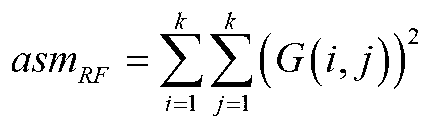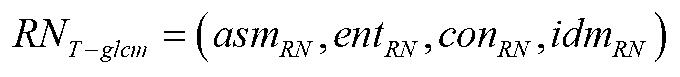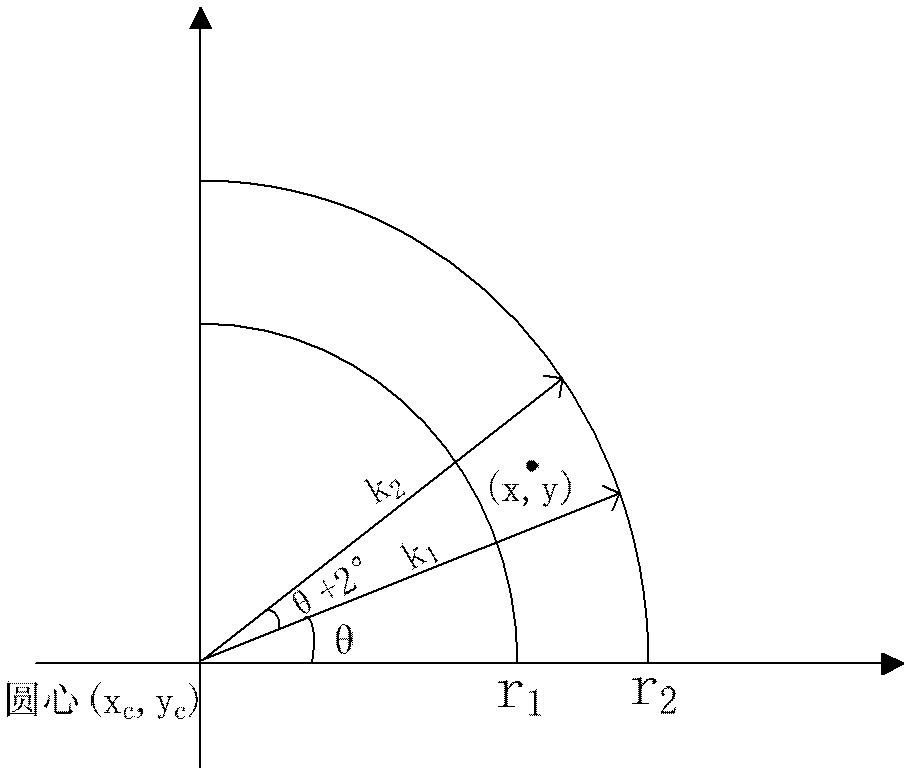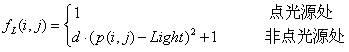Patents
Literature
2732 results about "Grey level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
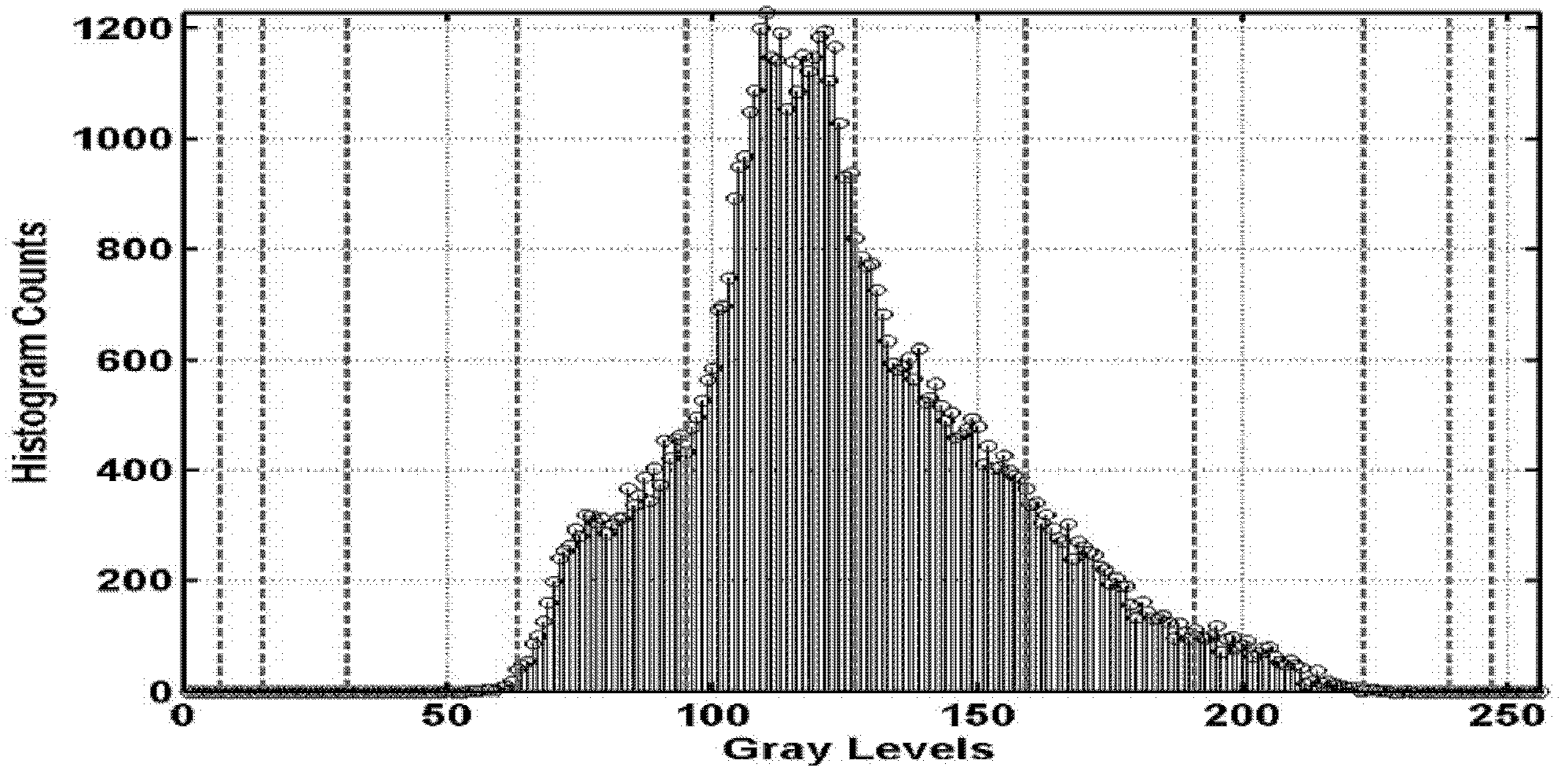
Gray level. A shade of gray assigned to a pixel. The shades are usually positive integer values taken from the gray-scale. In a 8-bit image a gray level can have a value from 0 to 255.
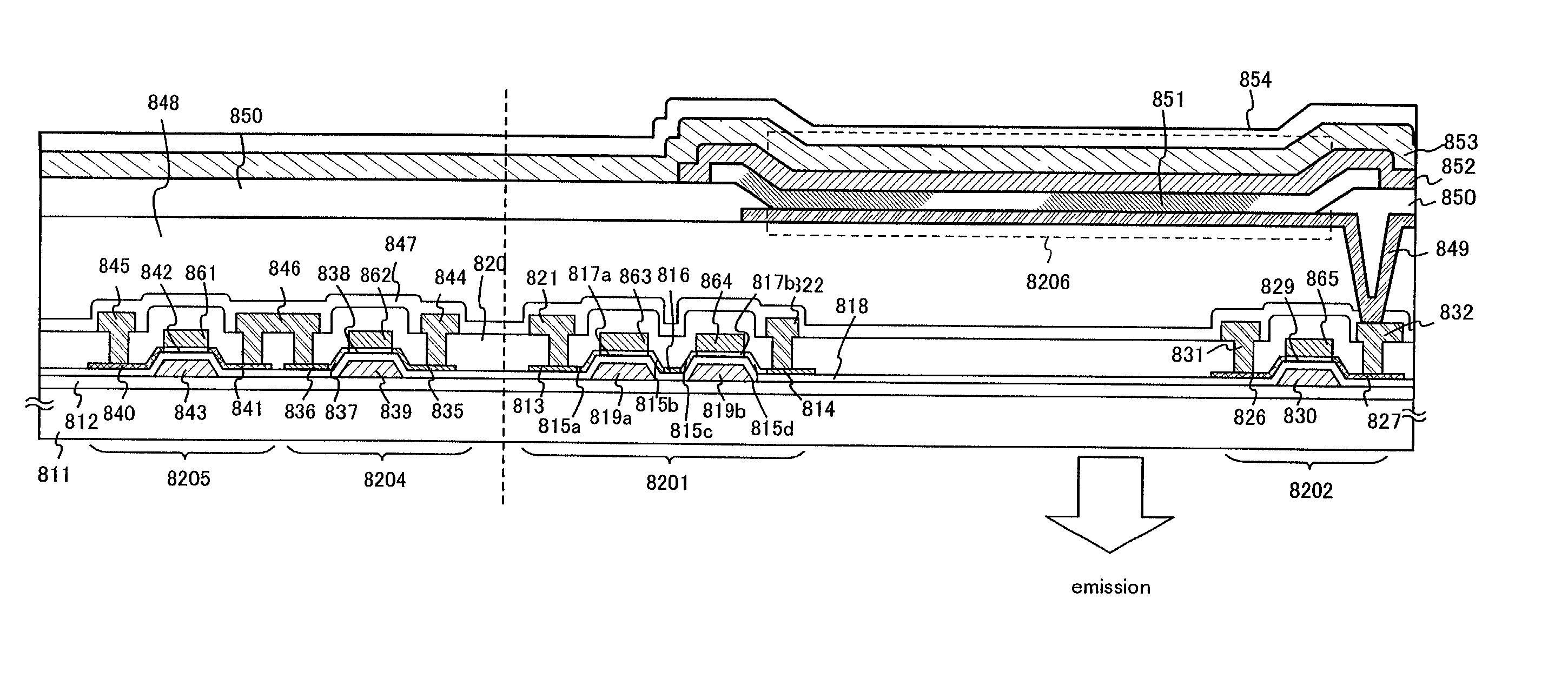
Light emitting device
An active matrix light emitting device which is capable of clear color display of multiple gray scales is provided. The light emitting device has a pixel portion, and the pixel portion has a plurality of pixels. Each of the plurality of pixels has an EL element, a first EL driver TFT, a second EL driver TFT, a switching TFT, and an erasure TFT. The first EL driver TFT and the second EL driver TFT are connected in parallel.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
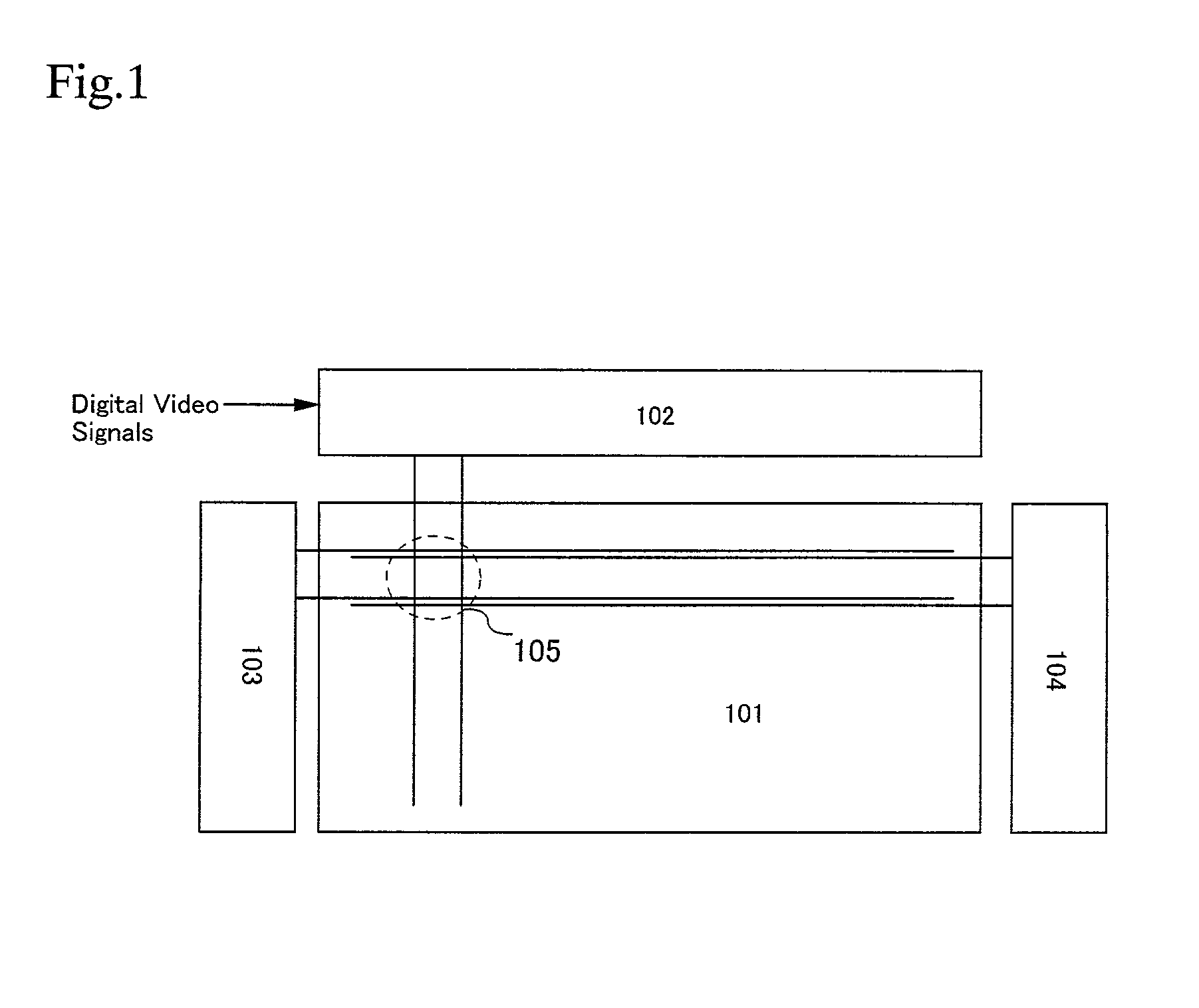
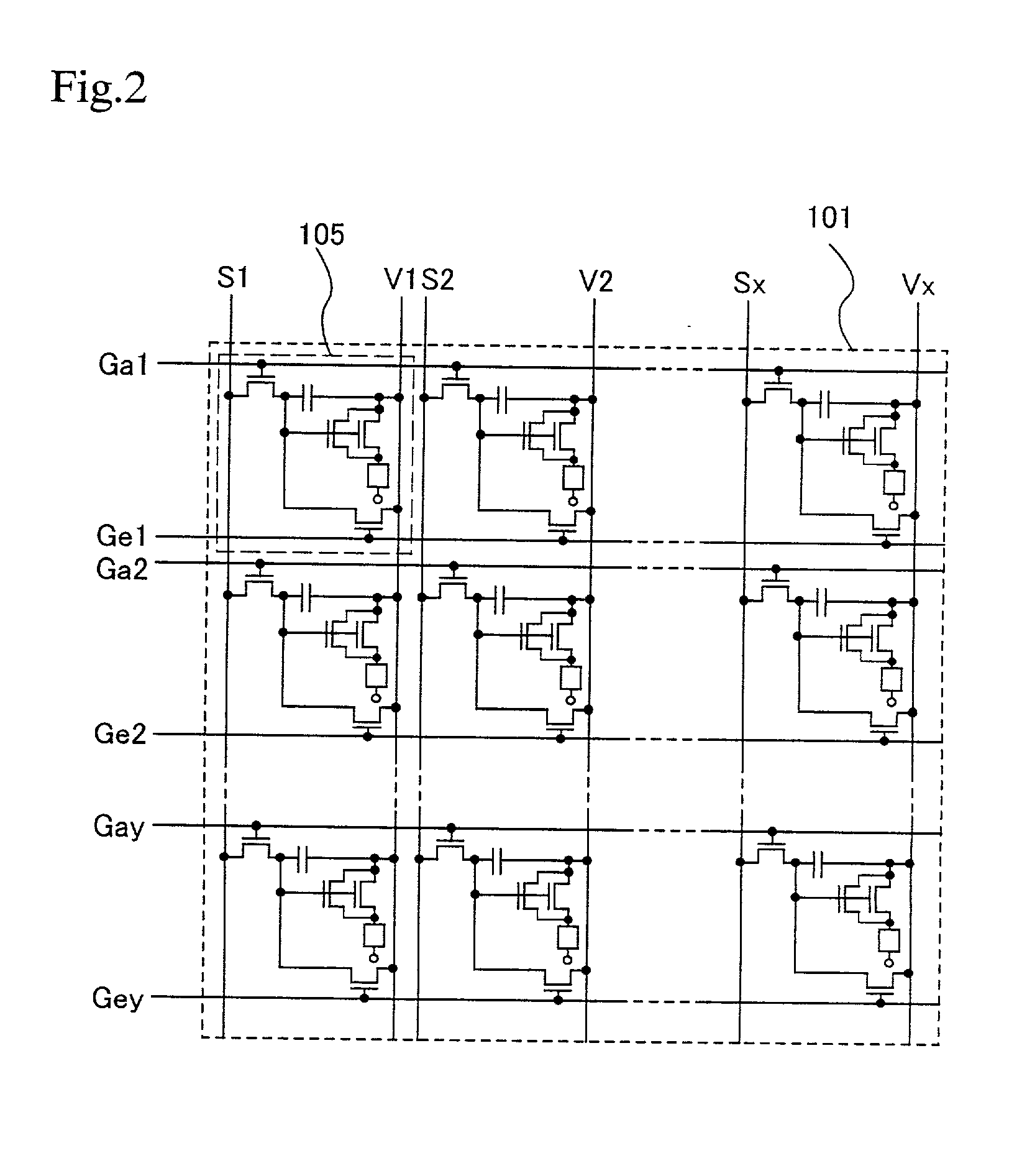
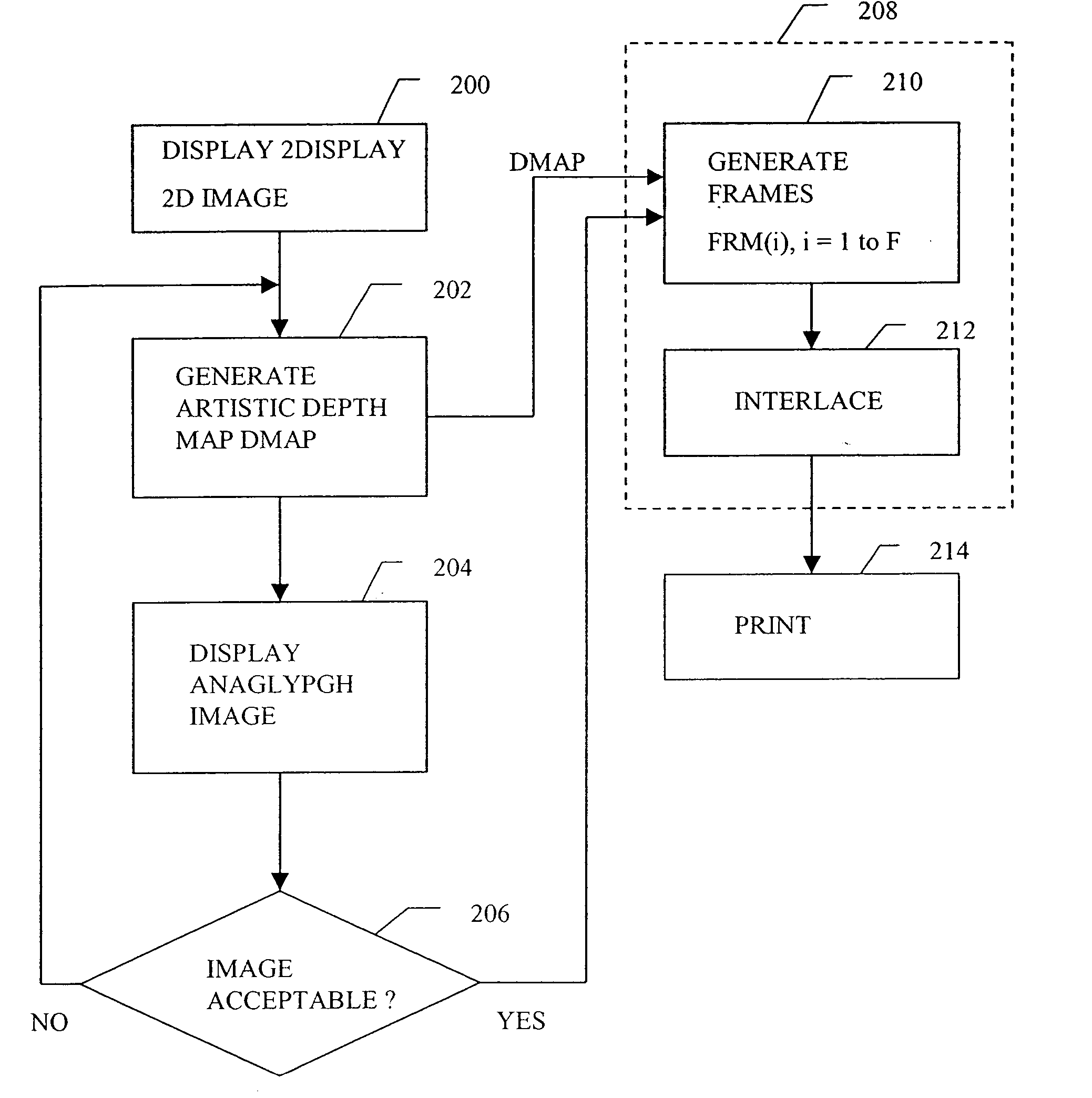
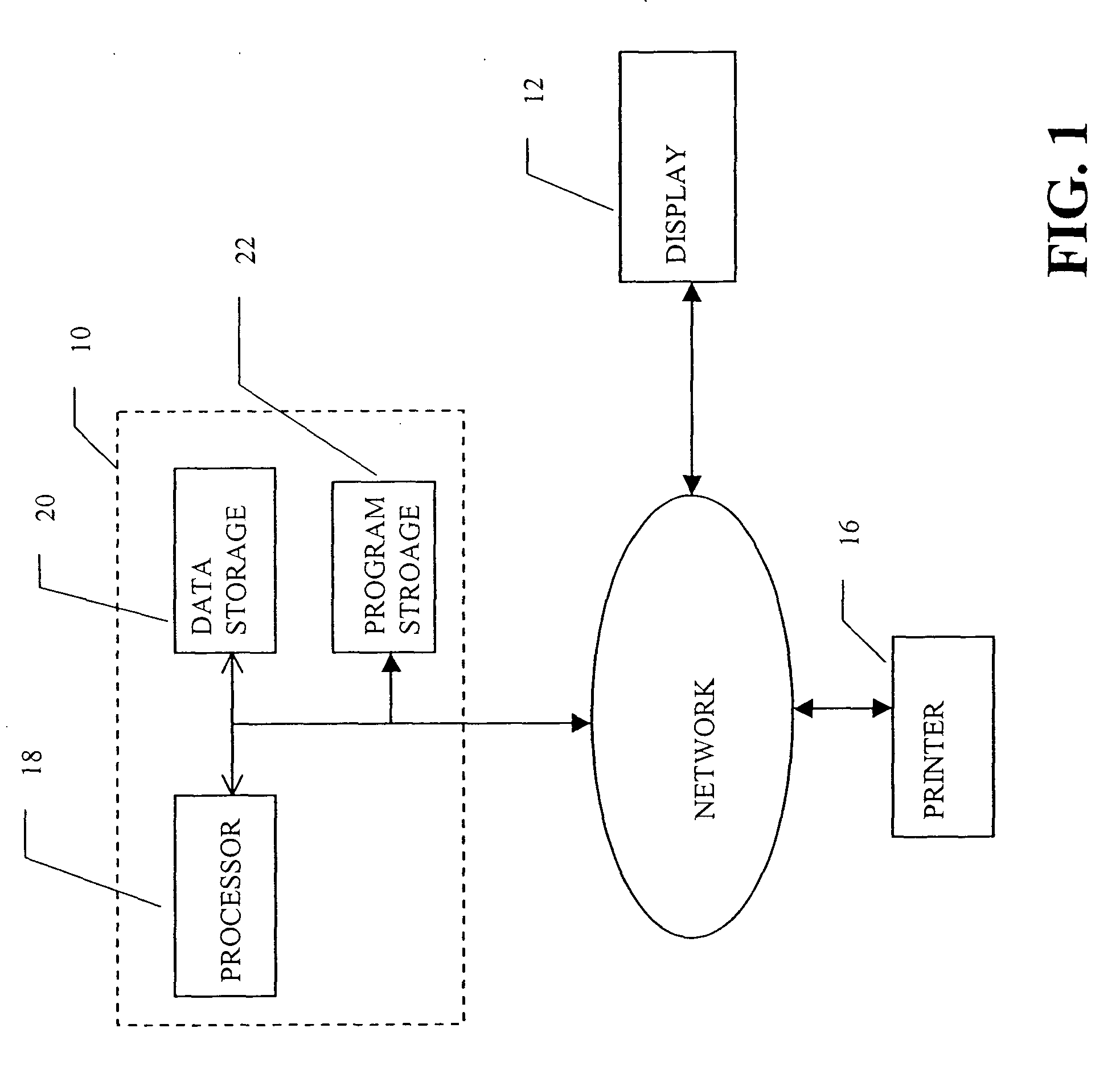
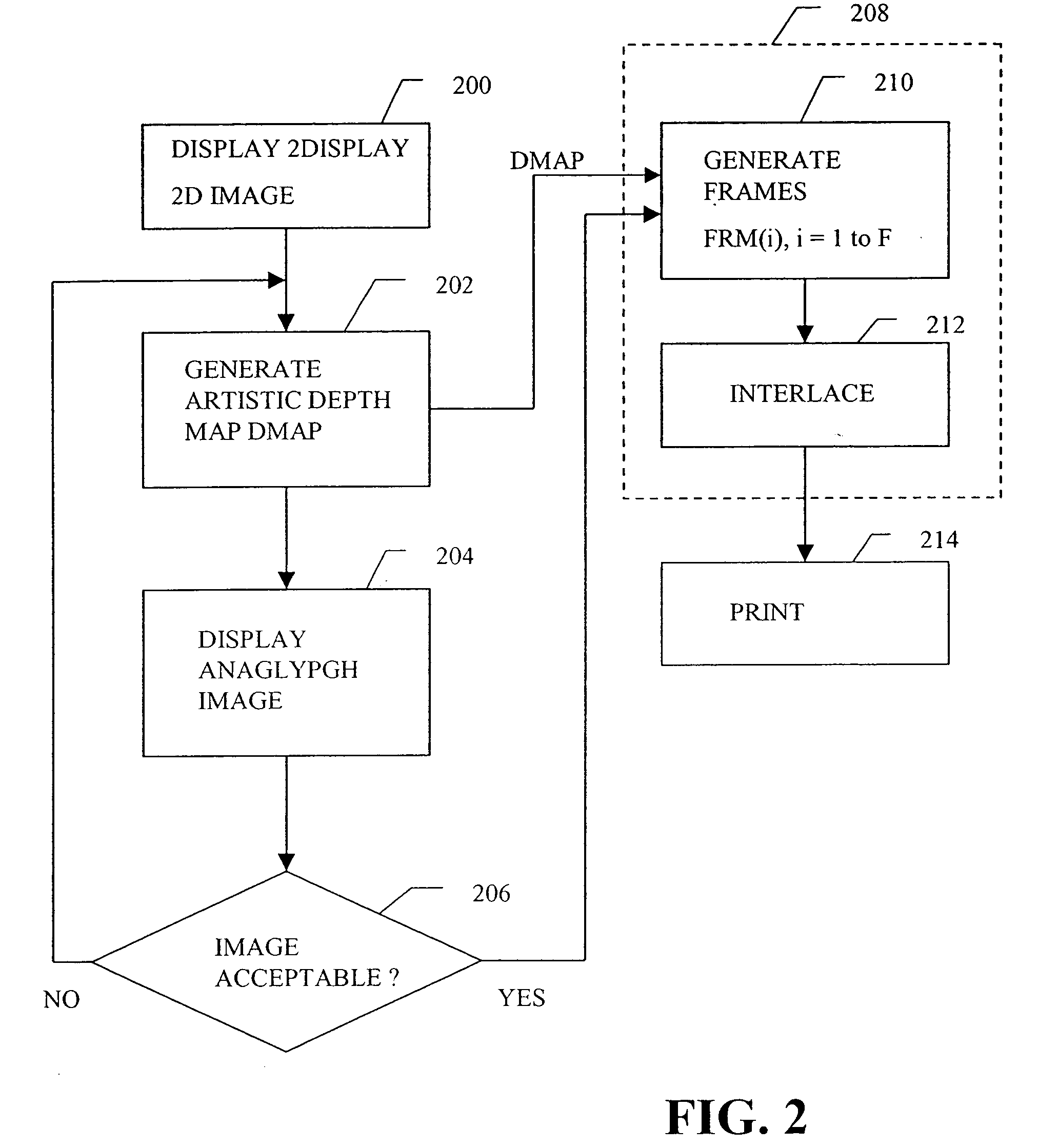
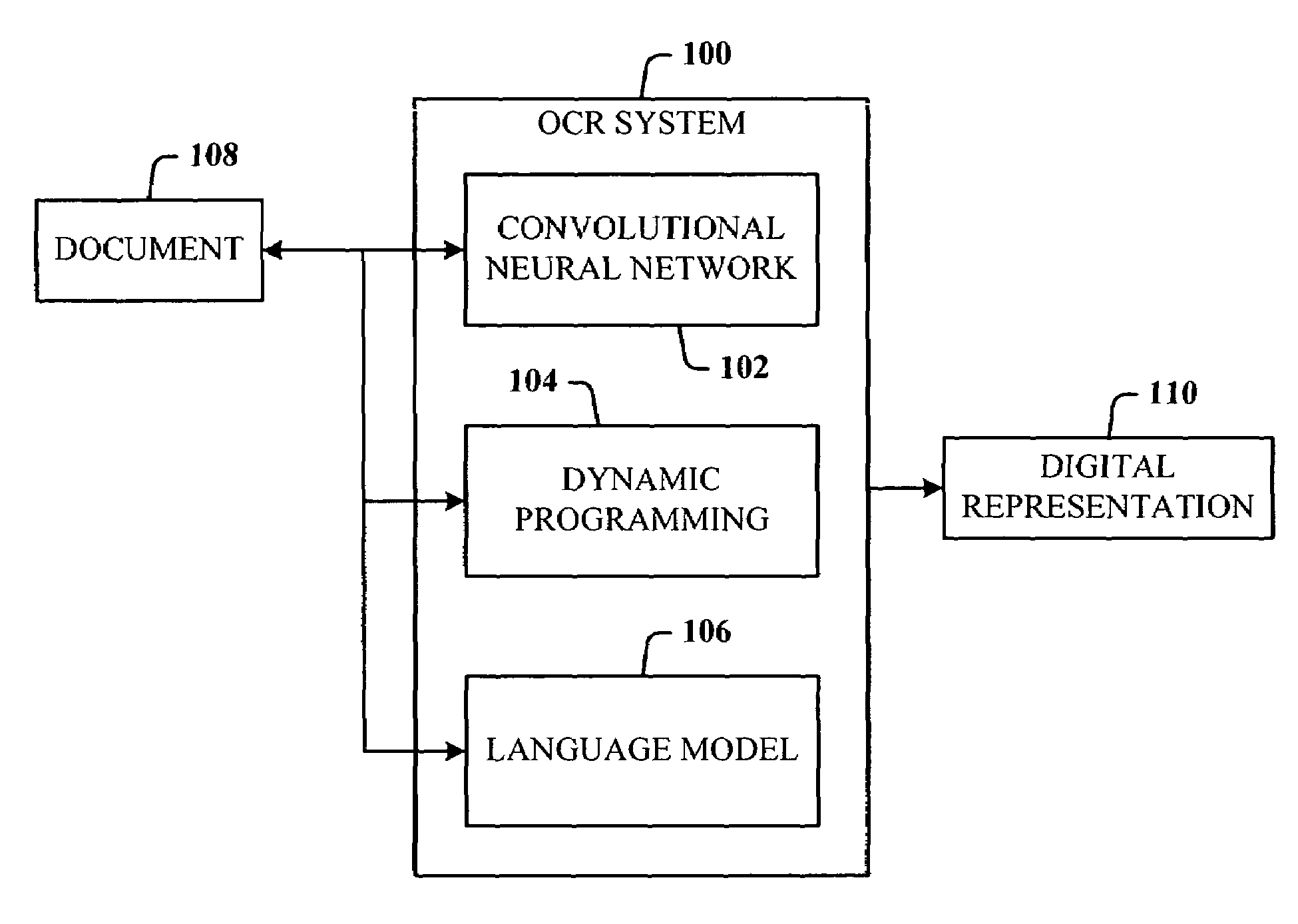
