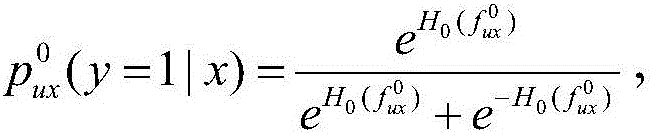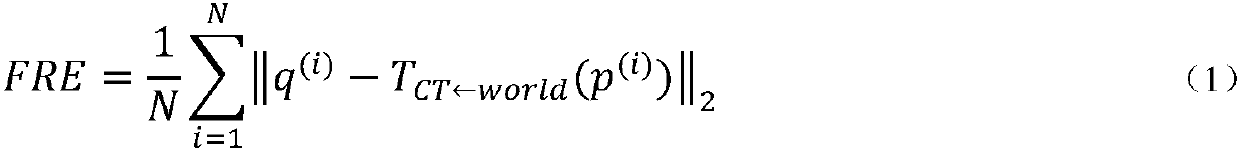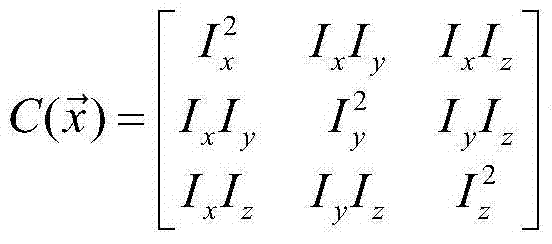Patents
Literature
148 results about "Three dimensional ct" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
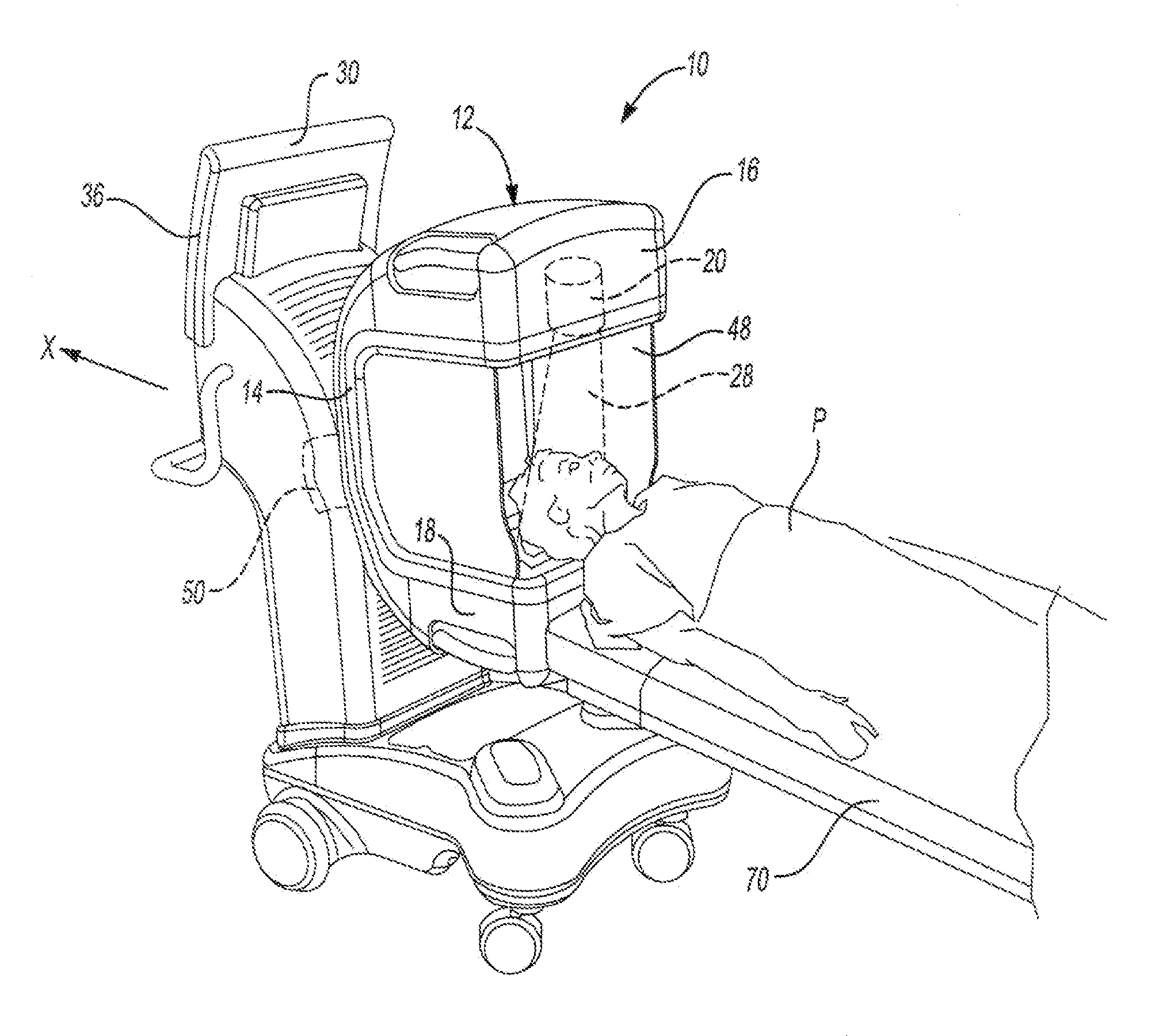
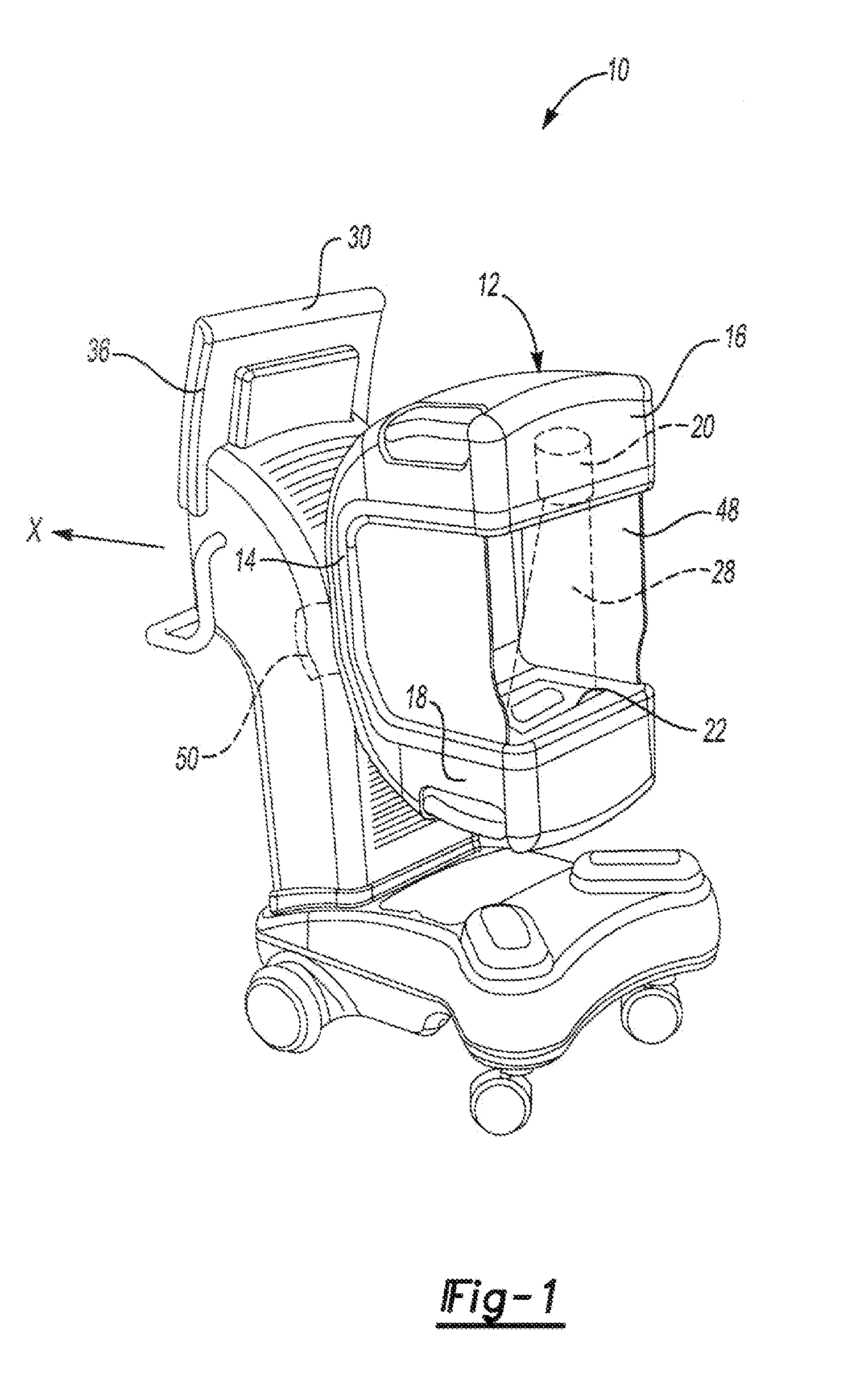
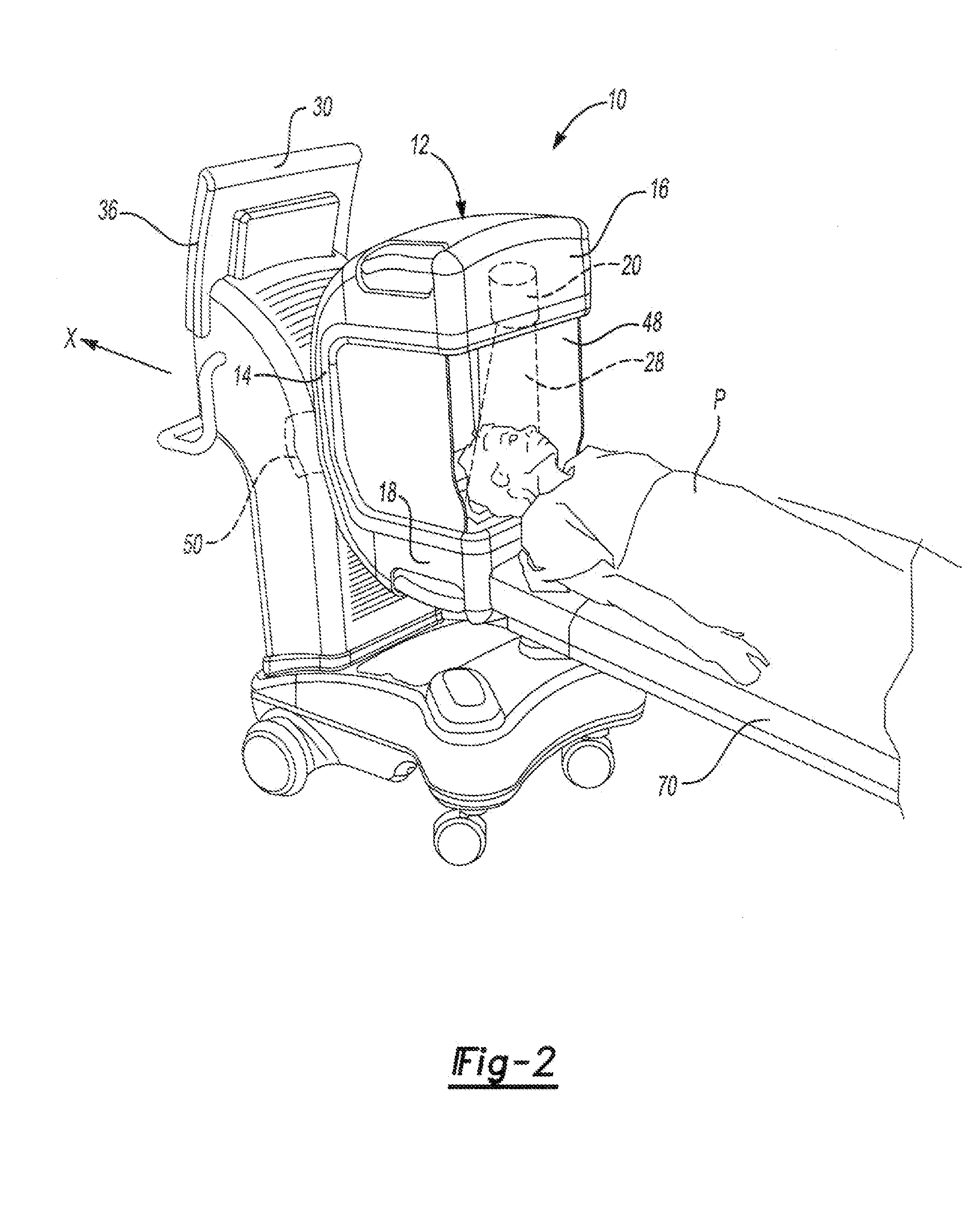
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS20060195004A1Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
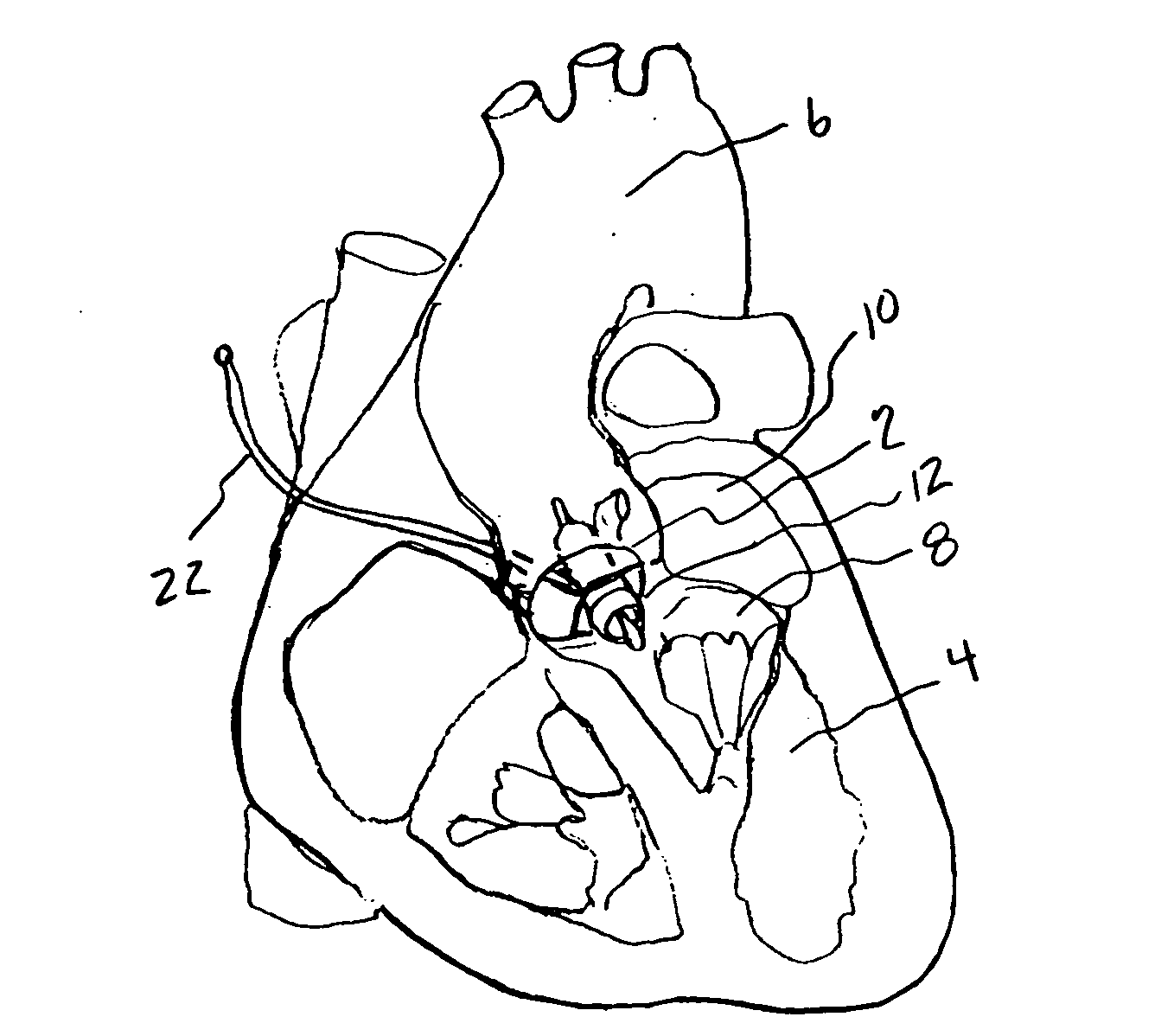
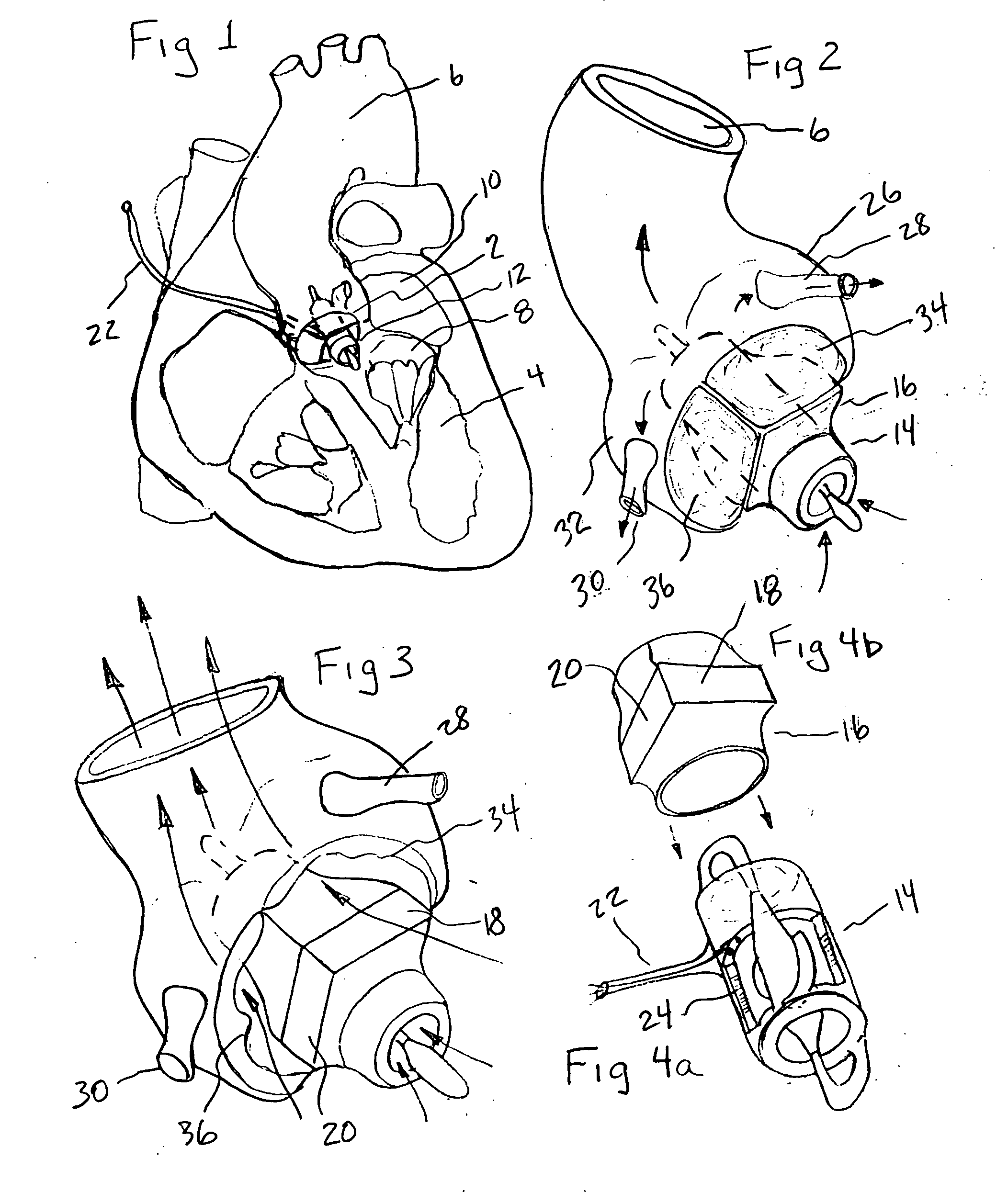
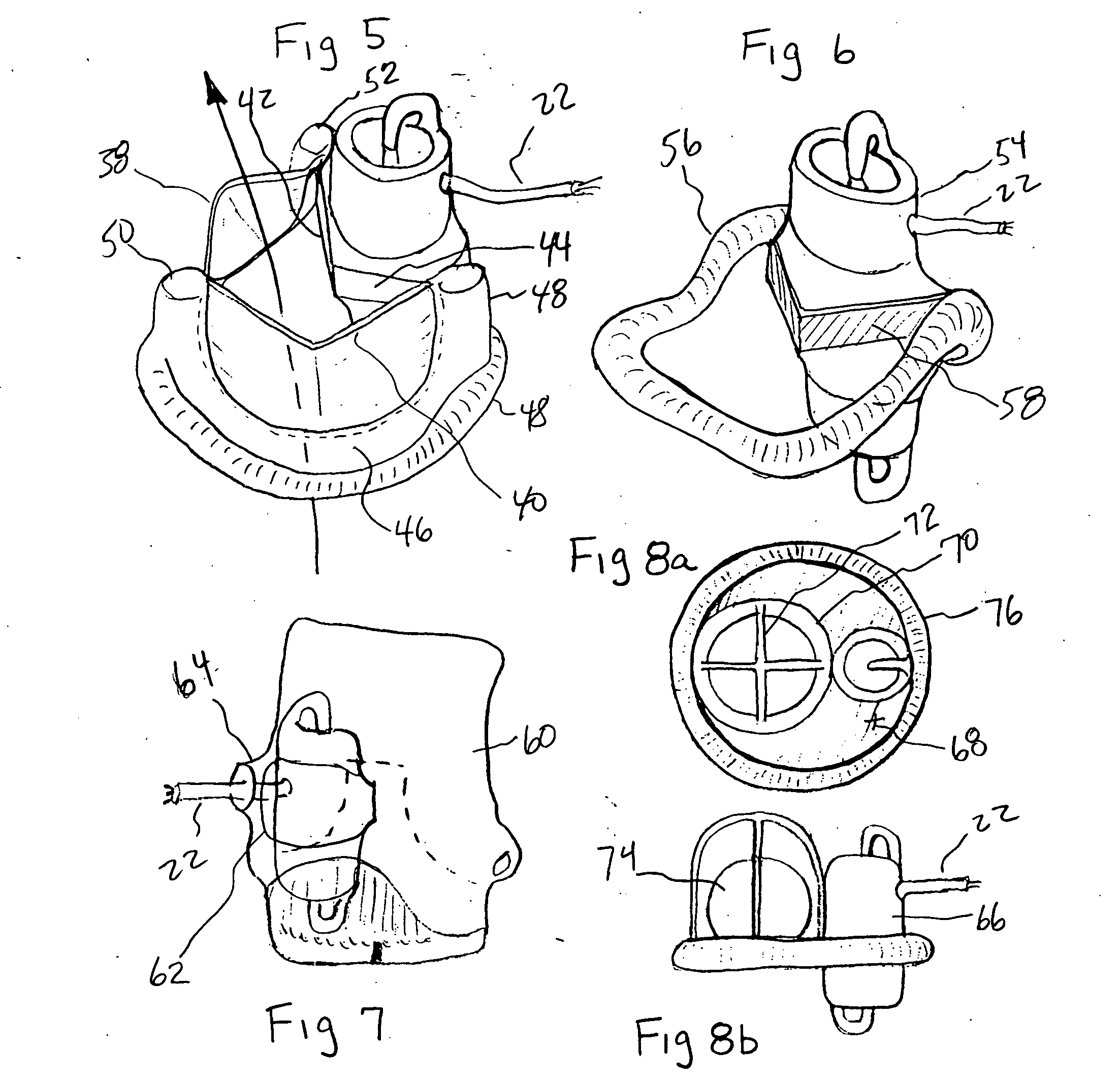
A tiny electrically powered hydrodynamic blood pump is disclosed which occupies one third of the aortic or pulmonary valve position, and pumps directly from the left ventricle to the aorta or from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. The device is configured to exactly match or approximate the space of one leaflet and sinus of valsalva, with part of the device supported in the outflow tract of the ventricular cavity adjacent to the valve. In the configuration used, two leaflets of the natural tri-leaflet valve remain functional and the pump resides where the third leaflet had been. When implanted, the outer surface of the device includes two faces against which the two valve leaflets seal when closed. To obtain the best valve function, the shape of these faces may be custom fabricated to match the individual patient's valve geometry based on high resolution three dimensional CT or MRI images. Another embodiment of the invention discloses a combined two leaflet tissue valve with the miniature blood pump supported in the position usually occupied by the third leaflet. Either stented or un-stented tissue valves may be used. This structure preserves two thirds of the valve annulus area for ejection of blood by the natural ventricle, with excellent washing of the aortic root and interface of the blood pump to the heart. In the aortic position, the blood pump is positioned in the non-coronary cusp. A major advantage of the transvalvular VAD is the elimination of both the inflow and outflow cannulae usually required with heart assist devices.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
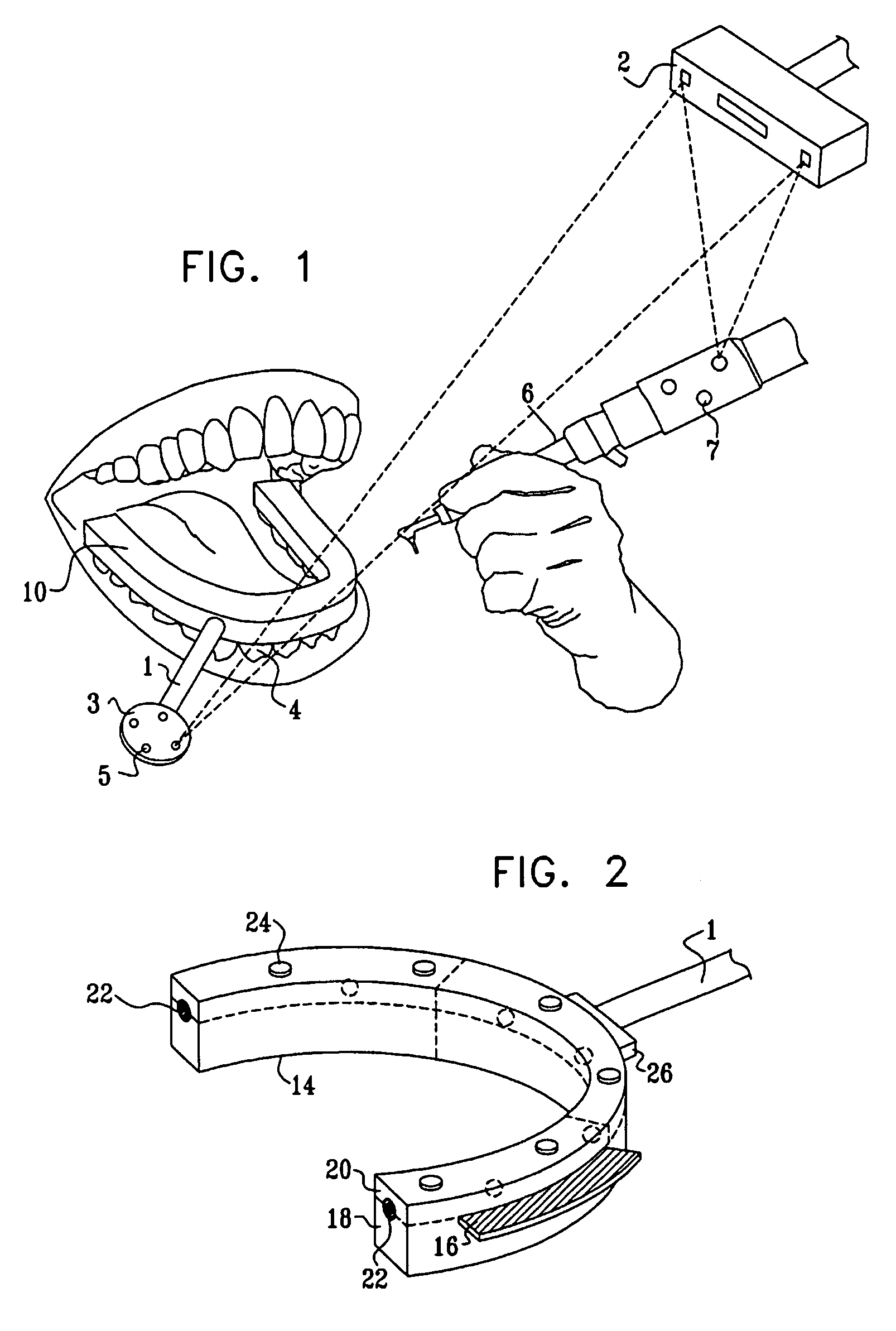
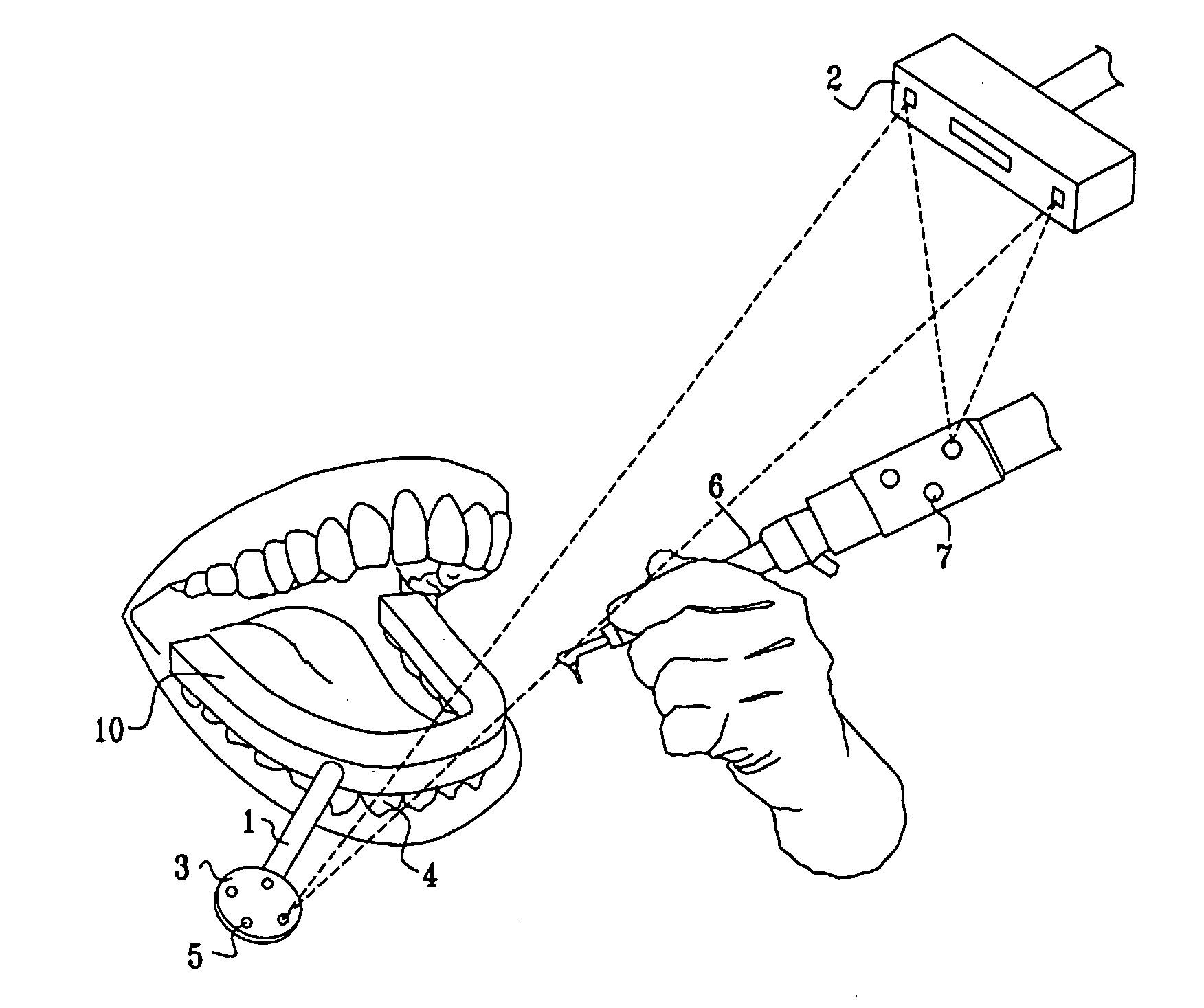
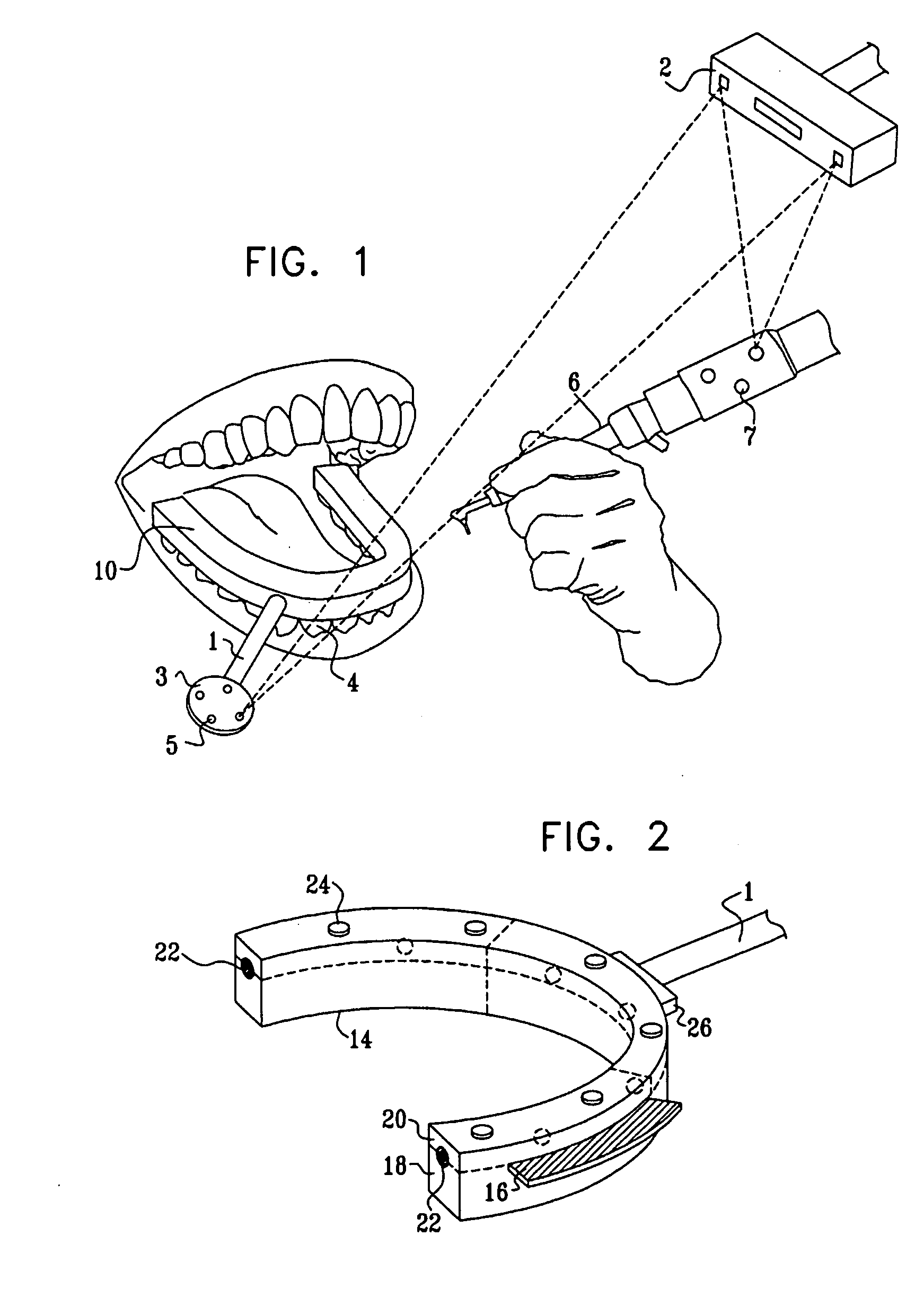
Image guided implantology methods
InactiveUS7457443B2Accurate dataEfficient use ofImpression capsImage analysisThree dimensional ctMri image
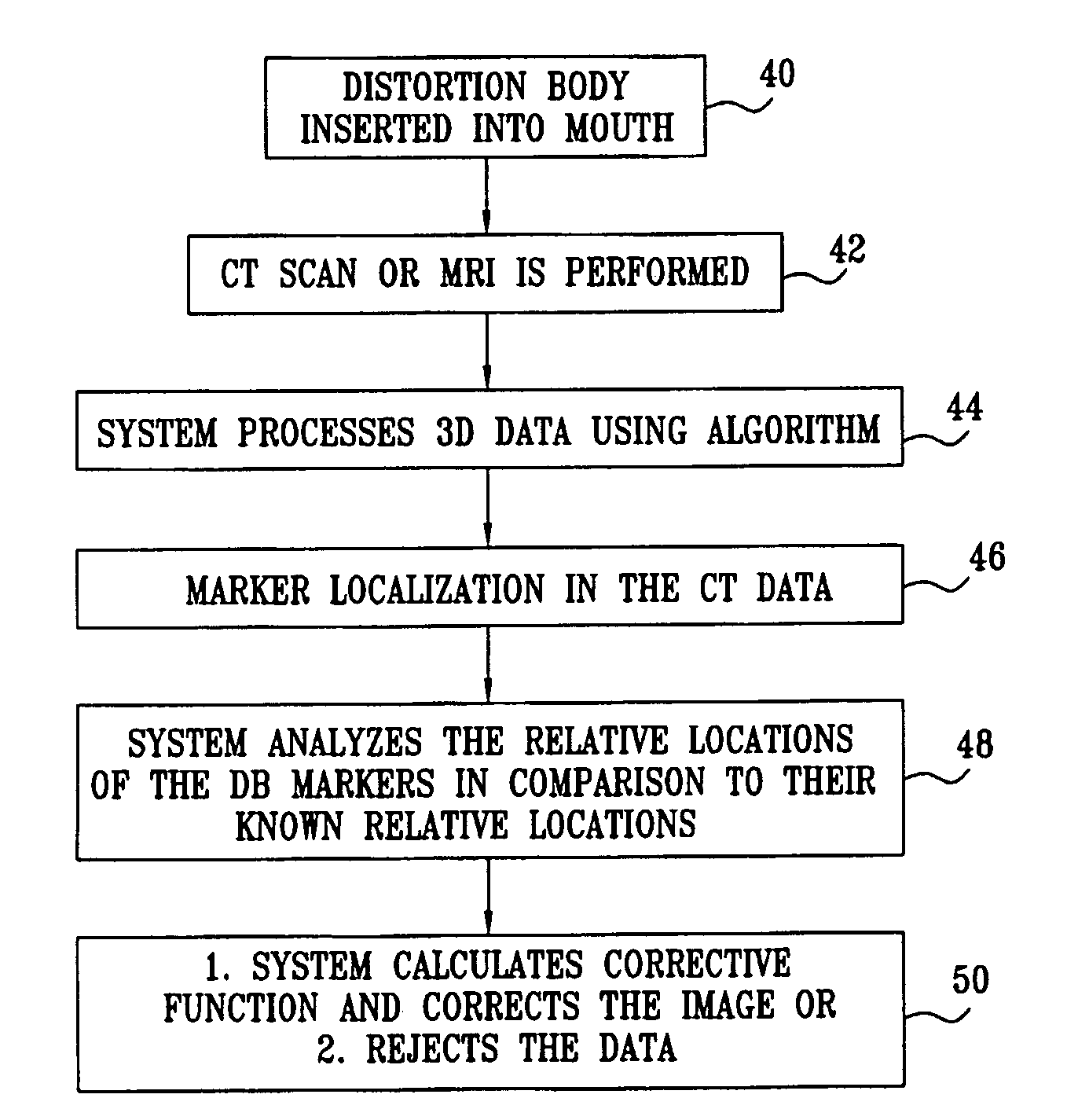
A method for correcting inherent distortions in a CT or MRI imaging process, or distortions arising from excessive patient movement during the scan by means of a registration device inserted into the mouth of the patient at the time the scan is being performed. The registration device incorporates a set of fiducial markers disposed in a predetermined three-dimensional pattern. The exact positions of the fiducial markers are known with respect to each other, thus providing a three-dimensional reference against which the resulting images can be compared. Additionally, a method whereby three-dimensional CT or MRI images taken prior to an operation, are accurately registered and integrated with real-time tracking positional data of the patient's body part and instruments operating thereon. Application is described for the drilling of a patient's jaw for the placement of dental implants.
Owner:IMAGE NAVIGATION LTD
Image guided implantology methods
InactiveUS20050163342A1Accurate dataEfficient use ofImpression capsImage analysisThree dimensional ctMri image
A method for correcting inherent distortions in a CT or MRI imaging process, or distortions arising from excessive patient movement during the scan by means of a registration device inserted into the mouth of the patient at the time the scan is being performed. The registration device incorporates a set of fiducial markers disposed in a predetermined three-dimensional pattern. The exact positions of the fiducial markers are known with respect to each other, thus providing a three-dimensional reference against which the resulting images can be compared. Additionally, a method whereby three-dimensional CT or MRI images taken prior to an operation, are accurately registered and integrated with real-time tracking positional data of the patient's body part and instruments operating thereon. Application is described for the drilling of a patient's jaw for the placement of dental implants.
Owner:IMAGE NAVIGATION LTD
Method for remodeling three-dimensional pore structure of core
The invention relates to a method for remodeling a three-dimensional pore structure of a core. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out high-resolution three-dimensional micro-CT (Captive Test) on a full diameter core so as to generate full diameter core CT data; selecting a core matrix from the full diameter core to carry out a higher-resolution three-dimensional micro-CT or a casting sheet experiment so as to obtain the information of a pore structure of the matrix; obtaining a secondary three-dimensional pore structure through three-dimensional CT remodeling by utilizing the full diameter core CT data; obtaining the three-dimensional pore structure of the matrix through the three-dimensional CT remodeling by utilizing the obtained information of the pore structure of the matrix or through geological statistics remodeling by utilizing sheet images; integrating the three-dimensional pore structure of the full diameter core with the three-dimensional pore structure of the matrix so as to obtain a three-dimensional fine pore structure of the core, which is provided with both secondary pore characteristics and matrix pore characteristics; and obtaining parameters of pore structures with different dimensions of the core and parameters of connectivity of three-dimensional space according to the three-dimensional fine pore structure of the core.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
