Patents
Literature
1351results about How to "Reliable measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
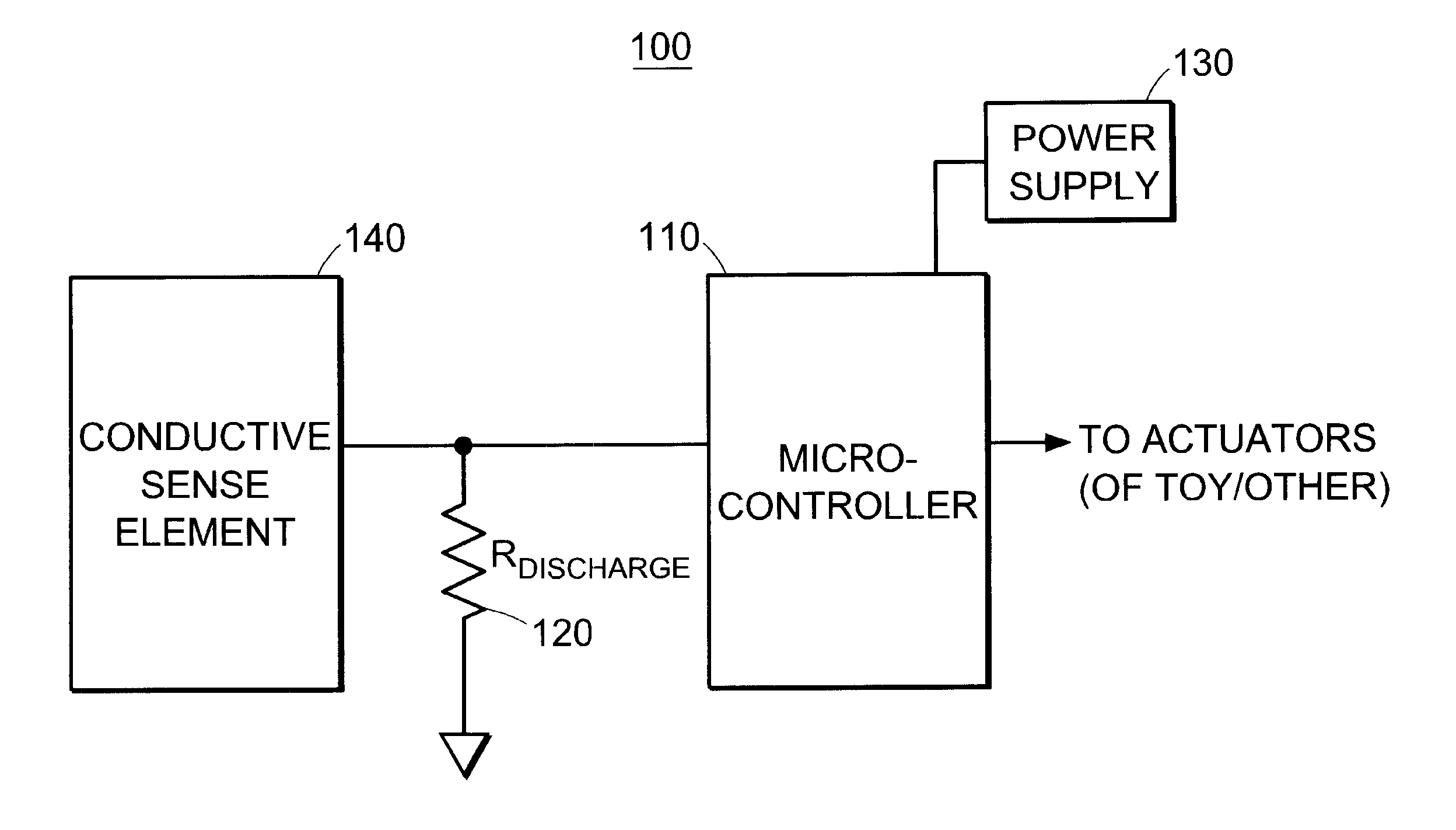
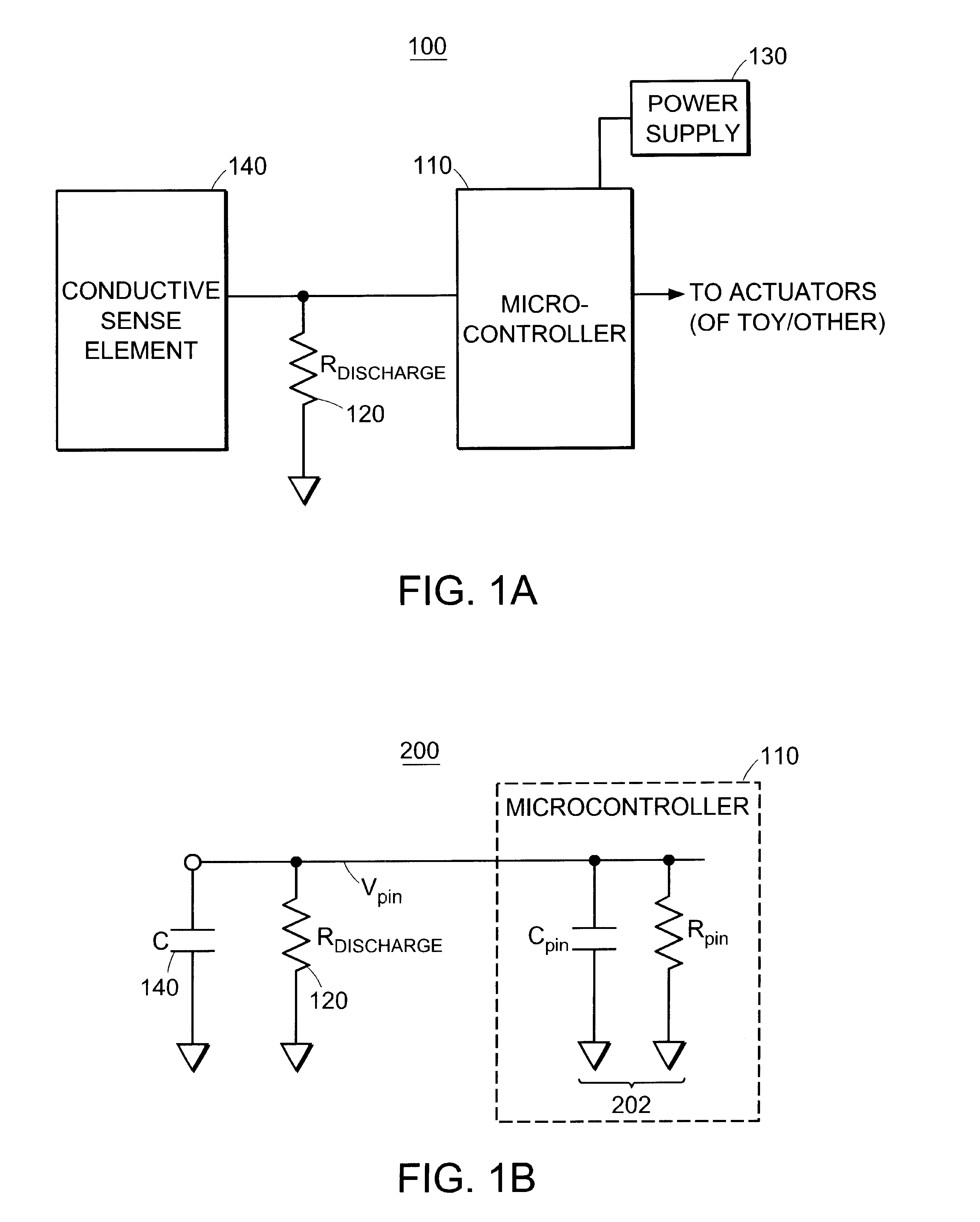
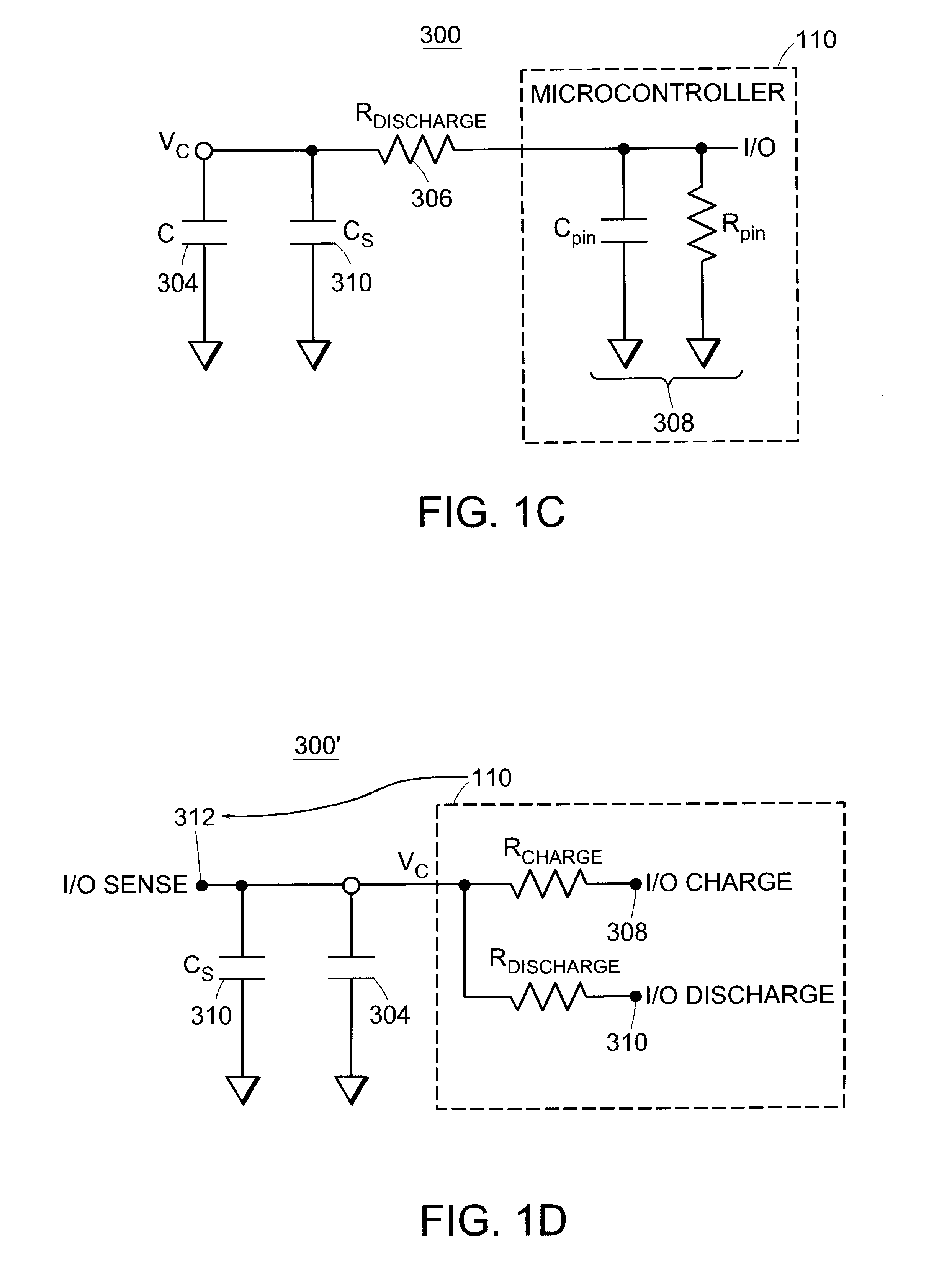
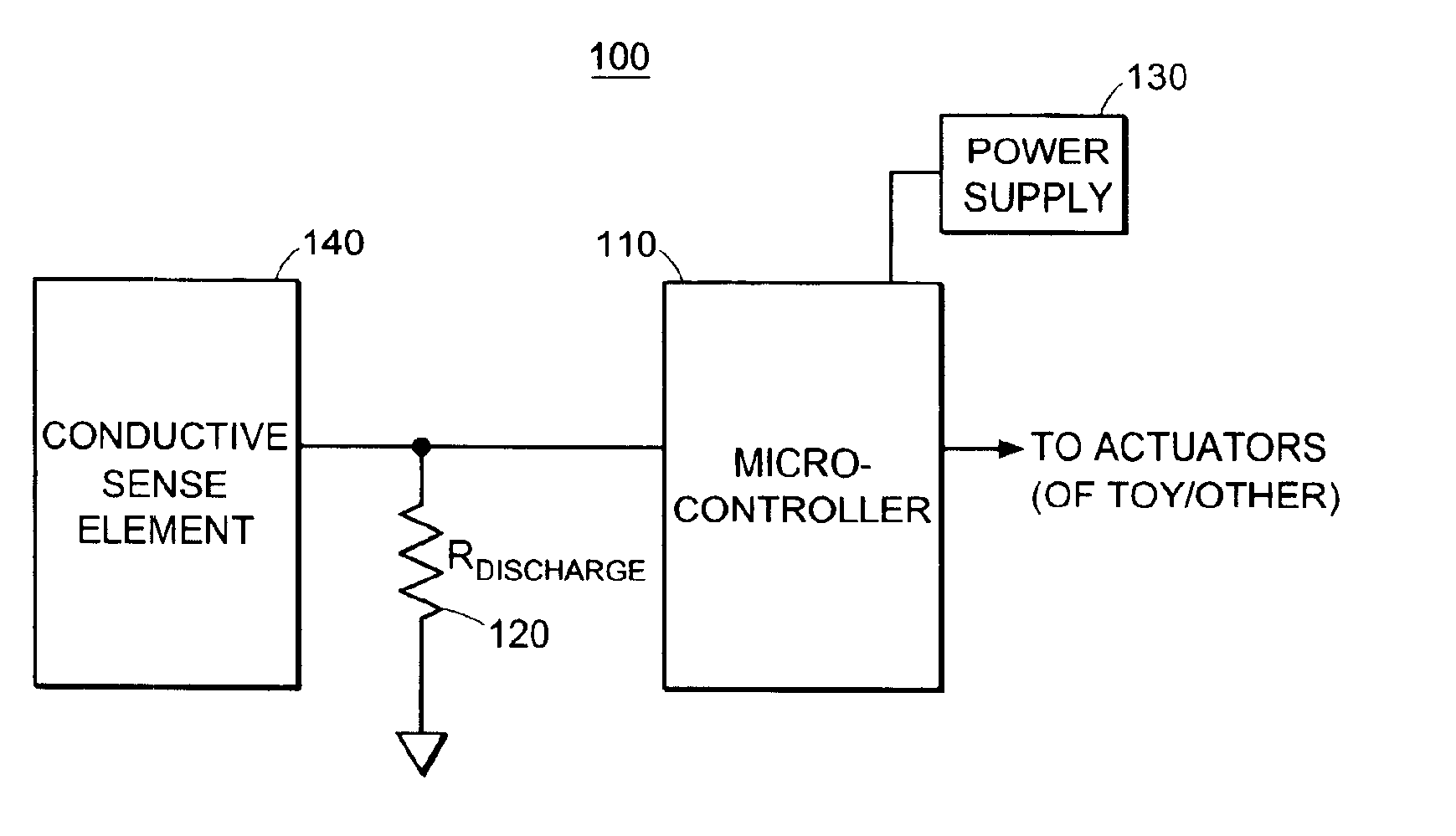
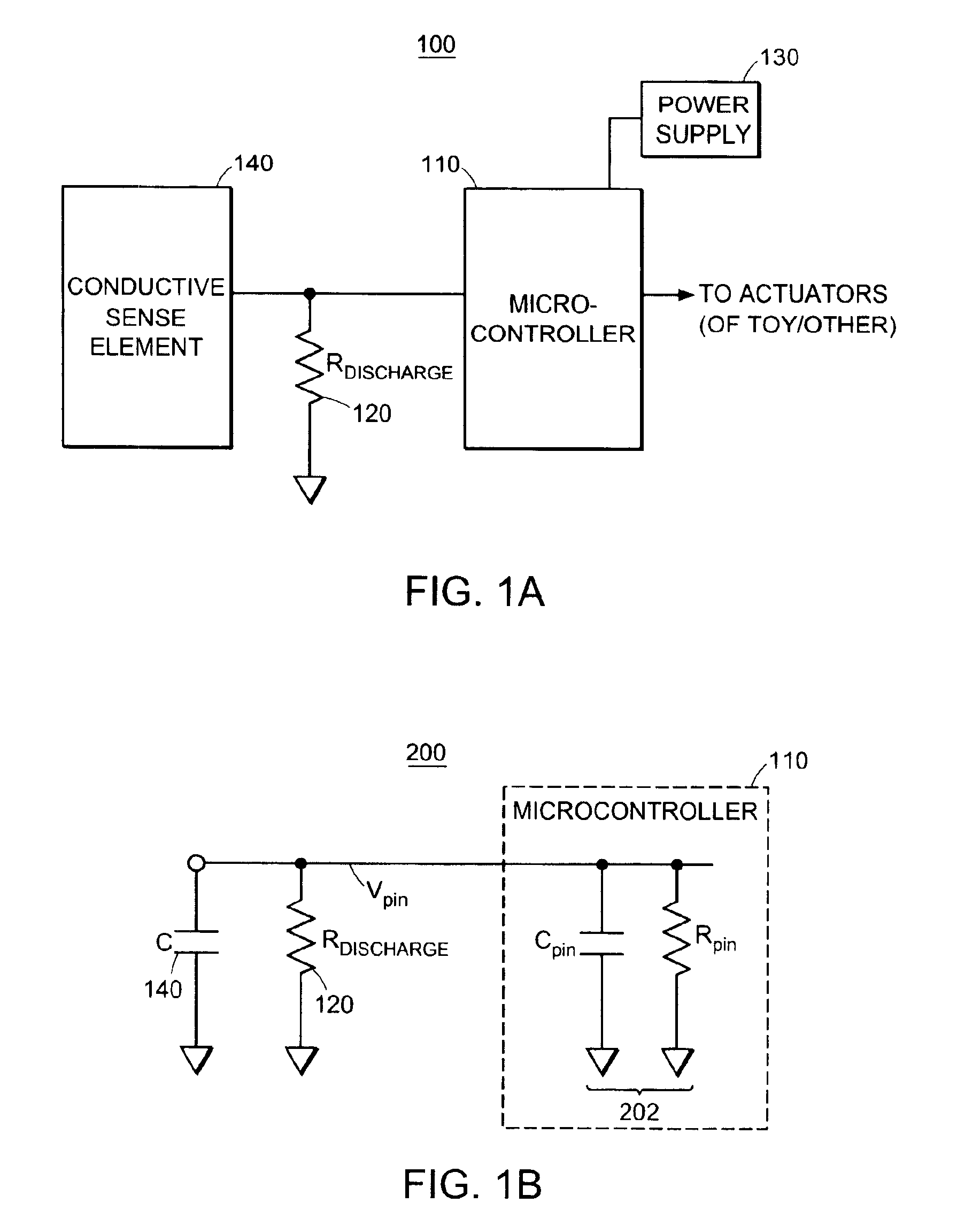
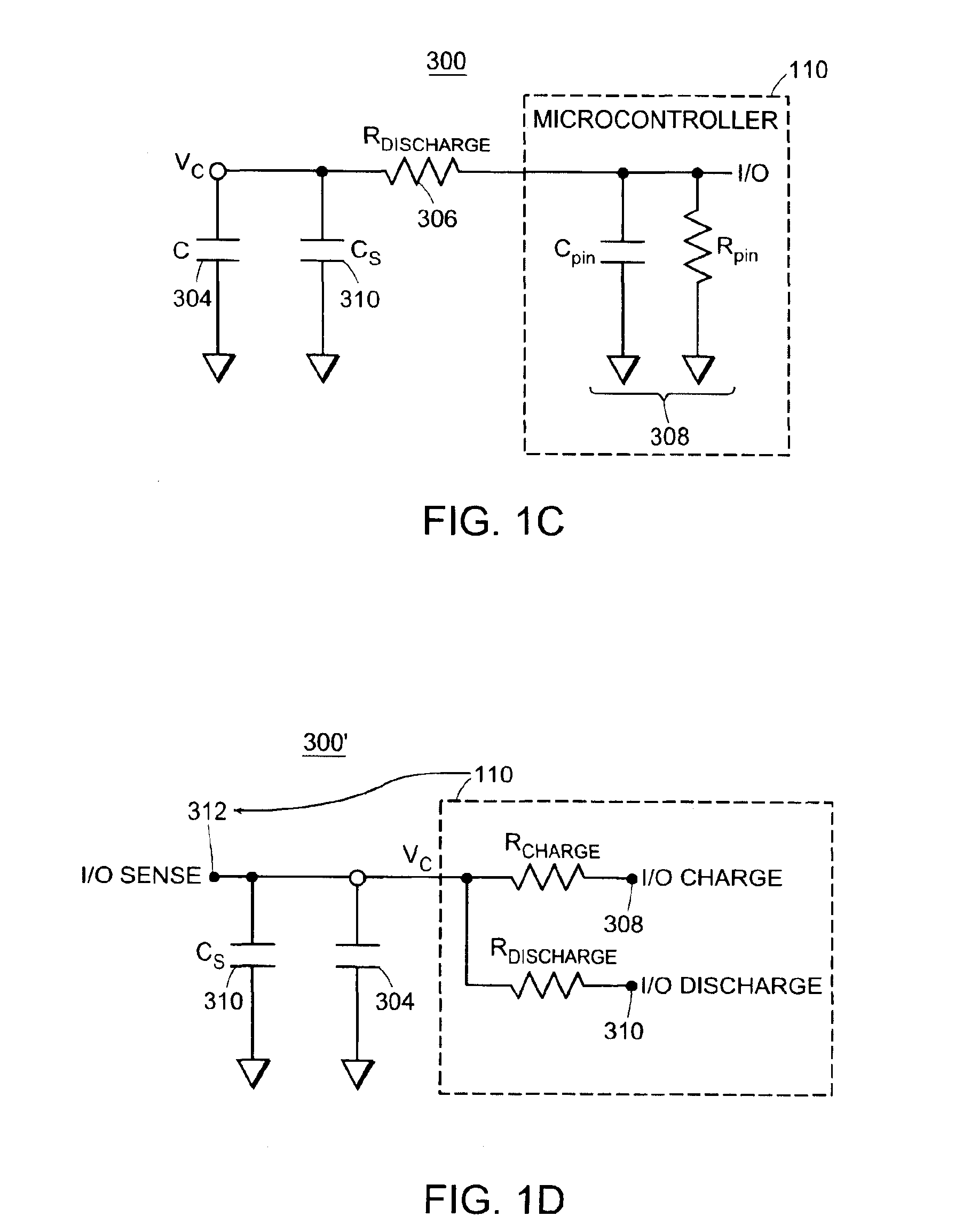
Capacitive sensor systems and methods with increased resolution and automatic calibration
InactiveUS6661239B1Small capacitance changeReliable measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceAutomatic recalibrationImage resolutionDigital signal processing
Methods and systems for capacitive proximity and contact sensing employ one or more simple sensors (which may be a conductive fiber or pattern of conductive ink) in communication with a microcontroller. Digital signal processing executed by the microcontroller enables resolution enhancement, automatic and continuous calibration, noise reduction, pattern recognition and the configuration of virtual sensors capable of detecting how an object incorporating the sensors is being manipulated.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Capacitive sensor systems and methods with increased resolution and automatic calibration
InactiveUS6940291B1Small capacitance changeReliable measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingFiberDigital signal processing
Methods and systems for capacitive proximity and contact sensing employ one or more simple sensors (which may be a conductive fiber or pattern of conductive ink) in communication with a microcontroller. Digital signal processing executed by the microcontroller enables resolution enhancement, automatic and continuous calibration, noise reduction, pattern recognition and the configuration of virtual sensors capable of detecting how an object incorporating the sensors is being manipulated.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Test element and test system for examining a body fluid
ActiveUS20080249435A1Improve user friendlinessEasy to integrateMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterLight guideOptical measurements
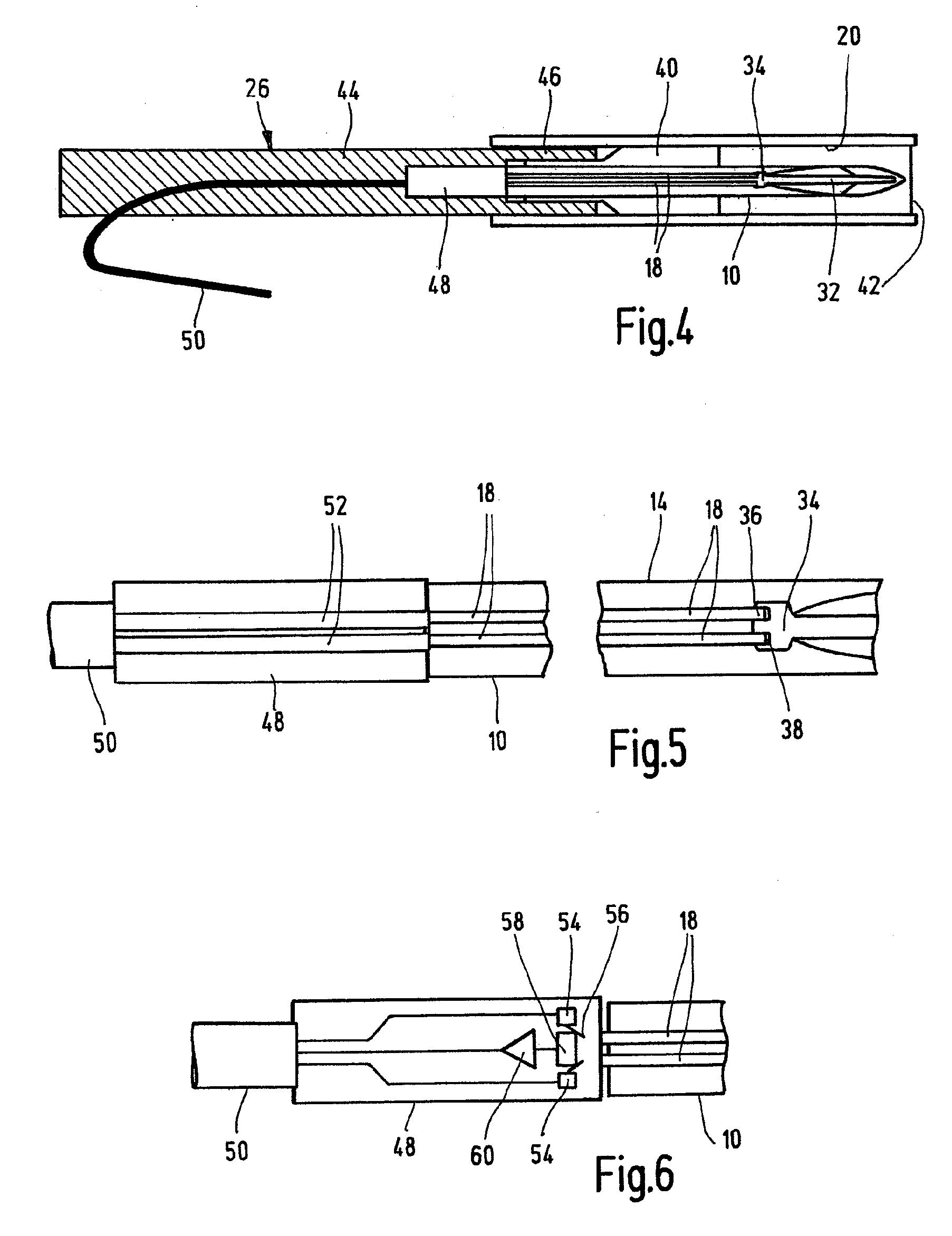
The invention relates to a test element as a single-use article for examining a body fluid, comprising a lancing member that can be inserted into a body part, a collecting area configured thereon for body fluid obtained by the lancing and at least one light guide for an optical measurement in the collecting area. The collecting area is formed by a collection recess of the lancing member which extends in the lancing direction and the light guide is integrated into the lancing member such that it is secure against displacement and the distal end thereof is arranged in a proximal measurement zone of the collection recess.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Sensor for blood component analysis
