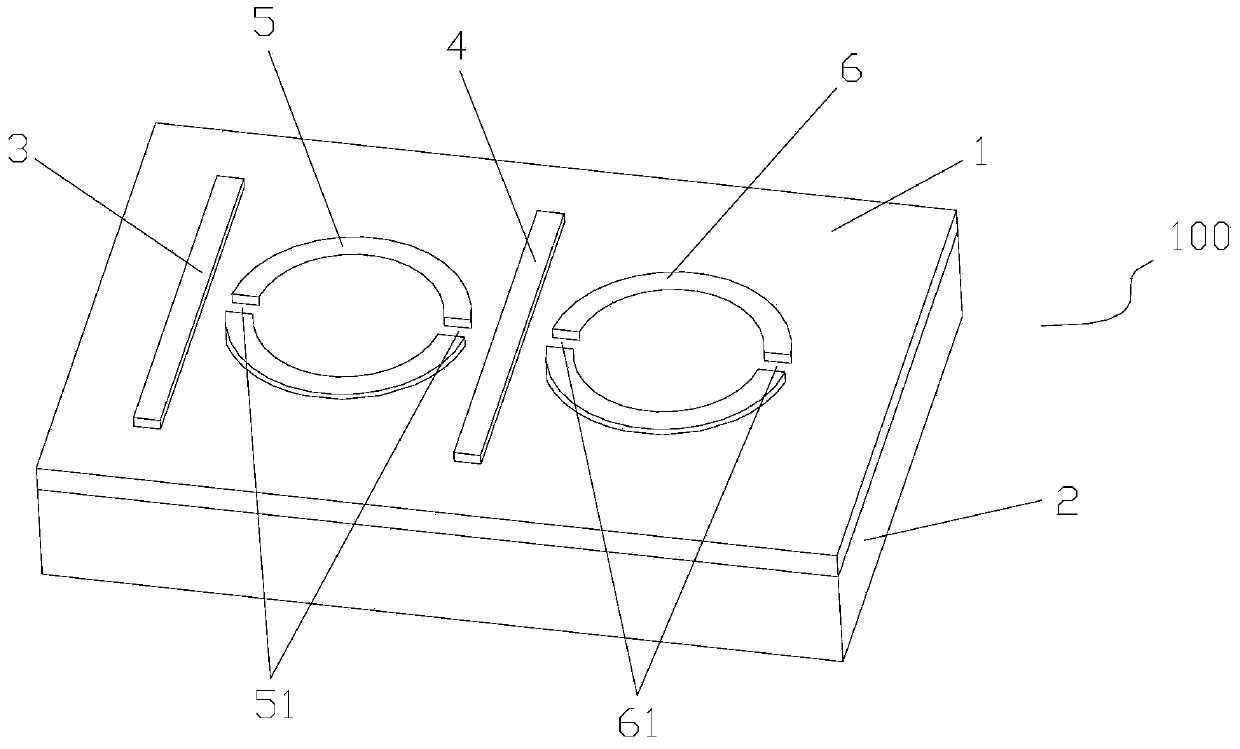
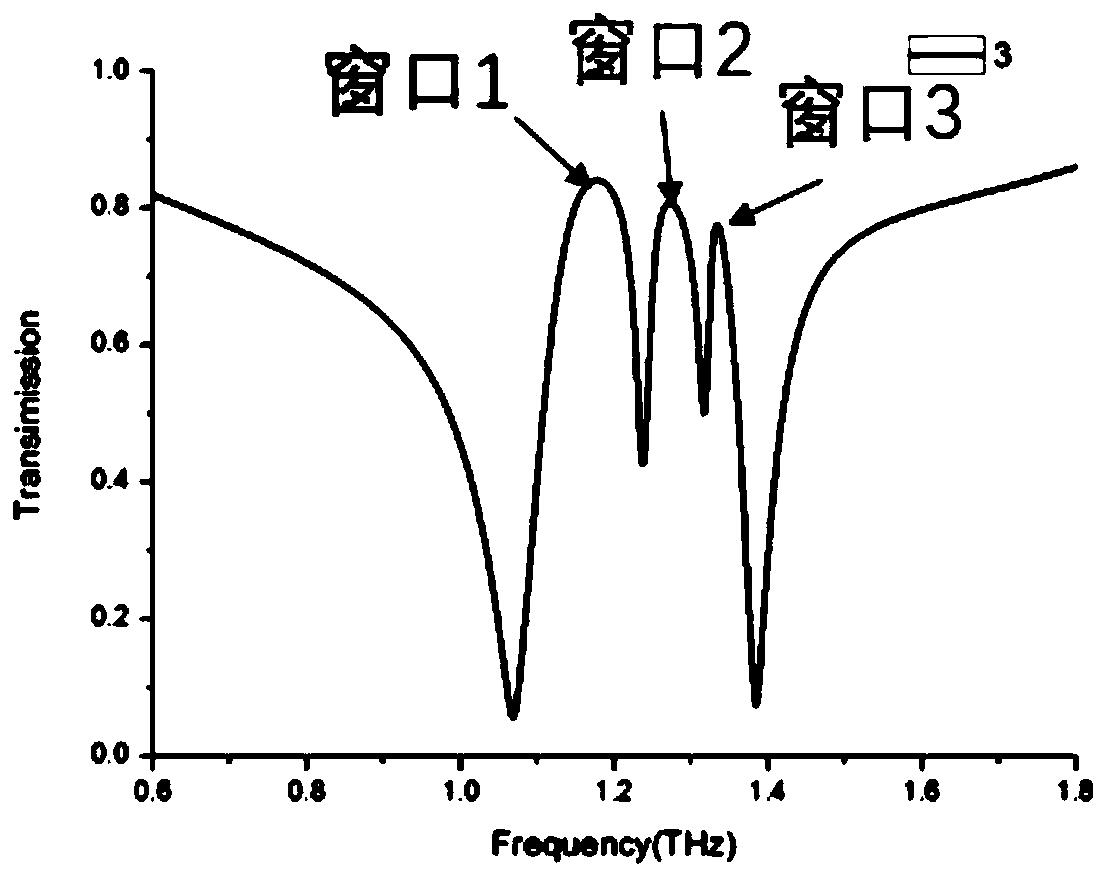
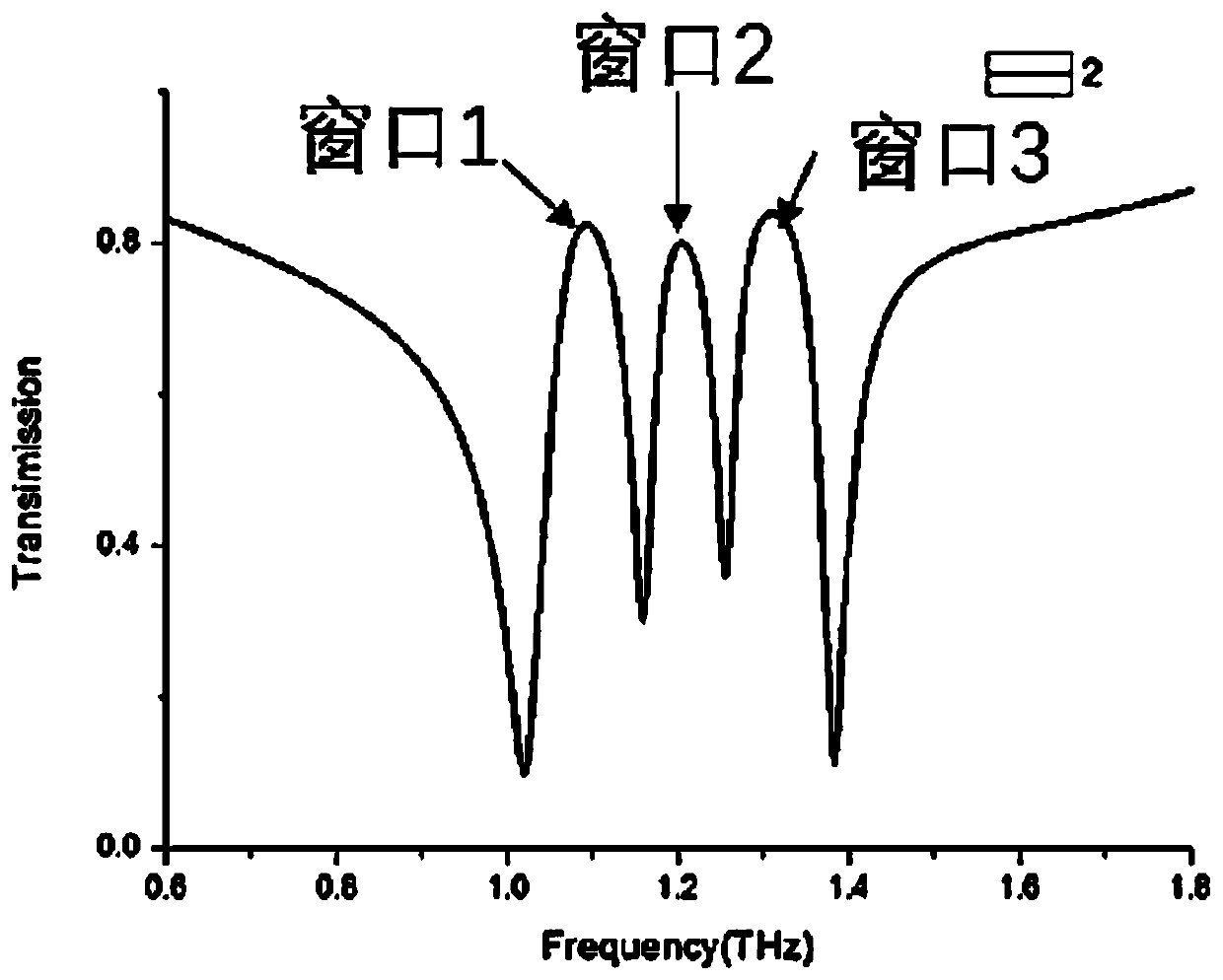
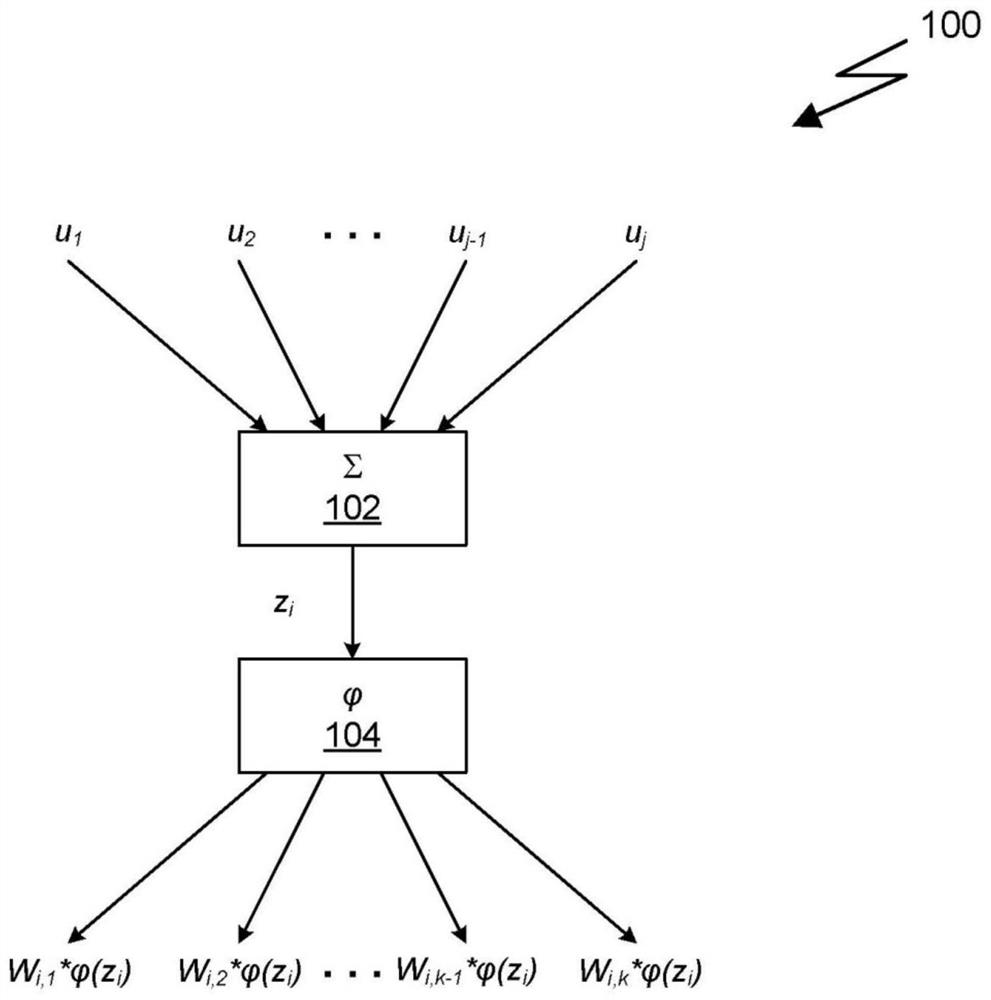
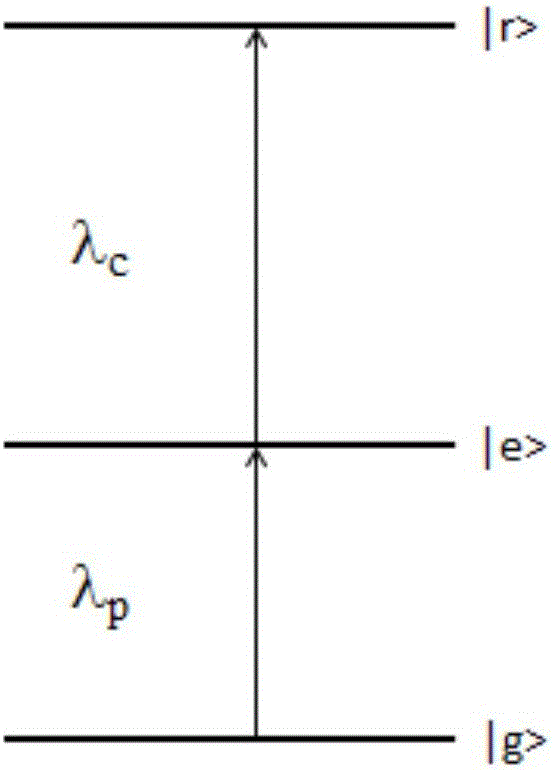Patents
Literature
113 results about "Electromagnetically induced transparency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
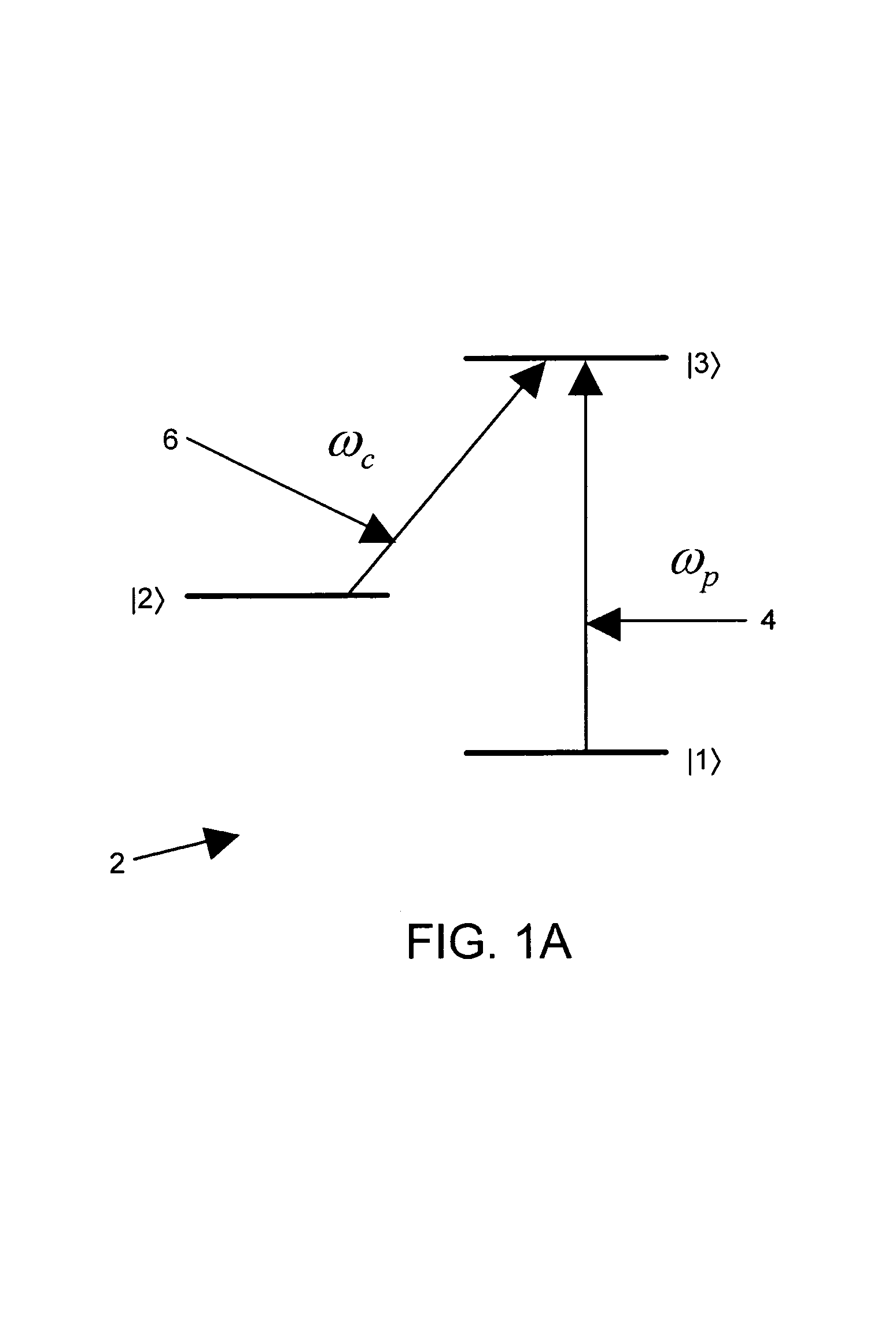
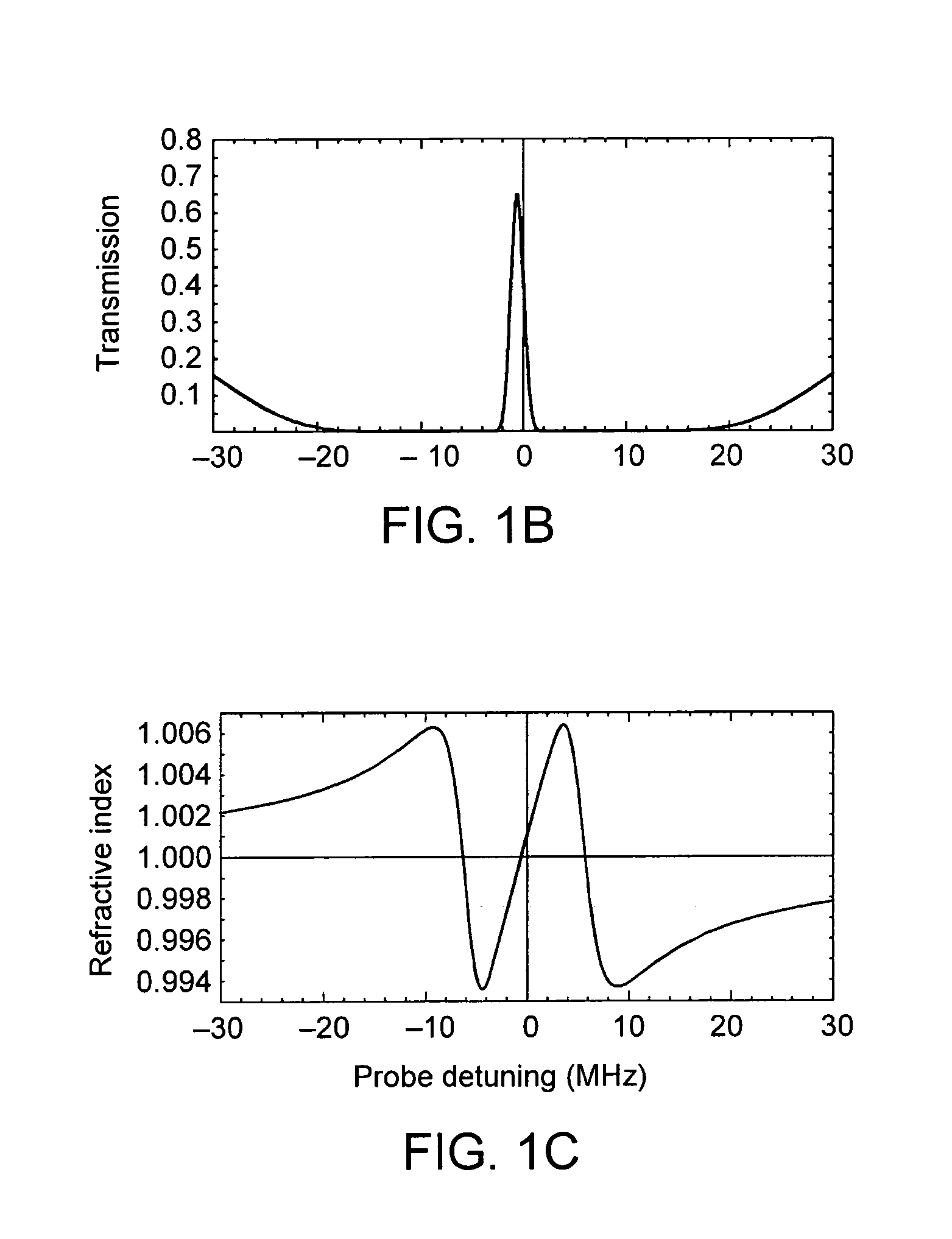
Electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) is a coherent optical nonlinearity which renders a medium transparent within a narrow spectral range around an absorption line. Extreme dispersion is also created within this transparency "window" which leads to "slow light", described below. It is in essence a quantum interference effect that permits the propagation of light through an otherwise opaque atomic medium.