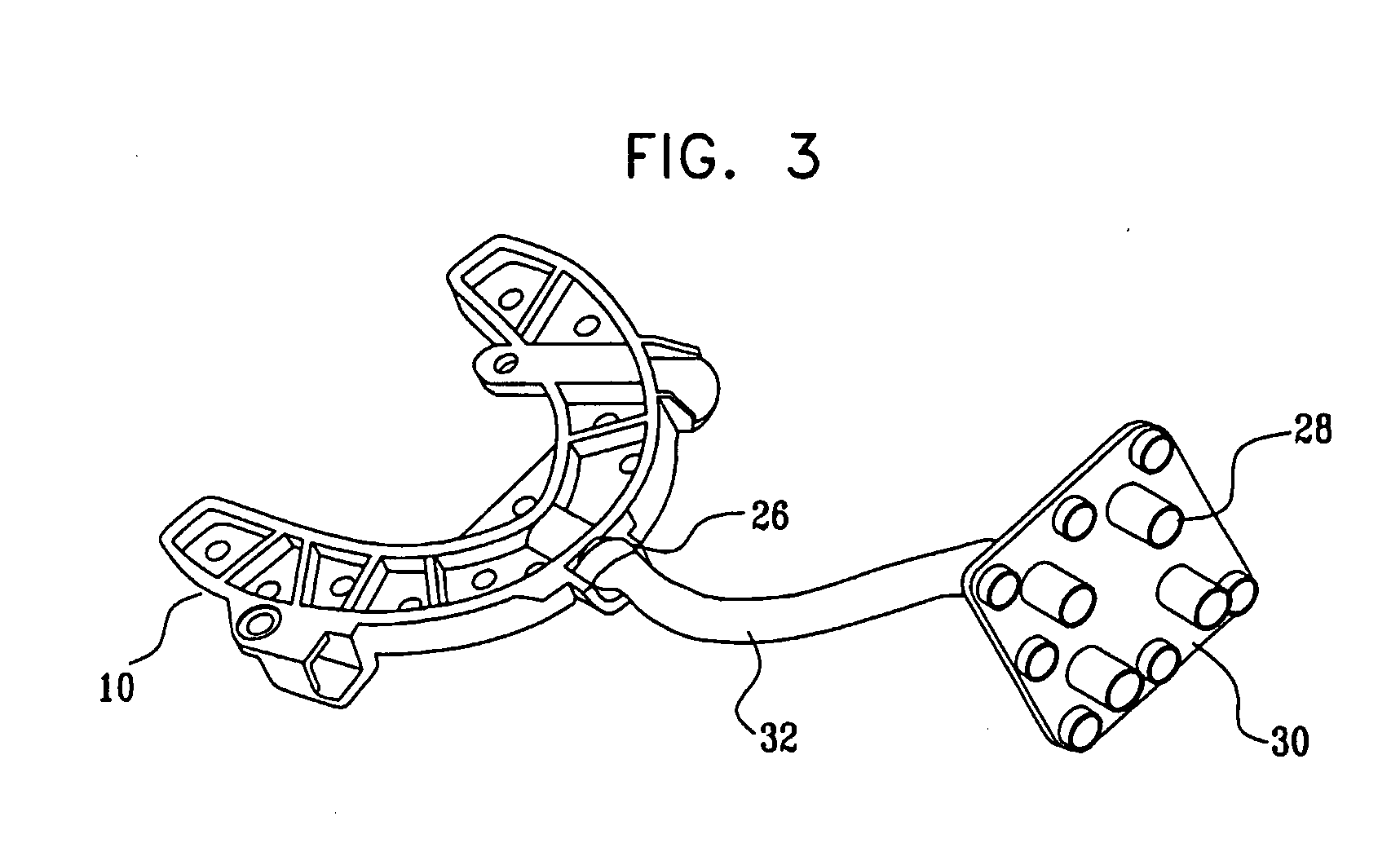
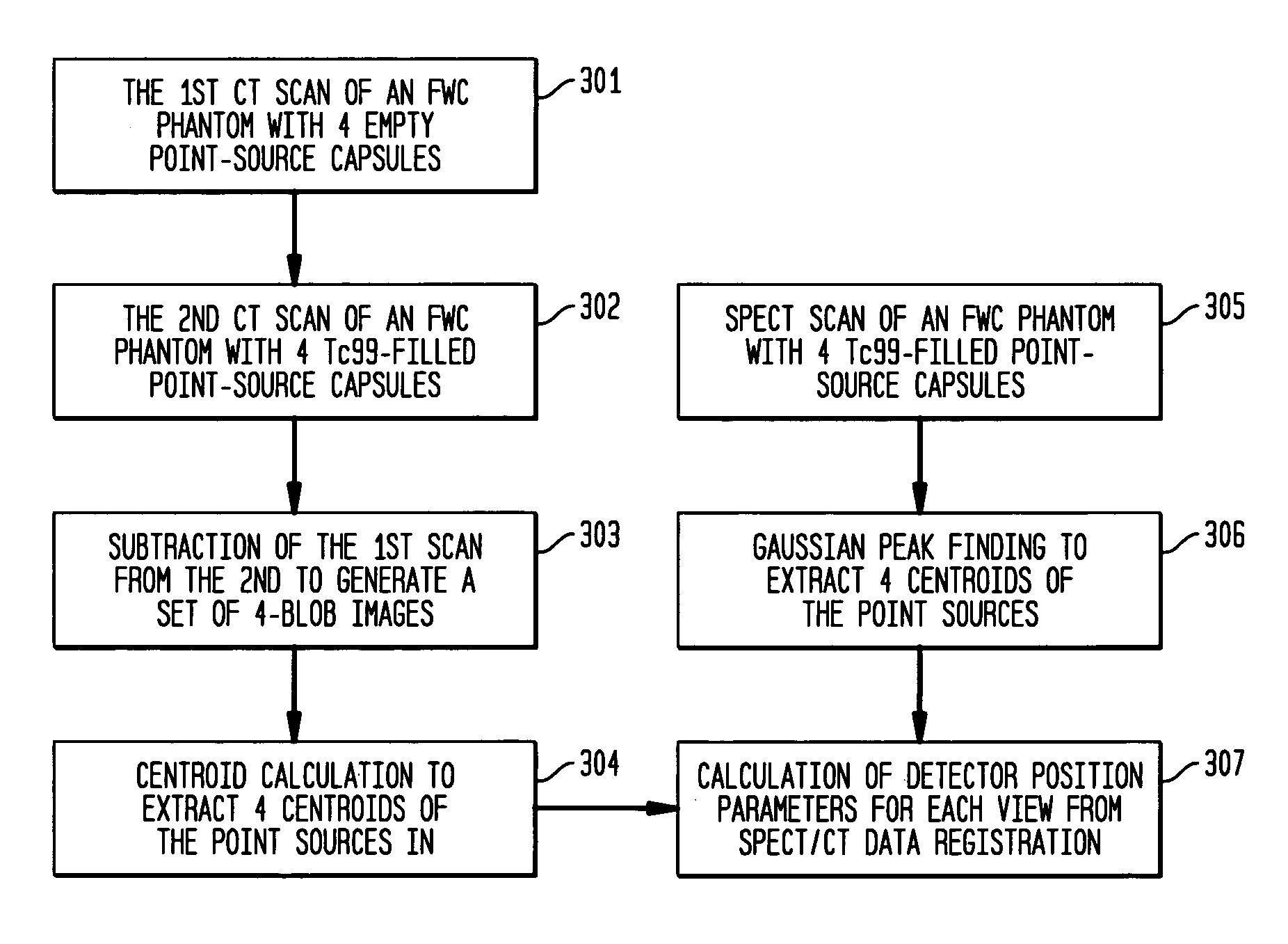
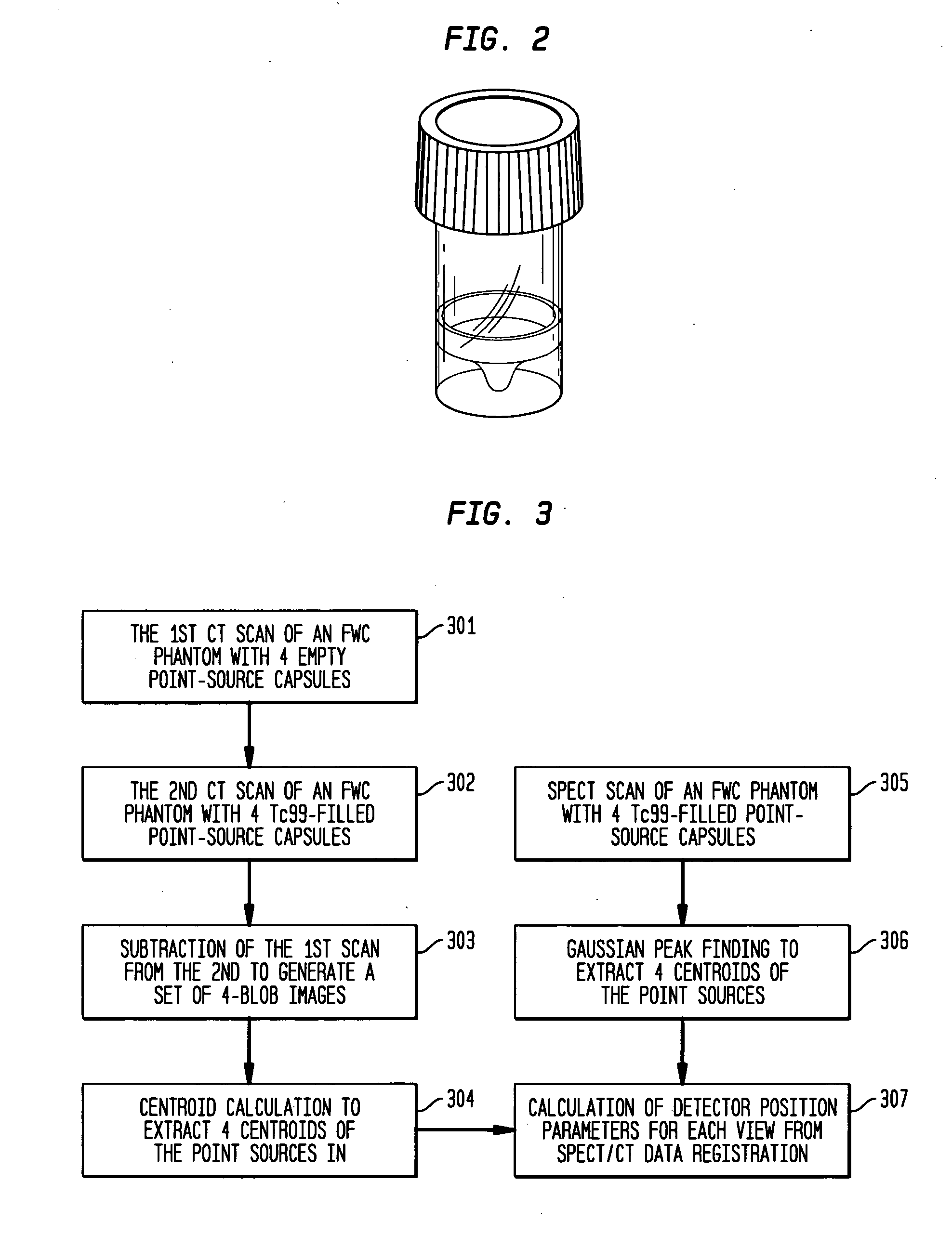
Detector head position correction for hybrid SPECT/CT imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20060214097A1Accurate image registrationSolve the real problemMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusThree dimensional ctProjection image
A system and method provide for more accurate SPECT / CT image registration. CT data is utilized to establish a global spatial coordinate system of a common test phantom. The common test phantom is then used to obtain a set of point source nuclear images. Three-dimensional CT point source data is mapped to a two-dimensional image plane of corresponding point source data, to obtain a pair of intersecting projection cones that are used to obtain a set of detector head position correction parameters to correct detector head positioning in the CT coordinate system when obtaining SPECT projection images of the same object.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
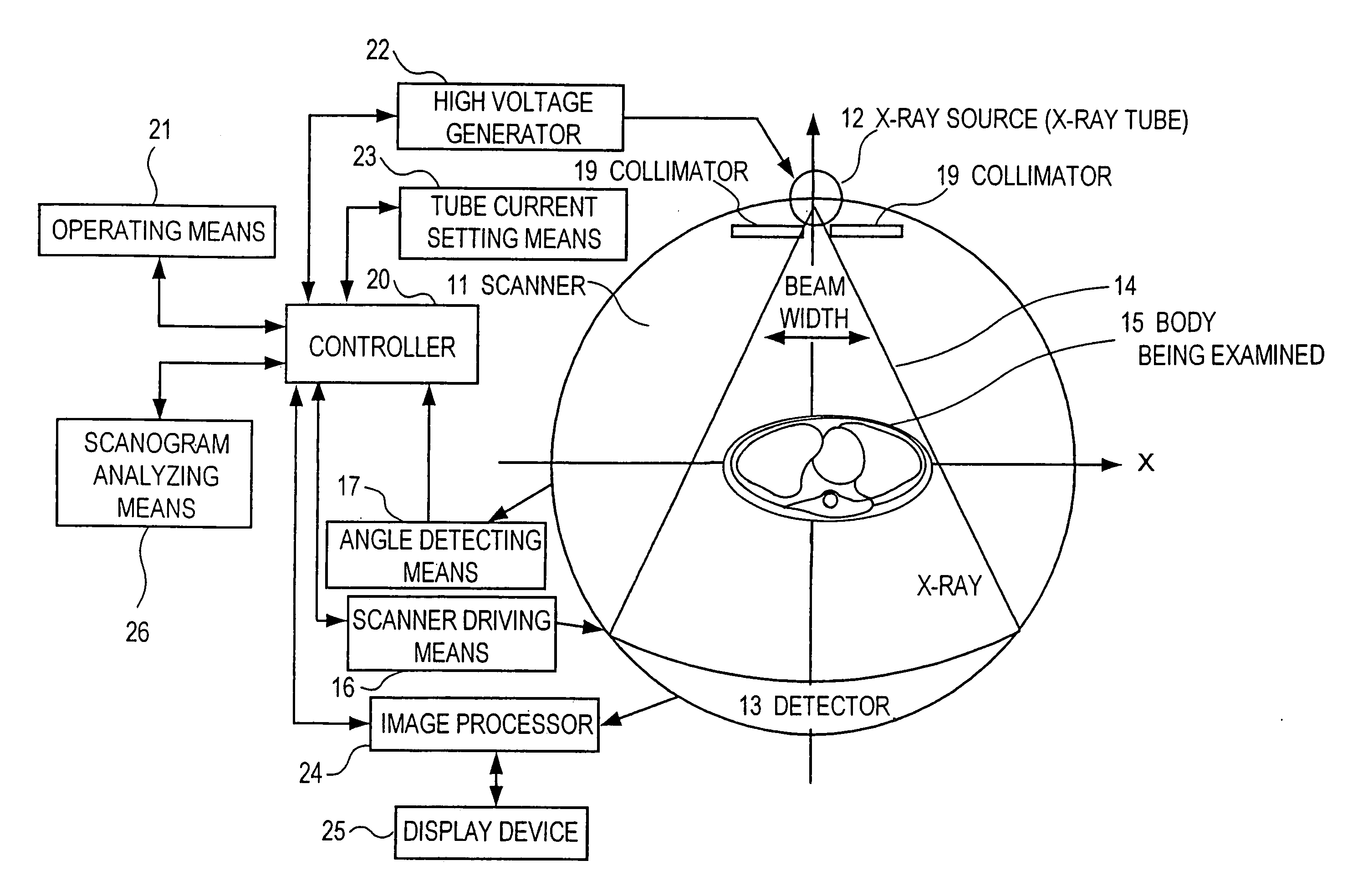
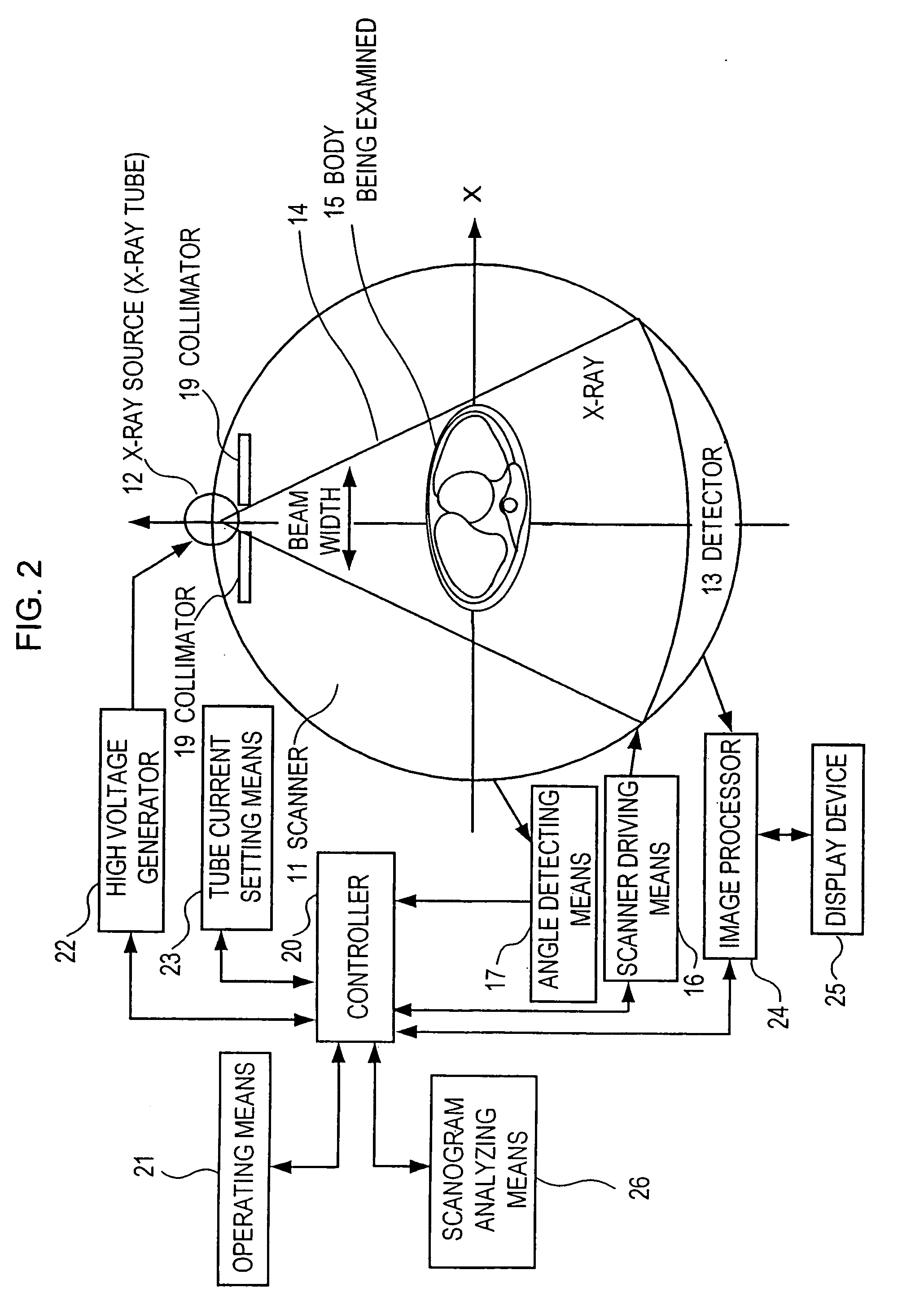
X-ray CT device and image displaying method therefor
InactiveUS7103139B2Shorten the timeEffective imagingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingThree dimensional ctPower flow
In an X-ray CT device, the scan conditions of the device are set, a three-dimensional X-ray passage length model of the body being examined is generated from a scanogram image of the body, the control pattern of the tube current is automatically set on the basis of the scan conditions and the three-dimensional passage length model, and the dose which will be given will be calculated and displayed on the basis of the control pattern of the tube current, and three-dimensional CT value model data of the body generated on the basis of a standard human body. The scanogram image of the body and the control pattern of the tube current are displayed next to each other or overlap to allow an operator to edit the control pattern while viewing the body, so that a suitable tube current can be set.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
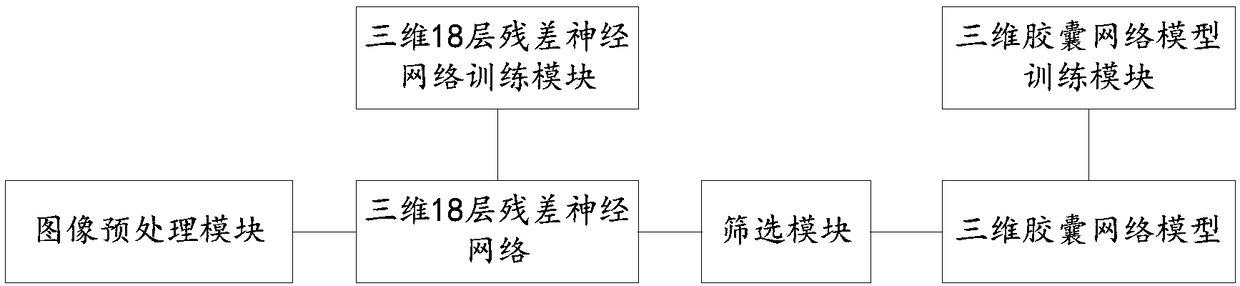
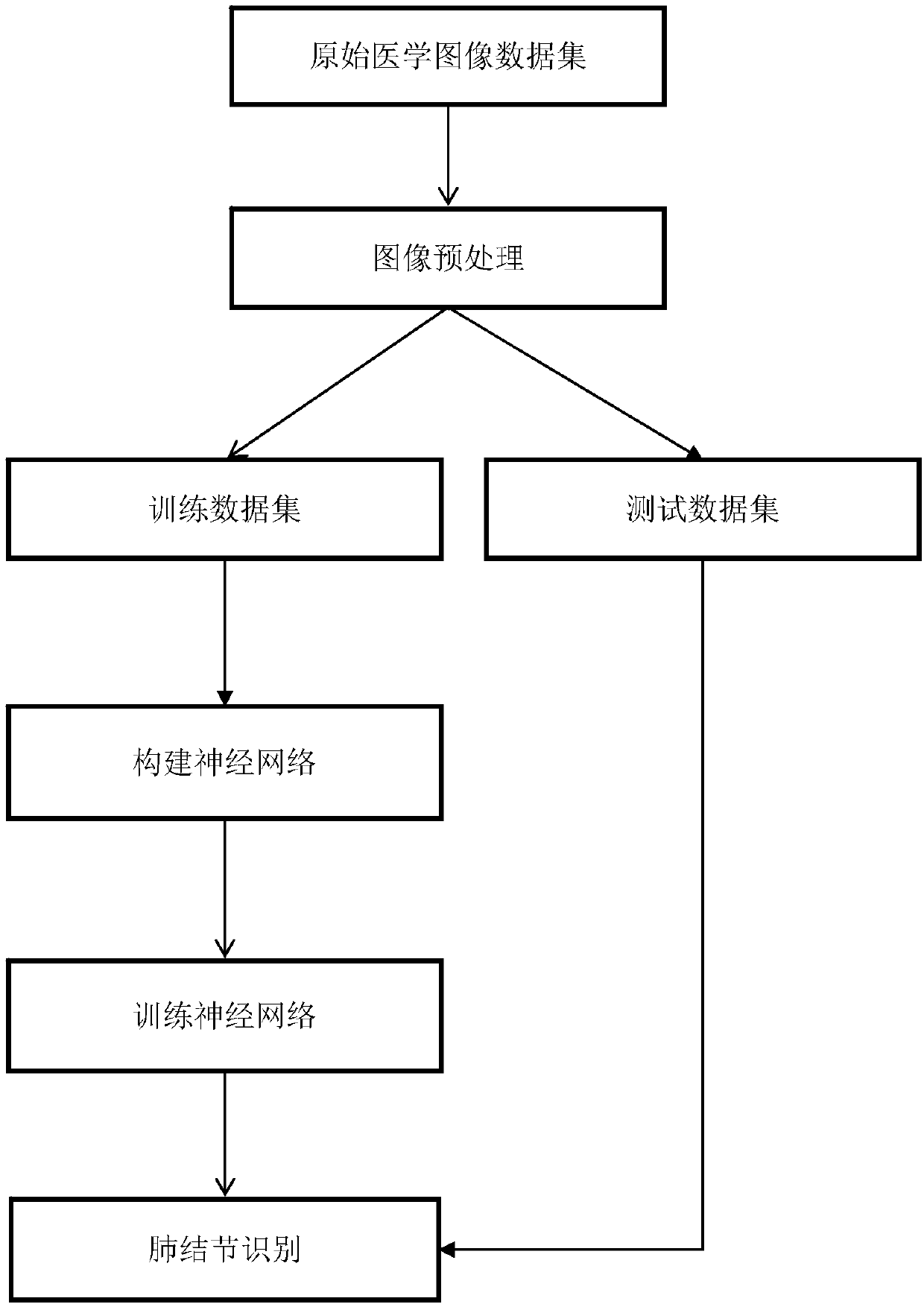
System and method of detecting pulmonary nodule
ActiveCN108830826AEasy to detectImprove recallImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional ctPulmonary nodule
The invention discloses a system and a method of detecting a pulmonary nodule. The system comprises an image preprocessing module, a three-dimensional RPN network model and a three-dimensional capsulenetwork model, wherein the image preprocessing module is used for preprocessing an original three-dimensional CT image to acquire a standard CT image; the three-dimensional RPN network model is usedfor detecting a first candidate pulmonary nodule from the standard CT image outputted from the image preprocessing module; and the three-dimensional capsule network model is used for carrying out false positive pulmonary nodule screening on the first candidate pulmonary nodule outputted by the three-dimensional RPN network model to acquire a pulmonary nodule detection result. According to the technical scheme provided in the invention, while the false positive pulmonary nodule detection rate is ensured to be lower, a high recall ratio is ensured to be realized for the pulmonary nodule, and thedetection method is simple and the detection speed is quick.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
CT image liver segmentation method and system based on automatic context model
ActiveCN105957066AImprove Segmentation AccuracyGood segmentation resultImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional ctPrior information
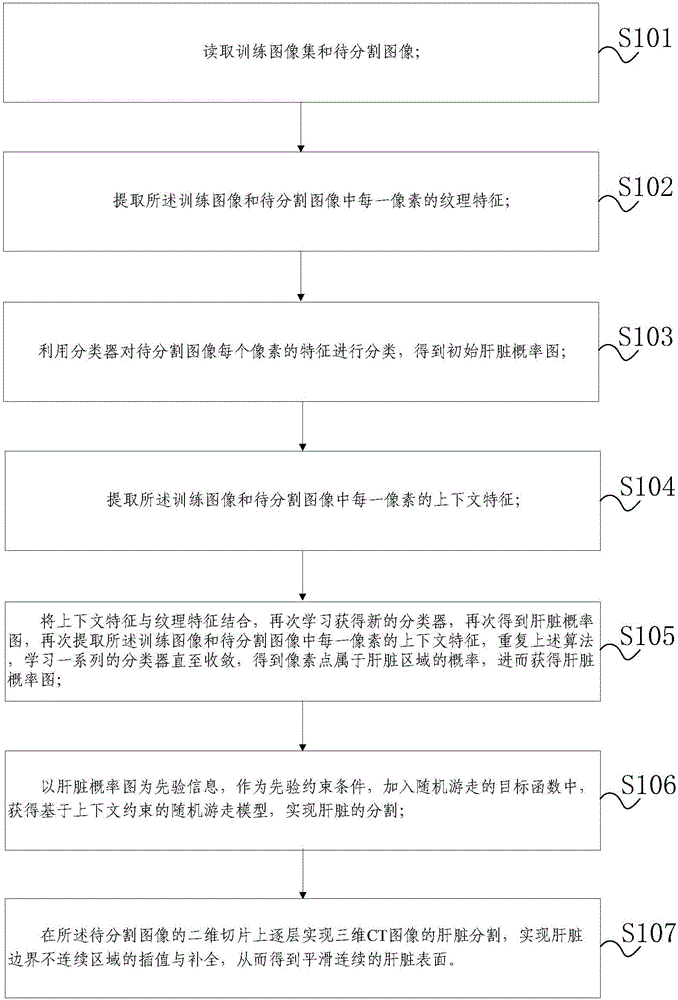
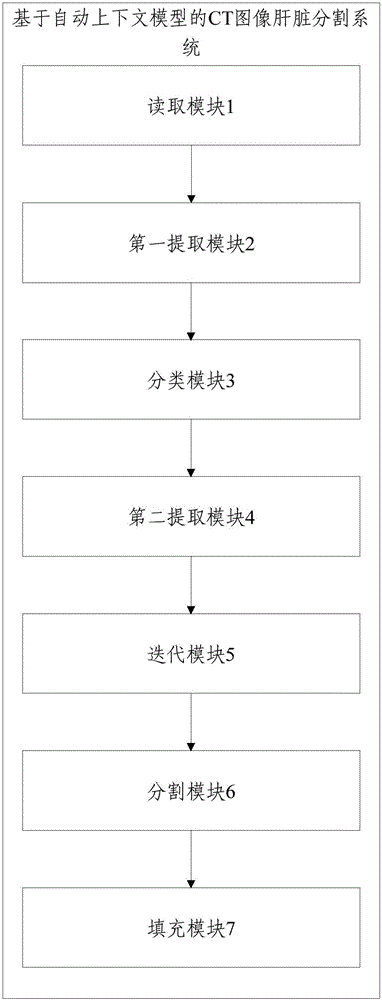
The invention discloses a CT image liver segmentation method and system based on an automatic context model and capable of increasing liver segmentation precision in a CT image. The method comprises steps of: reading a training image set and a to-be-segmented image; extracting the textural feature of each pixel in the images; classifying the feature of each pixel in the to-be-segmented image by using a classifier to obtain an initial liver probability graph; extracting the context feature of each pixel in the images; combining the context features with the textural features and learning a series of classifiers by means of iteration until convergence to obtain a liver probability graph; using the liver probability graph as prior information and adding the liver probability graph a prior constraint condition to a randomly walking objective function as to obtain a random walk model based on context constraint for segmenting the liver; achieving liver segmentation of a three-dimensional CT image layer by layer on a two-dimensional slice of the to-be-segmented image, and interpolation and complement of a liver bound discontinuous area so as to obtain a smooth continuous liver surface.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method
