Patents
Literature
53 results about "Biopsy methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
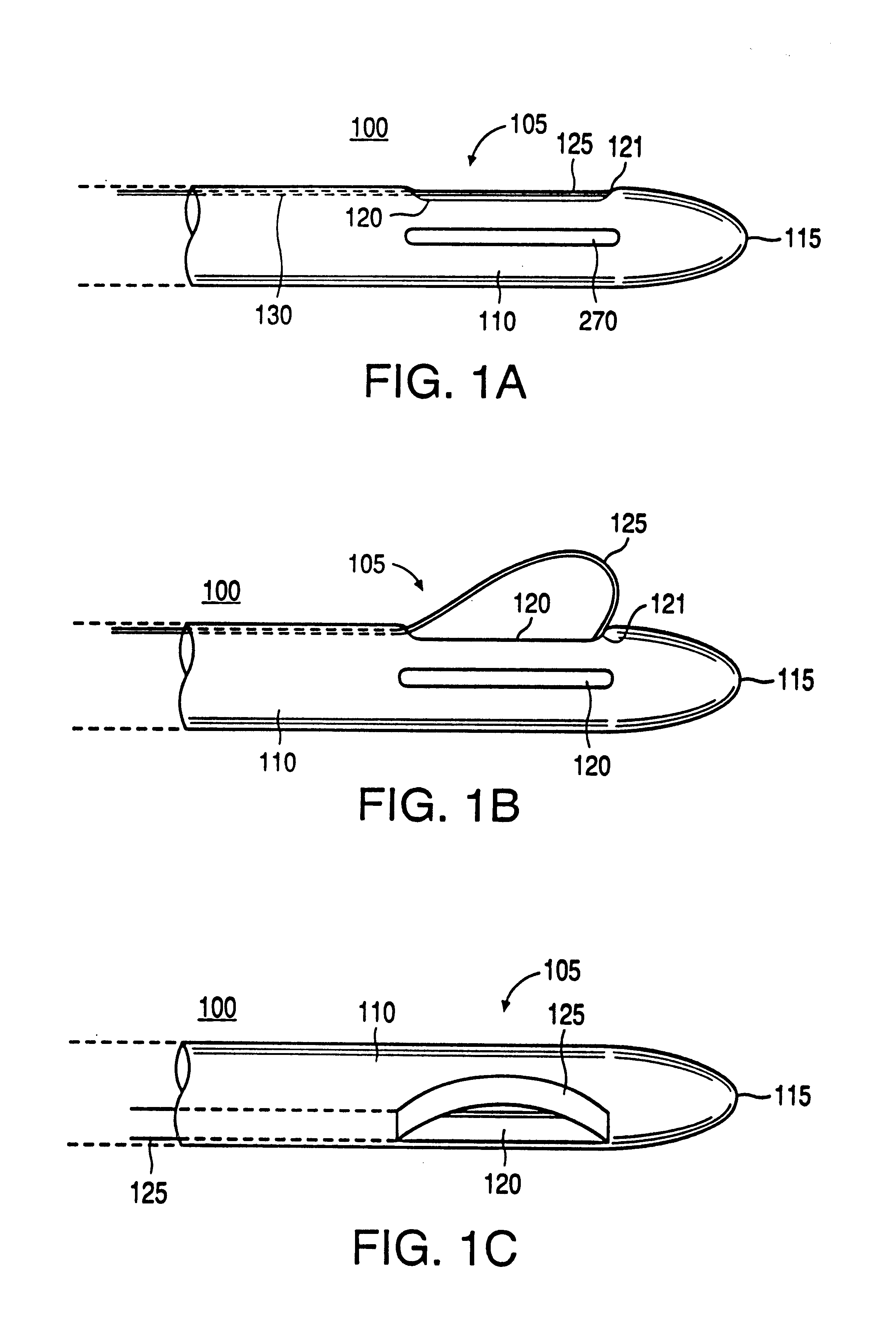
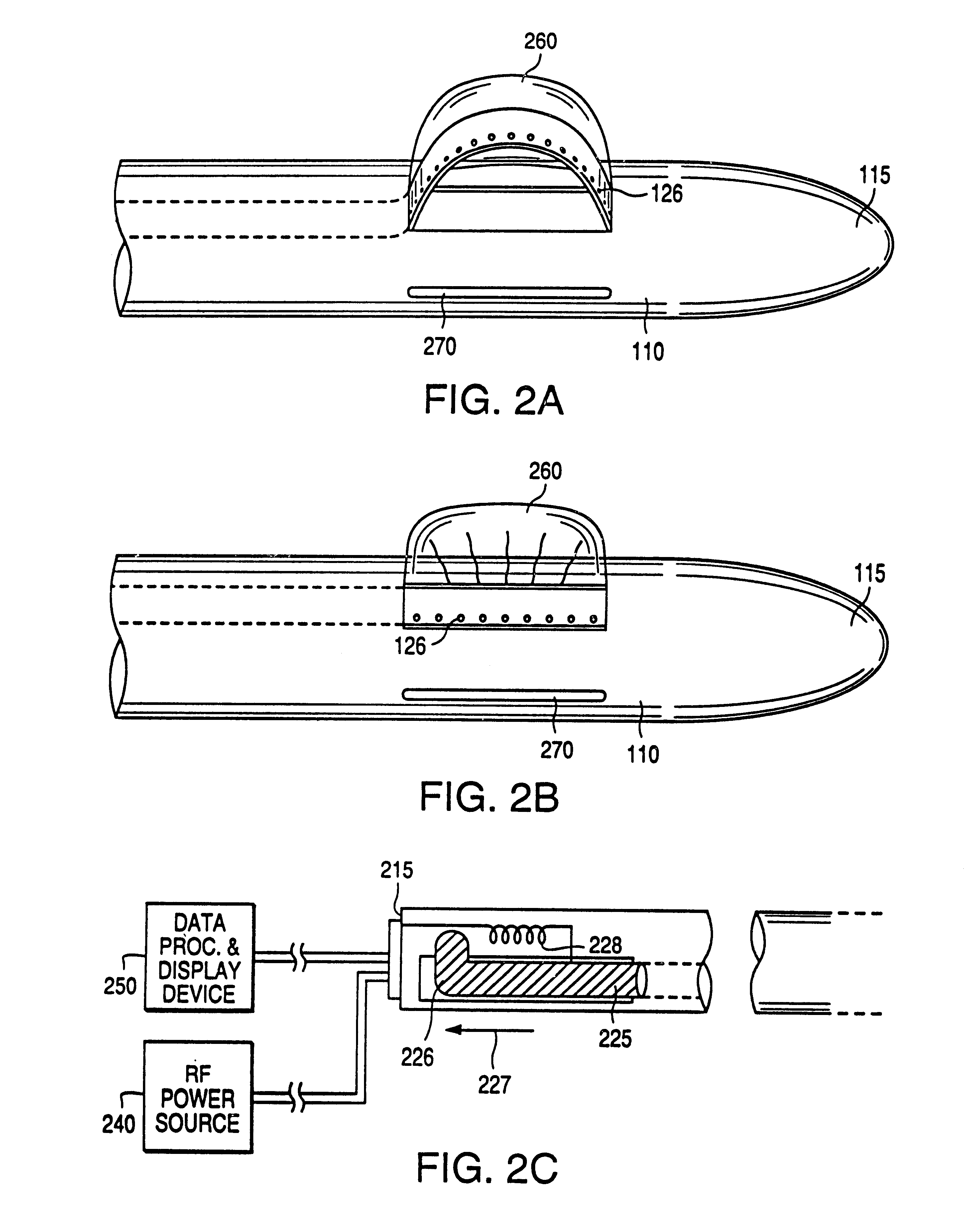
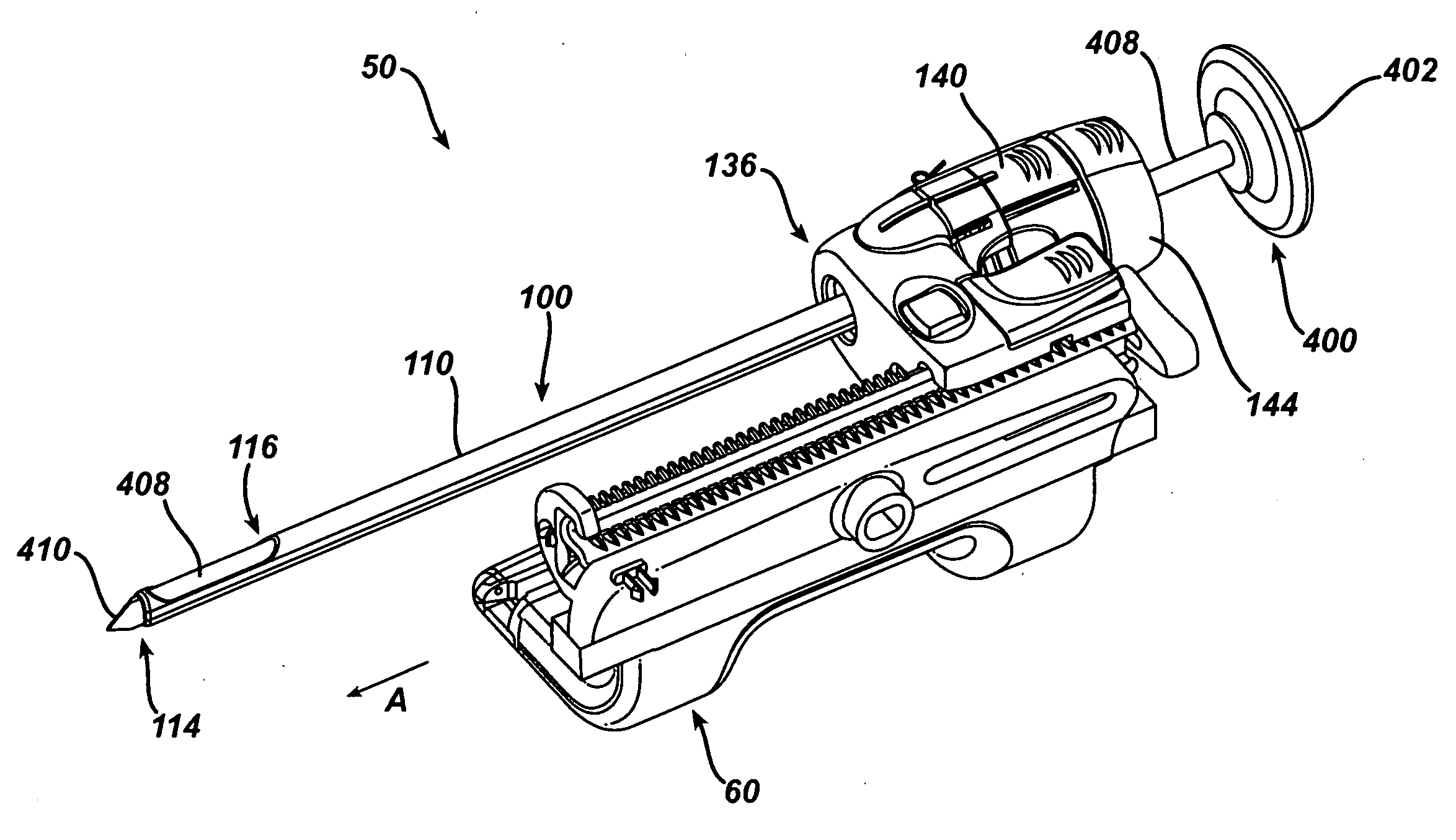
