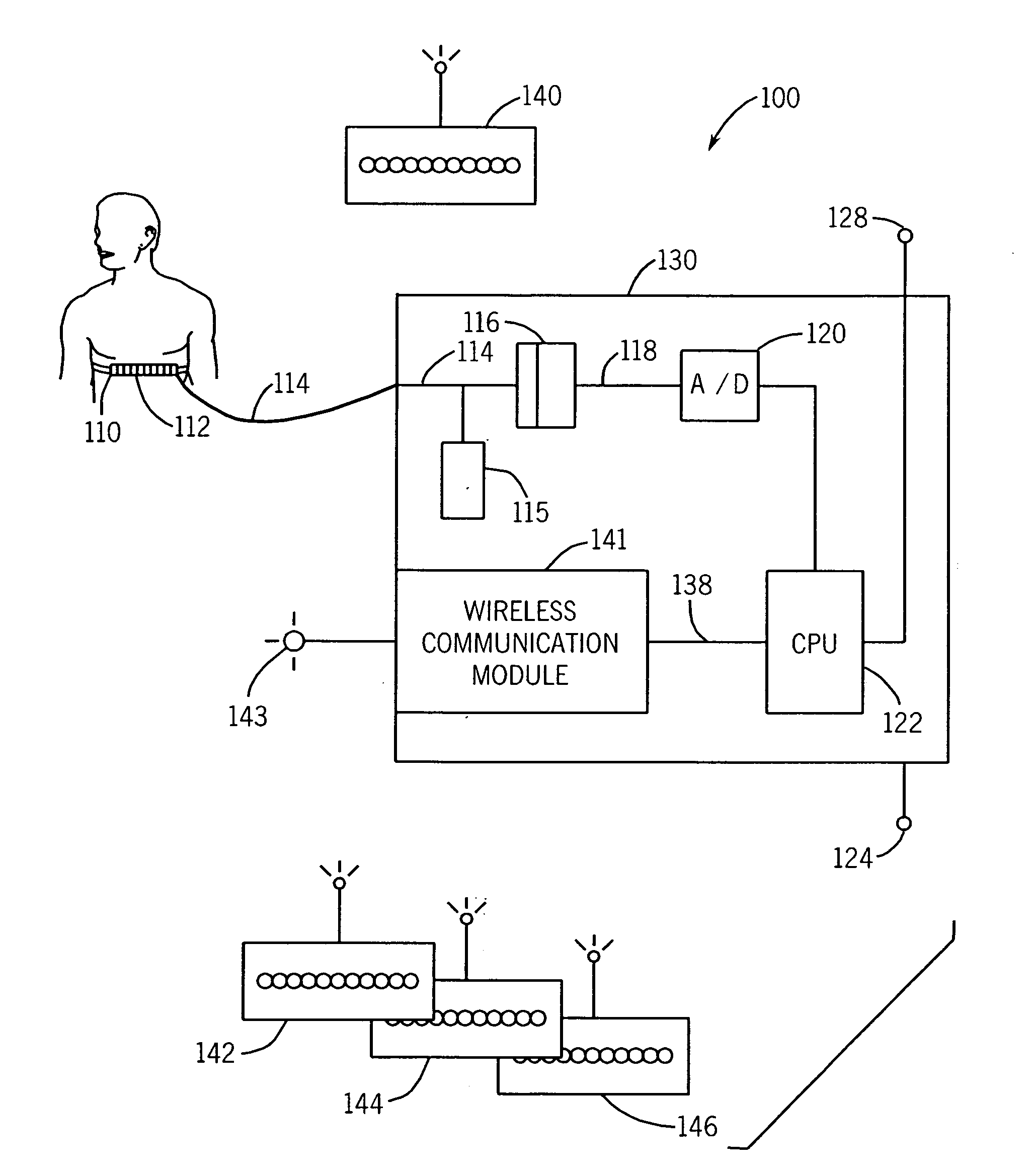
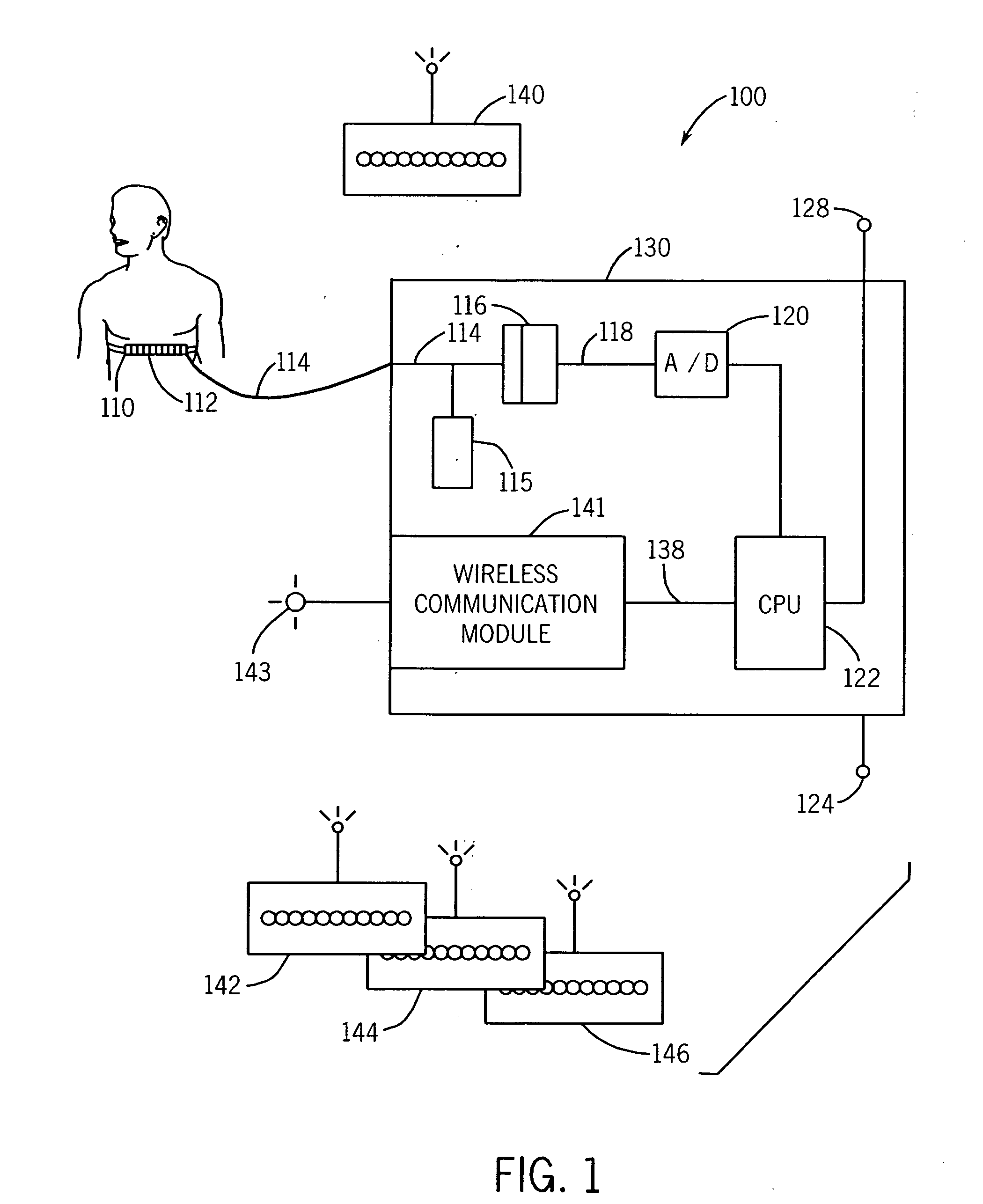
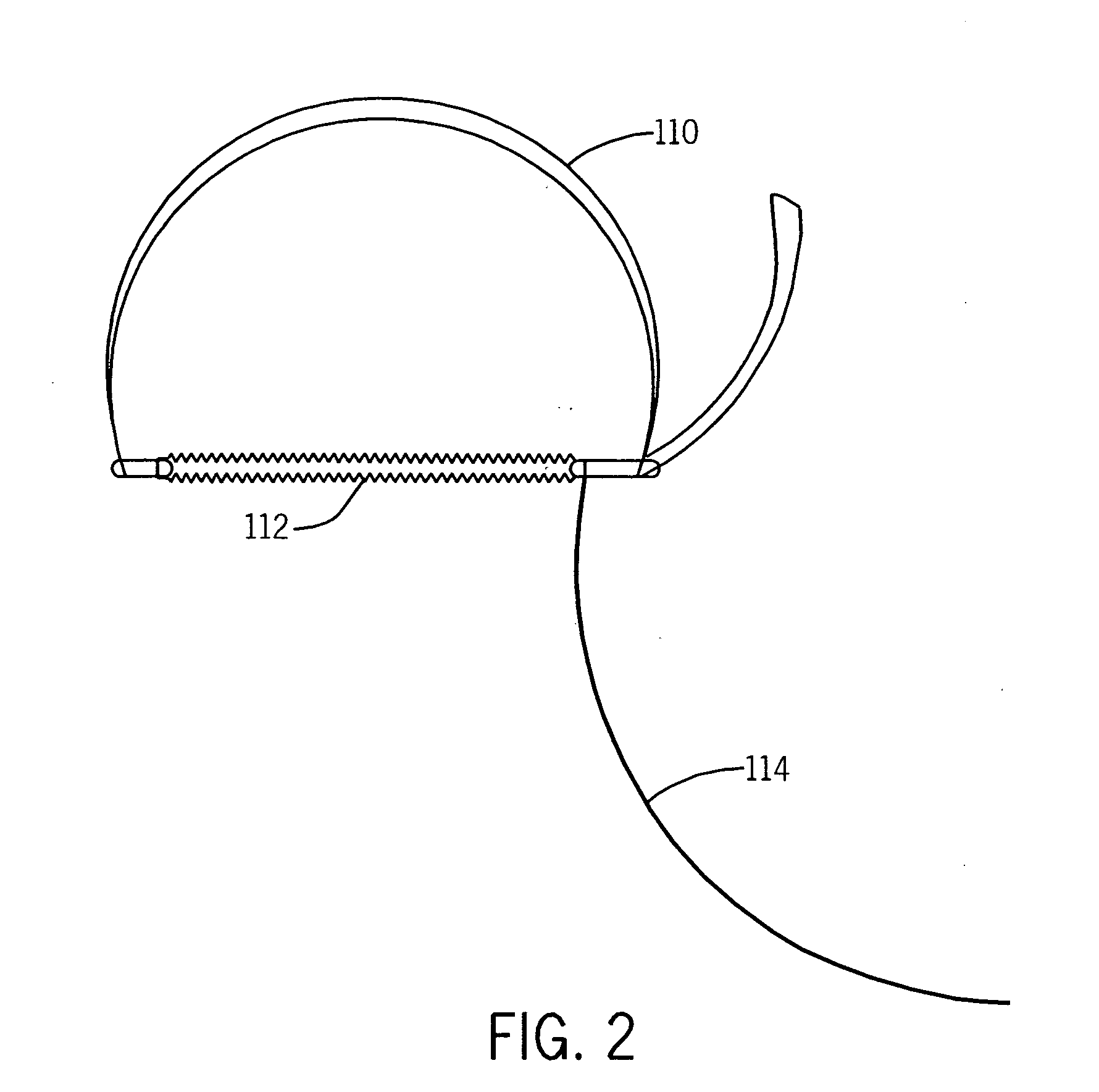
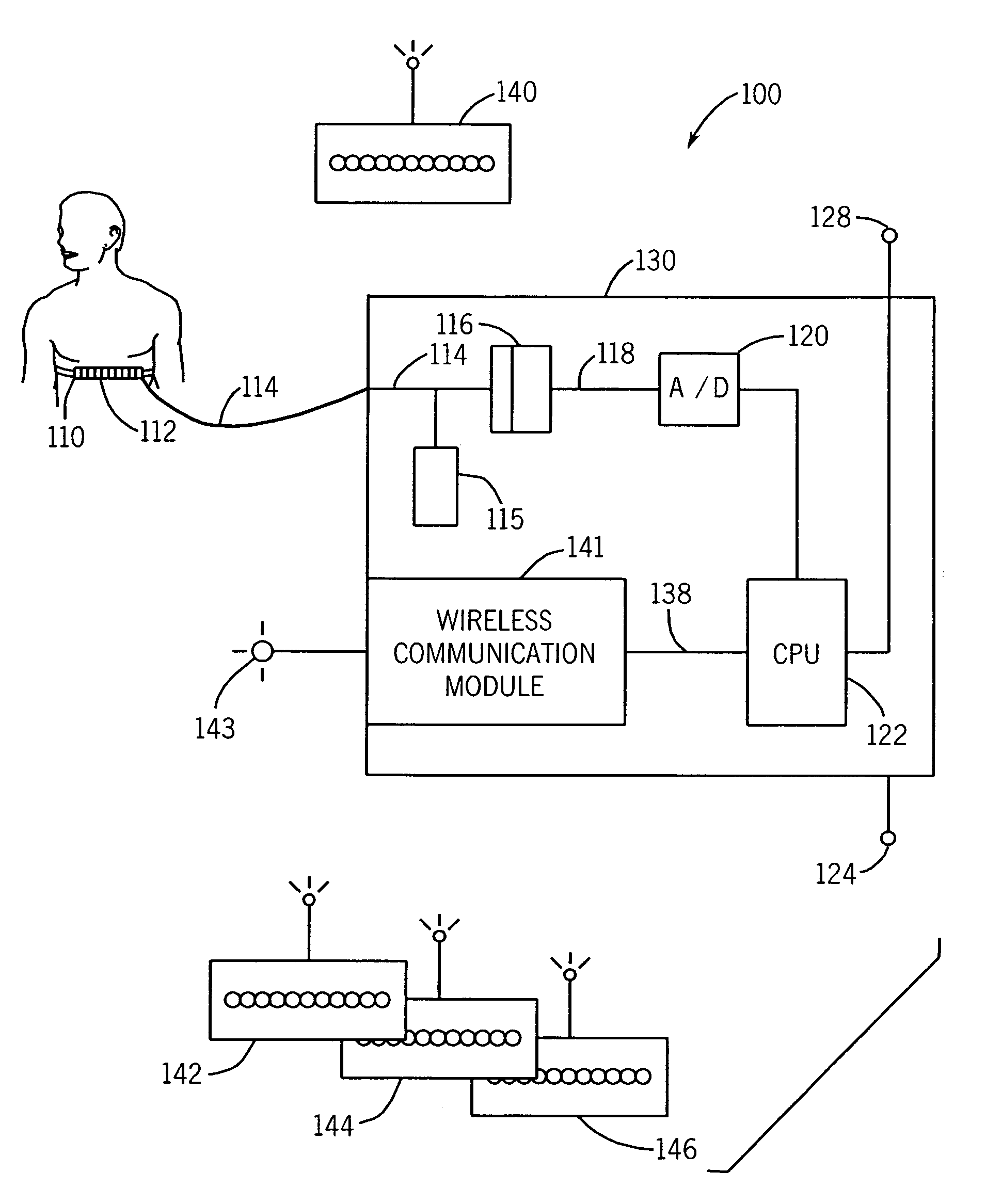
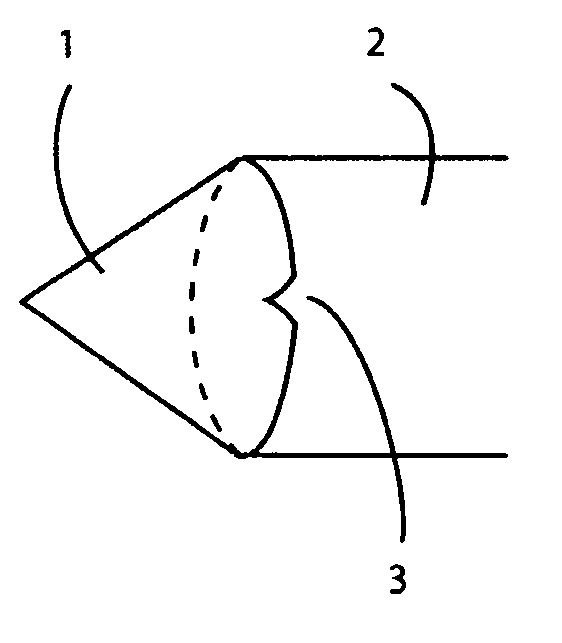Patents
Literature
96 results about "Target lesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In dermatology, a target lesion or bull's-eye lesion, named for its resemblance to the bull's-eye of a shooting target, is the typical lesion of erythema multiforme (EM) in which a vesicle is surrounded by an often hemorrhagic maculopapule. EM is often self-limited, of acute onset, resolves in three to six weeks, and has a cyclical pattern. EM lesions are multiform (polymorphous) and include macules, papules, vesicles, and bullae. Target lesions are also typical of erythema chronicum migrans.
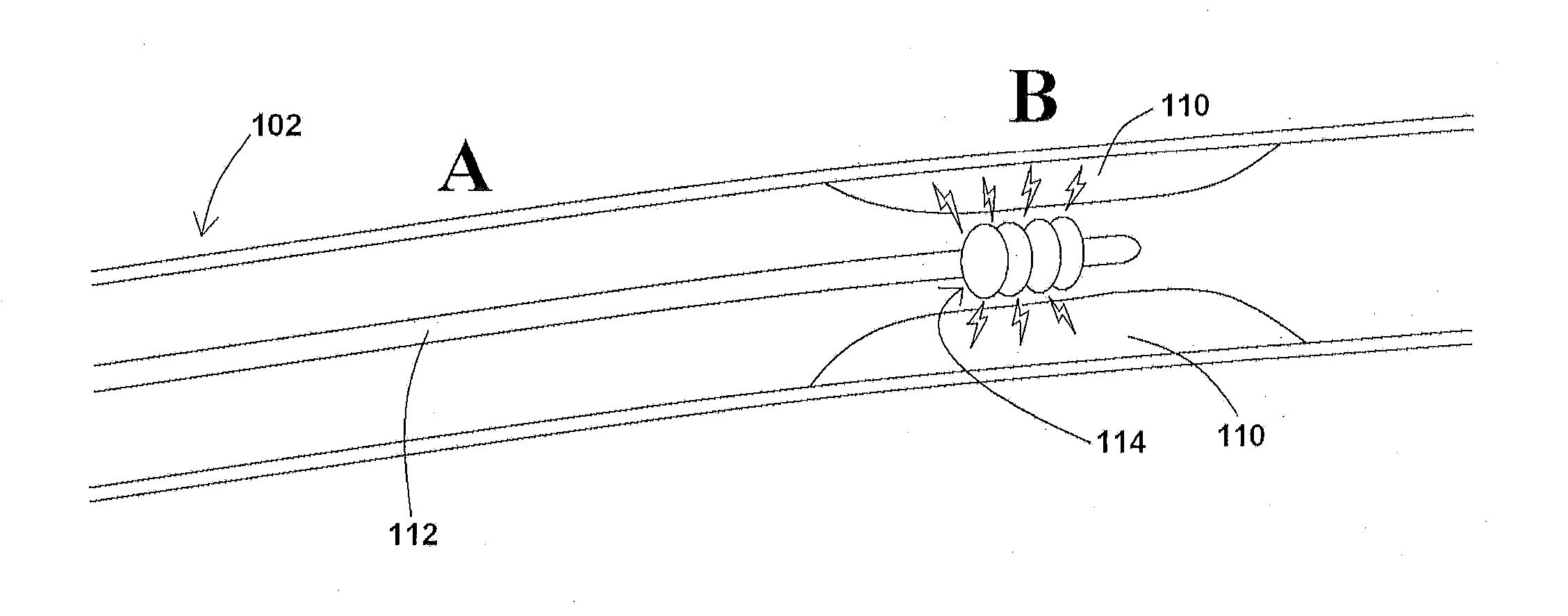
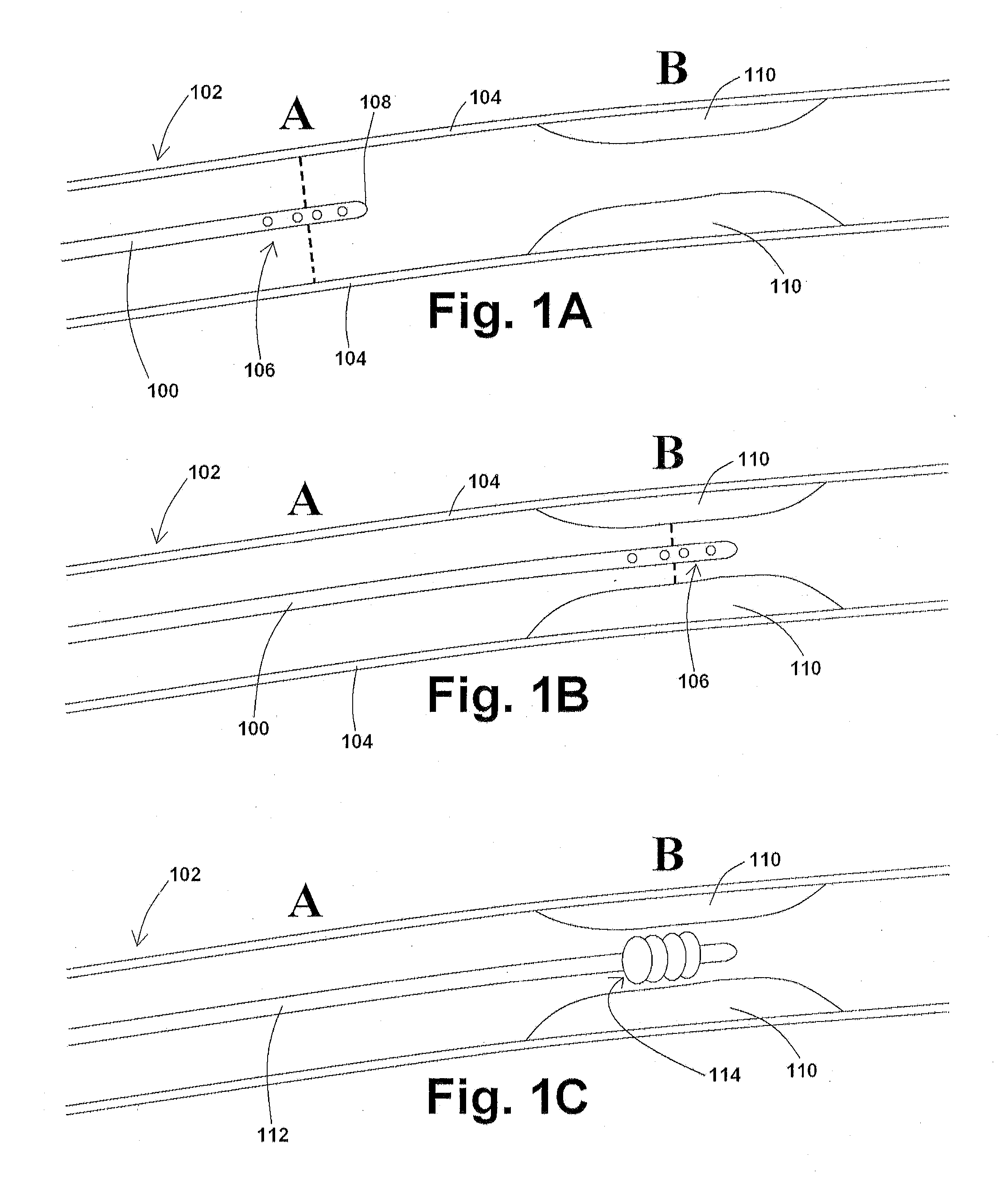
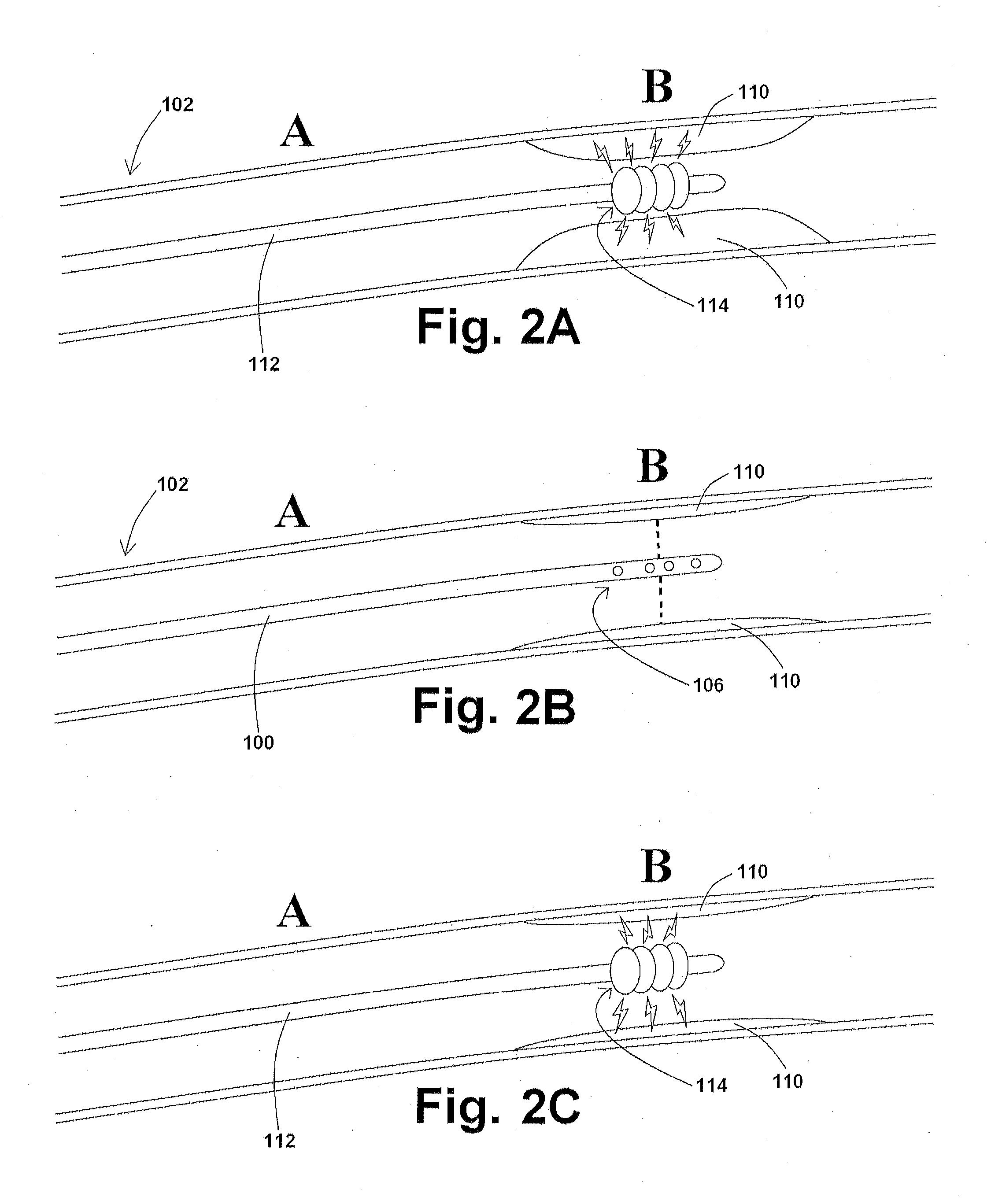
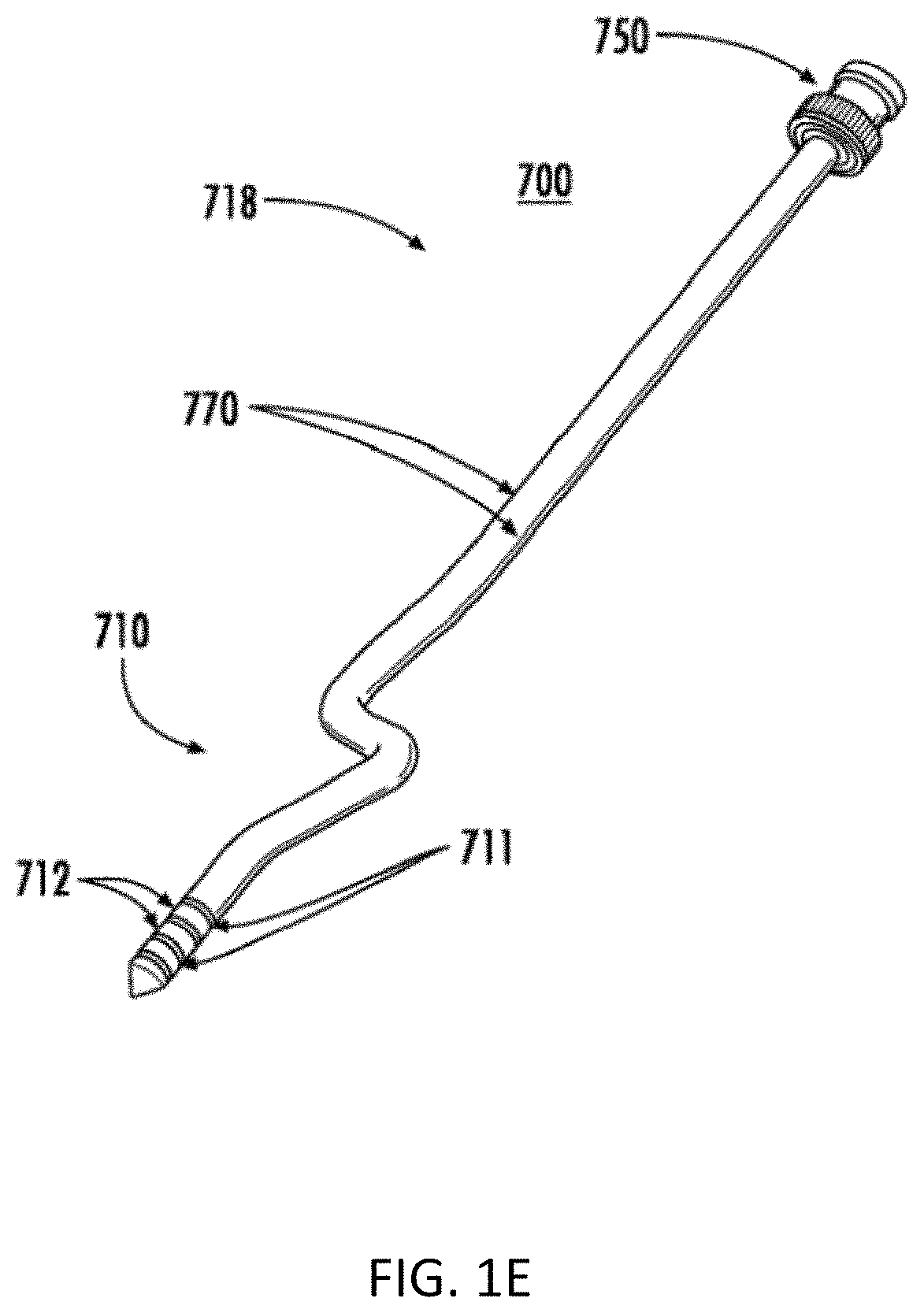
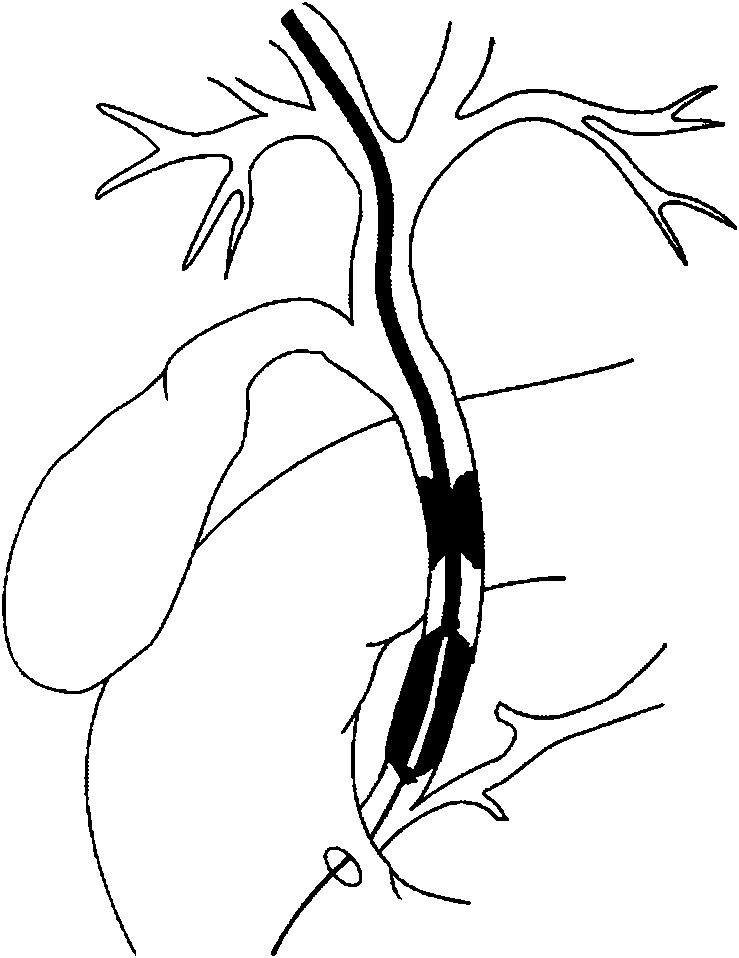
Devices, systems, and methods for removing targeted lesions from vessels
ActiveUS20100222786A1Easy to operate and controlFacilitate one or more fluid injectionsStentsCannulasStenotic lesionTyping
Devices, systems, and methods for removing targeted lesions from vessels. In at least one embodiment of a device for removing a stenotic lesion from a vessel, the device comprises a sizing portion capable of measuring a luminal size parameter when at least part of the device is positioned within a lumen of a luminal organ, a typing portion, wherein at least part of the at least one typing portion is capable of physically touching a portion of the luminal organ or a structure therein, and a treatment portion capable of removing at least part of a stenotic lesion from the luminal organ.
