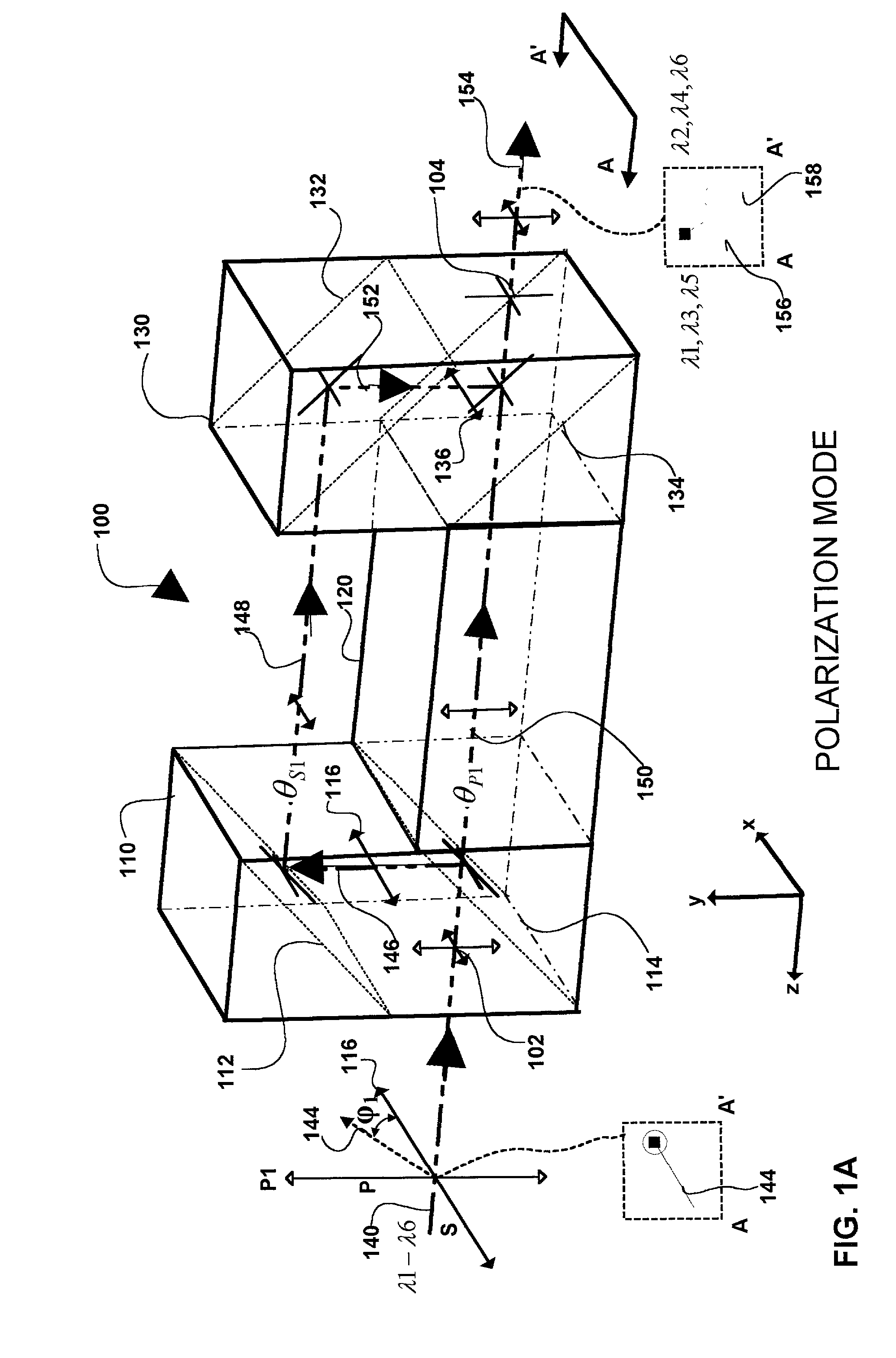
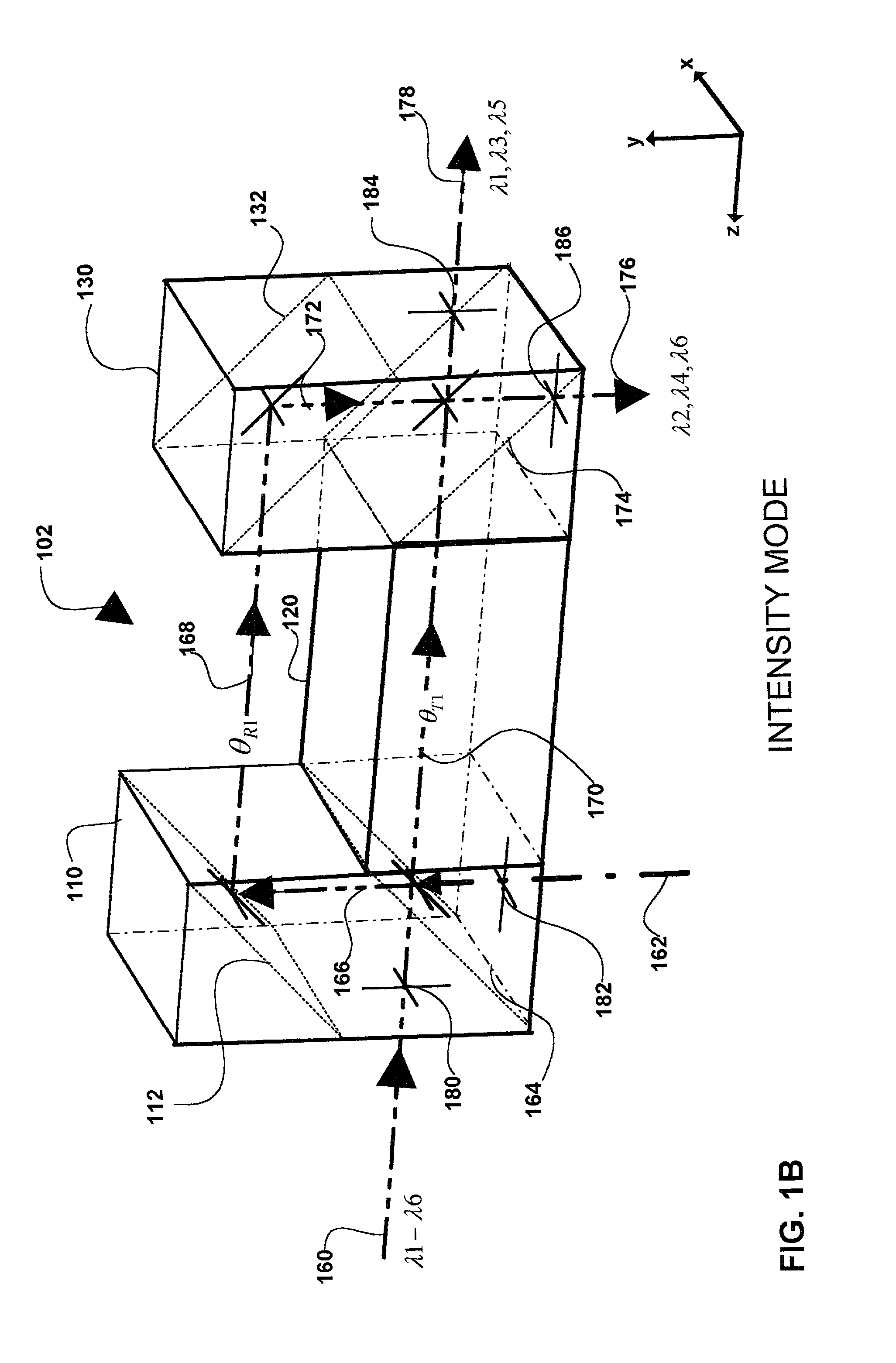
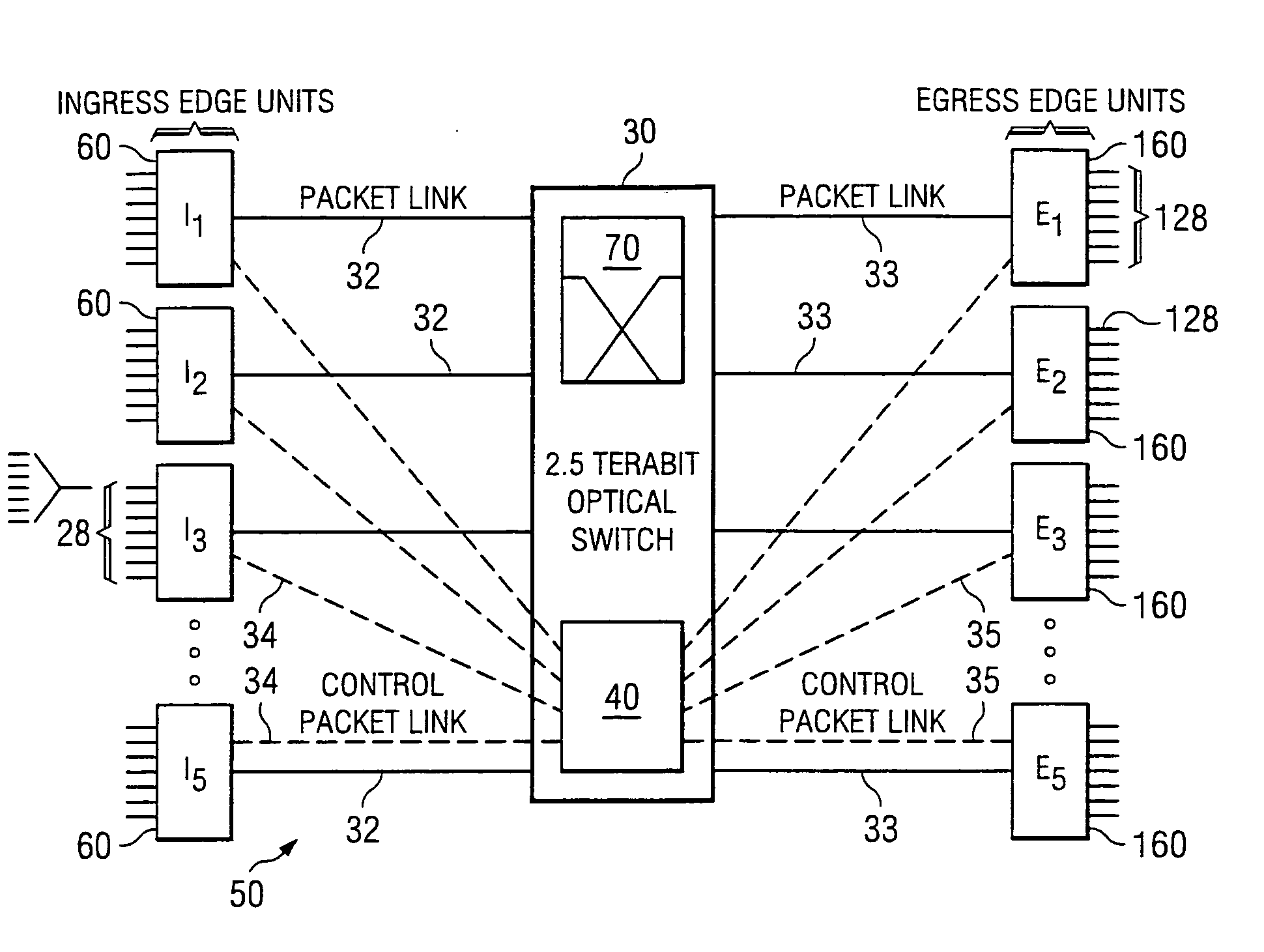
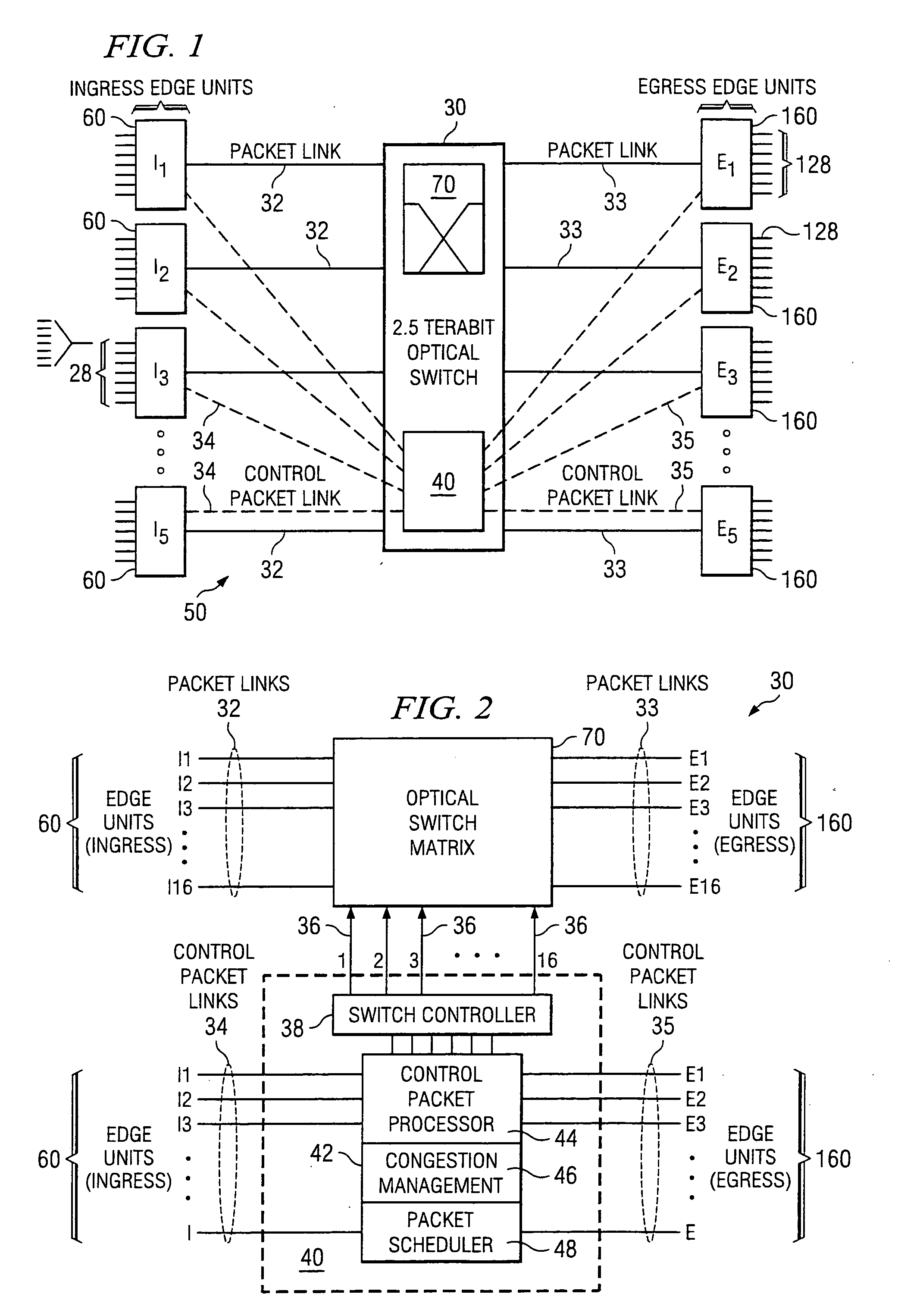
Patents
Literature
180 results about "Optical router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
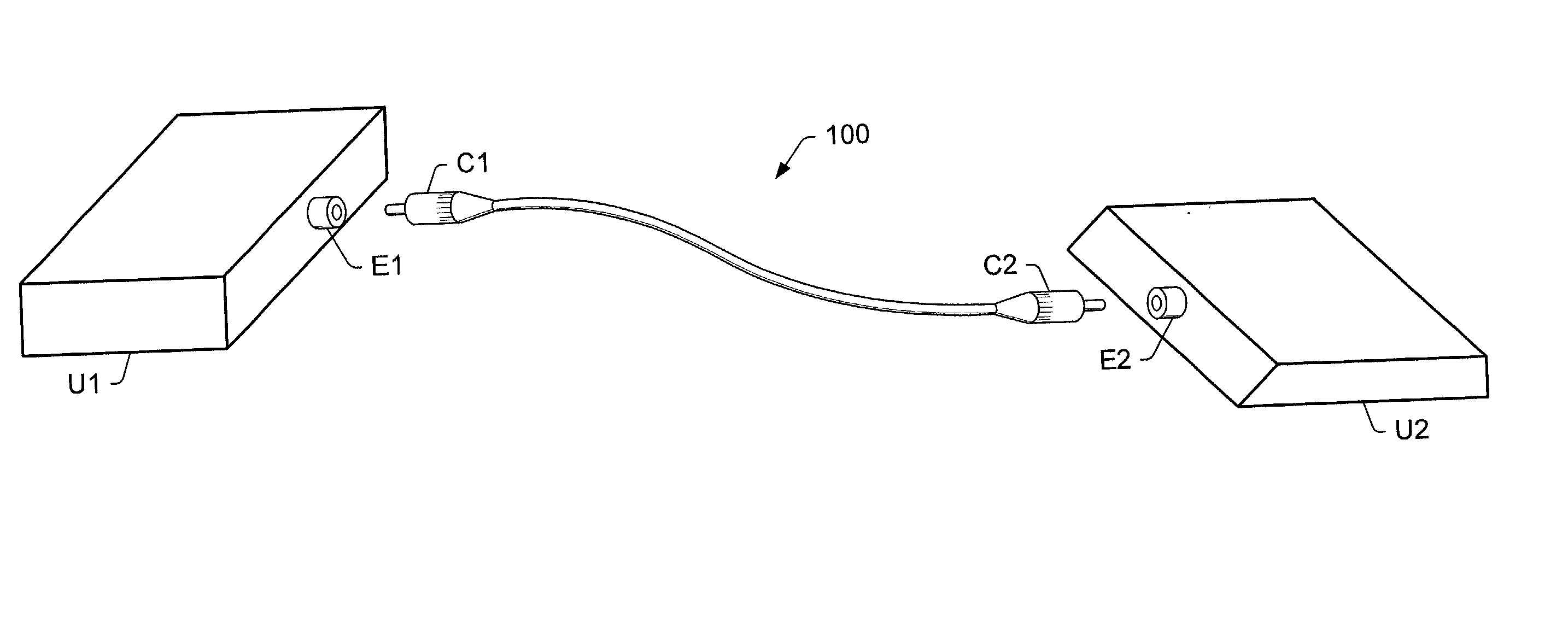
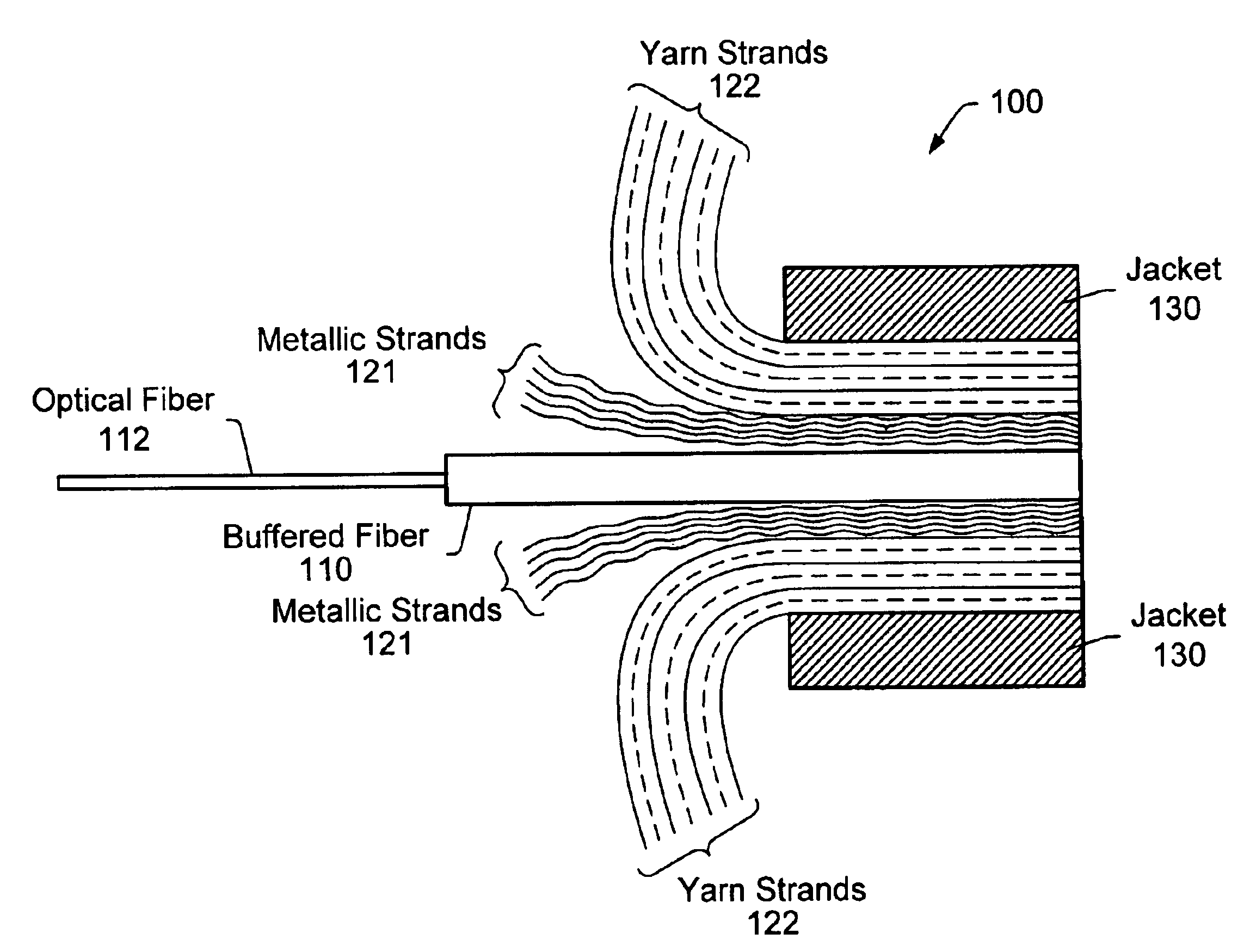
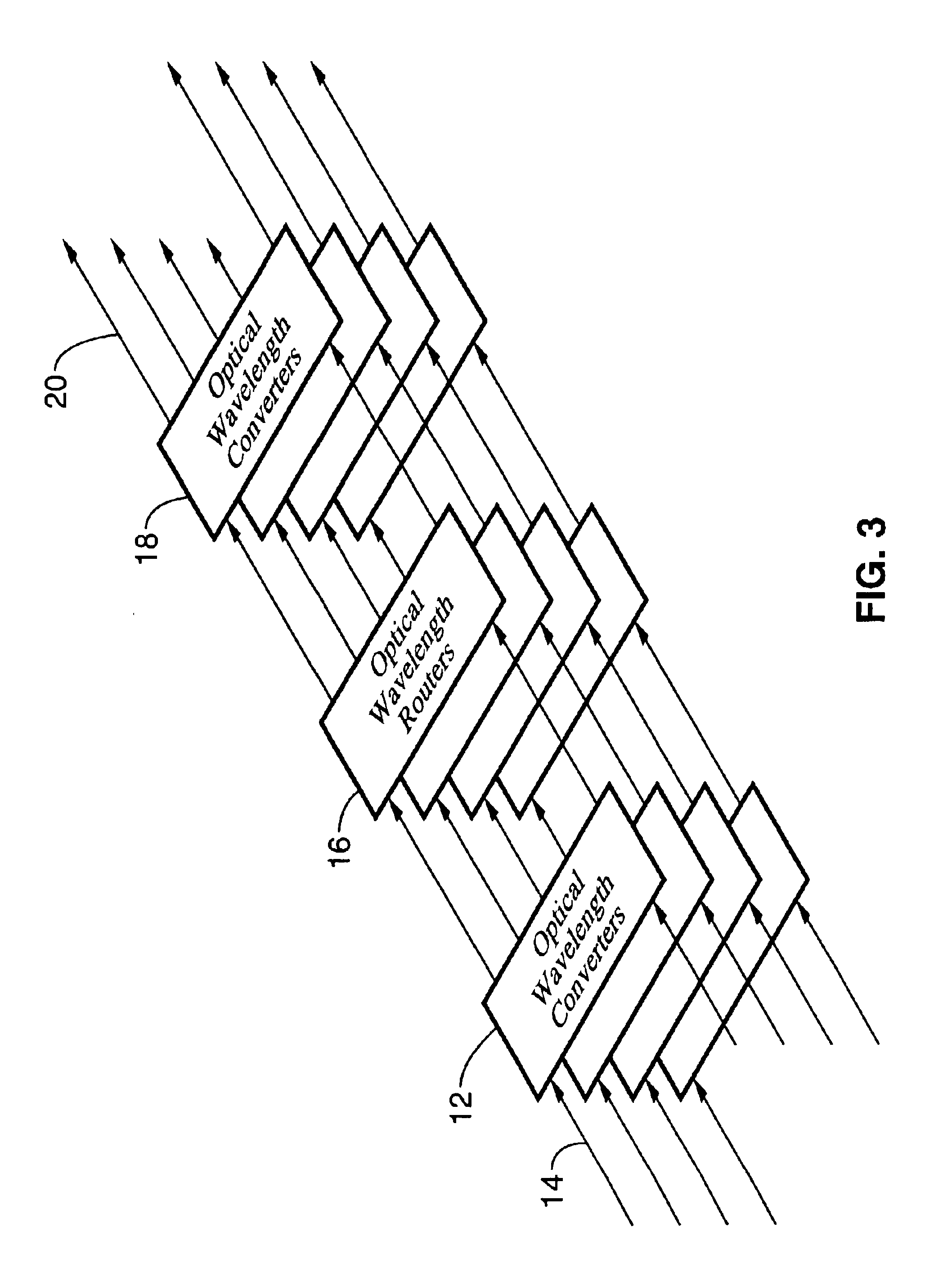
Hybrid electro-optic cable
InactiveUS20020126967A1Reduce initial system cost costReduce cost ongoing maintenance costCommunication cablesFlat/ribbon cablesElectricityFiber
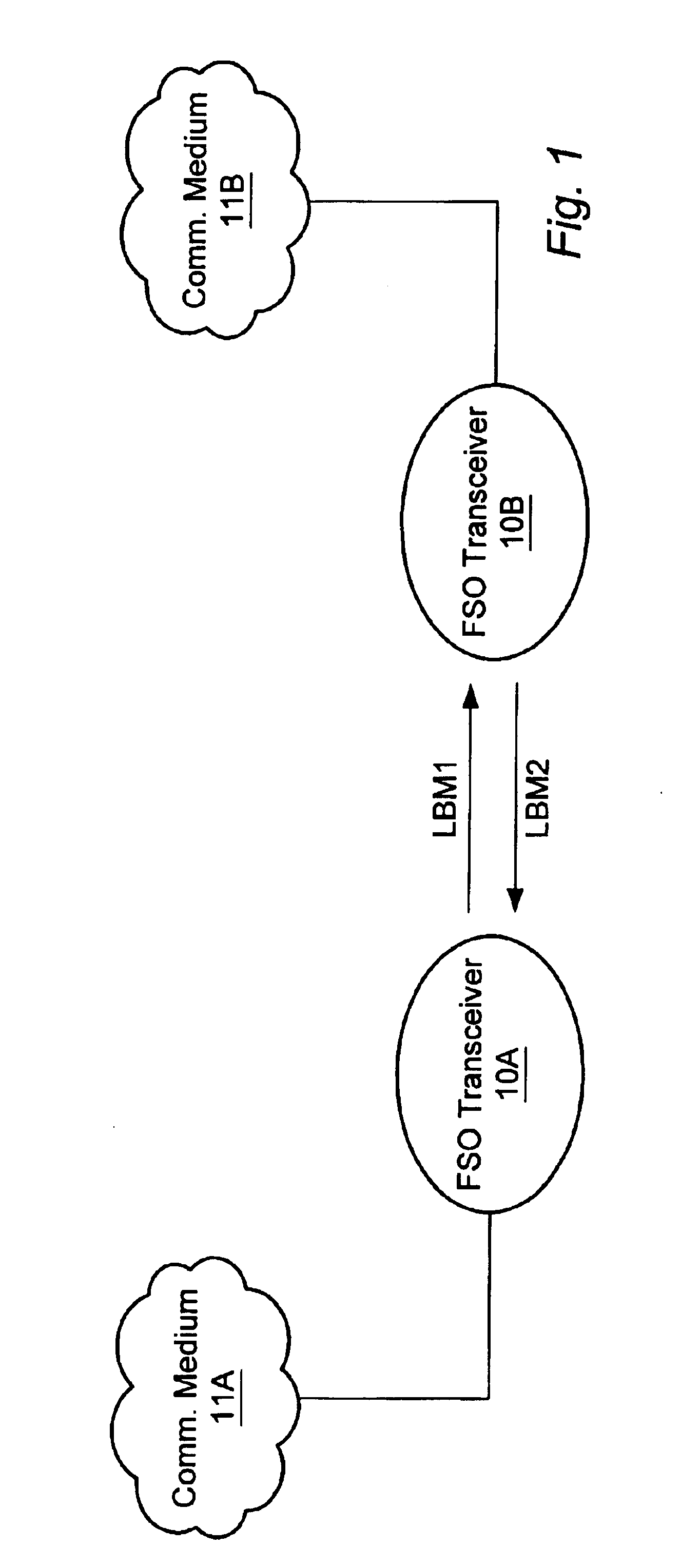
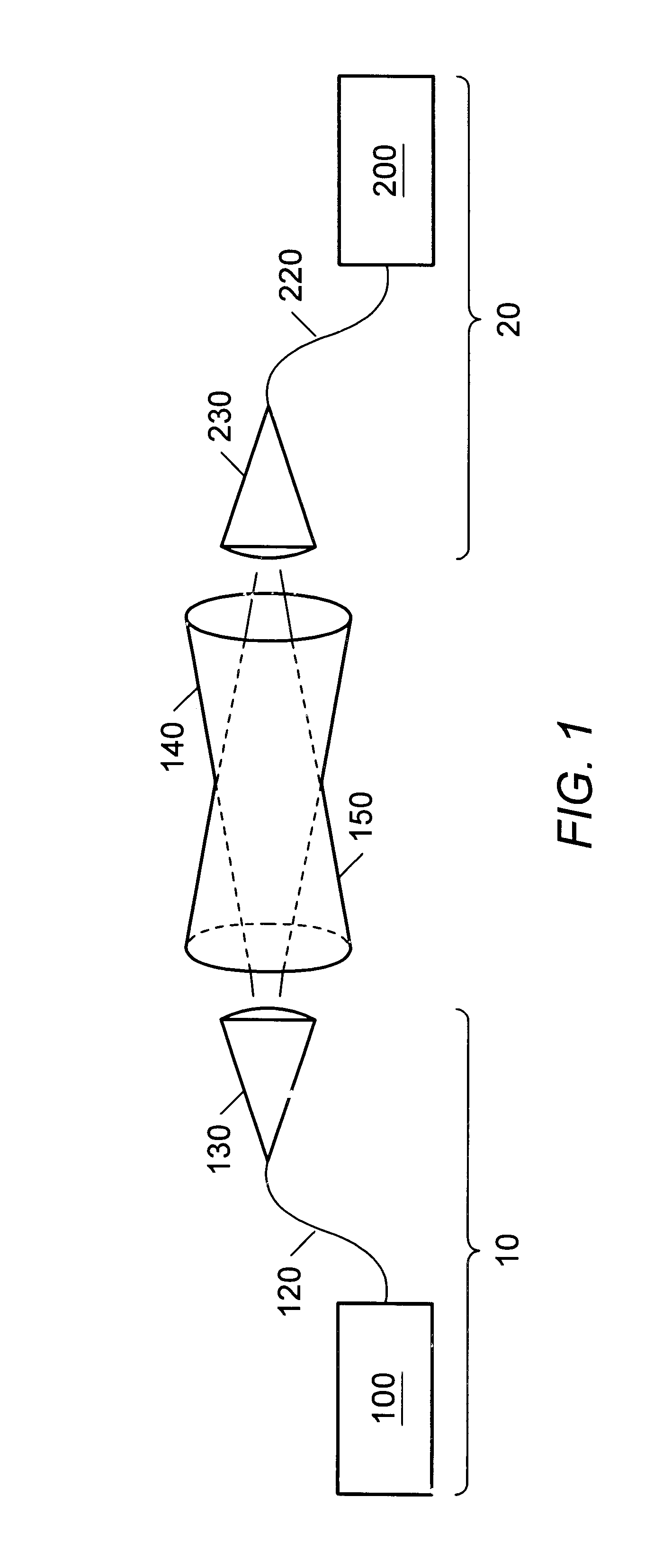
A hybrid cable comprising an optical fiber, an intermediate layer surrounding the optical fiber, and an electrically insulating jacket surrounding the intermediate layer. The intermediate layers include a collection of metallic strands. The hybrid cable may be used to establish simultaneous electrical and fiber-optic connection between two communication devices. Thus, the two communication devices may simultaneously transfer optical signals through the optical fiber and perform any of various electrical functions (power transfer, eye safety control) through the metallic strands. For example, an optical transceiver may couple to an optical antenna unit through the hybrid cable. Such an optical transceiver may serve as part of a point-to-point link, a point-to-multipoint link, and / or, a link between a primary transceiver unit and an optical router.