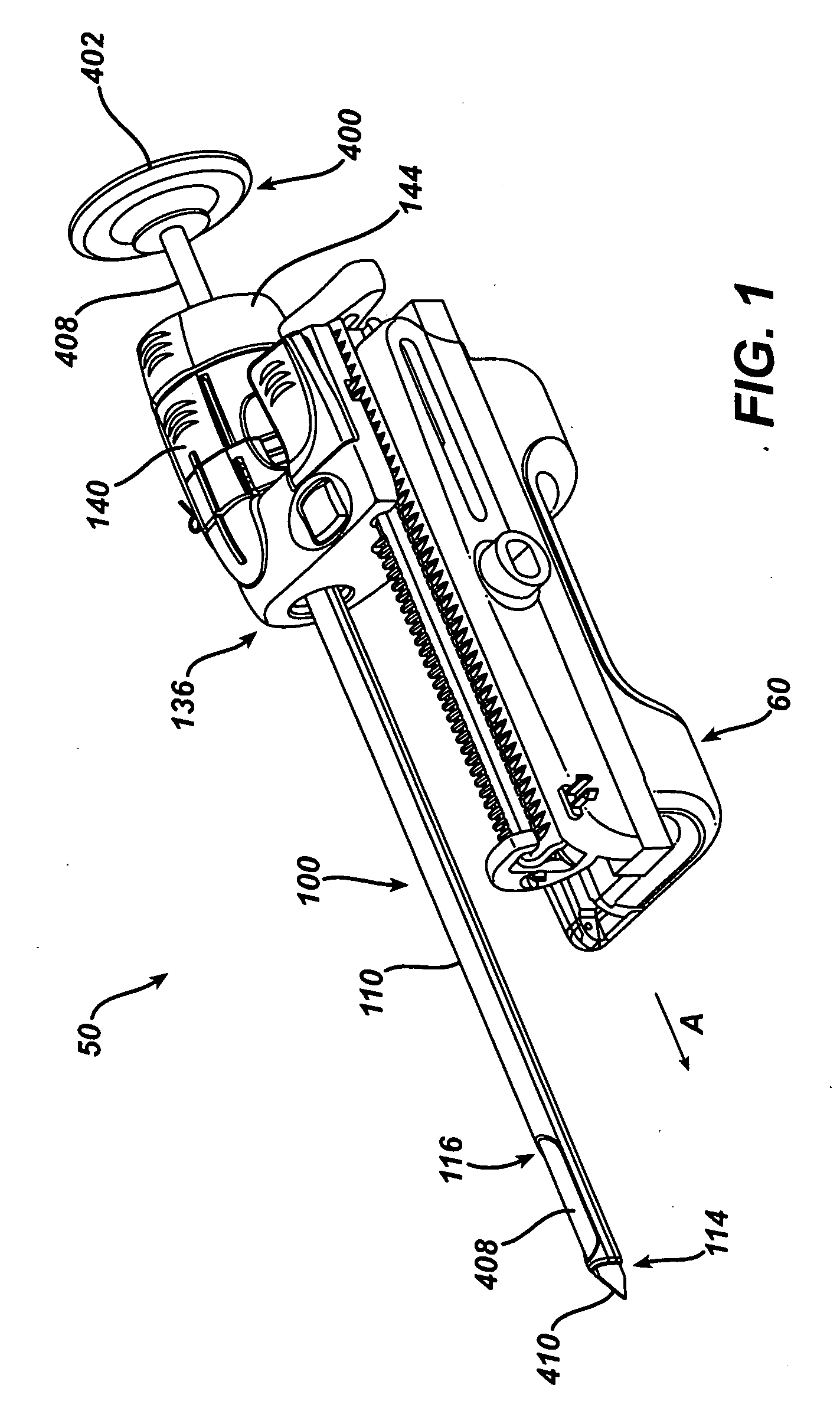
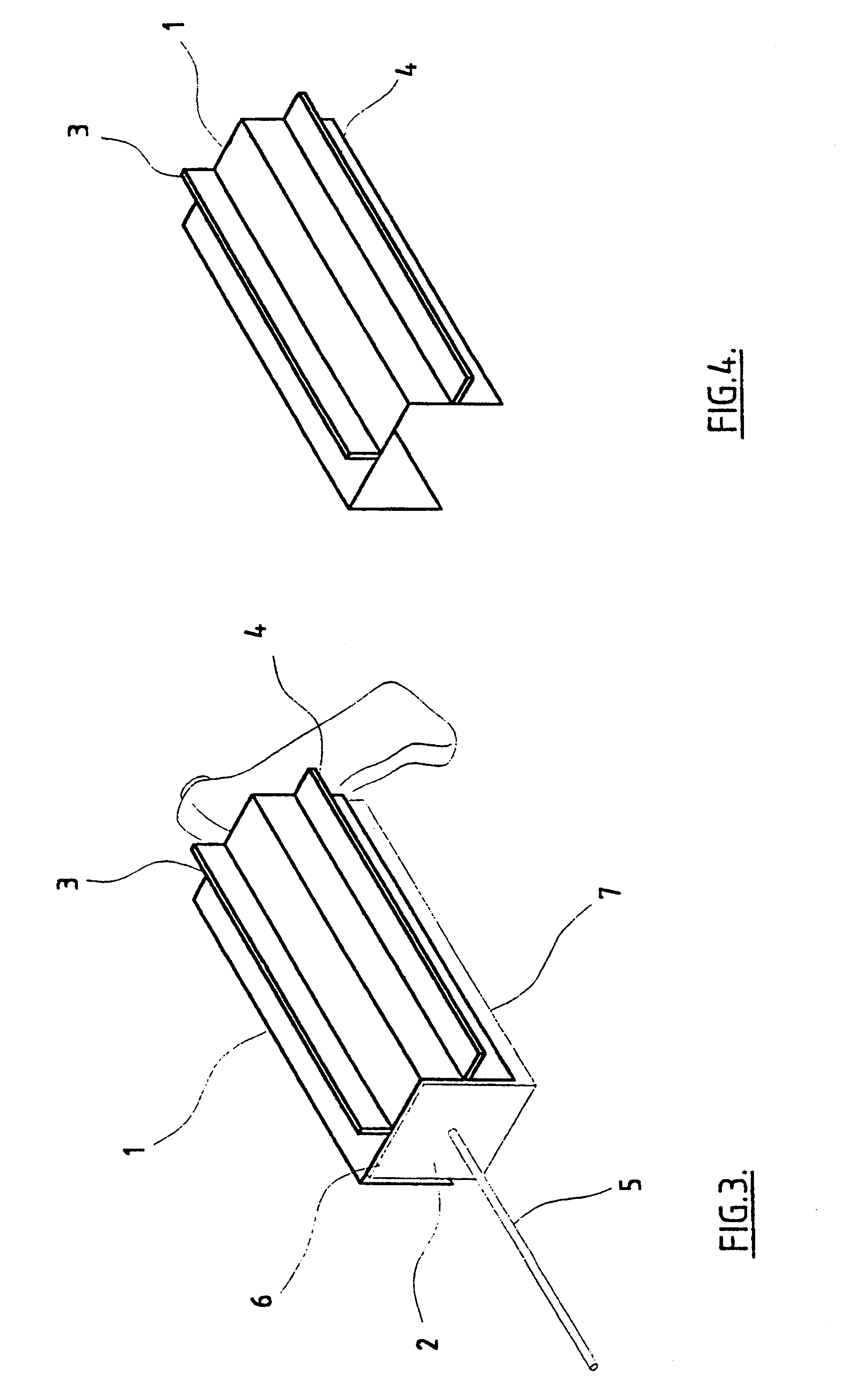
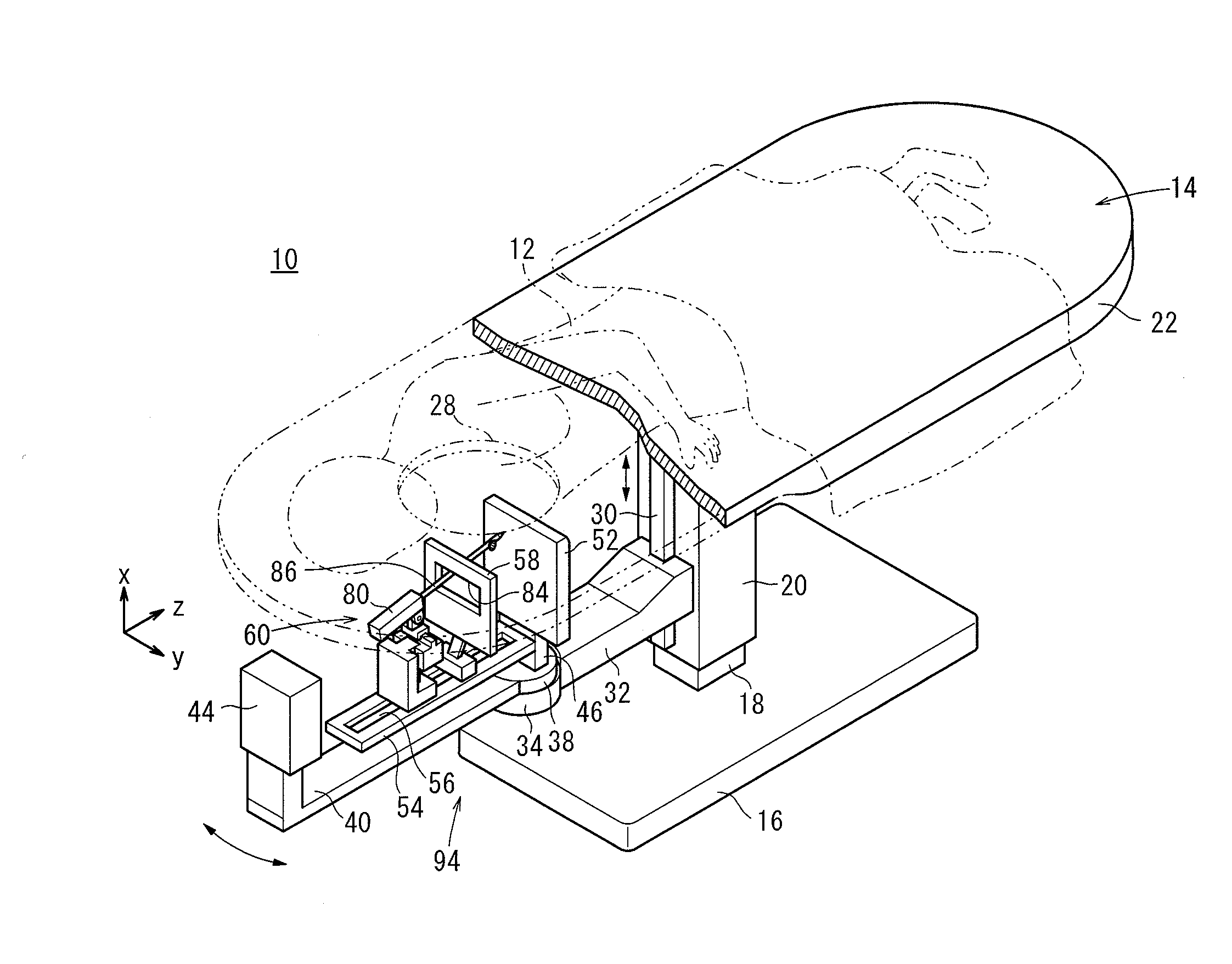
