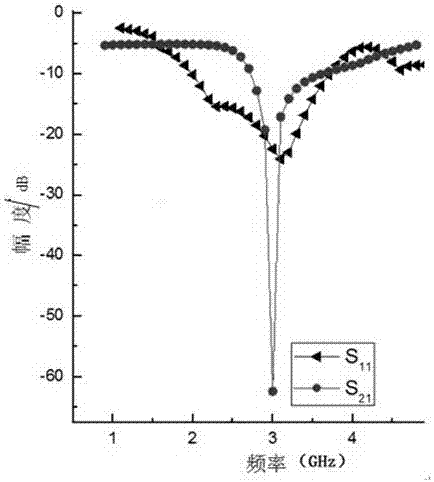
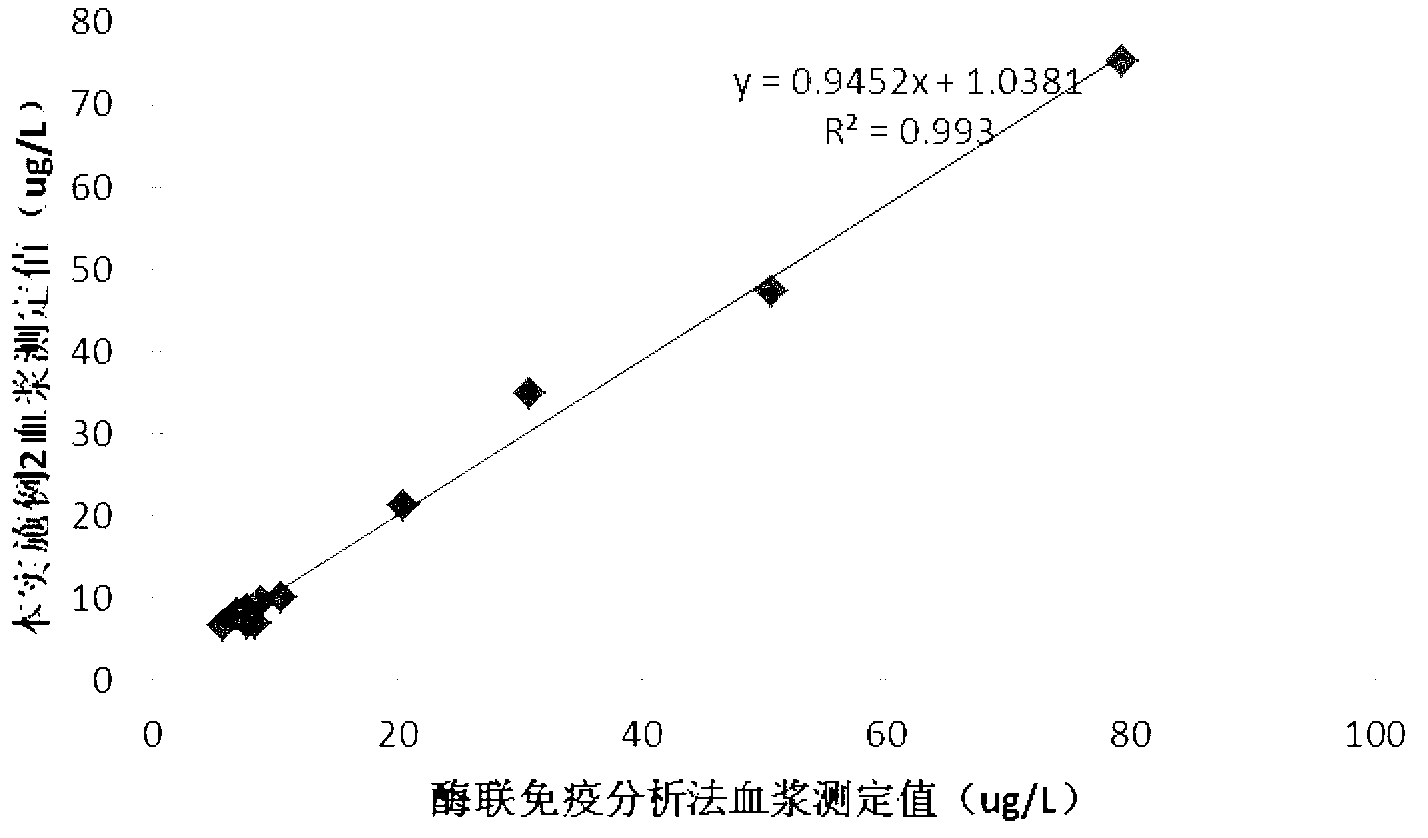
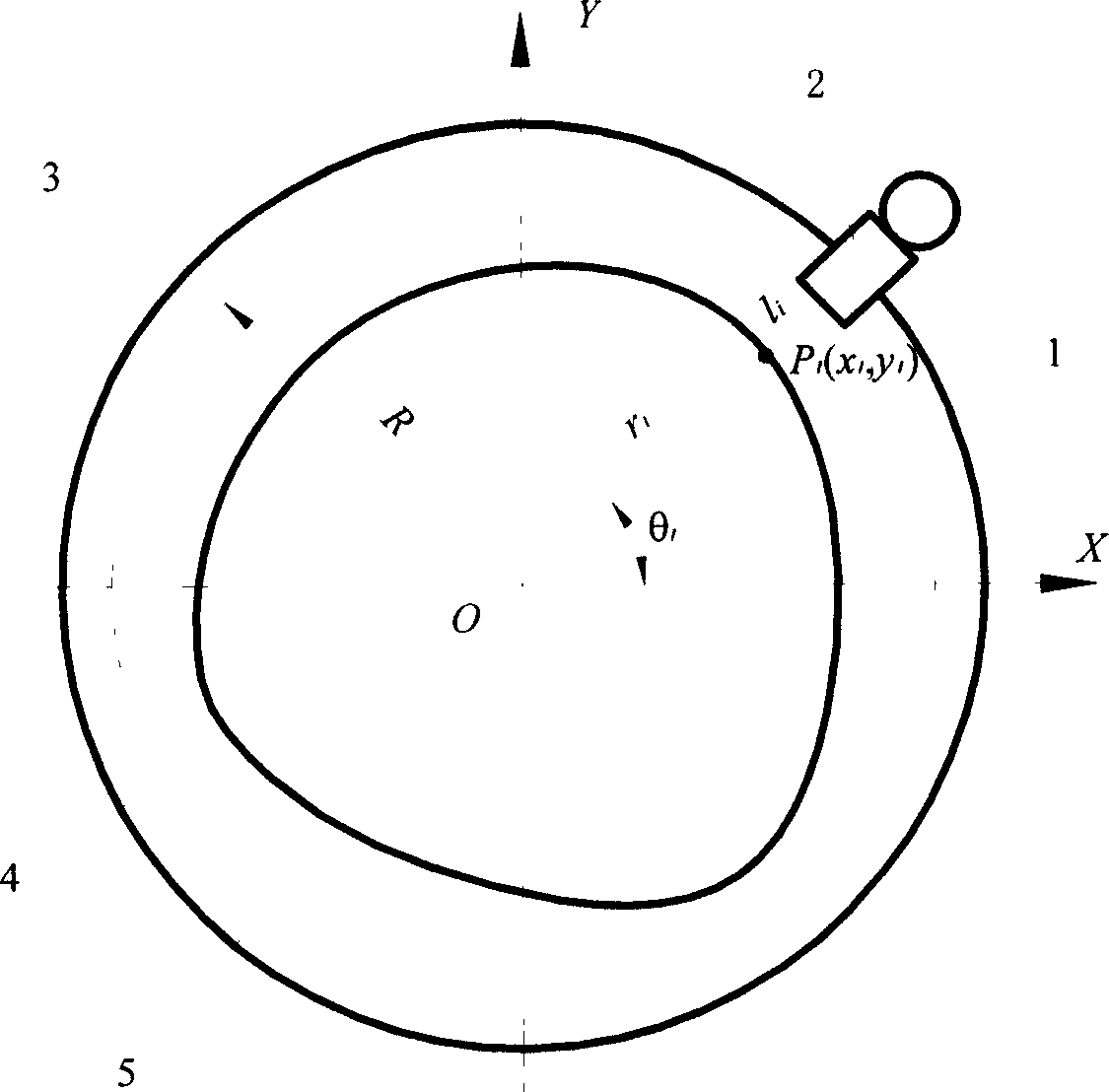Patents
Literature
1375results about How to "Accurate and reliable measurement results" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
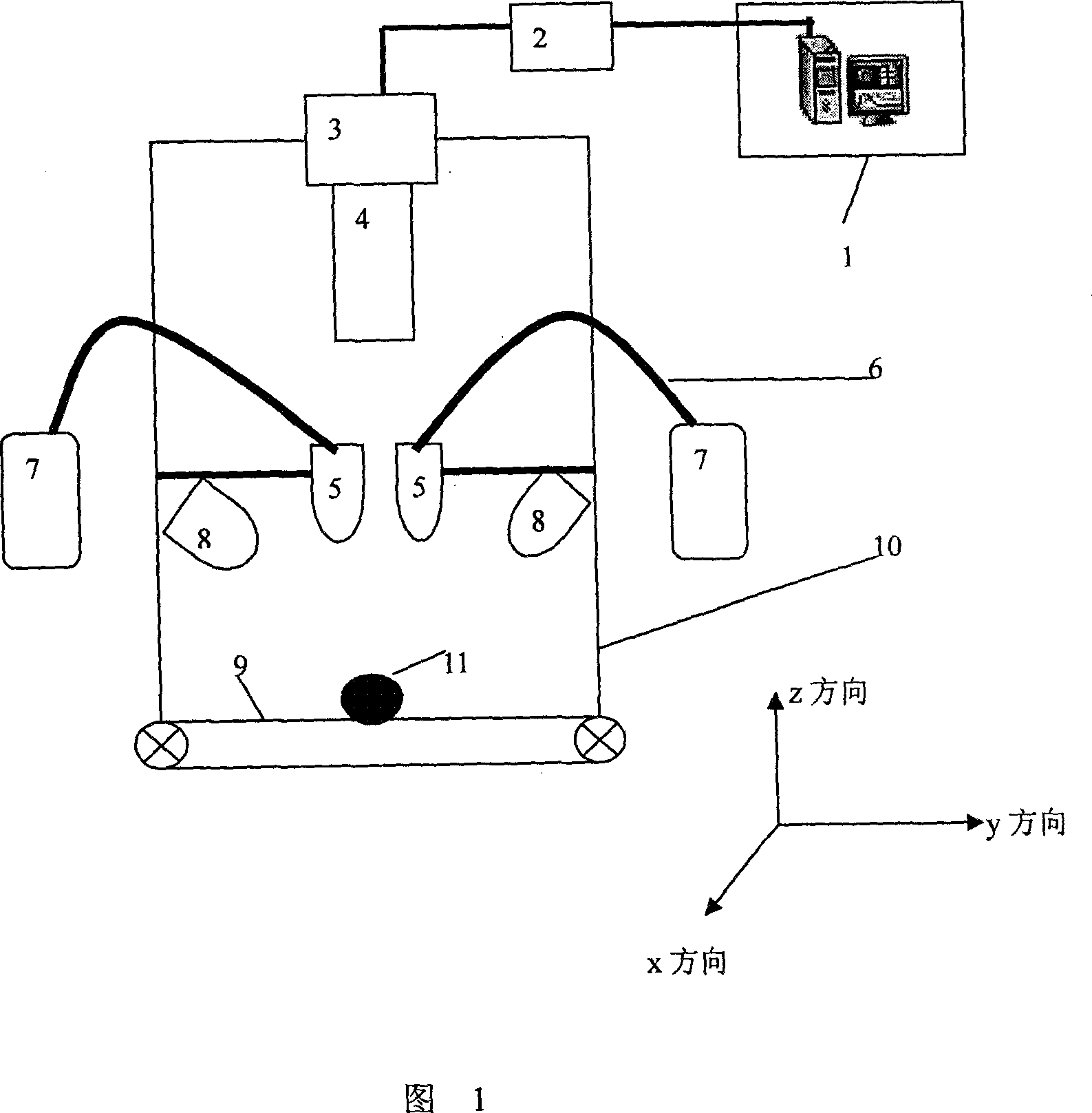
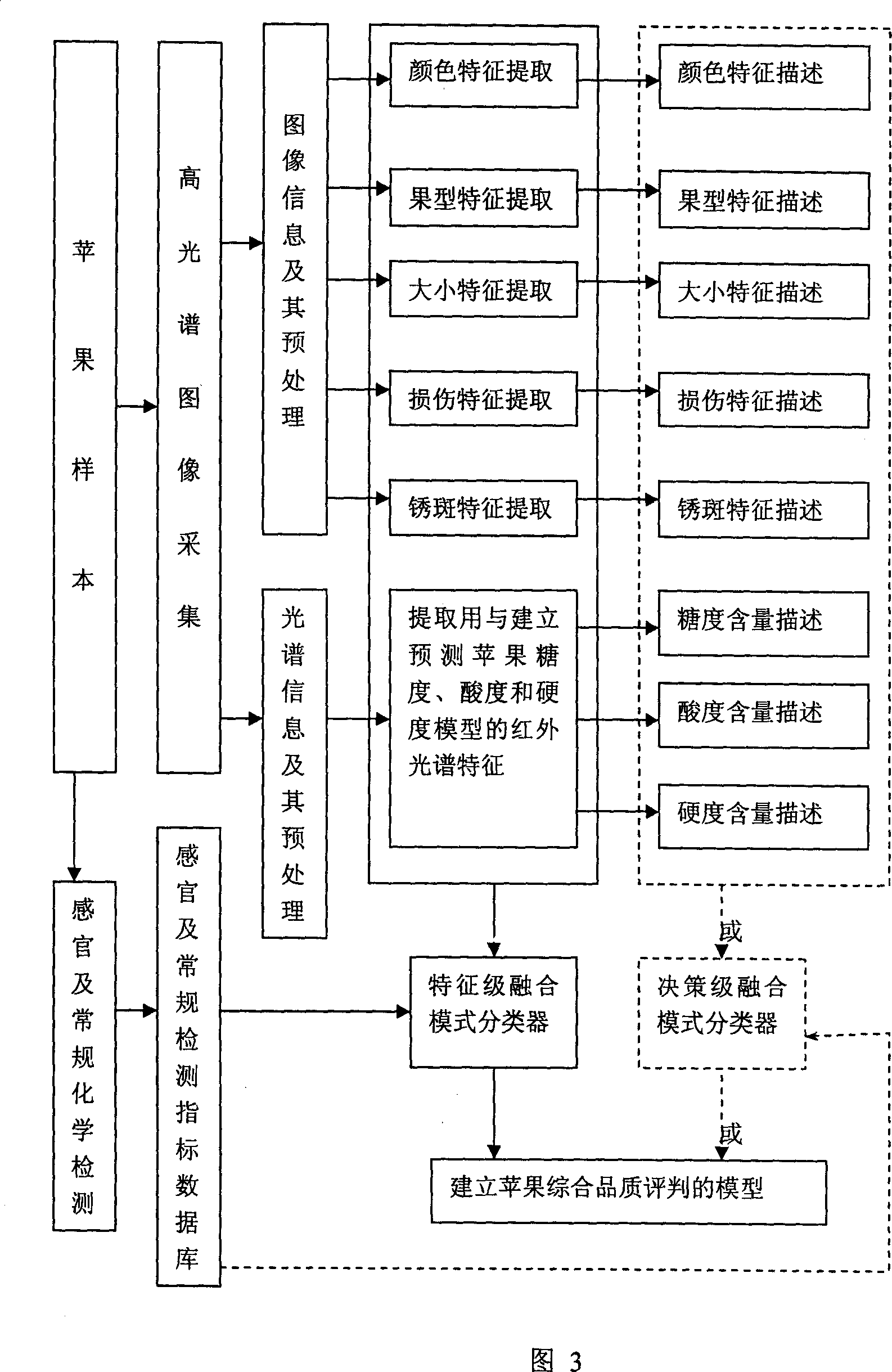
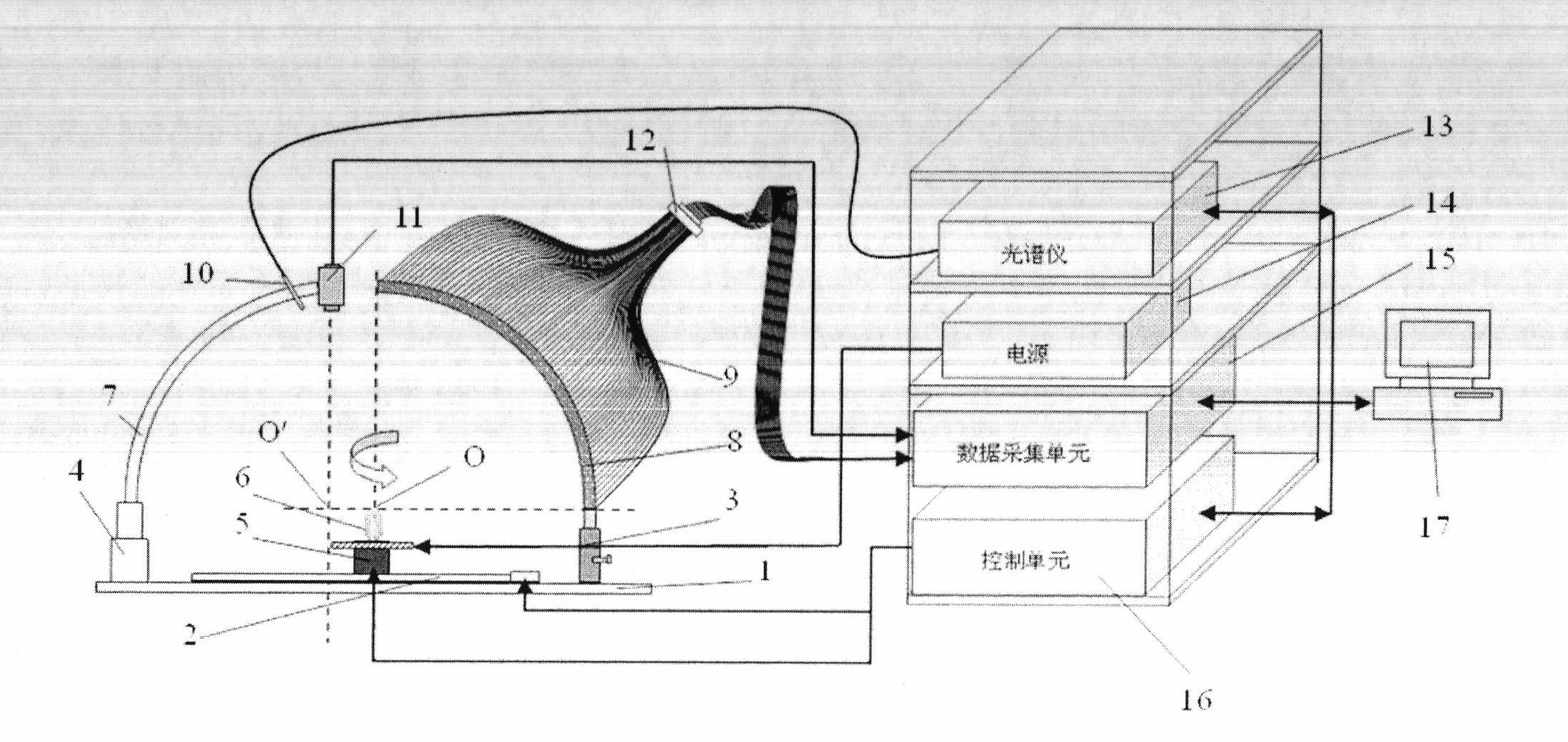
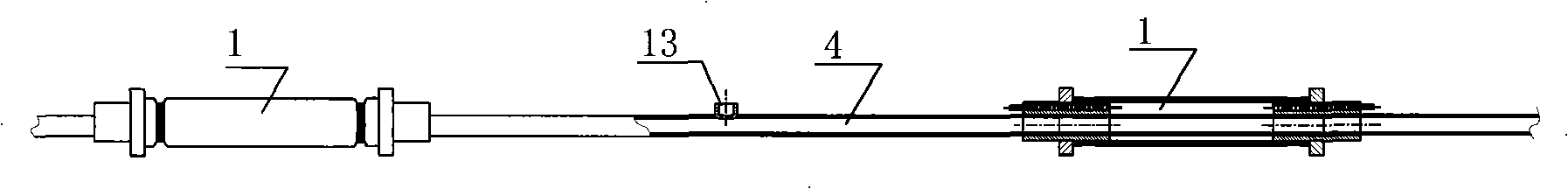
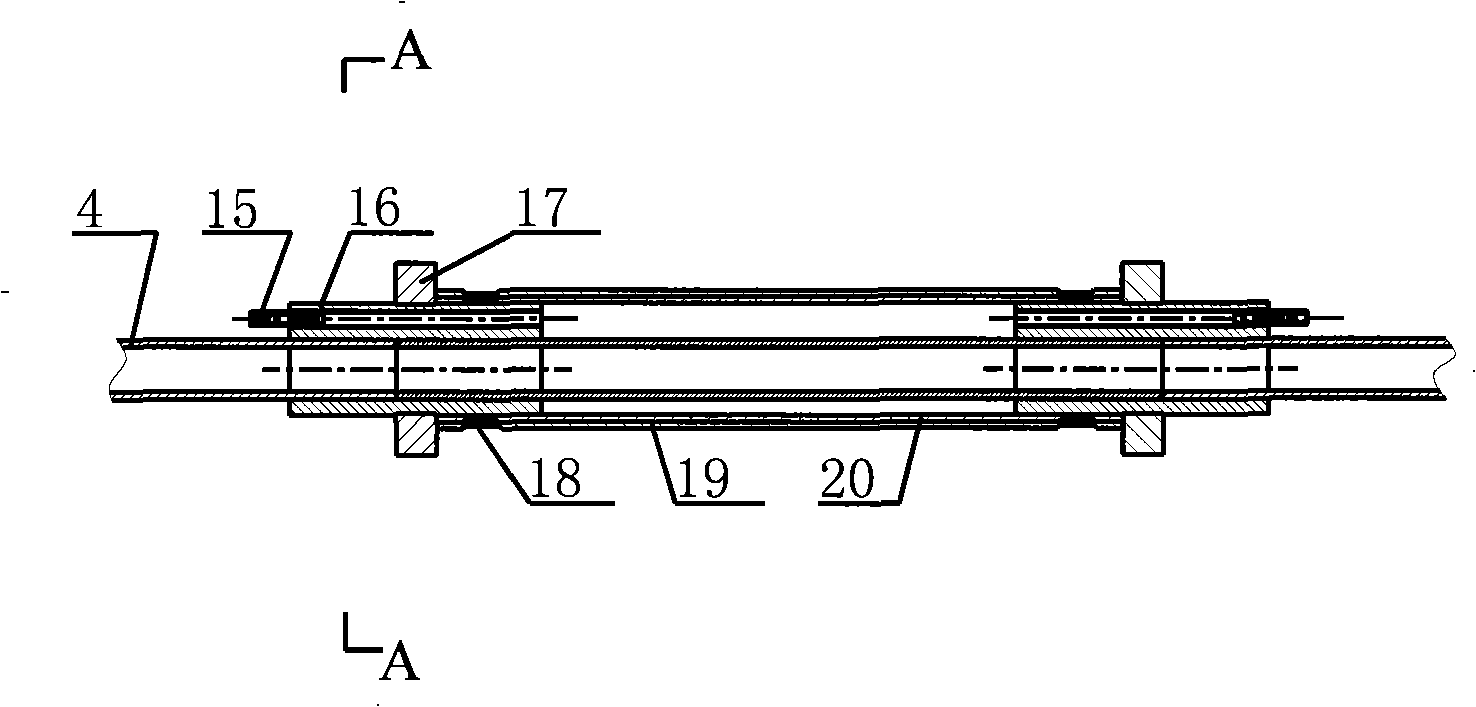
Non-destructive detection method and device for agricultural and animal products based on hyperspectral image technology
InactiveCN1995987AWith artificial intelligenceGuaranteed sampling qualityImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansNon destructiveAnimal product
The invention relates to high optical spectral image technique without harm to agricultural products. It can reflect the appearance of the agriculture products like color, shape, texture, dimension, scar and son on, and internal features like hardness, protein content and connected with knowledge base and experience of experts to make judgment. It can make quick, accurate, timely judgment of products, controlling the overall production with guarantee of the agriculture quality.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
LED optical parameter comprehensive testing device
ActiveCN102213615AEfficient use ofAccurate measurementSpectrum investigationColor measuring devicesFiberMeasuring instrument
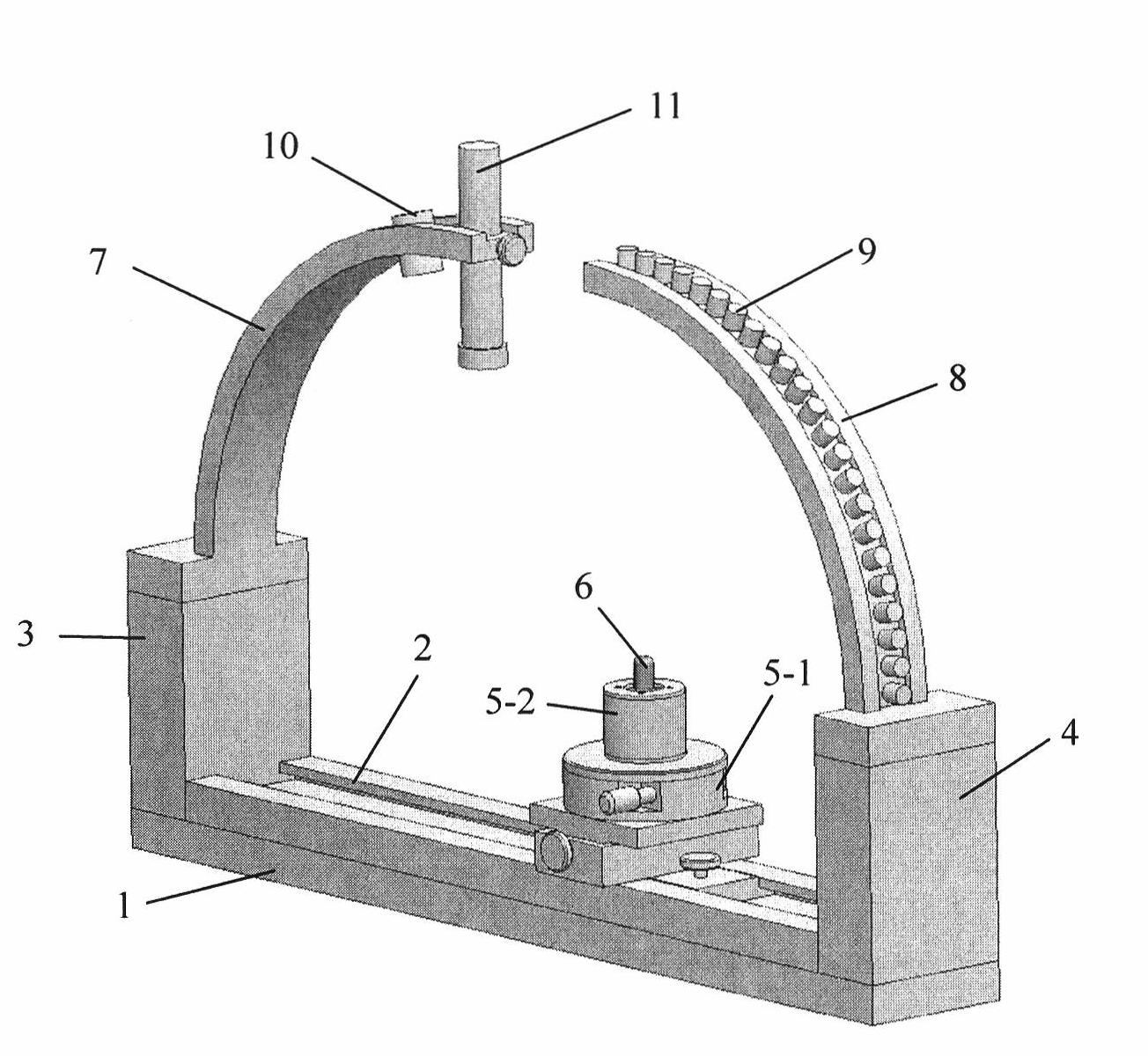
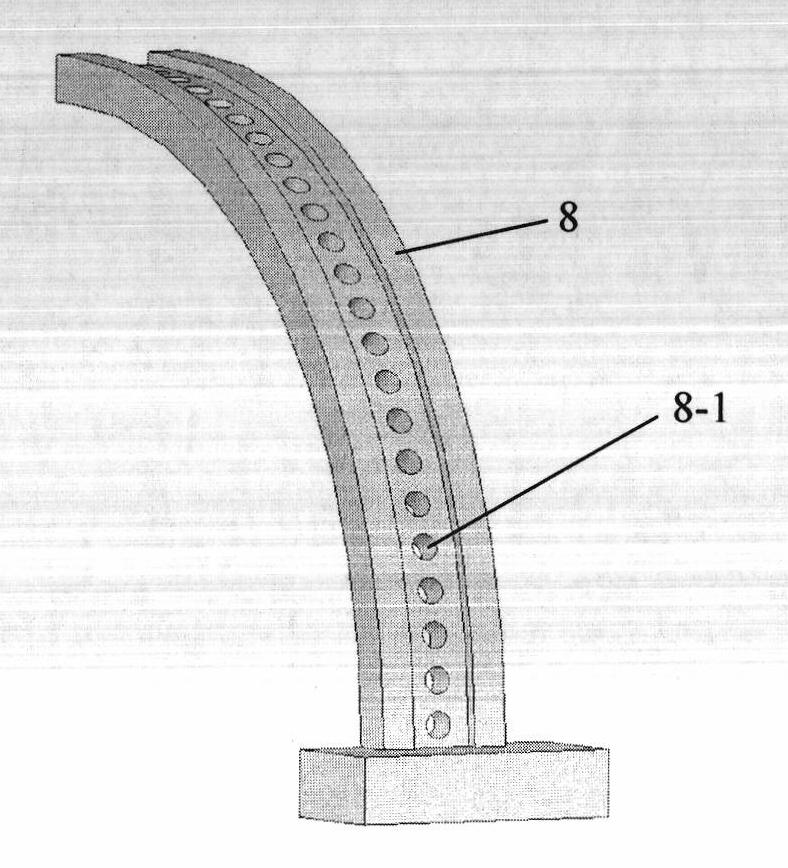
The invention discloses an LED optical parameter comprehensive testing device, belonging to the technical field of optical parameter measurement. The LED optical parameter comprehensive testing device is technically characterized in that one end of a horizontal base provided with a one-dimensional mobile platform is fixedly provided with an arc-shaped clamp provided with a fiber-optic probe and astandard luminosity probe, the other end of the horizontal base is fixedly provided with an arc-shaped light collector consisting of an arc fiber-optic array and a linear array CCD (Charge Coupled Device), and a rotary clamping table for holding an LED to be tested is arranged on the one-dimensional mobile platform; light information acquired by the fiber-optic probe is converted into a spectrum band by a spectrograph and then is sent into a computer, outputs of the standard luminosity probe and the linear array CCD are sent to the computer through the data acquisition unit, the computer performs corresponding processing and operation on measurement data through measurement software to finally obtain the luminescence characteristics of the LED to be tested. According to the invention, theproblem on comprehensively measuring the LED on a single measurement instrument is solved; and the LED optical parameter comprehensive testing device has the characteristics of simplicity for operation, compact structure, fastness for measurement, easiness for realization and the like.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND NO 205 RES INST
Method and device for detecting polarization extinction ratio of optical polarizer
InactiveCN102183360AHigh measurement accuracyAccurate measurementTesting optical propertiesFiber couplerPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
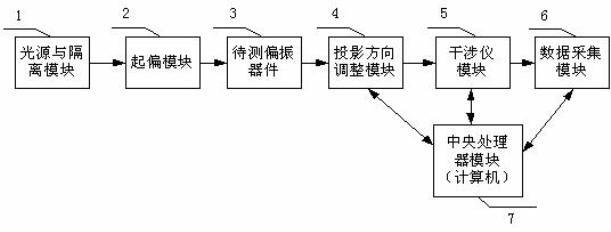