Owner:SEAFORT INT TRADING SRL
Hybrid electro-optic cable for free space laser antennas
InactiveUS6931183B2Reduce tensionEasy and efficient installationCommunication cablesFlat/ribbon cablesFiberElectricity
A hybrid cable comprising an optical fiber, an intermediate layer surrounding the optical fiber, and an electrically insulating jacket surrounding the intermediate layer. The intermediate layers include a collection of metallic strands. The hybrid cable may be used to establish simultaneous electrical and fiber-optic connection between two communication devices. Thus, the two communication devices may simultaneously transfer optical signals through the optical fiber and perform any of various electrical functions (power transfer, eye safety control) through the metallic strands. For example, an optical transceiver may couple to an optical antenna unit through the hybrid cable. Such an optical transceiver may serve as part of a point-to-point link, a point-to-multipoint link, and / or, a link between a primary transceiver unit and an optical router.
Owner:SEAFORT INT TRADING SRL
Ultra-low latency multi-protocol optical routers for the next generation internet
InactiveUS6925257B2Control performanceScalability limitationMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexThe InternetHemt circuits
An ultra-low latency optical router with a peta-bit-per-second total aggregate switching bandwidth, that will scale to a total connectivity of 1000 by 1000, and beyond by modular upgrades, that utilizes advanced optical technologies to achieve such high capacity with two to three orders of magnitude less volume and power requirements than the electrical router counter part, that serves as a universal engine to other optical routers being developed by vendors and researchers today, that can function in the context of circuit-switching, flow-switching, burst-switching, and packet-switching, that uses advanced wavelength conversion technology to effectively achieve three methods of contention resolution in the router: deflection in wavelength, deflection in space, and buffering in time, and that interfaces a local network to the Supernet.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
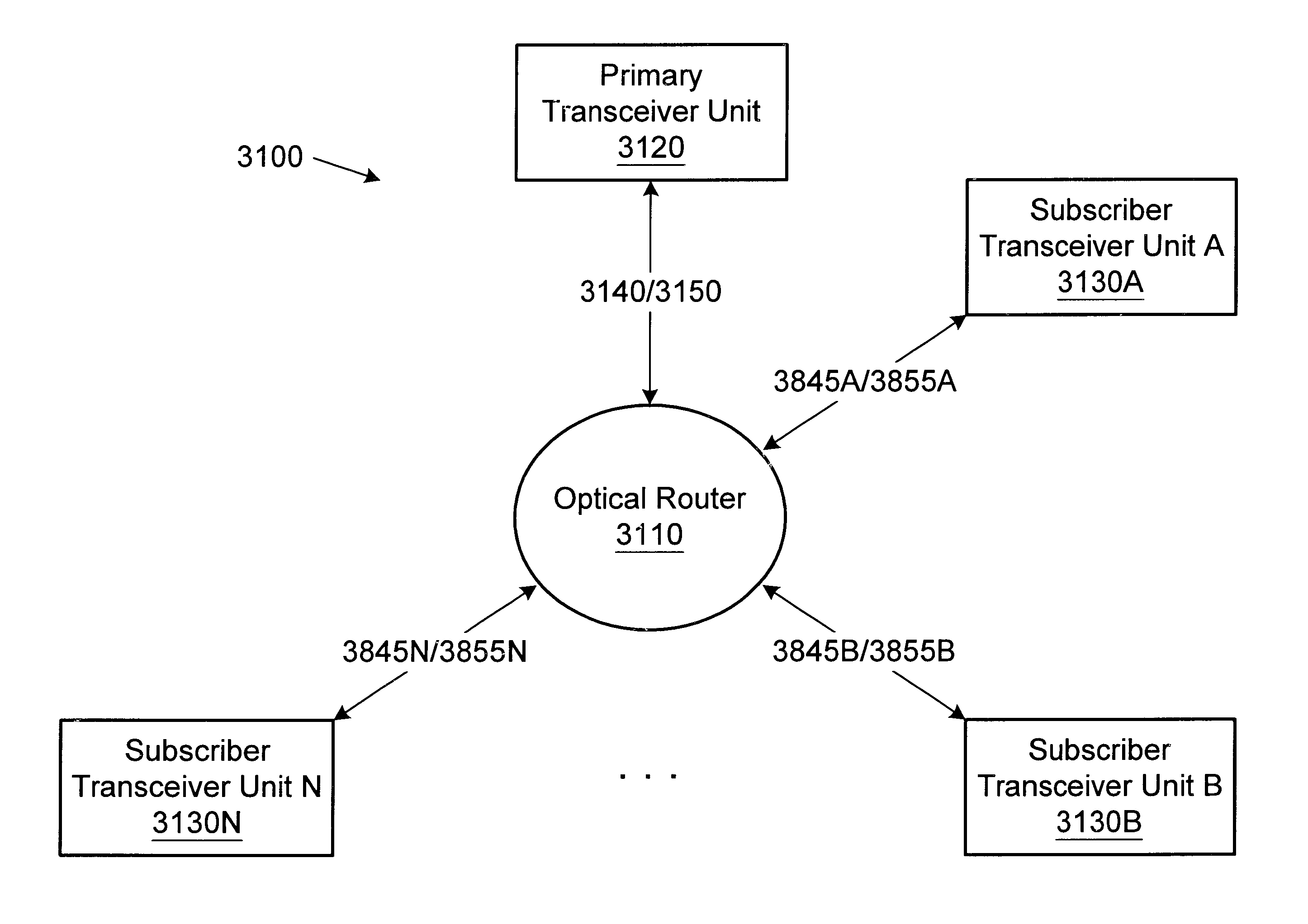
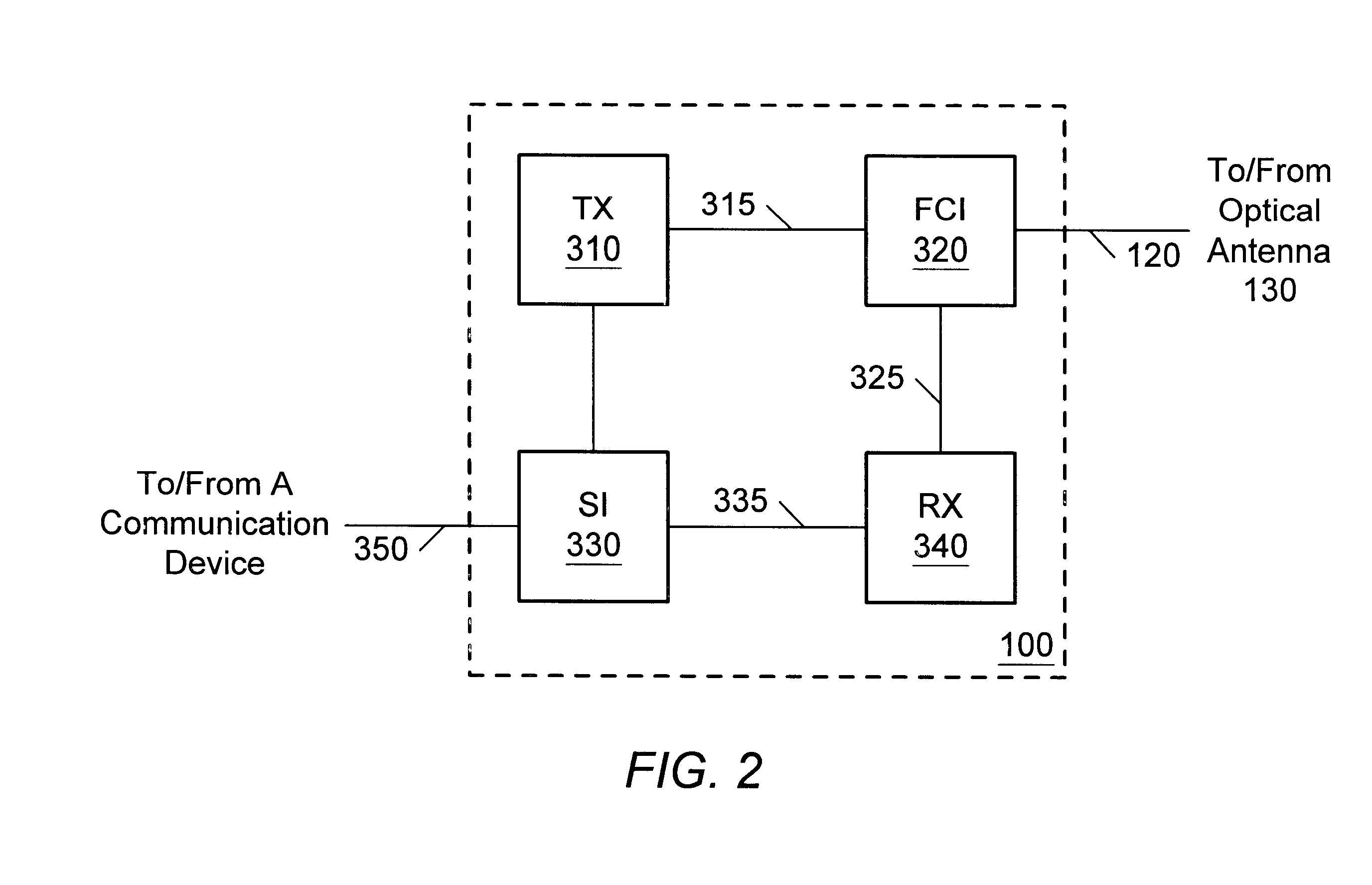
Wireless fiber-coupled telecommunication systems based on atmospheric transmission of laser signals
A wireless optical transceiver system which includes a passive optical antenna coupled by optical fiber to an active electronics module. The transceiver system receives and transmits light beams from / to the atmosphere,.and thereby communicates optically with a second optical transceiver. Receivers, transmitters, repeaters, switches, routers, etc., may be similarly organized, i.e. by coupling one or more passive optical antennas and an active electronics module with fiber-optic cable. Furthermore, various network toplogies and organizations may be arranged using one or more of the fiber-coupled transceivers, receivers, transmitters, repeaters, switches, routers, etc. Such components are admirably suited for use in various network configurations such as broadcast networks, point-to-multipoint networks, etc due to their low cost, ease of installation and antenna sighting, modularity, and upgradability. An optical router for establishing wireless channels to a number of subscribers may be configured based on demodulation and remodulation of light beams, or alternatively by redirecting light beams by adjustable deflections mirrors. A communications network infrastructure based on atmospheric light beam propagation is contemplated.
Owner:SEAFORT INT TRADING SRL +1
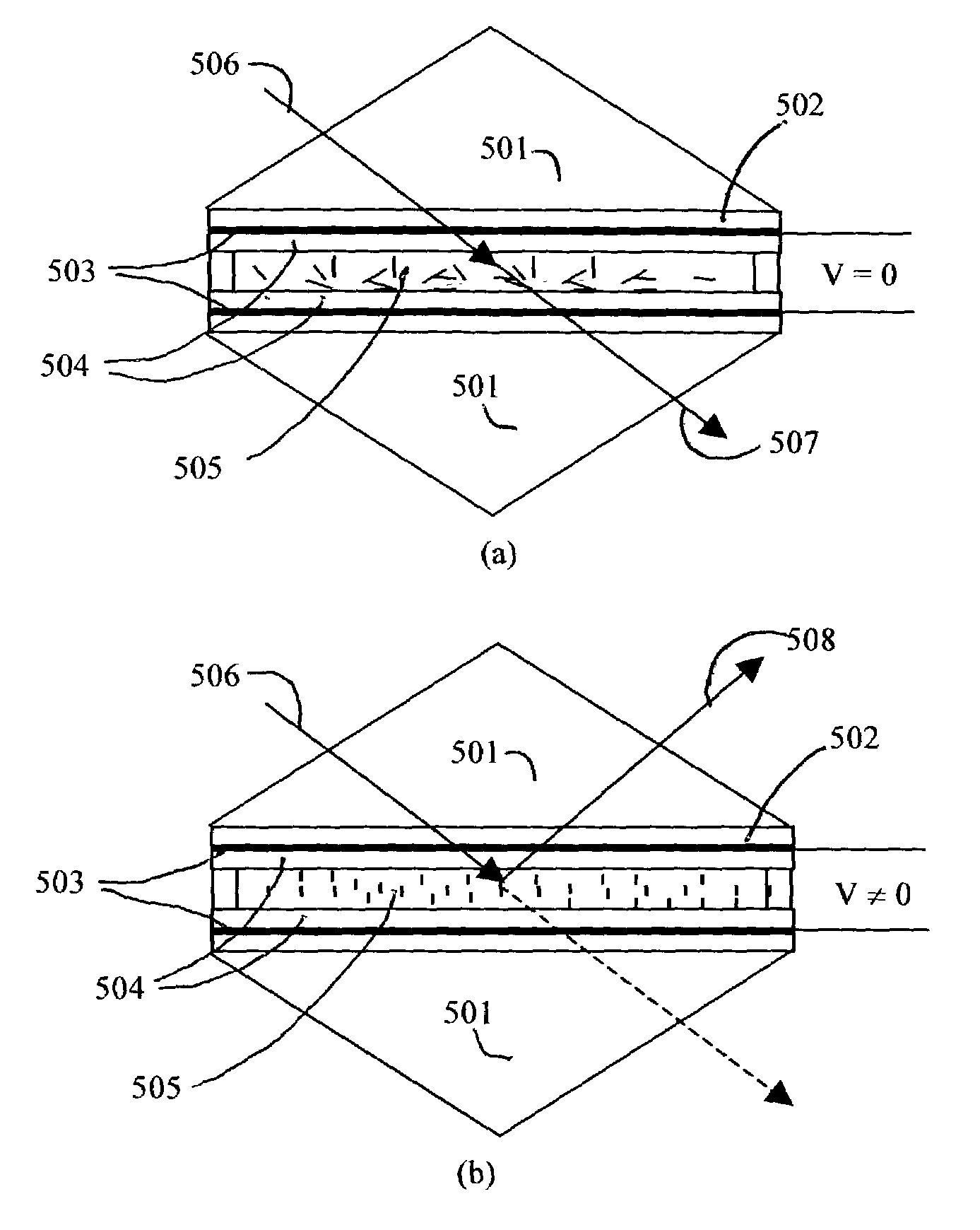
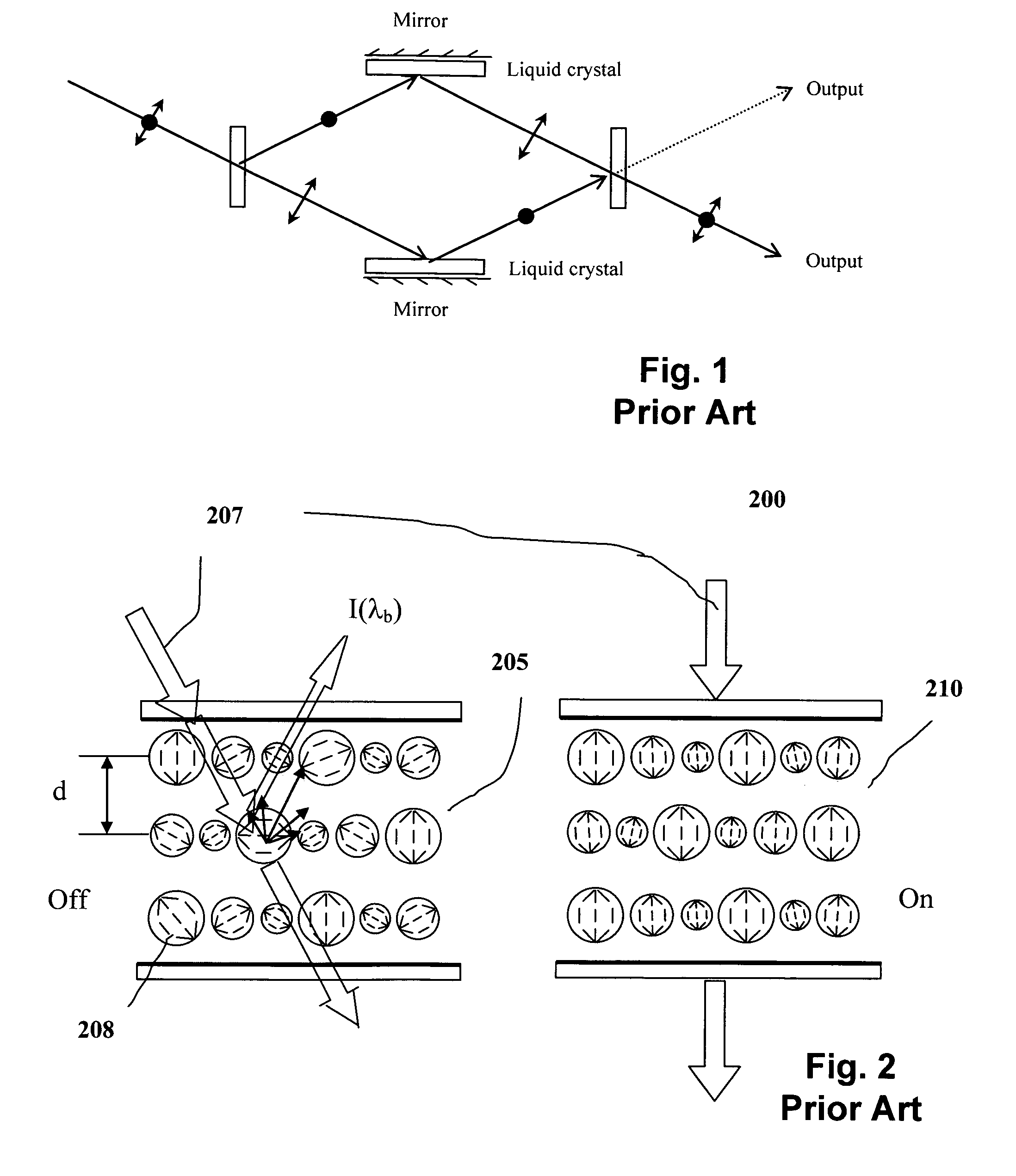
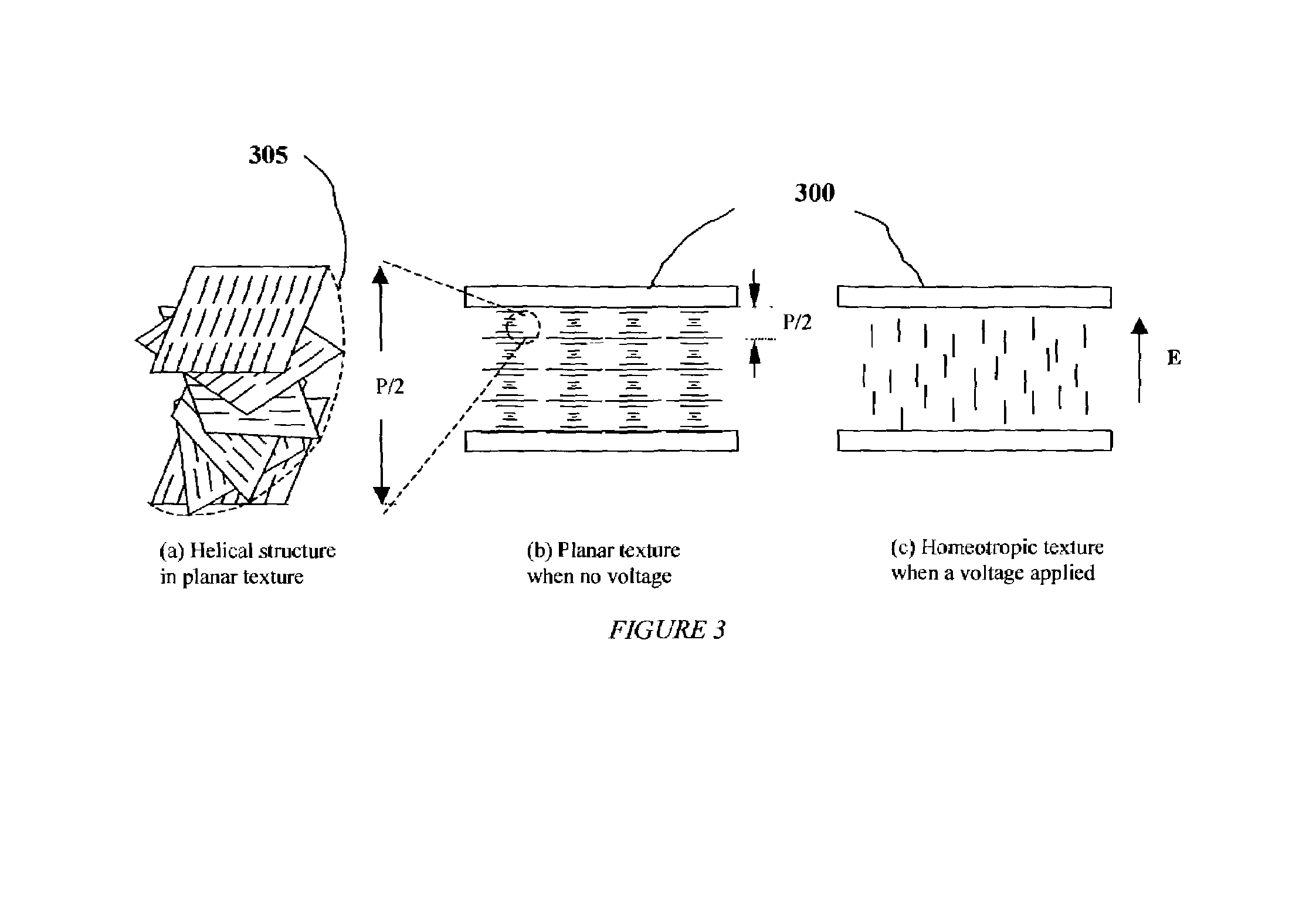
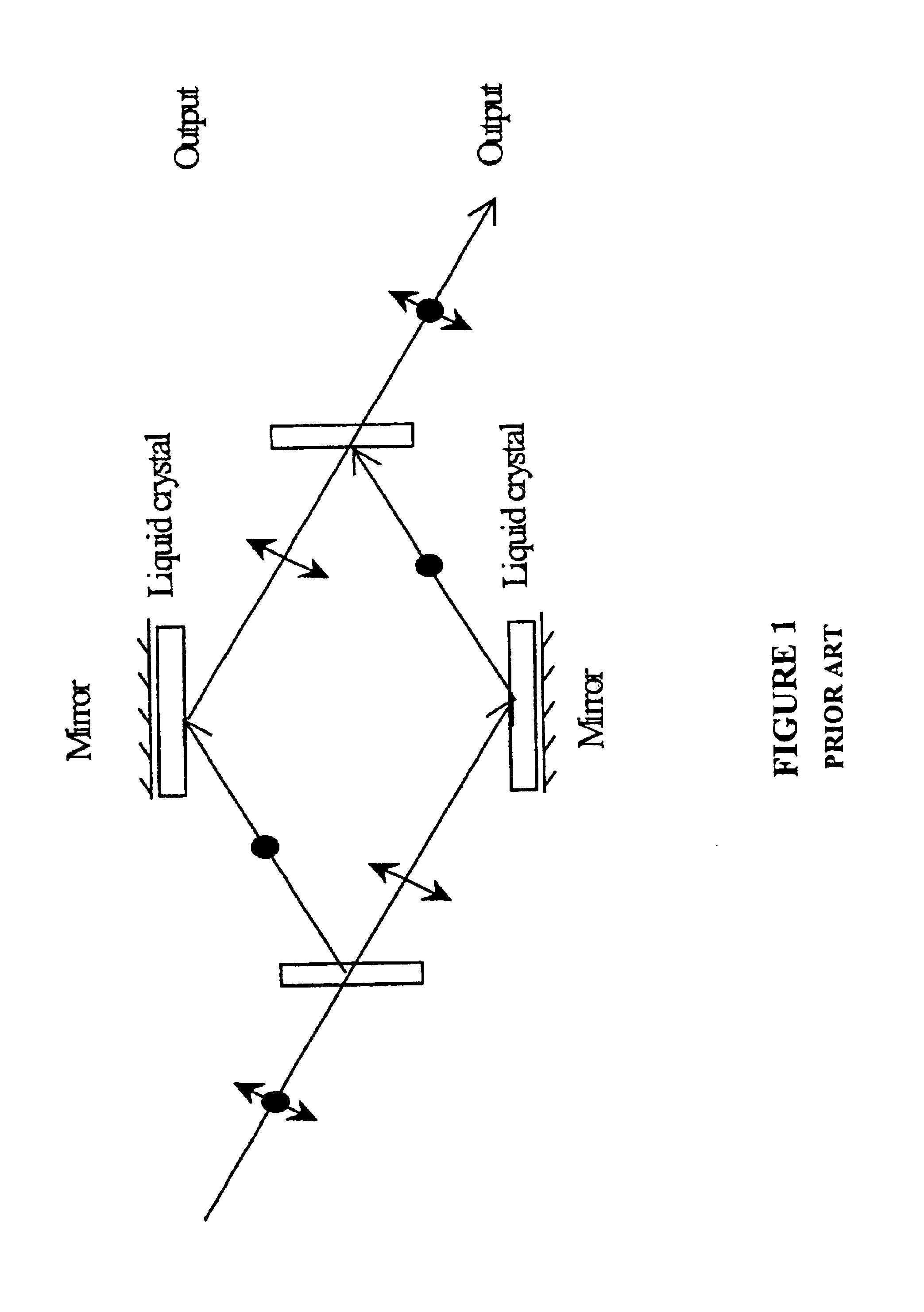
Optical switches made by nematic liquid crystal switchable mirrors, and apparatus of manufacture
InactiveUS6999649B1Liquid crystal compositionsCoupling light guidesElectricityManufacturing technology
Technology for constructing a single layer polarization insensitive electrically switchable liquid crystal mirror is disclosed which serves as the basic element for constructing an optical router switch array in free space as well as waveguide format. The optical router switch array includes a plurality of switchable liquid crystal mirror elements having liquid crystal arranged in stack cells and / or in a waveguide configuration. The resulted optical router switches are motionless, polarization insensitive, stable within the operational spectral region, and stable versus temperature. The invention also includes methods for manufacturing a single switchable liquid crystal mirror element and the optical switch arrays. The same technology is further extended to constructing an electrically tunable optical filter that is motionless and polarization insensitive.