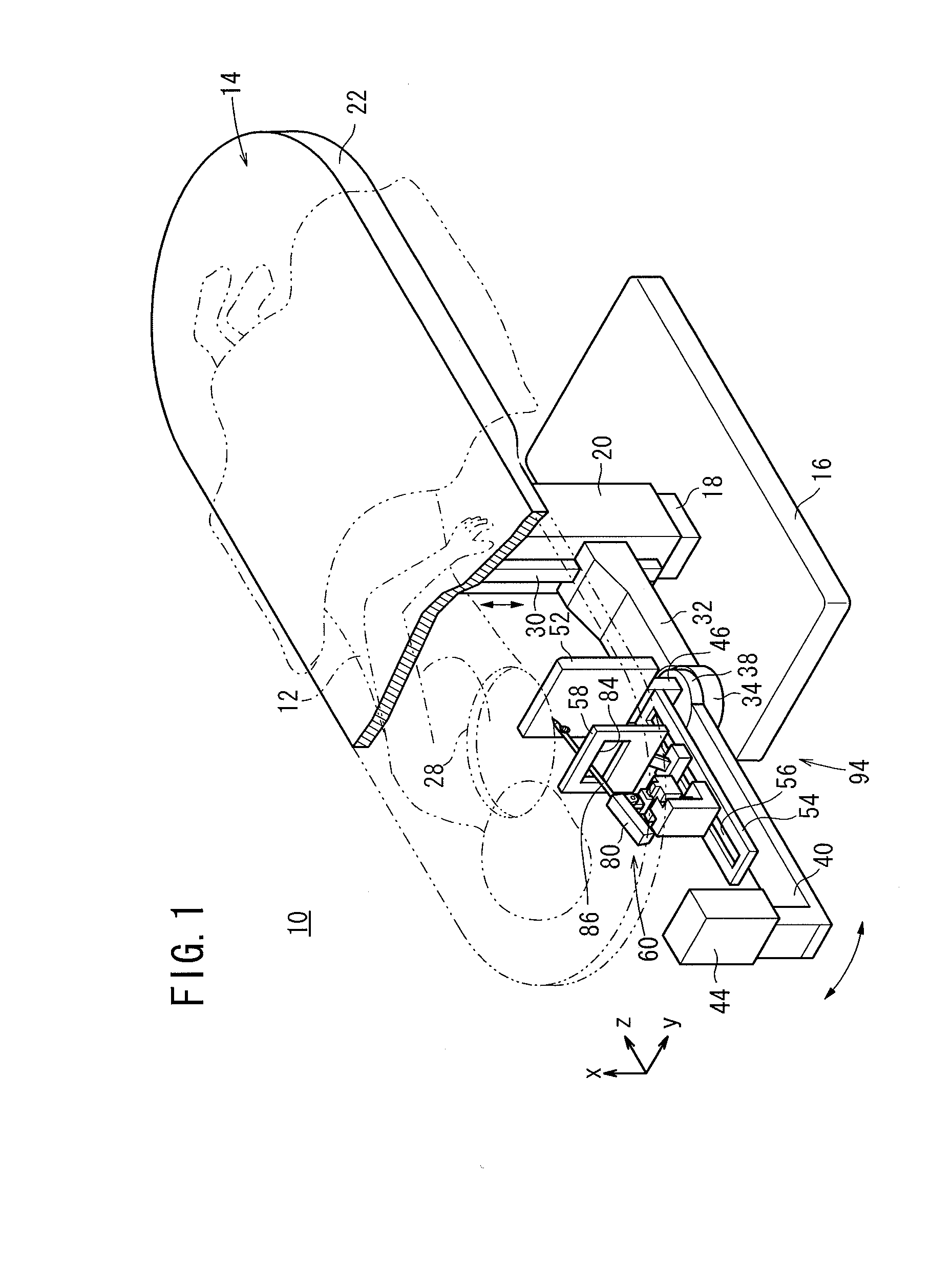
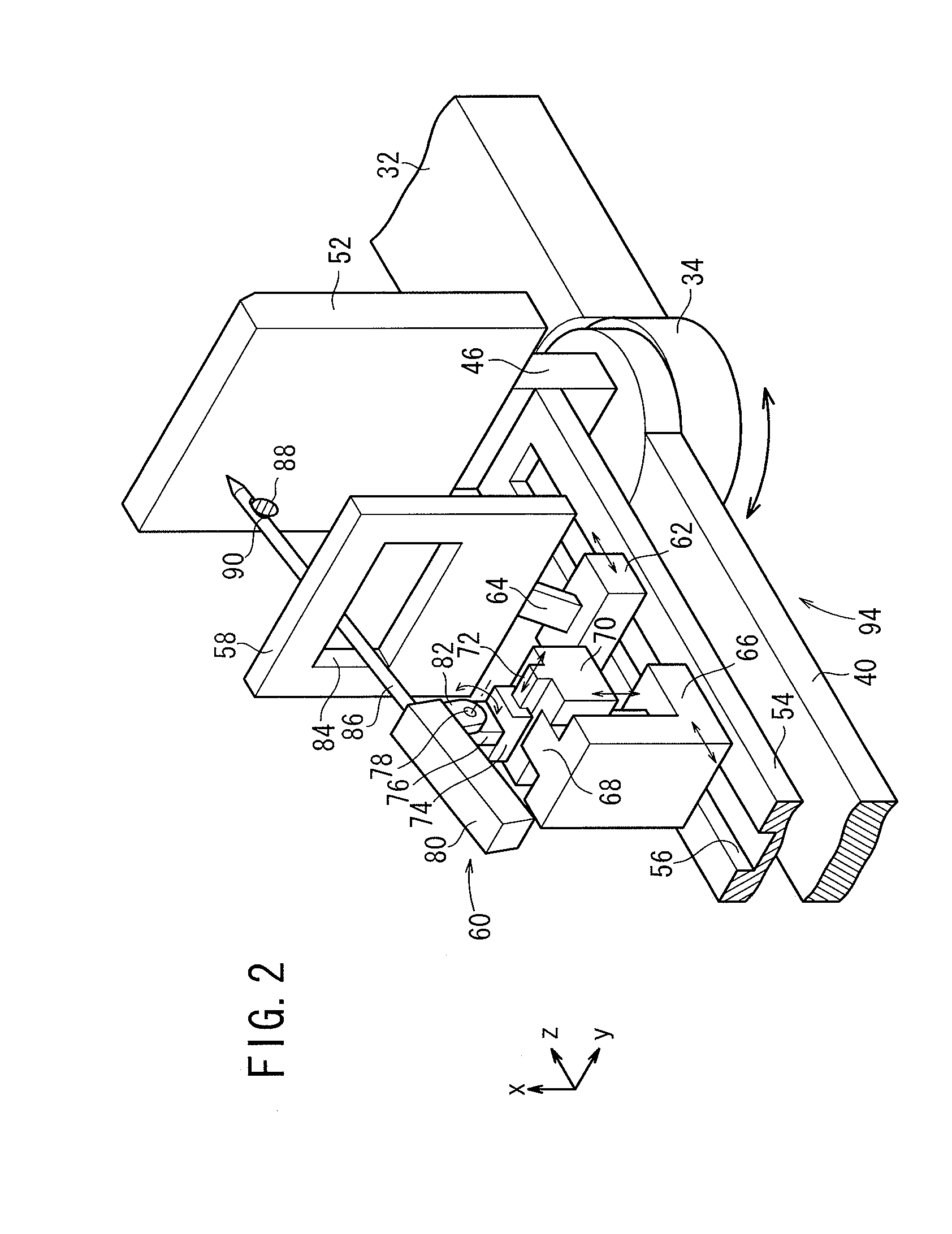
Excisional biopsy devices and methods