The invention provides a method and device for detecting a polarization extinction ratio of an optical polarizer. The detection method comprises the following steps of: making linear polarized light incident along a principal axis of an optical polarizer to be detected, and obtaining two light signals on two orthogonal optical axes at an outgoing end due to polarization crosstalk; interfering and carrying out photoelectric conversion and data acquisition on interfering light signals to obtain one group of discrete voltage signal values reflecting the interfering light intensity signals; and calculating coupling intensity h at each coupling spot based on a formula (1), and calculating an extinction ratio of the optical polarizer to be detected based on a formula (2). The device sequentially comprises a light source, an isolator module, a polarization module, the optical polarizer to be detected, a projection direction regulating module, an interferometer module, a data acquisition module and a central processor module. The invention has the advantage that the coupling intensity of the coupling spots is detected to induce the polarization extinction ratio, so that the measurement result is accurate. The invention is suitable for various optical polarizers, such as polarization maintaining fibers, polarization maintaining fiber couplers, polarizers and the like and has certain universality.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
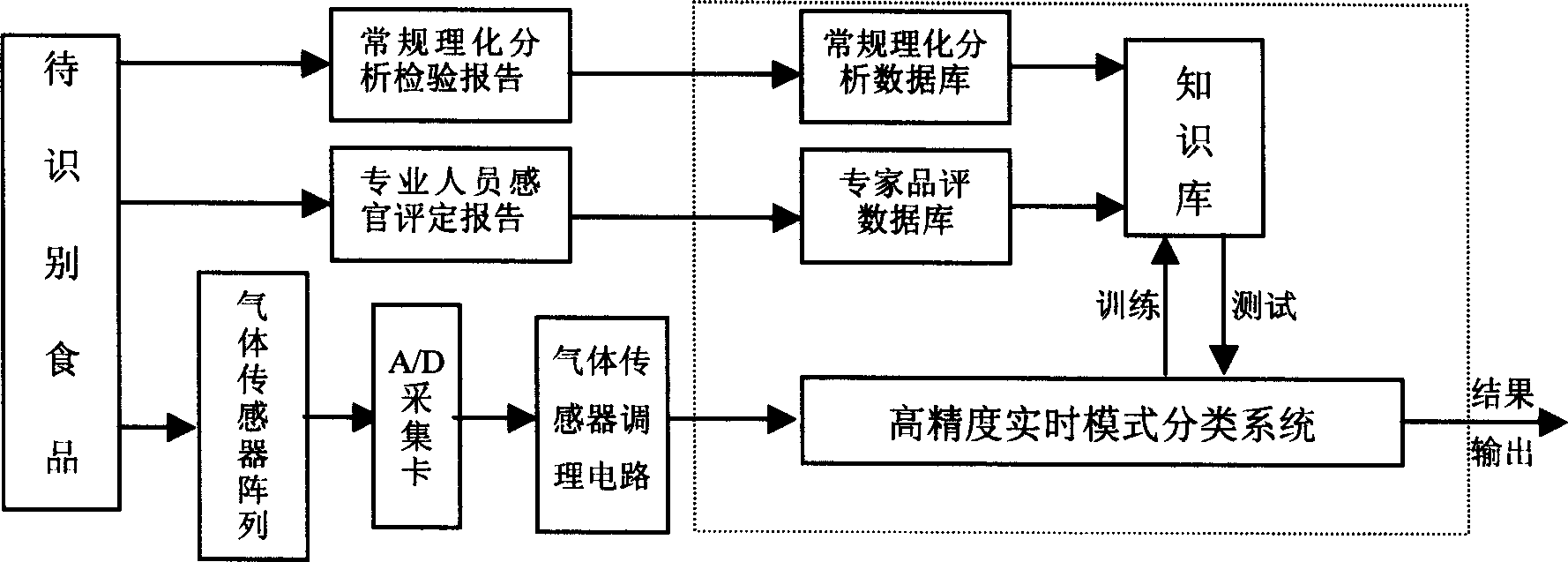
Fast non-destructive detection method and device of food smell based on gas sensor array technology
Some sample of relevant food is estimated by some professionals with their sensory organ or tested through conventional physical and chemical analysis to establish correlative data base. Some other sample is determined with sensor array through carrying the smell of the food to the sensor array reaction chamber via carrier gas, amplifying and filtering the signal from the sensor array, A / D conversion in A / D converter and data processing in computer. The result of computer processing is related with those in the established data base and one knowledge library is obtained through learning forthe determination of truth and quality of tested sample. The said method is fast and simple, needs no pre-treatment of the sample and organic solvent extraction, and has the artificial intelligent identification to unknown sample. The present invention facilitates the physical and chemical analysis of food products.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Complex monitor for automatically monitoring multiple parameters of water on line
InactiveCN102661923AEconomic savingsNo secondary pollutionColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial electrochemical variablesPrincipal component analysisUv vis absorbance
The invention discloses a method for automatically monitoring water quality indexes on line and a device for implementing the method. A method of combining an ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy and various sensors is adopted, dozens of water quality indexes including chemical oxygen demand and ammonia nitrogen can be measured at one time, measurement indexes can be configured in a building block mode according to requirements, and chemical agents are not required. According to the device, the constructed digital optical fiber spectrometer is taken as a core, ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrum data of a water sample is processed in a mode of sequentially combining wavelet de-noising, principal component analysis and a support vector machine, and water quality indexes such as chemical oxygen demand and biochemical oxygen demand of water are acquired. Various physical and electrochemical sensors acquire water quality indexes such as ammonia nitrogen, dissolved oxygen and conductivity. All hardware and software for implementing the method is put in a cabinet to form the device, and the device analyzes the introduced water sample under the control of an embedded industrial control computer system, and automatically monitors the water quality indexes in real time.
