Patents
Literature
382 results about "Resistive sensors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
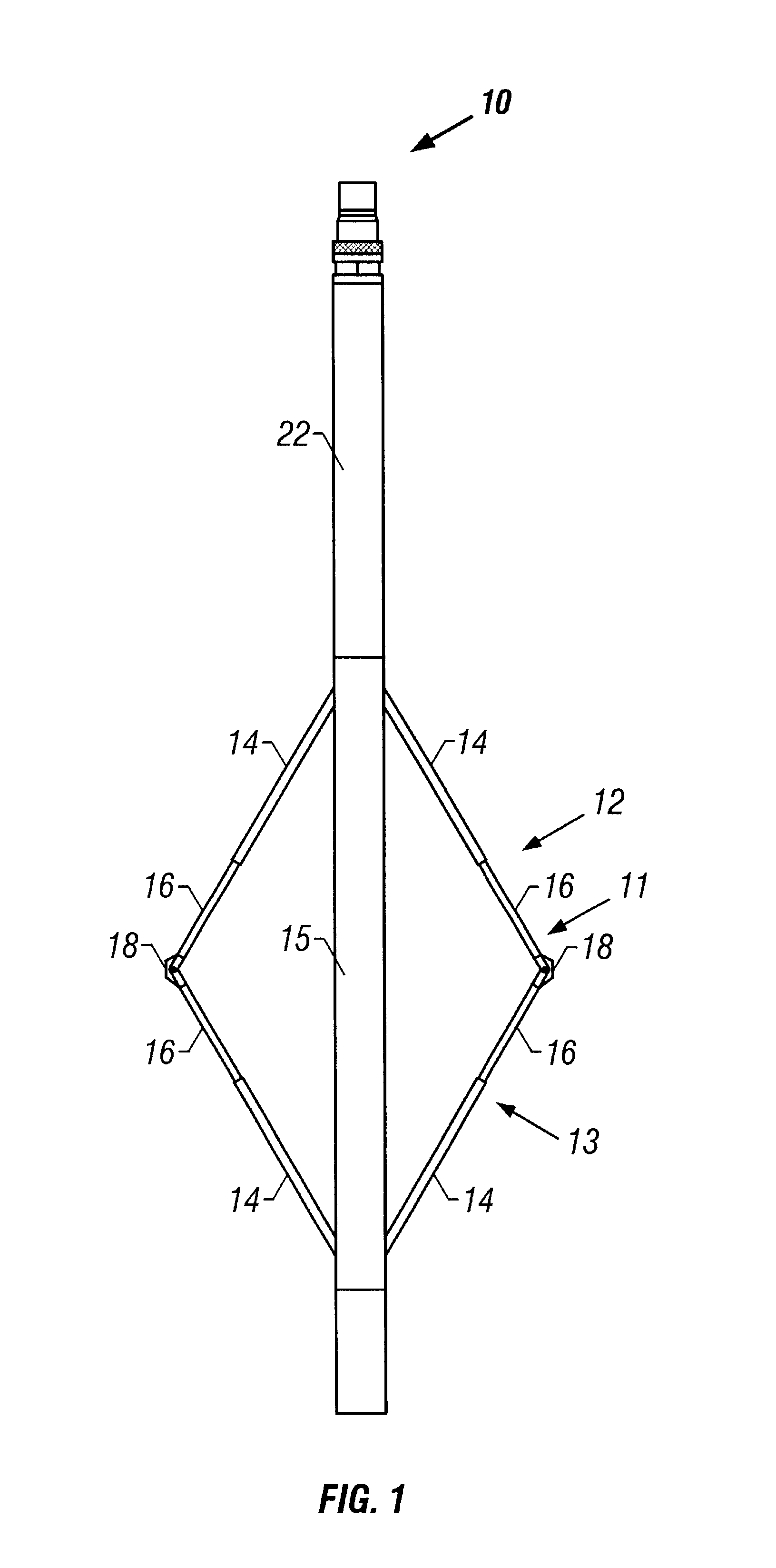
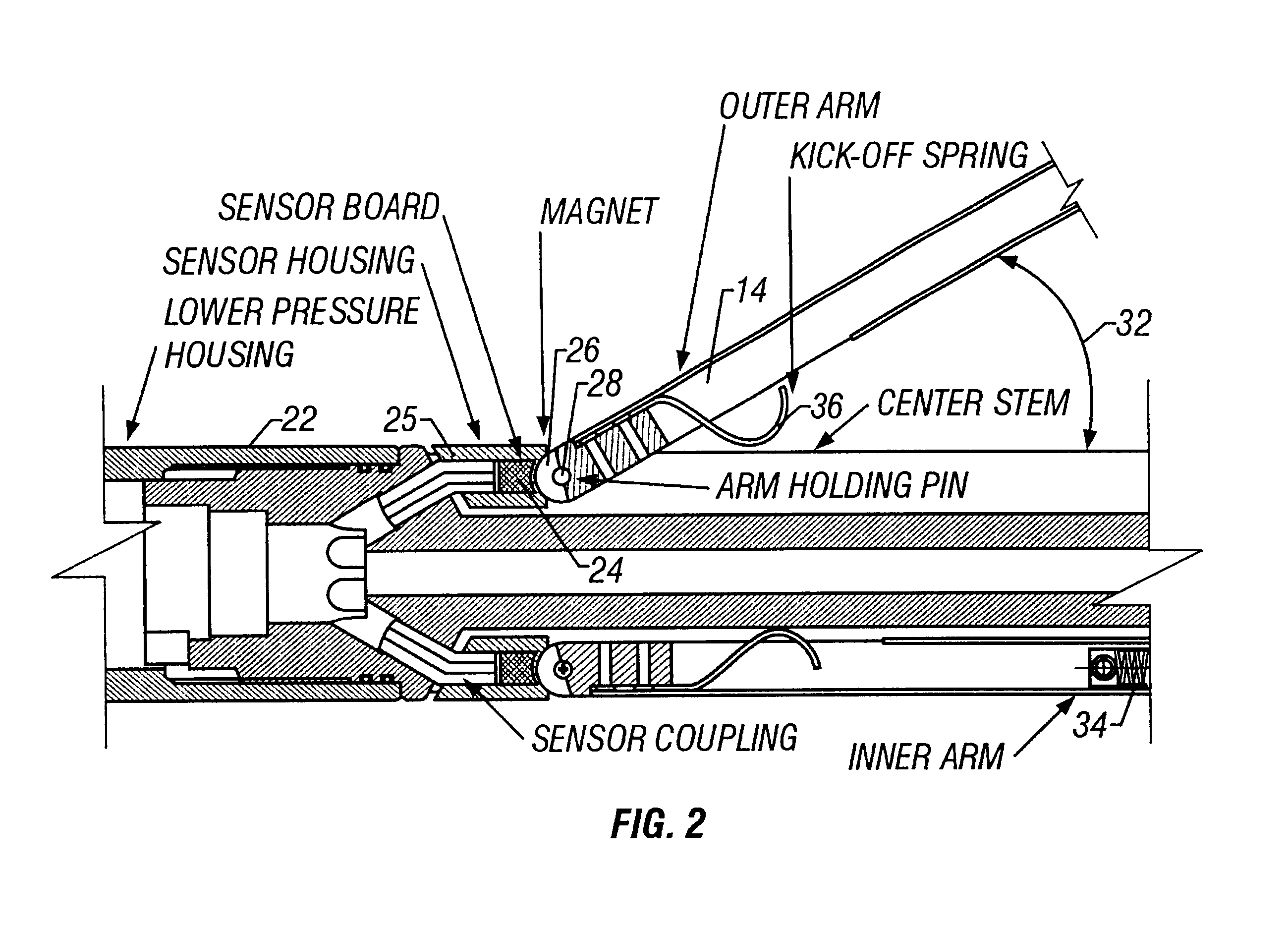
Blind-spot warning system for an automotive vehicle
InactiveUS7161472B2Improve responseNeed lessDetection of traffic movementAnti-collision systemsResistive sensorsMobile vehicle
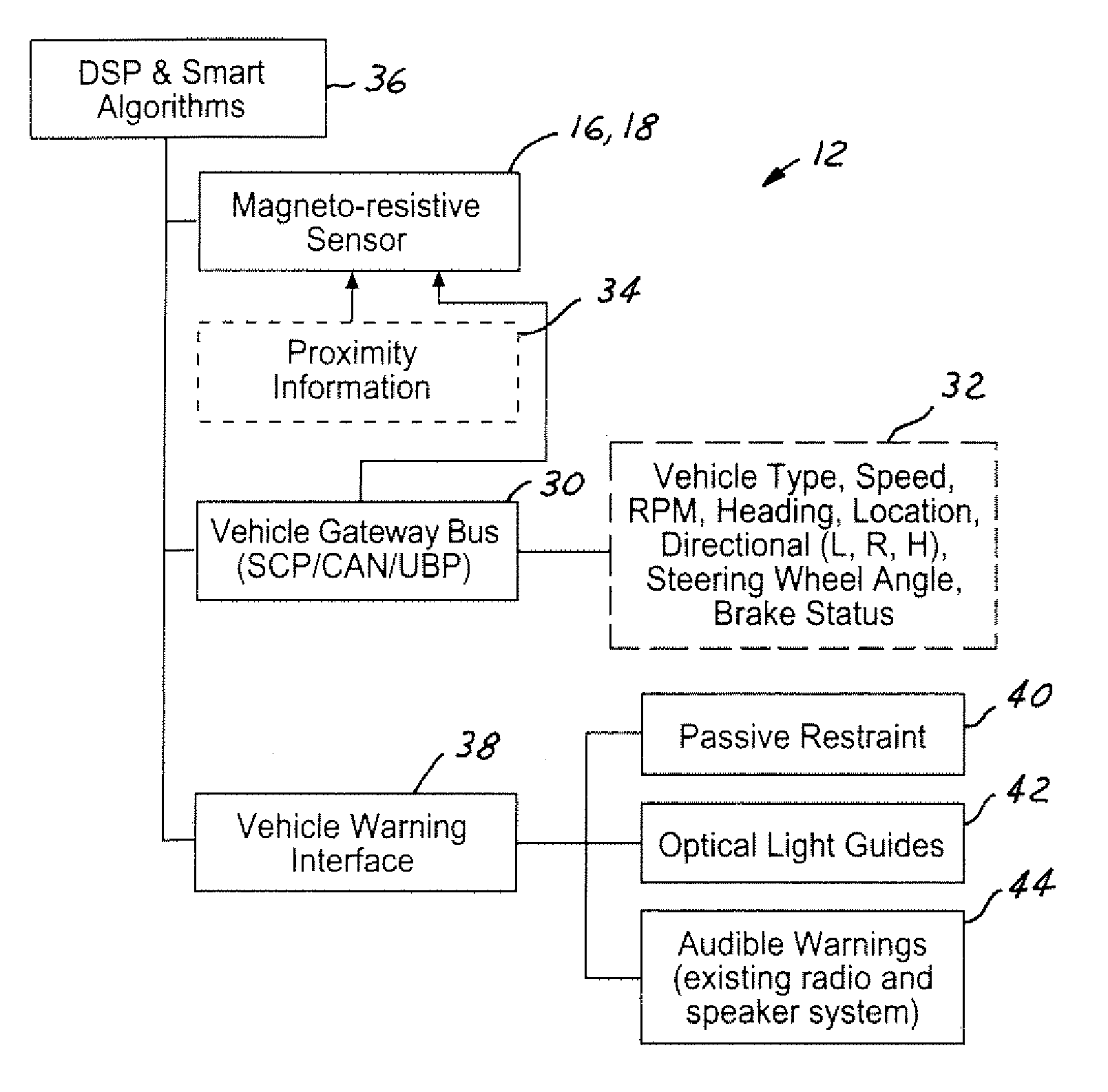
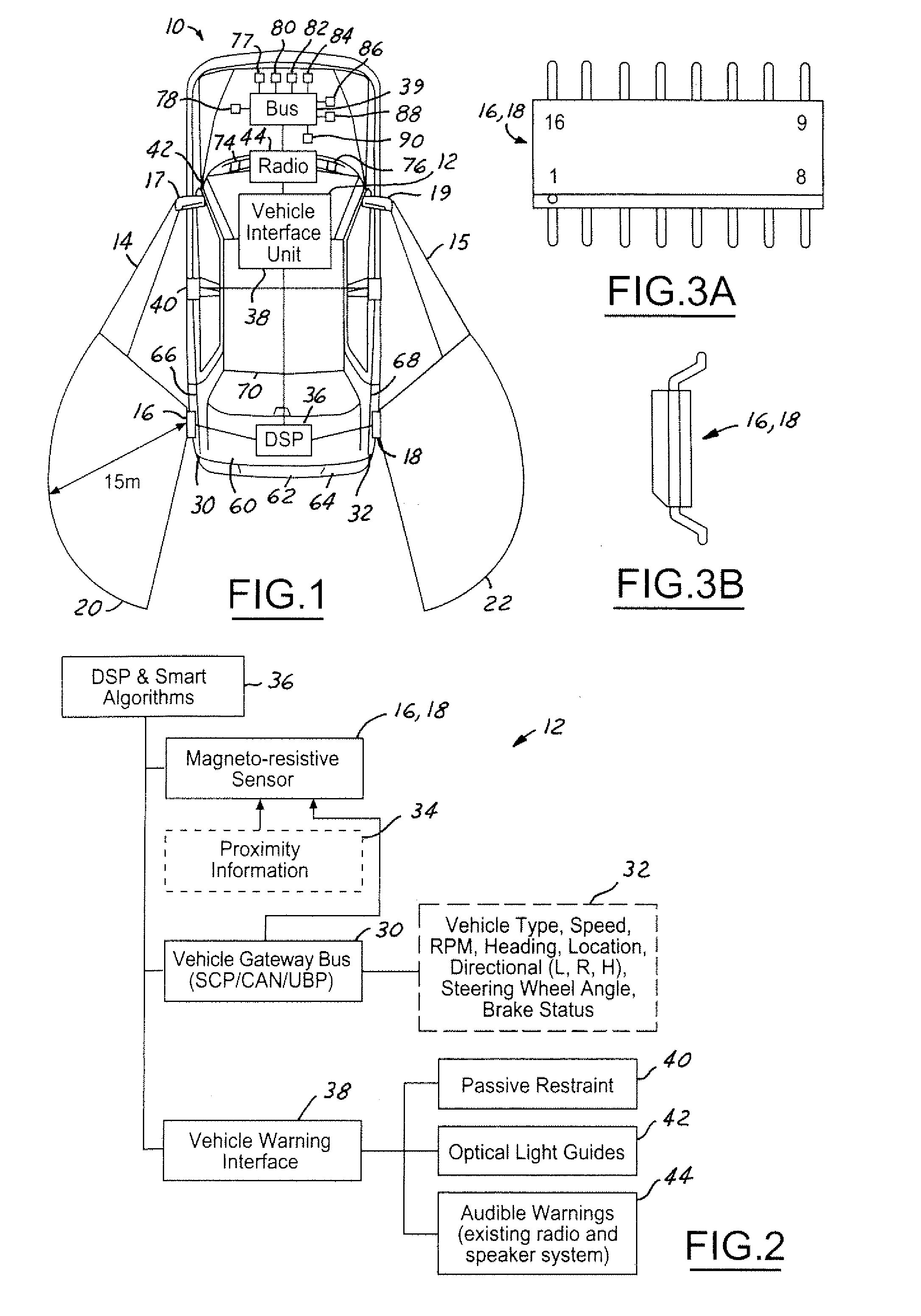
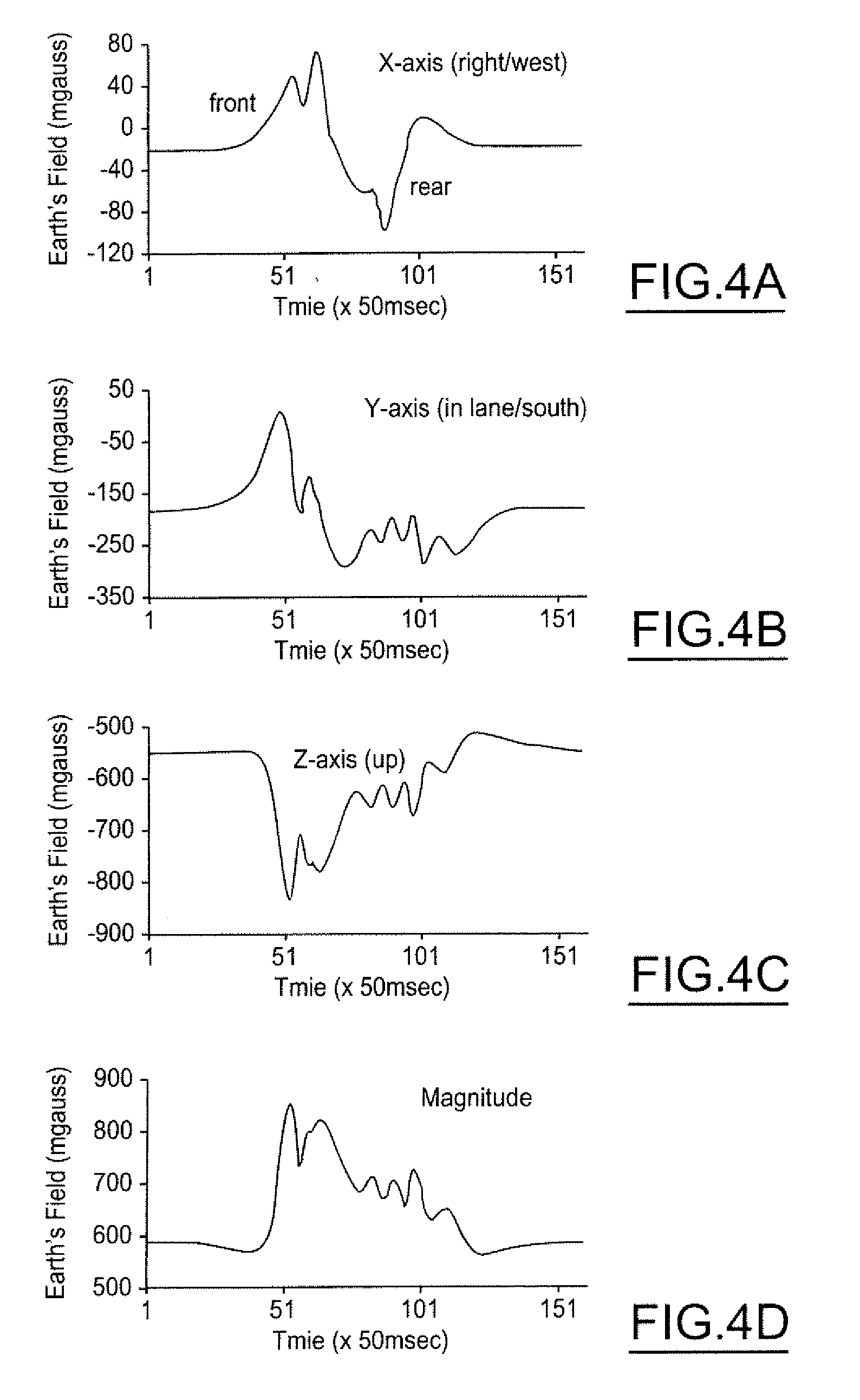
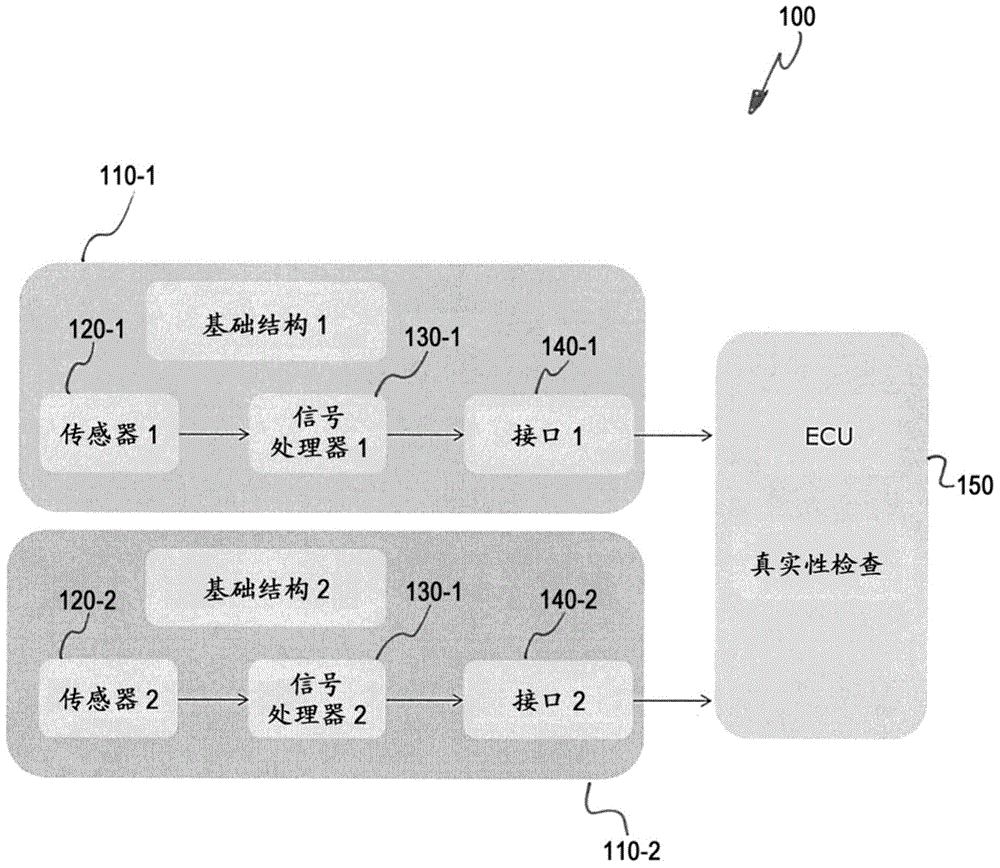
A host vehicle system includes a blind-spot warning system providing an indication to the host vehicle a target vehicle entering a blind-spot. The system includes a vehicle bus receiving various vehicle control signals, magneto-resistive sensors receiving proximity information as a function of magnetic field variations, a smart algorithm controller analyzing bus signals and sensor signals, and various vehicle collision systems such as passive restraints, optical light guides, and audible warnings operating in response to a threat from a target vehicle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
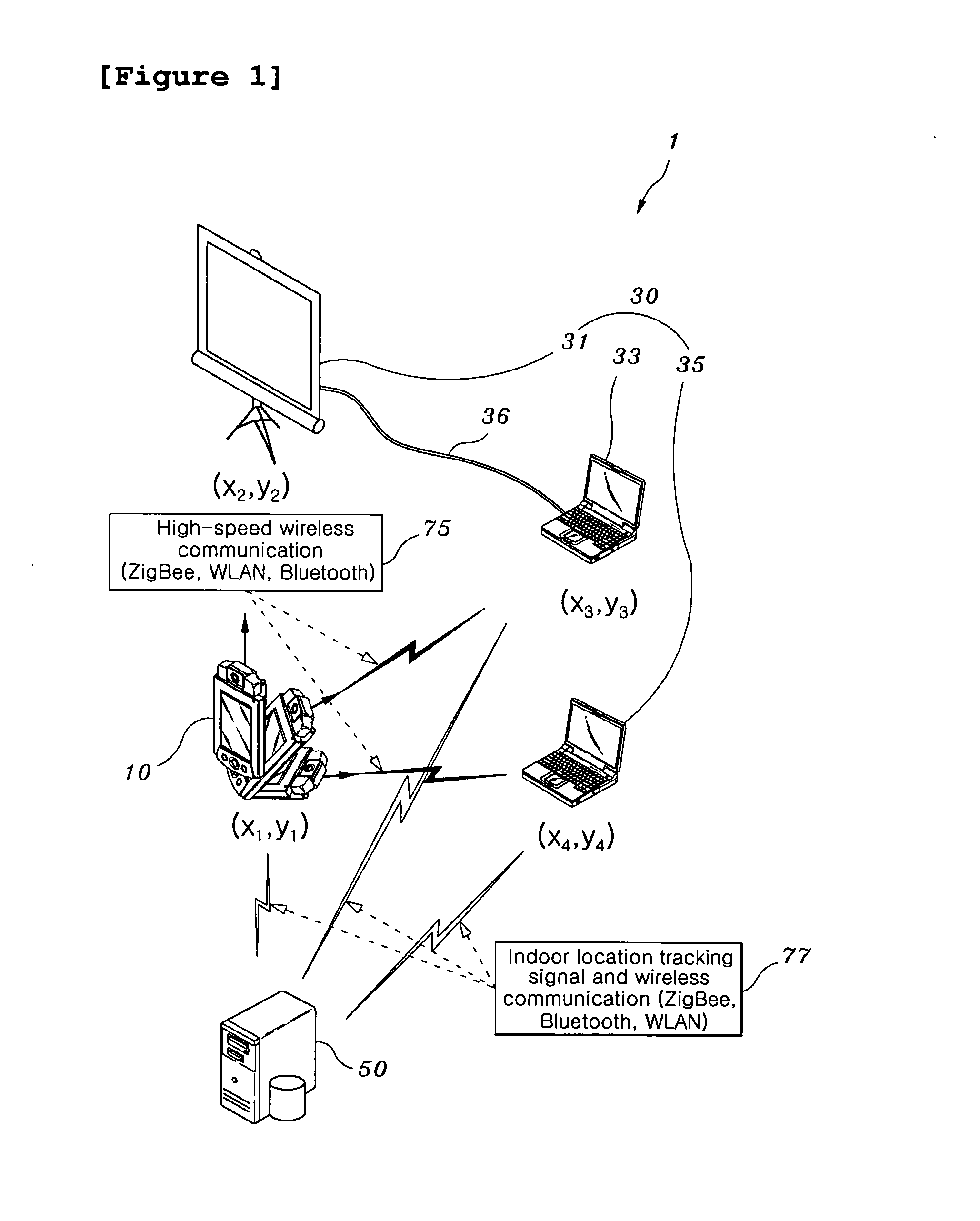
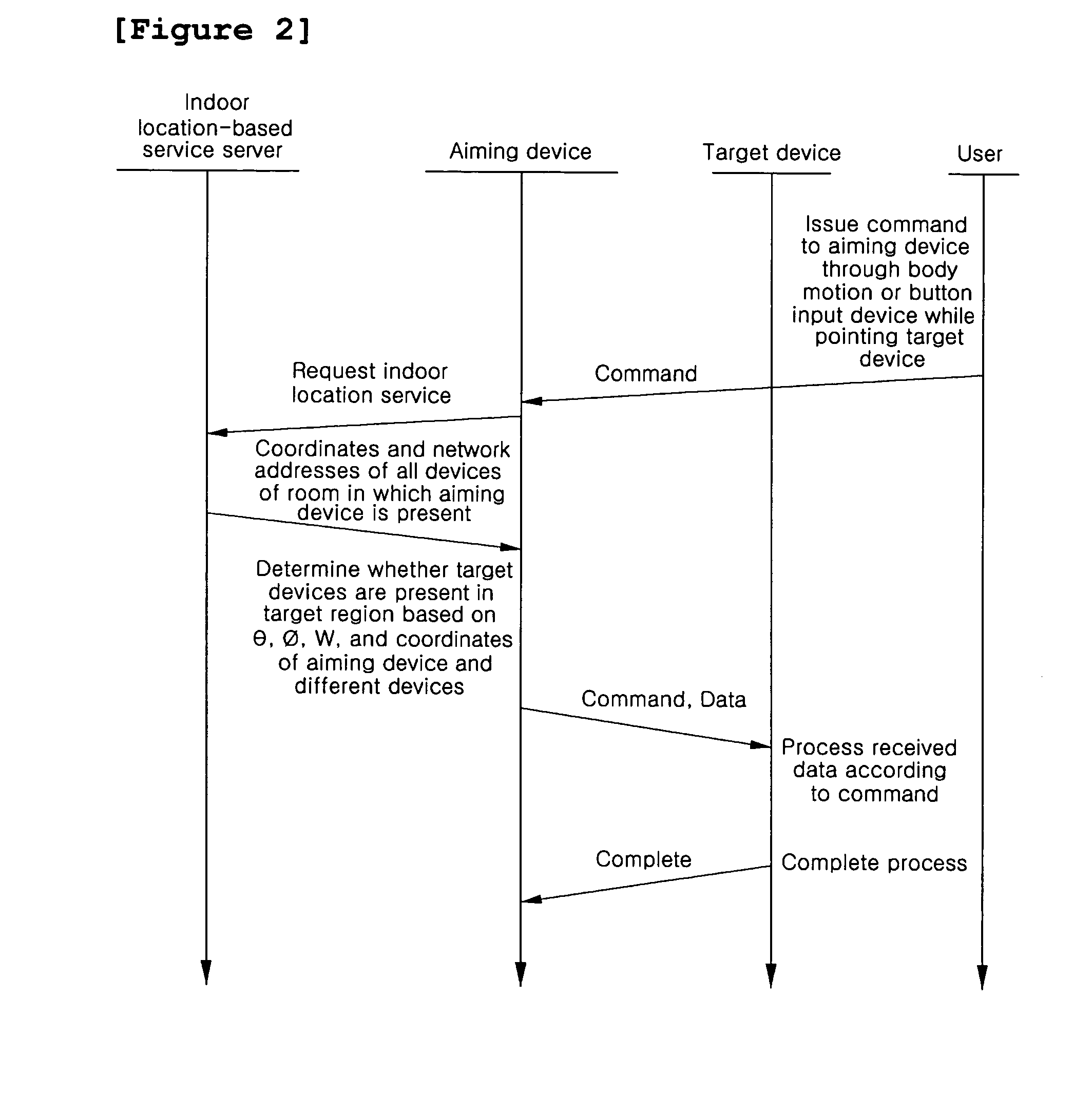
Intuitive real spatial aiming-based system, identification and communication methods using the same
InactiveUS20070066323A1Simple remote controlSimplify spacePosition fixationSubstation equipmentResistive sensorsLocation tracking
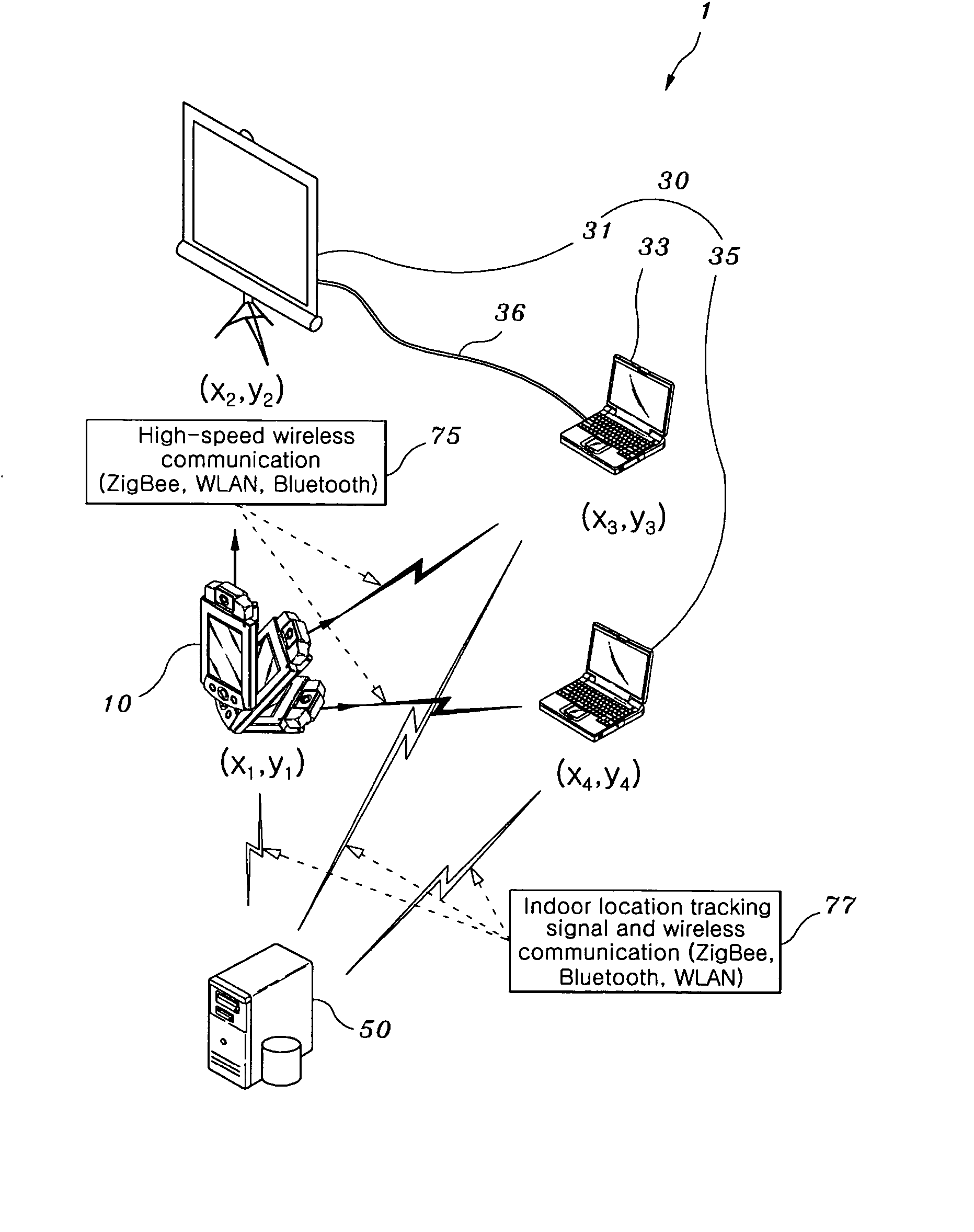
An intuitive real spatial aiming-based system, and identification and communication methods using the intuitive real spatial aiming-based system. The intuitive real spatial aiming-based system includes aiming device, target devices and an indoor location-based service server. The aiming device includes a mobile computer or a Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), which is provided with a first high-speed wireless communication means, a first location tracking sensor, and an electronic compass having a magneto resistive sensor for detecting a direction. The target devices each includes a fixed computer, a home appliance, a PDA, or a mobile communication terminal, which is selectively provided with second high-speed wireless communication means and a second location tracking sensor. The indoor location-based service server tracks the indoor locations and coordinates of the aiming device and the target devices in real time. To tolerate sensor's error, this patent presents an angle-based target region, a width-based target region, and a combination of the two regions.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Optical force sensor
InactiveUS20070014490A1Less potential damageReduce contact frictionForce measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionResistive sensorsEngineering
A force sensor particularly suited for use in an electronic stylus that senses the contact force on its nib for recording pen strokes and handwriting recognition. The sensor has a housing for a load bearing member for receiving an input force to be sensed and associated circuitry for converting the input force into an output signal indicative of the input force. The bearing member is movably mounted within the elongate body (up to 100 microns). The input force acting on the load bearing member is caused by contact on the nib. The load bearing member is biased against the direction of the input force. The force sensor also has a light source and photo-detector for sensing levels of illumination from the light source. Associated circuitry converts a range of illumination levels sensed by the photo-detector into a range of output signals, so that the illumination level sensed by the photo-detector varies with movement of the load bearing member within the elongate body such that the output signal from the circuitry is indicative of the input force. Using an optical sensor avoids the need to use a delicate piezo-resistive sensor that requires careful tolerancing during production.