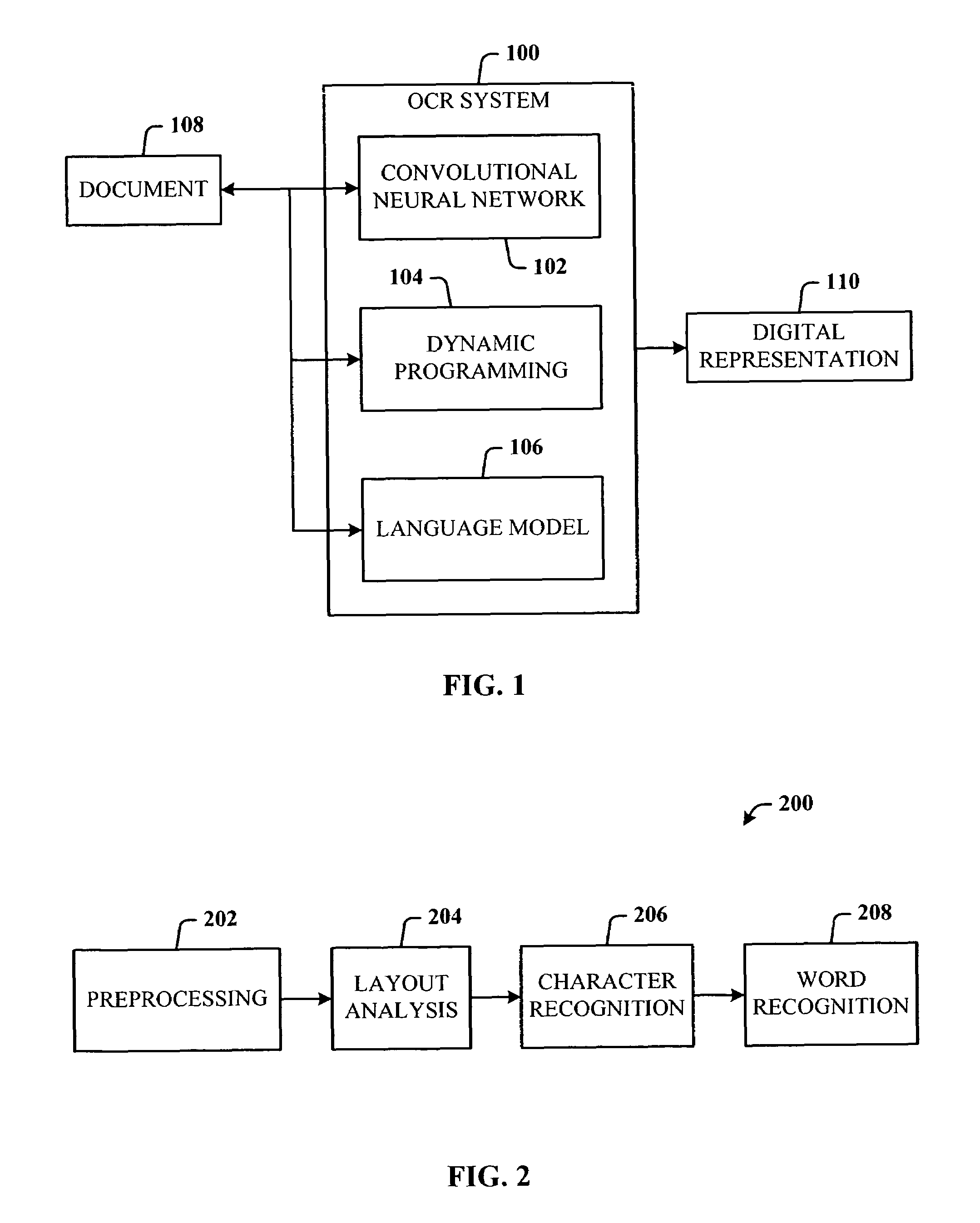
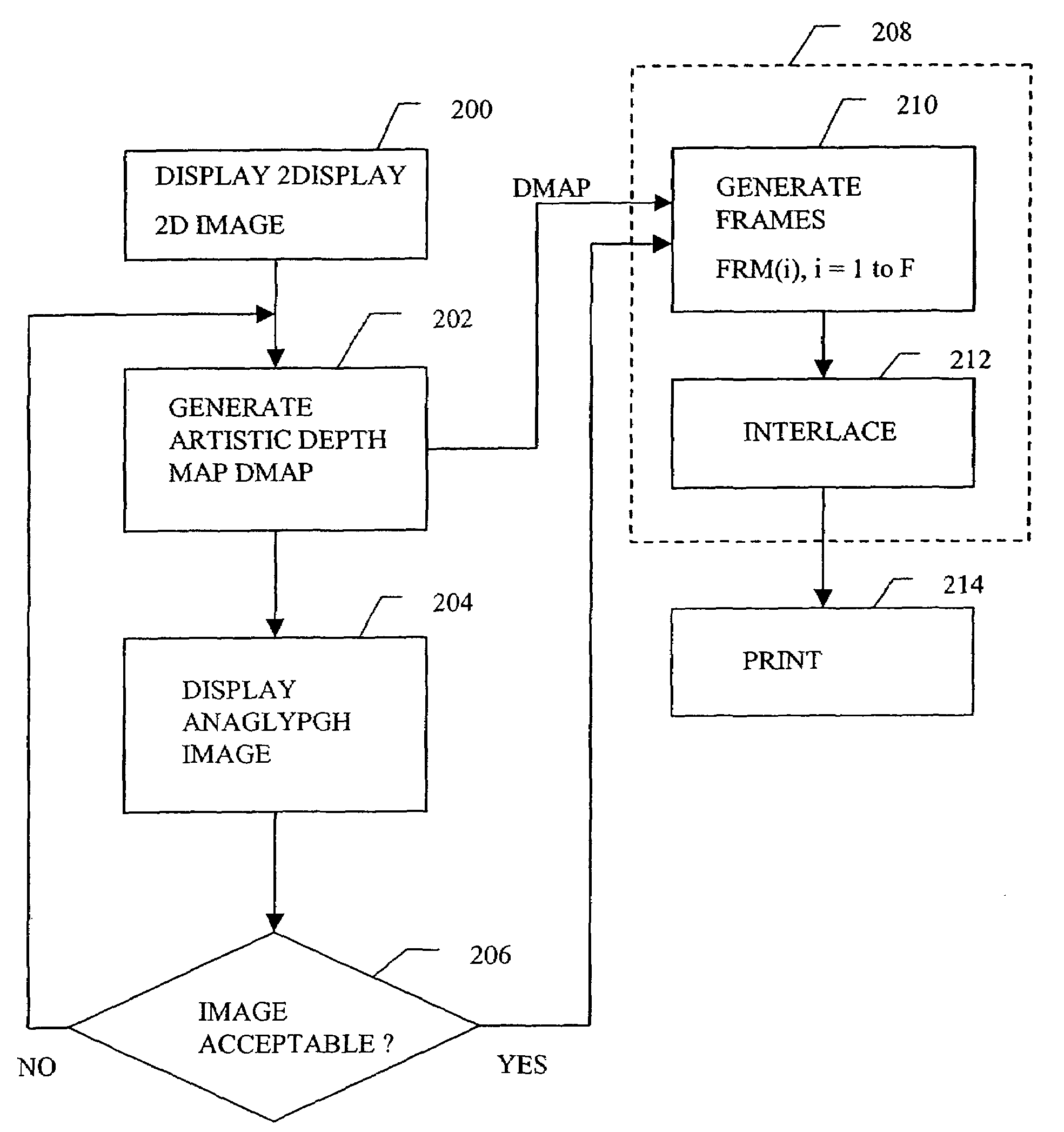
Multi-dimensional images system for digital image input and output
ActiveUS20040135780A1Character and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsInterlaced videoStereo pair
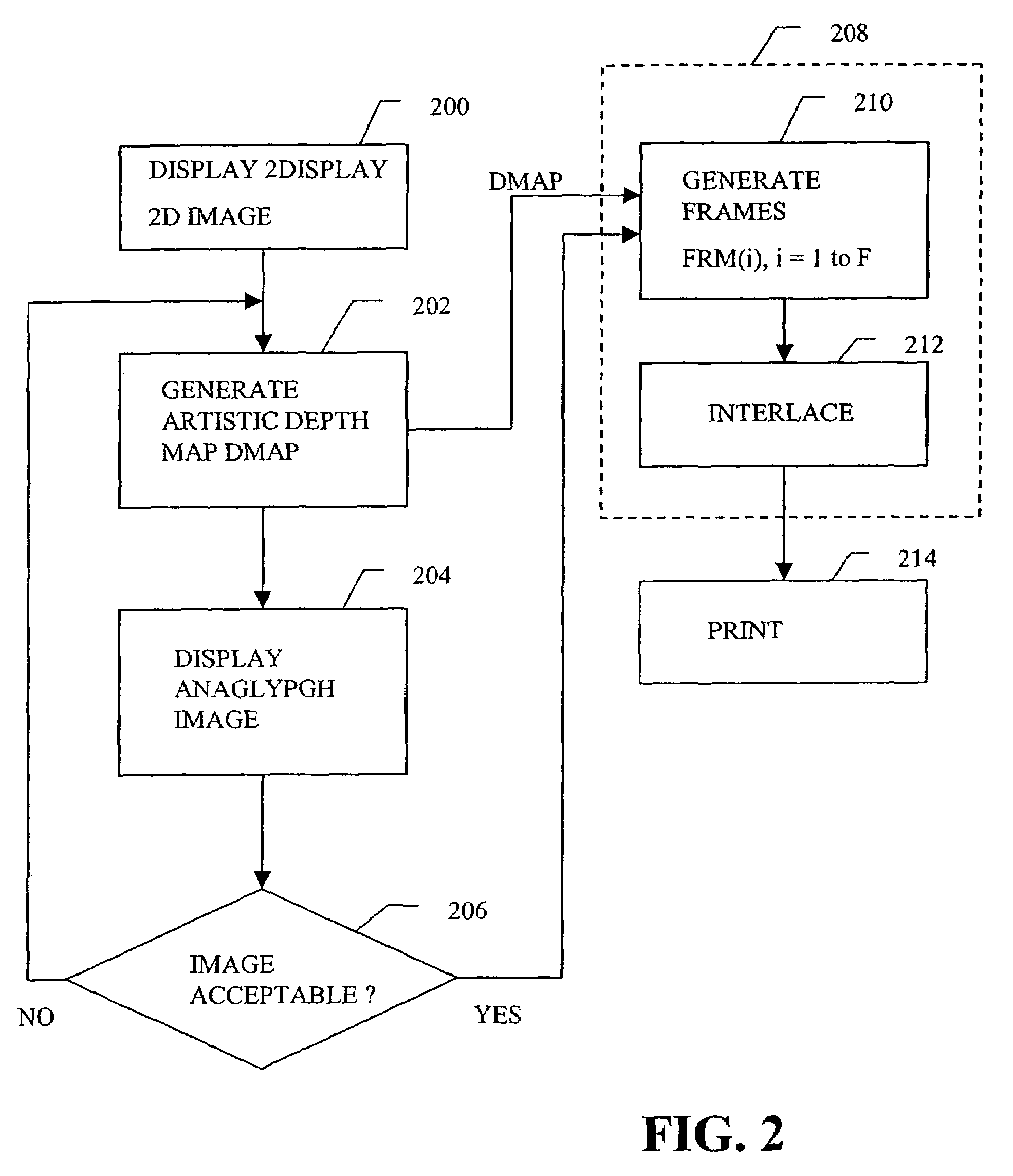
A two-dimensional image is displayed and a grey level image is drawn on said two-dimensional image defining a depth map. A stereo image pair is generated based on the depth map and an anaglyph image of the stereo image pair is displayed. Edits of the depth map are displayed by anaglyph image. A plurality of projection frames are generated based on the depth map, and interlaced and printed for viewing through a micro optical media. Optionally, a layered image is extracted from the two-dimensional image and the plurality of projection frames have an alignment correction shift to center the apparent position of the image. A measured depth map is optionally input, and a stereo pair is optionally input, with a depth map calculated based on the pair. The user selectively modifies the calculated and measured depth map, and the extracted layers, using painted grey levels. A ray trace optionally modifies the interlacing for optimization to a particular media.
