Patents
Literature
75results about How to "Highly miniaturized" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
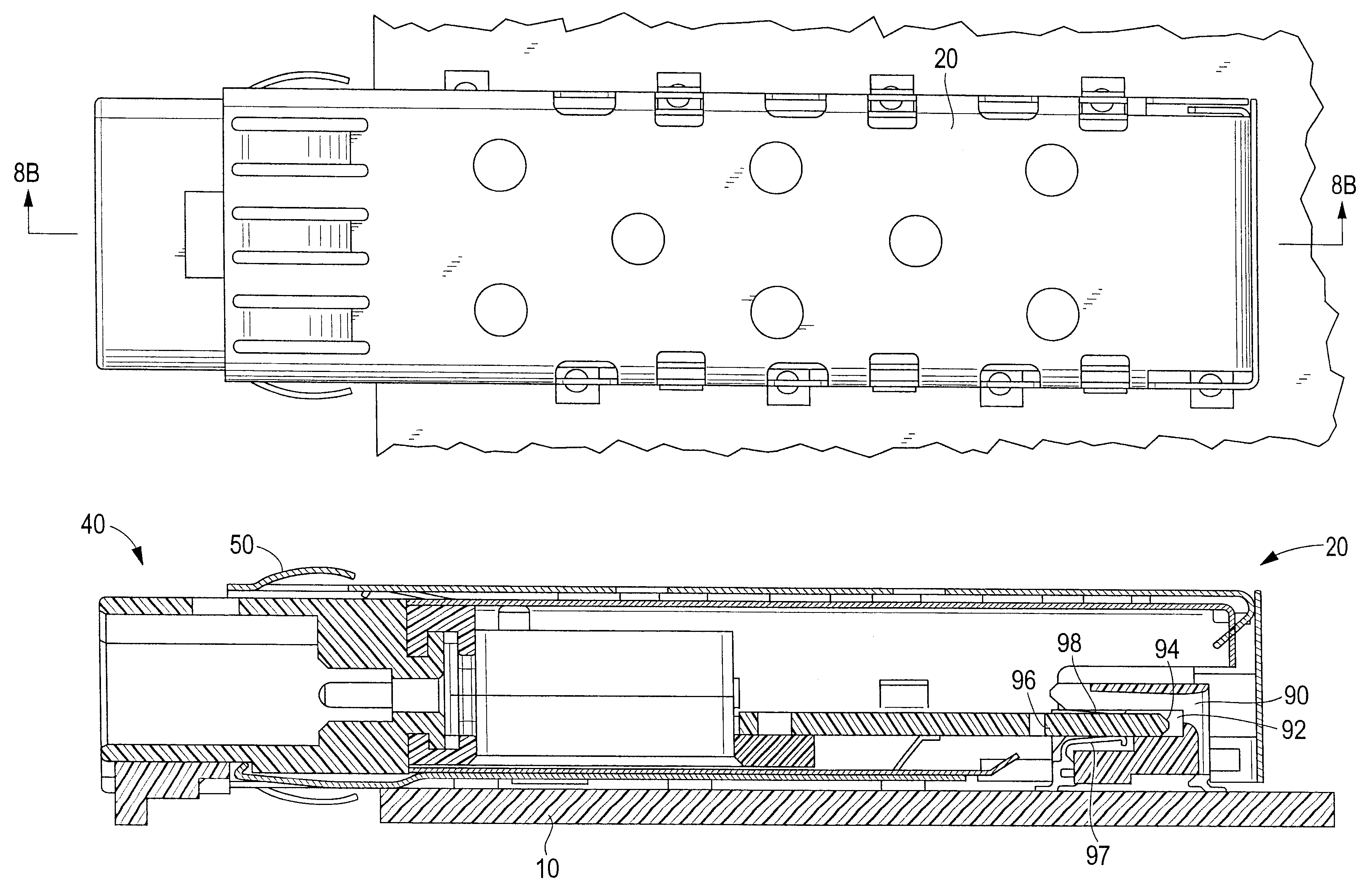
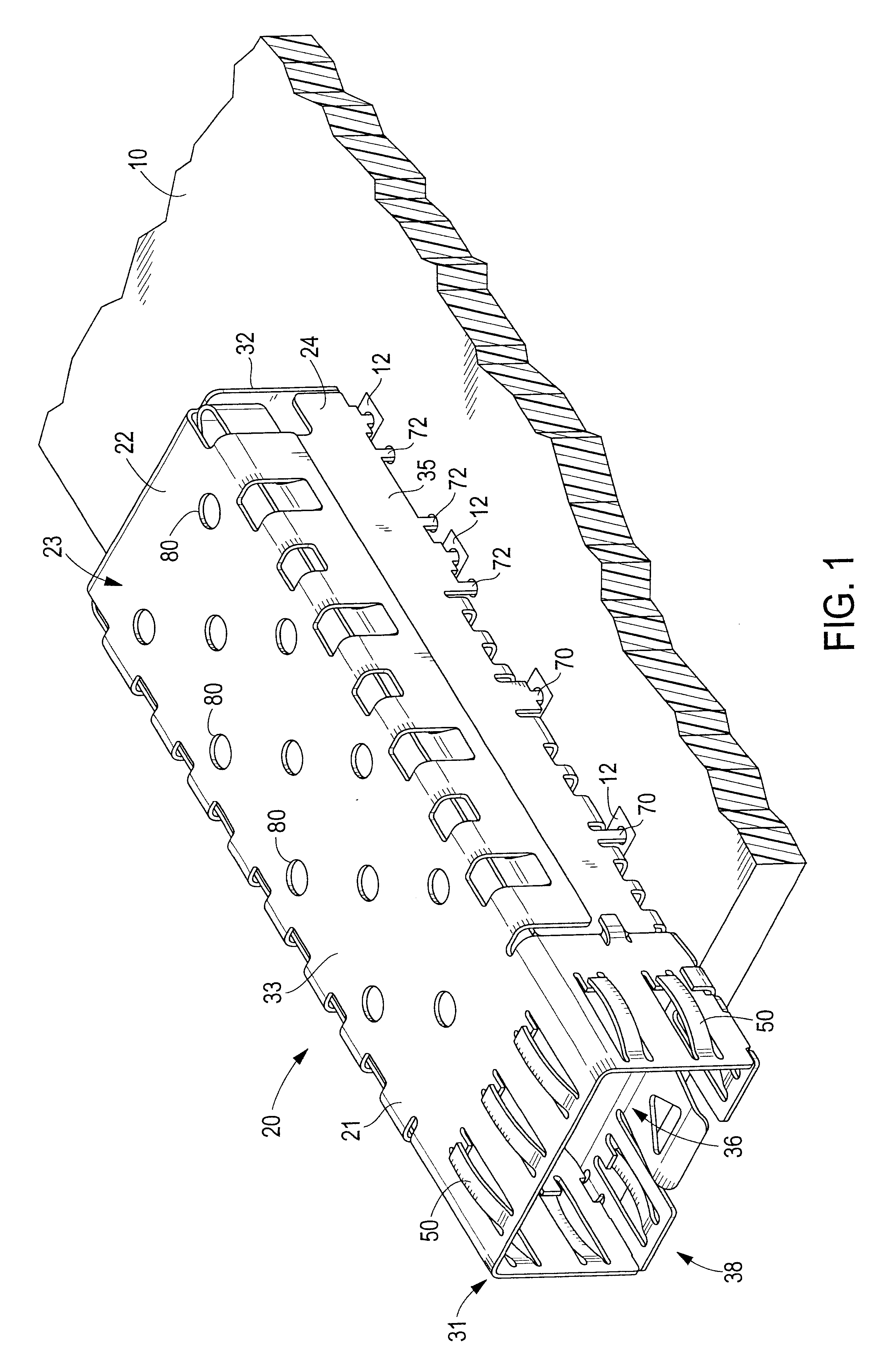
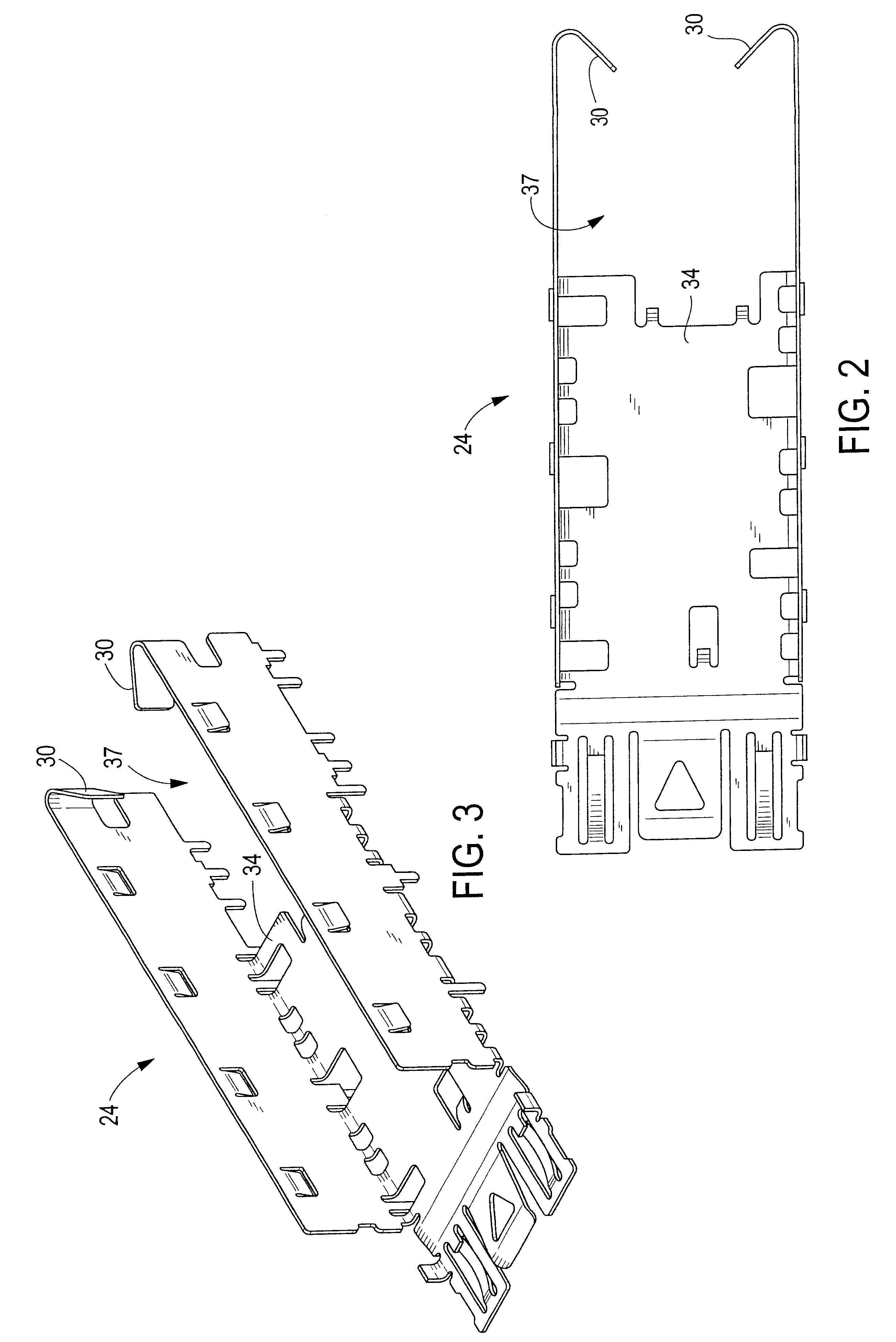
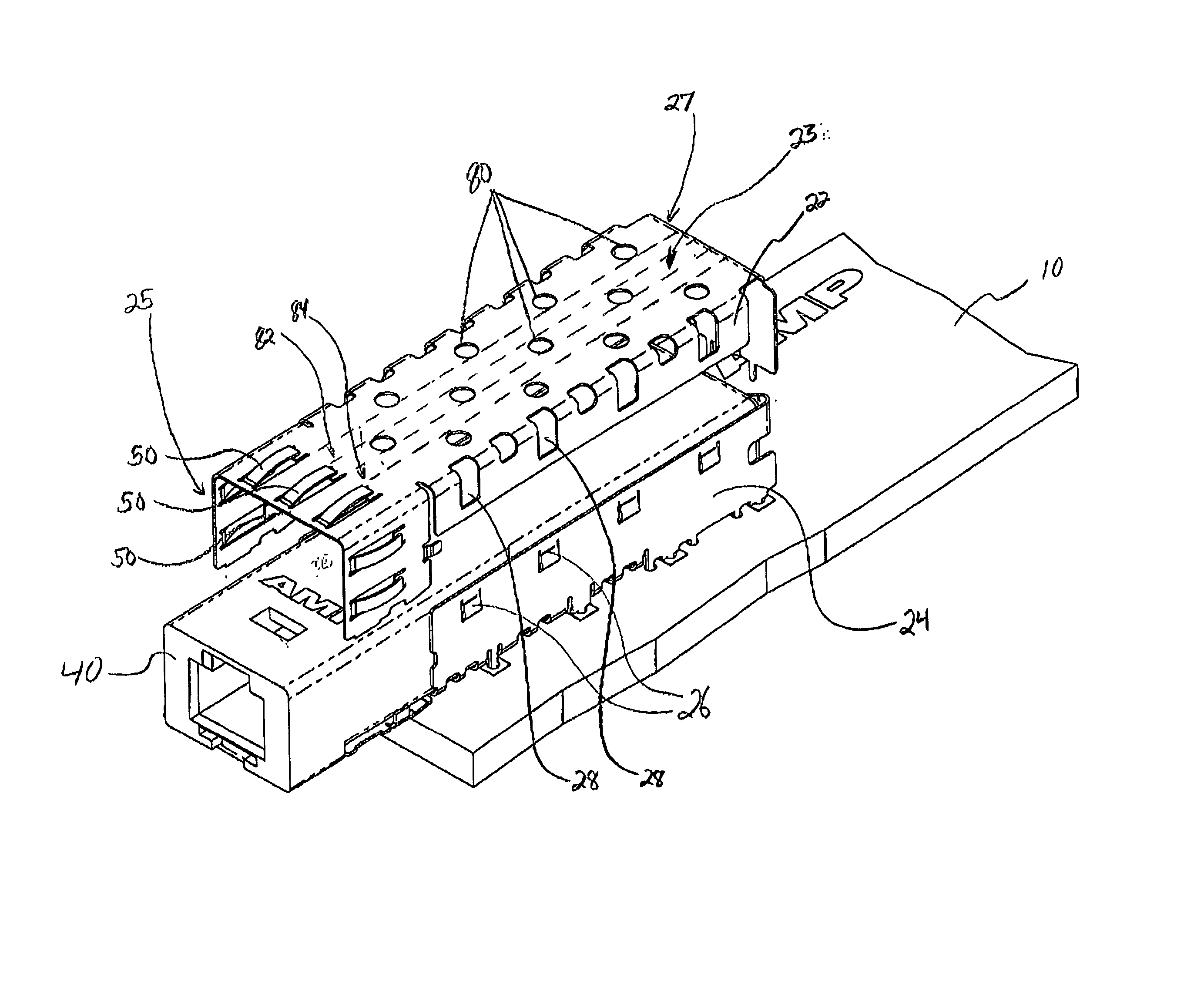
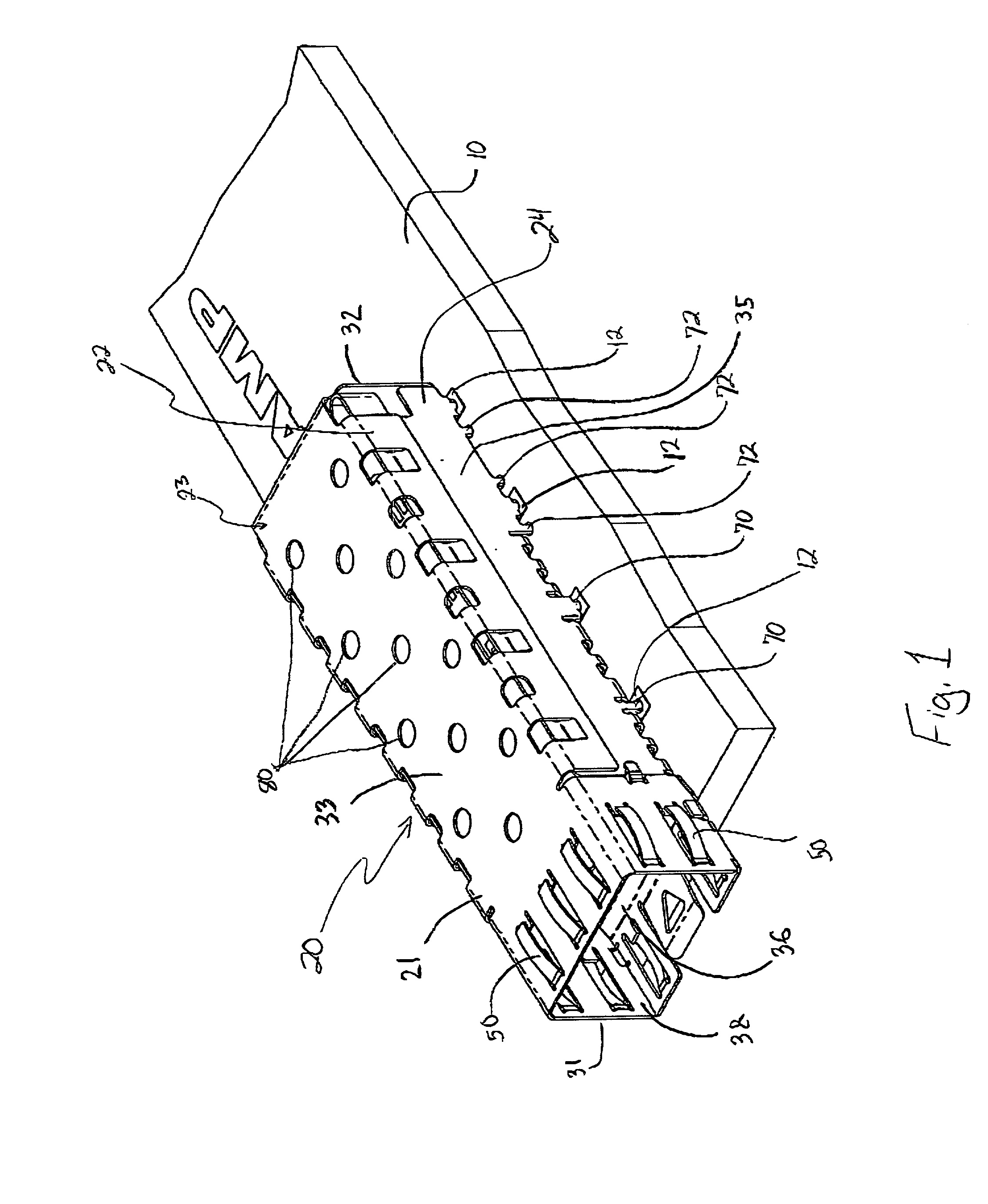
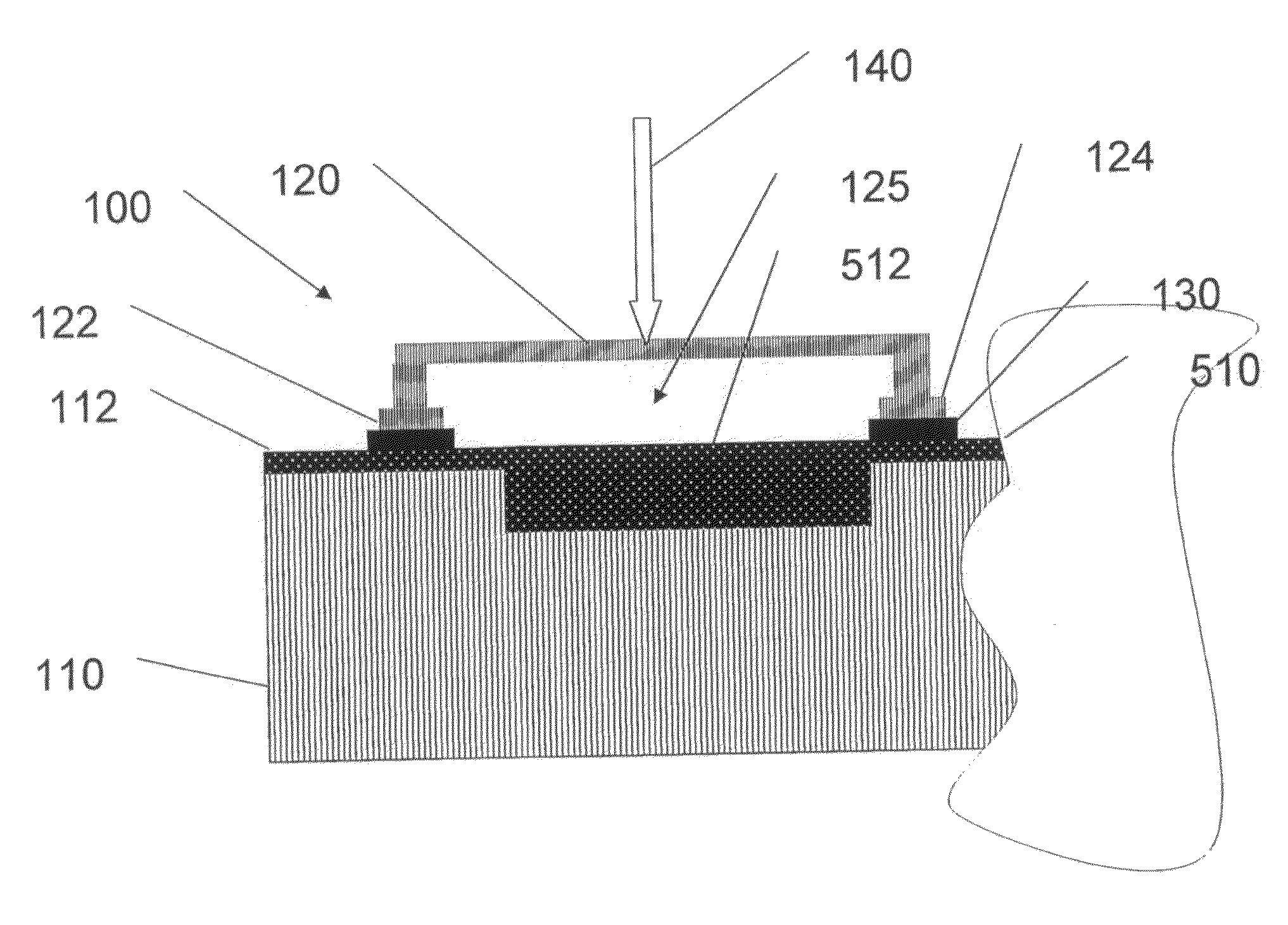
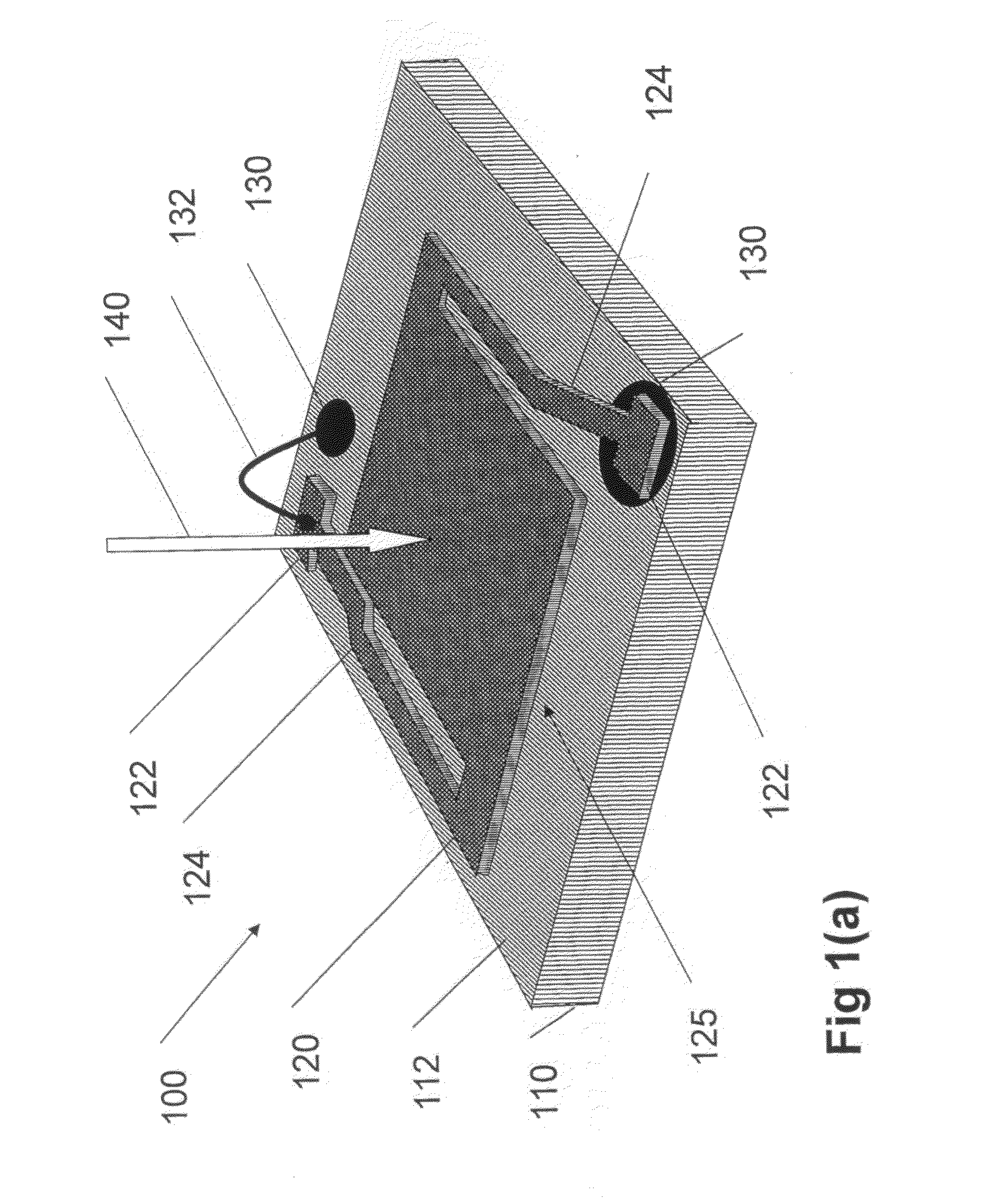
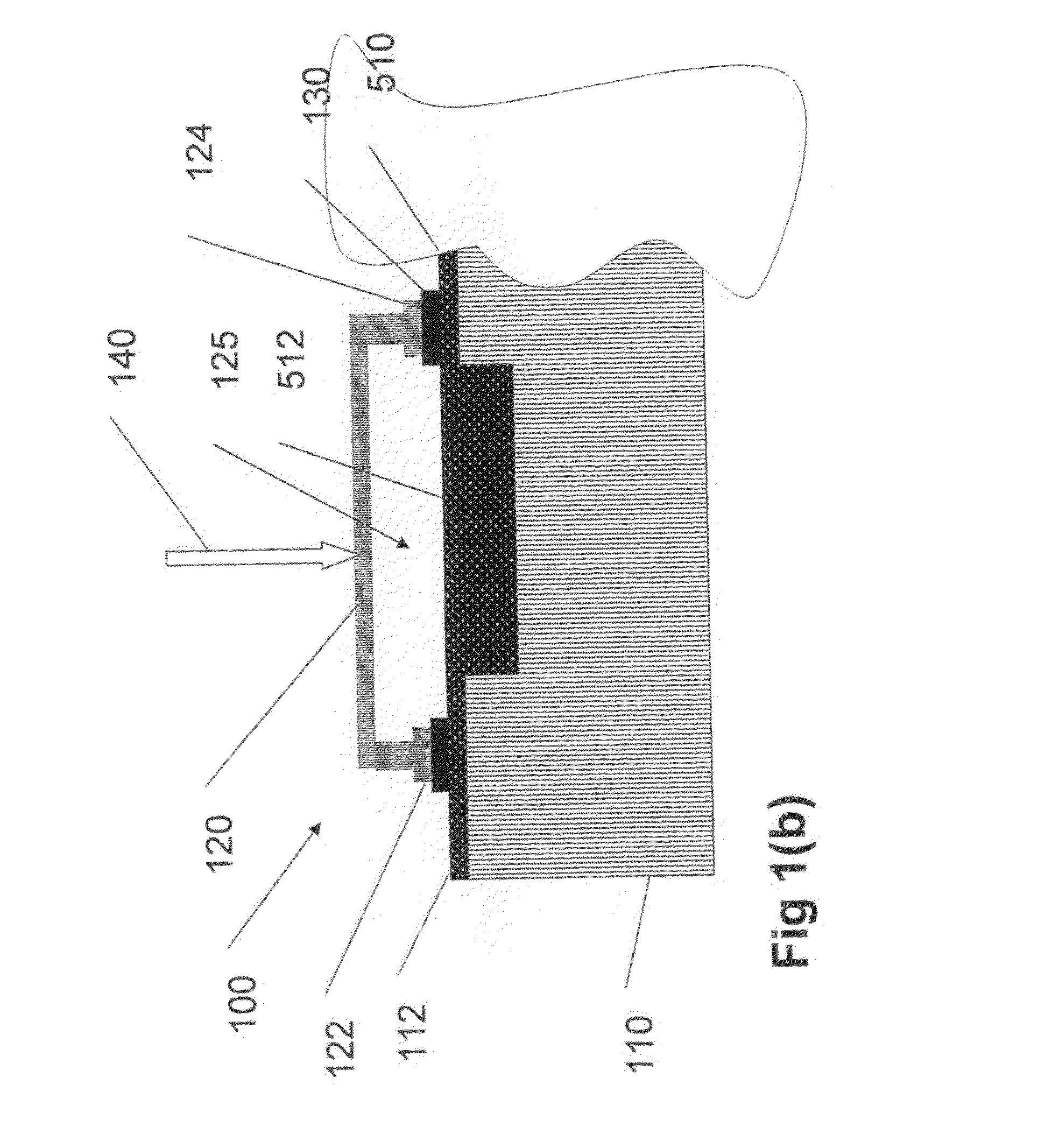
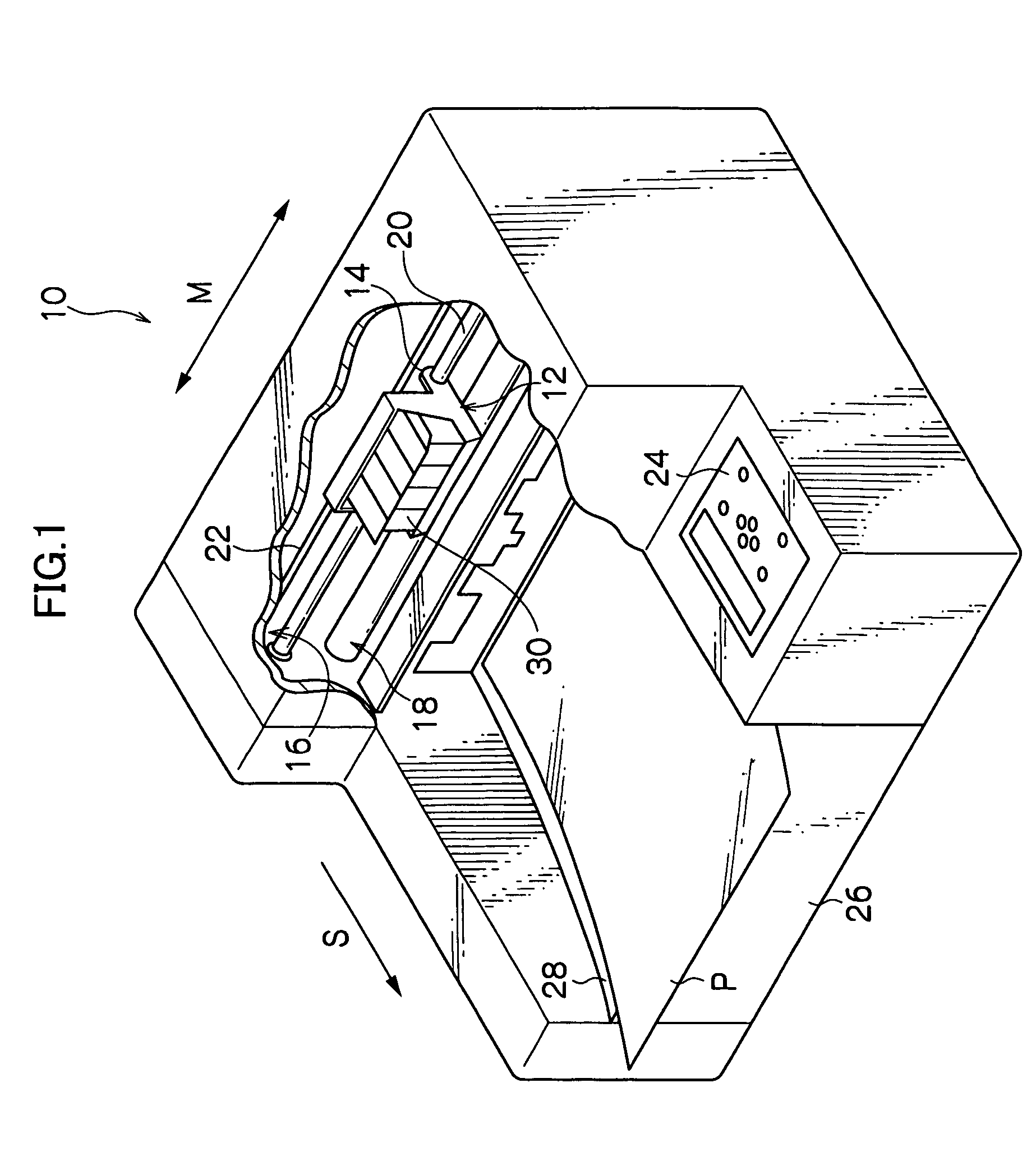
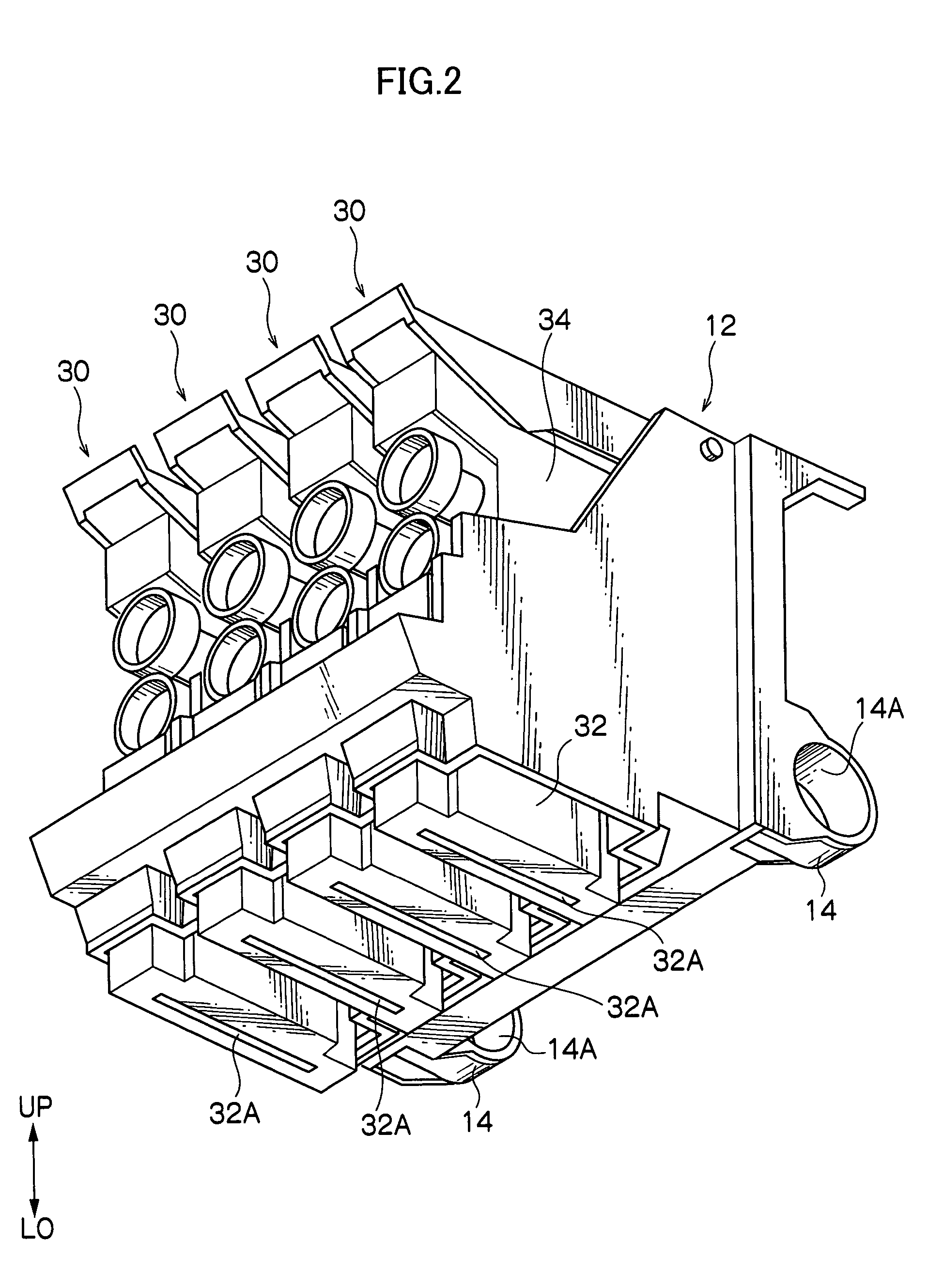
Pluggable module and receptacle
InactiveUS6517382B2High frequencyHighly miniaturizedMagnetic/electric field screeningContact members penetrating/cutting insulation/cable strandsElectrical connectionConductive materials
A receptacle for a pluggable module includes a housing having a front, a back wall, a top wall, a bottom wall, and side walls and defining a cavity for receiving a module. The bottom wall has a bottom opening to receive a receptacle connector, and the front has a front opening to receive the module. The walls of the housing are made from a conductive material. A plurality of elongated members extend down from the housing past the bottom wall. The elongated members are adapted for electrical connection to a host circuit board such that the walls of the housing are electrically connected to the host circuit board.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
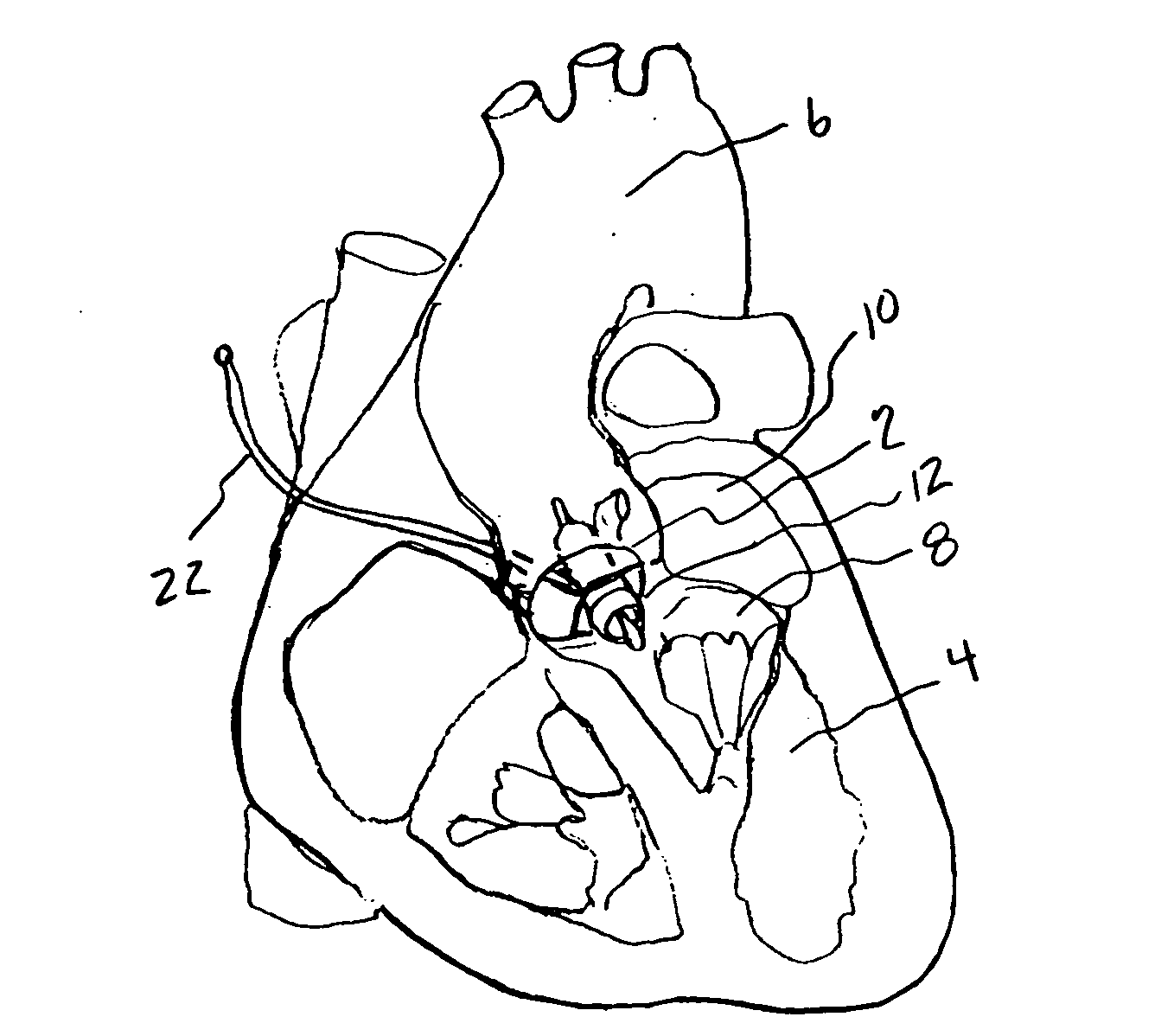
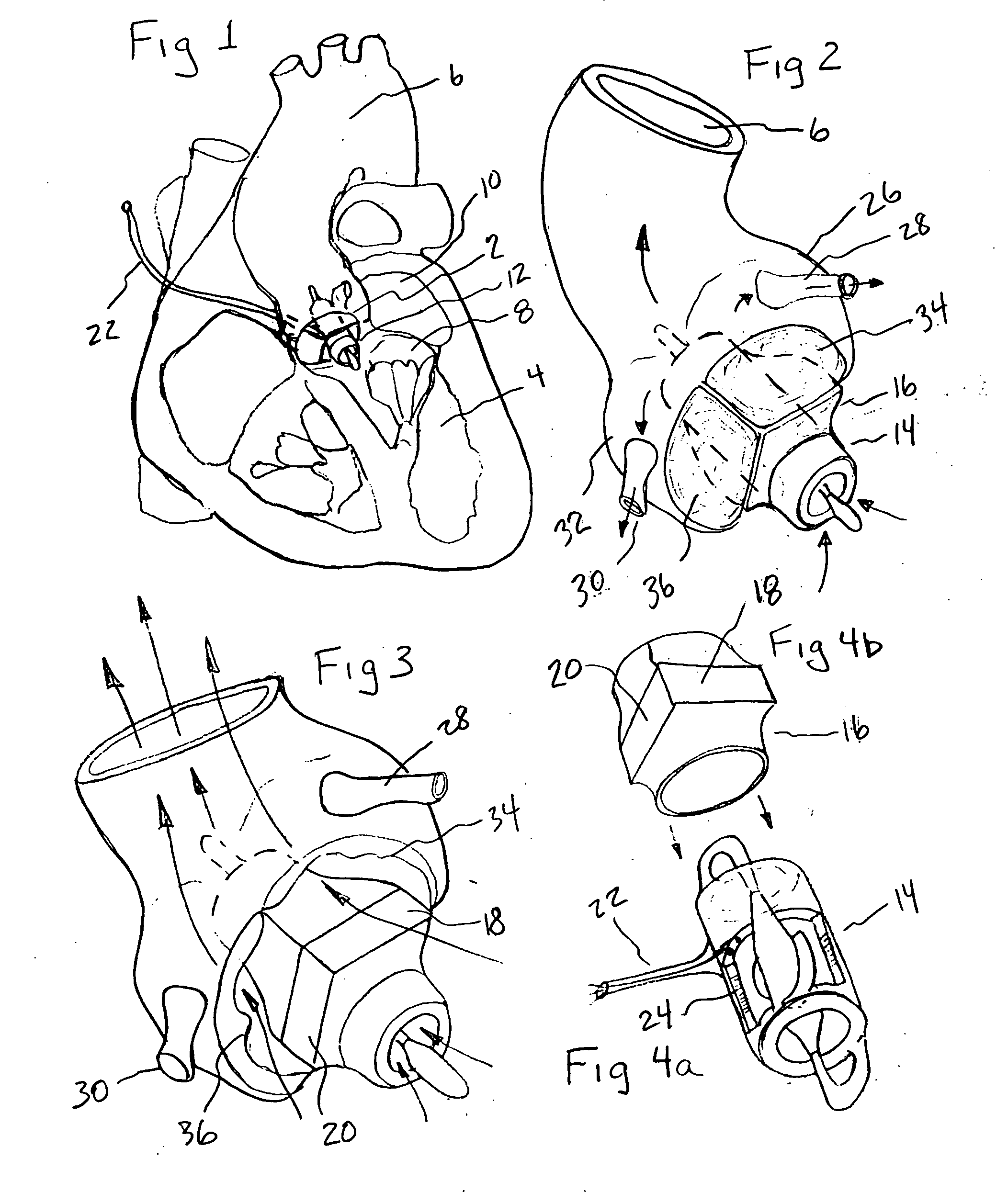
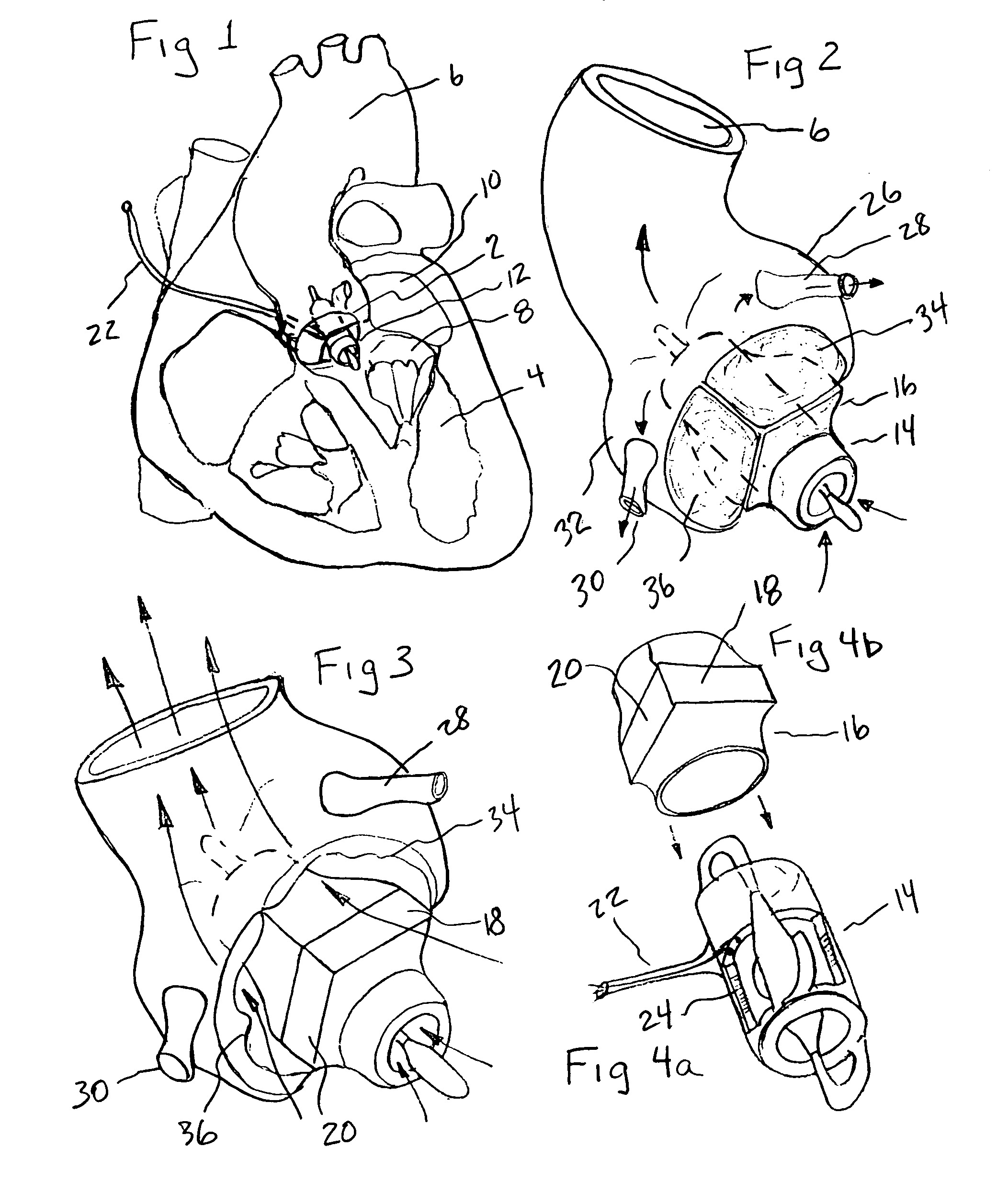
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS20060195004A1Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
A tiny electrically powered hydrodynamic blood pump is disclosed which occupies one third of the aortic or pulmonary valve position, and pumps directly from the left ventricle to the aorta or from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. The device is configured to exactly match or approximate the space of one leaflet and sinus of valsalva, with part of the device supported in the outflow tract of the ventricular cavity adjacent to the valve. In the configuration used, two leaflets of the natural tri-leaflet valve remain