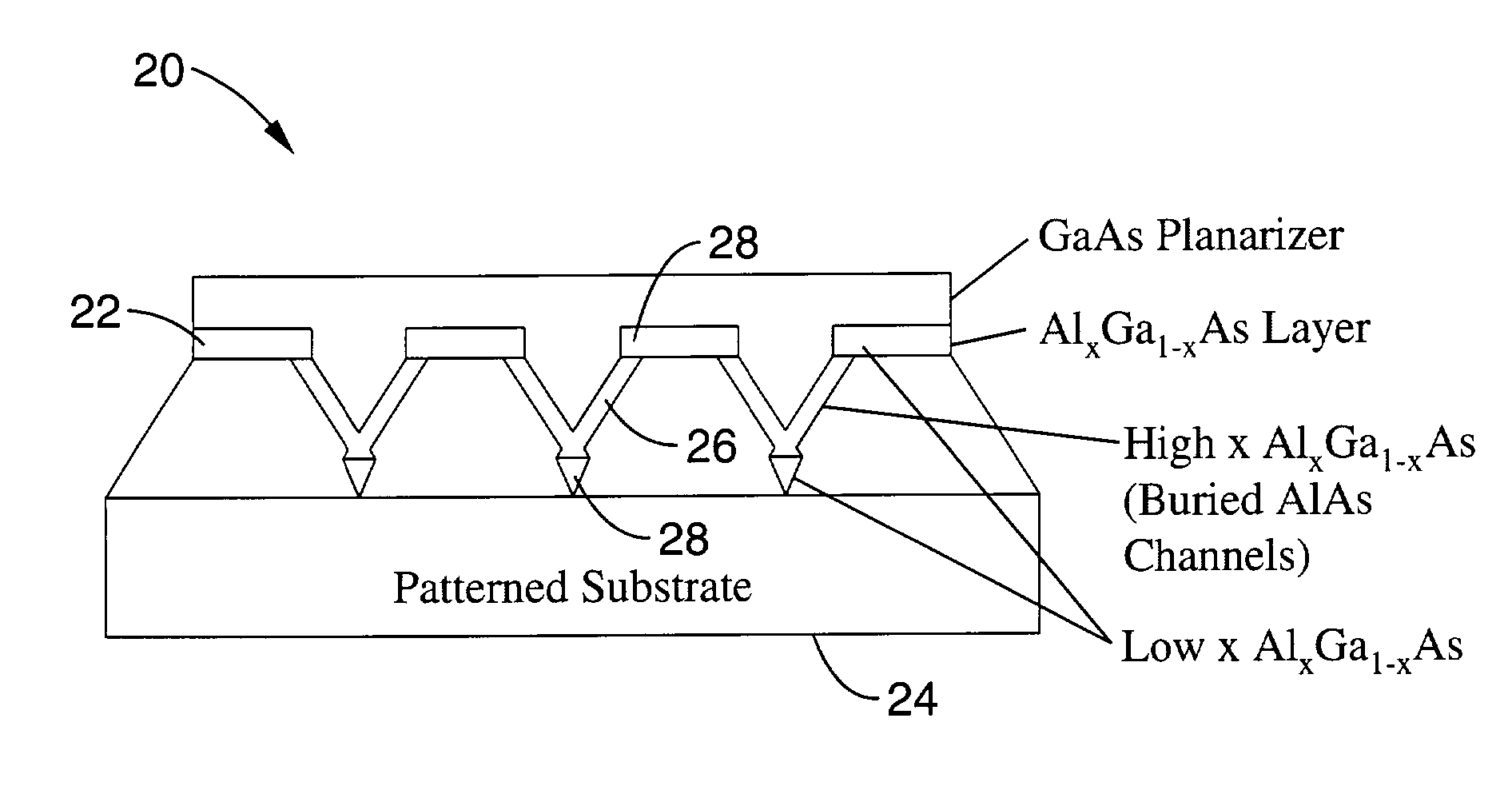
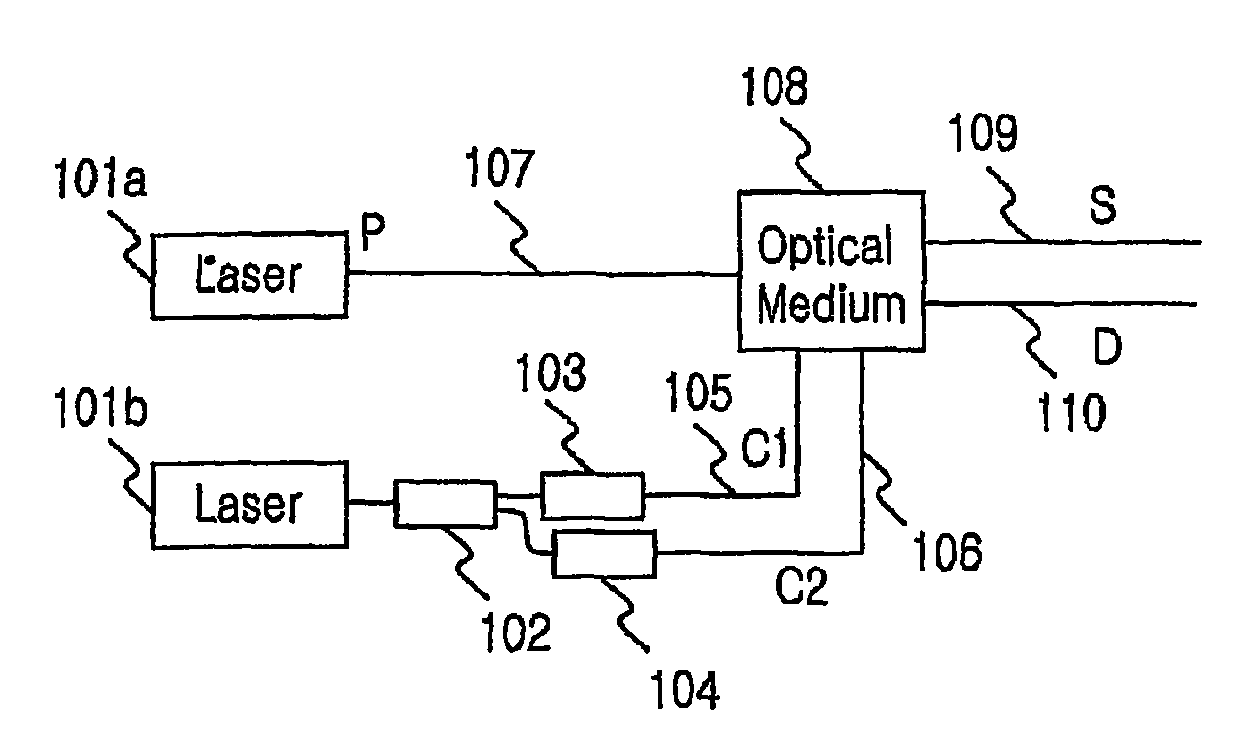
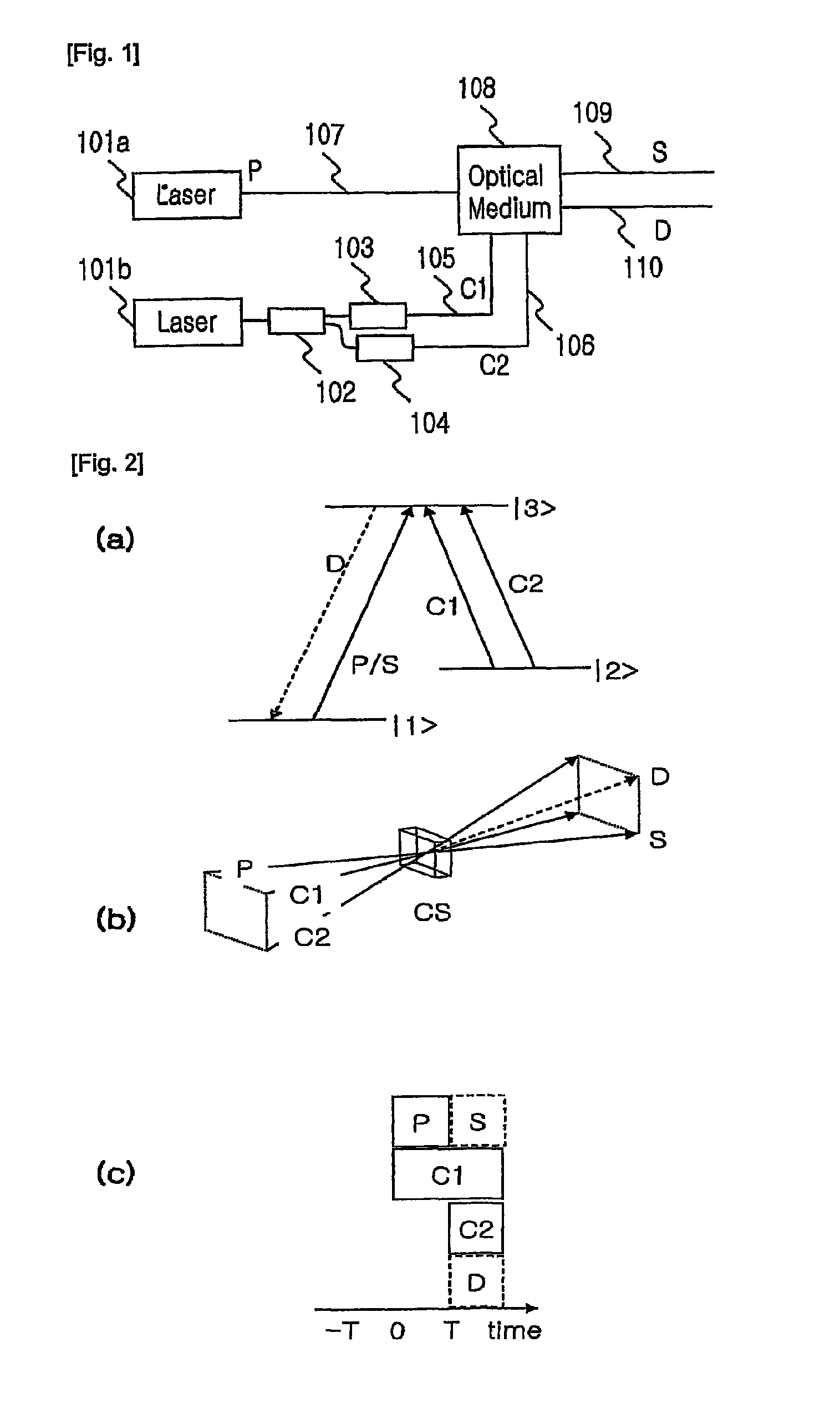
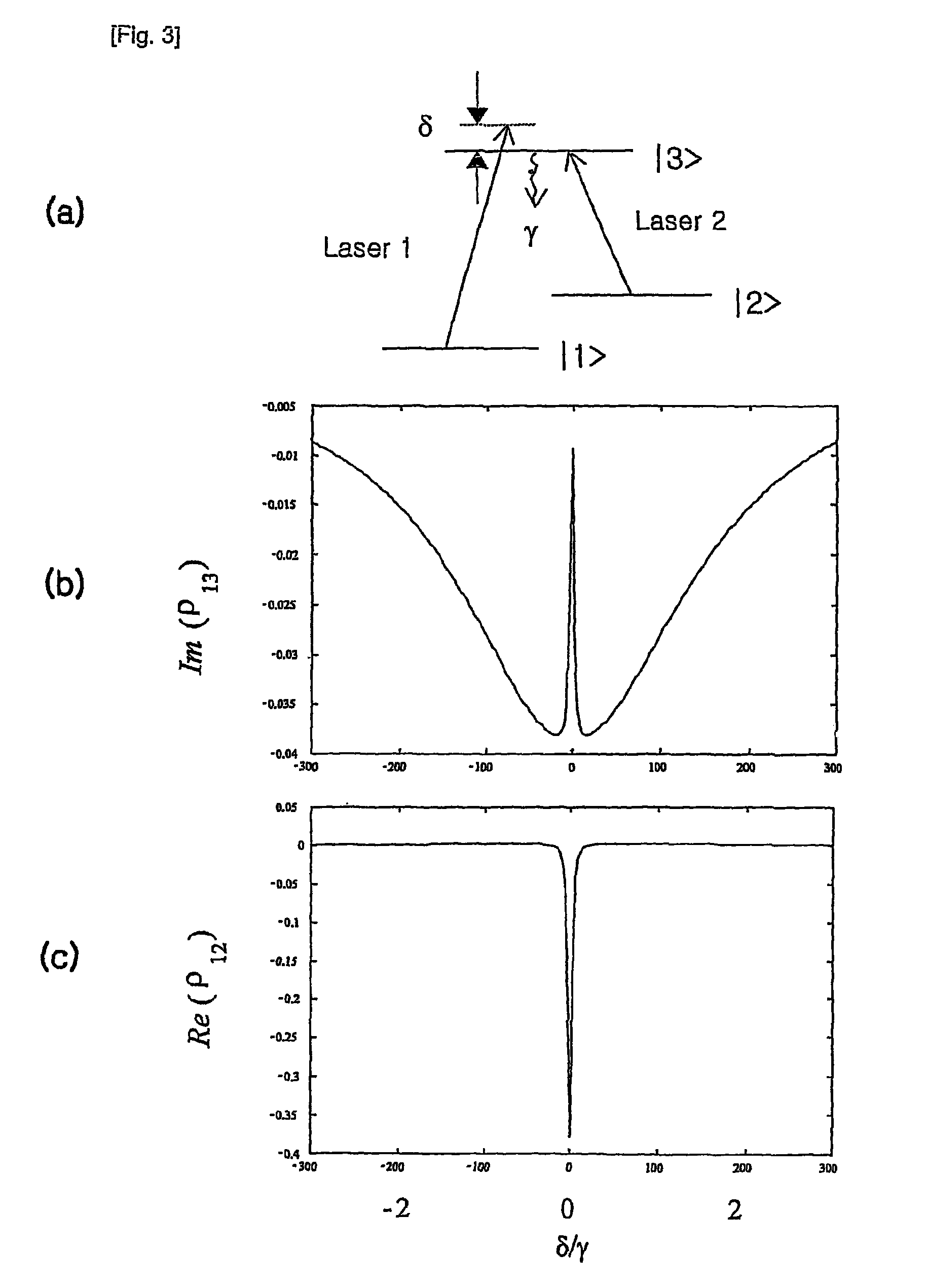
Variable semiconductor all-optical buffer using slow light based on electromagnetically induced transparency
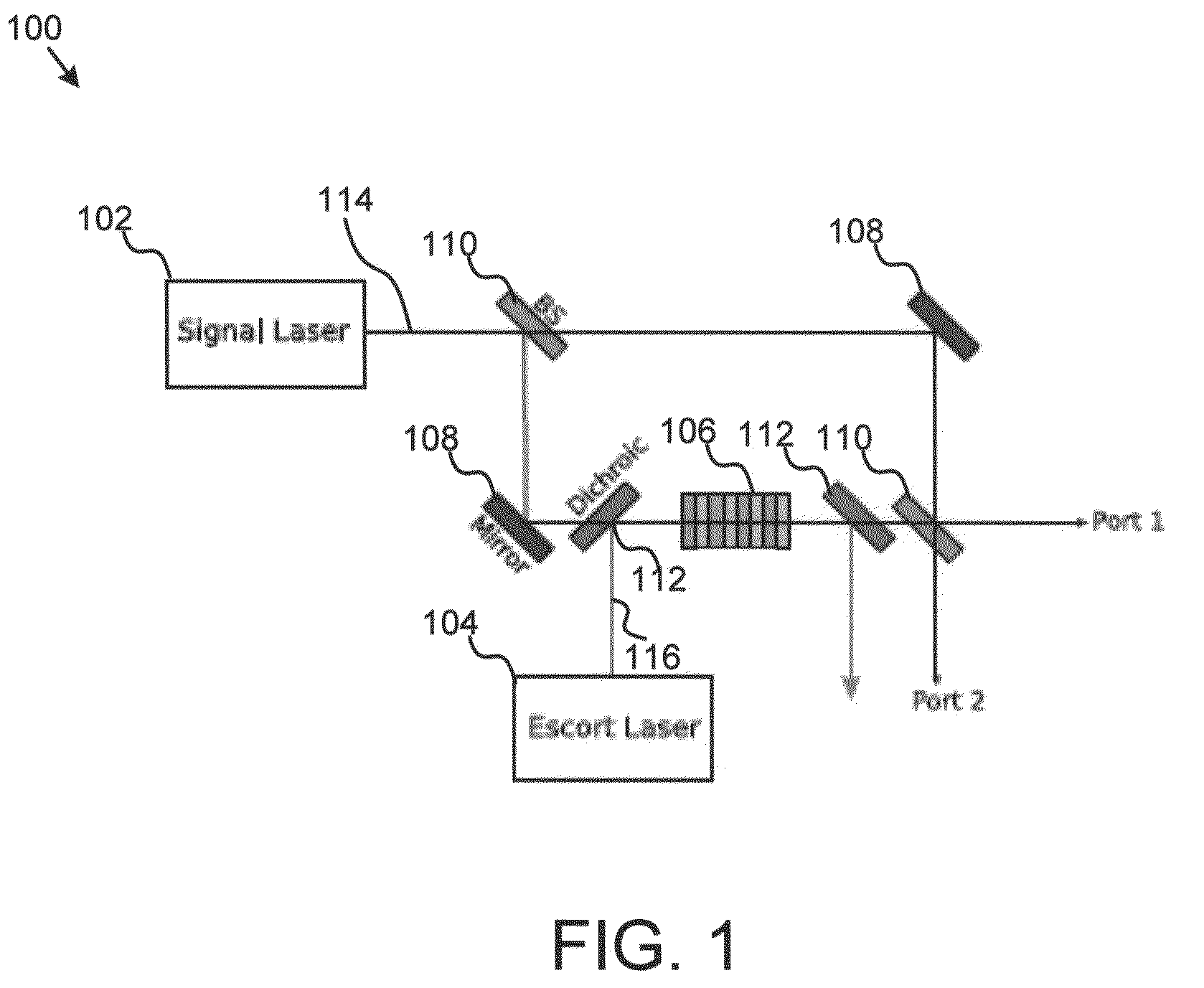
A variable semiconductor all-optical buffer and method of fabrication is provided where buffering is achieved by slowing down the optical signal using a control light source to vary the dispersion characteristic of the medium based on electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). Photonic bandgap engineering in conjunction with strained quantum wells (QWs) and quantum dots (QDs) achieves room temperature operation of EIT. Photonic crystals are used to sharpen the spectral linewidths in a quantum well structure due to its density of states and in a quantum-dot structure caused by the inhomogeneity of the dot size, typically observed in state-of-the-art QD materials. The configuration facilitates monolithic integration of an optical buffer with an amplifier and control laser to provide advantages over other material systems as candidates for optical buffers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
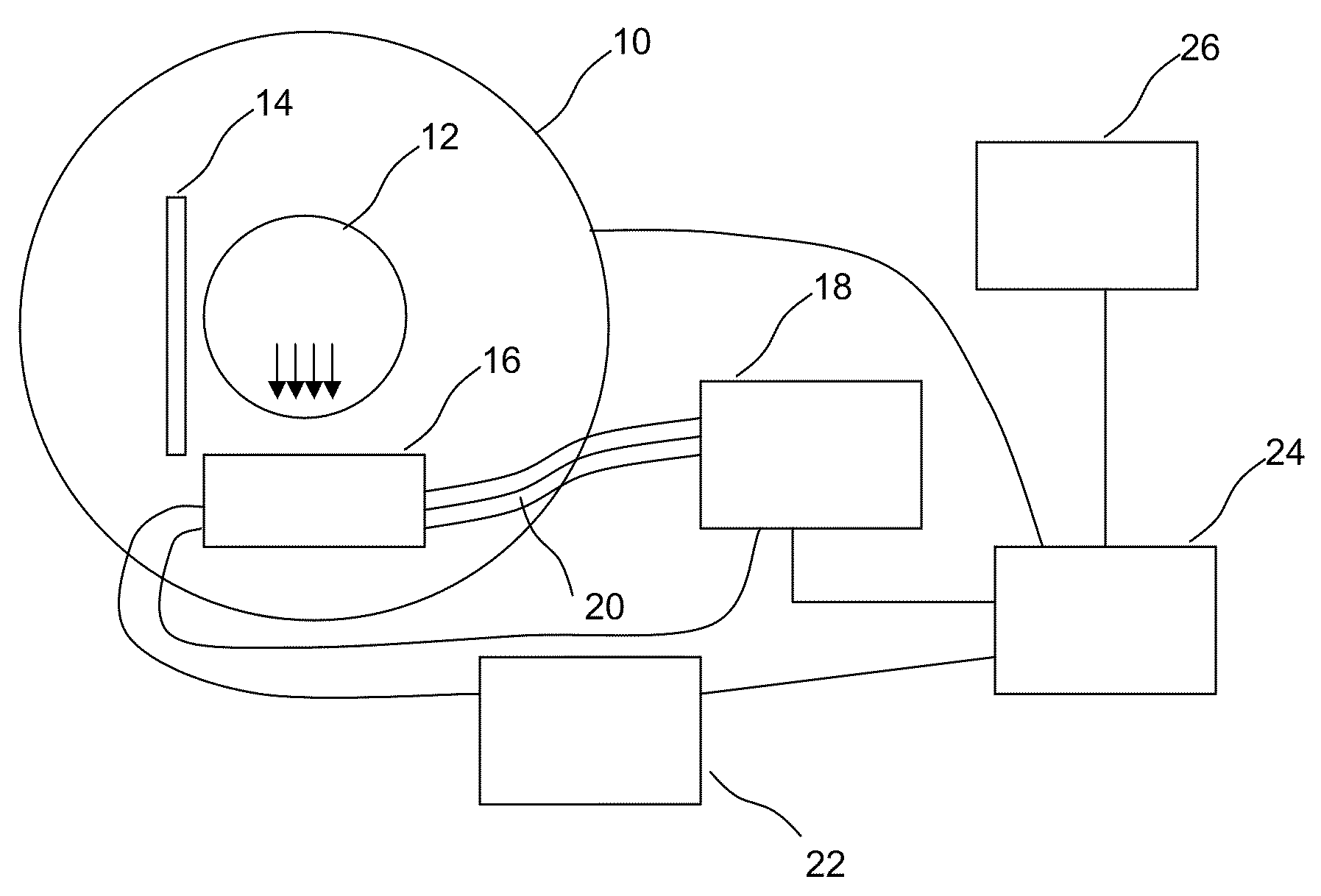
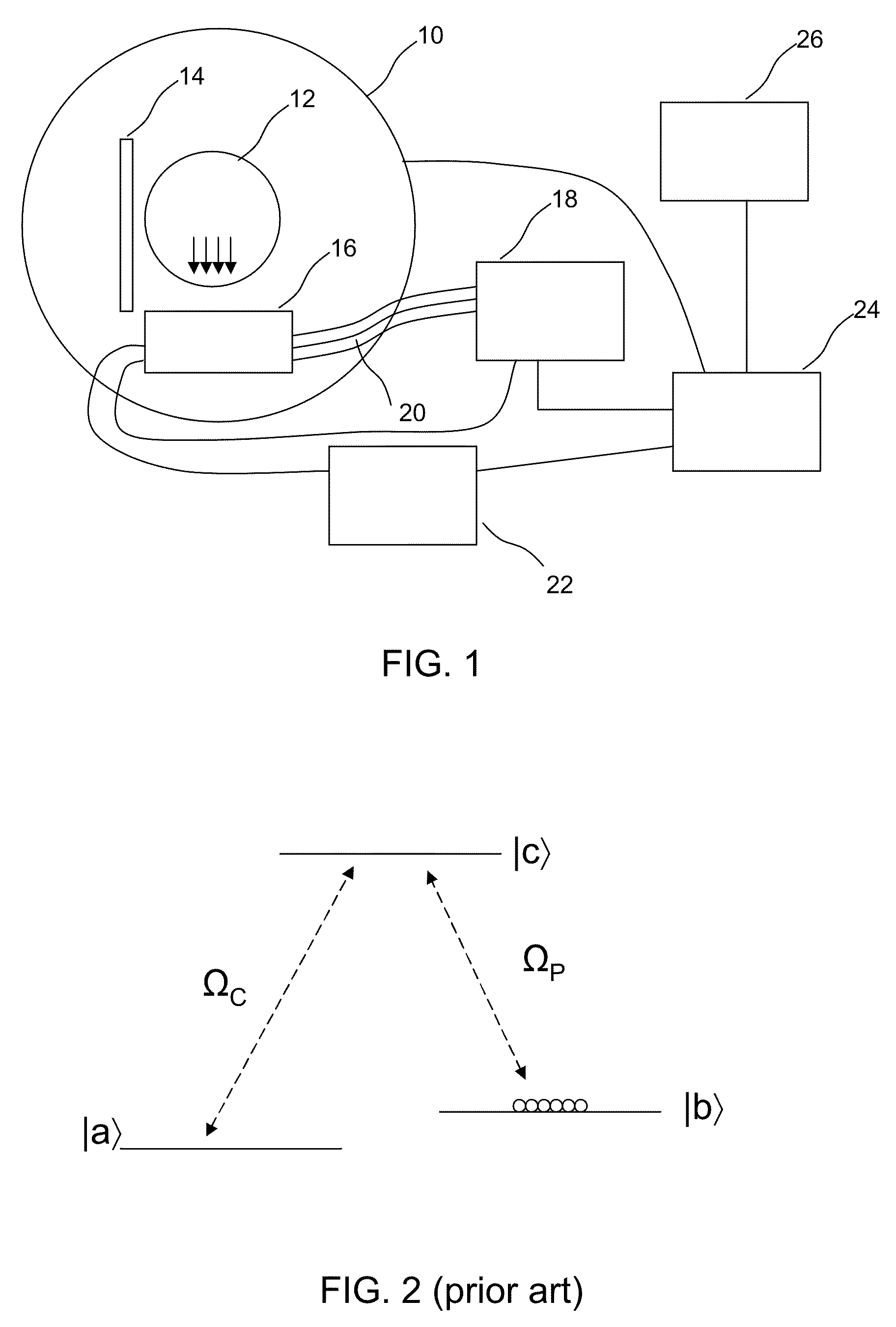
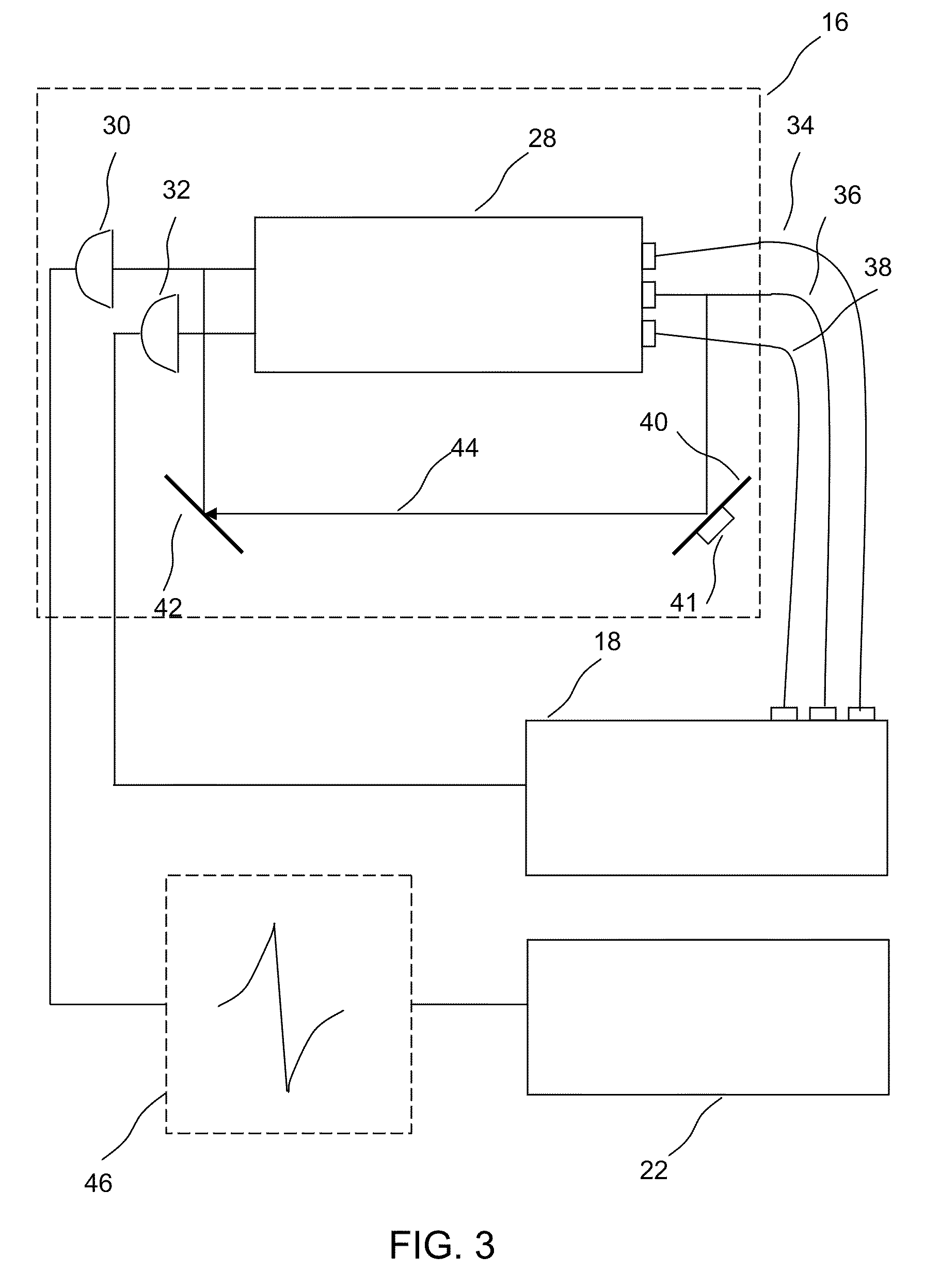
Method and Apparatus for Implementing EIT Magnetometry
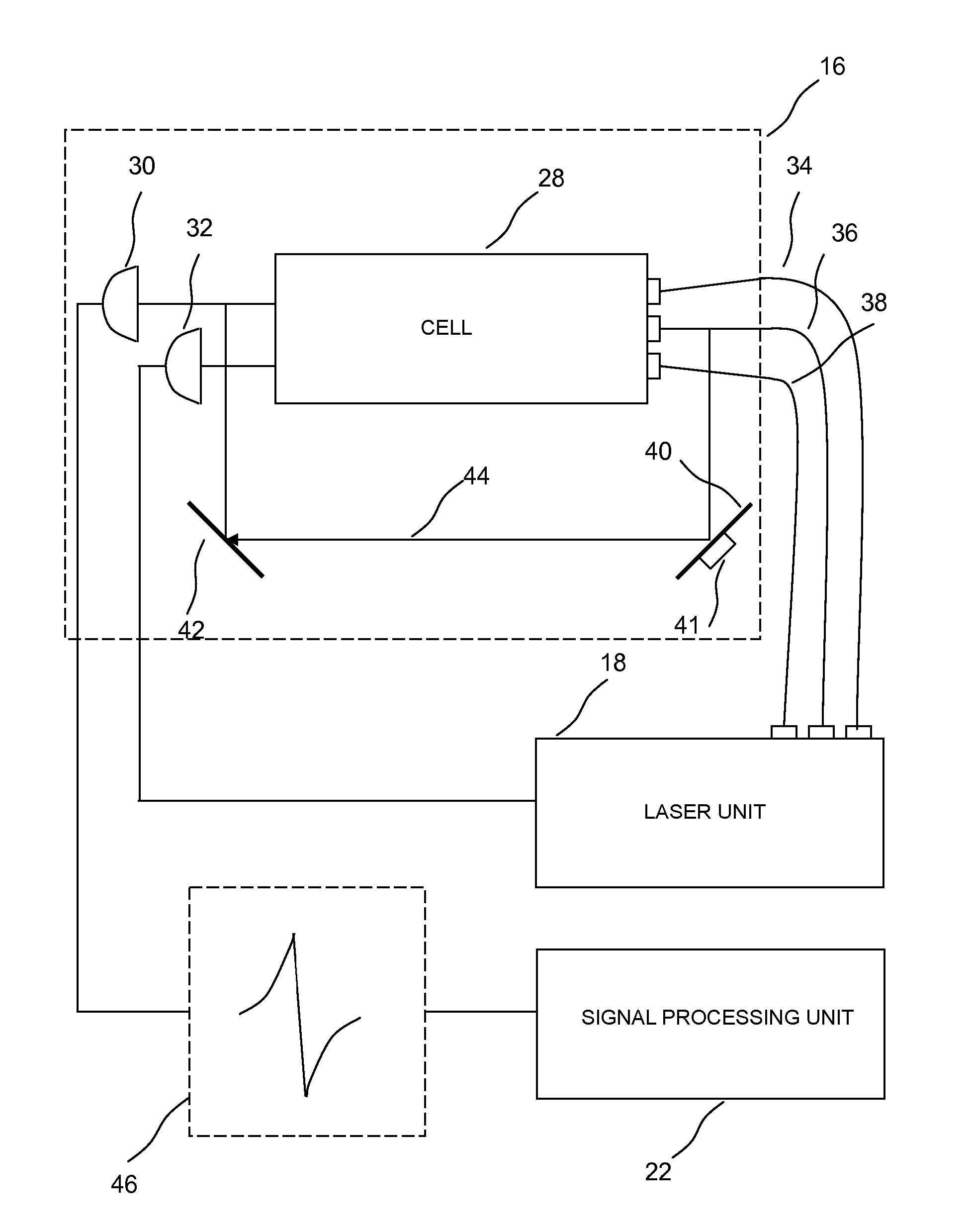
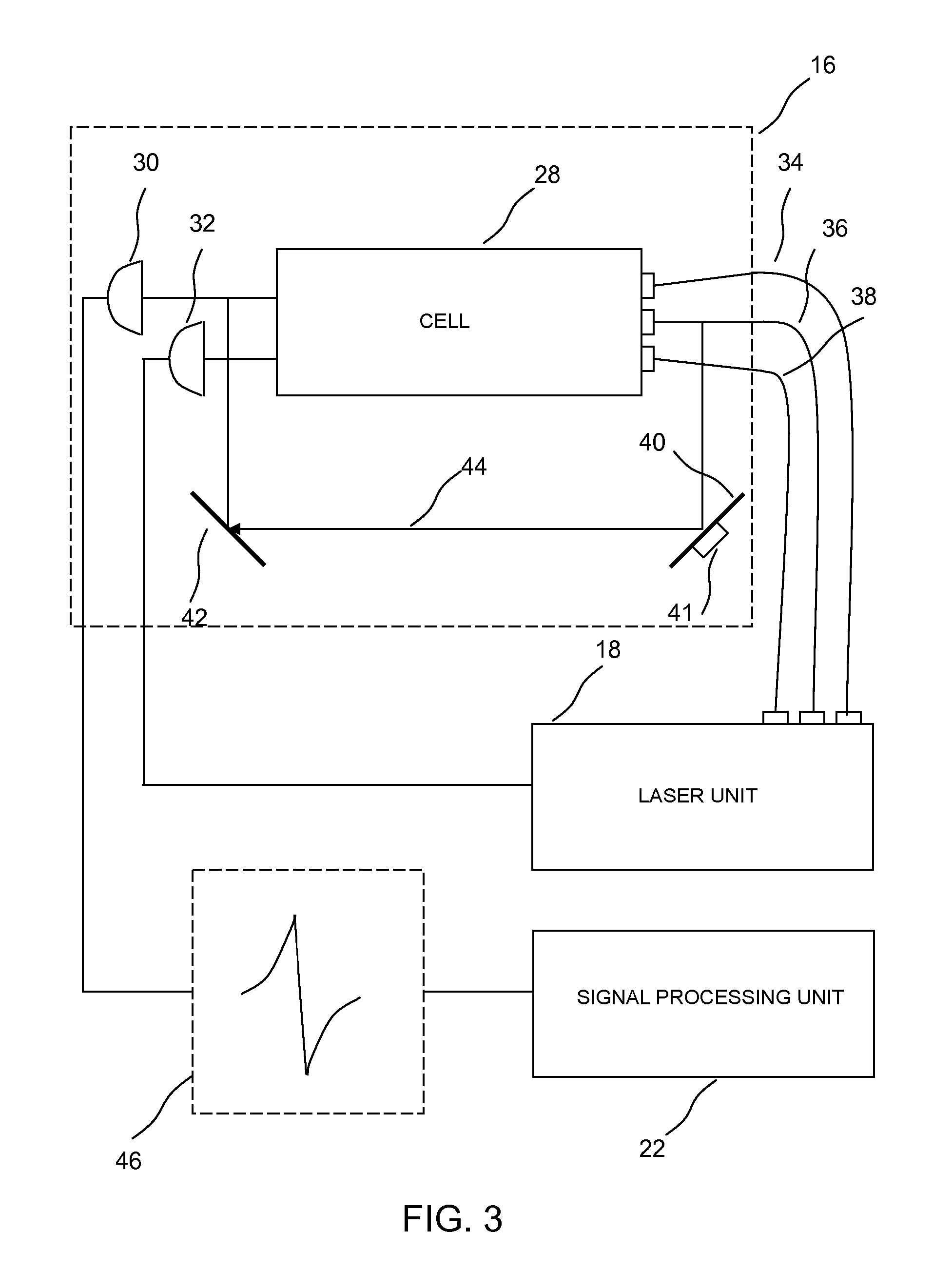
ActiveUS20090289629A1Applied imageMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesElectric/magnetic detectionPhase detectorLight beam
A magnetometer is provided comprising an atomic vapor in an enclosure, a source of light for preparing the vapor into a state exhibiting electromagnetically induced transparency, a first laser beam passing through the atomic vapor, a phase detector for detecting changes in phase of the first laser beam, and a controller which controls the light source and laser beam and receives the information detected by the phase detector in order to compute from those changes in phase a magnetic field strength in the presence of a selected background magnetic field of at least 0.001 T. Operation in the presence of a background field helps make this magnetometer suitable for diagnostic imaging applications.
Owner:ENTANGLEMENT TECH
Metamaterial-based terahertz adjustable polarized wave insensitive electromagnetically-induced transparency device
InactiveCN108390156AAvoid replacementSame electromagnetically induced transparencyAntennasAdhesiveWave detection
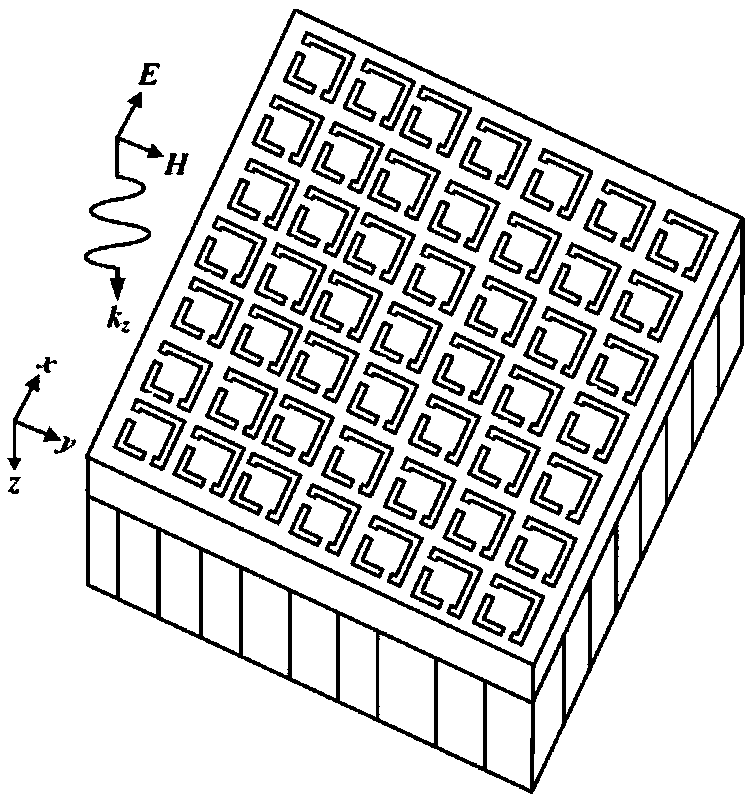