InactiveUS20050123443A1Reliable measurementLess painfulAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood collectionComing out
A sensor for blood component analysis, which allows even a trace amount of blood to be led to an analysis portion reliably. The sensor for blood component analysis includes a substrate, a spacer, and a cover. The cover is disposed on the substrate with the spacer intervening between the cover and the substrate, whereby a space that serves as an analysis portion and a channel for leading blood to the analysis portion is formed inside the sensor. Through holes are formed in the substrate and the spacer, respectively, so that a common through hole through which a needle of a lancet can pass is formed when the spacer is disposed on the substrate. The through hole of the spacer communicates with the channel and a top of the through hole of the spacer is covered with the cover, whereby a lancing portion is formed by the common through hole and a portion of the cover covering the top of the through hole of the spacer. In use, the sensor is placed at a position where blood collection is to be performed, the portion of the cover covering the lancing portion is broken through with the needle of the lancet so that the needle is allowed to pass through the common through hole to puncture the position, and blood that has come out is guided by a downwardly protruding burr formed when the cover is broken through so that the blood is led to the channel and flows through the channel to be led to the analysis portion.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
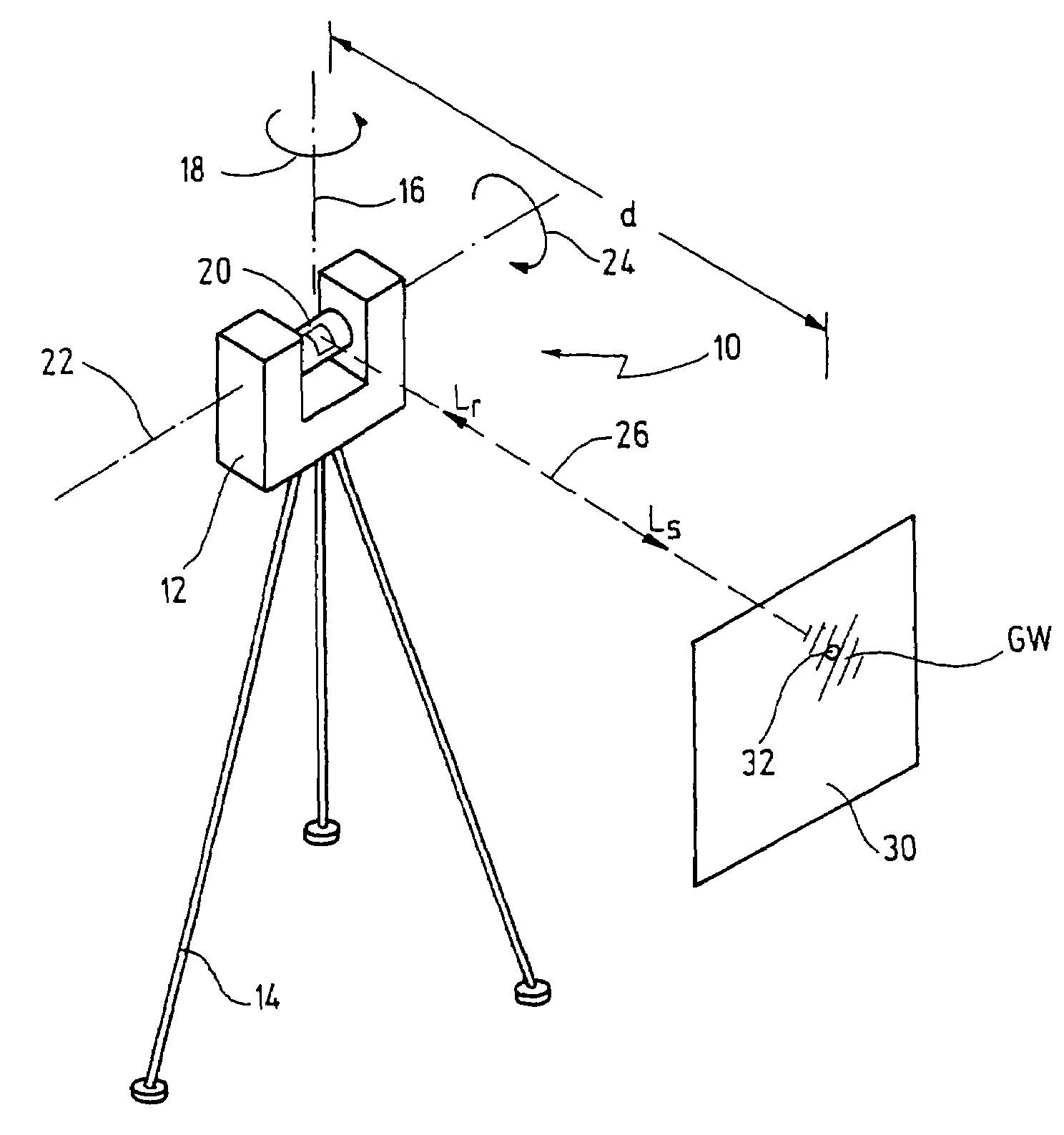
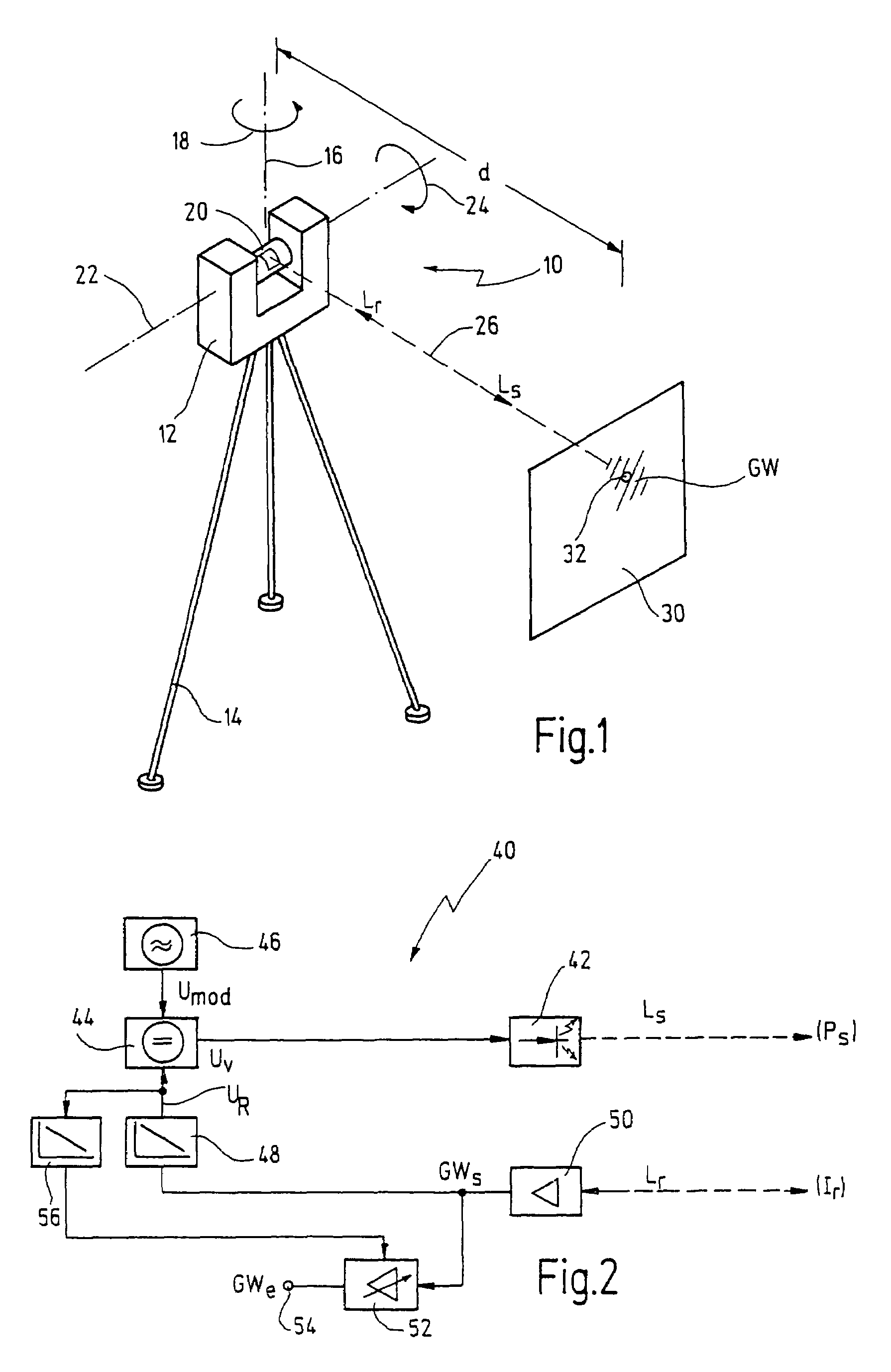
Laser scanner and method for optically scanning an environment
ActiveUS7193690B2Reduce transmit powerAvoid imaging errorsOptical rangefindersActive open surveying meansMeasurement pointLaser scanning
A laser scanner for optically scanning and measuring an environment comprises a light transmitter having a predetermined transmission power for emitting a light beam. The emitted light beam is reflected at a measurement point in the environment. The reflected light beam is received with a certain intensity by a receiver. The transmission power is adjustable as a function of the intensity of the reflected light beam. Furthermore, a gray-scale value of the measurement point is determined as a function of the transmission power adjusted.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
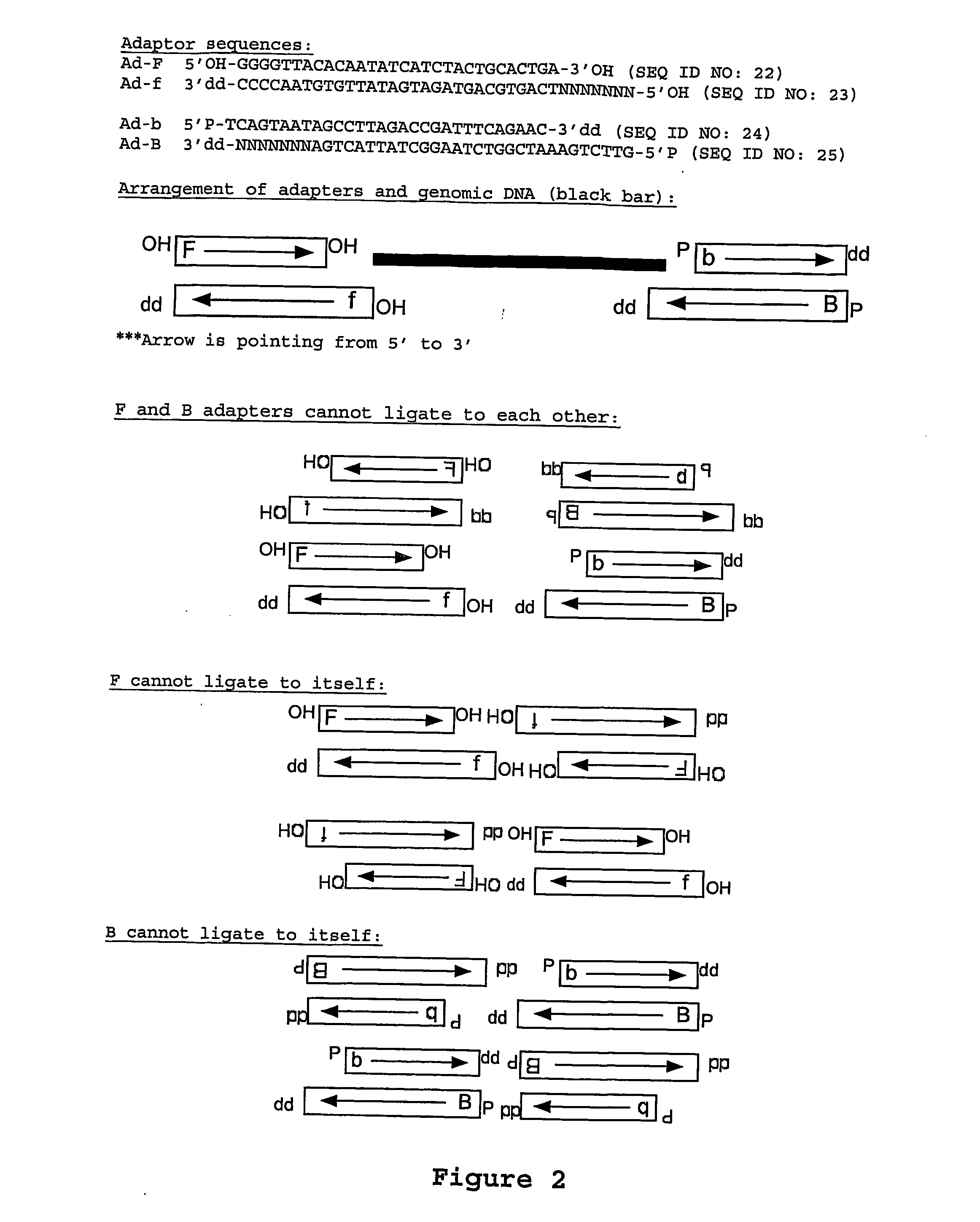
Random array dna analysis by hybridization
ActiveUS20070037152A1Reliable measurementSufficient amountMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsRandom arrayNucleic acid sequencing
The invention relates to methods and devices for analyzing single molecules, i.e. nucleic acids. Such single molecules may be derived from natural samples, such as cells, tissues, soil, air and water without separating or enriching individual components. In certain aspects of the invention, the methods and devices are useful in performing nucleic acid sequence analysis by probe hybridization.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