functional and the pump resides where the third leaflet had been. When implanted, the outer surface of the device includes two faces against which the two valve leaflets seal when closed. To obtain the best valve function, the shape of these faces may be custom fabricated to match the individual patient's valve geometry based on high resolution three dimensional CT or MRI images. Another embodiment of the invention discloses a combined two leaflet tissue valve with the miniature blood pump supported in the position usually occupied by the third leaflet. Either stented or un-stented tissue valves may be used. This structure preserves two thirds of the valve annulus area for ejection of blood by the natural ventricle, with excellent washing of the aortic root and interface of the blood pump to the heart. In the aortic position, the blood pump is positioned in the non-coronary cusp. A major advantage of the transvalvular VAD is the elimination of both the inflow and outflow cannulae usually required with heart assist devices.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
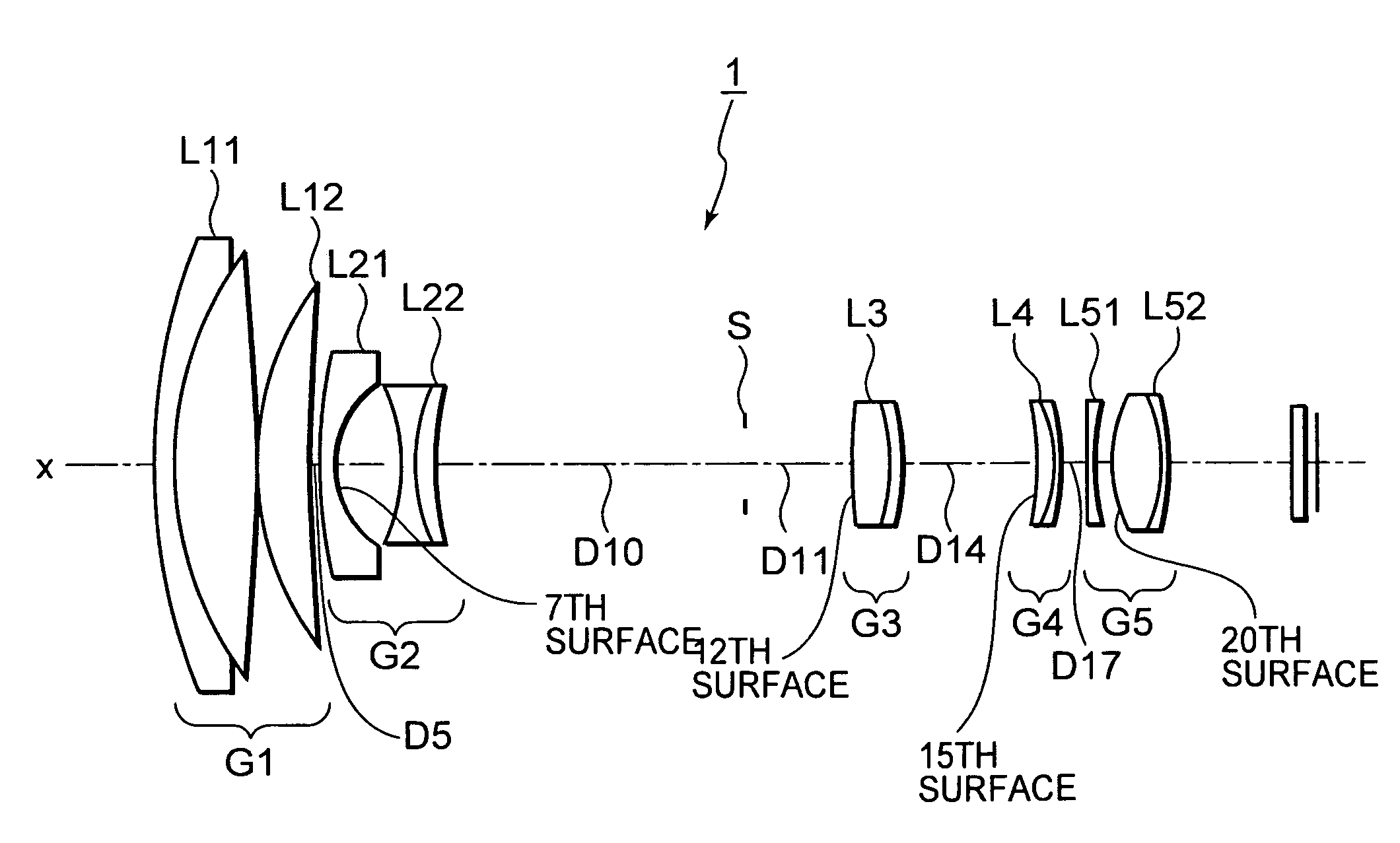
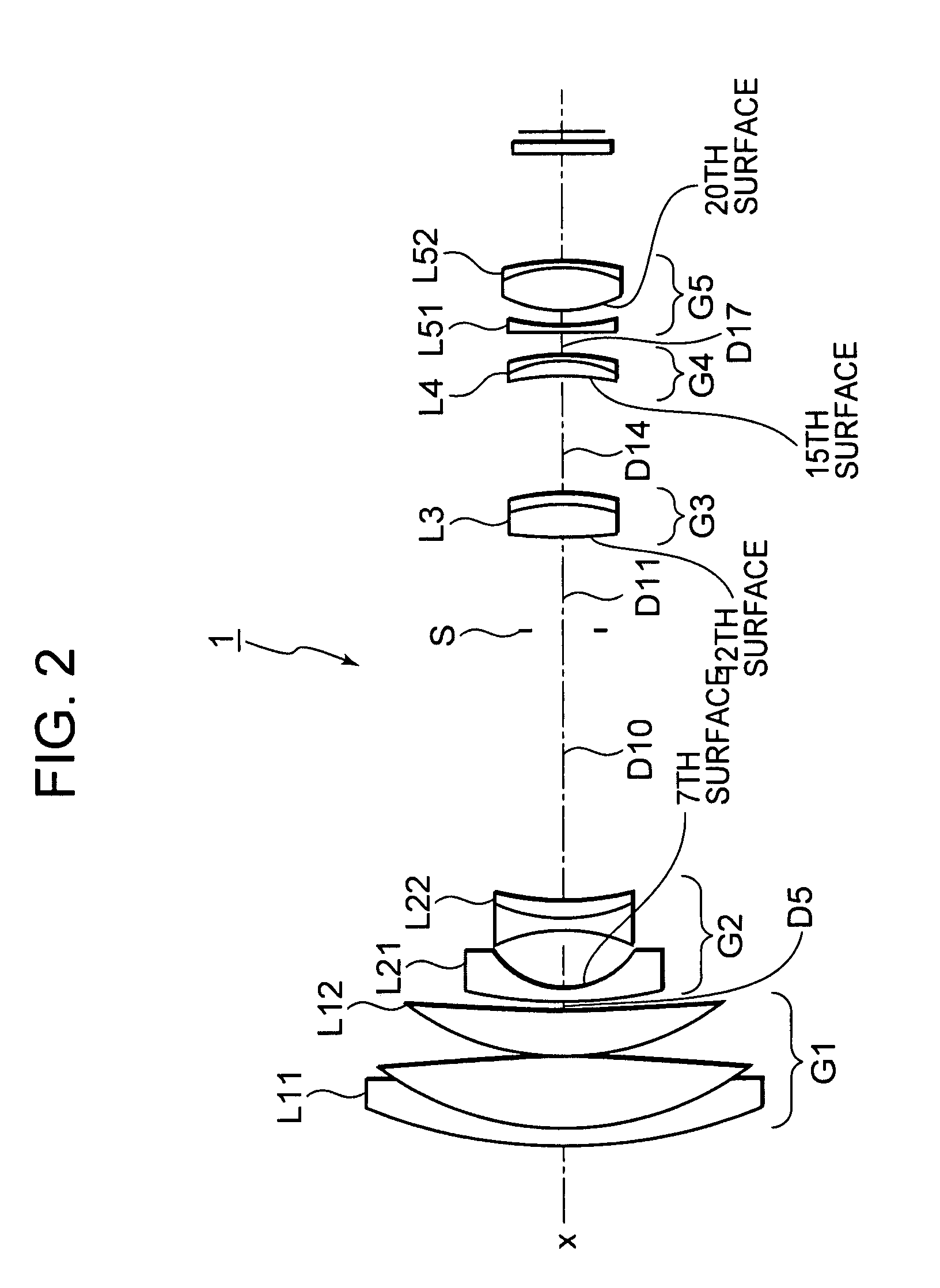
Variable focal length lens system and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7286304B1Highly miniaturizedHigh zoom ratioCamera body detailsLensOphthalmologyOptical axis
A variable focal length lens system includes: a first lens group having a positive refractive power; a second lens group having a negative refractive power; a third lens group having a positive refractive power; and a fourth lens group having a positive refractive power. As the lens position state changes from a wide-angle end state to a telephoto end state, at least each of the lens groups is mobile, the second lens group moves towards the image side and the third lens group moves towards the object side such that the gap between the first and the second lens group increases, and the gap between the second and the third lens group decreases, while the fourth lens group moves in the direction of the optical axis so as to compensate for changes in the position of the image plane which accompany movements of each of the lens group.
