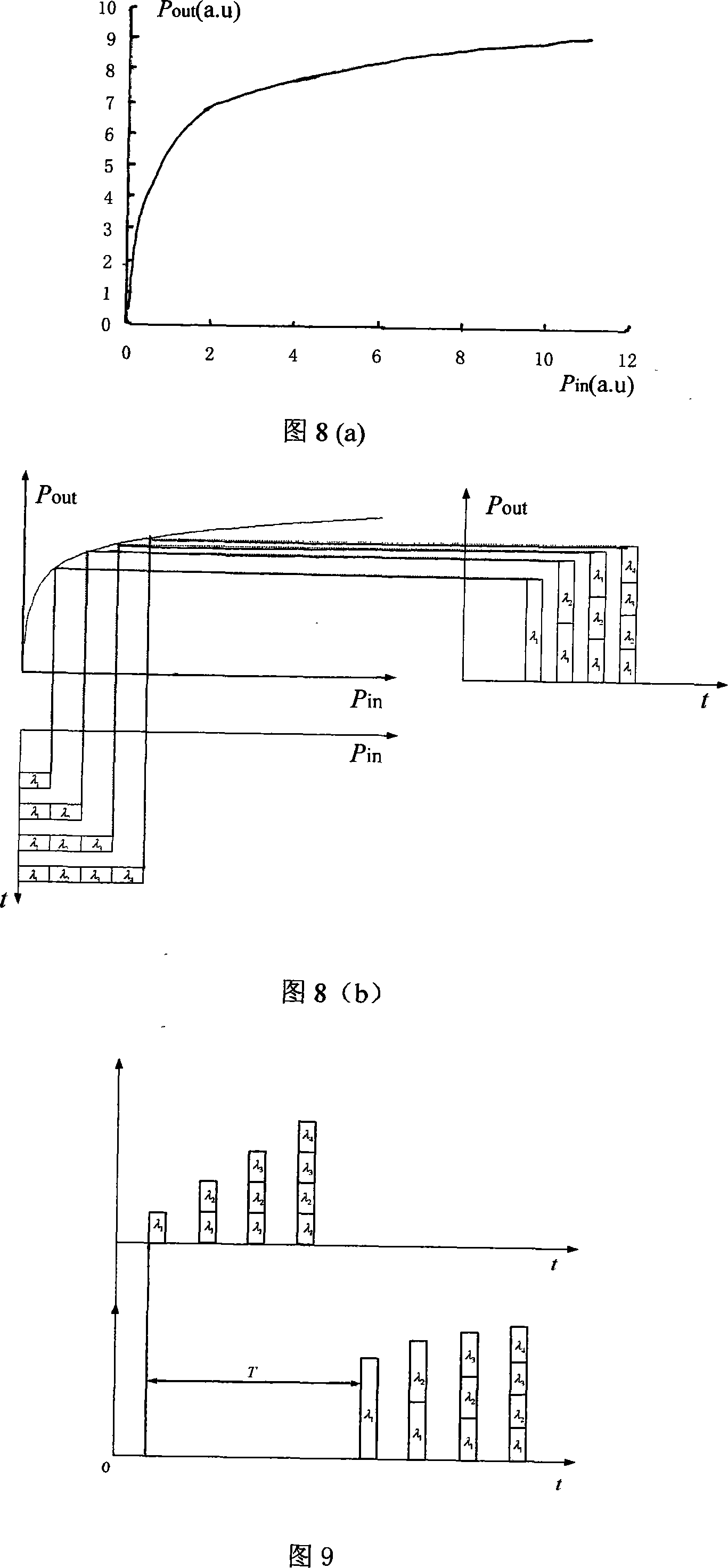
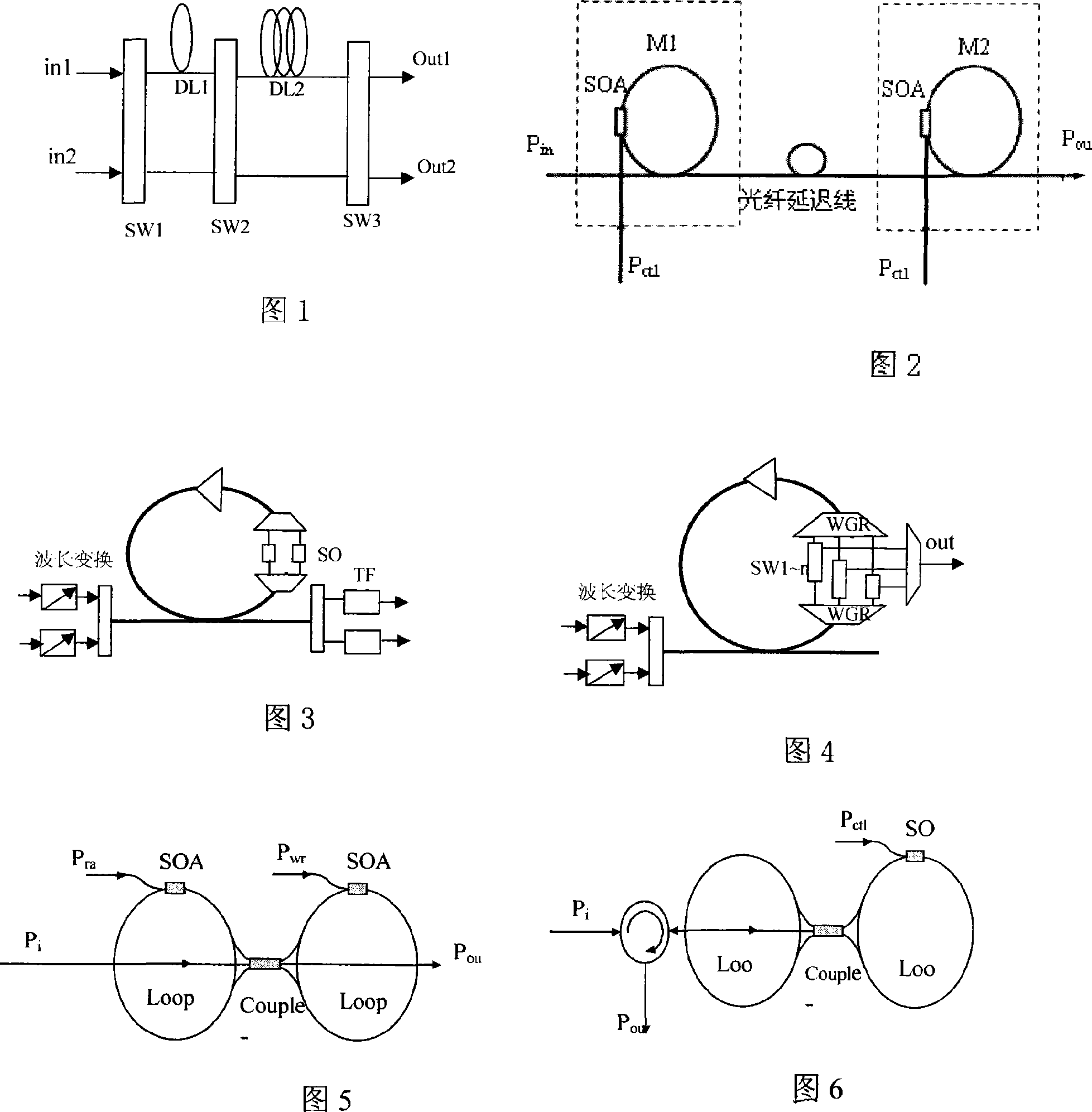
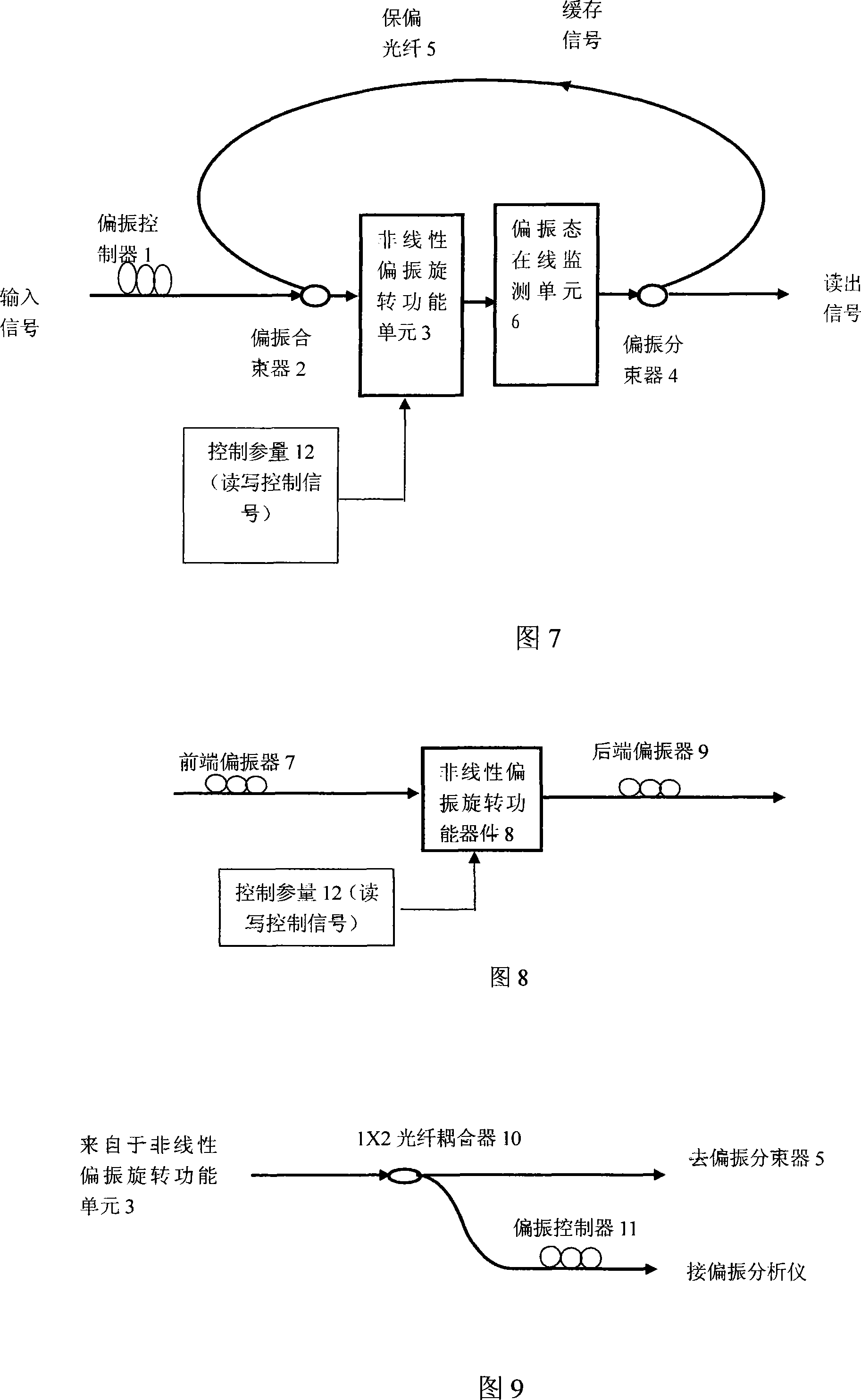
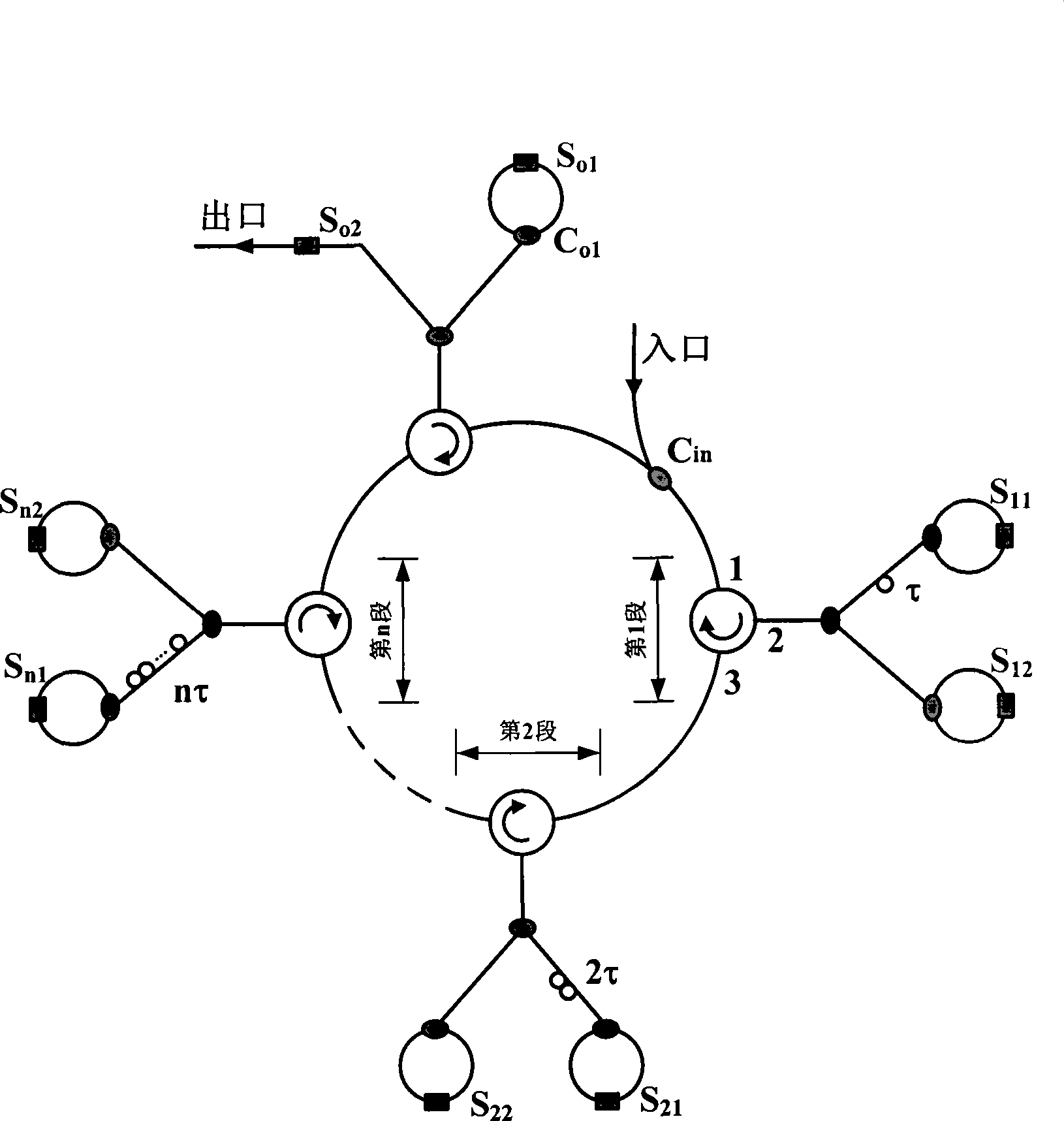
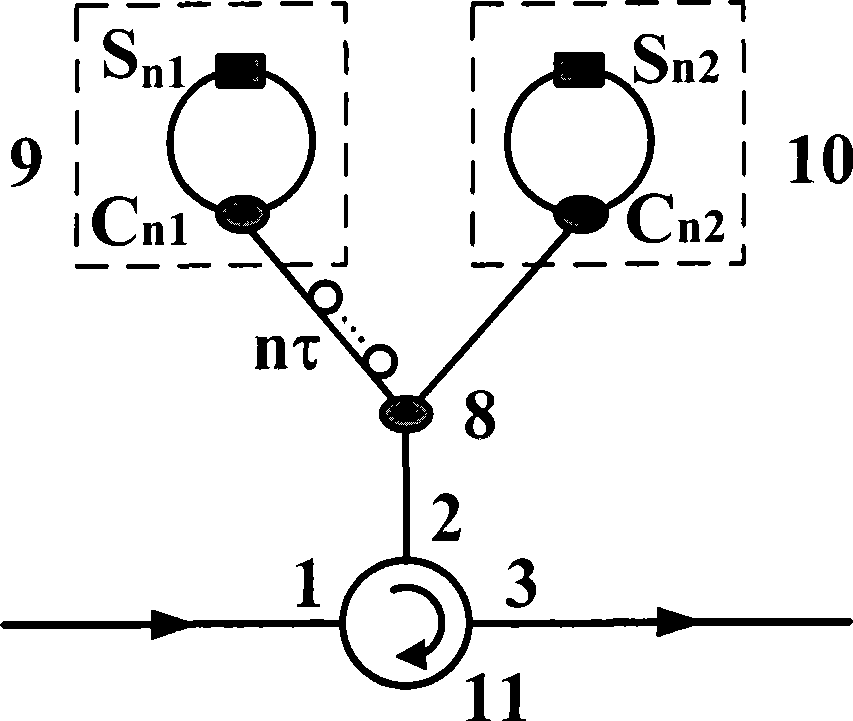
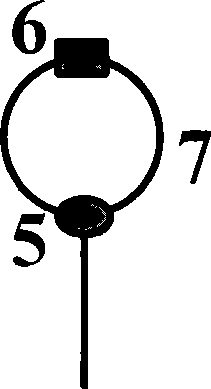
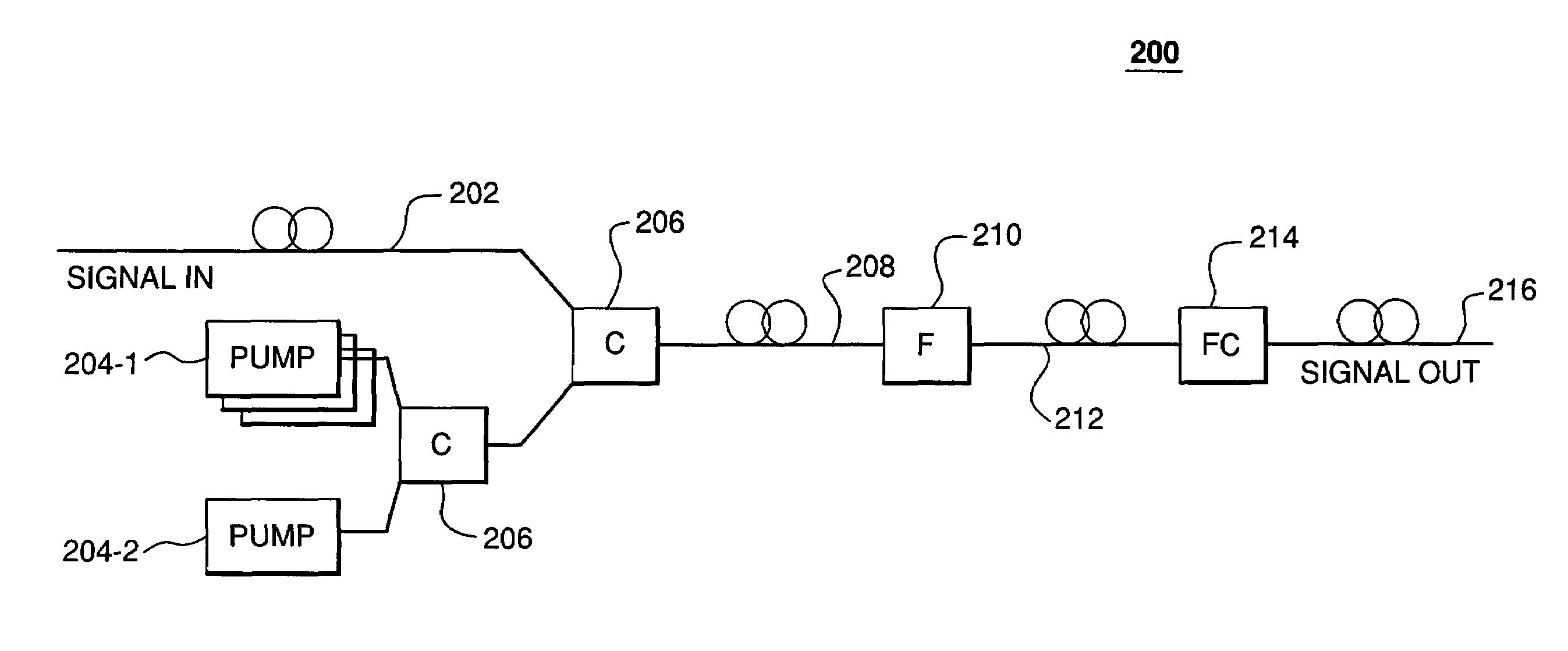
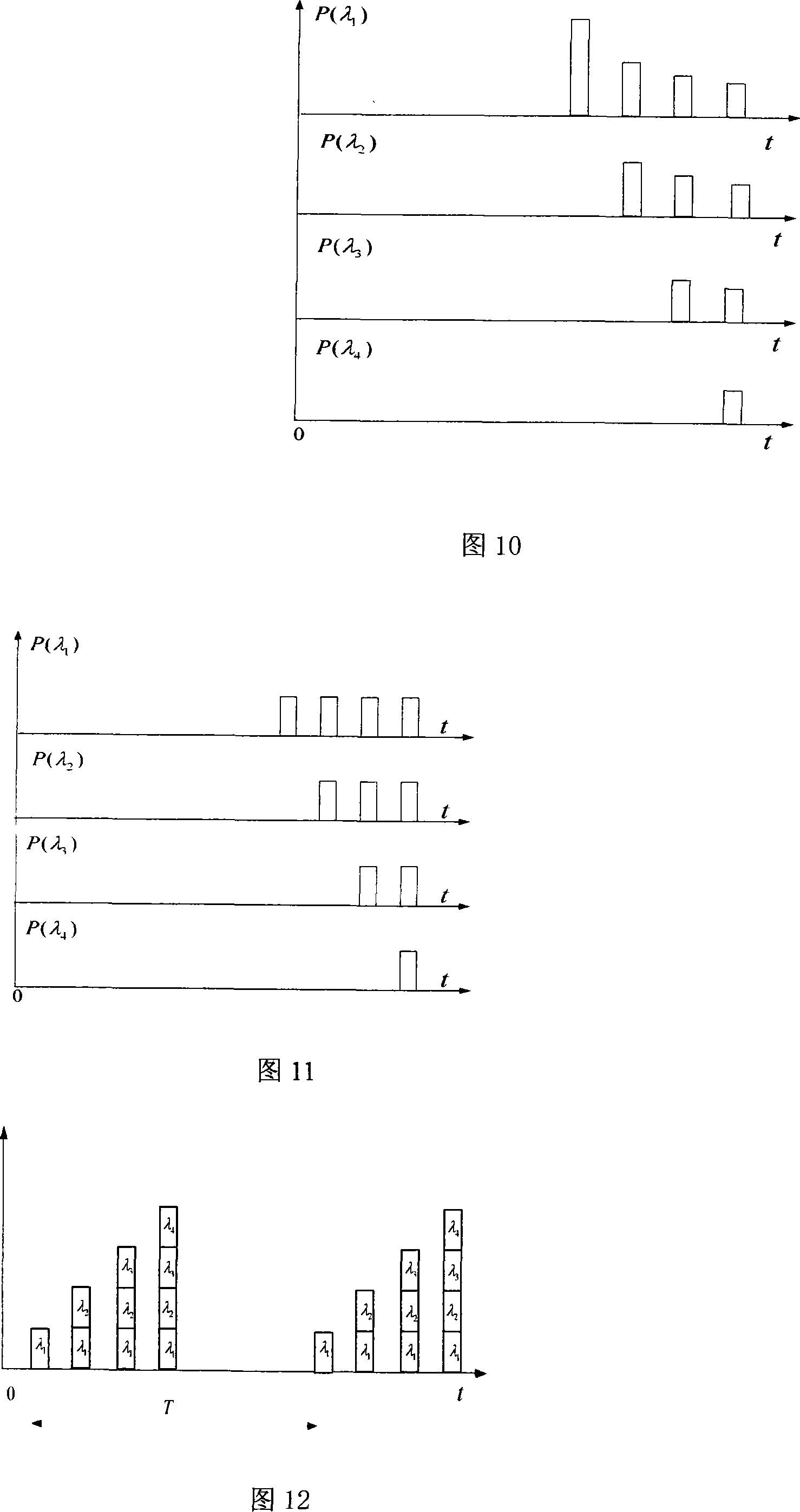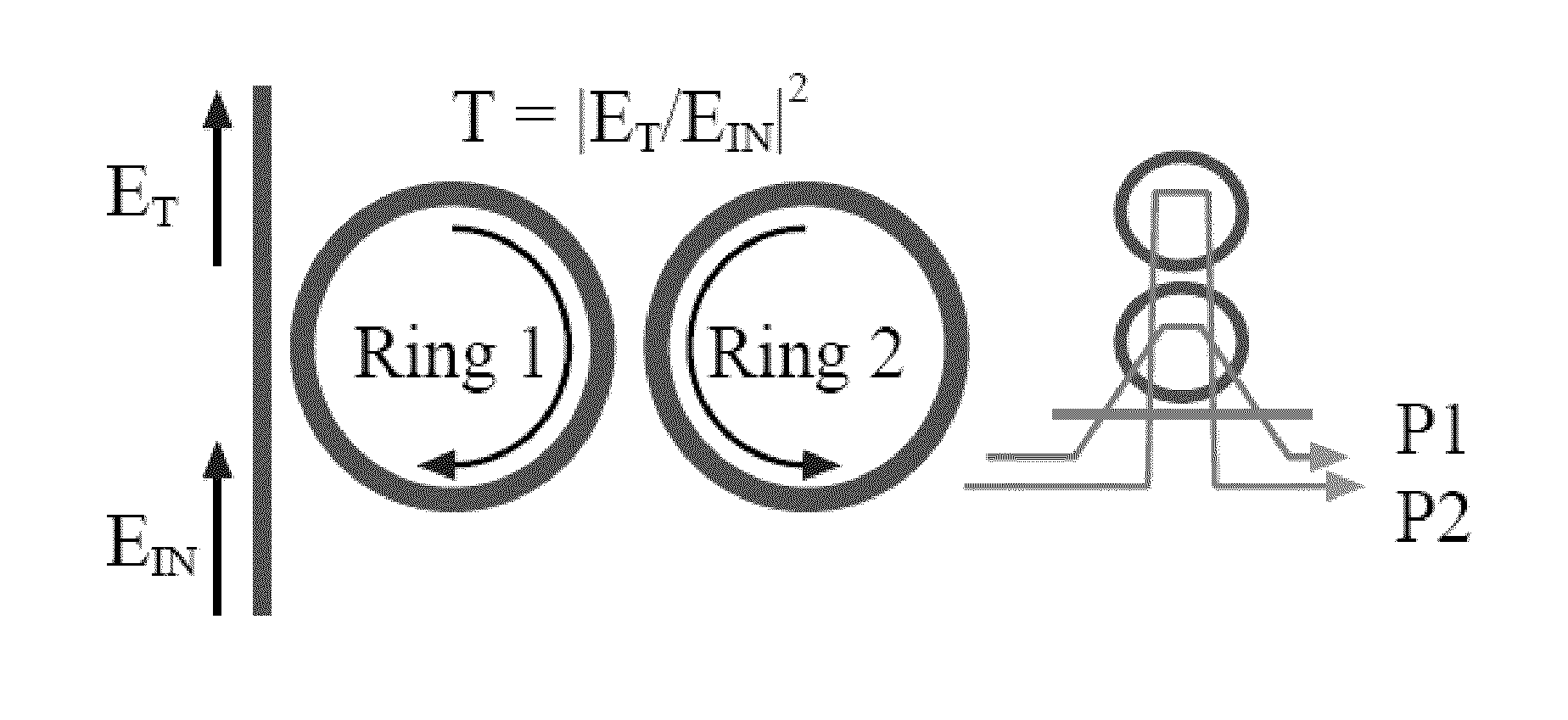Patents
Literature
85 results about "Optical buffer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
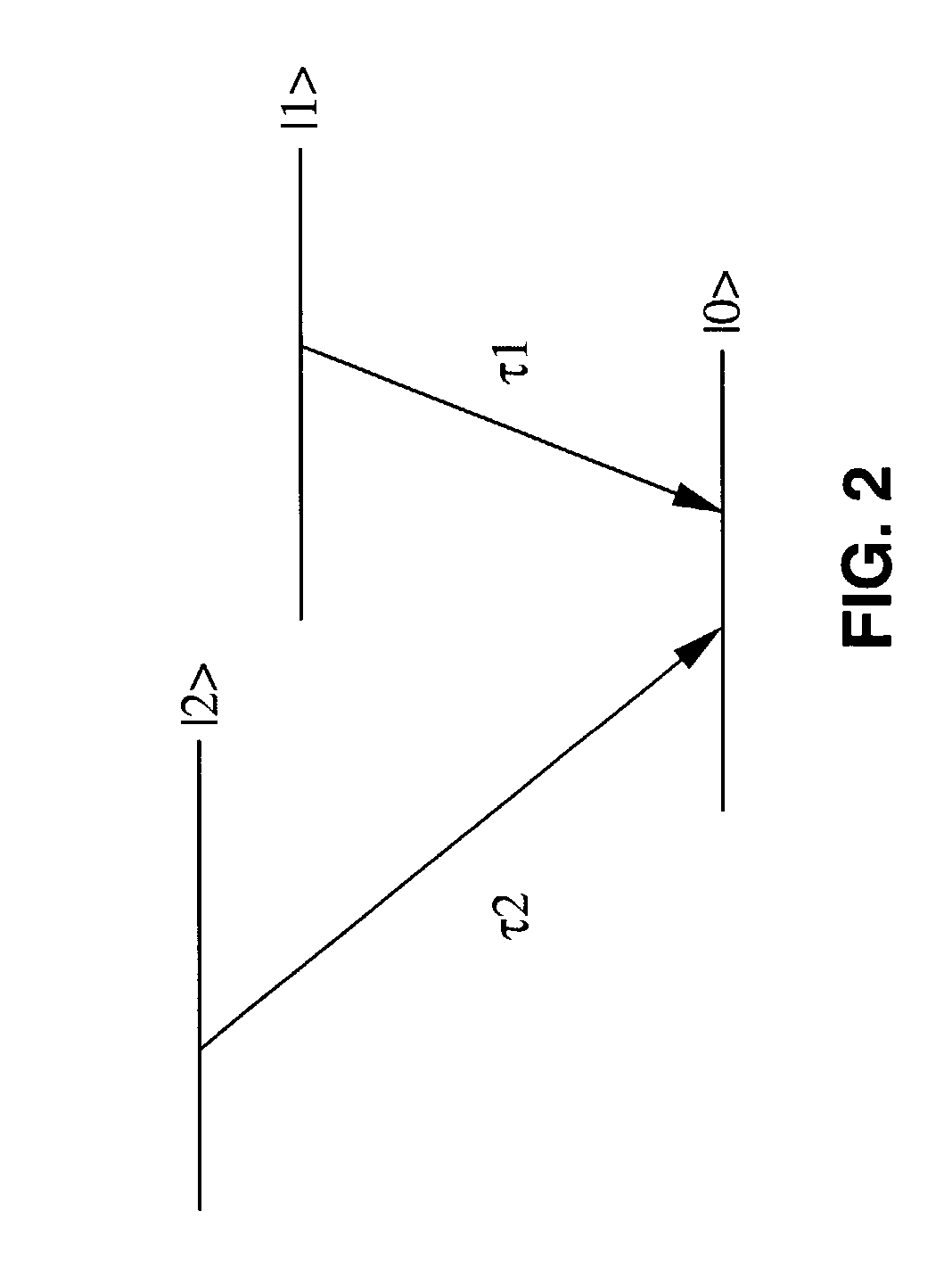
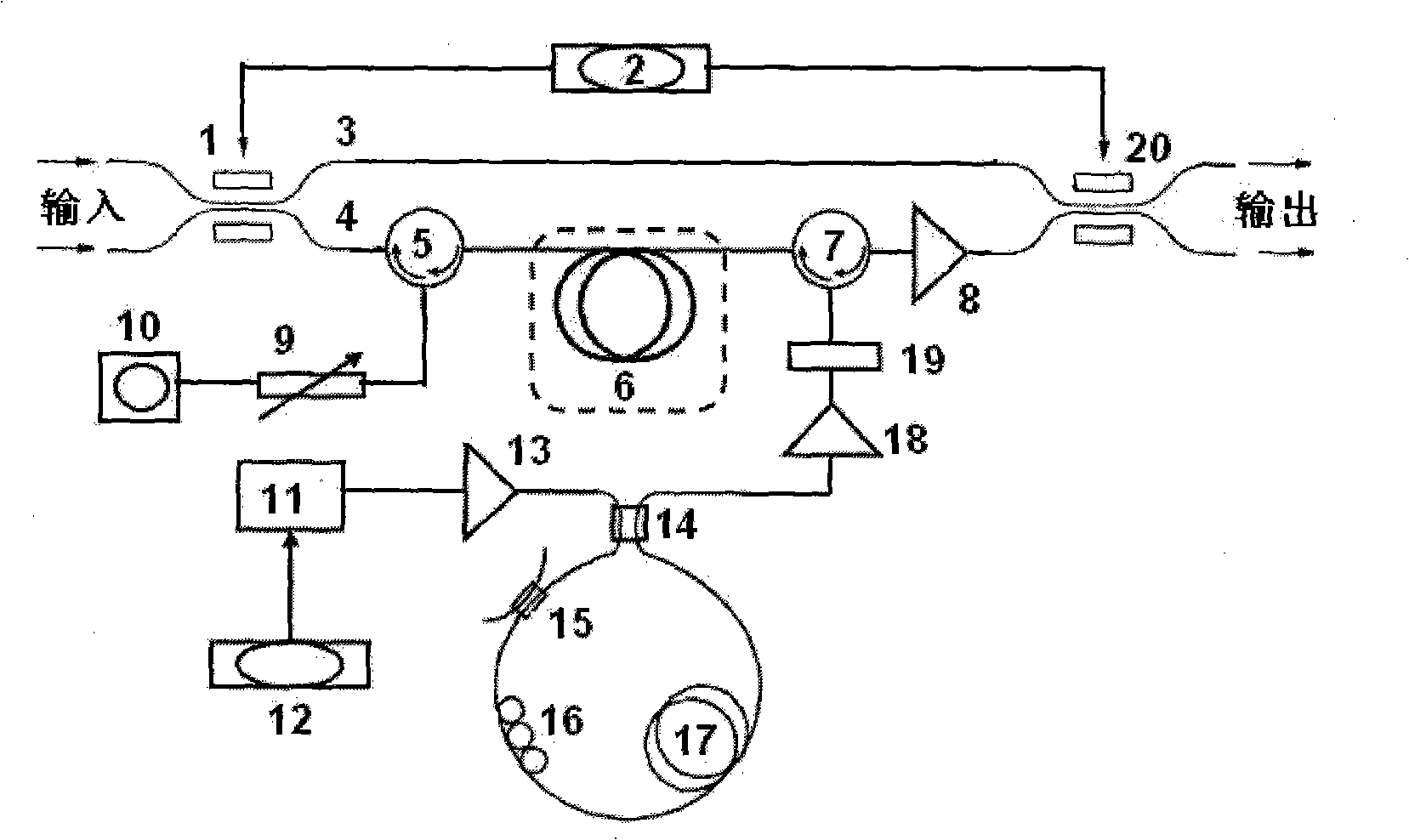
In telecommunications, an optical buffer is a device that is capable of temporarily storing light. Just as in the case of a regular buffer, it is a storage medium that enables compensation for a difference in time of occurrence of events. More specifically, an optical buffer serves to store data that was transmitted optically (i.e., in the form of light), without converting it to the electrical domain.