The invention discloses a metamaterial-based terahertz adjustable polarized wave insensitive electromagnetically-induced transparency device, and belongs to the fields of electromagnetic wave detection and sensor. The electromagnetically-induced transparency device comprises multiple basic units periodically arranged in the same direction; each basic unit comprises an upper layer graphene layer and a lower layer dielectric layer, and the dielectric layer is fixed on a substrate device; graphene is cut to form graphene square rings with openings in the adjacent edges; after the graphene layer is completely cut in one time, the middle part of the substrate device is hollow out; and finally, electroplating of a layer of conductive adhesive is carried out. The electromagnetically-induced transparency device has the same electromagnetically-induced transparency phenomenon on line polarized light in the x and y directions; when the polarized mode of incident wave is changed, device replacement is not needed; and in addition, an adjustable electromagnetically-induced transparency phenomenon can be realized by regulating the externally applied voltage without changing the device structure,thereby achieving important guidance significance and reference value on the development of an adjustable terahertz functional device.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Measurement method and measurement device for intensity of microwave electric field
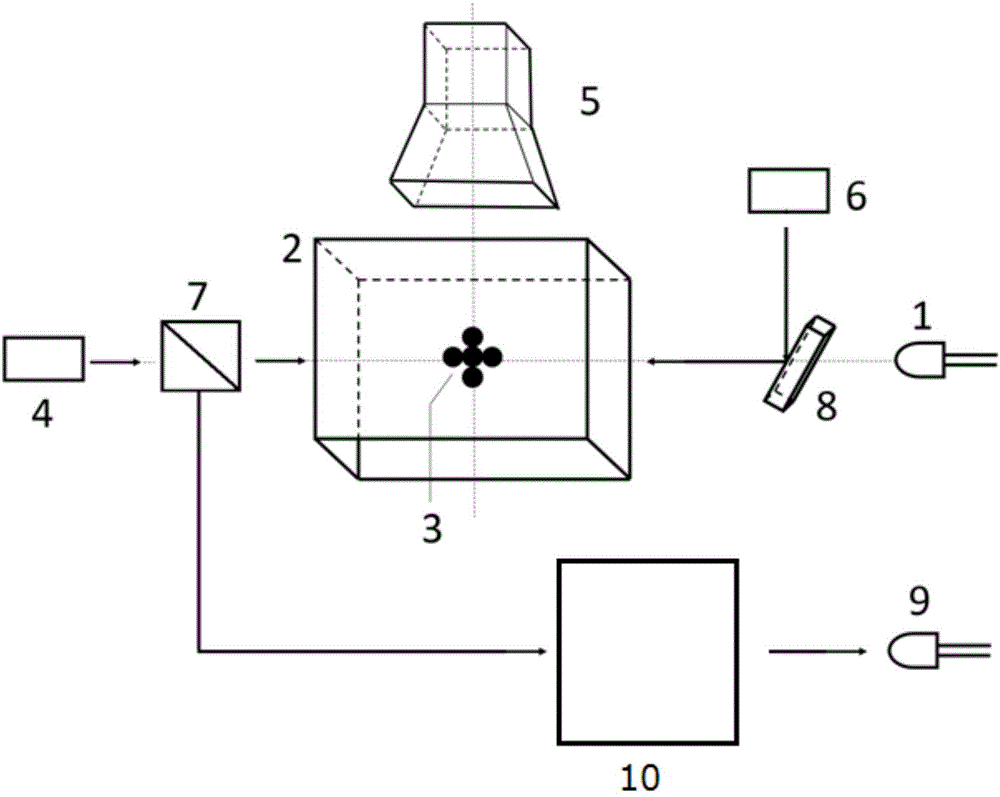
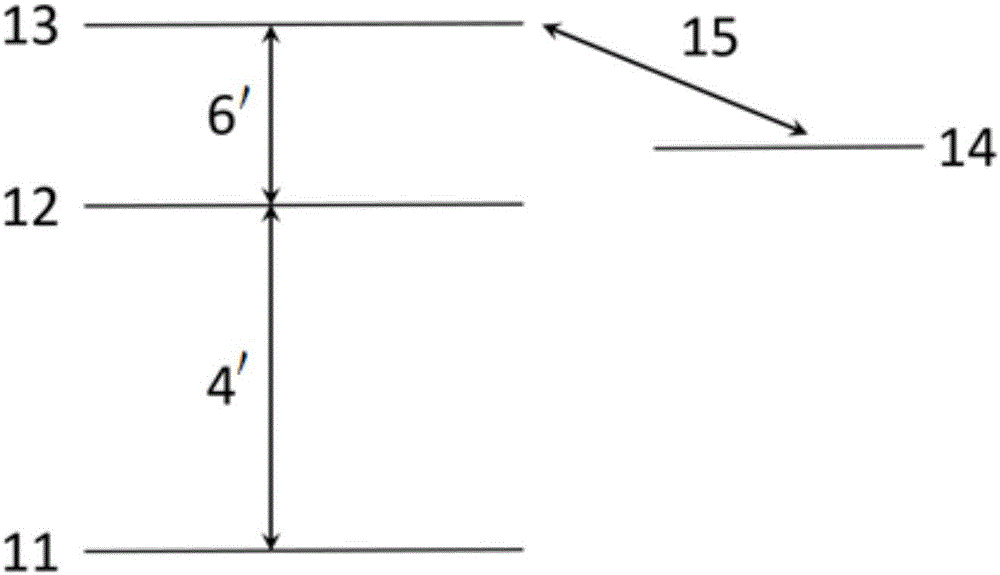
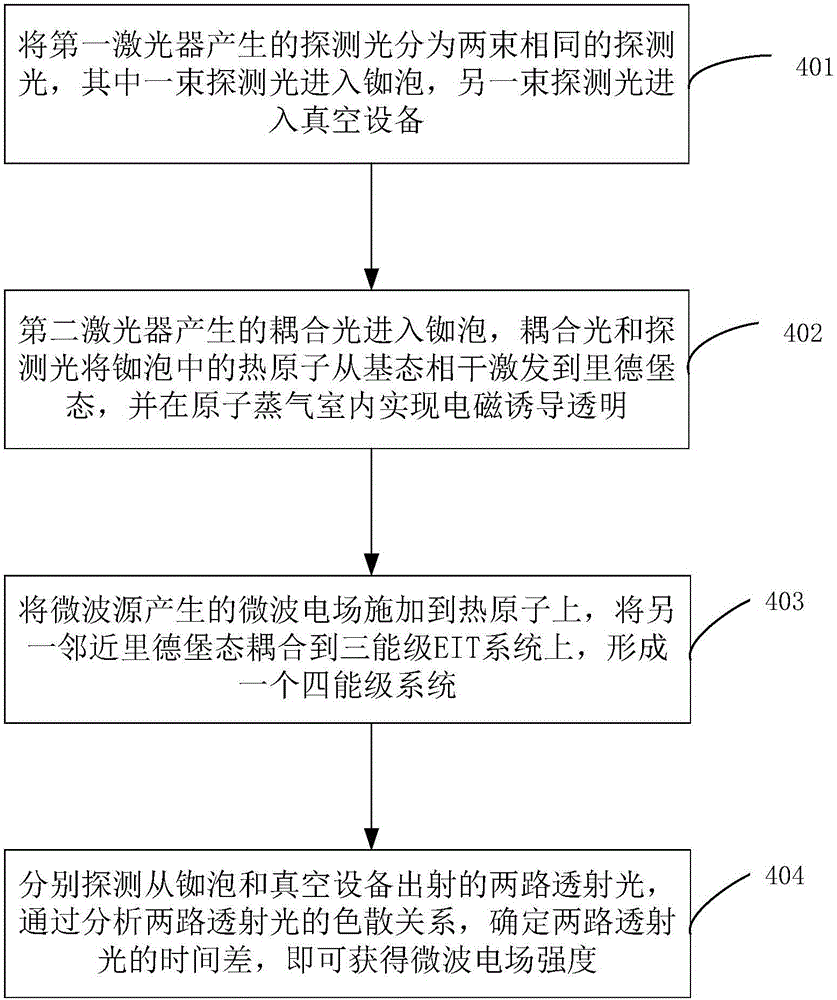
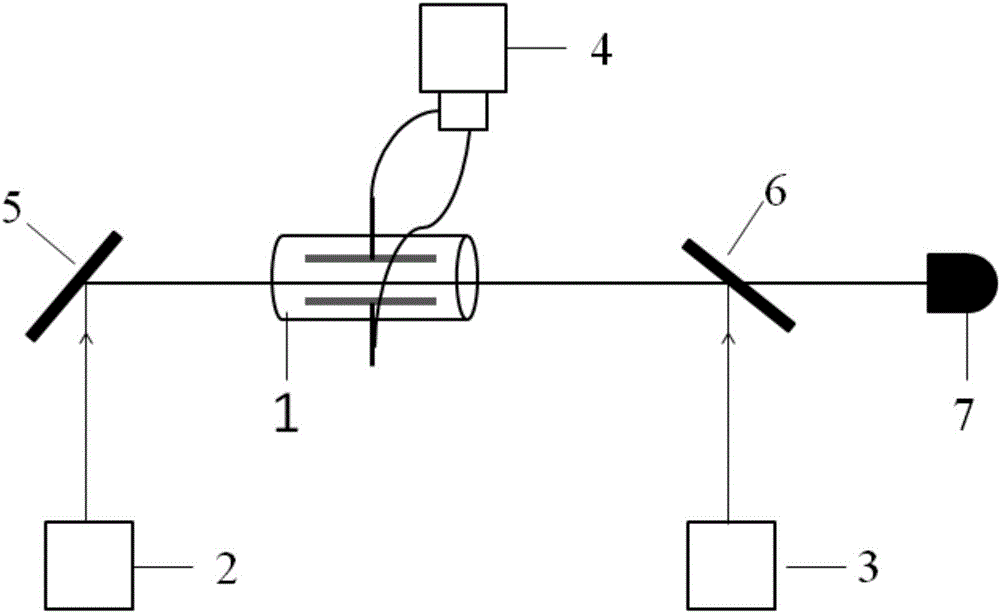
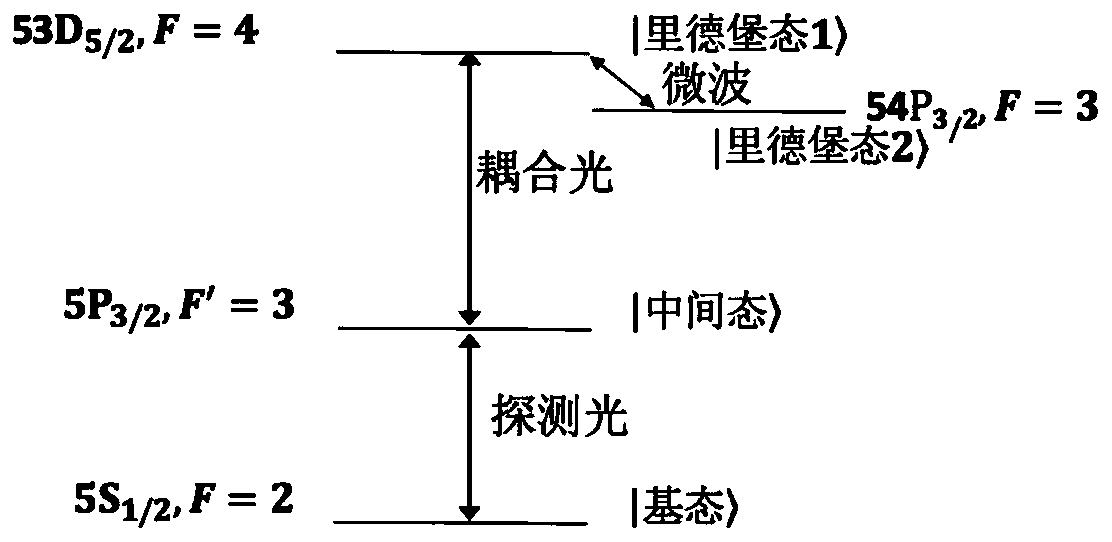
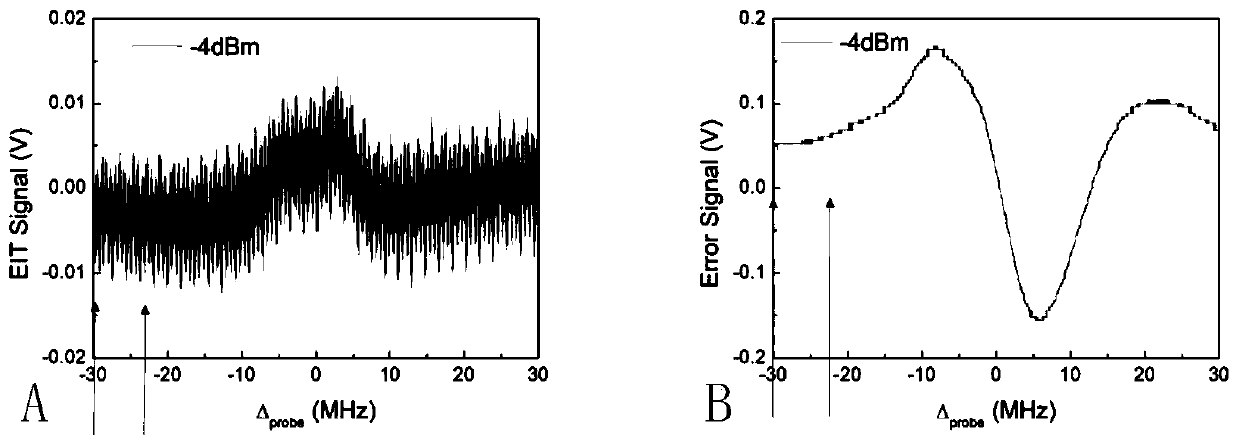
The invention discloses a measurement method and measurement device for the intensity of a microwave electric field. The measurement method includes the steps of splitting a probe light generated by a first laser into two beams of identical probe light, one of which enters a rubidium cell and the other of which enters vacuum equipment; coupling light, which is generated by a second laser, entering the rubidium cell, coherently exciting hot atoms in the rubidium cell from a ground state to a rydberg state by the coupling light and the probe light, and realizing electromagnetically induced transparency in an atomic vapor chamber; applying a microwave electric field generated by a microwave source onto the hot atoms, and coupling another adjacent rydberg state onto a three-level EIT system to form a four-level system; and respectively probing the two ways of transmission light emitted from the rubidium cell and the vacuum equipment, determining the time difference of the two ways of transmission light by analyzing a dispersion relation between the two ways of transmission light, and thus obtaining the intensity of the microwave electric field.