Owner:SICHUAN BELAM TECH
Diluting and sampling system for particle from fixed combustion source emission
InactiveCN1731127AReduce volumeWell mixedWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCombustionProduct gas
The invention relates to a fixed burning source emission particulate sampling system, which comprises an off-gas inlet system, a second diluter, a setting house and a sampling system positioned on the lower part of the setting house. It arranges a compressed air system on the first diluter and a sampler outlet with gas flow gauge and a superfluity gas outlet with gas flow adjusting valve on the outlet end; it arranges a dilution air supplying system and a gas flow gauge on the outlet of the second diluter and a plurality of pressure balance holes around the lower part of the setting house.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
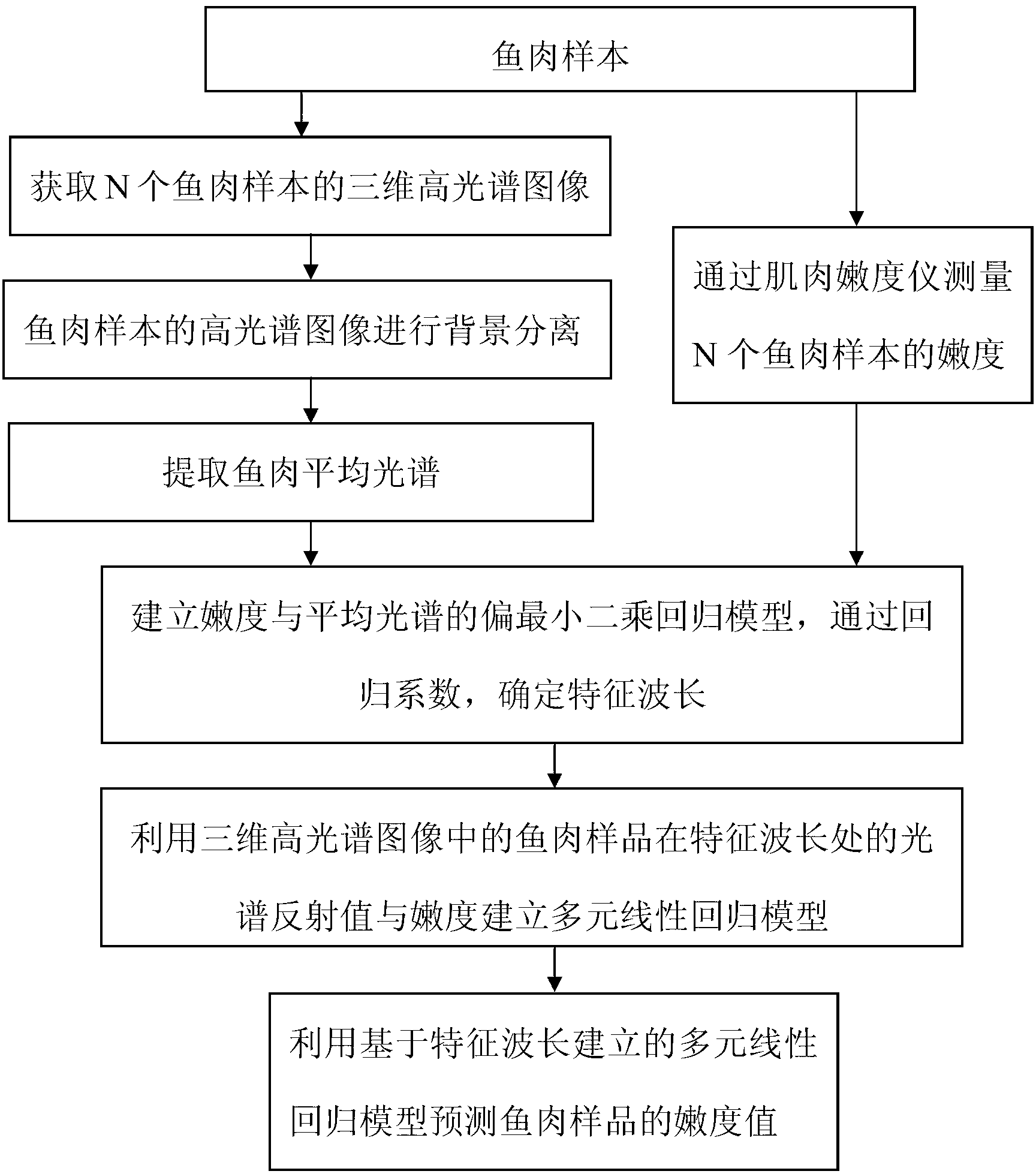
Fish tenderness hyperspectral detection method based on characteristic wave band
InactiveCN103257118AQuick checkEasy to detectColor/spectral properties measurementsVisible near infraredSpectral imaging
The invention discloses a fish tenderness hyperspectral detection method based on a characteristic wave band. The detection method comprises the following steps of: firstly, detecting fish tenderness according to the conventional detection method; then, with fish as a sample set, utilizing a near-infrared hyperspectral imager to carry out nondestructive detection on the fish, establishing a multi-element linear regression model of the tenderness and a characteristic wavelength, detecting a fish sample, and calculating the tenderness of fish sample according to the multi-element linear regression model of the tenderness and the characteristic wavelength. The fish tenderness hyperspectral detection method provided by the invention has the advantages that the fish tenderness is rapidly detected in an optimized manner through the characteristic wave band, the time of hyperspectral collection, detection and data analysis is greatly shortened, the detection efficiency is improved, and the fish tenderness hyperspectral detection method really provides theoretical support and research basis for on-line, rapid and nondestructive detection of food quality.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
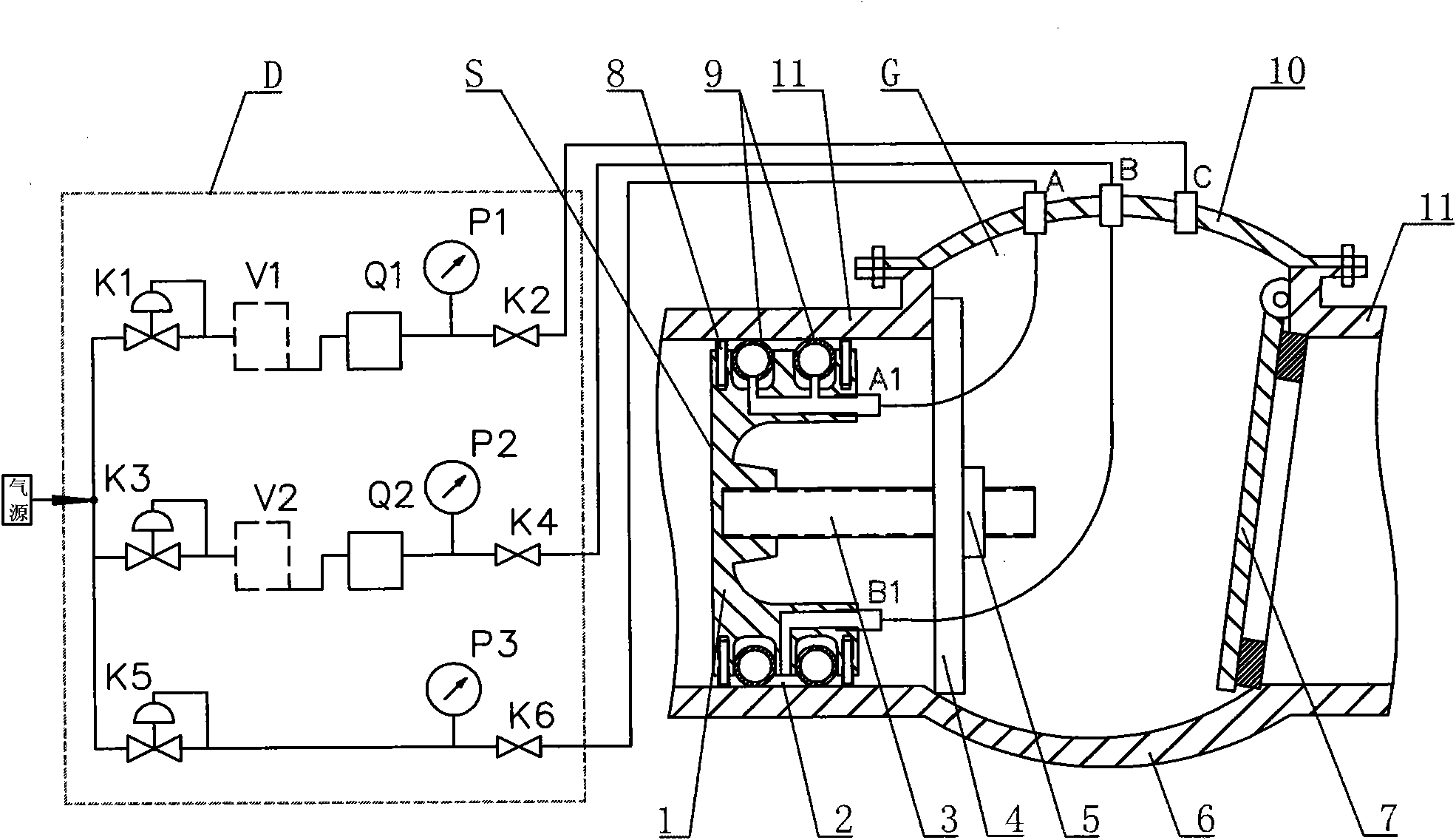
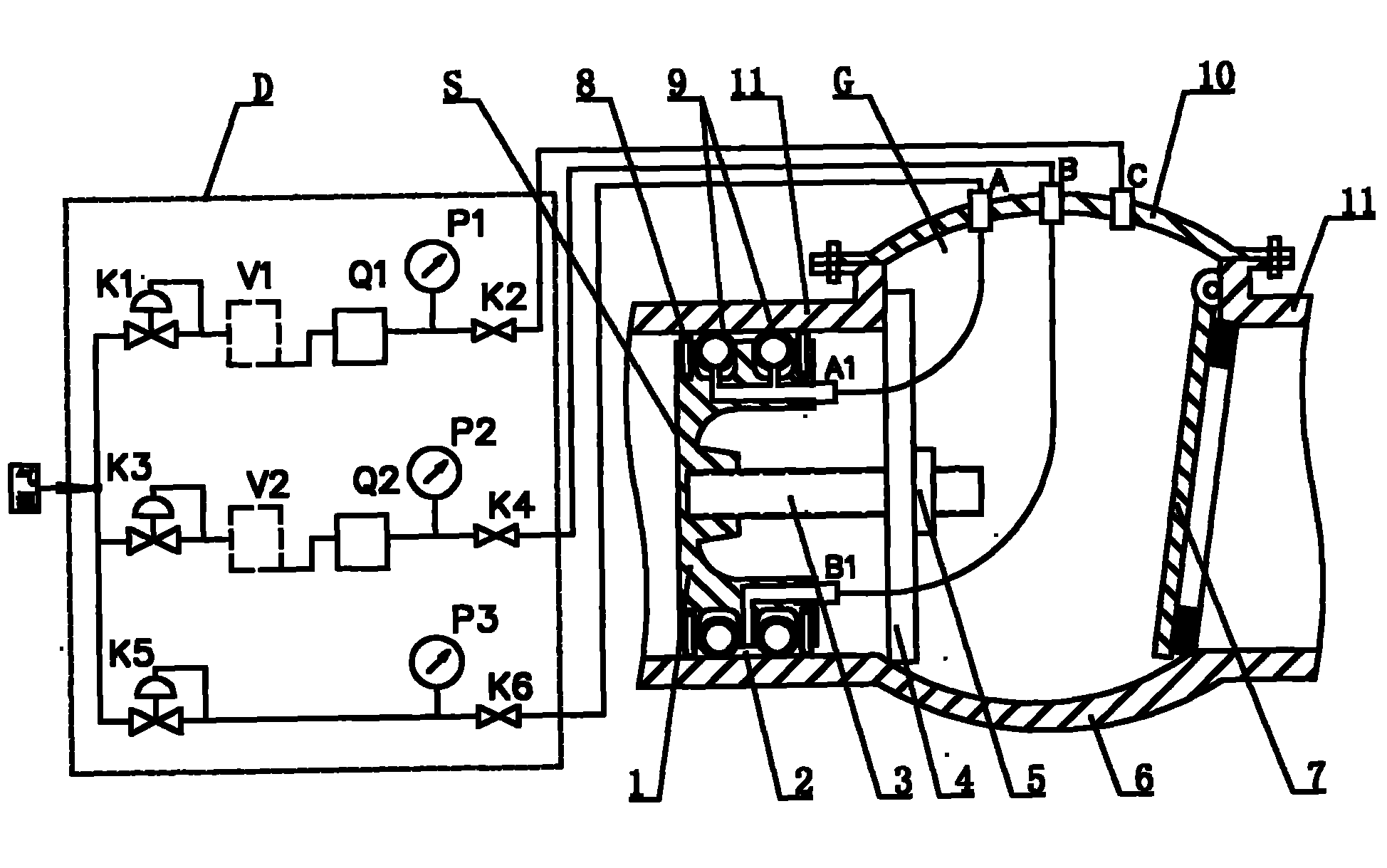
System and method for measuring section shape and size of heavy caliber steel pipe
InactiveCN1734233ATrue reflection of geometric featuresReflect geometric featuresMeasurement devicesInformation processingSize measurement
This invention discloses such a measurement and method of a large caliber steel tube cross-section shape, which belongs to the domain of geometric measurement technique. The measurement system of information processing mode and measurement mode is located in the small moving car, with the small car moving on the datum circular orbit. The input and output mode connect the information processing mode through the serial port. The measurement method is like this: testing a series of the steel tube surface and the radial distance of a certain known datum circular orbit radius in order to get a configuration point coordinates of the steel tube cross-section. When the amount of sampling points is abundant enough, we can get the accurate outline of steel tube. Then the information-processing mode counts the steel tube cross-section shape and dimension parameter.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Indirect measuring method for hypersonic speed wind tunnel turbulence scale
ActiveCN103969022AAccurate and reliable measurement resultsFunction relation simplificationAerodynamic testingEngineeringData collecting
The invention relates to wind tunnel turbulence scale measuring, in particular to an indirect measuring method for hypersonic speed wind tunnel turbulence scale. According to the indirection measuring method for hypersonic speed wind tunnel turbulence scale, a miniature airspeed head is used for measuring pressure pulsation in a hypersonic speed wind tunnel flow field, and then the turbulence scale is indirectly obtained according to relation conversion between pressure pulsation and speed pulsation. The method includes the steps of wind tunnel data collecting and data analyzing. According to wind tunnel data collection process, an adjustable device of the miniature airspeed tube is used for measuring pulsation pressure values at different positions of wind tunnel incoming flows, and other probes are used for measuring other wind tunnel data. According to the data analyzing process, the measured pressure pulsation values and other wind tunnel data are analyzed to obtain the function relation expression between pressure pulsation and speed pulsation in hypersonic speed airflows through deduction, and therefore the hypersonic speed wind tunnel turbulence scale is obtained through calculation. The function relation expression between pressure pulsation and speed pulsation is simple and clear, the hypersonic speed wind tunnel turbulence scale can be obtained only by pressure pulsation measurement and simple calculation, and the indirect measuring method is convenient and rapid to implement.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for detecting high speed rotating blade synchronous vibration parameters under speed change
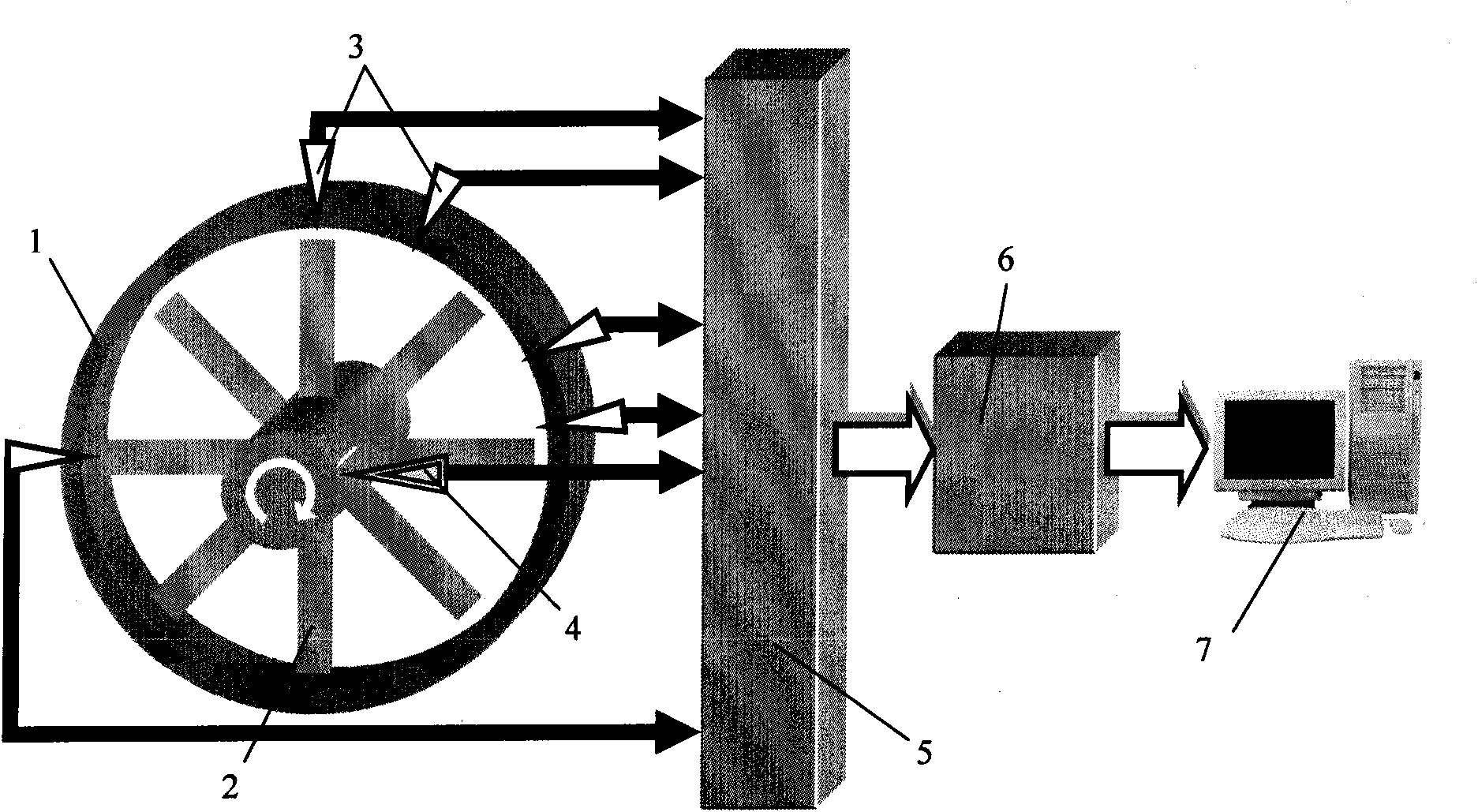
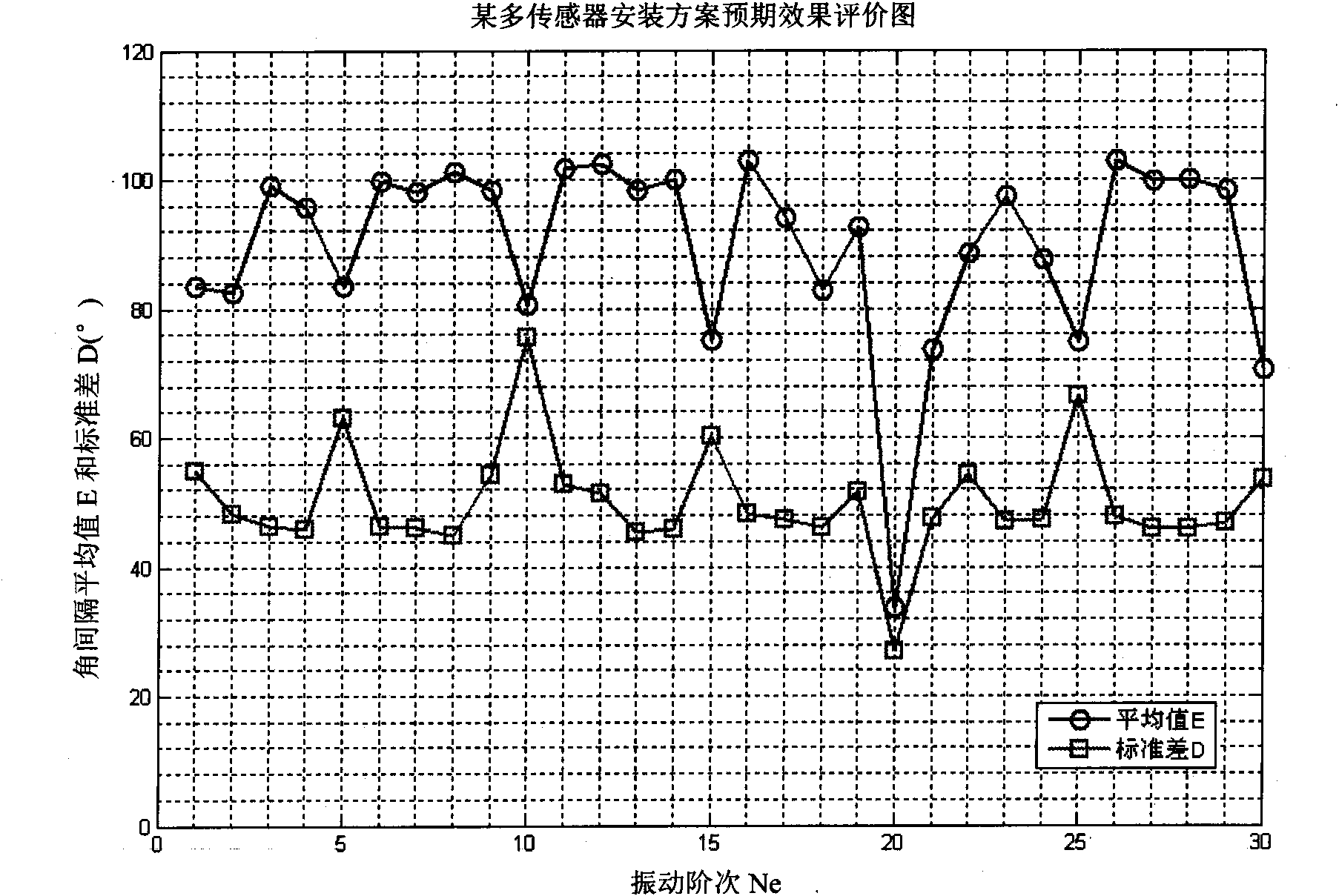
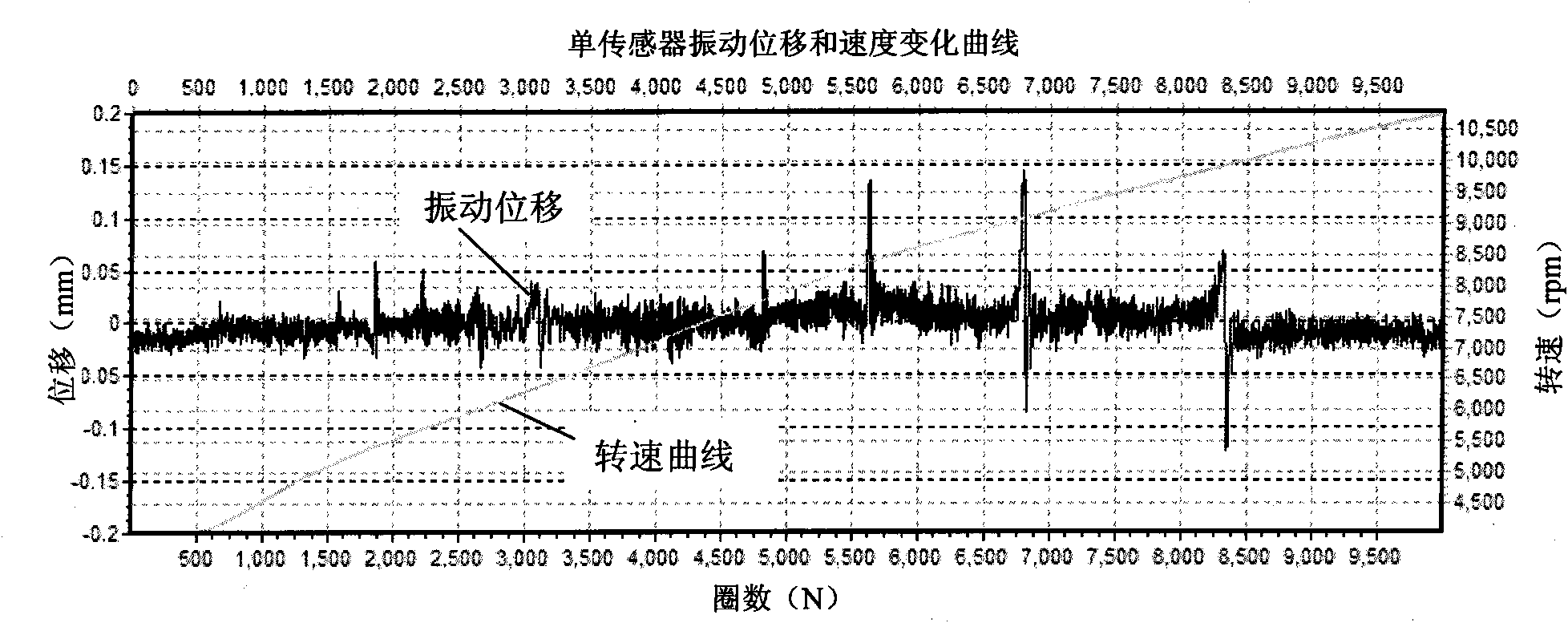
ActiveCN101625260AAdaptableAccurate and reliable measurement resultsVibration measurement in solidsResonant frequencyVibration measurementResonance
