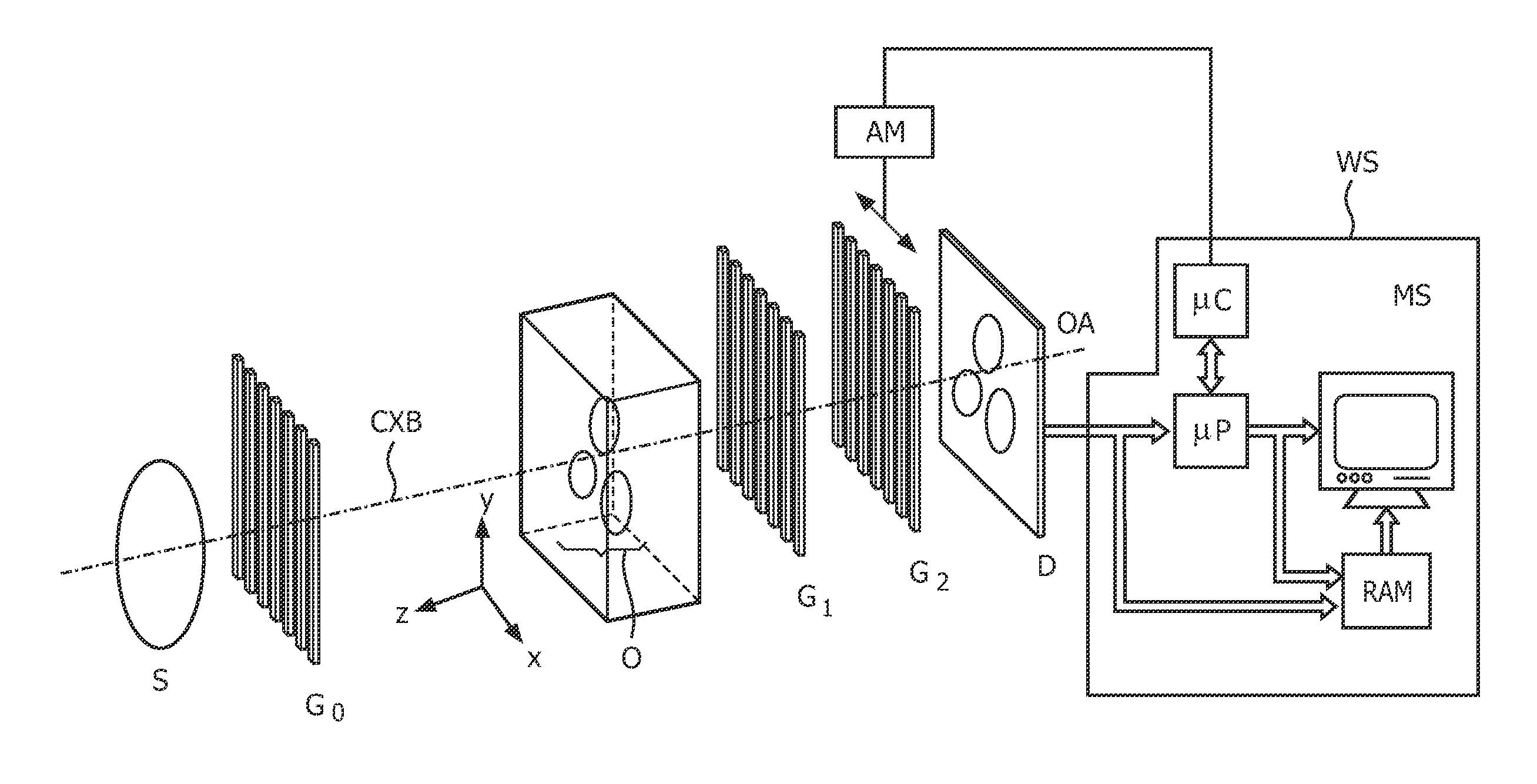
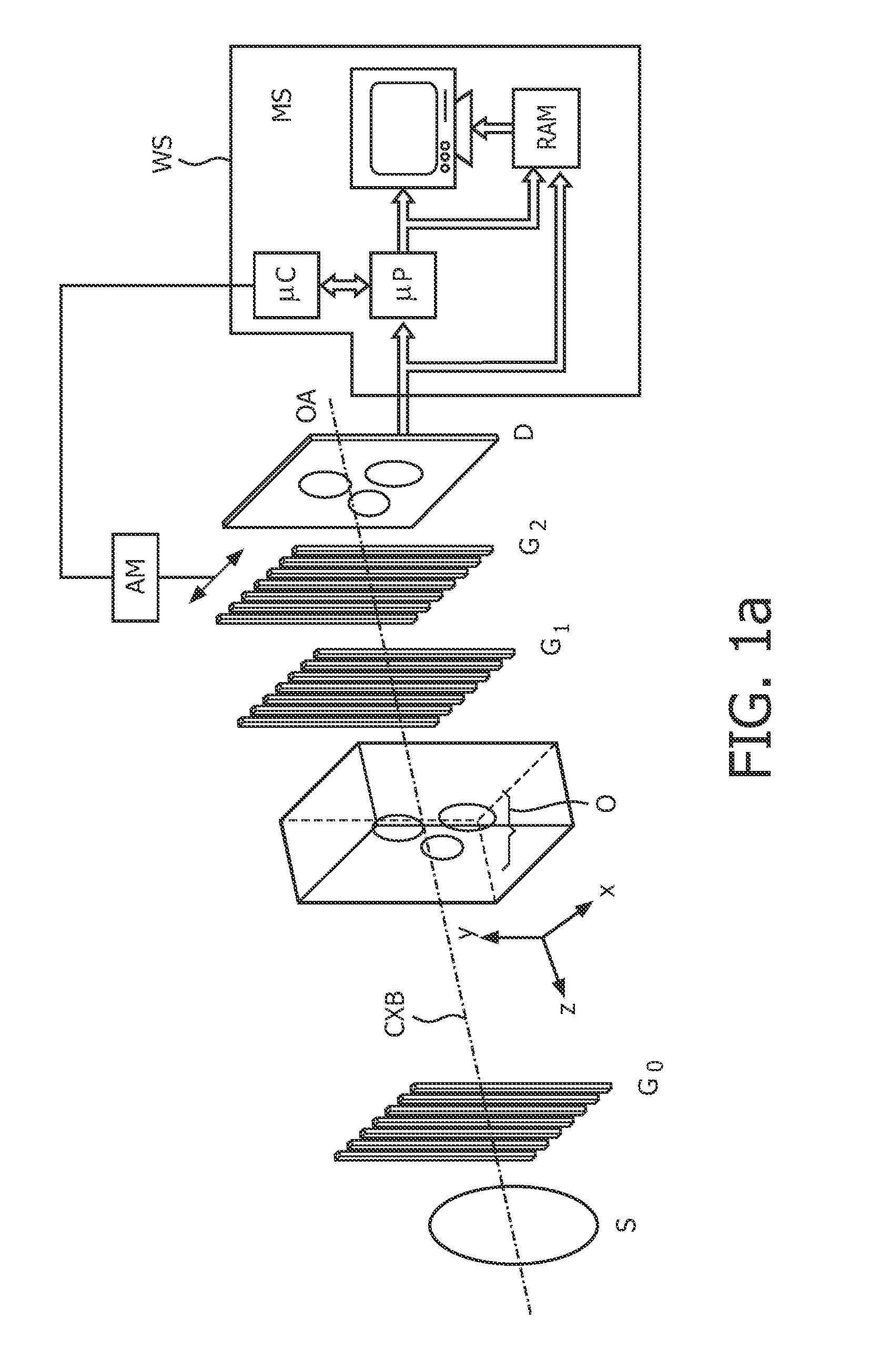
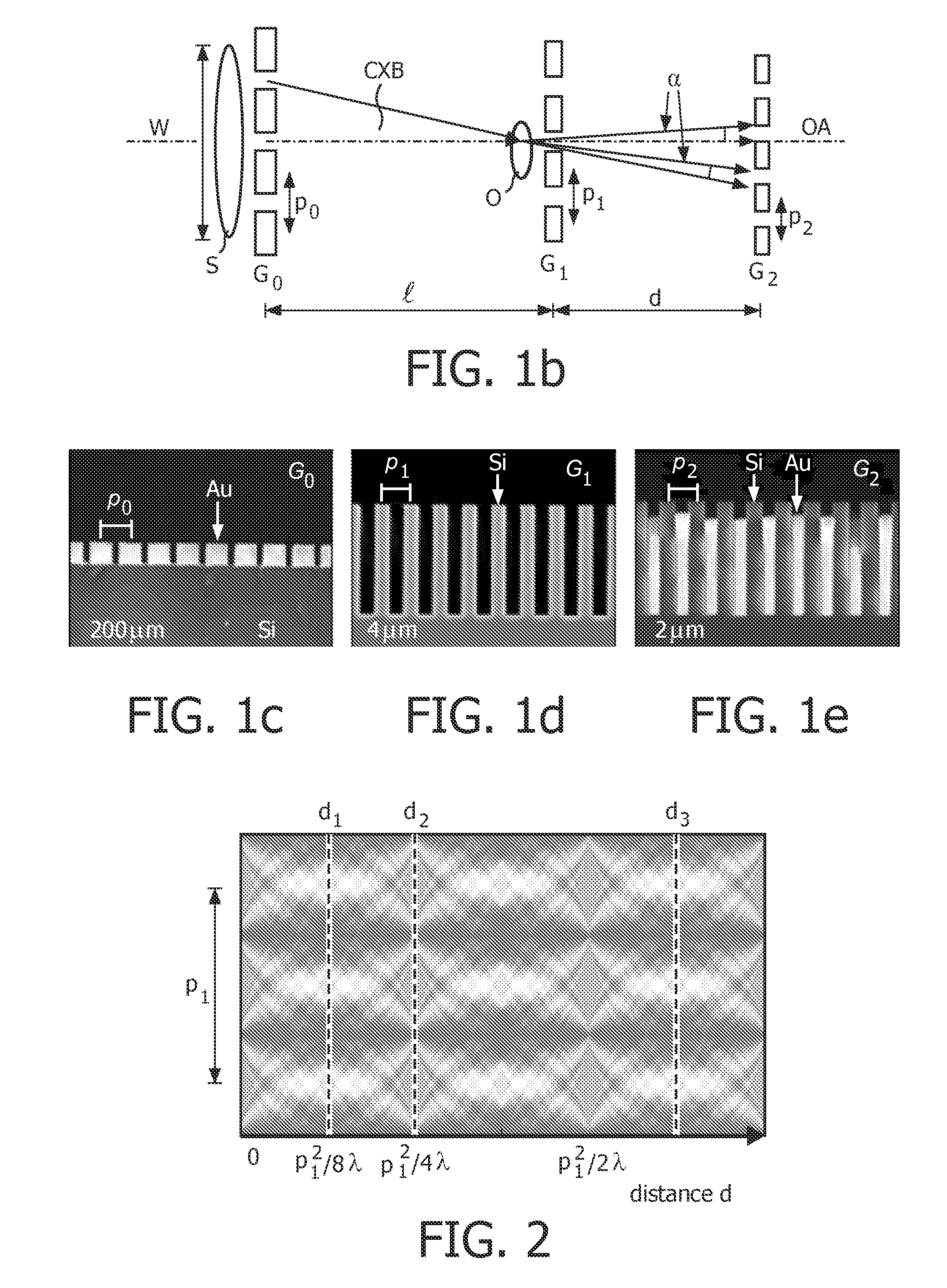
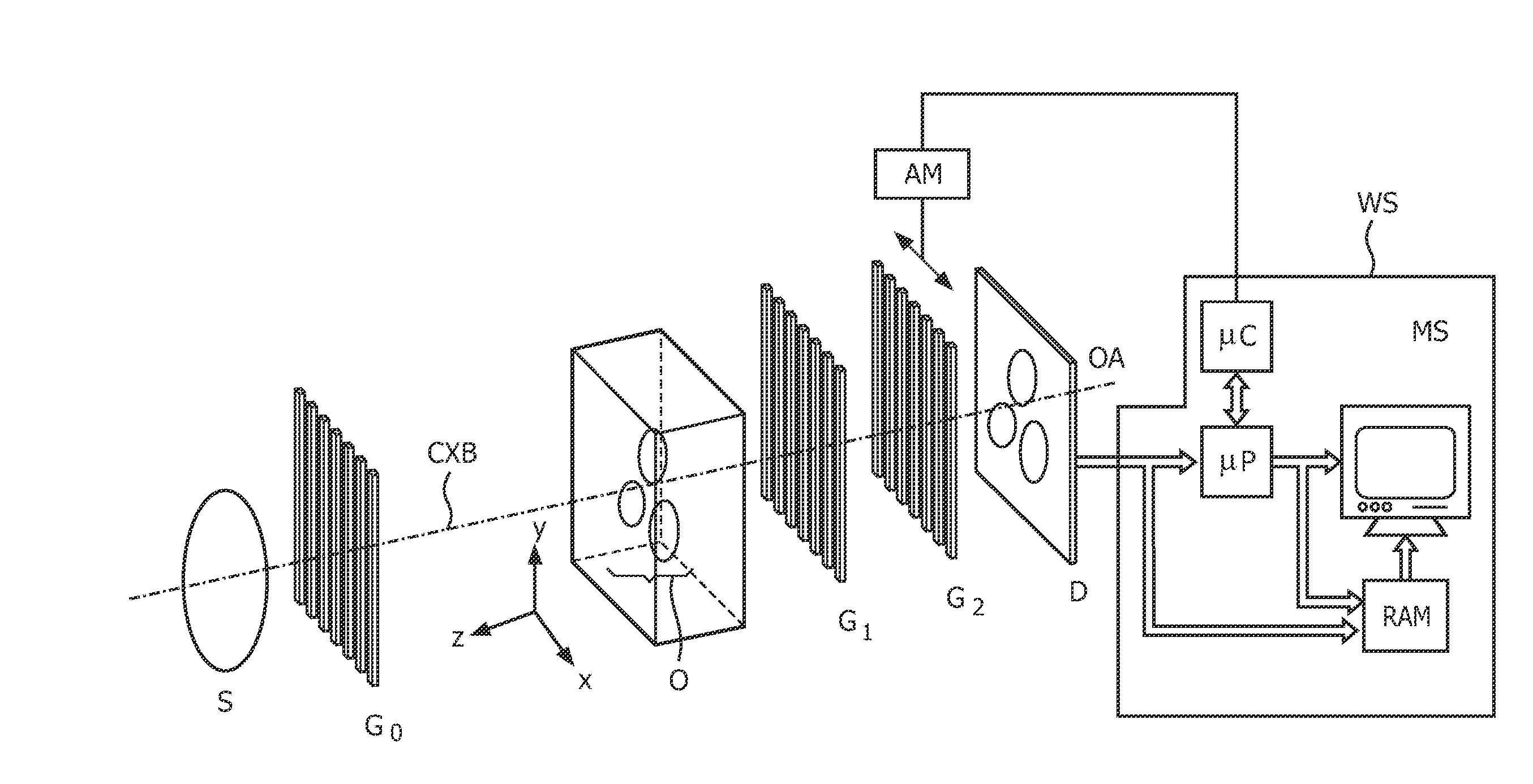
Patents
Literature
259 results about "Helical computed tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spiral computed tomography, or helical computed tomography, is a computed tomography (CT) technology in which the source and detector travel along a helical path relative to the object. Typical implementations involve moving the patient couch through the bore of the scanner whilst the gantry rotates.
Tetrahedron beam computed tomography
ActiveUS7760849B2Reduce exposureReduce the ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisSoft x ray
A method of imaging an object that includes directing a plurality of x-ray beams in a fan-shaped form towards an object, detecting x-rays that pass through the object due to the directing a plurality of x-ray beams and generating a plurality of imaging data regarding the object from the detected x-rays. The method further includes forming either a three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography, digital tomosynthesis or Megavoltage image from the plurality of imaging data and displaying the image.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
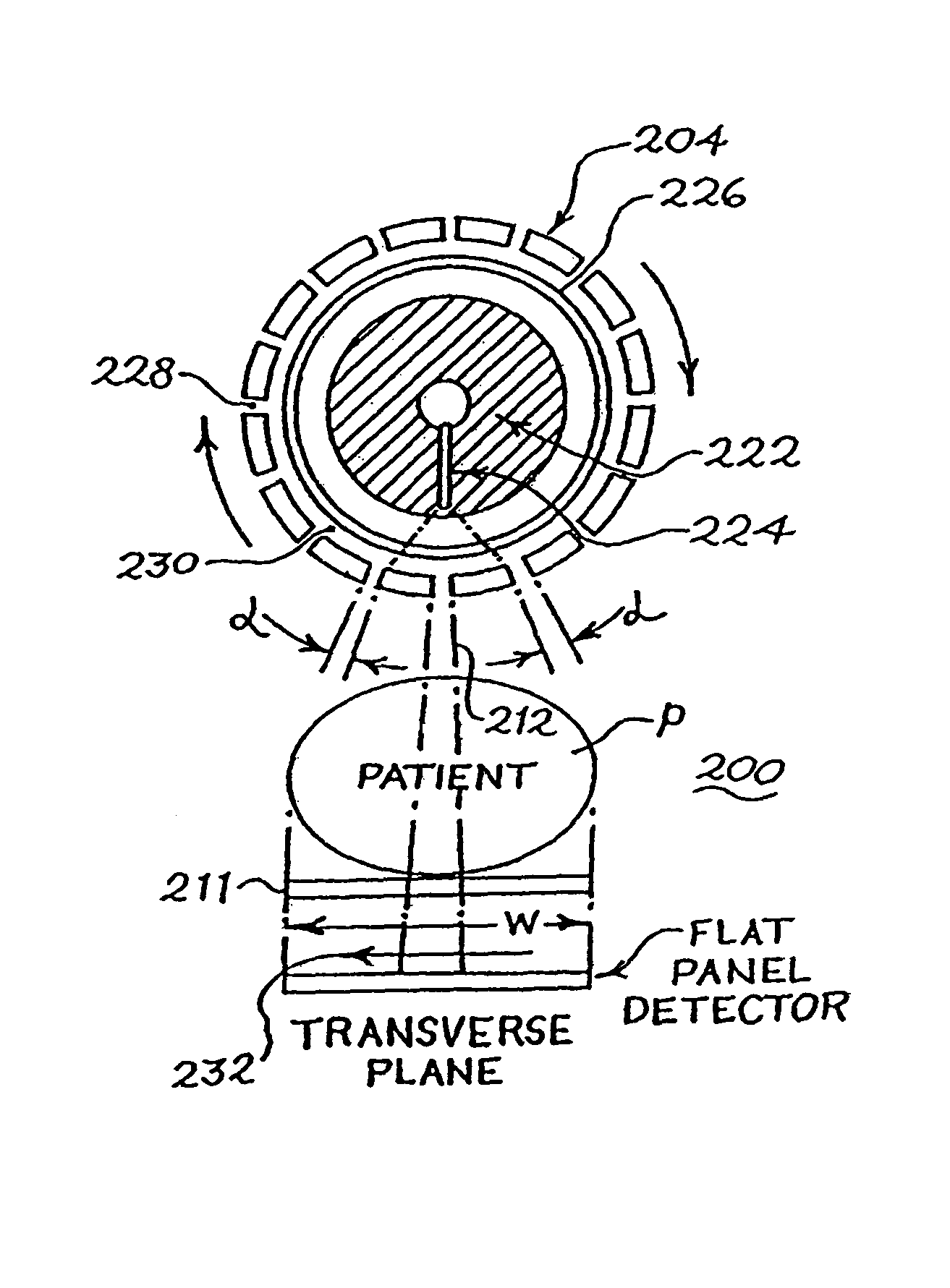
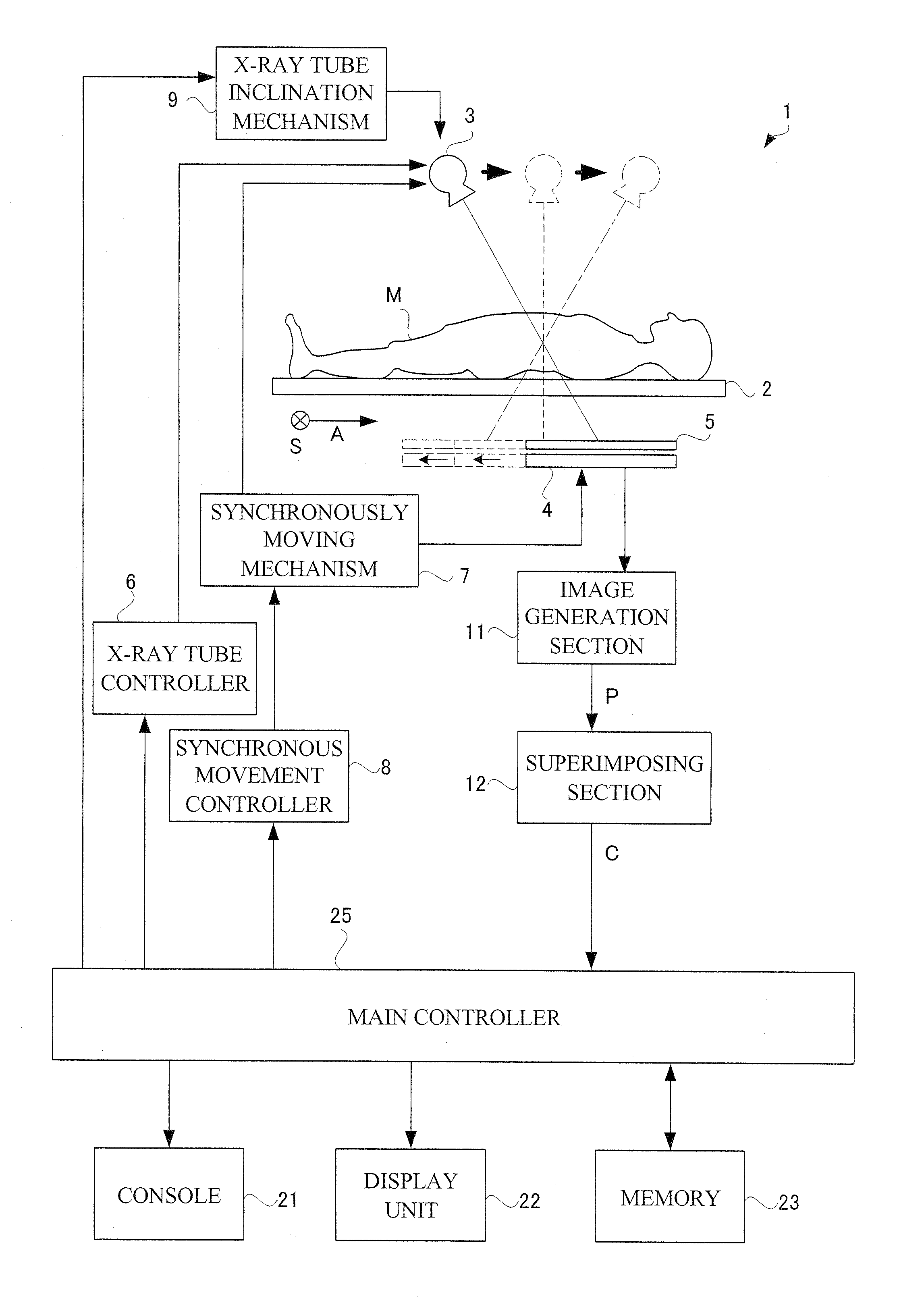
Radiographic apparatus
ActiveUS8798231B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFluoroscopic imageFluorescence
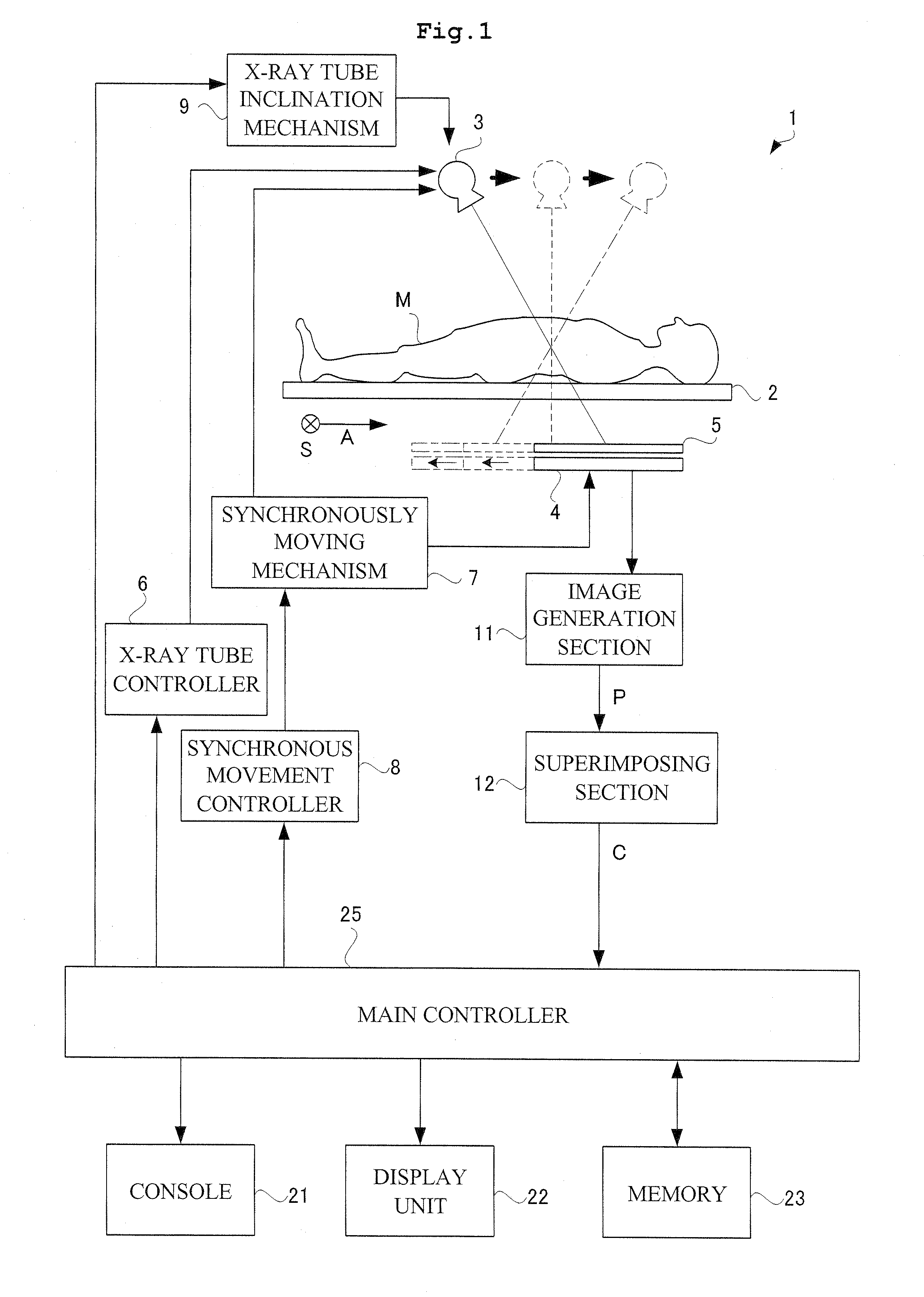
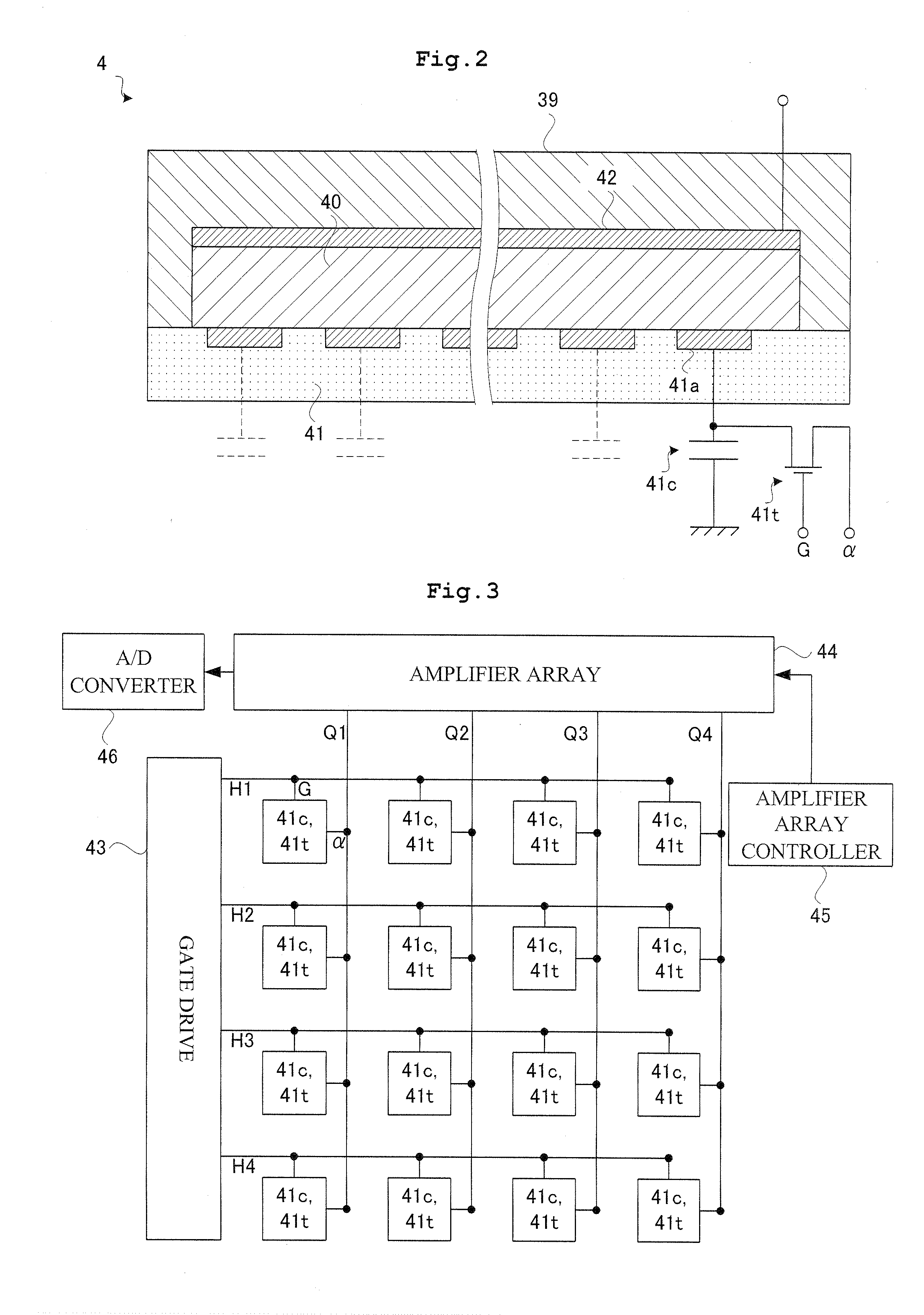
One object of this invention is to provide radiography apparatus with suppressed exposure to a subject in tomography mode. An FPD provided in X-ray apparatus according to this invention converts X-rays into electric signals, and thereafter amplifies the signals to output them to an image generation section. According to this invention, an amplification factor is higher in a tomography mode than in a spot radiography mode. A tomographic image is obtained through superimposing two or more fluoroscopic image. In comparison of the fluoroscopic images, they differ from one another in appearance of the false image. Accordingly, superimposing the images may achieve cancel of the false images. In this way, the tomographic image finally obtained has no false image.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method and apparatus for interferometry
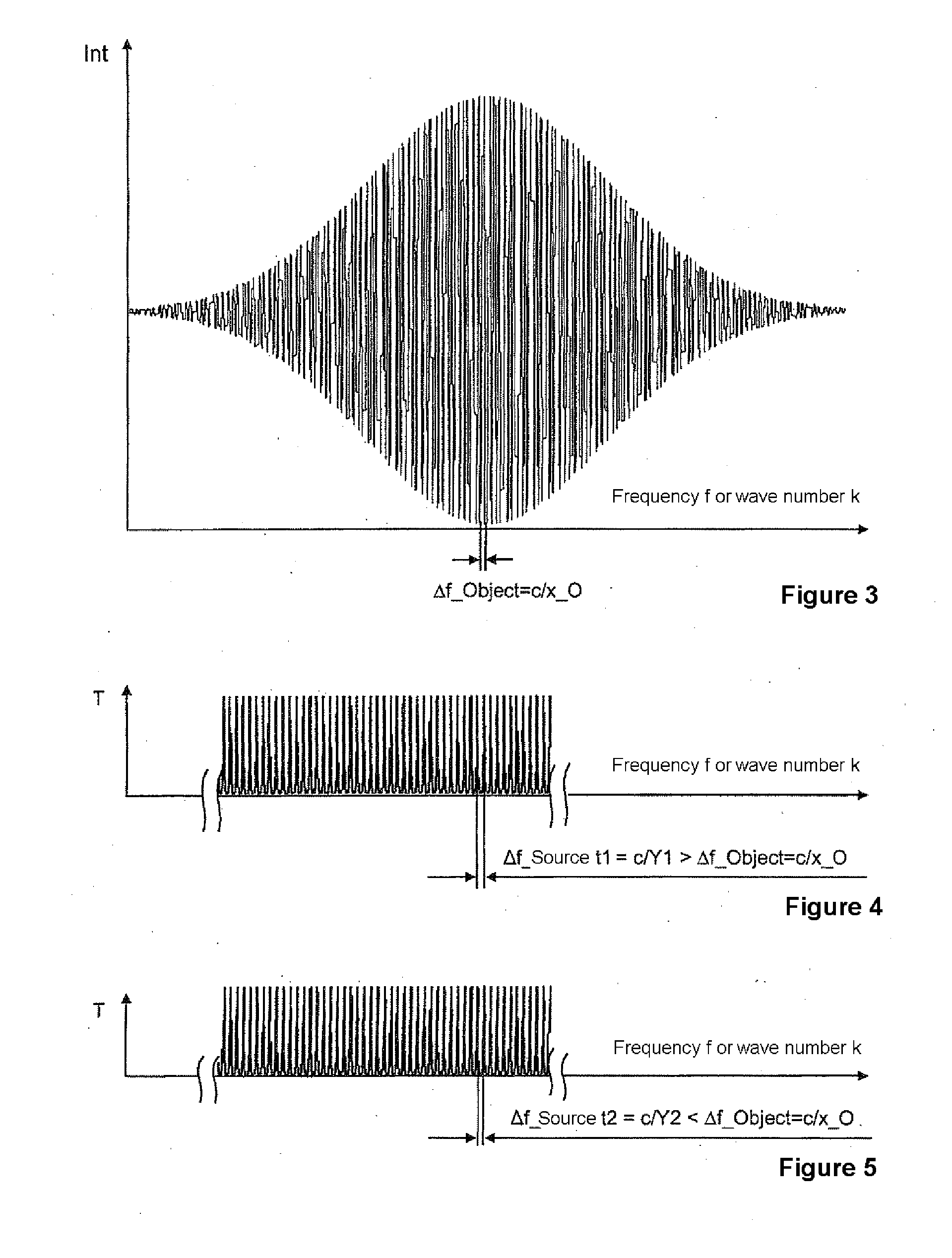
InactiveUS20110235045A1High measurementImprove scanning accuracyRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryHelical computed tomographyEngineering
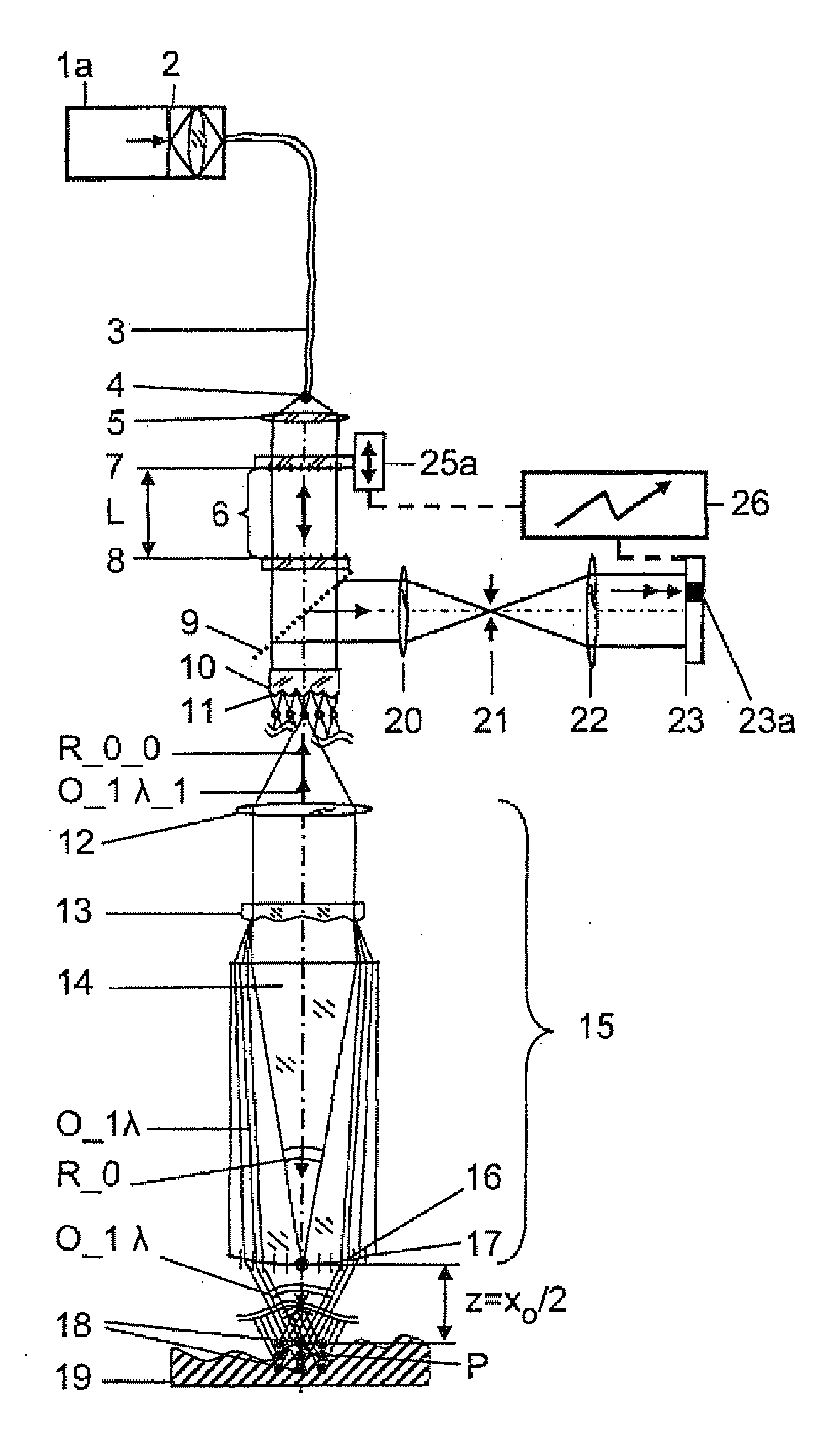
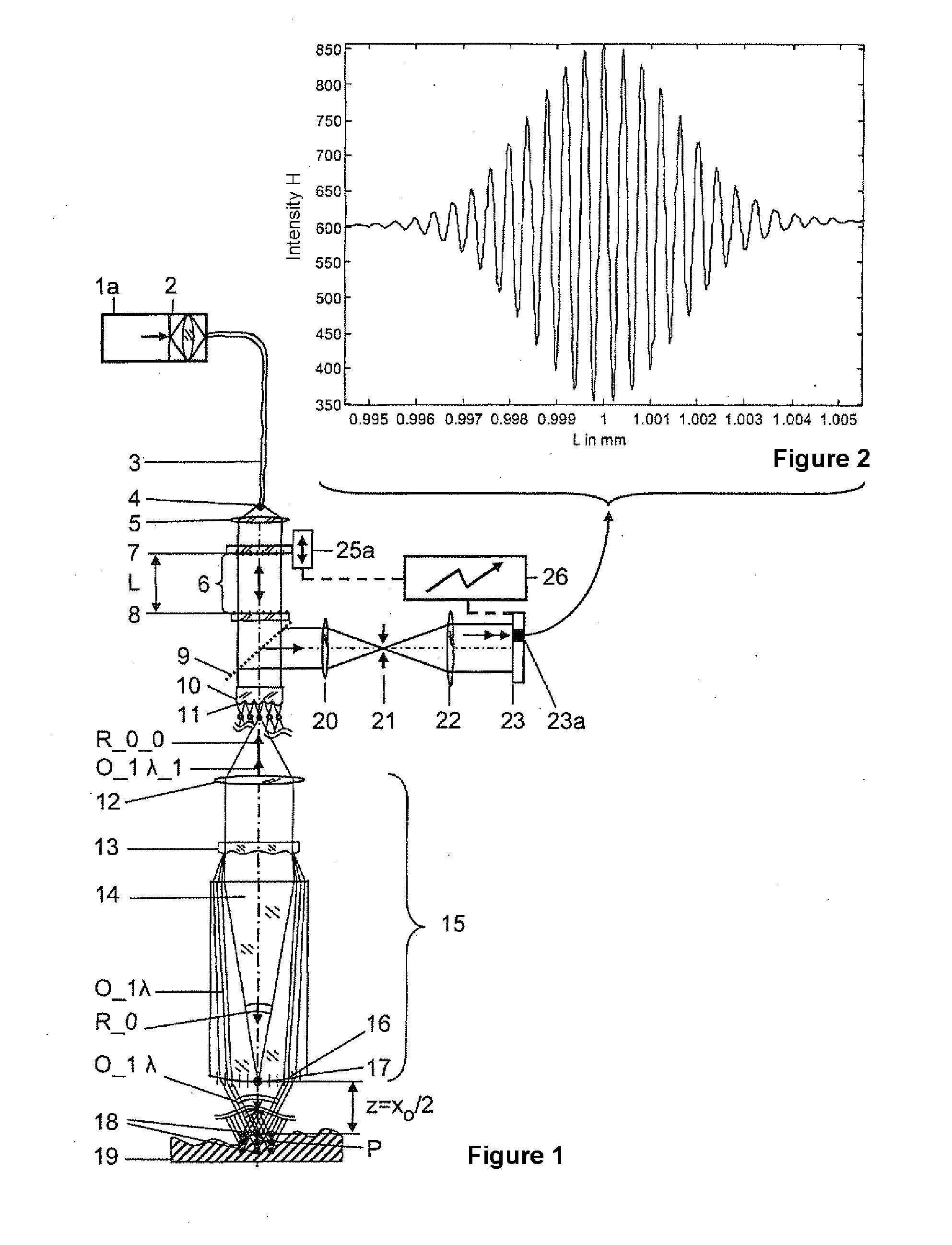
A method and an arrangement are provided for scalable confocal interferometry for distance measurement, for 3-D detection of an object, for OC tomography with an object imaging interferometer and at least one light source. The interferometer has an optical path difference not equal to zero at each optically detected object element. Thus, the maxima of a sinusoidal frequency wavelet, associated with each detected object element, each have a frequency difference Δf_Objekt. At least one spectrally integrally detecting, rastered detector is arranged to record the object. The light source preferably has a frequency comb, and the frequency comb differences Δf_Quelle are changed in a predefined manner over time in a scan during measuring. In the process, the frequency differences Δf_Quelle are made equal to the frequency difference Δf_Objekt or equal to an integer multiple of the frequency differences Δf_Objekt at least once for each object element.
Owner:UNIV STUTTGART
