Patents
Literature
5286results about "Electrical/magnetic solid deformation measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
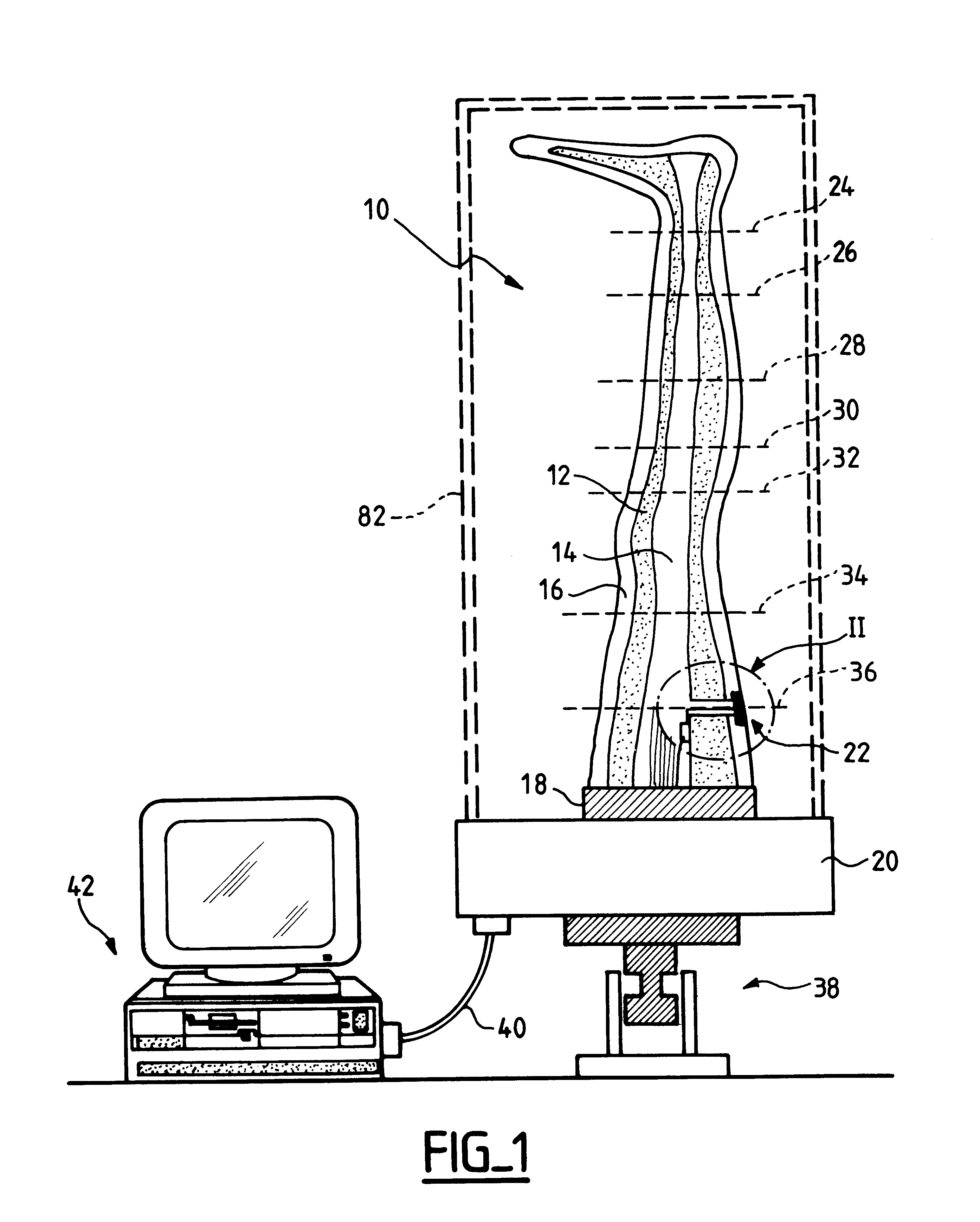
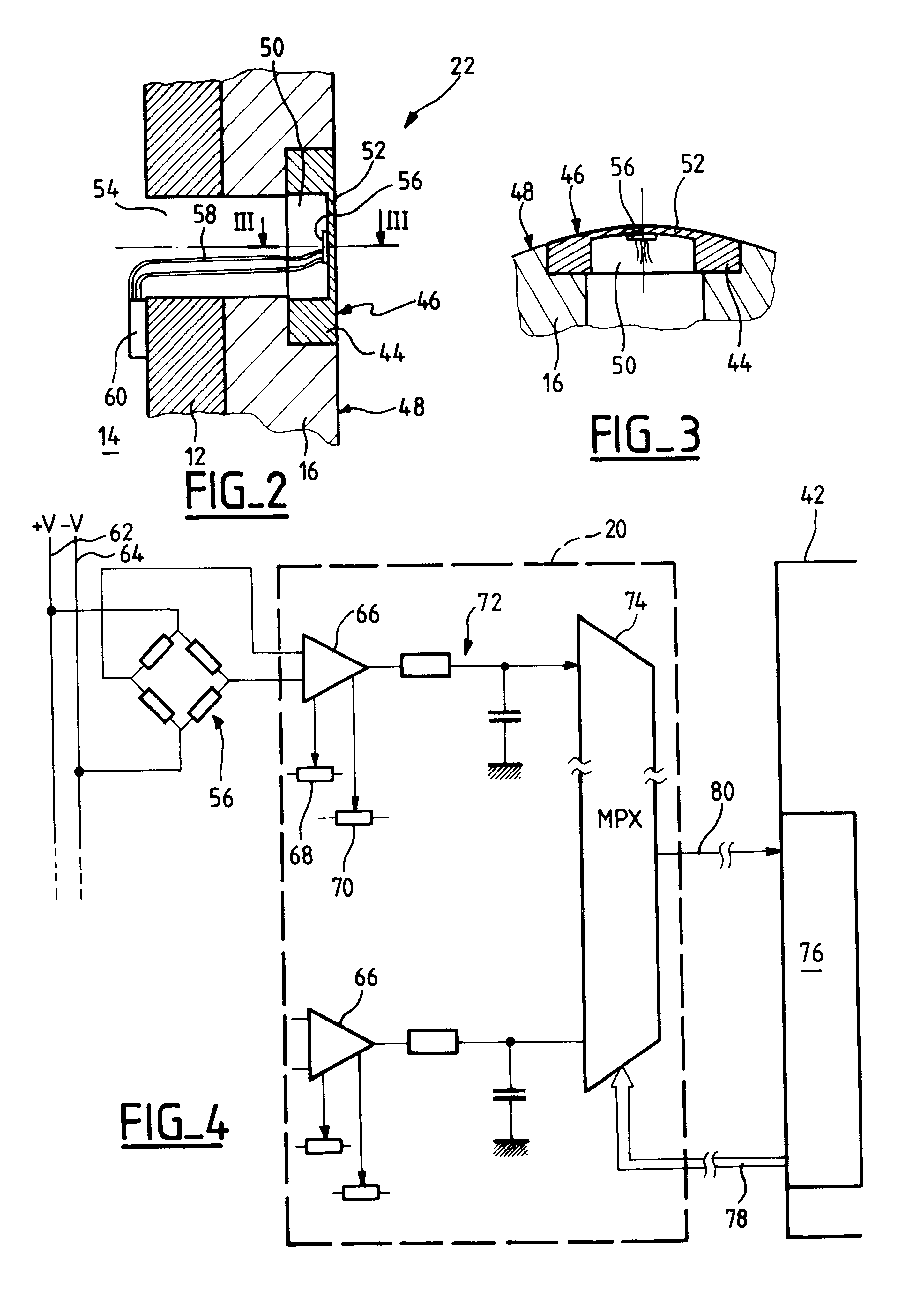
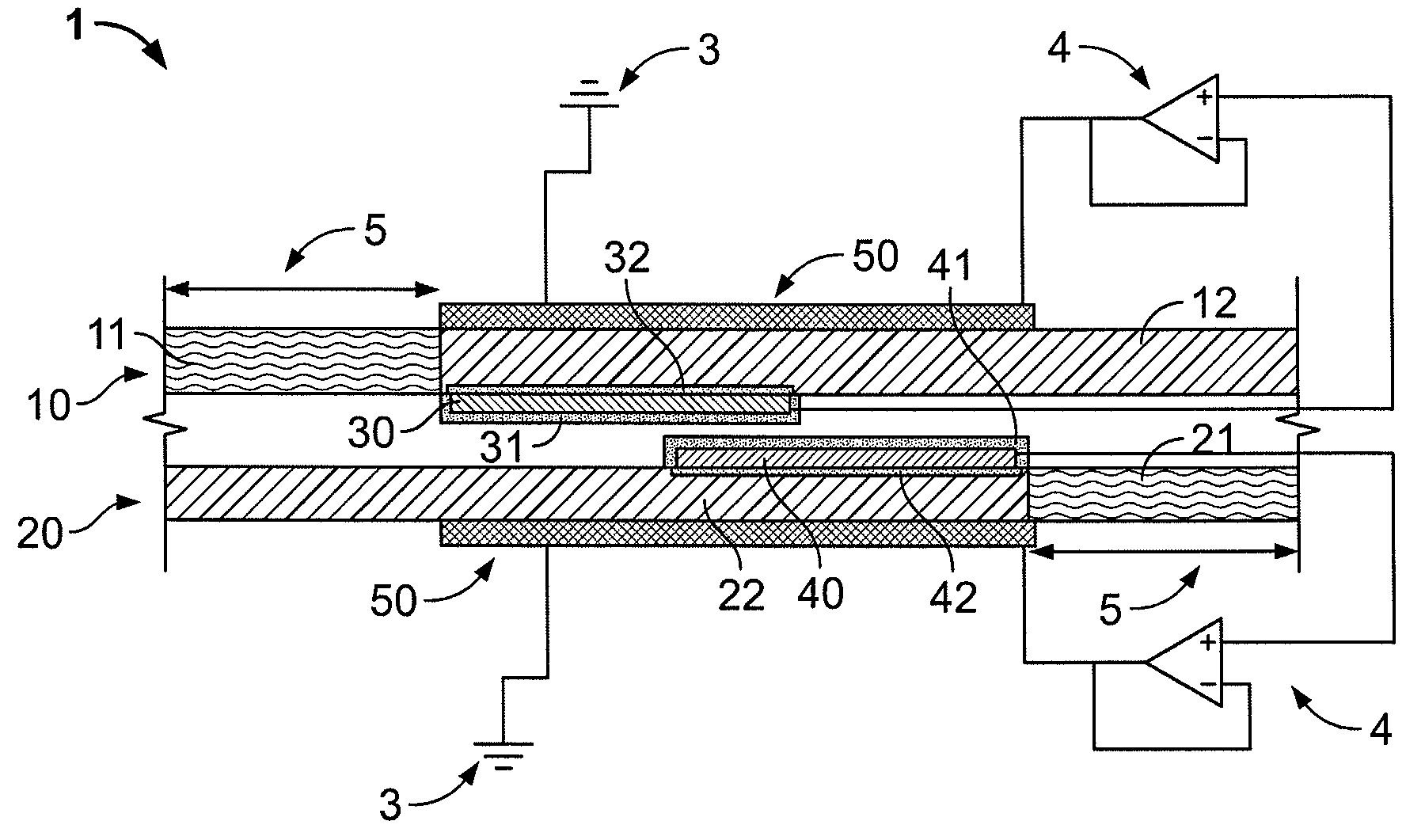
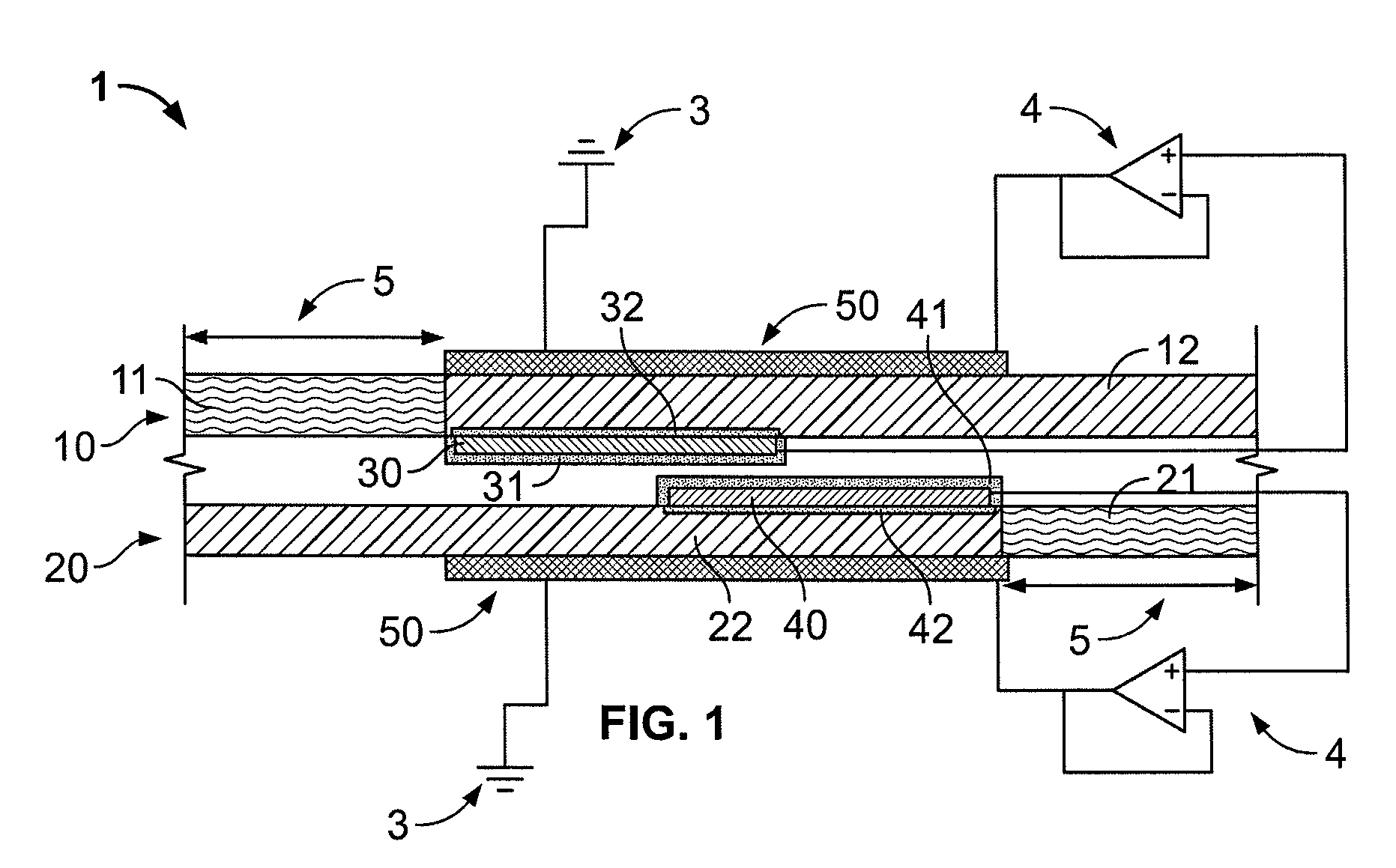
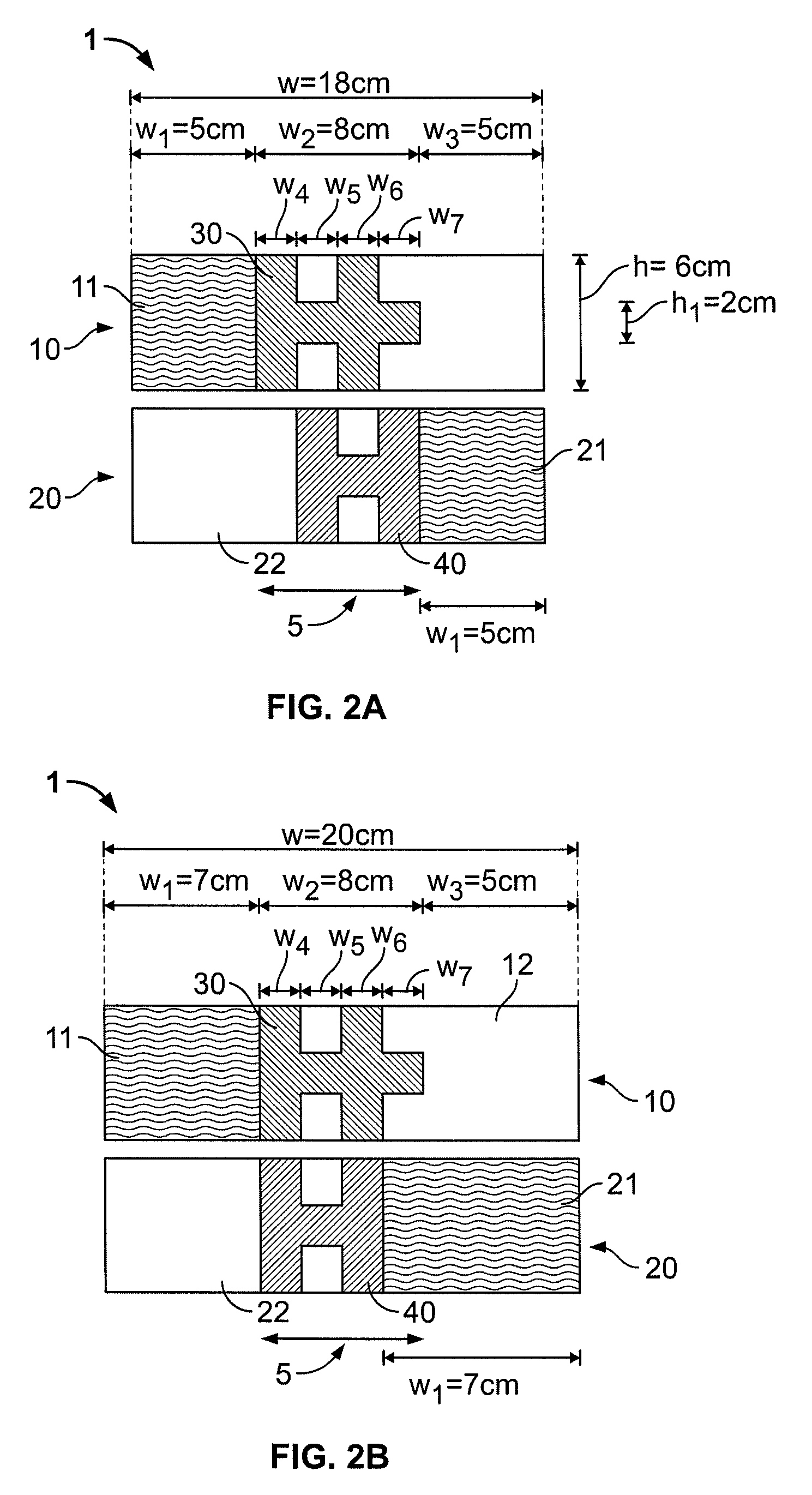
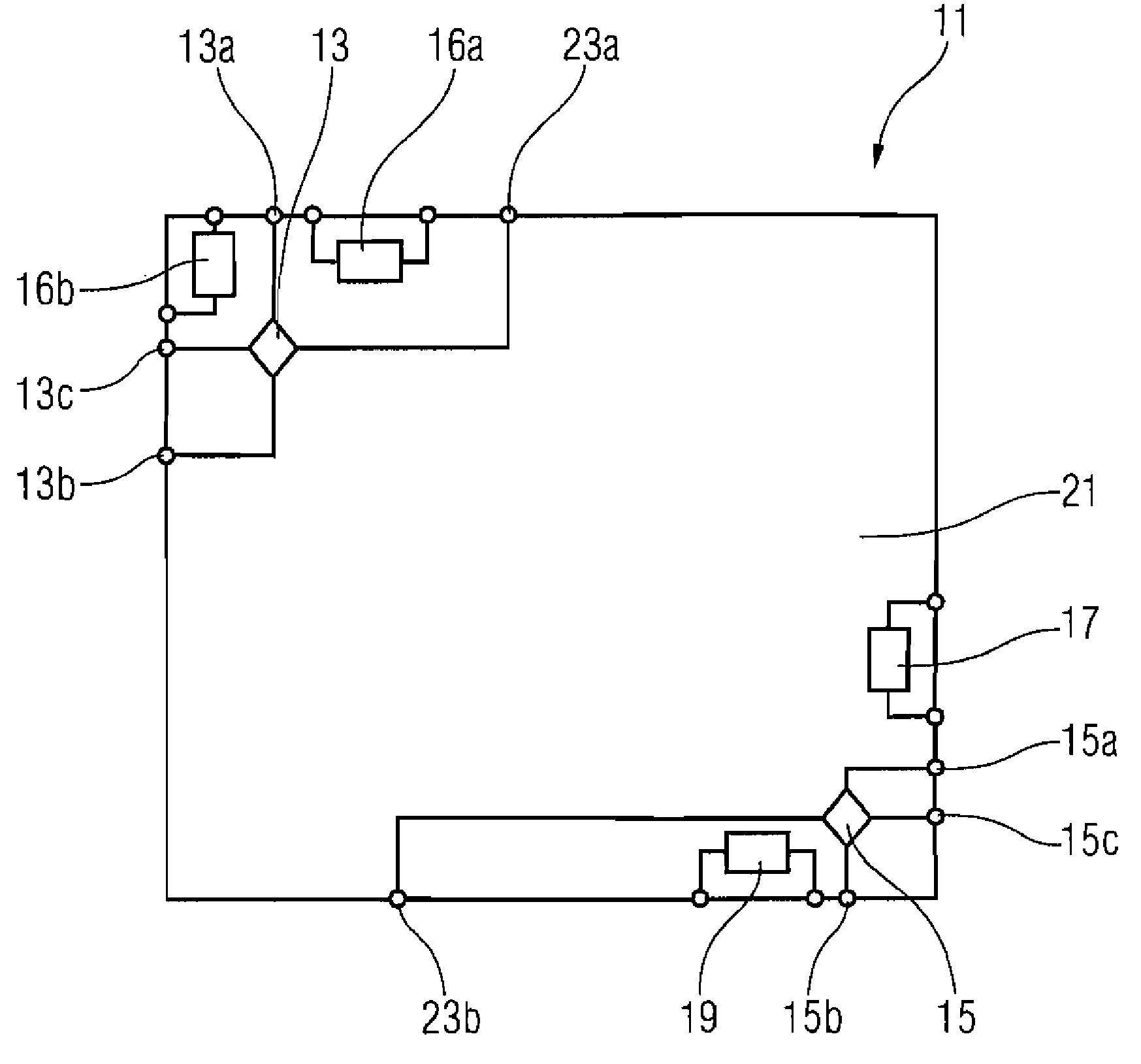
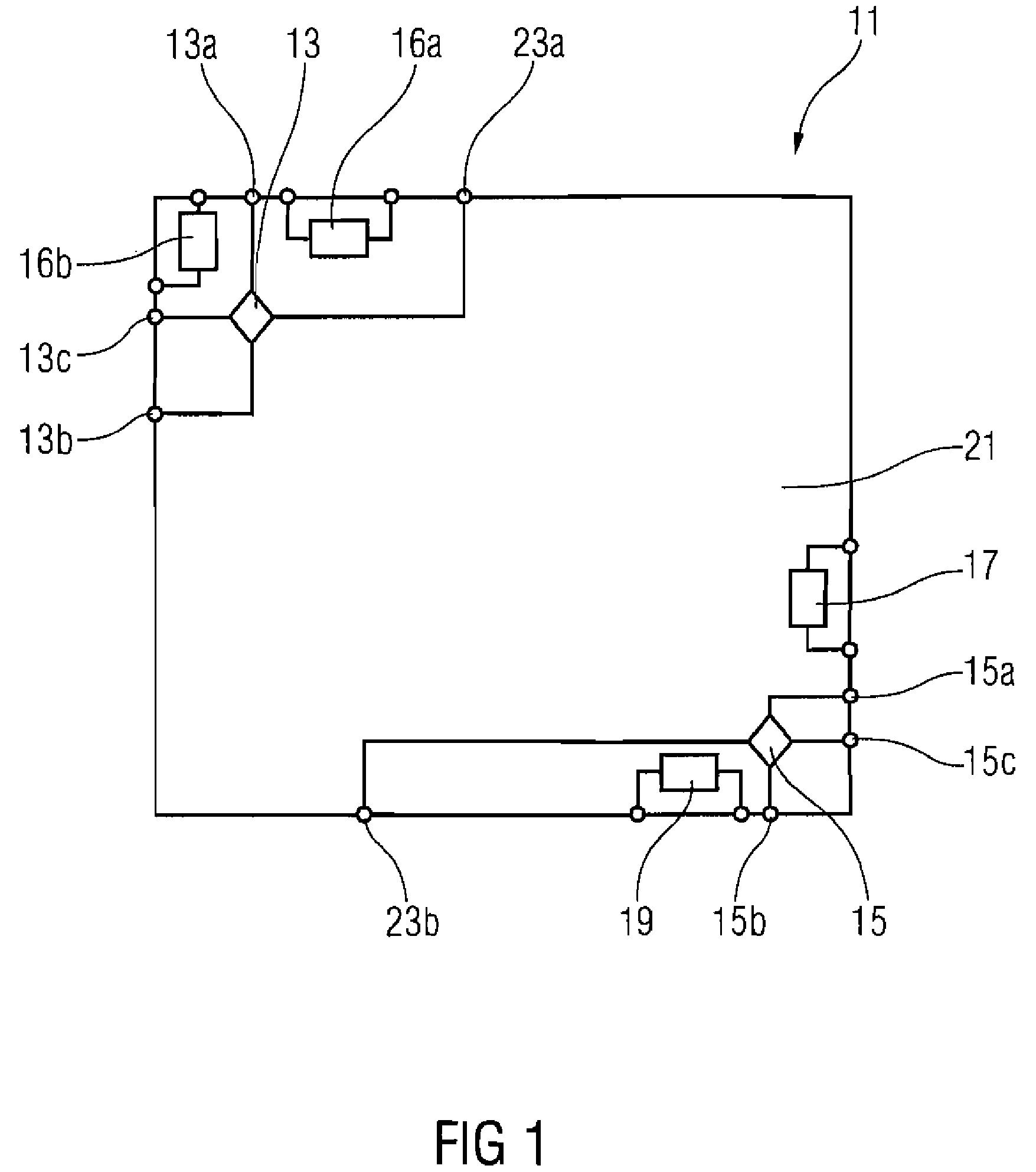
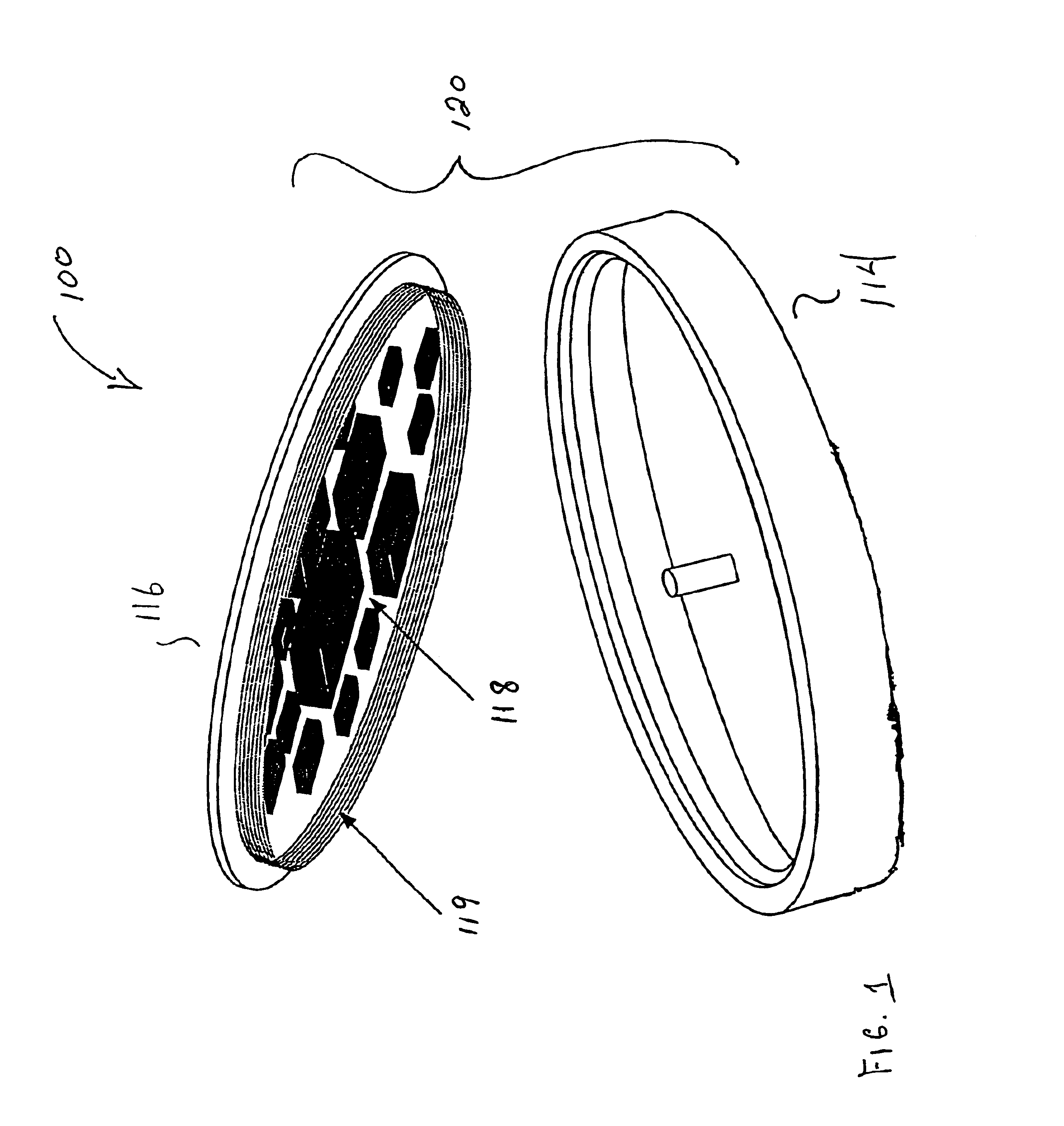
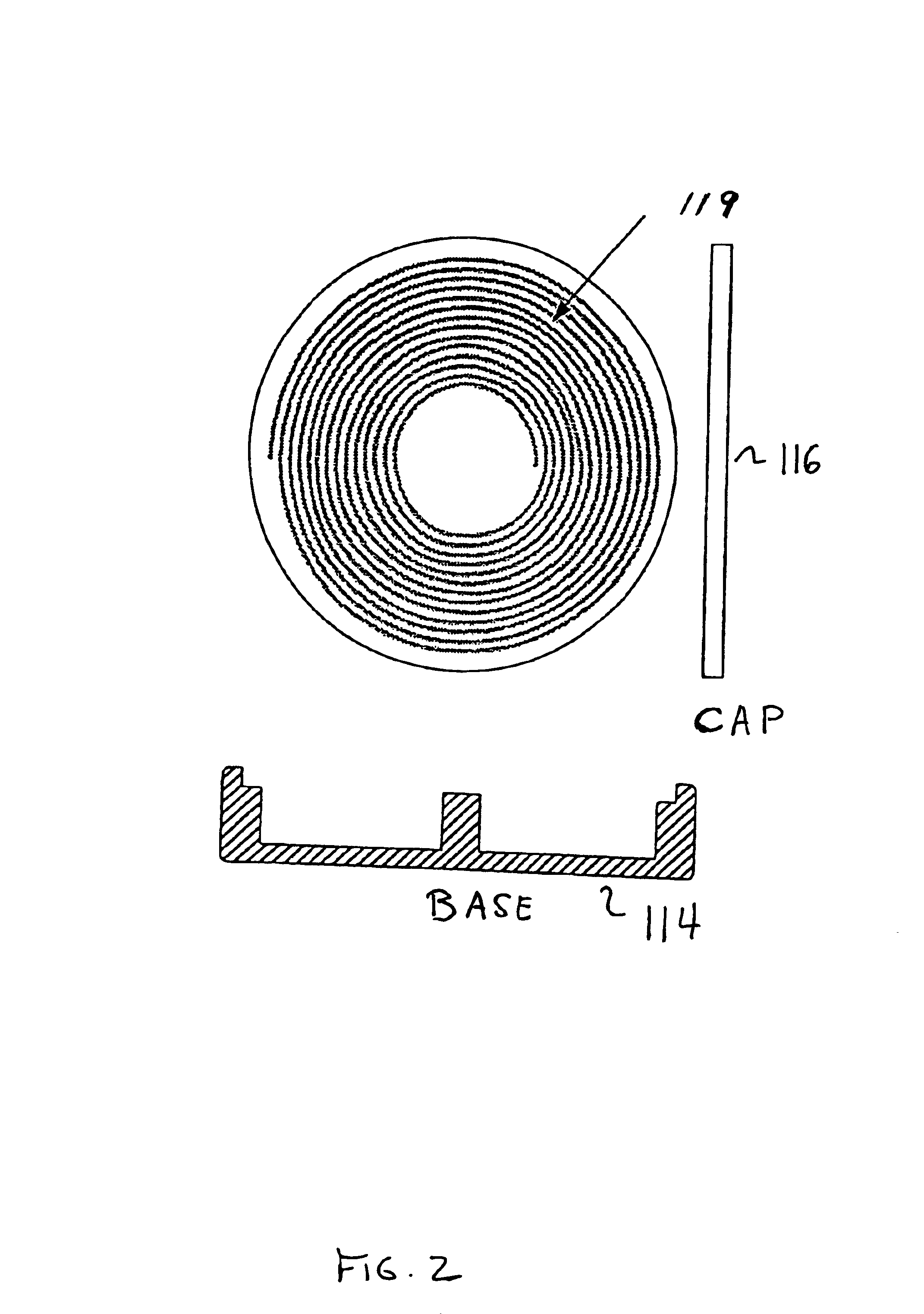
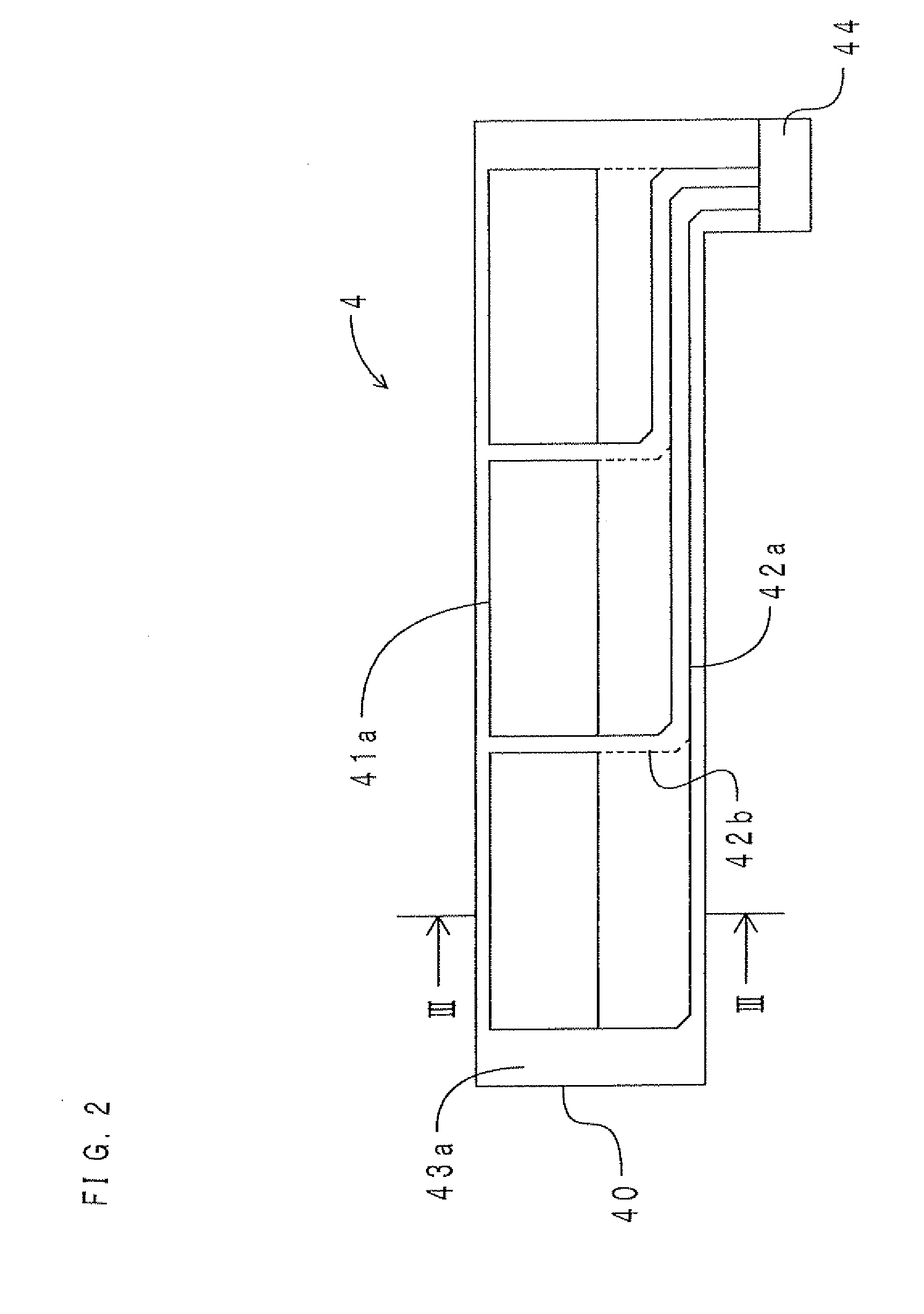
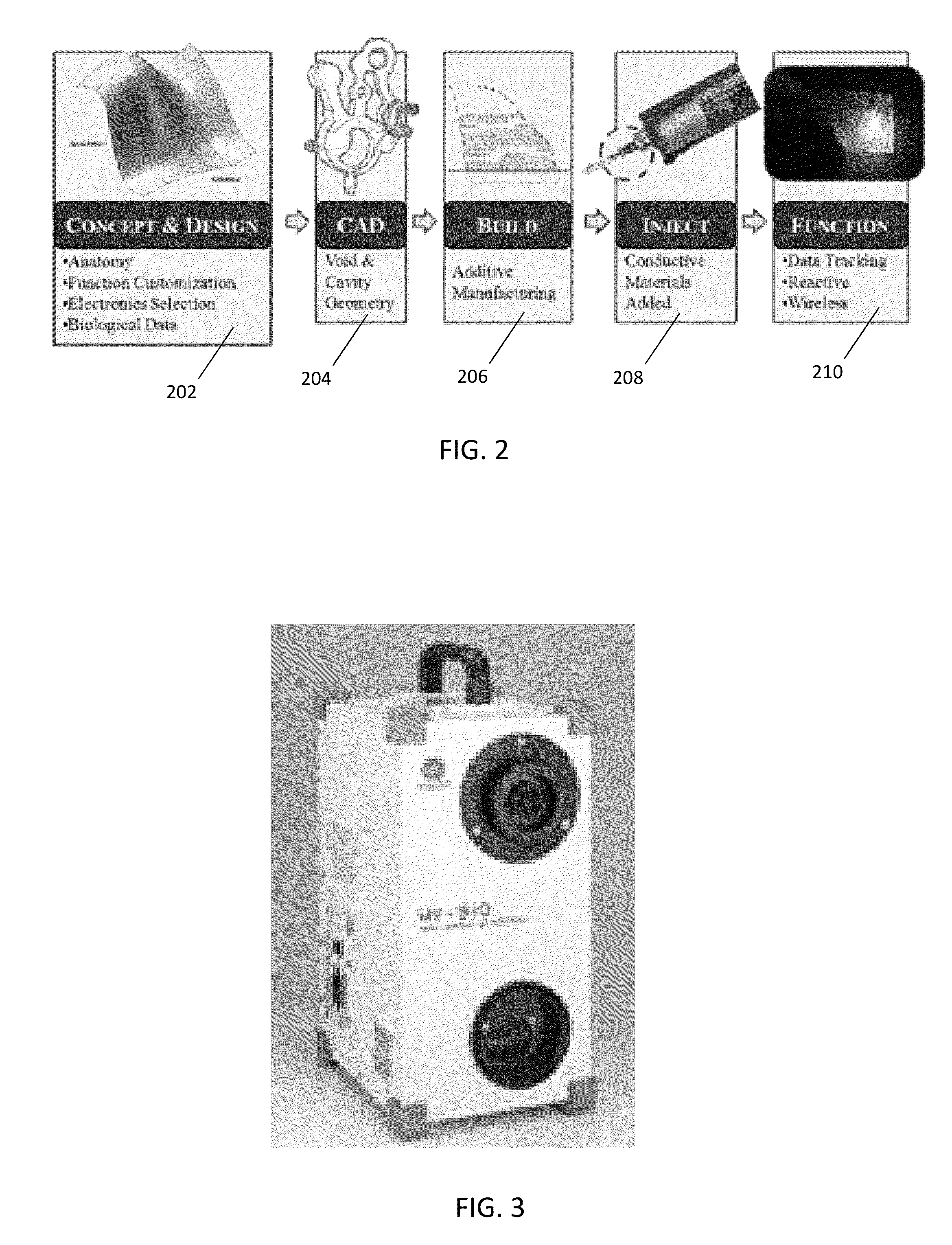
Strain monitoring system and apparatus
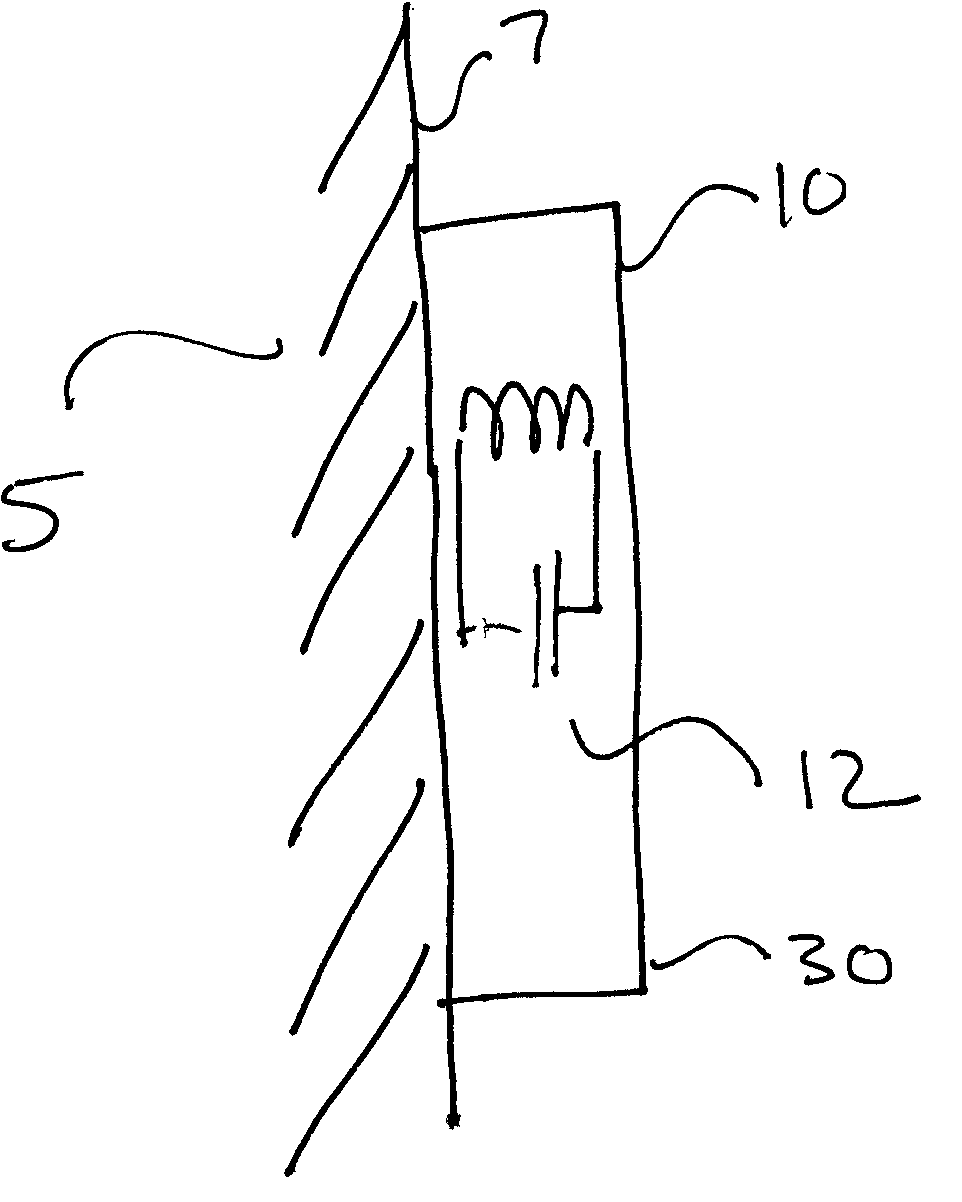
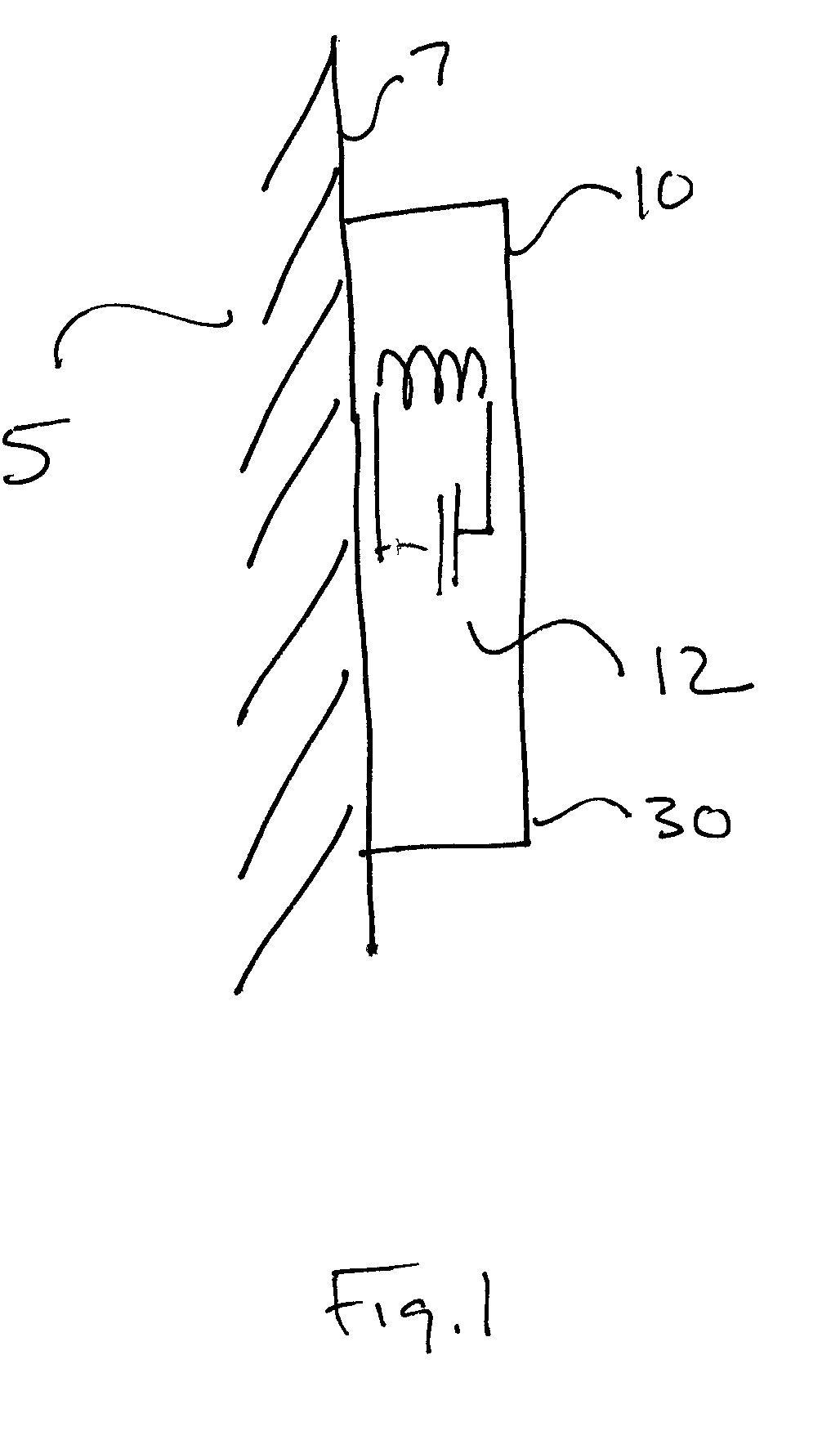
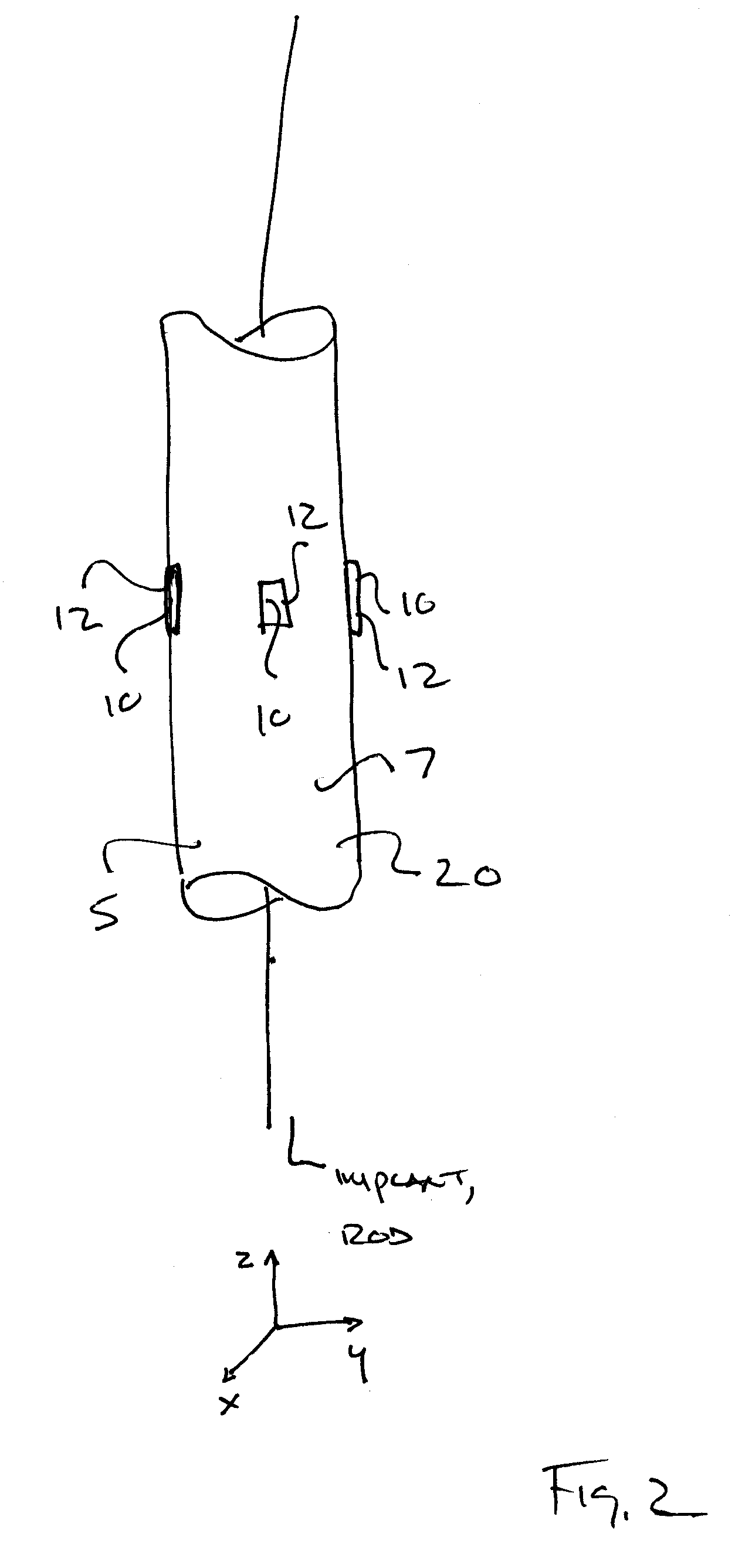
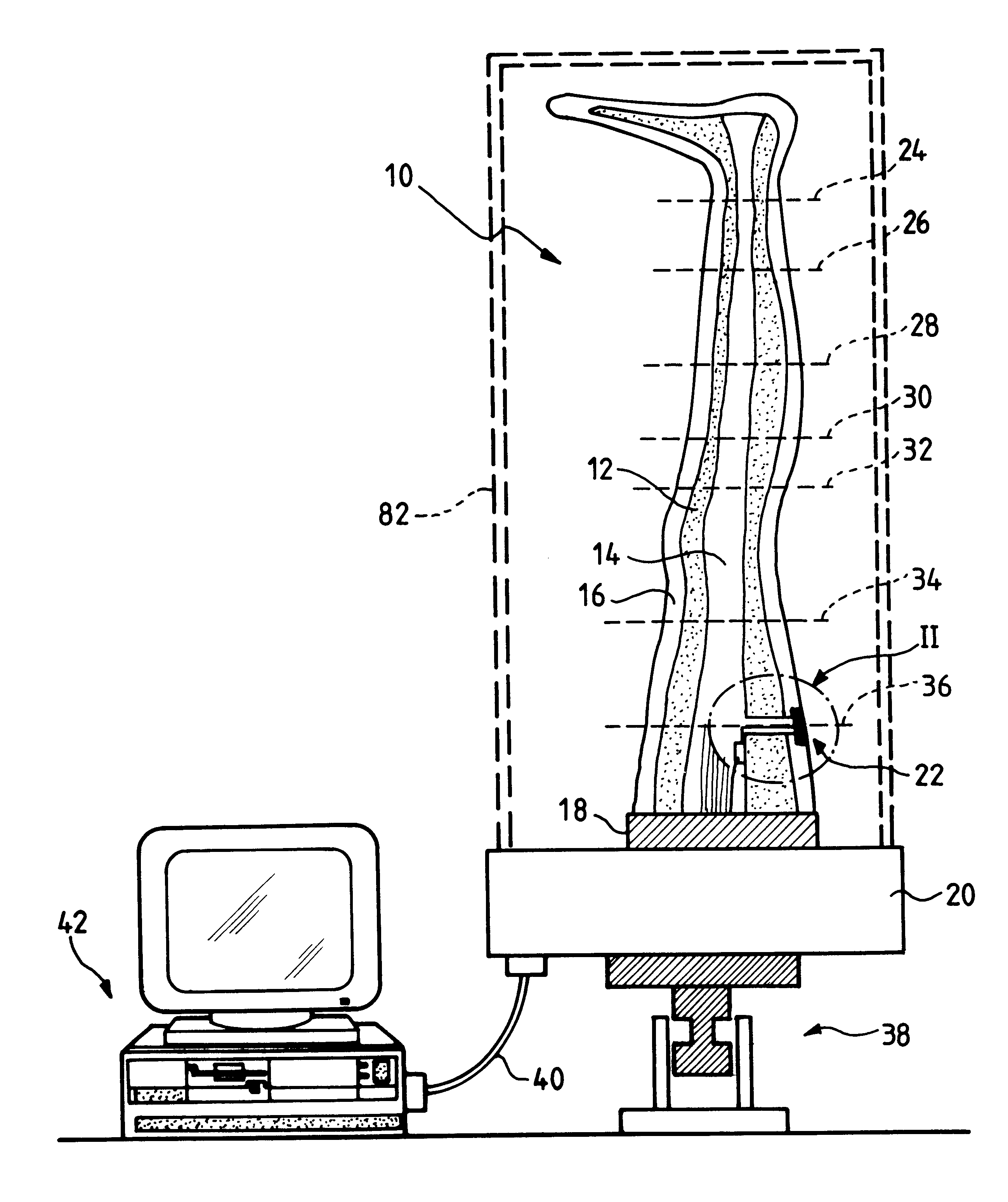
ActiveUS20090273353A1Internal osteosythesisResistance/reactance/impedenceElectromagnetic couplingBiological body
This application relates to an apparatus and system for sensing strain on a portion of an implant positioned in a living being. In one aspect, the apparatus has at least one sensor assembly that can be mountable thereon a portion of the implant and that has a passive electrical resonant circuit that can be configured to be selectively electromagnetically coupled to an ex-vivo source of RF energy. Each sensor assembly, in response to the electromagnetic coupling, can be configured to generate an output signal characterized by a frequency that is dependent upon urged movement of a portion of the passive electrical resonant circuit and is indicative of strain applied thereon a portion of the respective sensor assembly.