The invention relates to a method for detecting rotating mechanical blade vibration, in particular to a method for detecting high speed rotating blade synchronous vibration parameters under speed change, aiming at providing a method for detecting high speed rotating blade synchronous vibration parameters under speed change with high resolution preciseness and strong adaptability. The technical proposal of the invention comprises the following steps: step 1, determining a multi-sensor distribution scheme of blade tip timed vibration measurement: firstly pre-estimating the synchronous vibration frequency multiplication Ne possible to occur to the blade to be detected according to the actual detected rotating mechanical performance, and secondly determining the number and distribution condition of the mountable blade tip timed sensors and determining the mounting angles among the sensors according to the actual requirement of the rotating machinery; step 2, carrying out synchronous vibration measurement according to the above determined scheme; and step 3, adopting the traversal method to precisely obtain blade resonance frequency multiplication Ne, natural frequency fn and other parameters. The invention is mainly used for detecting rotating mechanical blade vibration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGXIN POWER MEASUREMENT & CONTROL TECH
Down-hole guiding height viewer and its observation method
InactiveCN101245701AImprove observation efficiencySimple structureBorehole/well accessoriesEngineeringObservation method
The invention discloses an underground high-conducting visualizer and an observation method thereof. The invention includes a plurality of plugging devices that are connected in series; a water injection pipeline between two neighboring plugging devices is provided with a water injection opening; one end of the water injection pipeline is connected with a water injection control platform; the plugging pipelines are mutually communicated by external connecting pipelines and are connected with expansion pipelines. When in use, firstly bores are drilled in the cover rocks needed observing; then the plugging devices connected in series are pushed into the preset position of the bores; gas is pumped into the expansion pipeline and then one section of the bores is plugged into a plurality of sections; water is injected into the water injection pipelines and the water injection opening on the water injection pipeline between the two neighboring plugging devices are opened in sequence; water is injected into the terrane that the section of bores lies in; finally the cranny growth situation inside the cover rocks is analyzed according to the water injection seepage discharge of each section of terrane. The underground high-conducting visualizer has simple structure, is convenient for use, can realize simultaneous plugging, water injection by section and multi-section seepage detection, improve the observing efficiency and has highly reliable detection result.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
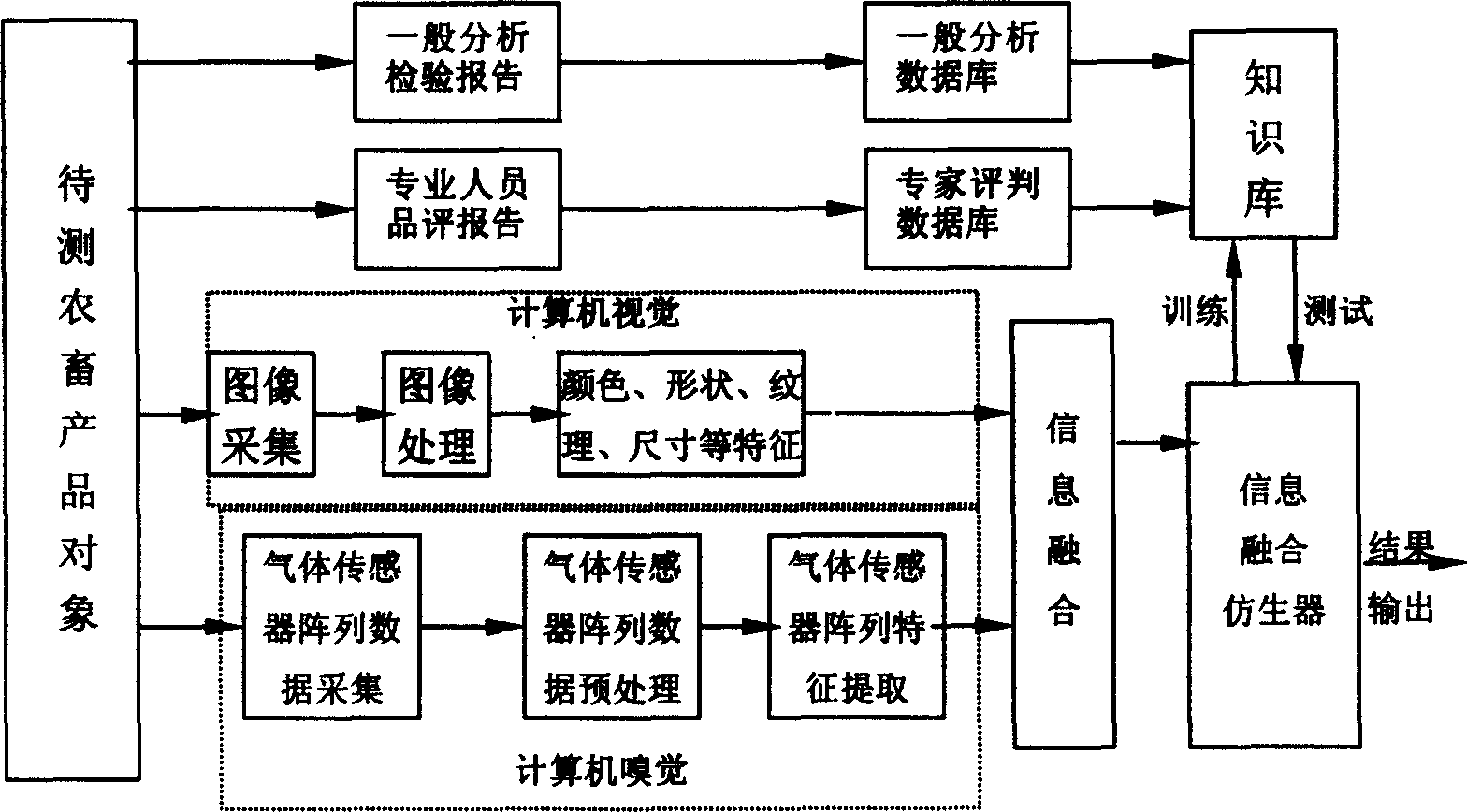
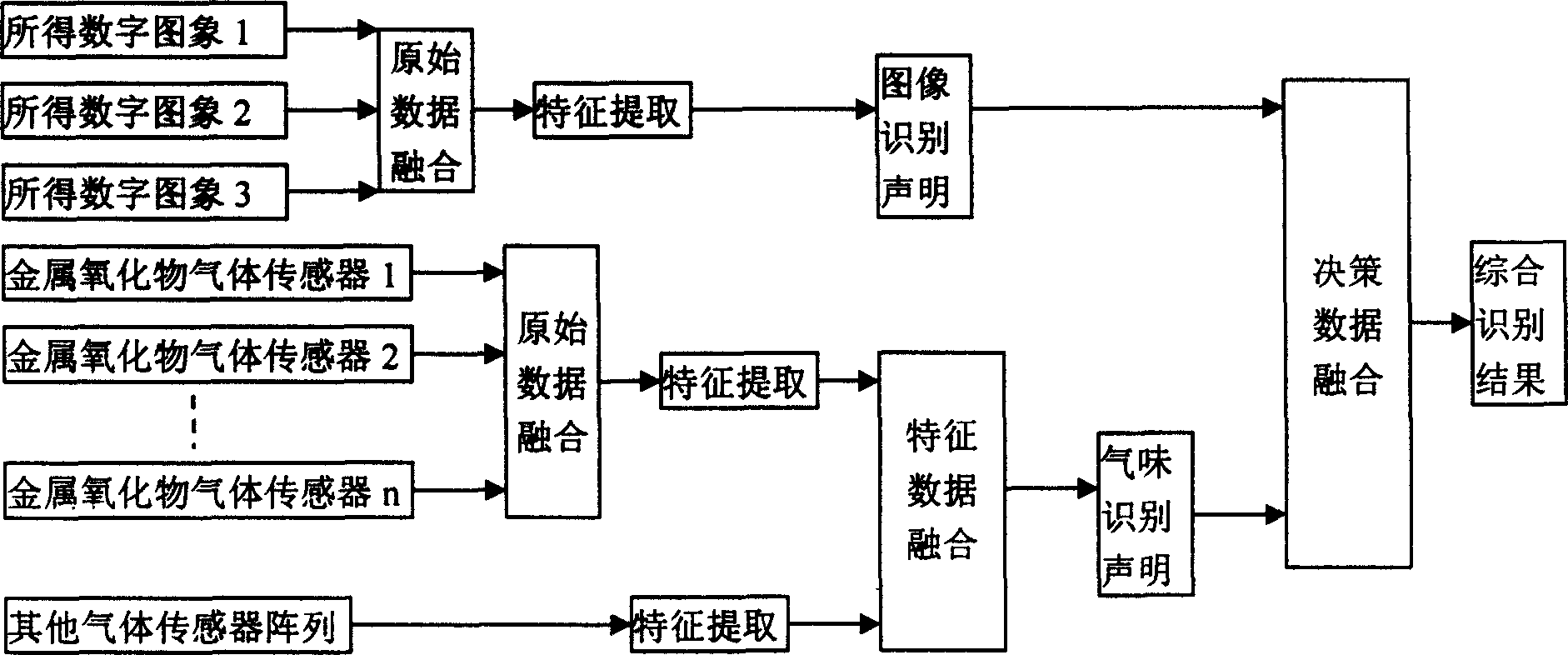
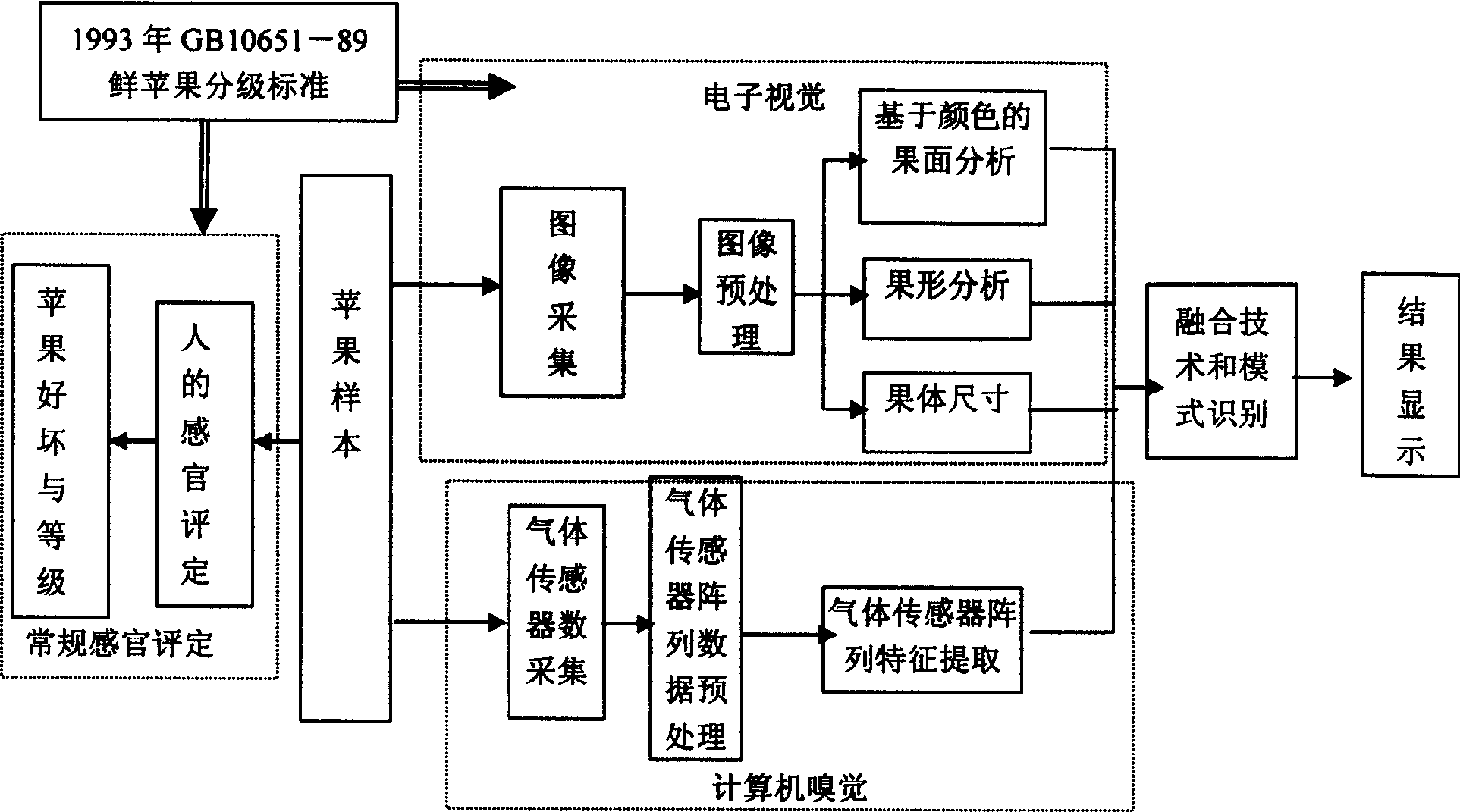
Agricultural and animal product nondestrctive detection method based on electronic visual sense and smell sense fusion technology and its device
InactiveCN1556412AHigh sensitivityExpand the scope of recognitionMaterial analysisCcd cameraHuman brain
Images of farm animal products taken by CCD camera through image acquisition card are transferred to computer. Under certain condition (temperature, humidity and flow rate), smells emitted from farm animal products through mini pump with no oil are sucked into reaction chamber, where signals are generated by array of gas sensor. The said signals through conditioning circuit, A / D acquisition card are transferred to computer. Computer for simulating human brain to treat vision data and smell data carries out syncretizing and pattern recognition processing. Combining with experts' knowledge in knowledge base as well as experiences, computer makes judgment for qualities of garden spgarden stuff, meat and corns etc. synthetically.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
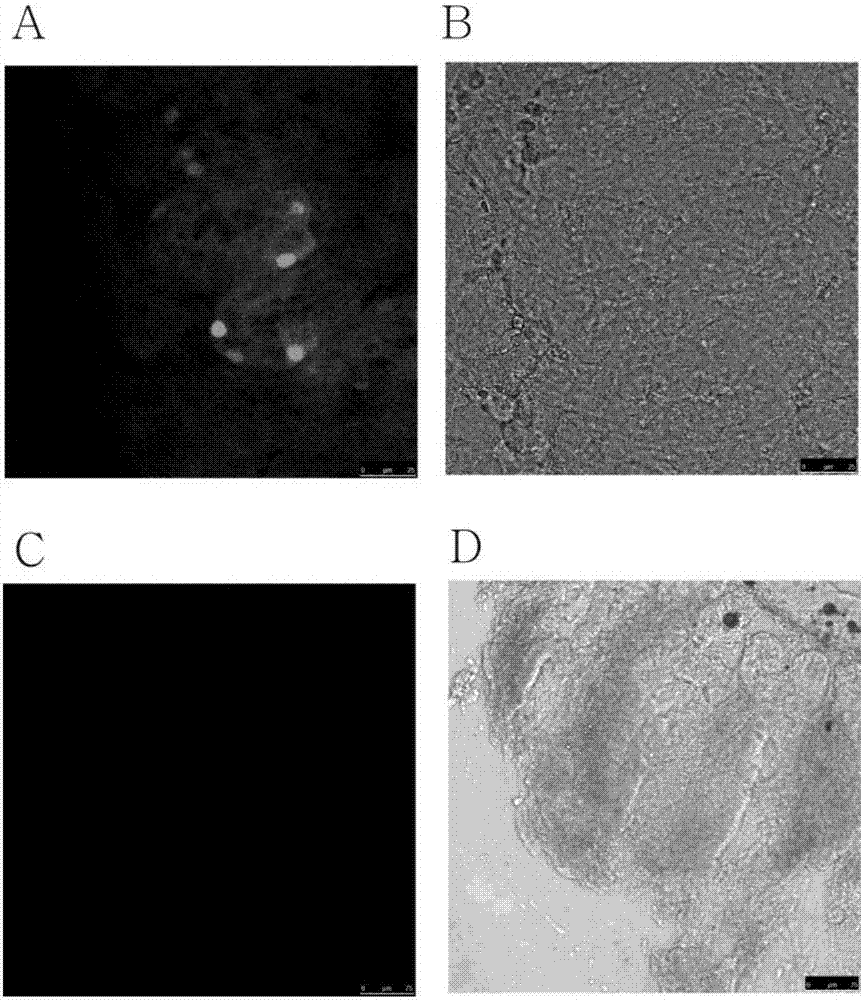
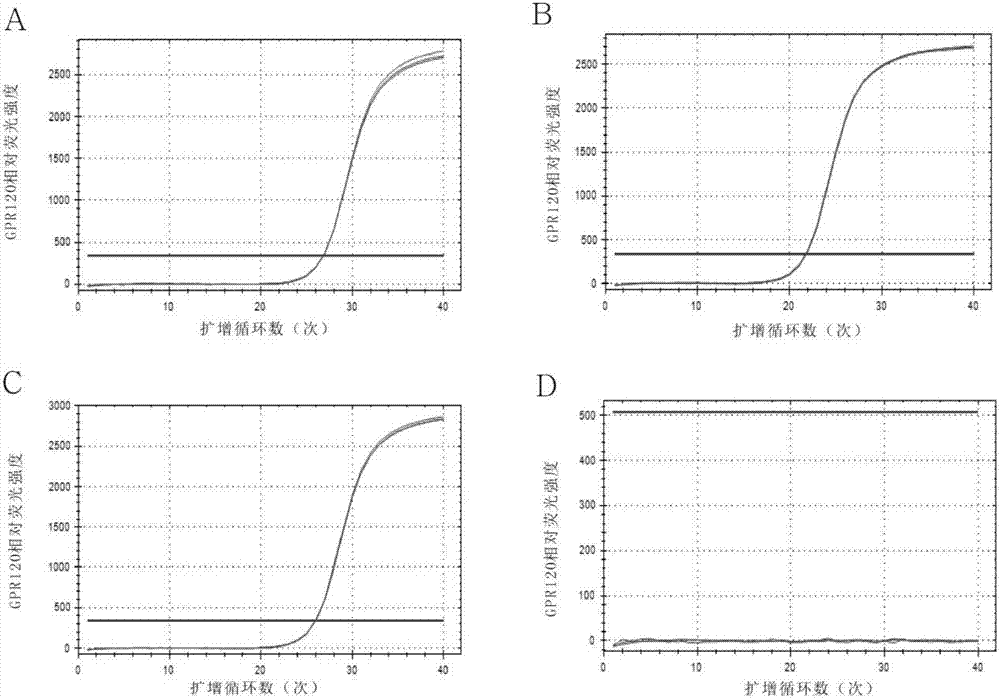
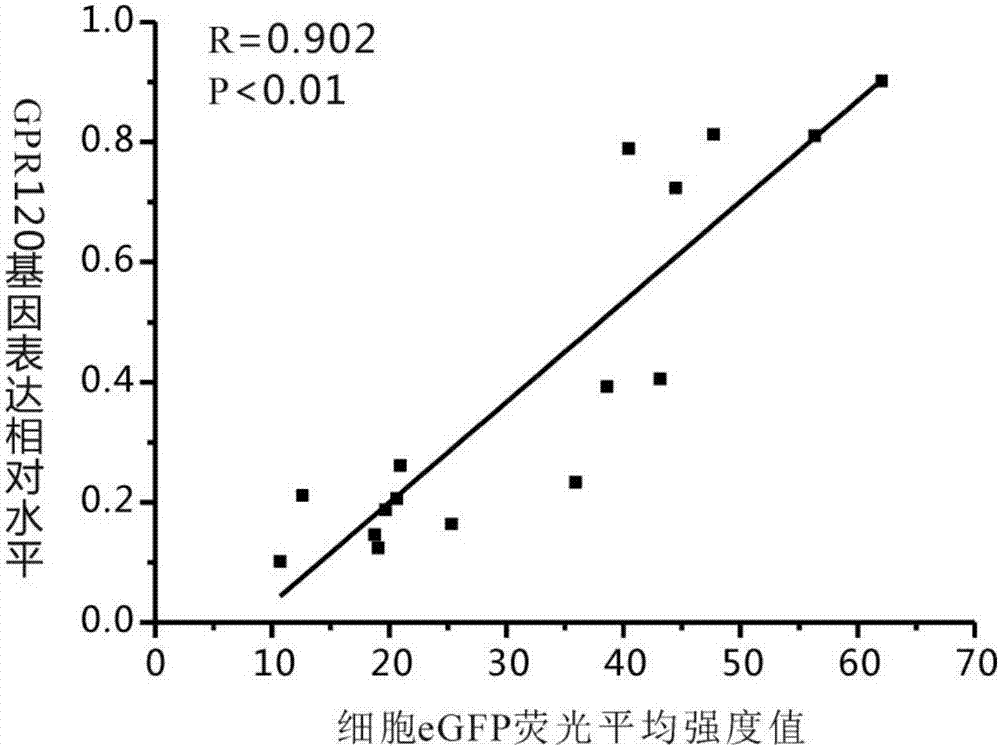
Detection method for expression of GPR120 gene based on eGFP, and application of eGFP to detection of expression of GPR120 gene
InactiveCN107227352AControl errorReduce the error between groupsMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRNA extractionGPR120
The invention discloses a detection method for the expression of a GPR120 gene based on eGFP. The detection method comprises the following steps: inserting an eGFP fragment to the specific site TAA of the termination codon of the GPR120 gene by using CRISPR / Cas 9 technology so as to obtain a transgenic model mouse with eGFP-labeled GPR120 positive cells; and carrying out excitation by using a fluorescence analyzer and determining the fluorescence intensity of the positive cells of the mouse. The method carries out real-time monitoring on the expression of the GPR120 gene so as to control and reduce errors among groups, guarantee the reliability of results and compensate for and overcome the problems of variability caused by comparison of different groups of histocytes and incapability of monitoring the changes of gene expression at a living cell level in the prior art. According to the invention, the expression level of the GPR120 gene can be immediately determined after collection of cells, and operations and reactions like RNA extraction, inverse transcription and PCR are omitted, so detection of the expression of the GPR120 gene is simpler.
