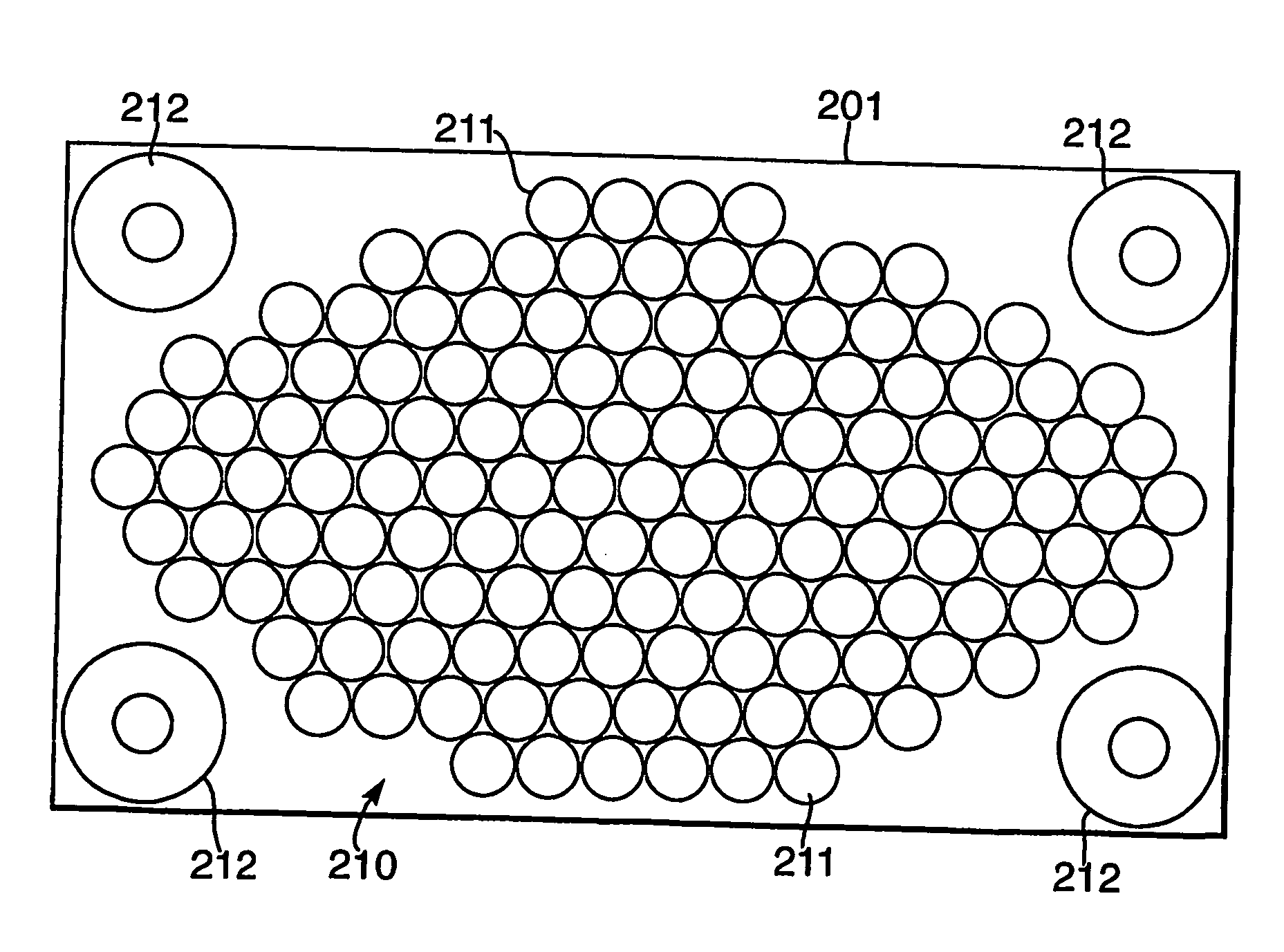
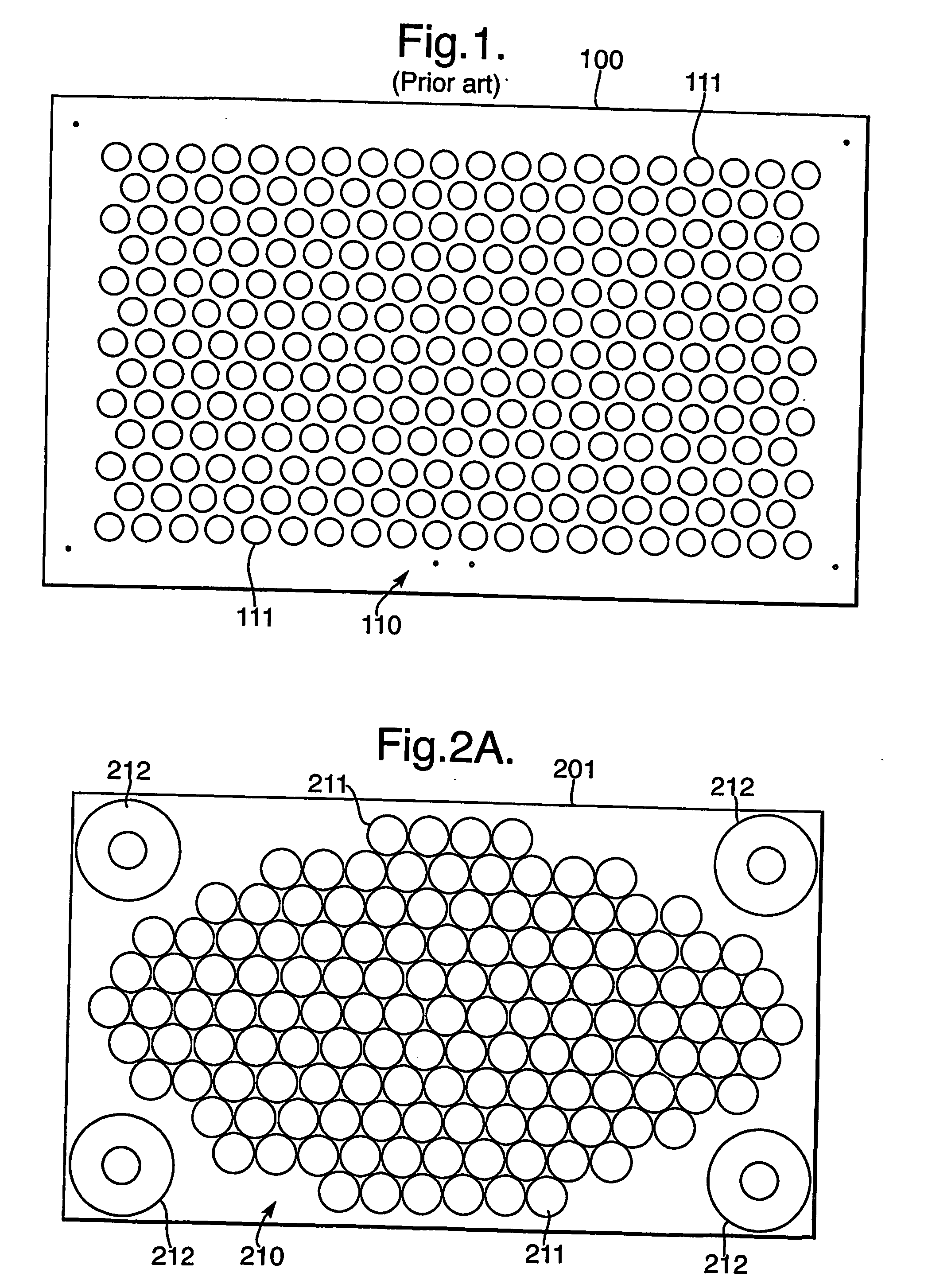
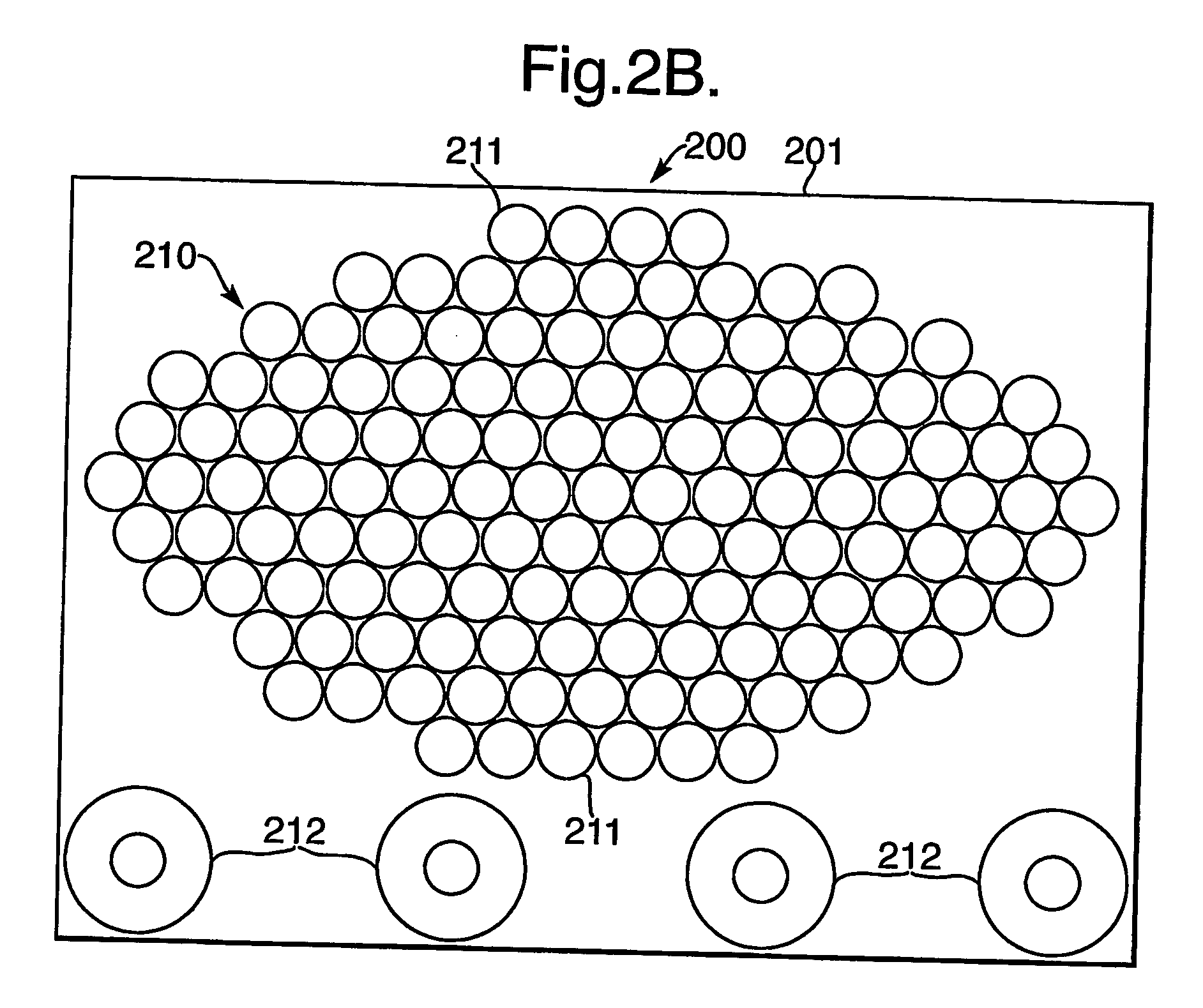
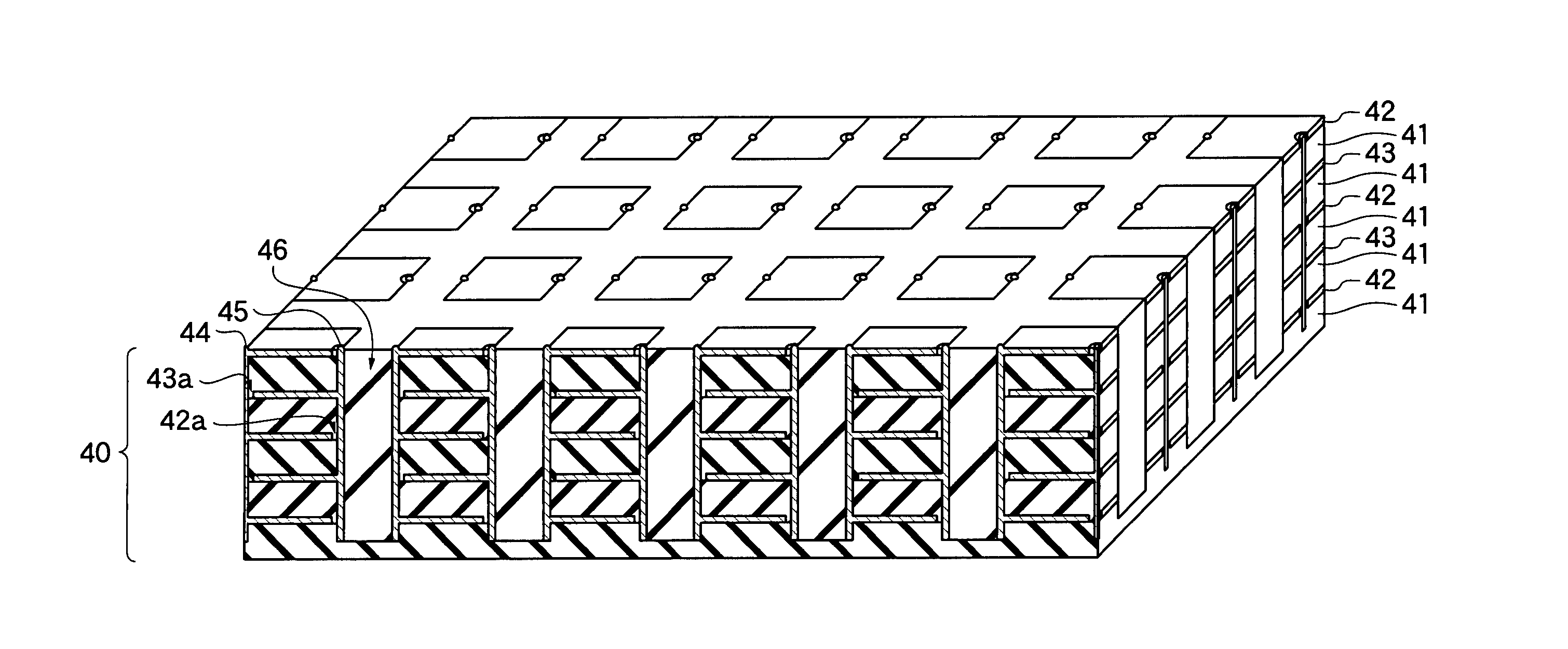
Patents
Literature
4154results about "Piezoelectric/electrostrictive transducers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
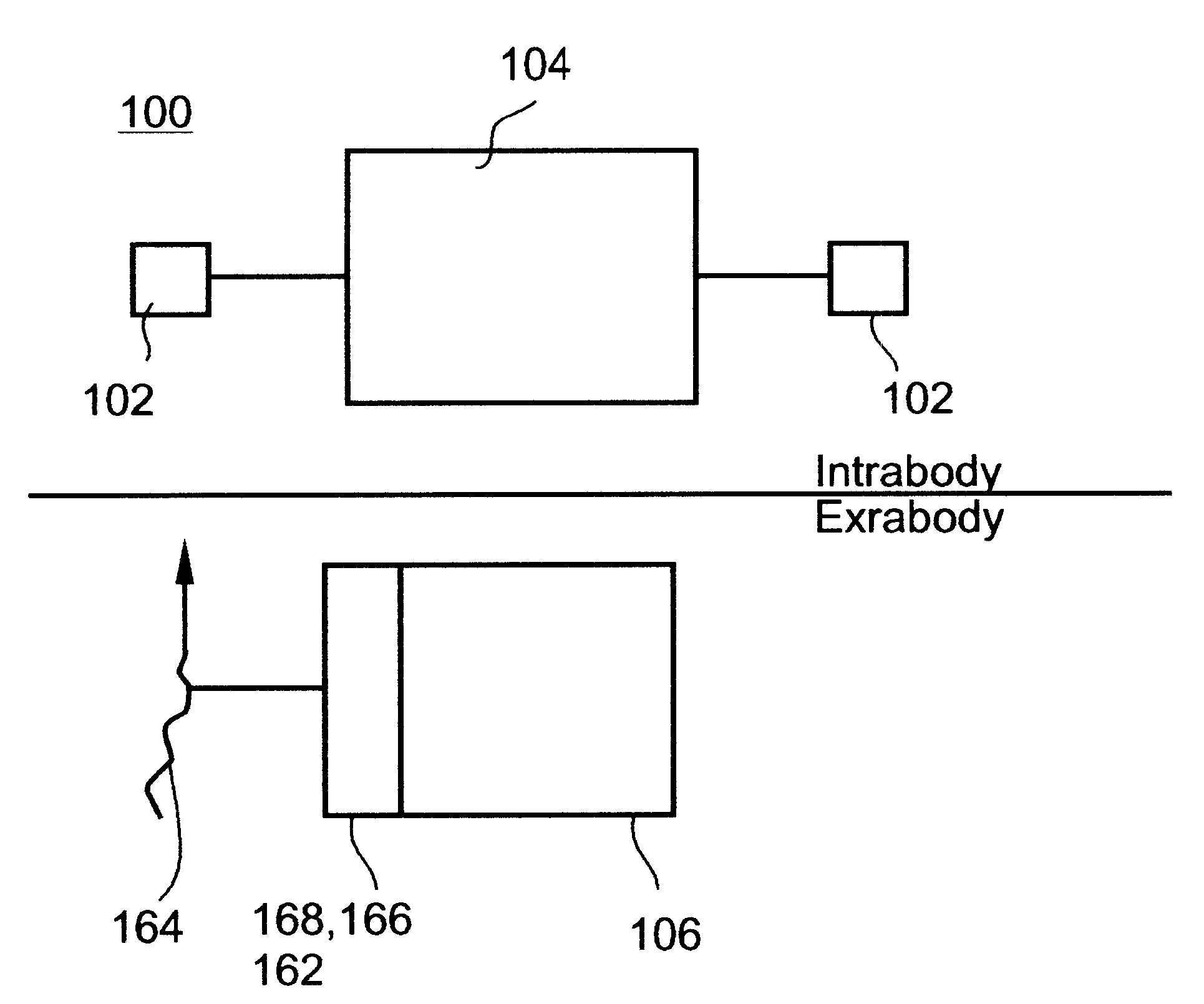
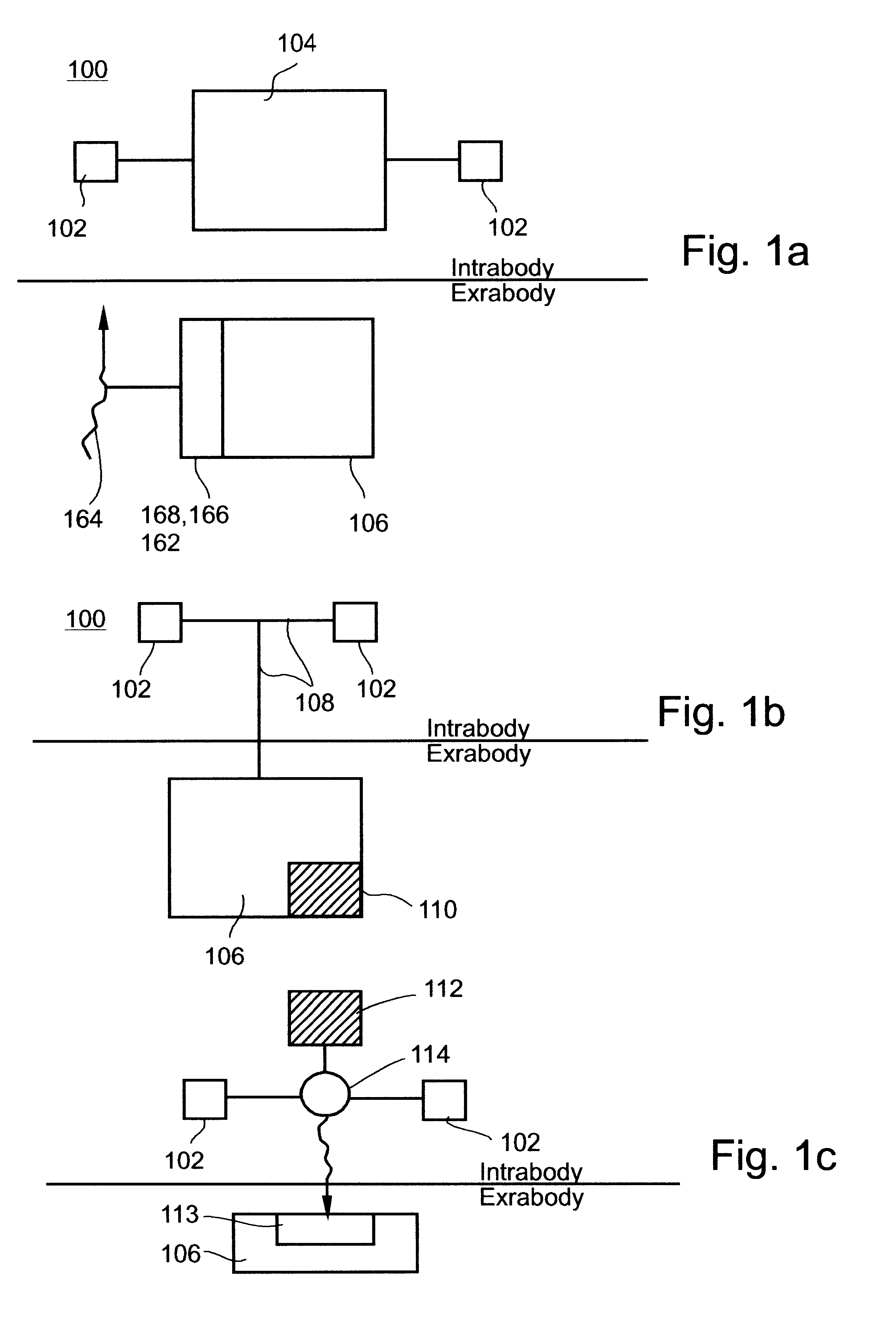
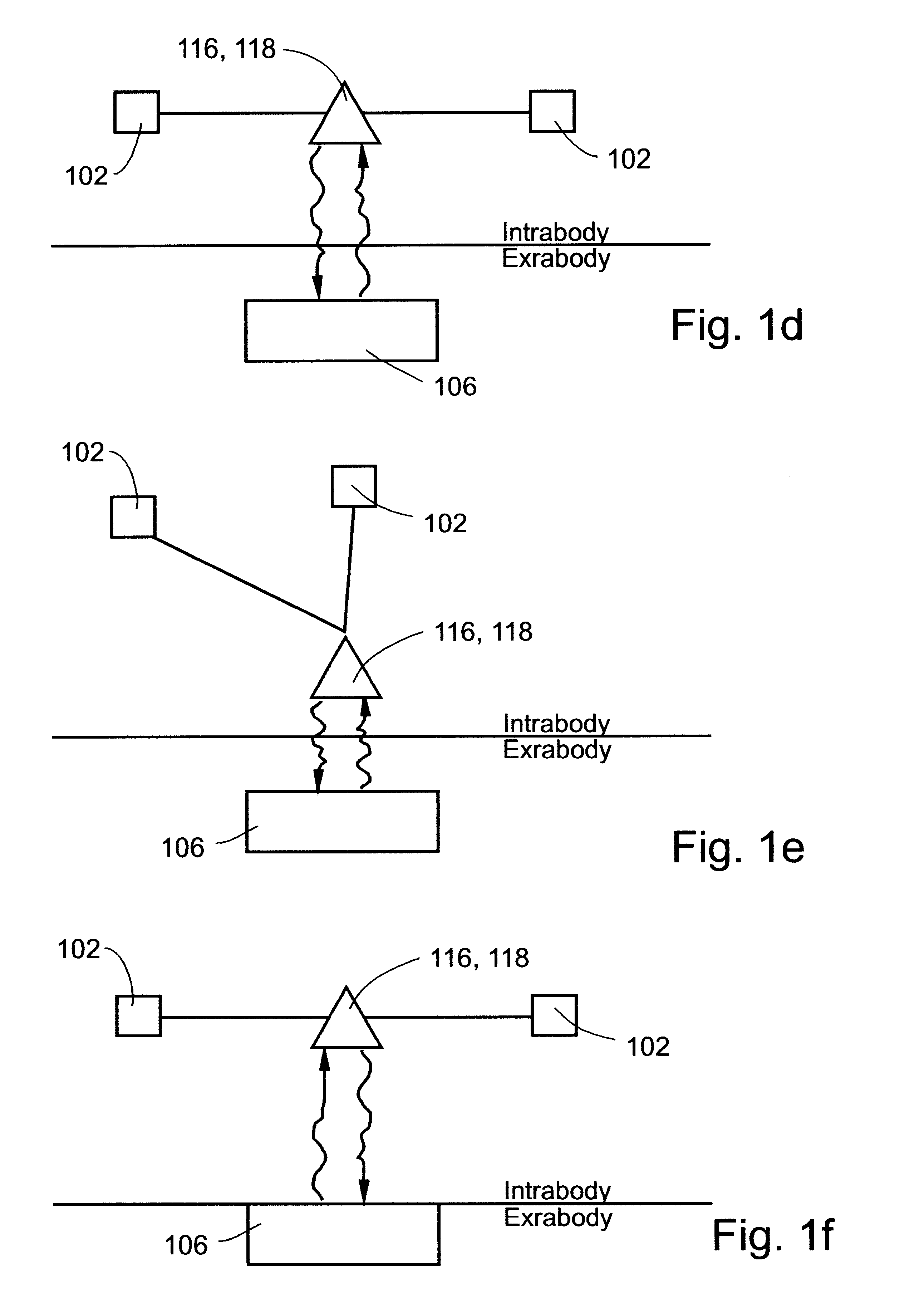
System and method for telemetrically providing intrabody spatial position
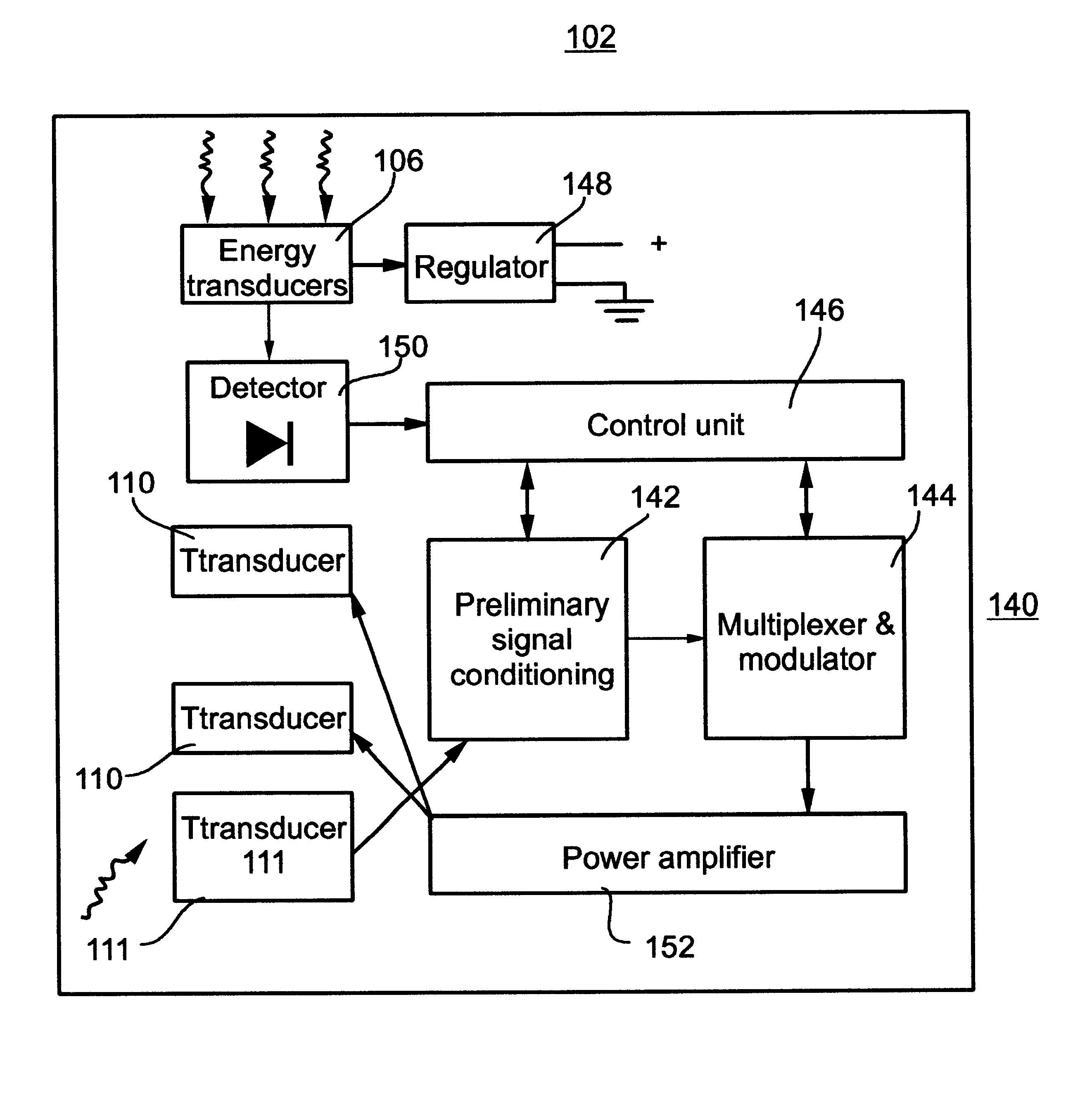
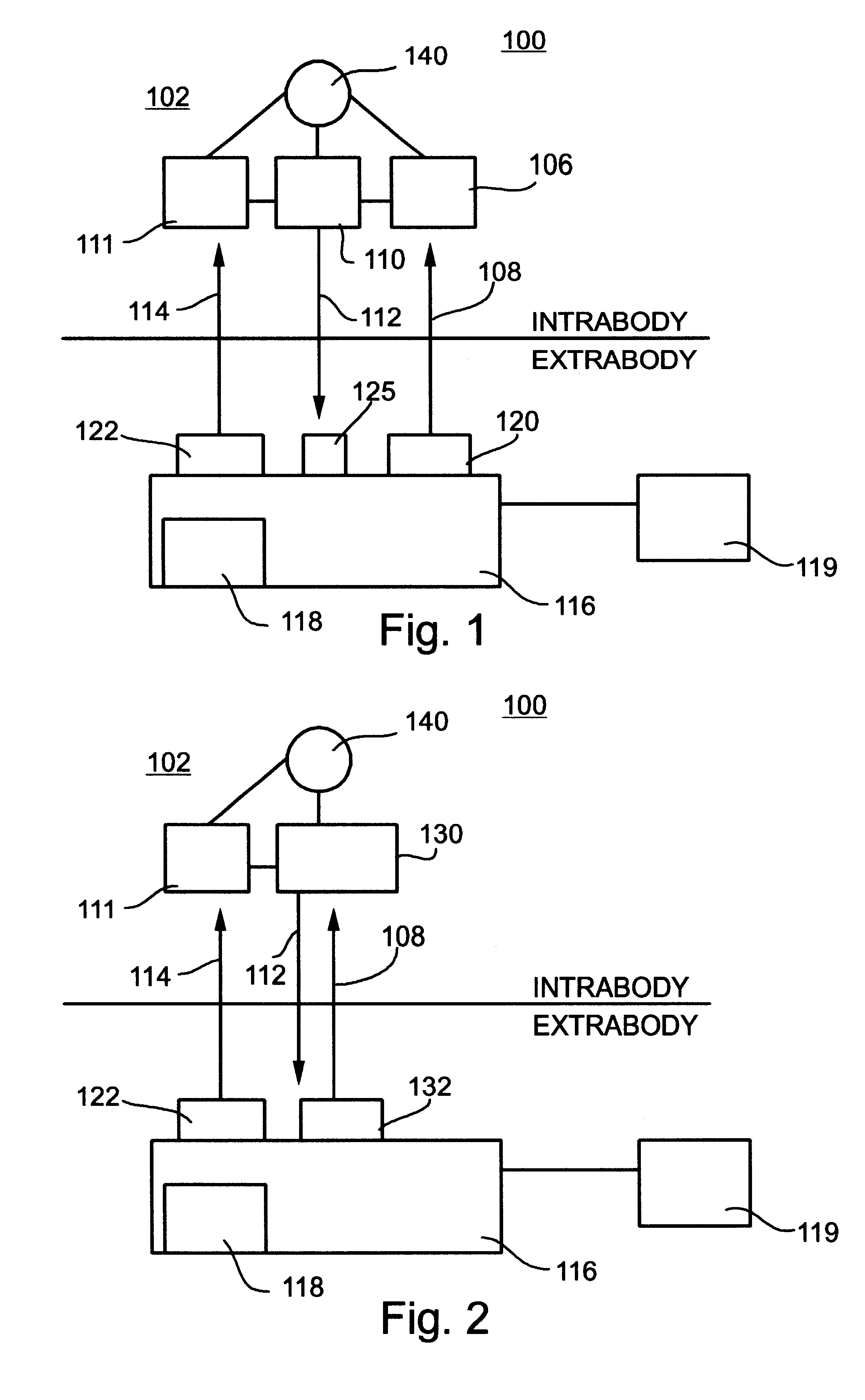
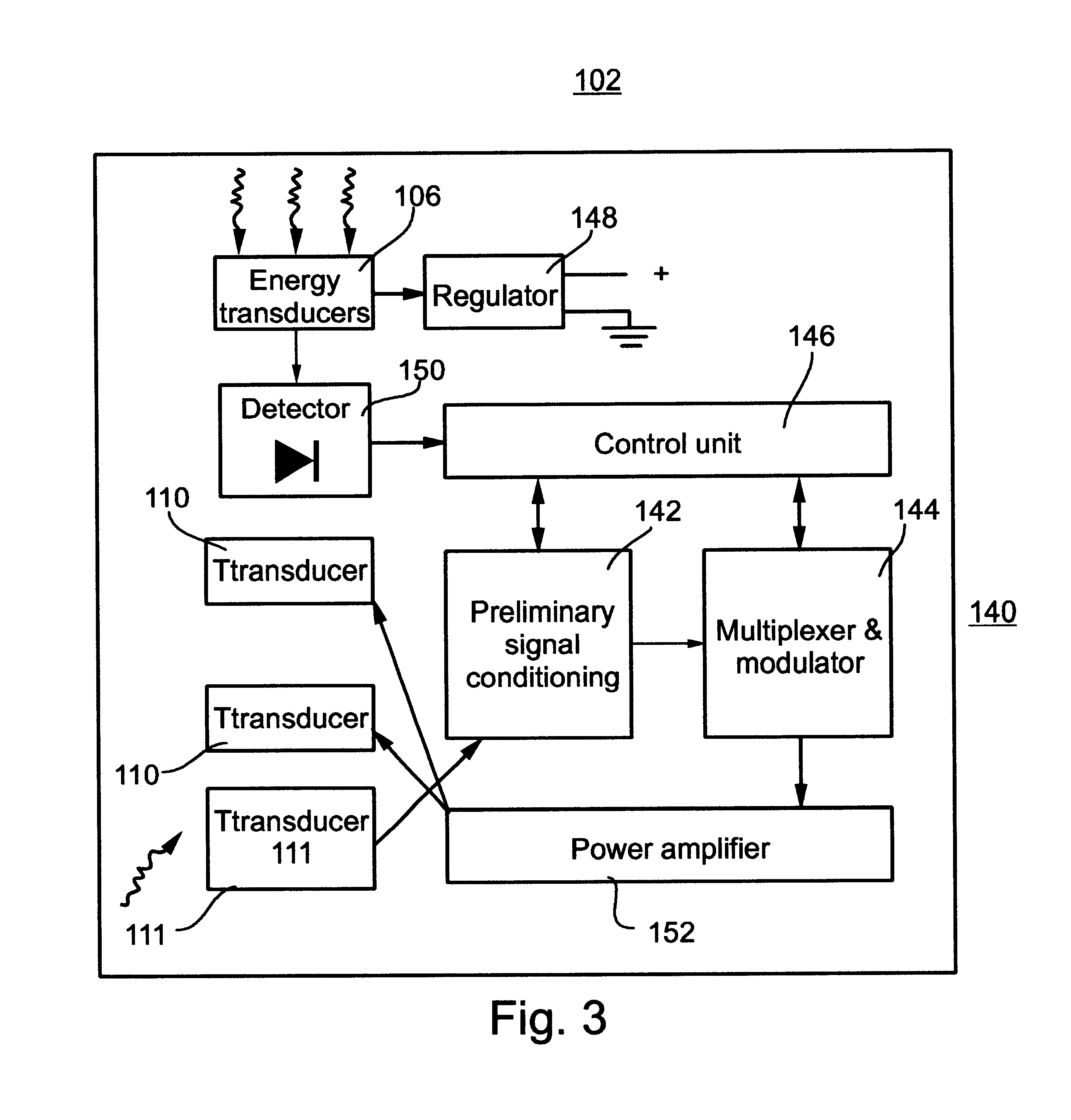
A telemetry system and method for providing spatial positioning information from within a patient's body are disclosed. The system includes at least one implantable telemetry unit which includes (a) at least one first transducer being for converting a power signal received from outside the body, into electrical power for powering the at least one implantable telemetry unit; (b) at least one second transducer being for receiving a positioning field signal being received from outside the body; and (c) at least one third transducer being for transmitting a locating signal transmittable outside the body in response to the positioning field signal.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
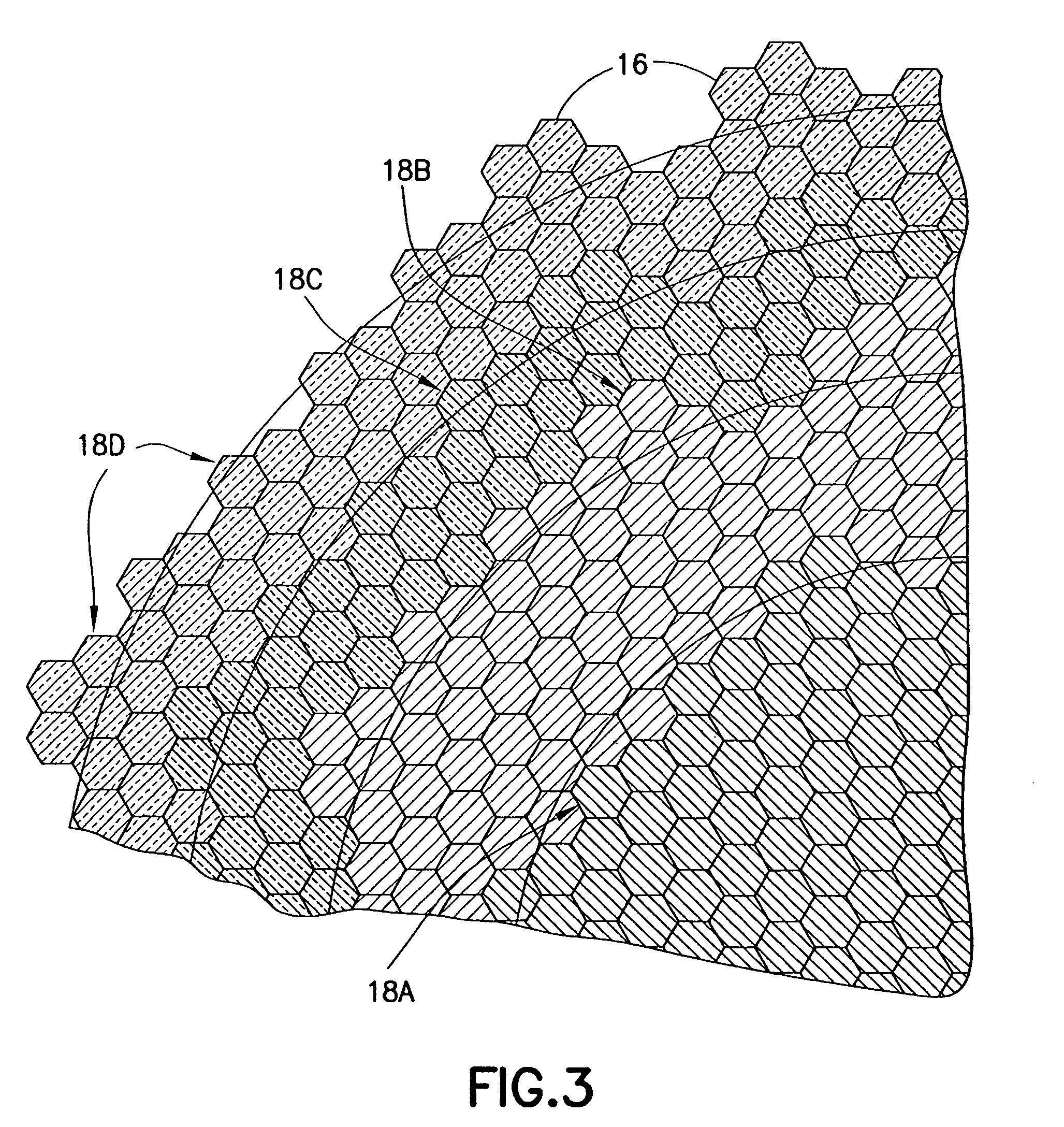
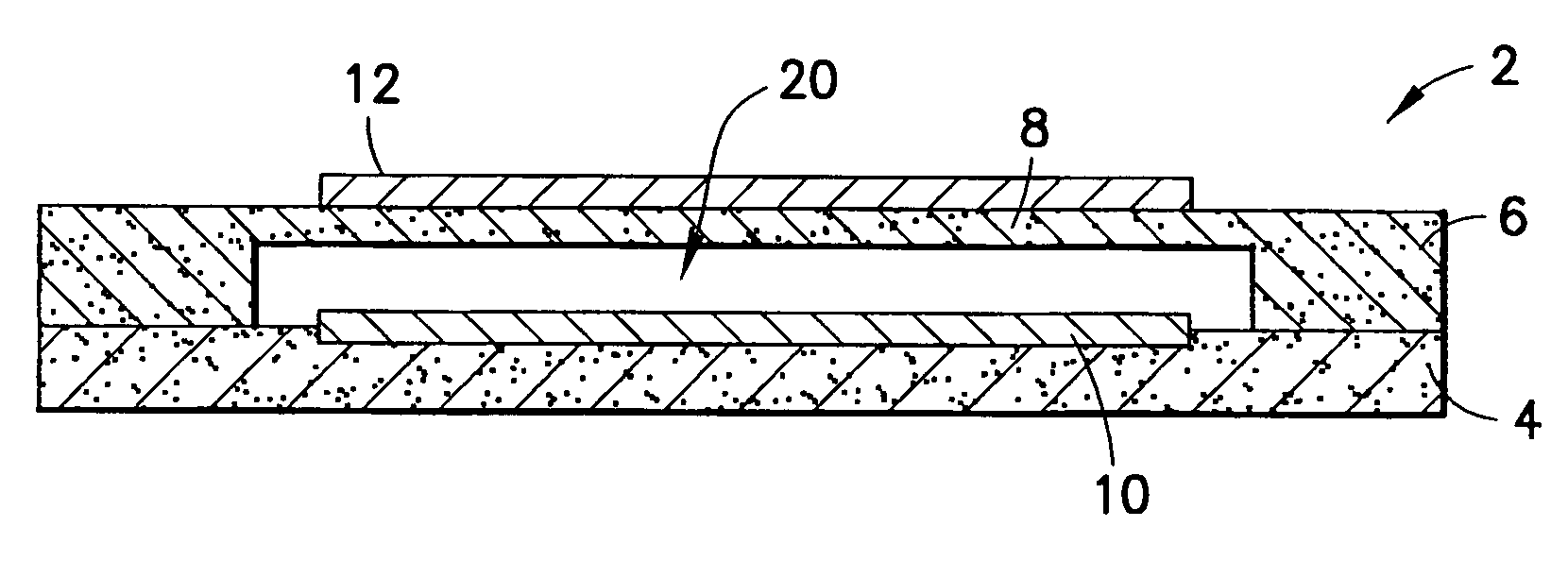
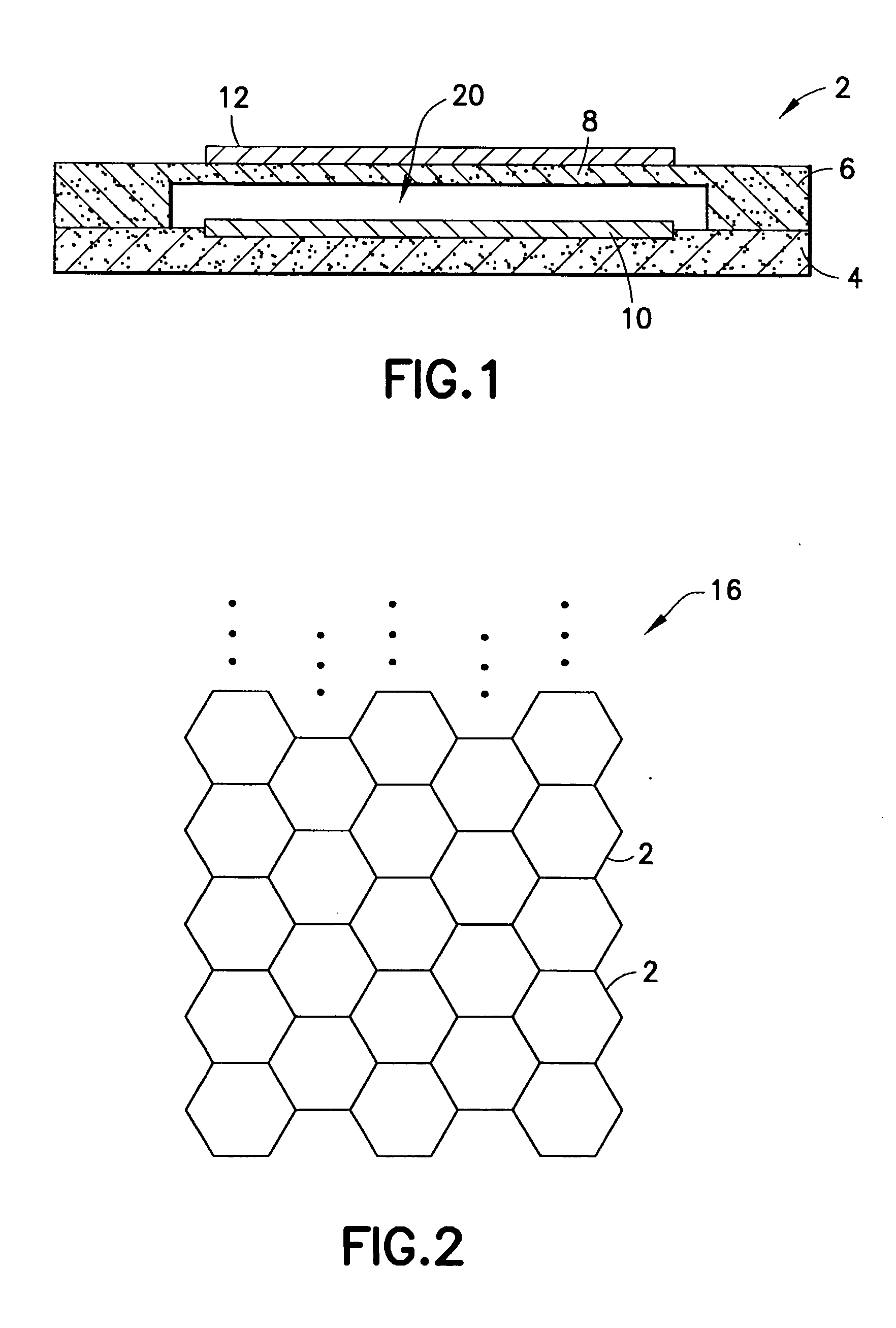
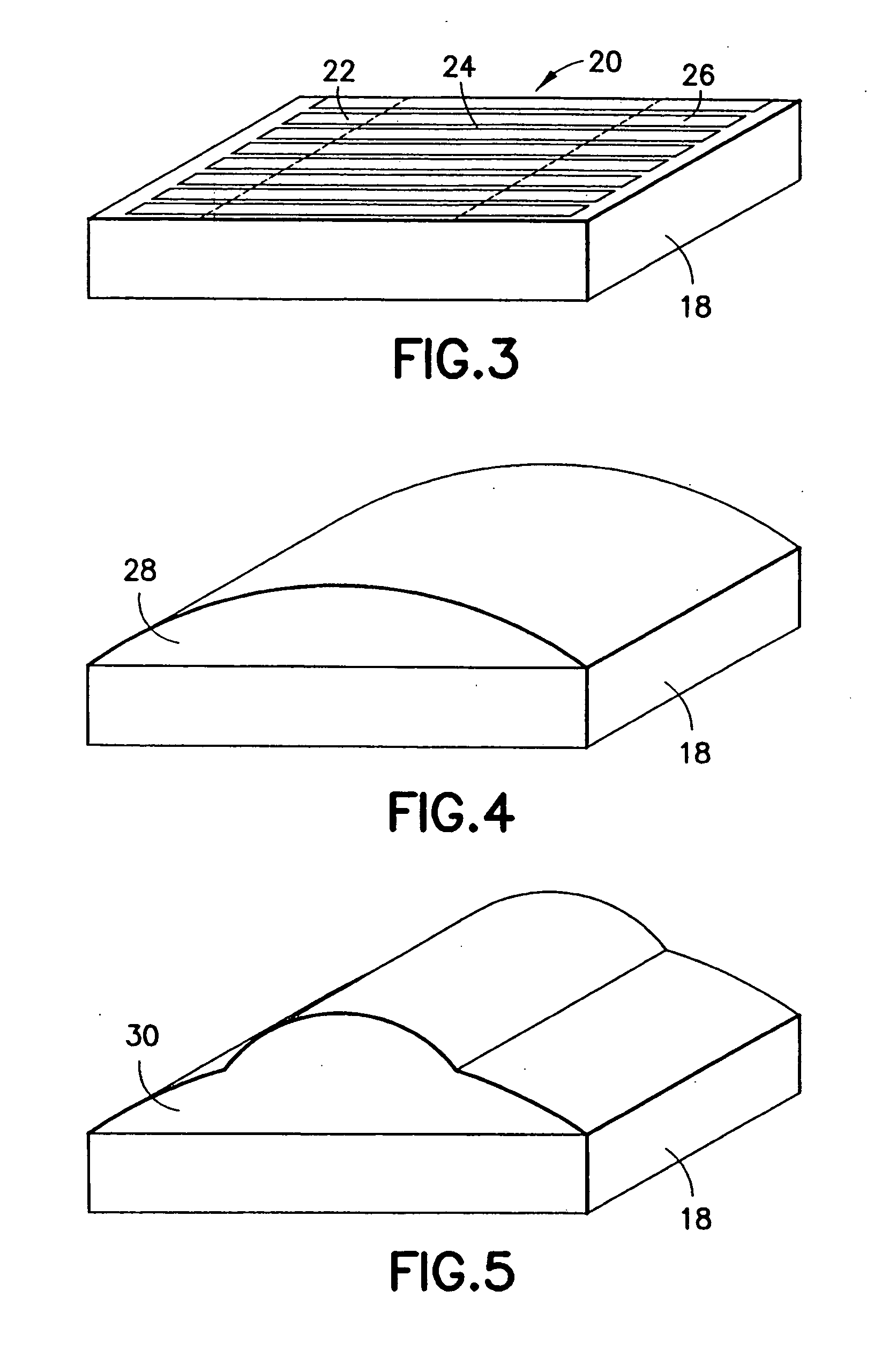
Acoustic device
InactiveUS6332029B1Spread fastGood effectTelevision system detailsElectrophonic musical instrumentsEngineeringBending stiffness
Acoustic device including a member extending transversely of its thickness and capable of sustaining bending waves at least over an intendedly consequentially acoustically active area of the transverse extent of said member, the member having, by reason of orderly design methodology disclosed and claimed, a distribution of resonant modes of its natural bending wave vibration at least over said area that is dependent on values of particular parameters of said members, including geometrical configuration and directional bending stiffness(es), which values have been selected to predetermine said distribution of natural resonant modes being consonant with required achievable acoustic action of said member for operation of said device over a desired operative acoustic frequency range.
Owner:NEW TRANSDUCERS LTD
Ultrasonic treatment and imaging of adipose tissue