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
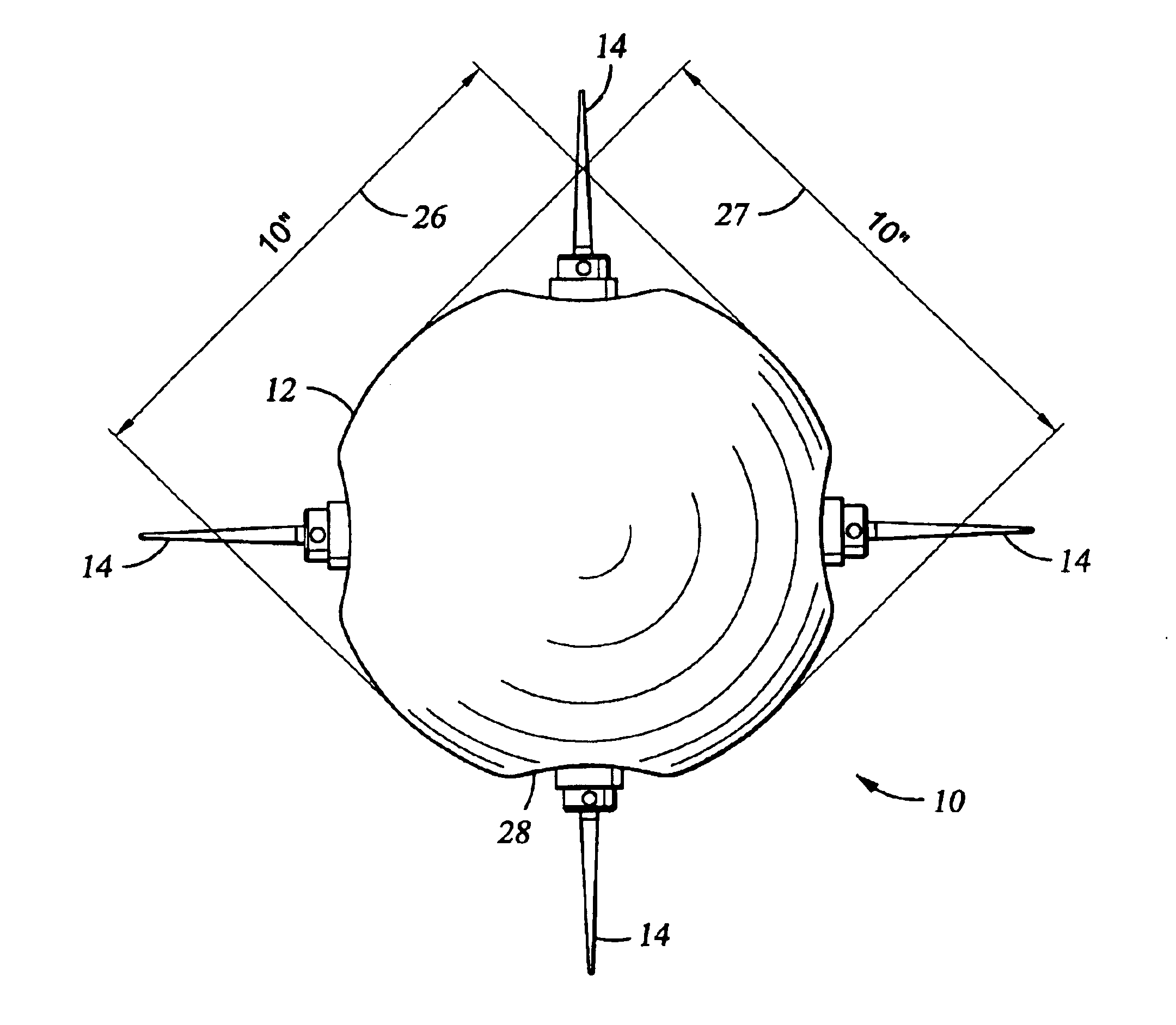
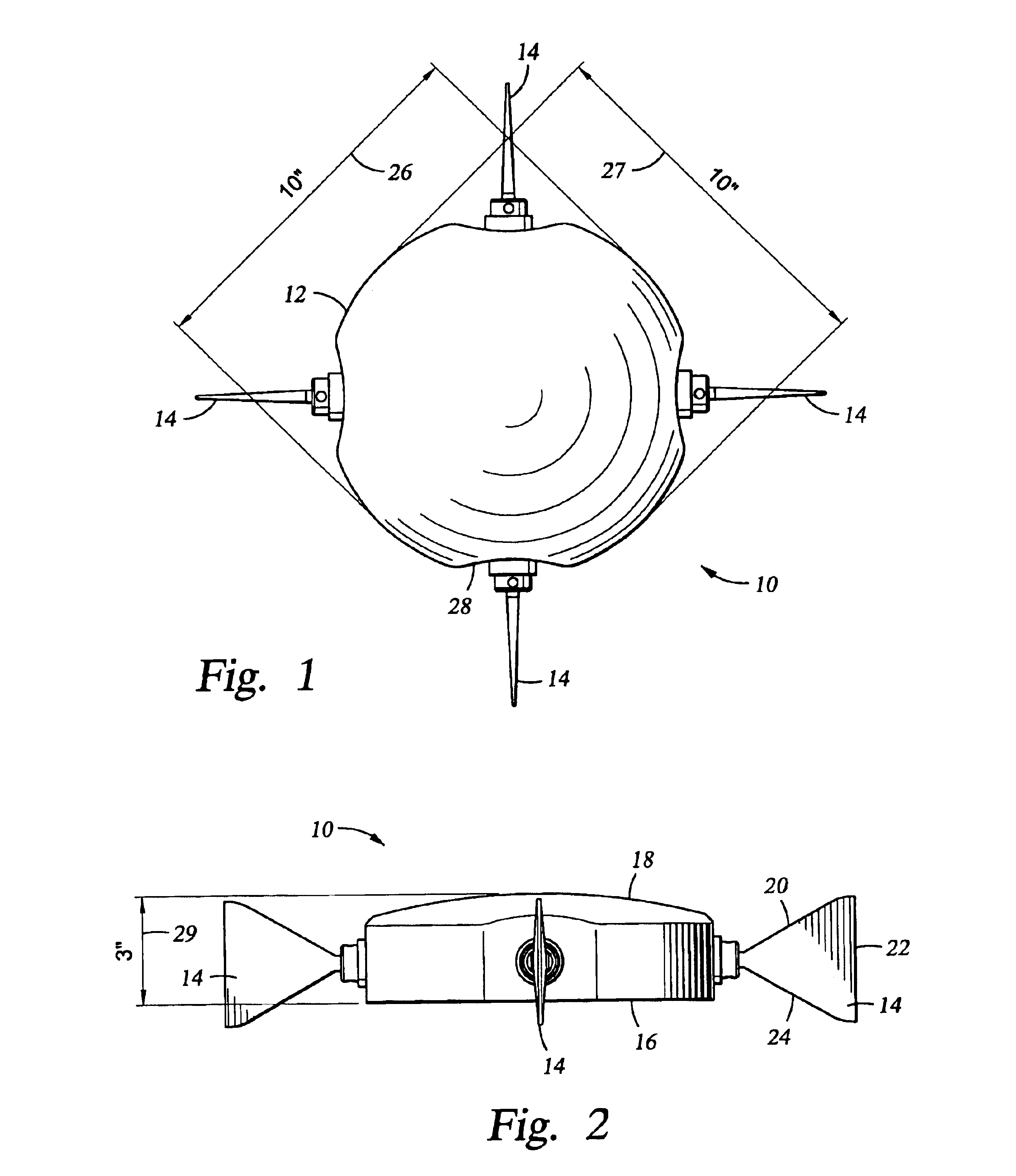
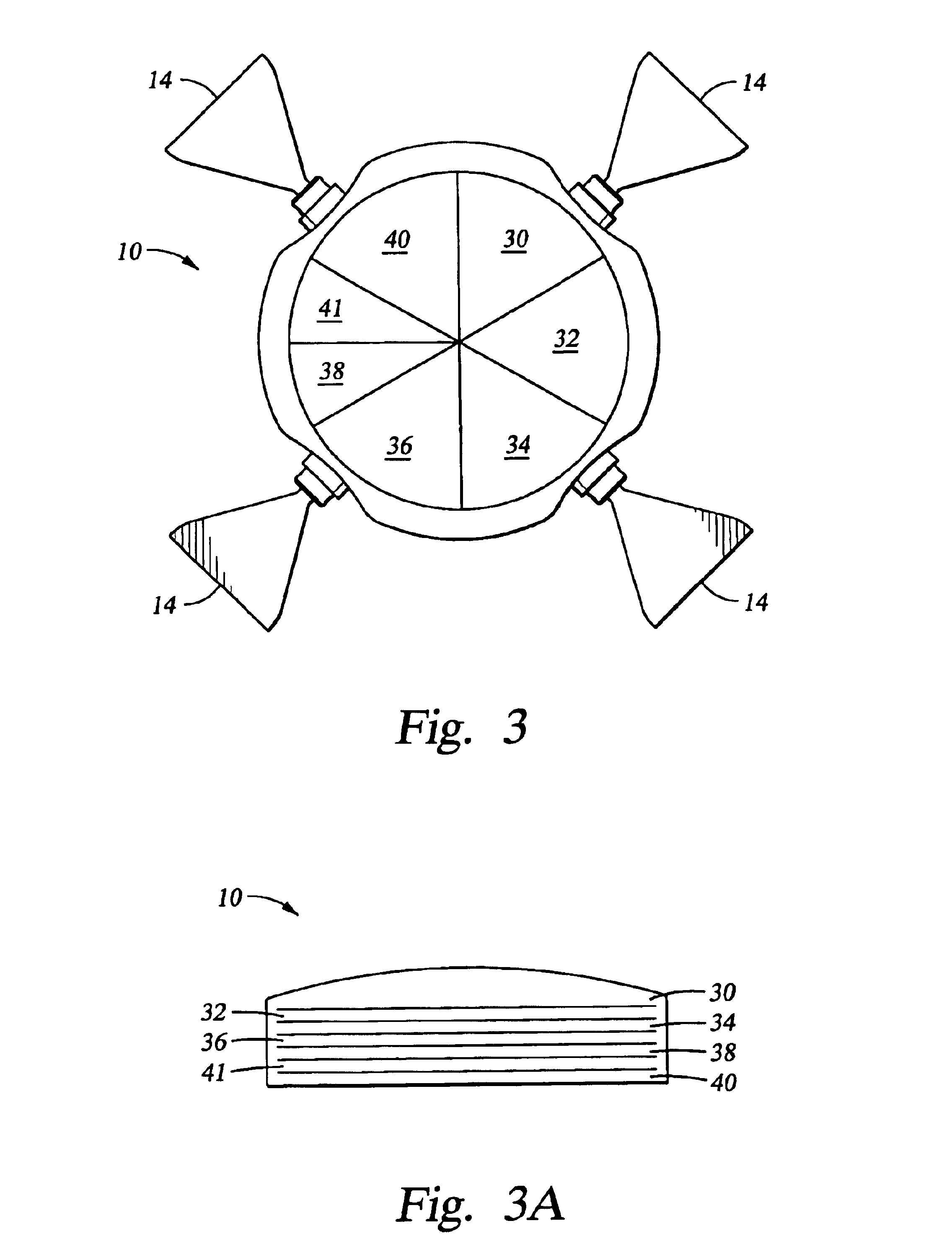
Device for measuring pressure points to be applied by a compressive orthotic device
The device comprises a rigid former reproducing the volume of a portion of the body and suitable for receiving the compressive orthosis. The former (10) incorporates a plurality of sensors (22) distributed over various points of the former and configured in such a manner as to avoid significantly modifying the surface profile of the former, the sensors essentially measuring the pressure applied locally on the former by the orthosis at the location of the sensor and perpendicularly to the surface of the former. Advantageously, at the location of the measurement point, each sensor comprises a thin wall capable of being subjected to microdeformation under the effect of the pressure applied by the orthosis, and means such as a strain gauge bridge, for example. The thin wall can constitute a portion of a support pellet which is fitted to the former in such a manner that its outside surface, which includes the thin wall, is flush with the outside surface of the former.