Owner:NIMS JERRY C
Displaying method for the display and display
InactiveCN101009083AUniform brightness distributionImprove light and dark uniformityCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Gray level
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Driving method to neutralize grey level shift for electrophoretic displays
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
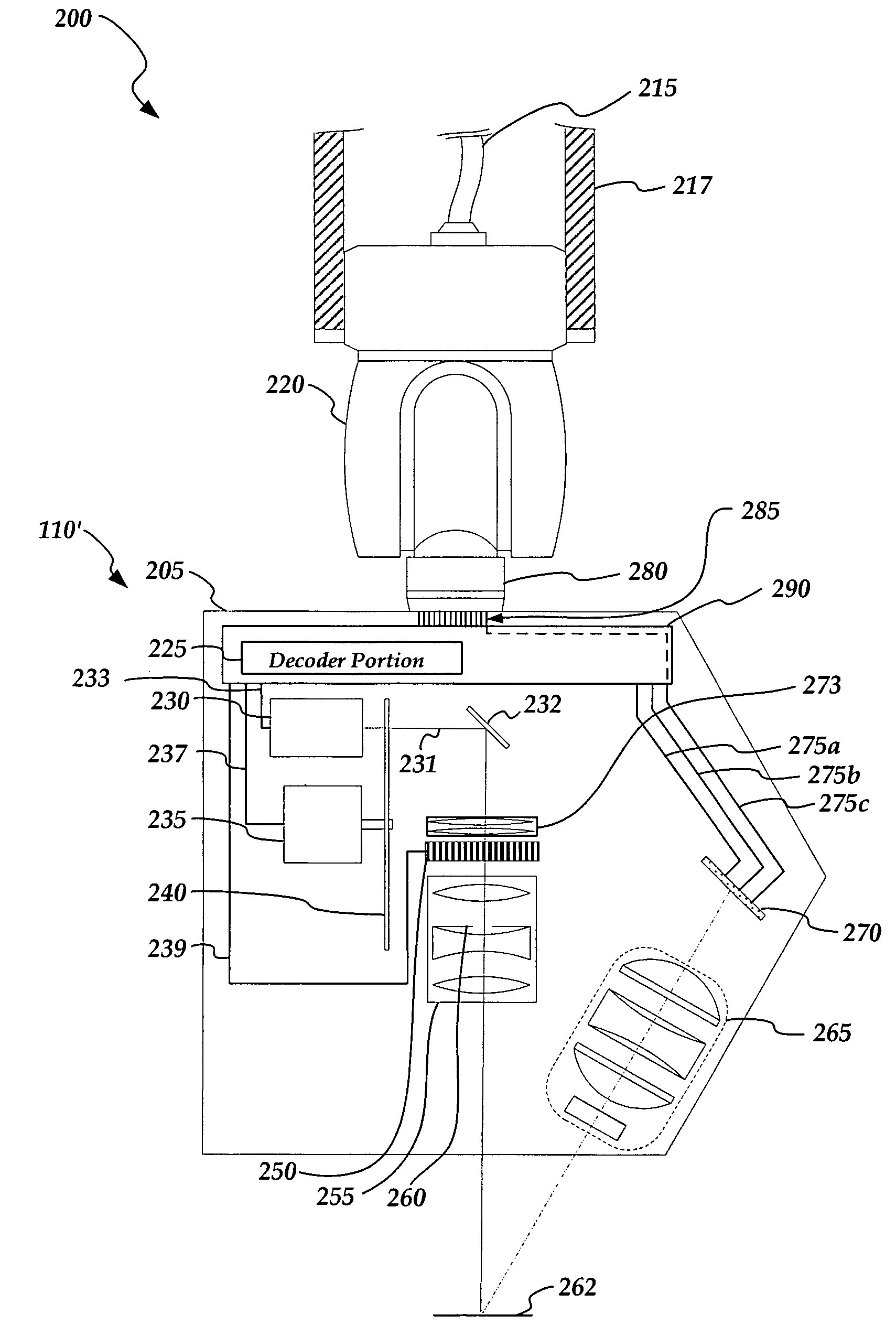
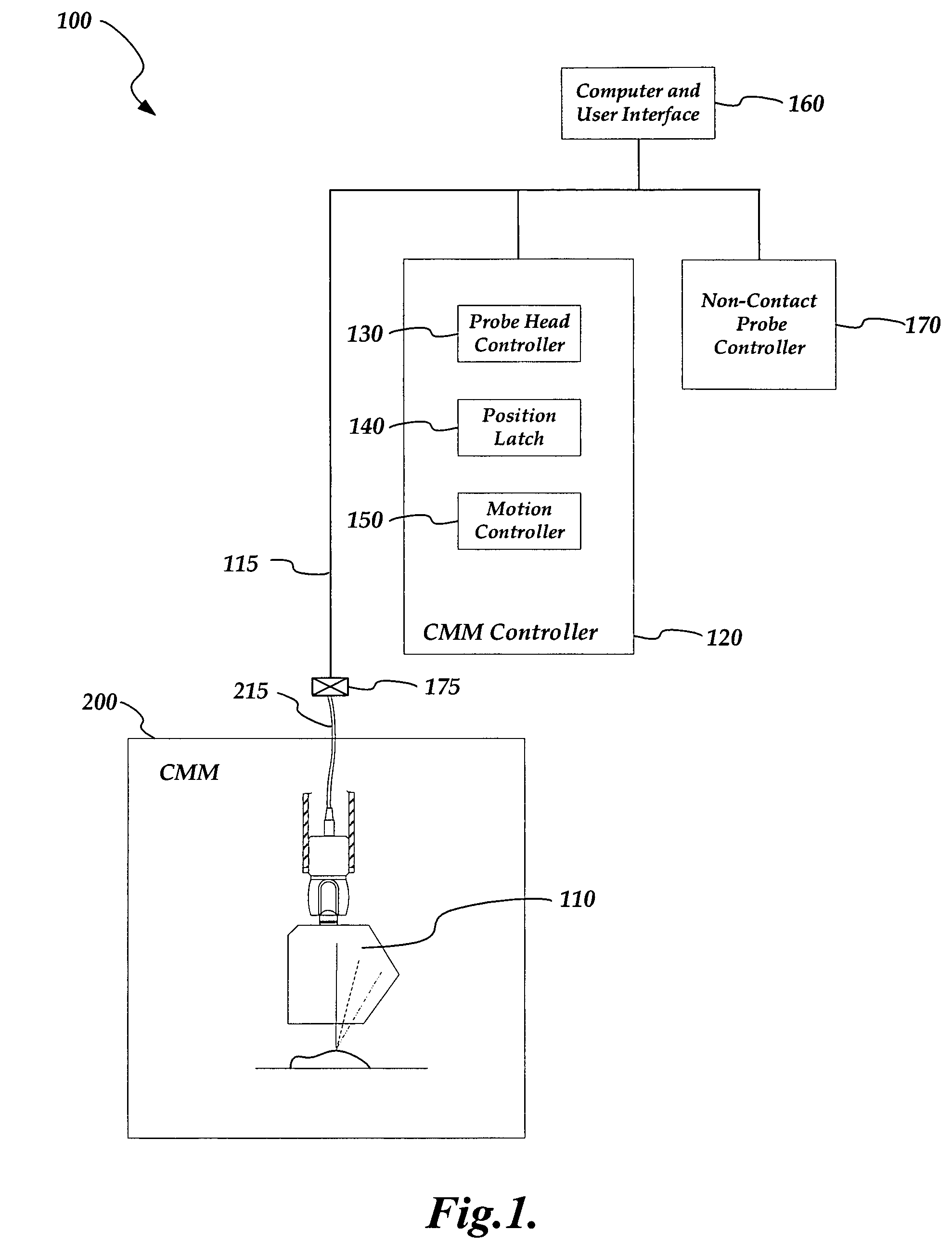
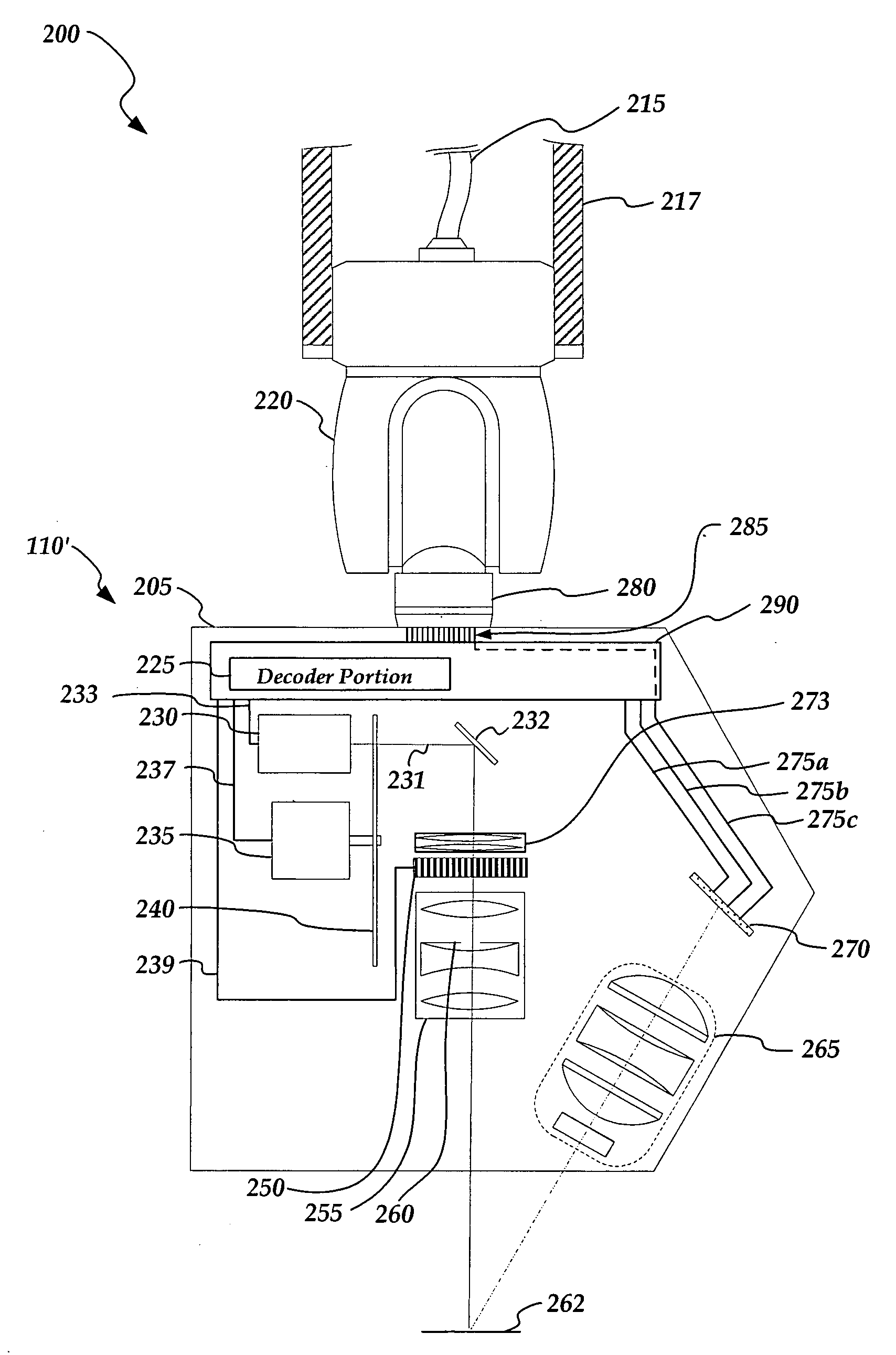
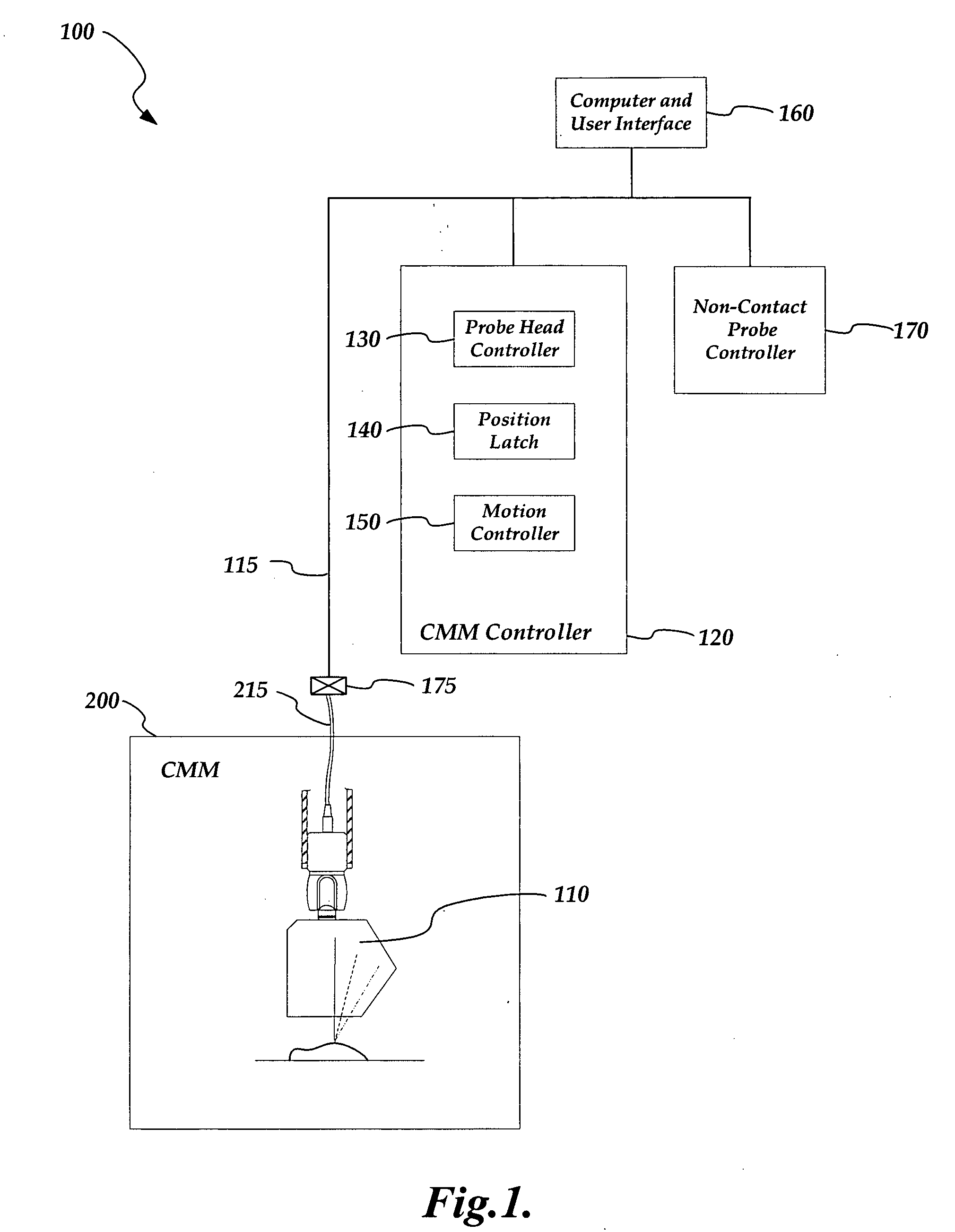
Non-contact probe control interface
ActiveUS7652275B2Existing systems can be upgraded more easilyEasy to upgradeImage analysisOptical rangefindersSpatial light modulatorControl signal
A probe control interface is provided for a structured light non-contact coordinate measuring machine probe. Portions of a video control signal for controlling the grey level of selected rows of pixels of a spatial light modulator of the probe can be decoded into control signals for additional probe components or functions that have been added to increase the measuring capabilities or versatility of the non-contact probe. By providing the additional probe component control signals in this manner, a versatile structured light non-contact probe system can be made compatible with a standard probe head autojoint system (e.g. a Renishaw™ type system), thus allowing the probe to be automatically exchanged with other standard probes and allowing existing systems to use the non-contact probe more easily. Various aspects of the probe control interface allow for relatively simple, compact, lightweight and robust implementation.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
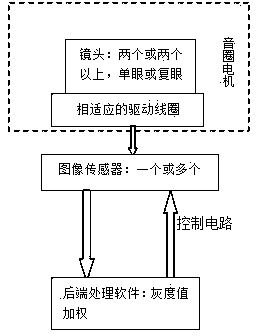
Novel three-dimensional image shooting module
InactiveCN103841404AAchieve shootingMiniaturizationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensCamera module
The invention relates to a novel three-dimensional image shooting module which can achieve synchronous focusing control over portable electronic product dual lens or multiple lens and three-dimensional image shooting. The module comprises a plurality of camera modules fixed on a voice coil motor, the voice coil motor which can bear the camera modules at the same time, an image sensor which is used for collecting shot image information, a control circuit and back end processing software which can carry out grey level weighting and three-dimensional image synthesis. The camera modules have the same parameters and are borne on the same voice coil motor, synchronous focusing can be carried out, the number of the image sensor can be one or more, the back end processing software carries out weighting according to a preset factor through the grey levels of two images during a focusing process, and feedback fine focusing is carried out after a comprehensive grey level is obtained. The shooting module can be used on a micromation portable electronic product conveniently for three-dimensional image shooting, and quality and shooting effect can be improved.
Owner:江西省一元数码科技有限公司 +1
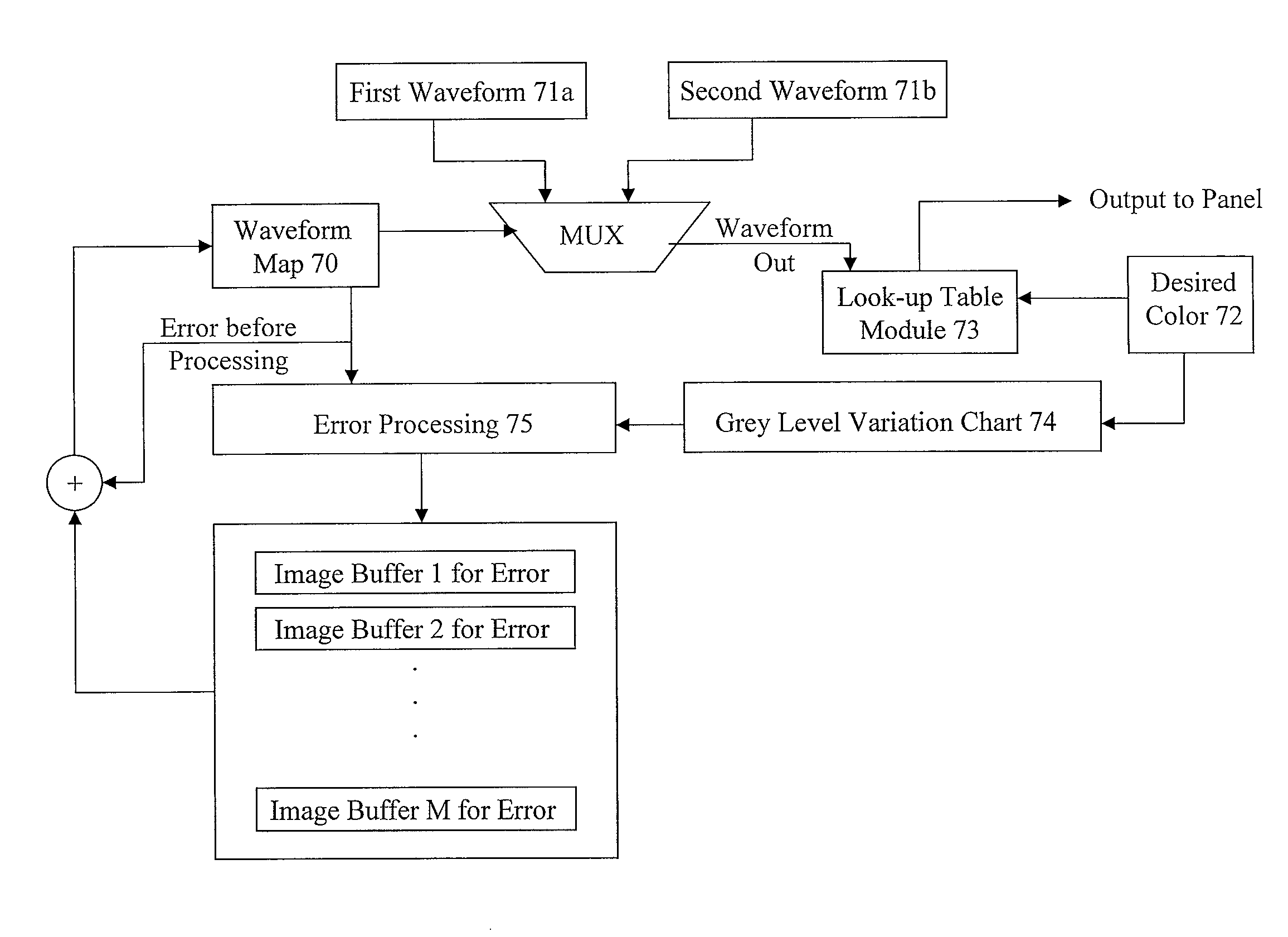
Spatially combined waveforms for electrophoretic displays
ActiveUS8576164B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectrophoresisDisplay device
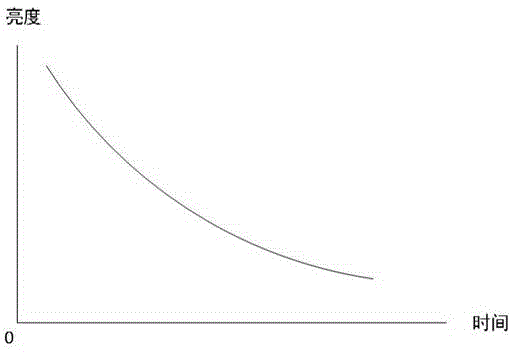
The present invention is directed to a driving method for compensating the response speed change of an electrophoretic display due to temperature variation, photo-degradation or aging of the display device, without a complex structure (e.g., use of sensors). This is accomplished by combining two waveforms, one of which causes the grey level to become dimmer and the other waveform causes the grey level to become brighter, as the response speed degrades.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
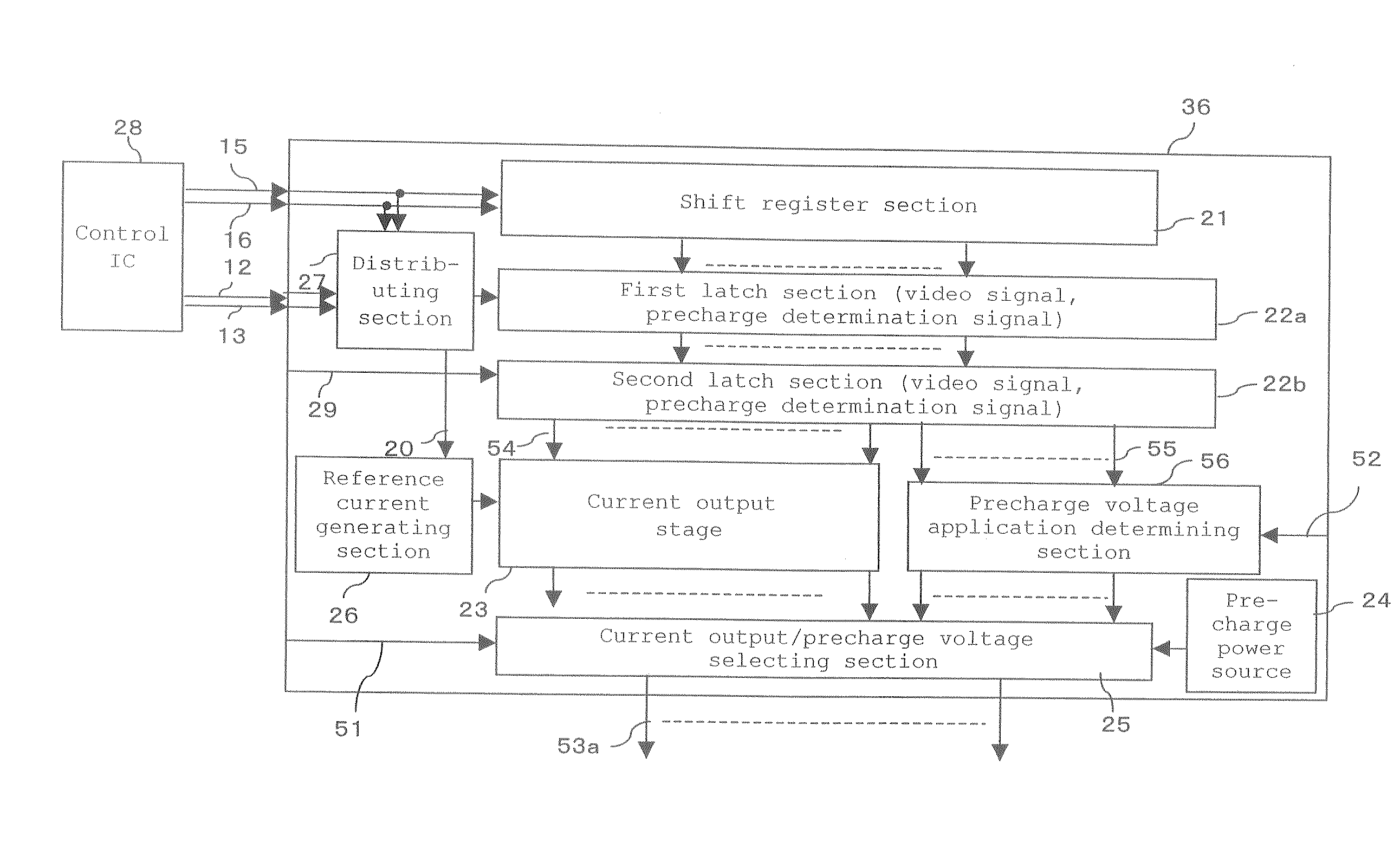
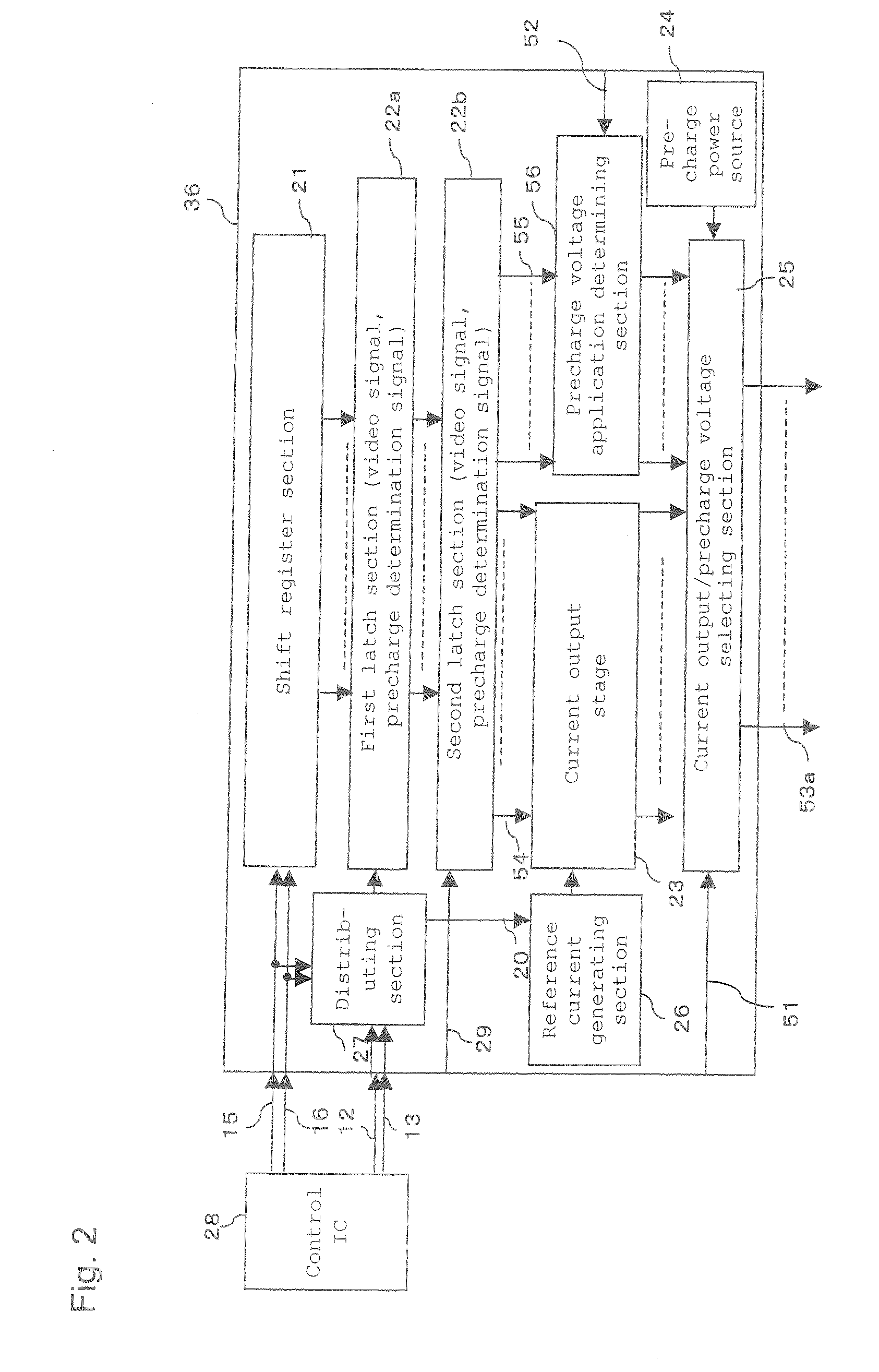
Driving method of self-luminous type display unit, display control device of self-luminous type display unit, current output type drive circuit of self-luminous type display unit
InactiveUS20070132674A1Suppress increase in circuit scale lowerElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesGray levelElectrical current
The method includes applying a gray level current corresponding to a display gray level to each of pixel circuits for a first period, applying a display current based on the gray level current to the self-luminescent elements during a second period succeeding the first period to display corresponding the display gray level, and applying a precharge current to the self-luminescent device during a third period before the first period on the basis of a predetermined first condition.
