Patents
Literature
67 results about "Contrast resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Contrast resolution is the ability to distinguish between differences in intensity in an image. The measure is used in medical imaging to quantify the quality of acquired images. It is a difficult quantity to define, because it depends on the human observer as much as the quality of the actual image. For example, the size of a feature affects how easily it is detected by the observer.
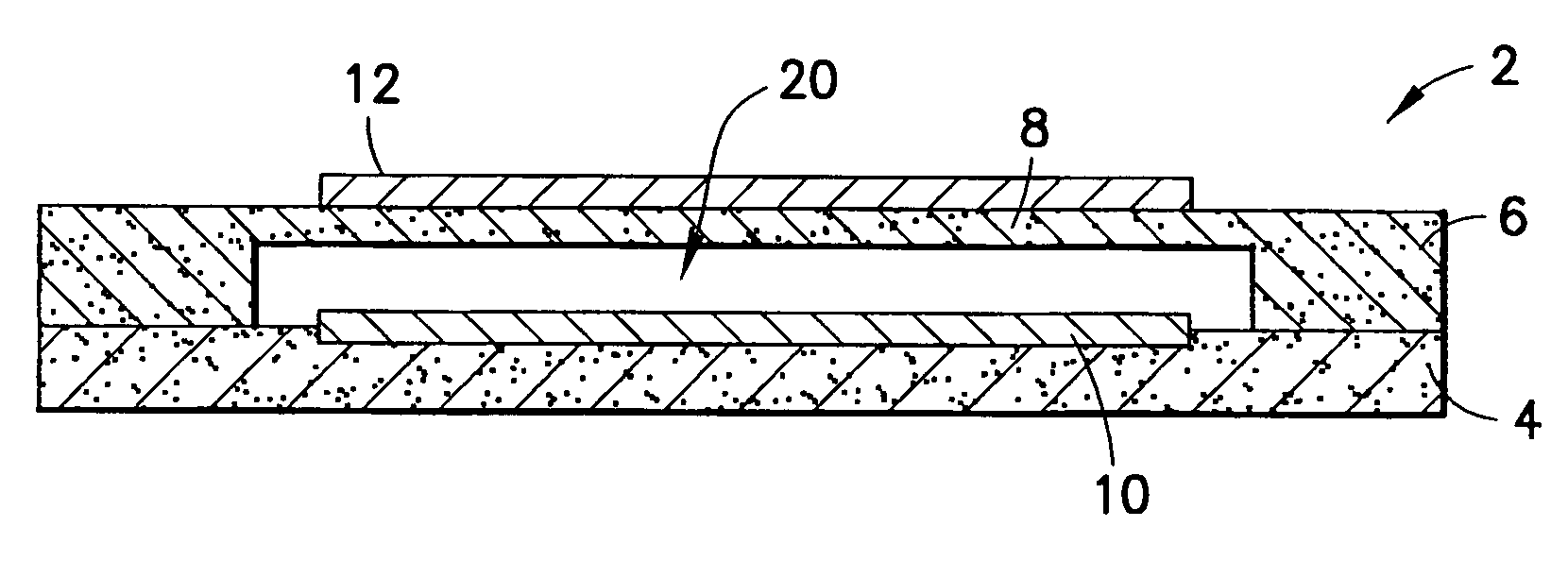
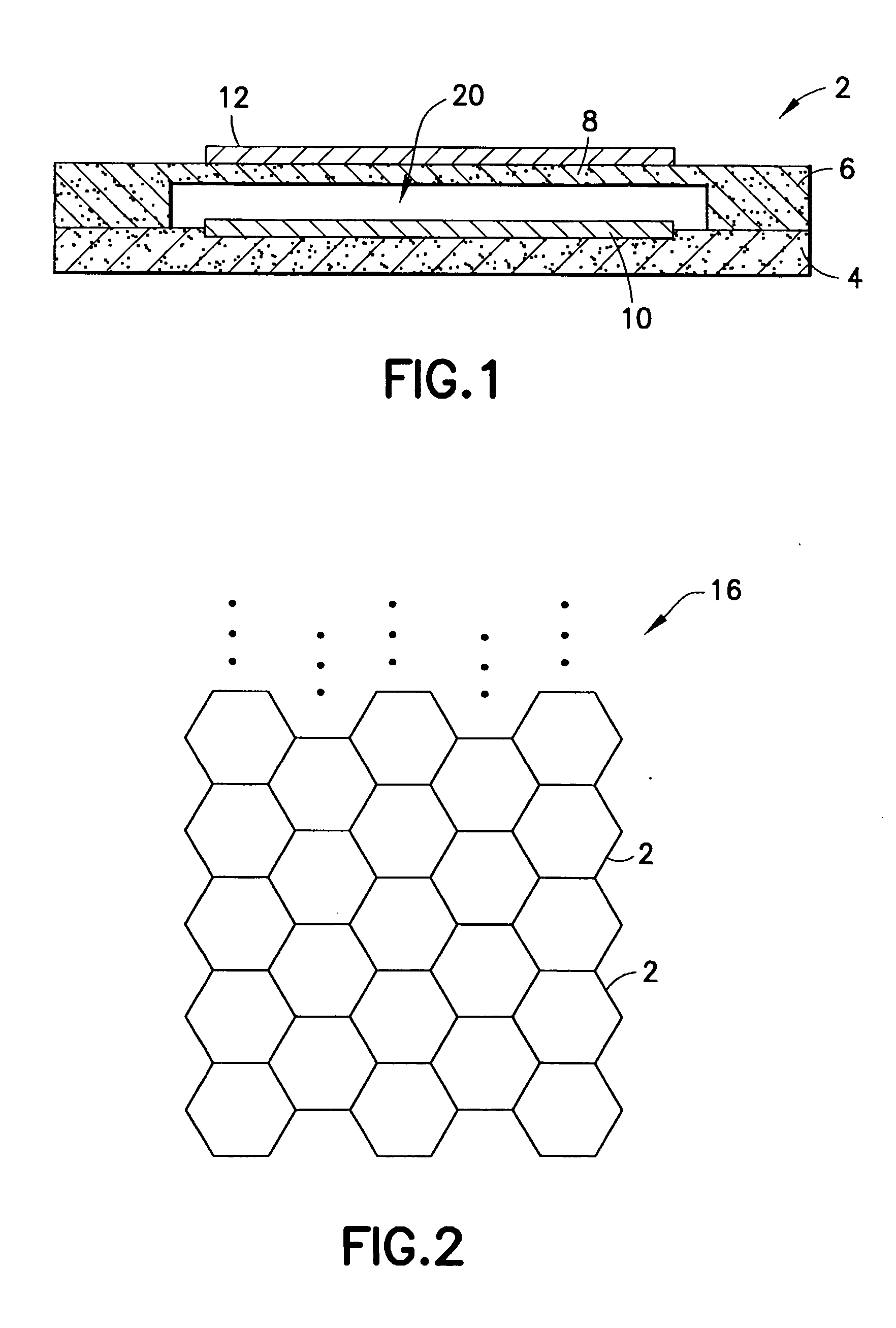
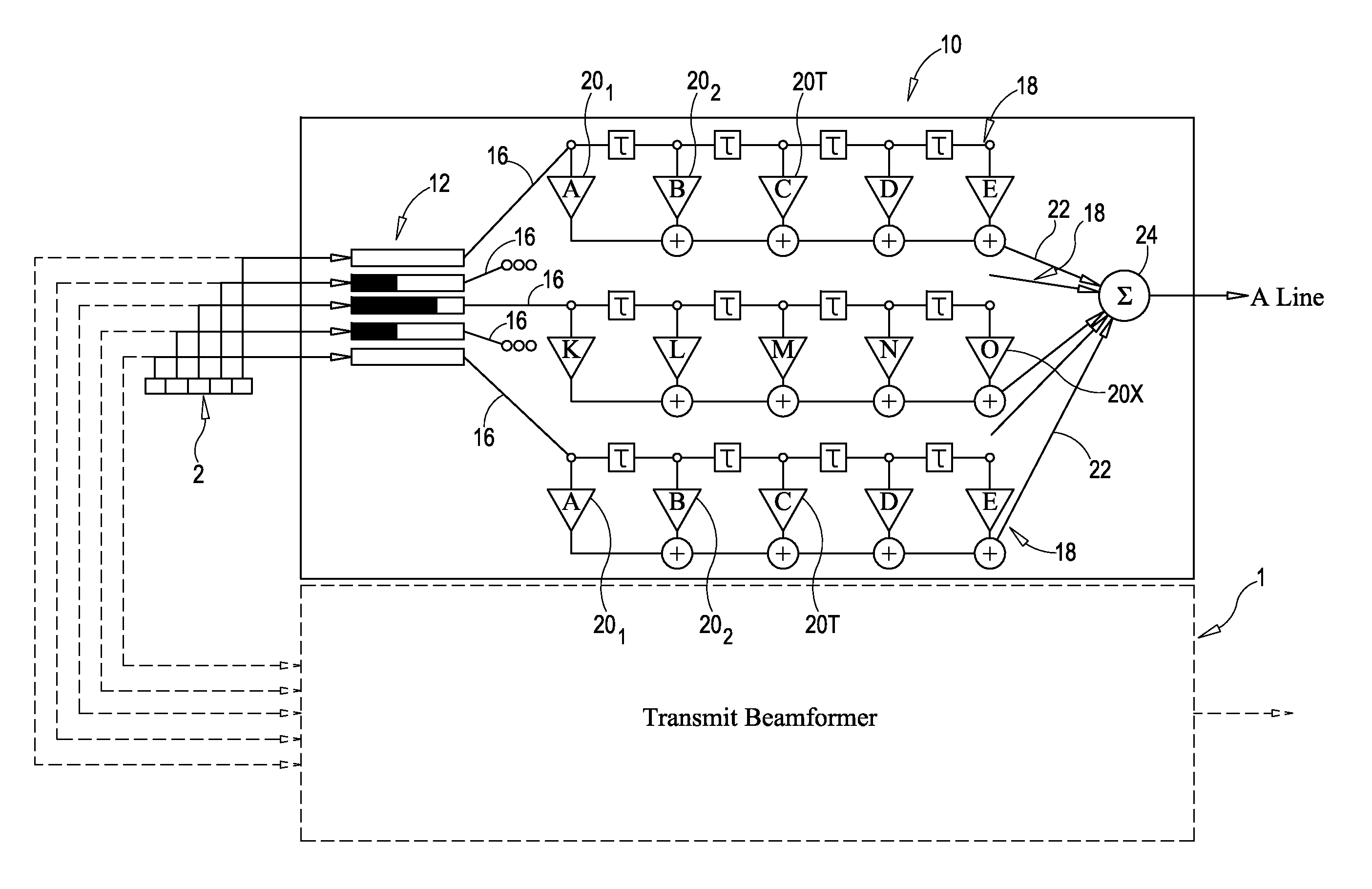
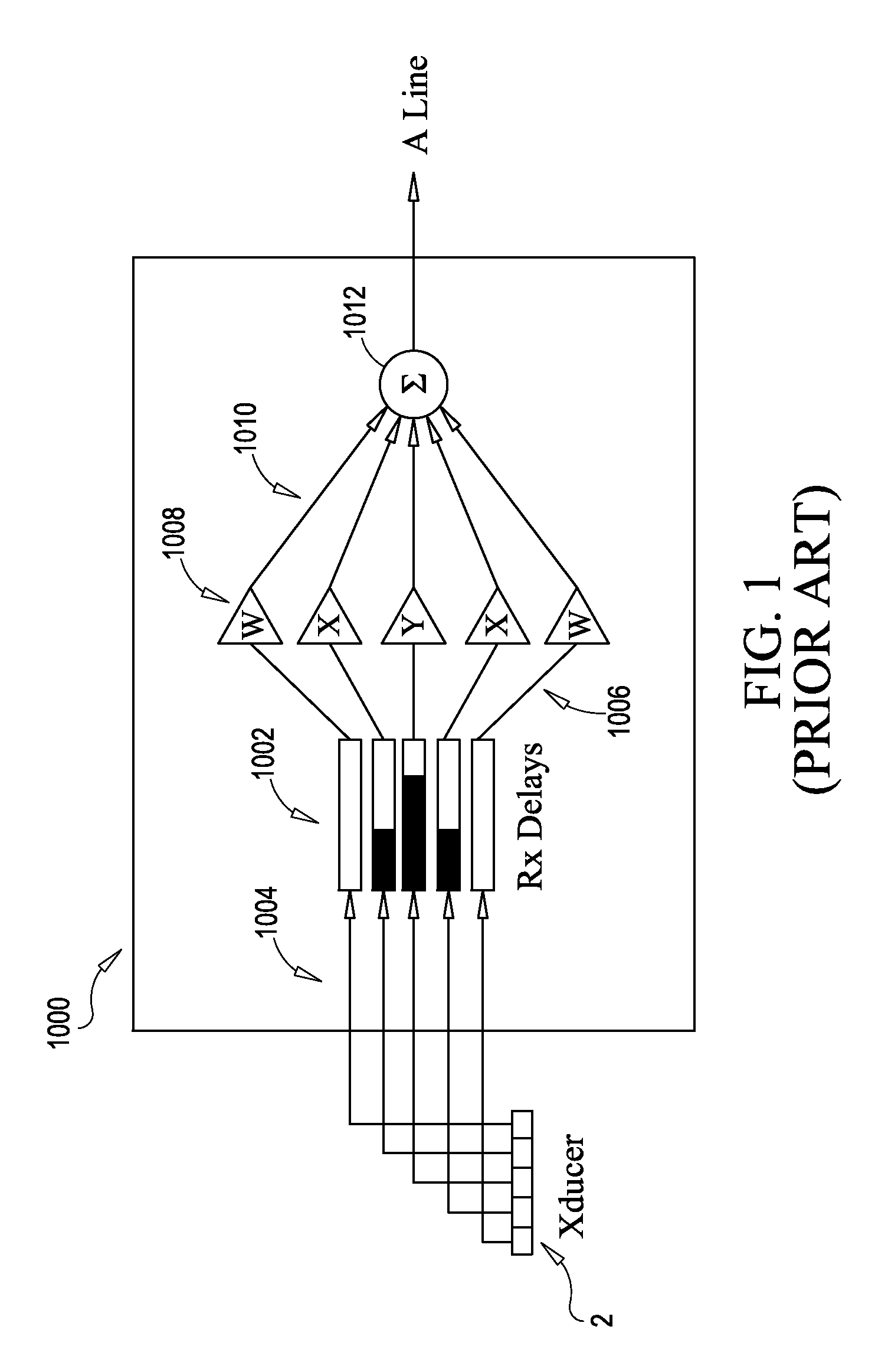
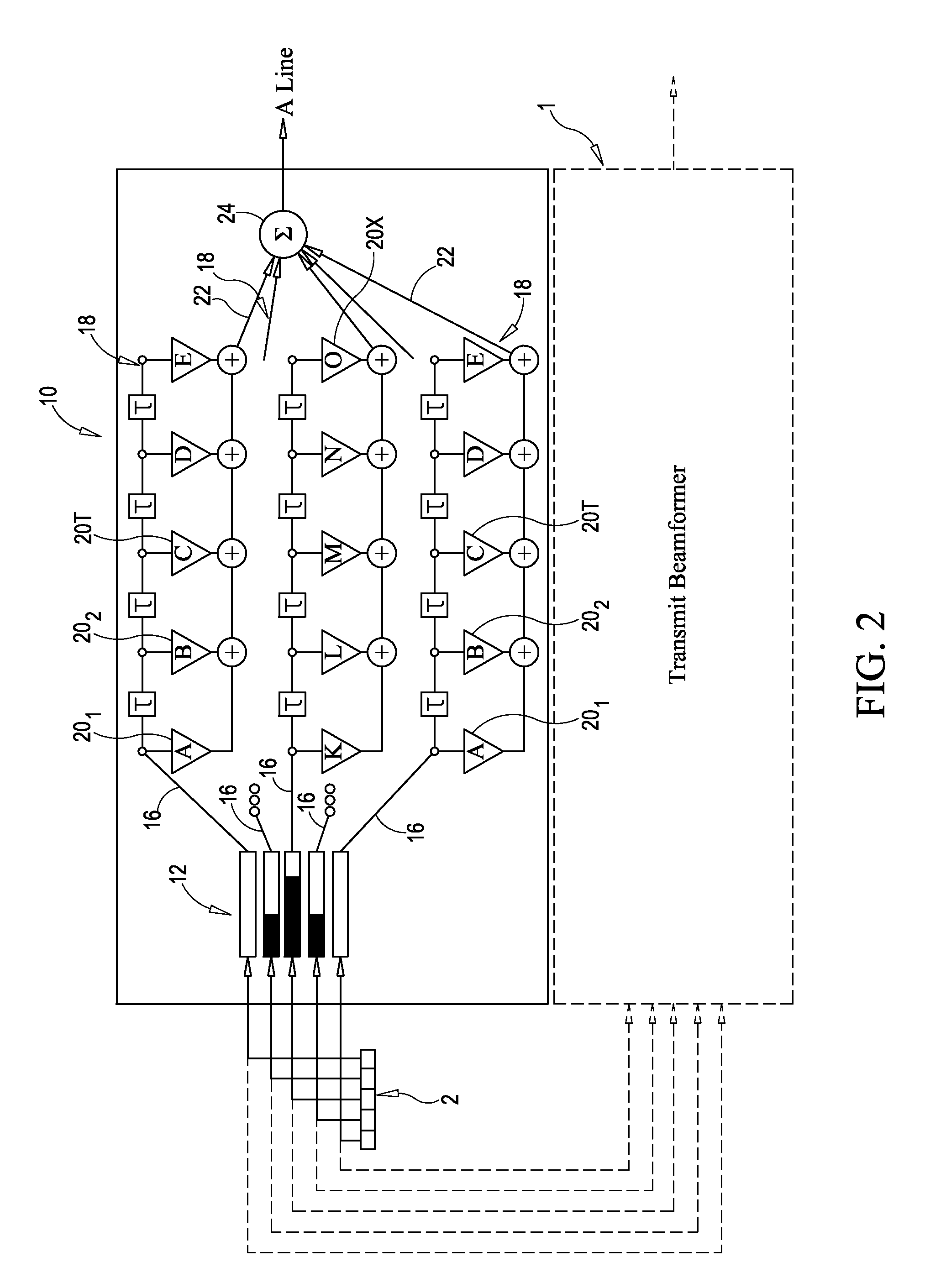
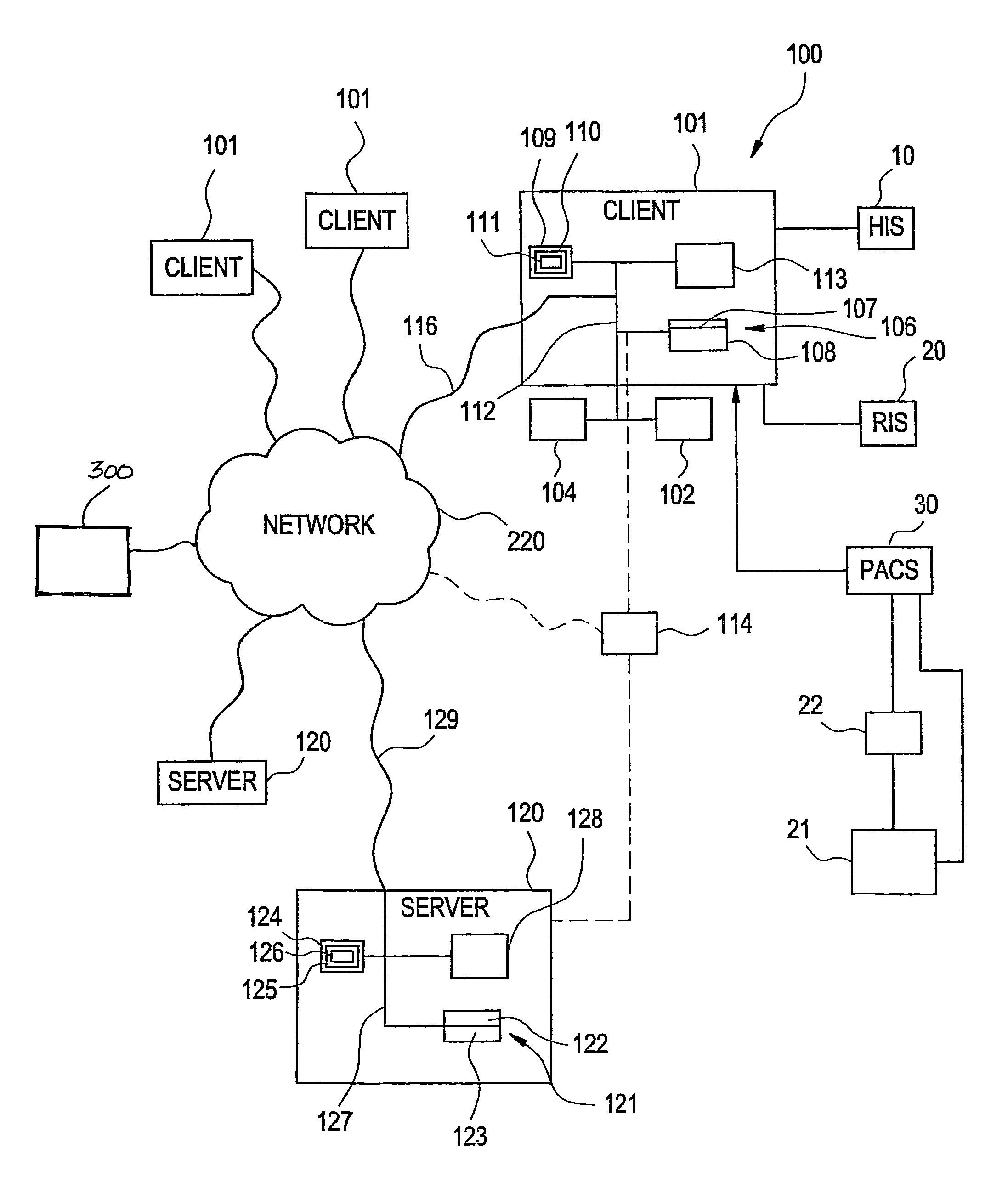
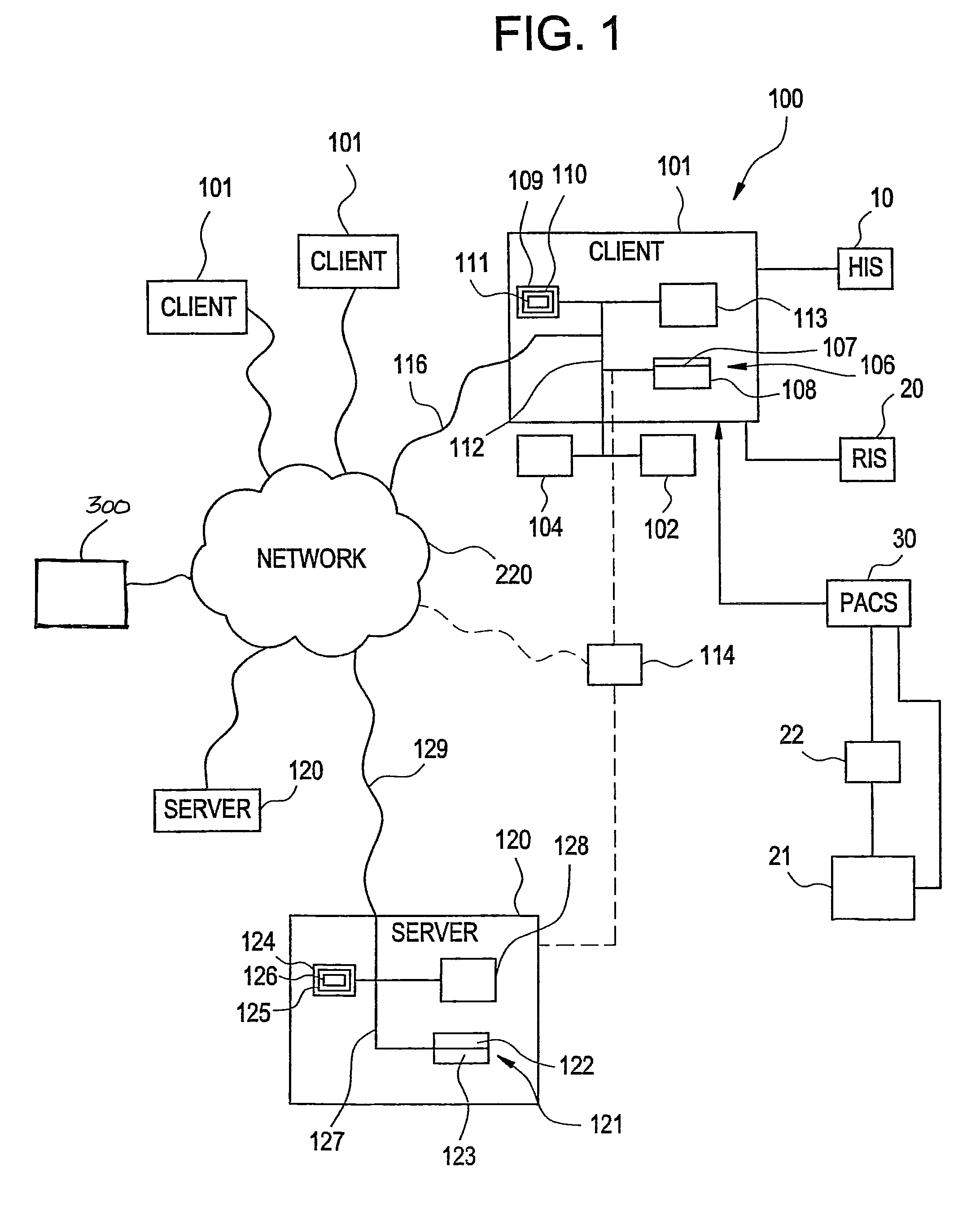
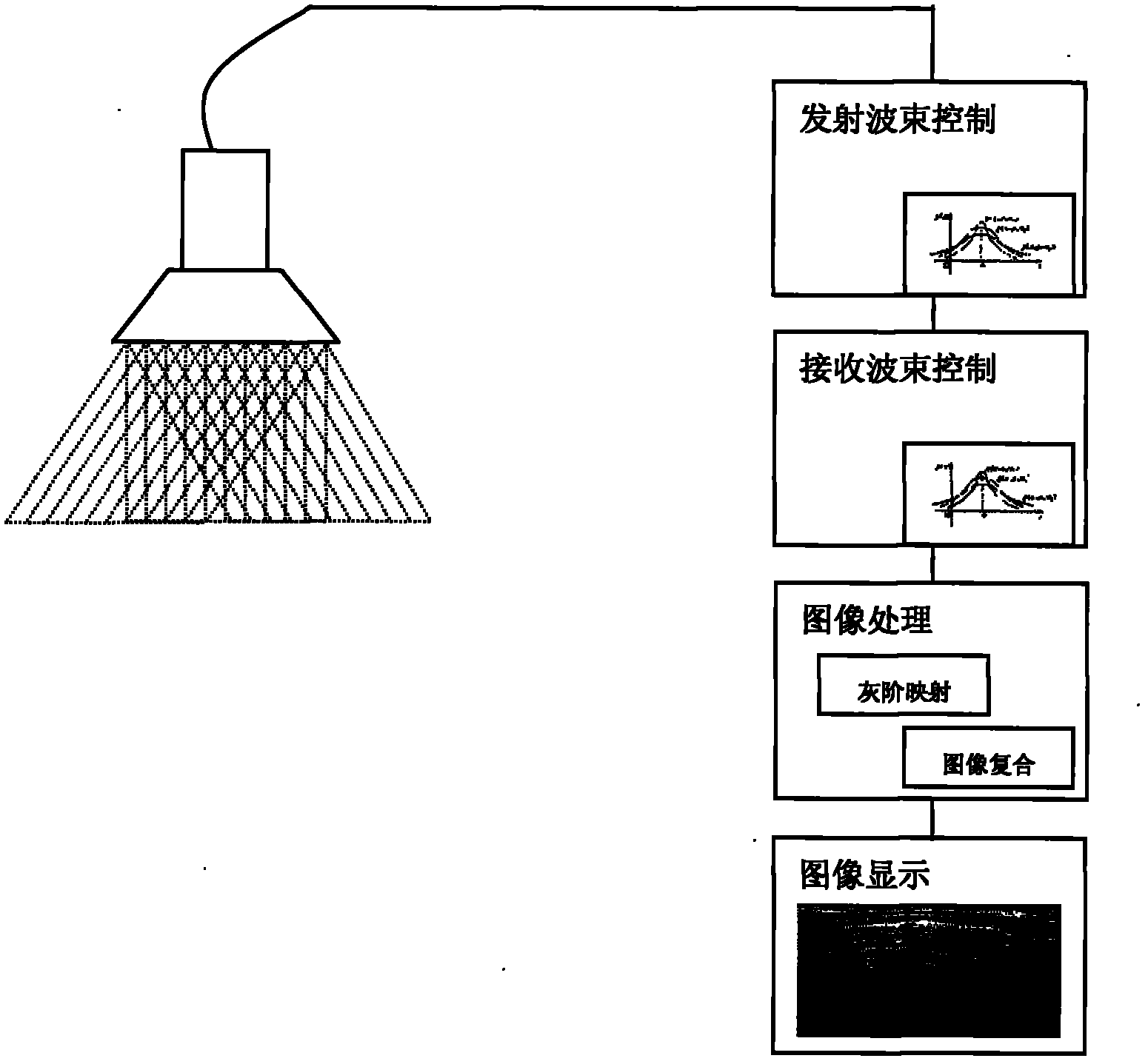
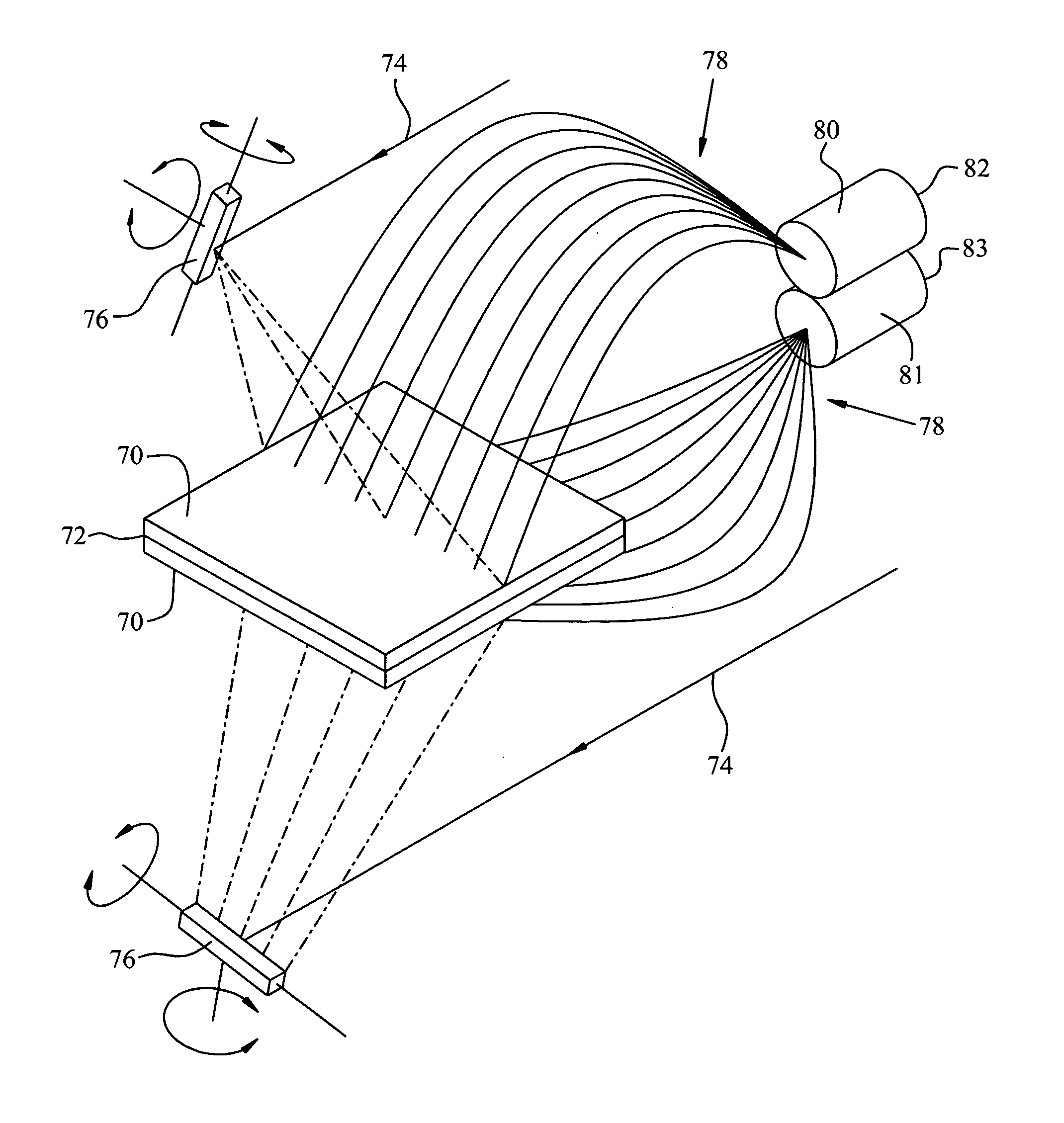
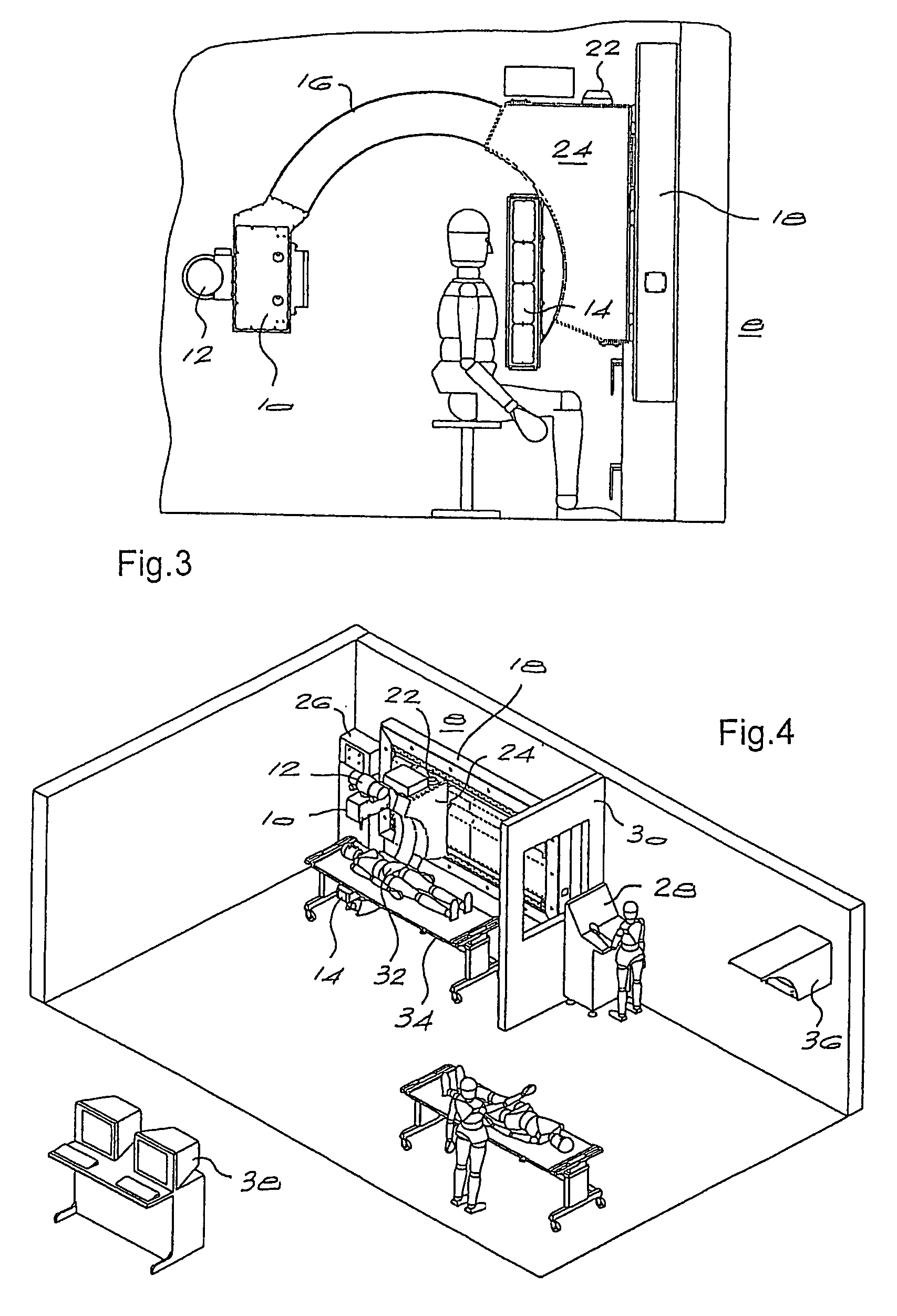
Focusing micromachined ultrasonic transducer arrays and related methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20050075572A1Improvement of contrast resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersContrast resolutionLight beam
A micromachined ultrasonic transducer array that focuses in the elevation direction. A curved lens is used to narrow the beam width in the elevation direction so that contrast resolution is improved and clinically relevant. Alternatively, a curved probe is formed by bending a micromachined substrate to have a predetermined curvature. The invention is further directed to methods of manufacturing such transducers.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Laser Optoacoustic Ultrasonic Imaging System (LOUIS) and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20130190595A1Increase contrastImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingHelical computed tomographyContrast resolution
Provided herein are the systems, methods, components for a three-dimensional tomography system. The system is a dual-modality imaging system incorporates a laser ultrasonic system and a laser optoacoustic system. The dual-modality imaging system has means for generate tomographic images of a volume of interest in a subject body based on speed of sound, ultrasound attenuation and / or ultrasound backscattering and for generating optoacoustic tomographic images of distribution of the optical absorption coefficient in the subject body based on absorbed optical energy density or various quantitative parameters derivable therefrom. Also provided is a method for increasing contrast, resolution and accuracy of quantitative information obtained within a subject utilizing the dual-modality imaging system. The method comprises producing an image of an outline boundary of a volume of interest and generating spatially or temporally coregistered images based on speed of sound and / or ultrasonic attenuation and on absorbed optical energy within the outlined volume.