Owner:SONY CORP
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS7479102B2Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
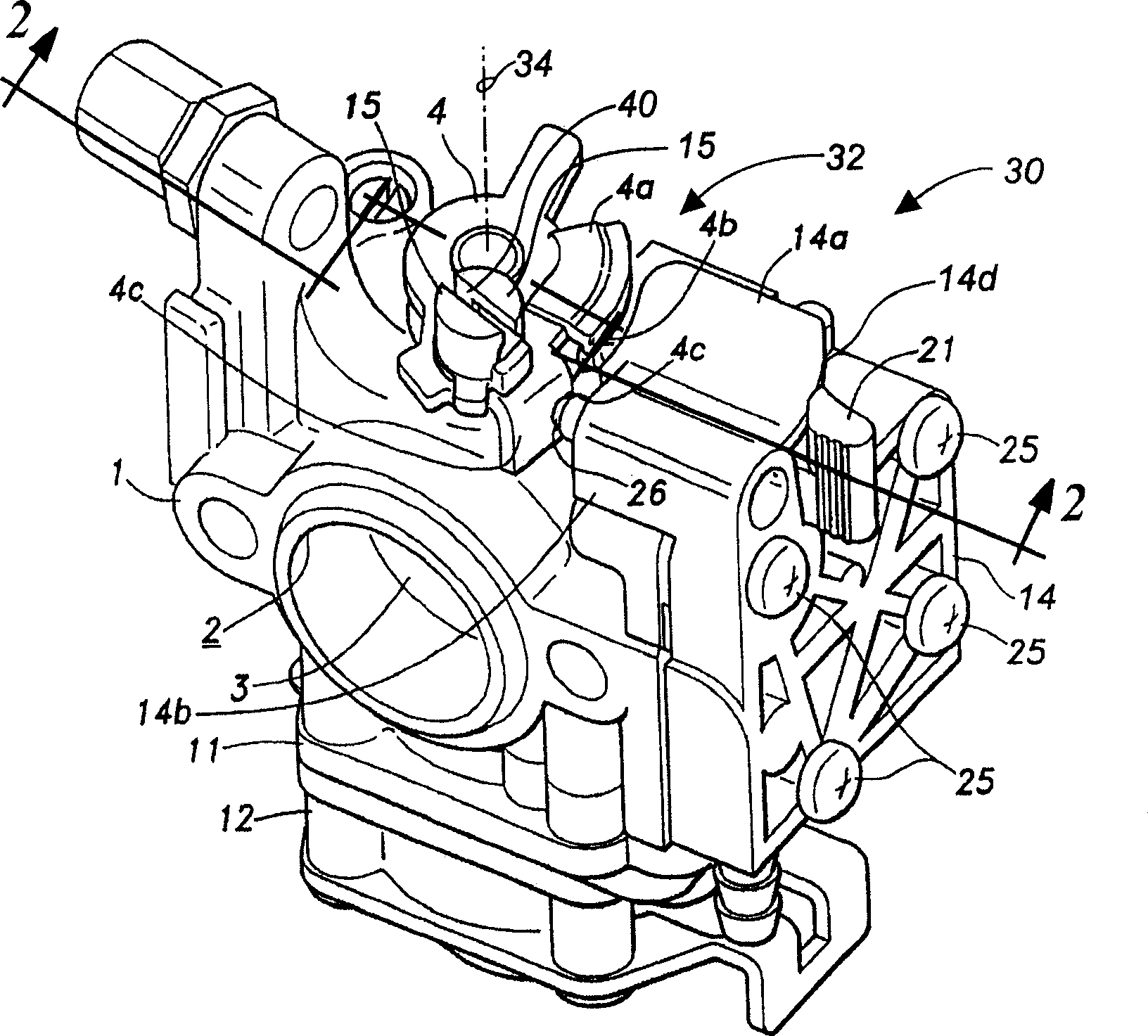
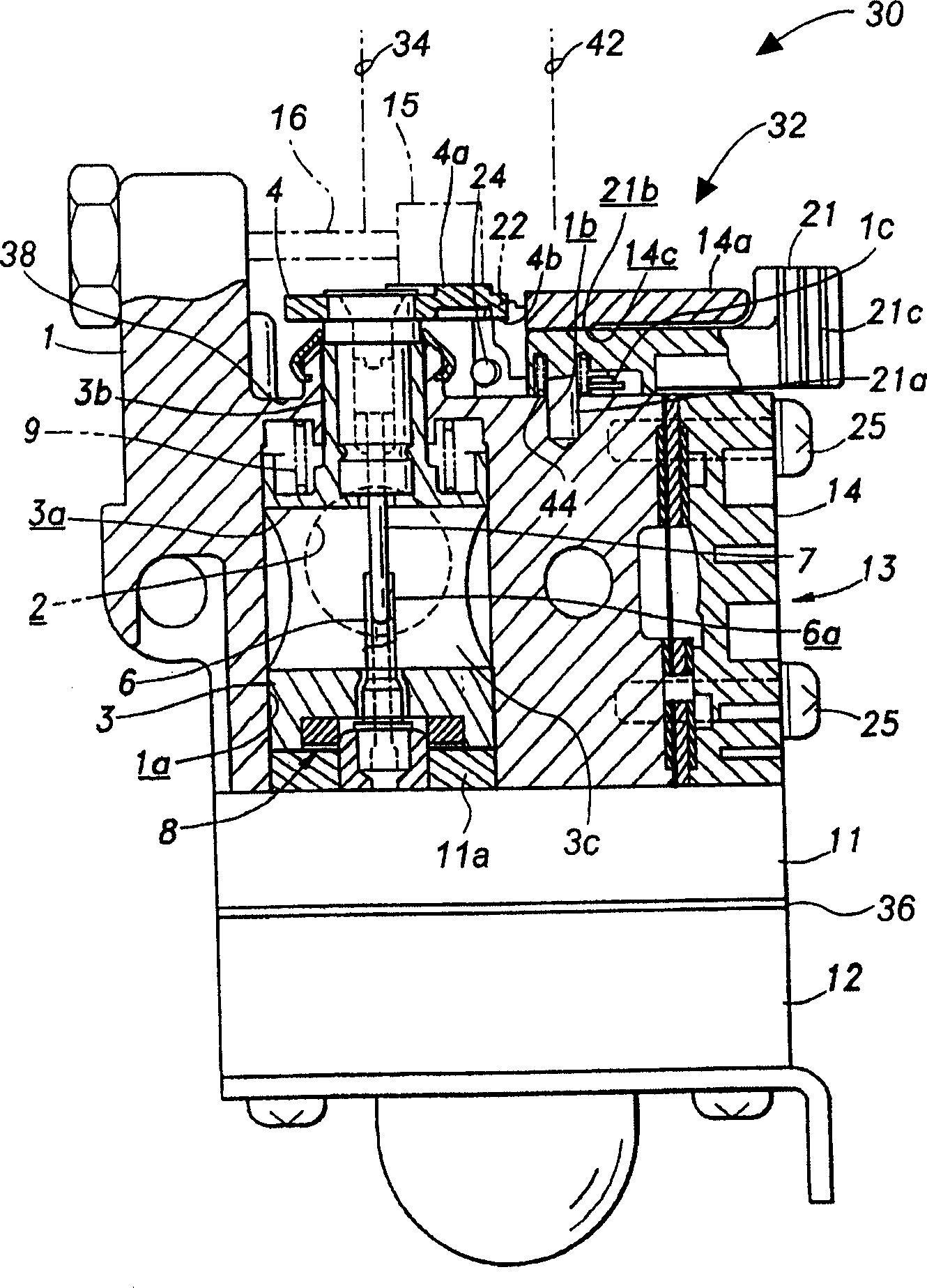
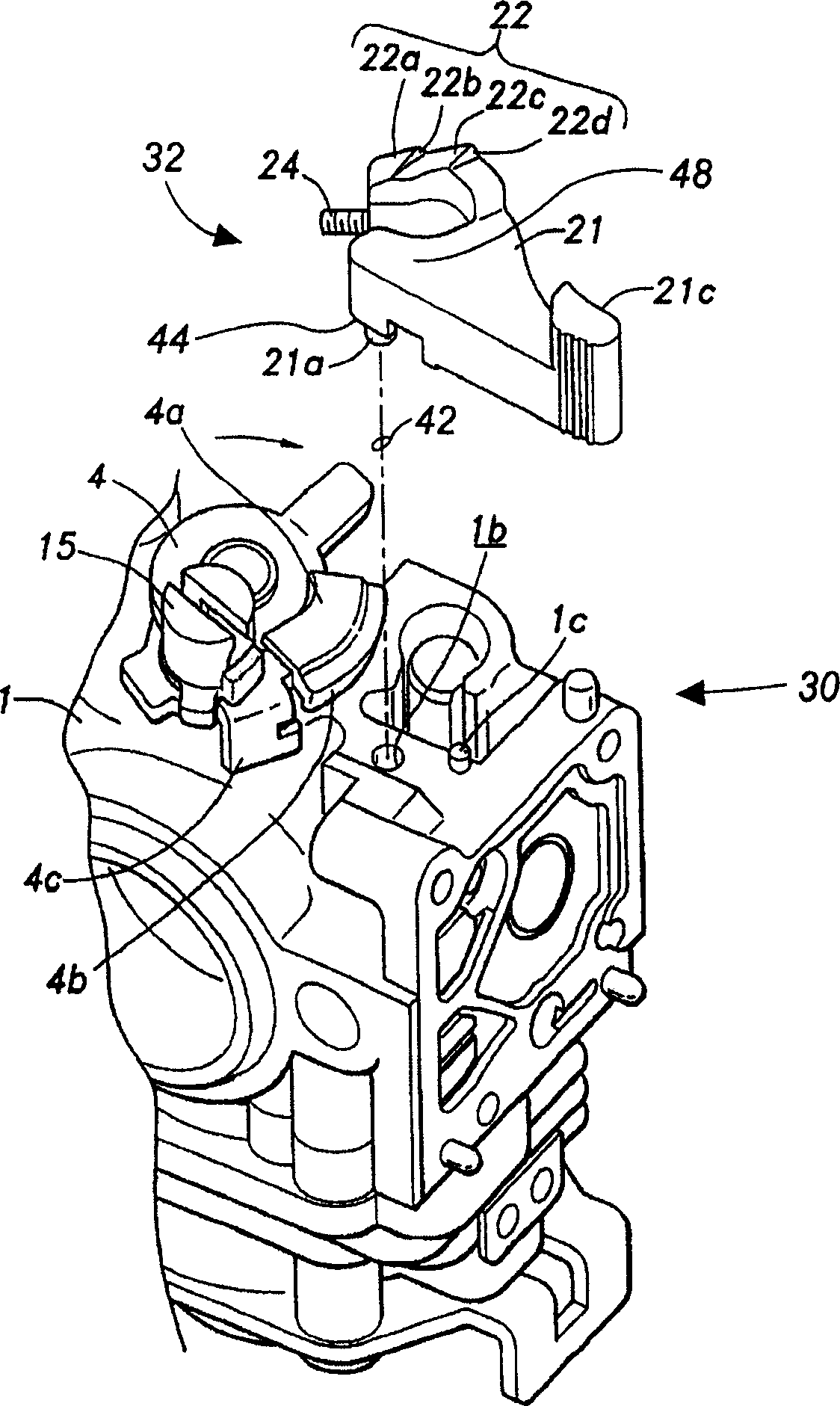
Engine start device of a rotary valve carburetor
InactiveCN1869425AIncrease concentrationPrevent axial movementMachines/enginesCarburettorsCombustionRotary valve
A compact engine start device of a combustion engine rotary-type carburetor overrides normal operation of a rotary throttle valve to provide a richer mixture of fuel-and-air to start a cold engine. Rotation of a start lever of the start device activates a releasable camming interface coupler causing the throttle lever to rotate about a rotary axis and axially lift partially out of the carburetor at prescribed angular and axial distances. This provides the engine, through a fuel-and-air mixing passage, with a controlled and enriched ratio and volume of a fuel-and-air mixture. Preferably, the start lever has a projecting rod that inserts into a hole in the carburetor body for rotation about an axis orientated substantially parallel to the rotary axis. An outward surface of the start lever is in rotational sliding contact with a low-profile, preferably cantilevered, retention arm preferably formed unitarily to a metering fuel pump cover engaged removably to the body of the carburetor, thus allowing rotational movement but preventing axial movement of the start lever. Because the start lever does not move axially to displace the rotary throttle valve, the height of the start lever is favorably minimized. Moreover, the start lever preferably has a knob for user interface at a distal end of the lever that conforms generally about the retention arm thus maximizing knob size yet not contributing to an increase in carburetor size.
Owner:WALBRO ENGINE MANAGEMENT
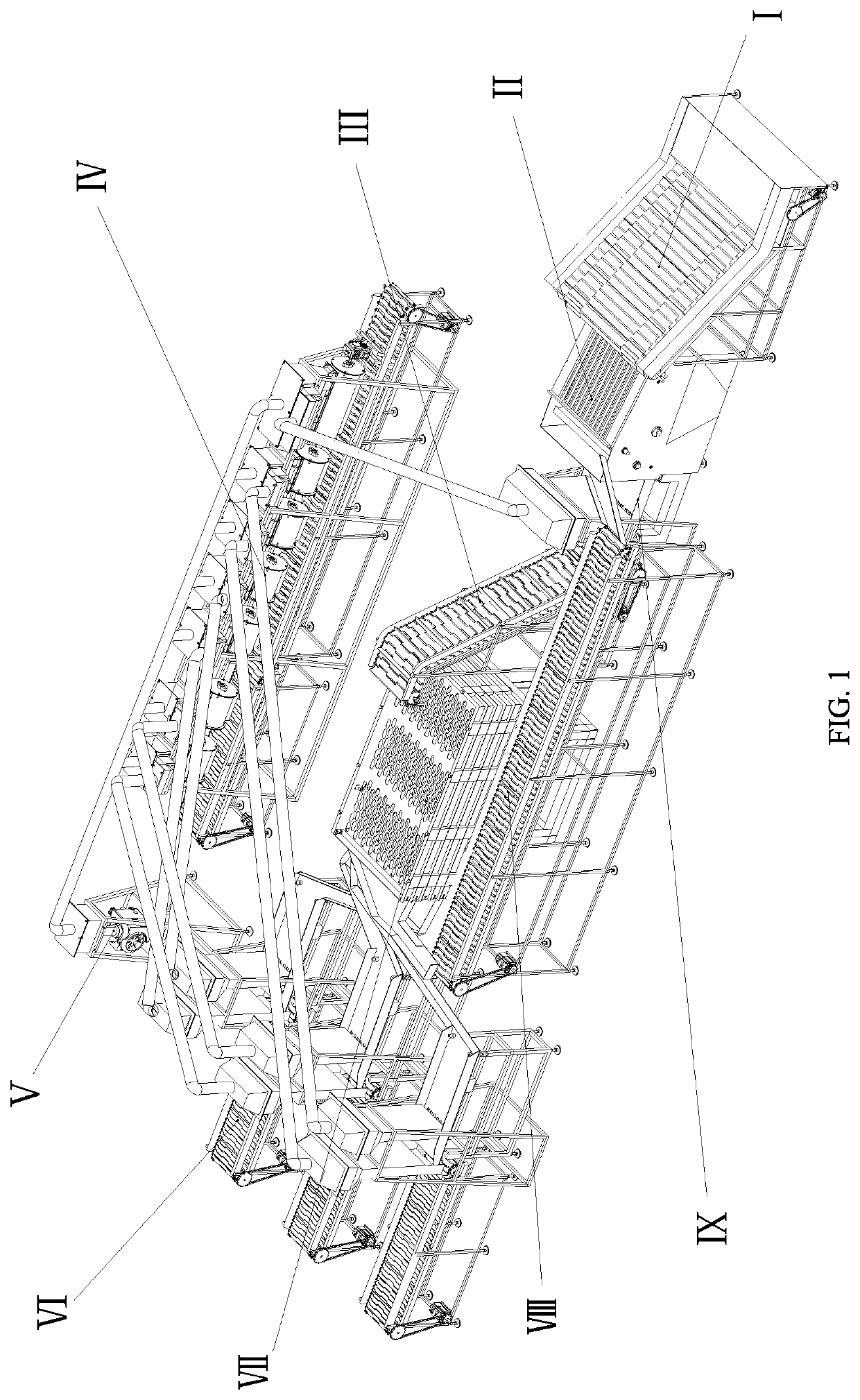
Automated production system for efficient walnut shell-breaking, kernel-taking and shell-kernel separation
PendingUS20200138083A1High speedHigh-efficiency walnut shell-breakingGas current separationHuskingWalnut NutProcess engineering
The disclosure discloses an automated production system for efficient walnut shell-breaking, kernel-taking and shell-kernel separation, solving the problem that the existing walnut shell breaking device cannot adapt to walnuts having different sizes and shell breaking rate and shell breaking efficiency cannot be ensured. The system can realize efficient shell-breaking, kernel-taking and shell-kernel separation on different varieties of walnuts, is quick in production speed and high in automation degree, and meanwhile is capable of improving entire kernel rate and kernel obtaining rate, reducing the damage rate of the walnut kernel and ensuring the high shell-breaking efficiency and thoroughness of shell and kernel separation.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY +1
Pluggable module and receptacle
InactiveUS20020068481A1High frequencyHighly miniaturizedMagnetic/electric field screeningContact members penetrating/cutting insulation/cable strandsElectrical connectionConductive materials
A receptacle for a pluggable module includes a housing having a front, a back wall, a top wall, a bottom wall, and side walls and defining a cavity for receiving a module. The bottom wall has a bottom opening to receive a receptacle connector, and the front has a front opening to receive the module. The walls of the housing are made from a conductive material. A plurality of elongated members extend down from the housing past the bottom wall. The elongated members are adapted for electrical connection to a host circuit board such that the walls of the housing are electrically connected to the host circuit board.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
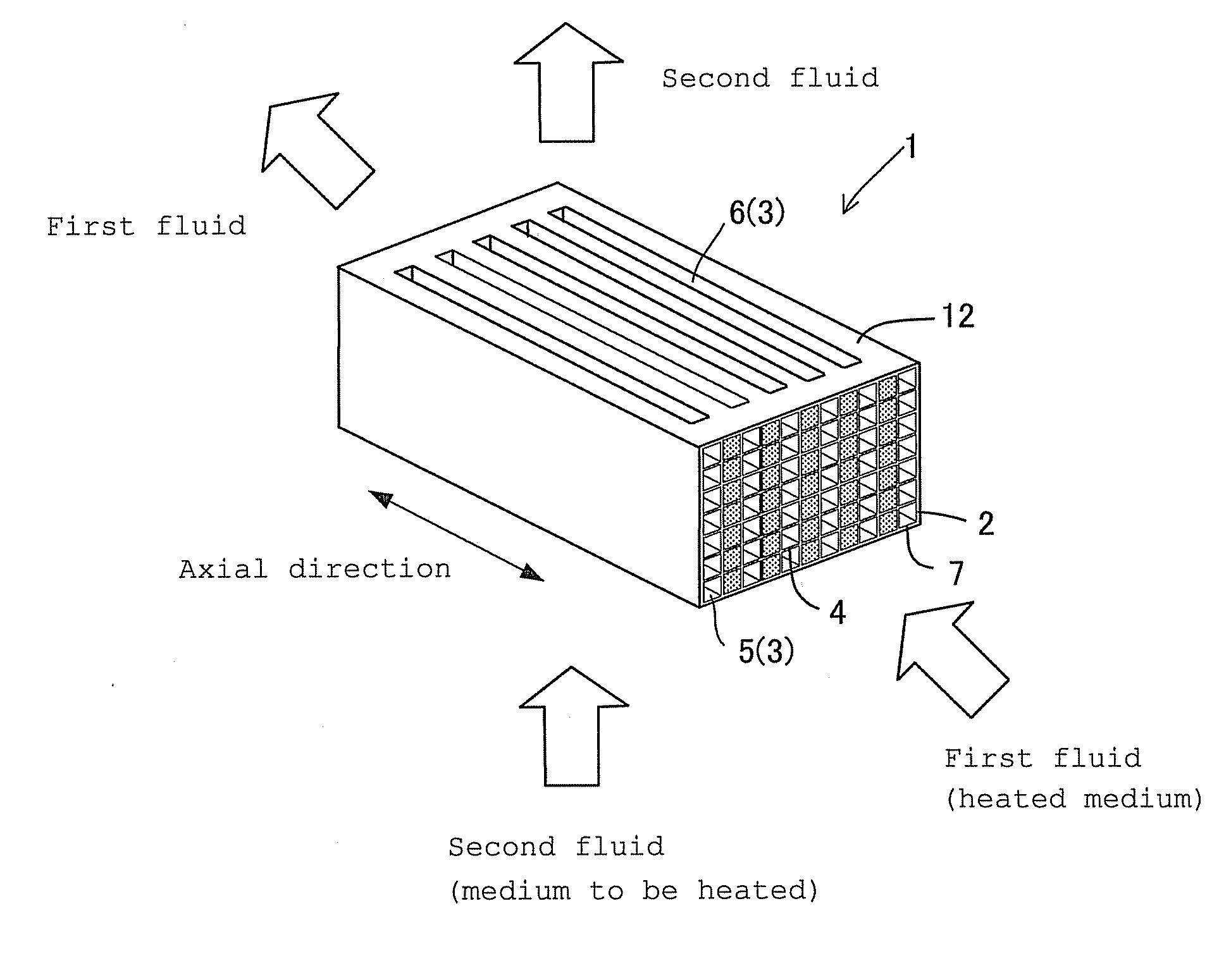
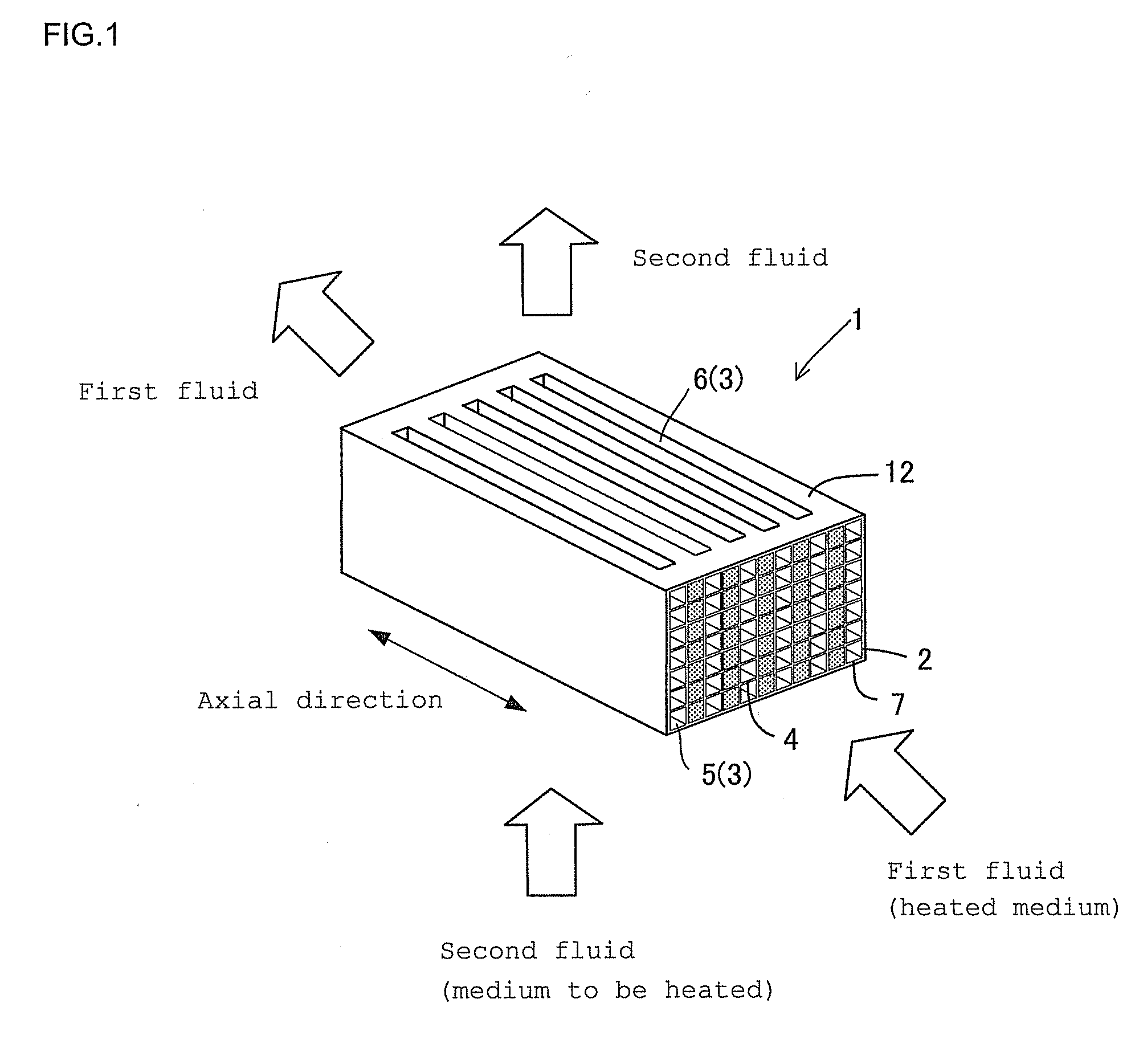
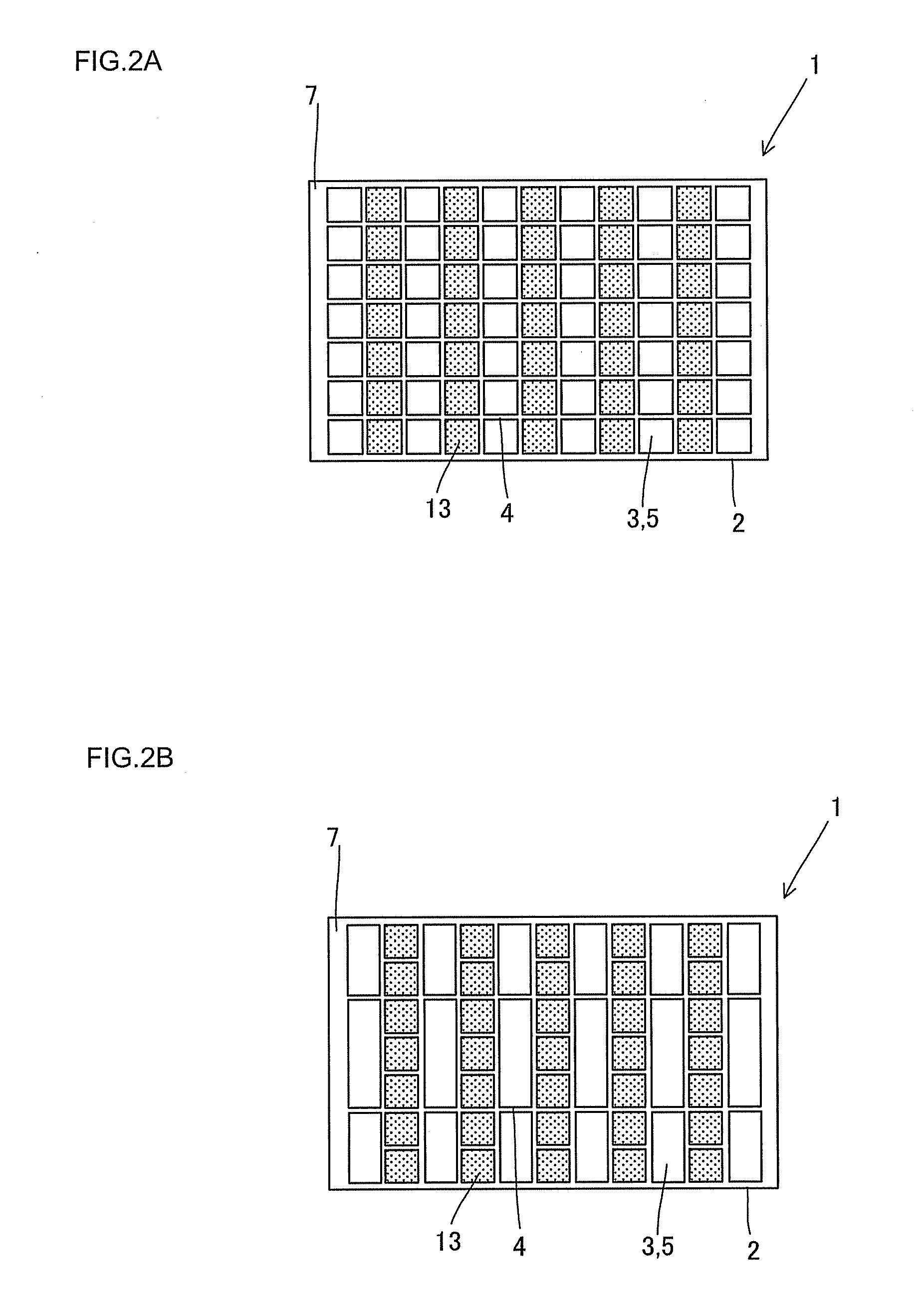
Ceramics heat exchanger and production method thereof
InactiveUS20100270011A1Improve heat exchange efficiencyHighly miniaturizedRecuperative heat exchangersMetal-working apparatusVolumetric Mass DensityEngineering
In a heat exchange element 1, first fluid circulation portions 5 having a honeycomb structure having a plurality of cells separated by ceramic partition walls 4, extending through in an axial direction from one end face 2 to the other end face 2, and allowing a heated medium as a first fluid to flow therethrough and second fluid circulation portions 6 being separated by ceramic partition walls 4, extending in the direction perpendicular to the axial direction, allowing a second fluid to flow therethrough, transferring heat to a medium to be heated as the second fluid are alternately formed as a unit. The cells 3 on the first fluid circulation portion 5 side are smaller than the cells 3 on the second fluid circulation portion 6 side, and the partition walls have a density of 0.5 to 5 g / cm3 and a thermal conductivity of 10 to 300 W / mK.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
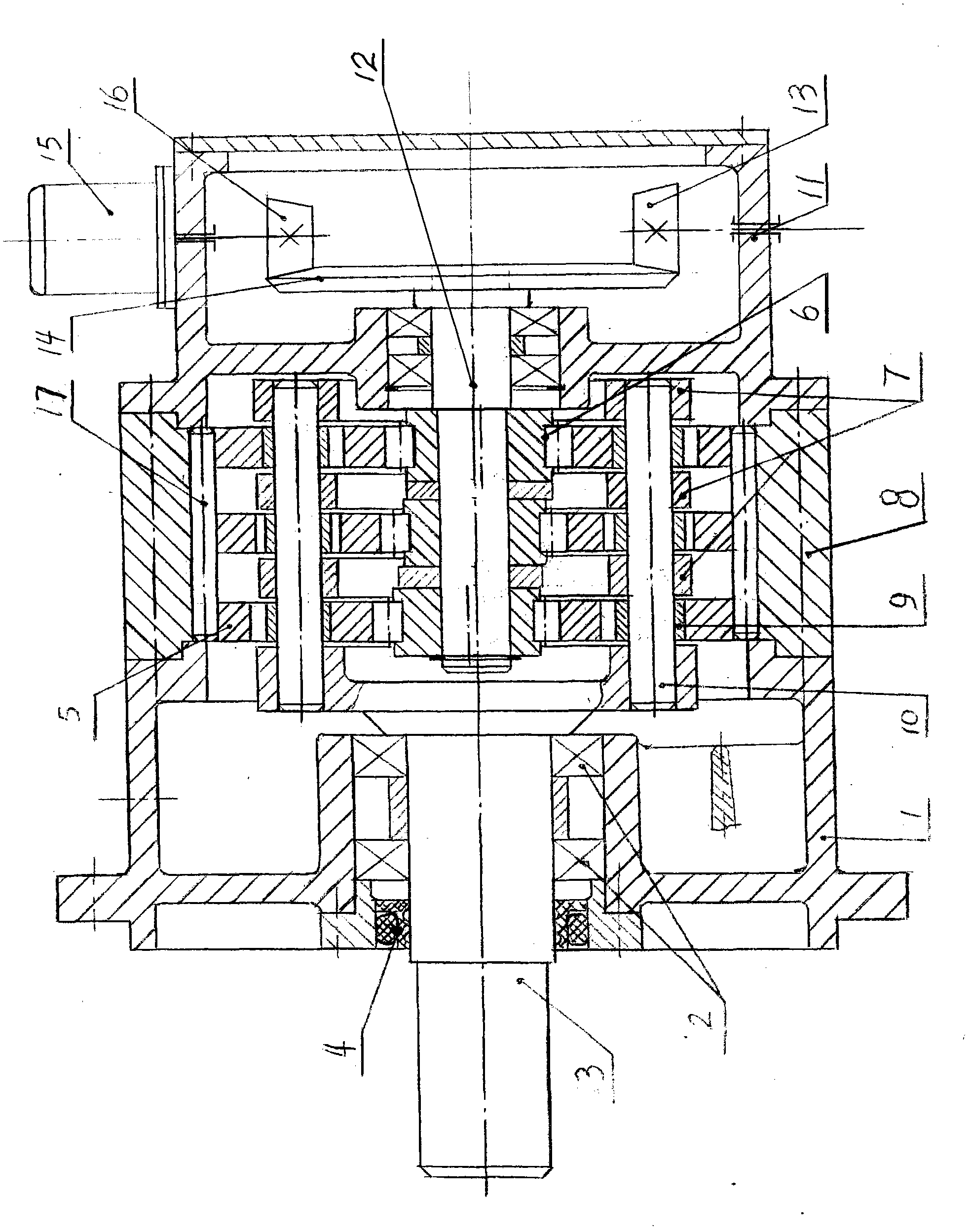
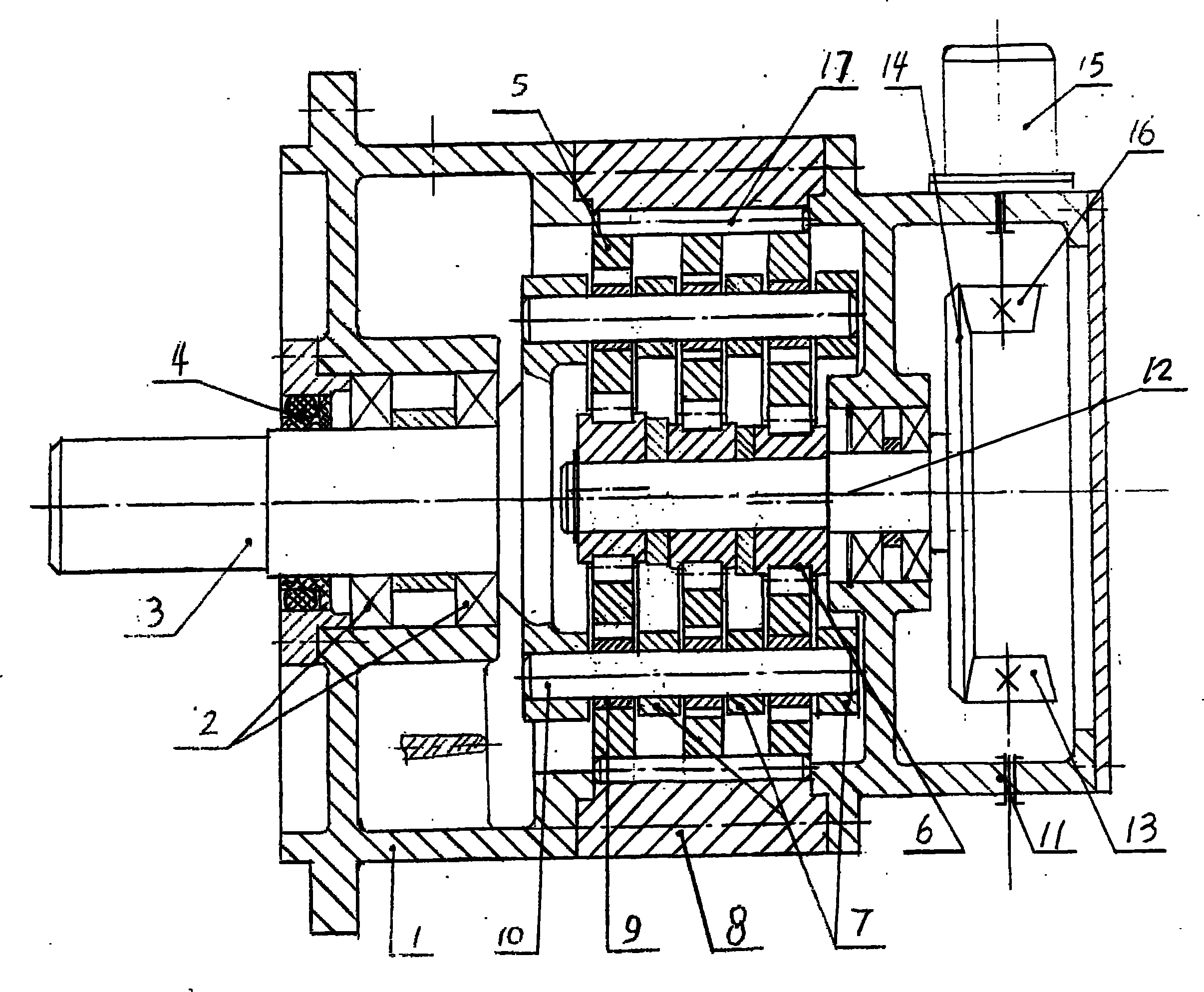
Bevel gear-double cycloid speed reduction device for rocket launching movable platform
InactiveCN101963208AImprove bending resistanceImprove bending performanceGearboxesToothed gearingsReduction driveRocket launch
The invention relates to the technical field of speed reducers, in particular to a bevel gear-double cycloid speed reduction device for a rocket launching movable platform. The device is a two-stage speed reduction device characterized by comprising a bevel gear pair and double-cycloid transmission, wherein (A) the cycloid transmission comprises a base, an output shaft, support bearings, a cycloid wheel, an eccentric bearing, an inner cycloid gear ring, a front base, an input shaft and a W output mechanism, the input shaft is supported in an inner hole of the front base through a bearing, the shaft extension end is connected with the eccentric bearing, and the input end is connected with a big bevel gear; the front base is integrated with the inner cycloid gear ring and the base in sequence; the output shaft is supported in the inner hole of the base through a bearing; and (B) two symmetrically installed small bevel gear shafts engaged with the big bevel gear are supported in wall holes of a front base box through bearings, and the small bevel gear shafts are connected with a motor; and another small bevel gear shaft is connected with a manual handle. The invention has the advantages of two-stage speed reduction, small axial size, light weight and high-degree lightweight; cycloid gear teeth are uninterrupted, so that the bearing capacity is greater than that of planet transmission with only four planet wheels; and the cost is low and is reduced to 40-55%.
