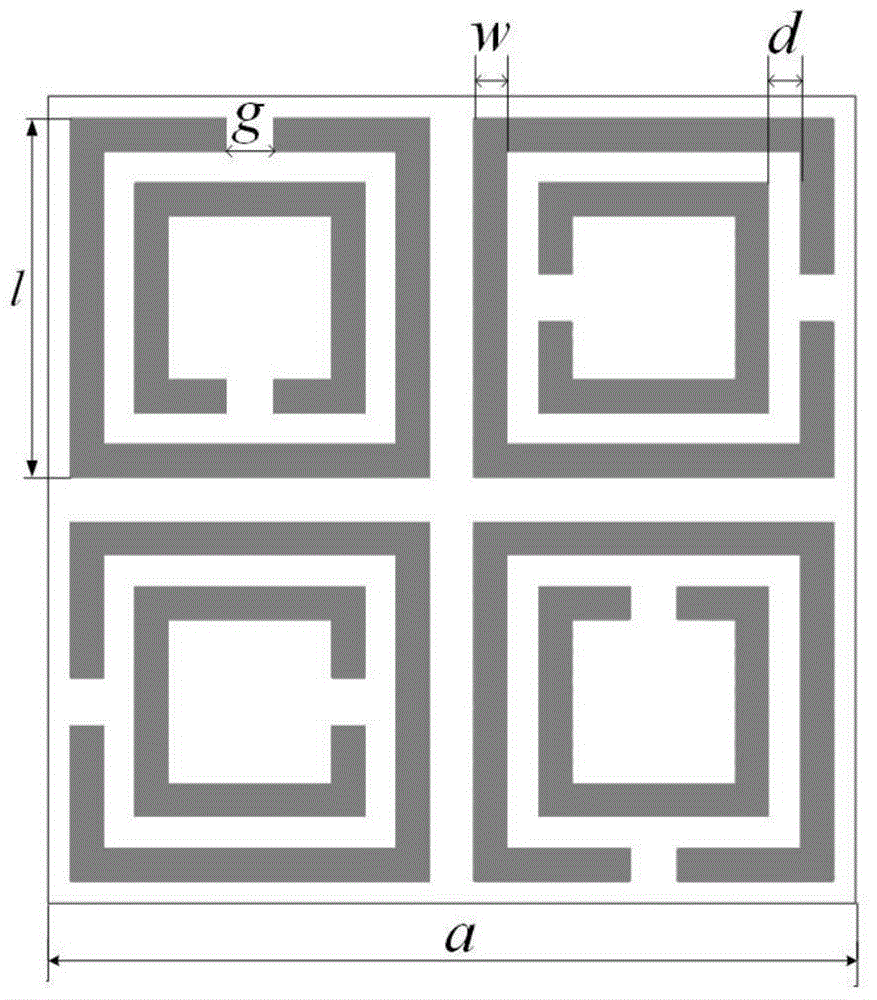
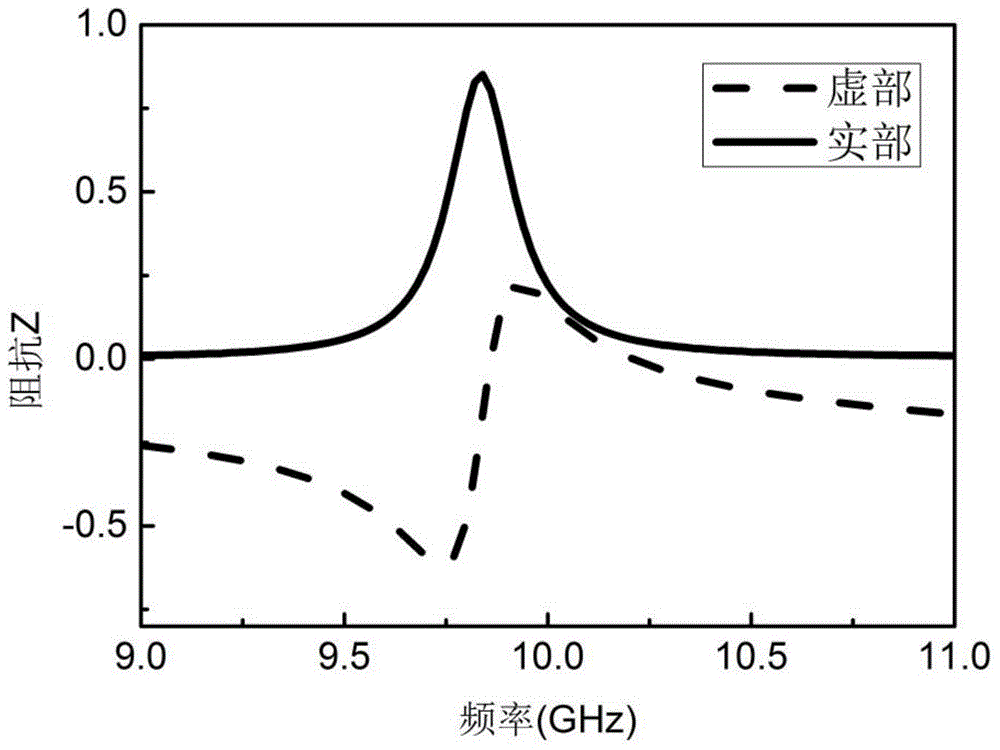
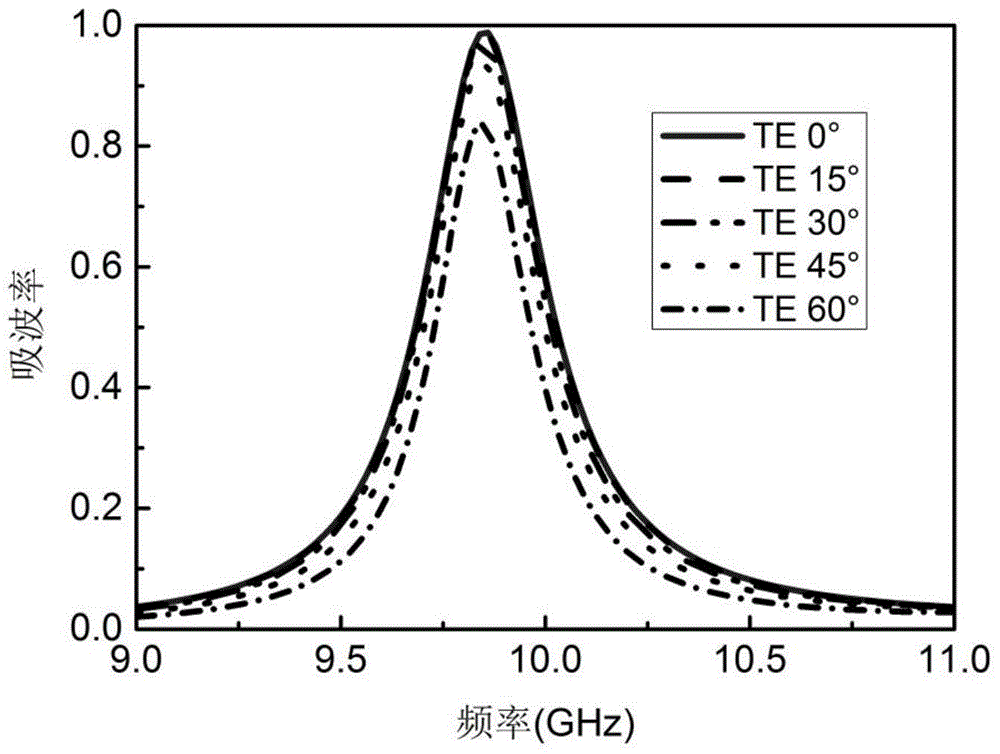
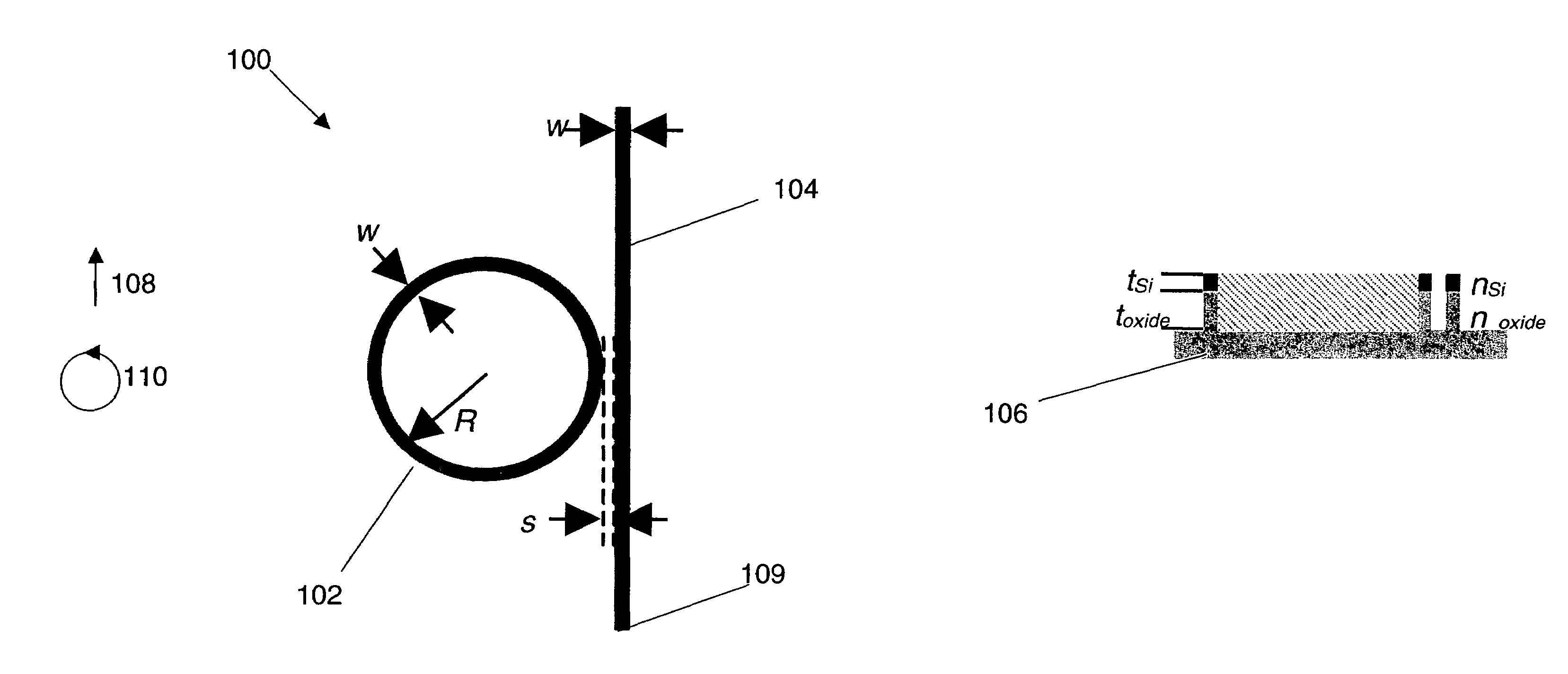
Patents
Literature
537 results about "Split-ring resonator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
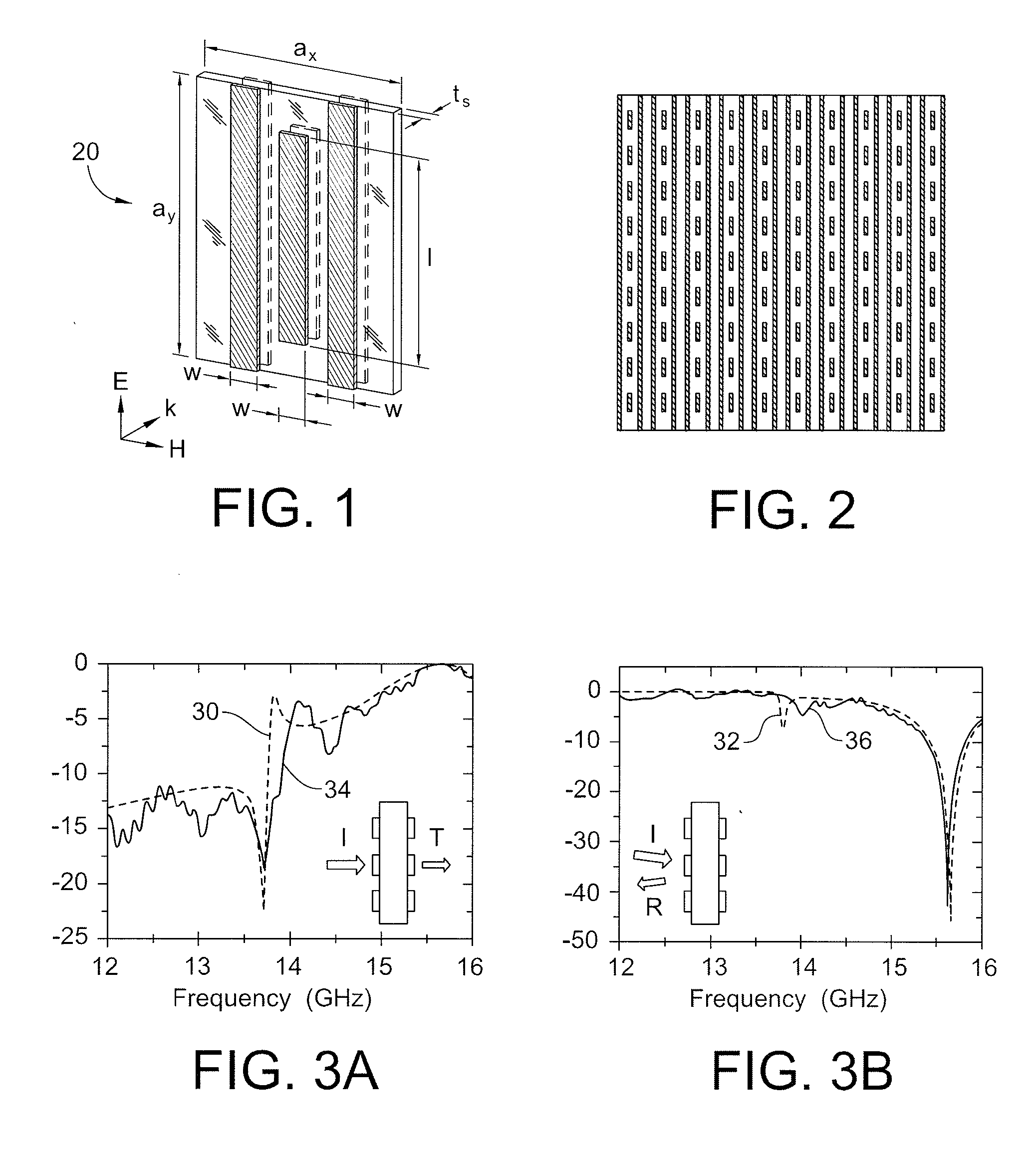
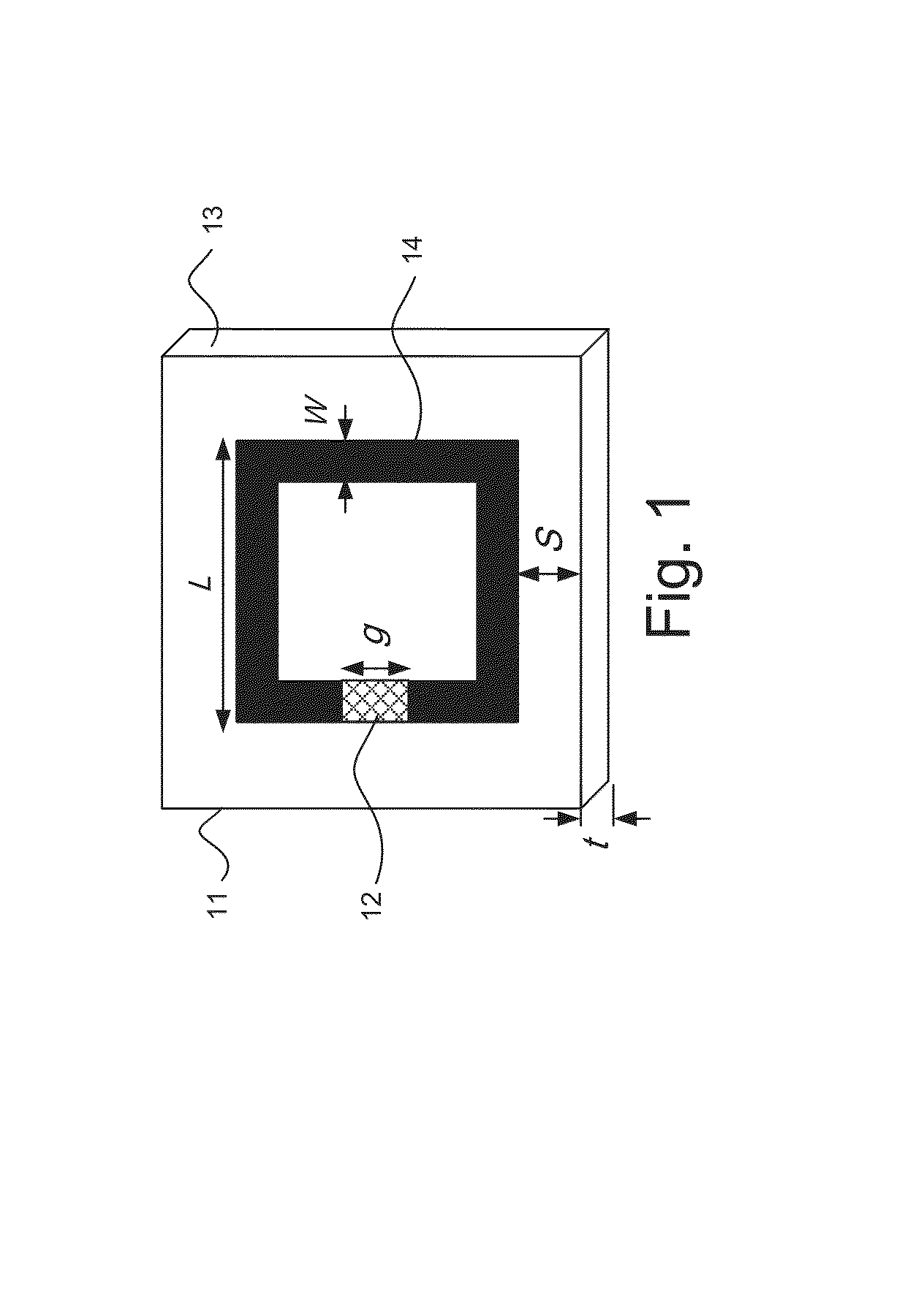
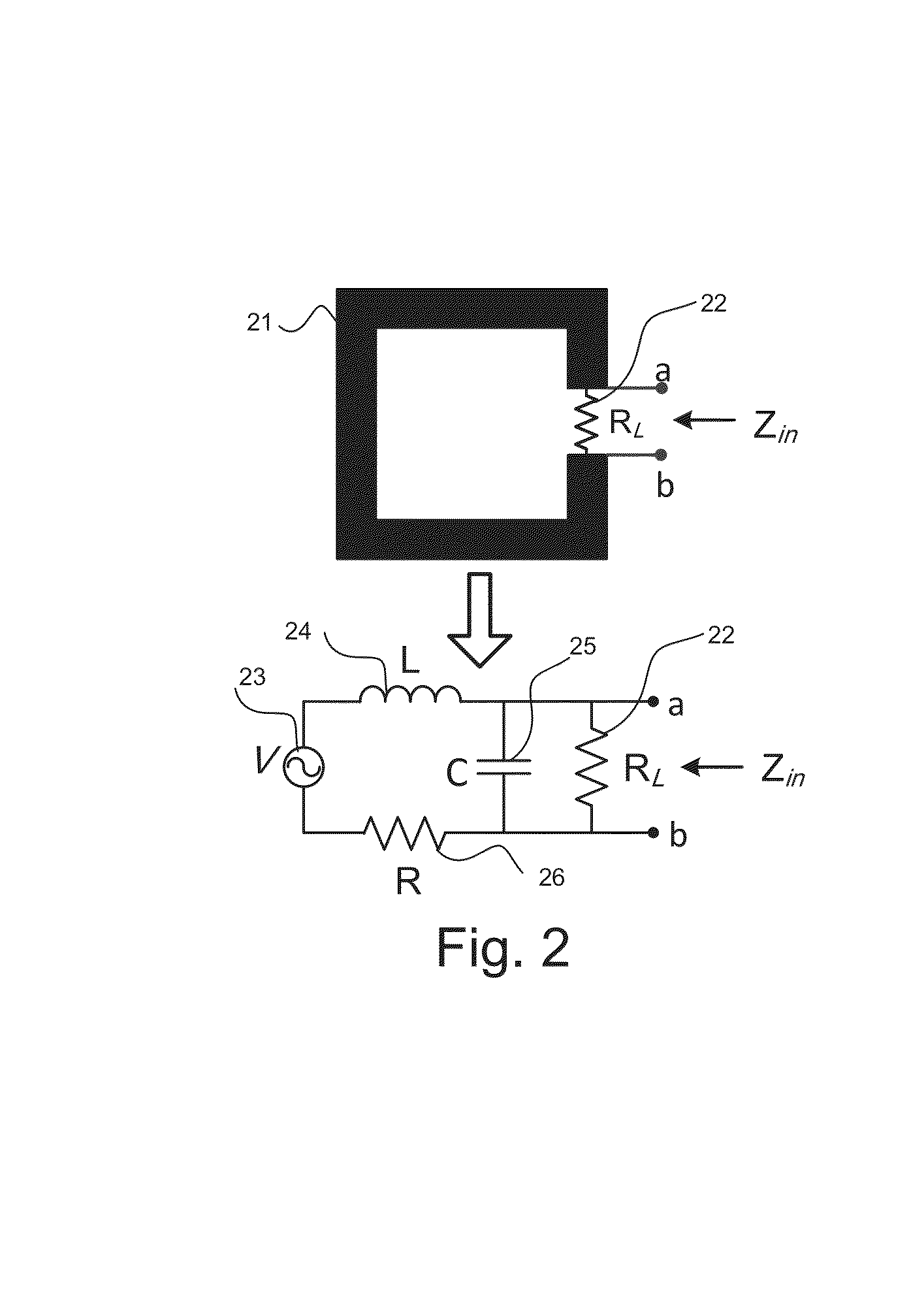
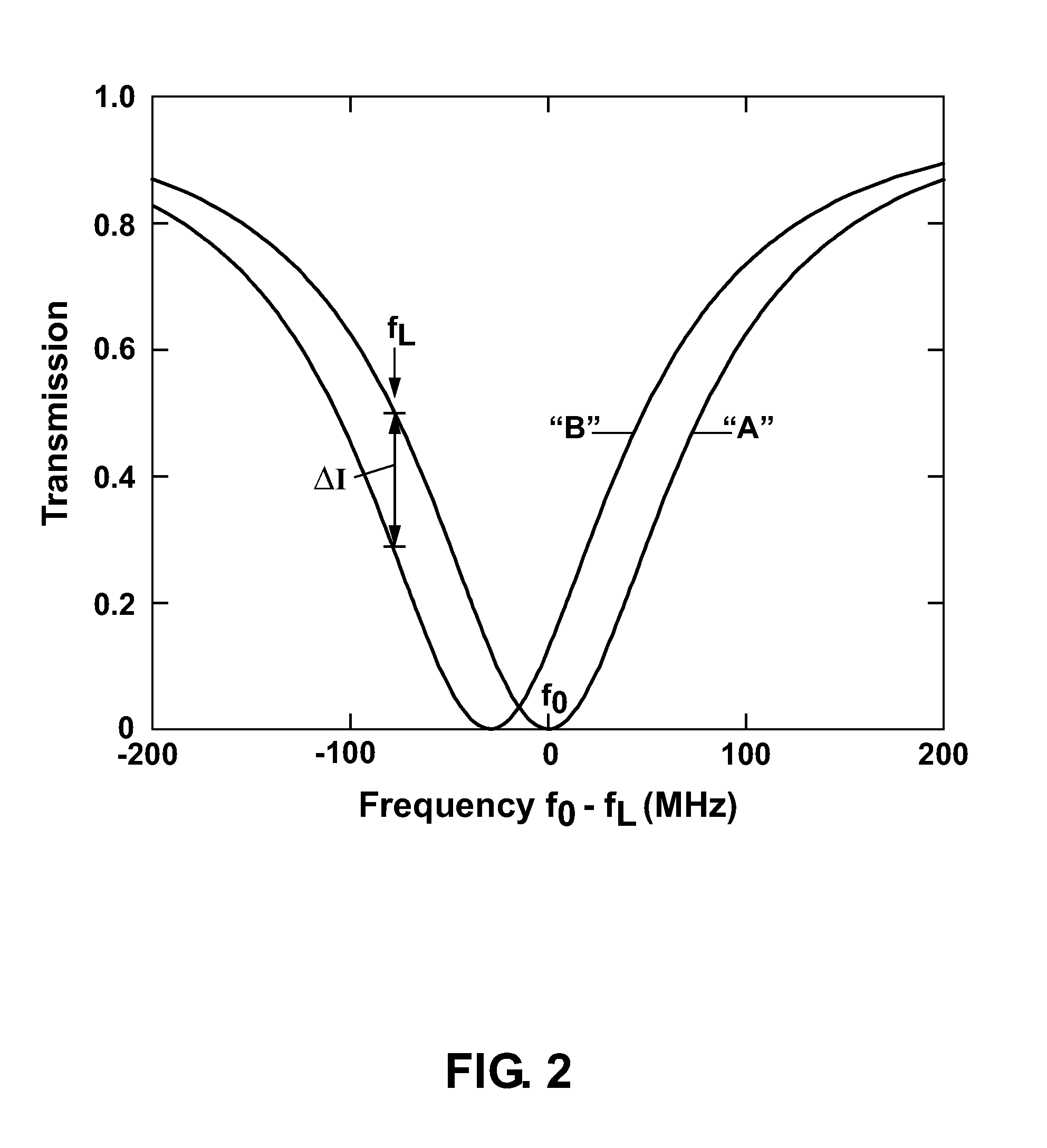
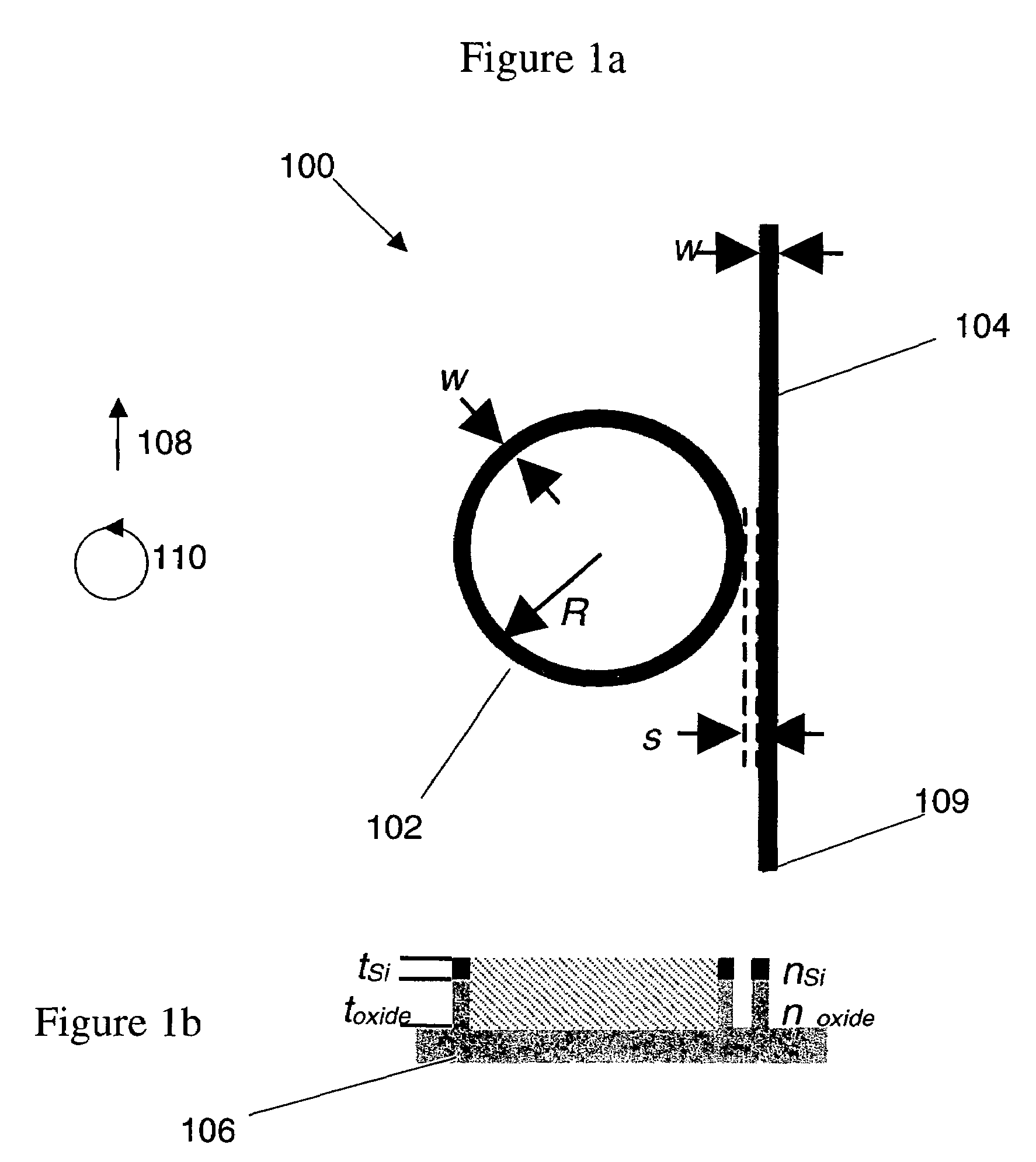
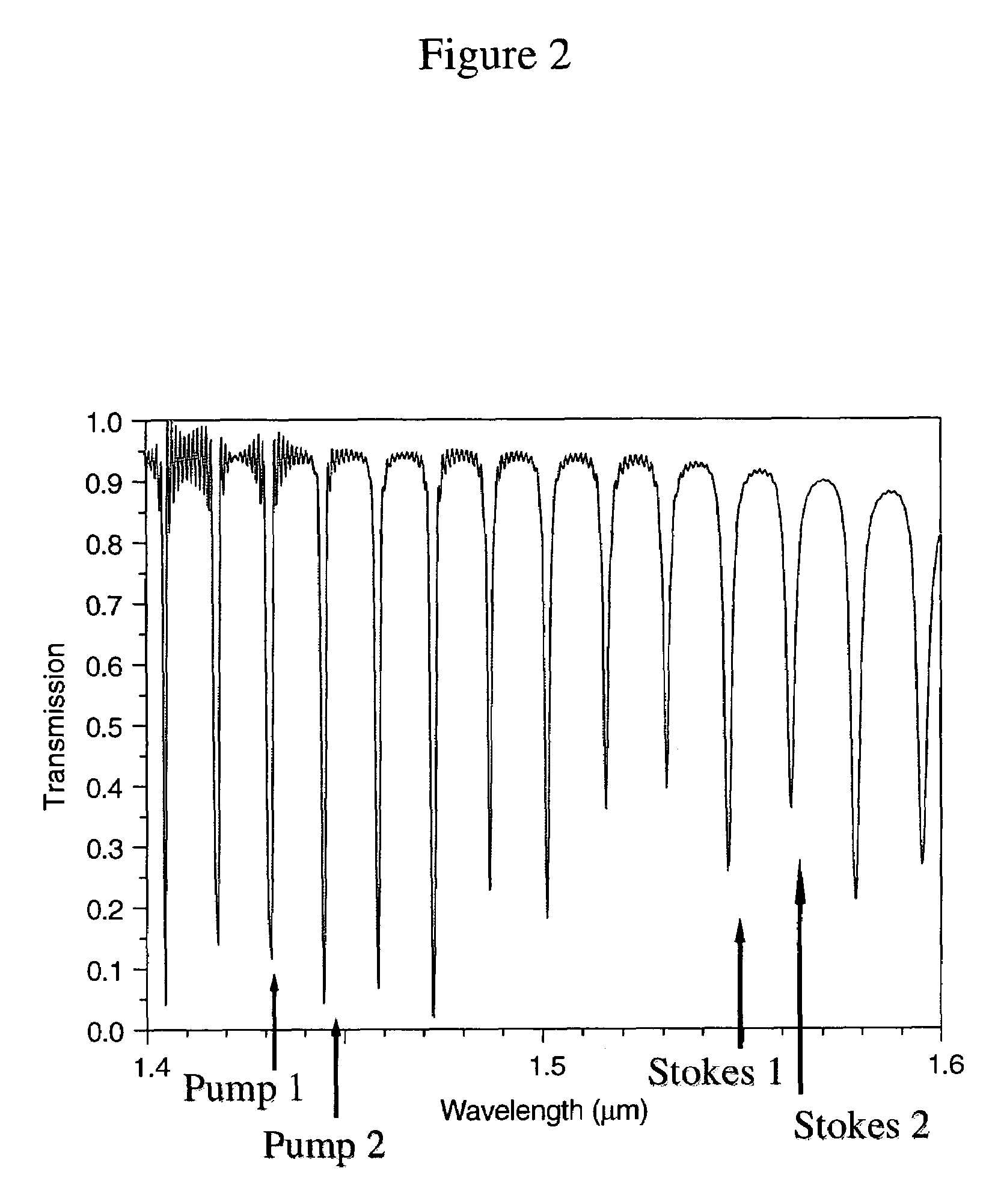
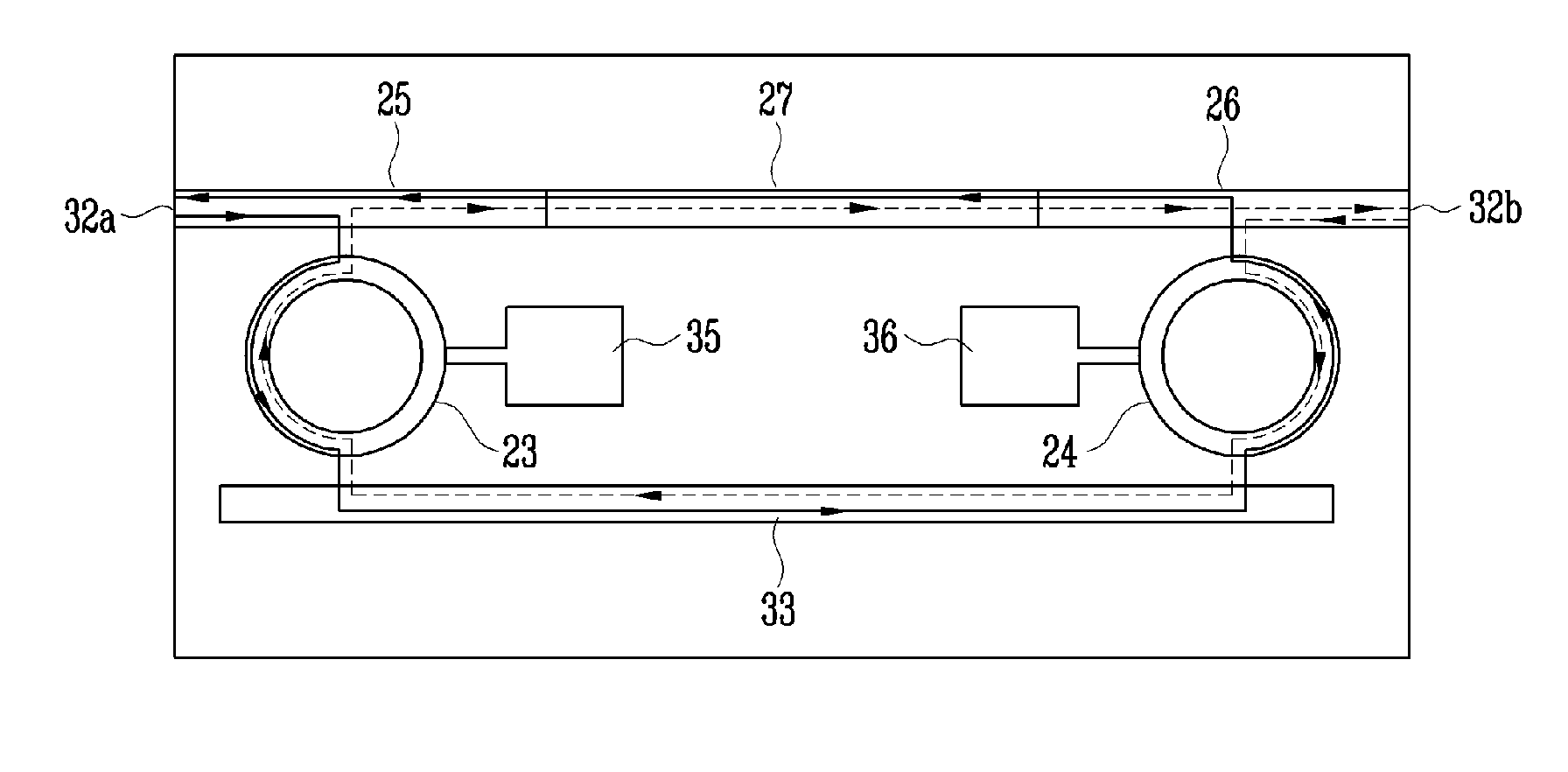
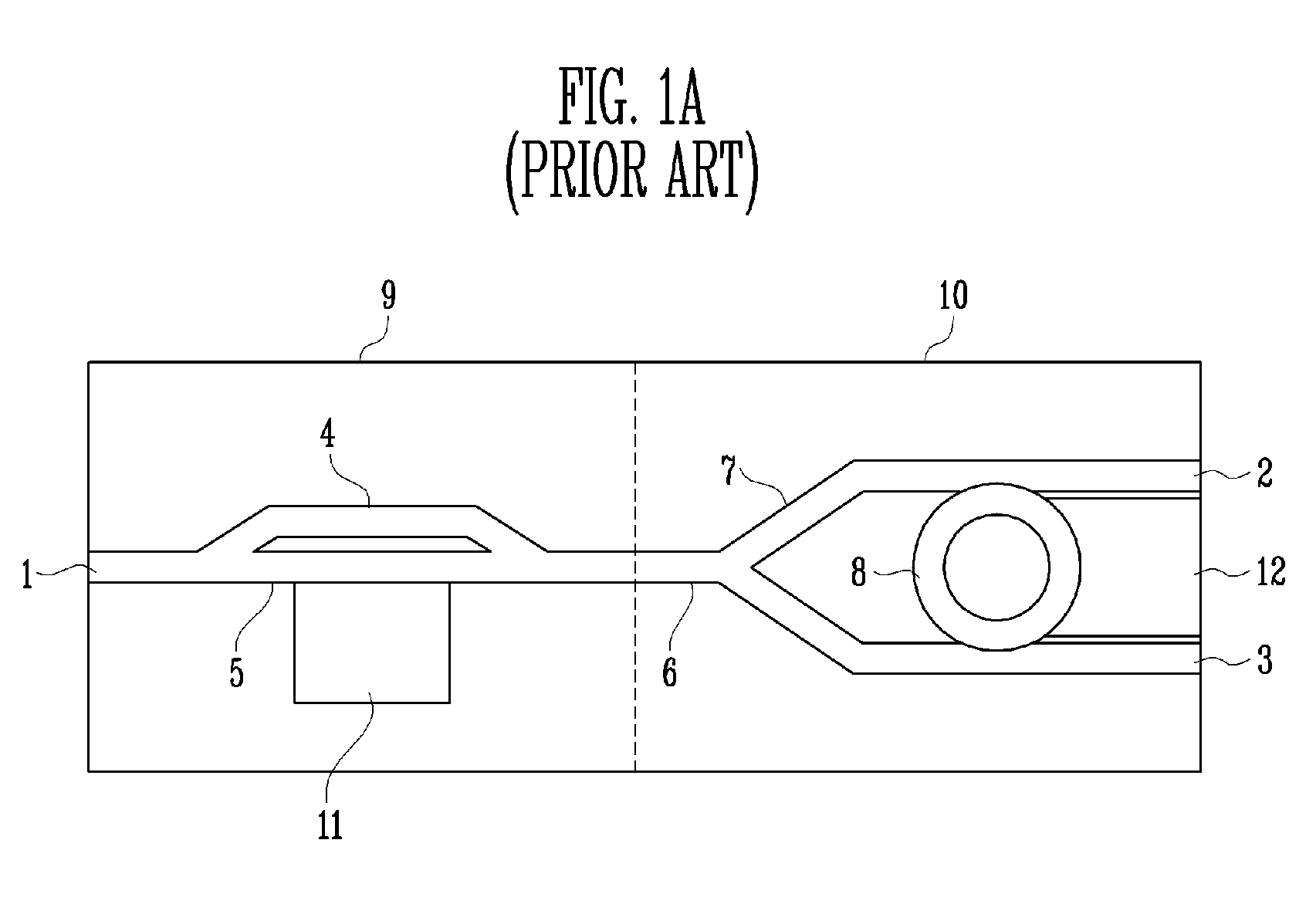