Owner:KENT OPTRONICS
Wavelength selective optical routers
InactiveUS6201909B1Wide wavelength band to be manipulatedLow insertion lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesBandpass filteringFiber
Using the wavelength selectivity and low loss characteristics of optical couplers, in which index of refraction gratings in a non-evanescent waveguide merged region reflect only a selected wavelength band, signal switching and control systems of novel characteristics are provided for multi-wavelength optical communication systems. In a router, for example, selected wavelengths or wavelength bands on an add / drop line can be added to or dropped from a main fiber, by cross switching between wavelength selective loops disposed sequentially in the lines. In a collector box, as another example, selected wavelength bundles can be routed from one fiber onto multiple fibers. In a bandpass filter a selected wavelength band is transmitted with low loss while those wavelengths outside the selected wavelength band are rejected with very high loss.
Owner:ARROYO OPTICS
Edge router for optical label switched network
InactiveUS20060008273A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexOptical routerClient-side
An edge router for interfacing an optical label switched core IP network with client networks, which may be electronically switched and operate with different protocol. The core network has a limited number of ports, each with an edge router, which receives packets from one or more associated client networks and queues them according to egress port on the core network and optionally additionally according to attribute of service. When a queue has exceed a maximum packet length or a timeout limit assigned to the queue, the packets including their headers are assembled into a super packet for transmission across the core network in optical form, preferably using optical routers incorporating wavelength conversion of payloads and switching according to an attached label. The edge router at the egress port disassembles the super packet into constituent packets for respective destinations on the client network.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS20090074414A1Maximize throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCross connectionStructure of Management Information
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
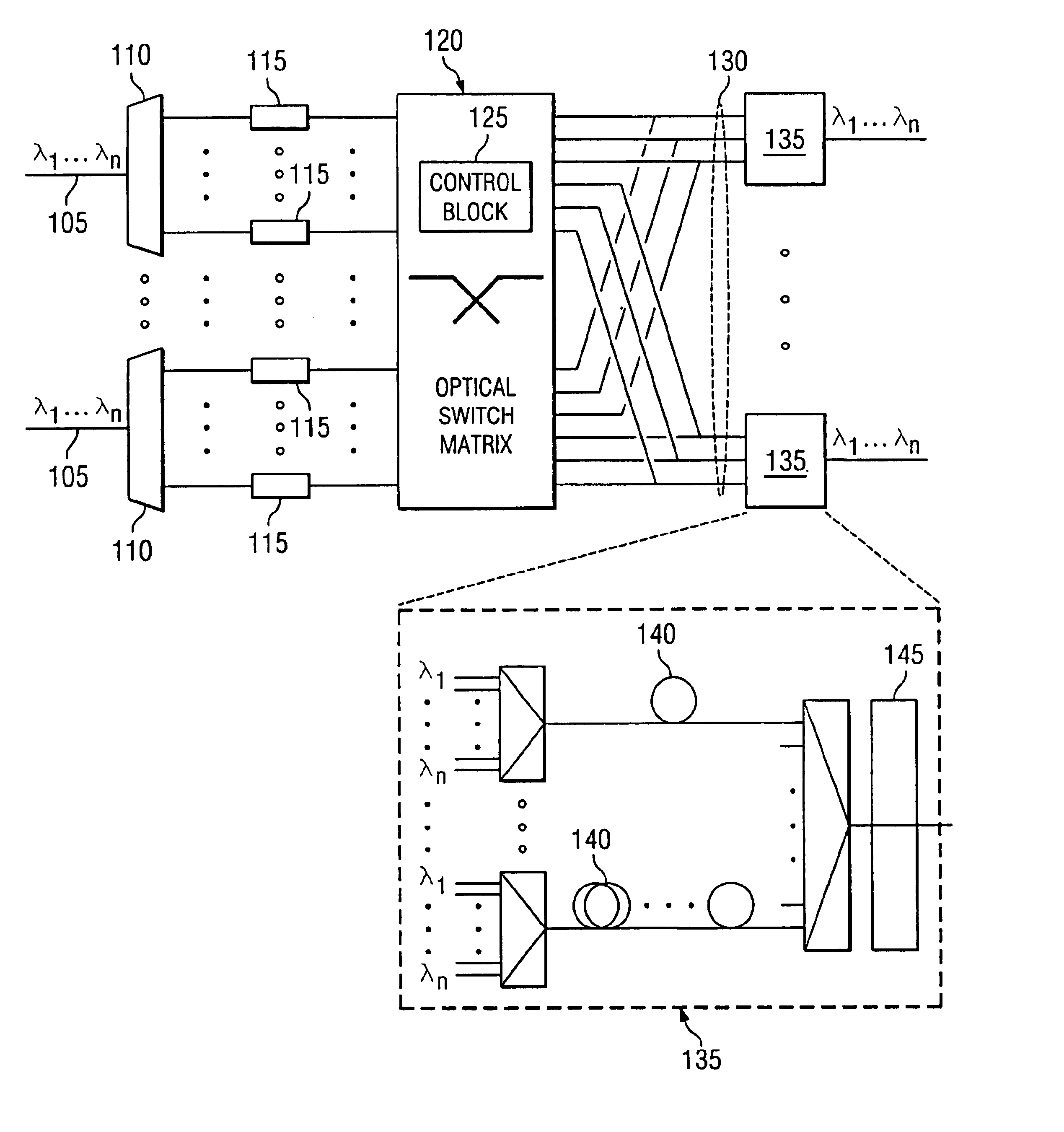
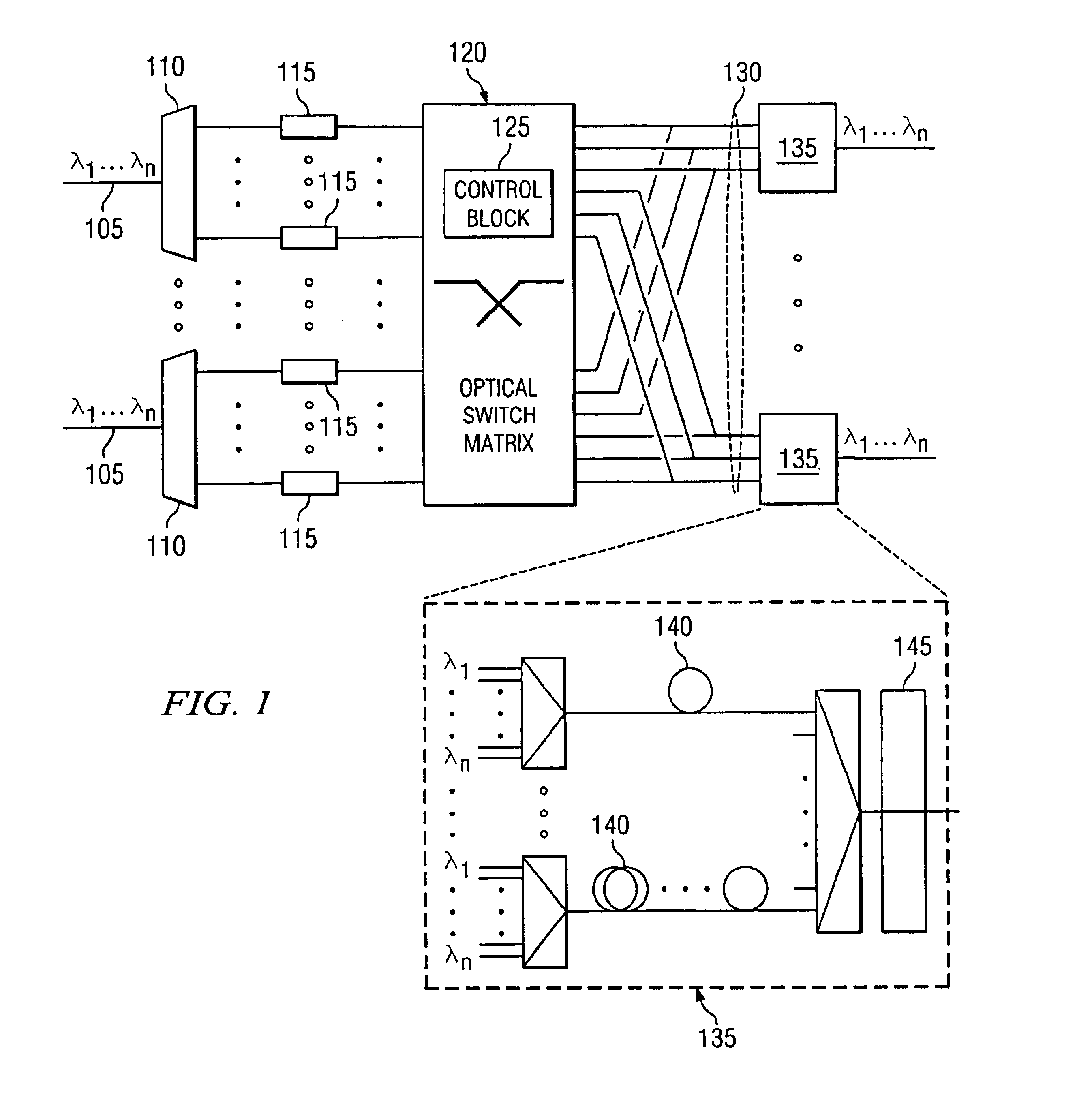
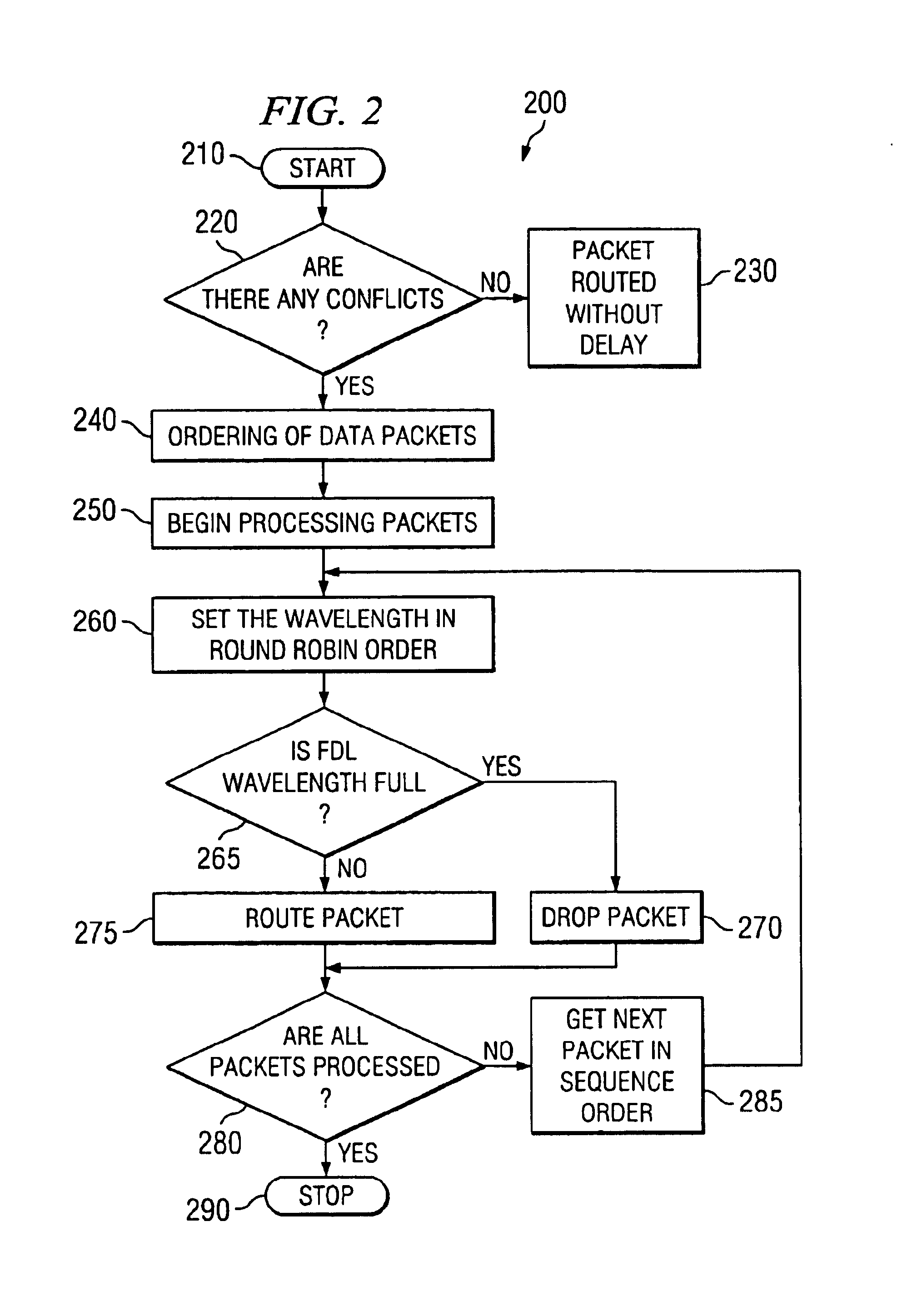
All-optical networking optical fiber line delay buffering apparatus and method
A method for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) fiber delay line (FDL) optical buffer routing and scheduling of conflicted variable length data packets through an optical router. The method includes ordering of each conflicted variable length data packet and selecting each of the data packets in turn for routing based on the ordering sequence selected. The sequentially assigned conflicted data packet is assigned a wavelength in the FDL optical buffer from (n) available wavelengths, wherein (n)=lambda1, lambda1, . . . , lambdan, lambda1, lambda1, . . . , lambdan, . . . . Each data packet is converted to the sequentially assigned wavelength (n) and routed to an optical buffer according to the wavelength assignment. If the wavelength of the FDL optical buffer is fully occupied the data packet is dropped.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
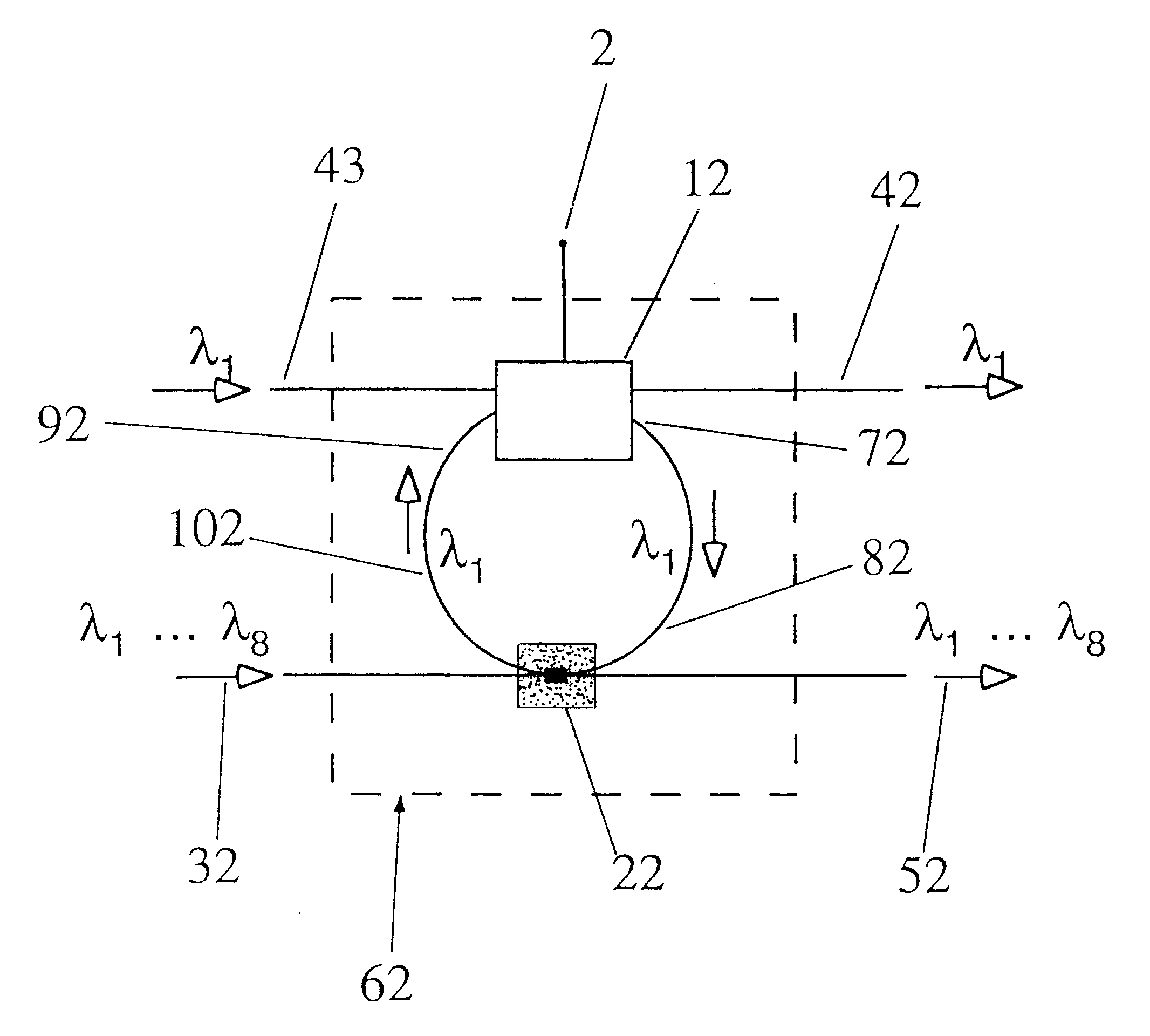
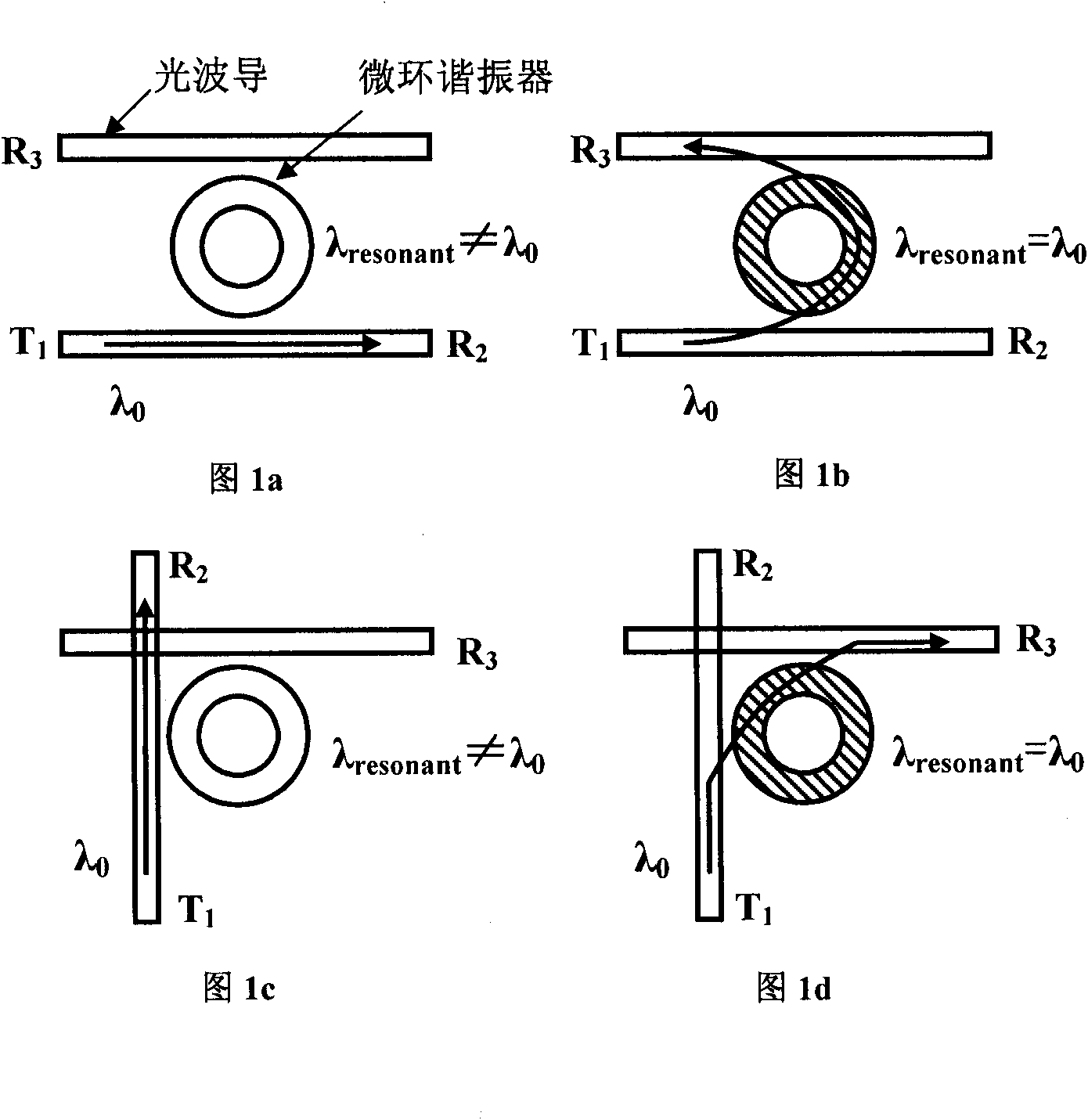
4*4 non-blocking optical router based on active micro-ring resonator
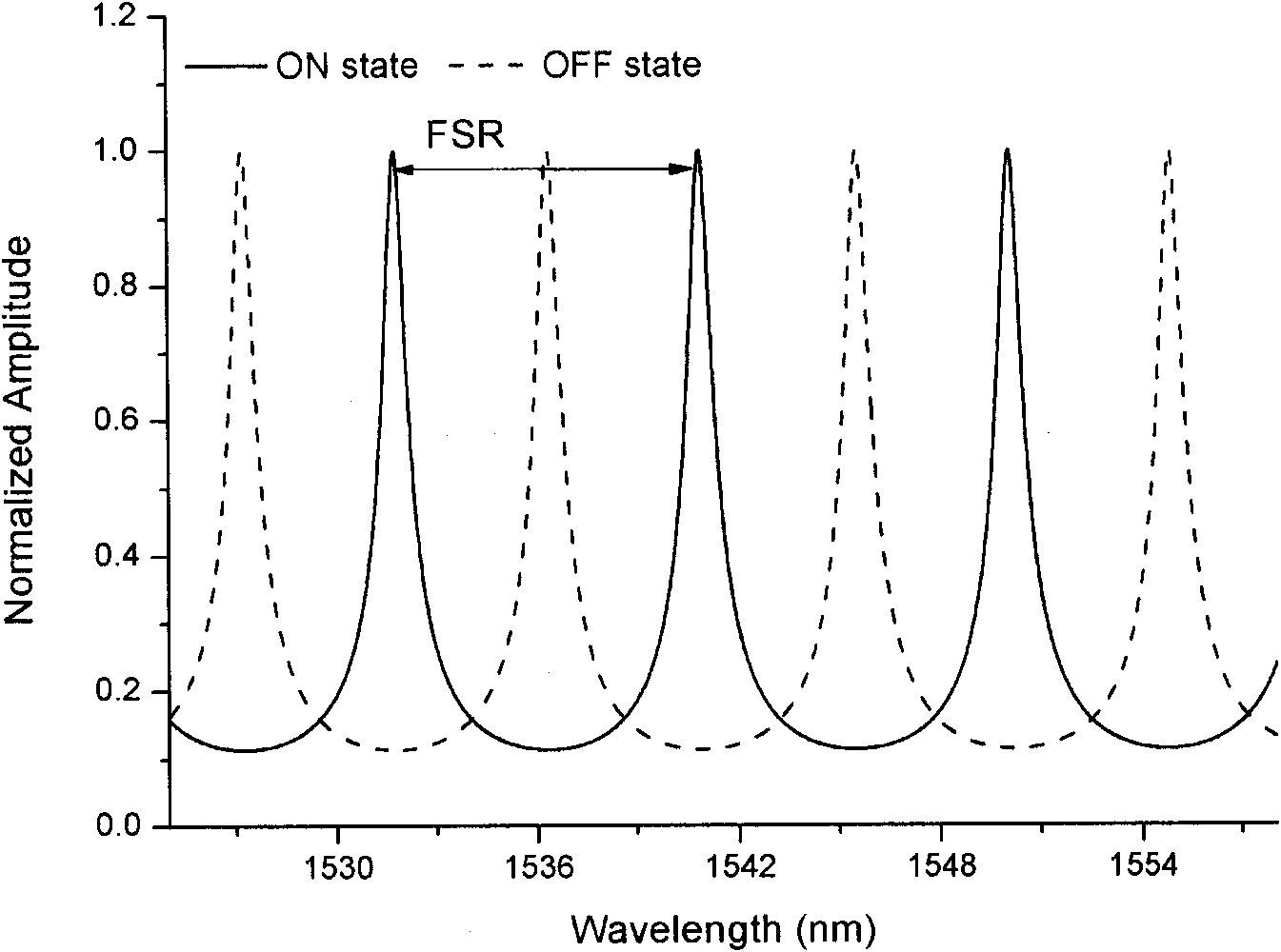