Owner:吴声震
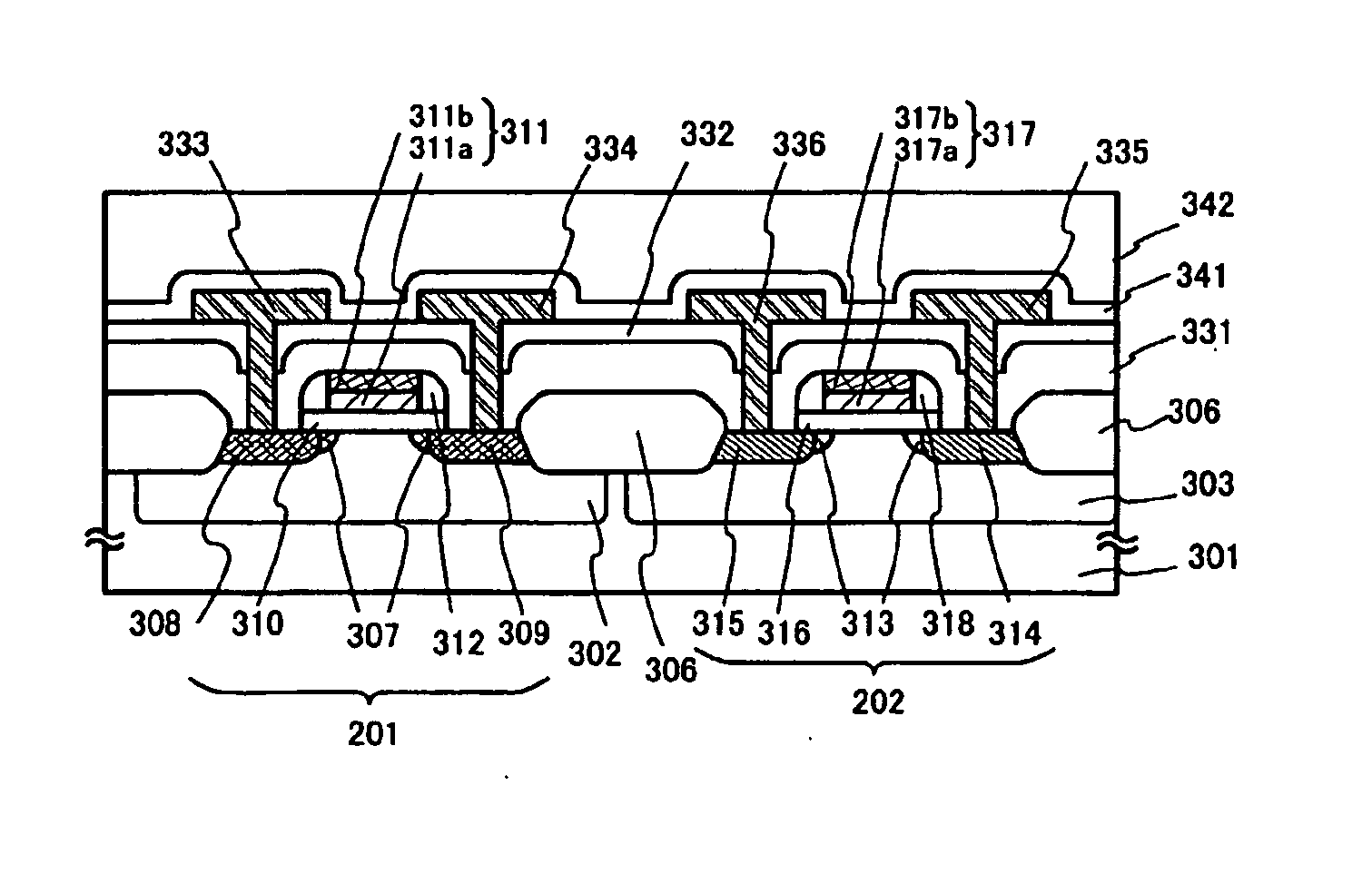
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
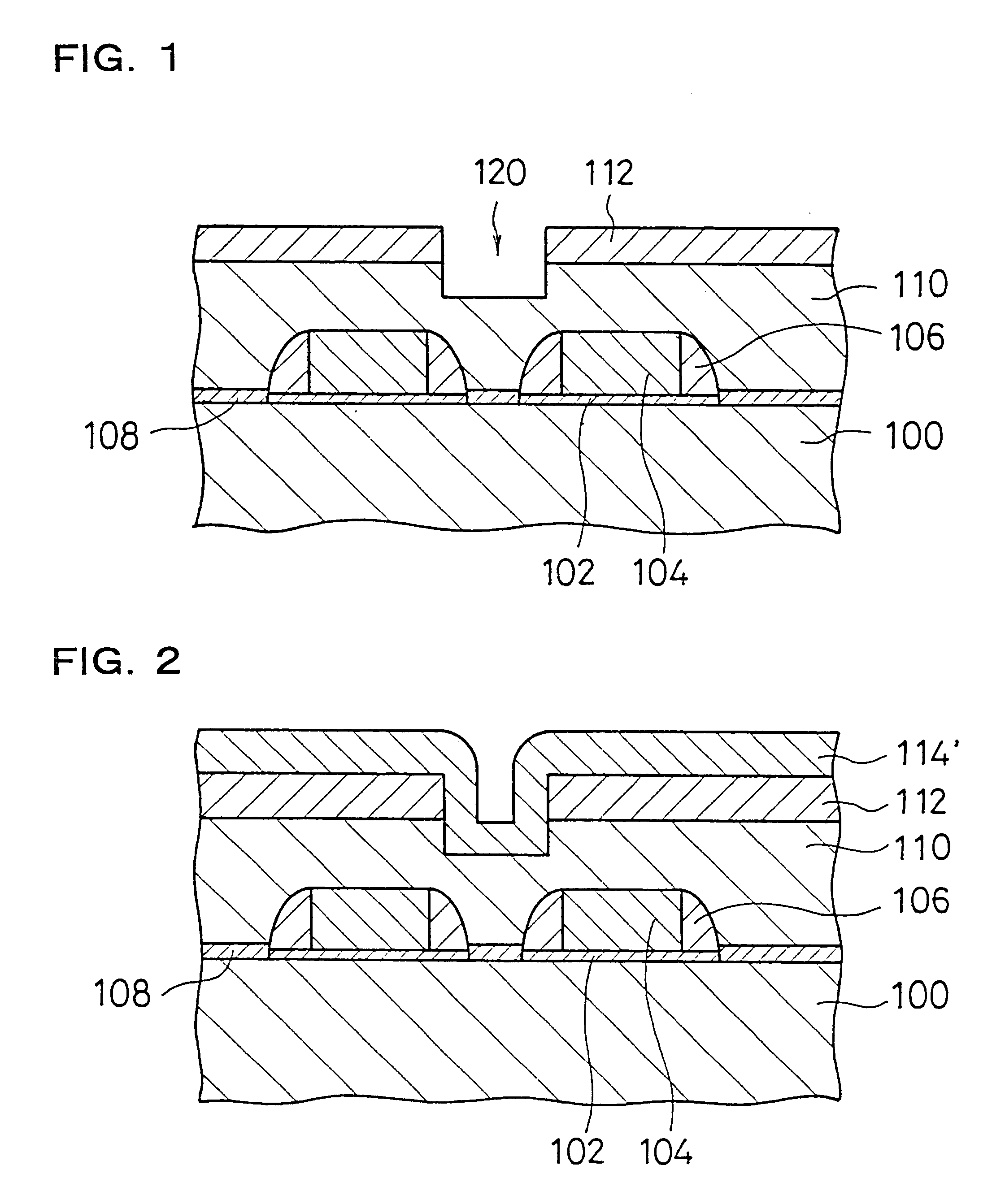
InactiveUS6368957B1Increase the diameterHigh film thicknessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor device
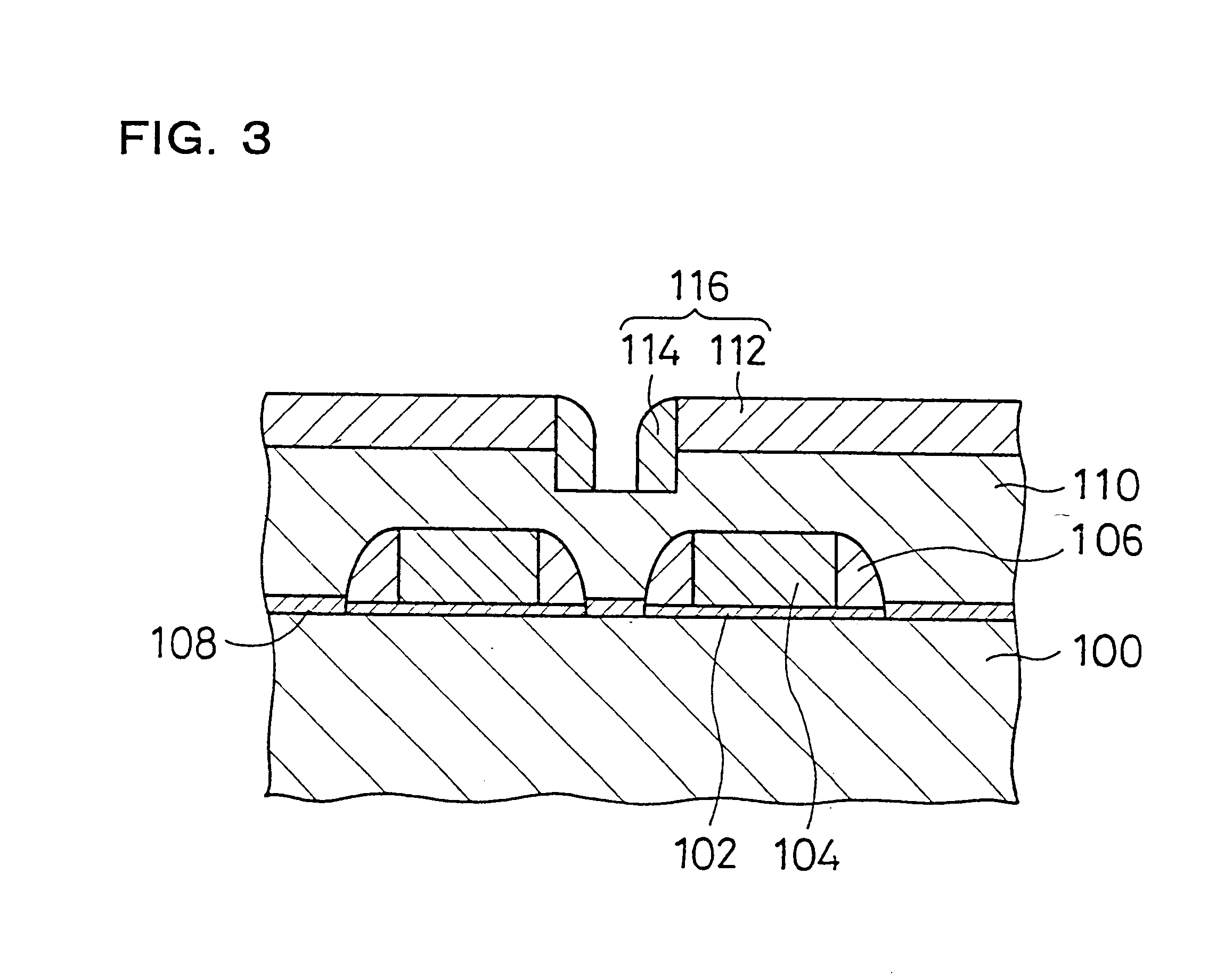
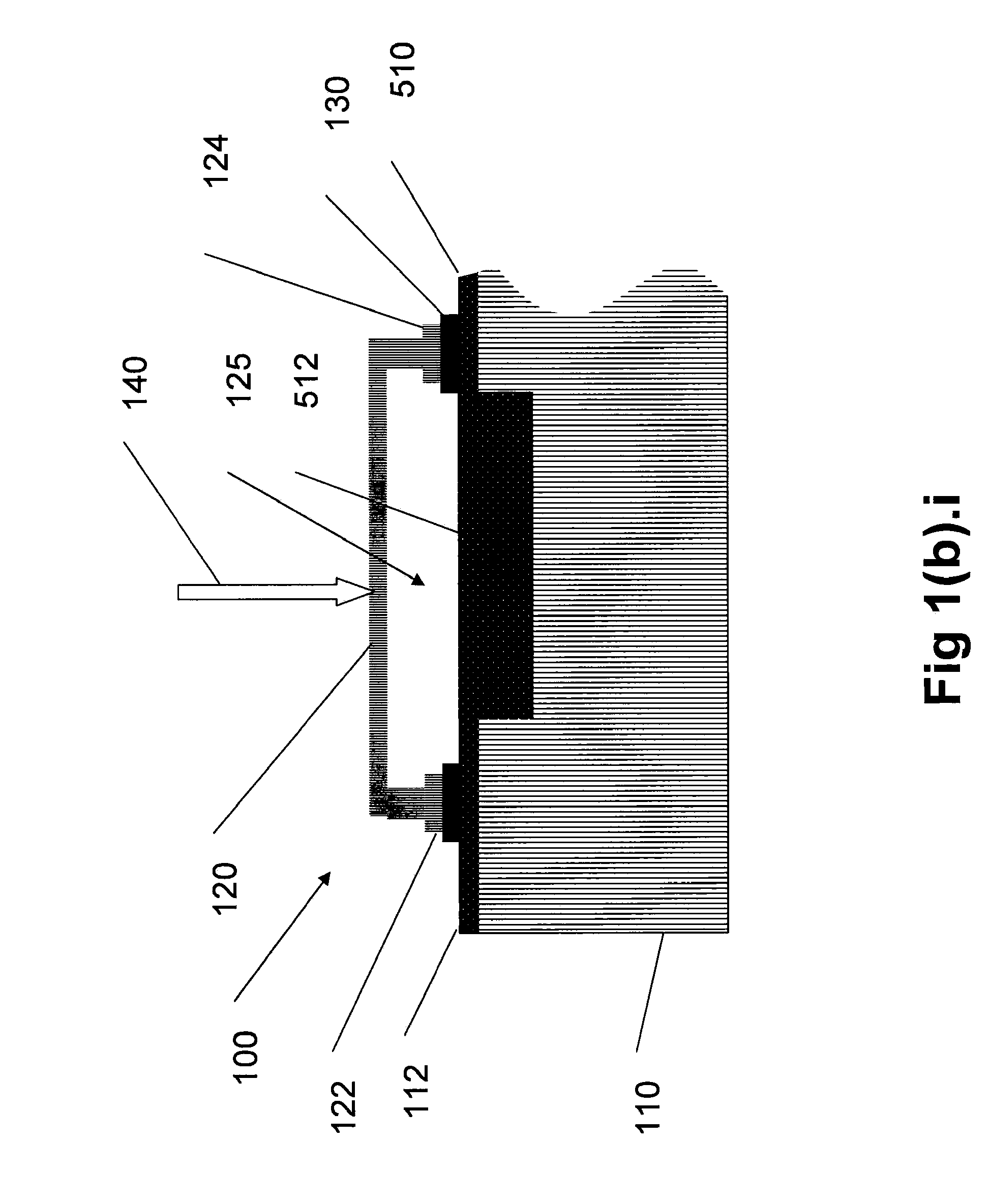
In the method for manufacturing a semiconductor device according to the present invention, after forming a BPSG film 110 on a silicon substrate 100, a preparatory hole 120 that reaches a specific depth and has a larger diameter than a contact hole 118 is formed at a position where the contact hole 118 (see FIG. 4) is to be formed at the BPSG film 110. Thus, polysilicon side walls 114 (see FIG. 4) formed at side portions of a polysilicon film 112 (see FIG. 4) are also formed at the side walls of the preparatory hole 120. As a result, the contact hole 118 (see FIG. 4) free of shape defects can be formed by using an etching mask 116 (see FIG. 4) constituted of the polysilicon film 112 and the polysilicon side walls 114. This structure prevents defects related to the shape of the hole and reduces electrical defects such as shorting.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device having an erasing gate
InactiveUS20090085090A1Highly miniaturizedGuaranteed high speed operationTransistorSolid-state devicesSalicideSurface layer
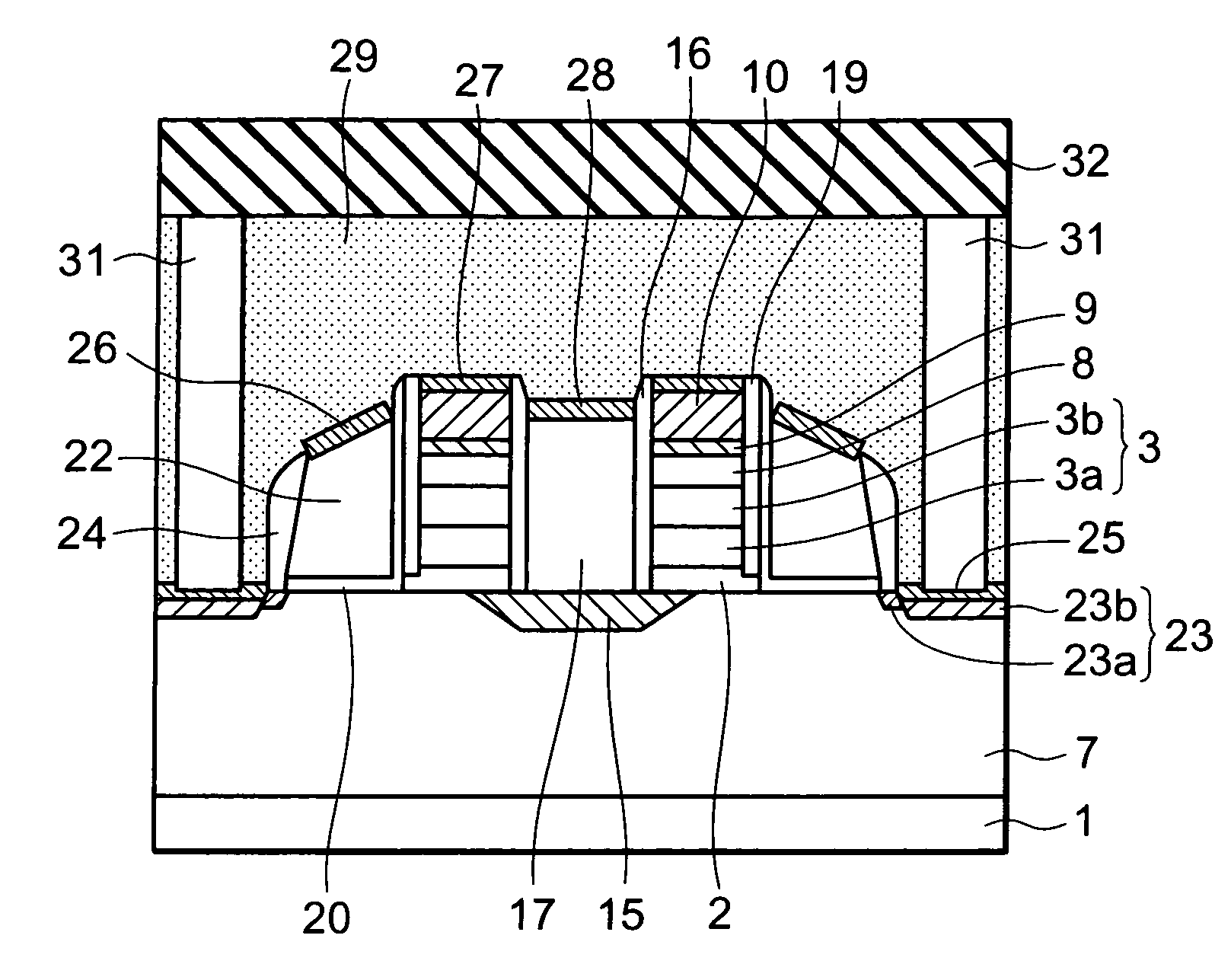
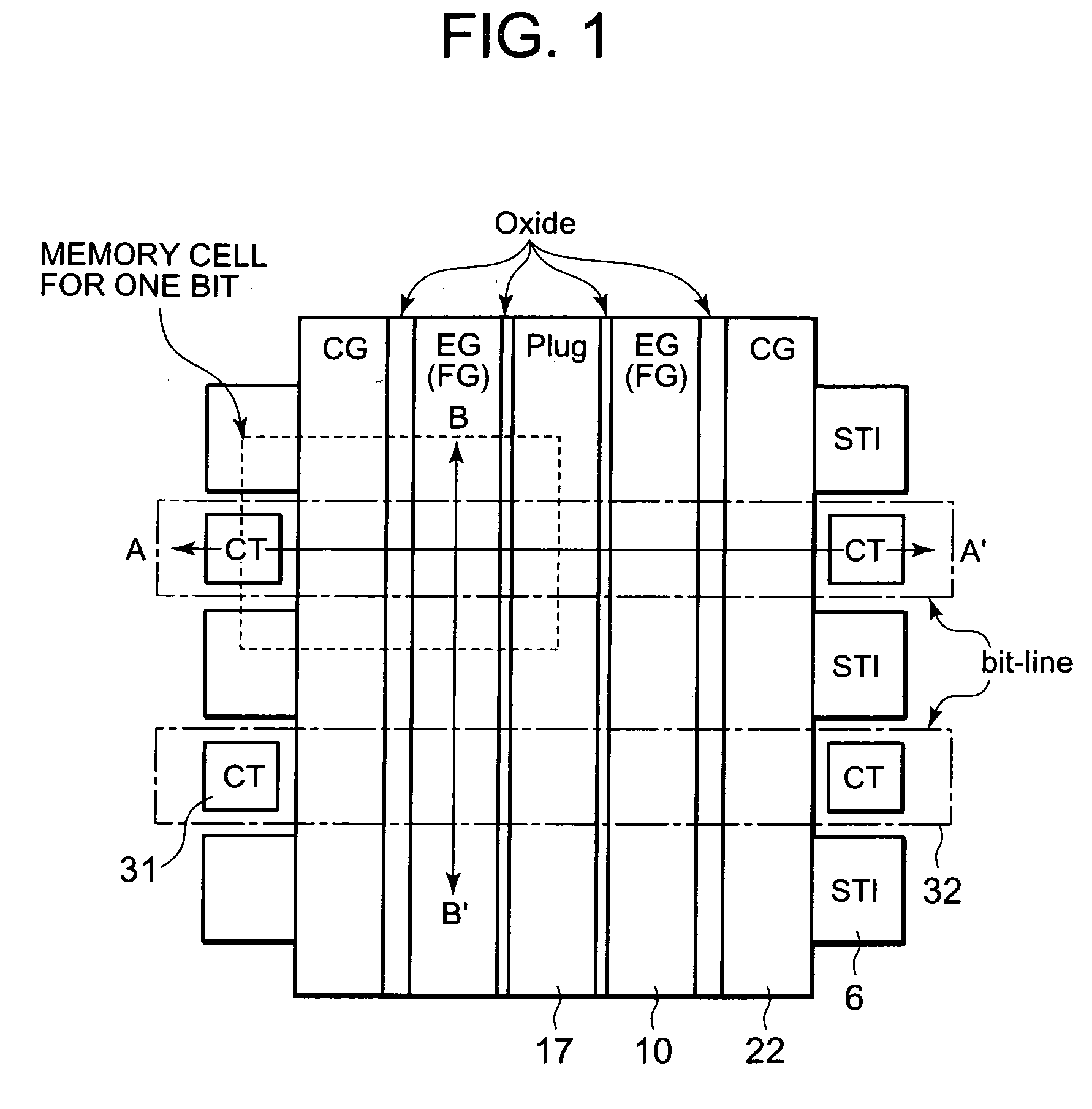
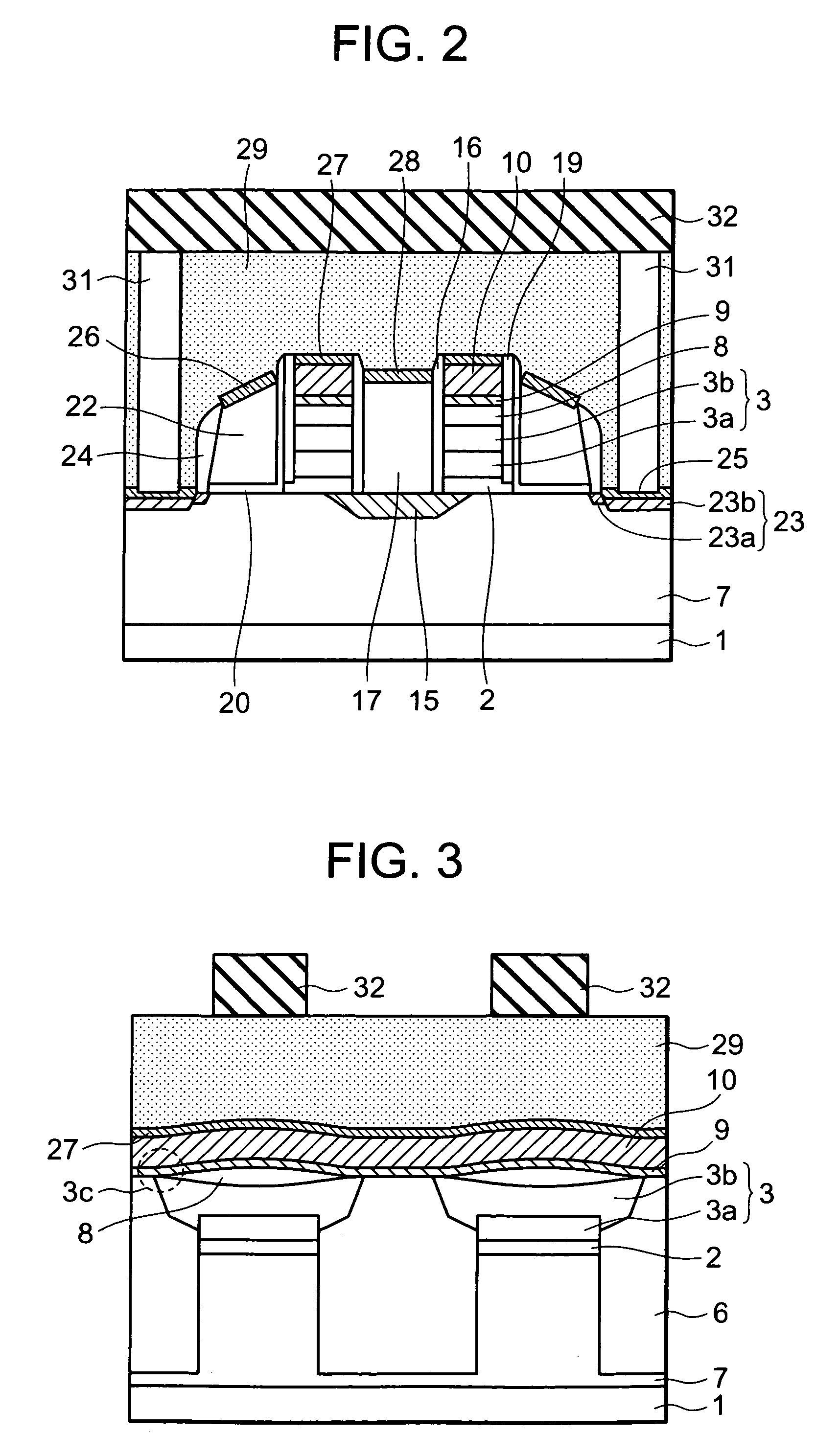
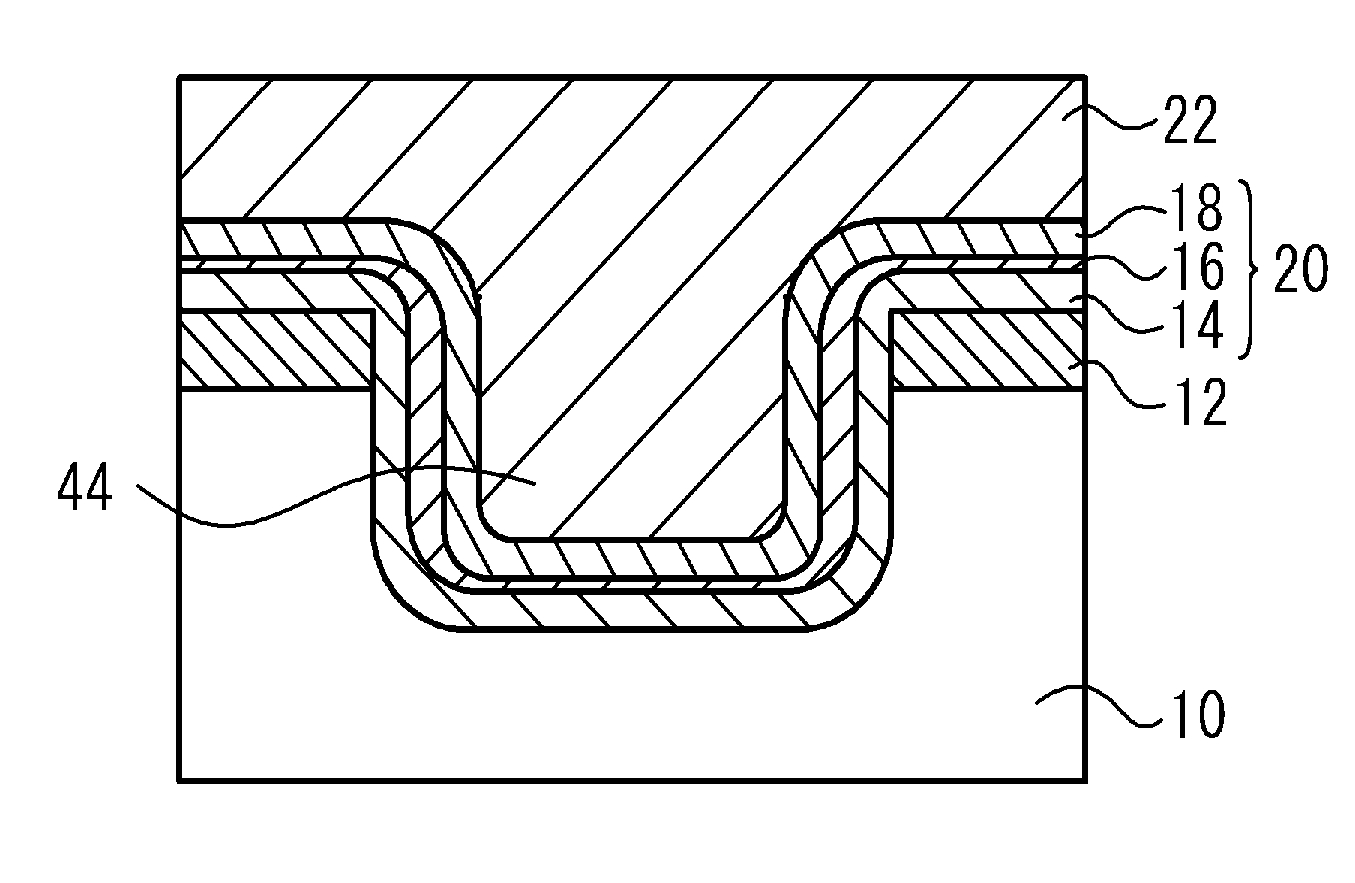
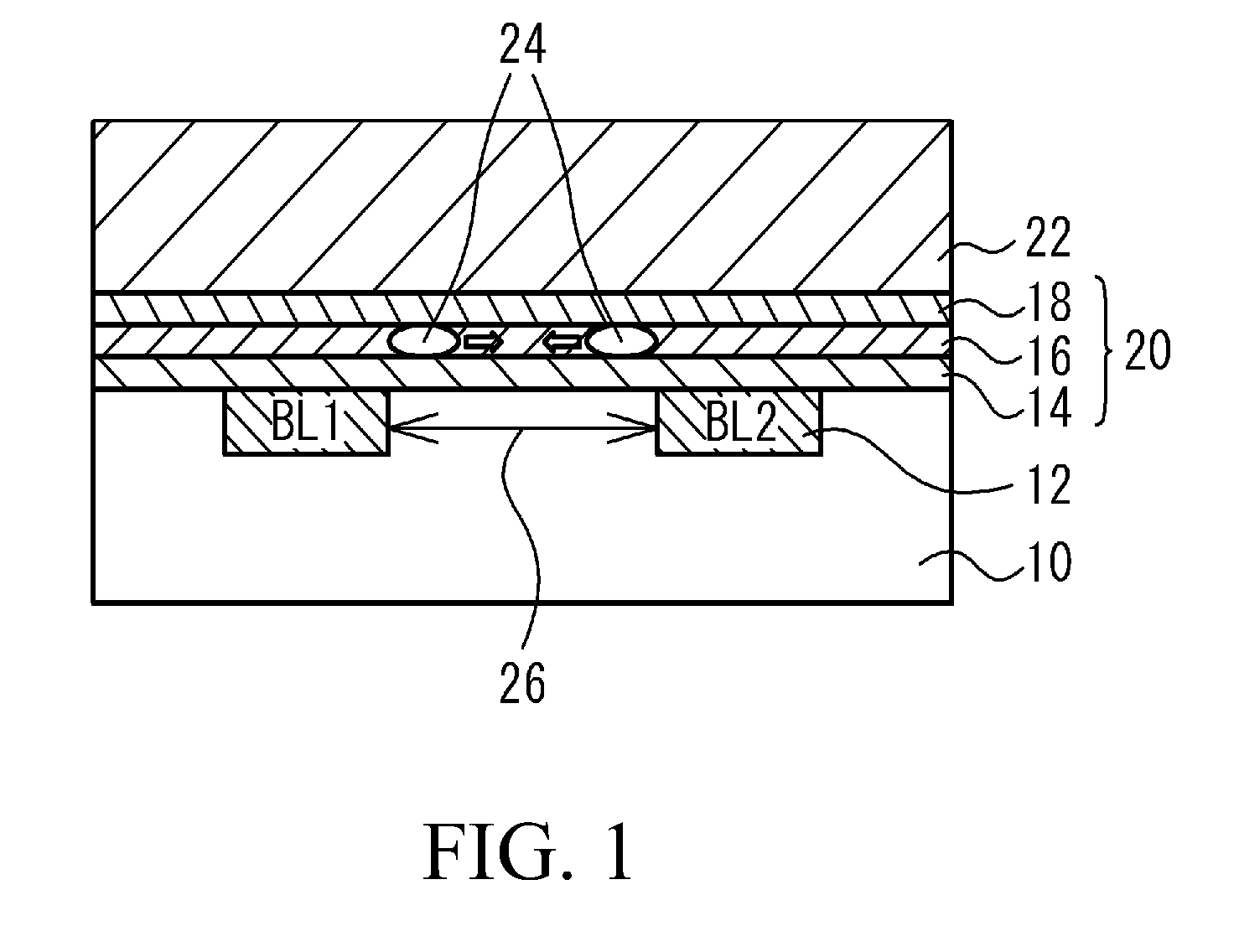
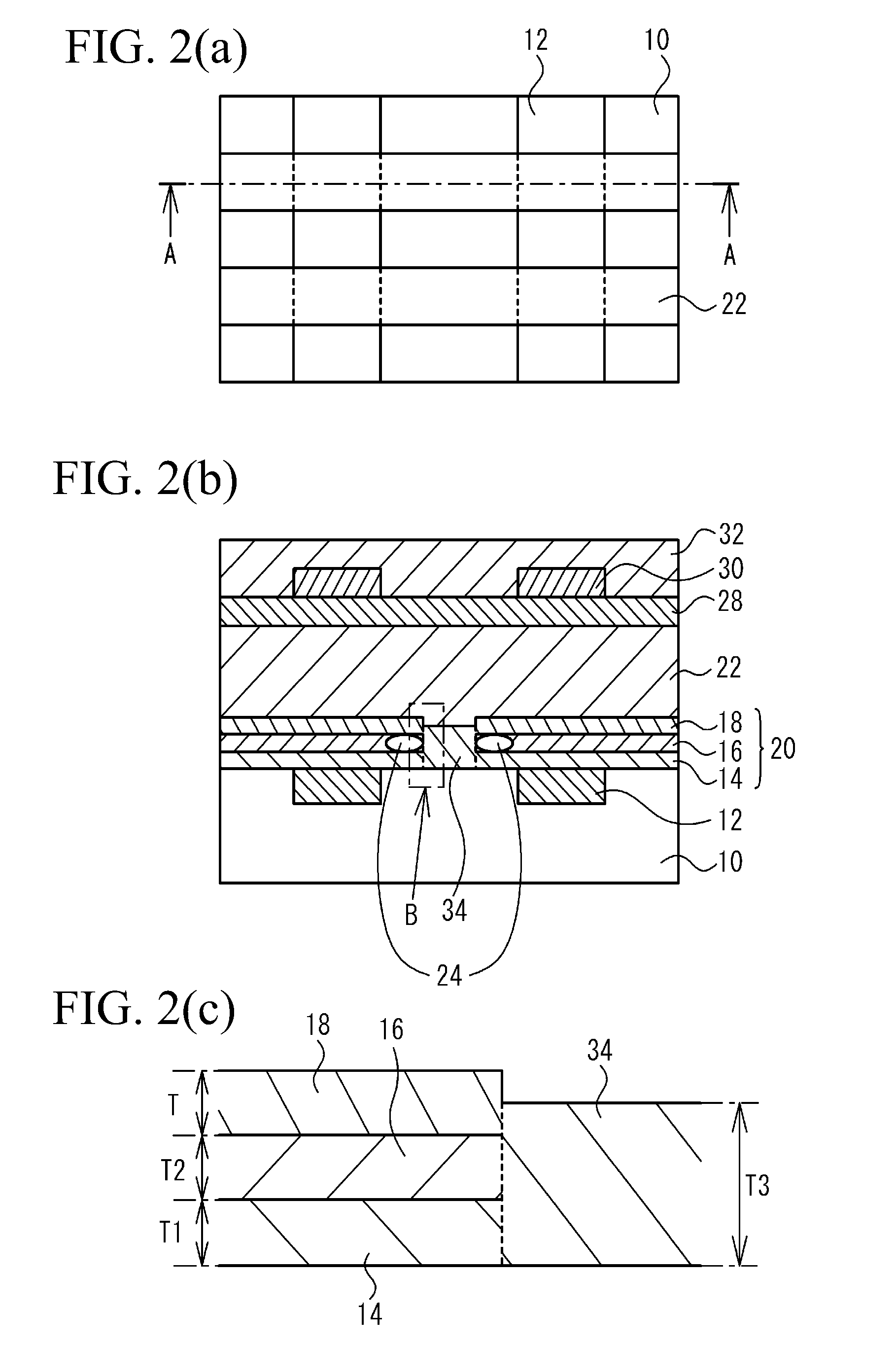
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor substrate; a floating gate formed above the semiconductor substrate; an erasing gate formed above the floating gate; a control gate formed above a channel region of a surface layer of the semiconductor substrate at a position corresponding to one lateral side of the floating gate and the erasing gate; a first silicide film formed on an upper surface of the erasing gate; and a second silicide film formed on an upper surface of the control gate, in which a height of the upper surface of the control gate is flush with / or lower than a height of the upper surface of the erasing gate. With such a device structure, the distance between the upper surface of the erasing gate and the upper surface of the control gate is large, and hence the probability of occurrence of the silicide short between the first silicide film formed on the upper surface of the erasing gate and the second silicide film formed on the upper surface of the control gate may be extremely lowered. Thus, further high speed, operation, miniaturization, and the lower voltage operation of the non-volatile semiconductor memory device having an erasing gate may be achieved.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Thermal detection and imaging of electromagnetic radiation
InactiveUS20110204231A1High sensitivityImprove performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaicsEnergy absorptionParticle physics
The current invention provides a method for improving the sensitivity of bolometric detection by providing improved electromagnetic power / energy absorption. In addition to its role in significantly improving the performance of conventional conducting-film bolometric detection elements, the method suggests application of plasmon resonance absorption for efficient thermal detection and imaging of far-field radiation using the Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) and the herein introduced Cavity Plasmone Resonance (CPR) phenomena. The latter offers detection characteristics, including good frequency sensitivity, intrinsic spatial (angular) selectivity without focusing lenses, wide tunability over both infrared and visible light domains, high responsivity and miniaturization capabilities. As compared to SPR, the CPR-type devices offer an increased flexibility over wide ranges of wavelengths, bandwidths, and device dimensions. Both CPR and SPR occur in metallic films, which are characterized by high thermal diffusivity essential for fast bolometric response.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same