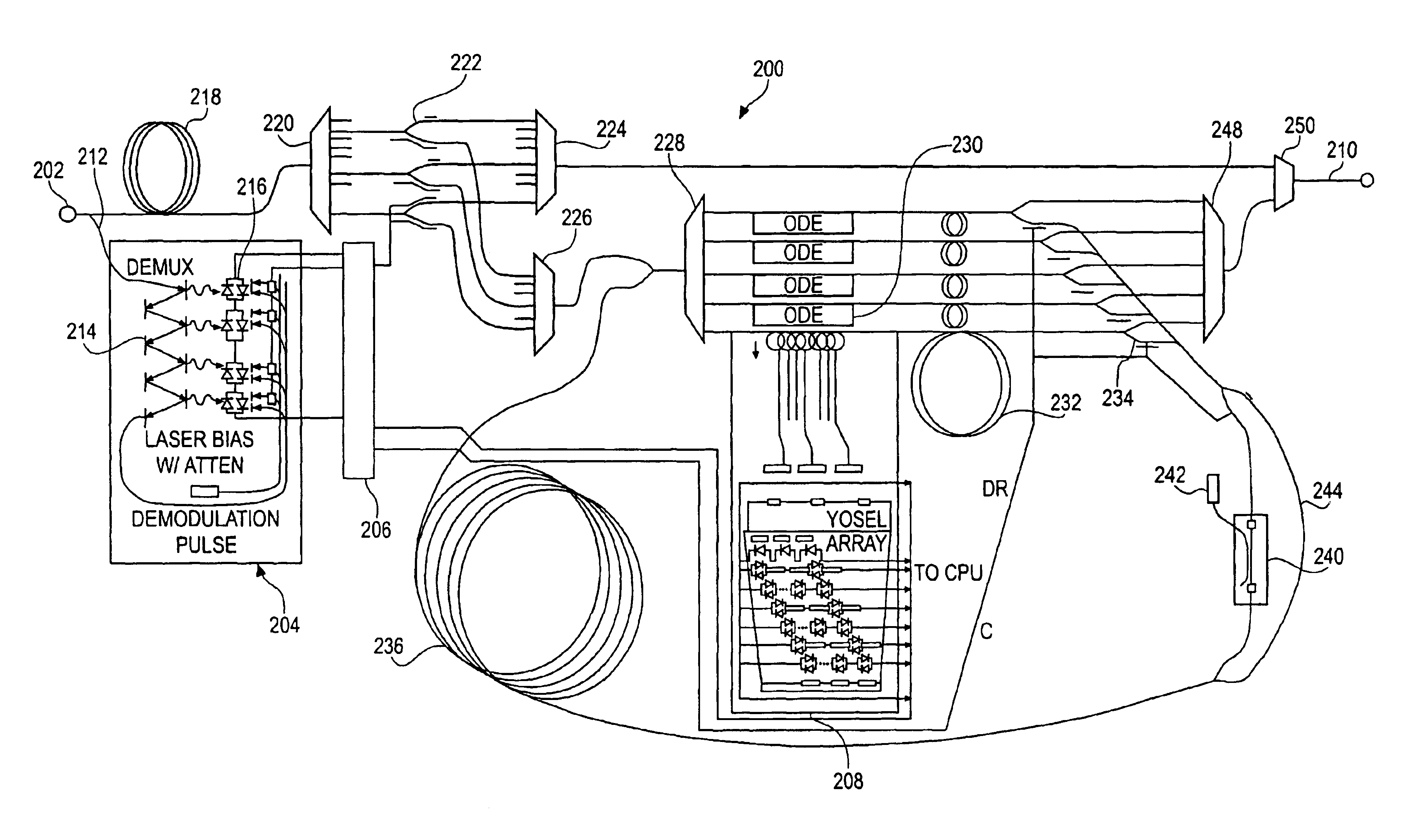
Node, data processing system, and data processing method
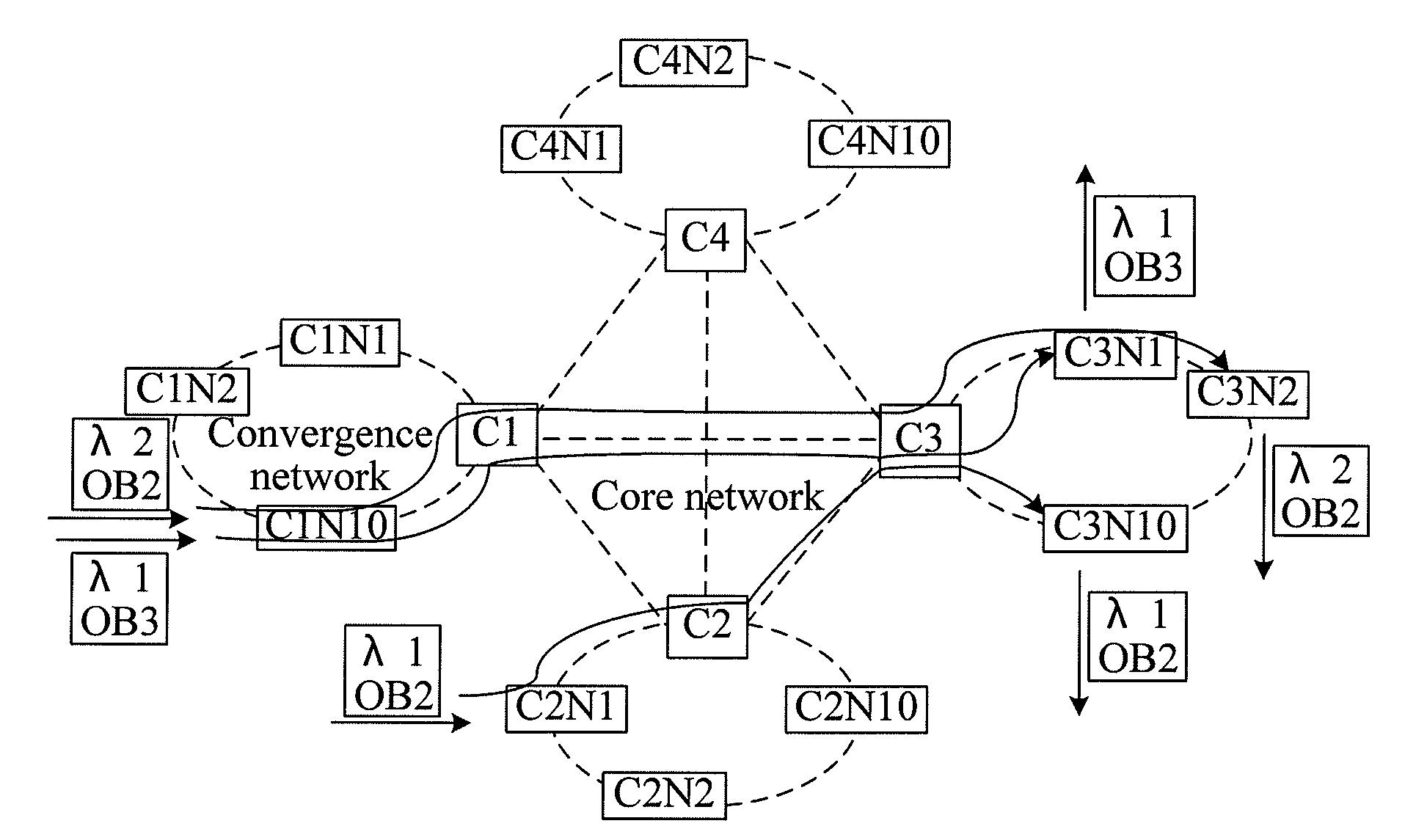
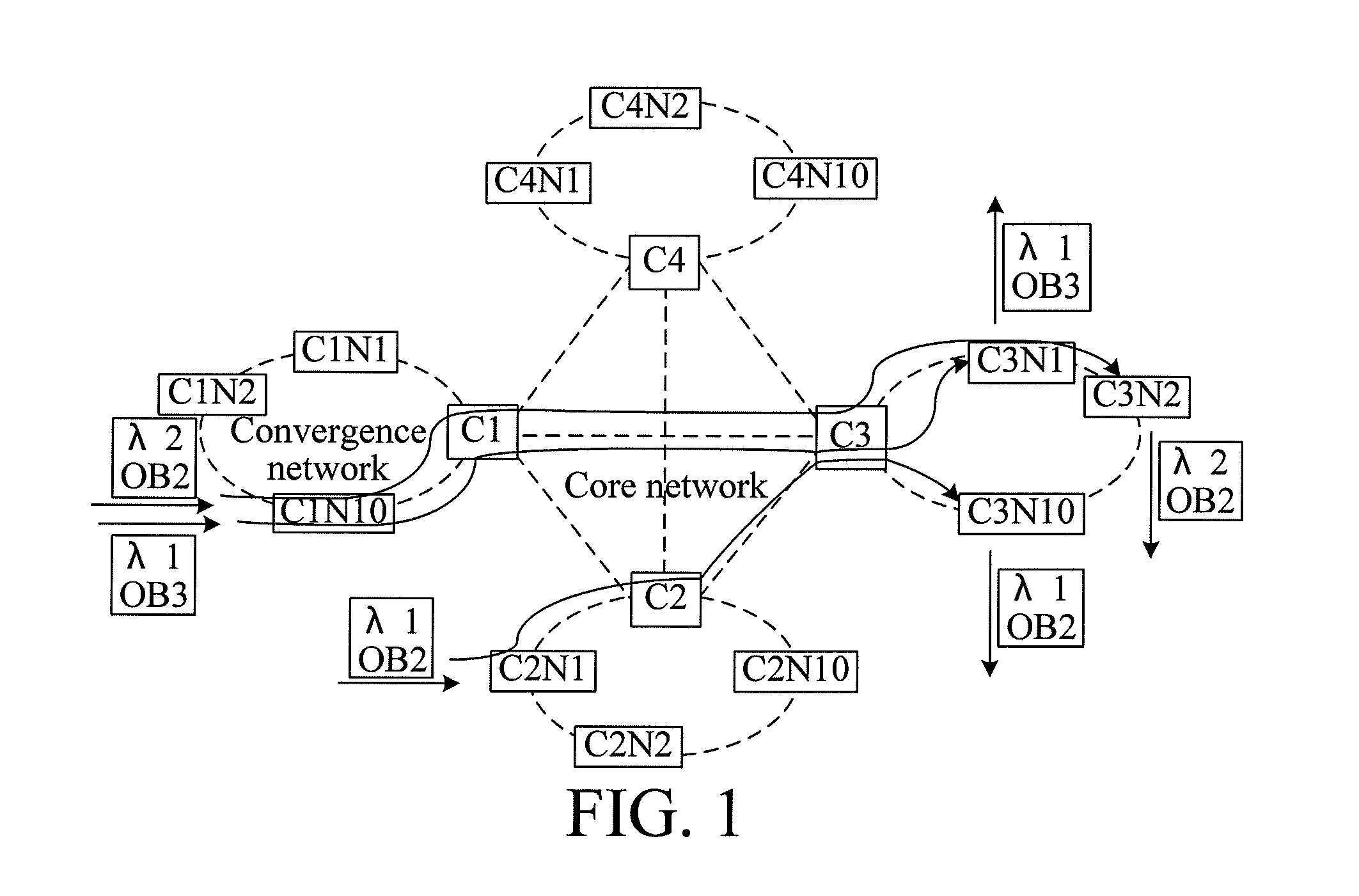
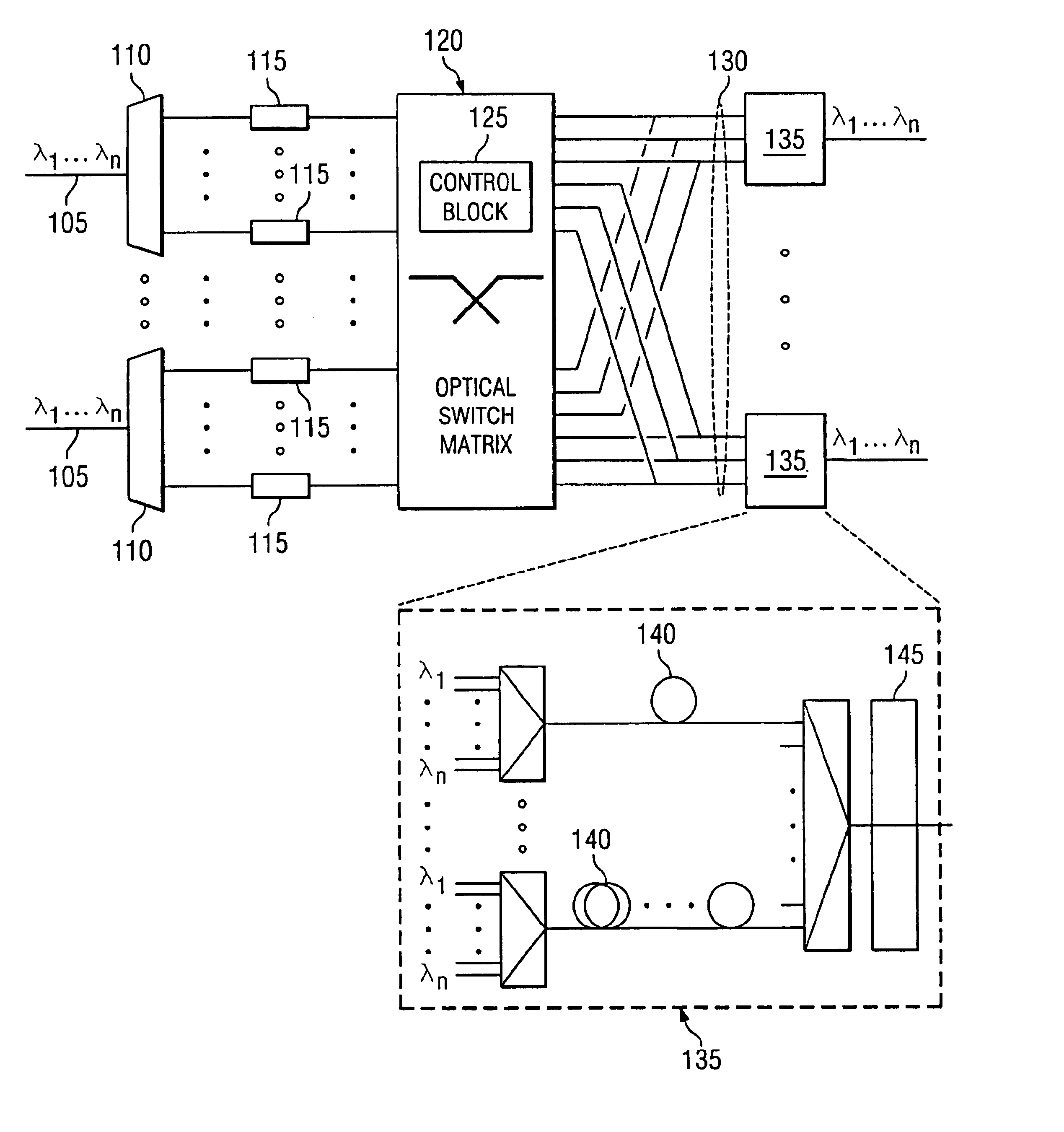
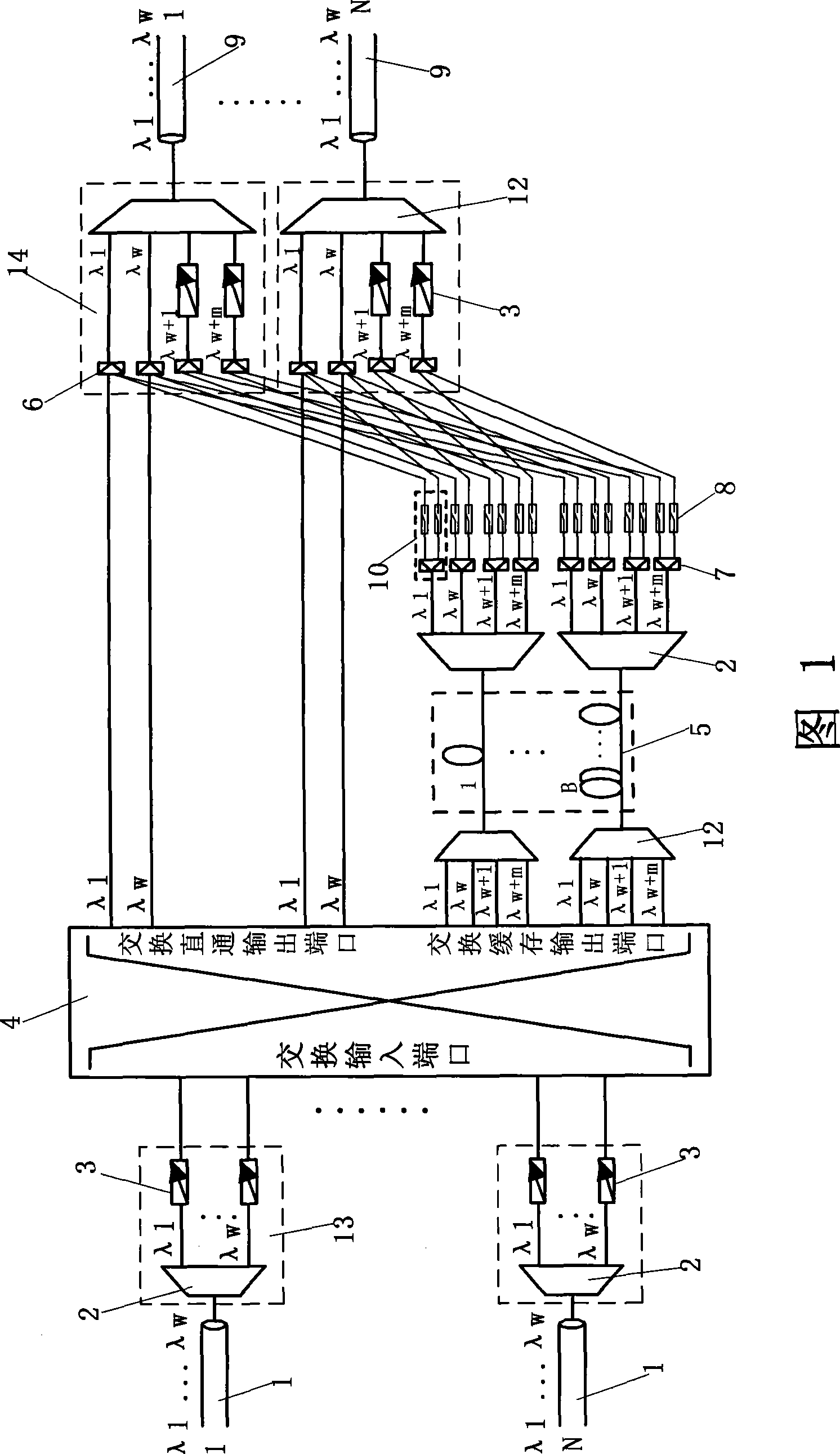
ActiveUS20110097090A1Reduce volume and power consumption and costIncrease in sizeMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexData processing systemCross connection
A node, a data processing system, and a data processing method are provided. The node includes a control module, adapted to generate synchronization information and Optical Burst (OB) configuration information; at least one synchronization processing module, adapted to perform a synchronization process on OB paths at a plurality of wavelengths according to the synchronization information; and a cross-connection module, adapted to perform, a cross-connection process on the OB paths, on which the synchronization process has been performed. The data processing system includes at least two nodes, where the nodes are connected through OB paths at one or more wavelengths, and the nodes are adapted to transfer service data through the OB paths. The technical solutions can reduce volume, power consumption, and costs of the nodes, and avoid a problem of generation of data conflict on an optical layer due to lack of optical buffers in all optical switching.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
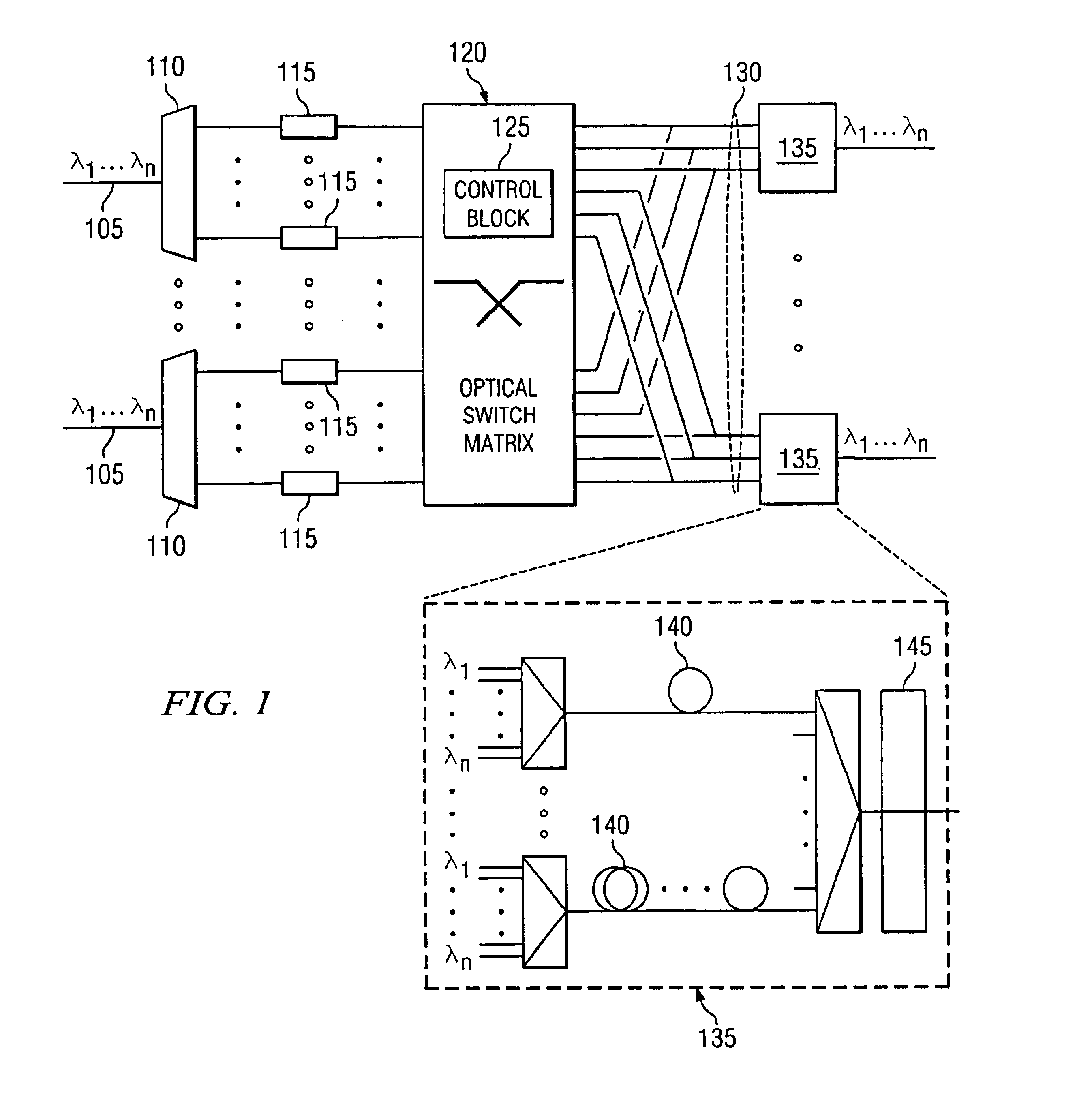
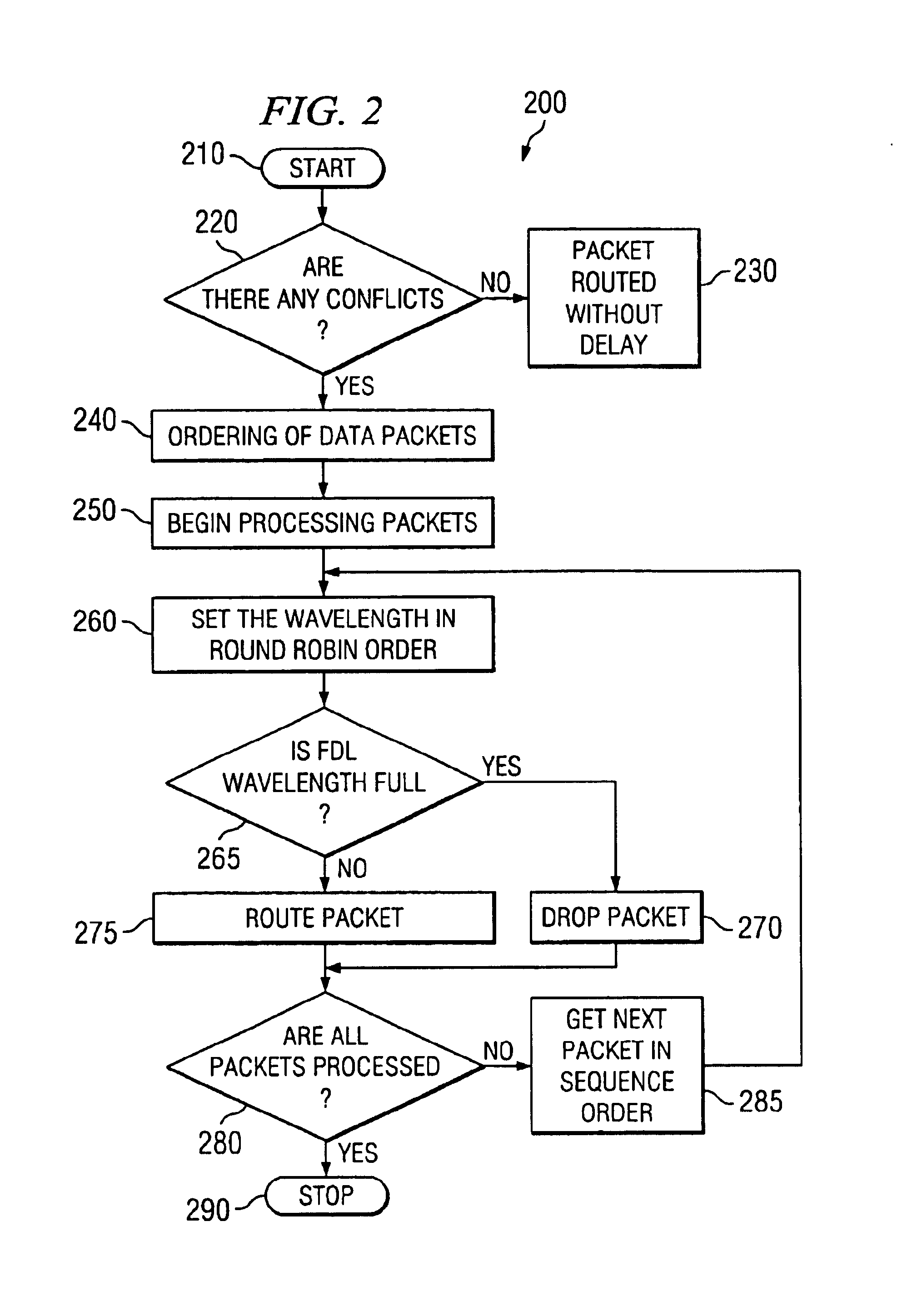
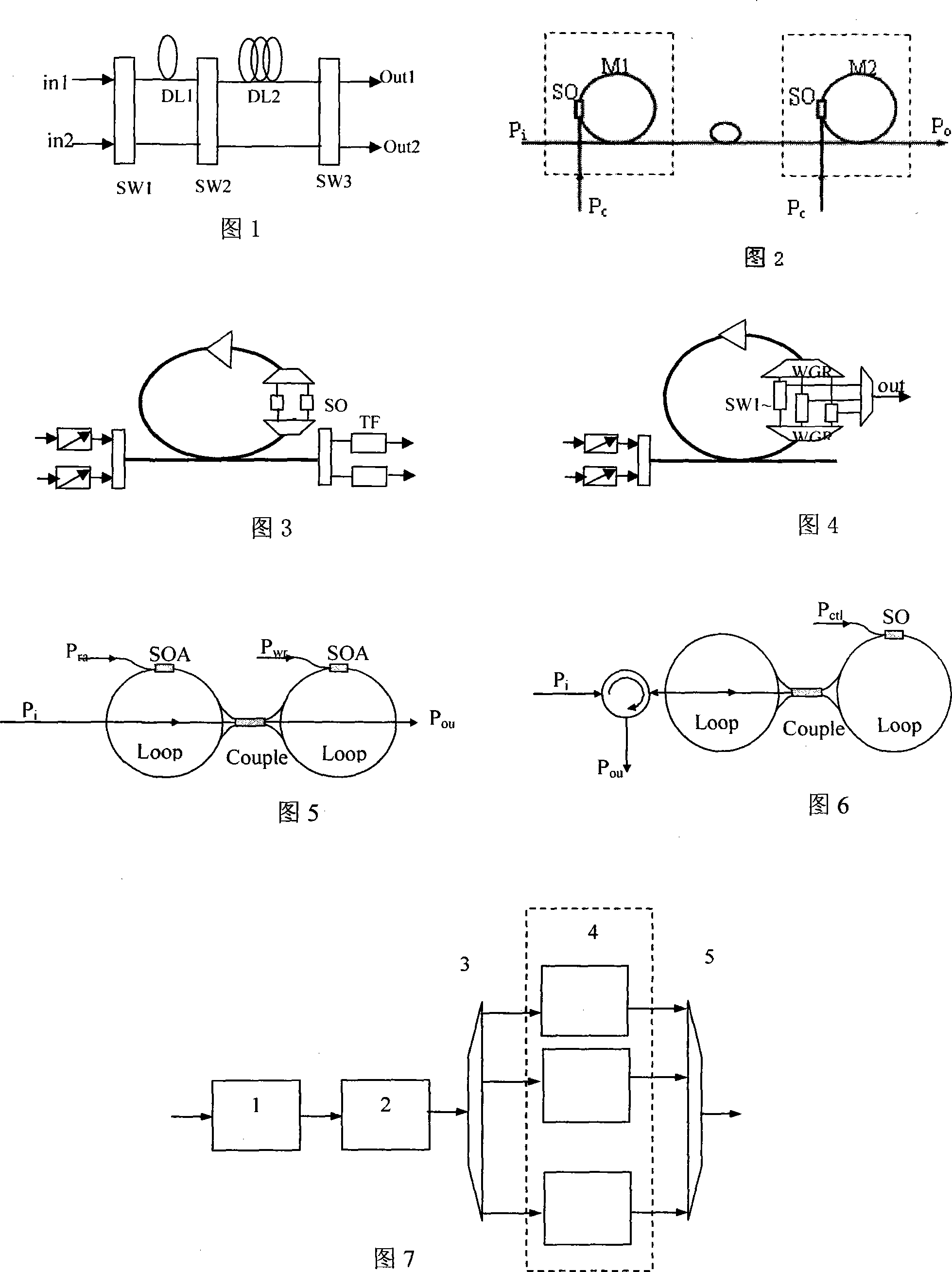
All-optical networking optical fiber line delay buffering apparatus and method
A method for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) fiber delay line (FDL) optical buffer routing and scheduling of conflicted variable length data packets through an optical router. The method includes ordering of each conflicted variable length data packet and selecting each of the data packets in turn for routing based on the ordering sequence selected. The sequentially assigned conflicted data packet is assigned a wavelength in the FDL optical buffer from (n) available wavelengths, wherein (n)=lambda1, lambda1, . . . , lambdan, lambda1, lambda1, . . . , lambdan, . . . . Each data packet is converted to the sequentially assigned wavelength (n) and routed to an optical buffer according to the wavelength assignment. If the wavelength of the FDL optical buffer is fully occupied the data packet is dropped.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
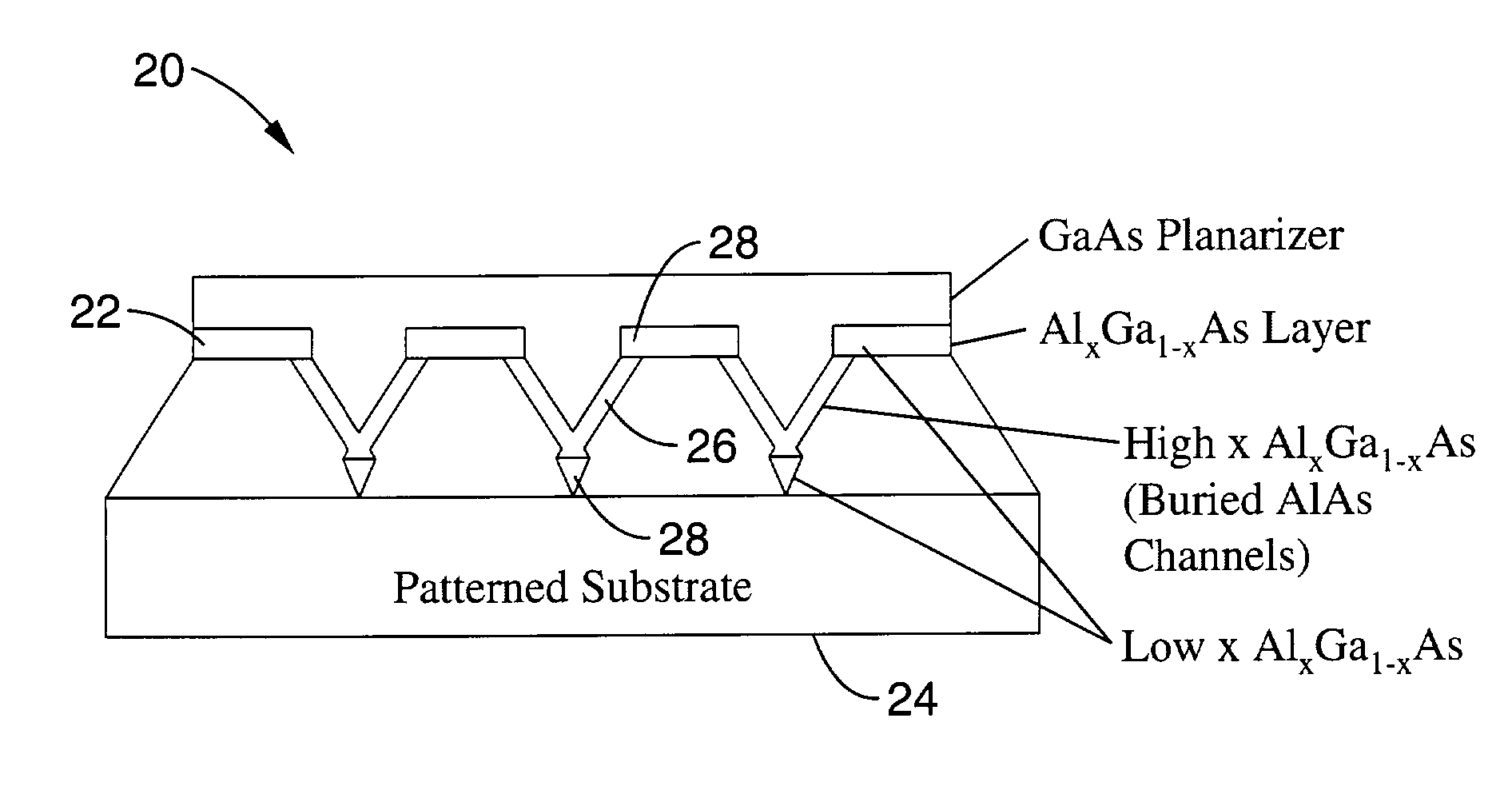
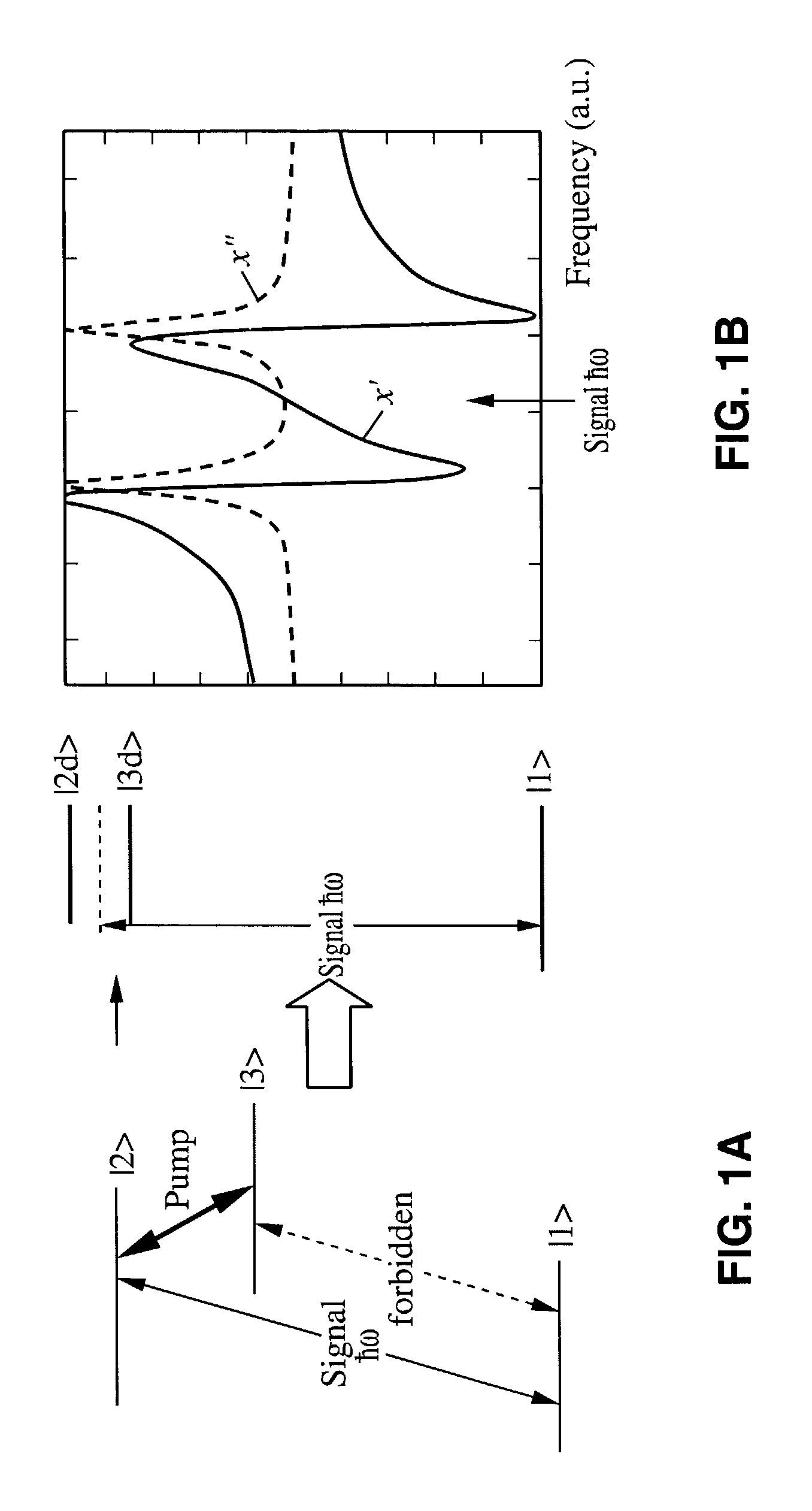
Variable semiconductor all-optical buffer using slow light based on electromagnetically induced transparency