Owner:INNOTHERA TOPIC INT
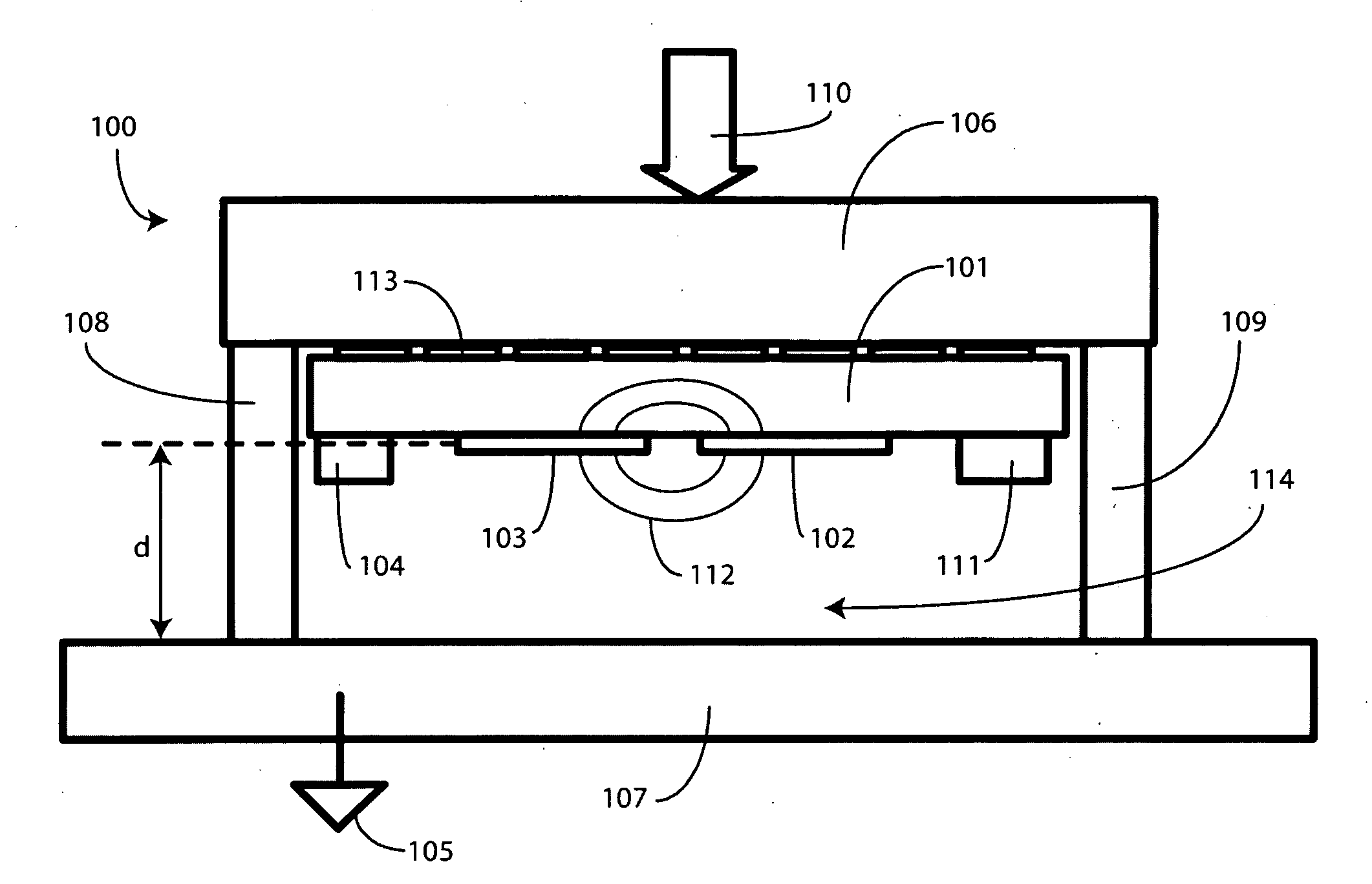
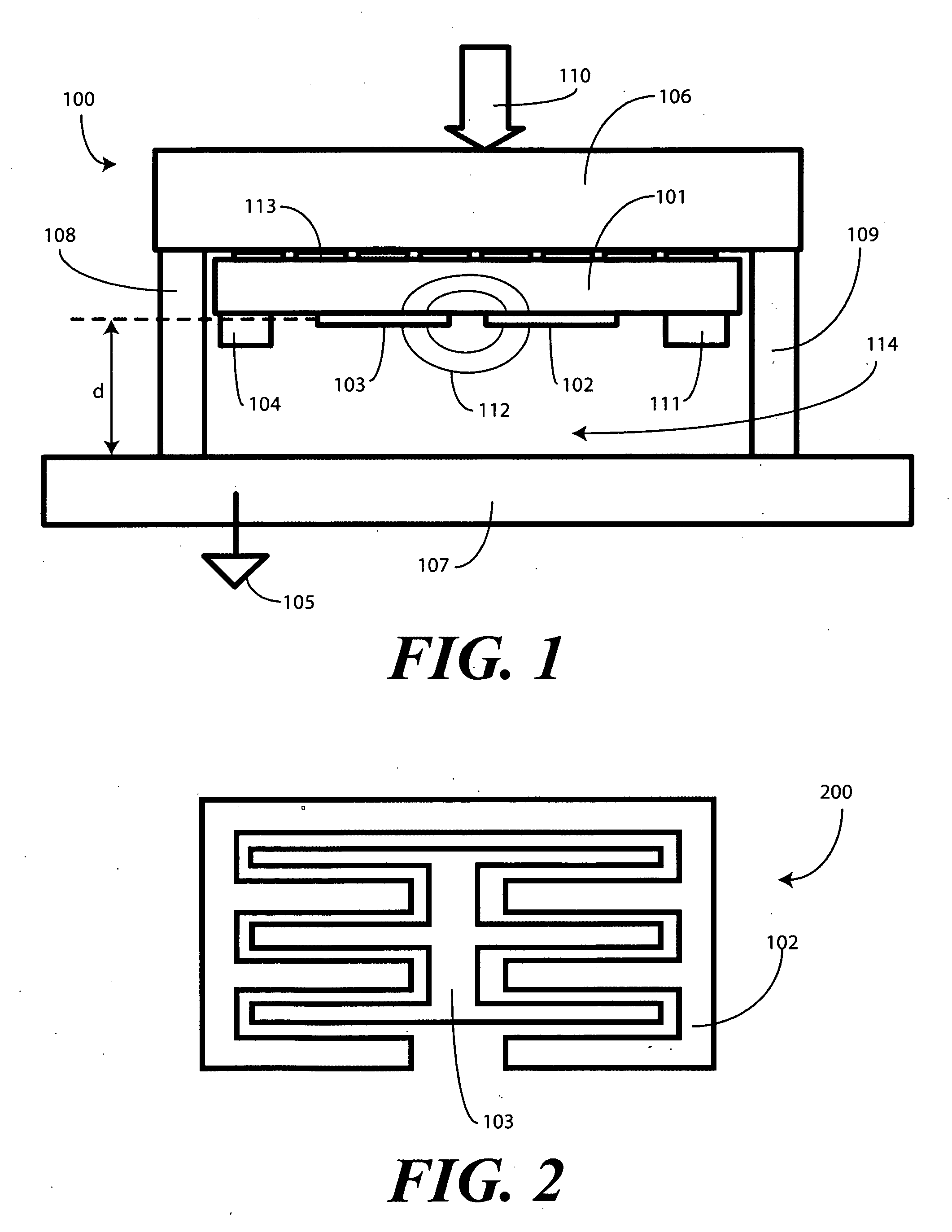
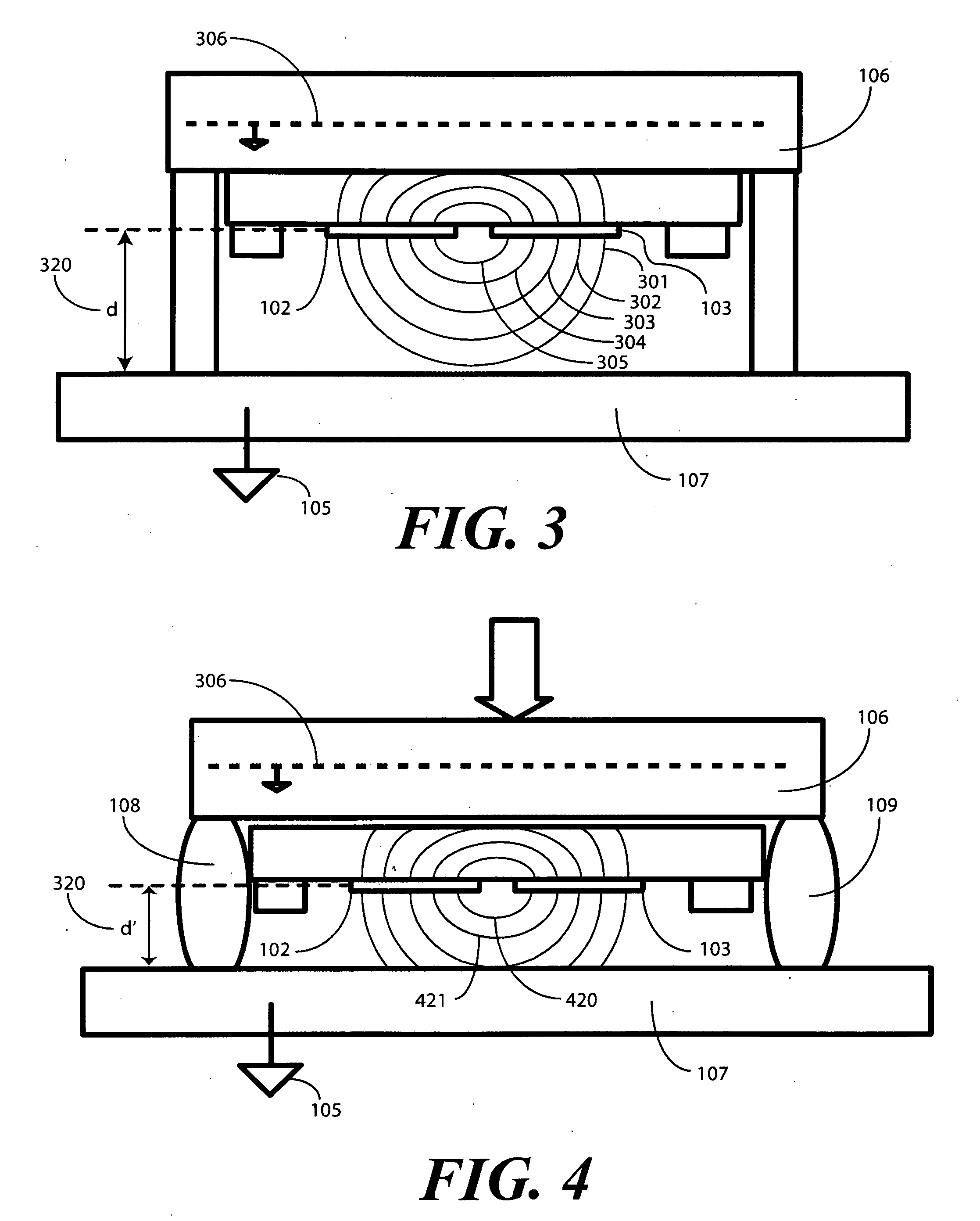
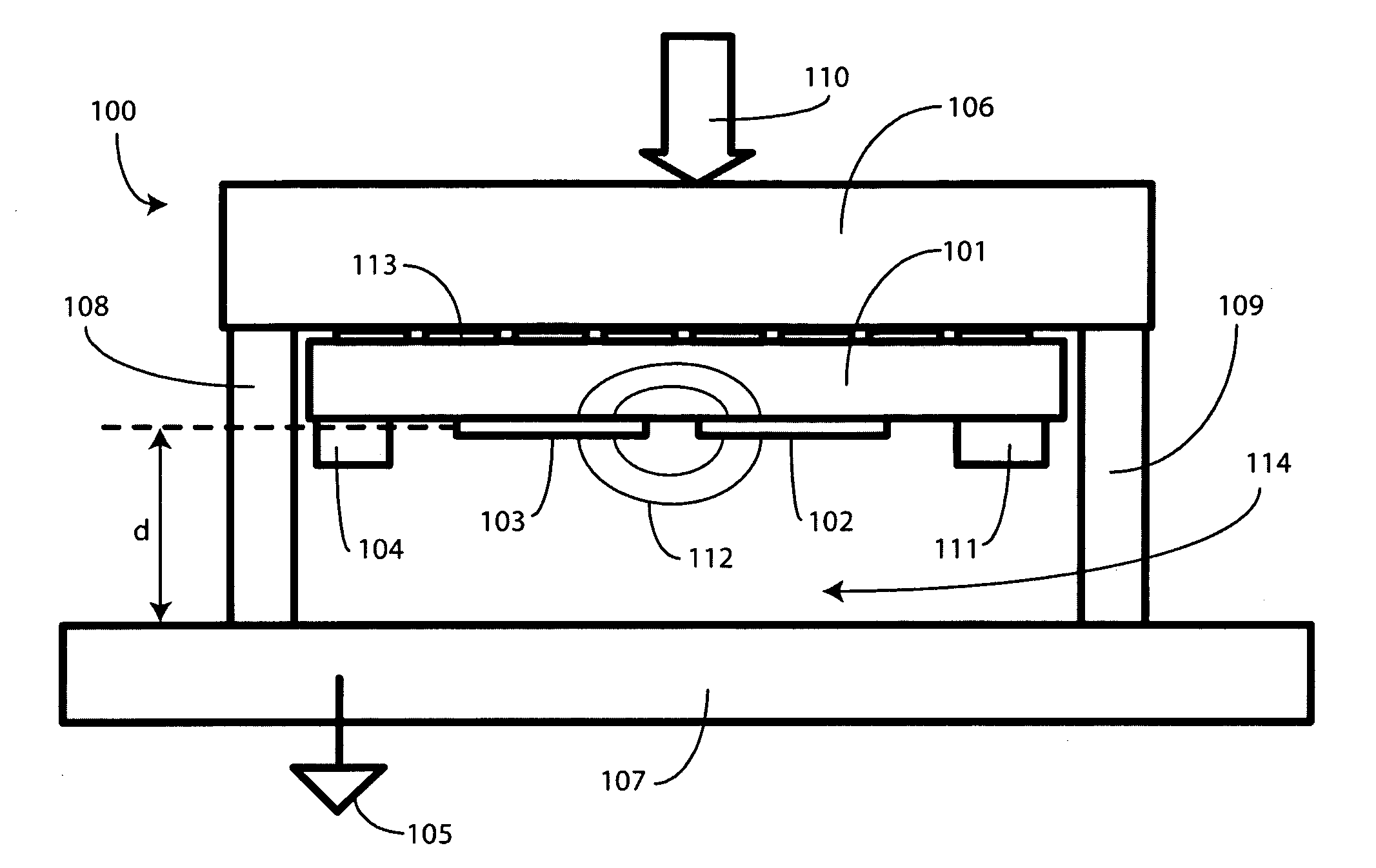
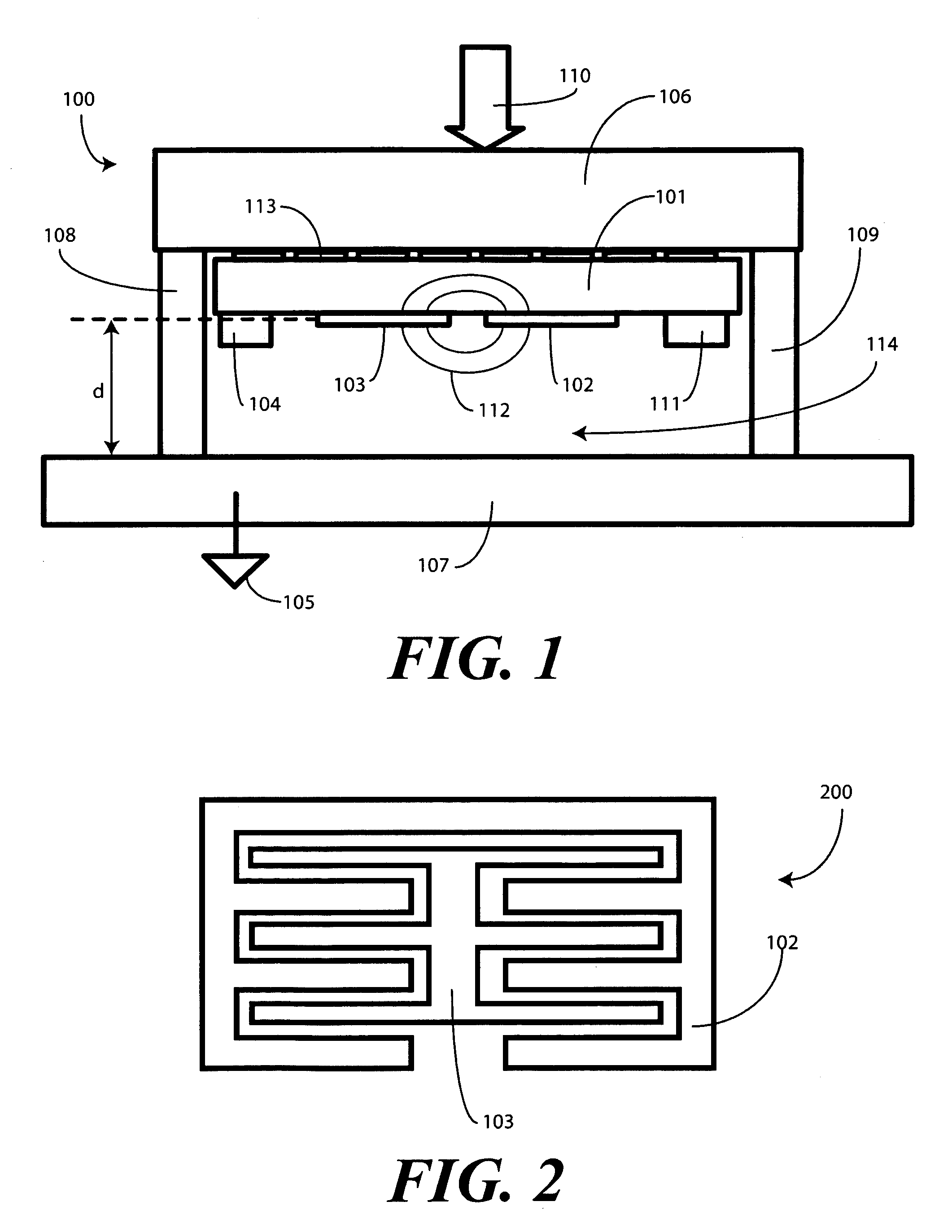
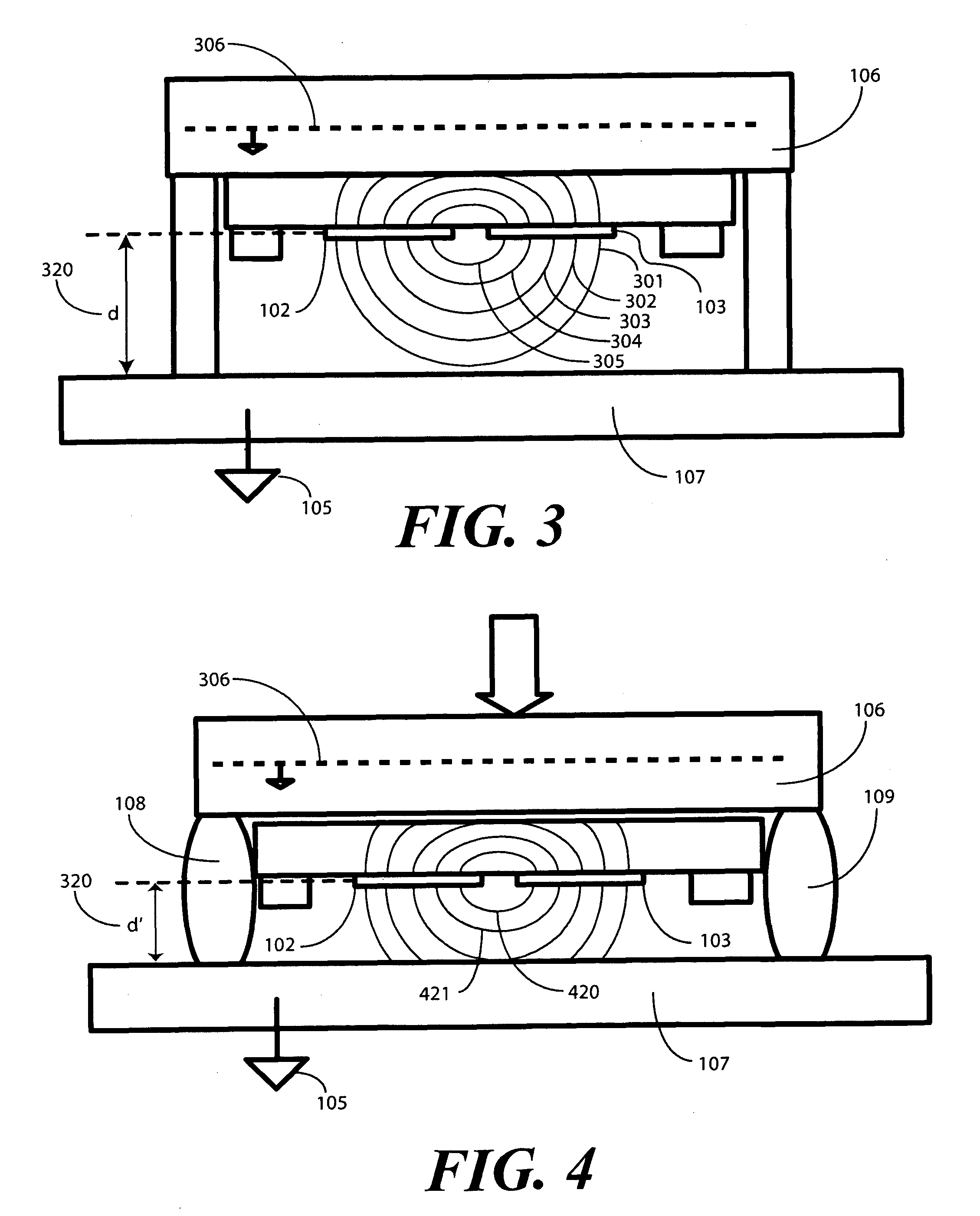
Single Sided Capacitive Force Sensor for Electronic Devices
A capacitive force sensor (100) includes a substrate (101) having at least one electrode pair (102,103) defining a capacitance disposed thereon. The substrate (101) is fixed relative to a first plate (106). A drive circuit (104) is configured to apply a voltage relative to a circuit ground (105) to the electrode pair (102,103). The first plate (106) is separated from a second plate (107) that is coupled to circuit ground (105) by a compliance member (108,109). The compliance member (108,109) is configured to oppose a compression force (110) while allowing the first plate (106) to physically move relative to the second plate (107). A capacitive detection circuit (111) is then configured to detect a change the capacitance when the compliance member (108,109) is compressed. The compression force (110) is then determined from the change in capacitance and the spring constant of the compliance member (108,109).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Pressure sensing or force generating device
ActiveUS20120055257A1Few contactsShorten the counting processPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceCapacitive effect
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a pressure sensing / force generating device comprising a non-planar substrate, a printed pressure sensitive element comprising (a) a piezoelectric material containing ink composition capable of producing a piezoelectric effect / piezoresistive effect and / or (b) a dielectric material containing ink composition capable of producing a capacitive effect. It also includes a first printed electrode comprising a conductive ink composition, and a second printed electrode comprising a conductive ink composition. The first and second electrodes are in electrical contact with the printed pressure sensitive element. The first and second printed electrodes and the printed pressure sensitive element collectively form a pressure sensitive junction, which is coupled to the non-planar substrate. The present invention further relates to medical devices comprising the pressure sensing / force generating device and methods of making such devices.
Owner:MICROPEN TECH CORP
Sensor device for real-time monitoring or relative movement using capacitive fabric sensors
InactiveUS7712373B2Accurately and precisely measuring respiratory functionForce measurementElectric/magnetic position measurementsParallel plateRelative motion
A capacitive sensor device, including electrode materials carried by fabric substrates, is provided for monitoring relative movement of an expanding and / or contracting structure, such as the mammalian chest and / or torso, corresponding to a performance parameter related, for example, to respiratory function. Some embodiments include non-woven fabric substrates comprising compliant portions configured to stretch only in a selected direction and non-compliant portions upon which electrode materials are disposed. In some embodiments, layers of fabric substrates, carrying corresponding first and second electrode materials, are configured to cooperate to form a parallel plate capacitive sensor having a variable capacitance corresponding to a relative motion of the fabric substrates.
