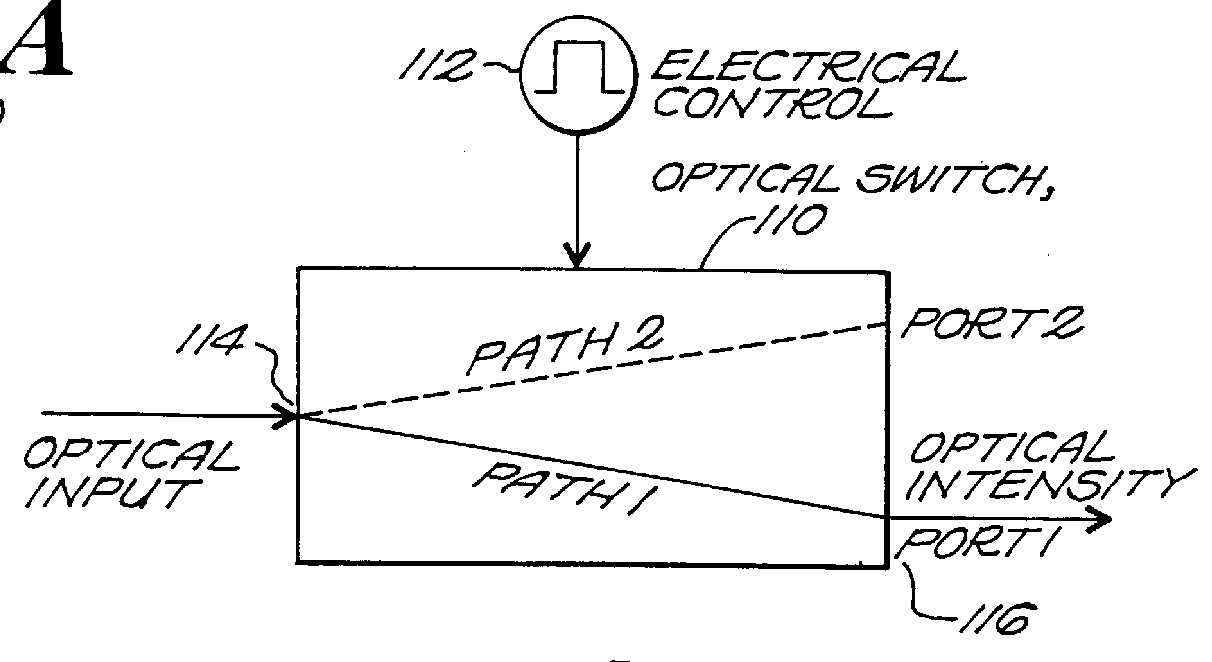
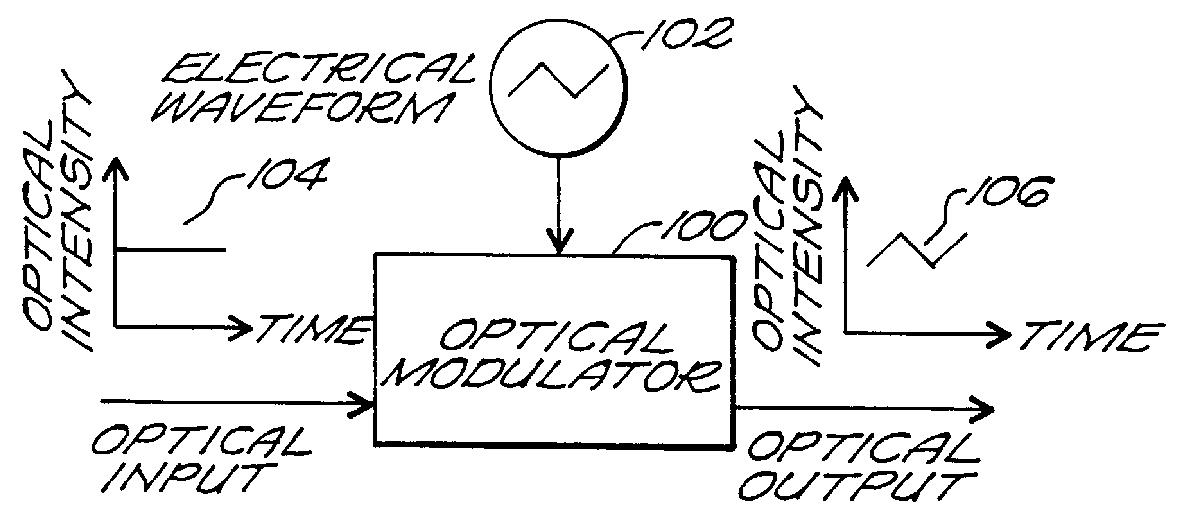
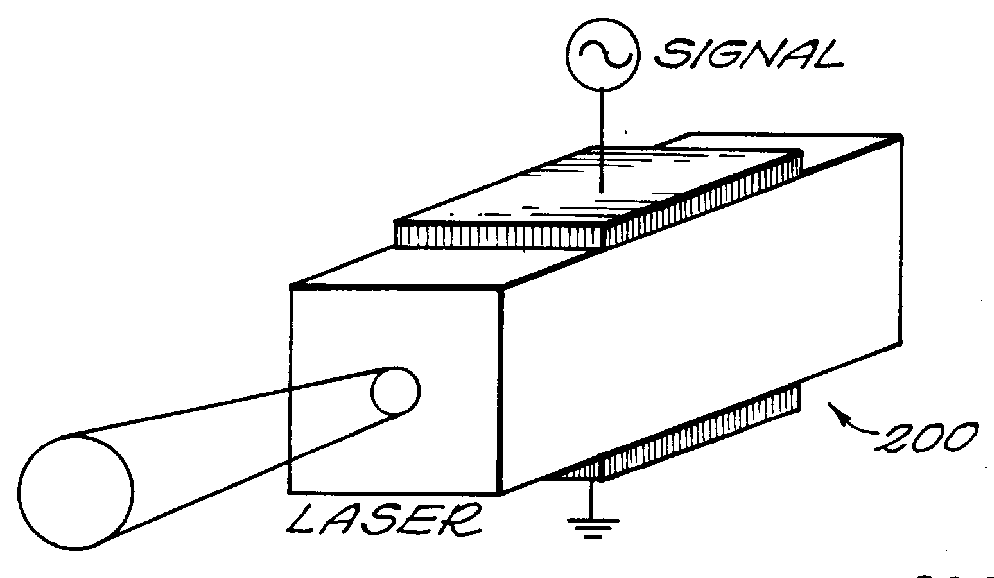
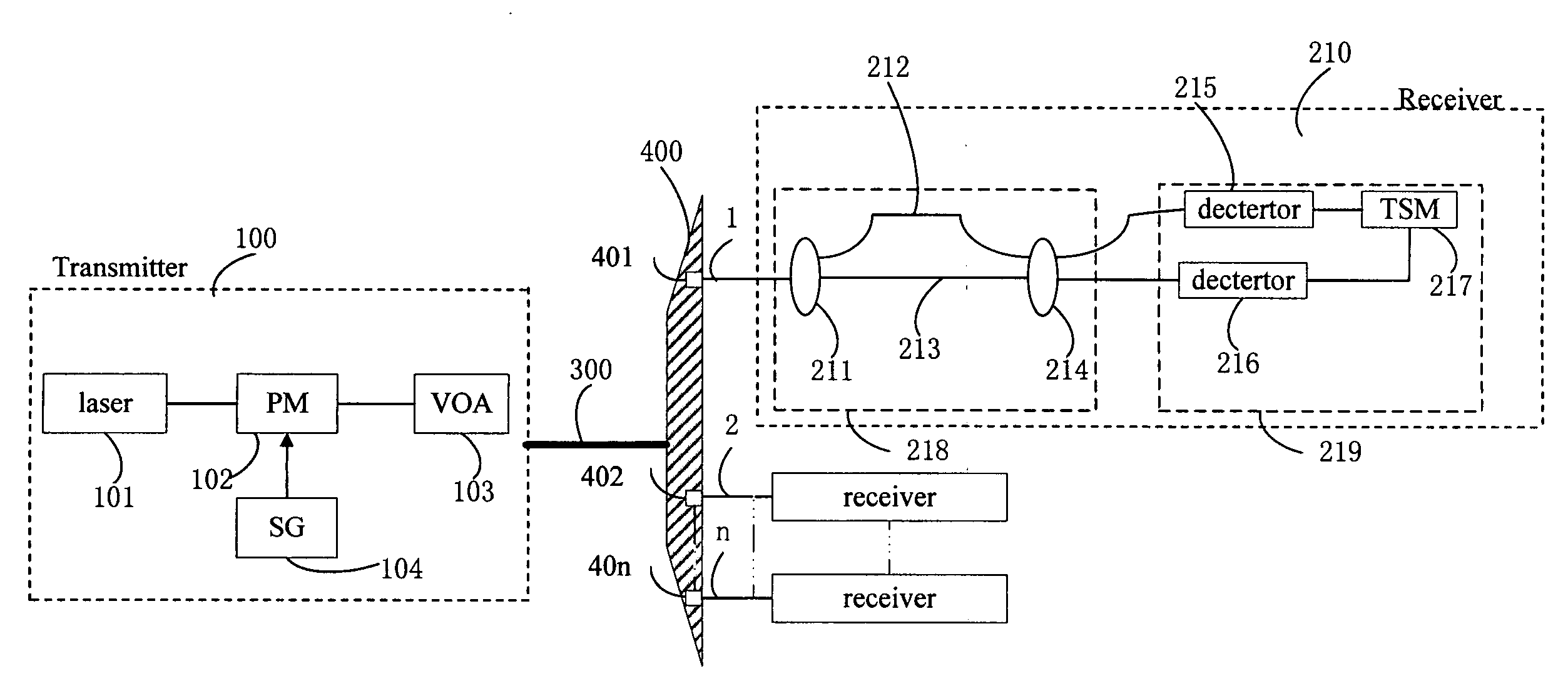
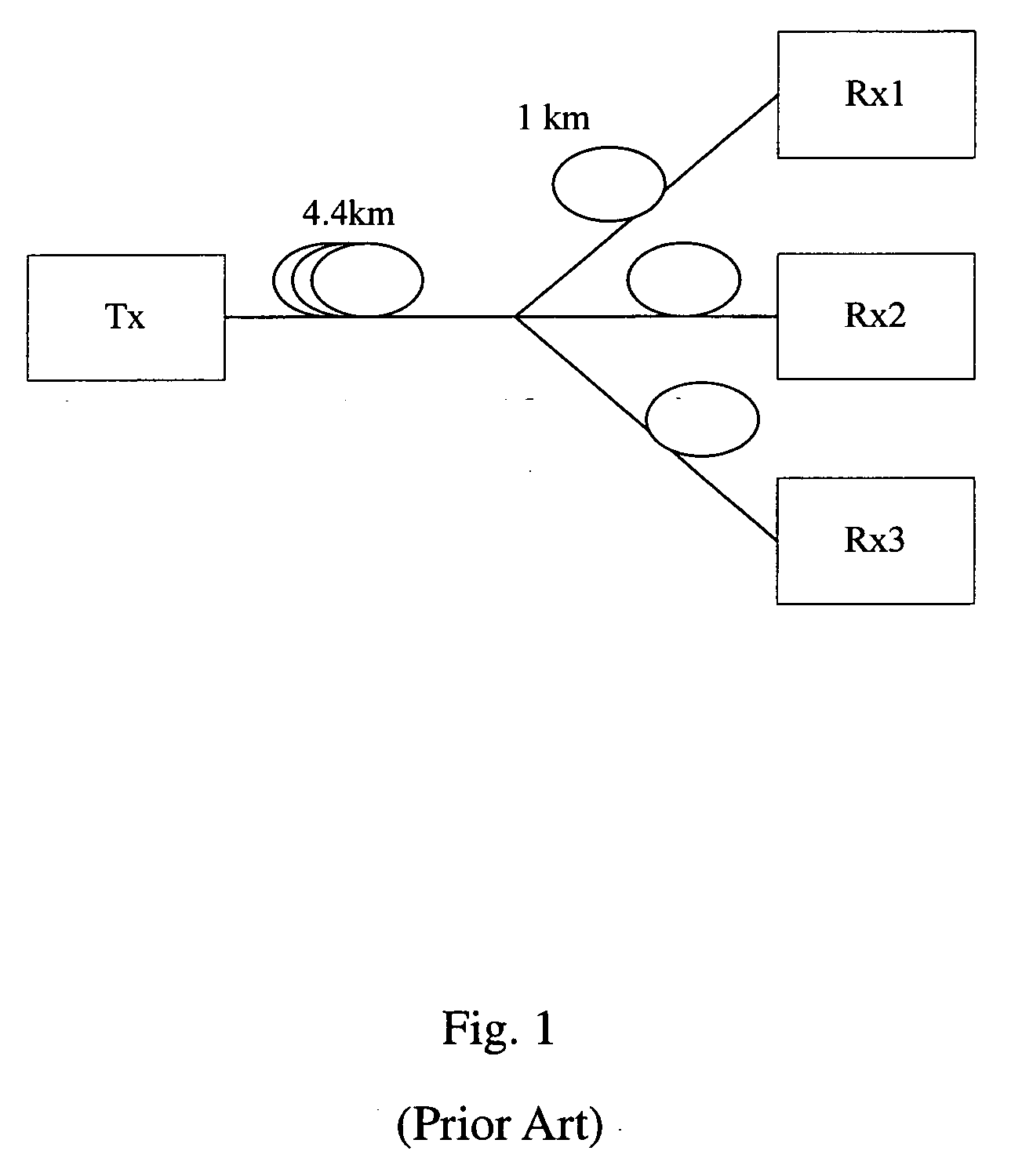
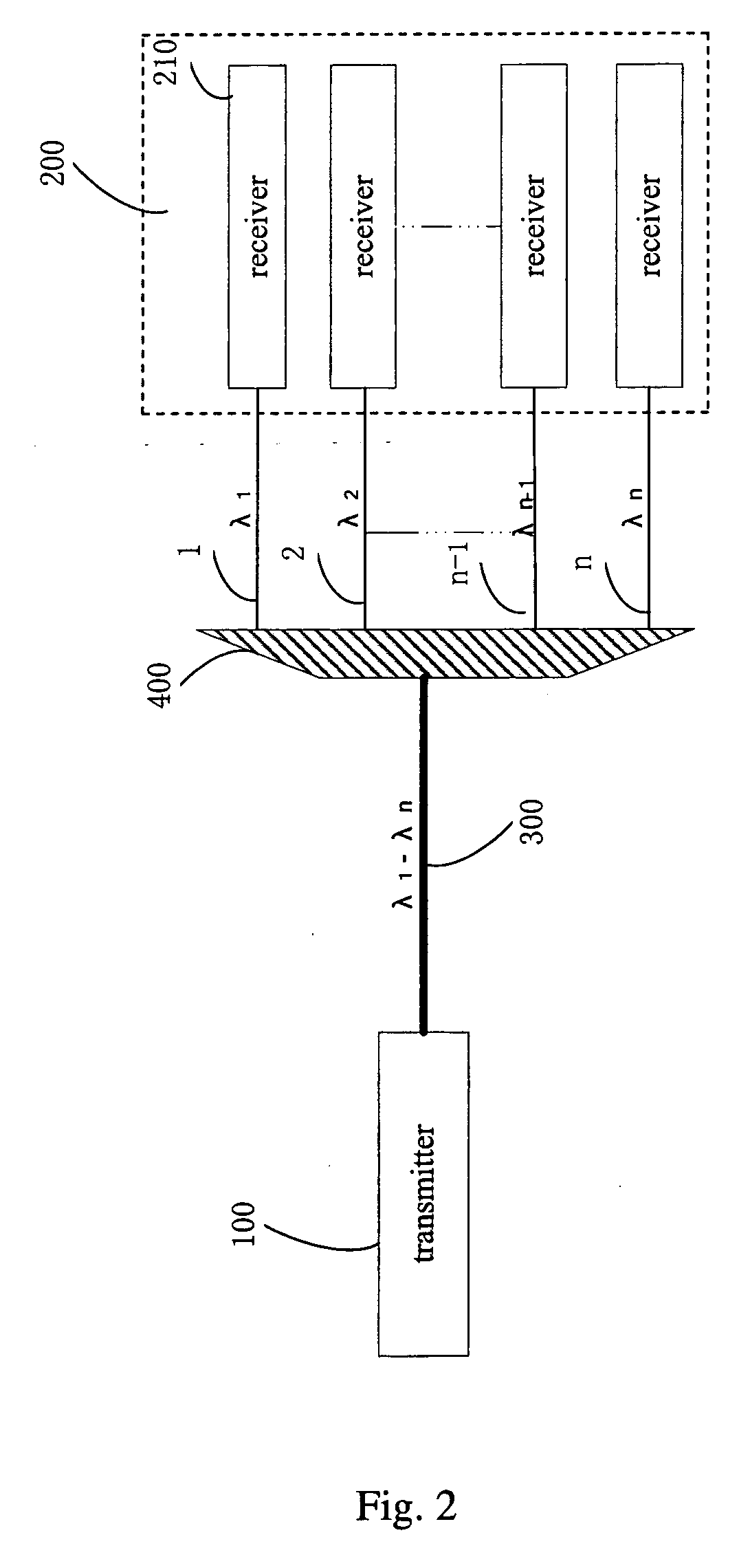
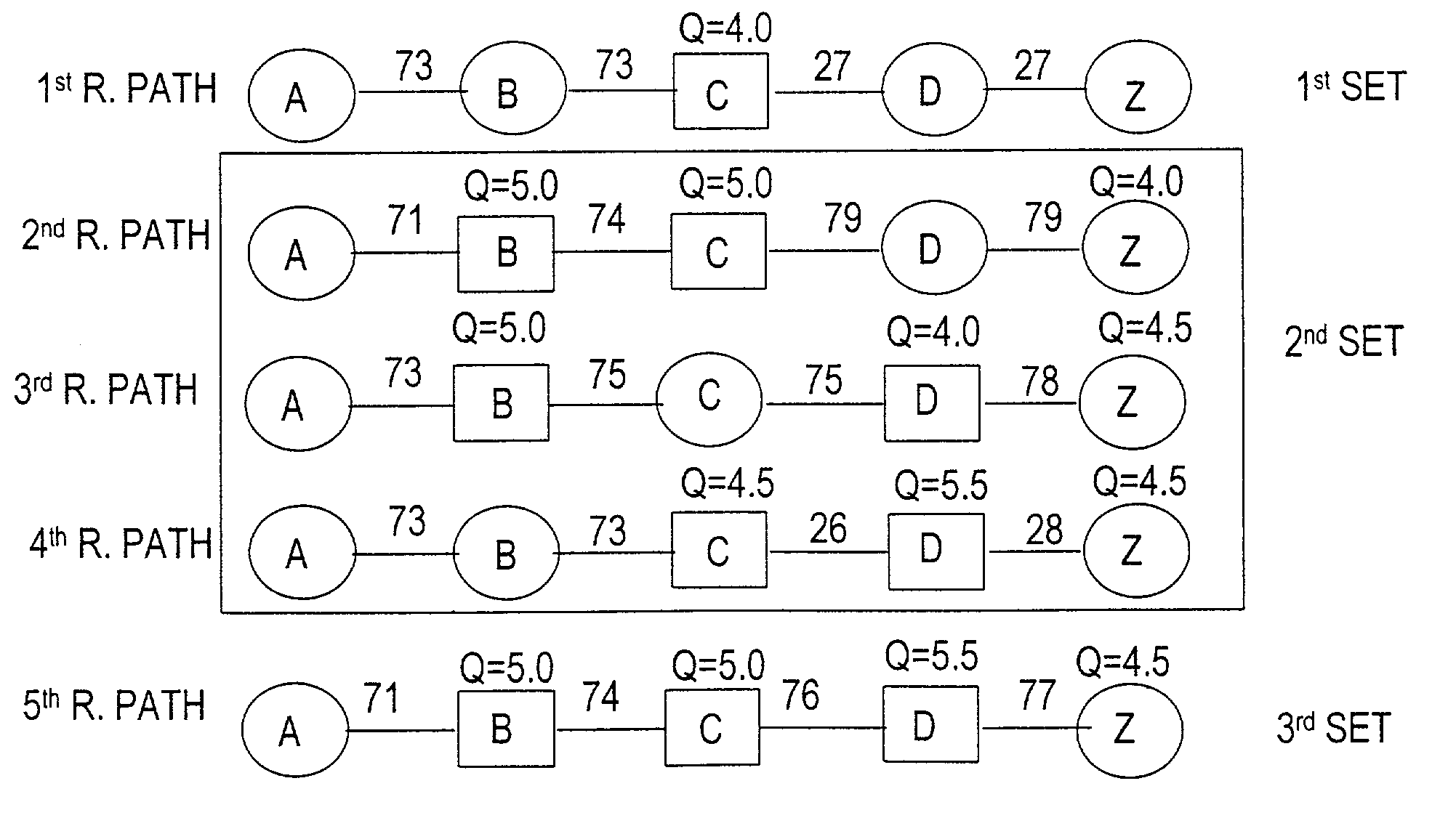
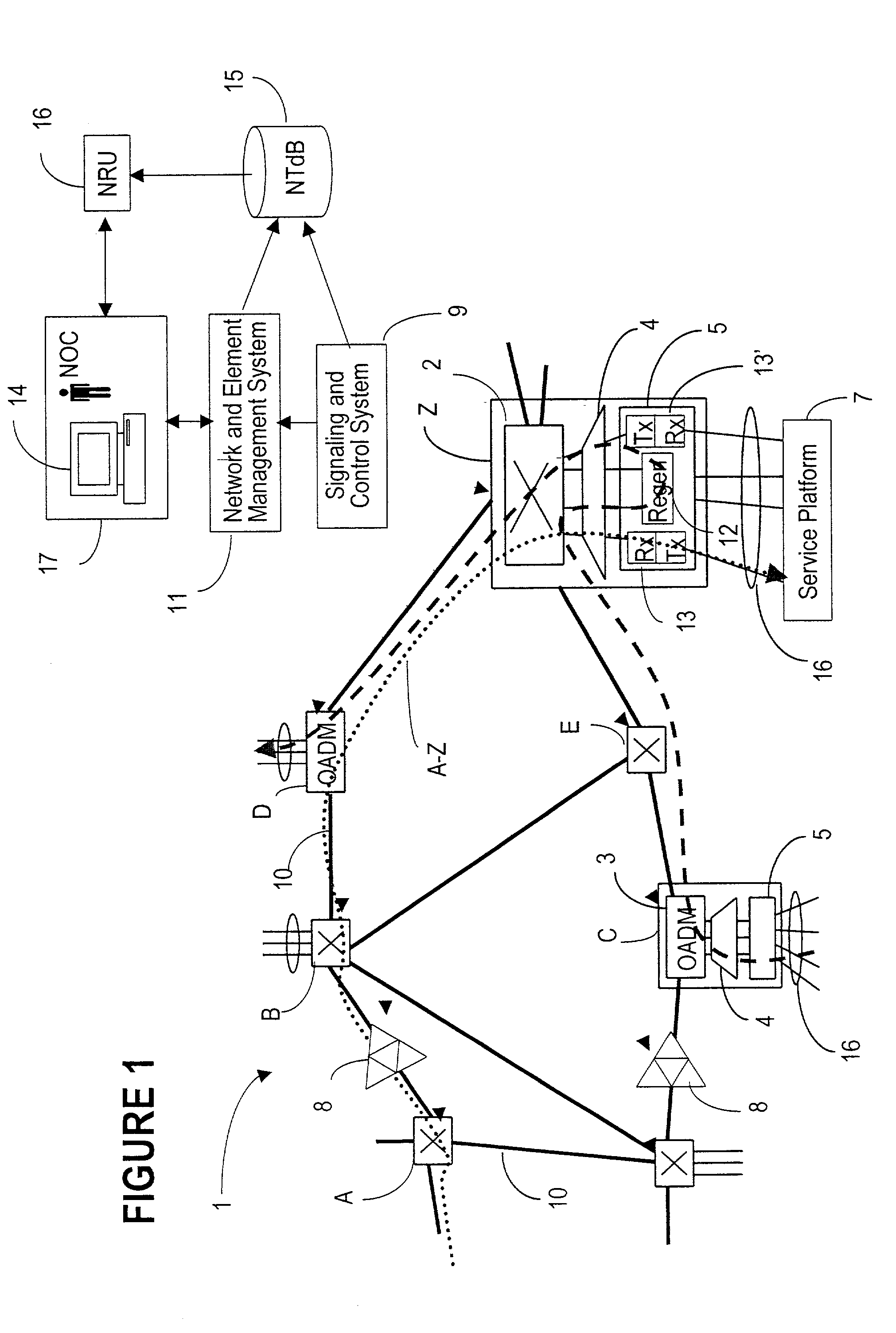
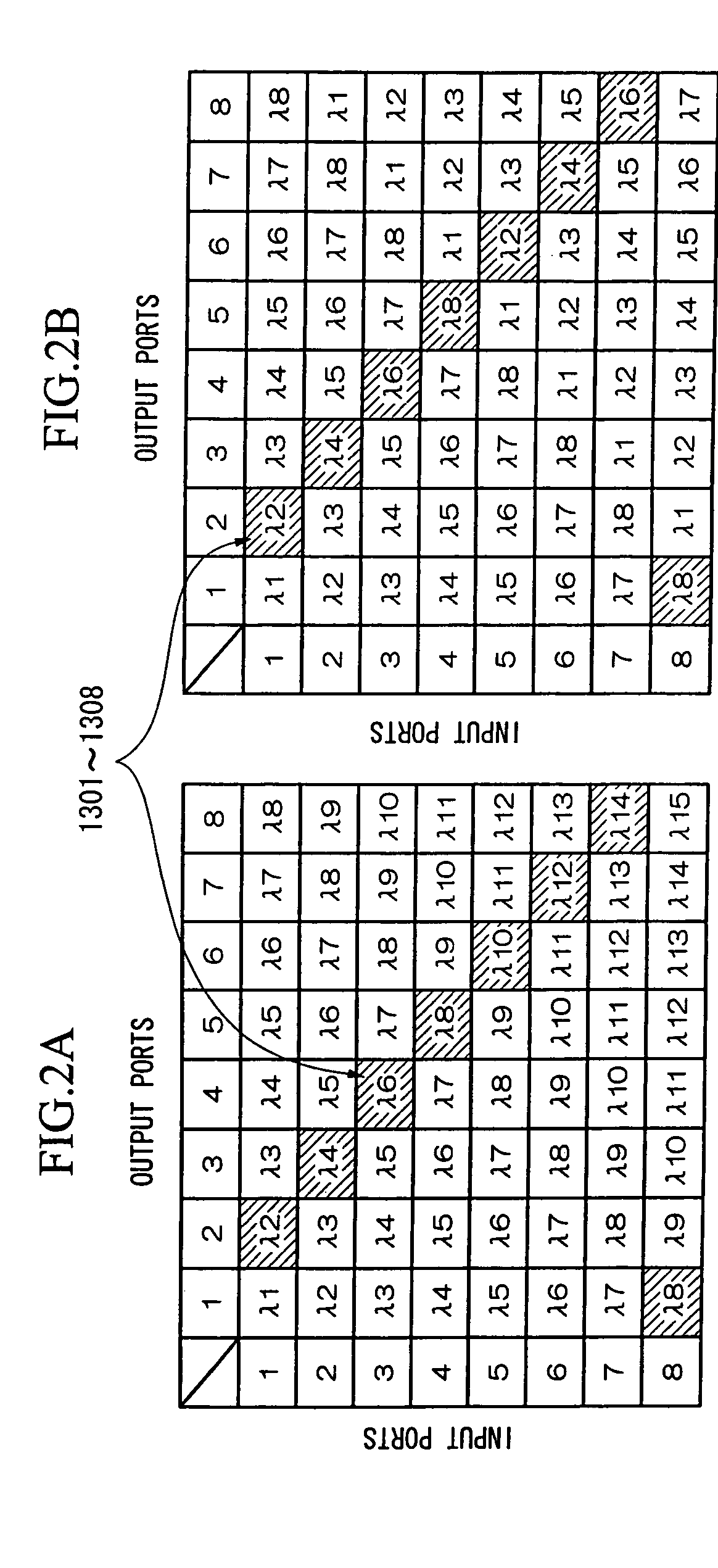
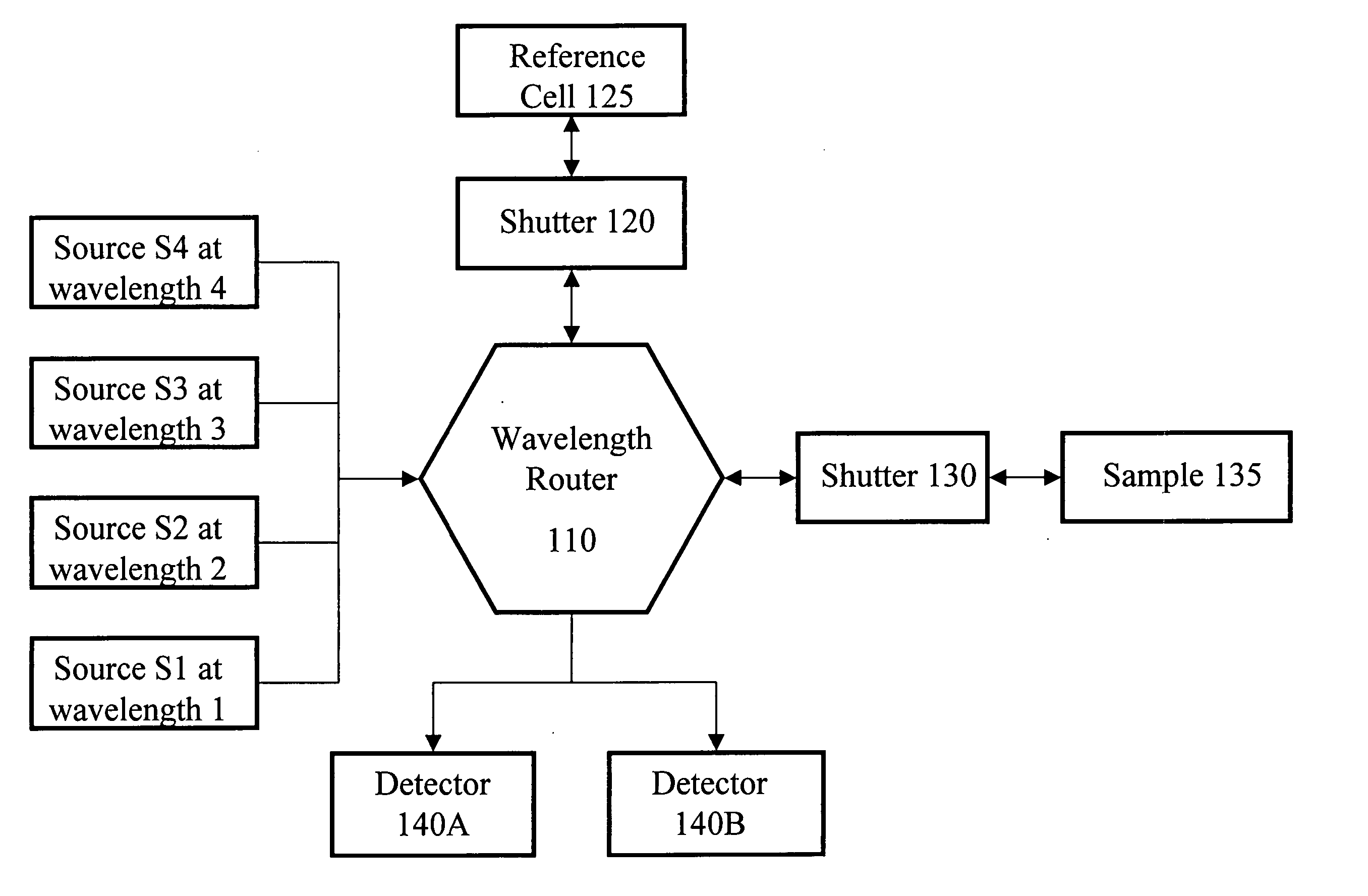
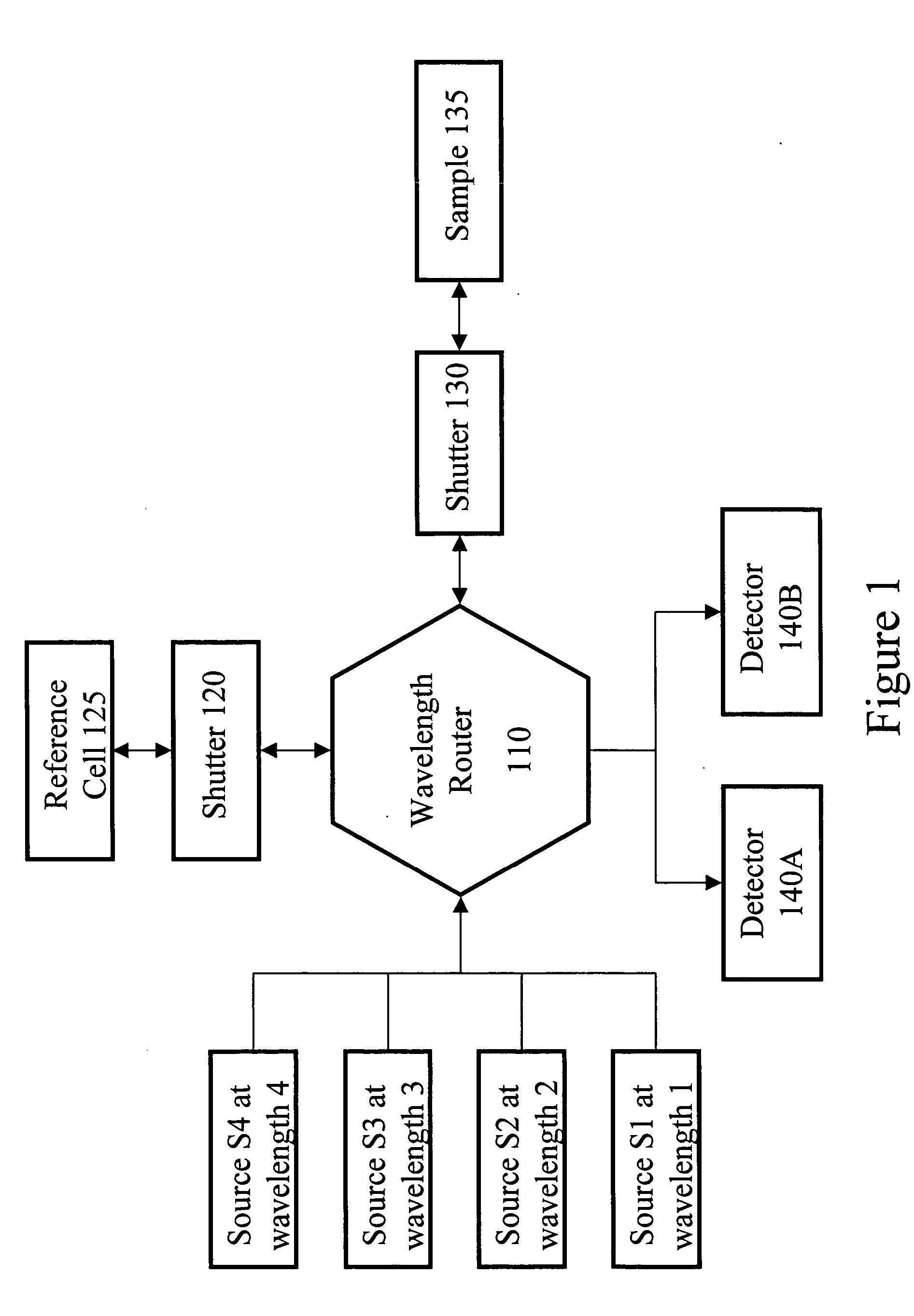
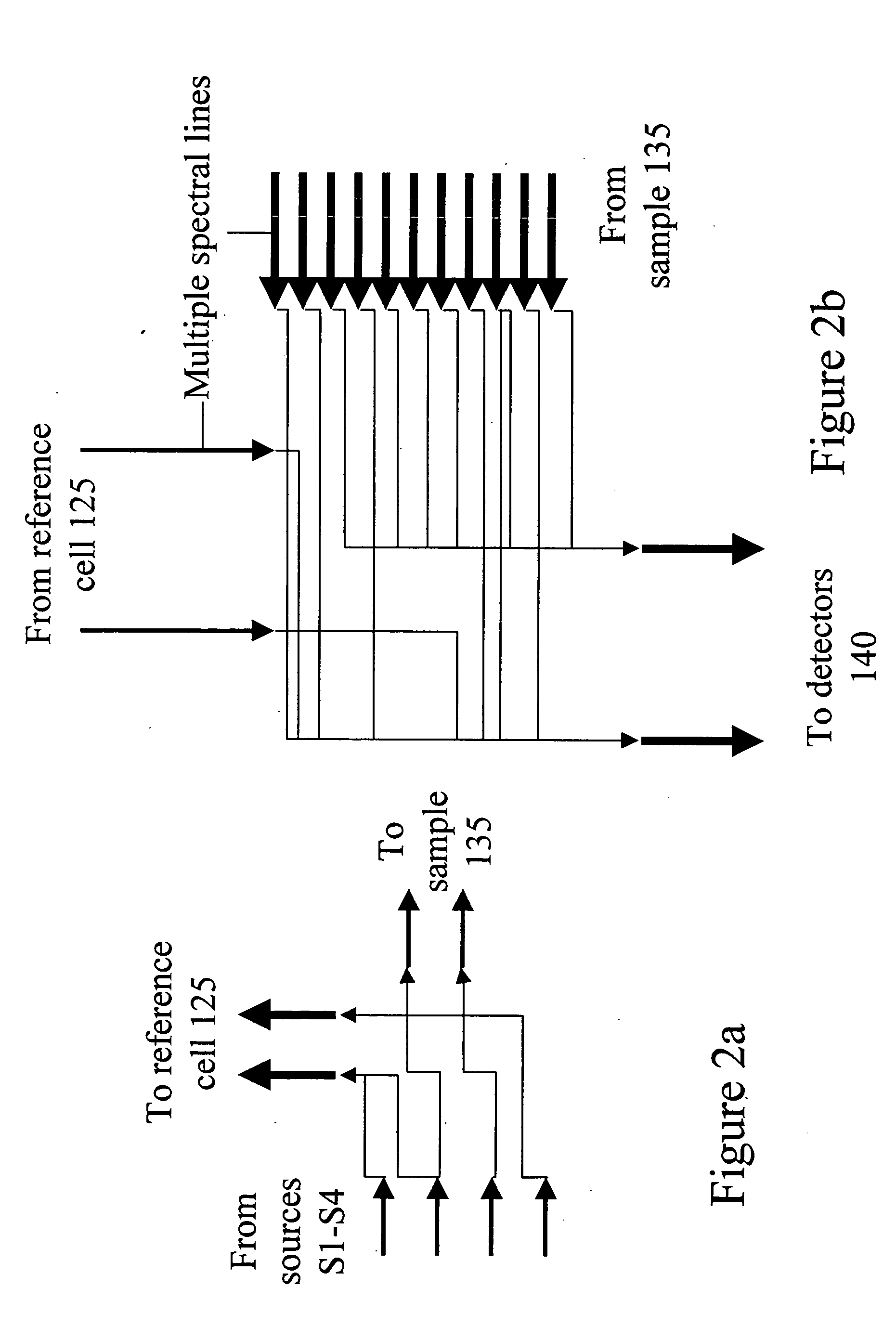
Patents
Literature
136 results about "Wavelength routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
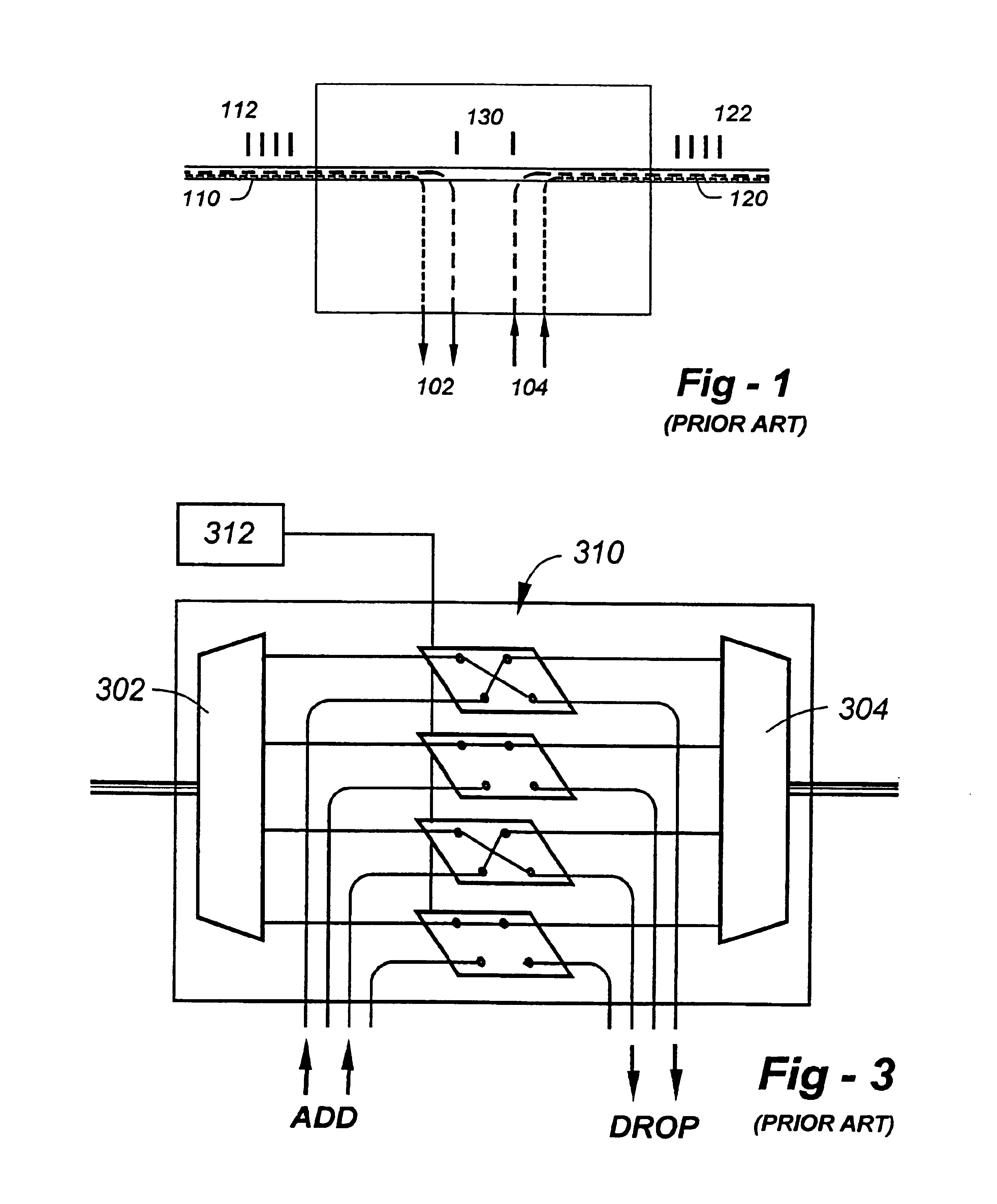
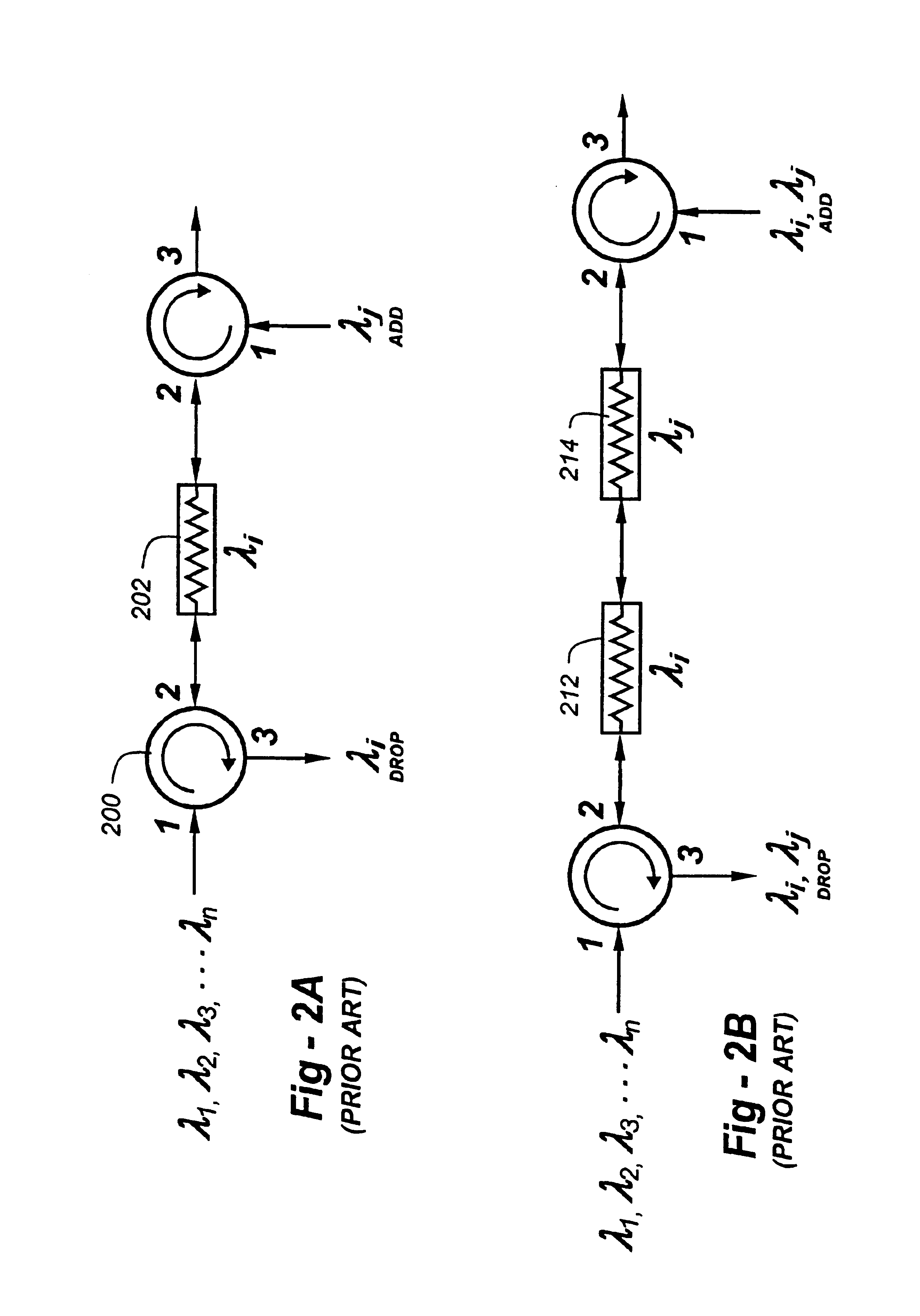
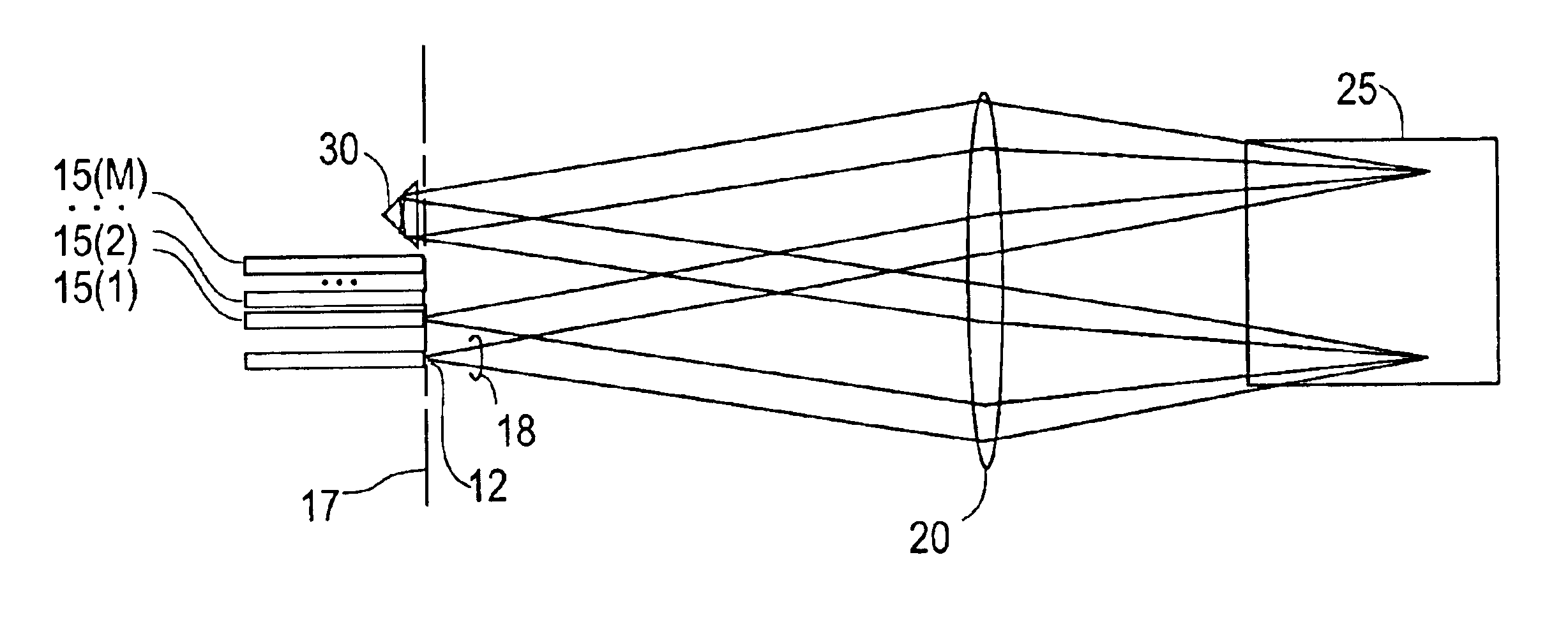
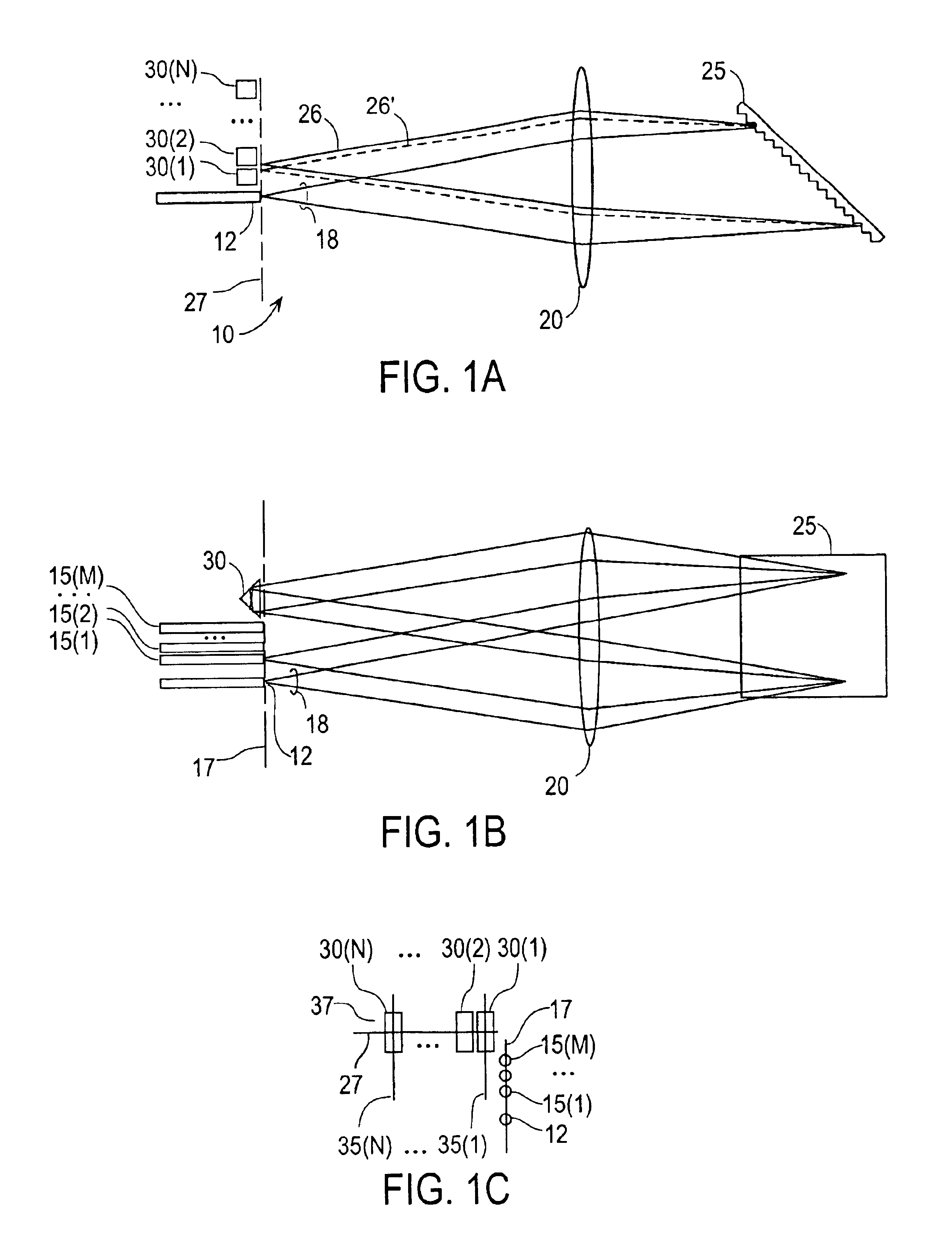
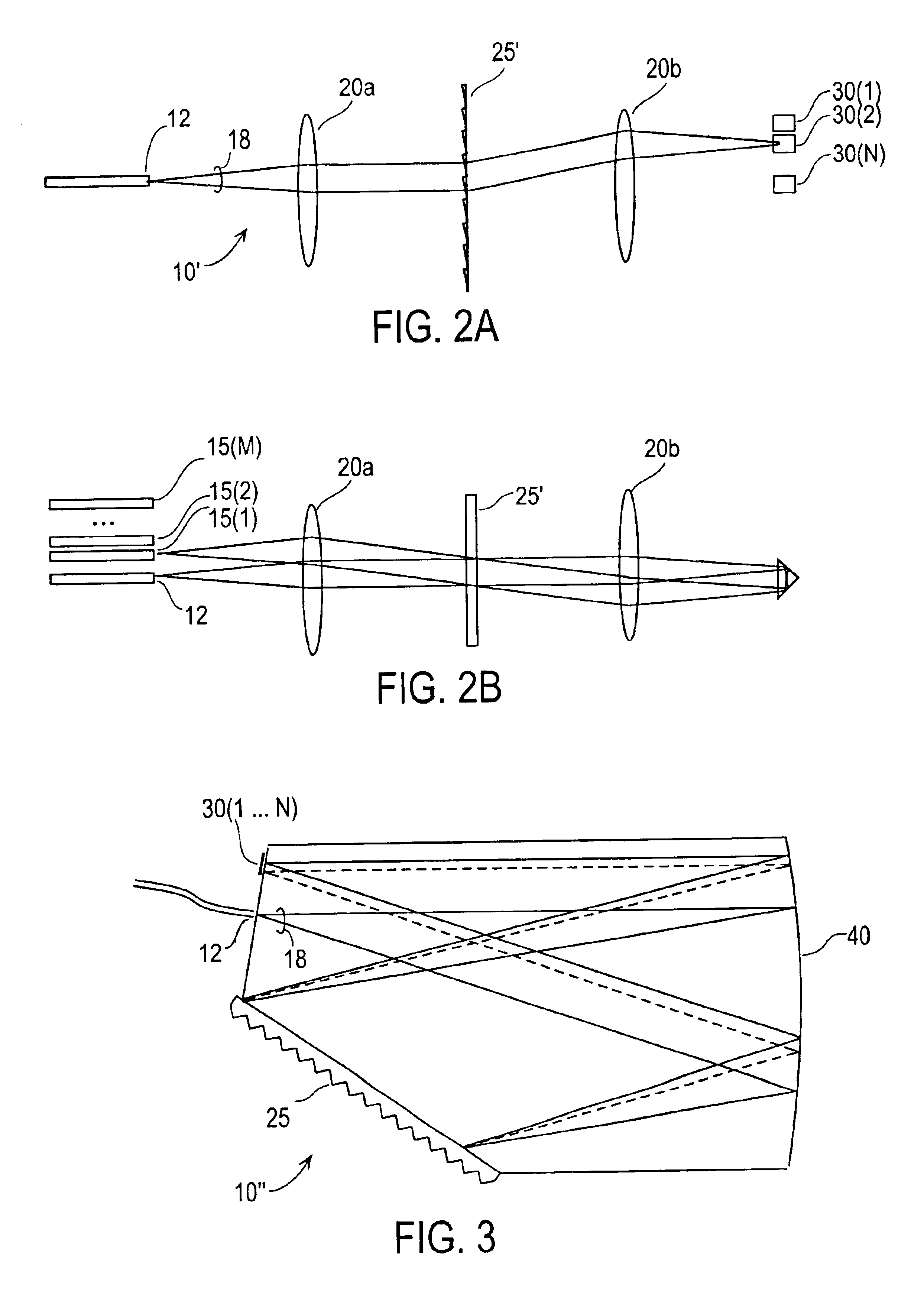
Resonator modulators and wavelength routing switches
InactiveUS6052495ASmall sizeImprove responseCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsClosed loopRefractive index
The invention provides an optical switch and modulator which uses a closed loop optical resonator. The optical resonator is a dielectric cavity whose primary function is to store optical power. Various structures are possible, and a particularly advantageous one is a ring shaped cavity. The wavelength response at the output port of a ring resonator side coupled to two waveguides is determined by the details of the resonator, and the coupling between the resonator and the waveguides. By coupling to adjacent resonators, the modulator response can be improved over that of a single resonator. One such improvement is in modulator efficiency, which is defined as the ratio of the change in optical intensity at the output, to a change in absorption in the ring waveguides. Absorption is used for switching and modulation without incurring significant optical attenuation. Another improvement involves making the resonance insensitive to small deviations in wavelength or index change. The latter improves fabrication tolerances and compensates for possible drift of the signal wavelength. Collectively, the behavior of multiple coupled resonators yields higher order responses.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods and system for quantum key distribution over multi-user WDM network with wavelength routing
ActiveUS20070065154A1Improve securitySystem simple and stableKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetwork linkLength wave