Owner:TOMOWAVE LAB INC
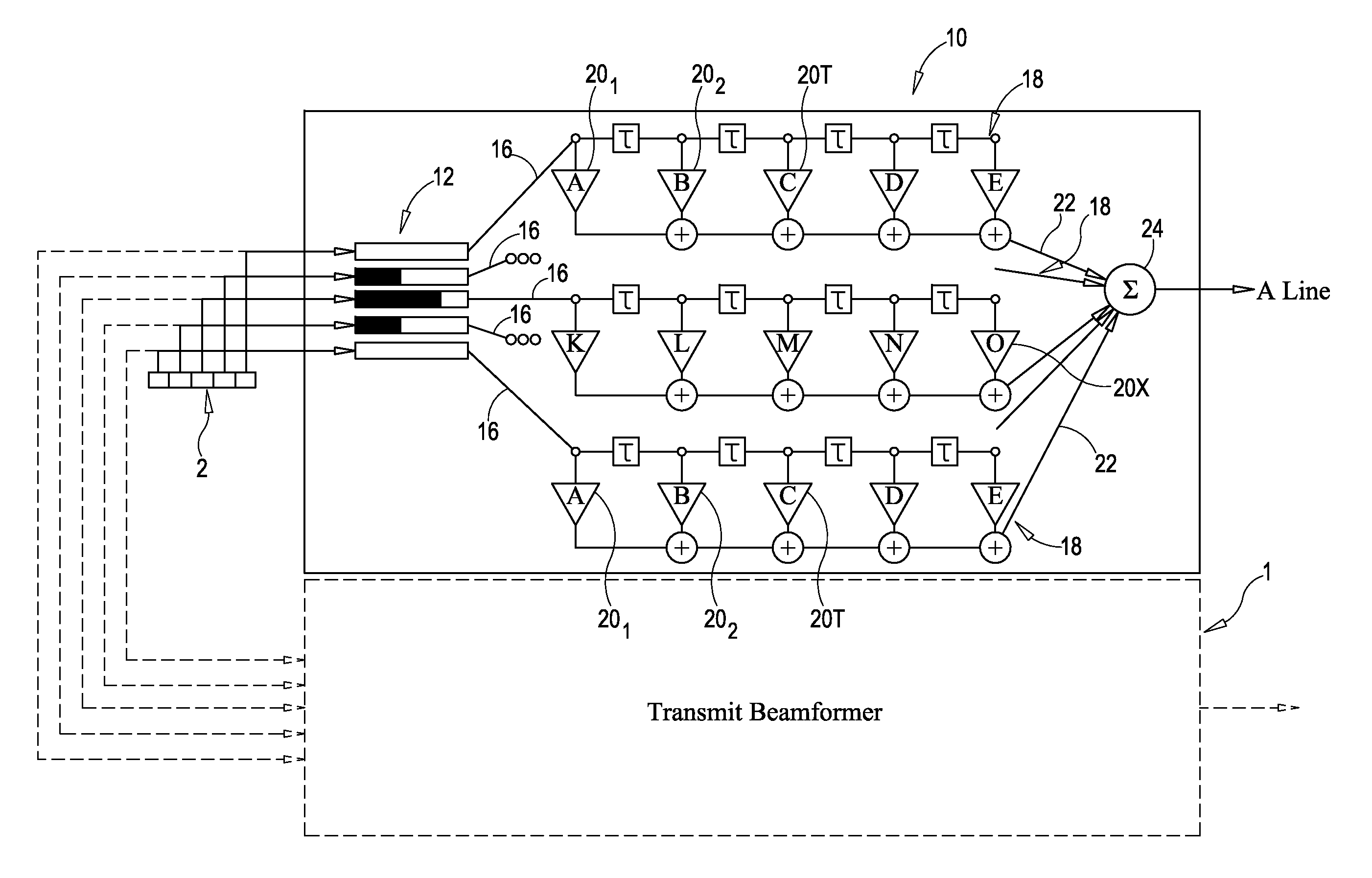
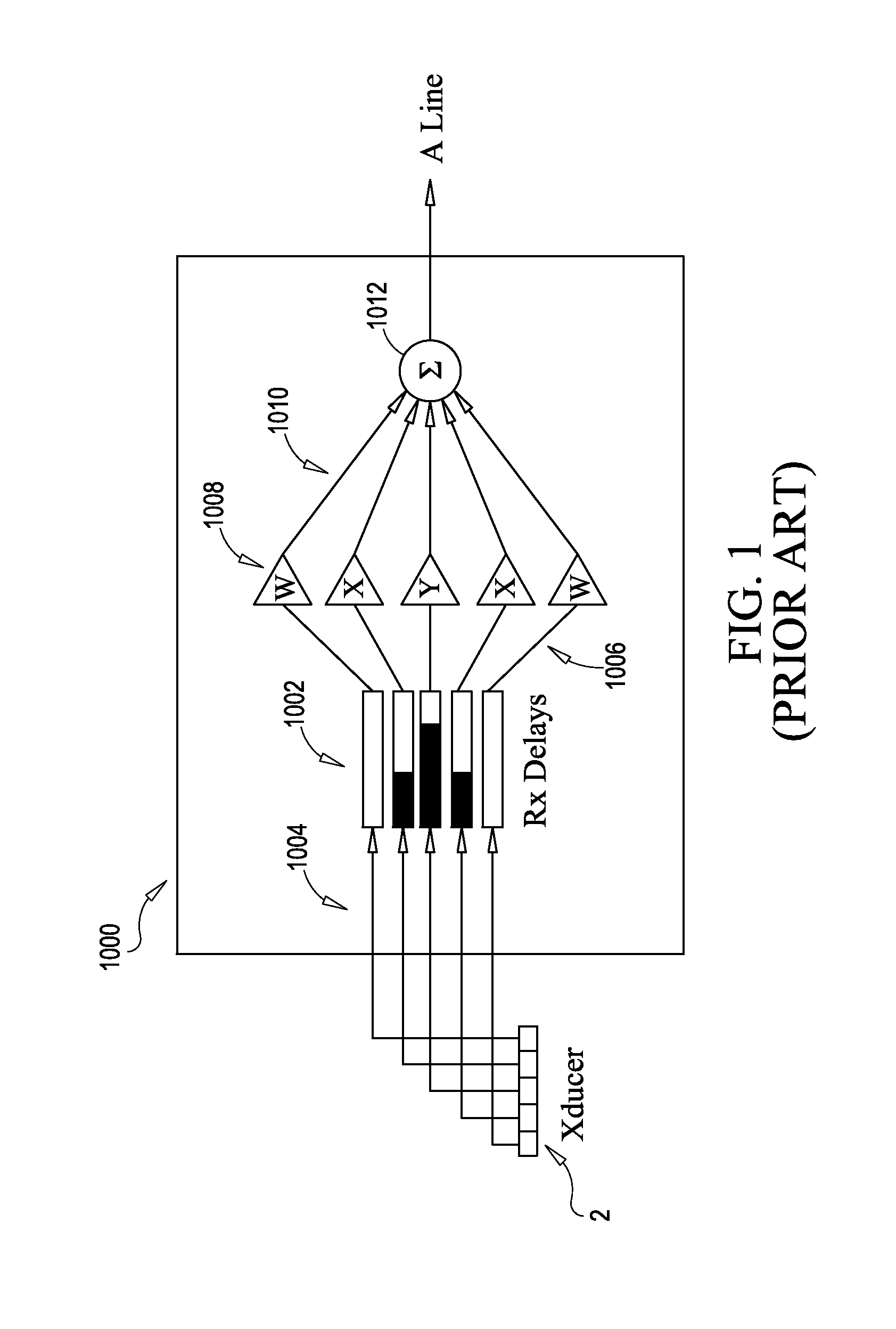
Imaging or communications system utilizing multisample apodization and method
ActiveUS20090299184A1Easy to optimizeMinimizing ratioUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFinite impulse responseCommunications system
Methods systems and system components for optimizing contrast resolution of an imaging or sensing system utilizing multiple channels of broadband data associated with an array of transducers. Channels or data are filtered by passing the channels of data through finite impulse response (FIR) filters on each channel. The filters each have multiple taps having tap weights pre-calculated as a function of distance of the array from an object that energy is being transmitted to or reflected from. The weights are pre-computed through a deterministic equation based on an a priori system model.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Ultrasound diagnosis apparatus
ActiveUS20090326377A1Uniform thin widthGood image dataUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationSonificationSound sources
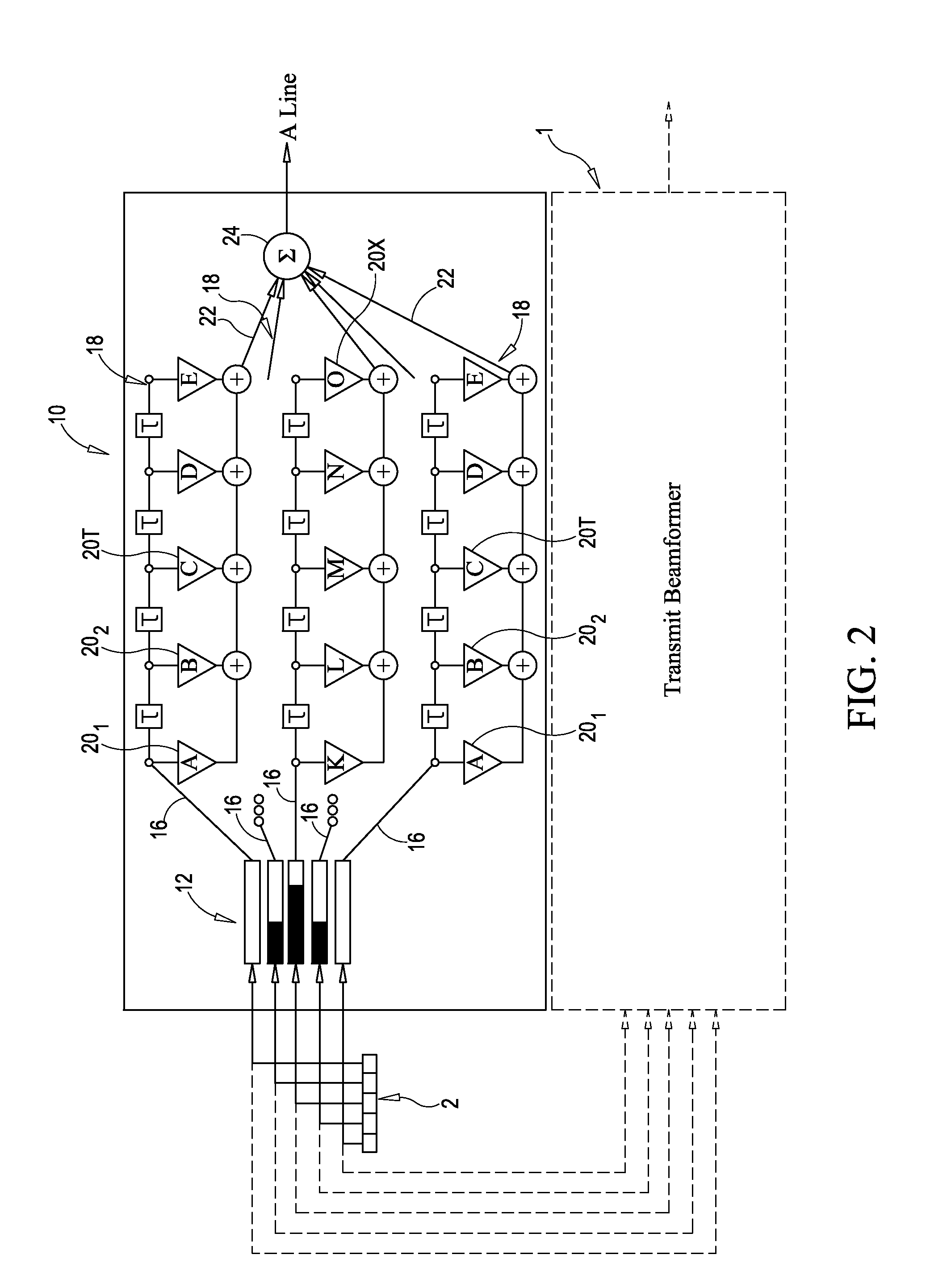
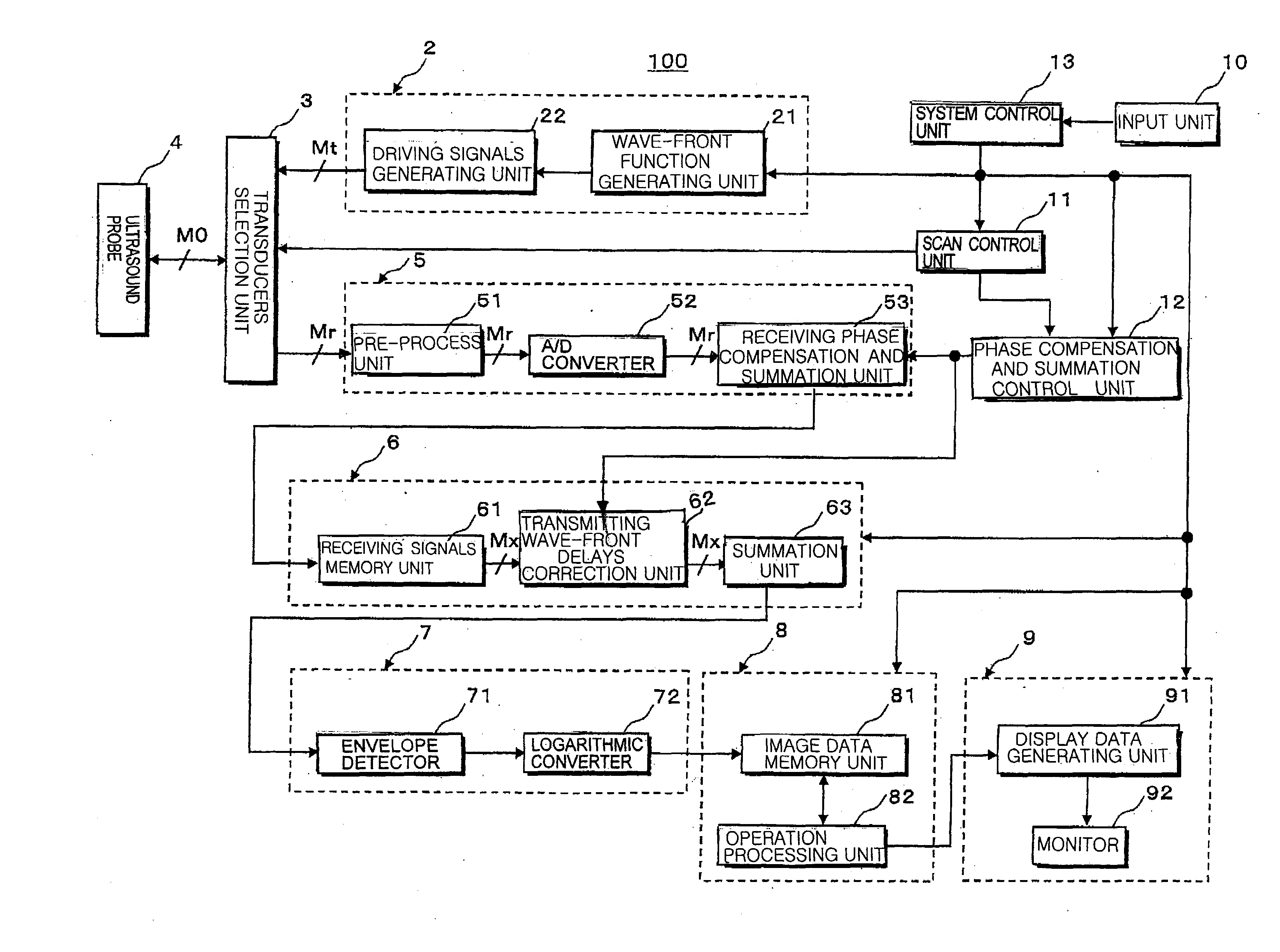
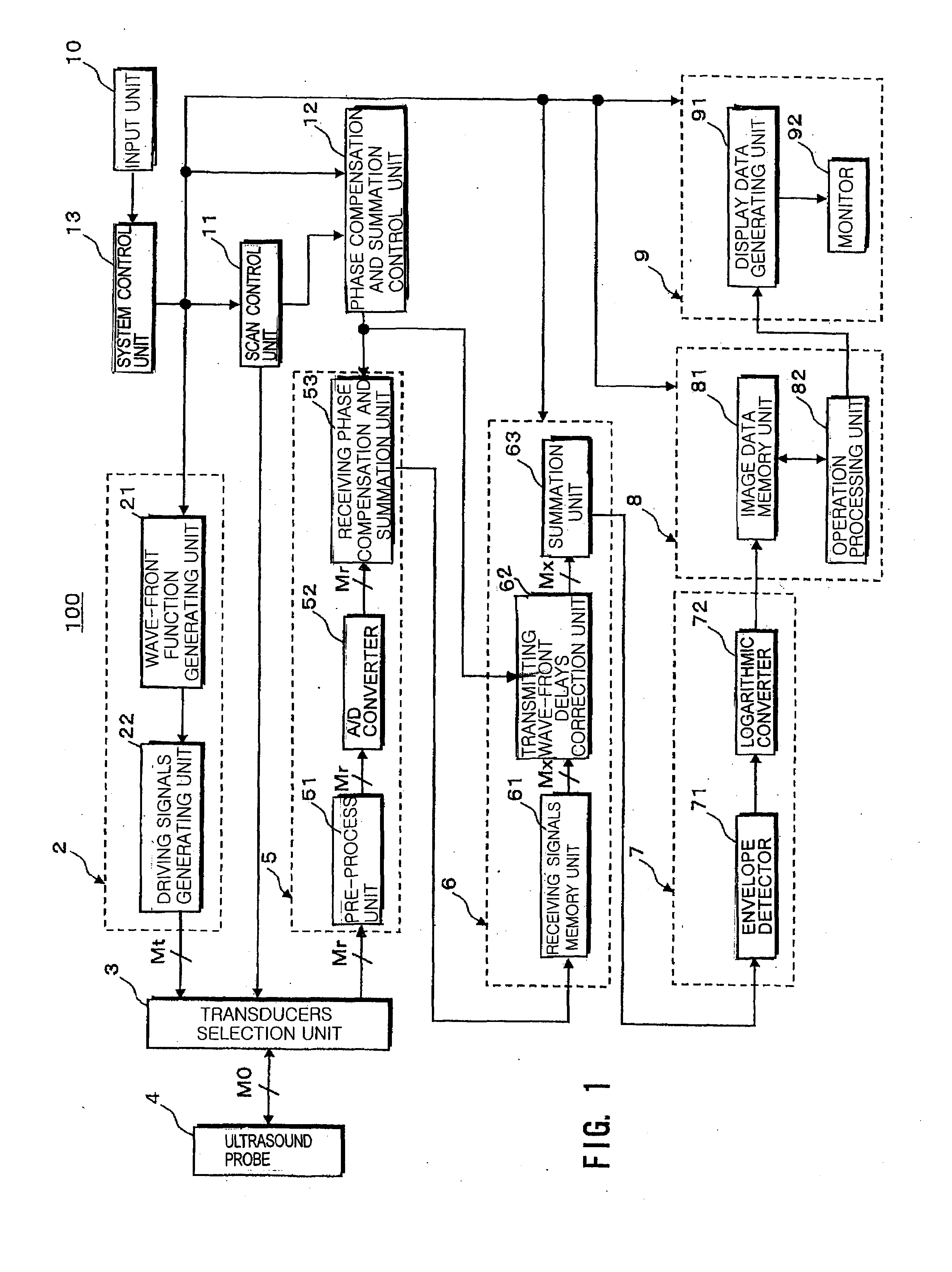
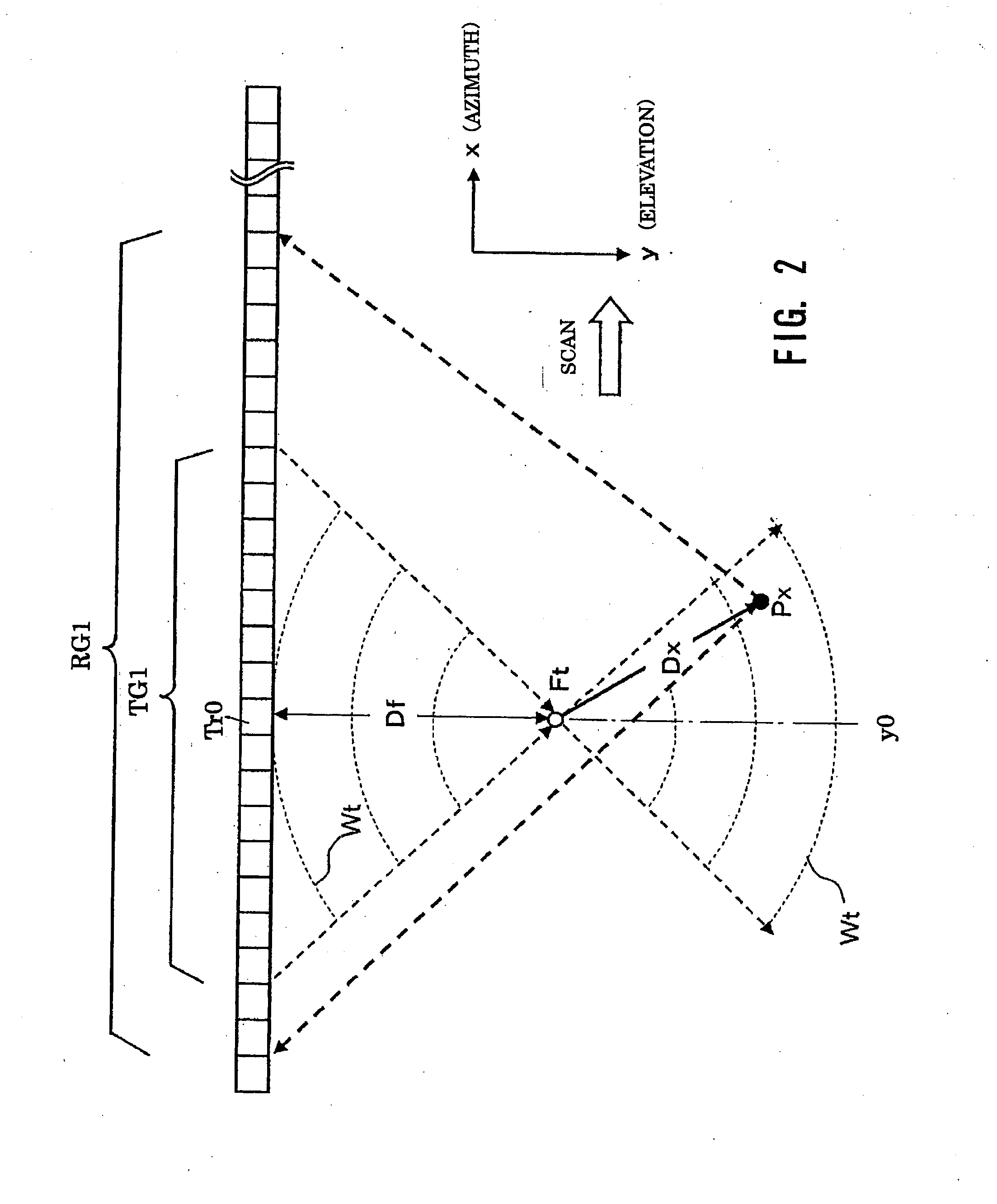
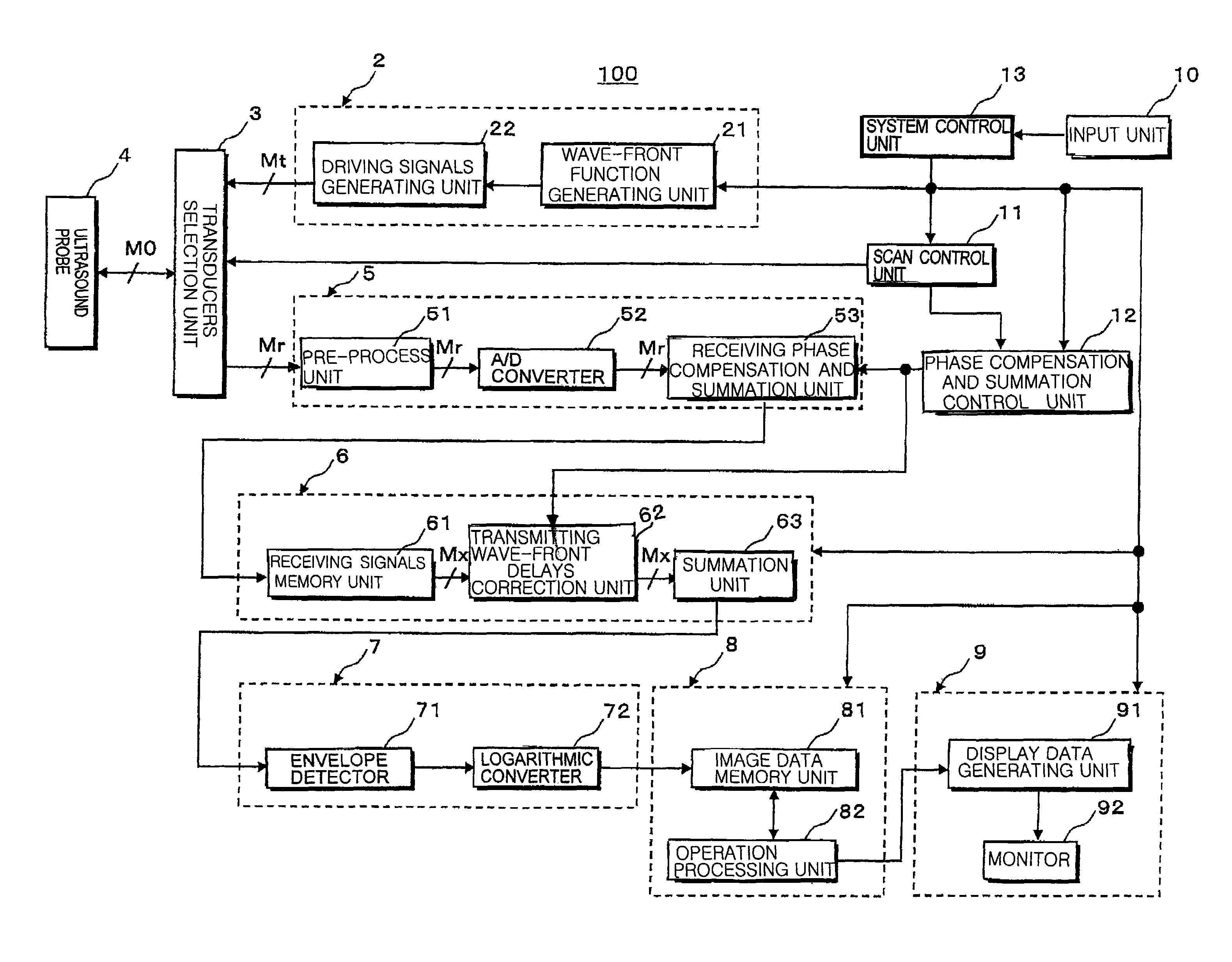
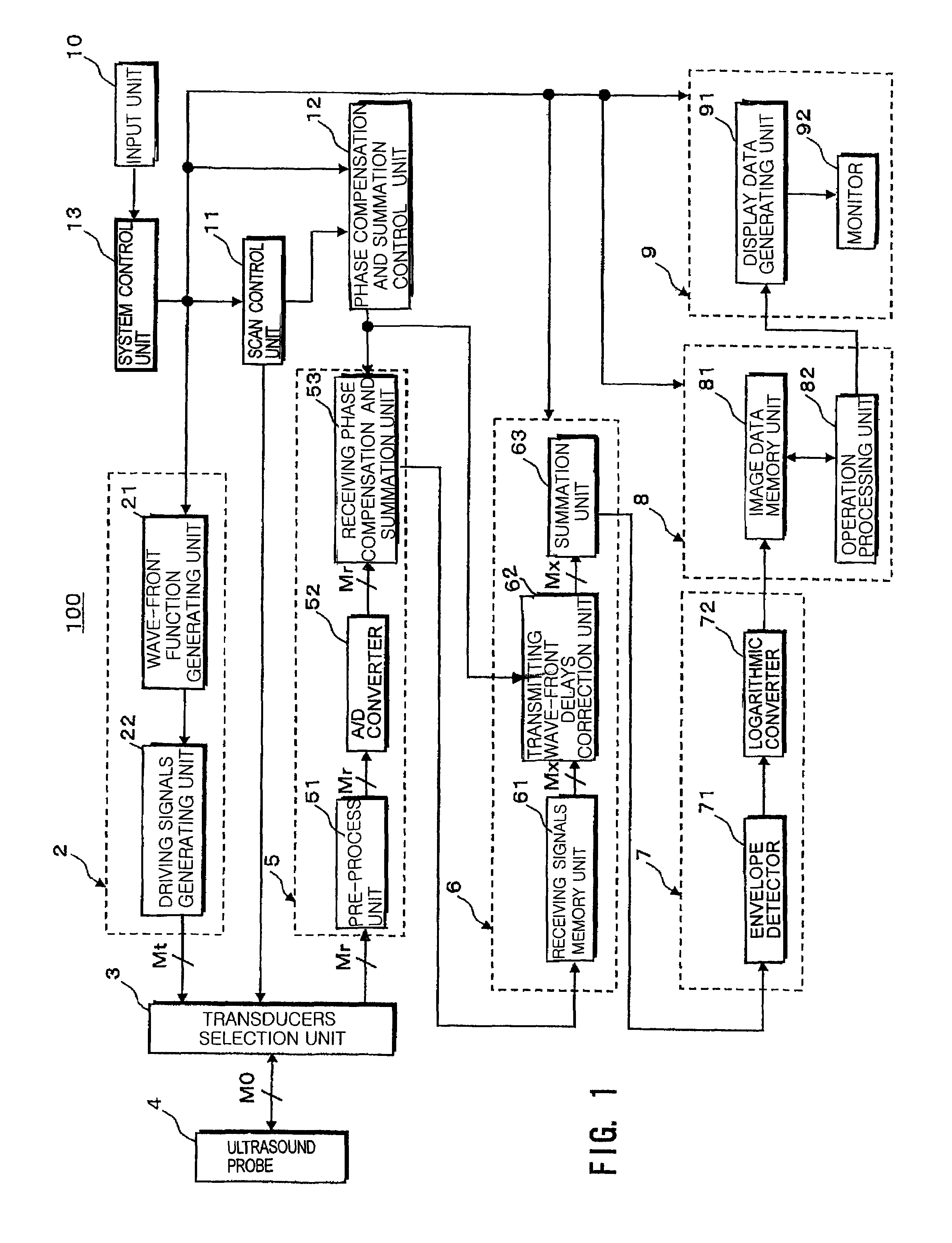
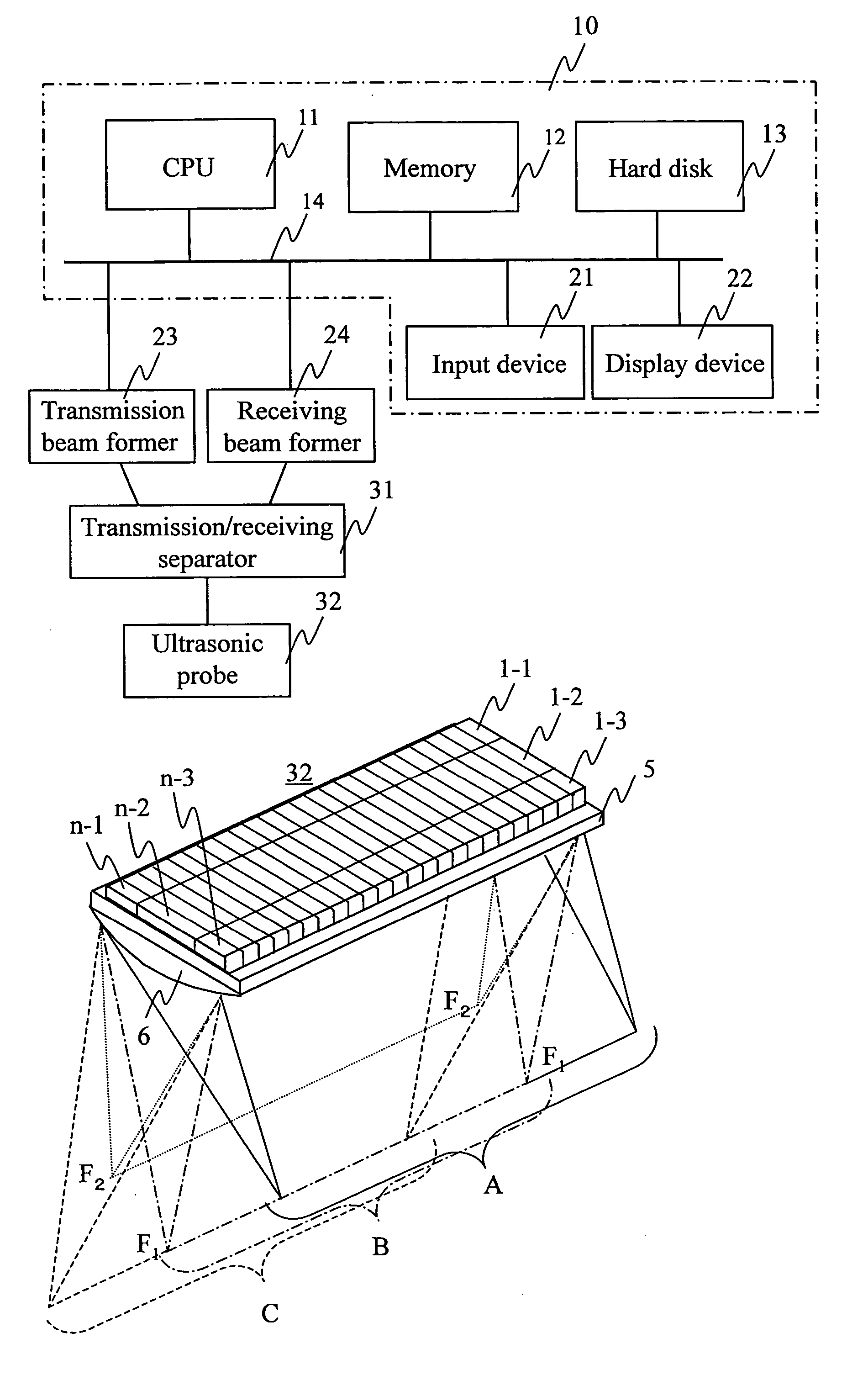
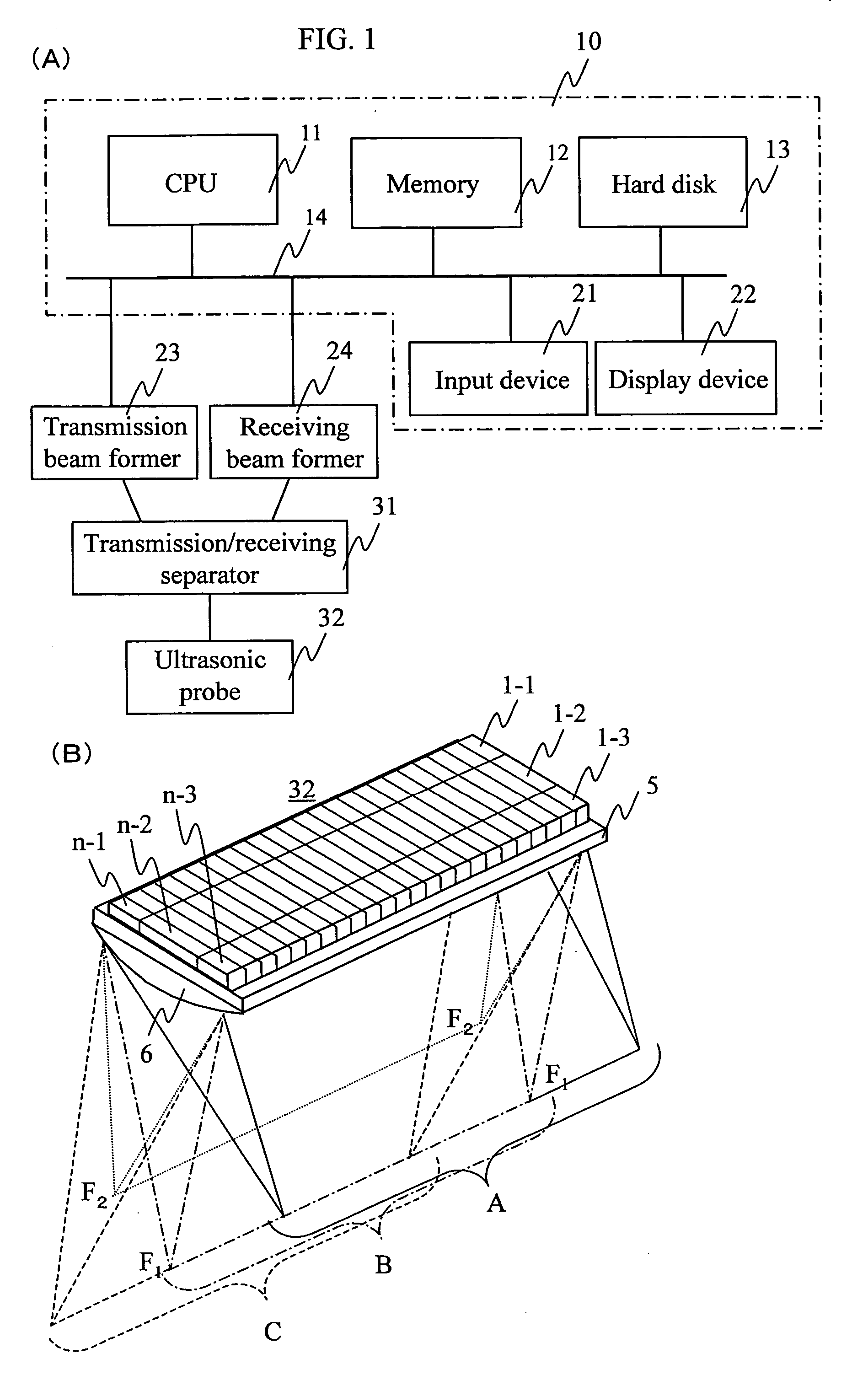
An ultrasound diagnosis apparatus that can acquire ultrasound image data of an excellent spatial resolution and contrast resolution by electrically controlling focusing points of transmission / reception waves so as to form transmitting beams and receiving beams having a substantially uniform thin beam width along an elevation direction in an object. Transmission ultrasounds emitted from a prescribed number of transducers are focused at a hypothetical point sound source. Transmitting wave-fronts propagated from the point sound source reflect at a plurality of observing points in the propagation area. Reception ultrasounds reflected at the observing points are received through a prescribed number of