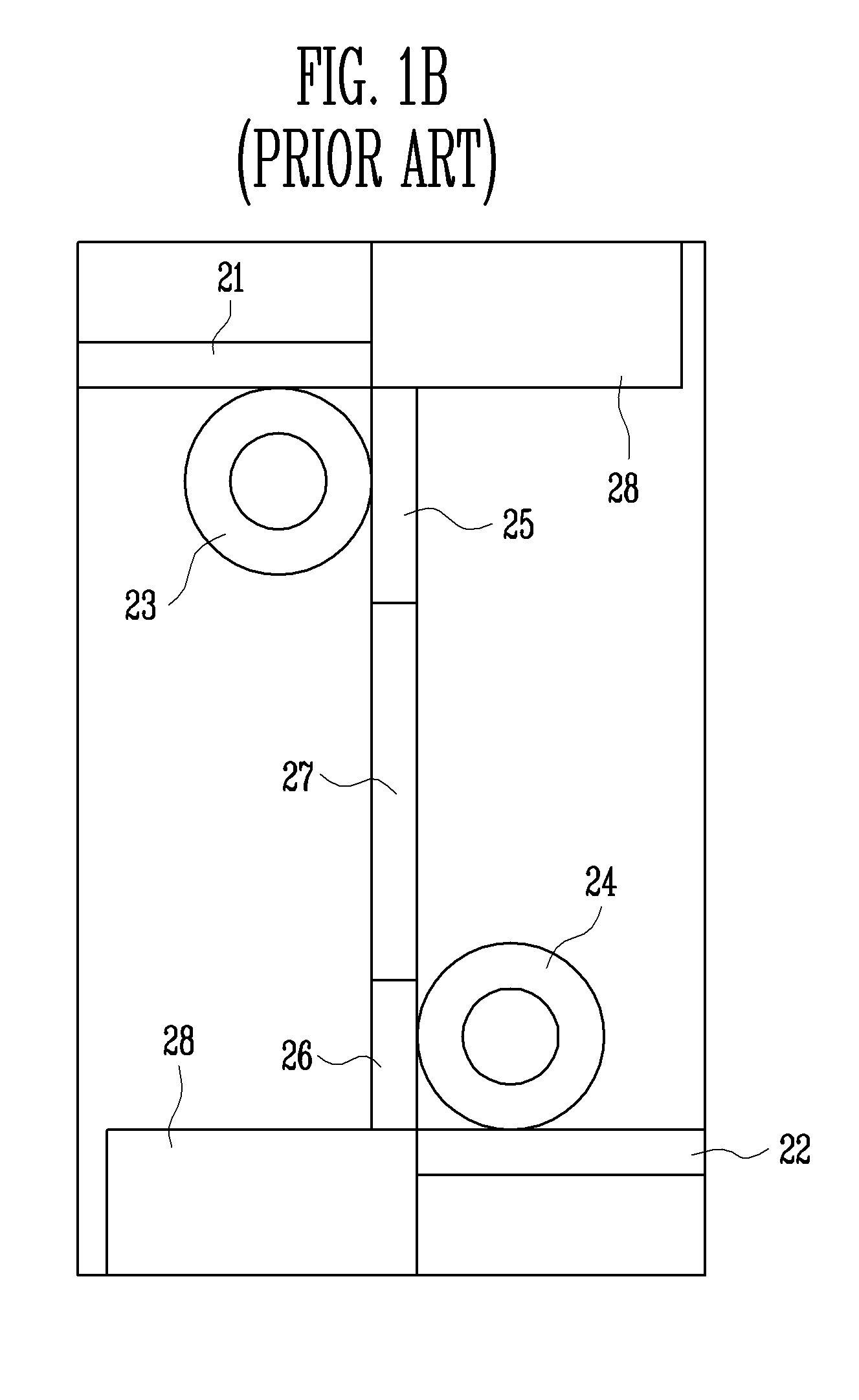
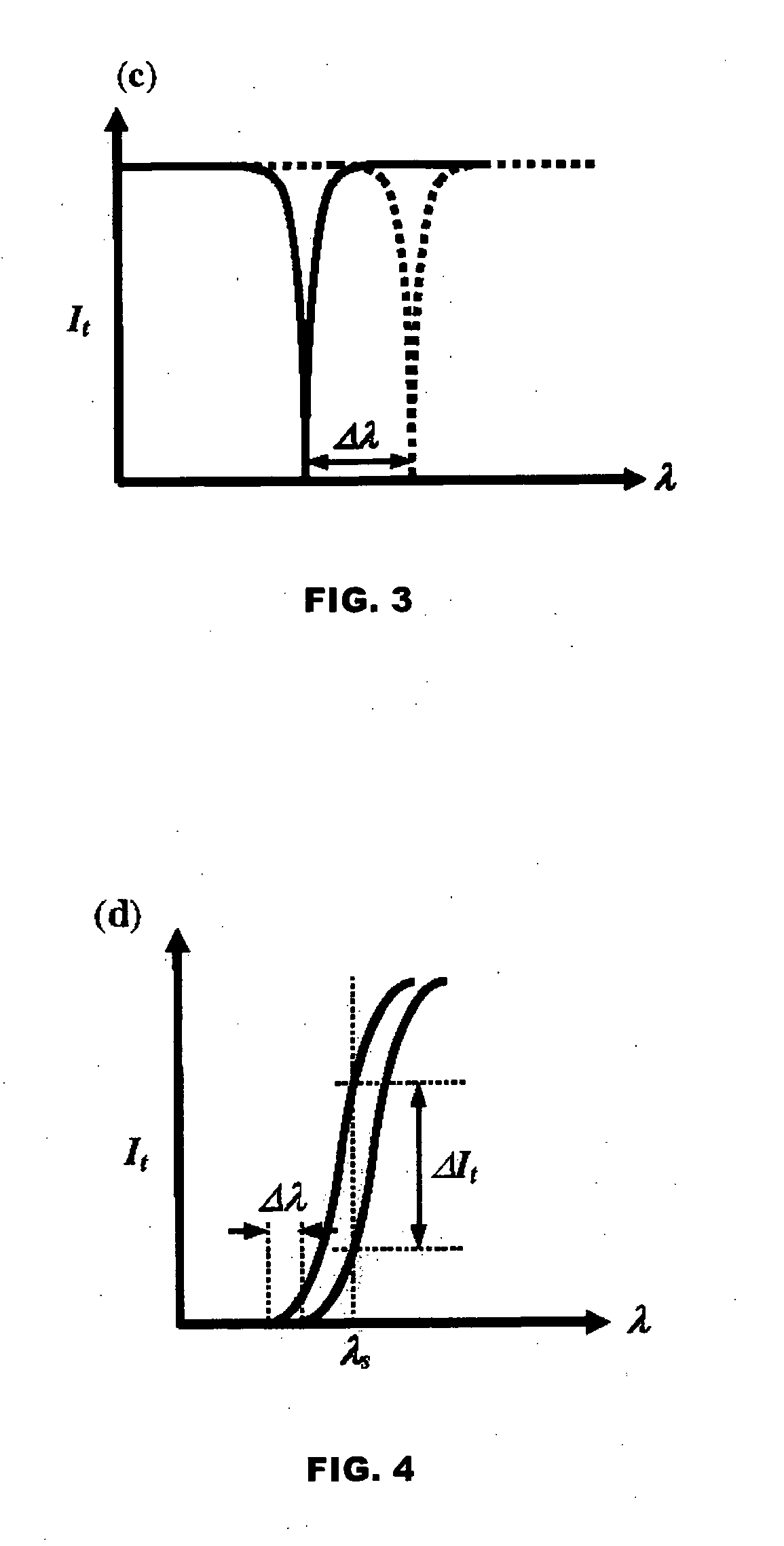
A split-ring resonator (SRR) is an artificially produced structure common to metamaterials. Their purpose is to produce the desired magnetic susceptibility (magnetic response) in various types of metamaterials up to 200 terahertz. These media create the necessary strong magnetic coupling to an applied electromagnetic field, not otherwise available in conventional materials. For example, an effect such as negative permeability is produced with a periodic array of split ring resonators.