A variable semiconductor all-optical buffer and method of fabrication is provided where buffering is achieved by slowing down the optical signal using a control light source to vary the dispersion characteristic of the medium based on electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). Photonic bandgap engineering in conjunction with strained quantum wells (QWs) and quantum dots (QDs) achieves room temperature operation of EIT. Photonic crystals are used to sharpen the spectral linewidths in a quantum well structure due to its density of states and in a quantum-dot structure caused by the inhomogeneity of the dot size, typically observed in state-of-the-art QD materials. The configuration facilitates monolithic integration of an optical buffer with an amplifier and control laser to provide advantages over other material systems as candidates for optical buffers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
All optical variable buffer queue useful in optical packet networks
InactiveUS20050053375A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical packetLength wave
A variable optical buffer queue, particularly useful either as an input or an output queue in an optical packet router in a wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) communication network. An input queue includes plural separately controllable optical delay units disposed on wavelength channels between a demultiplexer and tunable wavelength converters controlling switching through a wavelength router. An output queue includes for each output port of a wavelength router plural separately controllable optical delay units tuned to different wavelengths. The delay units may induce selective amounts of delay and may be implemented as a series of controlled microresonators coupled to waveguide. Such a structure is usable as a controllably accessible optical memory.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
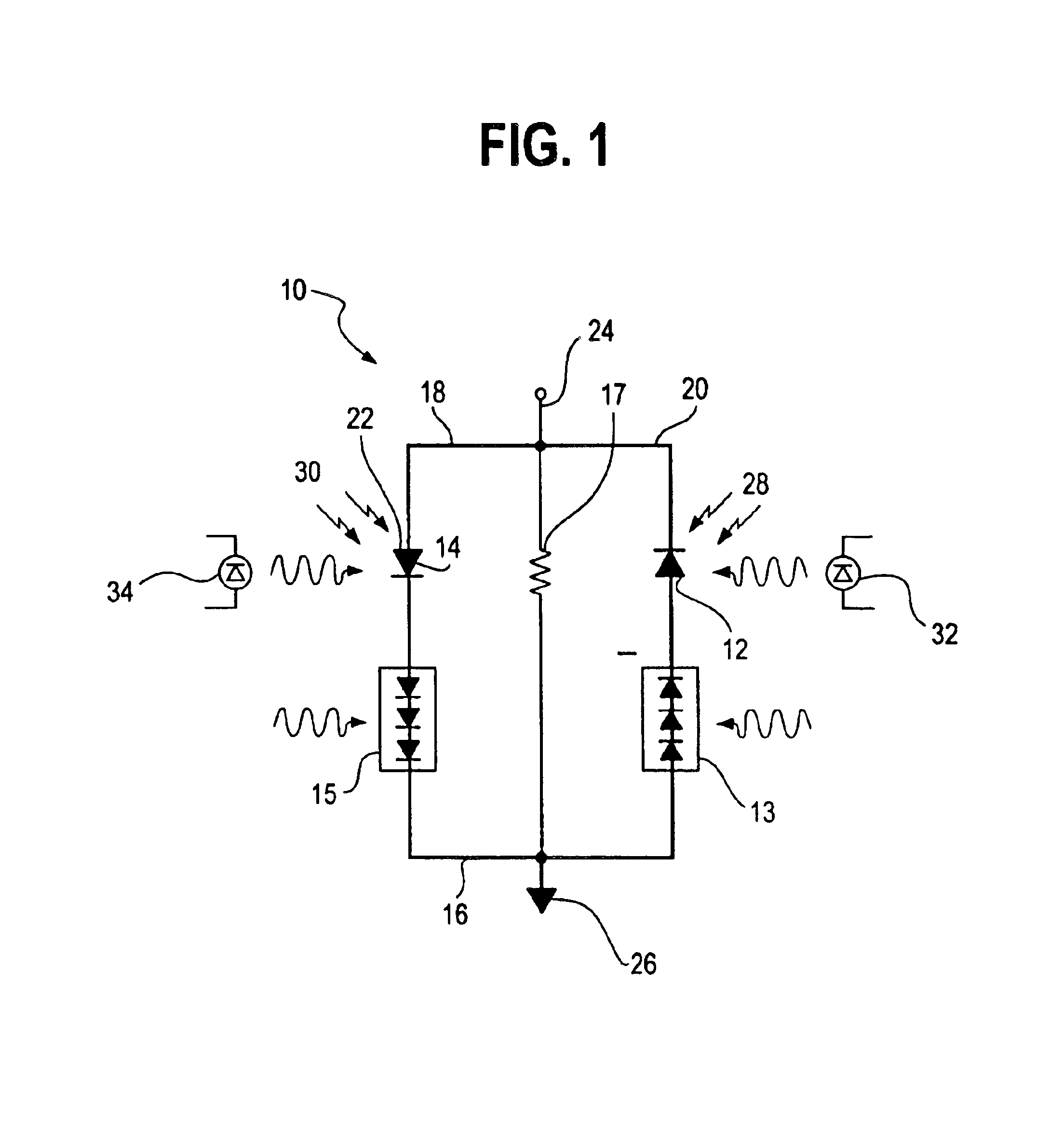
Wavelength associative addressing system for WDM type light packet steering
InactiveUS6904239B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTelevision system detailsFiberCross connection
A system and method are disclosed for carrying additional information data on multiplexed signals which are modulated on different wavelengths. An information code such as an address or control data for a particular data signal at a selected wavelength is overlaid on the parallel multiplexed signals. The information code may be overlaid by attenuation or changing the amplitude of the different signals. A separate marker channel at a separate wavelength is also multiplexed with the data signals to indicate the presence of an information code. An optical data detector array is used to optically determine the encoded address by comparing the signals with light levels and producing an output when a matching code is detected. The optical data detector array uses a series of detectors each corresponding to the wavelength of light signals carrying the information data. The detectors each have two photo detectors which are wired in parallel with each other to produce a voltage output when different light levels are detected on the two photo detectors. Using the information codes, an optical buffer may be realized which allows true optical switching of a data signal on detection of a matching information code. Alternatively, optical signals may be cross connected to balance data traffic through a fiber optic cable.