Owner:3DT HLDG
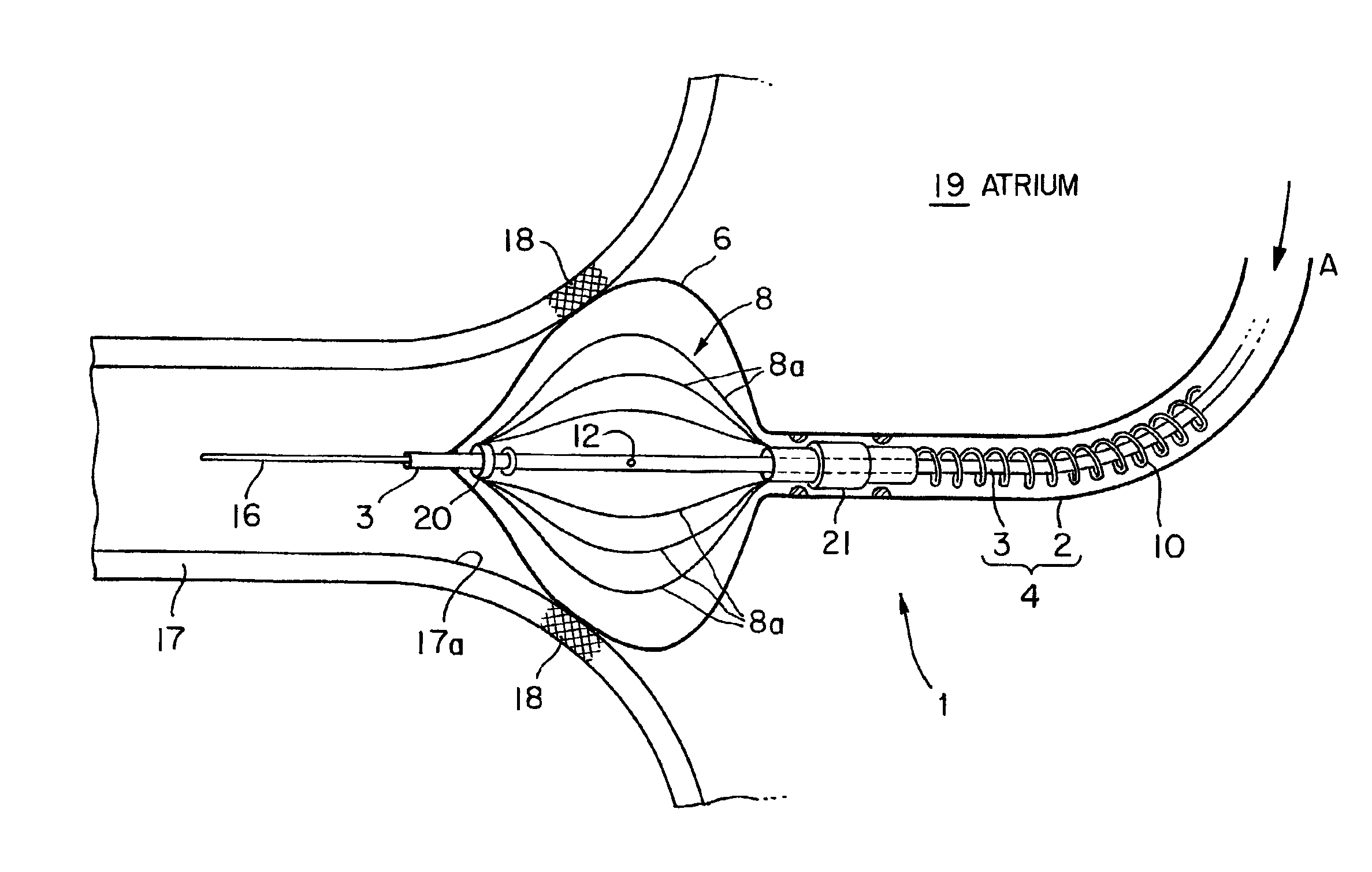
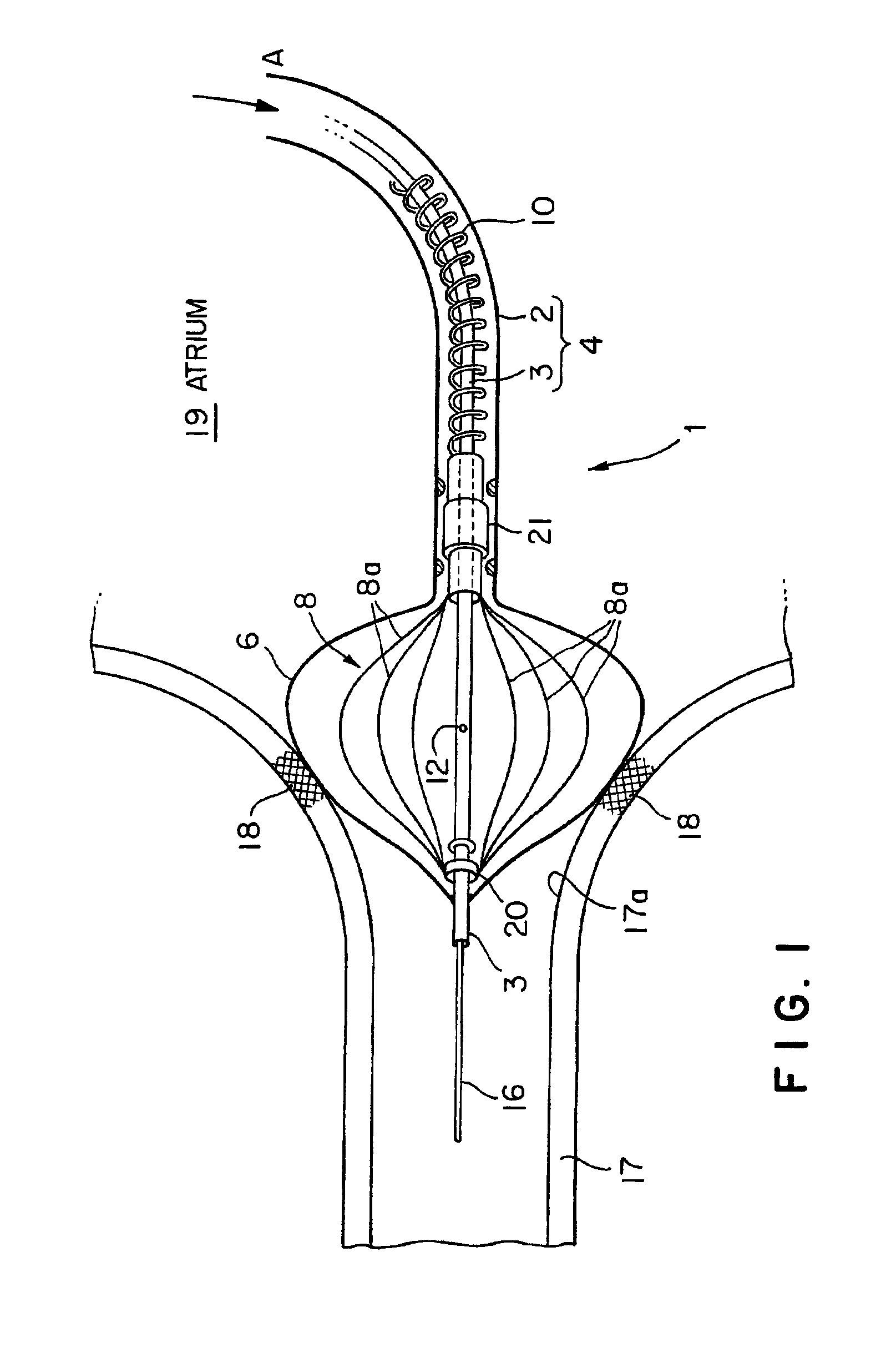
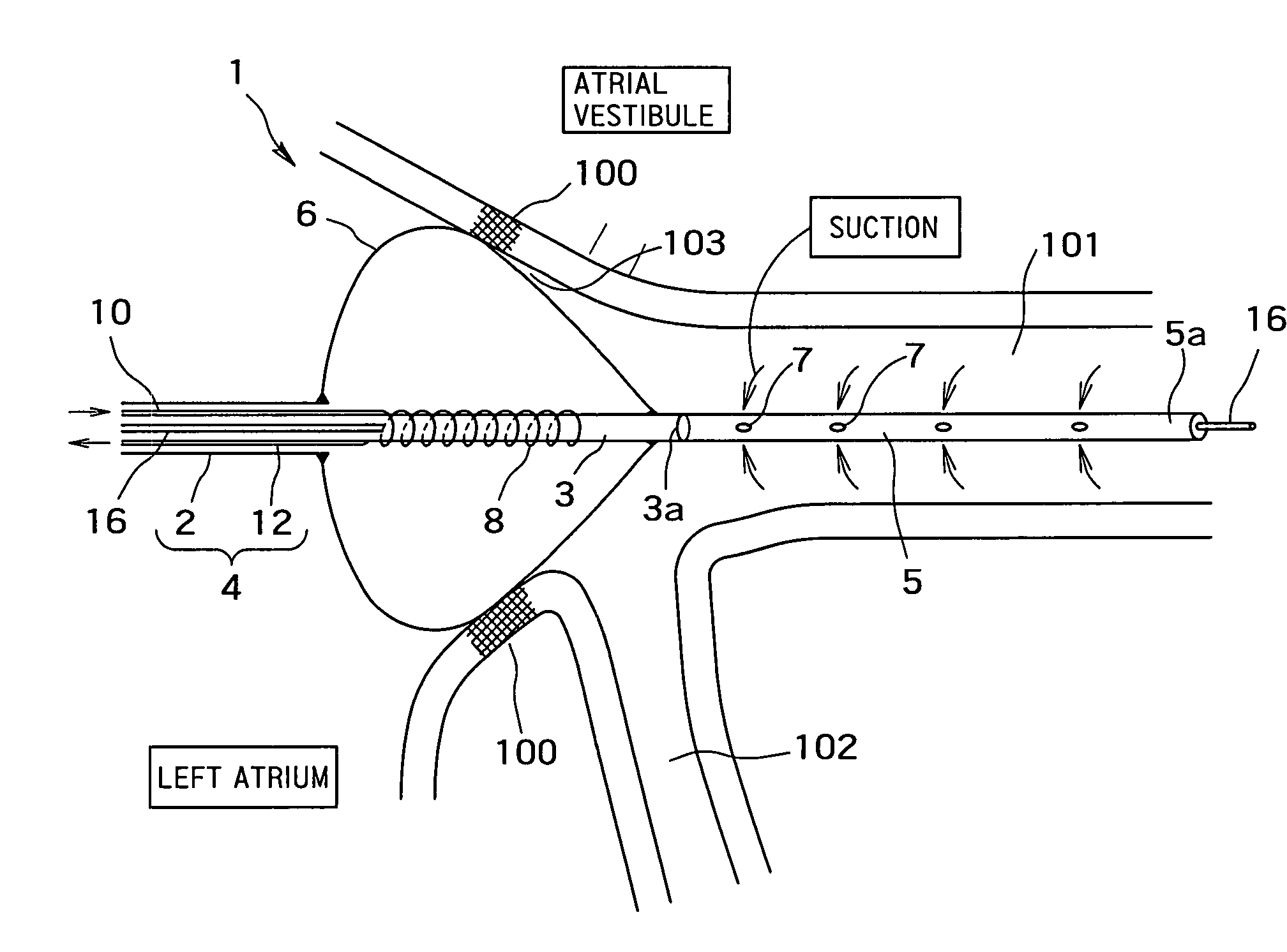
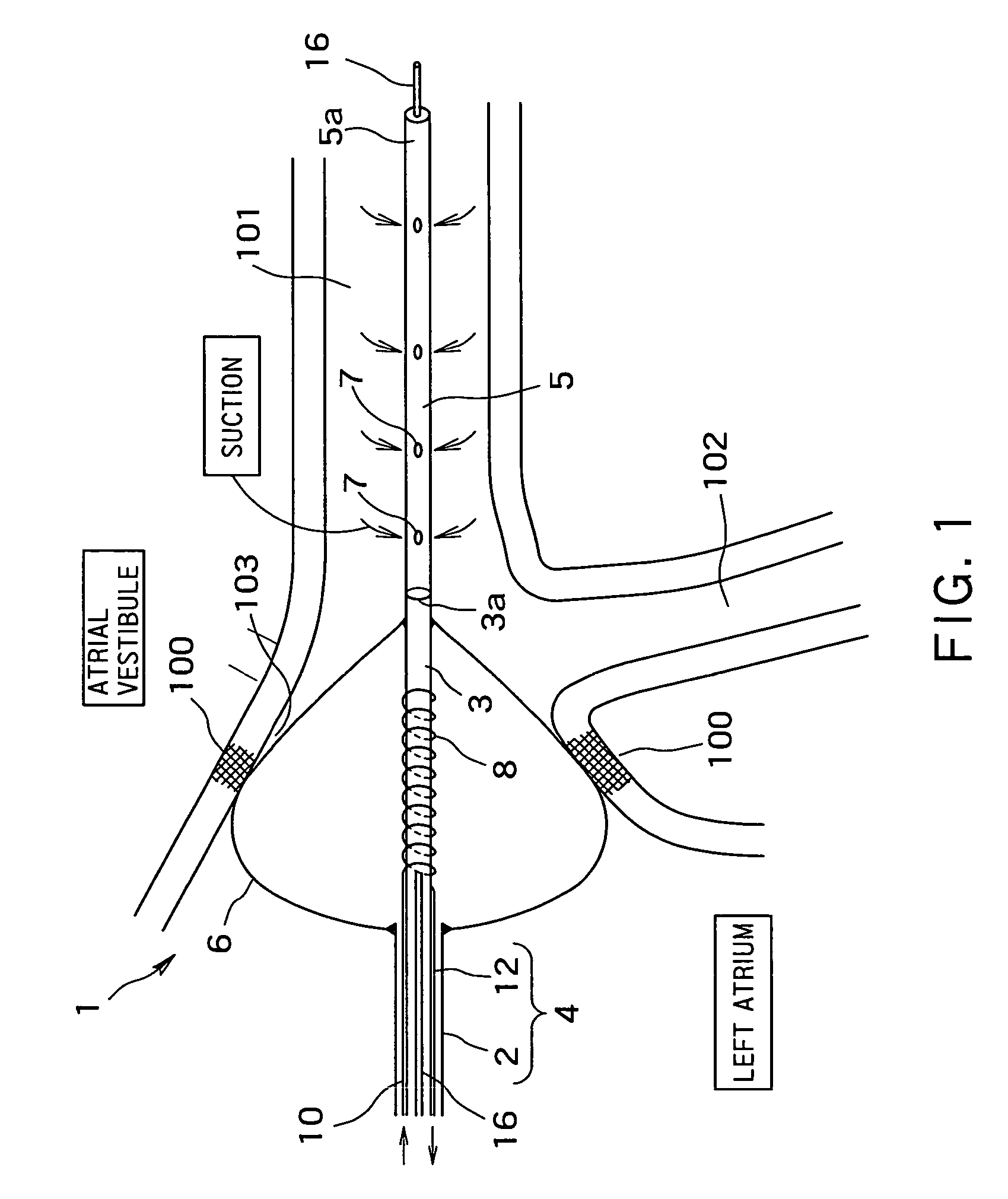
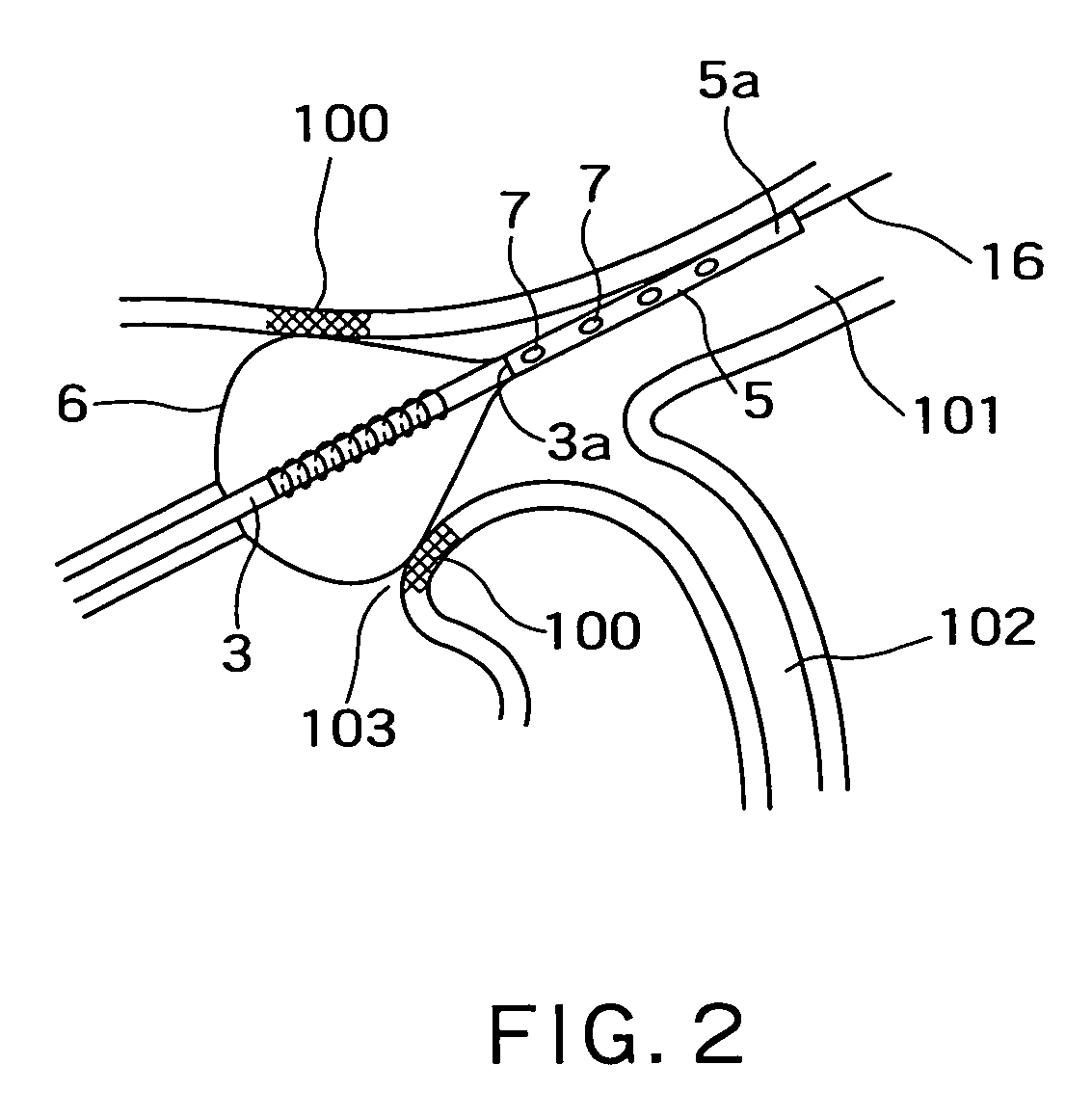
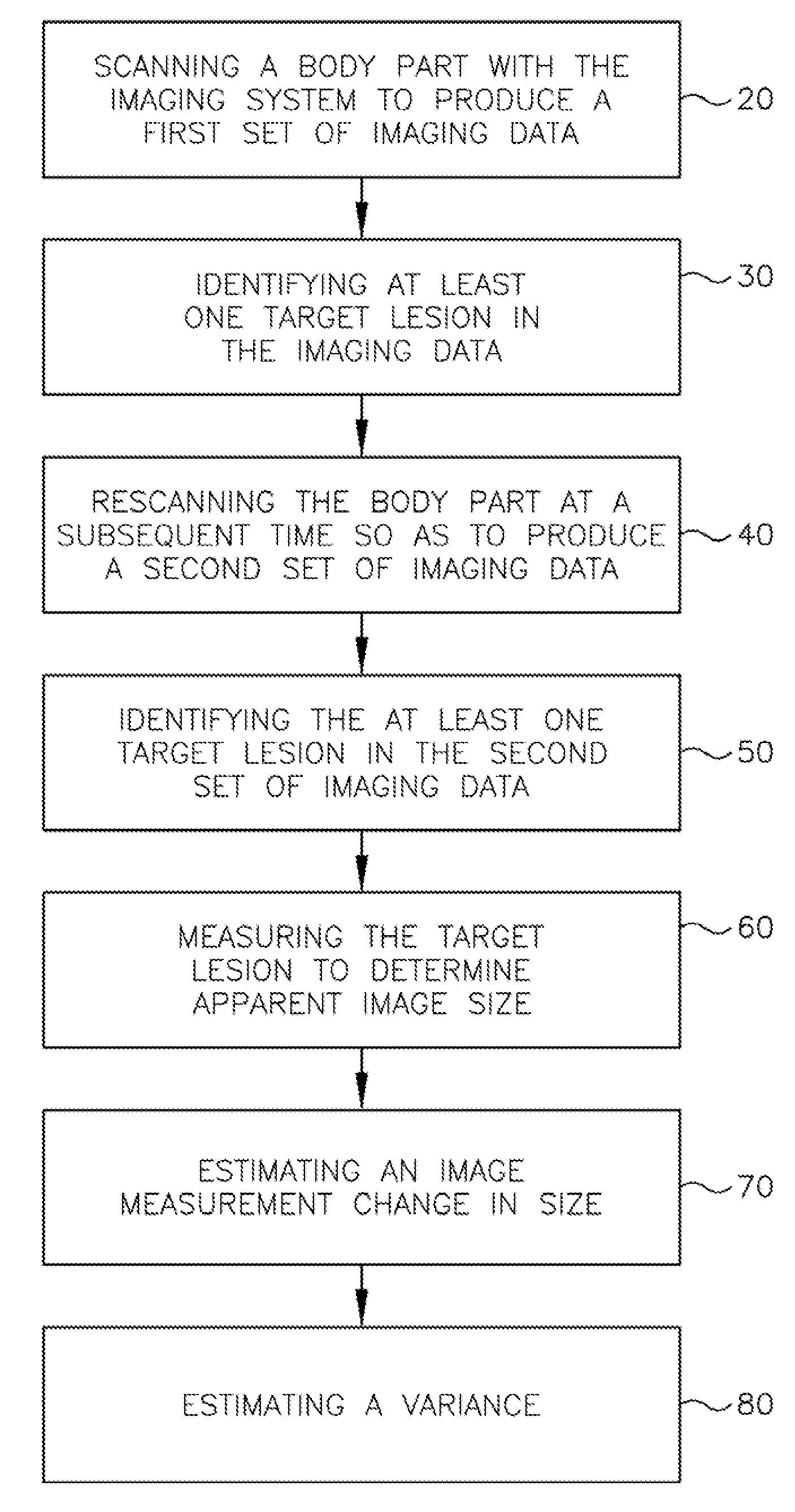
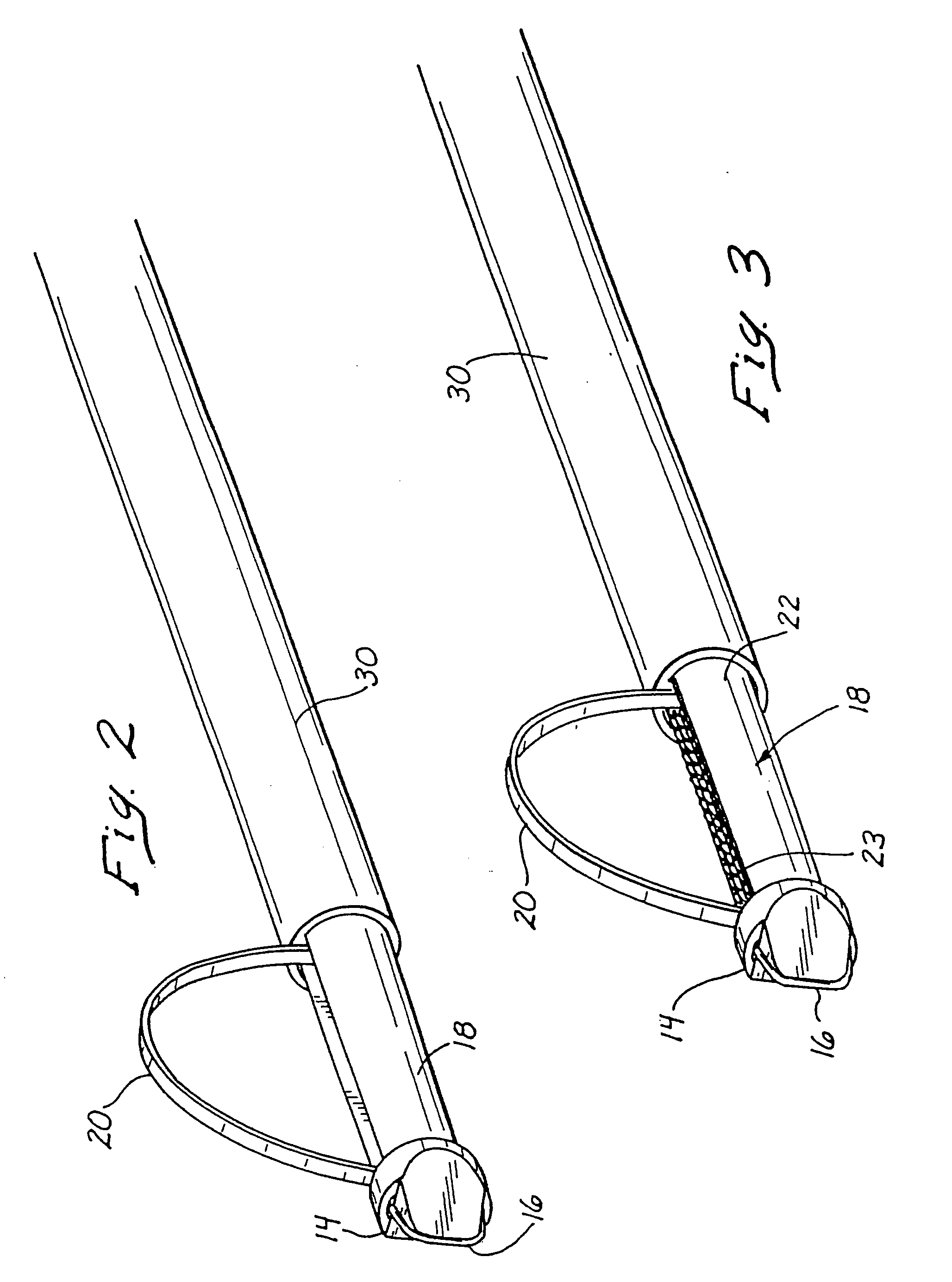
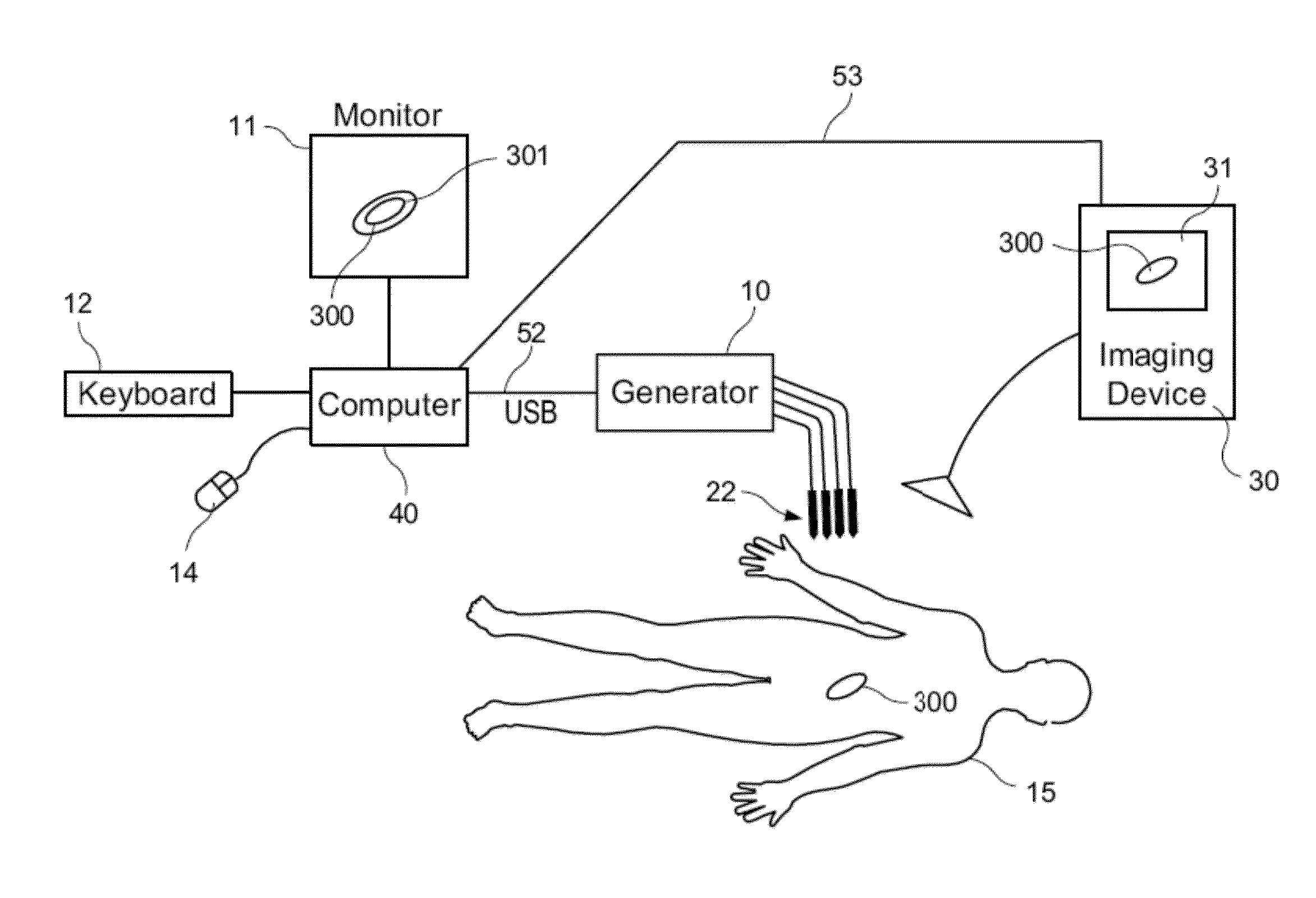
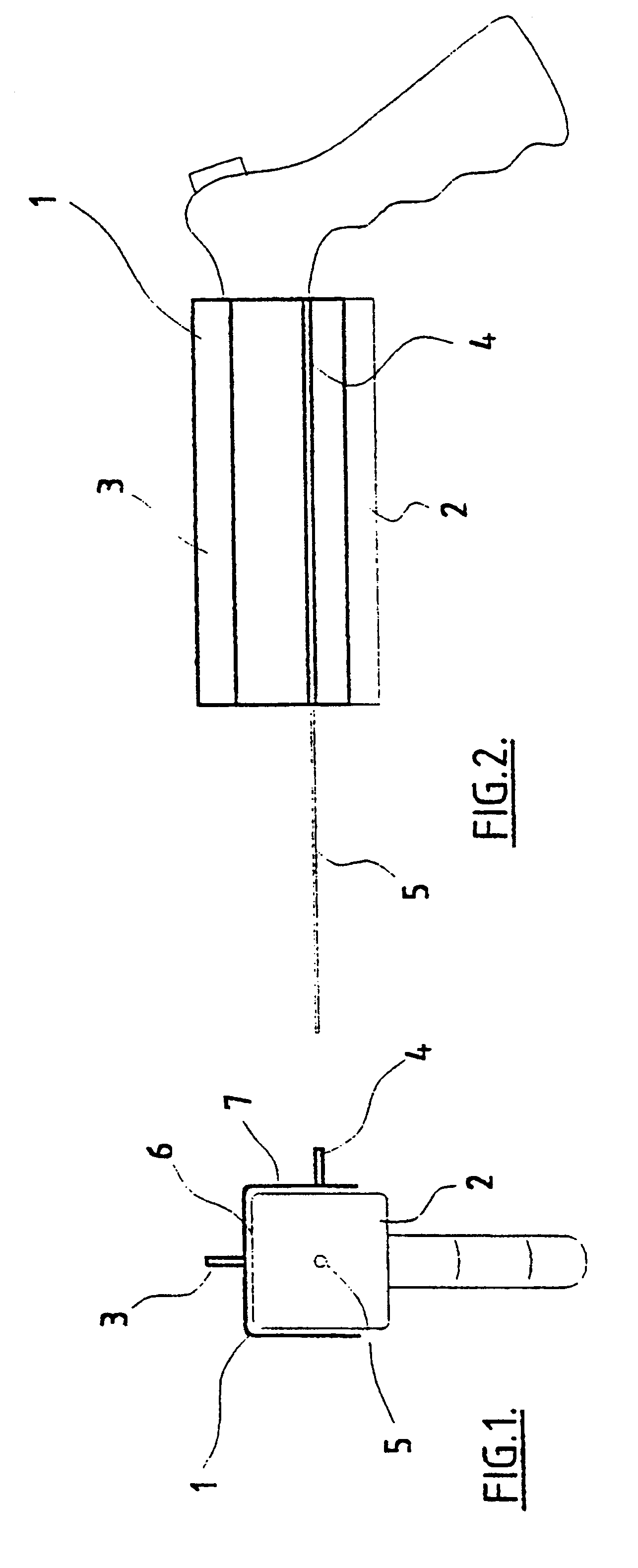
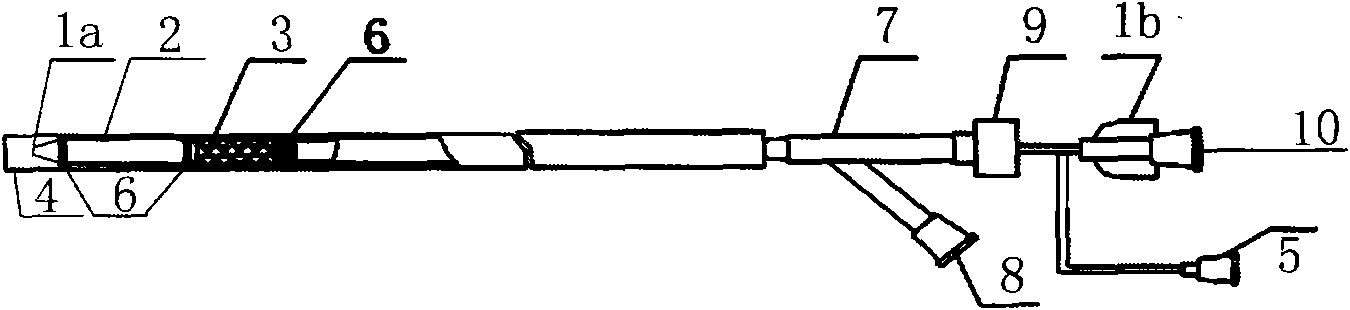
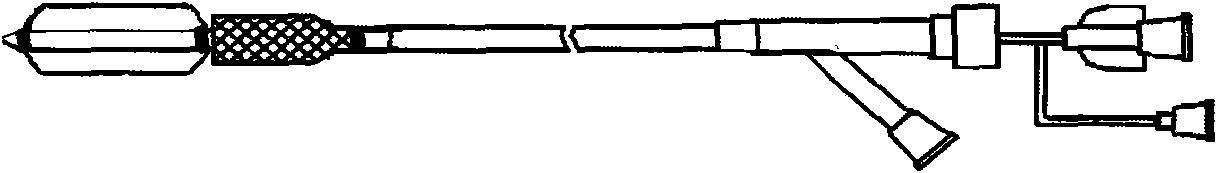
Radiofrequency thermal balloon catheter
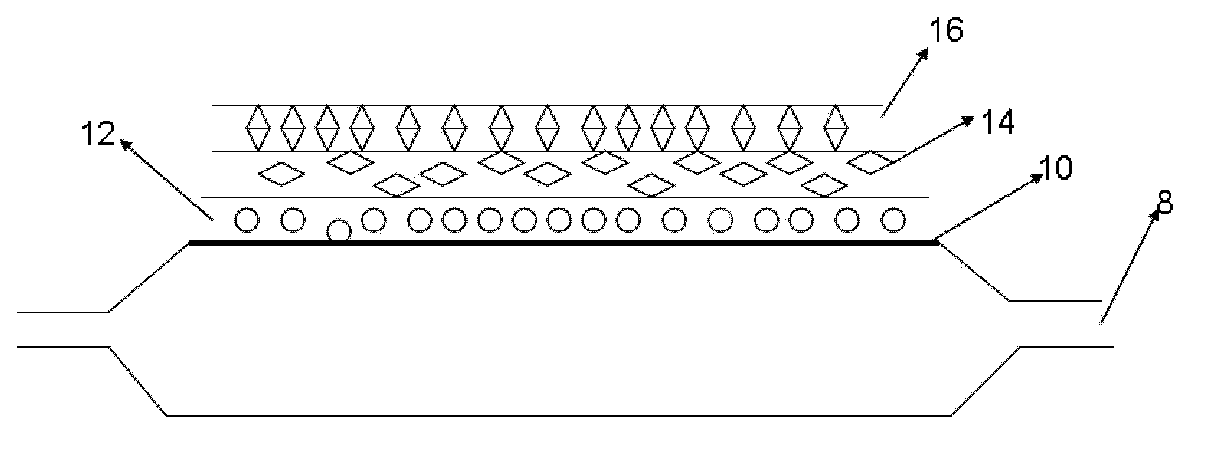
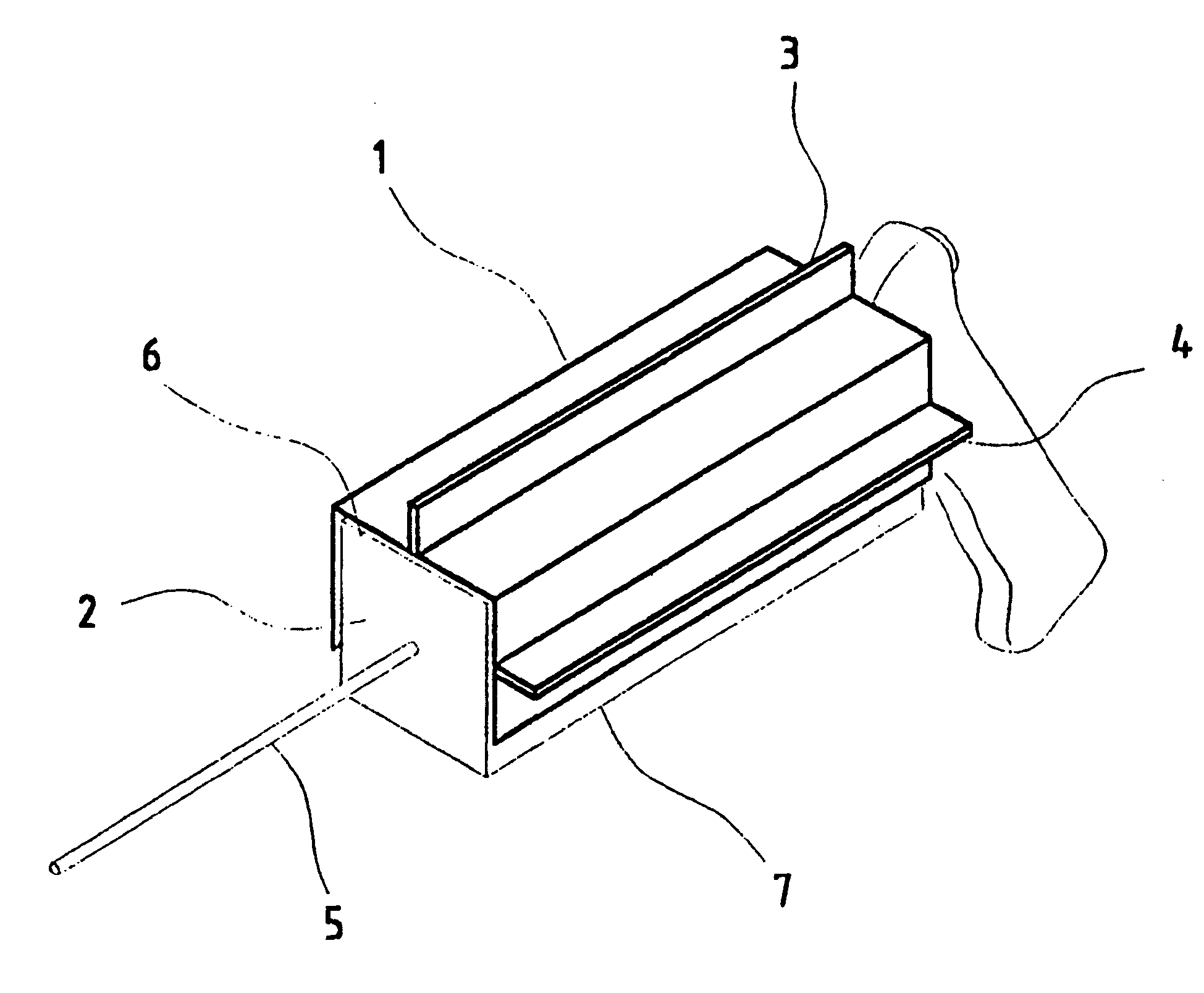
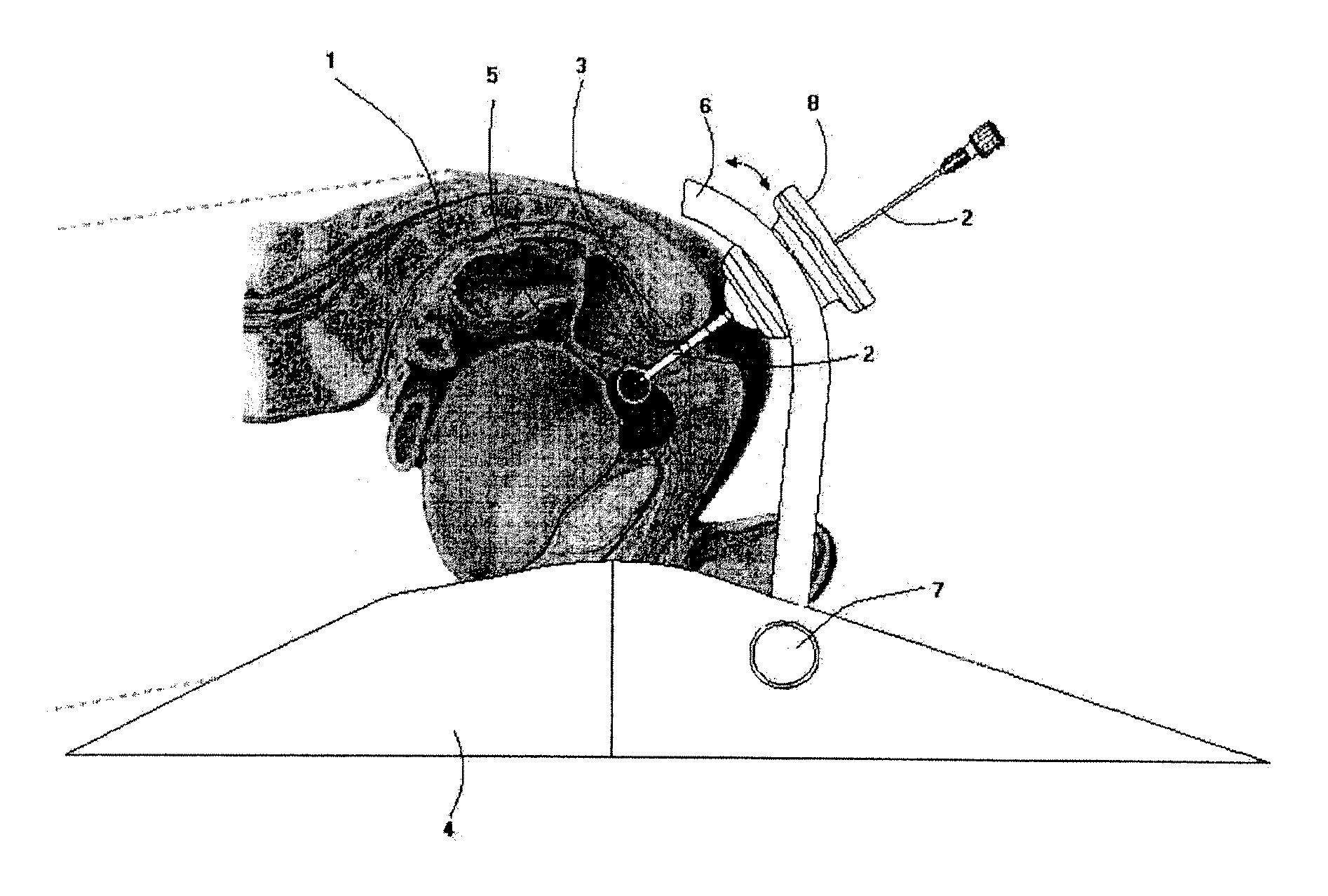
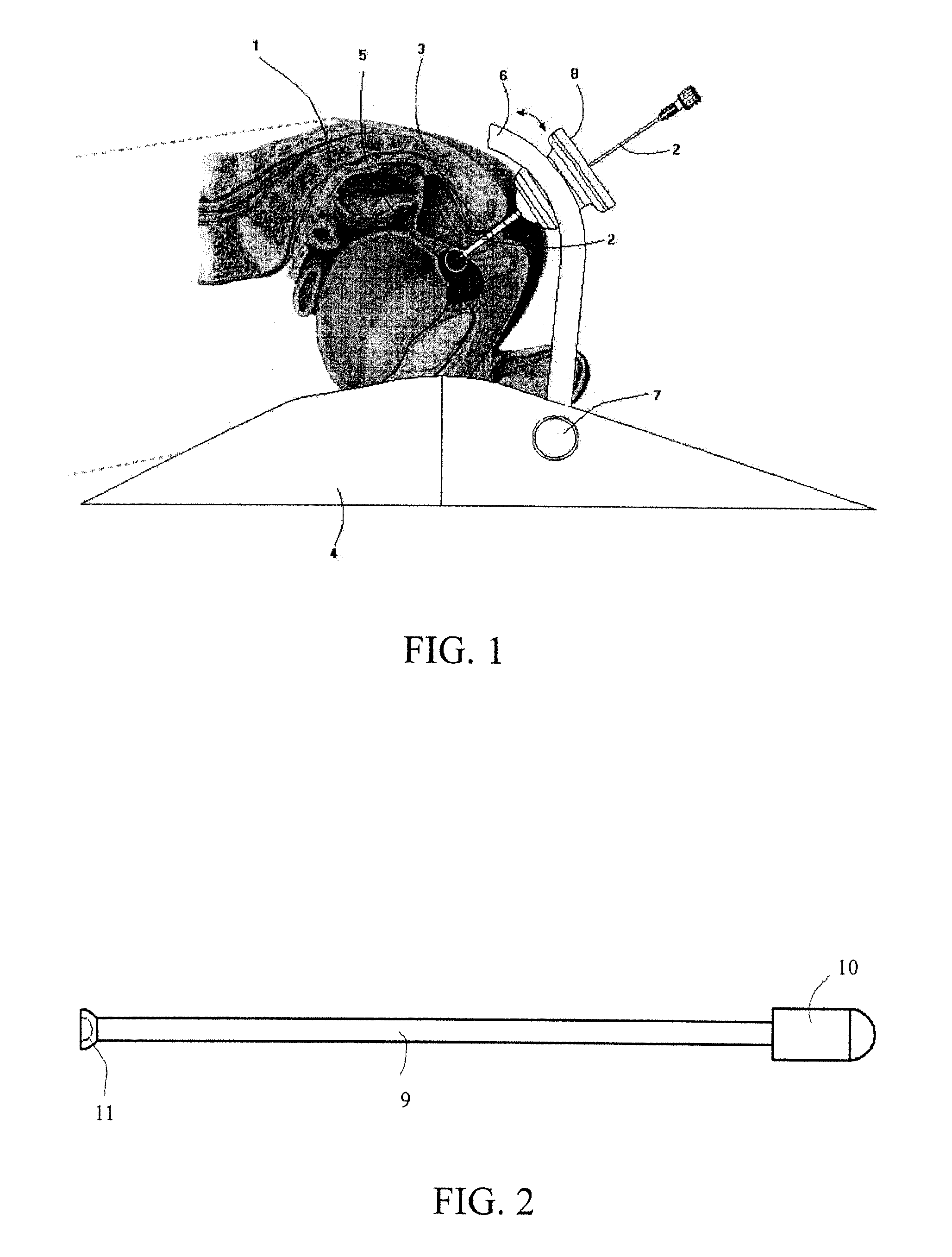
A radiofrequency thermal balloon catheter uniformly heats tissues in contact with the balloon to achieve thermotherapy such as ablation or hyperthermia safely and properly for a diseased part. The radiofrequency thermal balloon catheter includes a catheter (4) having an outer shaft (2) and an inner shaft 3 extended through the outer shaft so as to be slidable relative to the outer shaft, an inflatable balloon (6) capable of being inflated so as to be in contact with a target lesion (18) and provided between respective front end parts of the outer and the inner shaft, and a radiofrequency electrode (8) extended in a wall of the balloon or inside the balloon to be used for radiofrequency energy supply in combination with a counter electrode (53). The counter electrode is disposed at a predetermined position, for example, inside the balloon, in the wall of the balloon, in a position neighboring the balloon or on the patient's body surface. A lead wire (10) electrically connects to the radiofrequency electrode. A temperature sensor (12) is capable of sensing temperature of a liquid contained in the balloon. A temperature distribution uniformizing device (14) uniformizes the temperature distribution in the liquid contained in the balloon.