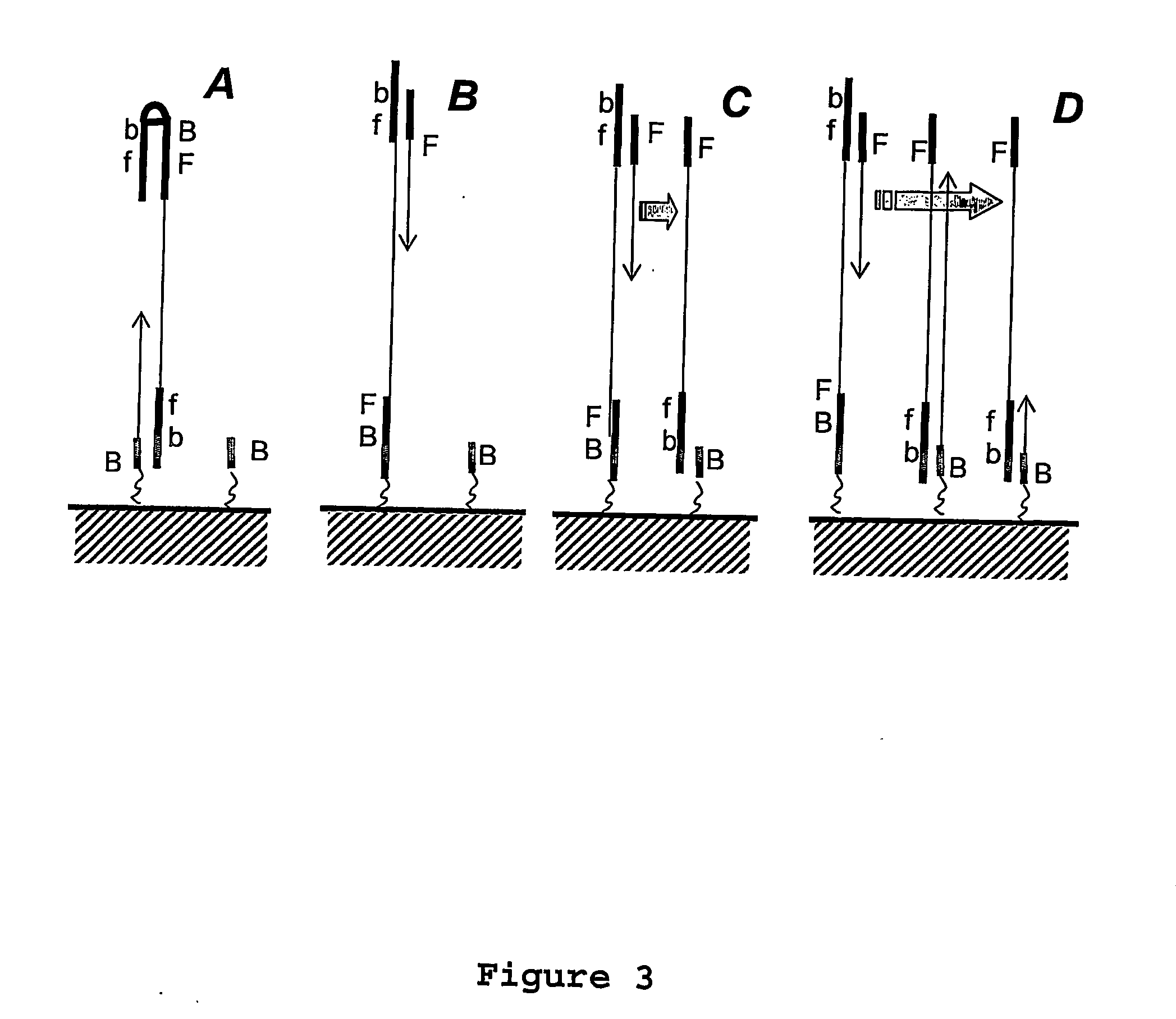
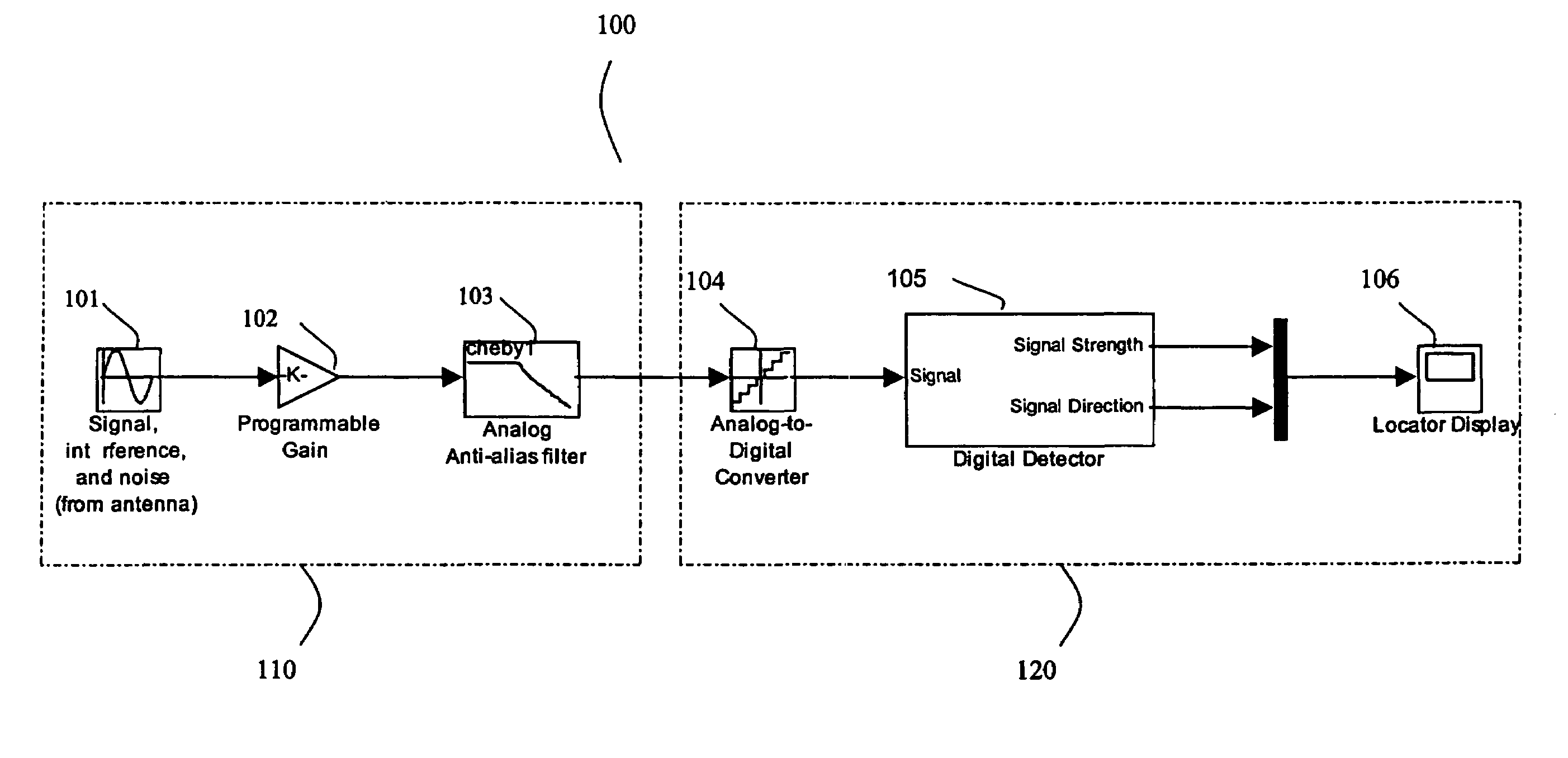
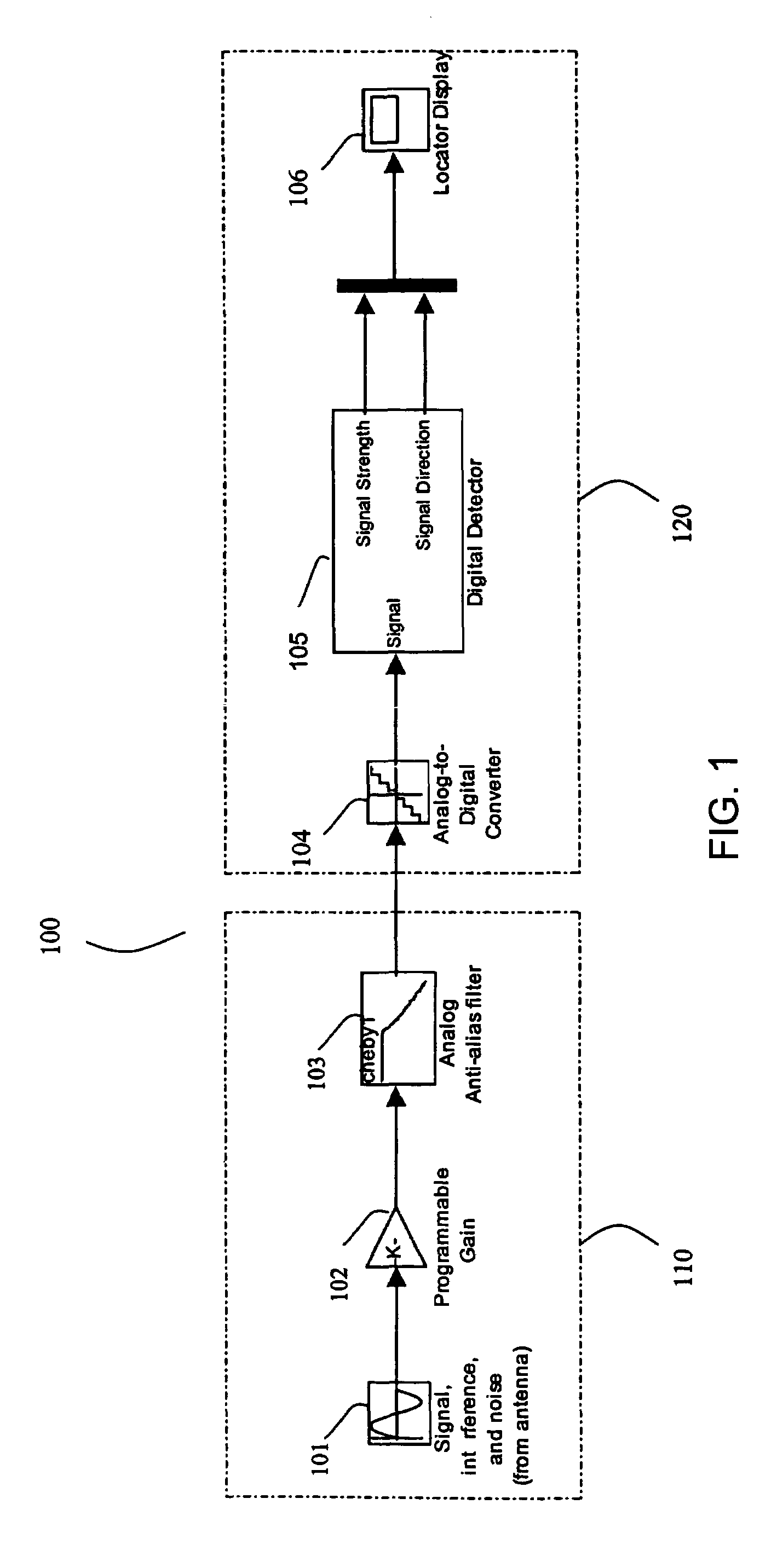
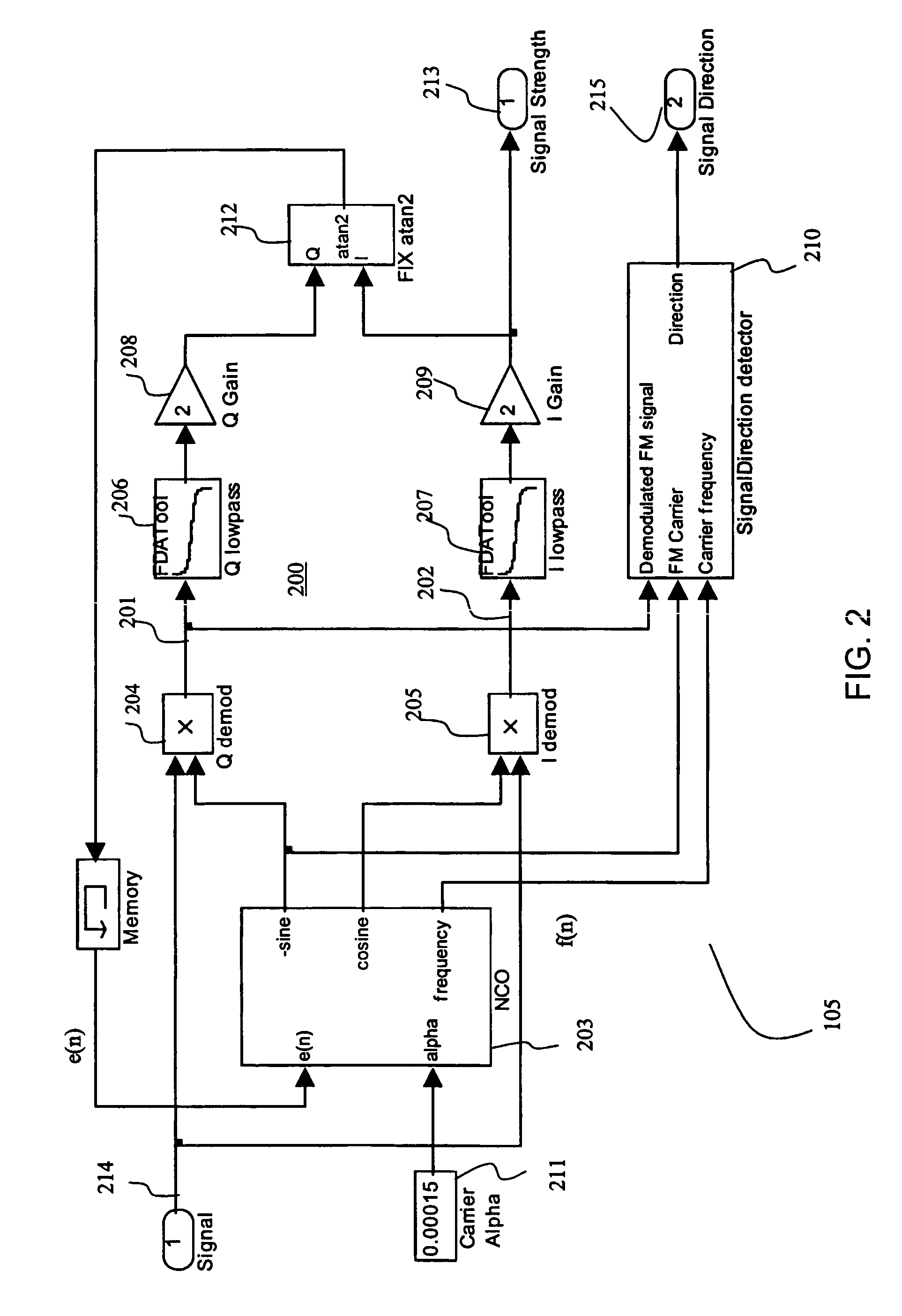
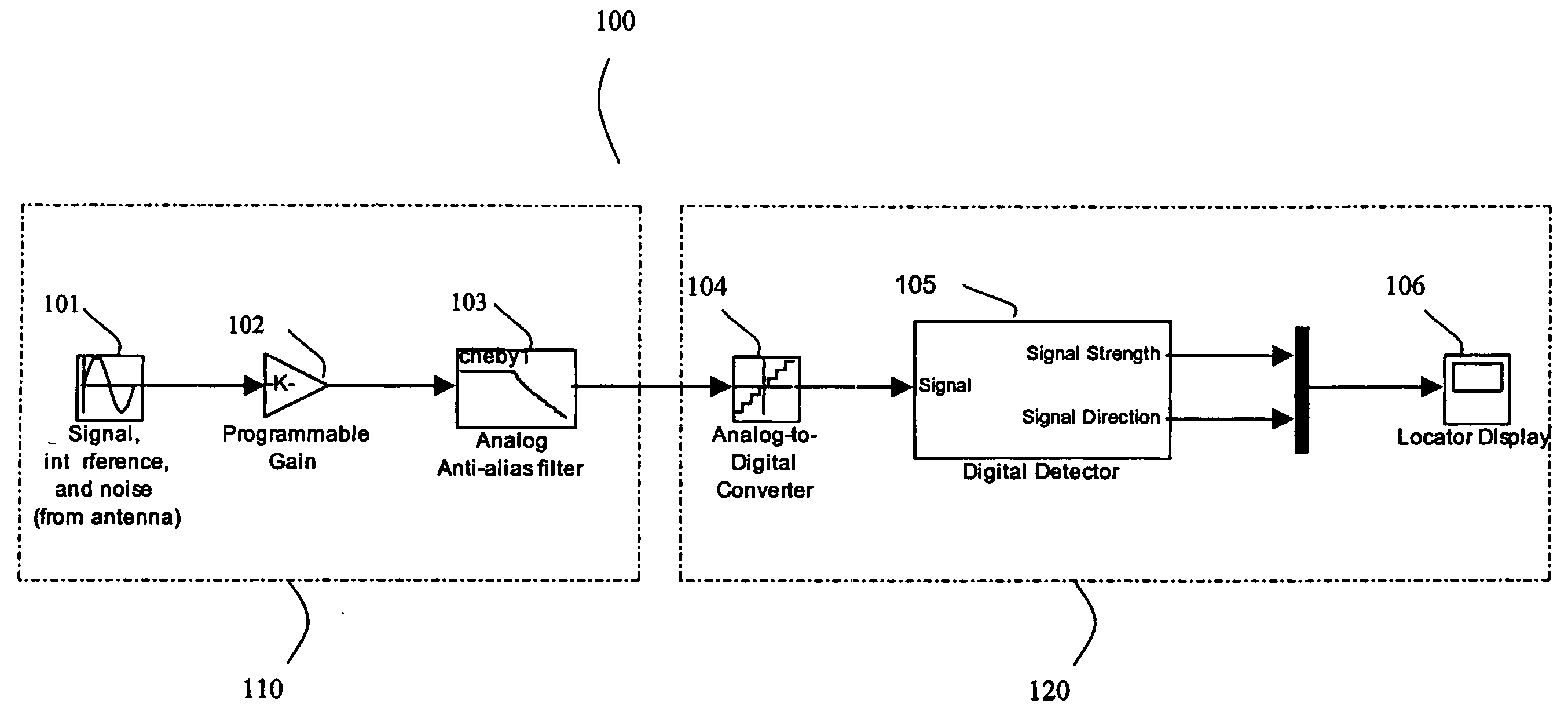
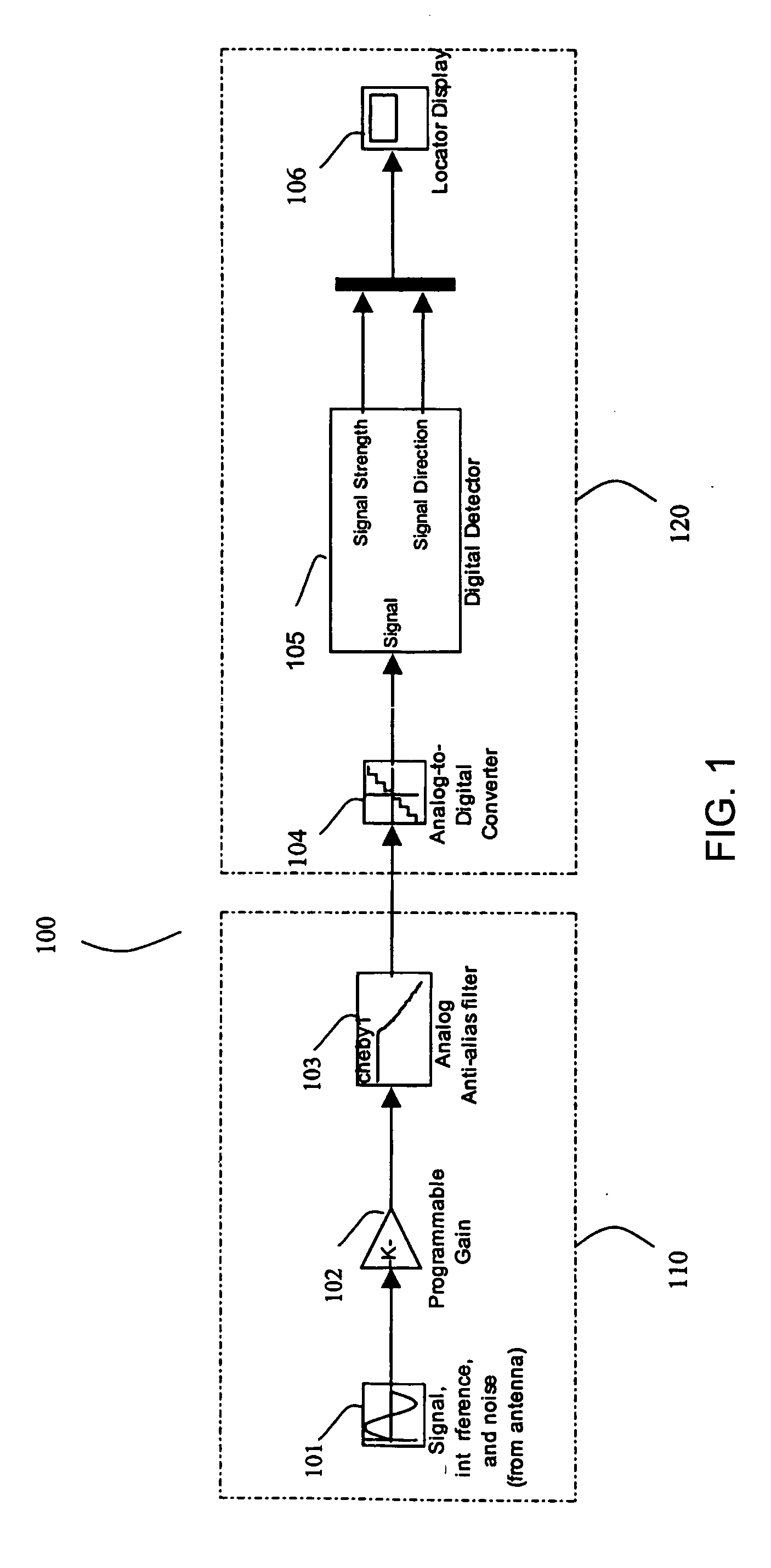
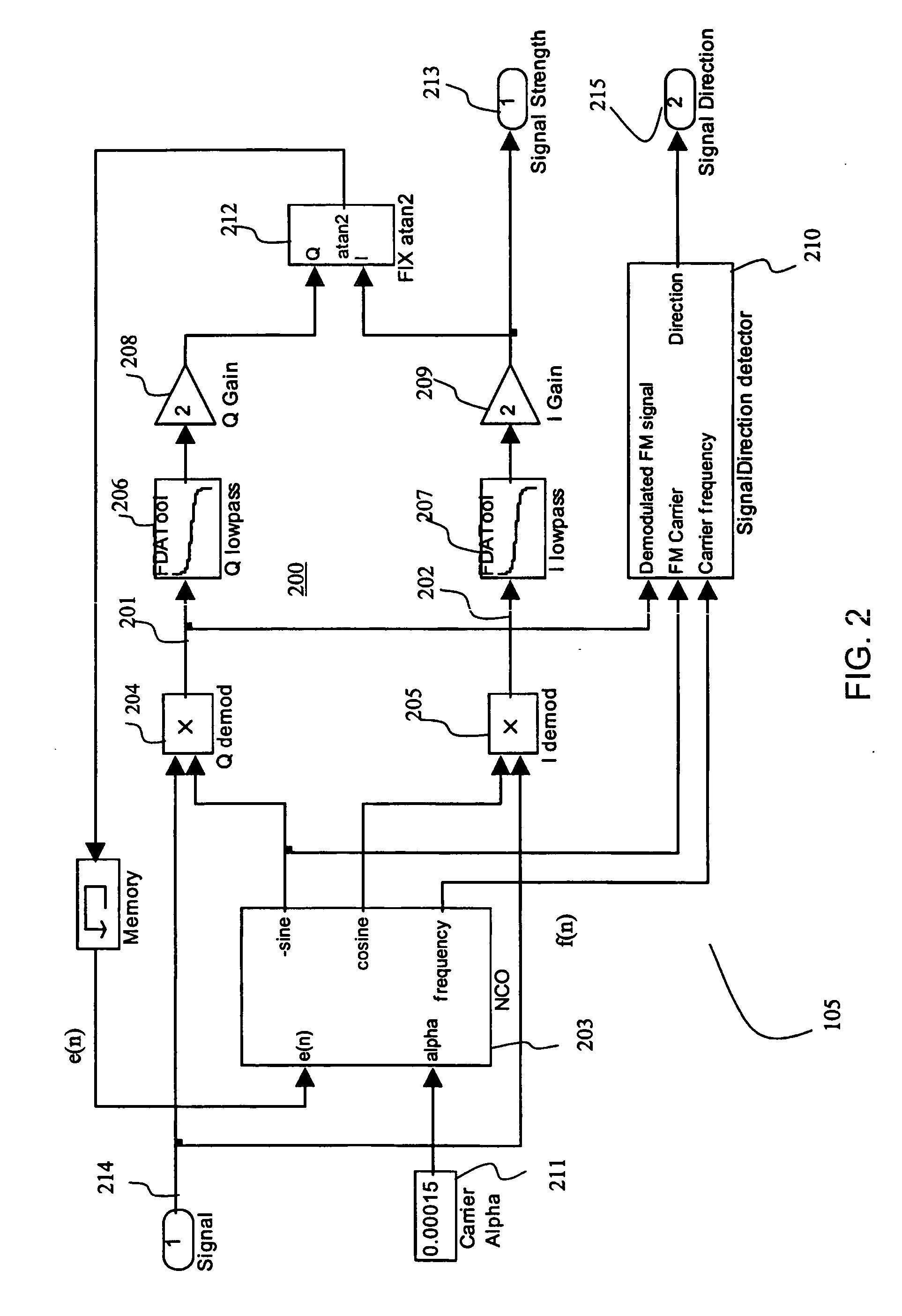
Method and apparatus for digital detection of electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction in metallic pipes and cables
InactiveUS7062414B2Low hardware requirementsWide resistance to component tolerancesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingCarrier signal
A new digital architecture for metallic pipe and cable locators, providing accurate estimation of the fundamental locate parameters, electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction, and utilizing a nested Digital Phase-Locked Loop (DPLL) structure is disclosed. The obstacles to signal direction measurement in low SINR environments using the signal select method are overcome and a more precise phase comparison between the carrier and the FM modulation signals is obtained. The architecture further significantly reduces analog front-end hardware requirements, offers wider resistance to component tolerances, lower calibration and test time, and provides flexible frequency selectivity. Locators according to the present invention provide accurate estimation of the fundamental physical parameters of line location (electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction) in extremely noisy environments, using Digital Signal Processing (DSP) methods.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Reconfigurable portable locator employing multiple sensor array having flexible nested orthogonal antennas
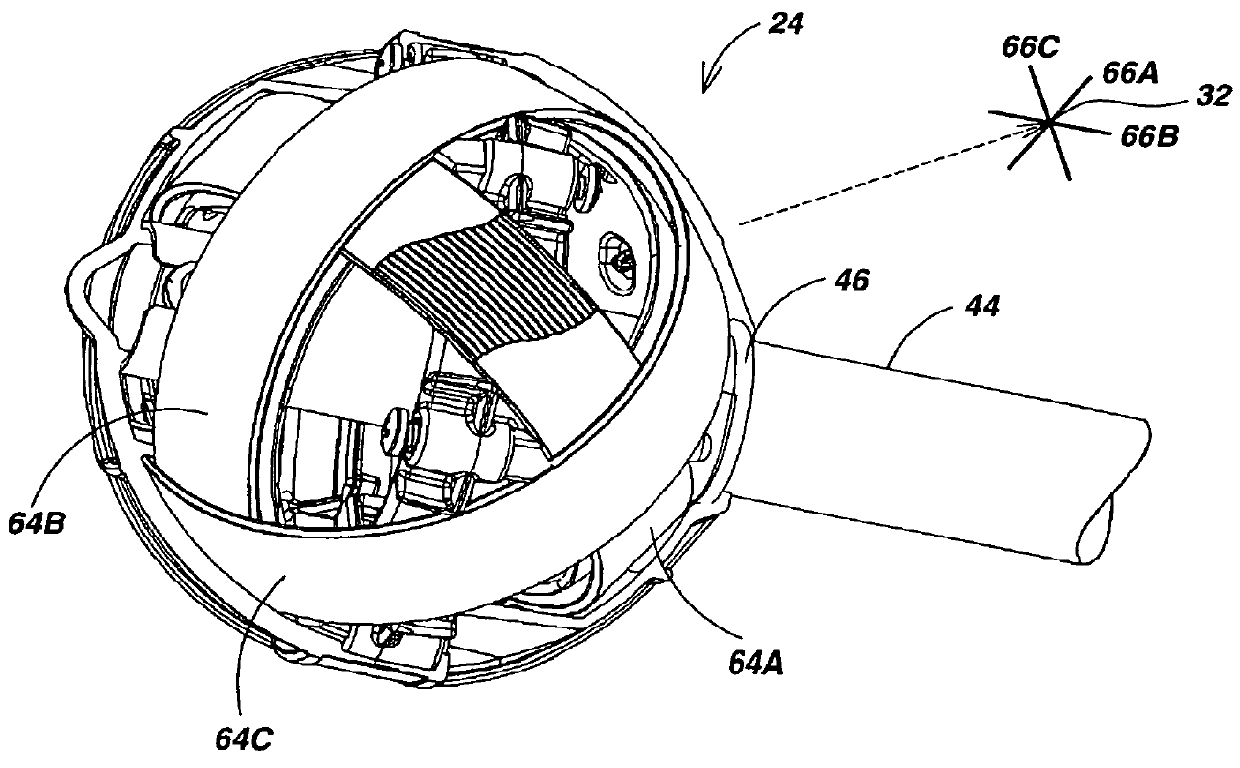
ActiveUS7518374B1High positioning accuracyImprove manufacturabilityMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementSensor array3d sensor
A portable locator for detecting a buried object characterized by an electromagnetic (EM) field emission employing three-dimensional (3D) sensor arrays each having three substantially-identical EM field sensors disposed on a flexible annular wall having a radial centroid defining a sensing axis. The flexible annular sensors are retained in substantial concentricity with the corresponding sensing axes disposed in substantial mutual orthogonality. A pair of 3D sensor arrays disposed on a first axis substantially orthogonal to a second axis defined by another pair of EM field sensors each having a sensing axis disposed along the second axis. The locator introduces a user-reconfigurable user interface (UI) employing a “sticky” ratcheting audio UI and a hollow hinge assembly for redisposing the sensor assembly from an operating to a storage disposition.