Owner:MERRITT CAREY +5
Sensing system for monitoring the structural health of composite structures
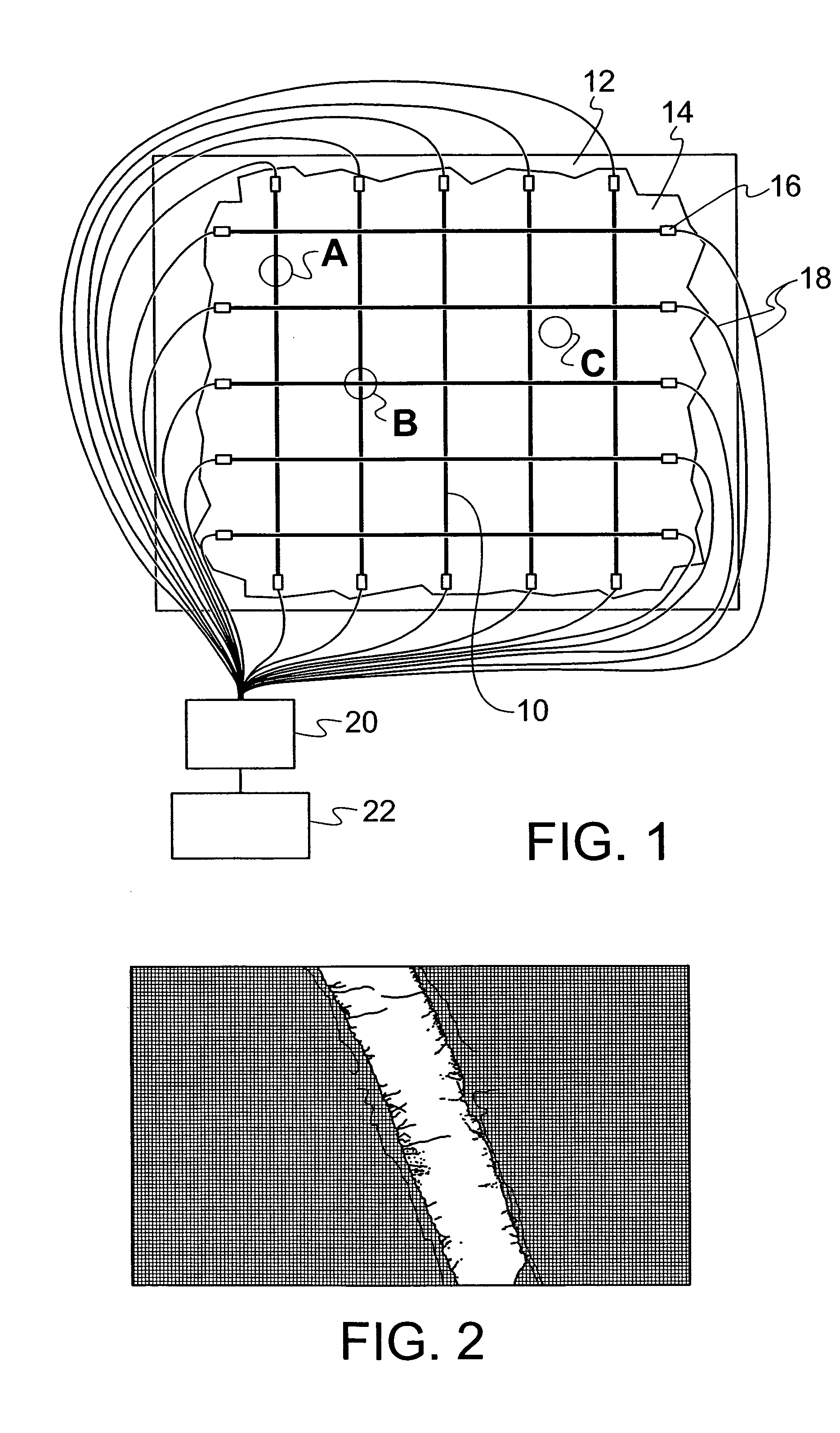
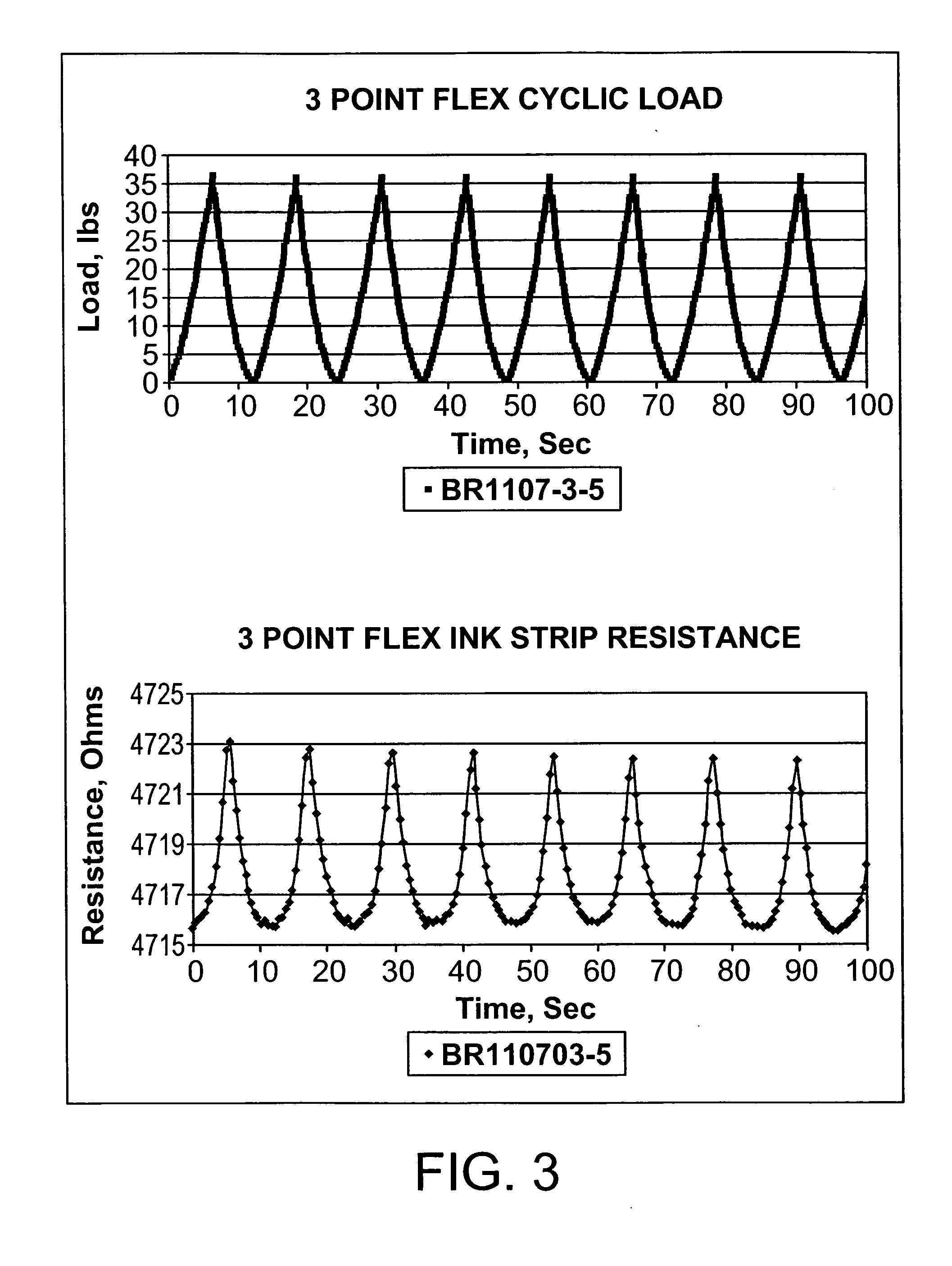
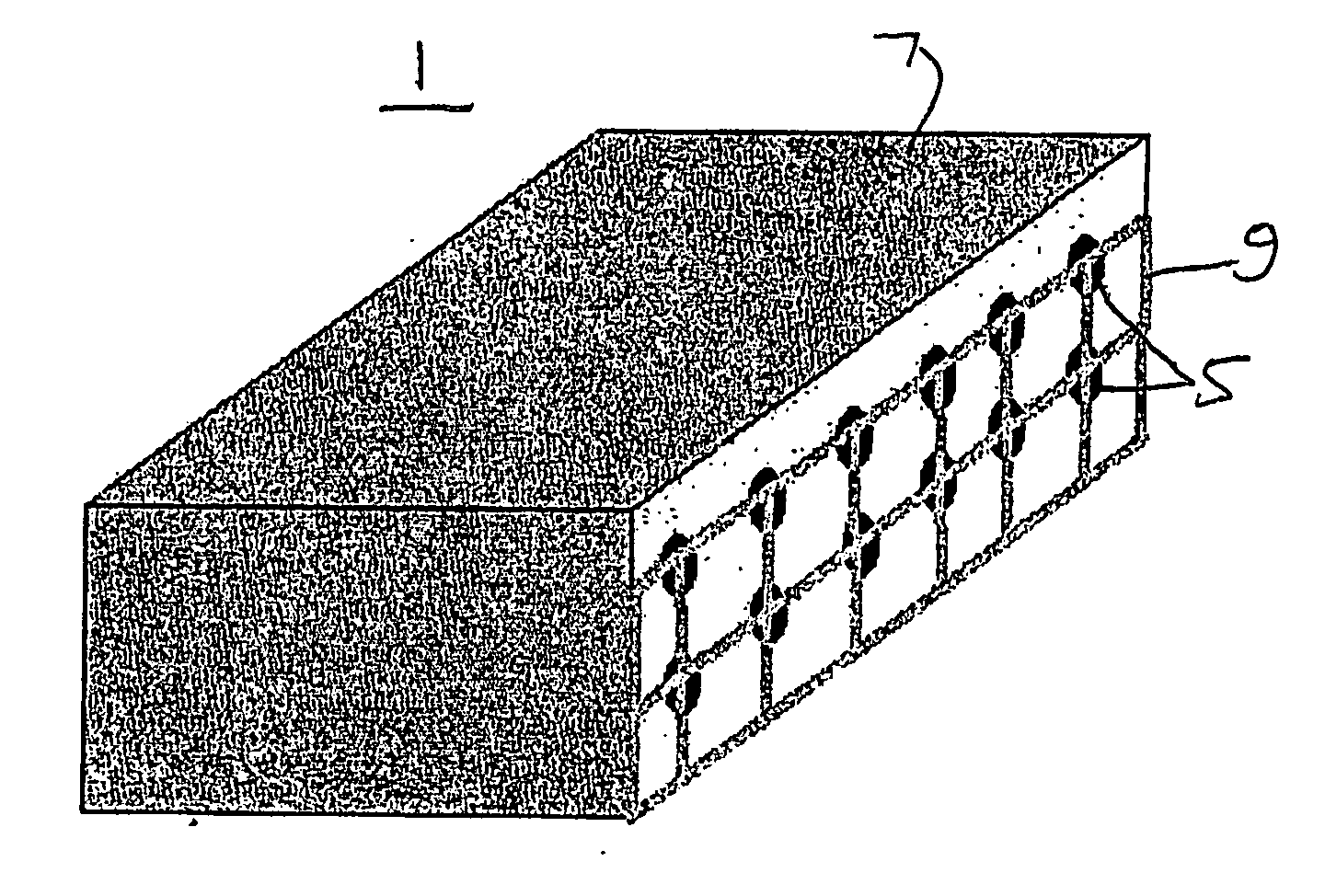
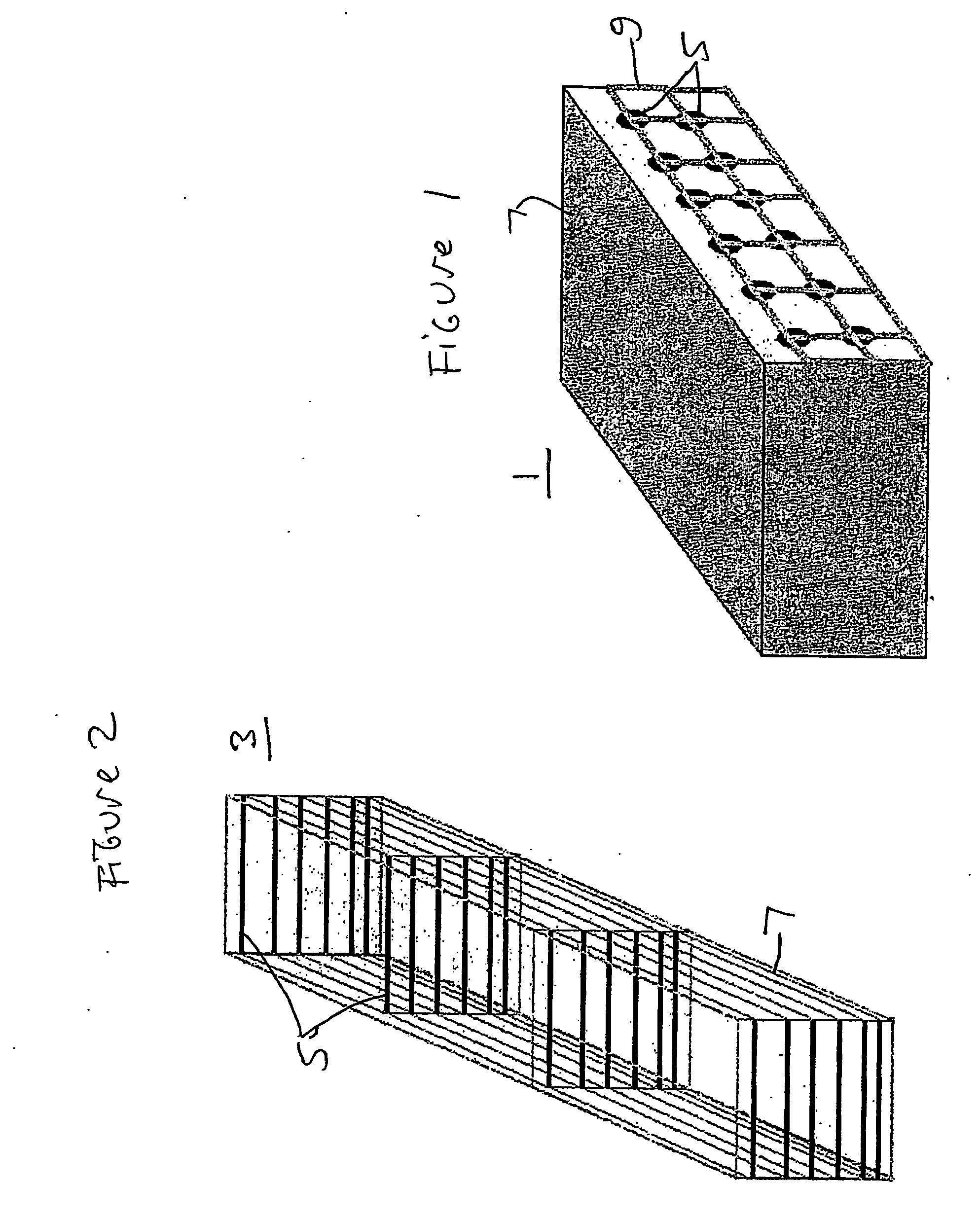
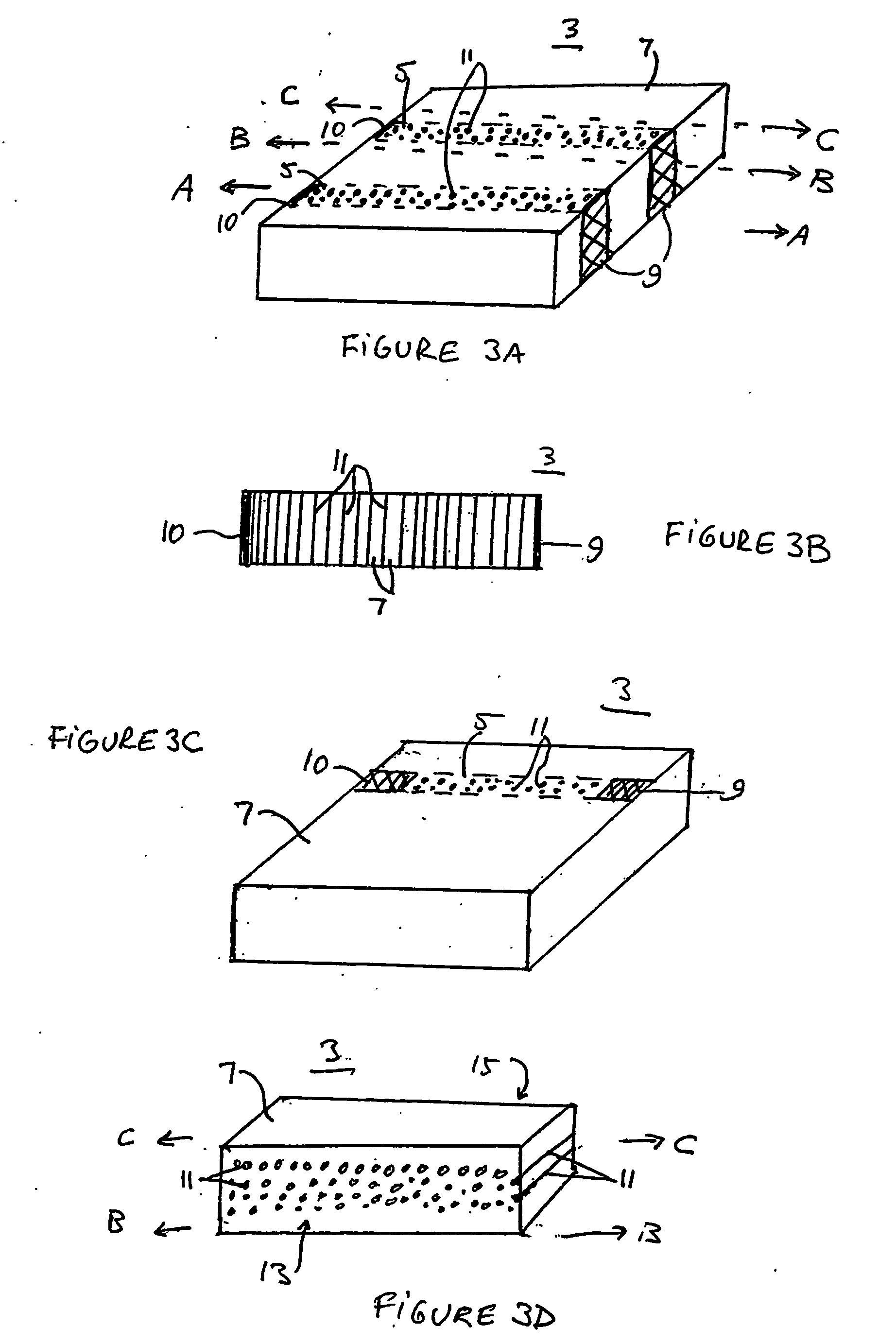
ActiveUS20050284232A1Easy to stickImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementGrid patternState of health
A sensing system for use in monitoring the structural health of a structure such as a polymeric matrix composite structure is provided. The system includes a sensor formed from a conductive ink containing carbon nanofibers and a polymeric resin, and a data acquisition system for acquiring and evaluating data from the sensor. The conductive ink may be applied directly to the structure to be monitored in the form of a grid pattern. Damage to the structure may be detected by measuring changes in resistance values detected from the sensor.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Systems and methods for maintaining load histories
Methods and systems for constructing a load history database for a structure is disclosed. In one embodiment, a method is disclosed that may include detecting a measurable parameter on the structure utilizing a sensor positioned on the structure and determining a value of external loads acting upon the structure based on the detected parameter. Further, the method may include evaluating the value of the external loads against a pre-established factor. Based on the evaluation, the value of the external loads are selectively stored in the load history database.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Method and apparatus for an ocean bottom seismic acquisition technique
InactiveUS6951138B1Enhanced couplingImproved vector fidelityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersForce measurementOcean bottomSurface ocean
A seismometer having a hydrodynamically efficient shaped body containing a seismic sensor or source, having a propulsion unit located and a control unit for directional control of the propulsion unit for guiding the seismometer to and from an ocean floor. The seismometer can be deployed from a surface ship, helicopter or airplane. The seismometer or surface support vessel contains a navigation unit for directing the control unit to a desired location on the ocean bottom. The apparatus provides a storage device for storing seismic data sensed by the seismic sensor. The navigation system sends a responsive directional command to the apparatus based on the current location and the desired location. Upon arrival at the desired ocean bottom location, the propulsion system acts to couple the apparatus to the ocean floor. A flight control system manages a plurality of the seismometers during navigation to and from the a ocean bottom.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
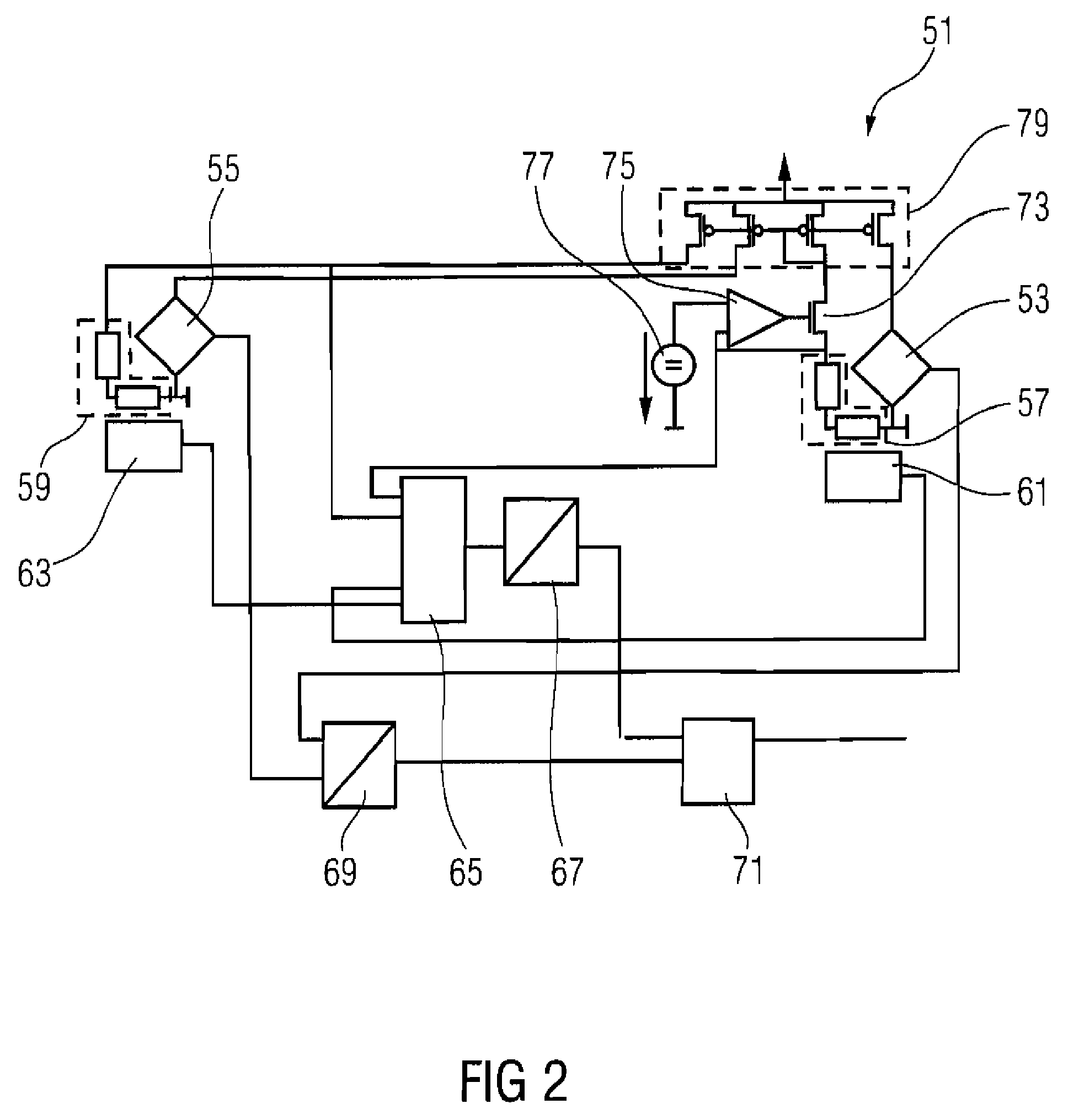
Magnetic field sensor apparatus
ActiveUS7474093B2Force measurement by measuring magnetic property varationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceStress sensorAcoustics
A magnetic field sensor apparatus includes a first magnetic field sensor and a second magnetic field sensor, arranged on a substrate in a spaced manner from each other, a first temperature sensor with an output for a first temperature sensor signal, a second temperature sensor with an output for a second temperature sensor signal, a first stress sensor with an output for a first stress sensor signal, and a second stress sensor with an output for a second stress sensor signal, wherein the first temperature sensor and the first stress sensor are arranged more closely to the first magnetic field sensor or at a location identical with the first magnetic field sensor, and the second temperature sensor and the second stress sensor are arranged more closely to the second magnetic field sensor than to the first magnetic field sensor or at a location identical with the second magnetic field sensor.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
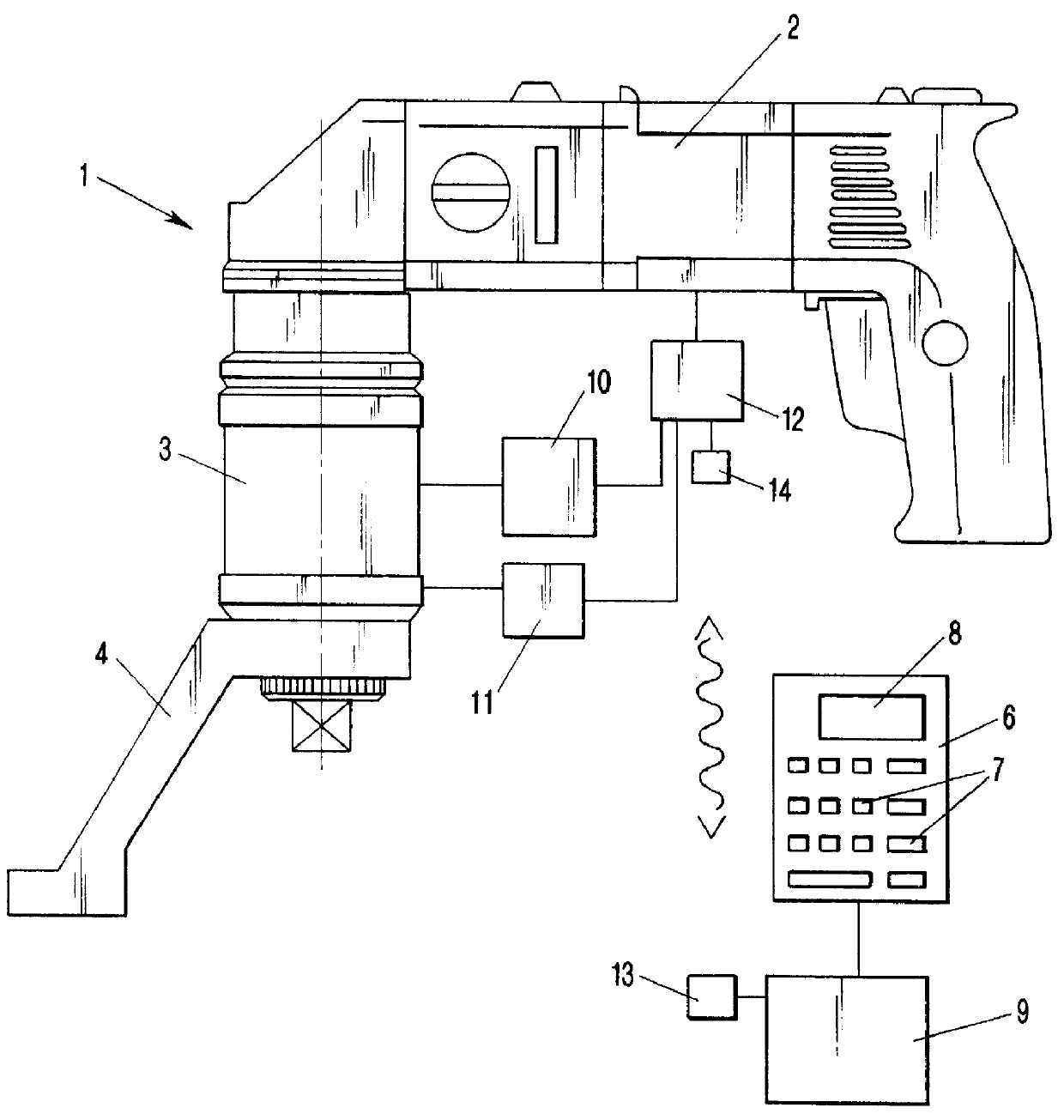
Power wrench
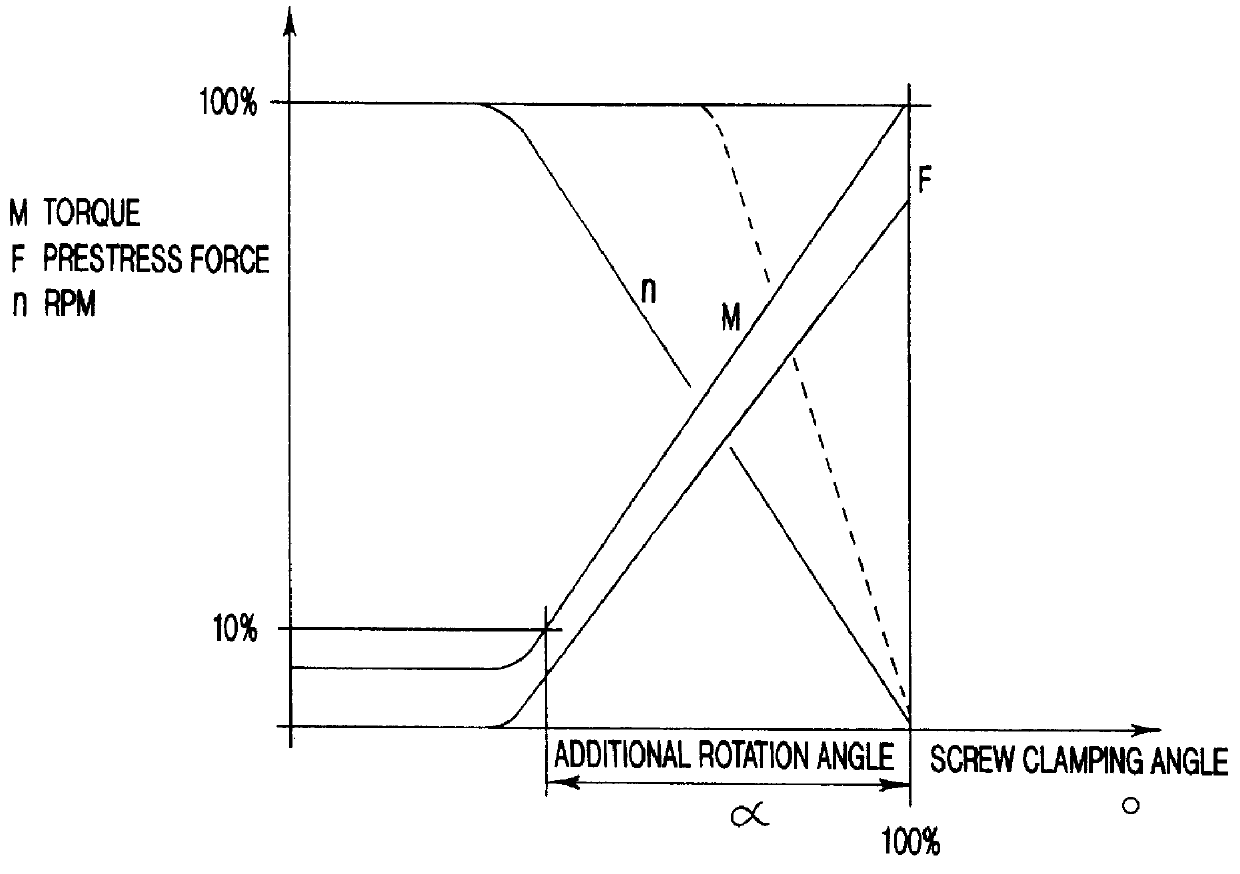
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 05974 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 16, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 16, 1999 PCT Filed Oct. 29, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 22263 PCT Pub. Date May 28, 1998A power screwdriver has a drive unit and an input circuit for inputting screw size, material quality, pitch, and clamping length of a screw. An evaluation circuit is provided for determining a nominal prestress force based on input screw size, material quality, and clamping length, for determining a nominal torque based on the nominal prestress force and the pitch, and for determining the screw clamping angle resulting from the nominal prestress force and the pitch. A sensing device for sensing the actual torque is provided, and a further sensing device for sensing the actual screw