Laser Optoacoustic Ultrasonic Imaging System (LOUIS) and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20130190595A1Increase contrastImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingHelical computed tomographyContrast resolution
Provided herein are the systems, methods, components for a three-dimensional tomography system. The system is a dual-modality imaging system incorporates a laser ultrasonic system and a laser optoacoustic system. The dual-modality imaging system has means for generate tomographic images of a volume of interest in a subject body based on speed of sound, ultrasound attenuation and / or ultrasound backscattering and for generating optoacoustic tomographic images of distribution of the optical absorption coefficient in the subject body based on absorbed optical energy density or various quantitative parameters derivable therefrom. Also provided is a method for increasing contrast, resolution and accuracy of quantitative information obtained within a subject utilizing the dual-modality imaging system. The method comprises producing an image of an outline boundary of a volume of interest and generating spatially or temporally coregistered images based on speed of sound and / or ultrasonic attenuation and on absorbed optical energy within the outlined volume.
Owner:TOMOWAVE LAB INC
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS8855265B2Reduce impactImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120099702A1Good estimateImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
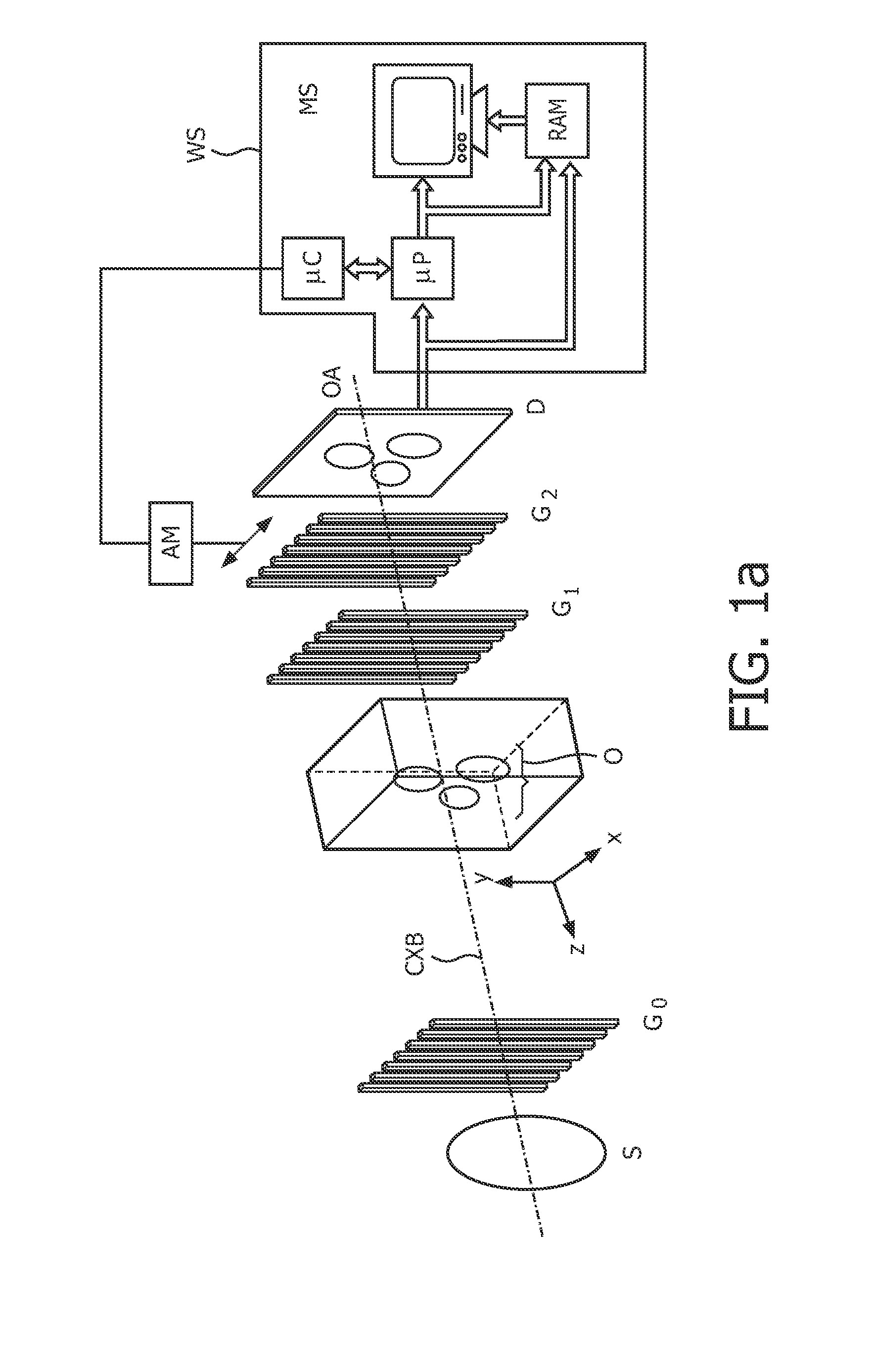
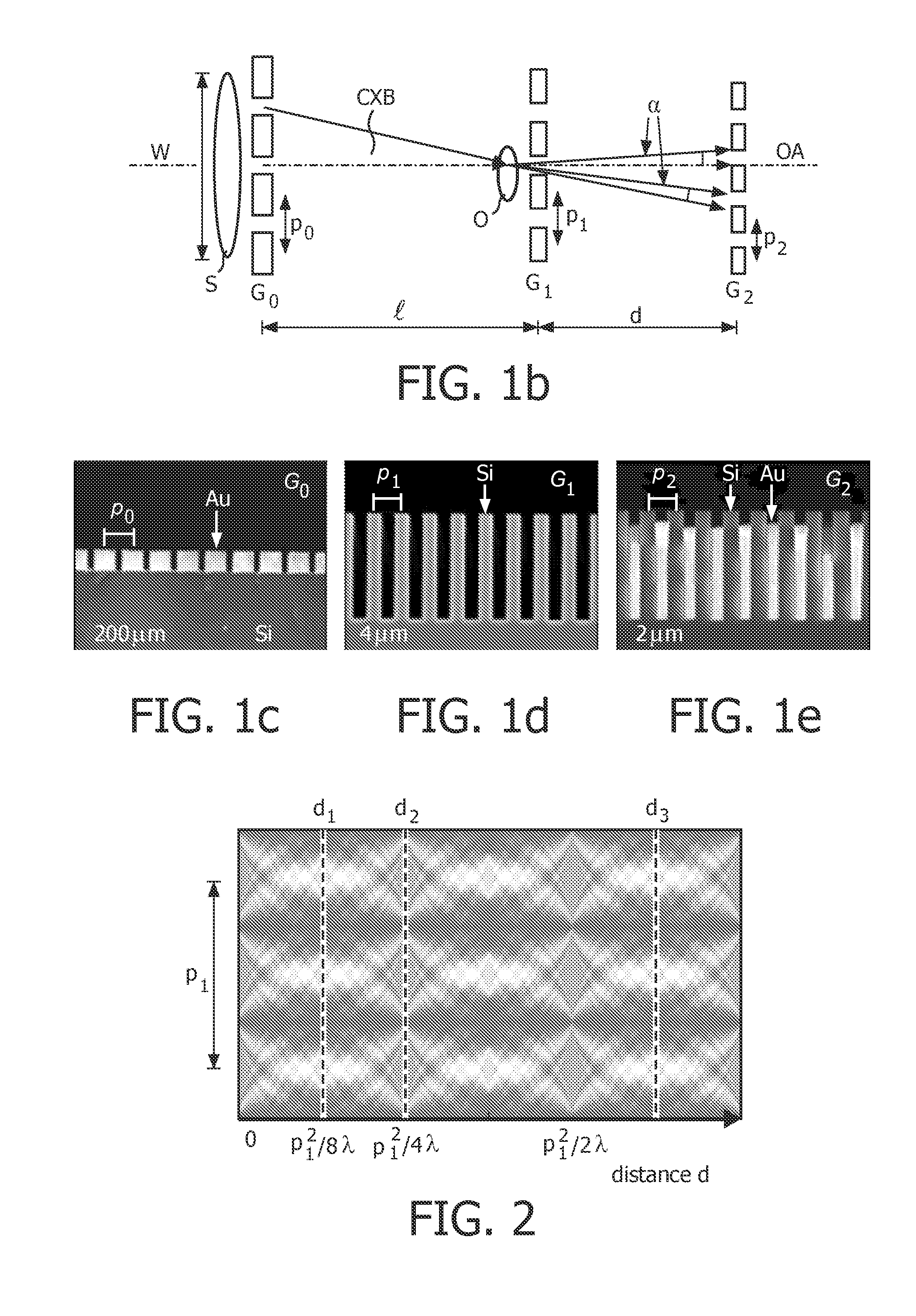
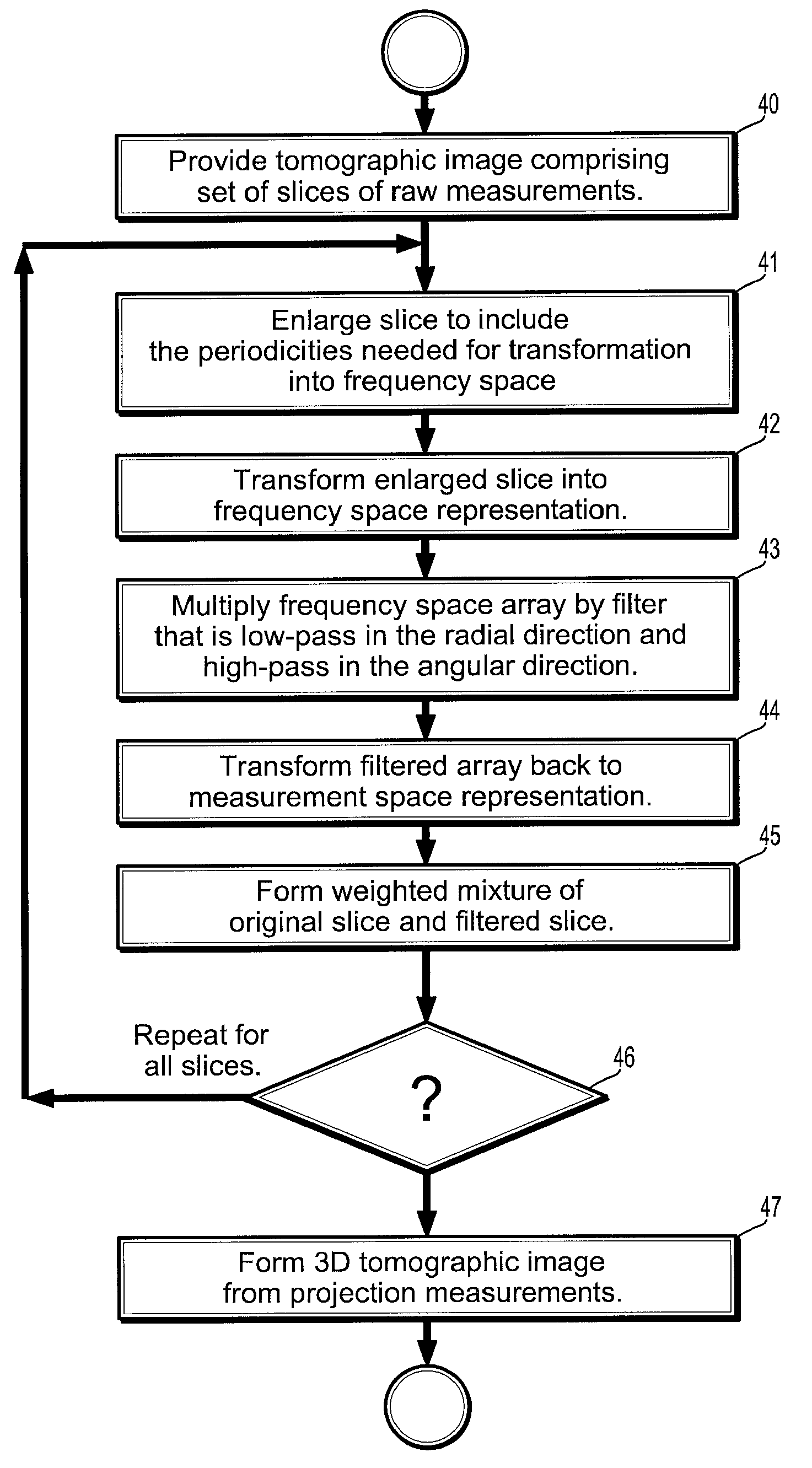
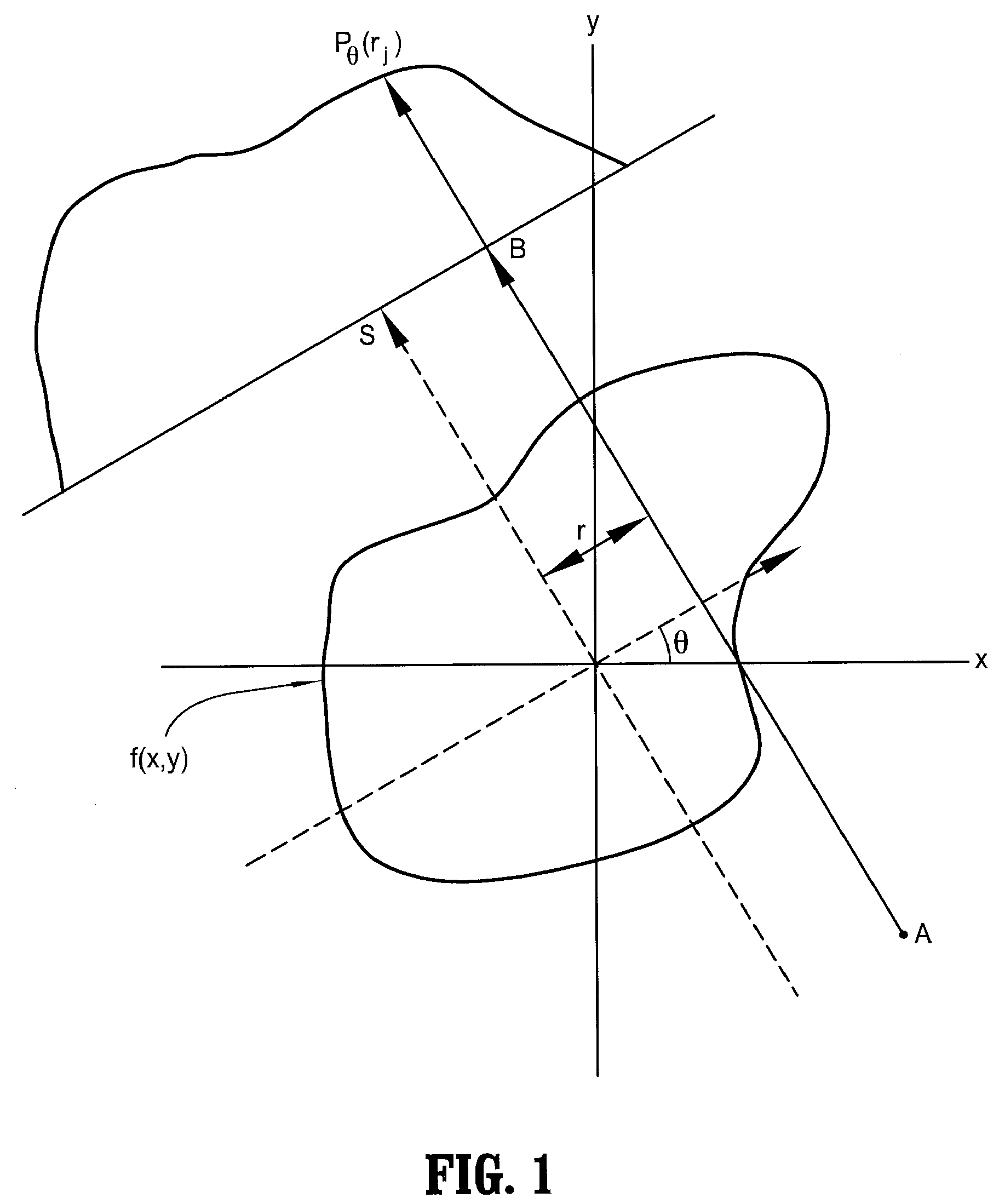
System and Method for Reducing Circular Artifacts in Tomographic Imaging
InactiveUS20080056549A1Reducing ring artifactReduce artifactsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhysicsA domain
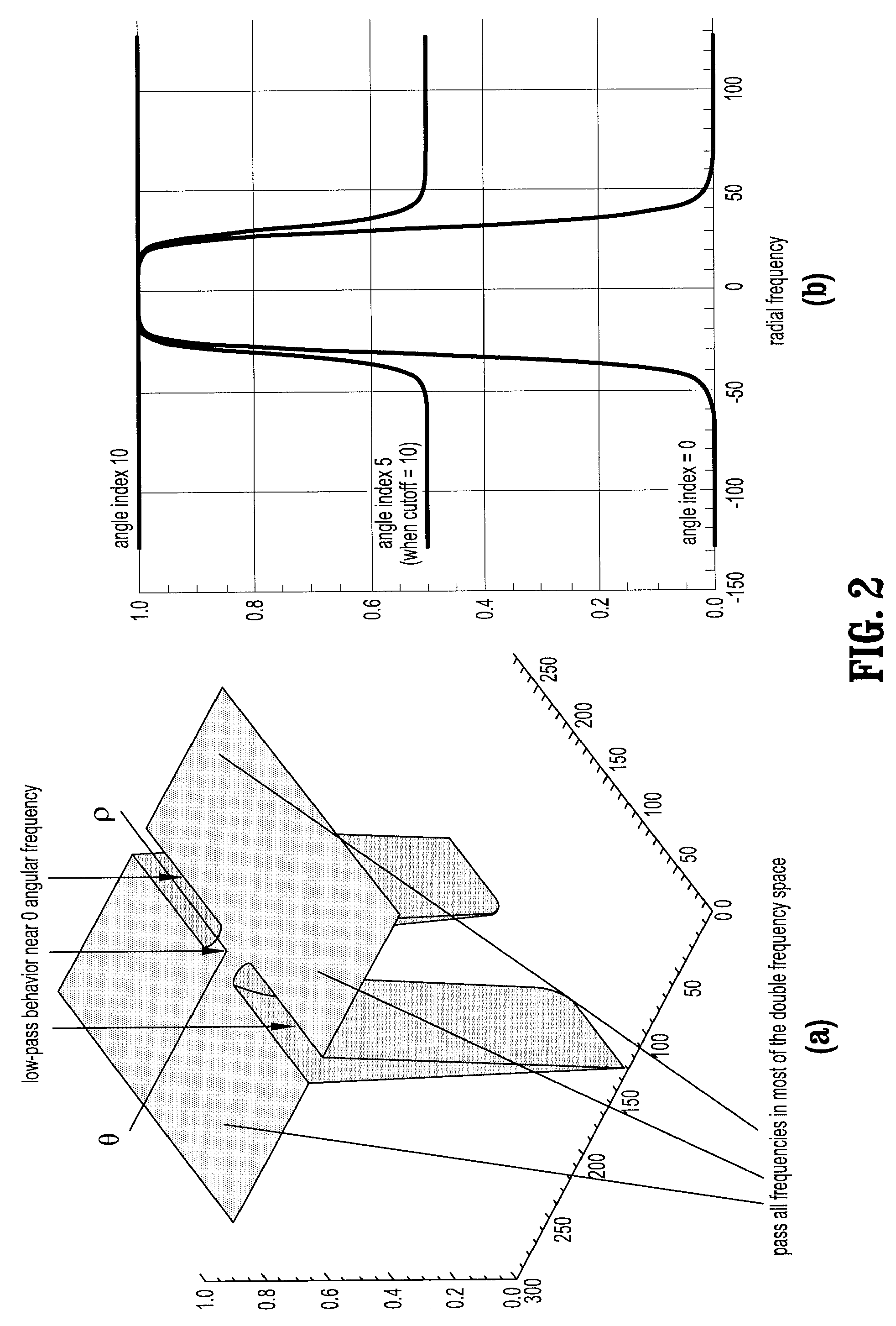
A method of reducing ring artifacts in tomographic images including providing an original digitized projection measurement comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a domain of points on an 2-dimensional grid, operating on said original projection measurement with a filter wherein features of high radial frequency and low angular frequency are attenuated, forming a weighted mixture of said filtered projection measurement and said original projection measurement wherein ring artifacts in said original tomographic image are substantially reduced, and reconstructing the projection measurement to form a tomographic image. Alternatively, a first tomographic image is reconstructed from said original projection measurement, a second tomographic image is reconstructed from said filtered projection measurement, and a weighted mixture is formed from said first tomographic image and said second tomographic image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Monitoring and Mapping of Atmospheric Phenomena
InactiveUS20090160700A1Rainfall/precipitation gaugesWeather condition predictionUltrasound attenuationTemporal information
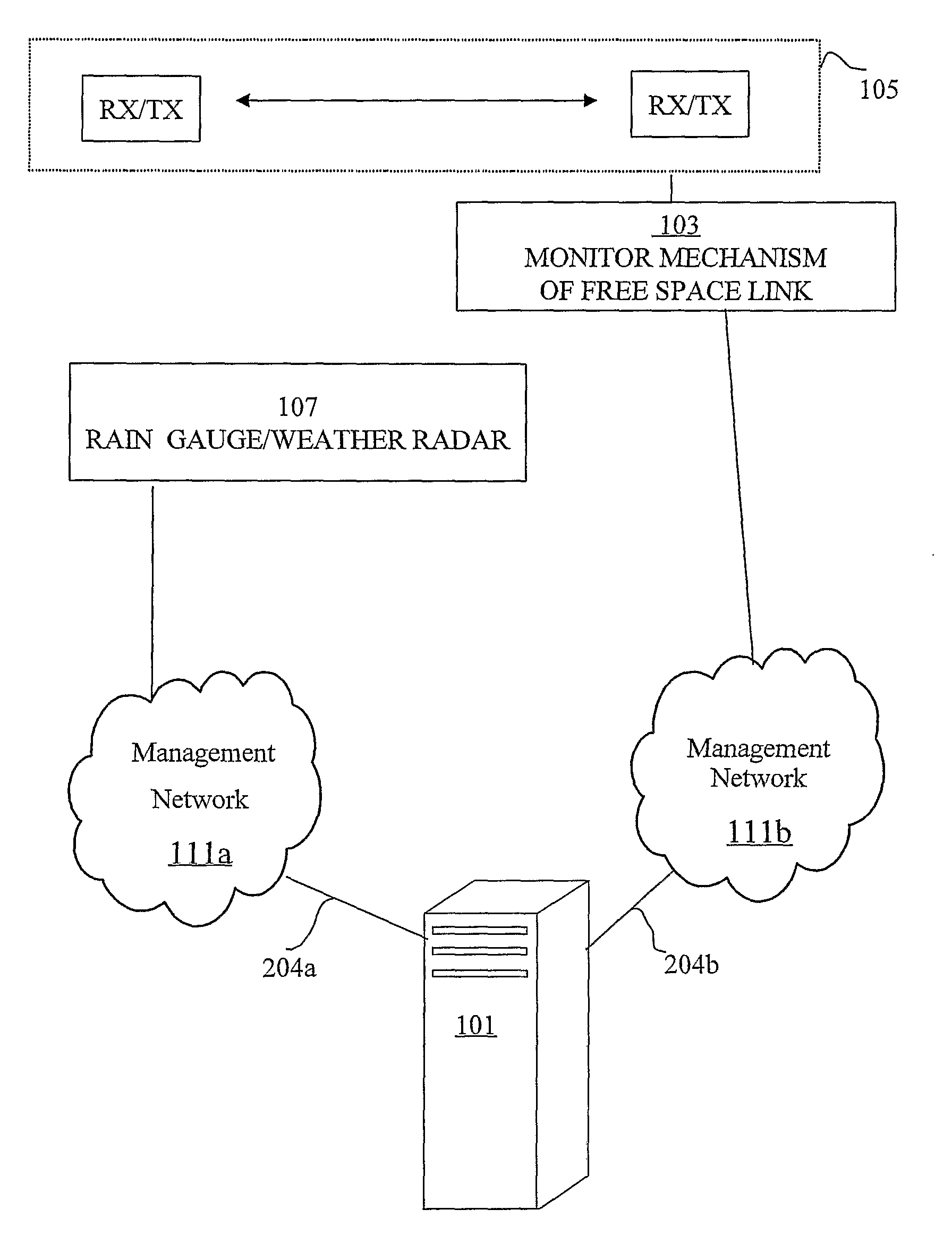
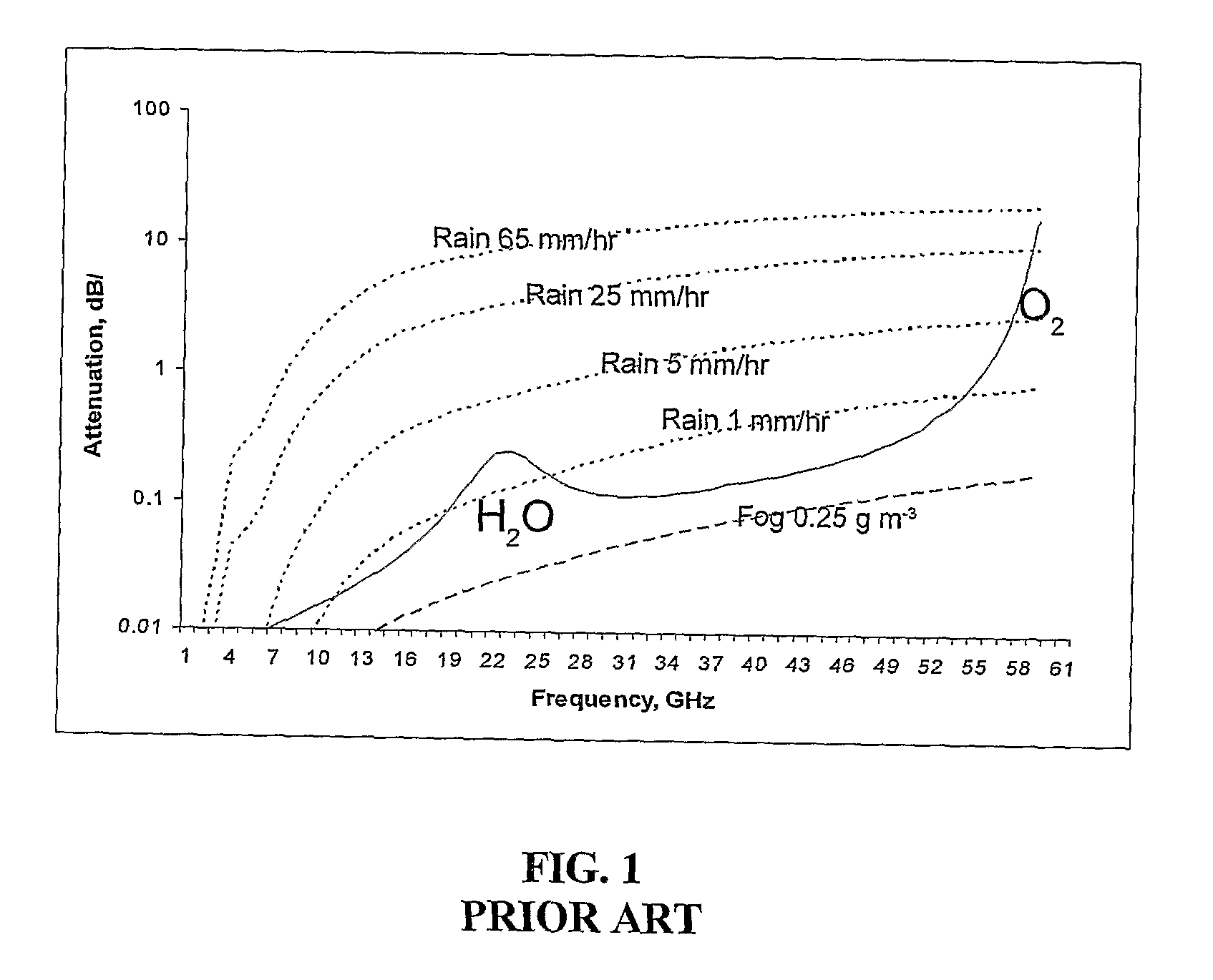
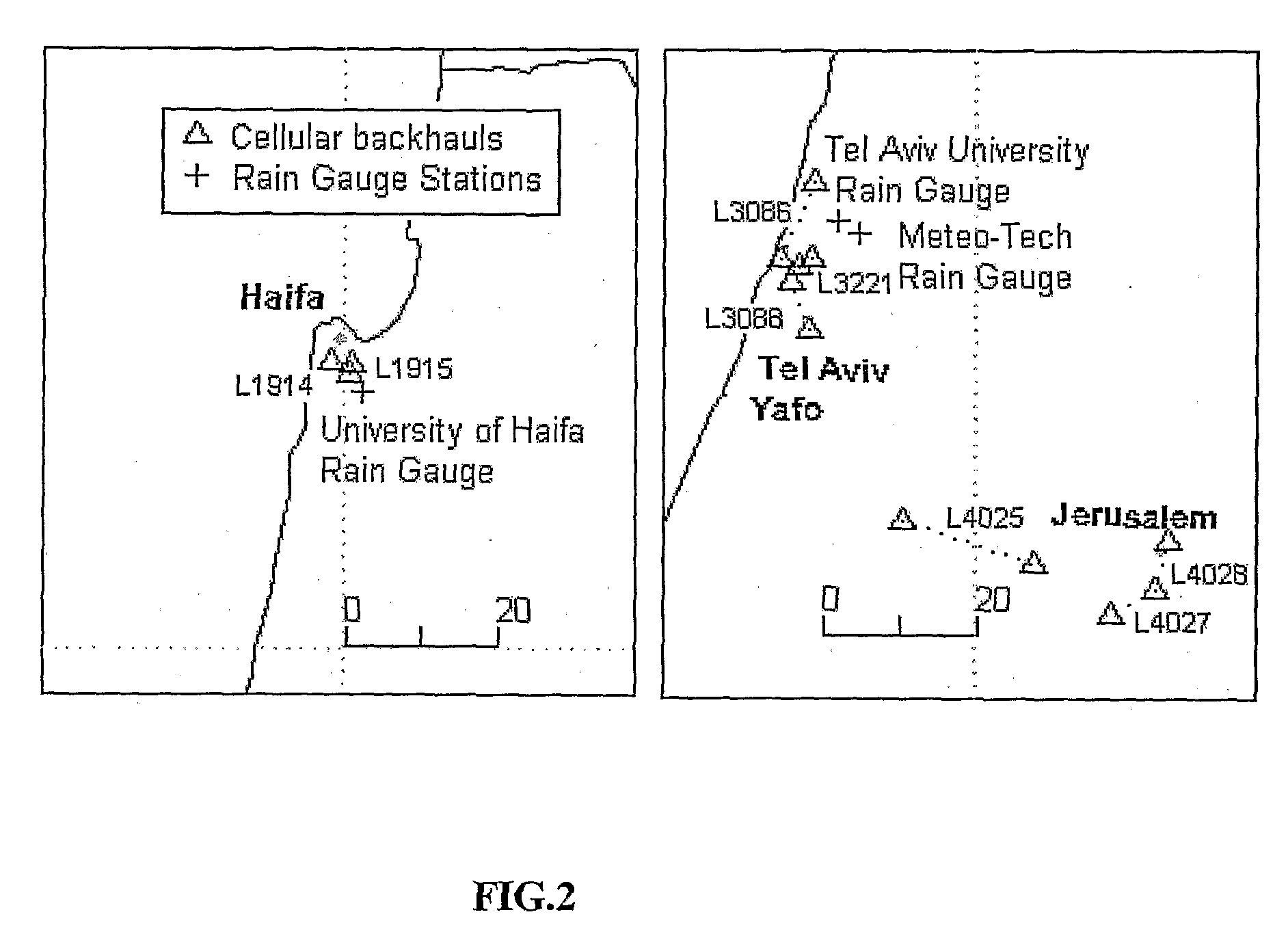
A computerized system for mapping an atmospheric phenomenon in a geographic region. Multiple free-space electromagnetic communications links are previously distributed in the geographic region. The system includes an interface to monitoring mechanisms attached respectively to the free-space electromagnetic communications links. The monitoring mechanisms respectively monitor attenuation levels of the free-space electromagnetic communications links. A processor simultaneously processes the attenuation levels, and maps in the geographic region the atmospheric phenomenon. The simultaneous processing preferably applies a