Owner:LIVESCRIBE
Monitoring physiological condition of a subject
InactiveUS20130165809A1Cheap, non invasive, accurate, small and disposableImprove securityRespiratory organ evaluationTelemetric patient monitoringResistive sensorsElectrical resistance and conductance
A system for monitoring breathing of a subject, the system comprising: (a) a wearable subject unit comprising: an elastic resistive sensor positionable such that breathing motion of the subject applies mechanical pressure to said elastic resistive sensor, wherein said elastic resistive sensor is configured to change its resistance responsive to the mechanical pressure, and a transmitter configured to wirelessly transmit a signal based on the change in resistance of the elastic resistive sensor; and (b) a platform unit comprising a receiver and being positionable in wireless transmission range with said subject unit, said platform unit configured to receive said signal from said subject unit and to issue an advisory signal indicative of the breathing of the subject.
Owner:DIGISENSE
Sensors and probes for mapping electromagnetic fields
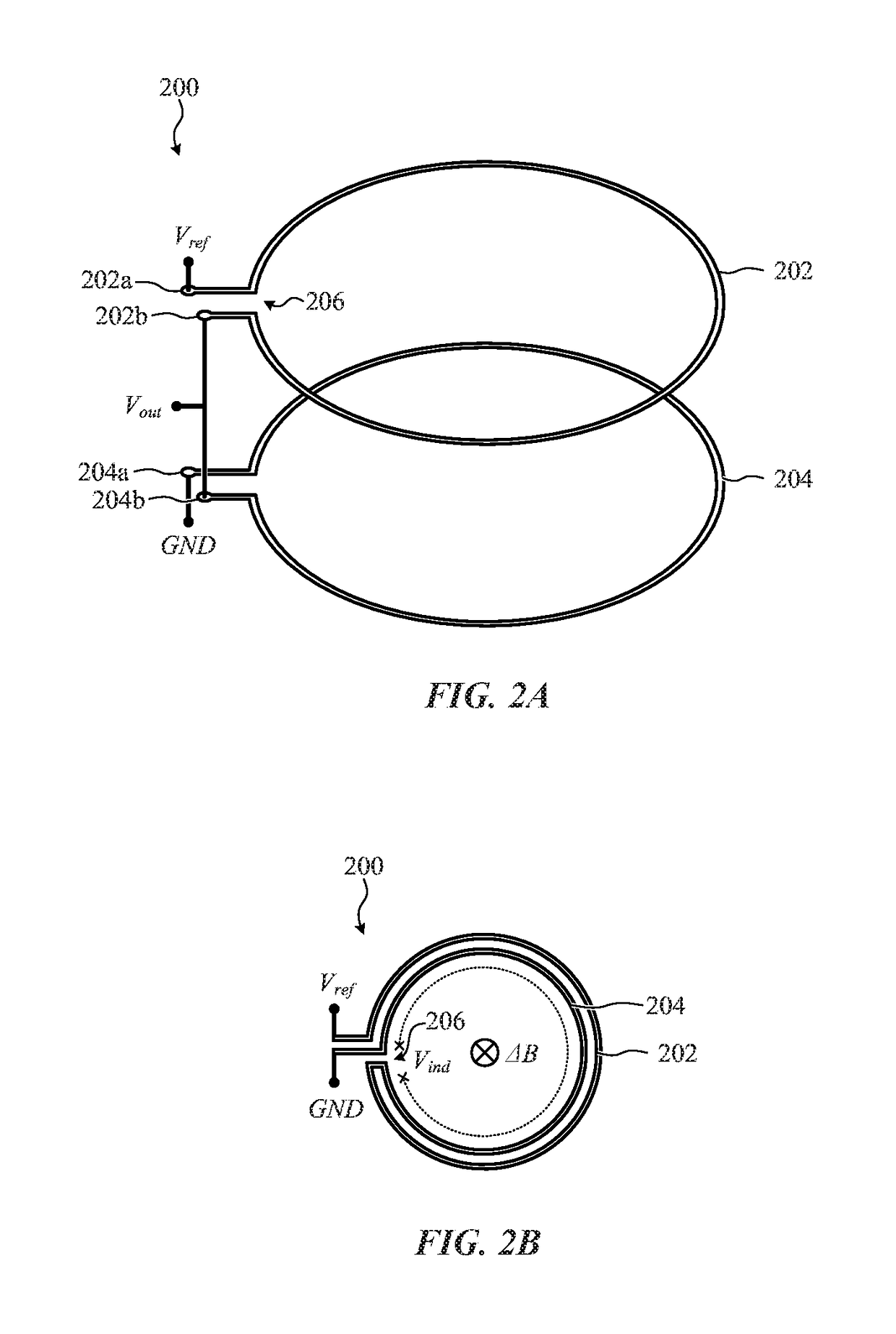
InactiveUS6933717B1Reduce areaHigh-resolution electromagnetic field mappingMagnetic property measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsResistive sensorsClassical mechanics
Products are disclosed for measuring electromagnetic fields. One embodiment has at least two coplanar magneto-resistive sensors. Each magneto-resistive sensor has a sensitive axis in the plane of the at least two coplanar magneto-resistive sensors. The at least two magneto-resistive sensors may be orthogonally arranged about a central point to measure orthogonal components of electromagnetic fields.
Owner:ALBANY INSTR
Use of magneto-resistive sensors for borehole logging
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
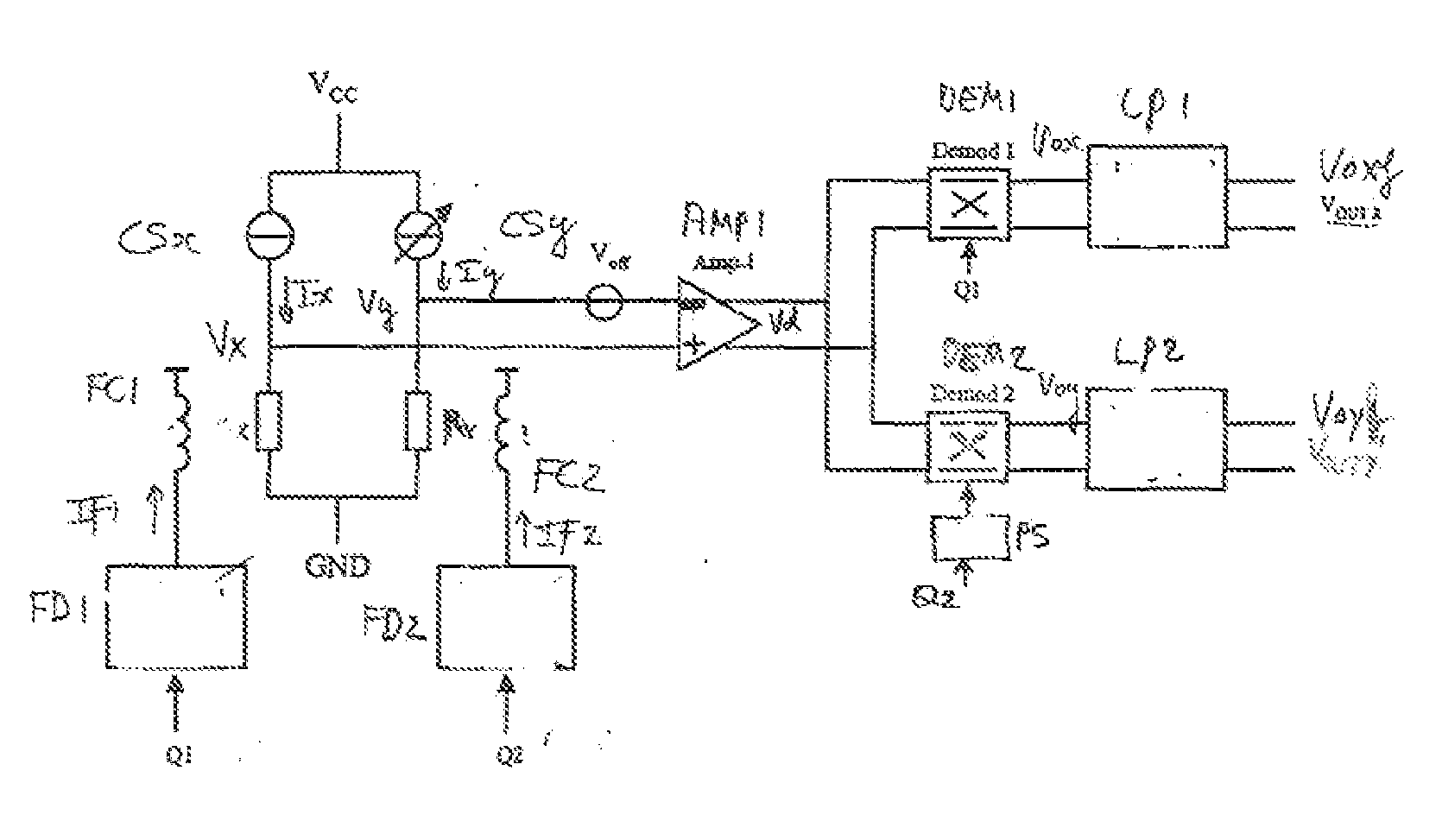
Magnetic field sensor circuit
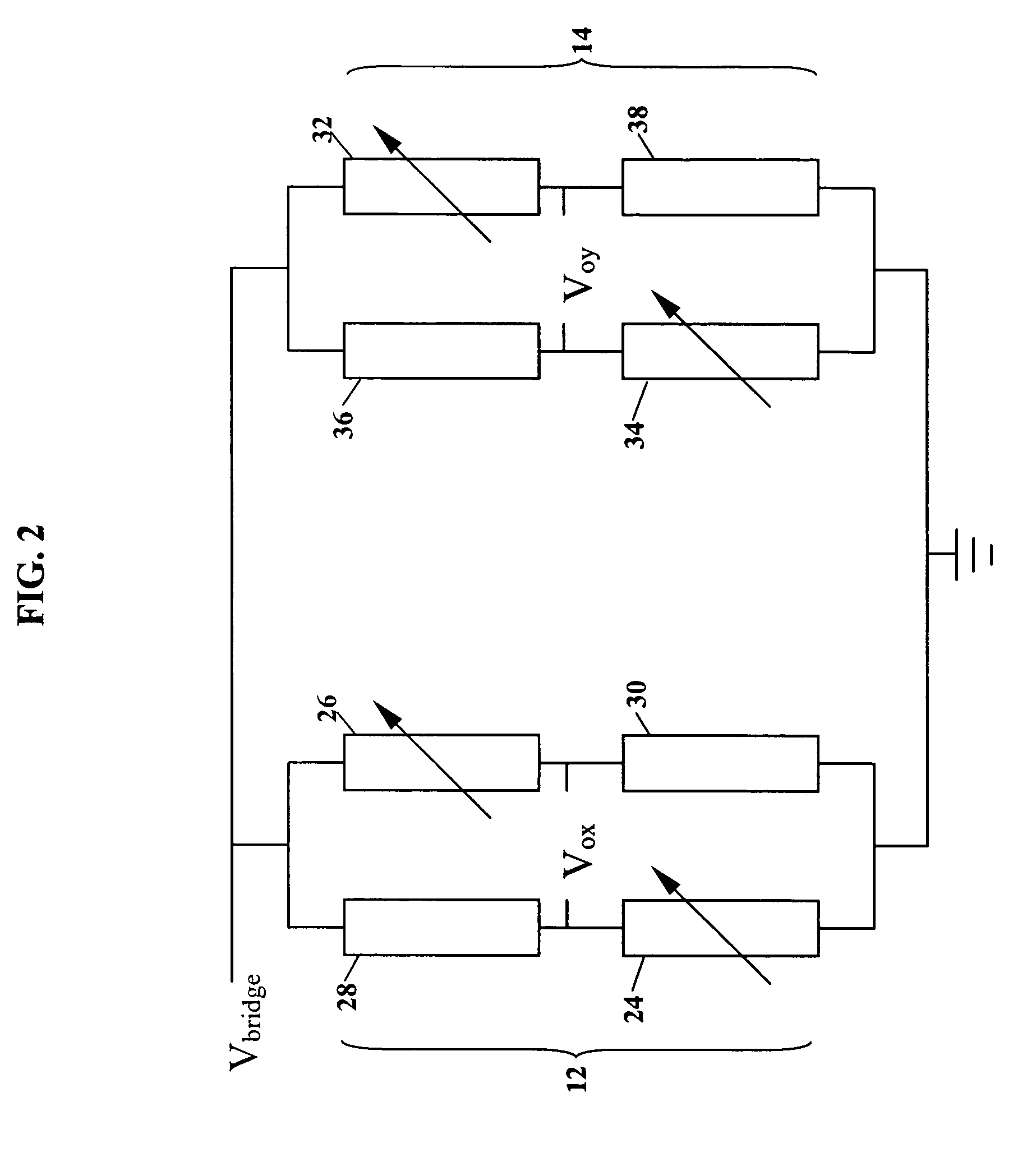
InactiveUS20100053789A1Improve performanceLess spaceNanomagnetismRecord information storageResistive sensorsPhase shifted
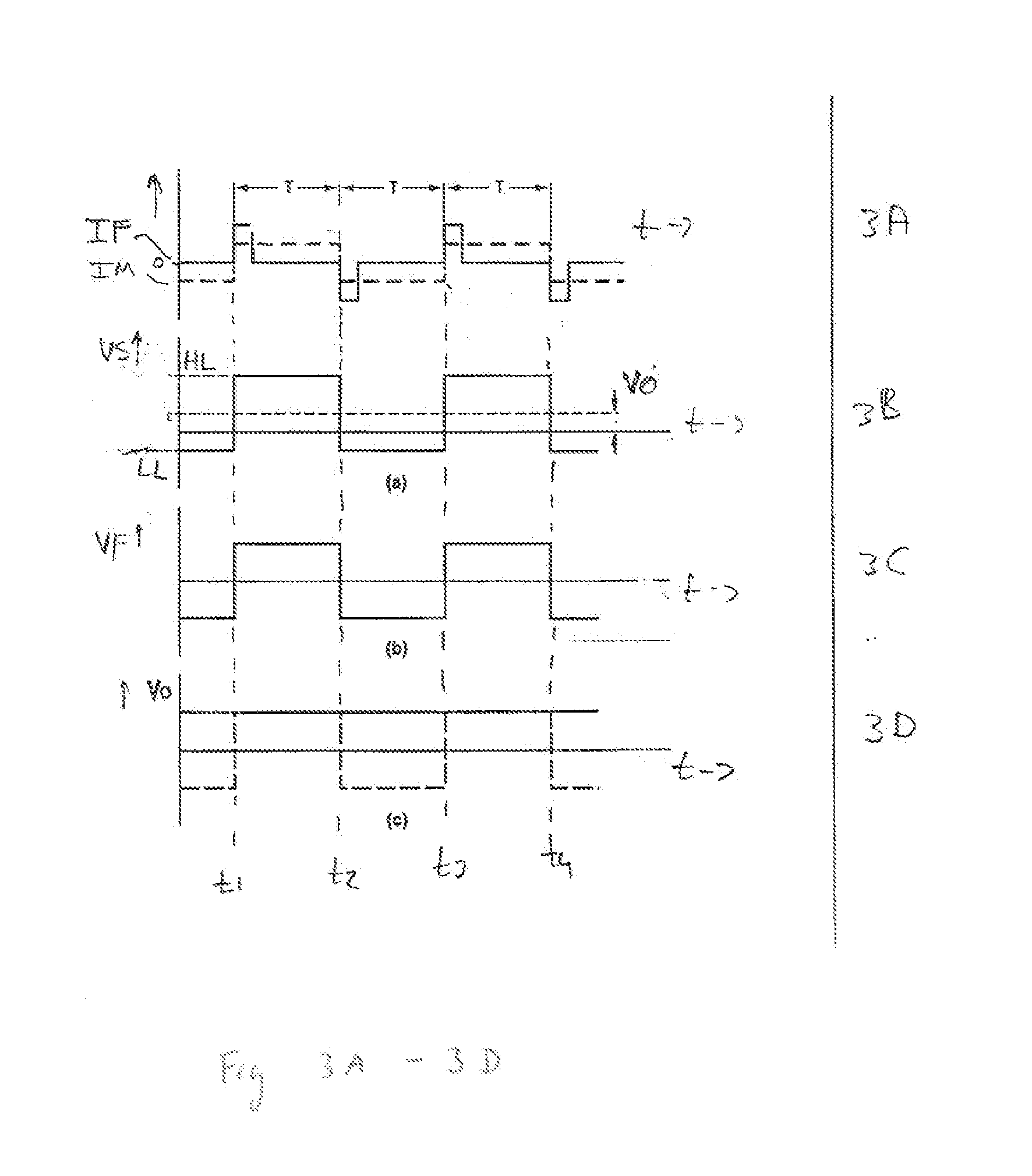
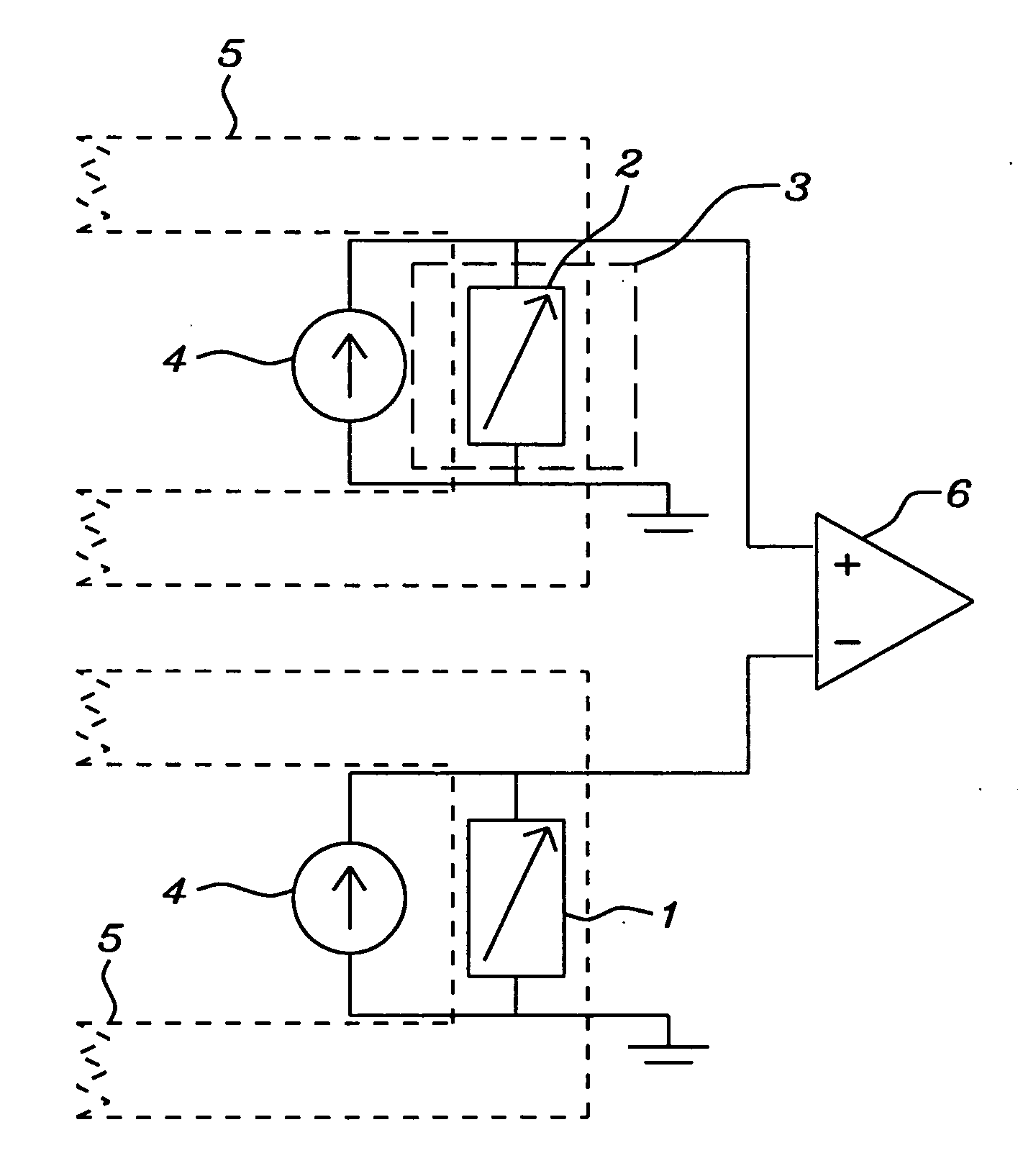
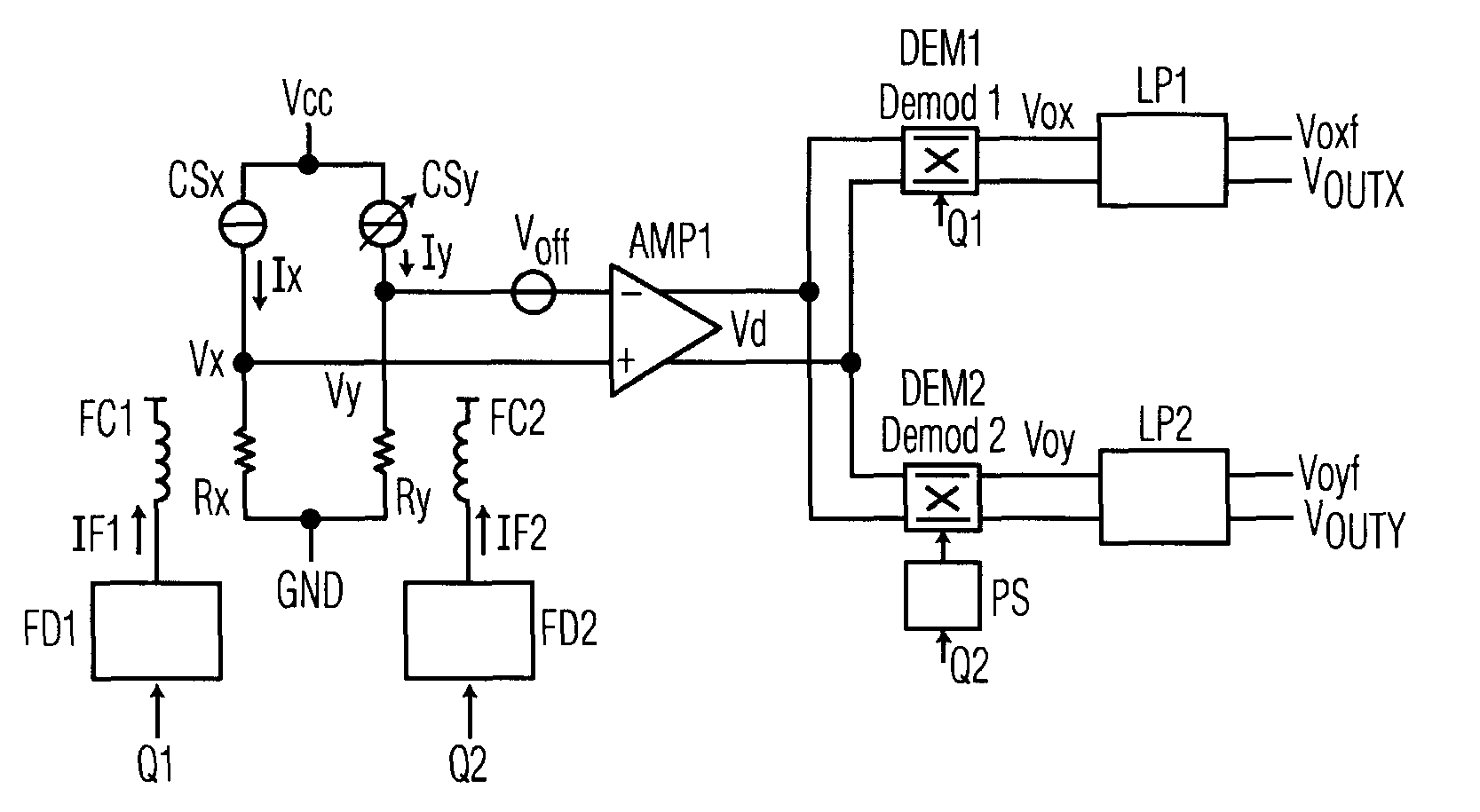
A magnetic field sensor circuit comprises a first magneto-resistive sensor (Rx) which senses a first magnetic field component in a first direction to supply a first sense signal (Vx). A first flipping coil (FC1) applies a first flipping magnetic field with a periodically changing polarity to the first magneto-resistive sensor (Rx) to cause the first sense signal (Vx) to have alternating different levels synchronized with the first flipping magnetic field. A second magneto -resistive sensor (Ry) senses a second magnetic field component in a second direction different than the first direction to supply a second sense signal (Vy). A second flipping coil (FC2) applies a second flipping magnetic field with a periodically changing polarity to the second magneto -resistive sensor (Ry) to cause the second sense signal (Vy) to have an alternating different levels synchronized with the second flipping magnetic field. The first flipping magnetic field and the second flipping magnetic field have a phase shift. A differential amplifier (AMP1) receives the first sense signal (Vx) and the second sense signal (Vy) to obtain a difference signal (Vd). A first synchronous demodulator (DEM1) receives the difference signal (Vd) and a first switching signal (Q1) being phase locked to the alternating different levels of the first sense signal (Vx) to supply a first output signal (Vox) indicating the first magnetic field component. A second synchronous demodulator (DEM2) receives the difference signal (Vd) and a second switching signal (Q2) being phase locked to the alternating different levels of the second sense signal (Vy) to supply a second output signal (Voy) indicating the second magnetic field component.
Owner:TITAN INTELLIGENCE TECH LTD
Systems, articles, and methods for electromyography sensors
Systems, articles, and methods for surface electromyography (“EMG”) sensors that combine elements from traditional capacitive and resistive EMG sensors are described. For example, capacitive EMG sensors that are adapted to resistively couple to a user's skin are described. Resistive coupling between a sensor electrode and the user's skin is galvanically isolated from the sensor circuitry by a discrete component capacitor included downstream from the sensor electrode. The combination of a resistively coupled electrode and a discrete component capacitor provides the respective benefits of traditional resistive and capacitive (respectively) EMG sensor designs while mitigating respective drawbacks of each approach. A wearable EMG device that provides a component of a human-electronics interface and incorporates such capacitive EMG sensors is also described.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Magneto-resistance based nano-scale position sensor
ActiveUS20100085041A1NanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsResistive sensorsMagnetic reluctance
A position sensor and method include a magnetic component, a first magneto-resistive sensor disposed in proximity to the magnet / coil; and a second magneto-resistive sensor disposed in proximity to the magnetic component and the first magneto-resistive sensor. The first magneto-resistive sensor and second magneto-resistive sensor are configured to sense changes in a stray magnetic field created by the magnetic component in accordance with a relative positional change between the magnetic component and the first and second magneto-resistive sensors.