InactiveCN104637061AFast and Accurate Guided TreatmentFast and accurate registrationImage enhancementImage analysisIn planeThree dimensional ct
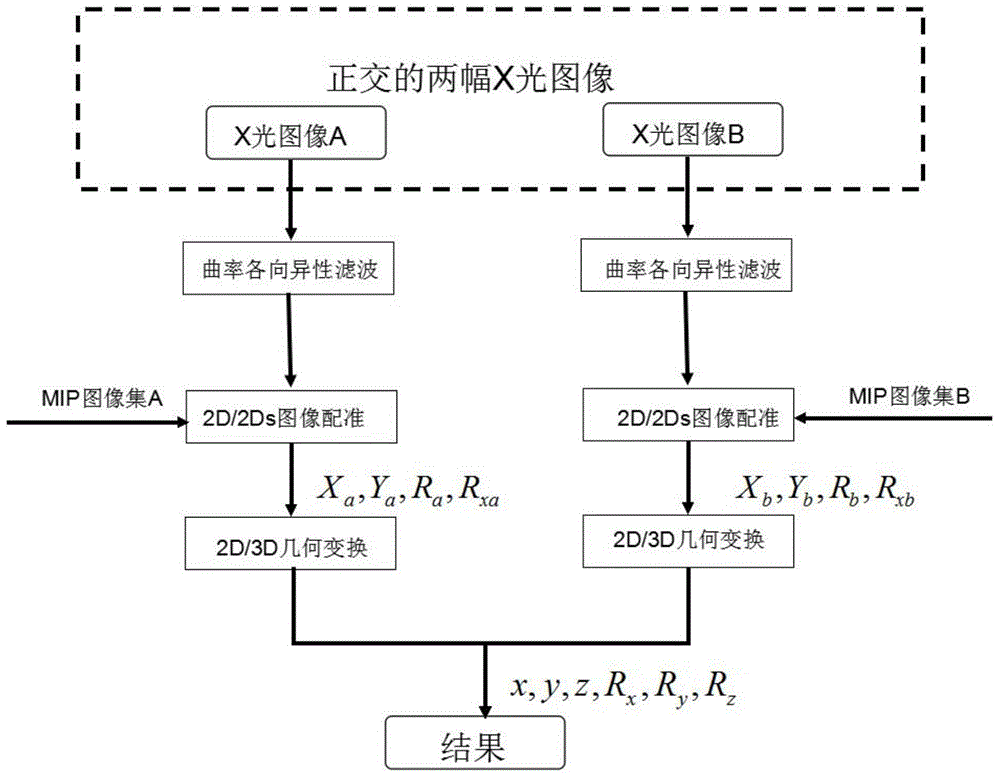
The invention provides a two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method, which can quickly carry out registration on an intra-operative two-dimensional X-ray image and a preoperative three-dimensional CT (Computed Tomography) image. The two-dimensional and three-dimensional medical image registration method comprises the following steps: carrying out filtering preprocessing on the three-dimensional CT image, projecting the three-dimensional CT image in two mutually-orthogonal plane systems to obtain two corresponding digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) sets according to a maximum intensity projection (MIP) algorithm; obtaining two two-dimensional X-ray images on another two orthogonal planes, and carrying out the filtering preprocessing on the two-dimensional X-ray image; carrying out traversal on the two DRR sets, and carrying out registration on the two DRR sets and another two orthogonal two-dimensional X-ray images so as to determine a corresponding most similar DRR as well as the in-plane position coordinate, the in-plane rotation angle and an out-of-plane rotation angle of the DRR; converting the coordinate and the angles to be under a three-dimensional CT image coordinate system to obtain six registration parameters. According to the method, the X-ray image and the CT image which is generated in advance can be subjected to accurate and quick real-time registration.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple source CT scanner
InactiveUS20060285633A1Expand field of viewReduced dimensionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingThree dimensional ctCt scanners
A CT scanner includes a plurality of cone-beam x-ray sources offset along a CT axis. A detector is positioned opposite the x-ray sources. The x-ray sources and detector are rotatable about the CT axis. The x-ray sources direct x-rays through the patient that are received by the detector at a plurality of rotational positions, thereby generating projections from the plurality of x-ray sources that are used to construct the three-dimensional CT image of the patient.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS7479102B2Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
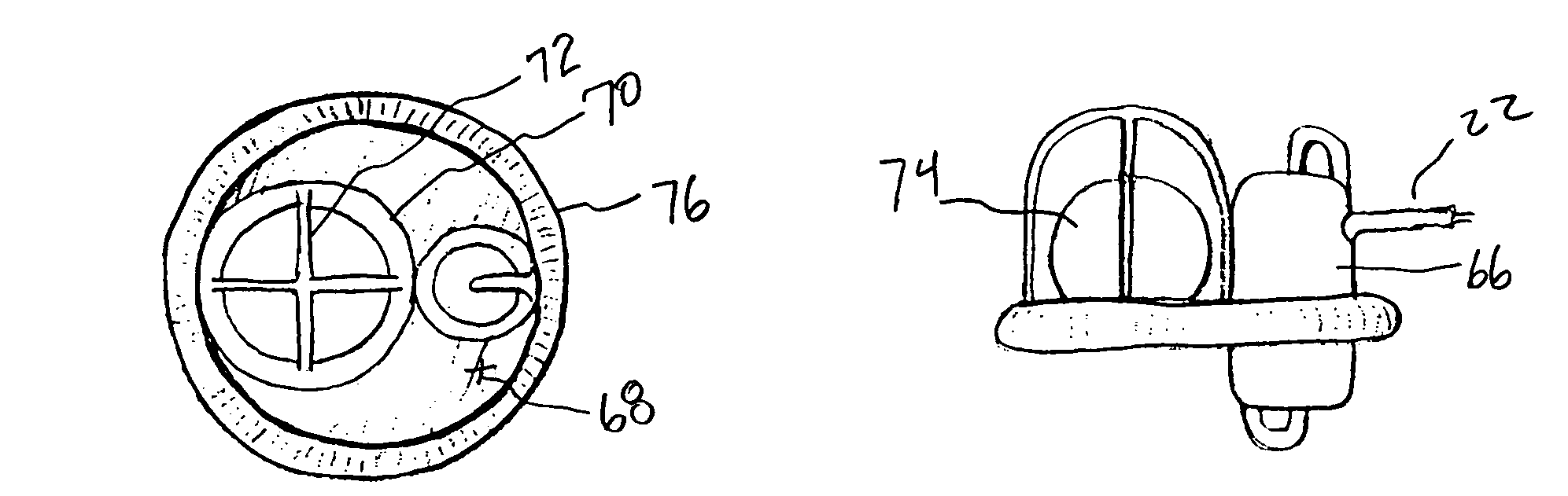
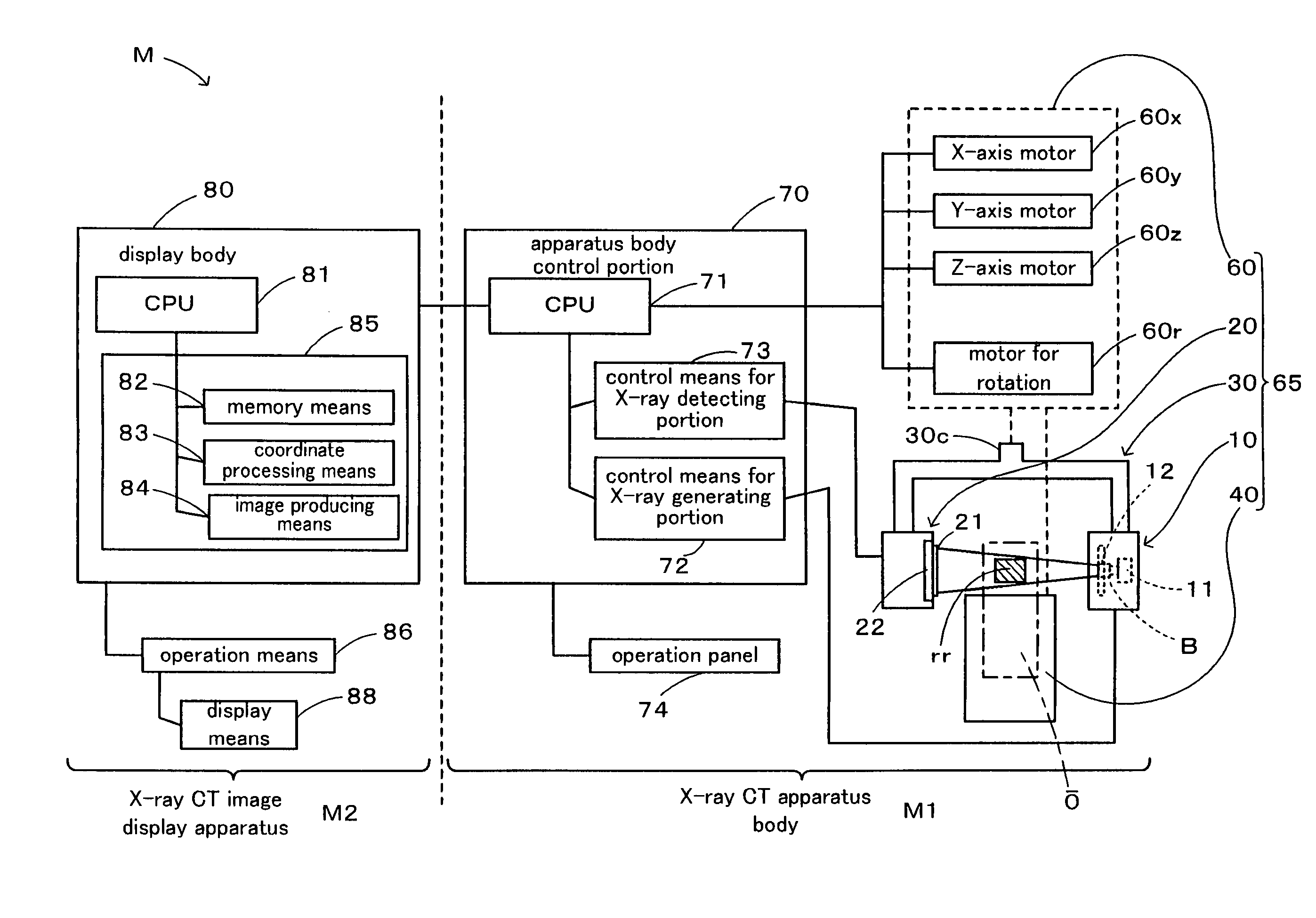
Display method of X-ray CT image of maxillofacial area, X-ray CT apparatus and X-ray image display apparatus
ActiveUS7787586B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingThree dimensional ctPresent method
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
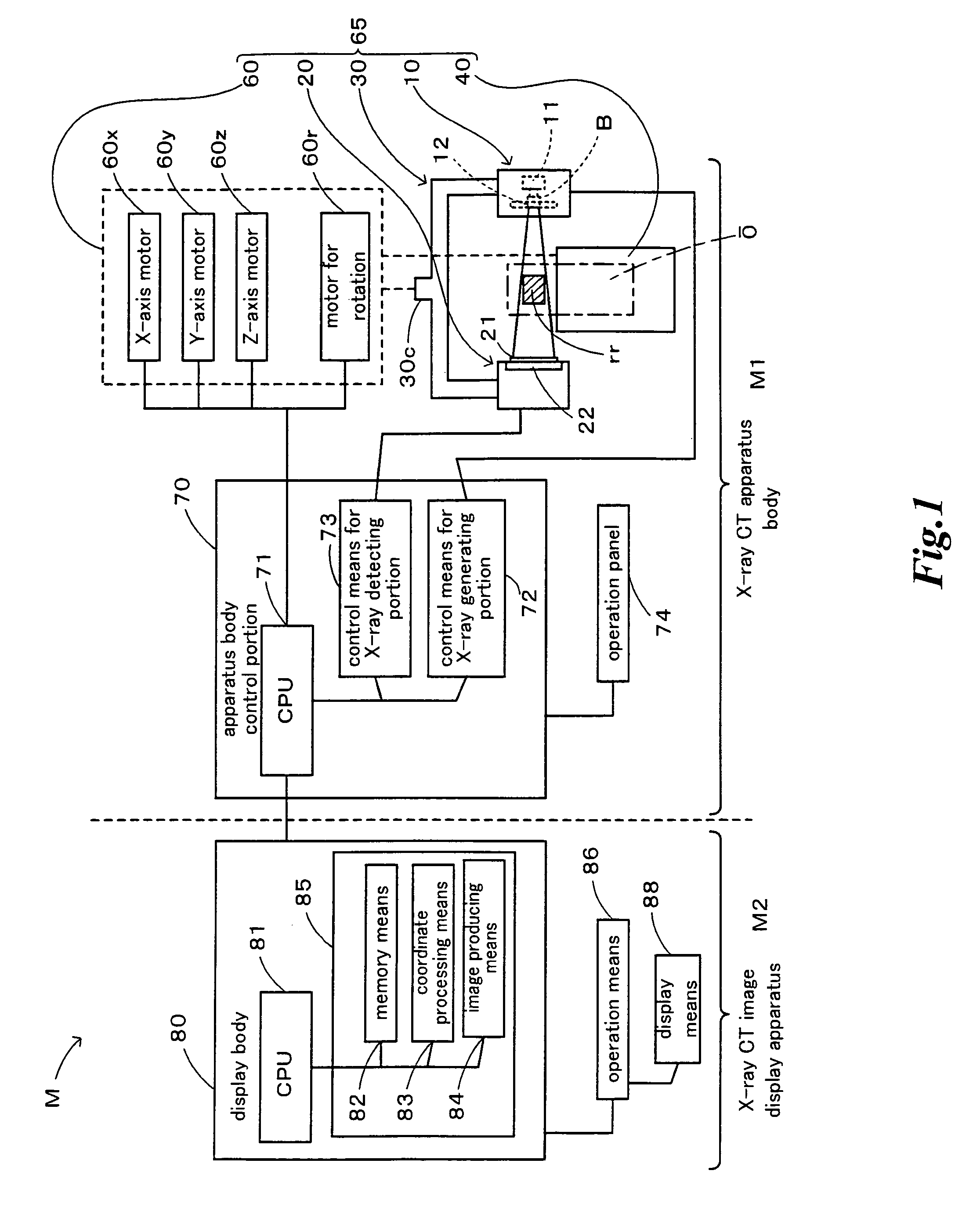
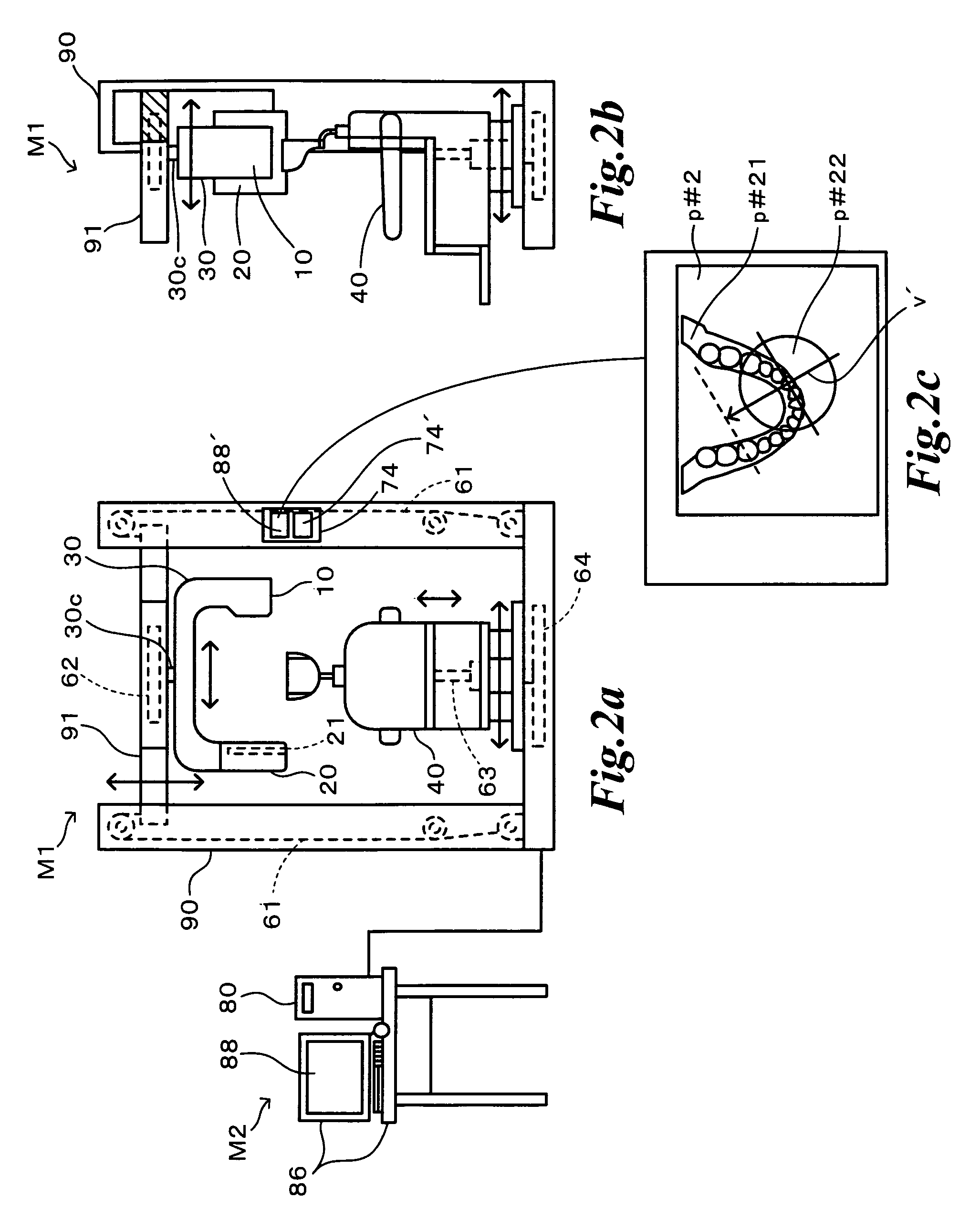
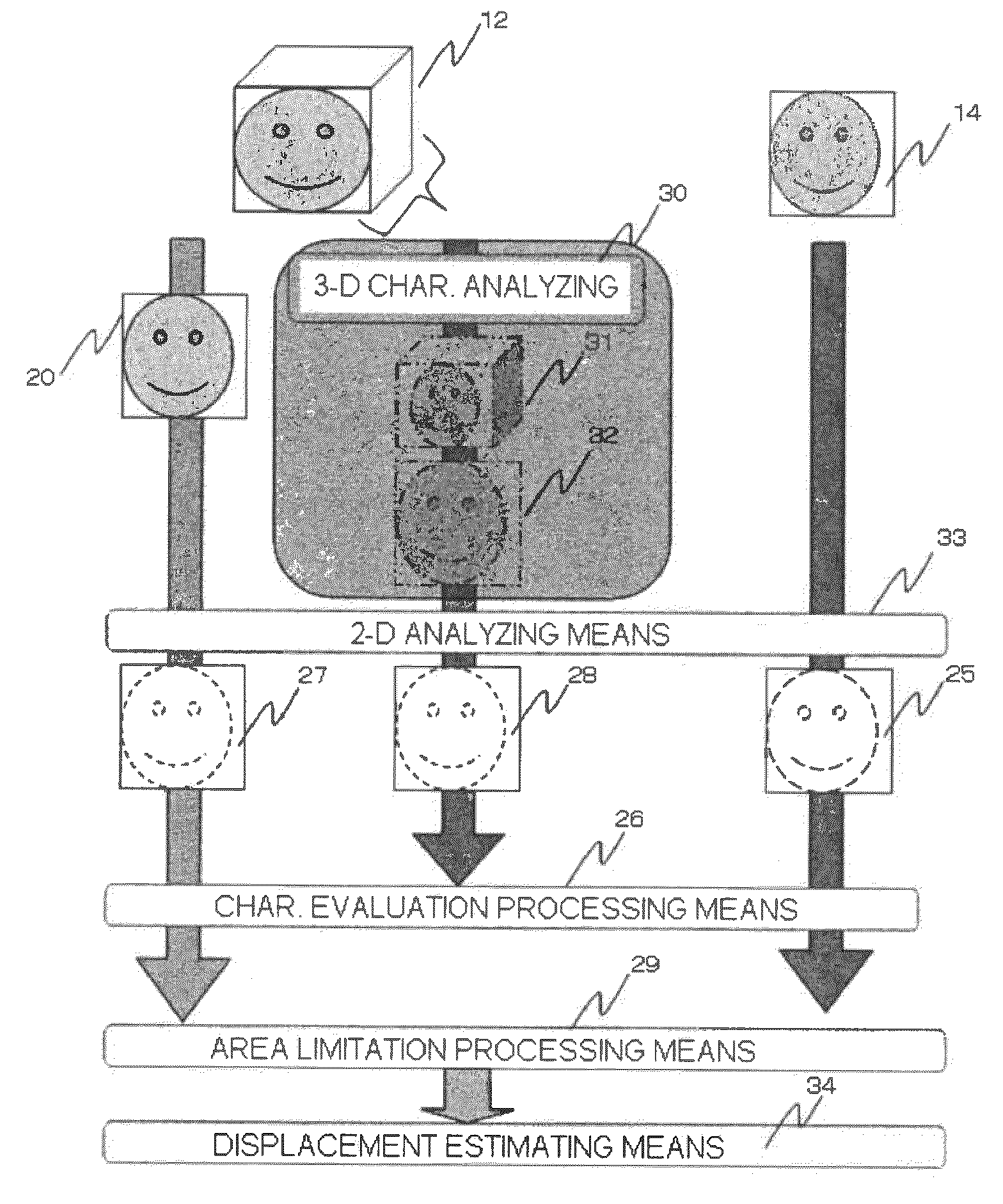
Patient registration system
InactiveUS20100246915A1Short timeImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingThree dimensional ctImaging processing
There is provided a patient registration system according to the present invention, including: a CT data capturing device; an X-ray television imaging device; and an image processing device for generating a two-dimensional DRR image based on the captured CT data, and then calculating an amount of displacement between a first diseased site position when the CT data is captured and a second diseased site position when the X-ray television image is captured. The image processing device carries out processes of: three-dimensional analysis for extracting an amount of three-dimensional characteristic from the three-dimensional CT data; two-dimensional analysis for extracting an amount of two-dimensional characteristic from both of the DRR image and the X-ray television image; characteristic evaluation for evaluating the extracted characteristic amounts; area limitation for selecting an area where the evaluated characteristic amounts are present; and displacement estimation for estimating an amount of displacement between the first diseased site position and the second diseased site position within the selected area, whereby achieving quick and accurate registration of patient.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Wide view-field three-D CT imaging method
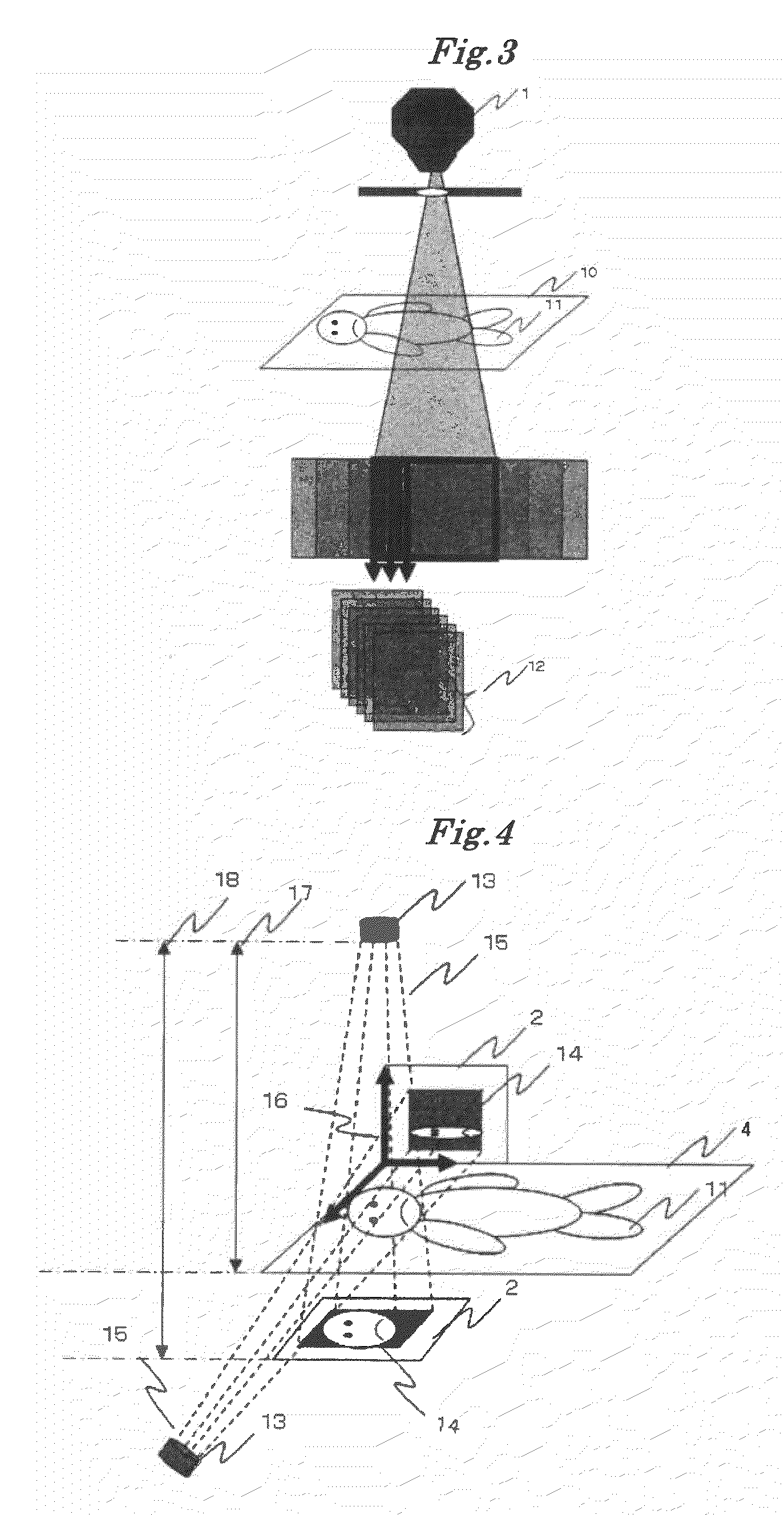
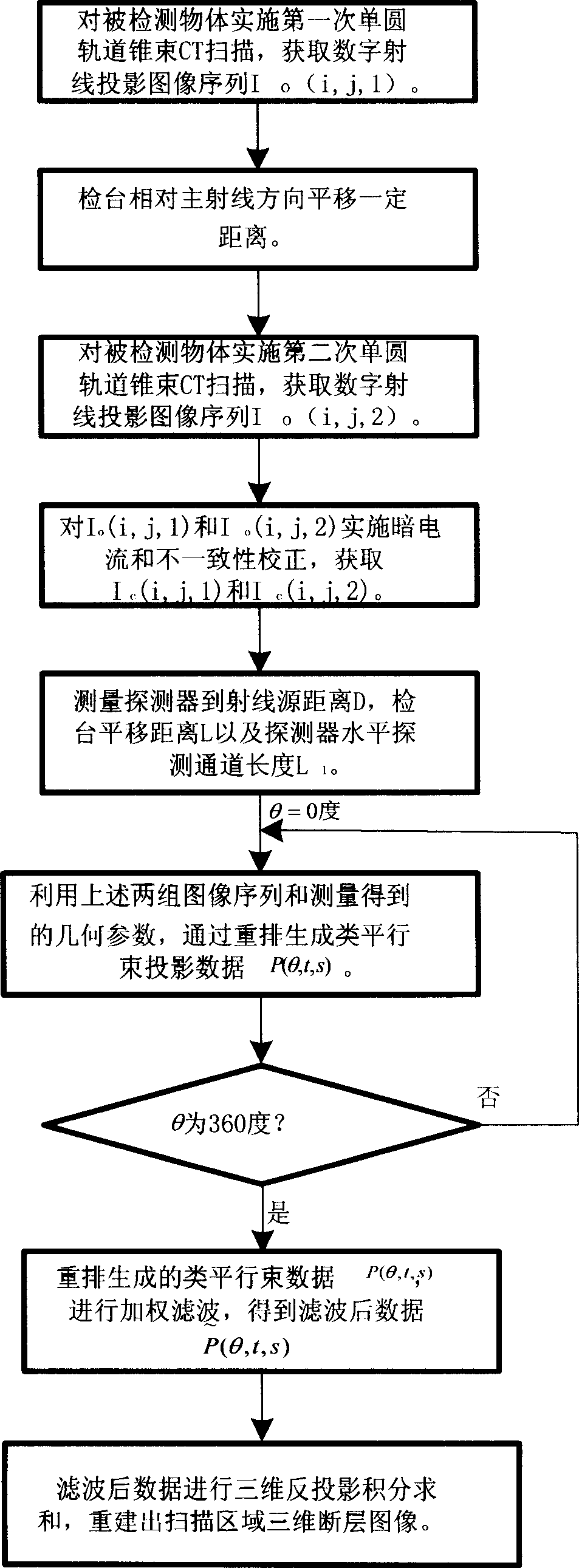
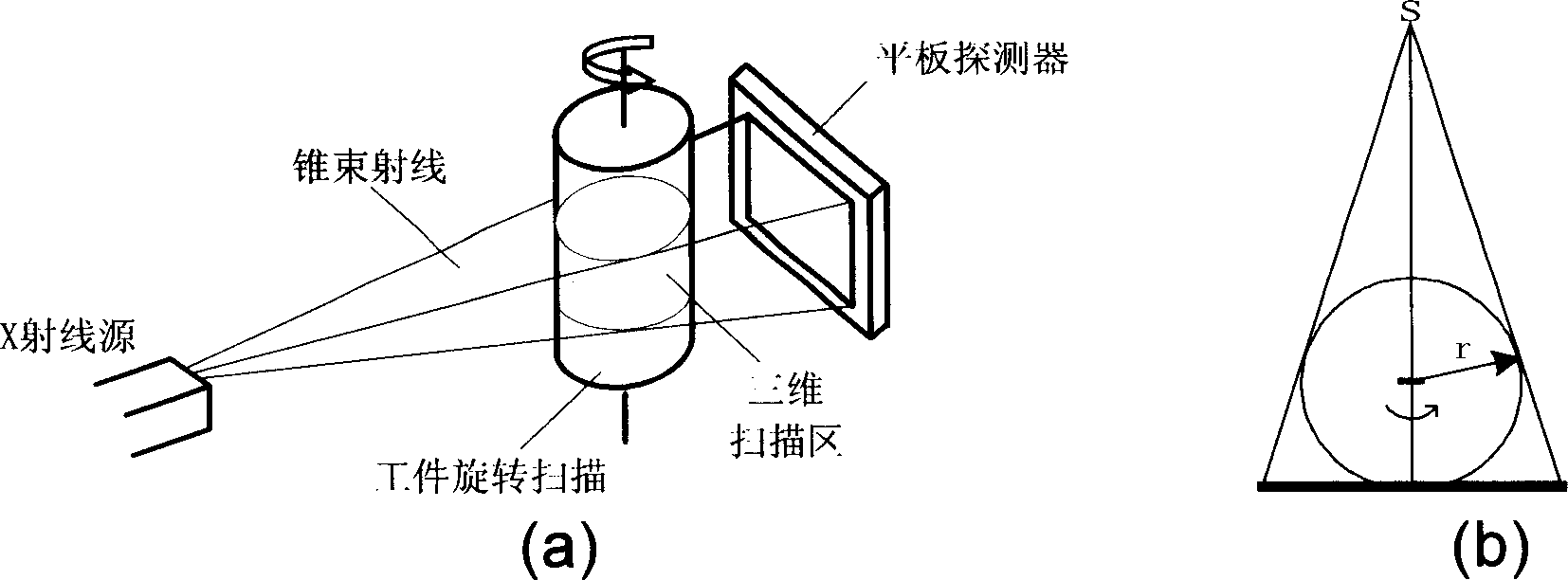
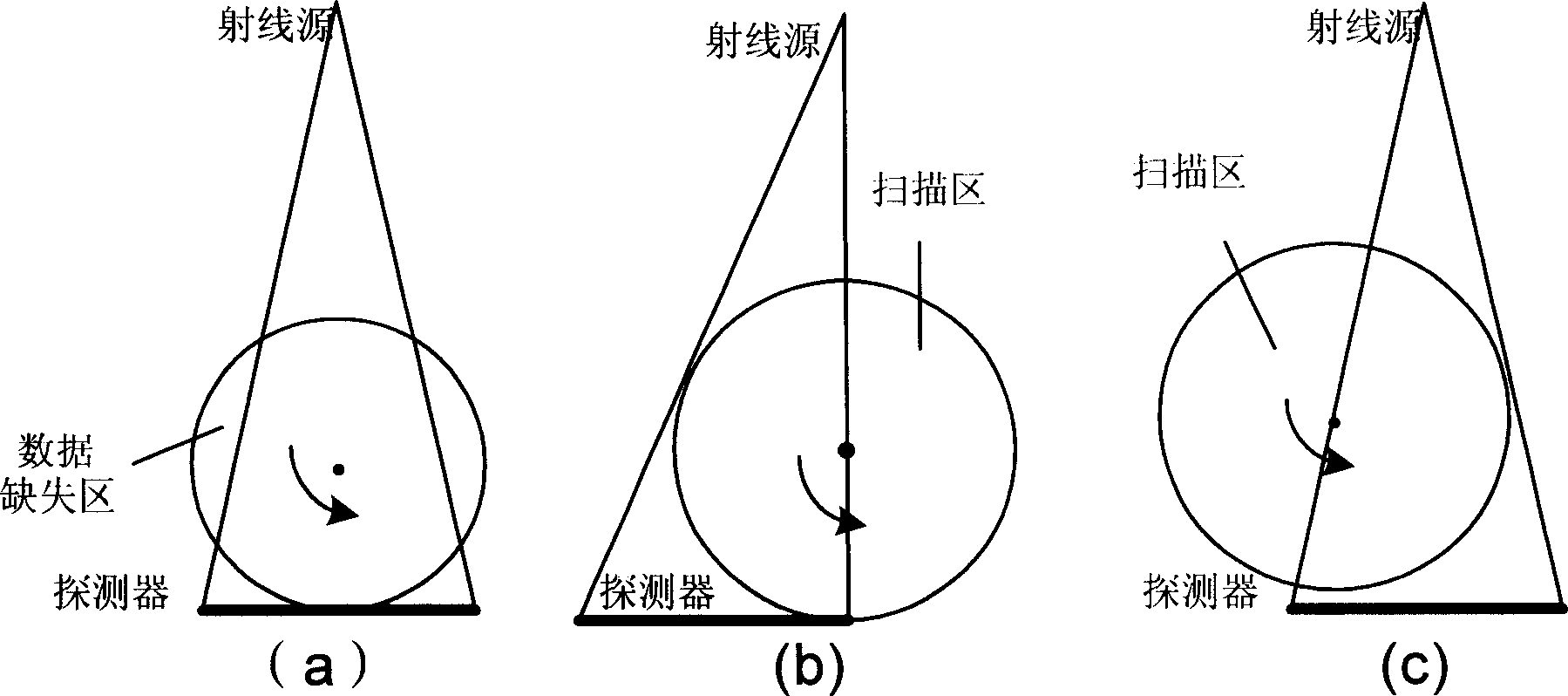
InactiveCN1865954AScan structure is simpleCompatibleComputerised tomographsTomographyDigital RayVisual field loss