Owner:TOSHIBA MATSUSHITA DISPLAY TECH
Low resolution OCR for camera acquired documents
ActiveUS7499588B2Low resolution OCRMaximum robustnessBiological modelsCharacter recognitionSingle processGrey level
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multi-dimensional images system for digital image input and output
Owner:NIMS JERRY C
Displays with large dynamic range
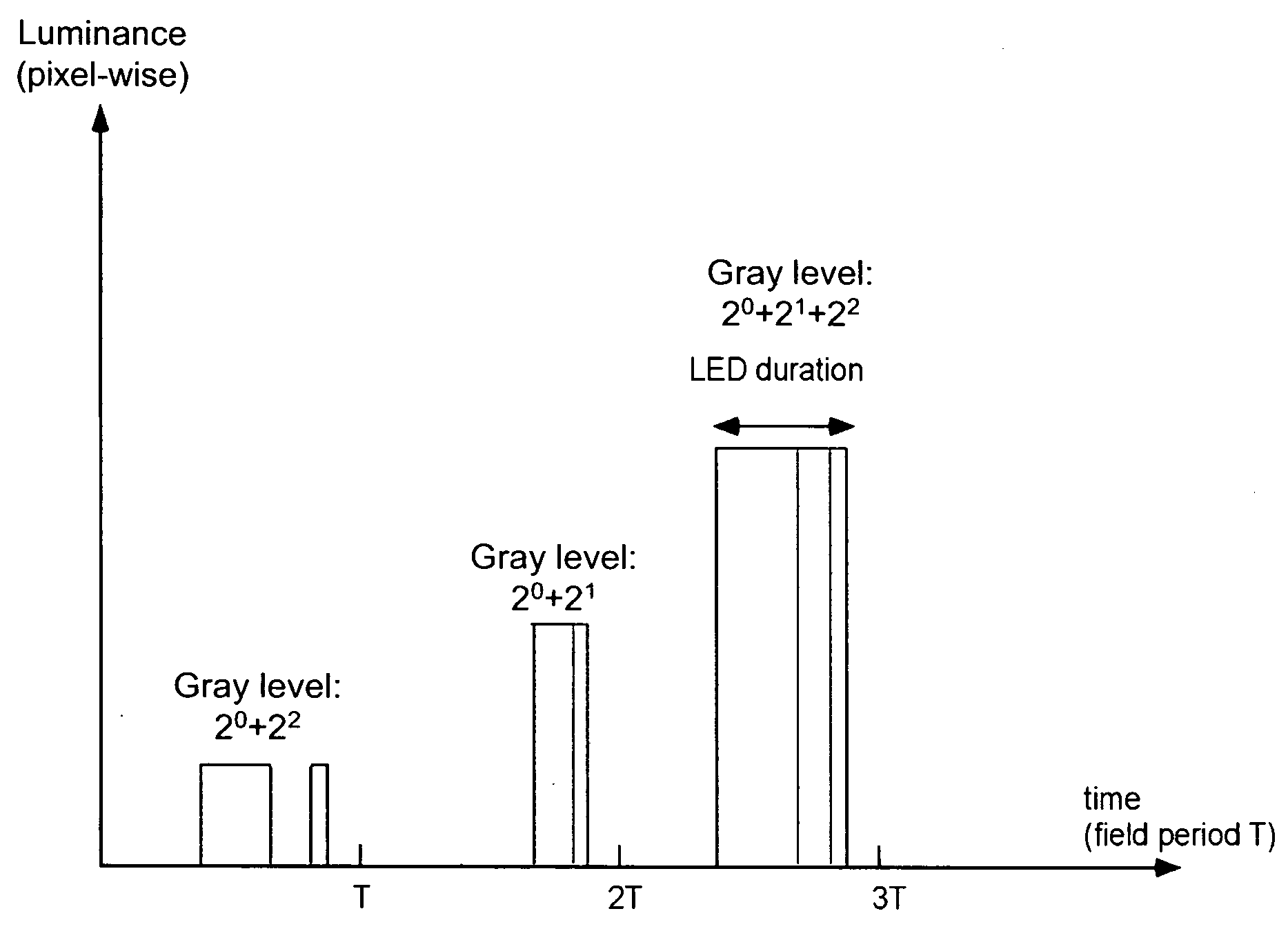
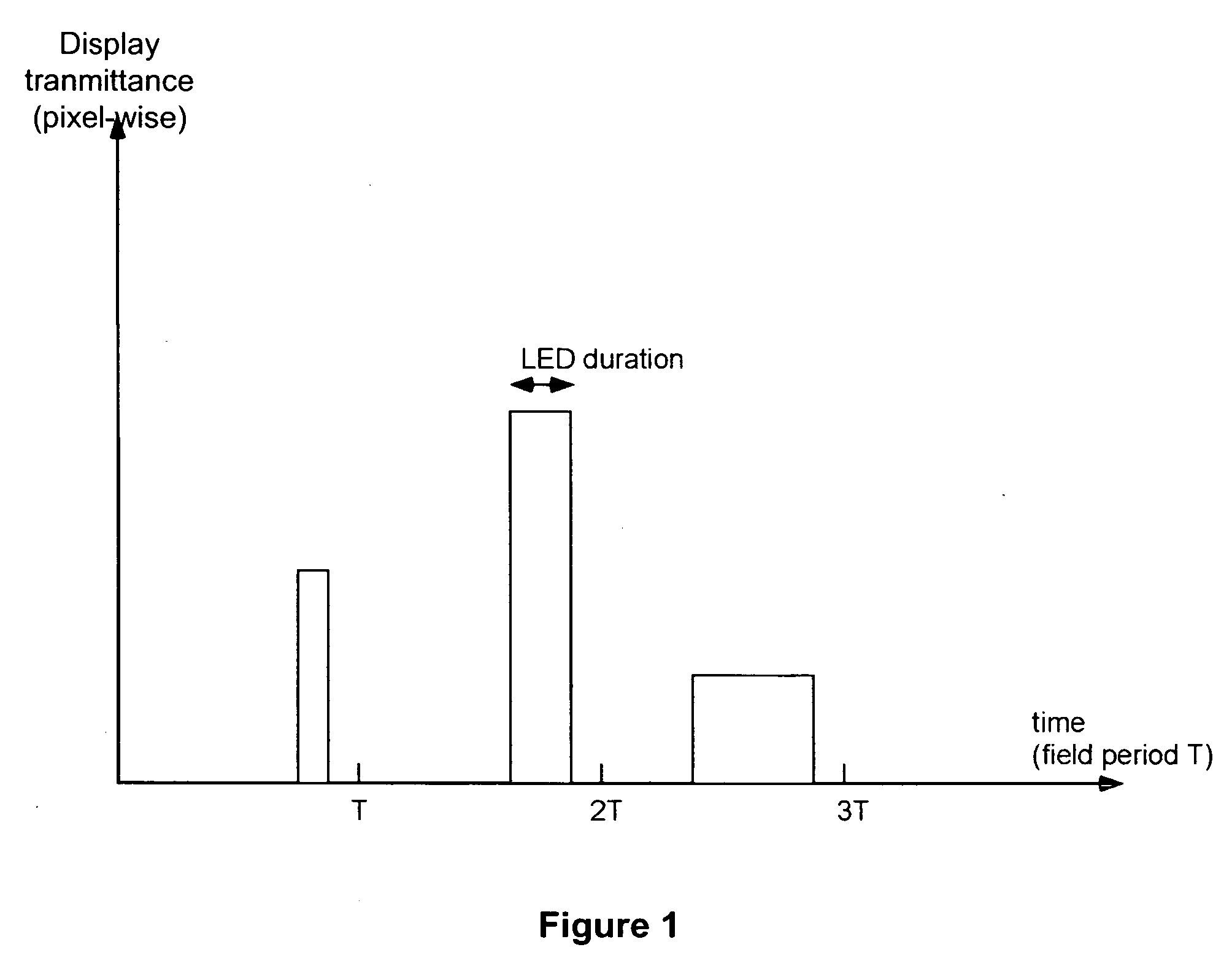
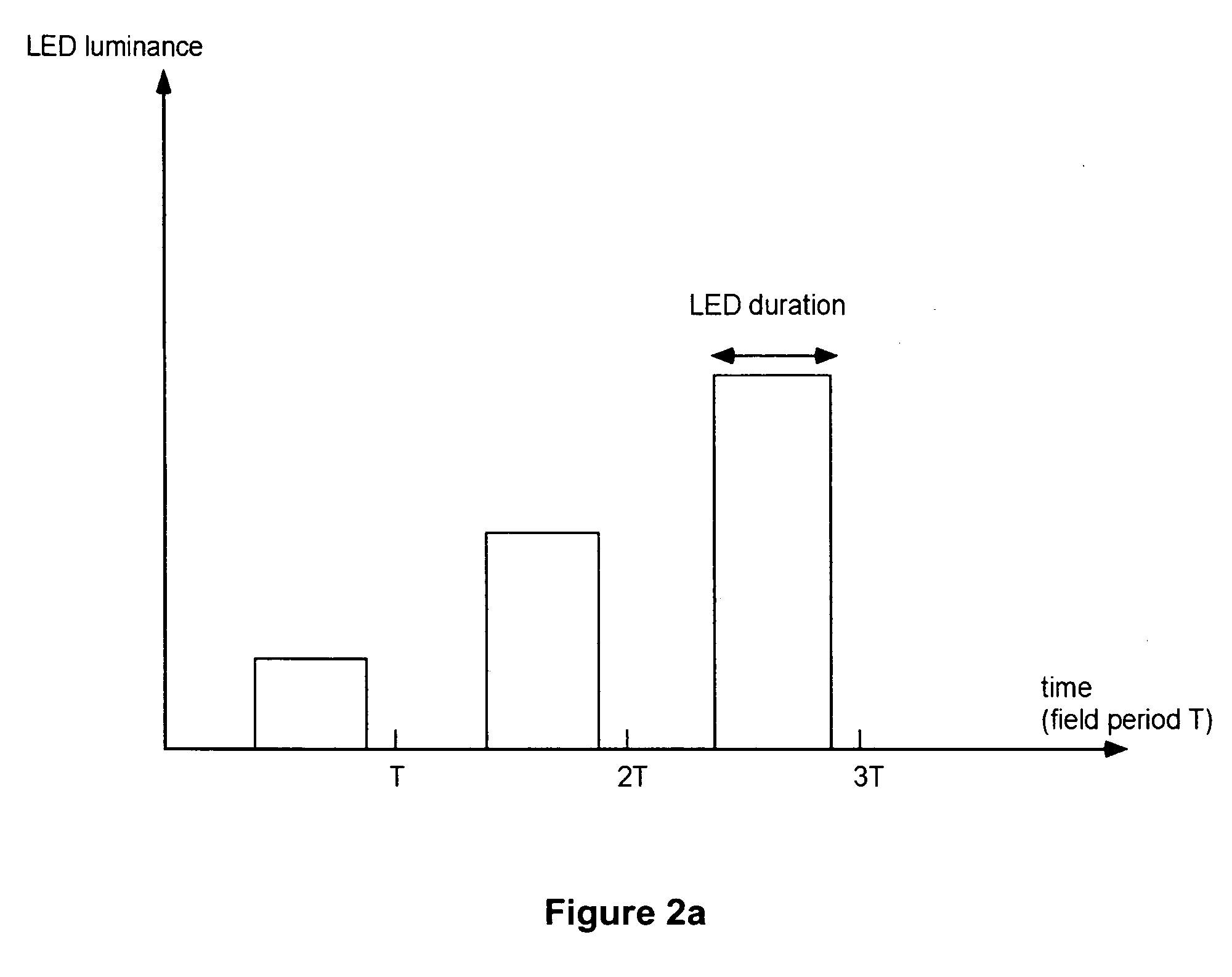
The specification and drawings present a new method, apparatus and software product for increasing a grey dynamic range of a display for displaying video data by providing a grey level, calculated for a reduced number of primary colors using a predetermined criterion, for each field of a frame set by the display by varying an amplitude or a subfield composition of a display driving signal and by varying a fluence of simultaneously lit backlight sources (e.g., LEDs) corresponding to selected two or more primary colors of the display. Thus, grey level resolution of the display can be increased to match the higher grey level resolution of the video data provided to the display
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
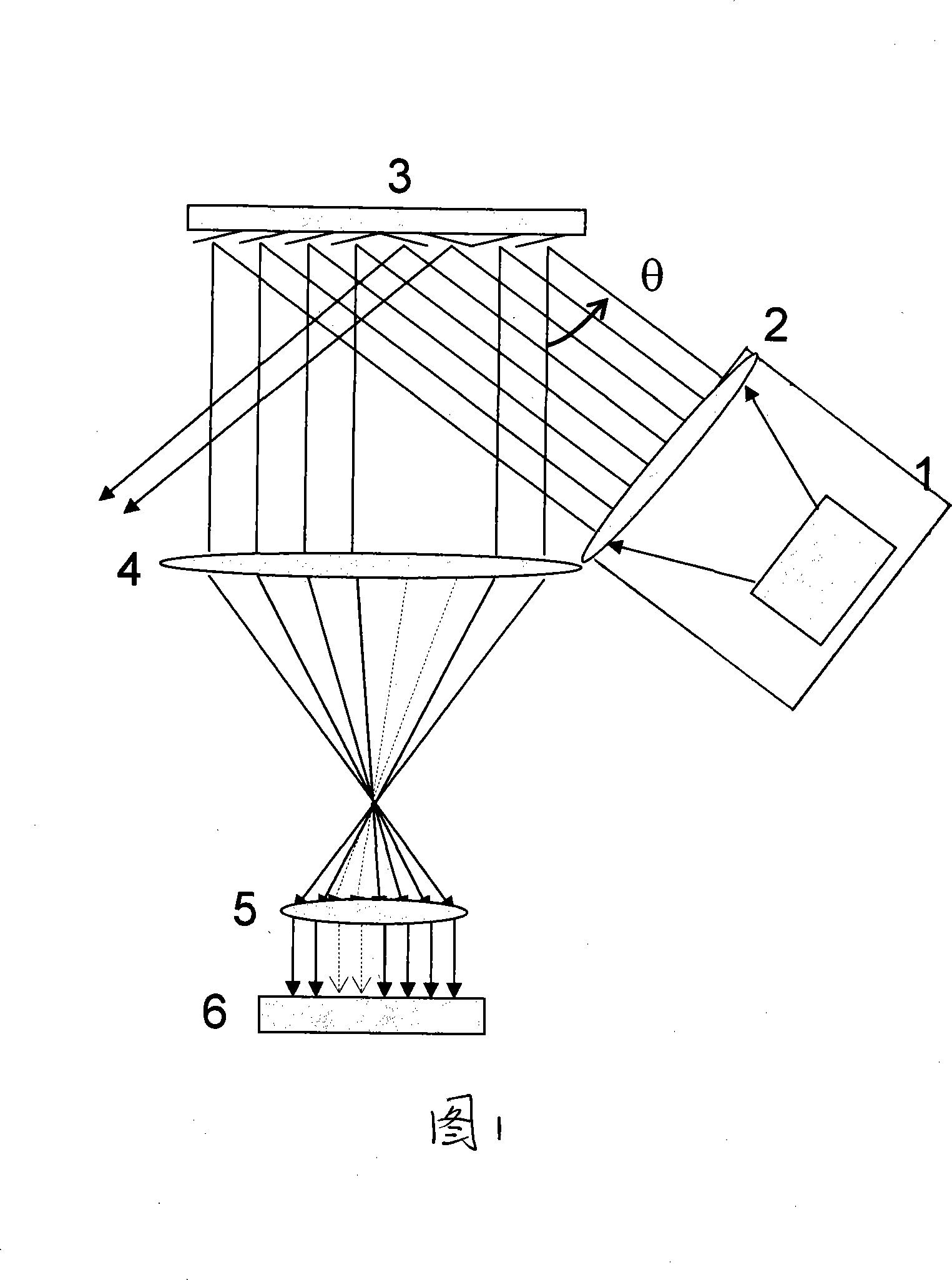
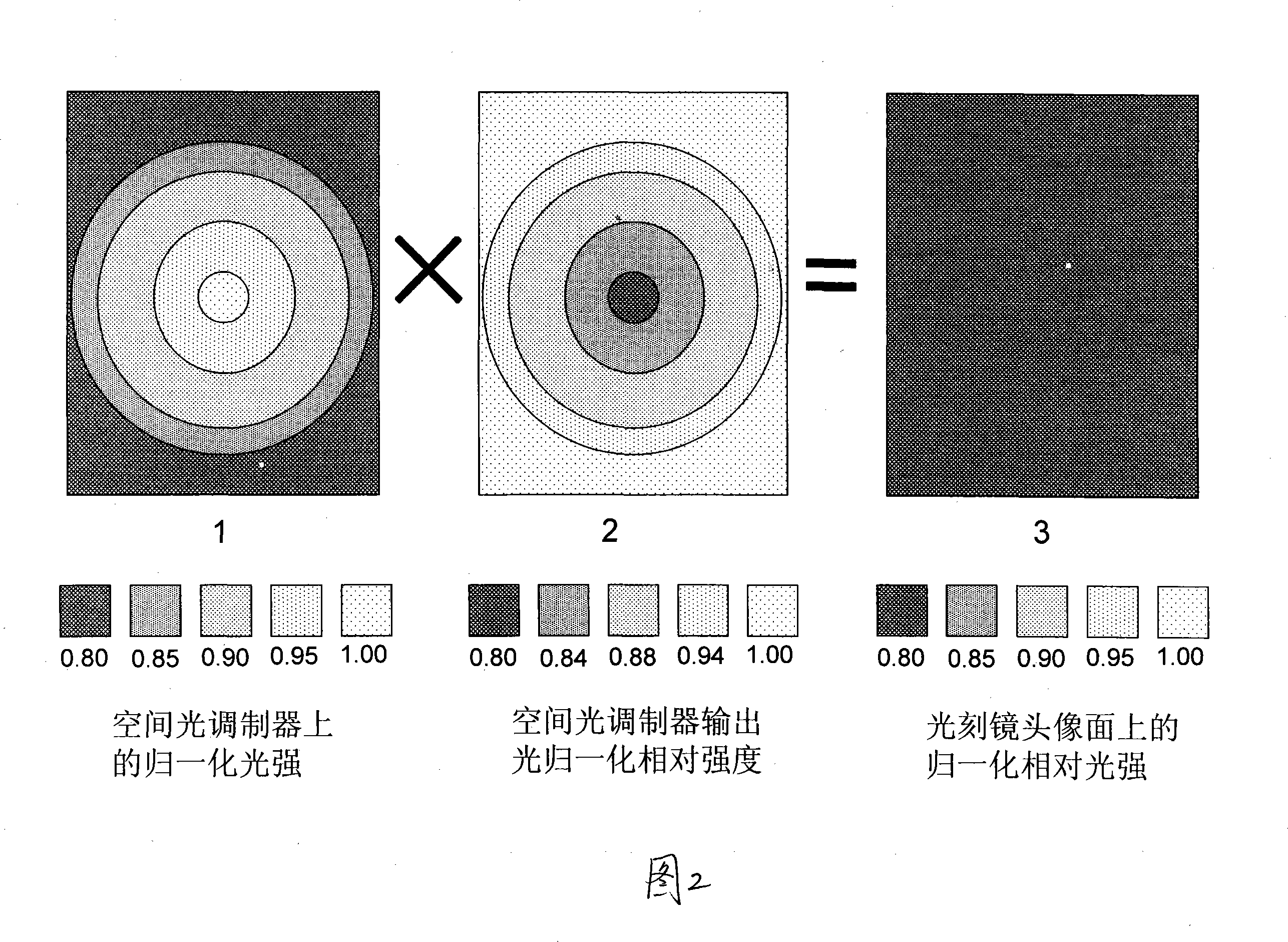
Method for improving photolithography exposure energy homogeneity using grey level compensation
InactiveCN101226343AImprove consistencyReduce designPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorHardness
The invention discloses a method for using gray scale compensation to improve photo-etching exposure energy uniformity, with wide application in non-mask photo-etching machine which uses spatial light modulator as image generator. The non-mask photo-etching machine provided with a spatial light modulator as image generator uses the gray scale modulation of the spatial light modulator, according to the image light strength distribution information of photo-etching objective lens collected by a CCD to modulate the light output of each pixel unit of the spatial light modulator to change the emission light field distribution on the image plane of the photo-etching objective lens. The invention uses the light strength distribution measured in the integration of some time or uses the energy distribution of the light emitted from each image plane position in a certain exposure time to make the exposure energy of each position uniform on the image plane. The invention can effectively reduce the design and assembly hardness of the lighting system of traditional photo-etching machine and reach better exposure energy uniformity.