An RTA method has a limitation on miniaturization. The RTA method needs a heating time of several seconds, and has a risk that impurities are diffused into a deep portion, since a semiconductor substrate is heated at a high temperature. Thus, the RTA method has a difficulty in responding miniaturization which is expected in the future. According to the present invention, a fundamental wave is used without putting laser light into a non-linear optical device, and laser annealing is conducted by irradiating an impurity diffusion layer with pulsed laser light having high intensity and a high repetition rate, so as to electrically activate the impurities. By the present invention, a thin layer on the surface of a silicon substrate can be partially melted to conduct activation. Further, the width of the region activated by laser-scanning once can be increased, and thus the productivity can be enhanced dramatically.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Cavity Plasmon Resonance Biosensing Device, Method And System
InactiveUS20110001975A1Promise detection capabilityPromising detection capabilityScattering properties measurementsPyrometry using electric radation detectorsLayered structurePneumatic pressure
The current invention provides a devices methods and systems for efficient biosensing using the Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) and Cavity Plasmon Resonance (CPR) phenomena. The miniature biosensor comprises a stratified structure having a channel for analyte form between a substrate and thin metallic absorber layer in which plasmon are resonantly excited. Presence of analyte in the channel, changes the resonance conditions, thus changing the energy absorbed by the biosensor. Bolometric signal from the absorber; layer or detection of the radiation not absorbed by the biosensor is used to detect, measure the concentration of, or monitor the analyte.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110076800A1High in functionality and integrationReliable manufacturingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
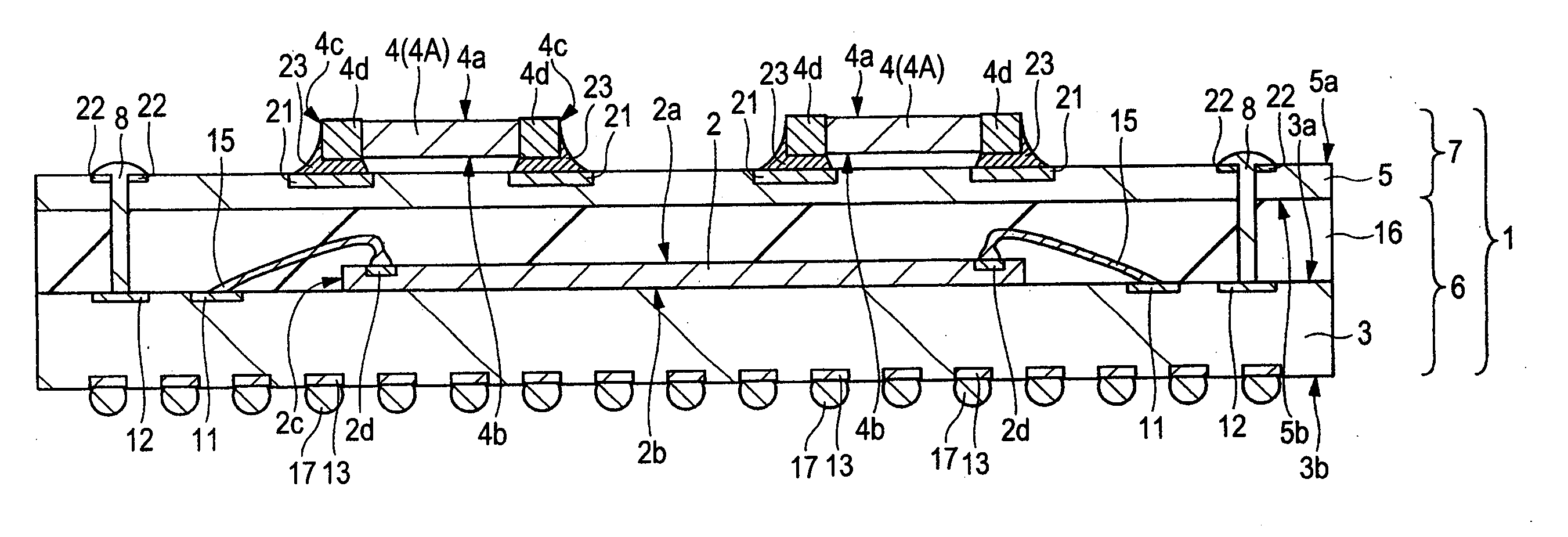
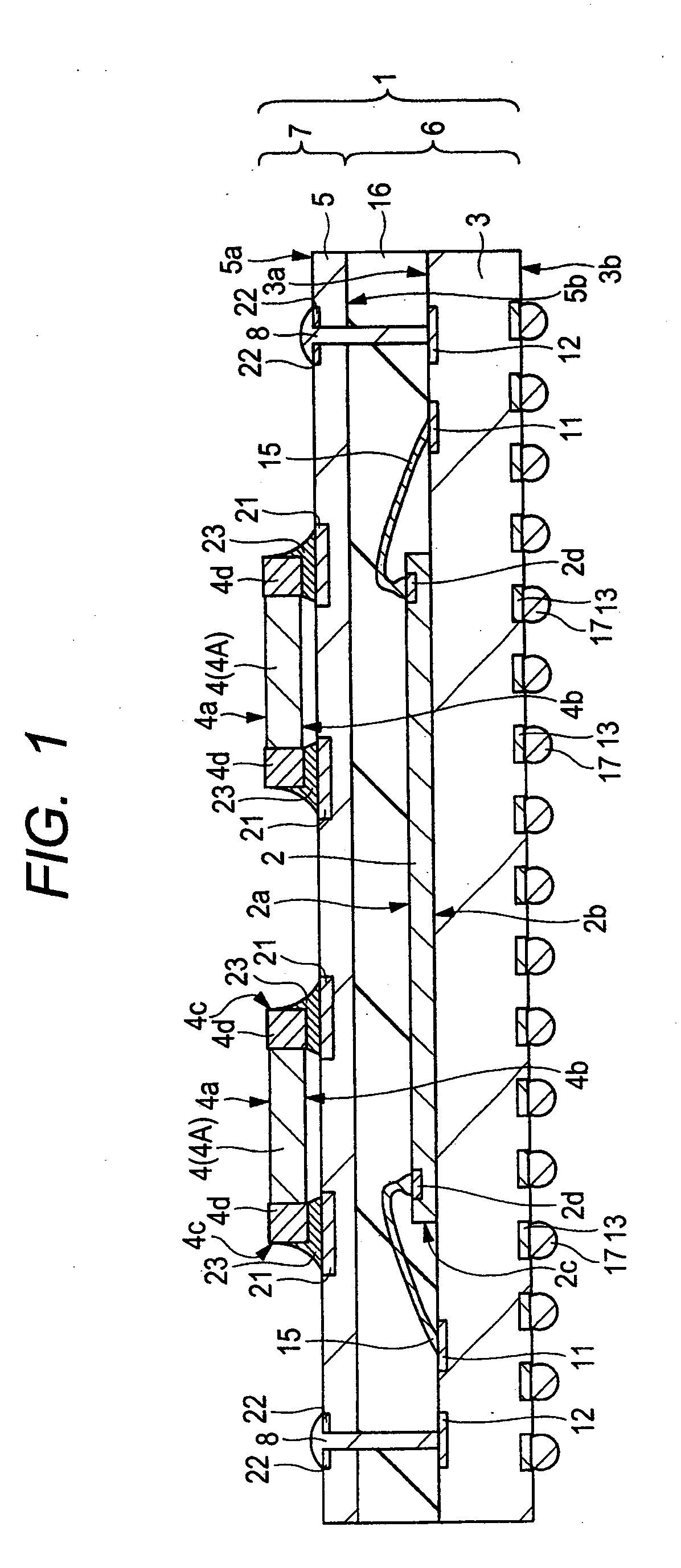
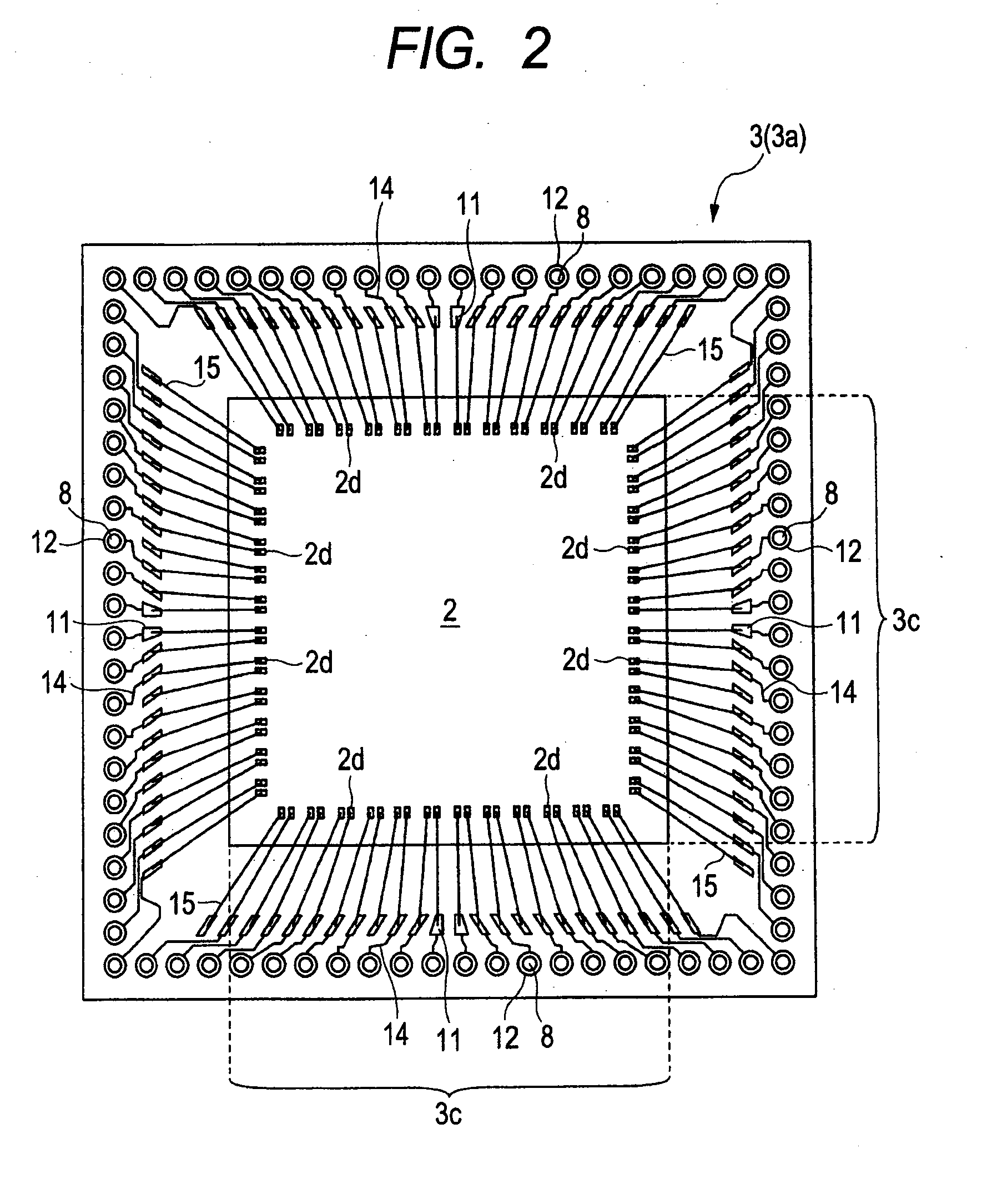
The reliability of a semiconductor device is improved. A sealing resin (sealed body) is formed between a sub-substrate (first base member) and a base substrate (second base member) that are provided individually and distinctly to be integrated therewith, and then, the sub-substrate is electrically coupled to the second base member. As a means for electrically coupling the sub-substrate to the base substrate, lands (first lands) formed on the sub-substrate and lands (second lands) formed on the base substrate are disposed such that the respective positions thereof are aligned. After through holes are formed from the lands of the sub-substrate toward the lands of the base substrate, a solder member (conductive member) is formed in each of the through holes.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Conductive Contact Holder
ActiveUS20090311890A1Simple assembly structureEasy to integrateElectrical measurement instrument detailsPrinted circuitsConductive materialsFirst insertion
A conductive contact holder includes an insulating holder member and a conductive block member. The insulating holder member is made of an insulating material and includes a first insertion hole through which a signal conductive contact inputting and outputting a signal to and from a circuit is directly inserted over substantially its full length. The conductive block member His made of a conductive material and includes a second insertion hole through which the ground conductive contact is inserted in partial contact therewith.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Method for forming interconnection structure
InactiveUS6040240ALower resistanceHighly integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCopper interconnect
Disclosed herein is a method for forming a copper interconnect in which a substrate having the copper interconnect is exposed to atmosphere after the substrate is cooled to a temperature below 160 DEG C. under a non-oxidizable atmosphere. The exposure of the substrate to a relatively high temperature conventionally makes an electric resistance between interconnects on the substrate higher to prevent high integration. In accordance with the present invention, the above electric resistance can be reduced to smoothly realize the high integration because of the exposure of the substrate to a relatively low temperature.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
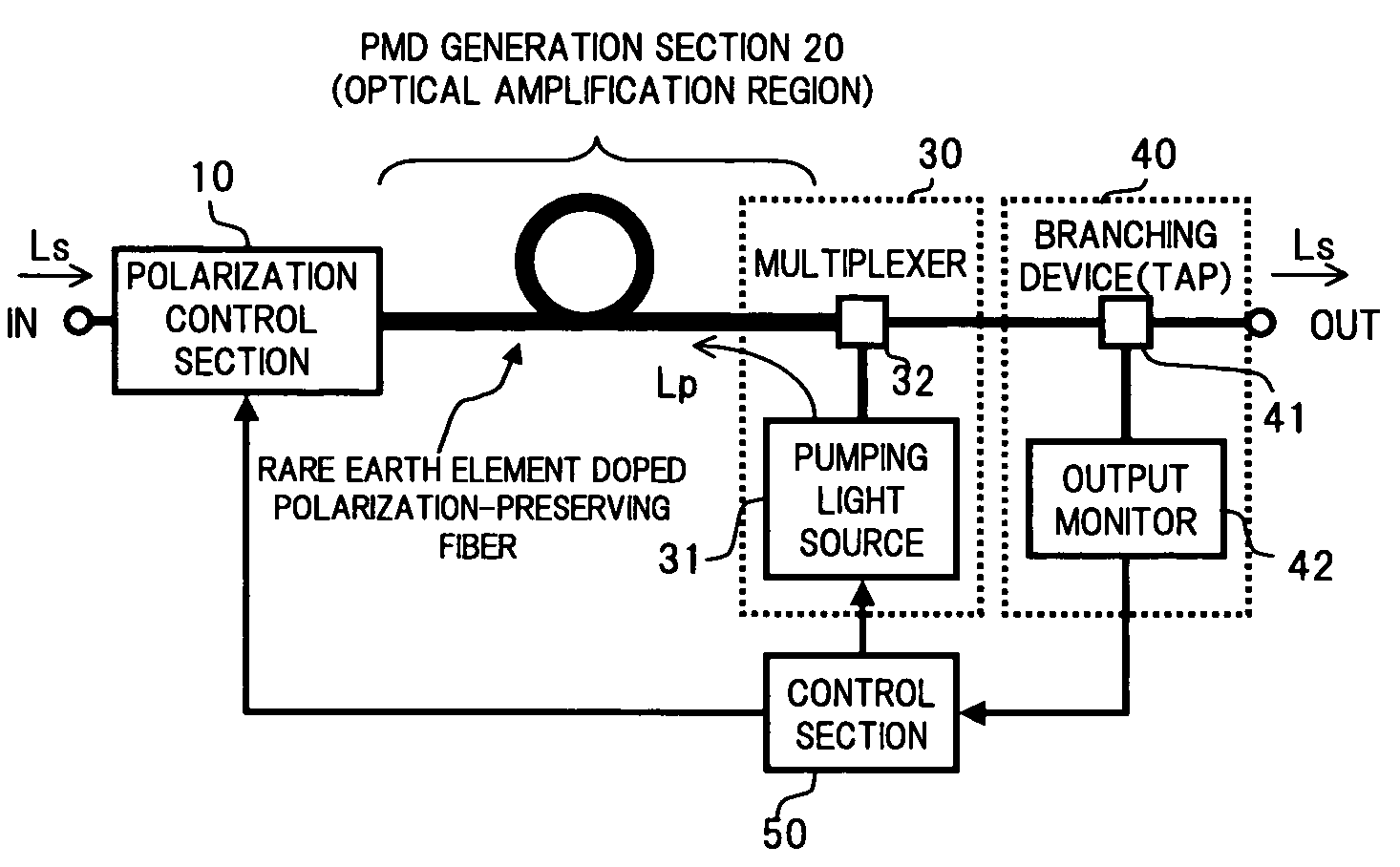
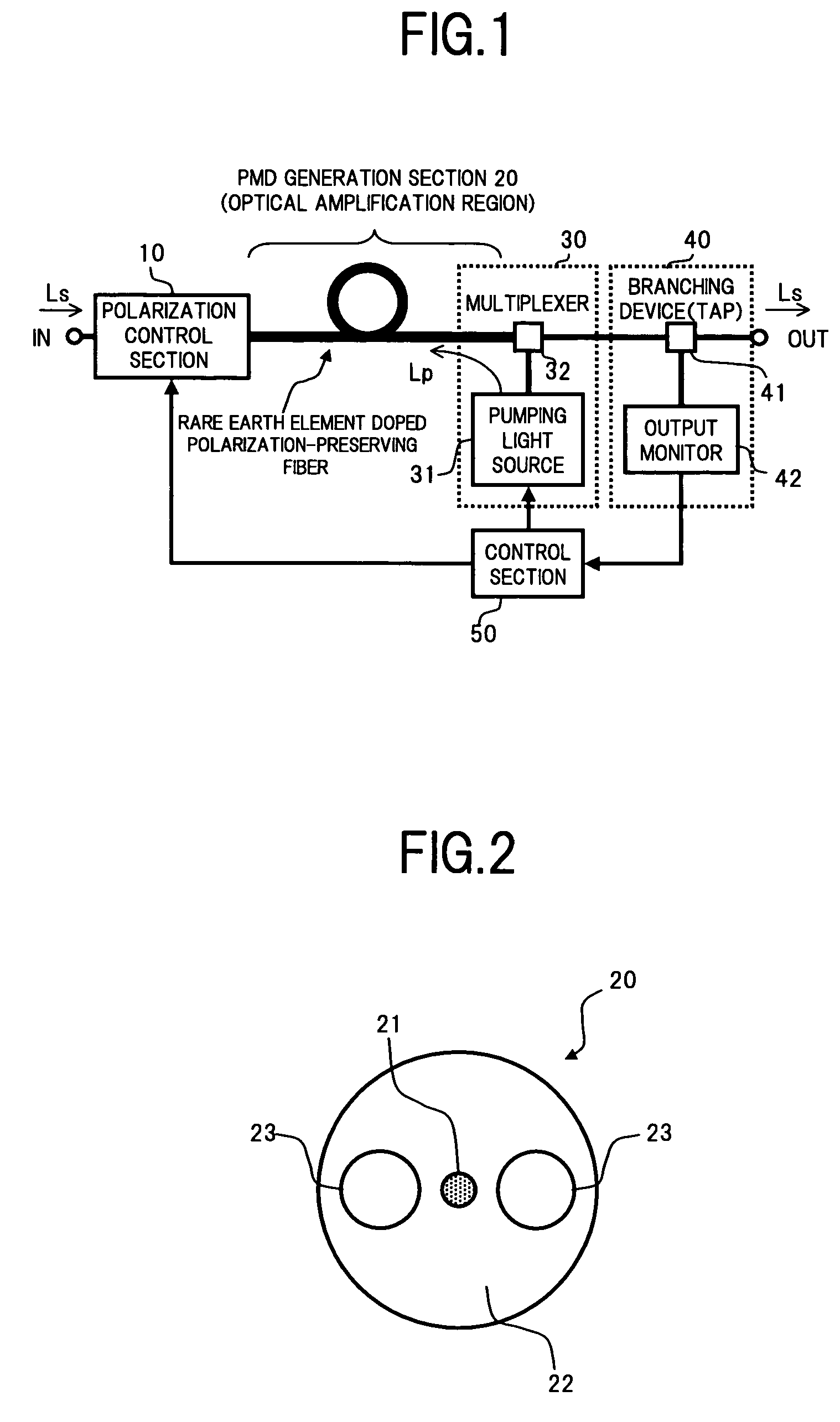