Owner:JAPAN ELECTEL
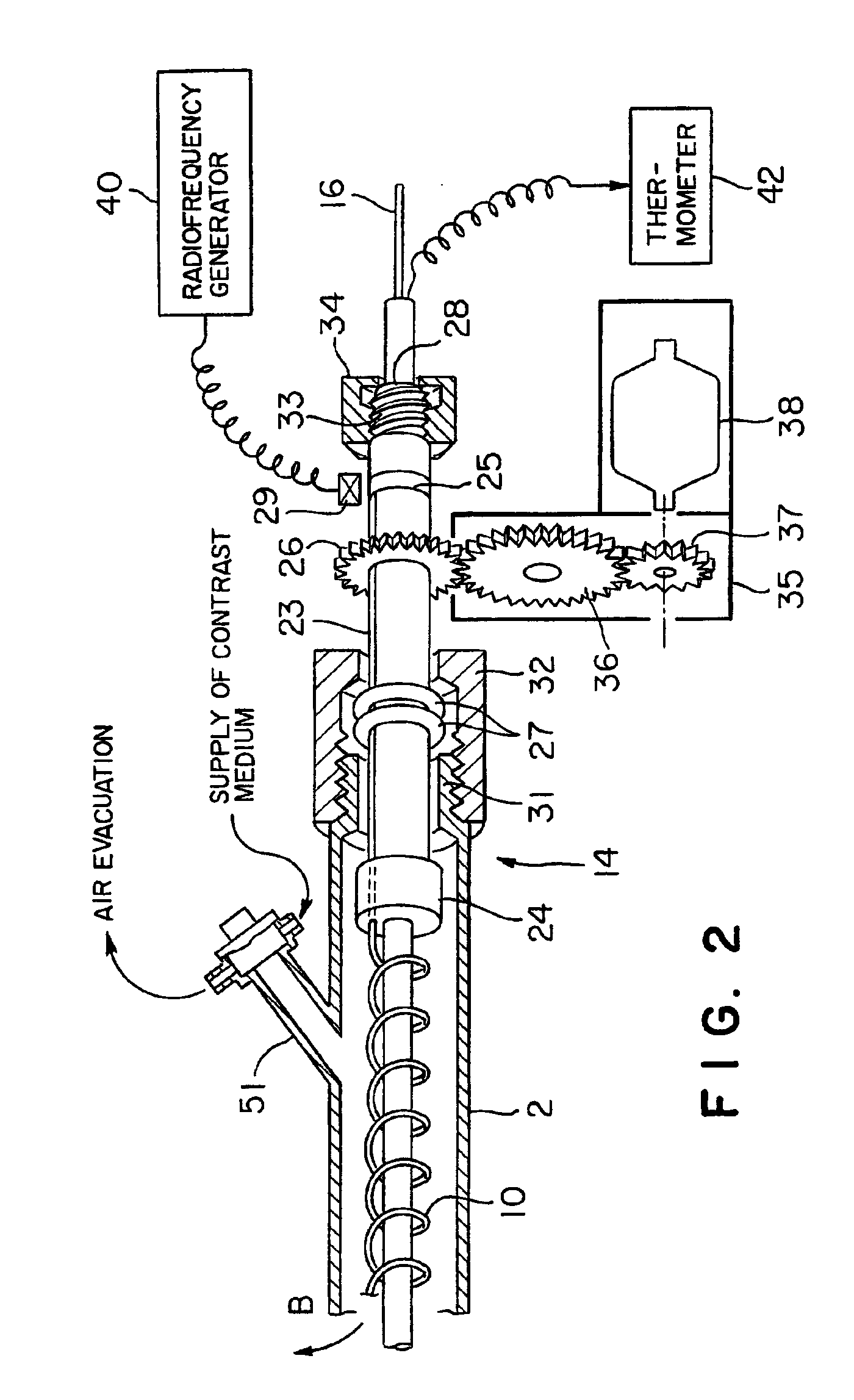
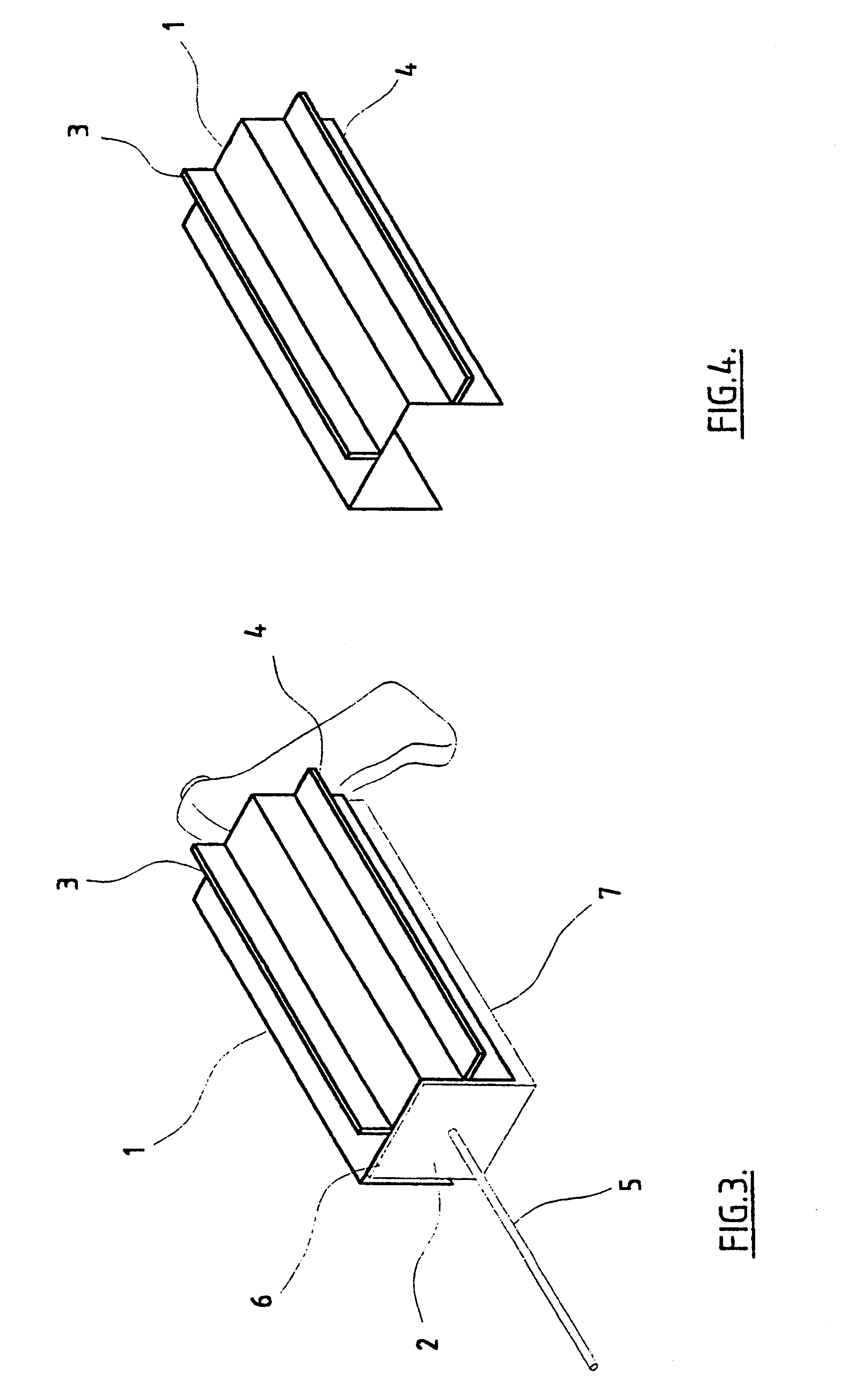
Radio-frequency heating balloon catheter
ActiveUS7112198B2Safely cauterizingShorten the timeCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingBalloon catheterRadio frequency
A radio-frequency heating balloon catheter is capable of cauterizing a target lesion in an atrial vestibule. The radio-frequency heating balloon catheter has a catheter tube including an outer tube and an inner tube slidably extended through the outer tube. An inflatable balloon is connected to an extremity of the outer tube and a part near an extremity of the inner tube, and is capable of coming into contact with a target lesion when inflated. A radio-frequency electrode serves as a counter to a surface electrode attached to a surface of a subject's body and is placed in a wall of the balloon or inside the balloon to supply radio-frequency power between the surface electrode and the radio-frequency electrode. A temperature sensor senses temperature inside the balloon, a guide shaft projects from the extremity of the inner tube and is capable of holding the balloon on the target lesion, and a guide wire extends through the catheter tube and the guide shaft.
Owner:JAPAN ELECTEL
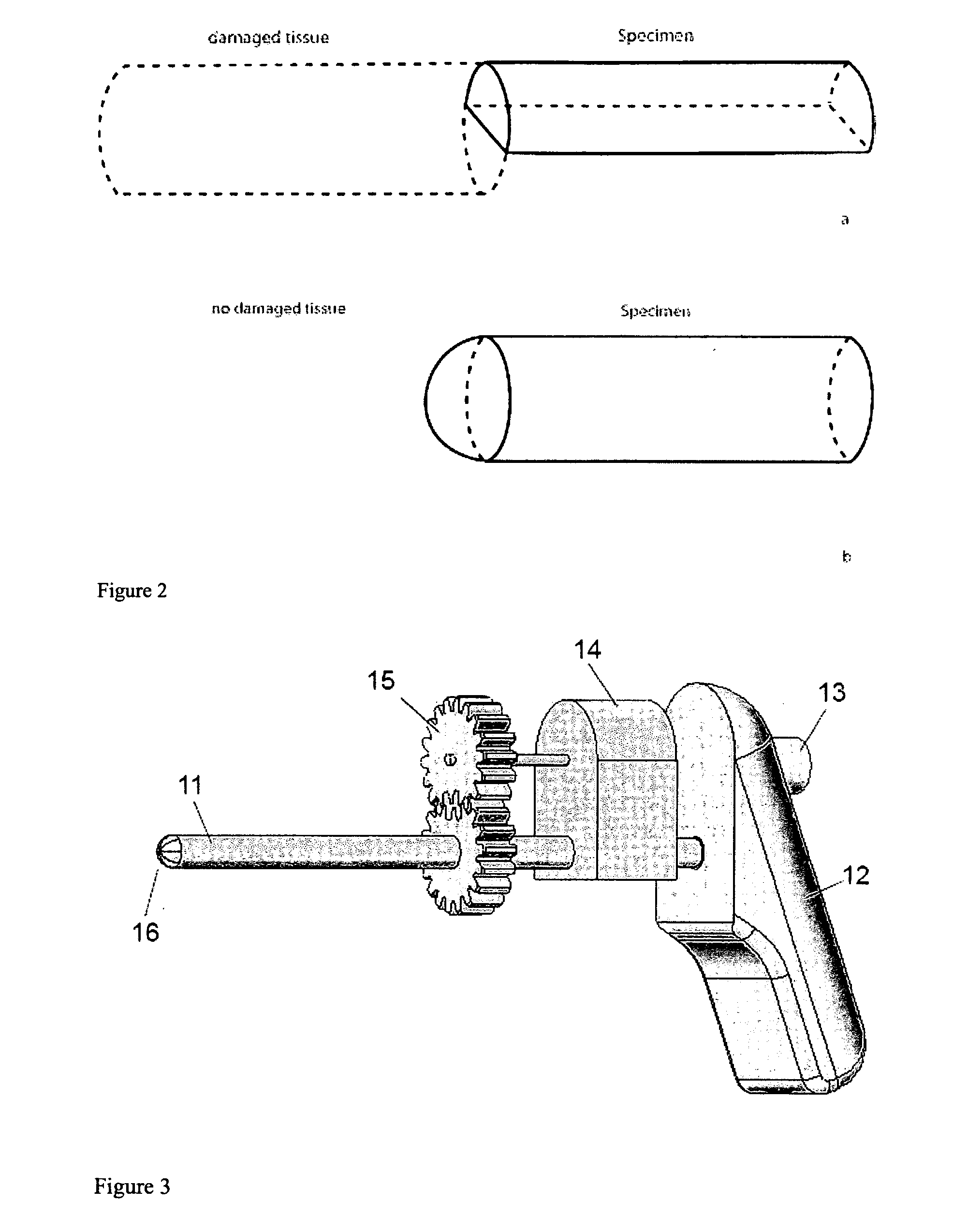
Method and device to obtain percutaneous tissue samples
InactiveUS20060122535A1Surgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityResonance
A new method and design for a percutaneous biopsy system that cuts only the tissue lesion specimen and that does not penetrate through or beyond the targeted tissue into intact tissue. The proposed mechanism operates only in the targeted lesion space and leaves healthy or unsuspicious tissue intact. The proposed biopsy mechanism will cut the specimen in front of the tip of the guiding needle. The device may be image guided by ultrasound, any x-ray based modality or magnetic resonance (MRI).
Owner:DAUM WOLFGANG
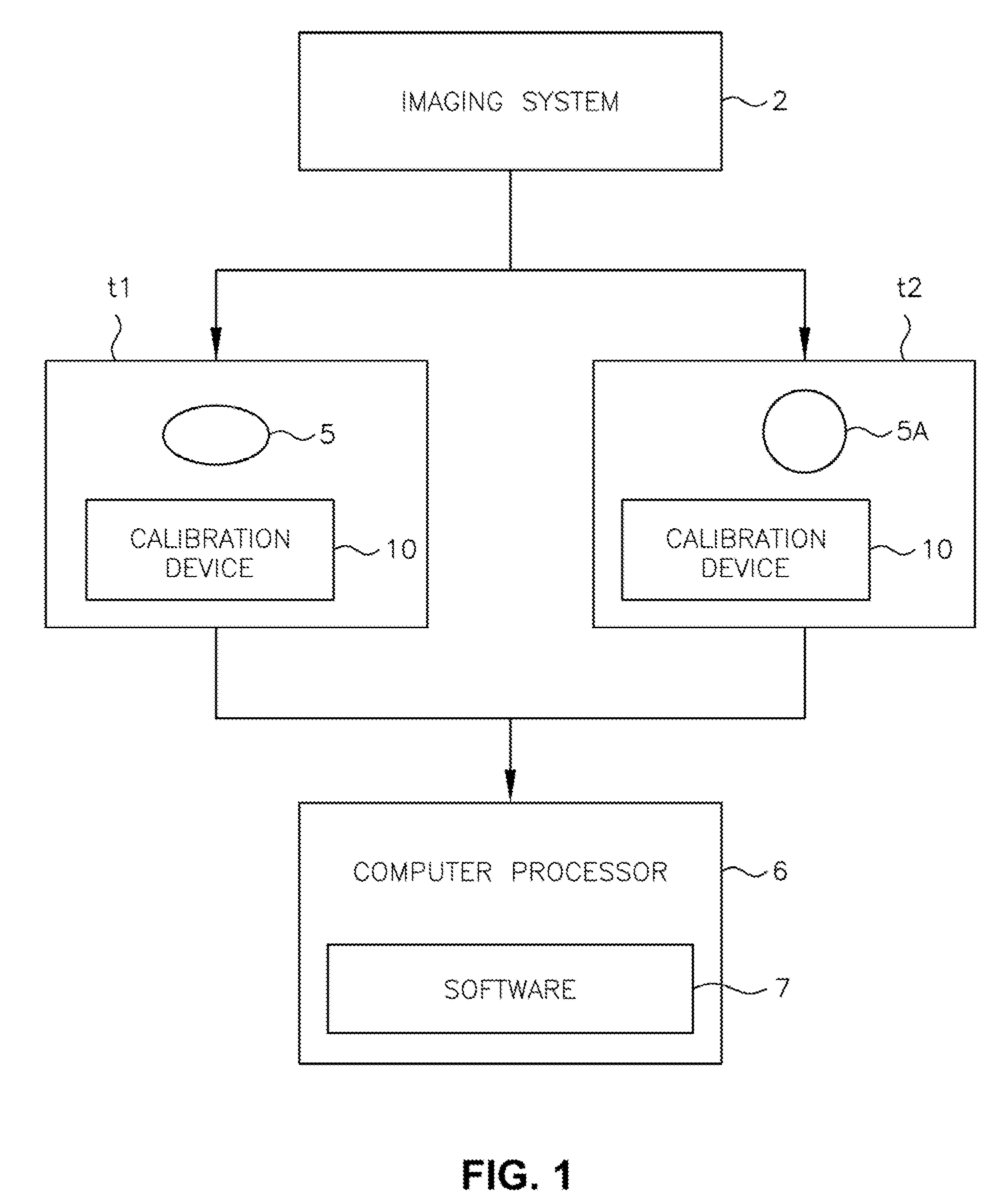
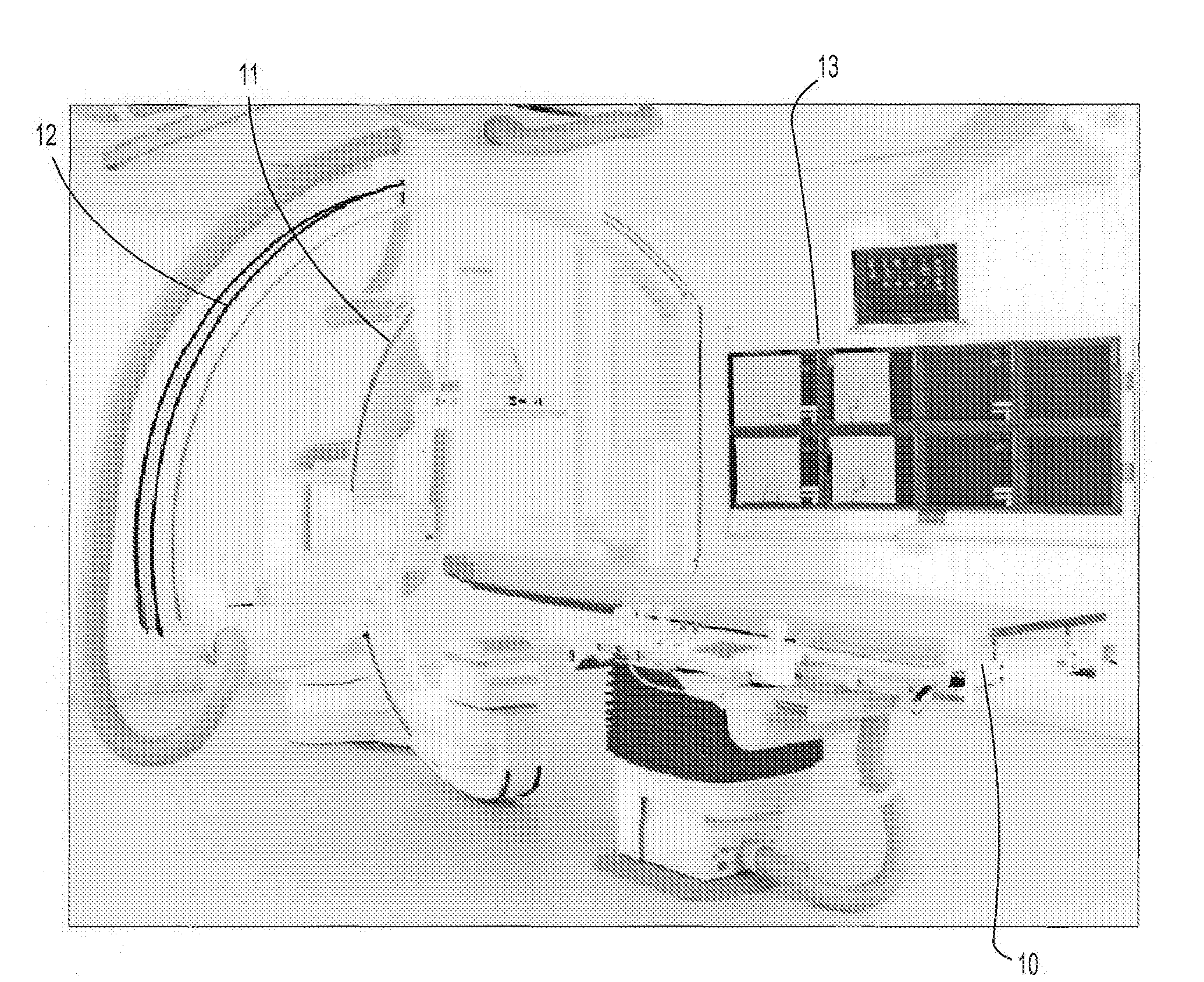
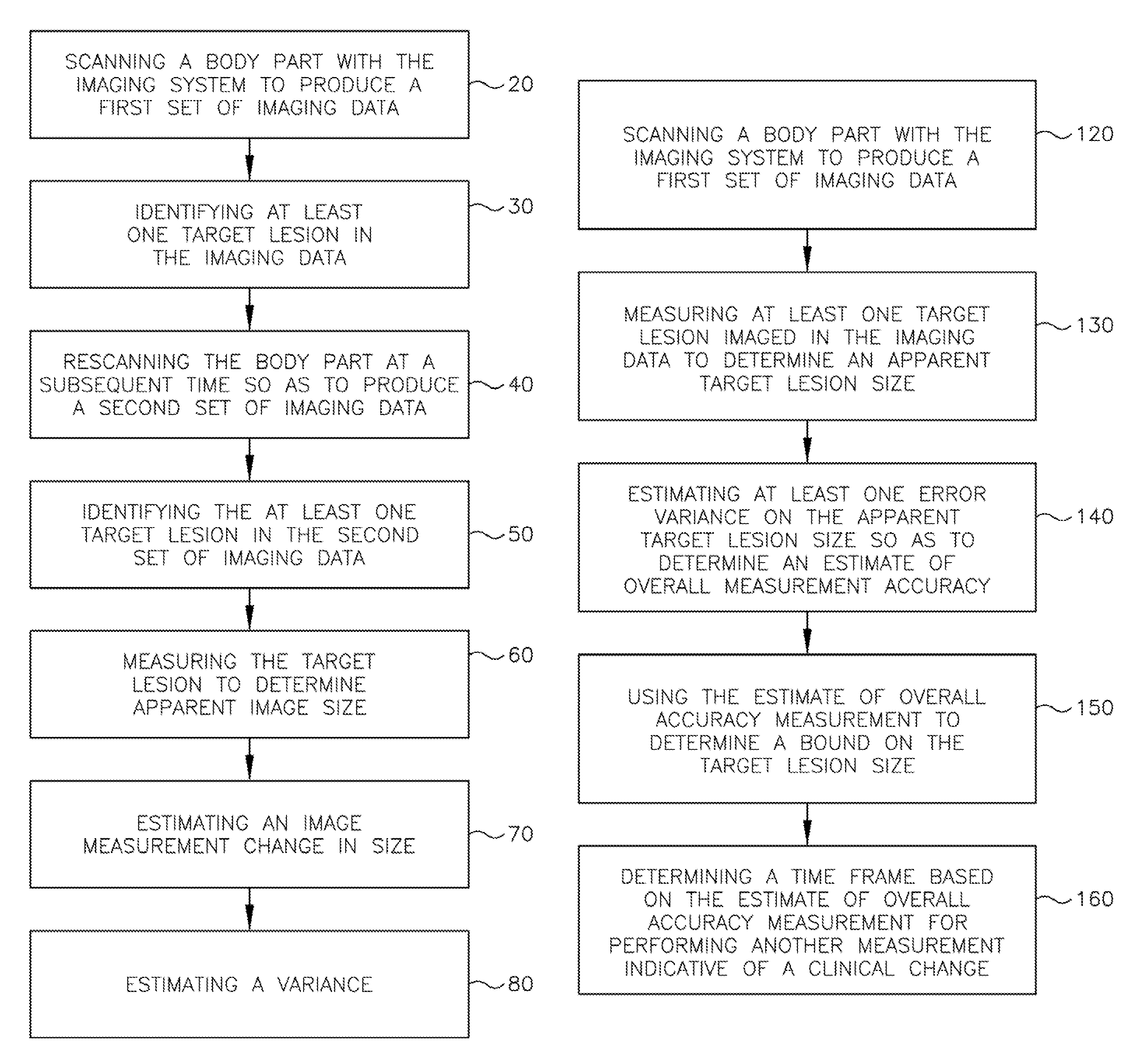
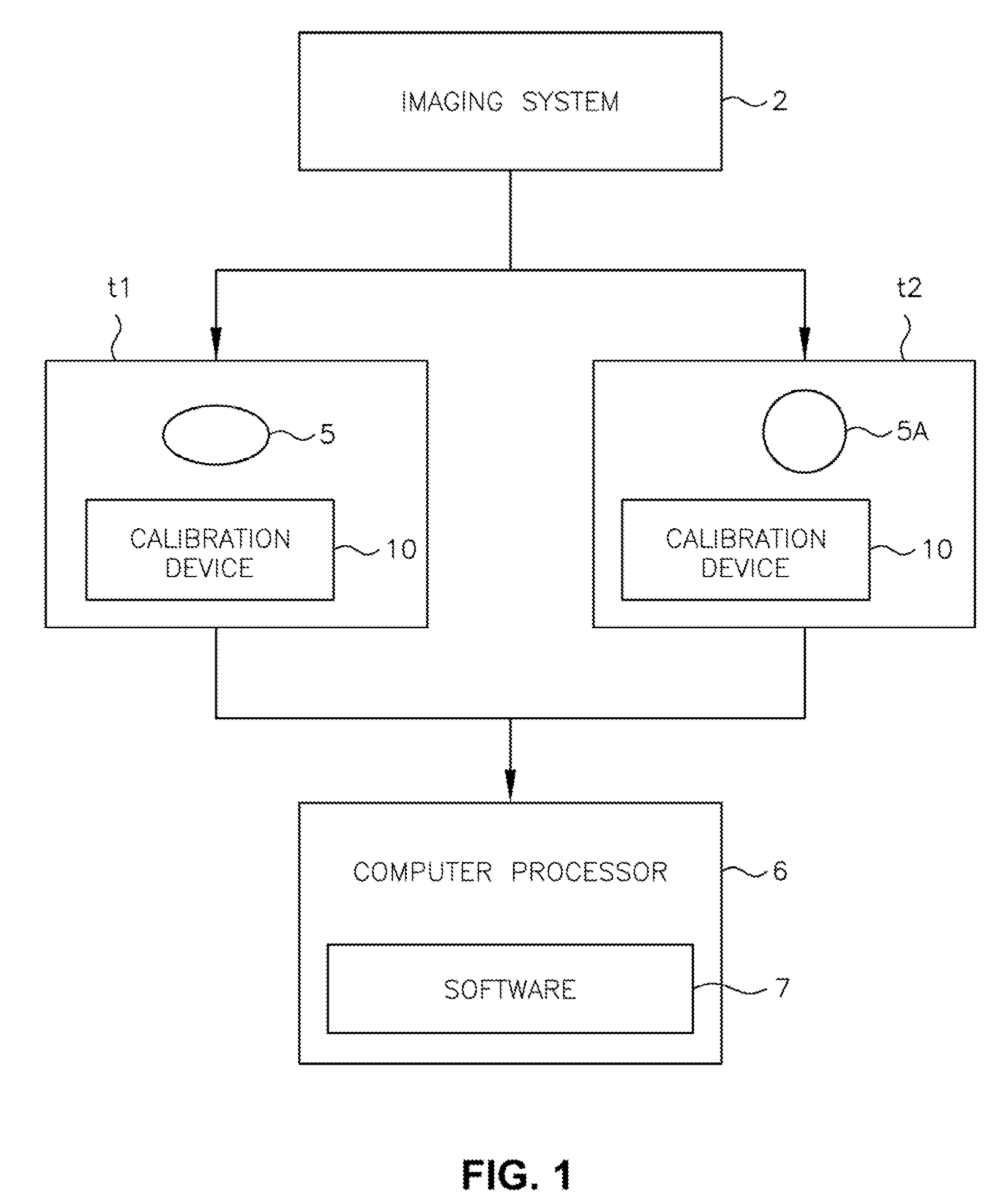
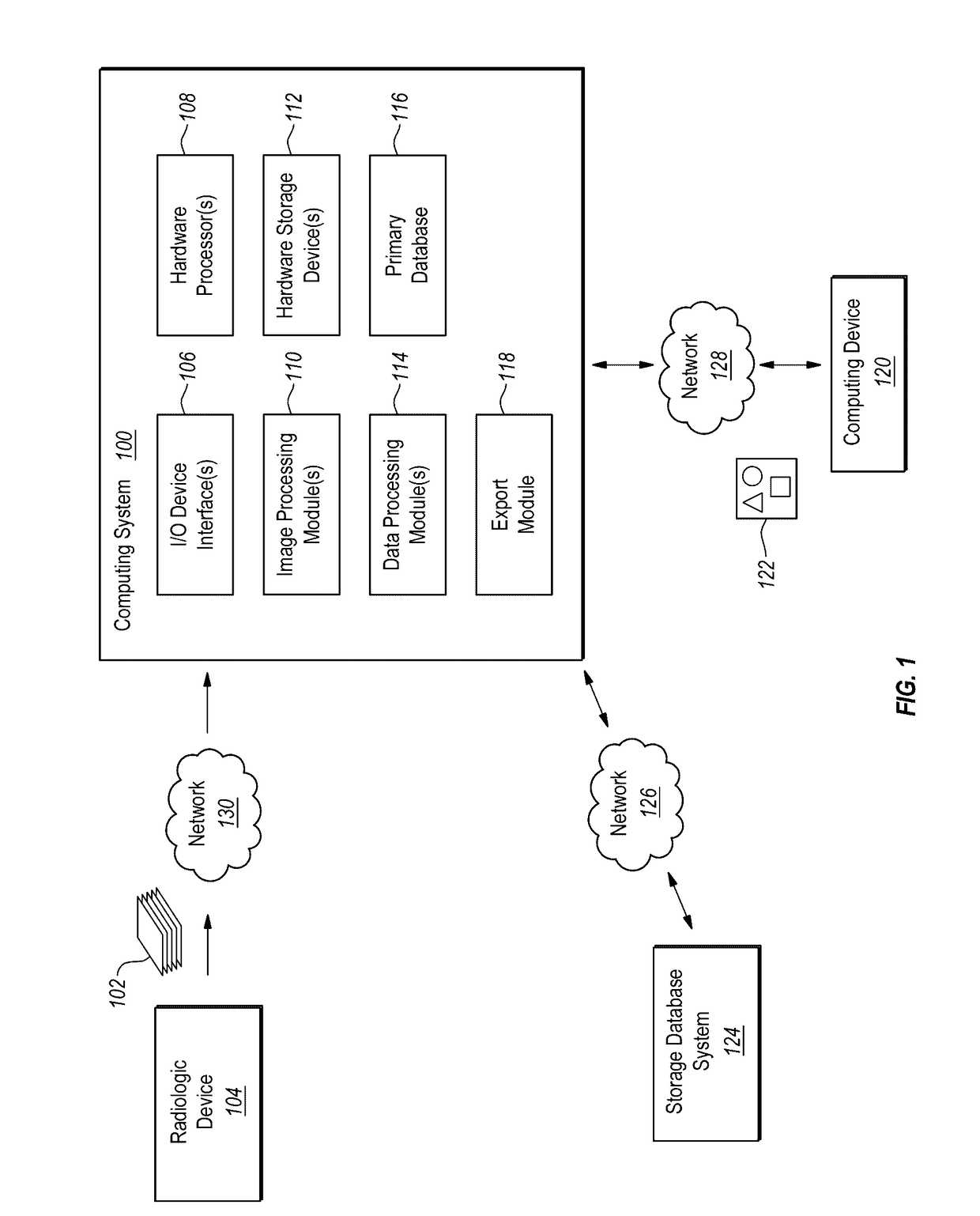
Medical imaging system for accurate measurement evaluation of changes in a target lesion
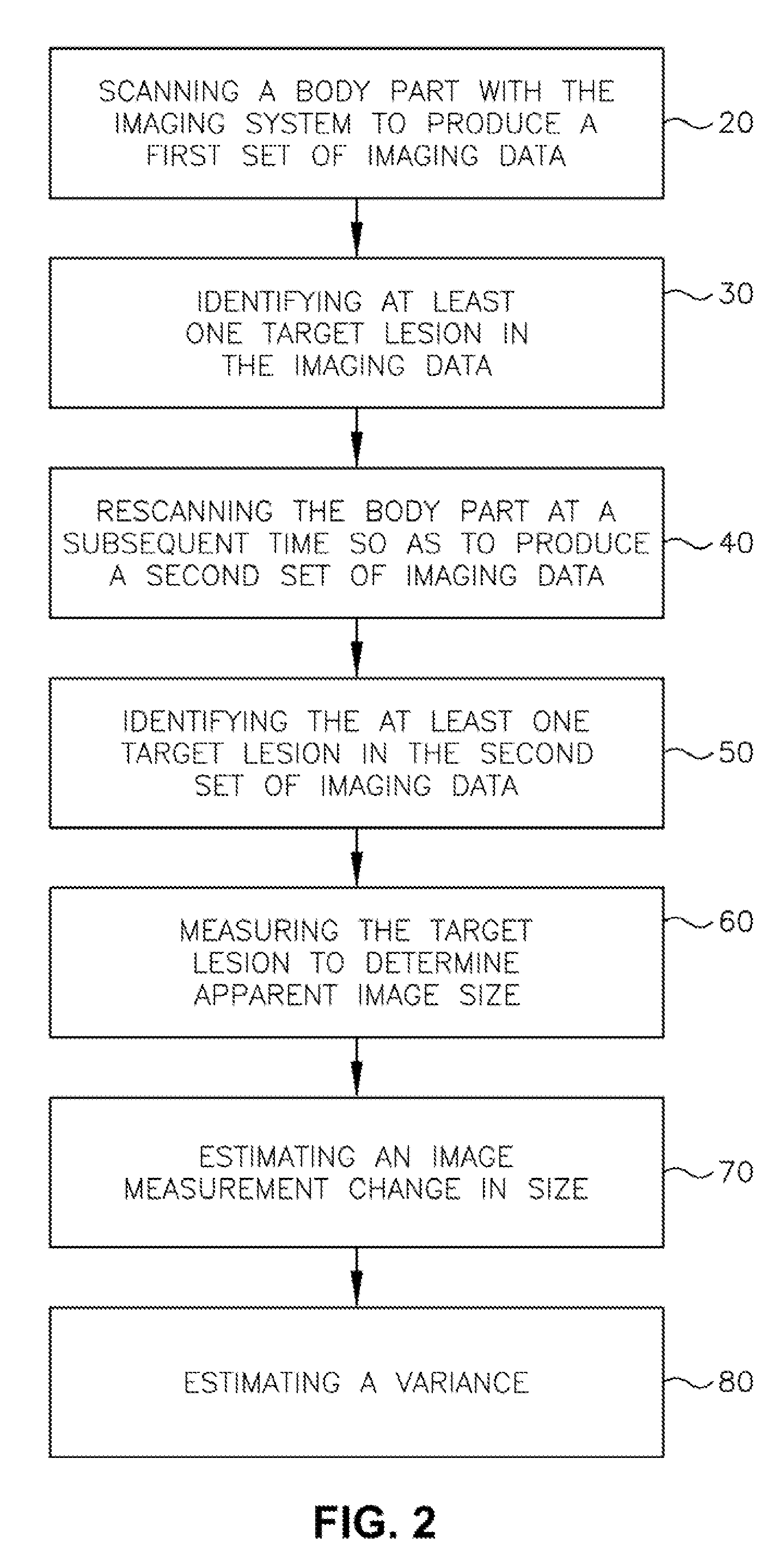
ActiveUS20070100226A1Shorten the lengthInformation can be usedImage enhancementImage analysisMeasurement evaluationMedical imaging
A body part is scanned to produce a first set of imaging data. A target lesion in the imaging data is identified. The body part is rescanned at a subsequent time so as to produce a second set of imaging data. The target lesion is identified in the second set of imaging data and the size of the target lesion is measured in the first and second sets of imaging data to determine two apparent image volumes corresponding to the first and second sets of imaging data. A change in size is estimated by comparing the first and second apparent lesion sizes. A variance on the change in size is estimated so as to determine a bound on the change in size measurement.