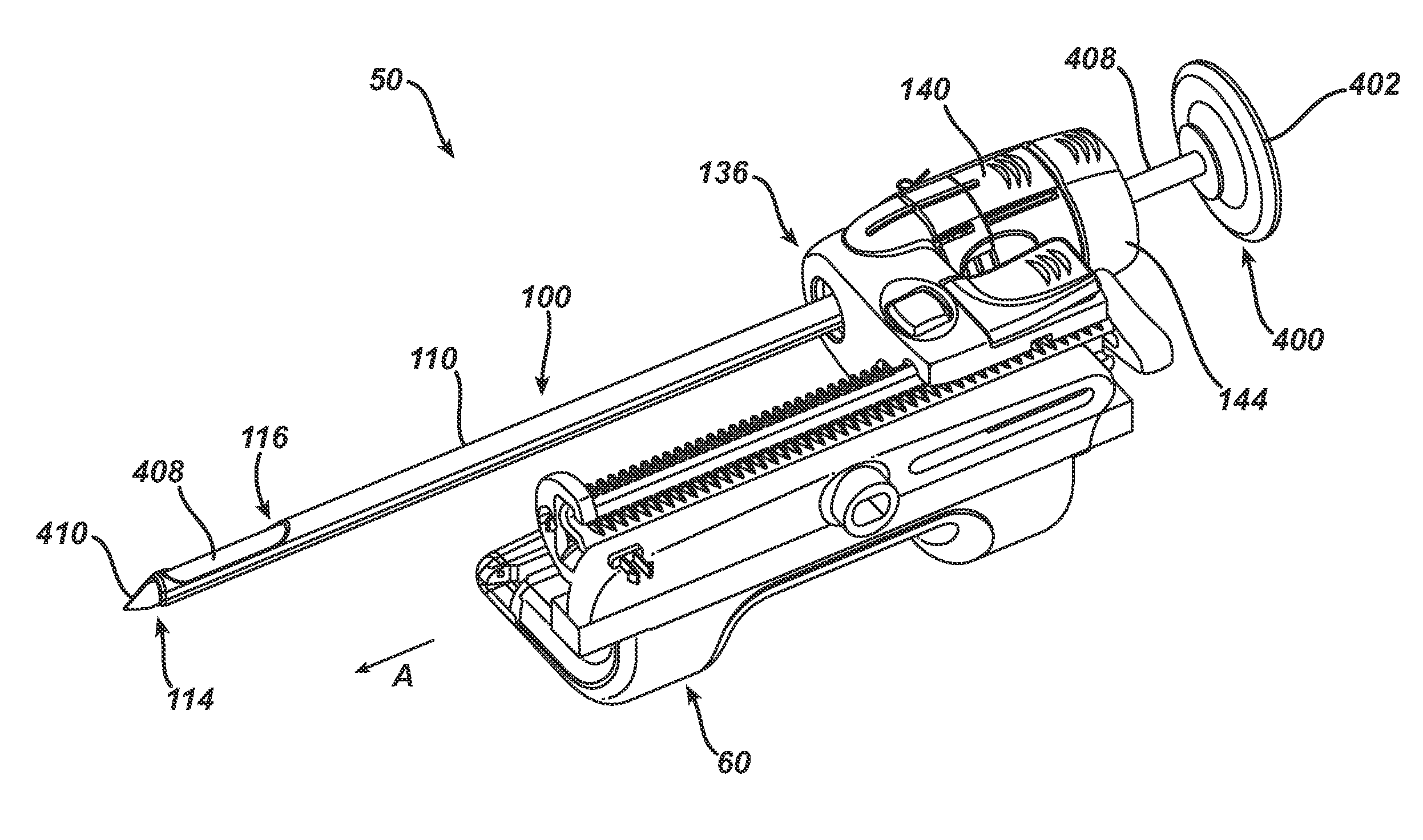
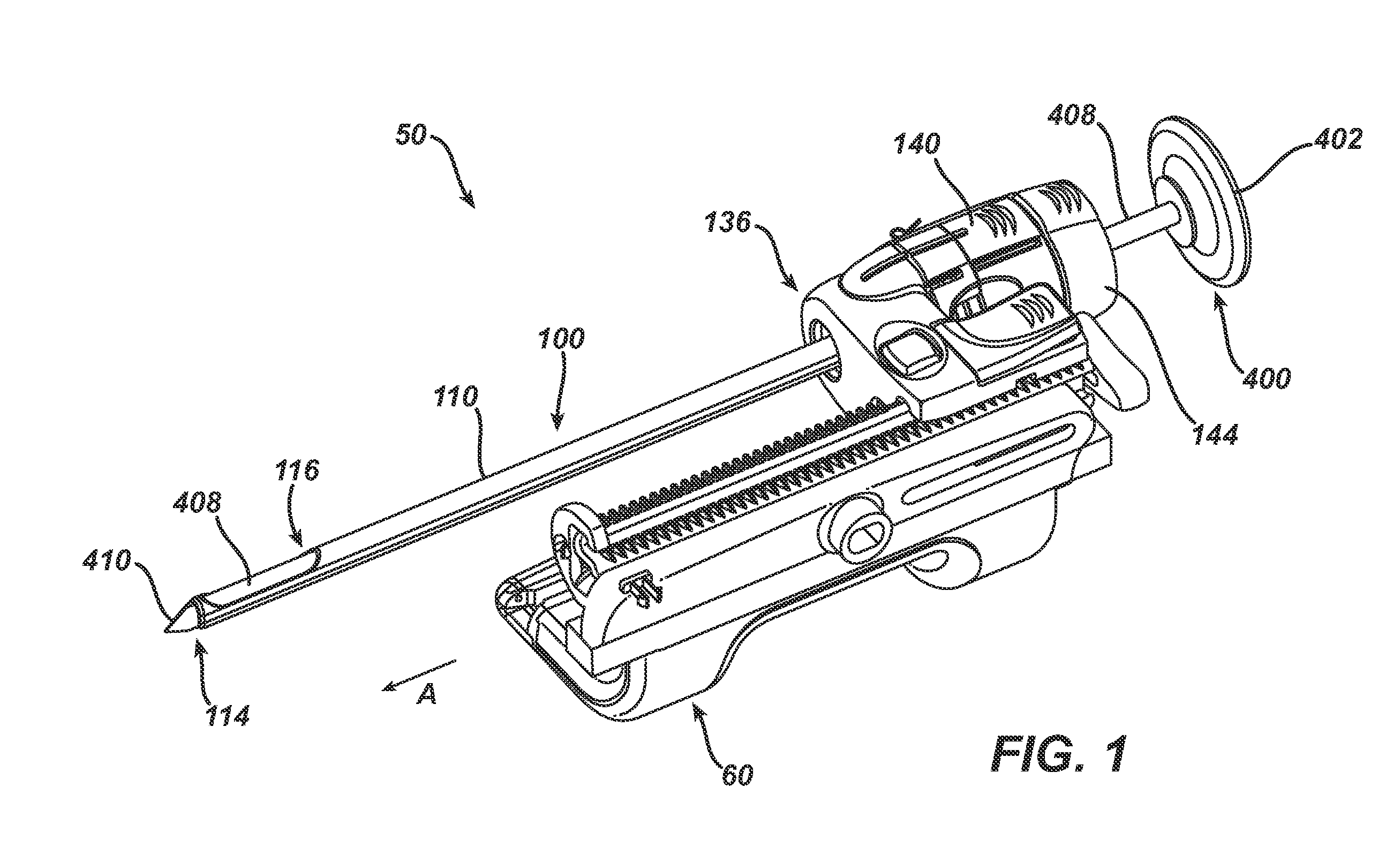