Owner:清远市天之衡量子科技有限公司
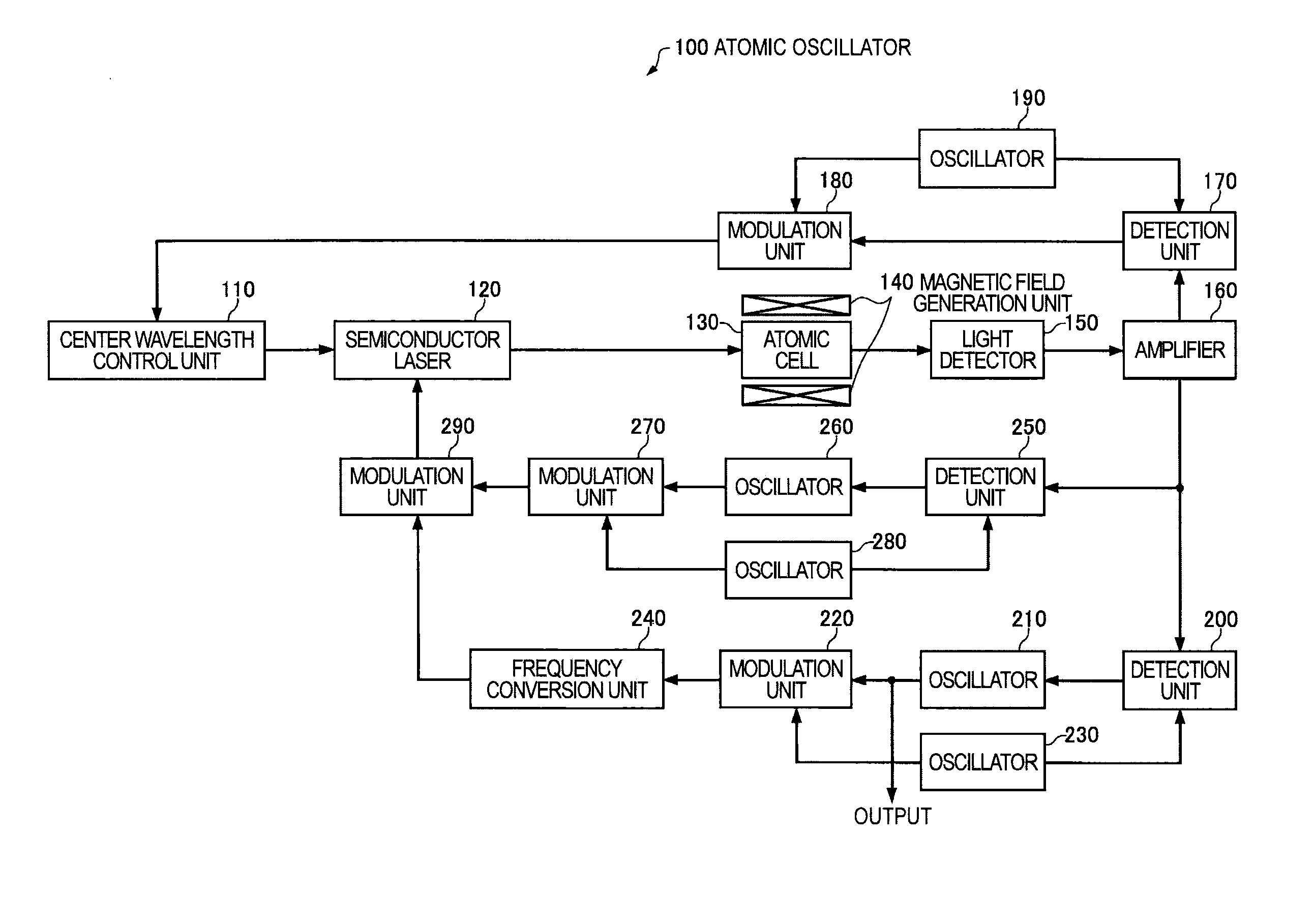
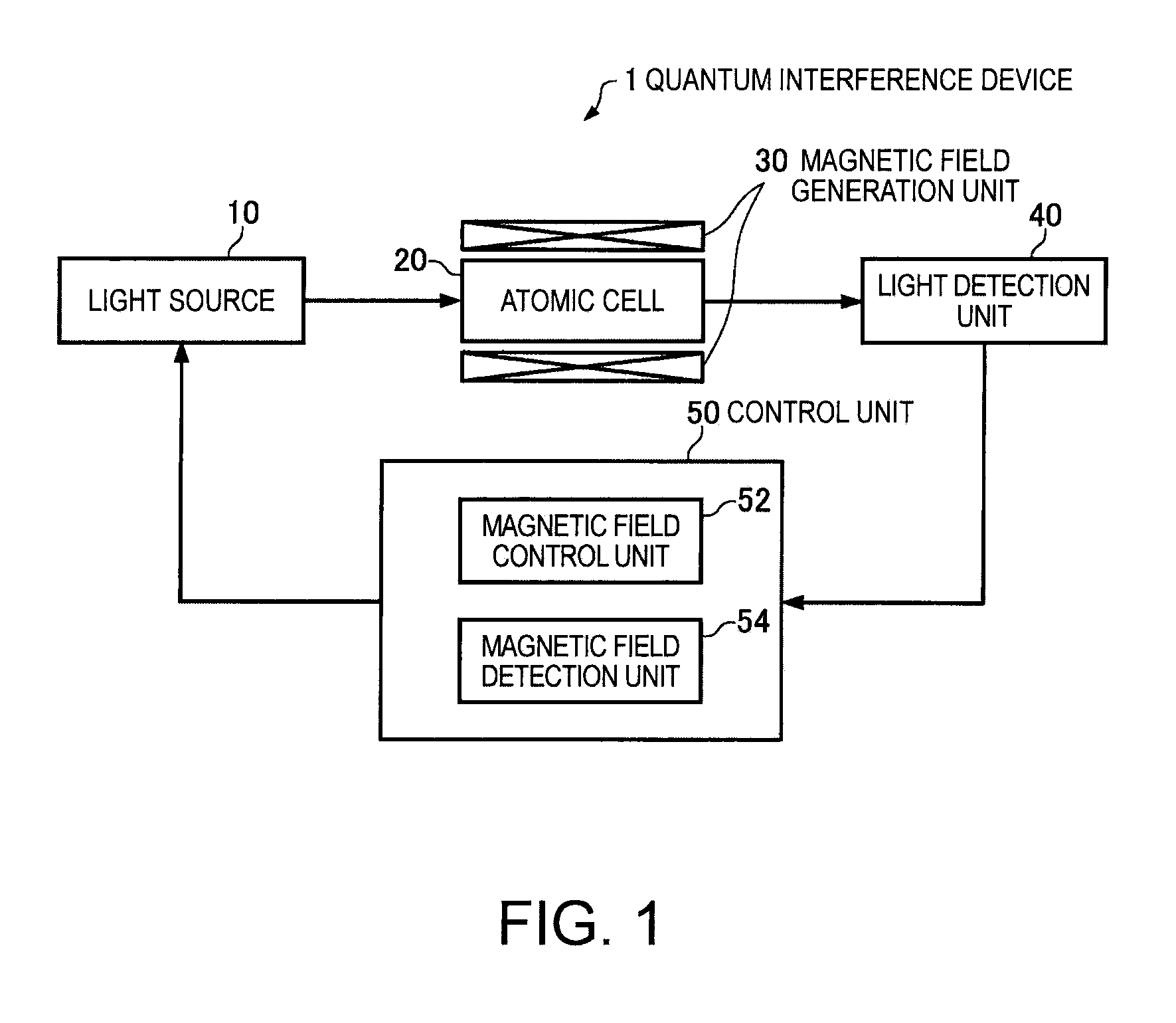
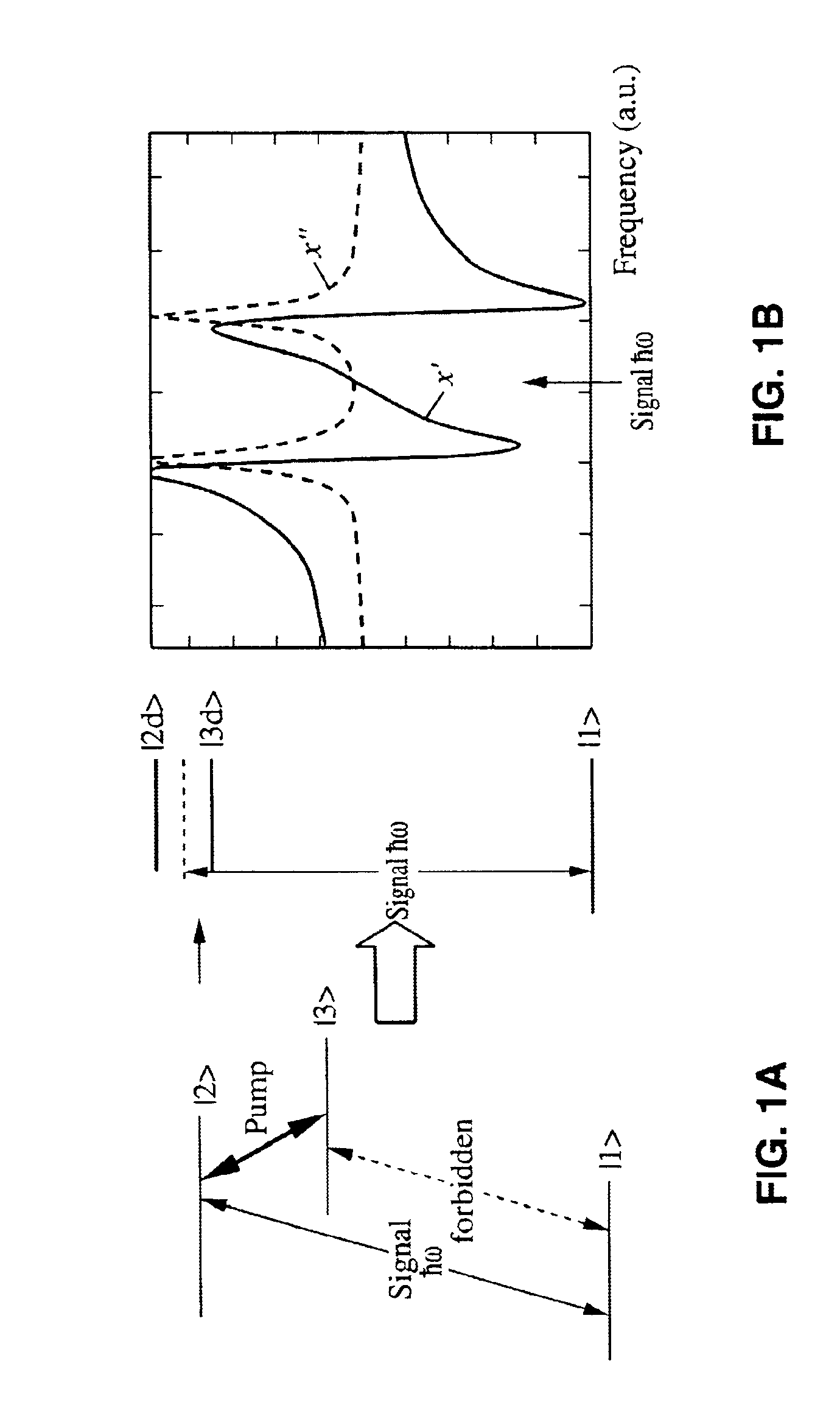
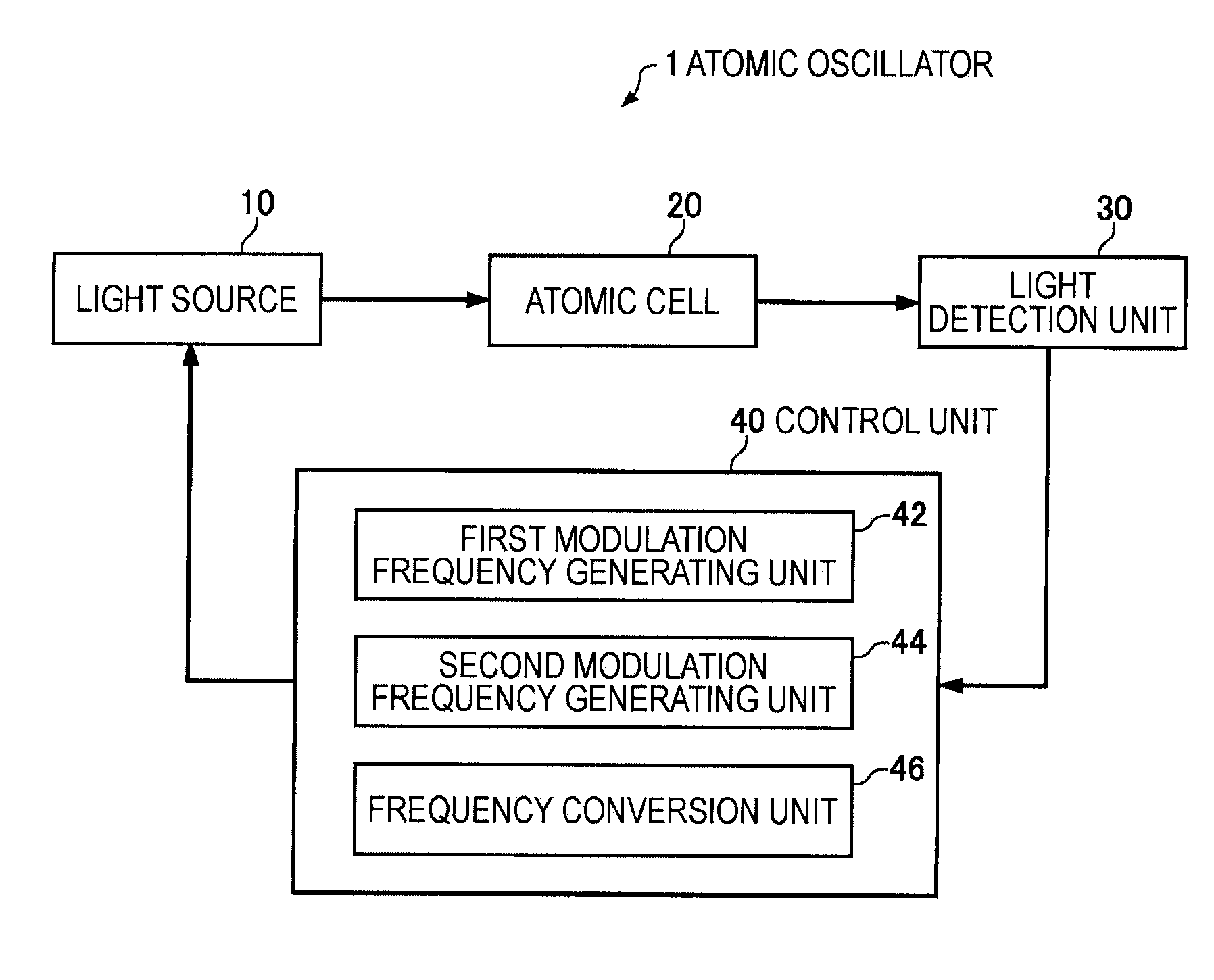
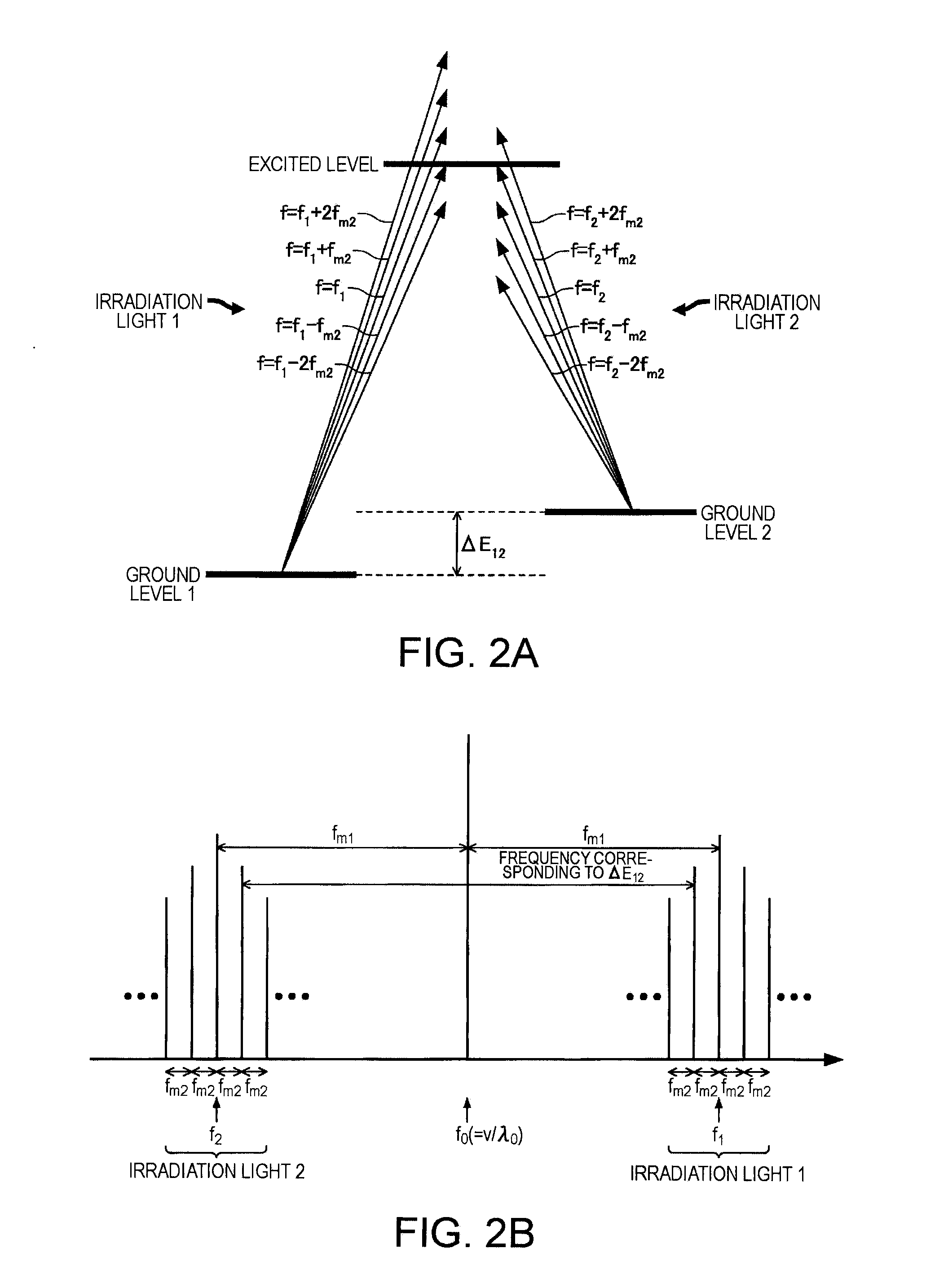
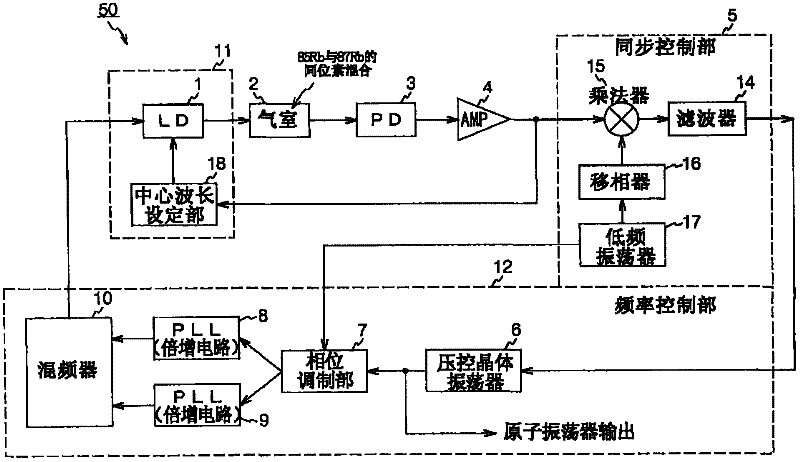
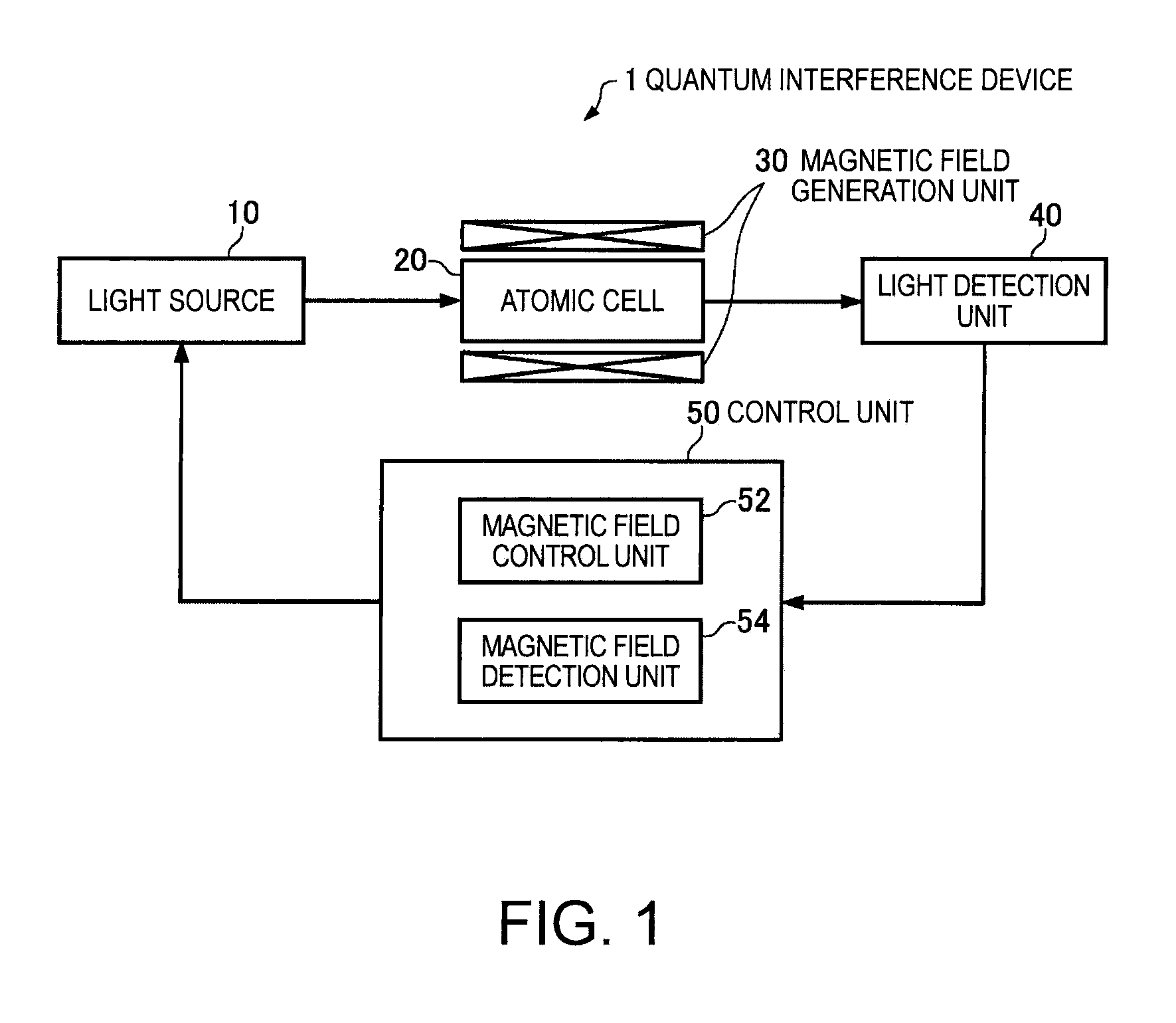
Quantum interference device, atomic oscillator and magnetic sensor
InactiveUS20110057737A1Increase incidenceImprove efficiencyPulse automatic controlGaseous masersGround stateAlkali metal
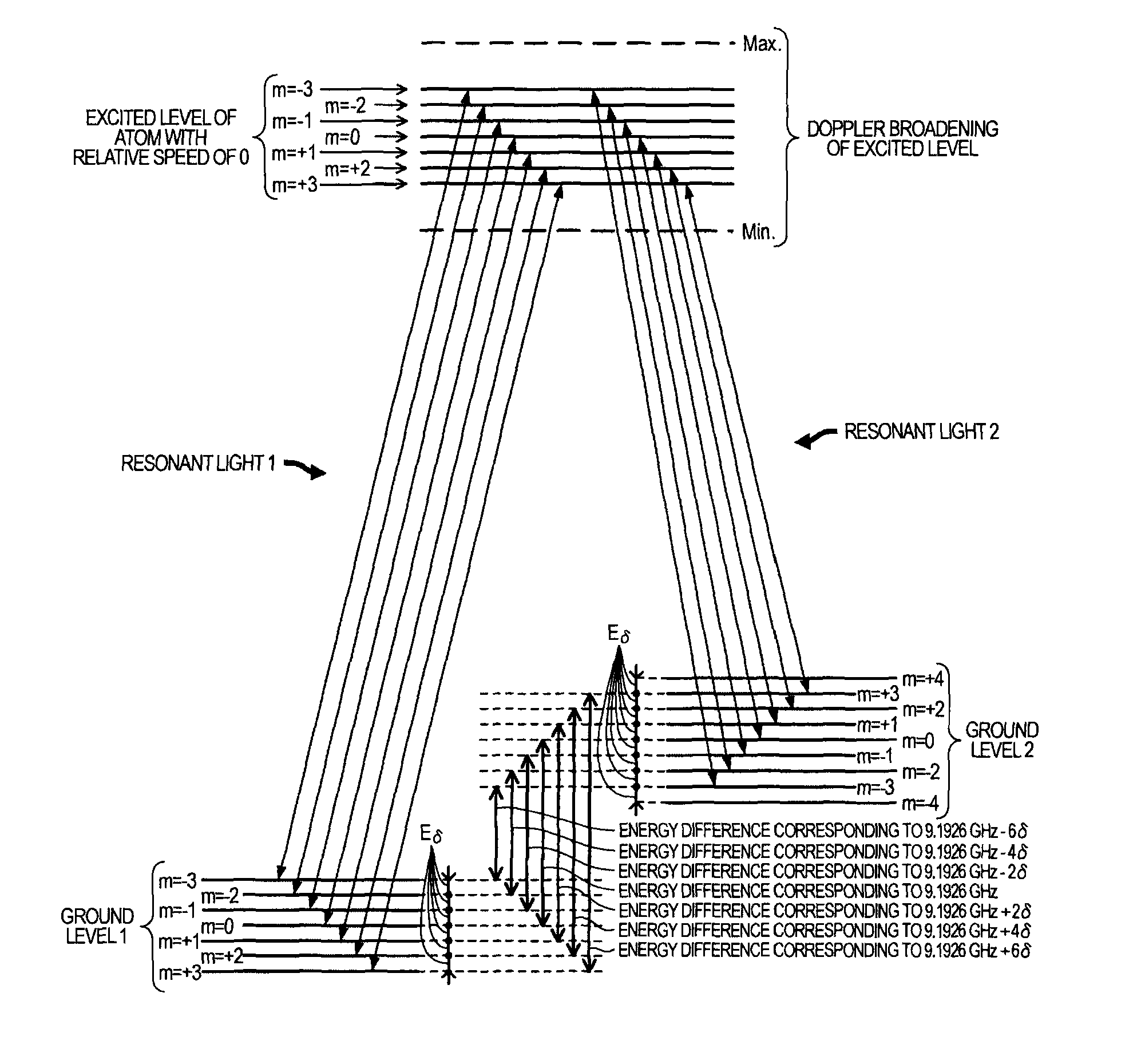
A quantum interference device for causing an electromagnetically induced transparency phenomenon to occur in an alkali metal atom by a resonant light pair including a first resonant light and a second resonant light, includes: a light source to generate a plurality of the first resonant lights different from each other in frequency by Δω and a plurality of the second resonant lights different from each other in frequency by Δω; a magnetic field generation unit that applies a magnetic field to the alkali metal atom; a light detection unit that detects intensities of lights including the first resonant lights and the second resonant lights passing through the alkali metal atom; and a control unit that controls to cause a frequency difference between the specified first resonant light and the specified second resonant light to become equal to a frequency difference corresponding to an energy difference between two ground levels of the alkali metal atom based on a detection result of the light detection unit, wherein the control unit controls at least one of the frequency Δω and intensity of the magnetic field generated by the magnetic field generation unit to satisfy at least one of 2×δ×n=Δω and Δω×n=2×δ (n is a positive integer) with respect to a frequency δ corresponding to an energy difference between two Zeeman split levels different from each other in magnetic quantum number by one among a plurality of Zeeman split levels generated in each of the two ground levels of the alkali metal atom by energy splitting due to the magnetic field.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
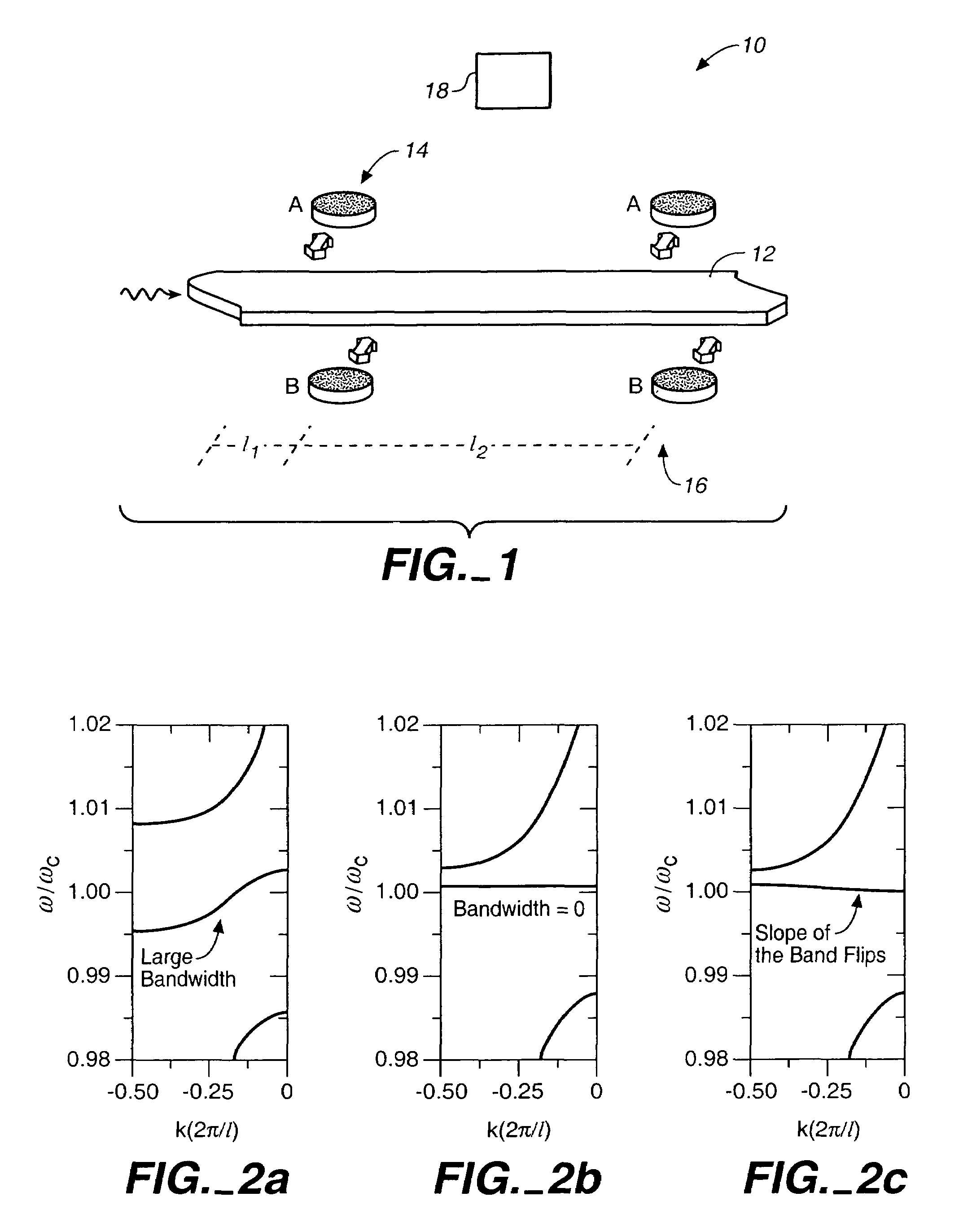
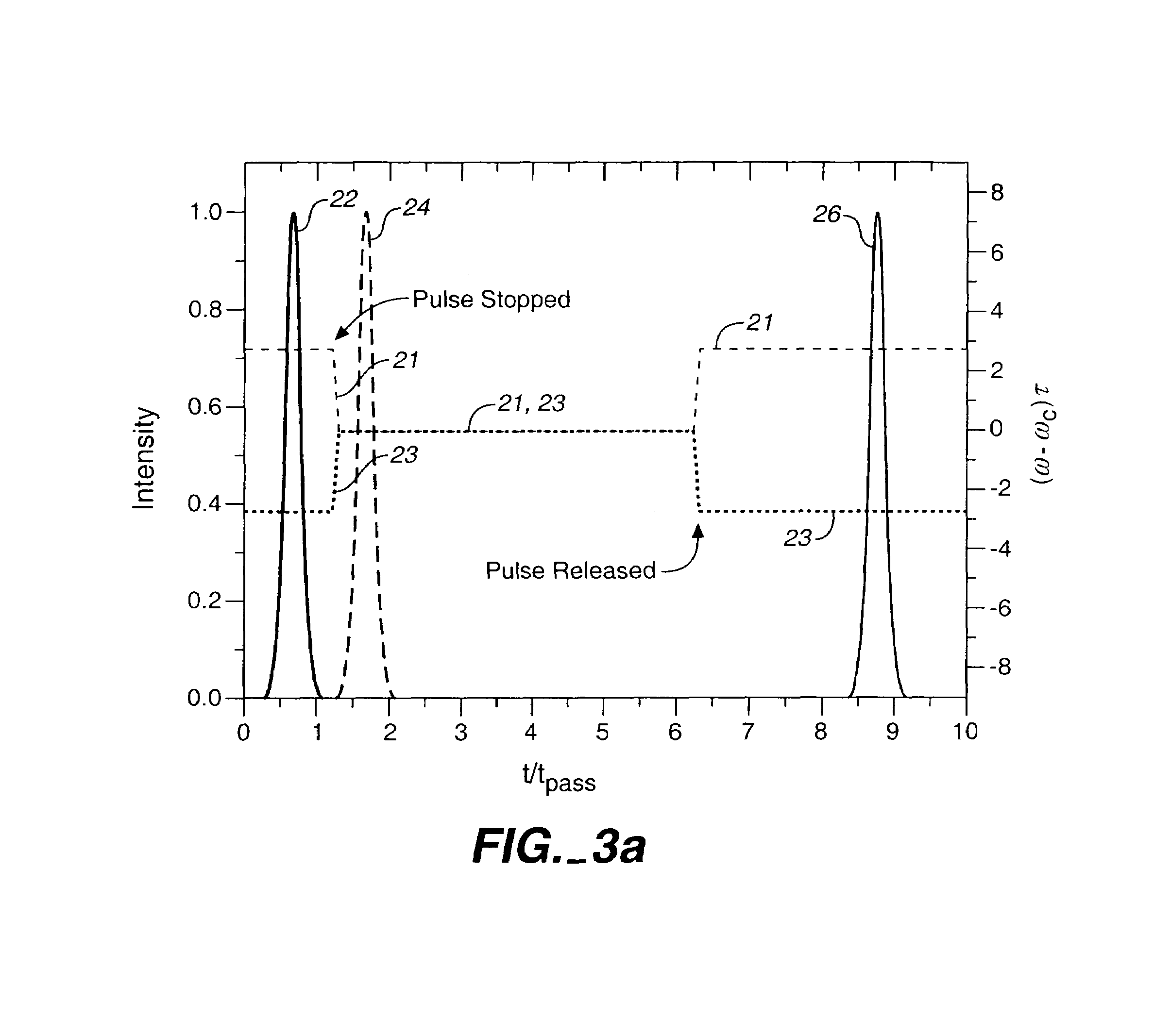
Stopping and time reversing light in a waveguide with an all-optical system
We introduce a new all-optical mechanism that can compress the bandwidth of light pulses to absolute zero, and bring them to a complete stop. The mechanism can be realized in a system consisting of a waveguide side-coupled to tunable resonators, which generates a photonic band structure that represents a classical analogue of the Electromagnetically Induced Transparency. The same system can also achieve a time-reversal operation. We demonstrate the operation of such a system by finite-difference time-domain simulations of an implementation in photonic crystals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