A system and a method for quantum key distribution over a multi-user wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) network are disclosed. The system comprises a tunable or multi-wavelength transmitter; a plurality of receivers, each assigned a receiving-wavelength; and a multi-user WDM network linking the transmitter to the receivers. The transmitter can select a receiver among the receivers to be communicated therewith and transmit quantum signals to the selected receiver over the WDM network. The quantum signals are at a wavelength equal to a receiving-wavelength of the receiver. Therefore the WDM network allows quantum signals to be communicated between the transmitter and the receivers by wavelength routing.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
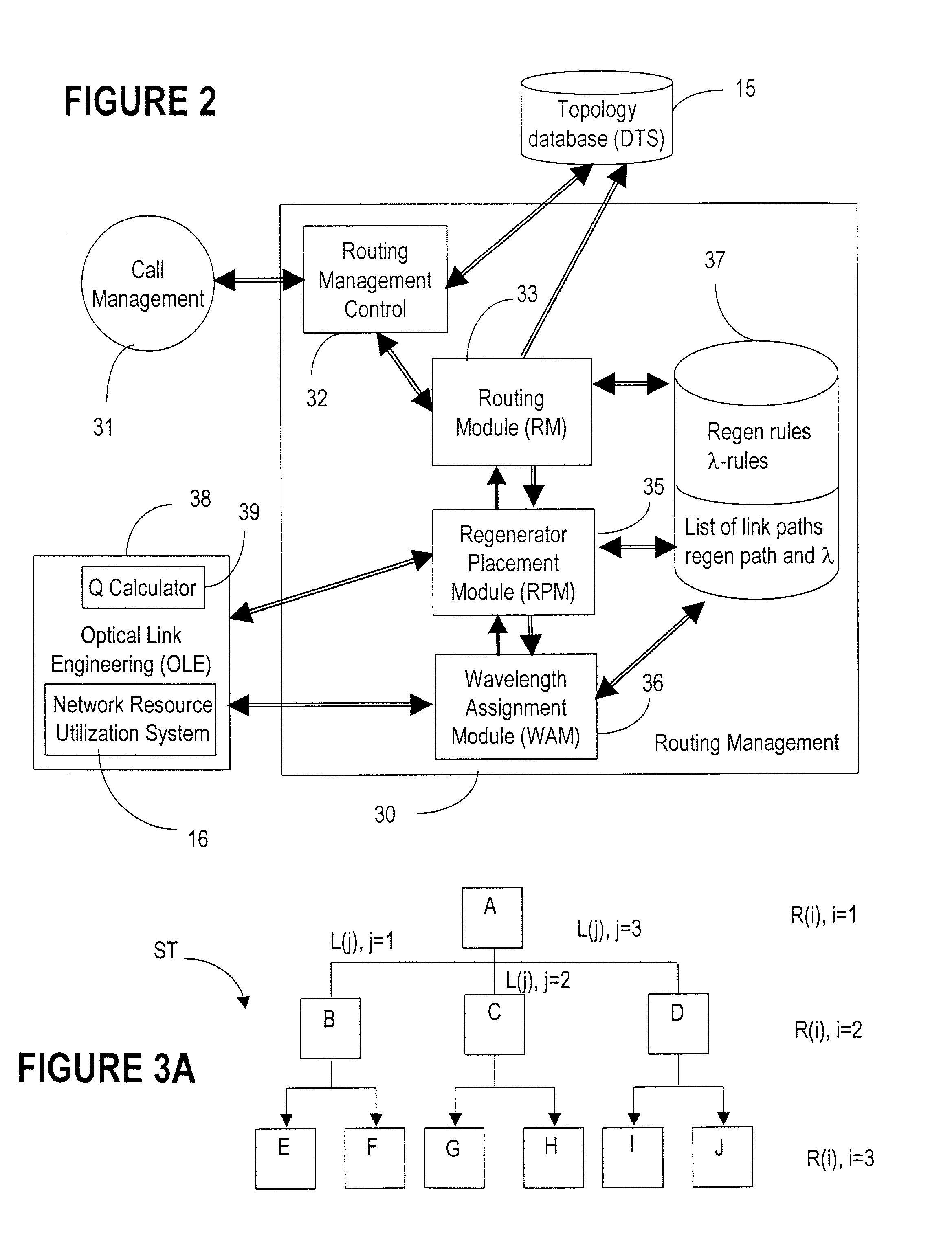
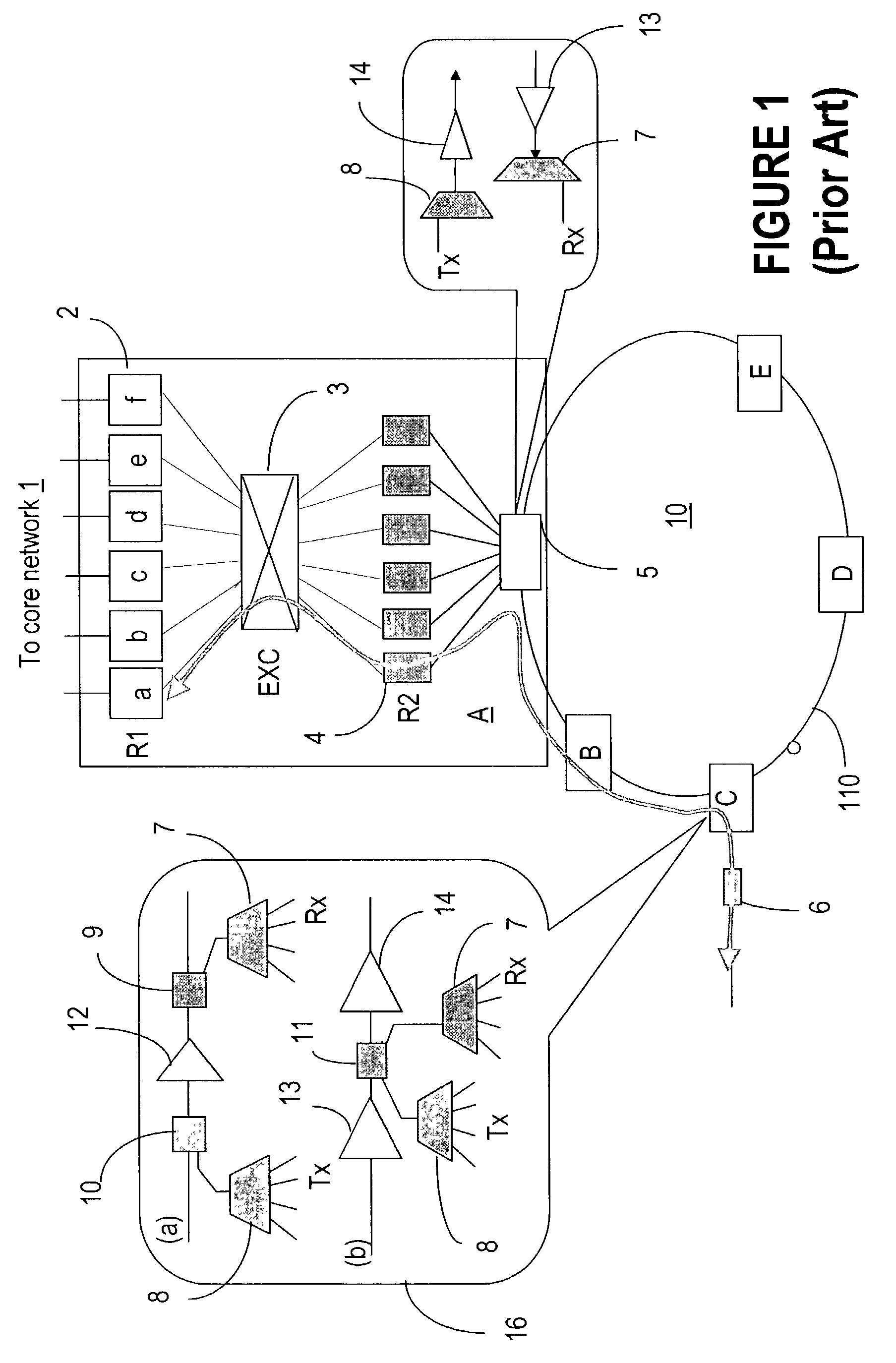
Wavelength routing and switching mechanism for a photonic transport network
InactiveUS7171124B2Flexibility of provisioningLow costLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhoton transmissionAutomatic routing
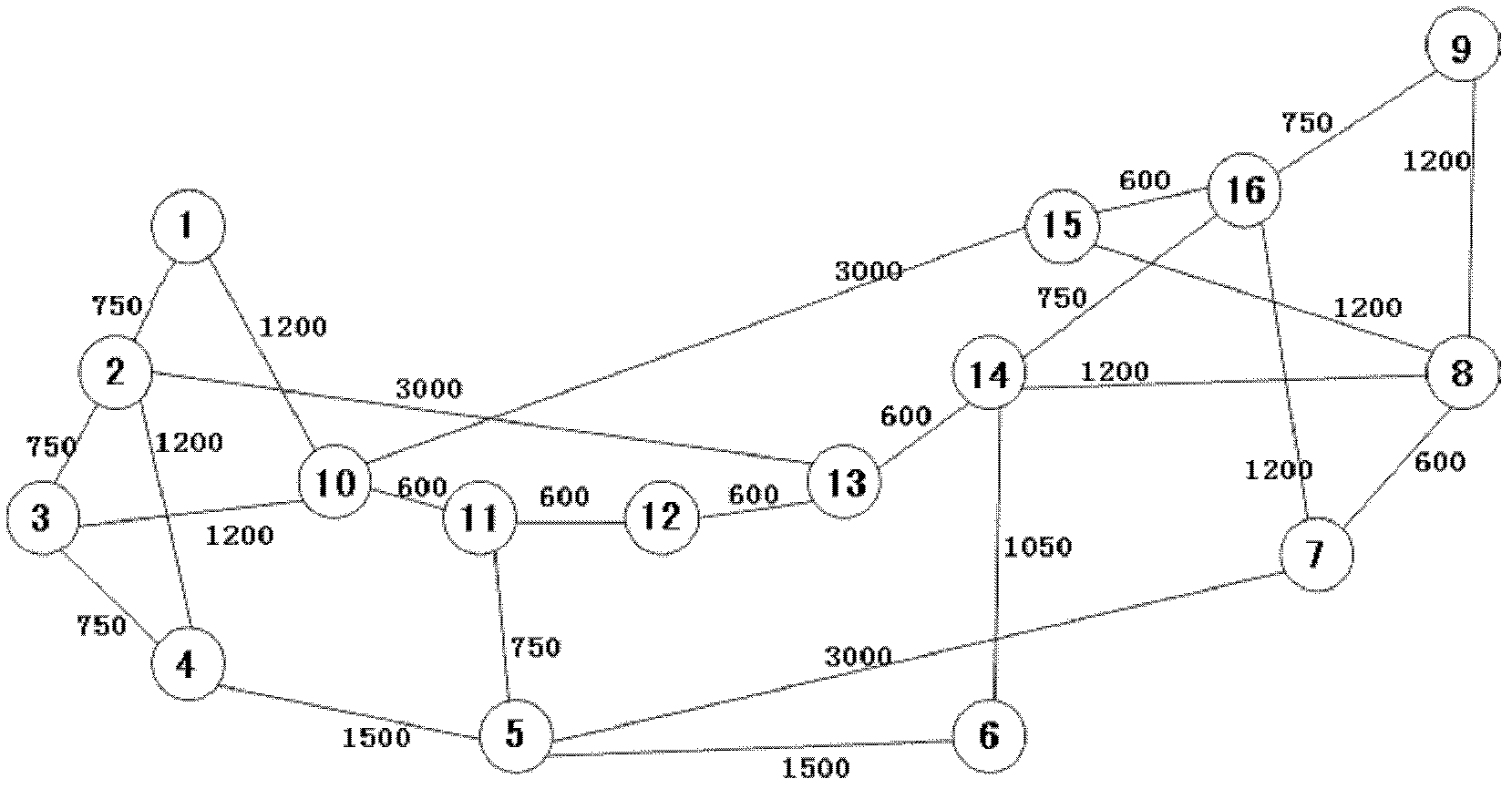
A connection between a source node and a destination node is automatically routed and switched in a WDM photonic network, on receipt of a connection request. A switching and routing mechanism selects a plurality of valid link paths using a path tree, where invalid branches are eliminated based on constraints received in the connection request, and on a link and path cost functions. A regenerator placement tree is used for determining a plurality of viable regenerator paths for each valid link path. On the regenerator placement tree, non-viable branches are eliminated based on constraints received with the request and on regenerator availability at the intermediate nodes along the respective path, and on the specification of these available regenerators. Next, the switching and routing mechanism assigns a set of wavelengths to each viable regenerator path, and estimates the performance of the path using a Q estimator. The regenerator paths are ordered according to their performance and the switching and routing mechanism attempts to setup a paths to serve the request, starting with the best path.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
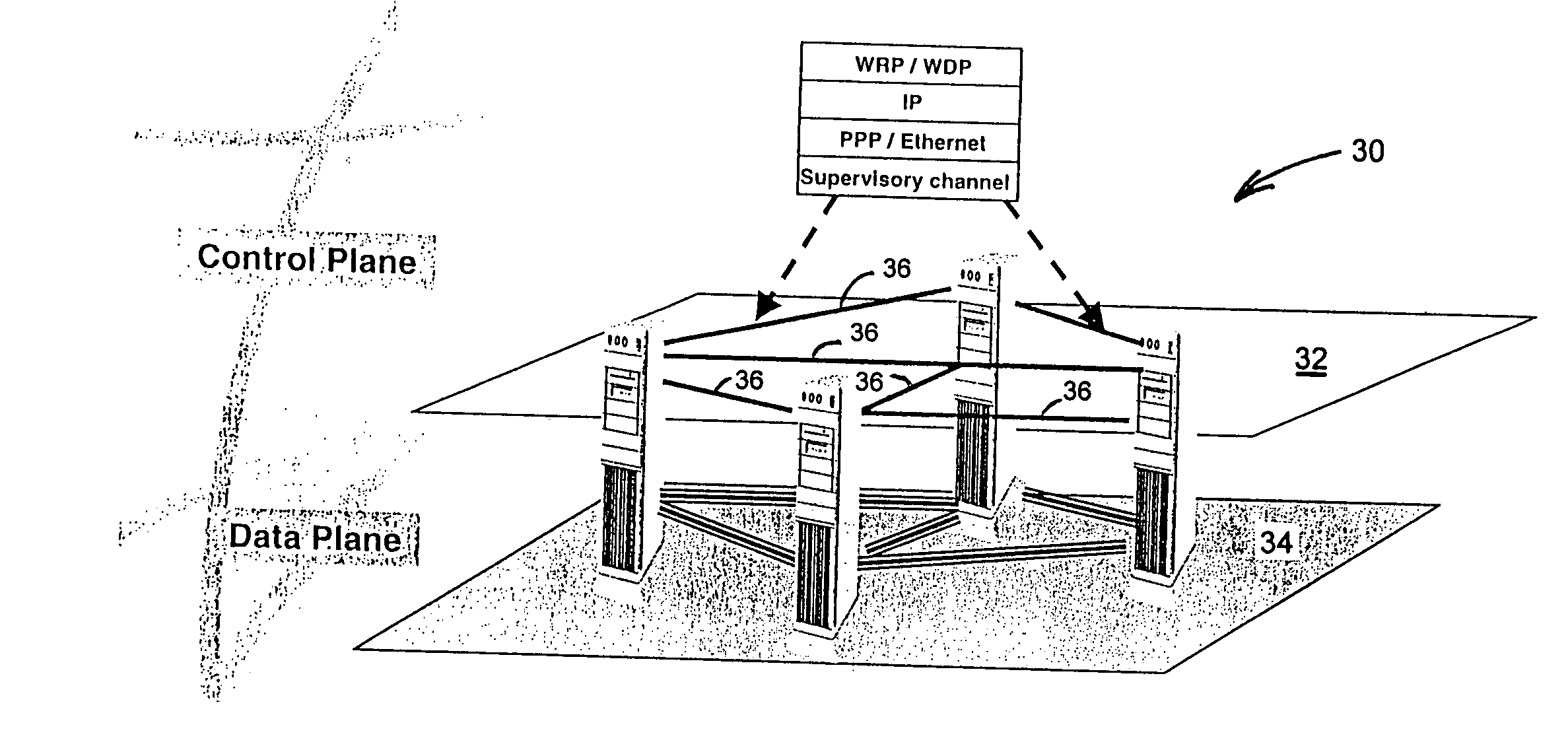
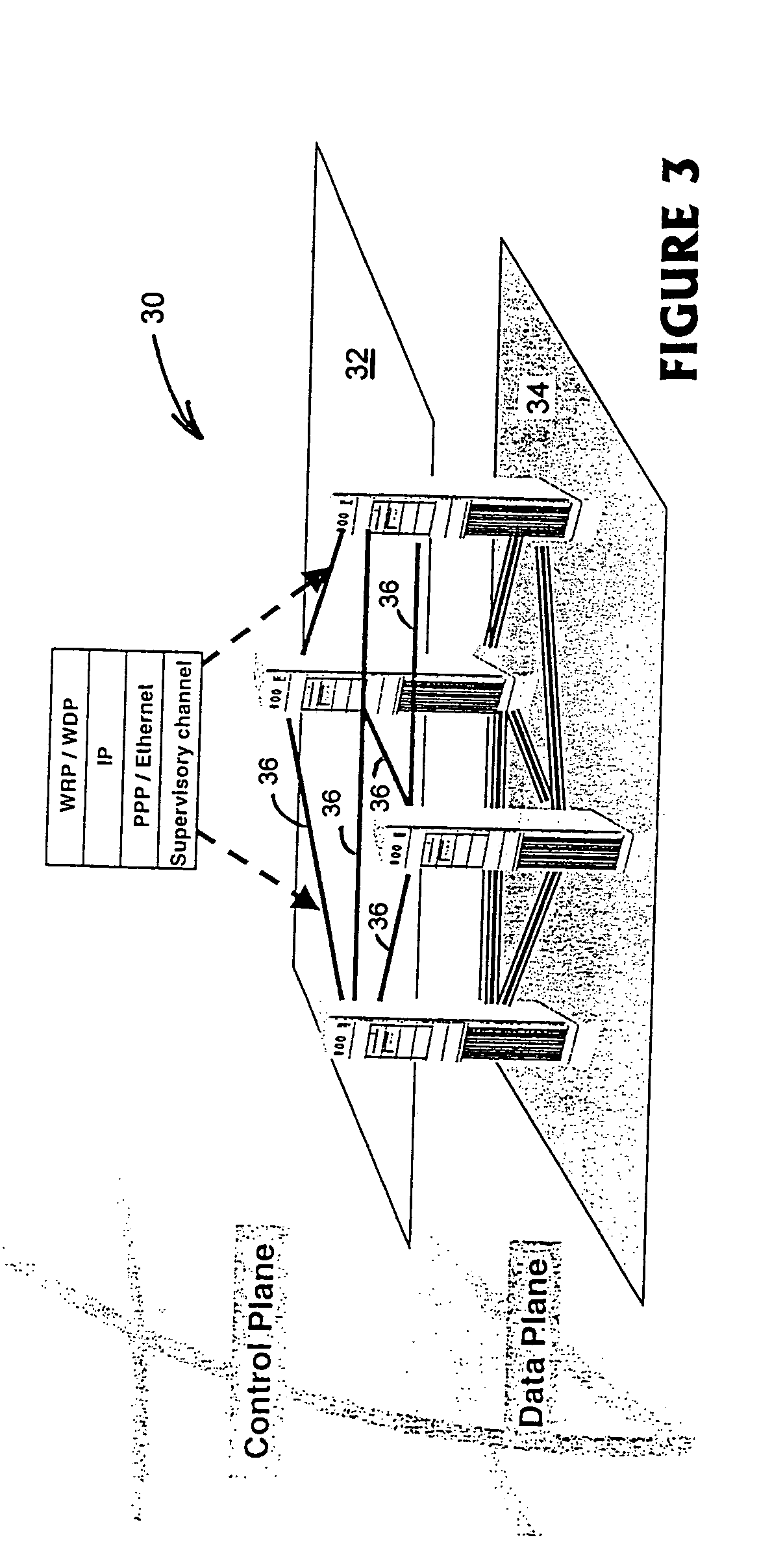
Supervisory control plane over wavelength routed networks
InactiveUS7190896B1Reduce complexityLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringTraffic capacityExchange network
A dedicated IP-based wavelength routing / signaling control plane for optically switched network, is provided. The IP-based control plane is an out-band routing / signaling mechanism and does not require optical-electrical-optical (OEO) conversion. The control plane can accommodate the various network topologies of the data plane and if one of the supervisory, or control channel fails, the IP-based control plane can re-route the traffic to destination. Using non-broadcasting addressable protocols the control plane selects a different path to re-direct the control information without declaring the whole communications trail down and without affecting the client traffic over the data path.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