non-linear model which relates the attenuation levels the atmospheric phenomenon, and solves a tomographic problem based on the non-linear model and the attenuation levels. The tomographic problem is preferably solved by an interactive algorithm based on consecutive refinement and linear inversion at each iteration. Alternatively, an interpolation is performed based on respective inverse distance from the communications links. Preferably, the interpolation is further based on respective lengths of communications links. A data interface preferably provides to subscribers temporal information related to the atmospheric phenomenon within portions of the geographic region.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Real time ultrasound monitoring of the motion of internal structures during respiration for control of therapy delivery
InactiveUS20060241443A1Organ movement/changes detectionChiropractic devicesHelical computed tomographyReal time ultrasound
A method of targeting therapy such as radiation treatment to a patient includes: identifying a target lesion inside the patient using an image obtained from an imaging modality selected from the group consisting of computed axial tomography, magnetic resonance tomography, positron emission tomography, and ultrasound; identifying an anatomical feature inside the patient on a static ultrasound image; registering the image of the target lesion with the static ultrasound image; and tracking movement of the anatomical feature during respiration in real time using ultrasound so that therapy delivery to the target lesion is triggered based on (1) movement of the anatomical feature and (2) the registered images.
Owner:CIVCO MEDICAL INSTR CO
Scanning slot cone-beam computed tomography and scanning focus spot cone-beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20070280408A1Minimize radiation doseAvoid artifactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhysicsTomography
A method of imaging an object that includes directing a plurality of x-ray beams in a fan-shaped form towards an object, detecting x-rays that pass through the object due to the directing a plurality of x-ray beams and generating a plurality of imaging data regarding the object from the detected x-rays. The method further includes forming either a three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography, digital tomosynthesis or Megavoltage image from the plurality of imaging data and displaying the image.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
3-d quantitative-imaging ultrasonic method for bone inspections and device for its implementation
InactiveUS20110112404A1Enabling useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsPorositySonification
The invention is a differential 3D Quantitative-Imaging Ultrasonic Tomography method for inspecting a layered system that is comprised of a heterogeneous object embedded in a volume of space that comprises layers having an acoustic impedance gradient between the layers providing non-linear beams travels. A transducer grid is attached to the surface of the layered system in a unilateral manner. By sequentially changing the distance between transmitter and receiver the fastest travel times of the ultrasonic oscillations are measured. A differential approach provides from the data the longitudinal wave velocities values for each elementary volume that make up an inspected volume. These values are used to construct two and three-dimensional maps of the longitudinal wave velocity values distribution in the inspected volume and the porosity values distribution in the heterogeneous object. By applying statistical treatment to the obtained data the longitudinal wave velocity in the inspected material matrix part is estimated.