The 3D CT imaging method for large view field comprises: (1) taking first single-circular orbit cone-beam CT scanning to obtain the first digital ray projection image sequence; (2) removing the platform vertical the main ray with some distance to take the second CT scanning and obtain the second image sequence; (3) correcting former two images for dark current and inconsistency; (4) recording distance from ray source to detector, former moved distance and detector level channel number; (5) with the projection rearrangement algorithm in this invention, rearranging former two images into self-contained quasi-parallel image sequence; (6) with the quasi-parallel ray reconstructing algorithm in this invention, reconstructing the 3D CT image. This invention can enlarge the view area more than 3 times with high efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Surgical navigation simulation method based on electromagnetic positioning technology and intraoperative image guidance
InactiveCN108420529ARealize real-time trackingSafe intraoperative real-time guidanceSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingThree dimensional ctComputation complexity
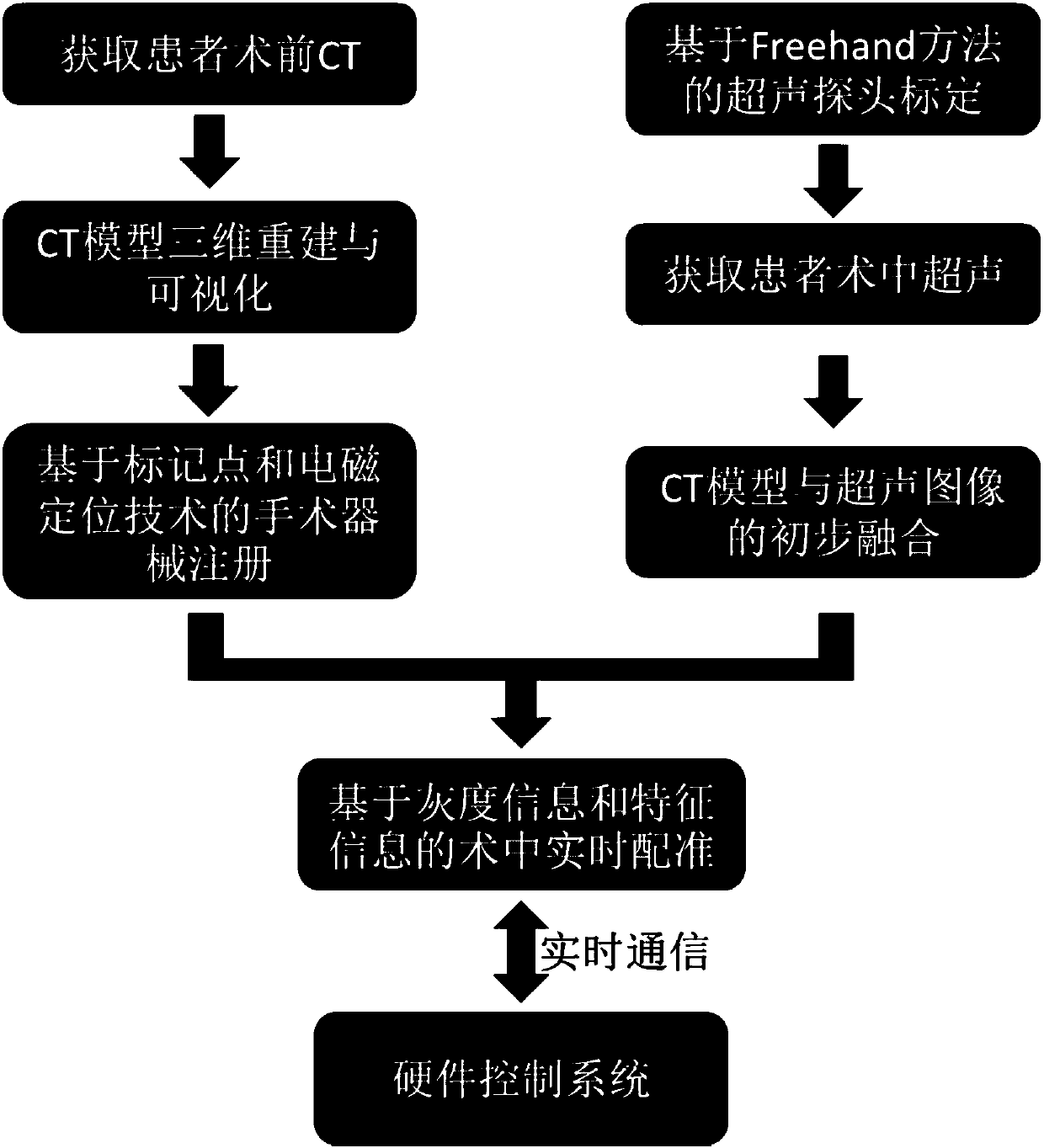
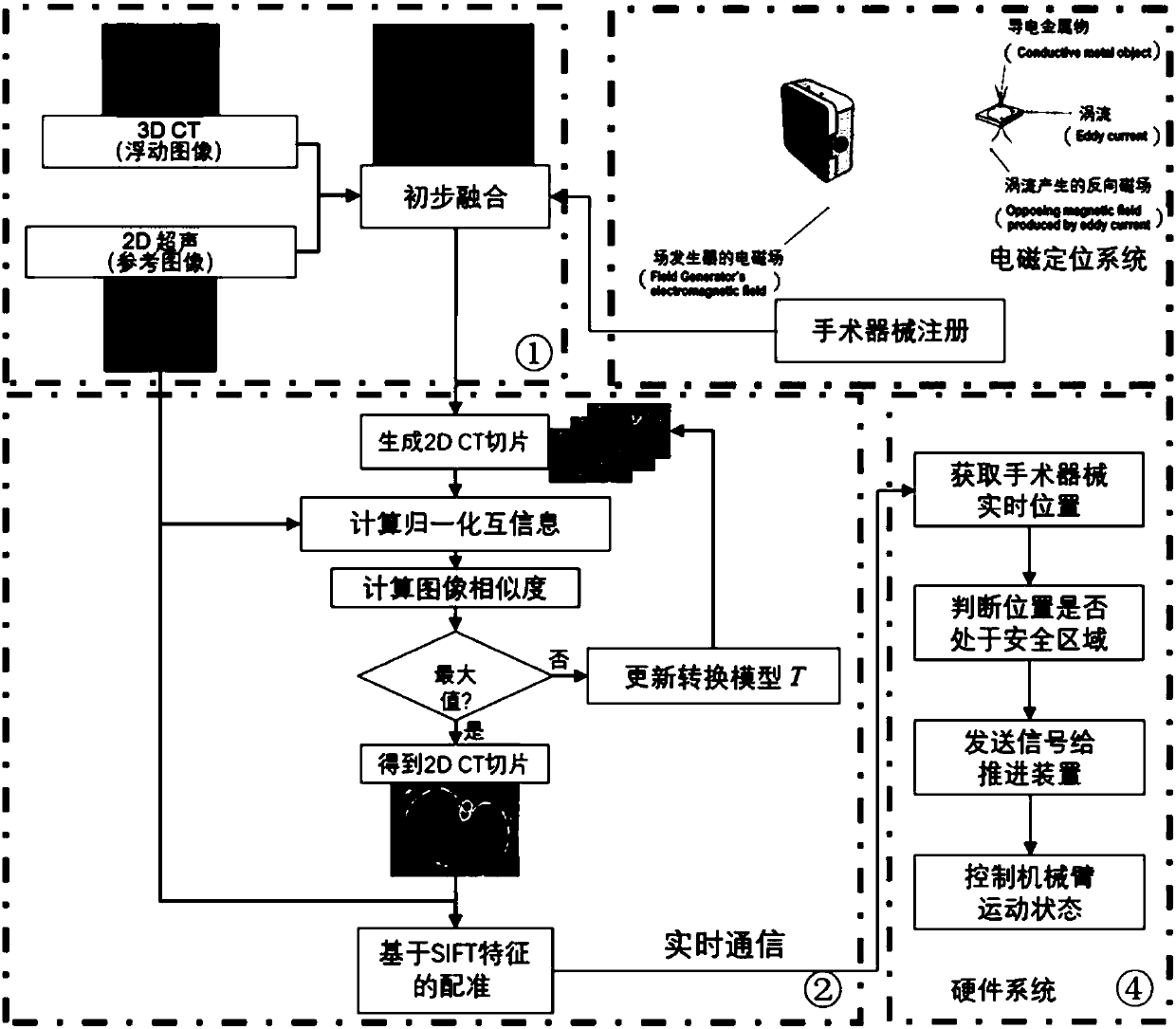
The invention relates to a surgical navigation simulation method based on an electromagnetic positioning technology and intraoperative image guidance. The surgical navigation simulation method comprises the steps that 1, a preoperatively shot CT image of a patient is obtained; 2, the preoperatively shot CT image of the patient is reconstructed into a three-dimensional CT model; 3, registration andvisualization of surgical instruments are achieved; 4, the electromagnetic positioning technology is utilized to achieve real-time tracing of the surgical instruments under an image coordinate system; 5, an ultrasonic probe is calibrated, an ultrasonic image is obtained during operation in real time, and preliminary fusion between the three-dimensional CT model and the ultrasonic image is achieved; 6, by utilizing grey information and characteristic information of the ultrasonic image and adopting a mutual information method and an automatic SIFT characteristic extraction method, real-time registering of the preoperative three-dimensional CT model and the intraoperative ultrasonic image in the surgical process is performed; 7, simulation control of surgical robot movements is achieved. Compared with the prior art, the surgical navigation simulation method has the advantages of high navigation precision, low calculation complexity, good stability and reliability, convenient achievement, low cost, good clinic applicability and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
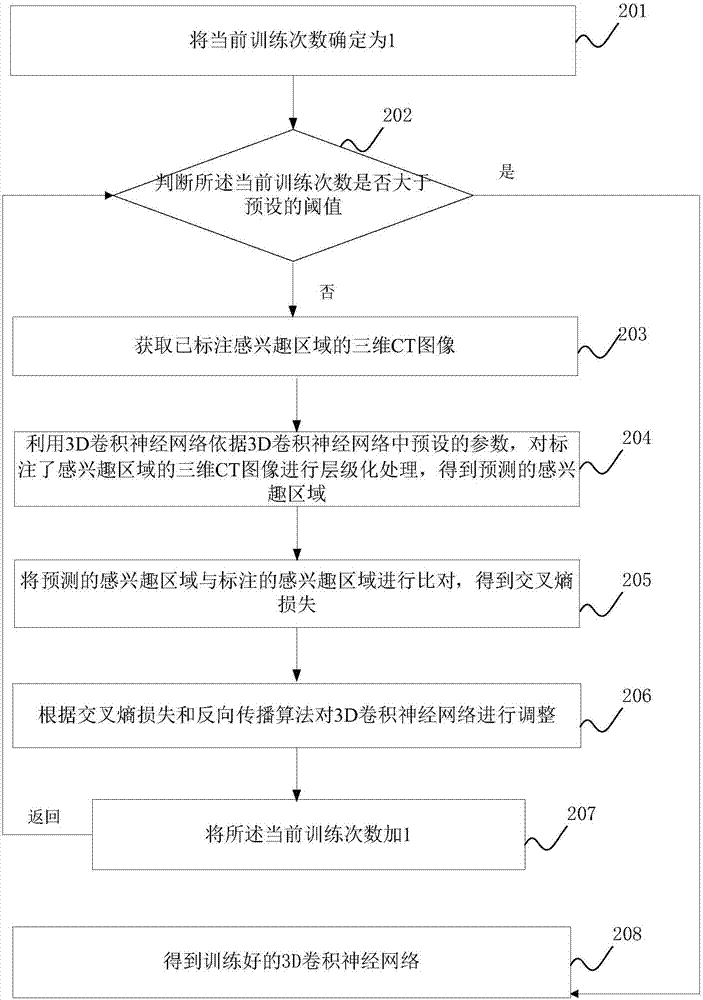
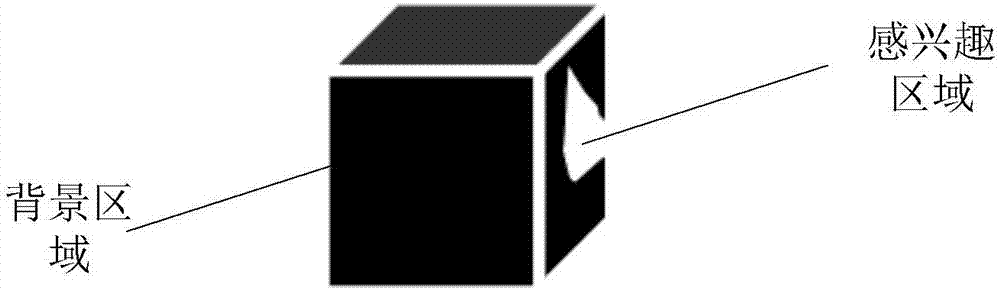
Method and apparatus for automatically identifying a region of interest in three-dimensional CT image
ActiveCN107480677AThe judgment result is accurateImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional ctComputer science
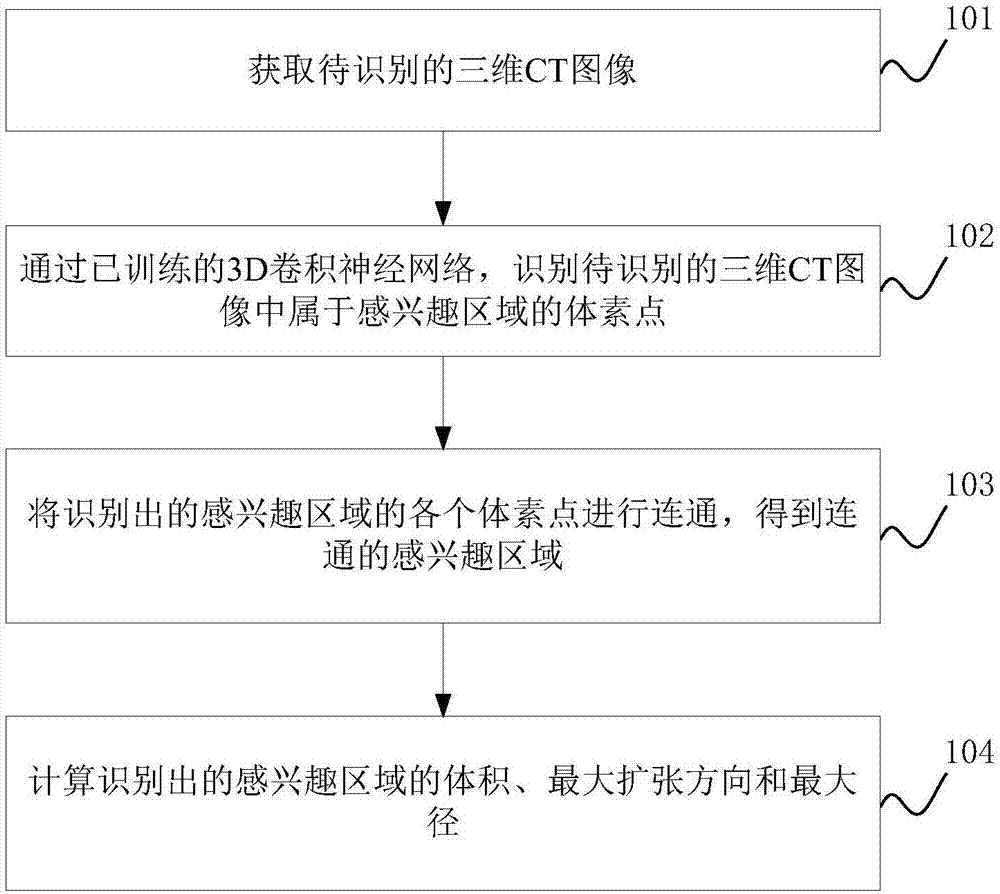
The present invention discloses a method and an apparatus for automatically identifying a region of interest in a three-dimensional CT image. The method includes: training a 3D convolution neural network through a three-dimensional CT image marked with a region of interest to obtain a 3D convolutional neural network with a high identification rate for the region of interest; then, through the trained 3D convolution neural network, identifying the obtained three-dimensional CT image and obtaining the region of interest; and calculating the volume, the expansion direction and the expansion diameter of the interest of interest. With the method of the embodiments in the invention, the region of interest representing the lesion can be obtained automatically and efficiently, and the identifying accuracy is also higher. In addition, the volume, the expansion direction and the expansion diameter of the lesion can be automatically calculated, therefore, helping the doctor to make a more accurate judgment of the condition of a patient.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD +1
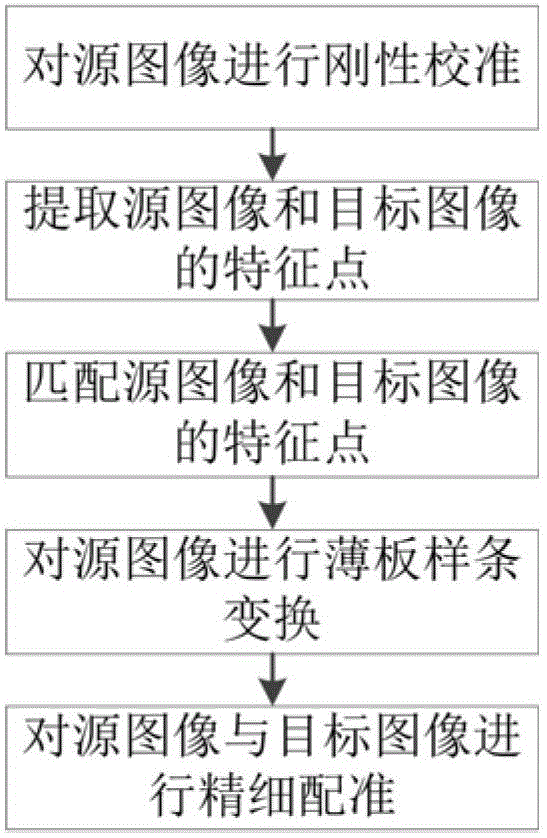
Non-rigid registering method of mouse three-dimensional CT image
InactiveCN103337065AReduce in quantityOvercome the shortcoming of too long registration timeImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional ctSource image
A non-rigid registering method of a mouse three-dimensional CT image comprises the following steps: A, a direction and a position of a source image of a mouse three-dimensional CT image are calibrated; B, a threshold segmentation algorithm is used to segment the mouse image to obtain a mouse bone of the source image and a mouse bone of a target image, a center of mass of a bone slice connected domain is extracted to serve as a characteristic point, so that a source image characteristic point and a target image characteristic point are obtained; C, the source image characteristic point and the target image characteristic point in the step B are matched, the matched characteristic point is used to calculate a thin plate batten transformation matrix, and a hierarchical transformation mode is used to carry out the thin plate batten transformation to the mouse source image; and D, the mouse source image after the thin plate batten transformation and the target image carry out a fine registering. According to the invention, when the characteristic points are extracted, the number of characteristic points is reduced; the hierarchical transformation mode is used to overcome the defect of long registering time; an automatic registering in the image registering is basically realized; and registering the three-dimensional mouse image is easier.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