Owner:XIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Two-interface cementing strength testing device of cementing sheath containing hydrates and ice stratum
InactiveCN105484729ASimple structureEasy to operateConstructionsTemperature controlPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a two-interface cementing strength testing device of a cementing sheath containing hydrates and an ice stratum. The testing device comprises a kettle shell base and a simulation sleeve which is vertically arranged in the middle of the kettle shell base. A polyvinyl alcohol membrane tube is arranged on the periphery of the simulation sleeve, an annular cavity is formed between the simulation sleeve and the polyvinyl alcohol membrane tube, a temperature control circulating bath sealing cover is arranged on the outer edge of the top of the kettle shell base in a surrounding mode, the position between the temperature control circulating bath sealing cover and the polyvinyl alcohol membrane tube is filled with a simulation stratum, the top of the simulation stratum is covered with a stratum kettle cover, the top of the simulation sleeve is covered with a pressurizing kettle cover which covers the top of the cavity, and a pressure device for pressurizing the pressurizing kettle cover is arranged above the pressurizing kettle cover. The testing device has the advantages that the structure is simple, installing and using are convenient, production cost is low, and a detection result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Combined microwave sensor and dielectric constant measurement method for measured object
ActiveCN107490727AAccurate measurementAccurate and reliable measurement resultsResistance/reactance/impedenceSpurlineDielectric permittivity
A combined microwave sensor comprises metal ground at the bottom layer, dielectric at the middle layer, an input port, an output port I, a branched line coupler, a power divider, an open resonant ring, a microstrip line I and a microstrip line II, wherein the input port, the output port I, the branched line coupler, the power divider, the open resonant ring, the microstrip line I and the microstrip line II are arranged in the top layer. The input port and the output port I are connected with a vector network analyzer. The output side of the branched line coupler is provided with an isolated port and the output port I. The input end of the power divider is connected with the input port. The output port II and the output port III are connected with an annular directional coupler through a microstrip line. The open resonant ring is arranged between the power divider, the branched line coupler and the two microstrip lines. The combined microwave sensor has advantages of effectively eliminating background noise, realizing testing for weak background signals, and ensuring large offset of the sensor resonant frequency through small disturbance of the tested object. Therefore the combined microwave sensor provided by the invention has higher sensitivity and higher accuracy in dielectric constant measurement and can be used in high-sensitivity testing with small dielectric constant change.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
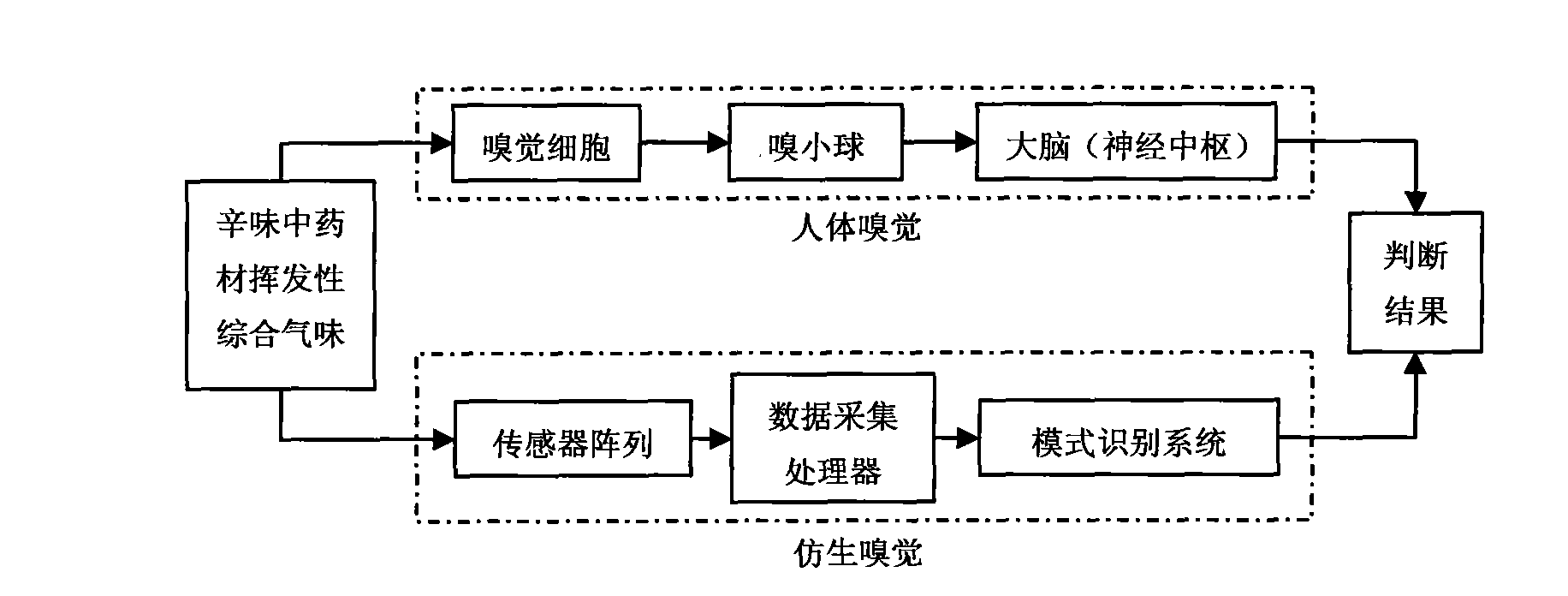
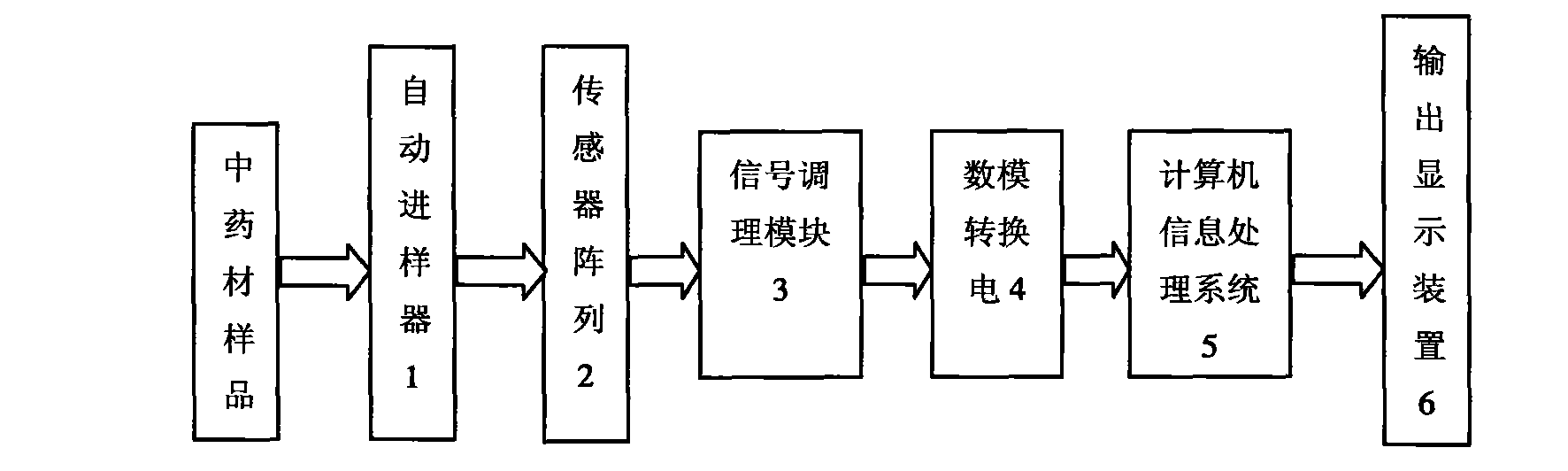
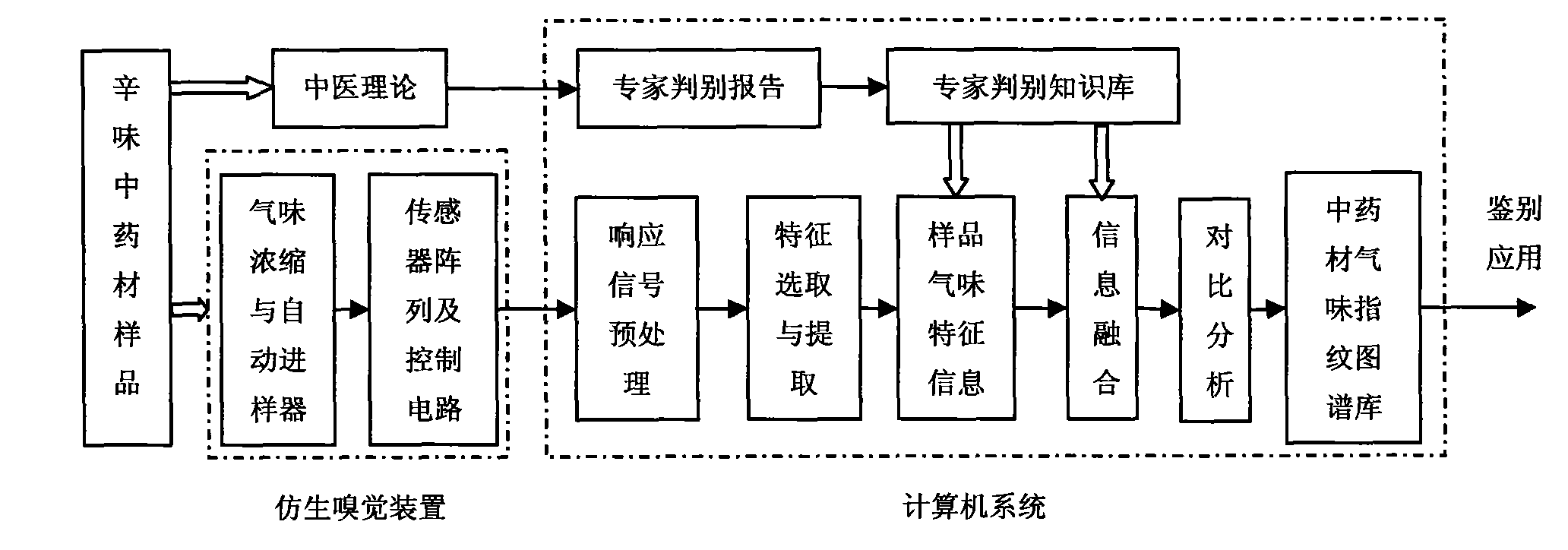
Pungent traditional Chinese medicine odor fingerprint map construction system and method based on bionic olfaction
InactiveCN101788517AImprove protectionDoes not affect healthBiological neural network modelsMaterial resistanceSensor arrayInformation processing
The invention discloses pungent traditional Chinese medicine odor fingerprint map construction system and method based on bionic olfaction. The pungent traditional Chinese medicine odor fingerprint map construction system based on bionic olfaction comprises a sensor array (2), a signal modulation module (3), a digital analog conversion circuit (4) and a computer information processing system (5), wherein the sensor array (2) is arranged on the position which can detect the odor of pungent traditional Chinese medicines, the input end of the signal modulation module (3) is connected with the output end of the sensor array (2), the output end of the signal modulation module (3) is connected with the input end of the digital analog conversion circuit (4), and the output end of the digital analog conversion circuit (4) is connected with the computer information processing system (5). The pungent traditional Chinese medicine odor fingerprint map construction system based on bionic olfaction has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and objective and reliable determination result. The pungent traditional Chinese medicine odor fingerprint map construction method based on bionic olfaction is simple and convenient.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
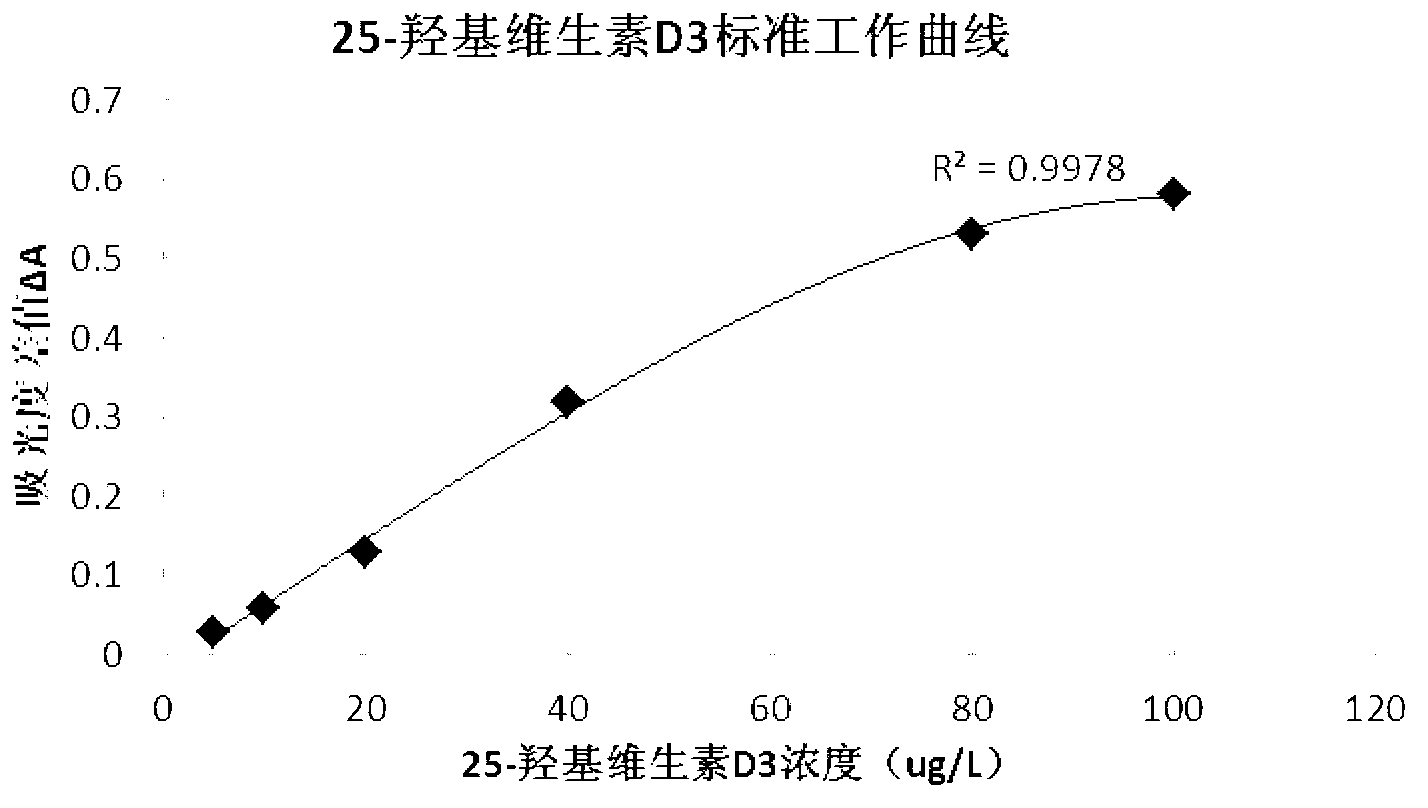
25-hydroxy-vitamin D3 detection kit, as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102998468AEasy to operateIncreased sensitivityBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesActive agent
The invention discloses a 25-hydroxy-vitamin D3 detection kit, as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The detection kit consists of a reagent I and a reagent II which are independent from each other, wherein the reagent I comprises the following components: a 25-hydroxy-vitamin D3-BSA conjugate, a biobuffer, a chelating agent, a surface active agent, a coagulant, a preservative, a stabilizer and water; the reagent II comprises the following components: rubber latex particles coated by a 25-hydroxy-vitamin D3 antibody, a biobuffer, a chelating agent, a surface active agent, a suspending agent, a preservative, a sealing agent, a stabilizer and water. The detection kit disclosed by the invention is high in detection sensitivity, high in specificity, accurate in quantification and wide in linear range, and is especially suitable for the detection of samples with extremely low 25-hydroxy-vitamin D3 content. In addition, the detection kit disclosed by the invention does not need to dilute the samples in advance in the detection process, facilitates the clinical use, and is easy to operate, low in detection cost and suitable for various full-automatic biochemical analyzers.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
A monitoring method for a surrounding rock and full face tunnel boring machine shield interaction process
ActiveCN105952465AEasy to installAccurate and reliable measurement resultsForce measurement by measuring frquency variationsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationRisk levelTunnel boring machine
The invention provides a monitoring method for a surrounding rock and full face tunnel boring machine shield interaction process. The method comprises the steps of: A, welding and installing pressure boxes to the outer surface of a shield for testing the extrusion force applied to the shield by surrounding rocks directly, placing cables of the pressure boxes in flexible cable-protecting casing pipes, and leading the cables into the shield and connecting the cables to a reading device; B, installing a surface strain sensor in each of the annular direction and the longitudinal direction of each monitoring point on the inner surface of the shield, and inversely calculating the extrusion force applied to the shield by the surrounding rocks according to the principle of elastic mechanics based on the tested annular and longitudinal strains of the inner surface of the shield; C, according to the acquired distribution rules of the extrusion force applied to the shield by the surrounding rocks, calculating the friction force borne by the shield on the premise of linear distribution of the extrusion force between two adjacent measuring points; D, according to the jamming state judging criteria and jamming risk coefficient calculation method, calculating whether the shield is jammed and giving early warning of a jamming risk level. The method solves the problem in monitoring of surrounding rock and shield interaction in a shield type TMB tunneling process, provides basis for the predictive analysis of jamming accidents and is of great importance for the safety of TBM tunneling.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Equal-pressure virtual isolation check valve sealing test method and equipment
ActiveCN101858817AEasy to installReduce volumeMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateHigh dosesEngineering
The invention relates to equal-pressure virtual isolation check valve sealing test method and equipment, which are realized through an equal-pressure virtual isolation sealing plug and a leak detector by the following steps of: firstly arranging the equal-pressure virtual isolation sealing plug in an outlet pipe of a tested check valve; filling pressure in the sealing ring and the annular space of the sealing plug through the test fluid of the leak detector, and carrying out virtual isolation on the outlet pipe of the tested check valve through a formed equal-pressure ring; then carrying out fluid filling on a cavity between the equal-pressure virtual isolation sealing plug and a valve plate in the tested check valve through the leak detector, and keeping the pressure in the cavity of the tested check valve to be constant; and subsequently detecting the supplemented flow value of the fluid, i.e. the leakage ratio of the valve, wherein the test fluid not only can be gas, but also can be a liquid. The invention has the characteristics of accurate and reliable testing result, short working time of testing personnel in a high-dose region, low acceptable dose and less time for installing an equal-pressure isolation plug body 1. A low-pressure sealing test is adopted for test pressure, and the test pressure is generally consistent with the test pressure of a nuclear power plant containment.