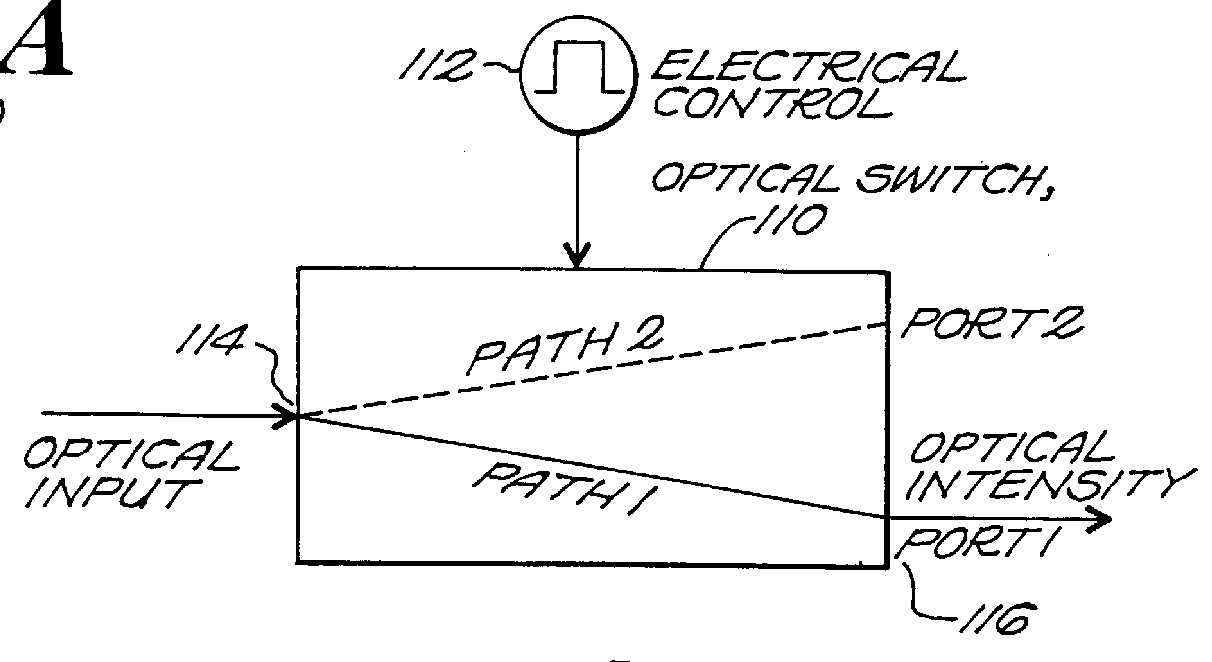
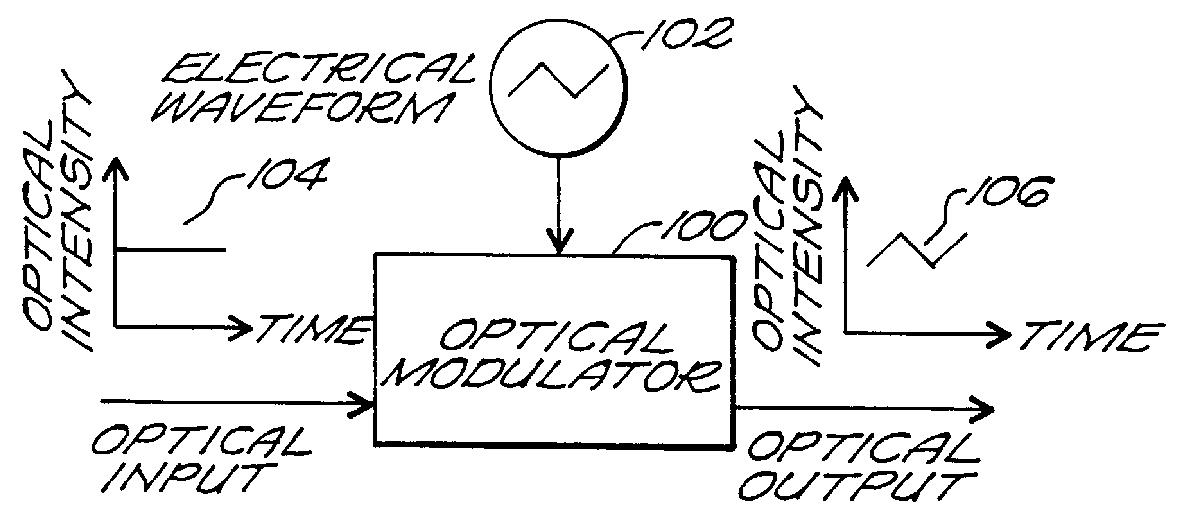
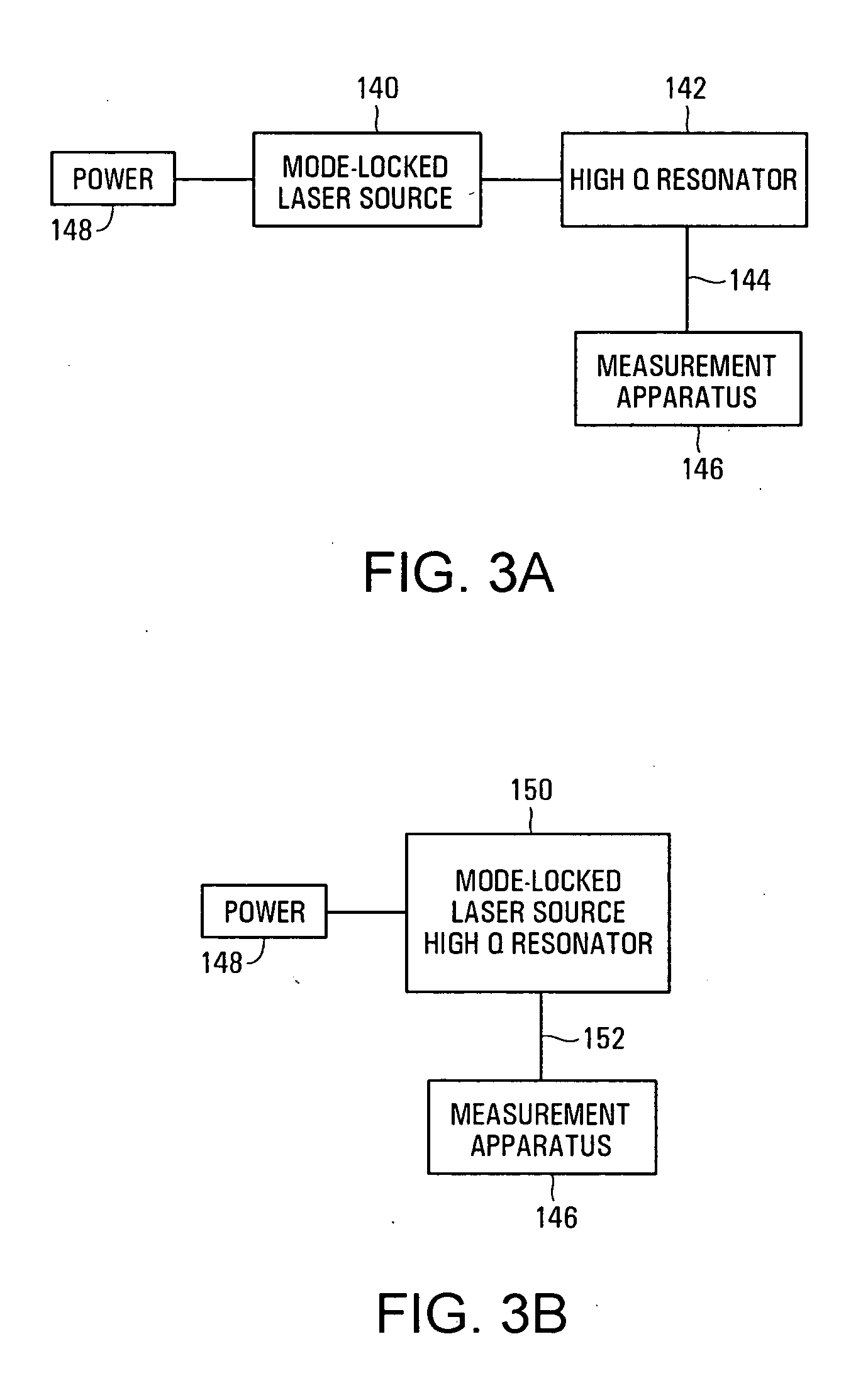
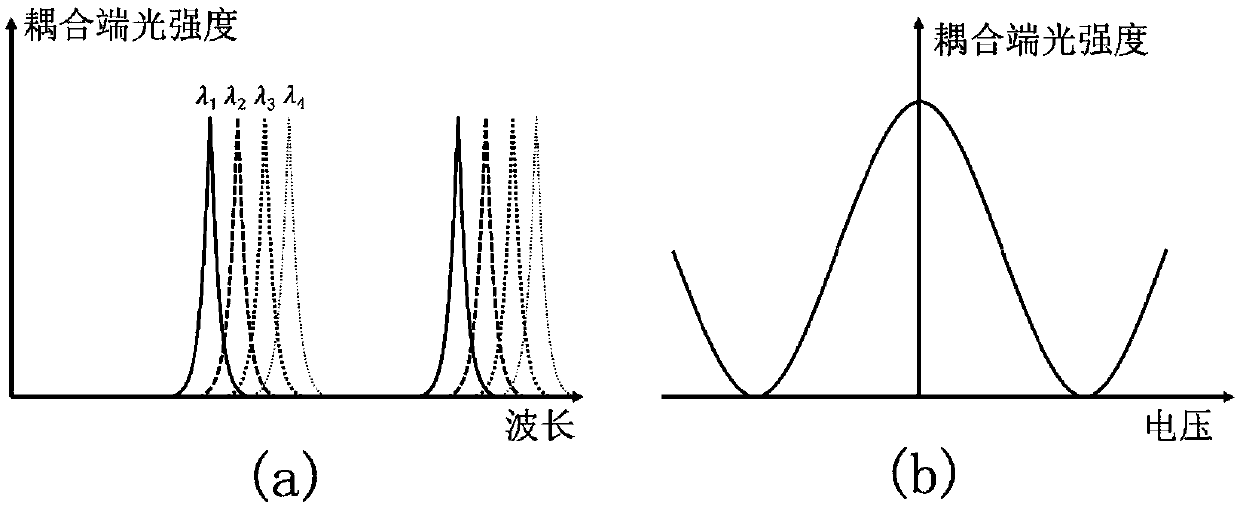
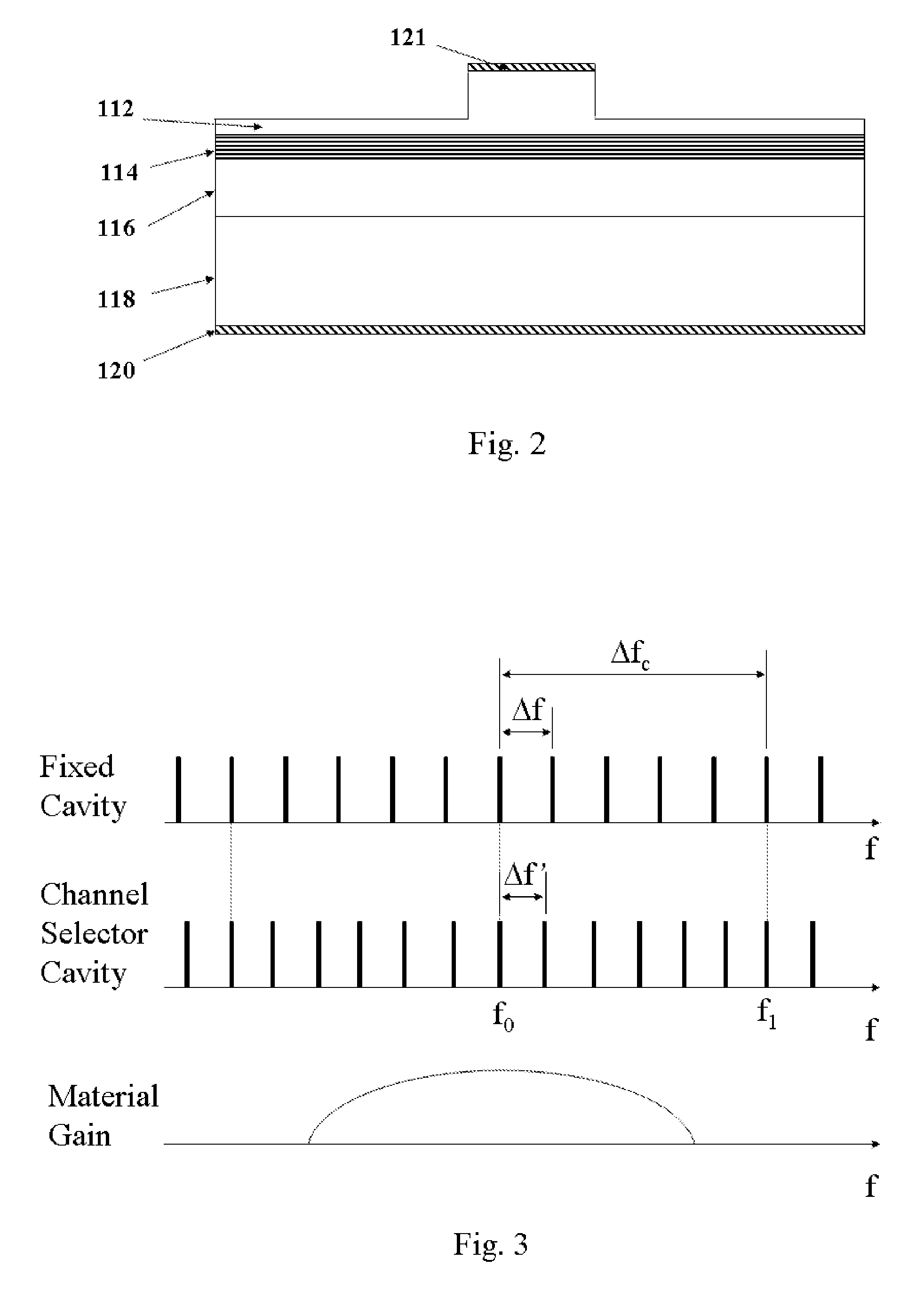
Resonator modulators and wavelength routing switches
InactiveUS6052495ASmall sizeImprove responseCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsClosed loopRefractive index
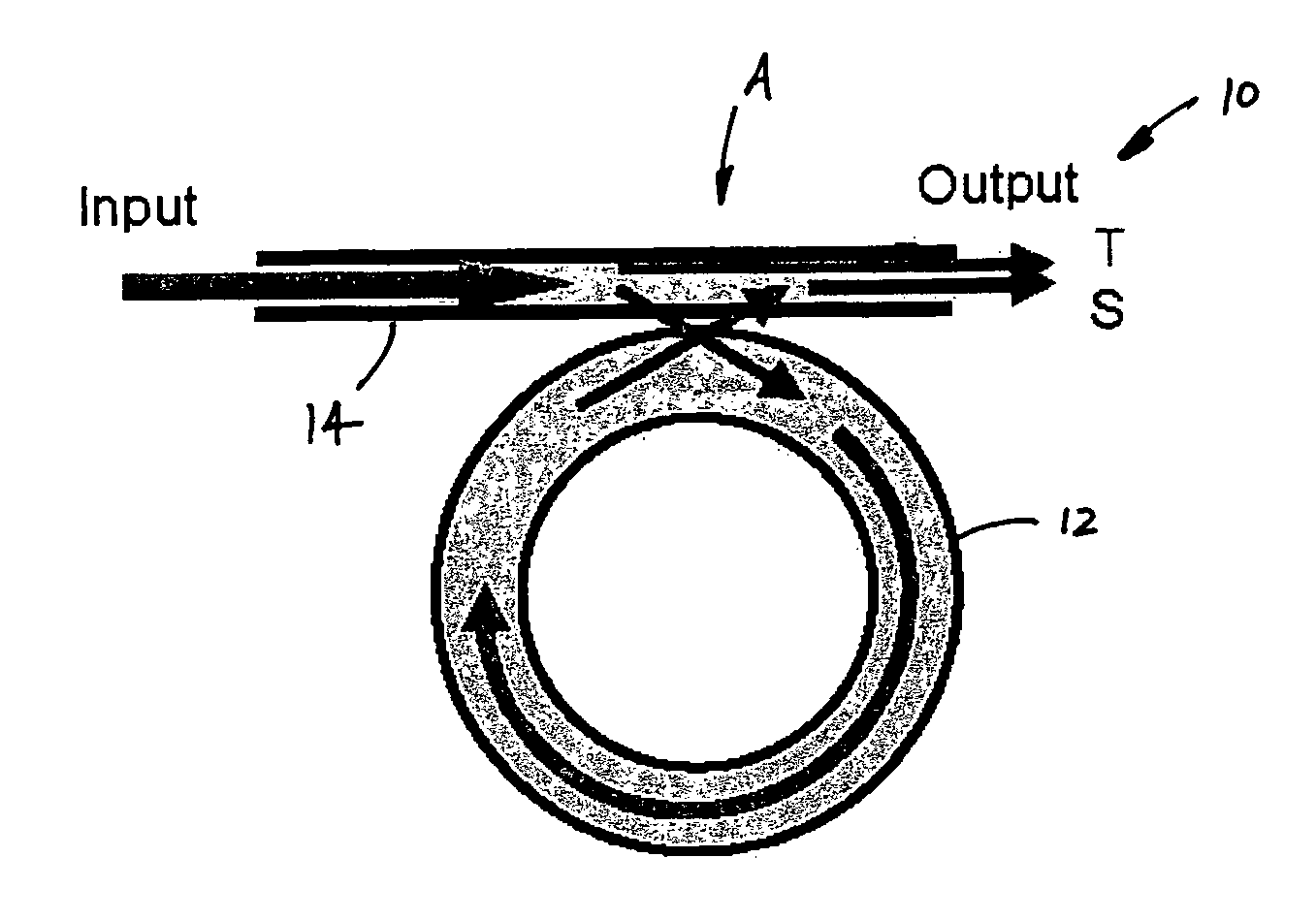
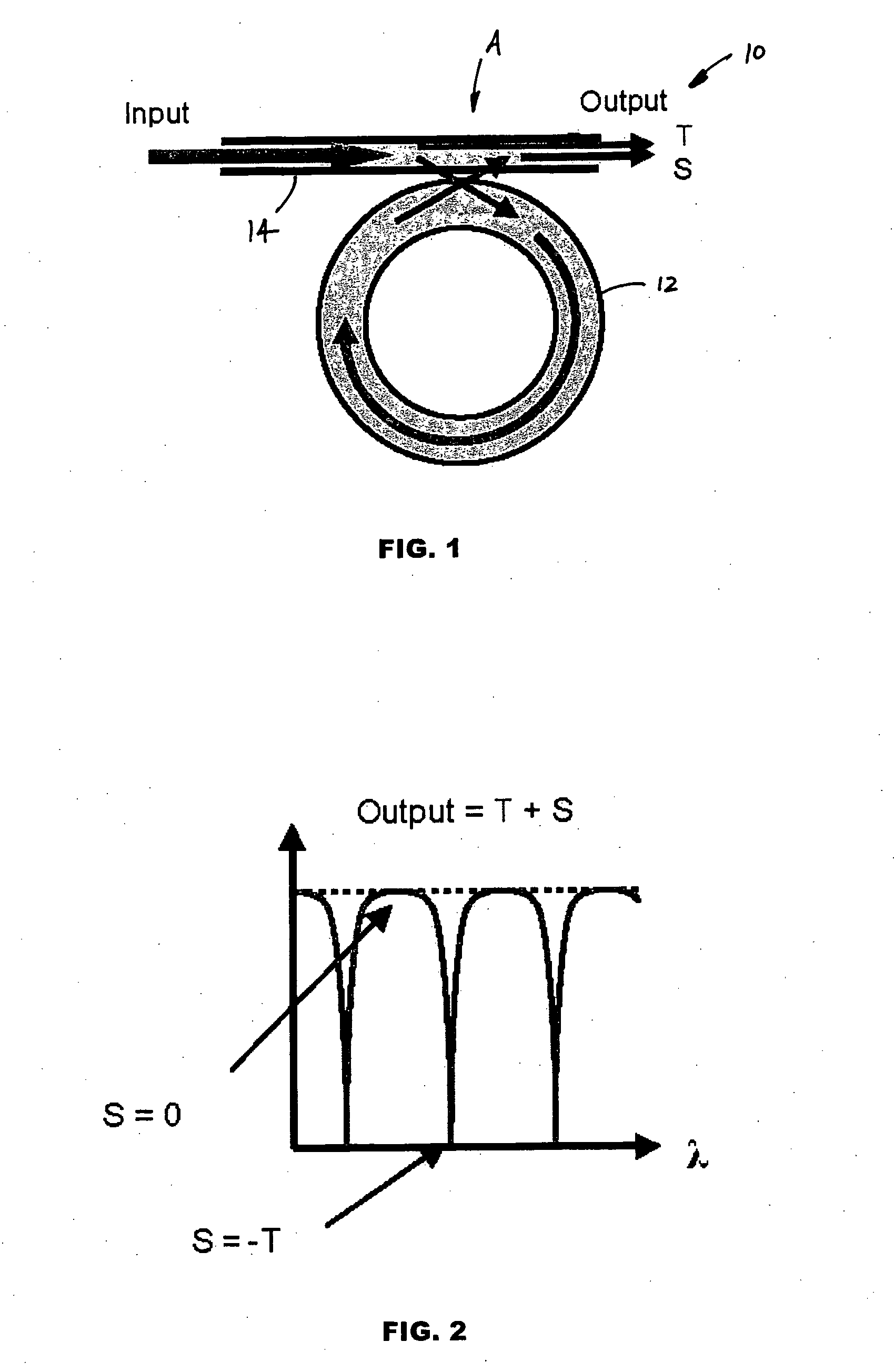
The invention provides an optical switch and modulator which uses a closed loop optical resonator. The optical resonator is a dielectric cavity whose primary function is to store optical power. Various structures are possible, and a particularly advantageous one is a ring shaped cavity. The wavelength response at the output port of a ring resonator side coupled to two waveguides is determined by the details of the resonator, and the coupling between the resonator and the waveguides. By coupling to adjacent resonators, the modulator response can be improved over that of a single resonator. One such improvement is in modulator efficiency, which is defined as the ratio of the change in optical intensity at the output, to a change in absorption in the ring waveguides. Absorption is used for switching and modulation without incurring significant optical attenuation. Another improvement involves making the resonance insensitive to small deviations in wavelength or index change. The latter improves fabrication tolerances and compensates for possible drift of the signal wavelength. Collectively, the behavior of multiple coupled resonators yields higher order responses.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
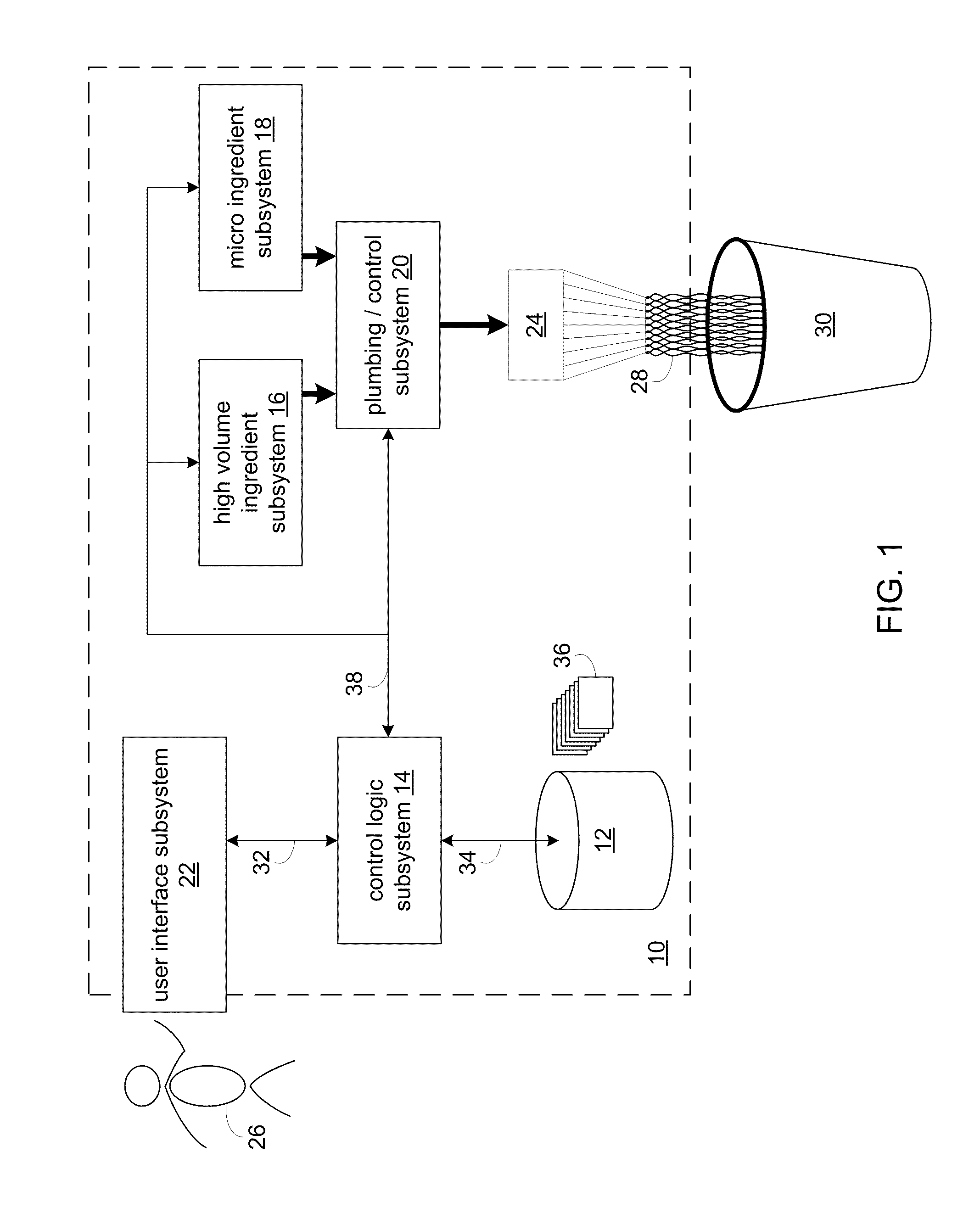
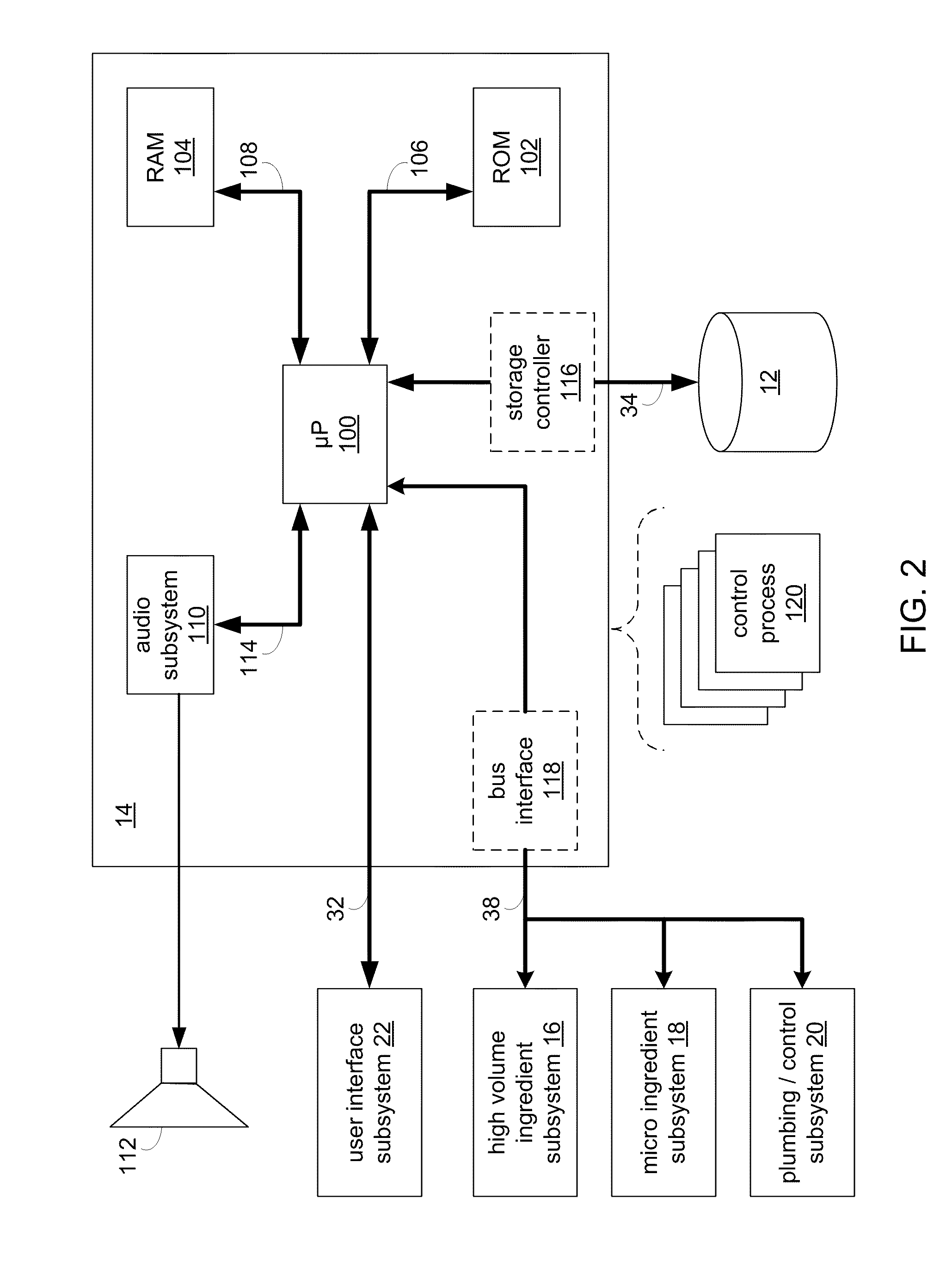
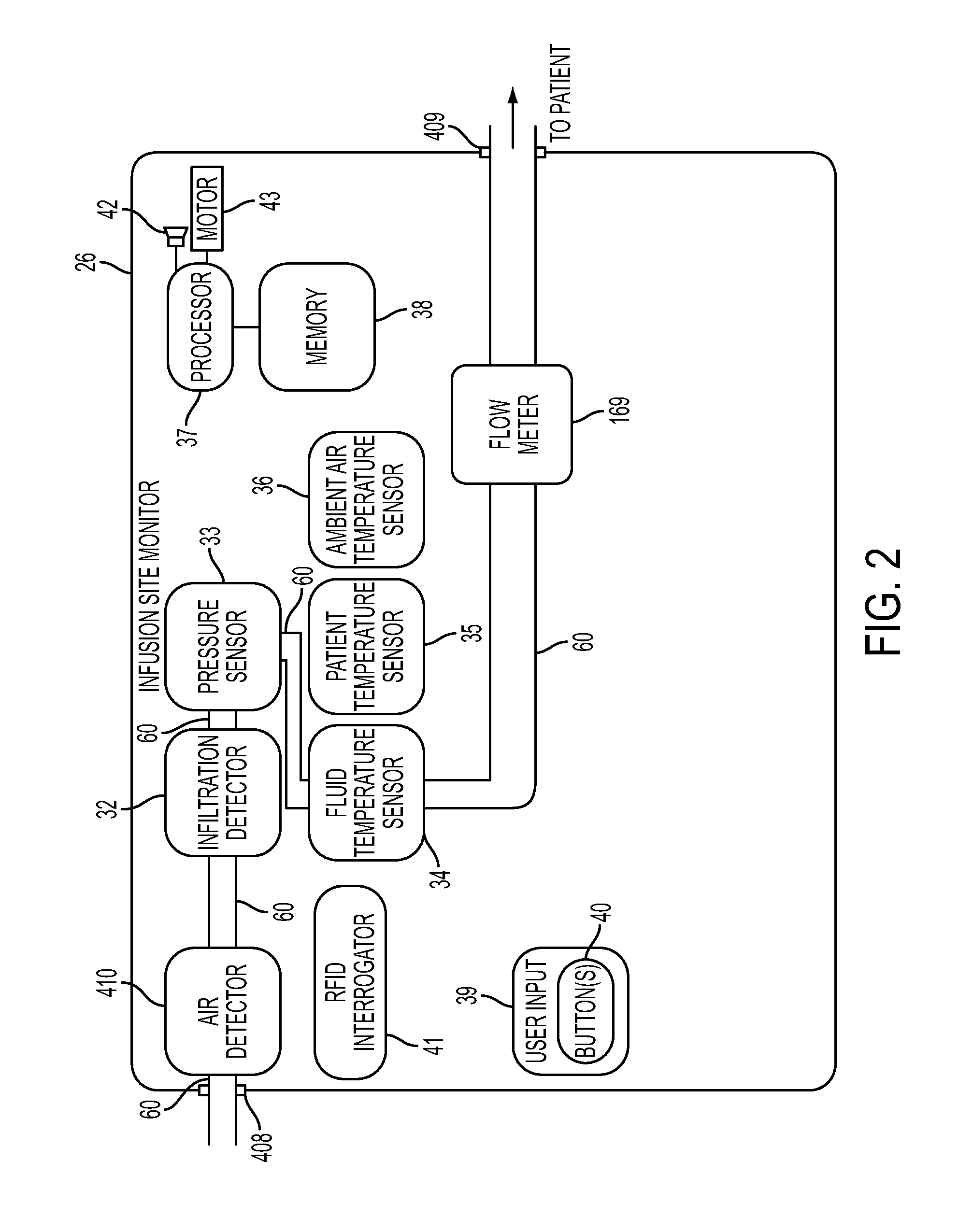
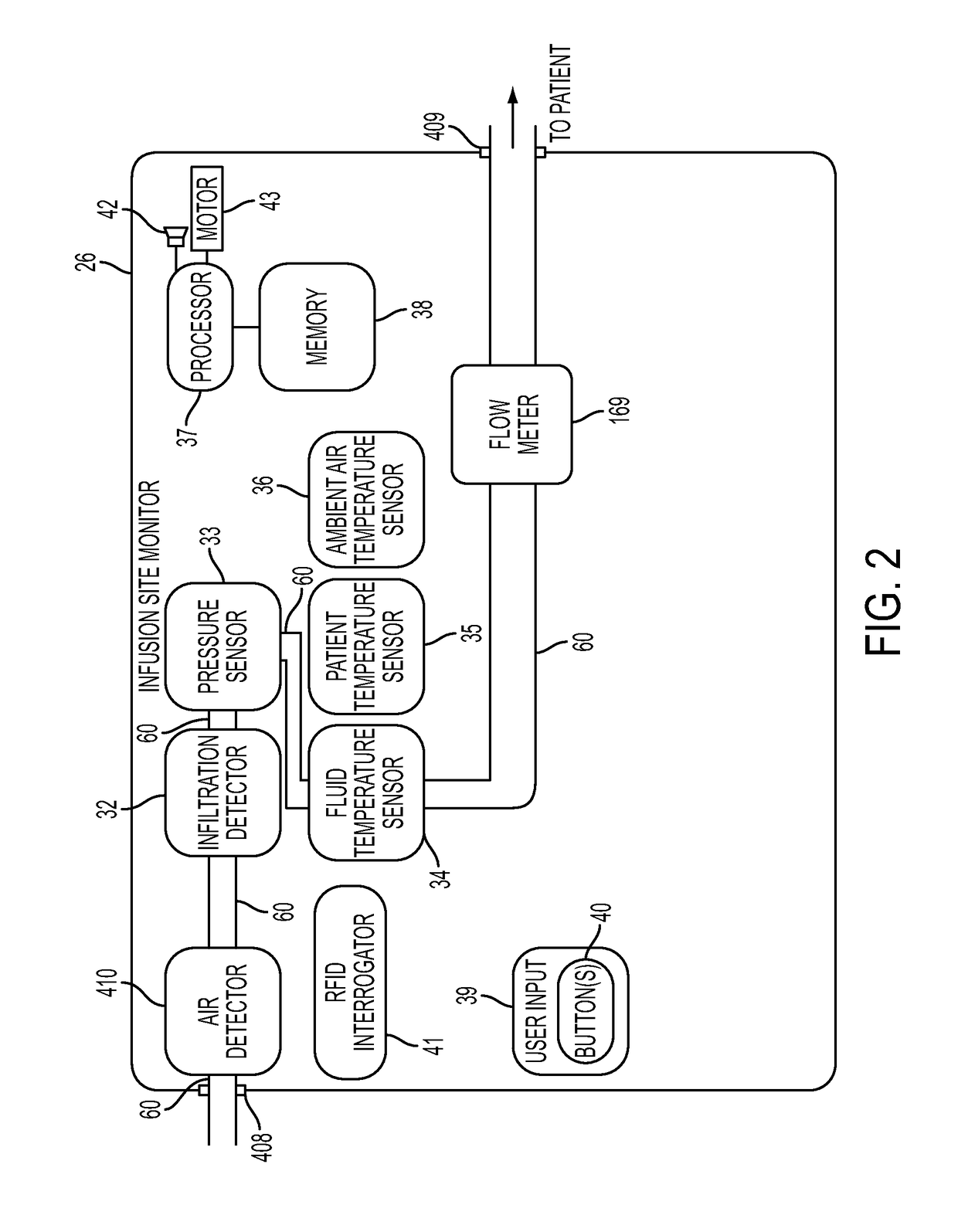
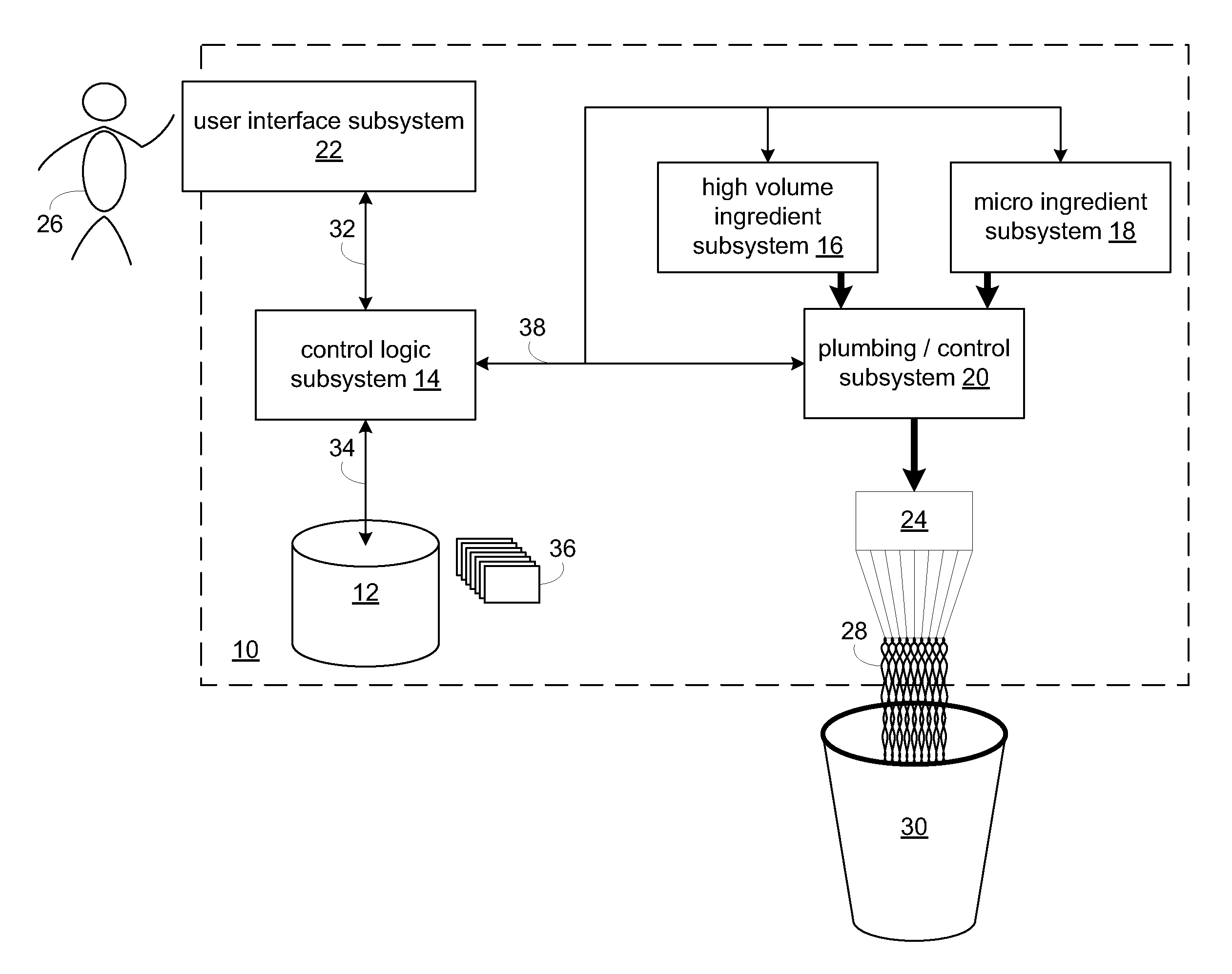
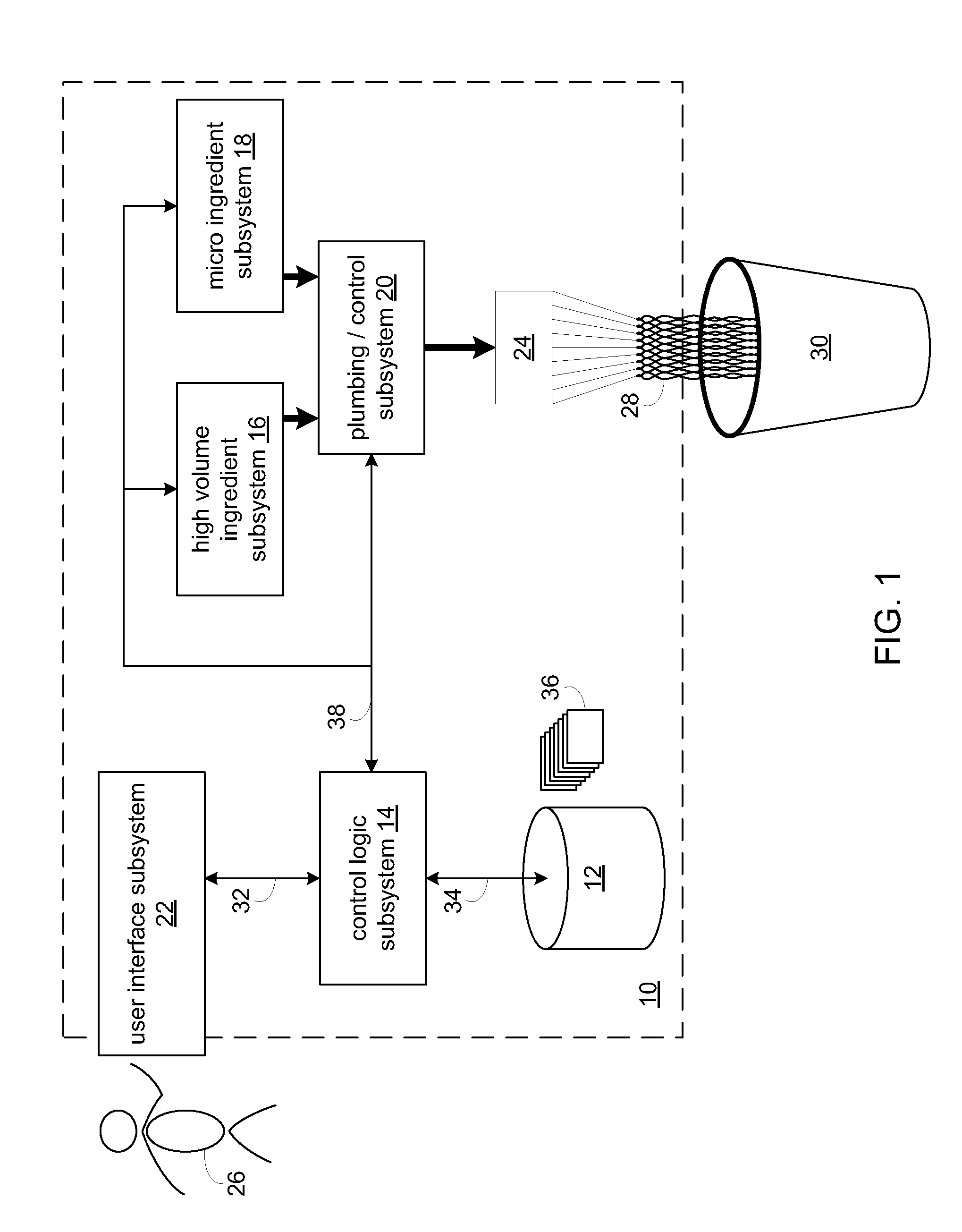
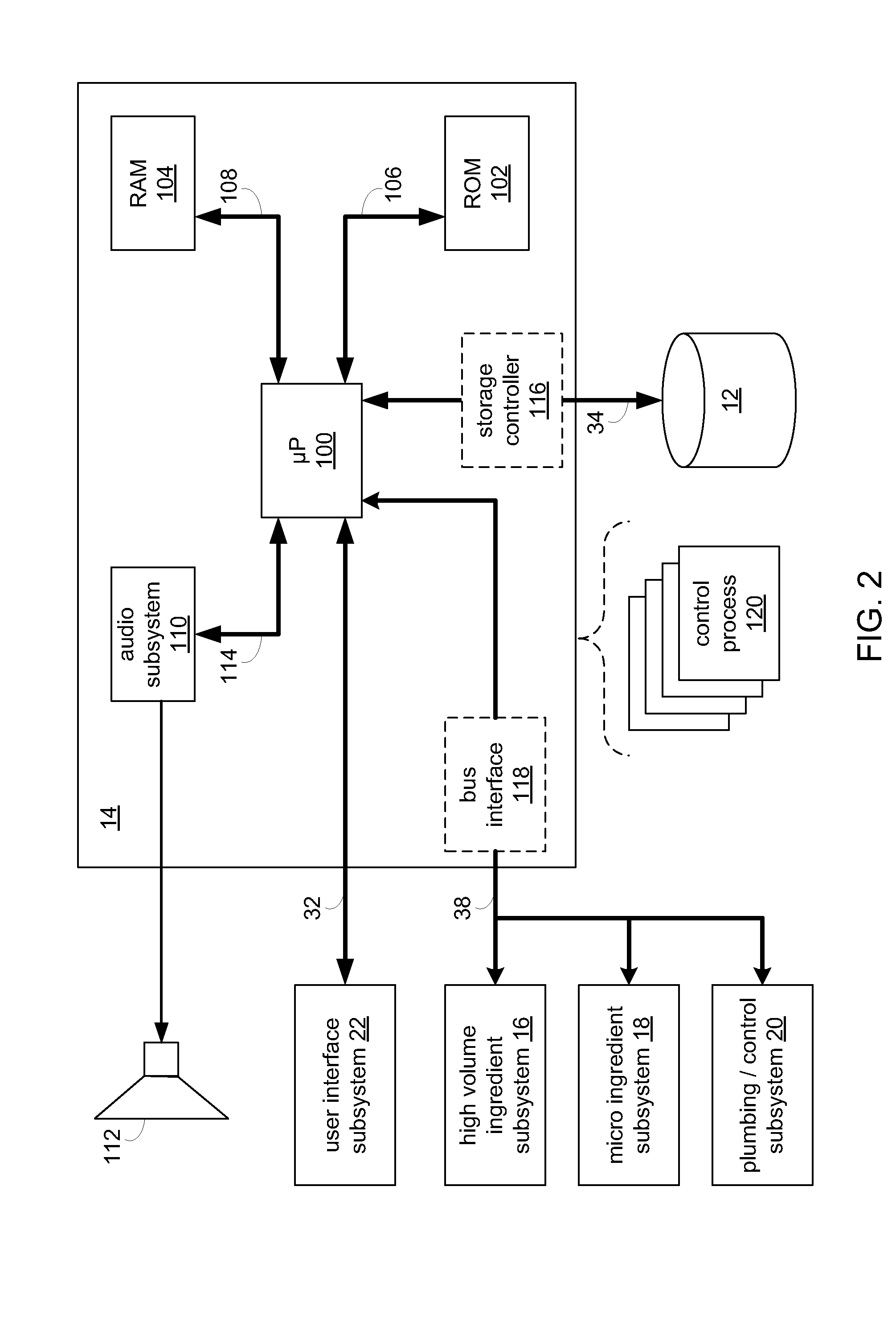
RFID system
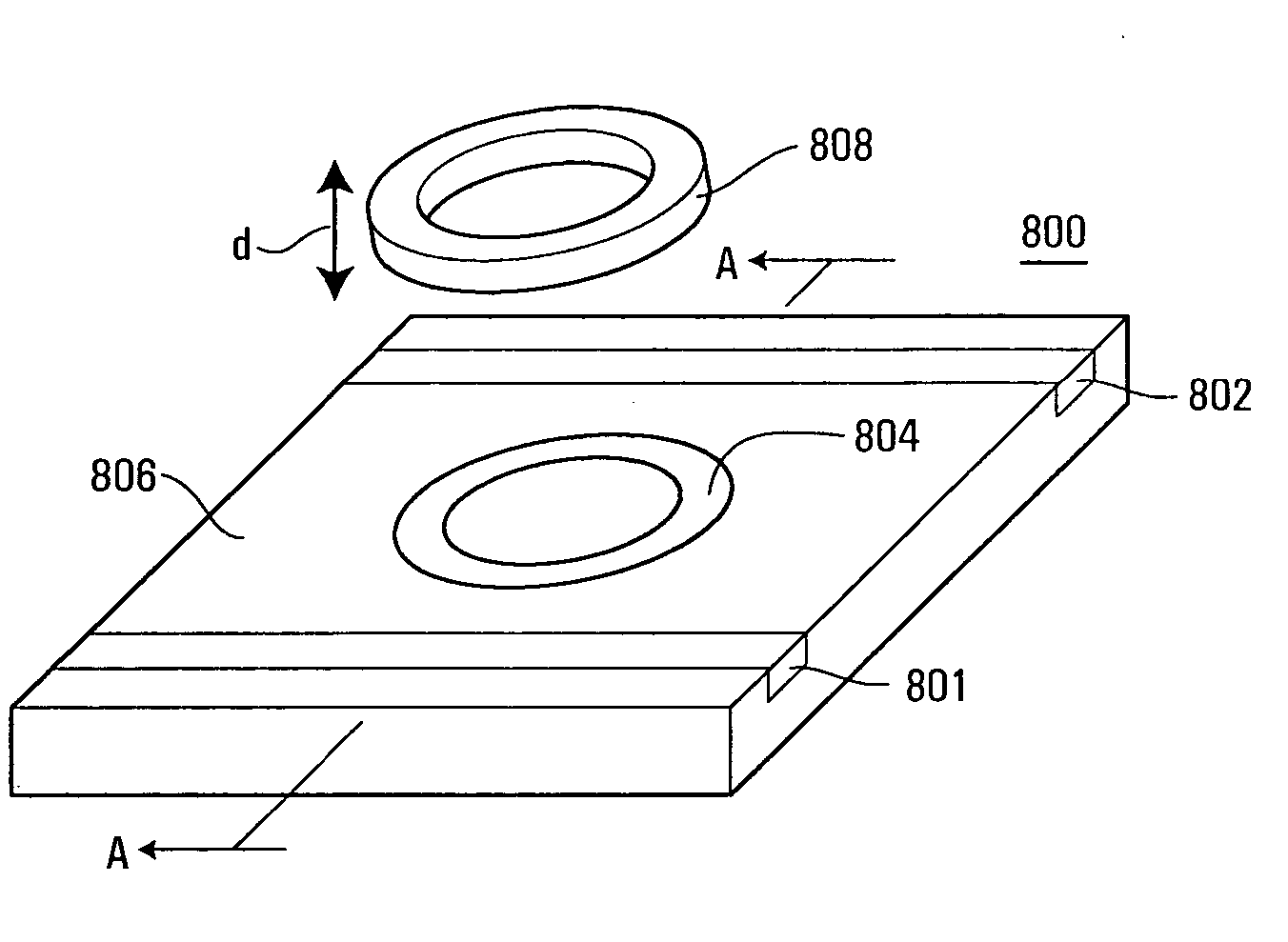
ActiveUS20090289796A1Impedance can be adjustedAntennas earthing switches associationResonatorsSplit ring resonatorsCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field focusing assembly includes a magnetic field generating device configured to generate a magnetic field, and a split ring resonator assembly configured to be magnetically coupled to the magnetic field generating device and configured to focus the magnetic field produced by the magnetic field generating device.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
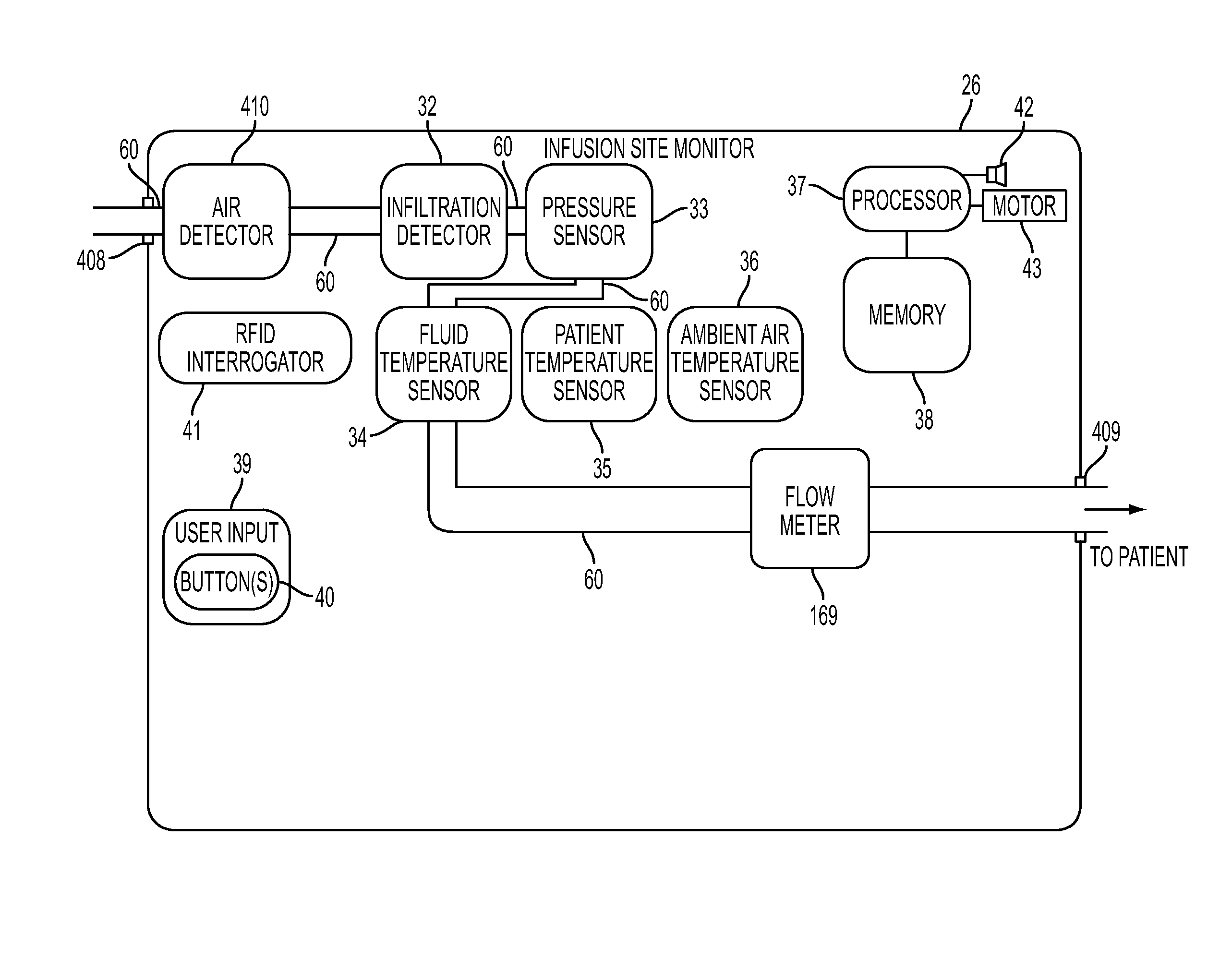
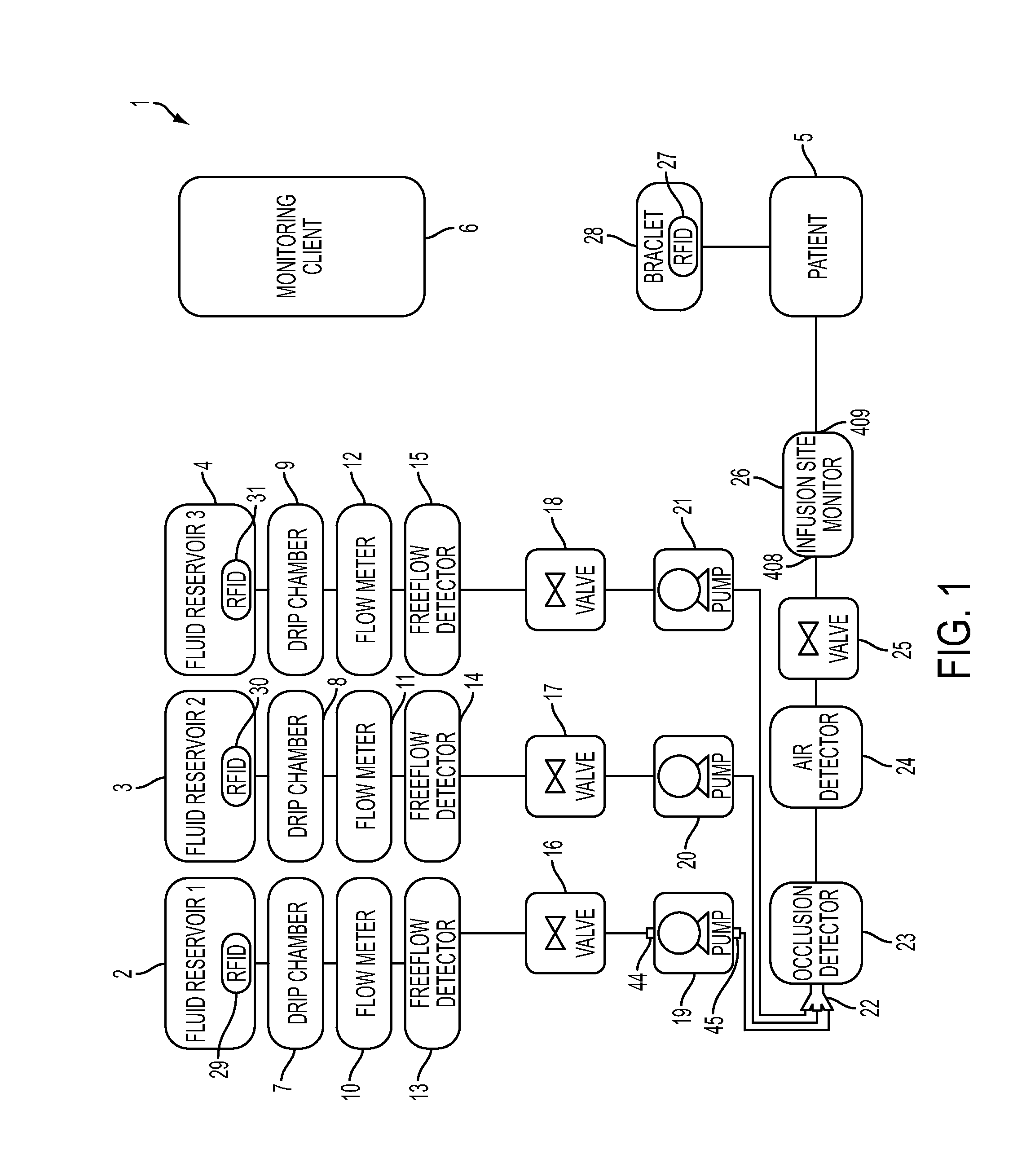
System, Method, and Apparatus for Bubble Detection in a Fluid Line Using a Split-Ring Resonator
ActiveUS20150033823A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansMicrowave rangeAcoustics
A system, method, and apparatus for detecting at least one condition of interest relating to a tube, e.g. the presence of an air bubble. In some embodiments, the sensor includes antennas, a split-ring resonator, a frequency generator capable of generating frequencies in the microwave range, and a detection component. The detection component may estimate at least one parameter of received microwave energy in order to determine if a condition of interest exists.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
System, method, and apparatus for bubble detection in a fluid line using a split-ring resonator
ActiveUS9719964B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansLine tubingMicrowave range
A system, method, and apparatus for detecting at least one condition of interest relating to a tube, e.g. the presence of an air bubble. In some embodiments, the sensor includes antennas, a split-ring resonator, a frequency generator capable of generating frequencies in the microwave range, and a detection component. The detection component may estimate at least one parameter of received microwave energy in order to determine if a condition of interest exists.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Temperature compensation mechanism for a micromechanical ring resonator
InactiveUS6859113B2Additional requirementAcceleration measurement using interia forcesImpedence networksVIT signalsAtomic physics
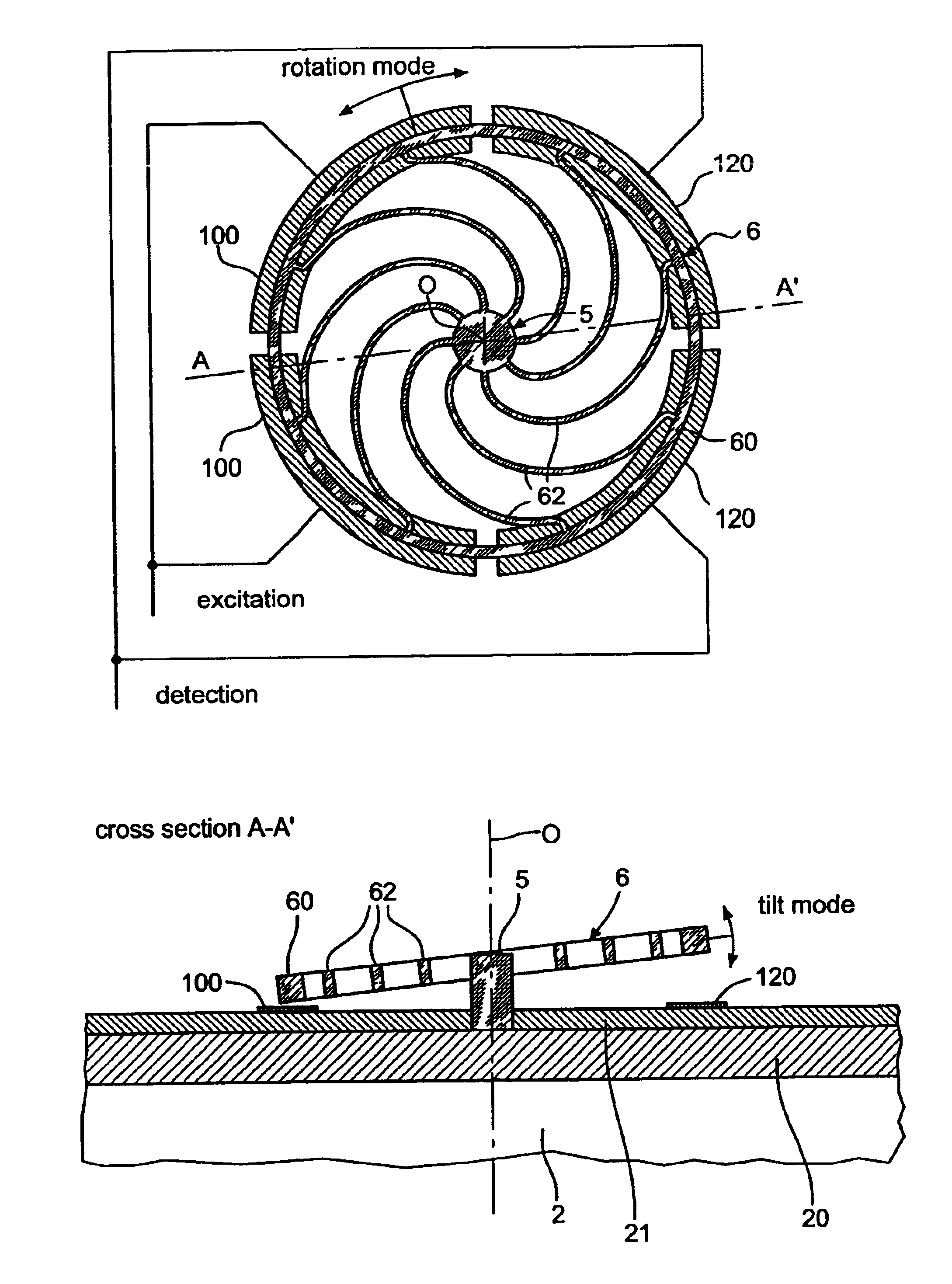