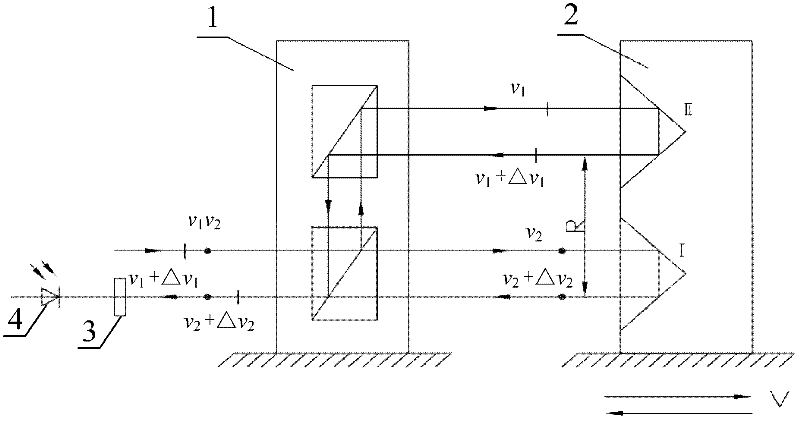
Angle measuring device and angle measuring method of double-frequency laser interferometer based on slow-light material
InactiveCN102564354AHigh detection sensitivityUsing optical meansSpectral hole burningPhotovoltaic detectors
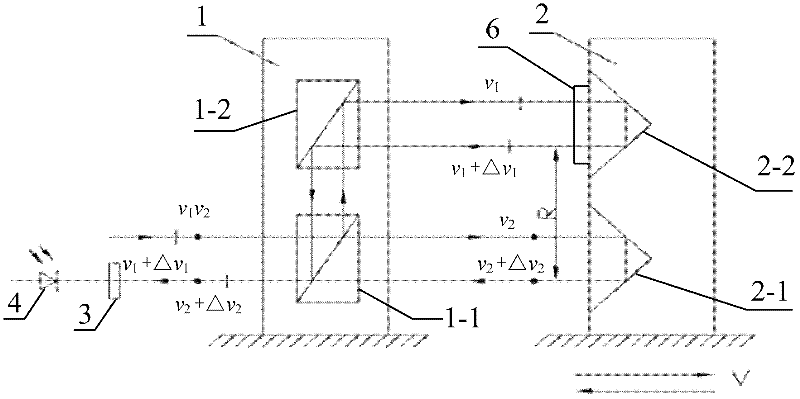
The invention provides an angle measuring device and an angle measuring method of a double-frequency laser interferometer based on a slow-light material, which relates to an angle measuring device and an angle measuring method of the double-frequency laser interferometer. The angle measuring device provided by the invention aims at solving the problem of low angle measuring sensitivity of the angle measuring device of the existing double-frequency laser interferometer. Double-frequency laser is divided into polarized light with frequency at v1 and polarized light with frequency at v2 through a polarization spectroscope in a polarization direction. The polarized light with the frequency at v1 enters a pyramid prism 1 to be reflected to the polarization spectroscope through the pyramid prism 1; the polarized light with the frequency at v2 is reflected to the slow-light material sequentially through a common corner reflector, the slow-light material and a pyramid prism 2 and then is reflected to the polarization spectroscope sequentially through the slow-light material and the common corner reflector to converge with polarized light reflected through the pyramid prism 1 at the position of the polarization spectroscope so as to form beat frequency; and converged light enters an optical detection face of a photoelectric detector after being subjected to transmission of a polarization reducing device. The angle measuring device and the angle measuring method provided by the invention are applicable to the electromagnetic induction transparency technology and the spectral hole burning technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for implementing EIT magnetometry
ActiveUS8054073B2Applied imageMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesElectric/magnetic detectionPhase detectorLight beam
A magnetometer is provided comprising an atomic vapor in an enclosure, a source of light for preparing the vapor into a state exhibiting electromagnetically induced transparency, a first laser beam passing through the atomic vapor, a phase detector for detecting changes in phase of the first laser beam, and a controller which controls the light source and laser beam and receives the information detected by the phase detector in order to compute from those changes in phase a magnetic field strength in the presence of a selected background magnetic field of at least 0.001 T. Operation in the presence of a background field helps make this magnetometer suitable for diagnostic imaging applications.