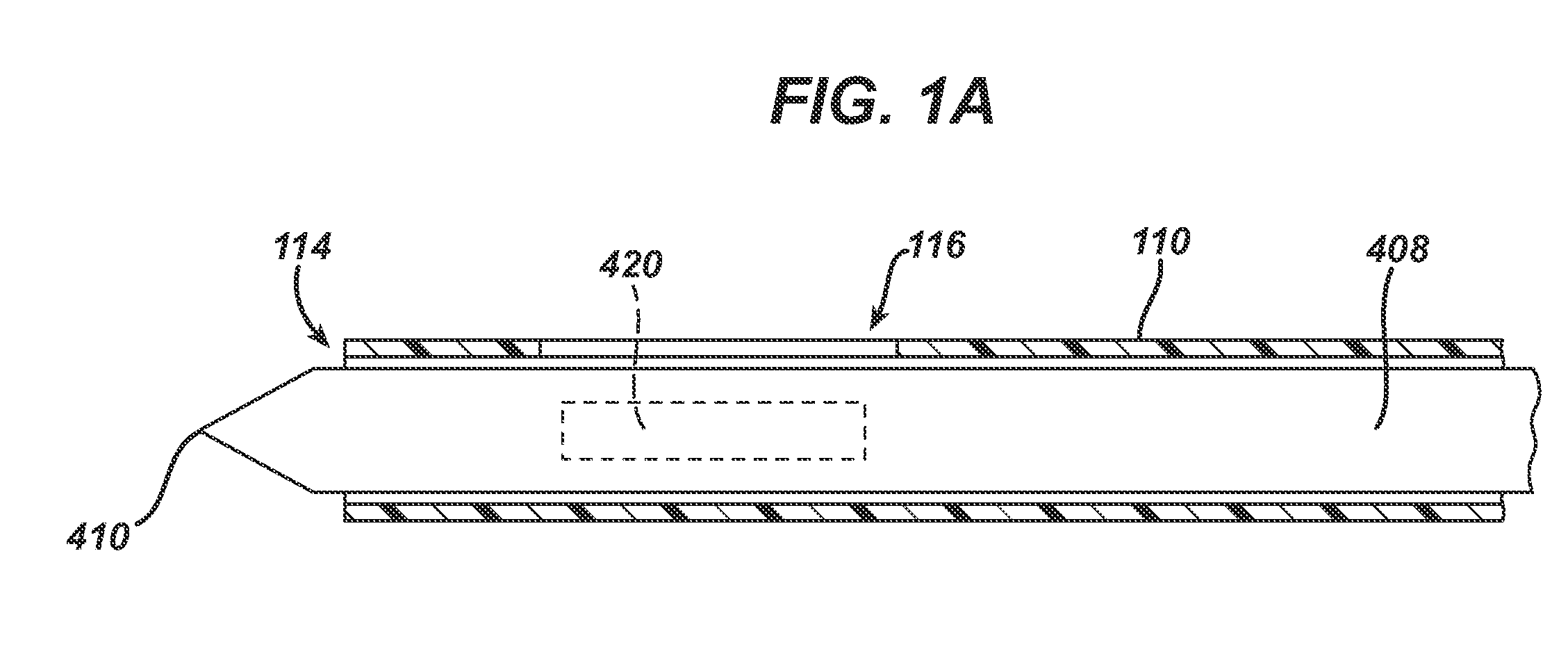
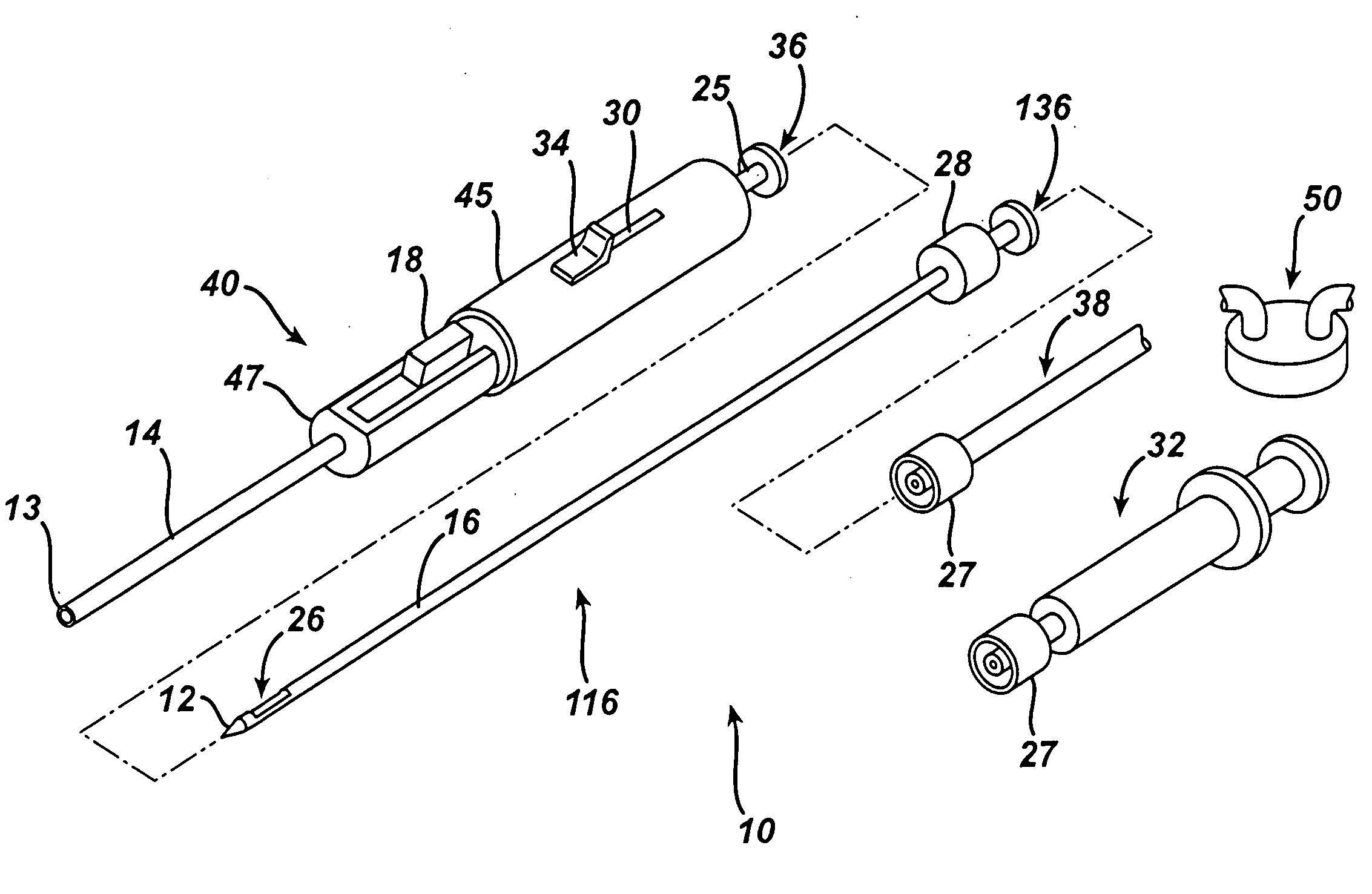
InactiveUS7303531B2Efficiently and safely