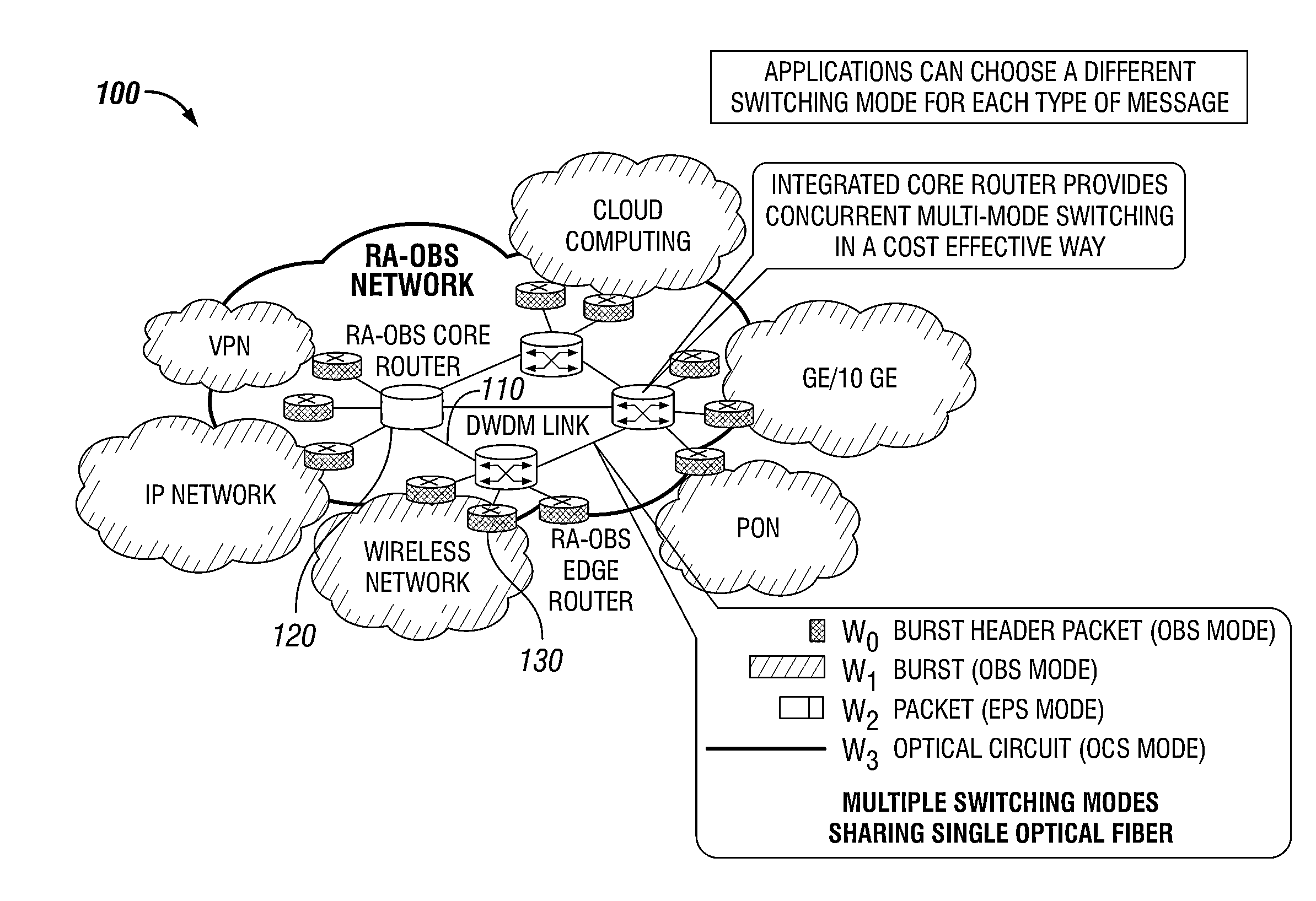
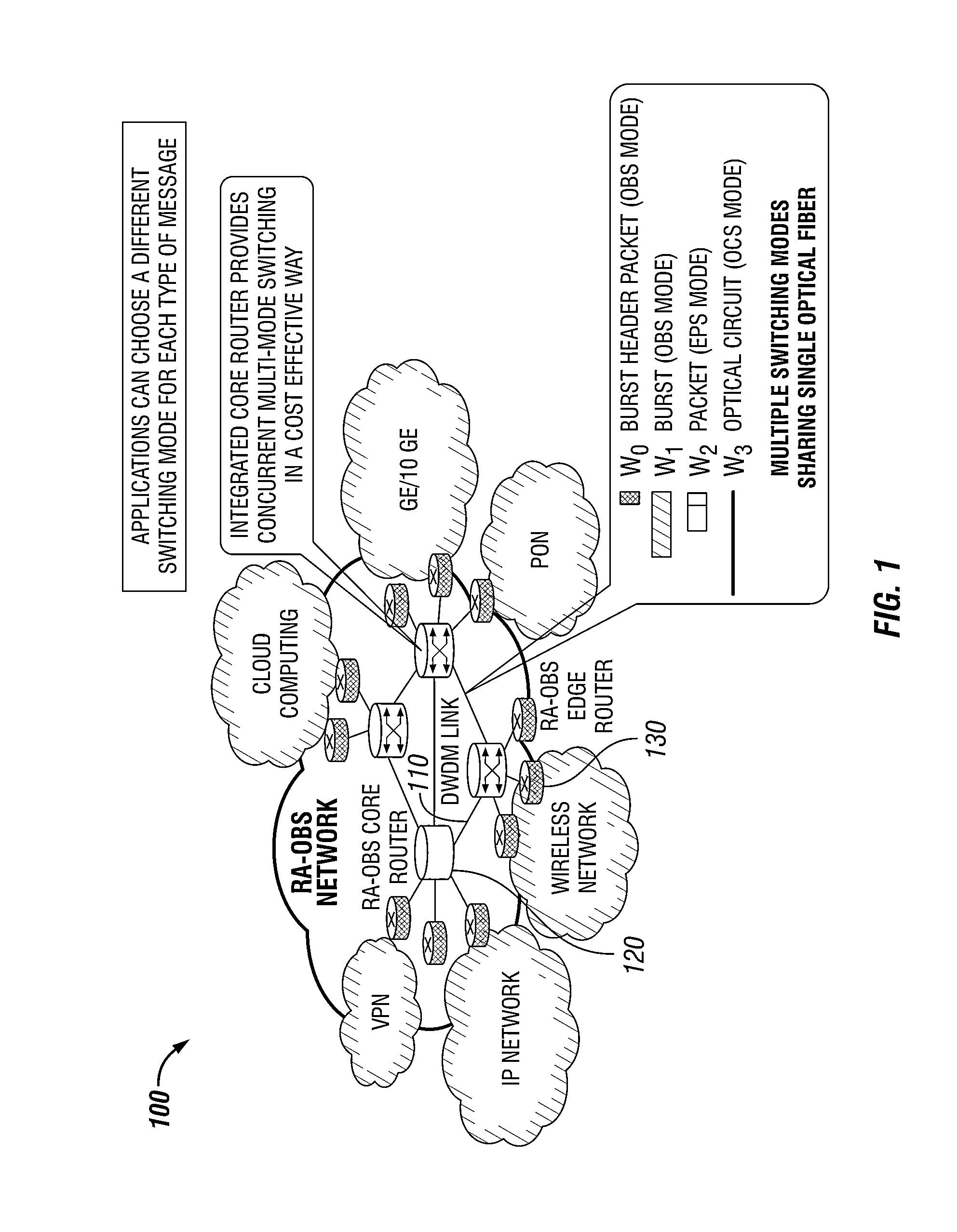
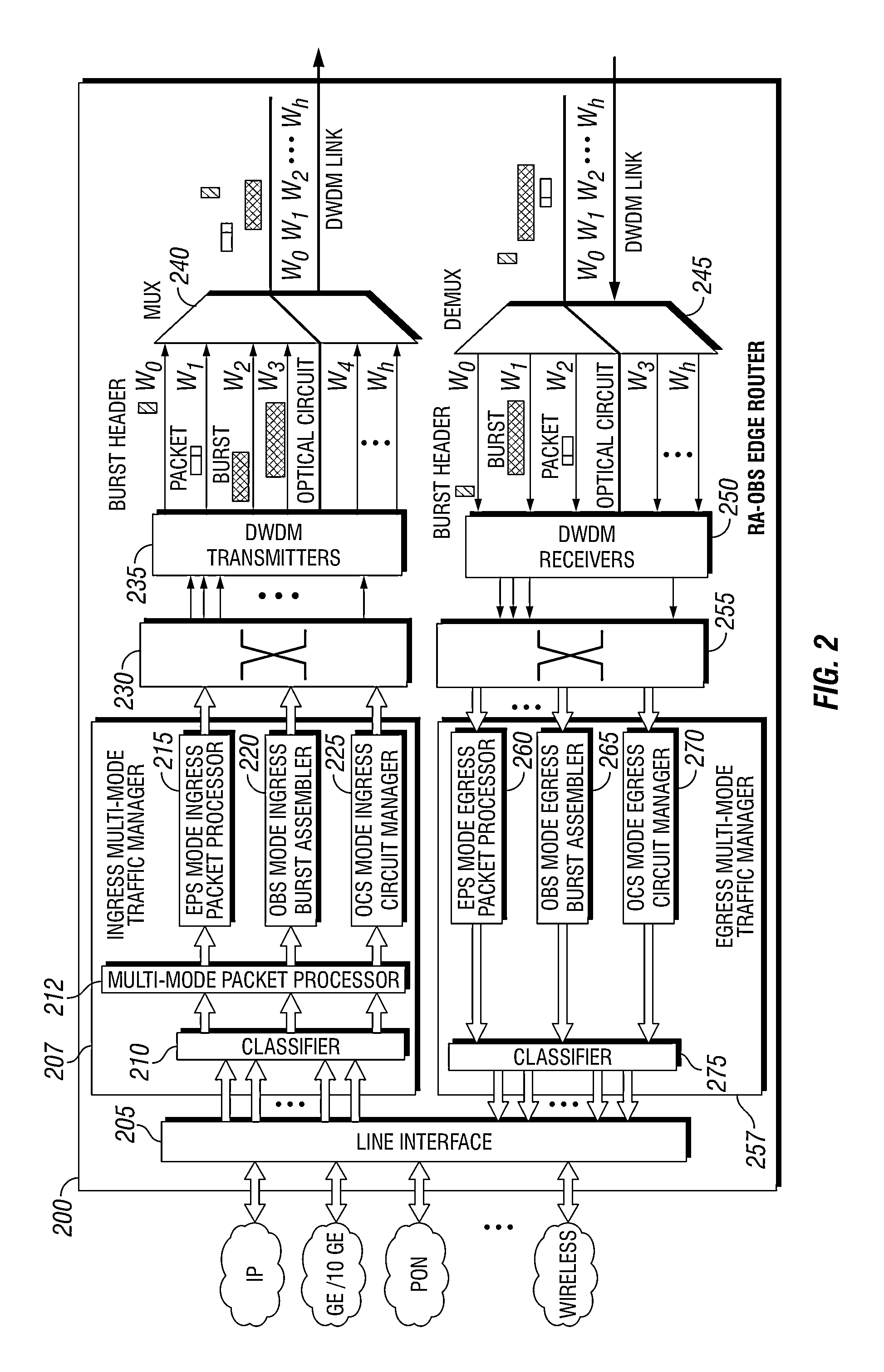
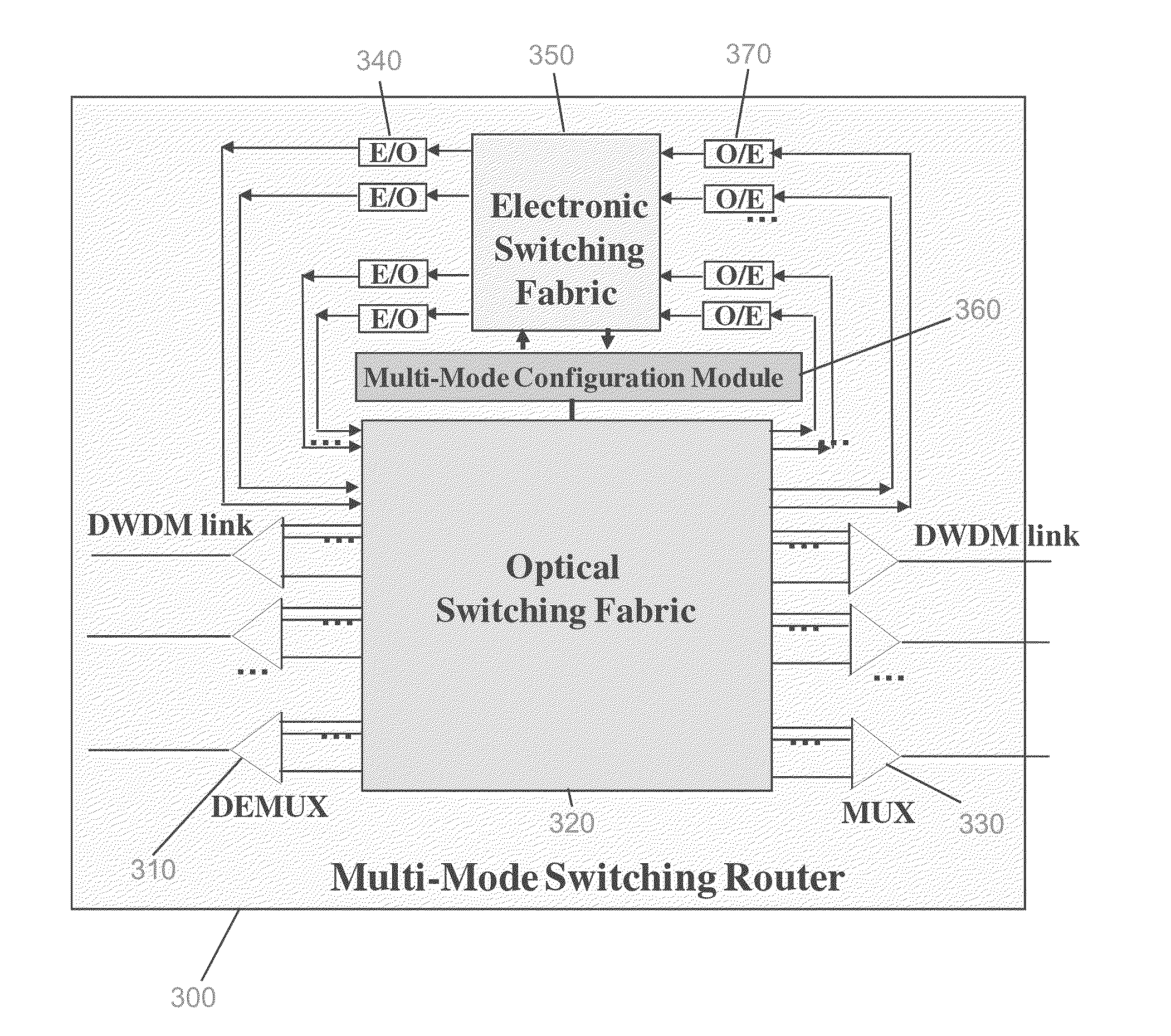
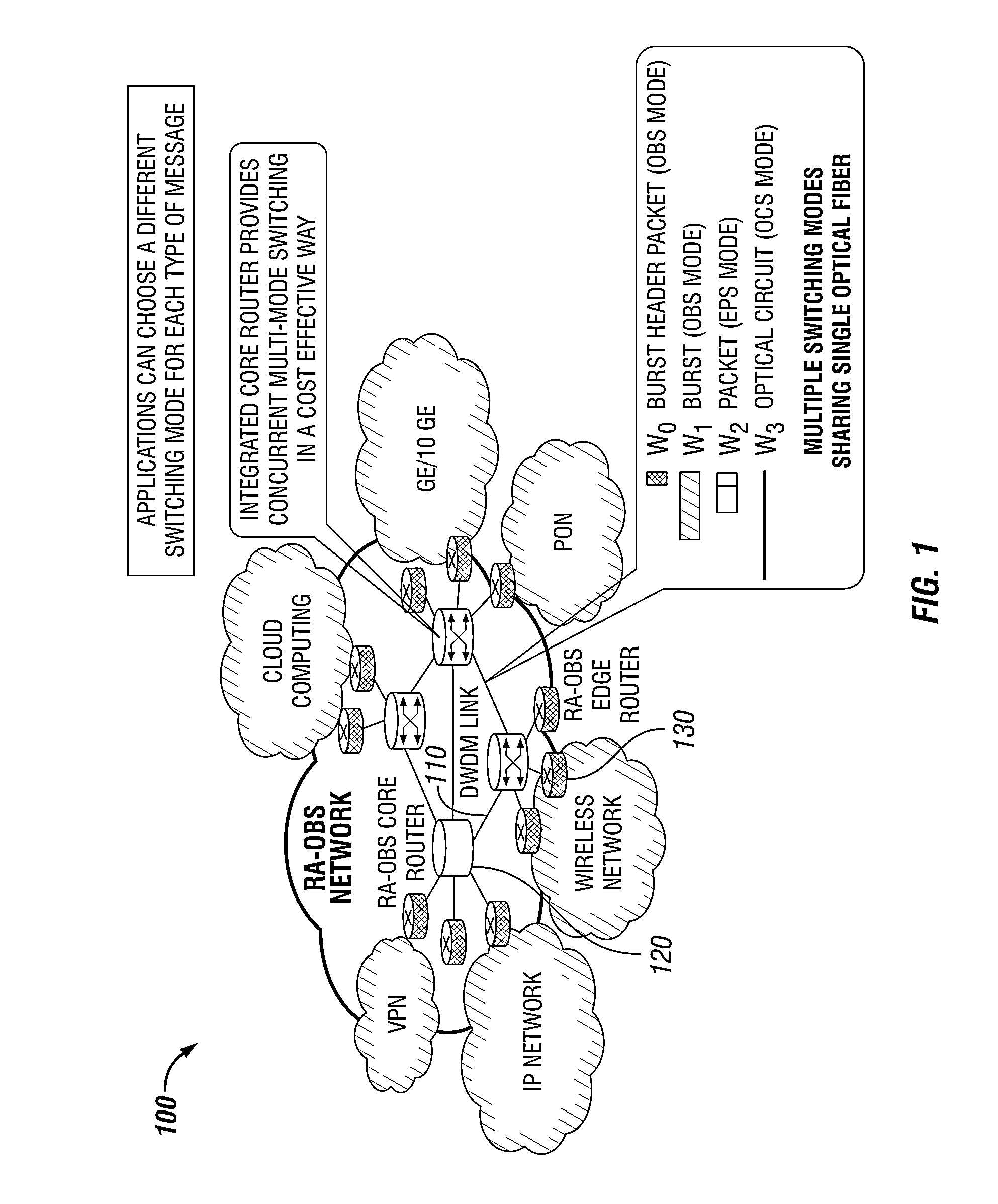
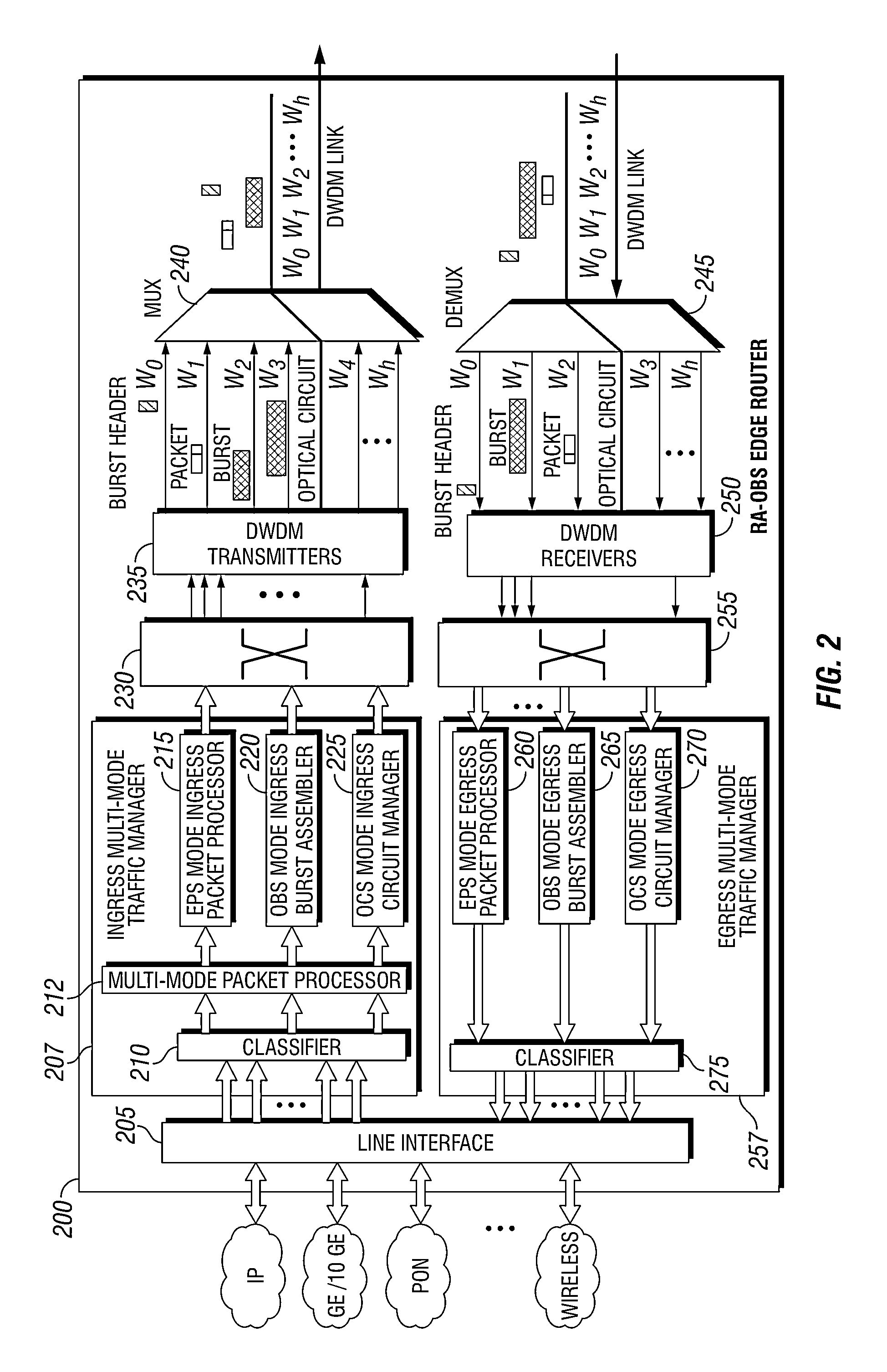
Methods and apparatuses for DWDM multi-mode switching router and dynamic multi-mode configuration and reconfiguration
ActiveUS20130051798A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexComputer architectureLength wave
A multi-mode configuration module for managing switching for an EPS, OCS, and OCS mode is provided. The multi-mode configuration module may include a multi-mode configuration processor, wherein said multi-mode configuration processor receives configuration information for an EPS, OCS, or OBS mode. The module may also provide an optical configuration processor coupled to said multi-mode configuration processor, wherein said optical configuration processor manages wavelength routing of an optical switching fabric; and an electronic configuration processor coupled to said multi-mode configuration processor, wherein said electronic configuration processor manages routing of an electronic switching fabric.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Optical Switching Architectures for Nodes in WDM Mesh and Ring Networks
ActiveUS20070237524A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerProtection mechanism
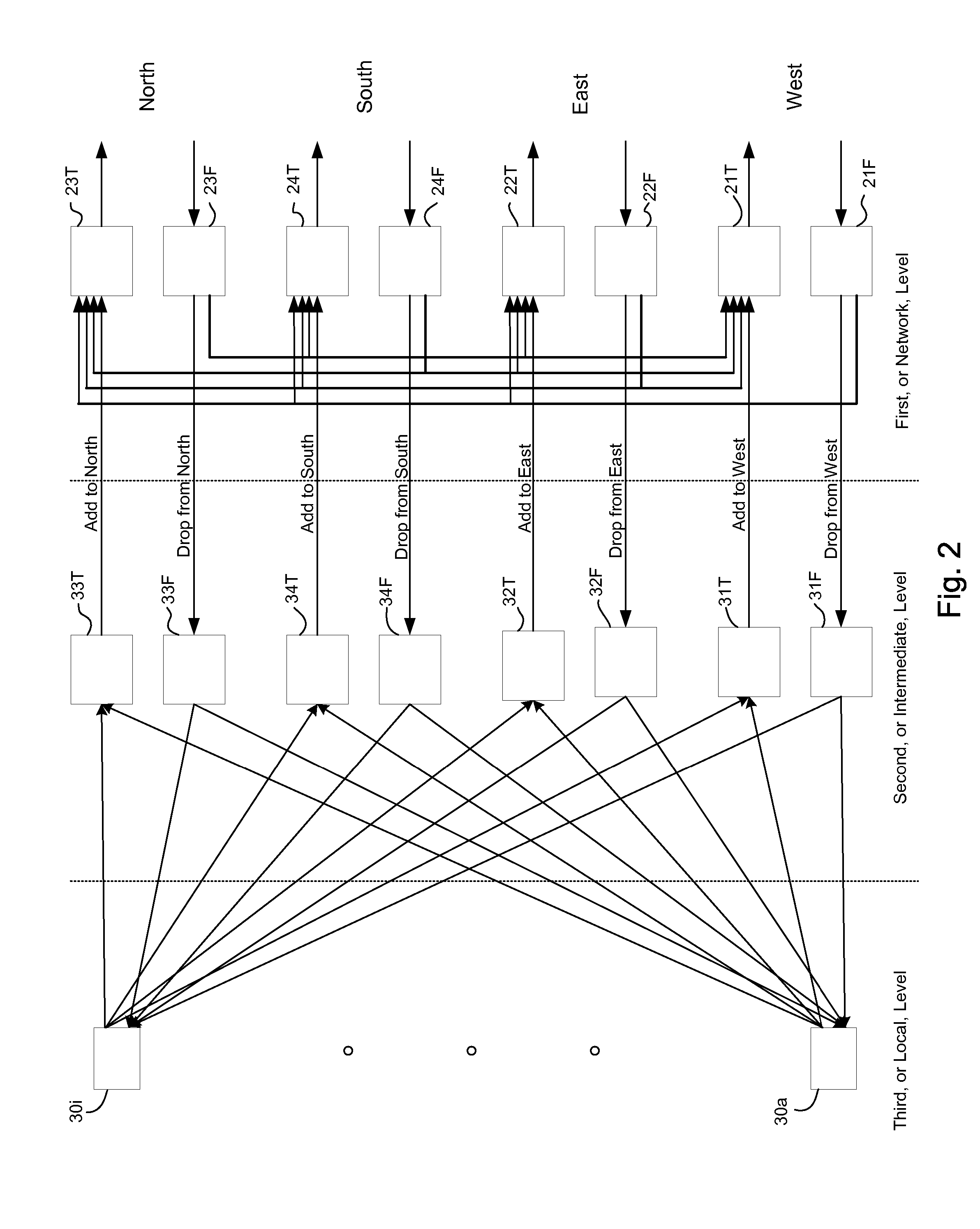
Switching architectures for WDM mesh and ring network nodes are presented. In mesh networks, the switching architectures have multiple levels - a network level having wavelength routers for add, drop and pass-through functions, an intermediate level having device units which handle add and drop signals, and a local level having port units for receiving signals dropped from the network and transmitting signals to be added to the network. The intermediate level device units are selected and arranged for performance and cost considerations. The multilevel architecture also permits the design of reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexers for ring network nodes, the easy expansion of ring networks into mesh networks, and the accommodation of protection mechanisms in ring networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
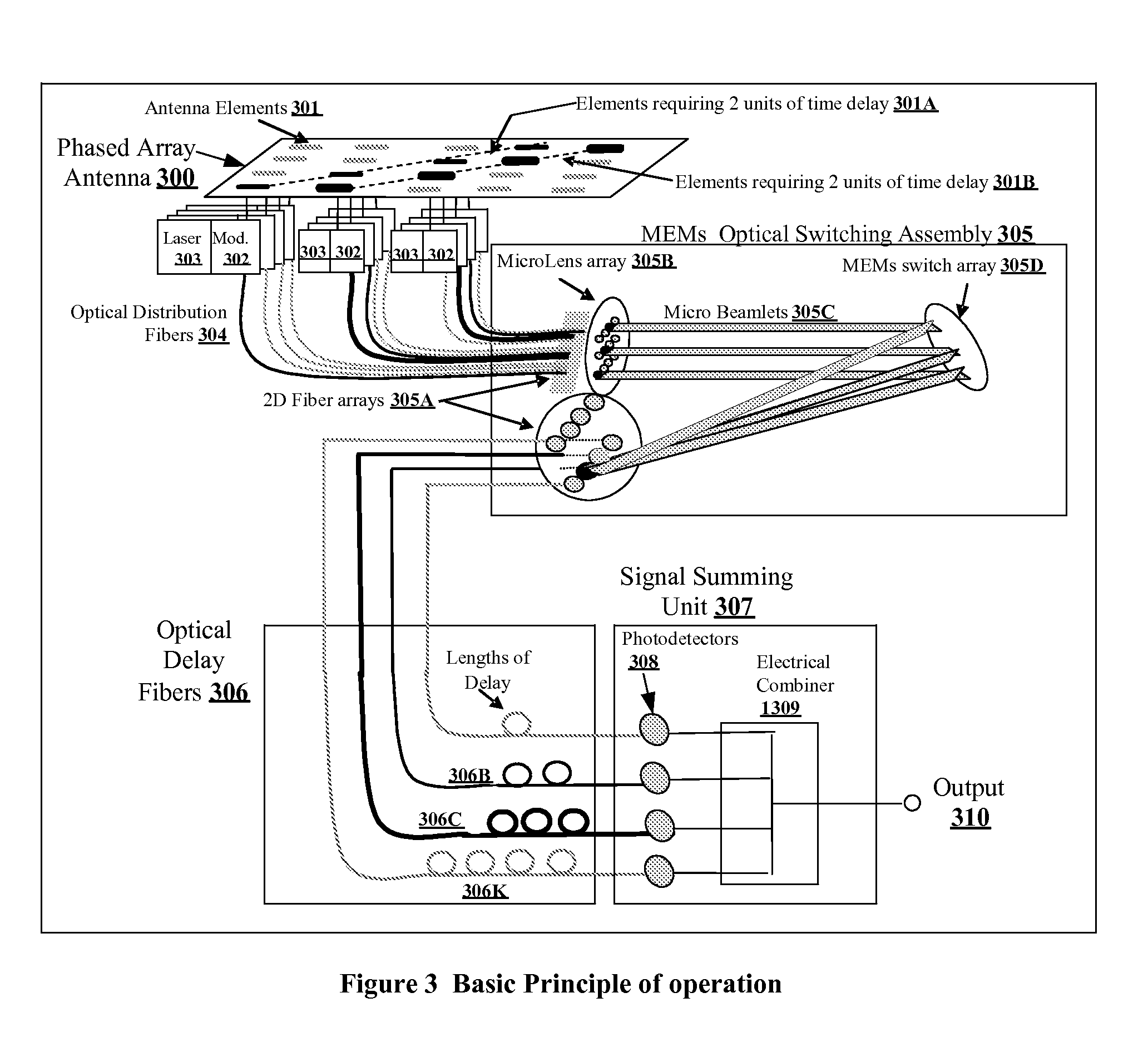
Multi Beam Photonic Beamformer
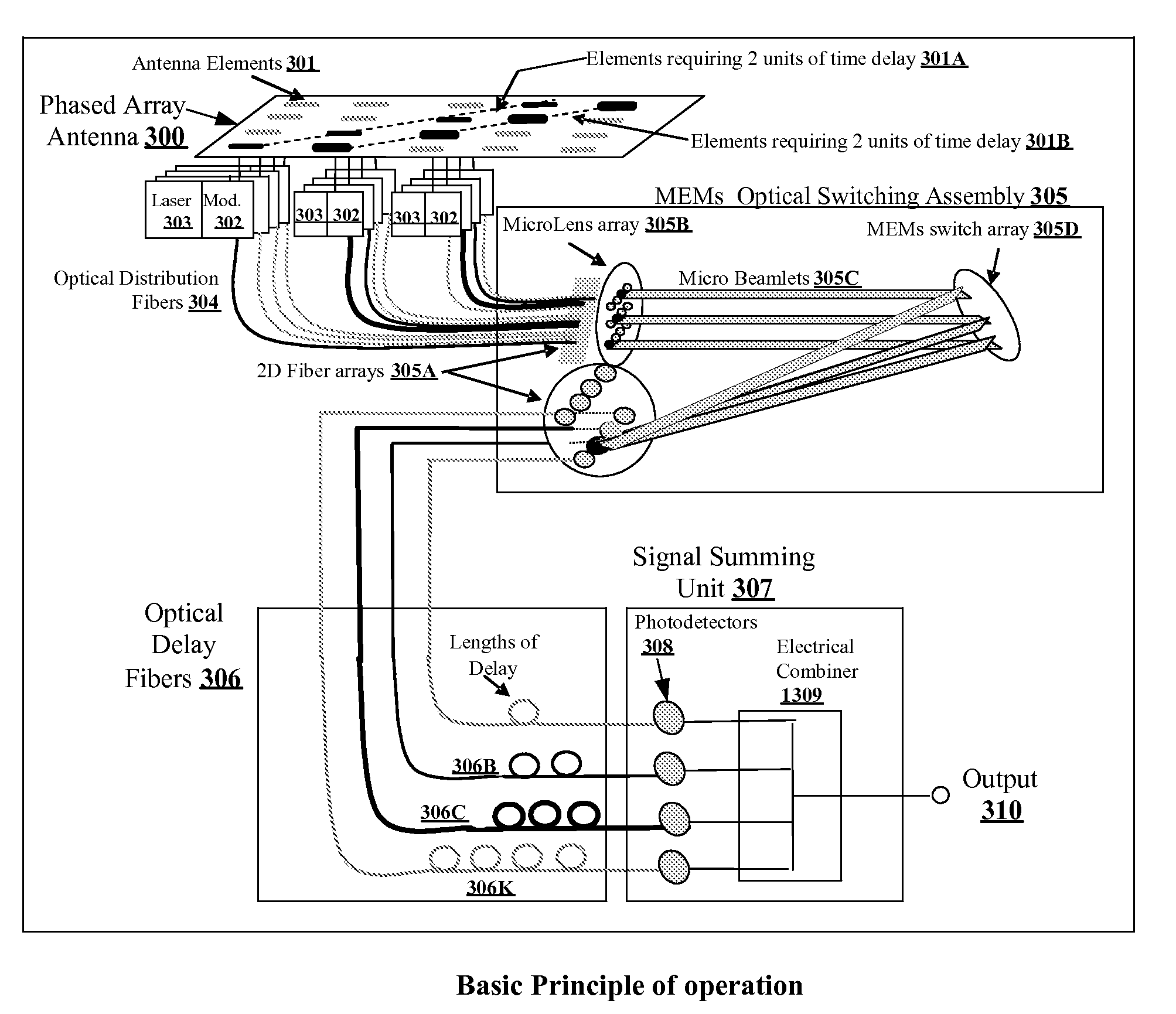