A system for the destruction of adipose tissue utilizing high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) within a patient's body. The system comprises a controller for data storage and the operation and control of a plurality of elements. One elements is a means for mapping a human body to establish three dimensional coordinate position data for existing adipose tissue. The controller is able to identify the plurality of adipose tissue locations on said human body and establish a protocol for the destruction of the adipose tissue. A HIFU transducer assembly having one or more piezoelectric element(s) is used along with at least one sensor wherein the sensor provides feed back information to the controller for the safe operation of the piezoelectric element(s). The sensor is electronically coupled to the controller, and the controller provides essential treatment command information to one or more piezoelectric element(s) based on positioning information obtained from the three dimensional coordinate position data.
Owner:LIPOSONIX
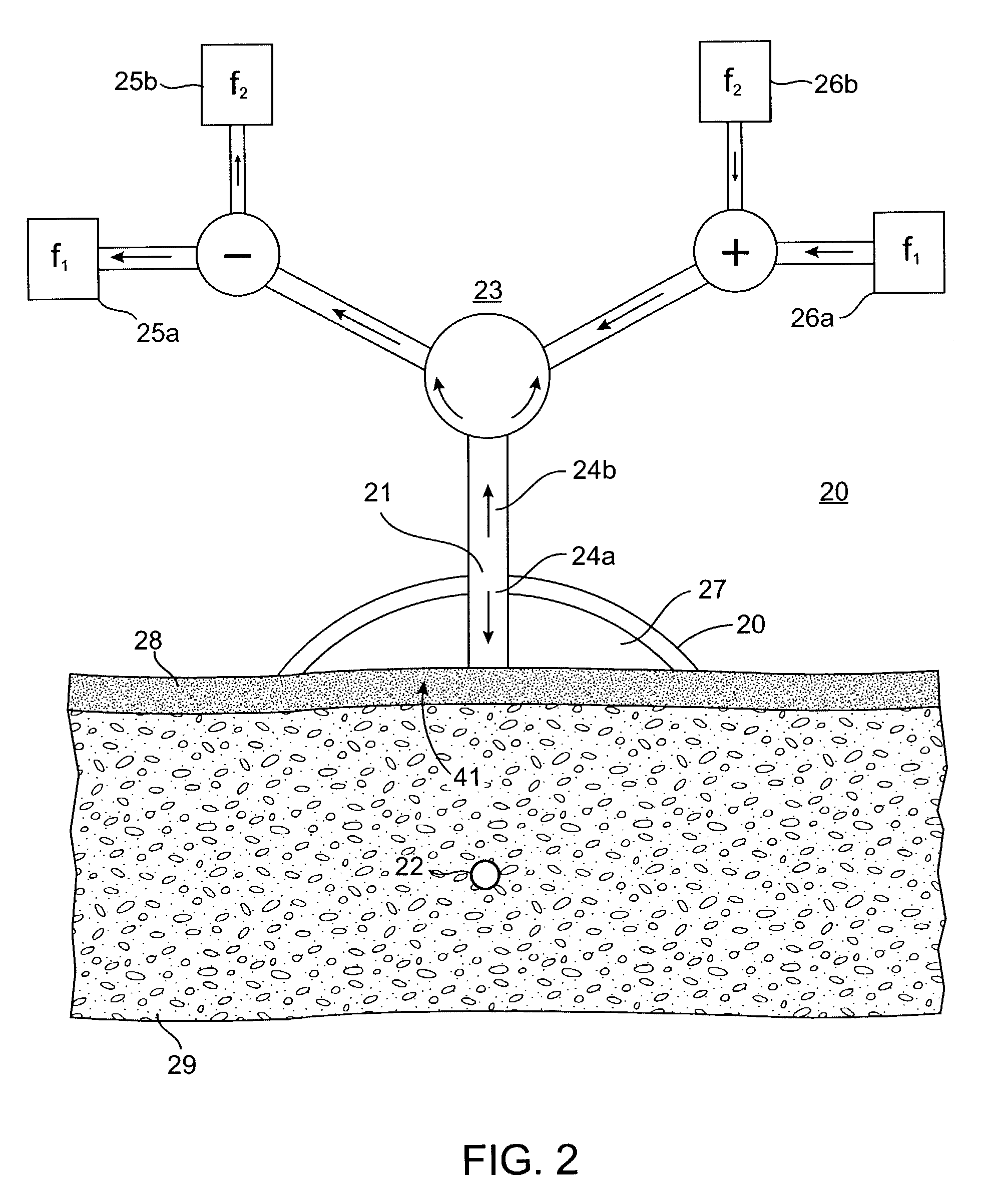
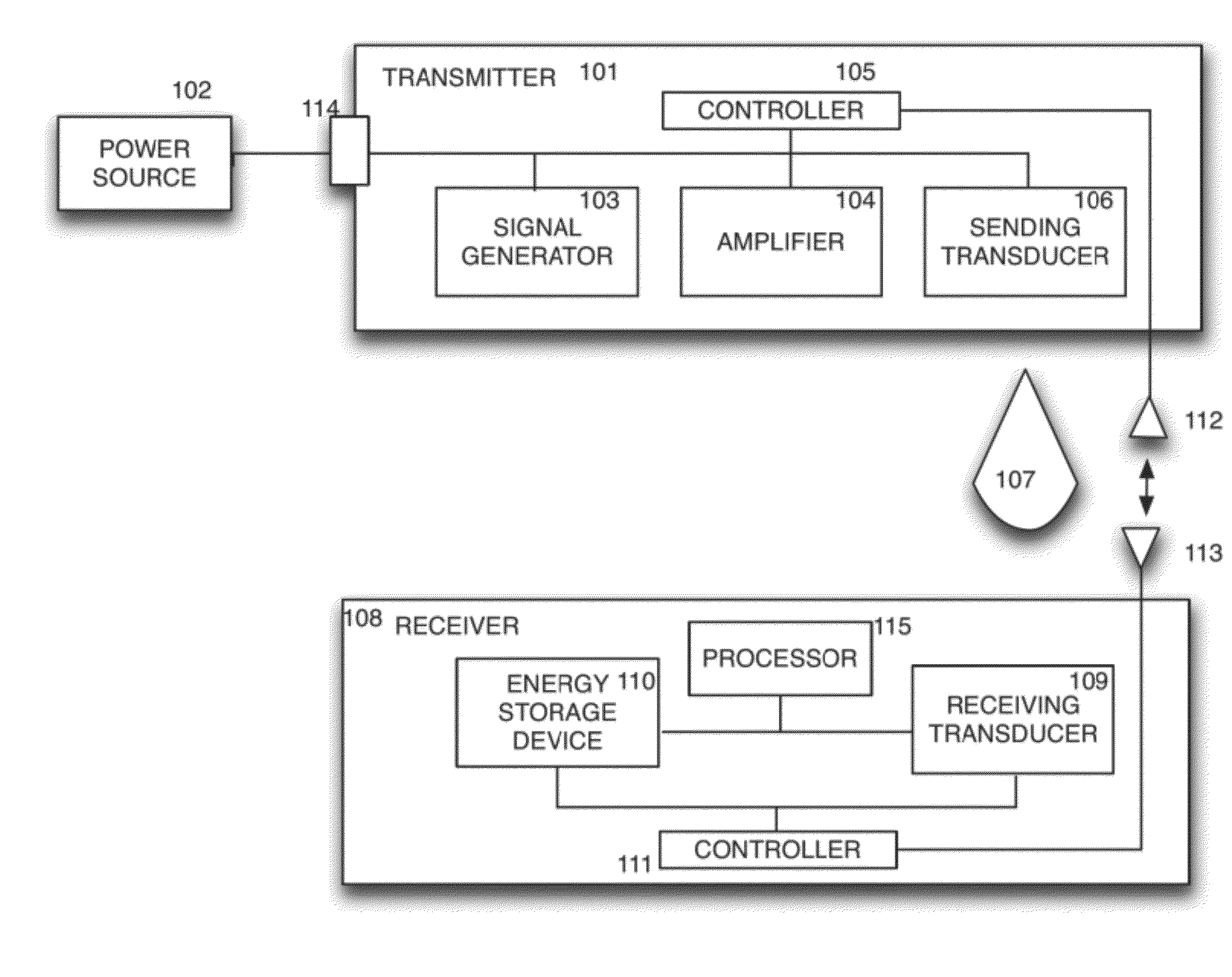
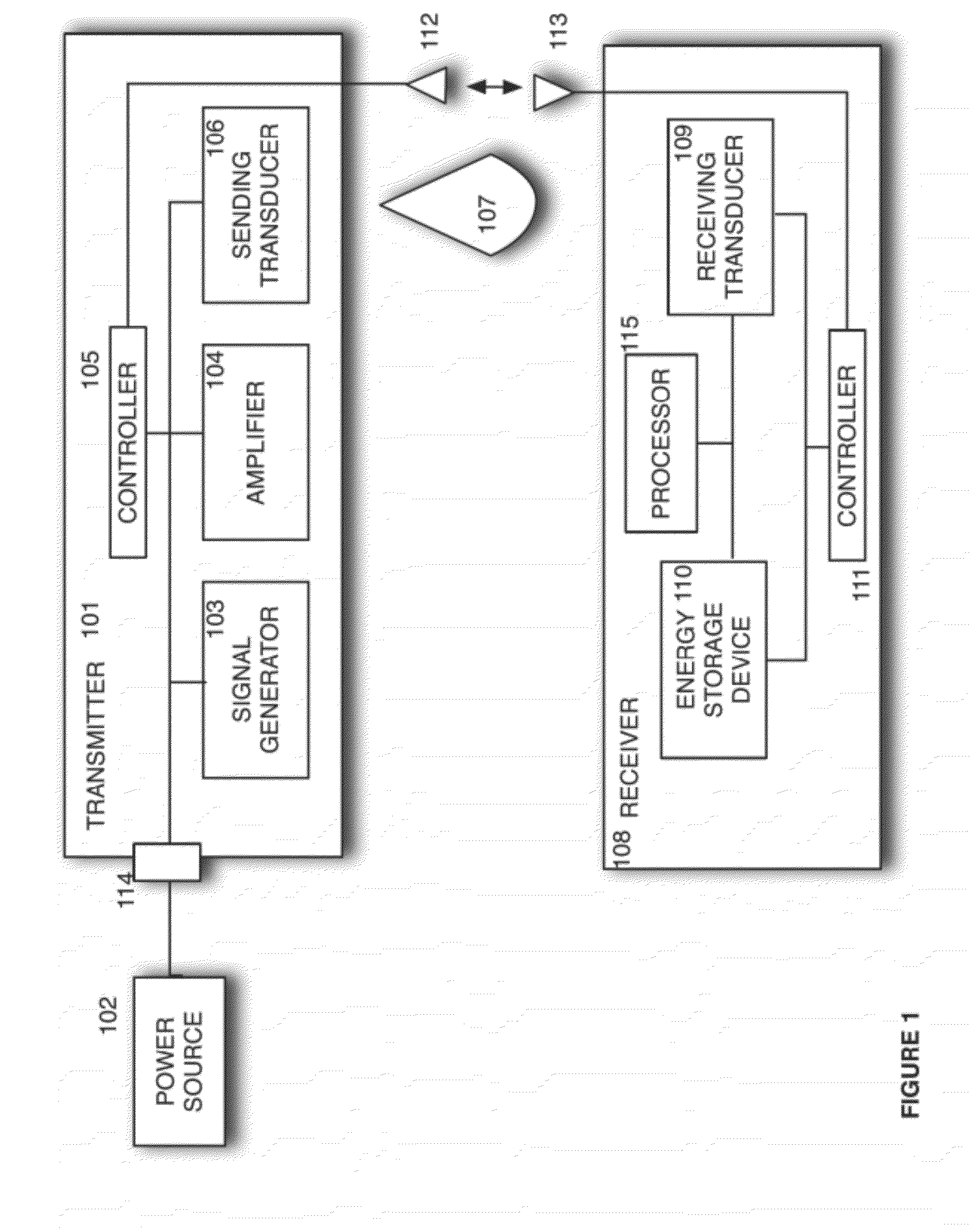
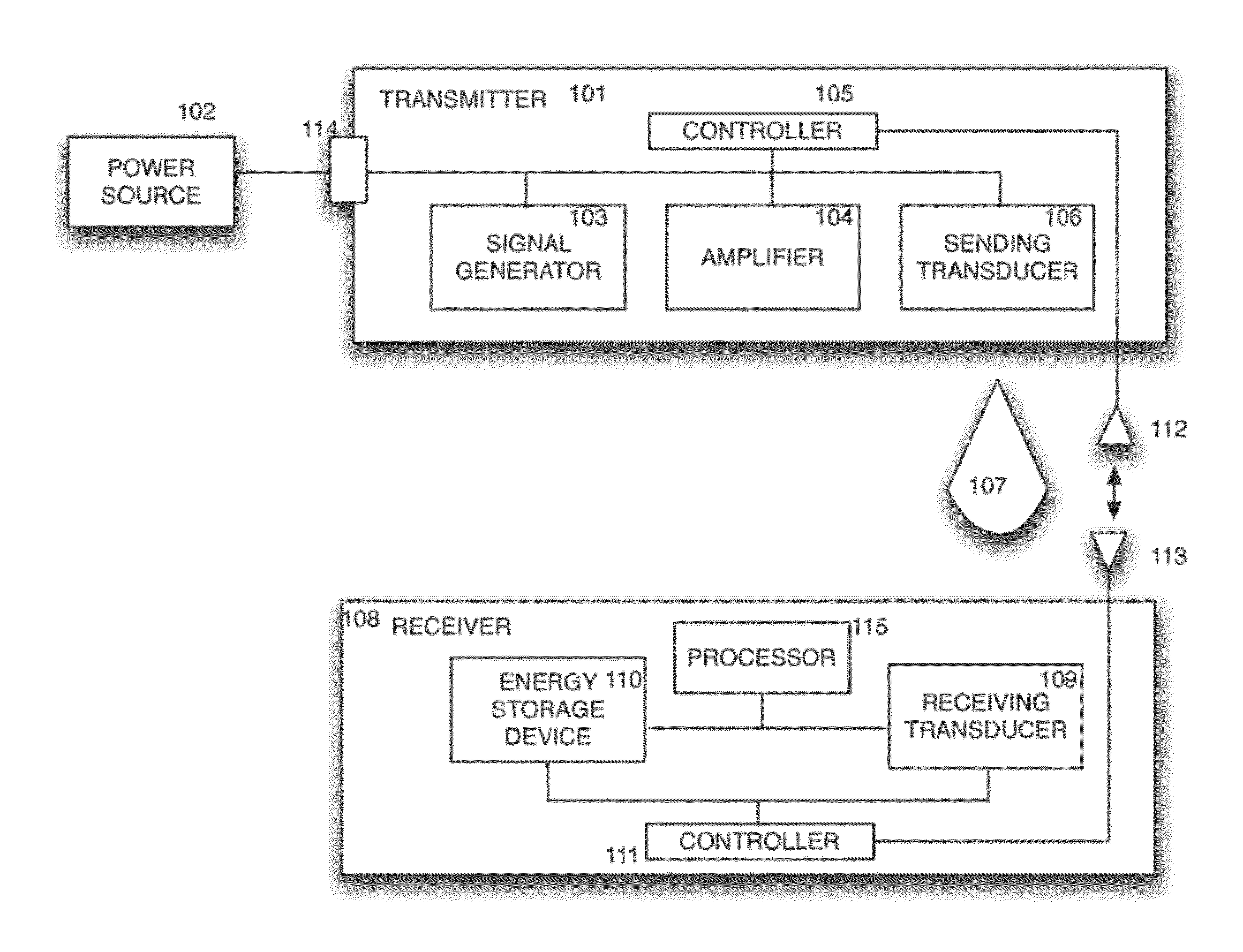
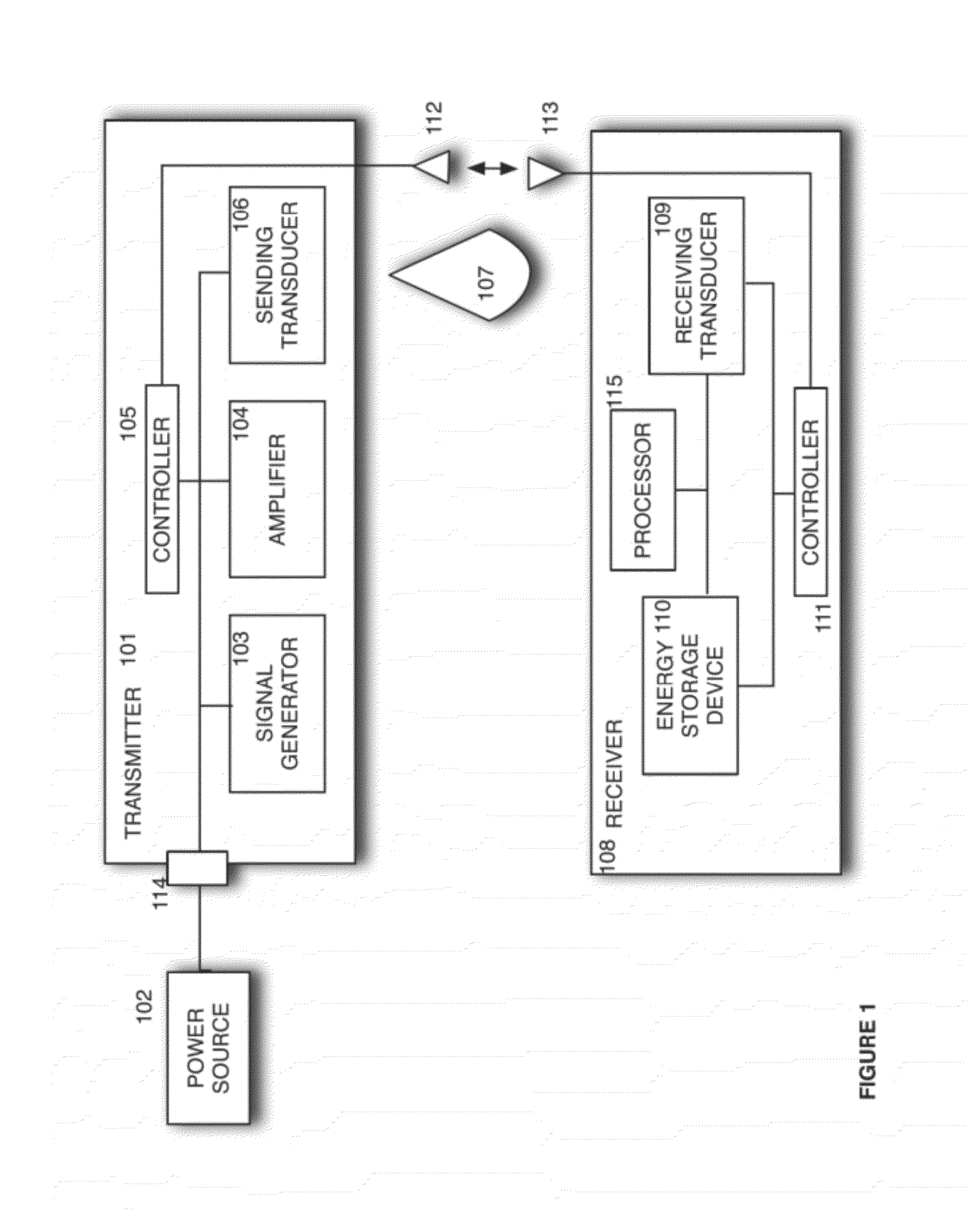
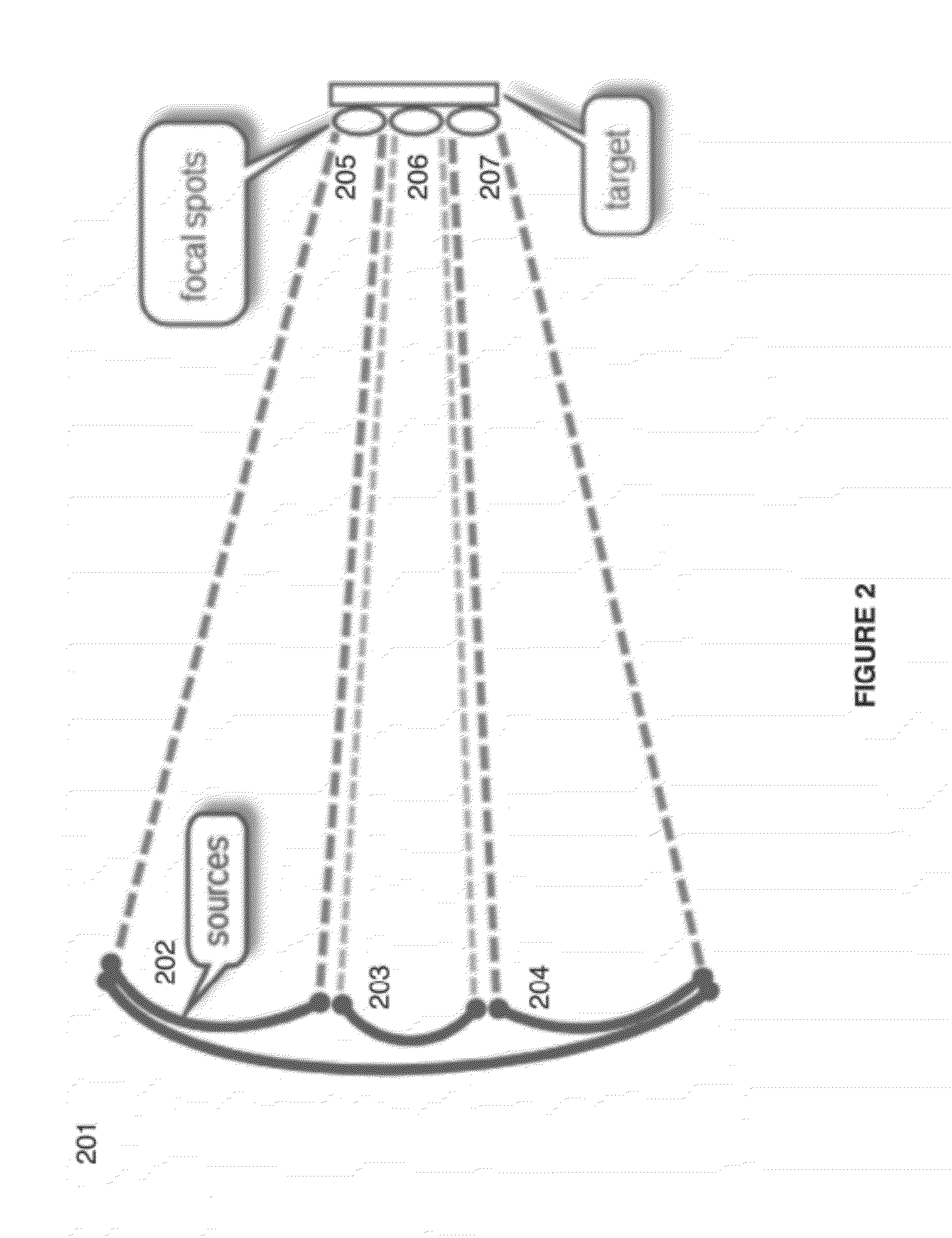
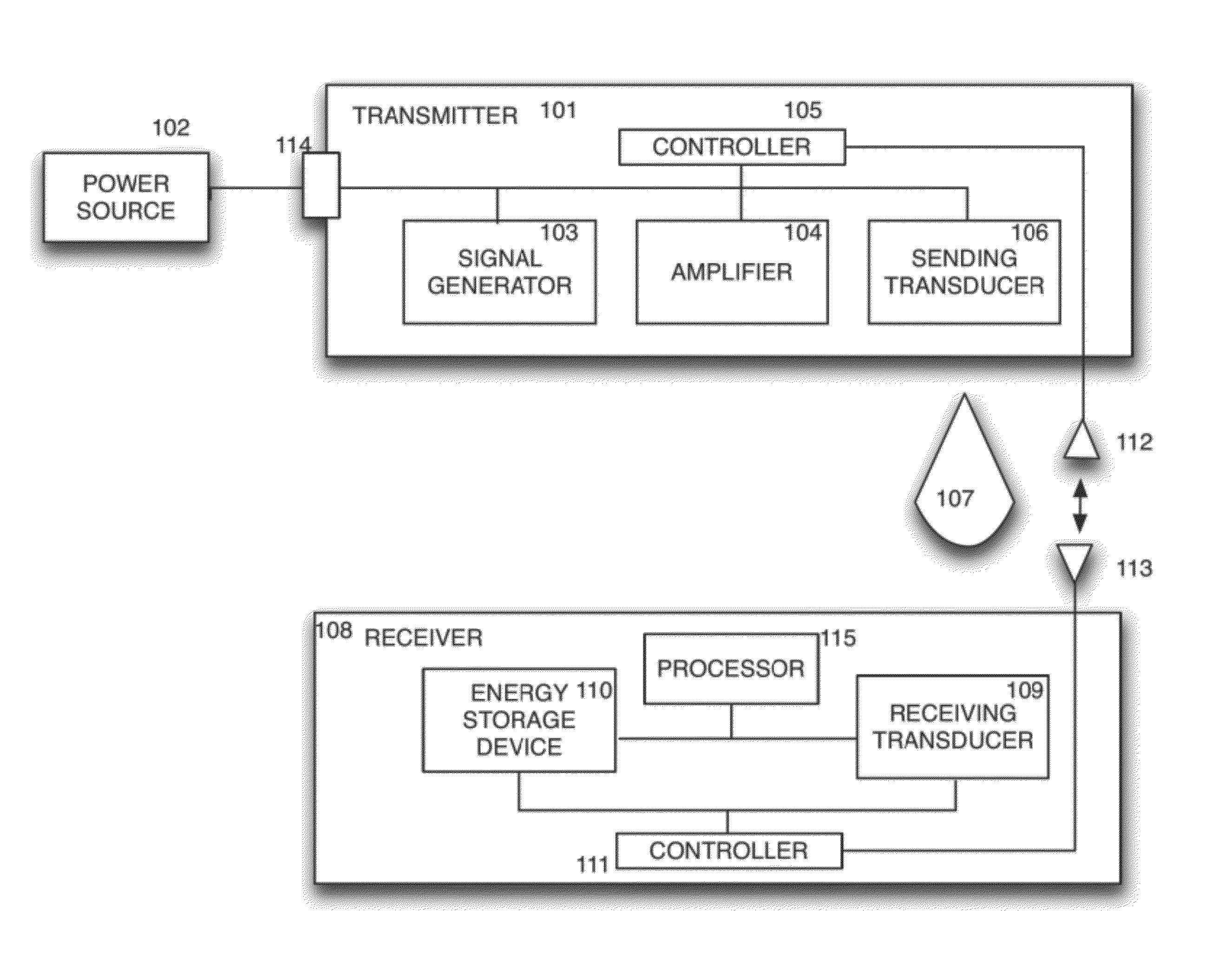
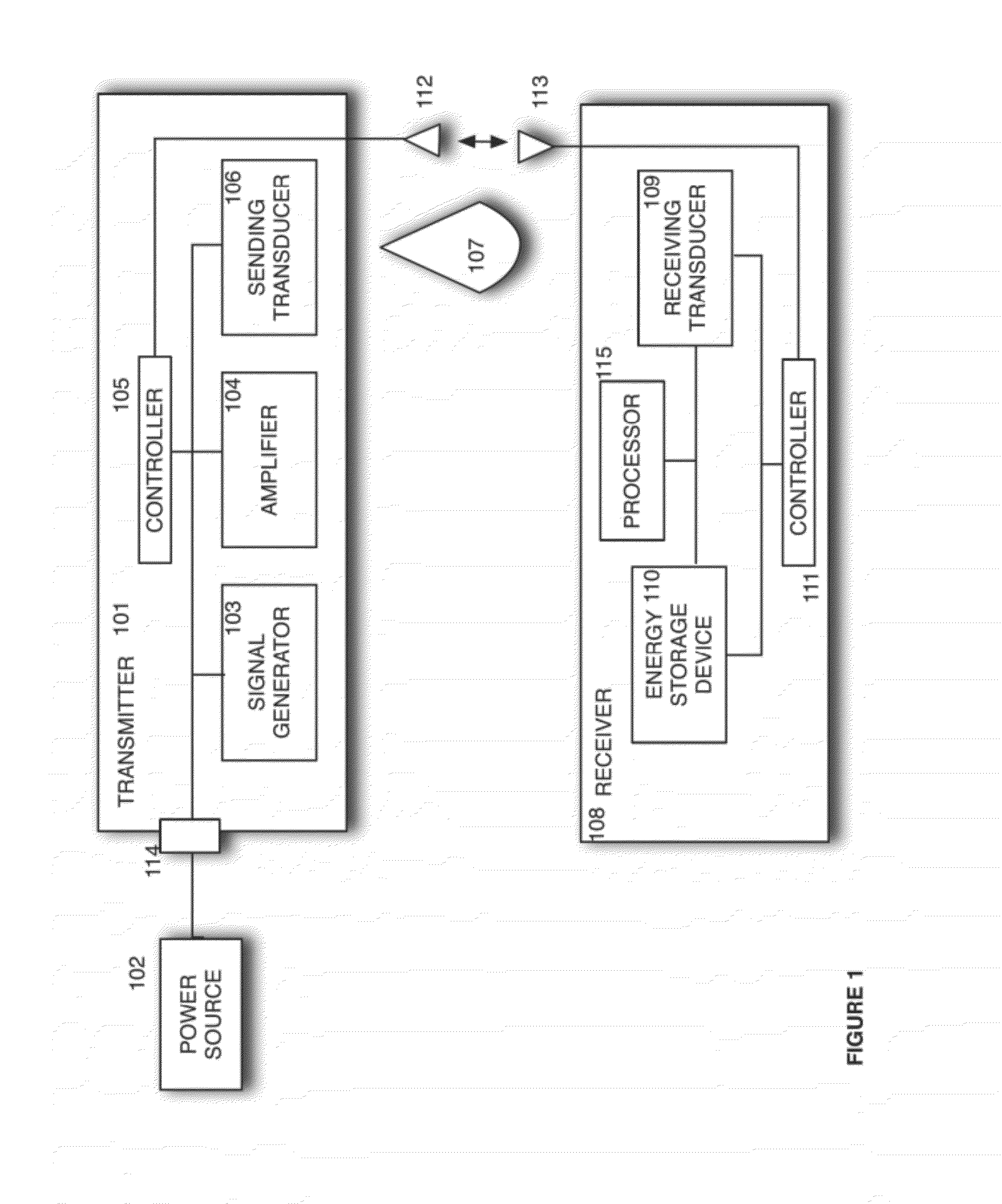
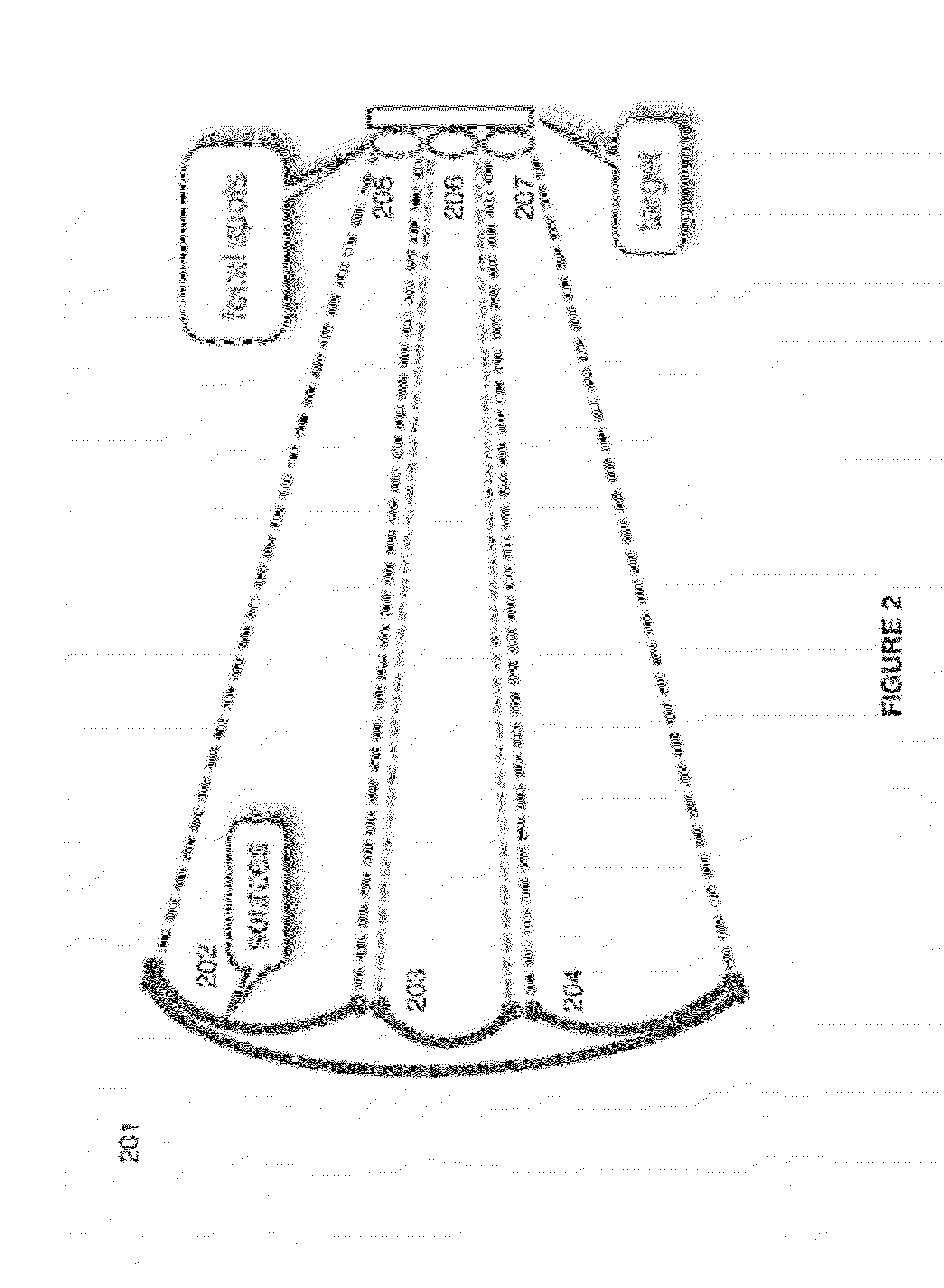
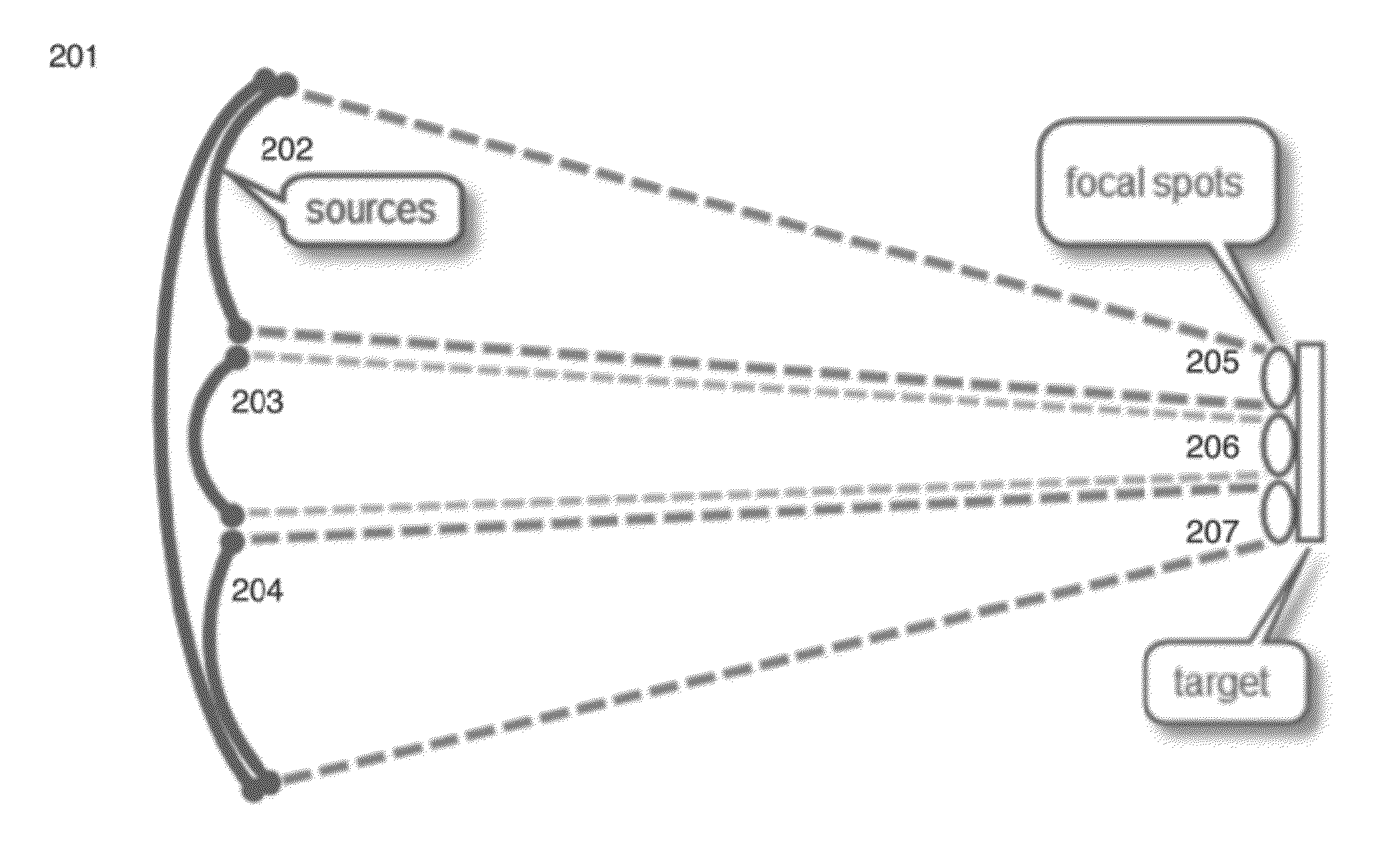
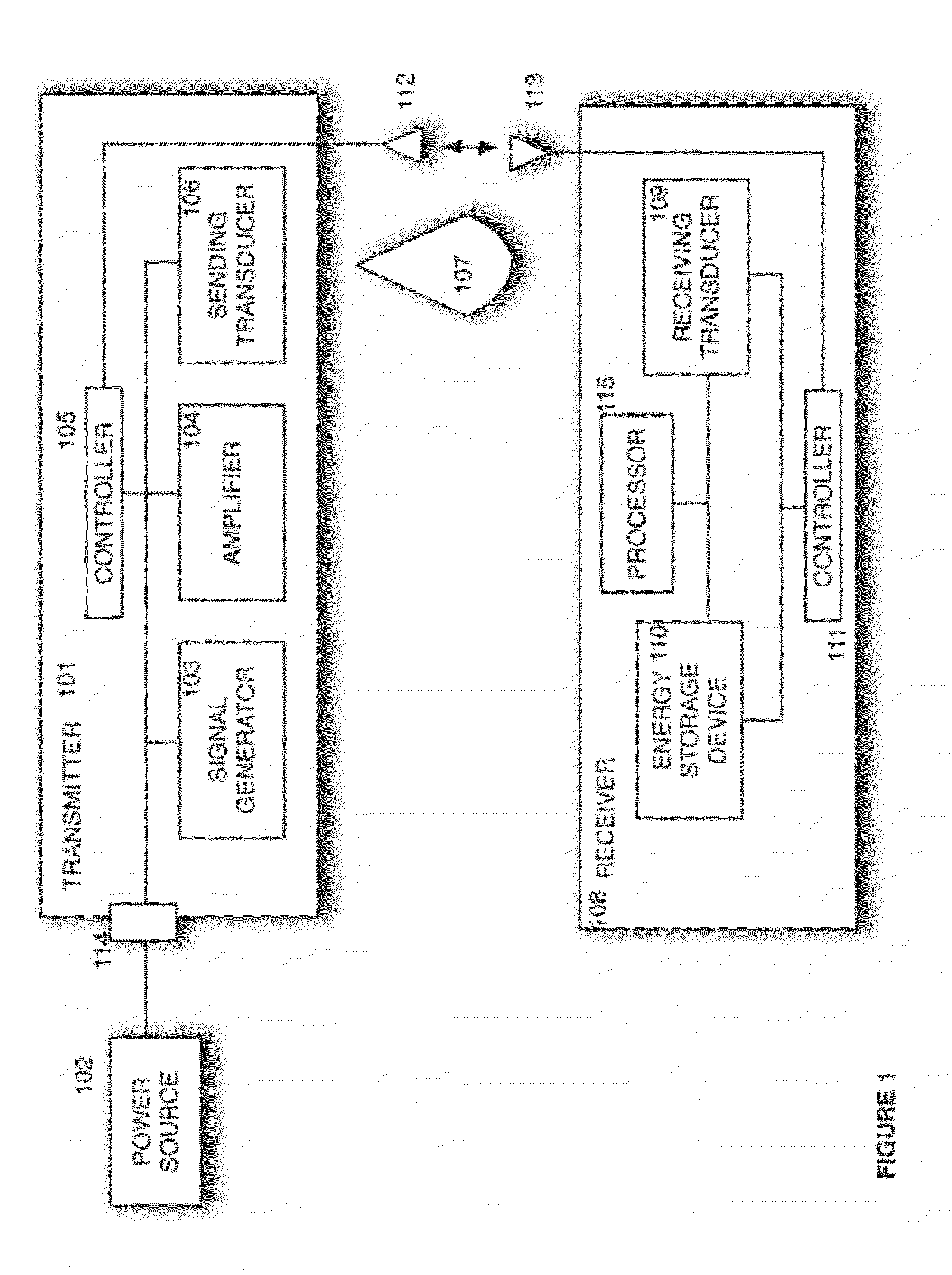
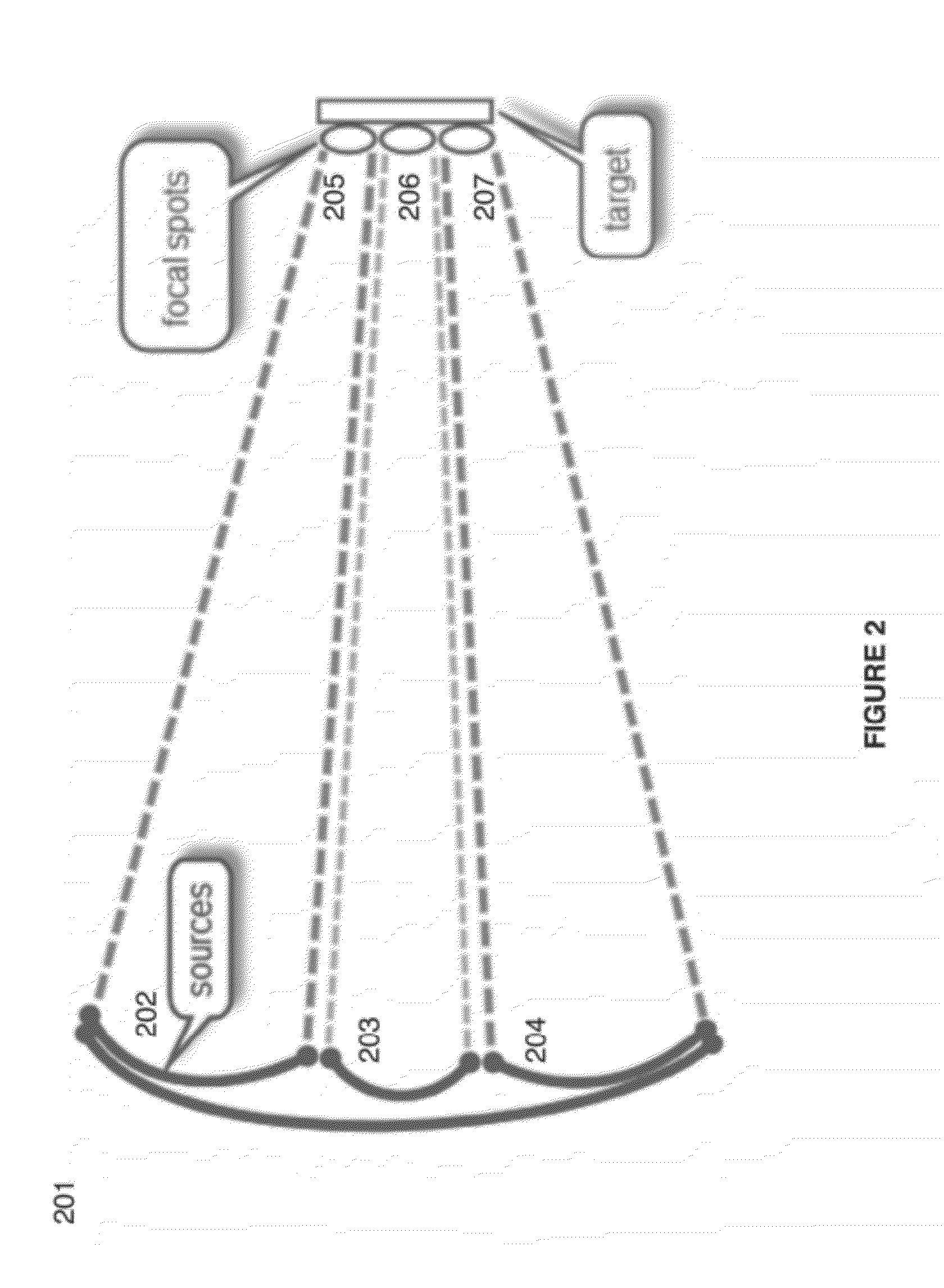
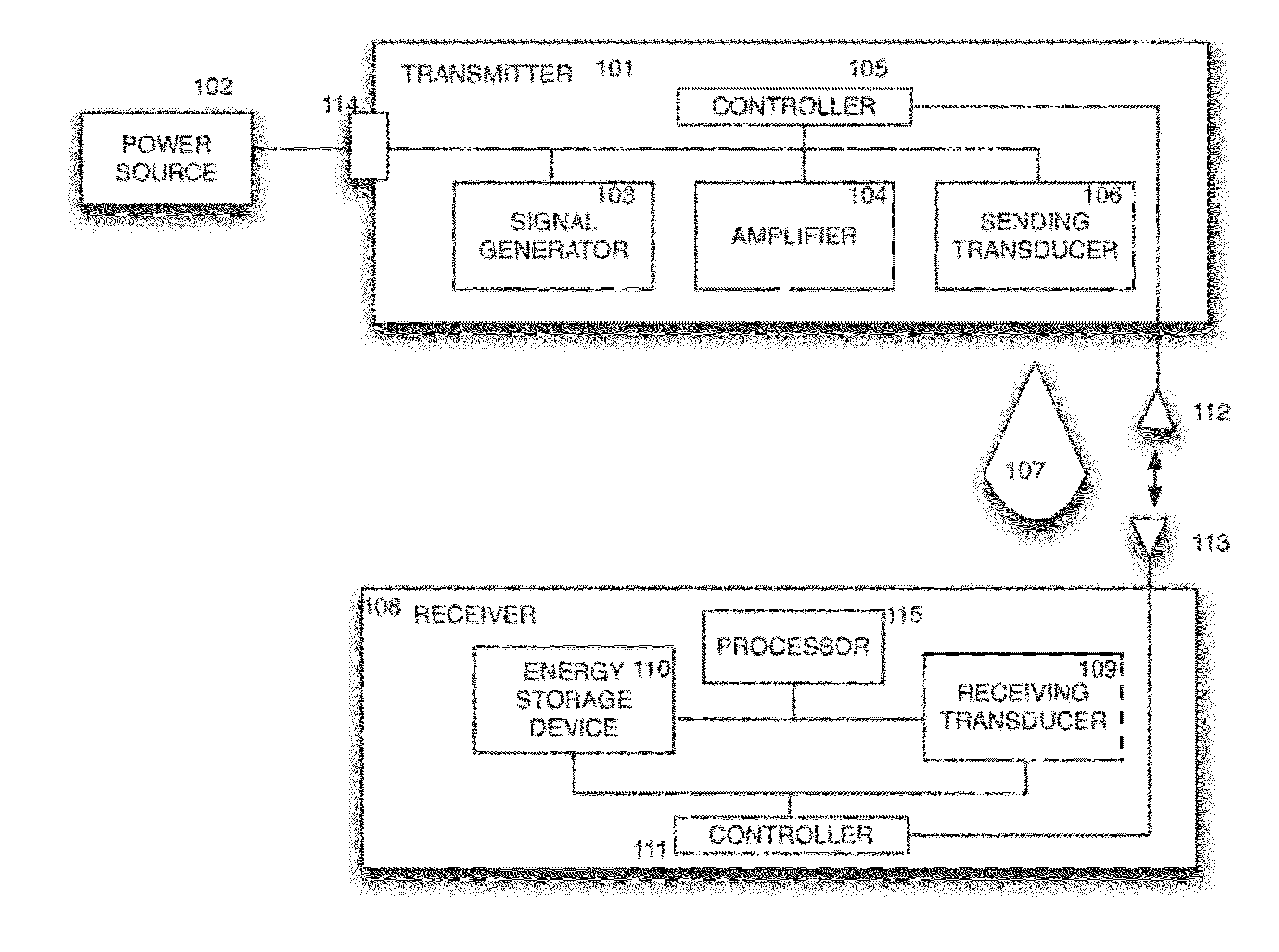
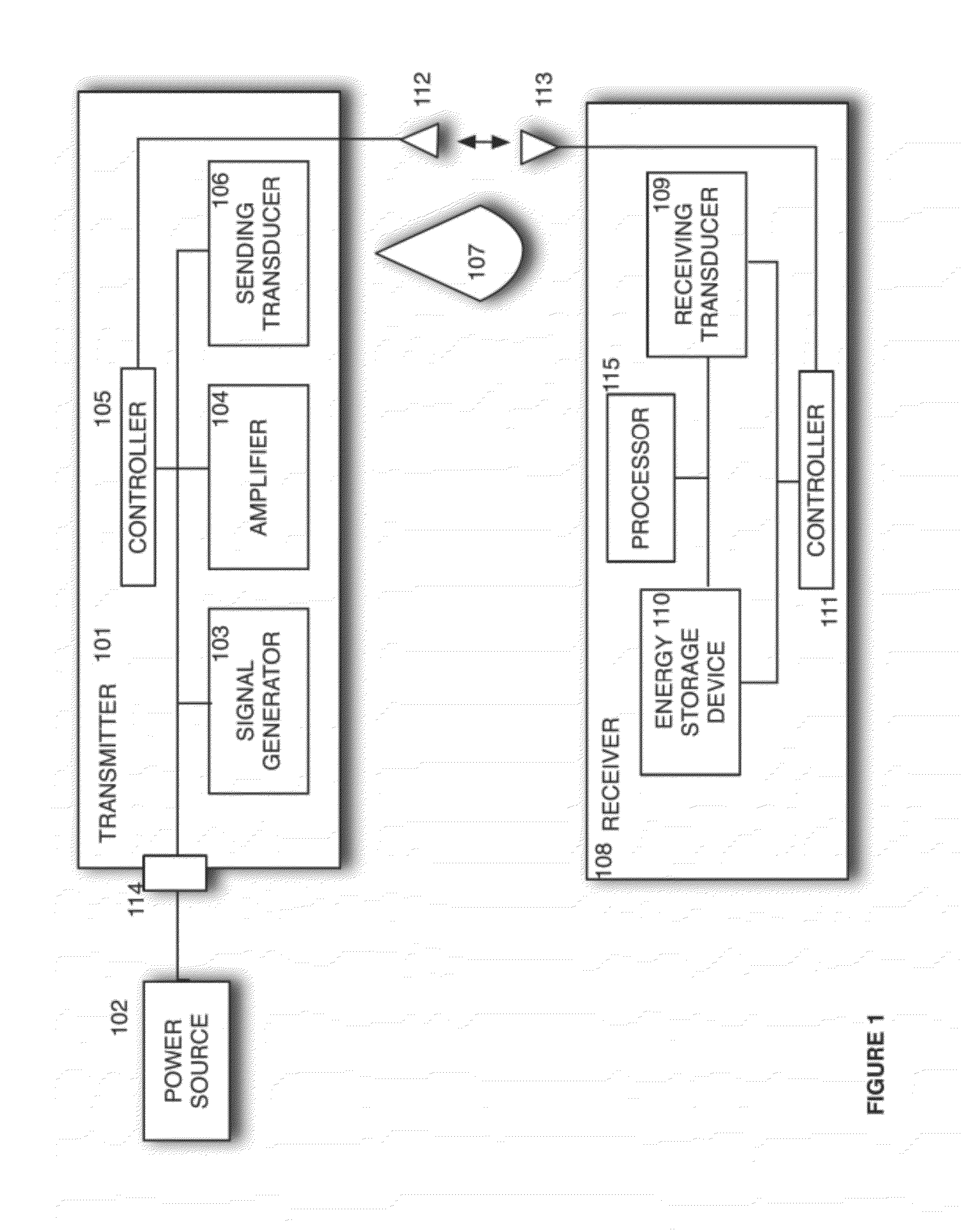
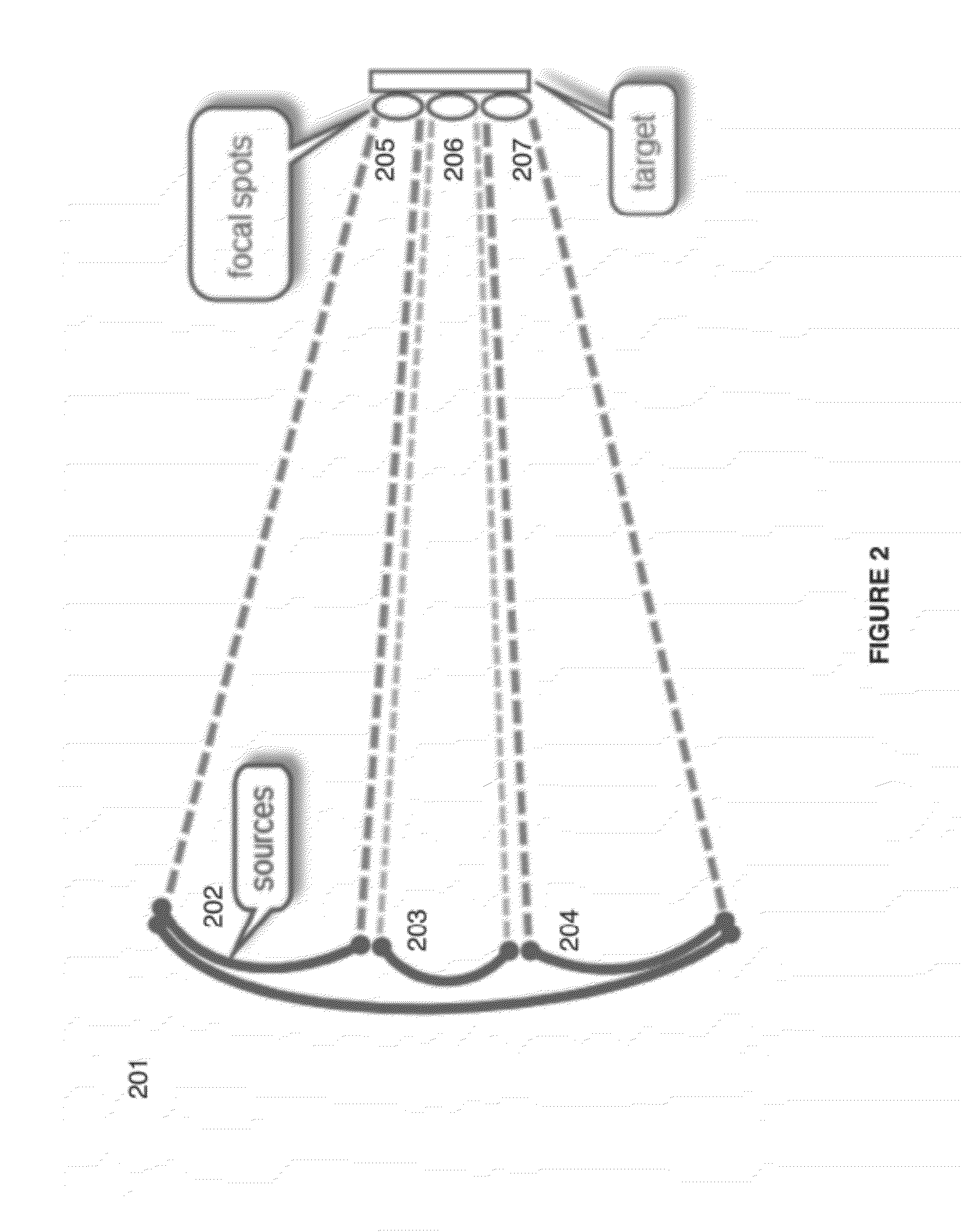
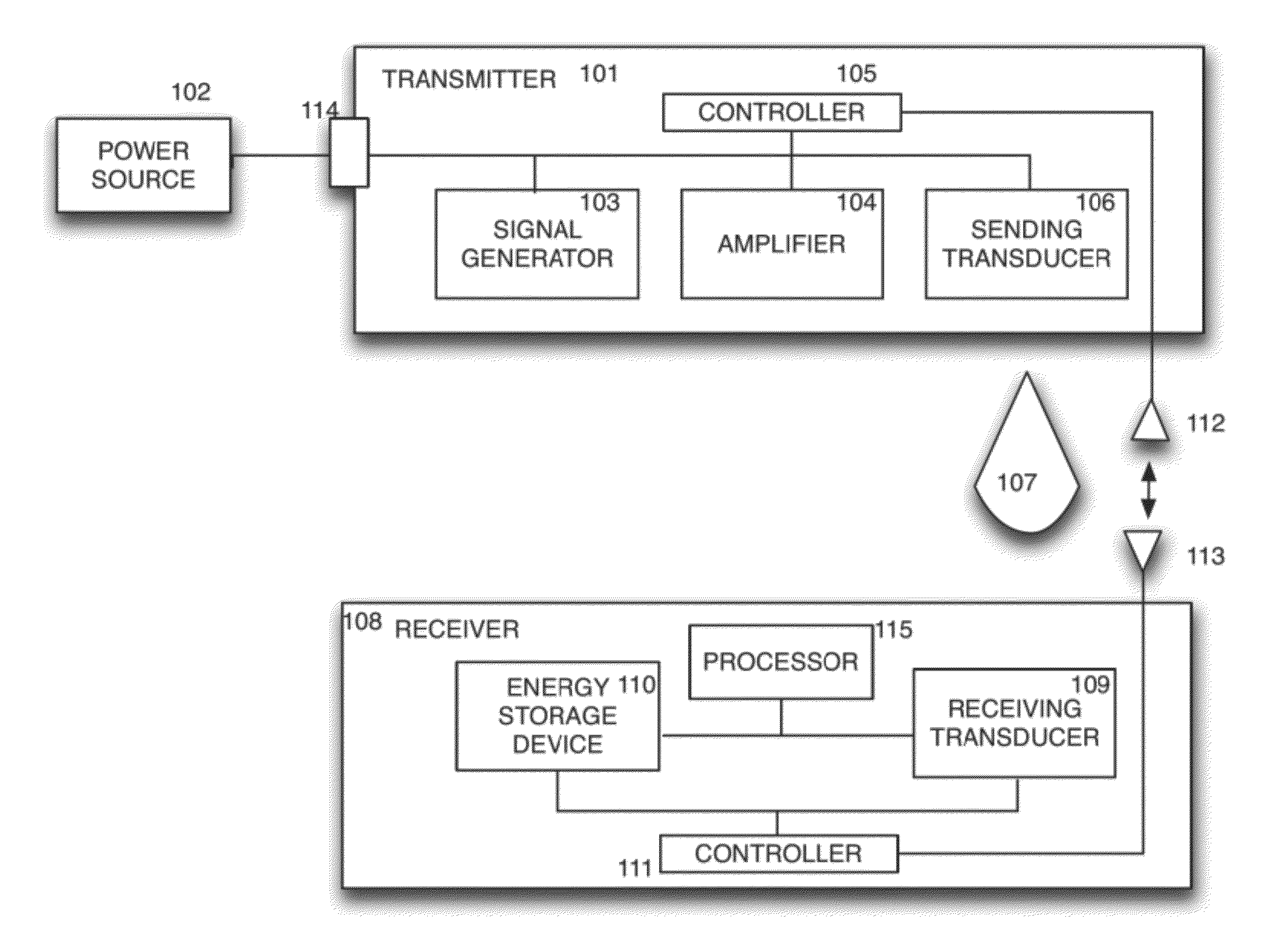
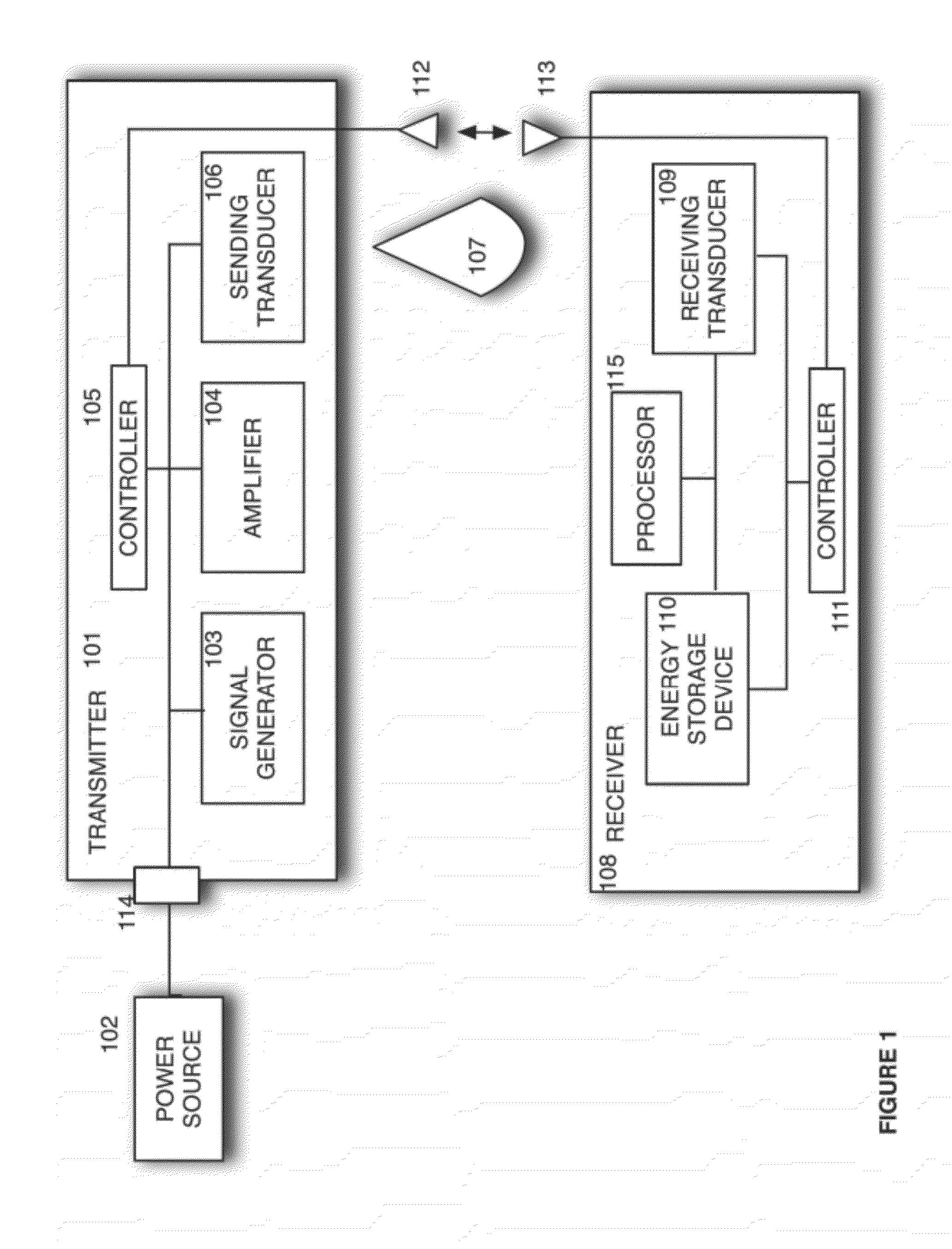
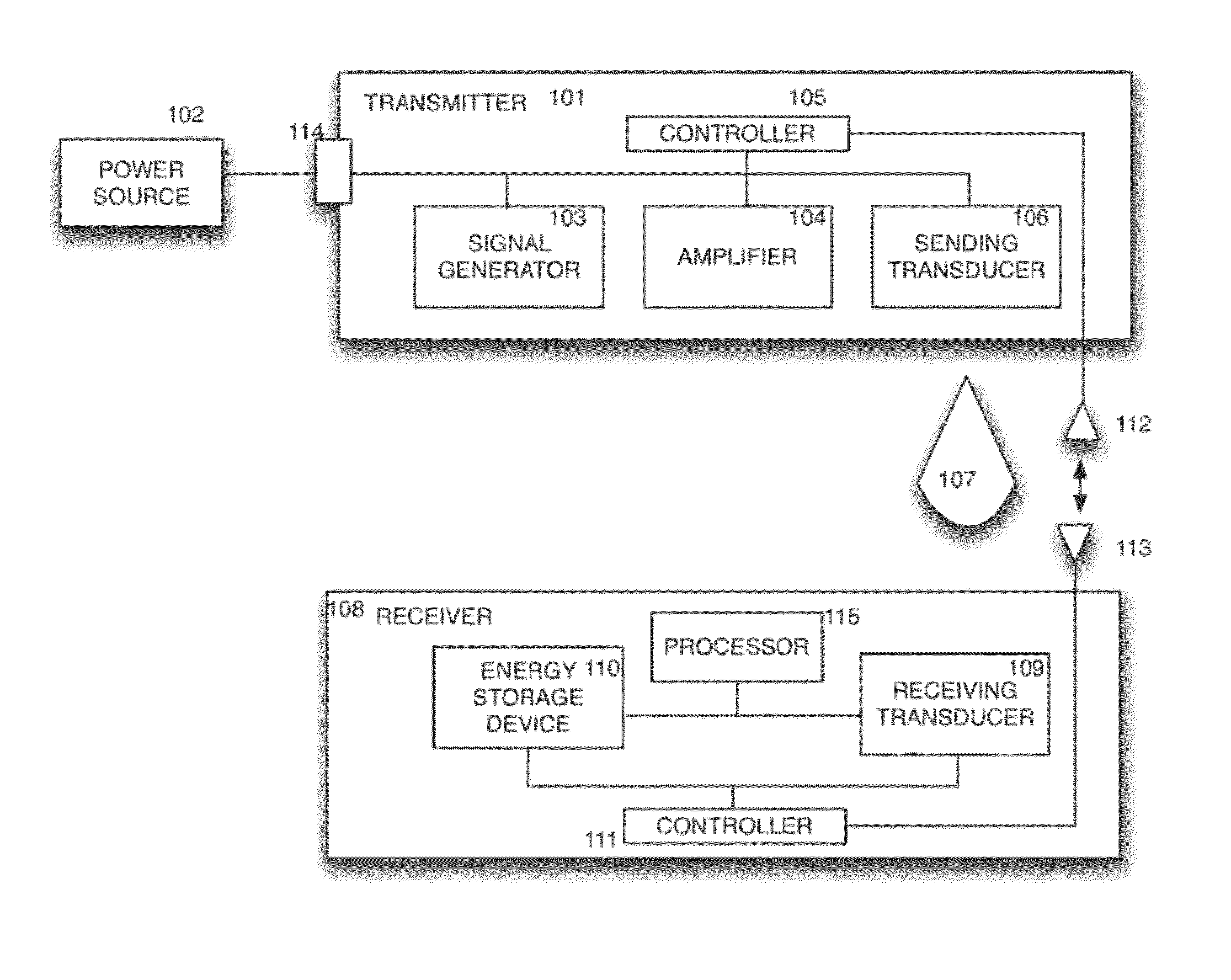
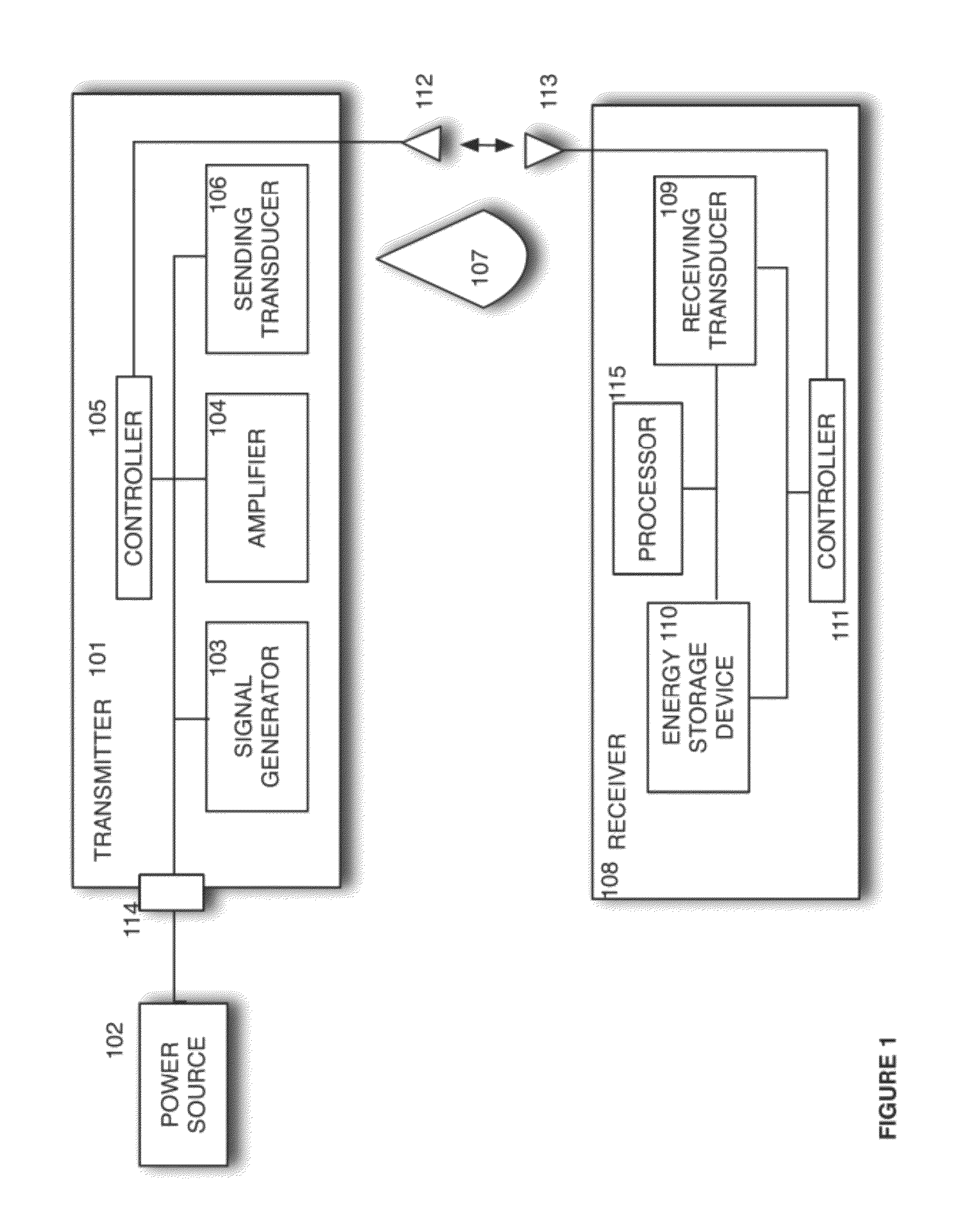
Sender communications for wireless power transfer
A signal generator generates an electrical signal that is sent to an amplifier, which increases the power of the signal using power from a power source. The amplified signal is fed to a sender transducer to generate ultrasonic waves that can be focused and sent to a receiver. The receiver transducer converts the ultrasonic waves back into electrical energy and stores it in an energy storage device, such as a battery, or uses the electrical energy to power a device. In this way, a device can be remotely charged or powered without having to be tethered to an electrical outlet.
Owner:UBEAM
Apodization methods and apparatus for acoustic phased array aperture for diagnostic medical ultrasound transducer
InactiveUS6258034B1Reduce side lobe side lobe image artifactLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyUltrasonographyAzimuth direction
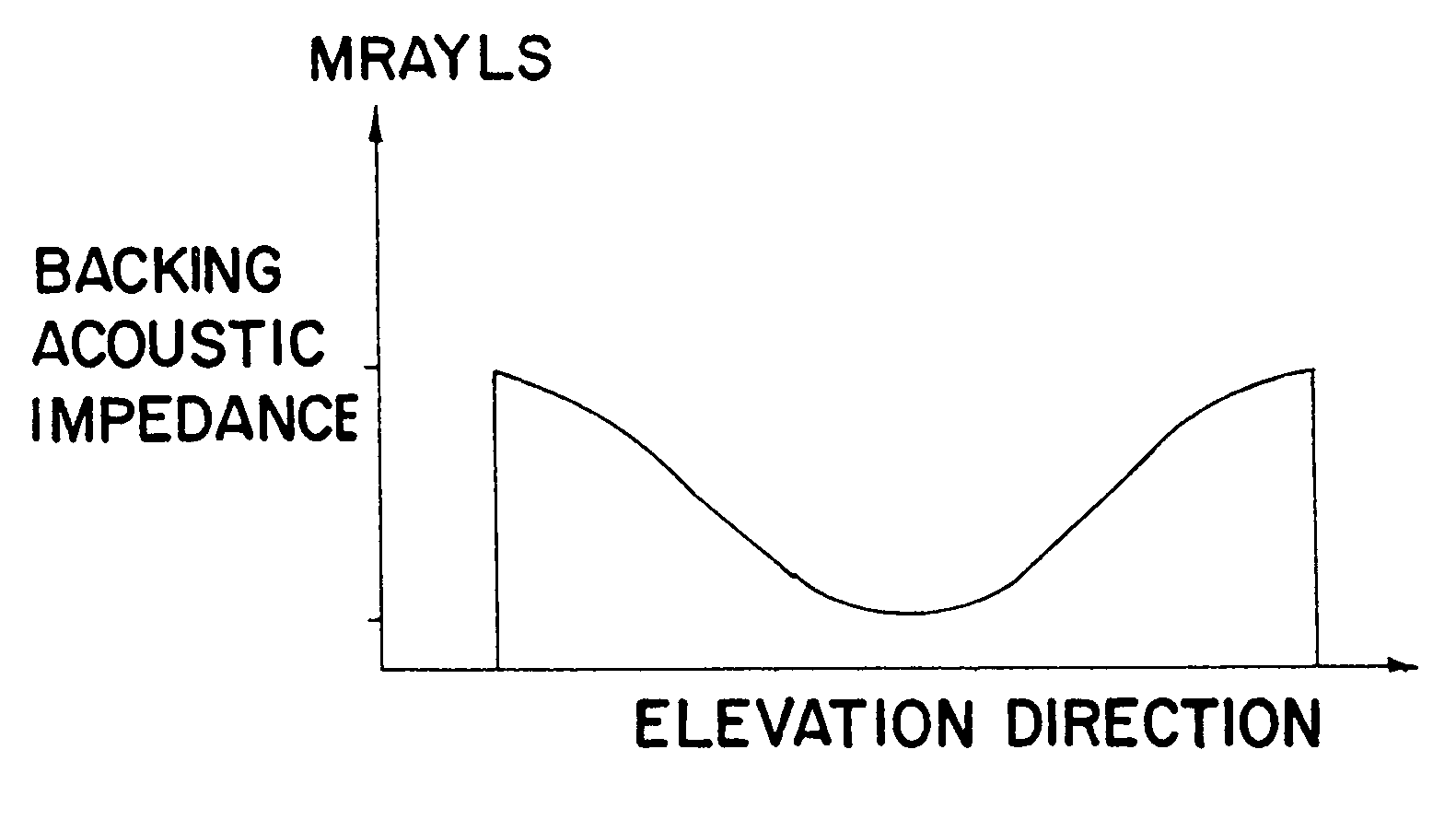
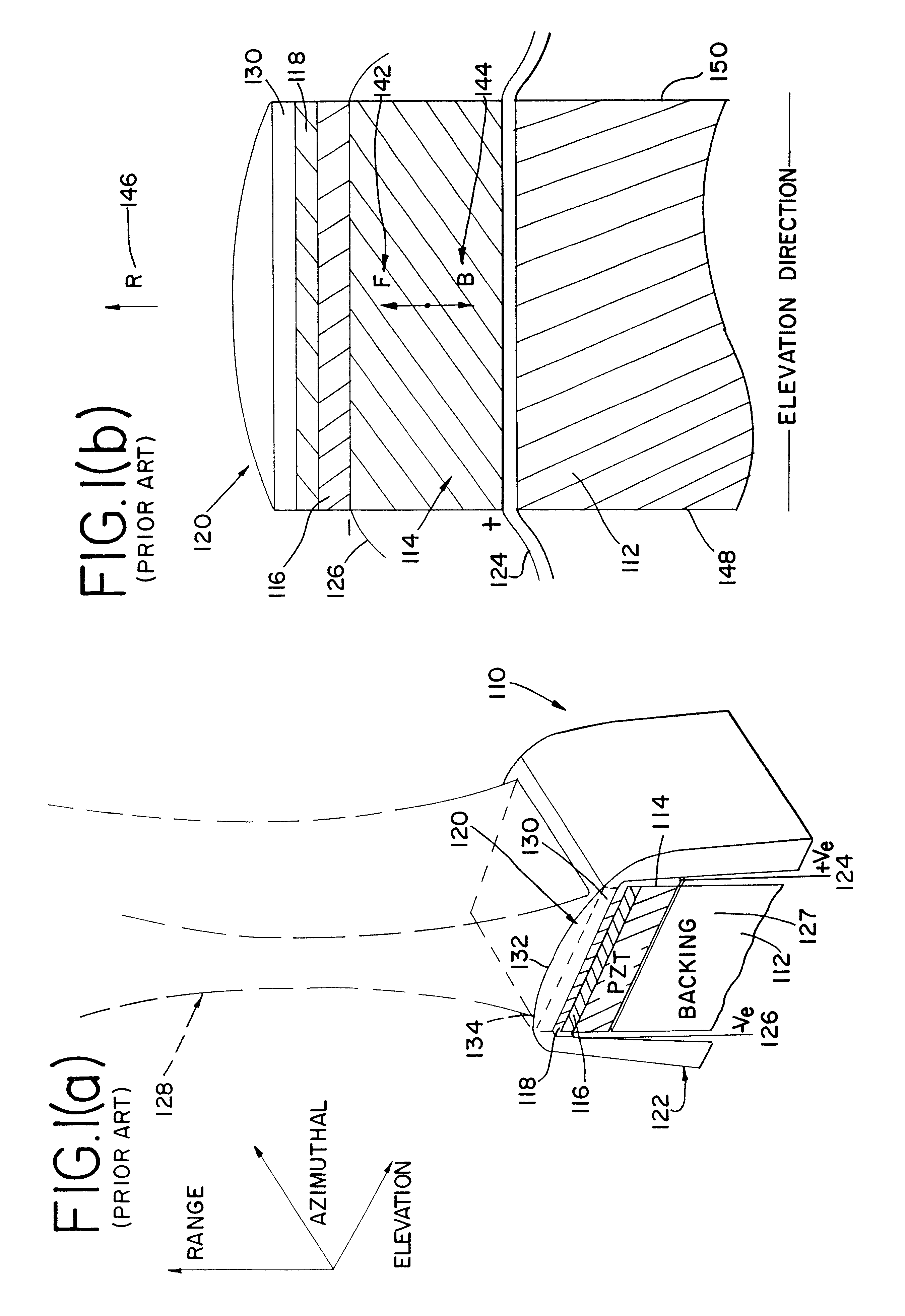
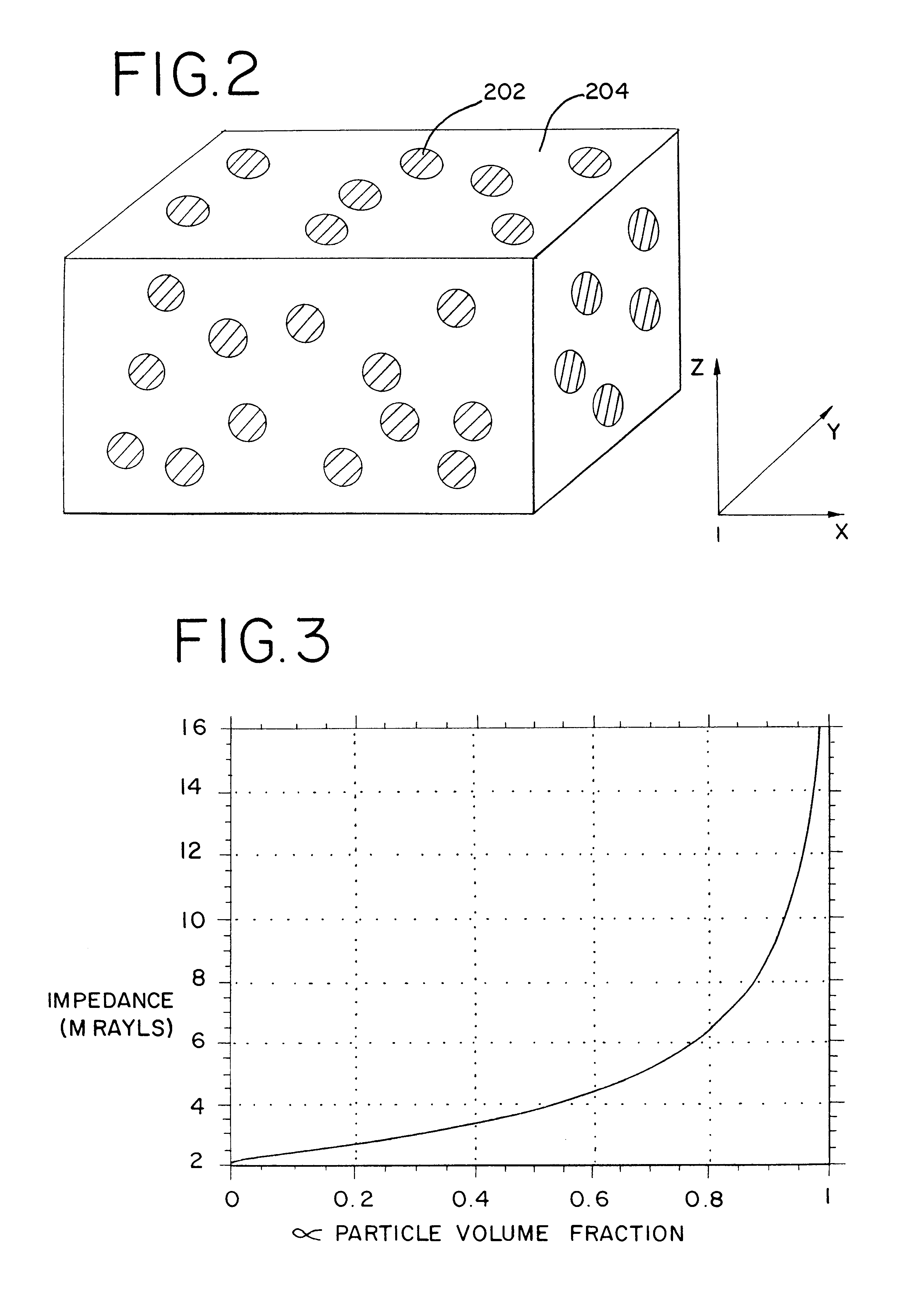