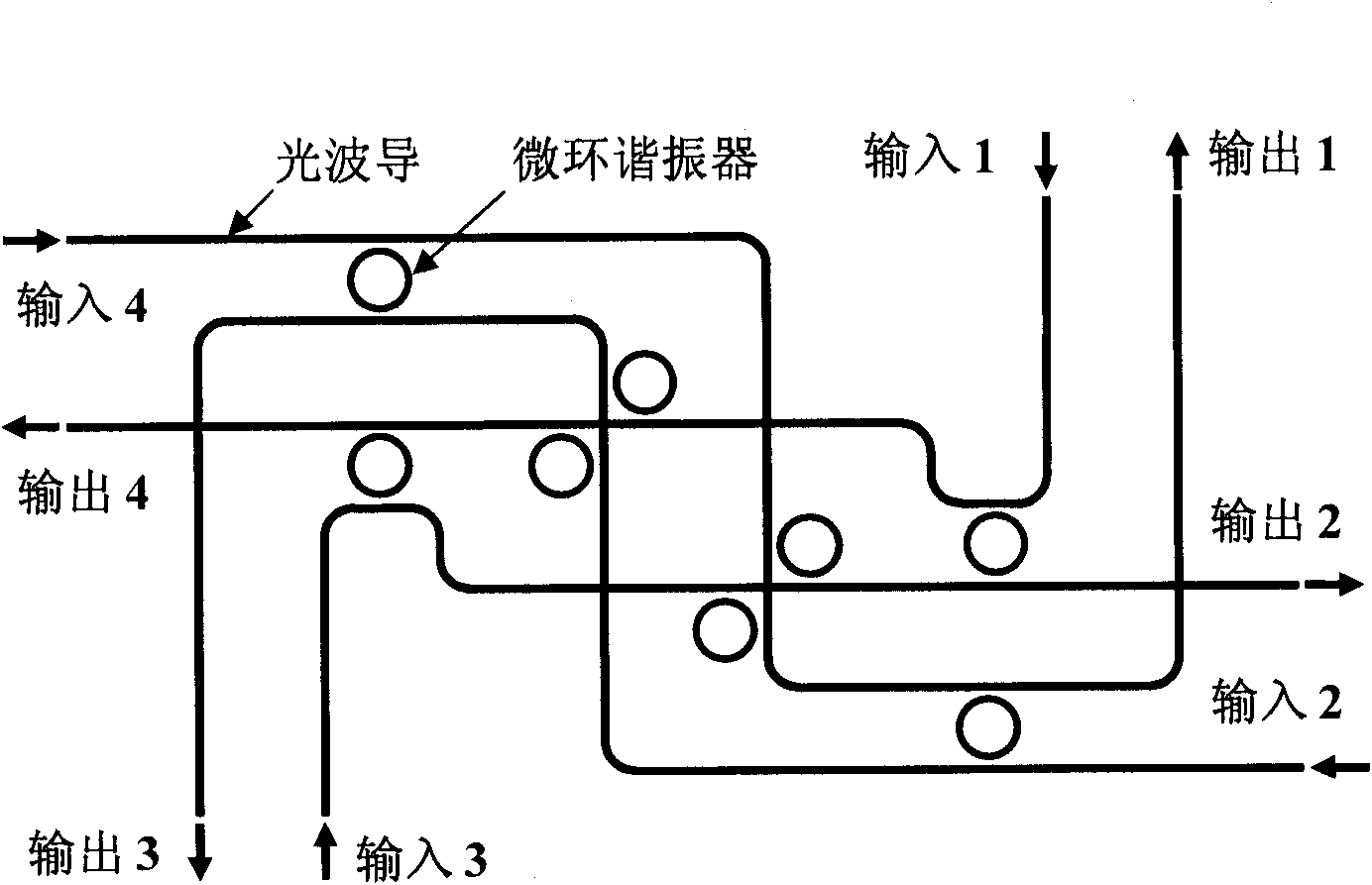
InactiveCN101872039AHigh information throughputLow insertion lossMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesOptical routerTwo-way communication
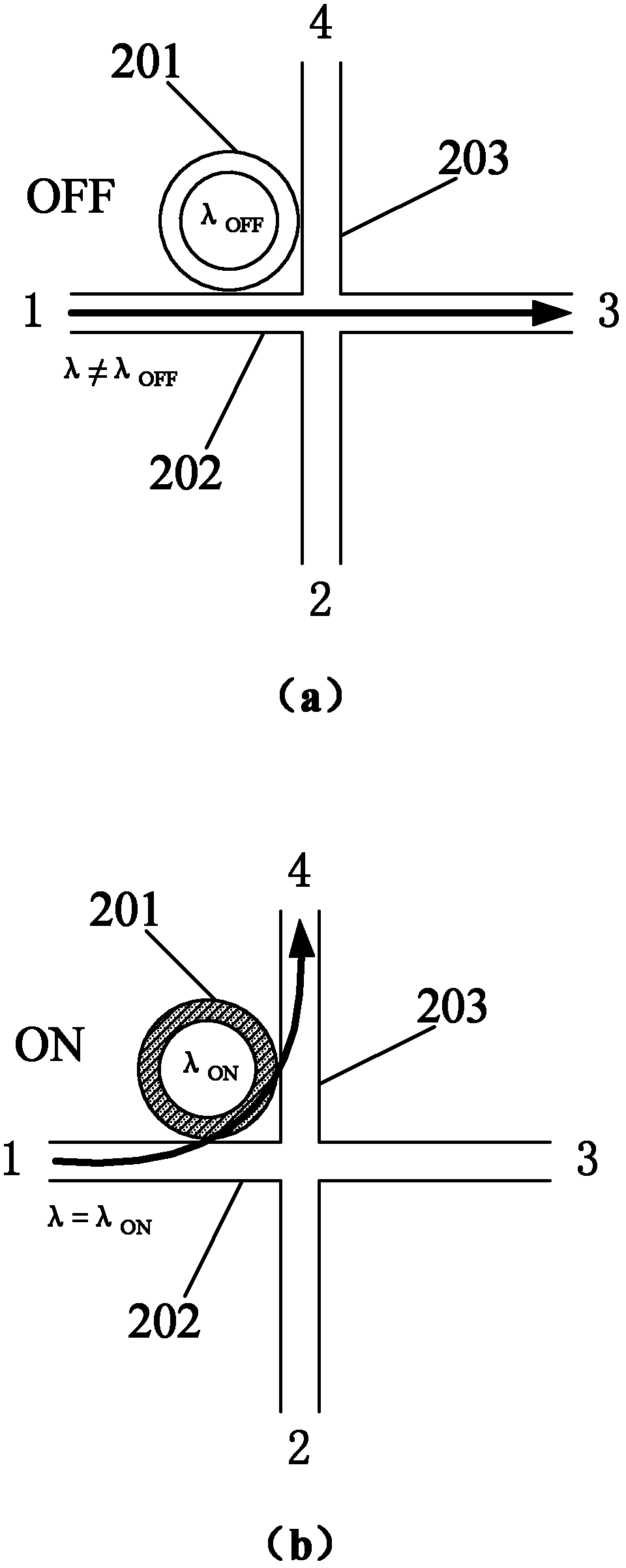
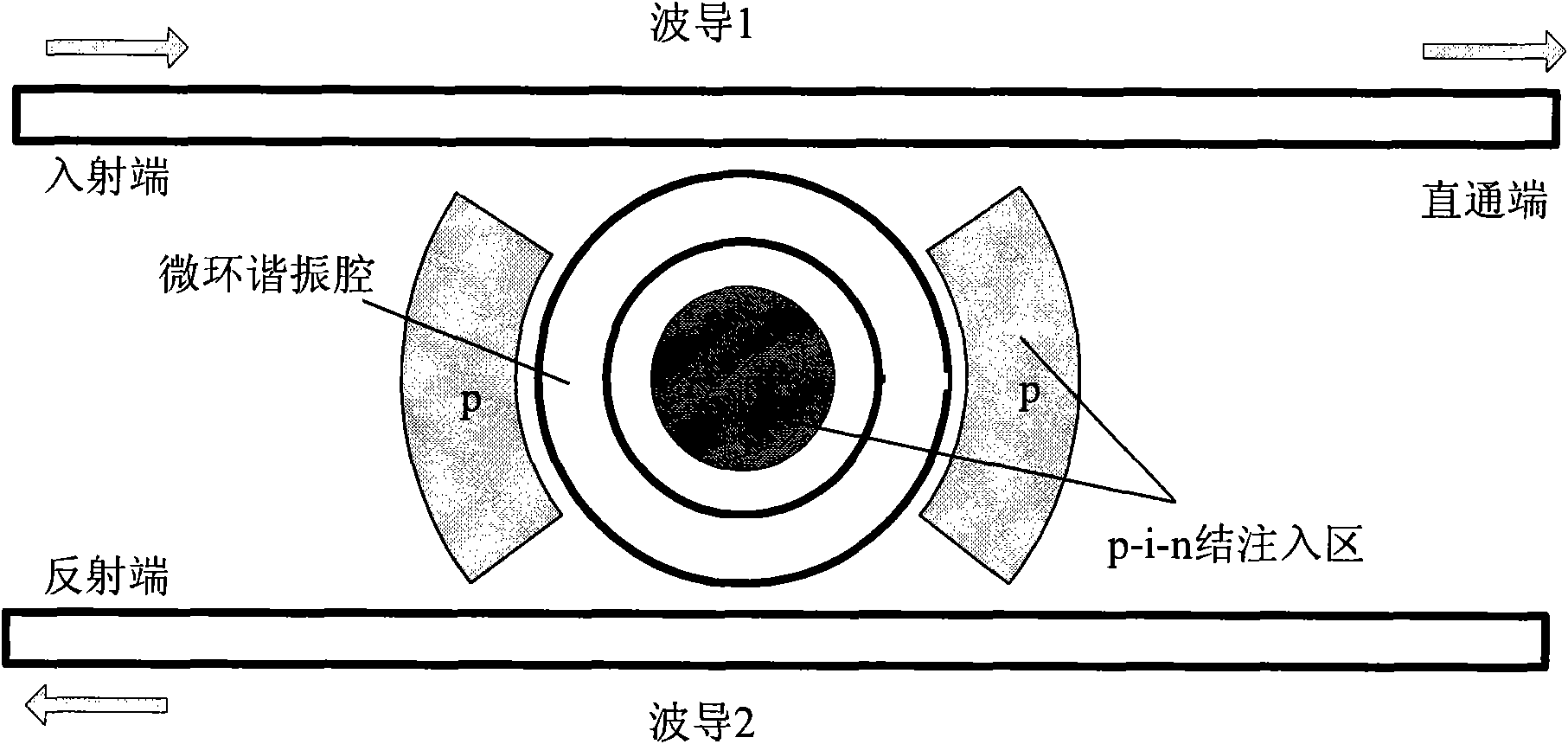
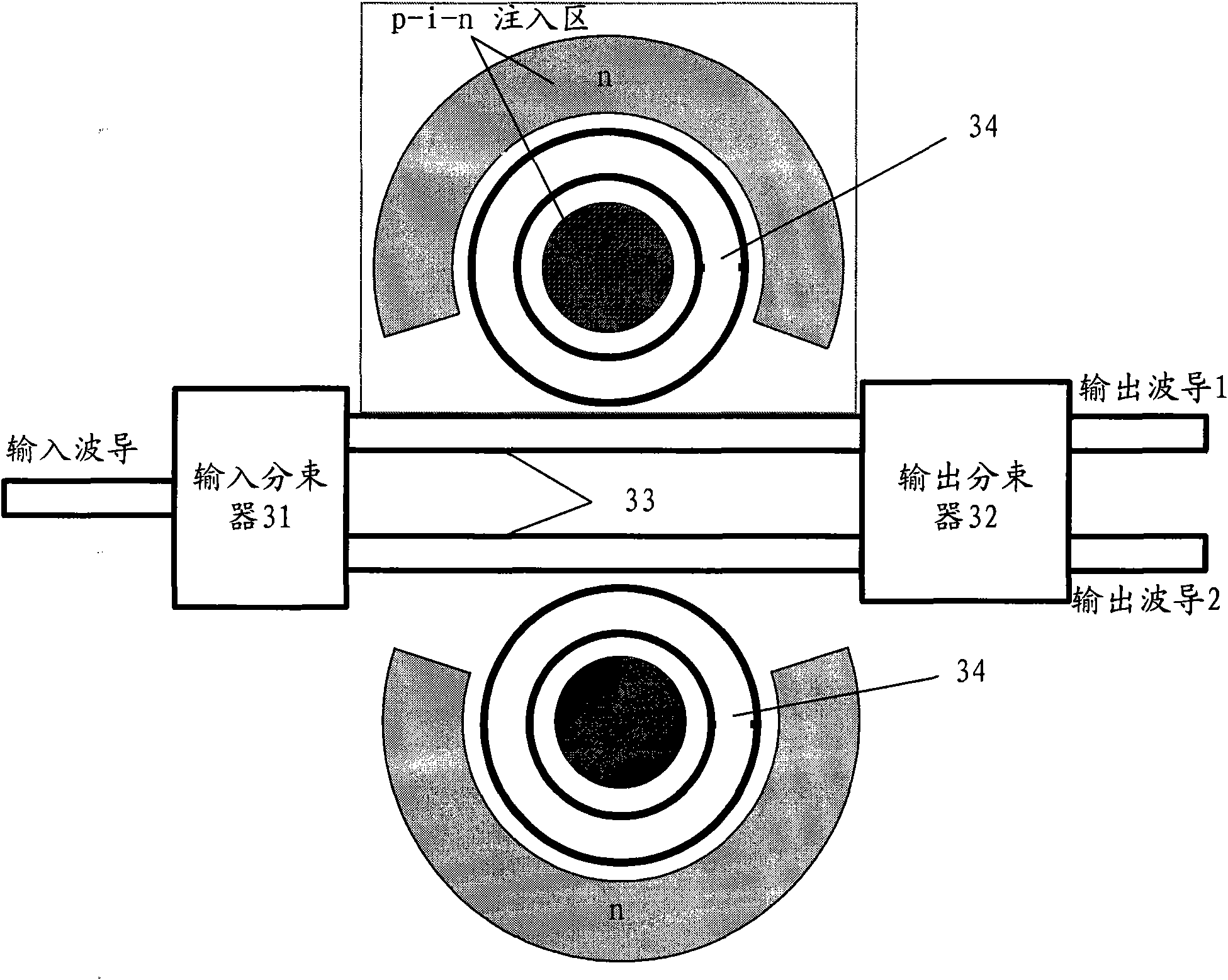
The invention discloses a 4*4 non-blocking optical router based on an active micro-ring resonator. The optical router comprises four parallel waveguide micro-ring resonator 1*2 optical switches and four crossed waveguide micro-ring resonator 1*2 optical switches, wherein the four parallel waveguide micro-ring resonator 1*2 optical switches are connected to the four crossed waveguide micro-ring resonator 1*2 optical switches, so that the optical router comprises only four input terminals and four output terminals, and each waveguide corresponding to the component is sequentially coupled with four micro-ring resonators from the input terminals to the output terminals, wherein two micro-ring resonators are used for downloading the optical signals at the input terminals of the waveguides to the output terminals of the other two waveguides; and the other two micro-ring resonators are used for uploading the optical signals at the input terminals of the two waveguides to the output terminals corresponding to the waveguides, thus achieving the non-blocking router switch among four two-way communication ports.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
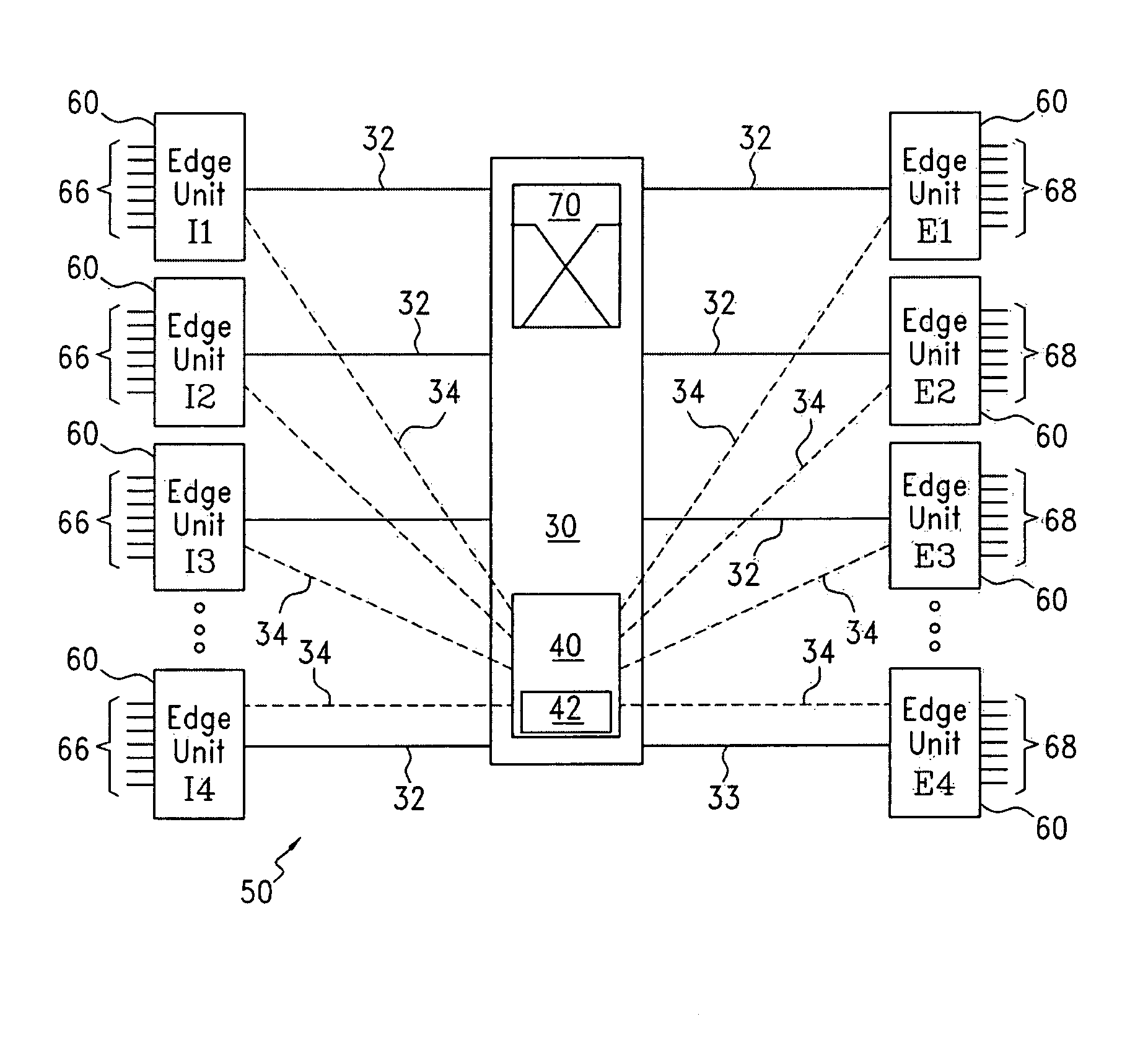
InactiveUS7426210B1Reduce complexityImprove data throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTime domainMicrowave
One embodiment of the present invention includes a router comprising an ingress edge unit with one or more ports and an egress edge unit with one or more ports connected by a switch fabric. The ingress edge unit can receive optical data and convert the optical data into a plurality of micro lambdas. The ingress edge unit can convert the incoming data to micro lambdas by generating a series of short-term parallel data bursts across multiple wavelengths. The ingress edge unit can also wavelength division multiplex and time domain multiplex each micro lambda for transmission to the switch fabric in a particular order. The switch fabric can receive the plurality of micro lambdas and route the plurality of micro lambdas to the plurality of egress edge units in a non-blocking manner.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Network audit tool
InactiveUS6950865B1Improve network performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksDevice typeFault analysis
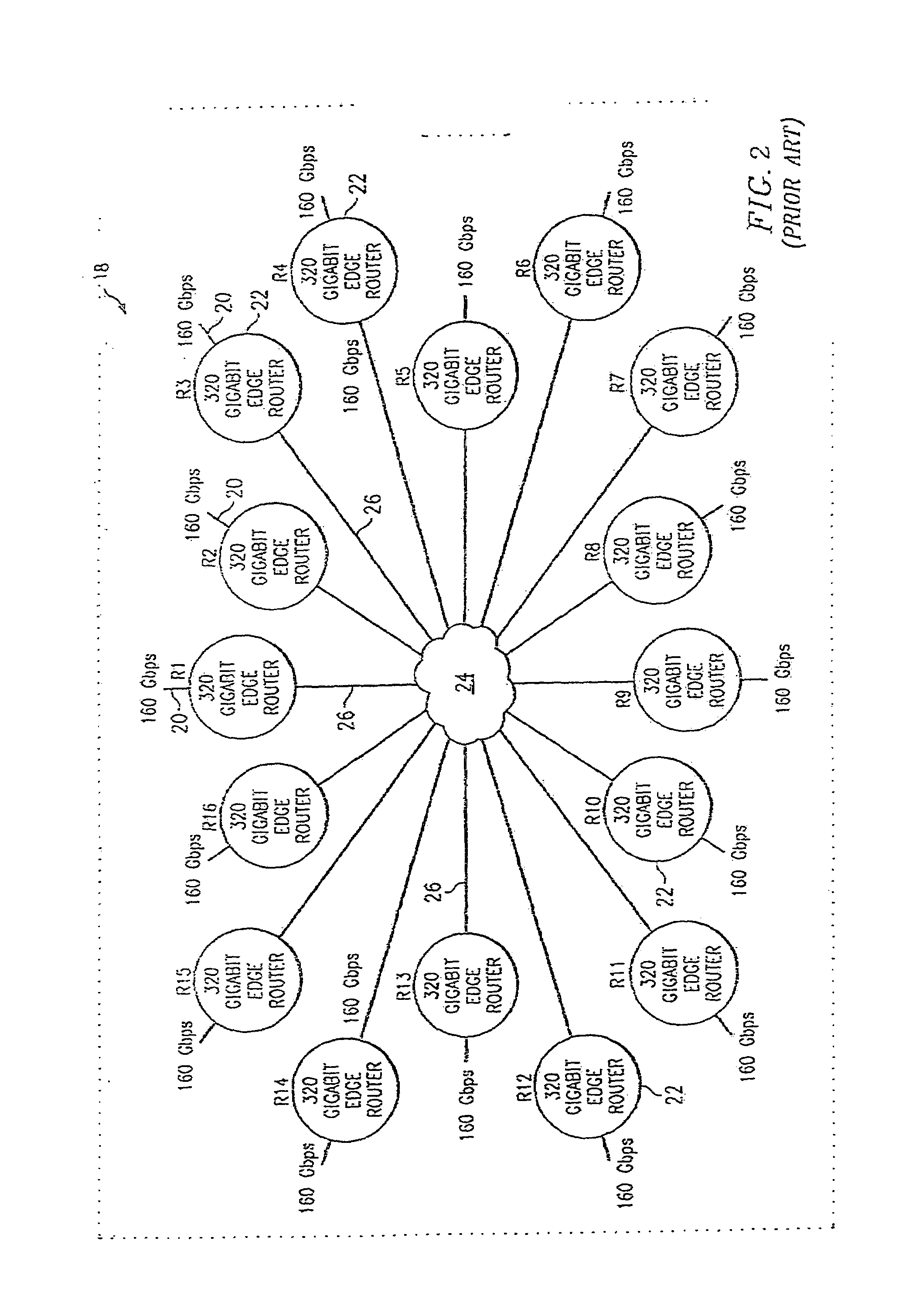
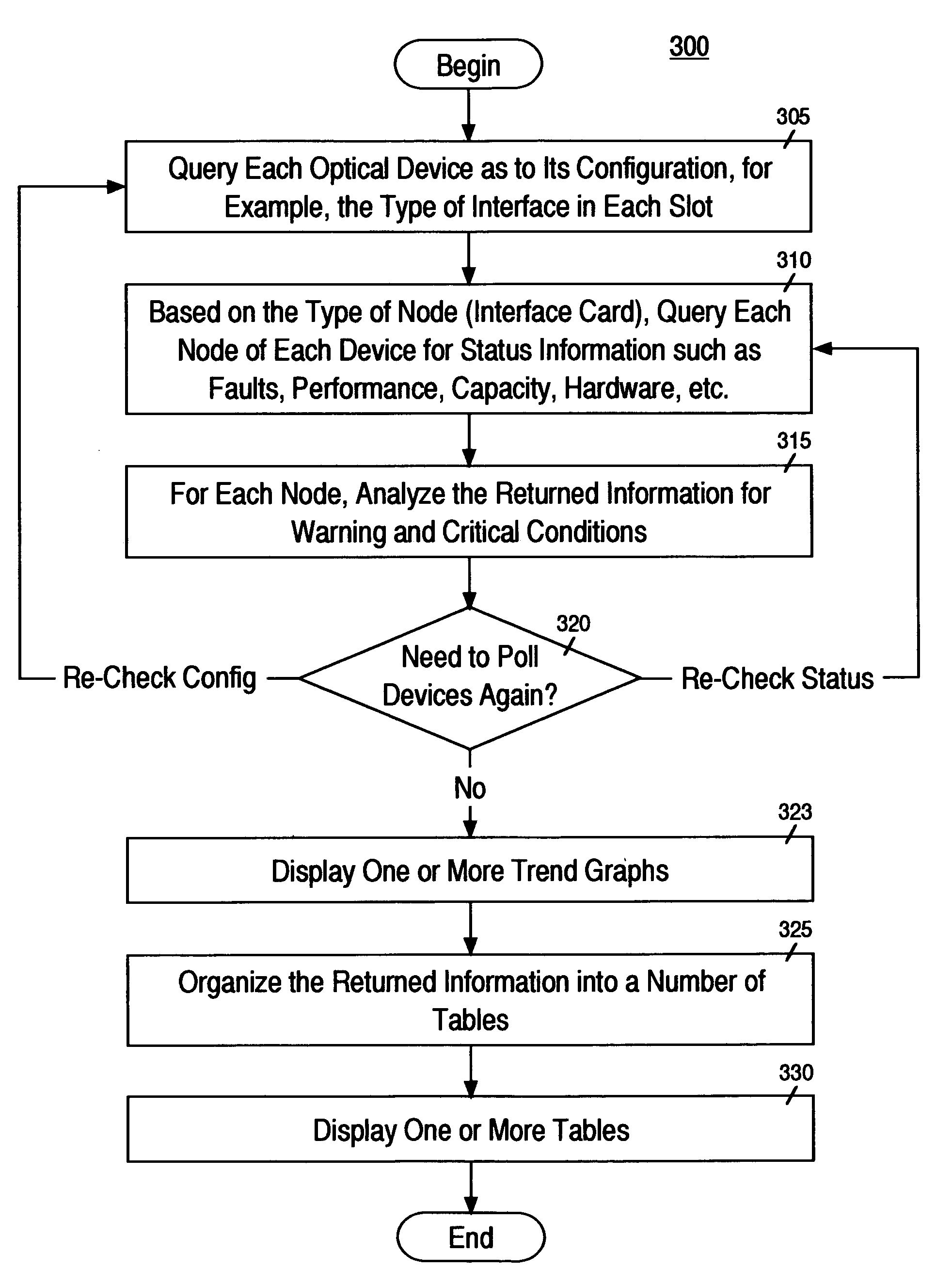
A method for automatically performing a network audit. The network may comprise a number of different types of devices, each with multiple possible configurations. In one embodiment, each device in a network is queried for its configuration. For example, a number of optical routers are queried as to what interface cards each has. All of the data may be collected from a single point in the network. Based on the responses, one or more status queries are issued to each device. Next, the process analyzes the responses according to a set of rules that are tailored for each possible device configuration. Then, one or more network audit tables are displayed. The tables have a similar look and feel regardless of the type of device or the device's configuration. For example, for each type of device configuration there may be tables pertaining to fault analysis, capacity and planning, configuration, and performance.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