Owner:IBM CORP
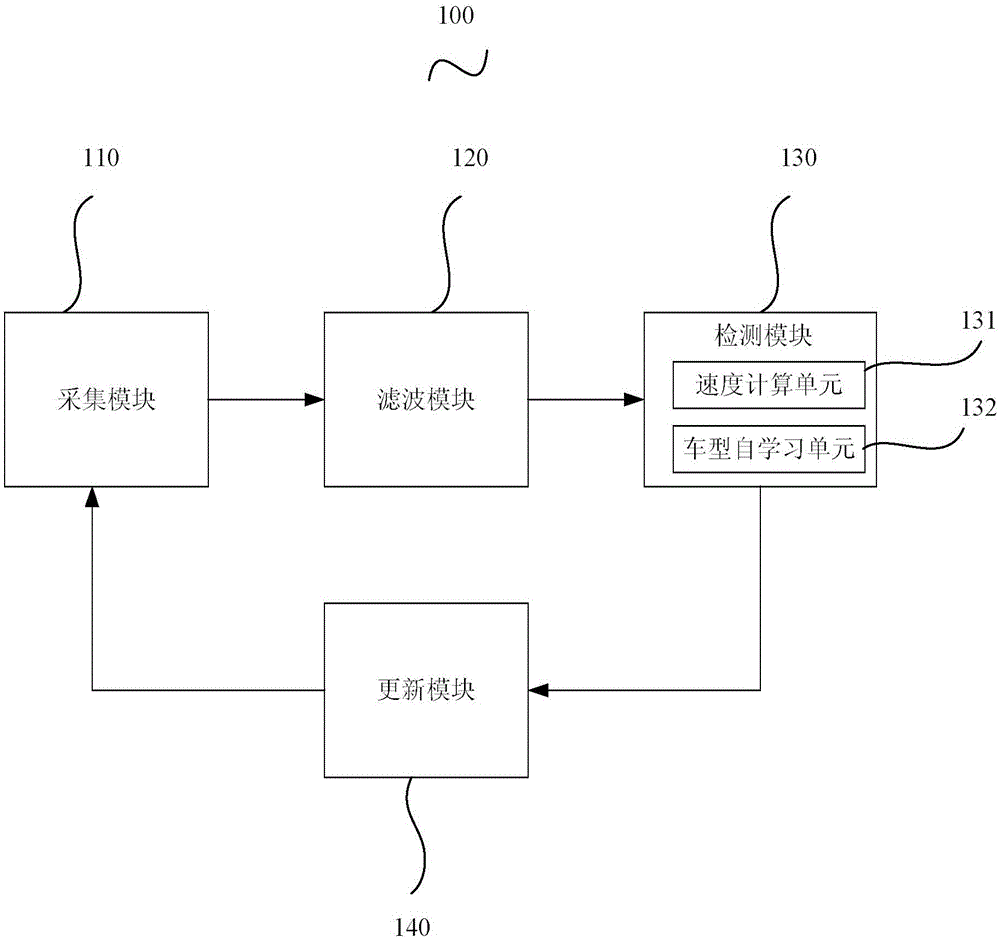
Road vehicle detection system and method
InactiveCN105096611AImprove detection accuracyAchieve precision measurementRoad vehicles traffic controlResistive sensorsEngineering
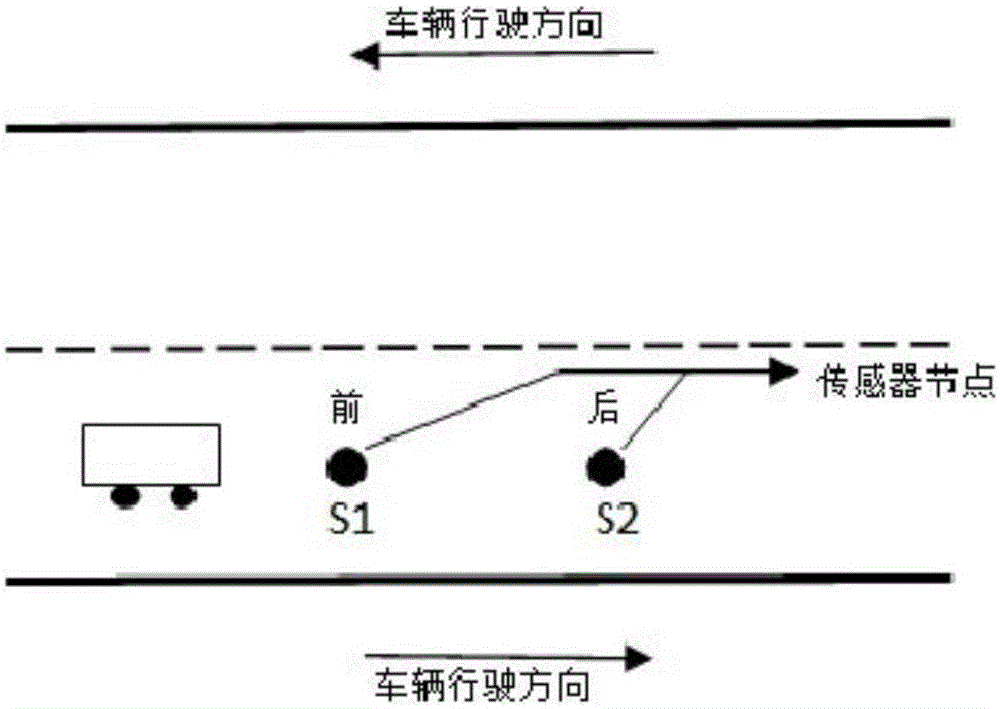
The invention provides a road vehicle detection system and method. An acquisition module acquires a three-dimensional geomagnetic signal in real time, a filter module filters the three-dimensional geomagnetic signal, and a detection module calculates the difference between the filtered three-dimensional geomagnetic signal and a reference line data and judges a vehicle state according to an algorithm model and X, Y and Z-axis geomagnetic values, so that the vehicle detection precision is effectively improved, and the defect of inaccuracy when the vehicle state is only judged by means of a threshold is overcome; and according to the road vehicle detection system, on the basis of vehicle detection, the acquisition module is designed into a subnet composed of a magneto-resistive sensor node and a routing node, and the running time and speed of a vehicle are detected in real time according to the routing node, so that vehicle flow, speed and vehicle model can be detected.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHENGSHENGYUAN IND
Method and apparatus for detecting presence of vehicle using a magnetic sensor employing a magneto-resistive effect
ActiveUS7427931B1Less sensitive to noiseImprove reliabilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficResistive sensorsSensor node
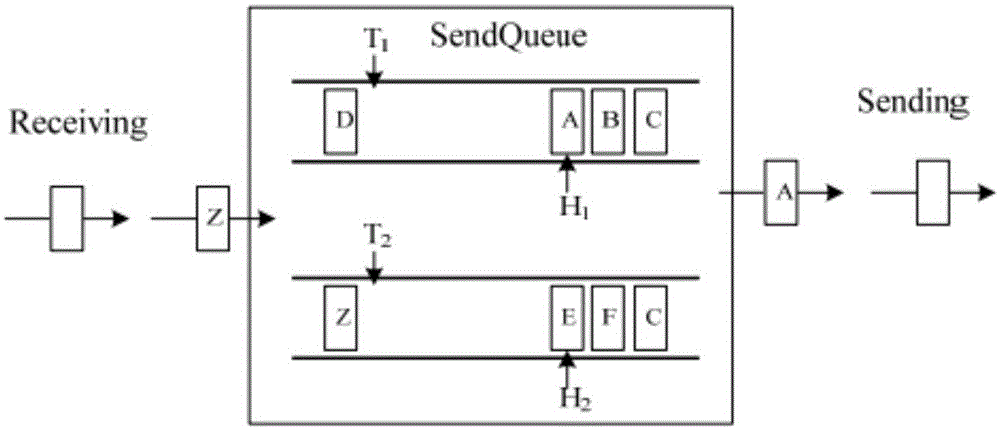
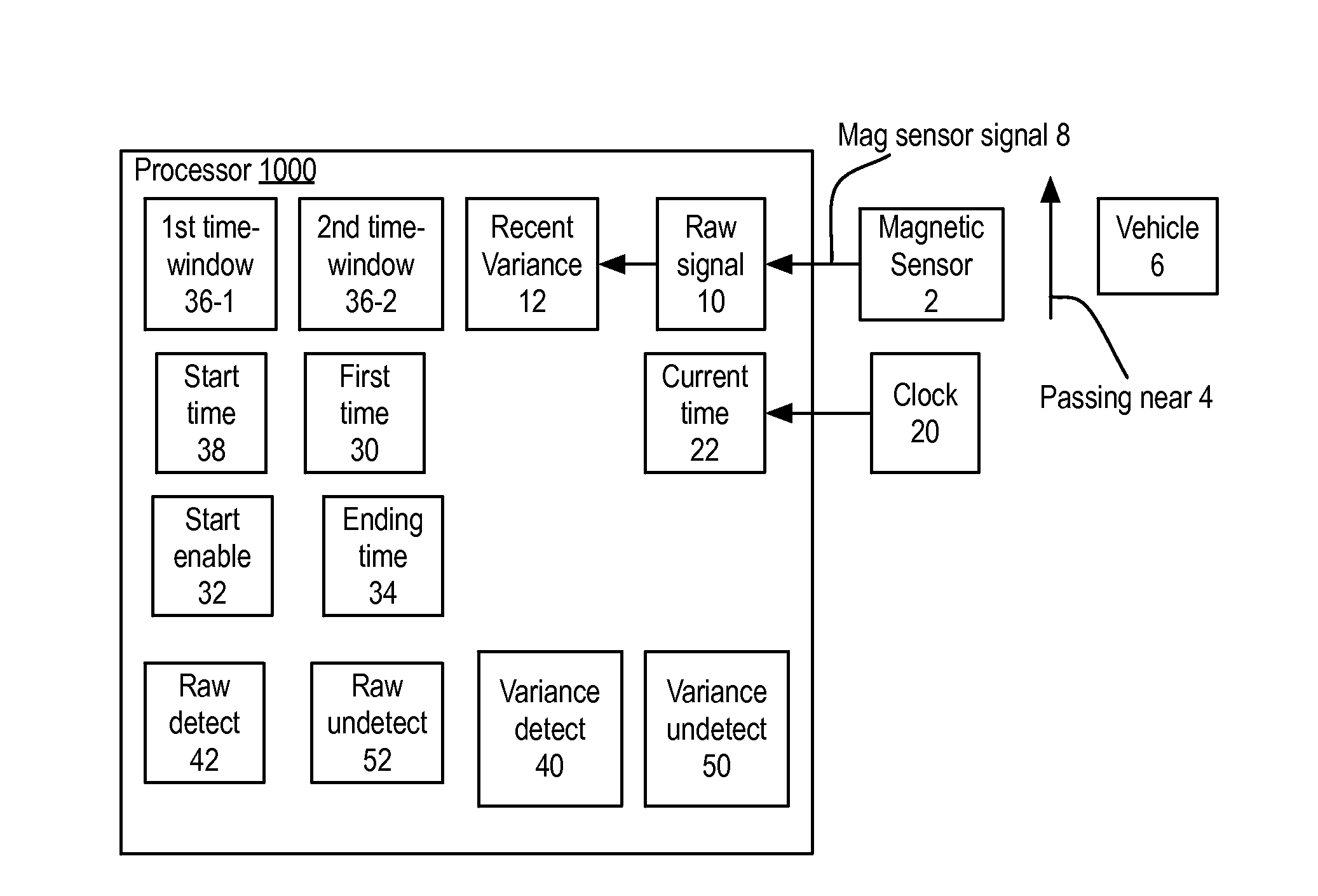
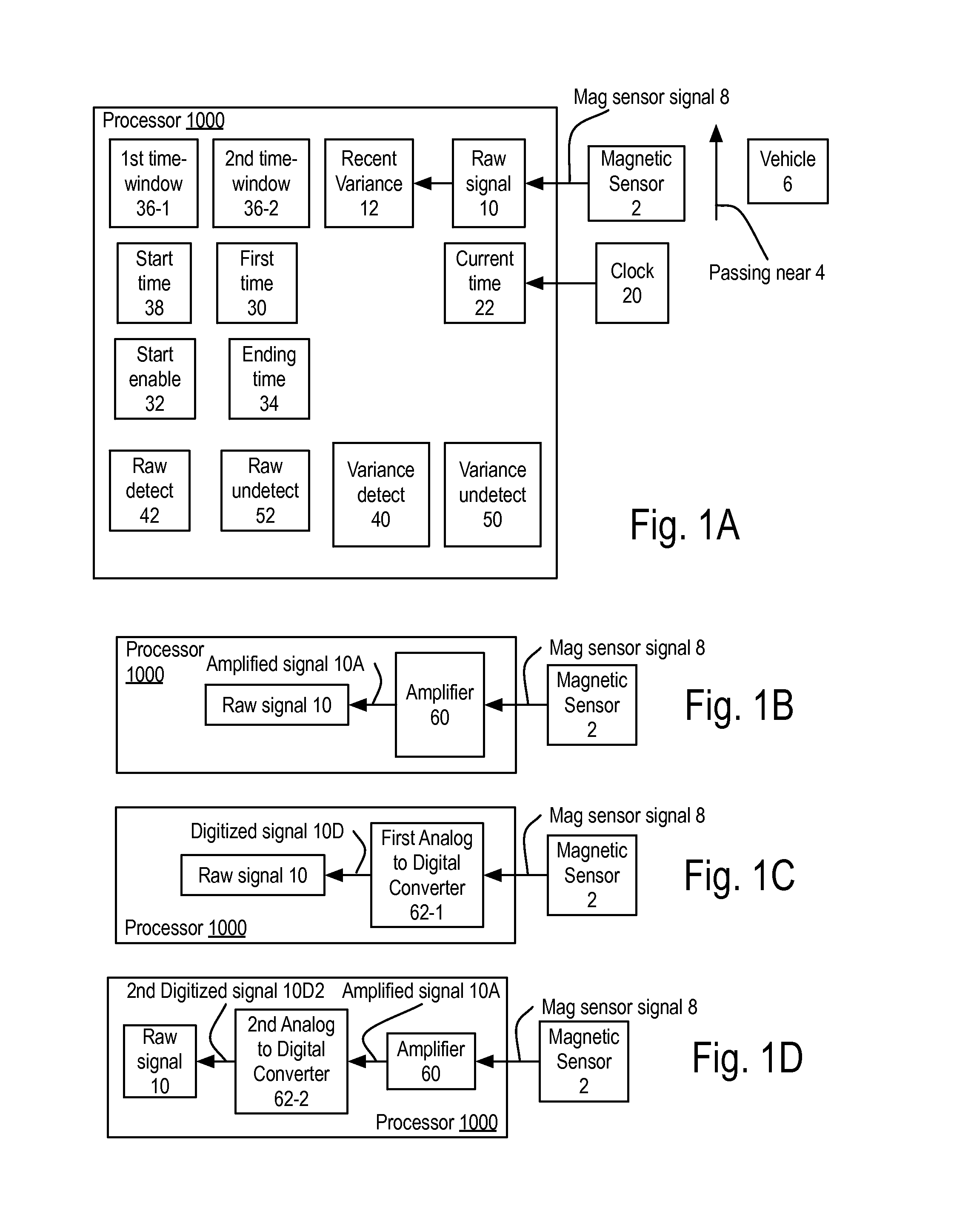
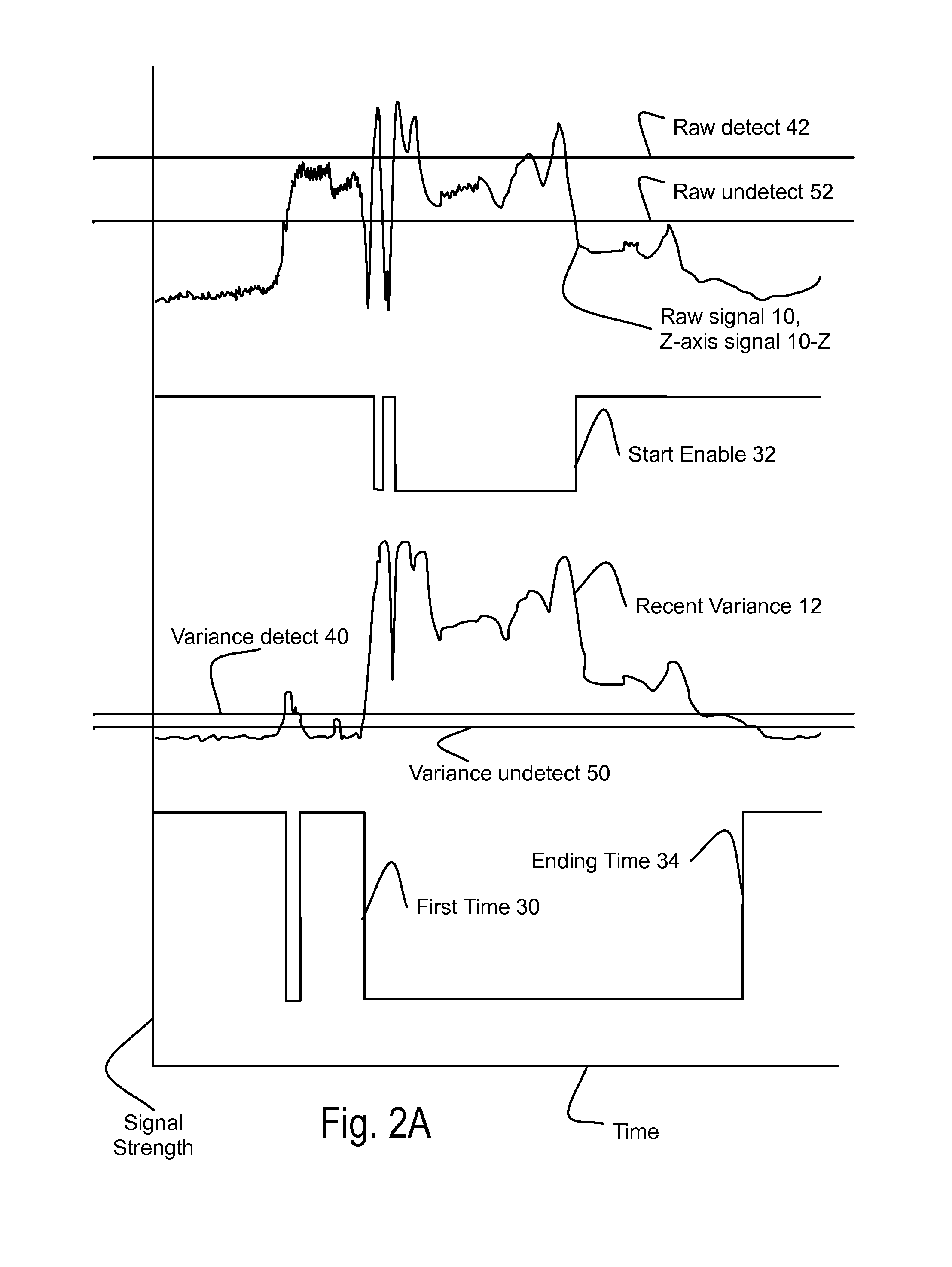
Method using raw signal from magneto-resistive sensor through the use of recent variance (RV) of raw signal (RS) for first-capture of first time RV crosses variance detect, second-capture start enable for first time when RS crosses above raw detect and RV above variance detect, third-capture ending time when RS crosses below raw undetect and RV below variance undetect. Starting and ending times are products of the process, often used for traffic flow counts. Apparatus supporting this method as a processor and / or a vehicular sensor node.
Owner:SENSYS NETWORKS
Isolated measurement circuit for sensor resistance
InactiveUS7592820B2Reliable indicationNo longer indicateBurglar alarm by openingResistance/reactance/impedenceResistive sensorsElectrical conductor
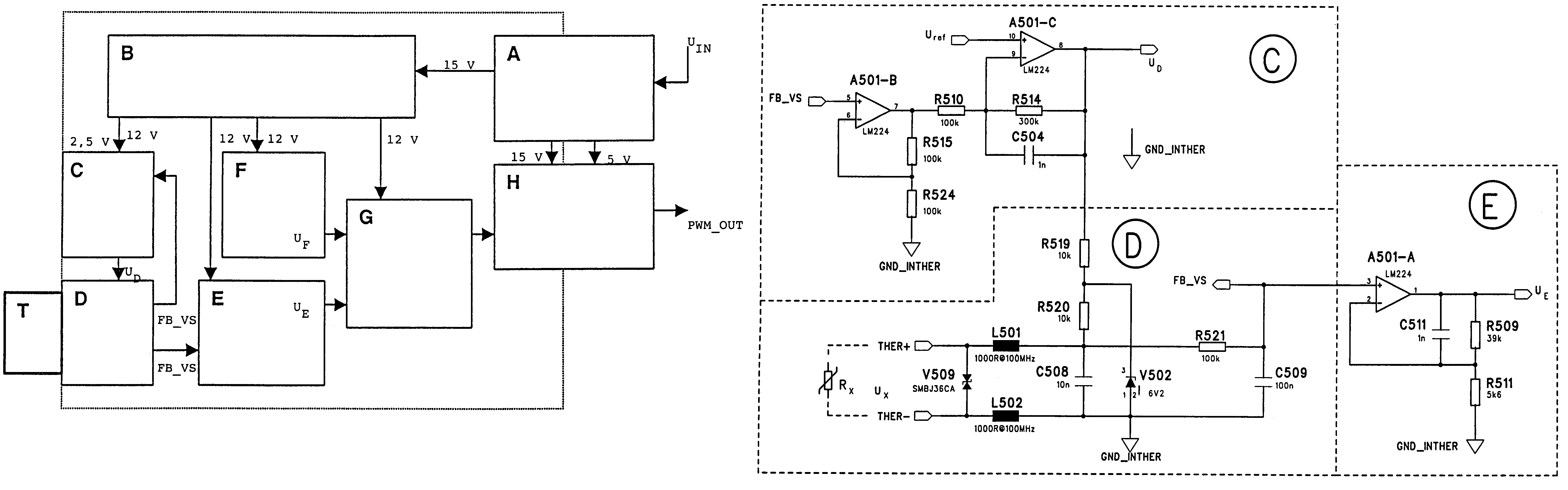
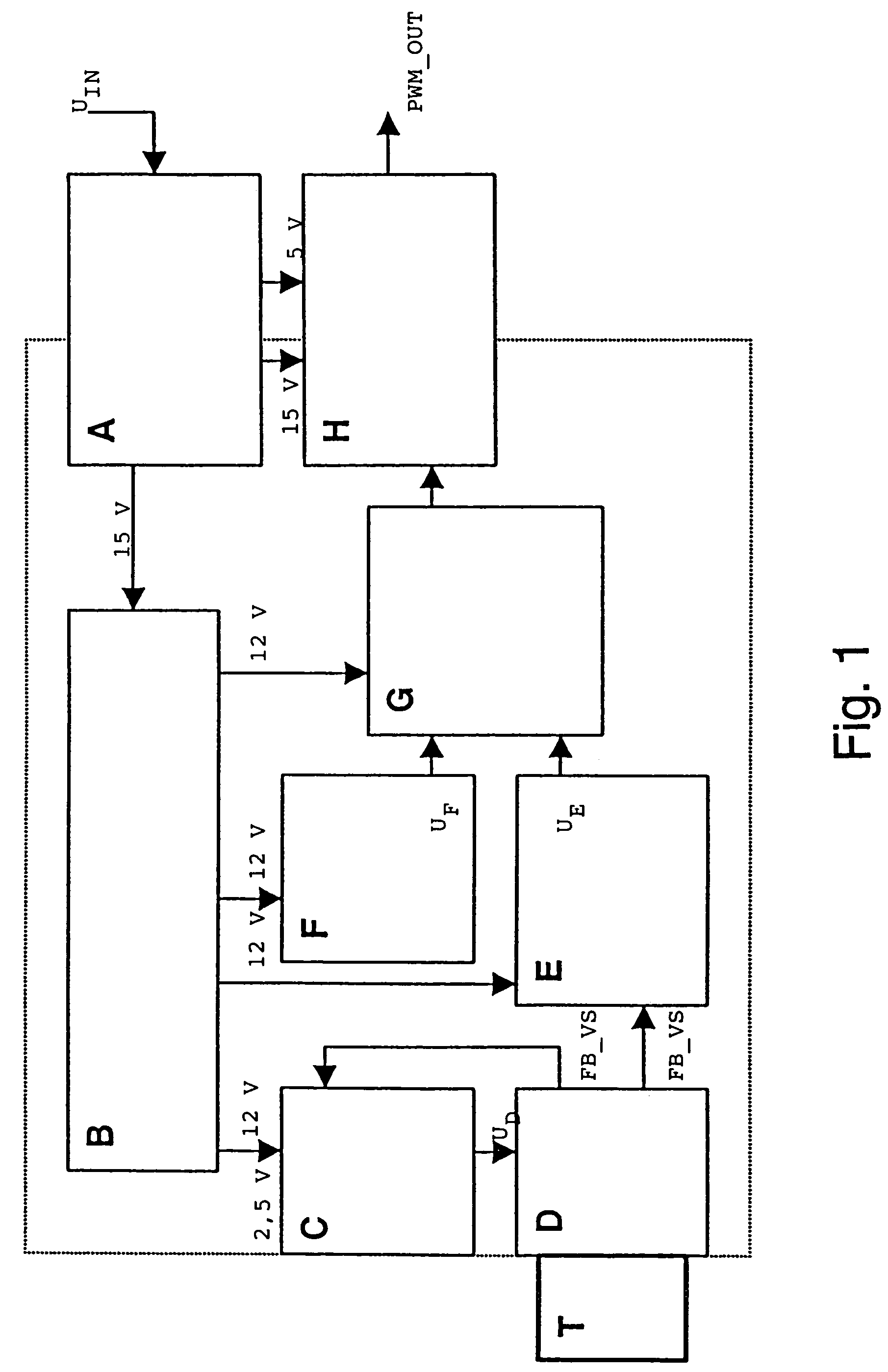
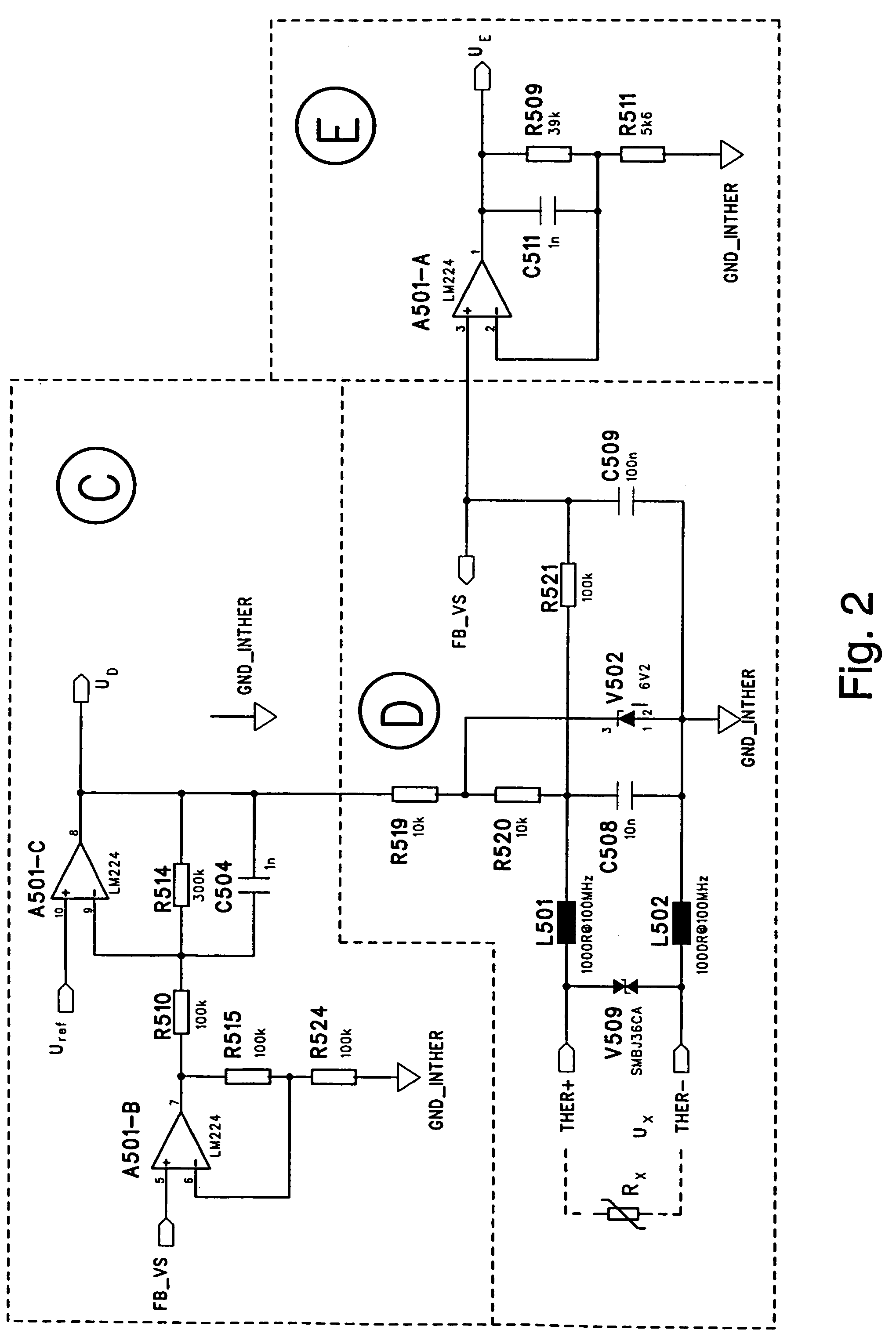
A circuit and method is disclosed for measuring the resistance of a resistive sensor, such as a PTC or NTC temperature sensor used for monitoring the temperature of the windings of an electric motor. The measurement circuit is based on an electronic circuit in which conductors from a sensor located in the object to be monitored are connected to an amplifier circuit in a feedback configuration that reduces the DC level supplied to the voltage divider when the sensor resistance increases. The measured signal is amplified and, using a comparator to compare it with the output voltage of a sawtooth generator, a continuous PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal is generated and transmitted in digital format to a SELV electronic circuit, for example through an opto-isolator. The essentially logarithmic signal amplification makes it possible to reliably distinguish between a short circuit in the sensor circuit and low values of sensor resistance.