Owner:GOUREVITCH ALLA
Method and apparatus for medical imaging using near-infrared optical tomography and flourescence tomography combined with ultrasound
ActiveUS20080058638A1High qualityGreat frequencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansTissue volumeFluorescence
Methods and apparatus for medical imaging using diffusive optical tomography and fluorescent diffusive optical tomography are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method for medical imaging comprises, scanning a tissue volume with near-infrared light to obtain structural parameters, wherein the tissue volume includes a biological entity, scanning the tissue volume with near-infrared light to obtain optical and fluorescence measurements of the scanned volume, segmenting the scanned volume into a first region and a second region, and reconstructing an optical image and a fluorescence image of at least a portion of the scanned volume from the structural parameters and the optical and fluorescence measurements. In another embodiment an apparatus for medical imaging is disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Nuclear medicine imaging system and method using multiple types of imaging detectors
ActiveUS20120248320A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyHelical computed tomographyNuclear medicine imaging
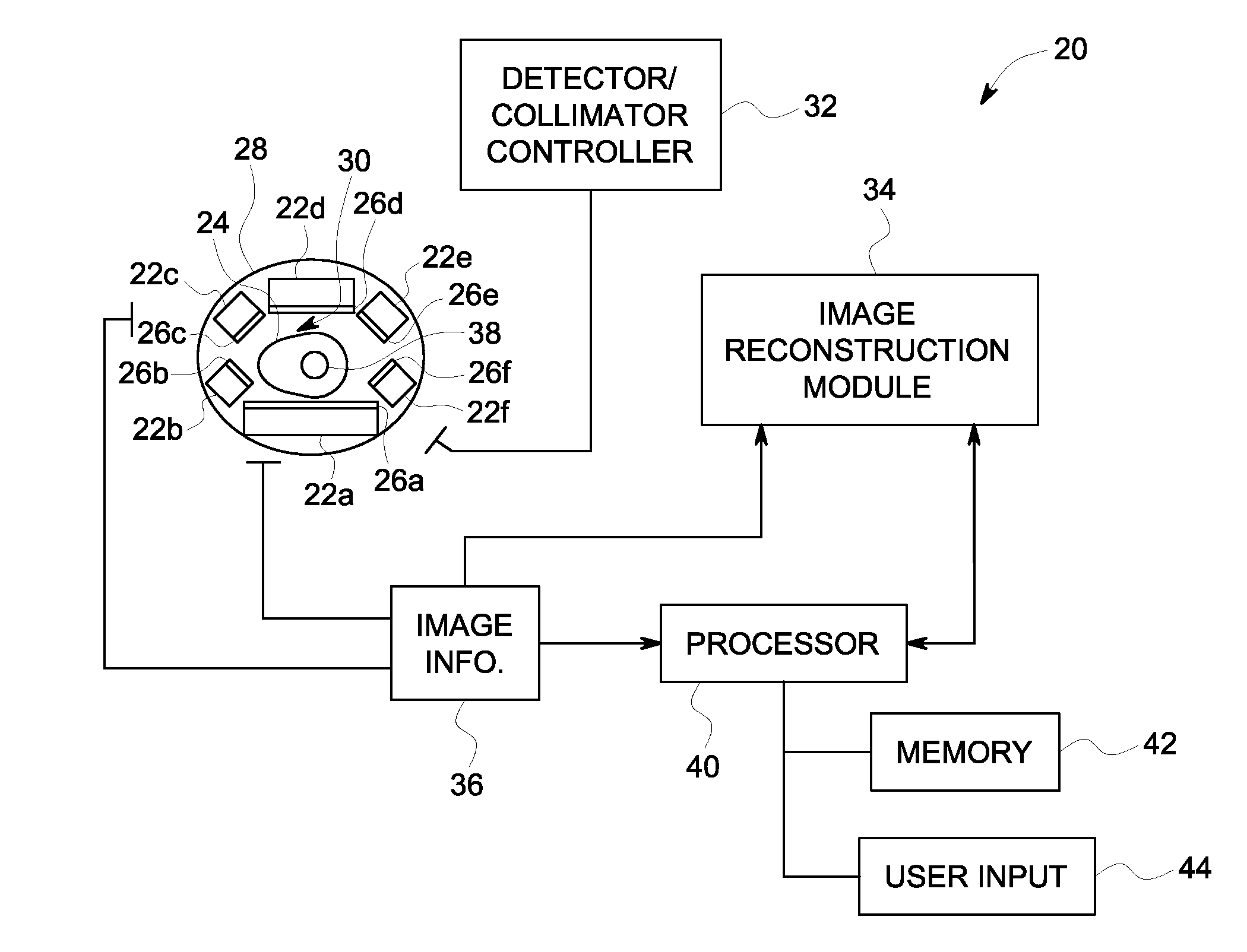
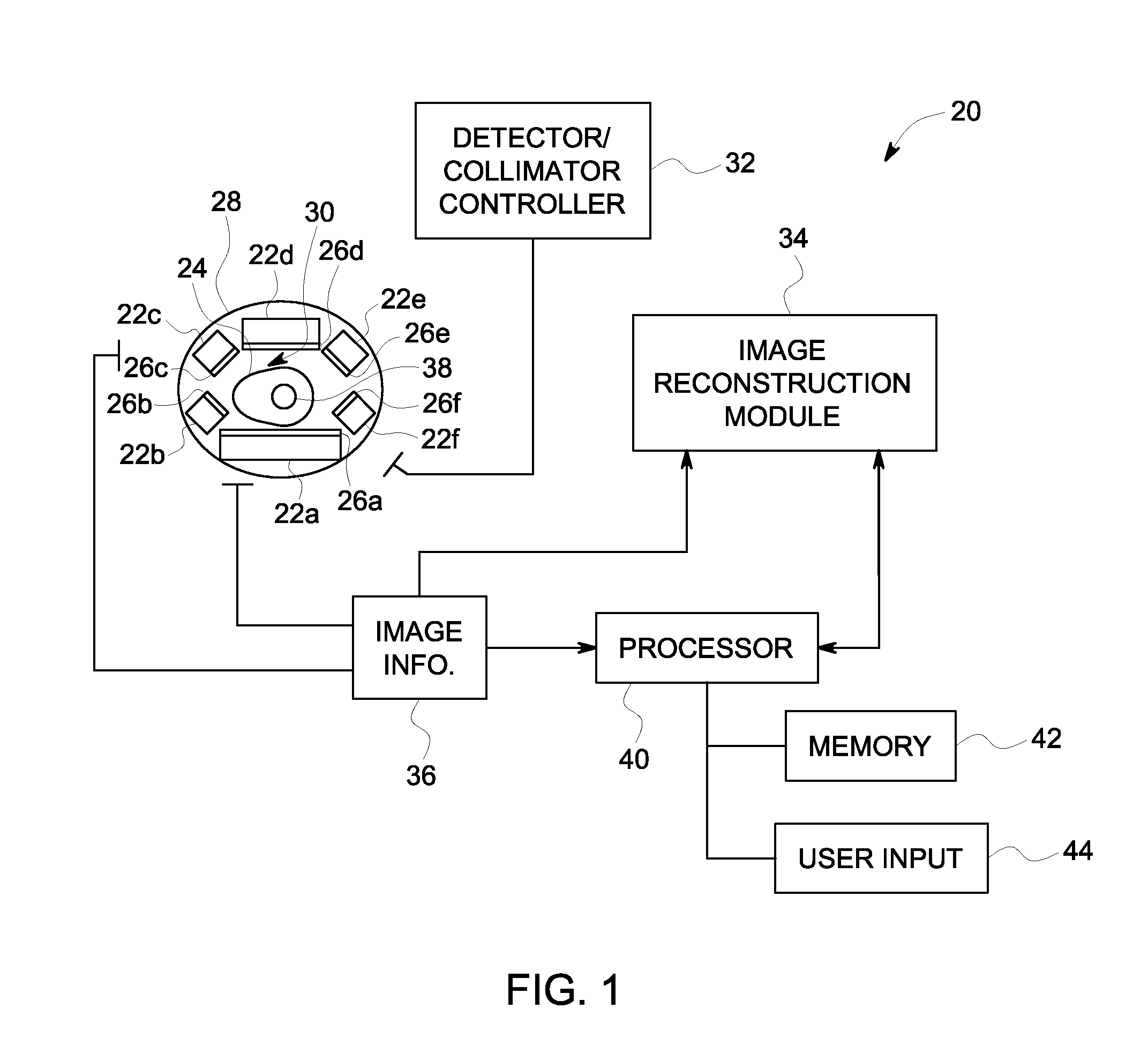
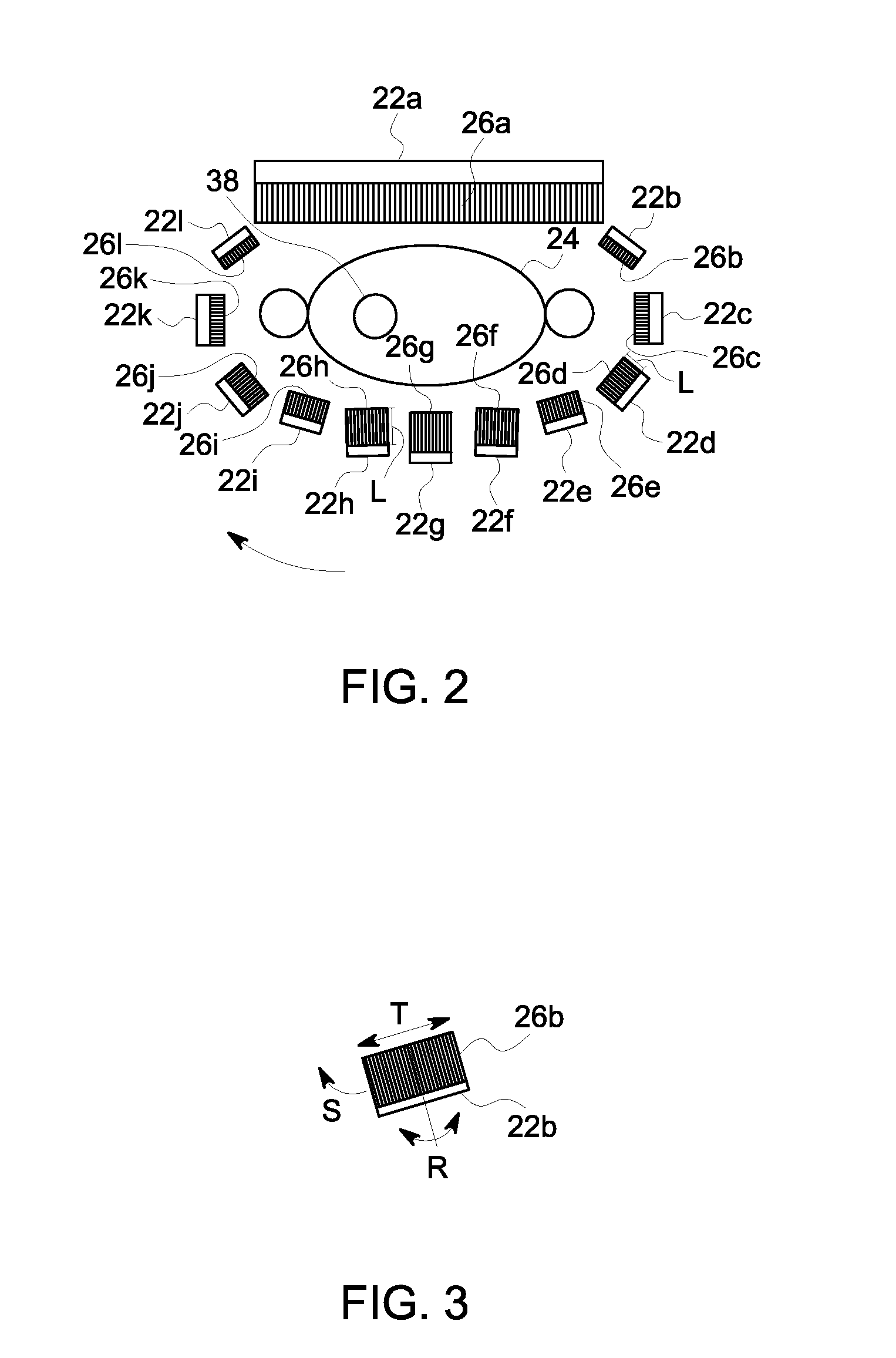
A Nuclear Medicine (NM) imaging system and method using multiple types of imaging detectors are provided. One NM imaging system includes a gantry, at least a first imaging detector coupled to the gantry, wherein the first imaging detector is a non-moving detector, and at least a second imaging detector coupled to the gantry, wherein the second imaging detector is a moving detector. The first imaging detector is larger than the second imaging detector and the first and second imaging detectors have different detector configurations. The NM imaging system further includes a controller configured to control the operation of the first and second imaging detectors during an imaging scan of an object to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) image information such that at least the first imaging detector remains stationary with respect to the gantry during image acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
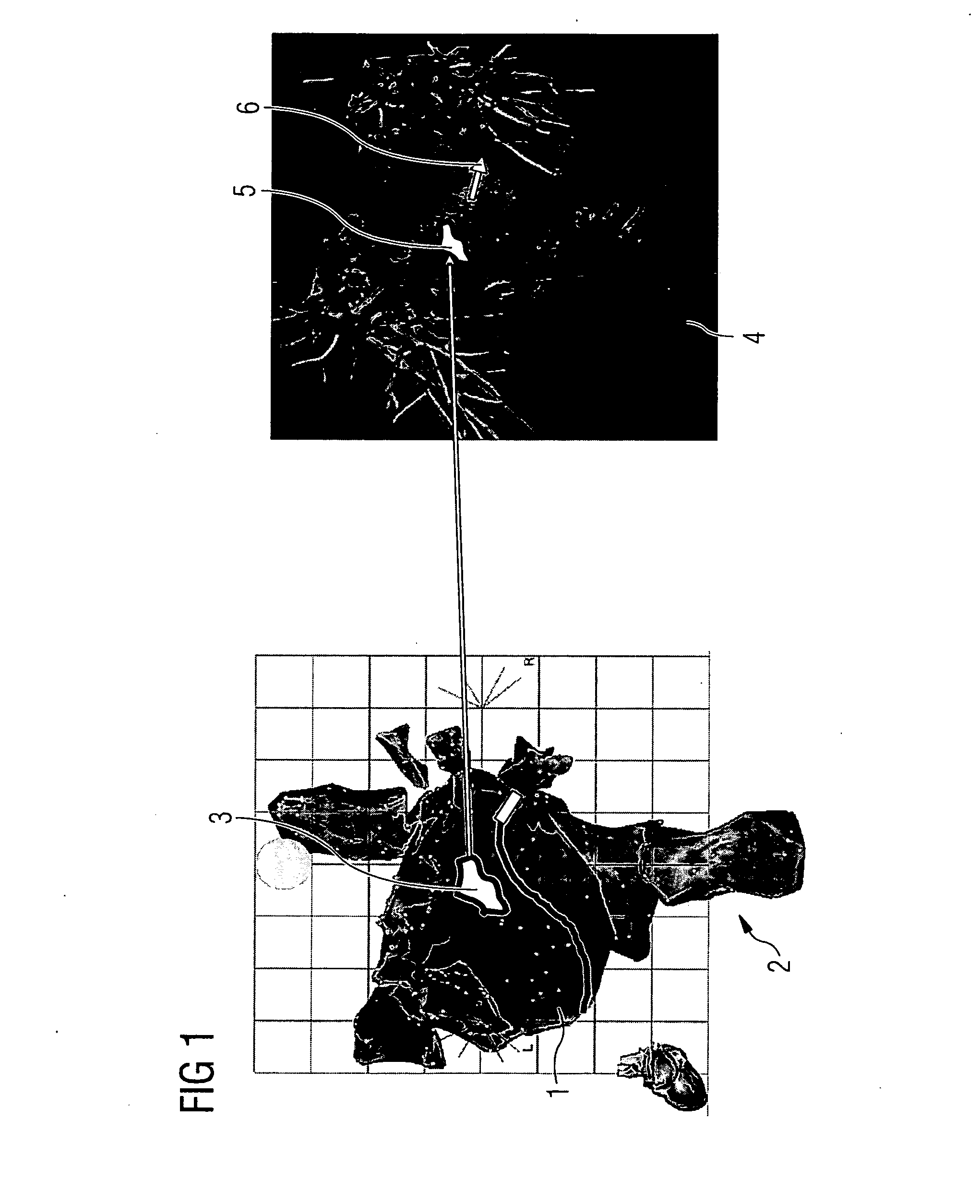
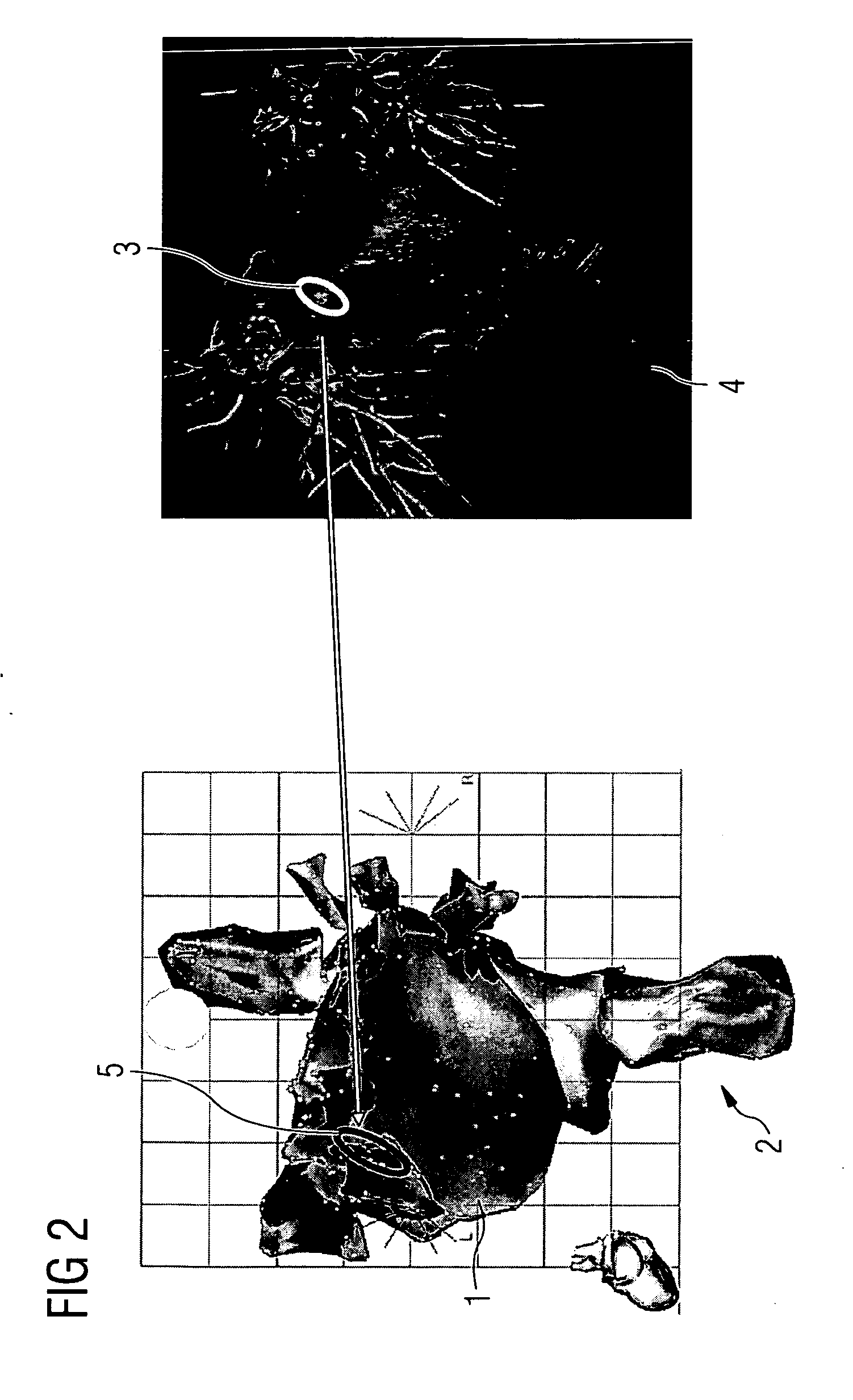
Method and apparatus for visually supporting an electrophysiological catheter application in the heart by means of bidirectional information transfer
InactiveUS20070167706A1Rapid overview of positionRapid overview of extentReconstruction from projectionSurgical instrument detailsElectricityInformation transmission
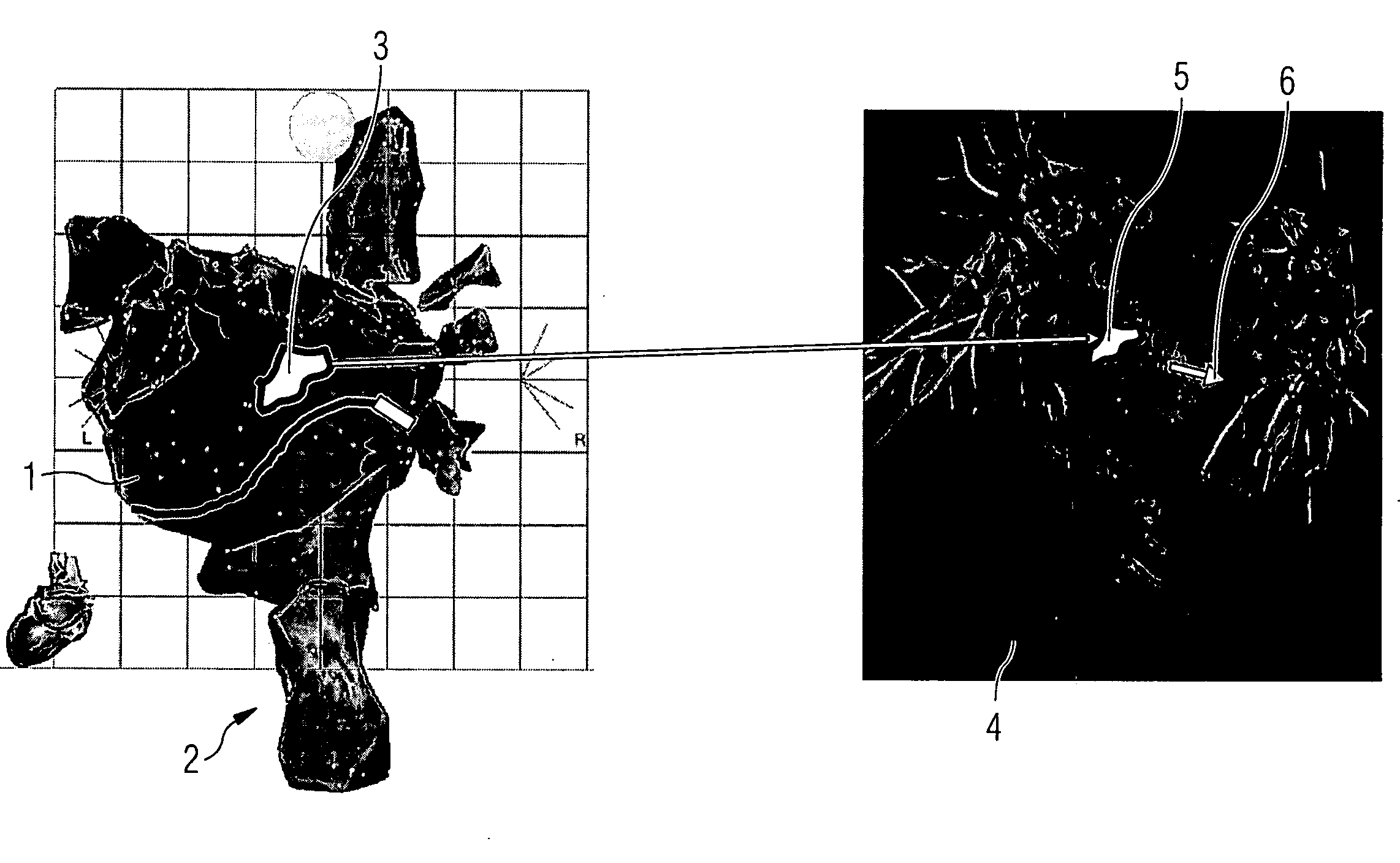
Method and apparatus for visually supporting an electrophysiological catheter application in the heart by means of bidirectional information transfer The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for visually supporting an electrophysiological catheter application in the heart. For the method, 3D image data of at least the heart, which is captured using a tomographic 3D imaging method prior to execution of the catheter application, and electroanatomical 3D mapping data of at least one area of the heart to be treated, which is captured during execution of the catheter application, is provided and the electroanatomical 3D mapping data and / or at least part of the 3D image data is displayed during execution of the catheter application. The method is characterized in that, in the electroanatomical 3D mapping data and / or the 3D image data, the contour of one or more areas (3) relevant to the catheter application is captured and transferred to the other system in each case on which the areas (3) are superimposed as a single polyline (5) in the representation (2, 4) of the electroanatomical 3D mapping data and / or 3D image data. The method proposed and the associated apparatus provide the user with a rapid overview of the areas relevant to the catheter application.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Q Tomography Method
ActiveUS20110273961A1Quality improvementSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTomographyFrequency shift
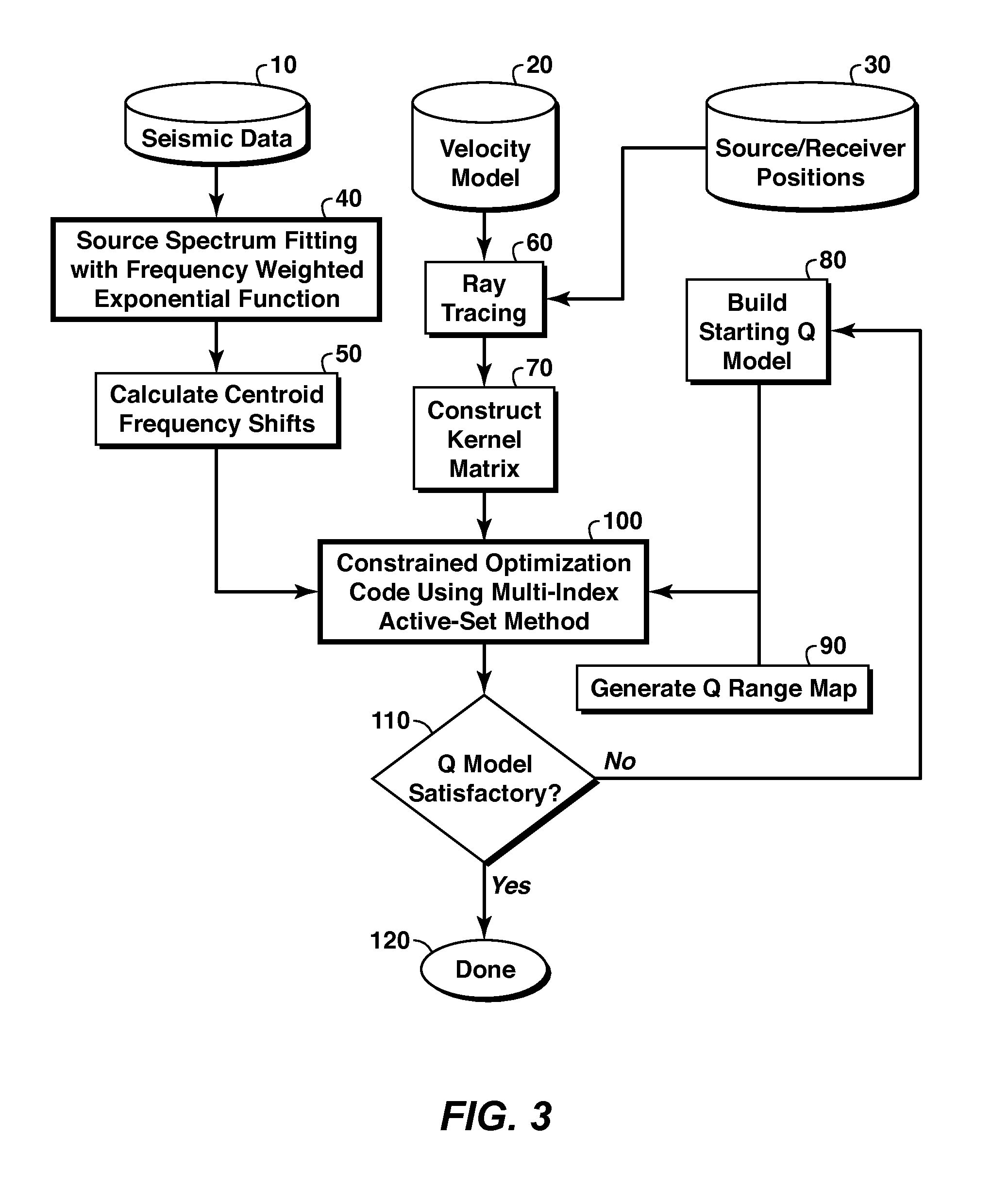