clamping angle is present. A control and switch-off device controls further rotation of the drive unit when the actual torque coincides with the nominal torque and switches off the drive unit when the actual screw clamping angle coincides with the nominal screw clamping angle. The nominal torque, based on which the additional rotation o f the drive unit is controlled until the nominal screw clamping angle is reached, is set to a value which is smaller than the torque corresponding to the nominal pretension force. An additional rotation angle of the drive unit, for reaching the nominal screw clamping angle corresponding to the nominal prestress force, is determined based on the difference between the nominal screw clamping angle and the adjusted screw clamping angle corresponding to the preset nominal torque and is used for switching off the drive unit.
Owner:HOHMANN JORG +1
Instrumented Tabular Device for Transporting a Pressurized Fluid
InactiveUS20070284112A1Low insertion lossDrilling rodsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationGratingEngineering
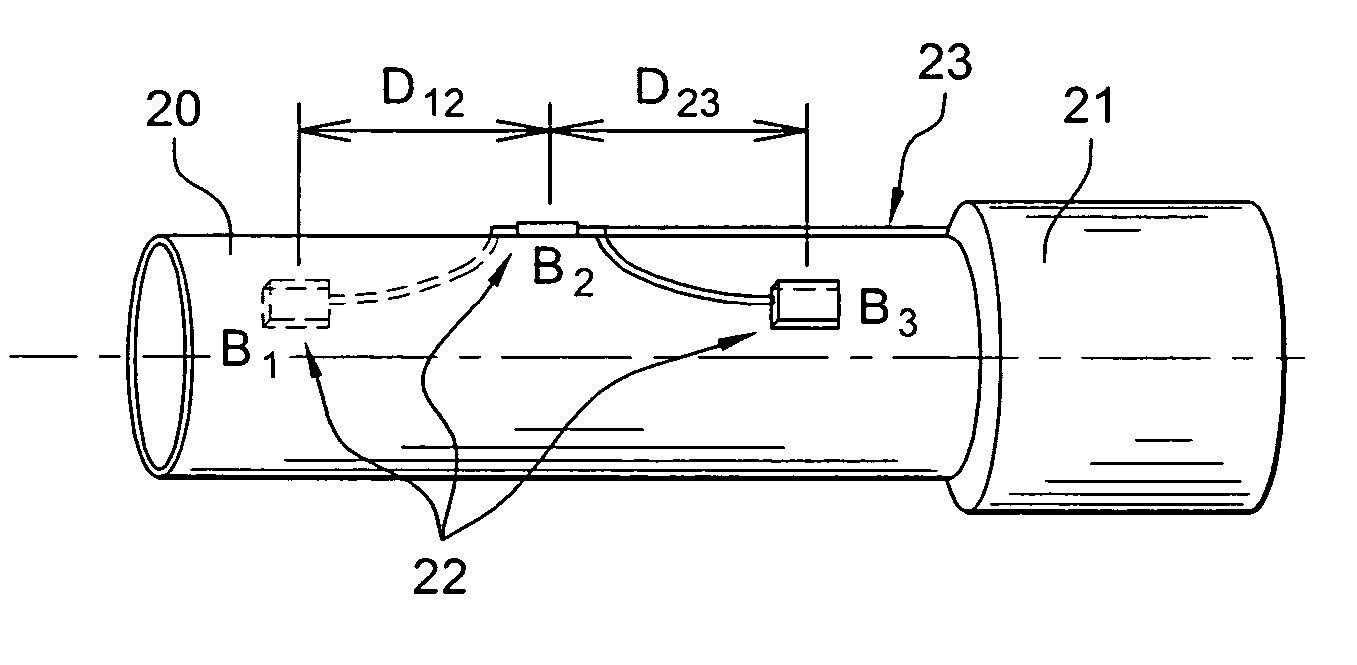
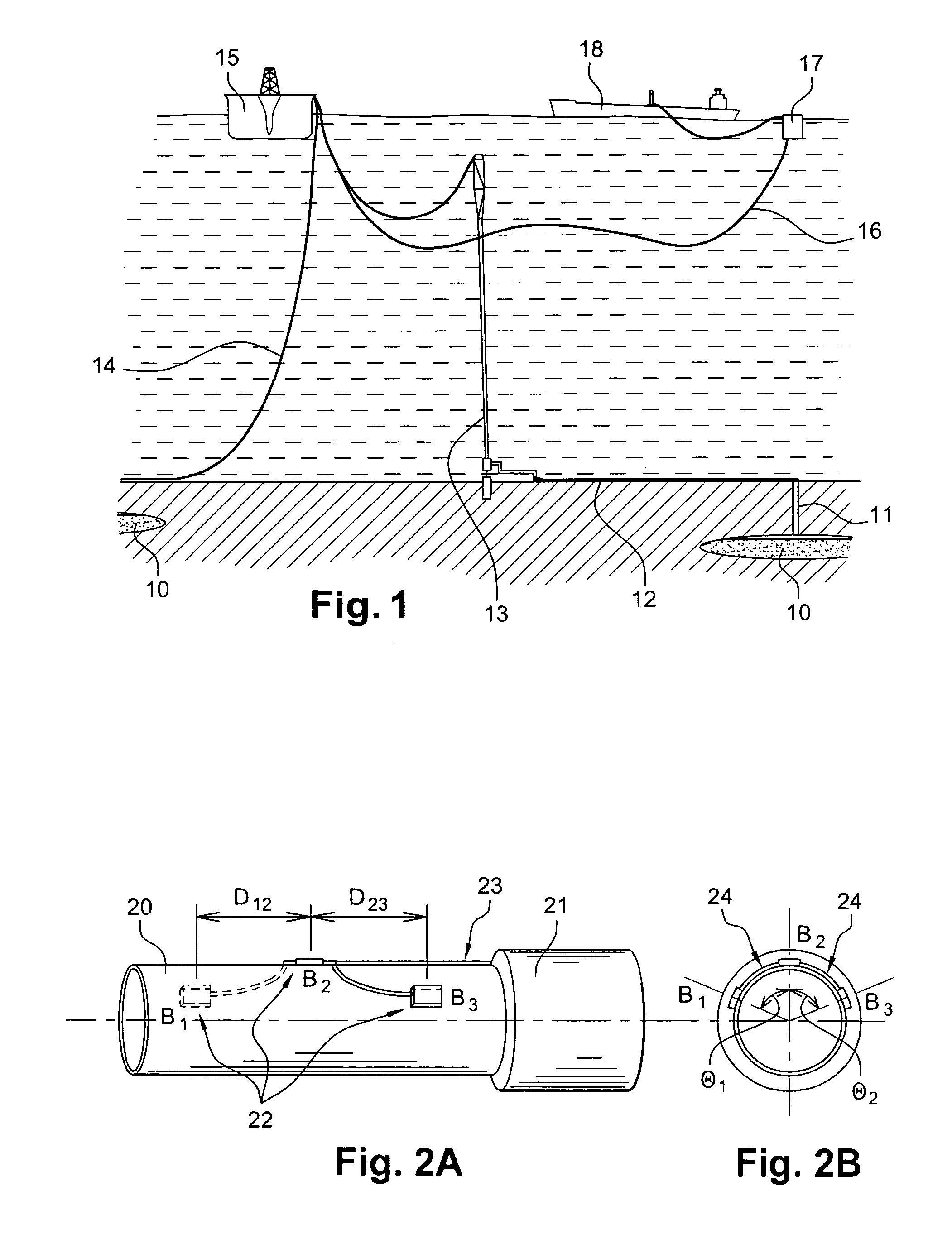
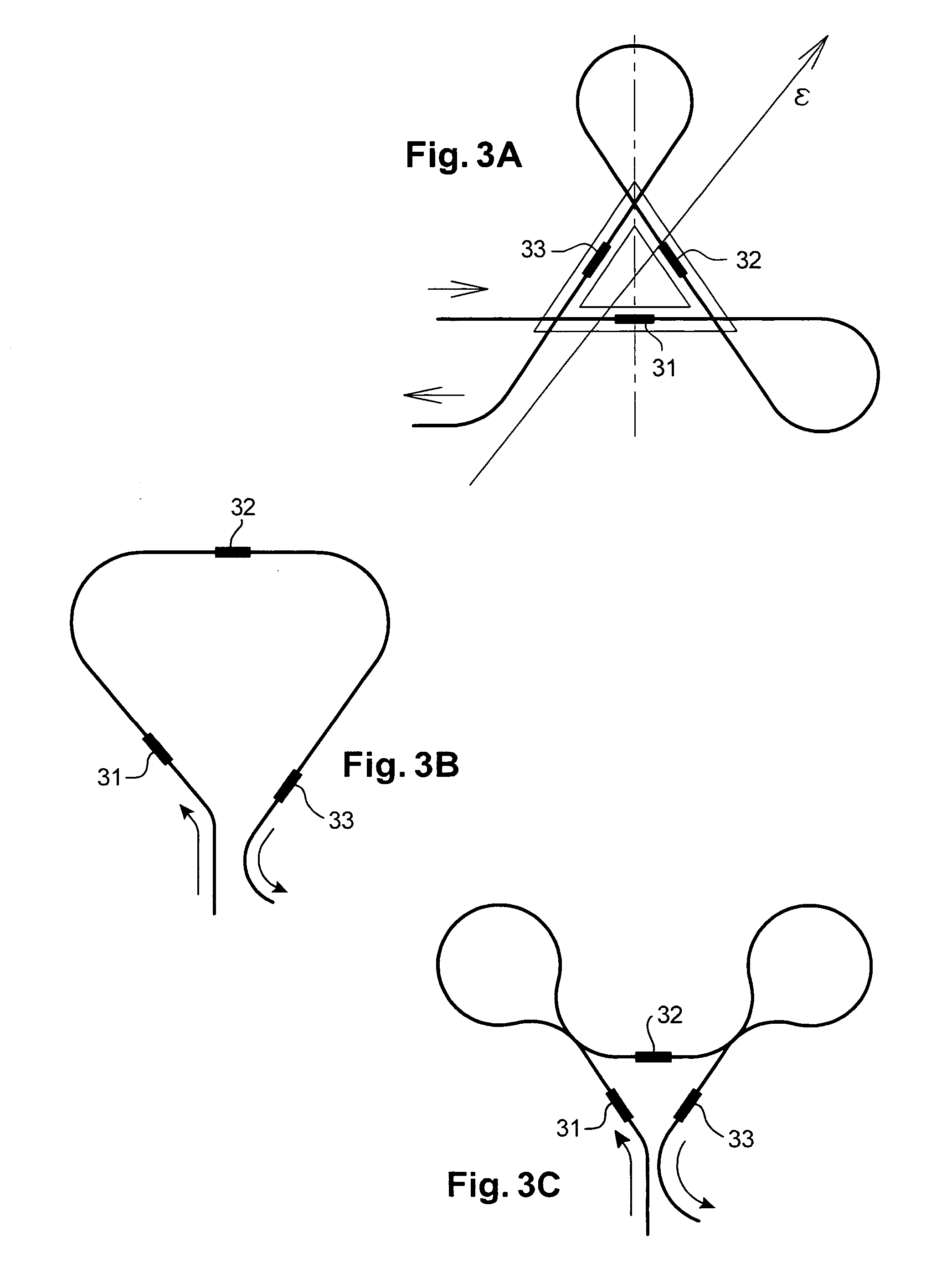
The invention relates to an instrumented tubular device for transporting a pressurized fluid notably in the field of oil exploration and in that of the transport of gas or hydrocarbons. This device comprises a tube (20) in which this fluid flows, with which are associated means for measuring the main deformations of this tube, and means for measuring the temperature of the fluid in the tube. This tube is equipped with measurement means integral with its surface and offset by at least one remote optical cable towards an electronic measurement system. These measurement means are means for assembling at least two non-parallel optical fibers which comprise at least three assemblies (B1, B2, B3) of at least two optical gages with Bragg gratings attached to at least three measurement locations (22) and connected to the remote optical cable (23) via optical fibers. At least one assembly further comprises a temperature gage.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
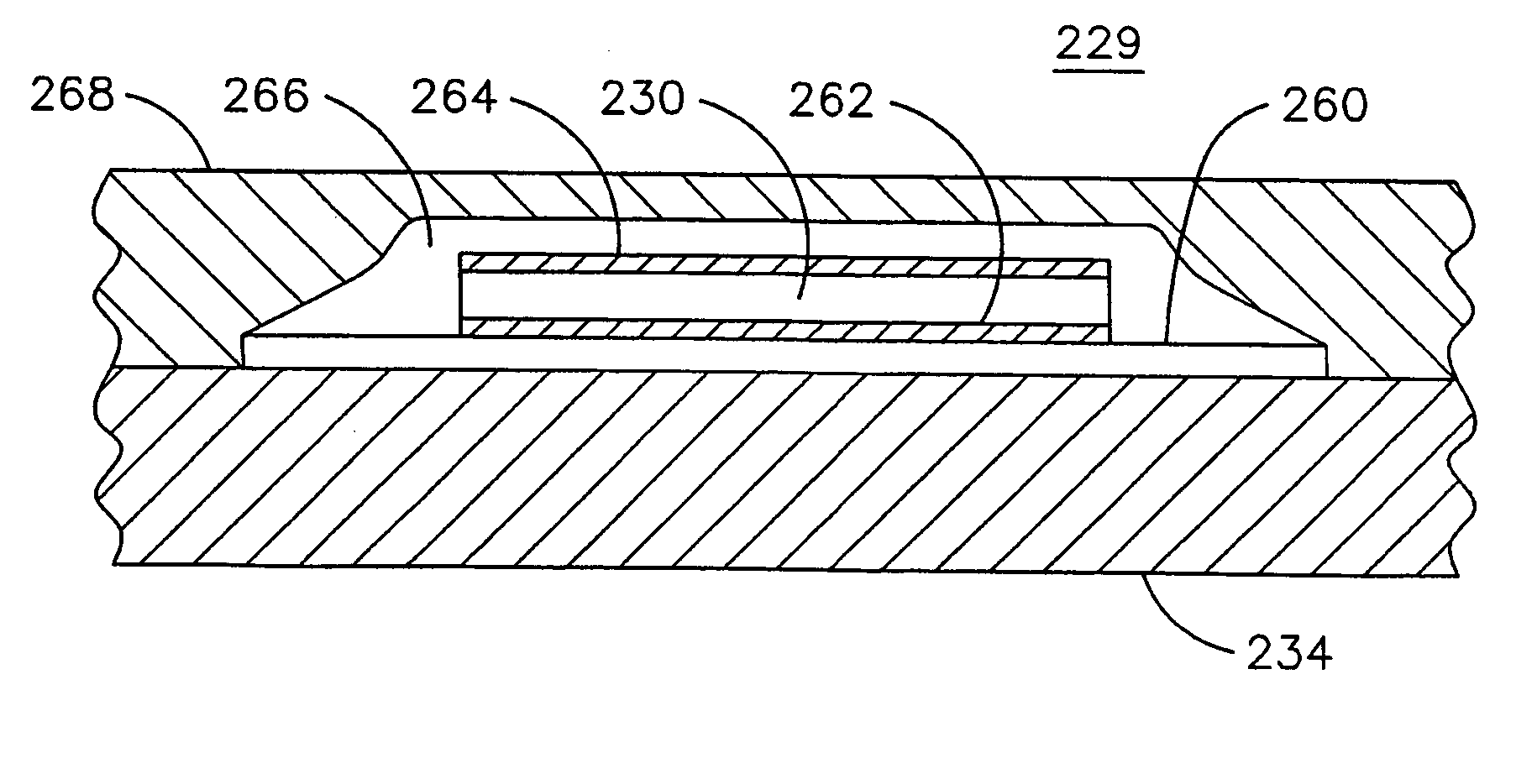
Method of instrumenting a component
A method of instrumenting a first component (210) for use in a combustion turbine engine (10) wherein the first component (210) has a surface contacted by a second component during operation of the combustion turbine engine (10). The method may include depositing an insulating layer (260) on the surface of the first component (210) and depositing a first conductive lead (232, 254) on the insulating layer (260). A piezoelectric material (230) may be deposited in electrical communication with the first conductive lead (232, 254) and a second conductive lead (236, 256) may be deposited in electrical communication with the piezoelectric material (230) and be insulated from the first conductive lead (232, 254) to form a sensor (50) for detecting pressure exerted on the surface of the first component (210) during operation of the combustion turbine engine (10).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
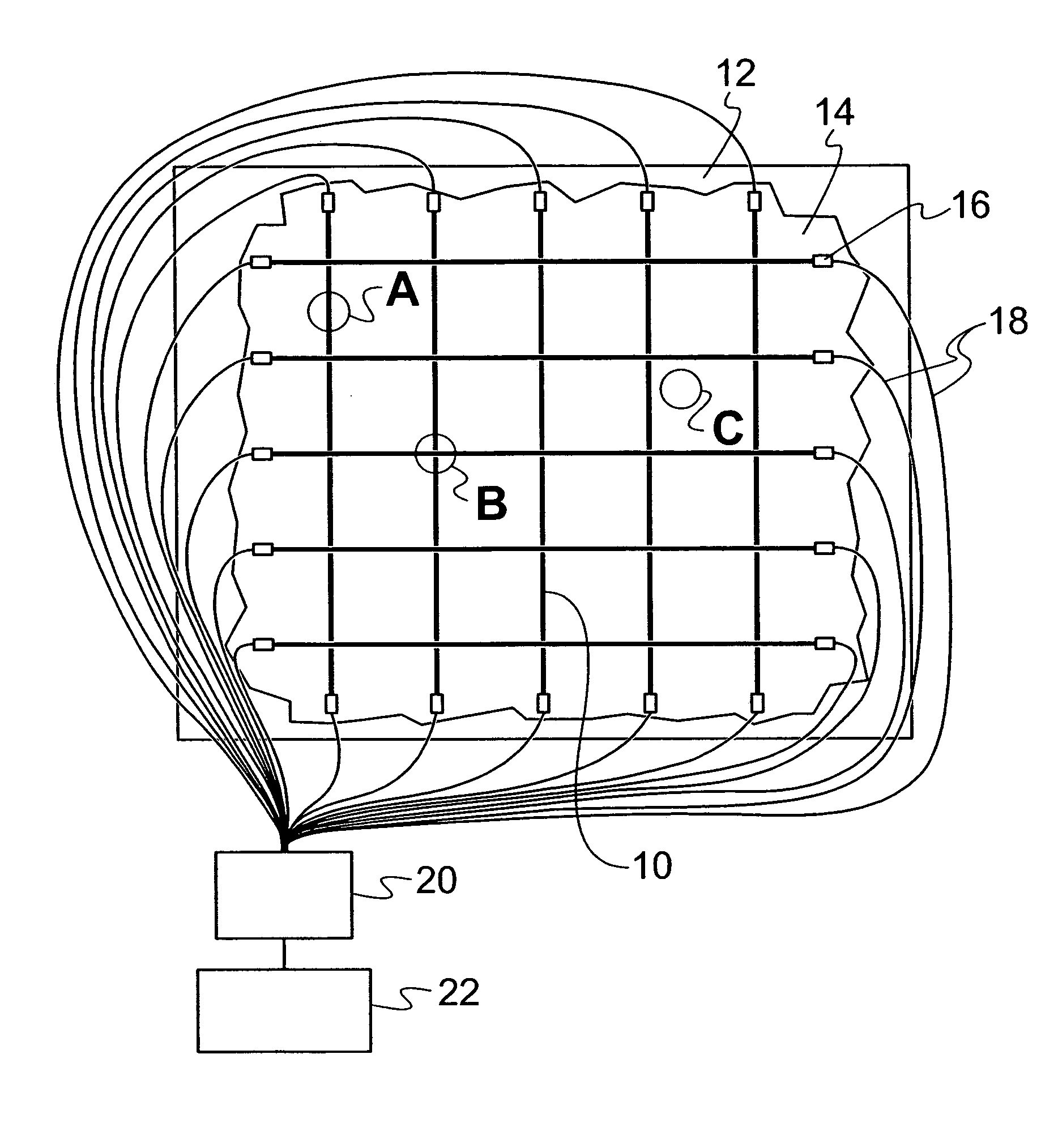
Wireless multi-functional sensor platform, system containing same and method for its use
InactiveUS6796187B2Small sizeLow costElectric signal transmission systemsForce measurementLine sensorTransmitted power
A multi-functional sensor system for simultaneously monitoring various parameters such as the structural, chemical and environmental conditions associated with a medium to be monitored, e.g., bridges, high-rise buildings, pollution zones, is provided wherein the system includes at least a plurality of wireless multi-functional sensor platforms embedded in the medium in which an interrogation unit transmits power and receives responses. Each wireless multi-functional sensor platform includes multiple channels for accommodating a plurality of sensor types to simultaneously monitor the parameters associated with the medium. Thus, the wireless sensor platforms are formed to include those sensor types which are considered germane to the intended medium to be monitored.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
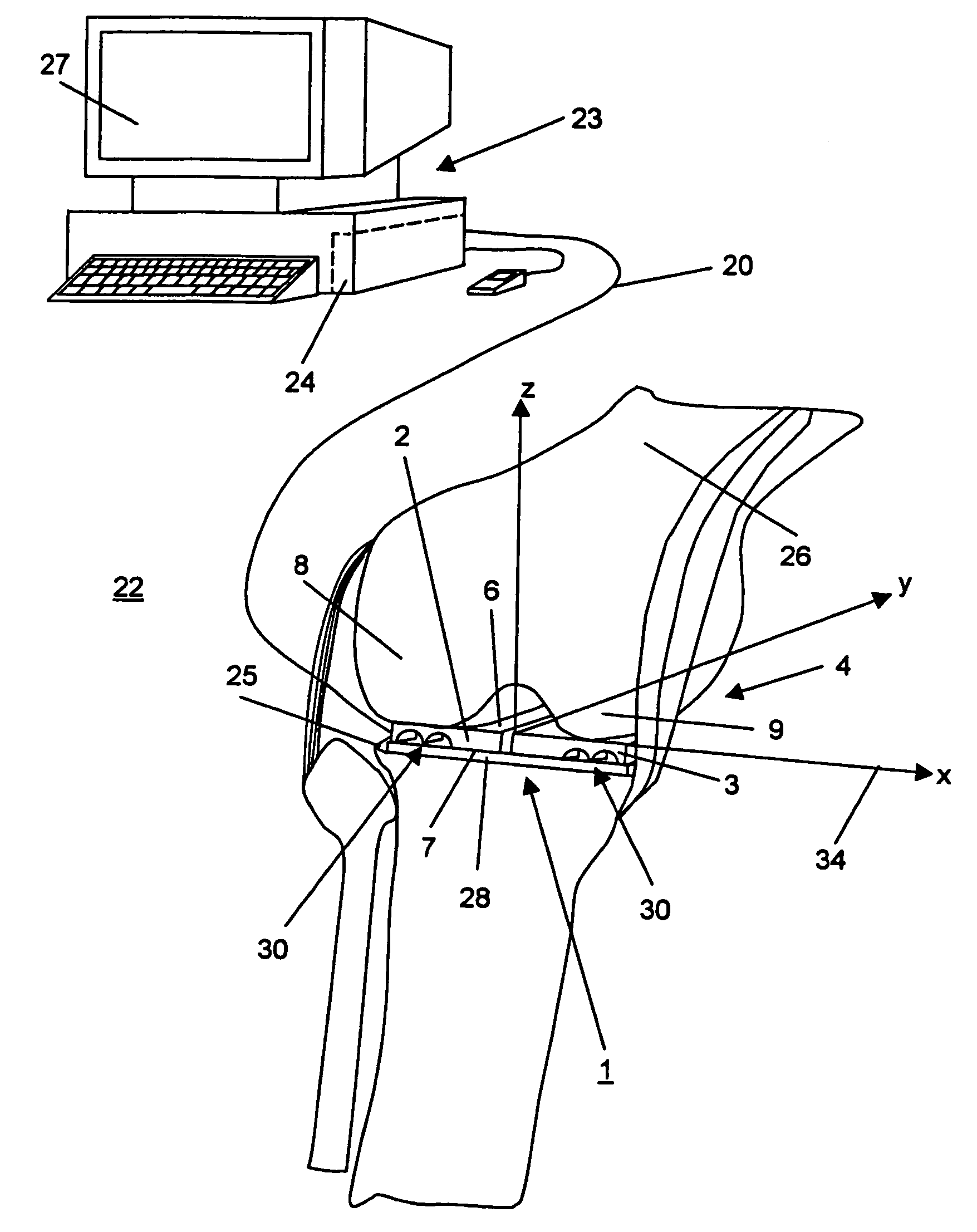
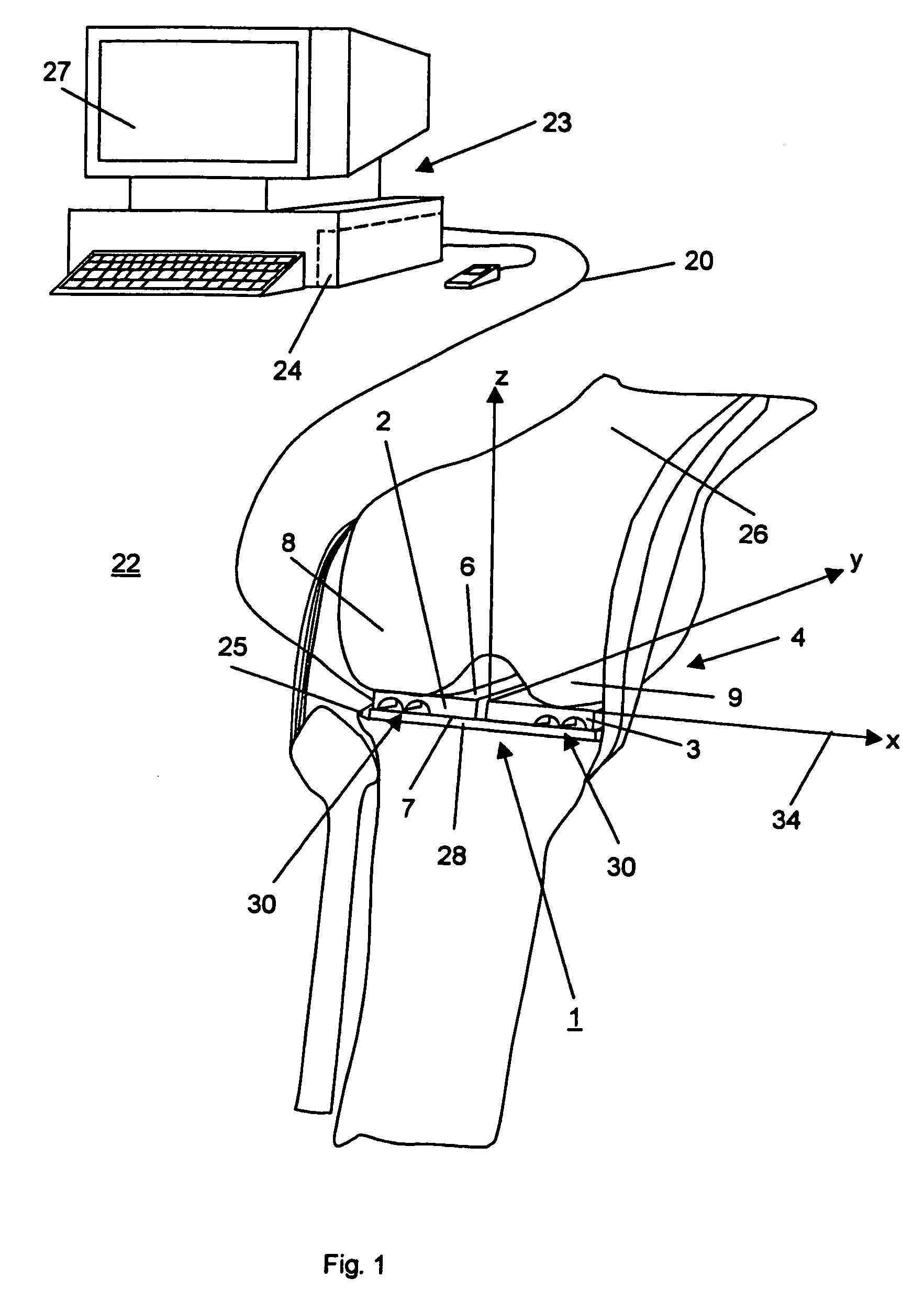
Device for measuring tibio-femoral force amplitudes and force locations in total knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS7412897B2Improve balanceImprove ergonomicsSurgeryForce measurementTotal hip arthroplastyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A probe used during a total knee arthroplasty for measuring forces and locations of their points of application and thereby moments includes two load sensitive plates t to be inserted in one joint-compartment of a knee joint each and each being provided with a top surface and a bottom surface. At least two load sensors may be situated on the top surfaces and / or the bottom surface of each load sensitive plate.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