Owner:CHOW ALAN
Multi-wave length parallel buffer full optical buffer
InactiveCN101127570AOvercoming cross modulationImprove signal-to-noise ratioWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Multiplexer
The utility model relates to an all-optical buffer of multiple wavelength parallel storage to solve parallel buffer problem of dense wave-division multiplex signal and consists of an input power equalizer, a light buffer unit, a wave-division multiplex-de-multiplexer, an output power equalizer set and a wave-division multiplexer. The utility model adopts the multiple wavelength parallel storage technique of power equalization - parallel buffer - de-multiplex - power equalization - re-multiplex to maintain the synchronous buffering of multiple wavelength signals, so that the cross modulation among multiple wavelength signals can be effectively overcome, the signal-to-noise ratio can be promoted and the good buffer memory performance can be gained. Free adjustment on the cycle multiple of multiple wavelength signals buffer period can be realized in the utility model and the reading and writing time can be controlled with light signal writing and reading. The reading time can be started as required after storing signals; the event triggering can be realized without preset in the buffer. With great flexibility, the utility model is a real all-optical buffer suitable to all-optical routers or all-optical exchangers.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
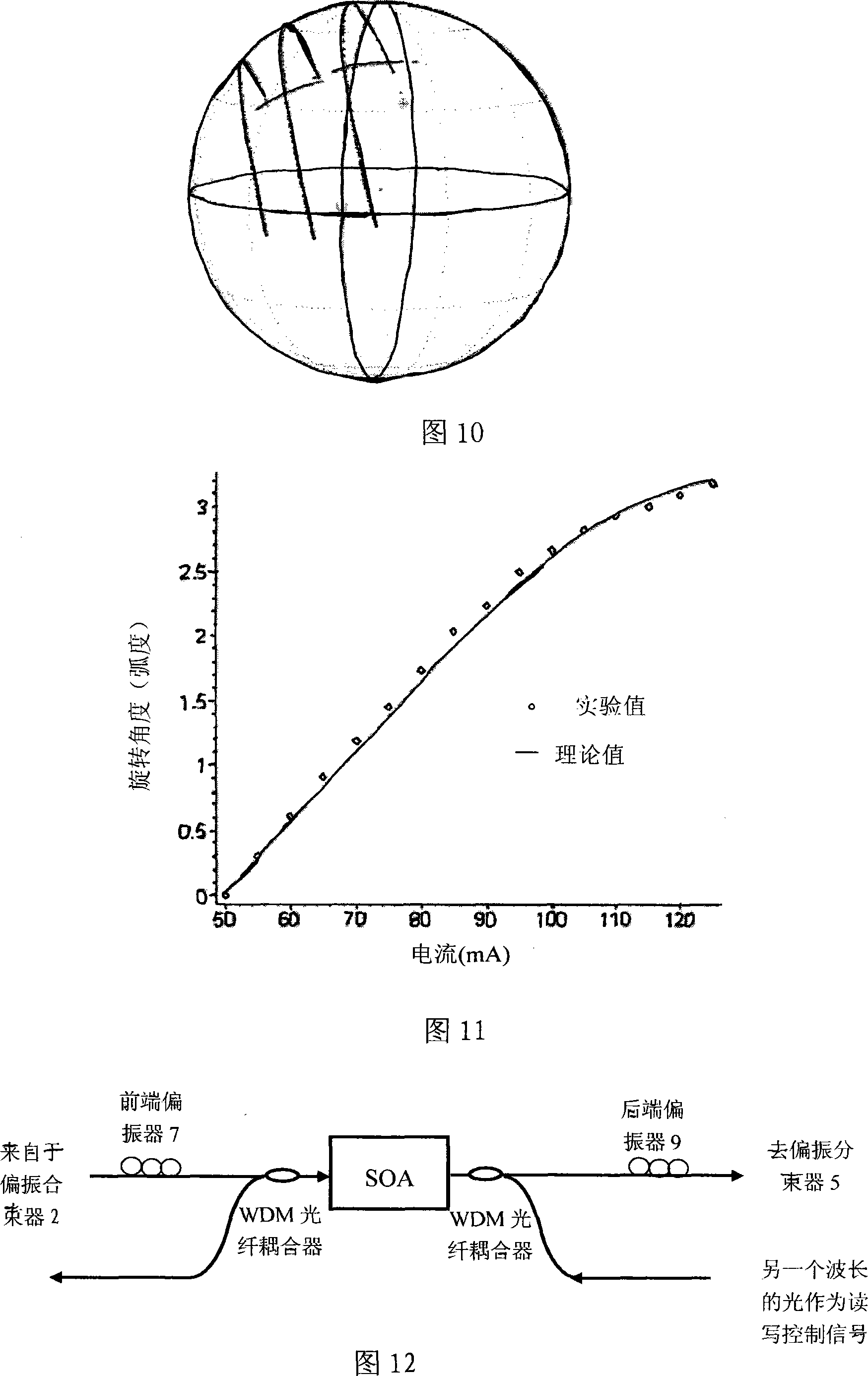
Polarization type optical caching device and regulating method thereof
InactiveCN101114886AFast reading and writing responseCascading convenienceWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesInstabilityPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
A polarization type optical buffer together with the adjusting method is designed for the low turning on and off speed and the instability of the avoiding polarization state, namely using the nonlinear rotation of the polarization state in a semiconductor optical amplifier or an optical fiber as a polarization control switch to realize the optical buffer to cache the data packet signal. The optical buffer consists of an input polarization controller, a polarization beam combiner, a nonlinear polarization rotation functional unit, a polarization beam splitter and a polarization maintaining fiber, wherein, the nonlinear polarization rotation functional unit consists of a front polarizer, a tail polarizer, the controllable non-linear rotation functional parts and an online monitoring unit of the polarization state composed by an optical fiber coupler and a polarization controller. The instability of the polarization can be avoided by adjusting the polarization type optical buffer to the polarized rotation. The polarization type optical buffer of the invention has the advantages that the reading and writing speed is high and the buffer depth of an optical fiber ring reaches above 90%, thereby being good for the cascade.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Dynamic reconfigurable multi-granularity optical buffer for all-optical switching network
InactiveCN1633108AUnlimited lengthSatisfy the requirements of optical cacheMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionFiberTime delays
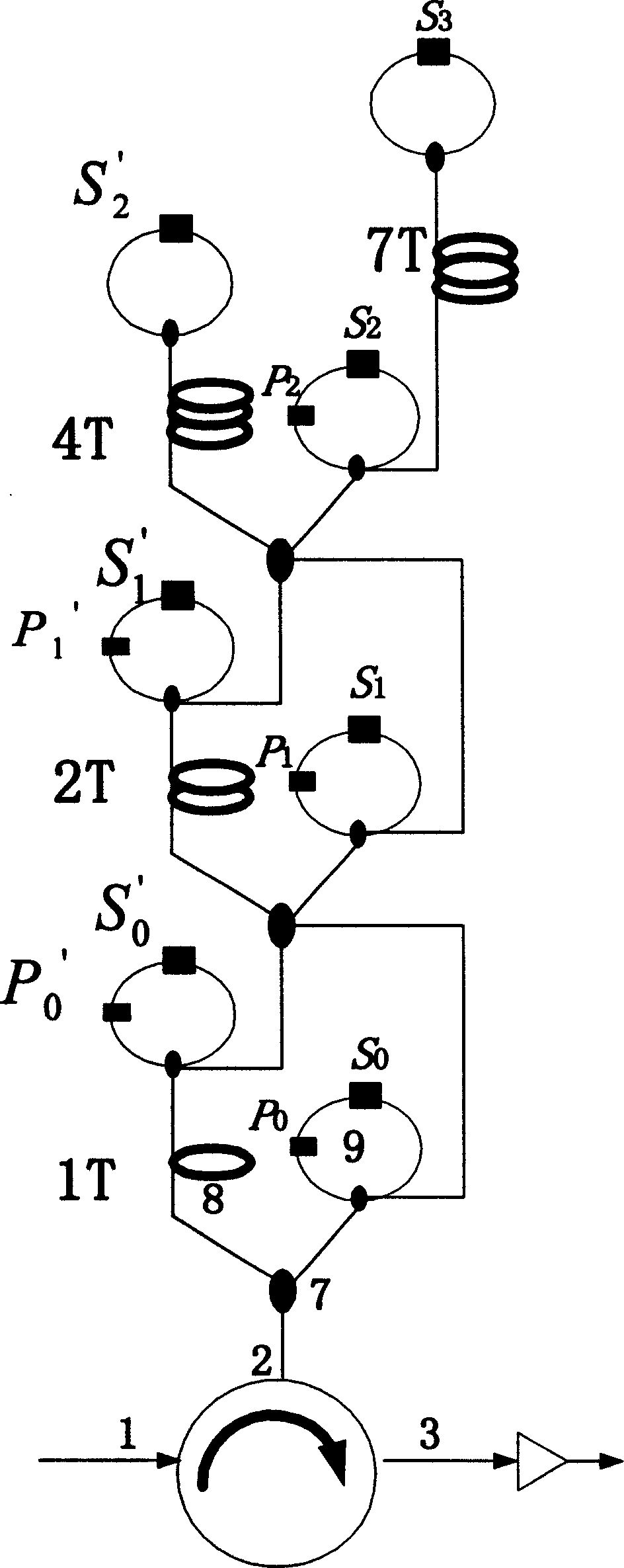
A full optical exchange net dynamic reconstructive multigrain optical buffer memory based on fiber delay lines and SOA gain optical switch has a read-write speed of nanosecond level to support data packet. The optical buffer memory cascaded by different grains of optical delay line trees, each tree is composed of four optical delay lines with different grains and provides the buffer storage time delay of 10 basic units by combination of two different grains of delay lines to the most, therefore, the optical buffer memory cascaded by two level optical delay line trees can provide the time delay of 100 basic units.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Variable semiconductor all-optical buffer using slow light based on electromagnetically induced transparency
A variable semiconductor all-optical buffer and method of fabrication is provided where buffering is achieved by slowing down the optical signal using a control light source to vary the dispersion characteristic of the medium based on electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). Photonic bandgap engineering in conjunction with strained quantum wells (QWs) and quantum dots (QDs) achieves room temperature operation of EIT. Photonic crystals are used to sharpen the spectral linewidths in a quantum well structure due to its density of states and in a quantum-dot structure caused by the inhomogeneity of the dot size, typically observed in state-of-the-art QD materials. The configuration facilitates monolithic integration of an optical buffer with an amplifier and control laser to provide advantages over other material systems as candidates for optical buffers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
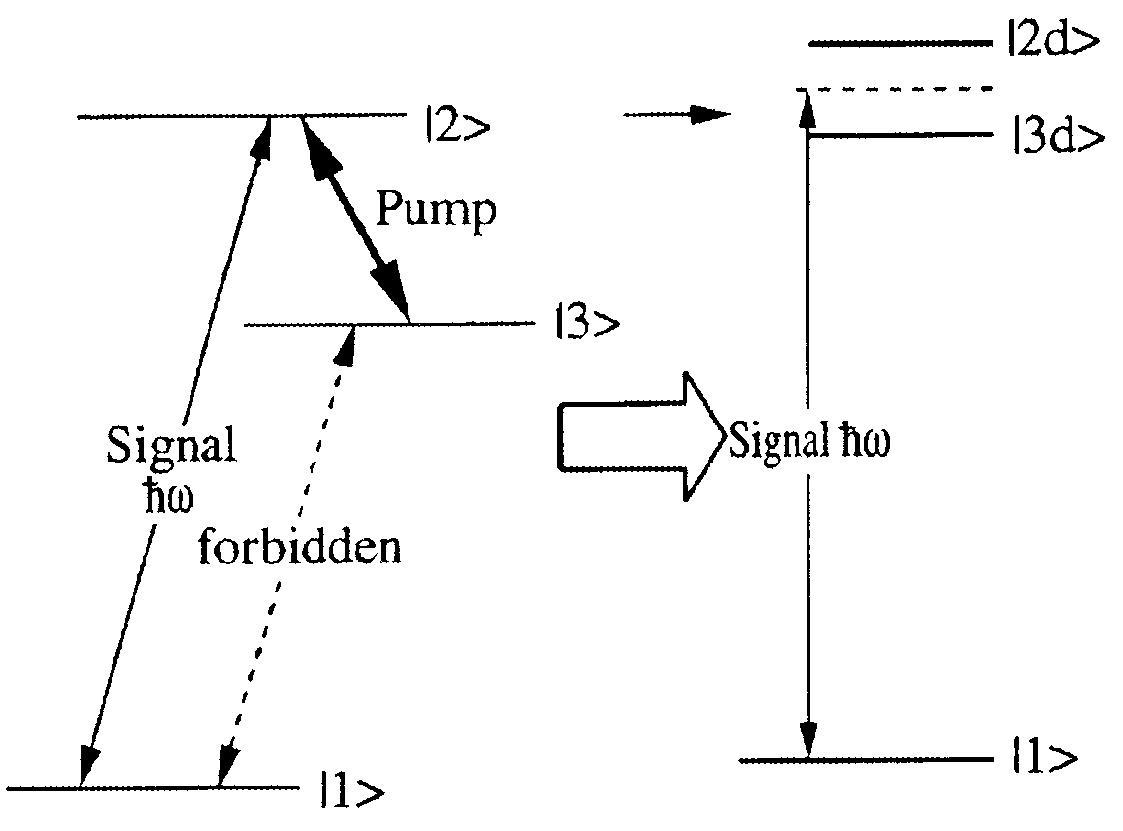
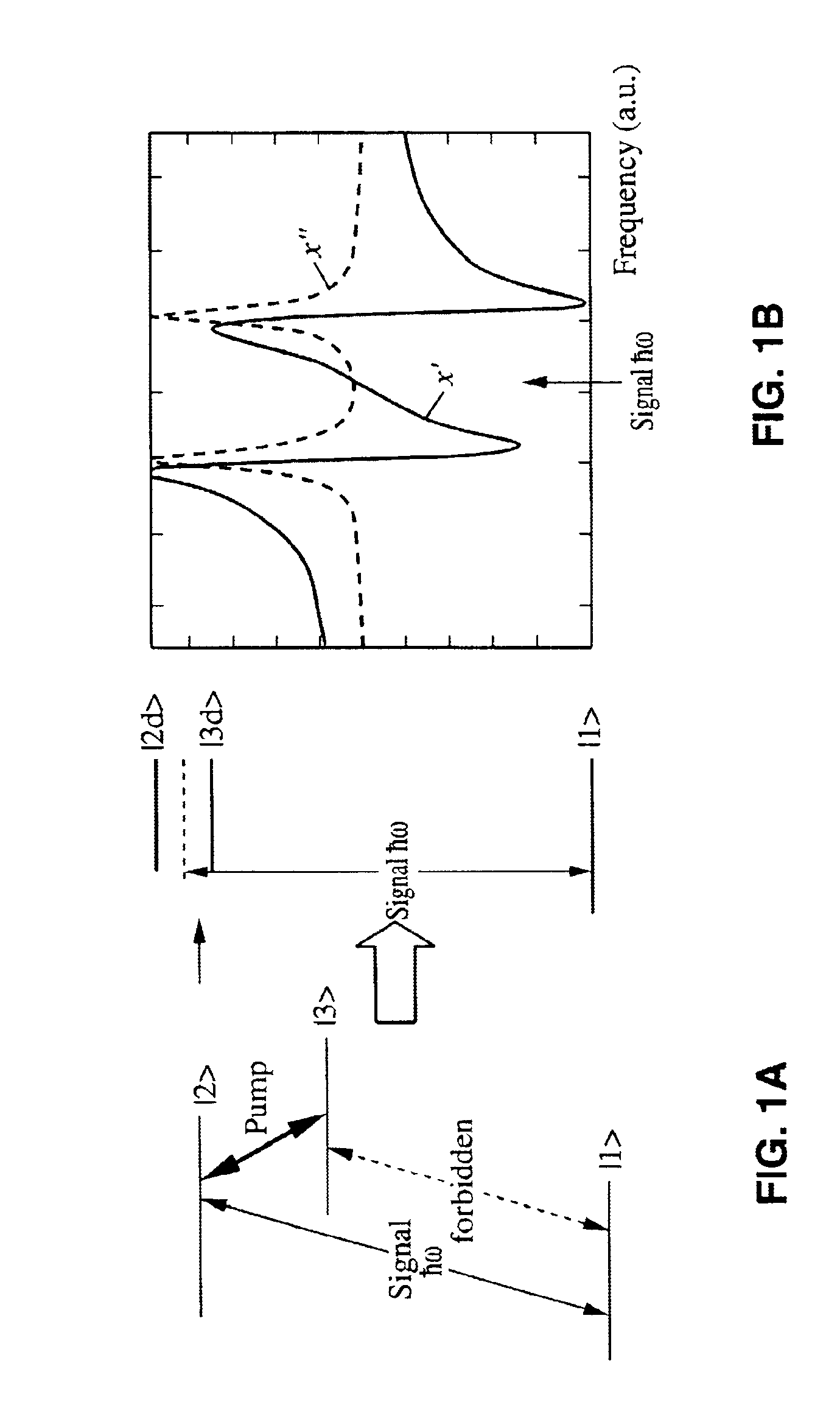
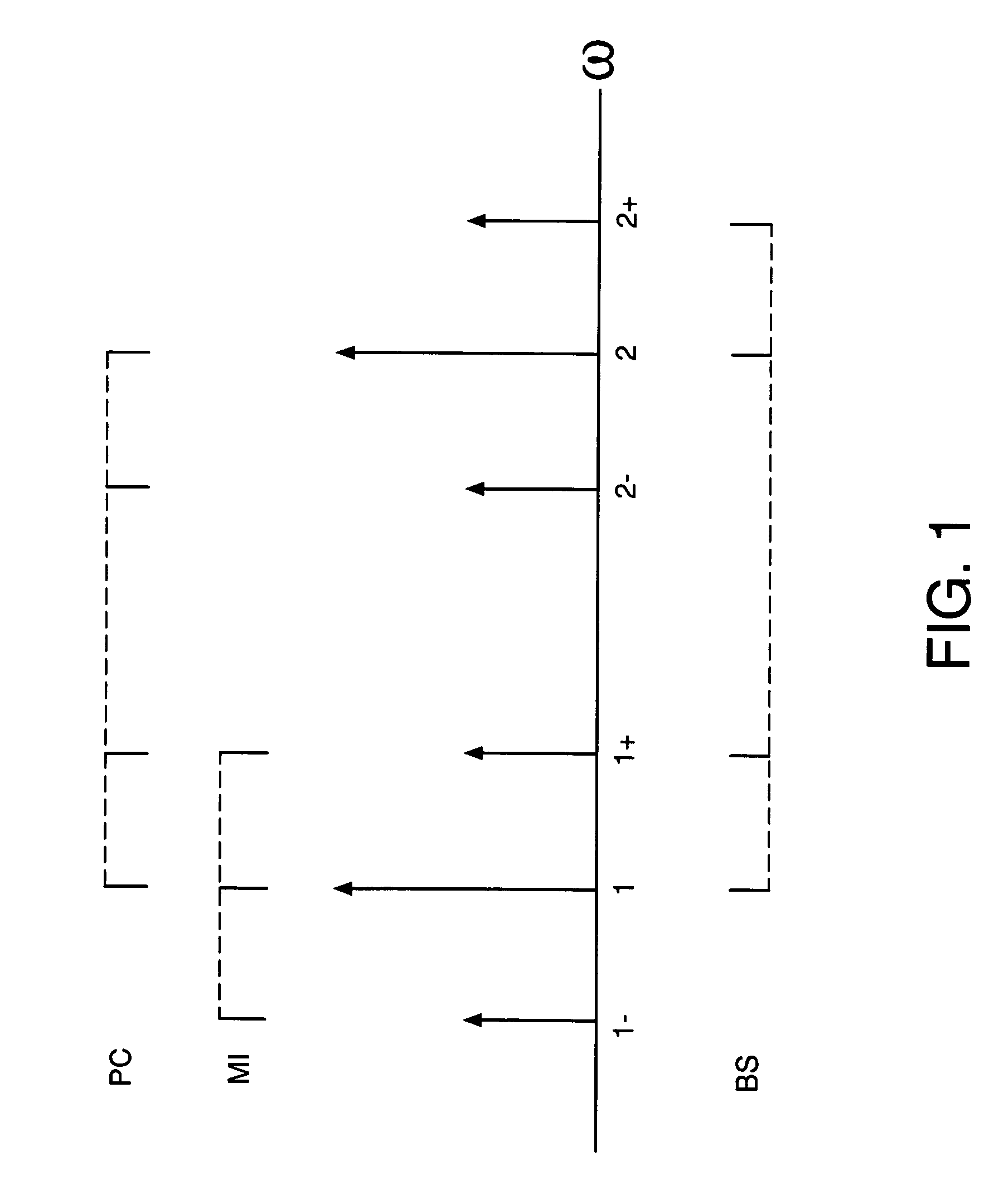
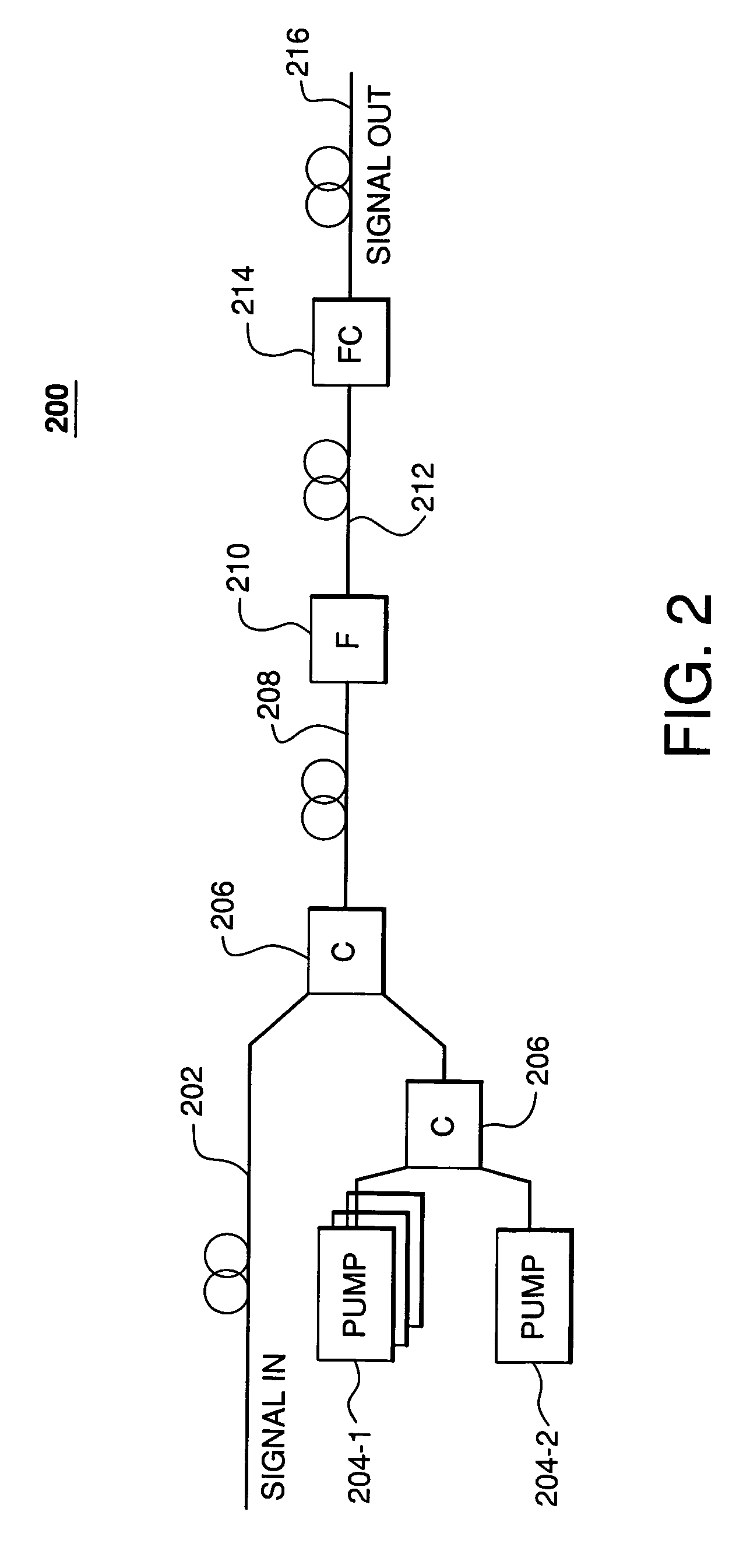
Optical buffer employing four-wave mixing
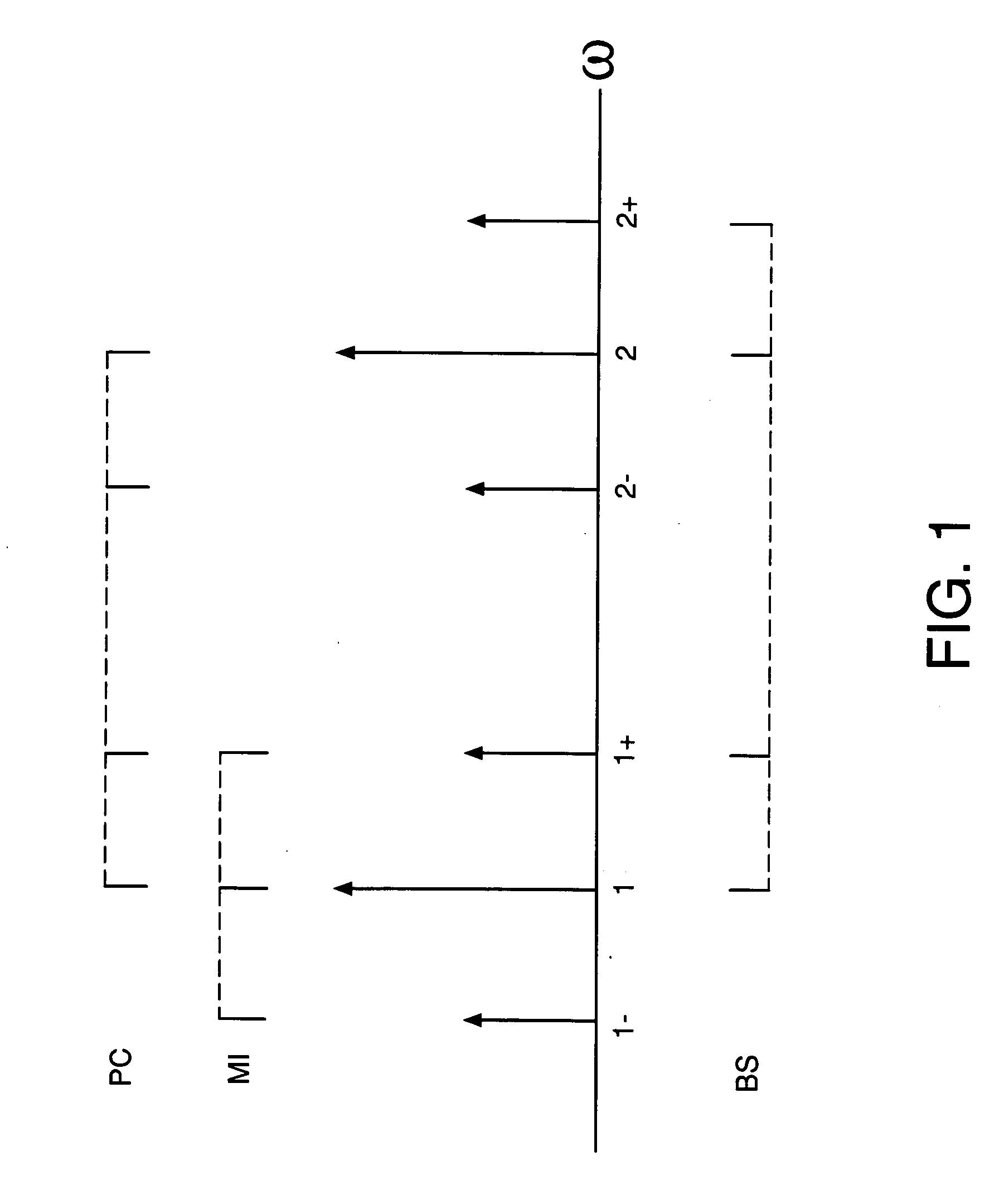
An optical buffer employing Bragg scattering (BS), in which two pump signals are combined with an input (data) signal in a four-wave mixing (FWM) medium to frequency convert the input signal into an idler signal, which is applied to a dispersive medium, in which the idler signal propagates at a speed different from that of the input signal. By selectively turning on and off a pump, e.g., at bit-level switching rates, the BS-based frequency conversion can be selectively performed on particular bits in the input signal, e.g., to generate an output signal having reordered bits. A BS-based optical buffer can (1) be tuned to achieve different amounts of delay; (2) support single-channel or multiple-channel, classical or quantal communications; (3) be implemented with co-phased pump-phase modulation to suppress stimulated Brillouin scattering, while inhibiting spectral broadening of the idler signal; and (4) provide polarization independence using standard polarization-diversity techniques.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
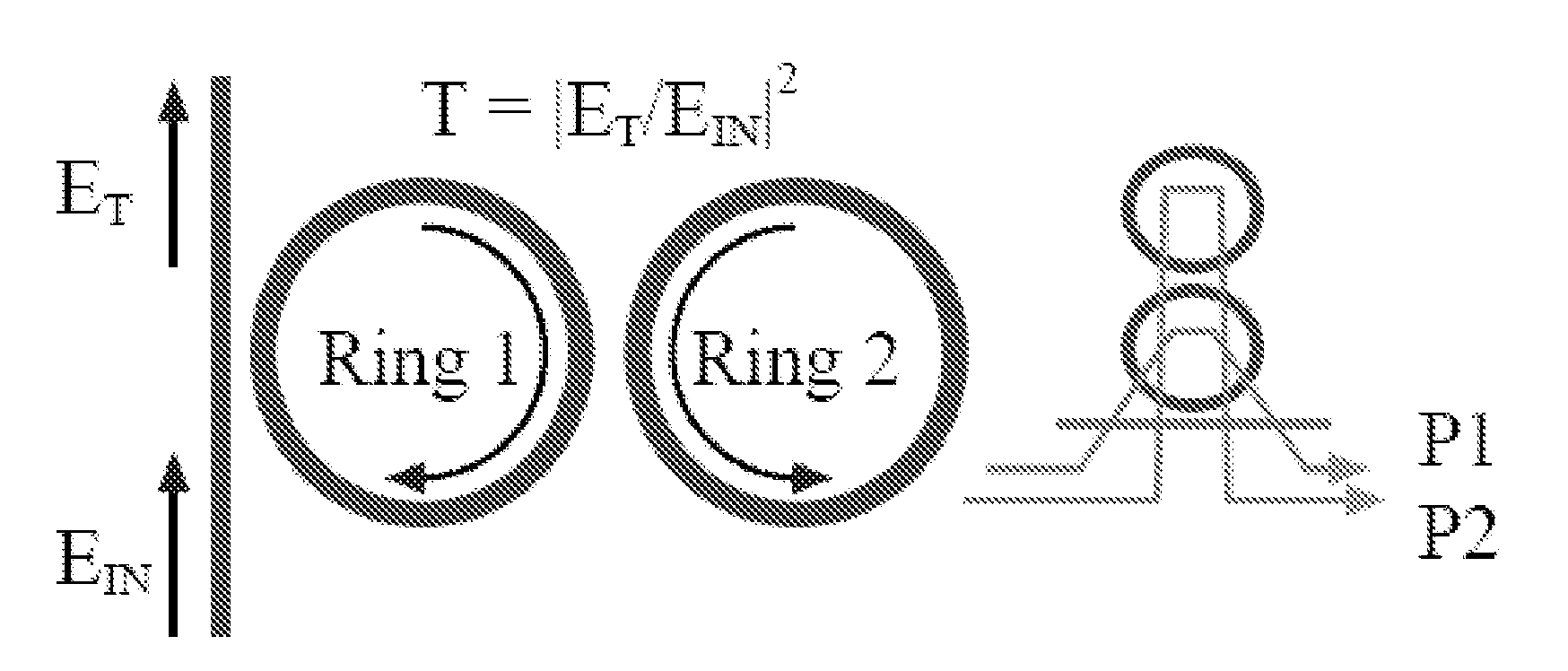