System and method for improving the efficiency of routers on the Internet and/or cellular networks and/or other networks and alleviating bottlenecks and overloads on the network
InactiveUS20080145050A1Simpler and flexible bufferingCheaply and easilyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical delay lineIndividual data
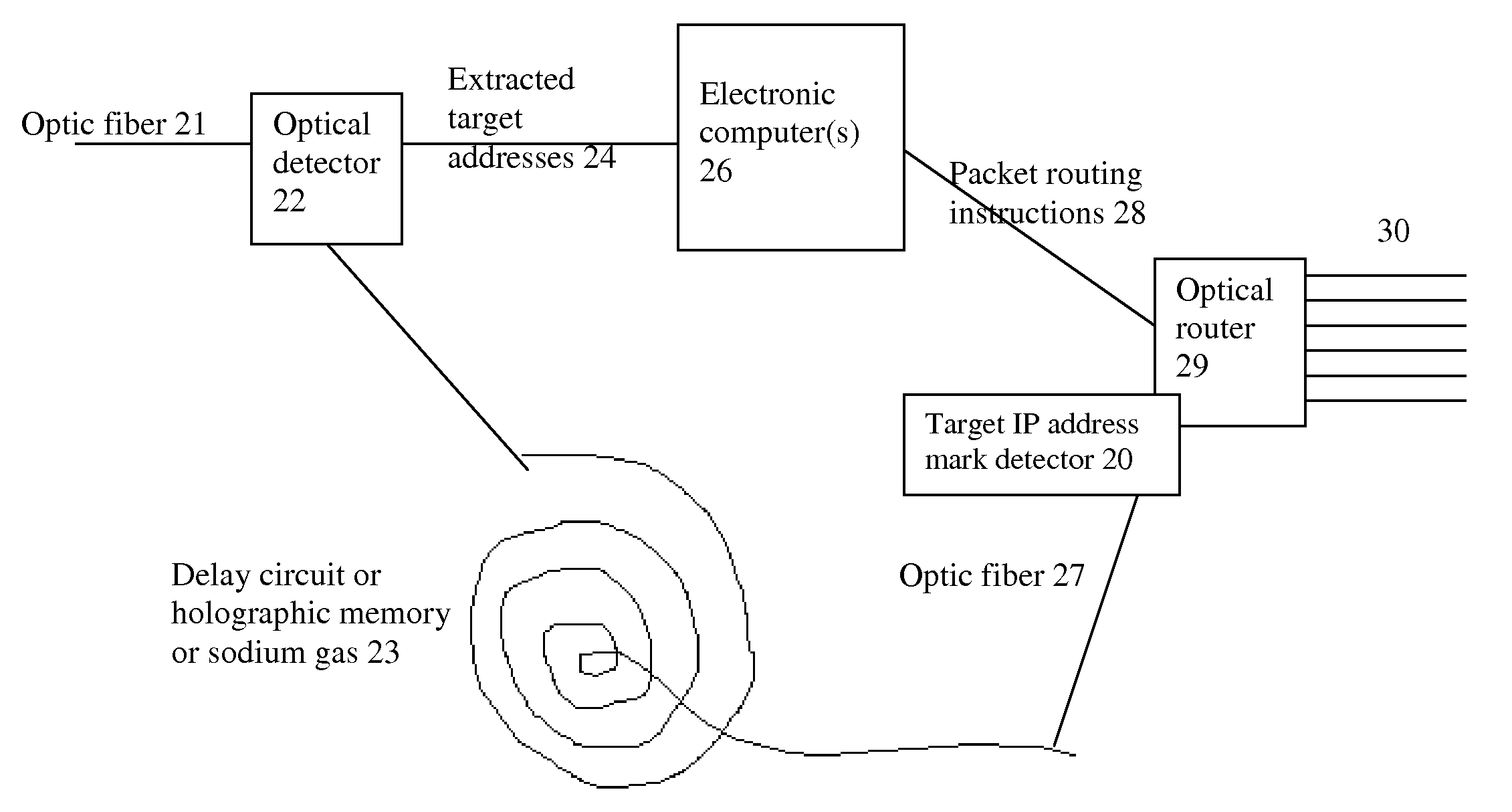
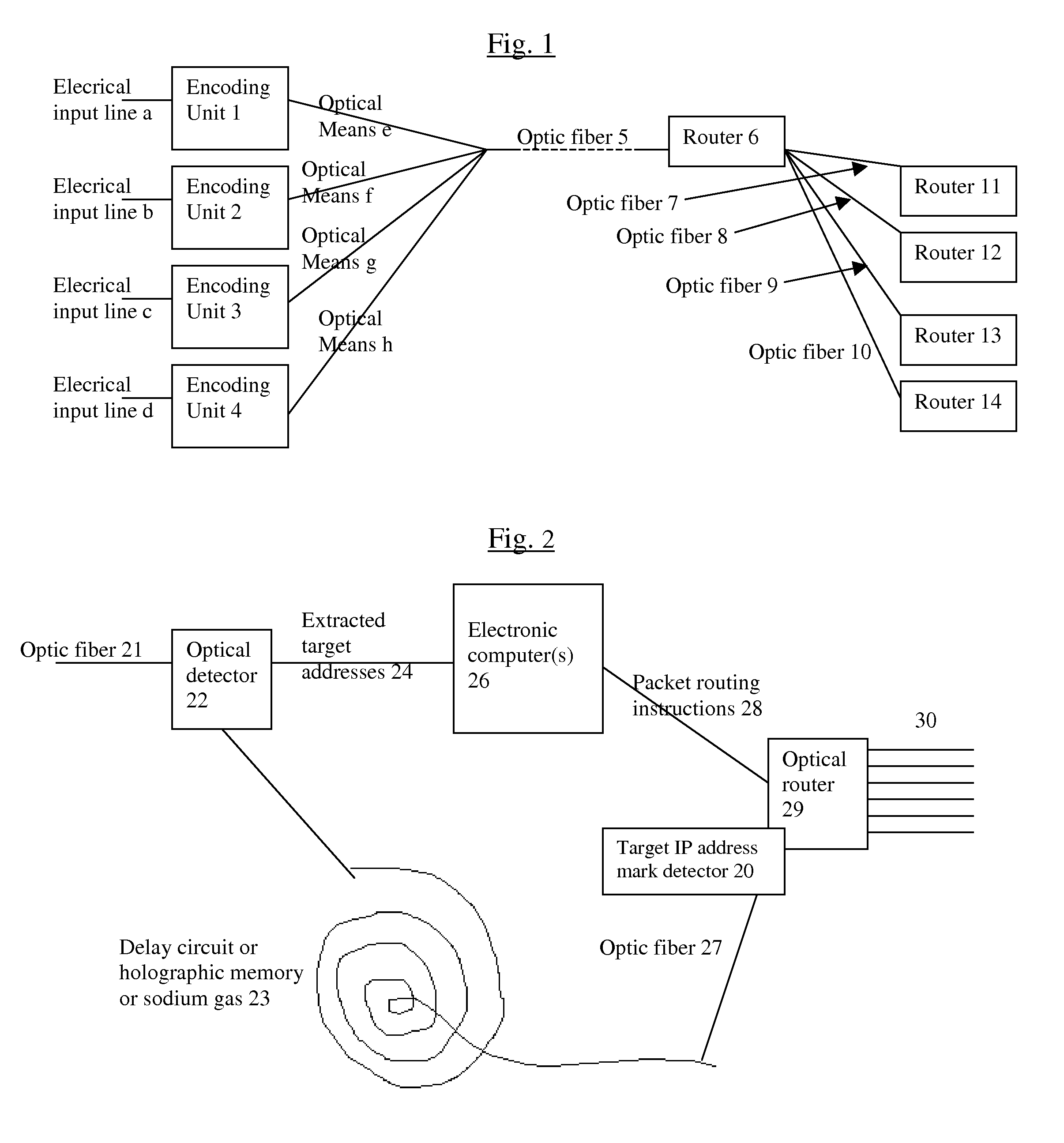
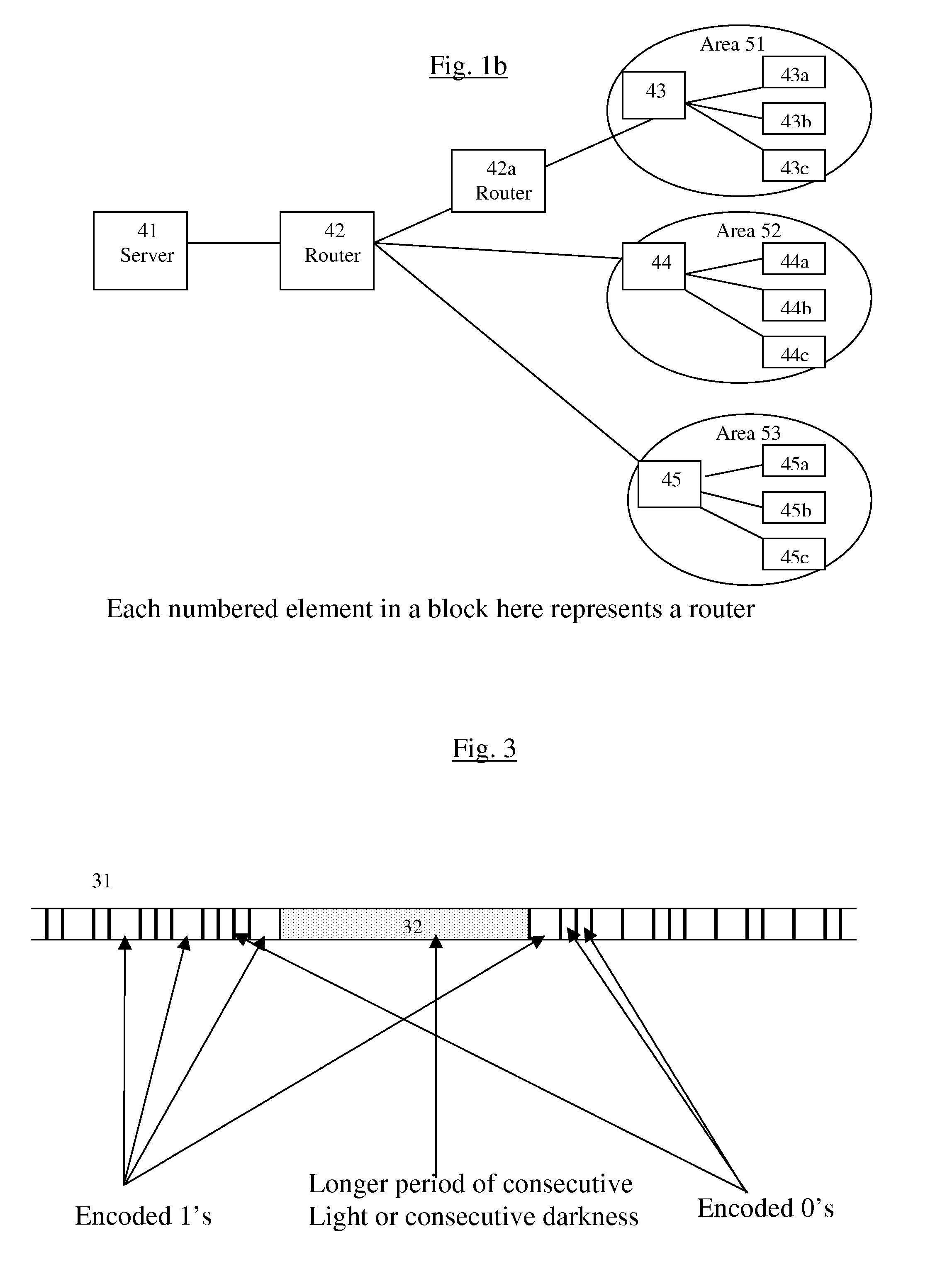
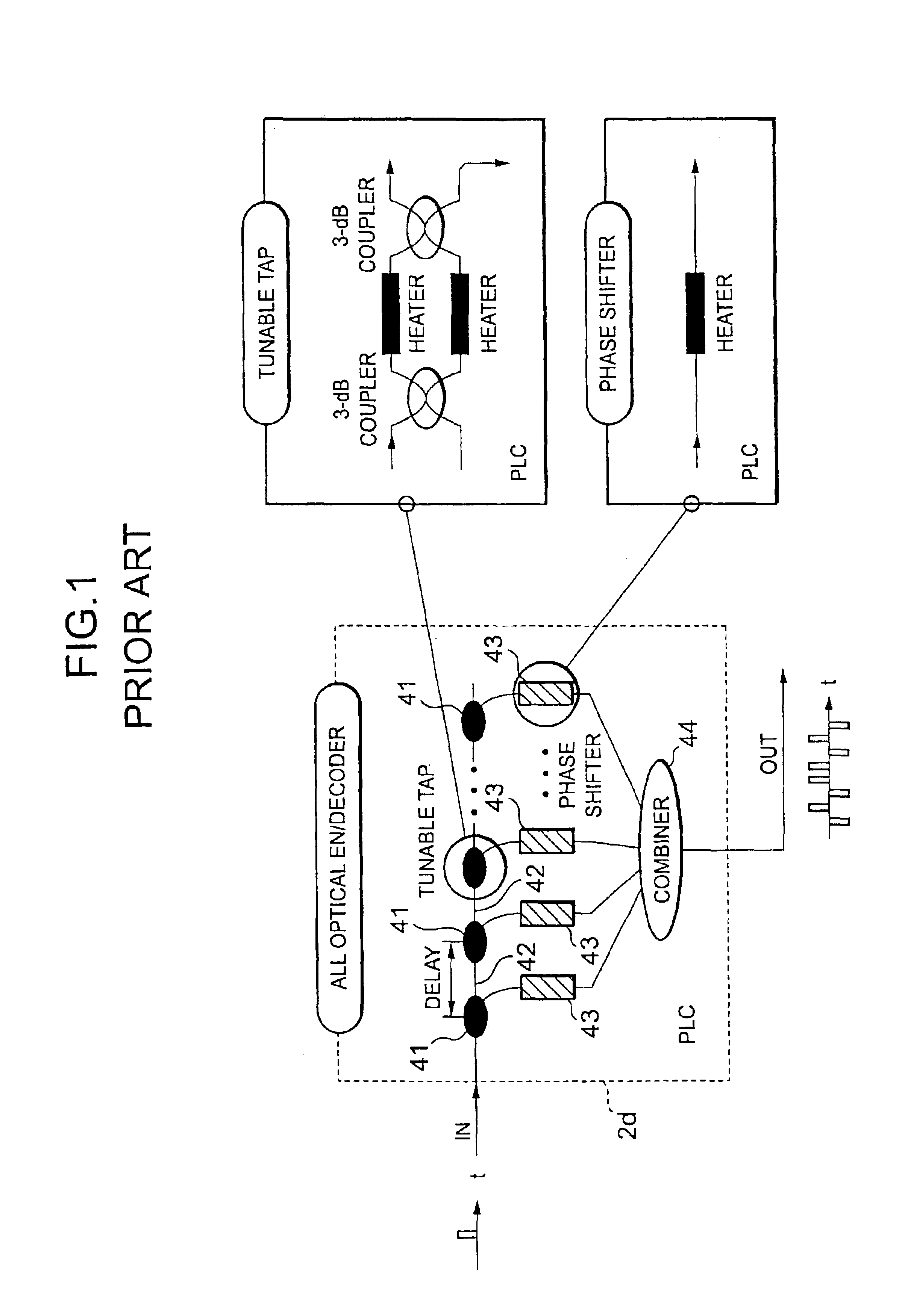
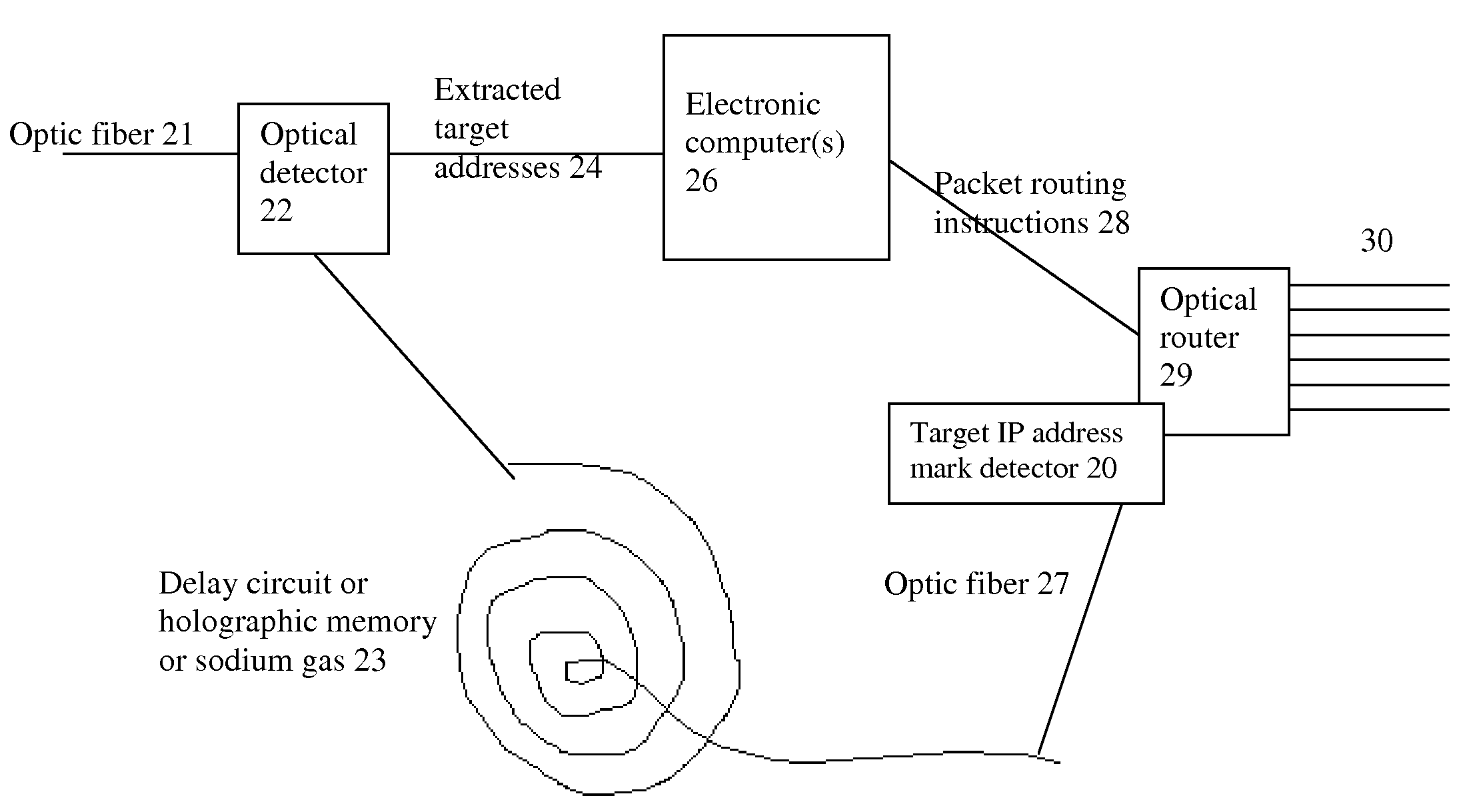
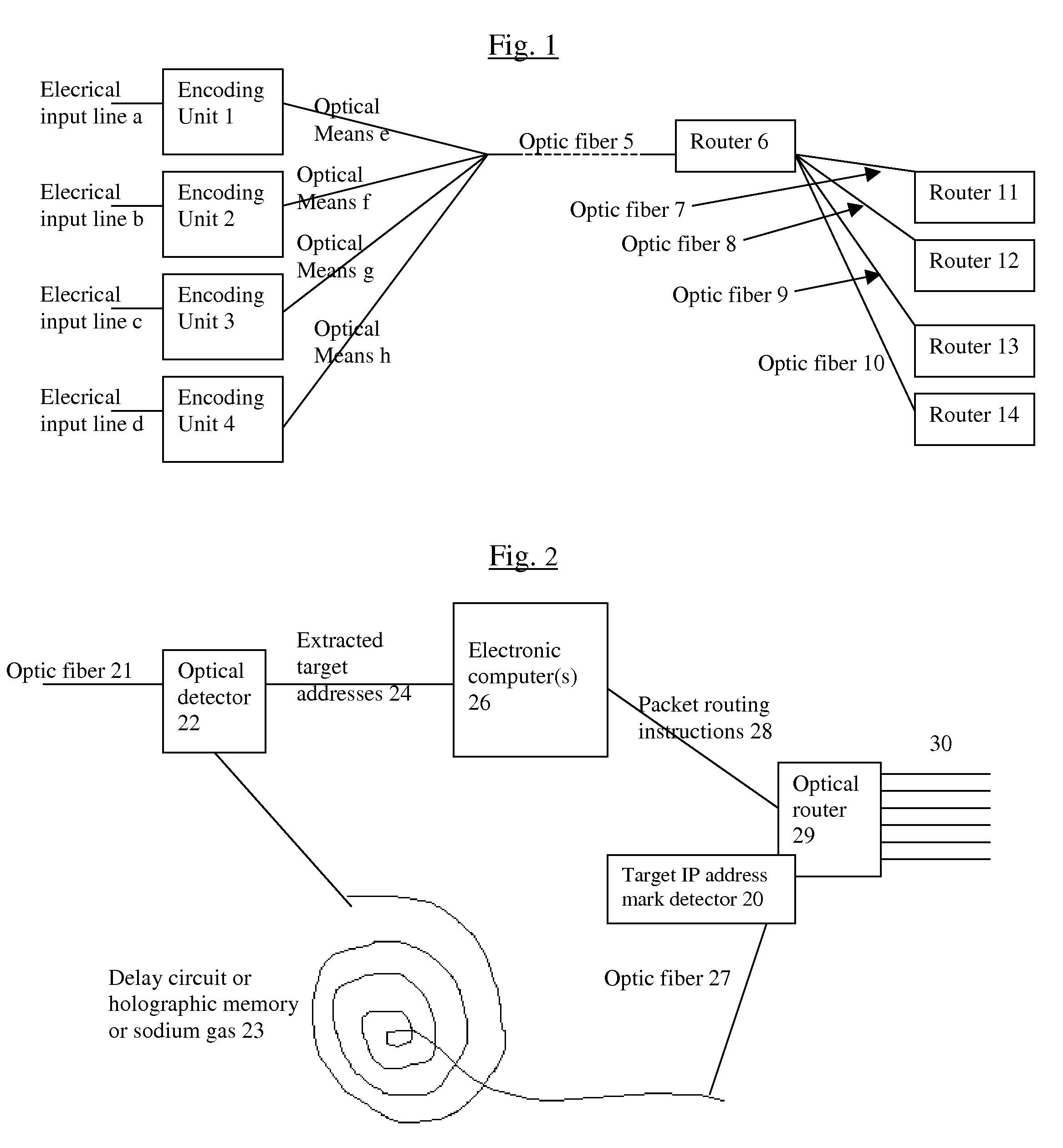
The biggest bottleneck in the Internet today is caused by the slow speed of routers, compared to the speeds that are achieved by optic fibers with DWDM (Dense Wave Division Multiplexing). Packet switching or something similar to it is needed not just for better utilization of the lines, but also because it is superior to circuit switching in many ways, such as better scalability as the Internet grows, better handling of traffic congestions, and better routing flexibility. But optical routers are currently unable to do packet switching except by translating the data to electronic data and then back, which is very inefficient. The present invention solves this problem by optically marking and detecting the packet headers or parts of them, translating at most only the headers or parts of them to electronics for making packet switching decisions, and keeping the rest of the packets in optical delay lines, and solving response-time problems in the router, so that the crude optical switches can execute the packet switching decisions at fast bit rates. This solution has very high scalability and becomes even more efficient when physical addresses are used. Another optimization described in this invention is improving routing efficiency and bandwidth utilization by grouping together identical data packets from the same source going to the same general area with a multiple list of targets connected to each copy of the data and sent together to the general target area. These grouped packets are then preferably broken down into smaller groups by the routers in the general target area and finally broken down to individual data packets for delivering to the final actual destinations. This optimization works best with Physical addresses, and can be very useful for example for optimizing the access to very popular sites such as for example Yahoo or CNN, and can be used also for example for more efficiently transferring streaming data, such as for example from Internet radio stations, or Internet TV stations which will probably exist in the next years. Another important optimization is a new architecture and principles for routing based on physical geographical IP addresses (such as for example based on GPS), in a way much more efficient than has been previously discussed in the literature that suggested using physical (geographical) addresses. This is preferably based on a hierarchy similar to a hierarchical road system, so that preferably the MAIN routers (and / or intermediary-level routers) are preferably also connected directly and preferably with high-bandwidth as peers between each other, without having to go through lower-level routers in order to reach their peers, so that once a higher-level router (and especially if it's one of the MAIN routers) decides to forward a packet (or a group of packets) to a higher-level peer, preferably the packets don't have to go through lower level routers. However, conversion from the current architecture to the new one can be done very easy, as shown in the description below.