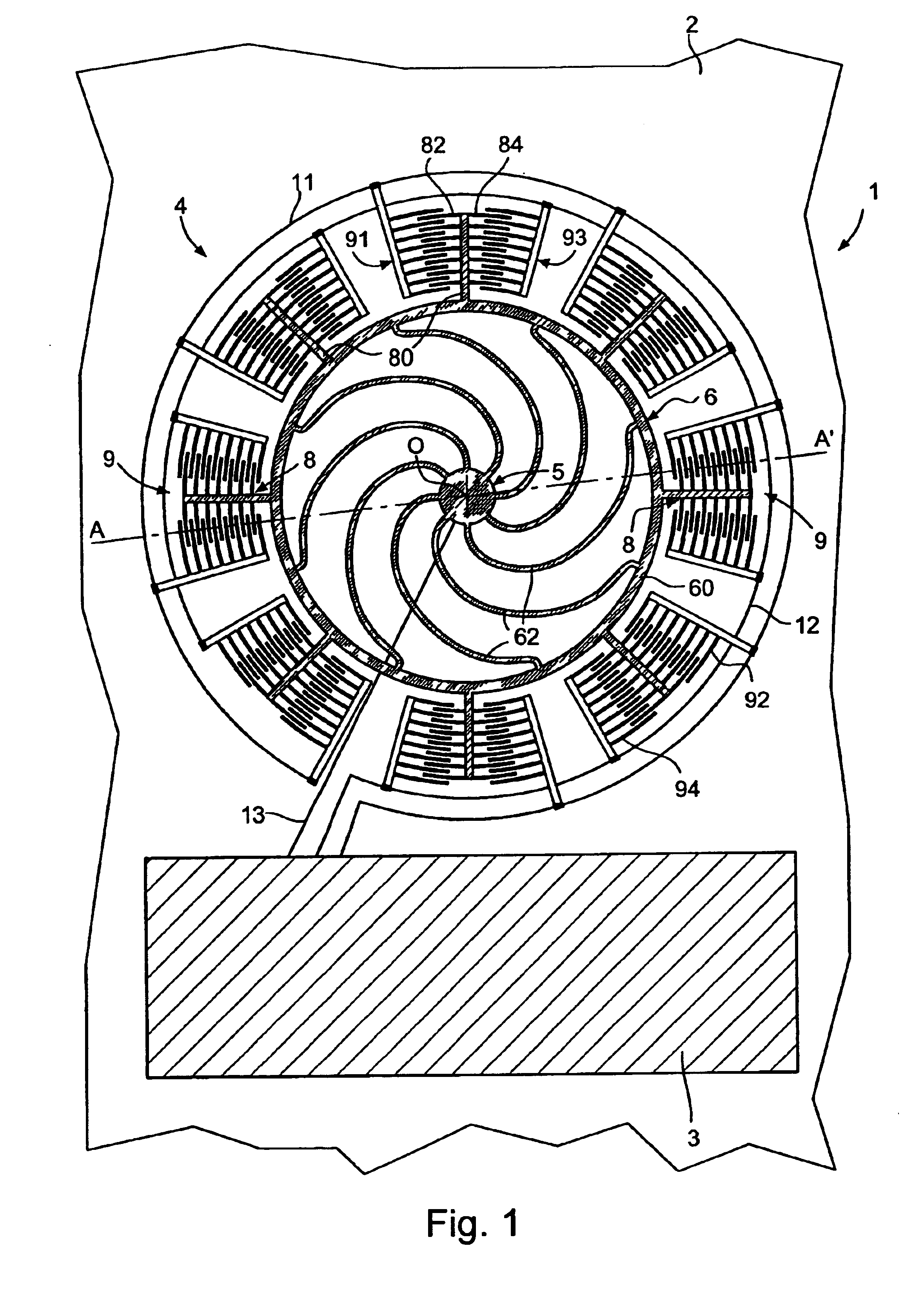
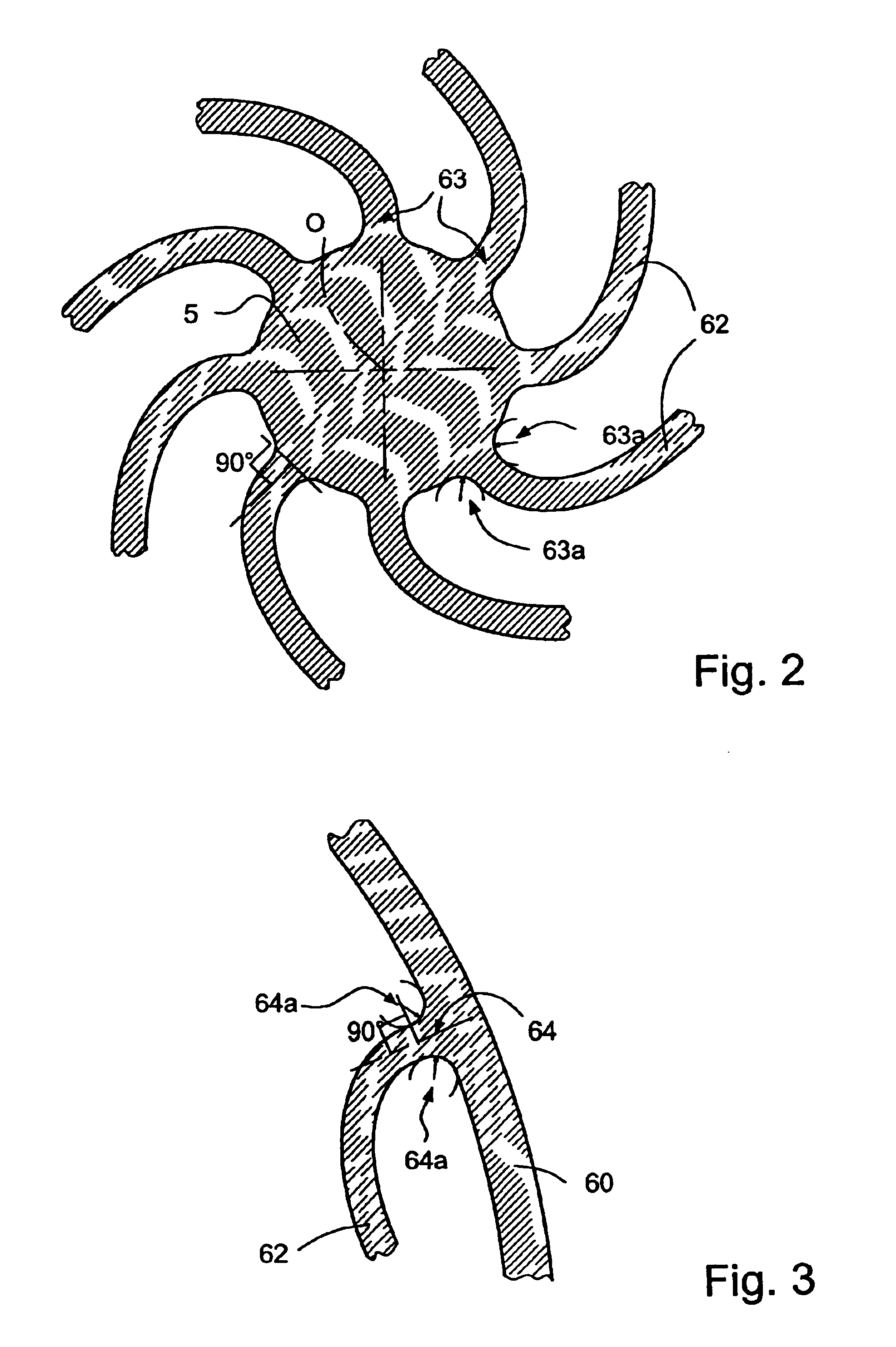
A time base including a resonator (4) and an integrated electronic circuit (3) for driving the resonator into oscillation and for producing, in response to the oscillation, a signal having a determined frequency. The resonator is an integrated micromechanical ring resonator supported above a substrate (2) and adapted to oscillate in a first oscillation mode. The ring resonator includes a free-standing oscillating structure (6). Electrodes (100, 120; 130, 150) are positioned under the free-standing oscillating structure in such a way as to drive and sense a second oscillation mode in a plane substantially perpendicular to the substrate and having a resonant frequency which is different from the resonant frequency of the first oscillation mode, a frequency difference between the resonant frequencies of both oscillation modes being used for compensating for the effect of temperature on the frequency of the signal produced by the time base.
Owner:ETA SA MFG HORLOGERE SUISSE
Structures With Negative Index Of Refraction
ActiveUS20070215843A1Easily fabricatedEasily experimentallyLiquid organic insulatorsNanoopticsCapacitanceRefractive index
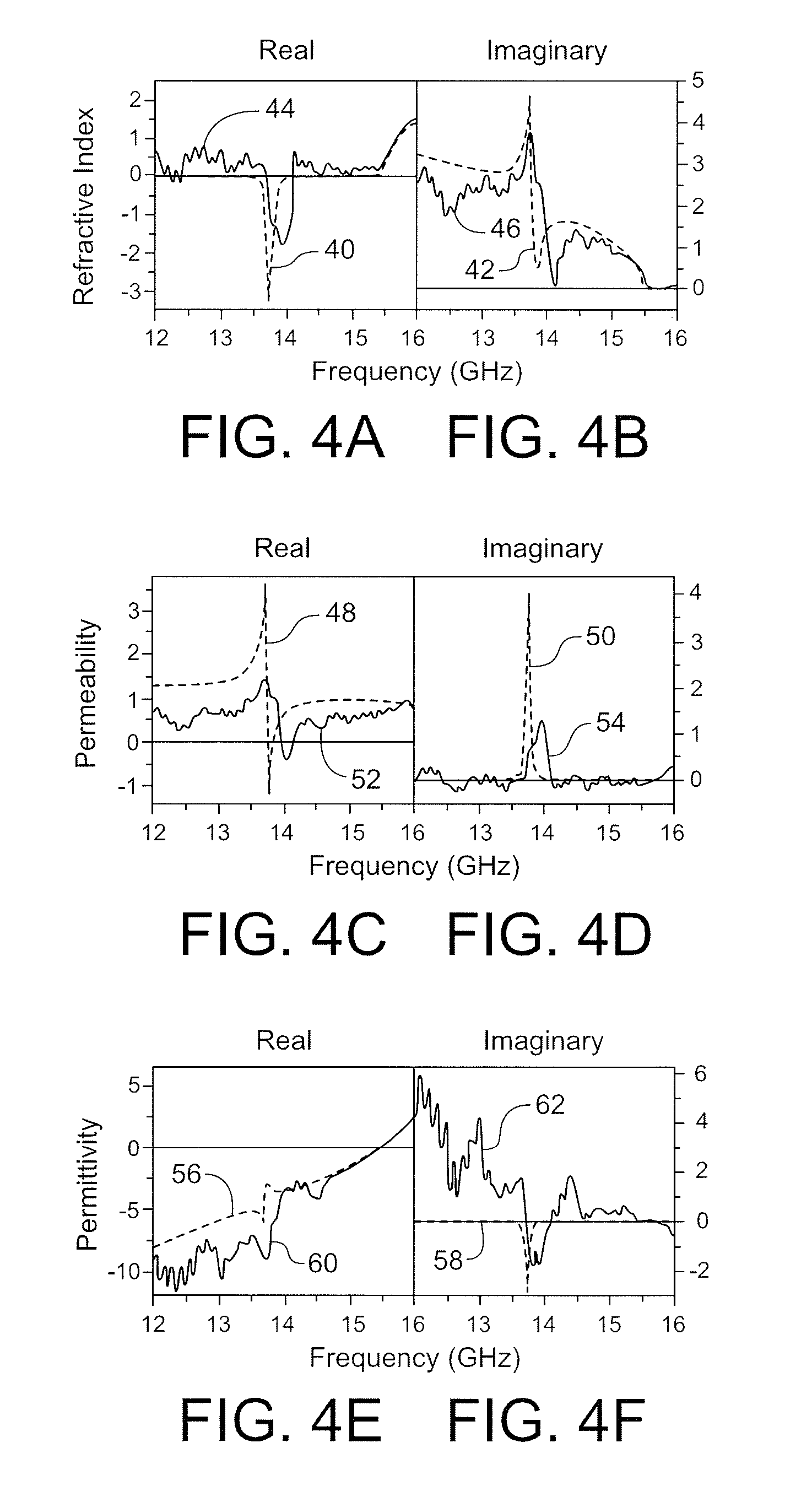
The invention provides simplified negative index materials (NIMs) using wire-pair structures, 4-gap single ring split-ring resonator (SRR), fishnet structures and overleaf capacitor SRR. In the wire-pair arrangement, a pair of short parallel wires and continuous wires are used. In the 4-gap single-ring SRR, the SRRs are centered on the faces of a cubic unit cell combined with a continuous wire type resonator. Combining both elements creates a frequency band where the metamaterial is transparent with simultaneously negative ε and μ. In the fishnet structure, a metallic mesh on both sides of the dielectric spacer is used. The overleaf capacitor SRR changes the gap capacities to small plate capacitors by making the sections of the SRR ring overlap at the gaps separated by a thin dielectric film. This technique is applicable to conventional SRR gaps but it best deploys for the 4-gap single-ring structures.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Tunable optical filter
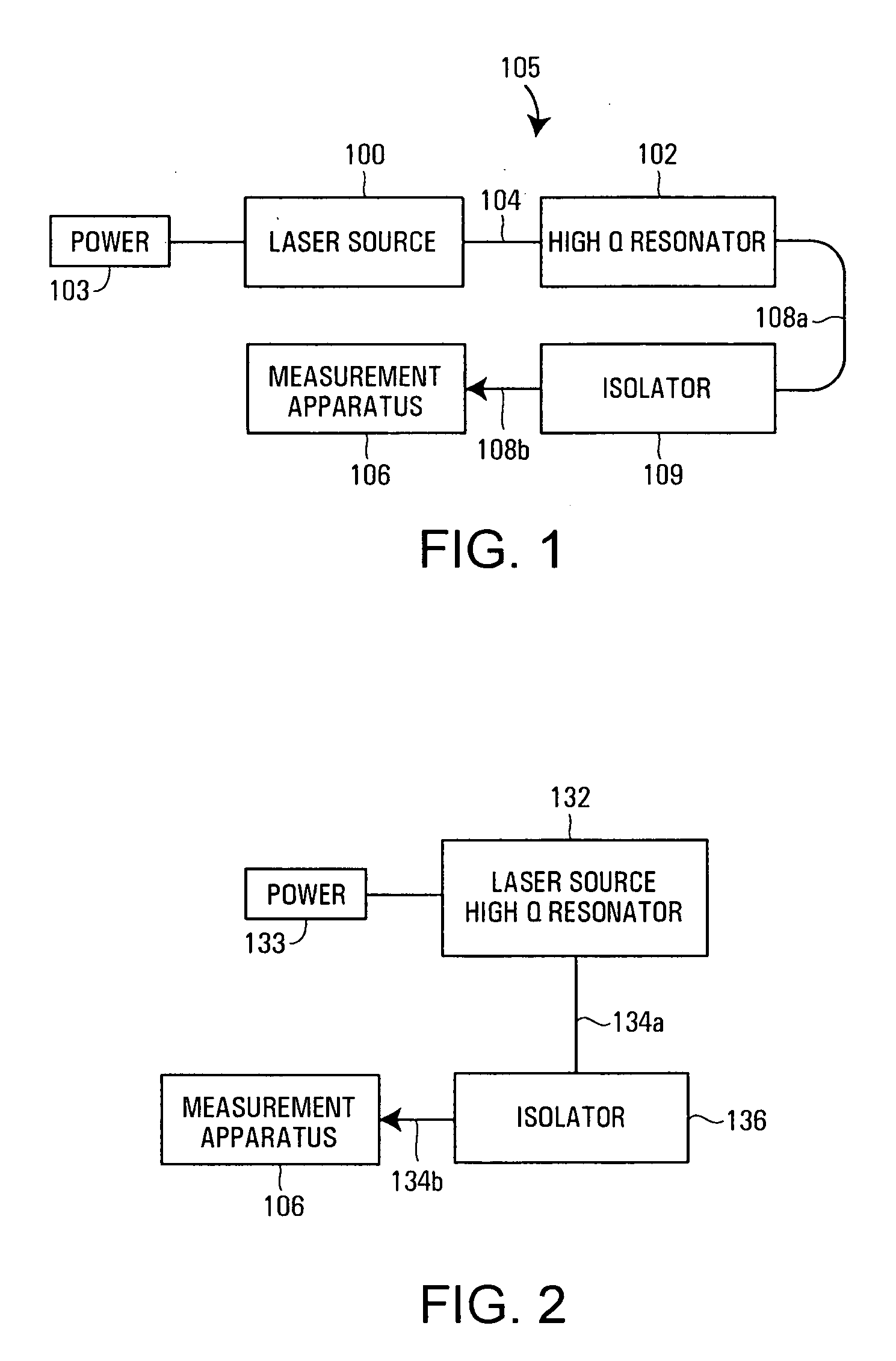
InactiveUS20040120638A1Cladded optical fibreLaser optical resonator constructionDielectric plateMicrosphere
A tunable filter having a resonator with a resonant frequency dependent upon a variable gap is provided. The variable gap may be controllably altered by use of an actuator. The resonator is a high Q resonator that may be formed by a ring resonator, microsphere, microdisc, or other high Q optical structures. Actuation is preferably achieved through an electrostatic actuator that moves a dielectric plate relative to the resonator in response to measured values of gap and temperature.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
Metamaterial Particles for Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting
InactiveUS20140266967A1Small sizeHigh bandwidthIndividually energised antenna arraysLoop antennasElectric power transmissionFrequency spectrum
Antennas developed for electromagnetic field energy harvesting, typically referred to as rectennas, provide an alternative electromagnetic field energy harvesting means to photovoltaic cells if designed for operation in the visible frequency spectrum. Rectennas also provide energy harvesting ability or power transfer mechanism at microwave, millimeter and terahertz frequencies. However, the power harvesting efficiency of available rectennas is low because rectennas employ traditional antennas whose dimensions is typically proportional or close to the wavelength of operation. This invention provides a device for electromagnetic field energy harvesting that employs a plurality of electrically-small resonators such as split-ring resonators that provide significantly enhanced energy harvesting or energy collection efficiency while occupying smaller footprint. The invention is applicable to electromagnetic energy harvesting and to wireless power transfer.
Owner:RAMAHI OMAR +2
Piezoelectric Transducers and Inertial Sensors using Piezoelectric Transducers
InactiveUS20100058861A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsElectricityGyroscope
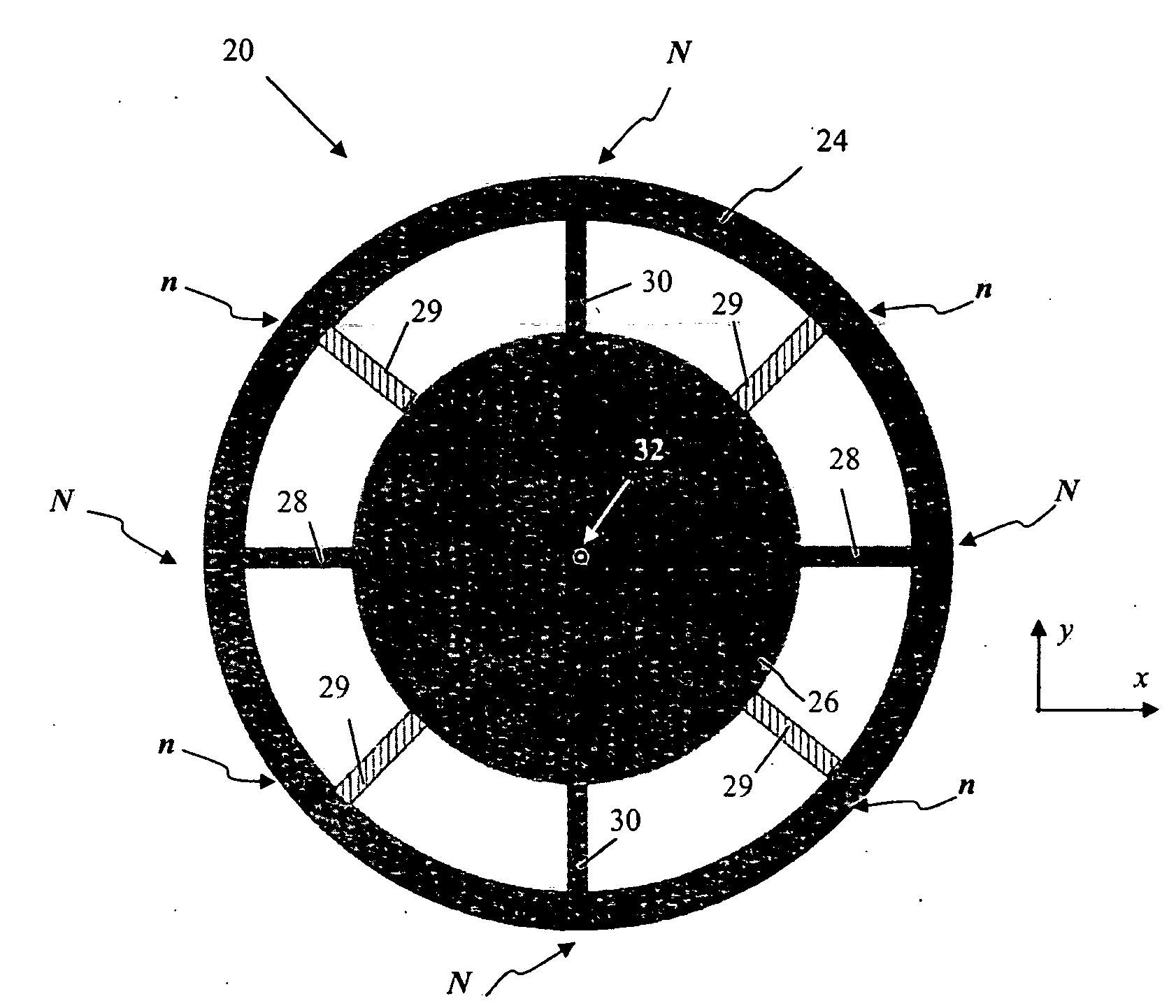
Transducers comprising a frame structure made of piezoelectric material convert energy, through piezoelectric effect, between electrostatic energy associated with voltage differential between the electrodes sandwiching the frame structure and mechanical energy associated with deformation of the frame structure. Inertial sensors such as gyroscopes and accelerators, including inertial sensors comprising ring resonators, utilize said transducers both to generate oscillations of their resonators and to sense the changes in such oscillations produced, in the sensors' frame of reference, by Coriolis forces appearing due to the movement of the sensors.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Photonic neural network convolutional layer chip based on micro-ring resonator
ActiveCN109639359AImprove energy consumption ratioDoes not consume energyWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersBusiness efficiencyHigh energy
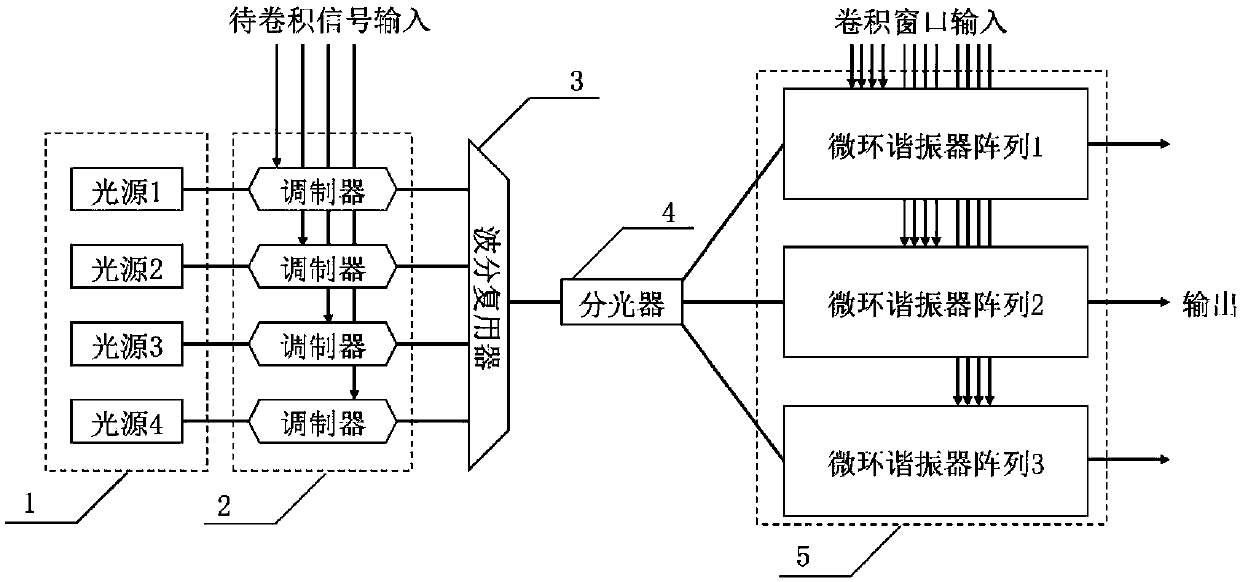
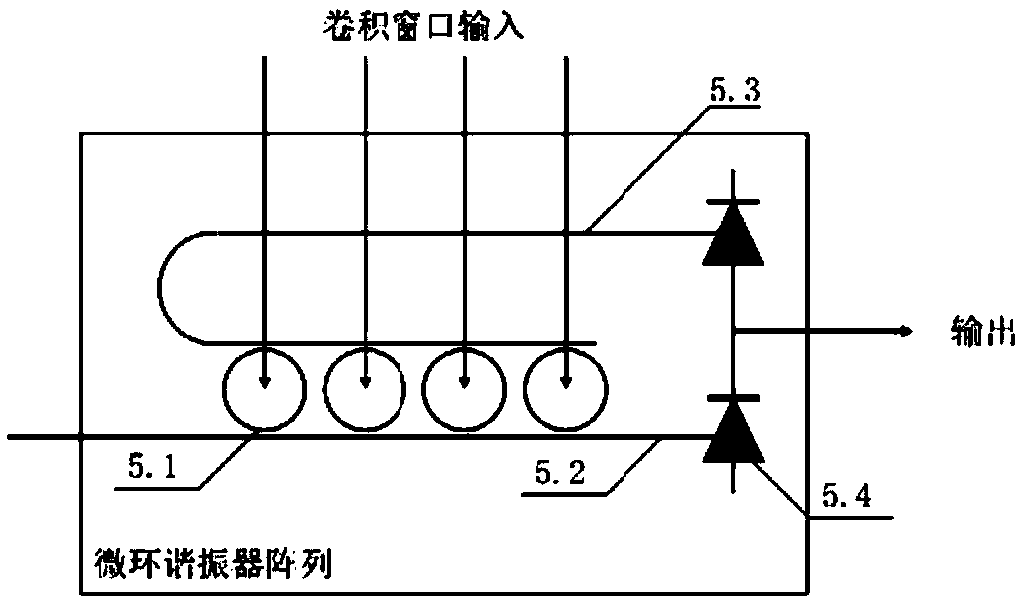
The invention discloses a photonic neural network convolutional layer chip based on a micro-ring resonator. The chip is universal to all deep learning technologies including convolutional calculation.According to the chip, vectorized to-be-calculated signals are loaded on different optical wavelengths by means of a wavelength division multiplexing mode. The micro-ring resonator and a balance photoelectric detector form a weight matrix, convolutional calculation of the to-be-calculated signals and the weight matrix can be completed, and a convolutional result is output. By utilizing the tunability of the integrated micro-ring resonator, the convolutional calculation of any numerical value can be realized. In addition, the speed of the convolutional calculation is increased to a constant level (that is, the speed of light) by using light as a numerical calculation medium, and the advantage of a higher energy efficiency ratio is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
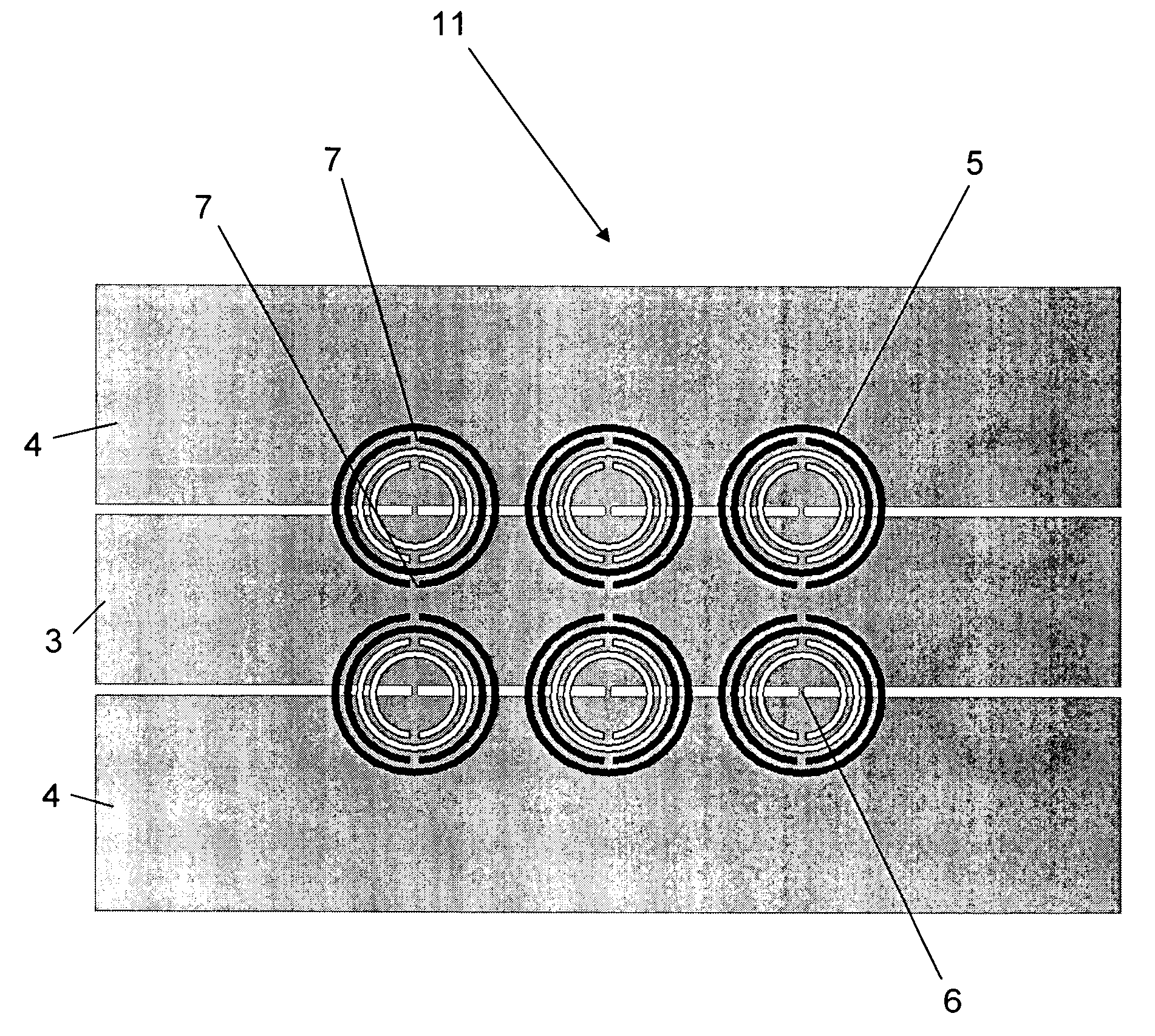
Filters and antennas for microwaves and millimetre waves, based on open-loop resonators and planar transmission lines
InactiveUS20070024399A1Good level of directivityGood level of polarisationResonatorsLoop antennasElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
Filter for microwaves and millimetER waves, characterised in that it comprises a planar transmission medium (1) that it includes a conductor strip (3), metallic ground plane (4) and dielectric substrate (2) and in that it includes at least one split rings resonator (5a, 5b, 5c, 5d, 5e and 5f)
Owner:AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF BARCELONA
Terahertz dual-band metamaterial based on electric resonance
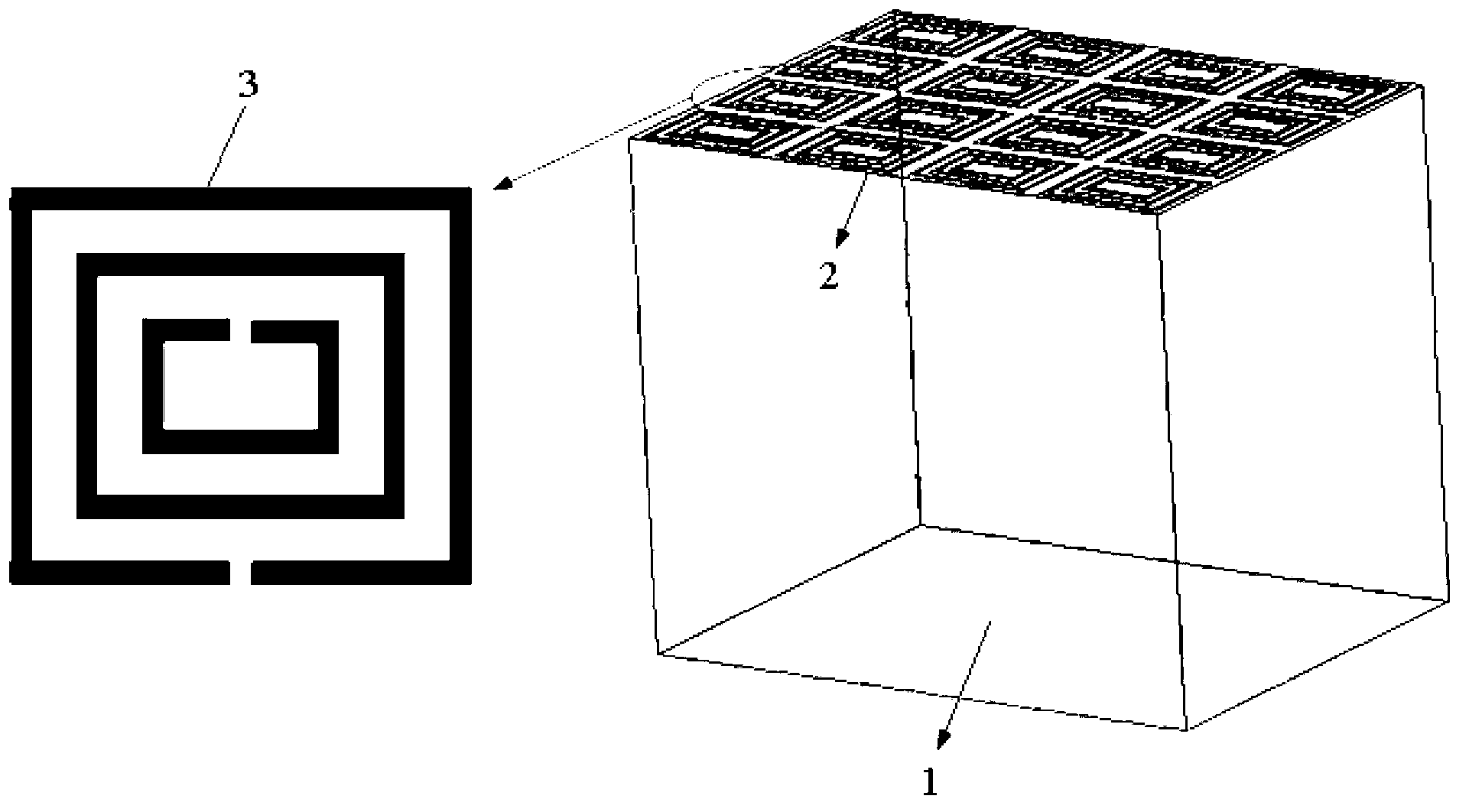
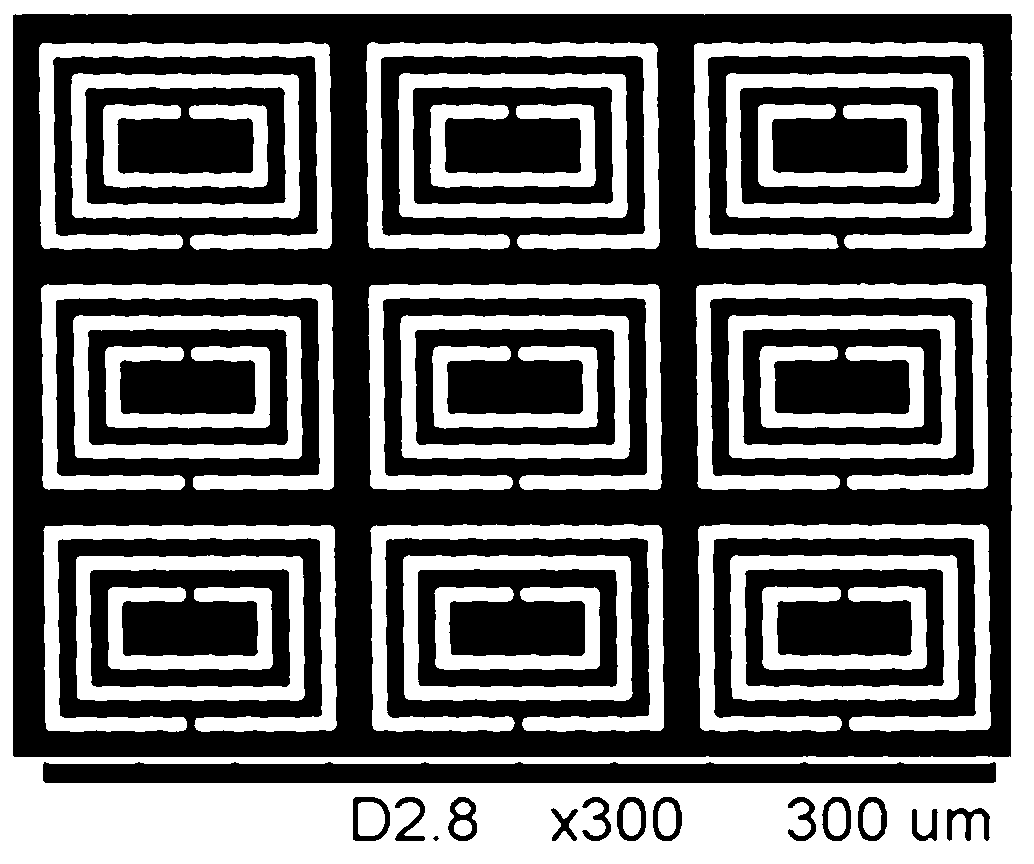
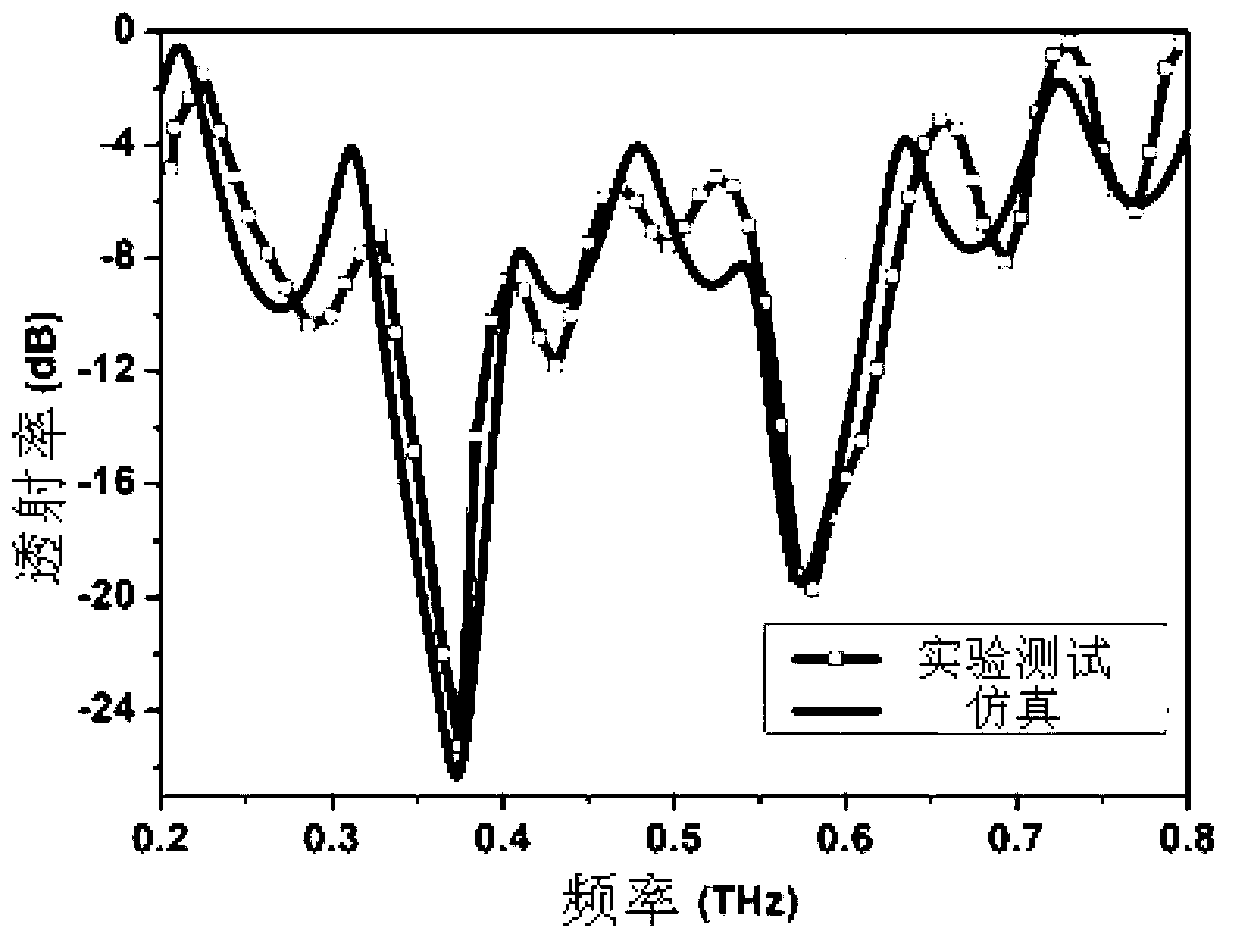
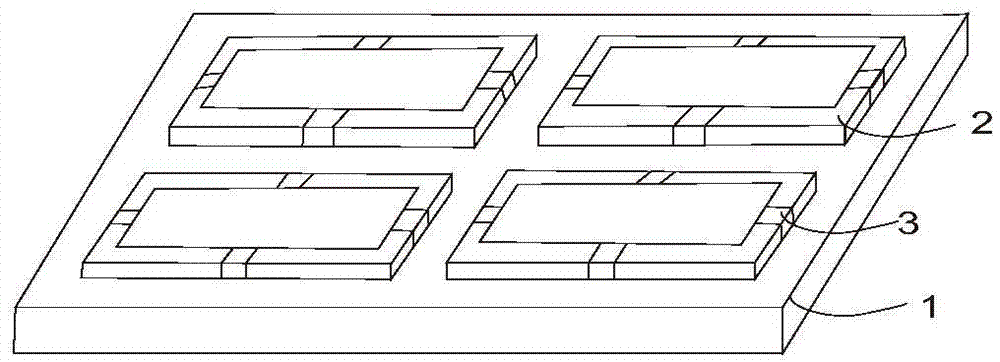
The invention relates to a terahertz dual-band metamaterial based on electric resonance. The metamaterial comprises a substrate and a metal layer unit, wherein the metal layer unit is provided with an electromagnetic resonance unit which comprises two split resonant rings and a closed ring; the closed ring is positioned between the two split resonant rings; and the metal layer unit is paved on the substrate in a periodic array manner. The terahertz double-band metamaterial is simple in structure and low in manufacturing cost, has the advantages of strong resonance, wide band and dual frequency points, can be effectively applied to terahertz function devices with various requirements on wide band design.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
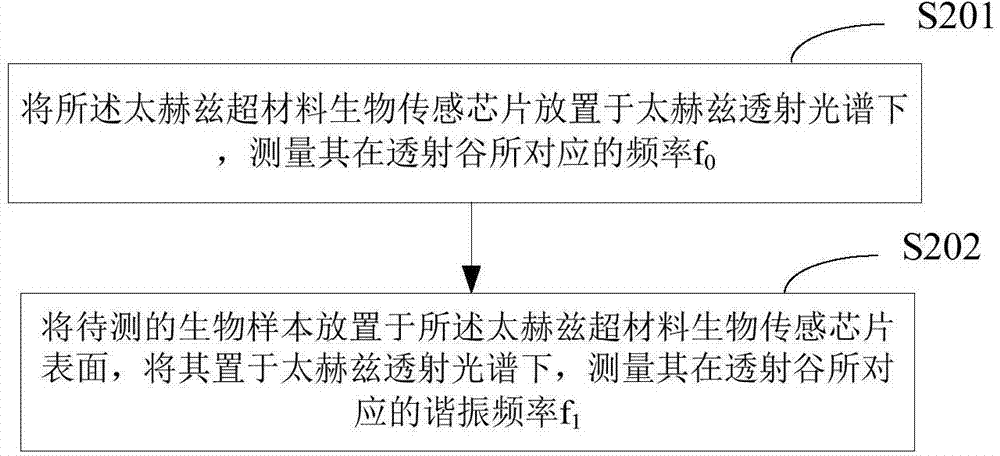
Terahertz metamaterial biosensing chip and testing method thereof
ActiveCN104764711AImprove uniformitySimple structural designMaterial analysis by optical meansTerahertz metamaterialsWavelength