Owner:HEFEI ADVANTOOLS SEMICON
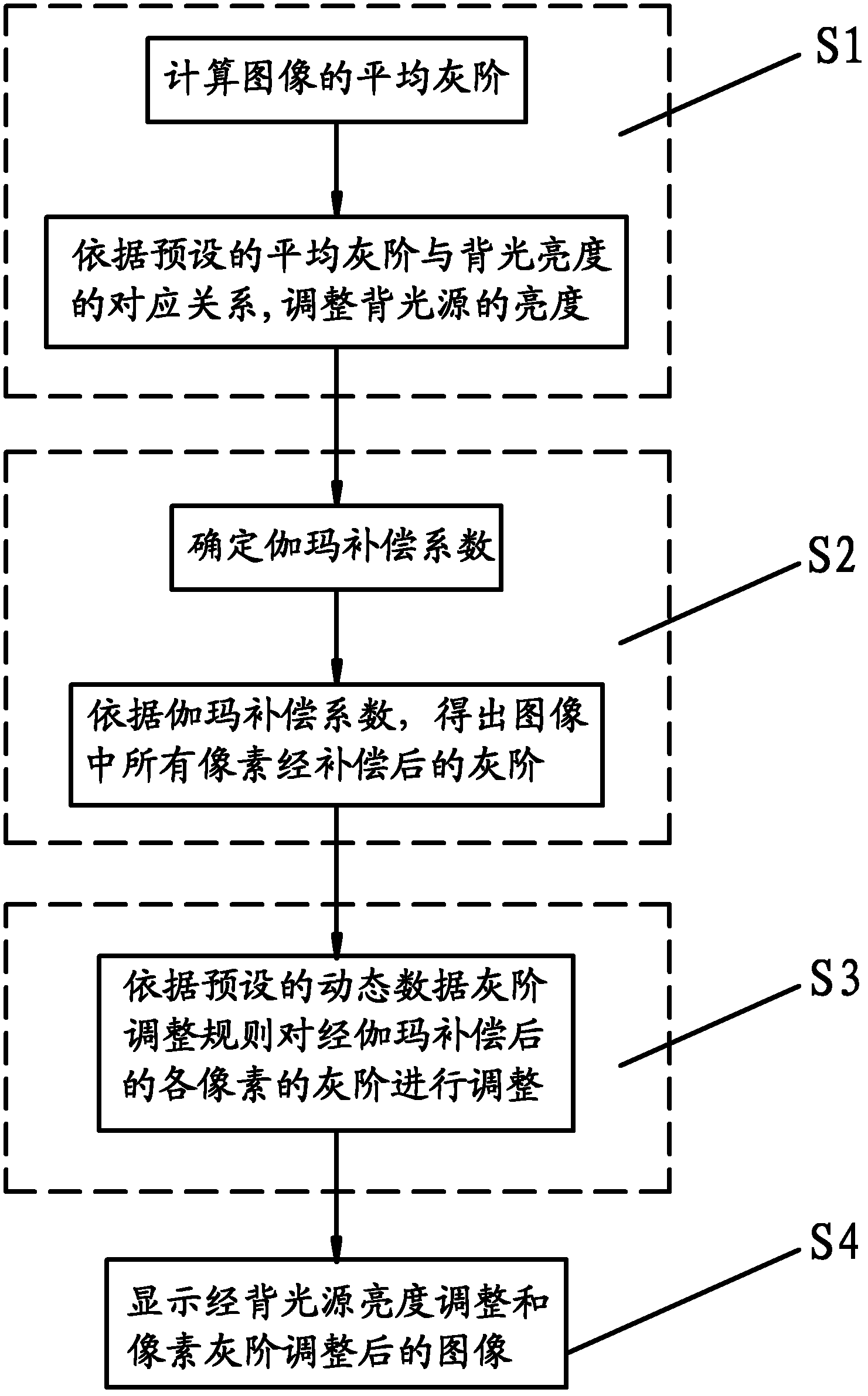
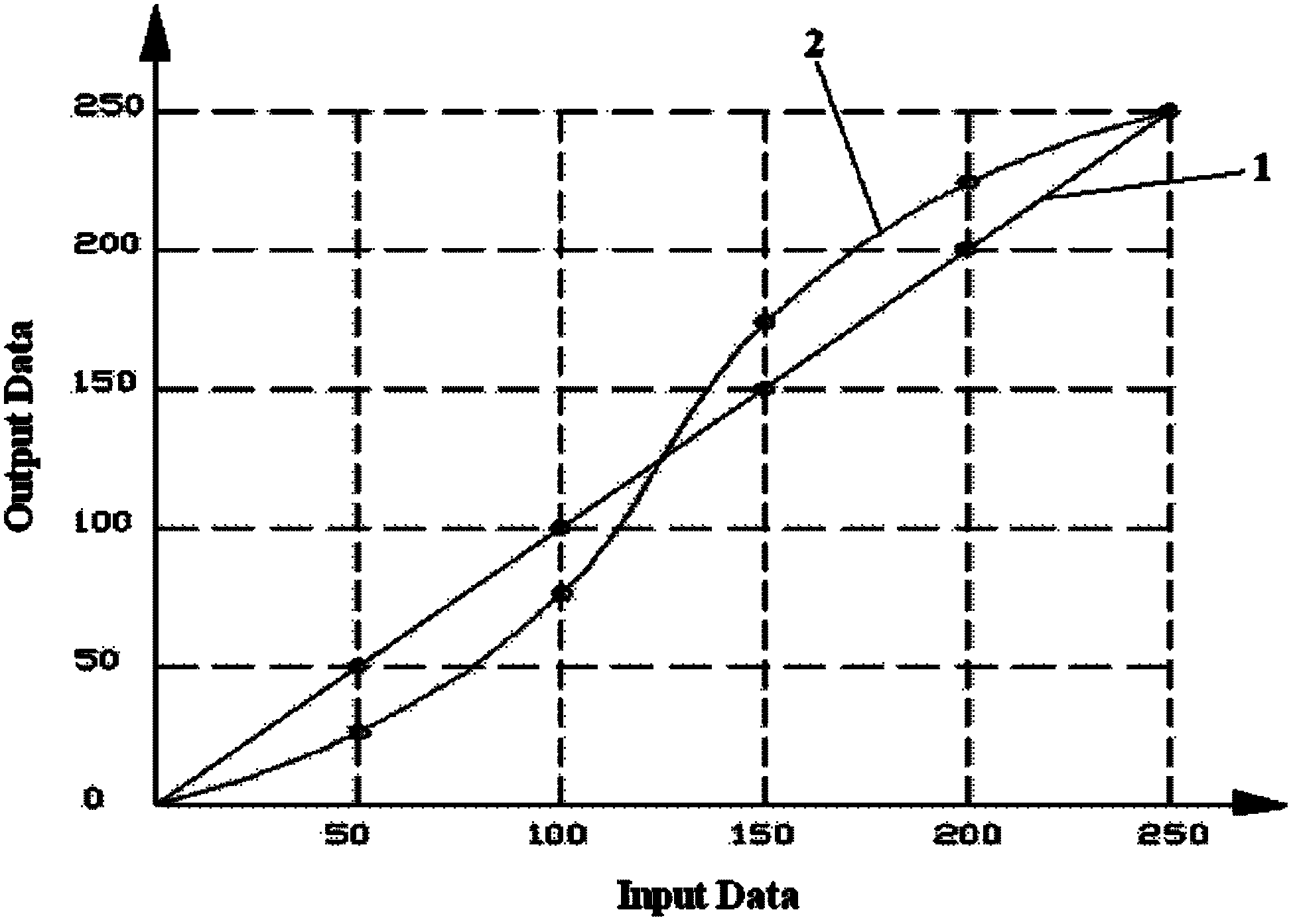
Method and device for improving image contrast, LCD TV (liquid crystal display television) set
InactiveCN102355561AIncrease contrastImprove display qualityTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayImage contrast
The invention discloses a method and device for improving image contrast and an LCD TV (liquid crystal display television) set. The method for improving image contrast comprises the following steps: adjustment of the brightness of a dynamic backlight: calculating the average gray-scale of all pixels in a frame of image, and according to a congruent relationship between a preset average gray-scaleand the brightness of the backlight, adjusting the brightness of the backlight; gamma compensation: according to a ratio of the original brightness of the backlight to the adjusted brightness, determining a gamma compensation coefficient, then, according to the gamma compensation coefficient, obtaining the gray-scales of all the pixels subjected to compensation in the image; and dynamic pixel gray-scale adjustment: according to a preset dynamic data gray-scale adjustment rule, adjusting the gray-scale of each pixel subjected to gamma compensation so as to obtain the gray-scale of each pixel subjected to adjustment, and displaying the image subjected to adjustment in the brightness of the backlight and the gray-scales of the pixels.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Image analysis
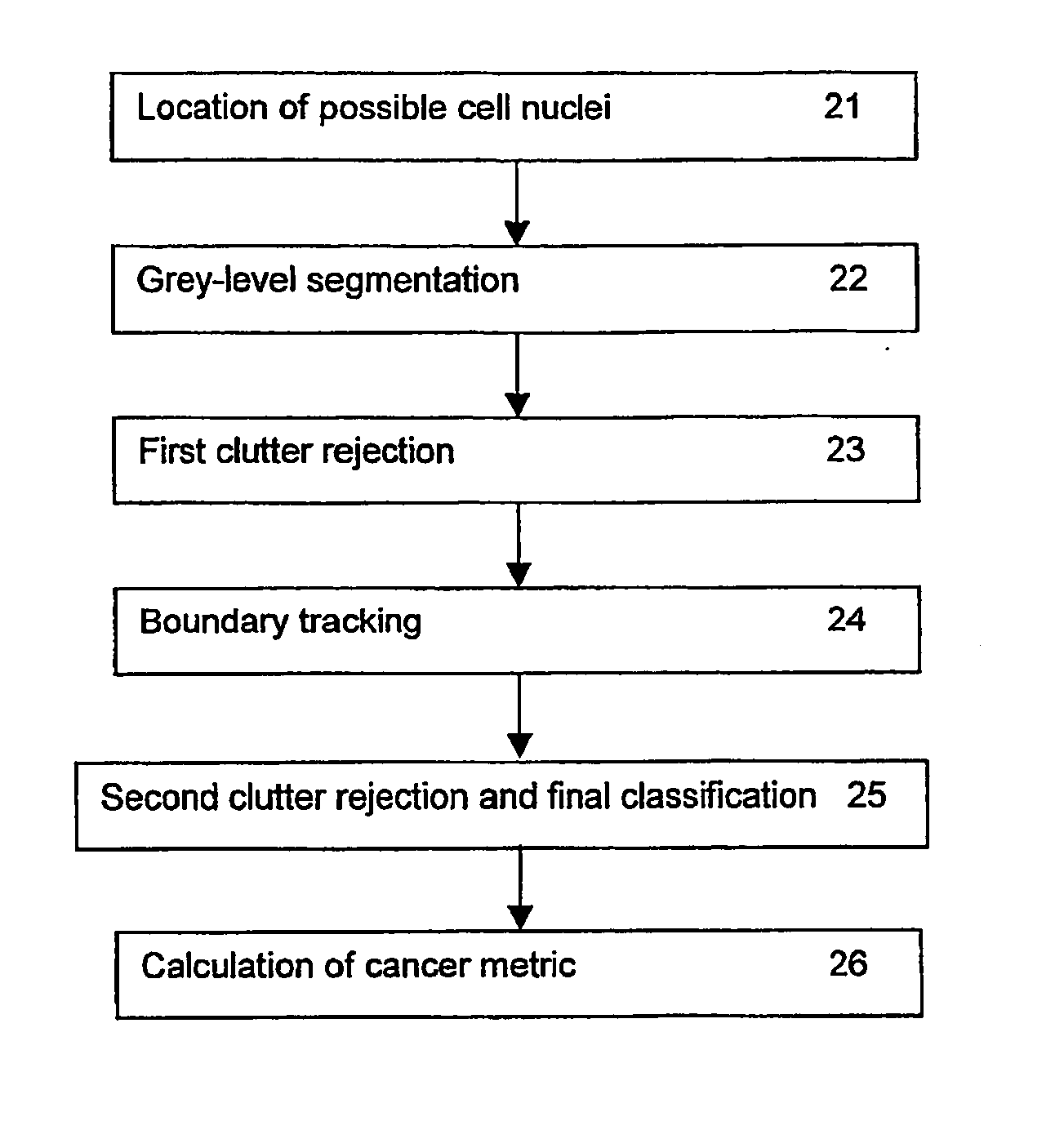
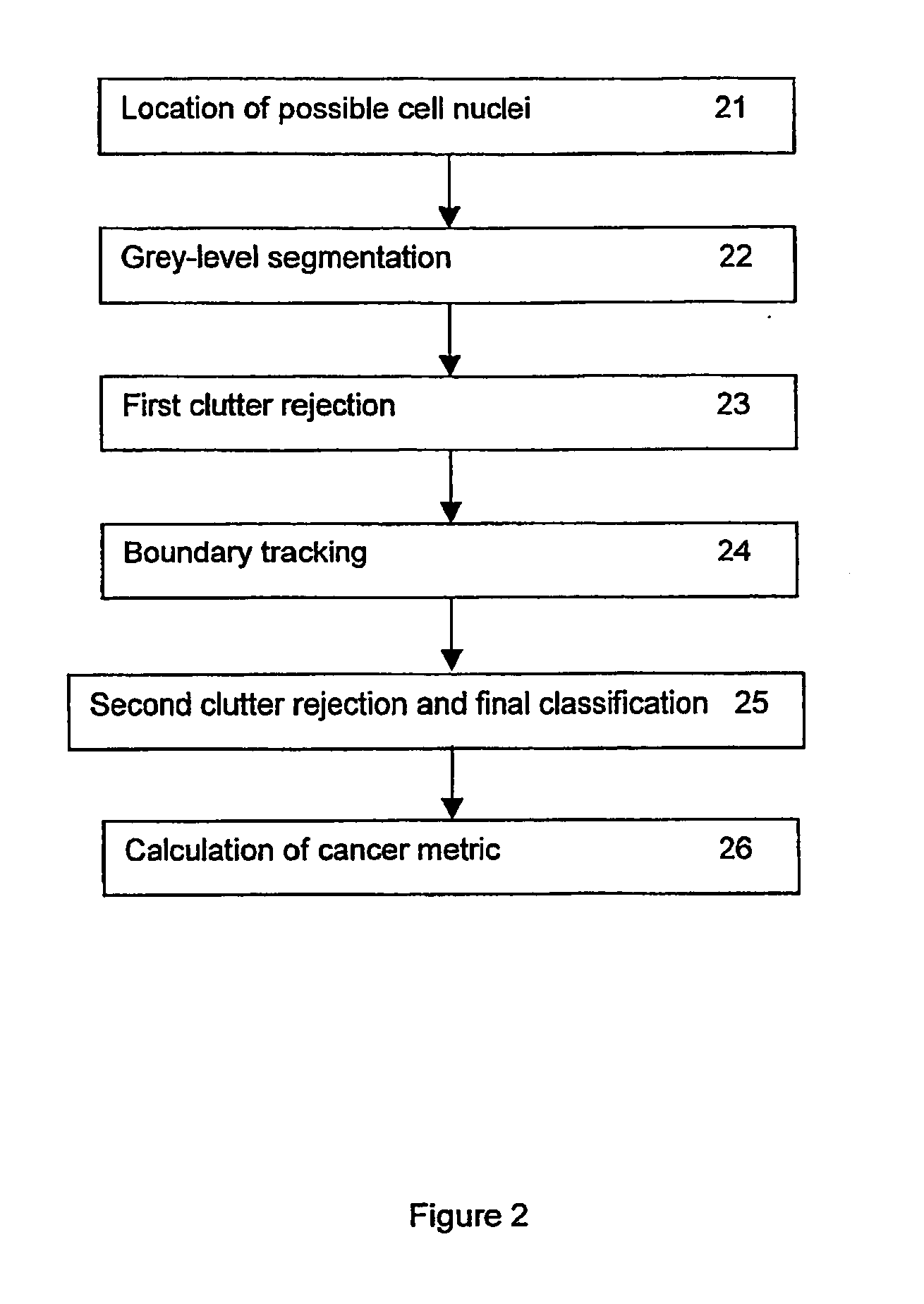
A method for the automated analysis of digital images, particularly for the purpose of assessing nuclear pleomorphism from images of histological slides for prognostication of breast cancer. The method includes the steps of identifying the locations of objects within the image which have intensity and size characteristics consistent with epithelial cell nuclei and deriving boundaries for those objects. Statistics concerning at least the shapes of the derived boundaries are calculated and clutter is rejected on the basis of those statistics and / or they are used to assign probabilities that the respective objects are epithelial cell nuclei, and a measure of the variability of at least the areas enclosed by such boundaries is then calculated. In one embodiment the boundaries are derived by seeking closed contours consisting of points of the same grey-level within regions centred on the locations of such objects. Another embodiment involves the deformation of a closed loop starting within the respective object, moving outward in stages in accordance with grey-level gradients around the loop, and selecting as the best fit to the real boundary the deformed loop which satisfies specified edge metrics.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
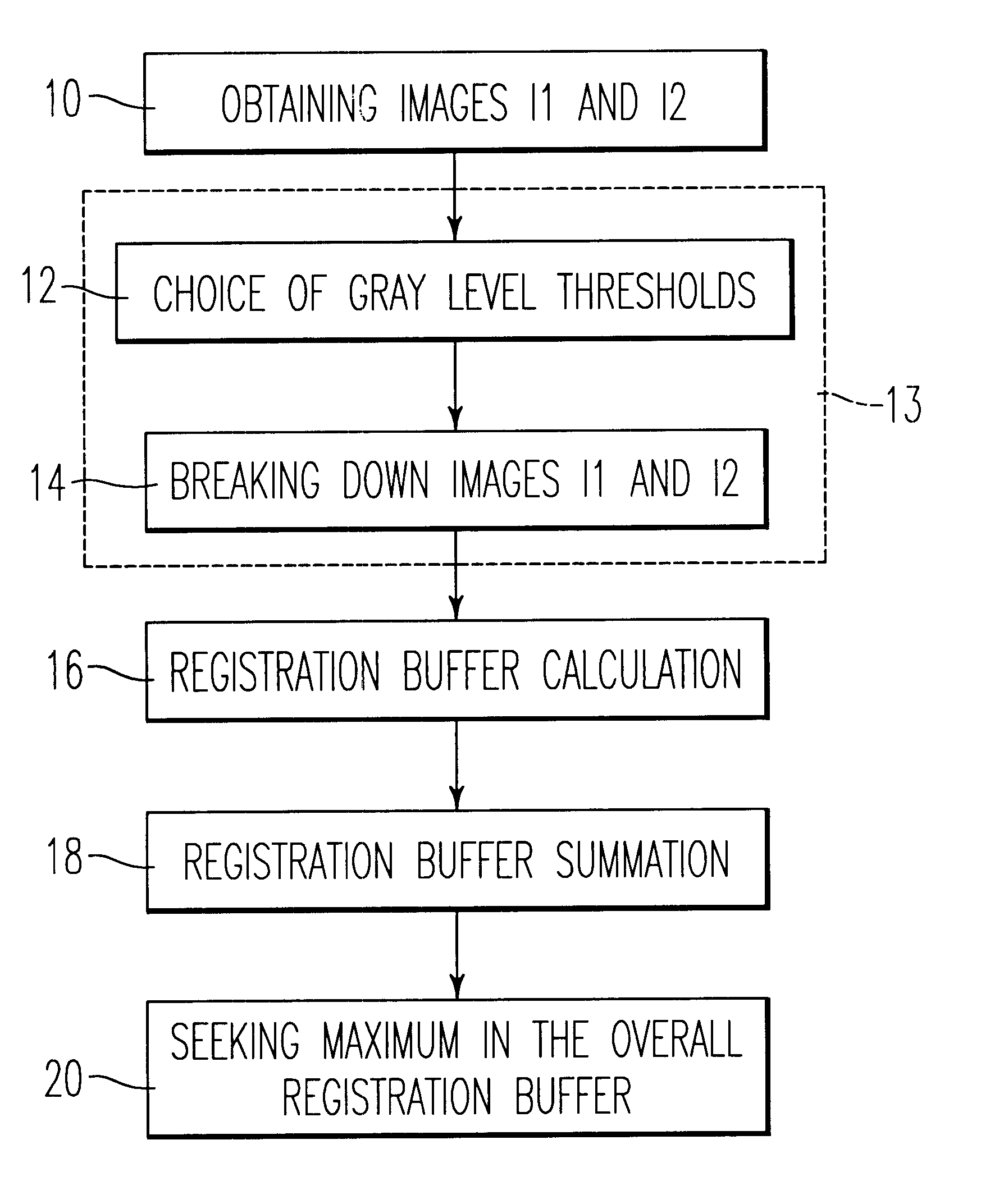
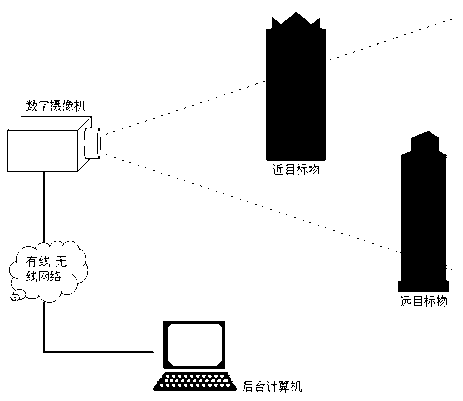
Process for the registration of two different images of the same object
The invention relates to a process for the registration of two different images of the same object consisting of breaking down each of the images into space components representing the distribution of the grey levels of the image, applying a phase registration method to the components to bring about a correspondence between the components of one image with those of the other image, summating all the results of the bringing into correspondence and detecting, in the image resulting from said sum, the maximum grey level defining the transformation between the two initial images.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Haze monitoring method based on computer vision
InactiveCN103218622ALow costEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorGrey level
Provided is a haze monitoring method based on computer vision. The monitoring method includes the steps: collecting data of pre-set far and near target regions which are dark in color in a scene, and giving haze monitoring results based on comparison of the computation of target object visual features and sample images under different haze conditions. Visual features expressing an image comprises color features containing pixel color saturation mean value and blue component mean value, shape features containing feature point number and edge pixel number, textural features containing grey level co-occurrence matrix features and wavelet transform sub-band coefficients, and feature vectors expressing differences between a far target object and a near target object. According to the haze monitoring method based on computer vision, a direct measurement method by means of visual features which is closely associated to manual observation of the haze in principle is put forward, comprehensive monitoring of haze conditions in an entire region is achieved easily, and high-precision monitoring results can be guaranteed with enough sample data.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Detection of Textural Defects Using a One Class Support Vector Machine
ActiveUS20110026804A1Small amount of timeImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorSupport vector machine