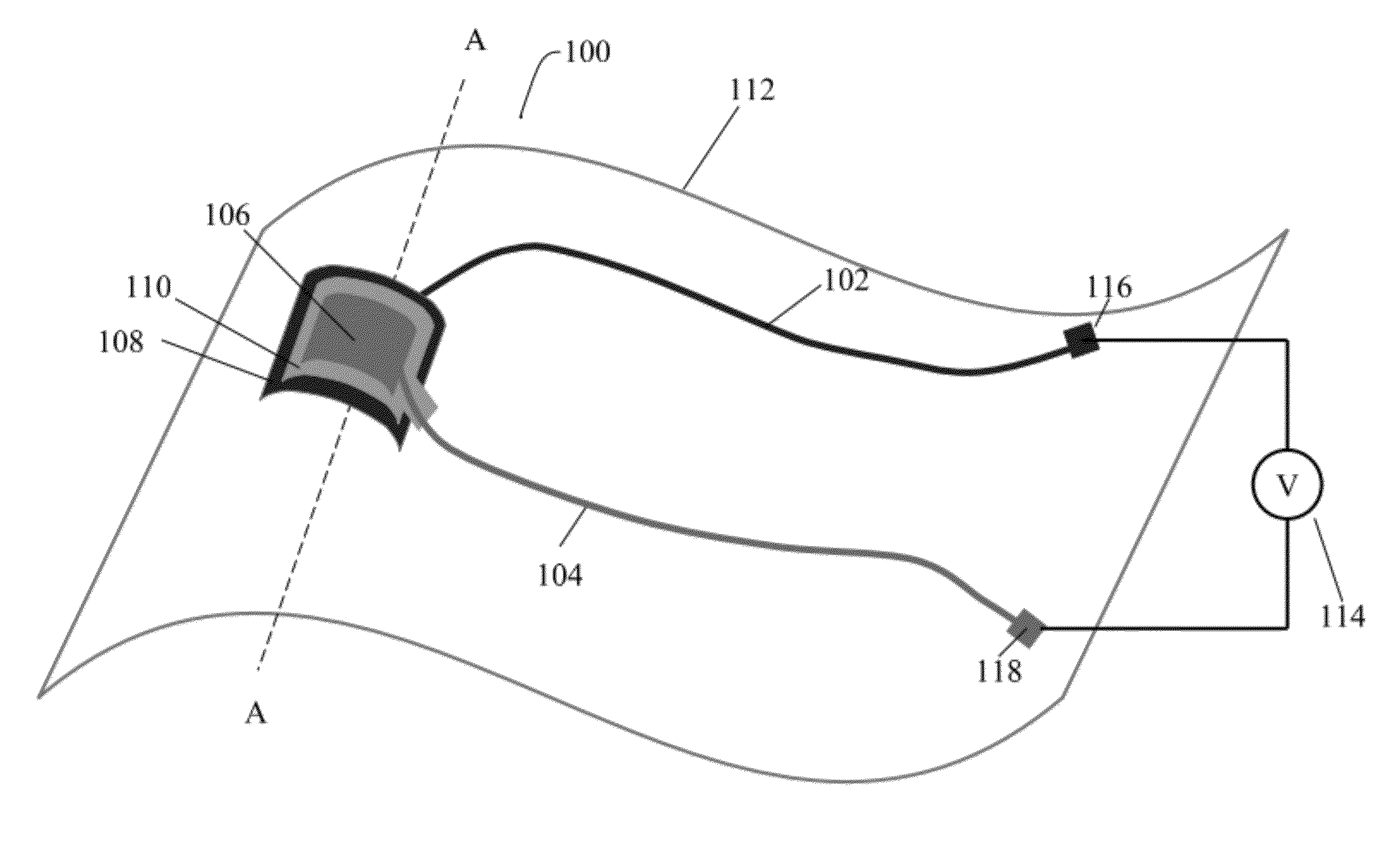
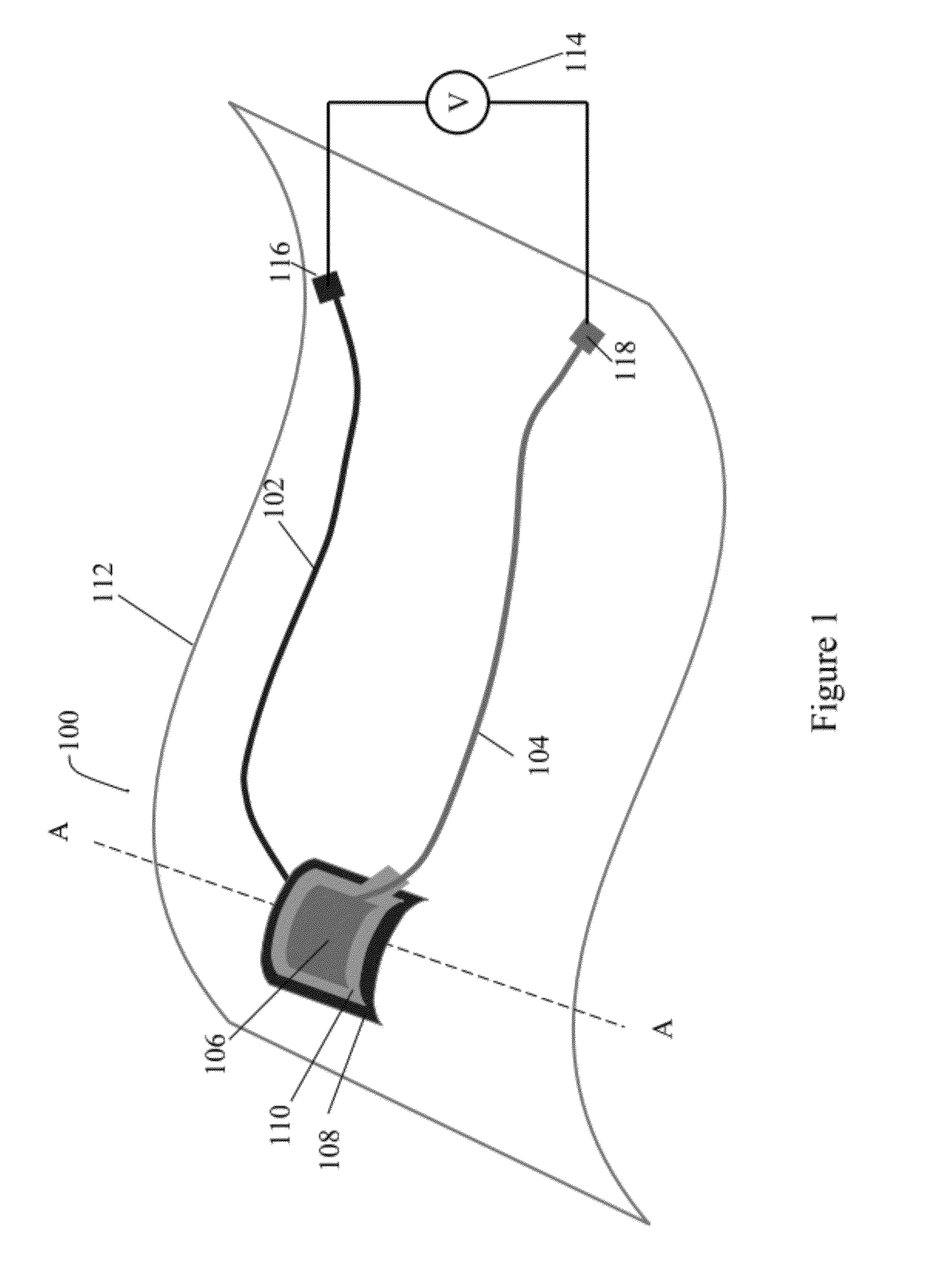
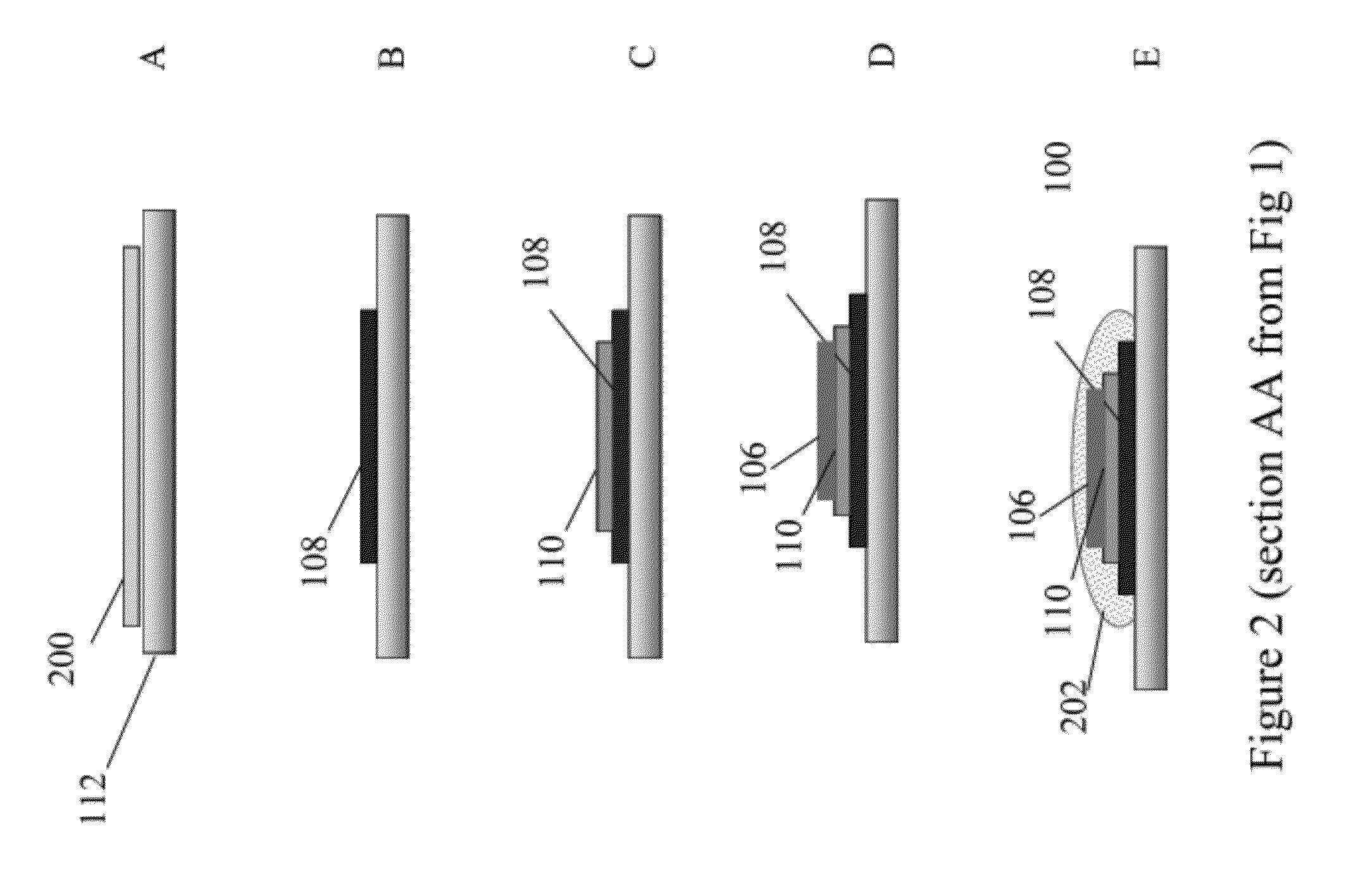
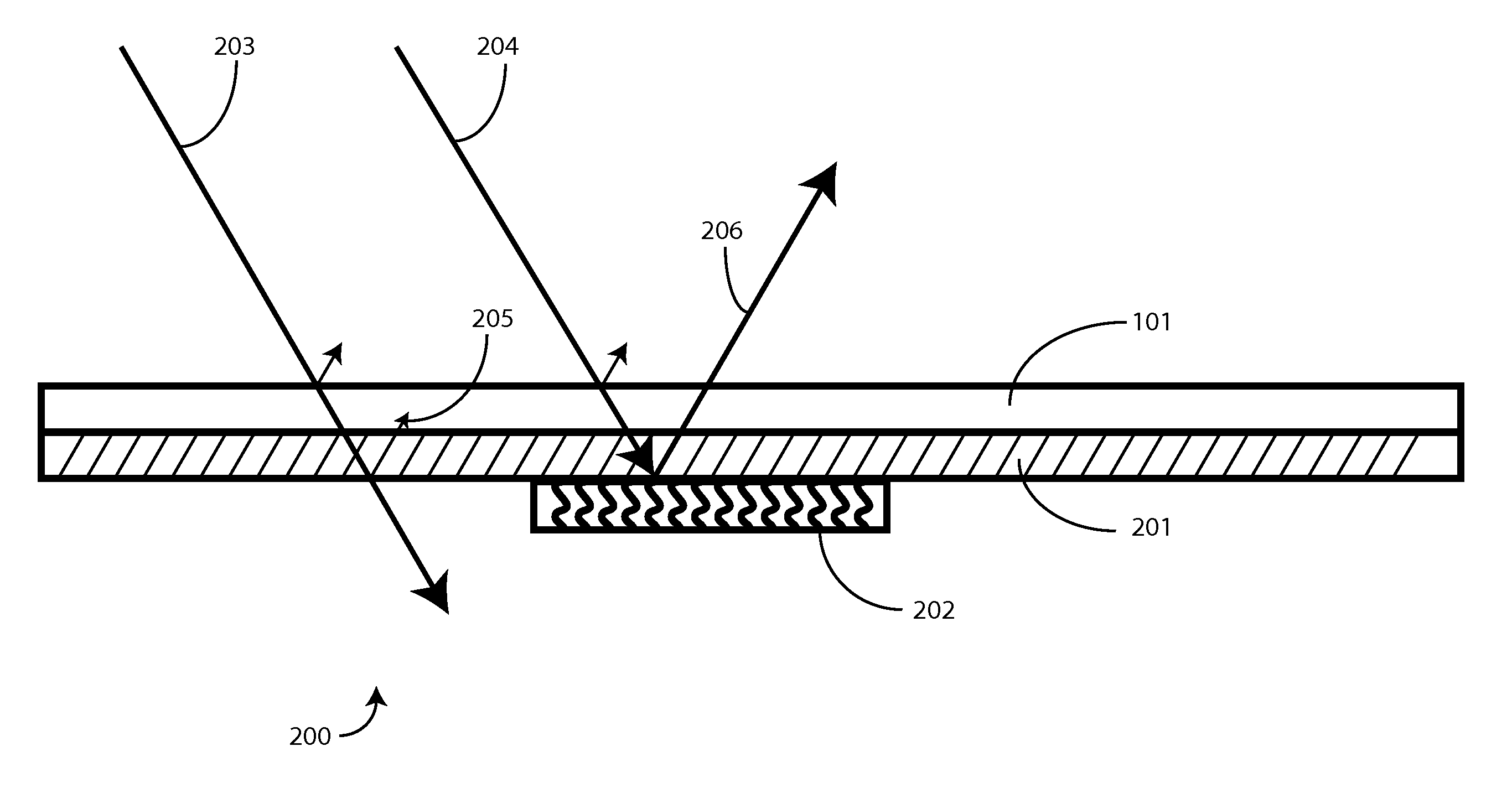
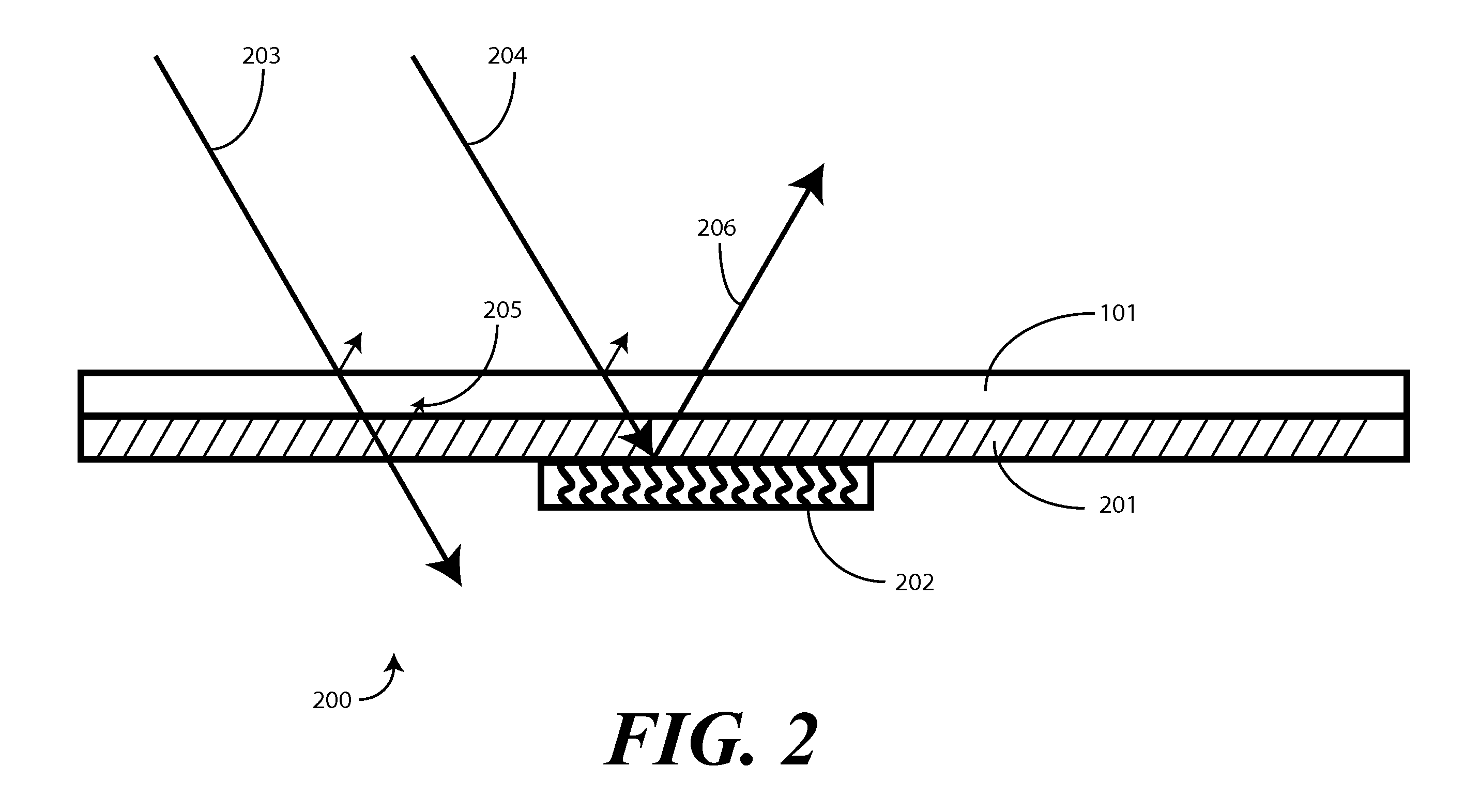
Electrically non-interfering printing for electronic devices having capacitive touch sensors
A capacitive sensor (200) for a touch sensitive electronic device (800) includes at least one graphic (401) visible to a user. The graphic (401) is configured so as to be non-electrically interfering with the electrode array of the capacitive sensor (200). A substrate (101), configured to transmit light, has a layer of capacitive sensor material (201) deposited thereon. The layer of capacitive sensor material (201) is electrically conductive and pellucid. A layer of selectively disposed electrically conductive material (202) is then electrically coupled to the layer of capacitive sensor material (201). The layer of selectively disposed electrically conductive material (202) is arranged as a graphic, which may be a logo, brand, or other mark. The layer of selectively disposed electrically conductive material (202) has a reflectivity that is greater than the layer of capacitive sensor material (201) so as to make the graphic (401) visible to a user.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
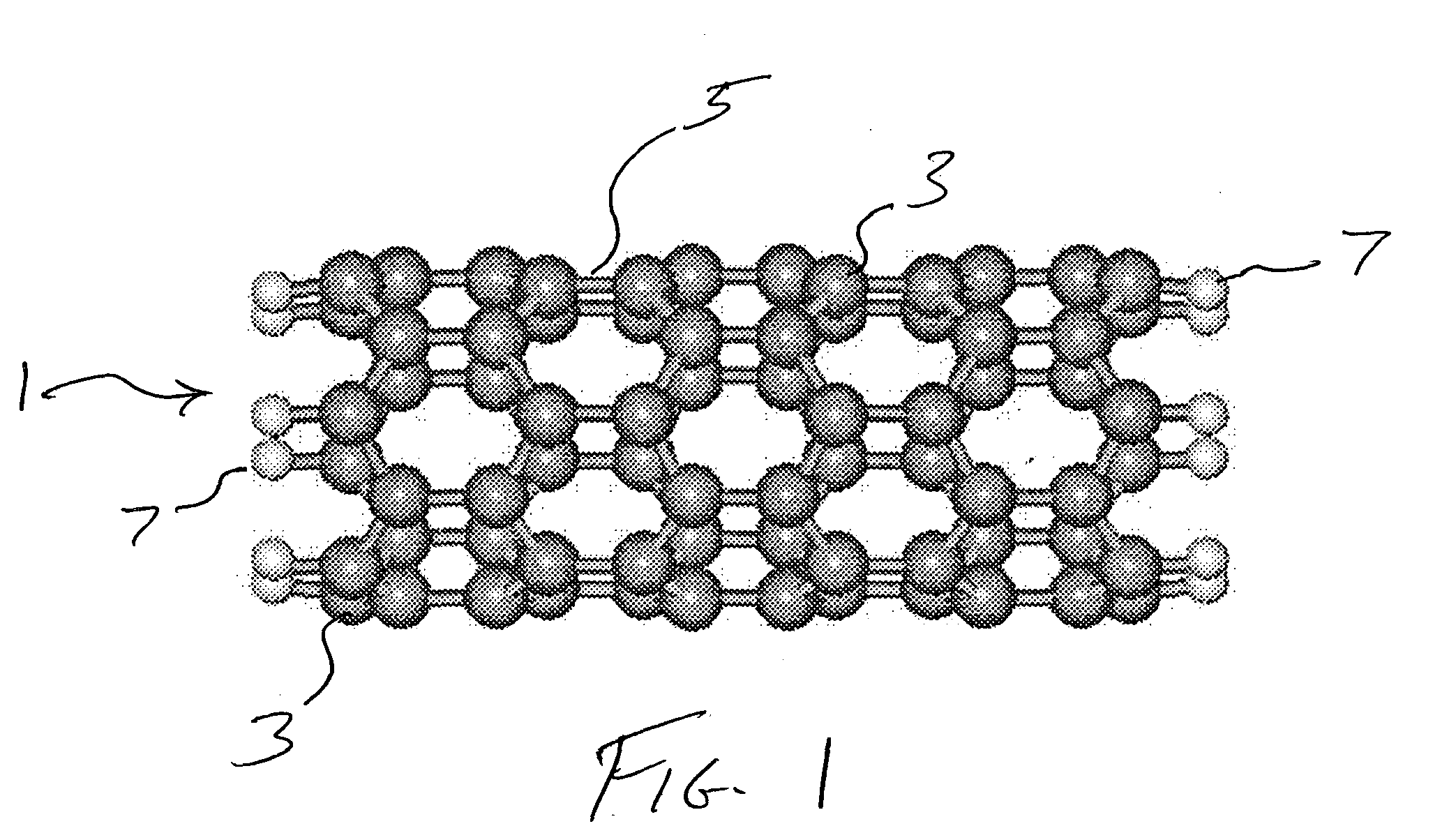
Defect controlled nanotube sensor and method of production
InactiveUS20050036905A1Avoid contactImprove defect densityMaterial nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsEngineeringMethods of production
Sensor for detecting a physical or chemical quantity, comprising a defect controlled nanotube. The sensor can be produced by post treating a nanotube with sufficient energy to modify at least one of density and type of defects in the nanotube, and associating the nanotube with a circuit capable of providing an output signal based upon change of electrical characteristic of the nanotube in response to stimulus of the nanotube.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
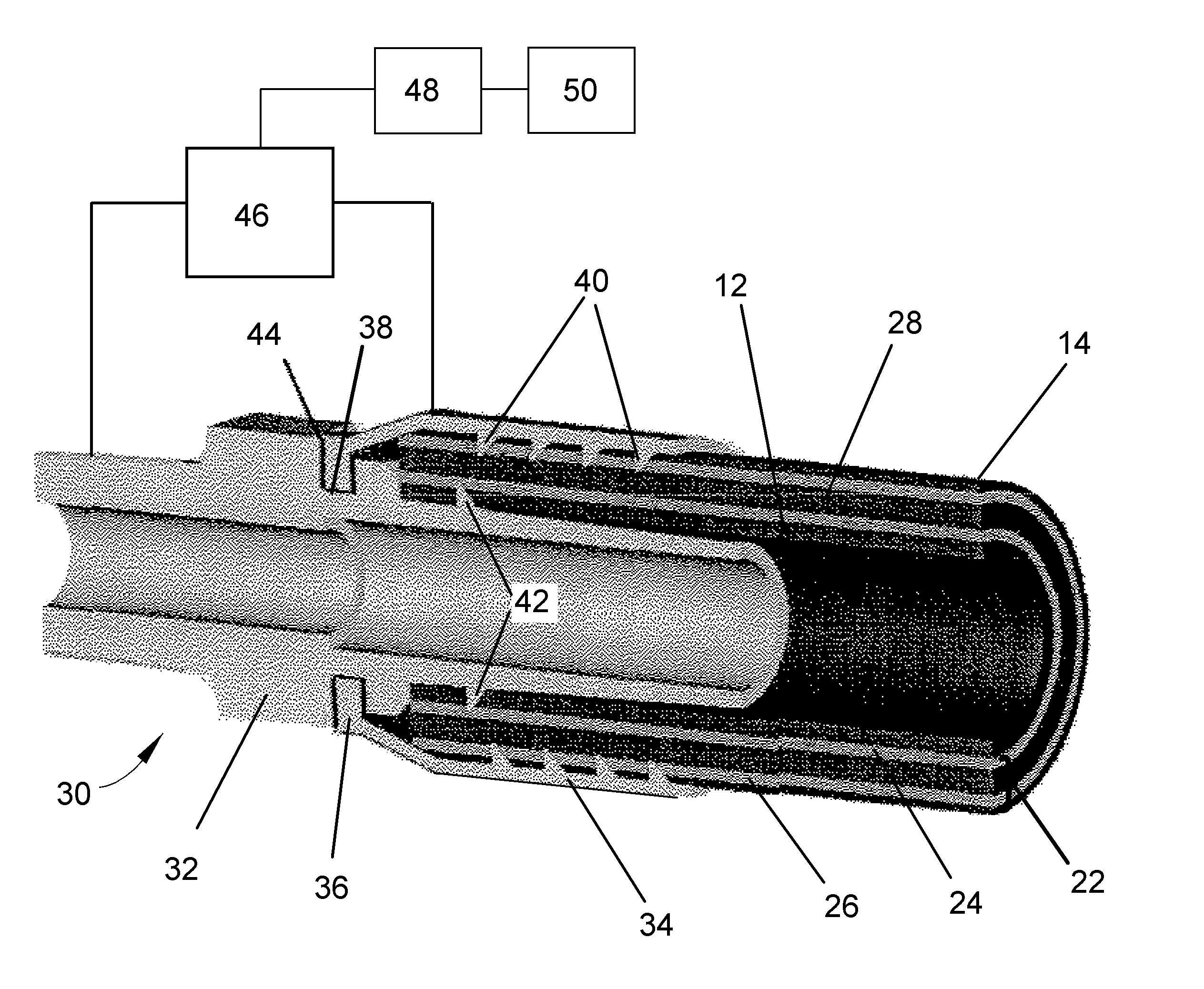
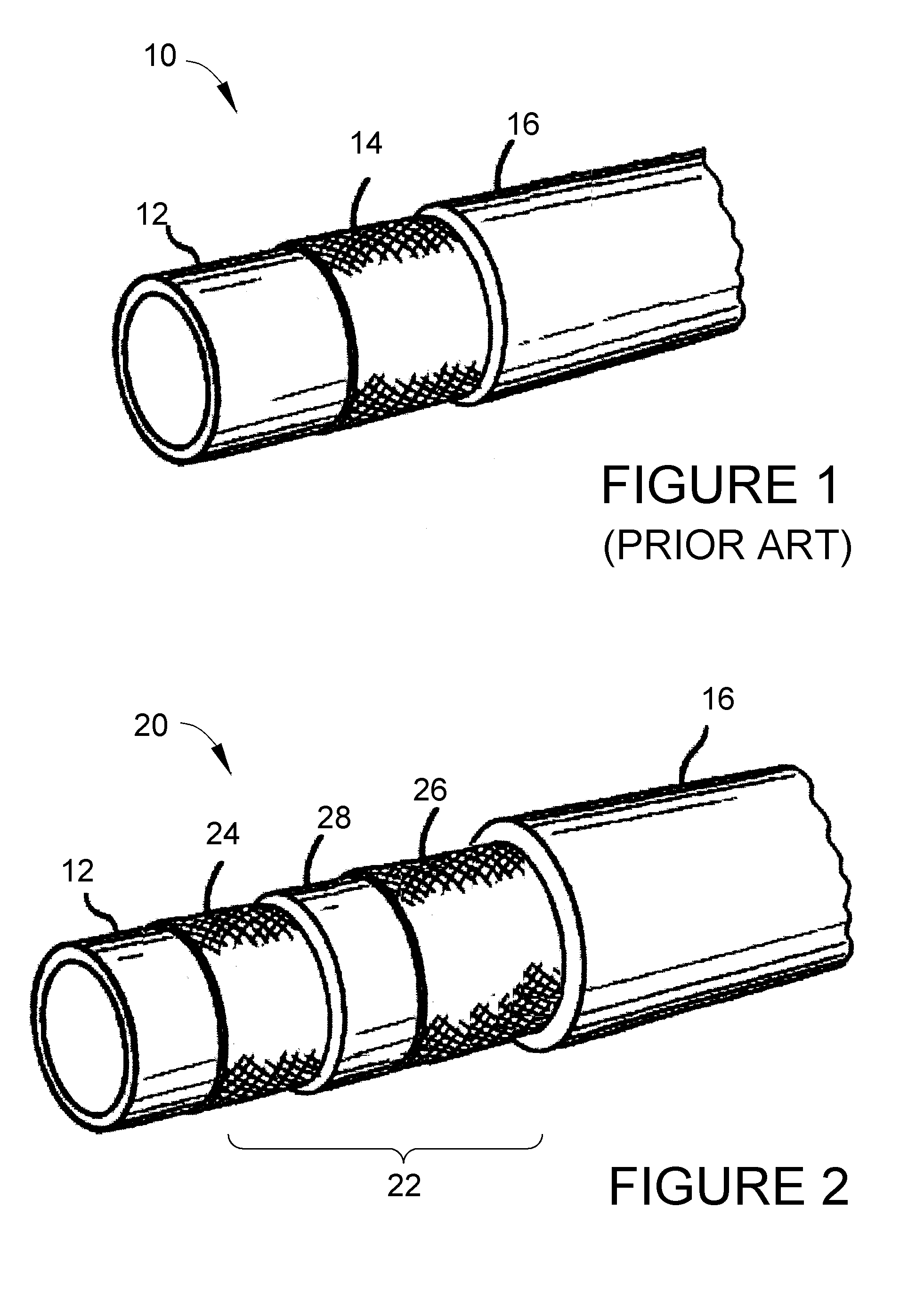
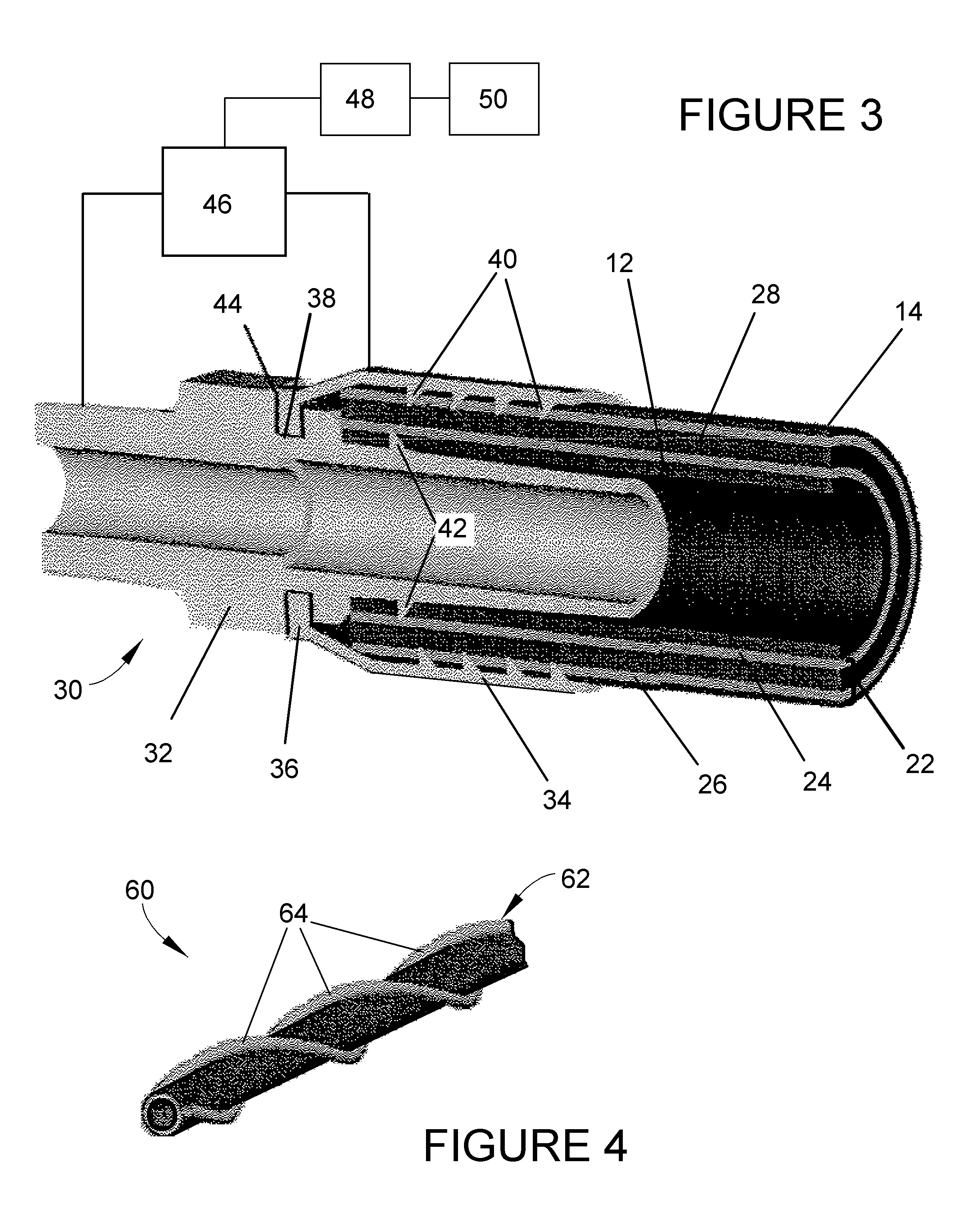
Hydraulic hose with integral life-sensing capability and method therefor
ActiveUS20060196252A1Detection of fluid at leakage pointTesting/calibration apparatusElectrical conductorProcess equipment
A system and method for predicting structural failure of a wall of a fluid containment vessel, such as a hydraulic hose or other type of pressurized conduit of types used in mobile machinery, automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and process equipment. The wall of the vessel has an innermost layer for contact with the fluid contained by the vessel, and an outermost layer parallel with the innermost layer. The system includes strain-sensing means between the innermost and outermost layers and comprising at least one conductor parallel to the innermost layer of the wall. The system and method entail sensing changes in an electrical property associated with the at least one conductor resulting from distortion of the wall of the vessel causing distortion of the at least one conductor.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
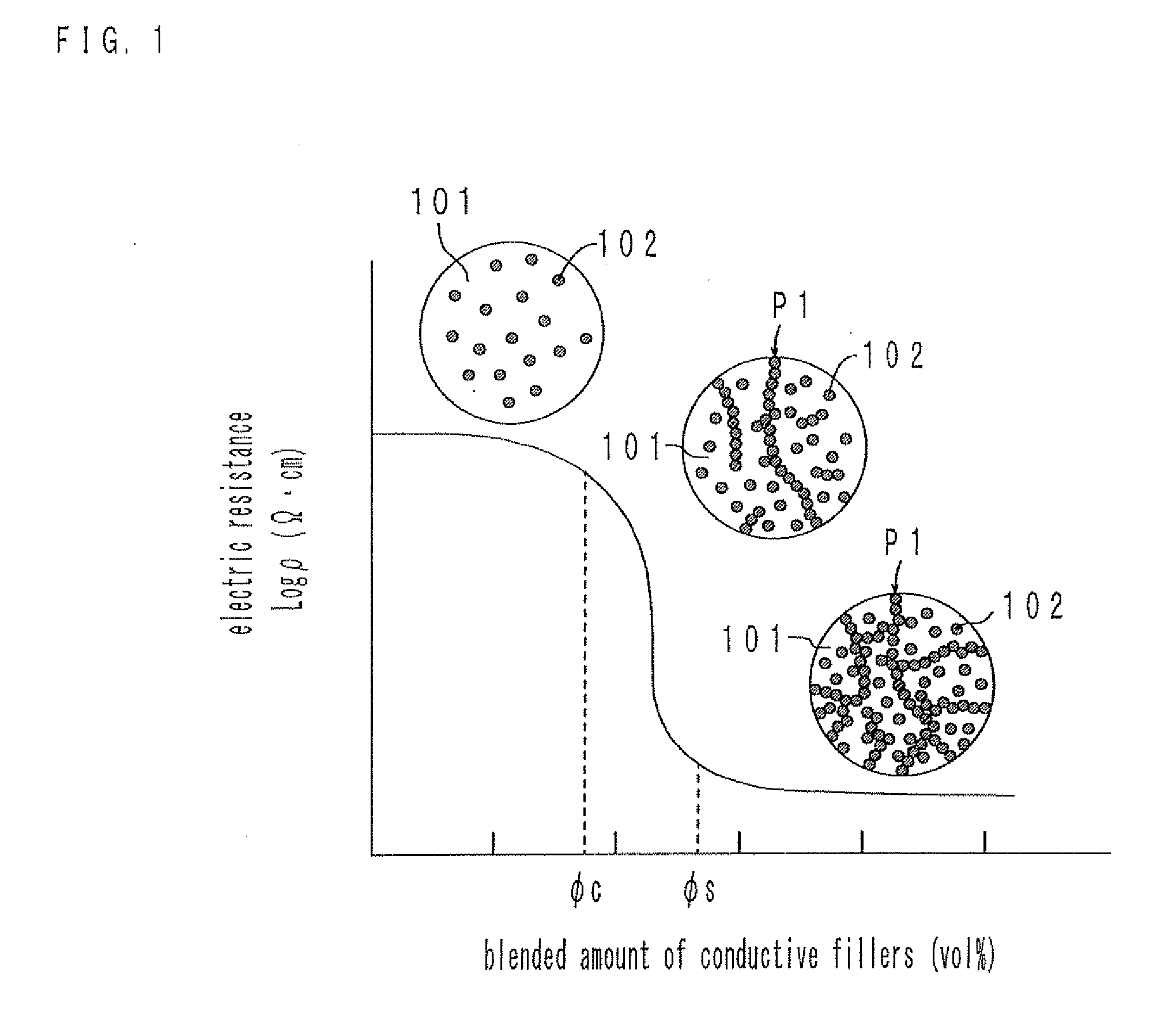
Capacitive sensor
ActiveUS20100033196A1Improve conductivityWell formedResistance/reactance/impedenceForce measurementElastomerCapacitive sensing
A capacitive sensor includes a dielectric layer made of an elastomer and a pair of electrodes arranged via the dielectric layer, and detects deformation on the basis of electrostatic capacity variation between the pair of electrodes. The pair of electrodes contain an elastomer and conductive fillers filled into the elastomer, are expandable and contractible in accordance with deformation of the dielectric layer, and exhibit little conductivity variation even when the pair of electrodes expand and contract. At least one of the dielectric layer and the electrodes is formed by a printing method using a dielectric layer coating containing a formation component of the dielectric layer or an electrode coating containing a formation component of the electrode.
Owner:TOKAI RUBBER IND LTD
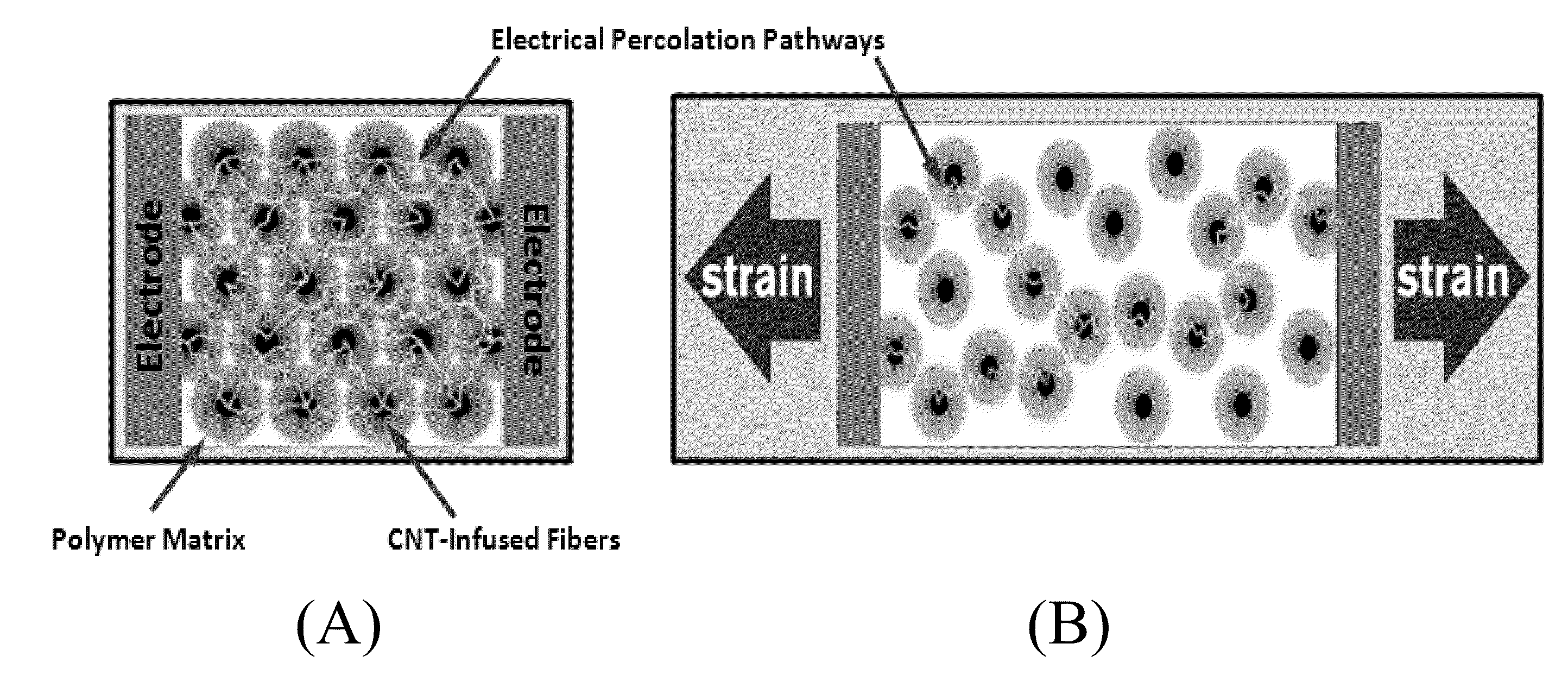
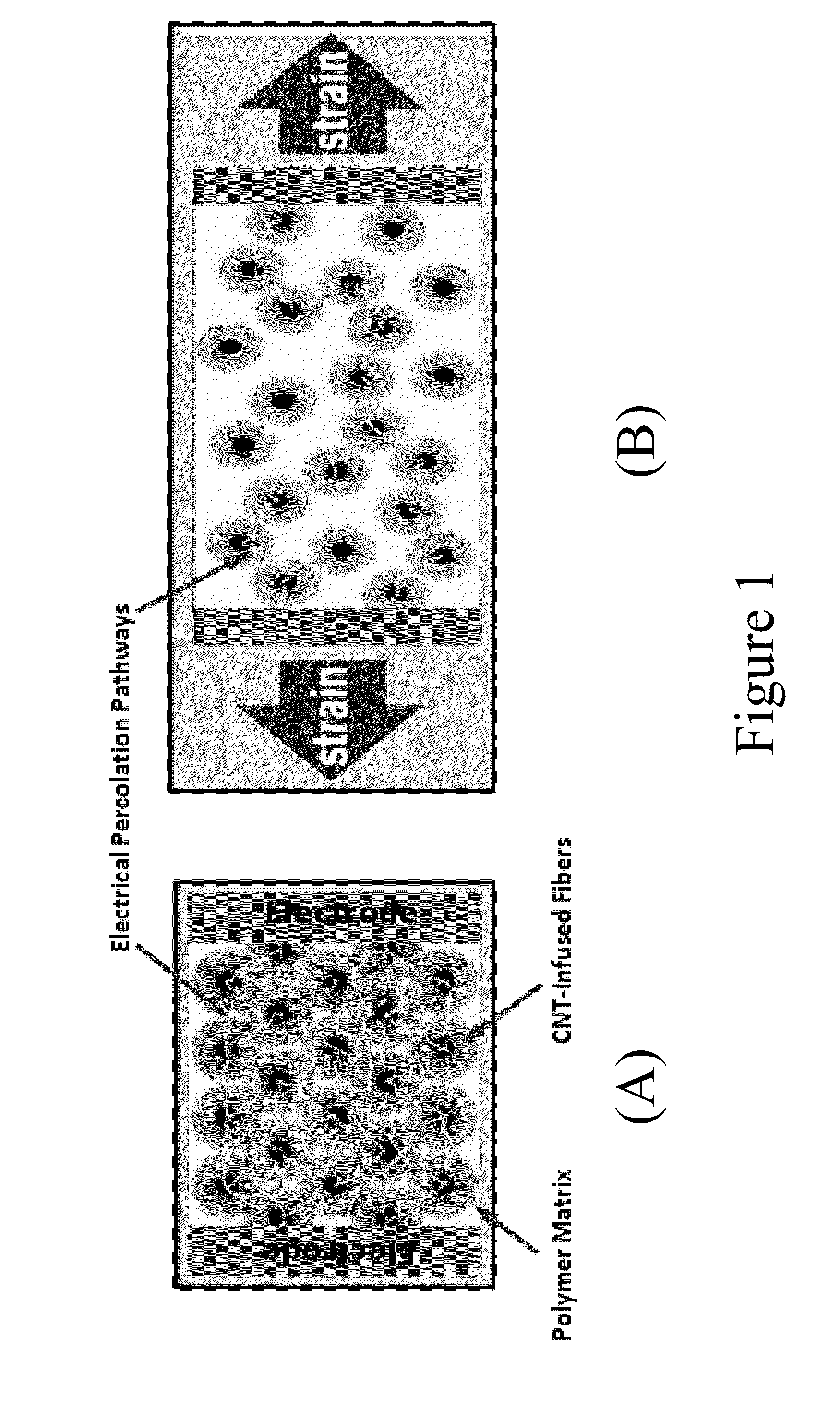
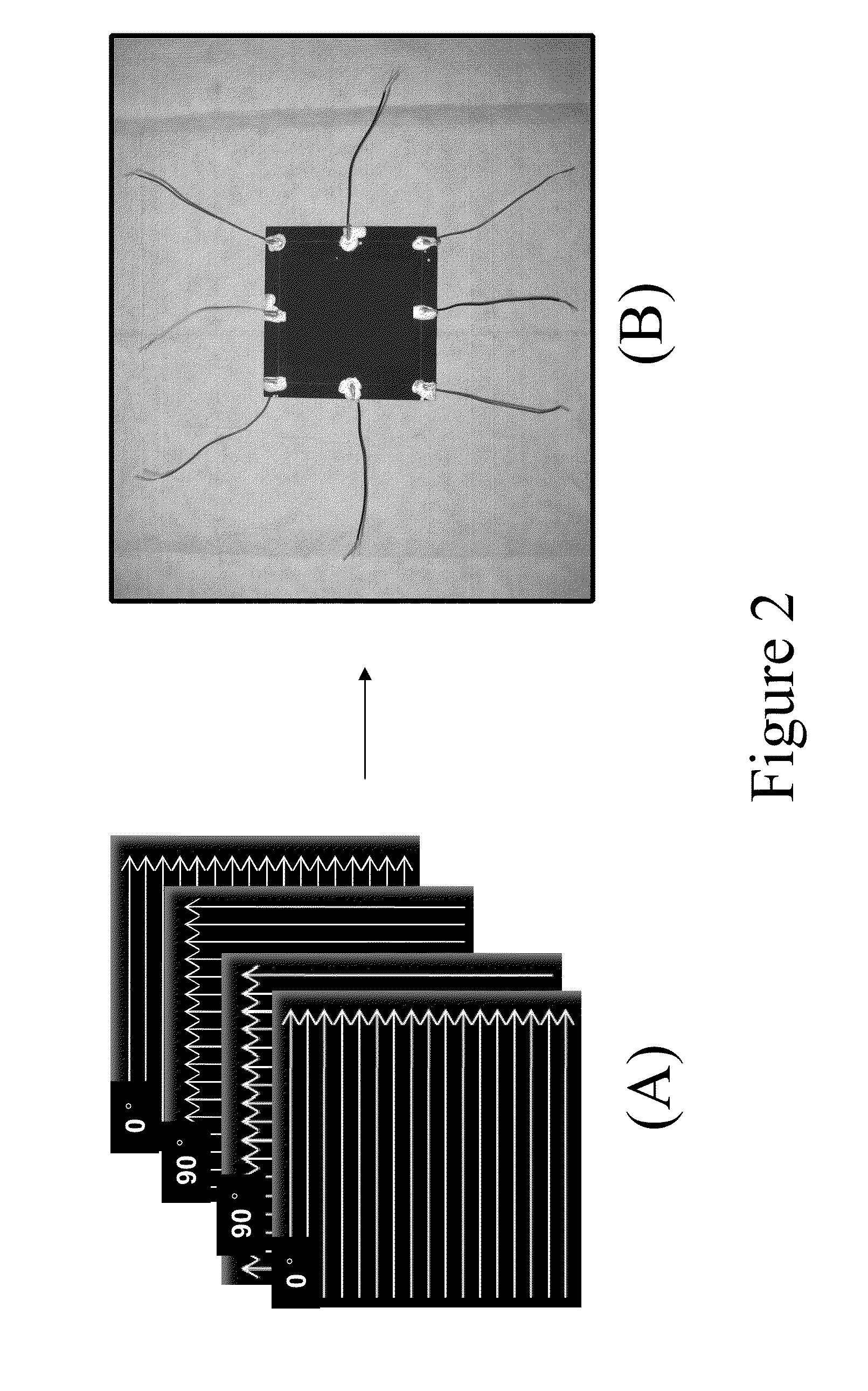
Damage-sensing composite structures
A composite includes a matrix material and a unidirectional array of carbon nanotube-infused fibers disposed in a portion of the matrix material. An article includes this composite and a network of electrodes disposed about the periphery of the composite. The electrodes send and receive an electrical charge. Such an article is included in a system, along with sensing circuitry and a source for supplying current to the network of electrodes. Such a system is used in a method that includes subjecting the article to a load that causes a condition in the composite including strain, fatigue, damage, or cracks, and monitoring the location of the condition.