Owner:ABB OY
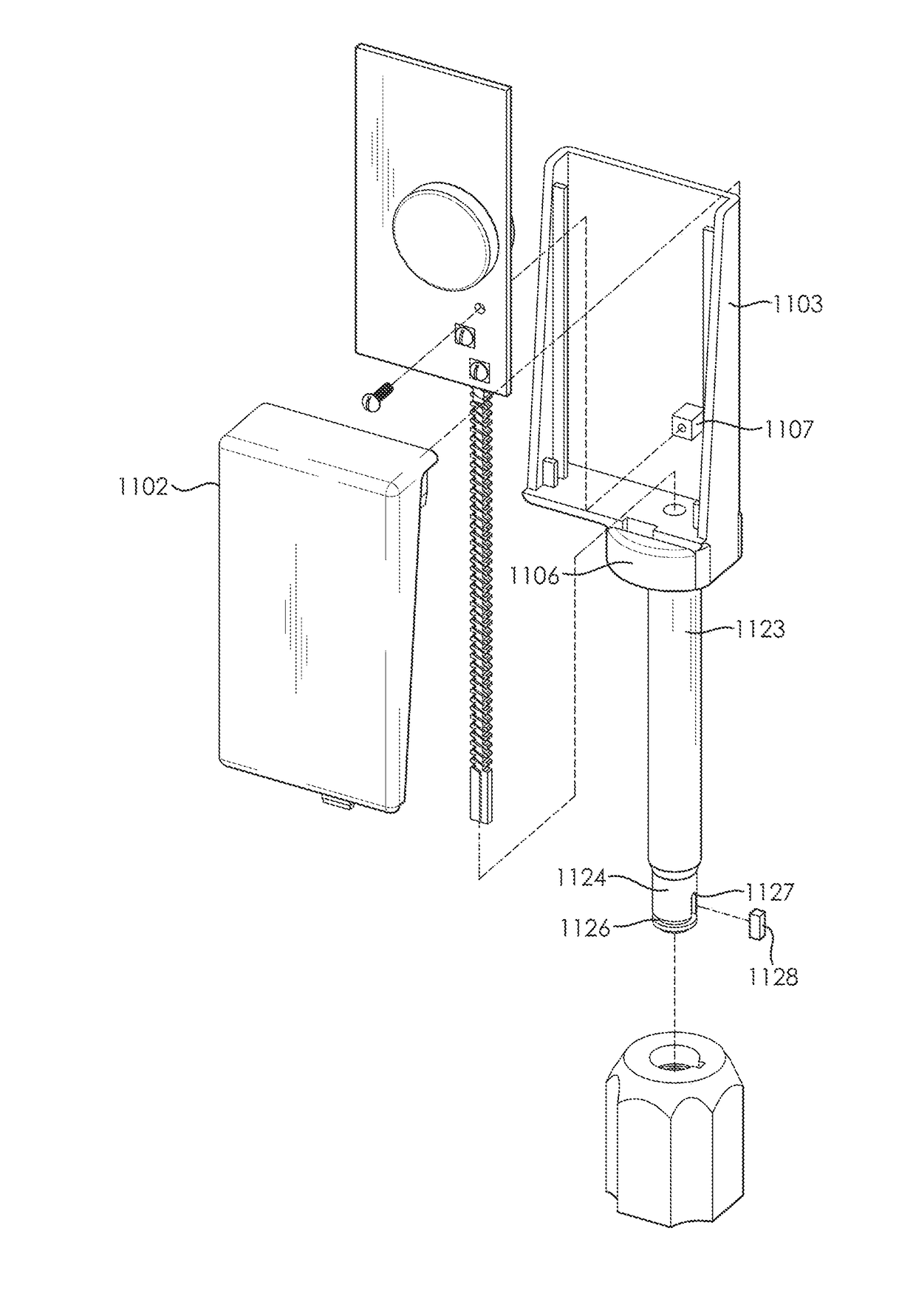
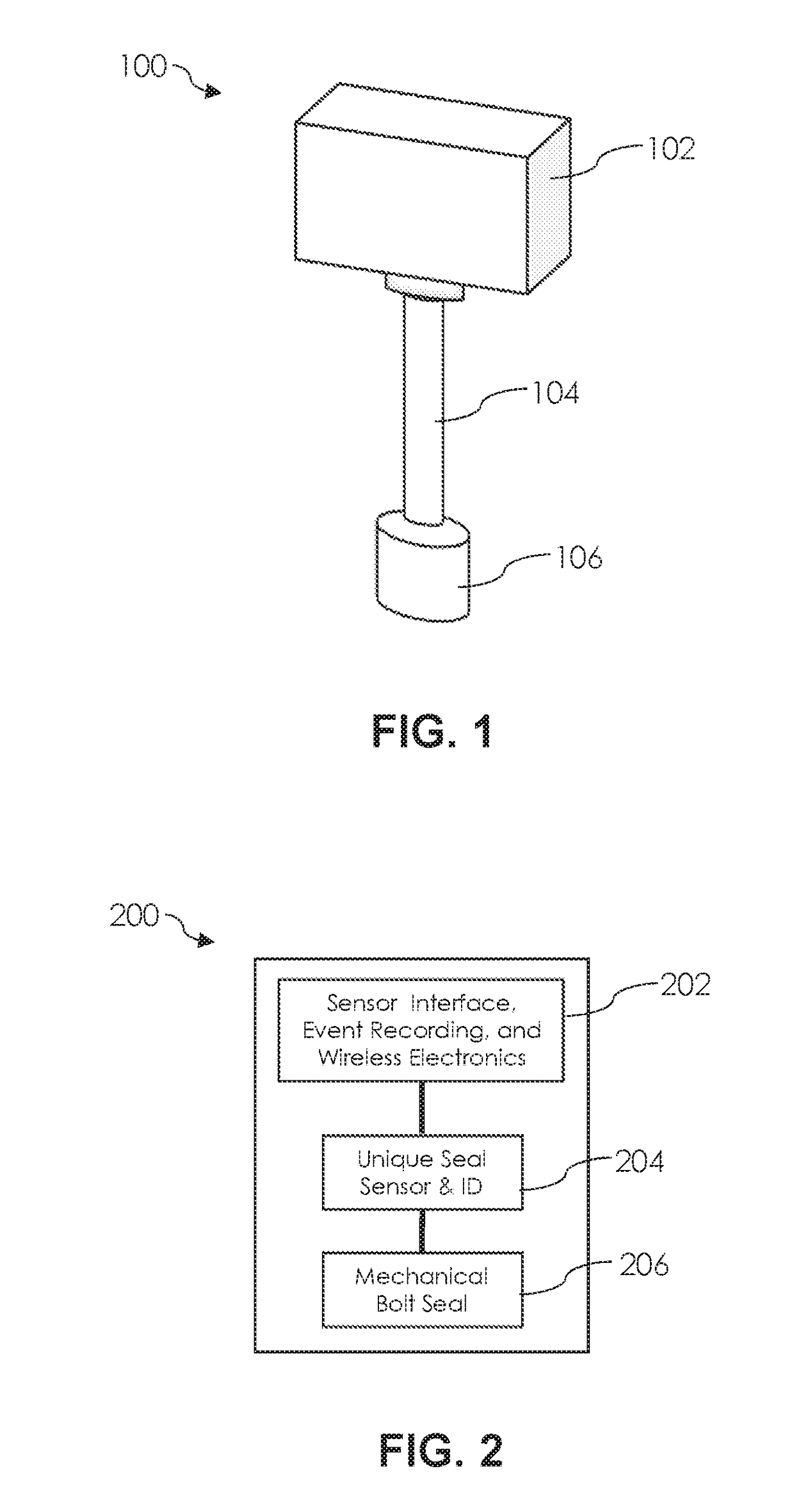
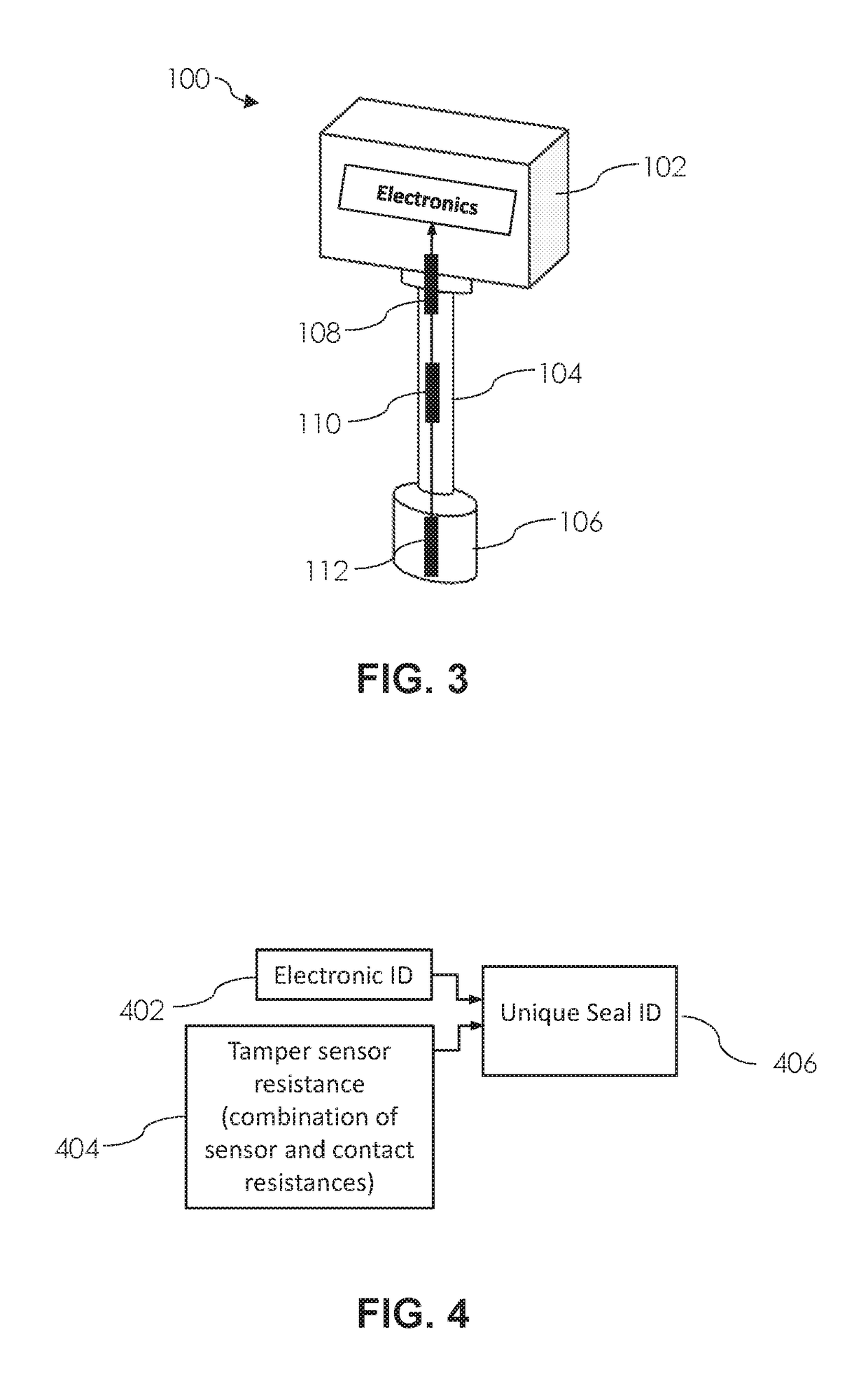
Tamper-proof electronic bolt-seal
ActiveUS20170103683A1Low costEasy to installBurglar alarm with fastening tamperingStampsElectrical resistance and conductanceTamper resistance
A tamper-proof bolt-seal incorporating a unique identification tamper detection sensor that cannot be restored or duplicated after the bolt. The sensor employs a resistive sensor wire embedded in the bolt. The resistive sensor wire has a randomized length to enable a unique resistive value for that sensor. The resistive value of the sensor is combined with an electronic identification code to create the unique seal identification for the tamper detection sensor, therefore giving the bolt a seal identification that is unique and that cannot be restored or duplicated.
Owner:EVIGIA SYST
Self-driven sensing system based on friction nano-generator
ActiveCN106949912ASolve power problemsImprove adaptabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsResistive sensorsMechanical energy
The invention provides a self-driven sensing system based on a friction nano-generator. The self-driven sensing system comprises the friction nano-generator for converting external mechanical energy into electrical energy to output an electrical signal to an external circuit; a resistive sensor directly connected to the friction nano-generator in order that the friction nano-generator supplies power to the resistive sensor for detecting a sensing signal; and an alarm connected in parallel with the resistive sensor and used for giving an acoustic and / or optical alarm signal when the sensing signal is greater than a signal threshold. The self-driven sensing system does not need any external power supply, solves the power supply of the sensor, improves the adaptability of Internet of Thing equipment, and is greatly reduced in size and weight. The system is greatly improved in terms of stability and controllability. The friction nano-generator and the sensor are separated from each other so that a friction material and a sensing material do not affect each other, thereby expanding a material selection range and achieving a practical application value.
Owner:苏州慧闻纳米科技有限公司
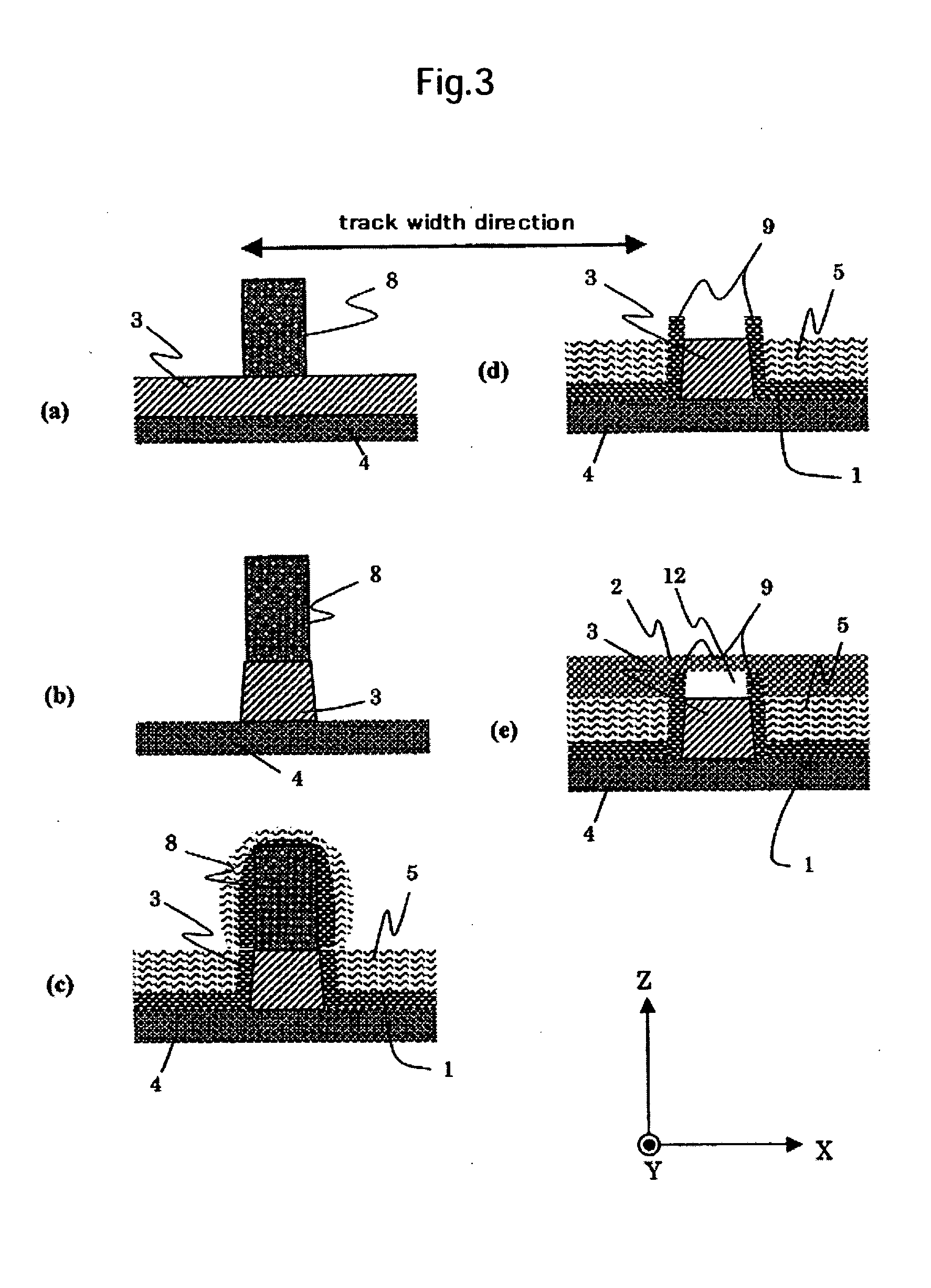
Magneto-resistive sensor with stopper layer and fabrication process
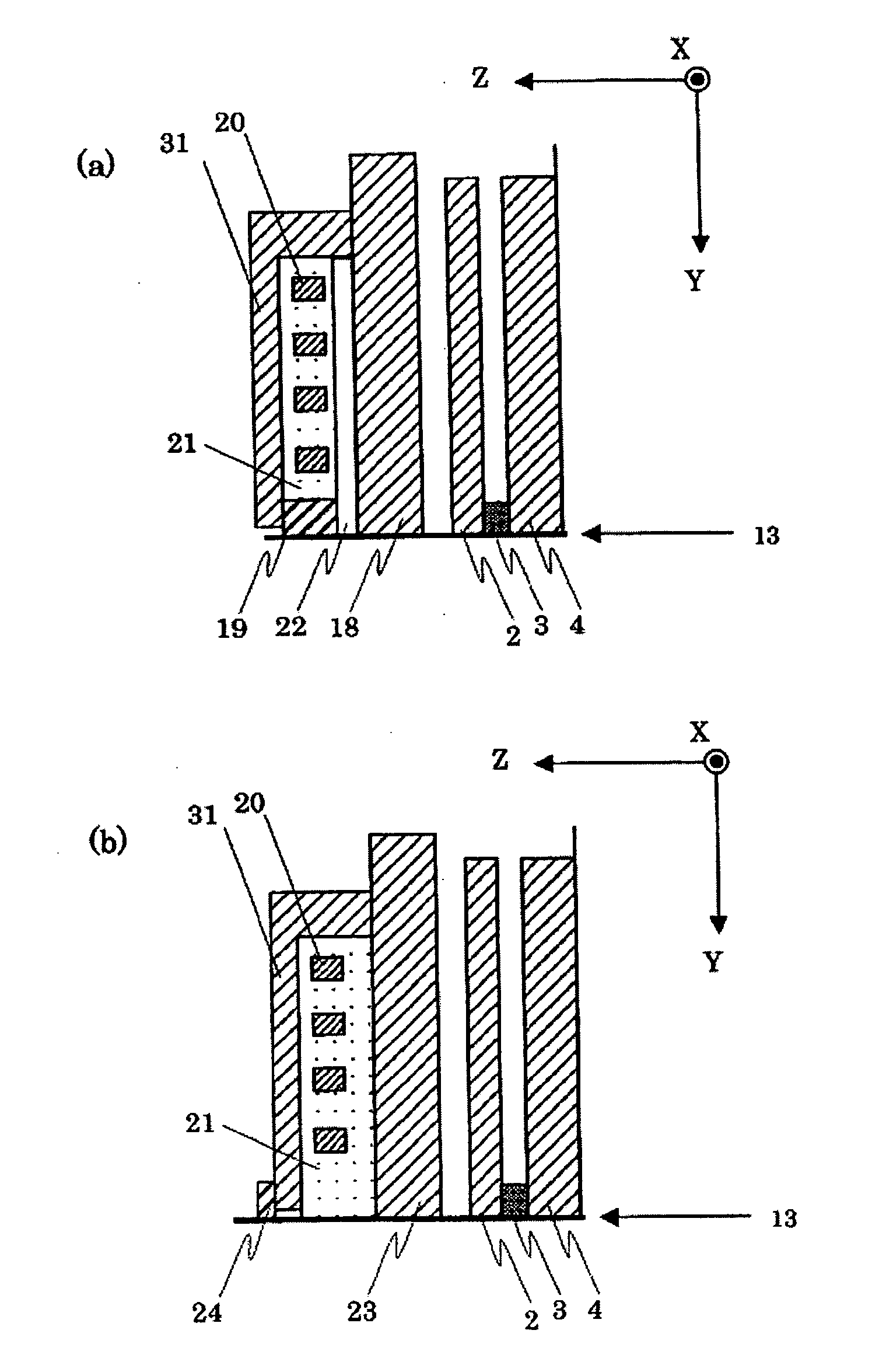
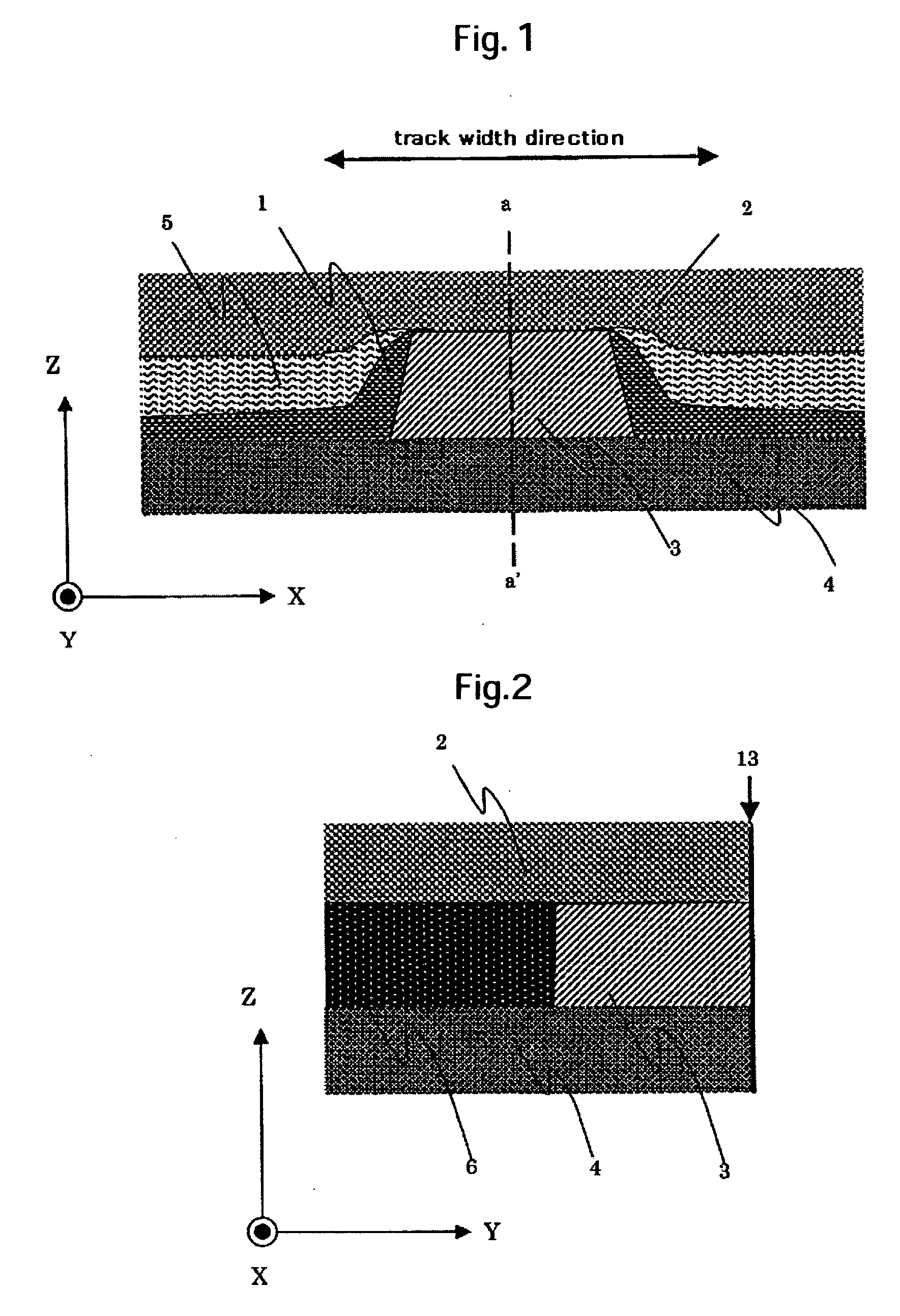
InactiveUS20060132983A1Increase heightEasy to useMagnetic measurementsRecord information storageResistResistive sensors
A high output magneto-resistive sensor is provided by suppressing leftover resist mask after lift-off and generation of a fence, and by making it easy to remove the redepositions deposited on the side wall in the track width direction or on the side wall in the sensor height direction of the magnetoresistive film. As a means to solve a fence and lift-off leftover of a resist in a process for forming a track and a process for forming a sensor height, a stopper layer is provided on the magnetoresistive film and the stopper layer on the refill film, and performing lift-off by CMP. By using a metallic material which has a small CMP polishing rate for at least the first stopper layer, the magnetoresistive film and the first stopper layer can be etched simultaneously and a pattern formed. As a result, decrease of the height of the resist mask by RIE can be suppressed and lift-off leftover can be prevented.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