Method for detecting textural defects in an image. The image, which may have an irregular visual texture, may be received. The image may be decomposed into a plurality of subbands. The image may be portioned into a plurality of partitions. A plurality of grey-level co-occurrence matrices (GLCMs) may be determined for each partition. A plurality of second-order statistical attributes may be extracted for each GLCM. A feature vector may be constructed for each partition, where the feature vector includes the second order statistical attributes for each GLCM for the partition. Each partition may be classified based on the feature vector for the respective partition. Classification of the partitions may utilize a one-class support vector machine, and may determine if a defect is present in the image.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Method and system for eliminating afterimage defect of static-state image display area
ActiveCN104318893AReduced grayscale attenuation varianceEliminate afterimageStatic indicating devicesReference typeGray level
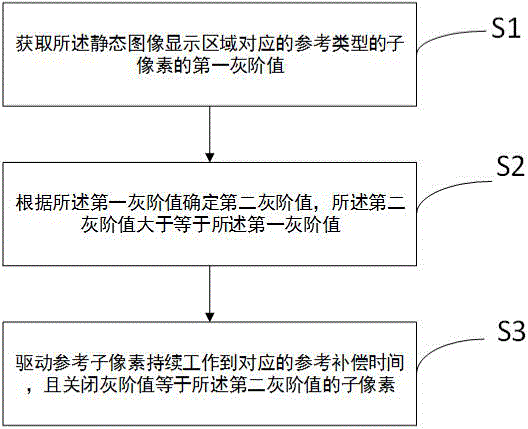
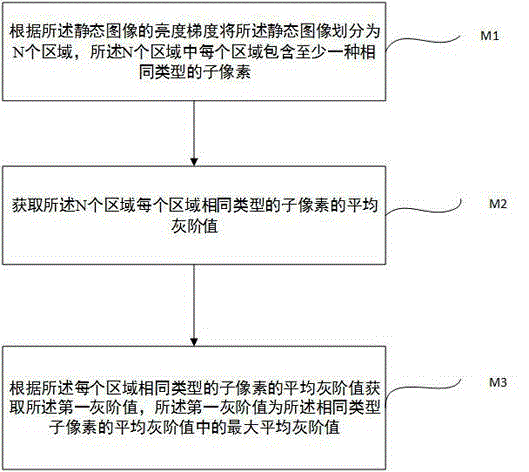
The invention discloses a method and system for eliminating an afterimage defect of a static-state image display area, and is applied to a self-luminous display apparatus. The static-state image display area comprises at least two sub pixels of the same type yet with different grayscale values. The method comprises: obtaining the first grayscale value of a sub pixel of a reference type corresponding to the static-state image display area, wherein the reference type is any one from RGB types, and the first grayscale value is the maximum grayscale value in the grayscale values of all the sub pixels of the reference type; according to the first grayscale value, determining a second grayscale value, the second grayscale value being greater than or equal to the first grayscale value; and driving a reference sub pixel to work continuously for corresponding reference compensation time, and closing a sub pixel whose grayscale value is equal to the second grayscale value, wherein the reference sub pixel is any one sub pixel of the reference type, whose grayscale value is smaller than the second grayscale value, and the reference compensation time is the continuous work time of the reference sub pixel. By using the technical scheme provided by the embodiments of the invention, once an image of the self-luminous display apparatus generates the afterimage defect problem, the problem can be rapidly eliminated.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
OLED module Gamma adjustment and calibration method and device
ActiveCN106328070AImprove regulation efficiencyImprove pass rateStatic indicating devicesColor temperatureTarget binding
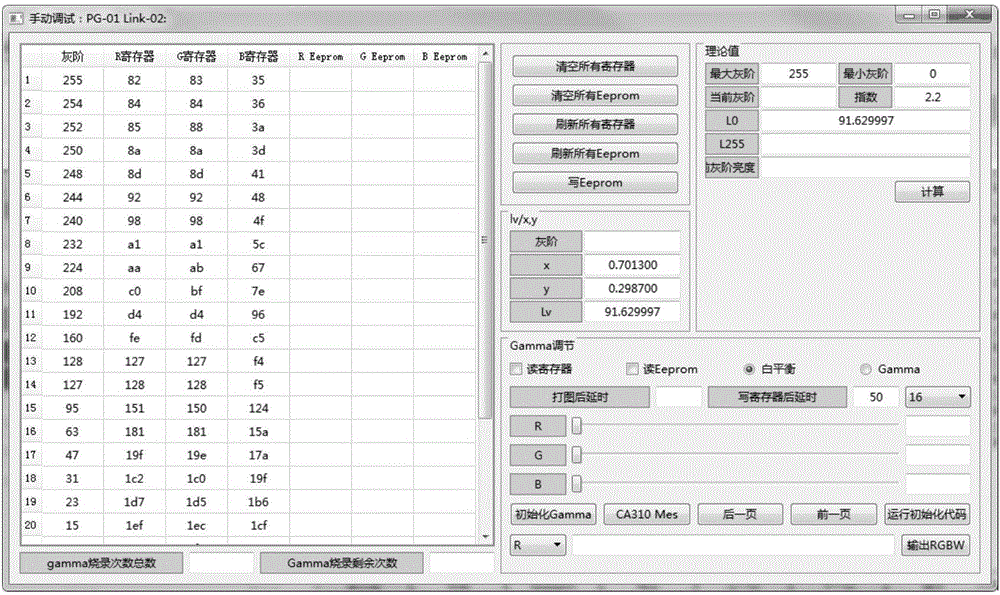
The invention discloses an OLED module Gamma adjustment and calibration method and device wherein the device comprises a PC, a controller, an image generator and an optical detection instrument. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the theoretical brightness values of a target binding point according to the brightness value of the highest gray level W255 and the brightness value of the lowest gray level W0, and determining the target brightness value and the target color coordinate value of the target binding point; adjusting the R and G register values so that the color coordinate value of the target binding point falls within the error range of the target color coordinate value; adjusting the R, G and B register values so that the brightness value of the target binding point falls within the error range of the target brightness value; According to the invention, it is possible to adjust the brightness and coordinate of a finished OLED module bounded with IC so that the brightness meets a Gamma 2.2 curve, that the color temperature conforms to the CIE 1931 standard, and that the registers are solidified and adjusted to the EEProm of the OLED module's IC, making the OLED module present the visual curves most consistent with the human eye and achieve the display effect with a specific color temperature.
Owner:WUHAN JINGCE ELECTRONICS GRP CO LTD
Forming 3D models using periodic illumination patterns
InactiveUS20120176380A1Simple computationHigh accuracyUsing optical means3D modellingImage sequencePattern recognition
A method for determining a three-dimensional model for a scene comprising: projecting a sequence of binary illumination patterns onto a scene; capturing a sequence of binary pattern images of the scene from a plurality of capture directions; projecting a sequence of periodic grayscale illumination patterns onto the scene, each periodic grayscale pattern having the same frequency and a different phase; capturing a sequence of grayscale pattern images from the plurality of capture directions; determining a range map for each capture direction by analyzing the captured binary pattern images and the captured grayscale pattern images; and determining the three-dimensional model for the scene responsive to the range maps determined for each capture direction.
Owner:KODAK ALARIS INC
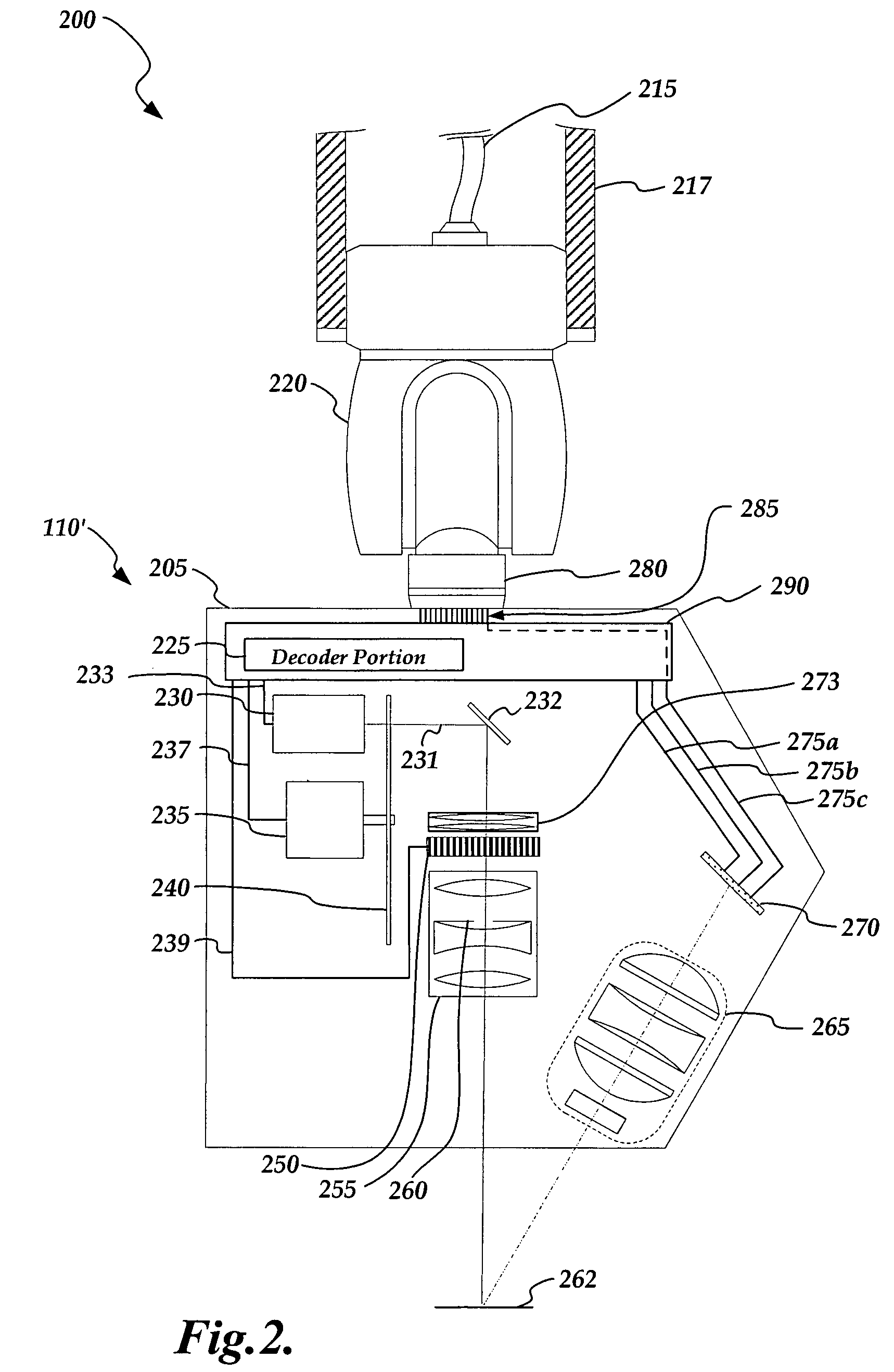
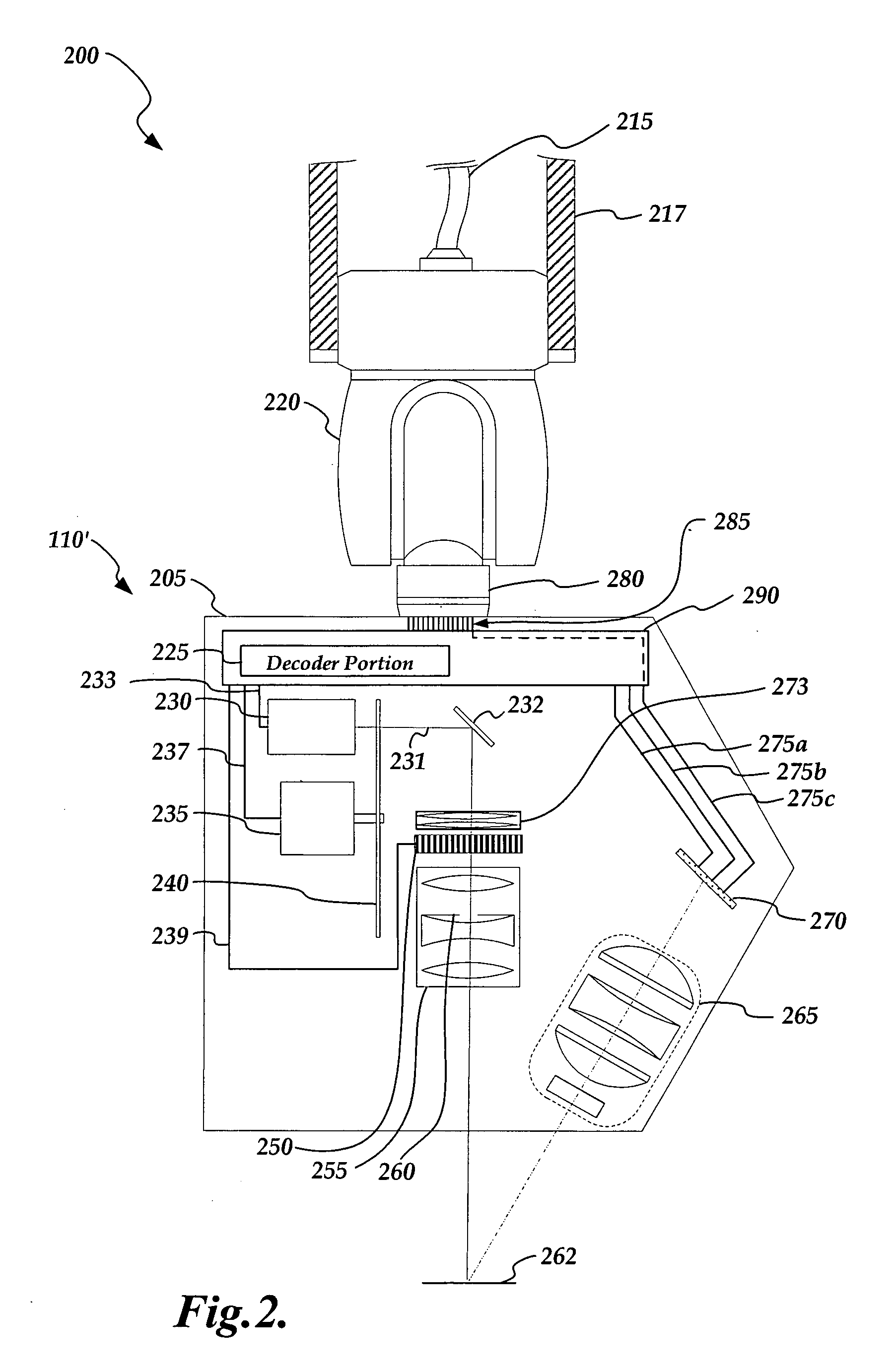
Non-contact probe control interface
ActiveUS20080024793A1Existing systems can be upgraded more easilyEasy to upgradeImage analysisOptical rangefindersSpatial light modulatorControl signal
A probe control interface is provided for a structured light non-contact coordinate measuring machine probe. Portions of a video control signal for controlling the grey level of selected rows of pixels of a spatial light modulator of the probe can be decoded into control signals for additional probe components or functions that have been added to increase the measuring capabilities or versatility of the non-contact probe. By providing the additional probe component control signals in this manner, a versatile structured light non-contact probe system can be made compatible with a standard probe head autojoint system (e.g. a Renishaw™ type system), thus allowing the probe to be automatically exchanged with other standard probes and allowing existing systems to use the non-contact probe more easily. Various aspects of the probe control interface allow for relatively simple, compact, lightweight and robust implementation.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