The invention provides a terahertz metamaterial biosensing chip and a testing method of the terahertz metamaterial biosensing chip. The terahertz metamaterial biosensing chip comprises a substrate and a sub-wavelength metallic split-ring resonator array attached on the substrate, wherein the substrate is made of a material having the absorption coefficient less than 0.5-1cm under the terahertz waveband; the sub-wavelength metallic split-ring resonator array comprises multiple split-ring resonator units, each split-ring resonator unit is a square metal frame; and the middle parts of the edges of the square metal frame are provided with same openings respectively. Compared with the existing biosensor, the terahertz metamaterial biosensing chip is made of the terahertz metamaterial, so that the uniformity of the terahertz metamaterial biosensor structure is improved, and the sensing sensitivity is improved due to the uniformity and simple structure design.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Thermal microphotonic sensor and sensor array
ActiveUS7667200B1Promote absorptionImprove insulation performanceRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansResonant cavitySensor array
A thermal microphotonic sensor is disclosed for detecting infrared radiation using heat generated by the infrared radiation to shift the resonant frequency of an optical resonator (e.g. a ring resonator) to which the heat is coupled. The shift in the resonant frequency can be determined from light in an optical waveguide which is evanescently coupled to the optical resonator. An infrared absorber can be provided on the optical waveguide either as a coating or as a plate to aid in absorption of the infrared radiation. In some cases, a vertical resonant cavity can be formed about the infrared absorber to further increase the absorption of the infrared radiation. The sensor can be formed as a single device, or as an array for imaging the infrared radiation.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Switching-controllable THz wave metamaterial perfect absorber and control method thereof
InactiveCN103247839AMature processing technologyEasy to prepareWaveguide type devicesOptical elementsVanadium dioxidePhase change
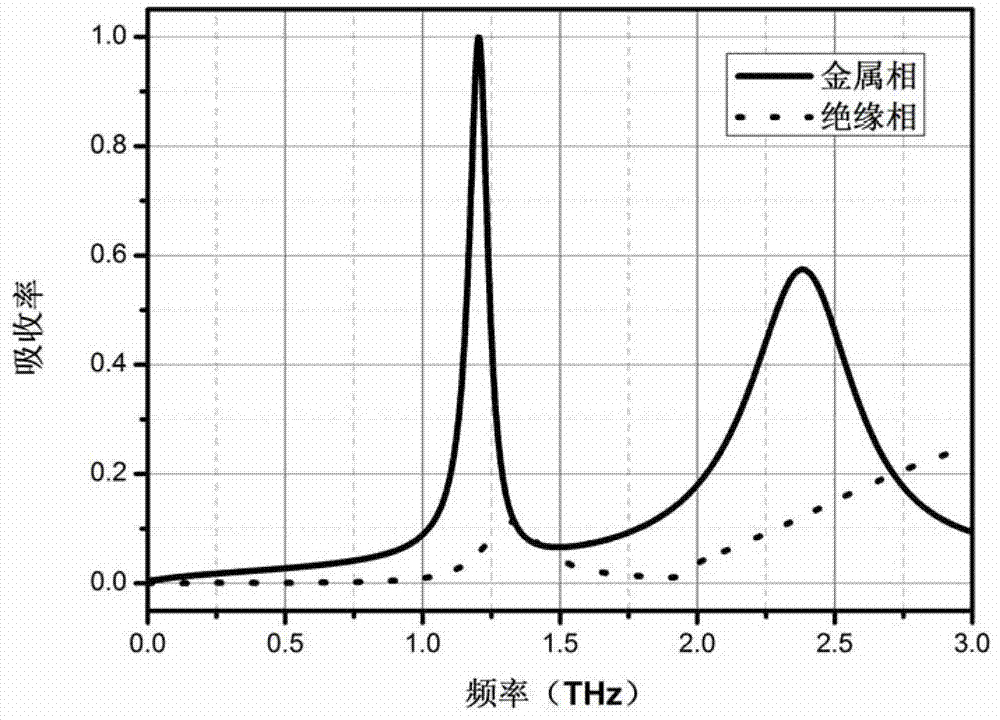
The invention relates to the field of metamaterial devices and provides a switching-controllable THz wave metamaterial perfect absorber (MPA) and a control method thereof. The switching-controllable THz wave metamaterial perfect absorber comprises a substrate, an MIT (metal-insulator transition) layer positioned on the substrate, a dielectric layer positioned on the MIT phase change layer and metal opening resonance units positioned on the dielectric layer and being in cyclic arrangement, and the on / off of the absorber at the resonance frequencies of the metal opening resonance units is realized through changing the conductivity of the MIT phase change layer. According to the invention, the variation of the conductivities of the MIT phase-change material before and after phase change is utilized to change the absorptivity of the absorber, so that the THz MPA can be turned on / off near the resonance frequency of the metal opening resonance units, initiative control of the electromagnetic transfer characteristics of THz wave bands at the specific frequency, and accordingly, a larger on-off ratio or modulation depth can be obtained; and the switching-controllable MPA adopting the substrate-vanadium dioxide-dielectric layer-SRRs (Split Ring Resonators) four-layer structure can control the conductivity of vanadium dioxide through an external field so as to control the absorptivity of the MPA.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tunable laser
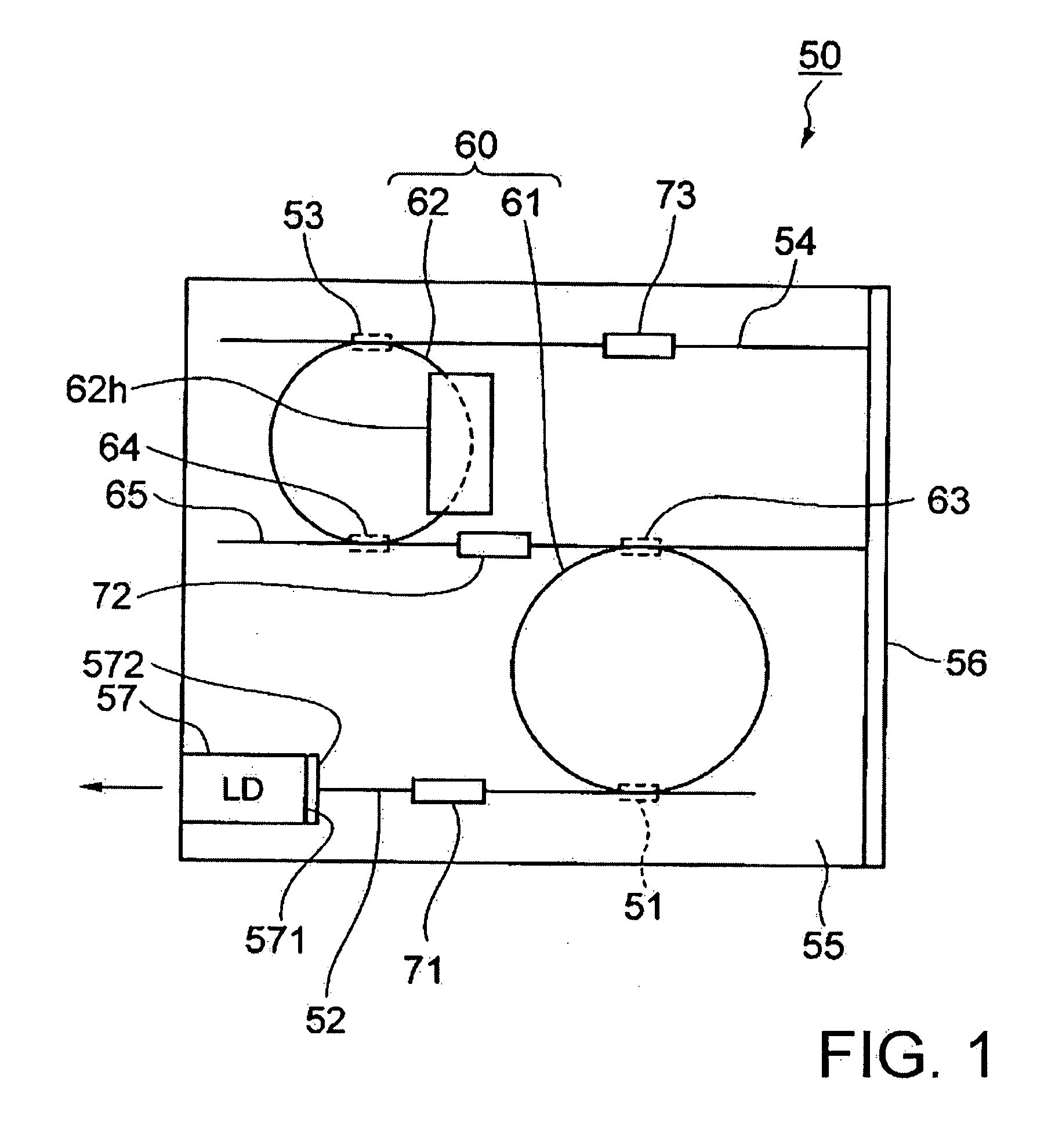
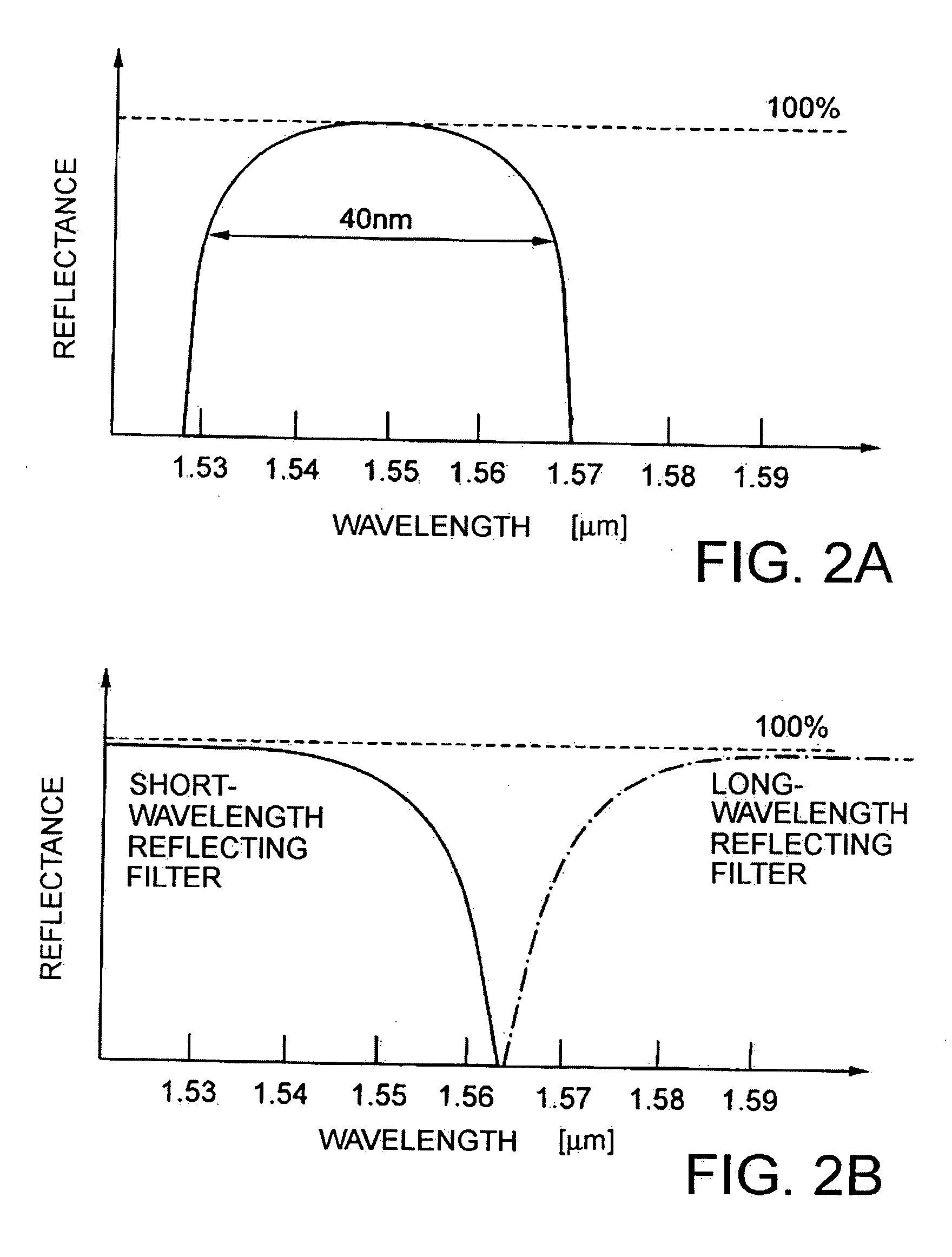
InactiveUS20060222039A1Improve reliabilityLow costLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionOptical reflectionOptical pathlength
A tunable laser has a multiple ring resonator comprising a plurality of ring resonators having respective ring-shaped waveguides and respective different optical path lengths, an input / output side optical waveguide coupled to the multiple ring resonator, an optical input / output device such as a laser diode coupled to the input / output side optical waveguide, a reflection side optical waveguide coupled to the multiple ring resonator, an optical reflector coupled to the reflection side optical waveguide for removing light at an unwanted wavelength and reflecting light at a required wavelength, and a wavelength varying mechanism for changing the resonant wavelength of the multiple ring resonator.