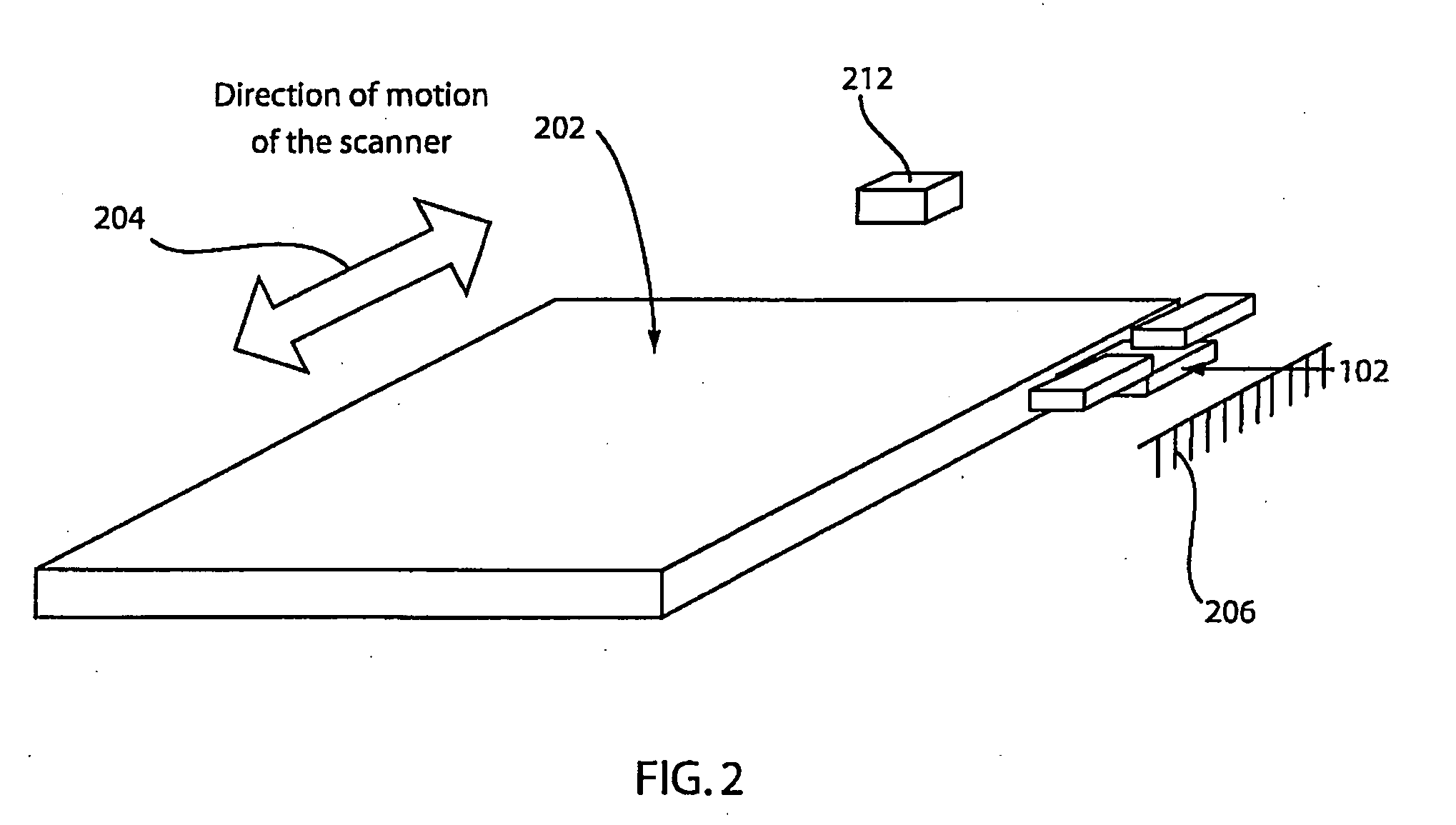
Fuel measuring device
InactiveUS7201052B2Reduce measurement errorLess measurement errorMachines/enginesLubrication indication devicesResistive sensorsMeasurement device
The present invention relates to a fuel measuring device, more particularly, to a fuel measuring device having a non-intrusive (or non-contact) structure between a rotor and a magneto resistive sensor, resulting in reducing of measurement errors that are usually caused by imperfect mechanical contact or corroded contacts.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
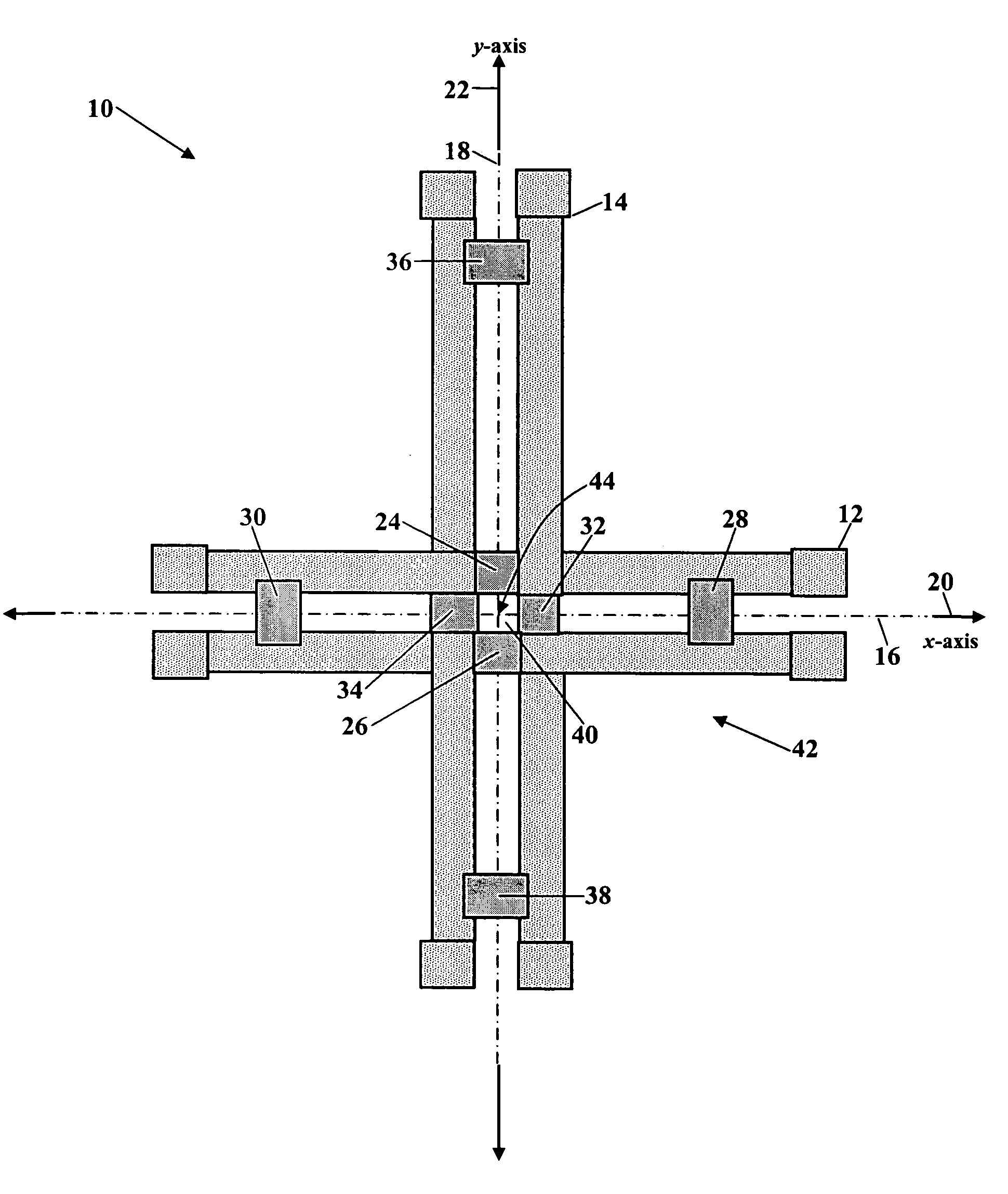
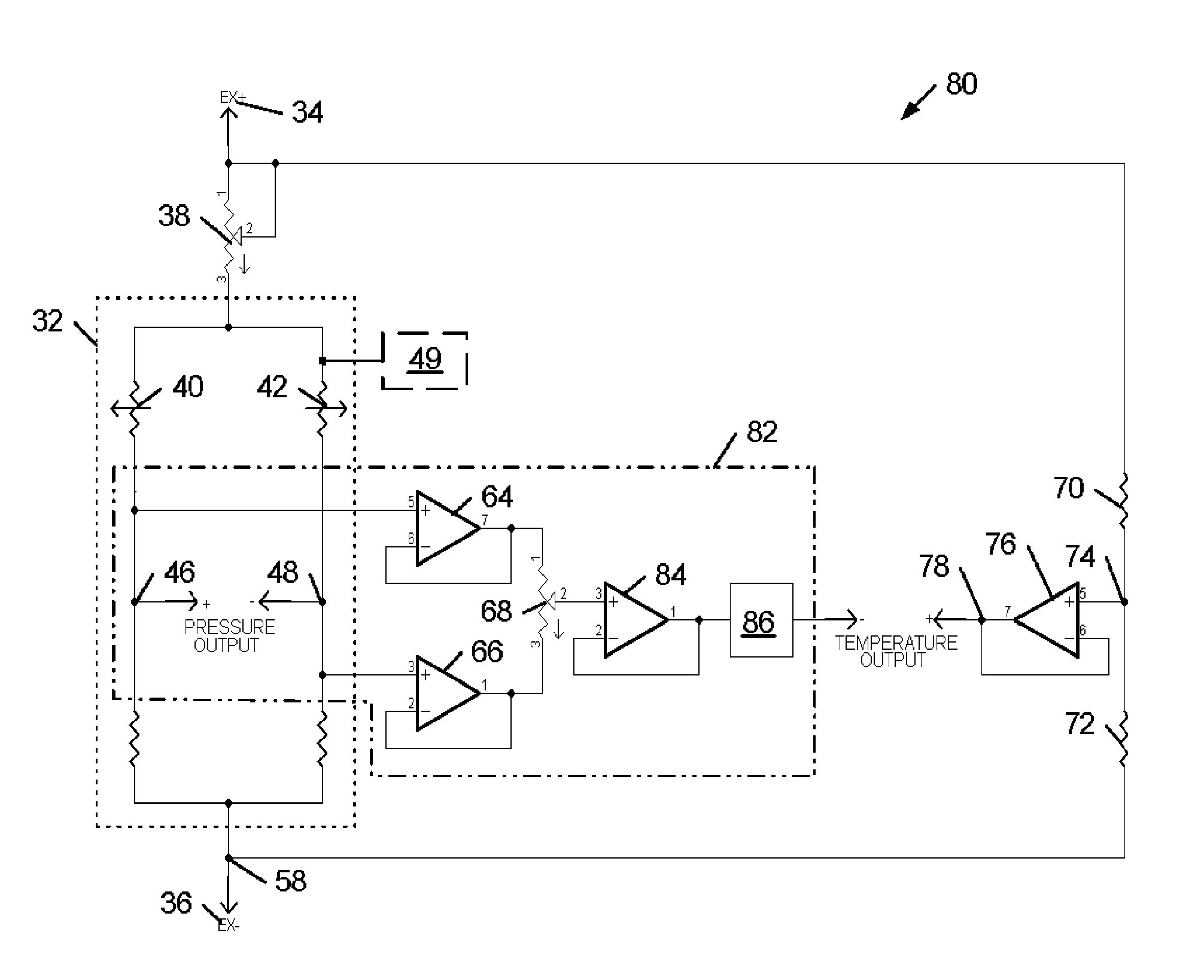
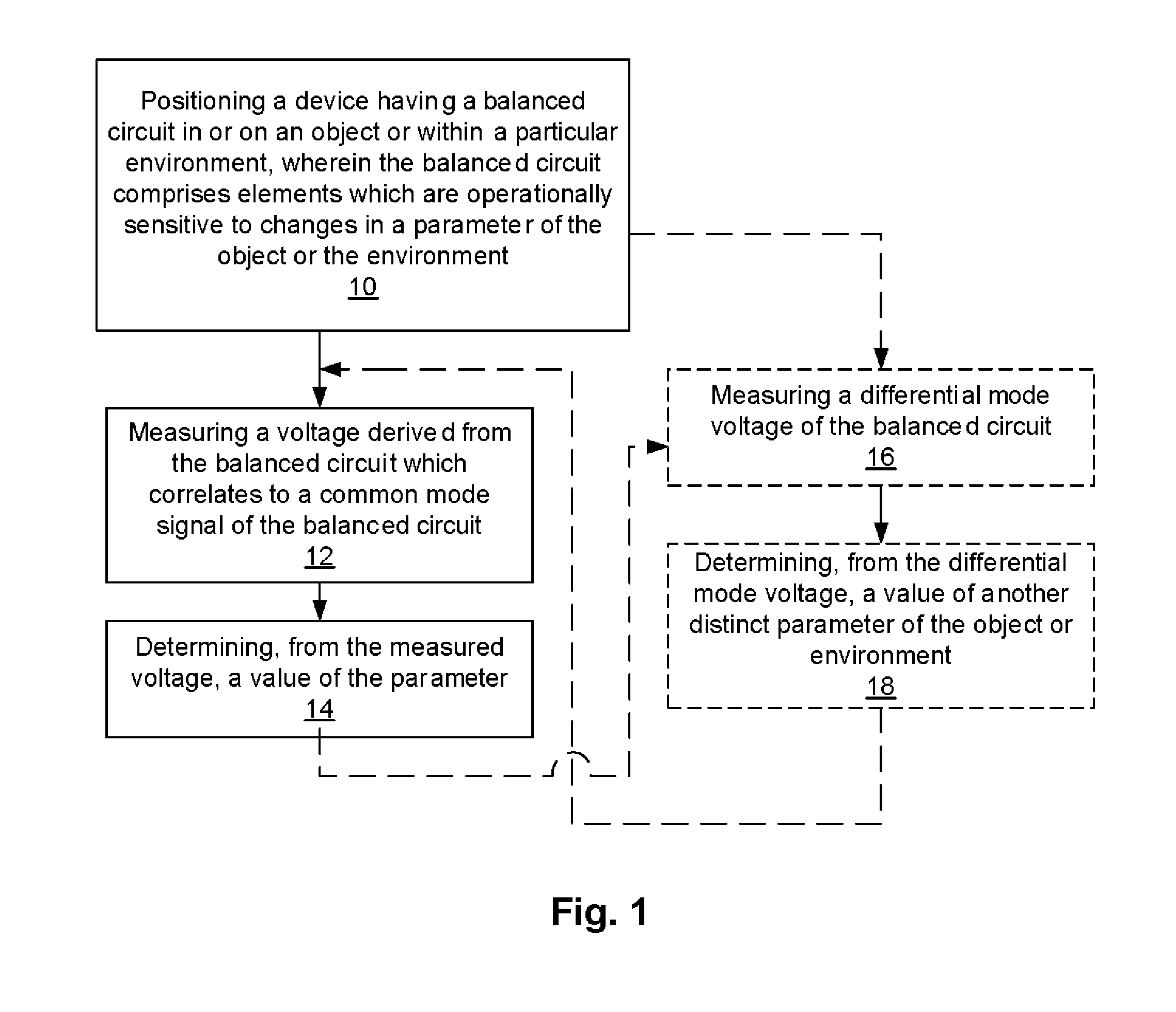
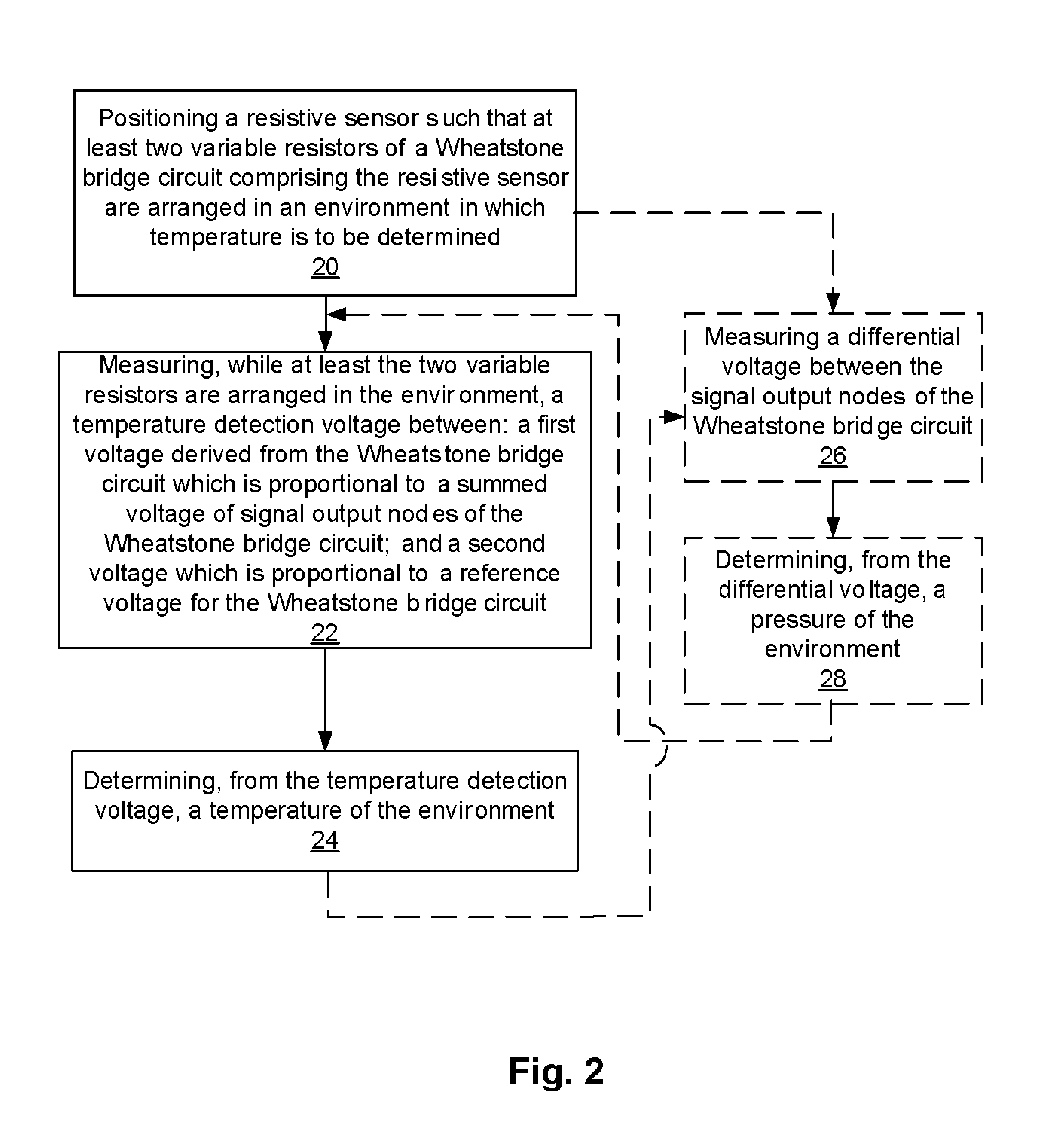
Methods, Devices, and Systems Which Determine a Parameter Value of an Object or an Environment From a Voltage Reading Associated With a Common Mode Signal of a Balanced Circuit
ActiveUS20140023112A1Thermometer detailsHumidity sensorsResistive sensorsElectrical resistance and conductance
A method for determining a value of a parameter of an object or an environment includes positioning a device having a balanced circuit in or on an object or within a particular environment, wherein the balanced circuit comprises elements which are operationally sensitive to changes in a parameter of the object or the environment. The method further includes measuring a common mode signal of the balanced circuit and determining, from the common mode signal, a value of the parameter. An exemplary implementation of the method includes determining temperature using a resistive sensor having a Wheatstone bridge circuit with two variable resistors and two fixed resistors. Embodiments of systems and devices configured to employ such methods are provided, particularly medical probes, electronic signal monitoring devices, and systems employing such devices.
Owner:MILLAR INSTR
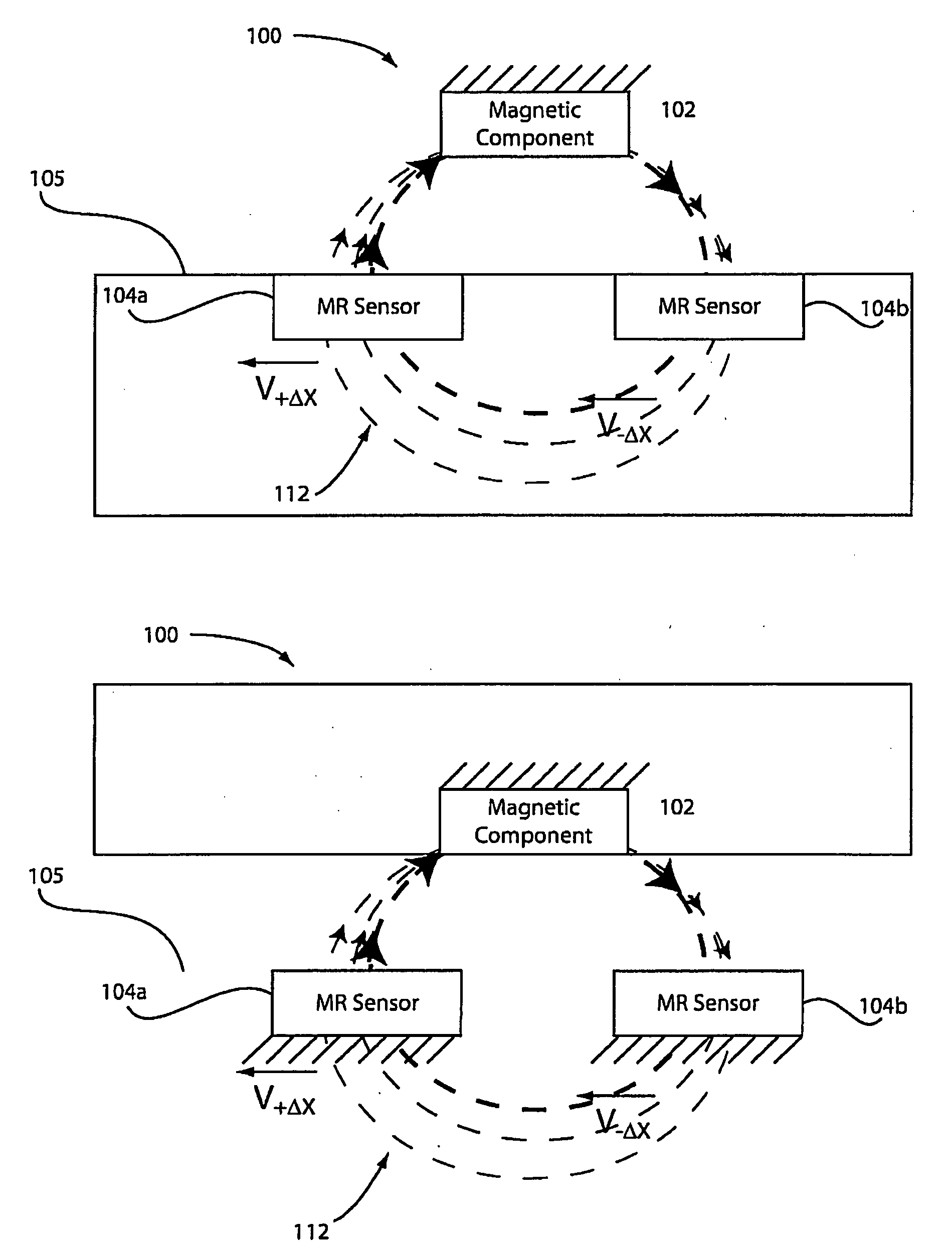
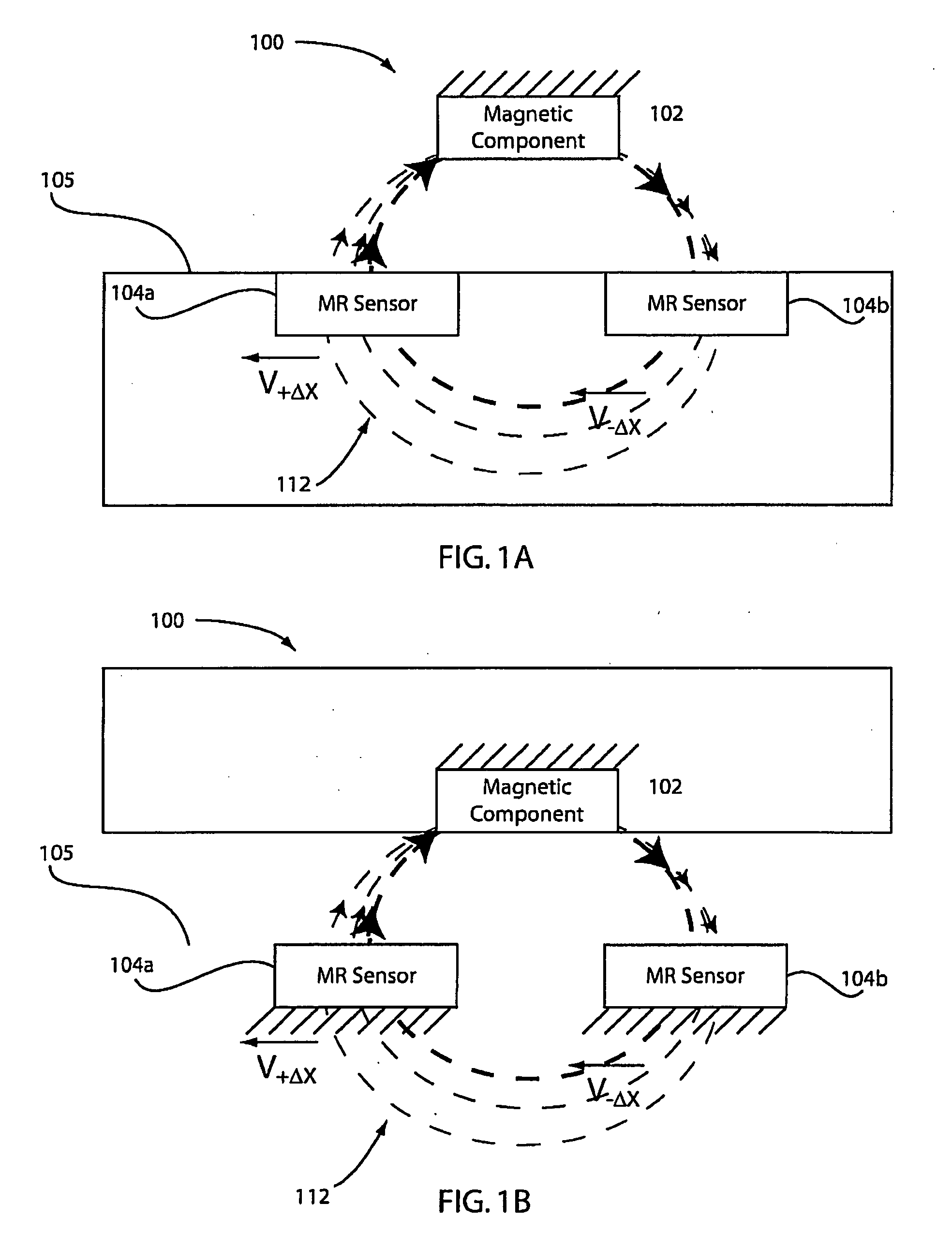
Elimination of errors due to aging in magneto-resistive devices
ActiveUS20100315928A1Reduce the impactReduce impact on measurement accuracyRecord information storageCarrier monitoringResistive sensorsEngineering
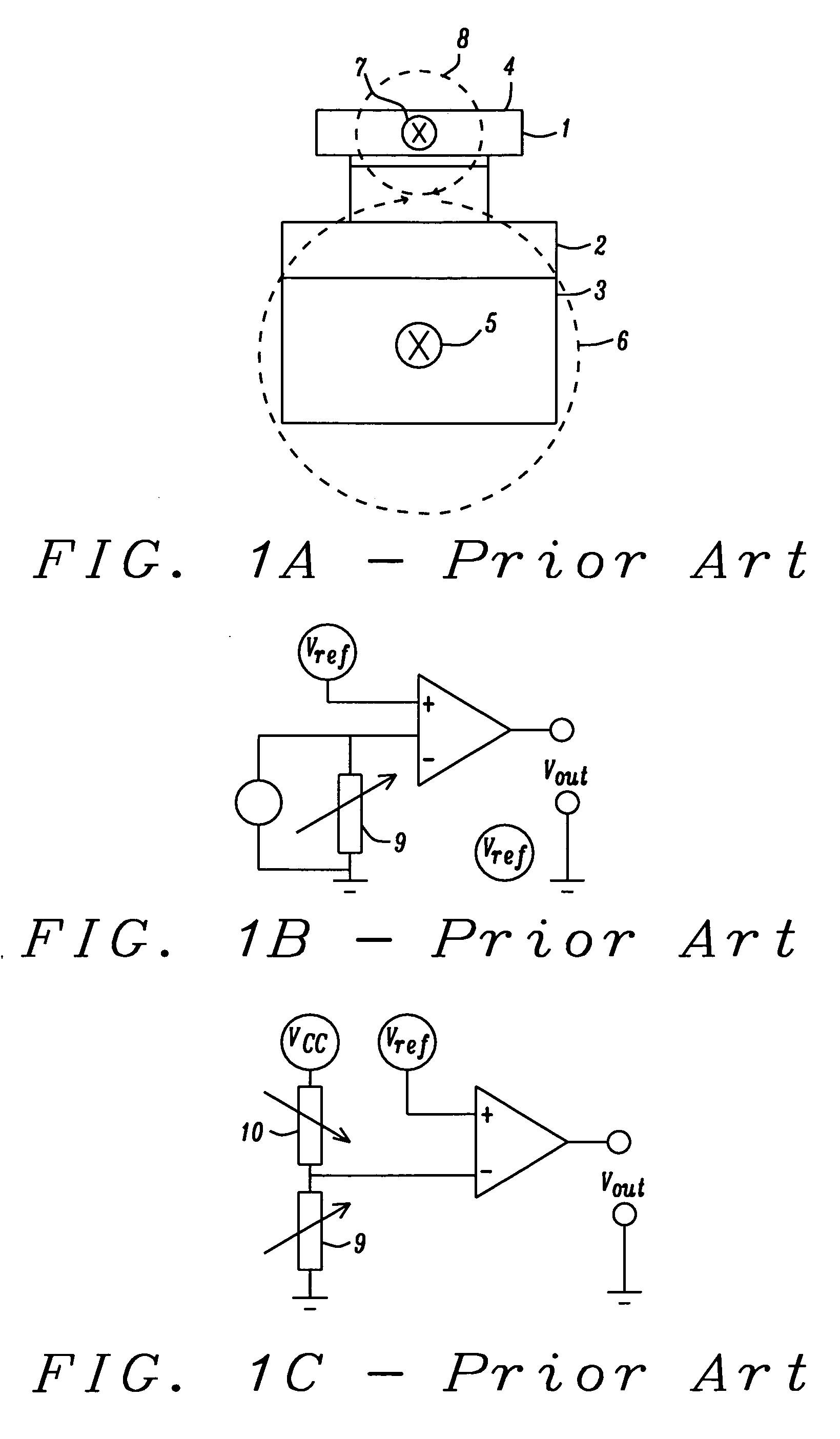
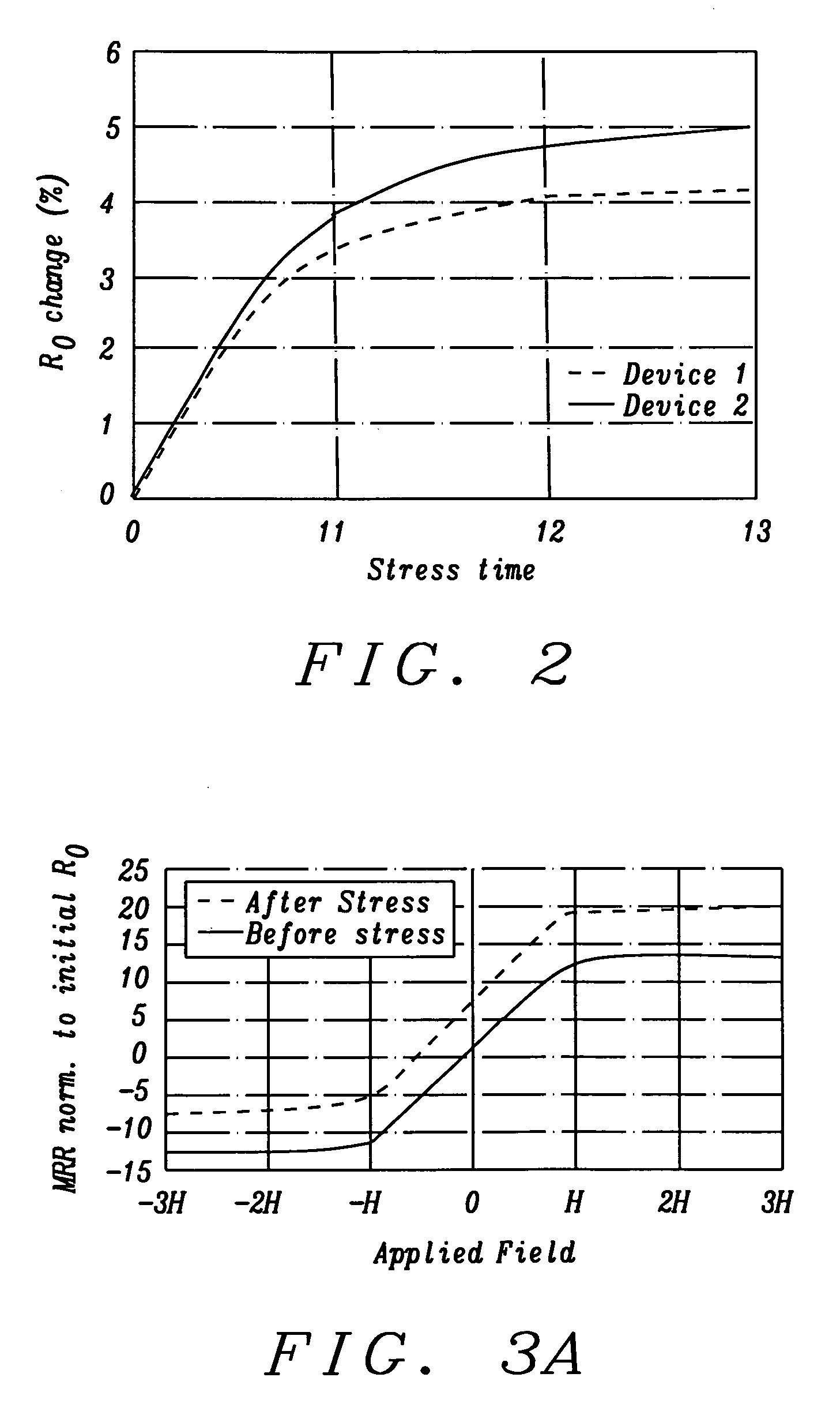
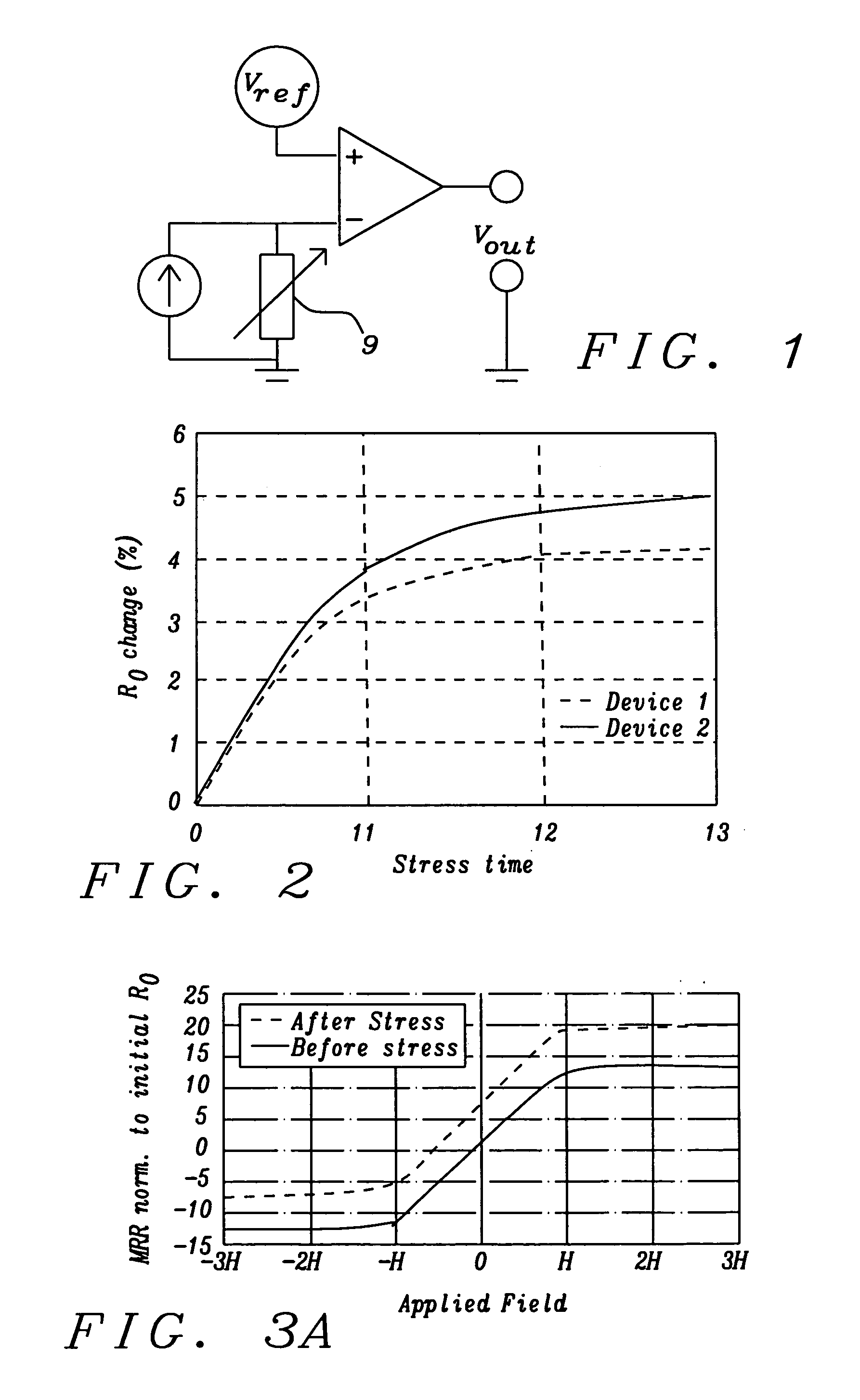
The problem of magneto-resistive sensor drift with age has been solved by normalizing the sensor's output relative to its output when it is in a selected reproducible state. Details for the method to accomplish this normalization are disclosed together with several examples of how the method can be utilized.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
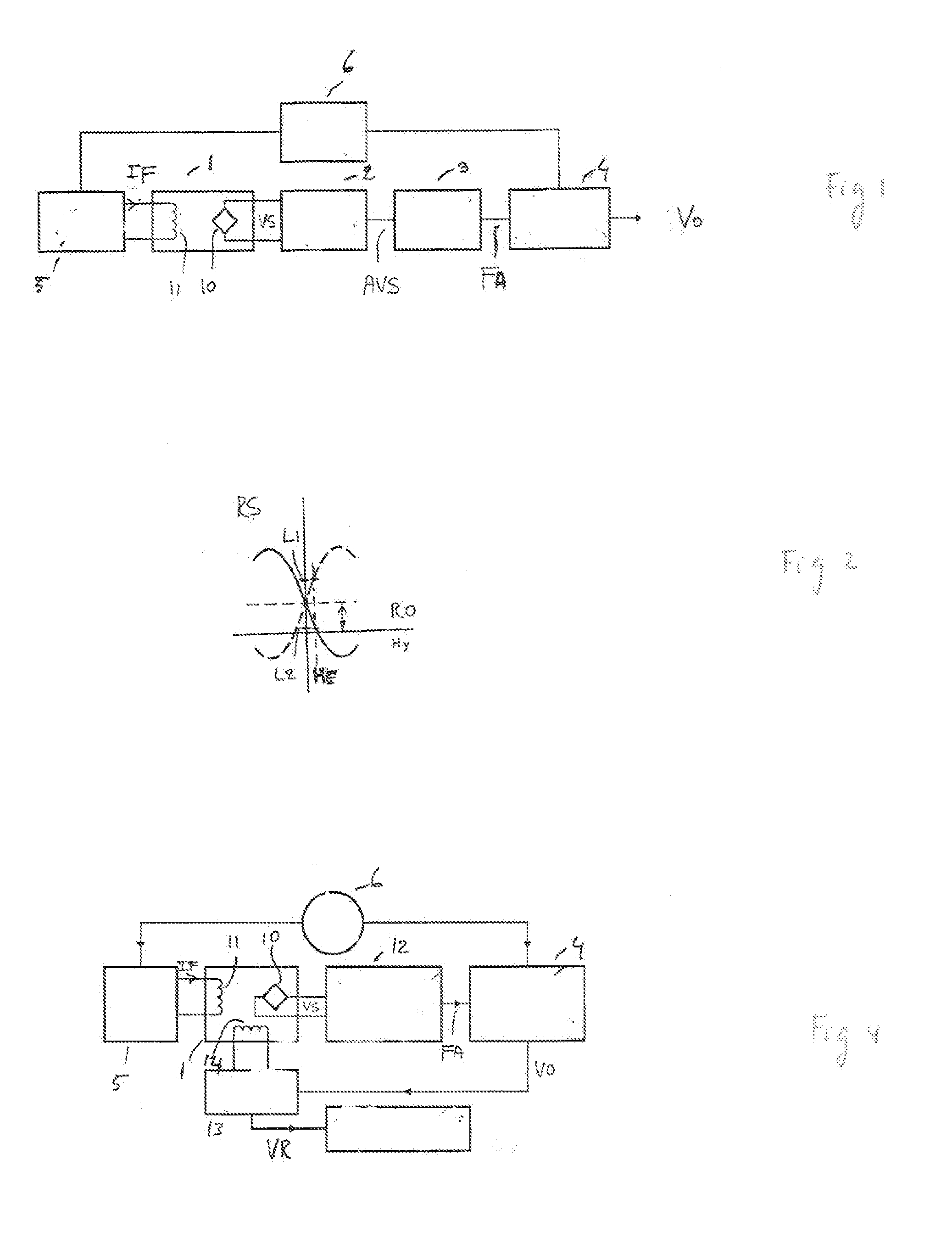
Open loop magneto-resistive magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS20110037458A1Improve accuracyEliminate the effects ofElectrical measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsResistive sensorsAcoustics
An apparatus and a general method to measure a magnetic field using magneto-resistive sensors in an open-loop configuration are disclosed. A key feature is the regular in-situ normalization of the sensors to compensate for the effects of sensor aging.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Method for measuring a physical parameter and electronic circuit for implementing the same