Method for reconstructing subsurface Q models (110) from seismic data (10) by performing ray-based (60), centroid frequency shift (50) Q tomography. The seismic source waveform's amplitude spectrum is approximated by a frequency-weighted exponential function of frequency (40), having two parameters to adjust to fit the frequency shift data, thereby providing a better fit to various asymmetric source amplitude spectra. Box constraints may be used in the optimization routine, and a multi-index active-set method used in velocity tomography is a preferred technique for implementing the box constraints (100).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Methods and systems for performing model-based iterative reconstruction
ActiveUS20130343624A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionX-rayJoint likelihood
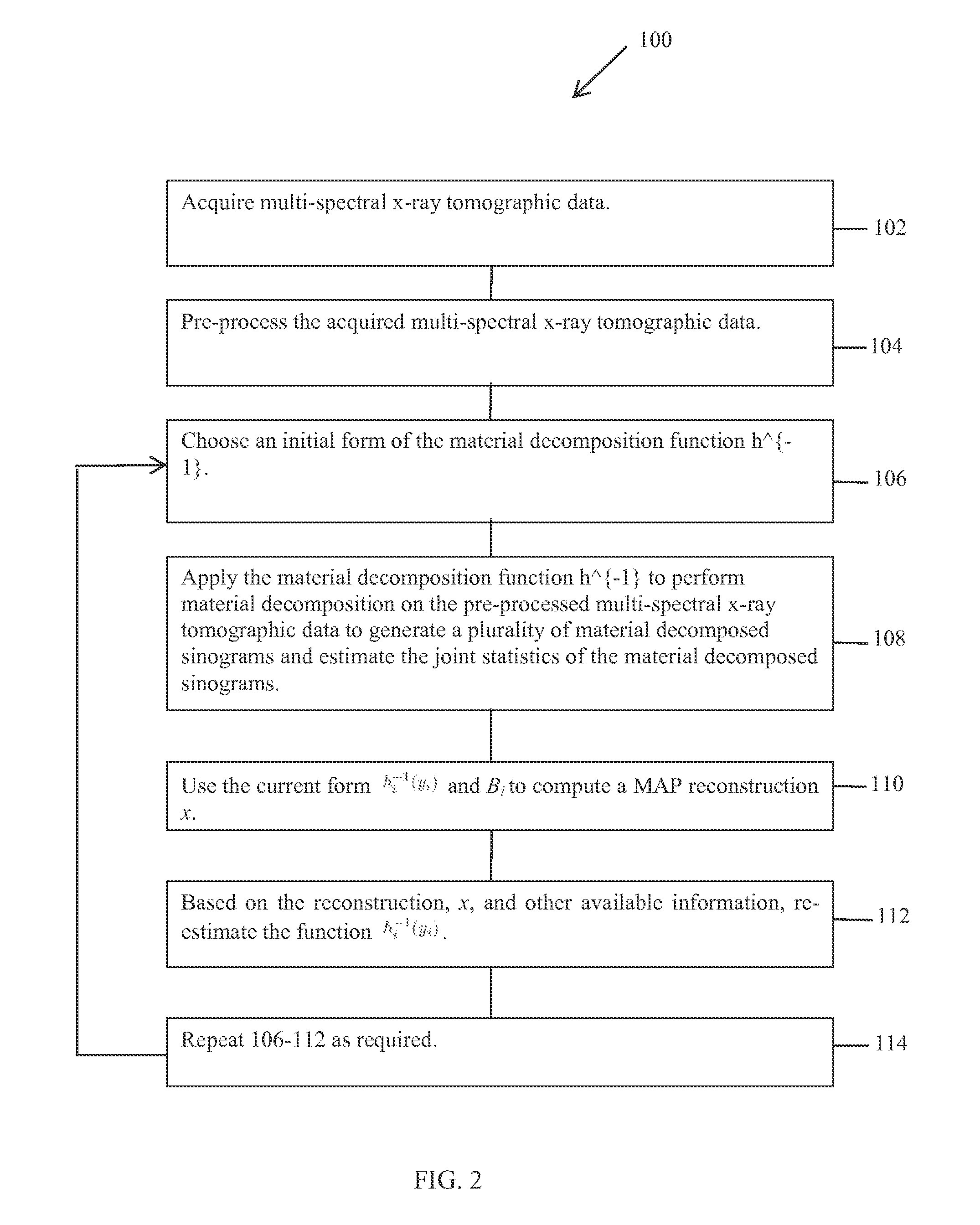
A method for reconstructing image component densities of an object includes acquiring multi-spectral x-ray tomographic data, performing a material decomposition of the multi-spectral x-ray tomographic data to generate a plurality of material sinograms, and reconstructing a plurality of material component density images by iteratively optimizing a functional that includes a joint likelihood term of at least two of the material decomposed sinograms. An x-ray tomography imaging system and a non-transitory computer readable medium are also described herein.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC +2
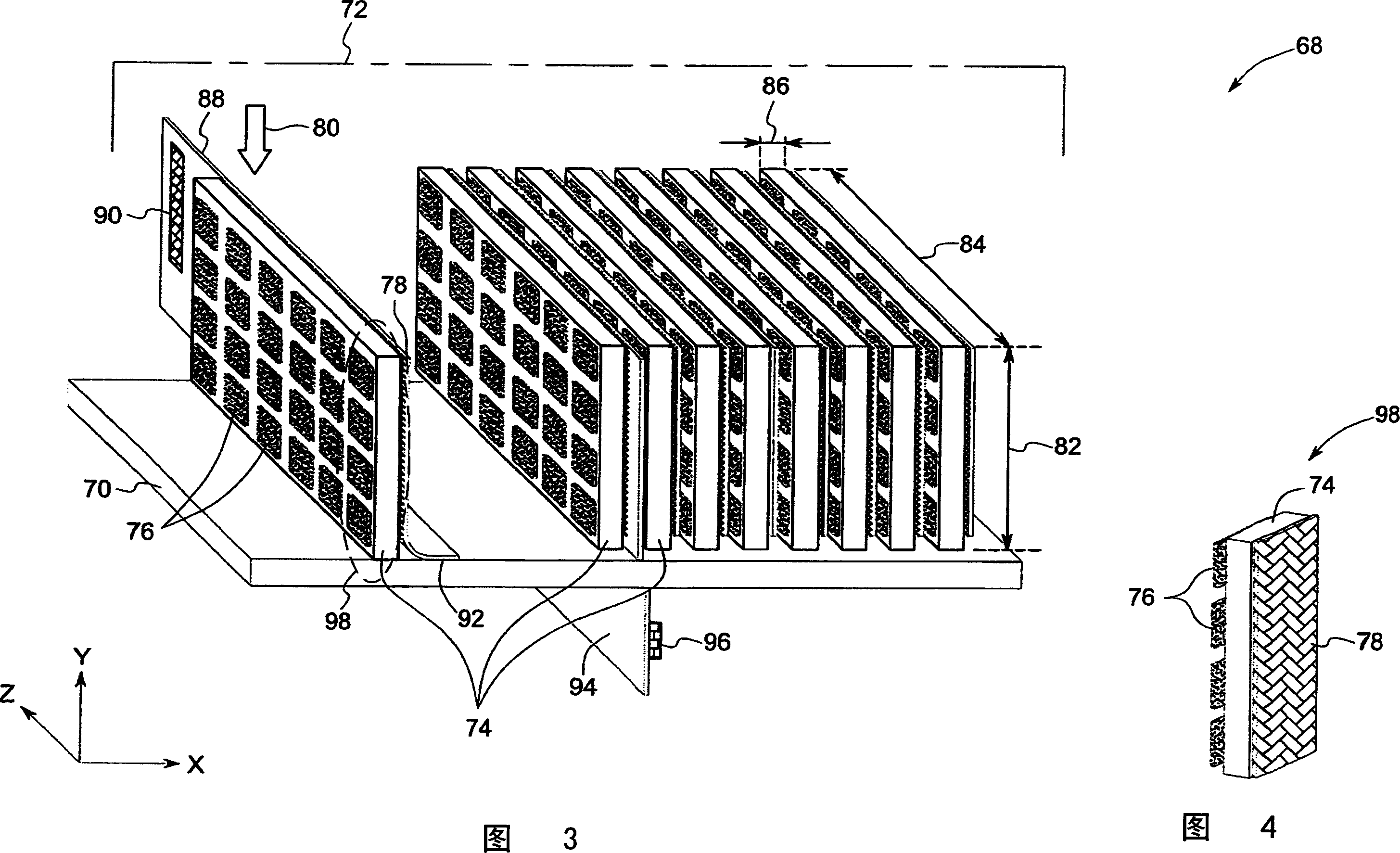
Multi-layer direct conversion computed tomography detector module
A computed tomography detector module is presented. The detector module includes a substrate having a topside and a bottom side. Additionally, the detector module includes a plurality of detector layers disposed on the top side of the substrate in a direction that is substantially orthogonal to the substrate, where each of the plurality of detector layers comprises a direct conversion material configured to absorb radiation, and where each of the plurality of detector layers comprises a first side and a second side. Further, the detector module includes a plurality of pixelated anode contacts is disposed on the first side of each of the plurality of detector layers. Also, the detector module includes a common cathode contact is disposed on the second side of each of the plurality of detector layers.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
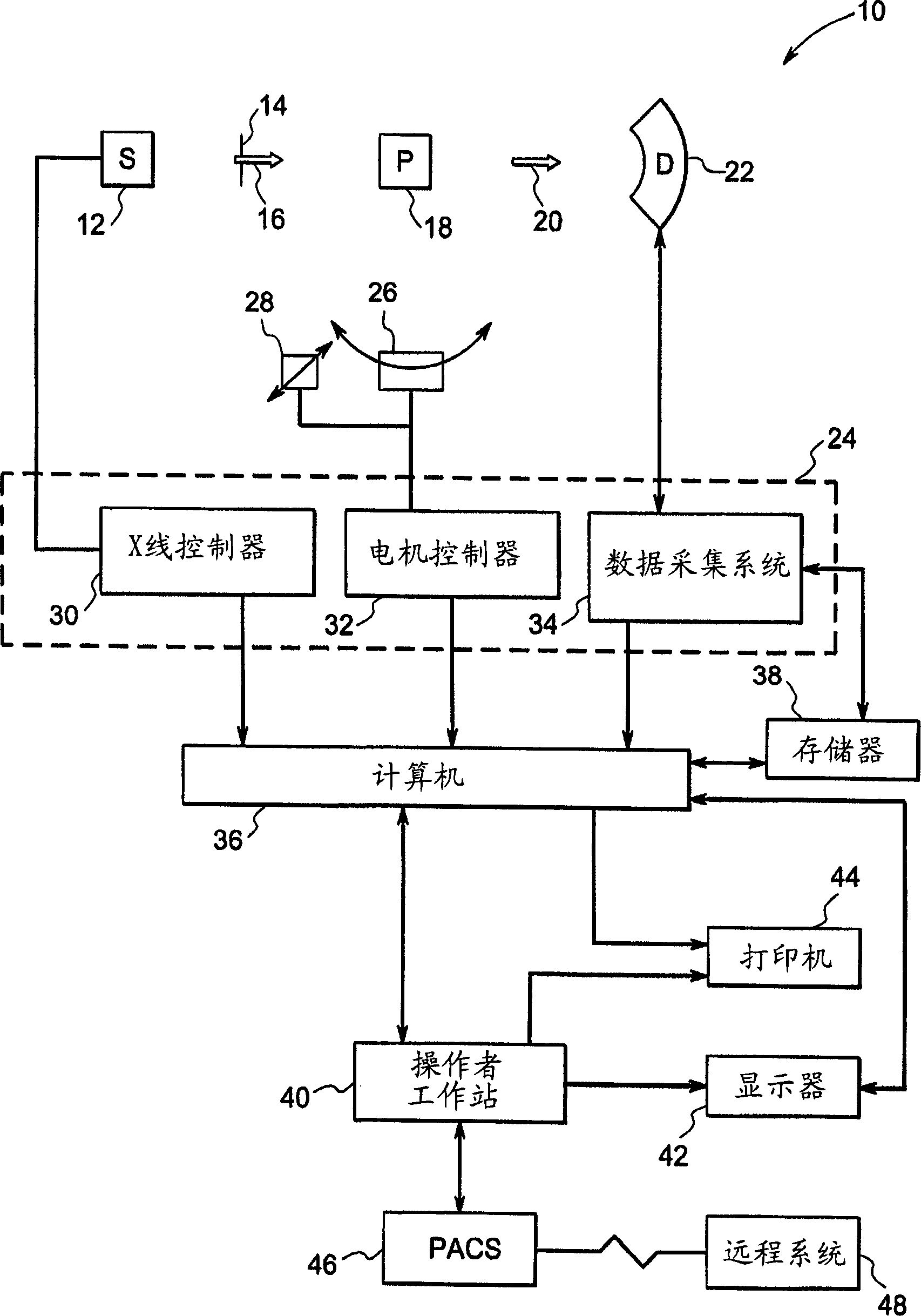
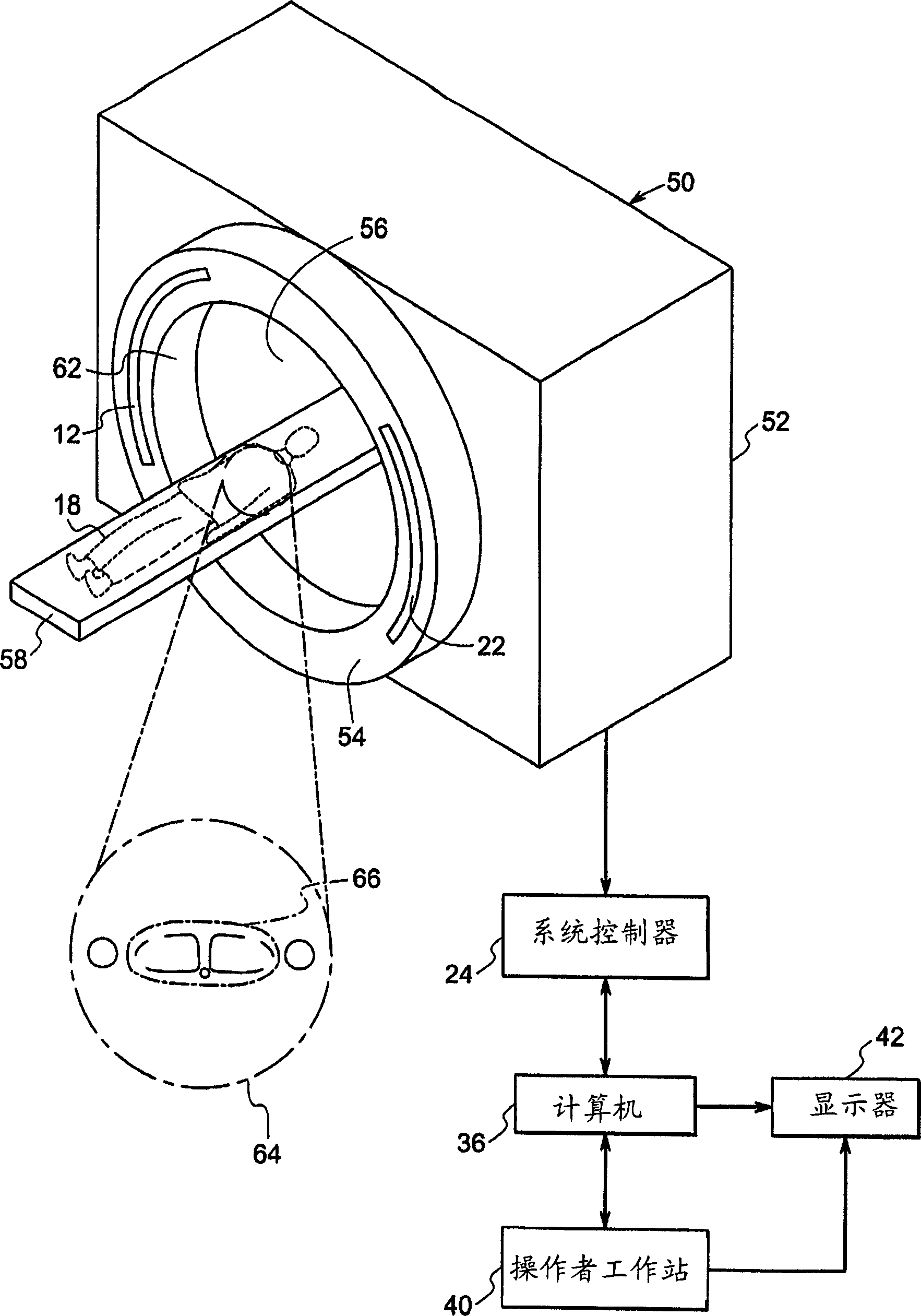
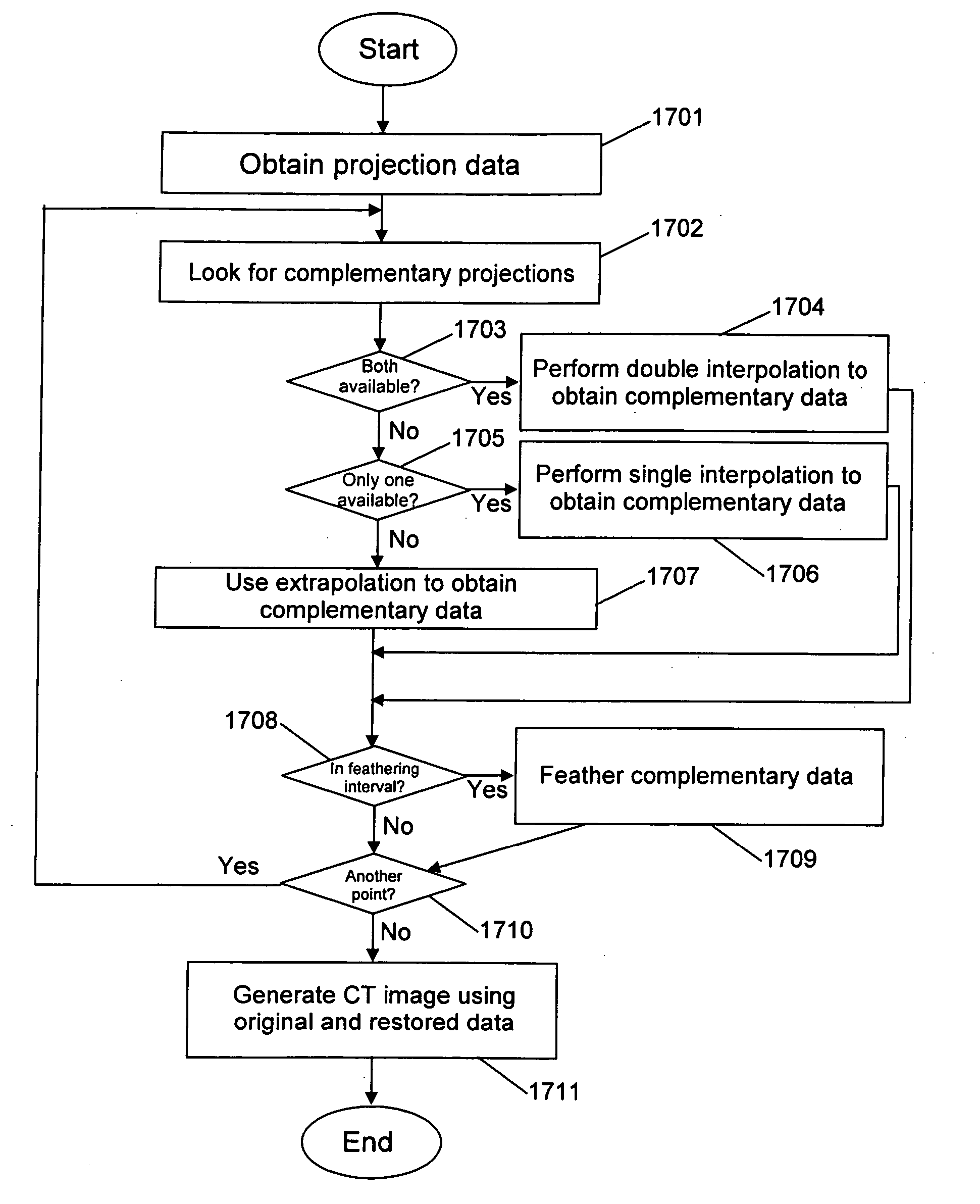
Method for restoring truncated helical cone-beam computed tomography data
InactiveUS20060104407A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical computed tomographyAlgorithm
A method, system, and computer program product for compensating for the unavailability of projection data of a scanned object at a selected point, the selected point located outside a detection range of a detector. The method include the steps of obtaining projection data of the scanned object, and compensating for the unavailability of the projection data at the selected point based on the obtained projection data and coordinates of the selected point relative to the detector. The compensating step includes determining at least one complementary projection angle and coordinates of at least one complementary point based on a source projection angle and the coordinates of the selected point relative to the detector, and estimating the projection data value at the selected point based on the acquired projection data, the at least one complementary projection angle, and the coordinates of the at least one complementary point.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
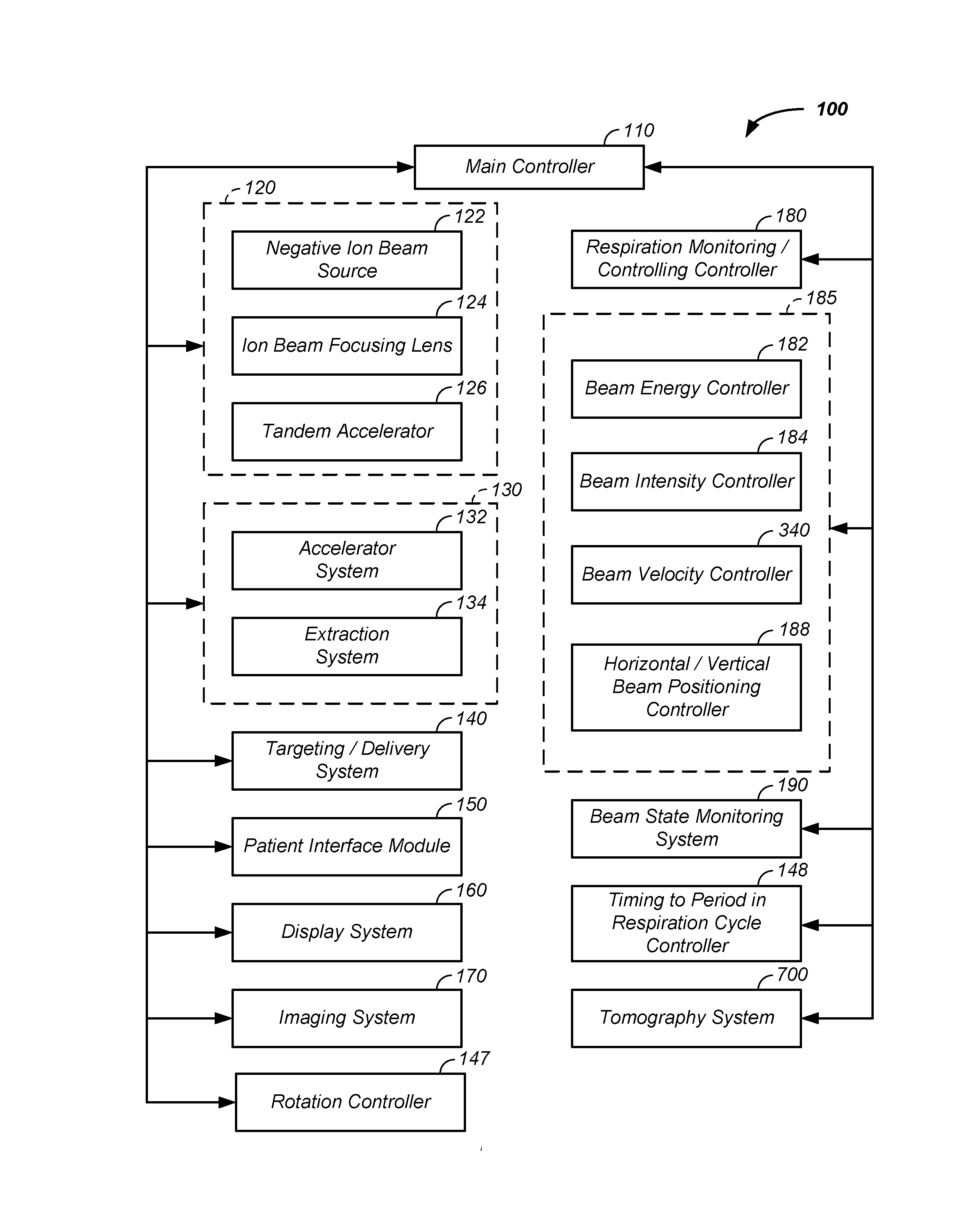
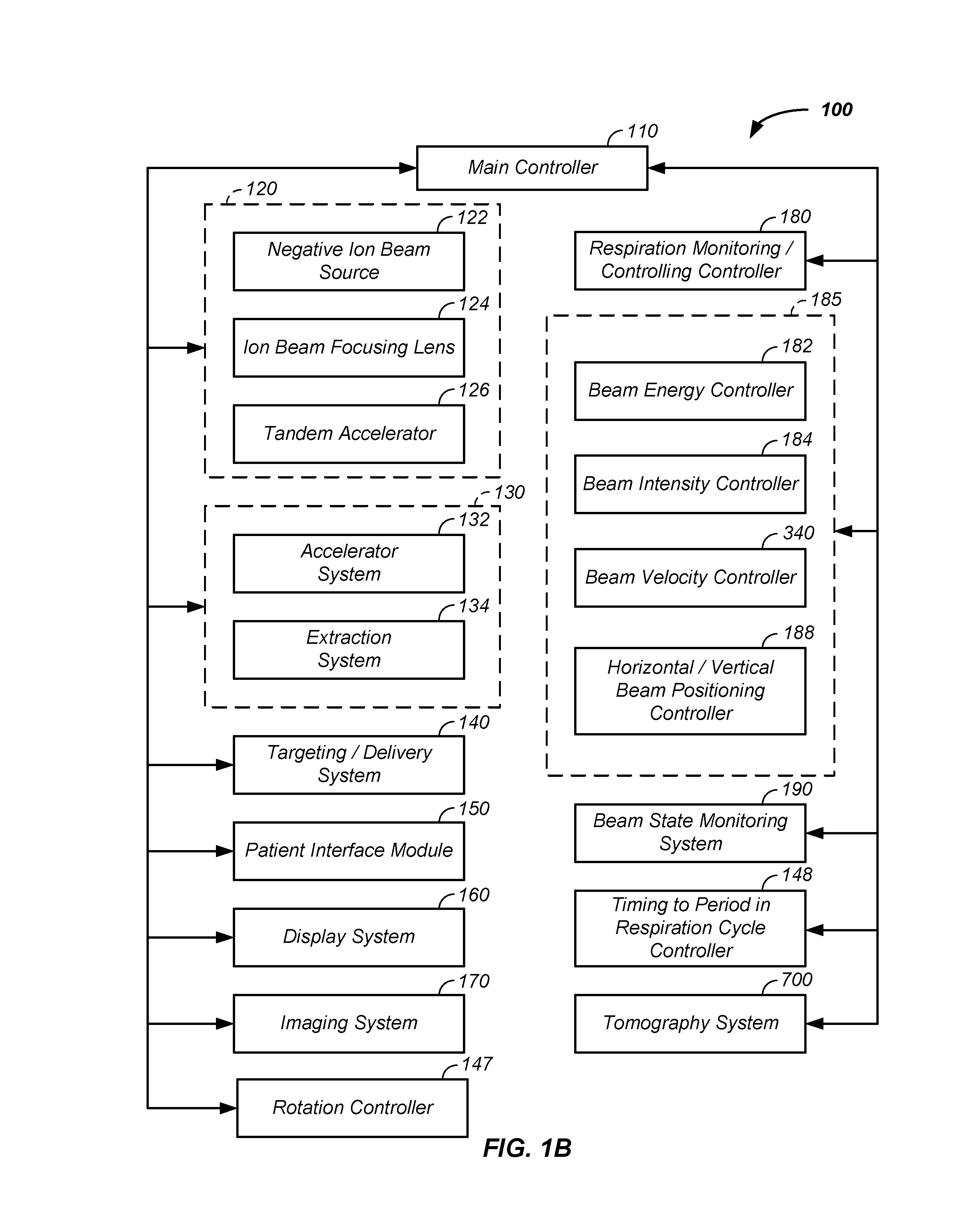
Charged particle - patient motion control system apparatus and method of use thereof
ActiveUS20160287907A1Beam deviation/focusing by electric/magnetic meansTomographyTomographyMolecular physics
The invention comprises a system for controlling a charged particle beam shape and direction relative to a controlled and dynamically positioned patient and / or an imaging surface, such as a scintillation plate of a tomography system and / or a first two-dimensional imaging system coupled to a second two-dimensional imaging system. Multiple interlinked beam / patient / imaging control stations allow safe zone operation and clear interaction with the charged particle beam system and the patient. Both treatment and imaging are facilitated using automated sequences controlled with a work-flow control system.