Owner:SEEKTECH
Omnidirectional portable appliance for steam cleaning hard or flexible surfaces
InactiveUS6031969ALow costStart fastUsing liquid separation agentCleaning machinesElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
The omnidirectional portable appliance for steam cleaning surfaces both hard and flexible, comprises a case provided with a handle, a water feed orifice, an electricity power cord, a cleaning head, a steam generator included in the case and a venturi device [means for selectively] delivering steam to the cleaning head. The instantaneous steam generator having low thermal inertia operates at atmospheric pressure and comprises a capillary body for storing in divided form all of the supply of water to be evaporated, [in divided form] the capillary body being compressed around [the electrical heater means which comprise] a [metal-clad] resistance element and a heater body constituted by a [having a] material that is a good conductor of heat, is overmolded on the resistance element and [thereon to form a heater body which] is associated with at least one heat transmission element connected to [the] a hottest portion of the heater body and provided with a temperature sensor enabling the control of power fed to the [metal-clad] resistance element to be optimized so as to be safe regardless of the orientation in three dimensions of the steam generator.
Owner:SUPERBA SAS
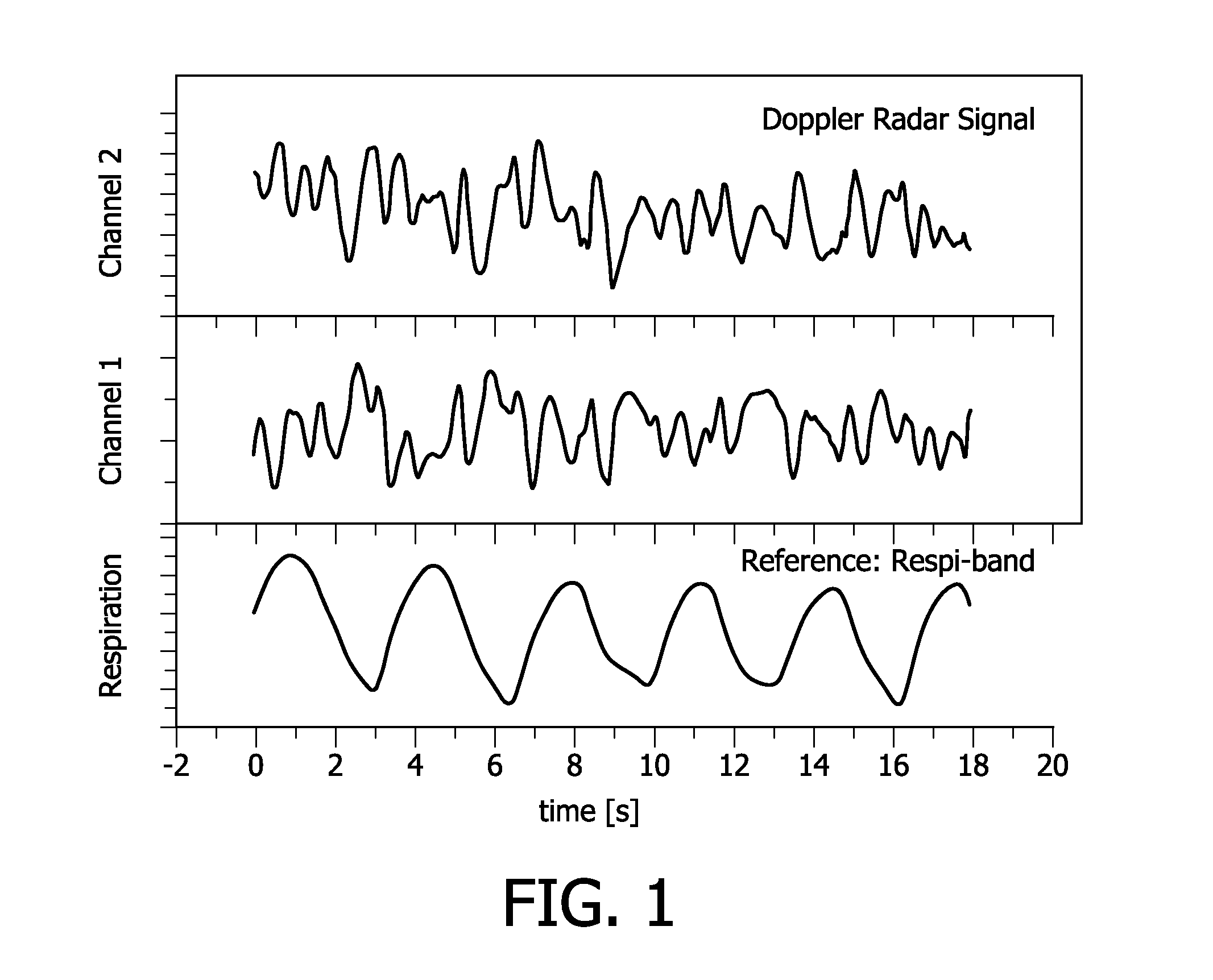
Contactless respiration monitoring of a patient
ActiveUS20110112425A1Easy to handleReliable of direction changeRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsPhase shiftedRadar
The invention relates to a method for detection of respiration of a patient comprising the following steps: emitting an electromagnetic signal towards the patient; receiving a reflected electromagnetic signal reflected from the patient; converting the reflected electromagnetic signal, yielding a first signal; phase-shifting the reflected electromagnetic signal and converting the phase-shifted reflected electromagnetic signal, yielding a second signal; determining a first vector being defined by the time derivatives of the first signal and the second signal, for a common first point in time; determining a second and vector being defined by the time derivatives of the first signal and the second signal, for a common second point in time; and calculating the scalar product of the normalized first vector and the normalized second vector as an indicator value for a change from expiration to inspiration of the patient or vice versa. A change from expiration to inspiration of the patient or vice versa is preferably indicated if the indicator value is below a threshold value, preferably below a value of 0. In this way, a possibility for contactless remote respiration monitoring of a patient based on the Doppler radar principle is provided which is reliable and easy to handle.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Tamper evident packaging
ActiveUS7170409B2Risk minimizationLess secureElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingPackagingLogistics managementTransceiver
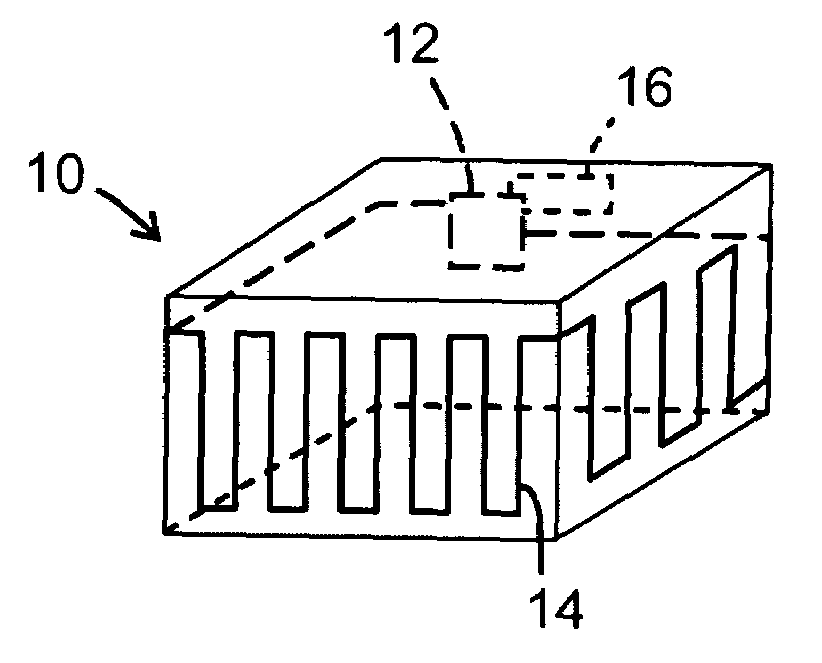
A packaging and a method for monitoring a packaging (10) of a disposable material in a chain of logistics. As an integral part of the packaging, the packaging has an electronic module (12) comprising electric energy supply means, data processing means, data storage nonvolatile memory means for storing information related to the packaging, time keeping means, and data transceiver means for transmitting and receiving said information in communication with a host computer (30). The electronic module also has sensor means (14, 20) for detecting a changed physical condition of the packaging and for signaling information representing said changed physical condition to the electronic module (12) to be stored in the memory means together with a notation of time from the time keeping means.