Owner:APPL NANOSTRUCTURED SOLUTIONS LLC
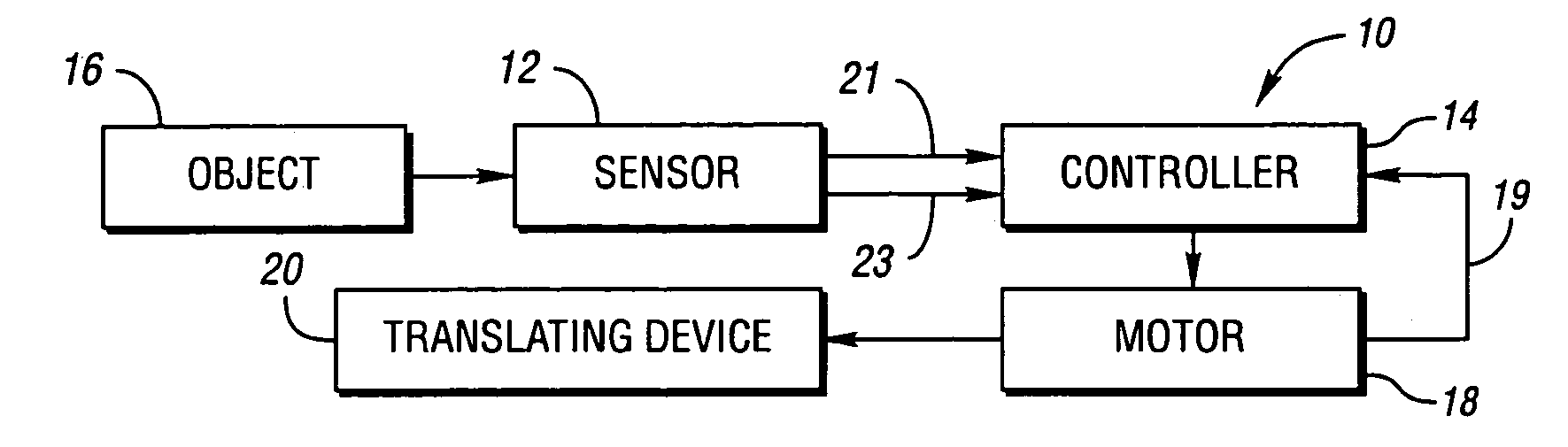
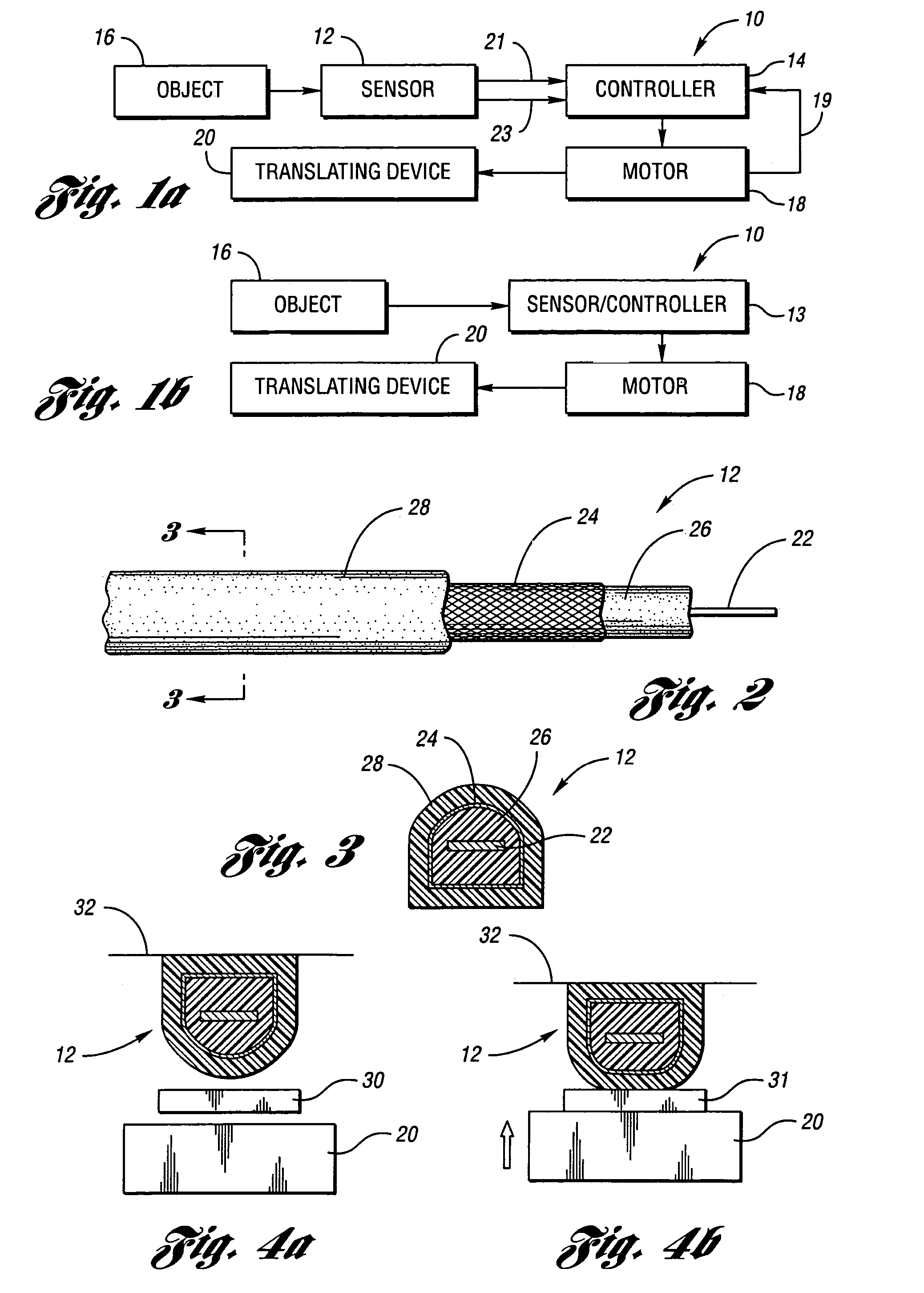
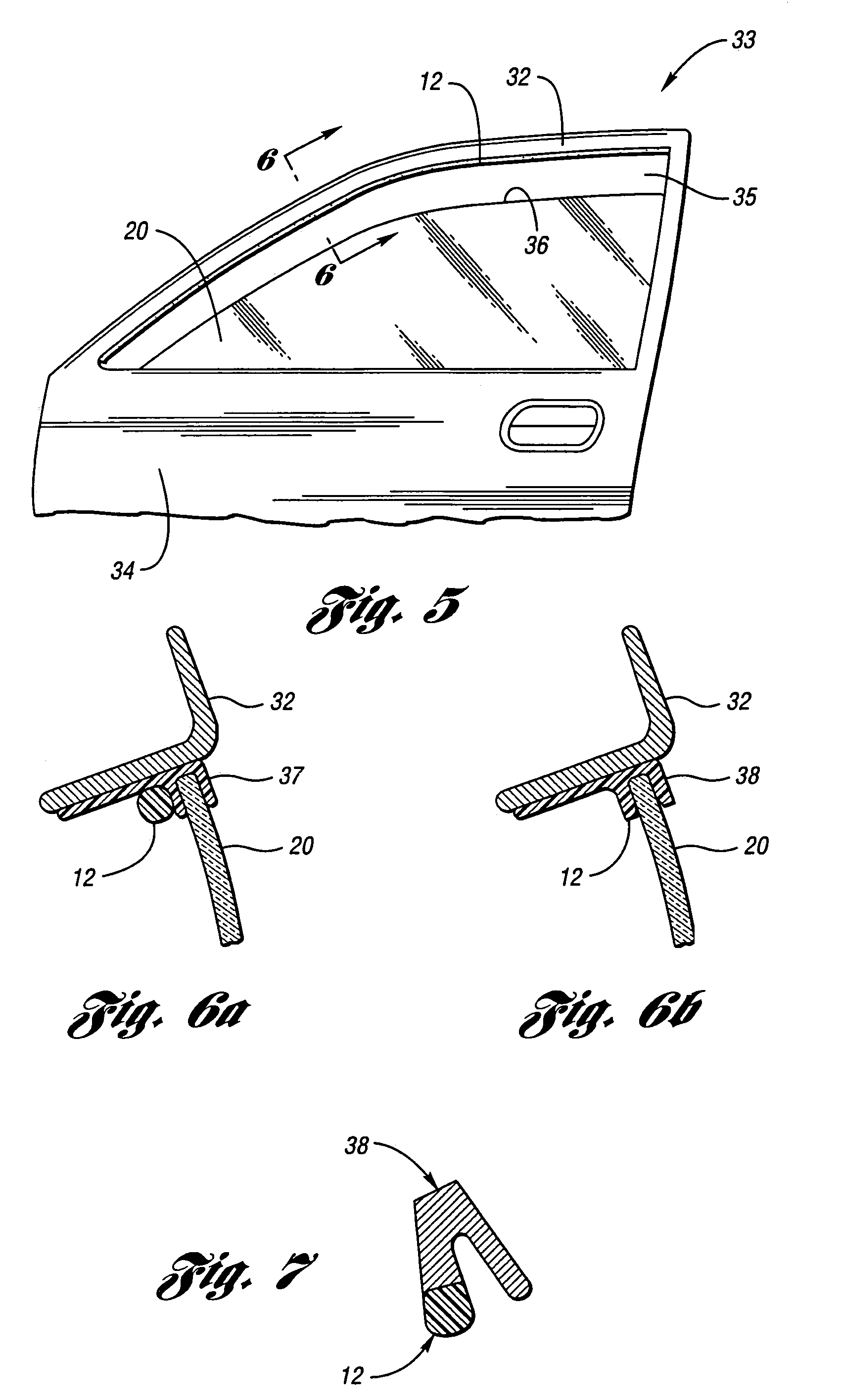
Anti-entrapment systems for preventing objects from being entrapped by translating devices
InactiveUS7132642B2Prevent any pinching of the objectHigher compressive forceVehicle seatsForce measurementDielectricElastomer
An anti-entrapment system for preventing an object from being entrapped by a translating device includes a capacitance sensor positioned adjacent to the translating device. The sensor has first and second conductors separated by a separation distance, a compressible dielectric element interposed between the conductors, and a non-conductive elastomer outer jacket encasing the conductors and the dielectric element. The sensor having a capacitance dependent upon the separation distance between the conductors. The capacitance changes in response to the separation distance changing as a result of the dielectric element compressing in response to a first object touching the outer jacket, and in response to a second conductive object coming into proximity with at least one of the conductors. A controller controls the translating device as a function of the capacitance in order to prevent the translating device from entrapping either object.
Owner:UUSI
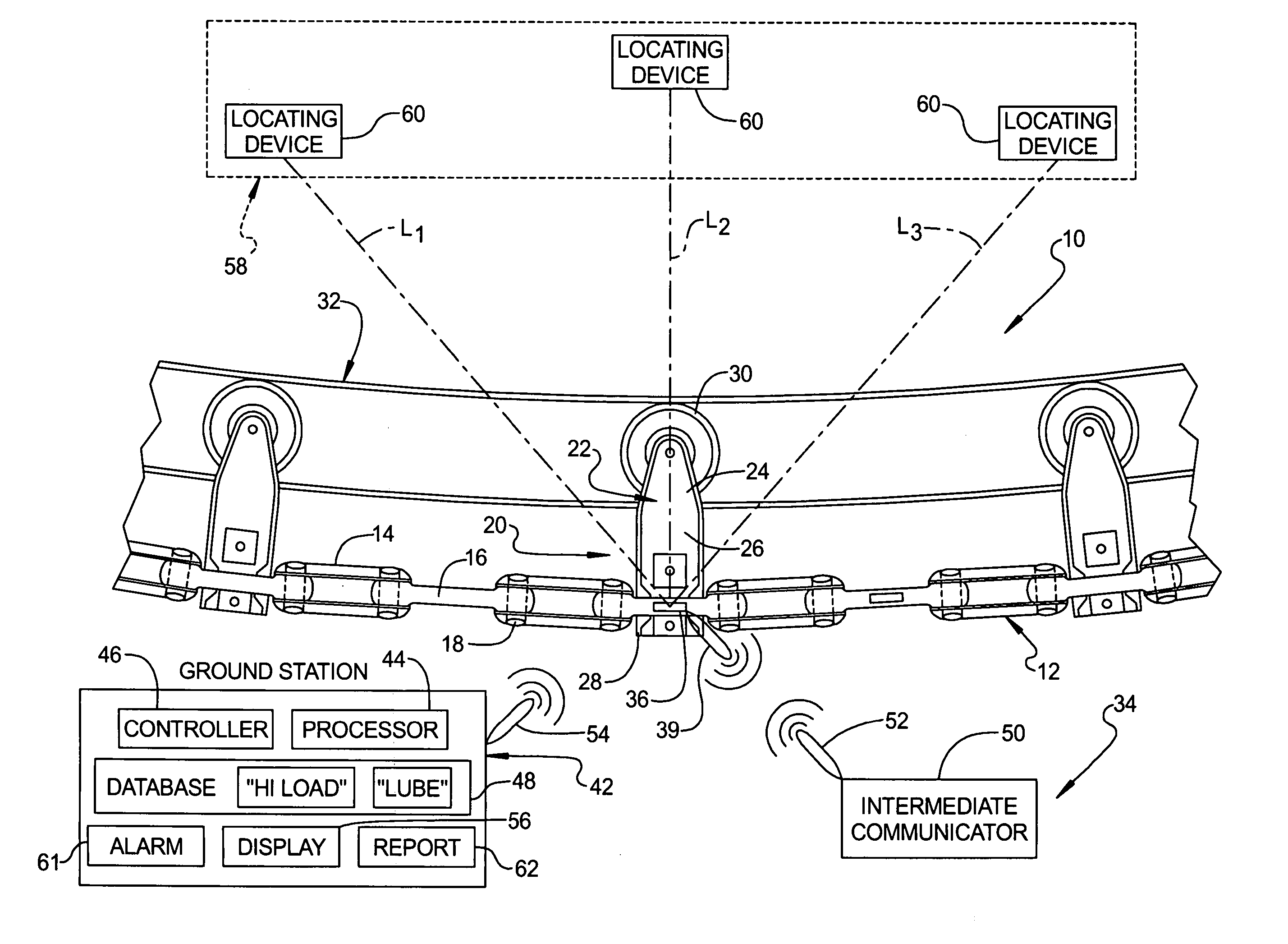
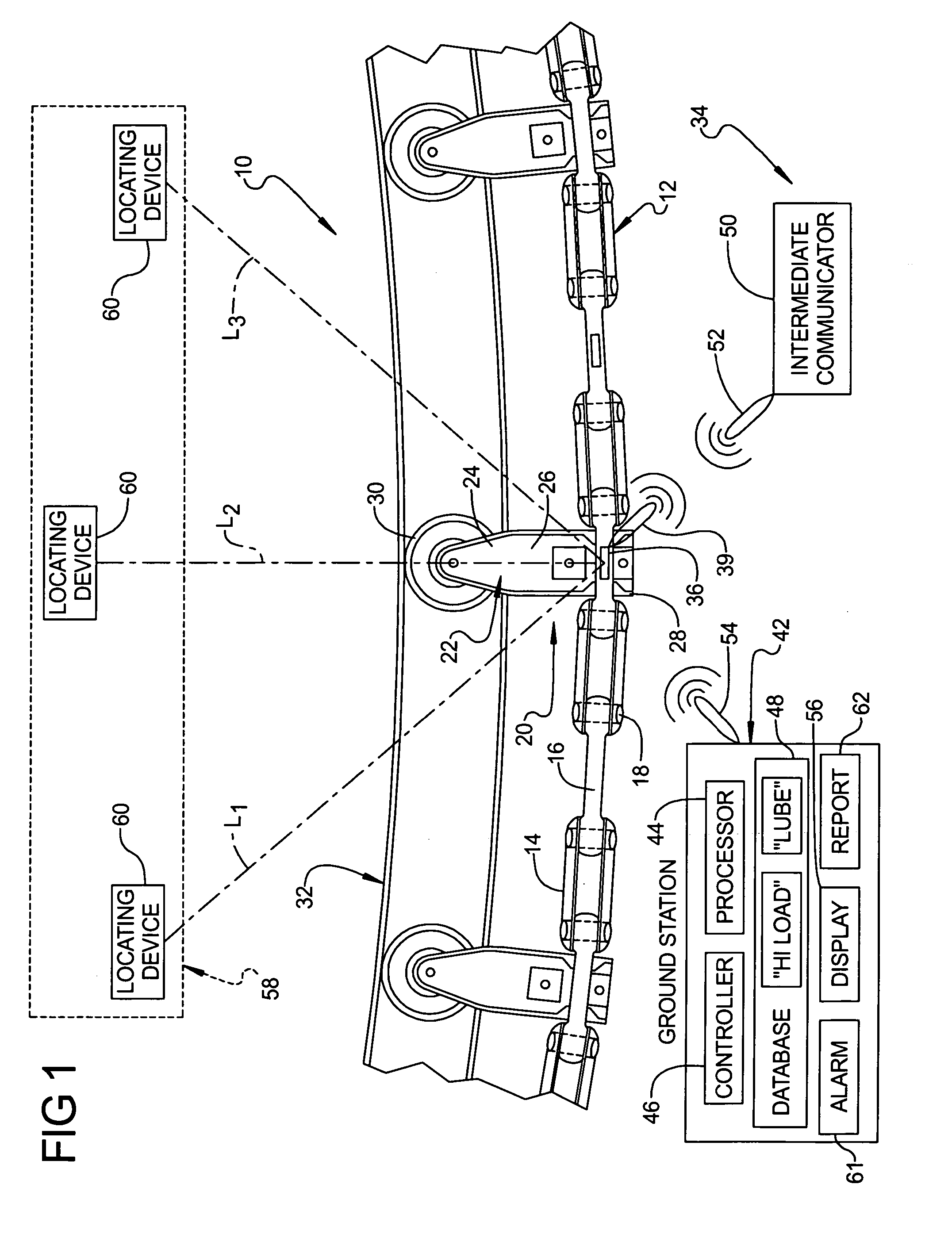
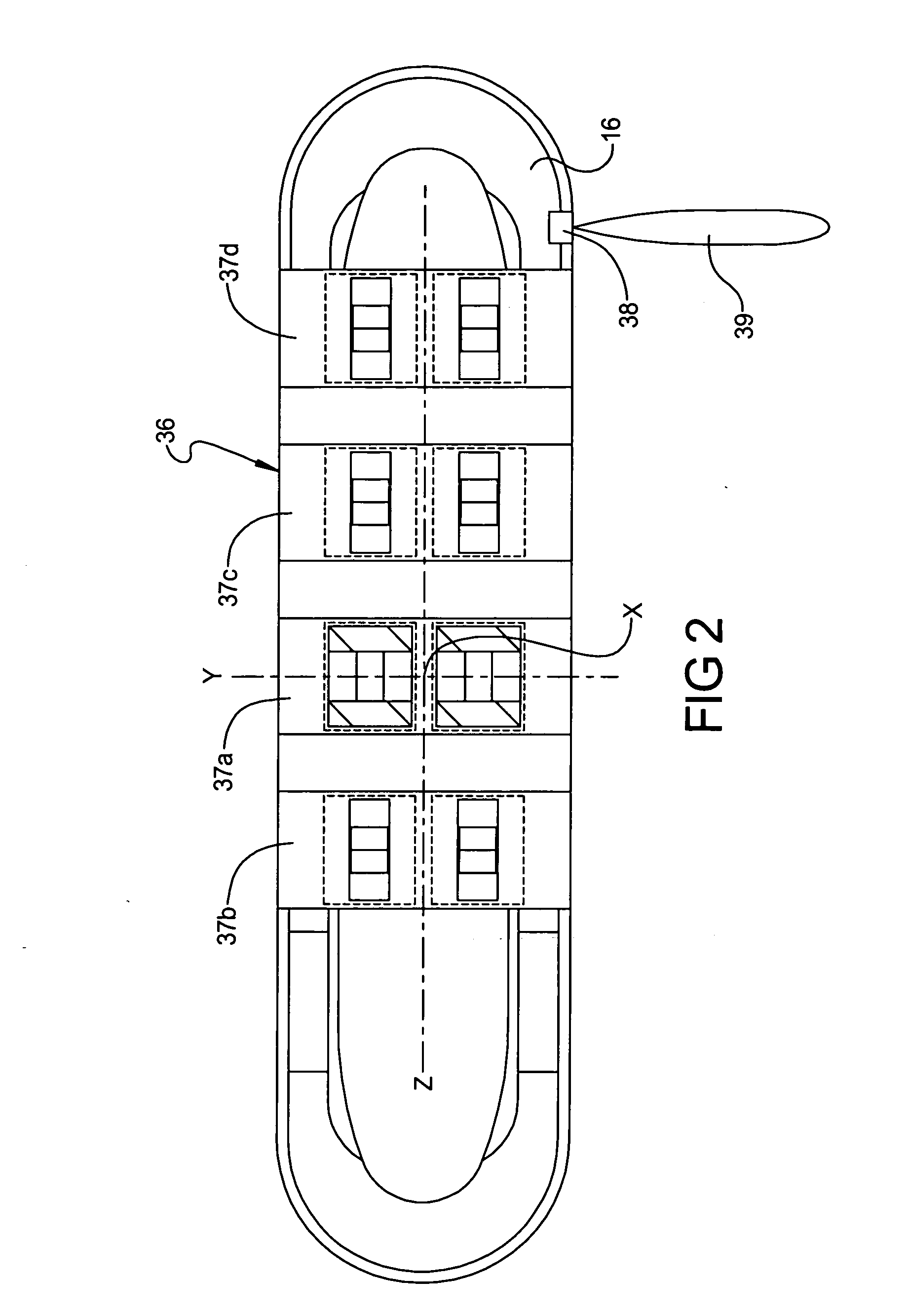
Conveyor diagnostic system having local positioning system
A conveyor diagnostic system for monitoring loading of a conveyor line assembly including at least one sensor component coupled to the conveyor line assembly. The sensor component is adapted for detecting loading of the conveyor line assembly and is further adapted for generating and transmitting a signal that is correlative of the loading of the conveyor line assembly. The conveyor diagnostic system also includes a ground station adapted to receive and process the signal that is correlative of the loading of the conveyor line assembly. Furthermore, the conveyor diagnostic system includes a local positioning system that is adapted for detecting the location of the sensor component in relation to a reference point. A method of using the conveyor diagnostic system is also disclosed.
Owner:FCA US
Customizable Embedded Sensors
InactiveUS20130079693A1Force measurement by permanent gauge deformationMeasurement apparatus componentsEngineeringEngineering physics
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
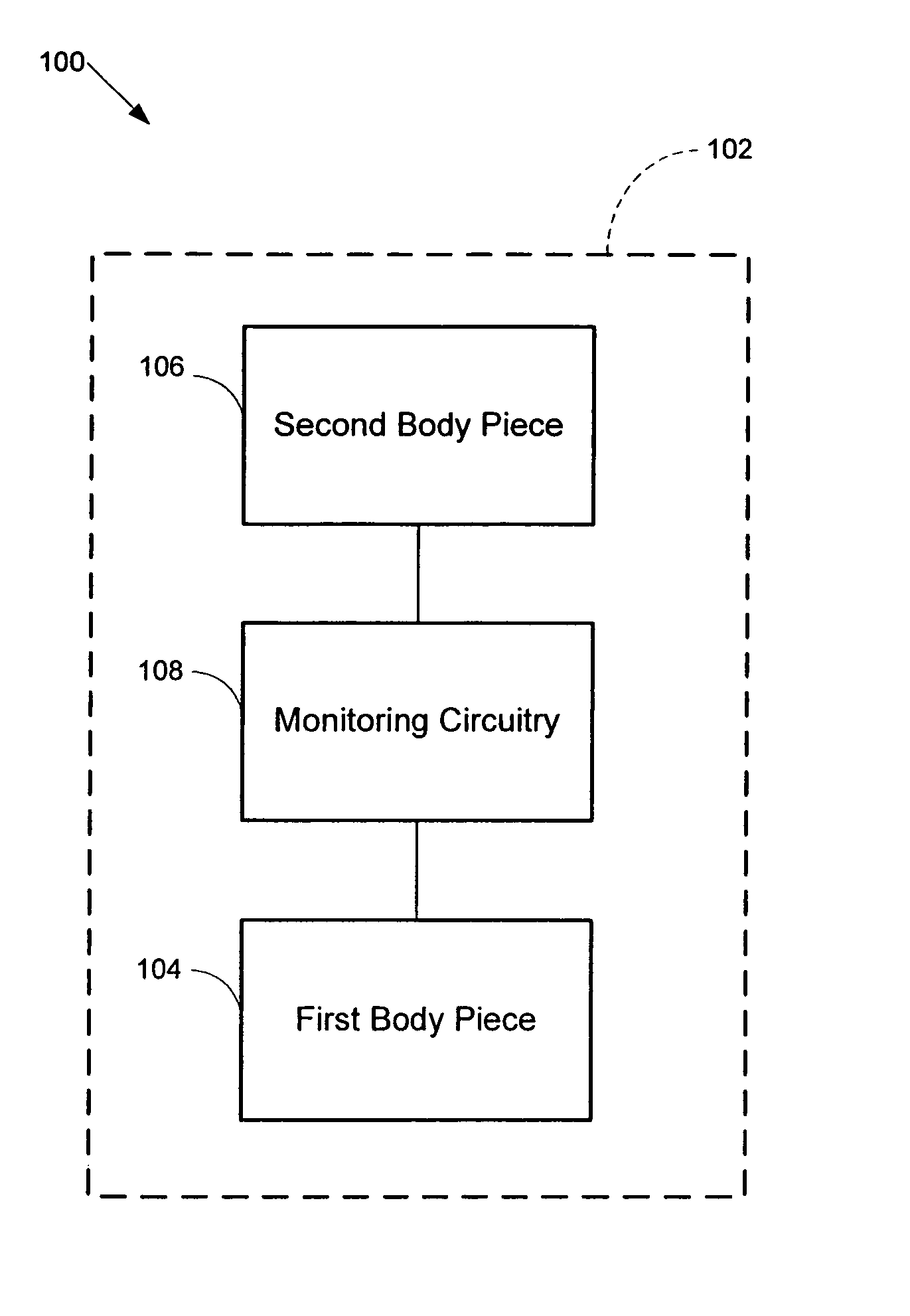
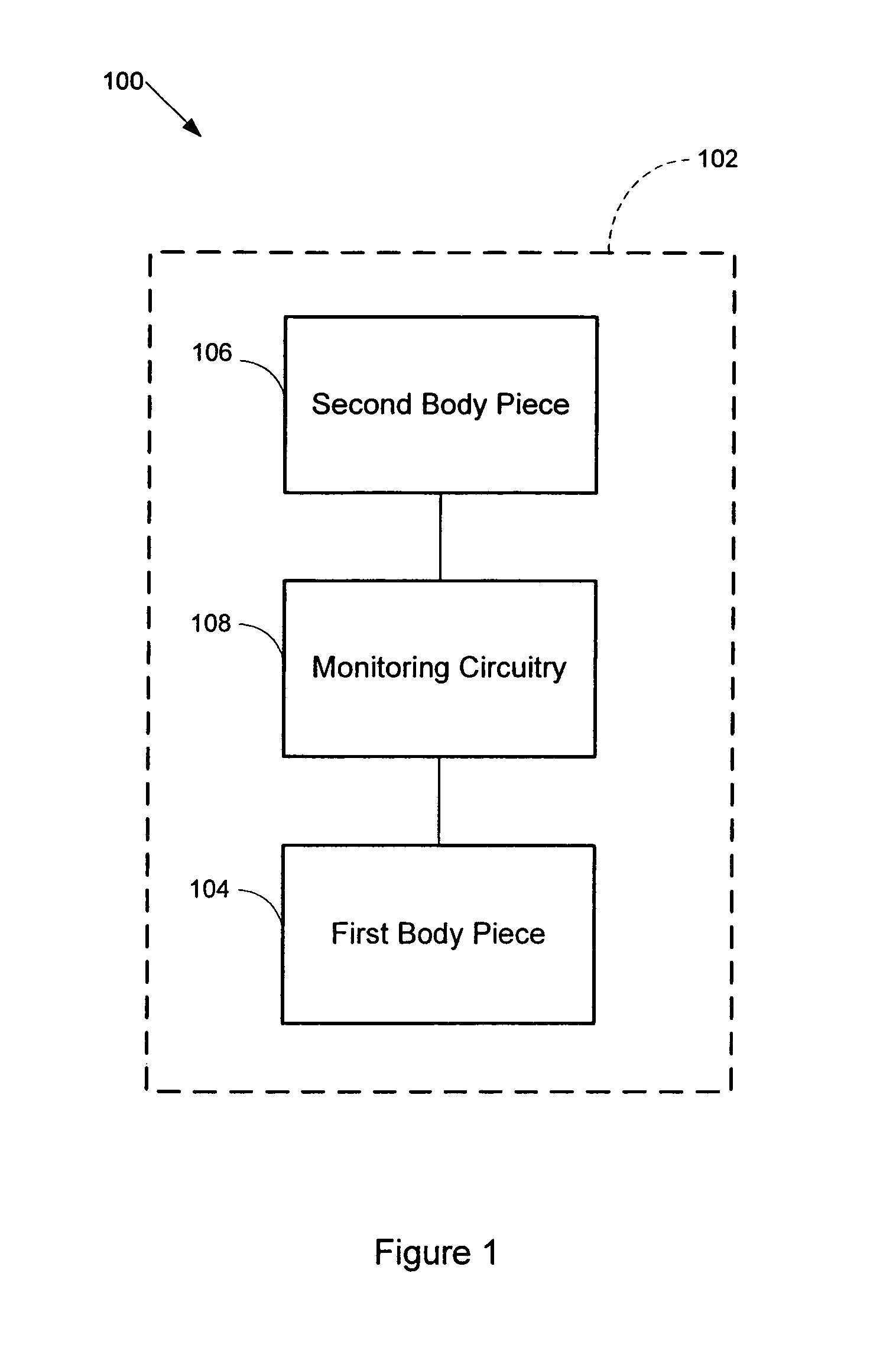
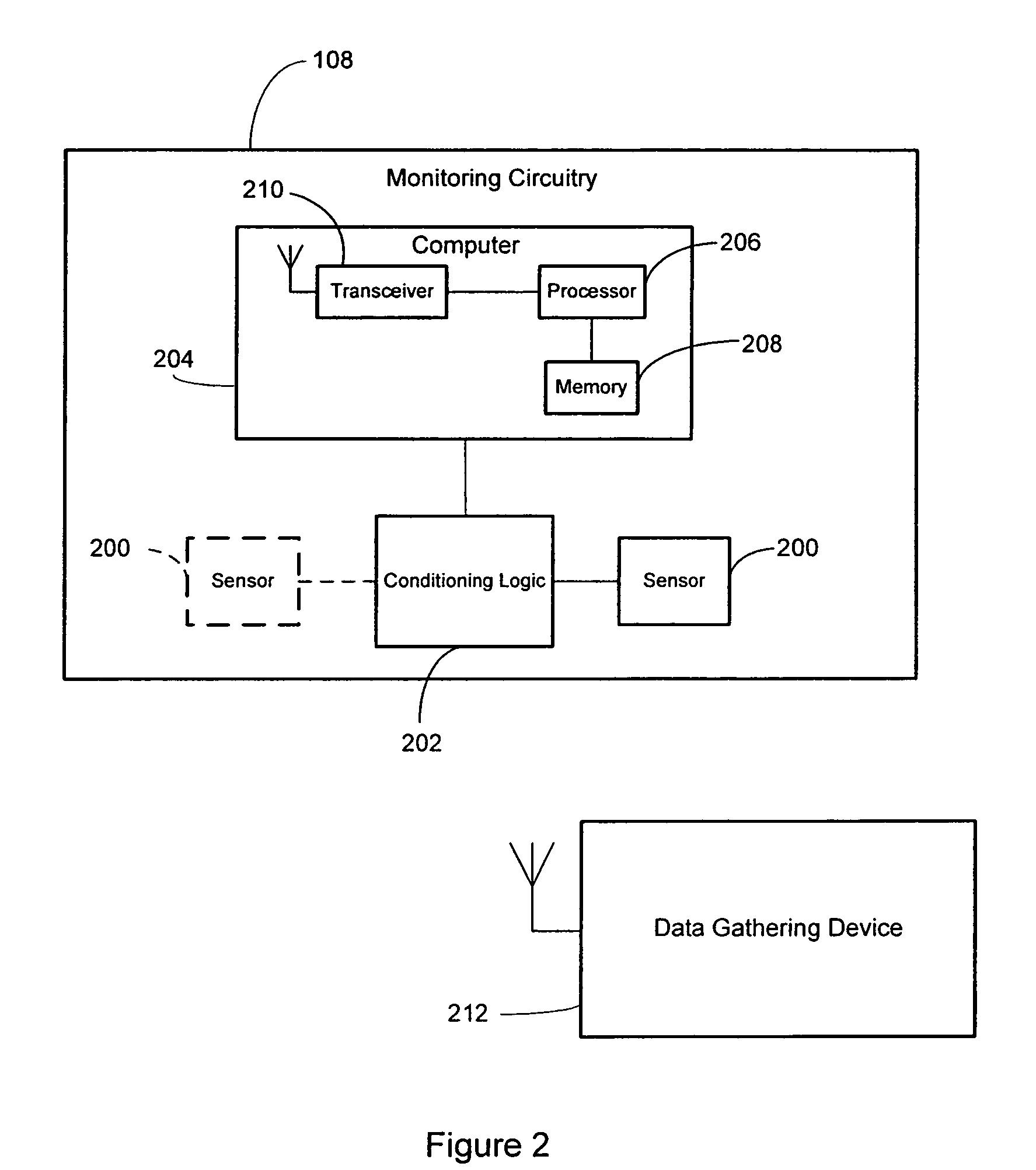
Force monitoring system
A system monitors dynamic forces between bearing surfaces. Based on sensed data, the system may model the forces on the bearing surfaces, analyze these forces, store data relating to these forces, and / or transmit data to an external data gathering device. The system includes a first body piece and a second body piece which mate together. The first and second body pieces comprise bearing surfaces that contact a material that may exert a force. A protrusion, such as a pole, post, or beam, extends from first body piece's bearing surface. At least one sensor is disposed on a pole. The at least one sensor detects a mechanical motion of the pole resulting from a force imposed on the body pieces, and generates data indicative of this force. A computer communicates with the at least one sensor and processes the sensed and / or modeled data.