ActiveUS20160003880A1Eliminate the effects ofLow frequency noiseAcceleration measurement using interia forcesResistance/reactance/impedenceResistive sensorsVoltage reference
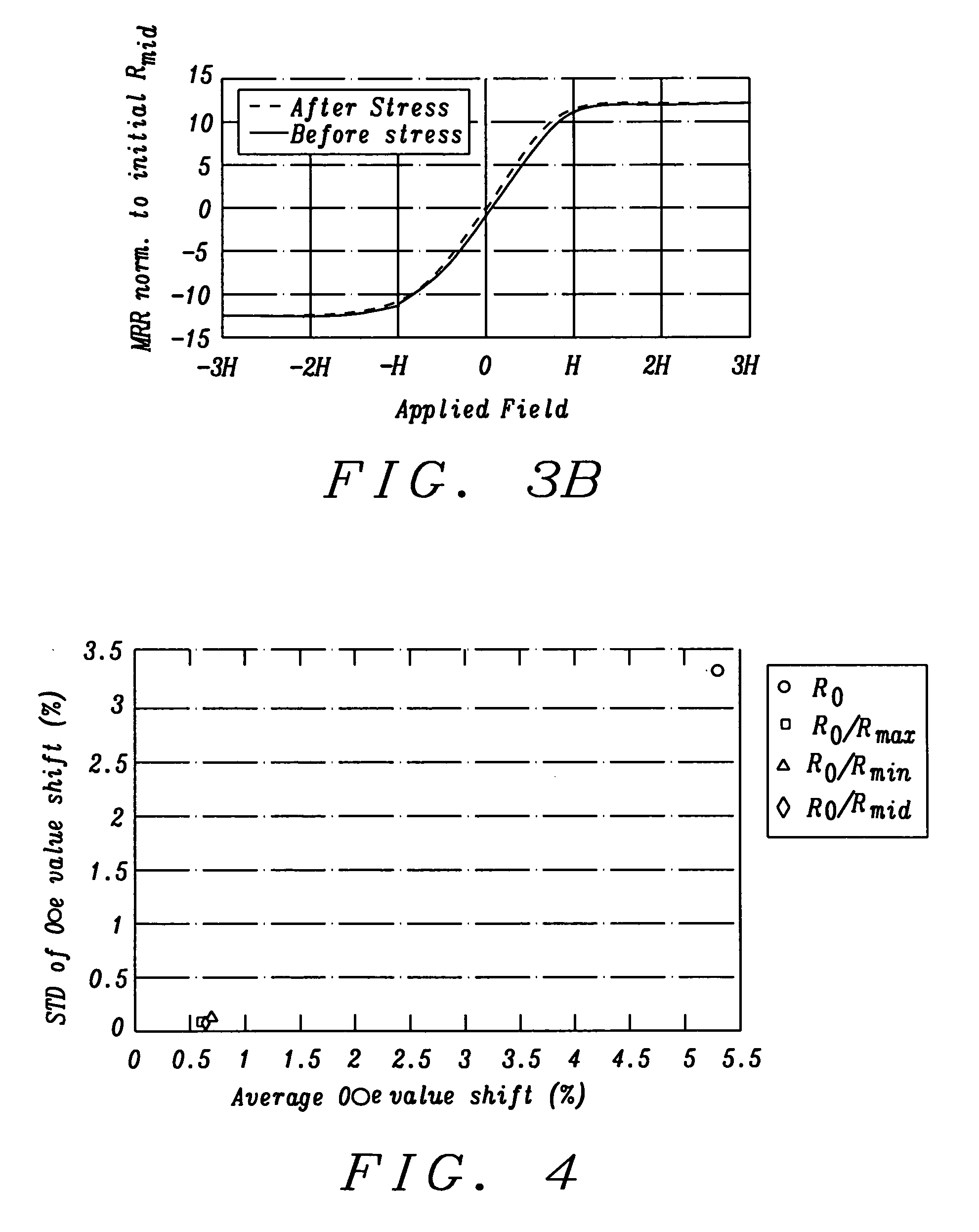
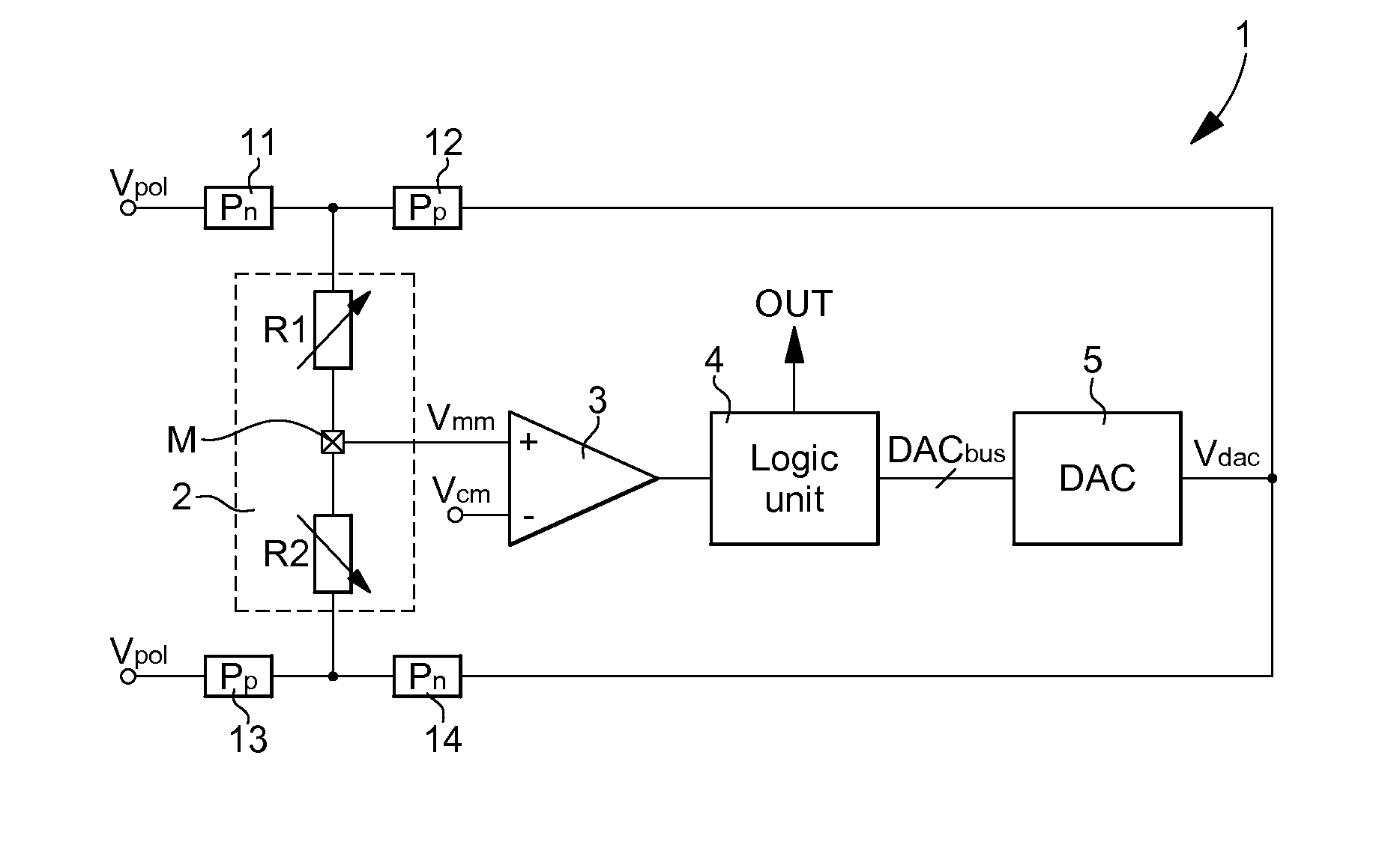
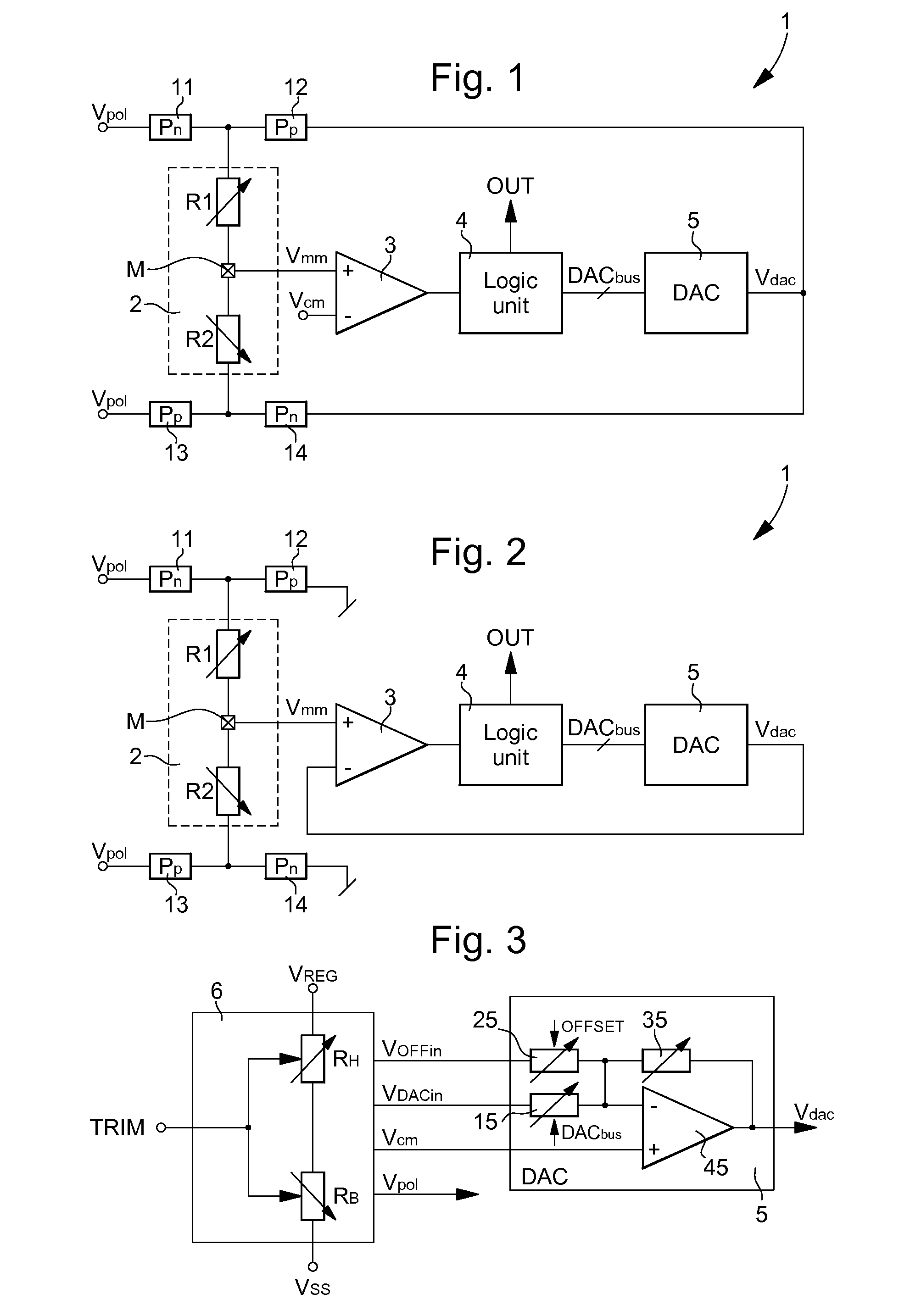
The physical parameter measurement method is performed using an electronic circuit (1) with a resistive sensor (2). The resistive sensor includes two resistors (R1, R2) mounted in series, whose connection node connected to a moving mass (M), is connected to a first input of an amplifier-comparator (3). A second input of the amplifier-comparator receives a reference voltage. One output of the amplifier-comparator is connected to a logic unit (4), which provides a digital output signal (OUT). A digital-to-analogue converter (5) provides a measurement voltage (Vdac), as a function of a digital signal provided by the logic unit, to the first resistor (R1) in a first phase of a measurement cycle, whereas the second resistor (R2) is polarized by a polarization voltage, and to the second resistor in a second phase, whereas the first resistor is polarized by a polarization voltage via a switching unit.
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
Wide-biphase-detector quality monitor for sensing of pin layer reversal
InactiveUS7738202B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageResistive sensorsData application
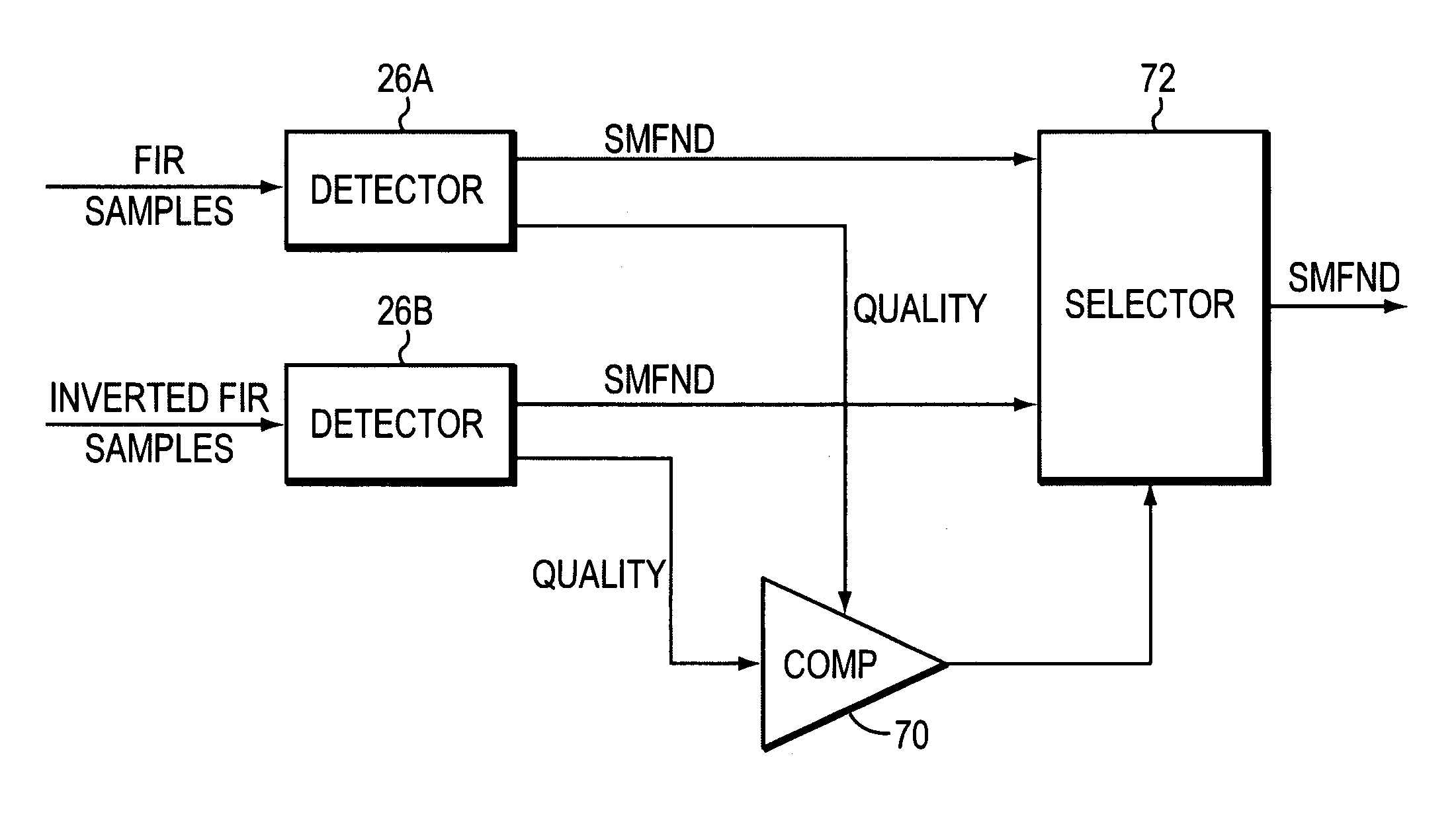
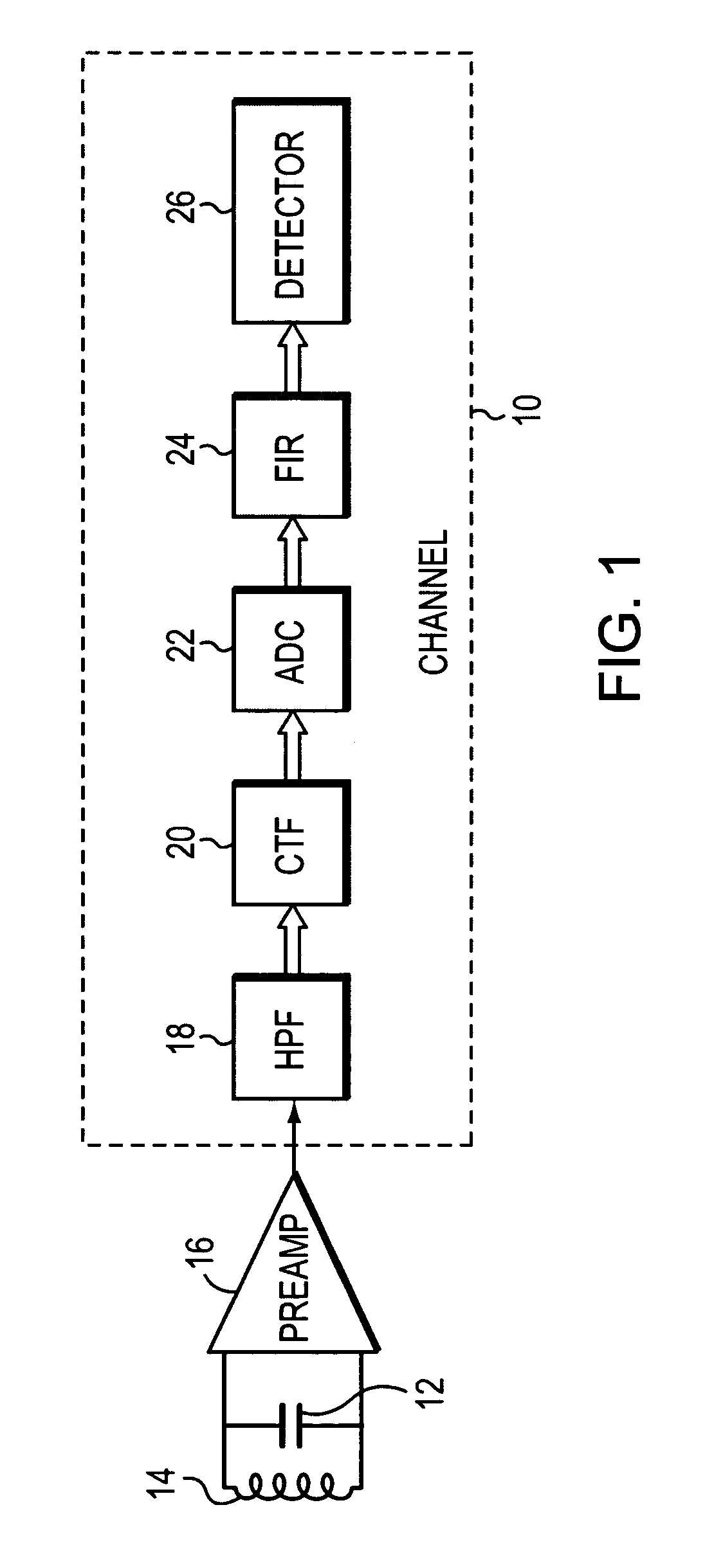
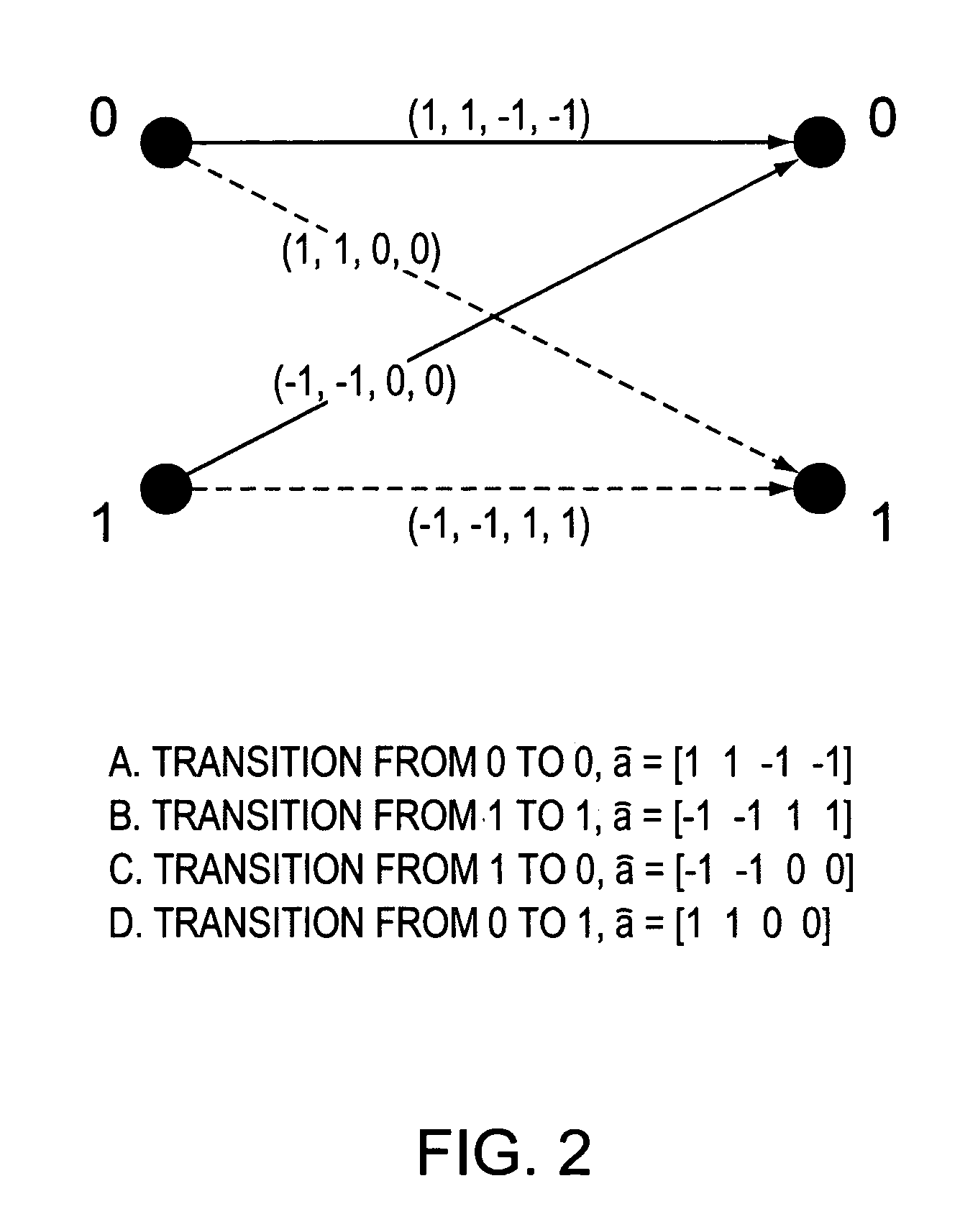
An apparatus and method are disclosed for decoding servo data recorded on a magnetic disk drive and detecting pinned layer reversals and signal errors, for example, errors due to noise. The servo data is encoded using wide-bi-phase encoding. This encoding is detected by a magneto-resistive sensor that senses the magnetization in domains passing by the sensor. The decoder includes an A / D converter for sampling the signals emitted by the sensor, to provide a sequence of the encoded data. A trellis, such as a Viterbi trellis, is employed to decode the samples generated by the converter. The trellis includes nodes representing states, connected by paths representing transitions, among the nodes. A quality value is generated for the transitions, the quality value representing the distance between each sample in the sequence output by the A / D converter and a corresponding expected sample. By applying servo data to two trellises, each corresponding to a different pinned layer magnetic orientation, and comparing the quality values produced, the correct pinned layer orientation may be selected.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
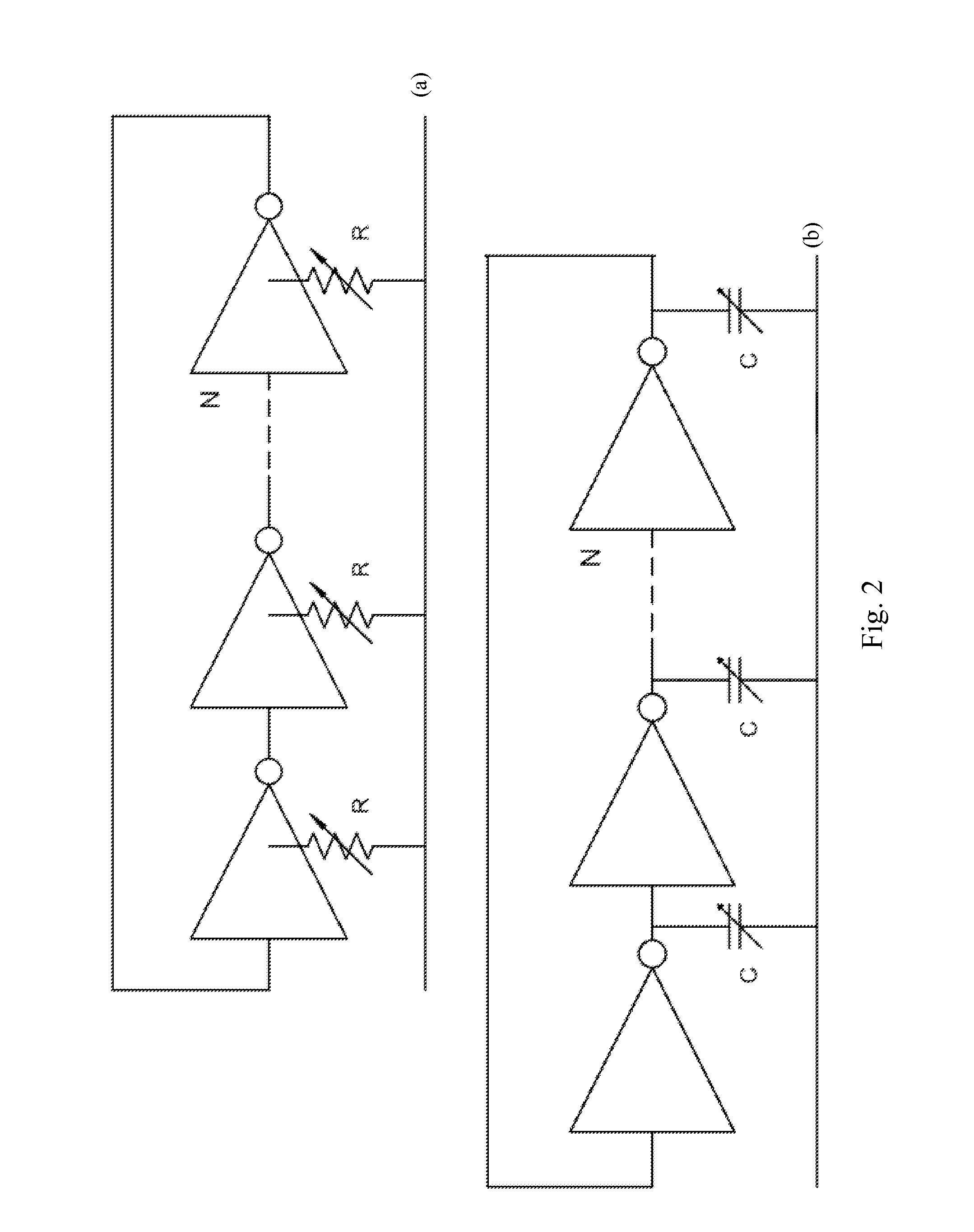
Magnetic Interference Avoidance in Resistive Sensors
ActiveUS20170261387A1Force measurementElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementResistive sensorsPower flow
A strain-responsive sensor incorporating a strain-sensitive element is disclosed. The strain-sensitive element includes a matched-pair of resistive structures disposed on opposite sides of a substrate. One resistive structure of the matched pair is coupled to a crossover, either a physical crossover or a soft crossover, such that current within the resistive structures of the matched pair flows in the same direction.