Owner:北京冶核技术发展有限责任公司
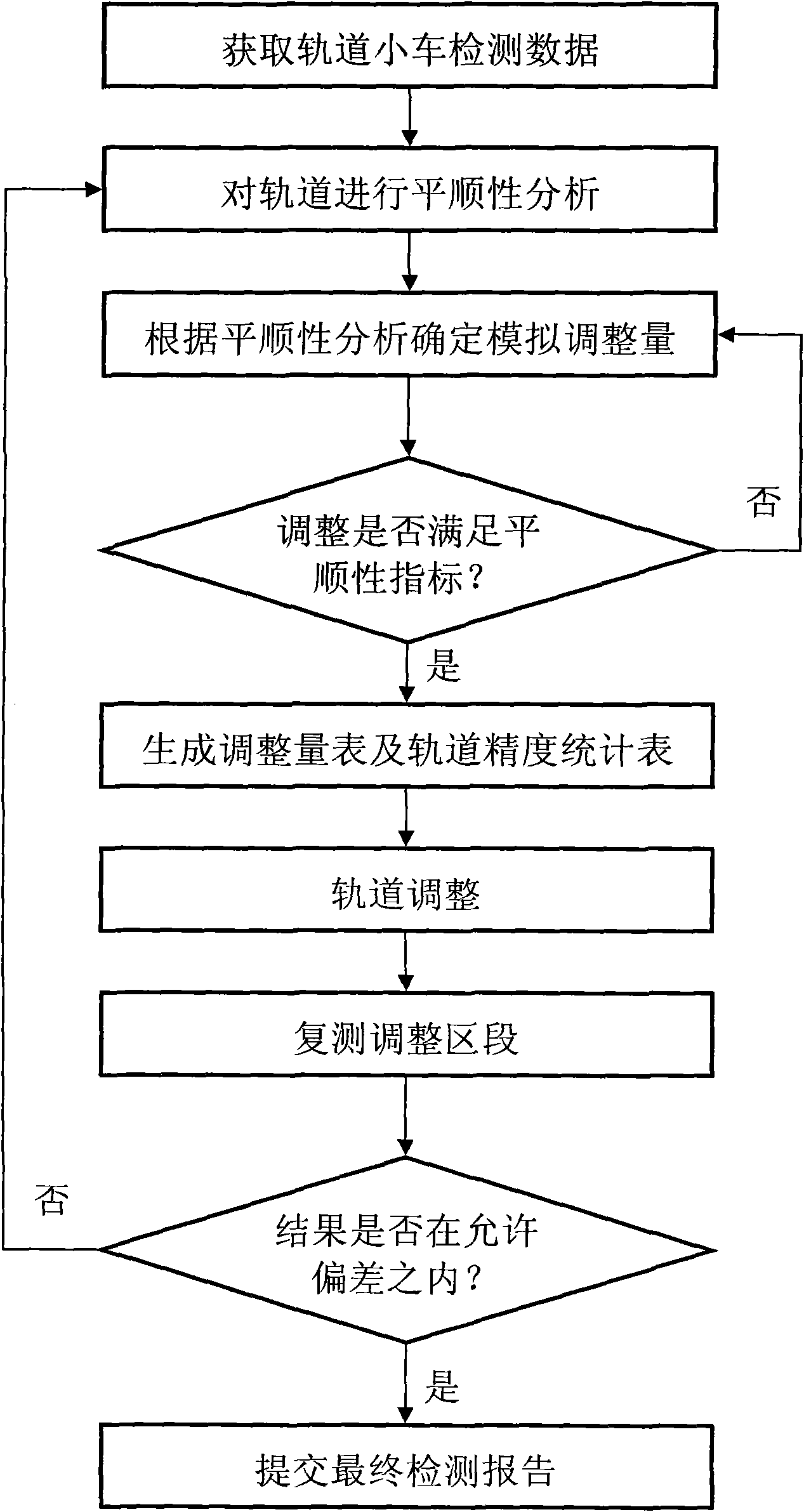
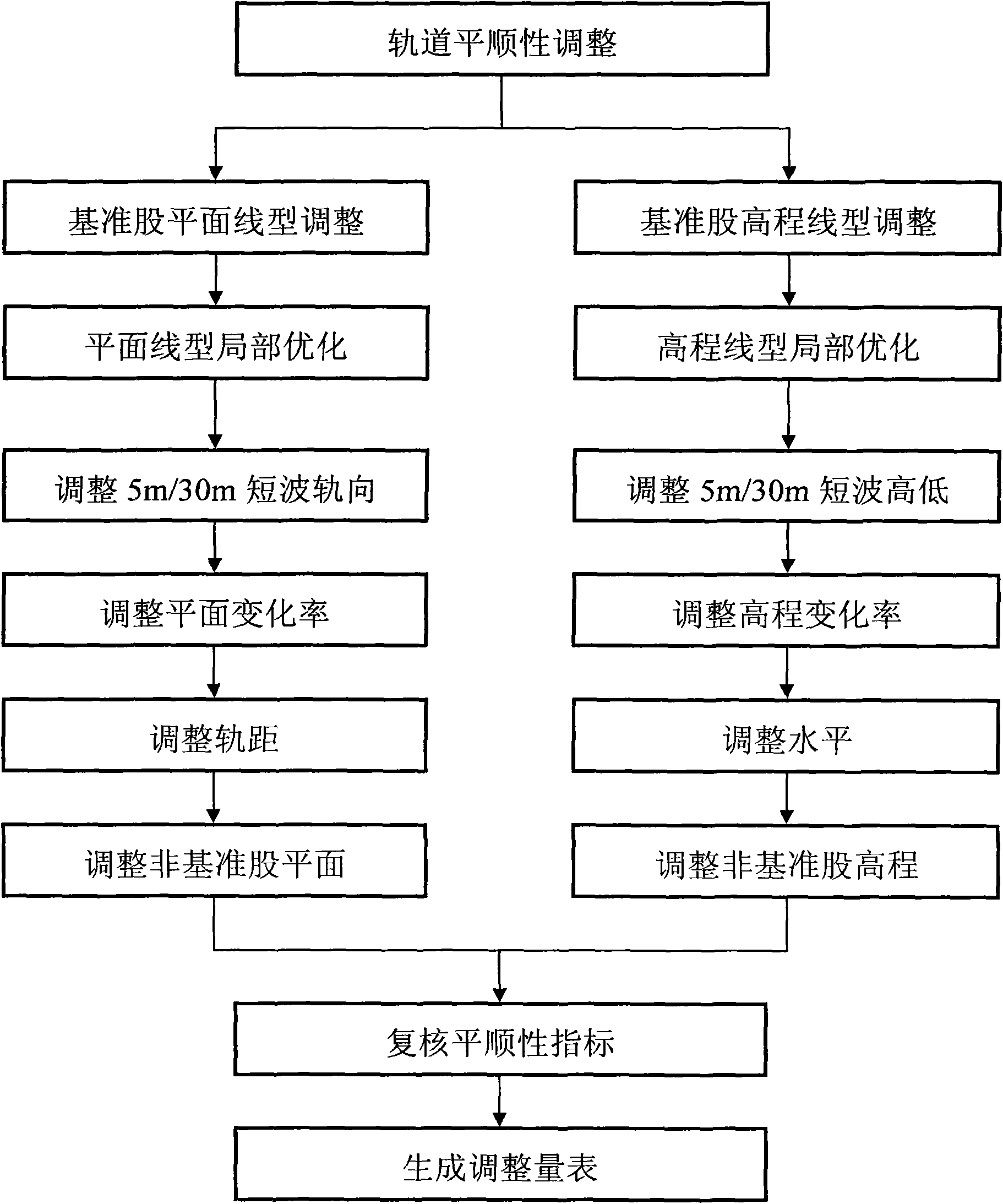
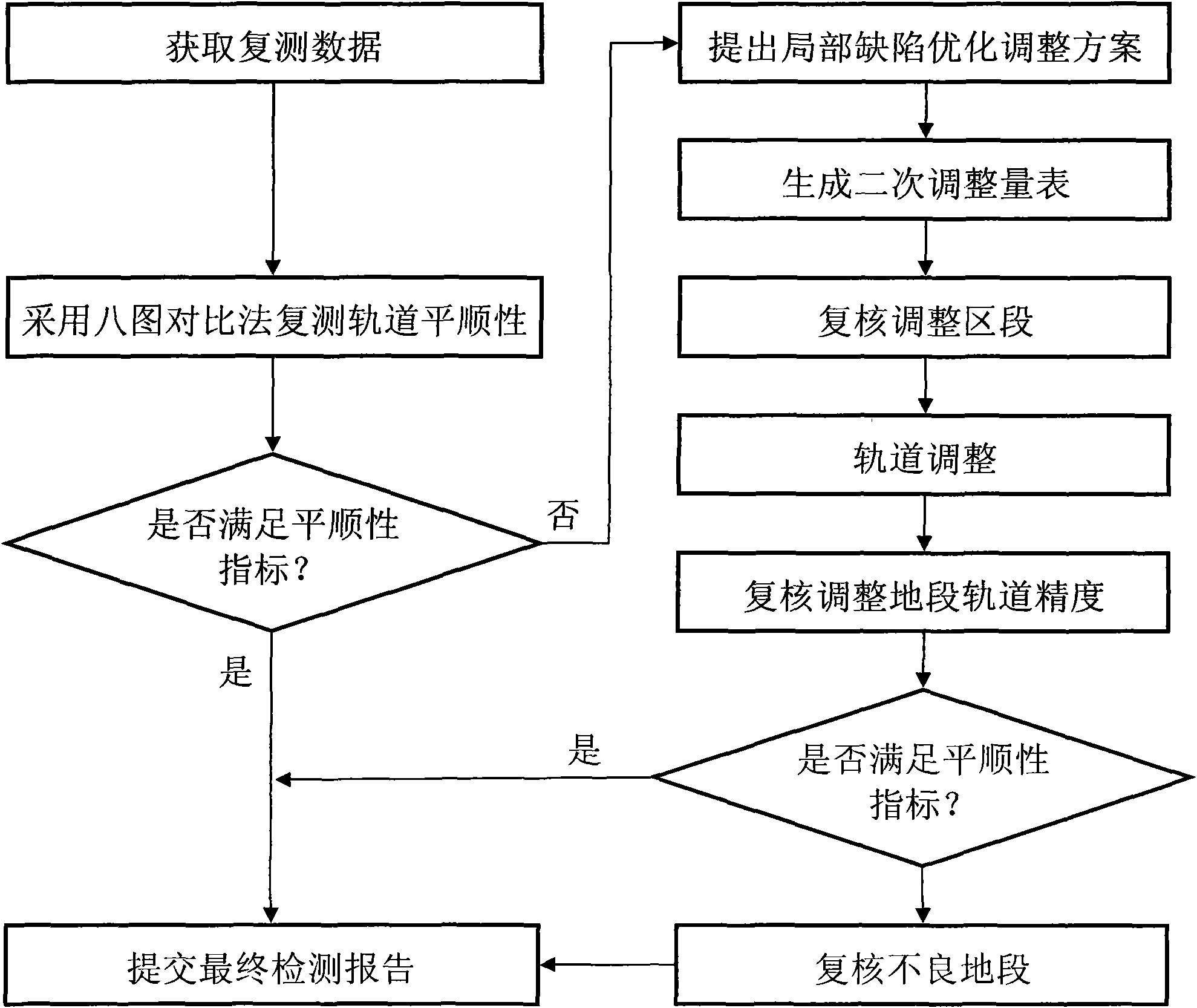
High-speed railway track static comfort analysis adjustment method
InactiveCN103132411AThe measurements are trueAccurate measurementRailway track constructionMeasuring apparatusEngineeringTotal station
The invention relates to a high-speed railway track static comfort analysis adjustment method which includes the steps of utilizing a track trolley to measure high-speed railway track parameters to acquire track static measurement data to acquire track static measurement data, after carrying out accurate positioning of the track trolley by using a total station and a control network of foundation piles; drawing the track static measurement data into an oscillogram according to a certain proportion relationship, drawing a variation trend line according to the overall trend of the oscillogram, and carrying out a comfort analysis over the track according to the drawn oscillogram and the variation trend line; calculating adjustment amount required in adjusting the track according to the result of the comfort analysis, and carrying out a site adjustment for the track; carrying out repetition measurement over the track adjusted on site, and carrying out a repeatedly measured data analysis of the adjusted track and local optimization adjustment; if the comfort index of the repeatedly measured data is not in the allowed deviation, getting back to analyze and adjust again, and then generating a track static comfort test report from the analysis and adjustment data.
Owner:刘彬 +1
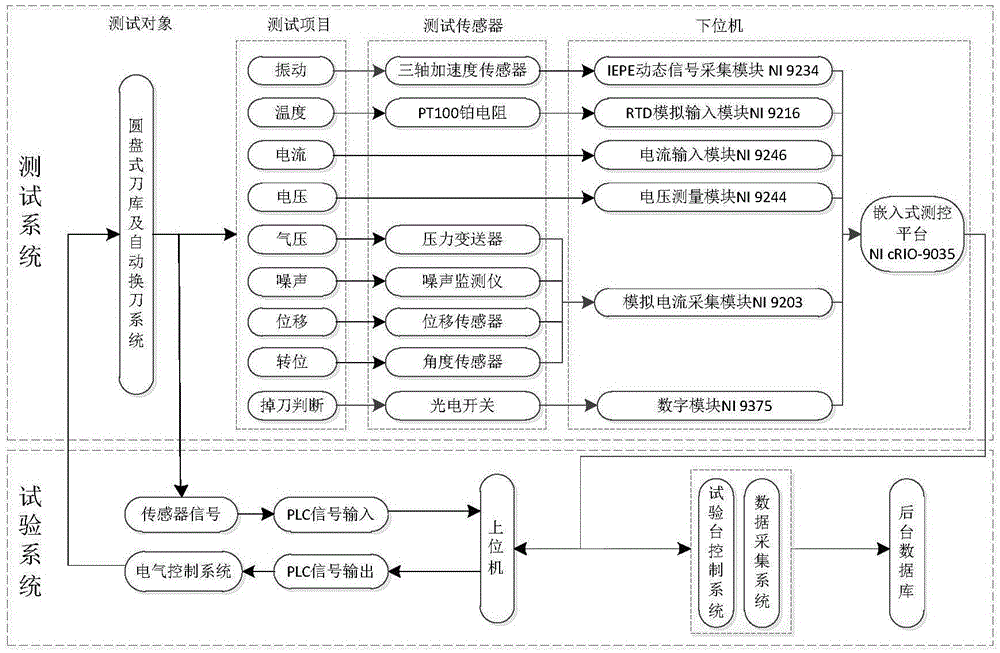
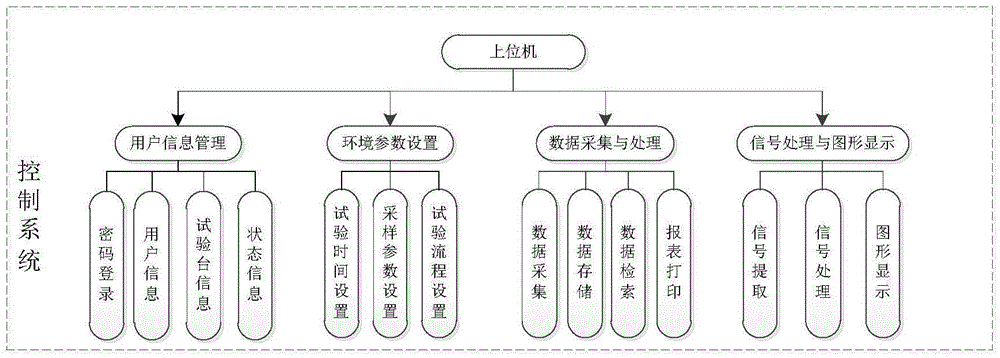
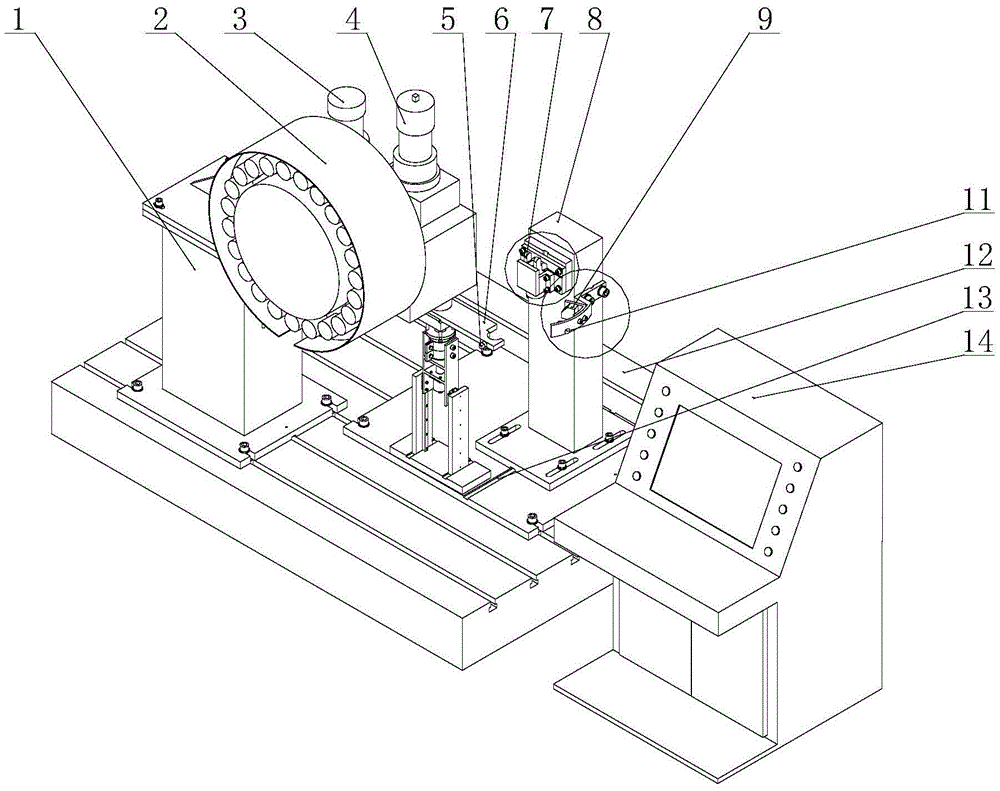
Disc-type tool magazine and automatic tool-changing system comprehensive performance detection platform
ActiveCN105573251AImprove performanceMany testing itemsProgramme controlComputer controlPilot systemControl system
The invention relates to the technical field of reliability test of a disc-type tool magazine and automatic tool-changing system for a machining center and specifically relates to a disc-type tool magazine and automatic tool-changing system comprehensive performance detection platform. The detection platform comprises a detection system, a test system and a control system. The detection system is used for finishing detection and collection of various parameters of the disc-type tool magazine and automatic tool-changing system; the test system is used for testing the reliability of the same-kind multi-dimension disc-type tool magazine and automatic tool-changing systems; and the control system is used for finishing setting of related test parameters in the test process and carrying out processing and analysis on the collected parameters, graphical display and test result display, and realizing comprehensive control of the detection system and the test system. The comprehensive performance detection platform is a test platform capable of loading the same-kind multi-dimension disc-type tool magazine and automatic tool-changing systems; and especially, the platform can carry out detection on the state and performance of the disc-type tool magazine and automatic tool-changing system and give corresponding analysis results.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Device for measuring rotational inertia and friction moment of ball screw
InactiveCN103900813AReal-timeAchieve preservationMachine gearing/transmission testingStatic/dynamic balance measurementFriction torqueCoupling
The invention relates to a device for measuring rotational inertia and friction moment of a ball screw. The device comprises a bottom plate, two linear guide rails, the ball screw, a torque sensor, a servo motor, a mobile platform and two friction moment measuring mechanisms. Each linear guide rail is provided with two sliding blocks. The two ends of the ball screw are supported by the part, located between the two linear guide rails, of the bottom plate in a rotary mode through a fixed supporting base and a floating supporting base. One end of the torque sensor is connected with the end, supported by the fixed supporting seat, of the ball screw through a coupler. An output shaft of the servo motor is connected with the torque sensor through a coupler. The