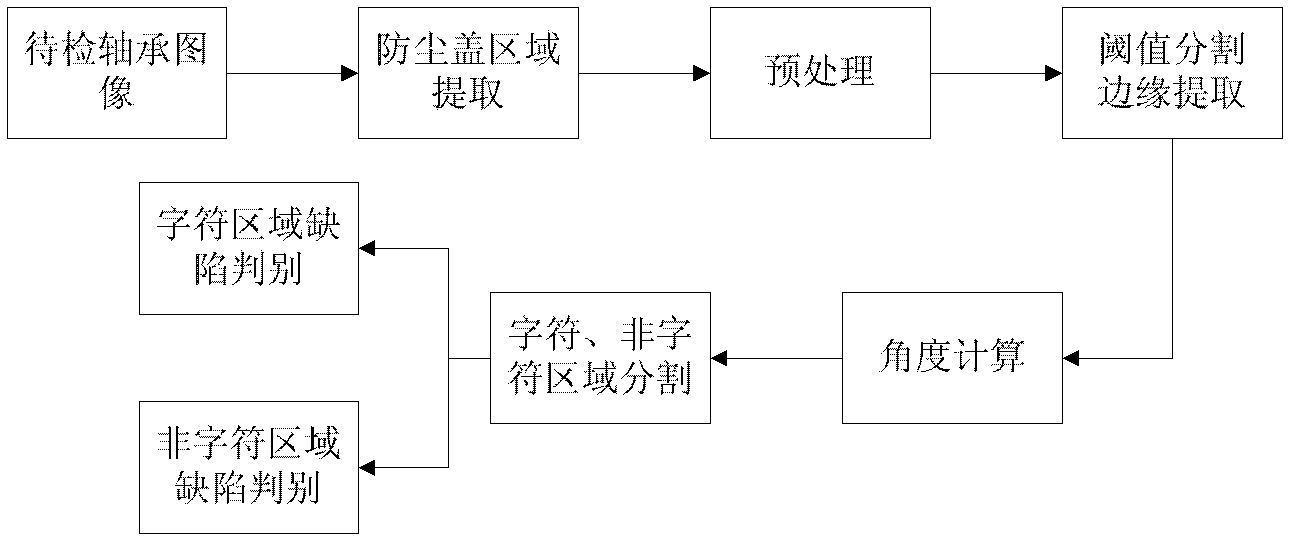
Method for detecting surface defects of dustproof cover of bearing based on machine vision
ActiveCN102636490AHigh speedAcquisition speed is fastOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMachine visionGrey level
The invention relates to a method for detecting surface defects of a dustproof cover of a bearing based on machine vision, which comprises the following steps: a, obtaining a gray level image of a to-be-detected bearing; b, carrying out separation on the gray level image so as to obtain a ring image of the dustproof cover of the bearing; c, carrying out grey level transformation and adaptive median filtering preprocessing on the ring image; d, carrying out threshold segmentation on the ring image by using a maximum interclass variance method, extracting an edge of the ring image of the dustproof cover of the bearing after threshold segmentation by using a Roberts edge detection operator; e, calculating the numbers of which the numerical values are 1 in the image area every two degrees for the ring image of the dustproof cover of the bearing; f, providing a template bearing image, and obtaining a deflection angle sigma through calculating; g, carrying out separation on the image so as to obtain character areas and non-character areas of the ring image of the dustproof cover of the bearing; and h, carrying out surface defect judgment on corresponding character areas and non-character areas in the ring image of the dustproof cover of the bearing according to the number of connected areas and the defect area. By using the method disclosed by the invention, automatic detection can be achieved, the visual detection workload of artificial detection is reduced, the detection efficiency is improved, and the method is safe and reliable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
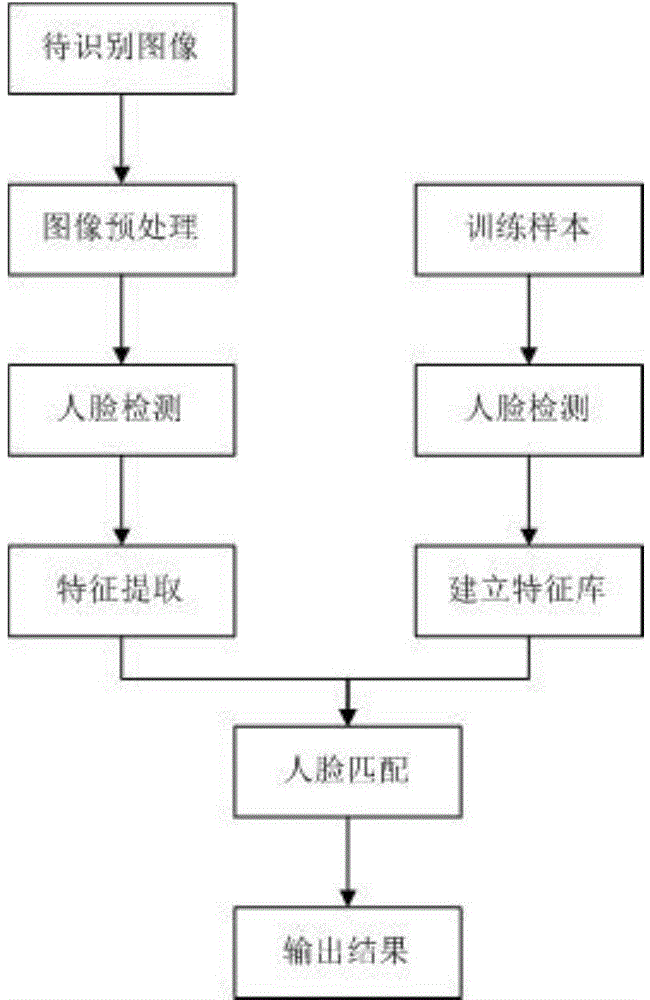
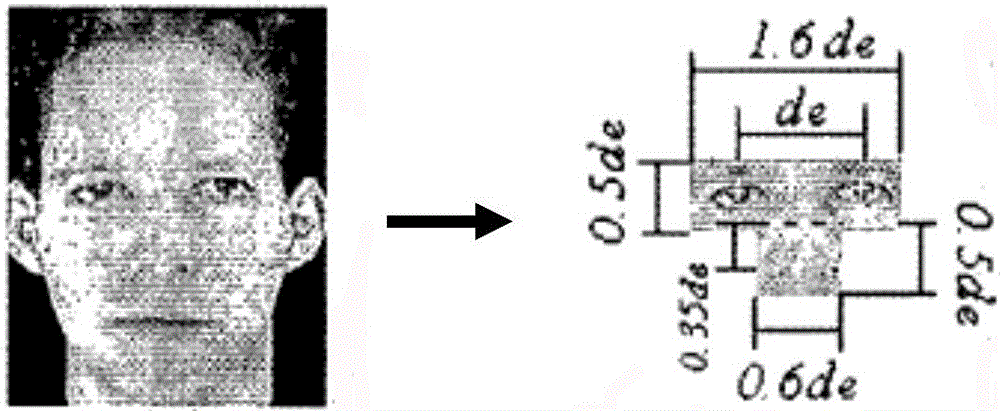
Face recognition method and system based on large-scale face database
ActiveCN104978550AHigh speedImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorFace detection
The invention discloses a face recognition method and system based on a large-scale face database. The recognition method comprises the following steps: obtaining a recognition image; image preprocessing: carrying out illumination compensation, graying, filtering denoising and normalization processing on an image to be detected to obtain a high-quality grey level image; face detection: detecting and positioning a face in a scene image, and separating the face from a background; characteristic extraction and expression: describing and modeling a face mode, and expressing the face by a characteristic vector; face matching: utilizing a similarity between the characteristic vector used for calculating the face image to be detected and a training sample to obtain discrimination information; and outputting a result. The face recognition method and system based on the large-scale face database not only improves the speed and the performance of face recognition under a large-scale database. Meanwhile, the face recognition method and system can be conveniently applied to the recognition field of other modes including facial expression recognition, face tracking and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JUNYU DIGITAL TECH
Method and device for evaluation of jointing regions on workpieces
ActiveUS20050041852A1Easy to checkEasy to recordArc welding apparatusCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringGrey level
Owner:PRECITEC VISION +1
Method of processing a video image sequence in a liquid crystal display panel
InactiveUS20050140626A1Television system detailsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayGrey level
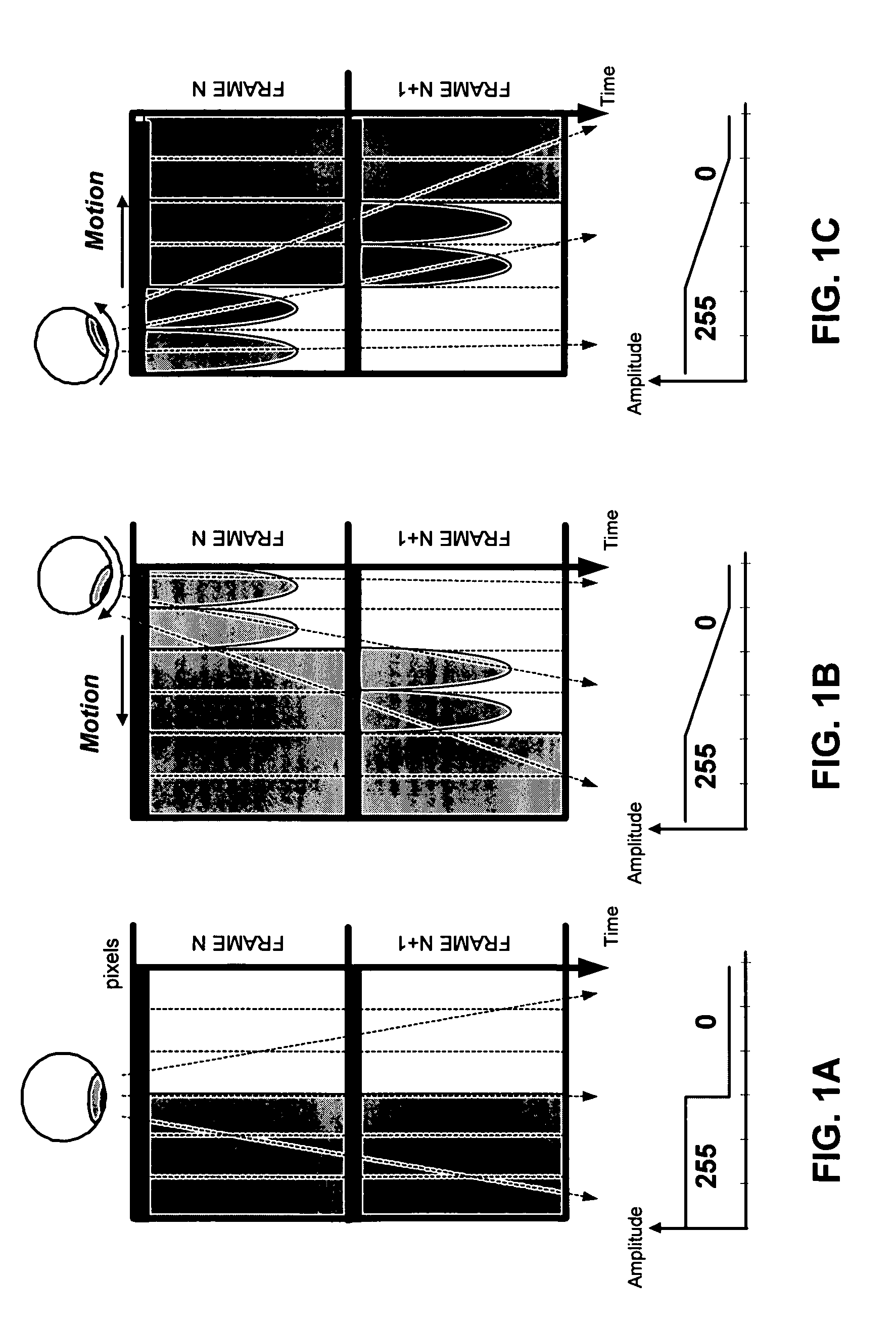
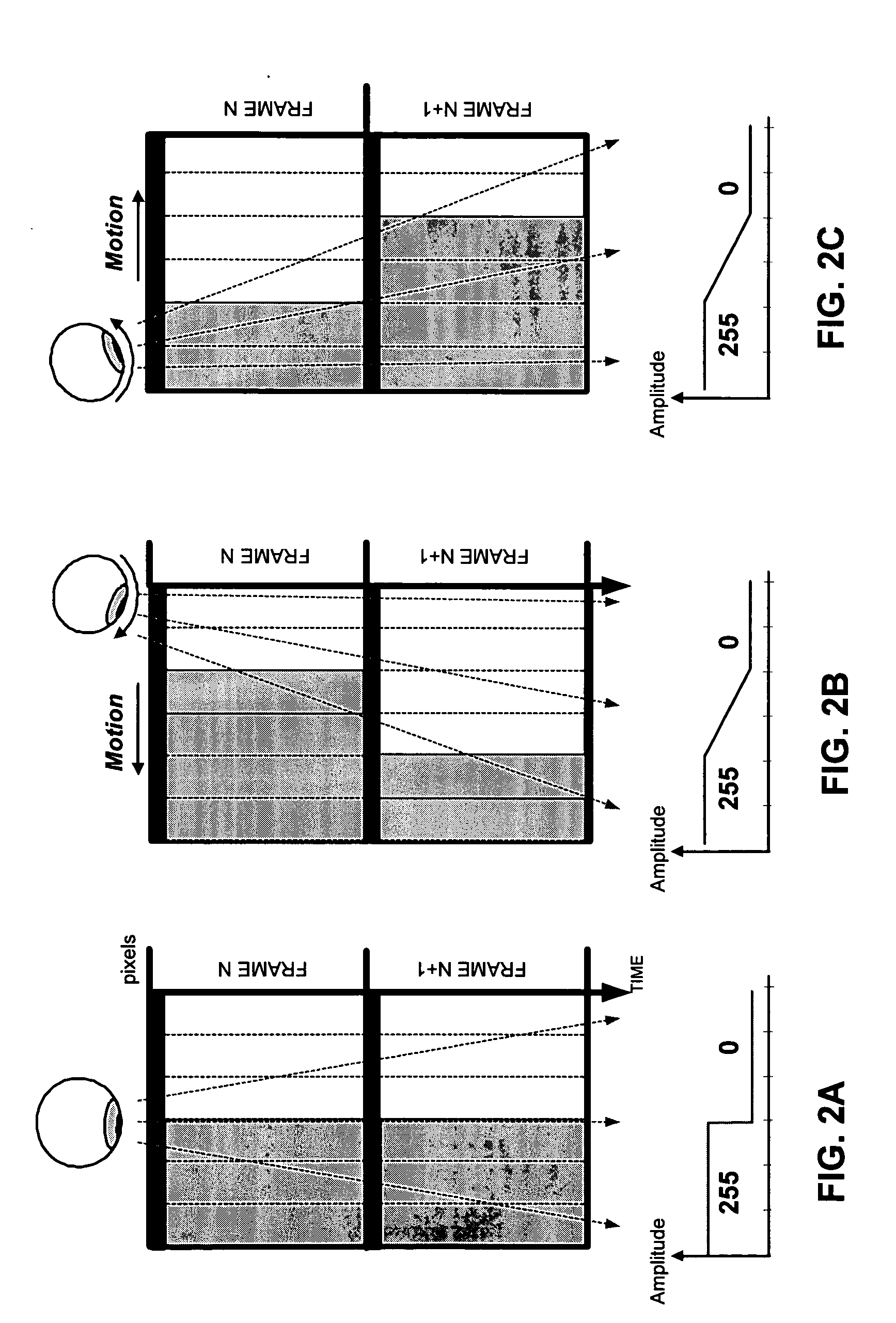
The present invention relates to a method of processing a video image sequence in a liquid crystal display panel and to a device for implementing this method. According to one embodiment of the invention, at least one motion-compensated image is generated for each group of m consecutive images of the sequence, m being greater or equal to 2, in order to obtain a group of n consecutive images, with n>m. Said group of n consecutive images replaces the group of m consecutive images into the sequence. Next, for each pixel having in a current image of the new sequence a current grey level and in the next image a different target grey level, an intercalary grey level is calculated which is higher or lower than said target grey level depending on whether said target grey level is respectively higher or lower than the current grey level of the pixel. Next, in the current image, the current grey level of the pixels is replaced with said calculated intercalary level. This method makes it possible to correct the blurring effects due to the mode of display and to the high response time of the LCD panel.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
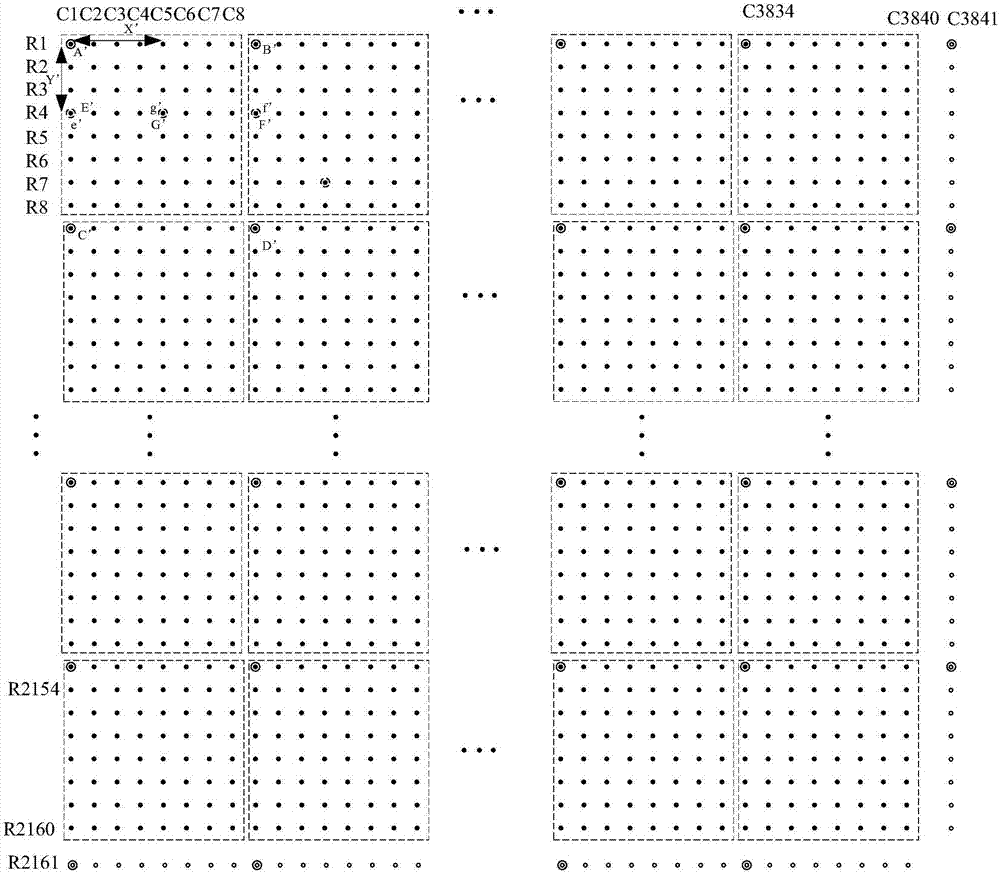
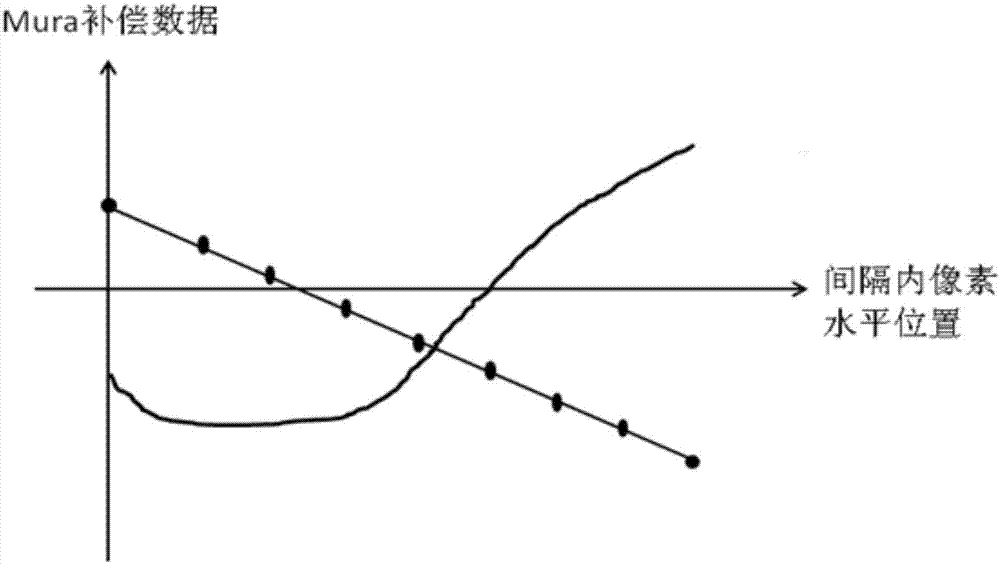
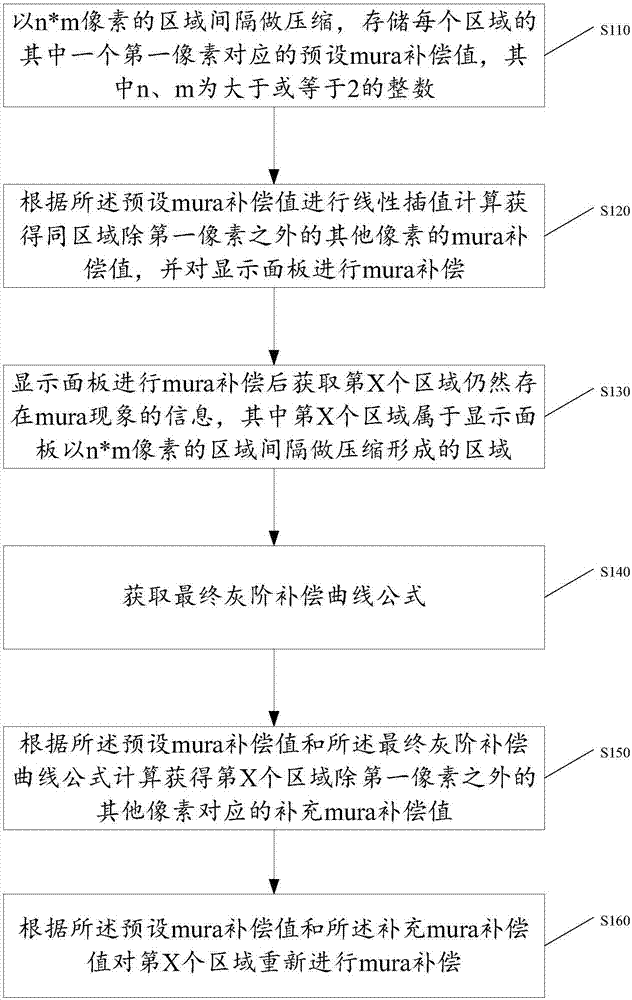
Mura phenomenon compensation method of display panel and display panel