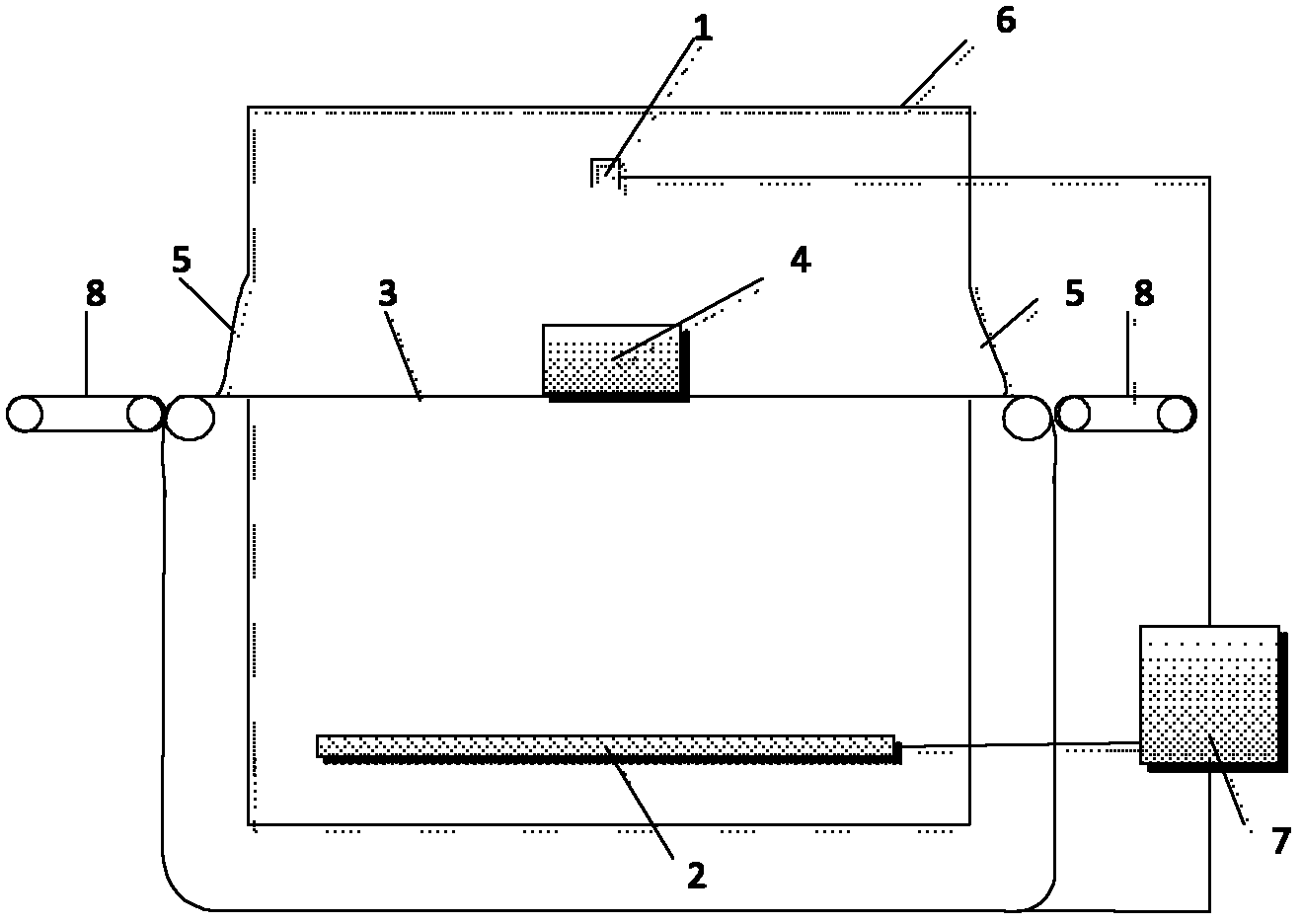
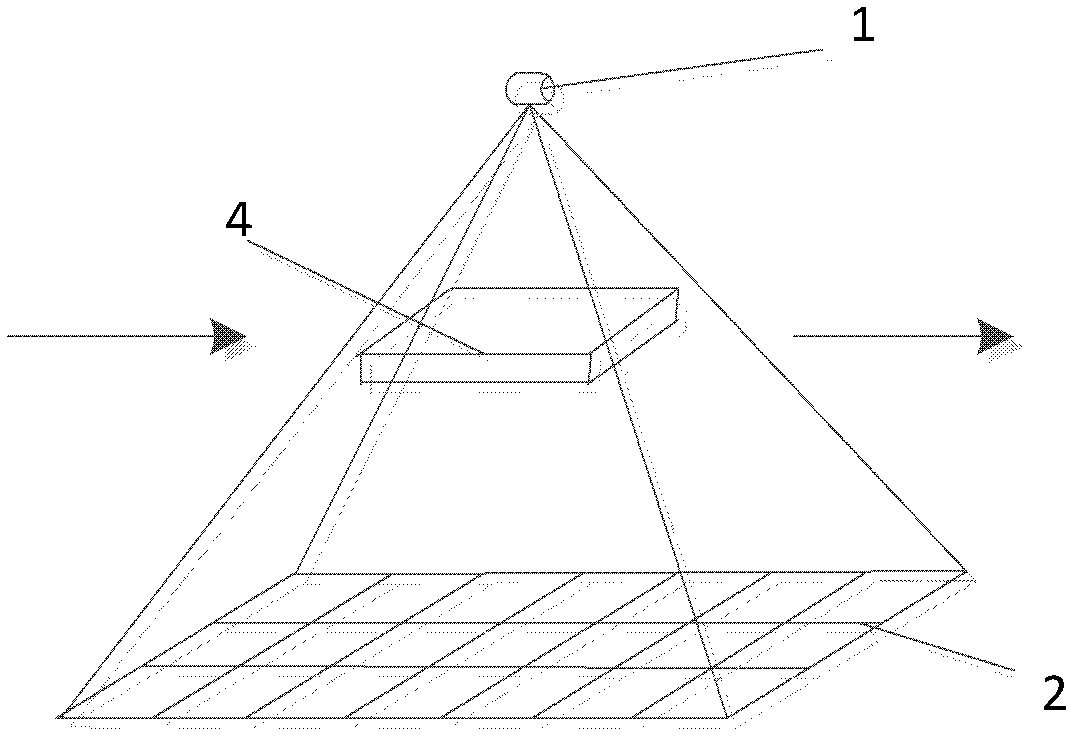
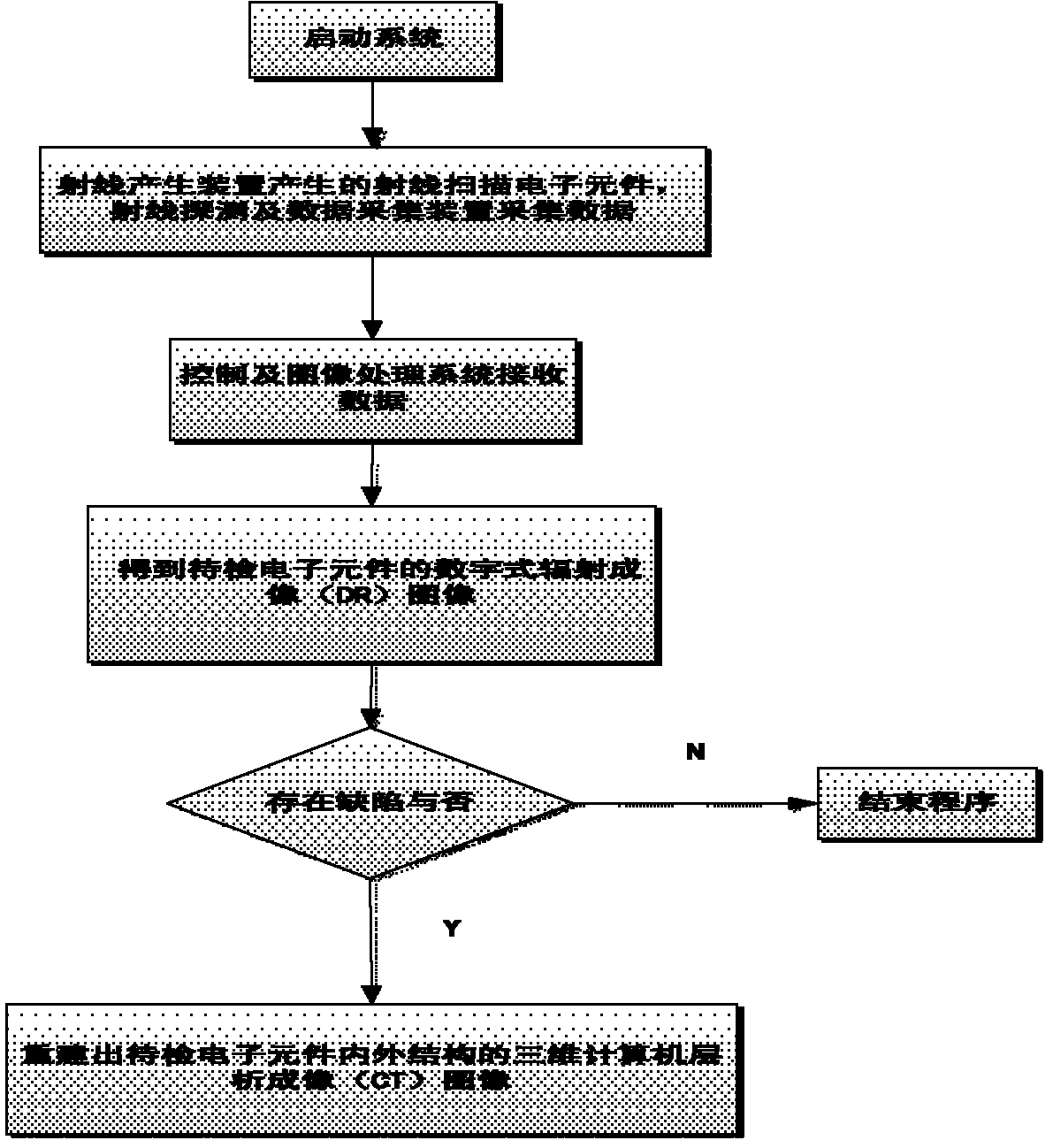
Method for online detecting electronic element by translational type micro focus CT (Computerized Tomography) detection device
ActiveCN102590248AImprove scanning efficiencyReduce volumeMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationThree dimensional ctProduction line
The invention discloses a method for online detecting an electronic element by a translational type micro focus CT (Computerized Tomography) detection device, and the method is realized as follows: when the detection is started, the electronic element is scanned by a conical ray beam generated by a ray generation device; and ray projection data is acquired by a ray detection and data acquisition device, and then is transmitted to a control and image processing system for imaging including digital radiation (DR) imaging and computerized tomography (CT) imaging. When the CT imaging is performed, the CT image can be reconstructed according to incomplete projection data acquired through ray scanning by the translational type conical beam and adopting translational type conical beam CT iterative reconstruction algorithm based on subdomain equalization and total variation minimization, so as to obtain a high quality three-dimensioanl CT image. The method is used for online detecting the electronic element on the production line with high precision, can perform amplification DR image and three-dimensional CT image for internal and external structures of the electronic element; the device has simple structure and high scanning efficiency; and further, material deficiency and assembly deficiency of the electronic element can be detected efficiently.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Ct scanner with automatic determination of volume of interest
InactiveUS20070237287A1Reduce X-ray exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingThree dimensional ctCt scanners
A CT scanner automatically determines a volume of change based upon anatomical changes in a patient. During surgery, the CT scanner takes a sufficient number of two-dimensional initial images using a full field of view. The CT scanner compares the initial images to pre-operative data. Based upon the comparison, the CT scanner automatically determines the volume of change plus some margin to define a volume of interest. The CT scanner then collimates an x-ray source to perform an intra-operative updated CT scan of the volume of interest. The CT scanner updates the pre-operative data with the data from the intra-operative updated CT scan of the volume of interest to form a fully updated three-dimensional CT image. The initial images and the pre-operative data can be taken at a lower resolution than the intra-operative updated CT scan of the volume of interest to reduce the x-ray exposure of the patient.
Owner:XORAN TECH
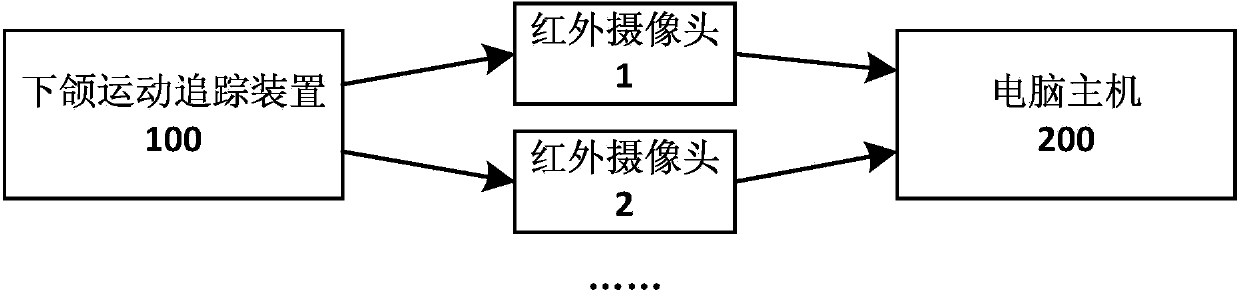
System and method for capturing and visualizing mandibular three-dimensional motion
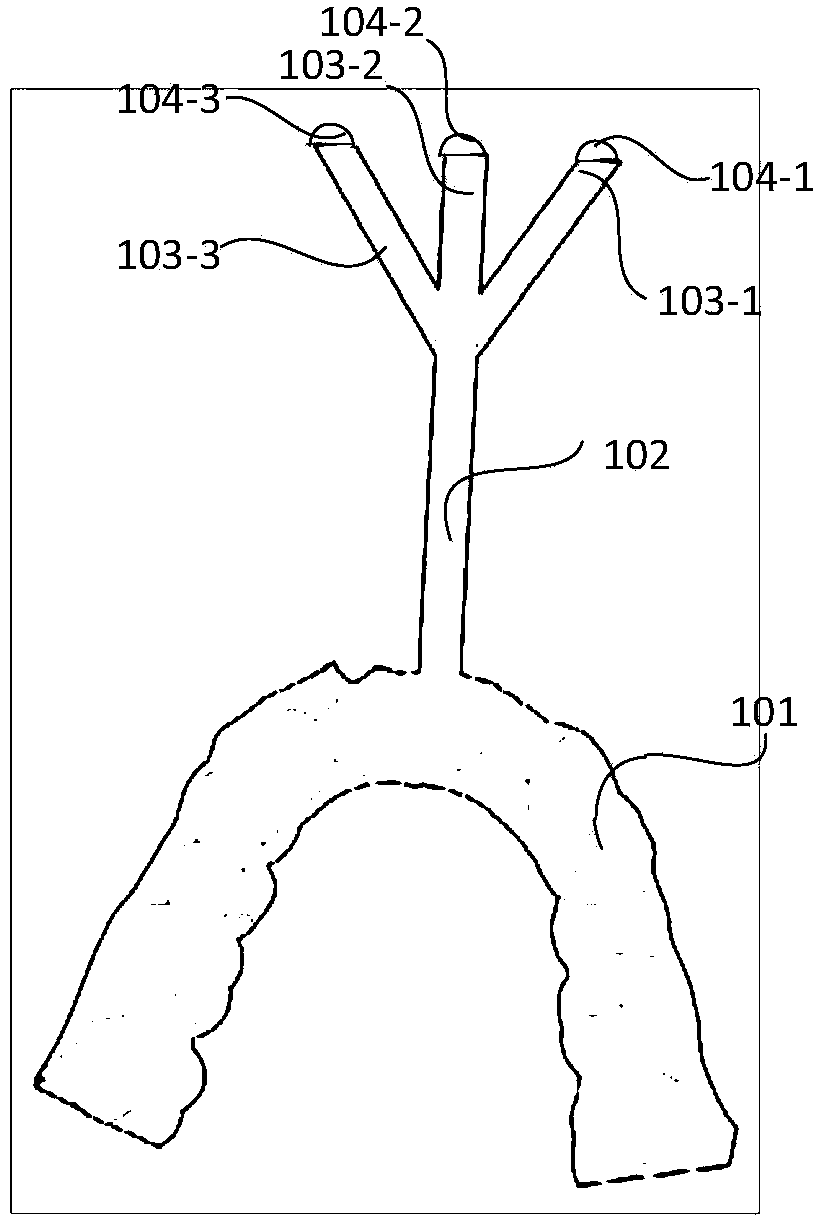
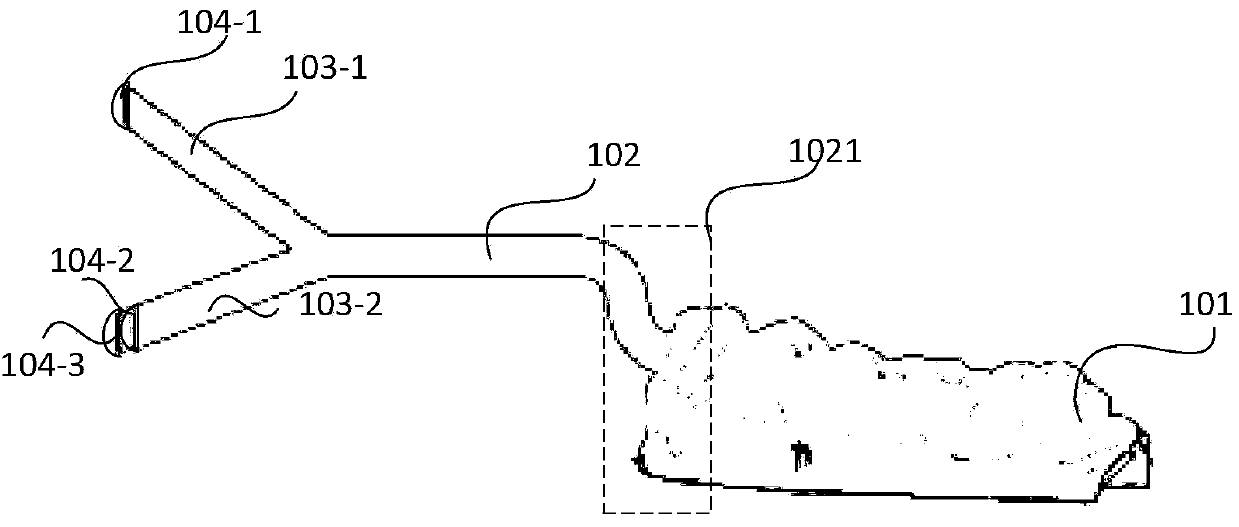
ActiveCN103690173AExact structure restorationRealize visual displayDentistryDiagnostic recording/measuringThree dimensional ctMotion capture
The invention discloses a system for capturing and visualizing mandibular three-dimensional motion. The system comprises a mandibular motion tracking device for designing and printing through a three-dimensional CT (Computed Tomography) model, at least two infrared cameras, and a host computer for analyzing shooting record data, wherein the mandibular motion tracking device comprises a rear end fixing device, a medium connecting rod, and three marking rods, wherein the three marking rods are arranged at the front end and are not co-planar; one end of each of the marking rods is connected to the medium connecting rod and while the other end of each of the marking rods is provided with a marker; the rear end fixing device is used for designing and printing through the three-dimensional CT model according to the external physical characteristics of lower teeth; the markers expose from the mouth and move together with the mandible; the host computer is used for recovering the overall motion of the mandible of a tested subject so as to determine whether the mandible motion and occlusal contacts are normal. The invention also provides a method for capturing and visualizing the mandibular three-dimensional motion. According to the technical scheme, the system and method have the advantages of low cost, high testing accuracy and the like, and is convenient to operate.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Estimation method and system for lung motion model
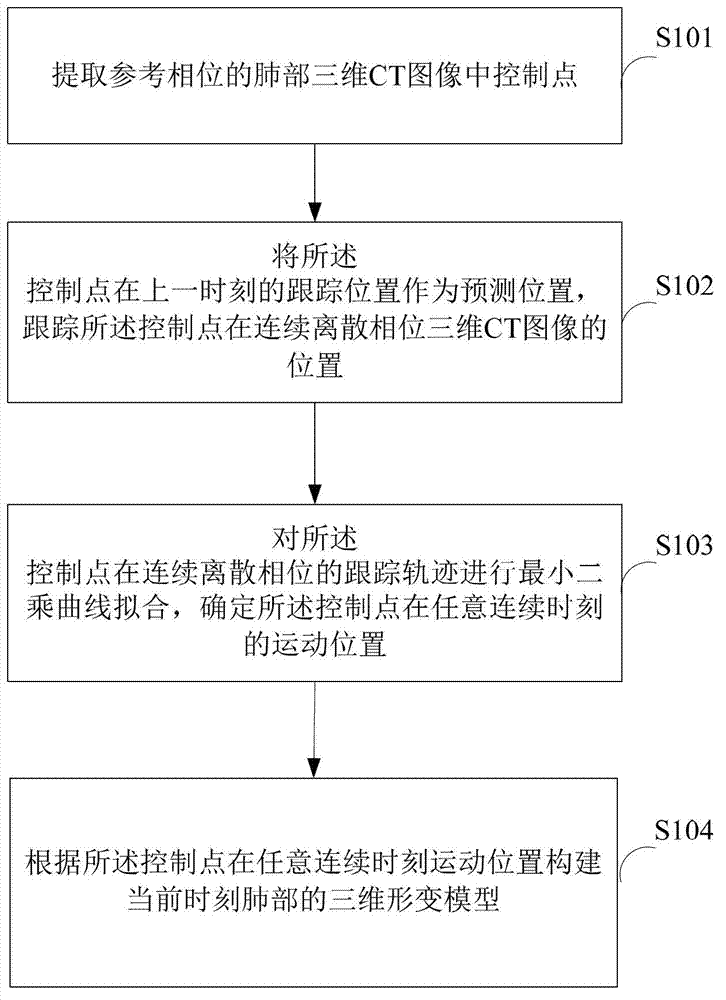
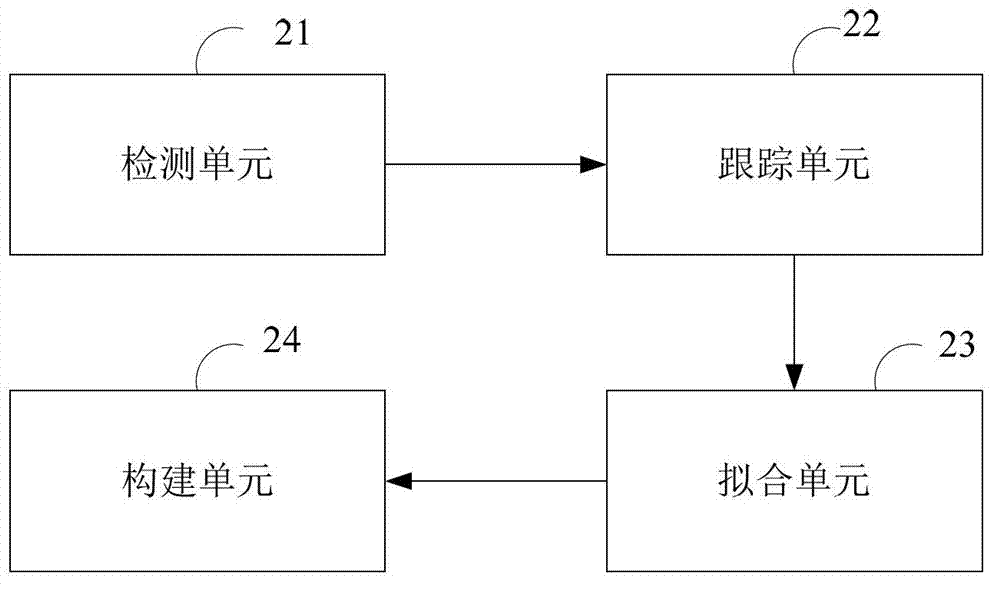
InactiveCN103761745AImprove correspondence accuracySolving the Respiratory Motion Estimation ProblemImage analysisComputerised tomographsThree dimensional ctVoxel