Owner:BARHON MAYER BATYA
Optical packet header identifier, optical router incorporating the same therein, and optical routing method using the router
InactiveUS6892001B2Simple configurationReduce power consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsGratingOptical packet
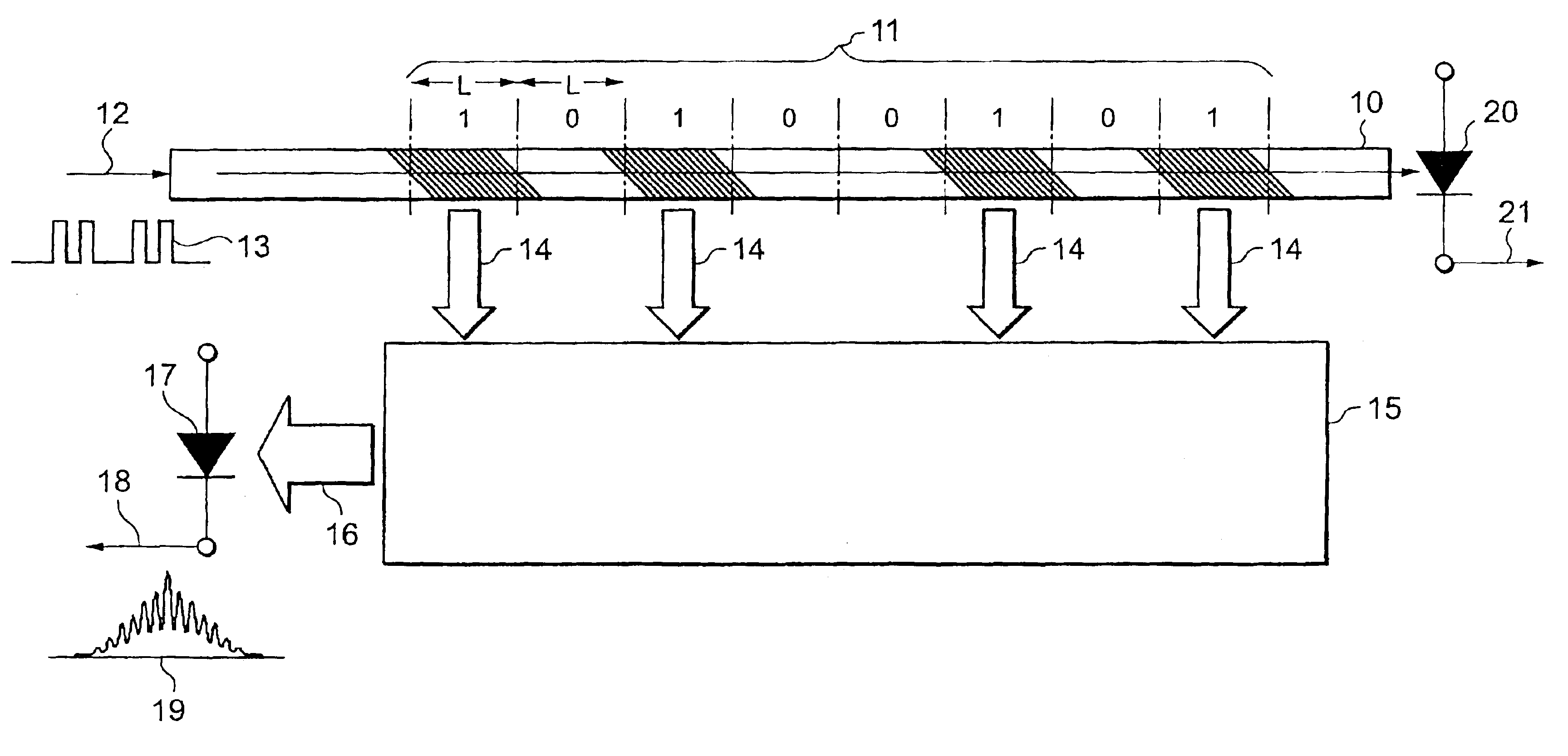
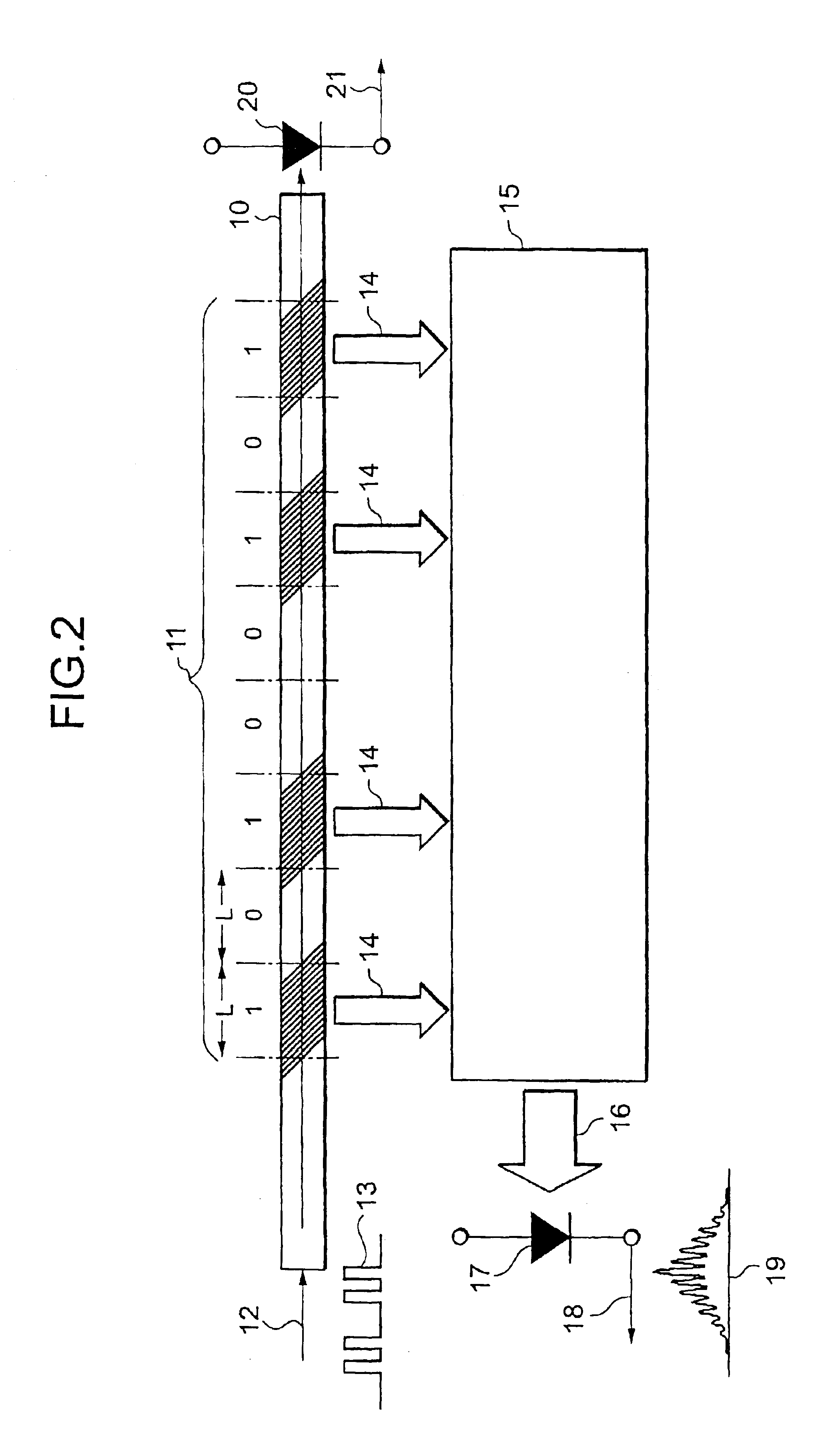
An optical packet header identifier having a simplified configuration and being superior in reliability, stability, and economical efficiency, an optical router incorporating the identifier therein, and a routing method using the optical router are provided. The optical packet header identifier includes an optical waveguide, optical focusing elements, and a photo receiver. Tilted gratings for diffracting an incident optical beam and emitting the beams as diffracted optical beams to the outside of the waveguide are formed within the optical waveguide. The tilted gratings are not formed uniformly in a longitudinal direction of a core of the optical waveguide, but are arranged at intervals. The length of a portion containing a set of gratings and the length of a portion containing no gratings can be defined in increments of length “L”. “L” equals to the spatial length which 1 bit in an optical signal occupies.
Owner:LASERFRONT TECH
System and method for improving the efficiency of routers on the internet and/or cellular networks and/or other networks and alleviating bottlenecks and overloads on the network
InactiveUS8073327B2Improving routing efficiency and bandwidth utilization efficiencyEfficient transferMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsIp addressThe Internet
Owner:BARHON MAYER BATYA
Method and apparatus for synchronized slotted optical burst switching
InactiveUS6963564B1Efficient and flexibleMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsFiberOptical burst switching
A network (4) includes optical routers (19), which route information in fibers (10). Each fiber carries a plurality of data channels (16), carrying data in data bursts (28) and a control channel, carrying control information in burst header packets (32). A burst header packet includes routing information for an associated data burst (28) and precedes its associated data burst. Information on the data channels and control channel is organized in synchronized slots. Multiple burst header packets occupy portions of a slot, referred to as micro-slots. When the burst header packets are received, an egress processor (52) schedules the routing of their associated bursts. The egress processor (52) determines a time at which a data burst can be scheduled for passing through an optical matrix (40) to the desired output channel group (the burst can be delayed via fiber delay lines (46) if necessary).
Owner:RPX CORP
Data center network system and data communication method based on software definition
ActiveCN103441942AReduce energy consumptionEmission reductionMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksTraffic characteristicData center
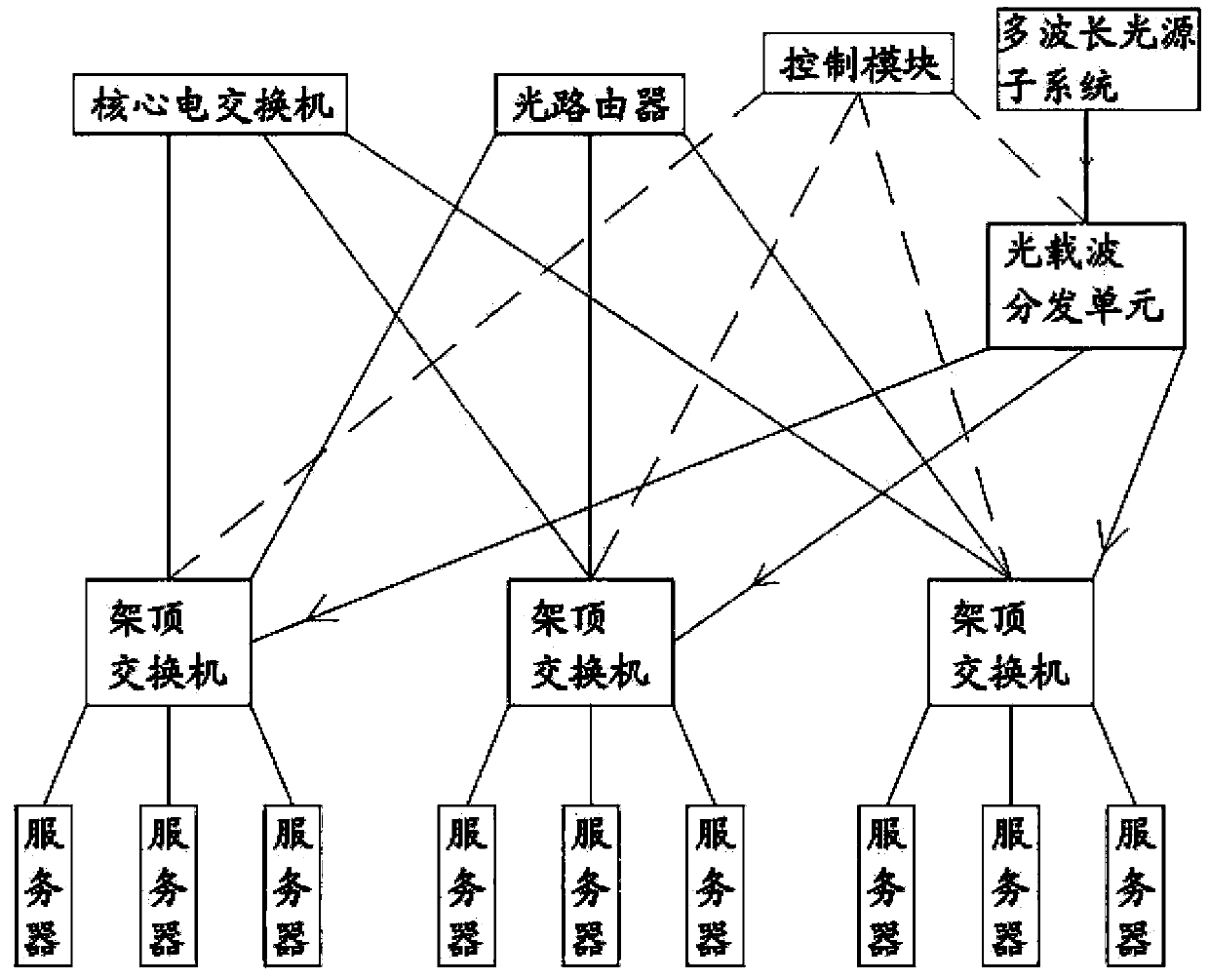
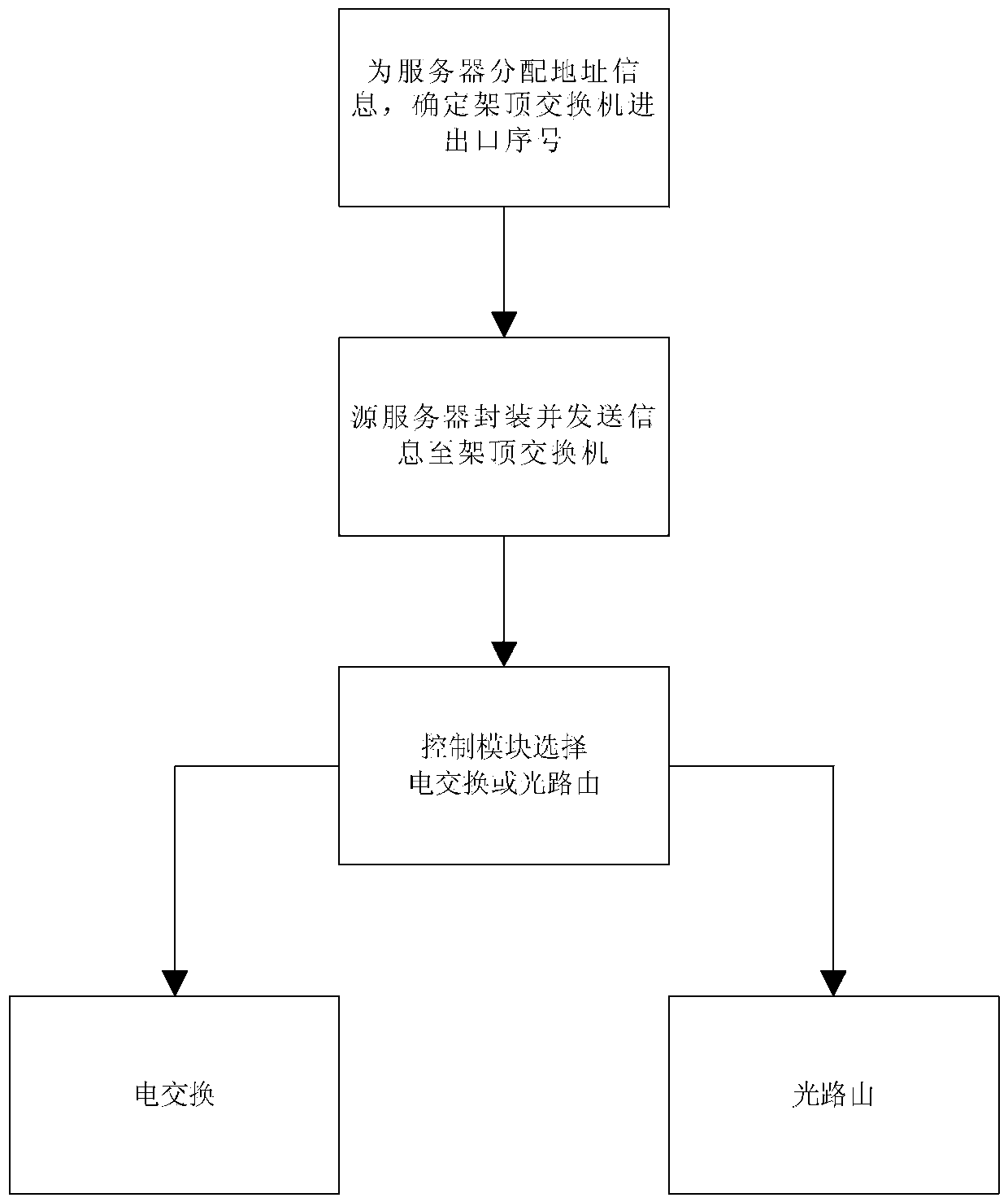
The invention provides a data center network system and data communication method based on software definition and relates to the technical field of cloud calculating data centers. The data center network system structurally comprises a core electric switch, an optical router, a top-of-rack switch, servers, a control module, an optical carrier wave distribution unit and a multi-wavelength light source subsystem. In data communication, communication optical carrier waves are allocated according to the address of the destination server of data and the traffic of the data; the data are sent to the top-of-rack switch after being packaged by the source server; the control module determines and selects an electric switching path or an optical routing path to forward the data according to the address of the destination server and the traffic characteristics of the data information and the corresponding routing algorithm. The top-of-rack switch performs light modulation on the data according to instructions of the control module and forwards the data to the corresponding electric switching or optical routing path. The data center network system and data communication method based on software definition have very good energy saving effect, are low in construction cost and improve the management efficiency of a data center network and the performance of the network.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
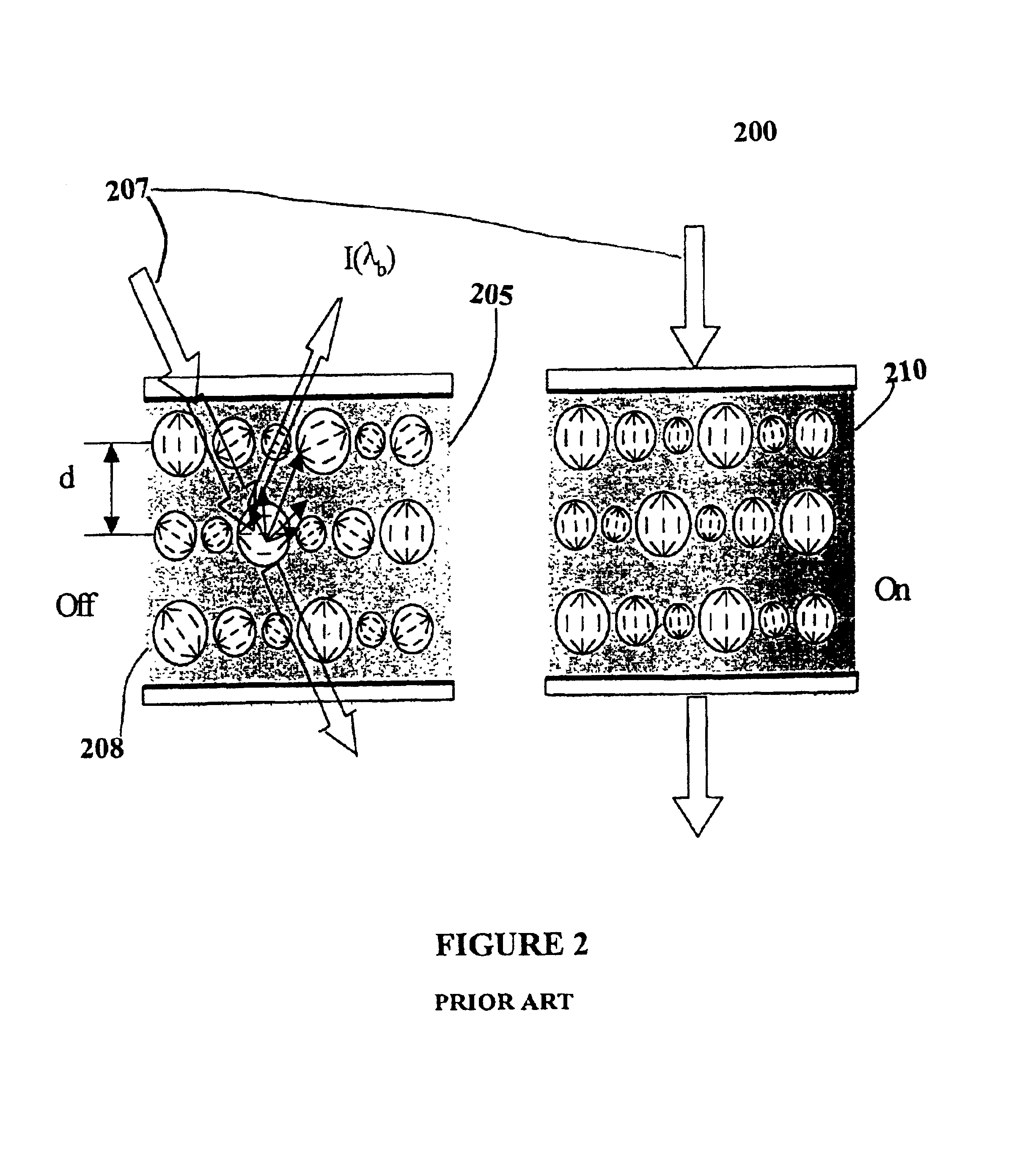
Optical router switch array and method for manufacture
InactiveUS6885414B1Simple configurationLow insertion lossLiquid crystal compositionsTelescopesElectricityGrating
An optical router switch array includes a plurality of switchable mirror elements having holographic liquid crystal arranged in stack cells. Each of the mirror elements is isolated electrically from the other switchable mirror elements by a plurality of substrates alternative arranged between the switchable mirror elements. Holographic gratings are formed on the holographic liquid crystal by exposure to holography at predetermined incident angles. A single switchable mirror element can also be provided in cases where an array is not required. The switchable mirror elements are polarization insensitive, stable within the operational spectral region, and stable versus temperature. The invention also includes methods for manufacturing a single switchable mirror element and the optical arrray.
Owner:KENT OPTRONICS
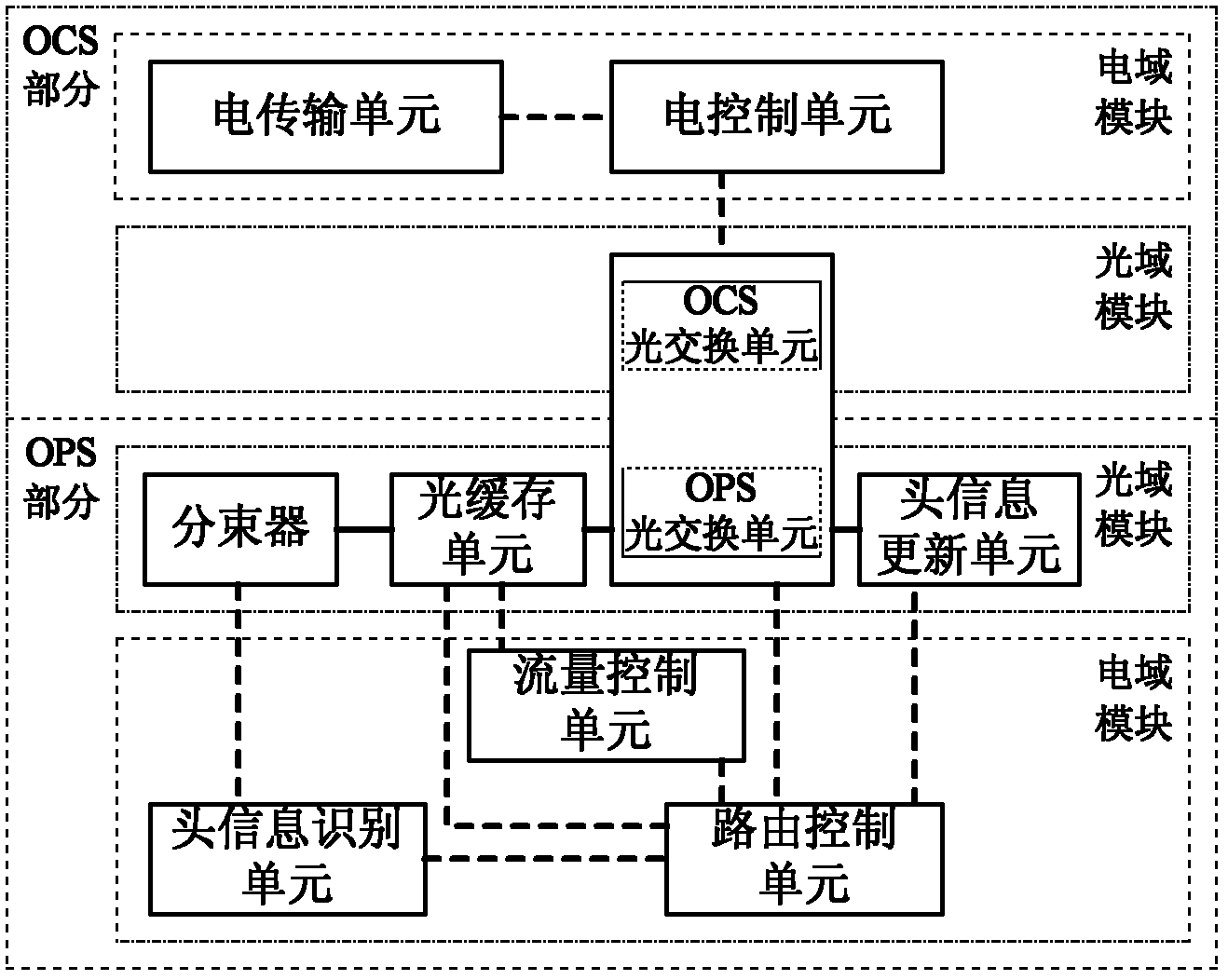
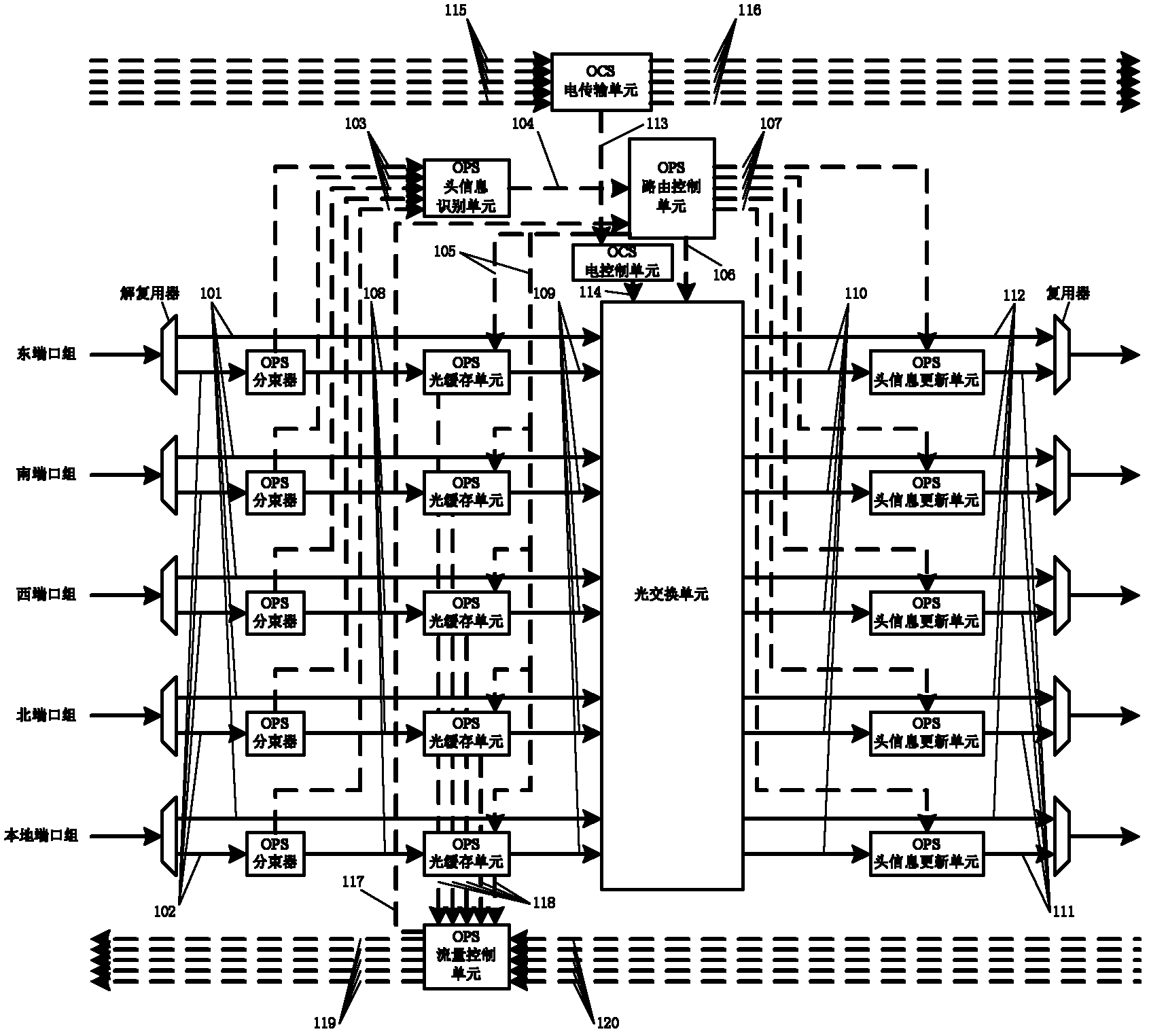
On-Chip Optical Router for Hybrid Switching
InactiveCN102281478AImprove resource utilizationReduce communication delayMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksResource utilizationOptical packet
The invention discloses an on-chip optical router for hybrid switching, which mainly solves the problems of high communication delay, low network transmission efficiency and low resource utilization rate facing a single exchange mechanism in the existing on-chip optical router. The router comprises an OCS (Optical Circuit Switching) part and an OPS (Optical Packet Switching) part, wherein each part is composed of an electric field module and an optical field module, the OCS electric field module establishes an optical link for the OCS optical field module according to electric link establishing information before transmitting messages, and the OPS electric field module provides control information for the OPS optical field module in a transmitting and switching process of optical packets. The OCS part is used for transmitting the messages for using an OCS switching mechanism, and the OPS part is used for transmitting the messages for using an OPS switching mechanism. The on-chip optical router respectively optimizes performances of different types of messages, has the advantages of less communication delay, high network transmission efficiency and high resource utilization rate, and is suitable for interconnections and communications in an on-chip optical network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High speed data classification system
InactiveUS20030231630A1Reduce processing burdenMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationGeneral purposeUltra high speed
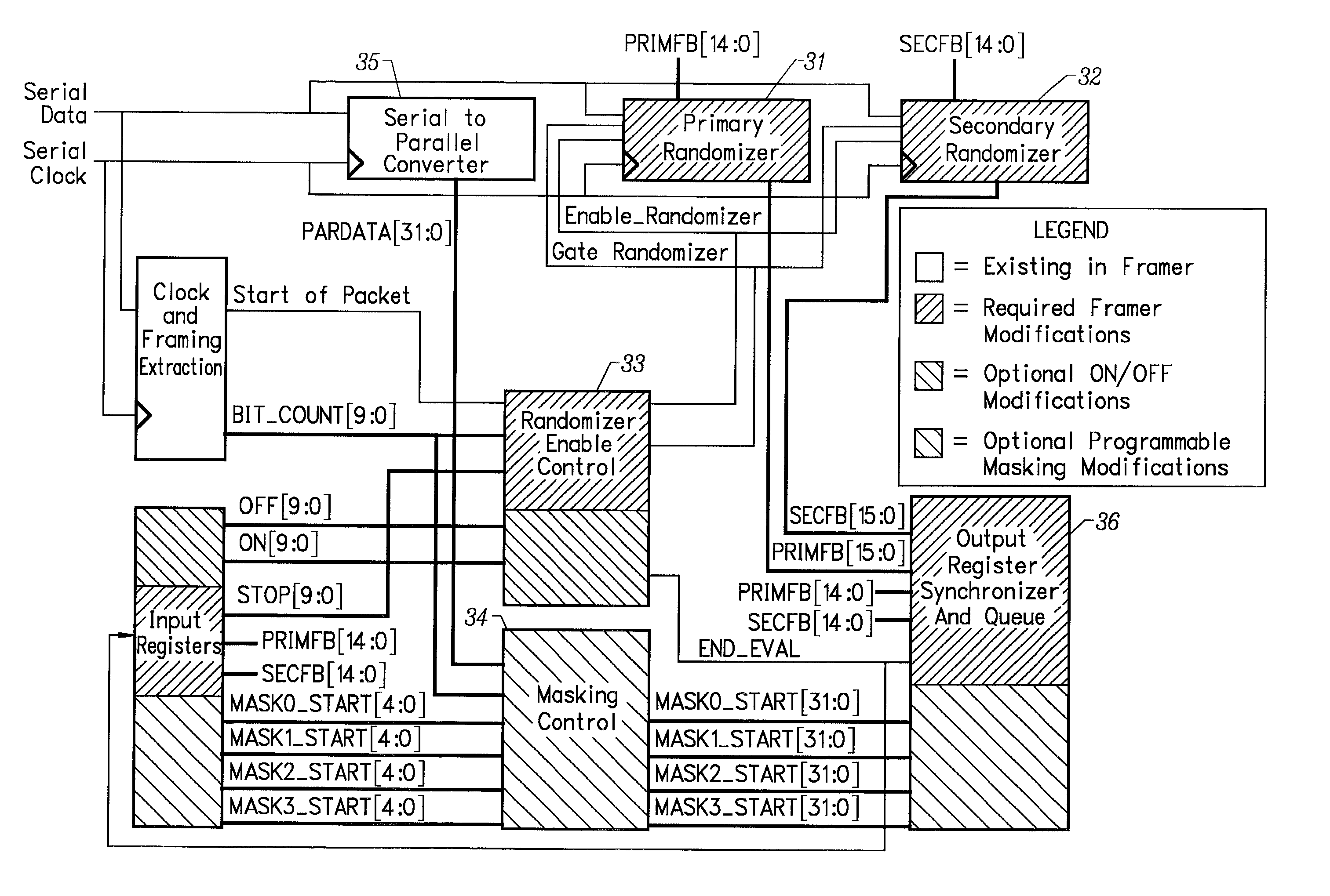
An optical network packet classification architecture is disclosed that addresses the packet classification requirements for OC-768 optical routers and beyond. The herein disclosed system is used for ultra-high speed packet classification of optical data at either the serial data stream level for maximum performance, or after it has been converted into parallel words of data. The presently preferred embodiment of the invention provides a system that operates in the receive path, where electronic data are provided by the optical interface to the data framer. The invention incorporates unique features into a traditional optical data framer chip and relies on a complex ASIC to permit the user to differentiate between up to 10,000 different patterns at ultra-high speeds. One purpose of the general purpose system disclosed herein is to eliminate the need for costly and power consumptive content addressable memory systems, or customer pattern specific ASICs, to perform network packet classification. The system operates on a principle of adaptive programmable randomization to permit a differentiation between the input vectors to be made. The invention dramatically reduces the processing burden required by high-speed optical routers or switches.