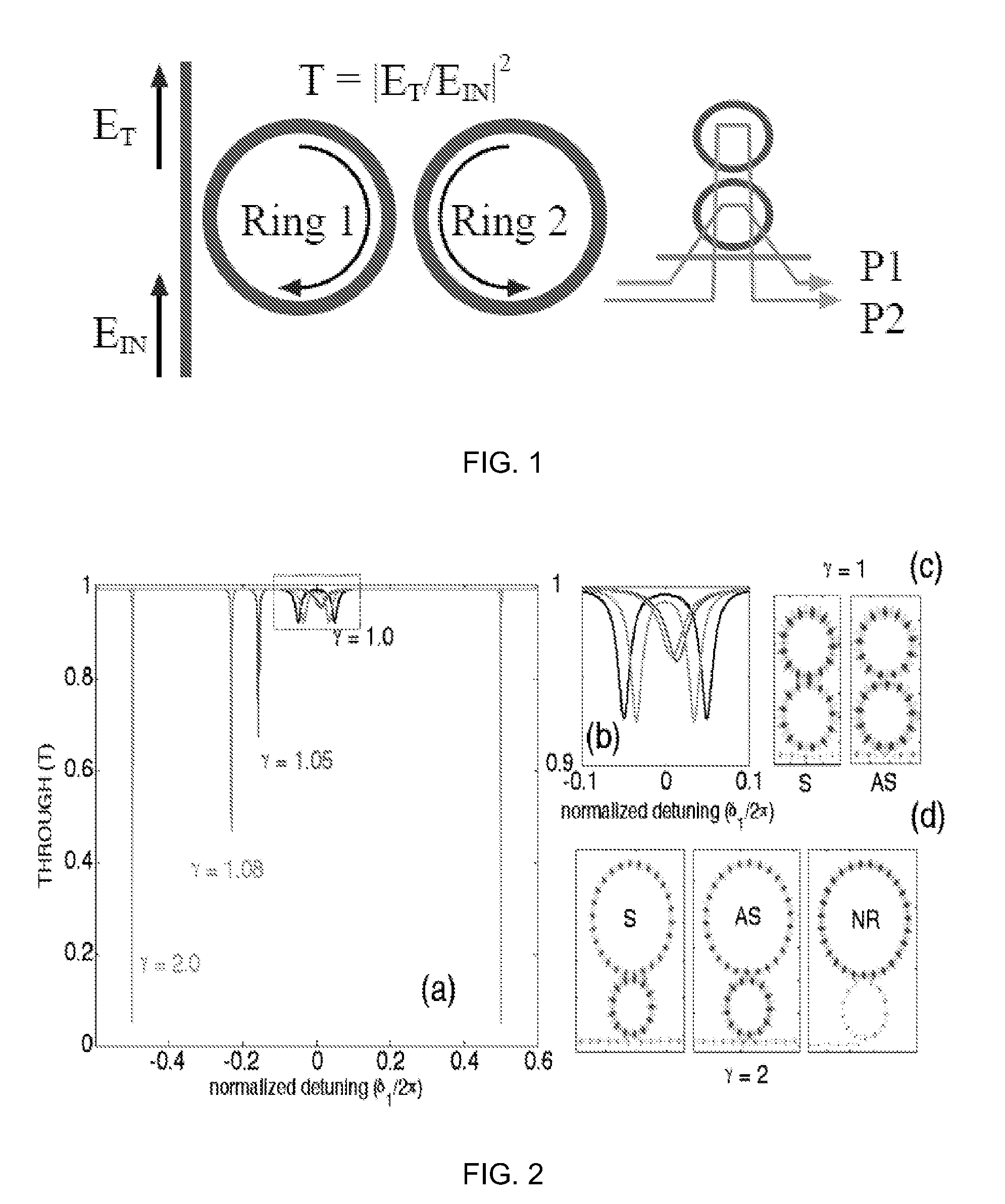
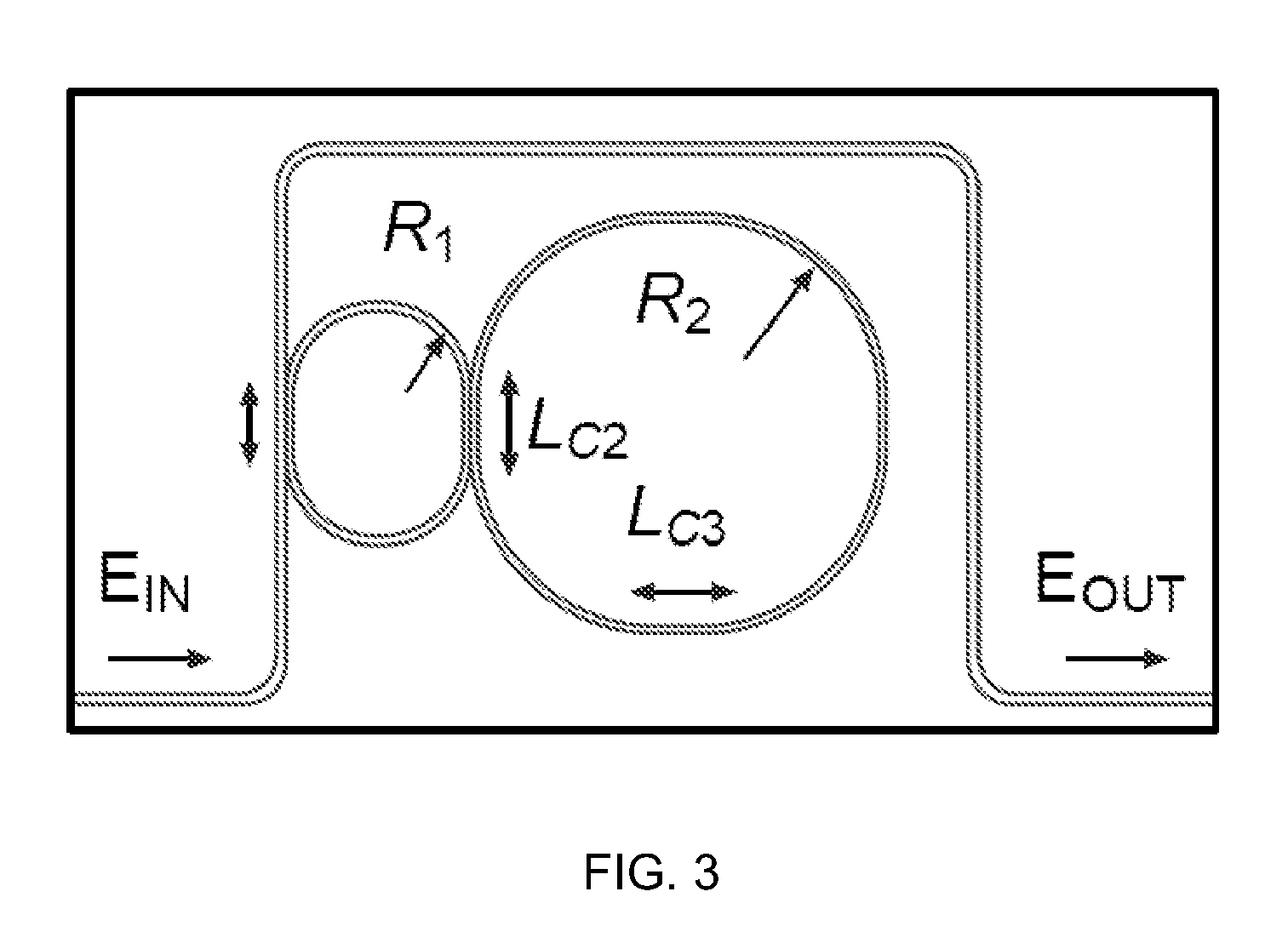
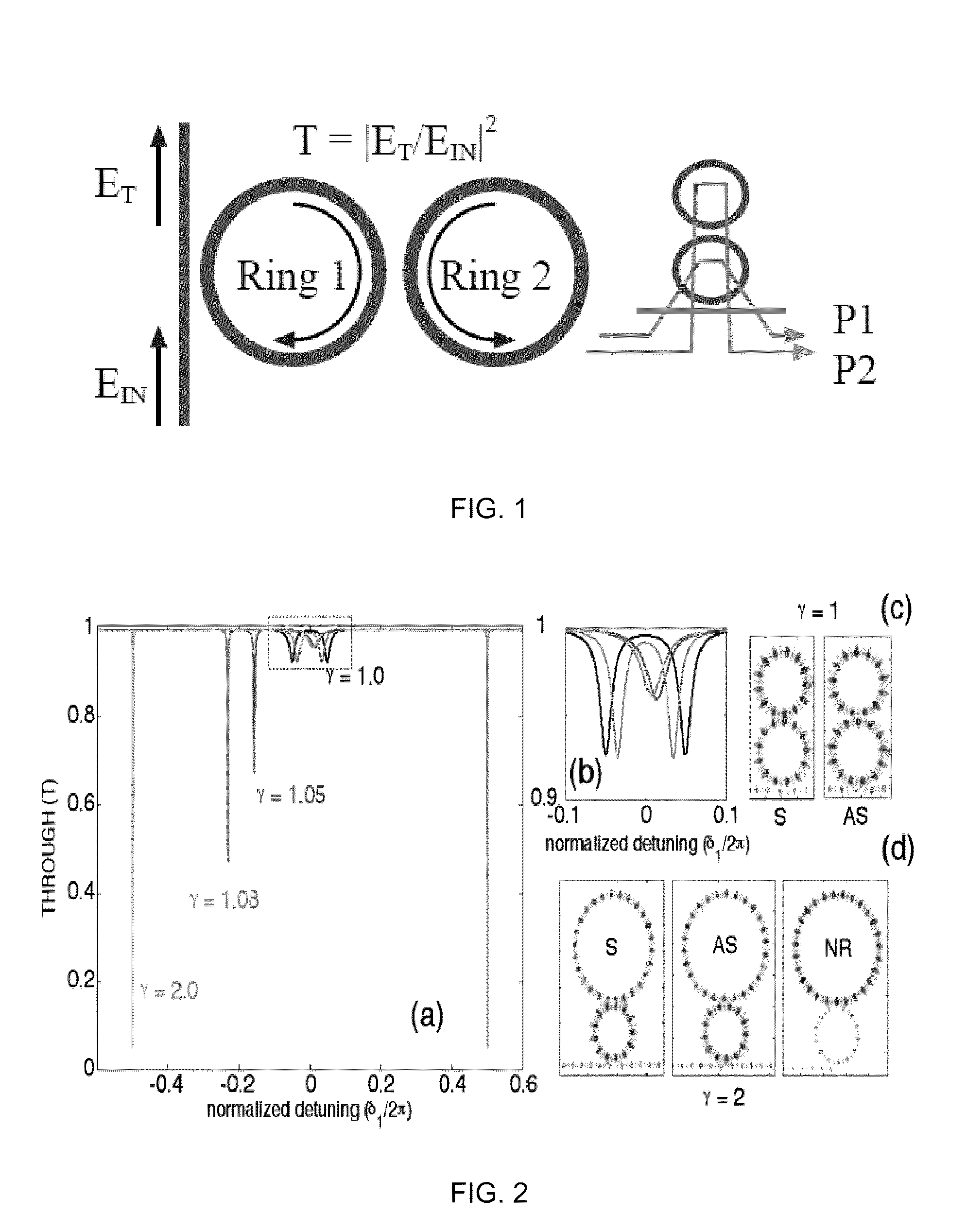
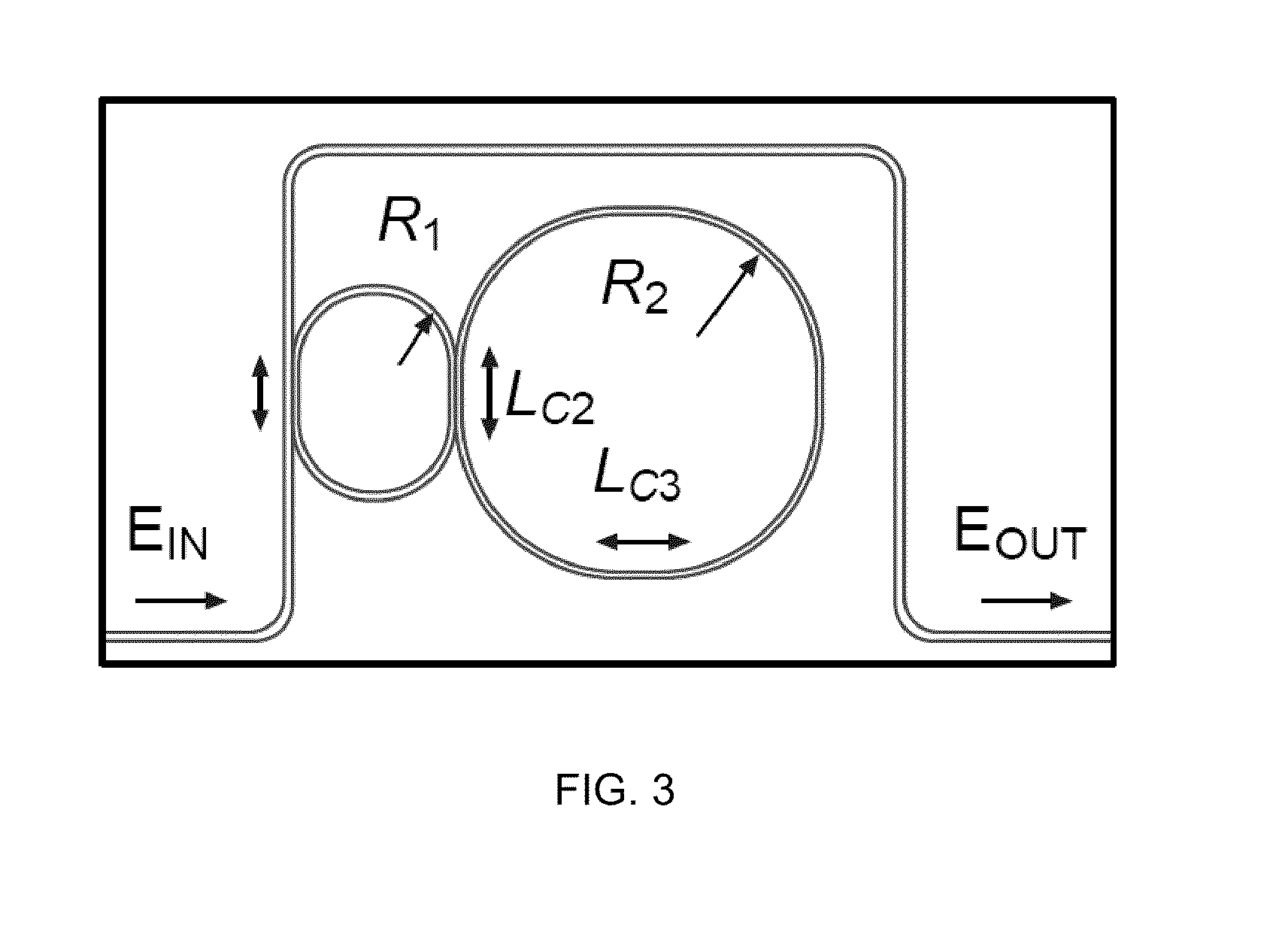
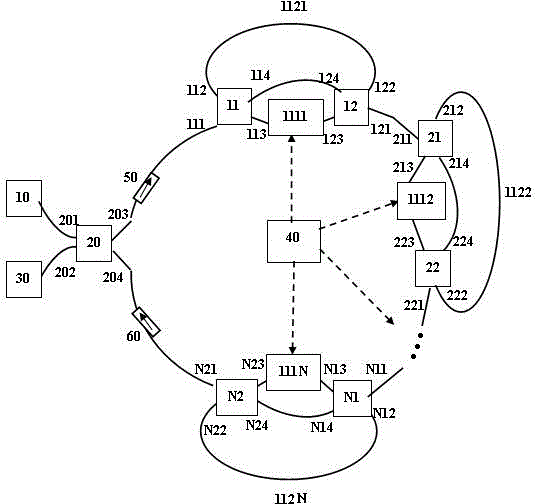
Two-ring optical buffer
A two-ring optical buffer comprising a first ring operatively connected to a waveguide and a second ring, the second ring being operatively connected to only the first ring, the second ring and the first ring having a circumferential ratio substantially equal to 2m, where m is an integer. A ratio of resonance splitting over resonance broadening may be approximately 0.6.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Sharing type optical packet switching node structure based on inside wavelength
InactiveCN101370315ALarge capacityAddress competitionMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime delaysOptical packet
The invention relates to a shared optical packet exchange node structure based on internal wavelength comprising wavelength-division demultiplexer, adjustable wavelength shifter, optic switch matrix, wavelength-division multiplex, optical fiber delay line, splitter, SOA light gate, passive coupler. Using a group of shared optical fibre delay line for solving competition of light grouping, and increasing optical buffer capacity by internal wavelength method, Solving FDL competition of shared optical cache; Each optical fibre delay line being degeneratively arranged, Each optical fibre delay line cache wavelength comprising transmission wavelength in input / output optical fiber, and also increasing proper internal wavelength to enlarge capacity of optical cache according to need, introducing extra internal wavelength to optical fibre delay line to enhance capacity of FDL optical cache; Node structure with compact appearance being simply controlled. Packet loss rate can be largely reduced for exchange node without increasing optical packet cache time delay, which effectively solves FDL competition problem of shared optical cache.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Optical delayer coupled through adopting multiple-mode interference
InactiveCN101881859AImprove working bandwidthSmall sizeCoupling light guidesResonant cavityTime delays
The invention discloses an optical delayer coupled through adopting multiple-mode interference, which adopts an all-pass filter structure; the all-pass filter structure is a structure of the sequent coupling of a plurality of micro ring resonant cavities and a bus waveguide, wherein the coupled segment between the micro ring resonant cavities and the bus waveguide is of a 2*2 multiple-mode interference coupler. Adopting the multiple-mode interference coupled structure, the invention can improve the coupling efficiency between the micro ring resonant cavities and the bus waveguide, and makes the optical delayer have wider operation bandwidth. The invention has high technical redundancy, is easy to manufacture, has small size, is suitable for dense integration, also has the characteristics of wide bandwidth and big time delay, the structural design with different splitting ratio increases the flexibility of the device application, and the delayer is suitable for being used as an optical buffer device of high-speed all-optical packet switching network in the future.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line supporting low-loss fundamental mode transmission
ActiveCN110596813AExtended propagation distanceLow Intermodal CrosstalkCoupling light guidesScattering lossEngineering
The invention discloses a silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line supporting low-loss fundamental mode transmission. A curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide is placed at the centers of curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguides; and two curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguides are annularly and helically arranged,an inner end of one curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguide is connected with one end of the curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide through a bending waveguide, the other end of the curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide is connected with the inner end of the other curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguidethrough another bending waveguide, and the entire silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line is arranged in a central symmetry manner. The silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line disclosed by the invention can effectively avoid mode mismatch loss and inter-mode crosstalk caused by the abrupt curvature change of the traditional structure, and can reduce the scattering loss introduced by a waveguide sidewall, thereby obtaining low-loss fundamental mode transmission in the silicon-based multimode helical waveguide, and the silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line has the advantages of low loss and compact structure and the like, and can be applied to optical buffers, optical delay lines and other systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
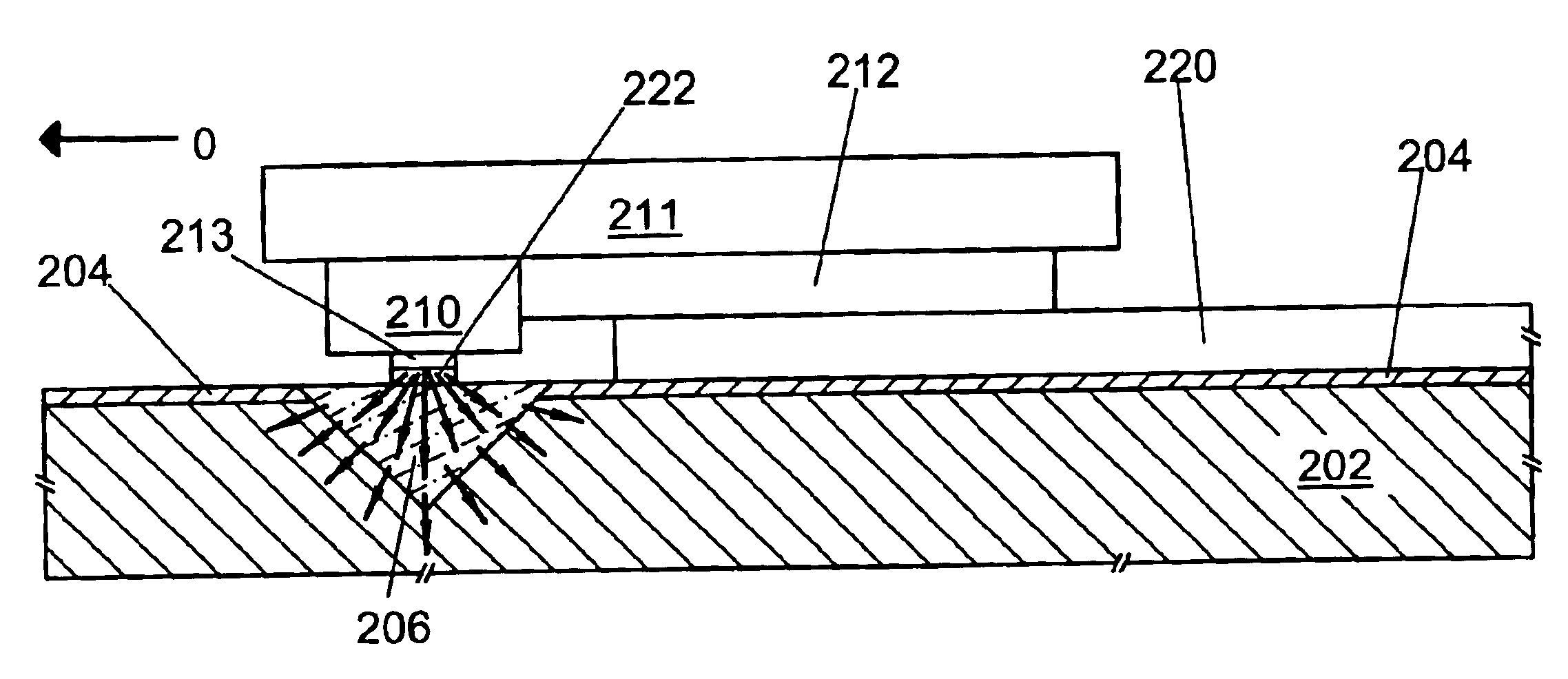
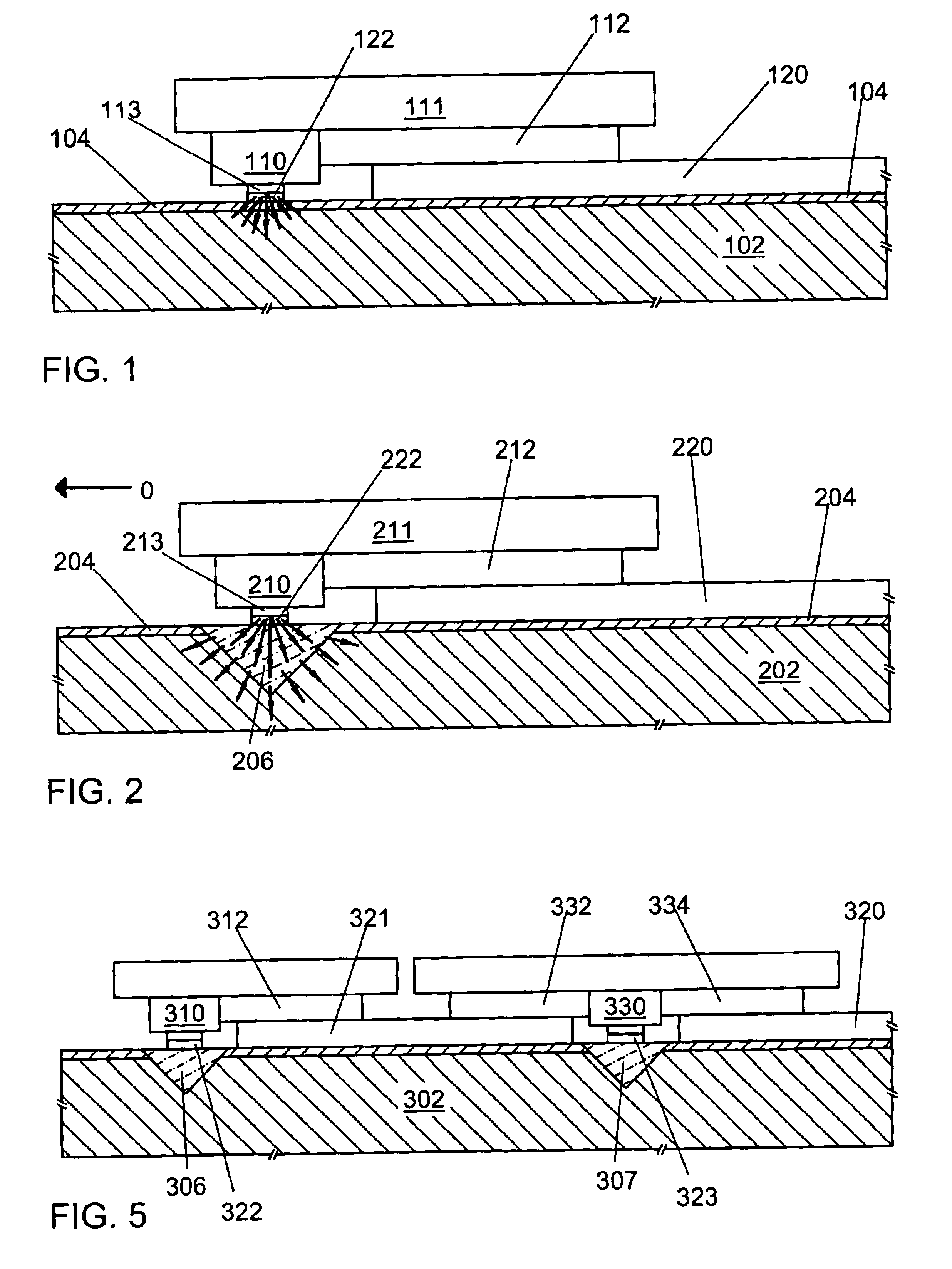
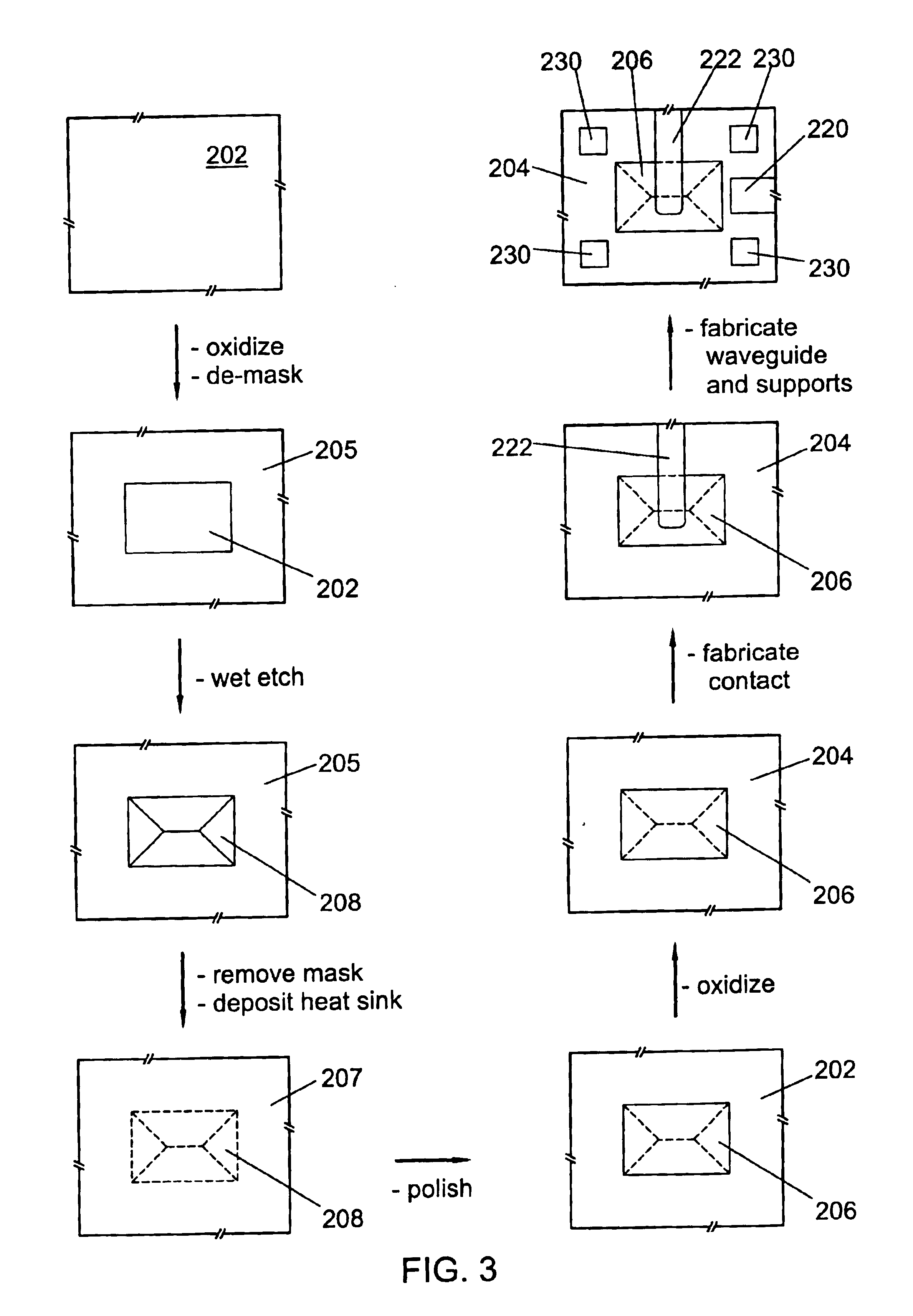
Heat sink for a planar waveguide substrate
InactiveUS6847748B2Improve thermal conductivityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexThermal contact
A recessed area formed on a substrate surface is filled with heat sink material to form a heat sink. The heat sink material has thermal conductivity greater than that of the substrate. The heat sink may have a substantially flat surface substantially flush with the substrate surface. The substrate may further include: a planar optical waveguide formed thereon positioned for optical coupling with an optical device mounted on the substrate in thermal contact with the heat sink; and / or an electrical contact layer formed thereon positioned for establishing electrical continuity with an optical device mounted on the substrate in thermal contact with the heat sink. The electrical contact may also provide thermal contact between the device and heat sink. The substrate may further include a low-index optical buffer layer formed on its surface. Materials for the substrate, buffer layer, and heat sink may include silicon, silica, and diamond, respectively.