Owner:YANKELEVITZ DAVID DR
System and method for intraoperative guidance of stent placement during endovascular interventions
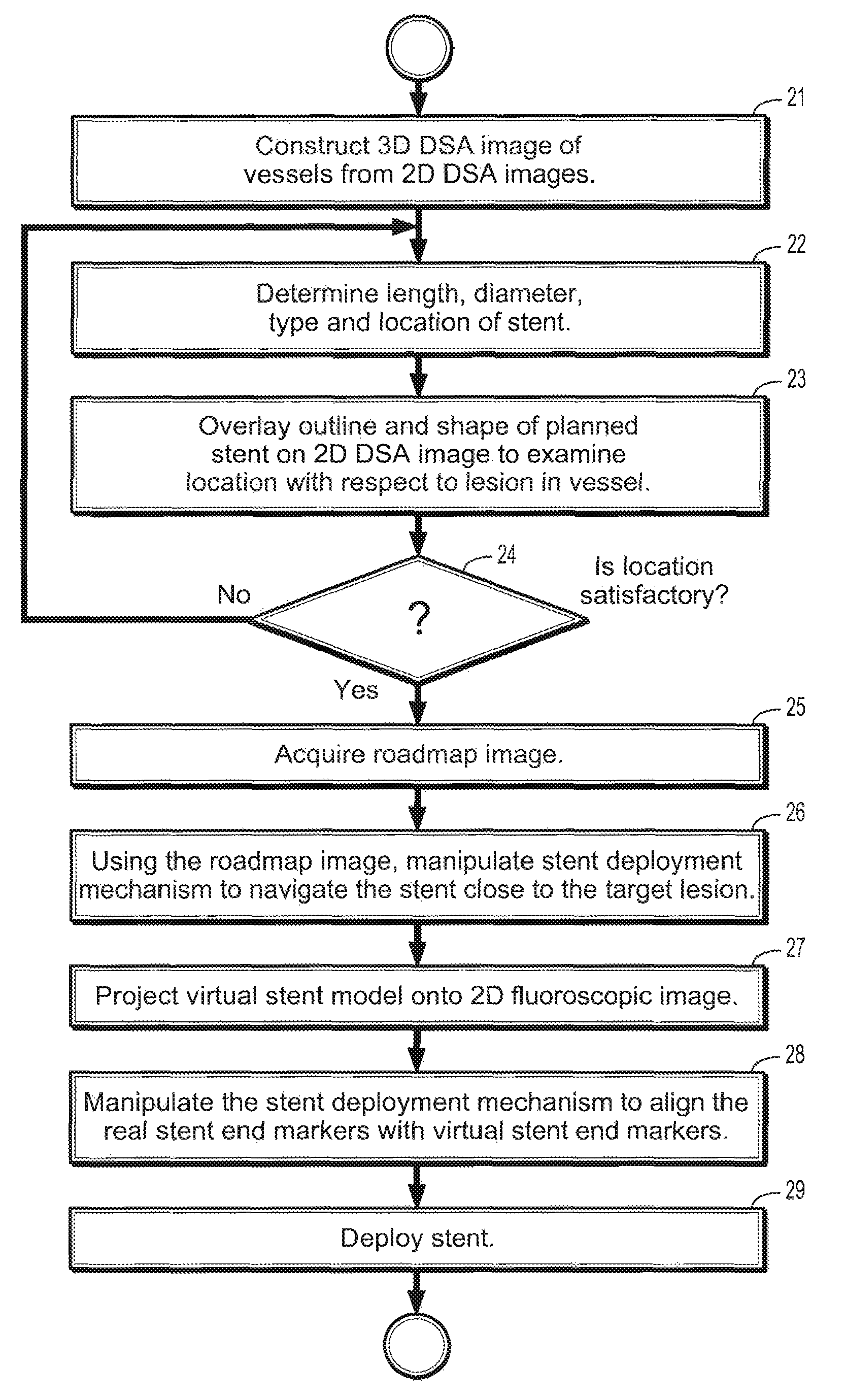
A method for guiding stent deployment during an endovascular procedure includes providing a virtual stent model of a real stent that specifies a length, diameter, shape, and placement of the real stent. The method further includes projecting the virtual stent model onto a 2-dimensional (2D) DSA image of a target lesion, manipulating a stent deployment mechanism to navigate the stent to the target lesion while simultaneously acquiring real-time 2D fluoroscopic images of the stent navigation, and overlaying each fluoroscopic image on the 2D DSA image having the projected virtual stent model image, where the 2D fluoroscopic images are acquired from a C-arm mounted X-ray apparatus, and updating the projection of the virtual stent model onto the fluoroscopic images whenever a new fluoroscopic image is acquired or whenever the C-arm is moved, where the stent is aligned with the virtual stent model by aligning stent end markers with virtual end markers.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Breast biopsy system and methods
InactiveUS20050010131A1Minimizing risk of migrationRaise the possibilitySurgical needlesInstrument handpiecesCancer cellSurgical department
An apparatus and method are provided for precisely isolating a target lesion in a patient's body tissue, resulting in a high likelihood of “clean” margins about the lesion when it is removed for diagnosis and / or therapy. This approach advantageously will often result in the ability to both diagnose and treat a malignant lesion with only a single percutaneous procedure, with no follow-up percutaneous or surgical procedure required, while minimizing the risk of migration of possibly cancerous cells from the lesion to surrounding tissue or the bloodstream. In particular, the apparatus comprises a biopsy instrument having a distal end adapted for entry into the patient's body, a longitudinal shaft, and a cutting element disposed along the shaft. The cutting element is actuatable between a radially retracted position and a radially extended position. Advantageously, the instrument is rotatable about its axis in the radially extended position to isolate a desired tissue specimen from surrounding tissue by defining a peripheral margin about the tissue specimen. Once the tissue specimen is isolated, it may be segmented by further manipulation of the cutting element, after which the tissue segments are preferably individually removed from the patient's body through a cannula or the like. Alternatively, the specimen may be encapsulated and removed as an intact piece.
Owner:SENORX
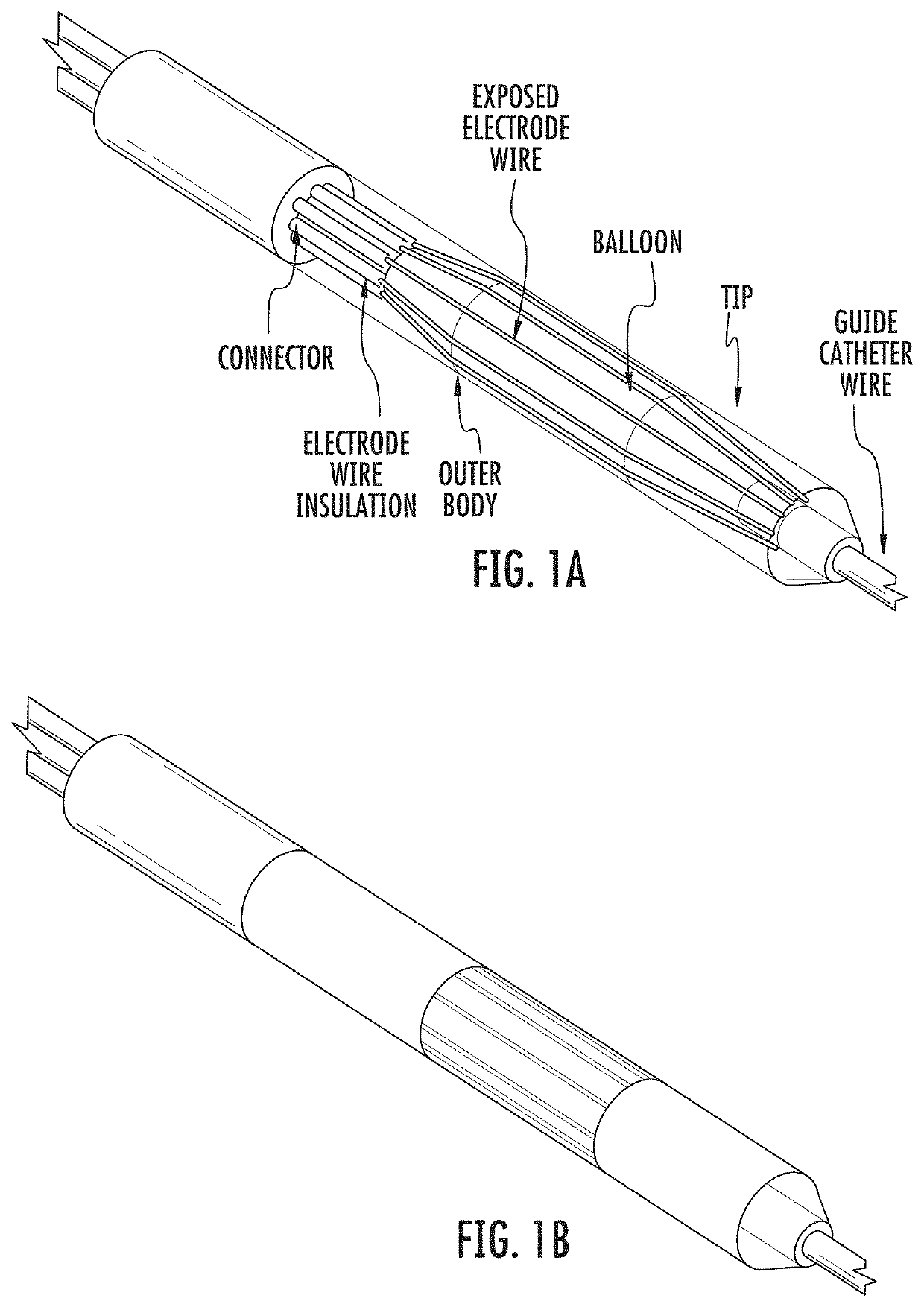
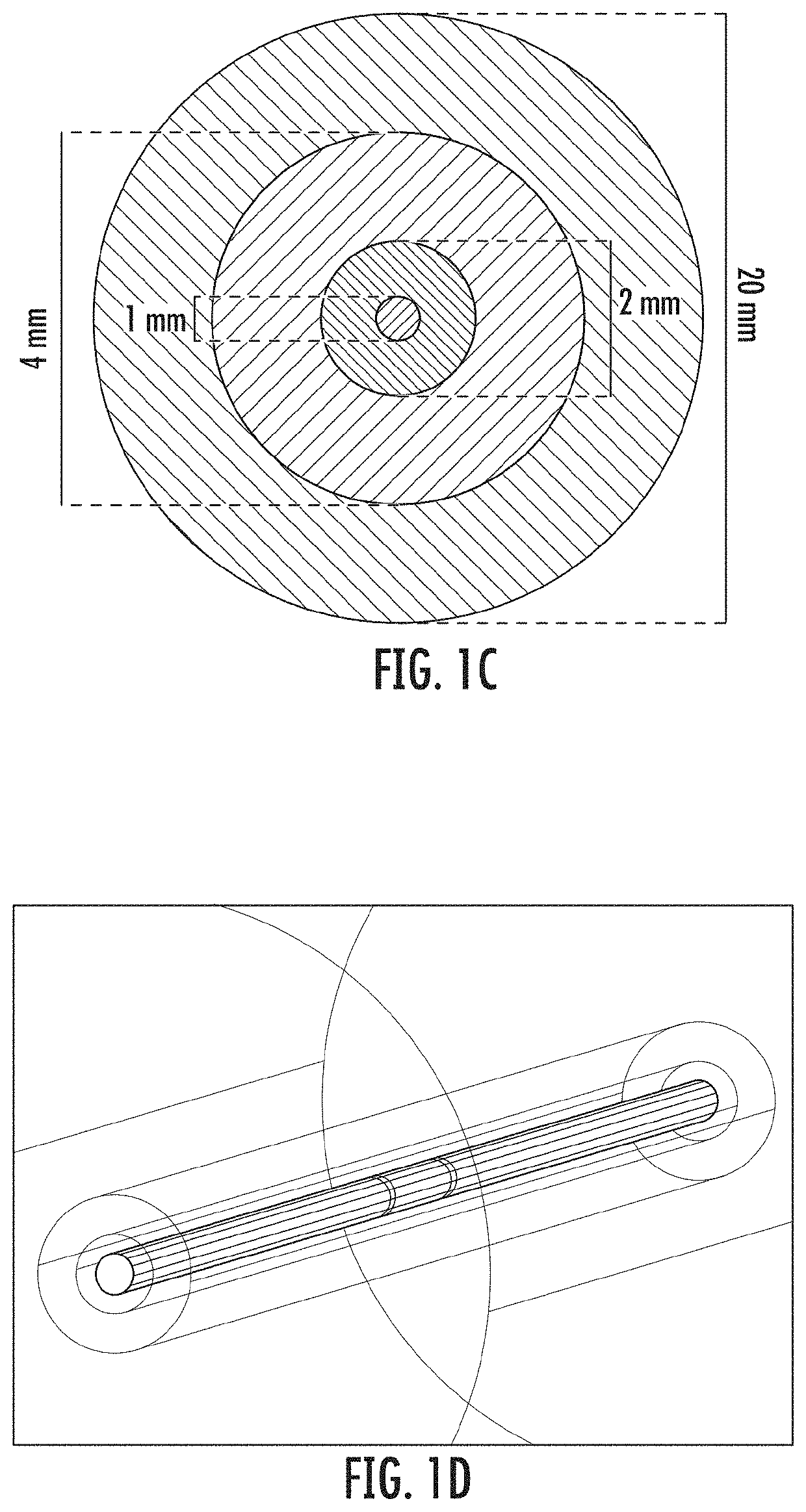
Device and Method for Electroporation Based Treatment of Stenosis of a Tubular Body Part
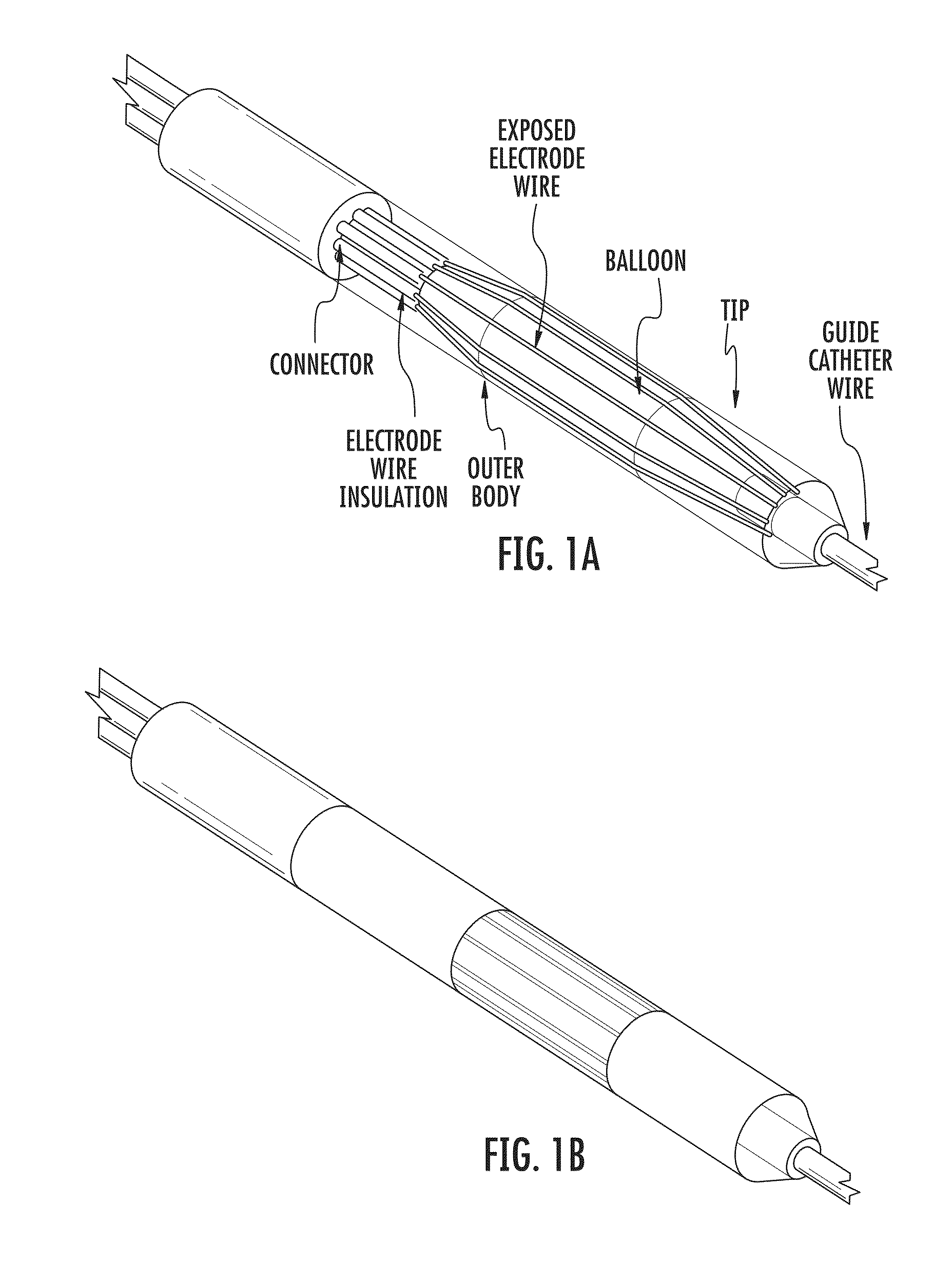
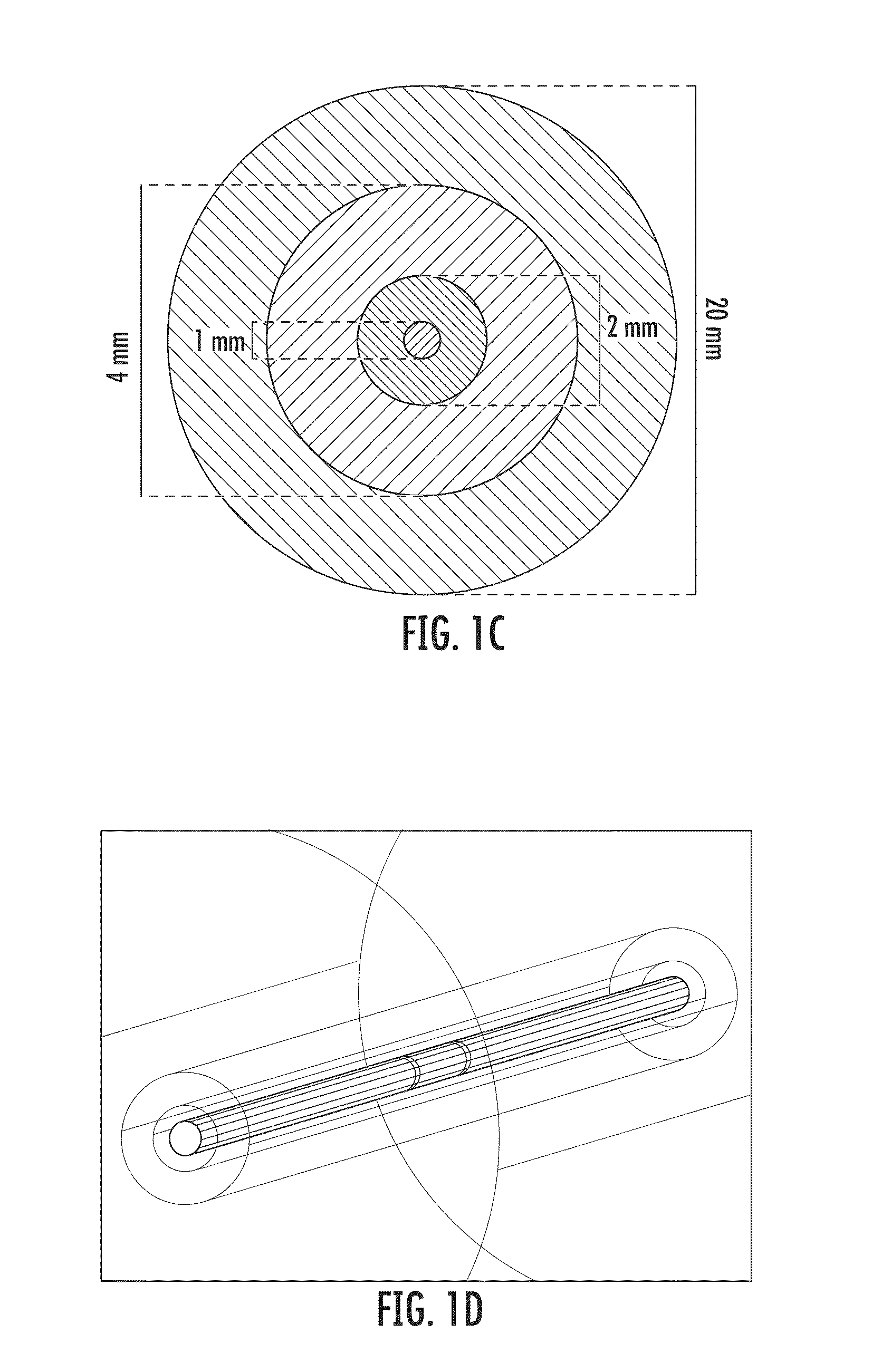
ActiveUS20130184702A1Less powerLess complexDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsIrreversible electroporationBalloon catheter
The present invention relates to medical devices and methods for treating a lesion such as a vascular stenosis using non-thermal irreversible electroporation (NTIRE). Embodiments of the present invention provide a balloon catheter type NTIRE device for treating a target lesion comprising a plurality of electrodes positioned along the balloon that are electrically independent from each other so as to be individually selectable in order to more precisely treat an asymmetrical lesion in which the lesion extends only partially around the vessel.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Breast biopsy system and methods
InactiveUS20050004492A1Raise the possibilityMinimizing risk of migrationSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCancer cellSurgical department
An apparatus and method are provided for precisely isolating a target lesion in a patient's body tissue, resulting in a high likelihood of “clean” margins about the lesion when it is removed for diagnosis and / or therapy. This approach advantageously will often result in the ability to both diagnose and treat a malignant lesion with only a single percutaneous procedure, with no follow-up percutaneous or surgical procedure required, while minimizing the risk of migration of possibly cancerous cells from the lesion to surrounding tissue or the bloodstream. In particular, the apparatus comprises a biopsy instrument having a distal end adapted for entry into the patient's body, a longitudinal shaft, and a cutting element disposed along the shaft. The cutting element is actuatable between a radially retracted position and a radially extended position. Advantageously, the instrument is rotatable about its axis in the radially extended position to isolate a desired tissue specimen from surrounding tissue by defining a peripheral margin about the tissue specimen. Once the tissue specimen is isolated, it may be segmented by further manipulation of the cutting element, after which the tissue segments are preferably individually removed from the patient's body through a cannula or the like. Alternatively, the specimen may be encapsulated and removed as an intact piece.