Owner:NEC CORP
Tunable Laser
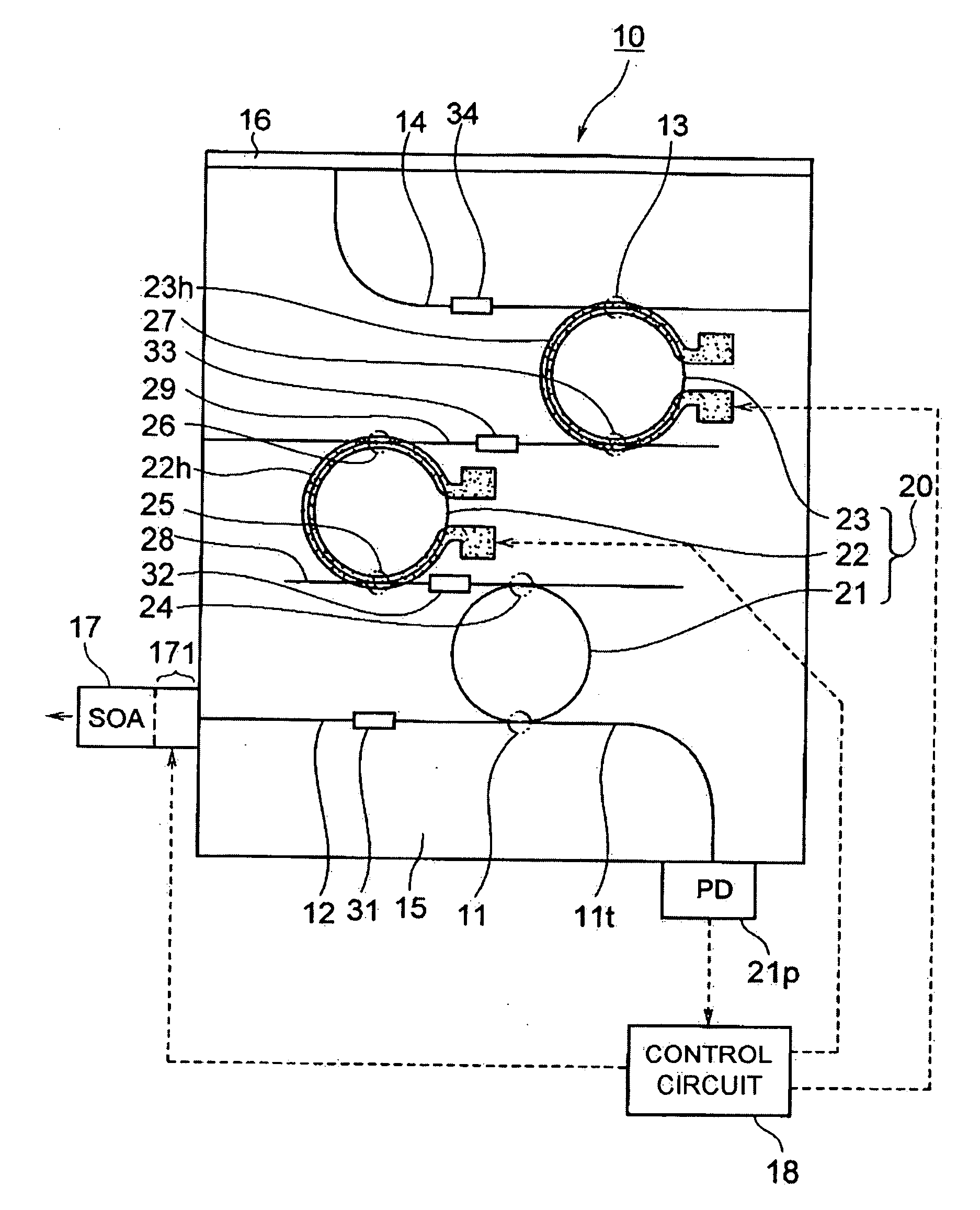
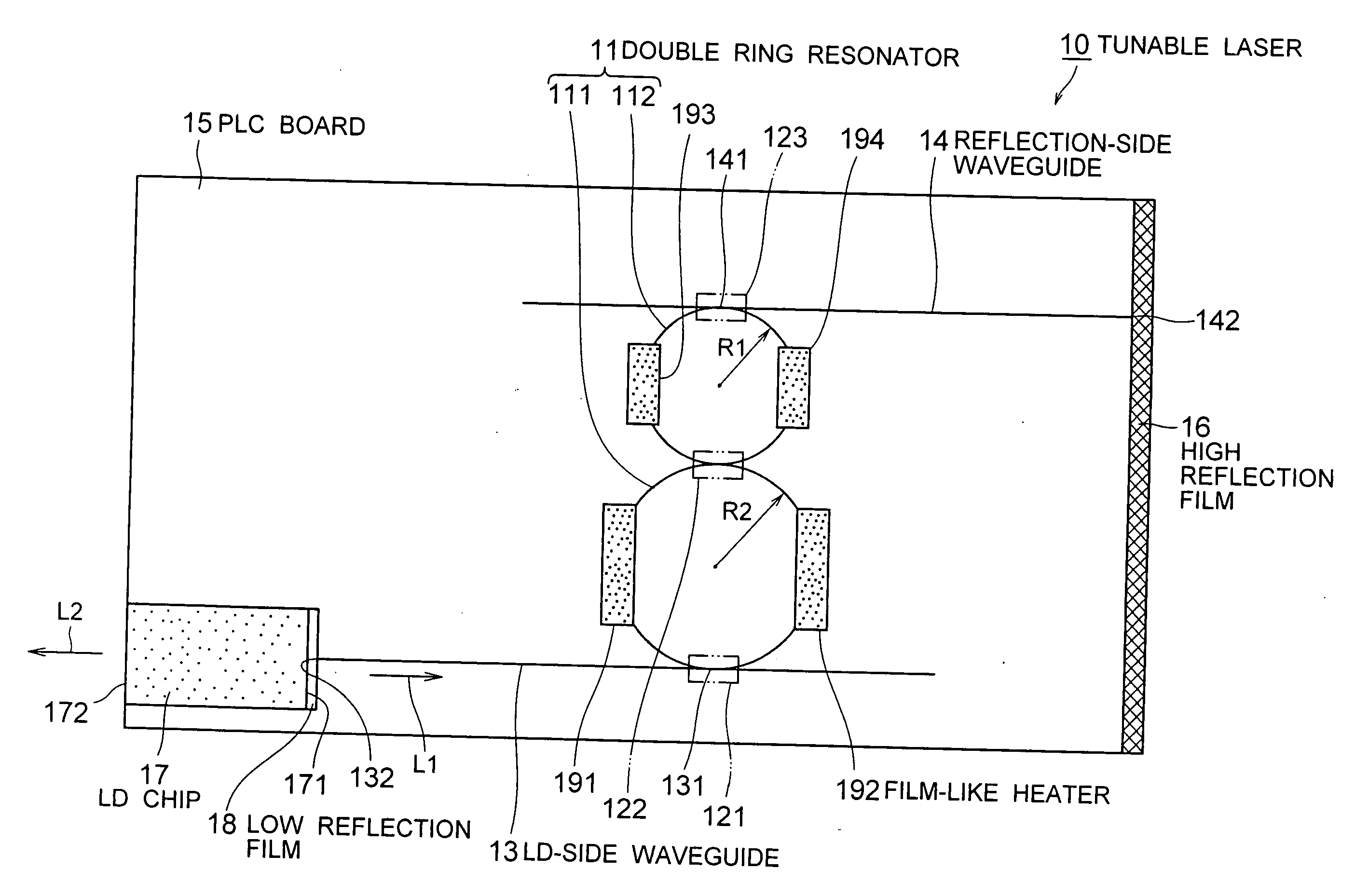
ActiveUS20080232409A1Promote generationHigh priceLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsResonance wavelengthWaveguide
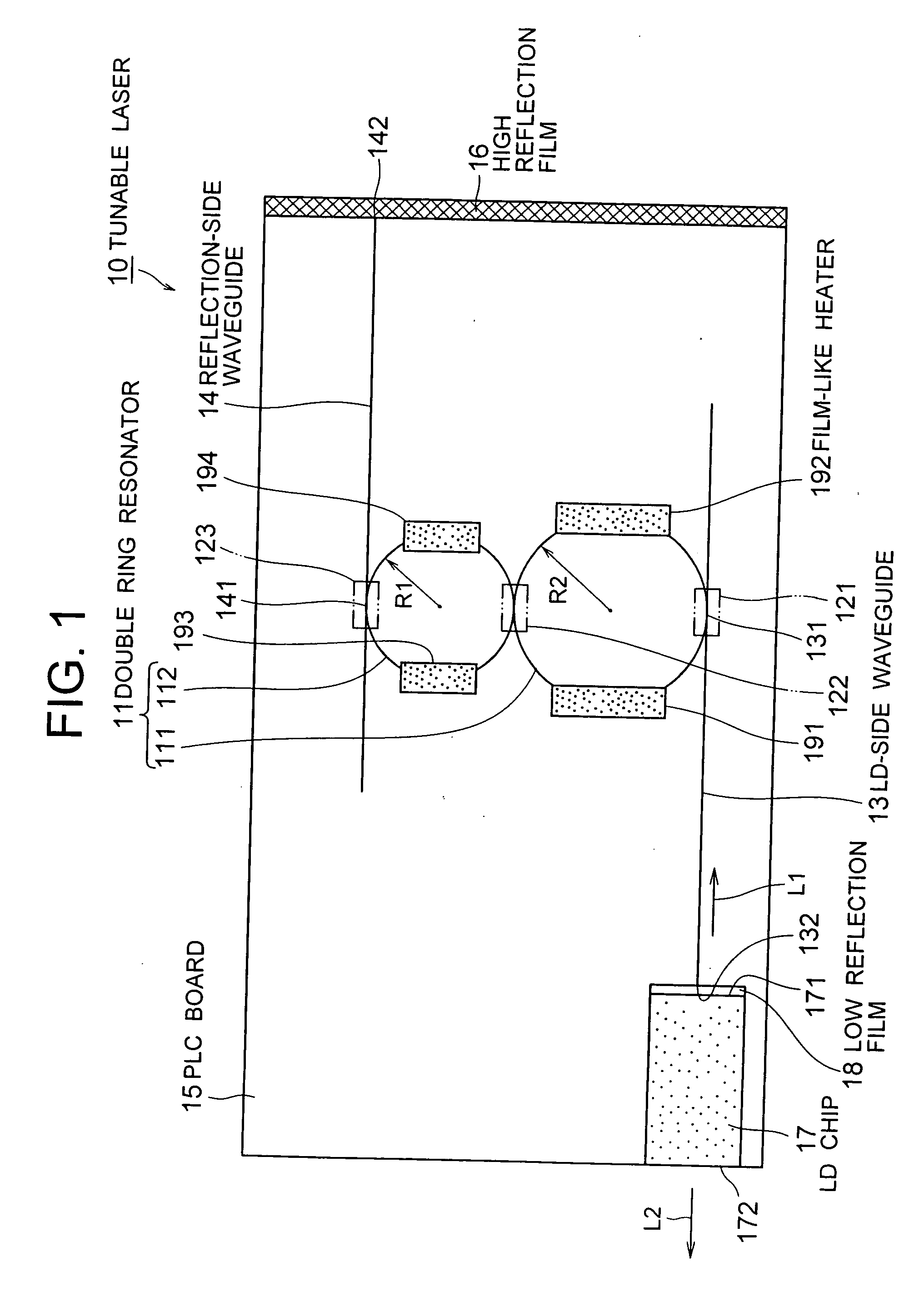
[Problems] To provide a tunable laser with high reliability and high performance, and of low cost.[Means for Solving Problems] A tunable laser (10) comprises a double ring resonator (11) where ring resonators (111, 112) of different sizes are coupled through a directional coupler (122), an LD side waveguide (13) connected at one end (131) to the ring resonator (111) through a directional coupler (123), a reflection side waveguide (14) connected at one end (141) to the ring resonator (112) through a directional coupler (123), a PLC board (15) on which the ring resonator (111) and the like are formed, a high reflection film (16) provided at the other end (142) of the reflection side waveguide (14), an LD chip (17) having a low reflection film (18) formed on either of two opposing emission end faces (171, 172) and coupled optically with the other end (132) of the LD side waveguide (13), and film-like heaters (191-194) for varying the resonance wavelength of the double ring resonator (11).
Owner:NEC CORP
Wavelength switchable semiconductor laser using half-wave coupled active double-ring resonator
ActiveUS20080123701A1Optimal single-mode selectivityOptical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesOptical pathlengthOptical coupler
A semiconductor laser comprises two optical ring resonators, each comprising an optical waveguide electrically pumped to provide optical gain. The two ring resonators have different round-trip optical path lengths, and are coupled to each other through a half-wave optical coupler. The half-wave optical coupler has a predetermined cross-coupling coefficient and a 180-degree cross-coupling phase. The cross-coupling coefficient is substantially less than the self-coupling coefficients in order to achieve an optimal single-mode selectivity of the laser. The first ring resonator has an optical path length such that its resonant wavelengths correspond to a set of discrete operating channels. The second ring resonator has a slightly different length so that only one resonant wavelength coincides with one of the resonant wavelengths of the first ring resonator over the operating spectral window. The lasing action occurs at the common resonant wavelength. In operation, at least a portion of the optical waveguide in each of the first and the second ring resonators are forward biased to provide substantially equal round-trip optical gains. The second ring resonator is tuned by varying the effective refractive index of a portion of the waveguide through an electrical means, resulting in wavelength switching among the set of discrete operating wavelengths as determined by the first ring resonator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
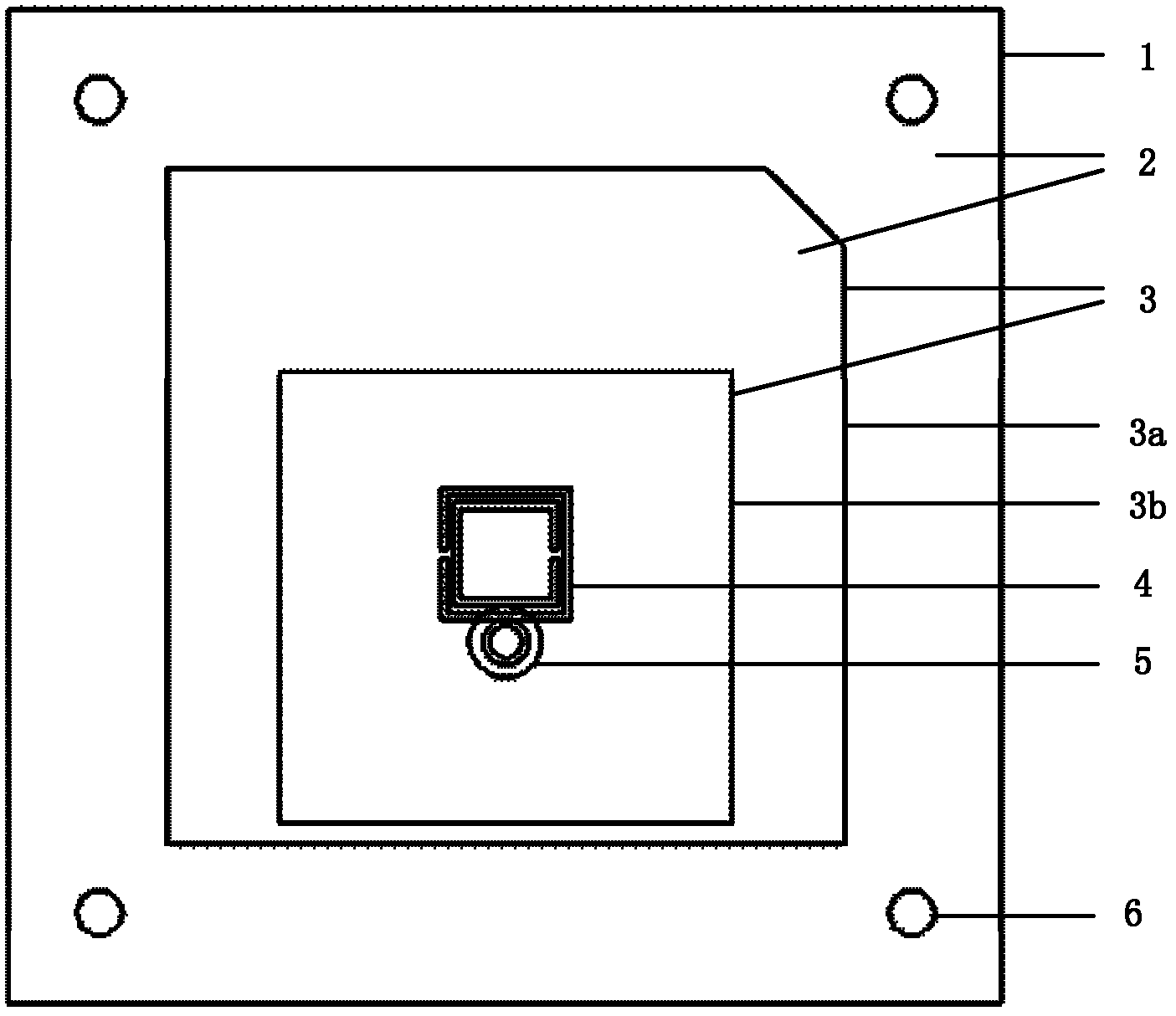
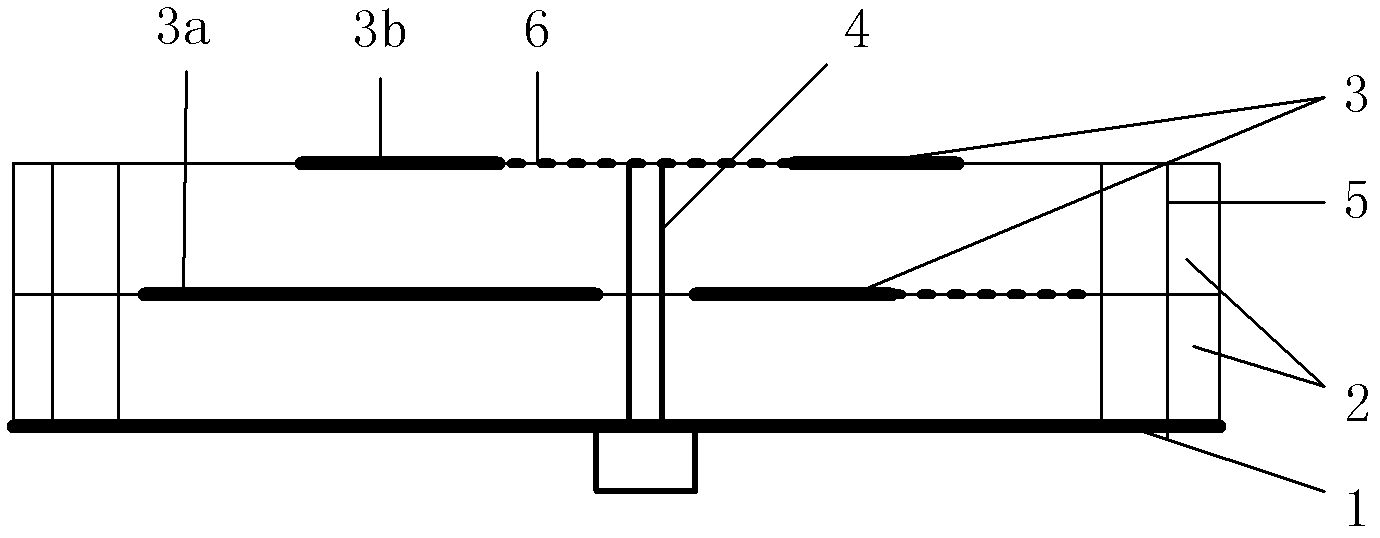
Single-fed dual-bandwidth wave beam circular polarization antenna
InactiveCN102610909AReduce areaIncrease electrical lengthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCircularly polarized antennaCoupling
The invention discloses a single-fed dual-bandwidth wave beam circular polarization antenna which comprises a metal floor (1), two layers of dielectric slabs (2), a radiation paster (3), a coaxial feed unit (4) and a metal bracket (5), wherein the radiation paster (3) comprises a coupling radiation paster (3a), from which a triangular corner is cut, and a main radiation paster (3b); complementary opening resonance rings (6) are etched on the main radiation paster (3b) and embedded with one another; the central points of the complementary opening resonance rings (6) are overlapped, and the opening directions are opposite; the main radiation paster (3b) is printed on the upper surfaces of the dielectric slabs (2); the coupling radiation paster (3a) is printed on the middle plane of the two layers of dielectric slabs (2); the coaxial feed unit (4) is arranged in the two layers of dielectric slabs (2) in a deviation manner; and the metal bracket (5) is symmetrically arranged on the four corners of the two layers of dielectric slabs (2). The dual-bandwidth circular polarization antenna with the characteristics of wide wave beam, high gain and low coupling is realized and can be applied to satellite communication.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Wide-angle polarization-insensitive low RCS meta-material wave absorber
InactiveCN104682013AWith incident anglePolarization insensitiveAntennasIncident waveRadar cross-section
The invention relates to a wide-angle polarization-insensitive low RCS (Radar Cross Section) meta-material wave absorber. The wide-angle polarization-insensitive low RCS meta-material wave absorber is applied to great reduction of a target echo, thereby achieving the stealth characteristic of a target. A basic unit of the wave absorber consists of four double-opening resonant rings which are rotationally symmetric, the transmission number of a meta-material unit in a working band is 0, the minimum reflection coefficient is minus 18.75dB, the maximum wave absorption rate is 98.9 percent, and a perfect wave absorbing effect is achieved. The TE and TM polarization incident wave within a range of minus 60 degrees to 60 degrees can be absorbed, the maximum decrement of an RCS in the working band can reach 12.35dB, and the effective stealth of the radar target is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
All-silicon raman amplifiers and lasers based on micro ring resonators
InactiveUS7532656B2Laser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionMicrowaveWhispering gallery
Devices for generating a laser beam are disclosed. The devices include a silicon micro ring having at least one silicon optical waveguide disposed at a distance from the micro ring. The radius and the cross-sectional dimension of the microring, the cross-sectional dimension of the waveguide, and the distance between the micro ring and the waveguide are determined such that one or more pairs of whispering gallery mode resonant frequencies of the micro ring are separated by an optical phonon frequency of silicon. Methods of manufacturing a lasing device including a silicon micro ring coupled with a silicon waveguide are also disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Wavelength tunable laser diode using double coupled ring resonator
InactiveUS20090154505A1Improve output characteristicsRapid wavelength tunabilityLaser detailsOptical light guidesProduction rateLength wave
A wavelength tunable laser diode using a double coupled ring resonator is provided. A new double coupled ring resonator structure is formed by a connection of two ring resonators having different radii so that stable laser oscillation occurs only in a resonant wavelength at which the two ring resonators are simultaneously resonated, and the effective refractive index of the two ring resonators is properly controlled differently for tunable laser oscillation wavelengths. The reproducibility of the optical coupling characteristics of the passive waveguides and the ring resonator can be assured by multi-mode couplers. This results in improved manufacturing productivity of the wavelength tunable laser diode. It is possible to amplify and output an output light without having an effect on oscillation wavelength characteristic by means of an optical amplifier integrated in an output end.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Low-loss four-port non-blocking optics router based on micro-ring resonator
InactiveCN103091784ASimple structureReduce areaOptical light guidesNetwork architectureOptical interconnect
The invention discloses a low-loss four-port non-blocking optics router based on micro-ring resonators. Through six cross waveguide micro-ring resonators and a parallel waveguide micro-ring resonator, an input end of a first port is coupled to an output end of a fourth port. An input end of a second port is coupled to an output end of the first port. An input end of the fourth port is coupled to an output end of a third port. The input end of the first port is coupled to the output end of the third port. An input end of the third port is coupled to an output end of the second port. The input end of the second port is coupled to the output end of the fourth port. A seventh micro-ring resonator is used for being connected with an optical channel from the fourth port to the first port and an optical channel from the second port to the third port. Due to the fact that the number of the micro-ring resonators is reduced to seven, the low-loss four-port non-blocking optics router based on the micro-ring resonators has the advantages of improving utilization efficiency of devices, simplifying the structure of a switch, decreasing area of the switch, reducing insertion loss and crosstalk of the switch due to the fact that the number of the cross waveguide micro-ring resonators is reduced to six, enhancing extendibility of the devices, being prone to establishing an on-chip optical interconnection network architecture and achieving high-speed transmission and exchange of optical signals.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