Owner:HOYA USA
Panoramic reconstruction of temporal imaging
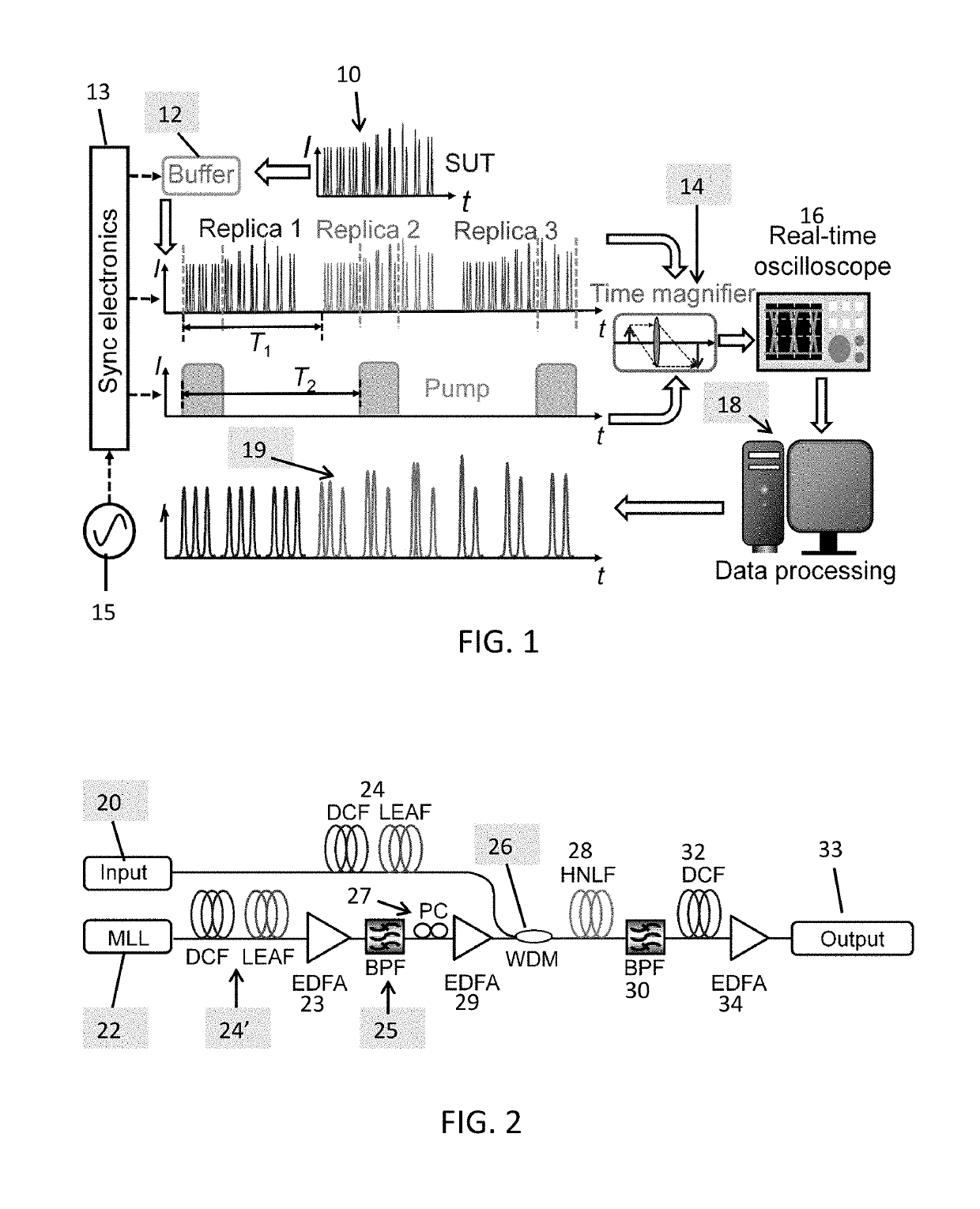
ActiveUS20190120696A1Sacrificing the temporal resolutionEnhancing TBWPOptical measurementsLaser detailsControl electronicsSynchronous control
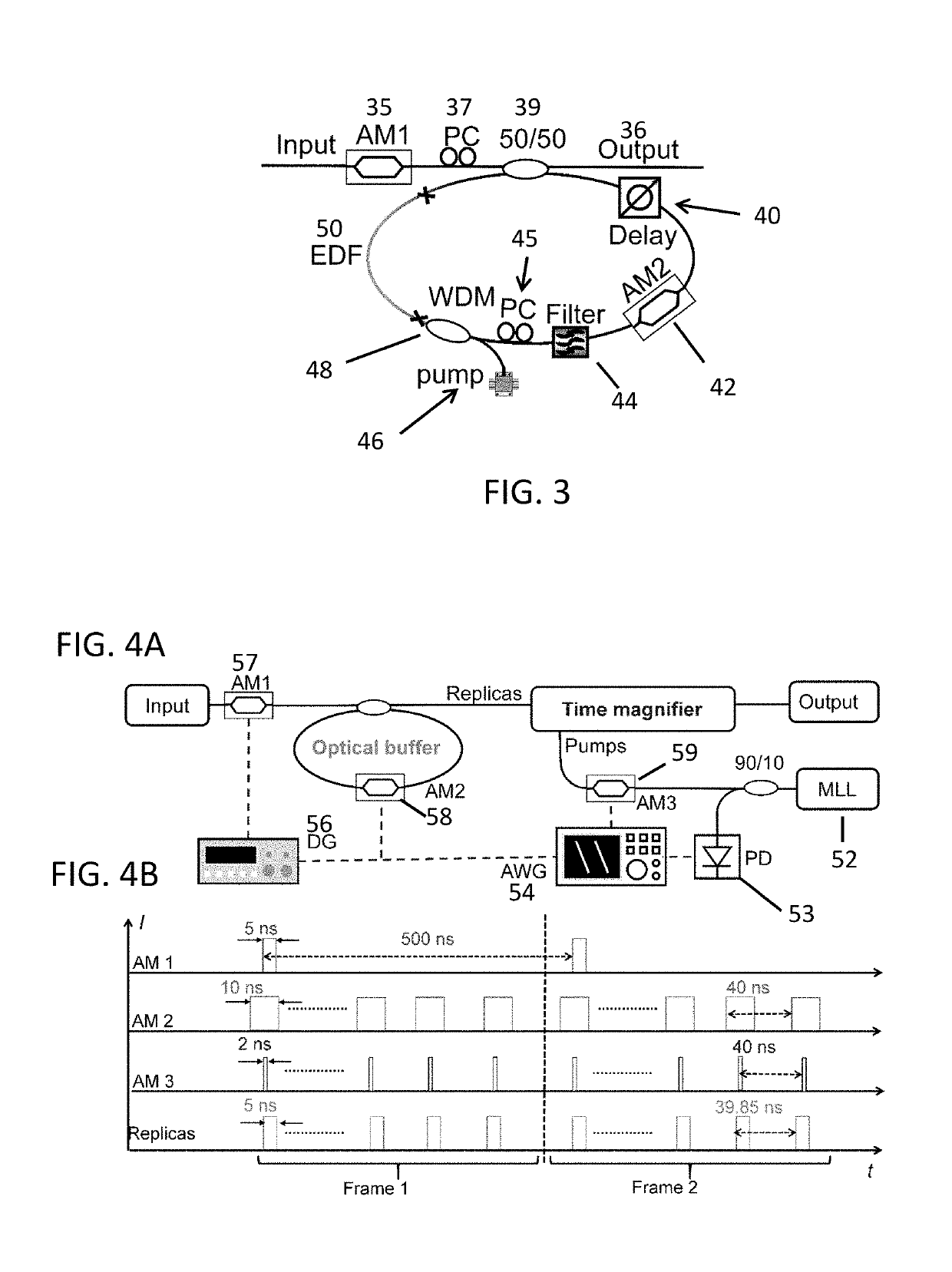
The panoramic-reconstruction temporal imaging (PARTI) system is a single-shot optical waveform measurement apparatus that achieves scalable record length and sub-picosecond resolution simultaneously for ultrafast non-repetitive waveform characterization, in analogy with the wisdom of stitching multiple mosaic images to achieve larger-field-of-view in the spatial domain. It consists of a high-fidelity optical buffer, a low-aberration time magnifier and synchronization-control electronics. For specific measurement circumstances, the PARTI system can also be carried out based on a passive optical buffer, which reduces the system complexity. The PARTI system is configured for real-time single-shot characterization of non-repetitive optical dynamic waveform that evolves over a time scale much larger than that of its ultrafast temporal details, i.e., optical dynamics with large time-bandwidth product.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
A full optical buffer based on proton crystal optical fiber
InactiveCN101262709AReduce pulse powerStrong nonlinear effectMultiplex system selection arrangementsCladded optical fibreProtonOptical power
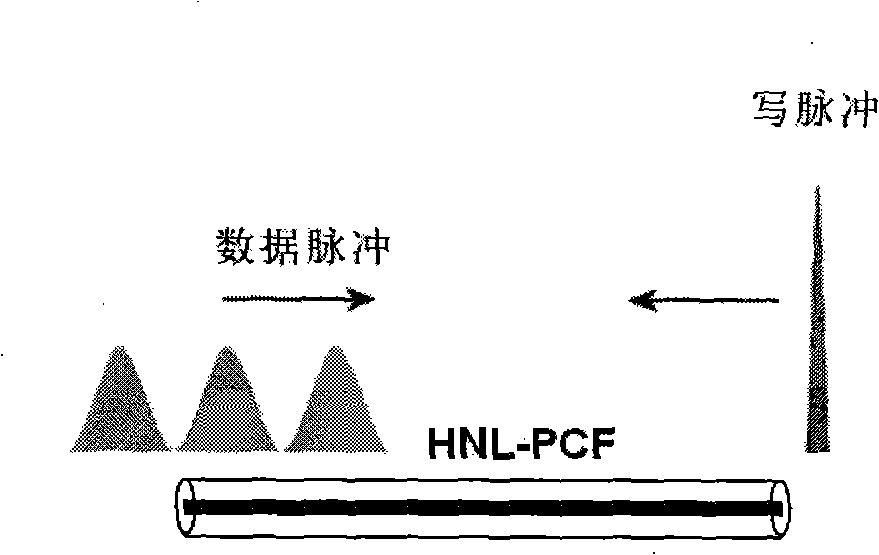
The invention relates to an all-optical buffer based on a photonic crystal fiber and pertains to the all-optical buffer devices in an optical network, which solves the problems that the existing optical buffers have high pump power and optical circuits are easy to be damaged. The invention comprises a data caching optical circuit which is composed of a highly-nonlinear photonic crystal fiber, etc., and a read and write control optical circuit. The invention is provided with a Mach-Zehnder switch at an input terminal and a Mach-Zehnder switch at an output terminal between which the data caching optical circuit and a direct data channel composed of the optical fiber pass through in parallel; the Mach-Zehnder switch at an input terminal and the Mach-Zehnder switch at an output terminal are controlled by a buffer on-off controller so as to select optical signals to pass through the direct data channel or the data caching optical circuit. The all-optical buffer of the invention can realize the continuous and controllable cache time of the optical signal under rather low pump optical power and has simple structure, low cost, a short signal storage medium, low energy consumption of the system as well as continuous and adjustable cache time, and has universality to the photonic crystal fiber of a small mode field.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
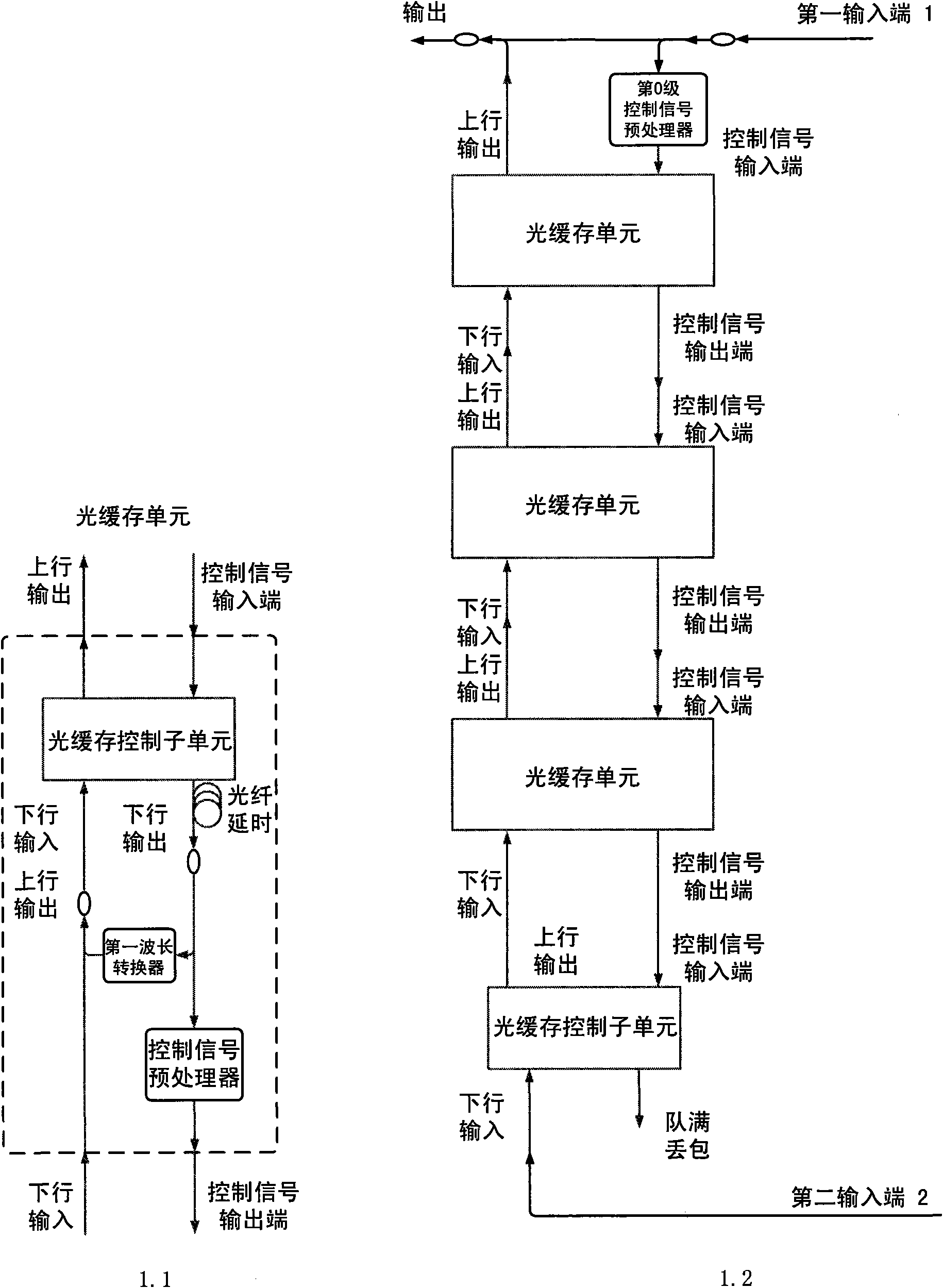
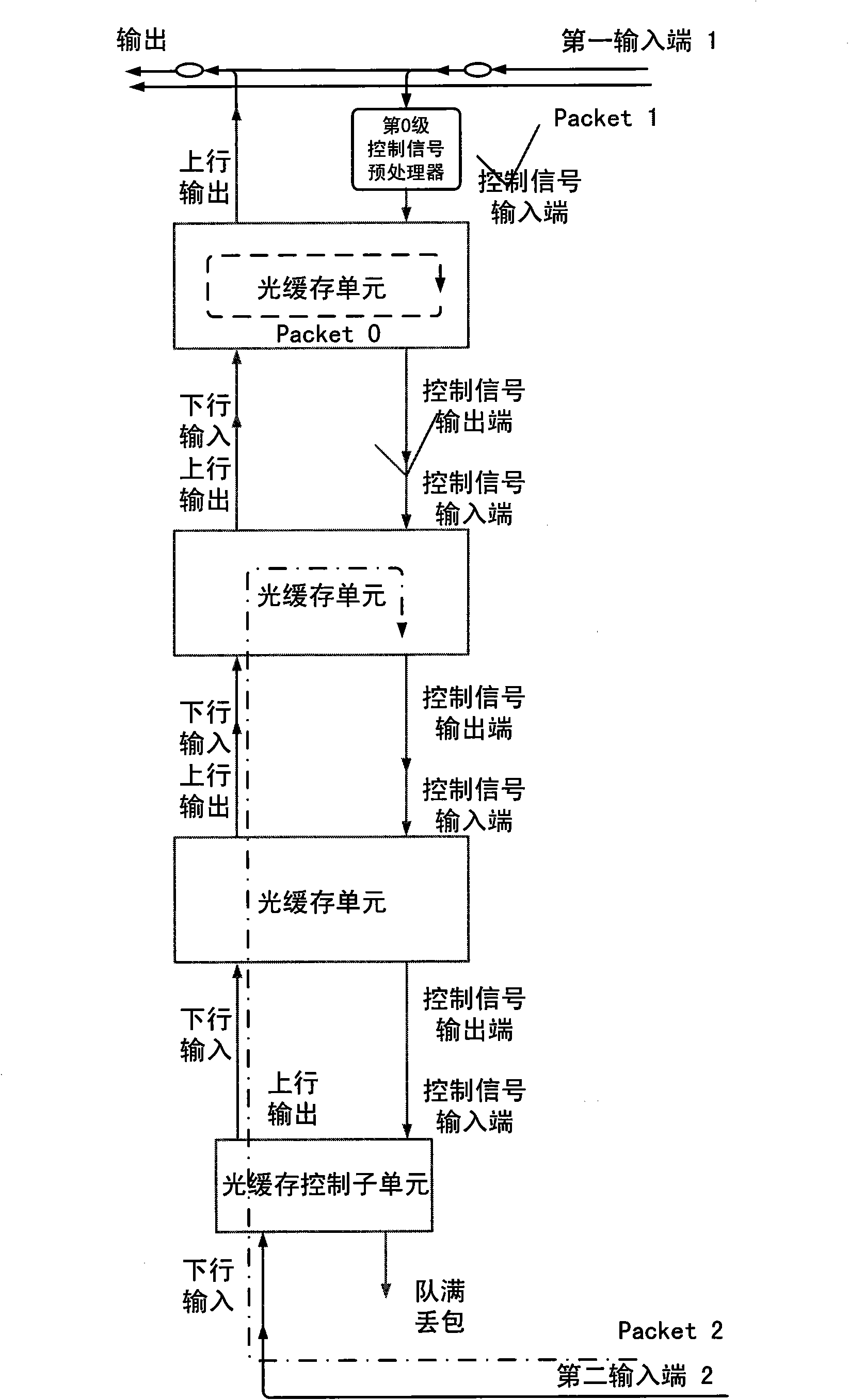
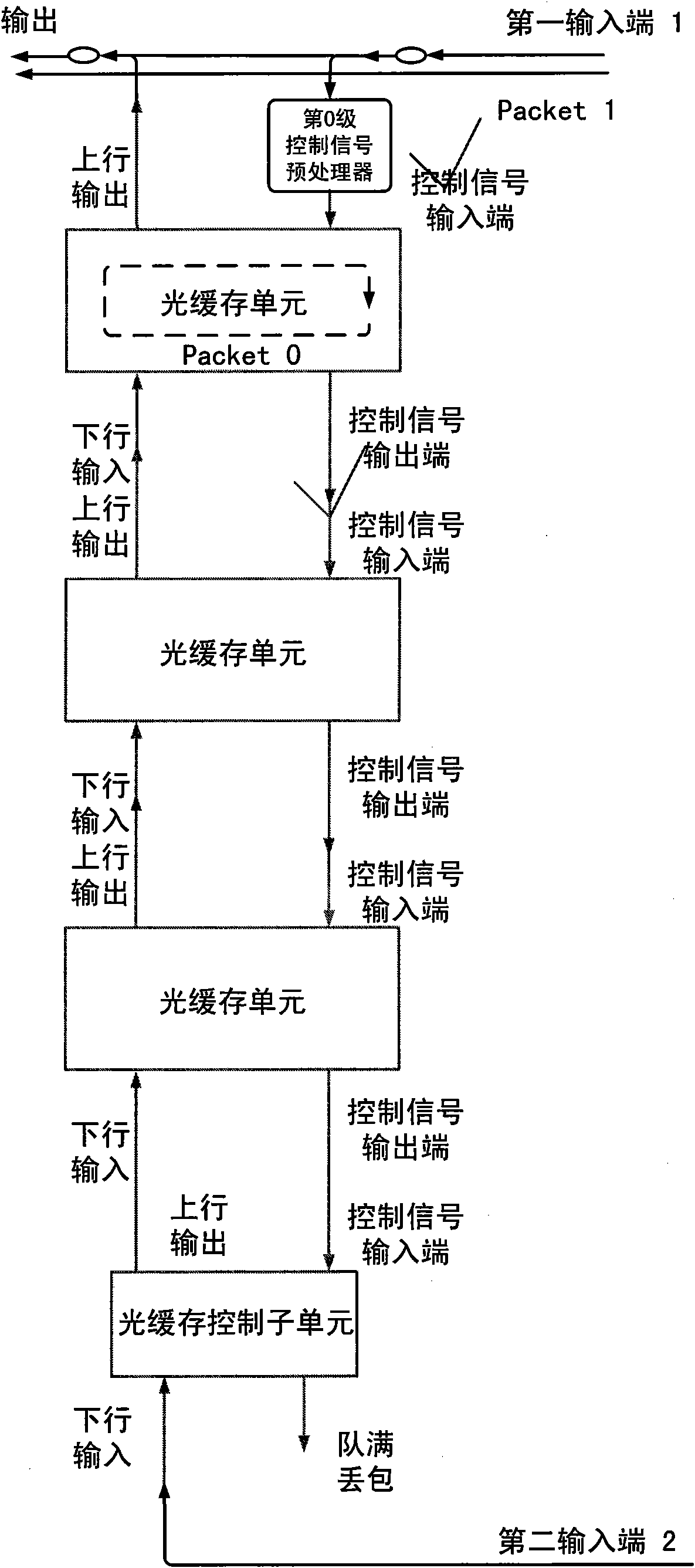
Queue-type all-optical buffer
InactiveCN101610435ADecide how long to storeDecision depthMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsControl signalOptical packet
The invention relates to a queue-type all-optical buffer, which belongs to the field of all-optical packet switching. The queue-type all-optical buffer is characterized in that the queue-type all-optical buffer is formed by cascade connection of a plurality of optical buffer units, and uplink output ends of each stage of the optical buffer units are sequentially connected with downlink input ends of the last stage, thereby constituting an uplink channel. Data packets which are input to each stage of the optical buffer units are determined to carry out the uplink output or the buffer at the stage by a control signal input end. A control signal output end of any i stage of the optical buffer units is connected with the control signal input end of the i+1 stage of the optical buffer units, thereby avoiding the situation that the i+1 stage of the optical buffer units output data to the i stage of the optical buffer units when the i stage of the optical buffer units have the buffer data packets. When two data packets simultaneously achieve the buffer, the data packet with high priority is directly output and the data packet with low priority is stored in the buffer. The queue-type all-optical buffer has the queue characteristics of first-in first-out and last-in last-out, can simultaneously process two data packets and has the advantages of easy expansion of storage capacity, no need of external control signals and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
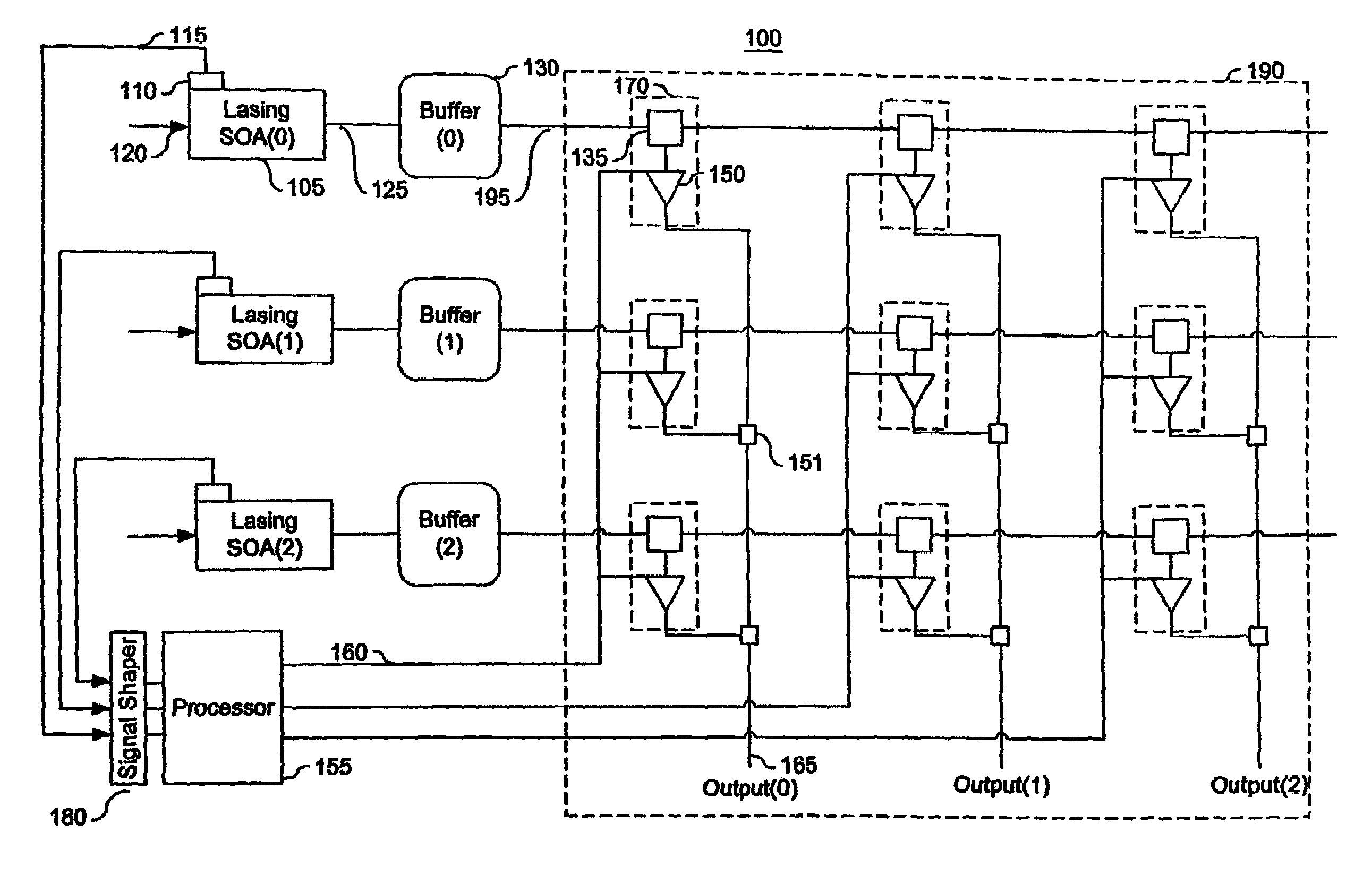
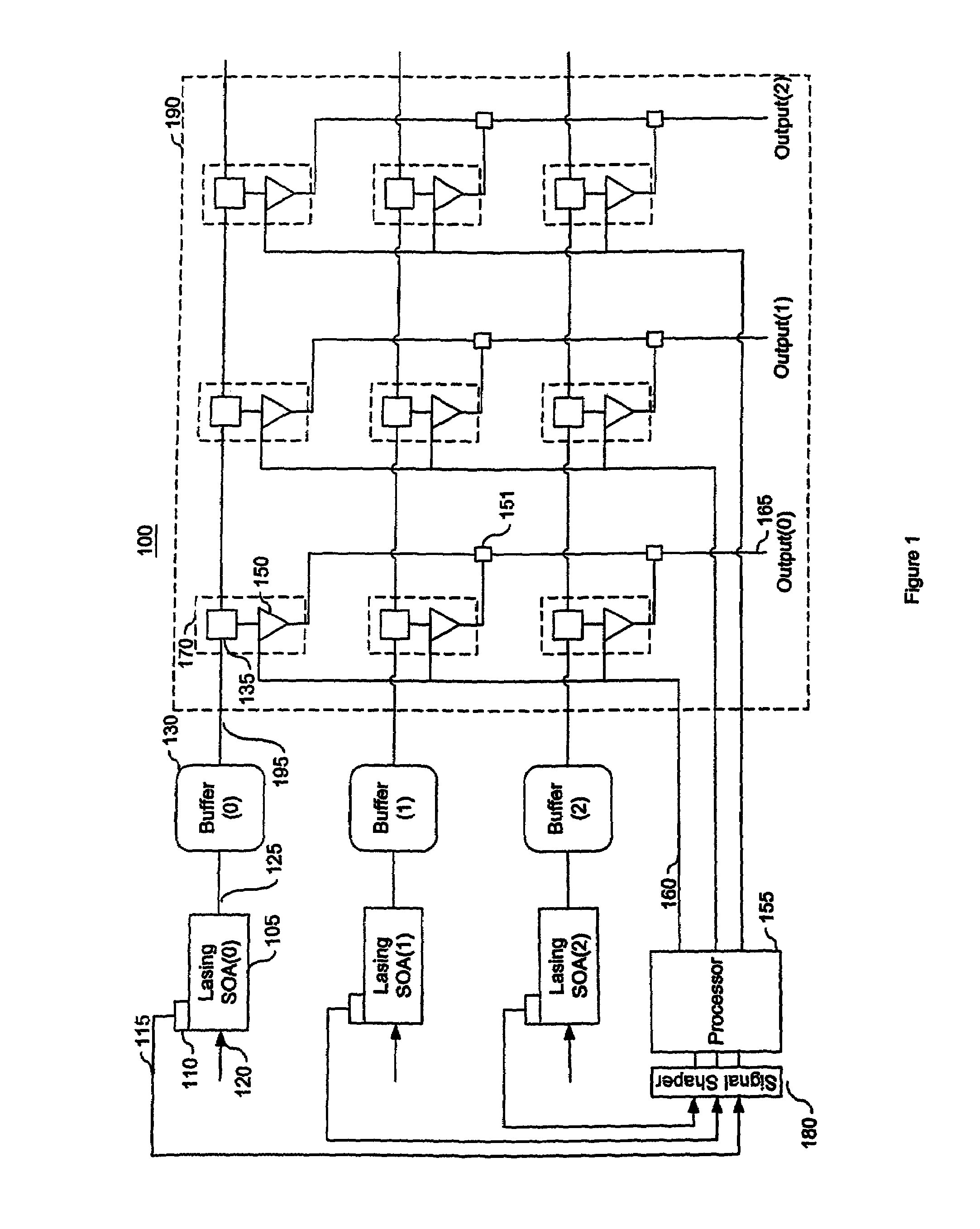
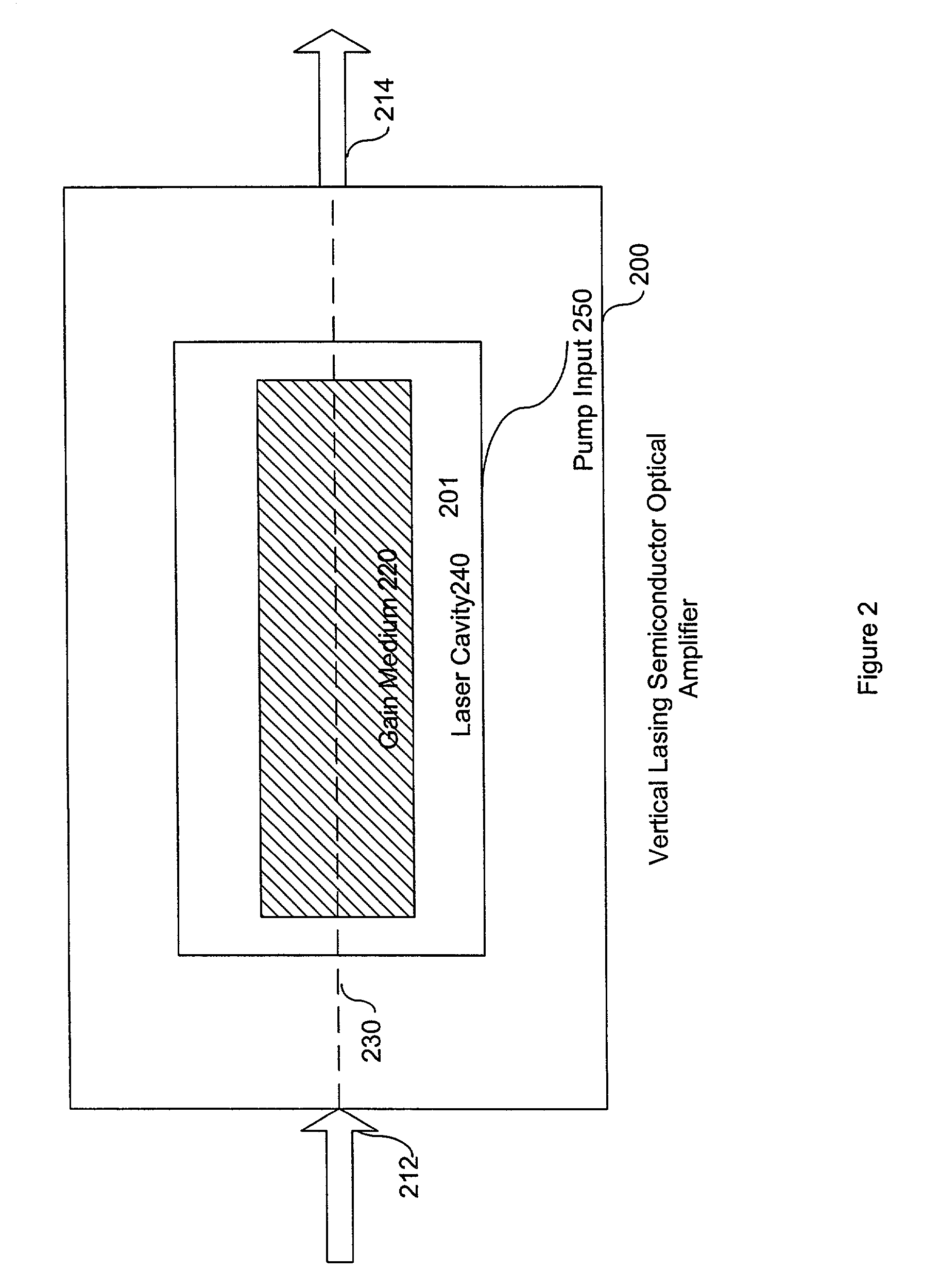
Optical crossbar using lasing semiconductor optical amplifiers
InactiveUS7046434B1Increase speedReduce in quantityMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsCrossbar switchDetector circuits
An optical crossbar switch is described that minimizes the number of electrical components and optimizes the conversion between optical and electrical signals. Utilizing various characteristics of lasing semiconductor optical amplifiers, the optical crossbar switch provides optical components in place of traditionally used electrical components. For example, an optical buffer is described that delays an optical signal a sufficient amount of time for a path to be created for the optical signal through the optical crossbar. Additionally, a monitor / detector circuit utilizes a ballast laser signal emitted from a lasing SOA during amplification of an optical signal in order to convert optical routing information to an electrical equivalent. As a result of the multiple uses of lasing semiconductor optical amplifiers, the bandwidth of the described optical crossbar switch is greater than traditional optical crossbar switches currently in use.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Two-ring optical buffer
A two-ring optical buffer comprising a first ring operatively connected to a waveguide and a second ring, the second ring being operatively connected to only the first ring, the second ring and the first ring having a circumferential ratio substantially equal to 2m, where m is an integer. A ratio of resonance splitting over resonance broadening may be approximately 0.6.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Adjustable-delay optical buffer based on ring-shaped resonant cavity
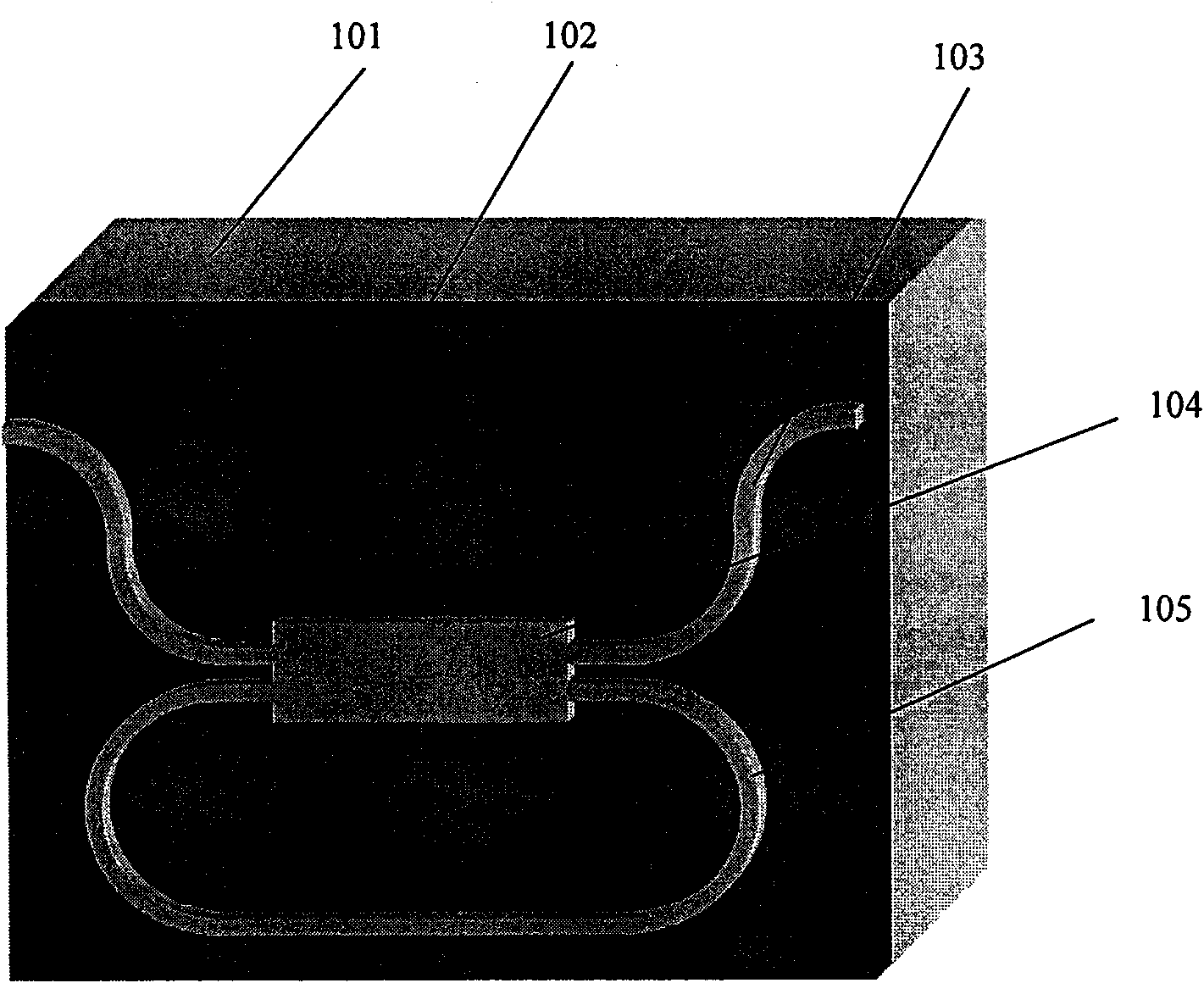
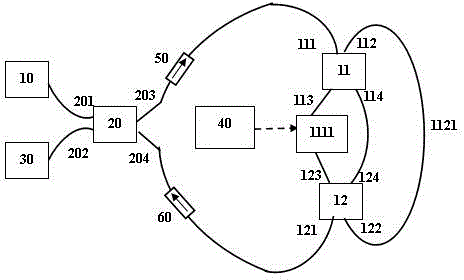