Owner:SONY CORP
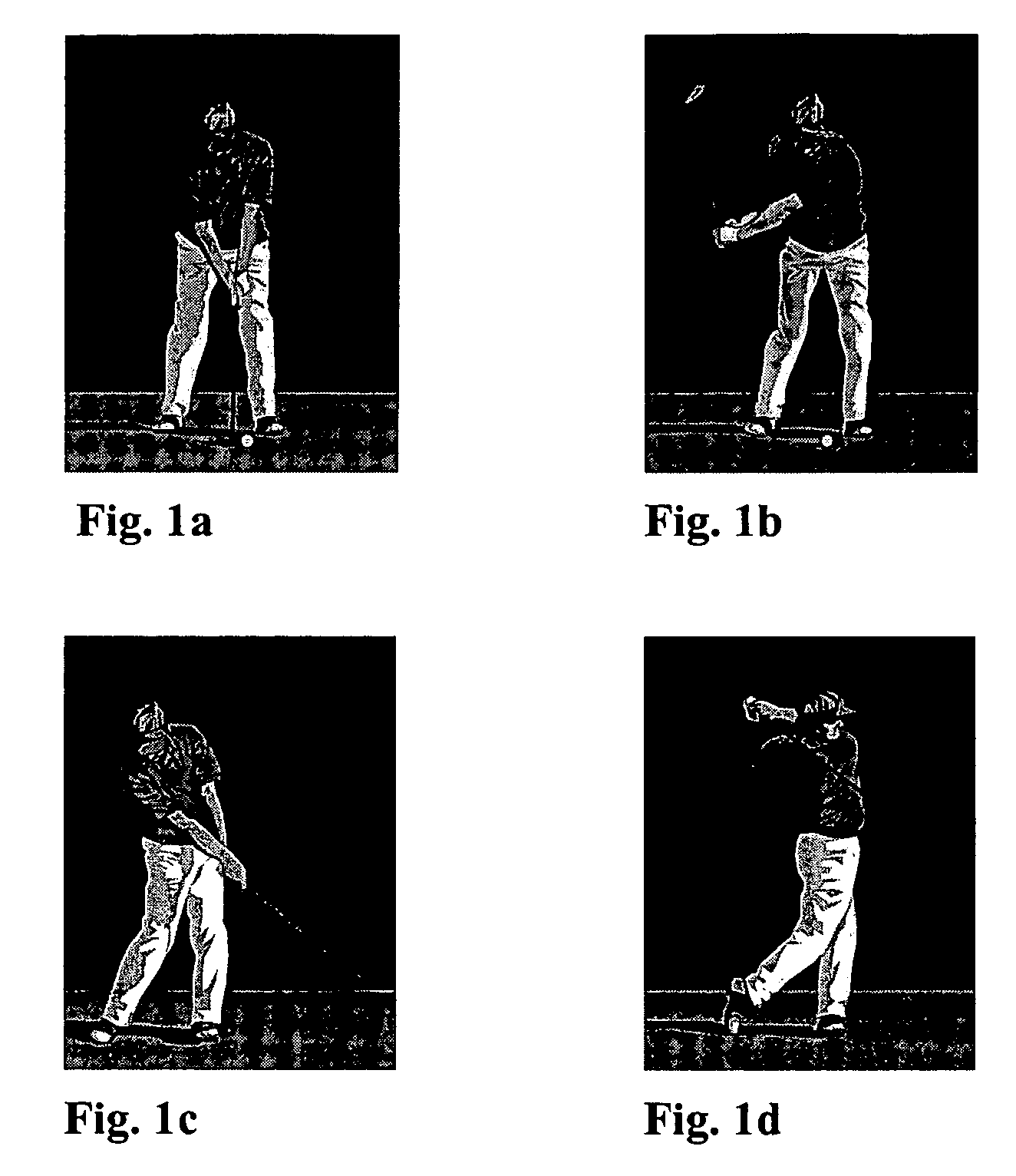
Golf device and method
ActiveUS20070010341A1Improve skillsImprove his or her skillsBall sportsGolf clubsElectric machineryEngineering
The invention relates to a portable device and a method for monitoring the performance a sportsman performing a plurality of motor acts, such as golf swings. The device comprises at least one sensor providing an output signal, the sensor being responsive to body movements of the sportsman. A signal processing unit is used for extracting data on the course of each of the plurality of motor acts from the sensor output signal, and a computing unit is used for determining, based on the data on the course of the plurality of motor acts, at least one characteristic number describing the repeatability of the motor act. By the means of the invention, the handicap number of the golfer can be predicted with good accuracy by monitoring several his or her subsequent swings.
Owner:SUUNTO OY
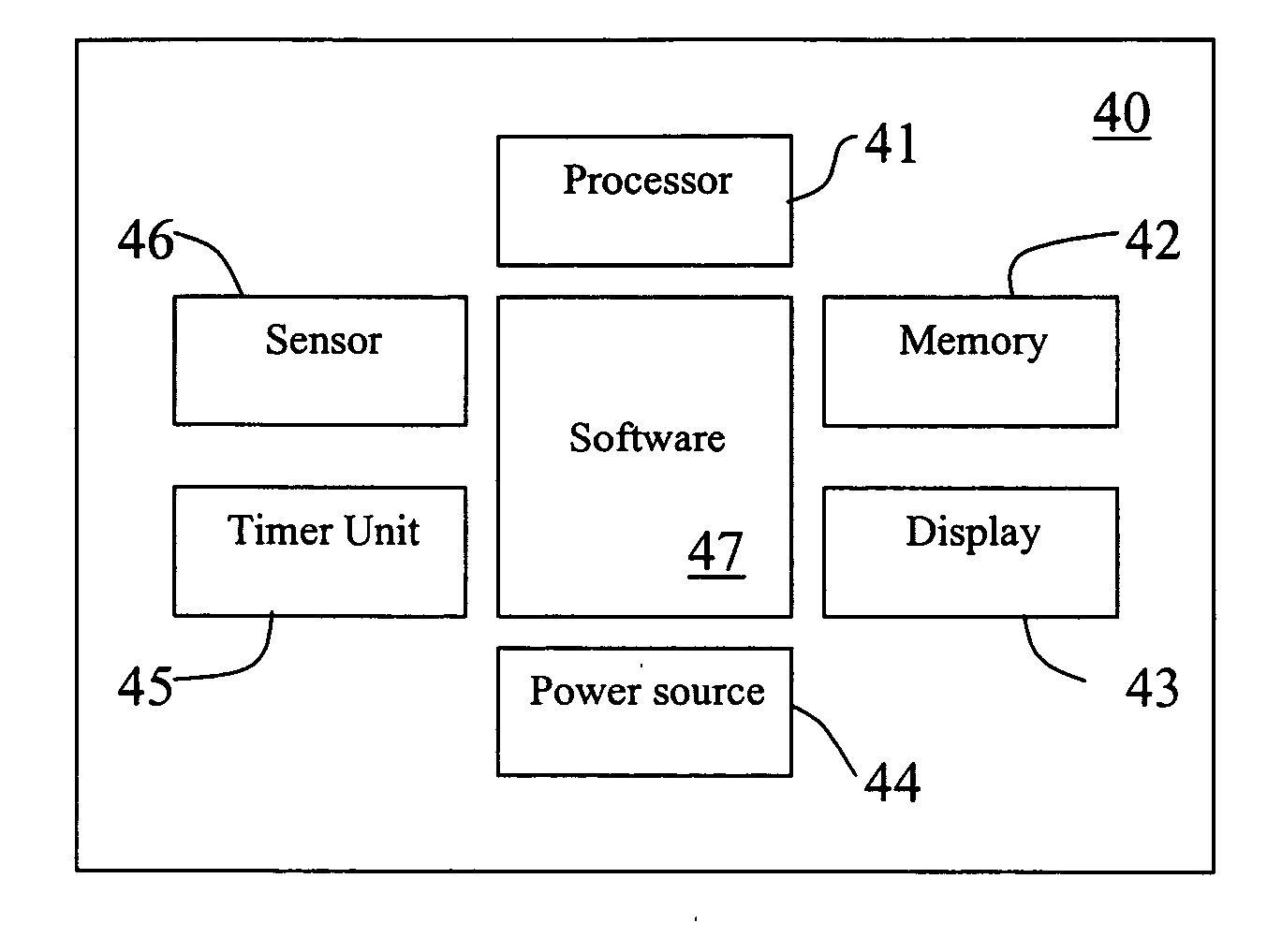
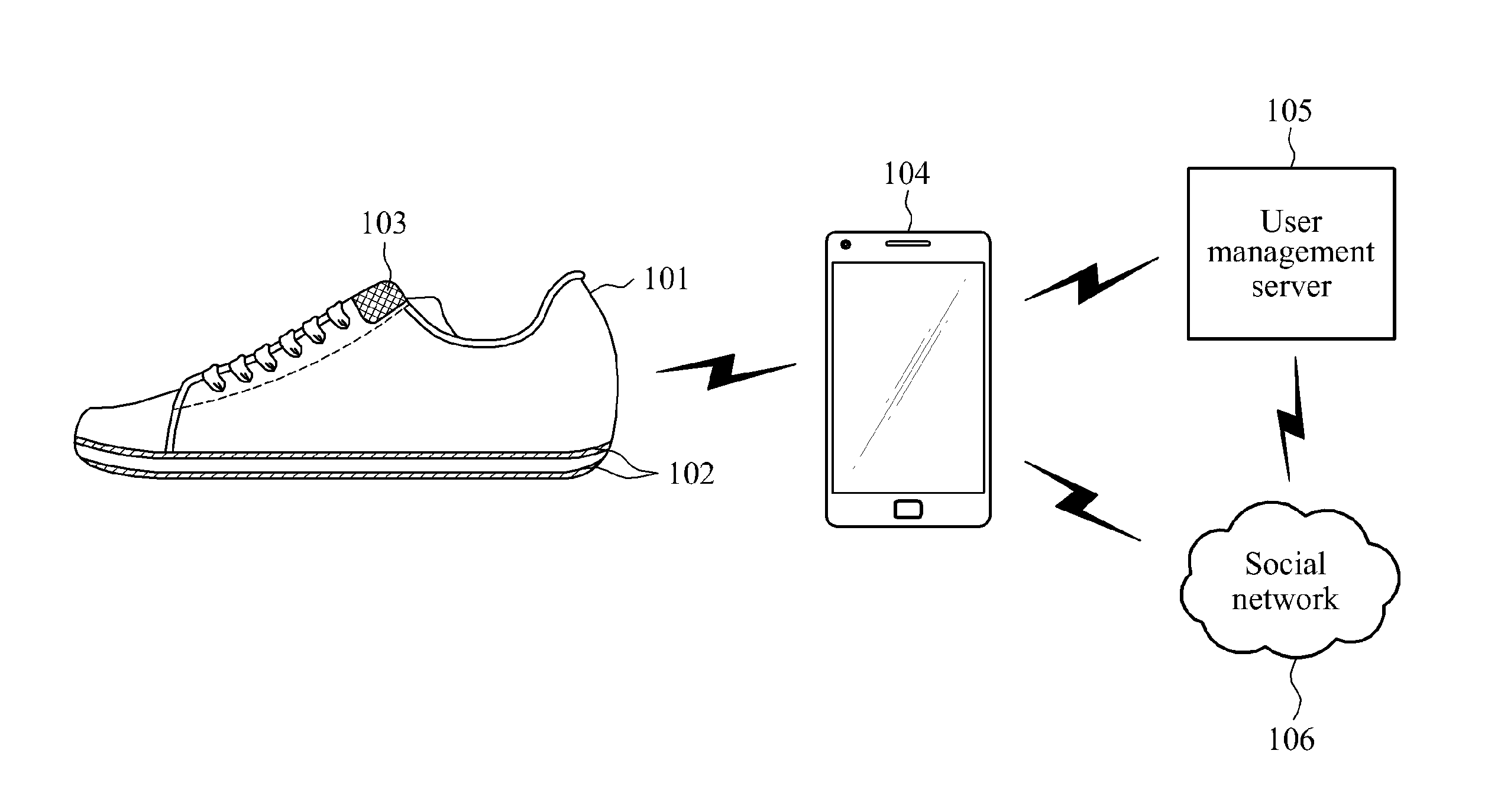
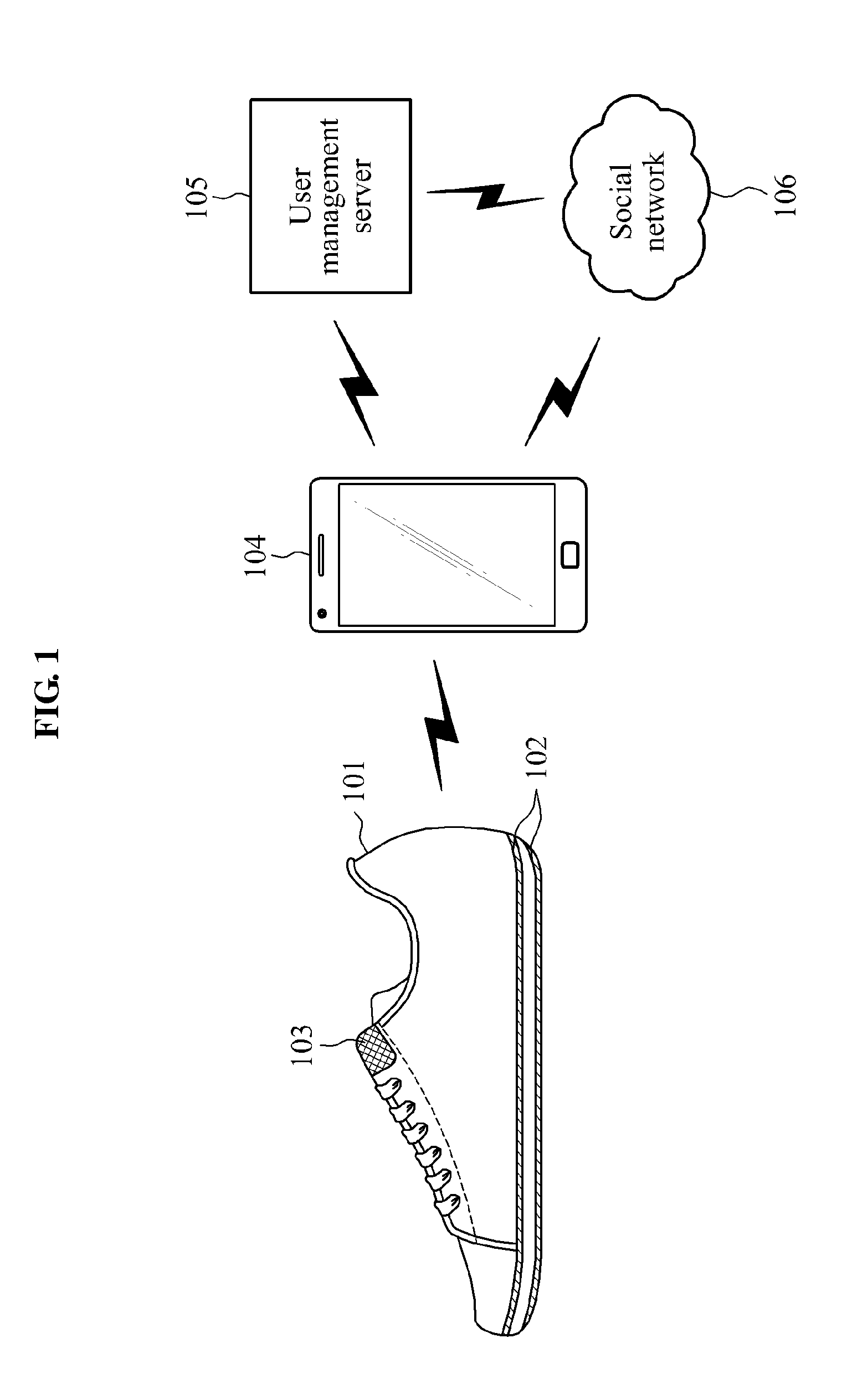
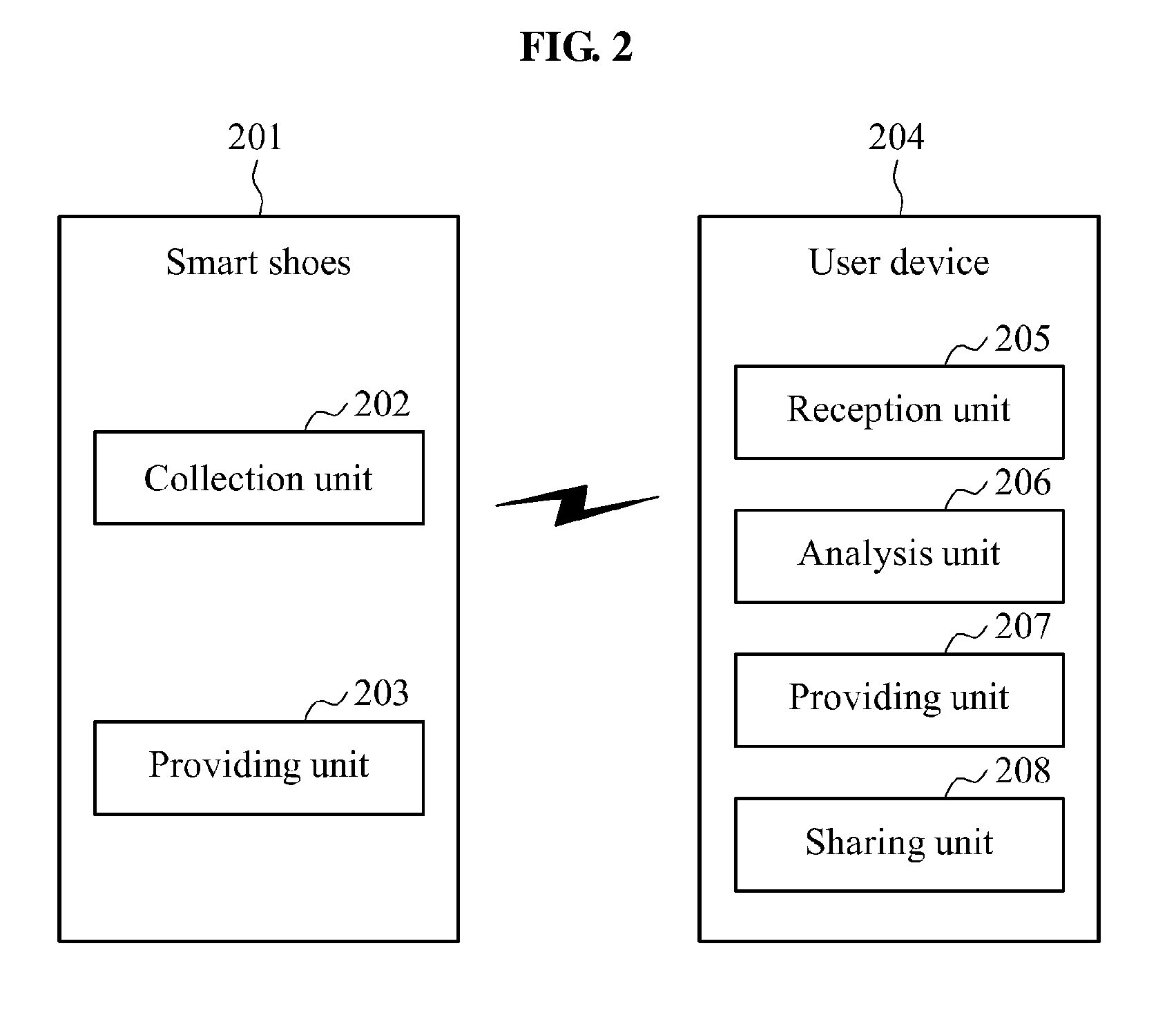
Smart shoes, method of providing sensor information to smart shoes, smart device and method of providing guidance program via smart device
ActiveUS20150182844A1Improve accuracyReliable weight measurementWeighing indication devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringUser deviceBooting
Smart shoes including a sensor unit including at least one sensor of a pressure sensor to sense a pressure in the smart shoes, a temperature sensor to sense a temperature in the smart shoes, an acceleration sensor to sense a movement of the smart shoes and an altitude sensor to sense an altitude, a controller to collect sensor information output by the at least one sensor and process the collected sensor information according to a request from a user device, and a providing unit to provide the processed sensor information to the user device.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
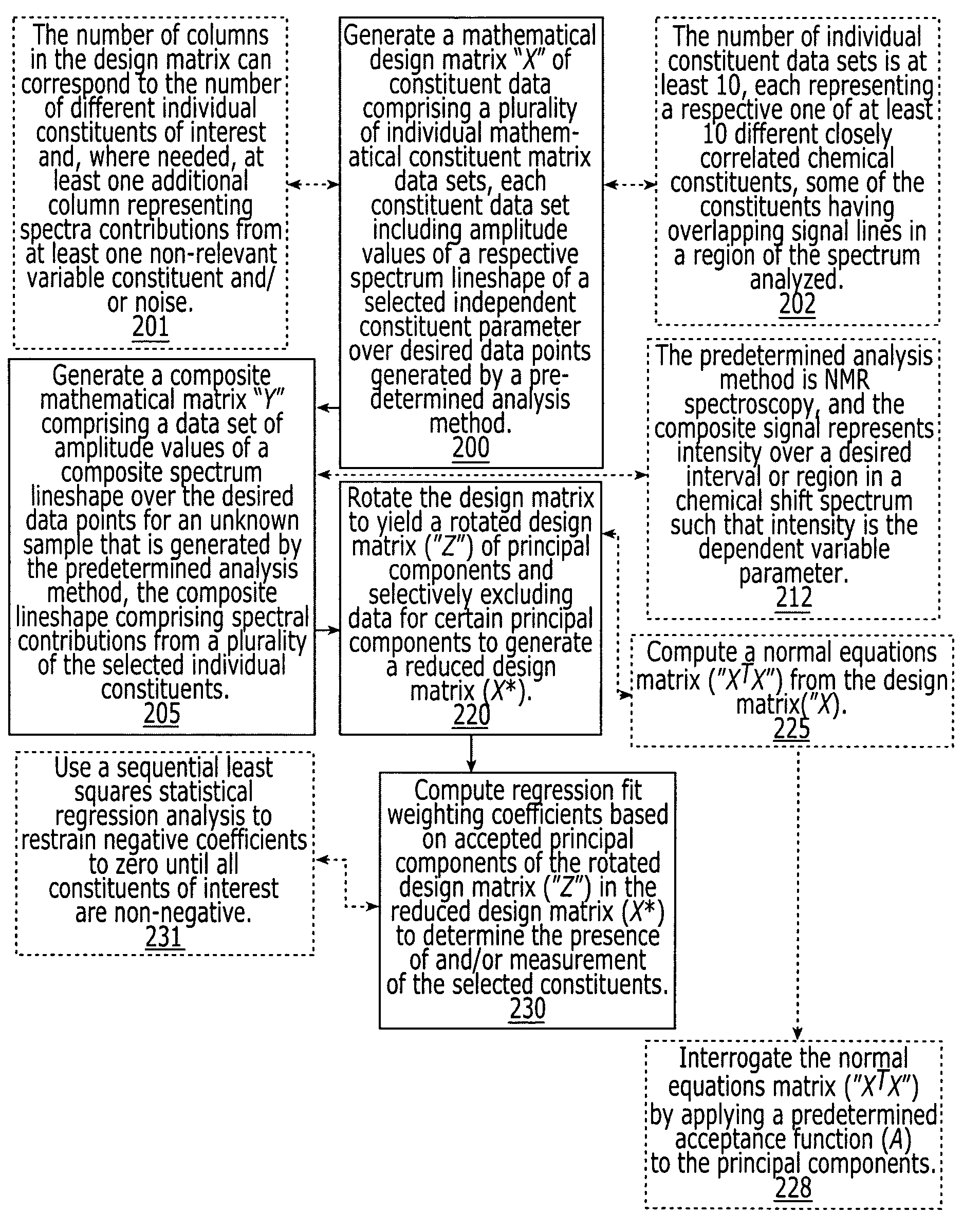
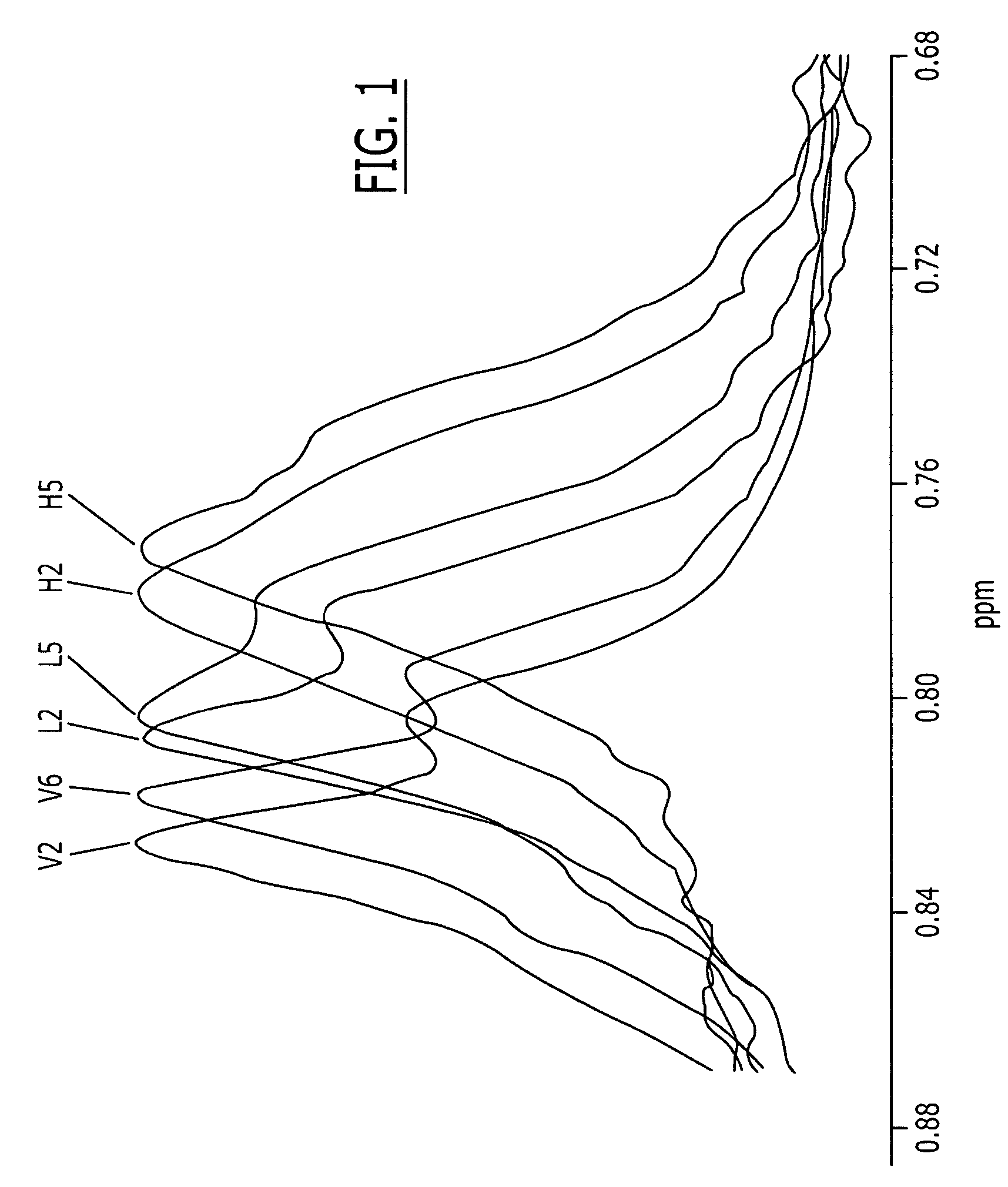
Methods, systems and computer programs for deconvolving the spectral contribution of chemical constituents with overlapping signals
ActiveUS7243030B2Improve robustnessImprove stabilityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringChemical compositionComputer science
Methods, systems and computer programs are configured to determine the presence of and / or a measurement for a plurality of constituents in a composite signal with closely correlated chemical constituents having overlapping signal lineshapes extending about a spectrum of interest obtained from a target sample undergoing analysis.
Owner:LIPOSCI
Detection of a target antigen irrespective of the presence or absence of a corresponding therapeutic antibody
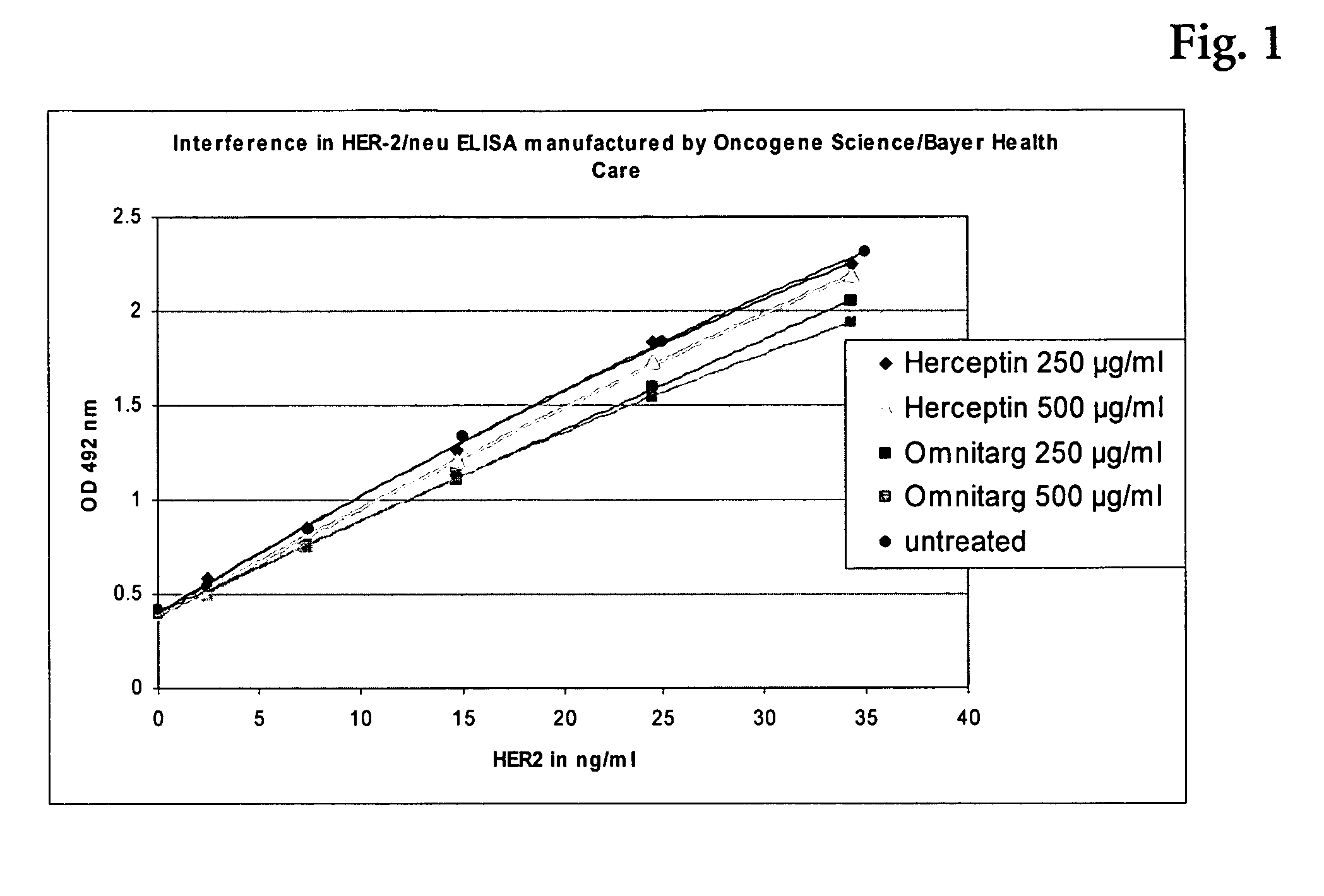
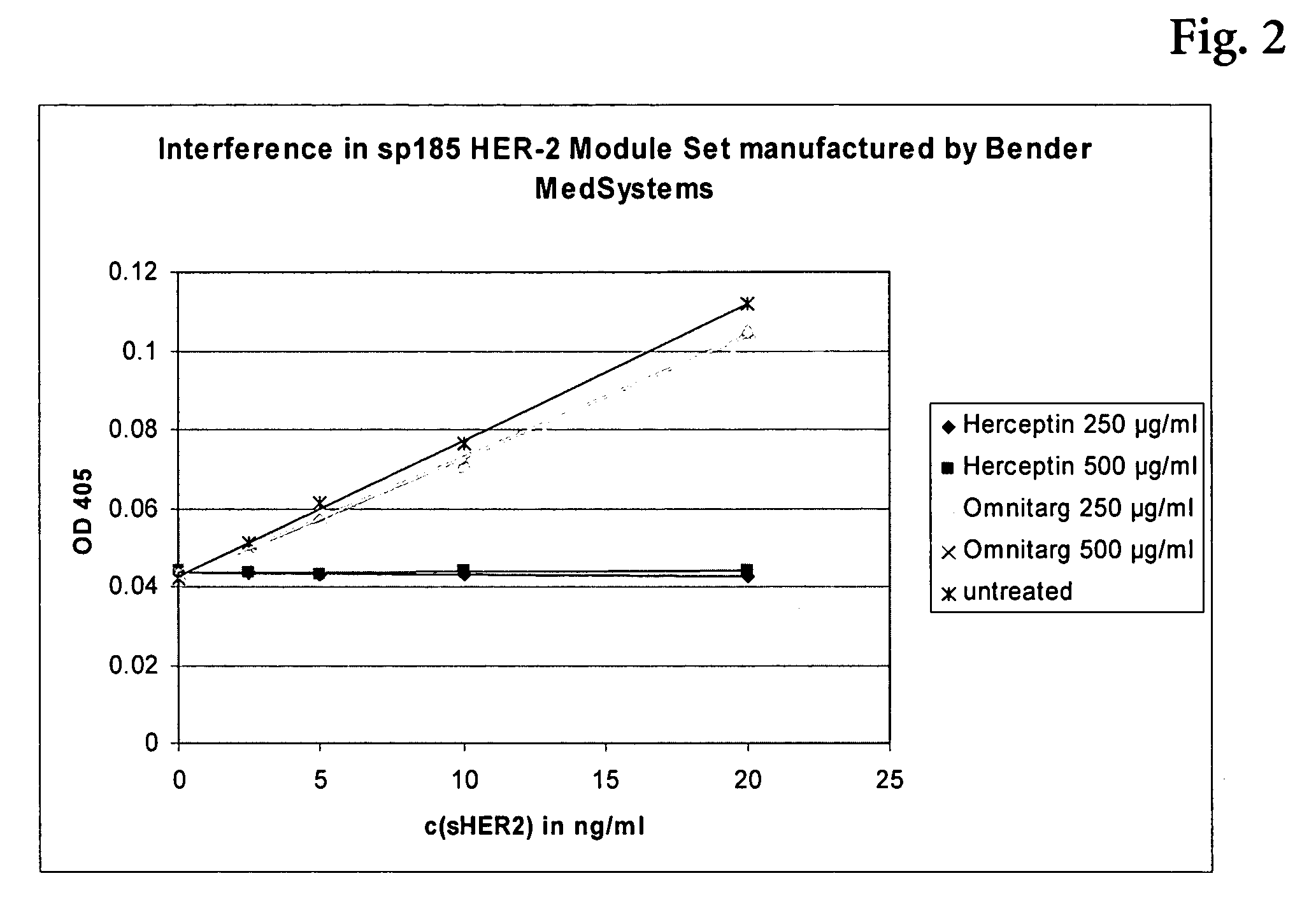
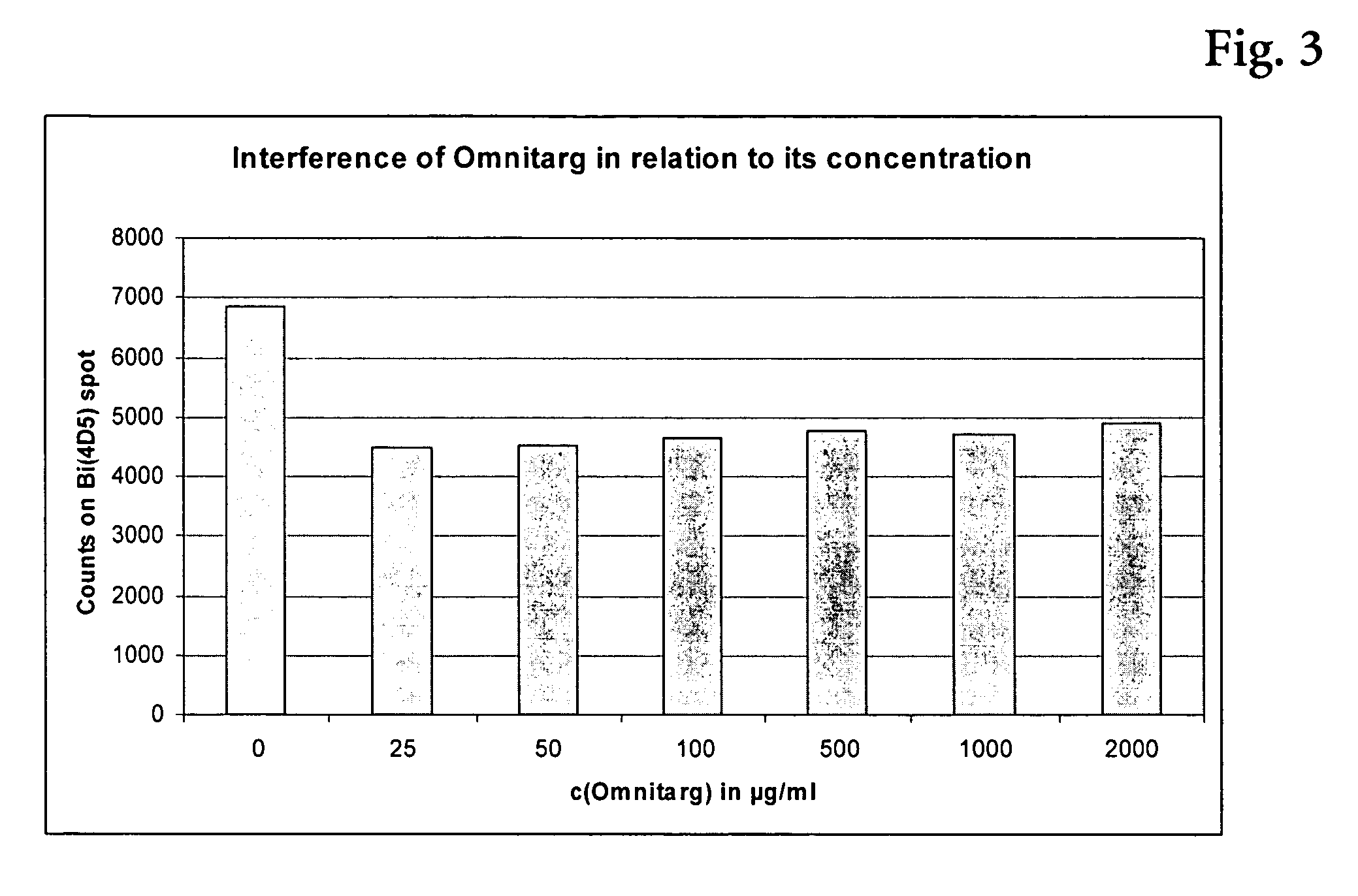
The present invention relates to the field of therapeutic antibodies. The invention especially relates to a method of detecting the target antigen of a therapeutic antibody in a sample comprising the steps of a) providing the sample to be analyzed, b) incubating said sample with said therapeutic antibody under conditions appropriate for binding of said therapeutic antibody to said target antigen, whereby a target antigen-therapeutic antibody-complex is formed, and c) detecting the complex formed in (b).