An apparatus and method using a backing block having a variable acoustic impedance as a function of elevation or azimuth, to achieve a desirable apodization of the aperture of an ultrasound transducer stacked with the backing block. The backing block has a gradient profile in acoustic impedance that changes from a minimum value to a maximum value along the elevation direction and / or azimuthal direction of the stacked ultrasound transducer. Typically, the backing block has an elevation gradient profile in acoustic impedance that increases from a minimum value of acoustic impedance near the center of the backing block to a maximum value of acoustic impedance at opposing lateral faces of the backing block. The backing block can be discretely segmented in acoustic impedance, with as many segments as are practically manufacturable. An individual segment can have a uniform or variable acoustic impedance. The backing block can be continuous in acoustic impedance, with a minimum acoustic impedance in the center and a maximum acoustic impedance at two or more planar lateral faces.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Receiver controller for wireless power transfer
ActiveUS20120299542A1Electromagnetic wave systemTransducer detailsElectric power transmissionAudio power amplifier
A signal generator generates an electrical signal that is sent to an amplifier, which increases the power of the signal using power from a power source. The amplified signal is fed to a sender transducer to generate ultrasonic waves that can be focused and sent to a receiver. The receiver transducer converts the ultrasonic waves back into electrical energy and stores it in an energy storage device, such as a battery, or uses the electrical energy to power a device. In this way, a device can be remotely charged or powered without having to be tethered to an electrical outlet.
Owner:UBEAM
Sender transducer for wireless power transfer
ActiveUS20120300592A1Transducer detailsAngle modulation detailsElectric power transmissionAudio power amplifier
A signal generator generates an electrical signal that is sent to an amplifier, which increases the power of the signal using power from a power source. The amplified signal is fed to a sender transducer to generate ultrasonic waves that can be focused and sent to a receiver. The receiver transducer converts the ultrasonic waves back into electrical energy and stores it in an energy storage device, such as a battery, or uses the electrical energy to power a device. In this way, a device can be remotely charged or powered without having to be tethered to an electrical outlet.
Owner:UBEAM
Receiver transducer for wireless power transfer
InactiveUS20120300593A1Transducer detailsAngle modulation detailsElectric power transmissionAudio power amplifier