InactiveCN104393921AFlexible handlingAvoid congestionCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionResonant cavityOptical isolator
The invention discloses an adjustable-delay optical buffer based on a ring-shaped resonant cavity, wherein the connection of each part is as follows: a first port of an optical coupler (20) is connected with a to-be-buffered optical signal (10), a third port of the optical coupler (20) is connected with buffer unit input (111) of a first ring-shaped resonant cavity buffer unit by an optical isolator (50) to form an optical signal input part; a second port of the optical coupler (20) is connected with an optical oscilloscope (30), a fourth port of the optical coupler (20) is connected with output of an optical isolator (60) to form an optical signal output part; output (121, 221, ..., N21) of the first to the N-th ring-shaped resonant cavity buffer units are respectively connected with input (211, 311, ..., N11) of the second to the N-th ring-shaped resonant cavity buffer units and the input of the second optical isolator (60) to form an optical signal buffer part; and a bit generator (40) is used for controlling a first to a N-th optical phase modulators (1111, 1112, ..., 111N) to form an optical signal delay regulating part.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Optical memory and logic using cross-switches
InactiveUS6963677B1Digital storageCoupling light guidesTotal internal reflectionRandom access memory
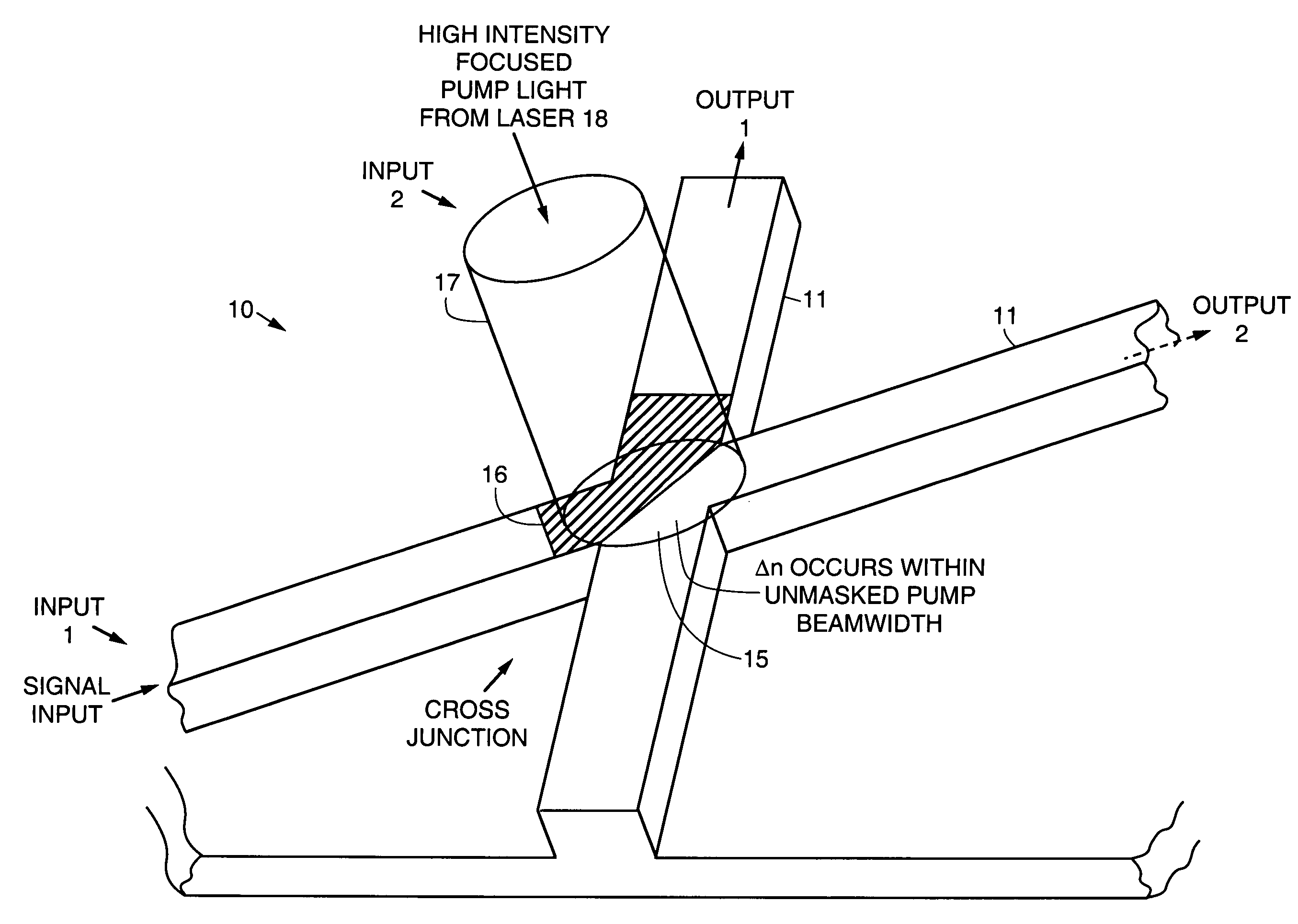
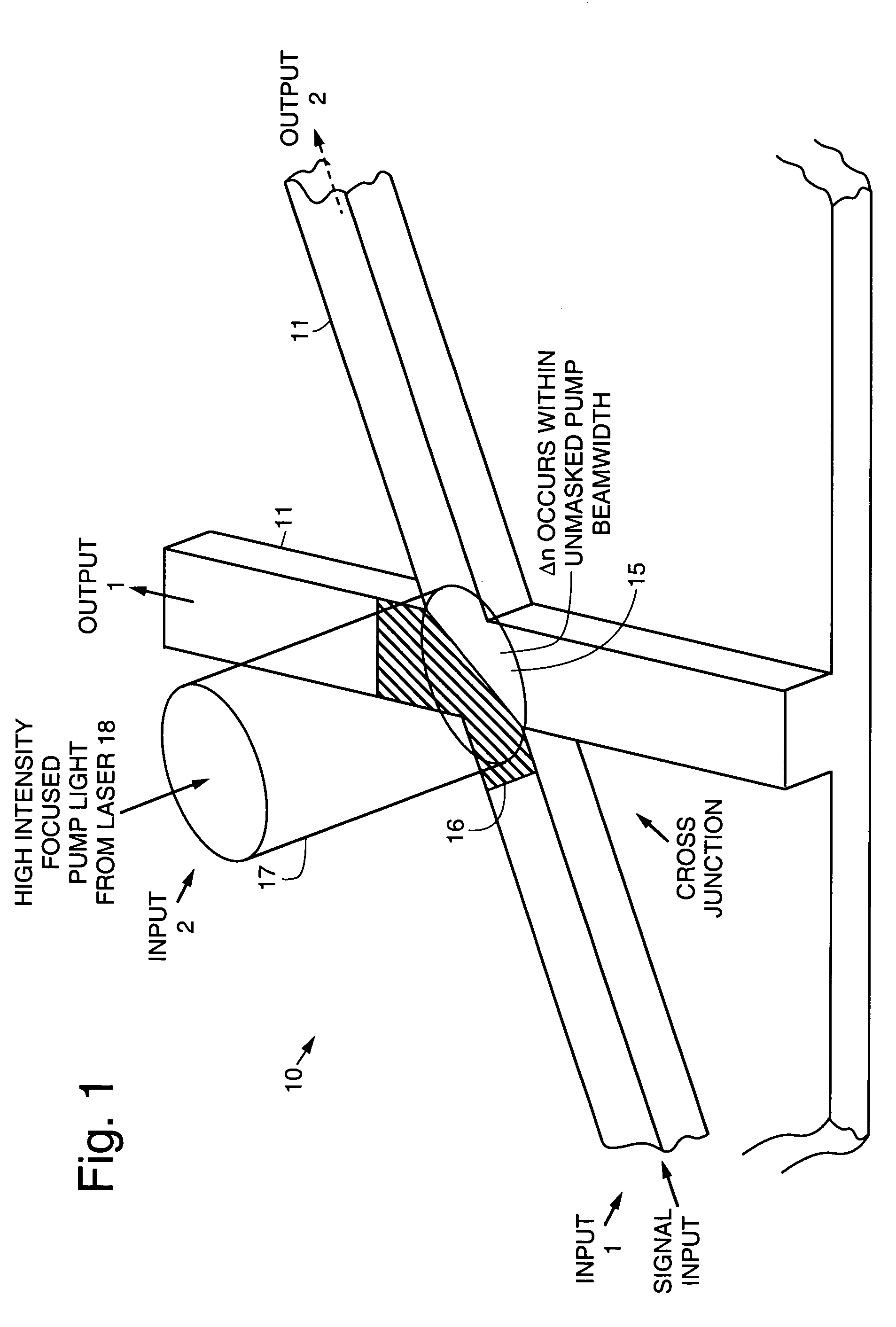
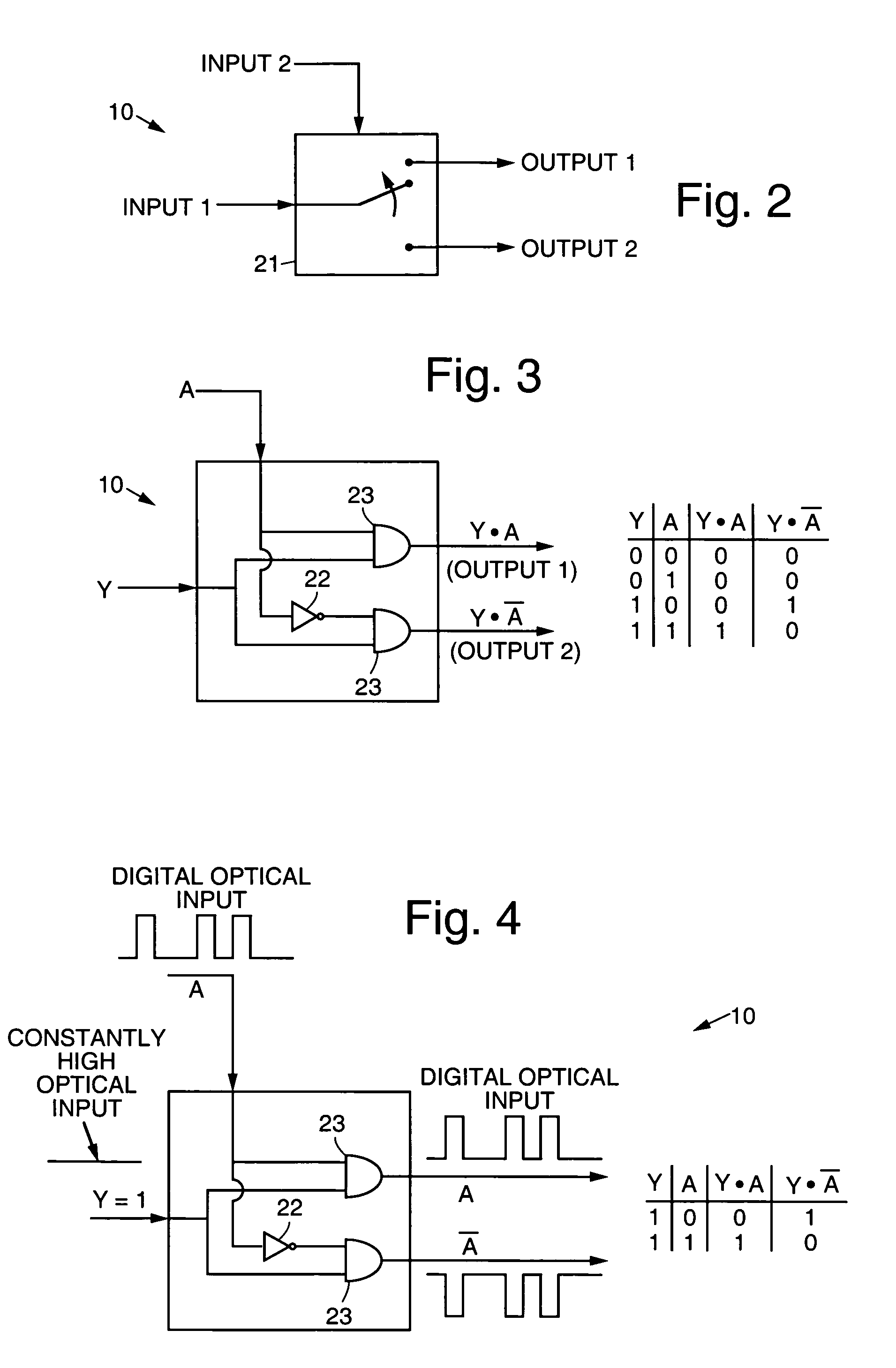
An all-optical, asynchronous binary storage cell implemented by optically induced total internal reflection cross-junction waveguide switches. The term “all-optical” refers to directing of optical data signals as a result of optical control signal inputs without the need for conversion between optical and electrical domains. The binary cell is a building block for a programmable all-optical random access memory (AORAM) device. The AORAM device enables circuits and networks that require optical buffers.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Optical buffer with adjustable delay time and output wavelength
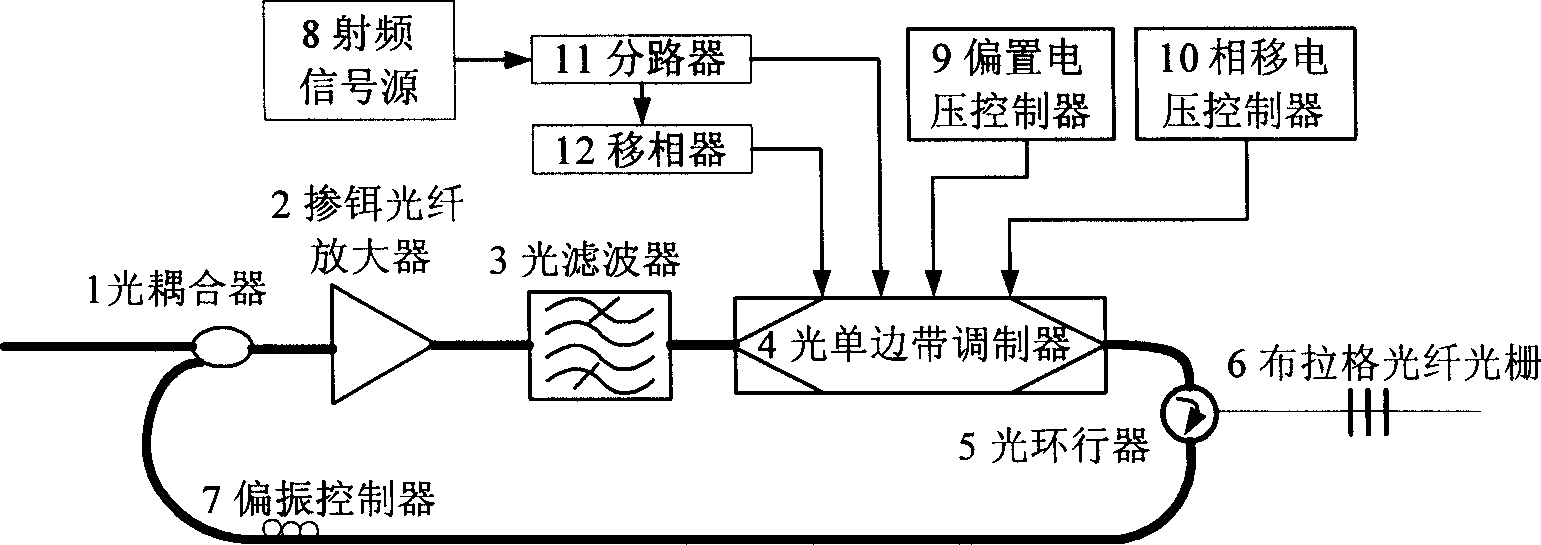
InactiveCN1866809AMeet performance requirementsGood signal to noise ratioMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingErbium doping
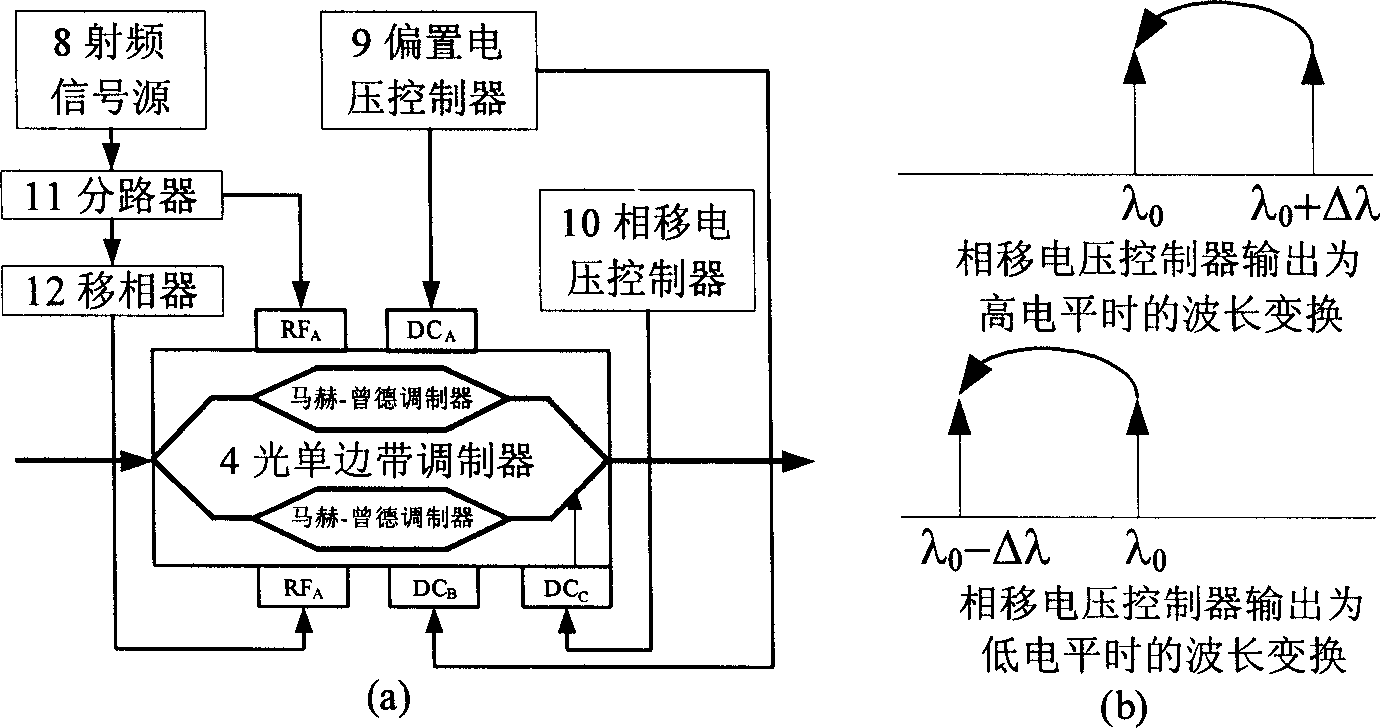
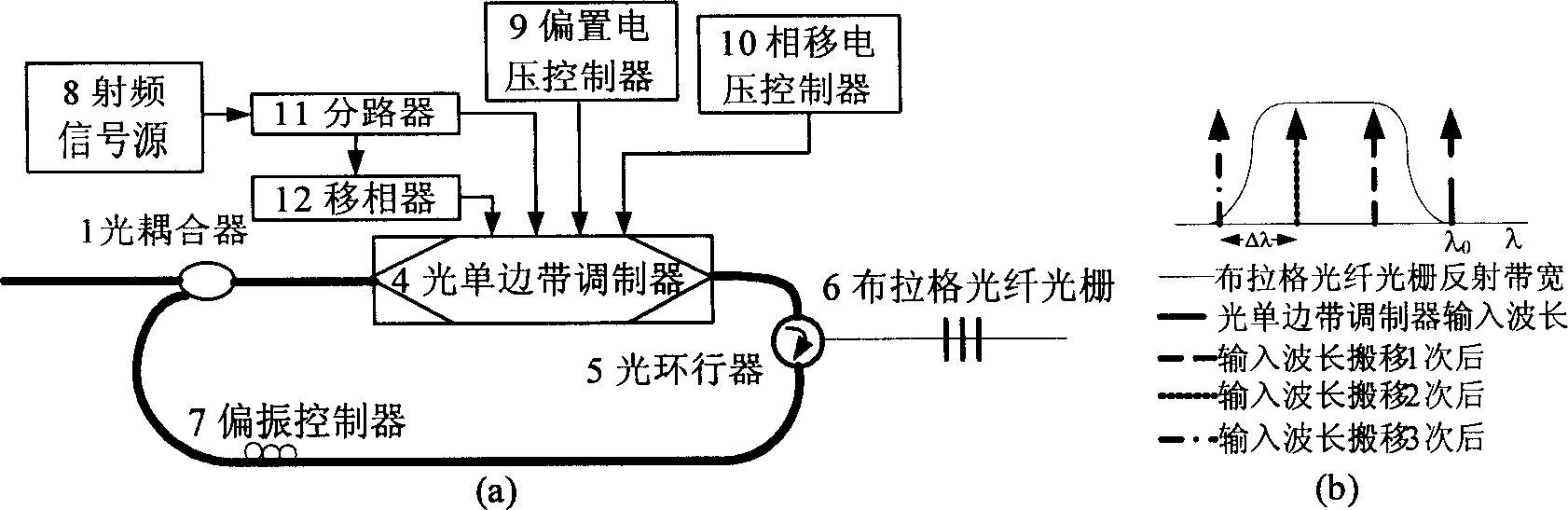
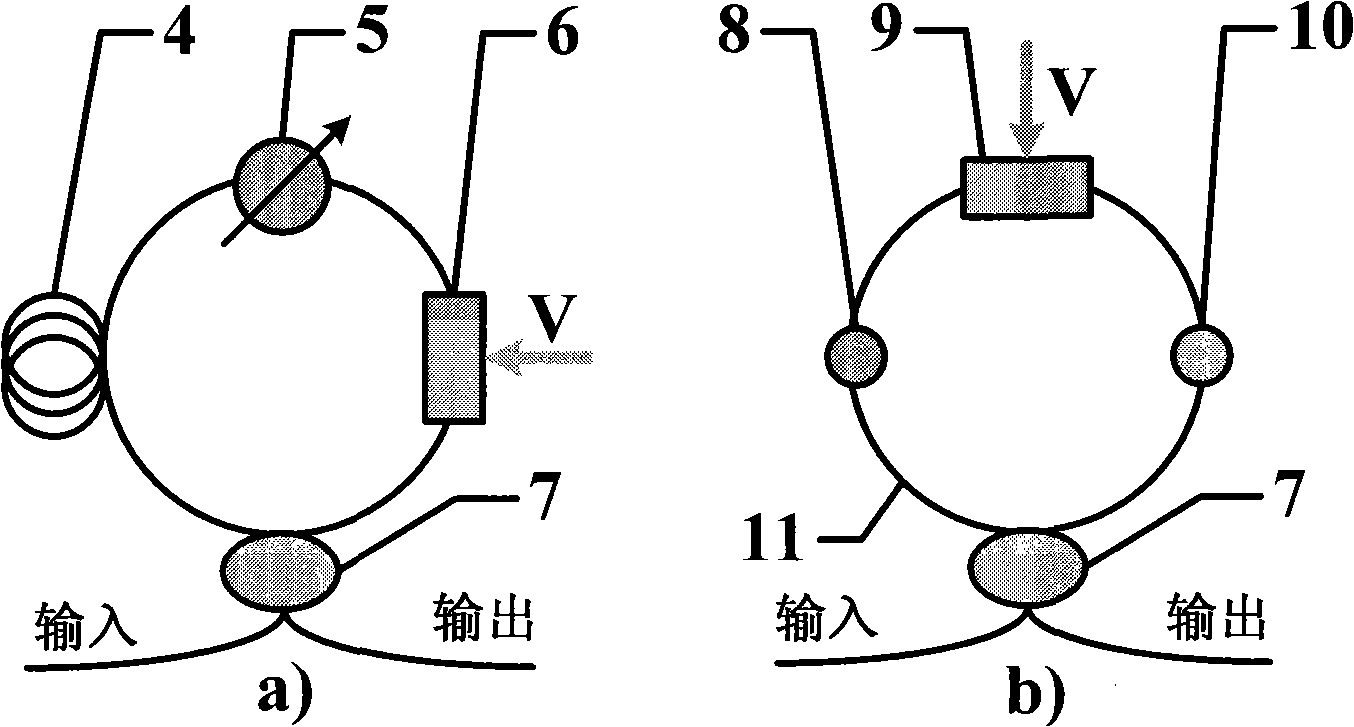
The invention discloses a delay time and export wavelengh adjustable optical buffer memory, which is characterized by the following: one of two input of the 2 X1 optical coupler is input port of optical buffer memory which connect outside; another port connects polarization controller; output of 2X1 optical coupler connects erbium-doped fiber amplifier; output of erbium-doped fiber amplifier connects input of optical electric filter; the output of optical electric filter links up optical single sideband demodulator; the radiofrequency signal source, bias voltage controller, phase voltage controller connect to control port of optical single selvage modulator; the output of optical single selvage modulator connects input of circulator; the output of circulator links up Bragg's fibre-optical pattern; the loopback port of circulator connects polarization controller. The invention adjusts the dalay time and export wavelengh, which reduces the power damage.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fast dynamic configurable optical grouping caching device in full optical network
InactiveCN101344614AFunction increaseReduce physical sizeWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical packetFiber ring
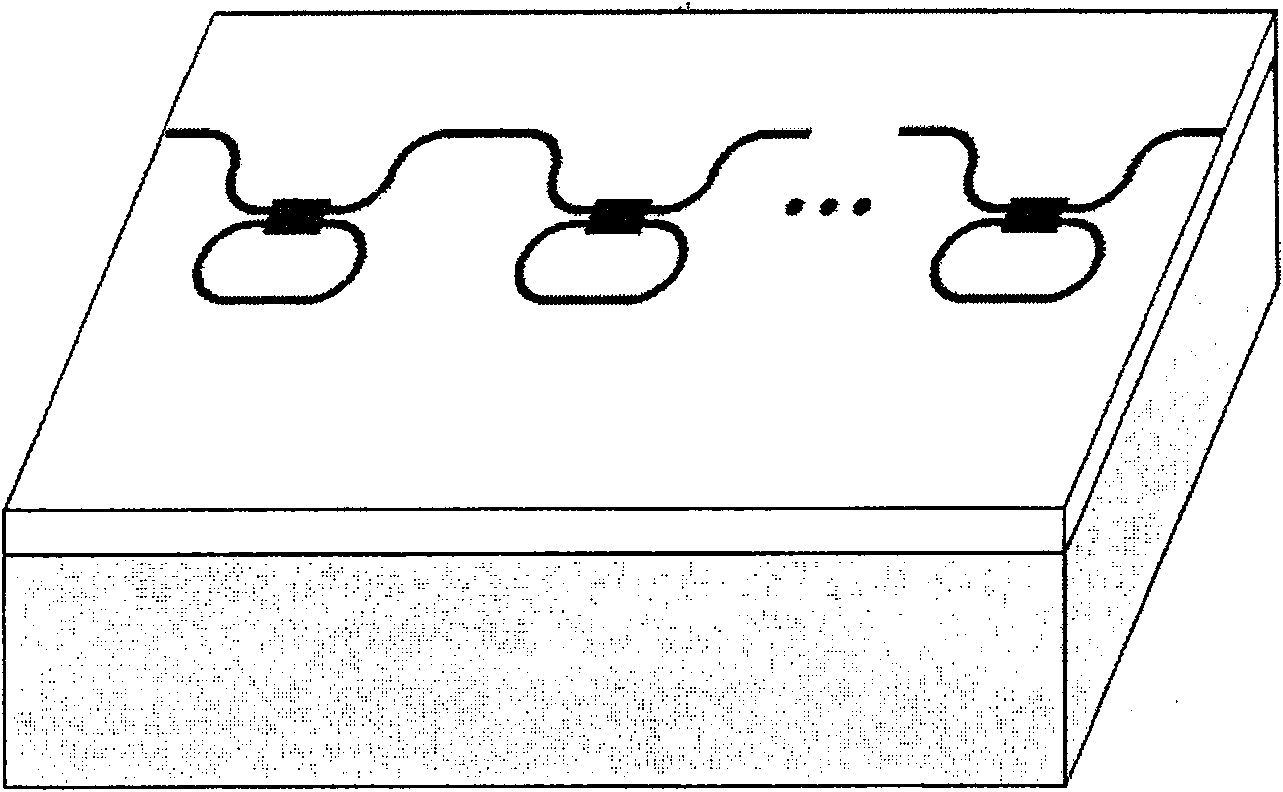
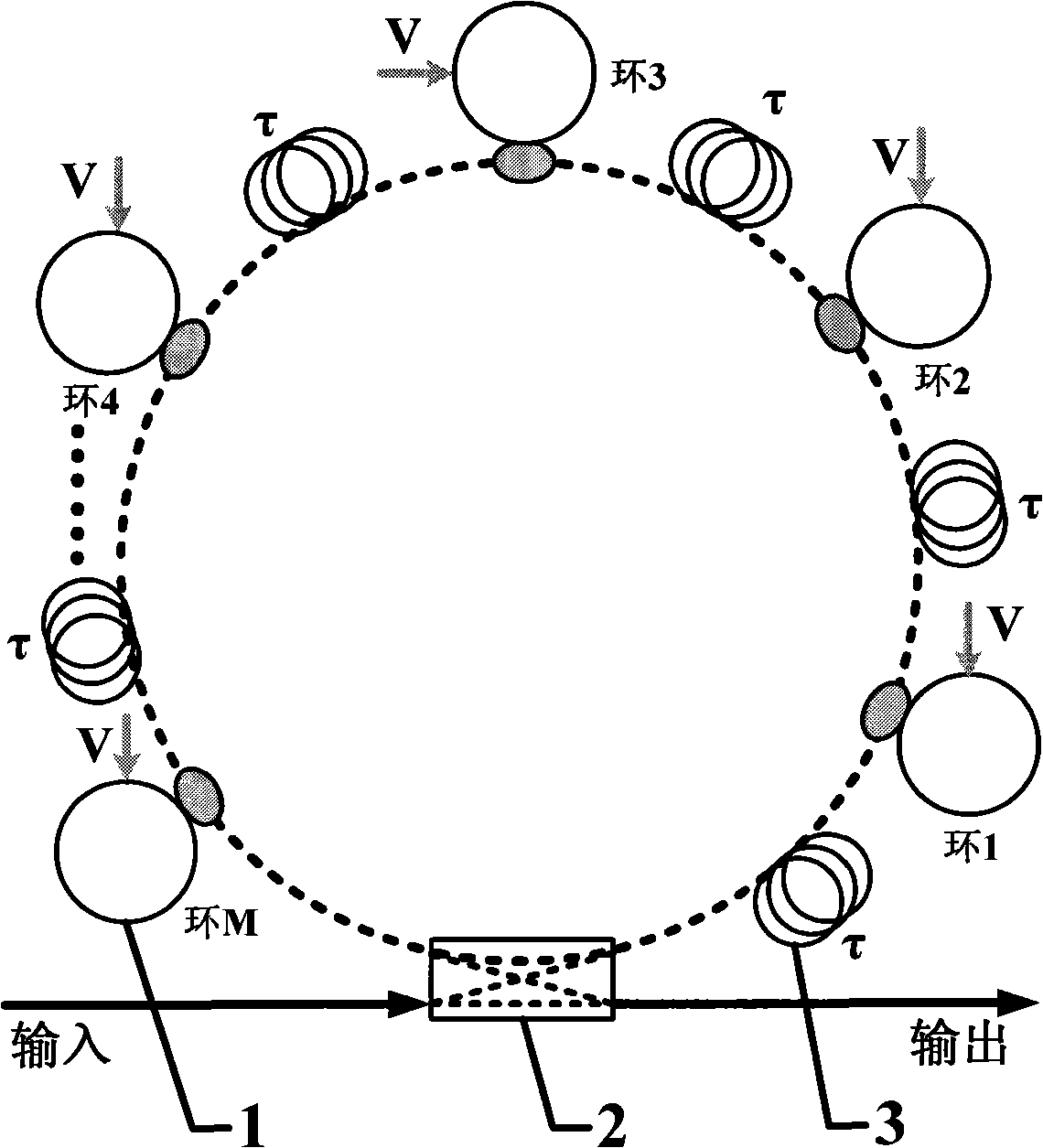
The invention relates to an all-optical network quick-dynamic configurable optical packet buffer. M Sagnac interference rings with reflex-transmission functions and M optical fiber delay lines are mutually by interval welded and connected in series; the optical fibers at the head and tail ends are welded with an input end and an output end of a 2 times 2 quick optical switch to form a buffer fiber ring. The other couple of the input end and output end of the 2 multiplied by 2 quick optical switch are adopted as the input and output ends of optical packet signals. The optical buffer of the invention enhances the re-cycle optical fiber buffering capability and provides the diverse buffer path options by embedding the Sagnac interference rings and optical fiber delay lines by interval on the basis of the existing re-cycle optical fiber ring of the traditional 2 multiplied by 2 quick optical switch so as to realize the time-slot exchanging for a plurality of optical packets and the quick-dynamic configuration of buffering time while supplying a plurality of optical packets. The invention has the advantages that the optical buffering time dynamic scope is wide; the reconfiguration time is short; the physical volume is small; the power cost is low and the potential expansibility is high, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Elastic optical group exchanging method and node equipment based on dicyclic all-optical buffer storage
InactiveCN1527615ABig amount of dataIncrease profitElectromagnetic transmissionData switching networksData streamResilient Packet Ring
The present invention provides grouped exchange method and equipment with buffering time adjustable all-optical buffer storage in elastically optical grouped cyclic network. Frame structure of unequal frame header rate and net load rate is adopted, optical / electric / optical conversion on frame header, rather than whole optical data frame, from the cycle is completed to obtain routing information, and the net load of the data frame is buffer stored in optical buffer storage. Based on the routing information of the frame header, it is determined whether the frame is made down from the present node or transferred to the downstream of the cyclic network. Utilizing the read / write controllable dicyclic all-optical buffer storage and the control algorithm to regulate the buffer storage time can overcome competition between the re-transmitted data and the data transmitted to the cyclic network, eliminate optical data flow conversion bottle neck, reduce obstruction and raise bandwidth utilization.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Optical fibre connecting mechanism
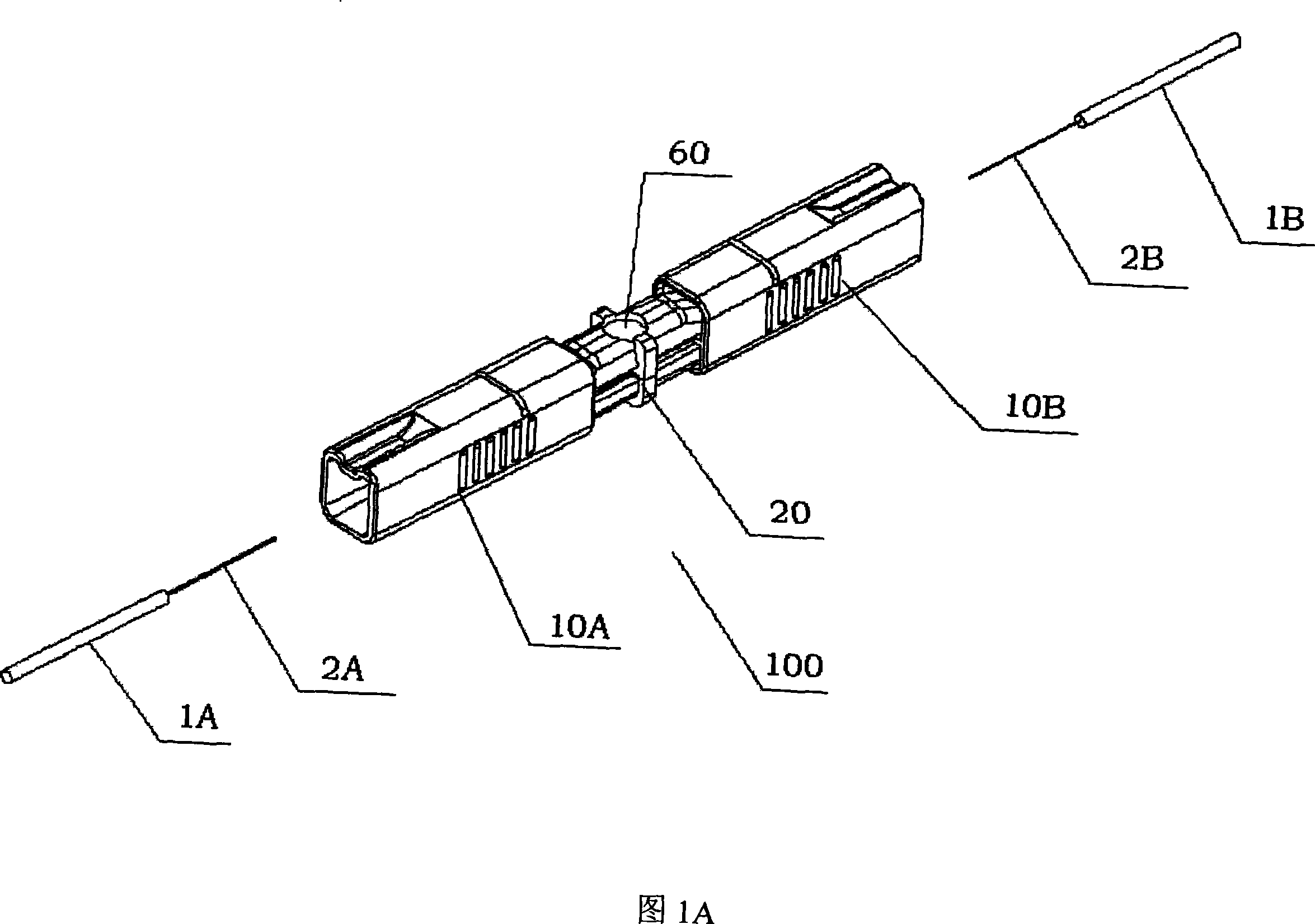