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Method, Device and Computer-Readable Medium for Evaluating Prevalence of Different Patient Postures
InactiveUS20080194998A1Improve efficiencyRepeatable signalPerson identificationMedical automated diagnosisBody posturePostural orientation
In a method, device and compute-readable medium for evaluating the prevalence of different postures of a patient, signals are sensed that indicate the posture of the patient during a monitoring period having a predetermined length, specific body postures of the patient are determined during this monitoring period from the sensed signals, the amount of time the patient spends in each of the specific postures is measured, information regarding each specific posture, and the associated amount of time spent in that posture, are stored, and the prevalence of the different postures of the patient is evaluated by classifying the stored information with respect to specific postures and the amount of time in each posture position.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Use of magneto-resistive sensors for borehole logging
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Cooking container comprising temperature sensor provided with fixing member
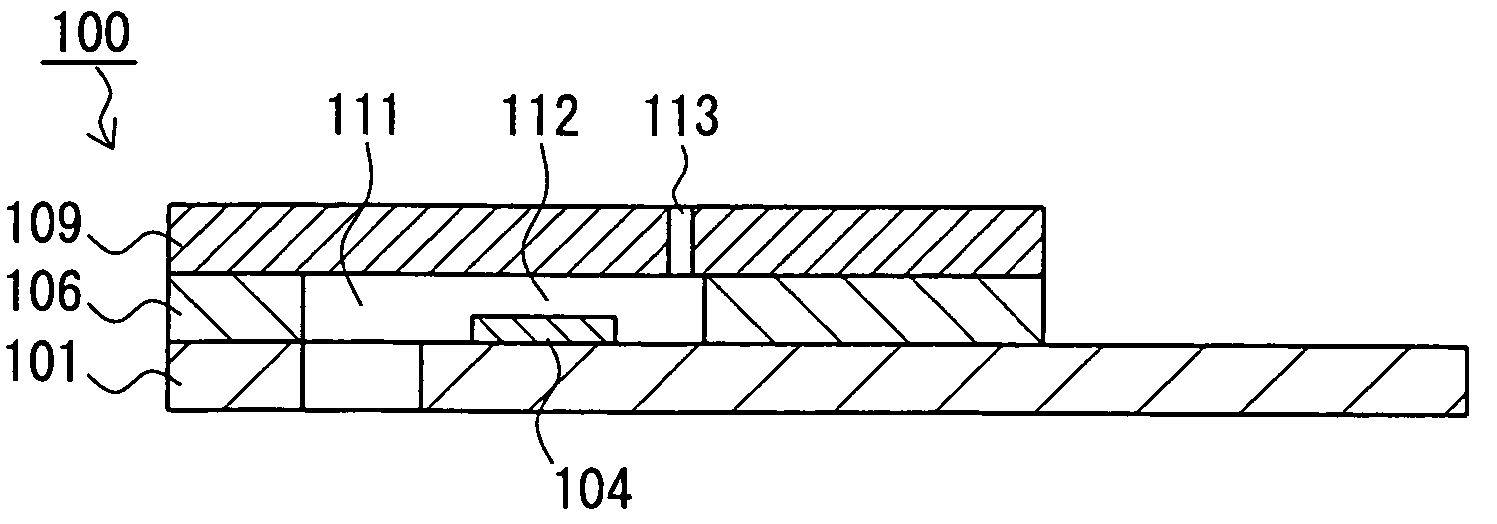
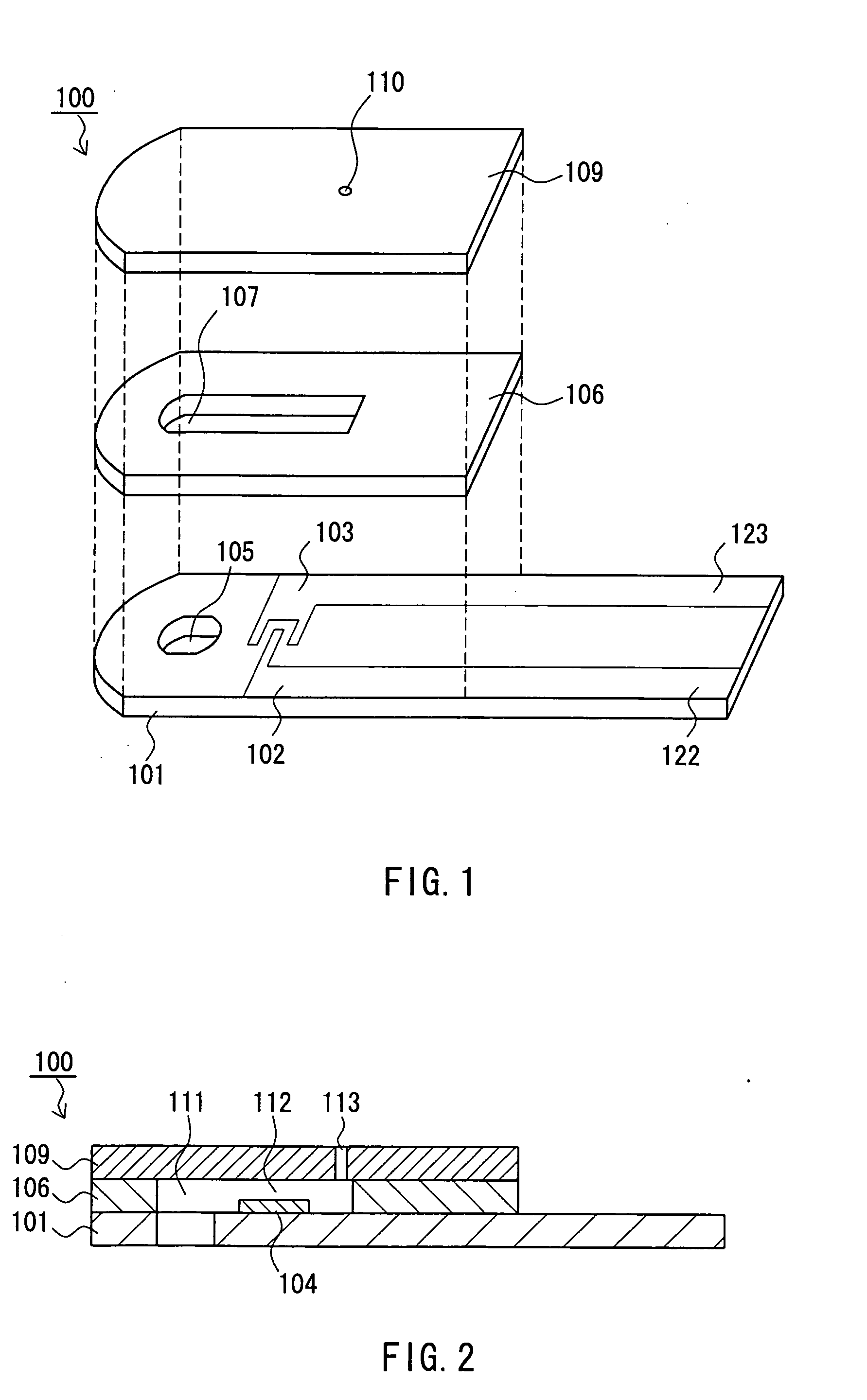
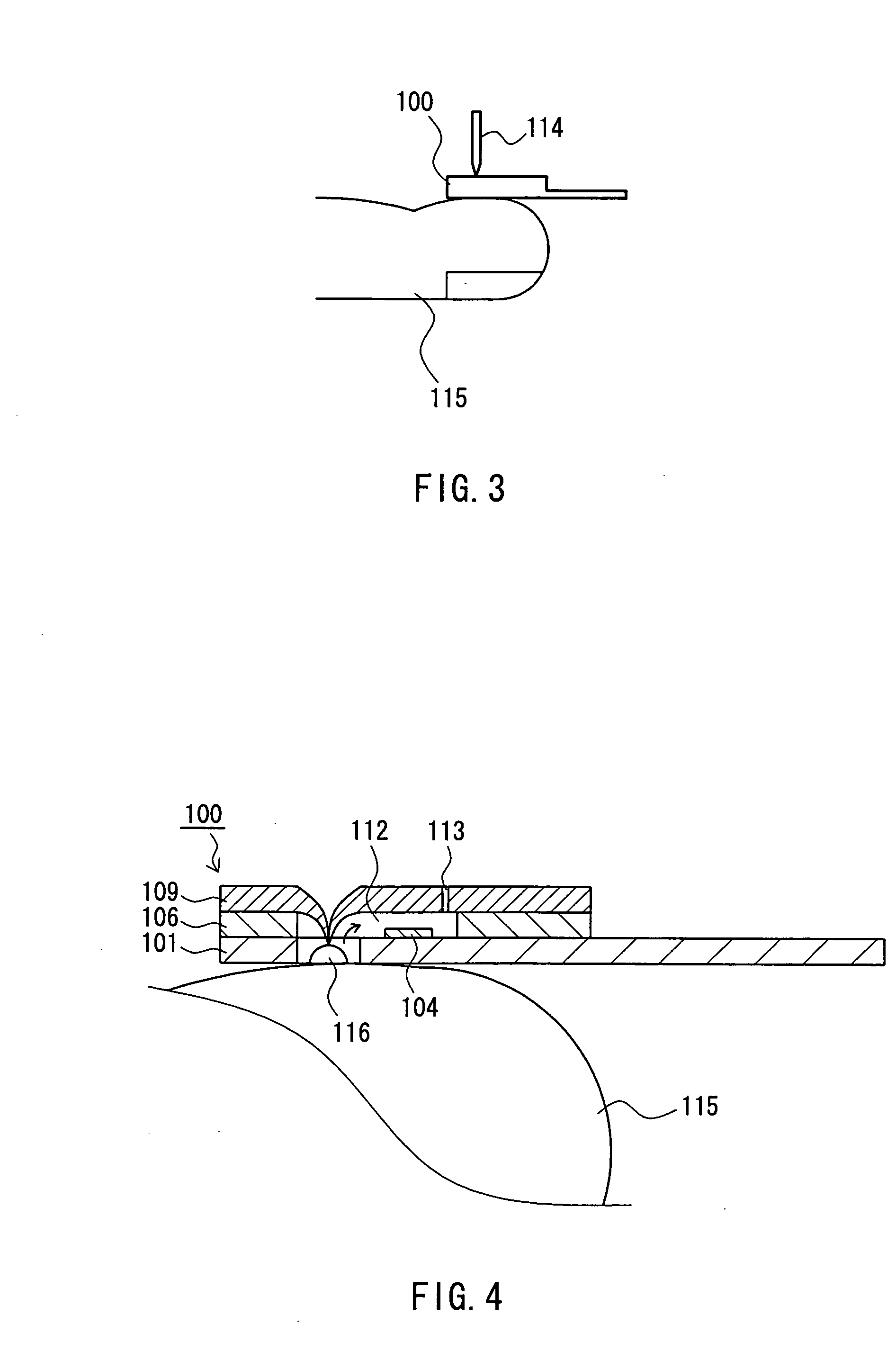
ActiveCN105142473AReliable measurementThermometer detailsKitchen equipmentElectrical conductorBiomedical engineering
Owner:SEB SA
Angular and axial position sensor arrangement
ActiveUS9244438B2Minimum of space and computational powerReduce manufacturing costElectric windingAnalogue-digital convertersAngular degreesEngineering
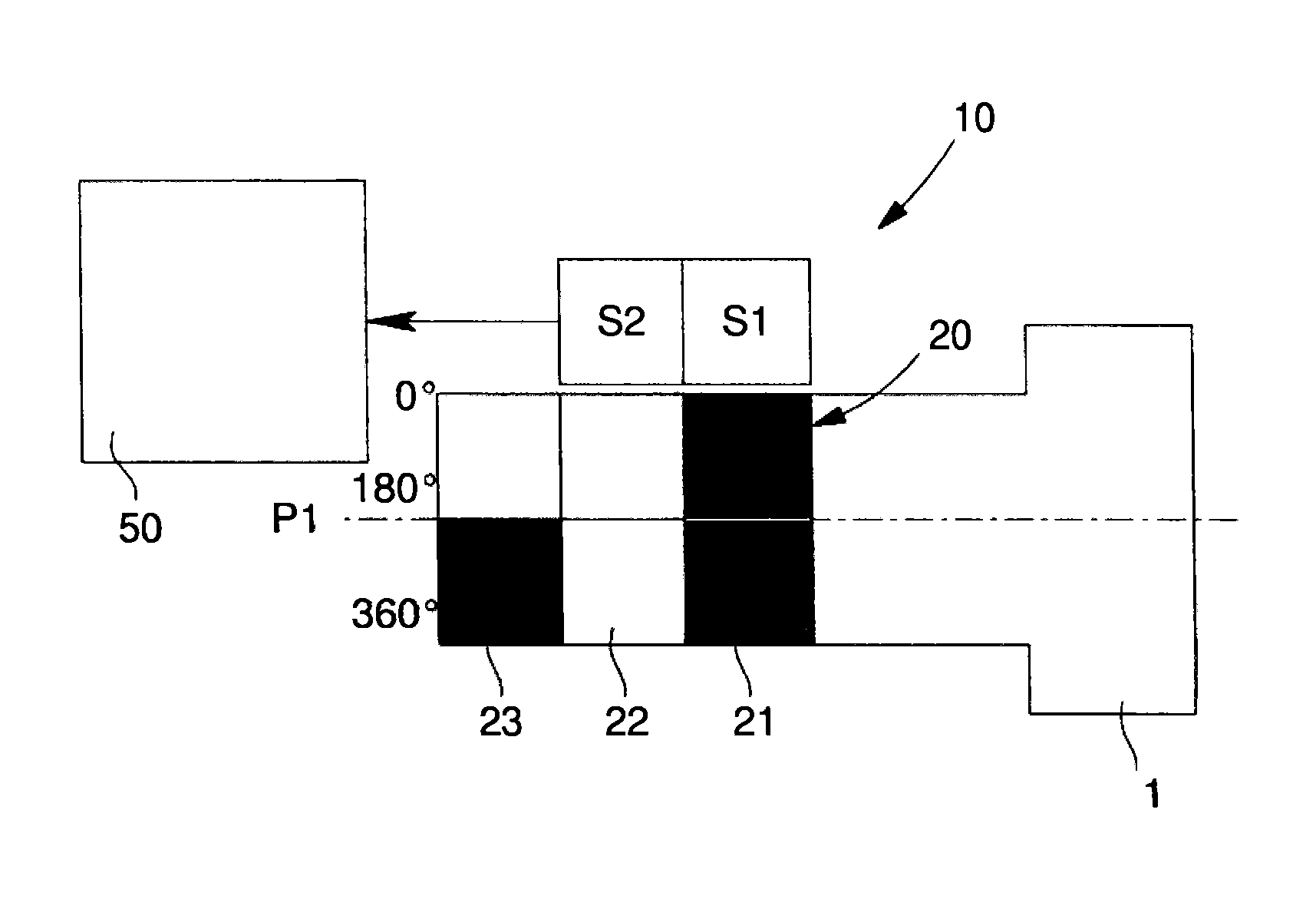
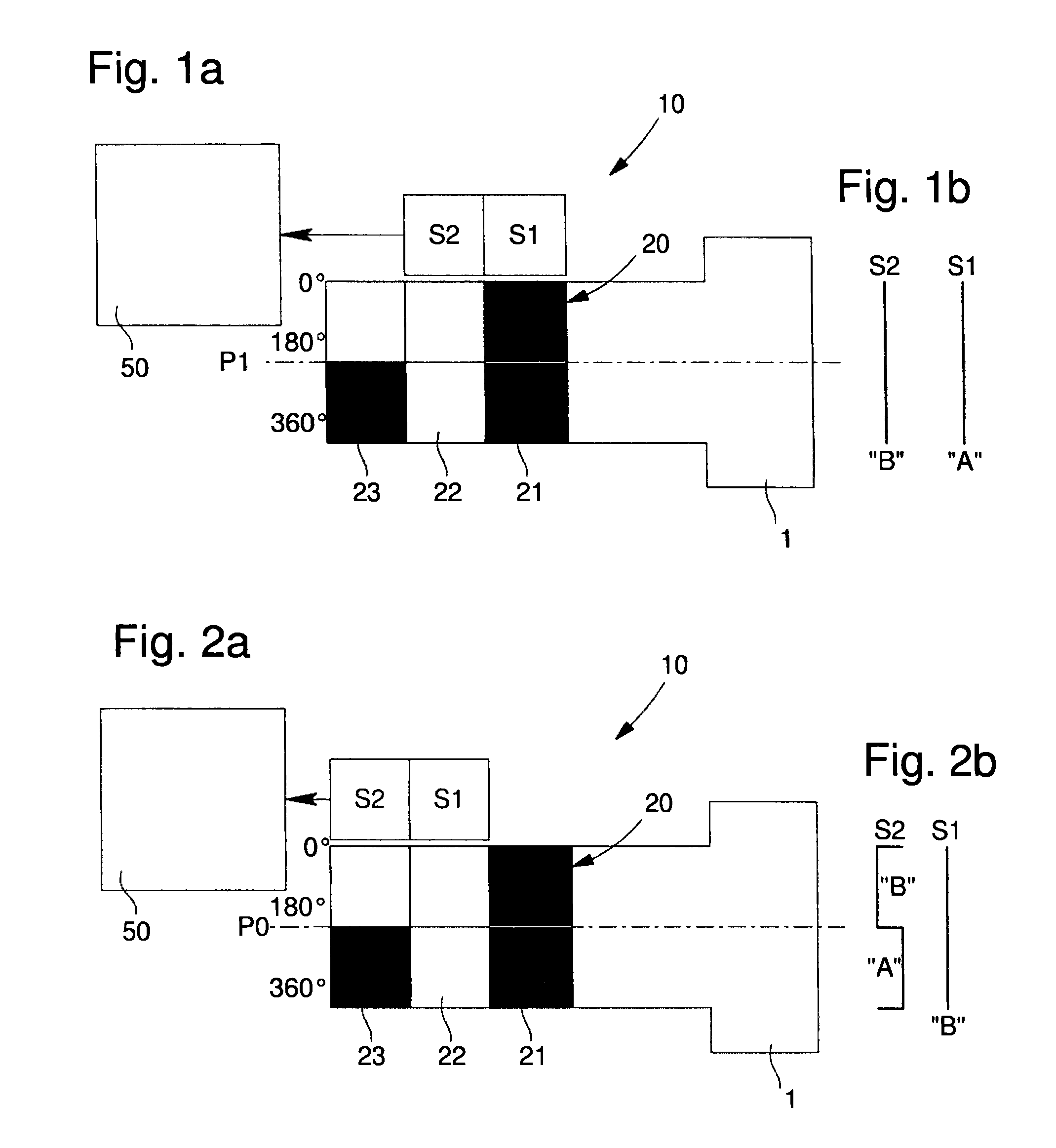
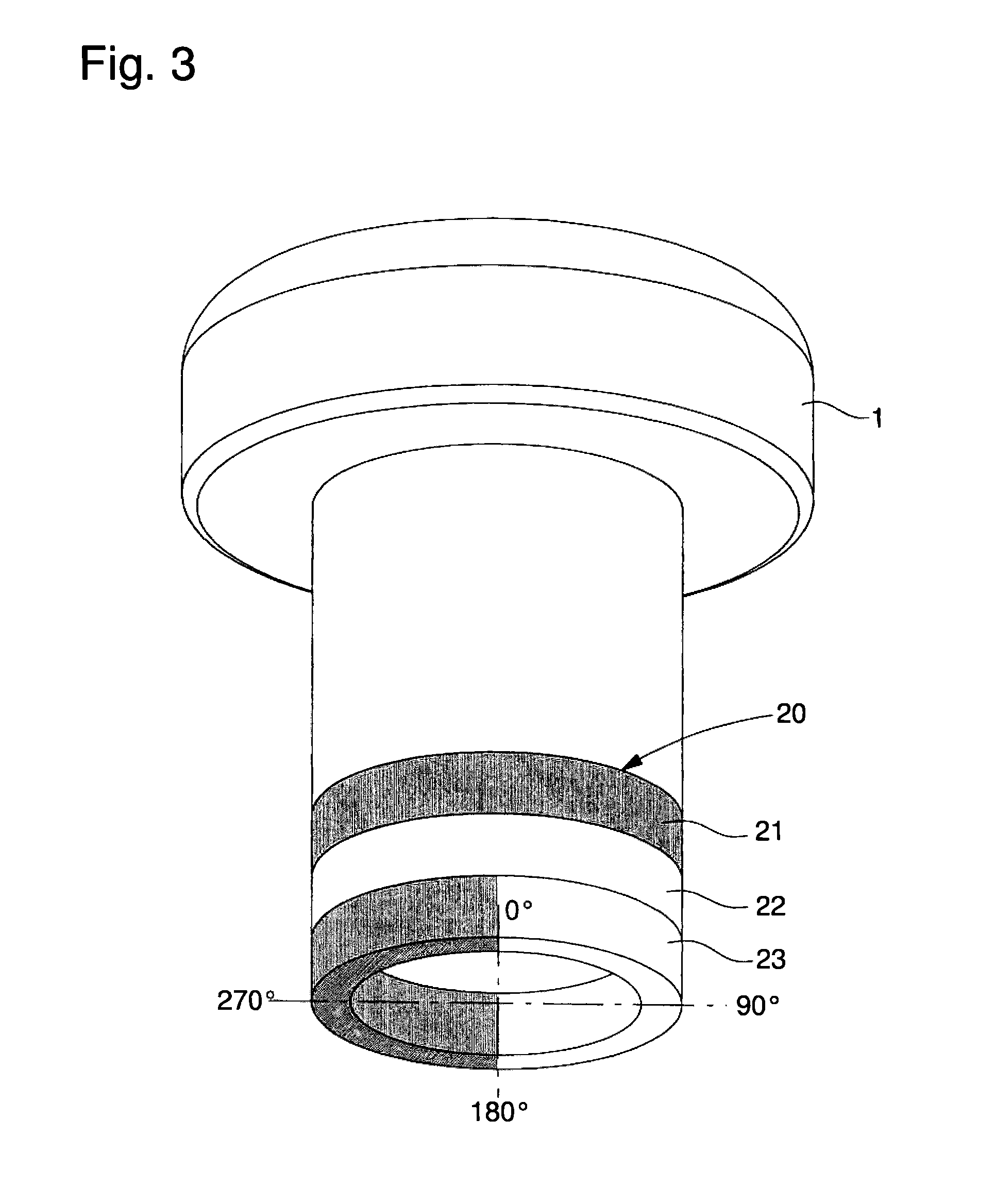
The angular and axial position sensor arrangement includes several sensors arranged adjacently, and aligned parallel to the axis of an encoded member that is angularly and axially displaceable relative to the sensors. The encoded member includes N−1 axial detection encoded rings with value A along their entire circumference and includes an Nth axial detection encoded ring that is axially adjacent with value B, different from value A, along its entire circumference. The values of axial detection encoded rings are distinguishable by the sensors overlapping some axial detection encoded rings. The encoded member includes several angular detection encoded rings axially adjacent to the Nth axial detection encoded ring. The angular detection encoded rings include a coding pattern composed of A and B values along their circumference to determine angular position by some sensors overlapping them.
