Method and apparatus for determining differential group delay and polarization mode dispersion
A polarization and polarization-related technology, applied in the structure of optical resonator cavity, testing of machine/structural components, structure/shape of active medium, etc., can solve the wrong estimation, reduce the maximum measurable PMD value, limit the maximum measurable length And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0147] In the figures, identical or similar components bear the same reference numerals in different figures, where appropriate with a symbol indicating differences.
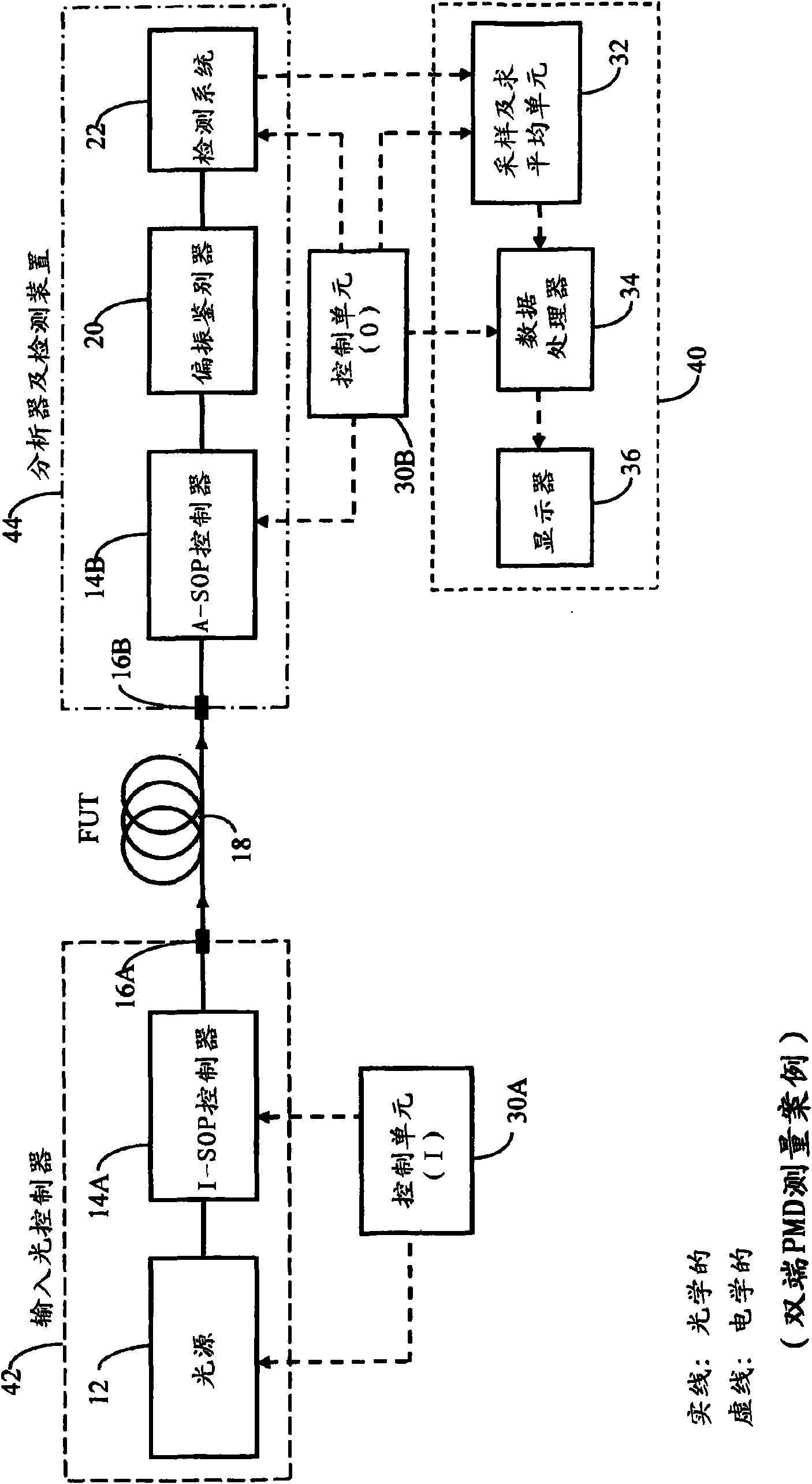
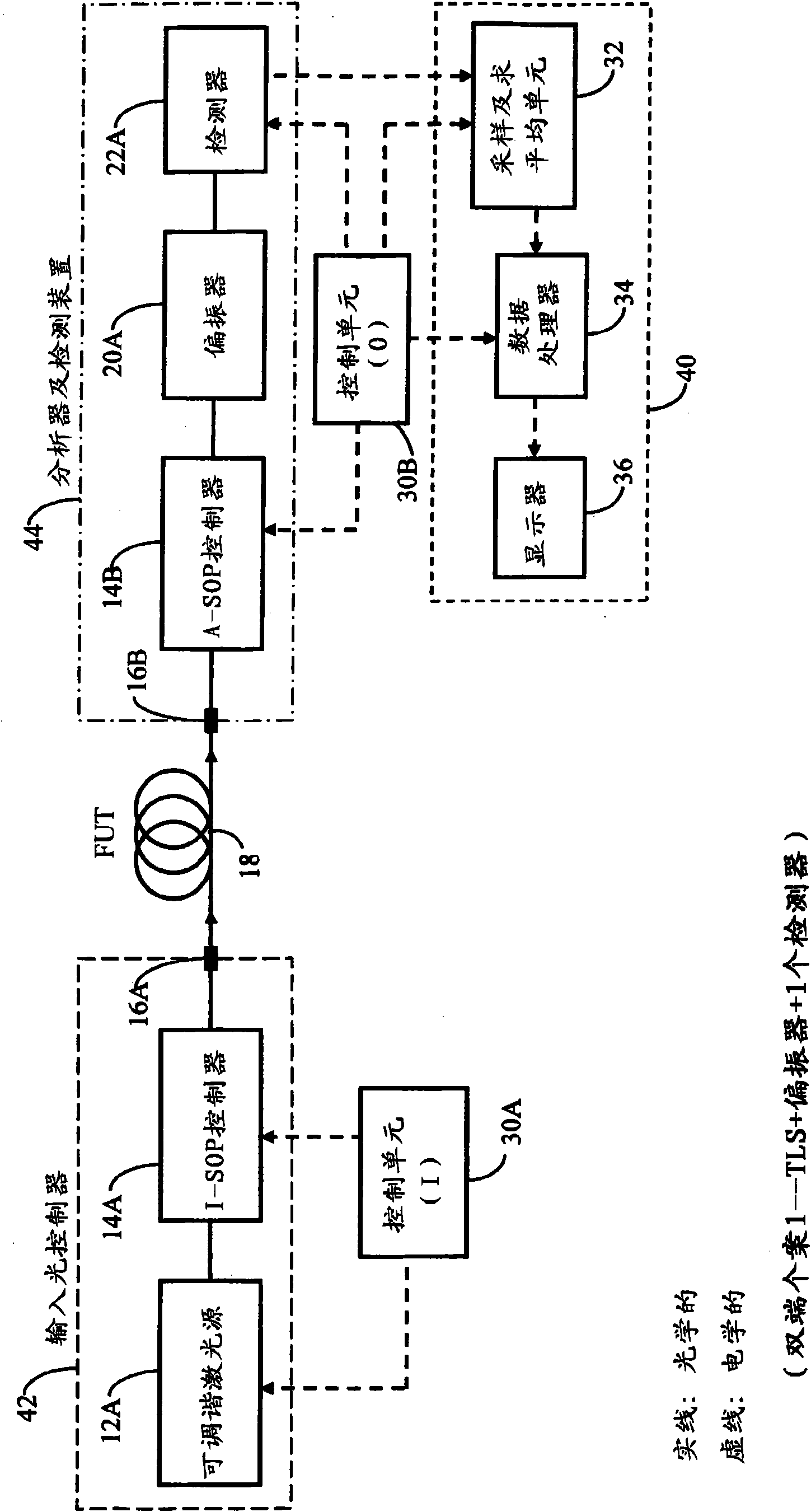
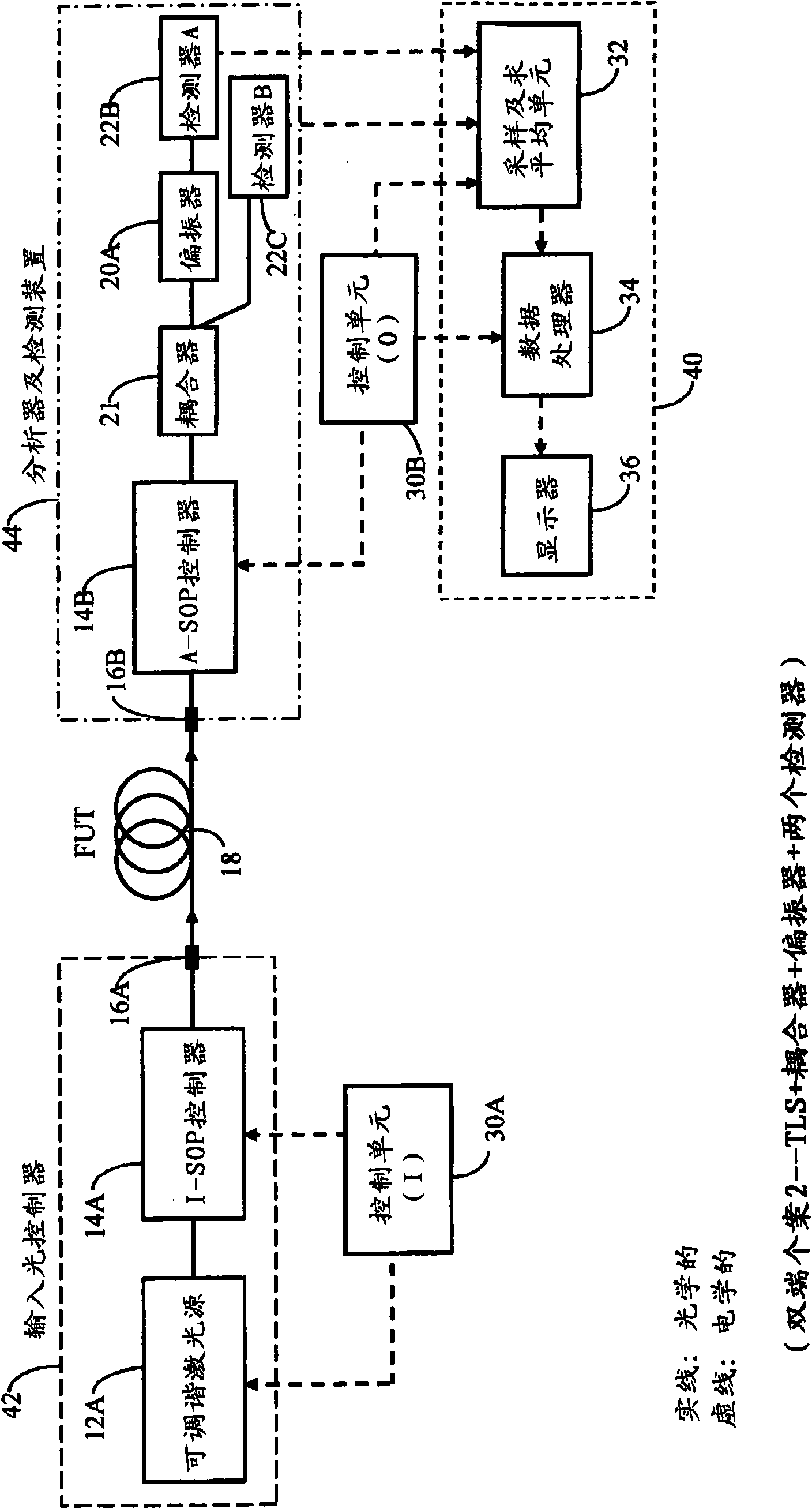
[0148] The various aspects of the invention, as well as their respective implementations, are based on the same underlying theory. The embodiment of these aspects can advantageously be used for: for narrow optical channel or in specified broad wavelength range, to PMD or depend on the double-ended measurement of the DGD of wavelength, single-ended overall PMD measurement, single-ended cumulative PMD measurement and Other related variants.
[0149] In each of the preferred embodiments of the invention described below, there will generally be three main parts, namely (i) an input light controller, (ii) an analyzer or detection unit, and (iii) an analog and digital processing unit, along with One or more control units. In the so-called double-ended case, the input light controller will be located at the near end ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com