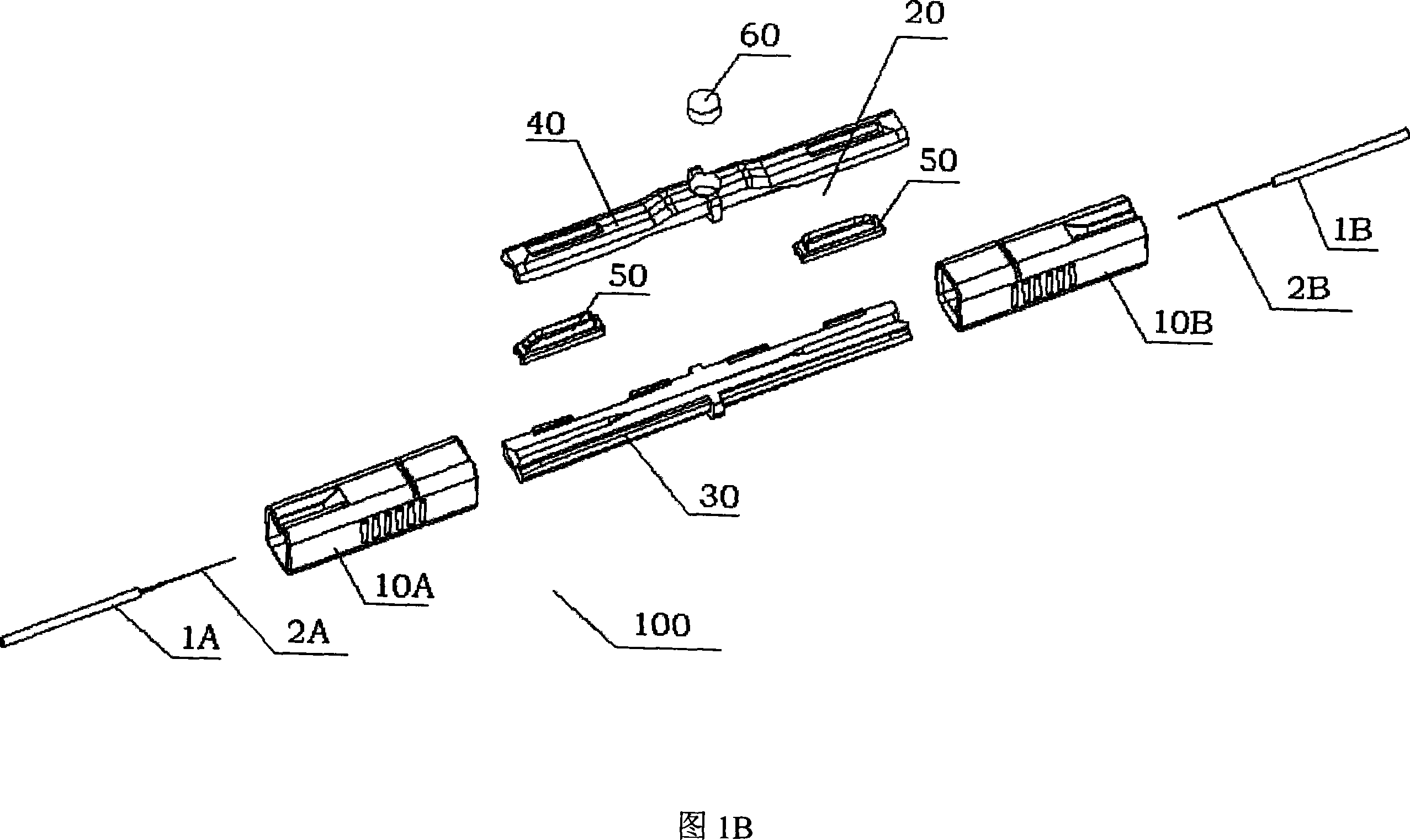
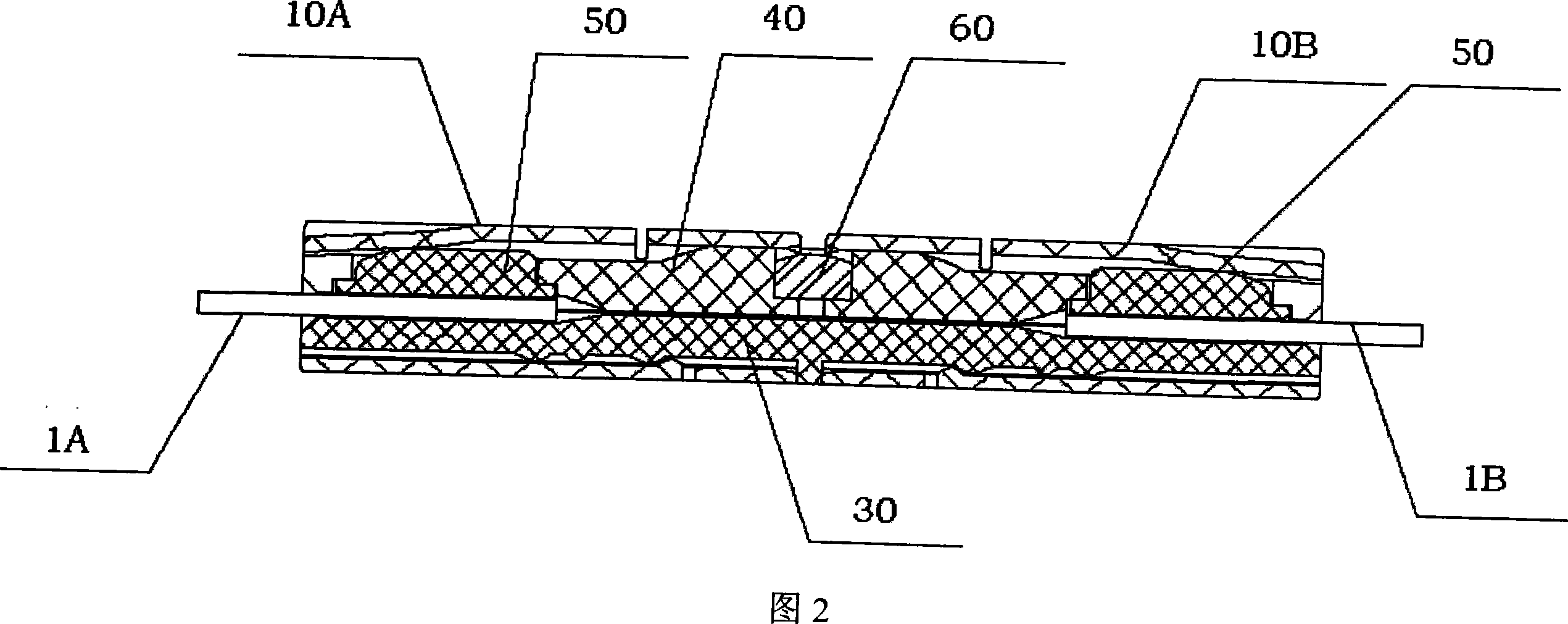
The invention provides an optical fiber connecting device which can connect every optical fiber with buffer covering layer but not need any other precise special optical fiber jointing device to improve the processing efficient. The optical fiber connecting device includes the jointing part and the shell. By the moving of shell in jointing part, the naked optical fiber can keep the connecting in jointing apparatus. At the same time, by the moving, the buffer layer holding part can press the optical buffer layer tightly to make optical fiber between the jointing parts and endure some axial and side outside force but has no influence to the optical connecting character.
Owner:NANJING HUAMAI TECH
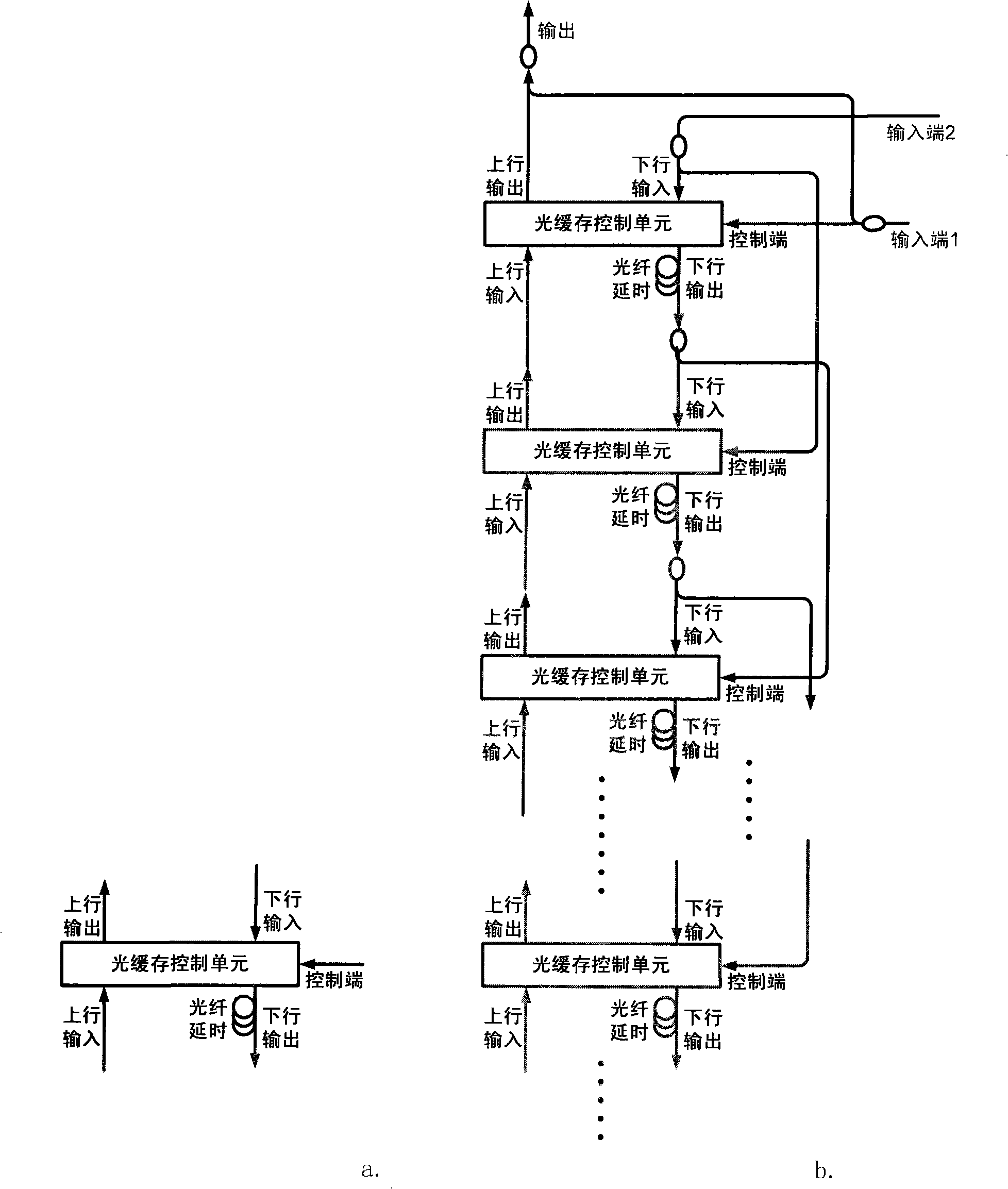
Stack type whole optical caching device
InactiveCN101350672ADecide how long to storeDecision depthMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesOriginal dataUplink transmission
The present invention relates to a stack type fully optical buffer, and belongs to the field of fully optical packet switching. The buffer is characterized by consisting of a plurality of cascading light guide units; the downlink output end of the light guide unit of each level is orderly connected with the downlink input end of lower level, so as to form a downlink channel; the uplink input end of each level is orderly connected with the uplink input end of higher level, so as to form an uplink channel. The data packet which is transmitted into the light guide unit of each level is controlled by a control end for uplink transmission or downlink transmission. The i-level downlink output end is connected with the control end of the level of i plus 2, so as to prevent the levels of i and i plus 2 from simultaneously transmitting the data to the level of i plus 1. When two data packets arrive to the buffer simultaneously, the data packet of higher priority is directly transmitted outwards, and the data packet of lower priority is stored in the buffer; and the storage depth of the original data packet in the buffer is deepened by one level. The fully optical buffer has the first-in but last-out, and last-in but first-out characteristics, the capability of simultaneously processing two data packets, and the advantages of easy expansion of the storage capacity, no requirement for additional control signals, and so on.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Switching method and node structure supporting burst packet and IP grouping
InactiveCN101155121AReduce in quantityReduce blocking rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLoss rateNetwork packet
The invention provides an all optical switching method of two kinds of grain sizes and node structure for supporting burst packet / IP grouping. The invention uses electric buffer memory instead of the optical buffer memory difficult to implement. The IP transmission character of 'make the best' is used, the IP grouping transmitted between the adjacent nodes and / or the IP grouping with low request of QoS is stored by electric buffer memory. The burst packets book the information of network resource to make the IP grouping insert into the inter space between the burst packets to transmit. The IP grouping passes through the OBS node just like sandglass, and the burst packet is transmitted in the light field. The said method can effectively reduce the amount of the burst packets in network and the data is equably distributed on a wavelength channel using an electric random access memory. The invention not only provides statistical multiplex capacity of high performance, but also greatly reduces the blocking rate of network and data loss rate.
Owner:君创物业管理(深圳)有限公司
Self-adaptive elastic ring optical buffer for variable length optical packet
InactiveCN101448183AEliminate length constraintsFlexible cache timeMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesFiberOptical packet
A self-adaptive elastic ring optical buffer for a variable length optical packet includes an annular structure consisting of basic buffer units with different buffer delays, wherein the on / off state of the basic buffer unit determines whether the optical packet is buffered in the unit, and the on / off control optical packet at the outlet is continuously buffered or read out. The selection of the number of turns of the buffer and the buffer unit can enable the self-adaptive elastic ring optical buffer to be adapted to optical packet buffer with arbitrary lengths, thereby obviating the restriction of a feedback structure on the length of the optical packet. In addition, the self-adaptive elastic ring optical buffer has larger buffer delay change range, bidirectional delay dynamic reconstruction capability, optional delay budget and more compact structure in comparison with a feedforward structure. The separated read-write control and the annular structure can ensure the optical packet in the buffer to be directly read out without influencing the buffering optical packet, so that the cascade structure has a plurality of queuing functions. Based on fiber delay line and SOA gain switch, the self-adaptive elastic ring optical buffer also has the advantages of nanosecond-scale reconstruction capability, lower ASE noise accumulation and power loss, low cost, high stability, simple implementation, etc.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Optical buffer employing four-wave mixing
An optical buffer employing Bragg scattering (BS), in which two pump signals are combined with an input (data) signal in a four-wave mixing (FWM) medium to frequency convert the input signal into an idler signal, which is applied to a dispersive medium, in which the idler signal propagates at a speed different from that of the input signal. By selectively turning on and off a pump, e.g., at bit-level switching rates, the BS-based frequency conversion can be selectively performed on particular bits in the input signal, e.g., to generate an output signal having reordered bits. A BS-based optical buffer can (1) be tuned to achieve different amounts of delay; (2) support single-channel or multiple-channel, classical or quantal communications; (3) be implemented with co-phased pump-phase modulation to suppress stimulated Brillouin scattering, while inhibiting spectral broadening of the idler signal; and (4) provide polarization independence using standard polarization-diversity techniques.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com