Owner:THE SWATCH GRP RES & DEVELONMENT LTD
Method of making an alumina deposit on a substrate covered in sic
ActiveUS20080264176A1Improve toughnessEnhancing mechanical anchoringMolten spray coatingWave amplification devicesThermal sprayingStrain gauge
The invention relates to a method of depositing an alumina coating on a part having a silicon carbide surface. The method comprises the following steps:a) depositing a silicon adhesion underlayer on the SiC surface by chemical vapor spraying; andb) depositing a coating on the silicon adhesion underlayer by atmospheric thermal spraying.The invention also provides a device for measuring deformation, which device comprises a first alumina coating obtained by atmospheric thermal spraying onto the silicon adhesion underlayer deposited on the silicon carbide layer covering the substrate of the part, a free filament strain gauge placed on the coating, and an additional alumina coating obtained by atmospheric thermal spraying onto the strain gauge.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Reconfigurable portable locator employing multiple sensor array having flexible nested orthogonal antennas
InactiveUS8203343B1Improve usabilityWithout affecting locator performance and accuracyMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementSensor array3d sensor
A portable locator for detecting a buried object characterized by an electromagnetic (EM) field emission employing three-dimensional (3D) sensor arrays each having three substantially-identical EM field sensors disposed on a flexible annular wall having a radial centroid defining a sensing axis. The flexible annular sensors are retained in substantial concentricity with the corresponding sensing axes disposed in substantial mutual orthogonality. A pair of 3D sensor arrays disposed on a first axis substantially orthogonal to a second axis defied by another pair of EM field sensors each having a sensing axis disposed along the second axis. The locator introduces a user-reconfigurable user interface (UI) employing a “sticky” ratcheting audio UI and a hollow hinge assembly for redisposing the sensor assembly from an operating to a storage disposition.
Owner:SEEK TECH
Method and apparatus for digital detection of electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction in metallic pipes and cables
ActiveUS20050096879A1Reduced analog front-end hardware requirementWide resistance to componentAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingCarrier signal
A new digital architecture for metallic pipe and cable locators, providing accurate estimation of the fundamental locate parameters, electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction, and utilizing a nested Digital Phase-Locked Loop (DPLL) structure is disclosed. The obstacles to signal direction measurement in low SINR environments using the signal select method are overcome and a more precise phase comparison between the carrier and the FM modulation signals is obtained. The architecture further significantly reduces analog front-end hardware requirements, offers wider resistance to component tolerances, lower calibration and test time, and provides flexible frequency selectivity. Locators according to the present invention provide accurate estimation of the fundamental physical parameters of line location (electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction) in extremely noisy environments, using Digital Signal Processing (DSP) methods.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Locator with apparent depth indication
ActiveUS7332901B2Easy to measureGood user interfaceMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementSensor arrayElectromagnetic field
A human-portable utility locator system for locating and tracing a buried utility line characterized by an electromagnetic field emission. The locator may include a horizontal spaced sensor pair for detecting the horizontal field asymmetry of the emitted field in one or more independent frequency bands, which is employed to assist in determining an accurate “virtual depth” measurement for producing detection events. An event detector may be disposed to detect events corresponding to extremum in the B-field gradient with respect to time and a user interface (UI) coupled to the event detector signals the detected event to a user. In a preferred embodiment, one pair of spaced-apart 3D magnetic sensor arrays is disposed substantially orthogonal to another intermediate spaced-apart pair of sensors.
Owner:SEEK TECH
Vibrating micro-mechanical sensor of angular velocity
ActiveUS20090260437A1Reliable measurementImprove performanceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMechanical sensorMeasurement device
The invention relates to measuring devices used in measuring angular velocity and, more precisely, to vibrating micro-mechanical sensors of angular velocity. The sensor of angular velocity according to the invention is adapted to measure angular velocity in relation to two or three axes, and at the least two seismic masses (34-36, 52-53, 71-75) of the sensor of angular velocity are adapted to be activated into primary motion vibration by means of a common mode. The structure of the sensor of angular velocity according to the invention enables reliable measuring with good performance, particularly in small size vibrating micro-mechanical sensors of angular velocity.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
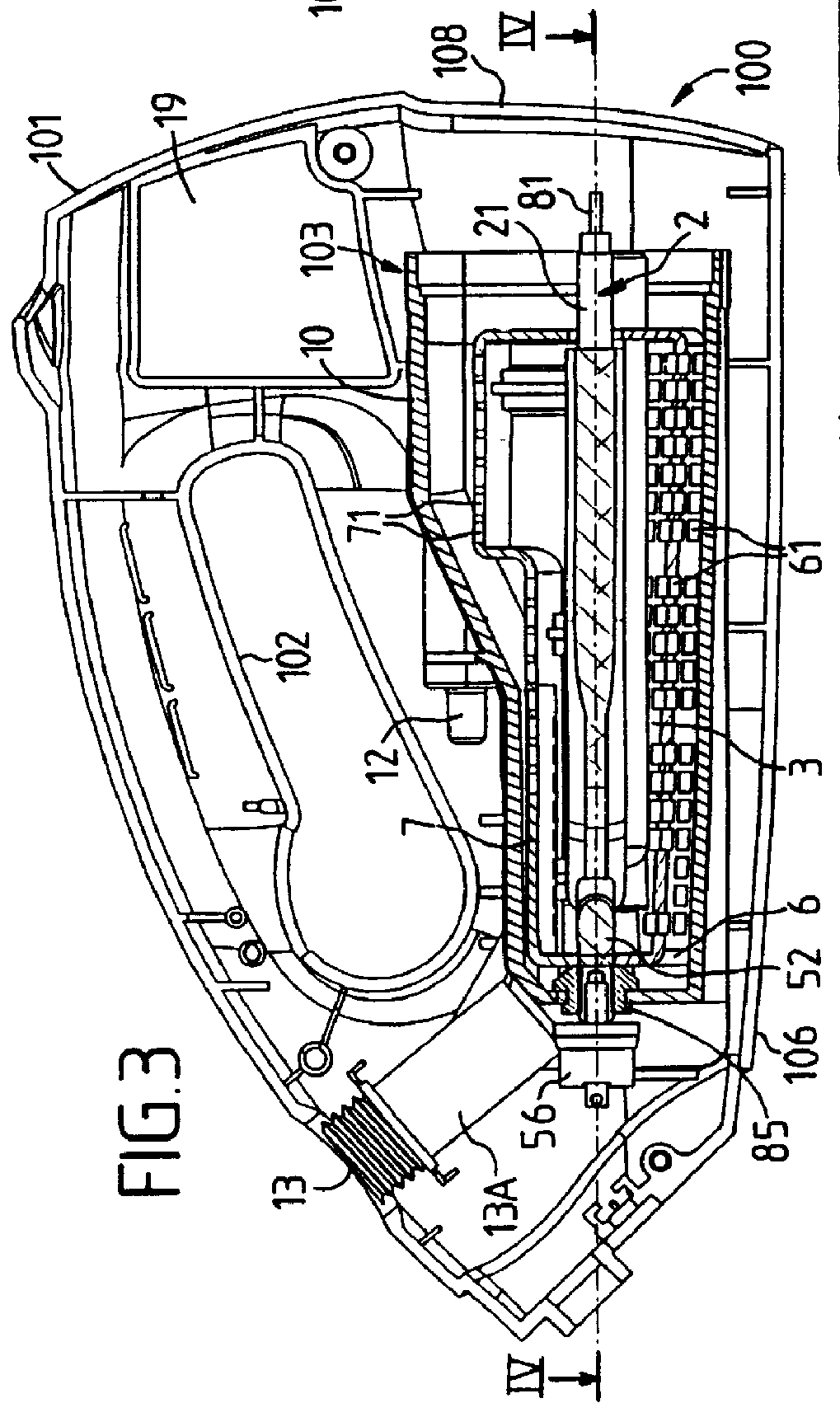
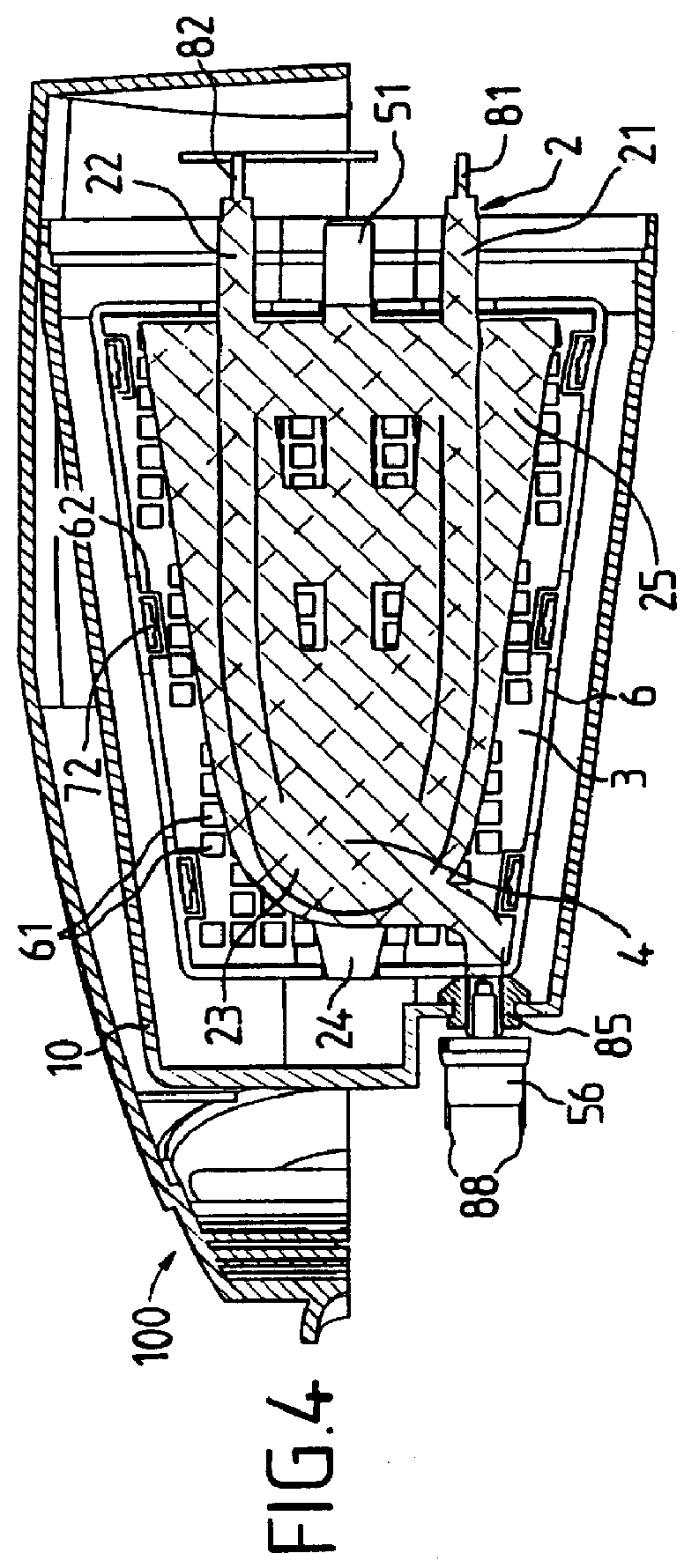
Camera Arrangement in a Motor Vehicle
InactiveUS20090085755A1Easy to installReliable measurementTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMoisture sensor
The invention presented herein is about a camera arrangement for a motor vehicle, comprised of a housing that can be attached on the inside of a windshield of a motor vehicle, at least one camera residing in the housing, a moisture sensor installation capable of detecting the moisture on the windshield, where the moisture sensor installation is a non-optical moisture sensor installation.
Owner:HELLA KGAA HUECK & CO
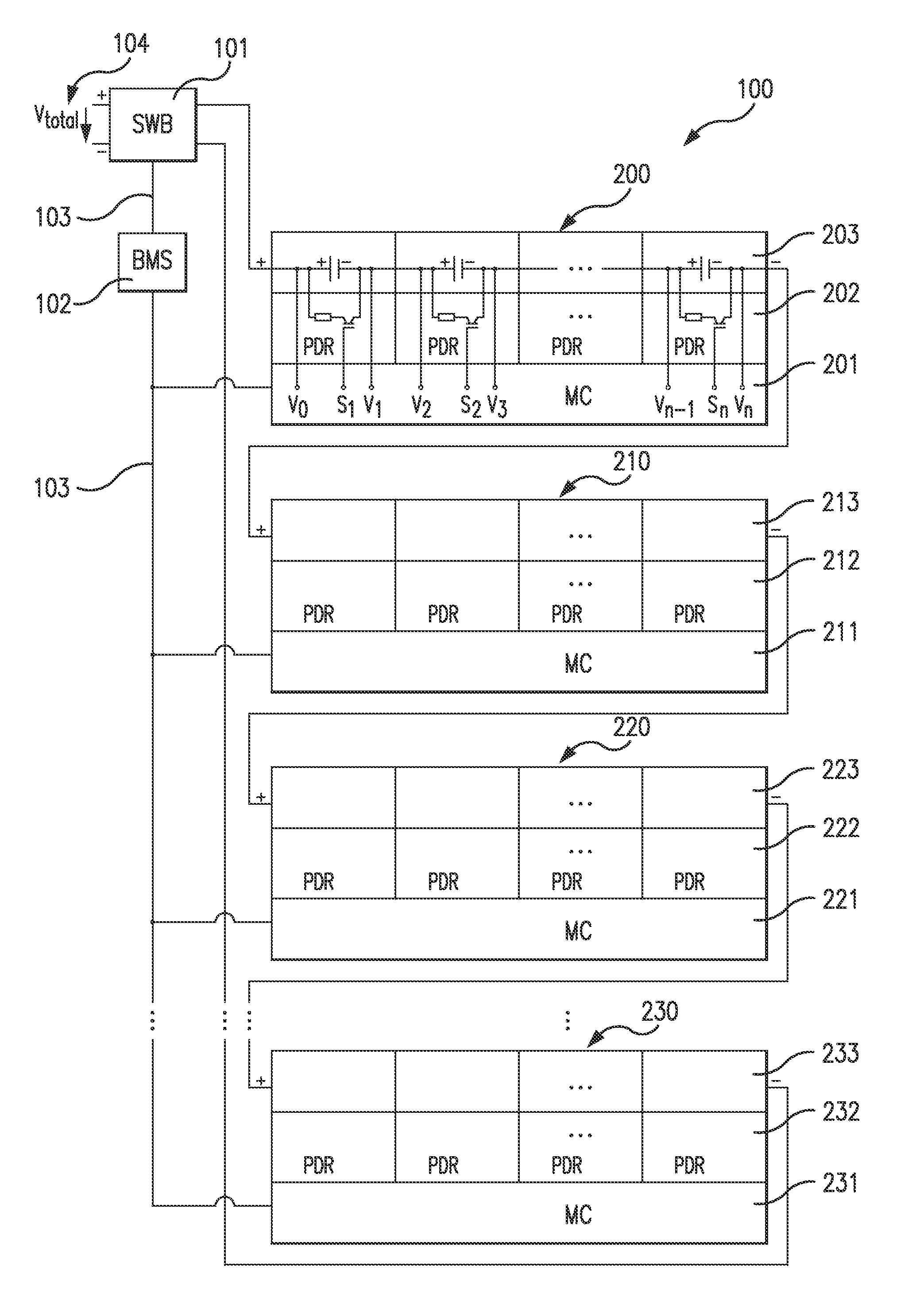
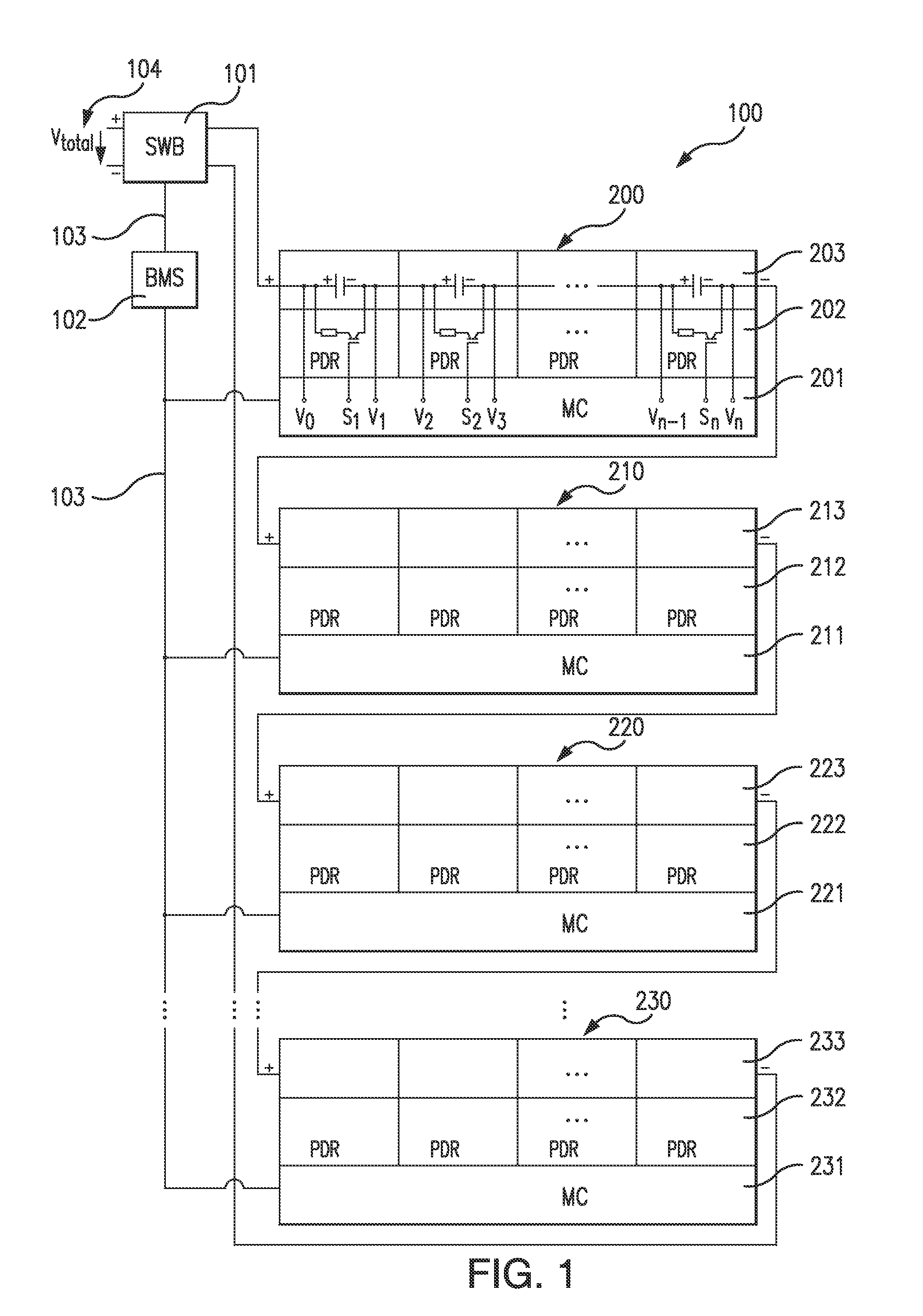
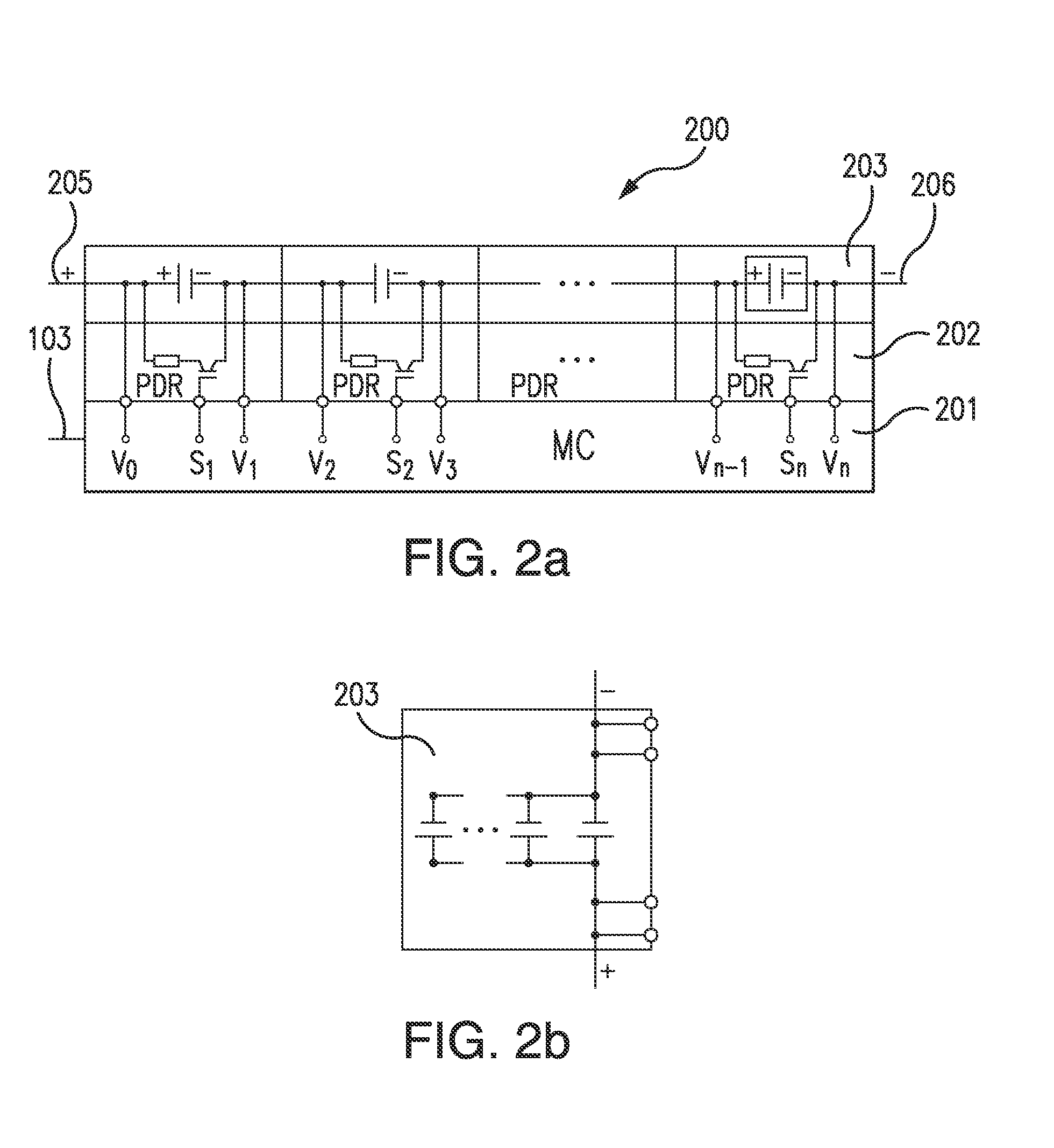
Balancing Voltage for a Multi-Cell Battery System
ActiveUS20120139491A1Reliable measurementA large amountCharge equalisation circuitElectric devicesElectricityCharge current
A method for balancing voltage for a multi-cell battery system, in which the battery system includes at least two parallel groups of cells connected in series and in which the parallel group of cells includes at least one battery cell, includes: charging the battery system by keeping the voltage of all parallel groups of cells less than or equal to a second threshold voltage value, while at least the voltage of one group of parallel cells is less than or equal to a first threshold voltage; and while at least the voltage of one group of parallel cells is less than or equal to a second threshold voltage; and while the charging current is above a predefined minimal current. The method further includes measuring the voltage of each parallel group of cells while electrical loads are shut off and dissipating energy in each of the parallel group of cells of the amount that is represented by the voltage difference between the individual parallel group of cells and the parallel group of cells with the lowest voltage.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG +1
Locator with apparent depth indication
ActiveUS20060232259A1Easy to measureReliable horizontal field asymmetry measurementMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementSensor arrayElectromagnetic field
A human-portable utility locator system for locating and tracing a buried utility line characterized by an electromagnetic field emission. The locator may include a horizontal spaced sensor pair for detecting the horizontal field asymmetry of the emitted field in one or more independent frequency bands, which is employed to assist in determining an accurate “virtual depth” measurement for producing detection events. An event detector may be disposed to detect events corresponding to extremum in the B-field gradient with respect to time and a user interface (UI) coupled to the event detector signals the detected event to a user. In a preferred embodiment, one pair of spaced-apart 3D magnetic sensor arrays is disposed substantially orthogonal to another intermediate spaced-apart pair of sensors.