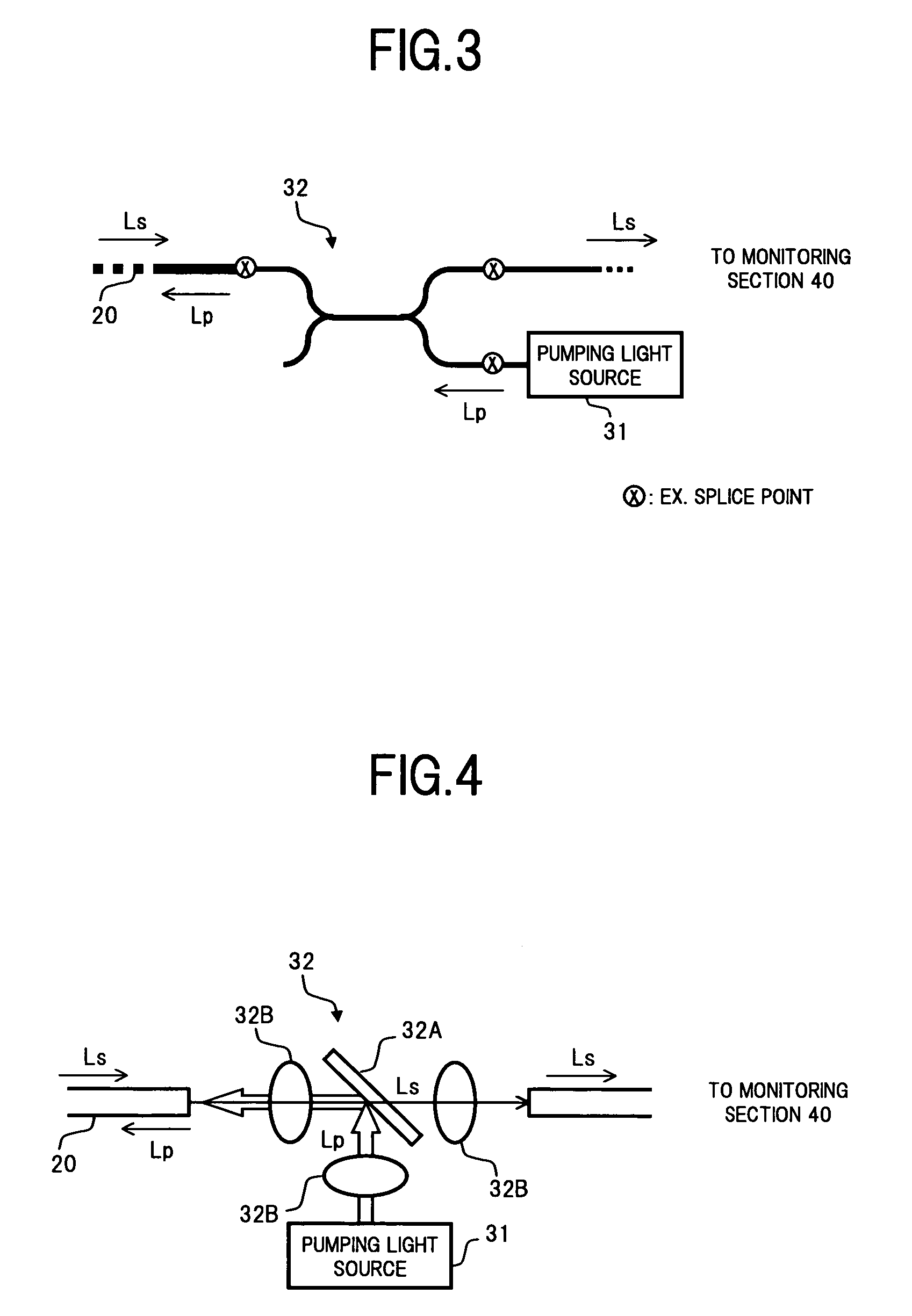
Optical amplifier having polarization mode dispersion compensation function
InactiveUS7268936B2Function increaseLow costLaser detailsPolarisation multiplex systemsRare-earth elementFiber
An object of the present invention is to provide at low cost, a highly functional and small size optical amplifier, which realizes a polarization mode dispersion (PMD) compensation function and an optical amplifying function, with a simple construction. To this end, the optical amplifier of the present invention comprises: a polarization control section that controls the polarization state of input signal light; a PMD generation section that receives the signal light from the polarization control section at a polarization-preserving fiber thereof doped with a rare earth element, and gives a differential group delay between orthogonal polarization mode components of the signal light to perform PMD compensation and at the same time amplifies the signal light; a pumping light supply section that supplies pumping light to the polarization-preserving fiber; a monitoring section that monitors the PMD generation state of the signal light from the PMD generation section, and the like; and a control section that controls the polarization control section and the pumping light supply section based on the monitor results of the monitoring section.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Battery pack
ActiveCN102386449AHighly miniaturizedImprove bond reliabilitySmall-sized cells cases/jacketsPrinted circuit aspectsSolderingBattery cell
The invention provides a battery pack having improved product reliability by minimizing a height of a solder portion when a multi-cell is connected to a printed circuit module (PCM) in series or parallel, and including a connecting circuit board. The battery pack comprises one or more battery cells, a connecting circuit board connected to the one or more battery cells, a conductive lead electrically coupled to the circuit board, a printed circuit module having an opening where the conductive lead is inserted, and a solder portion formed through soldering connection, wherein the conductive lead is inserted into the opening, and has an insertion portion for inserting into the opening, a bend portion bending from the insertion portion and an recess from which the insertion portion is separated.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Composite antenna and portable telephone
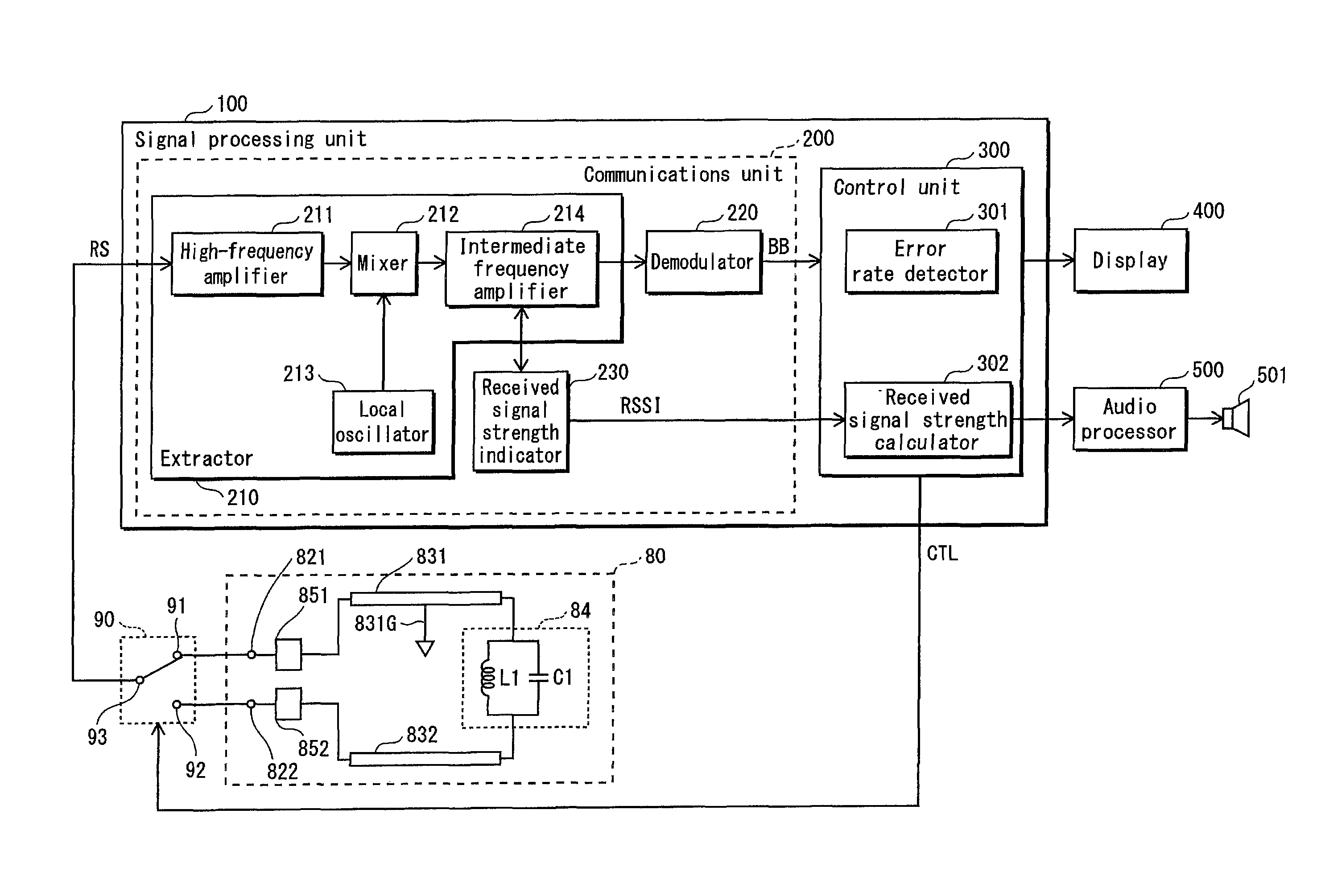
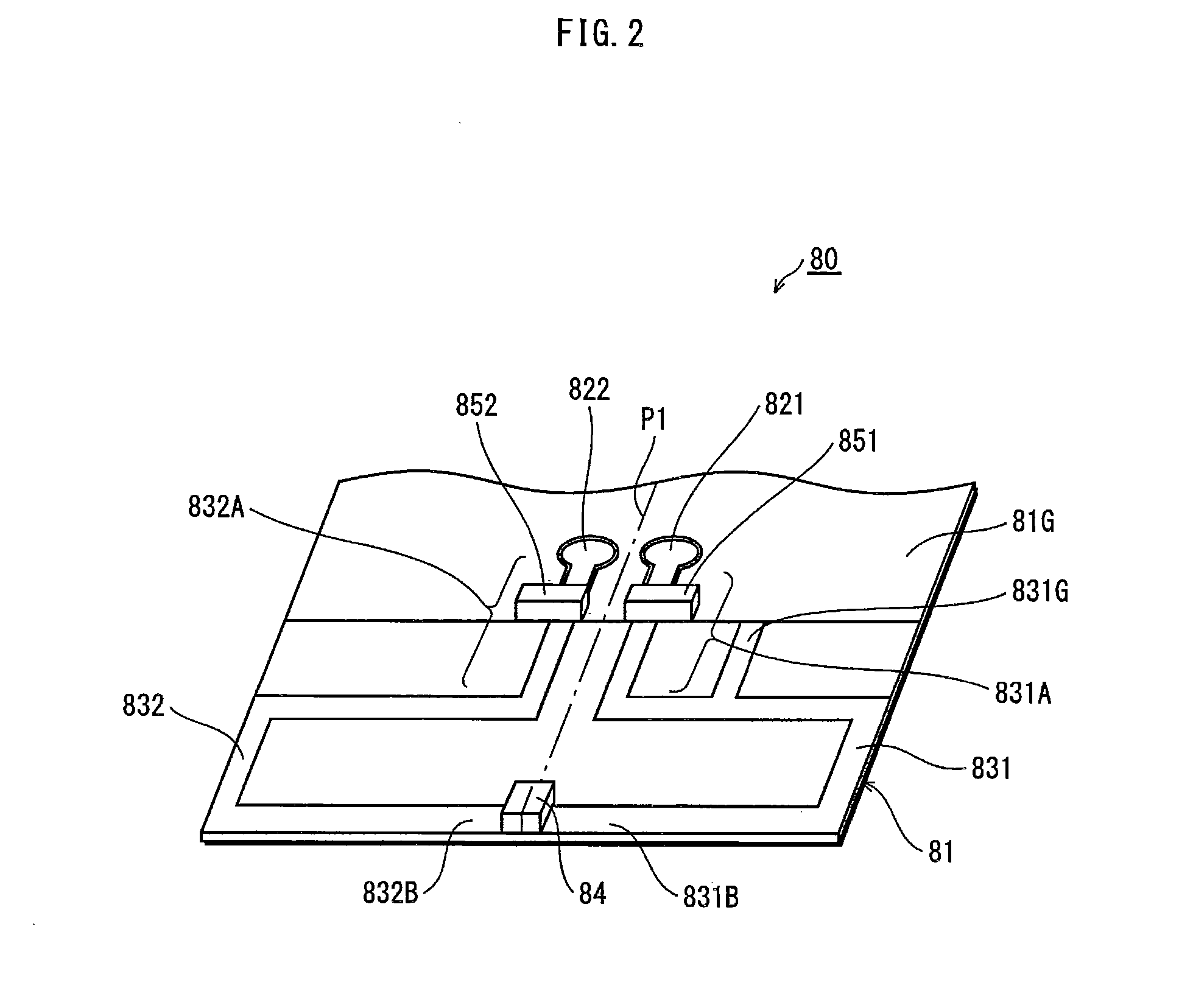
ActiveUS8600462B2MiniaturizationHighly miniaturizedSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringAntenna element
A complex antenna has a first antenna element and a second antenna element each connected at one end to a different feed point and connected to each other at the other end through a parallel resonant circuit. Each antenna element has the same resonant frequency as the parallel resonant circuit. A mobile phone has an antenna switch with a first port connected to the first antenna element, a second port connected to the second antenna element, and a third port that can be connected to one of the first port and the second port and switched therebetween. A signal processing unit causes the antenna switch to connect the third port to the first port or to the second port and detects a signal captured by one of the antenna elements from the output of the third port.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
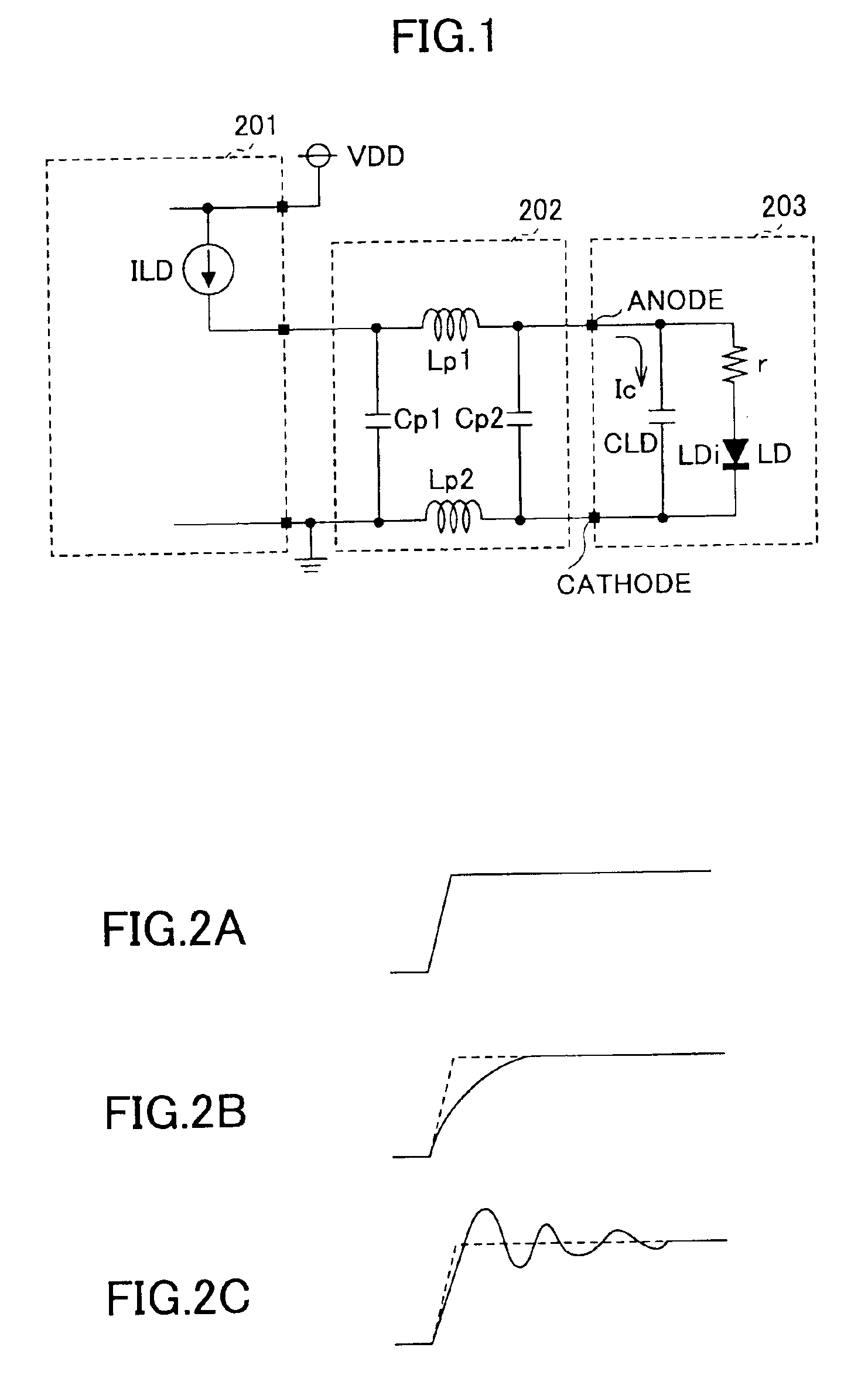
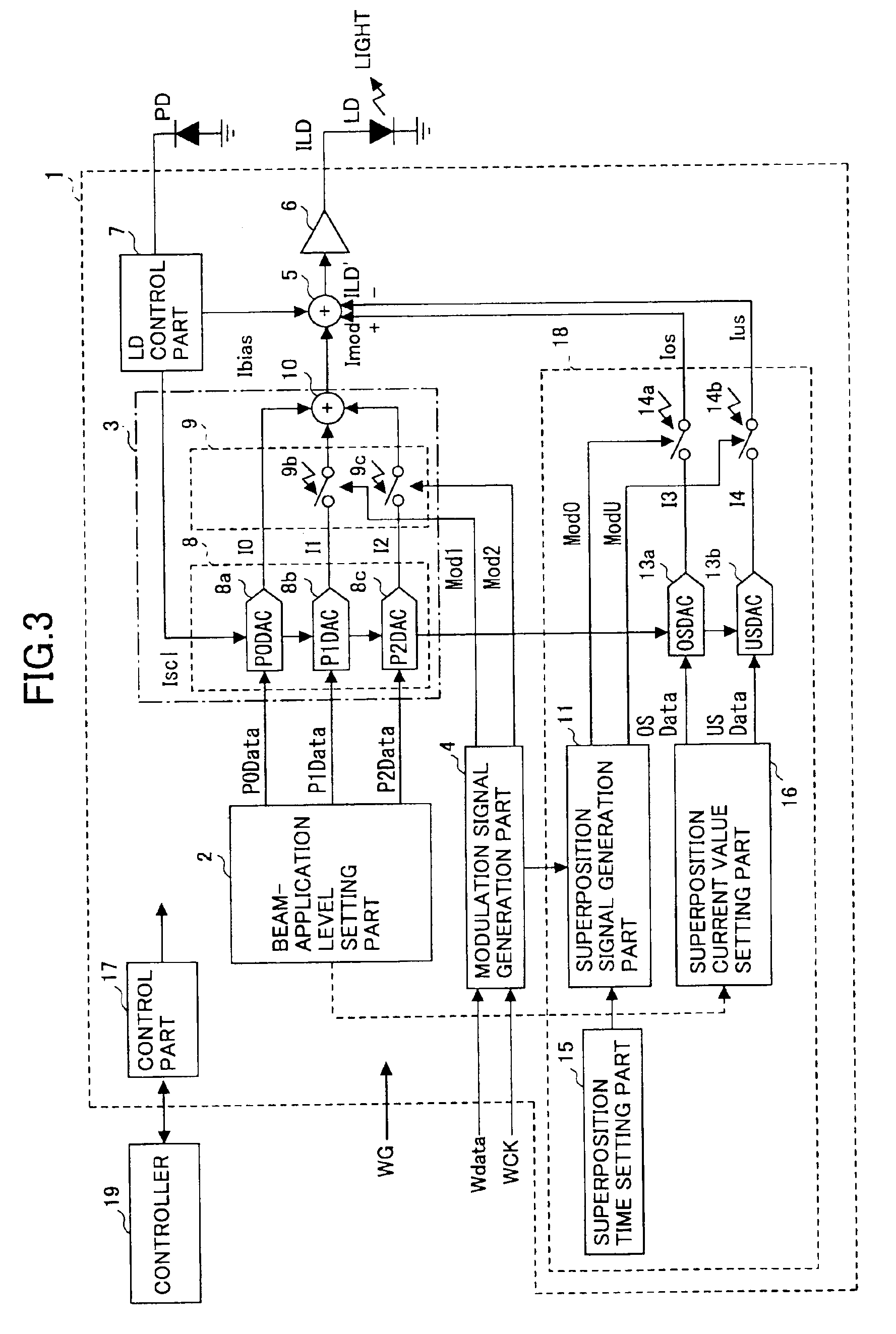
Light source drive, optical information recording apparatus, and optical information recording method
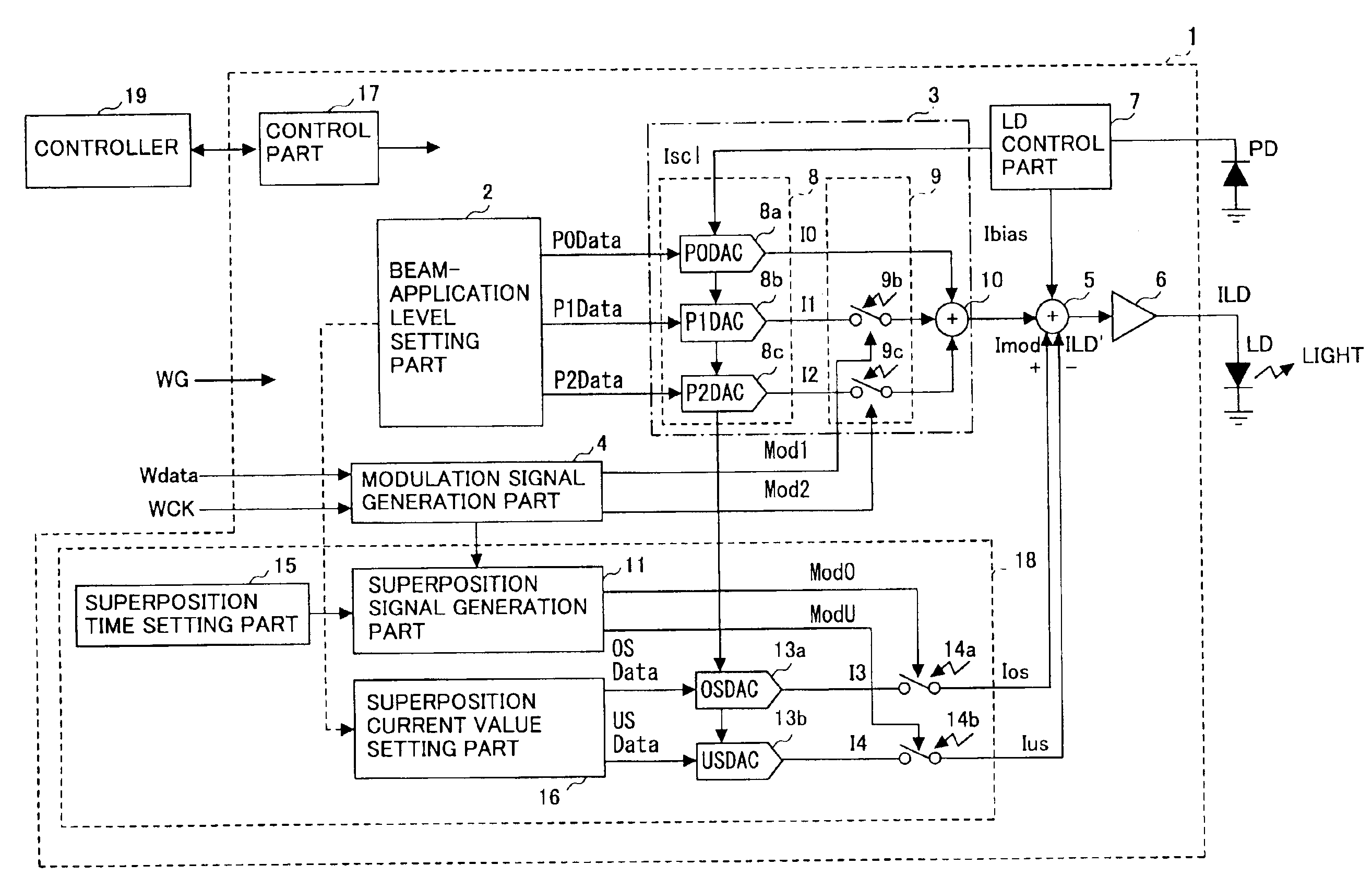
ActiveUS6954415B2High resolutionFine control of record mark formationTelevision system detailsLaser detailsDriving currentCapacitance
A light source drive which modulates a light source so as to cause the same to emit a light, includes: a superposition current generation part which generates a superposition current approximately corresponding to a charging / discharging current needed for a capacitance occurring in parallel to the light source for a predetermined time period near at least one of a rising-up part and a decaying-down part of a waveform of a drive current for the light source; and an addition / subtraction part which adds to or subtracts from the drive current the superposition current generated by the superposition current generation part.