Owner:PROTOM INT HLDG CORP
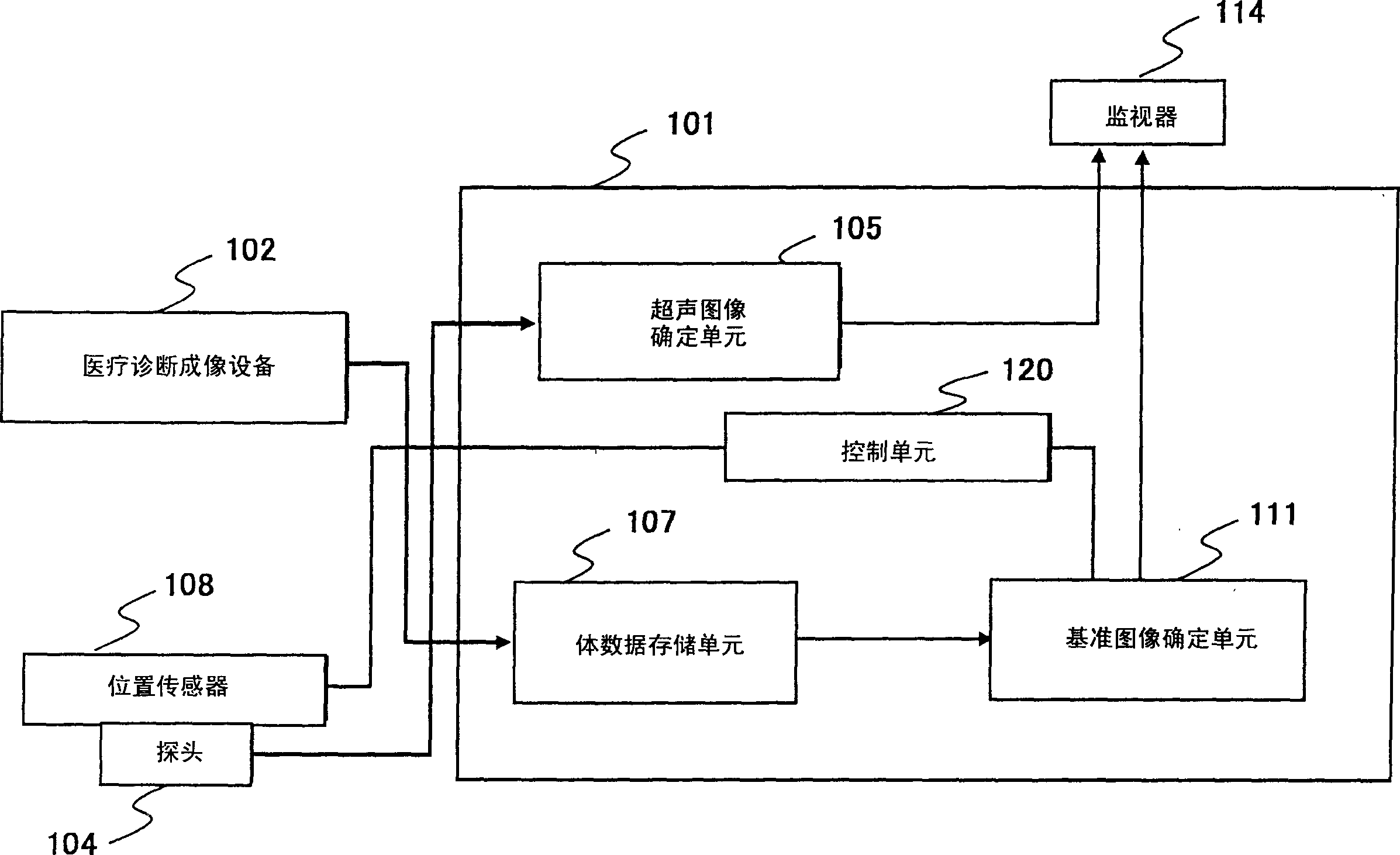
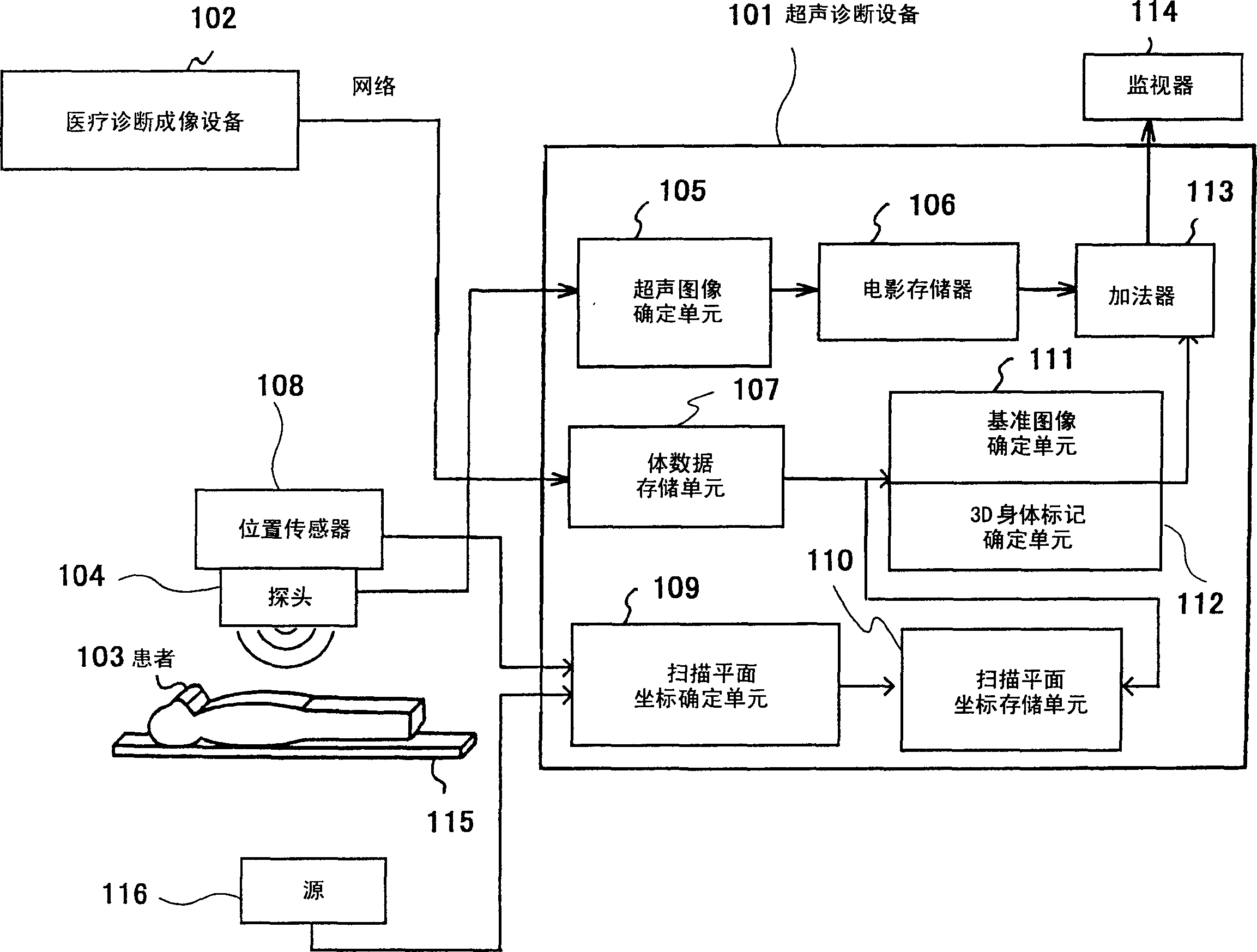
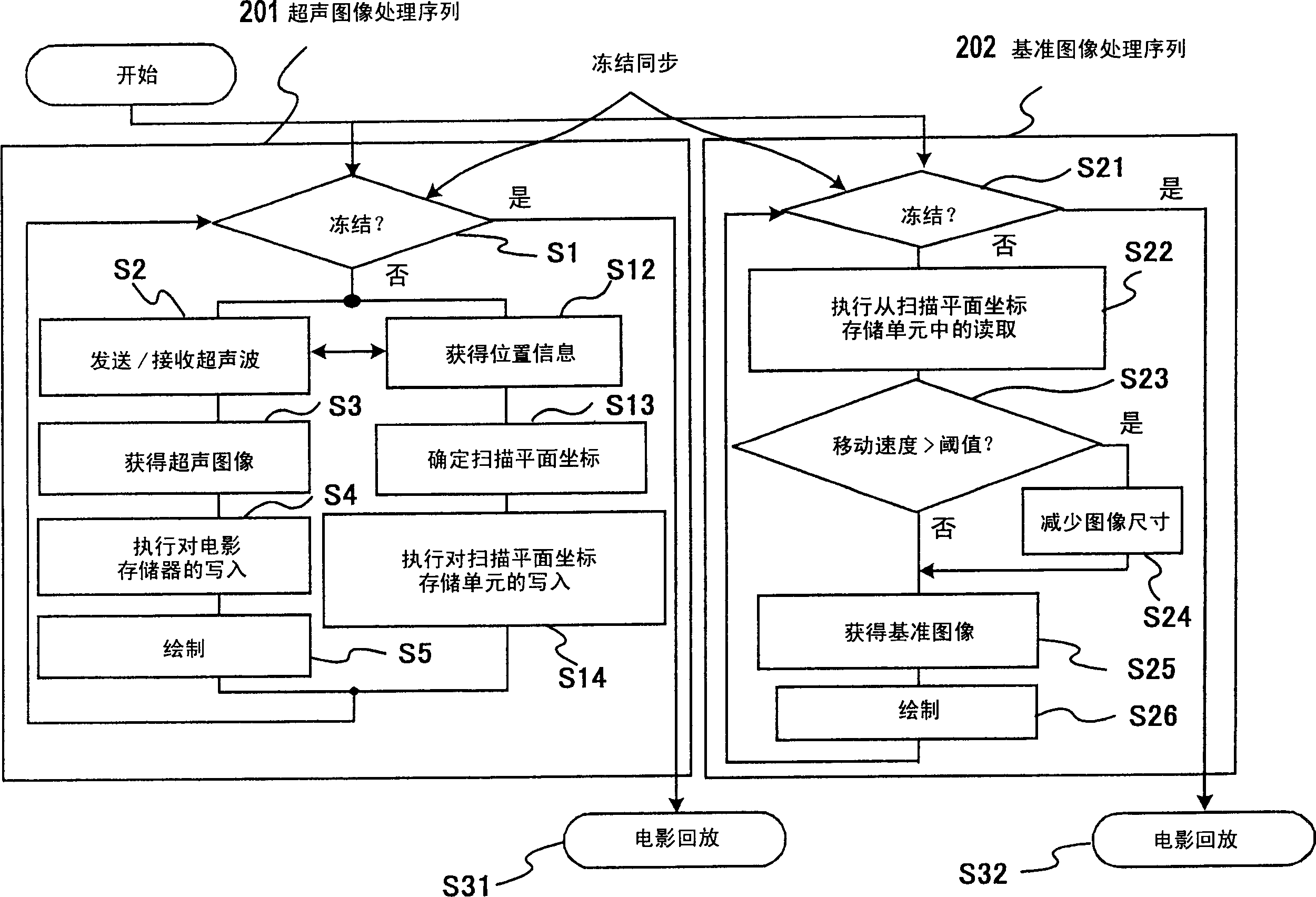
Reference image display method for ultrasonography and ultrasonograph
ActiveCN1805711AIncrease freedomHigh precisionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
Ultrasonograms (105, 106) are created by means of ultrasonic probe (104). Volume image data is created previously by using an image diagnosis apparatus (102) and stored in a volume data storage unit (107). From the stored volume image data, a tomogram corresponding to the scan surface of the ultrasonic images is extracted, and a reference image (111) is formed from the tomogram. The ultrasonograms and the reference image are displayed on the same screen (114). An area of the reference image corresponding to the viewing area of the ultrasonogram is extracted, and a reference image of the same portion as that of the ultrasonic image is displayed as a fan image and / or displayed with the same magnification as that of the ultrasonograms.
Owner:HITACHI HEALTHCARE MFG LTD
System and method for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20130077737A1Easy accessRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsX-rayHorizontal axis
A cone beam computed tomography system with a horizontally disposed, cylindrical gantry and a method for its use are provided. The cylindrical gantry includes a rotatable cylindrical frame fixed to a support frame. A cone beam X-ray source and X-ray detector are mounted to the circumference of the cylindrical frame at diametrically opposed positions. The cylindrical frame is actuated to revolve the X-ray source-detector arrangement around a horizontal axis, thereby scanning a recumbent subject positioned in the aperture of the cylindrical frame.
Owner:QUEENSLAND RAIL LIMITED
Connection adapter, optical tomographic imaging apparatus, program for executing imaging method and memory device for the program
InactiveUS20100103374A1Small installation spaceOptimize and adjust the structureOthalmoscopesFundus cameraLight guide
Provided is a connection adapter that is capable of constituting an optical tomographic imaging apparatus having a small installation space and high use efficiency. A connection adapter is disposed between the fundus camera main body portion and a camera portion to be attached to the fundus camera main body portion for imaging a surface image of a fundus as an object in an optical tomographic imaging apparatus, and connects them in a detachable manner. The connection adapter includes: a first light guide unit for guiding tomographic image measuring beams guided from the fundus camera main body portion for imaging the tomographic image to a tomographic imaging portion; and a second light guide unit for guiding fundus image measuring beams guided from the fundus camera main body portion for imaging the surface image of the fundus to the camera portion.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods apparatus assemblies and systems for implementing a ct scanner
InactiveUS20110122990A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersEngineering
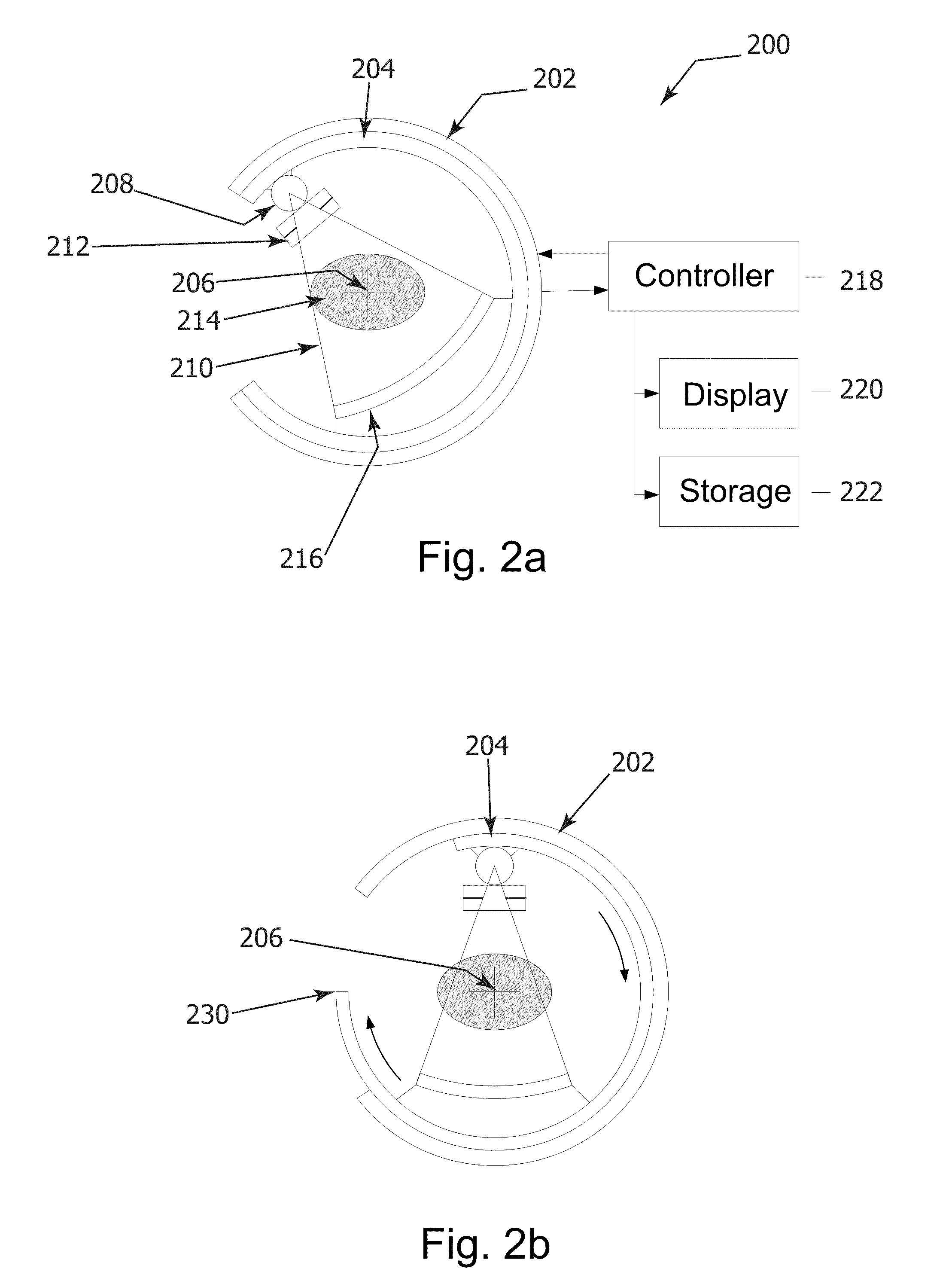
Disclosed is a Computer Tomography (CT) system including a gantry having first and second semicircular support elements which are concentric with one another. Each of the first and second semicircular support elements has a missing sector and at least one of the missing sectors may be of an angle of 180 degrees or less. A controller may be adapted to regulate relative rotational positions between said first and second support elements.