Owner:ORTHO SENSING TECH
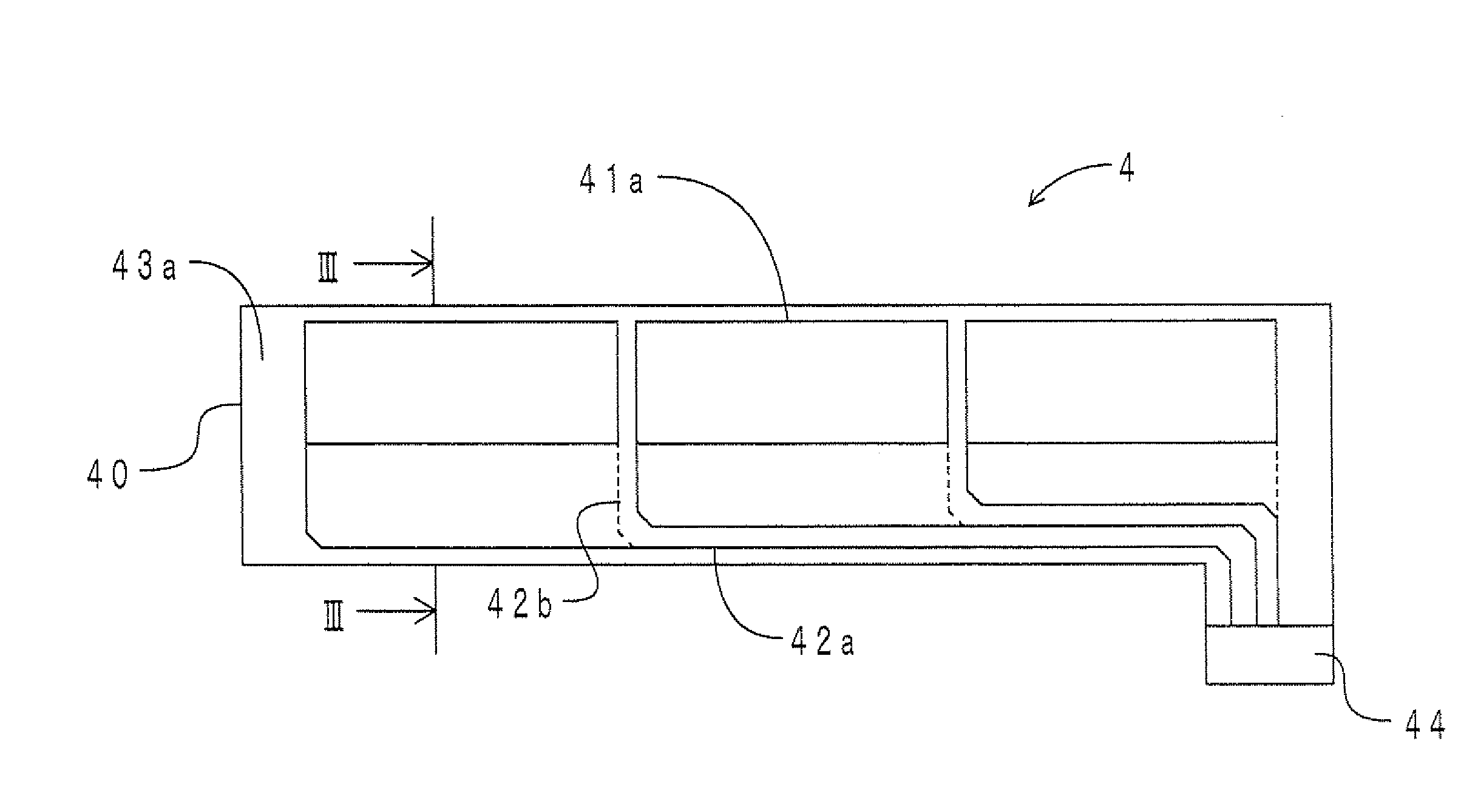
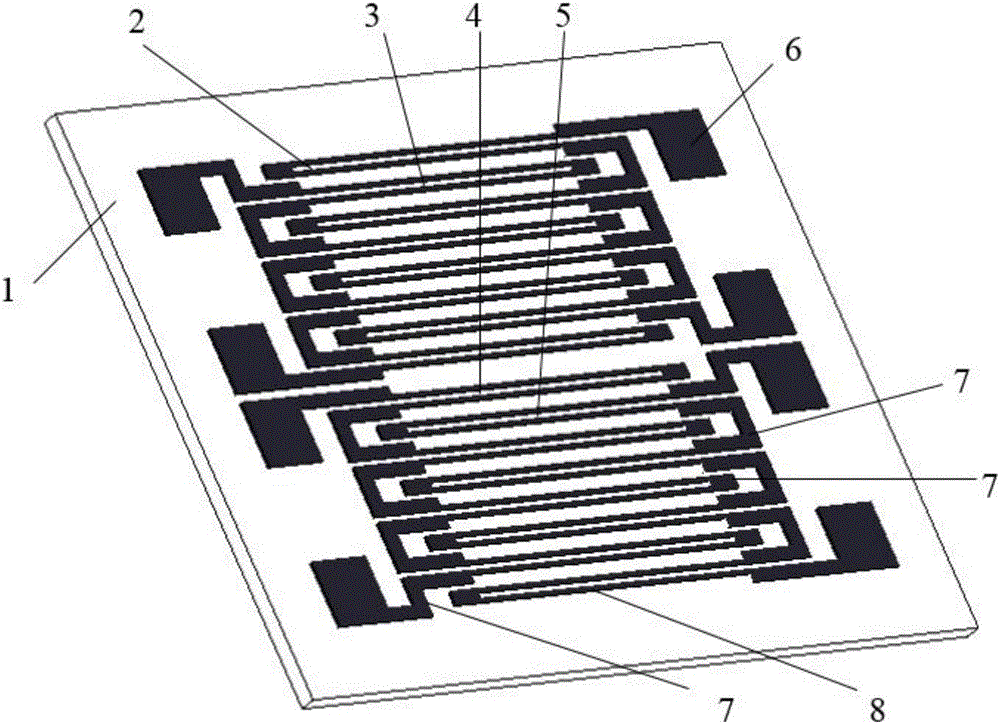
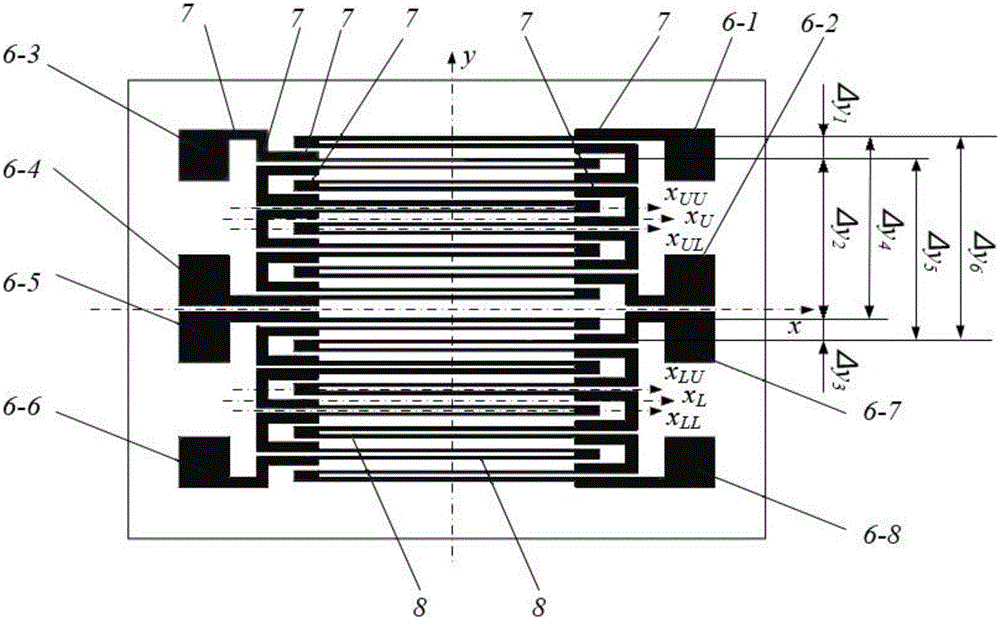
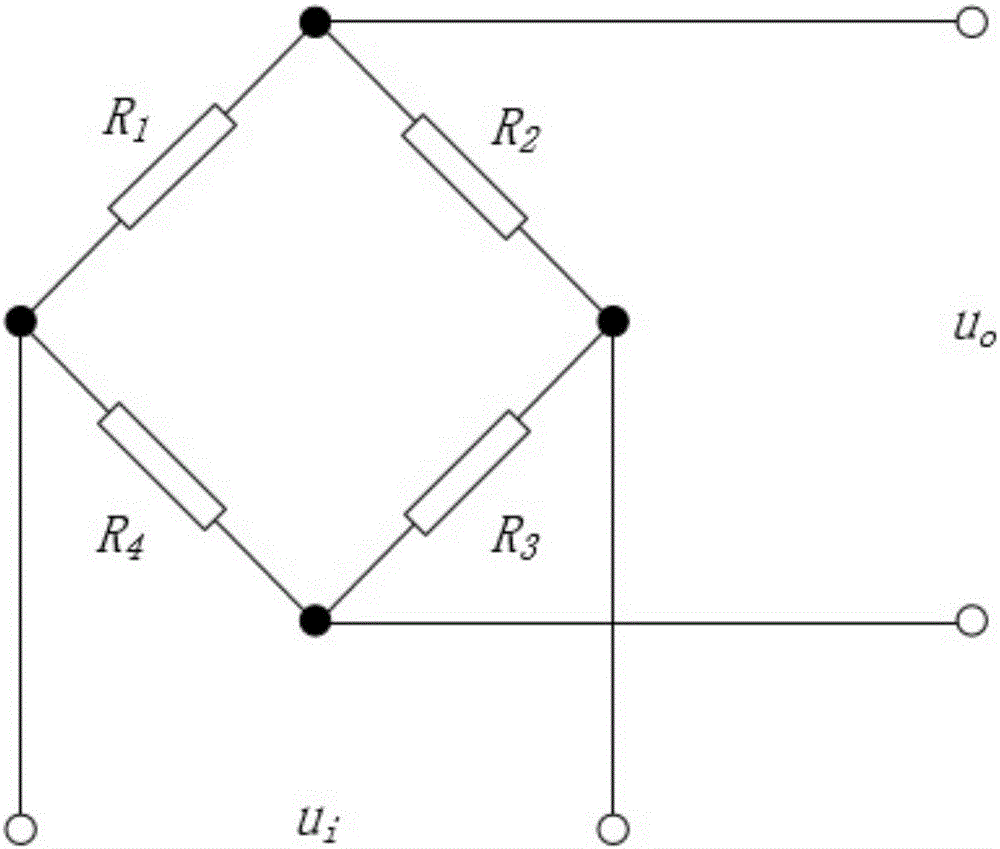
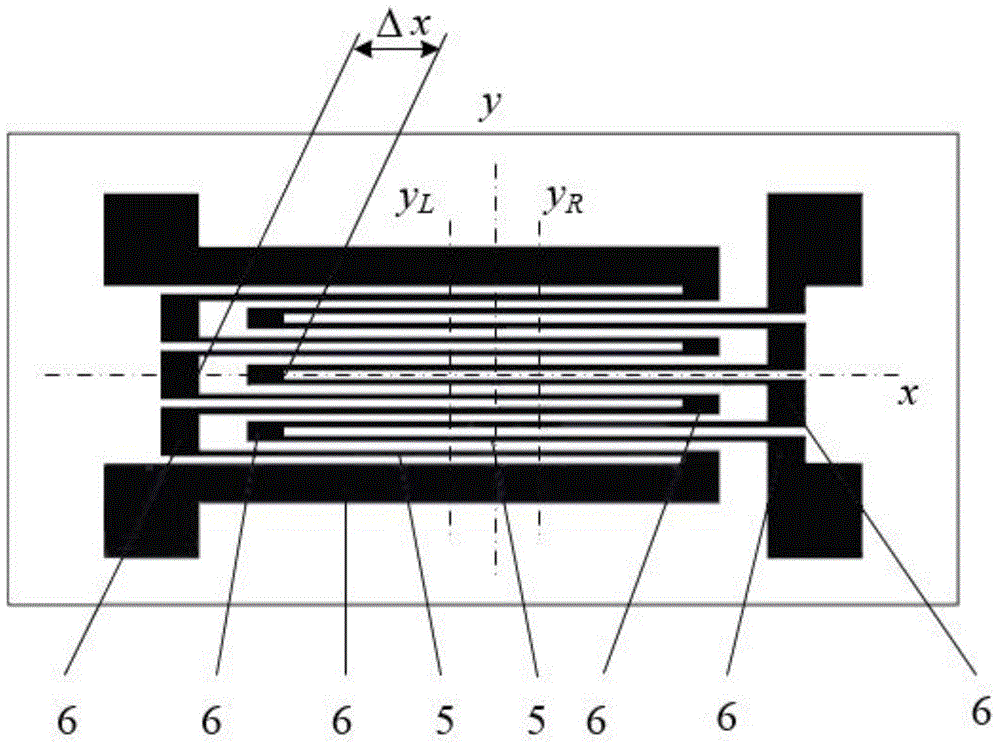
Lateral deviation full-bridge double-interdigital metal strain gauge capable of measuring surface strain lateral partial derivatives
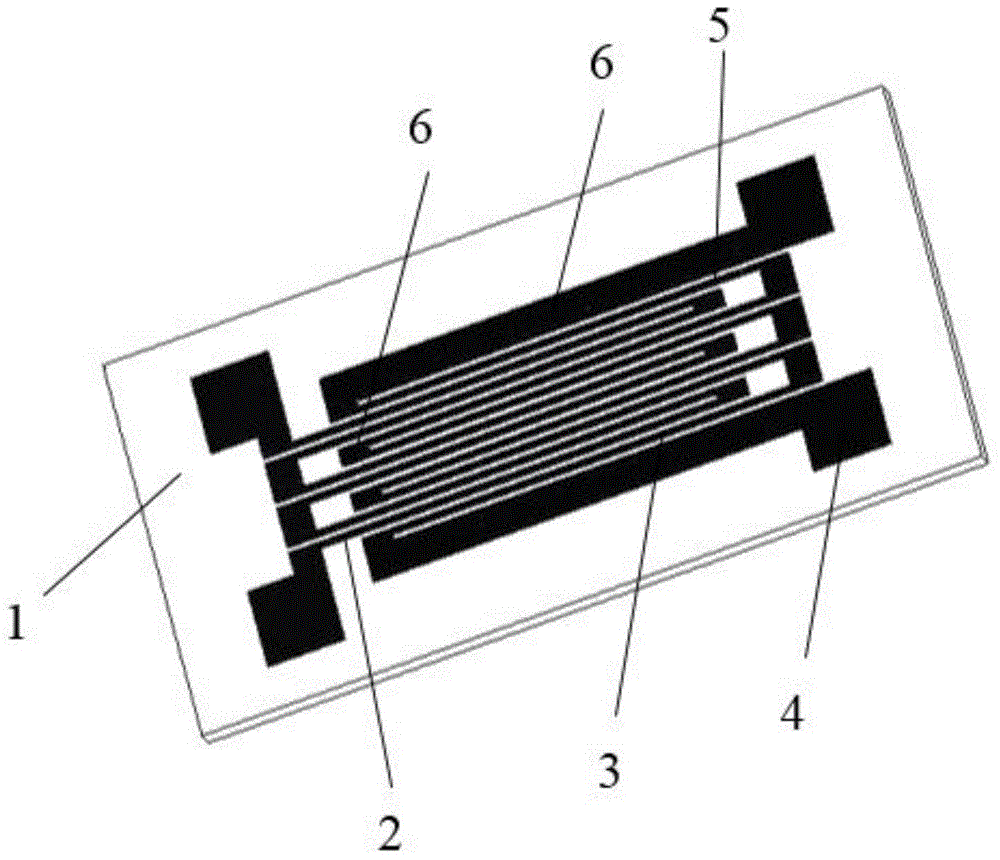
InactiveCN105004262AEfficient detection of surface strain lateral first orderEfficient detection of second order partial derivativesElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceFull bridge
The invention relates to a lateral deviation full-bridge double-interdigital metal strain gauge capable of measuring surface strain lateral partial derivatives, which comprises a base and four sensitive grids, and is characterized in that both ends of each sensitive grid are respectively connected to an outgoing line, each sensitive grid comprises a sensitive section and a transition section, and axes of the sensitive sections are straight lines and parallelly arranged in the same plane; in the plane determined by the axes of the sensitive sections, the axis direction of the sensitive sections is an axial direction, and the direction perpendicular to the axial direction is a lateral direction; the four sensitive grids are consistent in resistance, the resistance variation amount is consistent under the same strain, the four sensitive grids are called as an upper-upper sensitive grid, an upper-lower sensitive grid, a lower-upper sensitive grid and a lower-lower sensitive grid from top to bottom along the lateral direction, the upper-upper sensitive grid and the upper-lower sensitive grid are arranged in an interdigital mode, and the lower-upper sensitive grid and the lower-lower sensitive grid are also arranged in the interdigital mode; and centers of the four sensitive grids have no deviation in the axial direction and have deviation in the lateral direction. The lateral deviation full-bridge double-interdigital metal strain gauge not only can measure the strain, but also can effectively detect a lateral first-order derivative and a lateral second-order derivative of the surface strain.
Owner:山东尔湾海洋智能科技有限公司
Single sided capacitive force sensor for electronic devices
ActiveUS7784366B2Force measurement by measuring magnetic property varationUsing electrical meansDriver circuitEngineering
A capacitive force sensor (100) includes a substrate (101) having at least one electrode pair (102,103) defining a capacitance disposed thereon. The substrate (101) is fixed relative to a first plate (106). A drive circuit (104) is configured to apply a voltage relative to a circuit ground (105) to the electrode pair (102,103). The first plate (106) is separated from a second plate (107) that is coupled to circuit ground (105) by a compliance member (108,109). The compliance member (108,109) is configured to oppose a compression force (110) while allowing the first plate (106) to physically move relative to the second plate (107). A capacitive detection circuit (111) is then configured to detect a change the capacitance when the compliance member (108,109) is compressed. The compression force (110) is then determined from the change in capacitance and the spring constant of the compliance member (108,109).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Moving device in pipe lines
InactiveUS20050284233A1Easy to moveEasy to switchRailway tunnelsHollow article cleaningRemote controlEngineering
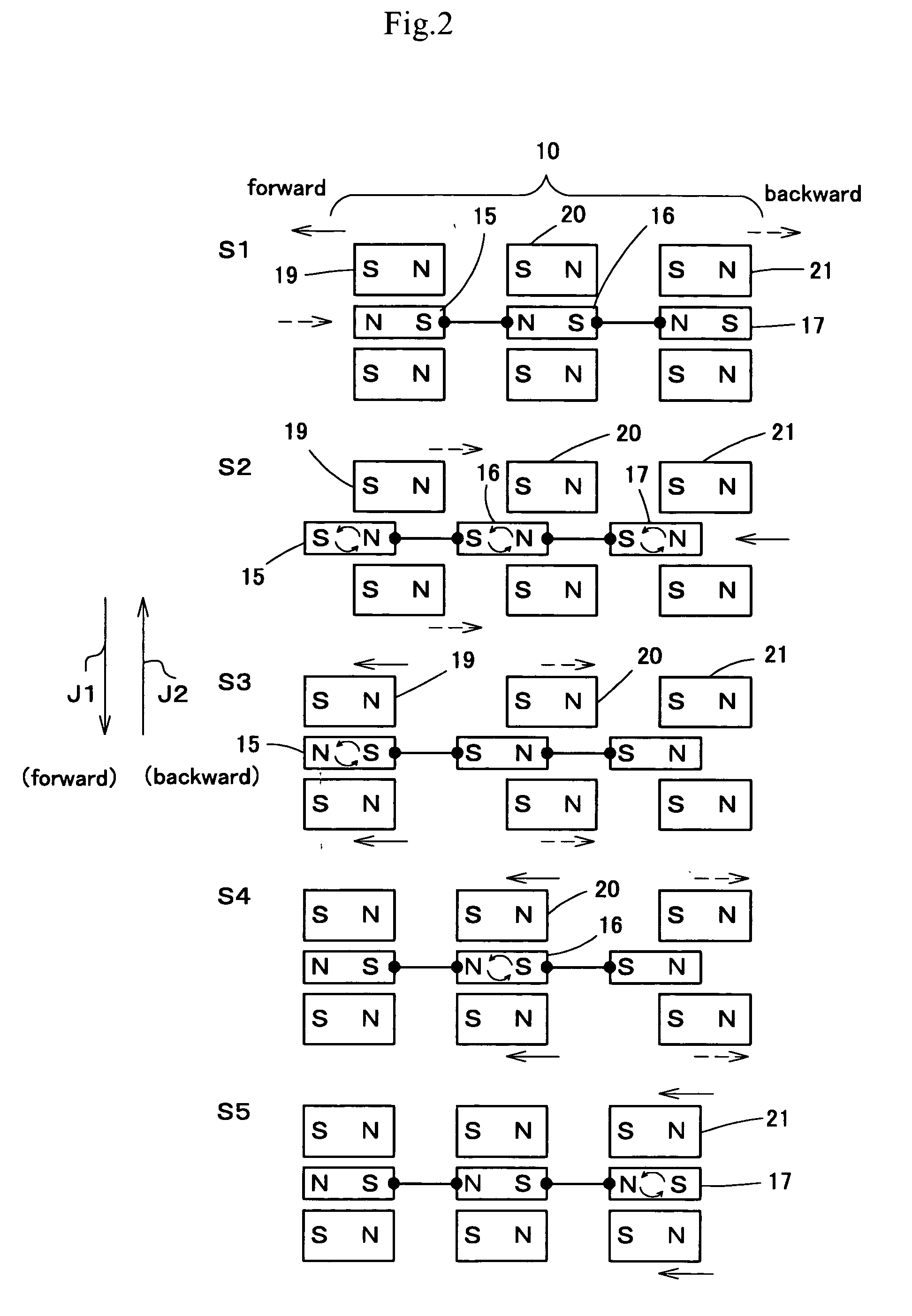
A moving device in pipe lines is provided, which allows easy switching of moving / stopping and remote control of the switching by only electric wires enabling easy operation in the inside of small diameter pipe lines. The moving device 10 in pipe lines comprises a guide frame 11 in which a line of three or more coils 15, 16, 17 is interconnected flexibly in the direction of magnet flux, ring-shaped permanent magnets 19, 20, 21 provided around the periphery of the guide frame slidably in the direction of the shaft, and a control means such as computers etc. to control by a preset program selecting the direction of turning on of the coils.
Owner:NIPPON CABLE SYSTEM INC
Anti-entrapment system
ActiveUS7162928B2Prevent any pinching of either objectVehicle seatsForce measurementElectrical conductorEngineering
An anti-entrapment system for preventing objects from being entrapped by a translating device includes a capacitance sensor positioned adjacent to the translating device and a controller. The sensor has first and second conductors separated by a separation distance and a compressible dielectric element interposed between the conductors. The conductors have a capacitance dependent upon the separation distance. The capacitance of the conductors changes in response to a geometry of the sensor changing as a result of either conductor or the dielectric element deforming in response to a first object touching the sensor. The capacitance of the conductors changes in response to a second conductive object coming into proximity with either conductor. The controller receives a signal from the sensor indicative of the capacitance of the conductors, and controls the translating device as a function of the capacitance of the conductors to prevent the translating device from entrapping either object.
Owner:UUSI
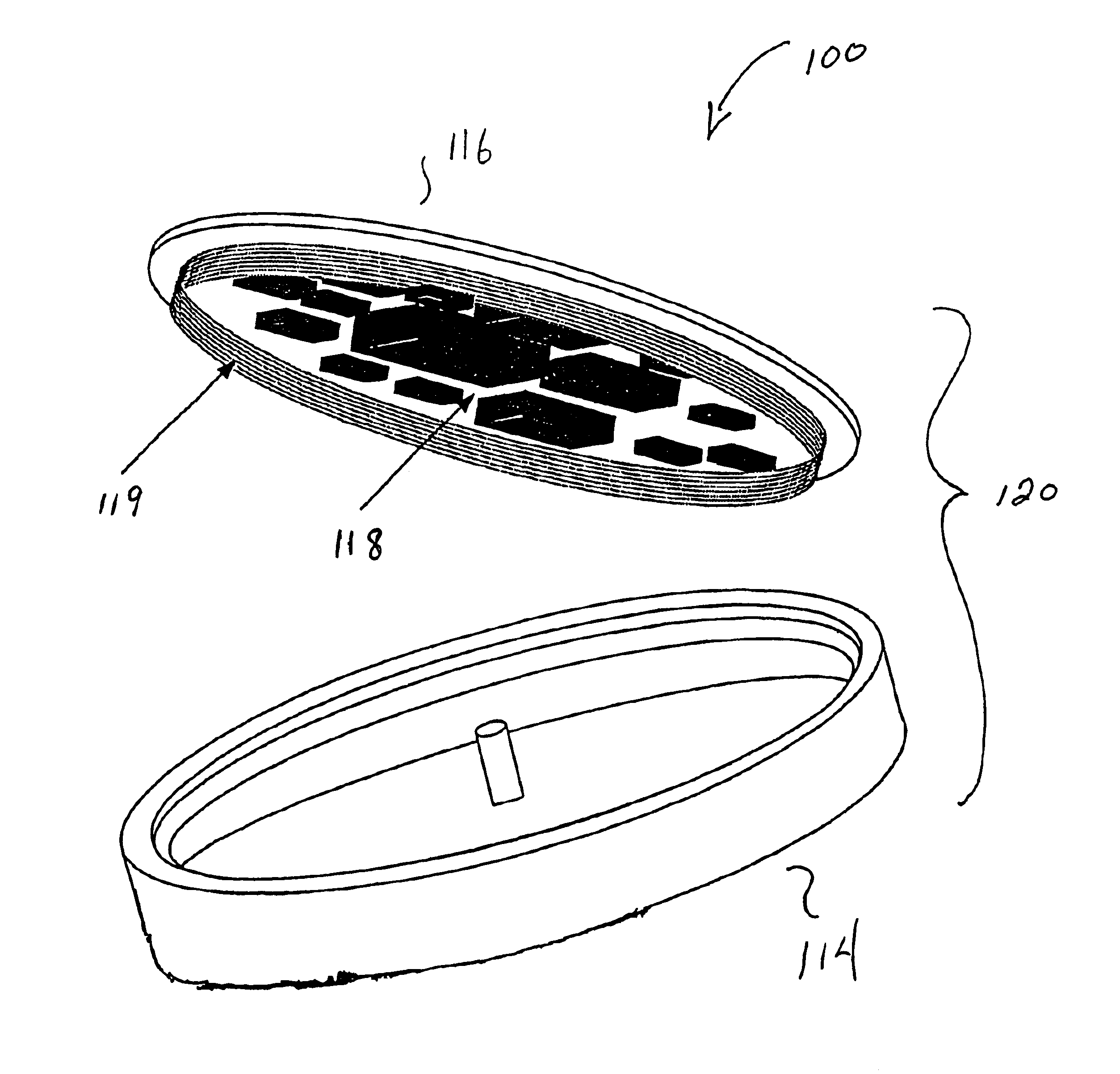
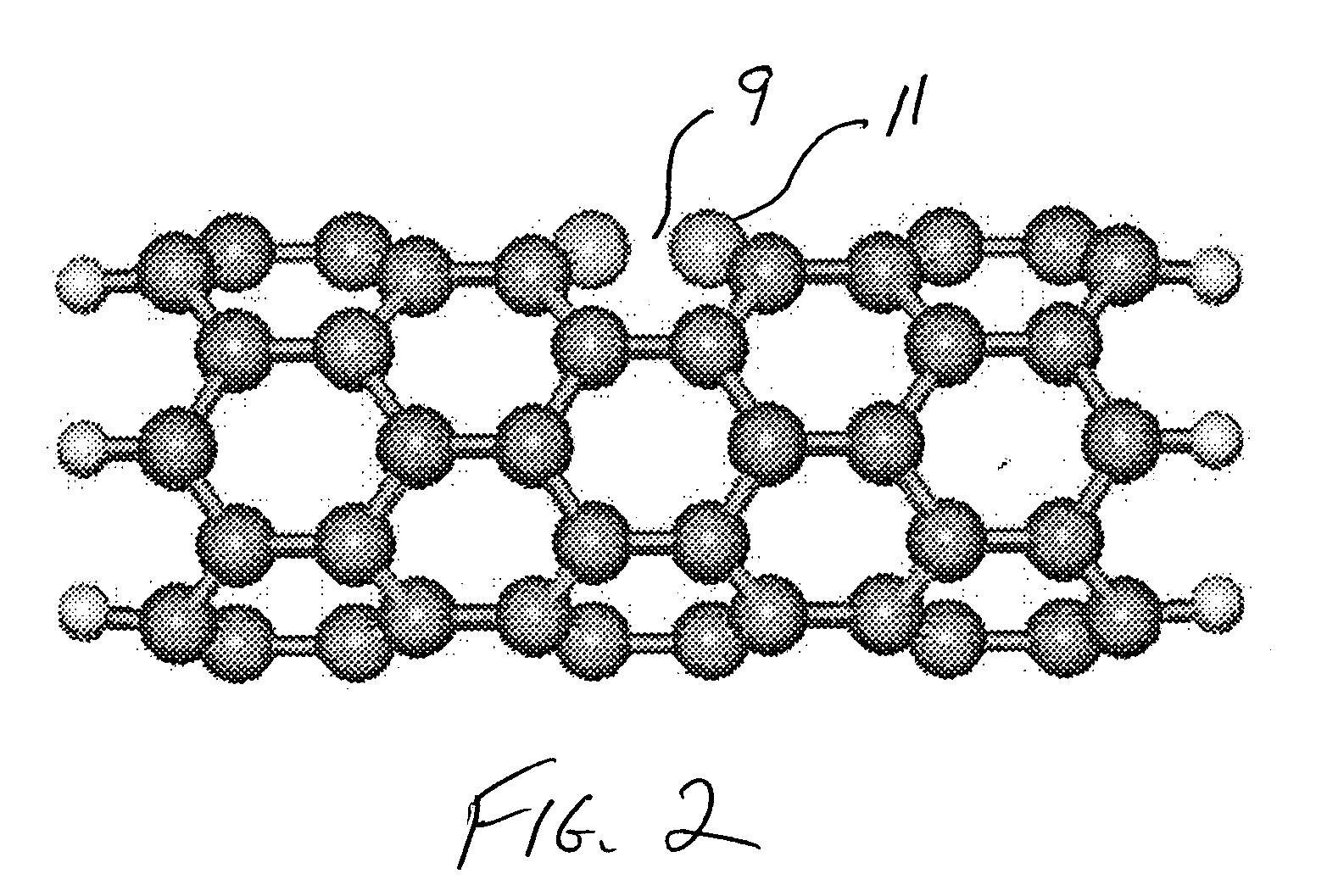
Embedded nanotube array sensor and method of making a nanotube polymer composite
ActiveUS20070138010A1Material nanotechnologyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPolymer compositesMaterials science
A method of producing polymer / nanotube composites where the density and position of the nanotubes (11) within the composite ca be controlled. Carbon nanotubes (11) are grown from organometallic micropatterns. These periodic nanotube arrays are then incorporated into a polymer matrix (7) by deposing a curable polymer film on the as-grown tubes. This controlled method of producing free-standing nanotube / polymer composite films may be used to form nanosensor (3) which provide information regarding a physical condition of a material (20), such as an airplane chassis or wing, in contact with the nanosensor (3).
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Axial deviation double-sensitive grid interdigital metal strain plate capable of measuring axial deviation of surface strain
ActiveCN105091731AEffective detection of axial partial derivatives of surface strainElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceStrain gauge
The invention discloses an axial deviation double-sensitive grid interdigital metal strain plate capable of measuring axial deviation of surface strain. The metal strain plate comprises a substrate and two sensitive grids, wherein two ends of each sensitive grid are respectively connected with a leading-out line, the two sensitive grids are fixed on the substrate, each sensitive grid comprises a sensitive section and a transition section, and the axes of all the sensitive sections are linear, parallel and within the same plane; the direction perpendicular to the axial direction which is the direction of the axes of the sensitive sections in the plane determined by the axes of the sensitive sections is a transverse direction; the two sensitive grids are consistent in resistance variation under the same strain, and are respectively a left sensitive grid and a right sensitive grid in the axial direction from left to right; and on the plane determined by the axes of the sensitive sections, the left sensitive grid and the right sensitive grid are arranged in an interdigital mode. The metal strain plate can be used for measuring strain and effectively detecting axial first-order deviation of the surface strain.
Owner:江苏明泰工程机械制造研究院有限公司
Wireless multi-funtional sensor platform, system containing same and method for its use
InactiveUS20040004554A1Electric signal transmission systemsForce measurementLine sensorTransmitted power
A multi-functional sensor system for simultaneously monitoring various parameters such as the structural, chemical and environmental conditions associated with a medium to be monitored, e.g., bridges, high-rise buildings, pollution zones, is provided wherein the system includes at least a plurality of wireless multi-functional sensor platforms embedded in the medium in which an interrogation unit transmits power and receives responses. Each wireless multi-functional sensor platform includes multiple channels for accommodating a plurality of sensor types to simultaneously monitor the parameters associated with the medium. Thus, the wireless sensor platforms are formed to include those sensor types which are considered germane to the intended medium to be monitored.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com