A signal generator generates an electrical signal that is sent to an amplifier, which increases the power of the signal using power from a power source. The amplified signal is fed to a sender transducer to generate ultrasonic waves that can be focused and sent to a receiver. The receiver transducer converts the ultrasonic waves back into electrical energy and stores it in an energy storage device, such as a battery, or uses the electrical energy to power a device. In this way, a device can be remotely charged or powered without having to be tethered to an electrical outlet.
Owner:UBEAM
Receiver communications for wireless power transfer
InactiveUS20120300588A1Transducer detailsAngle modulation detailsElectric power transmissionAudio power amplifier
A signal generator generates an electrical signal that is sent to an amplifier, which increases the power of the signal using power from a power source. The amplified signal is fed to a sender transducer to generate ultrasonic waves that can be focused and sent to a receiver. The receiver transducer converts the ultrasonic waves back into electrical energy and stores it in an energy storage device, such as a battery, or uses the electrical energy to power a device. In this way, a device can be remotely charged or powered without having to be tethered to an electrical outlet.
Owner:UBEAM
Sender controller for wireless power transfer
InactiveUS20120299541A1Electromagnetic wave systemTransducer detailsElectric power transmissionAudio power amplifier
A signal generator generates an electrical signal that is sent to an amplifier, which increases the power of the signal using power from a power source. The amplified signal is fed to a sender transducer to generate ultrasonic waves that can be focused and sent to a receiver. The receiver transducer converts the ultrasonic waves back into electrical energy and stores it in an energy storage device, such as a battery, or uses the electrical energy to power a device. In this way, a device can be remotely charged or powered without having to be tethered to an electrical outlet.
Owner:UBEAM
System and method for monitoring pressure, flow and constriction parameters of plumbing and blood vessels
InactiveUS6237398B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringPulsatile flow
The present invention provides a system and method of quantifying flow, detecting a location of an obstruction and quantifying a degree of the obstruction in a pipe characterized in pulsatile flow. The method includes the steps of (a) attaching at least two spaced pressure sensors onto inner walls of the pipe; (b) using the at least two spaced pressure sensors for recording pressure records associated with each of the at least two pressure sensors within the pipe; and (c) using the pressure records for quantifying the pulsatile flow in the pipe, for detecting the location of the obstruction in the pipe and for quantifying the degree of the obstruction in the pipe.