Owner:APPLE INC
Temperature switch with resistive sensor
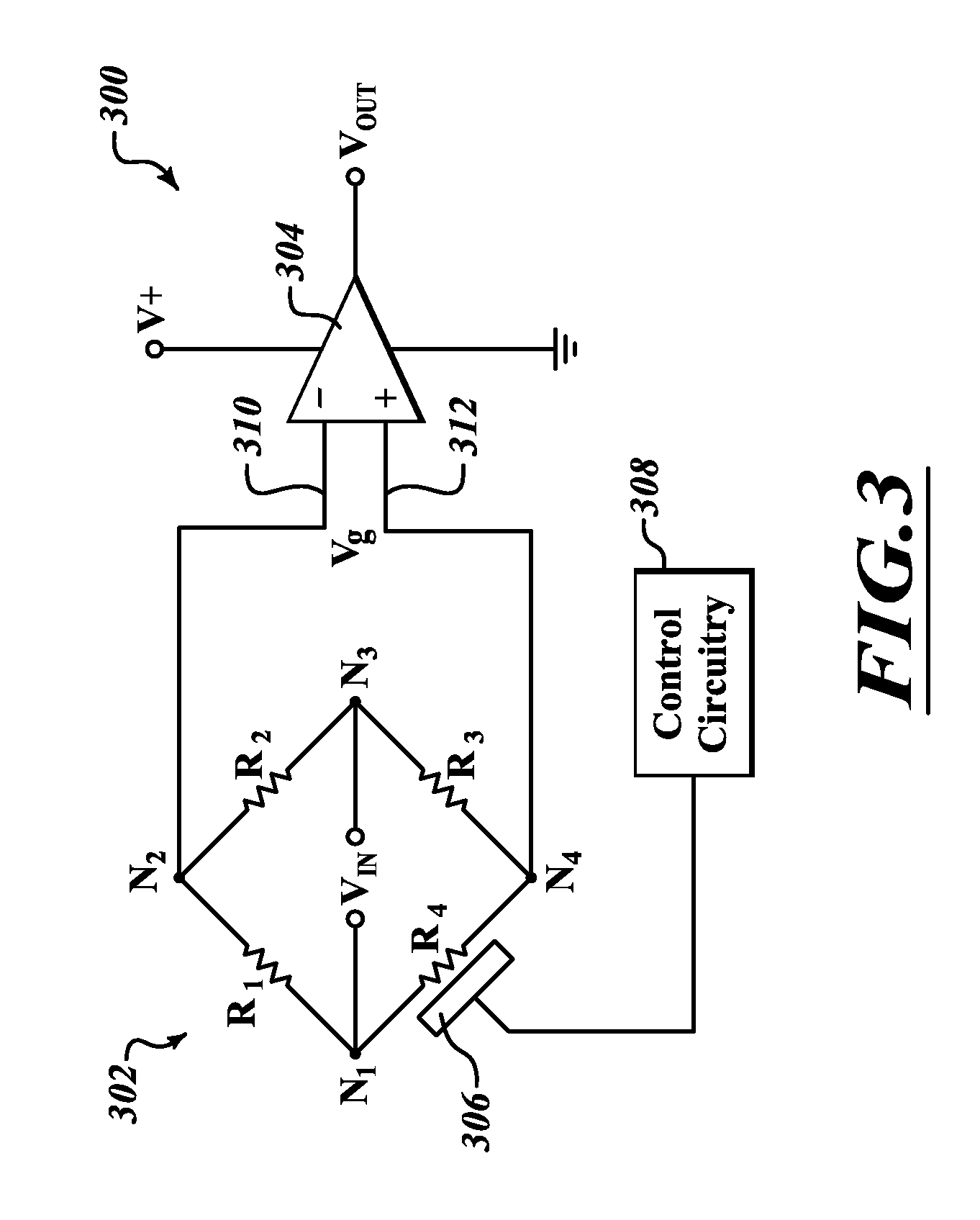
InactiveUS20130168815A1Accurate temperatureThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsSolid-state devicesResistive sensorsElectrical resistance and conductance
The present disclosure is directed to a device and a method for forming a precision temperature sensor switch with a Wheatstone bridge configuration of four resistors and a comparator. When the temperature sensor detects a temperature above a threshold, the switch will change states. The four resistors in the Wheatstone bridge have the same resistance, with three of the resistors having a low temperature coefficient of resistance and the fourth resistor having a high temperature coefficient of resistance. As the temperature increases, the resistance of the fourth resistor will change. The change in resistance of the fourth resistor will change a voltage across the bridge. The voltage across the bridge is coupled to the comparator and compares the voltage with the threshold temperature, such that when the threshold temperature is exceeded, the comparator switches the output off.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS PTE LTD
Magnetic field sensor circuit
InactiveUS7818890B2Improve performanceLess spaceNanomagnetismRecord information storageResistive sensorsPhase shifted
A magnetic field sensor circuit comprises a first magneto-resistive sensor (Rx) which senses a first magnetic field component in a first direction to supply a first sense signal (Vx). A first flipping coil (FC1) applies a first flipping magnetic field with a periodically changing polarity to the first magneto-resistive sensor (Rx) to cause the first sense signal (Vx) to have alternating different levels synchronized with the first flipping magnetic field. A second magneto -resistive sensor (Ry) senses a second magnetic field component in a second direction different than the first direction to supply a second sense signal (Vy). A second flipping coil (FC2) applies a second flipping magnetic field with a periodically changing polarity to the second magneto -resistive sensor (Ry) to cause the second sense signal (Vy) to have an alternating different levels synchronized with the second flipping magnetic field. The first flipping magnetic field and the second flipping magnetic field have a phase shift. A differential amplifier (AMP1) receives the first sense signal (Vx) and the second sense signal (Vy) to obtain a difference signal (Vd). A first synchronous demodulator (DEM1) receives the difference signal (Vd) and a first switching signal (Q1) being phase locked to the alternating different levels of the first sense signal (Vx) to supply a first output signal (Vox) indicating the first magnetic field component. A second synchronous demodulator (DEM2) receives the difference signal (Vd) and a second switching signal (Q2) being phase locked to the alternating different levels of the second sense signal (Vy) to supply a second output signal (Voy) indicating the second magnetic field component.
Owner:TITAN INTELLIGENCE TECH LTD
Network architecture for wirelessly interfacing sensors at ultra low power
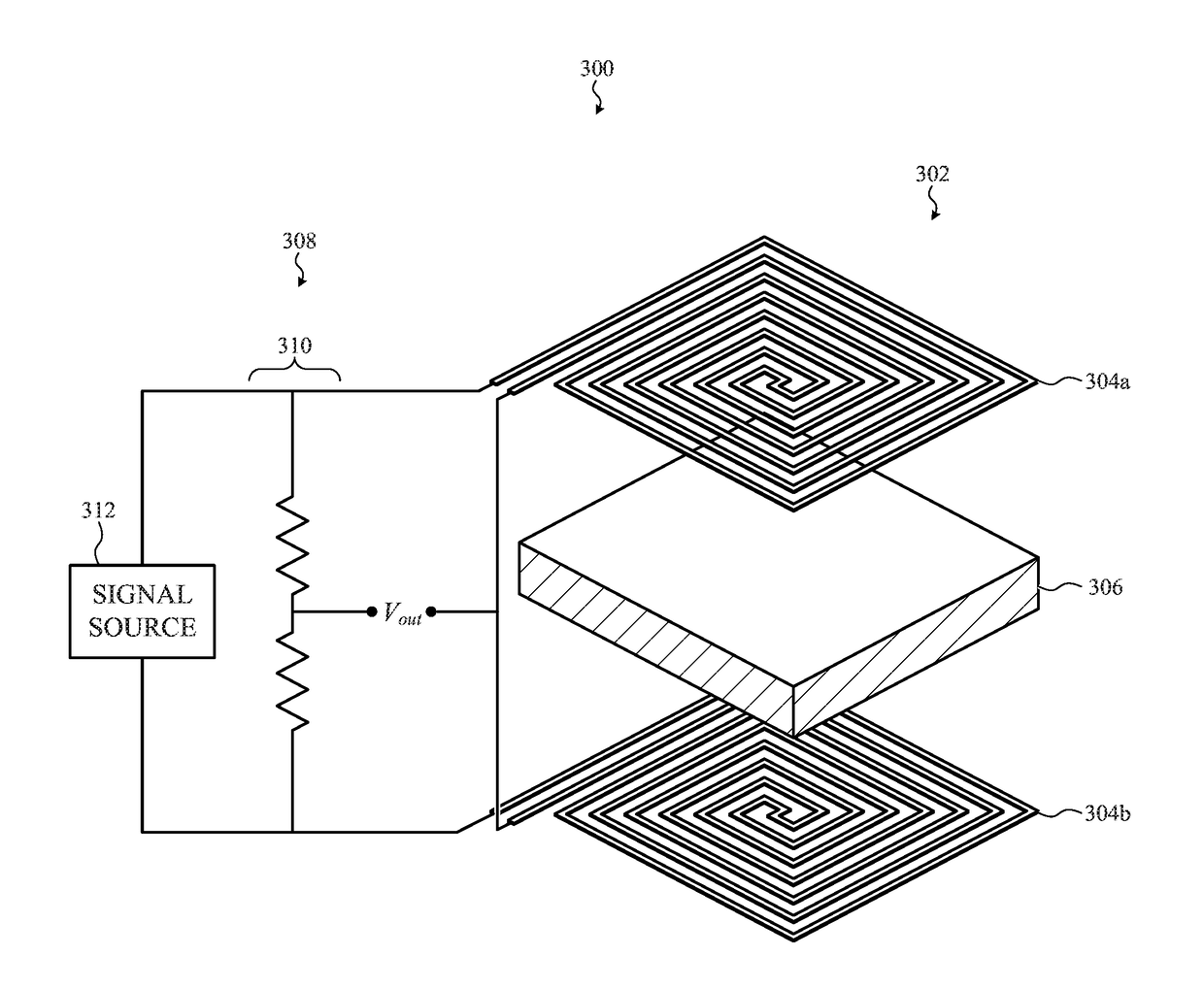
InactiveUS20100308980A1Limiting and reducing power consumptionReduce Design ComplexityElectric signal transmission systemsMobile data collection deviceResistive sensorsShortest distance
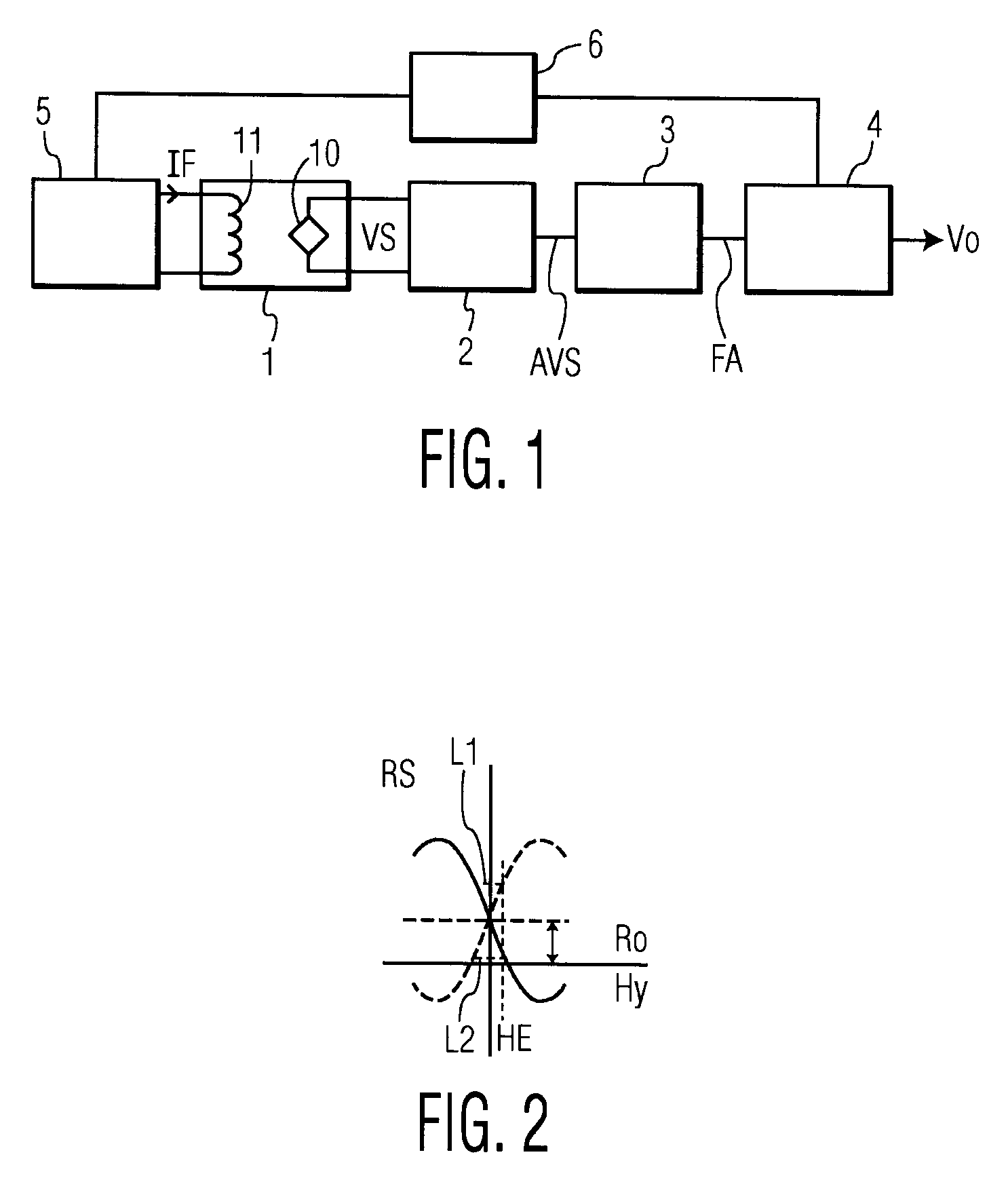
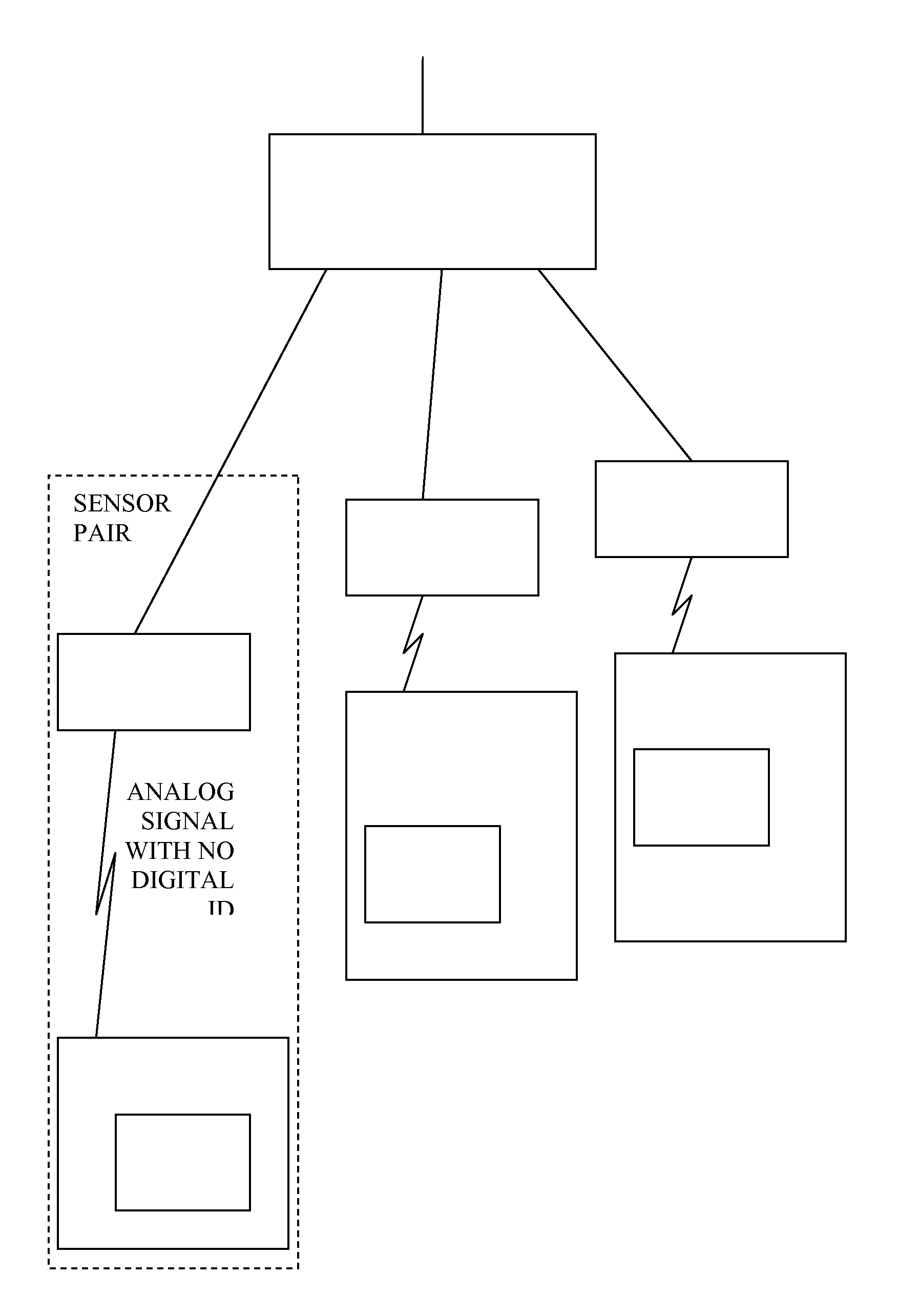
A sensing network is described, consisting of a multiplexing reader and one or more sensor pairs, each sensor pair comprising a transponder and a dedicated reader, dedicated to that transponder, each transponder having a sensor. Each sensor pair is able to wirelessly interface and power both capacitive and resistive sensors at a short distance with high efficiency. By providing a dedicated reader for each transponder, each link can be optimized and there is no need for the dedicated reader to distinguish between signals from other transponders. The transponder generates an analog signal directly using a sensor or analog memory value and sends it by modulation to the dedicated reader. So, the dedicated readers do not need to have circuitry to demodulate a digital signal or ID code. The transponder includes the sensors and their electronic circuits and can be optionally remotely powered by the dedicated reader through the wireless link. The expected consumption of the dedicated reader can be lower than 200 μW.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
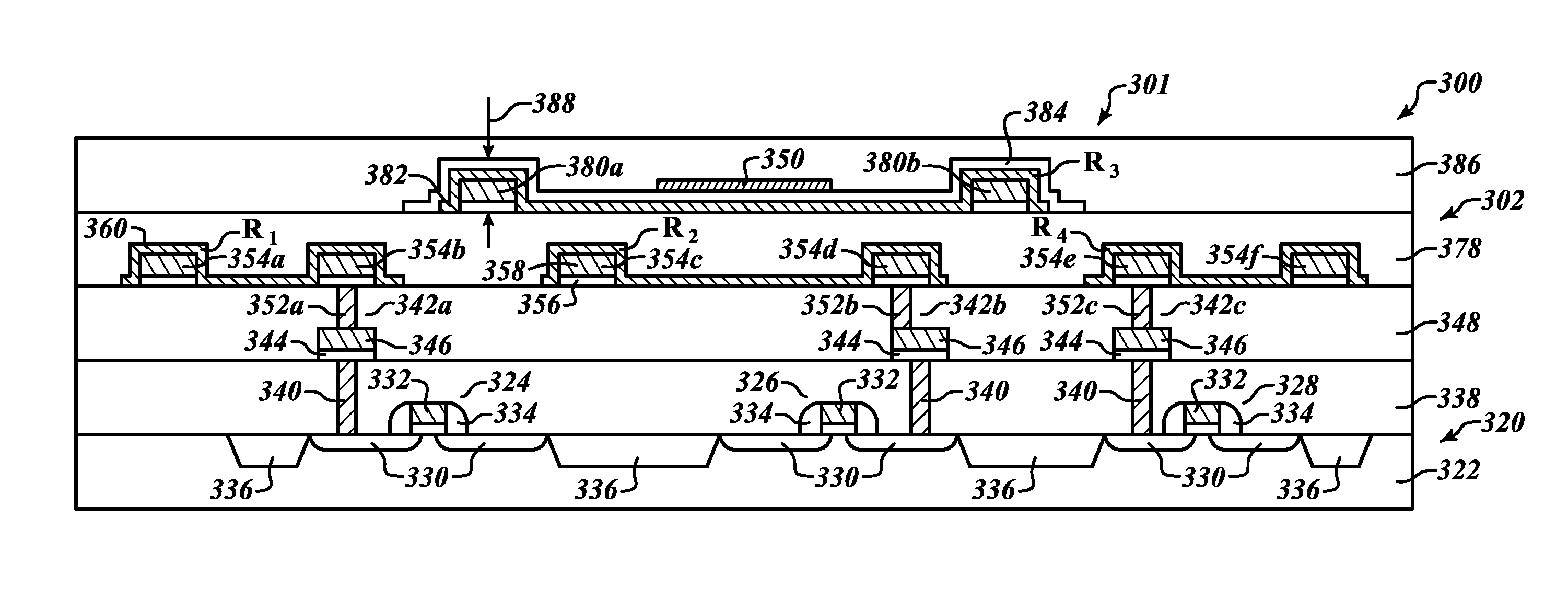
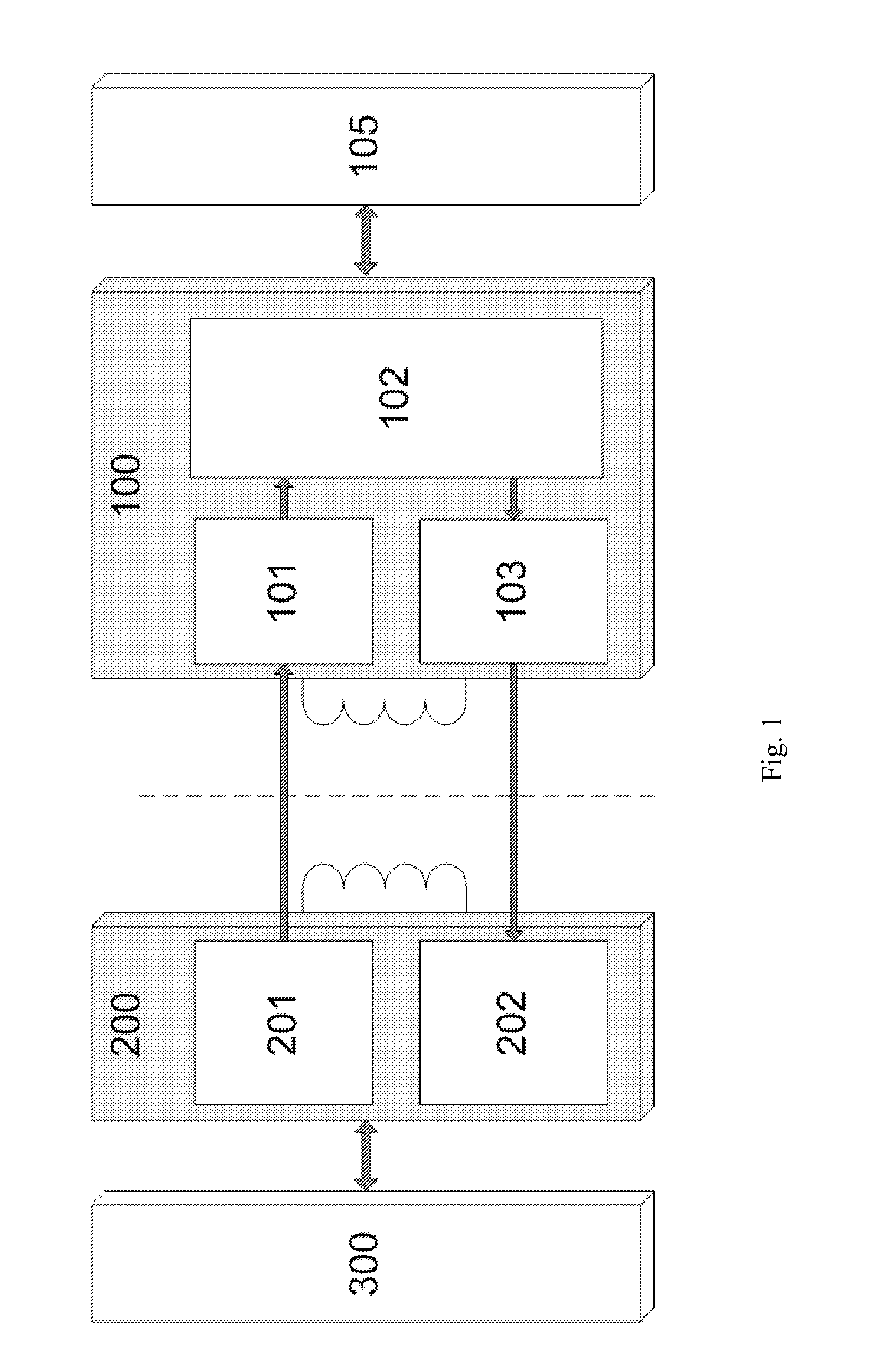