The invention is applicable to the field of image processing and provides an estimation method and system for a lung motion model. The method includes: extracting a control point in a lung three-dimensional CT image of a reference phase; using a tracking position at a previous moment of the control point as a prediction position and tracking the position of the control point in a continuous-discrete-phase three-dimensional CT image; performing least-square curve fitting on the continuous-discrete-phase pursuit path of the control point and determining the motion position of the control point at any continuous time; and constructing a three-dimensional deformation model of the lung at a current time according to the motion position of the control point at any continuous time and obtaining lung motion position estimation of any voxel of the lung of the reference phase at any time. The estimation method and system for the lung motion model adopts an image registration algorithm based on a mark point so that the method is small in calculation quantity, high in calculation speed and capable of estimating the motion model of the lung effectively.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Three-dimensional CT core image super-resolution reconstruction method
ActiveCN105006018AHigh-resolutionThe pore structure features are clear and obviousGeometric image transformationComputerised tomographsThree dimensional ctFeature extraction
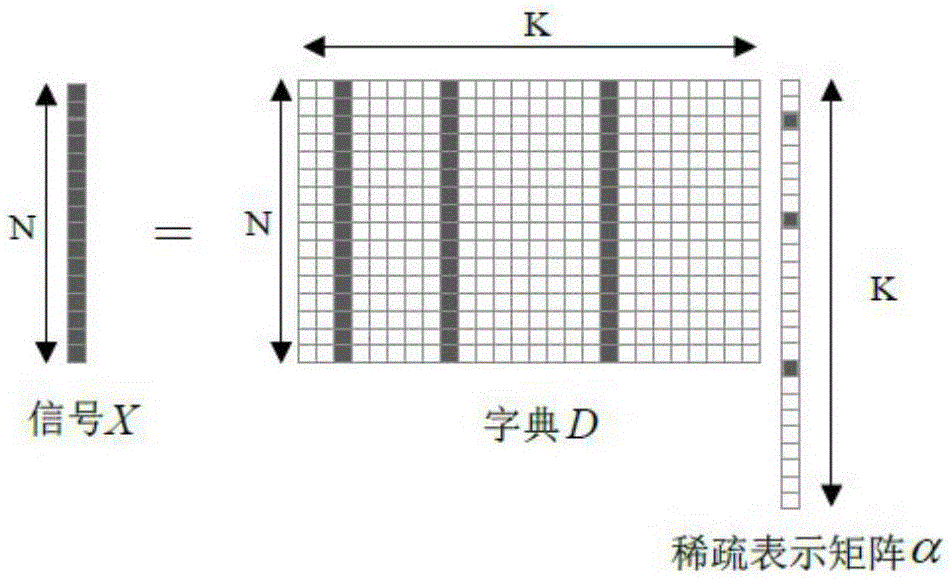
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional core image super-resolution reconstruction method. The method comprises the steps of: performing degradation on a three-dimensional CT core image, and performing decomposition and feature extraction on the degraded three-dimensional image to obtain a feature block 2; performing dictionary training on an extraction feature application algorithm to obtain a low-resolution dictionary Dl and a sparse coefficient alpha; performing decomposition and feature extraction on the input three-dimensional image to obtain a feature block 1; according to the feature block 1 and the sparse coefficient alpha, obtaining a high-resolution dictionary Dh of the input three-dimensional CT core image; according to the feature block 1 and the low resolution dictionary Dl, obtaining a new sparse coefficient beta; according to the high-resolution dictionary Dh and the new sparse coefficient beta, obtaining a three-dimensional high-resolution image block; performing up-sampling on the three-dimensional CT core image by using an interpolation algorithm and obtaining an enlarged three-dimensional image; and filling the enlarged three-dimensional image with the three-dimensional high-resolution image blocks to obtain an enlarged three-dimensional core sample model. According to the three-dimensional core image super-resolution reconstruction method, the problem of a contradiction between the resolution of the three-dimensional CT image and the sample dimension is solved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Three-dimensional CT image segmentation method and three-dimensional CT image segmentation device
ActiveCN105513036AAccurate removalImprove accuracyImage analysisComputerised tomographsThree dimensional ctDisease area
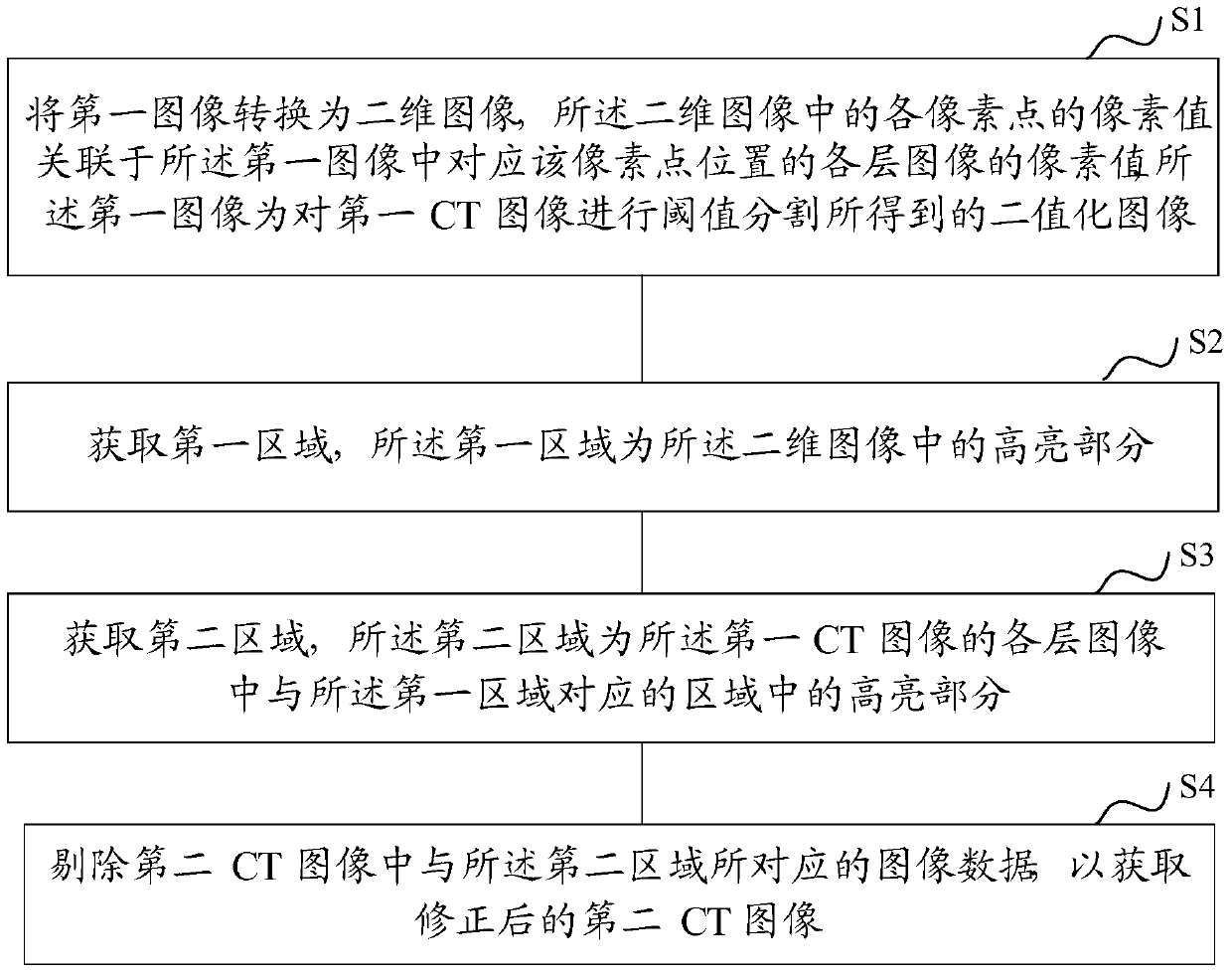
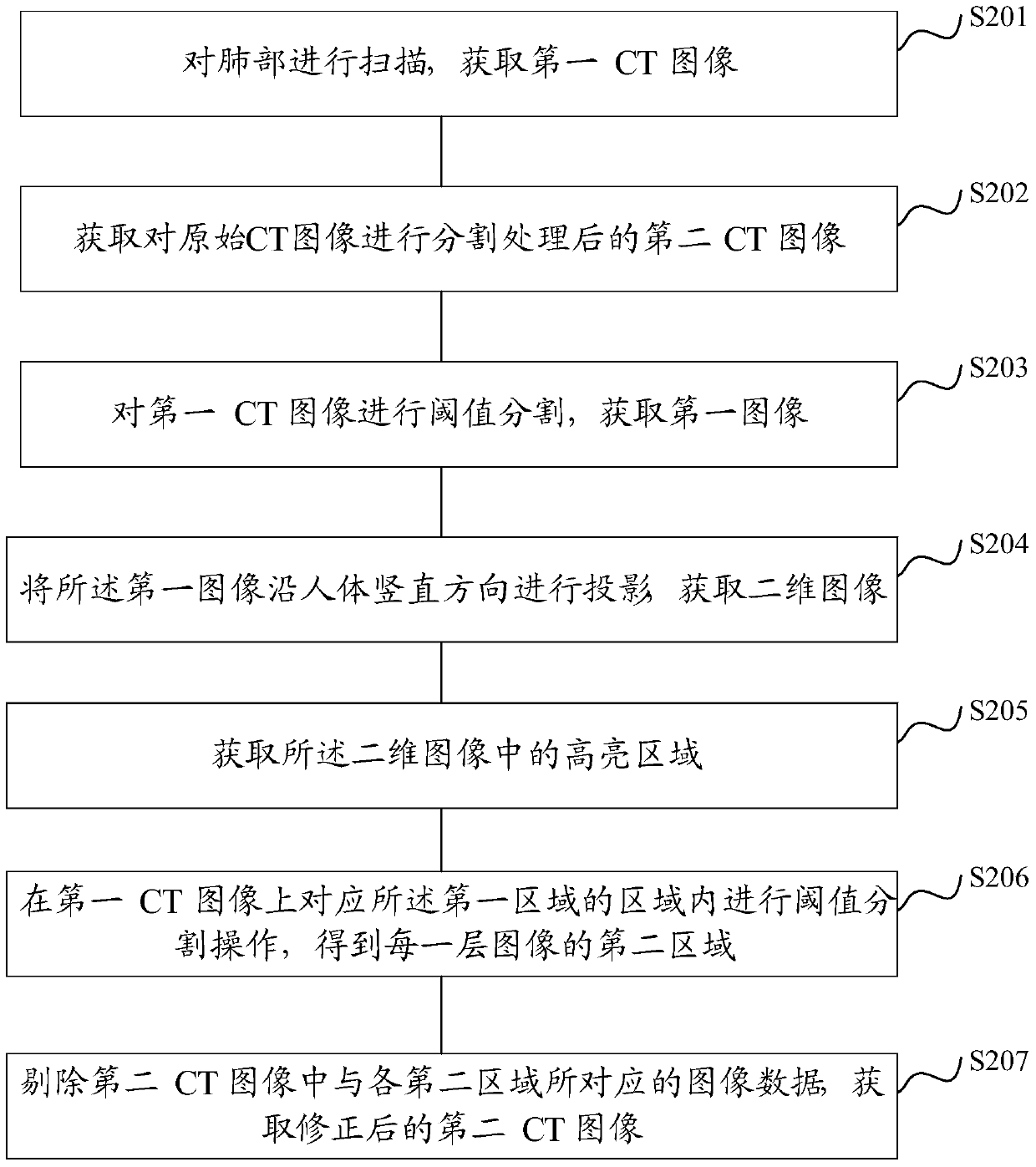
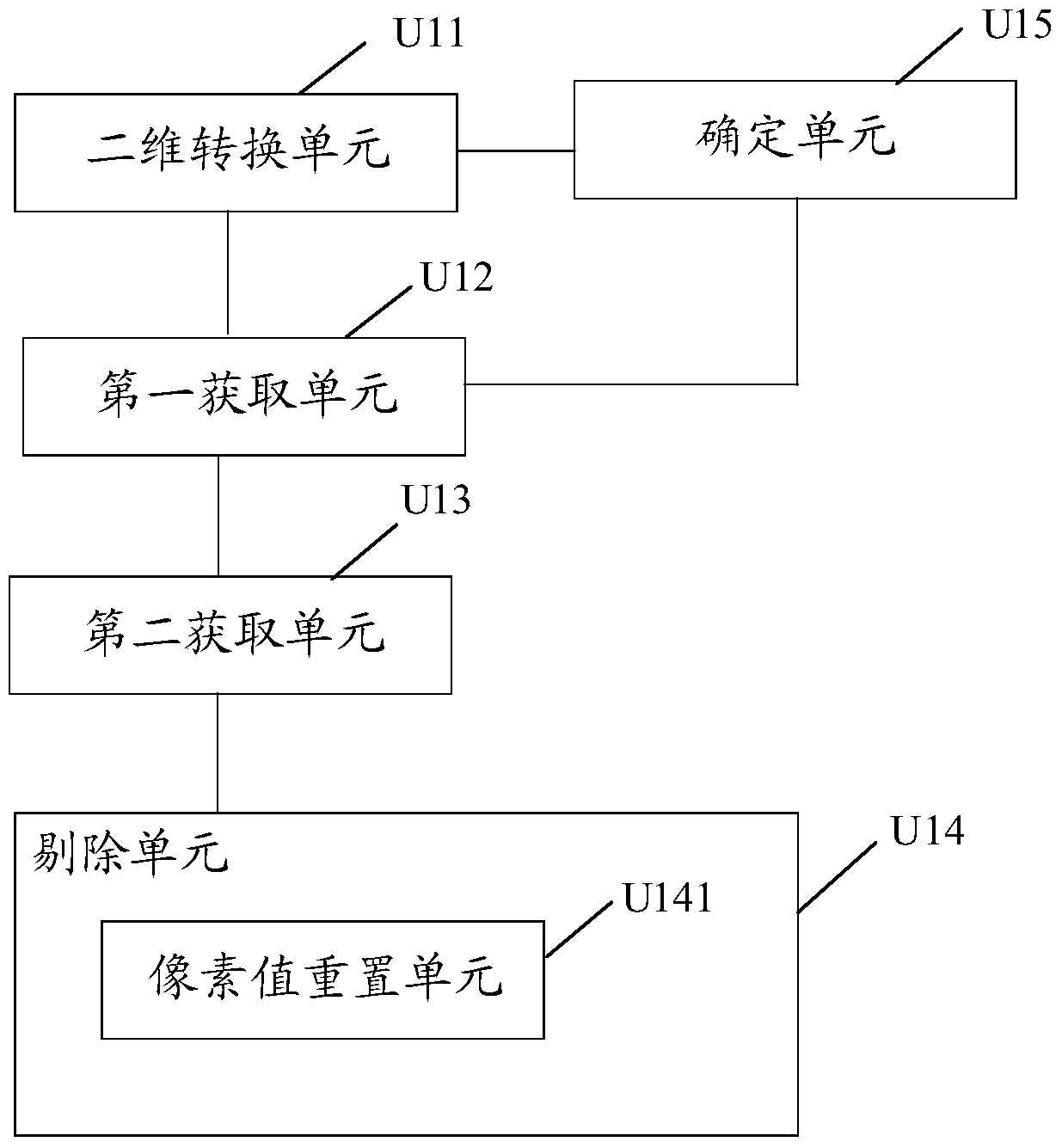
The invention discloses a three-dimensional CT image segmentation method and a three-dimensional CT image segmentation device. The three-dimensional CT image segmentation method is characterized in that a first image can be converted into a two-dimensional image, and the first image is a binary image acquired by adopting threshold segmentation of a first CT image; a first area is acquired, and is the high light part of the two-dimensional image; a second area is acquired, and is the high light parts of the areas of the images of different layers of the first CT image corresponding to the first area; image data of a second CT image corresponding to the image data of the second area can be eliminated, and the corrected second CT image can be acquired. The method provided by the invention is advantageous in that the bone and other normal-appearing areas of the second CT image can be effectively eliminated, and the accuracy of the human tissue segmentation result can be improved, and therefore the accuracy of the disease diagnosis result including the diseased areas can be guaranteed, and the diagnosis accuracy can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
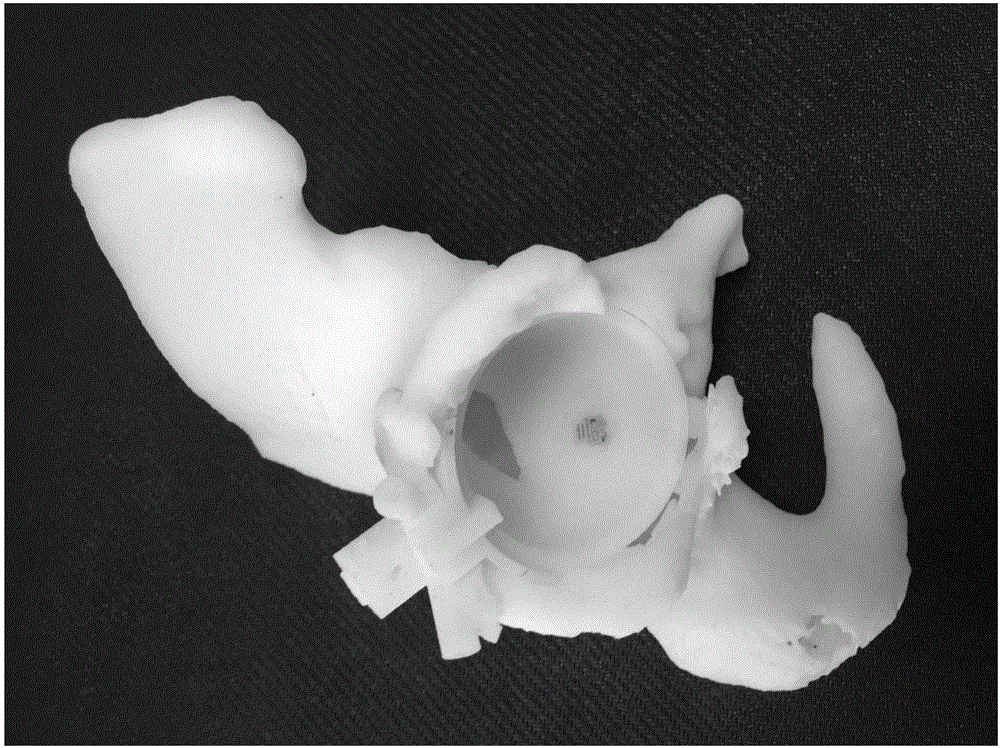
Method for preparing acetabulum side model and guide plate based on three-dimensional reconstruction technology
ActiveCN106388978AQuickly determine the locationQuickly determine file sizeBone implantJoint implantsThree dimensional ctComputed tomography
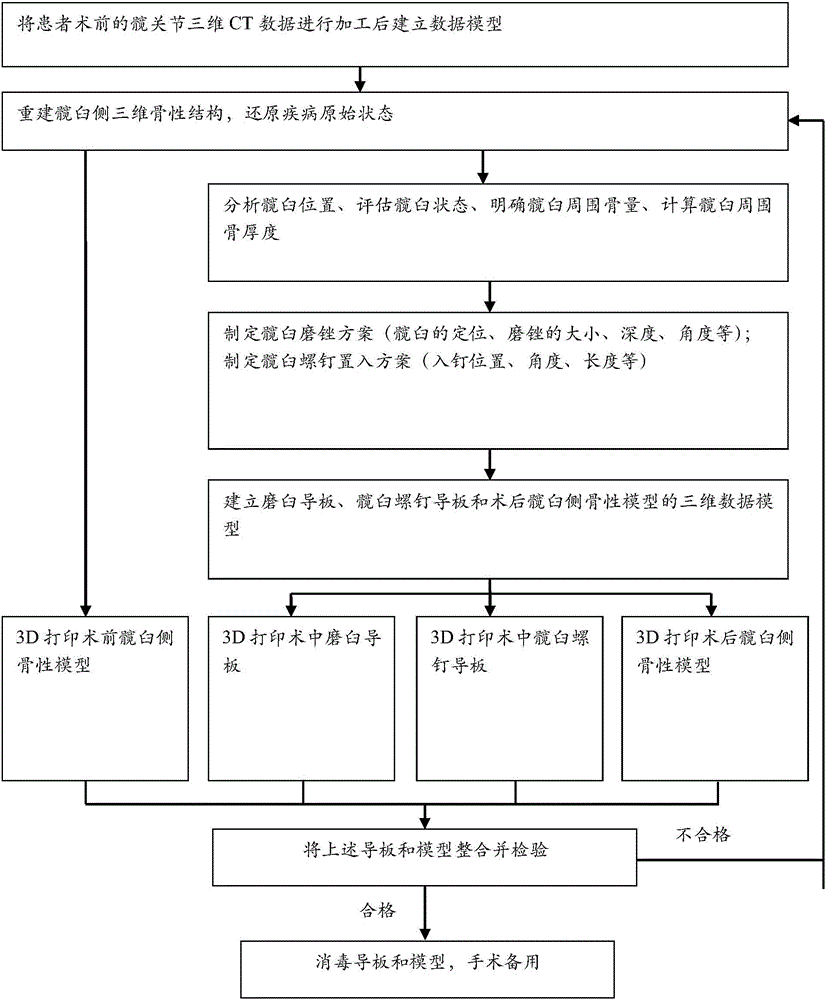
The invention discloses a method for preparing an acetabulum side model and a guide plate based on a three-dimensional reconstruction technology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a digital three-dimensional data model after three-dimensional CT (Computed Tomography) data of a preoperative hip joint of a patient is processed, reconstructing a three-dimensional bony structure of an acetabulum side, and restoring an original state of a disease; secondly, making an acetabulum mill filing and acetabulum screw embedding scheme by analyzing an acetabulum position, estimating an acetabulum state, clearing the mass of bones around an acetabulum and calculating the thickness of the bones around the acetabulum, and performing three-dimensional modelling on the guide plate and the model; thirdly, preparing a preoperative acetabulum side osseous model, an intra-operative grinding mortar guide plate, an intra-operative acetabulum screw guide plate and a postoperative acetabulum side osseous model by utilizing a 3D (Three-dimensional) printer; fourthly, integrating and inspecting the guide plate and the model, redesigning if the guide plate and the model are unqualified, and disinfecting the guide plate and the model and putting the guide plate and the model into an operation if the guide plate and the model are qualified.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