Owner:TELESENSE
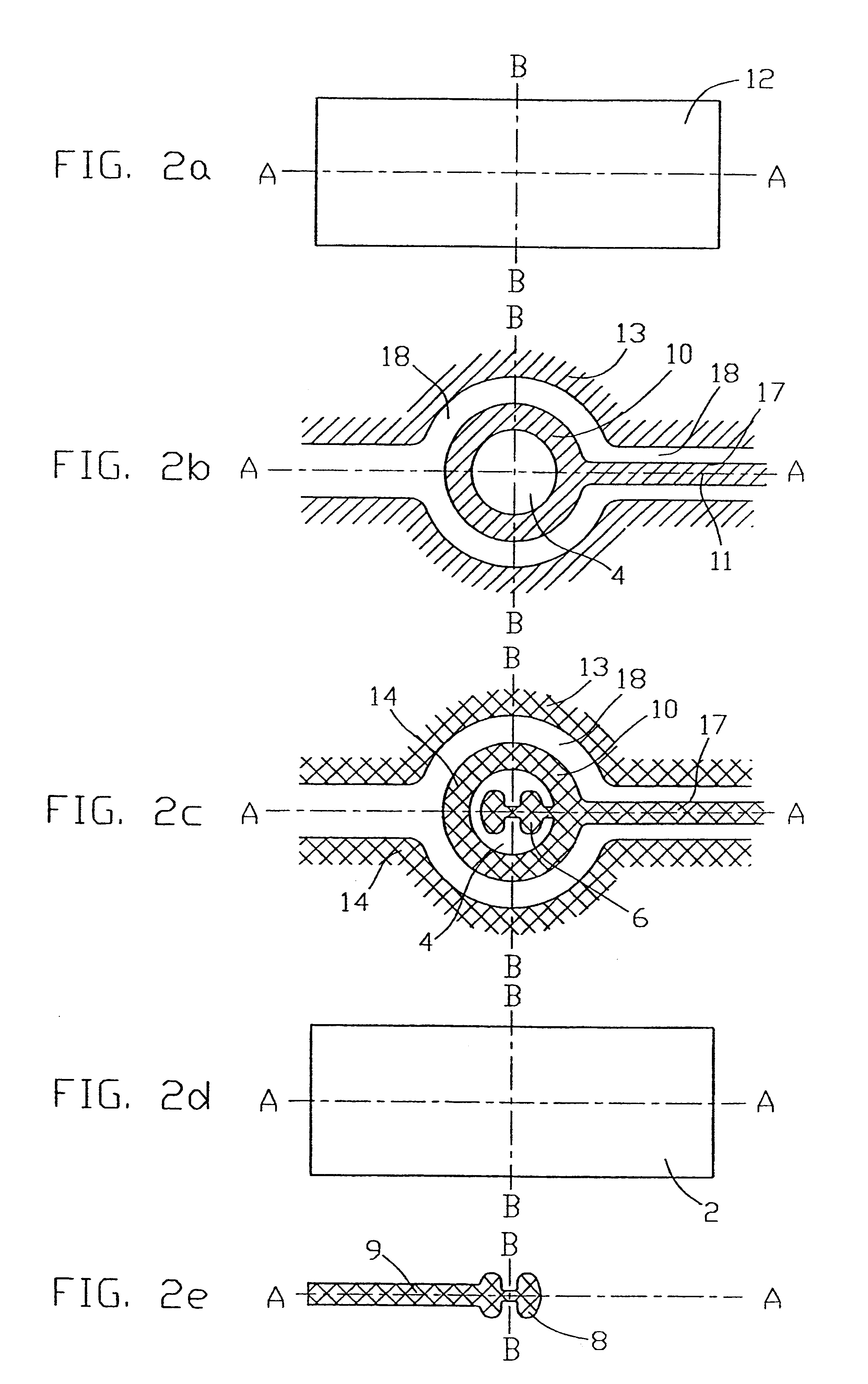
Ultrasound transducers for imaging and therapy
InactiveUS7063666B2Reduce in quantityReducing cross-talk and heatingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectrical resistance and conductanceSonification
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
Receiver communications for wireless power transfer
InactiveUS9001622B2Transducer detailsAngle modulation detailsElectric power transmissionAudio power amplifier
A signal generator generates an electrical signal that is sent to an amplifier, which increases the power of the signal using power from a power source. The amplified signal is fed to a sender transducer to generate ultrasonic waves that can be focused and sent to a receiver. The receiver transducer converts the ultrasonic waves back into electrical energy and stores it in an energy storage device, such as a battery, or uses the electrical energy to power a device. In this way, a device can be remotely charged or powered without having to be tethered to an electrical outlet.
Owner:UBEAM
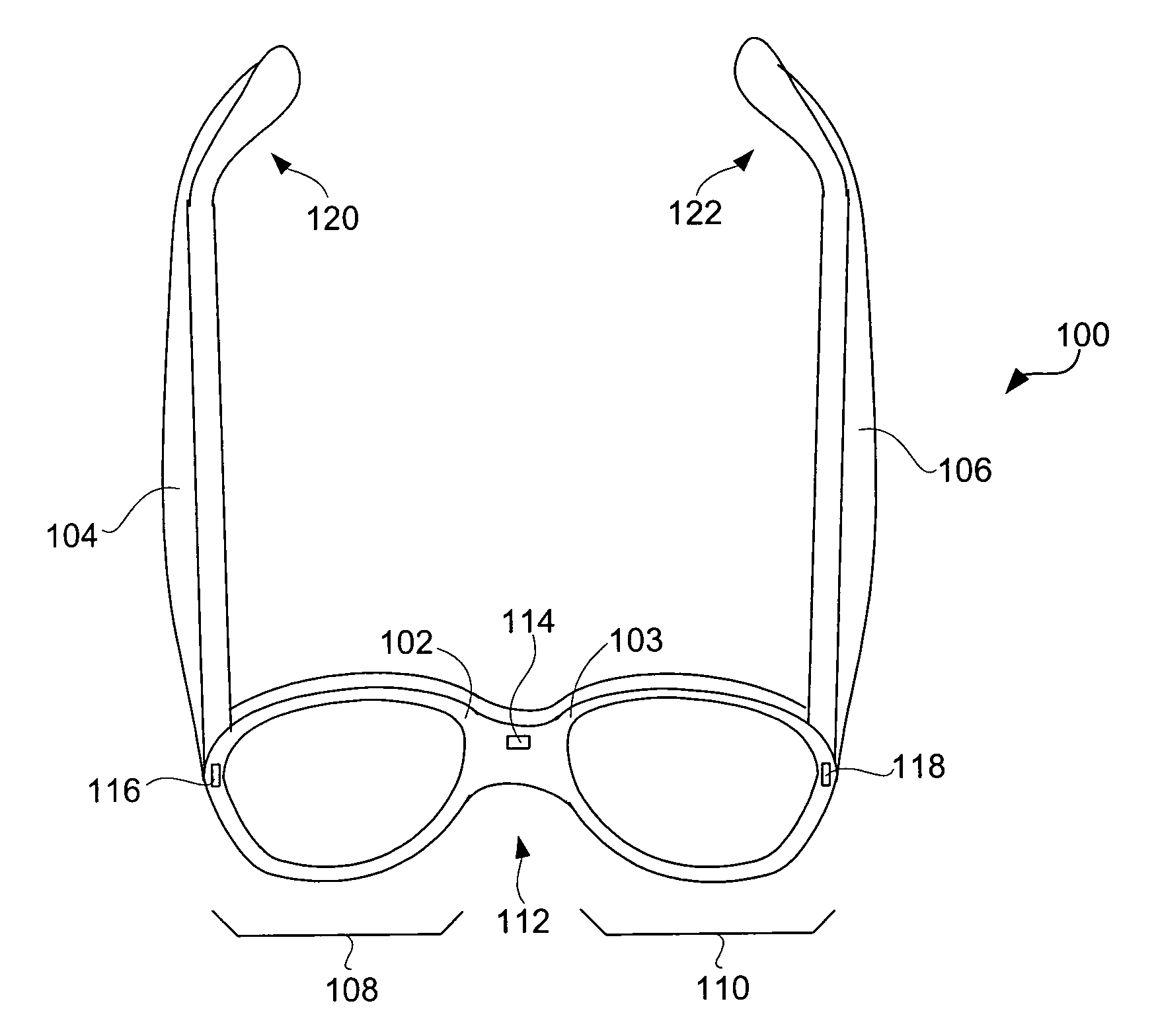
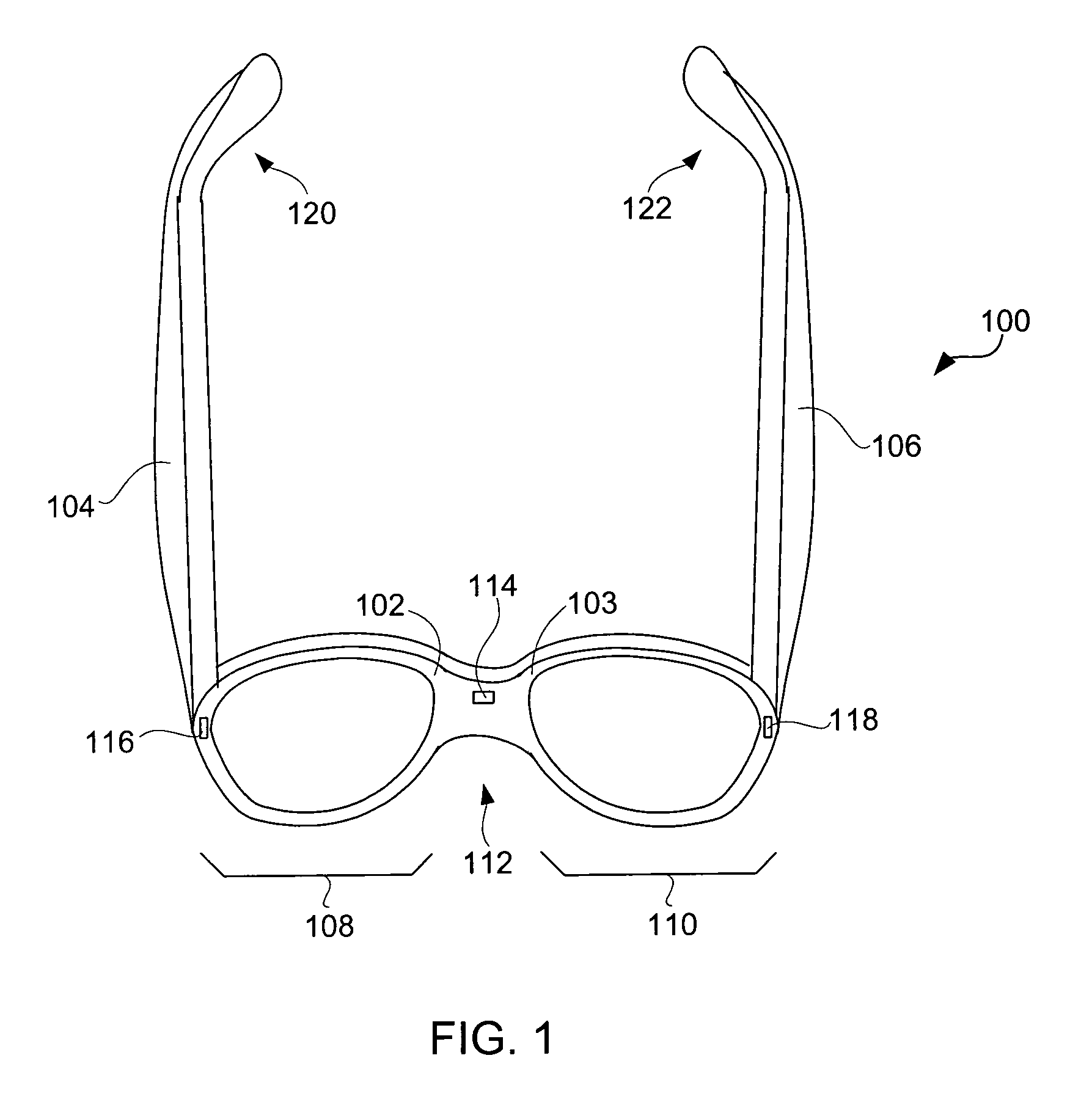
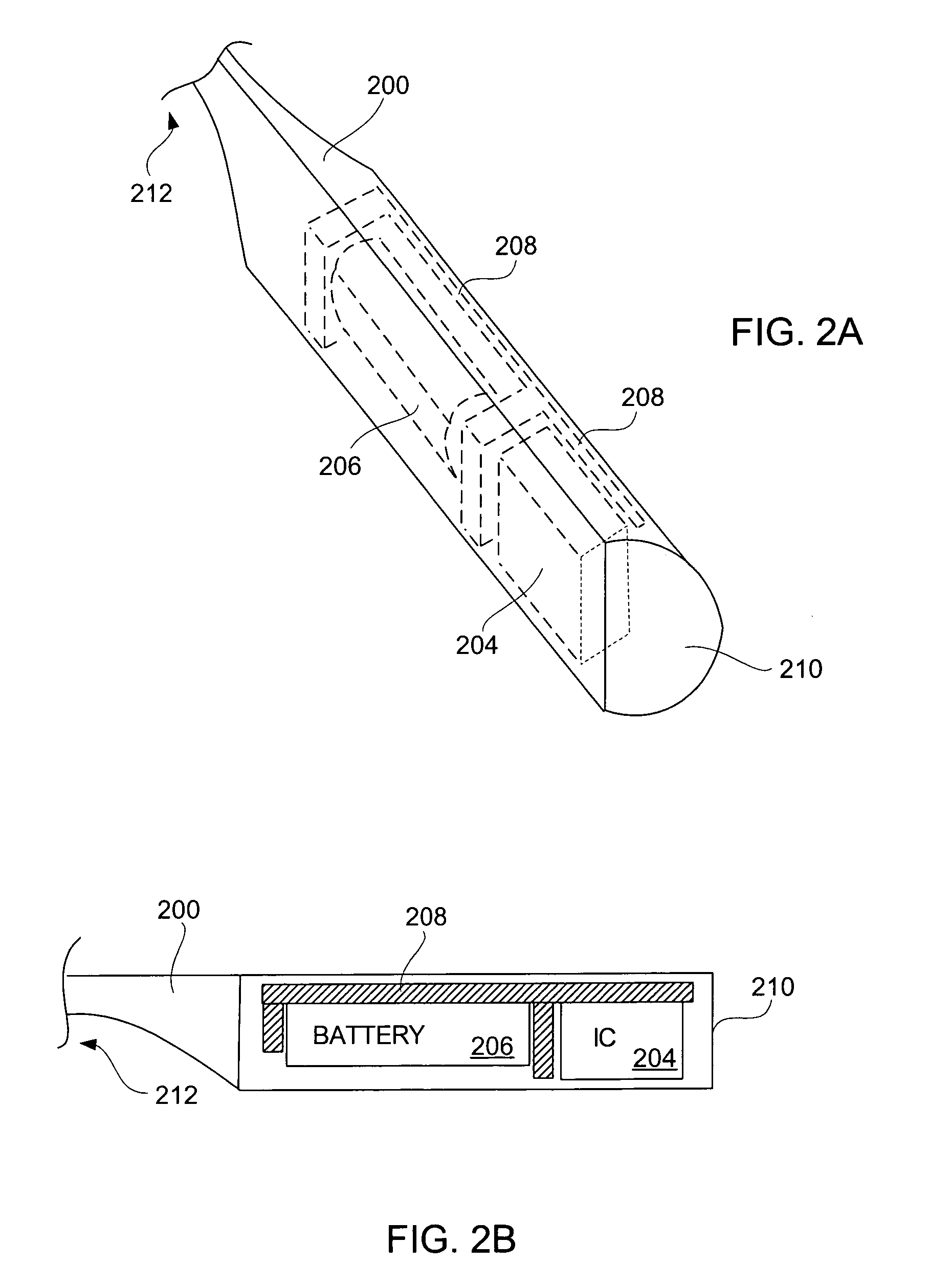
Eyeglasses for wireless communications
Owner:INGENIOSPEC +2
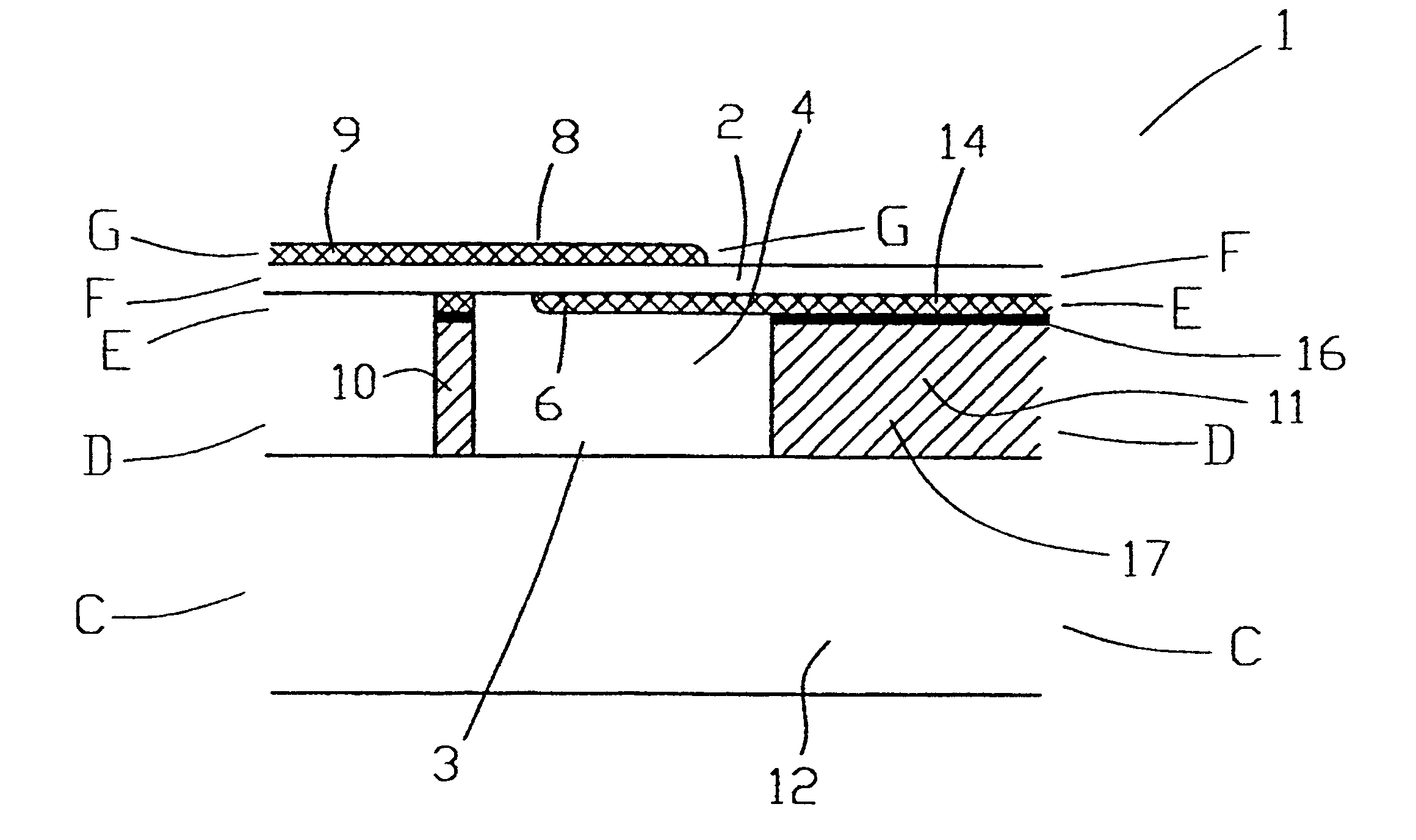
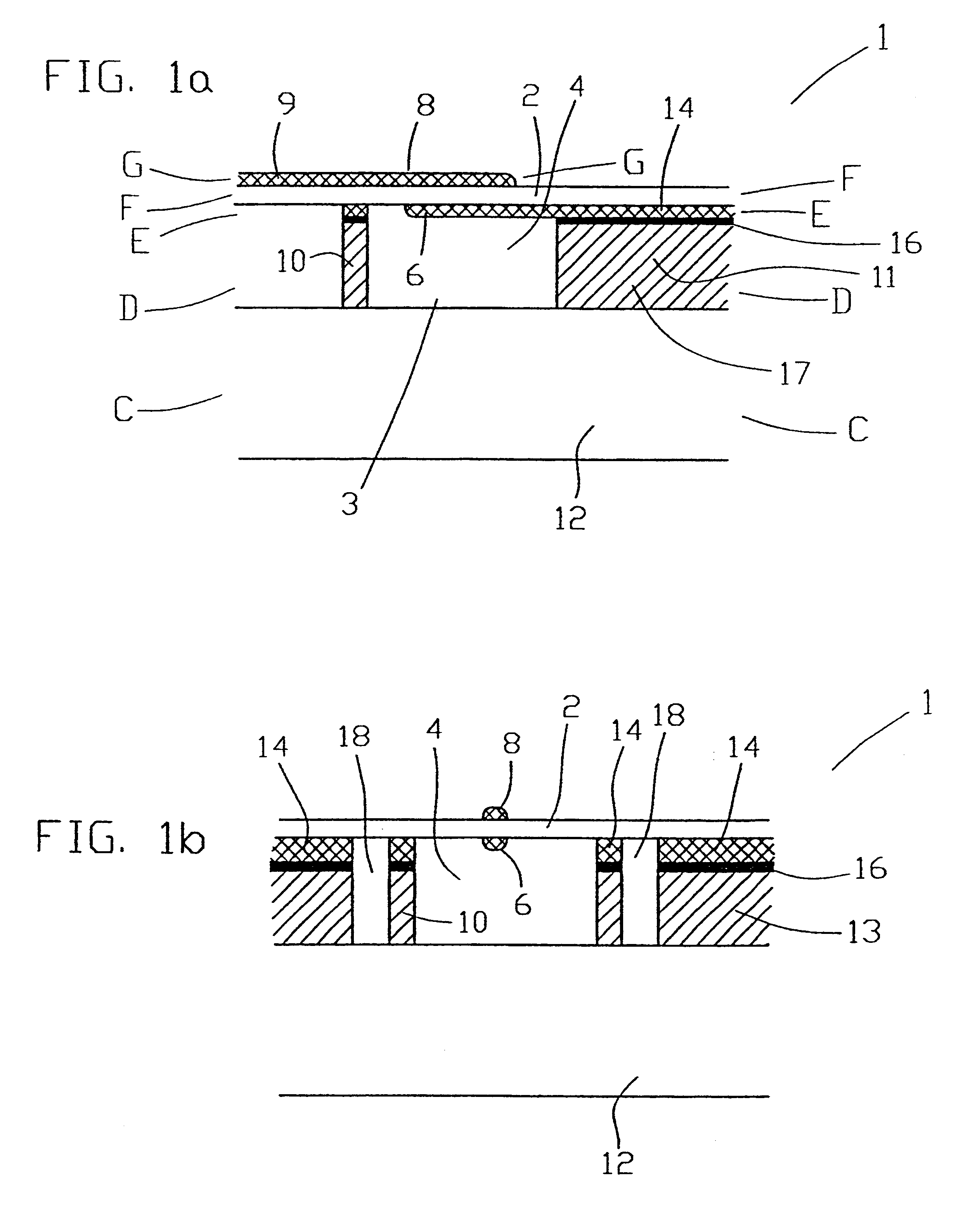
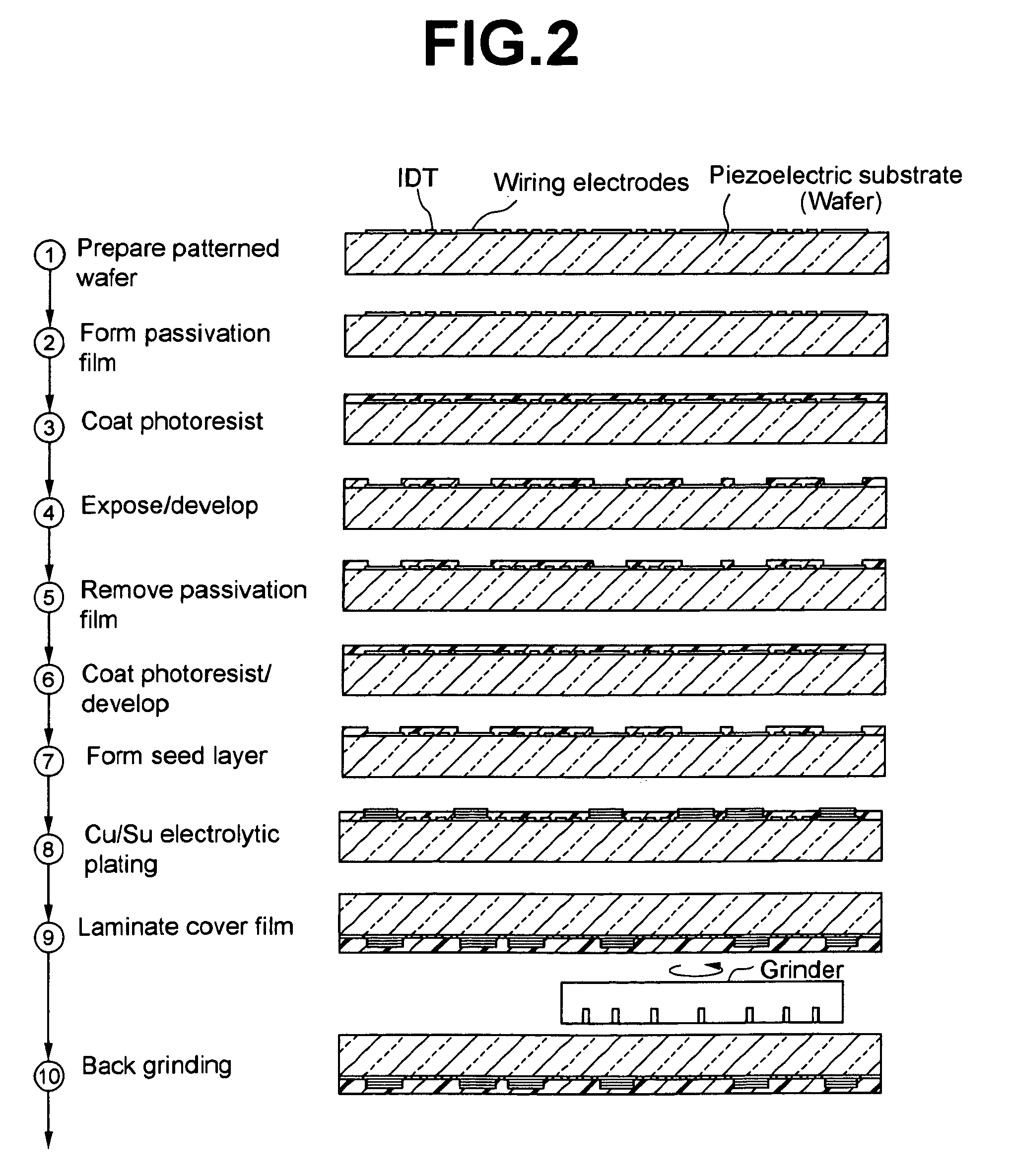
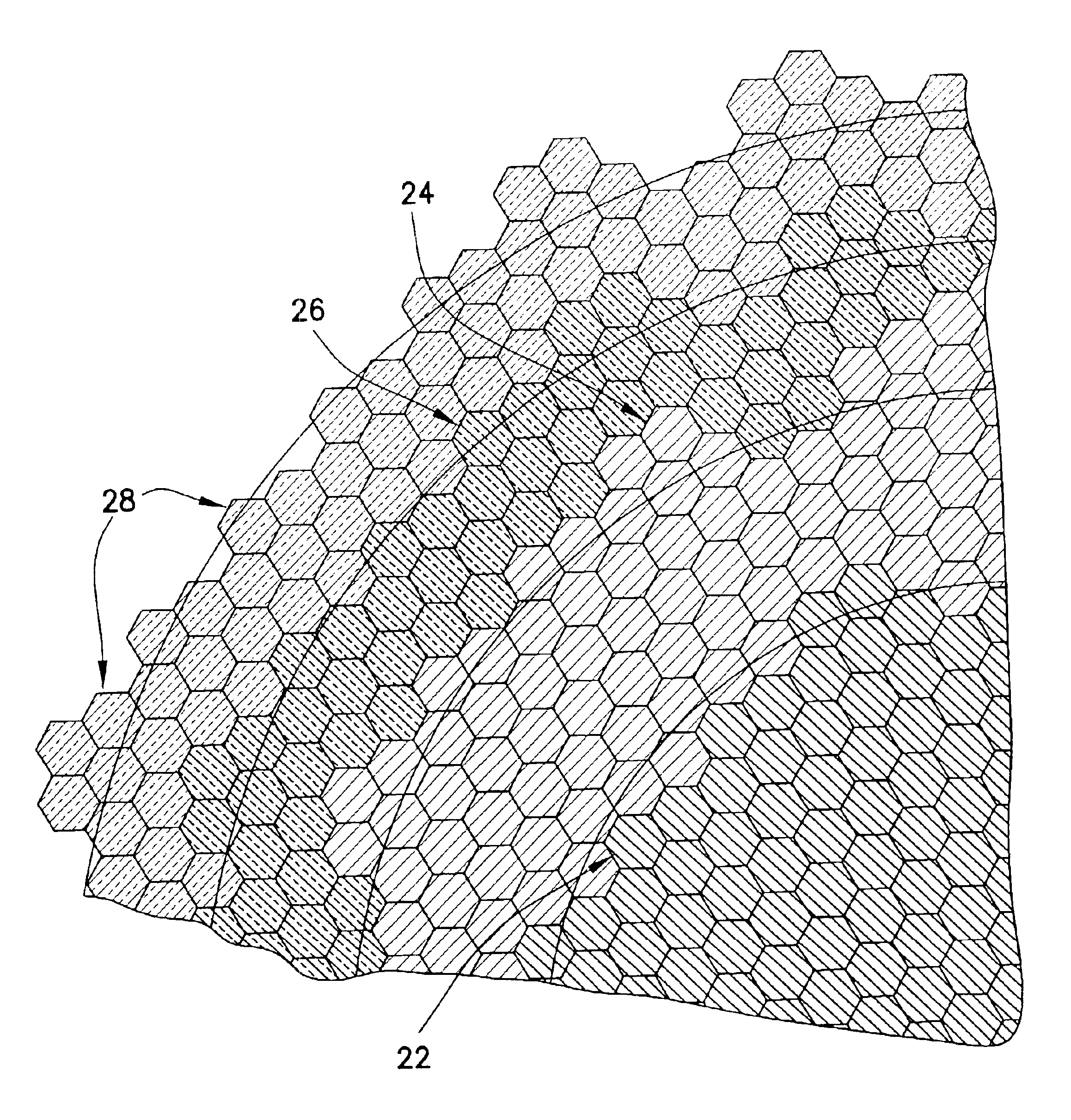
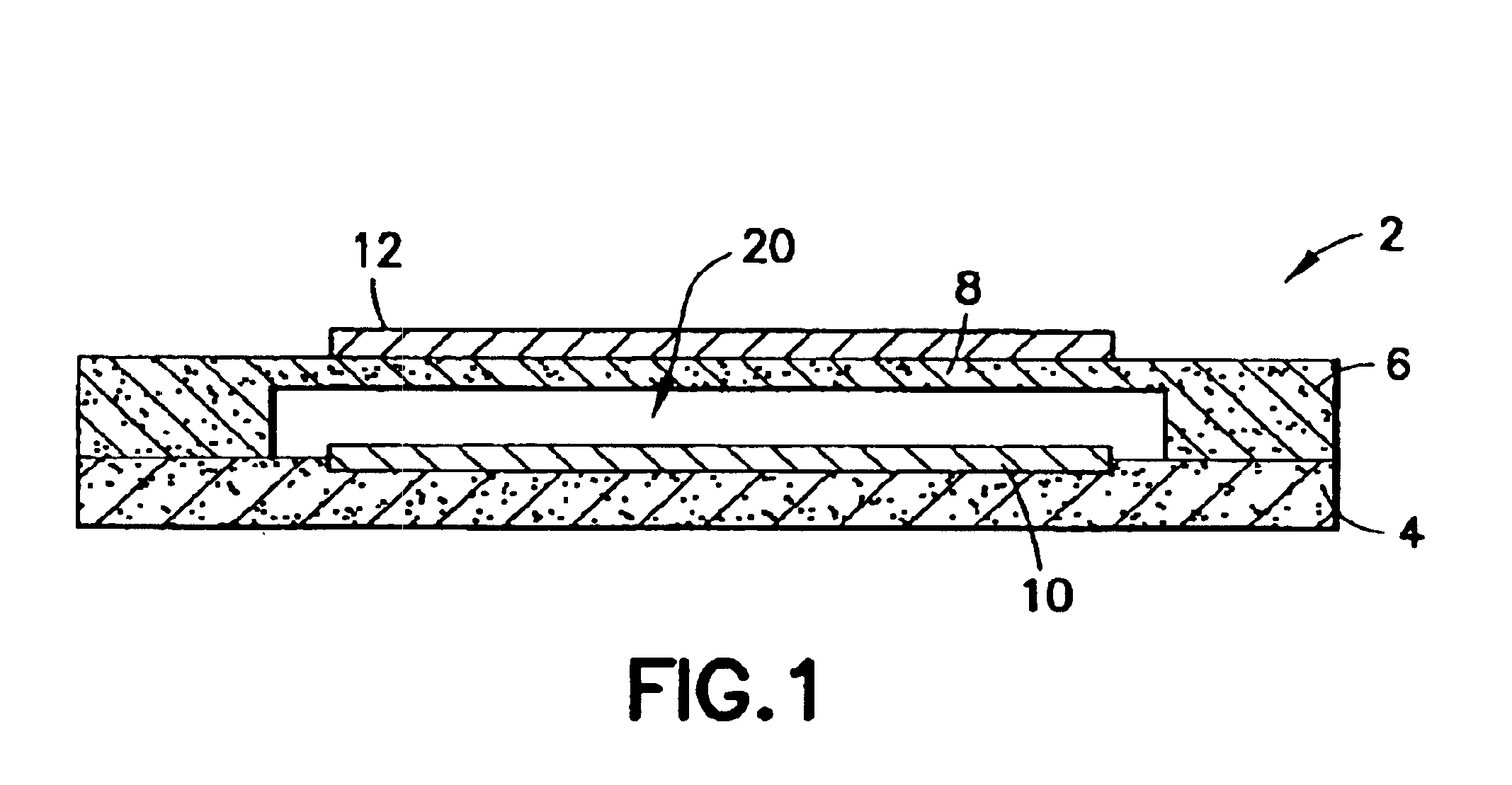
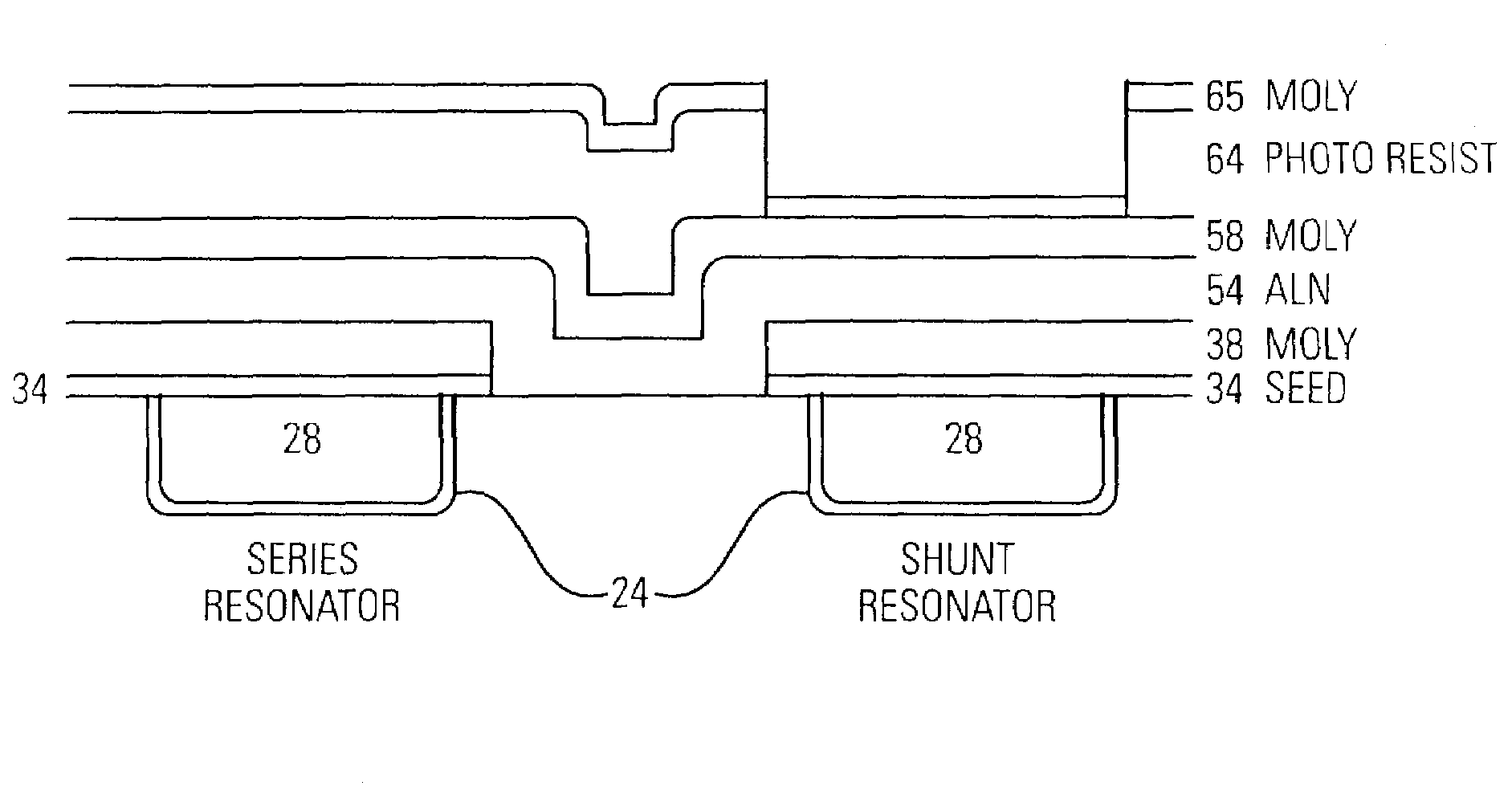
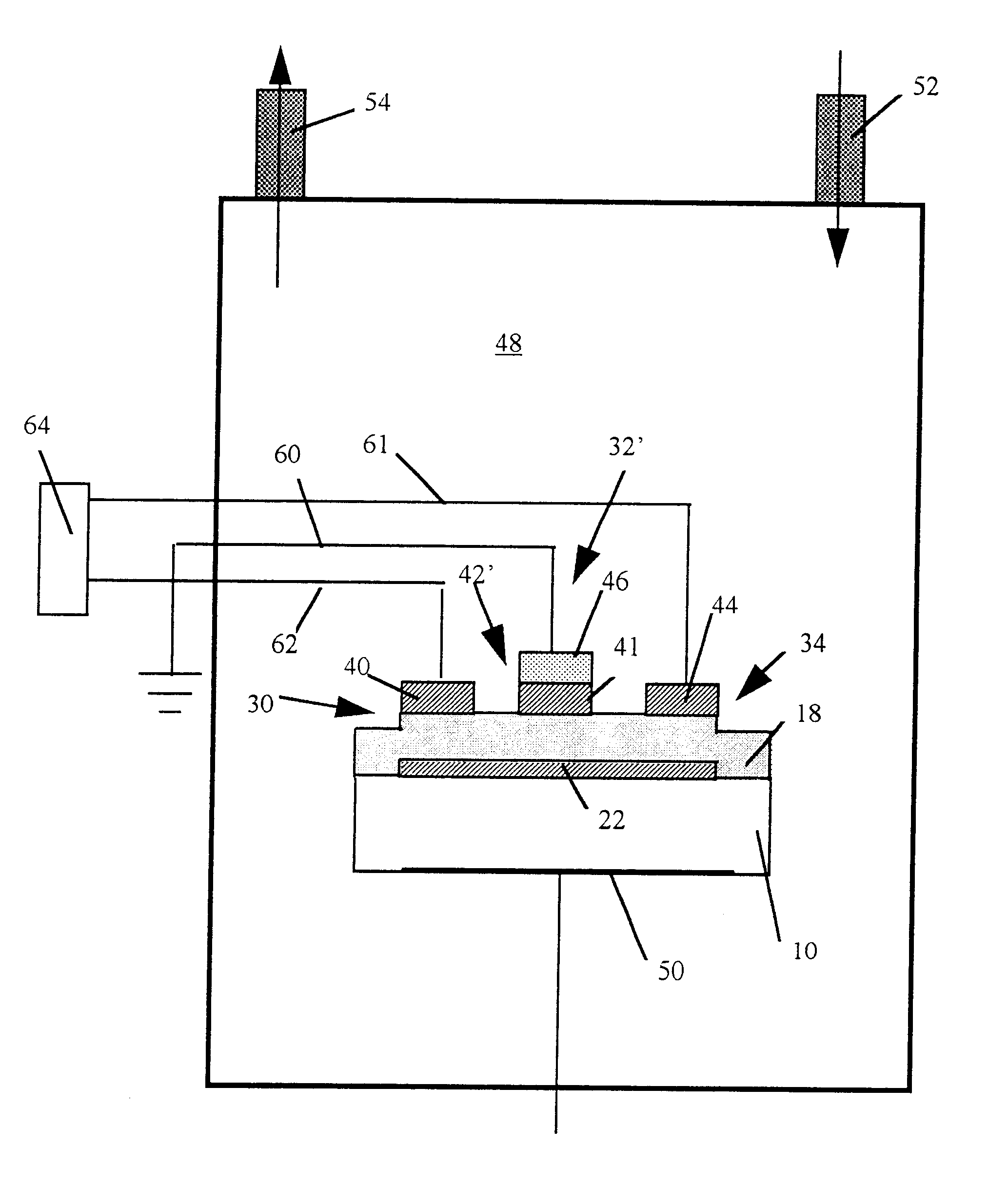
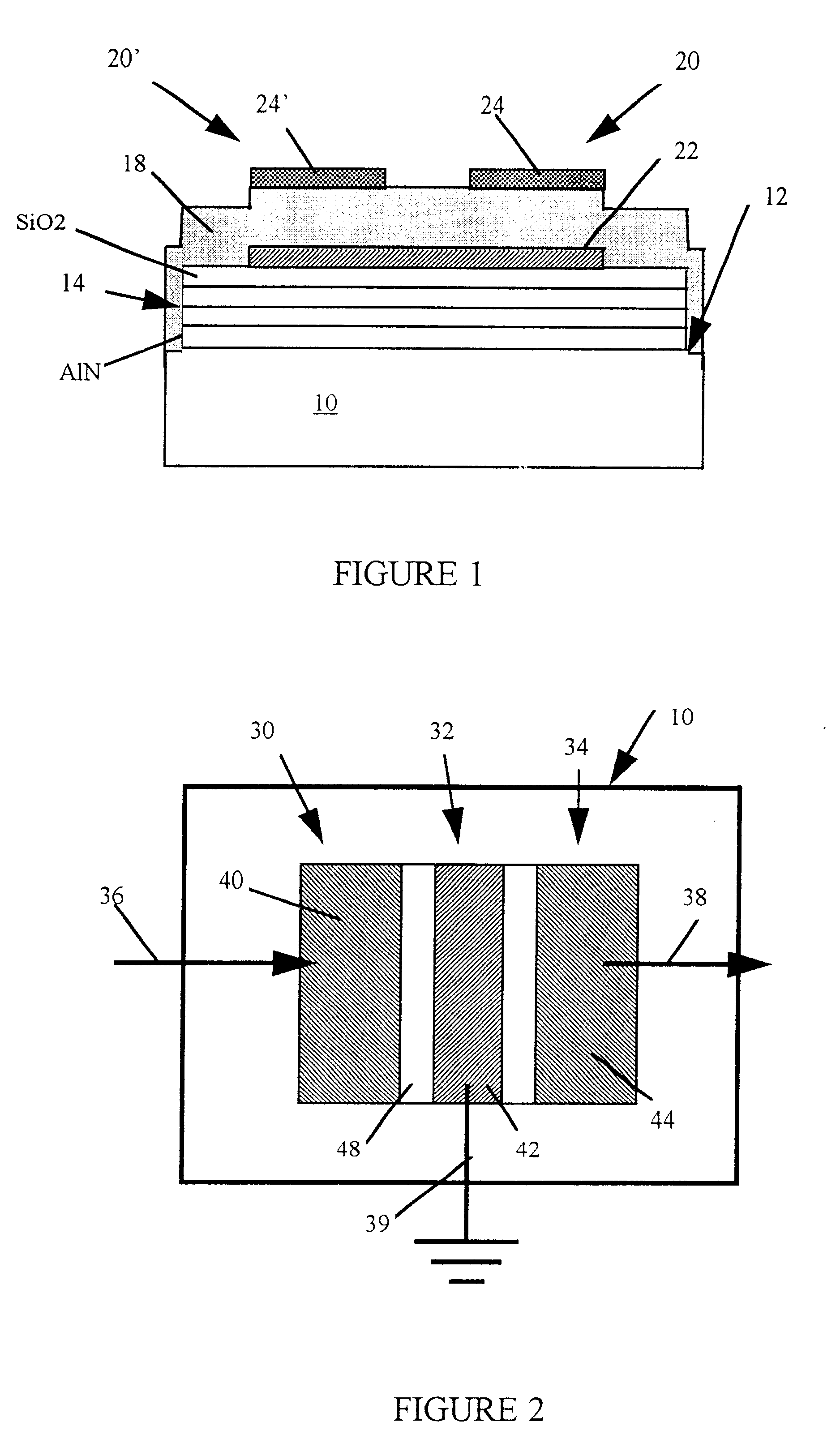
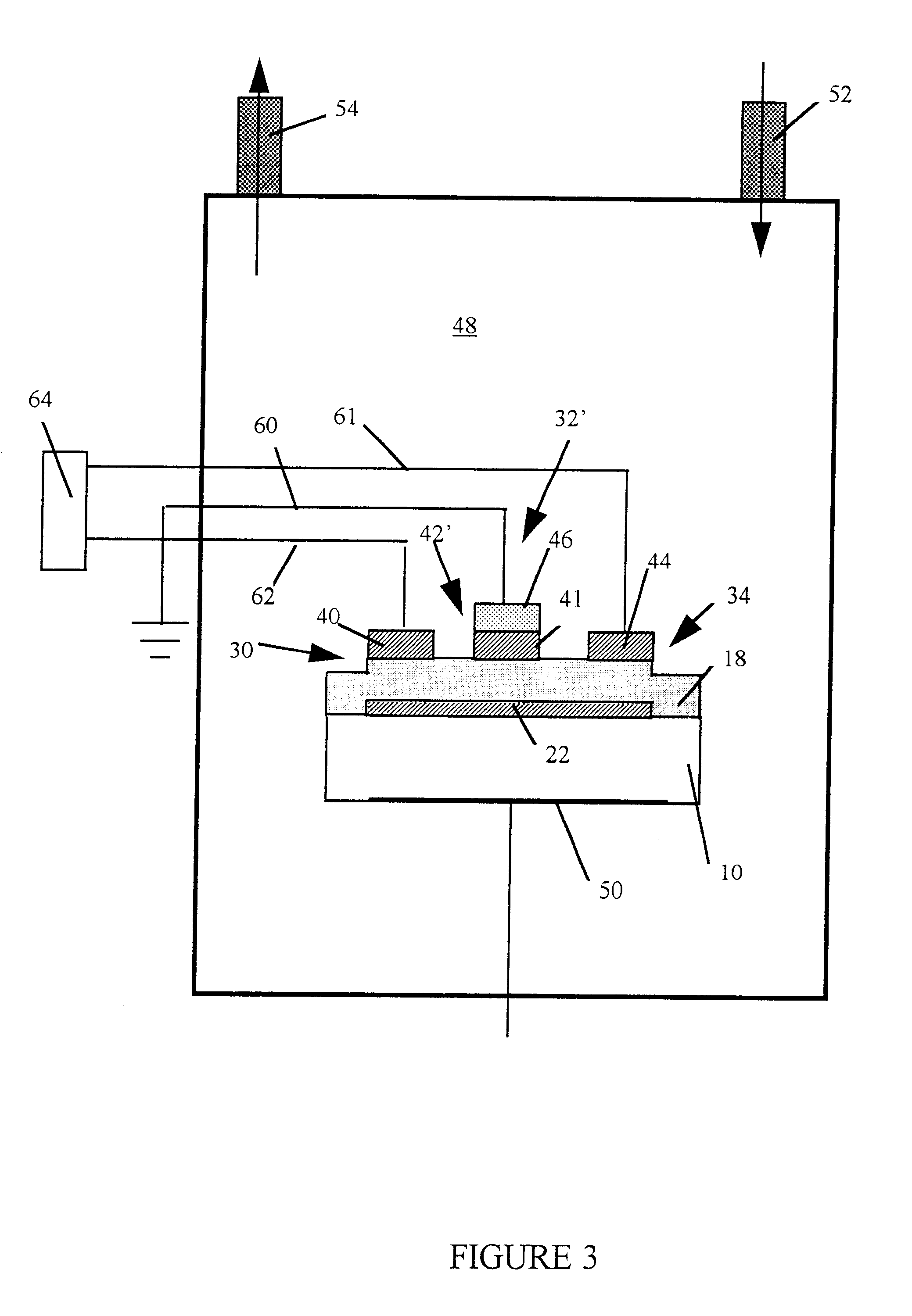
Resonator with seed layer
InactiveUS6828713B2Quality improvementPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksNitrideResonator
A thin-film resonator having a seed layer and a method of making the same are disclosed. The resonator is fabricated having a seed layer to assist in the fabrication of high quality piezoelectric layer for the resoantor. The resonator has the seed layer, a bottom electrode, piezoelectric layer, and a top electrode. The seed layer is often the same material as the piezoelectric layer such as Aluminum Nitride (AlN).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
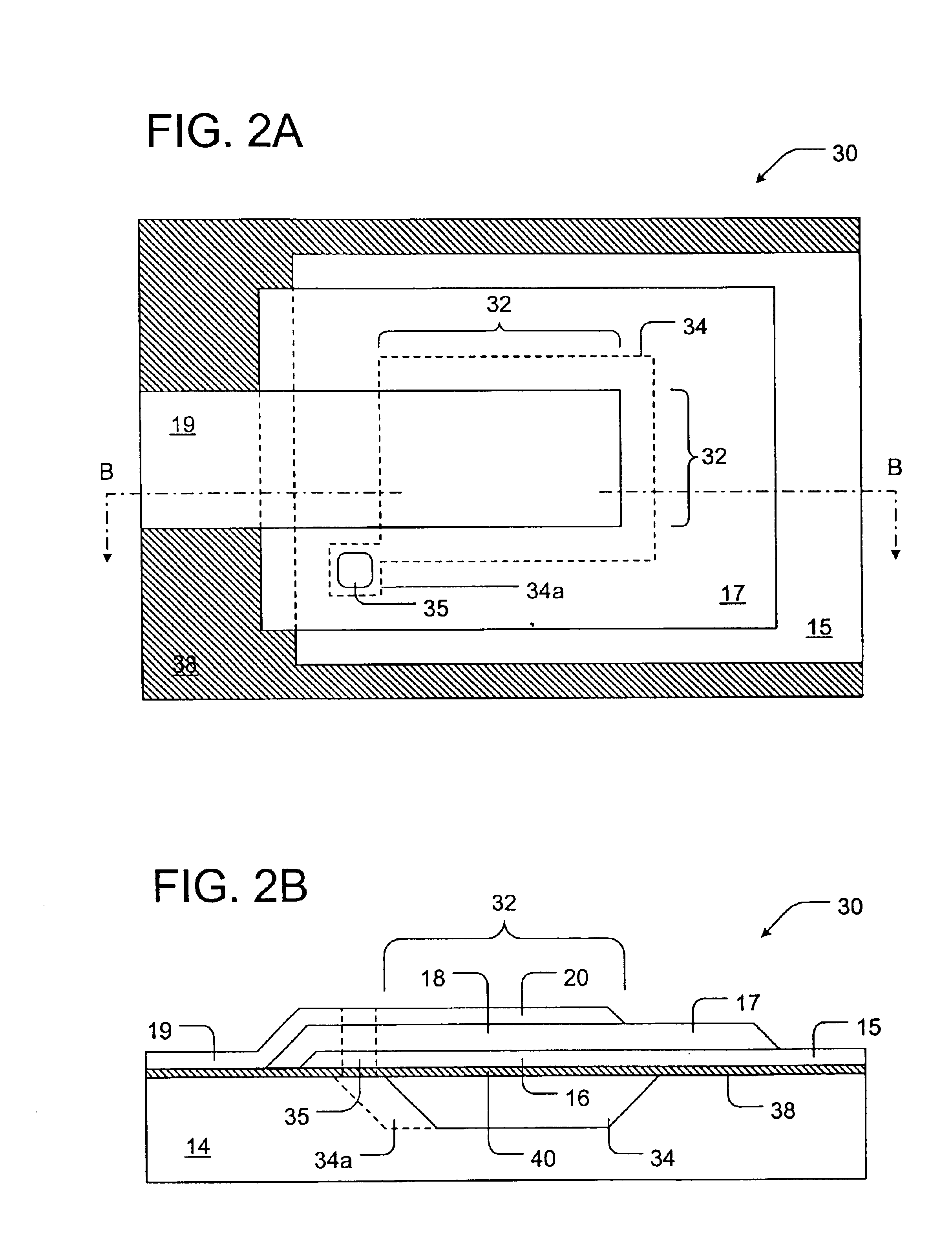
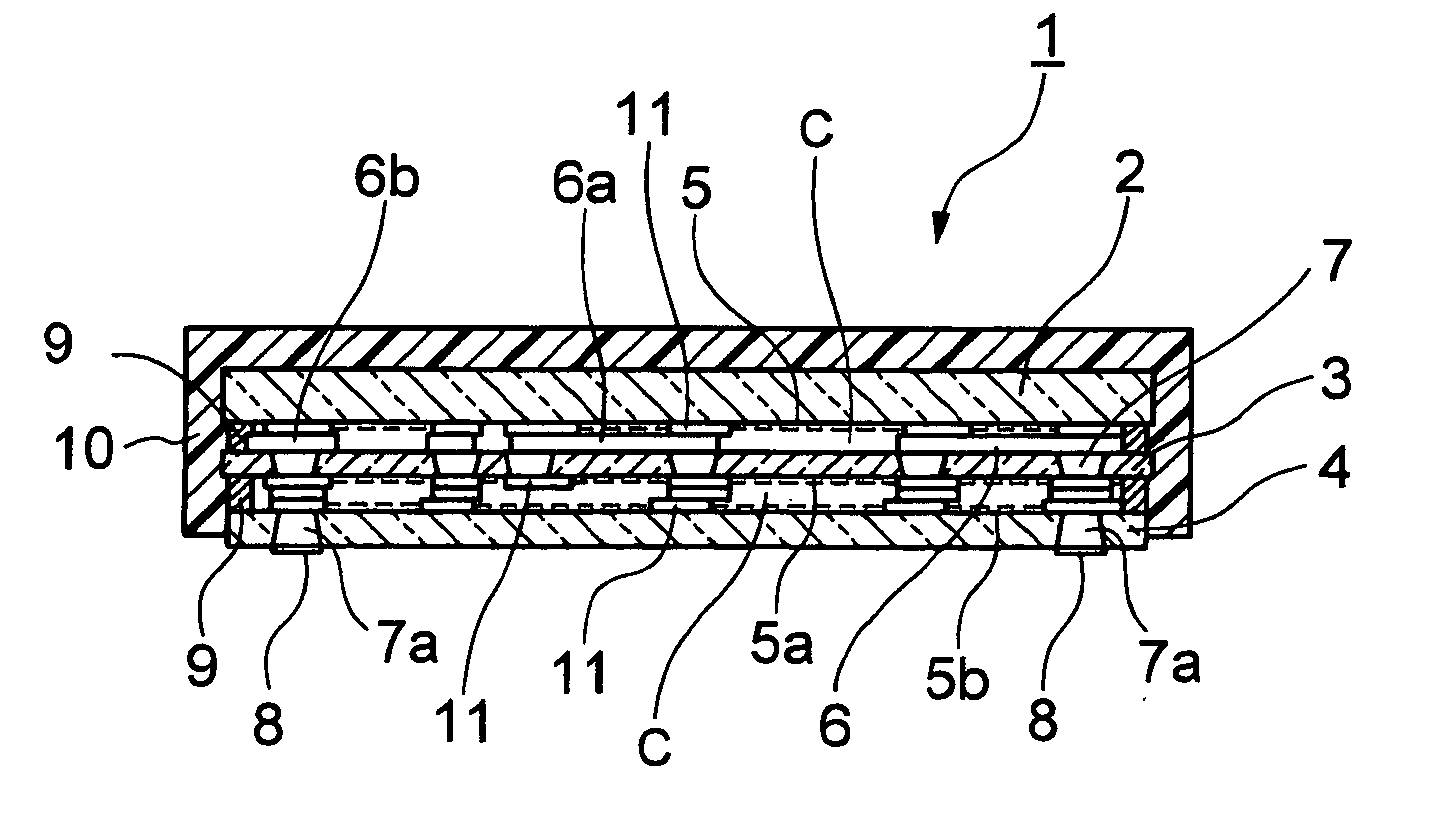
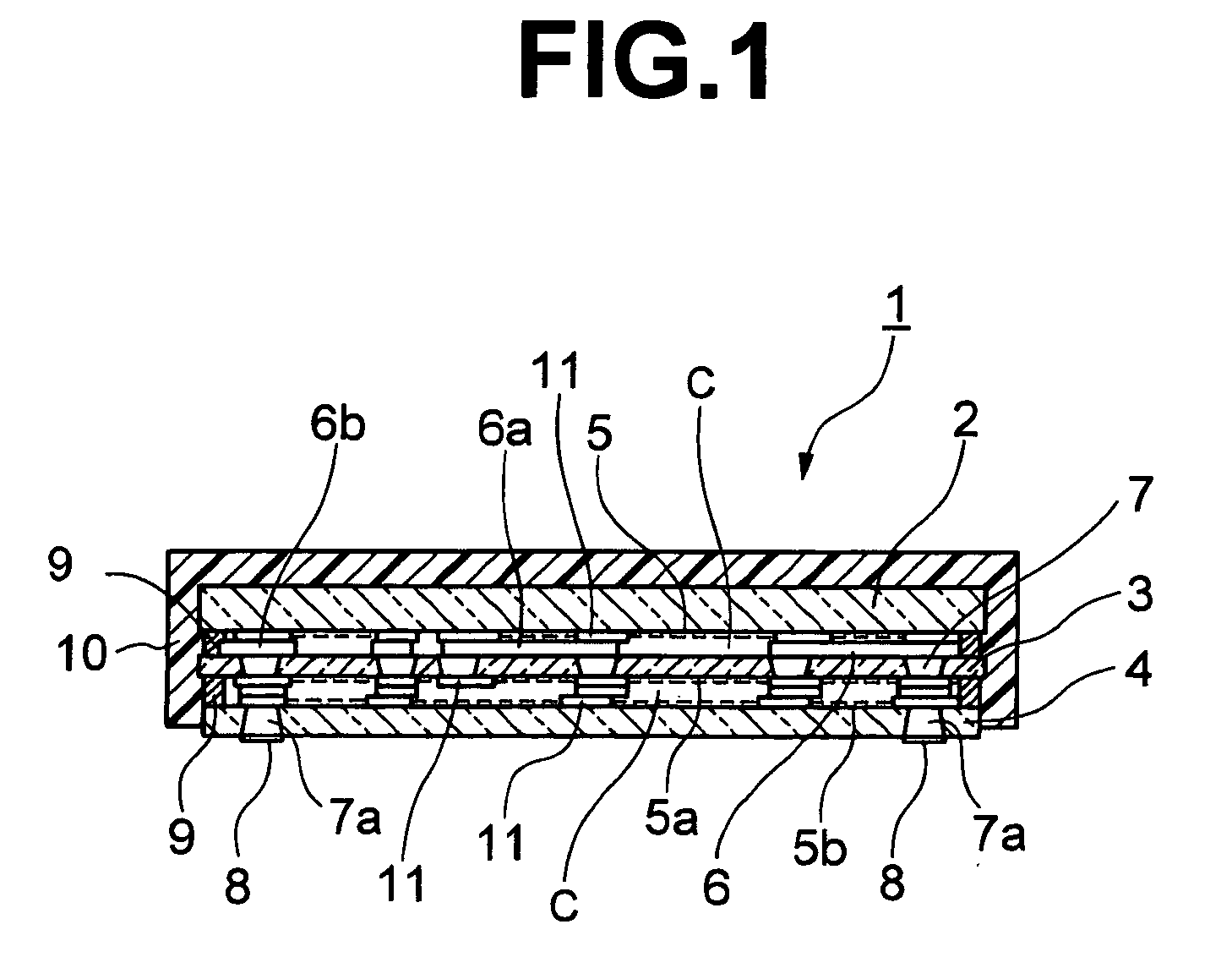
Piezoelectric component and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100045145A1Small sizeIncrease the number ofPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksElectrical and Electronics engineeringPiezoelectric substrate