A true time delay beamformer for RF / microwave phased array antenna systems using multiple laser sources, optical modulators to convert the electrical signal to a modulated optical signal, standard optical fiber for creating time delays, dispersive optical fiber for creating delays, optical splitting and / or switching section, photodetectors to convert the modulated optical signal to an electrical signal, and a signal combining section. The true time delay beamformer has the capability to create multiple simultaneous RF / microwave antenna beams. One (more lasers) is used to source one (or more) wavelengths of light to the optical modulator. The signal from one (or more) antenna elements drive the optical modulator. The light from the optical modulator passes through the standard optical fibers and / or the dispersive optical fibers to create time delay variation for one optical modulator relative to another allowing for the formation of RF / microwave beams. Fixed location RF / microwave beams can be generated by a static network of standard and / or dispersive optical delay fibers. Steering of the location of the RF / microwave beams can be accomplished by an optical switching mechanism which could be based on MEMs and / or wavelength routing based switching. Finally, all the signals for a RF / microwave beam are summed to form a single output. The summing can occur either optically before the photodetectors and / or electrically after the photodetectors.
Owner:COWARD JAMES F
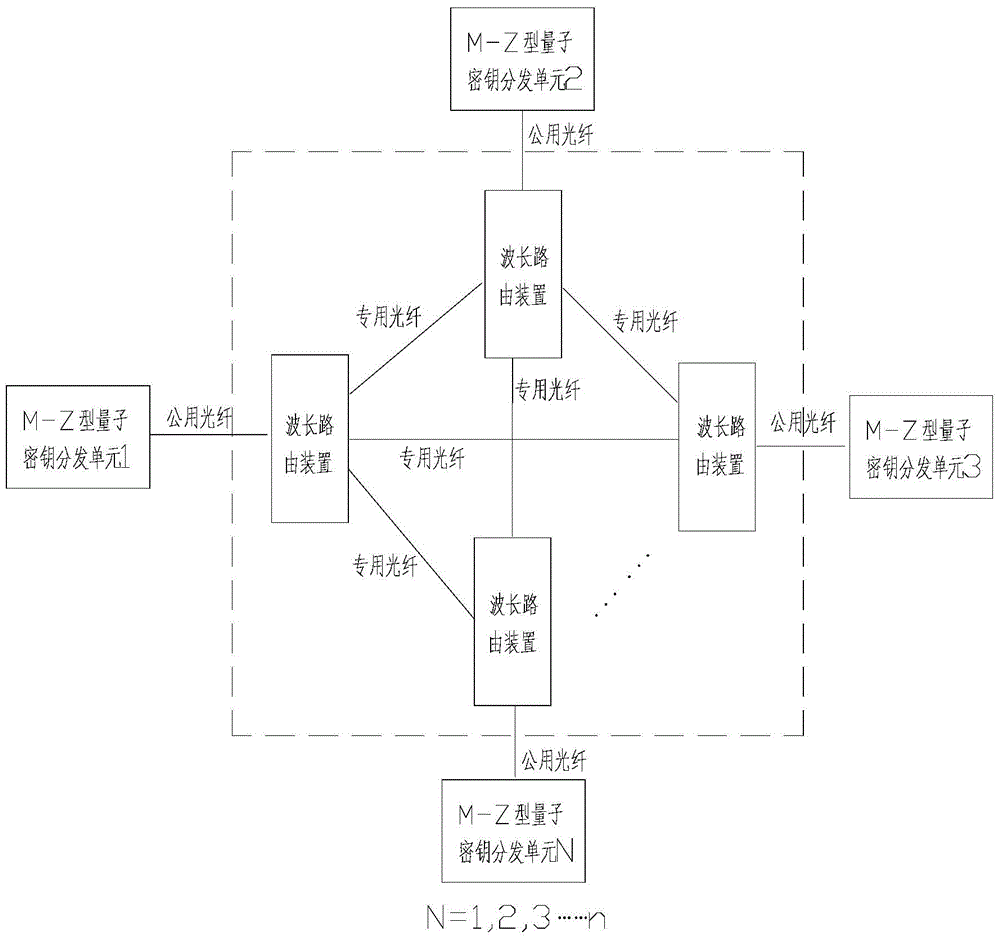
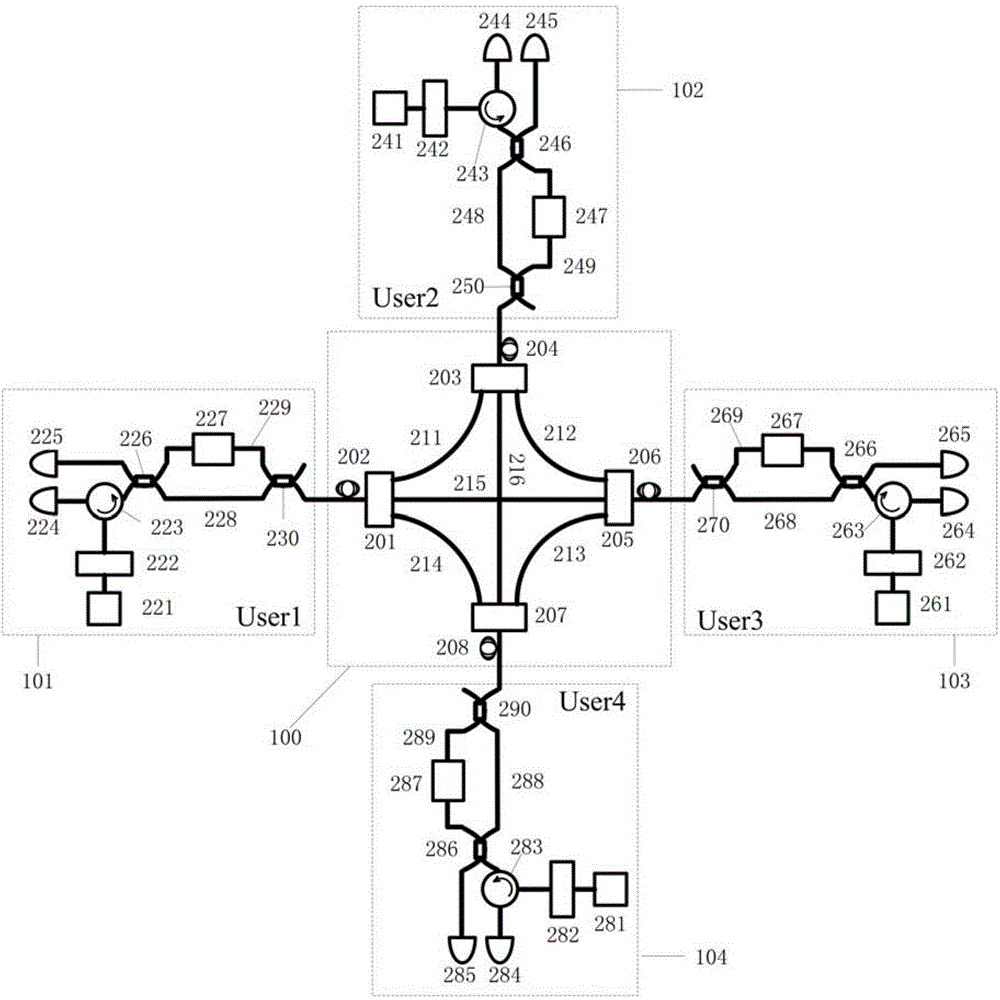
Multiuser QKD network system based on M-Z interferometer, and secret key distribution method thereof
ActiveCN104935428AImprove transmission stabilityReduce bit error rateKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationComputer hardwareWavelength
The invention discloses a multiuser QKD network system based on an M-Z interferometer, and a secret key distribution method thereof. The system comprises a mesh network structure unit and N M-Z type quantum secret key distribution units. The mesh network structure unit comprises public fibers, wavelength router devices and special-purpose fibers. One port of any one wavelength router apparatus is connected with one public fiber and is respectively correspondingly connected with other wavelength router devices through the special-purpose fibers. The N M-Z type quantum secret key distribution units are connected with the mesh network structure unit through the public fibers, and any one M-Z type quantum secret key distribution unit can communicate with other M-Z type quantum secret key distribution units through the mesh network structure unit, such that simultaneous communication among users is realized. The system provided by the invention is simple in integral structure, realizes intercommunication between any two users and among N users, is less influenced by an increase of the user number in terms of single-channel performance, and has quite good full-network expansibility and security.