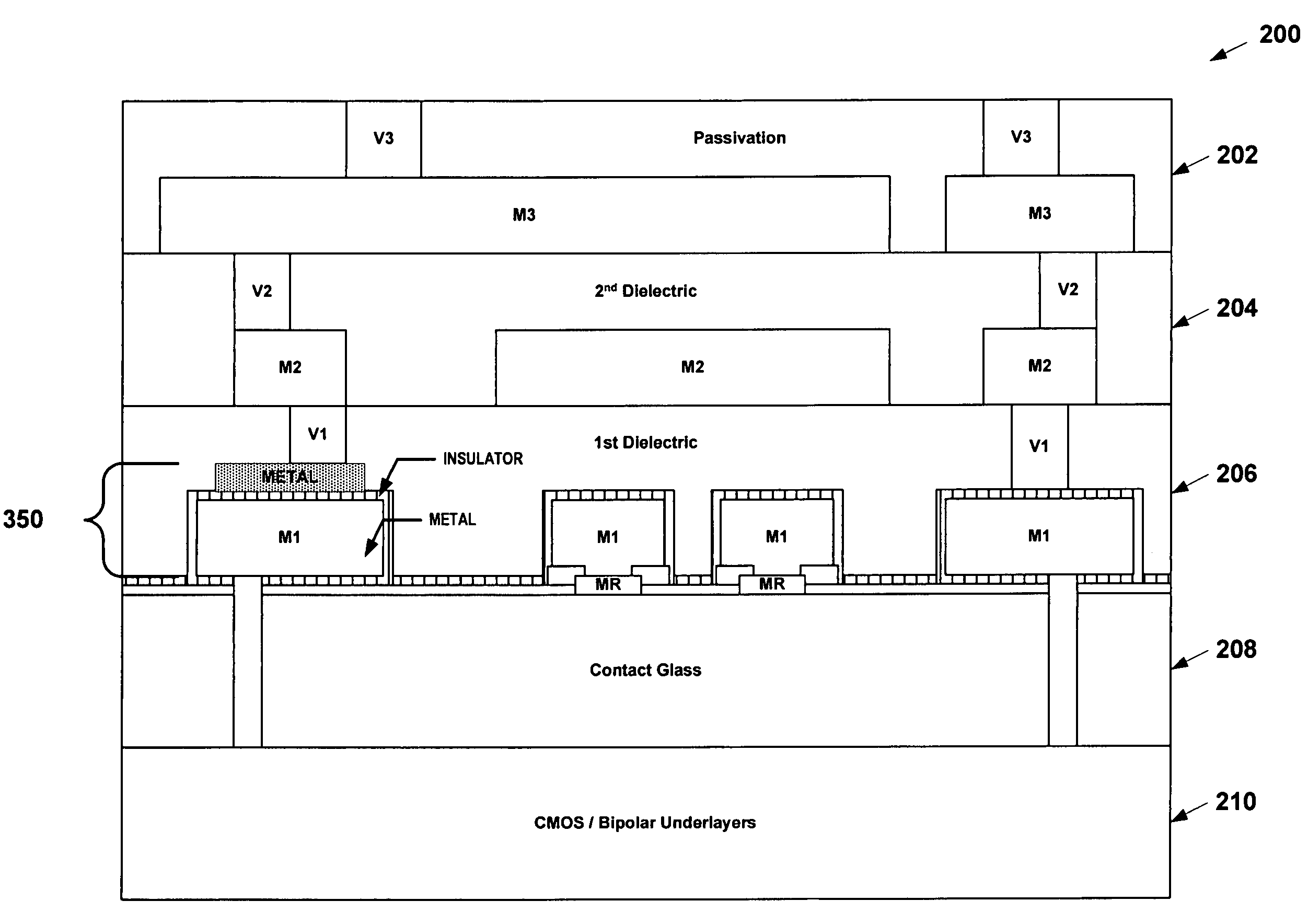
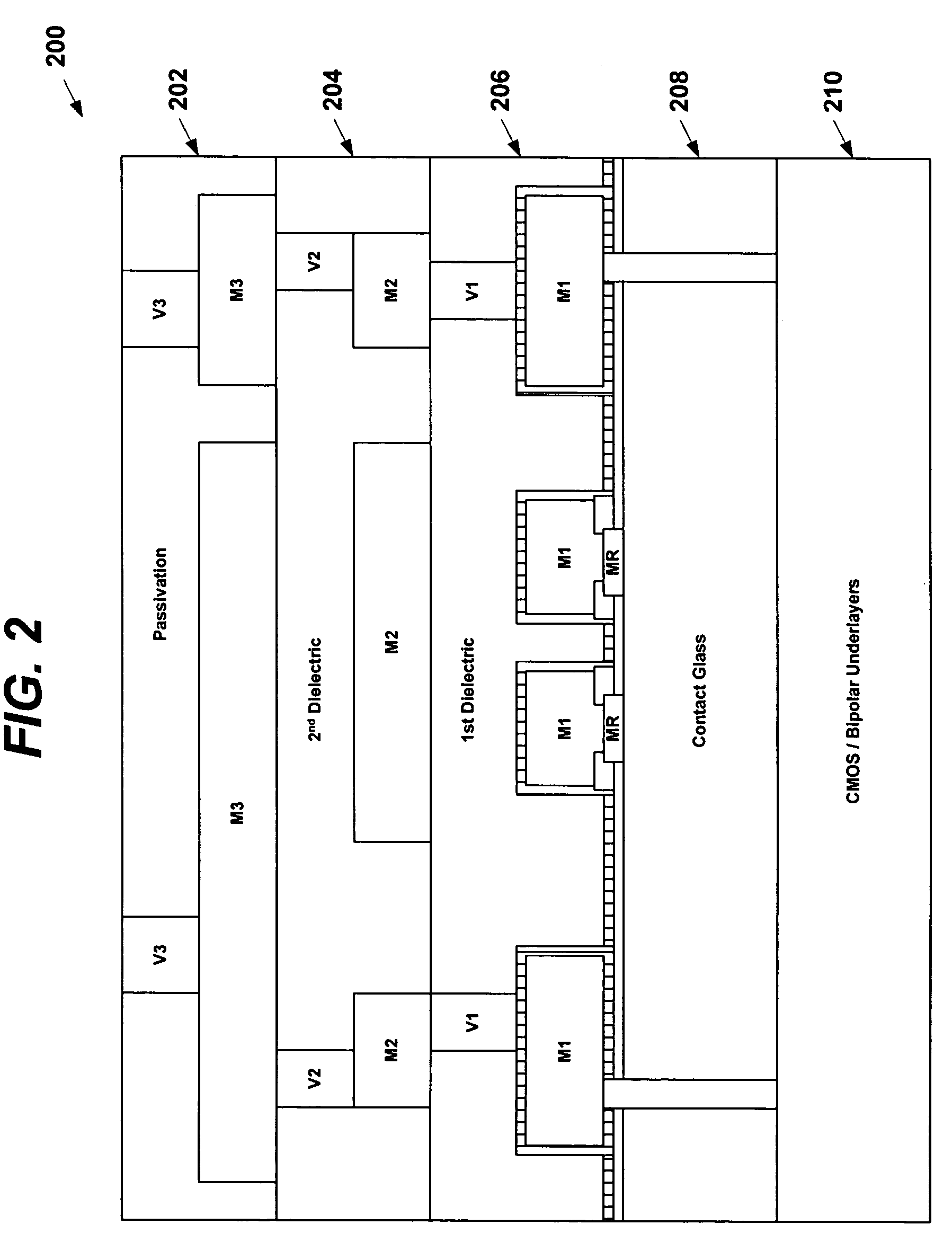
Semiconductor device and magneto-resistive sensor integration
A magnetic-sensing apparatus and method of making and using thereof is provided. The sensing apparatus may be fabricated from semiconductor circuitry and a magneto-resistive sensor. A dielectric may be disposed between the semiconductor circuitry and the magneto-resistive sensor. In one embodiment, the semiconductor circuitry and magneto-resistive sensor are formed into a single package or, alternatively, monolithically formed into a single chip. In another embodiment, some of the semiconductor circuitry may be monolithically formed on a first chip with the magneto-resistive sensor, while other portions of the semiconductor circuitry may be formed on a second chip. As such, the first and second chips may be placed in close proximity and electrically connected together or alternatively have no intentional electrical interaction, Exemplary semiconductor devices that might be implemented include, without limitation, capacitors, inductors, operational amplifiers, set / reset circuitry for the magneto-resistive sensors, accelerometers, pressure sensors, position sensing circuitry, compassing circuitry, etc.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
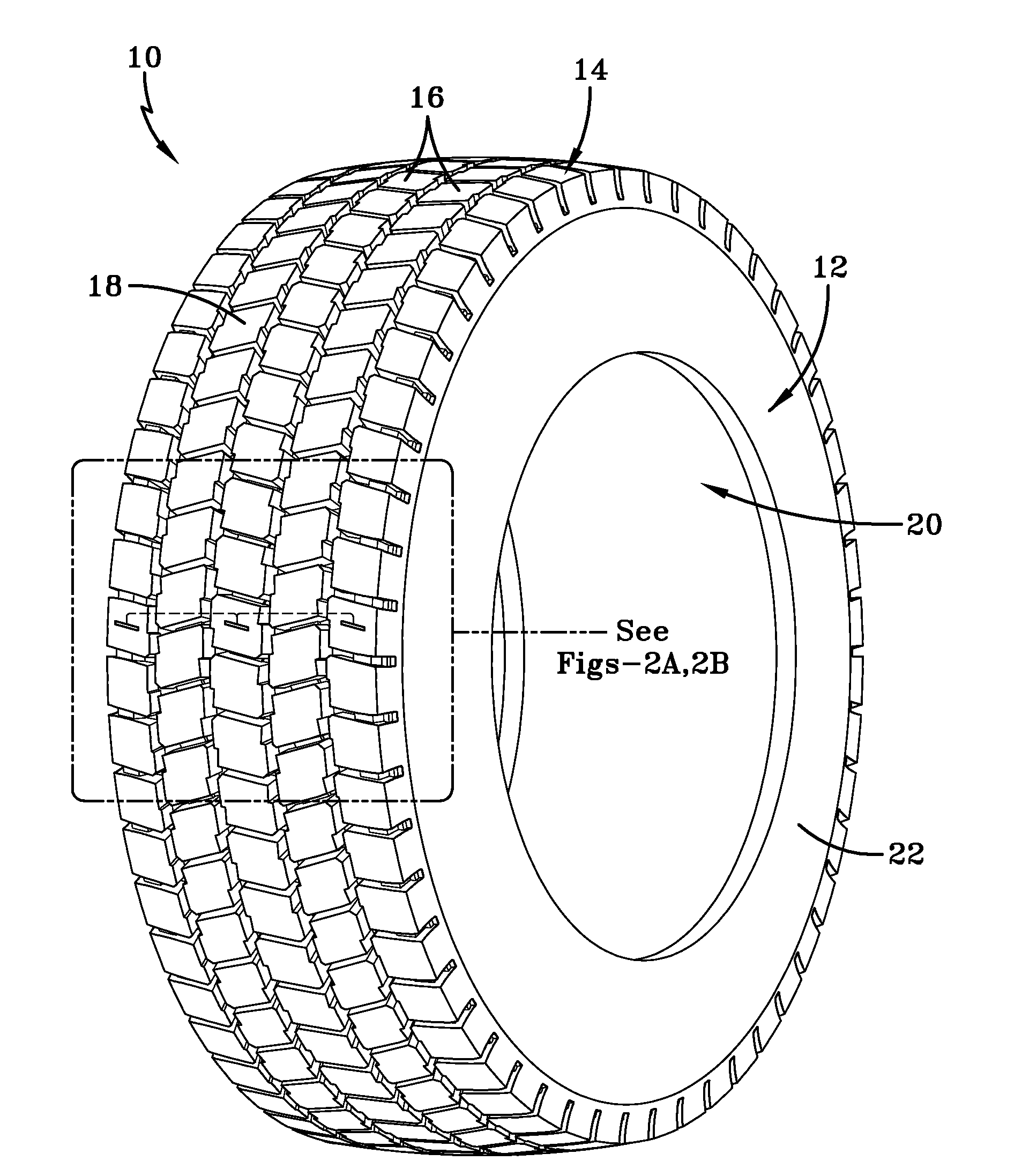
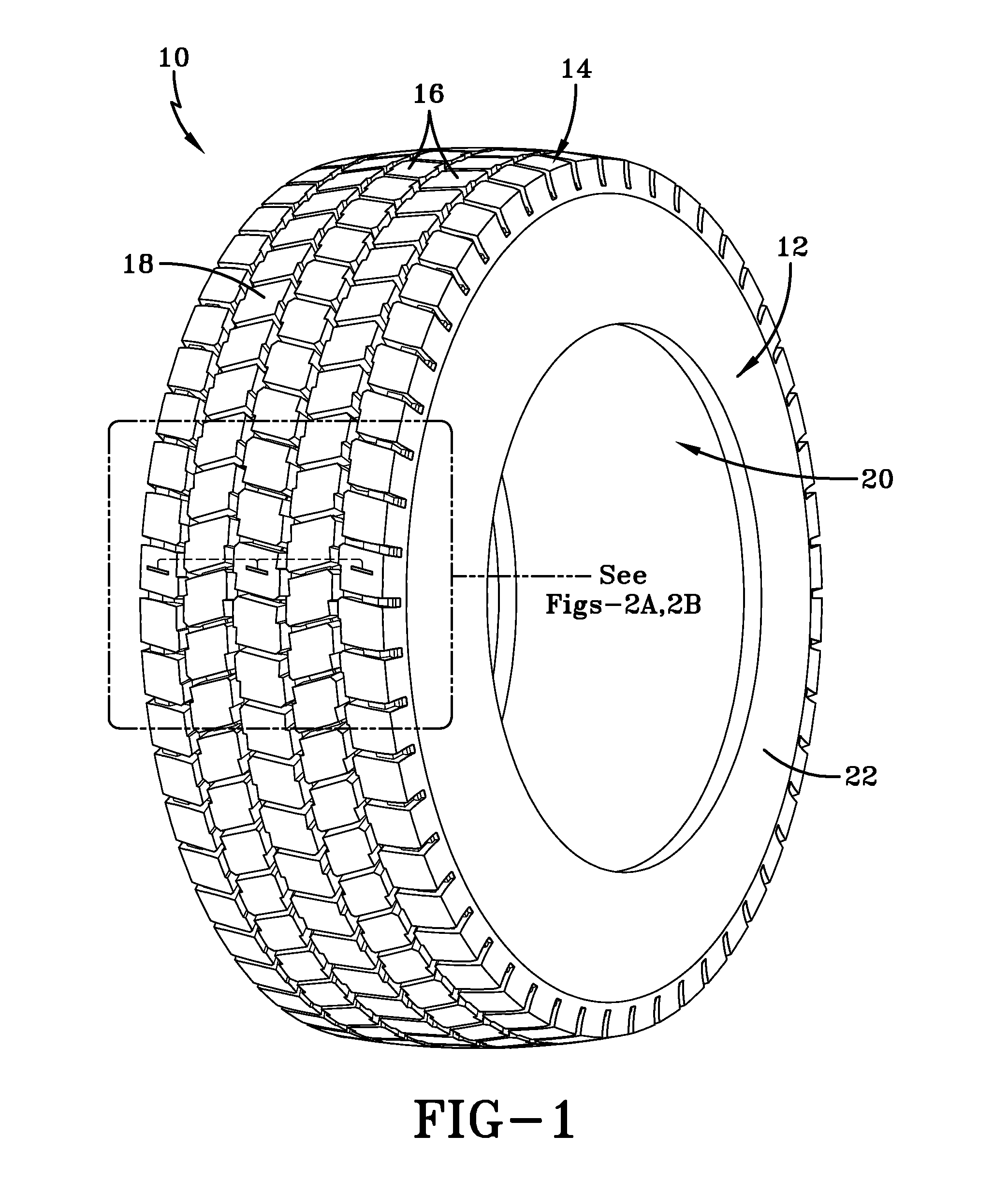
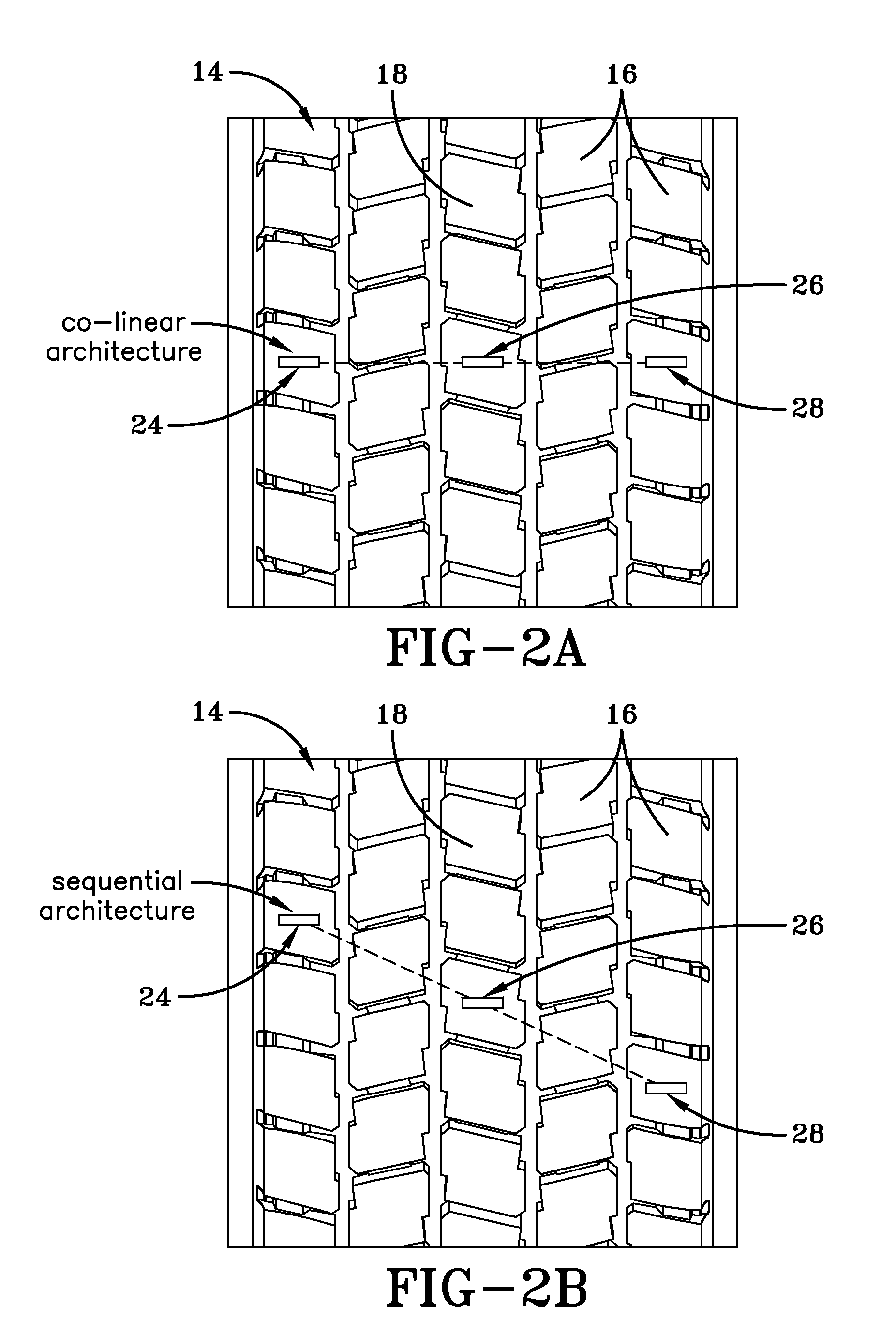
Method of tread wear sensor installation in a tire
ActiveUS20140360256A1Change resistanceTyre tread bands/patternsRoads maintainenceResistive sensorsTread
A method of installing a tread wear sensor in a tire includes configuring multiple tread wear indicators to each include a stack of sacrificial resistive sensor elements. The stacks of resistive sensor elements are affixed to respective selected tread lugs positioned at dispersed axial locations across a tire tread region. The resistive sensor elements sacrificially abrade and a change in resistance in each stack is measured. Connector assemblies within the tire carcass cavity are positioned radially opposite the selected tread lugs. A needle projection from each of the connector assemblies is inserted radially outward through the tire carrying leads which engage and establish electrical contact with a respective stack of resistive sensor elements.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Method for identifying compounds that affect a transport of a protein through menbrane trafficking pathway
InactiveUS20090294303A1Quality improvementHighly controllableImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsResistive sensorsElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Blast source based dam nondestructive detecting system
InactiveCN1991357AComprehensive monitoringAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSeismologyResistive sensorsGeophone
The invention discloses a lossless detection system for big bam based on the blasting source that consists of blasting source, receiving system, data recording system and data analyzing and processing system. The receiving system includes differential resistance sensor sets, vibrating wire sensor and geophone laid on the surface of bam. The geometrical position of the blasting source is located on the geometrical center or geometrical centerline. The invention adopts the blasting with known equivalent, and the acoustics parameters of elastic wave are received by the sensor berried on the surface and the interior of bam, then acoustics parameters and waveform change are analyzed by the computer, and the disadvantages and the extent of disadvantages can be determined, and the dynamic monitor for the bam can be realized.
Owner:CHINA GEZHOUBA GROUP CO LTD +1
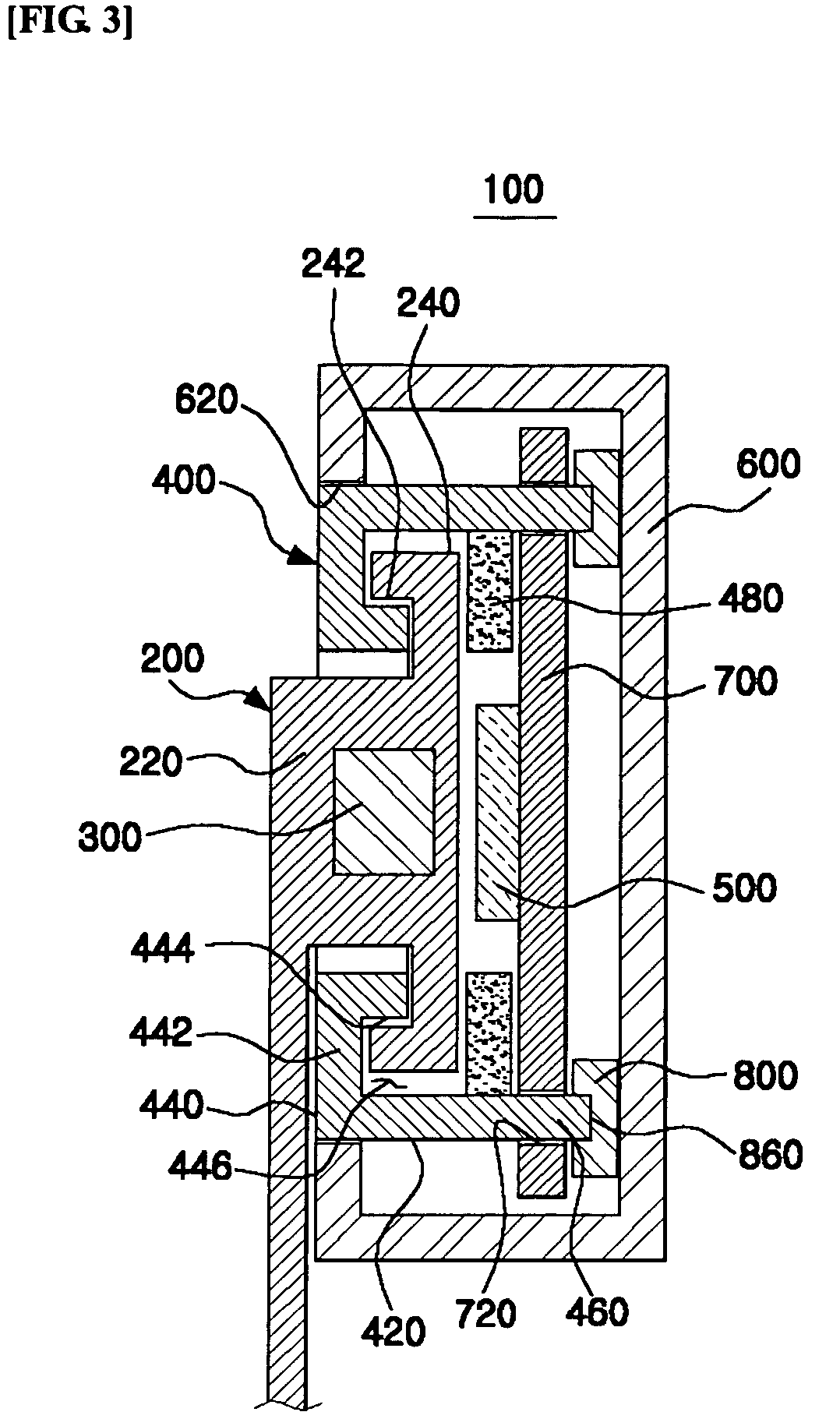
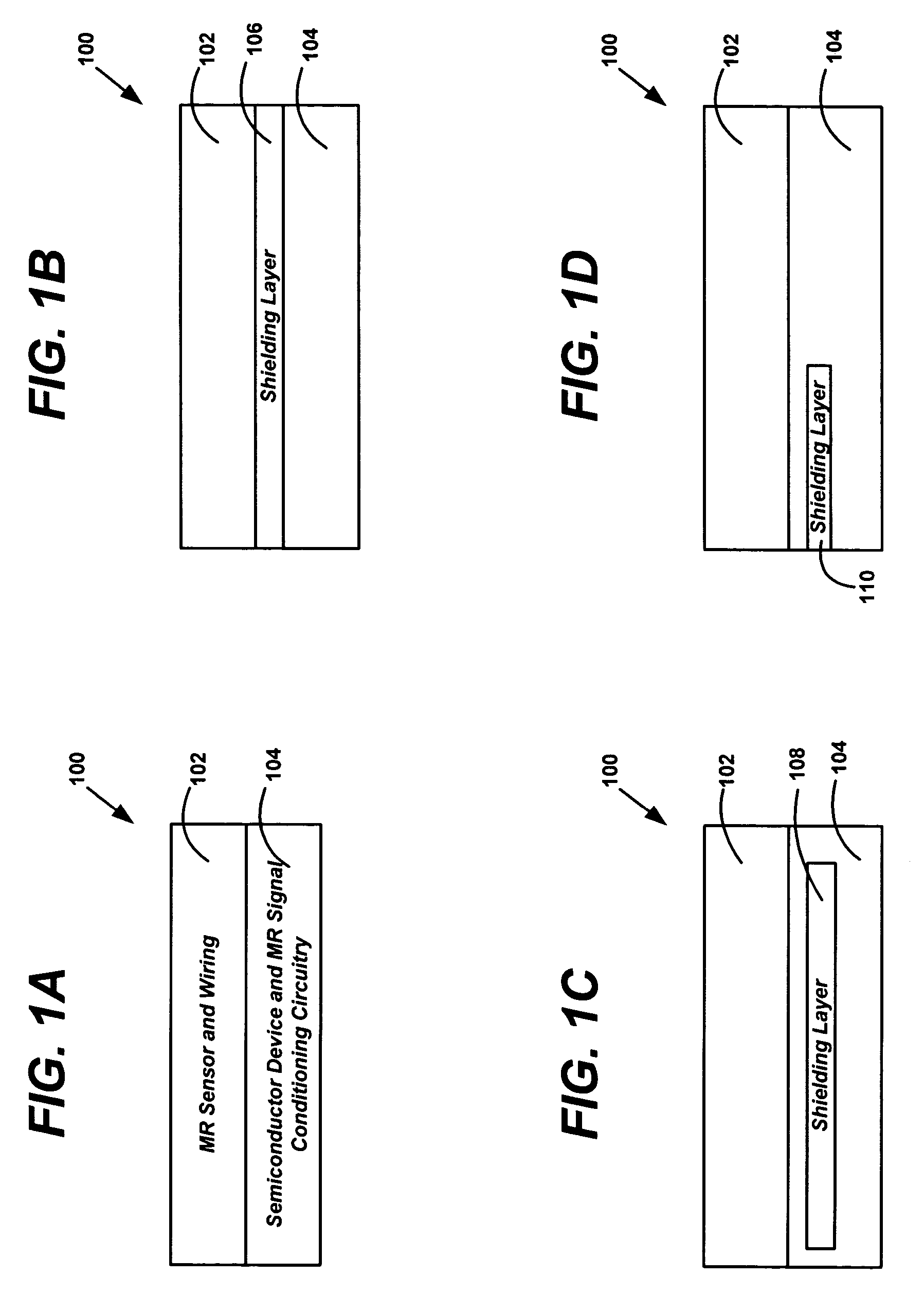
Sensor device and method
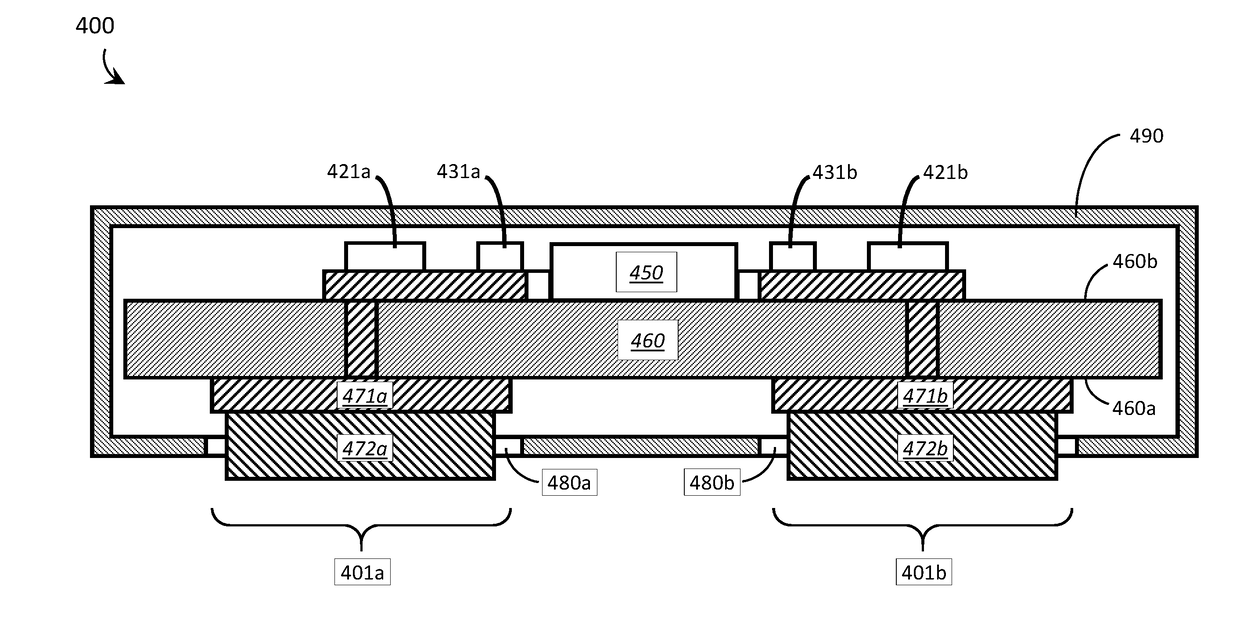
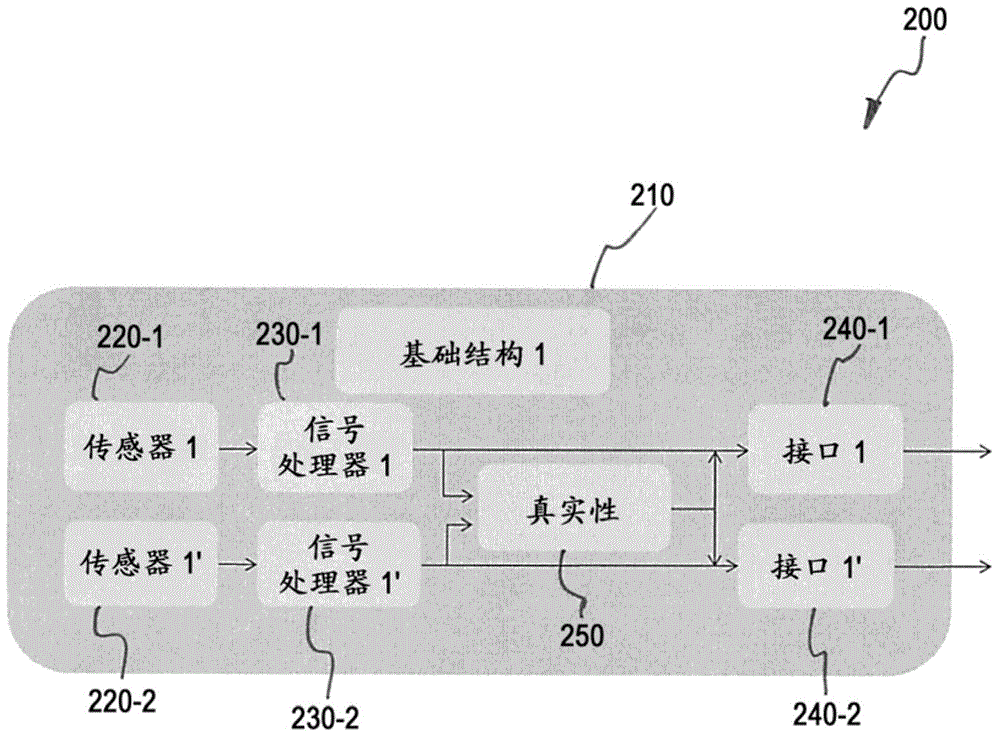
Embodiments relate to a sensor device including a layer stack 600, the layer stack 600 including at least ferromagnetic and non-magnetic layers formed on a common substrate 620. The sensor device 600 further includes at least a first magneto-resistive sensor element 711 provided by a first section 611 of the layer stack 600. The first magneto-resistive sensor element 711 herein is configured to generate a first signal. The sensor device 600 also includes a second magneto-resistive sensor element 712 provided by a second section 612 of the layer stack 610. The second magneto-resistive sensor element 712 herein is configured to generate a second signal for verifying the first signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com