An object of the present invention is to; miniaturize, increase the capacity, and reduce the price of piezoelectric components. The present invention relates to a piezoelectric component and a manufacturing method thereof, characterized in that: there are bonded and laminated at least two or more piezoelectric elements in which comb-teeth electrodes, wiring electrodes having element wirings that are arranged adjacent to the comb-teeth electrodes, and electrode terminals connected to the wiring electrodes, are formed on a principal surface of a plurality of piezoelectric substrates, while forming hollow sections between the respective piezoelectric elements; through electrodes are formed in the respective piezoelectric substrates so as to pass therethrough; the through electrodes are connected to the electrode terminals; and the piezoelectric substrates are sealed by a resin sealing layer.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
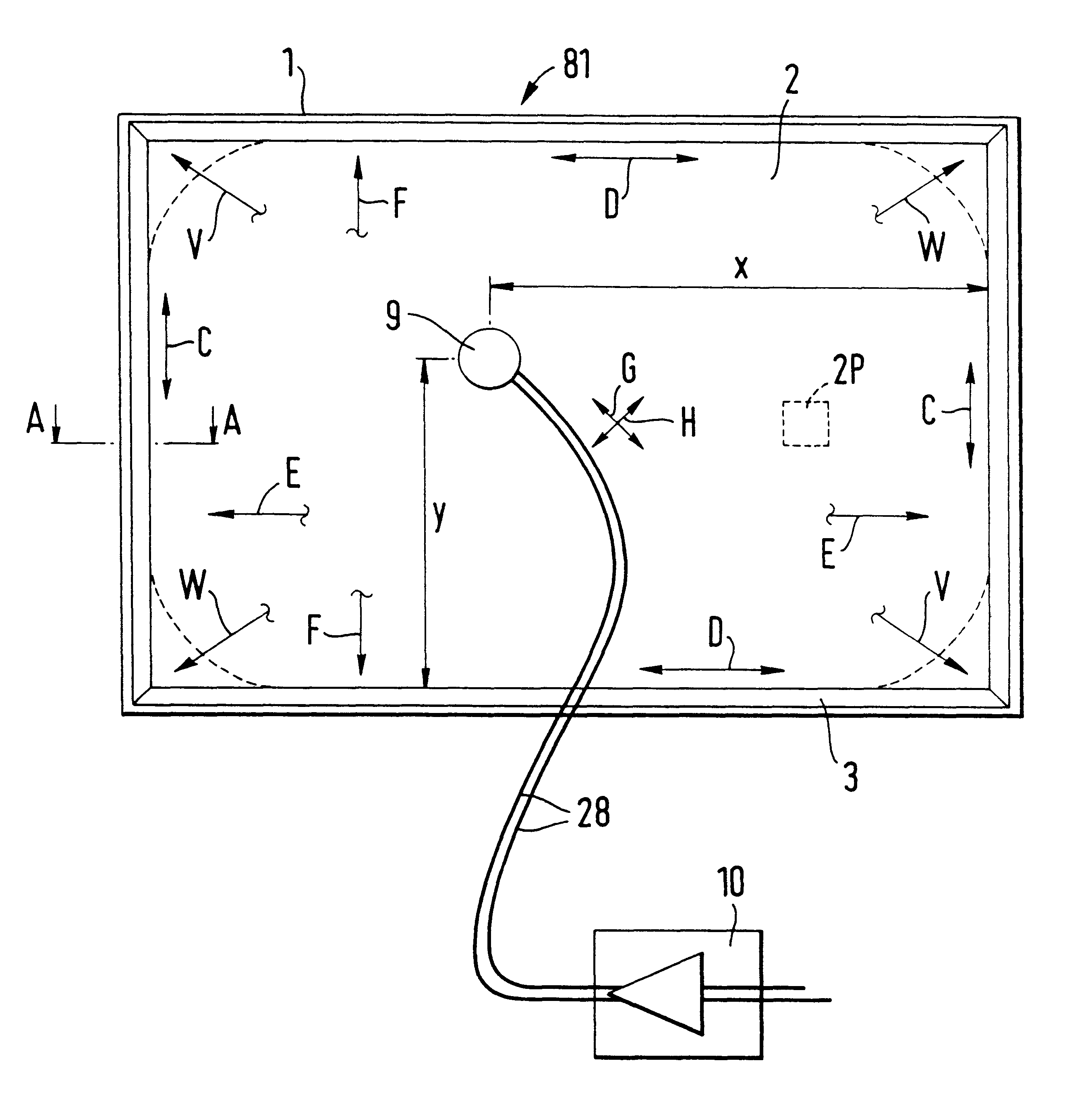
System and method for directing and monitoring radiation
A system for monitoring, directing and controlling the dose of radiation in a medical procedure for irradiating a specific region of a patient's body. In its generic form, the system includes at least one sensor being implantable within, or in proximity to, the specific region of the patient's body, the at least one sensor being for sensing at least one parameter associated with the radiation. The system further includes a relaying device which is in communication with the sensor(s). The relaying device serves for relaying the information outside of the patient's body.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
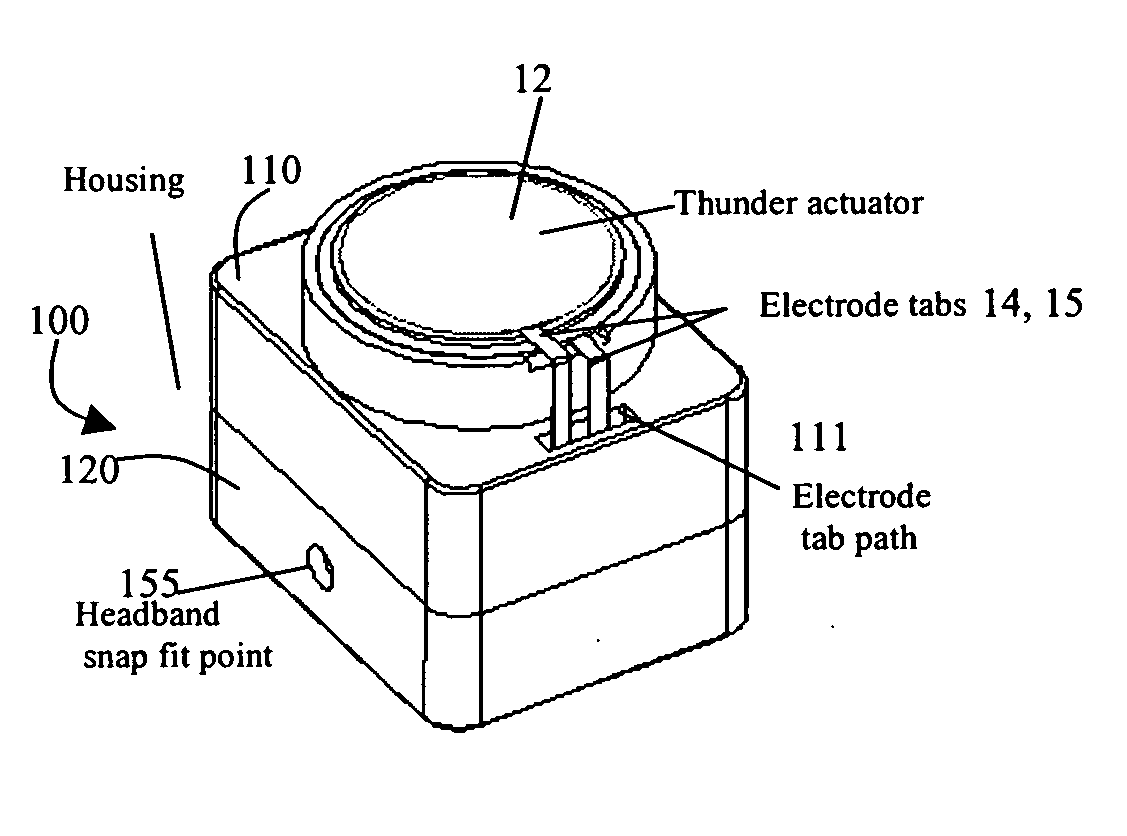
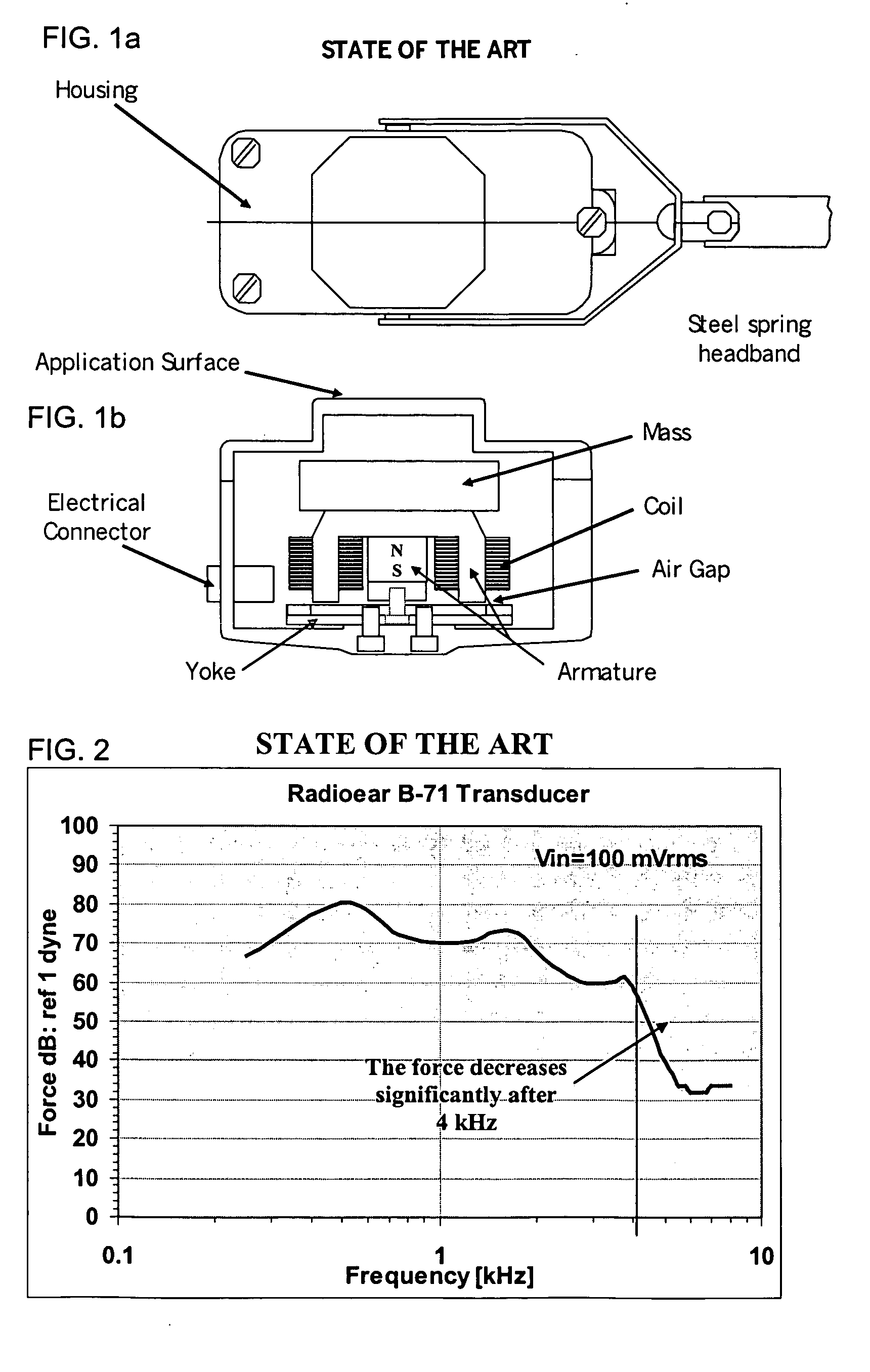
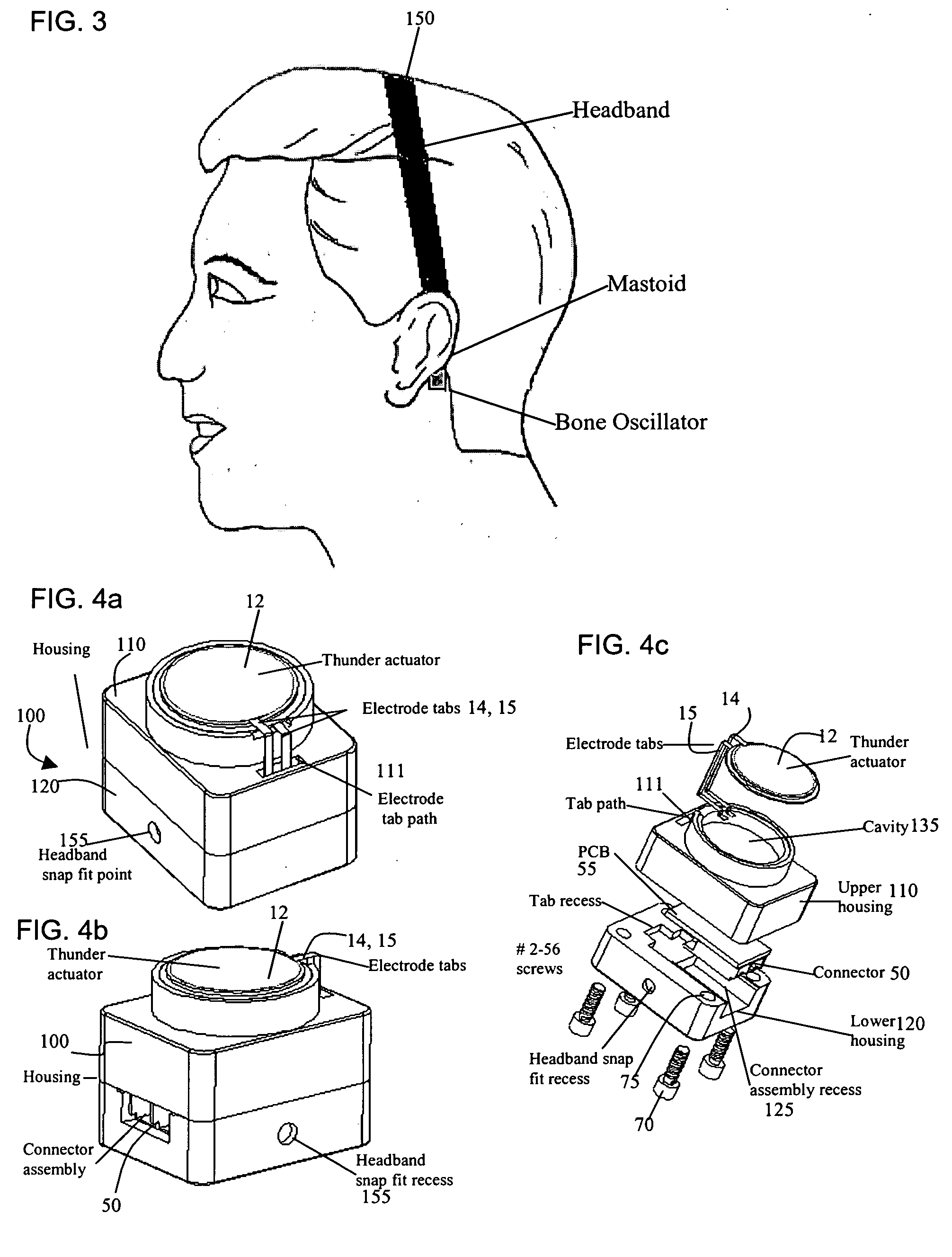
Bone-conduction hearing-aid transducer having improved frequency response
InactiveUS20070041595A1Eliminates soldering wireEliminate useRecord carriersPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersFrequency spectrumBone structure
A hearing-aid device and a method for transmitting sound through bone conduction are disclosed. The hearing-aid device comprises a piezoelectric-type actuator, housing and connector. The piezoelectric actuator is preferably a circular flextensional-type actuator mounted along its peripheral edge in a specifically designed circular structure of the housing. During operation, the bone-conduction transducer is placed against the mastoid area behind the ear of the patient. When the device is energized with an alternating electrical voltage, it flexes back and forth like a circular membrane sustained along its periphery and thus, vibrates as a consequence of the inverse piezoelectric effect. Due to the specific and unique designs proposed, these vibrations are directly transferred trough the human skin to the bone structure (the skull) and provide a means for the sound to be transmitted for patients with hearing malfunctions. The housing acts as a holder for the actuators, as a pre-stress application platform, and as a mass which tailors the frequency spectrum of the device. The apparatus exhibits a performance with a very flat response in the frequency spectrum 200 Hz to 10 kHz, which is a greater spectrum range than any other prior art devices disclosed for bone-conduction transduction which are typically limited to less than 4 kHz.