receiving transducers so as to generate a plurality of channels of receiving signals. The receiving signals are focused by performing receiving phase compensation and summation so that the observing point becomes a reception focusing point. The phase compensated and summed receiving signals are focused by performing wave-front phase compensation and summation in order to correct transmitting delays due to the propagation distances between the transmitting focusing point and the observing points.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
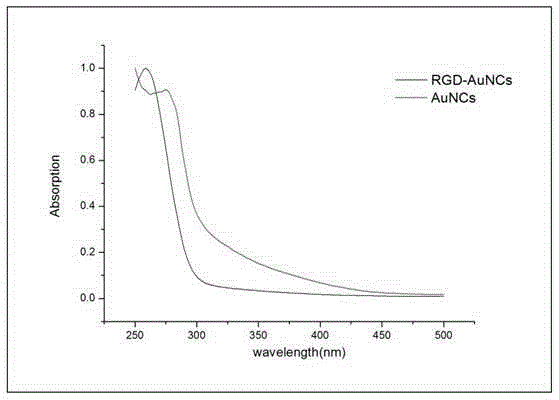
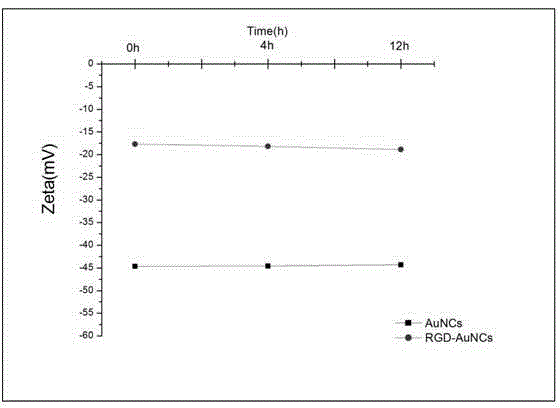
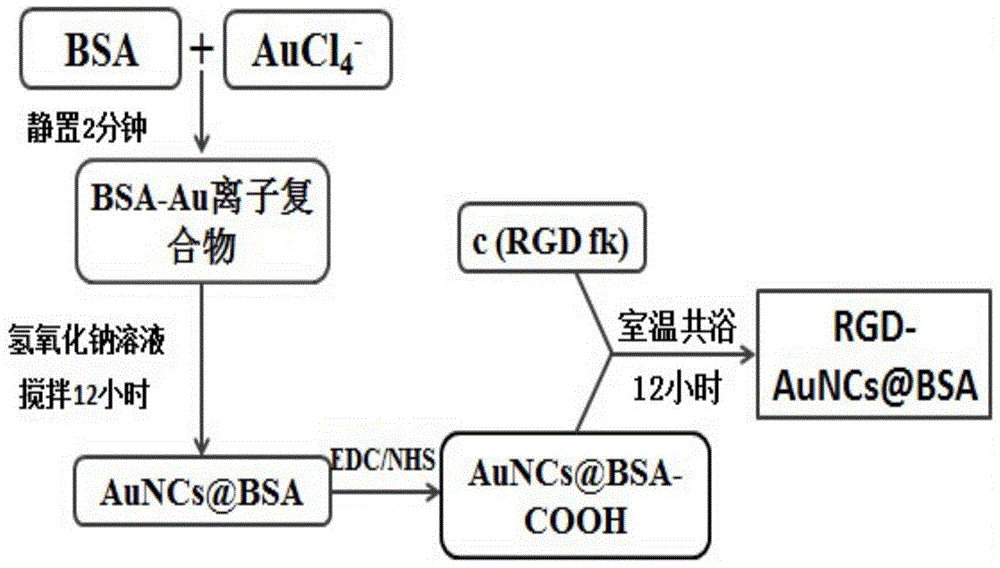
RGD-labeled fluorescent gold nano-cluster preparation method
InactiveCN105363043ASmall particle sizeLow cytotoxicityX-ray constrast preparationsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellSide effect
The present invention discloses a RGD-labeled fluorescent gold nano-cluster preparation method, which comprises: preparing gold nanoparticles with a particle size of less than 2 nm by using a BSA method; and carrying out an amidation reaction on the prepared gold nano-cluster and RGD having amino to obtain the RGD-labeled fluorescent gold nano-clusters. According to the present invention, the obtained gold nano-cluster (Au Nanoclusters, AuNCs) is the novel precious metal fluorescent nanometer material, and has characteristics of simple preparation conditions, simple preparation steps, near-infrared light emitting under a visible light source, small particle size, good monodispersity, good stability, low toxic-side effect, high safety, stable fluorescent property, and high CT imaging contrast resolution; a small amount of expression of integrin [alpha]v[beat]3 exists in most normal tissues and mature vascular endothelial cells while the over-expression of the integrin [alpha]v[beat]3 exists in a variety of cancer cells and neovessel endothelial cells, and the ligand is called RGD polypeptide sequence; and the RGD is selected as the targeting molecule, and the AuNCs and the RGD polypeptide sequence are conjugated to prepare the RGD-labeled fluorescent gold nano-cluster RGD-AuNCs@BSA.