Owner:GUANGDONG INCUBATOR TECH DEV CO LTD
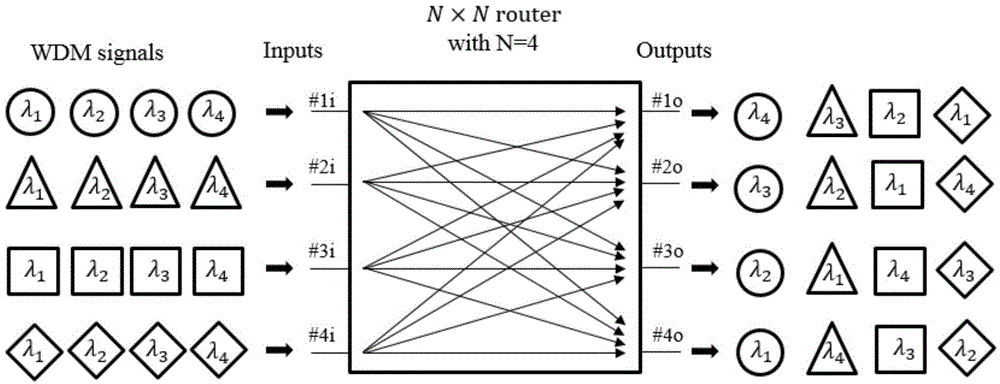
Wavelength routing system
ActiveUS20100054741A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingWavelength demultiplexer
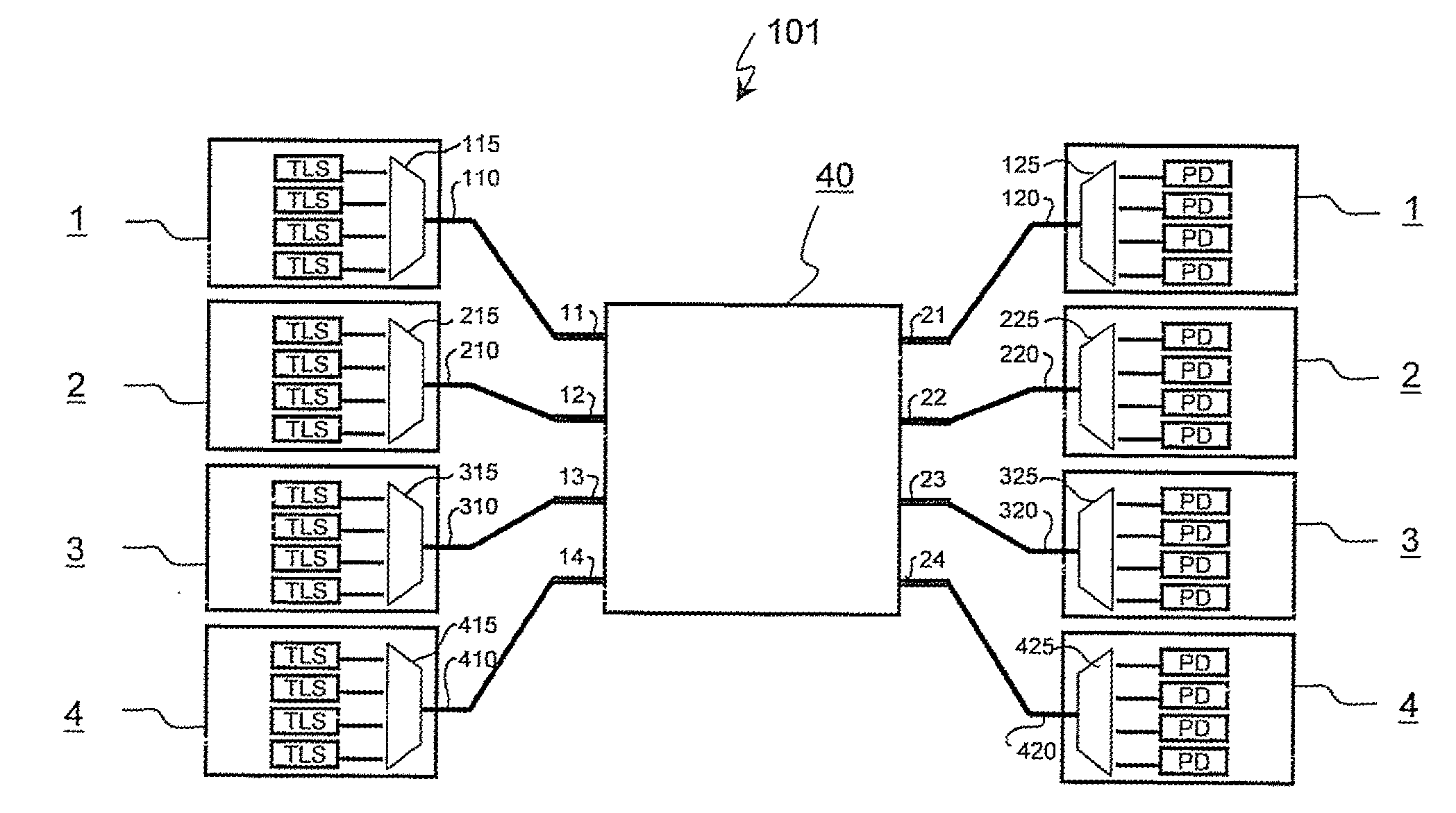
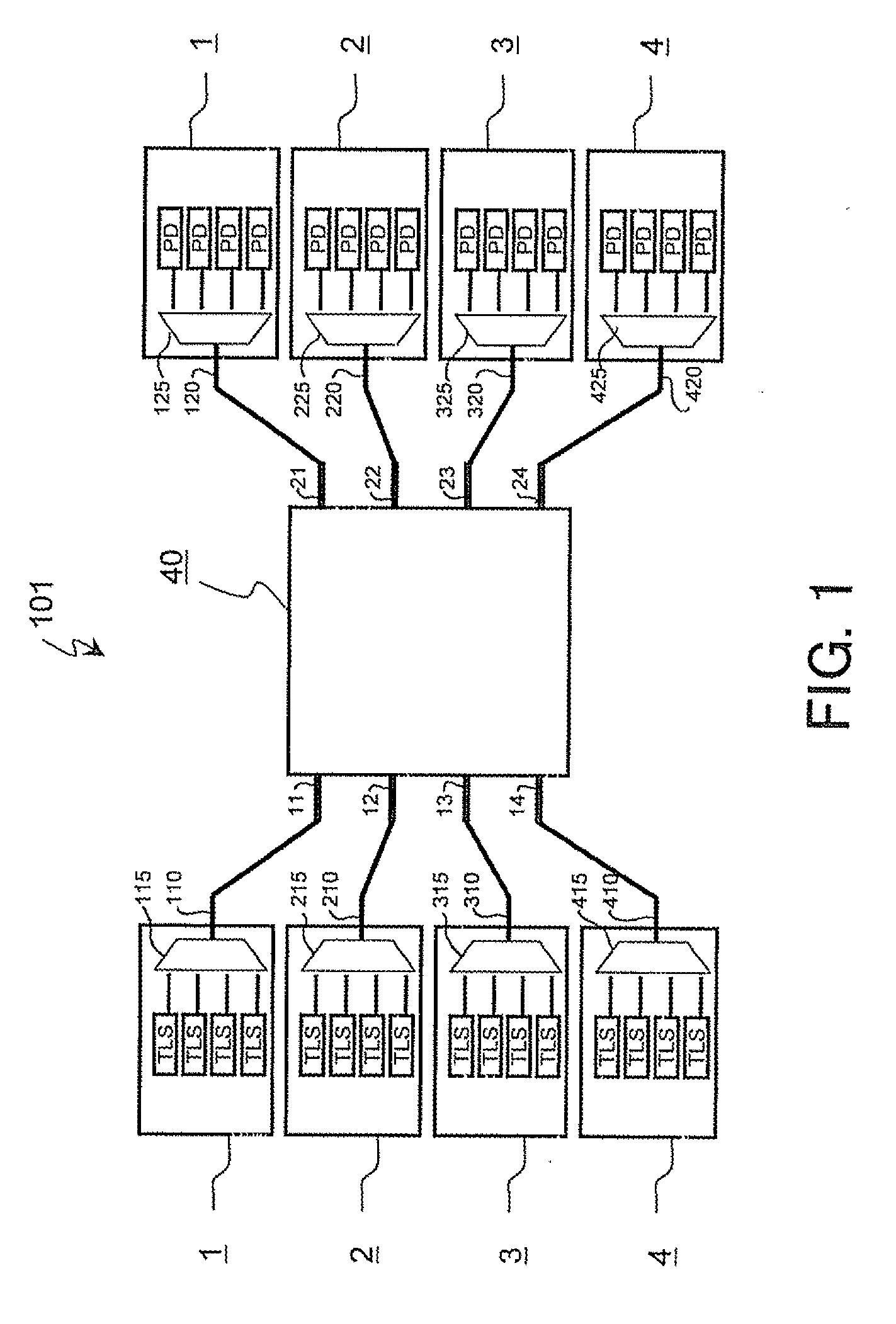
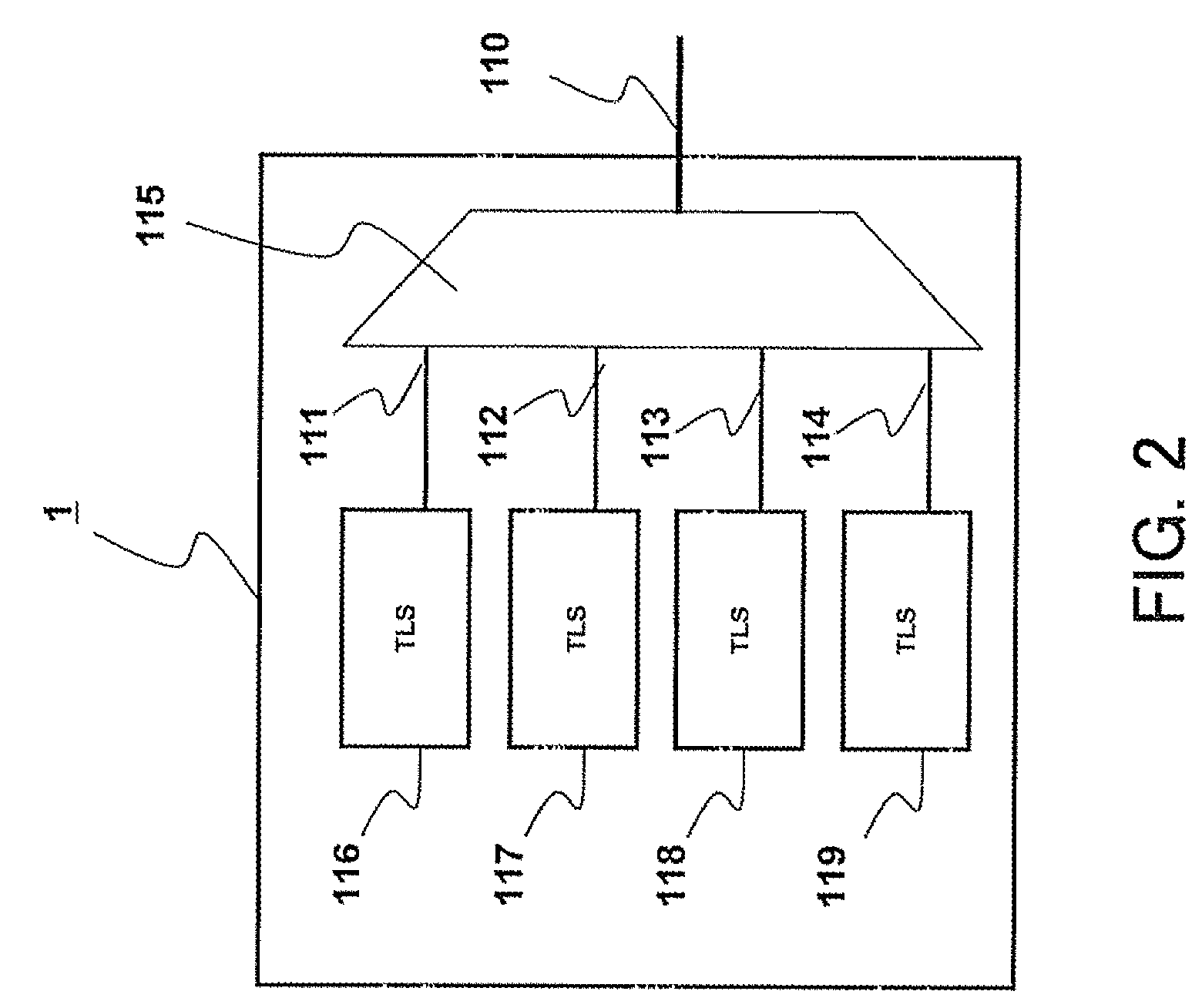
A wavelength routing system includes a plurality of nodes (1, 2, 3, 4) and an array waveguide grating (40) having a routing property and optically connected to the plurality of nodes. Each of the nodes has a plurality of light sources (TLS) outputting lights at different wavelengths to the array waveguide grating, respectively, and a wavelength demultiplexer (125, 225, 325, 425) having a periodic property, demultiplexing a light output from the array waveguide grating, and outputting demultiplexed lights. The wavelength demultiplexer is set a channel period which is different from that of the array waveguide, and which is more than or equal to a number of output ports of the wavelength demultiplexer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Configurable wavelength routing device
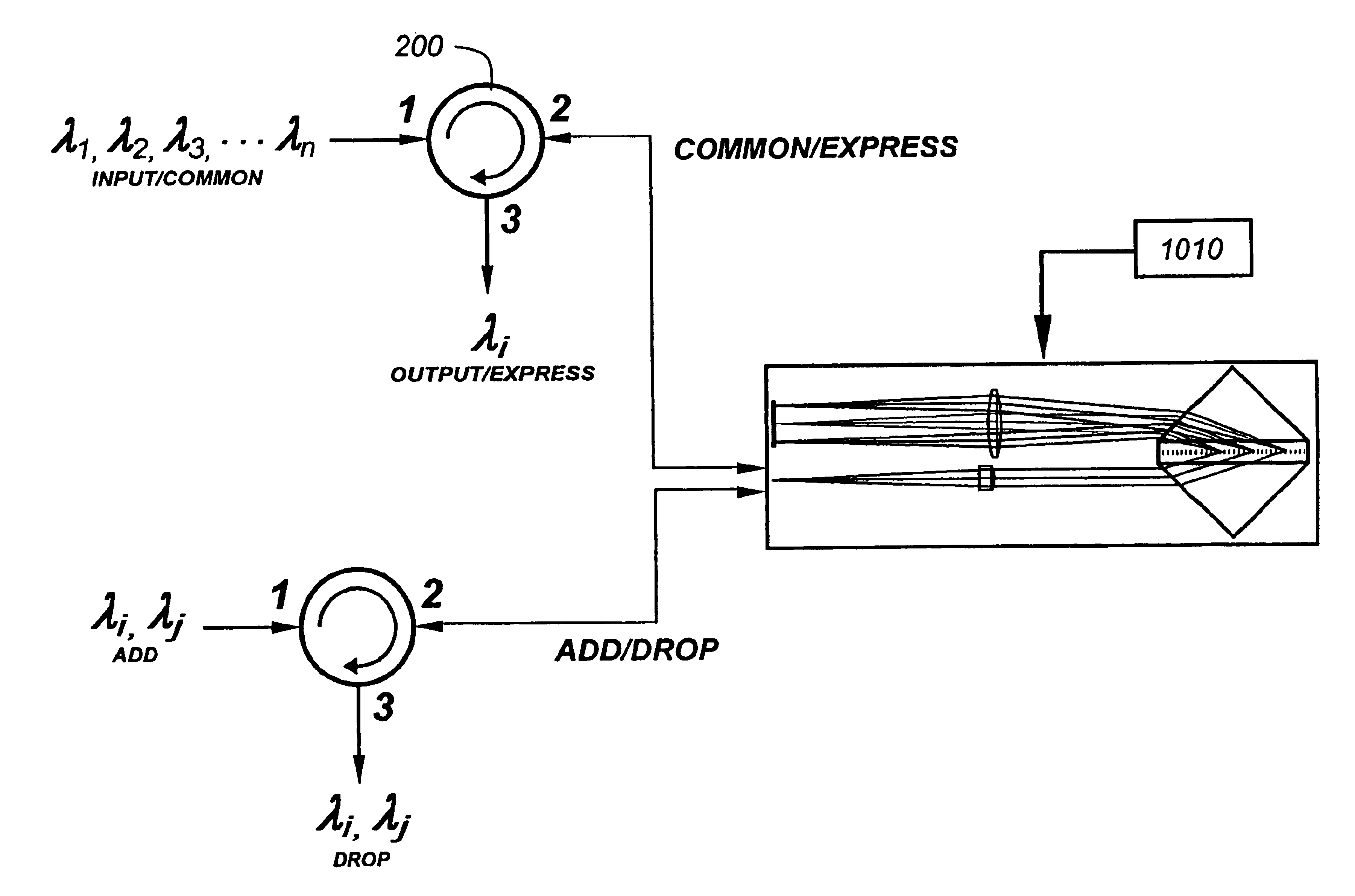
A dispersive optical element and positionable micromirrors are deployed to implement a configurable wavelength routing device for add / drop and other applications. Input light is dispersed and imaged onto a focal plane where there is disposed an array of light redirection elements operative to decenter wavelengths on a selective basis. In the preferred embodiment, the dispersive optical element is a grating or grating / prism featuring a high degree of dispersion allowing the input and return paths to be parallel and counter-propagating, both for a compact size and to facilitate a lateral shifting in a localized area. The inputs and outputs may be implemented in conjunction with optical fibers, with a lens being used to collimate light prior to illumination of the grating. A focusing lens is preferably used to form a nominally telecentric image of the dispersed spectrum at the image plane. A control mechanism is provided to locate individual mirrors of the array in one of at least two positions, to effectuate the selective wavelength routing. In the preferred embodiment, the mirrors are 90 degree V-mirrors, translatable within the plane of the telecentric image, such that in one position, a common port is coupled to an express port and whereas, in another position, a common port is placed in communication with an add / drop port.
Owner:KAISER OPTICAL SYST INC
Multi-grain optical router based on optical burst switch
InactiveCN1381963ACapable of dynamic wavelength routingReduce the probability of packet lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionGranularityControl channel
A multi-granular light router based on optical burst exchange can support both burst-class and dynamic wavelength routing-class light exchange. Its core optical router uses dual-light-switch matrix for different exchange granularities. Its marginal optical router can support electric IP access and optical dynamic wavelength routing network access. Any input wavelength can be converted to any output wavelength, so the whole network has dynamic wavelength routing power. A mixed signalling mode is used. It is compatible with the current optical network with dynamic wavelength routing and the frture optical network with burst exchange.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Wavelength router
InactiveUS6097517AEasy to assembleSmall sizeMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsMultiplexingLength wave
A wavelength router has first ports each receiving or providing a first multiwavelength optical signal having wavelengths, and second ports each providing or receiving second multiwavelength optical signals having multiplexed wavelengths. The number of multiplexed wavelengths of the second multiwavelength optical signal is smaller than the number of wavelengths of the first multiwavelength optical signal. The first multiwavelength optical signal is demultiplexed into the second multiwavelength optical signal. The second multiwavelength optical signals are multiplexed into the first multiwavelength optical signal. The first multiwavelength optical signal has a number N of multiplexed wavelengths, and the second ports are divided into M sets of second ports. The first multiwavelength optical signal is demultiplexed into optical signals having a number N / M of multiplexed wavelengths, which are supplied to the M sets of second ports.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Method, device and system for routing protocol message issuance and routing computation
InactiveCN101820556ASave resourcesMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetwork communicationLength wave
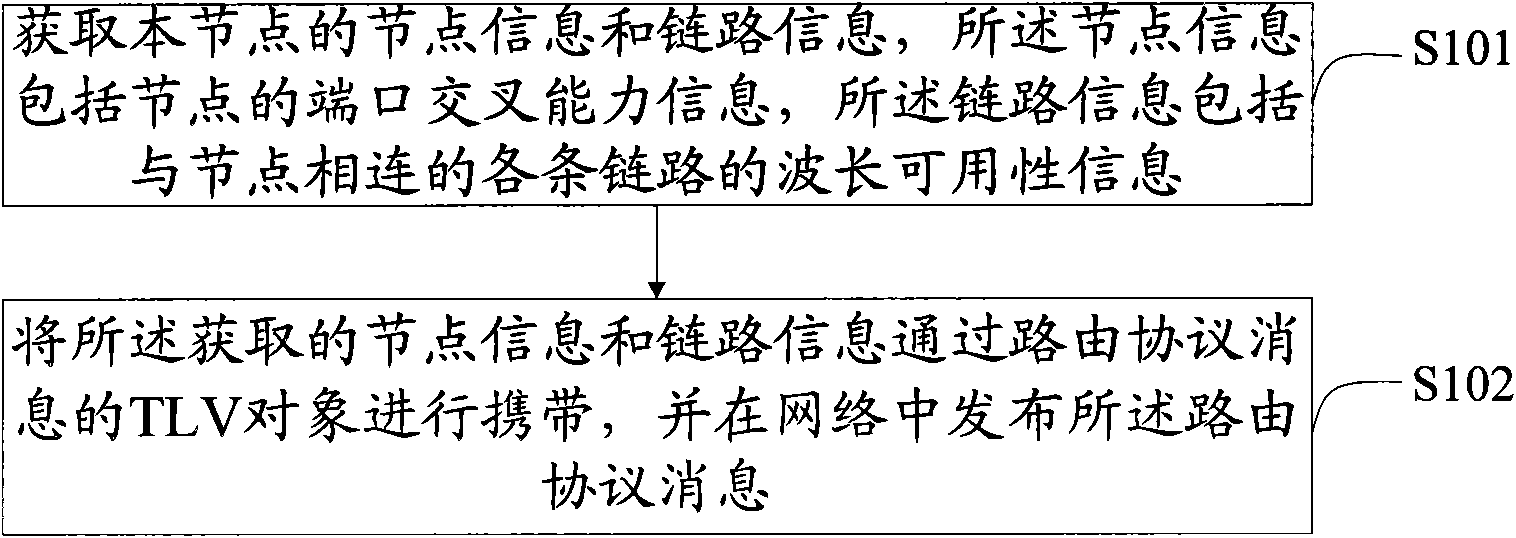
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for routing protocol message issuance and routing computation, relates to the an optical network communication technology and aims at solving the problems of excessively long time for establishing routing or re-routing and low wavelength utilization efficiency in the current wavelength routing. The method for the routing protocol message issuance comprises the following steps: obtaining node information and link information of a node, wherein the node information comprises port crossing capacity information of the node, and the link information comprises wavelength availability information of all links connected with the node; and carrying the obtained node information and the link information through a type-length-attribute object of a routing protocol message and issuing the routing protocol message in a network. The embodiment of the invention is applicable to the routing issuance and the computation in the wave division network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Optical communication network system, wavelength routing apparatus, communication node, optical path managing method for use in optical cross connect apparatus, and apparatus for that method
InactiveUS20060051094A1Improve transmission performanceExcel in flexibilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingMultiplexer
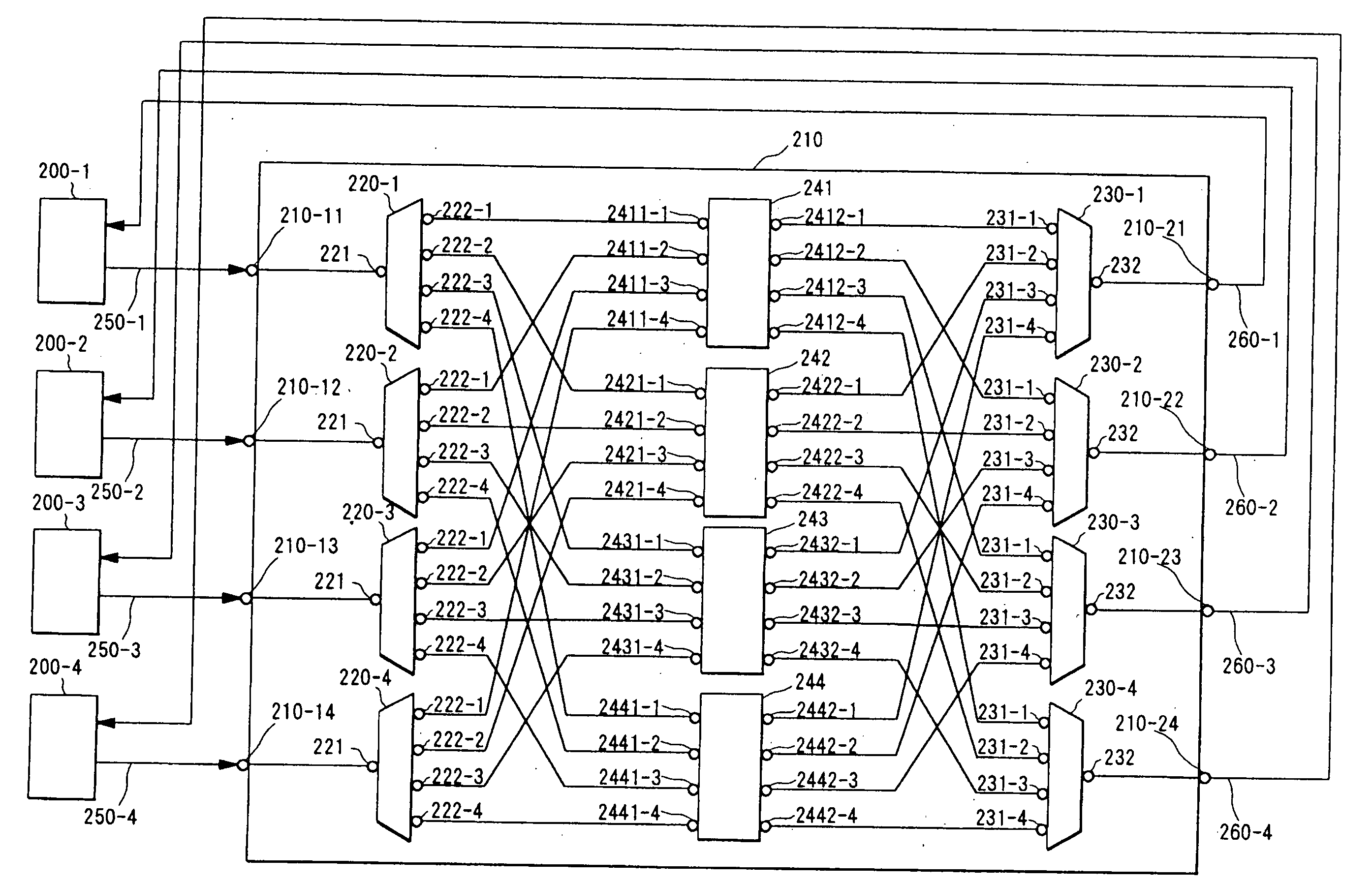
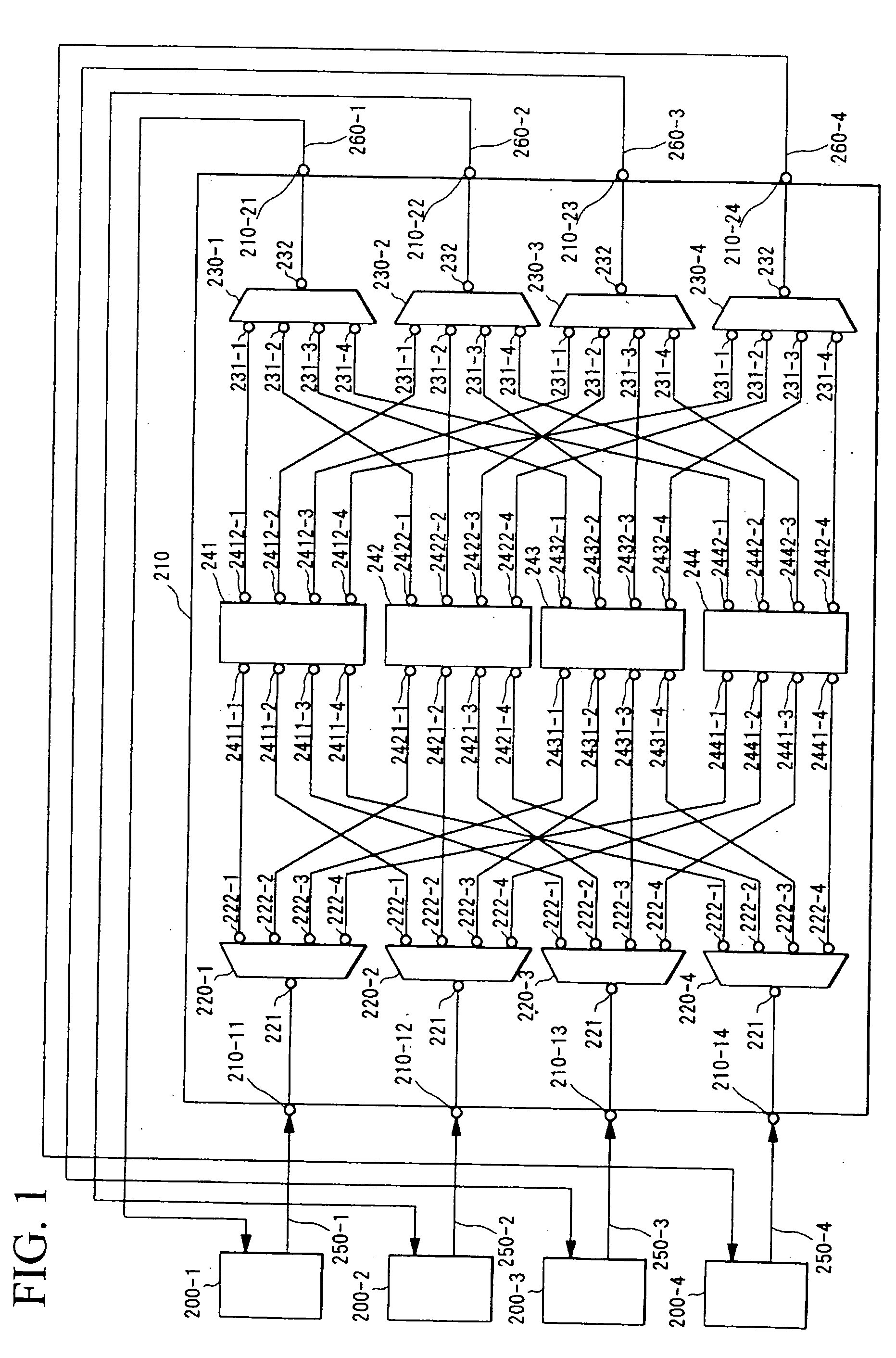
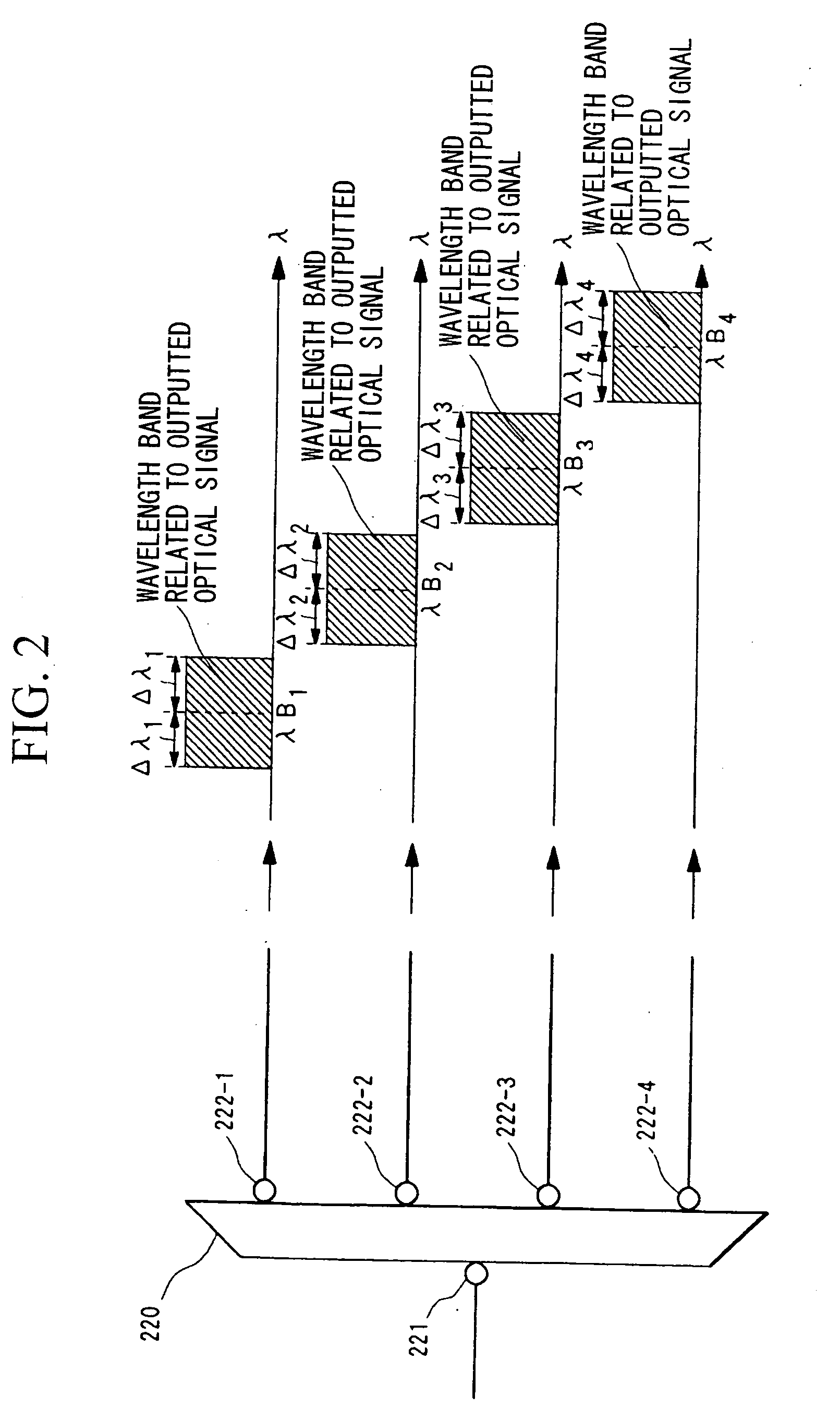
An optical communication network system and a wavelength-routing device and a communication node therefor are provided which can easily increase the optical paths between communication nodes, which are capable of expanding transmission capacity, and which excel in flexibility and expandability. An optical signal within a wavelength band (λBm±Δλm) which has been transmitted from a predetermined communication node (200-1 through 200-4) is subjected to wavelength-band demultiplexing of the wavelength bands by wavelength-band demultiplexers (220-1 through 220-4) of a wavelength-routing device (210), and is then subjected to wavelength-routing by arrayed-waveguide gratings (241 through 244) according to the wavelength bands, and furthermore is multiplexed with optical signals of other wavelength bands by wavelength-band multiplexers (230-1 through 230-4), and after having been outputted, is transmitted to a communication node. In this manner, by varying the wavelength band (λBm±Δλm) of the wavelength of the optical signal which is transmitted from the communication node, it becomes possible to establish a single optical path between the communication nodes for each wavelength band.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Wavelength routing on an optical metro network subtended off an agile core optical network
ActiveUS7200331B2Eliminating expensive electrical switchWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar-type electromagnetic networksEngineeringLength wave
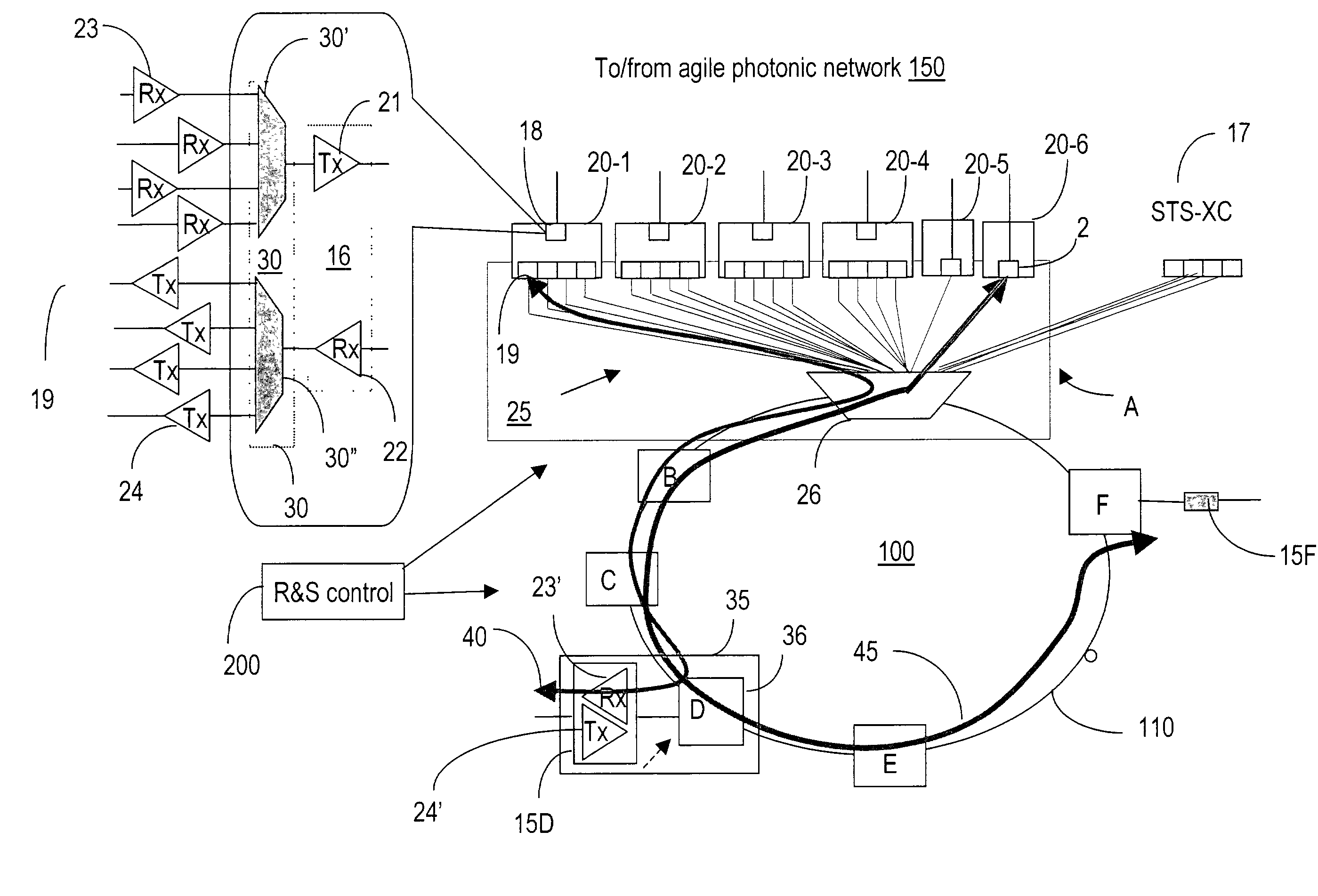
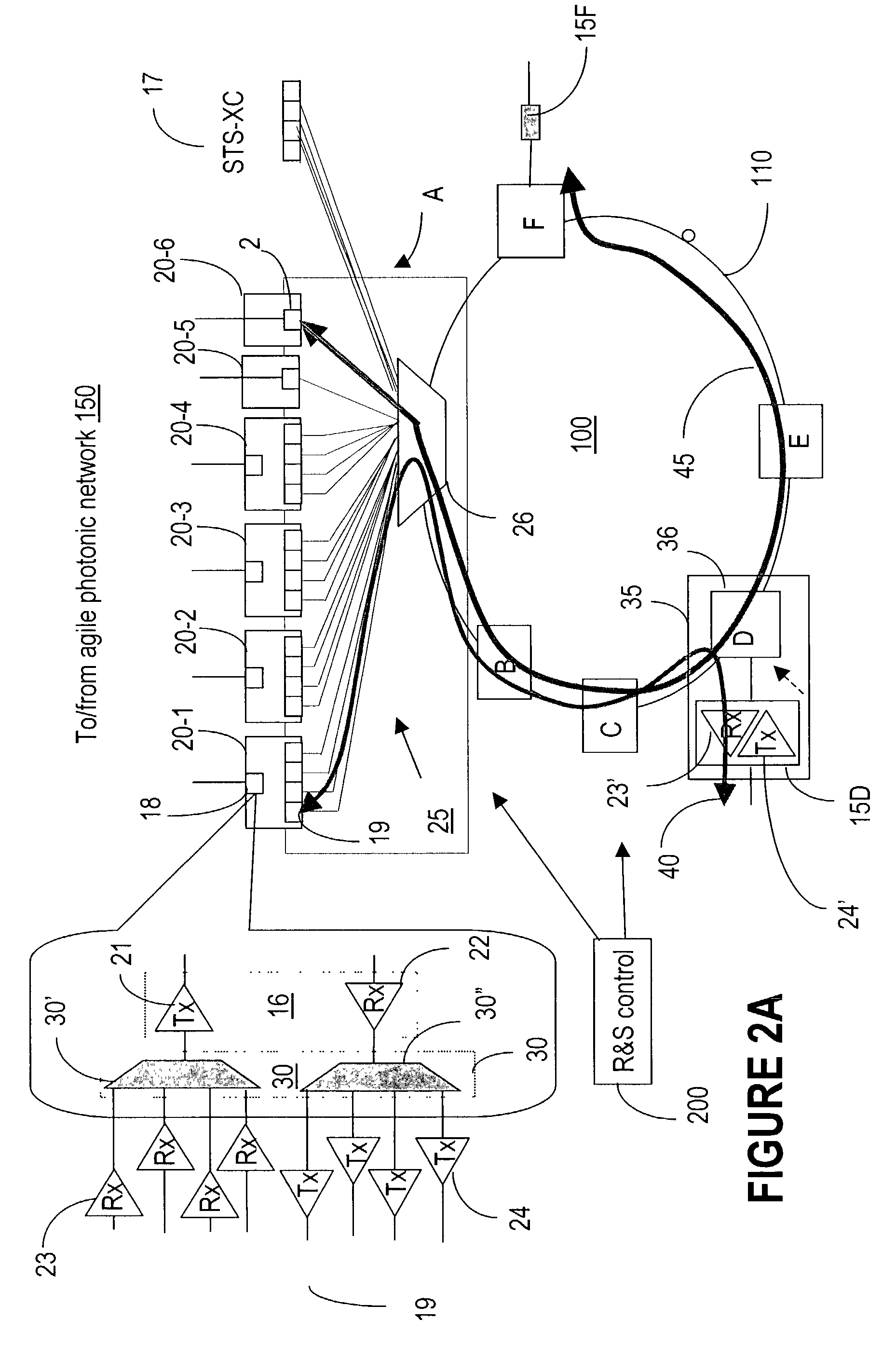
The is directed to extending wavelength routing on a metro network subtended off an optical agile network. Flexibility on the subtended metro network is obtained by either tuning the head-end transmitter on a metro wavelength that is the operating wavelength of the route to a specified tail-end node (tunable source, fixed wavelength-route dependency) or / and tuning a specified route to the metro wavelength (fixed source, tunable wavelength-route dependency). The routes may be tuned at one or both ends.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Wavelength router
InactiveUS6868205B2Flexible routingMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSpectral bandsLength wave
A wavelength router that selectively directs spectral bands between an input port and a set of output ports. The router includes a free-space optical train disposed between the input ports and said output ports, and a routing mechanism. The free-space optical train can include air-spaced elements or can be of generally monolithic construction. The optical train includes a dispersive element such as a diffraction grating, and is configured so that the light from the input port encounters the dispersive element twice before reaching any of the output ports. The routing mechanism includes one or more routing elements and cooperates with the other elements in the optical train to provide optical paths that couple desired subsets of the spectral bands to desired output ports. The routing elements are disposed to intercept the different spectral bands after they have been spatially separated by their first encounter with the dispersive element.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
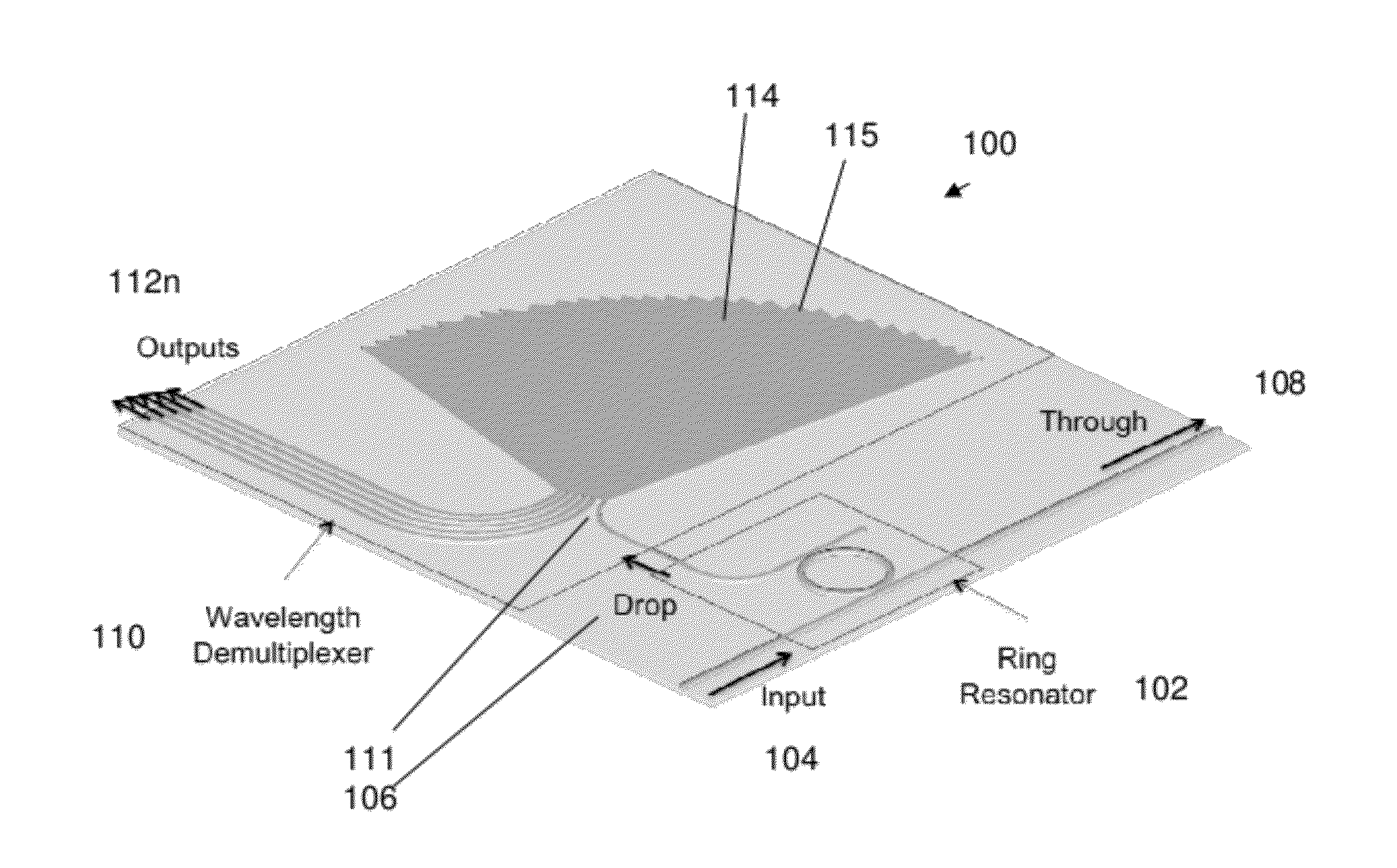
Optical apparatus, method, and applications
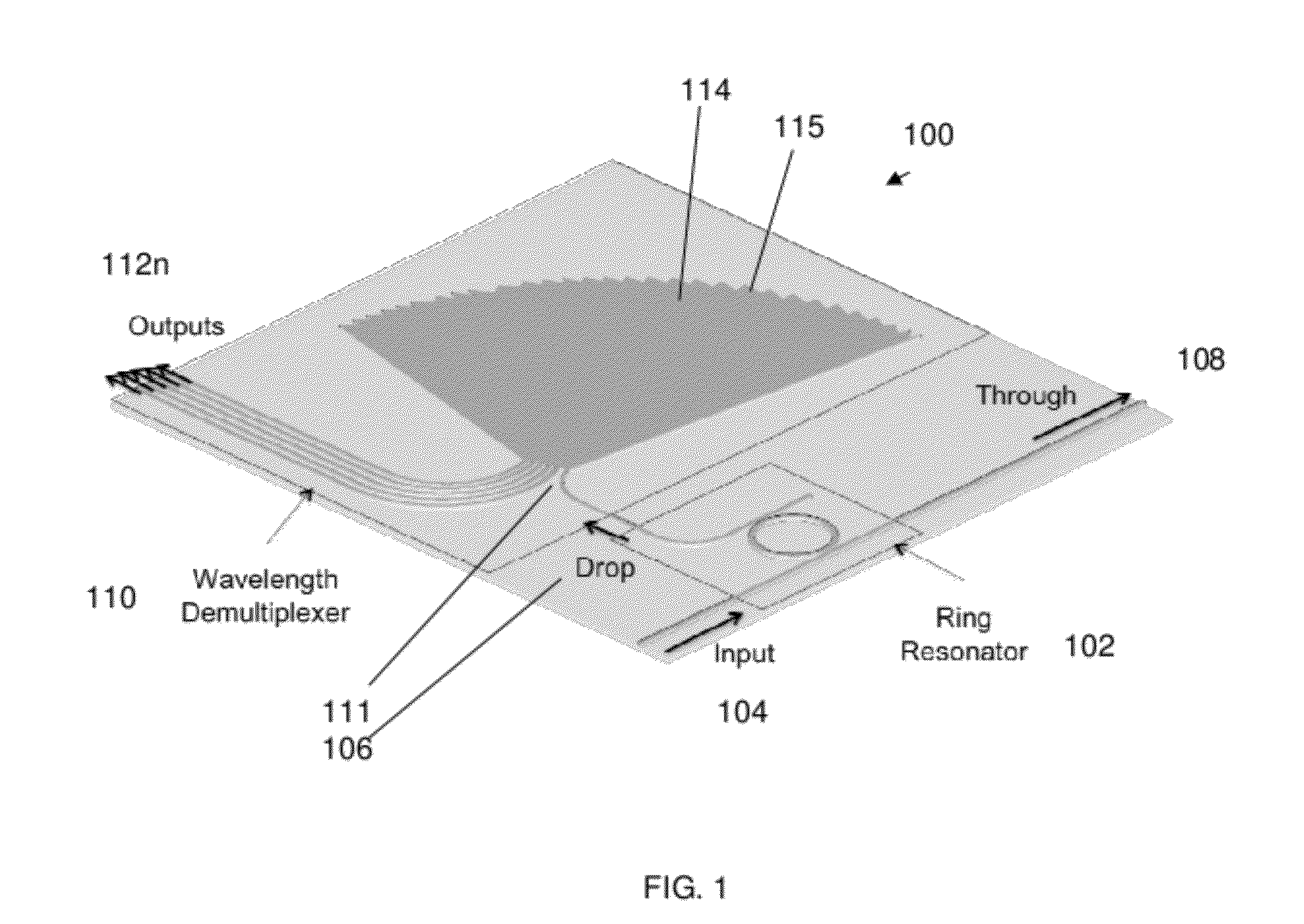
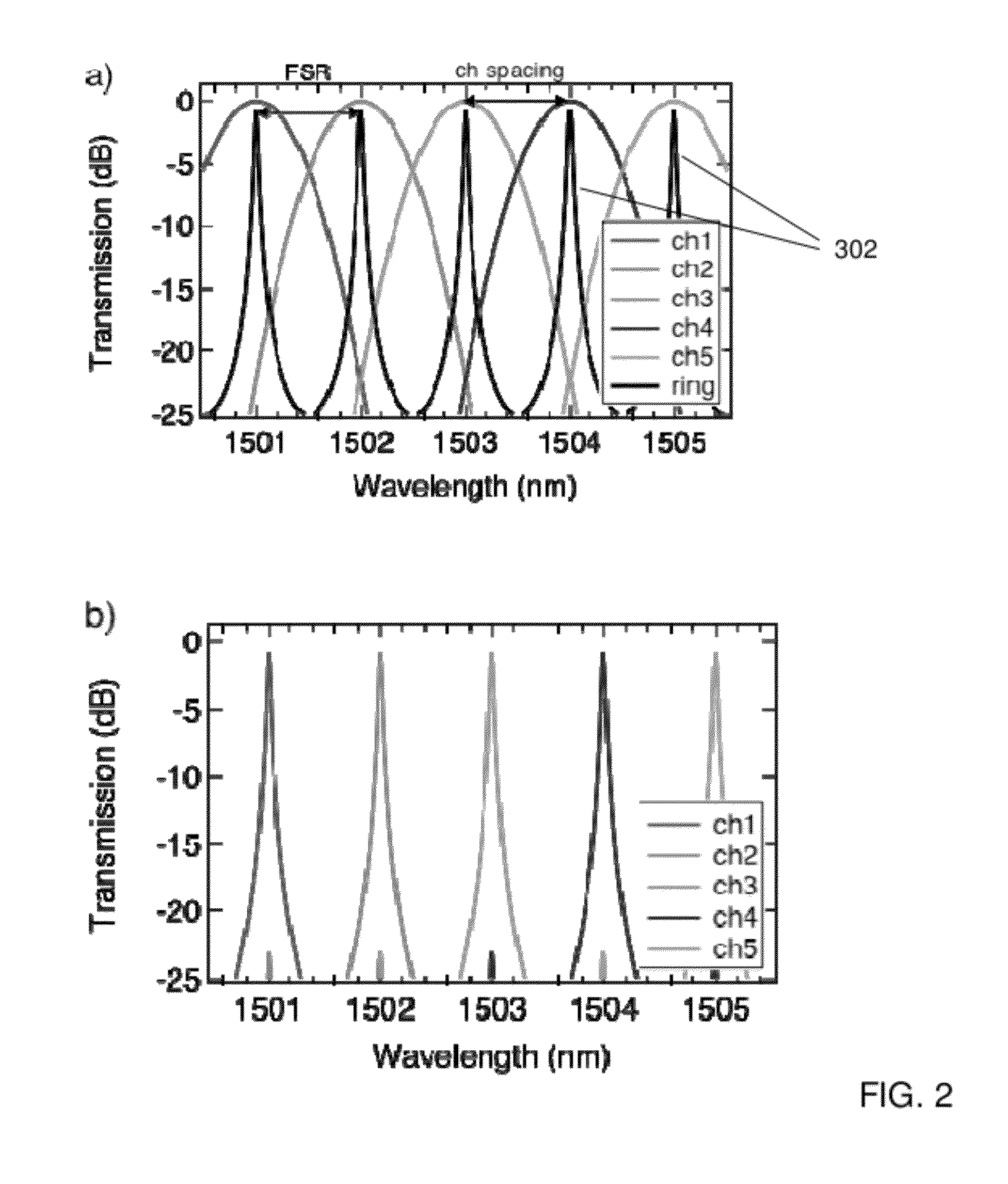
ActiveUS20120177060A1High resolutionEfficient solutionWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexResonant cavityChannel density
A high resolution, wide spectral range, optical apparatus that includes an optical resonator cavity and a wavelength demultiplexer, arrangeable in multiple configurations. A method for increasing the resolution of a wavelength demultiplexer involves inputting light into an optical resonant cavity; inputting a plurality of different resonant output wavelengths to a wavelength demultiplexer; and routing each different resonant wavelength to a different output waveguide of the demultiplexer to generate a demultiplexer output spectrum. The method further involves performing either a time serialization or a space serialization procedure to increase the channel density and fully cover the spectrum of interest.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Optical communication system
InactiveUS7522837B2Highly reliably and flexibly connectLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsGratingCommunications system
An optical communication system is constructed which enables highly reliable and flexible connection to communication nodes connected to a path establishment circuit, by utilizing wavelength-routing characteristics of a path establishment circuit such as an arrayed waveguide grating. The optical communication system has multiple communication nodes having a signal output port and signal input port pair, and a path establishment circuit having multiple optical input ports and multiple optical output ports which are set so that optical signals input from the respective optical input ports are output to predetermined optical output ports corresponding to the wavelengths of the optical signals.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
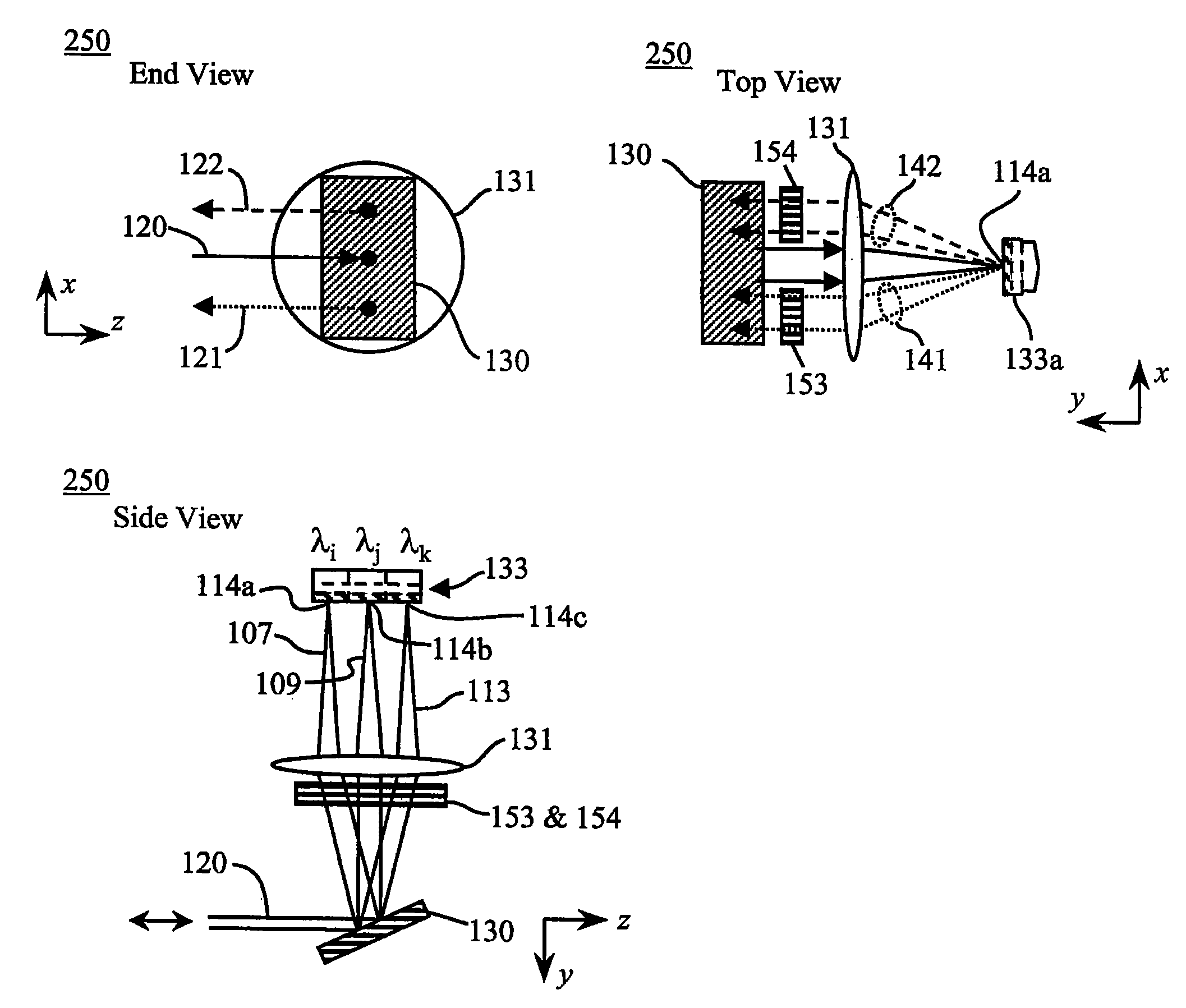
Measuring analytes from an electromagnetic spectrum using a wavelength router
InactiveUS20050124870A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioIncreasing input optical powerRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyAnalyteElectromagnetic spectrum
Weak signals scattered from analytes at multiple wavelengths can be summed to illuminate either a single detector or a multiplicity of detectors, offering the possibility of concentrating the spectral energy on a smaller total detector area. In addition, a method is disclosed whereby a calibration of the resulting signal for a given analyte can be obtained by means of measuring the quantity of water in the sample volume and by means of measuring the salinity of the fluid in the sample volume.