Owner:ARINETA
X-ray ct system for producing projecting and tomography contrast phase contrasting photo
InactiveCN101044987AHigh radiation burdenHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHandling using diaphragms/collimetersGratingHelical computed tomography
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Generating contrast-enhanced image data based on multi-energy x-ray imaging
InactiveCN107133995AHigh contrast-to-noise ratioReduce image noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPhysicsTomography
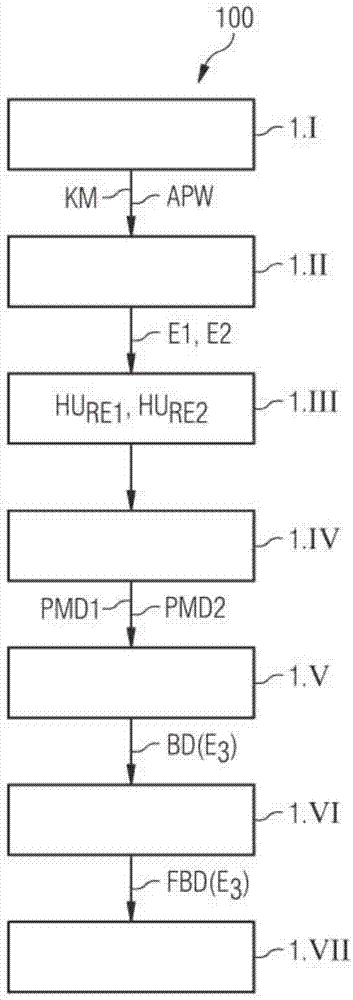
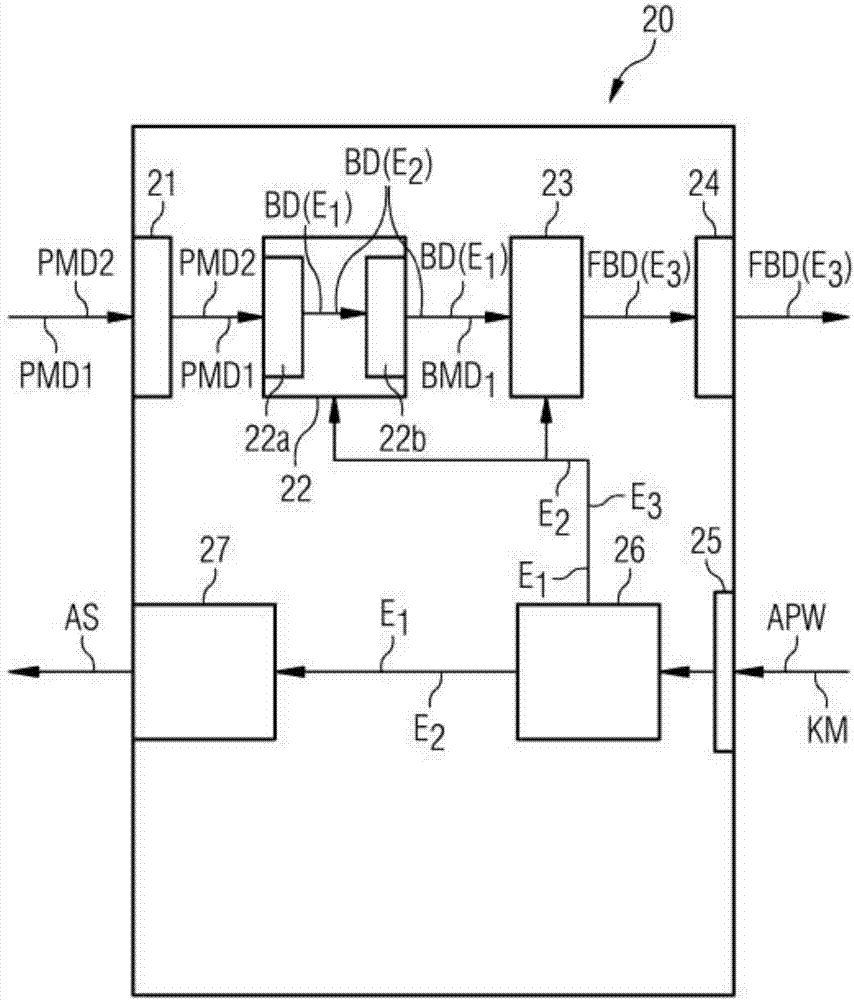
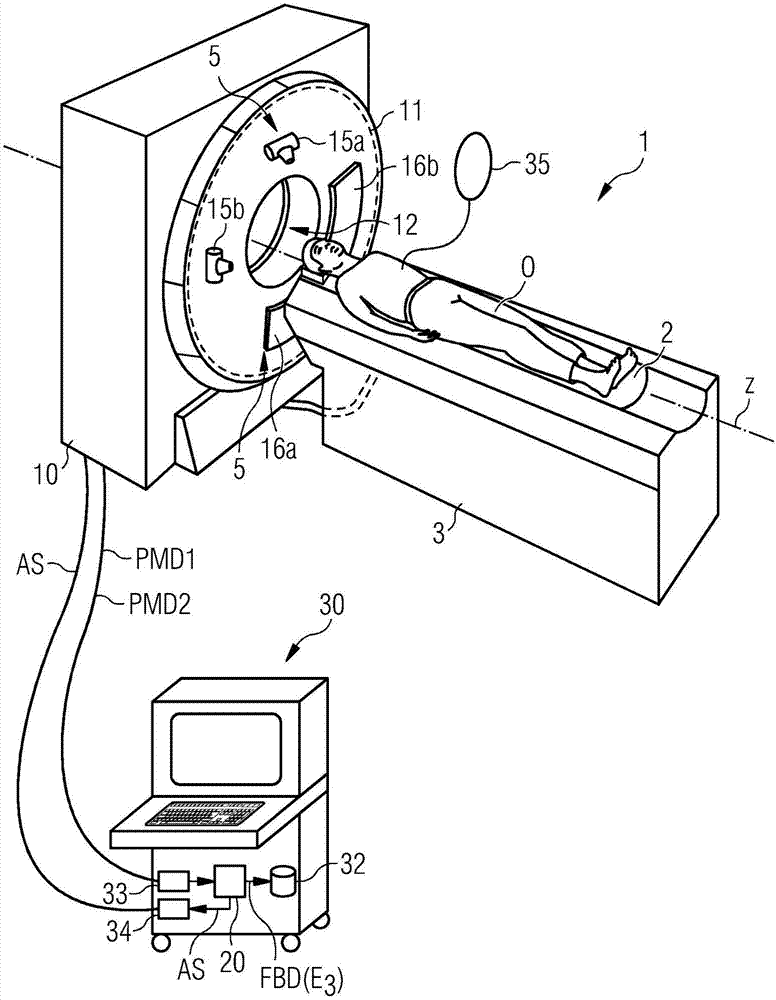
An X-ray imaging method (100) is for generating contrast-enhanced image data (BD) relating to an examination region (FOV) of an object (O) to be examined. Perferably a CT-X ray imaging method is disclosed. In an embodiment of the method, first contrast-agent influenced measured X-ray projection data (PMD1) with a first X-ray energy spectrum (RE1) and at least one set of second contrast-agent influenced measured X-ray projection data (PMD2) with a second X-ray energy spectrum (RE2) are acquired from the examination region. Subsequently, image data assigned to a third X-ray energy spectrum with a third mean energy (E3), based on the first and at least second measured X-ray projection data is reconstructed based on the first and at least second measured X-ray projection data that has been acquired. A mean energy of the first X-ray energy spectrum and a mean energy of the second X-ray energy spectrum are selected as a function of a dimension parameter value of the object that is to be examined. The invention also describes an image data generating device (20) and a computer tomography system (1).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Device and method for tomography and digital x-ray radiography of a flexible riser
InactiveUS20030142783A1Less stray radiationUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSensor arrayHelical computed tomography
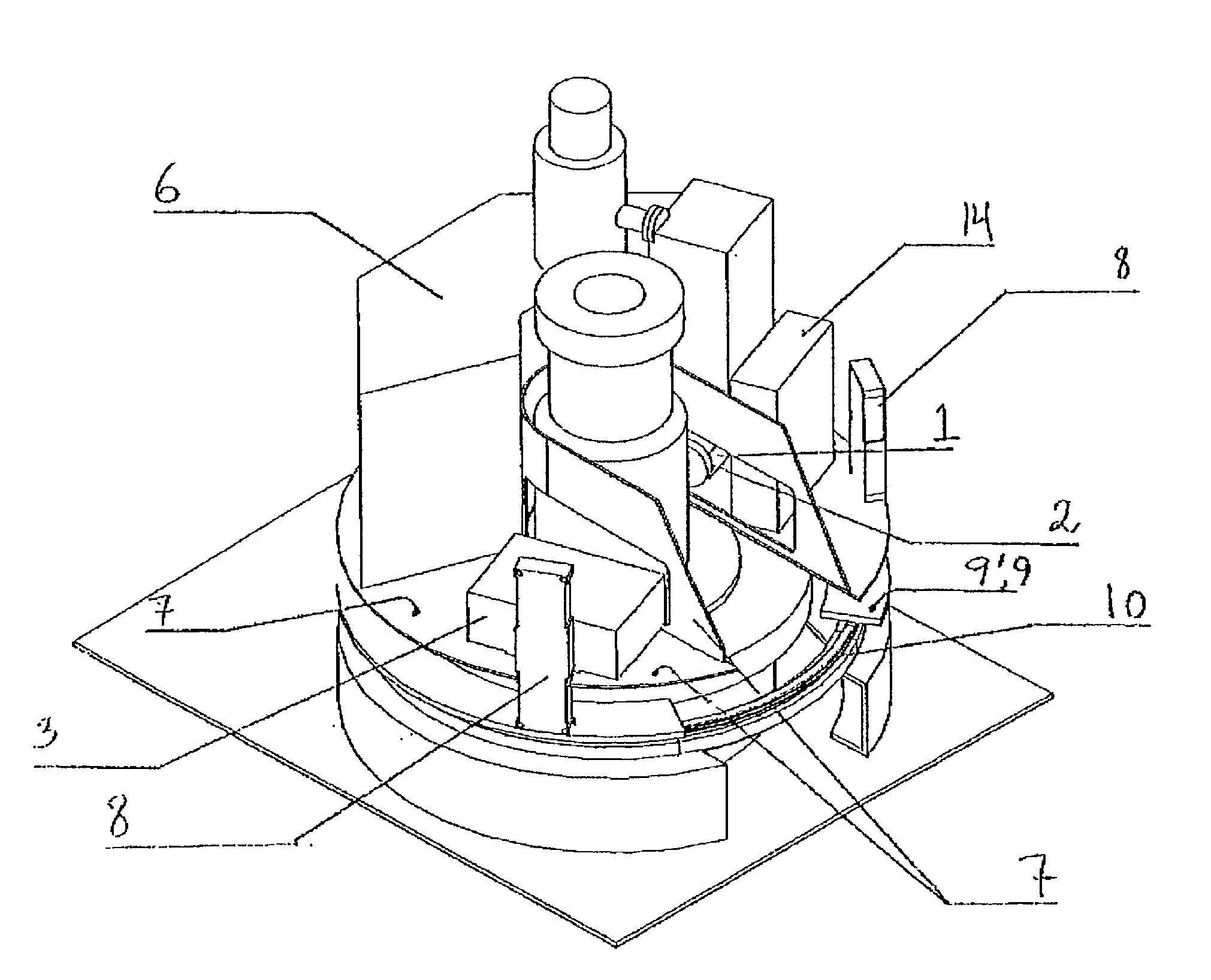
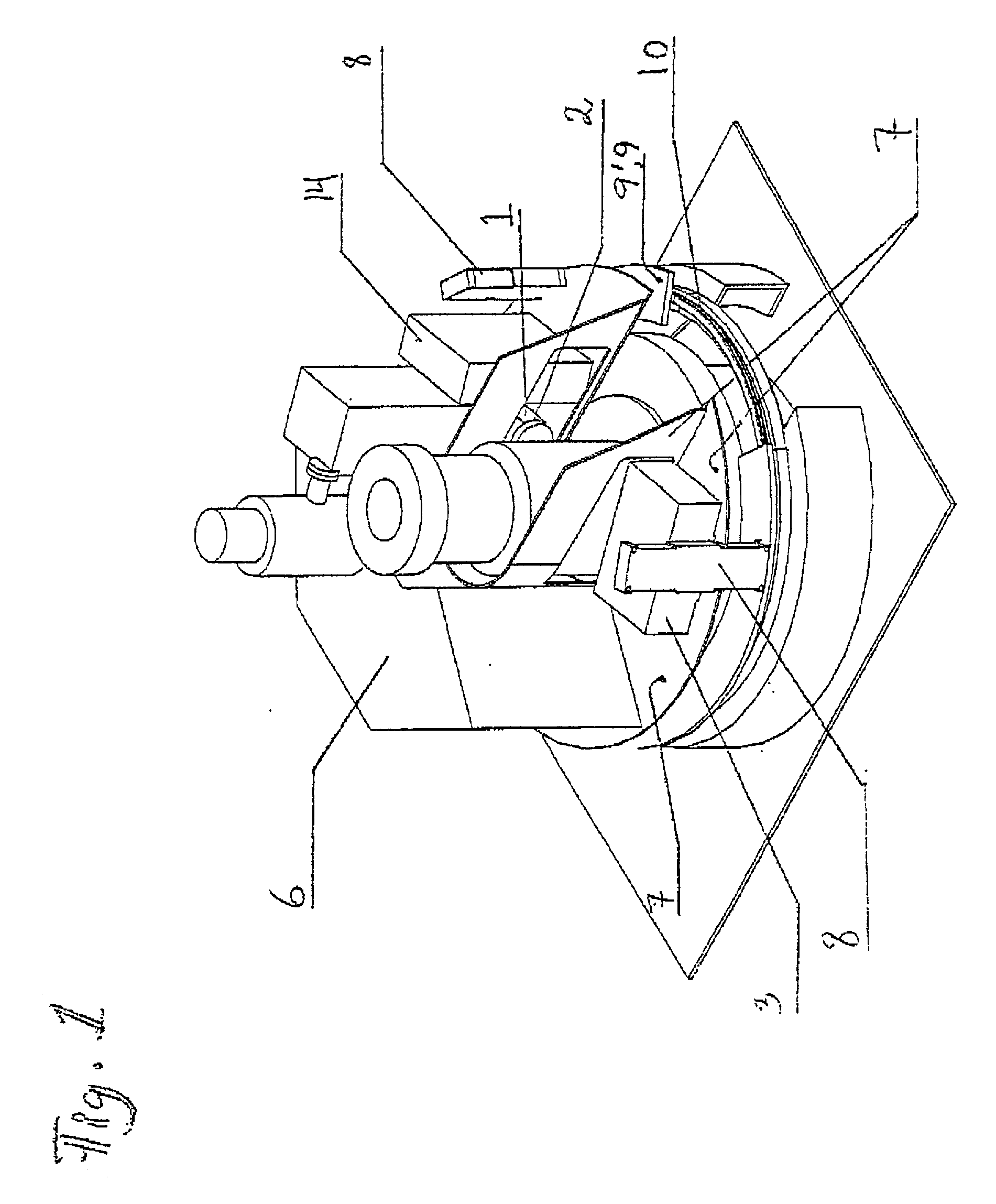
An x-ray radiography tomography device for a flexible riser, particularly a riser end fitting on a riser hangoff block on a petroleum platform, the x-ray radiography device comprising the following features: a) an x-ray source (1) of about 6 to 9 MeV arranged for directing said x-rays generally through an adjacent and an opposite sidewall portion of said riser; b) a collimator (2) arranged between said x-ray source (1) and said sidewall of said riser pipe being adjacent to said source (1), said collimator (2) arranged for directing radiation said x-rays in a beam fan generally extending in a plane perpendicular to a long axis of the riser; c) a sensor array (3) for receiving said x-ray beam fan after passage throug said riser pipe, said array comprising a plurality of scintillation detectors (30), said sensor array (3) arranged generally opposite of said source (1) with respect to said riser tube, and extending along a line extending generally perpendicular to said axis of said riser; d) an internal frame (7) for rotating the x-ray source (1), the collimator (2) and the sensor array (3) generally about said axis of said riser, said framework arranged on a circular guide rail (10) mounted around said flexible riser hangoff block.