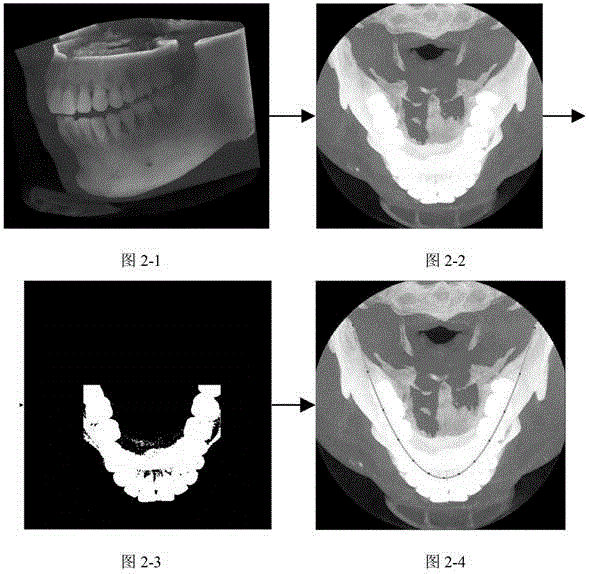
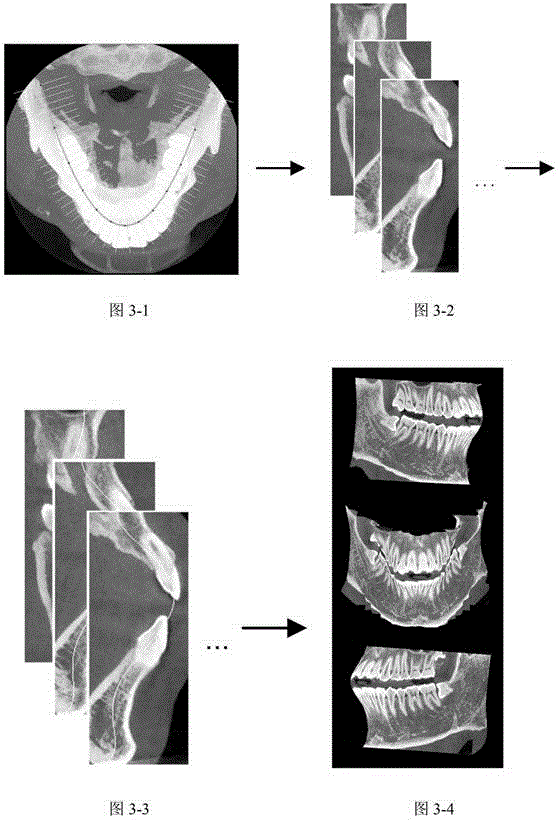
Method for extracting panoramic image from three-dimensional conical beam CT data of dentistry department
ActiveCN105608747AIdentify anatomyStructural solutionDetails involving 3D image dataGeometric image transformationAnatomical structuresThree dimensional ct
The invention relates to a method for extracting panoramic image from three-dimensional conical beam CT data of a dentistry department, and the method comprises the following steps: (1), generating a dental arch curve according to the three-dimensional conical beam CT data of the dentistry department; (2), extracting a three-dimensional oral cavity panoramic curved surface according to the generated dental arch curve; (3), expanding the three-dimensional oral cavity panoramic curved surface and obtaining an oral cavity panoramic image. The method can extract a tooth curved surface faultage image through the three-dimensional CT data, solves problems of structure overlapping and image fuzzy, and improves the diagnosis precision. The method can obtain a single-frame oral cavity panoramic image, and the single-frame oral cavity panoramic image can display all teeth. The method can clearly recognize the anatomical structure of teeth, such as enamel, dentin and dental pulp, effectively avoids image fuzzy caused by perspective, and has no structure overlapping.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
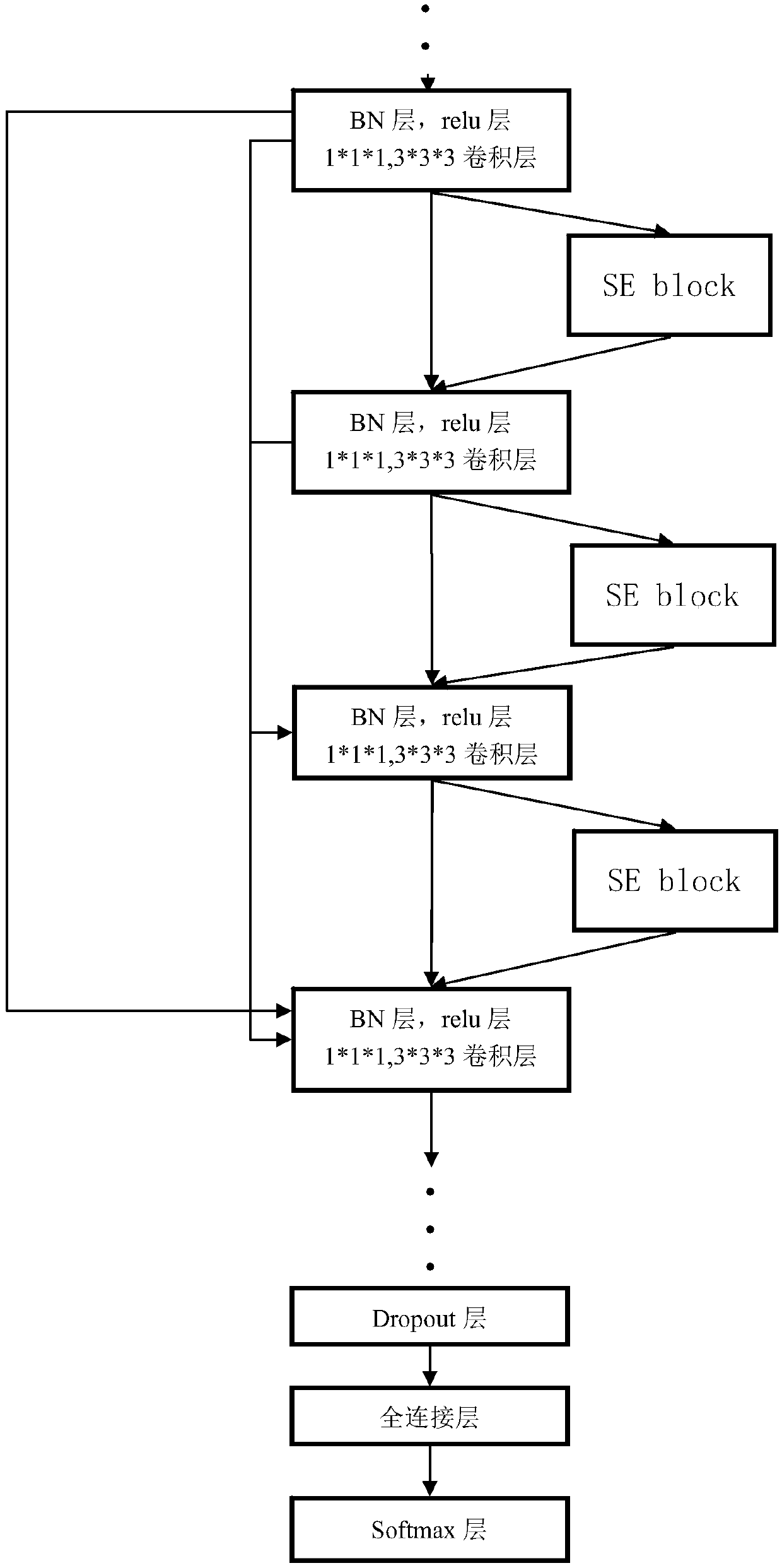
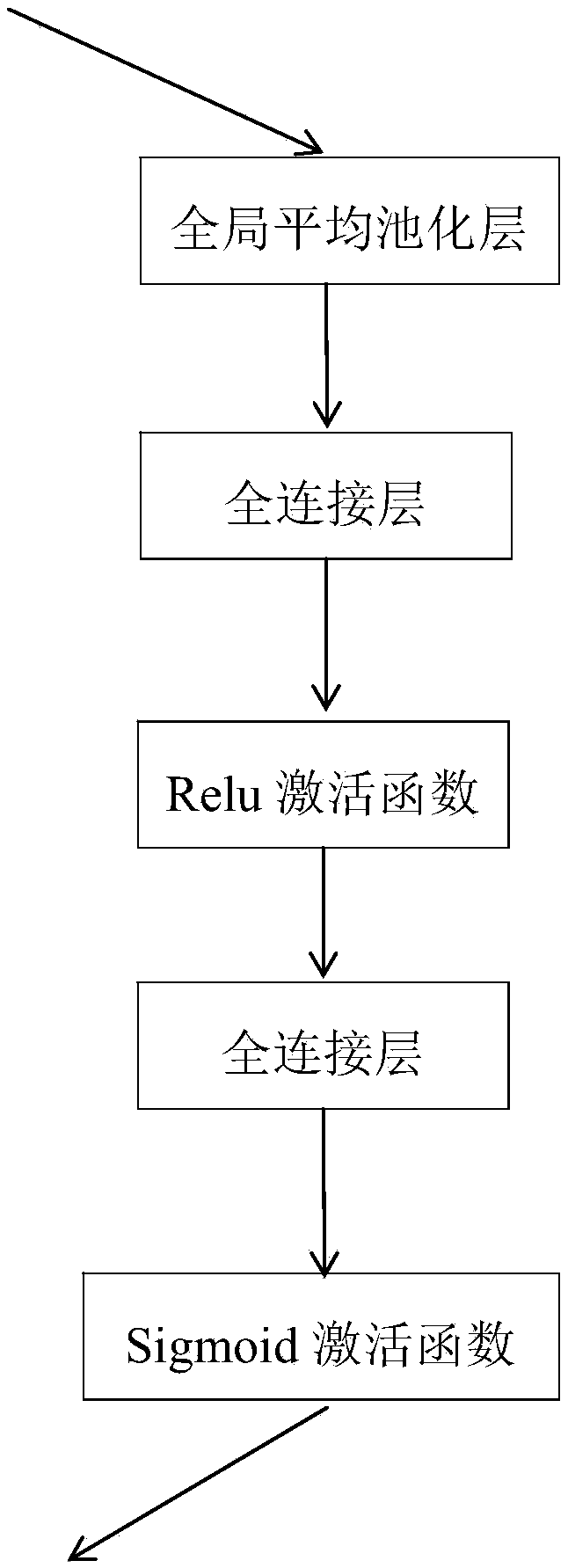
A three-dimensional pulmonary nodule recognition method based on convolution neural network
ActiveCN109544510AImprove recognition accuracyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional ctPulmonary nodule
The invention relates to the field of medical image analysis and the field of depth learning, which is a three-dimensional lung nodule identification method based on a convolution neural network. Themethod comprises the following steps: a lung three-dimensional CT image data set is pretreated, and the pretreated CT image data set is divided into a training data set and a test data set; A neural network model combining DenseNet and SENet is established, and its super parameters are set. The training data set is imported into the neural network model, and the stochastic gradient descent algorithm and the learning rate decrease gradually are used to train the neural network model. After the model converges sufficiently, the model structure and weight parameters are saved and deduced, and thetrained neural network model is obtained. Using neural network model to test each group of three-dimensional CT images in the test data set, the recognition results of lung nodules were obtained. This method can be used to analyze whether there are pulmonary nodules and their specific locations in 3D CT images, which can solve the problem of low accuracy of pulmonary nodules recognition caused bygradient disappearance, gradient explosion or degradation of deep convolution neural network.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Segmentation method of viscera and internal blood vessels thereof in surgical planning system
ActiveCN102663416AOvercoming the deficiency of error accumulationImprove robustnessImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree dimensional ctPattern recognition
The invention relates to a segmentation method of medical images, and specifically relates to a segmentation method of viscera and internal blood vessels thereof in a surgical planning system. The method designs a segmentation method of images of liver parenchyma, portal veins and hepatic veins based on minimal supervised classification of the three-dimensional CT images of the viscera and internal tubular tissues thereof. The method applies methods of statistics and spatial information, introduces high credible points, and obtains segmentation results based on arrival time of fast march of grey level. The method assumes that spatially adjacent points belong to a same organ, and performs segmentation calculation on the images by using a classification algorithm based on the above assumption, wherein the segmentation calculation comprises the steps of: acquiring estimated values of parameters of a Gaussian mixture distribution model; selecting the high credible points; and calculating the mean value of the grey level of the images and calculating the arrival time by using a fast marching algorithm to obtain arrival time images of three tissue classifications. According to the invention, good robustness and good anti-noise interference capability are obtained, accumulated errors are eliminated effectively, classification accuracy is improved, and great application value in clinical treatment is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU DIKAIER MEDICAL TECH