Owner:REDOX BIOMEDICAL
Intelligent wavelength routing optical network node structure supporting link management protocol
InactiveCN1547337ASimple structureLow costData switching by path configurationStar-type electromagnetic networksProcess mechanismEngineering
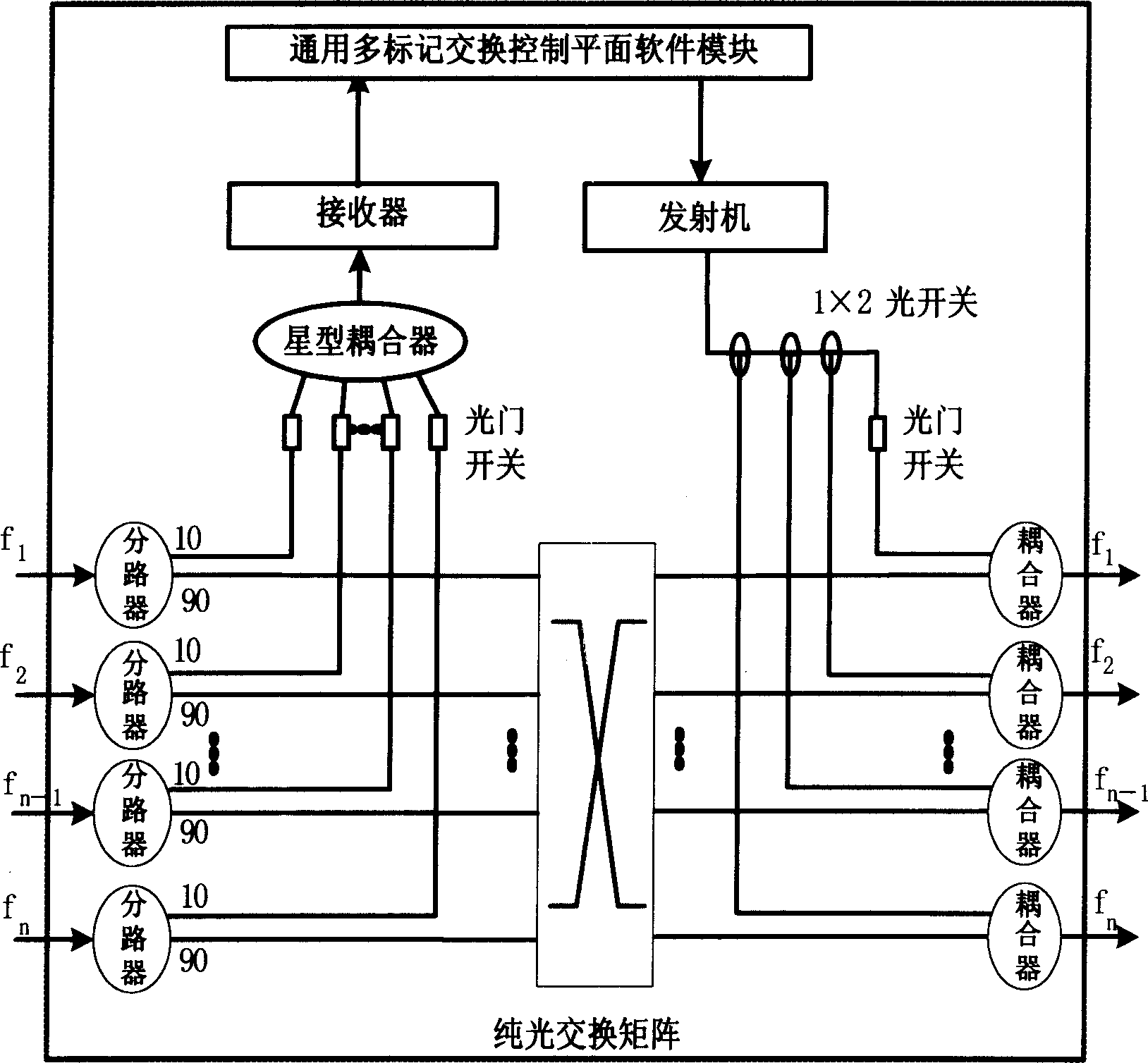
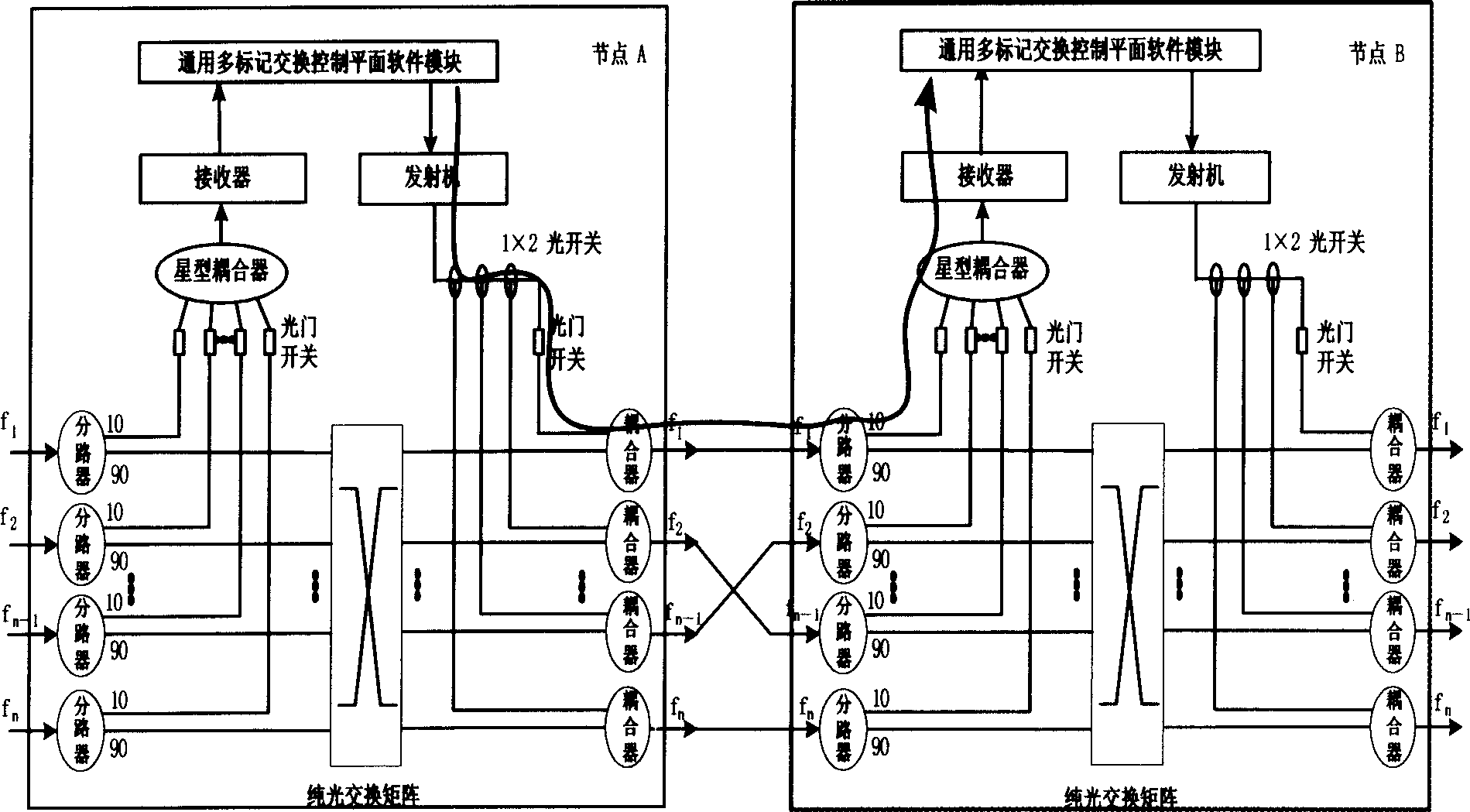
The invention discloses a structure with intelligent wavelength routing optical network nodes which supports the link management protocol, the transmit-couple- exchange structures are added to the present simple optical exchanger, the input part of the transmit-couple- exchange structure is made up of several 1x2 branching unit, the optical door switches with the same quantity, one star-coupler and receiver; the output part is made up of one transmitter, several 1x2 optical switches, one optical door switch and several 2x1 coupler. The message format controlled and transmitted by control plane software modules with universal multi-mark exchange is in line with the data package format and processing mechanism defined by the link management protocol (LMP), the transmit-couple-exchange structure ensures that the data from control plane software modules can select any output optical fiber through the node and be transmitted to the others nodes. The invention can support adjacent nodes automatically verify and detect the relation of optical fiber connection between two adjacent nodes, the corresponding relation of all ports on one node can be automatically detected by the follow-up route signal command and transmitting and coupling structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Optical Transport Switching Node with Framer
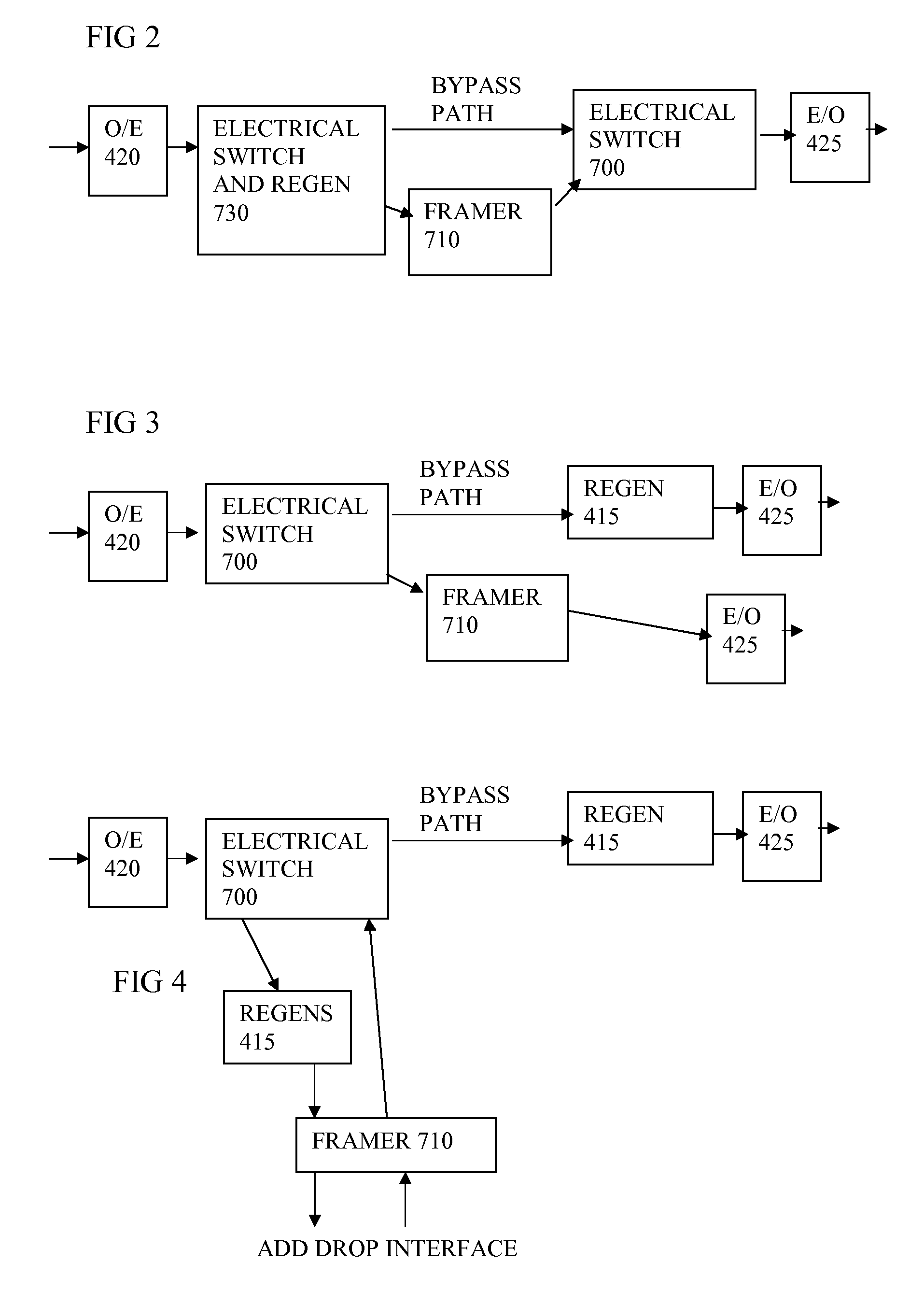
InactiveUS20120250580A1Reduce power consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCommunications systemControl signal
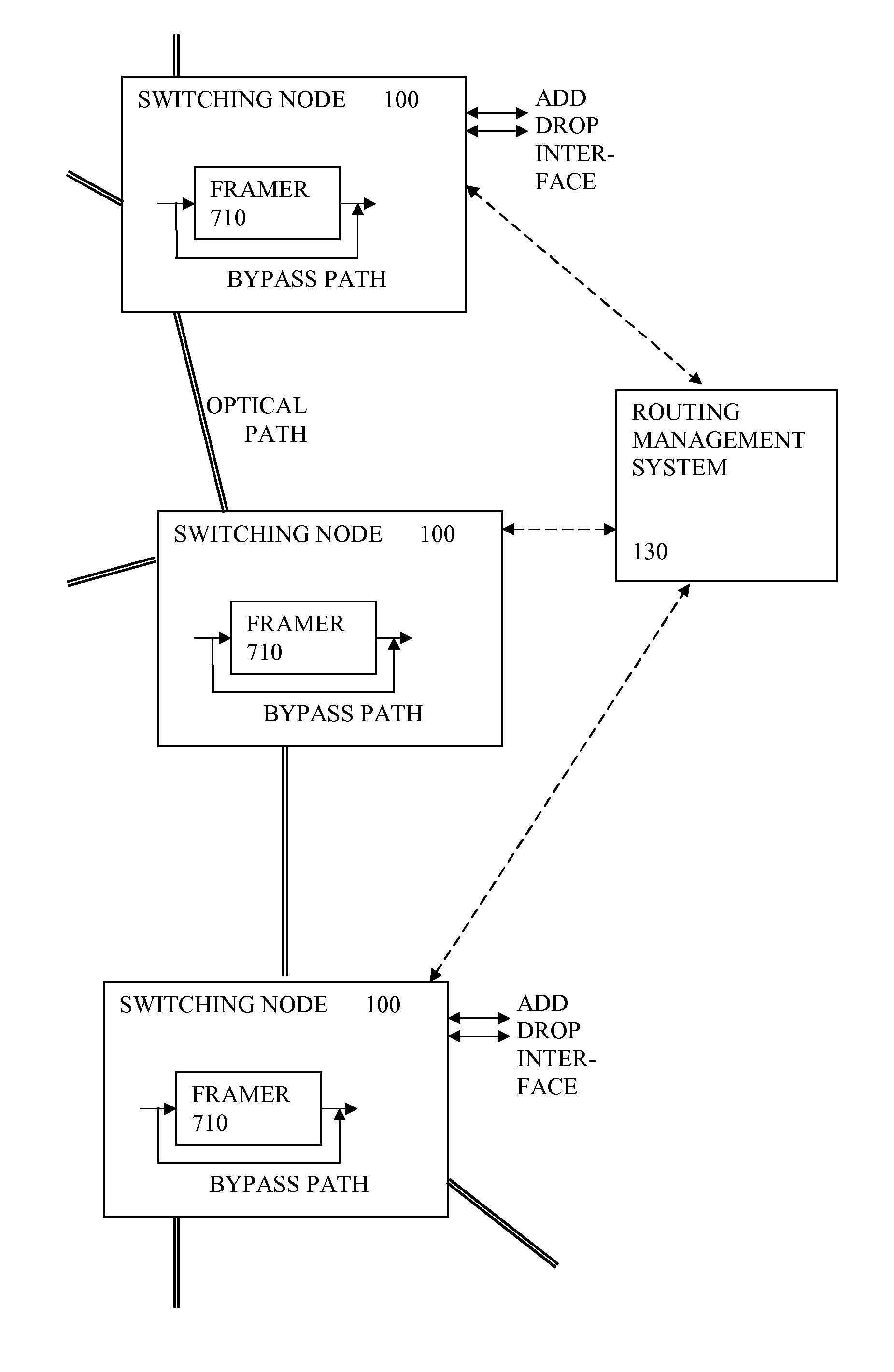
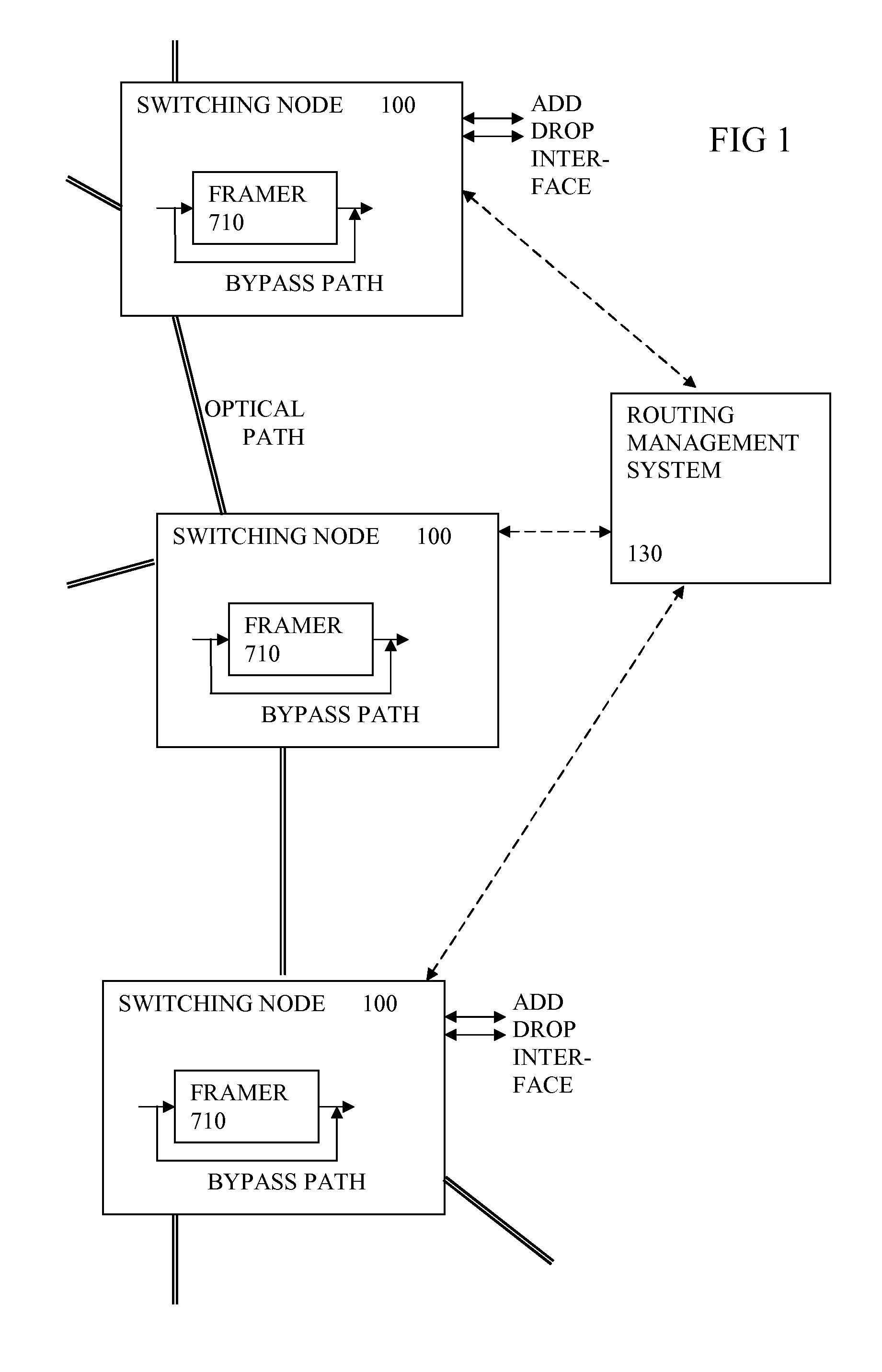
A switching node for an optical communication system has an electrical switch, coupled to switch electrical signals from an input converter to a selected one of the outputs, and has a framer for reading or writing optical transport overhead information from or to the electrical signals. A bypass path is provided so that at least some of the signals being switched can bypass the framer. This can enable each node to be more efficient or handle more signals, since the framer no longer has to process all the signals. A reduction in power consumption can result. A method of configuring the switching node can involve a management system receiving information about the network, determining a new wavelength routing configuration and sending control signals to the node to configure the switches and control which signals use the bypass path.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for planning dynamic business wavelength route optical network
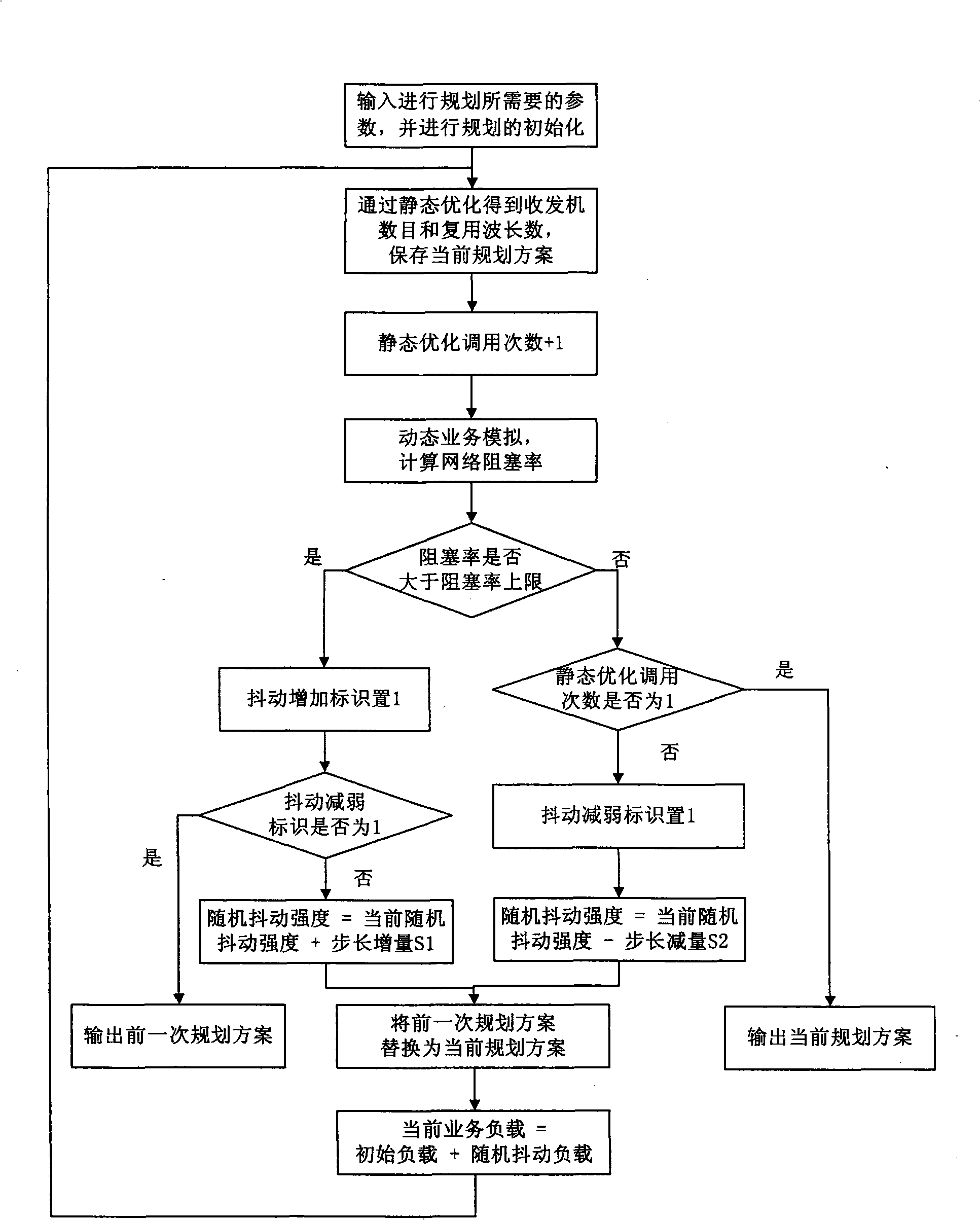
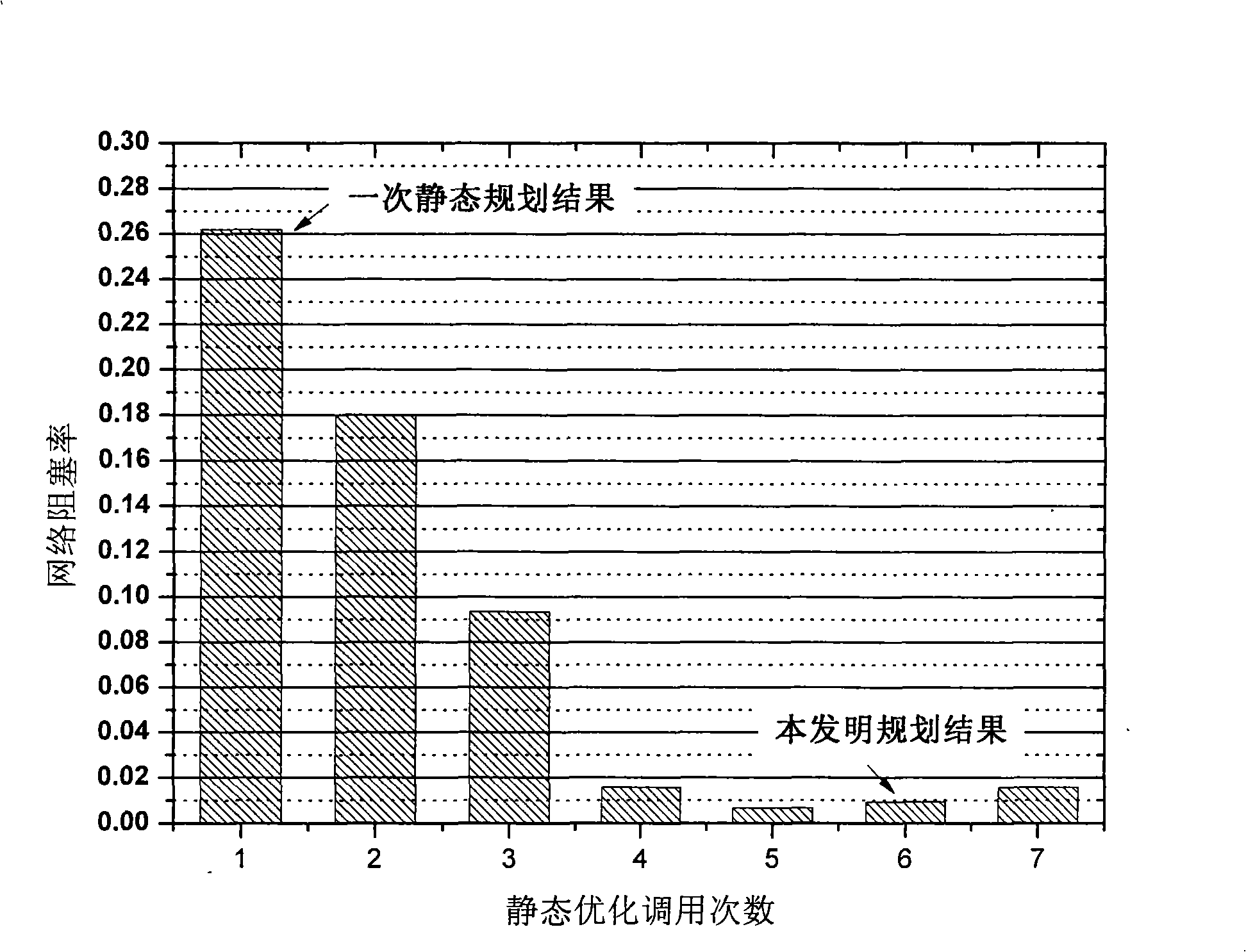
InactiveCN101409596AReduce blocking rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsStatic optimizationTransceiver
The invention relates to a method for panning a wavelength routing optical-fiber network of dynamic state service, belonging to the technical field of network communication. Parameters needed by the plan of the optical-fiber network are set and input, the number of transceivers of each optical cross connect node and multiplexing wavelength value of each optical fiber in an optimal optical-fiber network in a static state are obtained by using a static optimization method and taken as the input of dynamic service analogy, and then the blocking rate of the network is obtained. The strength of service randomized jitter is regulated according to the blocking rate of the network, and the plan of the optical-fiber network can be completed by using the static optimization method for a plurality of times. The method has the advantages that based on the static optimization method, the method can ensure the overall optimization character of the panning results, meanwhile, the wavelength routing optical-fiber network which is obtained by the plan can adapt to service dynamic performance through the verification of the blocking rate, thus ensuring the blocking rate of lower network of the dynamic service to be lower than the upper limit of the blocking rate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
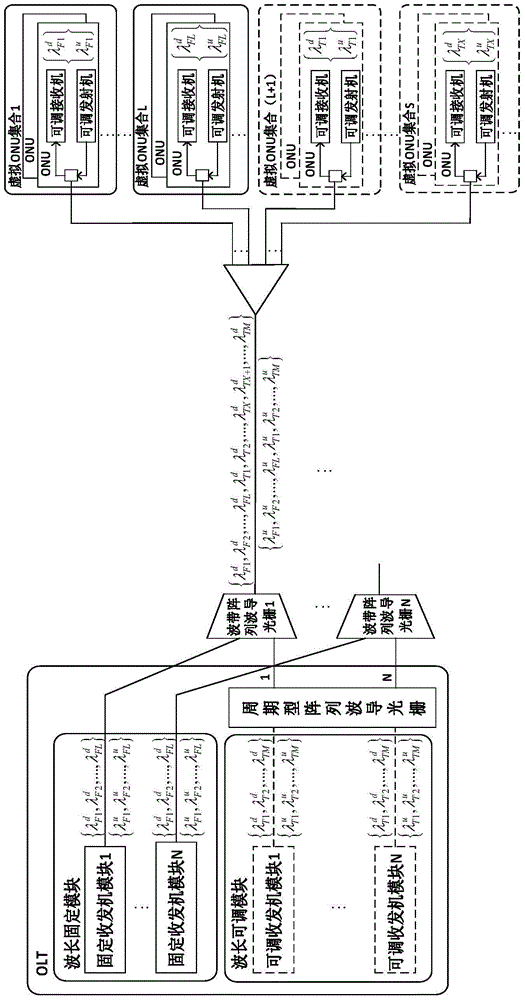
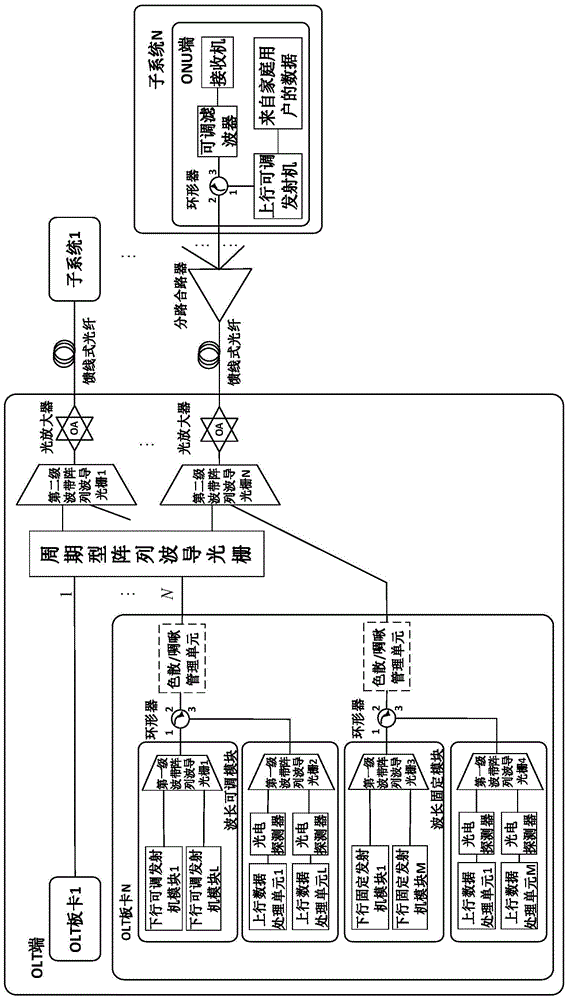
TWDM-PON (Time Wavelength Division Multiplexing-Passive Optical Network) system and method based on wavelength-fixed and wavelength-adjustable lasers
ActiveCN105007546APerfectly compatibleConducive to smooth upgradeMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingTransceiver
The invention provides a TWDM-PON (Time Wavelength Division Multiplexing-Passive Optical Network) system based on wavelength-fixed and wavelength-adjustable lasers. The TWDM-PON system based on the wavelength-fixed and wavelength-adjustable lasers comprises a plurality of sub-systems, wherein the sub-systems comprise optical line terminals, wavelength routing modules, waveband demultiplexing-multiplexing modules, light amplifiers, feeder line optical fibers and sub-passive optical networks. At the optical line terminal, through combination of a fixed transceiver module and an adjustable transceiver module, the most basic communication demand of a network is ensured at a fixed wavelength, and resources are allocated flexibly in the network through the adjustable transceiver module in order to meet the user's flow requirement varying in real time of a user. The invention also provides a TWDM-PON method based on the wavelength-fixed and wavelength-adjustable lasers. Through adoption of the method, flexible resource allocation can be realized, and compatibility with an existing TWDM-PON network can be realized. The method has the advantages of low cost and low energy consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods and apparatuses for DWDM multi-mode switching router and dynamic multi-mode configuration and reconfiguration
ActiveUS9306698B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer architectureComputer module
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
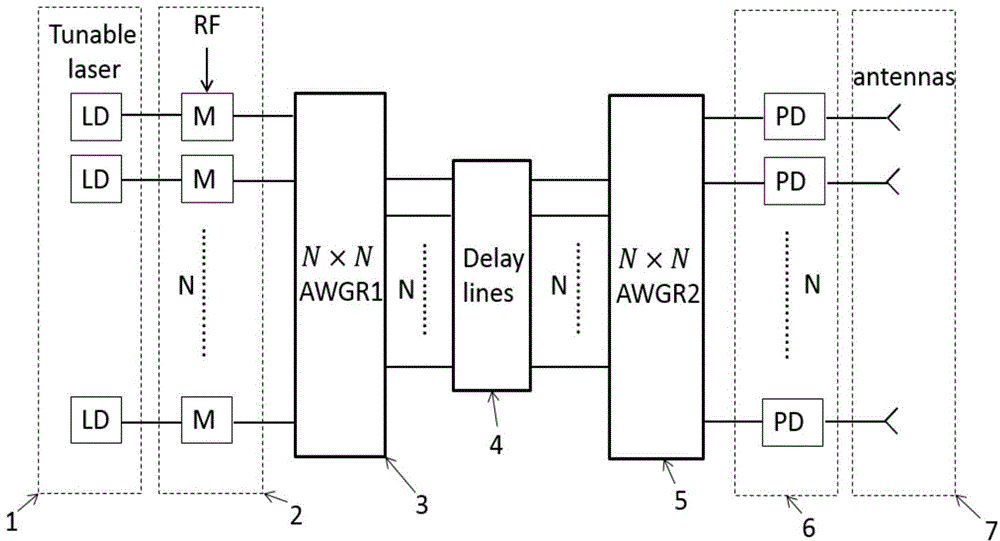
Optically controlled phased array radar system based on wavelength routing