two friction moment measuring mechanisms are arranged on the two sides of a screw nut base respectively. Each friction moment measuring mechanism comprises a cantilever. A connecting sleeve is arranged at the tail end of each cantilever. Each connecting sleeve is connected with a sliding bar through a vertical linear bearing. The other end of each sliding bar is connected with a pressure sensor. Each sliding bar is sleeved with a spring. The bottom of each pressure sensor is connected with a universal ball. The bottom of each universal ball makes contact with a linear slab which is parallel to the ball screw. The linear slabs are tightly connected to the bottom plate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
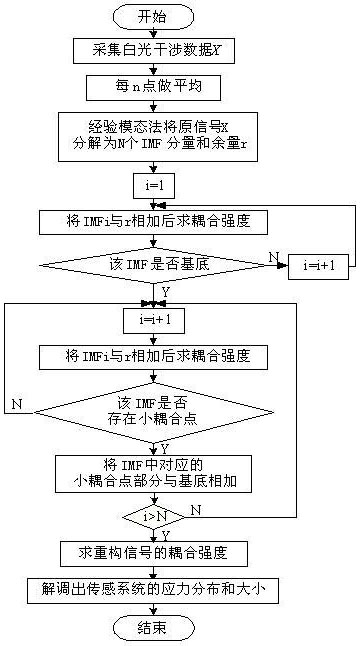
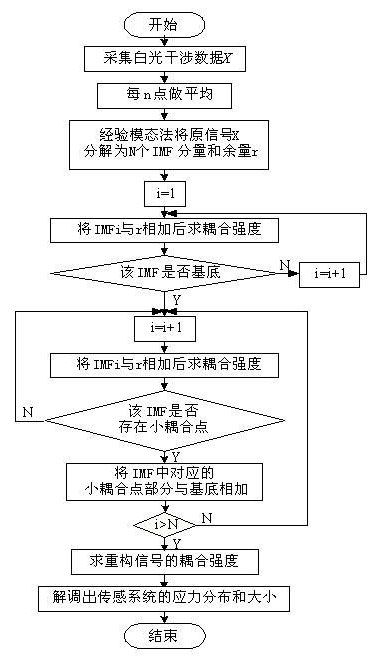
Data demodulation method for polarization maintaining fiber stress sensing
InactiveCN102095538AAccurate measurementAccurate and reliable measurement resultsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)System testing
The invention discloses a data demodulation method for polarization maintaining fiber stress sensing. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring an interference signal by using a polarization maintaining fiber stress sensing test system to acquire photovoltage data; pre-processing the photovoltage data, averaging every n points to acquire new photovoltage data, and data volume; decomposing a photovoltage data signal into an intrinsic mode function (IMF) component and an allowance by an experimental mode method; finding out a basic component and identifying a small coupling point; reconstructing coupling intensity of a signal, and calculating the stress magnitude through intensity of each coupling point so as to realize the distributed detection of a system; and calculating indexes which can show the system test accuracy, such as a signal-to-noise ratio and the like. The method can effectively improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the polarization maintaining fiber stress sensing system, and improves the identification capacity of weak coupling points and the sensitivity of a coupling test. Under the environment of relatively low signal-to-noise ratio, microstress can be detected well.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
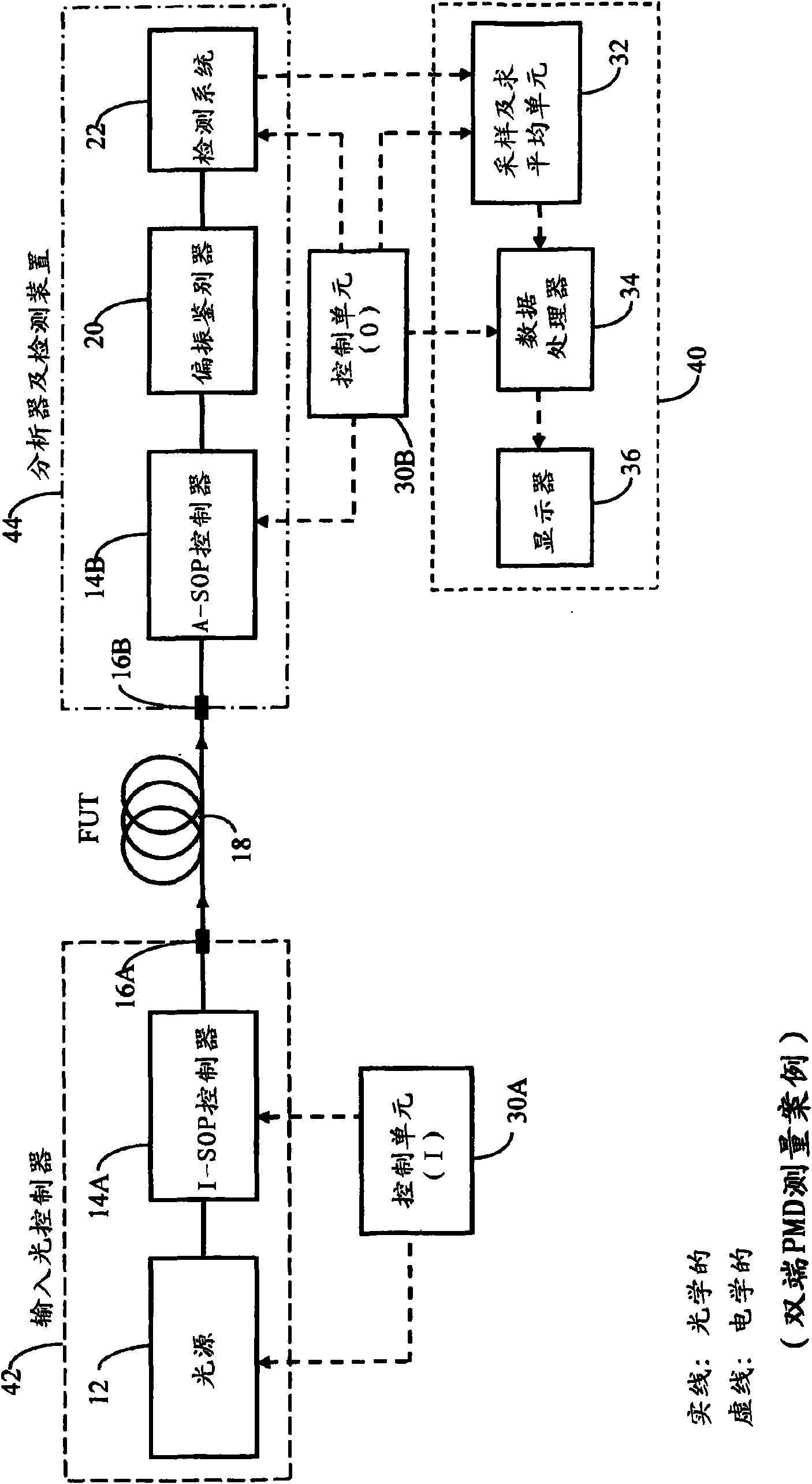
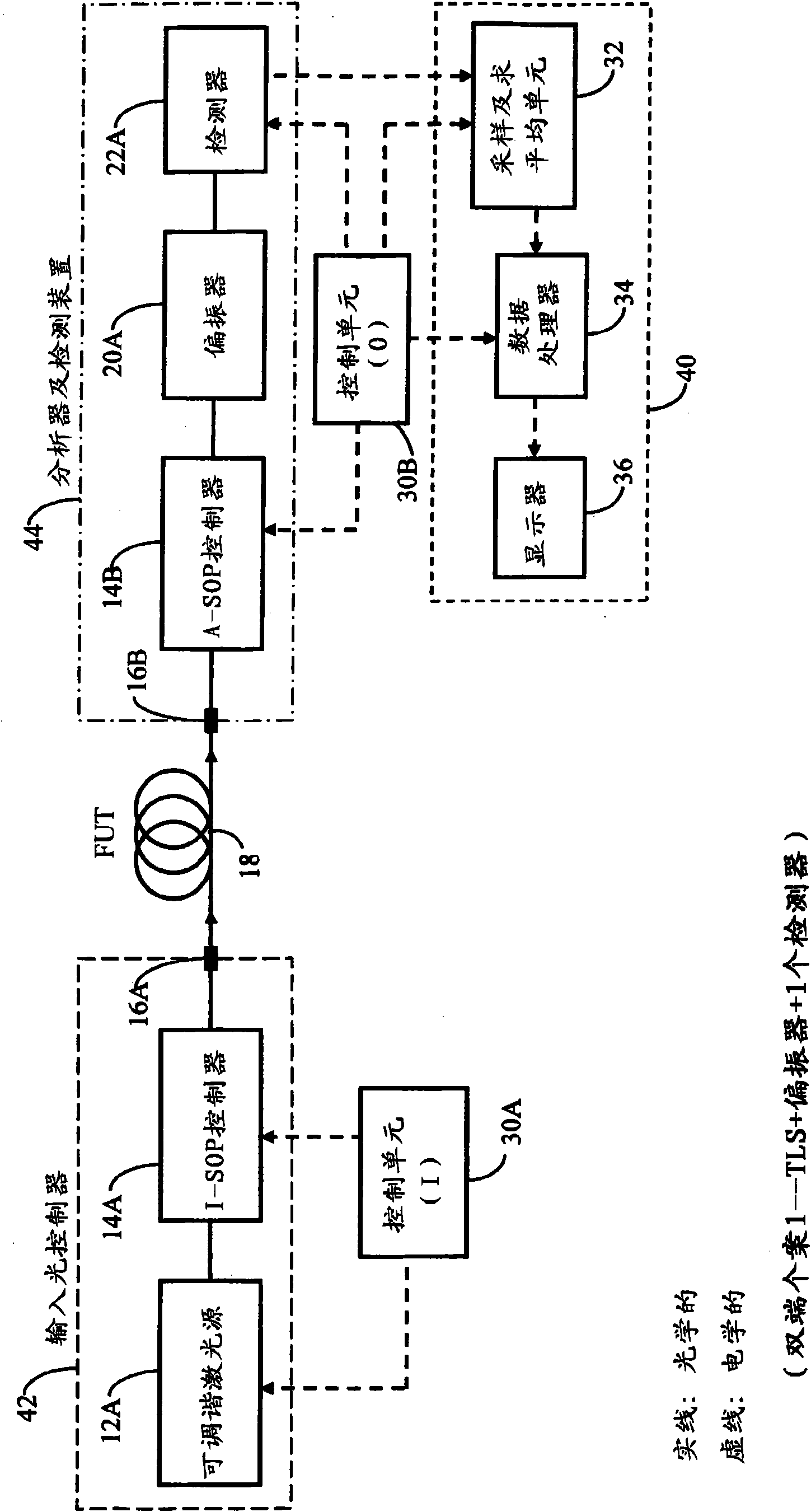
Method and apparatus for determining differential group delay and polarization mode dispersion
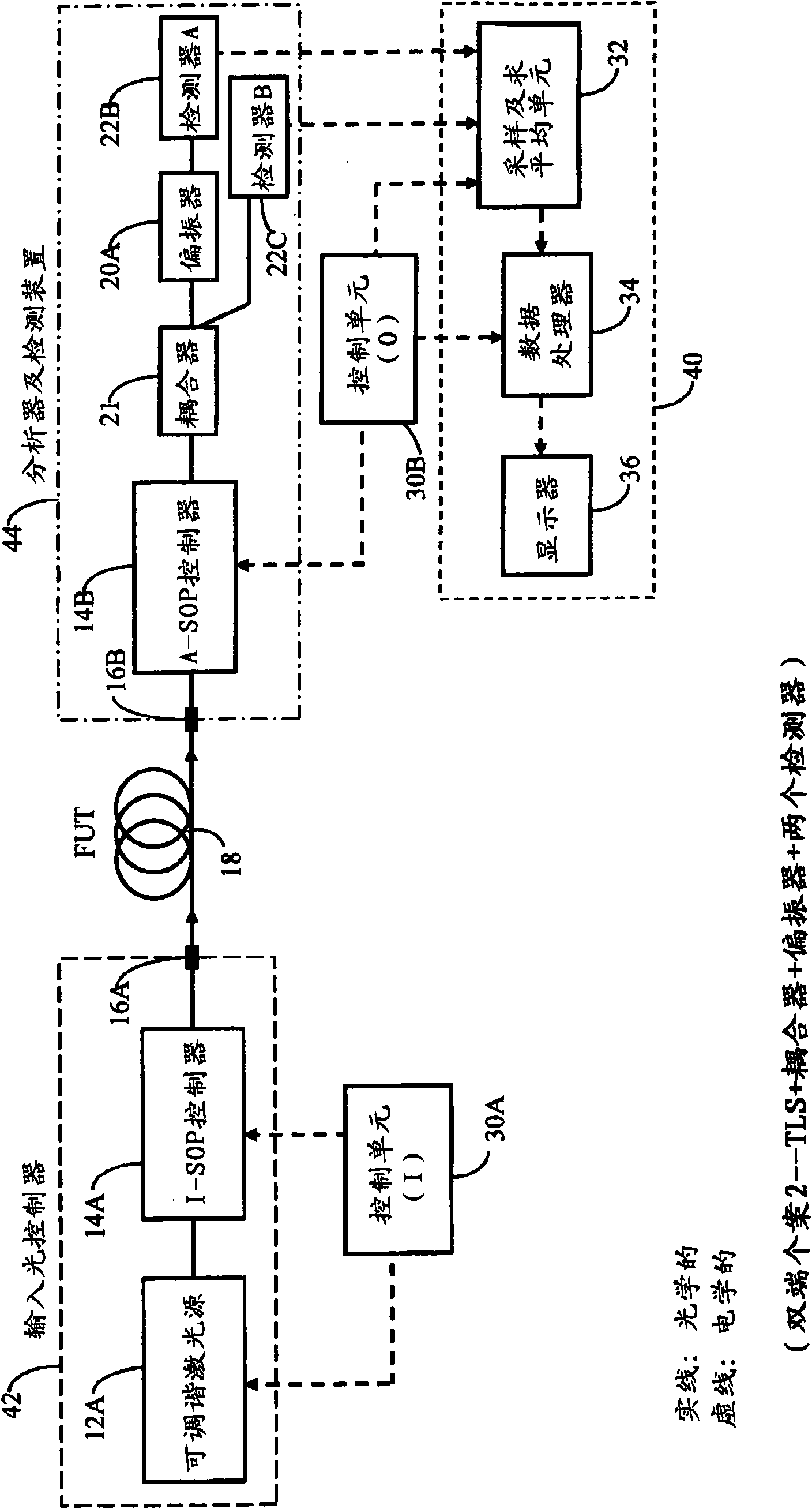
ActiveCN101688819ALow stability requirementsAccurate and reliable measurement resultsLaser optical resonator constructionLaser arrangementsMean squareOptical frequencies
A method and apparatus for measuring at least one polarization-related characteristic of an optical path (FUT) uses a light input unit connected to the FUT at or adjacent a proximal end of the FUT anda light output unit connected to the FUT at or adjacent its proximal or distal end. The light input unit injects into the FUT at least partially polarized light having a controlled state of polarization (I-SOP). The output light unit extracts corresponding light from the FUT, analyzes and detects the extracted light corresponding to at least one transmission axis (A-SOP), and processes the corresponding electrical signal to obtain transmitted coherent optical power at each wavelength of light in each of at least two groups of wavelengths, wherein the lowermost (lambda 1) and uppermost (lambdau) said wavelengths in each said group of wavelengths are closely- spaced. A processing unit than computes at least one difference in a measured power parameter corresponding to each wavelength in awavelength pair for each of the at least two groups, the measured power parameter being proportional to the power of the said analyzed and subsequently detected light, thereby defining a set of at least two measured power parameter differences; computes the mean-square value of said set of differences; and calculating the at least one polarization-related FUT characteristic as at least one predetermined function of said mean-square value, the predetermined function being dependent upon the small optical frequency difference between the wavelengths corresponding to the said each at least said two pairs of closely-spaced wavelengths.