Method and system for partitioning construction in CT image
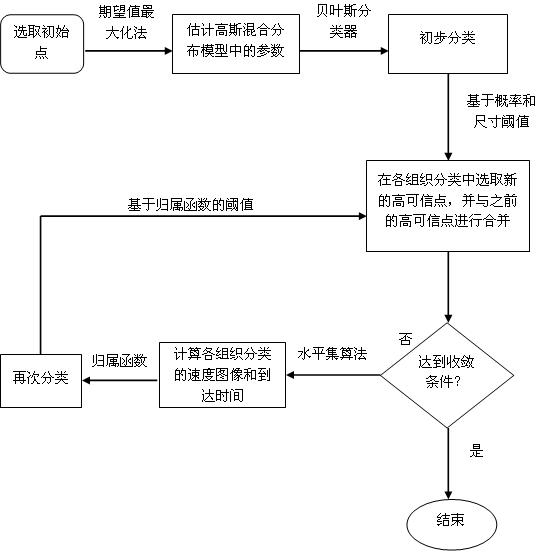
ActiveCN104143190AInteractive Split QuickOvercome the disadvantage that the energy value has a greater advantageImage analysisThree dimensional ctCurrent point
The invention provides a method and system for partitioning a construction in a CT image. The method includes the steps that the opacity of the CT image is adjusted, and a construction structure in the CT image is obtained; the construction to be partitioned is determined in the obtained construction structure, interactive partition is conducted on one layer of the CT image of the construction to be partitioned, the processes are that firstly, the gradient vector is used for constructing an energy cost function of the CT image under the opacity, a seed point is selected at the position close to the construction to be partitioned, the optimal path, generated according to the energy cost function, between a current point and the seed point is the outline of the image of one layer of the CT image of the construction to be partitioned, secondly, the outline of a layer adjacent to the layer where the outline is located is generated, thirdly, outlines of the images of all layers in the CT image of the construction to be partitioned are generated according to the iteration method, fourthly, the outlines of the images of all the layers in the CT image of the construction to be partitioned are combined to obtain the three-dimensional construction to be partitioned. By means of the method and system for partitioning the construction in the CT image, interactive partition can be conducted on the three-dimensional CT image rapidly and accurately.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
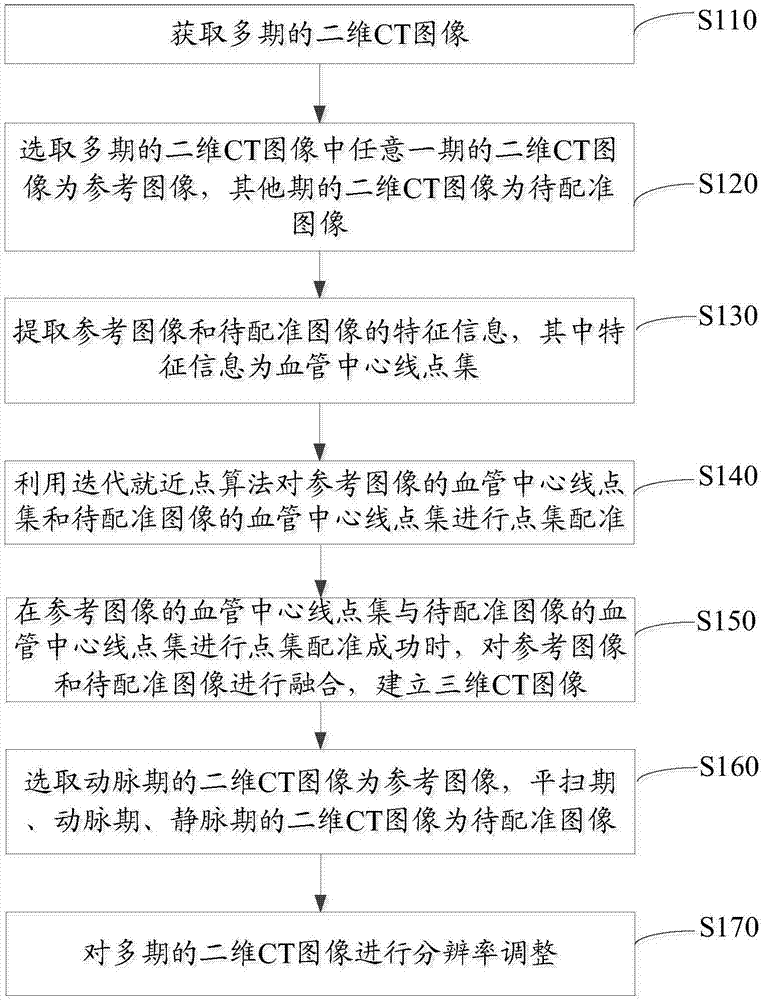
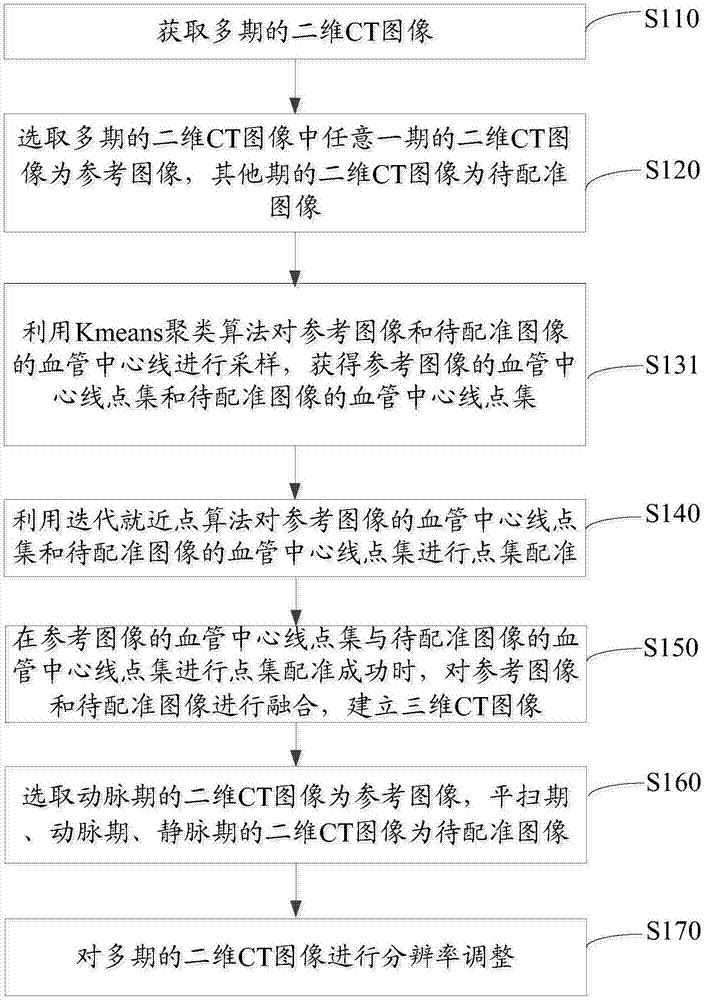
Three-dimensional fusion method and system of CT images
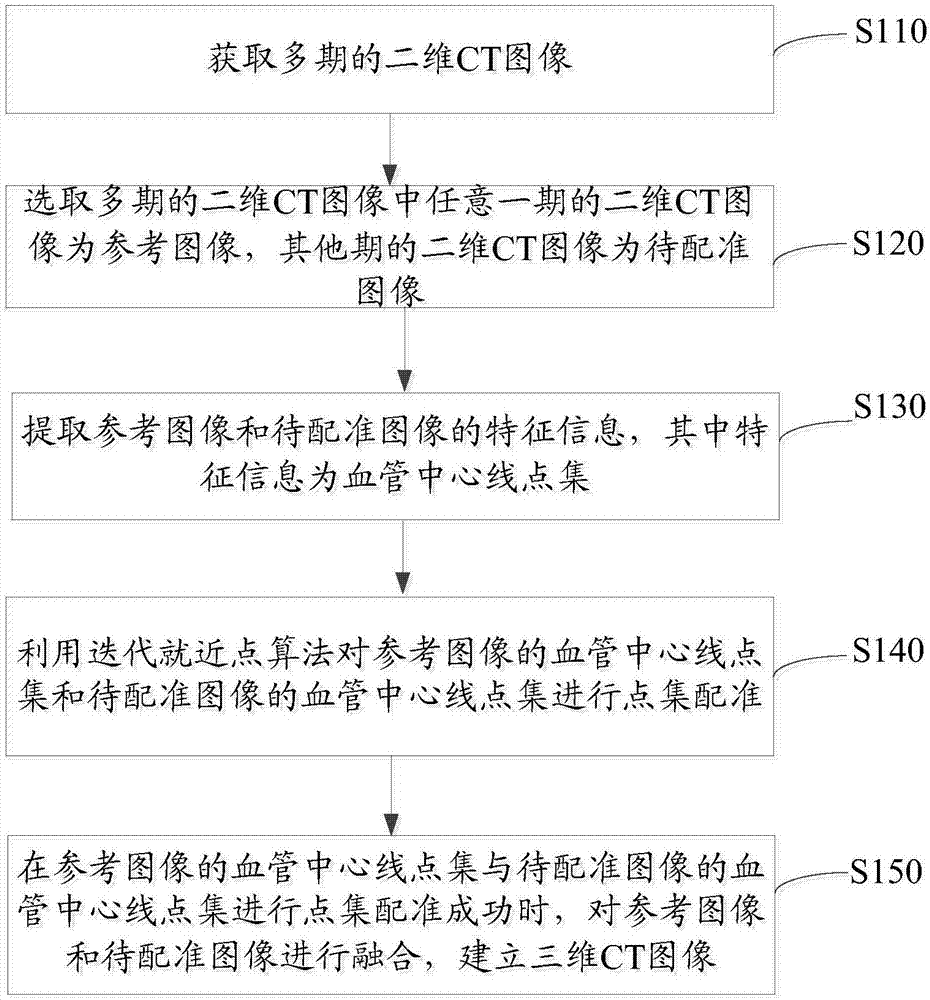
InactiveCN107451983ARealize visualizationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional ctReference image
The invention relates to a three-dimensional fusion method of CT images. The method comprises the steps that multiple periods of two-dimensional CT images are acquired; any period of a two-dimensional CT image is selected from multiple periods of two-dimensional CT images and is used as a reference image, and other periods of two-dimensional CT images are images to be registered; the characteristic information of the reference image and the images to be registered is extracted, wherein the characteristic information is vessel center line point sets; an iterative near point algorithm is used to carry out point set registering on the vessel center line point set of the reference image and the vessel center line point set of the images to be registered; and if the point set registering of the vessel center line point set of the reference image and the vessel center line point set of the images to be registered is successful, the reference image and the images to be registered are fused to create a three-dimensional CT image. According to the invention, multiple periods of two-dimensional CT images are registered; the three-dimensional CT image is established through fusion; and the CT images are visualized, which helps to improve the accuracy of the medical diagnosis.
Owner:THE SIXTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
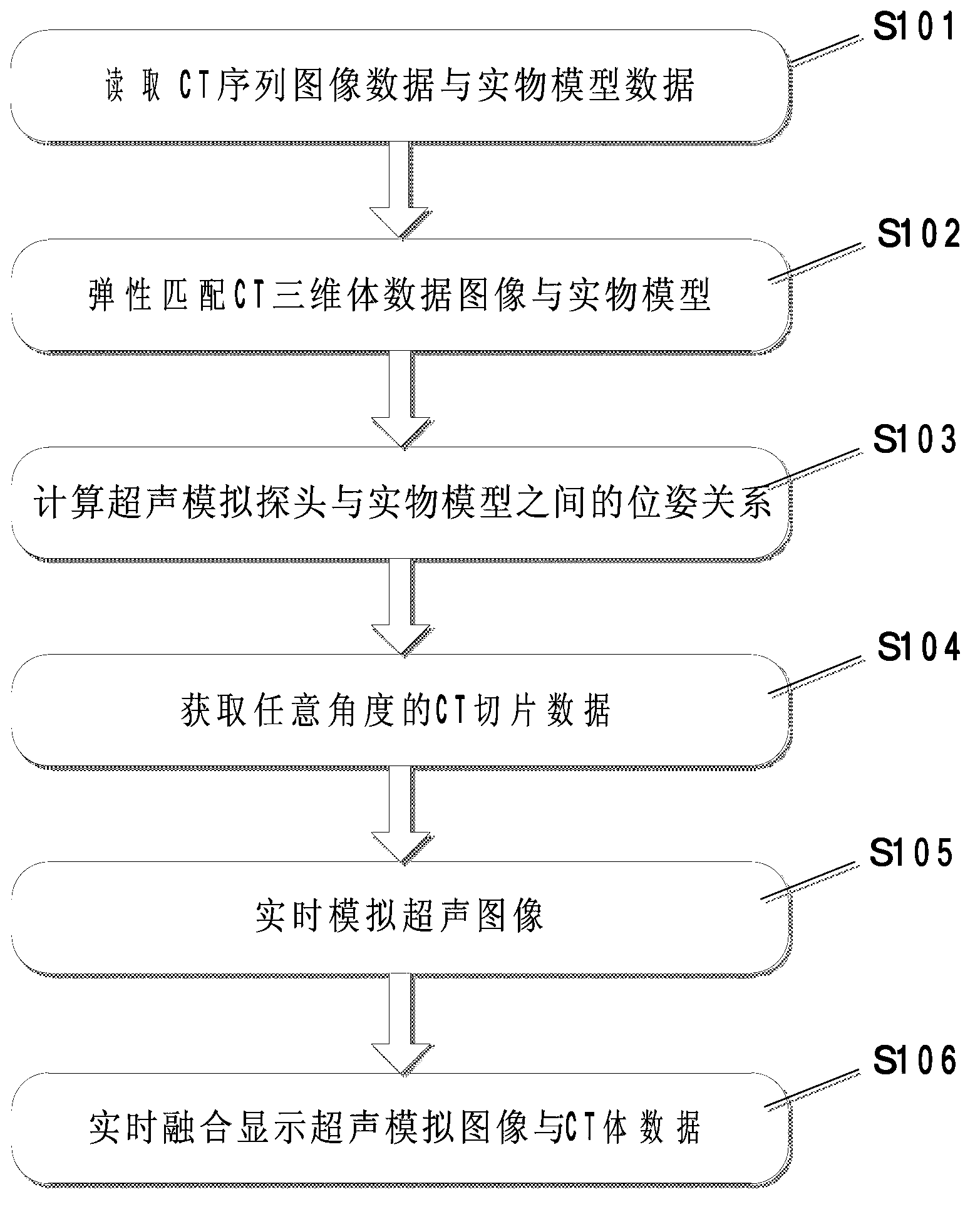
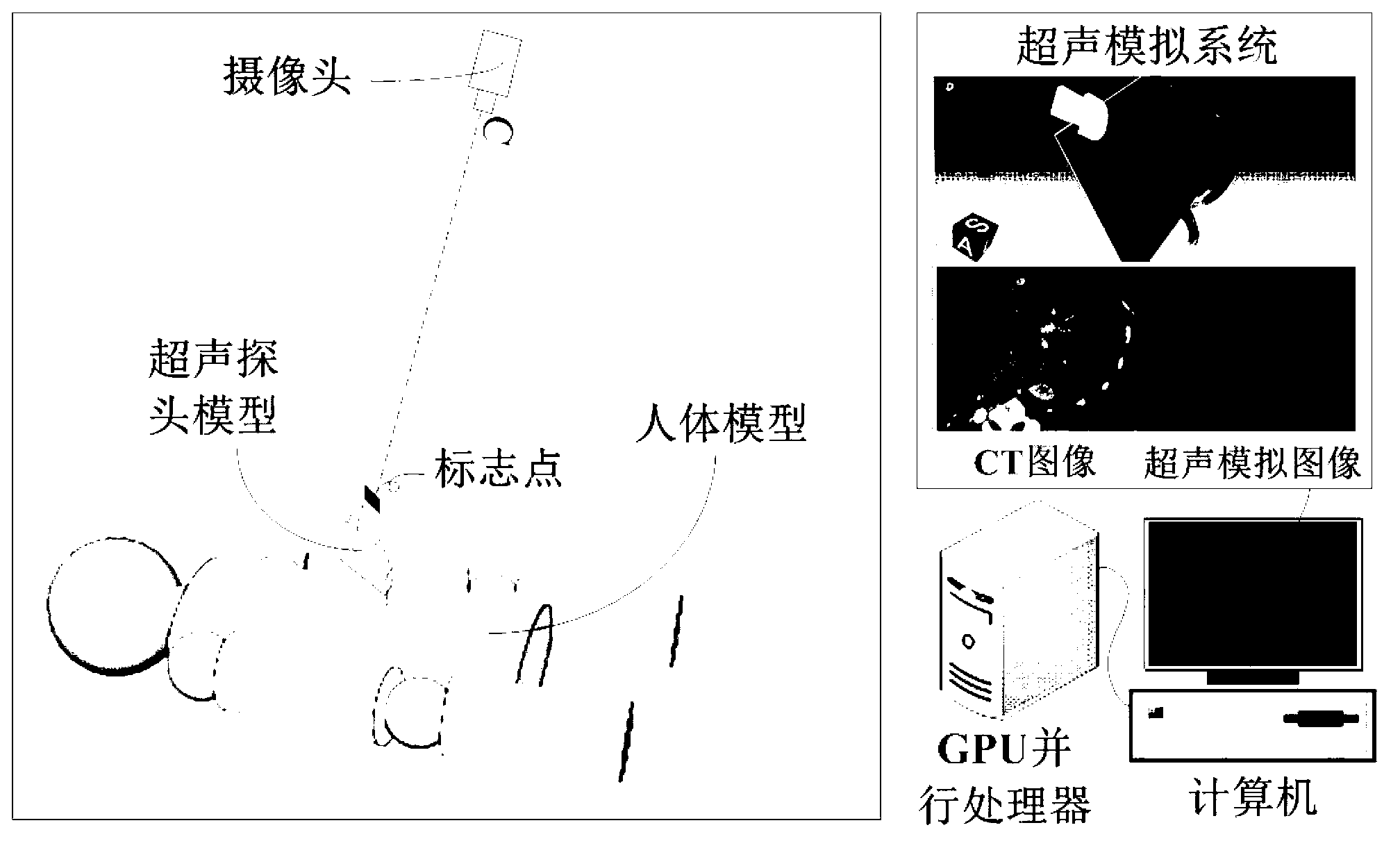
Ultrasonic training system based on CT (Computed Tomography) image simulation and positioning
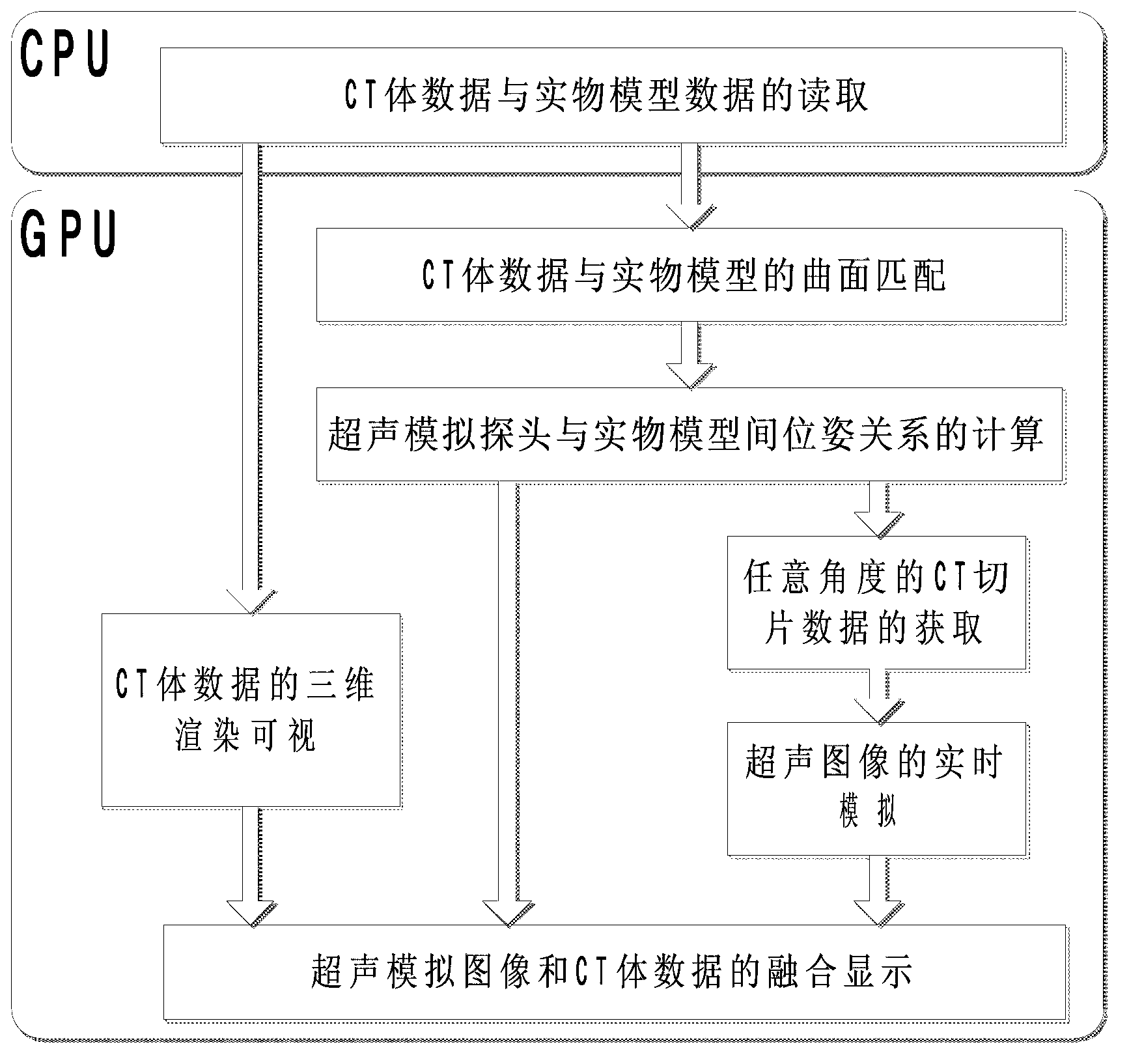
ActiveCN103295455AReduce computational complexityThe pose matrix is accurateEducational modelsHuman bodyThree dimensional ct
The invention provides an ultrasonic training system based on CT (Computed Tomography) image simulation and positioning. Ultrasound image simulation and CT volumetric data rendering are accelerated to be achieved through a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) and the real-time performance of the system is improved. A curved surface matching module is used for performing surface matching on read human body CT volumetric data and physical model data with a physical model as the standard and achieving elastic transformation of a curved surface based on an interpolation method of thin plate splines; an ultrasonic simulation probe position tracking module is used for performing real-time calculation on ultrasonic simulation probe positions relative to the physical model by a marking point tracking method and obtaining arbitrary angle CT slice images according to a position matrix; an image enhancement and ultrasonic image simulation generation module is used for improving the vessel contrast ratio in CT images by a multi-scale enhancement method and achieving the ultrasound image simulation based on the CT volumetric data; and an integration display module is used for accelerating to achieve rendering display of the CT volumetric data based on CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) and integrating and displaying ultrasound simulation images and three-dimensional CT images according to the obtained position matrix.
Owner:ARIEMEDI MEDICAL SCI BEIJING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com