Owner:FACE INT
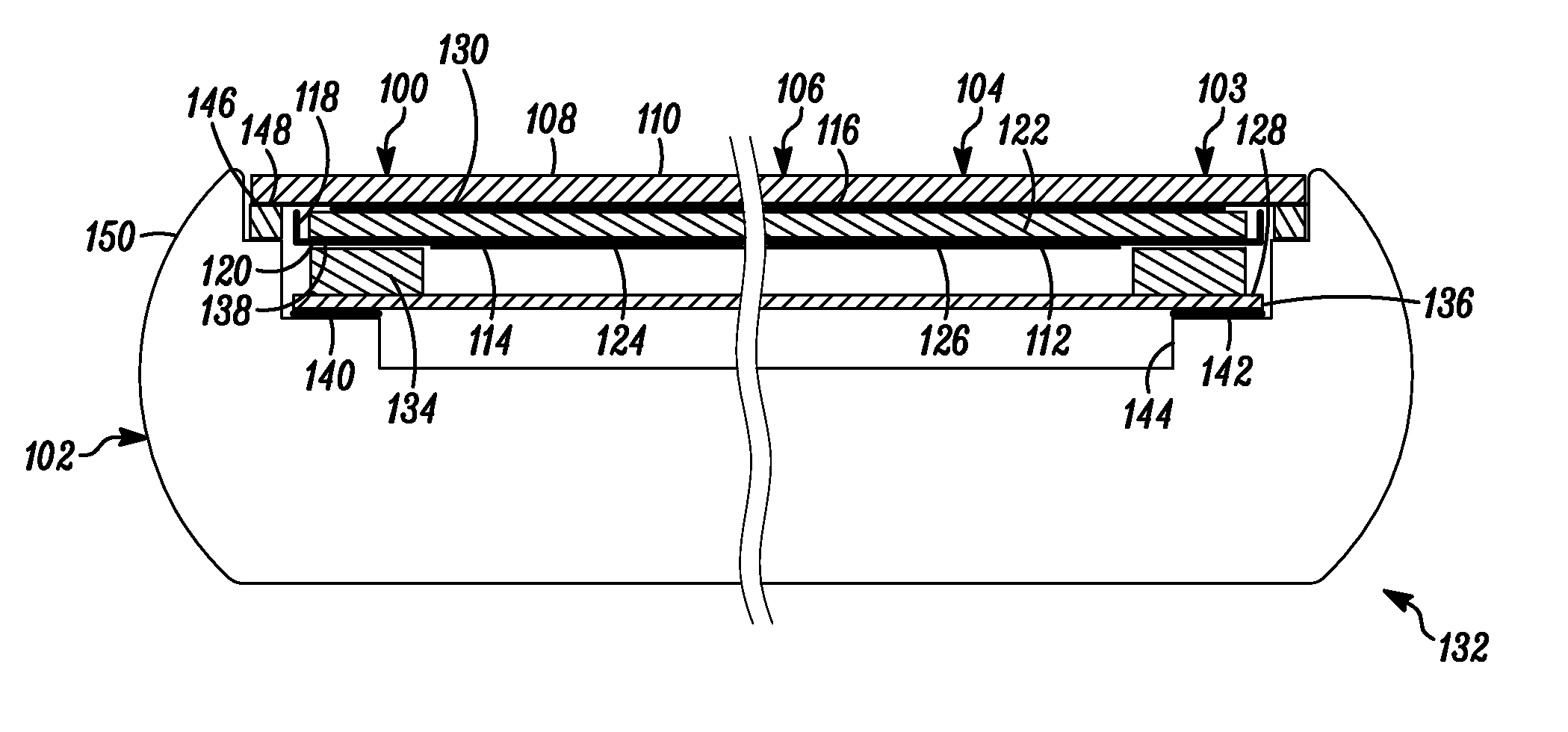
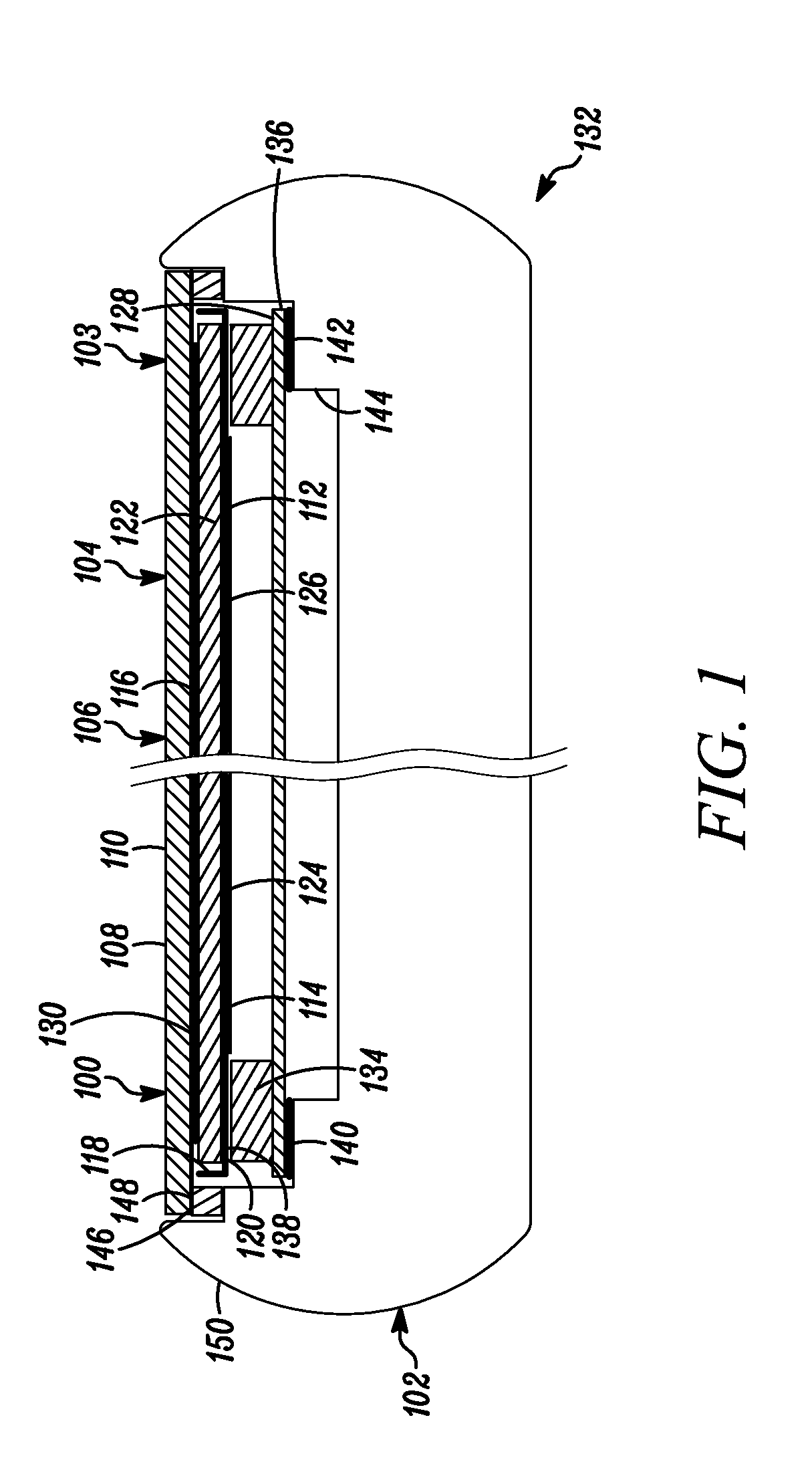
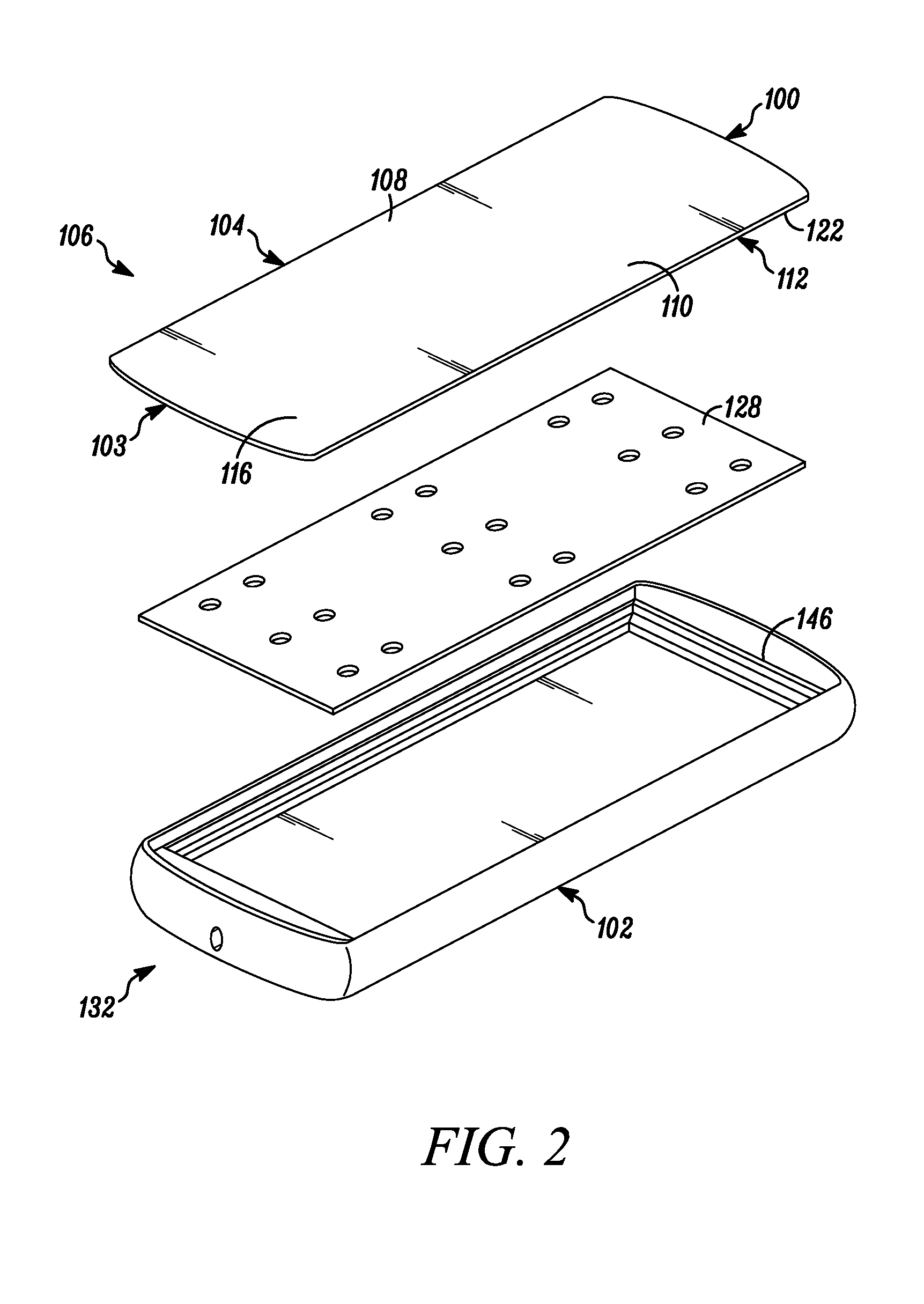
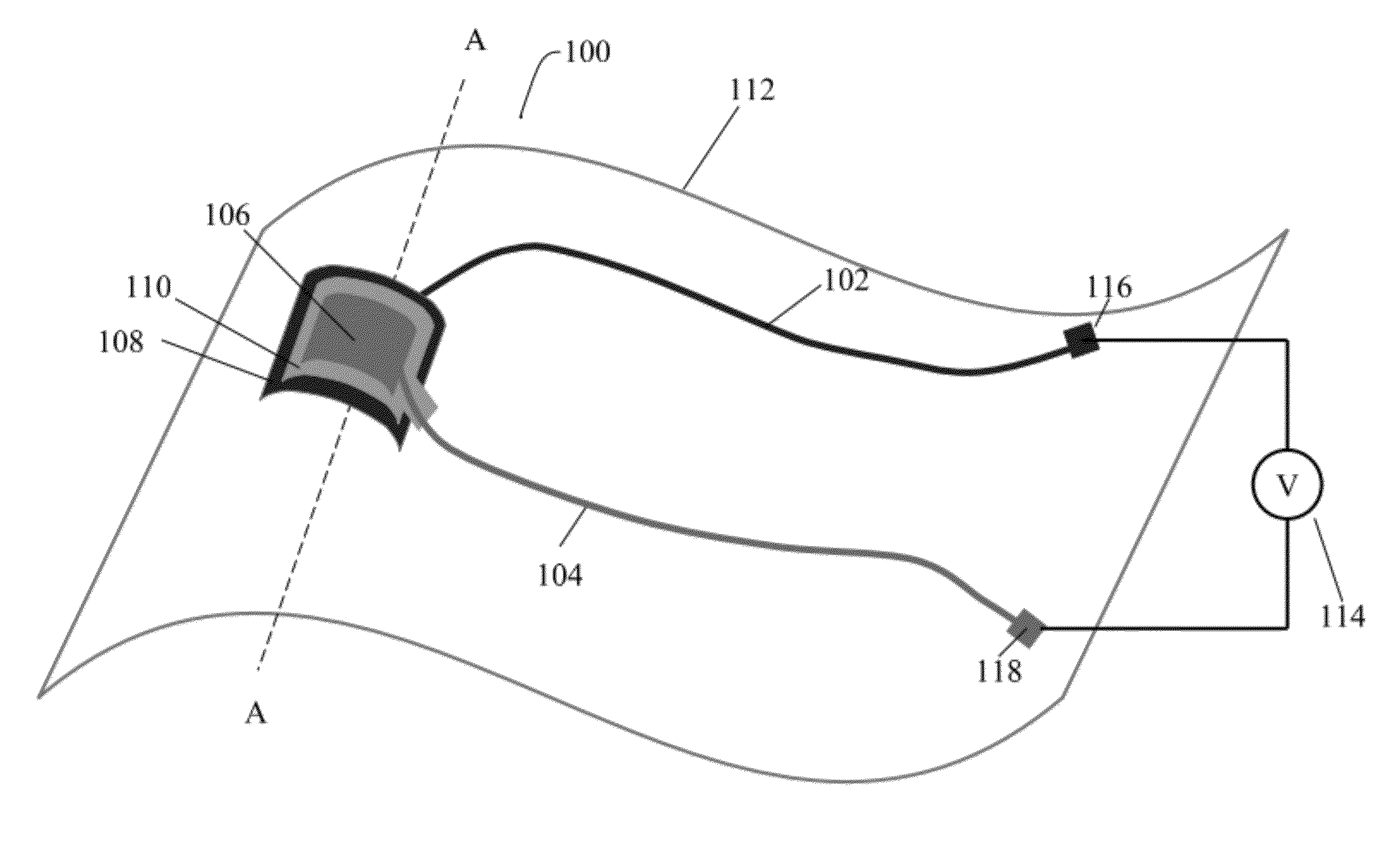
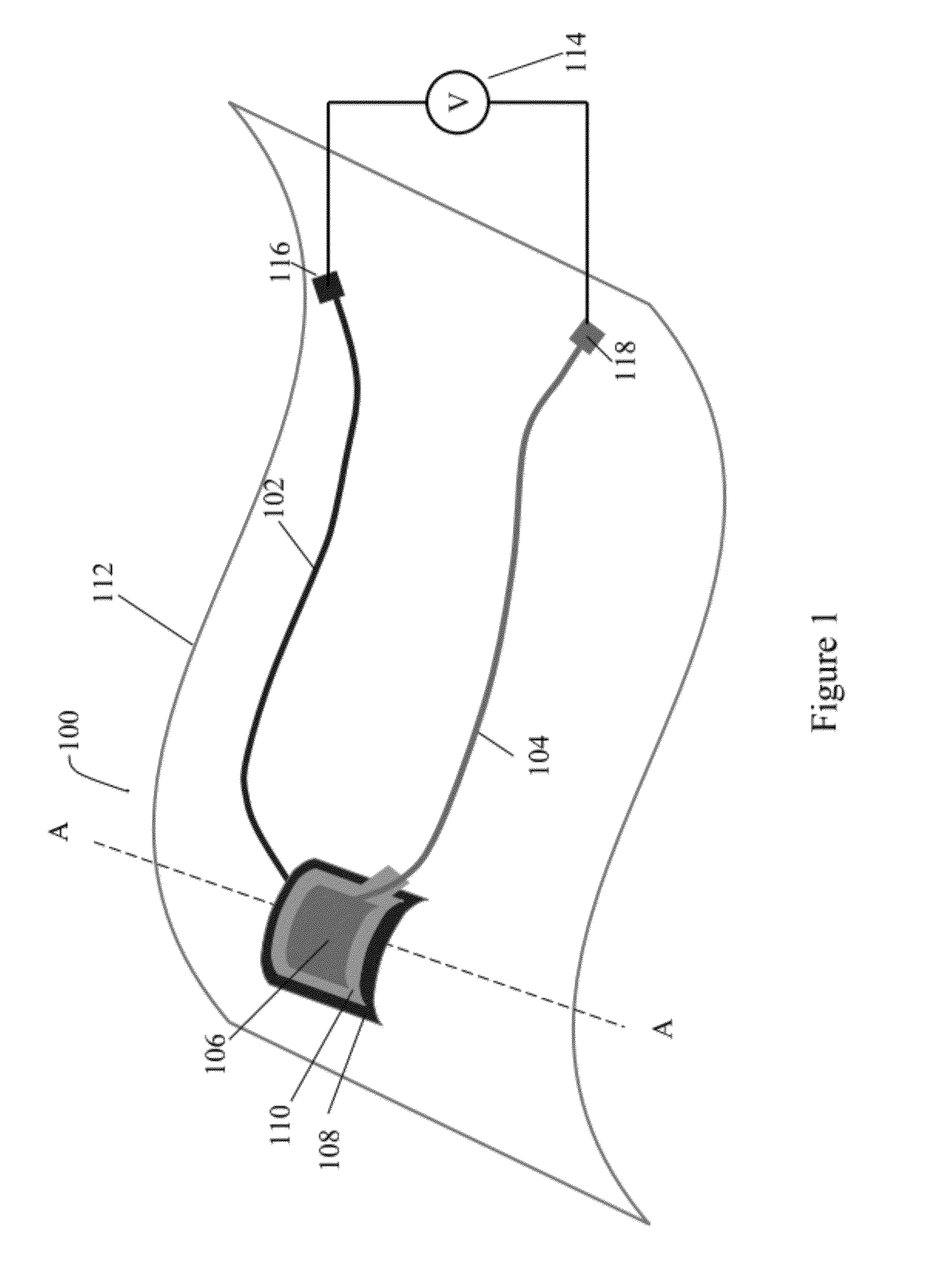
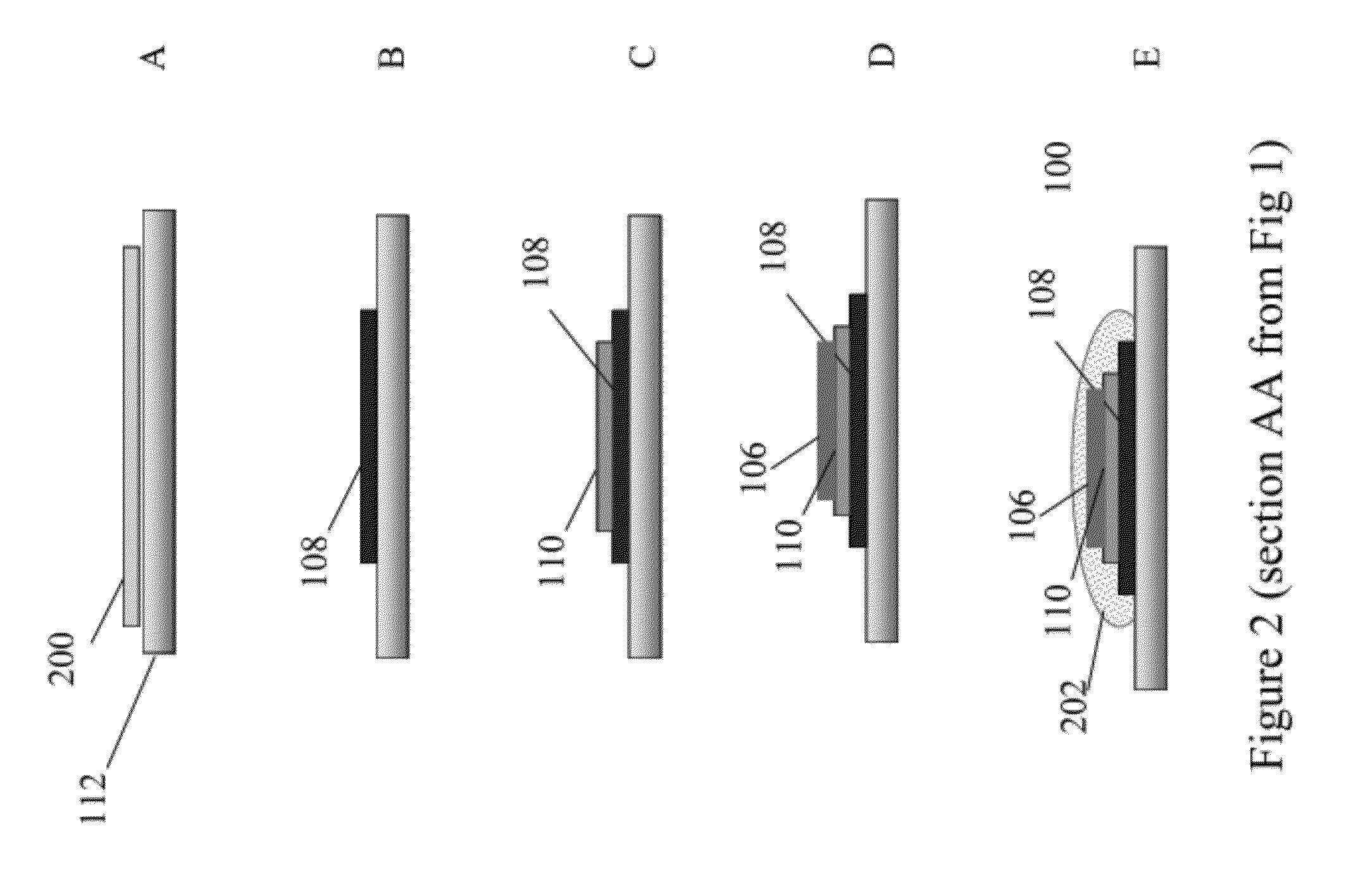
Display Structure with Direct Piezoelectric Actuation
InactiveUS20100225600A1Improve the display effectEasy to useBone conduction transducer hearing devicesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersHand heldEngineering
A user friendly display structure (100) for an electronic device (102), such as a touch screen hand held communications device, is provided with piezoelectric elements (126) bonded or otherwise secured directly to the back of a display module (112) generates effective haptics and sound localized to the display area. Actuation of piezoelectric elements (126) in the display structure (100) generates bending motion of the entire display structure (100) which provides haptics feedback to fingers operating on the display structure (100) as well as generates sound by turning part or the entire display into a speaker.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Pressure sensing or force generating device
ActiveUS20120055257A1Few contactsShorten the counting processPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceCapacitive effect
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a pressure sensing / force generating device comprising a non-planar substrate, a printed pressure sensitive element comprising (a) a piezoelectric material containing ink composition capable of producing a piezoelectric effect / piezoresistive effect and / or (b) a dielectric material containing ink composition capable of producing a capacitive effect. It also includes a first printed electrode comprising a conductive ink composition, and a second printed electrode comprising a conductive ink composition. The first and second electrodes are in electrical contact with the printed pressure sensitive element. The first and second printed electrodes and the printed pressure sensitive element collectively form a pressure sensitive junction, which is coupled to the non-planar substrate. The present invention further relates to medical devices comprising the pressure sensing / force generating device and methods of making such devices.