Owner:STATOIL ASA PETRO SA (NO)
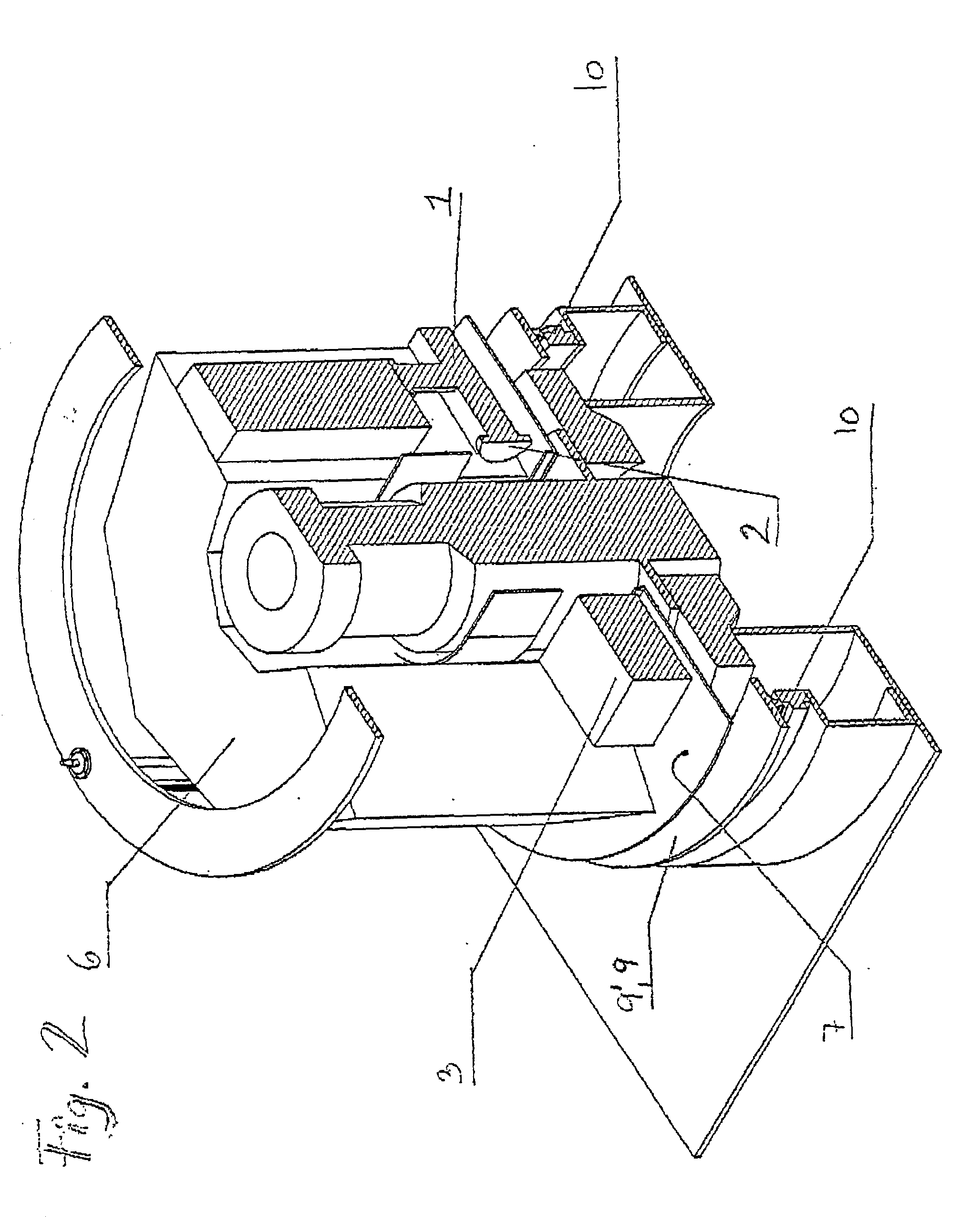
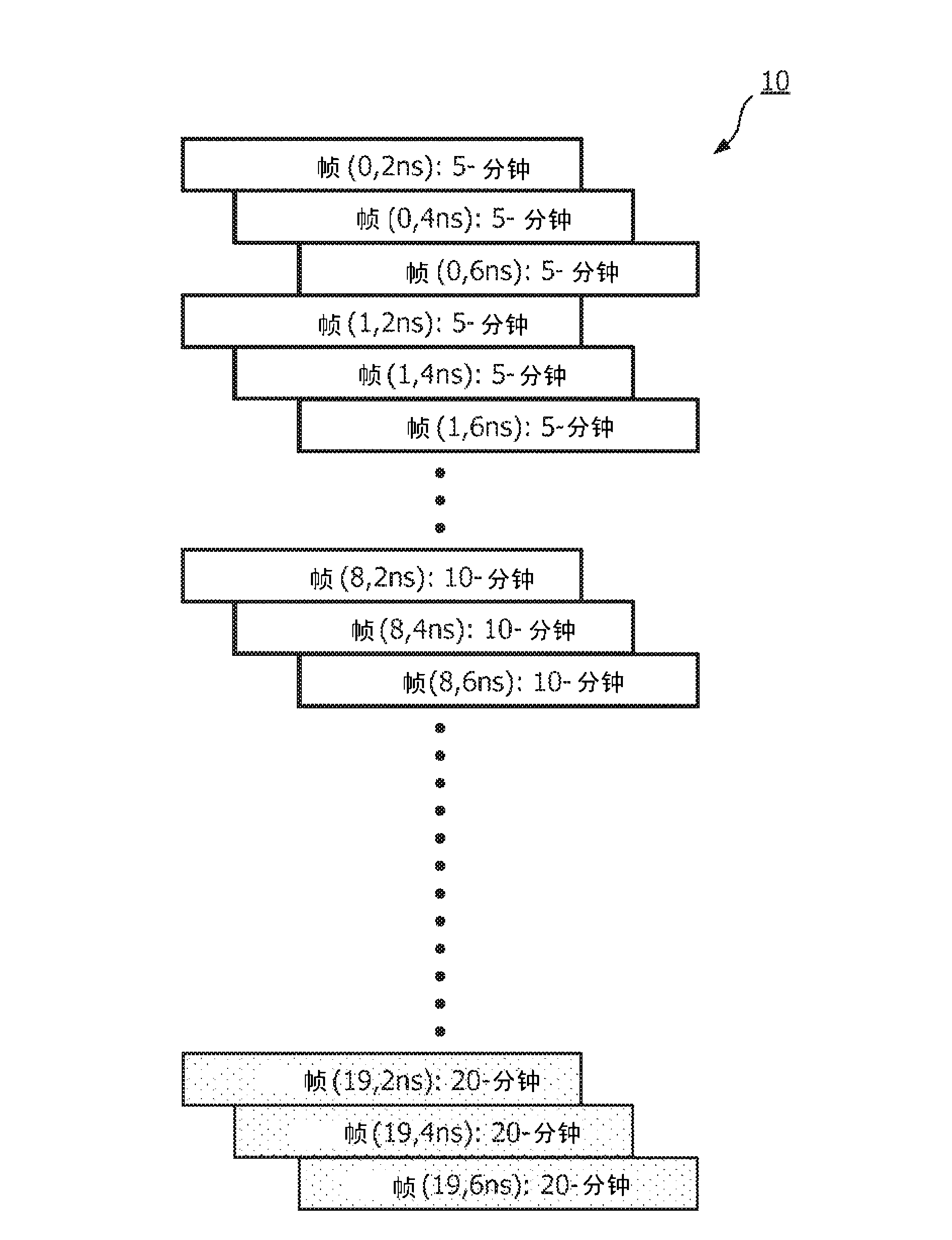
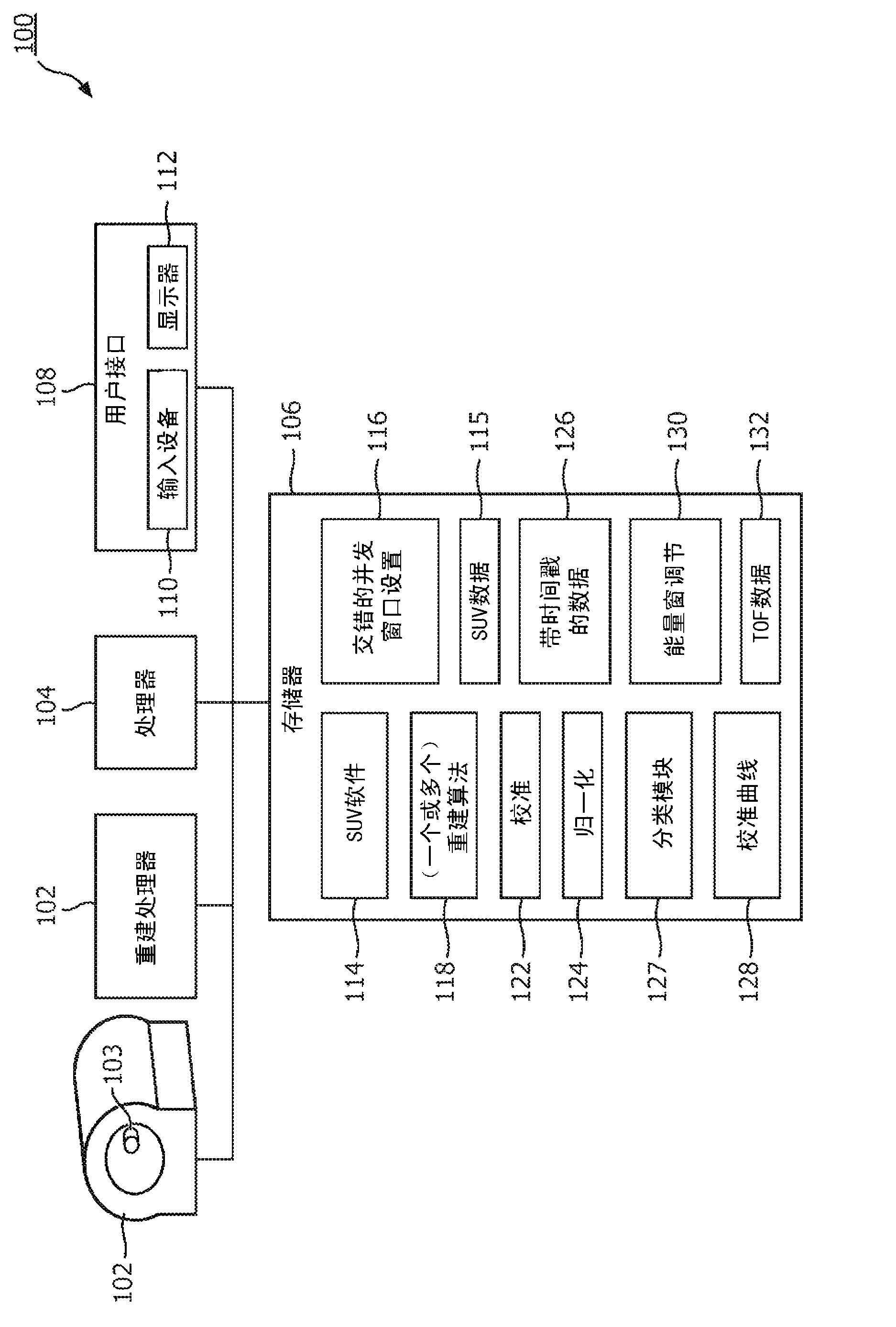
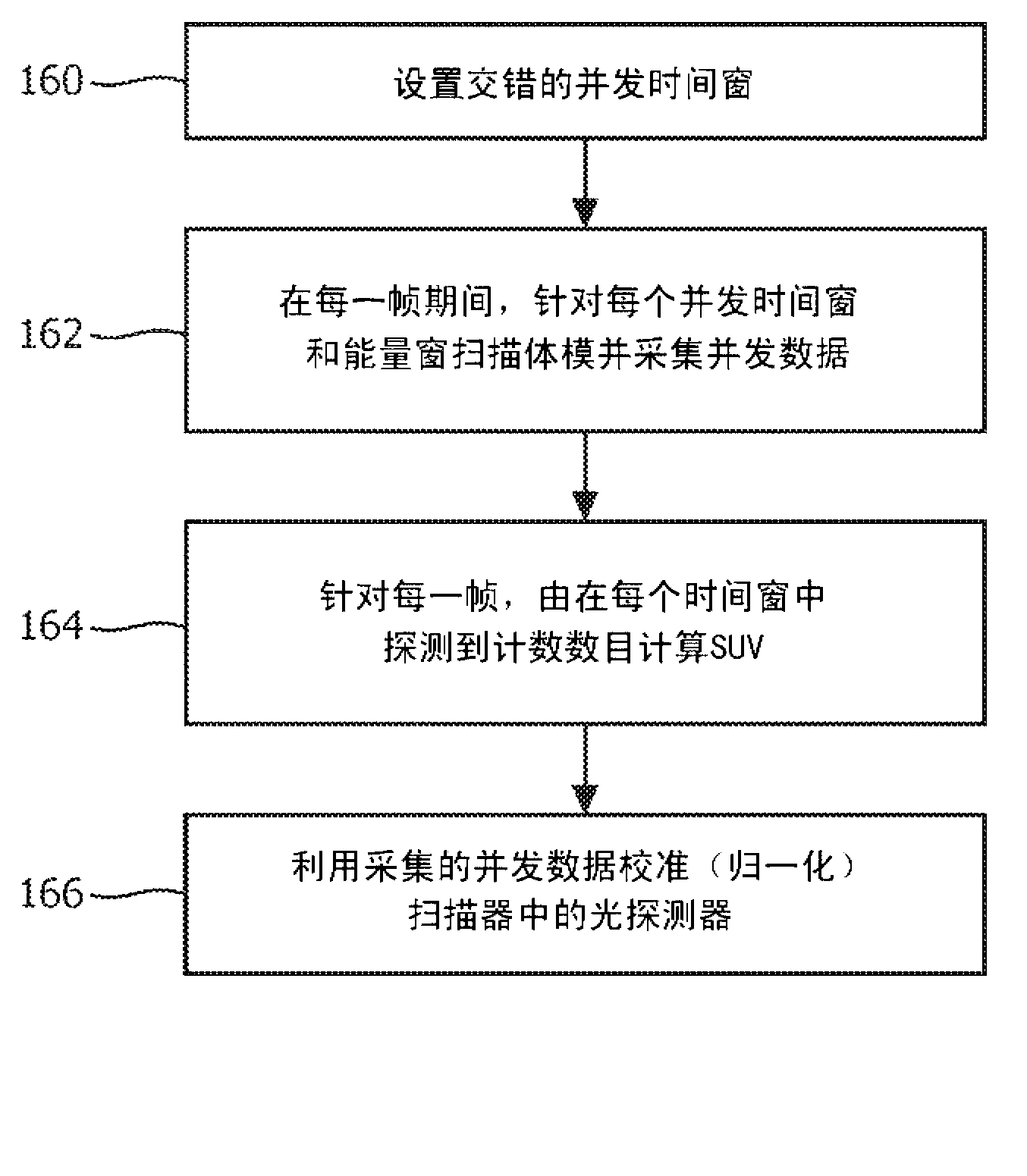
PET calibrations with varying coincidence windows
ActiveCN103221841AReduce calibration timeTomographyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentEnergy windowCompanion animal
When calibrating a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner, a radioactive calibration phantom is scanned over a period of several half lives to acquire a plurality of frames of scan data. Interlaced timing windows are employed to facilitate acquiring coincidence data for a plurality of coincidence timing windows and energy windows during a single calibration scan. Coincident events are binned according to each of a plurality of selected coincidence windows, and the PET scanner is calibrated for each of the plurality of coincidence timing windows using data acquired from the single calibration scan.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
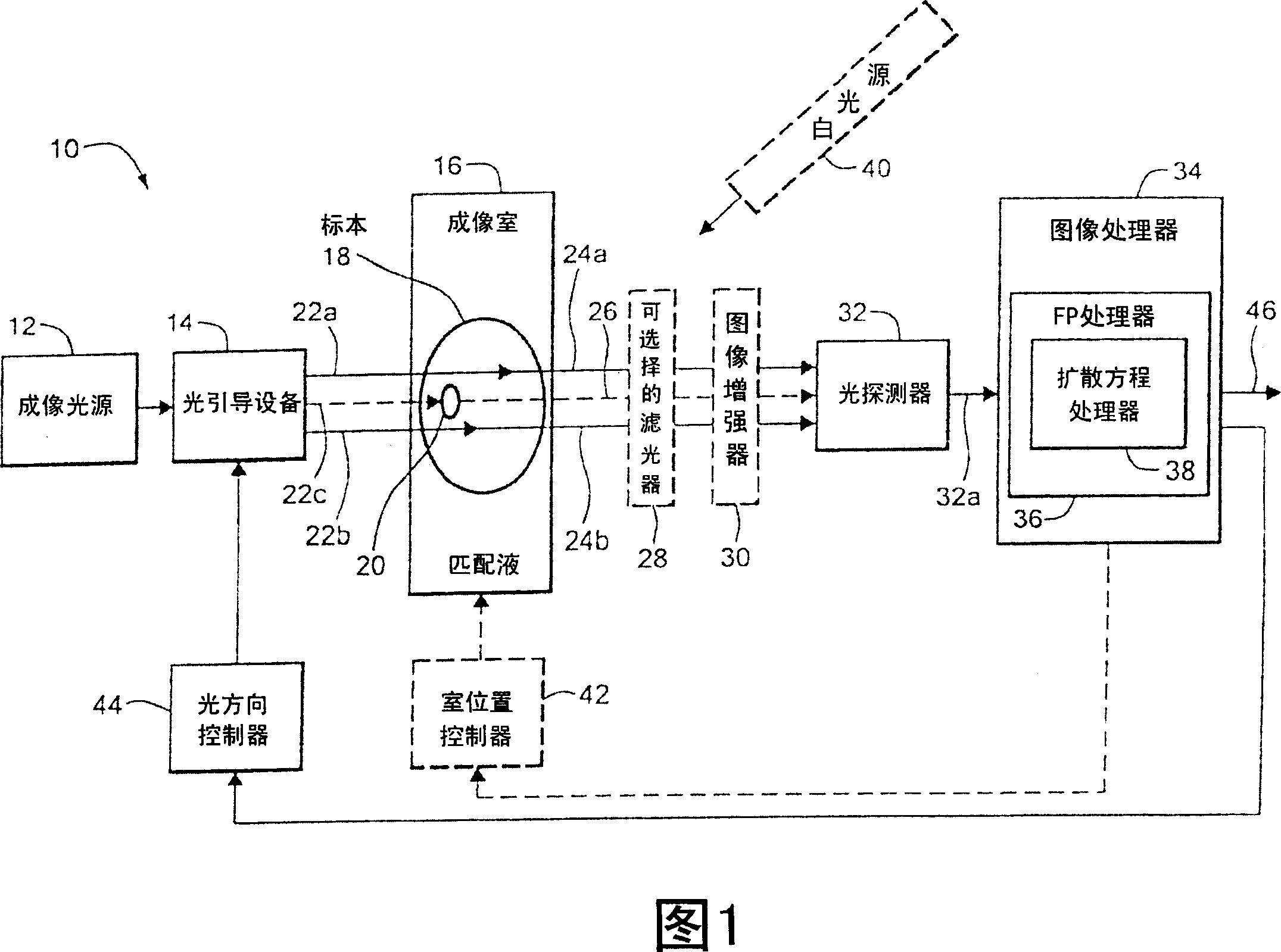
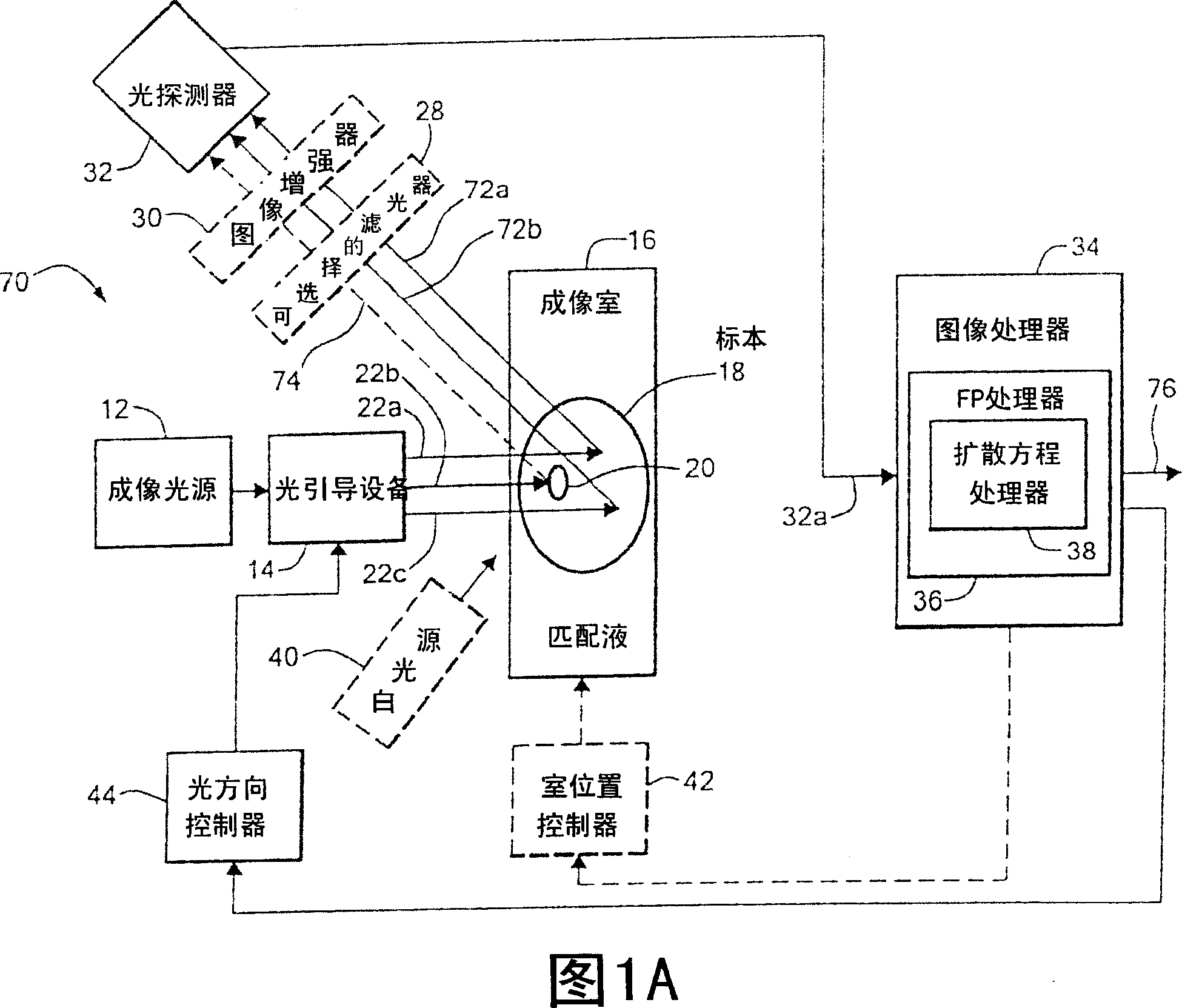
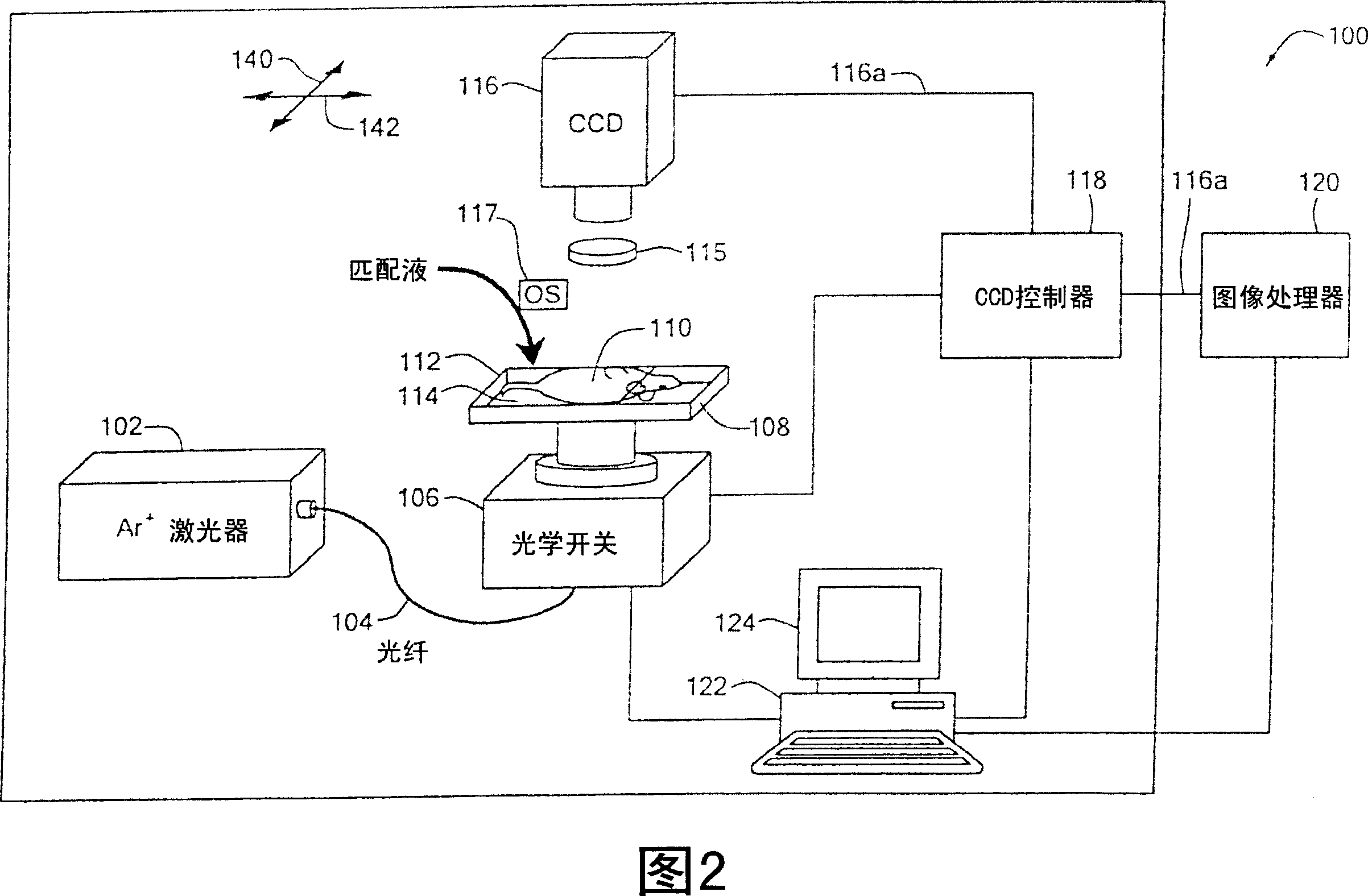
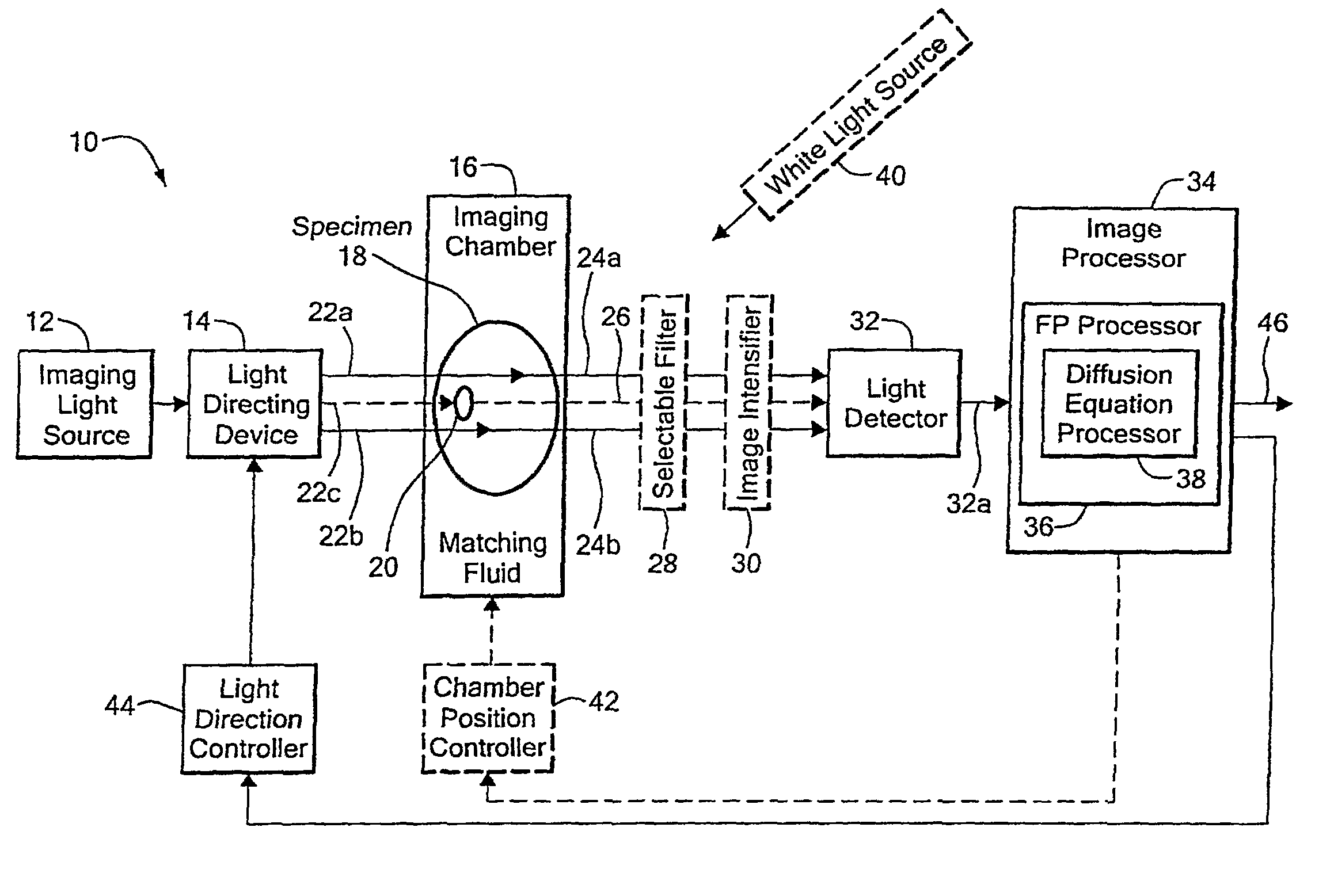
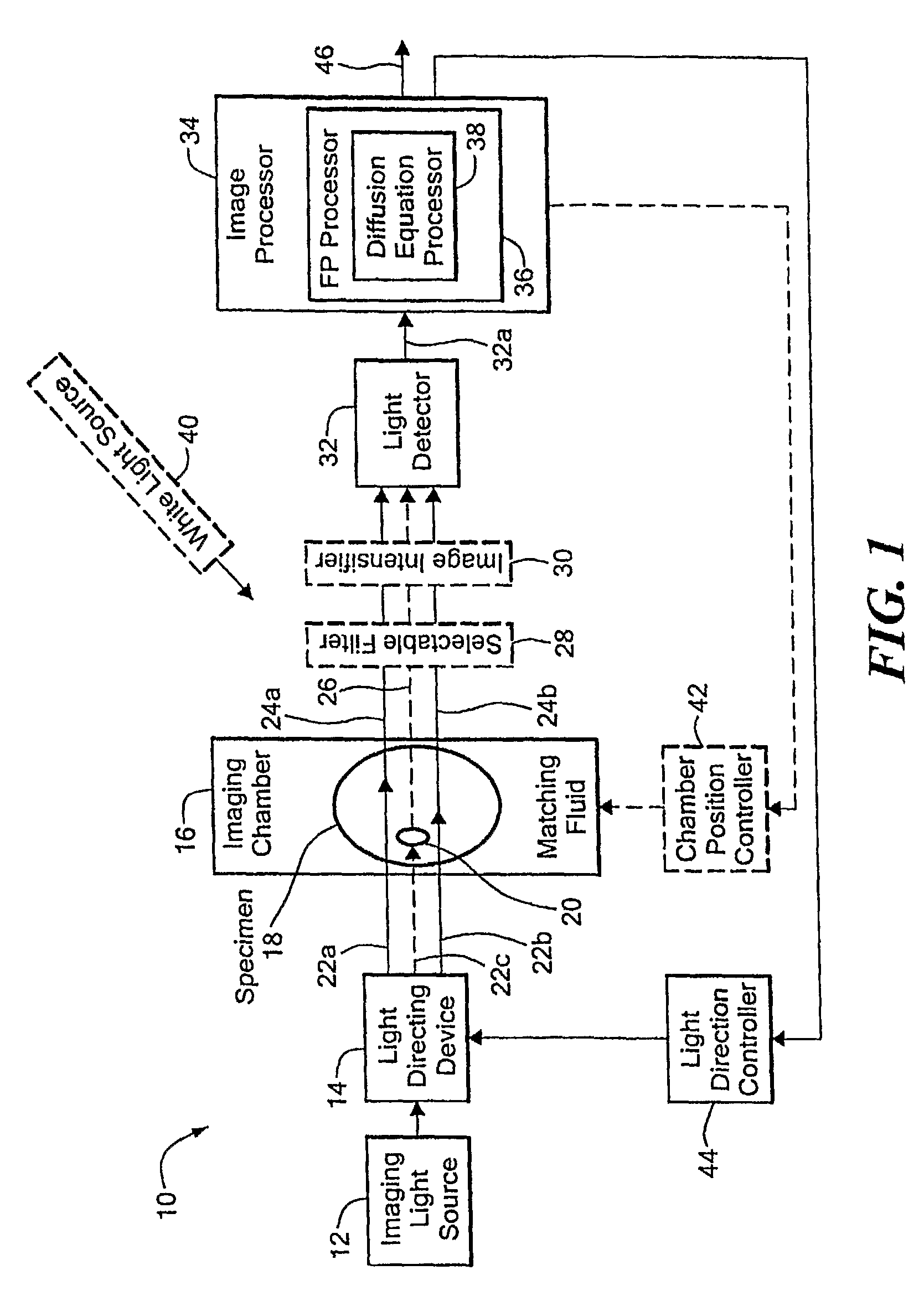
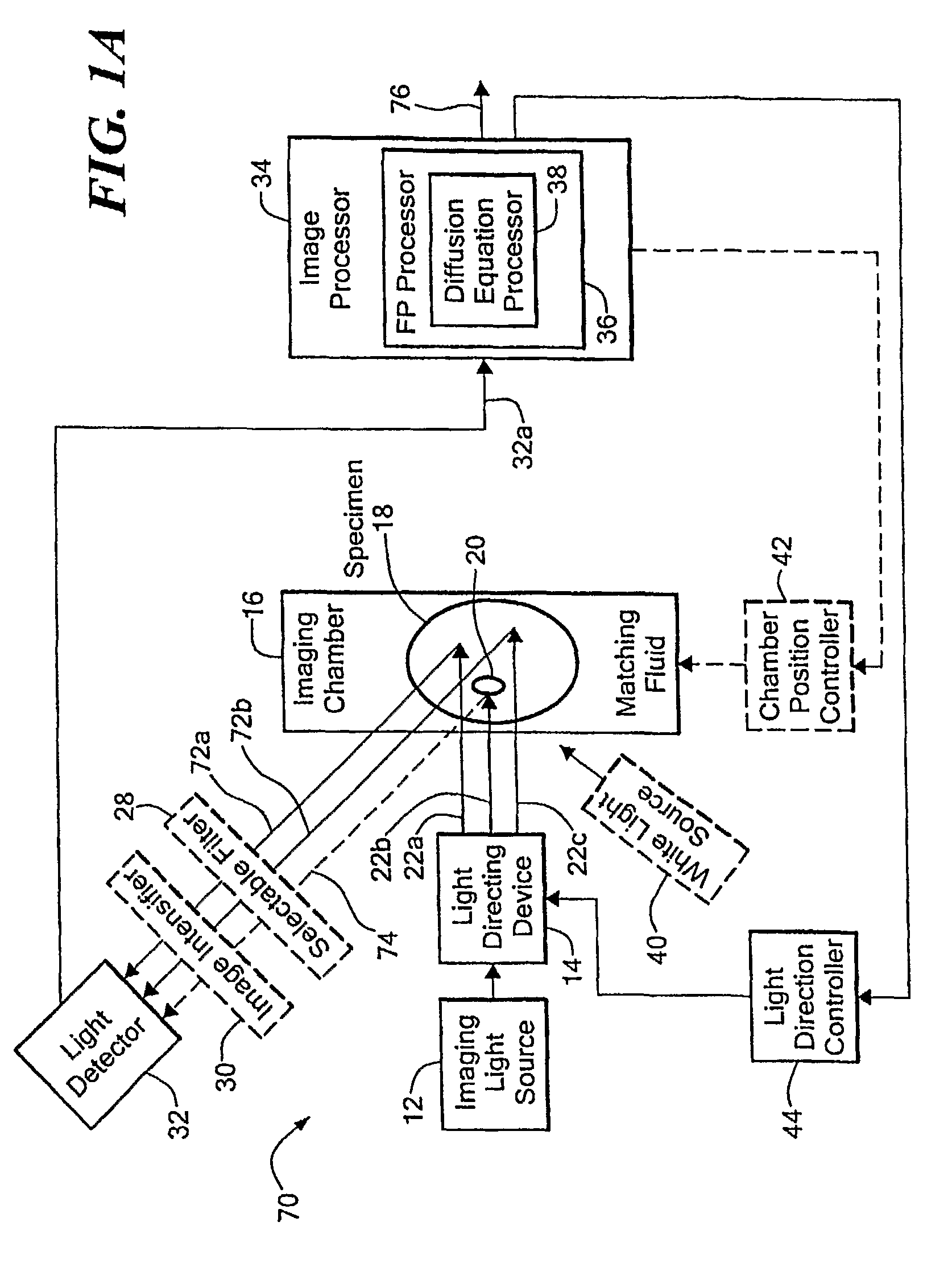
Method and system for tomographic imaging using fluorescent proteins
A system for optical tomography includes an apparent light source adapted to project excitation light toward a specimen having fluorescent proteins therein, wherein the excitation light enters the specimen becoming intrinsic light within the specimen, wherein the intrinsic light is adapted to excite fluorescent light from the fluorescent proteins, and wherein the intrinsic light and the fluorescent light are diffuse. A method of optical tomography includes generating the excitation light with the apparent light source, wherein the intrinsic light and the fluorescent light are diffuse.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and system for tomographic imaging using fluorescent proteins
A system for optical tomography includes an apparent light source adapted to project excitation light toward a specimen having fluorescent proteins therein, wherein the excitation light enters the specimen becoming intrinsic light within the specimen, wherein the intrinsic light is adapted to excite fluorescent light from the fluorescent proteins, and wherein the intrinsic light and the fluorescent light are diffuse. A method of optical tomography includes generating the excitation light with the apparent light source, wherein the intrinsic light and the fluorescent light are diffuse.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com