Method and system for tomographic imaging using fluorescent proteins
A fluorescent protein, optical tomography technology, used in diagnosis, application, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., to solve problems such as limiting the quality of final optical tomography images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
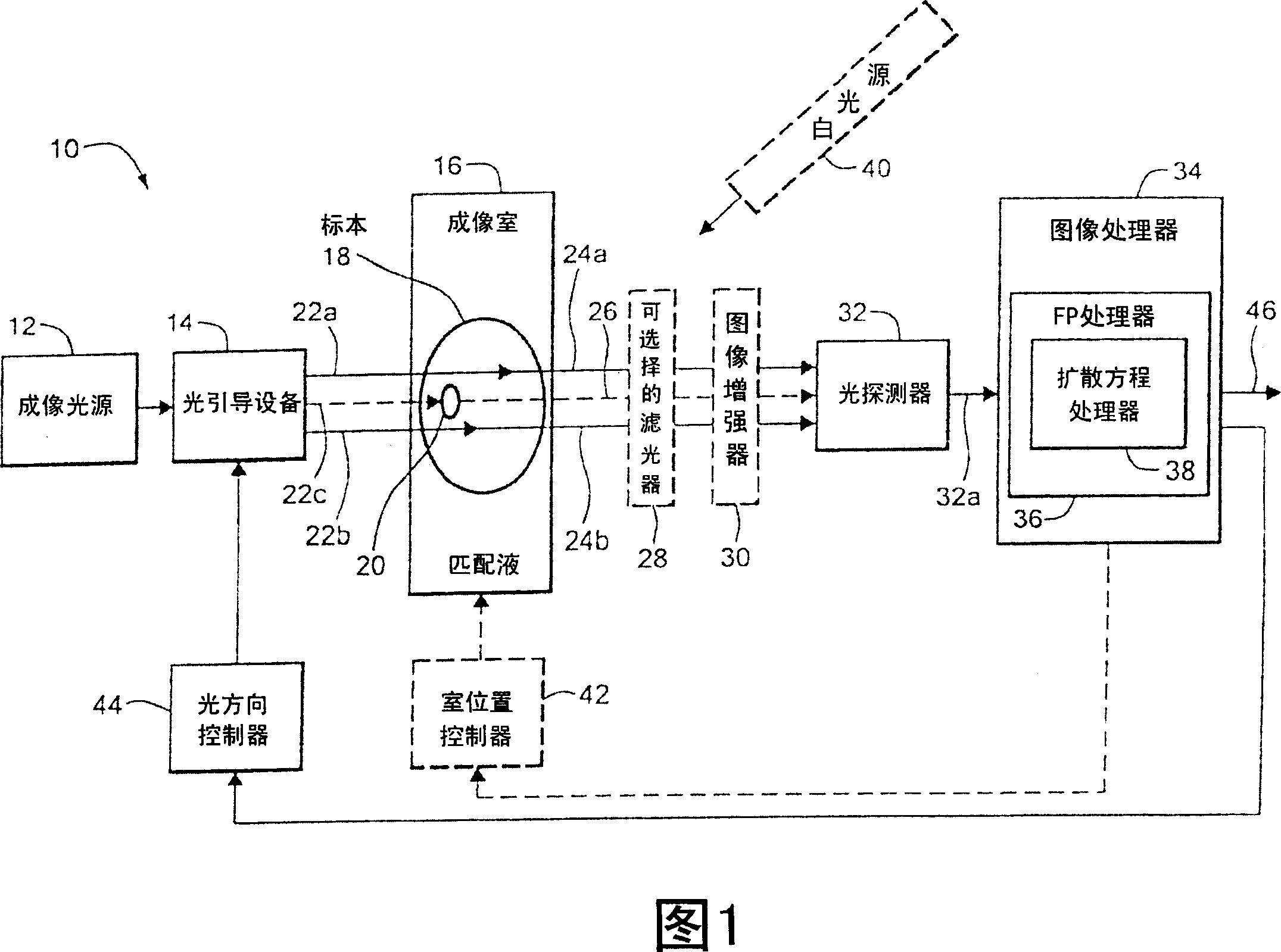
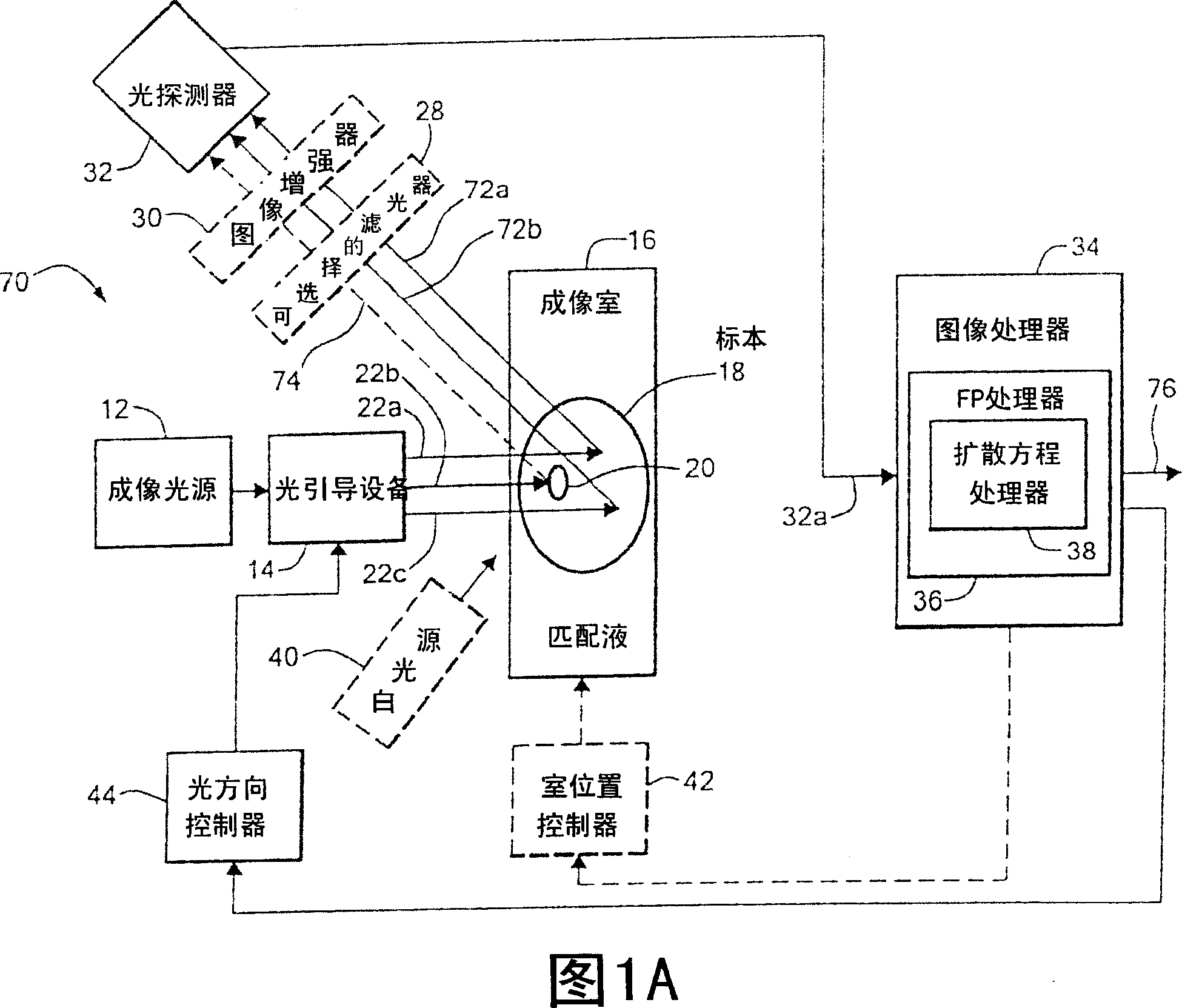
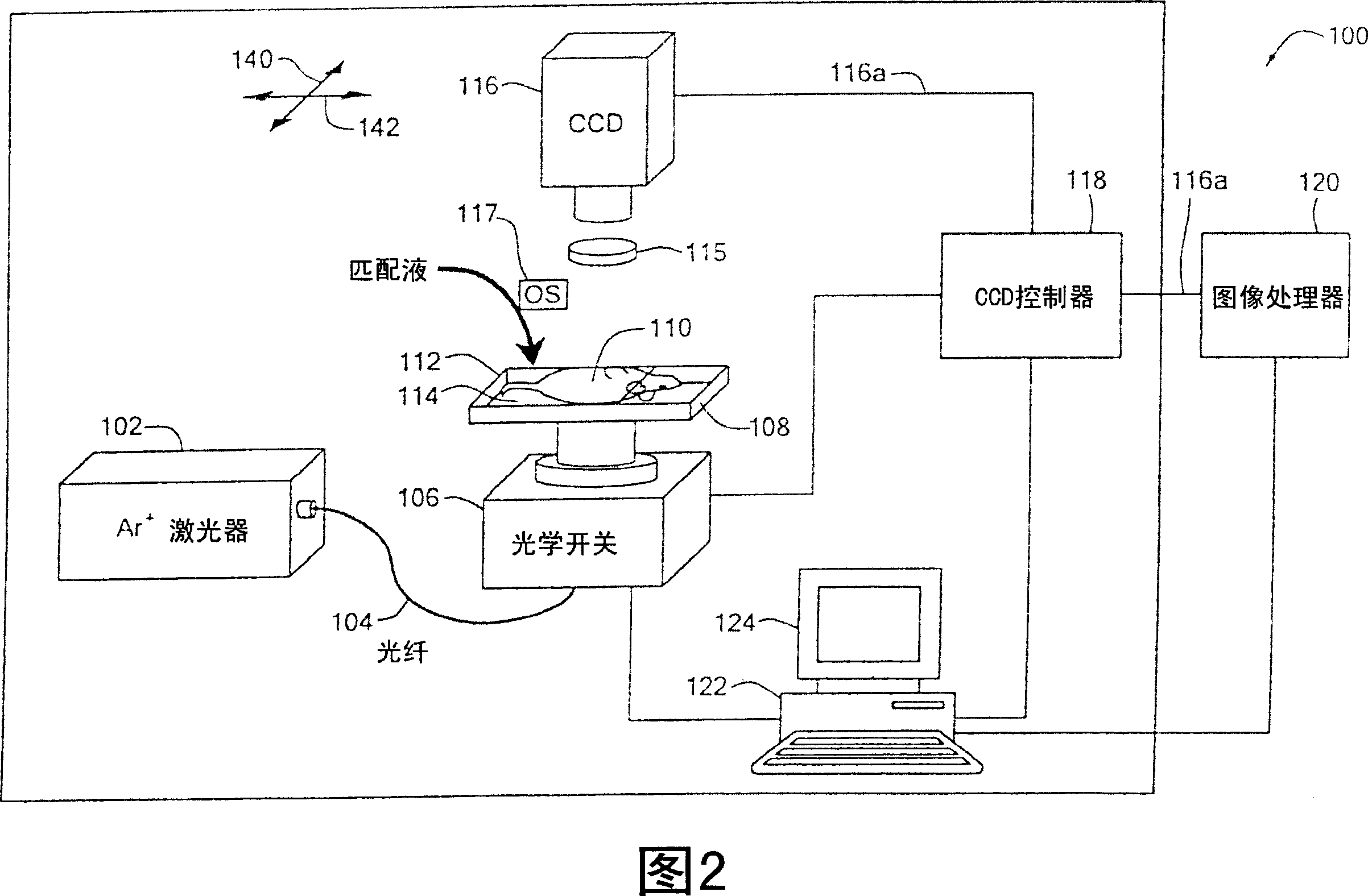
[0035] Before introducing the imaging methods and systems, some introductory concepts and terminology are explained. As used herein, "phantom" refers to the test object being imaged. The phantom is typically an artifact, such as a piece of plastic, with diffuse light propagation properties similar to living tissue. As another example, the phantom can be a glass vial with cells expressing a fluorescent protein (ie, fluorescently labeled) therein.
[0036] As used herein, the term "apparent light source" is used to describe a single light source projected to multiple physical positions or angles, each providing an apparent light source.
[0037] As used herein, the term "excitation" light is used to describe light produced by an excitation source, such as an apparent source, which travels toward a specimen to be imaged before entering the specimen. Once in the specimen, the light is referred to herein as "intrinsic" light. This intrinsic light is absorbed and scattered in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com