Owner:屈晓超
Imaging or communications system utilizing multisample apodization and method
ActiveUS8744155B2Minimizing ratioOptimization of contrast resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFinite impulse responseContrast resolution
Methods, systems and system components for optimizing contrast resolution of an imaging or sensing system utilizing multiple channels of broadband data associated with an array of transducers. Channels or data are filtered by passing the channels of data through finite impulse response (FIR) filters on each channel. The filters each have multiple taps having tap weights pre-calculated as a function of distance of the array from an object that energy is being transmitted to or reflected from. The weights are pre-computed through a deterministic equation based on an a priori system model.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
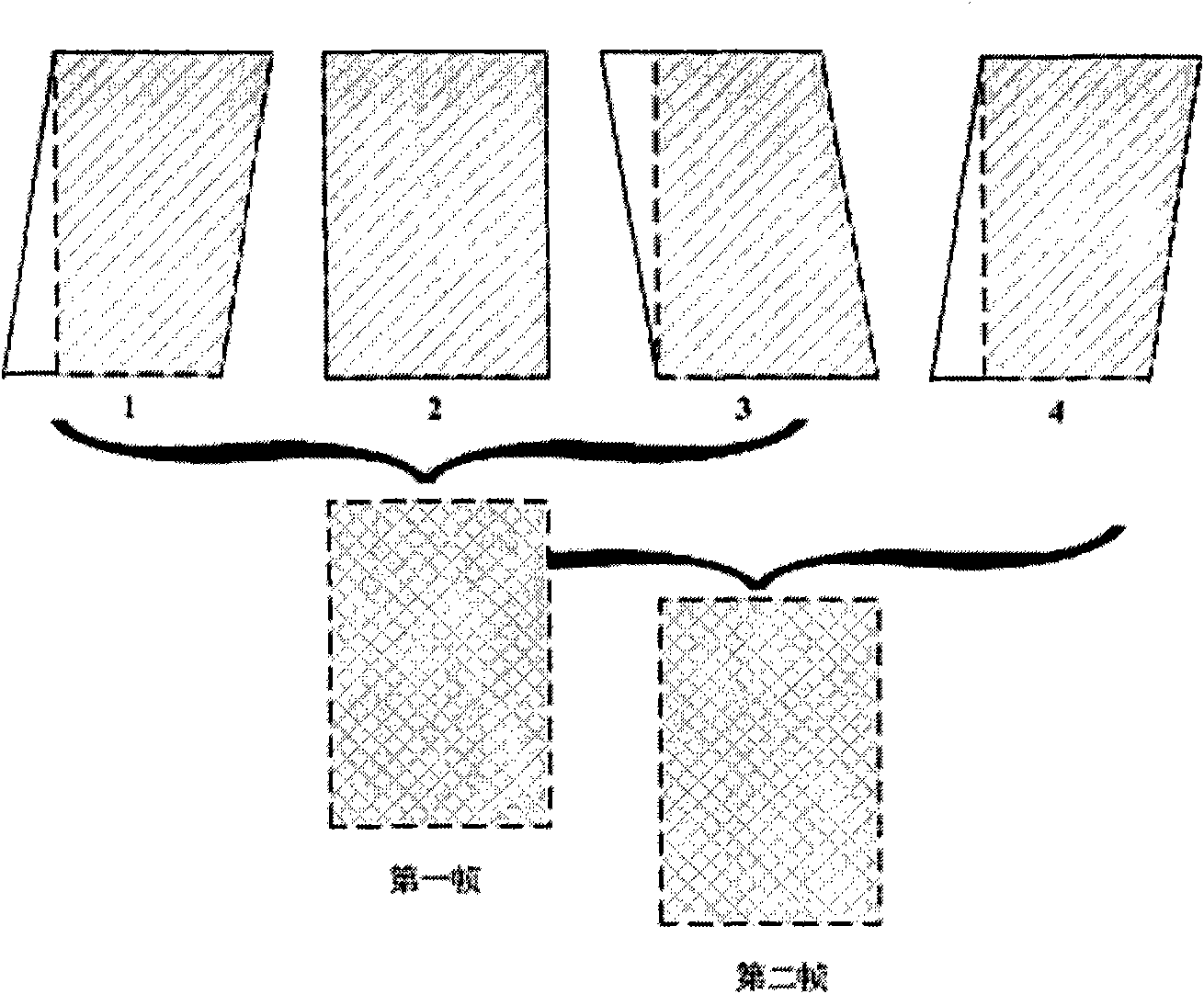
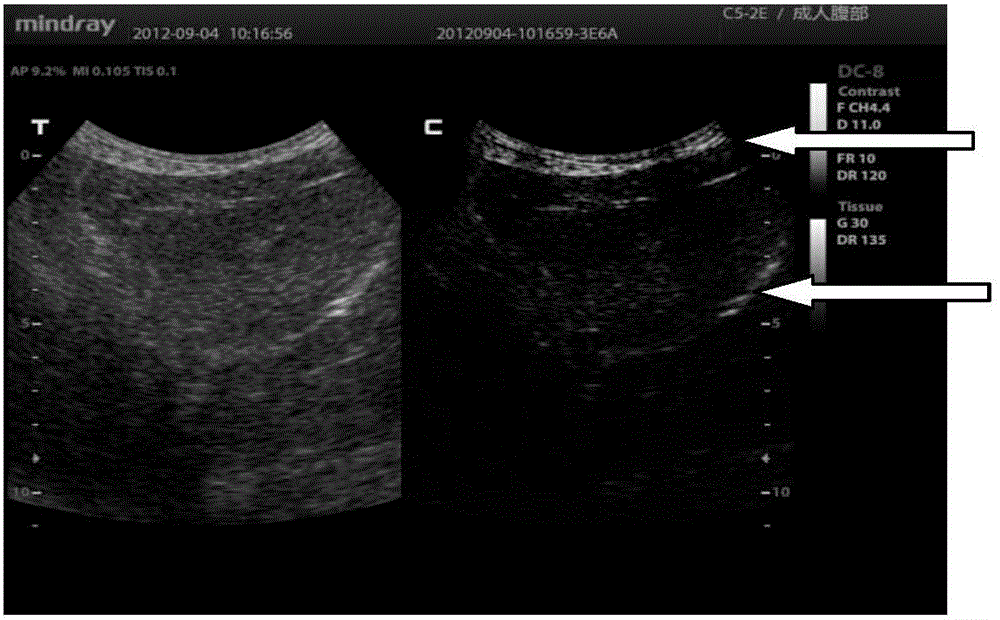
Spatial fusion method and spatial fusion device for ultrasonic imaging and ultrasonic imaging system
ActiveCN101617946AGuaranteed contrast resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationUltrasonic imaging
The invention discloses a spatial fusion method and a spatial fusion device for ultrasonic imaging and an ultrasonic imaging system comprising the device. The method comprises a fusion step and a rotary stretch step, wherein the fusion step is used for weighing and fusing a scanned and converted multi-angle image; and the rotary stretch step is used for adjusting the gray-scale distribution of the weighed and fused image make the gray-scale distribution basically same as the gray-scale distribution of the image to be fused through rotation and stretching under the condition of not changing image mean value gray-scale mapping. By using the technical scheme, the image gray-scale level of which the space is fused can be retained, and the contrast resolution of the image is ensured.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
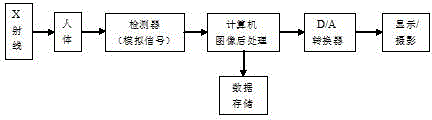
High resolution imaging system for digital dentistry
InactiveUS9384864B2Improve comfortSmall sizeX-ray/infra-red processesRadiation diagnostics for dentistryDosimetry radiationHigh resolution imaging
The invention provides methods and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray photon (including gamma ray photon) and particle radiation for dental x-ray imaging, radiation monitoring, and related industrial and scientific applications. Flat or shaped small (and small hybrid) area storage phosphor plates, available in multiple sizes, are encased in SP-carriers and used as detectors for intraoral dental x-ray imaging as a replacement for analog x-ray film and digital x-ray cameras, offering good detection efficiency, high spatial and contrast resolution, and a wide dynamic range. After removal of the SP-carrier, a small area storage phosphor plate is loaded into a dental storage phosphor scanner for readout. Intermediate and large area storage phosphor plates (including hybrid versions) are suitable for non-intraoral dental x-ray imaging. Suitable storage phosphors may be used in radiation monitoring, replacing current detectors employed in a film badge format. Simple external readers or electronic SP-carriers can provide data readout and thus enable dosimetry.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Multi-functional medical imaging quality assurance sensor
ActiveUS8333508B2Character and pattern recognitionRadiation diagnosticsQuality assuranceContrast resolution
The present invention relates to a method of providing a quality assurance program for a medical imaging examination, including measuring quality assurance metrics, including at least one of motion, contrast resolution, spatial resolution, radiation does, noise, and anatomic positioning, using a quality assurance sensor; performing an analysis the quality assurance metrics data, comparing the data with norms for same; and providing quality assurance recommendations in real-time for adjustment of the quality assurance metrics during the examination. The sensor includes a sensor body having an upper surface and a flat lower surface, the flat lower surface being divided into more than one portioned segment; a plurality of sensors and test patterns embedded into said flat surface within each portioned segment; wherein the sensors and test patterns in each portioned segment take predetermined quality assurance metrics, to optimize image acquisition during the examination.
Owner:REINER BRUCE
Digital X-ray image contrast enhancement processing method
InactiveCN104574284AIncrease visibilityImage enhancementMicroscope image processingContrast resolution
The invention discloses a digital X-ray image contrast enhancement processing method, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The digital X-ray image contrast enhancement processing method is characterized by comprising the following steps: according to X-ray imaging characteristics, dynamically expanding an interesting human body area image, and dynamically compressing non-human body image information, thereby effectively increasing the contrast of interesting area images; implementing detail enhancement and multi-scale contrast resolution enhancement on images adjusted within a dynamic range, and adjusting the naked eye watching effect of acquired images, thereby completely displaying human body information to a diagnosis doctor. The digital X-ray image contrast enhancement processing method has the advantages that human body image details are conspicuously highlighted, all information of the images can be watched in the same window, lung marking, lung marking tail end renal vessels, bone marking, muscle levels, brain vessels and the like can be all clearly displayed, and the diagnosis skill level can be greatly improved. In addition, on the basis of airspace image processing, the method is high in processing speed and can be applied to a dynamic image processing system.
Owner:NANJING PERLOVE RADIAL VIDEO EQUIP
Ultrasound diagnosis apparatus
ActiveUS8485977B2Improve spatial resolutionUniform thin beam widthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationSound sourcesSonification
An ultrasound diagnosis apparatus that can acquire ultrasound image data having excellent spatial resolution and contrast resolution by electrically controlling focusing points of transmission / reception waves so as to form transmitting beams and receiving beams having substantially uniform thin beam width along an elevation direction. Ultrasounds emitted from a prescribed number of transducers are focused at a hypothetical point sound source. Wave-fronts reflect at a plurality of observing points. Ultrasounds reflected at the observing points are received through a prescribed number of transducers generating a plurality of channels of receiving signals, which are focused by performing phase compensation and summation so that the observing point becomes a reception focusing point. The receiving signals are focused to correct transmitting delays due to propagation distances between the transmitting focusing point and the observing points.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Adaptive infrared image enhancement method based on visual contrast resolution
ActiveCN108257099AGood brightness perceptionSuppress background noiseImage enhancementImage analysisContrast resolutionThree stage
The invention requests to protect an adaptive infrared image enhancement method based on a visual contrast resolution model. Based on the fact that the resolution of human eye vision differs obviouslyin different grayscale ranges, the grayscale value of an image is divided into three stages which correspond to the dark vision, the middle vision and the bright vision of the human eyes respectively, and then, corresponding human eye visual contrast resolution models are established. According to the obtained grayscale difference between an image target and background and the models, the image target is adaptively mapped to a human eye sensitive area and the image background is mapped to a human eye insensitive area, and simulation and verification are carried out through an actual infraredimage. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple implementation process, small amount of computation and obvious image enhancement effect, and has application and popularization values.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
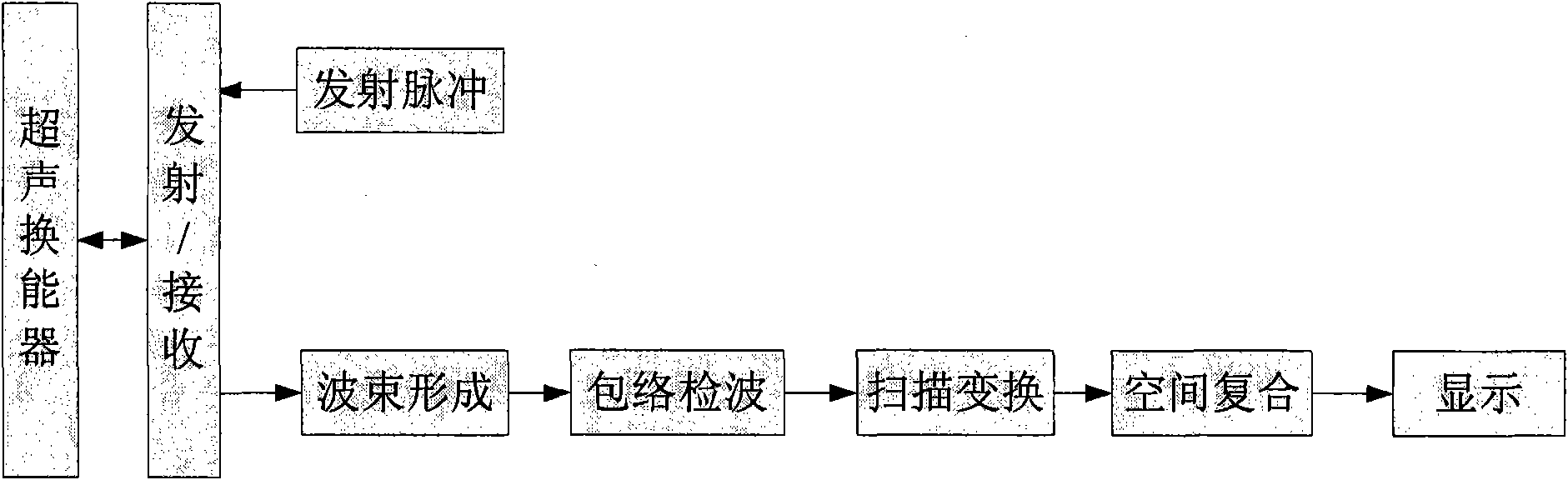
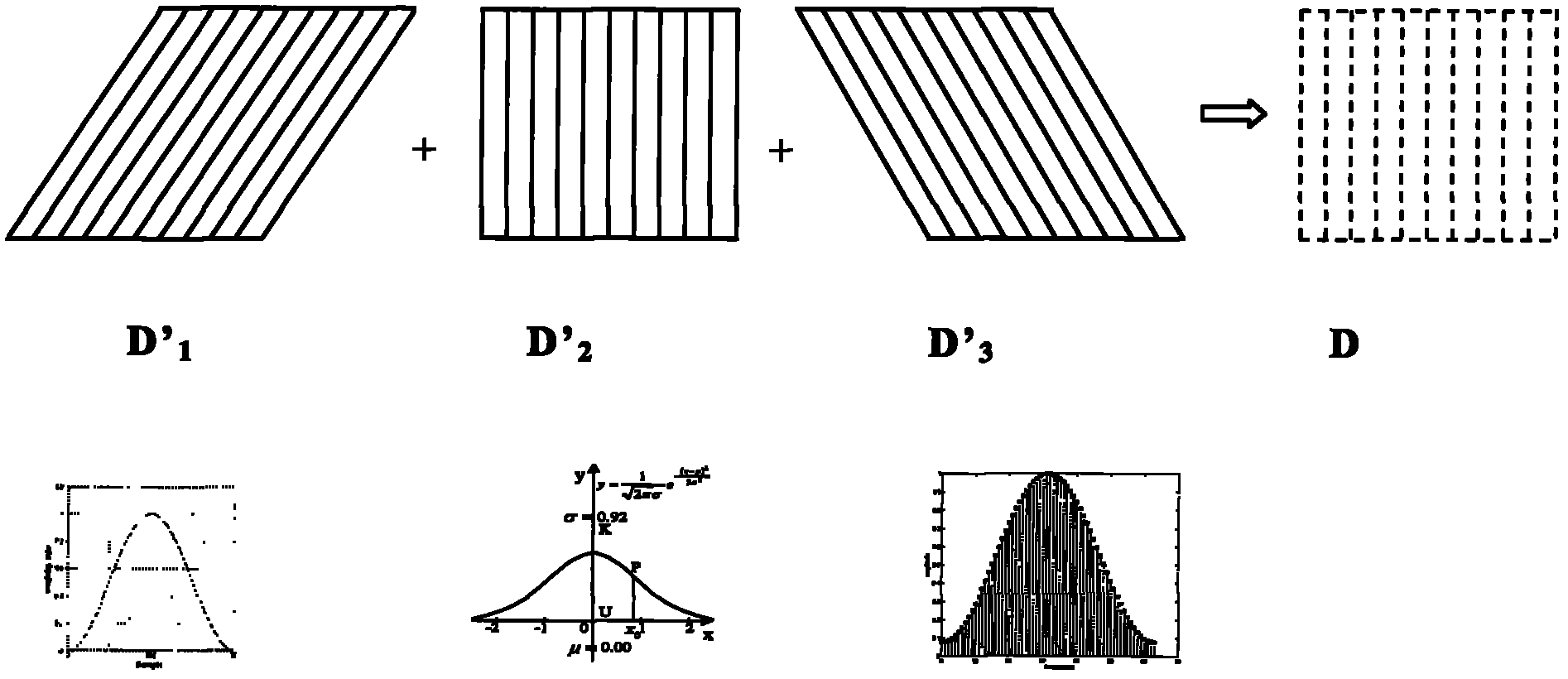
Space compound imaging method in ultrasonic diagnosis
InactiveCN102038519ABoost image dataEnhance beam signal strengthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationContrast resolution
The invention discloses a space compound imaging method in ultrasonic diagnosis. The method has the following advantages: window function processing is carried out on wave beam signals in transmitting and receiving channels during ultrasonic scanning in N directions respectively, then the obtained initial ultrasonic image data in N directions are processed through a histogram equalization algorithm or matching algorithm, and then space compound imaging is carried out on the processed ultrasonic image data to obtain the final ultrasonic image; the technicians in the field need to carry out debugging; and appropriate window function processing is selected, thus enhancing the wave beam signal intensity of the diagnosed part in the target tissue, and an appropriate histogram equalization algorithm or matching algorithm is conductive to further elevating the image data on the diagnosed part and enhancing the information of the diagnosed part in the final ultrasonic image, so the contrast resolution of the final ultrasonic image and hierarchy of the tissue structure are better and more useful information of the diagnosed part is displayed.