Owner:RICOH KK
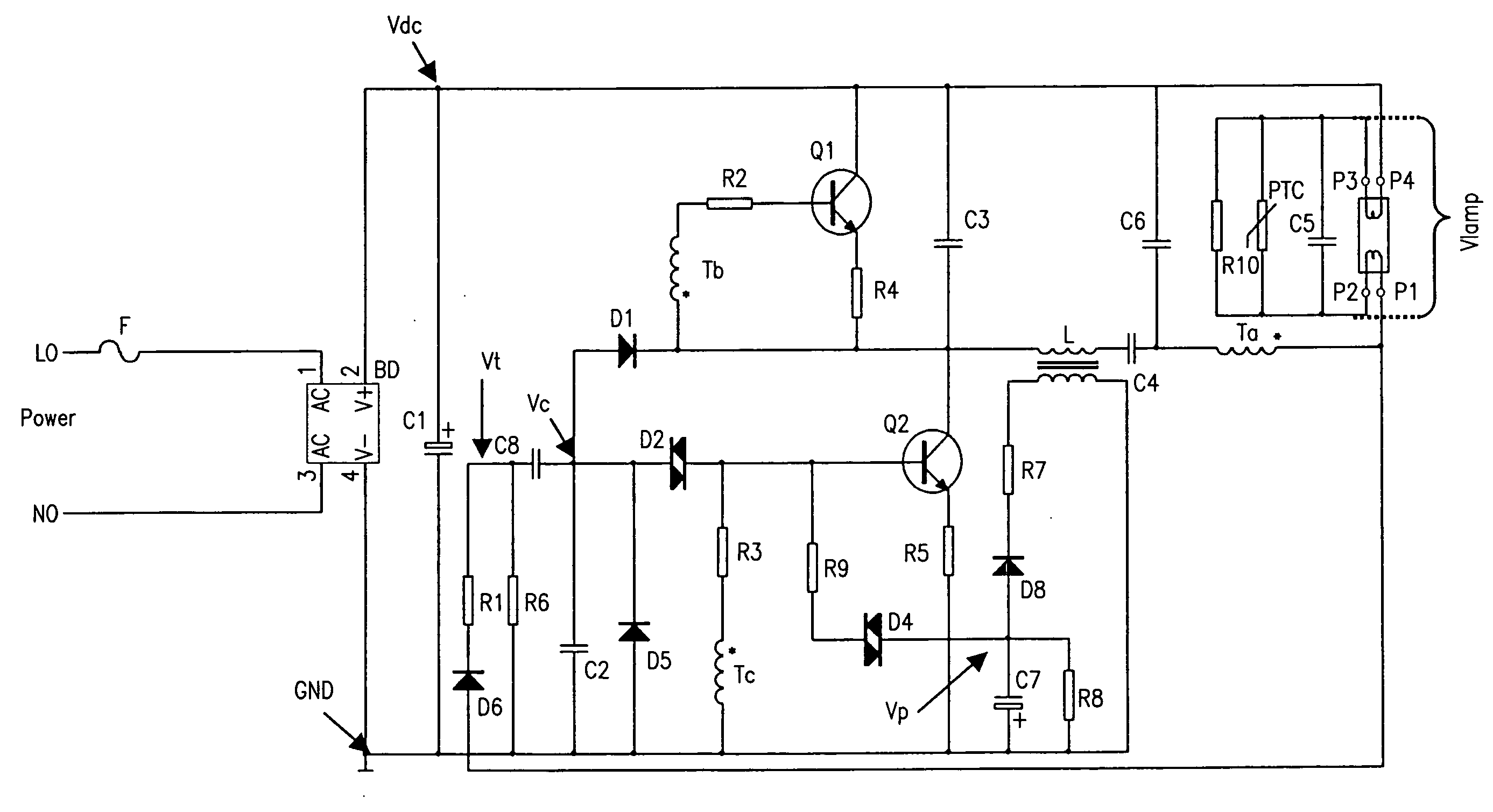
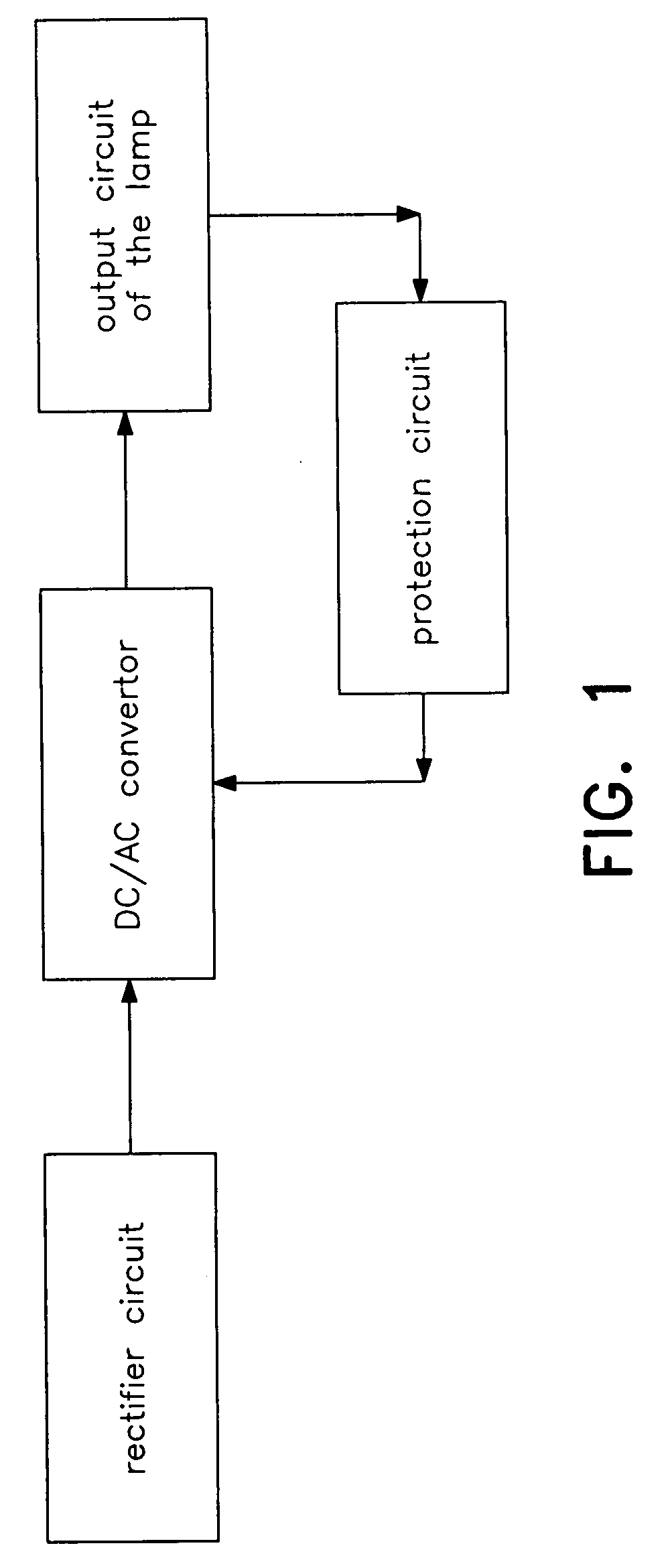
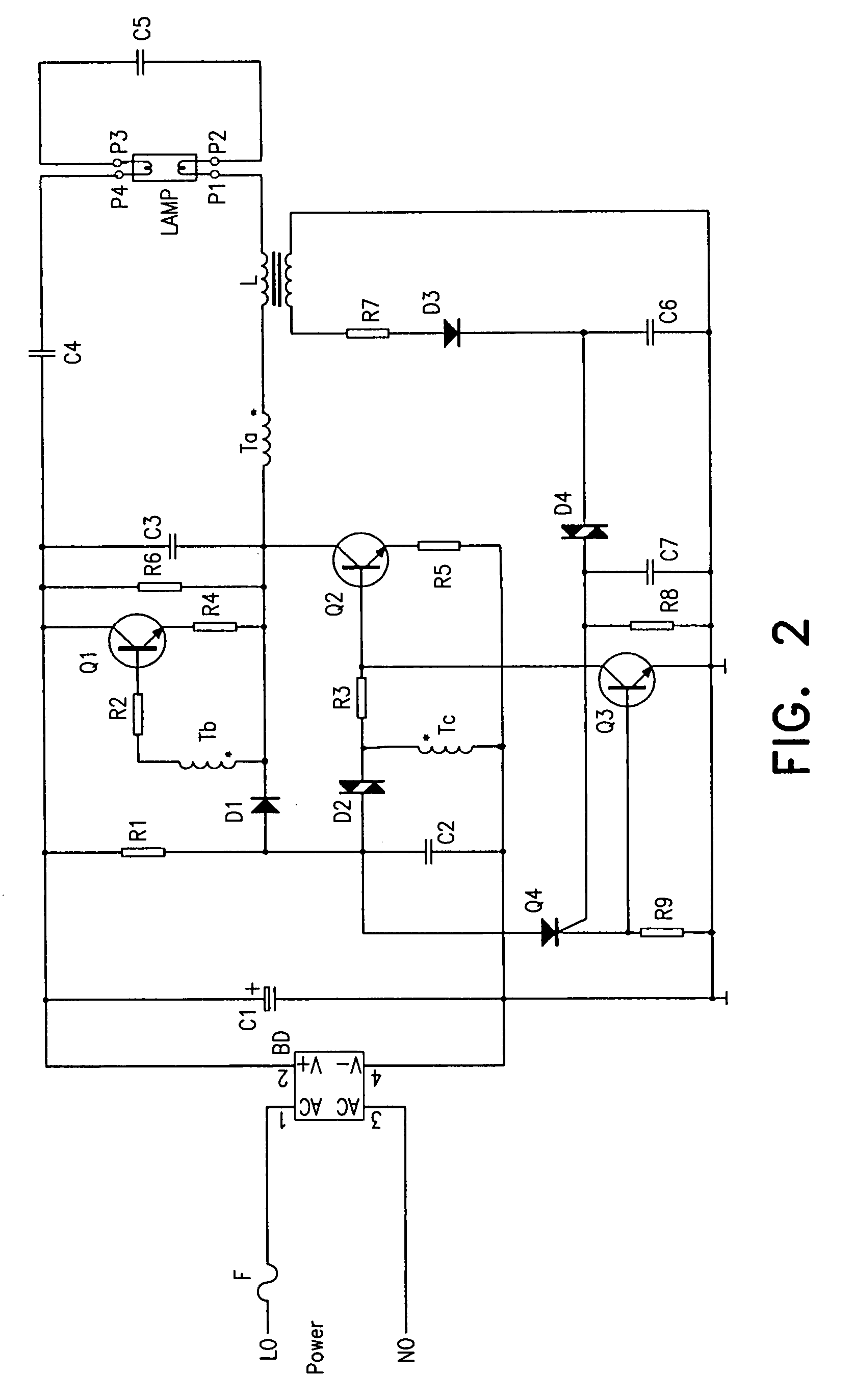
Circuit of the electronic ballast with the capability of automatic restart
InactiveUS20080061713A1Improve reliabilityLow costElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementCapacitanceEngineering
This present invention discloses a circuit of the electronic ballast with the capability of automatic restart. It includes a rectifier circuit, a trigger circuit of automatic restart, a DC / AC convertor, a output circuit of the lamp, and a circuit of abnormal protection. Its main feature is that there is a discharge loop in the trigger circuit, so it can realize automatic restart only after changing the lamp tube or connecting the lamp pin without turning off the power source when the lamp tube is abnormal and enters into protecting condition or any of the lamp pins is in poor contact. Because the trigger recourse Vt is led out from the lamp loop, when the power source is switched on, the DC / AC convertor is triggered to start after insuring good contact between the lamp tube and the lamp holder, accordingly realizes the self-check function of the connection for the lamp tube. Furthermore, because primary side winding Ta of oscillating coil T of the present invention is connected in series between the lamp pin P1 and the common end of feed-through capacitor C4 and by-pass capacitor C6, the primary side winding Ta of oscillating coil T will disconnect the power source when the lamp is in open circuit or any of the lamp pins is in poor contact. Therefore, the circuit will not come into protecting condition despite the by-pass capacitor C6, which results in the simplification of the task program.
Owner:DONGYANG TOSPO LIGHTING
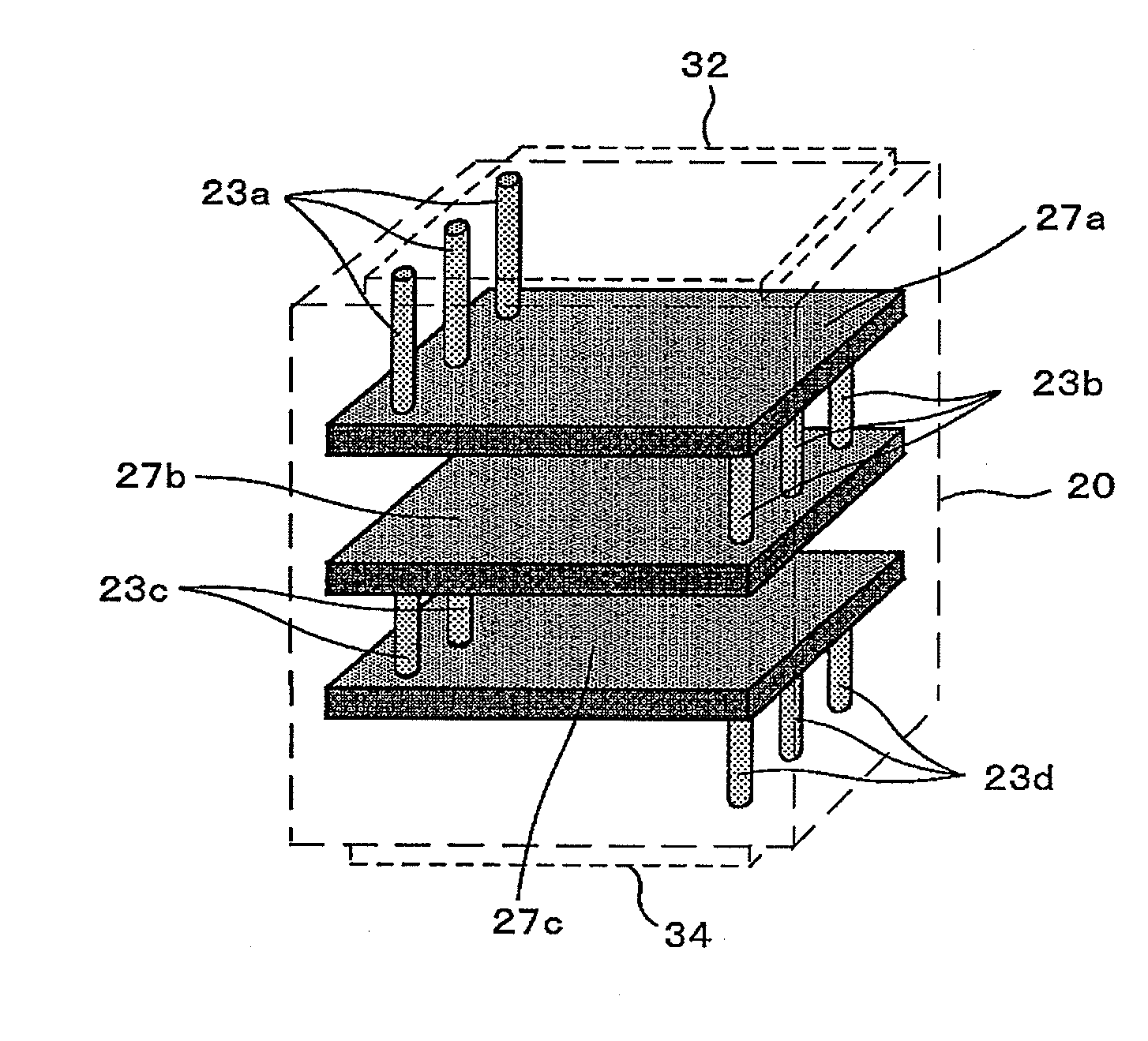
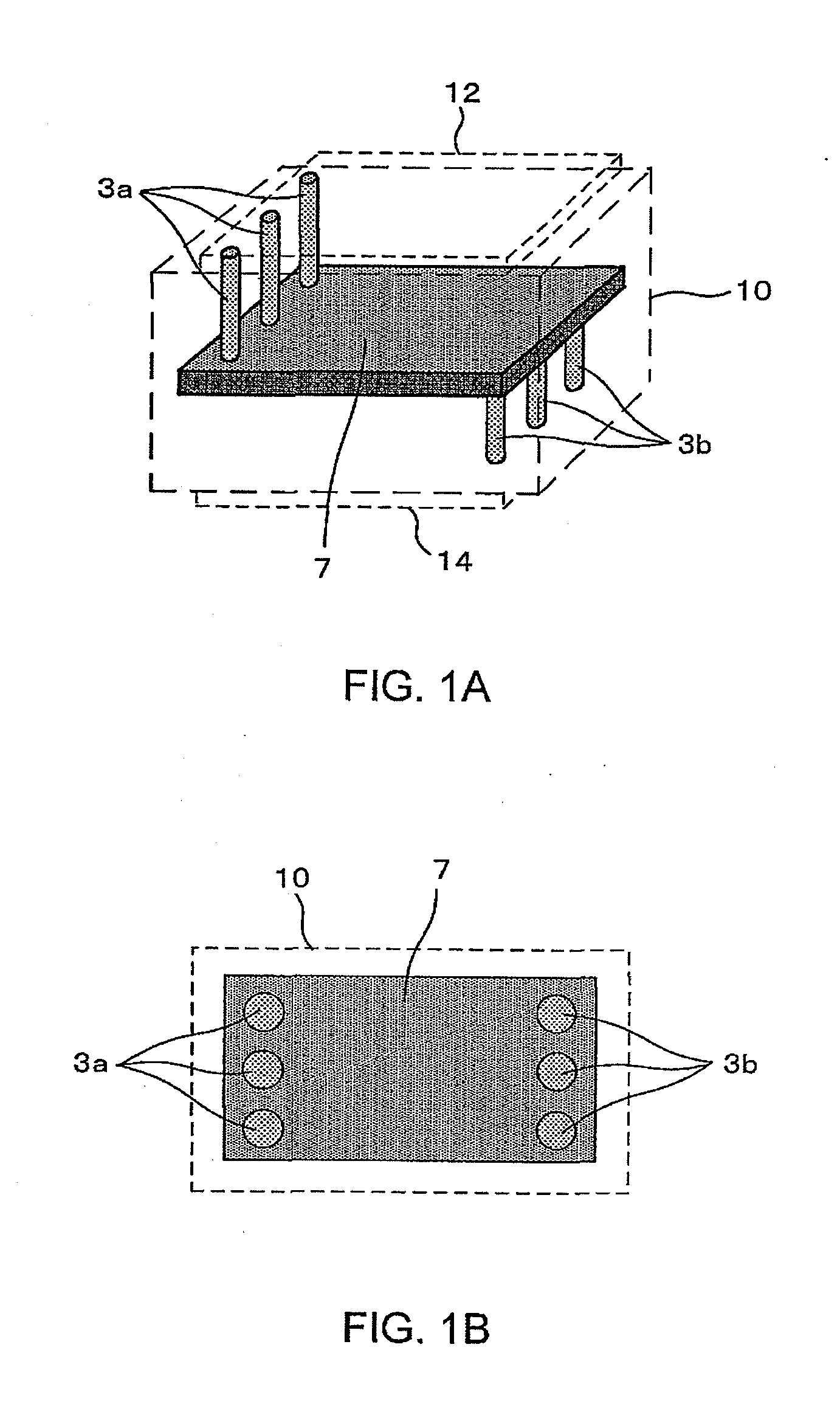
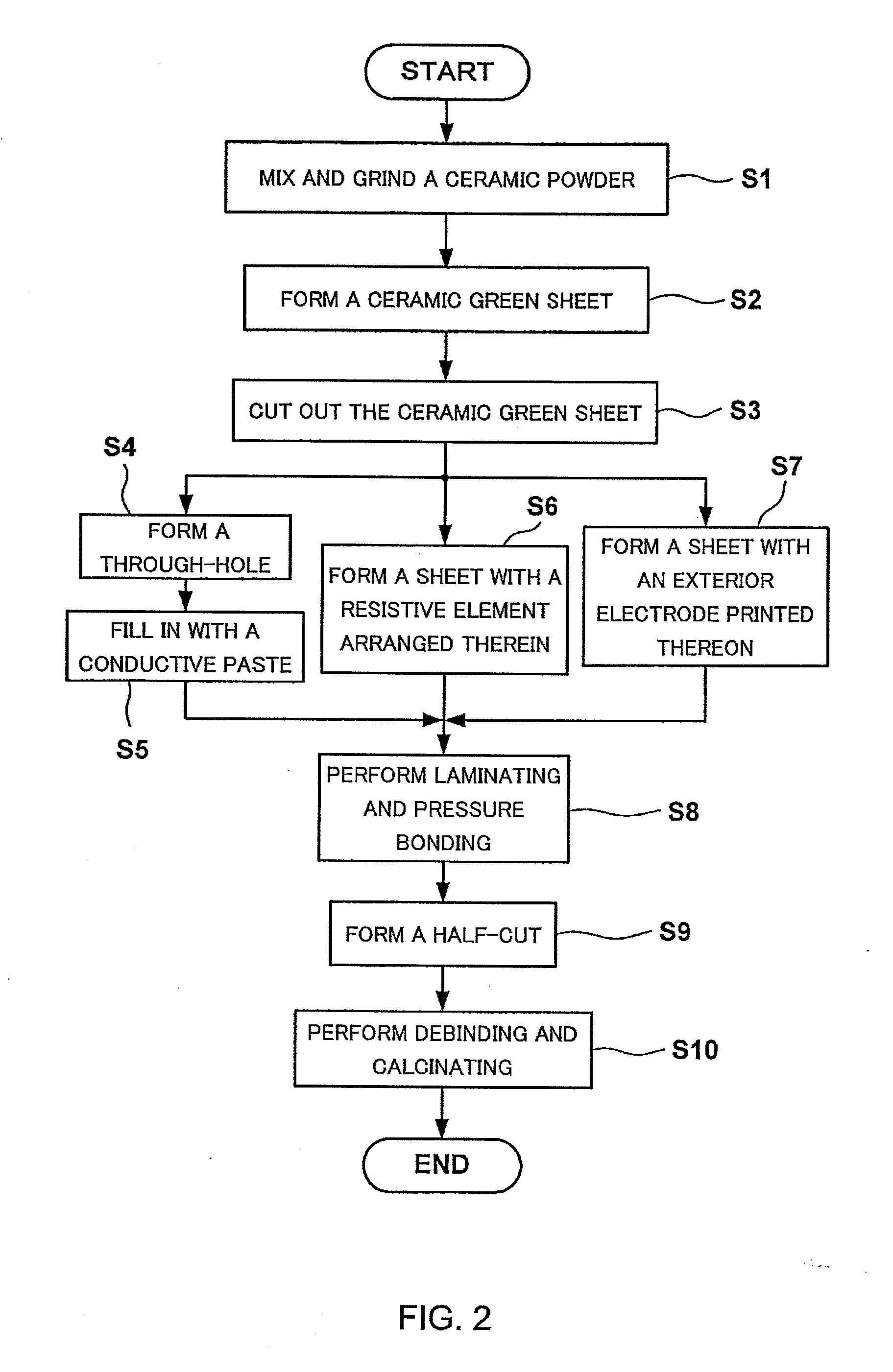
Laminated body and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20100097172A1Variation in resistanceImprove connectivityResistor terminals/electrodesPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringCeramic substrate
A laminated body and fabrication method thereof, which allow space saving and control of variation in internal layer resistance, are provided. When forming an internal-layer resistive element 7 in a multilayer ceramic substrate 10, the internal-layer resistive element 7 is connected to exterior electrodes (an upper surface electrode 32 and an undersurface electrode 34) via multiple via-electrodes 3a and 3b arranged in parallel, without a pad electrode adopted in the conventional laminated body. Moreover, in a multilayer ceramic substrate having multiple internal-layer resistive elements arranged in a multilayer structure, multiple internal-layer resistive elements are directly connected via multiple via-electrodes arranged in parallel.