Owner:MICROPEN TECH CORP
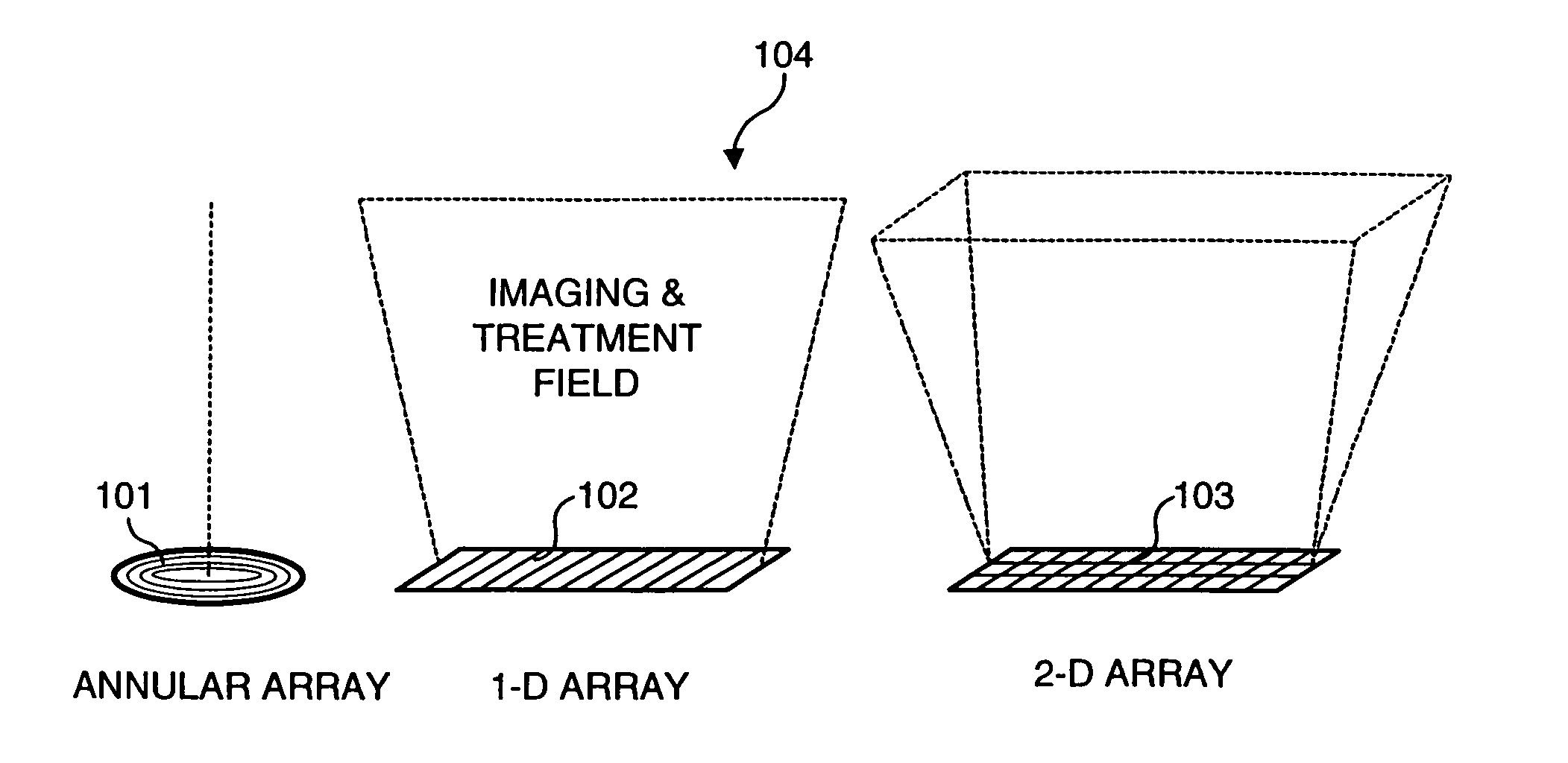
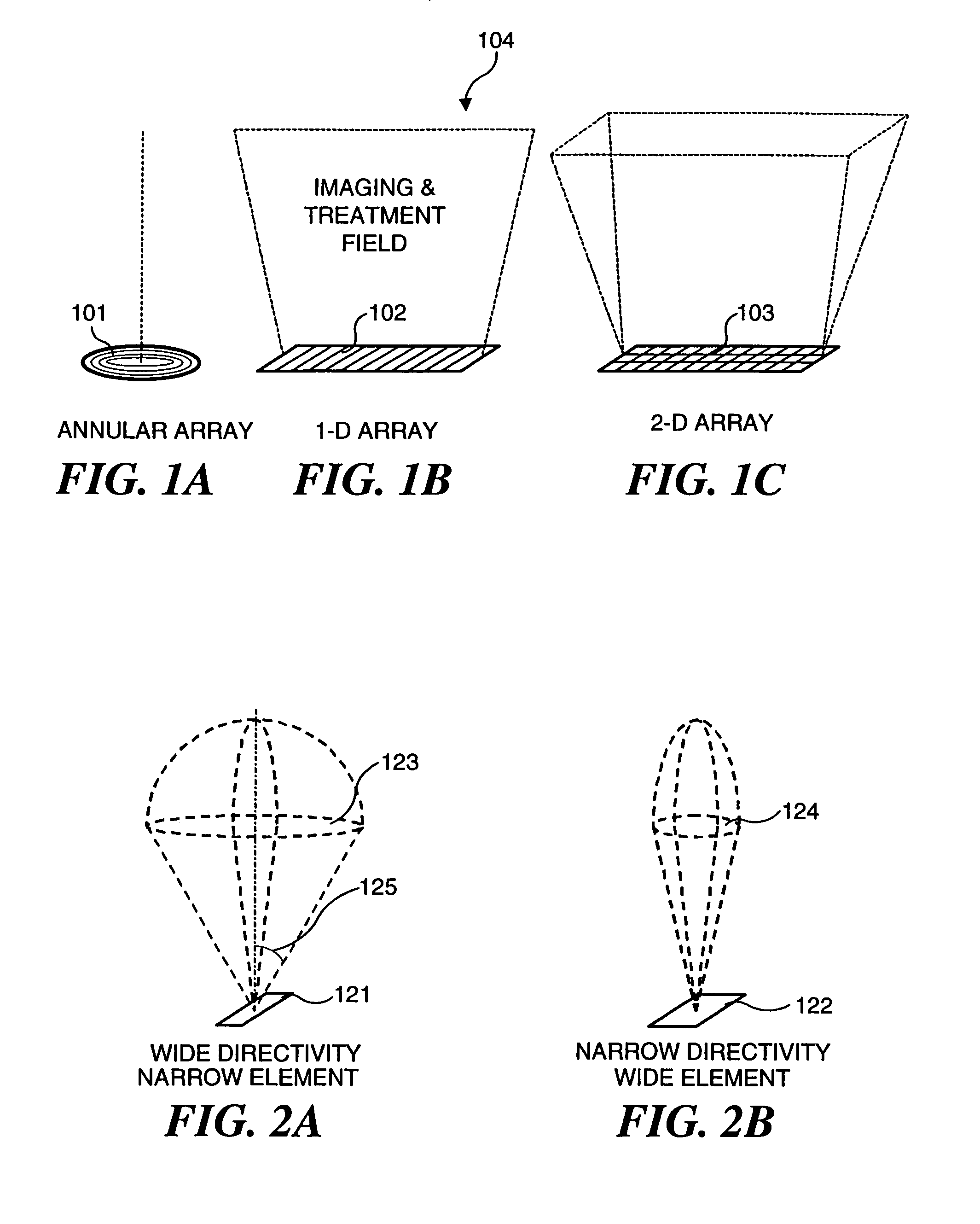
Mosaic arrays using micromachined ultrasound transducers
InactiveUS6865140B2Optimal acoustic image qualityImprove image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBurglar prevention lockingSonificationUltrasonic sensor
An ultrasound transducer array includes a multiplicity of subelements interconnected by a multiplicity of microelectronic switches, each subelement comprising a respective multiplicity of micromachined ultrasound transducer (MUT) cells. The MUT cells within a particular subelement are hard-wired together. The switches are used to configure the subelements to form multiple concentric annular elements. This design dramatically reduces complexity while enabling focusing in the elevation direction during ultrasonic image data acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for fabricating an acoustical resonator on a substrate
InactiveUS7275292B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksSurface levelMaterials science
Method for fabricating an acoustical resonator on a substrate having a top surface. First, a depression in said top surface is generated. Next, the depression is filled with a sacrificial material. The filled depression has an upper surface level with said top surface of said substrate. Next, a first electrode is deposited on said upper surface. Then, a layer of piezoelectric material is deposited on said first electrode. A second electrode is deposited on the layer of piezoelectric material using a mass load lift-off process.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for forming plated terminations
InactiveUS7152291B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesElectrolytic capacitorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTermination problemEngineering
Improved method steps for terminating multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are formed with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. Electrode and dielectric layers are provided in an interleaved arrangement and selected portions of the electrode layers are exposed. Electrically isolated anchor tabs may optionally be provided and exposed in some embodiments. Termination material is then plated to the exposed portions of the electrode layers until exposed portions of selected such portions thereof are connected. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Nano-Piezoelectronics
InactiveUS20080067618A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesNanometreSemiconductor
A semiconducting device includes a substrate, a piezoelectric wire, a structure, a first electrode and a second electrode. The piezoelectric wire has a first end and an opposite second end and is disposed on the substrate. The structure causes the piezoelectric wire to bend in a predetermined manner between the first end and the second end so that the piezoelectric wire enters a first semiconducting state. The first electrode is coupled to the first end and the second electrode is coupled to the second end so that when the piezoelectric wire is in the first semiconducting state, an electrical characteristic will be exhibited between the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Tuning mechanical resonators for electrical filter
InactiveUS6307447B1Multiple-port networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyHelical resonatorPhysics
The present invention is a method for adjusting different resonant frequencies of a plurality of mechanical resonators formed on a common substrate, in a case where the resonant frequencies of the resonators are a function of each resonator thickness. According to this method the resonators are each formed with an etchable top electrode layer which includes a material having different etching properties as a topmost layer for each of the resonators having different resonant frequencies. By selectively etching these etchable layers one at a time in the presence of the others, one may adjust the resonant frequencies of each of the resonators without need to mask the resonators during the etching process. Associated with this method there is a resonator structure having a top electrode structure having a topmost layer having different etching characteristics for different resonators.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
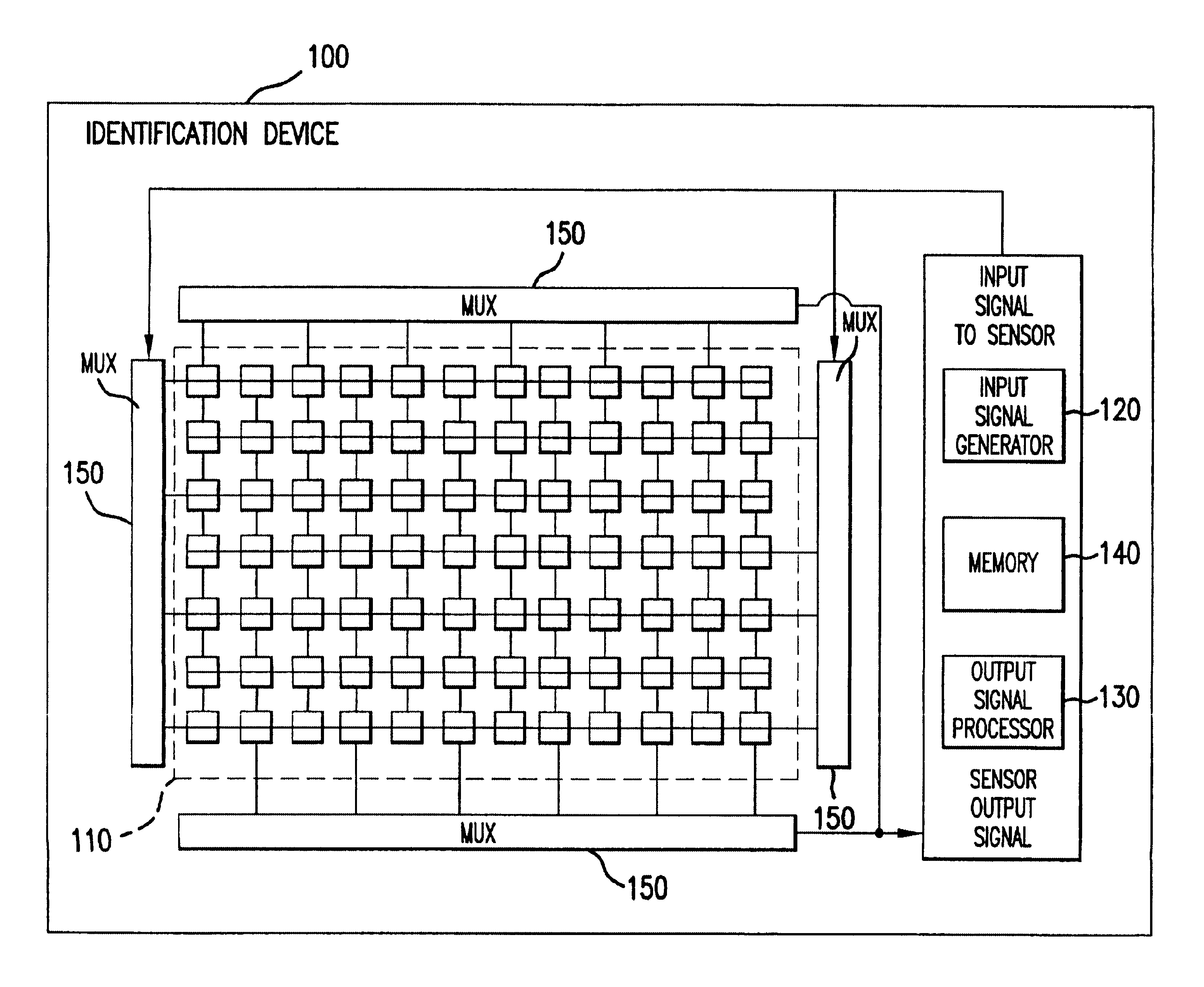
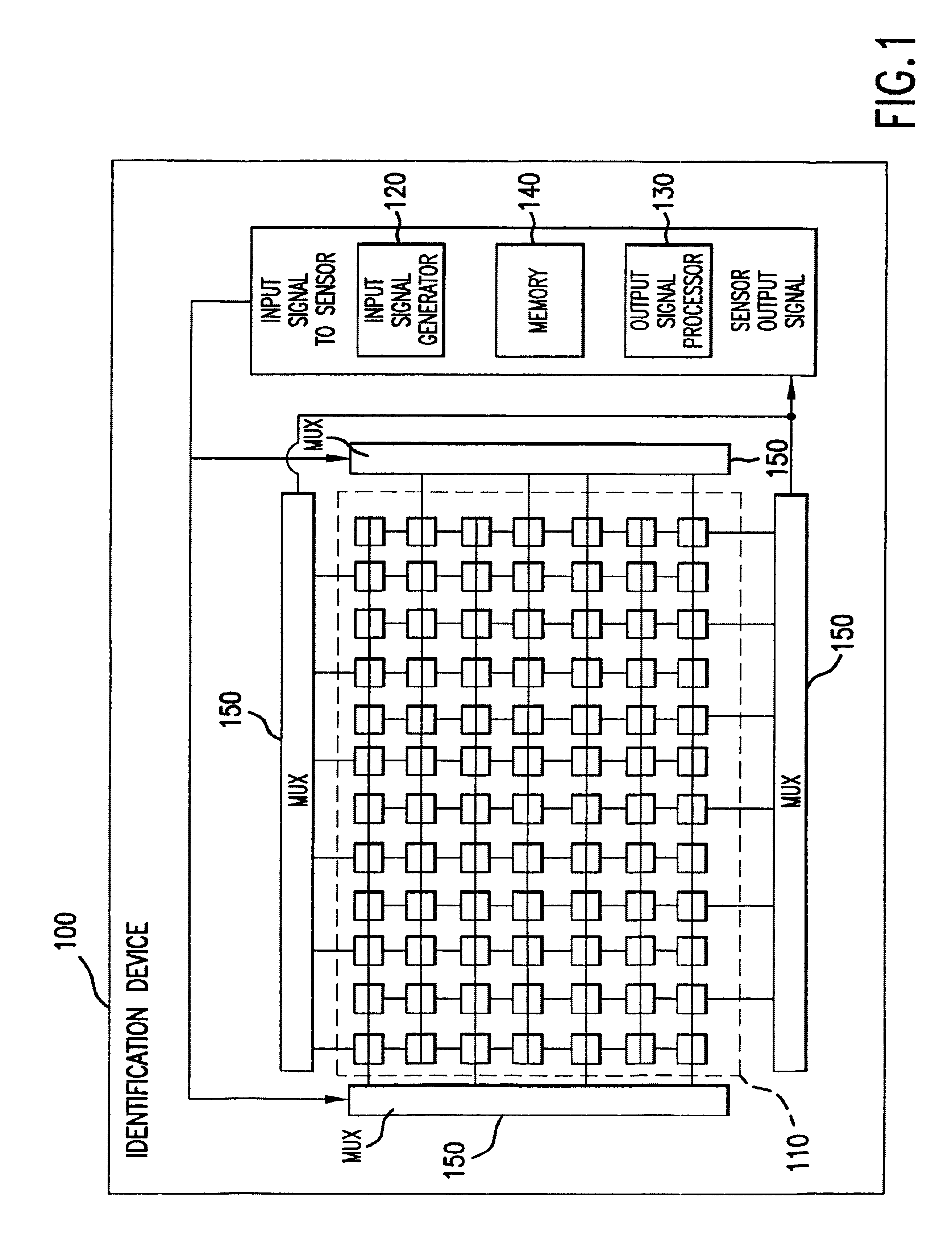
Piezoelectric identification device and applications thereof
InactiveUS6720712B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPerson identificationBiometric dataEngineering
An identification device having a piezoelectric sensor array is used to obtain biometric data. Multiplexers are switched to control the sensor. The device has several operating modes for obtaining a variety of biometric data, including an impedance detection mode, a voltage detection mode, an imaging mode, and a Doppler-shift detection mode. The presence of a fingerprint on the sensor can be used to turn-on the device. The device is capable of capturing a fingerprint, forming a three-dimensional map of a finger bone, and / or determining the direction and speed of arteriole and / or capillary blood flow in a finger. A single pixel or a group of pixels can be detected and readout to a memory. The device can be used as an electronic signature device. The device can operate as part of a personal area network, using a public service layer according to the invention.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP +1
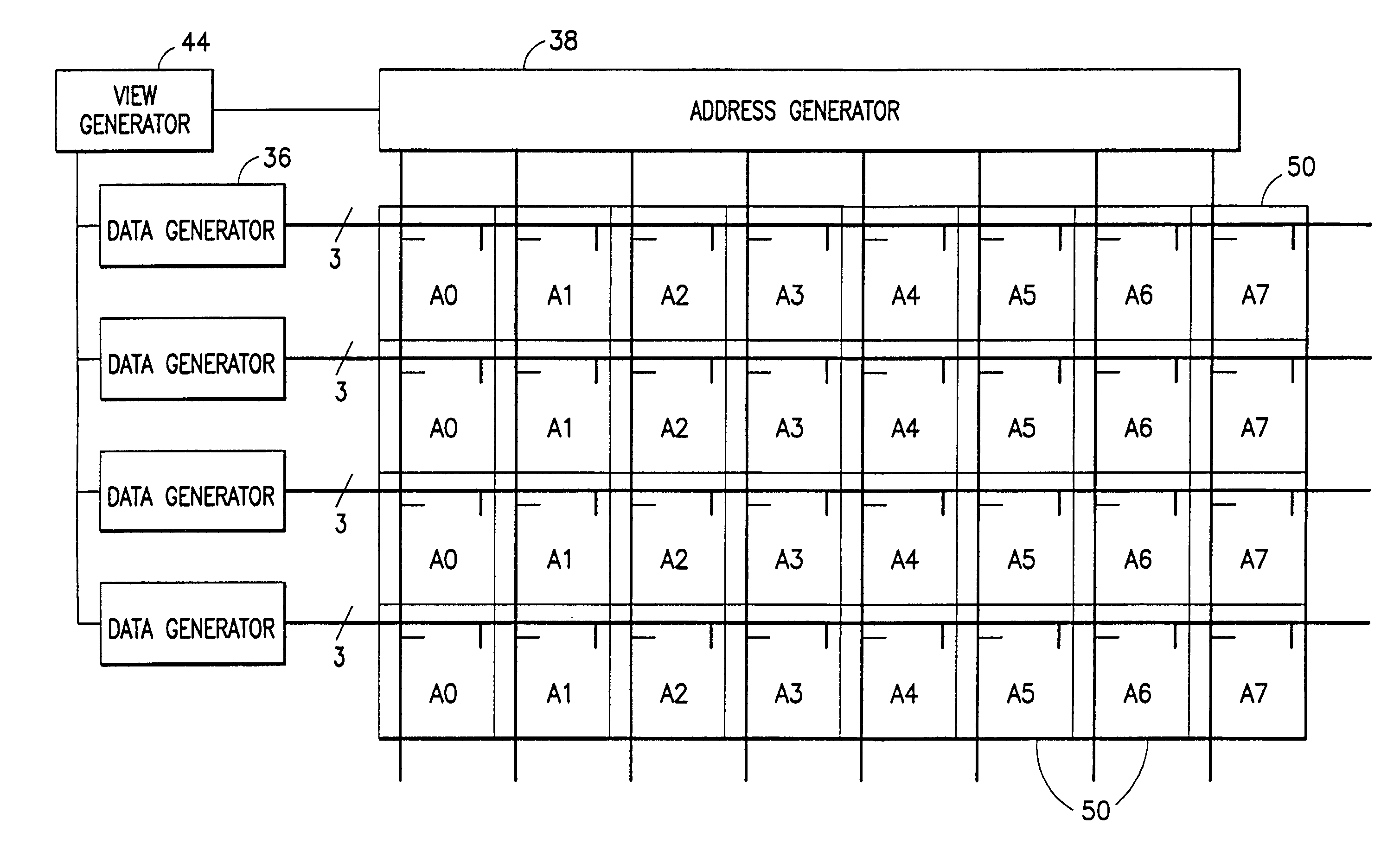
Method and apparatus for controlling scanning of mosaic sensor array
InactiveUS7313053B2Quick configurationMinimize powerUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsComputer hardwareSensor array
A scanning architecture that makes it possible to update only those ultrasonic transducer subelements of a mosaic transducer array that change from view to view. The configuration of the switch matrix is fully programmable. The switch matrix includes access switches that connect subelements to bus lines and matrix switches that connect subelements to subelements. Each subelement has a unit switch cell associated therewith, each unit switch cell comprising at least one access switch, at least one matrix switch, and addressing and control logic. Optionally, each unit switch cell also includes latches for storing the future switch states of the switches to be programmed. The switches themselves have memory for storing their current switch states.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
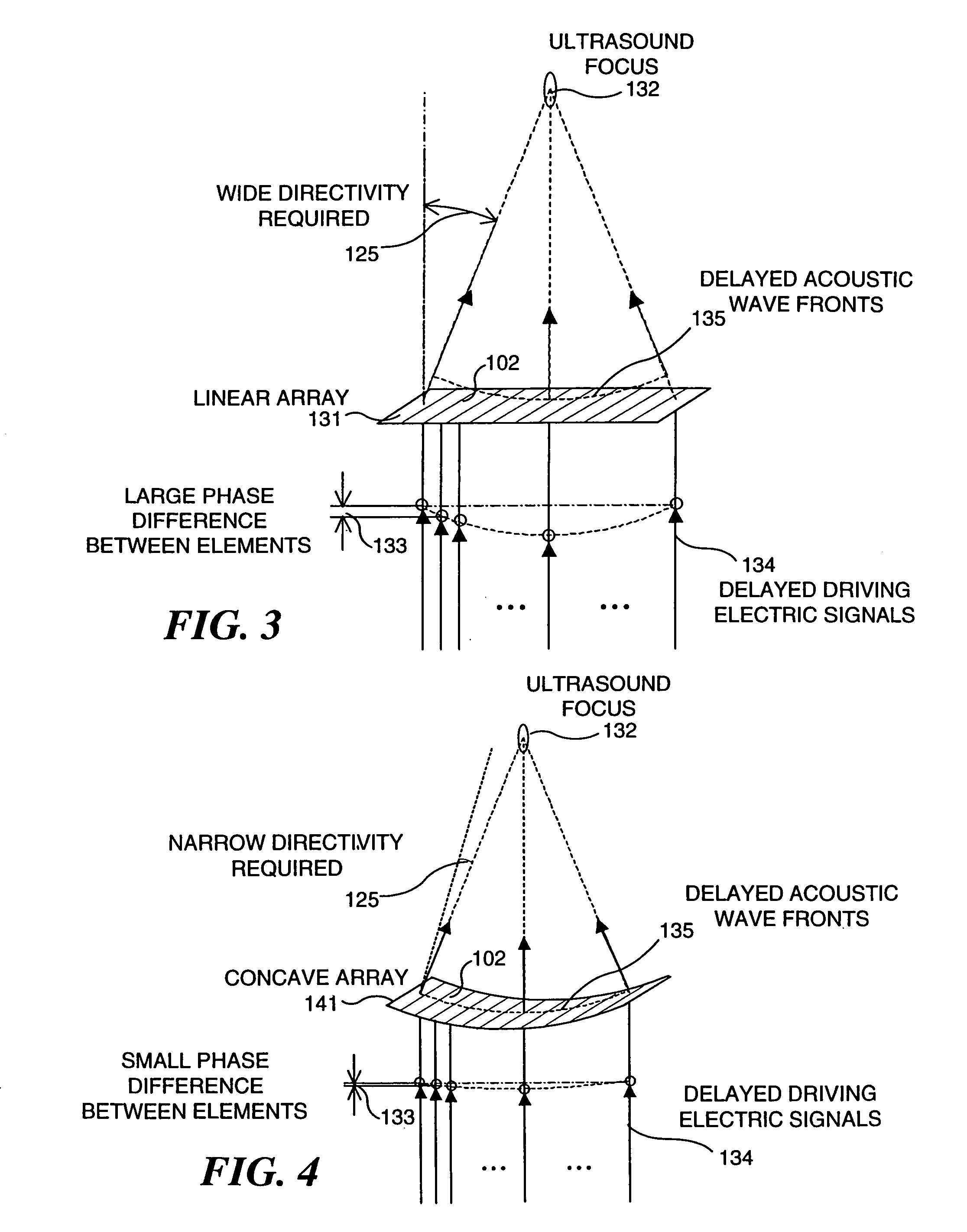
Focusing micromachined ultrasonic transducer arrays and related methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20050075572A1Improvement of contrast resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersContrast resolutionLight beam
A micromachined ultrasonic transducer array that focuses in the elevation direction. A curved lens is used to narrow the beam width in the elevation direction so that contrast resolution is improved and clinically relevant. Alternatively, a curved probe is formed by bending a micromachined substrate to have a predetermined curvature. The invention is further directed to methods of manufacturing such transducers.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sound beam loudspeaker system
InactiveUS20060204022A1Large directivityLow costTelevision system detailsMicrophonesTransducerEngineering
A loudspeaker system is described including an array of electro-acoustic transducers capable of generating steerable beams of sound and additional transducers adapted to reproduce low frequency sound being placed at the perimeter of said array.
Owner:1 LIMITED ST JOHN S INNOVATION CENT
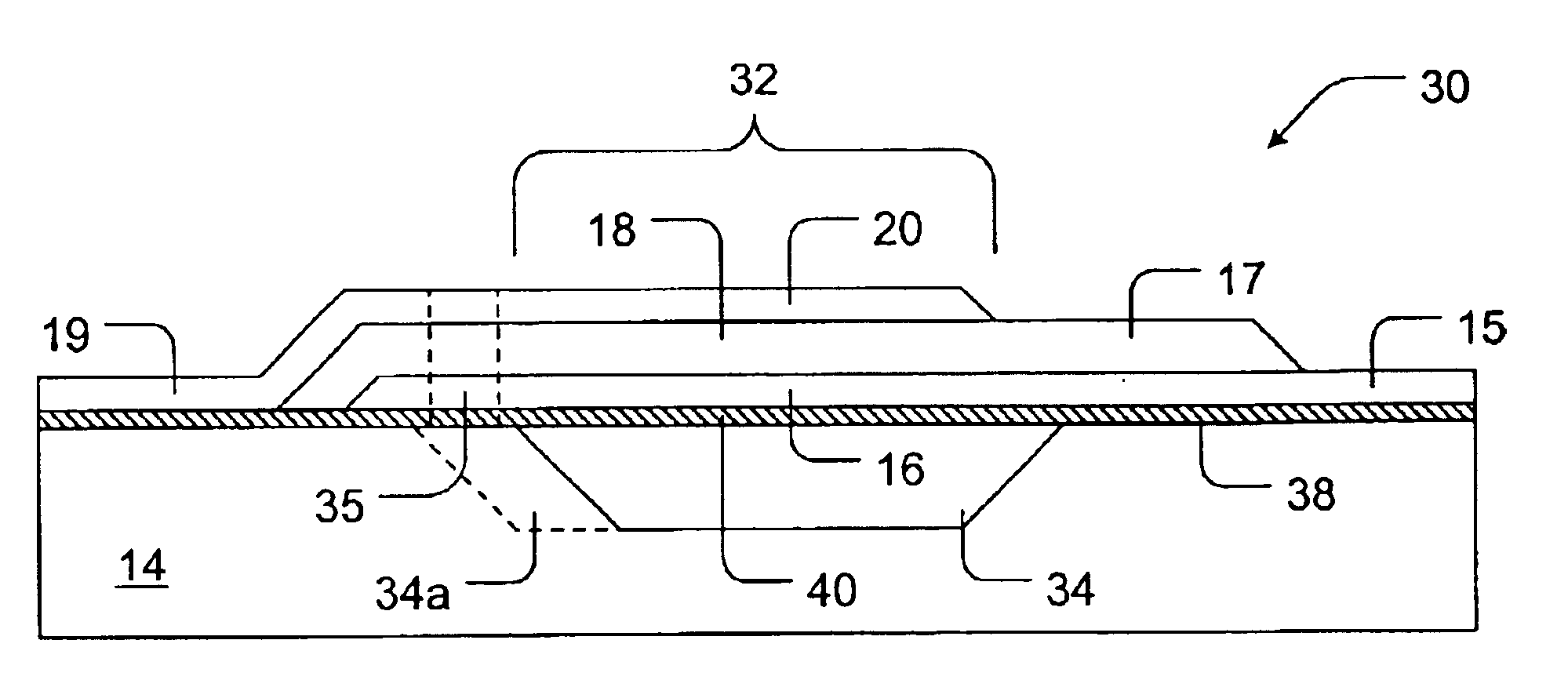
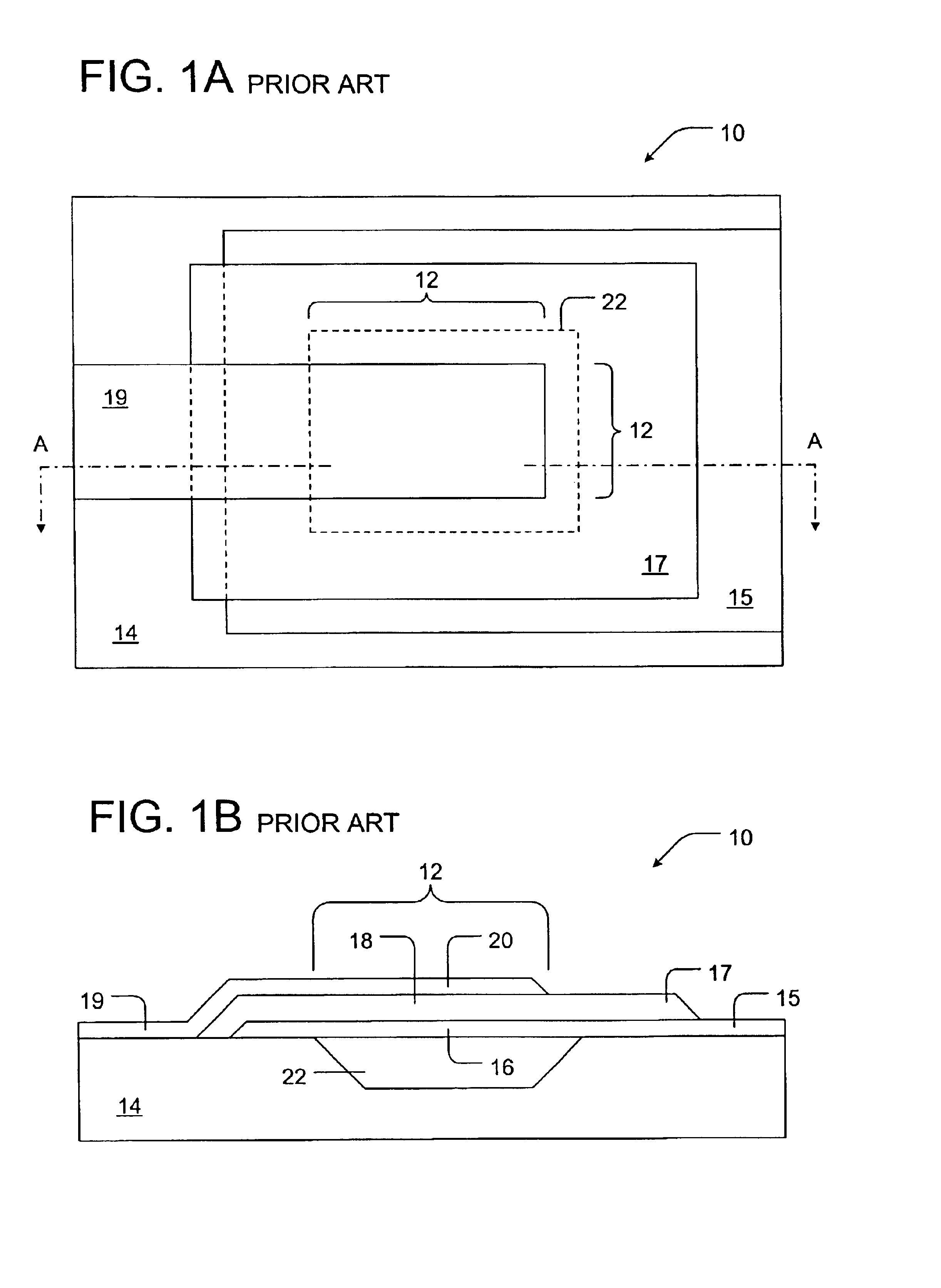
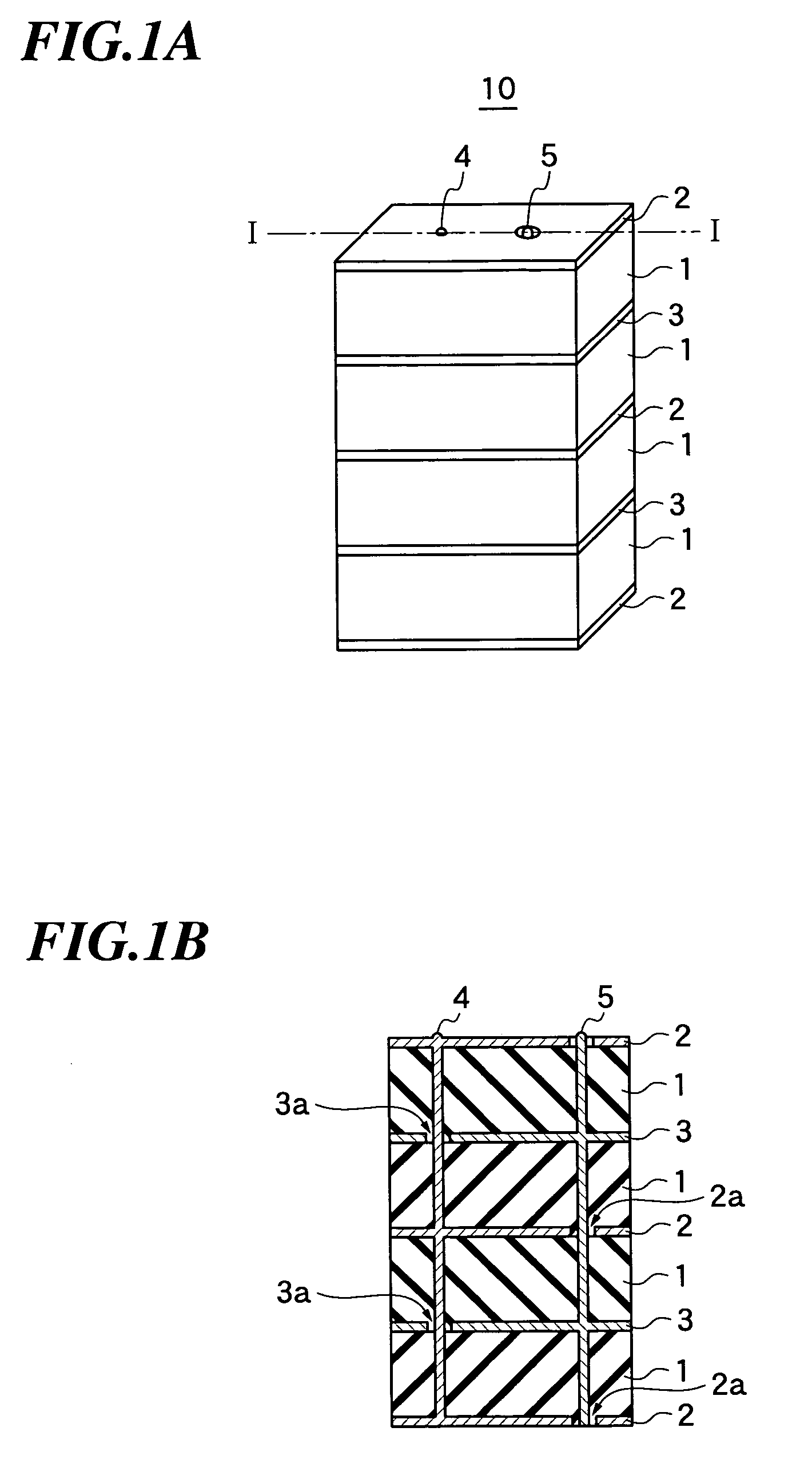
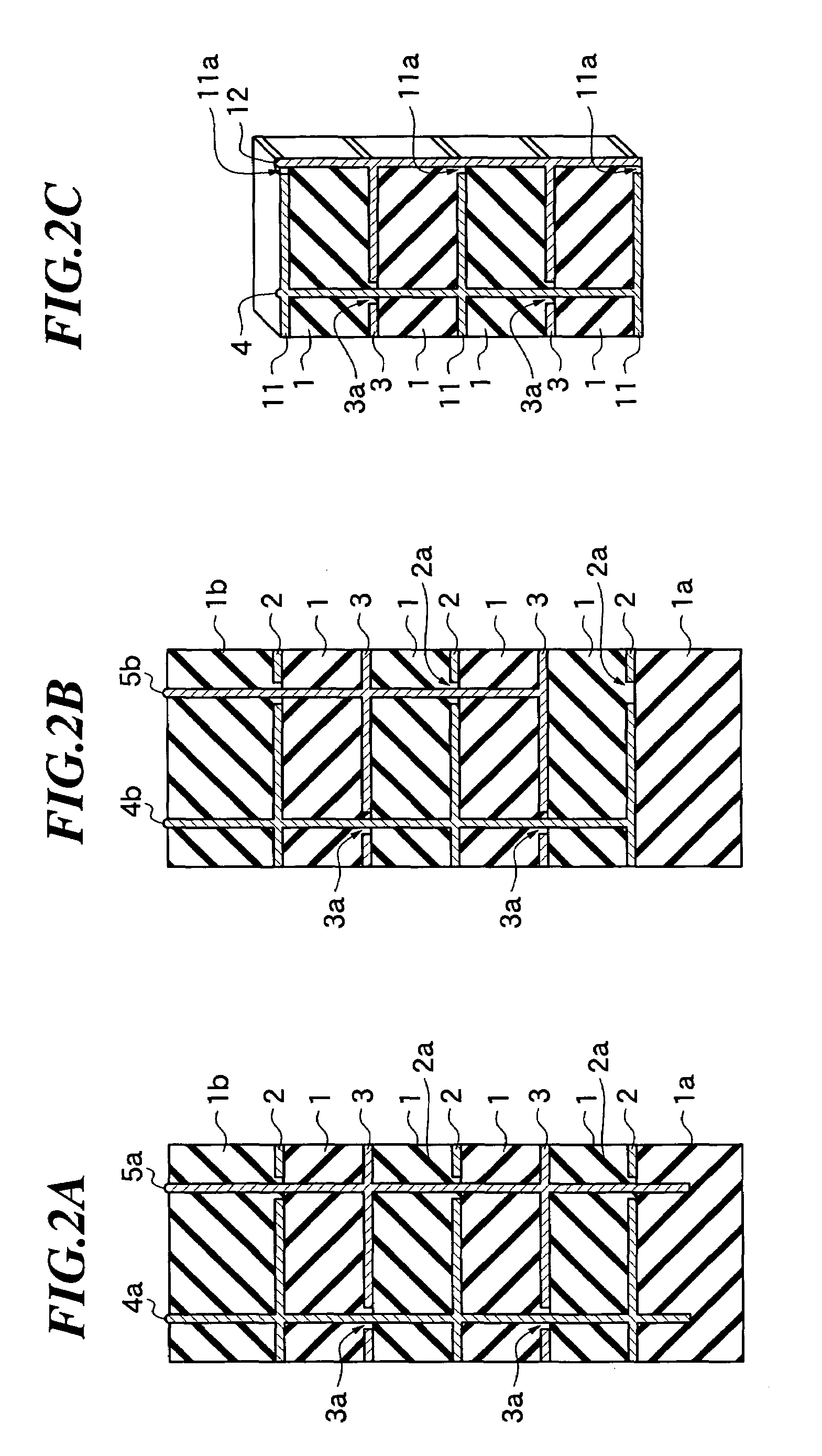
Laminated structure and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7061166B2Not easy to damageWell formedPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringInterconnection
A laminated structure in which interconnections can be easily formed for electrodes and in which the damage of an insulating layer attributed to stress is relieved. The laminated structure includes a laminated piece having a first electrode layer provided with a first insulating region, a piezoelectric material layer, and a second electrode layer provided with a second insulating region at a position different from that of the first insulating region, a first interconnection line electrically connected to the first electrode layer while passing through the second insulating region provided in the second electrode layer, and a second interconnection line electrically connected to the second electrode layer while passing through the first insulating region provided in the first electrode layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Popular searches
Telemetry/telecontrol selection arrangements Surgery Diagnostic recording/measuring Alarms Subscribers indirect connection Volume/mass flow by differential pressure Microscale sensors Piezoelectric/electrostrictive devices Piezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devices Digital data processing details
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com