Owner:SENORX
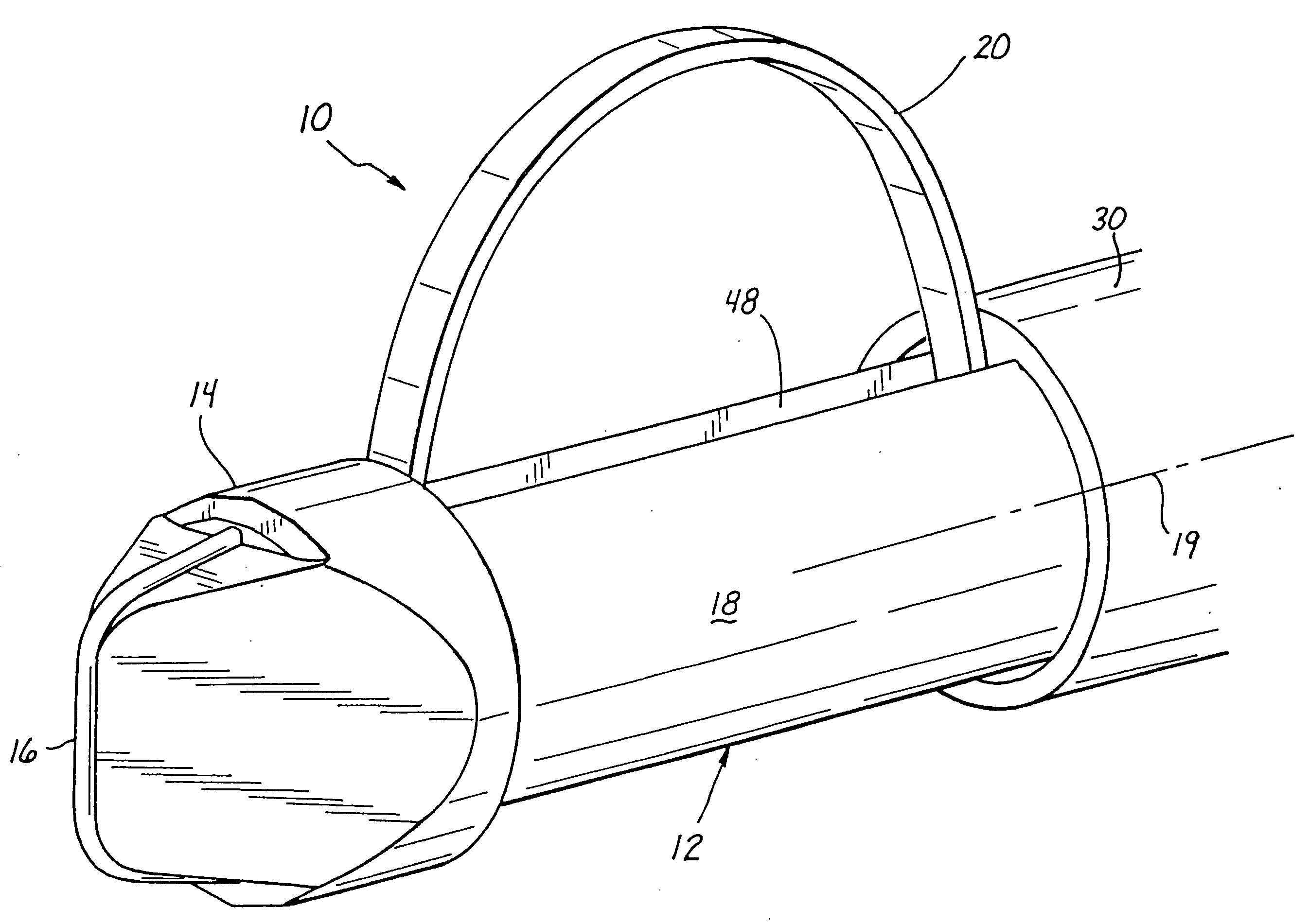
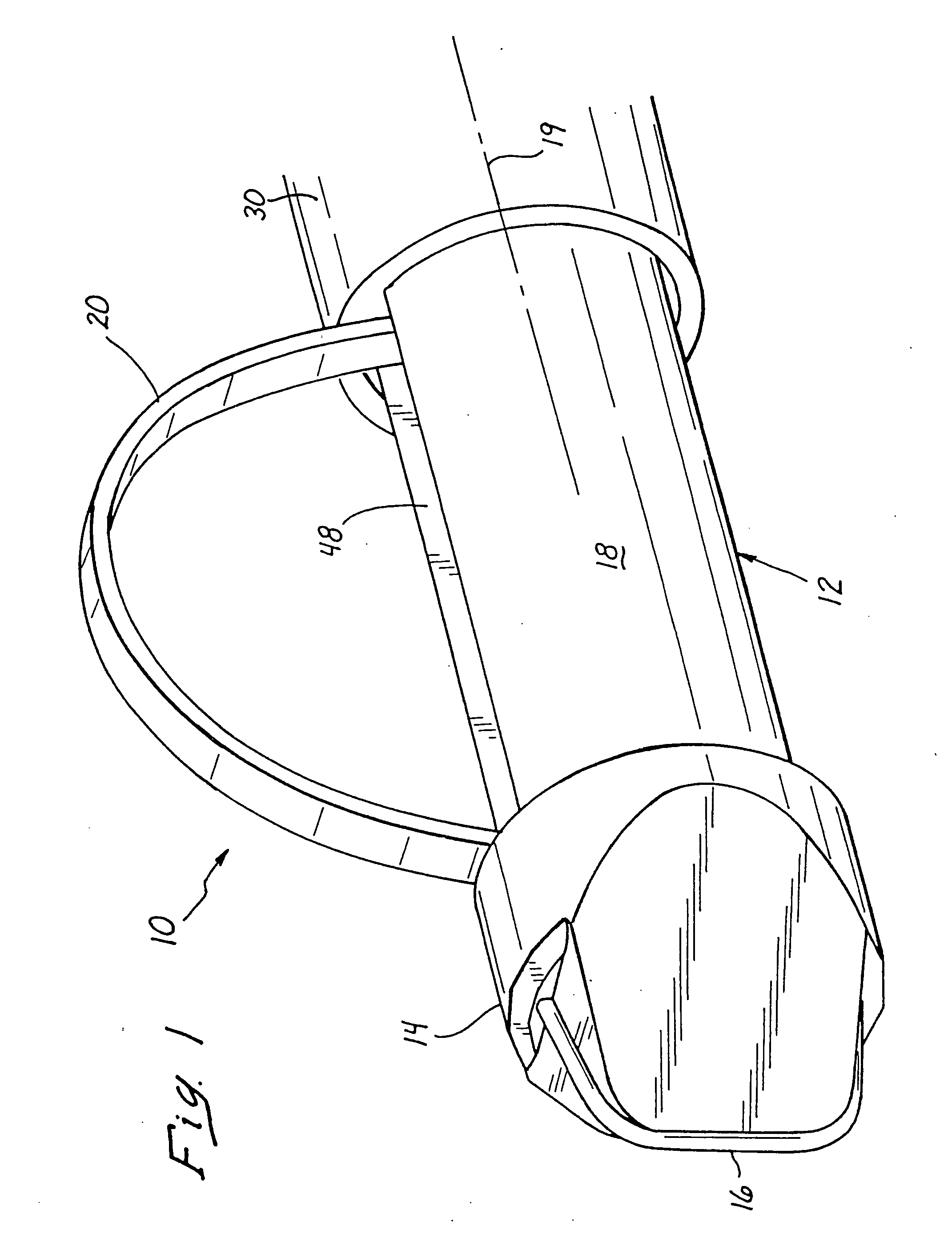
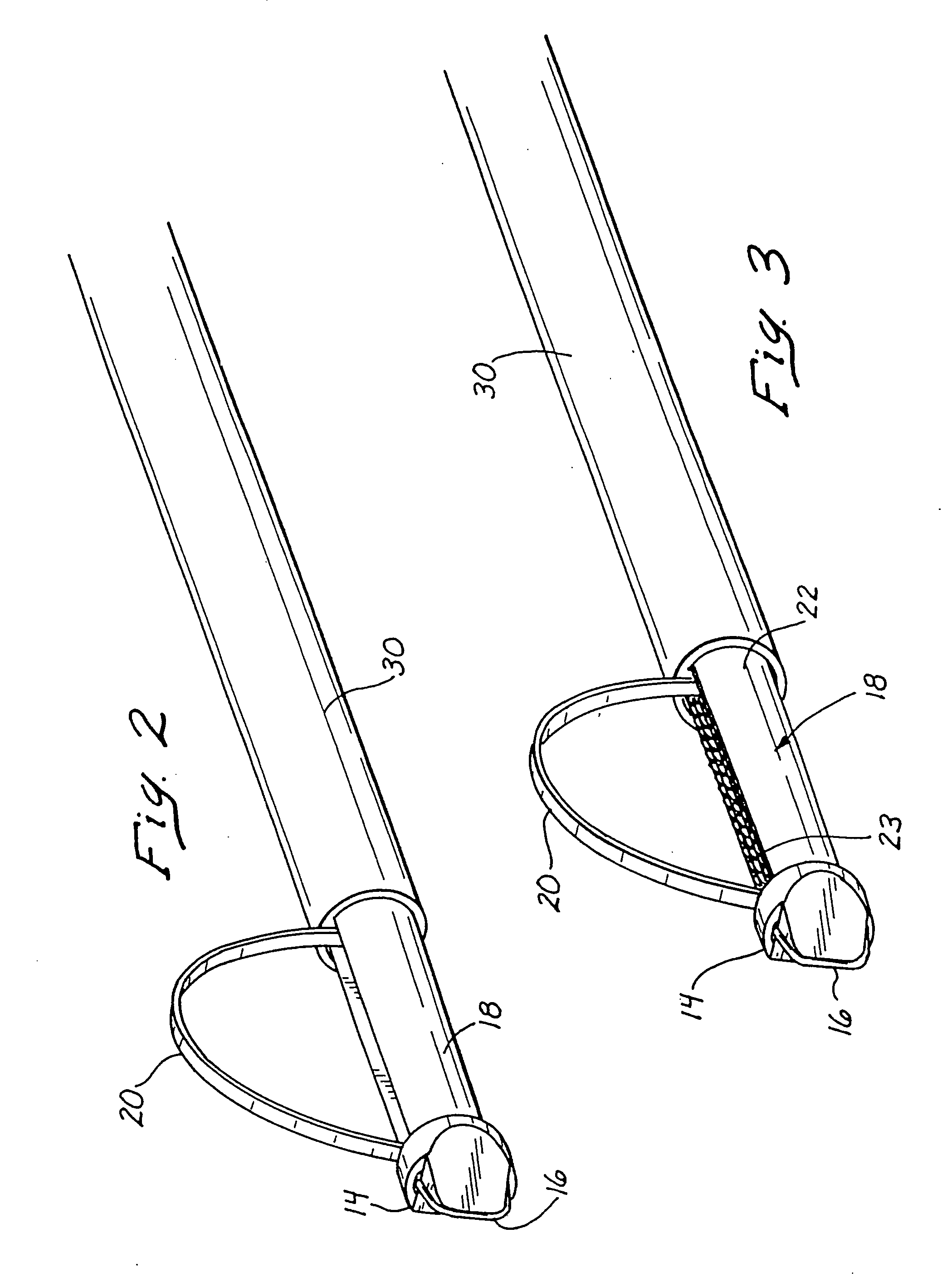
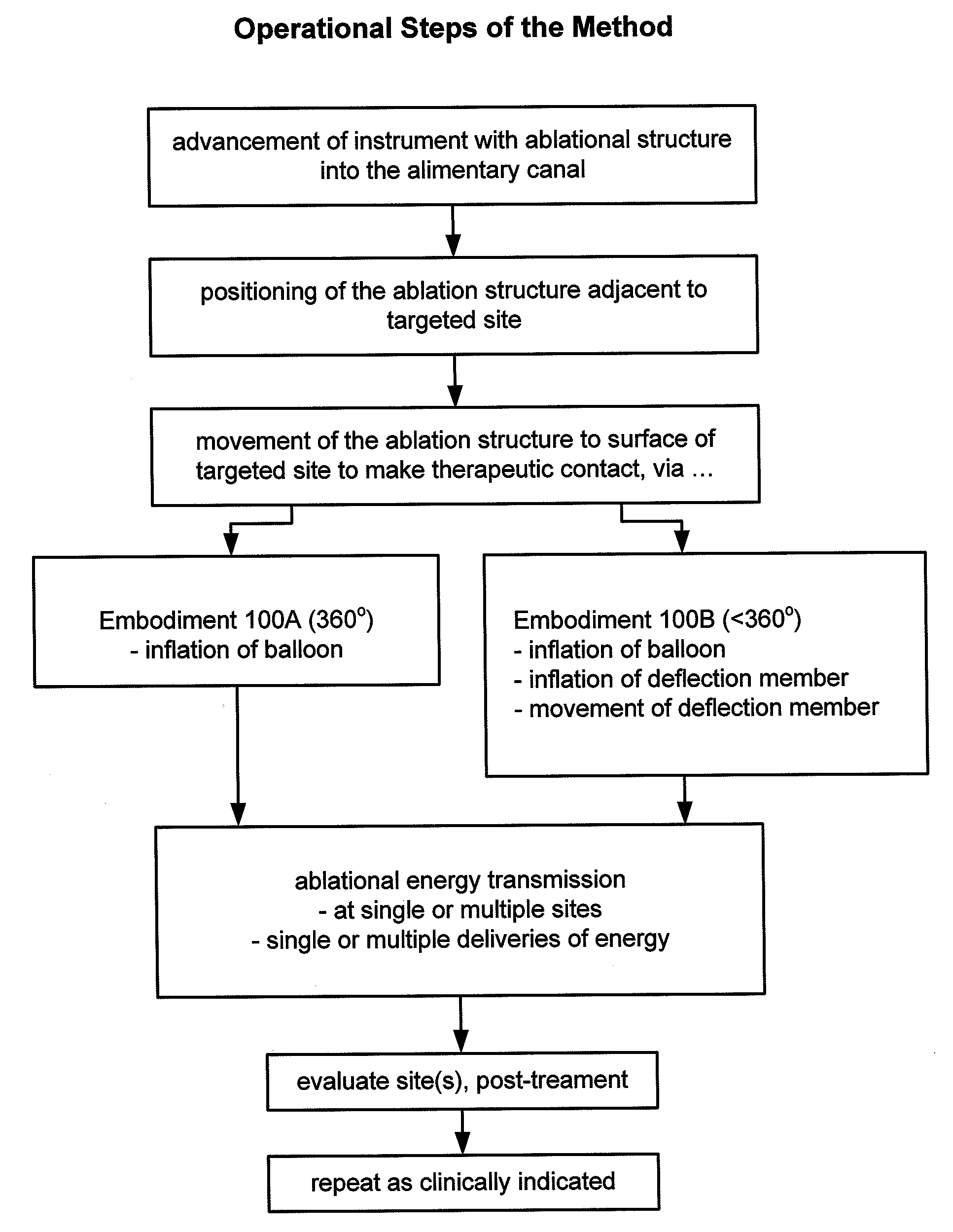
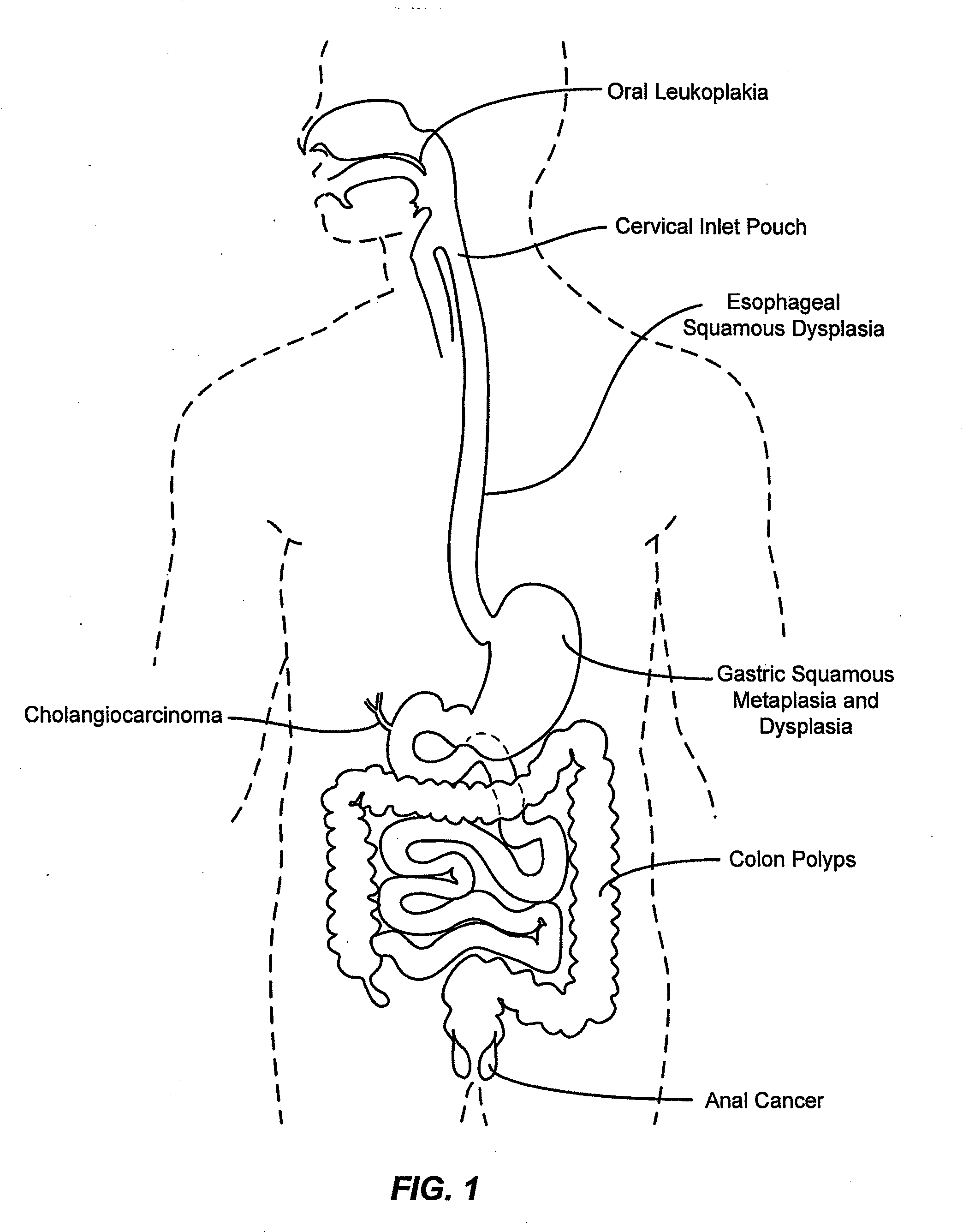
Method and Apparatus for Ablation of Benign, Pre-Cancerous and Early Cancerous Lesions That Originate Within the Epithelium and are Limited to the Mucosal Layer of the Gastrointestinal Tract
InactiveUS20090012518A1Enhance therapeutic contactSmooth connectionDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingEpitheliumOesophageal tube
Devices and methods are provided for ablating areas of the gastrointestinal tract affected with certain benign, pre-cancerous, or early cancerous lesions that originate within the epithelium and are limited to the mucosal layer of the gastrointestinal tract wall. Examples of such lesions include benign conditions such as cervical inlet patch (ectopic gastric mucosa in the upper esophagus), as well as pre-cancerous and cancerous conditions such as intestinal metaplasia / intra-epithelial neoplasia / early cancer of the stomach, squamous intra-epithelial neoplasia and early cancer of the esophagus, oral and pharyngeal leukoplakia, flat colonic polyps, anal intra-epithelial neoplasia (AIN), and early cancers of the anal canal. Ablation, as provided the invention, commences at the epithelial layer of the gastrointestinal wall and penetrates deeper into the gastrointestinal wall in a controlled manner to achieve a successful patient outcome, the latter of which is defined generally as eradication of the targeted lesion, and / or a change in the targeted lesion to prevent or forestall patient morbidity. Embodiments of the device include an ablational electrode array that spans 360 degrees and an array that spans an arc of less than 360 degrees.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical imaging system for accurate measurement evaluation of changes in a target lesion
ActiveUS7876939B2Shorten the lengthShort time intervalImage enhancementImage analysisSize measurementMeasurement evaluation
A body part is scanned to produce a first set of imaging data. A target lesion in the imaging data is identified. The body part is rescanned at a subsequent time so as to produce a second set of imaging data. The target lesion is identified in the second set of imaging data and the size of the target lesion is measured in the first and second sets of imaging data to determine two apparent image volumes corresponding to the first and second sets of imaging data. A change in size is estimated by comparing the first and second apparent lesion sizes. A variance on the change in size is estimated so as to determine a bound on the change in size measurement.
Owner:YANKELEVITZ DAVID DR
Real time ultrasound monitoring of the motion of internal structures during respiration for control of therapy delivery
InactiveUS20060241443A1Organ movement/changes detectionChiropractic devicesHelical computed tomographyReal time ultrasound
A method of targeting therapy such as radiation treatment to a patient includes: identifying a target lesion inside the patient using an image obtained from an imaging modality selected from the group consisting of computed axial tomography, magnetic resonance tomography, positron emission tomography, and ultrasound; identifying an anatomical feature inside the patient on a static ultrasound image; registering the image of the target lesion with the static ultrasound image; and tracking movement of the anatomical feature during respiration in real time using ultrasound so that therapy delivery to the target lesion is triggered based on (1) movement of the anatomical feature and (2) the registered images.