Owner:EXFO
Method for measuring initial attitude of high-speed rotating projectile body at muzzle
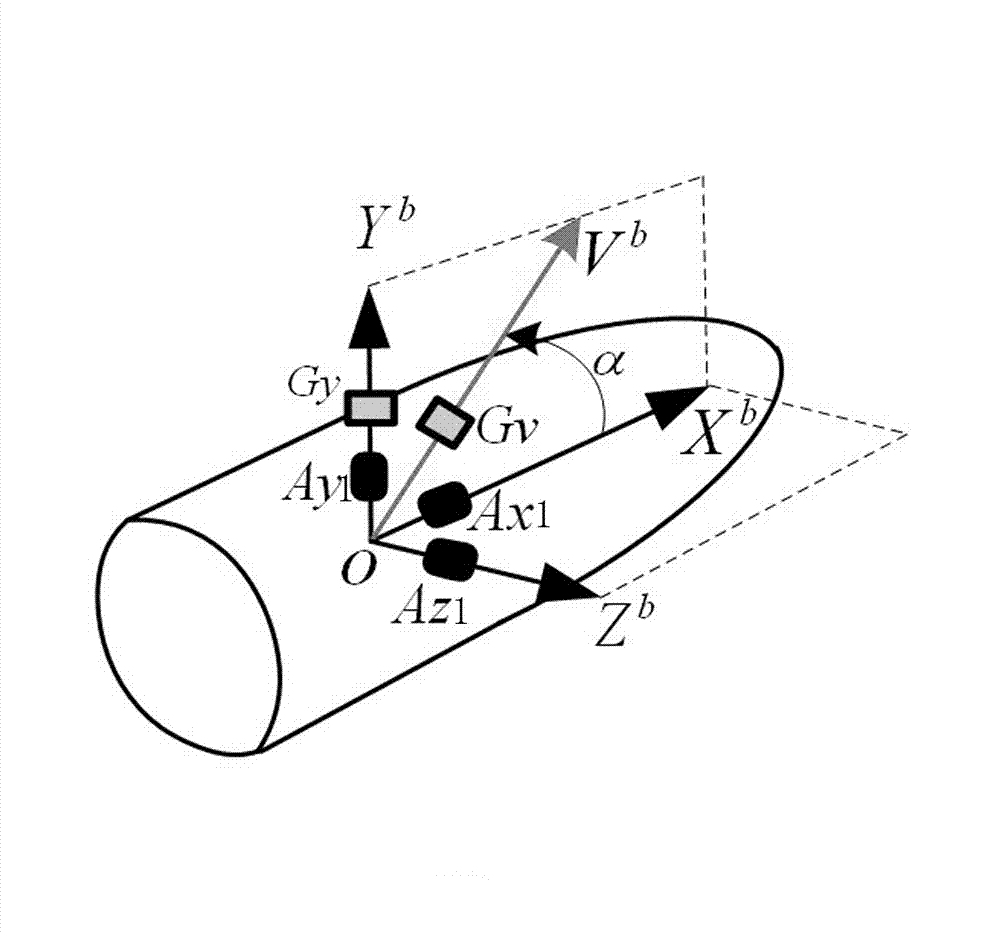
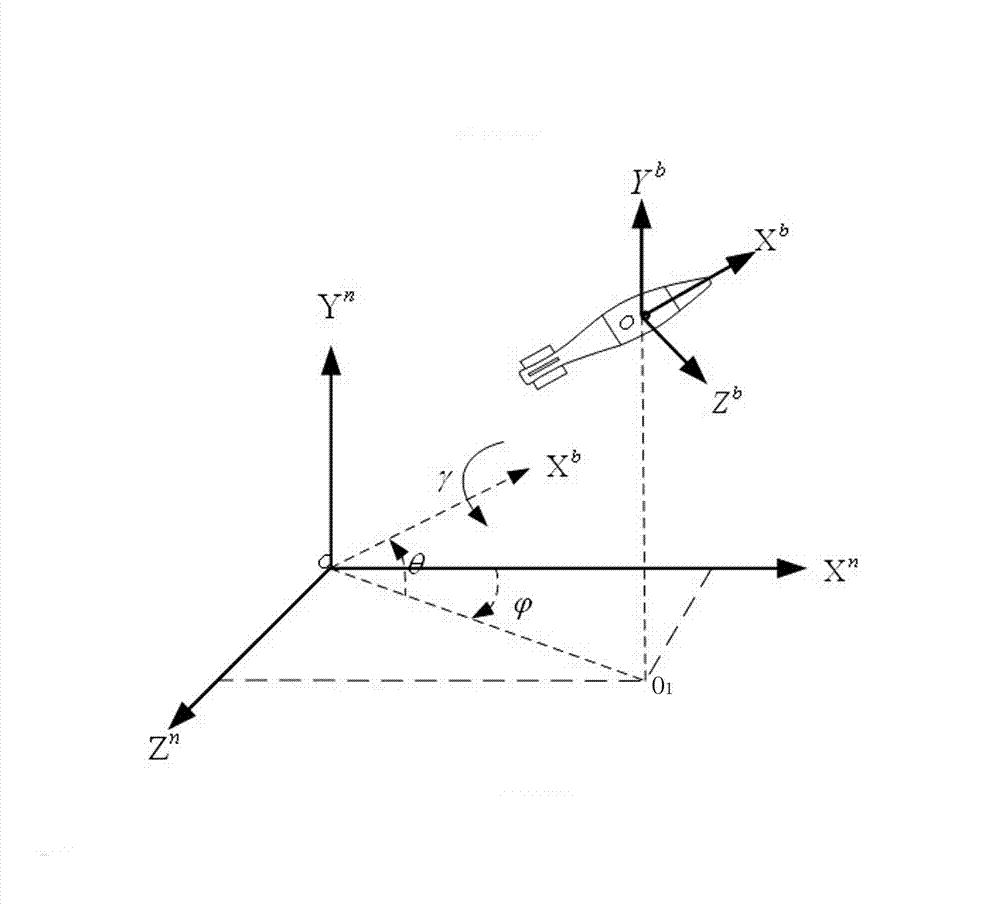
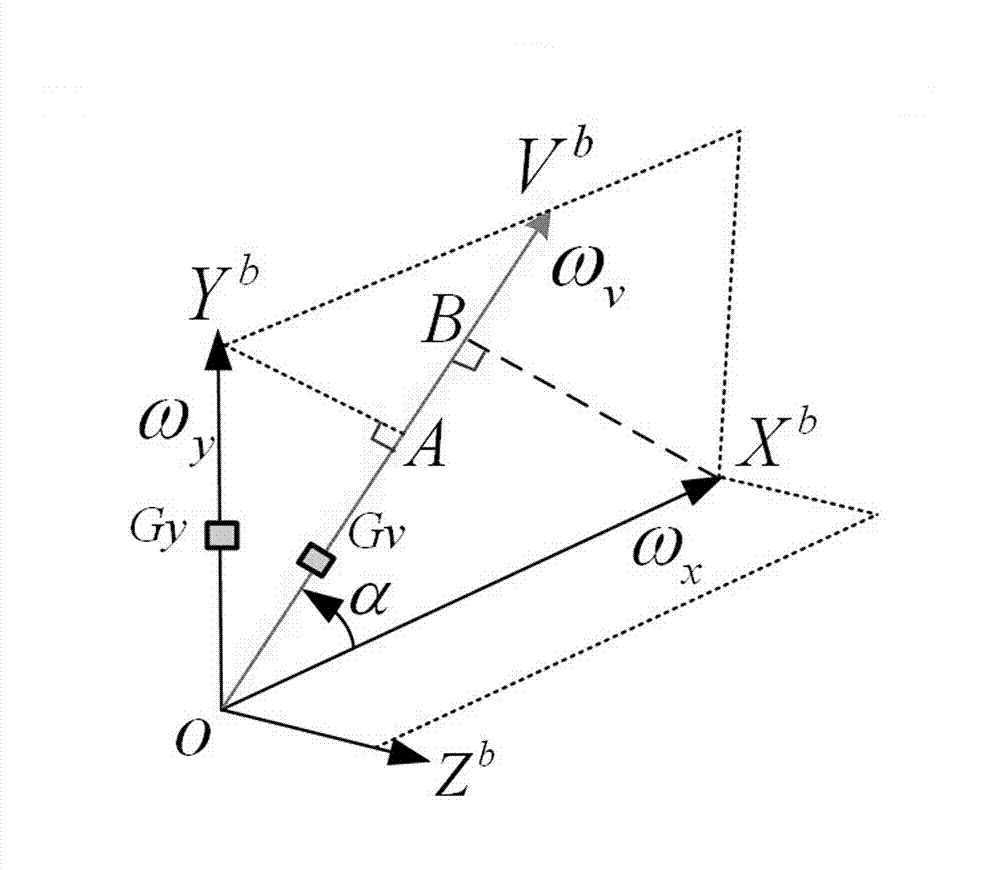
ActiveCN103075930ASolving High-Precision Measurement ProblemsReasonable designAmmunition testingNavigation instrumentsMeasurement problemSmall range
The invention relates to a technique for measuring an initial attitude of a high-speed rotating projectile body at a muzzle, in particular to a method for measuring the initial attitude of the high-speed rotating projectile body at the muzzle based on a three-axis micro electro mechanical system (MEMS) accelerator and two nonorthogonal distributed MEMS gyroscopes to solve the problem of accurately measuring the high-speed rotating projectile body with high axial overload and high angular speed. The method for measuring the initial attitude of the high-speed rotating projectile body at the muzzle comprises the following steps: (I) establishing a cannon emission coordinate system as a reference coordinate system, setting an emission point of the projectile body in a barrel as an original point of the reference coordinate system, and arranging the barrel in an XnOYn plane of the reference coordinate system; establishing a projectile body coordinate system, setting a projectile body core as an original point of the projectile body coordinate system, and enabling an axis to be along the axial direction of the projectile body; and in the whole process of emitting the projectile body to the muzzle, ensuring that the yaw angle of the projectile body is zero and the pitch angle is not changed. The design is reasonable, and the measurement problem that the range and the accuracy are conflicted when the axis angular rate of the projectile body is measured is solved through the two high-precision small-range gyroscopes.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Detection method of multiresidue of 5 nitrofuran metabolites and chloramphenicol in shrimp
ActiveCN106124653AImprove extraction efficiencyOvercoming the limitations of separate assaysComponent separationMetaboliteQuantitative accuracy
A detection method of a nitrofuran metabolites and chloramphenicol multiresidue in shrimp belongs to the technical field of aquatic products detection. The method is as below: hydrolyzing a sample with hydrochloric acid, subjecting nitrofuran metabolites to derivatization by using 2-nitrobenzaldehyde, adjusting the pH value to 6.5-7.5, adding acetonitrile, adding an extraction salt package; conducting liquid-liquid extraction of a target compound by using acetonitrile; purifying and concentrating a supernatant; then determining by a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer, and quantifying by an internal standard method. The method uses a novel sample extraction and purification mode for simultaneous analysis and determination of two prohibited drugs with the highest detection rate in shrimp, overcomes the limitations of separate determination of two drugs in the detection method of the prior art, improves the extraction efficiency of chloramphenicol in actual positive samples, greatly improves the work efficiency, shortens the work time and saves reagent consumption and labor costs. The method adopts the isotope internal standard method for quantification, the determination result is more accurate and reliable, has high sensitivity, and good reproducibility and quantitative accuracy.
Owner:青岛菲优特检测有限公司
Cardiovascular function detection method based on multi-channel pulse wave form analysis and device thereof
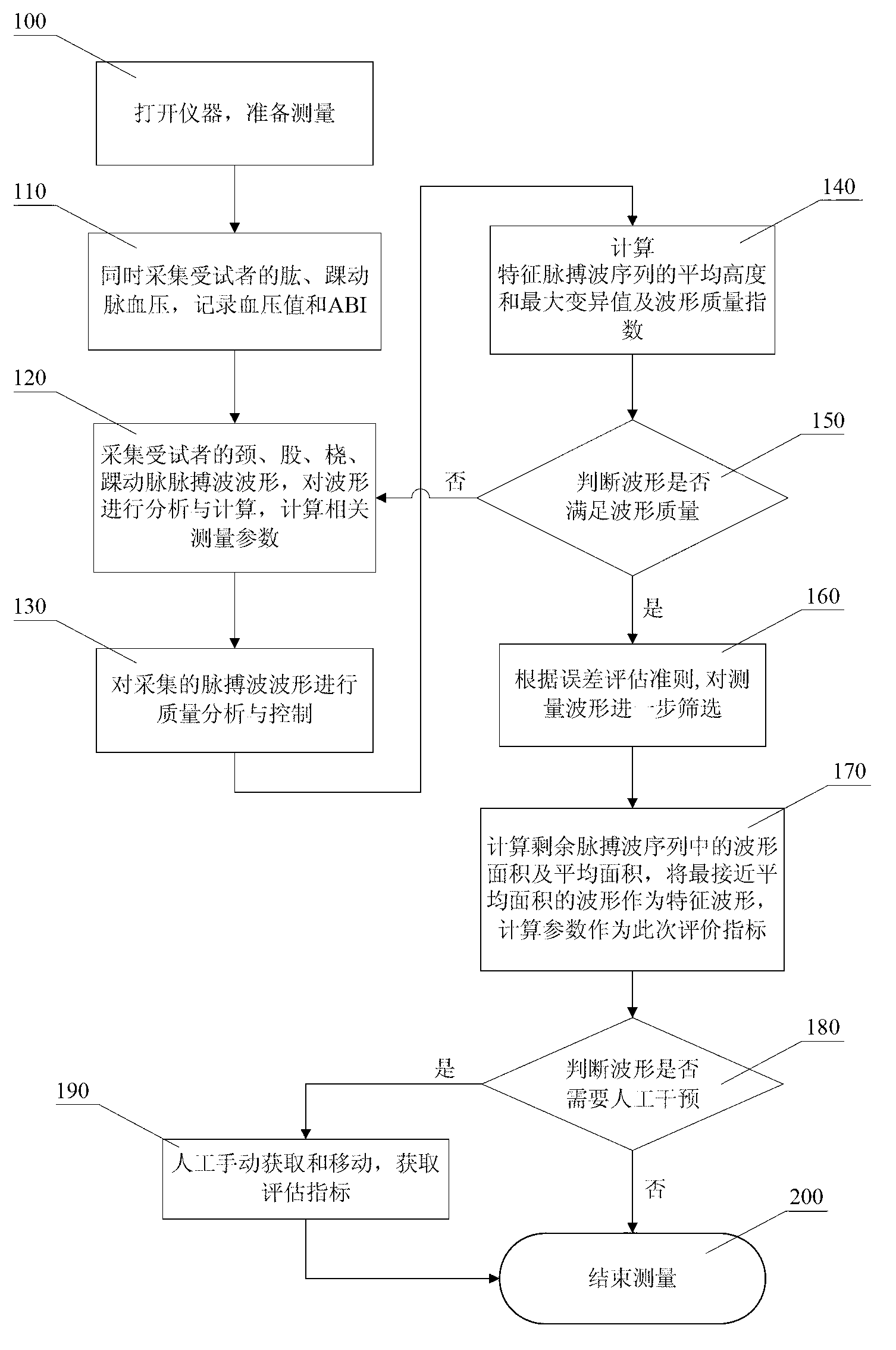
The invention discloses a cardiovascular function detection method based on multi-channel pulse wave form analysis and a device thereof. A cardiovascular function evaluation index system suitable for health screening and personal dynamic detection is built by collecting blood pressure of upper limbs and lower limbs and multi-channel pulse wave form of neck, thigh, radio and ankle, and quality analysis and control can be conducted on evaluation index in the system. Simultaneously, the device is convenient to operate, low in cost and capable of well meeting requirements of large crowd for cardiovascular disease screening.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry method for determining content of uranium in uranium niobium alloy
InactiveCN104597174AEasy to measureOvercoming Disadvantages of Susceptibility to InterferenceComponent separationElement analysisDecomposition
The invention discloses an isotope dilution mass spectrometry method for determining the content of uranium in a uranium niobium alloy. A formula for calculating the content of uranium in the uranium niobium alloy is derived according to an isotope dilution mass spectrometry principle. A decomposition process of the uranium niobium alloy is researched, the sampling quantity and the amount of a diluent are optimized, and the influences of mass spectrum line interference and alloy element interference on a measurement result are discussed. The method comprises the following steps: adding nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid to quantitatively dissolve the uranium niobium alloy, adding a quantitative amount of a uranium isotope diluent to directly prepare a mixed sample solution, determining the mixed solution and the uranium isotope proportion in the uranium niobium alloy sample through mass spectrometry, and calculating the content of uranium in the uranium niobium alloy. Quantitative separation of uranium is not needed by the determined method. An XRF technique, an ICP-AES technique and an element analysis technique are used to measure the content of niobium and the total content of impurity elements in the uranium niobium alloy, and back stepping is carried out to obtain the corresponding uranium content order in order to verify the accuracy of the analytical result, and the obtained result is consistent with a result obtained through the experiment method. When the method disclosed in the invention is used to analyze the uranium niobium alloy sample, the relative standard uncertainty of determination results is 0.2% (6 determinations), and the expanded uncertainty is 0.5% (95% confidence level).
Owner:青岛齐力铸钢有限公司
Method for measuring wettability of lithium battery electrolyte or lithium ion battery electrolyte on battery material
InactiveCN102866084AEffective assessmentOptimizing the standing processSurface/boundary effectEngineeringLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to a method for measuring wettability of lithium battery electrolyte or lithium ion battery electrolyte on a battery material, and the battery standing time is optimized according to the experimental results. Simultaneously, the precise measuring methods with the different degrees of wettability are distinguished. The invention provides a method for measuring electrolyte wettability at low temperature, so that the method provided by the invention is convenient and fast, the detected result accuracy is high, and the wettability of the electrolyte on the battery material is comprehensively and effectively evaluated, the battery standing technology is optimized according to the wetting speed, and the preparation efficiency of the batteries is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CHEM REAGENTS
Continuous drilling flowrate process capable of predicting coal draft outburst and its apparatus
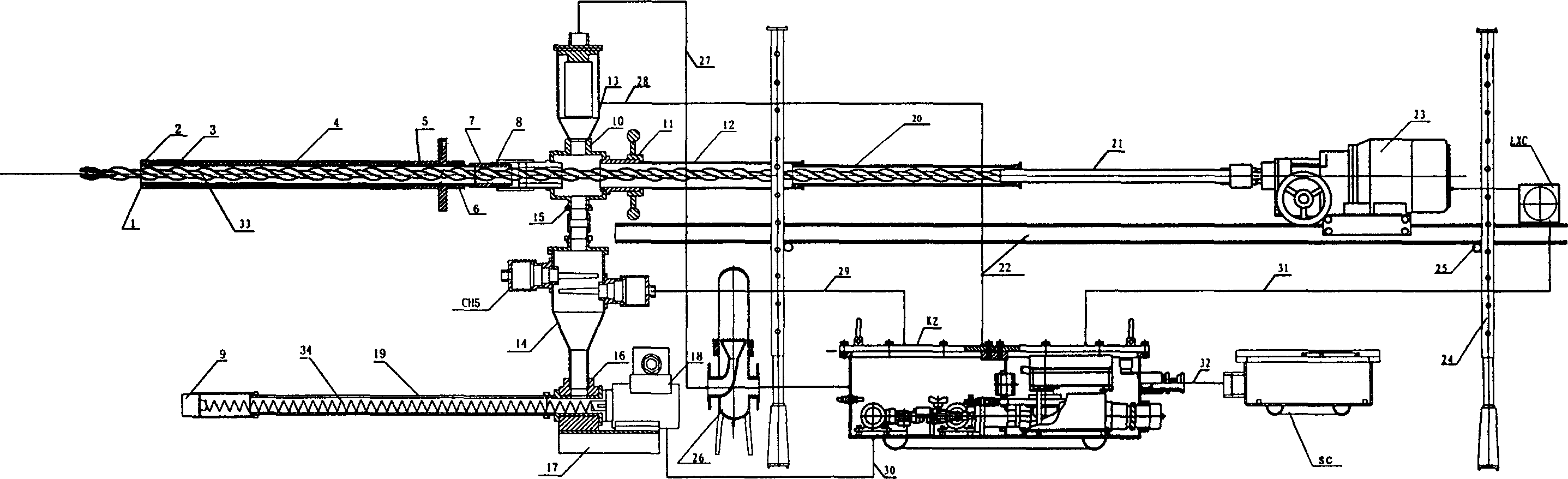
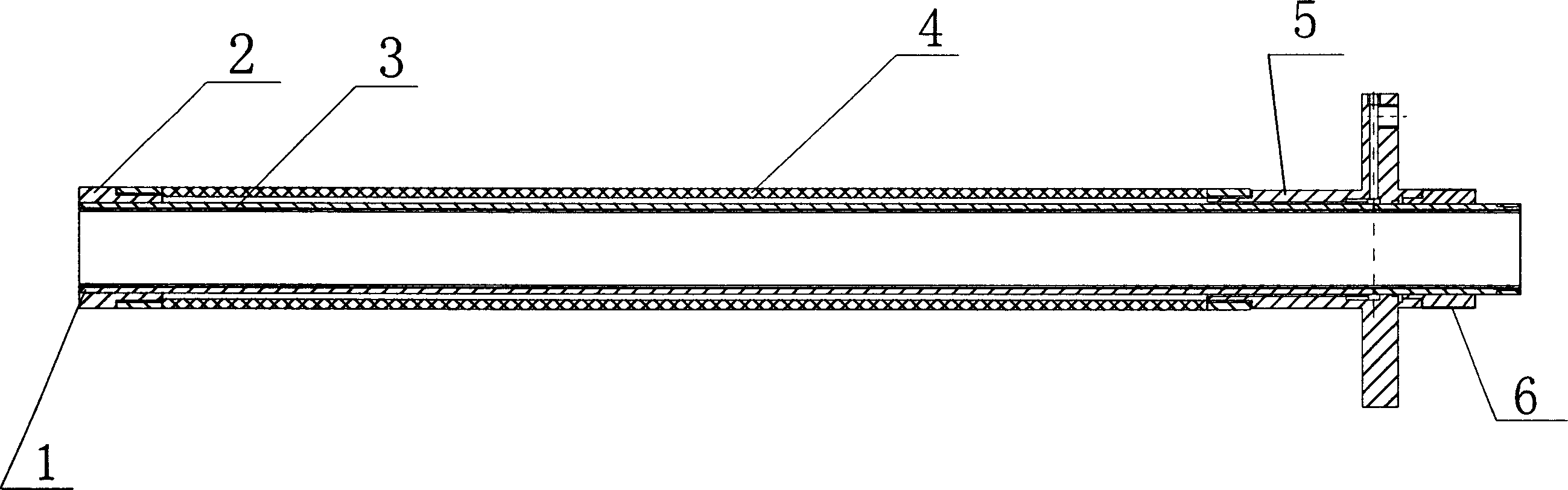
InactiveCN1847620APerceived heightControl startMining devicesDust removalData acquisitionEngineering
The present invention is continuous drilling flow rate capable of predicting coal draft outburst and its apparatus. By means of the method of drilling holes in the coal bed drilling direction for data acquisition and the apparatus comprising hole sealing capsule unit, solid-gas separator, filter, coal bit controller, electric rock drill with connected displacement sensor LXC, controller unit KZ with explosion resistant enclosure and connected computer data acquisitor SC, the present invention can determine the gas distribution in the drilling direction, obtain the gas flow rate distribution curve along the drilling depth during coal bed drilling process, so as to determine the distance of soft coal containing high pressure gas to the ground, judge the distance to the place with maybe outburst. The present invention has compact reasonable structure, high accuracy and stable and reliable measurement result, and may be used widely.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com