Owner:MESSENGER TERABIT NETWORKS
Optical switch
The embodiment of the invention discloses an optical switch relating to the optical communication field and solves the problems of low extinction ratio and sensitivity to optical signal wavelength of the existing optical switch. In the embodiment of the invention, a group of micro-ring resonators are arranged on two waveguide arms to control the phase position outputting the optical signal in the waveguide arms, thus, the state of the optical signal output by an output beam splitter at last in the optical switch can be adjusted to realize the function of the optical switch. The embodiment of the invention is mainly used in a device directly carrying out optical switch and optical router in optical communication, saves O / E conversion and E / O conversion when the optical communication carries out router switch.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
High speed data classification system
InactiveUS7170891B2Increase speedReduce processing burdenMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationGeneral purposeUltra high speed
An optical network packet classification architecture is disclosed that addresses the packet classification requirements for OC-768 optical routers and beyond. The herein disclosed system is used for ultra-high speed packet classification of optical data at either the serial data stream level for maximum performance, or after it has been converted into parallel words of data. The presently preferred embodiment of the invention provides a system that operates in the receive path, where electronic data are provided by the optical interface to the data framer. The invention incorporates unique features into a traditional optical data framer chip and relies on a complex ASIC to permit the user to differentiate between up to 10,000 different patterns at ultra-high speeds. One purpose of the general purpose system disclosed herein is to eliminate the need for costly and power consumptive content addressable memory systems, or customer pattern specific ASICs, to perform network packet classification. The system operates on a principle of adaptive programmable randomization to permit a differentiation between the input vectors to be made. The invention dramatically reduces the processing burden required by high-speed optical routers or switches.
Owner:MESSENGER TERABIT NETWORKS
Region-based photoelectric double-layer network-on-a-chip and routing method
InactiveCN101917333AReduce areaReduce complexityData switching switchboardsElectromagnetic transmissionResource utilizationData information
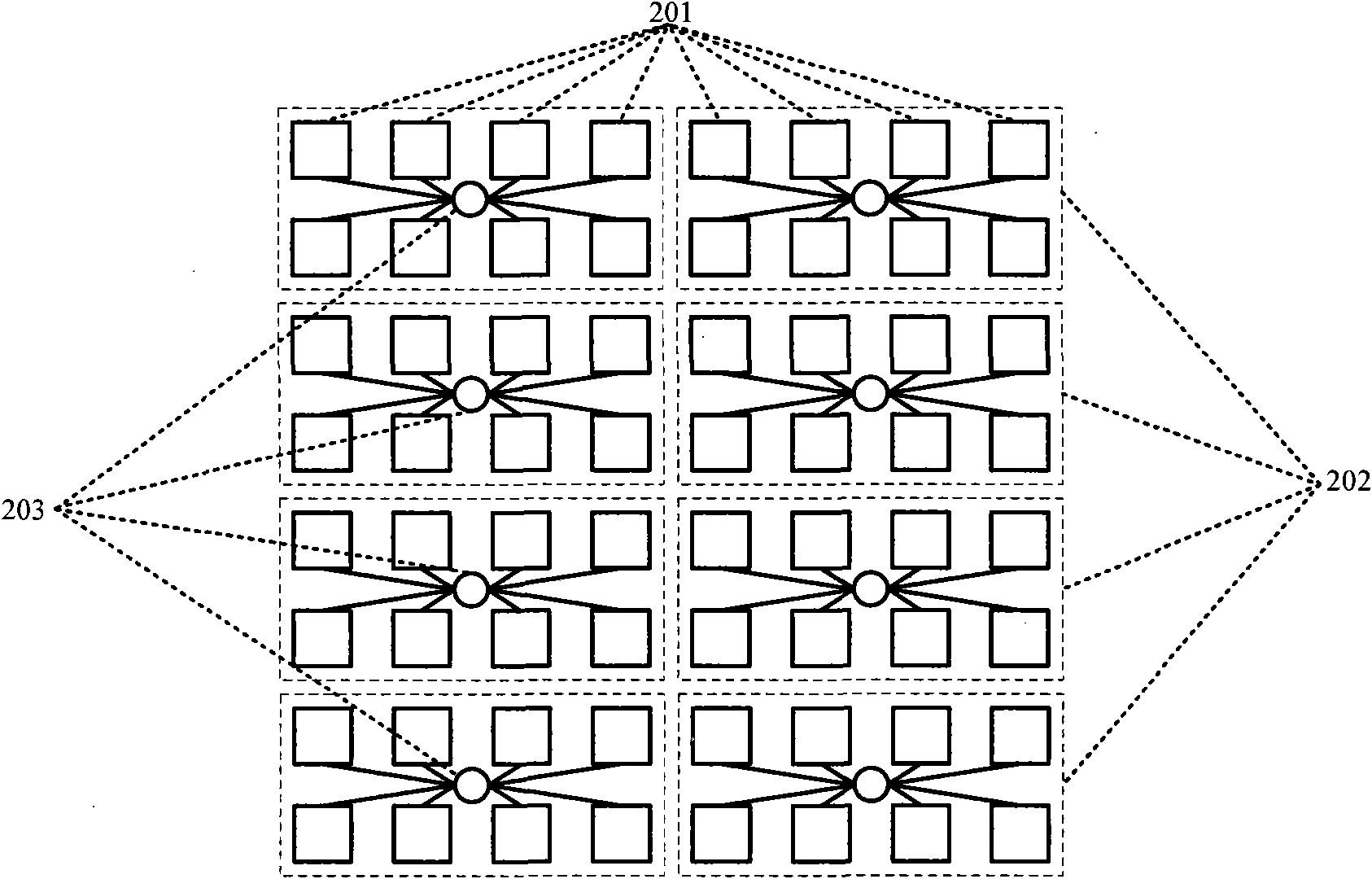
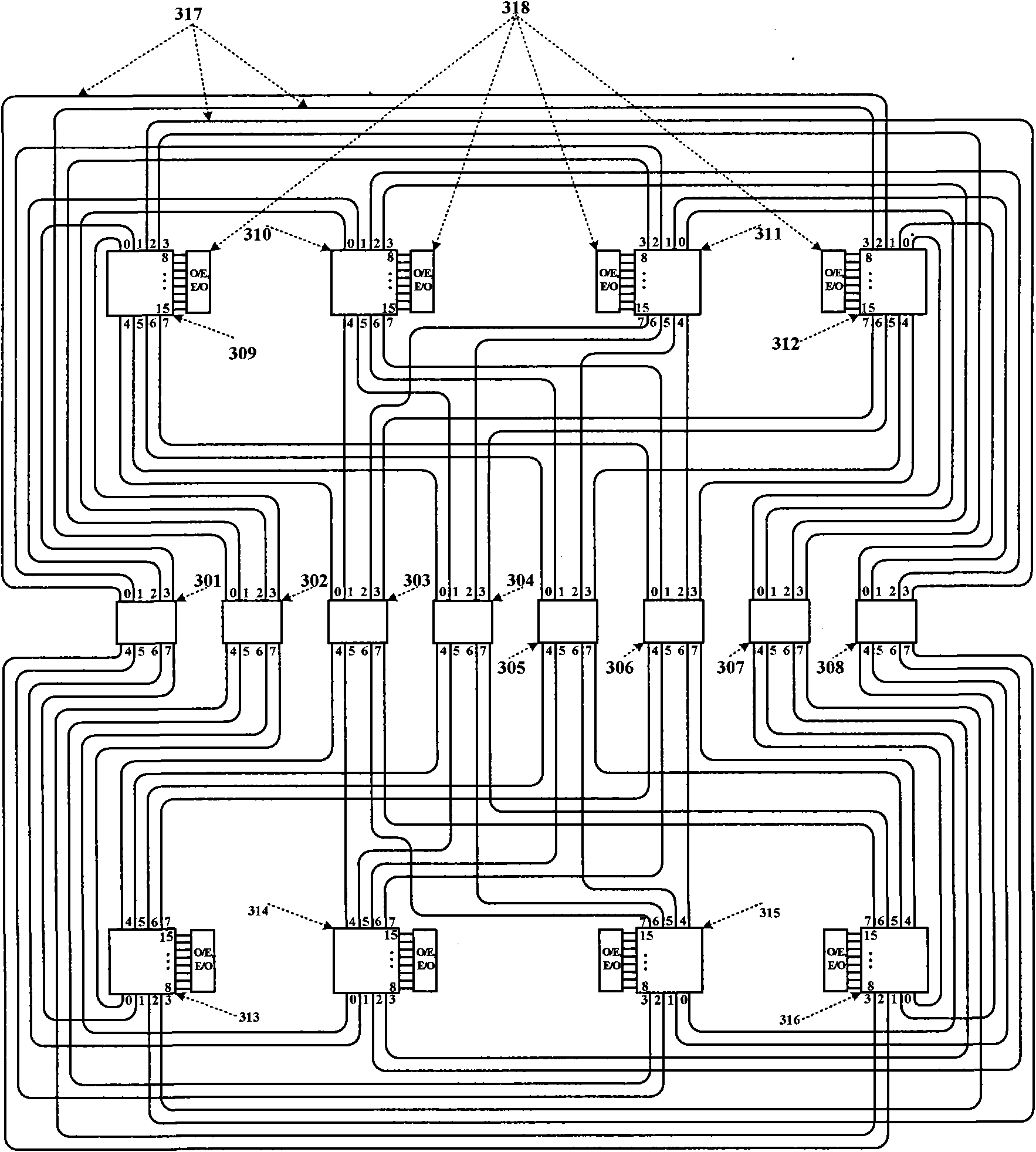
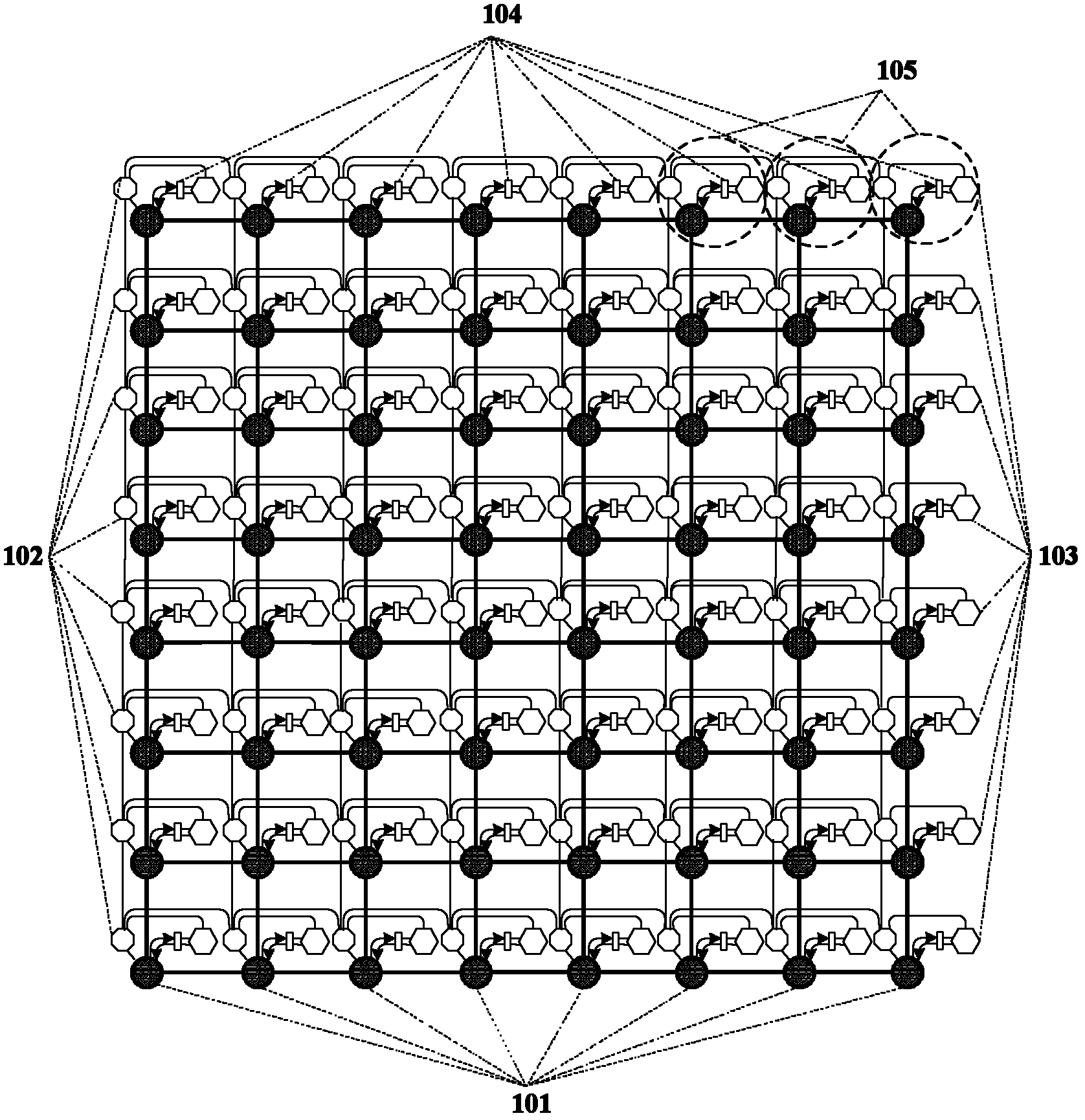
The invention discloses a region-based photoelectric double-layer network-on-a-chip and a routing method for solving the problem of serious network congestion of the traditional network. The system comprises 64 processor cores, 8 electrical crossing matrix modules, 8 8-port optical routers and 8 16-port optical routers; the 64 processor cores are divided into 8 regions; in each region, one electrical crossing matrix module mutually connect the 8 processor cores uniformly; and among the regions, the electrical crossing matrix modules, the 8-port optical routers and the 16-port optical routers connects all the regions into an integrated network. When two communication parties are in the same region, data information can be exchanged directly through the electrical crossing matrix modules; and when the two communication parties are not in different regions, the data information can be exchanged among regions through the electrical crossing matrix modules, the 8-port optical routers and the 16-port optical routers. The invention can improve the resource utilization rate and can be used for the interconnection among cores on a chip and optimizing data transmission among the processor cores.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
Optical network-on-chip system based on wavelength allocation and communication method of system
InactiveCN102638311AIncrease profitImprove scalabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionInterconnectionOptical router
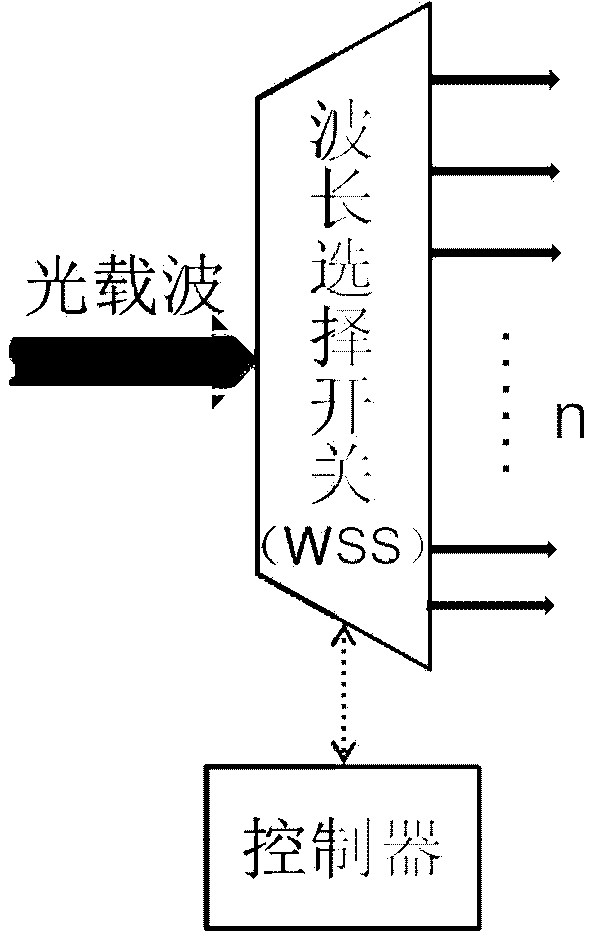
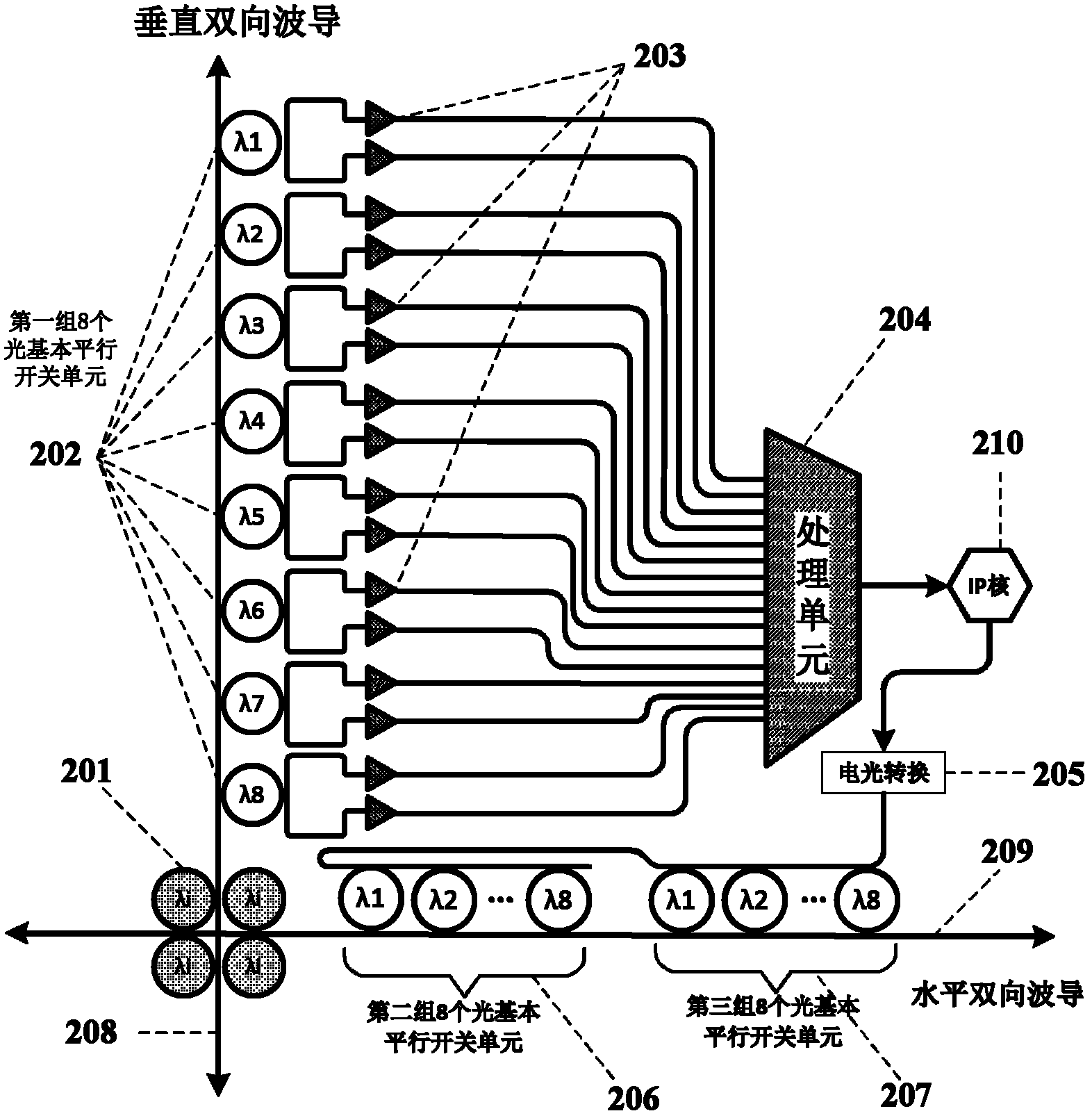
The invention discloses an optical network-on-chip system based on wavelength allocation and a communication method of the system, which mainly solve the problem of too many adopted wavelength, complex optical router structure and poor network expansibility when the conventional optical network-on-chip system adopts a wavelength division multiplexing technology. An optical router of the optical network-on-chip system comprises a criss-cross waveguide, four same micro-ring resonators and three groups of optical basic parallel switch units, and an optical signal is bidirectionally transmitted by single waveguide. The communication method of the optical network-on-chip system comprises the following steps: building a two-dimensional coordinate and distributing wavelength; determining the coordinates of a source node and a target node; according to the source node and the target node, determining the communication path of the optical signal, and modulating the wavelength; making an appointment to an optical link by making an appointment to the input port and the output port of the optical router of an intermediate steering node; and transmitting the optical signal along the appointed optical link, and releasing the optical link. According to the optical network-on-chip system, the wavelength use ratio of a wavelength division multiplexing optical network-on-chip can be effectively improved, the structure of the optical router is simplified, and the optical network-on-chip system is suitable for inter-core interconnection and communication of the optical network-on-chip.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-grain optical router based on optical burst switch
InactiveCN1381963ACapable of dynamic wavelength routingReduce the probability of packet lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionGranularityControl channel
A multi-granular light router based on optical burst exchange can support both burst-class and dynamic wavelength routing-class light exchange. Its core optical router uses dual-light-switch matrix for different exchange granularities. Its marginal optical router can support electric IP access and optical dynamic wavelength routing network access. Any input wavelength can be converted to any output wavelength, so the whole network has dynamic wavelength routing power. A mixed signalling mode is used. It is compatible with the current optical network with dynamic wavelength routing and the frture optical network with burst exchange.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for an optical filter
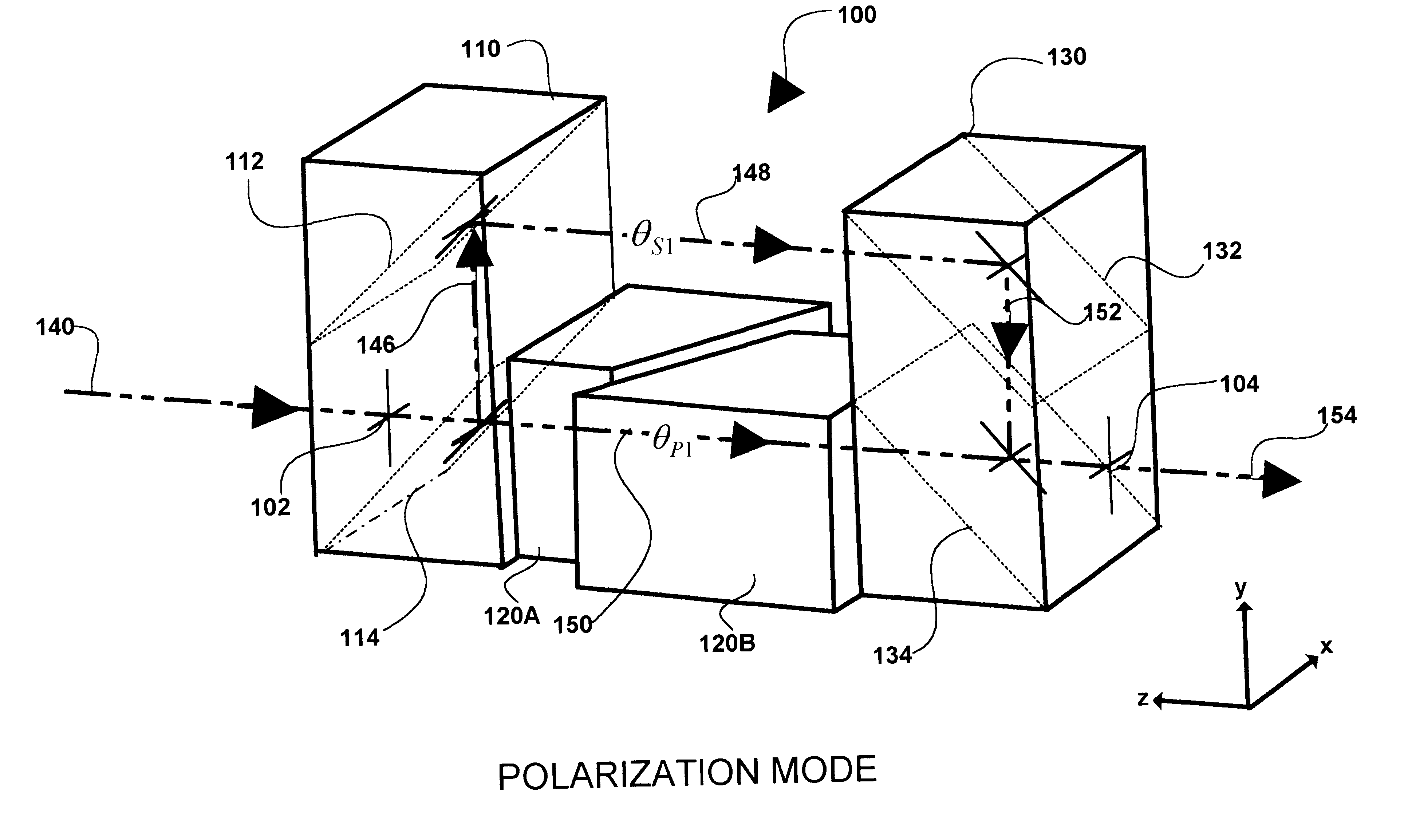
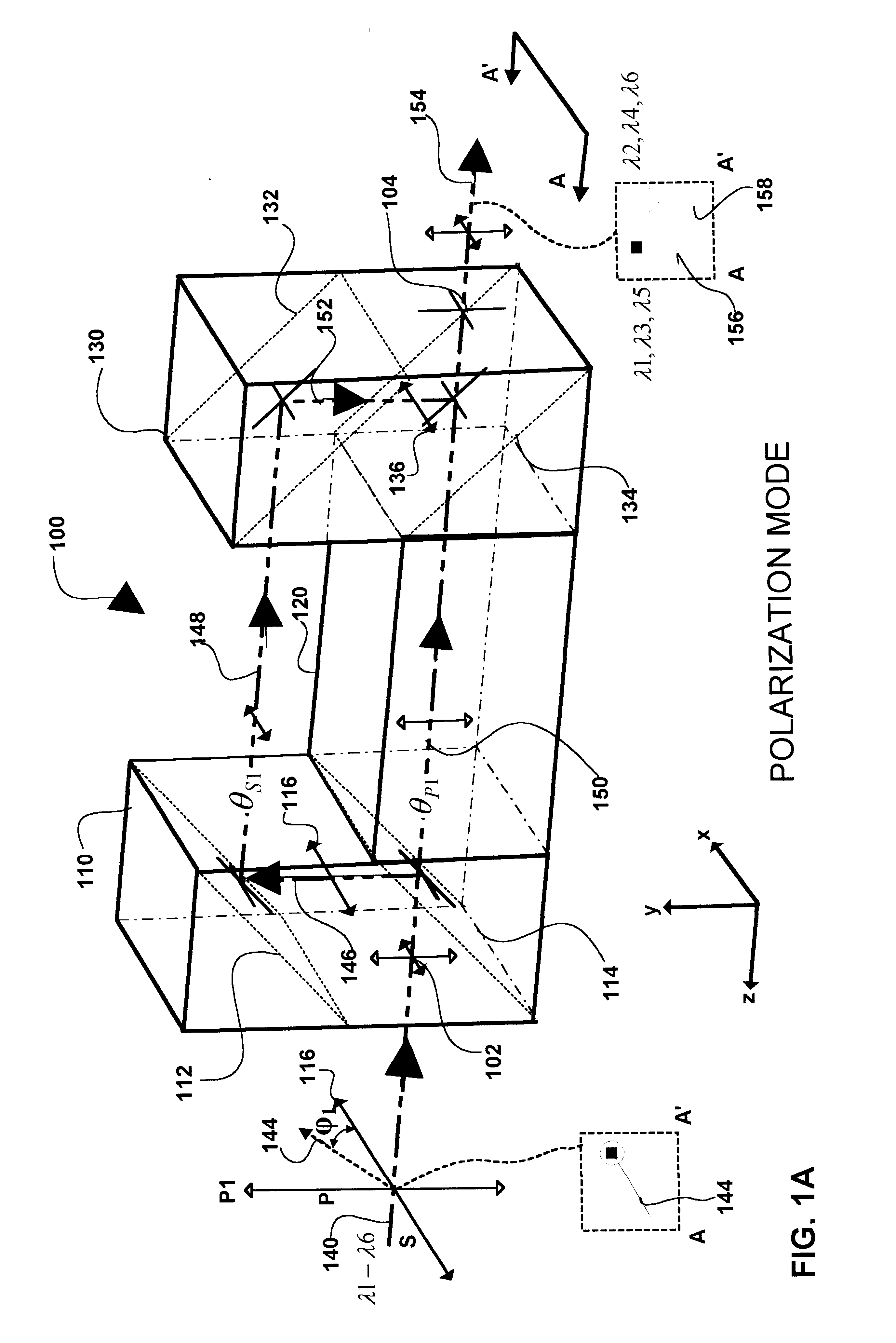
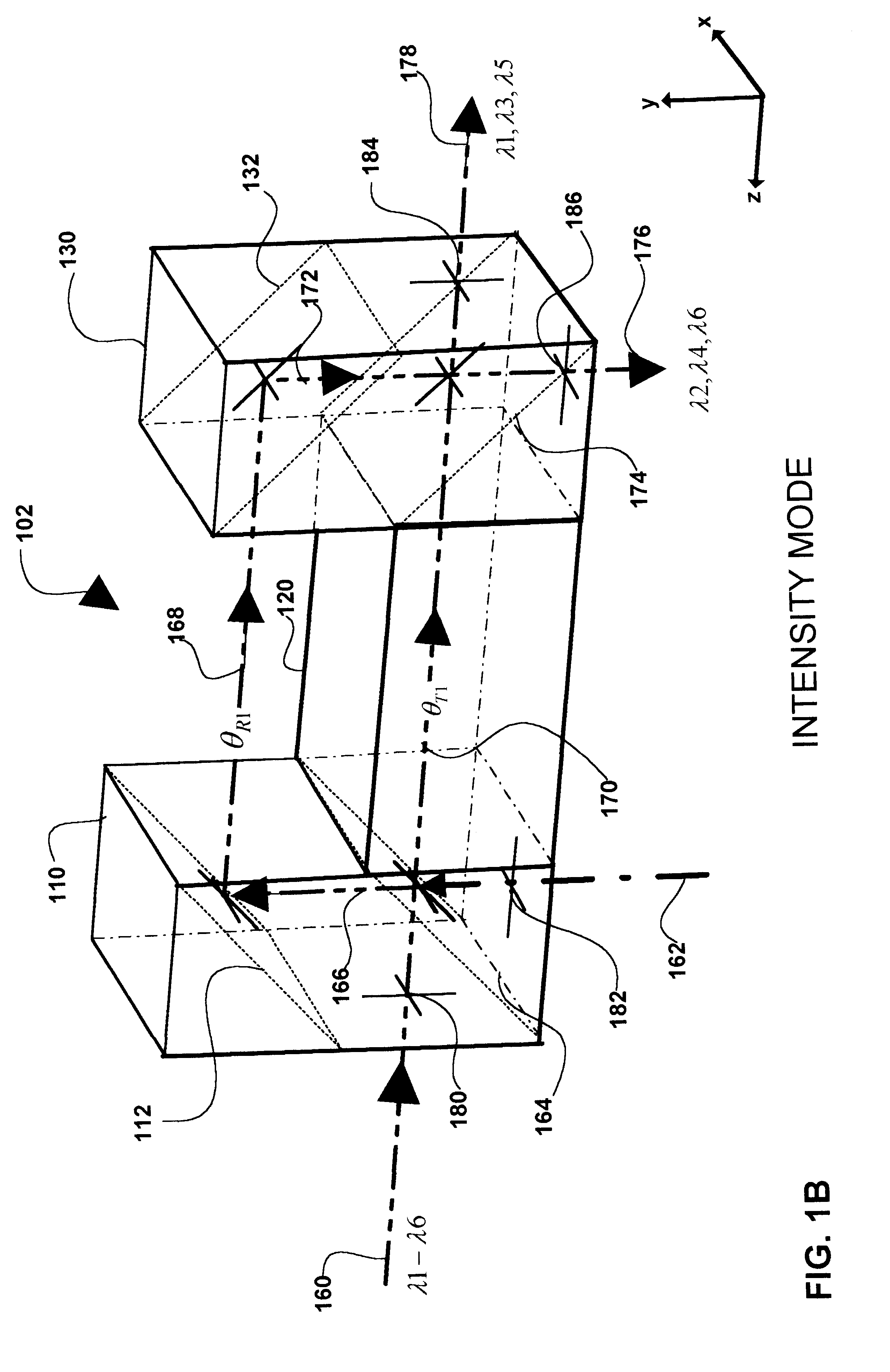
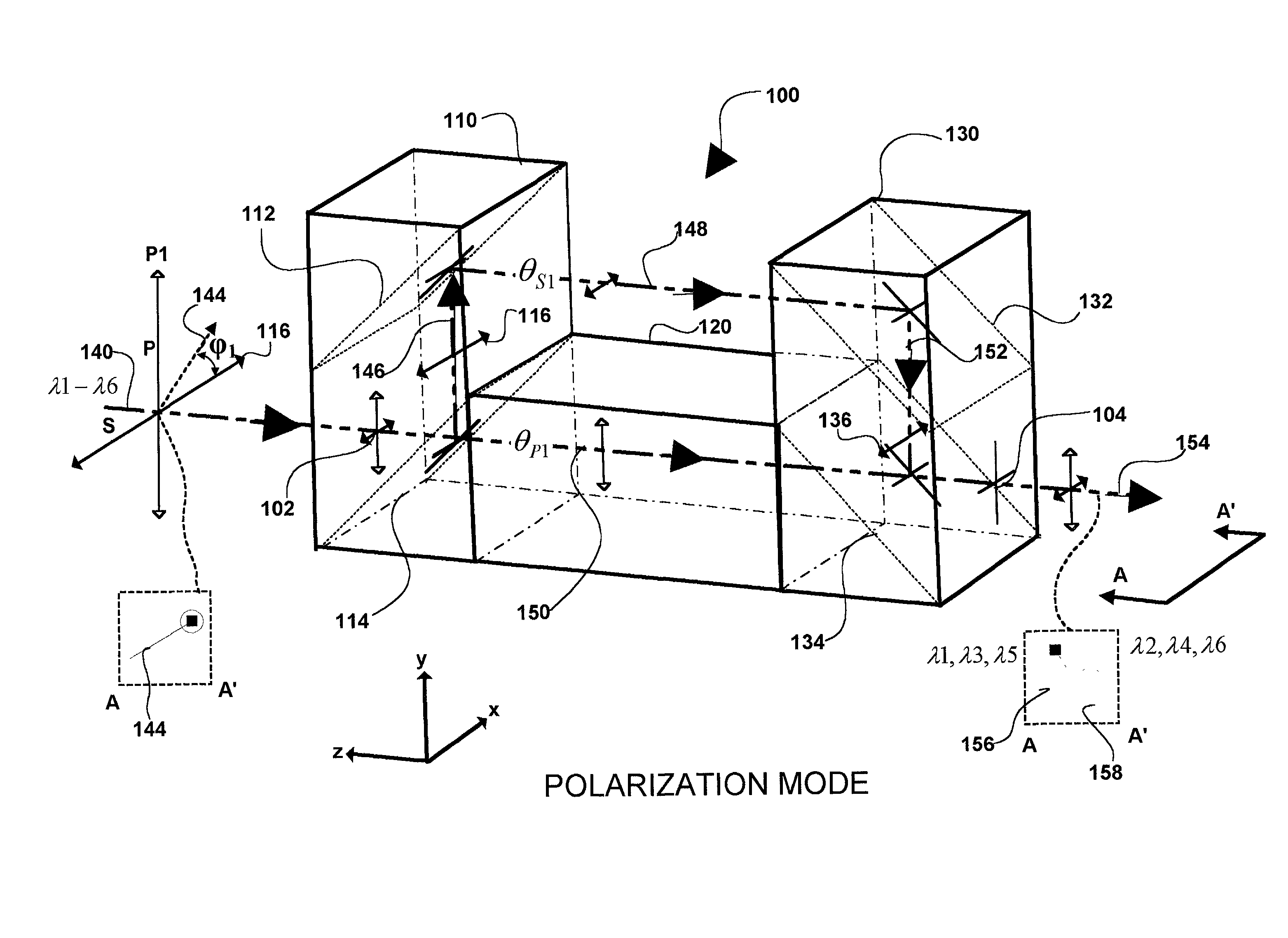
InactiveUS6694066B2Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideBeam splitterOptical pathlength