Owner:CIVCO MEDICAL INSTR CO
Photodynamic therapy for selectively closing neovasa in eyeground tissue
A method is provided for selectively occluding neovascular vessels formed in the ocular fundus of an eye, which includes intravenously administering a mono-L-aspartyl chlorin compound to a patient; subsequently estimating an appropriate time point when the mono-L-aspartyl chlorin compound has decreased in its concentration or has been eliminated from the retinal normal vascular vessels of the patient but is still remaining at an appropriate concentration in the vascular walls of the neovascular vessels of the ocular fundus; irradiating a laser light at a 664 nm-wavelength which is initiated at the appropriate time; and using the irradiation of the laser light to target lesions comprising the neovascular vessels, at a controlled power.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
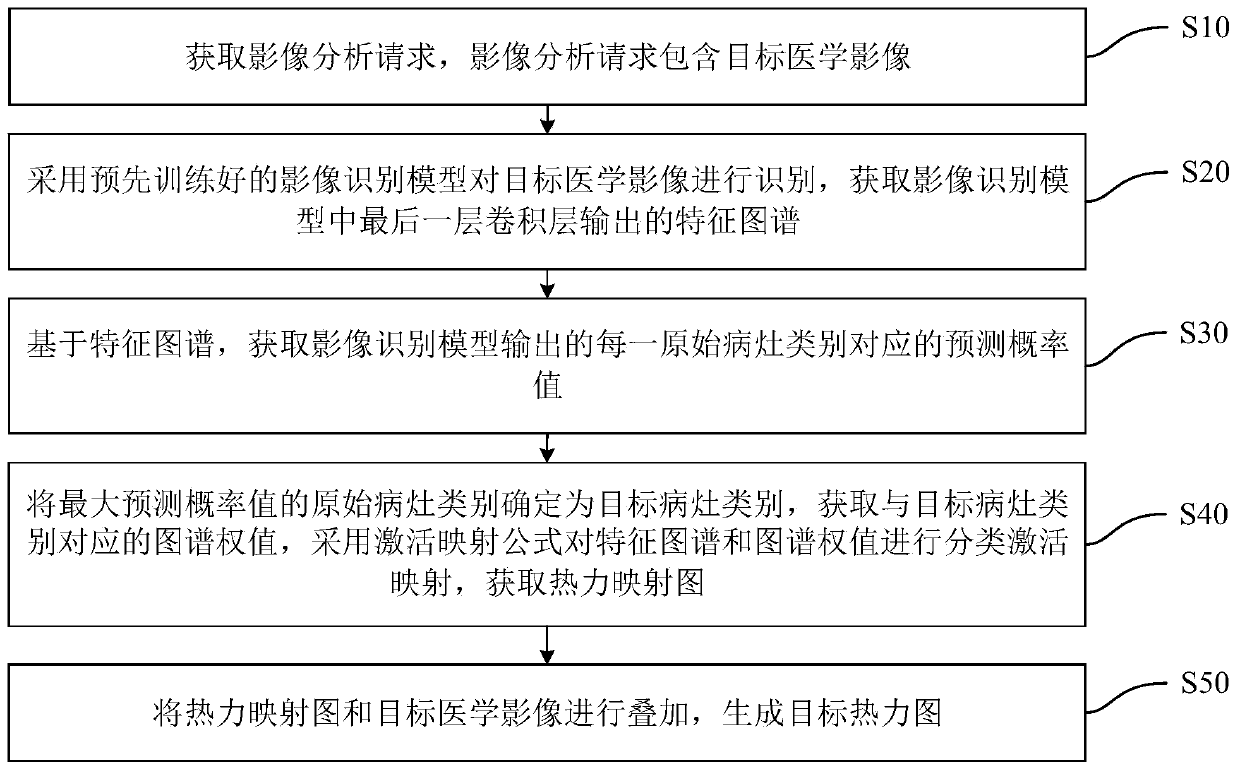
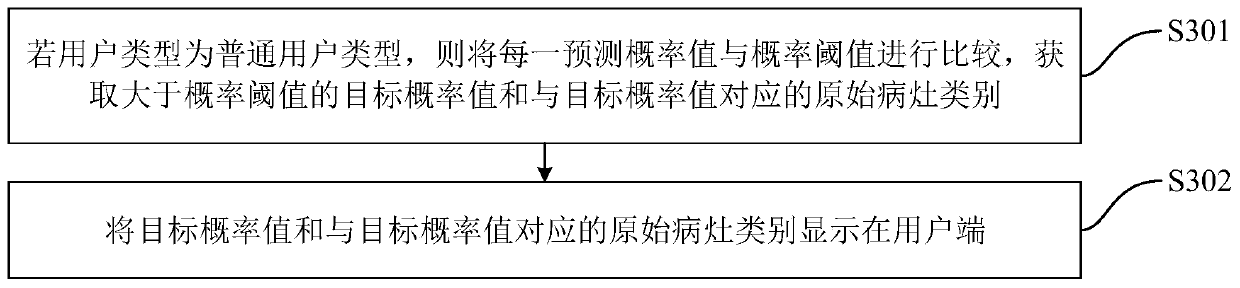
Medical image interpretation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN110136103AImprove recognition rateEasy diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisImaging interpretationImaging analysis
The invention discloses a medical image interpretation method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an image analysis request which comprises a target medical image; adopting a pre-trained image recognition model to recognize the target medical image, and obtaining a feature map output by the last convolutional layer in the image recognition model; based on the feature map, obtaining a prediction probability value corresponding to each original focus category output by the image recognition model; determining the original lesion category with the maximum prediction probability value as a target lesion category; obtaining a map weight corresponding to a target lesion category, carrying out classified activation mapping on a characteristic map and the map weight by adopting an activation mapping formula, obtaining a thermodynamic mapping map, superposing the thermodynamic mapping map and a target medical image, generating a target thermodynamic map, and improving an image recognition rate.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Motion monitor system for use with imaging systems
ActiveUS20070172029A1Precise positioningAccurate dataRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsUpper abdomenCt fluoroscopy
A bellows-based patient breath-hold monitoring and feedback system for use in intermittent mode CT fluoroscopy-guided biopsies of the lung or upper abdomen where respiratory motion is a problem. Breath-hold monitoring and feedback with the bellows system allows a patient to perform consistent breath-holds at a preselected level, which in turn, optimizes intermittent mode CT fluoroscopy-guided biopsies of the lung or upper abdomen by allowing target lesions to be reliably visualized.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Motion monitor system for use with imaging systems
A bellows-based patient breath-hold monitoring and feedback system for use in intermittent mode CT fluoroscopy-guided biopsies of the lung or upper abdomen where respiratory motion is a problem. Breath-hold monitoring and feedback with the bellows system allows a patient to perform consistent breath-holds at a preselected level, which in turn, optimizes intermittent mode CT fluoroscopy-guided biopsies of the lung or upper abdomen by allowing target lesions to be reliably visualized.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
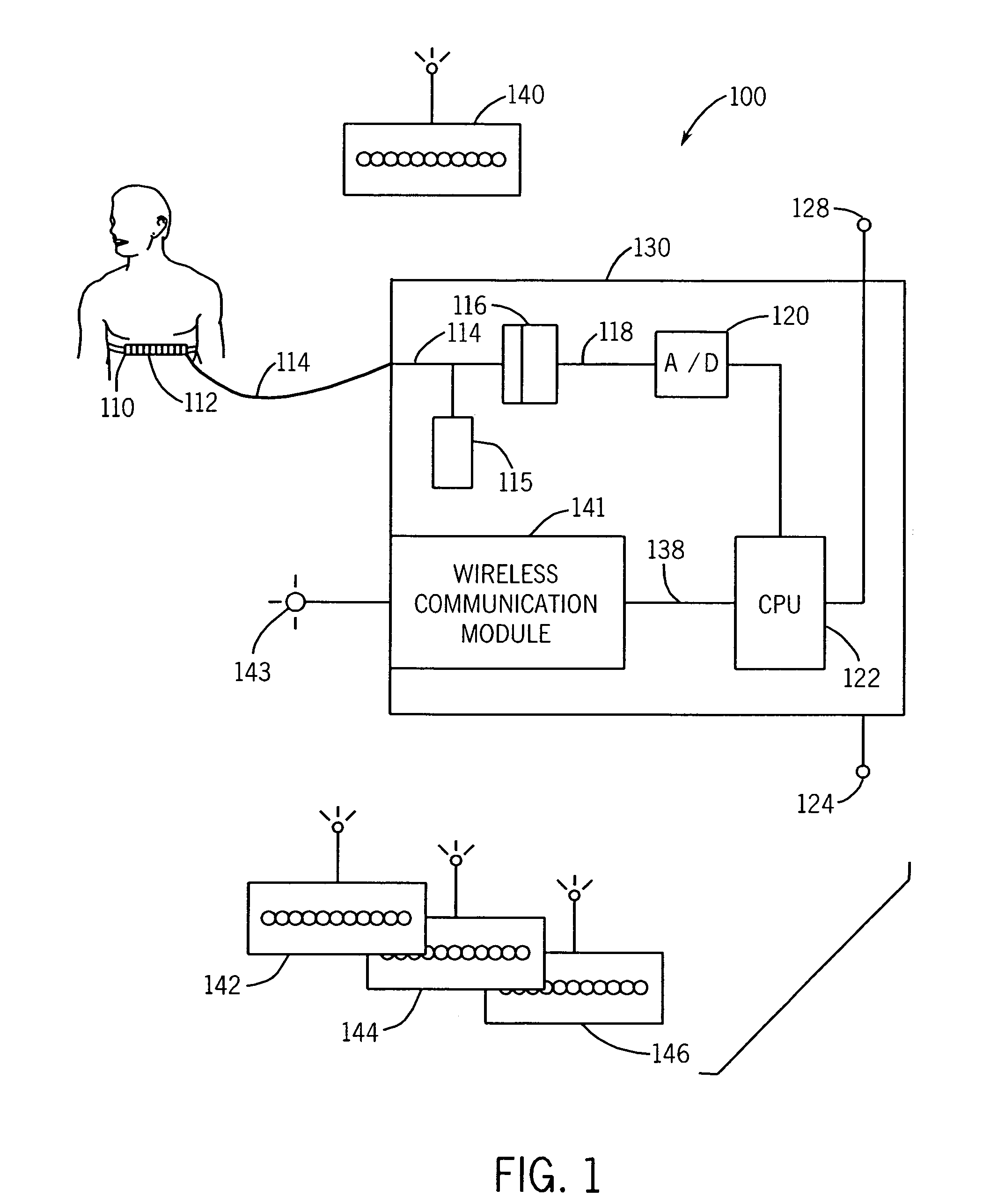
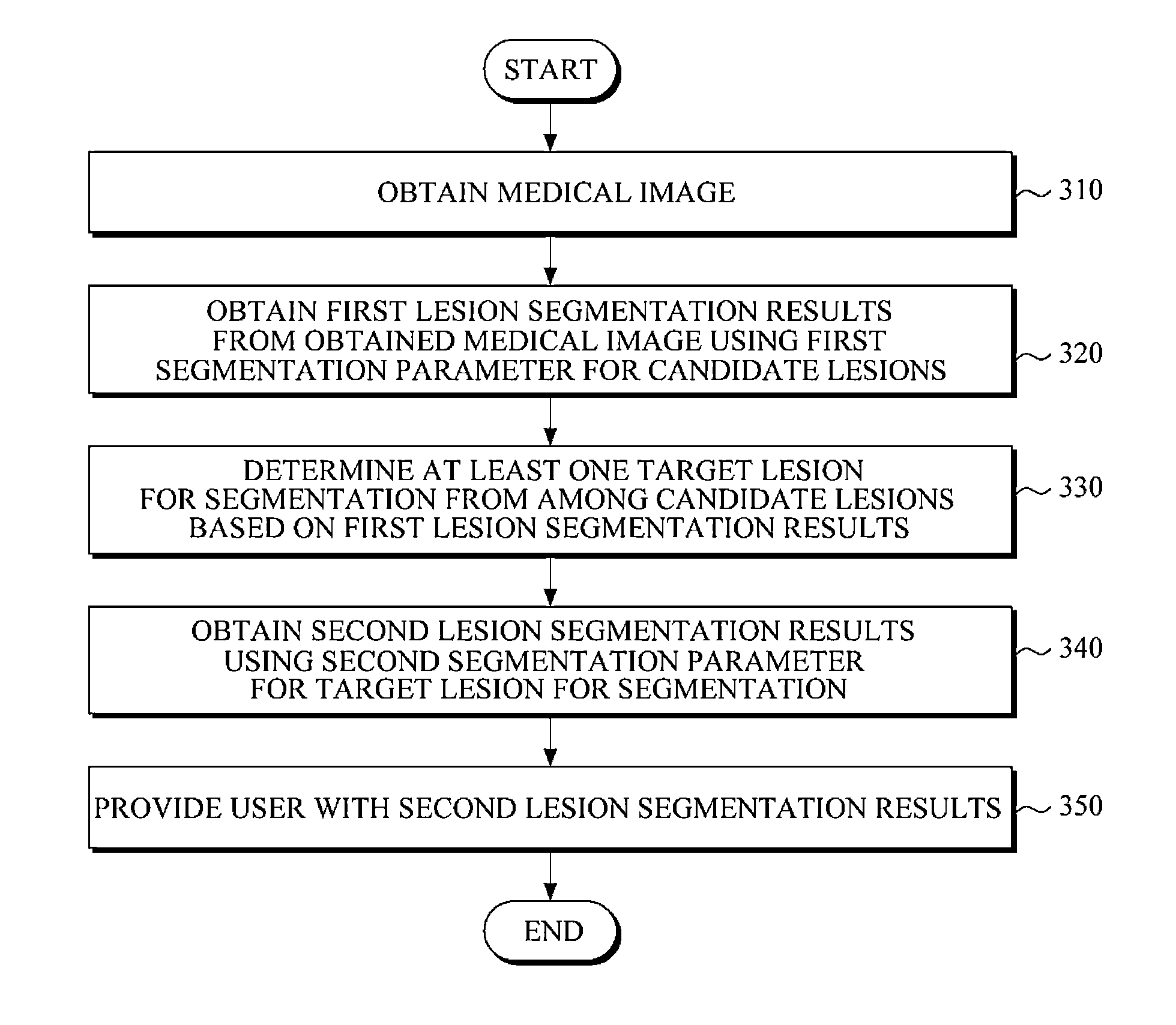
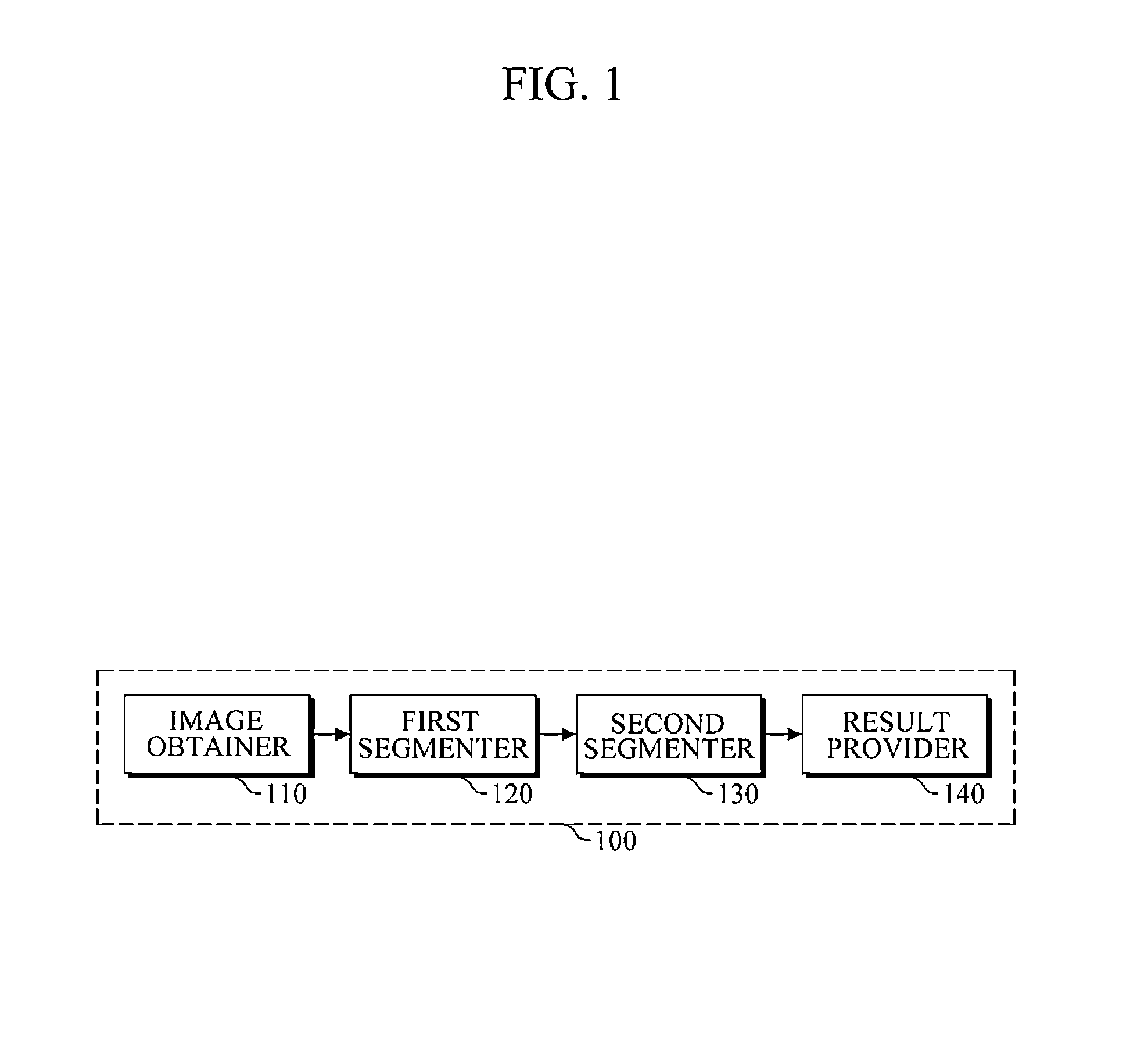
Apparatus and method for lesion segmentation in medical image
ActiveUS20140241606A1Cancel noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionLesion segmentation
An apparatus and method are provided including a first segmenter and a second segmenter. The first segmenter is configured to generate a first segmentation result from a medical image using a first segmentation parameter for a candidate lesion. The second segmenter is configured to determine a target lesion to segment from among the candidate lesion based on the first segmentation result, and generate a second segmentation result using a second segmentation parameter to segment the target lesion.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Device and method for electroporation based treatment of stenosis of a tubular body part
InactiveUS20200323576A1Less powerLess complexDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingBalloon catheterVascular Stenosis
The present invention relates to medical devices and methods for treating a lesion such as a vascular stenosis using non-thermal irreversible electroporation (NTIRE). Embodiments of the present invention provide a balloon catheter type NTIRE device for treating a target lesion comprising a plurality of electrodes positioned along the balloon that are electrically independent from each other so as to be individually selectable in order to more precisely treat an asymmetrical lesion in which the lesion extends only partially around the vessel.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
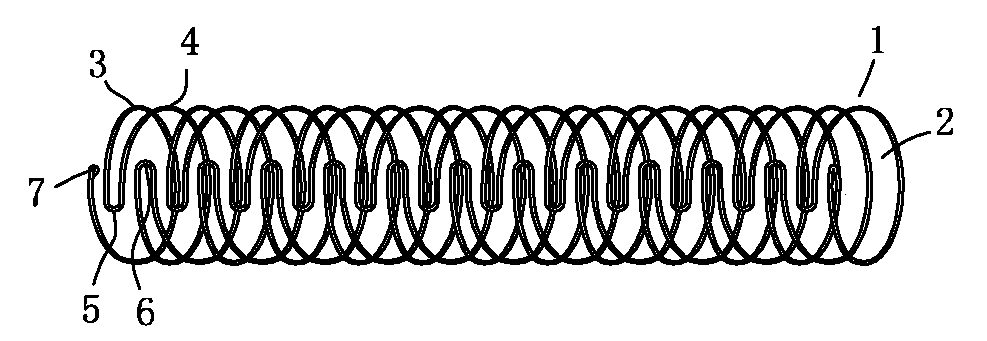
Medicine elution balloon device
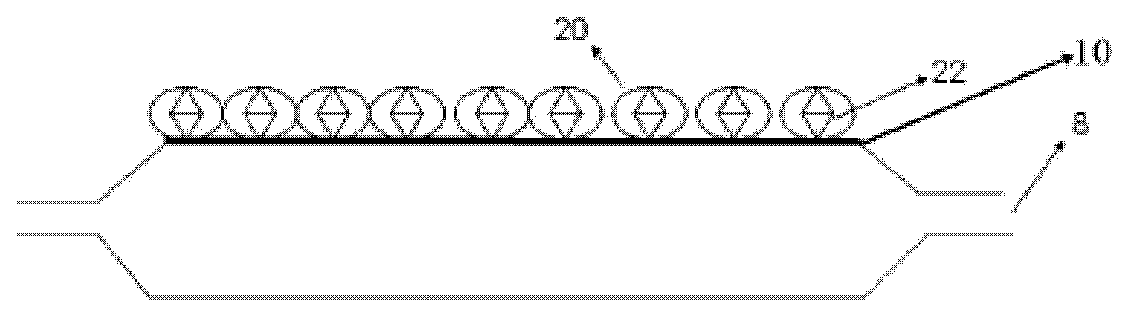
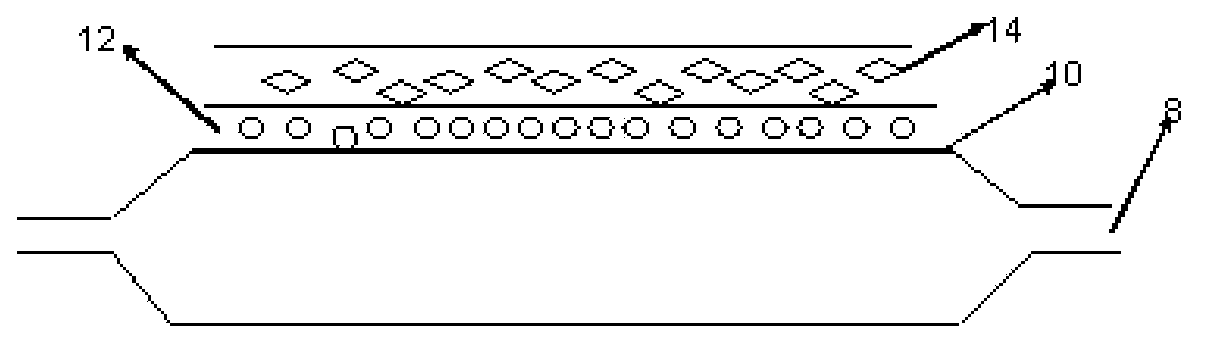
A drug-eluting balloon apparatus comprises a balloon surface (10), a polymer layer (14) that comprises drugs or both drugs and additives, and one or multiple drug layers or drug-and-additive layers (16). When a balloon (8) expands at a target lesion, the polymer layer (14) and the drug layers or the drug-and-additive layers (16) fall off the balloon surface (10) and bond on a blood vessel wall. The polymer layer (14) of the drug-eluting balloon apparatus can prevent a great loss of drugs during a pushing process of the balloon (8), and can also protect the drugs bond on the blood vessel wall from being brushed by blood, thus improving a drug utilization rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI VASOLUTIONS MEDTECH CO LTD
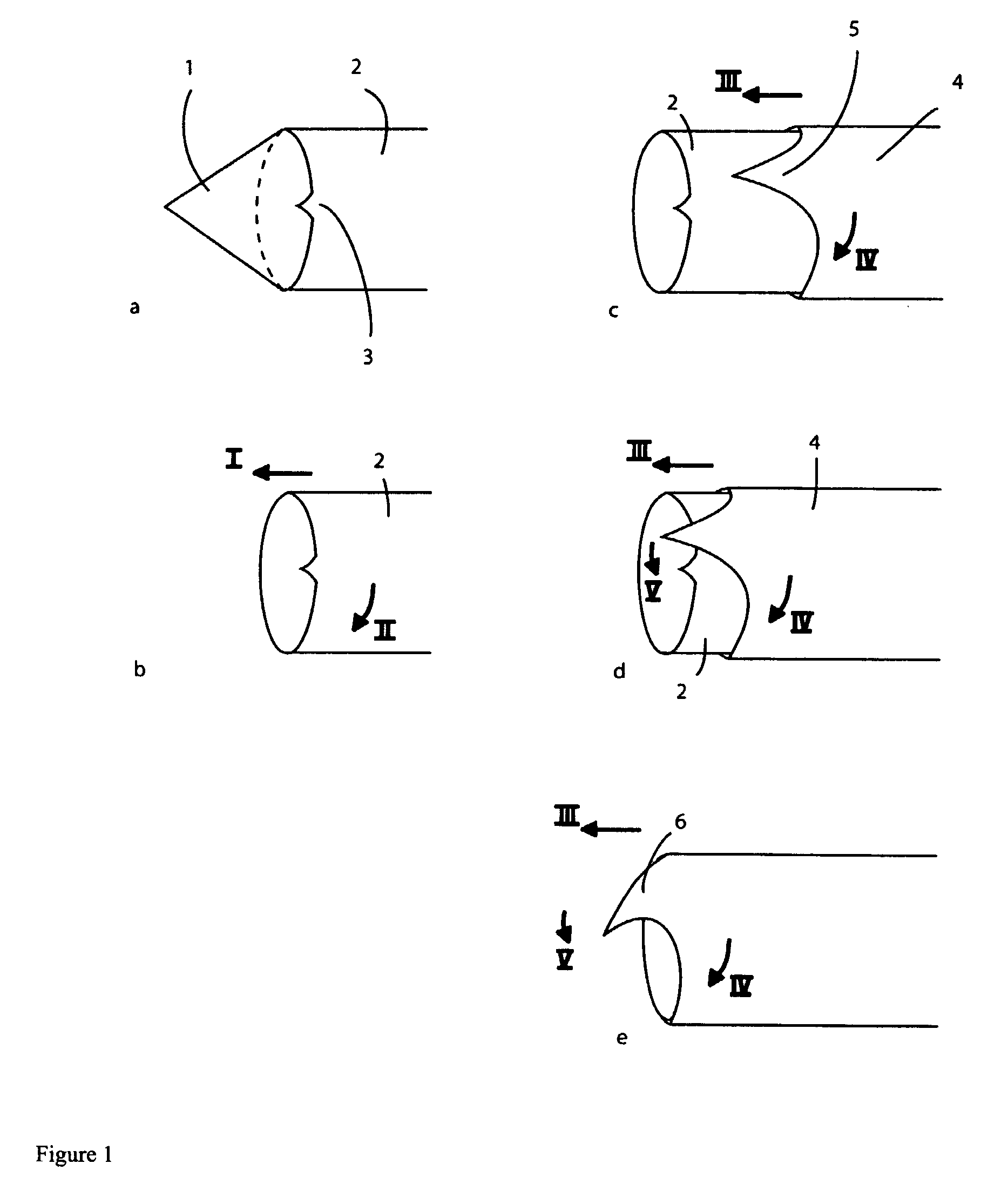
Biopsy method and device
InactiveUS6176835B1Minimize shadowsSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy methodsSkin surface
This invention relates to a method of performing accurate biopsies, particularly core breast biopsies, and a device for facilitating the accuracy of the taking of biopsies. The device involves the provision of guiding members or wing-type projections on at least two sides of the barrel of a biopsy gun. Each guiding member is parallel to the axis of a biopsy needle attached to the gun and there are at least two guiding members projecting from the barrel of the gun substantially perpendicular to one another. Each guiding member is preferably in line with the needle, so that in use the biopsy needle is in the plane of each guiding member. The device may be in the form of a biopsy gun with the guiding members integrally formed or affixed, or it may be in the form of an attachment for attaching to a conventional biopsy gun. The method of the invention involves a means of guiding a biopsy needle to a calculated site of a target lesion; identifying a location on the skin surface directly between the calculated site and a source of electromagnetic radiation, including a light source; positioning a biopsy needle tip at that location; monitoring shadows on the skin surface created by guiding members on a biopsy gun to which the biopsy needle is attached, each guiding member projecting from a side of the biopsy gun, in a parallel axis to the needle attached or held by the gun, and at least two of the guiding members substantially perpendicular to one another; and guiding the biopsy needle to the calculated site by minimizing the shadows so that the needle remains substantially parallel to the electromagnetic radiation beam.
Owner:MURRAY PACHAL FAMILY TRUST TRUSTEES MURRAY PACHAL JAN PACHAL ROBERT PARKINSON
Device and method for electroporation based treatment of stenosis of a tubular body part
ActiveUS10702326B2Less powerLess complexDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringBalloon catheter
The present invention relates to medical devices and methods for treating a lesion such as a vascular stenosis using non-thermal irreversible electroporation (NTIRE). Embodiments of the present invention provide a balloon catheter type NTIRE device for treating a target lesion comprising a plurality of electrodes positioned along the balloon that are electrically independent from each other so as to be individually selectable in order to more precisely treat an asymmetrical lesion in which the lesion extends only partially around the vessel.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Vascular reconstructive support frame
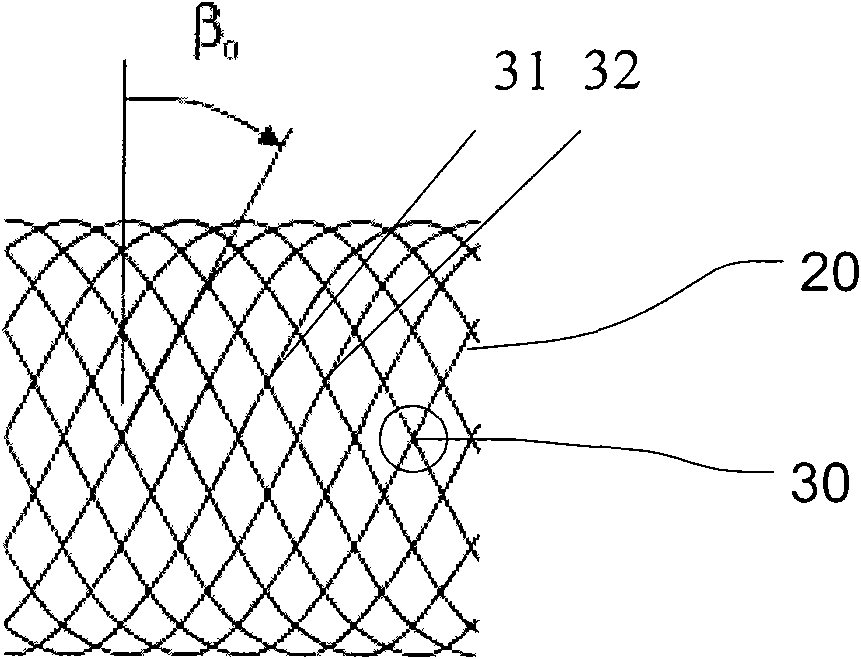
ActiveCN101991477APromote growthGuaranteed normal growthStentsBlood vesselsHigh densityInsertion stent
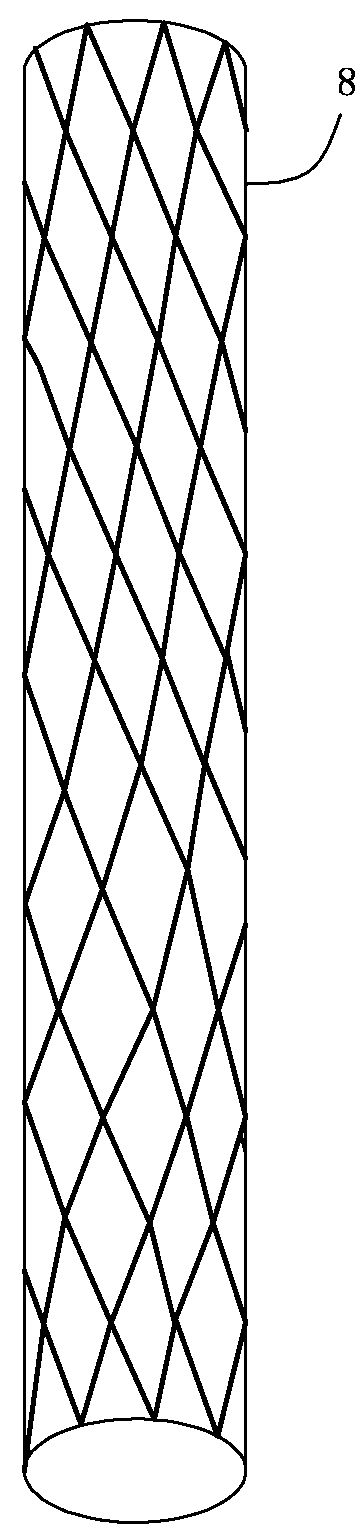
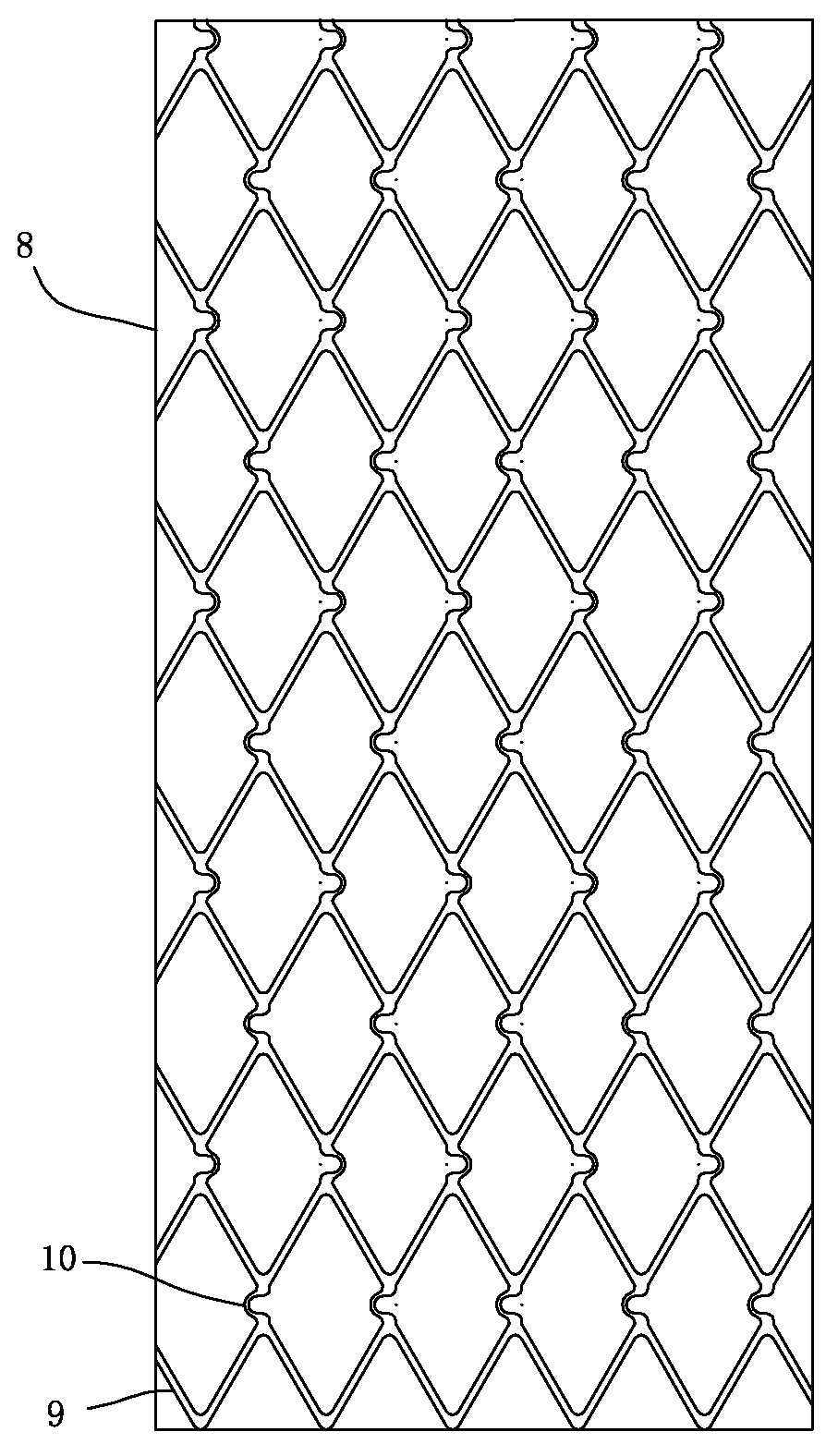
The invention provides a vascular reconstructive support frame which is in a net-pipe-shaped structure and is provided with a plurality of net holes formed by interlacing a plurality of wire chains, wherein each wire chain is continuous, and nodes of the net holes are movable. The vascular reconstructive support frame of the invention has high softness and flexibility, can pass through curve and fine brain blood vessels to reach a target lesion, and can maintain the smooth blood vessel inner cavity along the curve blood vessels. In addition, the support frame has high-density net holes, and can obviously change the blood circulation in the aneurysm so that the blood can be resorted for forming blood clots and organic solids.