Owner:KOA CORP
Cycloid speed-reducing device of rocket launching movable platform
InactiveCN101963209AImprove bending resistanceAxial dimension shortToothed gearingsReduction driveRocket launch
The invention relates to the technical field of speed reducers, in particular to a cycloid speed-reducing device of a rocket launching movable platform, which is characterized in that the cycloid speed-reducing device is a two-stage speed-reducing device comprising a bevel gear pair and a cycloid transmission, wherein (A) the cycloid transmission comprises a base, an output shaft, a supporting bearing, a cycloid gear, an eccentric bearing, a needle-tooth shell, a needle-tooth pin, a front base, an input shaft and an W output mechanism, wherein an input shaft is supported on an inner hole of the front base by bearings, the shaft-extension end of the input shaft is connected with the eccentric bearing, and the input end is connected with a large bevel gear; the front stand is sequentially connected with the needle-tooth shell and the base; the output shaft is supported on the inner hole of the base by the bearings; and (B) two symmetrical small bevel gear shafts meshed with the large bevel gear are both supported in a box wall hole of the front base by the bearings, wherein one small bevel gear shaft is connected with a motor, and the other small bevel gear shaft is connected with amanually-operated handle. The cycloid speed-reducing device has the advantages of two-stage speed reduction, short axial size, light weight and high quantization; in addition, as cycloid gear teeth and semi-buried teeth are continuous, the cycloid speed-reducing device has larger bearing capacity than that of a planetary transmission with only four planet gears; moreover, the cost of the cycloid speed-reducing device is lowered by 40%-55%.
Owner:郑雪霞
Semiconductor storage device and operating method of the same
ActiveUS20090073742A1Highly miniaturizedHigh readingNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage device includes: reading blocks; third wirings; reading switches; a control circuit; and evaluating circuits. The reading blocks includes first and second wirings extended in a first and second direction, respectively, and resistive storage elements arranged at points where the first and second wirings intersect. The third wirings is extended in the second direction and provided correspondingly to the second wirings. The reading switches are arranged between the third and second wirings. The control circuit controls the reading switches and supplies currents or the like to the first wirings. The evaluating circuits are connected to the third wirings and evaluate the currents or the like. When data is read out, the control circuit selects a selection reading block and a selection first wiring and supplies the currents or the like, and the evaluating circuits execute the evaluations of the currents or the like in the third wirings.
Owner:NEC CORP
Composite dielectric and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20050263744A1High dielectric constantLoss of characteristicLayered productsConductive materialDielectric lossDielectric permittivity
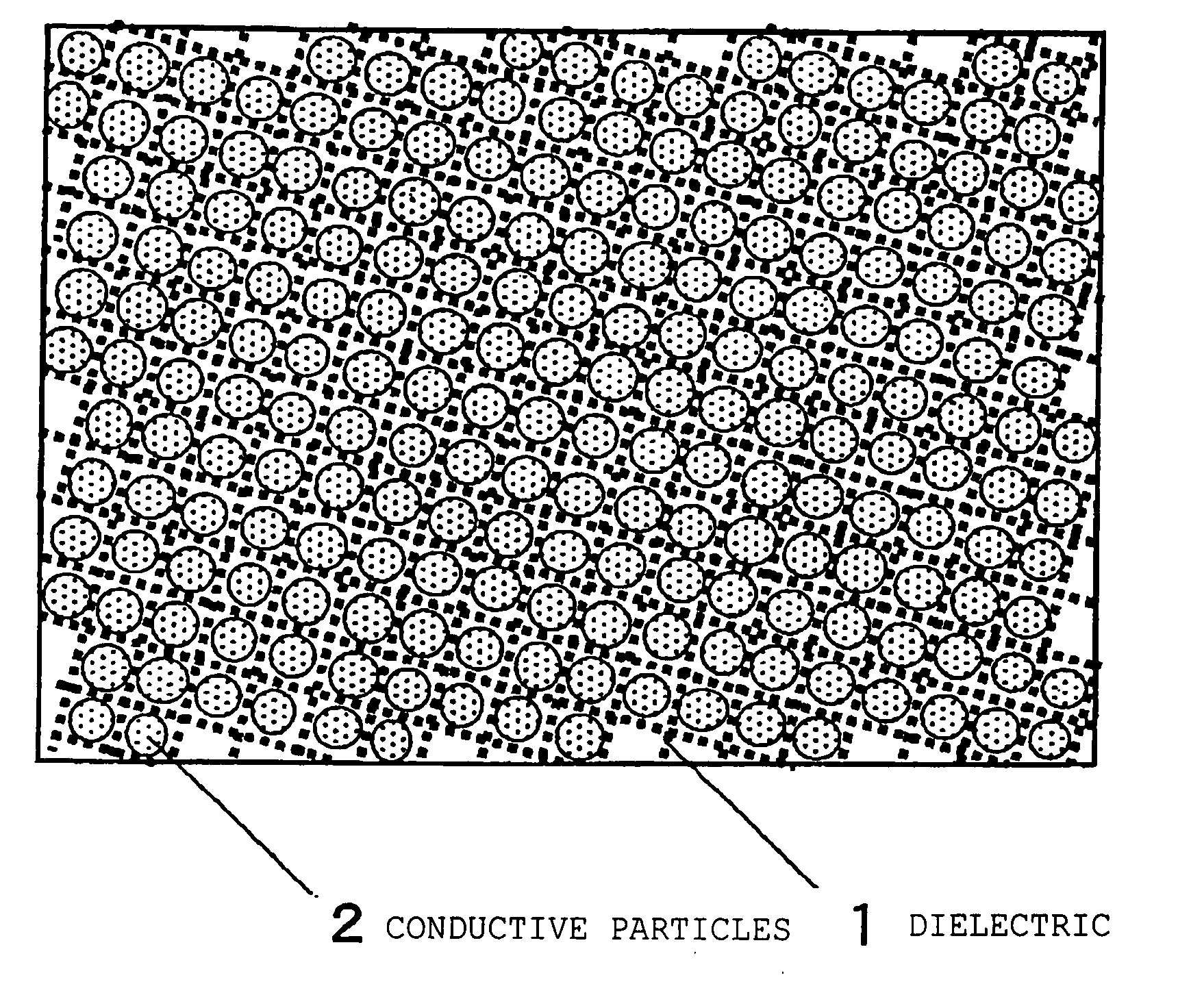
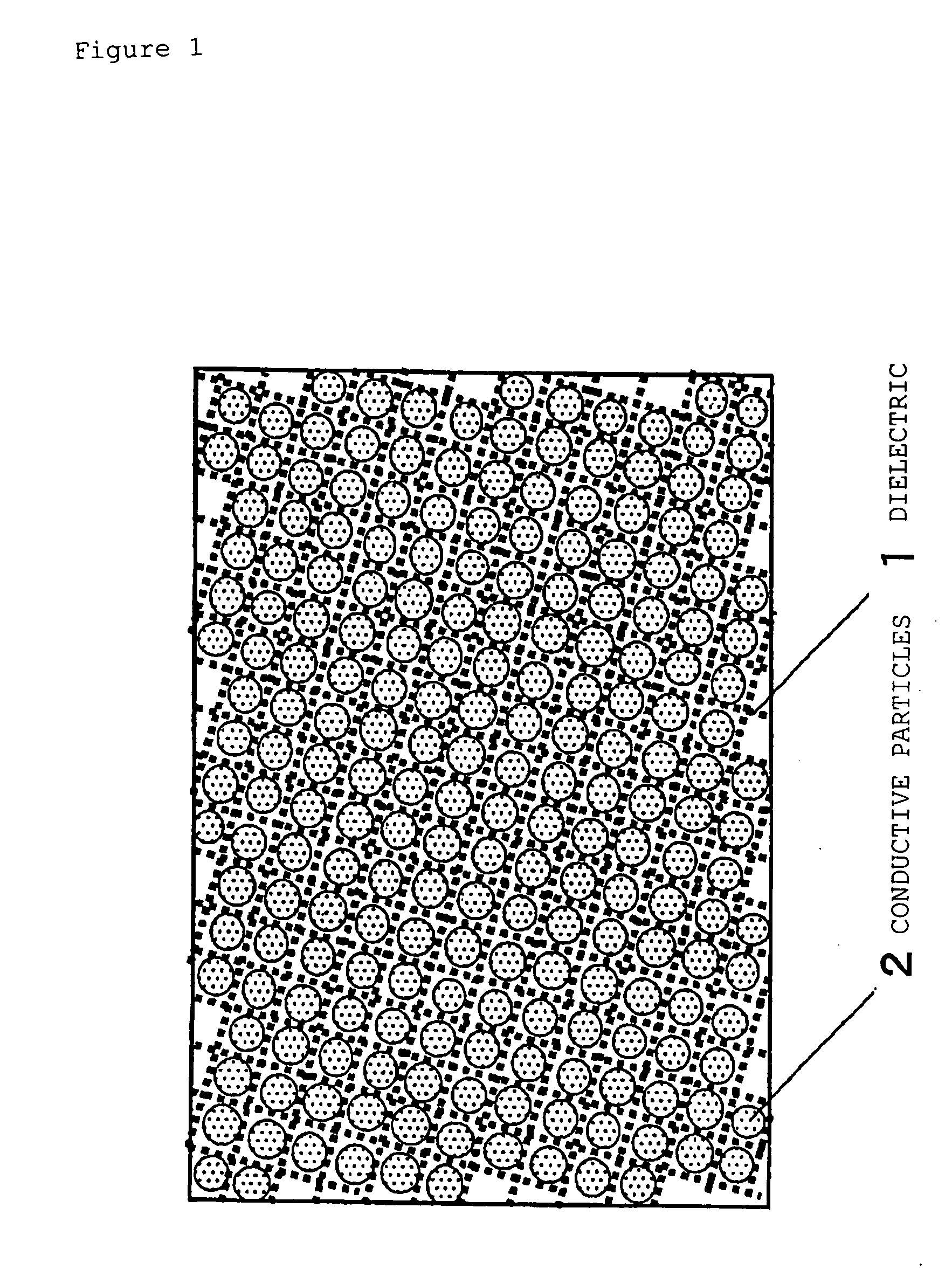
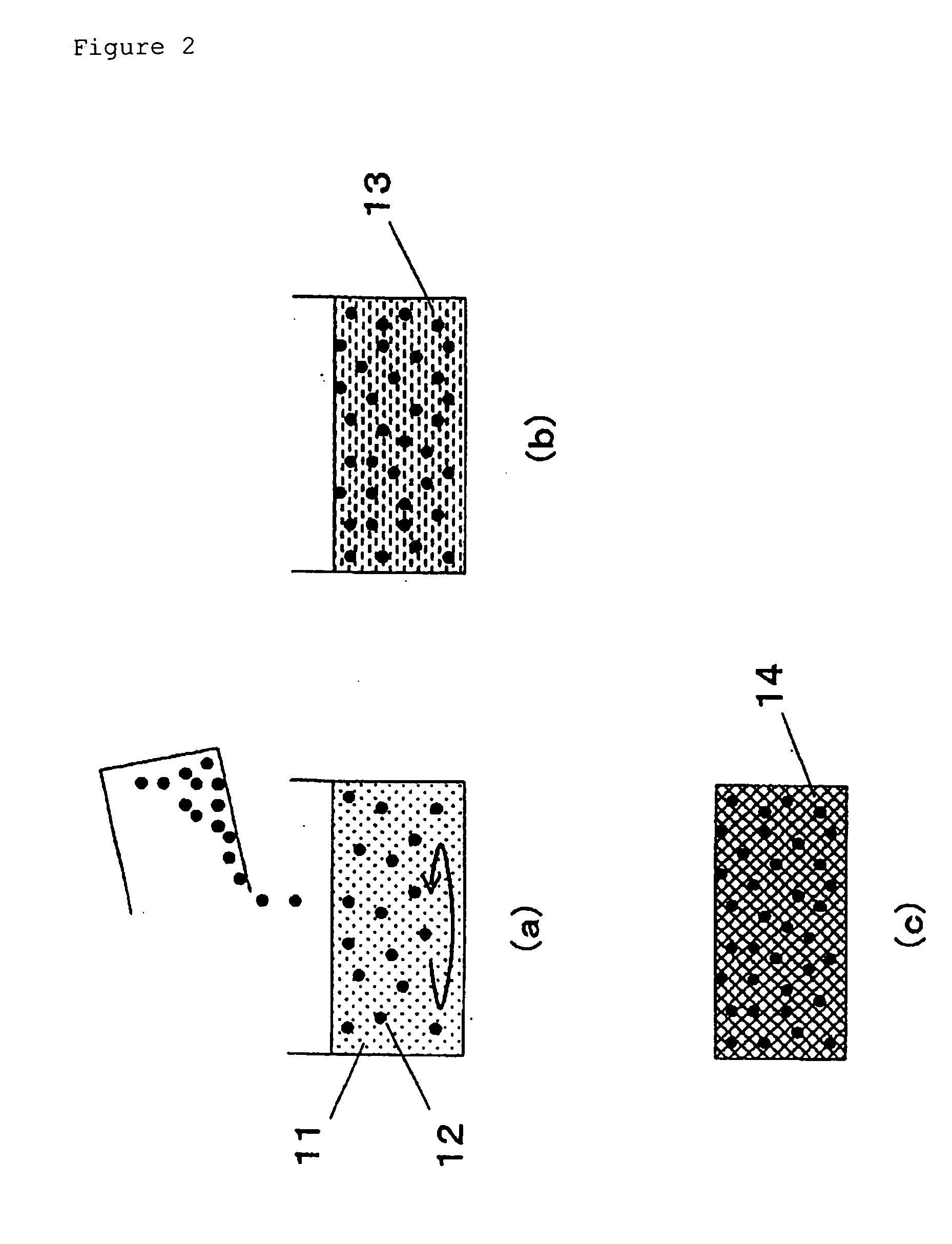
It is a principal object of the present invention to provide a dielectric having a high relative dielectric constant and dielectric loss minimized in high frequency bands. That is, the present invention relates to a composite dielectric comprising conductive particles dispersed in a porous body of inorganic oxide, wherein 1) the relative dielectric constant εr of the dielectric in high frequency bands of 1 GHz or more is 4 or more, and 2) the dielectric loss tans of the dielectric in high frequency bands of 1 GHz or more is 2×10−4 or less, and to a manufacturing method therefor.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20080224275A1Highly integratedHighly miniaturizedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBit lineEngineering
A semiconductor device includes bit lines provided in a semiconductor substrate; an ONO film that is provided along the surface of the semiconductor substrate and is made of a tunnel oxide film, a trap layer, and a top oxide film; and an oxide film that is provided on the surface of the semiconductor substrate in the middle between the bit lines and contacts the side face of the ONO film, in which the film thickness of the oxide film is larger than the sum of the thicknesses of the tunnel oxide film and the top oxide film, and smaller than the thickness of the ONO film.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
Inkjet recording head
An inkjet recording head includes: nozzles that jet ink droplets; pressure chambers that communicate with the nozzles and contain ink; a diaphragm that configures part of the pressure chambers; an ink pool chamber that pools ink to be supplied to the pressure chambers via ink flow paths; and piezoelectric elements that cause the diaphragm to be displaced, wherein the ink pool chamber is disposed opposite from the pressure chambers with the diaphragm being disposed therebetween, and drive ICs that apply a voltage to the piezoelectric elements are mounted on a piezoelectric element substrate formed to include the diaphragm.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
High-torque cycloidal speed-reduction device of rocket launching moving platform
InactiveCN102032321AImprove bending resistanceAxial dimension shortRocket launchersToothed gearingsRocket launchReduction drive
The invention relates to the technical field of a speed reducer, in particular to a high-torque cycloidal speed-reduction device of a rocket launching moving platform. The high-torque cycloidal speed-reduction device of the rocket launching moving platform is characterized in that: a two-stage speed-reduction device is formed through cycloidal transmission of a bevel gear pair and three cycloidal wheels, wherein, (A) the cycloidal transmission is constituted by a base, an output shaft, a supporting bearing, three cycloidal wheels with 120 degrees of phase angles, an eccentric bearing, a pin gear housing, a gear pin, a front base, an input shaft and a W-shaped output mechanism, wherein the input shaft is supported in an inner hole of the front base by a bearing, the shaft extension end of the input shaft is connected with the eccentric bearing, and the input end is connected with a bevel gear wheel; the front base is sequentially integrated with the pin gear housing and the base; and the output shaft is supported in the inner hole of the base by a bearing; and (B) two systematical bevel pinion shafts which are meshed with the bevel gear wheel are supported in a box wall hole of the front base by a bearing, and one bevel pinion shaft is connected with a motor and the other bevel pinion shaft is connected with a manual handle. The high-torque cycloidal speed-reduction device of the rocket launching moving platform has the beneficial effects that: (a) two-stage reduction is adopted, the axial size is short, the weight is small and the height is lightened; (b) cycloidal gear teeth and half-buried teeth are not broken, and three cycloidal wheels are adopted, therefore, the bearing capacity of three cycloidal wheels is higher than that of epicyclic transmission of four planet wheels; and (c) the cost is reduced by 40-55 percent.
Owner:吴声震
Detector for detecting liquid crystal module
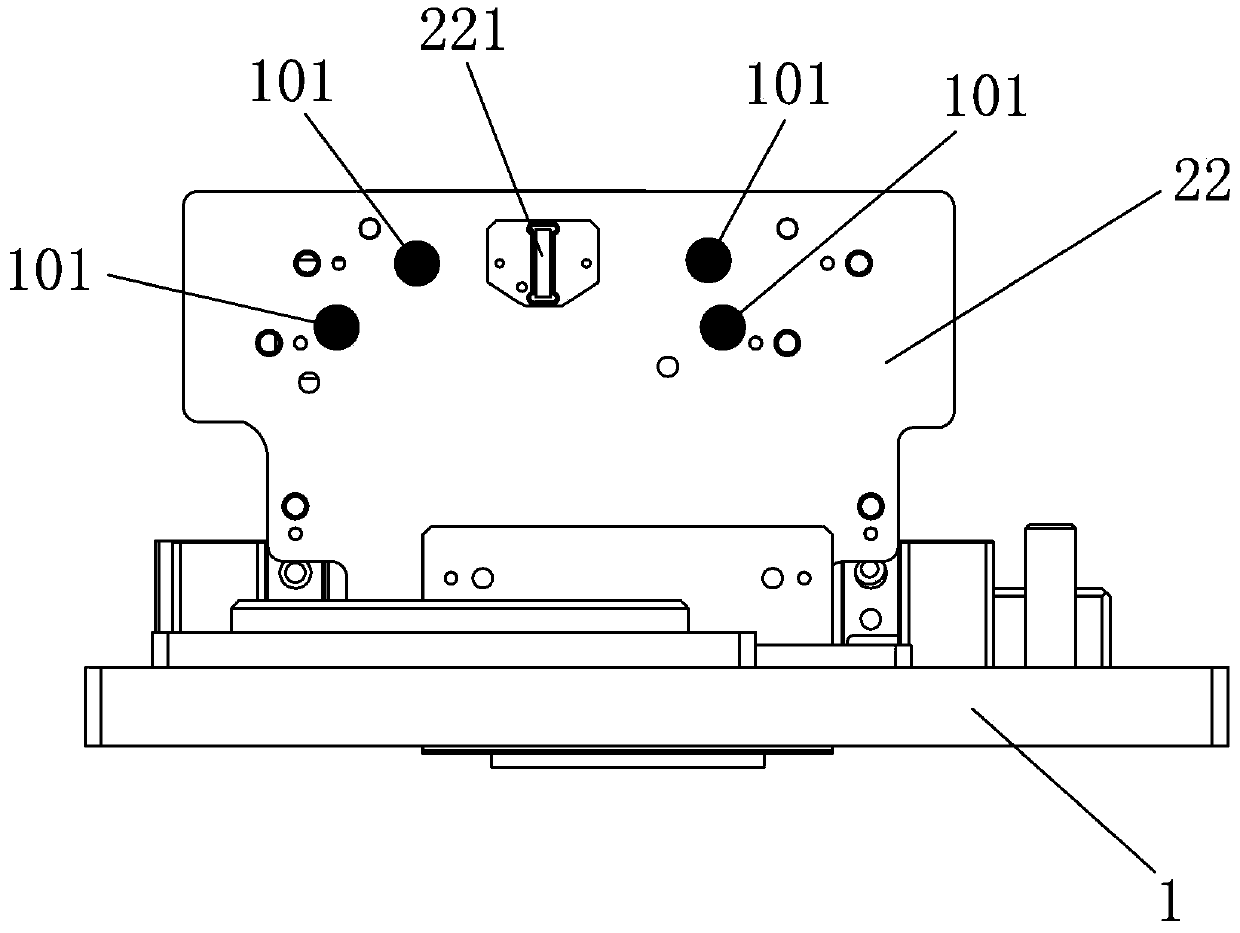
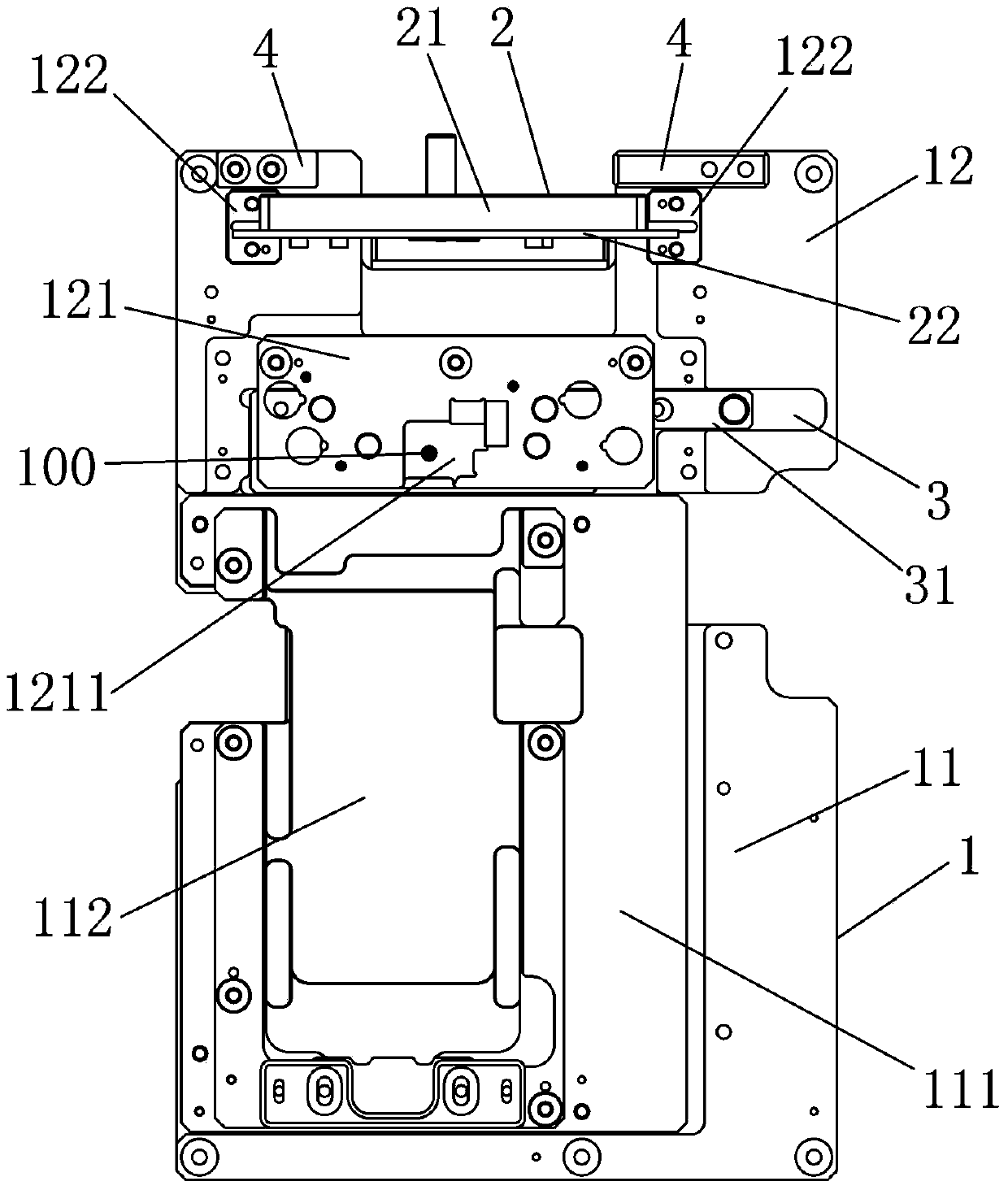
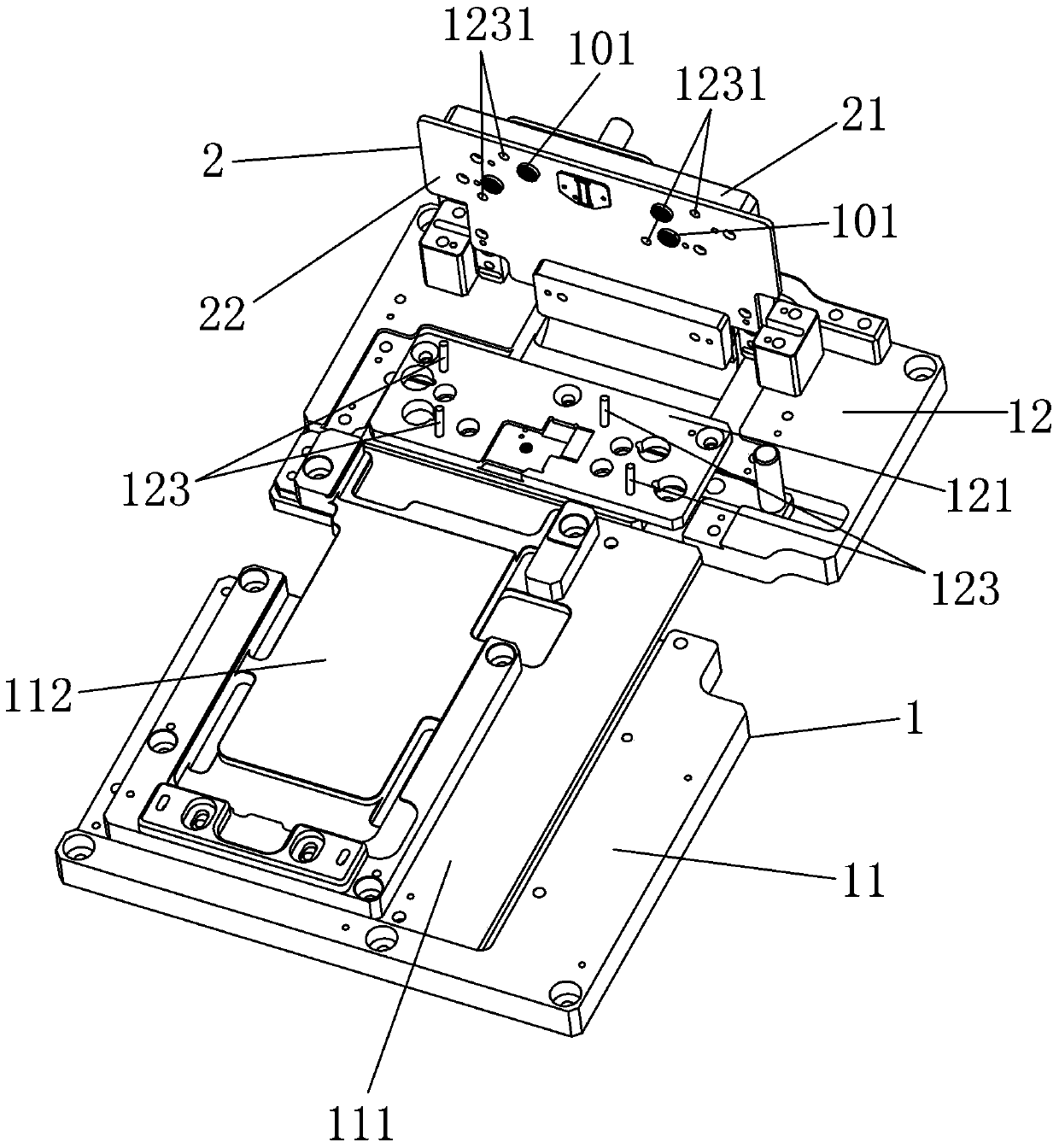
ActiveCN103424902AEasy to operateHighly miniaturizedEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsMeasurement instrument housingEngineeringLiquid crystal
The invention discloses a detector for detecting a liquid crystal module. The detector comprises top plates and an overturn assembly, wherein the top plates comprise the first top plate and the second top plate, the first top plate is used for carrying the module to be detected, and the overturn assembly is arranged on the second top plate in a turnover mode; the overturn assembly comprises at least one substrate fixing plate, wherein at least one detection substrate is arranged on the substrate fixing plate, and the detection substrate is provided with at least one connector detection port used for detecting a connector of the module to be detected. According to the detector for detecting the liquid crystal module, the module to be detected is convenient to replace in the operation process, the fault rate of the connector detection ports on the module to be detected is reduced, the service life of the connector detection ports on the detection substrates is prolonged, production efficiency is effectively improved, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU HUAXING YUANCHUANG TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com