Owner:VINNO TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
High resolution imaging system for digital dentistry
InactiveUS20110182406A1Improve comfortIncrease contrastRadiation diagnostics for dentistryConversion screensHigh resolution imagingContrast resolution
The invention provides methods and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray photon (including gamma ray photon) and particle radiation for dental x-ray imaging, radiation monitoring, and related industrial and scientific applications. Flat or shaped small (and small hybrid) area storage phosphor plates, available in multiple sizes, are encased in SP-carriers and used as detectors for intraoral dental x-ray imaging as a replacement for analog x-ray film and digital x-ray cameras, offering good detection efficiency, high spatial and contrast resolution, and a wide dynamic range. After removal of the SP-carrier, a small area storage phosphor plate is loaded into a dental storage phosphor scanner for readout. Intermediate and large area storage phosphor plates (including hybrid versions) are suitable for non-intraoral dental x-ray imaging. Suitable storage phosphors may be used in radiation monitoring, replacing current detectors employed in a film badge format. Simple external readers or electronic SP-carriers can provide data readout and thus enable dosimetry.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Ultrasonographic device and ultrasonographic method
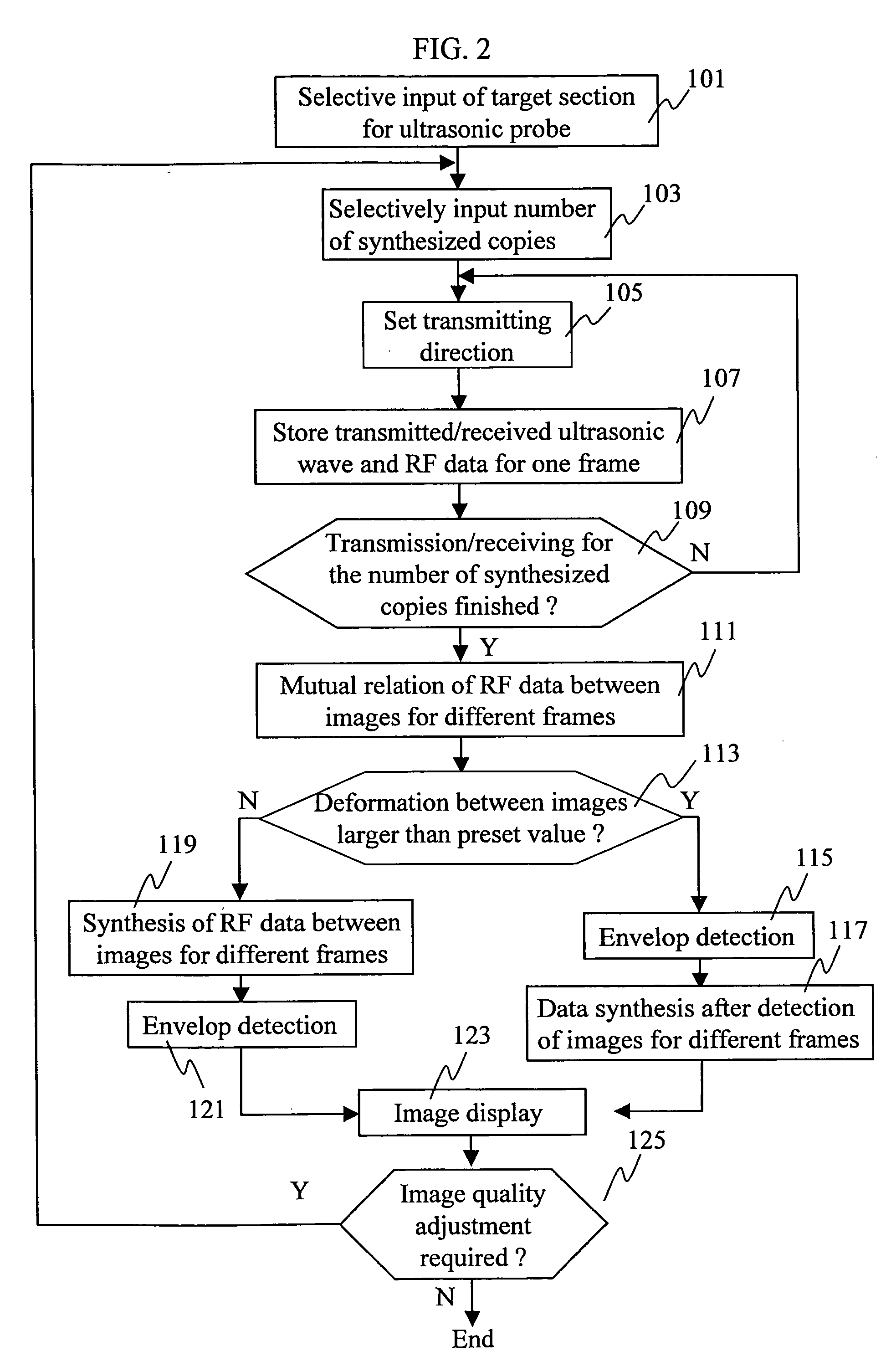
InactiveUS20060173334A1Improvement of contrast resolutionLittle degradationBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingContrast resolution
In an ultrasonic imaging device having an image synthesizing unit, correlation between images to be synthesized is computed for balancing between an improvement in contrast resolution and an improvement in spatial resolution, and an amount of displacement between the images is computed. When the amount of displacement is large, the signals after envelop detection are synthesized. When the amount of displacement is small, RF signals are synthesized. Alternatively, the mixing frequency may be variable according to the amount of displacement, and the balance between an improvement in spatial resolution and that in contract resolution is achieved according to a degree of the positional displacement.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Scanning x-ray apparatus
InactiveUS20070195935A1Increase widthImprovement of contrast resolutionHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputerised tomographsContrast resolutionControl system
Linear scanning x-ray apparatus generates a collimated fan beam which is moved together with a detector relative to a subject to generate a composite x-ray image of the subject An adjustable collimator varies the width of the imaging beam in the scan direction. A control system responds to adjustment of the collimator to combine output signals of groups of two or more pixels in the detector, in order to optimize the contrast resolution of the image signals for a given spatial resolution. The invention provides a collimator for use in the apparatus.
Owner:LODOX SYST
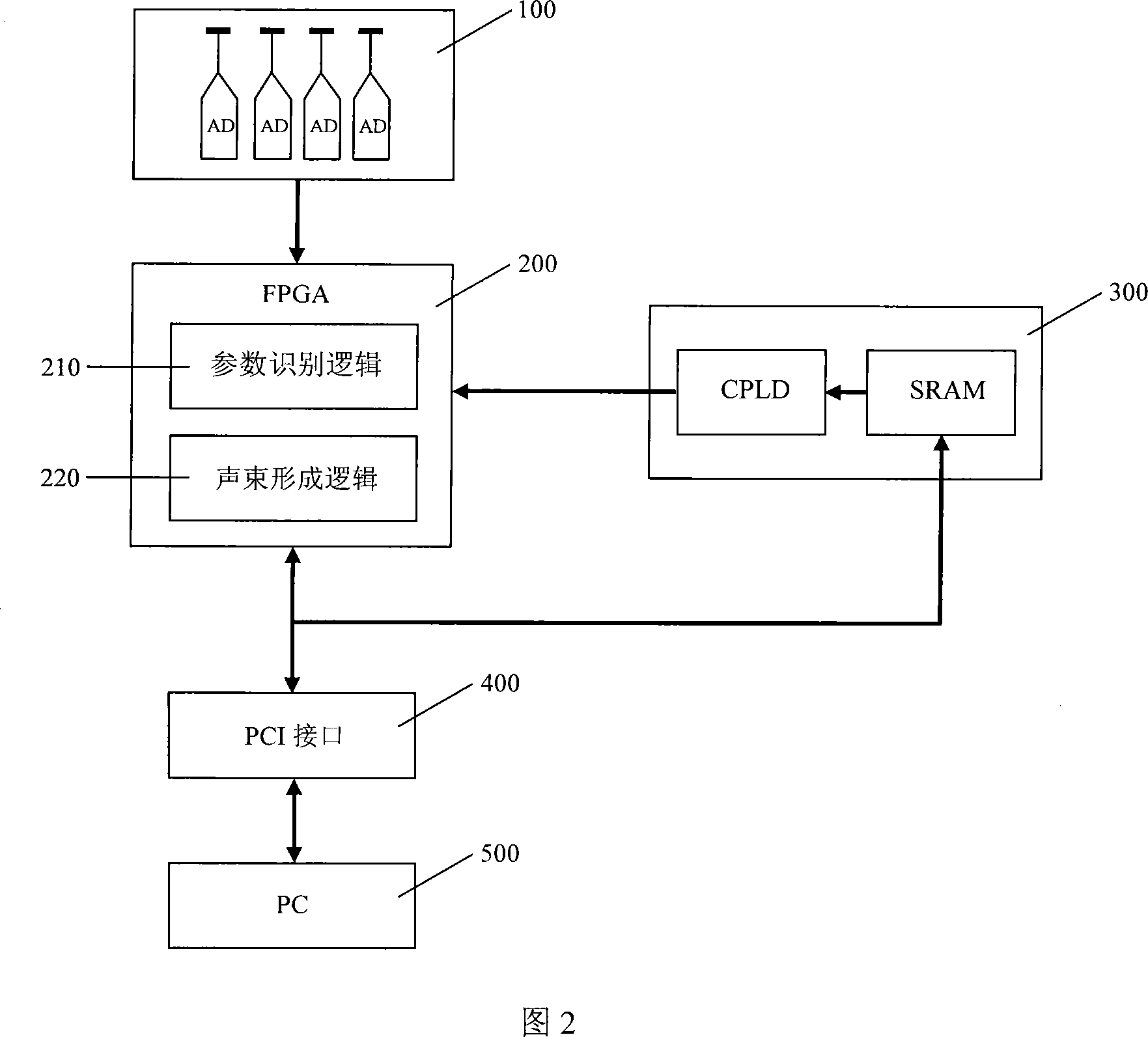
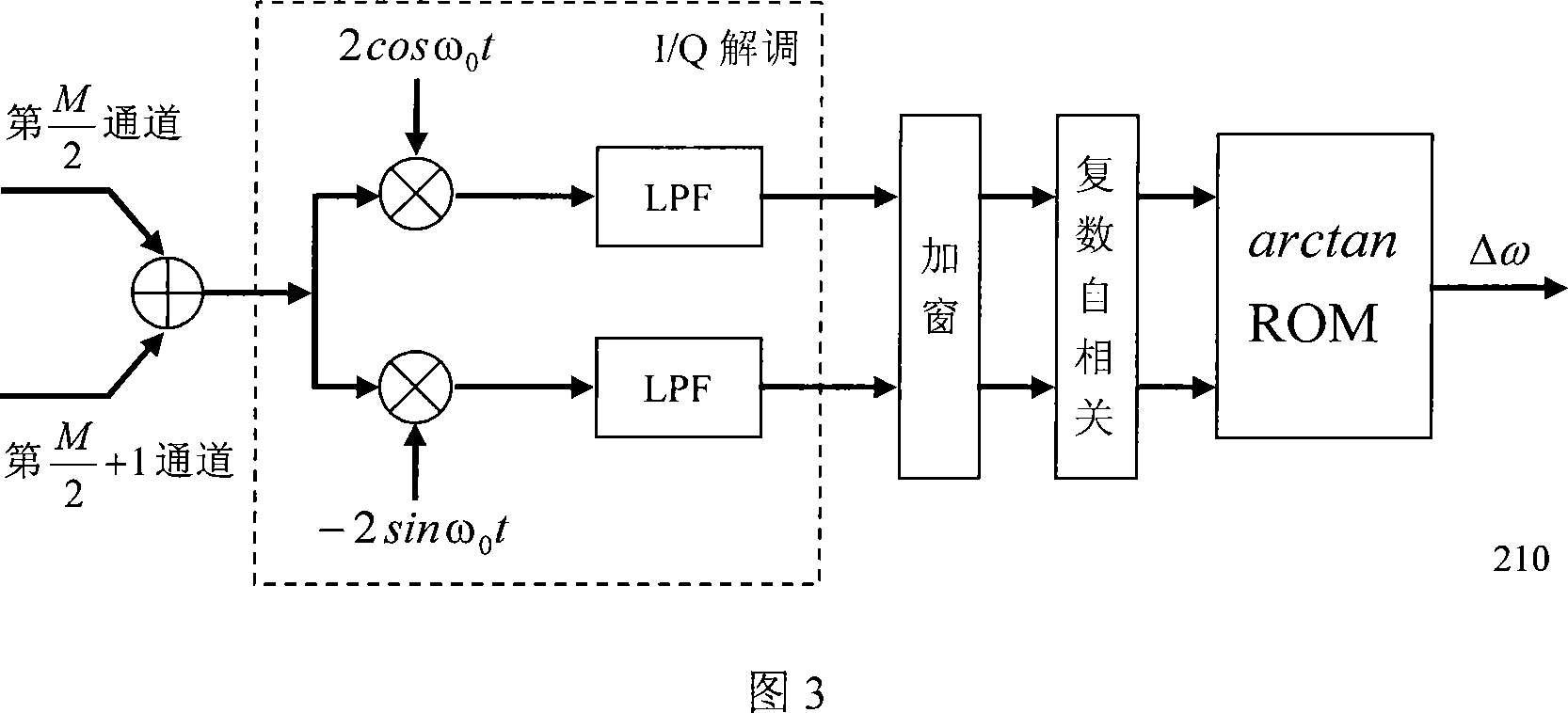
Dynamic self-adjusting sound beam forming device
InactiveCN101125092AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationUltrasonographySonification
The present invention relates to a dynamic self-adjusting sound beam forming device, which pertains to the field of medical ultrasound imaging. The present invention adopts a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) to realize the sound beam forming logic and makes use of the online reconfigurable feature of the FPGA to deploy the parameter identification logic to FPGA firstly, then the FPGA can carry out the estimation and identification of the characteristics of the ultrasonic echo of a measured target and save the identification results on an upper computer, the upper computer can adjust the focused delay parameter of the beam forming device according to the identification results and then deploy the beam forming logic to the FPGA to carry out the ultrasound scanning work. The present invention can adjust the focused delay parameter of the beam forming according to the characteristics of the current measured target by increasing the identification process of the characteristics of the measured target, so the present invention can obtain the best focus effects of the ultrasound for the different groups of people and the different inspection sites, thus effectively improving the transverse resolution and the contrast resolution of the ultrasonic images and having broad application prospect in the medical ultrasound system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
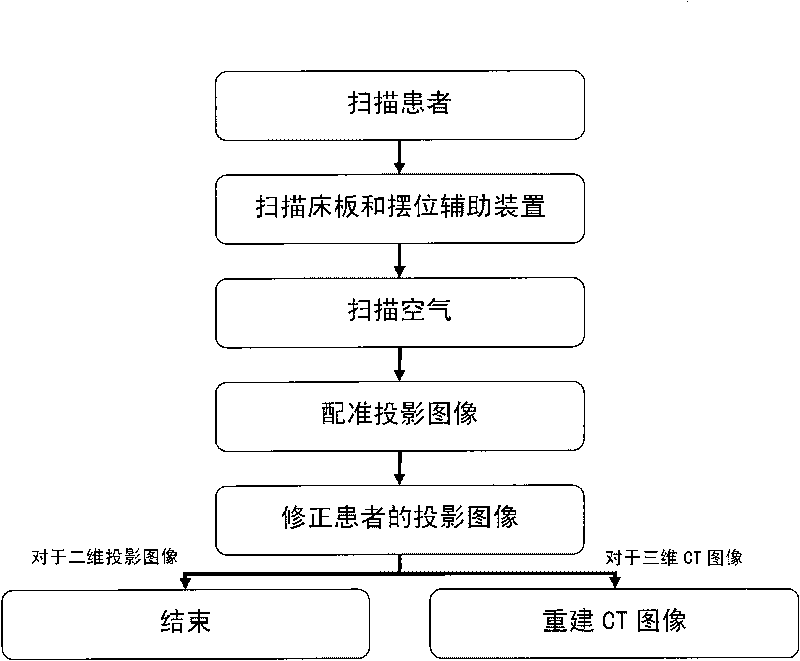
Method for correcting effect of bed board and positioning auxiliary device on image quality
InactiveCN101721222AQuality improvementComputerised tomographsTomographyThree dimensional ctAnatomical structures
The invention discloses a method for correcting effect of a bed board and a positioning auxiliary device on image quality. The method comprises the following steps that: a patient gets up out of a bed after conventional scanning; the bed board and the positioning auxiliary device are scanned individually without changing the scanning parameters and the positions of the bed and the positioning auxiliary device; then the air is scanned by moving away the bed board and the positioning auxiliary device. As for a two-dimensional projection image, each frame of projection images obtained by scanning the patient with the bed board and the positioning auxiliary device is corrected by using projection data of the geometric positions corresponding to three scanning processes and according to an exponential attenuation rule of X ray in a substance and the energy response characteristic of a detection panel; and as for a three-dimensional CT image, the three-dimensional CT image of the patient is reconstructed by using the corrected projection image. As a result, the images of the bed board and the positioning auxiliary device in the two-dimensional projection image and the three-dimensional CT image can be deducted to reduce image artifacts caused by the bed board and the positioning auxiliary device, improve the contrast resolution of a soft tissue and achieve a clearer anatomical structure.