Owner:ENTANGLEMENT TECH
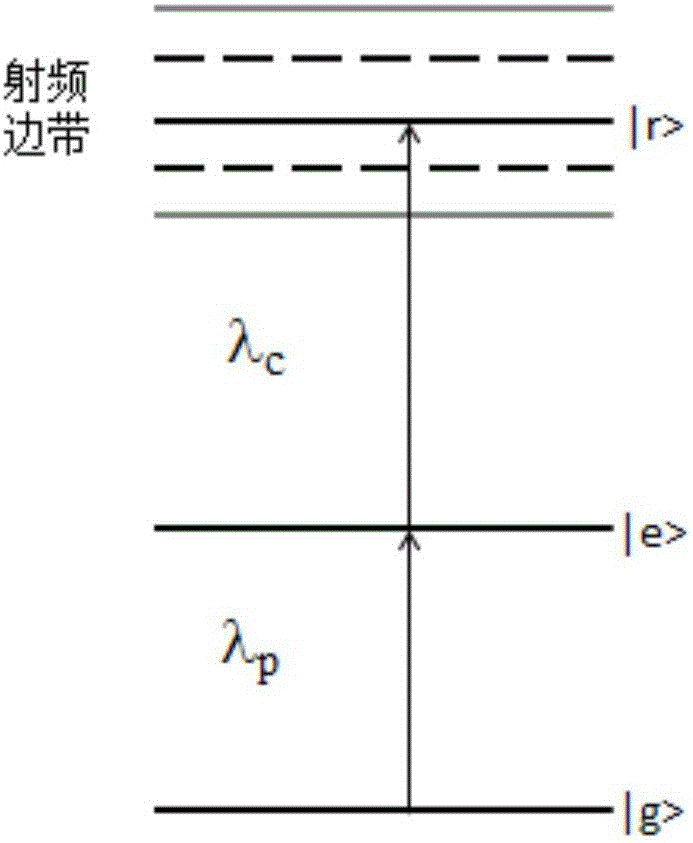
Radio frequency electric field correcting method and device based on Rydberg atom quantum coherence effect
ActiveCN106842095AOvercome the disadvantage of large errorNo distractionElectrical measurementsRydberg atomLaser light
The invention relates to a radio frequency electric field correcting method and device based on a Rydberg atom quantum coherence effect, and aims to solve the technical problem that an existing electric field measuring method has large errors. According to the adopted technical scheme, a glass cesium bubble provided with a pair of parallel electrode plates is used as a cesium atom sample cell, cesium atoms form electromagnetically induced transparency under the action of probe light sent by two laser light sources and coupling light, the electromagnetically induced transparency has Stark frequency shift and split under the action of a radio frequency electric field and generates dipole sidebands at the Rydberg energy level modulated by the radio frequency electric field, multiple energy level cross points are formed in the Stark spectrum, each cross point serves as a datum point for correcting the electric field, each datum point corresponds to an accurate electric field value, and then the determined electric value is used for correcting the radio frequency electric field. The device is composed of a cesium atom sample cell, two laser light sources, a radio frequency source, a high-reflectivity reflector, a dichroic mirror and a photoelectric detector.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Variable semiconductor all-optical buffer using slow light based on electromagnetically induced transparency
A variable semiconductor all-optical buffer and method of fabrication is provided where buffering is achieved by slowing down the optical signal using a control light source to vary the dispersion characteristic of the medium based on electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). Photonic bandgap engineering in conjunction with strained quantum wells (QWs) and quantum dots (QDs) achieves room temperature operation of EIT. Photonic crystals are used to sharpen the spectral linewidths in a quantum well structure due to its density of states and in a quantum-dot structure caused by the inhomogeneity of the dot size, typically observed in state-of-the-art QD materials. The configuration facilitates monolithic integration of an optical buffer with an amplifier and control laser to provide advantages over other material systems as candidates for optical buffers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Quantum interference device, atomic oscillator, and magnetic sensor
ActiveUS20100201452A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyPulse automatic controlGaseous masersCenter frequencyQuantum
A quantum interference device includes: gaseous alkali metal atoms; and a light source for causing a resonant light pair having different frequencies that keep a frequency difference equivalent to an energy difference between two ground states of the alkali metal atoms, the quantum interference device causing the alkali metal atoms and the resonant light pair to interact each other to cause an electromagnetically induced transparency phenomenon (EIT), wherein there are a plurality of the resonant light pairs, and center frequencies of the respective resonant light pairs are different from one another.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
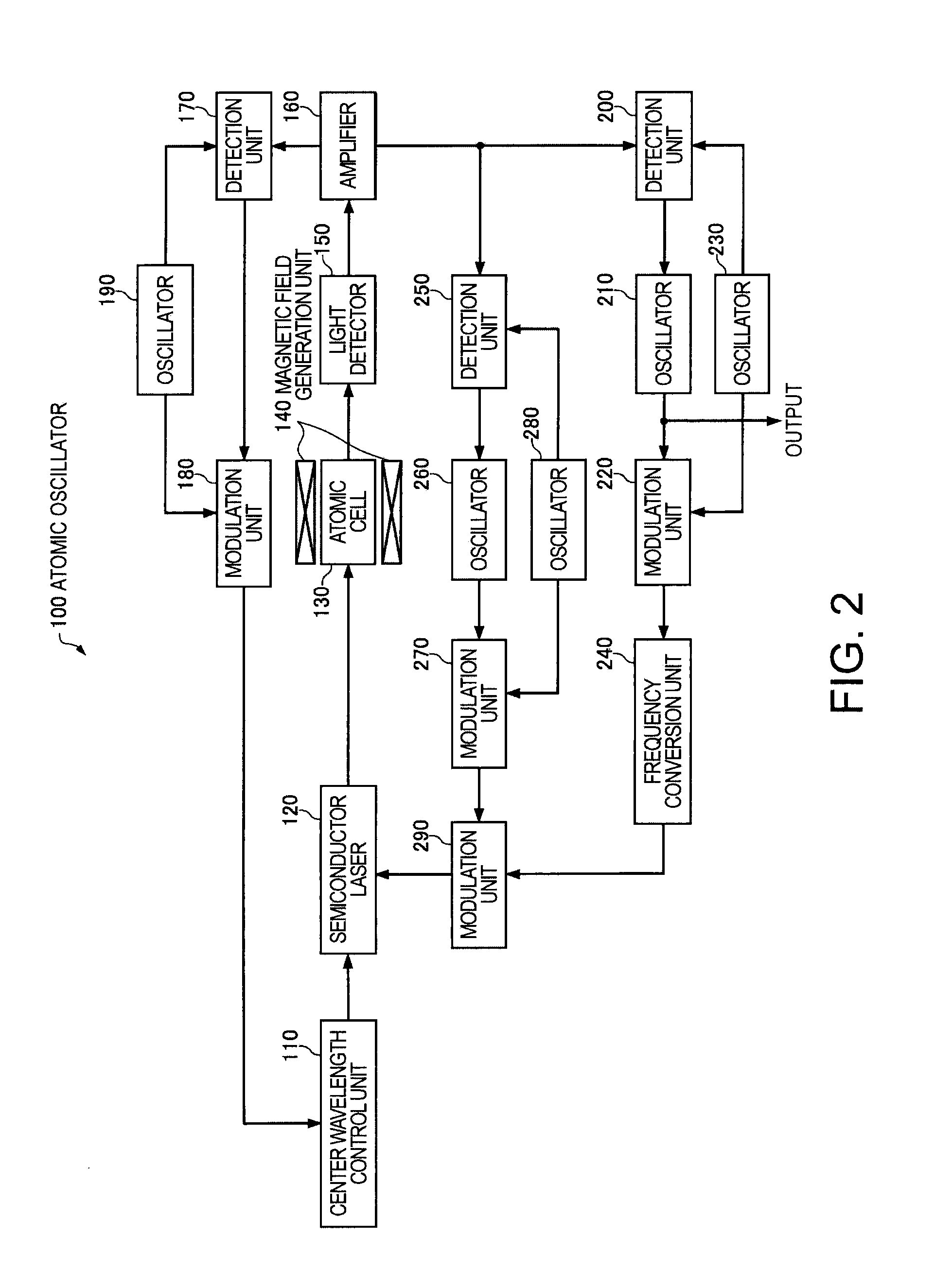
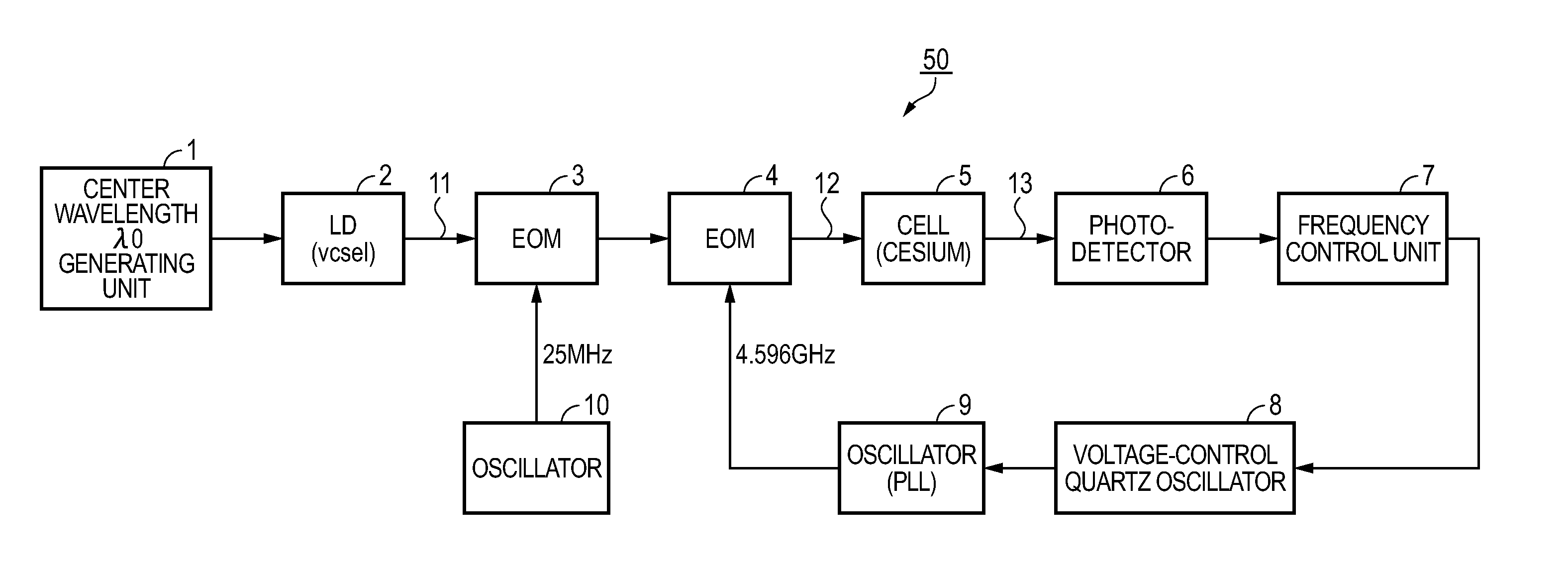
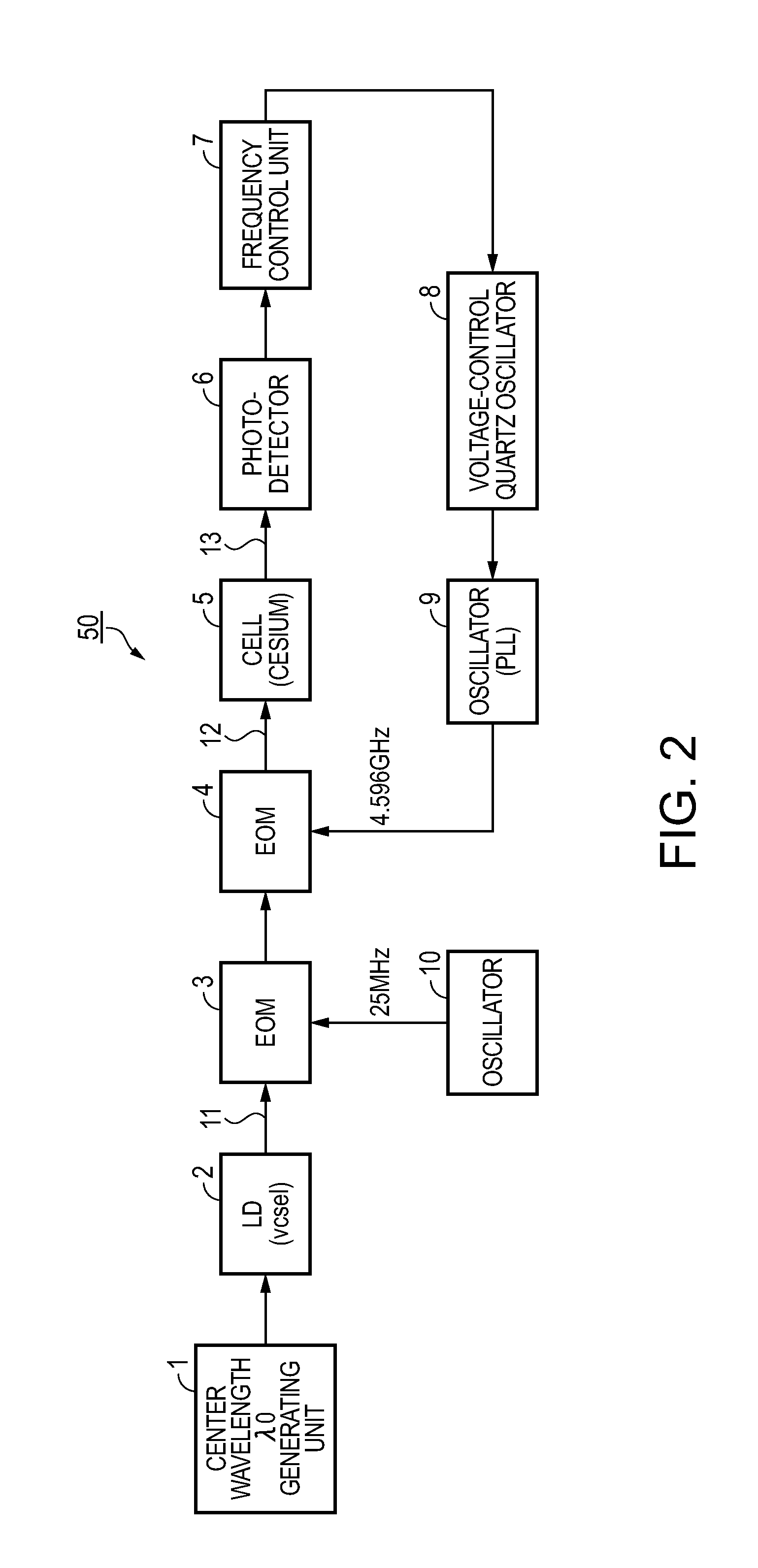
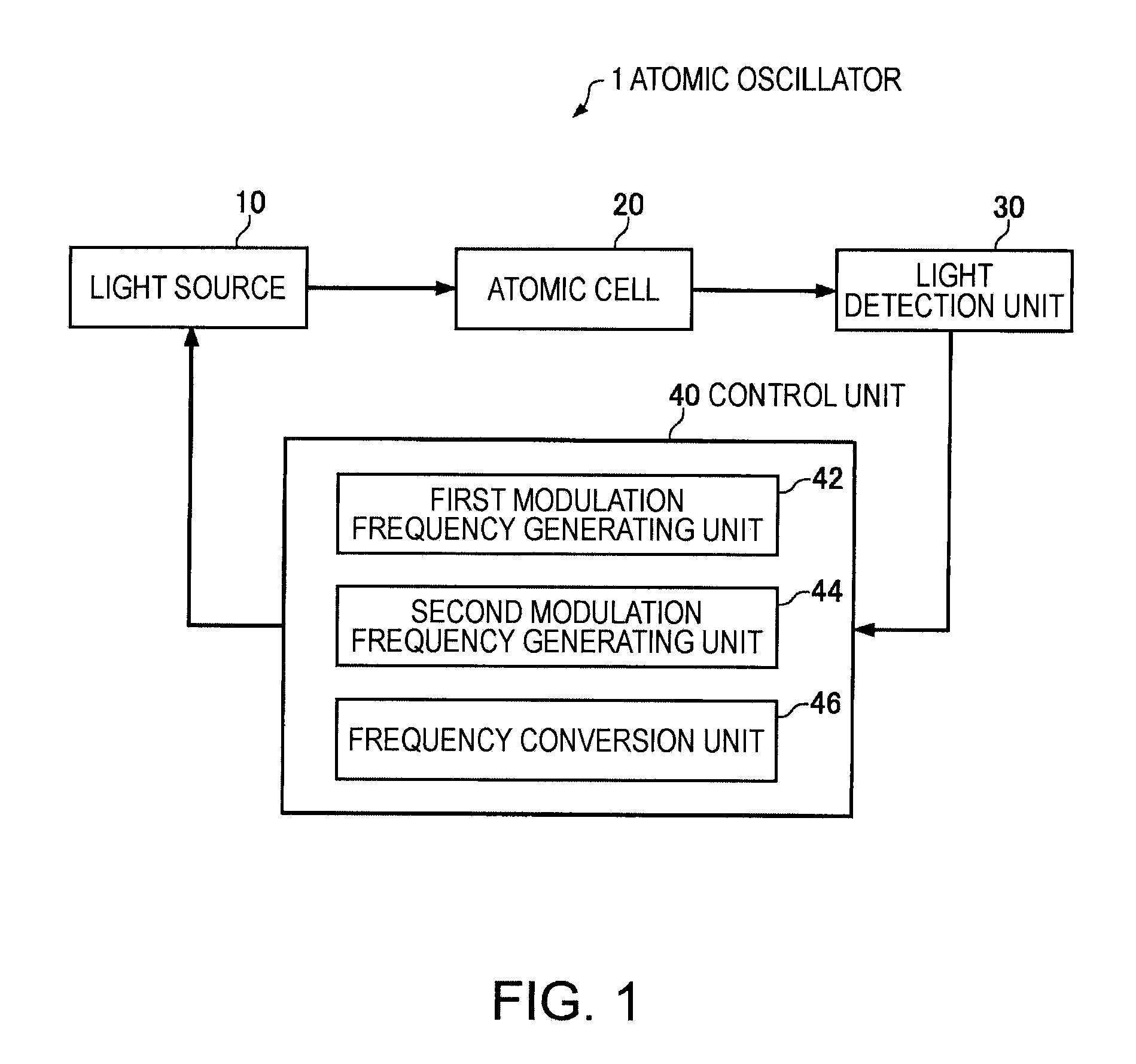
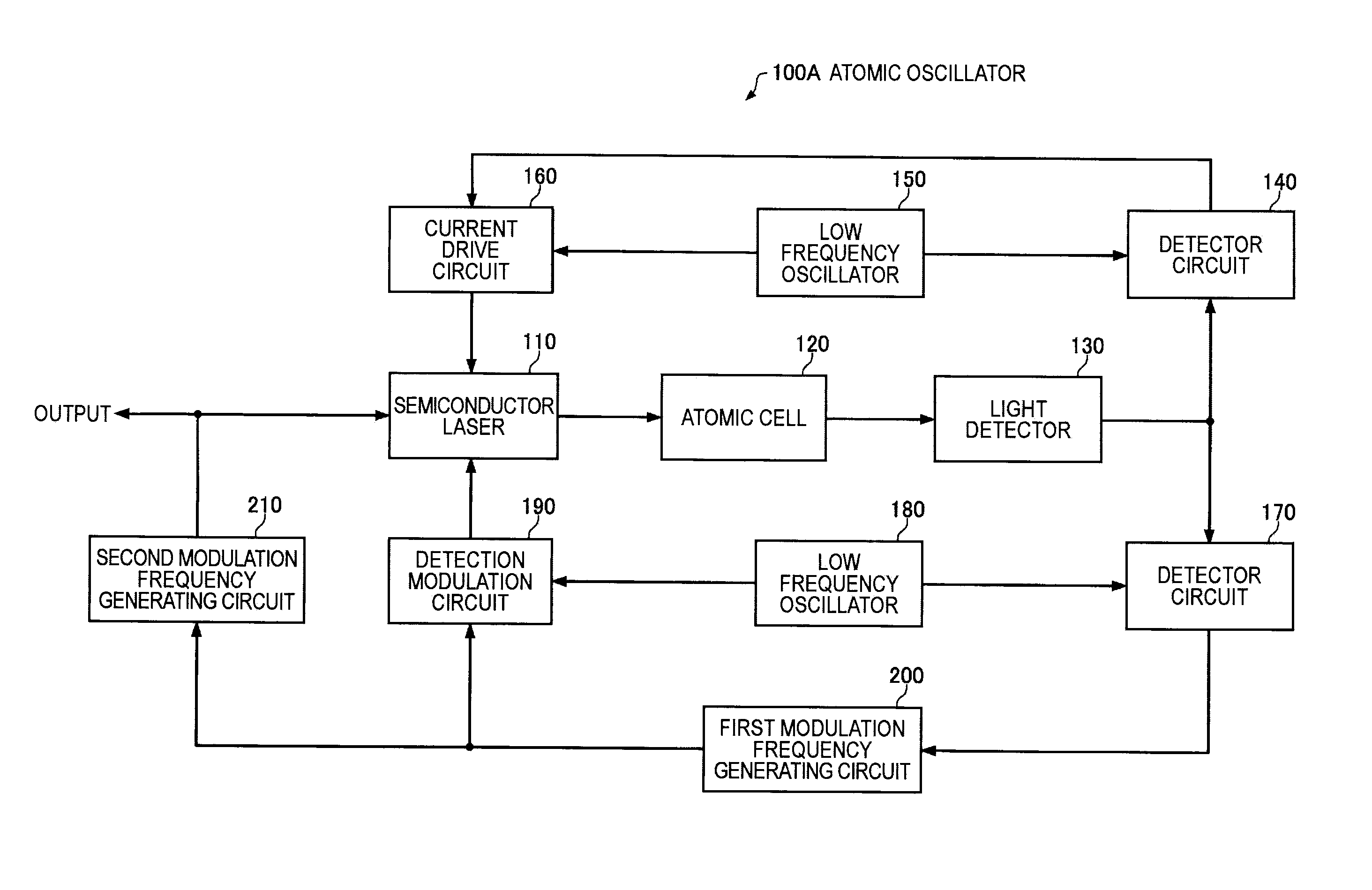
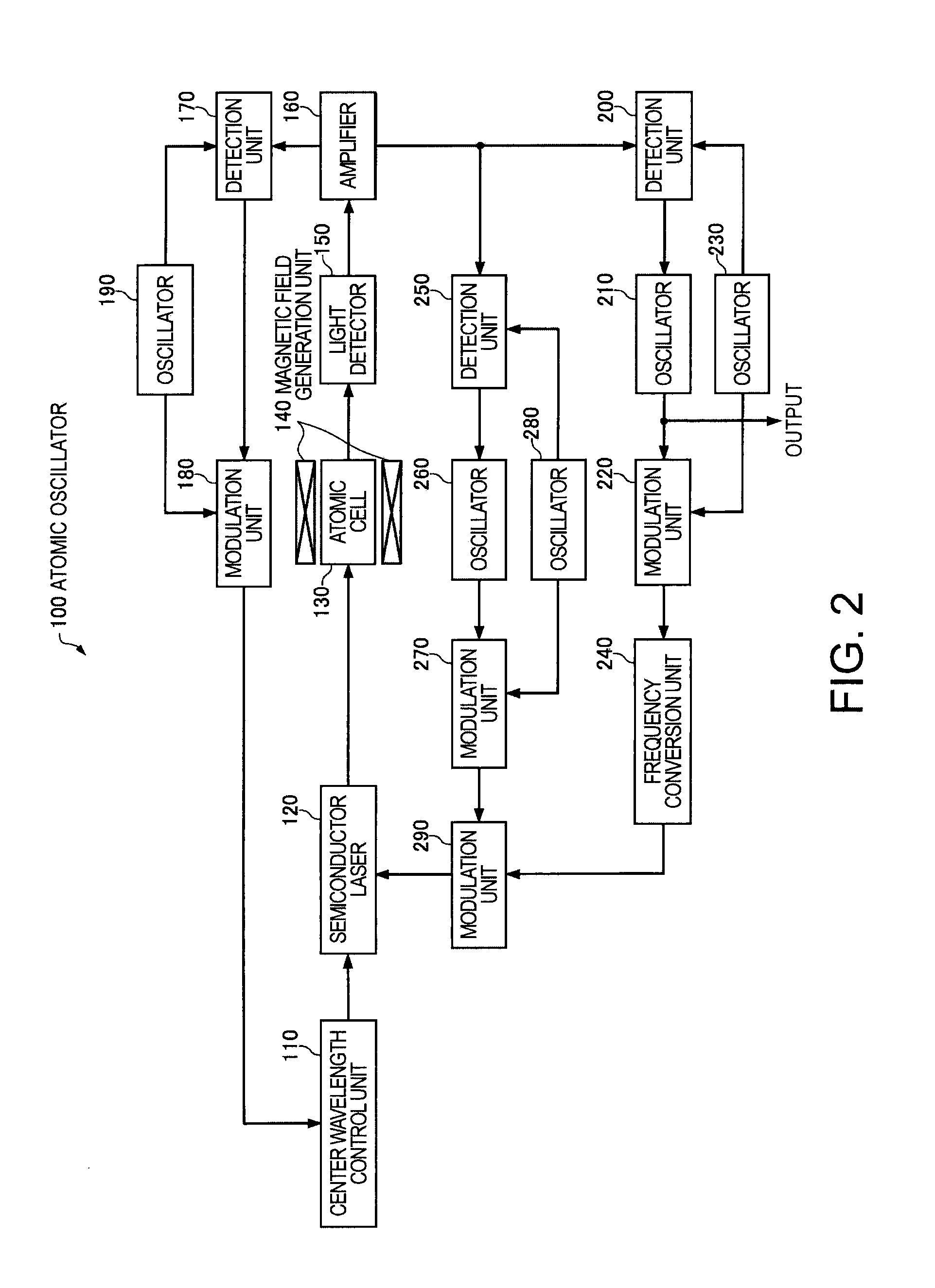
Atomic oscillator
ActiveUS20110109395A1Simple structureIncrease freedomPulse automatic controlGaseous masersIrradiationCenter frequency
An atomic oscillator using an electromagnetically induced transparency phenomenon caused by irradiation of a resonant light pair to an alkali metal atom, includes: a light source that generates a first light having a center frequency f1 and a plurality of frequency components different from each other in frequency by Δf, and a second light having a center frequency f2 and a plurality of frequency components different from each other in frequency by Δf; a light detection unit that detects intensities of lights including the first light and the second light passing through the alkali metal atom; and a control unit that controls, based on a detection result of the light detection unit, to cause a frequency difference between a specified frequency component of the first light and a specified frequency component of the second light to be equal to a frequency corresponding to an energy difference between two ground levels of the alkali metal atom, wherein a frequency difference between the center frequency f1 of the first light and the center frequency f2 of the second light is different from the frequency corresponding to the energy difference between the two ground levels of the alkali metal atom.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Waveguide filter based on electromagnetically induced transparency
InactiveCN103972623ALower quality factorImproved stop-band rejectionWaveguide type devicesTransmission zerosOut of band rejection
The invention discloses a waveguide filter based on electromagnetically induced transparency. The waveguide filter comprises an upper cavity, a lower cavity, a medium substrate, a signal input port and a signal output port, wherein the upper cavity and the lower cavity form a standard rectangular waveguide, and the medium substrate is inserted into the portion between the upper cavity and the lower cavity of the standard rectangular waveguide. A rectangular metal ring, an out-of-band rejection sheet, two rows of metallized through holes and a grounding epitaxial band are arranged in a metal micro-strip structure on the front face of the medium substrate, and two symmetric C-shaped resonance structures and a grounding epitaxial band are arranged on a metal micro-strip structure on the back face of the medium substrate. The rectangular metal ring located on the front side of the medium substrate and the two symmetric C-shaped resonance structures located on the back face of the medium substrate interact to generate a passing band of an electrically induced transparent window and a passing band of a magnetically induced transparent window, namely, the electromagnetically induced transparency effect is formed, upper sidebands and lower sidebands of the passing bands of the waveguide filter obtained through the effect are respectively provided with a transmission zero, high selectivity is achieved, and the waveguide filter is compact in structure and easy to design.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and device for improving microwave electric field intensity measurement signal-to-noise ratio through Zeeman frequency modulation
ActiveCN111308228AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove the signal-to-noise ratio of intensity measurementsElectrostatic field measurementsNoiseParticle physics
The invention provides a method and device for improving the microwave electric field intensity measurement signal-to-noise ratio through Zeeman frequency modulation. The method comprises the following steps: the frequency of coupling light is locked on the resonance transition of the intermediate state and the Rydberg state 1; the microwave frequency is locked on the resonance transition of the Rydberg state 1 and the Rydberg state 2, the frequency of the detection light is scanned near the resonance transition frequency of the ground state and the intermediate state, and the spectrum of thedetection light after penetrating through an atom pool is measured so as to obtain the spectrum of the AT split signal of the Rydberg electromagnetic induction transparency EIT; the position of the atomic energy level of the sample is modulated by using an alternating-current magnetic field, and frequency modulation is performed on the spectrum; and the spectrum of the AT split signal of the Rydberg electromagnetic induction transparent EIT is demodulated to obtain a dispersive frequency discrimination signal of the EIT-AT split spectrum. According to the method and device, the atomic energy level is modulated through the alternating magnetic field, frequency modulation is equivalent to spectrum frequency modulation, the problem of residual amplitude does not exist naturally, and meanwhilean experiment system is simpler and more convenient.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES +1
Terahertz band metamaterial sensor based on quasi-electromagnetically induced transparency (quasi-EIT) effect
ActiveCN108572162AHigh Q valueHigh Refractive Index SensitivityPhase-affecting property measurementsDark modeMicrometer
The invention claims a terahertz band metamaterial sensor based on quasi-electromagnetically induced transparency (quasi-EIT) effect. The terahertz band metamaterial sensor comprises a dielectric layer and a metamaterial of a sub-wavelength metal array on the dielectric layer, wherein the sub-wavelength metal array is composed of a plurality of open circular resonant rings and open square resonantrings. Under the excitation of terahertz waves, the open circular resonant rings and the open square resonant rings separately exhibit a bright mode and a dark mode; when the two resonant rings are combined and the space between the two is 80.0-85.0 micrometers, the bright and dark modes are coupled to each other, destructive interference is generated, realizing the quasi-EIT effect is realized,and sharp transmission peaks are produced near resonance points. The sensitivity of the terahertz band metamaterial sensor is measured according to the amount of translation of the frequency of the sharp transmission peaks generated by the quasi-EIT effect in the transmittance spectrum within the unit refractive index change, so as to realize the refractive index sensing function in the frequencyrange of 400 GHz to 800 GHz.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