The present invention provides optical filters that can be used in a range of telecommunications applications including optical multiplexers / demultiplexers, optical routers, and optical gain scalers. The optical filter is modular, using two or more couplers with a pair of delay paths between each pair of couplers in a sequence to generate a range of optical filter functions. The desired filter profile / function is obtained by proper selection of the coupling ratio for each coupler and by the length of each pair of delay paths. The couplers may be implemented as polarization or intensity beam splitters positioned along the optical path. Each coupler couples in controllable amounts, one or two inputs with the corresponding pair of delay paths. Where a coupler is implemented as a polarization beam splitter, the coupling is accomplished by input to the coupler of polarized light and by the subsequent separation of orthogonal "P" and "S" components of that light onto corresponding ones of the pair of delay paths. Where coupling is implemented with an intensity beam splitter, the coupling is accomplished by input of light with the percentage of reflection and transmission of the light determining the coupling ratio or percentage of the light input onto corresponding ones of the pair of delay paths. The pair of delay paths includes in an embodiment of the invention, passive thermal stabilization. The passive thermal stabilization of the filter(s) is accomplished by a plurality of optical elements positioned in and defining the optical path length of each member of the pair of paths. These optical elements are designed so that the optical path length difference between the pair of delay paths remains substantially invariant across a range of temperatures.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Method and apparatus for an optical filter
InactiveUS20020154845A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideBeam splitterOptical pathlength
The present invention provides optical filters that can be used in a range of telecommunications applications including optical multiplexers / demultiplexers, optical routers, and optical gain scalers. The optical filter is modular, using two or more couplers with a pair of delay paths between each pair of couplers in a sequence to generate a range of optical filter functions. The desired filter profile / function is obtained by proper selection of the coupling ratio for each coupler and by the length of each pair of delay paths. The couplers may be implemented as polarization or intensity beam splitters positioned along the optical path. Each coupler couples in controllable amounts, one or two inputs with the corresponding pair of delay paths. Where a coupler is implemented as a polarization beam splitter, the coupling is accomplished by input to the coupler of polarized light and by the subsequent separation of orthogonal "P" and "S" components of that light onto corresponding ones of the pair of delay paths. Where coupling is implemented with an intensity beam splitter, the coupling is accomplished by input of light with the percentage of reflection and transmission of the light determining the coupling ratio or percentage of the light input onto corresponding ones of the pair of delay paths. The pair of delay paths includes in an embodiment of the invention, passive thermal stabilization. The passive thermal stabilization of the filter(s) is accomplished by a plurality of optical elements positioned in and defining the optical path length of each member of the pair of paths. These optical elements are designed so that the optical path length difference between the pair of delay paths remains substantially invariant across a range of temperatures.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
System and method for slot deflection routing at optical router/switch
InactiveUS20060147208A1Eliminates and reduces disadvantage and problemReduce underutilizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexDeflection routingOptical router
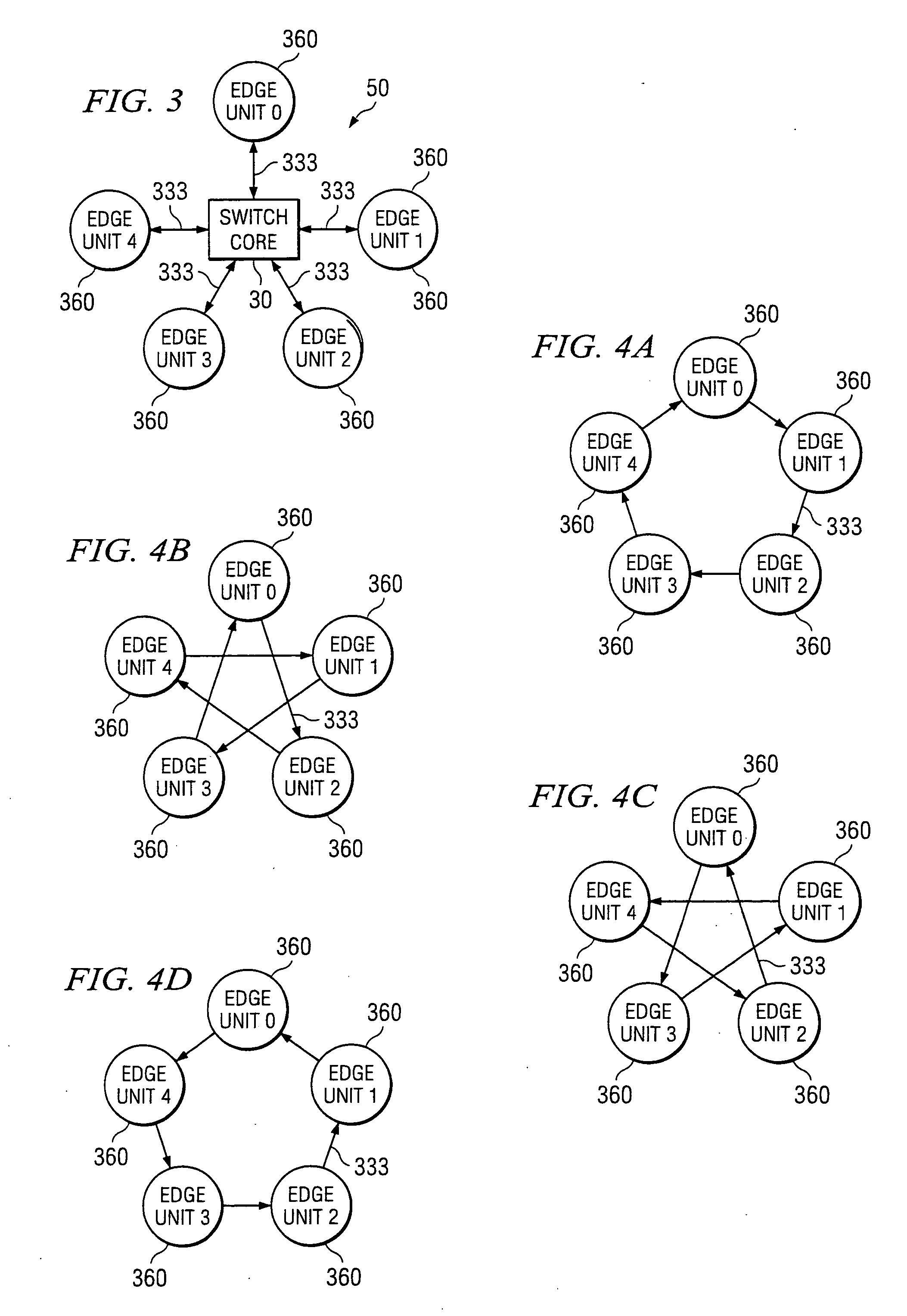
The present invention provides a system and method for slot deflection routing of optical data packets. The method of the present invention includes the steps of establishing a schedule pattern that includes a plurality of time slots. The schedule pattern includes at least one time slot in which an ingress edge unit can communicate with a destination egress edge unit, at least one time slot in which the ingress edge unit can communicate with a intermediate edge unit, and at least one time slot in which the intermediate edge unit can communicate with the destination egress edge unit. The present invention also includes receiving a data packet at the ingress edge unit and determining if the schedule pattern allocates sufficient bandwidth to send the data packet from the ingress edge unit to the destination egress edge unit without deflecting the data packet through an intermediate edge unit. If enough bandwidth has been allocated, the data packet can be sent to the destination edge unit from the ingress edge unit without deflection. Alternatively, if enough bandwidth has not been allocated, the data packet can be deflected to an intermediate edge unit prior to being communicated to the destination egress edge unit.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
WiFi (wireless fidelity) access system based on visible light transmission and data frame transformation method
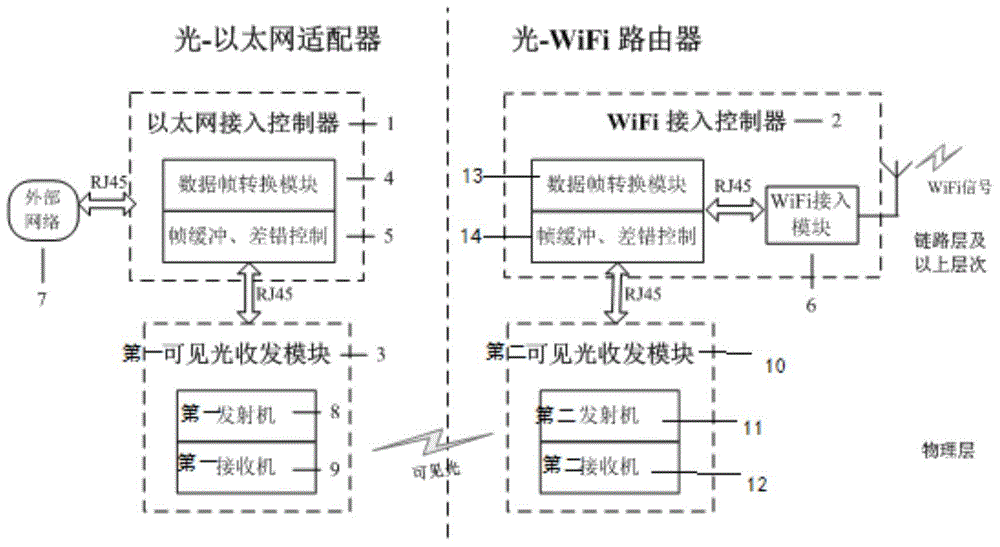
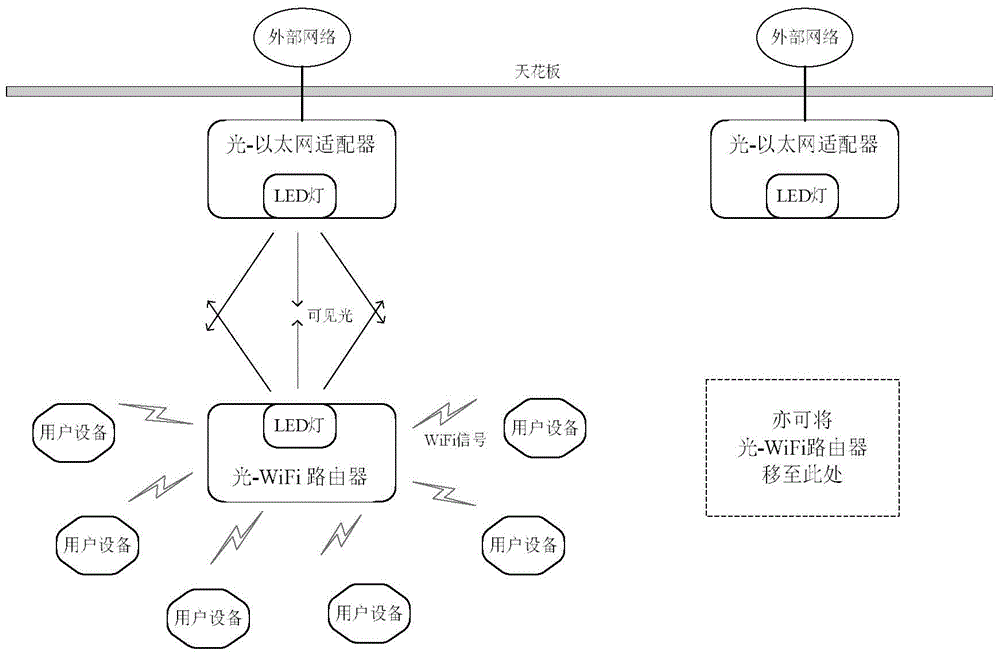
InactiveCN104618019AAvoid inconvenienceIncrease flexibilityClose-range type systemsTransceiverThe Internet
The invention discloses a WiFi access system based on visible light transmission. The WiFi access system based on visible light transmission comprises a light-Ethernet adapter and a light-WiFi router, wherein the light-Ethernet adapter comprises an Ethernet access controller and a first visible light transceiver module, wherein the Ethernet access controller is connected to the Internet and is also connected to the first visible light transceiver module through twisted pair cables; the light-WiFi router comprises a WiFi access controller and a second visible light transceiver module, wherein the second visible light transceiver module is connected with the WiFi access controller through twisted pair cables; the first visible light transceiver module and the second visible light transceiver module are connected through visible light transmission.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical interleaver and filter cell design with enhanced clear aperture
InactiveUS7173763B2Improve integrityEasy to packMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrismsMultiplexerOptical processing
An optical interleaver for use in a range of telecommunications applications including optical multiplexers / demultiplexers and optical routers. The optical device includes an optical processing loop which allows multi-stage performance characteristics to be achieved with a single physical filtration stage. Optical processing on the first leg and second legs of the loop is asymmetrical thereby improving the integrity of the optical signals by effecting complementary chromatic dispersion on the first and second legs. A fundamental filter cell within the interleaver filters optical signals propagating on each of the two legs of the optical loop which intersects the fundamental filter cell.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com