Owner:戴建荣 +1
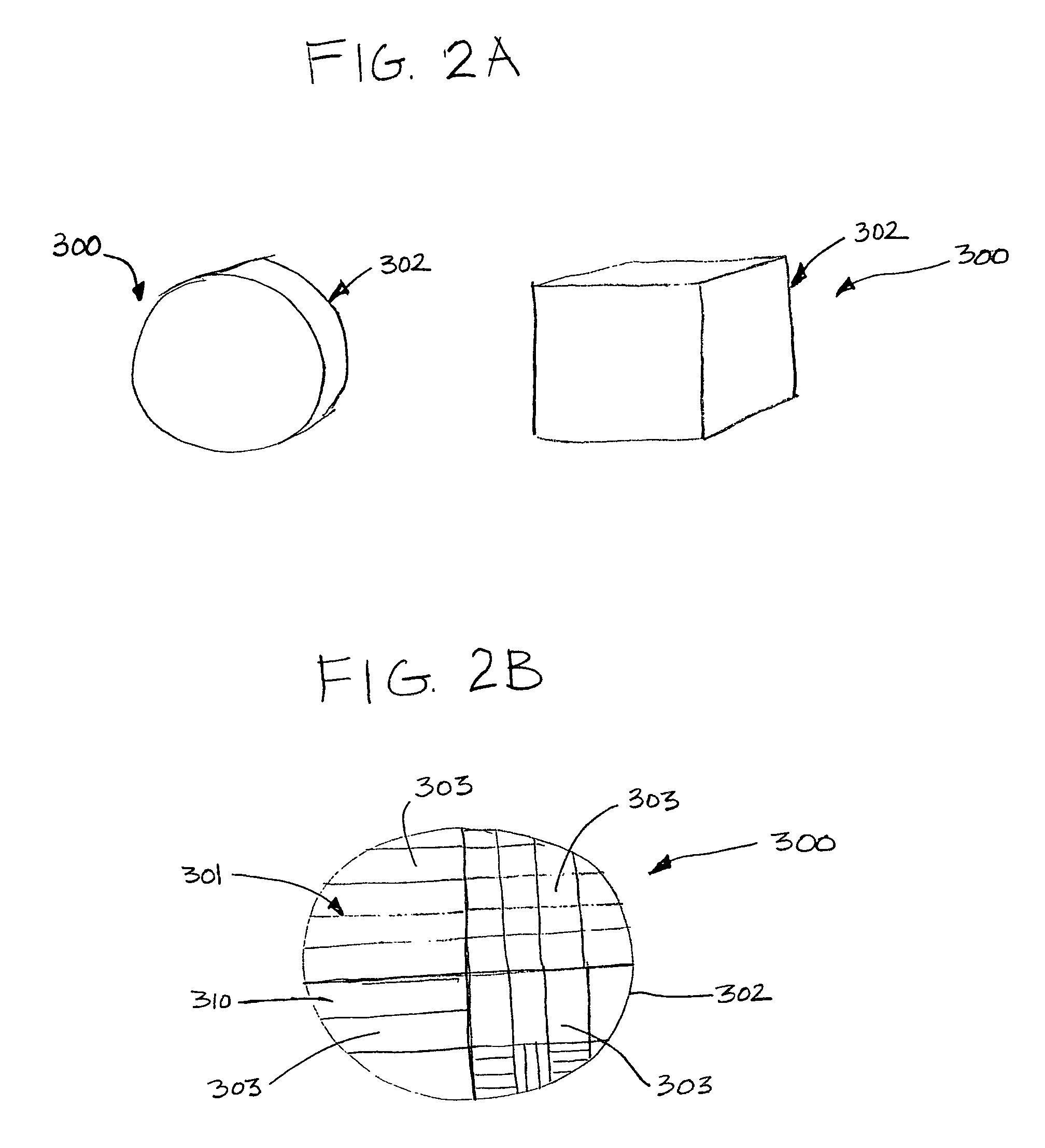
Phantom for evaluating performance of magnetic resonance imaging apparatus using ultra high field
ActiveUS20160282439A1Reduce the overall heightPrevent water leakageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsHuman bodyImaging condition
The present invention relates to a phantom for evaluating performance of an ultra high field Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) apparatus. Specifically, the present invention relates to a multi-purpose phantom which can grasp a degree of diagnostic capability of an MRI apparatus using a comprehensive result of imaging conditions and variables and simultaneously analyze and evaluate performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), performance of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) and metabolic components of a human body within a predetermined range of error and limit. The phantom for evaluating performance of an ultra high field Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) apparatus may include: an outer container opened and closed using a stopper and formed with an insertion hole for injecting components of a liver metabolite and a lipid; an inner container for quantitatively evaluating the components of the liver metabolite and the lipid, acquiring an MRI image using a spin echo sequence, and acquiring a relaxation time through spectroscopy using a single voxel technique of the MRI apparatus; a geometric accuracy evaluation apparatus installed at an upper end portion of the outer container in a shape of three-dimensional lattice type frame; slice position evaluation apparatuses of different shapes, capable of measuring a position of a slice in a middle of the outer container; a contrast resolution evaluation apparatus configured of a plurality of holes in the middle of the outer container to perform evaluation at regular intervals; a spatial resolution evaluation apparatus installed inside the outer container, in which a plurality of hole bundles configured of space evaluation holes is formed to have a same diameter and arranged in an evaluation frame in parallel at regular intervals to have holes of different diameters in each of the hole bundles; a slice thickness evaluation apparatus installed at a height a same as that of the spatial resolution evaluation apparatus and attached to the outer container to be formed in a shape of a stair; and a brain metabolite evaluation apparatus configured of a plurality of layers at a lower portion of the outer container.
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Biological magnetic photoacoustic combined endoscopic imaging method
InactiveCN107049252AHigh sensitivityHigh resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSonificationSignal on
The invention relates to a biological magnetic photoacoustic combined endoscopic imaging method. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of establishing a multi-layer cavity tissue cross section model, performing numerical simulation on the ultrasonic echo imaging, photoacoustic imaging and induction type magnetoacoustic imaging processes in a cavity channel to acquire a tissue reflected ultrasonic echo signal and tissue generated photoacoustic and magnetoacoustic signals on the cross section of the cavity channel; and performing optimal weighted summation on the three ultrasonic signals to acquired a fused combined imaging signal. The cavity tissue reflected / scattered ultrasonic echo signal and the tissue generated photoacoustic and magnetoacoustic signals which are received by an ultrasonic transducer in a time-share mode are fused in the signal layer. Compared with the traditional method, the method has the advantages that the combined imaging signal acquired by the method can retain the shape structure and the component information of the tissue more, the reestablished combined image has extremely high spatial resolution, contrast ratio, sensitivity and contrast resolution, and can accurately display the position, the shape and the functional components of each tissue in the wall of the cavity channel.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Scanning x-ray apparatus
InactiveUS7519160B2Increase widthIncrease contrastHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputerised tomographsSoft x rayContrast resolution
Linear scanning x-ray apparatus generates a collimated fan beam which is moved together with a detector relative to a subject to generate a composite x-ray image of the subject. An adjustable collimator varies the width of the imaging beam in the scan direction. A control system responds to adjustment of the collimator to combine output signals of groups of two or more pixels in the detector, in order to optimize the contrast resolution of the image signals for a given spatial resolution. The invention provides a collimator for use in the apparatus.
Owner:LODOX SYST
Eyeglass lens with high color contrast degree and manufacturing method
ActiveCN103984044AEffective filteringBlock scattered lightOptical partsOptical elementsCooking & bakingContrast resolution
The invention discloses an eyeglass lens with the high color contrast degree and a manufacturing method. The lens is composed of a base piece and a strengthening film layer, the base piece is formed by mixing and modulating high-molecular polymer, dispersing agents or solvents and ultraviolet light absorbers, the lens is formed by moulding the base piece, then, the lens is soaked in liquid silicide, and therefore the surface of the lens is coated with the silicide, and after heat baking and drying, the strengthening film layer is formed. According to the eyeglass lens with the high color contrast degree, the contrast resolution of the eyes to the colors can be relatively improved, most harmful ultraviolet rays can be effectively filtered out, a user can distinguish sceneries more easily, and therefore eye fatigue can be effectively relieved. Due to the effect of the polarizing coating layer, scattered rays harmful to vision are effectively blocked, and the user can watch the sceneries more clearly so that the effect of facilitating visual observation and enriching the colors can be achieved.
Owner:XIAN JINRUI OPTICS
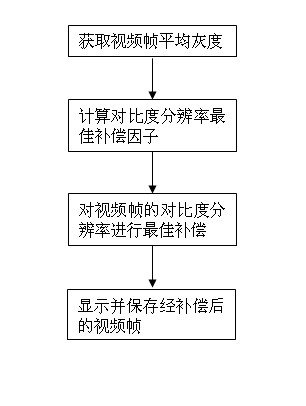
Adaptive bottom video online mining system and method based on contrast resolution compensation
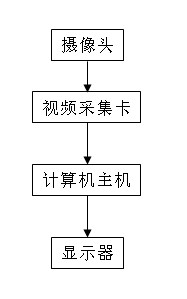
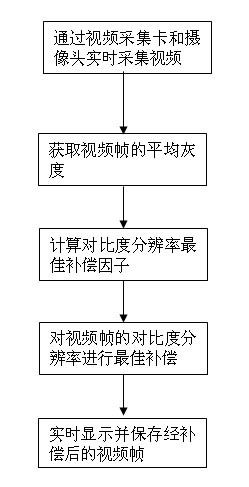
InactiveCN102186054ARealize the underlying online miningMake up for the lack of contrast resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMachine visionIlluminance
The invention provides an adaptive bottom video online mining system and method based on contrast resolution compensation. The system comprises a camera, a video capture card, a computer host and a display. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a video image transmitted from the camera by utilizing the video capture card; calculating the average gray of a current video frame; calculating the best compensation factor of contrast resolution according to the average gray; compensating the contrast resolution of the video frame by applying the best compensation factor; and displaying the compensated video in real time, and storing. By adopting the technical scheme in the invention, the video capture in a low illumination level environment can be compensated in real time, and bottom online mining of the real-time video images in the low illumination level environment can be realized, so that the defect of insufficient contrast resolution of people in a scotopic vision environment is overcome, and machine vision in the scotopic vision environment is realized.
Owner:谢丹玫 +3
Window setting method and device for image diagnosis system
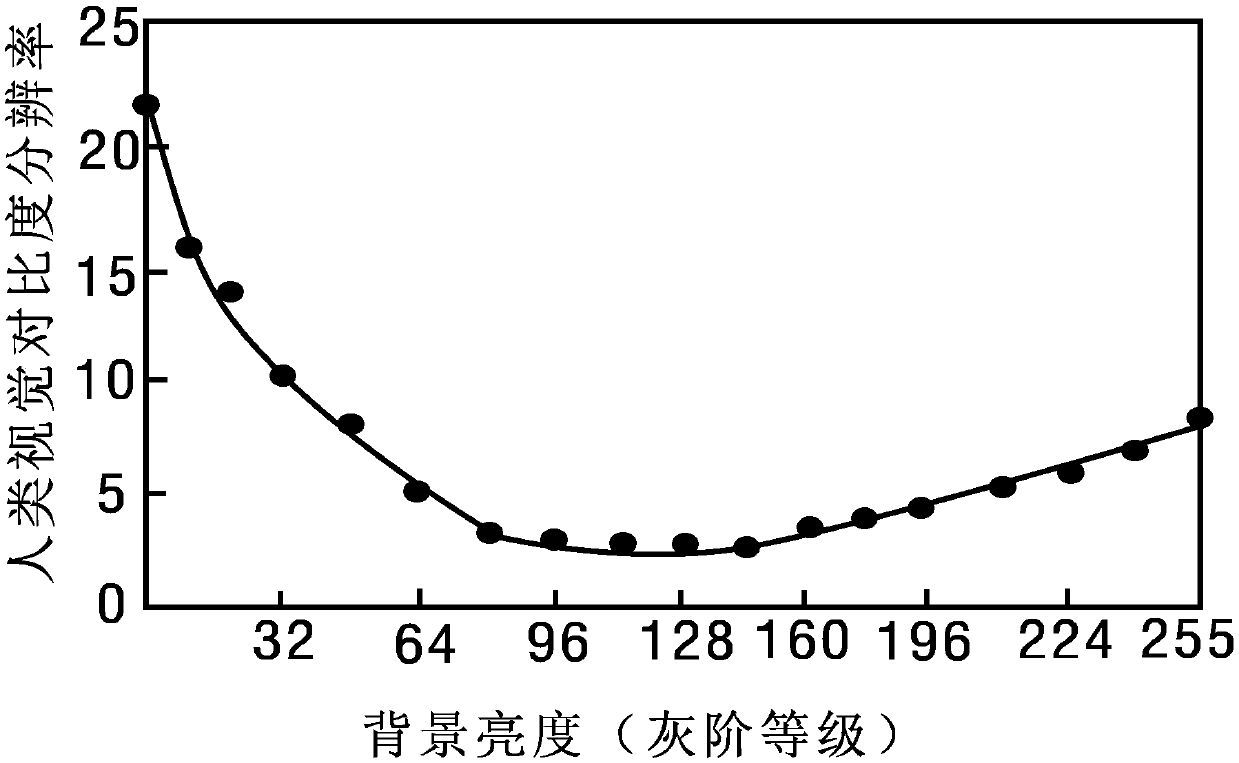
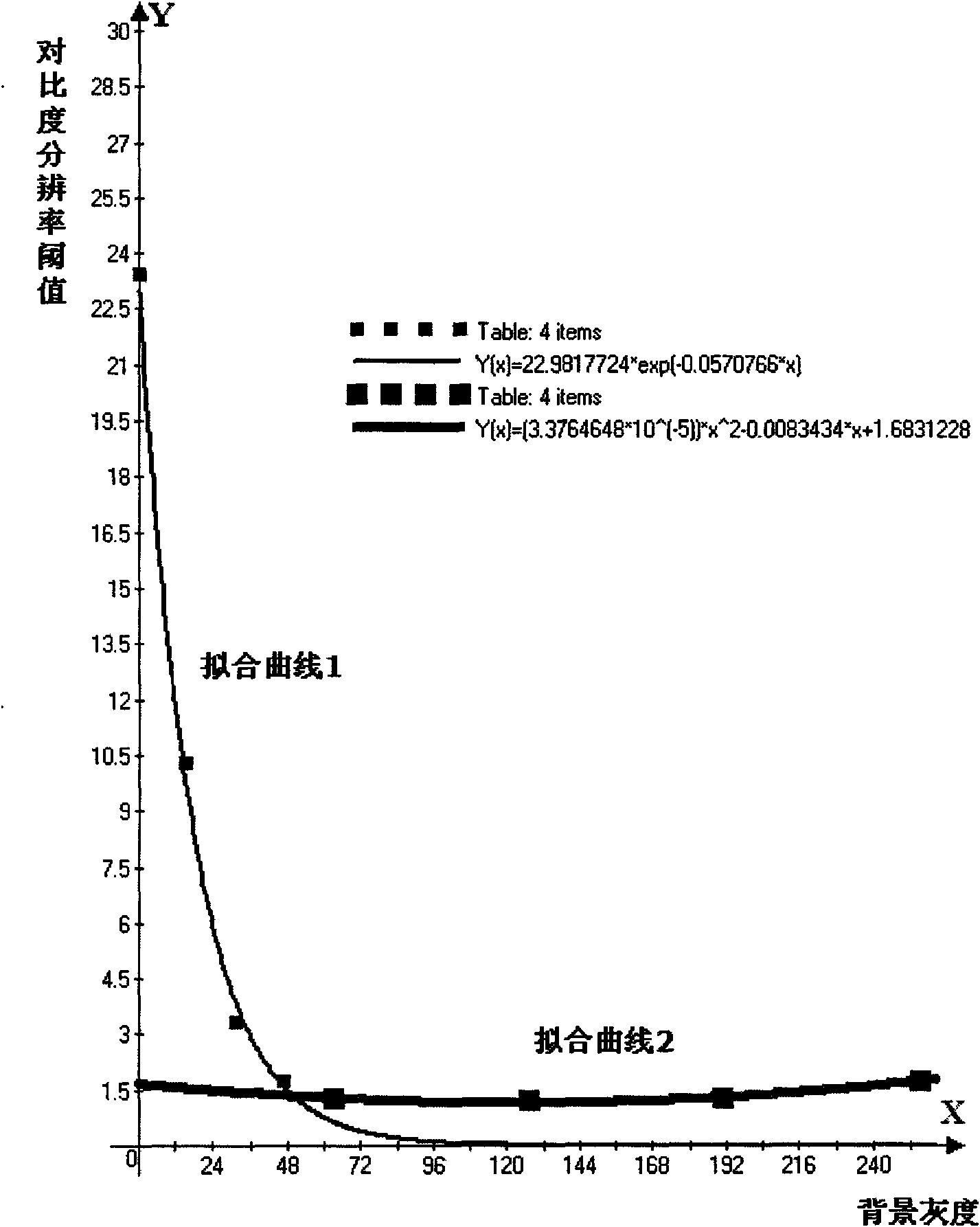
ActiveCN109993159AIncrease contrastMaximize Visual VisibilityImage enhancementImage analysisImage diagnosisContrast resolution
The invention provides a window setting method and device for an image diagnosis system. A window setting device determines a target object source point and a background source point in the image; aninterested target object region and a corresponding background region are respectively determined according to the target object source point and the background source point; according to the pixel gray scale mean value of the target object area and the pixel gray scale mean value of the background area, and based on the corresponding relation between the human vision contrast resolution and the background brightness, the corresponding target object expected display gray scale and the background expected display gray scale are determined; and a target window width and a target window positionset by a display window are determined according to the pixel gray average value of the target object area, the pixel gray average value of the background area, the expected display gray of the targetobject and the expected display gray of the background. The window setting is based on human visual characteristics, so that the image contrast most suitable for naked eye observation is provided fora user.