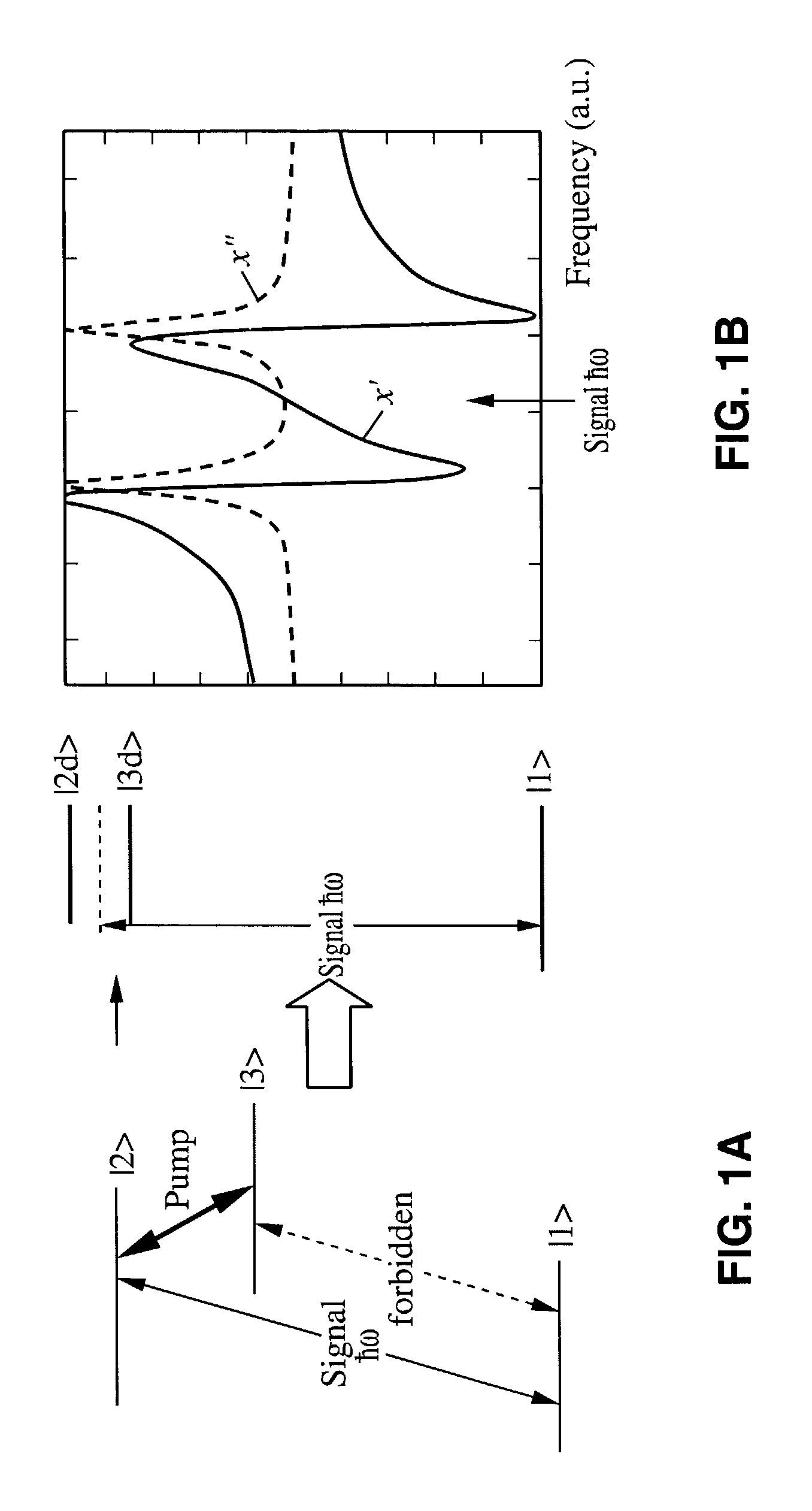
Using electro-magnetically induced transparency in photonic crystal cavities to obtain large non-linear effects
InactiveUS7031585B2Add nonlinearityOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsPhotonic crystal cavityPhotonic crystal structure
A photonic crystal structure includes a microcavity (point defect). The photonic crystal structure (or just the microcavity) is doped with materials that exhibit electro-magnetic induced transparency (EIT) so as to increase the non-linear properties of the photonic crystal.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Adjustable and controllable spatial electromagnetic induction transparent metamaterial device
The invention discloses an adjustable and controllable spatial electromagnetic induction transparent metamaterial device. The device comprises a substrate and a metal unit array which is positioned on the substrate and can be used for generating an electromagnetic induction transparent phenomenon, wherein the metal unit array comprises a plurality of metal units which are distributed in an array form; each metal unit comprises a first metal microstructure and a second metal microstructure; each first metal microstructure comprises a first metal pattern; each second metal microstructure comprises a second metal pattern; each first metal microstructure and / or each second metal microstructure further comprises a semiconductor element. By adopting the adjustable and controllable spatial electromagnetic induction transparent metamaterial device, the problem of incapability of easily and rapidly adjusting and controlling the working frequency of the electromagnetic induction transparent metamaterial in the prior art can be effectively solved, and a large modulation depth and a high switching speed can be realized. The device can be widely applied to the technical fields of slow light modulation, optical switches, sensors, wireless communication and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fast all-optical switch
An apparatus, system, and method for fast all-optical switching is presented. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a first light transmitting medium. The apparatus may also include a second light transmitting medium coupled to the first light transmitting medium and disposed to form an interface region between the first light transmitting medium and the second light transmitting medium. Additionally, the apparatus may include a plurality of Lambda atoms disposed in the interface region, the Lambda atoms adapted to cause Electromagnetically-Induced Transparency (EIT) in the interface region in response to an incident photon.
Owner:UTI LLP
Delayed optical logic gates
ActiveUS20100232001A1Easy to handleMultiplex system selection arrangementsLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesInformation processingThree level
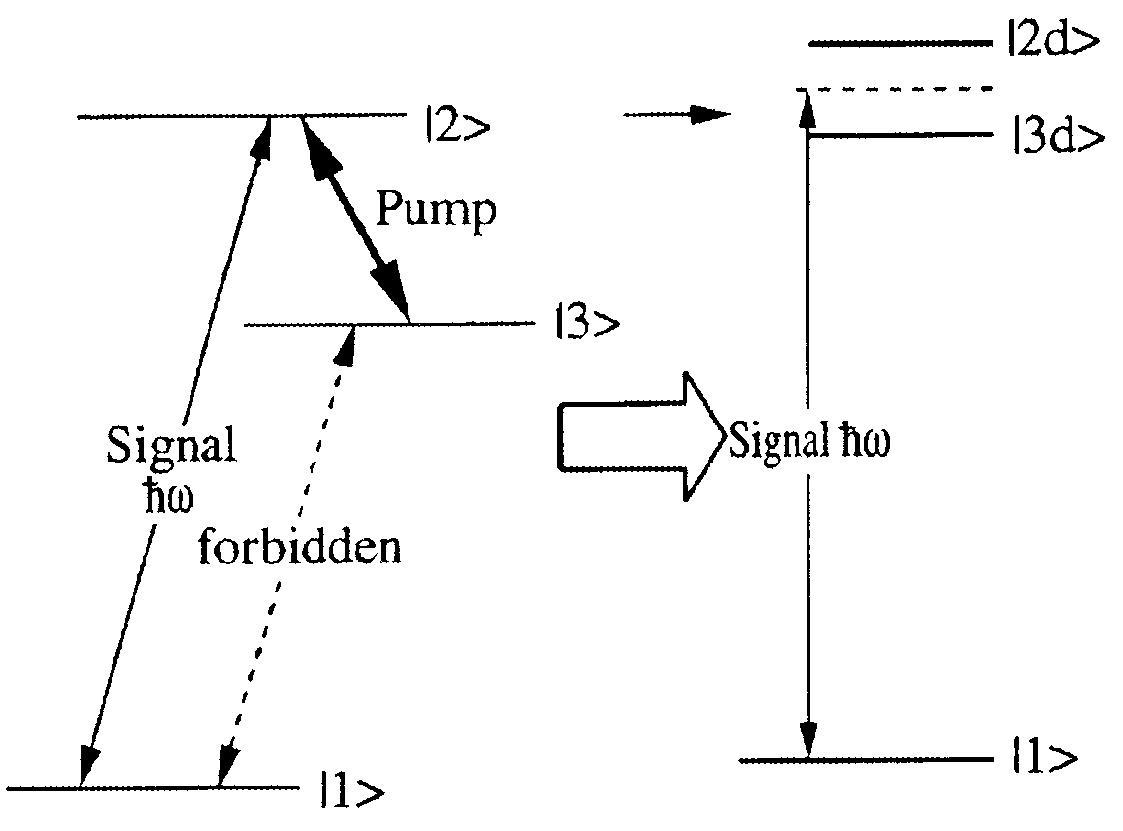
A system, method, and apparatus for delayed optical logic gates based on slow light and enhanced nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes, where a single or multiple delayed optical routers are utilized for dark resonance interactions in which two-color lasers interact with a three-level nonlinear optical medium comprised of two ground states and one excited state through the nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes. The delayed optical logic mechanism is based on combination of single or multiple dark resonance-induced two-photon coherence conversion via slow light phenomenon. The two-photon coherence induced on the ground states is optically detected via nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes. The nondegenerate four-wave mixing generation is enhanced owing to dark resonance or electromagnetically induced transparency. The gating time and bandwidth of the present delayed optical logic gates is invariant to the delayed time of the delayed optical router because IN and OUT bandwidth across the nonlinear medium must be same. The present invention of delayed optical logic gates have potential to keep up ultra-high-bandwidth optical information processing using relatively slow electronic processing devices.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Grapheme based resonance controller
The invention provides a grapheme based resonance controller and relates to the field of group delay adjustable controllers. The invention solves a problem that an electric field polarization direction of electromagnetic waves is single when a grapheme based light-shade mode is coupled to an EIT structure. The controller includes a rectangular resonance controller composed of a plurality of adjustable resonance units. Each adjustable resonance unit has a rectangular structure and is composed of a rectangular silicon substrate, a SiO2 coating and a resonance ring arranged from bottom up in sequence. Each resonance ring includes a No.1 grapheme nanometer band and a No.2 grapheme nanometer band, wherein the No.1 grapheme nanometer band has a long strip shaped structure while the No.2 graphemenanometer band has a U shaped ring structure and one part of the long strip shaped structure overlaps with one side wall of the U shaped ring structure and said part and said side wall are coplanar.The resonance rings are used for realizing energy coupling between the No.1 grapheme nanometer bands and No.2 grapheme nanometer bands under electromagnetic induction, so that electromagnetically induced transparency with adjustable window frequency of the resonance adjustable resonance units is generated. The controller provided by the invention is mainly used for storage of optical signals.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Delayed optical router/switch
ActiveUS8135277B2Relaxes switching performanceIncrease speedFibre transmissionOptical multiplexData trafficElectron
A system, method, and apparatus for delayed optical router based on slow light and nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes are presented, in which three laser pulses interact with a three-level nonlinear optical medium composing two closely spaced ground states and an excited state. The delayed optical routing mechanism is based on a slow light phenomenon, in which a group velocity of an incoming input signal pulse is slowed down due to quantum coherence induced refractive index change. The two-photon coherence induced on the ground states via electromagnetically induced transparency is optically recovered via nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes. The nondegenerate four-wave mixing generation is enhanced owing to absorption cancellation. In this case, the individual pulse switching / routing time is limited by the coherence decay time that is much faster than population decay time, where the population decay-time is a limiting factor of conventional switching devices. In the present invention of the delayed optical router the overall switching / routing time, however, is controlled to be delayed by using the slow light. Even though the overall switching / routing time can be delayed, the switching bandwidth of the present invention is not degraded at all because the input and output signal's group velocity across the delayed optical router is still same. Therefore, the present invention of the delayed optical router gives an advantage of wide-bandwidth optical data traffic control using a narrow-bandwidth processing unit such as an electronic device. Another advantage is signal amplifications owing to the dark-resonance enhanced nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH +1
All-dielectric metamaterial EIT (electromagnetically induced transparency)-like resonance device
The present invention discloses an all-dielectric metamaterial EIT (electromagnetically induced transparency)-like resonance device. The all-dielectric metamaterial EIT (electromagnetically induced transparency)-like resonance device comprises a planar waveguide and a two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator; the planar waveguide comprises a first dielectric layer; the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator is composed of cuboid dielectric bars which are arranged at the upper surface of the first dielectric layer and are in two-dimensional periodic distribution; the refractive index of the cuboid dielectric bars is greater than the refractive index of the first dielectric layer; the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator has a resonant characteristic, so that the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator can generate a series of Mie resonance according to the Mie resonant principle; the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator has a grating-like effect, so that the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator can make incident waves diffracted and coupled with the guided mode of the planar waveguide; and an EIT-like effect can be generated through controlling the interaction of Mie resonance and guided mode resonance. With the all-dielectric metamaterial EIT (electromagnetically induced transparency)-like resonance device of the invention adopted, high-quality factor resonance and high resonance intensity can be achieved, and a high group refractive index can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
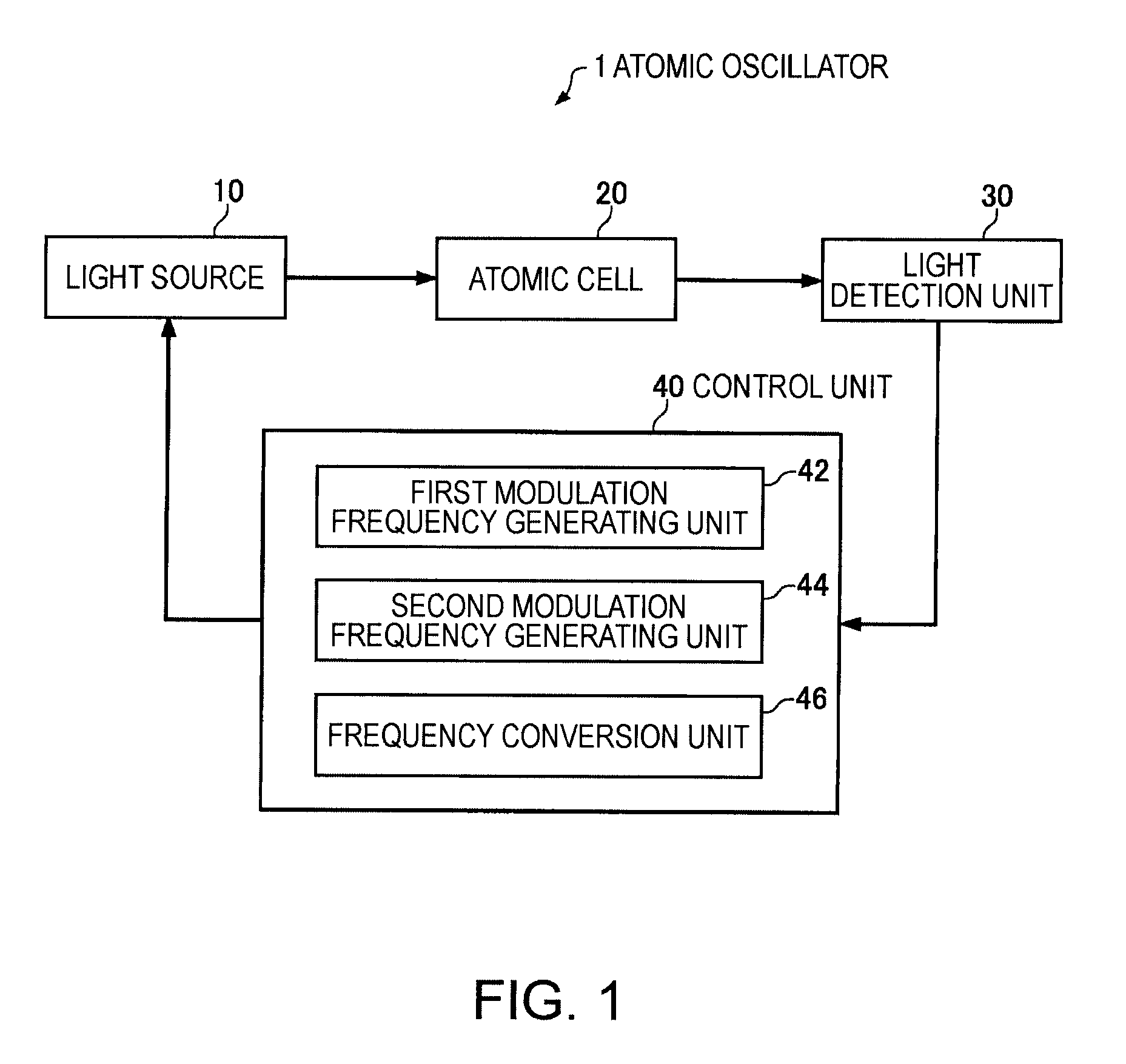
Atomic oscillator
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Atomic oscillator
ActiveUS8314661B2Simple structureIncrease freedomPulse automatic controlGaseous masersCenter frequencyElectromagnetic induction