ActiveCN106910483AImprove the display effectImprove MuraStatic indicating devicesComputer scienceBrightness perception
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
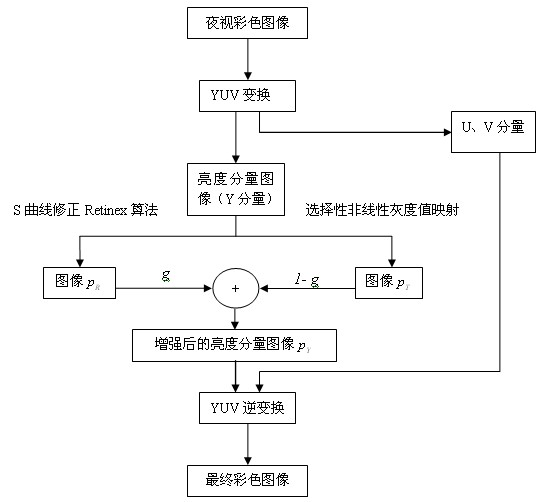
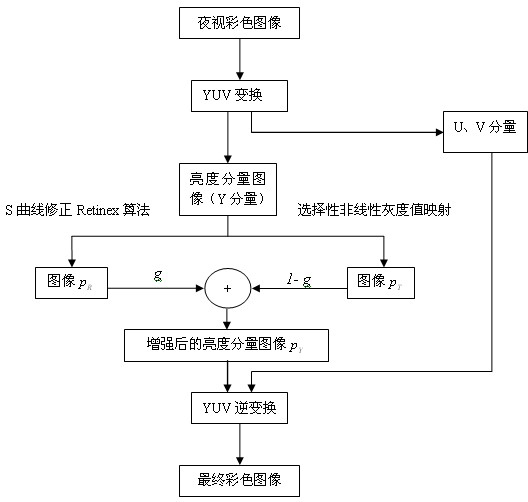
Colorized night vision image brightness enhancement method applicable to automotive assisted driving system
InactiveCN102231206AEfficient removalRecovery details displayImage enhancementNight visionVisual observation
The invention provides a colorized night vision image brightness enhancement method applicable to an automotive assisted driving system. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, transforming a night vision colorized image from a red, green and blue (RGB) space to a luma and chroma (YUV) space to overcome the shortcoming of color distortion caused by direct processing of the night vision colorized image in the RGB space; then processing a brightness component image by using an S-curve correction Retinex algorithm so as to enhance the detail and the brightness of the image; enhancing the brightness component image by a selective nonlinear grey level mapping method and keeping good shadow information; and finally, performing weighed fusion on the two enhanced images by a weighed fusion method and inversely transforming the weighed fusion brightness component image and a UV component image to the RGB space for displaying. The enhanced image acquired by the method keeps the necessary shadow information and has the detail and the brightness applicable to vision observation; and the night vision colorized image has a good enhancement effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
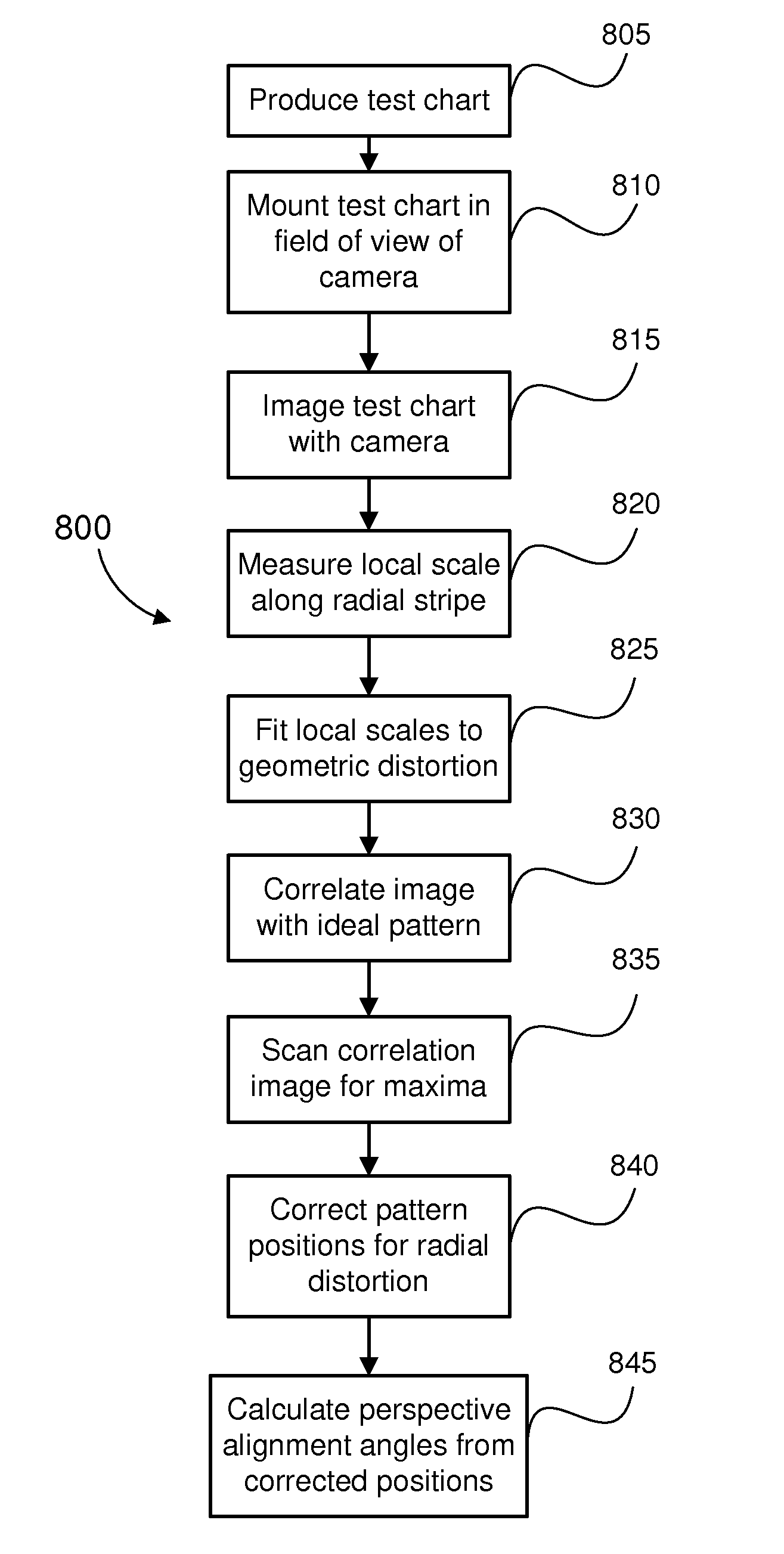
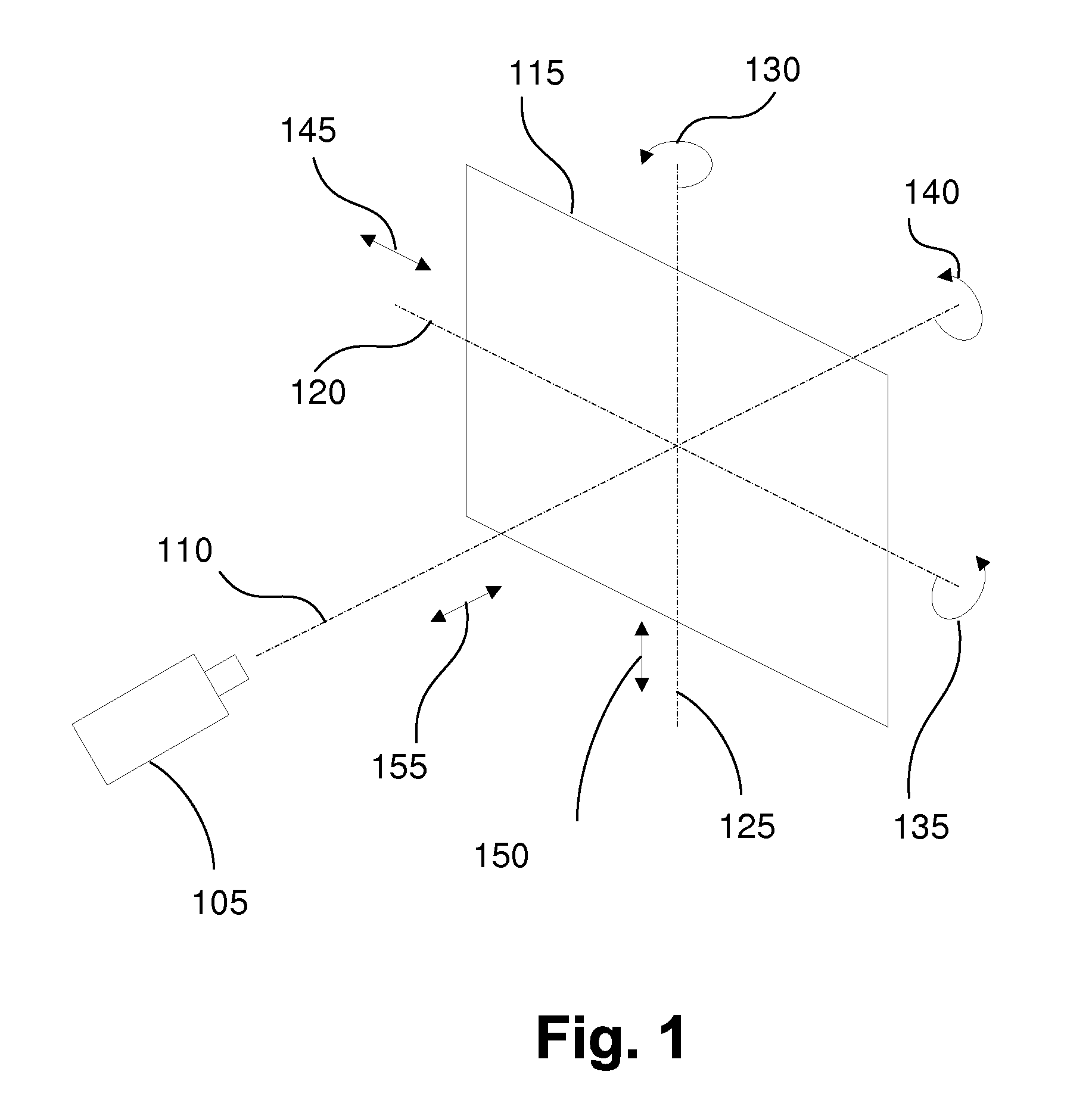
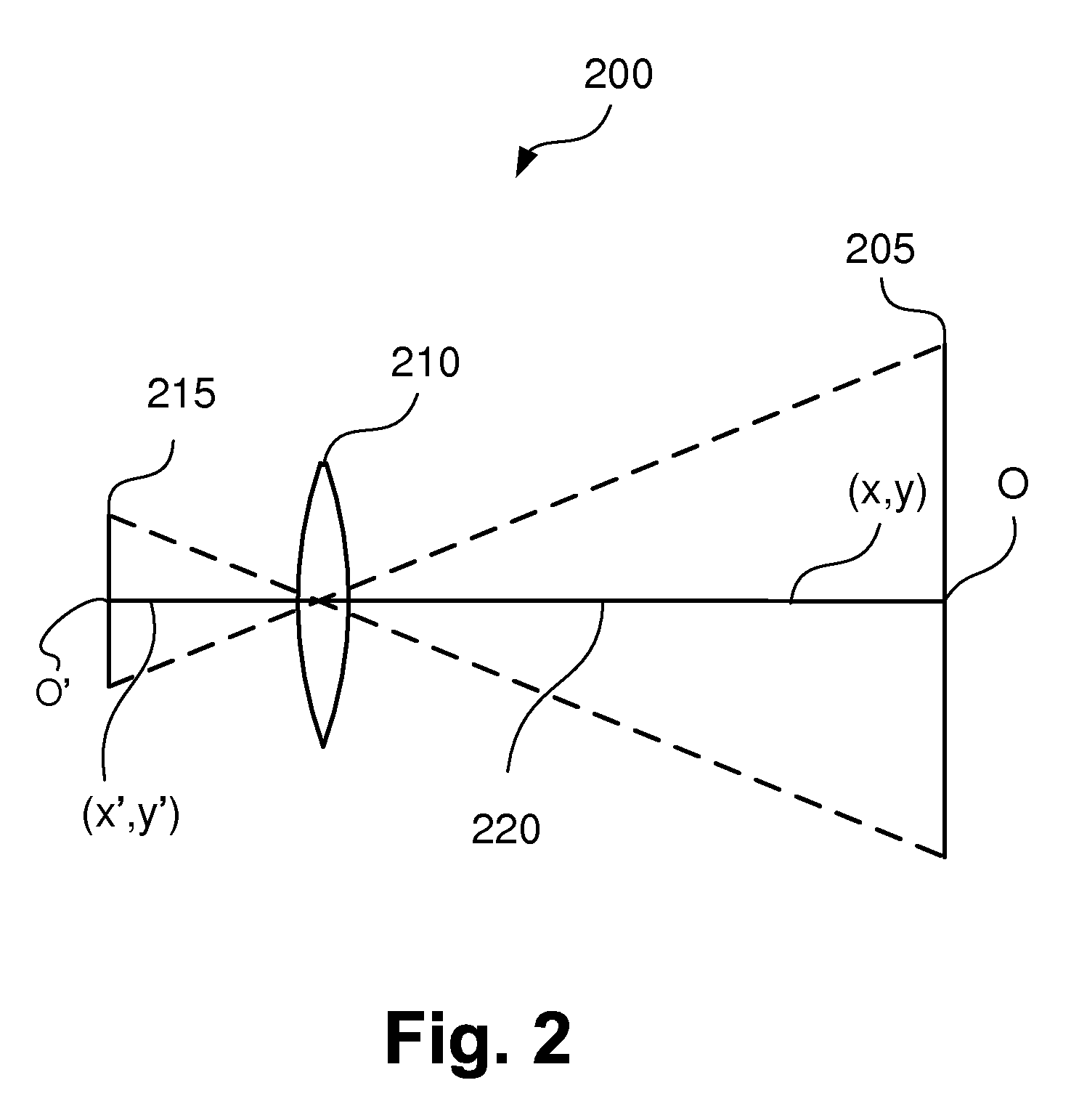
Geometric parameter measurement of an imaging device
ActiveUS20090161945A1Overcome disadvantagesAccurately determinedImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersGrey levelComputer vision
Disclosed is a method of determining at least one three-dimensional (3D) geometric parameter of an imaging device. A two-dimensional (2D) target image is provided having a plurality of alignment patterns. The target image is imaged with an imaging device to form a captured image. At least one pattern of the captured image is compared with a corresponding pattern of the target image. From the comparison, the geometric parameter of the imaging device is then determined. The alignment patterns include at least one of (i) one or more patterns comprising a 2D scale and rotation invariant basis function, (ii) one or more patterns comprising a 1D scale invariant basis function, and (iii) one or more patterns having a plurality of grey levels and comprising a plurality of superimposed sinusoidal patterns, the plurality of sinusoidal patterns having a plurality of predetermined discrete orientations. Also disclosed is a two-dimensional test chart for use in testing an imaging device, the test chart comprising a plurality of alignment patterns, at least one of said alignment patterns including one of those patterns mentioned above.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and system for improving visual angle complexion color shift of liquid crystal display
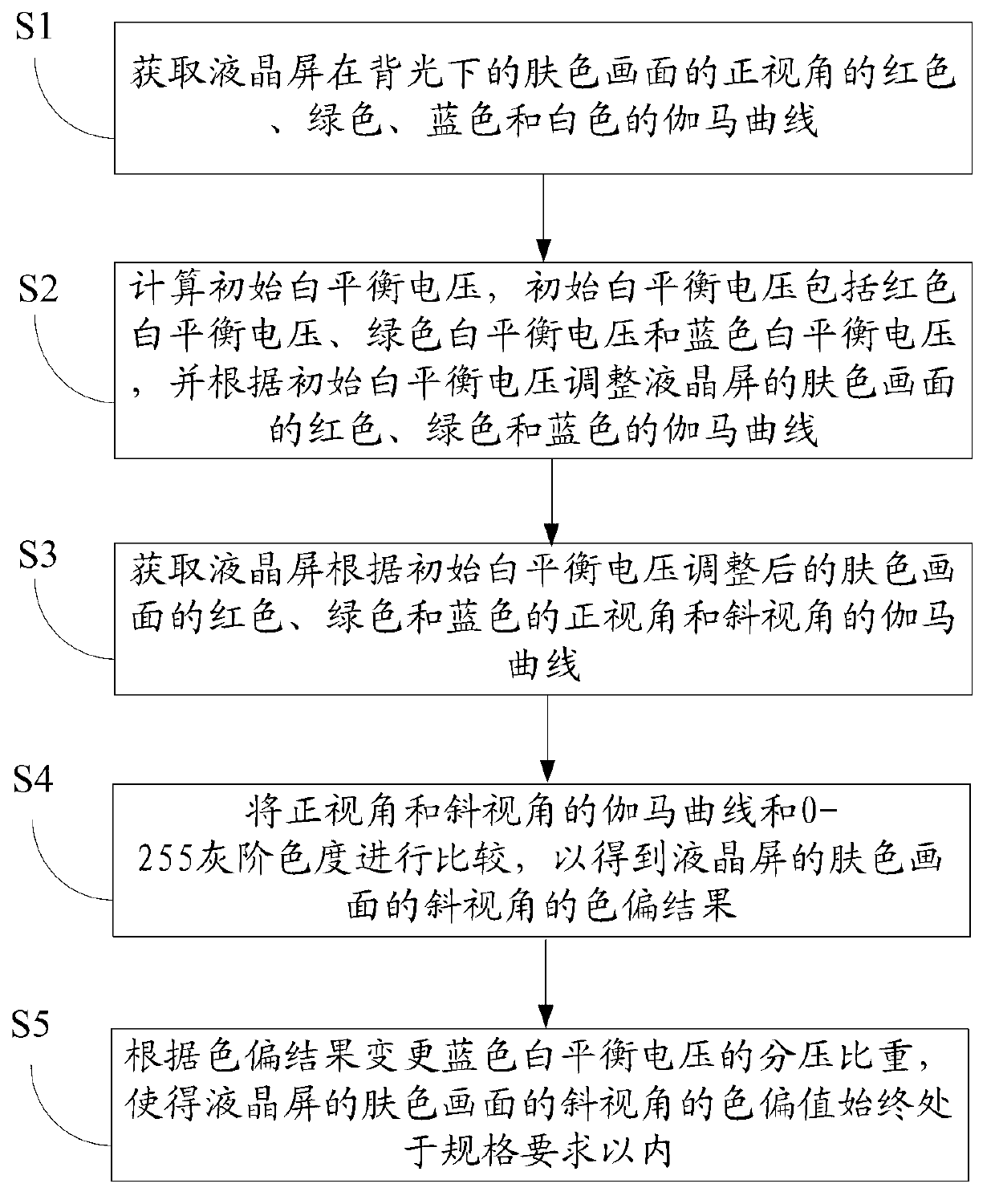
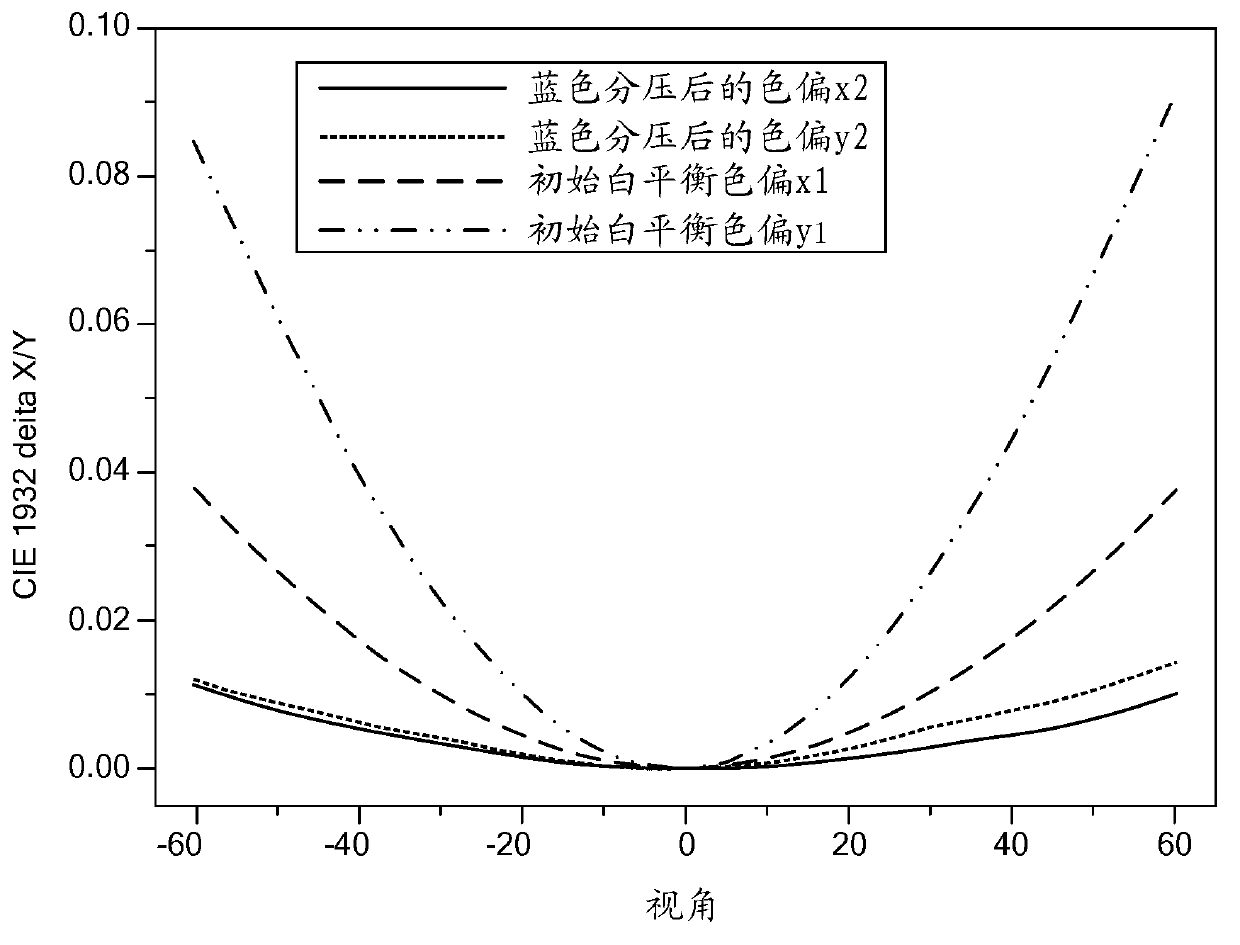
ActiveCN103106884AColor signal processing circuitsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayColor shift
The invention discloses a method and a system for improving visual angle complexion color shift of a liquid crystal display. The method is as follows: comparing gamma curves of front angles and squint angles of red, green and blue after adjustment according to initial white balanced voltage with 0-255 gray scale chrominance; and changing the partial pressure proportion of white balanced voltage of the blue according to color shift results so that color shift values of the squint angles of complexion pictures of the liquid crystal display can be within a range of specification requirements all the time. By means of the method, the color shift values of the squint angles of the complexion pictures of the liquid crystal display can be within the range of the specification requirements all the time.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Liquid-crystal panel and drive method therefor
ActiveCN104900203AGuaranteed display qualityOvercoming the problem of non-smooth changesStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
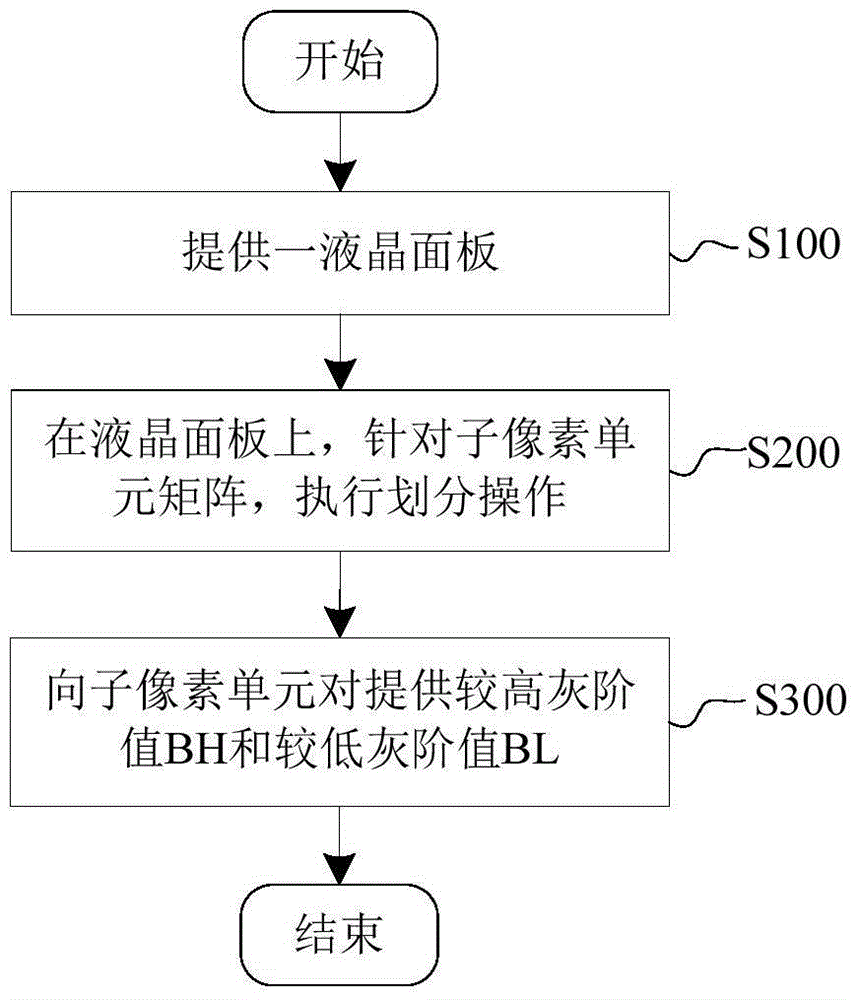
The invention discloses a liquid-crystal panel and a drive method therefor. The method comprises the steps: providing the liquid-crystal panel, wherein the liquid-crystal panel comprises an M*N pixel unit matrix and each pixel unit sequentially consists of a red sub-pixel unit, a green sub-pixel unit, and a blue sub-pixel unit, thereby enabling the liquid-crystal panel to comprise an M*(3*N) sub-pixel unit matrix; performing dividing operation for the sub-pixel unit matrix; providing a higher-gray-scale-value BH for the first sub-pixel unit in the sub-pixel unit of each color; providing a lower-gray-scale-value BL for the second blue sub-pixel unit in the sub-pixel unit of each color; and enabling the brightness curve of the sub-pixel unit of each color at an inclined angle to approach a preset Gamma curve. According to the invention, the color bias, generated when a user watch the liquid crystal display from a side or at an inclined angle, can be reduced.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com