Owner:MICROPORT NEUROTECH SHANGHAI
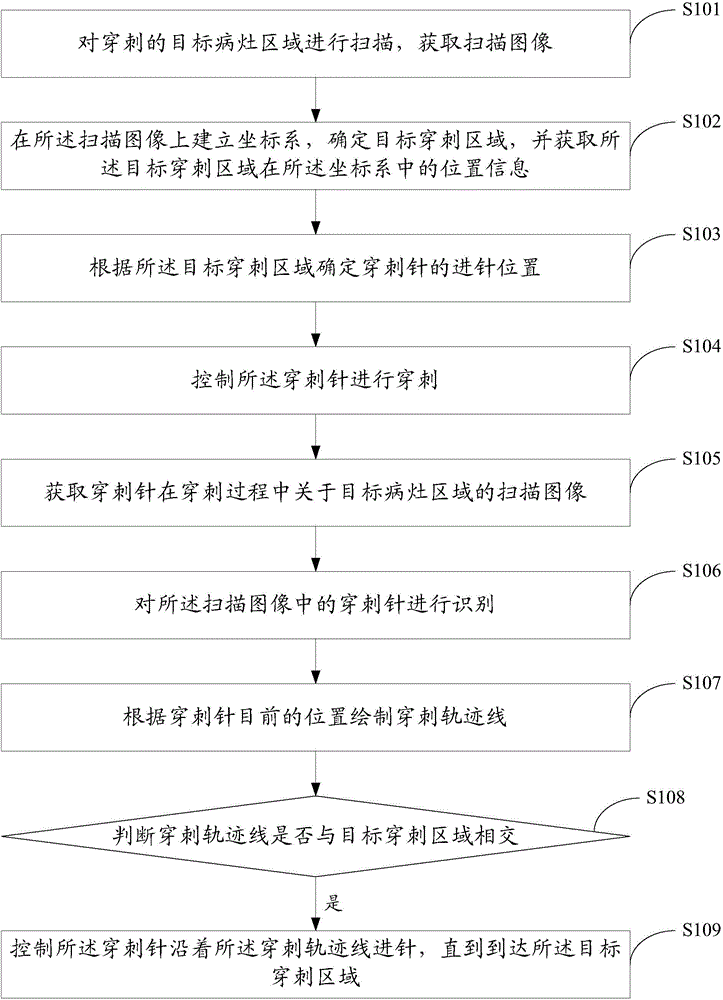
Intelligent puncturing method and device
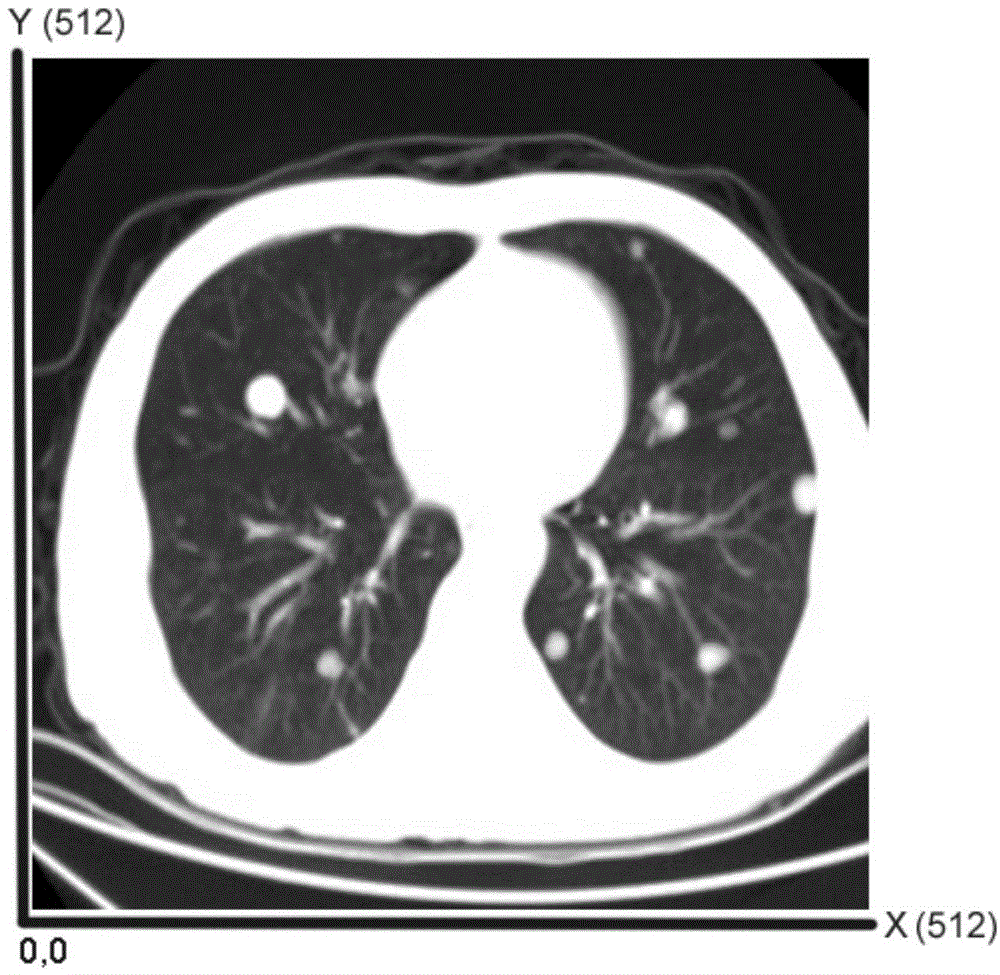
ActiveCN104605917ARelieve painRealize intelligent punctureMedical imagingSurgical needlesRadiologyTarget lesion
The embodiment of the invention discloses an intelligent puncturing method. The intelligent puncturing method is characterized by comprising the steps of obtaining a scanning image of a puncture needle for a target lesion region in the puncturing process; recognizing the puncture needle in the scanning image; according to the target position of the puncture needle, drawing a puncturing trajectory; judging whether the puncturing trajectory intersects with the target puncturing region or not, wherein the target puncturing region represents the target lesion region; if the puncturing trajectory intersects with the target puncturing region, controlling the puncture needle to be inserted along the puncturing trajectory until reaching the target puncturing region. The embodiment of the invention further discloses an intelligent puncturing device. According to the intelligent puncturing method and device, intelligent puncturing is achieved, the puncturing efficiency and success rate are improved, and pain of a patient is effectively relieved.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
Schlemm tube expansion bracket and combined body thereof
The invention relates to a Schlemm tube expansion bracket and a combined body of the Schlemm tube expansion bracket. The expansion bracket is a hollow cylindrical shell; the cylindrical surface is formed by a continuous round curve loop bent and folded from an alloy wire; the surface of the alloy wire is coated with a coating of 10-50 microns, and the coating comprises an adhesive bottom layer and a drug layer. The tube expansion bracket disclosed by the invention can reduce the damage to the wall of a Schlemm tube, reduces restenosis and multiplication occurrence rate of a cavity of the Schlemm tube, and has good soft performance. The Schlemm tube expansion bracket disclosed by the invention can effectively and lastingly release the drug on a narrow lesion site, and guarantees local precise drug delivery of a target lesion point while reducing a serious damage on the wall of the Schlemm tube caused by the bracket wall, and therefore, the restenosis occurrence rate of the Schlemm tube can be effectively reduced, thereby achieving the purposes of promoting aqueous humour discharge, reducing intraocular tension and treating glaucoma.
Owner:BEIJING TONGREN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Method and apparatus for MR-guided biopsy
An MR-guided biopsy, for example, prostate biopsy, is performed by a mechanical tool for stabilizing the patient in prone position and for guiding the biopsy needle into defined targeted lesions in the prostate gland. The patient can lay prone in the MRI. The apparatus can guide an MR-visible, sterile needle sleeve, which can have a hollow tube filled with contrast media, through the anus onto the inner wall of the colon. Due to the visibility of the contrast media in the sleeve, the apparatus can be guided to the exact position. The sleeve can incorporate a tube within the contrast media filled sleeve to insert the biopsy needle and to push this needle forward into the prostate. The apparatus can utilize various mechanical mechanisms to stereotactically move the needle or needle sleeve in various directions.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Balloon catheter
ActiveCN111135433AStrong push capabilityEffectively pass throughBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterSurgical riskVasodilation
The present invention discloses a balloon catheter. The balloon catheter comprises a catheter assembly with opposite proximal and distal ends, an expandable balloon located at the distal end of the catheter assembly, a first Luer lock connector connected with the proximal end of the catheter assembly, a folding sleeve pipe movably arranged at the outside of the expandable balloon in a sleeve manner, and a second Luer lock connector connected with the proximal end of the folding sleeve pipe, wherein the proximal and distal ends of the expandable balloon are respectively arranged at the periphery of the catheter assembly in a sleeve manner, and are sealed. The folding sleeve pipe can be used as a reinforcing pipe of the catheter assembly to improve the pushing property of a push rod. Compared with the prior art, if a lesion is severe in narrow degree and is relatively complicated, the balloon catheter can more easily transport the distal balloon into the middle of the lesion, and can directly retract the balloon at the target lesion location, vasodilation is performed through multiple repetitions, the surgery risk is reduced, and the surgery time is shortened.
Owner:GUANGDONG BROSMED MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
System and method for intraoperative guidance of stent placement during endovascular interventions
A method for guiding stent deployment during an endovascular procedure includes providing a virtual stent model of a real stent that specifies a length, diameter, shape, and placement of the real stent. The method further includes projecting the virtual stent model onto a 2-dimensional (2D) DSA image of a target lesion, manipulating a stent deployment mechanism to navigate the stent to the target lesion while simultaneously acquiring real-time 2D fluoroscopic images of the stent navigation, and overlaying each fluoroscopic image on the 2D DSA image having the projected virtual stent model image, where the 2D fluoroscopic images are acquired from a C-arm mounted X-ray apparatus, and updating the projection of the virtual stent model onto the fluoroscopic images whenever a new fluoroscopic image is acquired or whenever the C-arm is moved, where the stent is aligned with the virtual stent model by aligning stent end markers with virtual end markers.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
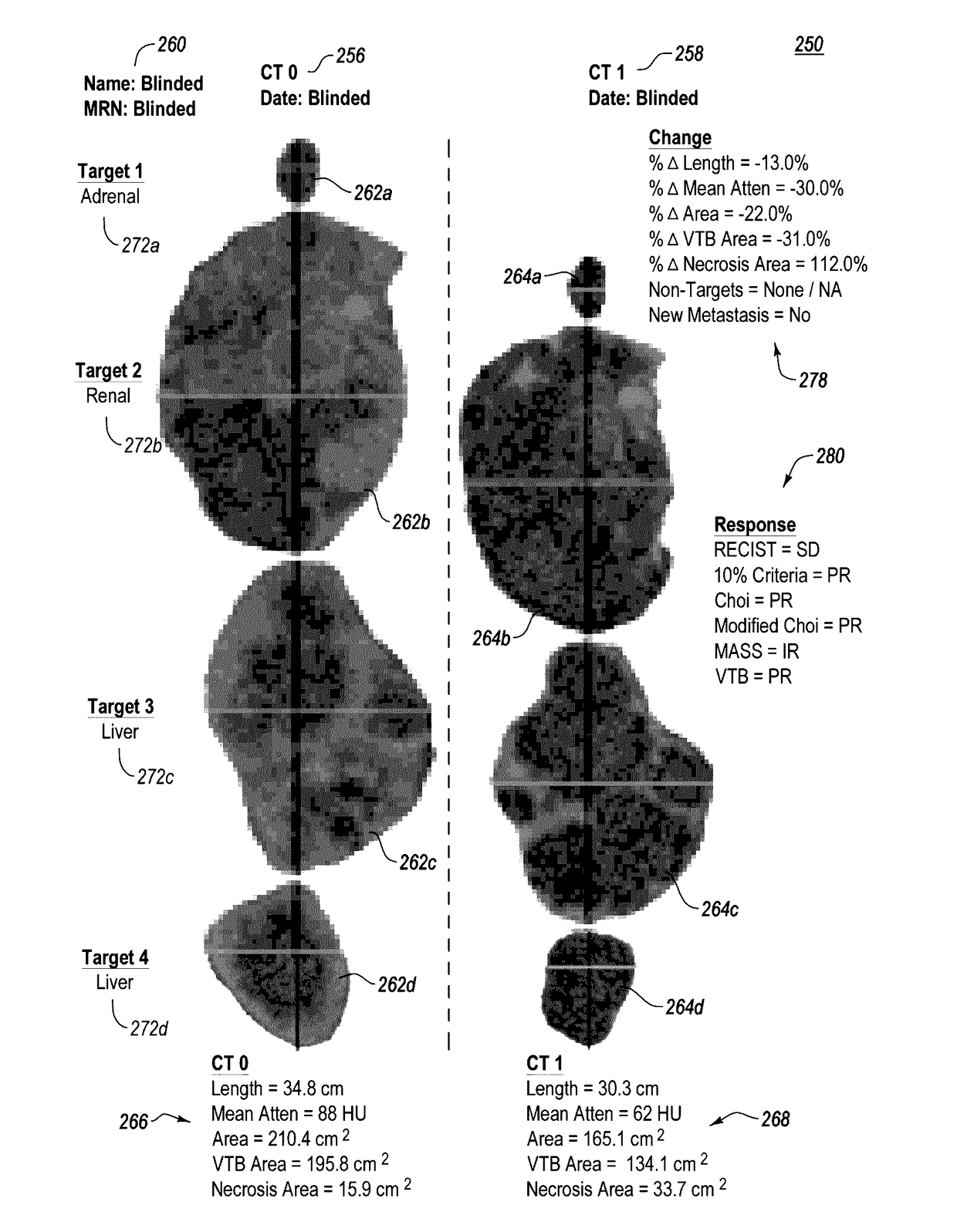
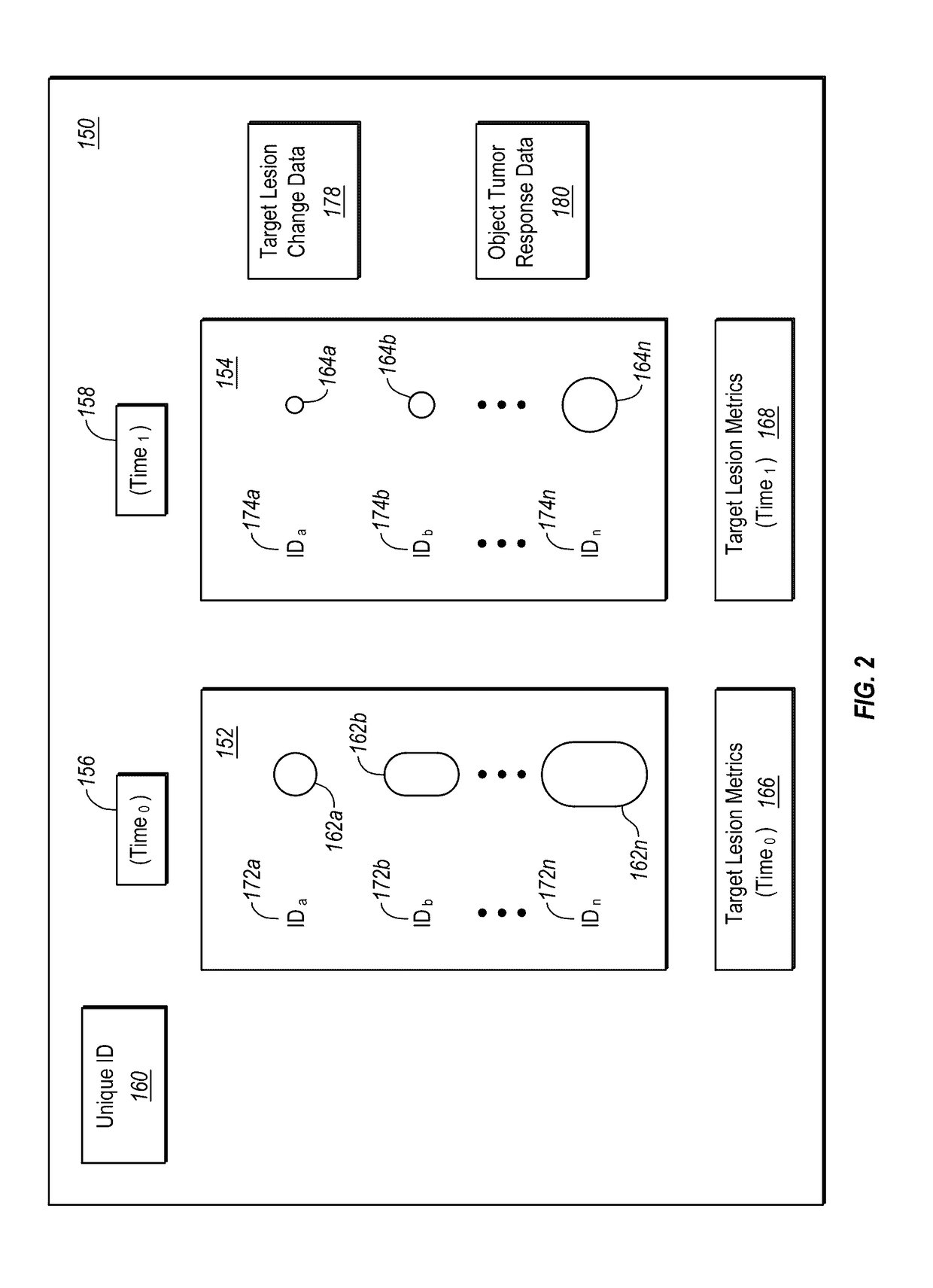
Computer-assisted tumor response assessment and evaluation of the vascular tumor burden
ActiveUS20170119334A1Accurately tumor responseEfficient responseImage enhancementImage analysisAbnormal tissue growthTumor response
A computerized method for determining an objective tumor response to an anti-cancer therapy using one or more cross-sectional images can comprise receiving one or more cross-sectional images that comprise one or more cross-sectional slices of digital medical image data and identifying one or more target lesions within the one or more cross-sectional images. The method can also comprise analyzing at least one of the target lesions with an image-processing module configured to identify a total range of pixel intensities and restrict the total range of pixel intensities to a first restricted range that corresponds to pixel intensities representative of vascularized tumor. Further still, the method can comprise deriving a vascular tumor burden for the at least one of the one or more target lesions and determining the objective tumor response for the at least one of the one or more target lesions based on the vascular tumor burden.
Owner:AI METRICS LLC
Intracavity stent conveying system for pre-implanting saccule at front end
The invention relates to an intracavity stent conveying system for pre-implanting a saccule at a front end, which belongs to the field of medical apparatuses. The saccule and a stent are designed integrally in the system; the saccule is designed at the far end of the stent; the saccule is arranged on an inner core and is separated from the stent, but is connected with the stent end to end; the farend and the near end of the saccule are provided with heavy metal markers not transmitting X rays; the stent is arranged at the near end of the saccule and is positioned in a cavity gap between the inner core and an outer sleeve; and the near end of the outer sleeve is provided with a safety lock. The release of the stent depends on the withdrawal of the outer sleeve relative to the inner core; and the stent can be released by unscrewing the safety lock, fixing the inner core and withdrawing the outer sleeve. The saccule can expand target lesions before releasing the stent, can anchor the inner core during releasing the stent, and can further expand the stent after releasing the stent. The intracavity stent conveying system makes stent implantation simpler, saves medical cost, shortens operation time, and reduces complications; and the saccule can anchor the inner core of the conveying system in operation so as to release the stent accurately.
Owner:王于 +1
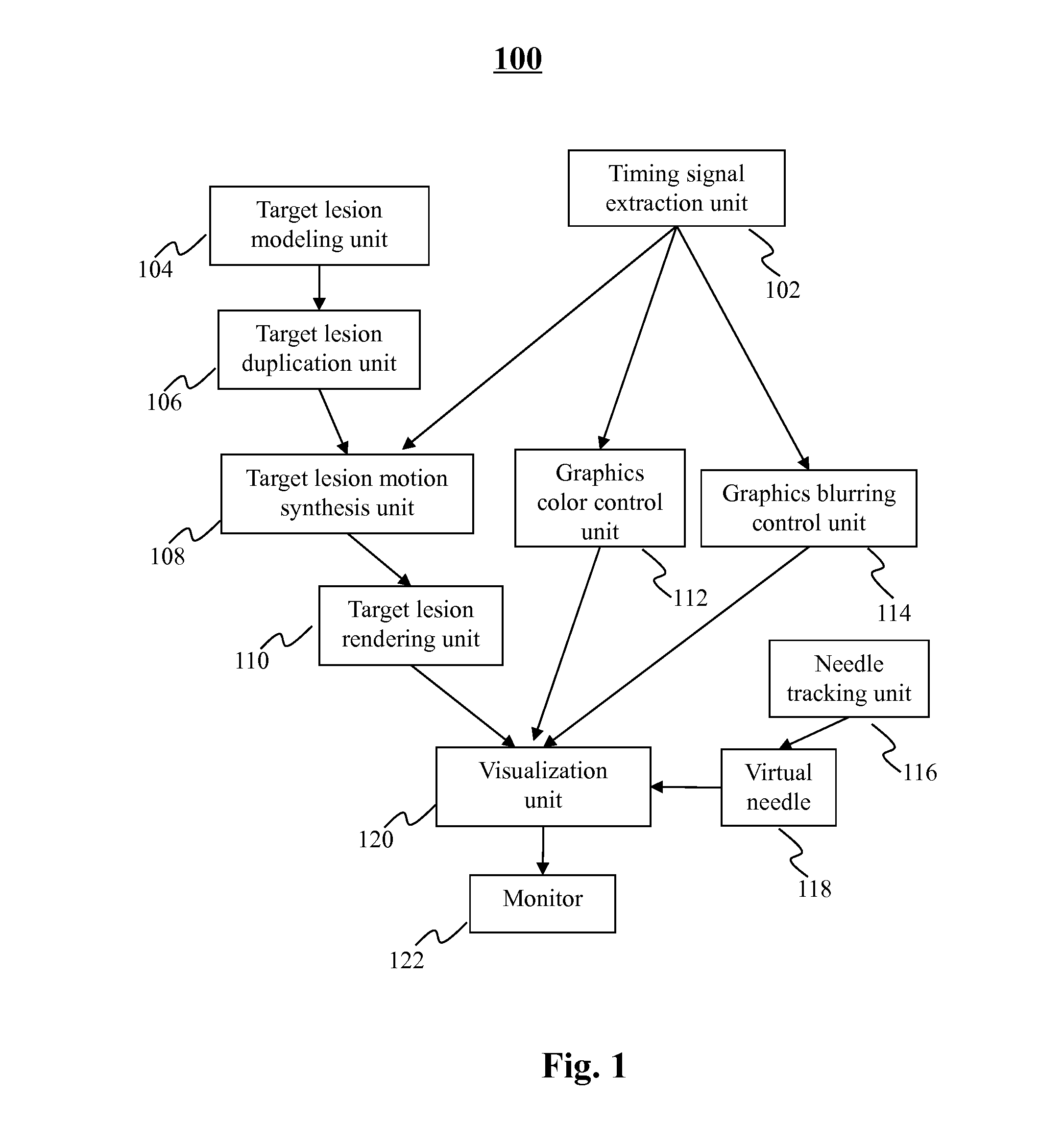
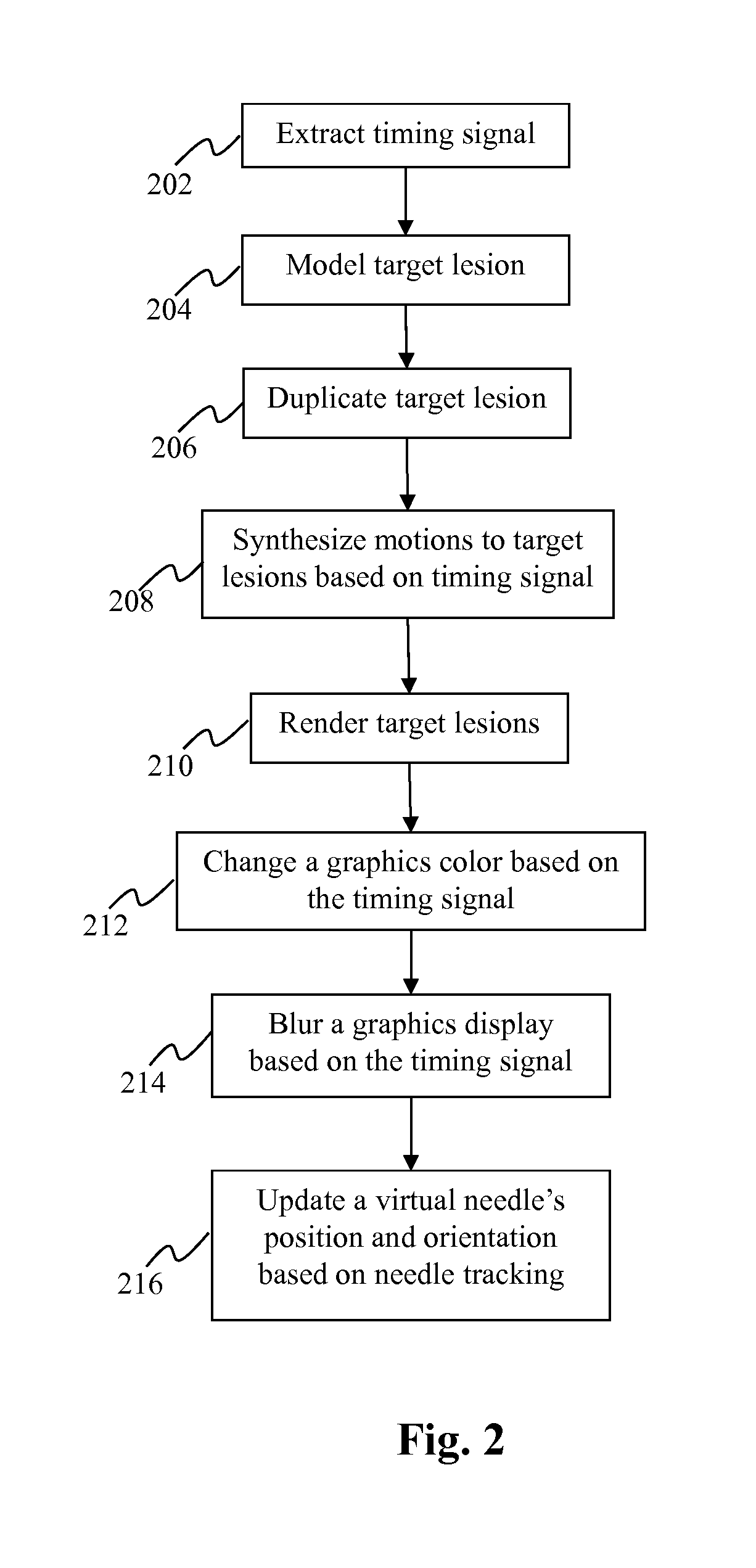
Method and system for displaying a timing signal for surgical instrument insertion in surgical procedures
The present teaching relates to surgical procedure assistance. In one example, a plurality of similarity measures are determined between a first set of positions and a plurality of second sets of positions, respectively. The first set of positions is obtained with respect to a plurality of sensors coupled with a patient in an image captured prior to a surgical procedure. The plurality of second sets of positions are obtained from the plurality of sensors and change in accordance with movement of the patient. A target lesion is segmented in the image captured prior to the surgical procedure to obtain a lesion display object. The lesion display object is duplicated to generate a plurality of lesion display objects. The plurality of lesion display objects are presented on a display screen so that a distance between the plurality of lesion display objects changes in accordance with the plurality of the similarity measures.
Owner:EDDA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com