The invention discloses an optically controlled phased array radar system based on wavelength routing. N tunable semiconductor lasers emit multiple paths of optical wave signals different in wavelength; microwave signals are loaded and modulated through respective modulators, transmitted to a first array waveguide grating router, transmitted to a second array waveguide grating router through a delayed linear array and transmitted to N semiconductor detectors for demodulation; the semiconductor detectors emit the demodulated microwave signals through an antenna. The tunable semiconductor lasers are used to change the wavelengths for switching the delayed linear array, so that the use of a large amount of optical switches is avoided; with an integrated optics method, an overlapping problem of fiber Bragg gratings is solved, the two array waveguide grating routers and the delayed linear array are integrated on the same substrate, and the precision of the delay line length is guaranteed, so that the stability of the system is improved, the cost is reduced, and the system has the advantages of small size, low loss, light mass, high precision, electromagnetic interference resistance and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Equalizing optical wavelength routers
InactiveUS7298540B2Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveWavelength routing
A dynamic equalizing optical channel router includes an input port for receiving a wavelength division multiplexed composite optical signal comprising a plurality of channels; at least one output port; a diffraction grating optically coupled to the input and output ports; a lens optically coupled to the diffraction grating at a side opposite to the input and output ports; an array of steering devices optically coupled to the lens at a side opposite to the diffraction grating, wherein each channel is reflected by a different steering device of the array; and a plurality of attenuators, wherein each channel reflected by the array traverses one of the attenuators and the diffraction grating to the at least one output port. The router is able to dynamically adjust optical intensity of each wavelength channel by a different amount while also performing the function of wavelength routing.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Full-light controlled optical switch system
InactiveCN101237294AImprove performanceRealize the function of optical switchWavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionContinuous lightControl signal
The invention relates to an all-optical controlled optical switch system, wherein, a control signal is continuous light with different wavelengths, and can realize the output of input optical signals from one or a plurality of output ports. Input signal light is divided into two parts; when control light exists, the optical information of one part of input signal light is firstly converted onto the control light through a wavelength converter, the control light with different wavelengths passes through a wavelength routing module, then is separated, and is output from corresponding ports of the wavelength routing module; the other part of signal light is changed into the continuous light through a traveling wave semi-conductor optical amplifier, split through a coupler, and then is input into each second-stage wavelength converter; the control light with the information and the continuous light the wavelength of which is the same as that of the input signal light undergo second wavelength transformation in each second-stage wavelength converter, and the output of the second wavelength converters is the output of the all-optical controlled optical switch system. The invention solves the problem of the all-optical controlled optical switch.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for configuring regenerators in wavelength division multiplexing optical network
InactiveCN102523170ASmall amount of calculationReduce blocking rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical packetLength wave
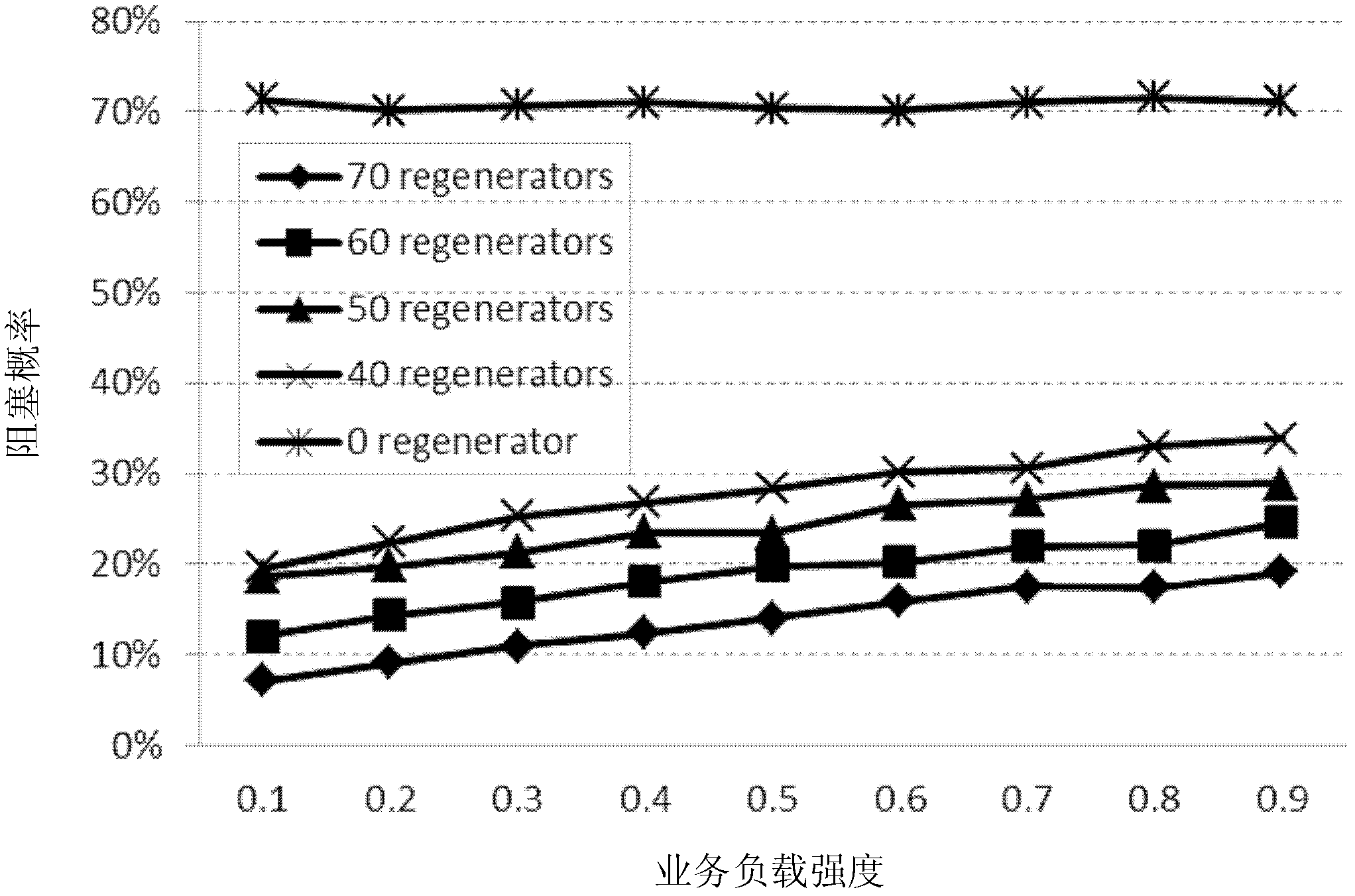
The invention discloses a method for configuring regenerators in a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical network. In the method, heuristic linear programming and integer linear programming are respectively used for determining the route node positions of regenerators configured in a network and the quantity of regenerators configured on each node. In a known network topology, when the sum of configurable regenerators is limited, the regenerators are reasonably configured by adopting the method, so that the limitation of optical fiber physical transmission impairments is lowered, and the rate of network congestion caused by the reason that a target node can not correctly recover the original information is reduced. The method is not related to network service types, and by adopting the method, the minimum conservatism that the network is not related to network can be obtained. Besides, as the method is not related to network exchange type, the configuration result of the regenerators in the WDM network, which is obtained by adopting the method, can be applied to not only a wavelength routing network but also an optical packet switching network.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Methods and system for quantum key distribution over multi-user WDM network with wavelength routing
ActiveCN101208890AImprove communication efficiencyWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhotonic quantum communicationNetwork linkLength wave
A system and a method for quantum key distribution over a multi-user wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) network are disclosed. The system comprises a tunable or multi-wavelength transmitter; a plurality of receivers, each assigned a receiving-wavelength; and a multi-user WDM network linking the transmitter to the receivers. The transmitter can select a receiver among the receivers to be communicated therewith and transmit quantum signals to the selected receiver over the WDM network. The quantum signals are at a wavelength equal to a receiving-wavelength of the receiver. Therefore the WDM network allows quantum signals to be communicated between the transmitter and the receivers by wavelength routing.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
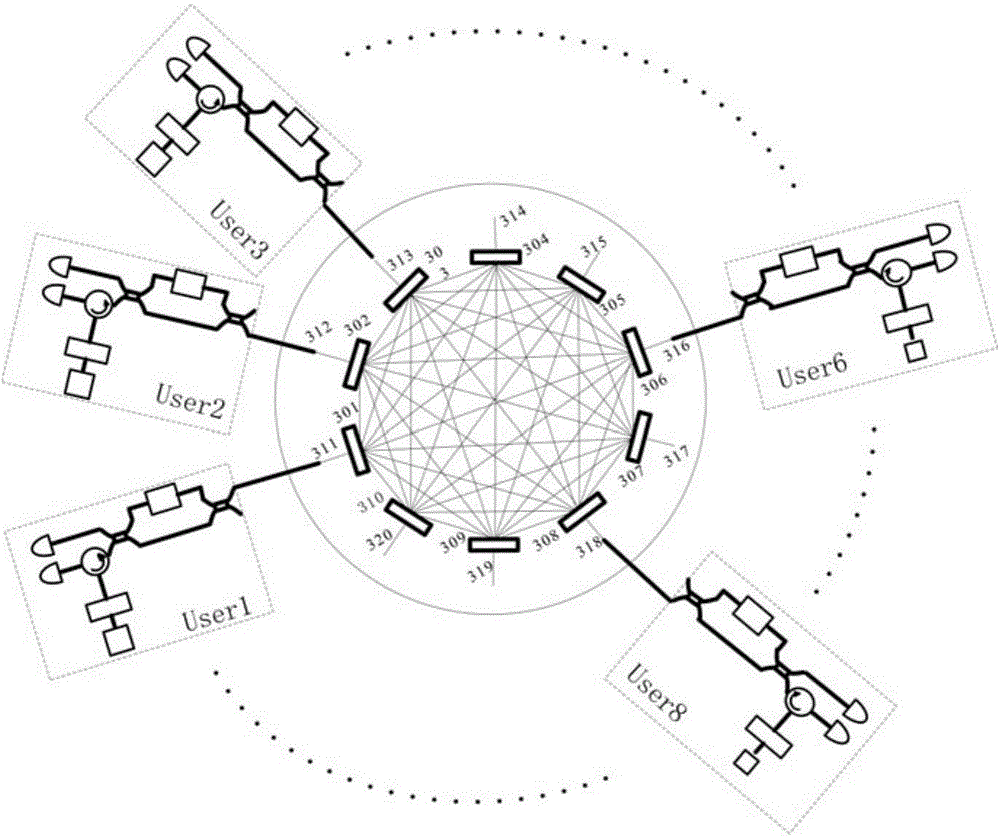
Limited wavelength all-to-all wavelength routing network configuration
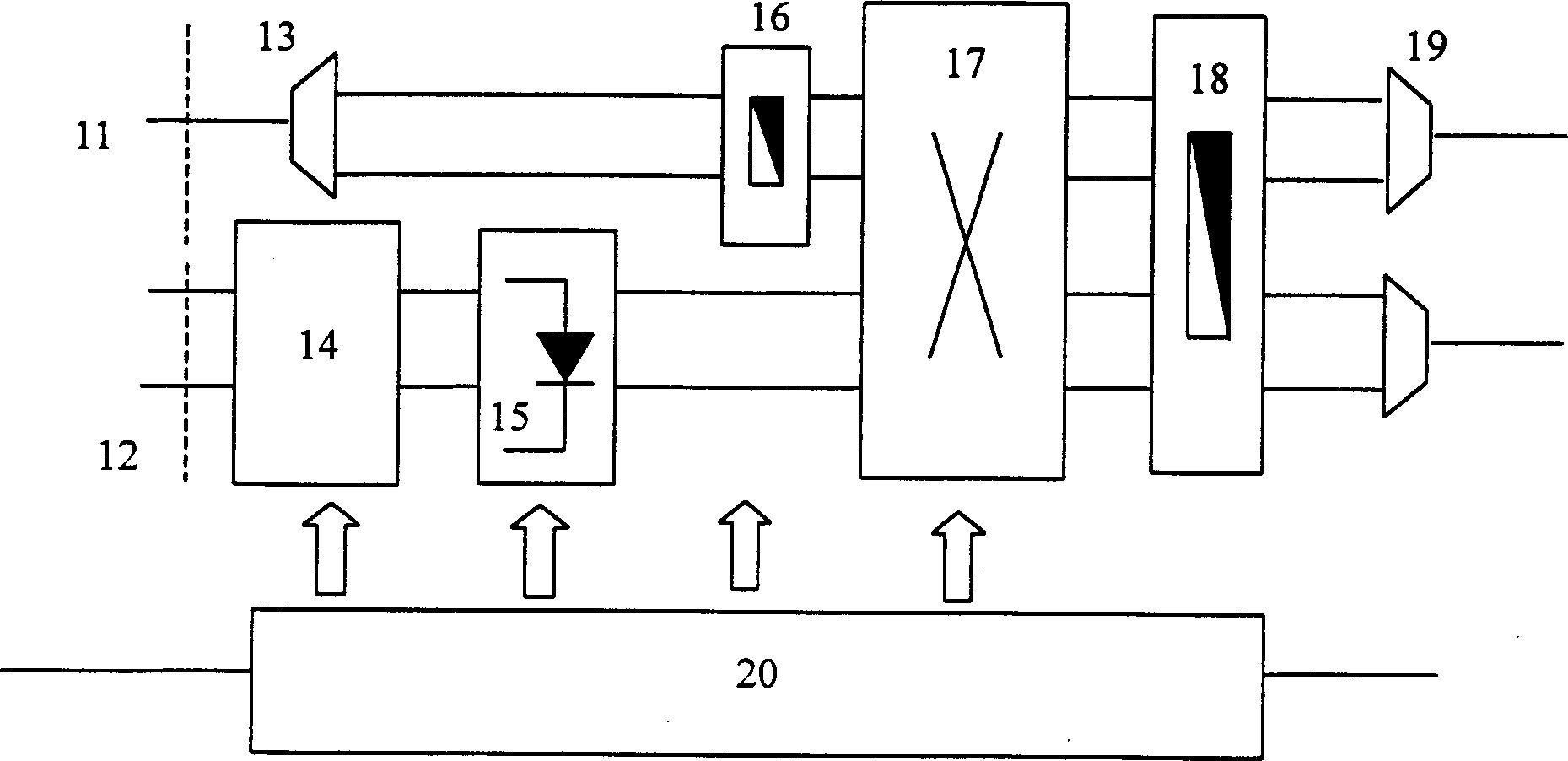
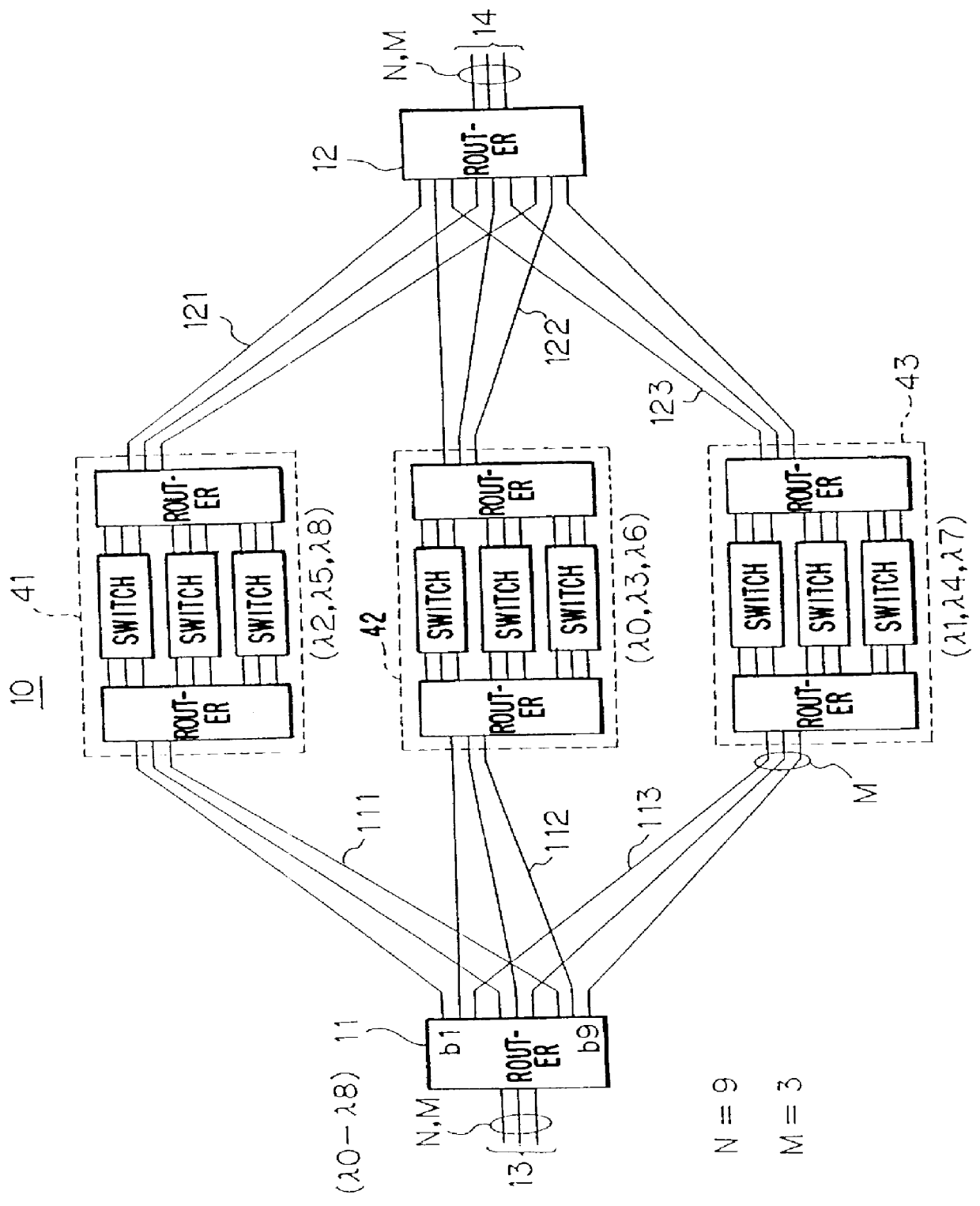
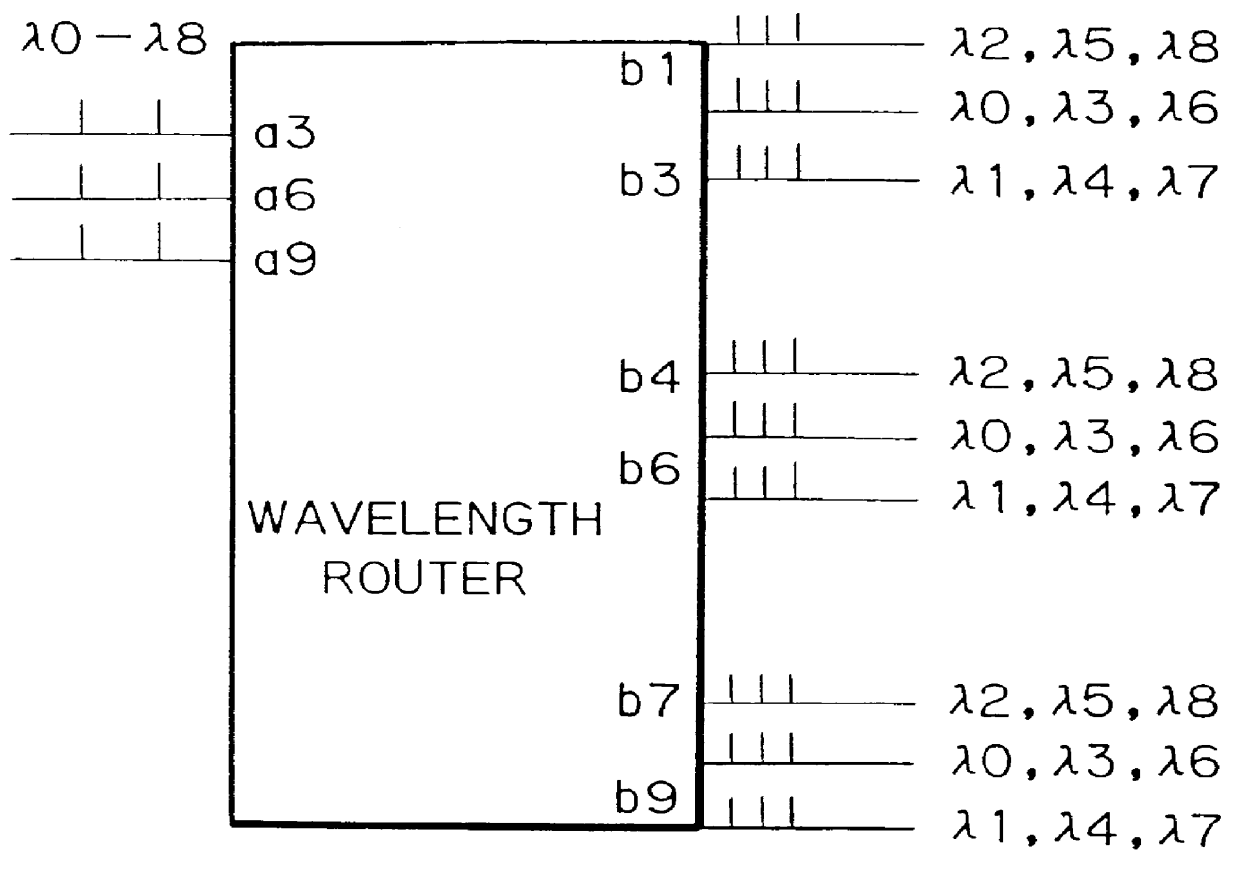
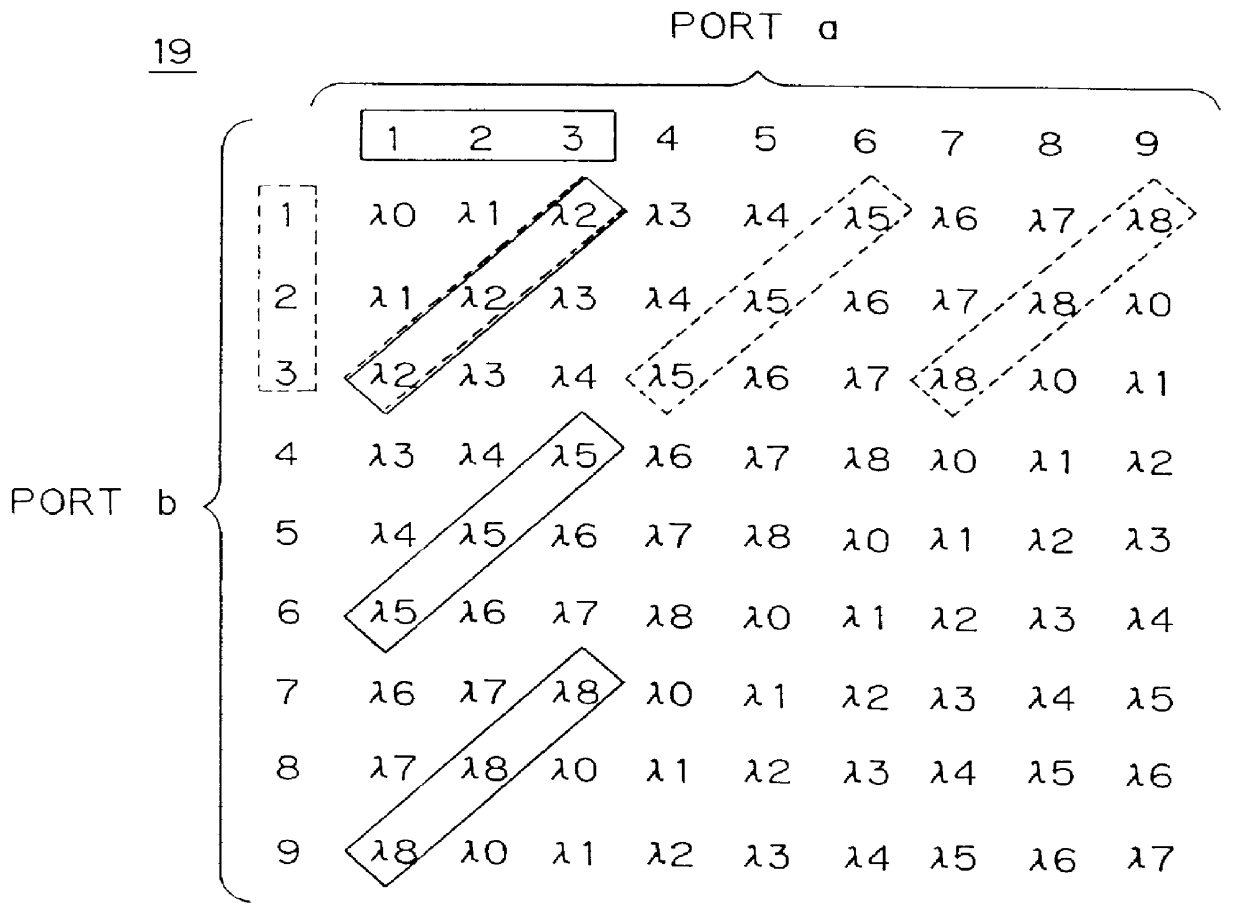
ActiveUS9401774B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveWavelength routing
A network configuration provides arbitration-free all-to-all connection between the nodes of the network utilizing wavelength routing devices and utilizing a limited number of wavelengths for routing optical signals to the nodes of the network.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE DIRECTOR NAT SECURITY AGENCY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com