Owner:SEEK TECH
Thermal Deposition Surface Treatment Method, System and Product
ActiveUS20080087359A1Increase ratingsDamaging internal stressLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingThermal depositionCoolant flow
A process for treating a workpiece, said process comprising the steps of: (c) altering the temperature of a workpiece surface wherein at least one condition selected from the group of: thermal treatment rate, relative motion between the surface and said thermal treatment rate, coolant flow rate onto said surface, heating flow rate onto said surface and the relative speed between the heating means or the cooling means and the surface is controllable; (d) simultaneously measuring temperatures at a plurality of locations over the surface of the workpiece; (c) determining an average temperature of the temperatures measured in step (b); (d) comparing the average temperature to a preselected minimum temperature and a preselected maximum temperature for the workpiece; and (e) automatically adjusting at least one of the controllable conditions if said average temperature is not between the preselected minimum temperature and the preselected maximum temperature for the workpiece. A system for performing a thermal treatment process and the resulting product are also provided. Standard deviations of all temperature readings and controlling the relative motion speed between the thermal coating deposition head and the workpiece provide another improvement for obtaining temperature uniformity over the workpiece surface.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Air-actuated muscle motion analog control platform device and posture control method
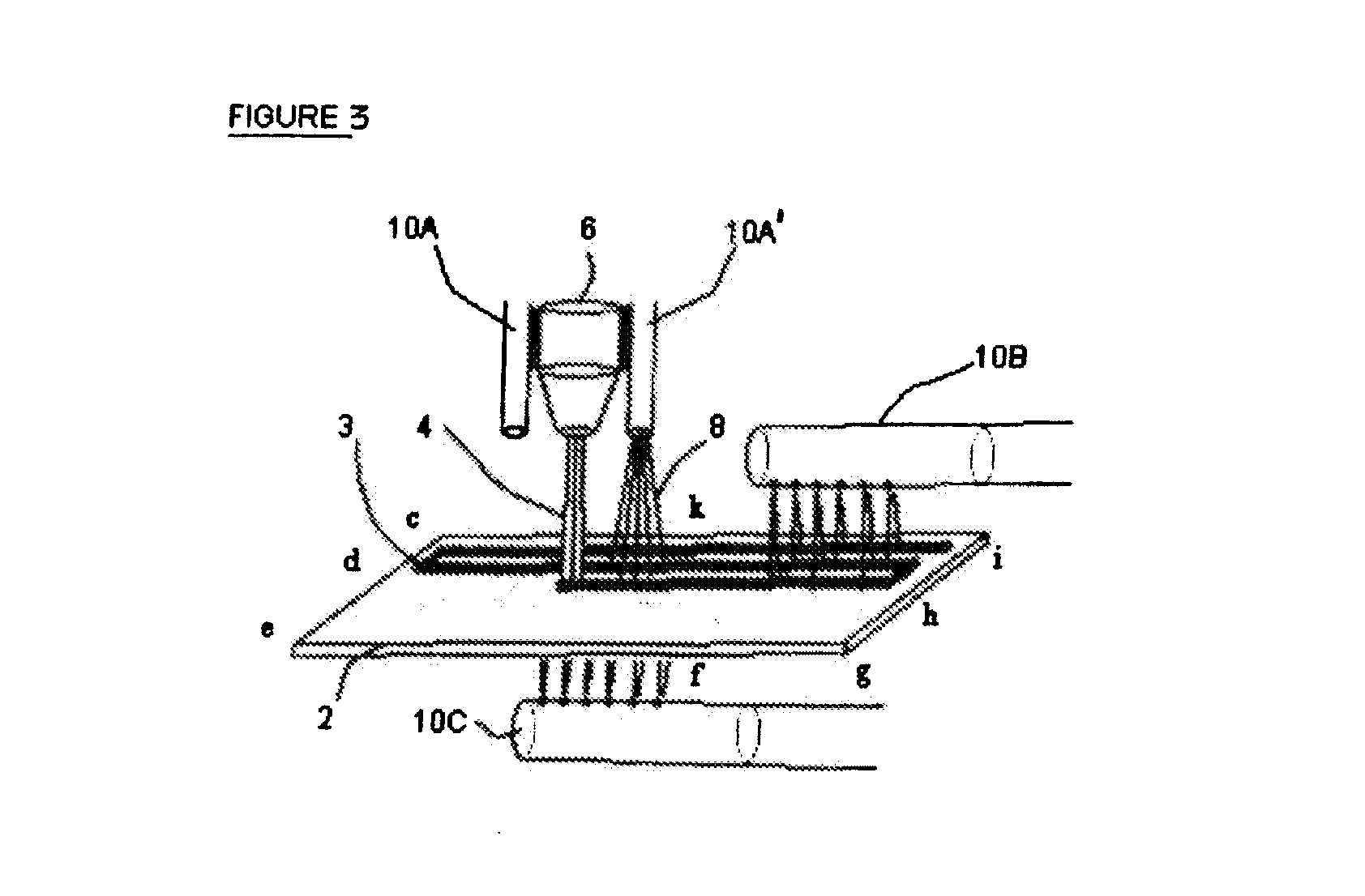
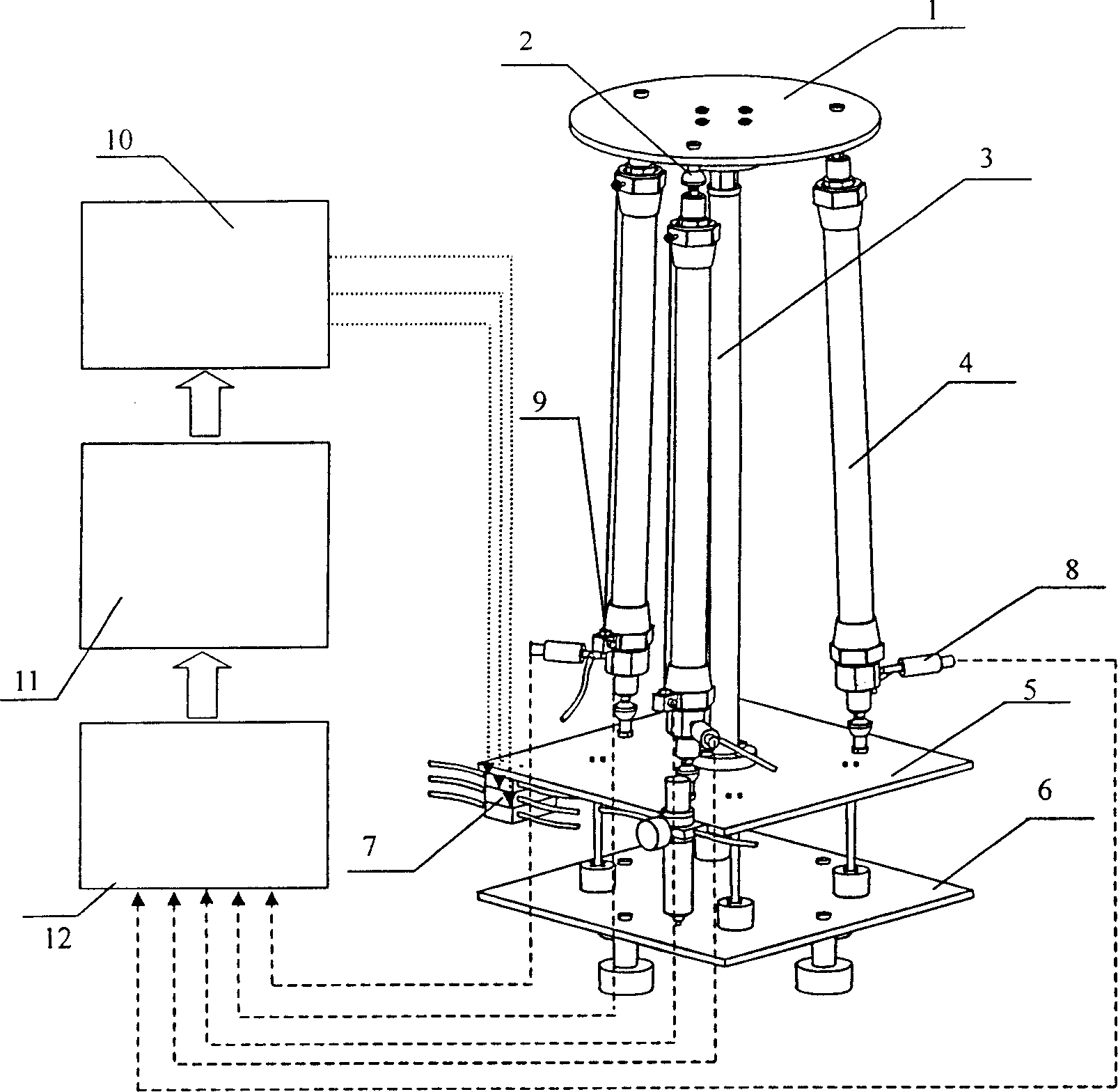
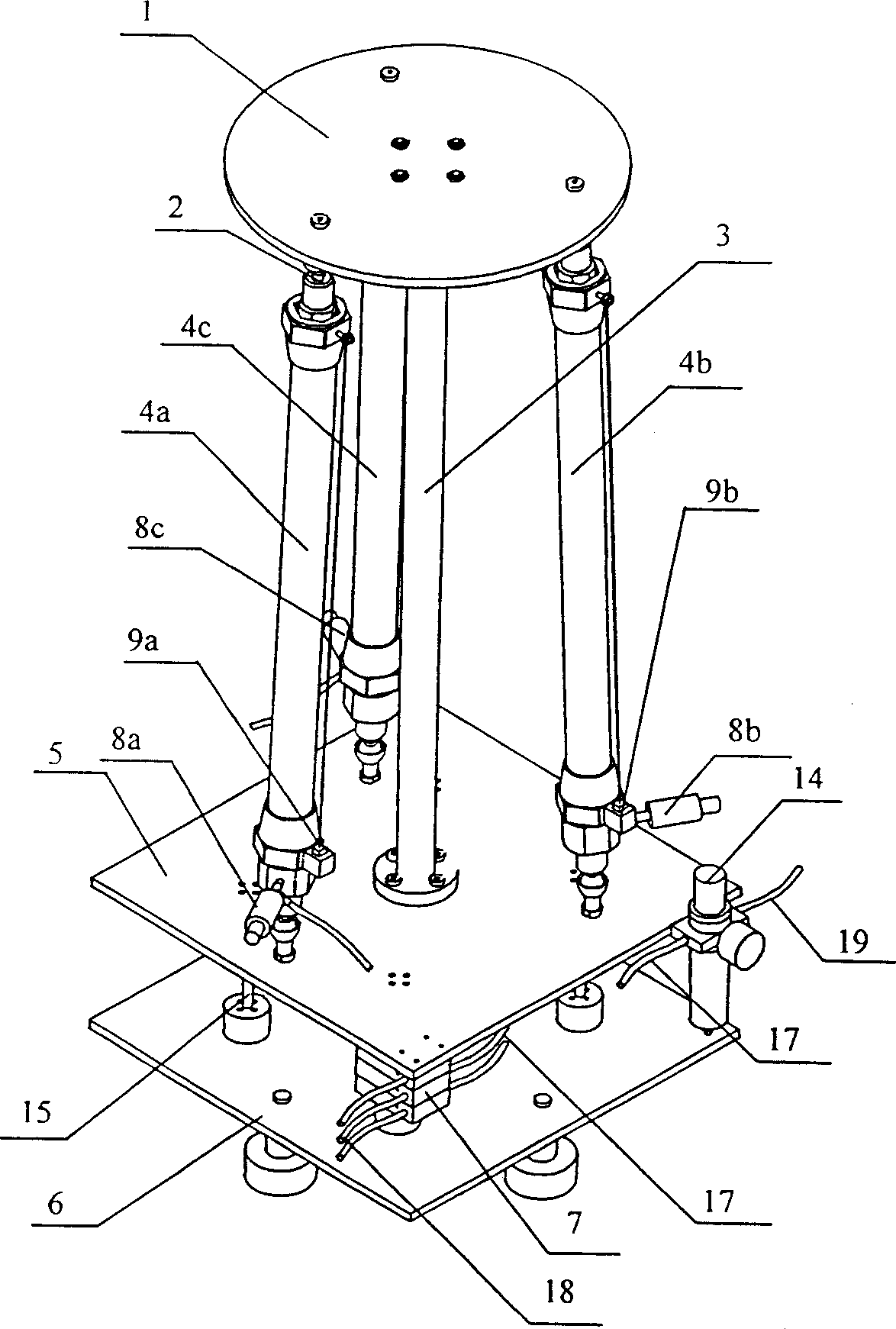
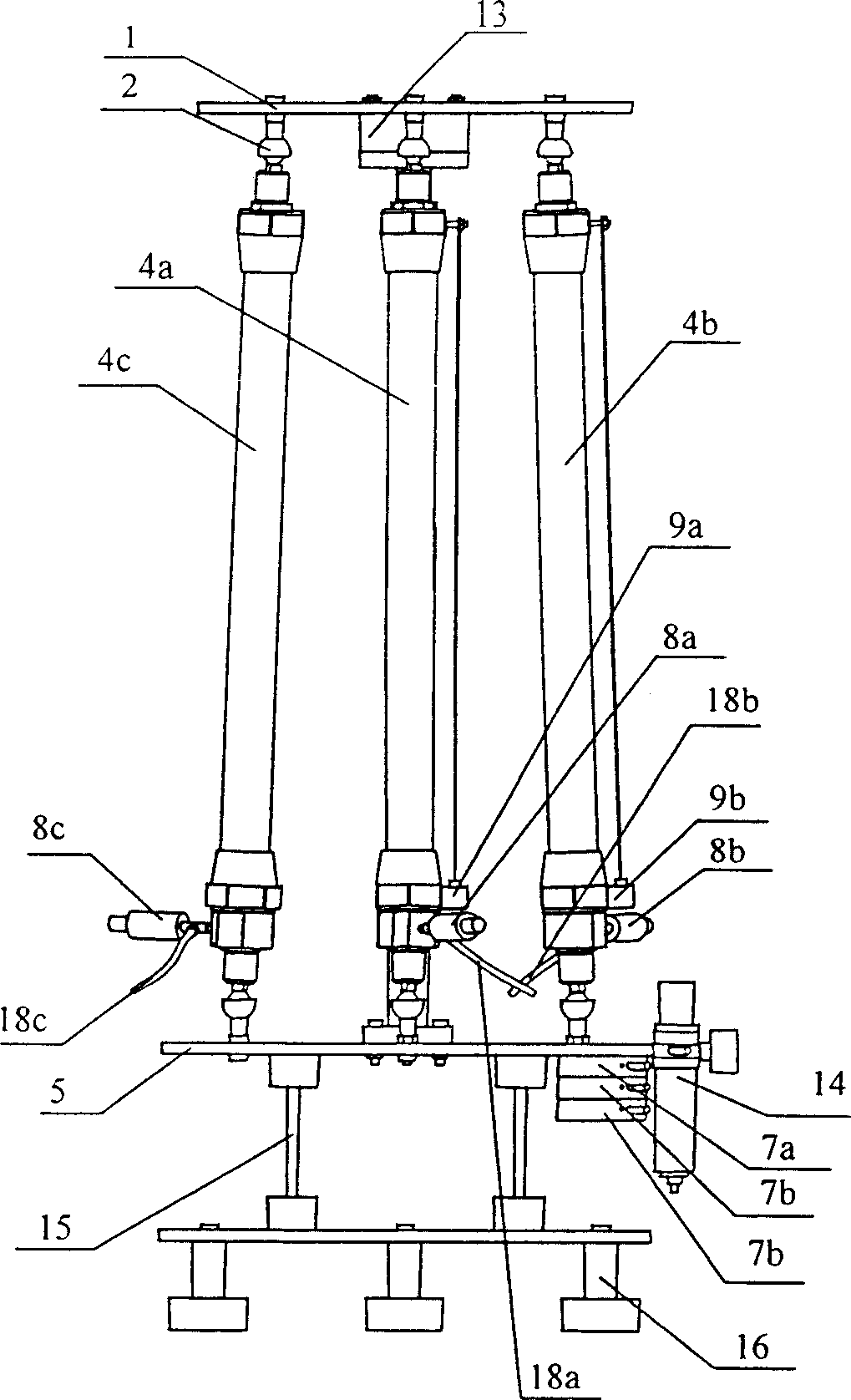
InactiveCN1909017AGreat effortReduce volumeCosmonautic condition simulationsAmusementsControl systemComputer module
The disclosed aerodynamic muscle motion simulation control platform comprises: three very same pieces of aerodynamic muscles connected to a central post and a fixed platform, a motion platform hinged to the muscles with uniform-distributed hinge points, and the central post to rigid connect with the fixed platform and hinge the motion platform through a central ball hinge with the hinge point on platform center to endow the motion platform two rotation DOF. Besides, the control system comprises an input conversion module, a controller, and an output drive amplification module. This invention is fit to different motion simulation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Complex monitor for automatically monitoring multiple parameters of water on line
InactiveCN102661923AEconomic savingsNo secondary pollutionColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial electrochemical variablesPrincipal component analysisUv vis absorbance
The invention discloses a method for automatically monitoring water quality indexes on line and a device for implementing the method. A method of combining an ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy and various sensors is adopted, dozens of water quality indexes including chemical oxygen demand and ammonia nitrogen can be measured at one time, measurement indexes can be configured in a building block mode according to requirements, and chemical agents are not required. According to the device, the constructed digital optical fiber spectrometer is taken as a core, ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrum data of a water sample is processed in a mode of sequentially combining wavelet de-noising, principal component analysis and a support vector machine, and water quality indexes such as chemical oxygen demand and biochemical oxygen demand of water are acquired. Various physical and electrochemical sensors acquire water quality indexes such as ammonia nitrogen, dissolved oxygen and conductivity. All hardware and software for implementing the method is put in a cabinet to form the device, and the device analyzes the introduced water sample under the control of an embedded industrial control computer system, and automatically monitors the water quality indexes in real time.
Owner:SICHUAN BELAM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com