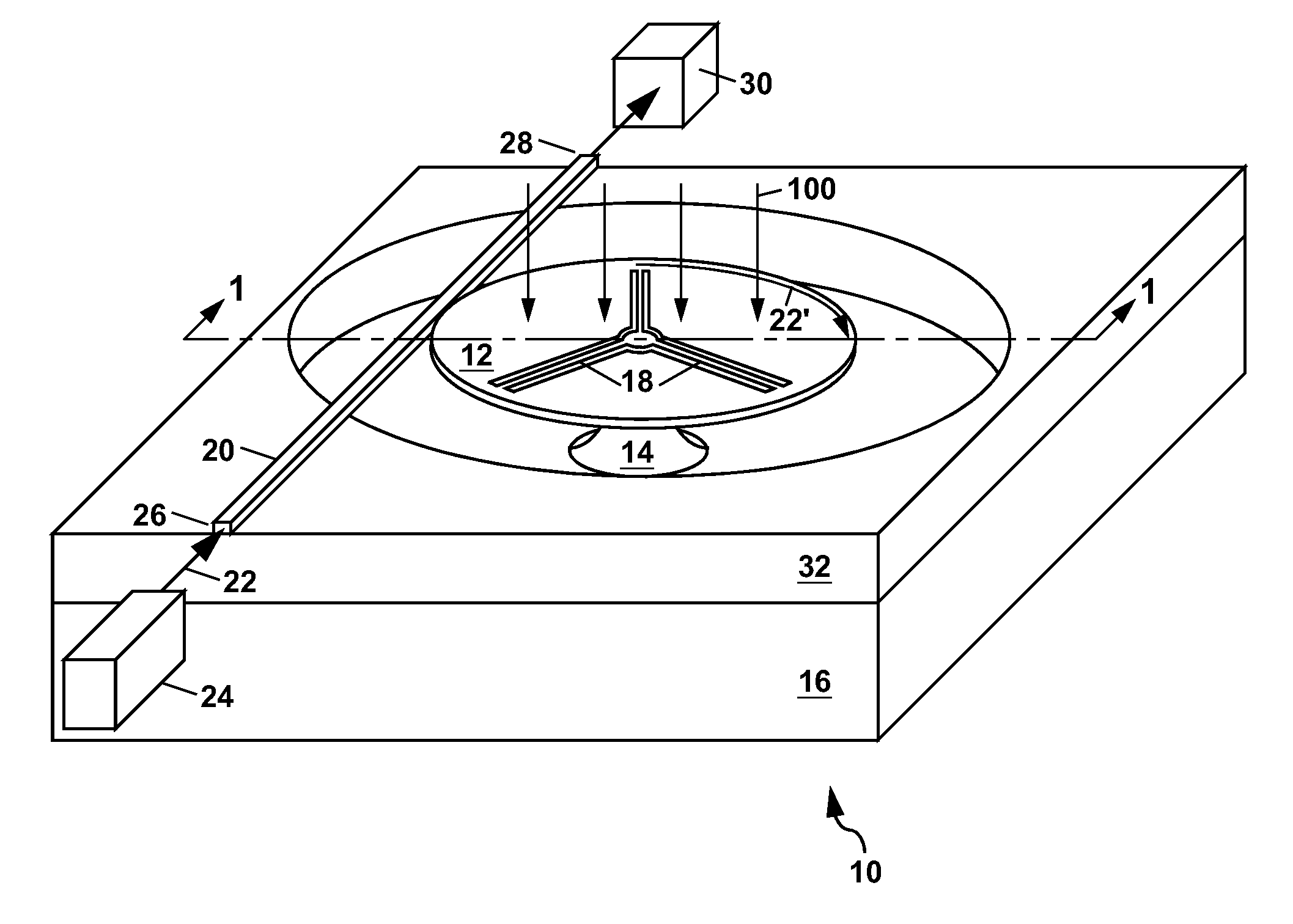
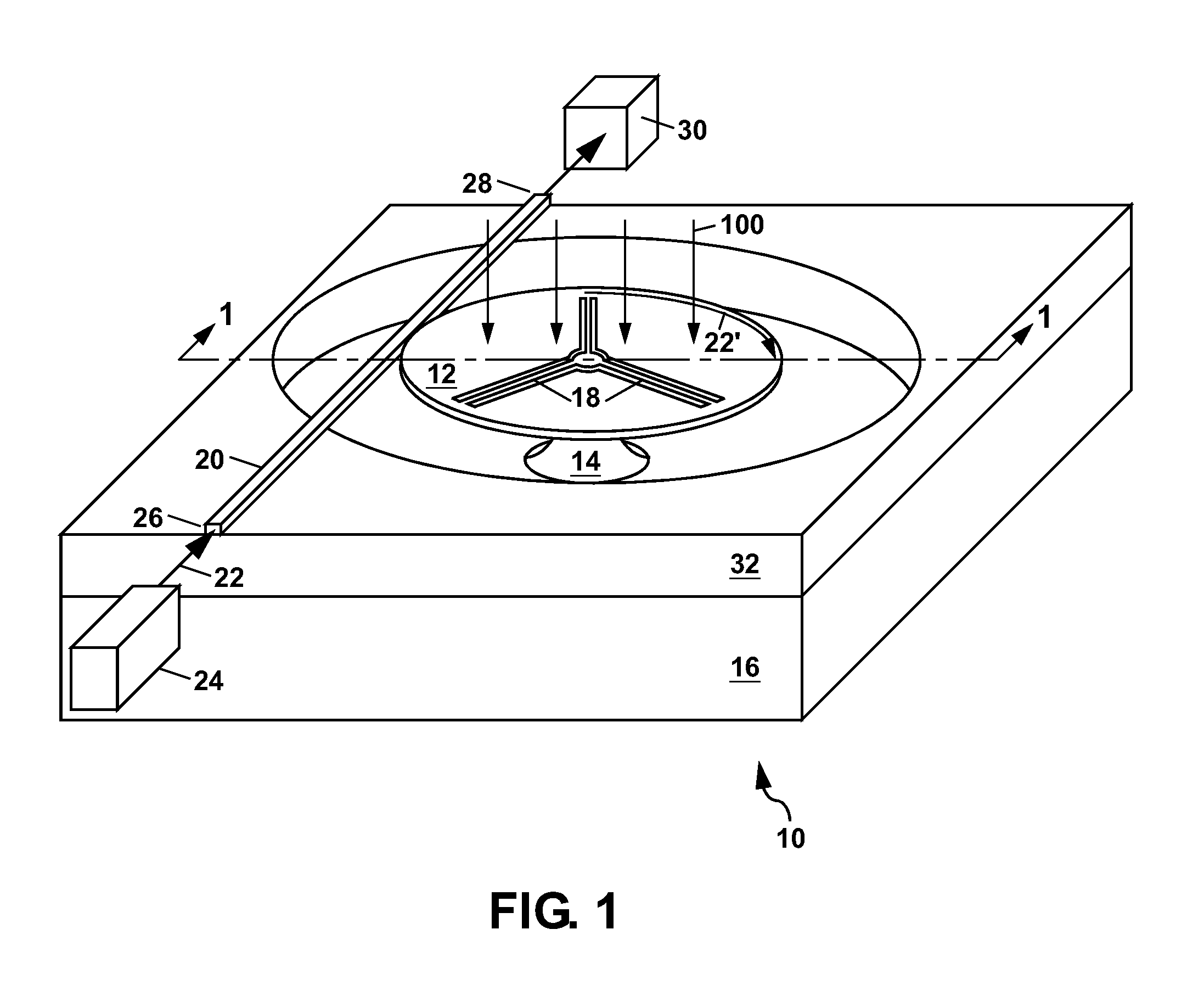
RFID system
ActiveUS20090295659A1Impedance can be adjustedBeverage vesselsAntennas earthing switches associationSplit ring resonatorsCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field focusing assembly includes a magnetic field generating device configured to generate a magnetic field, and a split ring resonator assembly configured to be magnetically coupled to the magnetic field generating device and configured to focus the magnetic field produced by the magnetic field generating device.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Hollow core fiber optical gyro
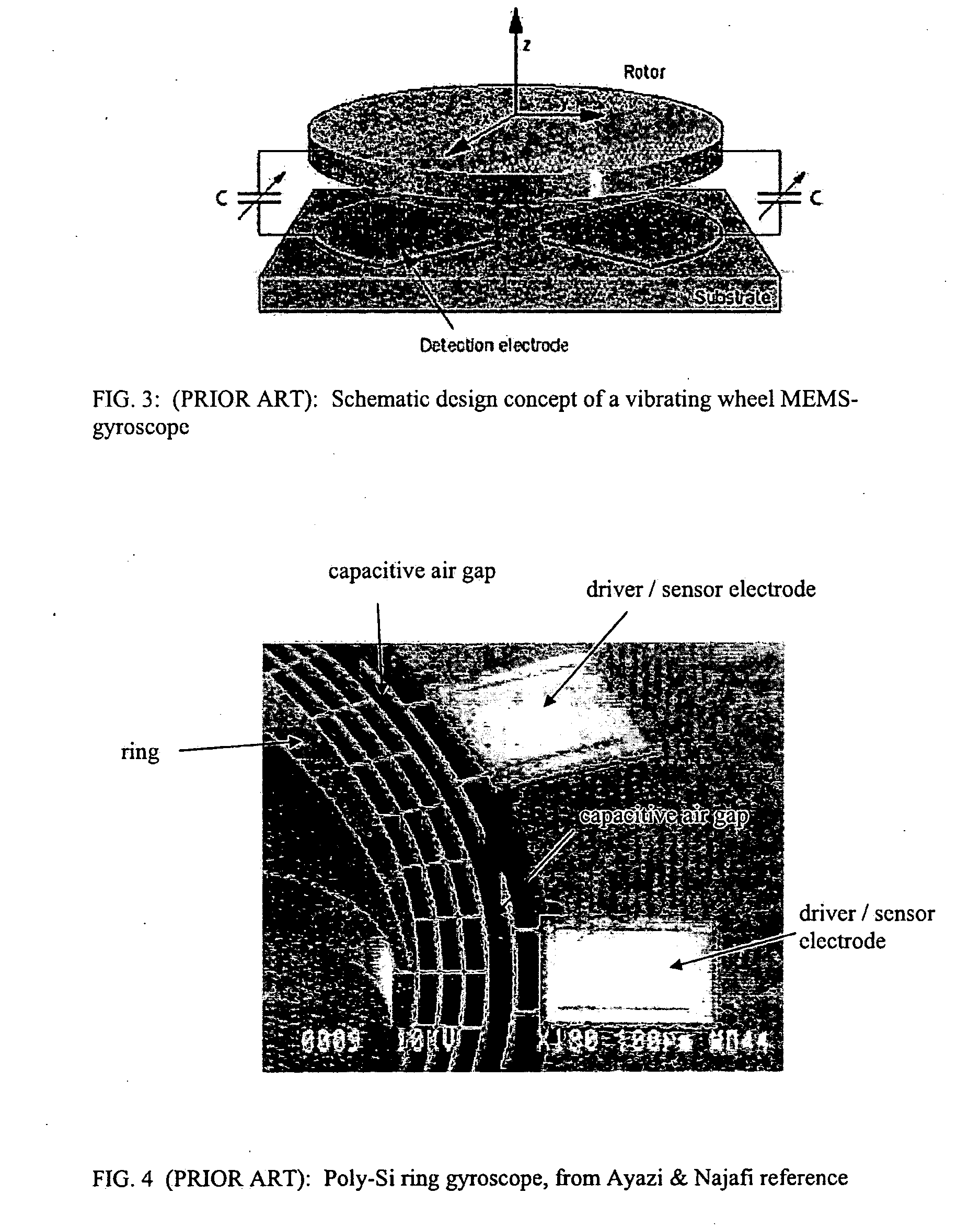
Apparatus is provided for a fiber optic gyro. The fiber optic gyro includes a ring resonator having first and second counter-propagating directions. The ring resonator includes a coil having an axis and an optical fiber having a hollow core. The ring resonator is configured to produce a first resonance frequency when a first light beam circulates through the hollow core in the first counter-propagating direction and produce a second resonance frequency when a second light beam circulates through the hollow core in the second counter-propagating direction. A difference between the resonance frequencies indicates a rotation rate of the fiber optic gyro about the axis.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Combined microwave sensor and dielectric constant measurement method for measured object
ActiveCN107490727AAccurate measurementAccurate and reliable measurement resultsResistance/reactance/impedenceSpurlineDielectric permittivity
A combined microwave sensor comprises metal ground at the bottom layer, dielectric at the middle layer, an input port, an output port I, a branched line coupler, a power divider, an open resonant ring, a microstrip line I and a microstrip line II, wherein the input port, the output port I, the branched line coupler, the power divider, the open resonant ring, the microstrip line I and the microstrip line II are arranged in the top layer. The input port and the output port I are connected with a vector network analyzer. The output side of the branched line coupler is provided with an isolated port and the output port I. The input end of the power divider is connected with the input port. The output port II and the output port III are connected with an annular directional coupler through a microstrip line. The open resonant ring is arranged between the power divider, the branched line coupler and the two microstrip lines. The combined microwave sensor has advantages of effectively eliminating background noise, realizing testing for weak background signals, and ensuring large offset of the sensor resonant frequency through small disturbance of the tested object. Therefore the combined microwave sensor provided by the invention has higher sensitivity and higher accuracy in dielectric constant measurement and can be used in high-sensitivity testing with small dielectric constant change.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
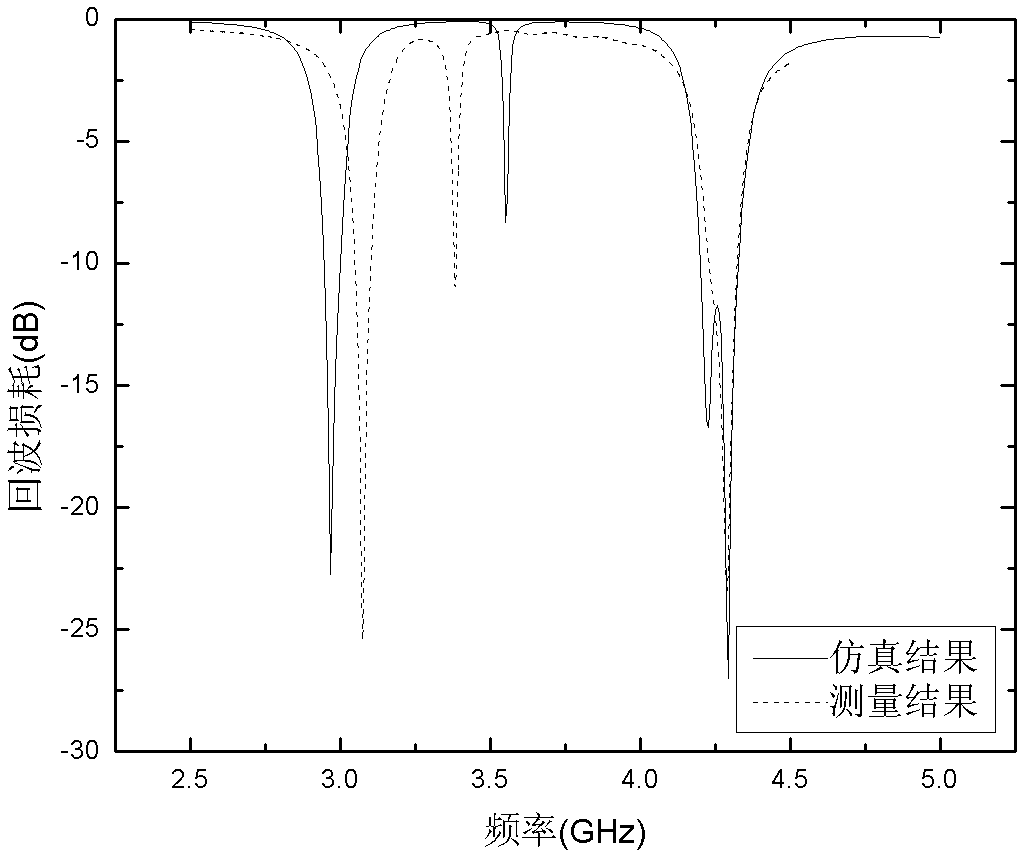
Ultra wideband antenna with four-notched band characteristics
InactiveCN102570023AReduce areaImproved high-frequency impedance matching characteristicsRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsUltra-widebandCoplanar waveguide
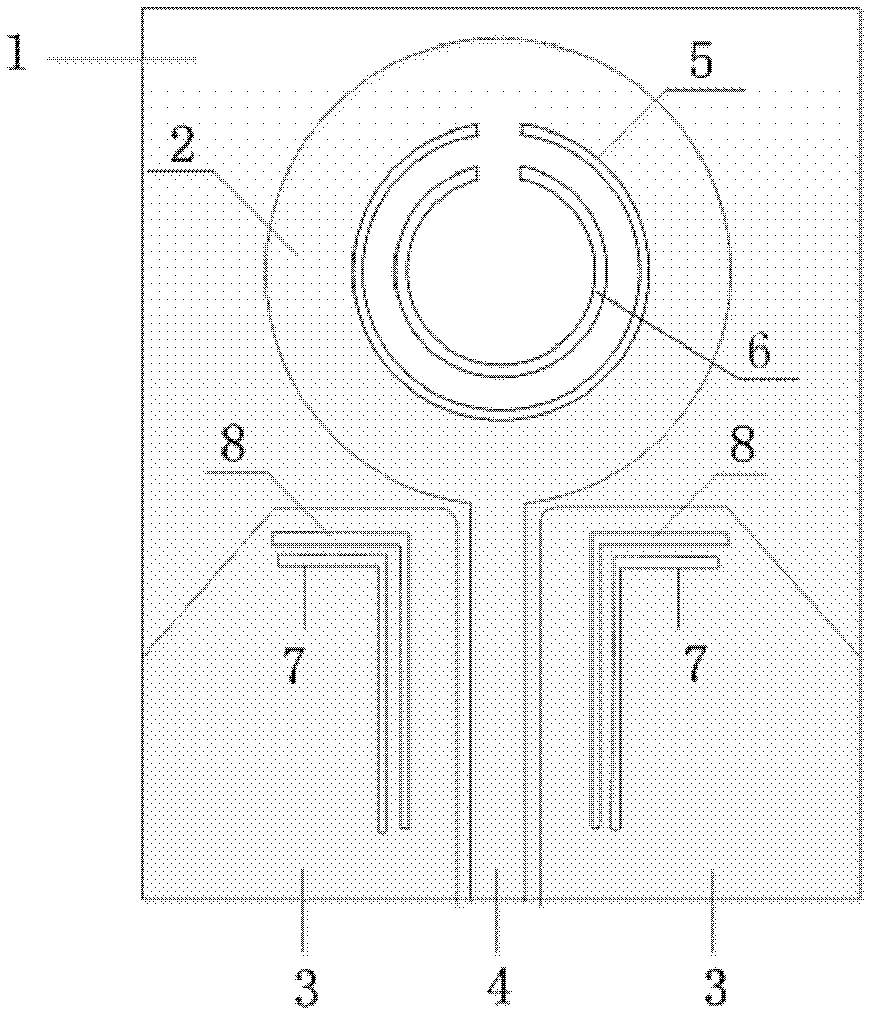
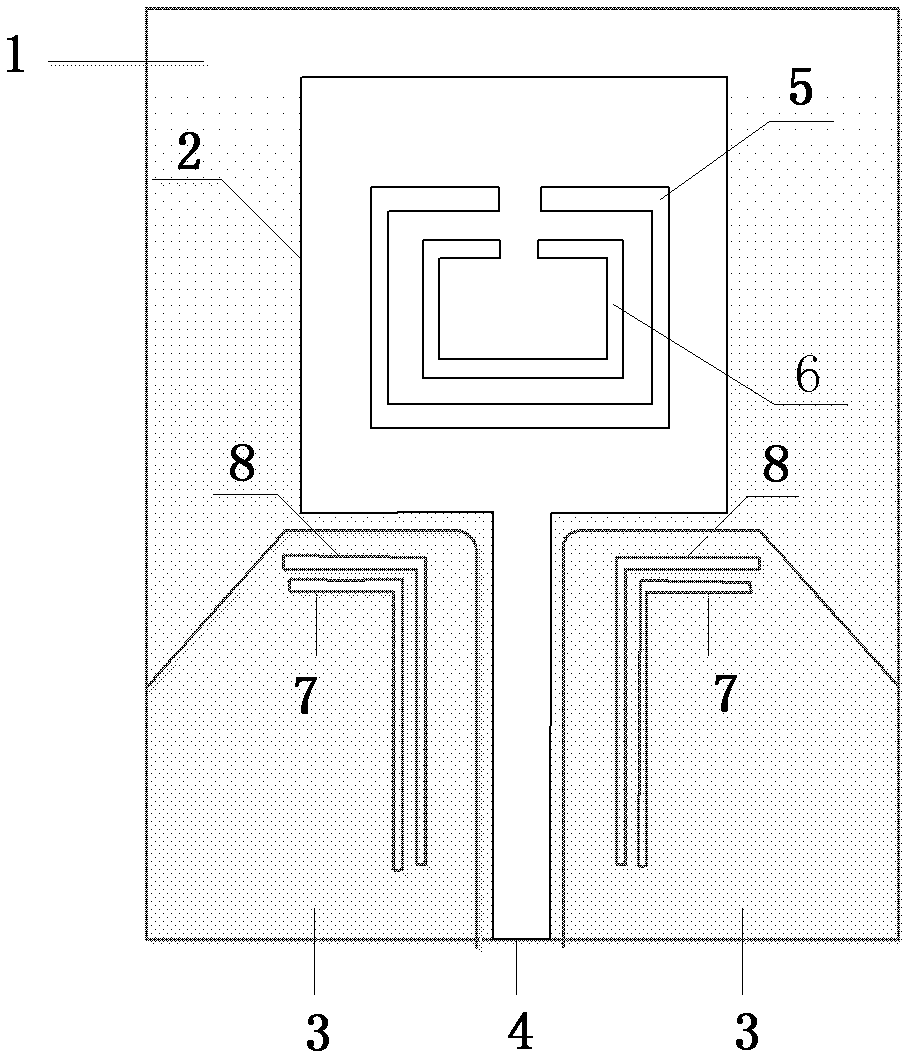
The invention discloses an ultra wideband antenna with four-notched band characteristics. The antenna comprises a dielectric substrate (1), a radiating unit (2), two coplanar waveguide grounding planes (3) and a coplanar waveguide feed micro-strip line (4), wherein all the radiating unit (2), the coplanar waveguide grounding planes (3) and the coplanar waveguide feed micro-strip line (4) are printed on the front surface of the dielectric substrate (1); two complementary split ring resonators (5 and 6) are etched on the radiating unit (2); the two coplanar waveguide grounding planes (3) are positioned on the two sides of the coplanar waveguide feed micro-strip line (4) respectively; two pairs of inverted L-shaped slots (7 and 8) are etched on the coplanar waveguide grounding planes (3); and the split ring resonators (5 and 6) and the inverted L-shaped slots (7 and 8) form four notched bands. The working band of the antenna covers 2 to 12GHz, interference signals in the ultra wide working band can be well suppressed, and the antenna can be used for ultra wideband antenna communication.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Substrate integrated waveguide split ring resonator-based microwave band pass filter
ActiveCN102013537ASteep out-of-band attenuationReduce volumeWaveguidesUltrasound attenuationBand-pass filter
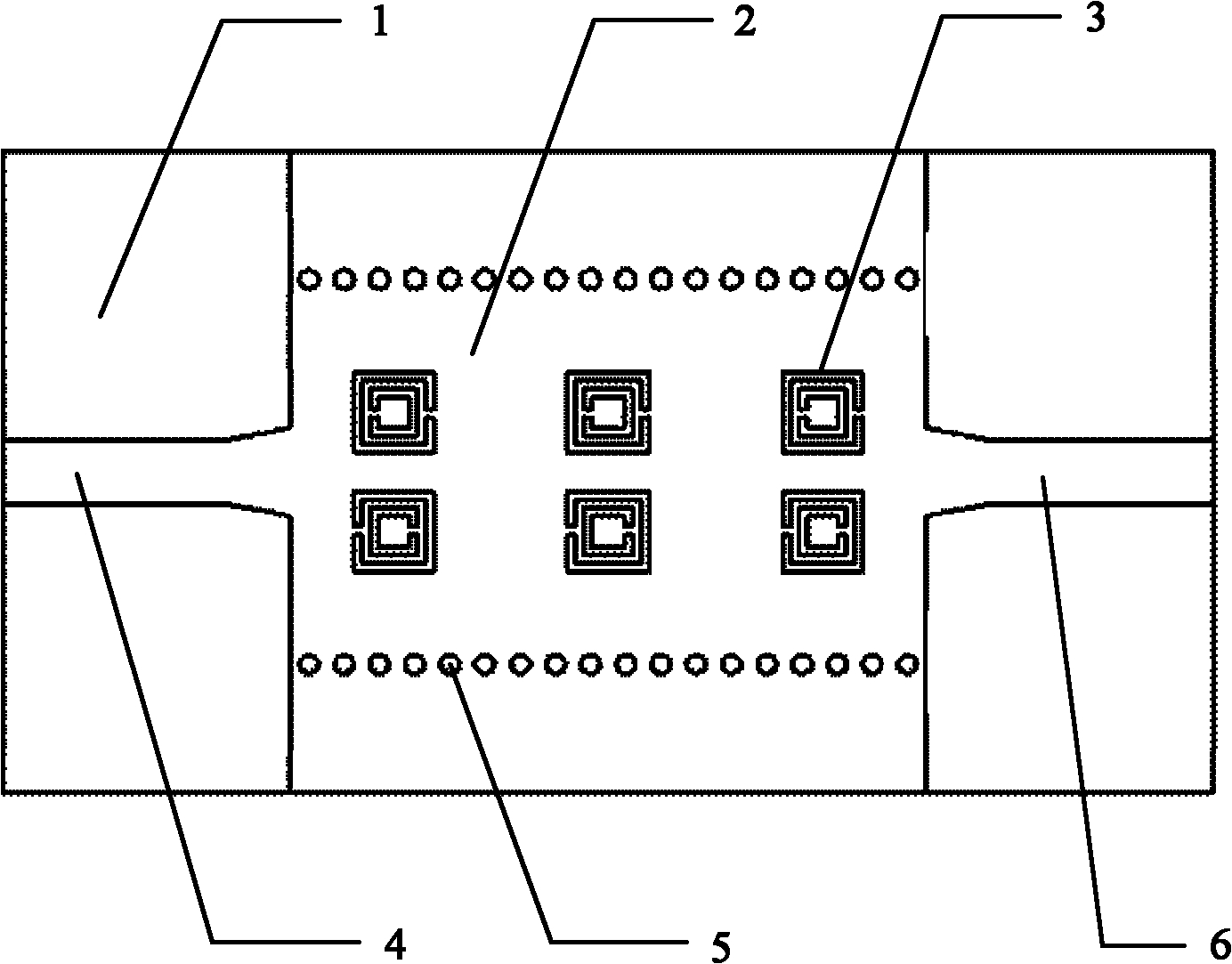
The invention discloses a substrate integrated waveguide split ring resonator-based microwave band pass filter. The microwave band pass filter comprises a substrate integrated waveguide which is formed by fixing two rows of metal members on a dielectric substrate, wherein the two ends of the substrate integrated waveguide are connected with a micro-strip feed line respectively; the surfaces of both the micro-strip feed line and the substrate integrated waveguide are made of metal dielectric; the upper surface of the substrate integrated waveguide is positioned between the two rows of metal members to corrode an m*n split ring resonator array; and a row of dumbbell-shaped area bodies or dumbbell-shaped deformation areas are corroded corresponding to each line of split ring resonators on the lower surface of the substrate integrated waveguide between the two rows of metal members. The band pass filter has the advantages of out-of-band steep attenuation, small volume, light weight and high power capacity and is easy to be integrated with other planar microwave and millimeter-wave circuits, so that the band pass filter is expected to be applied to the microwave and millimeter-wave integrated circuit or a millimeter wave integrated circuit.
Owner:ZTE CORP
High Frequency Ultrasound Detection Using Polymer Optical-Ring Resonator
ActiveUS20080095490A1Detection noise increaseIncreased signal noiseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationUltrasound pulse
A polymer waveguide resonator device for high-frequency ultrasound detection having a optical resonator coupled to a straight optical waveguide which serves as input and output ports. Acoustic waves irradiating the waveguide induce strain modifying the waveguide cross-section or other design property. As a consequence, the effective refractive index of optical waves propagating along the ring is modified. The sharp wavelength dependence of the high Q-factor resonator enhances the optical response to acoustic strain. High sensitivity is demonstrated experimentally in detecting broadband ultrasound pulses from a 10 MHz transducer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
High gain slot array antenna based on left-hand material
The invention discloses a high-gain gap array antenna based on a left-handed material, which is characterized in that the antenna has a multilayer structure and comprises three metal layers of a gap radiating layer (1), a feeding layer (2) and a reflecting layer (3); two air layers are formed among three metal layers; a coaxial joint (4) is used for feeding; the gap radiating layer (1) is formed by etching ringent resonant ring gaps (6) and rectangular narrow strip gaps (5) on the metal layer; the gaps form a periodic array as an antenna radiation unit; the feeding layer (2) comprises a T-shaped power splitting system (8) and a plurality of metal conduction bands (9); an input port of the T-shaped power splitting system in a coaxial feeding point (7) is connected with an inner conductor of the coaxial joint (4); each output port of the T-shaped power splitting system is connected with each metal conduction band (9) respectively; the metal conduction band is positioned right below each row of the ringent resonant ring; the gap radiating layer (1) and the reflecting layer (3) act as underground metal; the underground metal and the metal conduction bands (9) form a stripline transmission line. The high-gain gap array antenna has the advantages of high gain, simple manufacture and low cost.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com