Owner:SIEMENS SHANGHAI MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
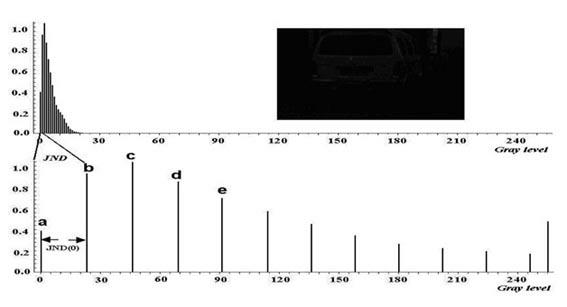
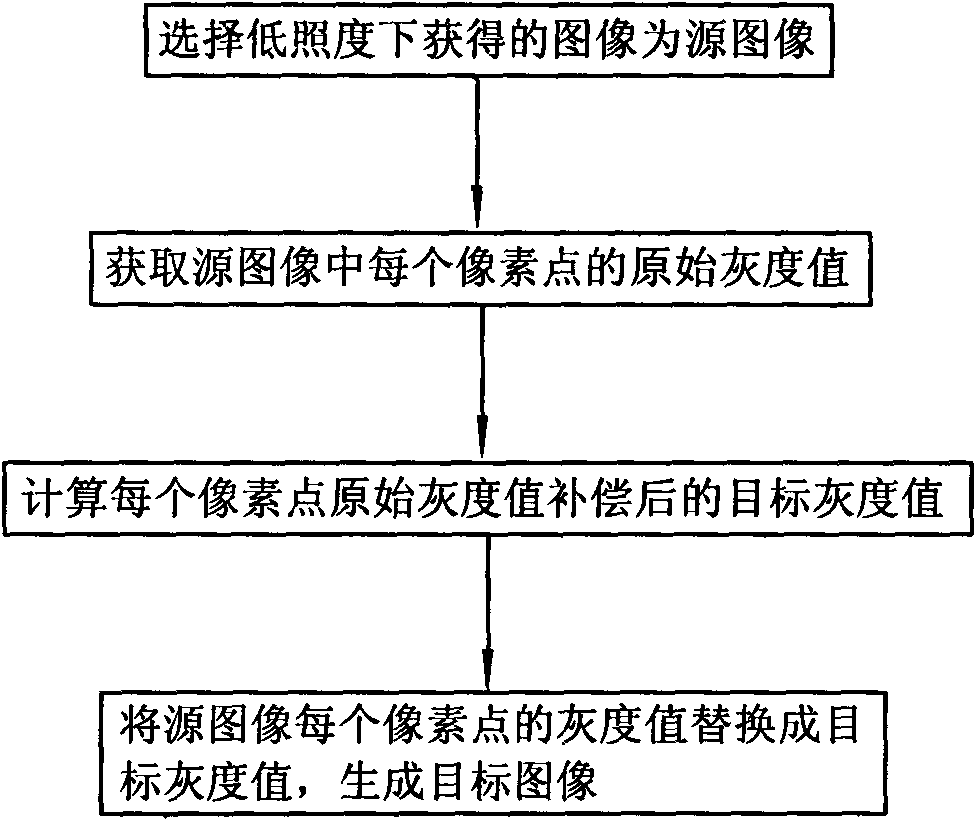
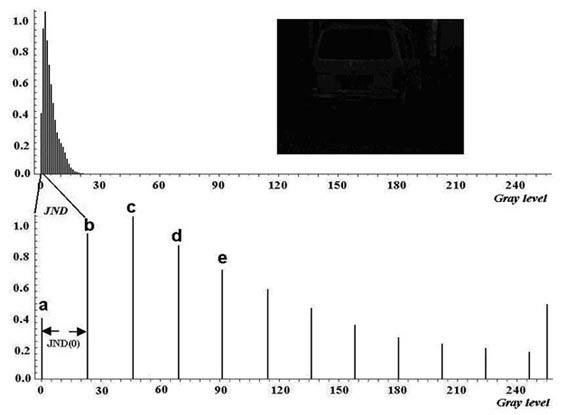
Nonlinear compensation process for human visual contrast
The invention discloses a nonlinear compensation process for human visual contrast , which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) selecting an image obtained in low light intensity as a source image; (2) acquiring the original gray value of each pixel of the source image; (3) calculating a target gray value of the compensated original gray value of each pixel; and (4) replacing the gray value of each pixel of the source image by the target gray value TG (x,y) to generate a target image. The invention changes images which are obtained in low light intensity and cannot be resolved by human vision into clear and resolved images by compensating the human visual contrast in low light intensity.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
High precision phantom commonly used by cone-beam CT
ActiveCN107348968ALow contrast resolutionImprove detection efficiencyRadiation diagnostics testing/calibrationContrast levelContrast resolution
The invention discloses a high precision phantom commonly used by cone-beam CT. The high precision phantom solves the problem that in the existing technology, no image quality detection phantom is suitable for Micro-CT and dental cone-beam CT at the same time, and the phantom has the effects of high detection efficiency and cost reduction. According to the technical scheme, the phantom includes a rectangular shell body 1 which is internally provided with a cylindrical cavity 2, and seven detection modules are arranged inside the cylindrical cavity 2, and includes a spatial resolution detection module, a low contrast resolution detection module, a three-dimensional pixel value detection module, a seam thickness detection module, a gland simulation module, a tooth bone simulation module and a geometric distortion and CT value calibration module.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
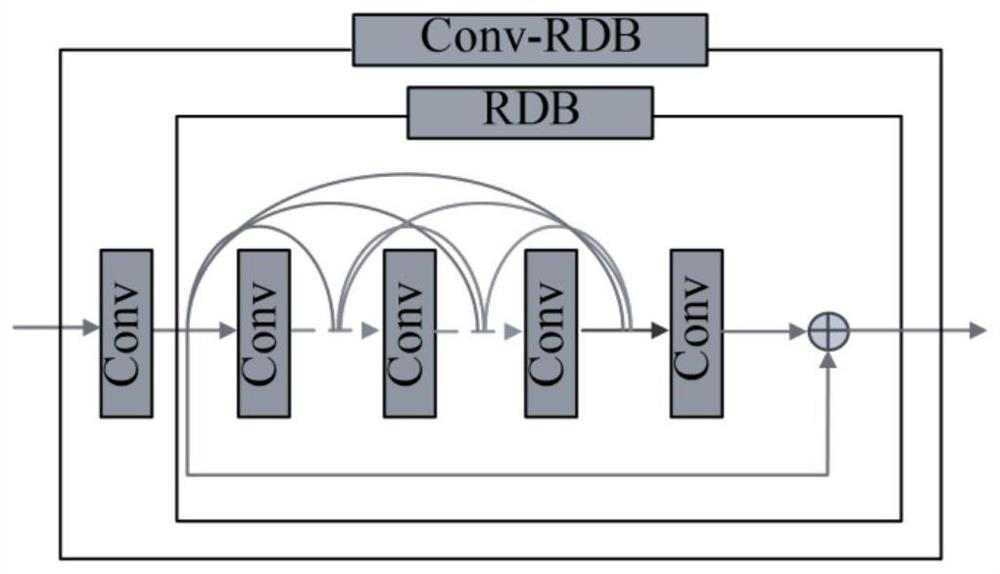
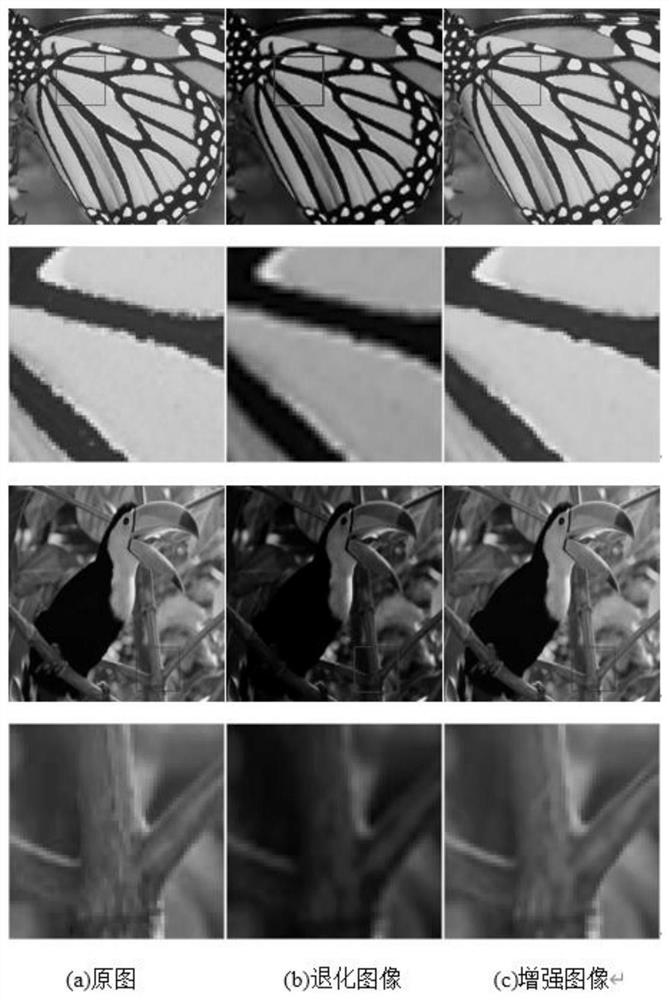
Hybrid degraded image enhancement method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN112801904AEnlarge image sizeIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisContrast resolutionSingle image
In order to solve the problem that a single image enhancement model cannot process a mixed degraded image, the invention provides a hybrid degraded image enhancement method based on a convolutional neural network, namely a fully convolutional sub-pixel residual dense network (FCSRDN), the network is based on the fully convolutional neural network (FCN), the residual network and the dense network are connected through a ResNet and a dense Net, and the enhanced model of the mixed degraded image based on the FCSRDN is used for enhancing the mixed degraded image based on the FCSRDN. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out feature fusion on an original image, finishing feature fusion of each level of the original image, carrying out up-sampling by combining a sub-pixel convolutional layer, and enlarging the size of the image to finally obtain an enhanced image. According to the method, network input of any size can be accepted, compared with an existing method, enhancement in the three aspects of contrast ratio improvement, resolution ratio improvement, denoising and the like can be completed at the same time, and good enhancement effects are achieved in all aspects.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Ultrasound contrast imaging method and apparatus
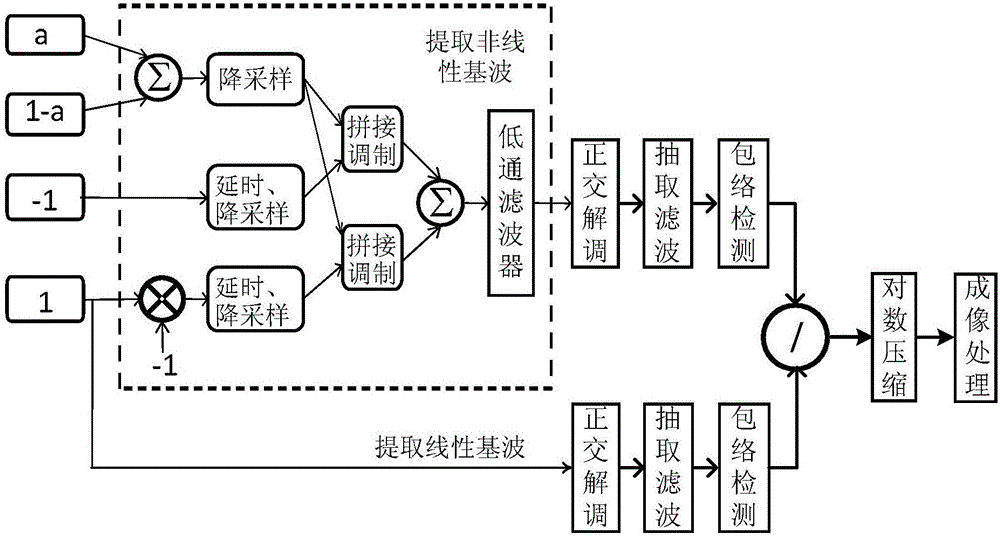
ActiveCN106061396AIncrease CTRHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsLinear componentSonification
The invention provides an ultrasound contrast imaging method and apparatus. The method comprises: S1. transmitting a plurality of pulse waveform sequences, and acquiring echo signals of various pulses; S2. processing echoes of the various pulses to extract non-linear components of the echoes, and acquiring amplitude information about the non-linear components; S3. selecting echoes of any one or more pulses for processing to extract linear components of the echoes, and acquiring amplitude information about the linear components; S4. using the amplitude information about the non-linear components and that of the linear components to generate a non-linear parameter; and S5. performing imaging processing on the non-linear parameter. In the method, by simultaneously using amplitude information about linear components and non-linear components of an echo to generate a non-linear parameter, and performing imaging after processing this parameter, tissue residues can be effectively inhibited, and the dynamic range of a contrast agent signal is increased, thereby improving the CTR and contrast resolution of a contrast image.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ultrasonic guided wave transducer, terminal equipment and fingerprint identification method
PendingCN110633601AImprove signal-to-noise ratioGuaranteed Spatial ResolutionPrint image acquisitionSonificationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
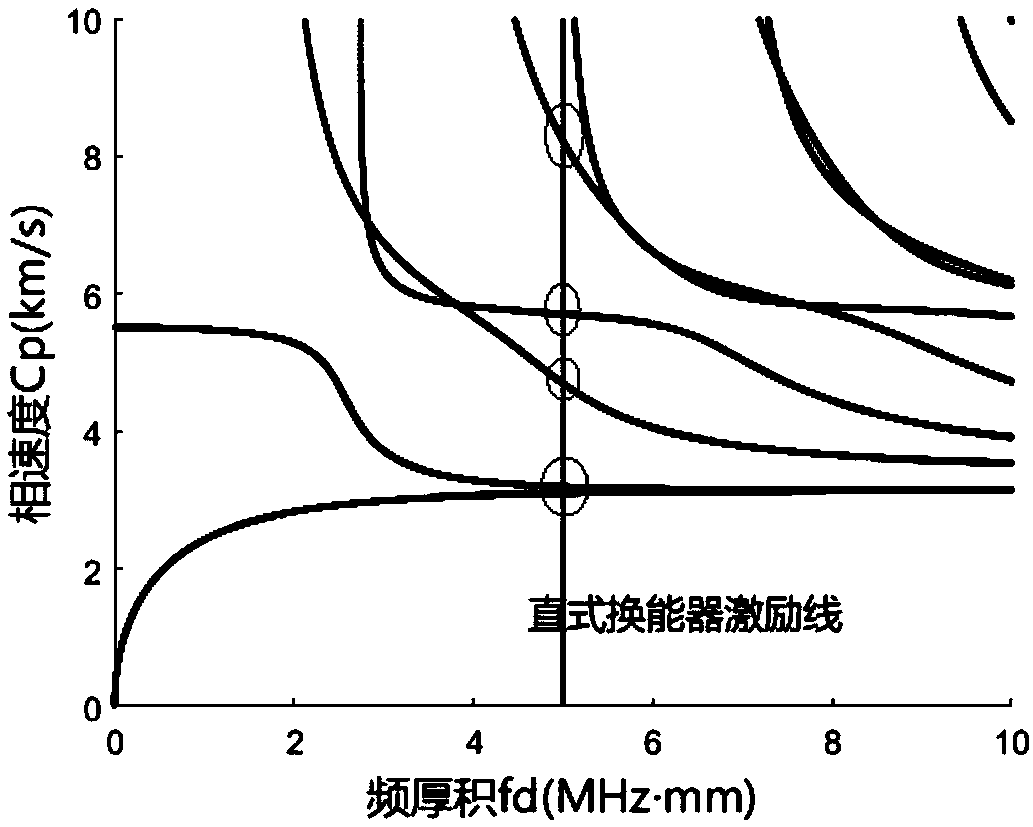
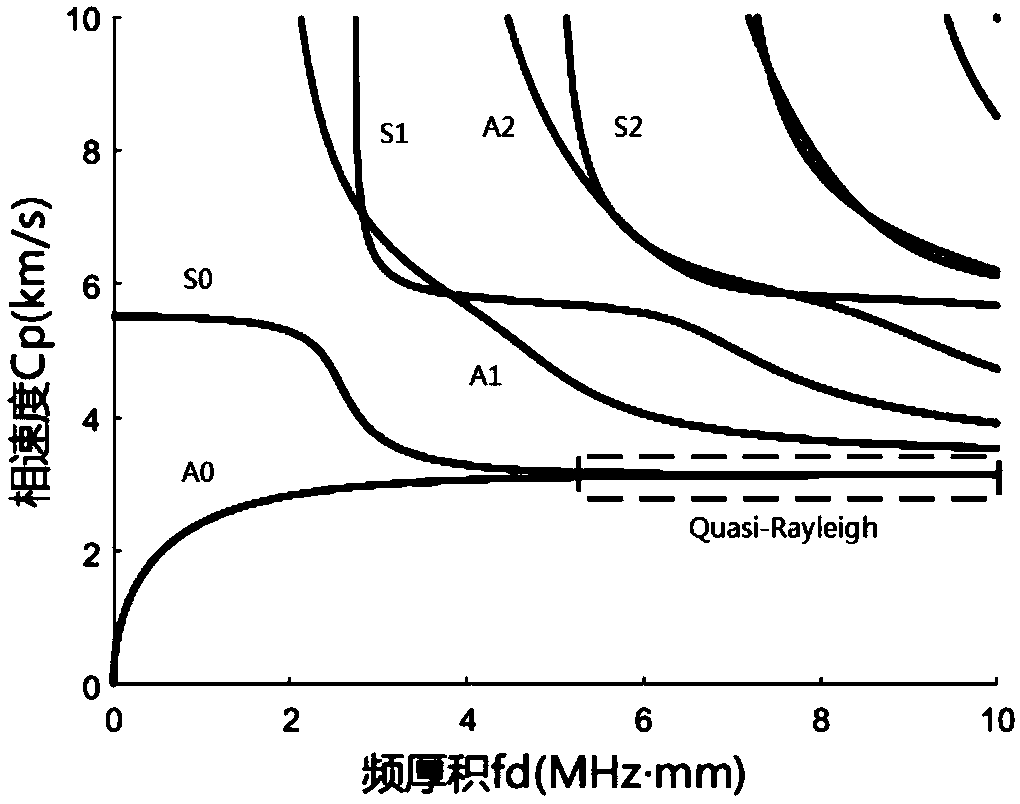
The embodiment of the invention relates to terminal equipment. The terminal equipment comprises a display screen and a processing circuit. The display screen comprises an ultrasonic guided wave transducer array, and the ultrasonic guided wave transducer array comprises at least one ultrasonic guided wave transducer. The at least one ultrasonic guided wave transducer can excite a Quasi-Rayleigh modal ultrasonic guided wave signal. The working frequency thickness product of the ultrasonic guided wave transducer is within the range of 5MHz. mm to 15MHz. mm. The at least one ultrasonic guided wavetransducer is used for transmitting an ultrasonic guided wave sound field signal. The processing circuit receives the scattered sound field signal, obtains a first fingerprint image according to thescattered sound field signal, and compares the first fingerprint image with a pre-stored second fingerprint image. When the first fingerprint image is matched with the second fingerprint image, an application operation is executed. The terminal excites an ultrasonic guided wave sound field with good characteristics and single mode on the display screen cover plate glass, weakens the influence of frequency dispersion characteristics of the sound field, eliminates coherent interference caused by multi-mode characteristics, improves the signal-to-noise ratio of a detection signal, and ensures thespatial resolution and contrast resolution of fingerprint imaging.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Self-adaptive bottom video mining method based on contrast resolution compensation
The invention provides a self-adaptive bottom video mining method based on contrast resolution compensation, comprising the steps of obtaining the original average gray of a video frame; obtaining the best compensation factor of the contrast resolution of the video frame according to the average gray press-down type; compensating the contrast resolution of the video frame by using the best compensation factor; displaying and memorizing the compensated video stream, thus completing the bottom video mining. In the invention, the self-adaptive bottom video mining on the video photographed under low luminance can be realized by the vision contrast resolution compensation method. The essential of the method is as follows: the contrast is replaced by sacrificing the information quantity that can not be sensed by human vision so as to mine the main information that is arranged in photos and can be sensed by human vision conveniently; and the method in the invention can be used for realizing the machine vision for bottom video mining.
Owner:刘晓华 +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com