An atomic oscillator using an electromagnetically induced transparency phenomenon caused by irradiation of a resonant light pair to an alkali metal atom, includes: a light source that generates a first light having a center frequency f1 and a plurality of frequency components different from each other in frequency by Δf, and a second light having a center frequency f2 and a plurality of frequency components different from each other in frequency by Δf; a light detection unit that detects intensities of lights including the first light and the second light passing through the alkali metal atom; and a control unit that controls, based on a detection result of the light detection unit, to cause a frequency difference between a specified frequency component of the first light and a specified frequency component of the second light to be equal to a frequency corresponding to an energy difference between two ground levels of the alkali metal atom, wherein a frequency difference between the center frequency f1 of the first light and the center frequency f2 of the second light is different from the frequency corresponding to the energy difference between the two ground levels of the alkali metal atom.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
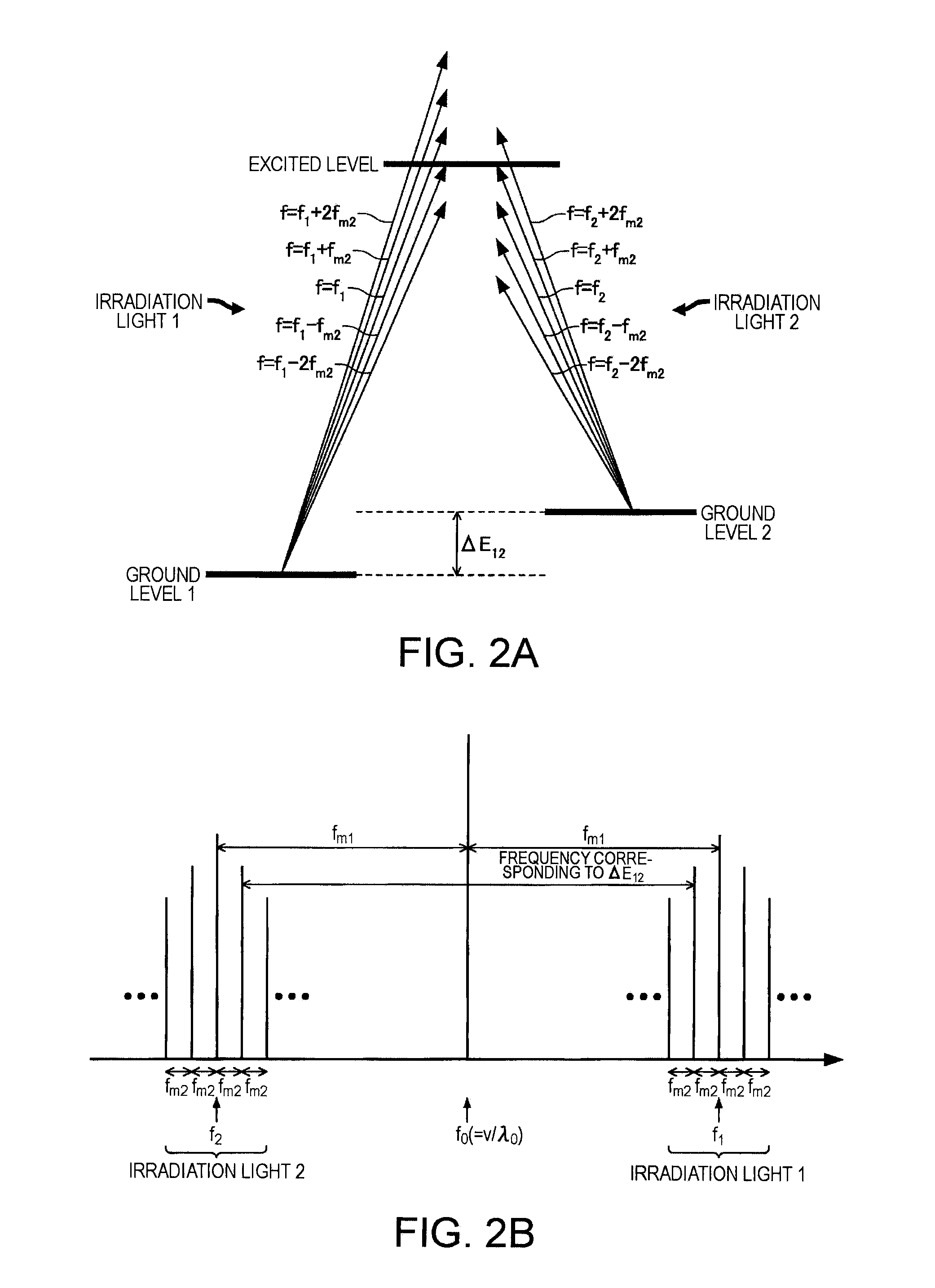
Quantum interference device, atomic oscillator and magnetic sensor
InactiveUS8279016B2Improve efficiencyPulse automatic controlGaseous masersMagnetic quantum numberGround state
A quantum interference device causing electromagnetically induced transparency in an alkali metal atom includes: a light source generating first and second resonant lights with frequency differences Δω; a magnetic field generator applying a magnetic field to the atom; a light detector detecting intensities of the first and second resonant lights passing through the atom; and a controller causing a frequency difference between specified first and second resonant lights to equal a frequency difference corresponding to an energy difference between two ground levels of the atom based on the detected light. The controller causes the frequency Δω or magnetic field intensity to satisfy 2×δ×n=Δω or Δω×n=2×δ. The frequency δ corresponds to an energy difference between two Zeeman split levels differentiated by one magnetic quantum number and generated in the two ground levels of the atom by energy splitting.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Microwave diode based on nonlinear electromagnetically induced transparency phenomenon
InactiveCN104253293ALower bistability thresholdIncrease contrastWaveguide type devicesDielectric plateMiniaturization
The invention relates to a microwave diode based on a nonlinear electromagnetically induced transparency phenomenon. The microwave diode includes a dielectric plate (4), a first copper foil layer (10) which is located at the bottom surface of the dielectric plate (4), an annular copper foil layer (6) which is arranged at the front surface of the dielectric plate (4), a first copper foil tape (8) which is arranged at the front surface of the dielectric plate (4), and a thin copper foil tape (5) which is arranged at the front surface of the dielectric plate (4); and one end of the thin copper foil tape (5) is vertically connected with the first copper foil tape (8), and the other end of the thin copper foil tape (5) is open circuited. Compared with the prior art, the microwave diode based on the nonlinear electromagnetically induced transparency phenomenon of the invention has the advantages of miniaturization, nondestructive cohesion, simple process, low cost, low threshold value, high contrast and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Delayed optical router/switch
ActiveUS20100232792A1Relaxes switching performanceIncrease speedFibre transmissionOptical multiplexData trafficElectron
A system, method, and apparatus for delayed optical router based on slow light and nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes are presented, in which three laser pulses interact with a three-level nonlinear optical medium composing two closely spaced ground states and an excited state. The delayed optical routing mechanism is based on a slow light phenomenon, in which a group velocity of an incoming input signal pulse is slowed down due to quantum coherence induced refractive index change. The two-photon coherence induced on the ground states via electromagnetically induced transparency is optically recovered via nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes. The nondegenerate four-wave mixing generation is enhanced owing to absorption cancellation. In this case, the individual pulse switching / routing time is limited by the coherence decay time that is much faster than population decay time, where the population decay-time is a limiting factor of conventional switching devices. In the present invention of the delayed optical router the overall switching / routing time, however, is controlled to be delayed by using the slow light. Even though the overall switching / routing time can be delayed, the switching bandwidth of the present invention is not degraded at all because the input and output signal's group velocity across the delayed optical router is still same. Therefore, the present invention of the delayed optical router gives an advantage of wide-bandwidth optical data traffic control using a narrow-bandwidth processing unit such as an electronic device. Another advantage is signal amplifications owing to the dark-resonance enhanced nondegenerate four-wave mixing processes.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH +1
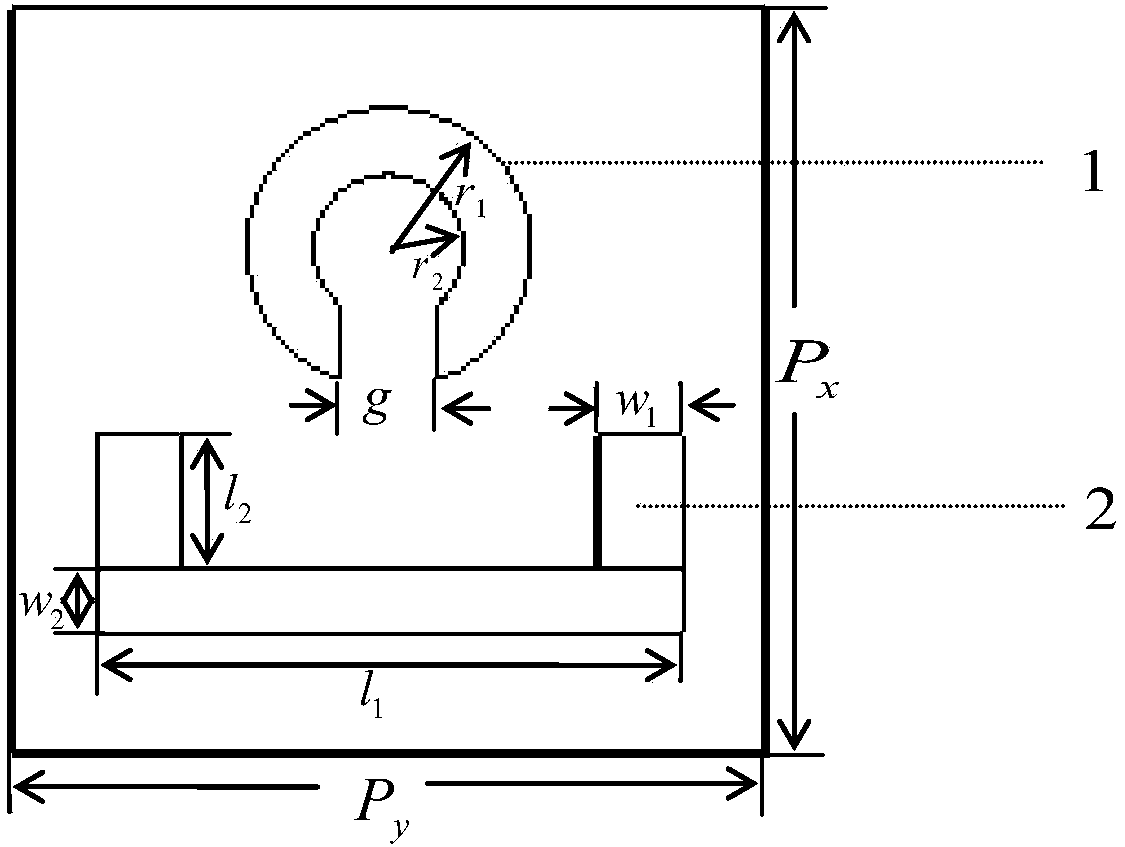
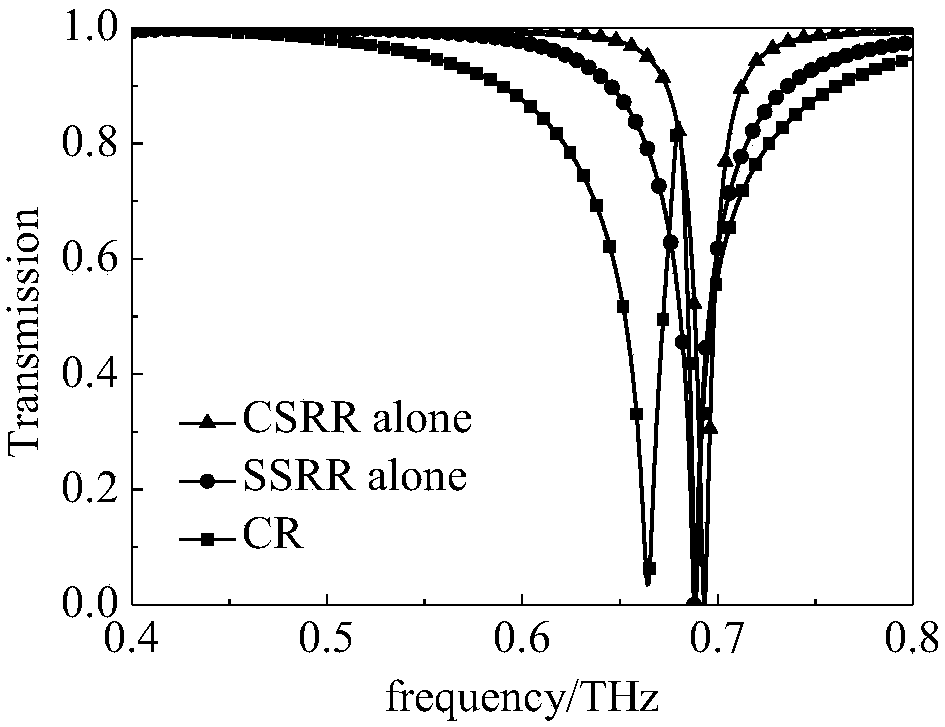
Multi-band electromagnetic induction transparent structure based on terahertz metamaterial
The invention discloses a multi-band electromagnetic induction transparent structure based on a terahertz metamaterial. The structure comprises a first dielectric substrate, a second dielectric substrate, a first metal strip, a second metal strip, a first metal symmetrical split-ring resonator and a second metal symmetrical split-ring resonator, wherein the second dielectric substrate is located below the first dielectric substrate, the first metal symmetrical split-ring resonator is located between the first metal strip and the second metal strip, and the second metal symmetrical split-ring resonator is located on the side, which is away from the first metal symmetrical split-ring resonator, of the second metal strip. Under the condition of incident electromagnetic field excitation, the metal strips and electromagnetic waves are in strong coupling to serve as bright-mode resonance; the metal symmetric split-ring resonators and electromagnetic waves are in weak coupling to serve as dark-mode resonance. Based on the coupling of the multi-band electromagnetic induction transparent structure based on the terahertz metamaterial and the incident electromagnetic field, a multi-band electromagnetic induction transparent phenomenon can be realized by a bright and dark mode near-field coupling principle.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
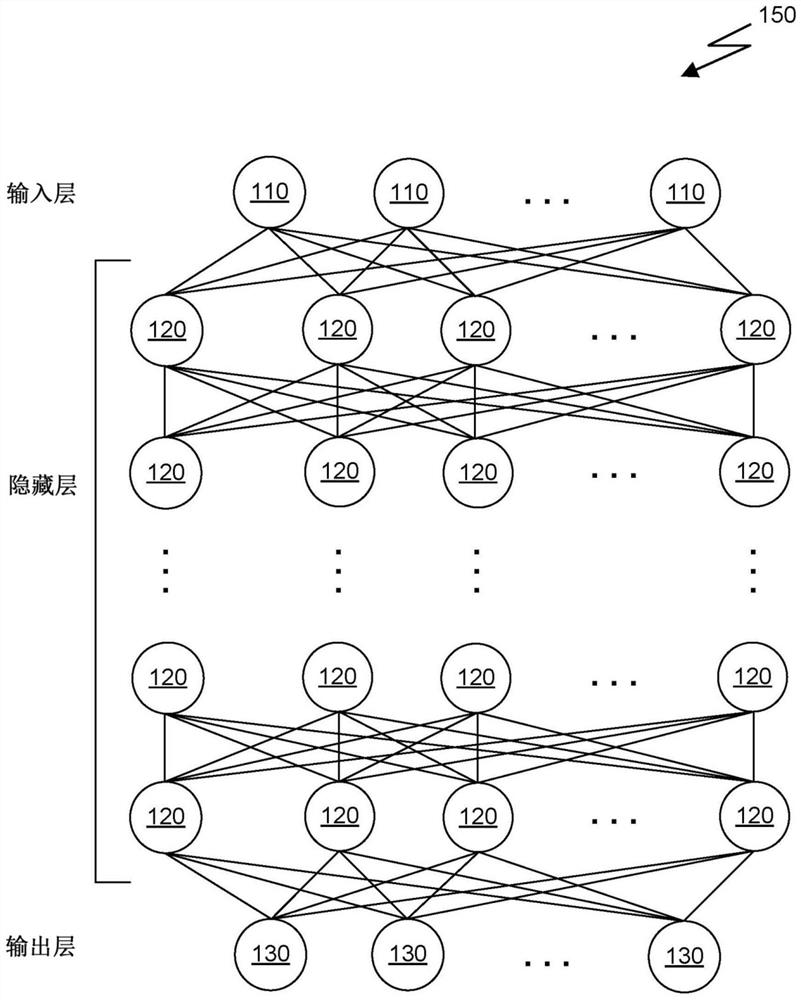
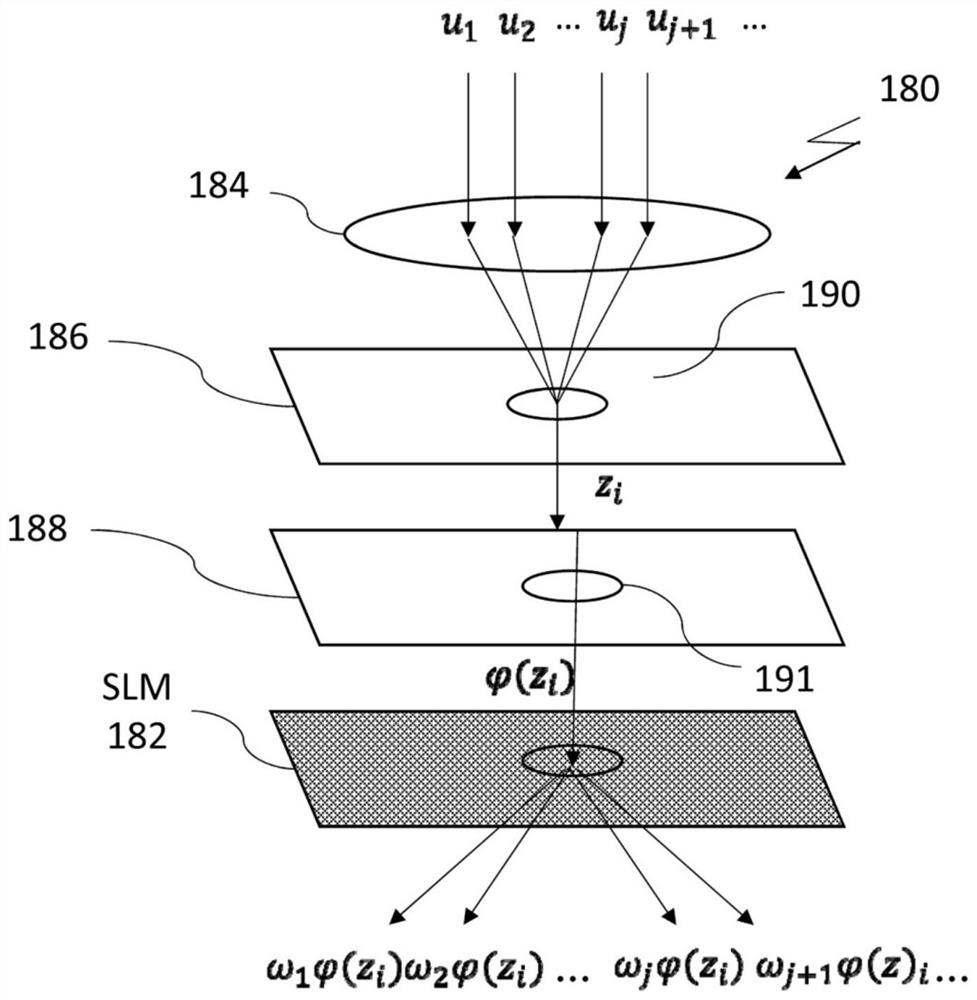
All optical neural network
An all-optical neural network that utilizes light beams and optical components to implement layers of the neural network is disclosed herein. The all-optical neural network includes an input layer, zero or more hidden layers, and an output layer. Each layer of the neural network is configured to simulate linear and nonlinear operations of a conventional artificial neural network neuron on an optical signal. In an embodiment, the optical linear operation is performed by a spatial light modulator and an optical lens. The optical lens performs a Fourier transformation on the set of light beams and sums light beams with similar propagation orientations. The optical nonlinear operation is implemented utilizing a nonlinear optical medium having an electromagnetically induced transparency characteristic whose transmission of a probe beam of light is controlled by the intermediate output of a coupling beam of light from the optical linear operation.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
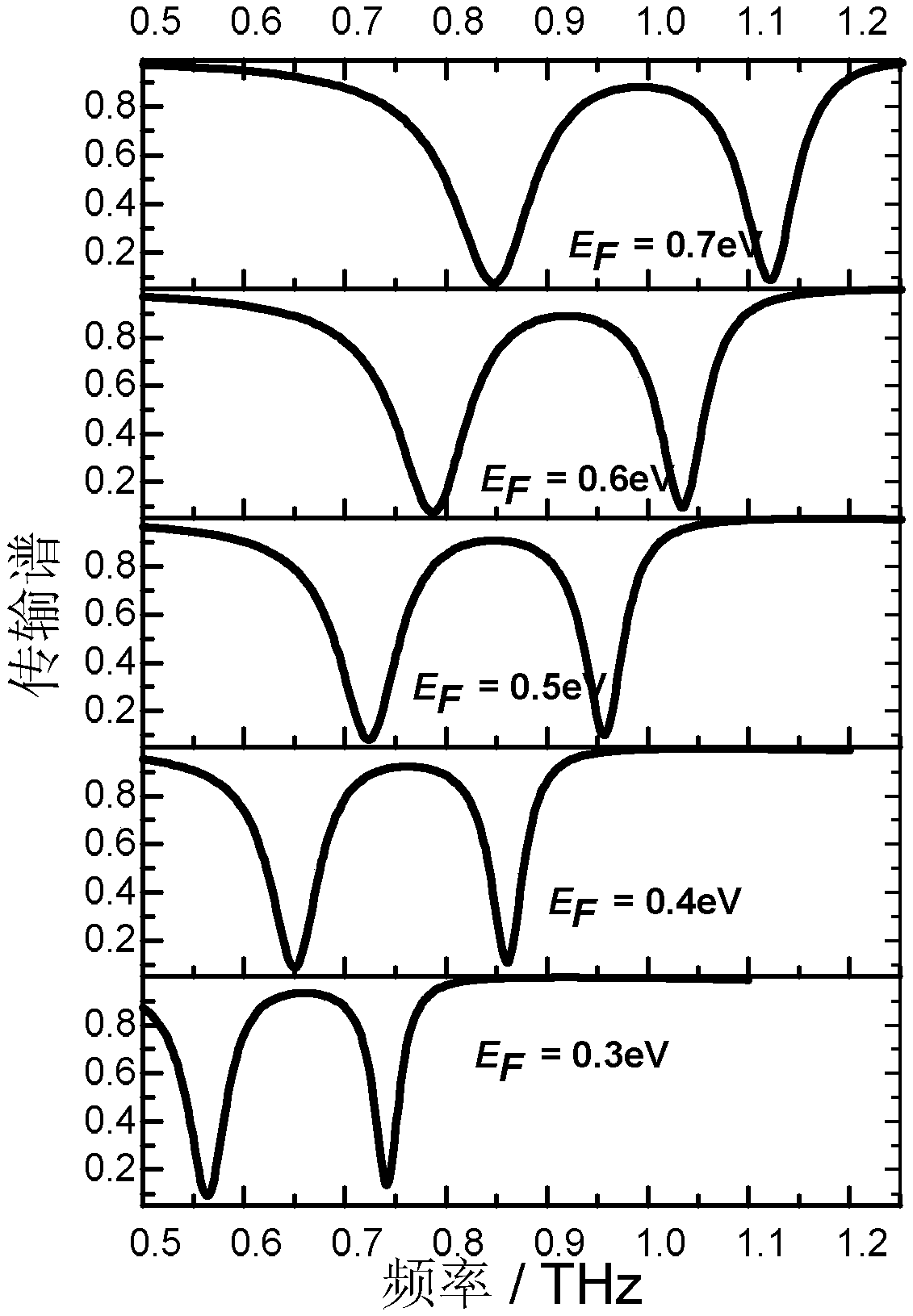
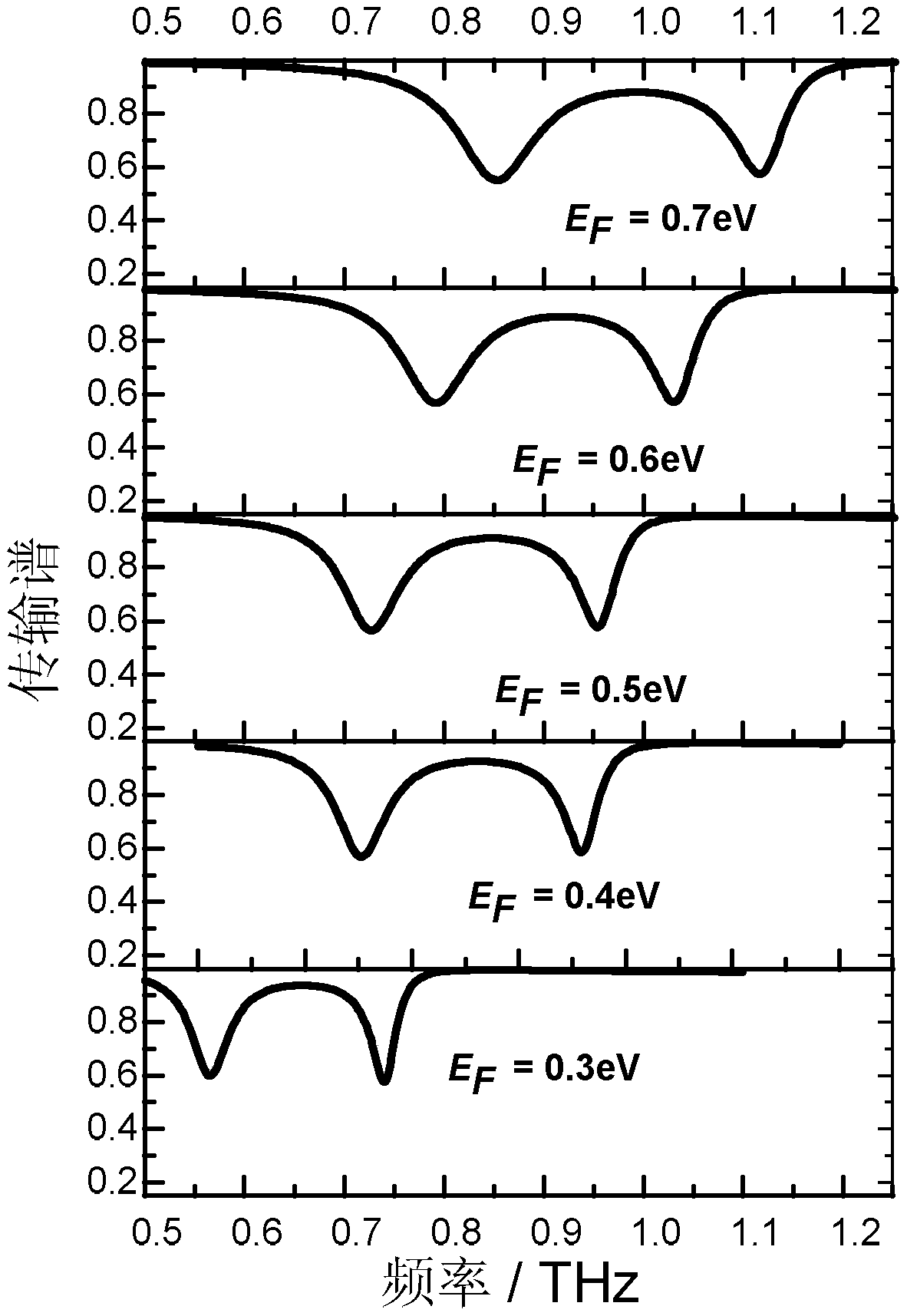
Polarization-insensitive adjustable electromagnetically induced transparent terahertz device
ActiveCN110246956ASymmetricalControl transfer characteristicsSuperconductor detailsDissimilar materials junction devicesExternal biasSlow light
The invention belongs to the field of metamaterial structures, and particularly relates to a polarization-insensitive adjustable electromagnetically induced transparent terahertz device. The device is composed of a substrate, a graphene layer, a metal layer and a metal electrode. The substrate comprises a silicon layer and a silicon dioxide layer covering the silicon layer. The graphene layer covers the upper surface of the silicon dioxide layer, and the graphene layer is composed of periodically arranged graphene square frame structures. The metal layer covers the upper surface of the silicon dioxide layer and is composed of periodically arranged cross-shaped metal unit structures. One electrode of the metal electrode is arranged at the edge of the graphene layer and is connected with the graphene layer, and the other electrode of the metal electrode is arranged at the edge of the silicon layer and is connected with the silicon layer. According to the invention, the electromagnetically induced transparency characteristic can be realized, the slow light effect is generated, the transmission characteristic and the slow light effect of the metamaterial device can be regulated and controlled through external bias voltage, and the group delay is effectively adjusted.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com