exciseMinimized in sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasBiopsy methodsTissue Collection
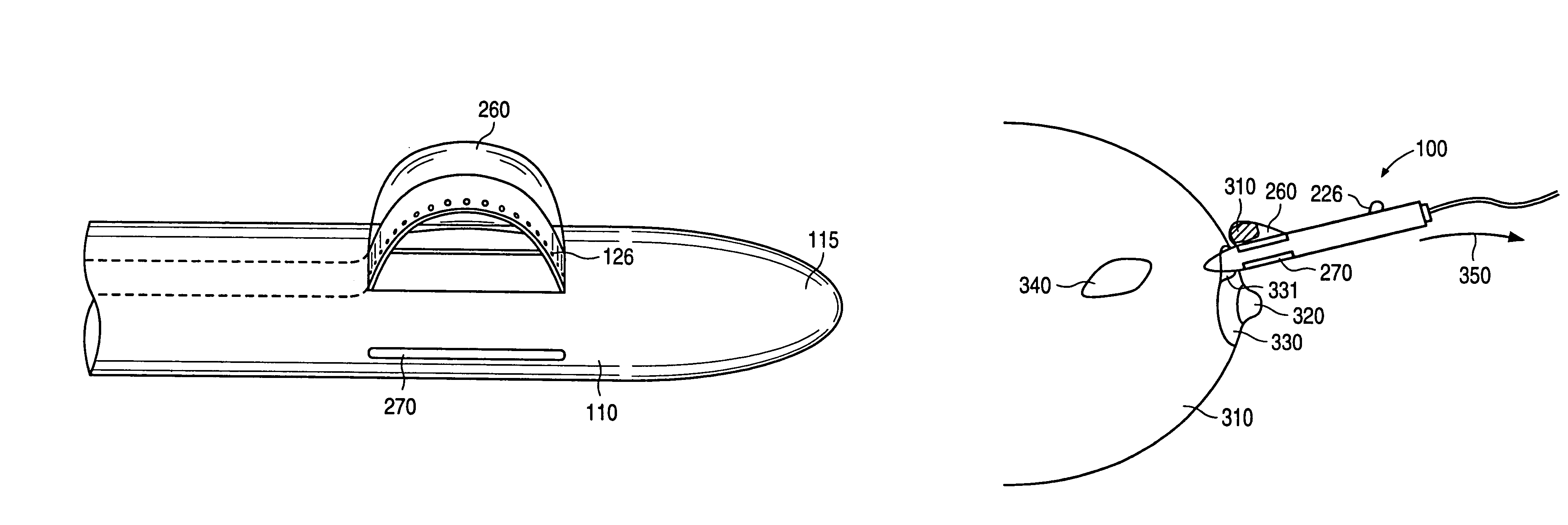
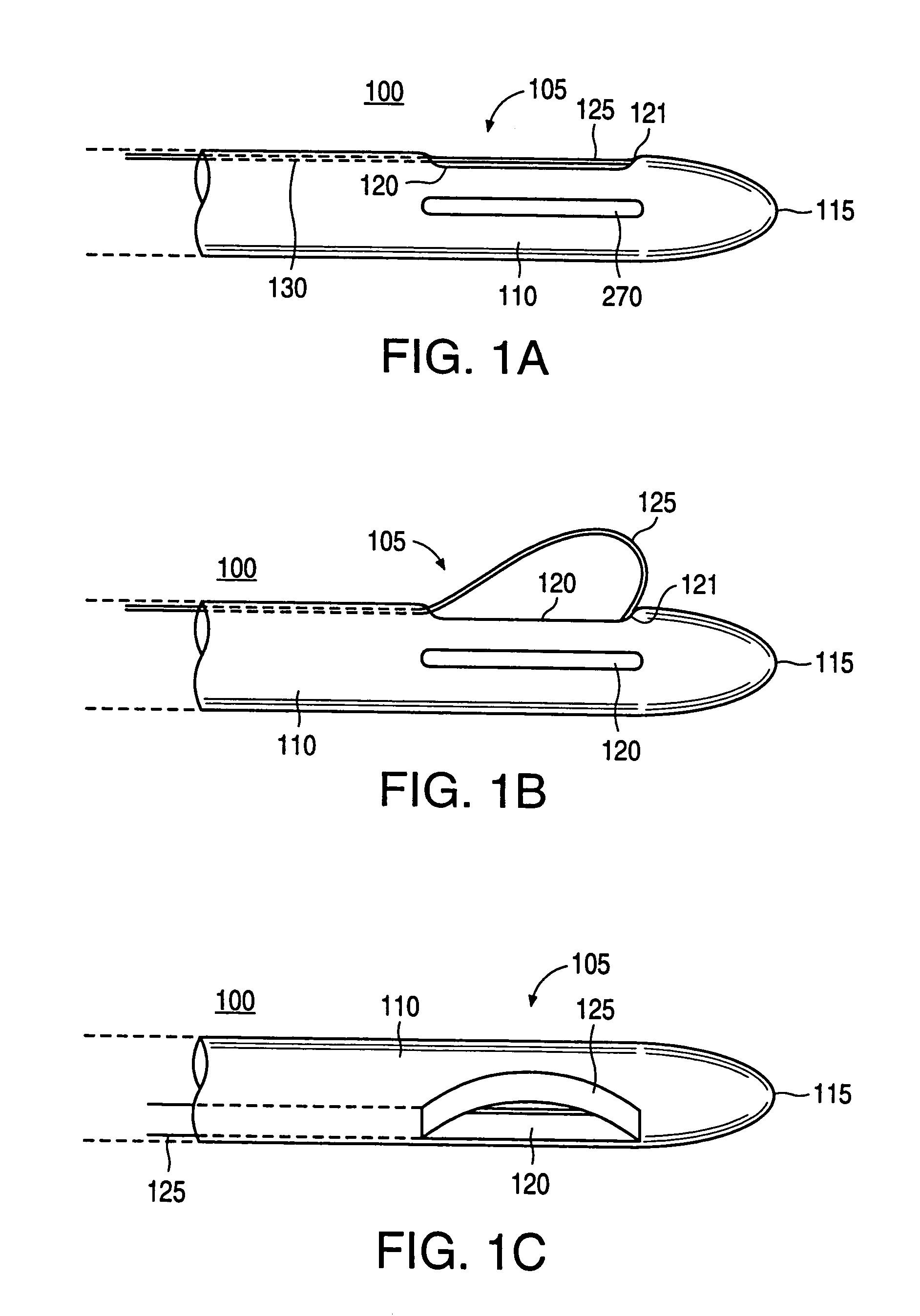
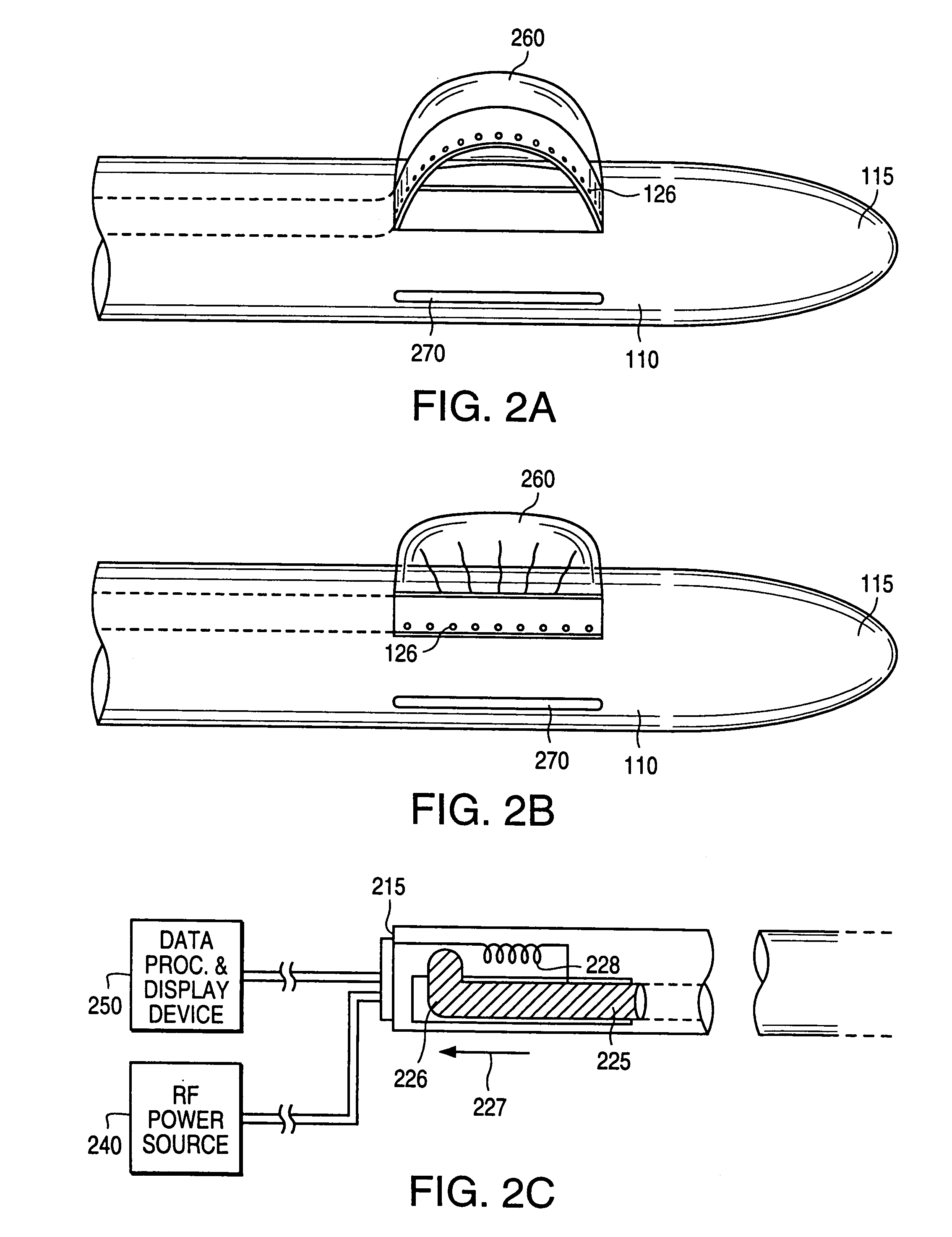
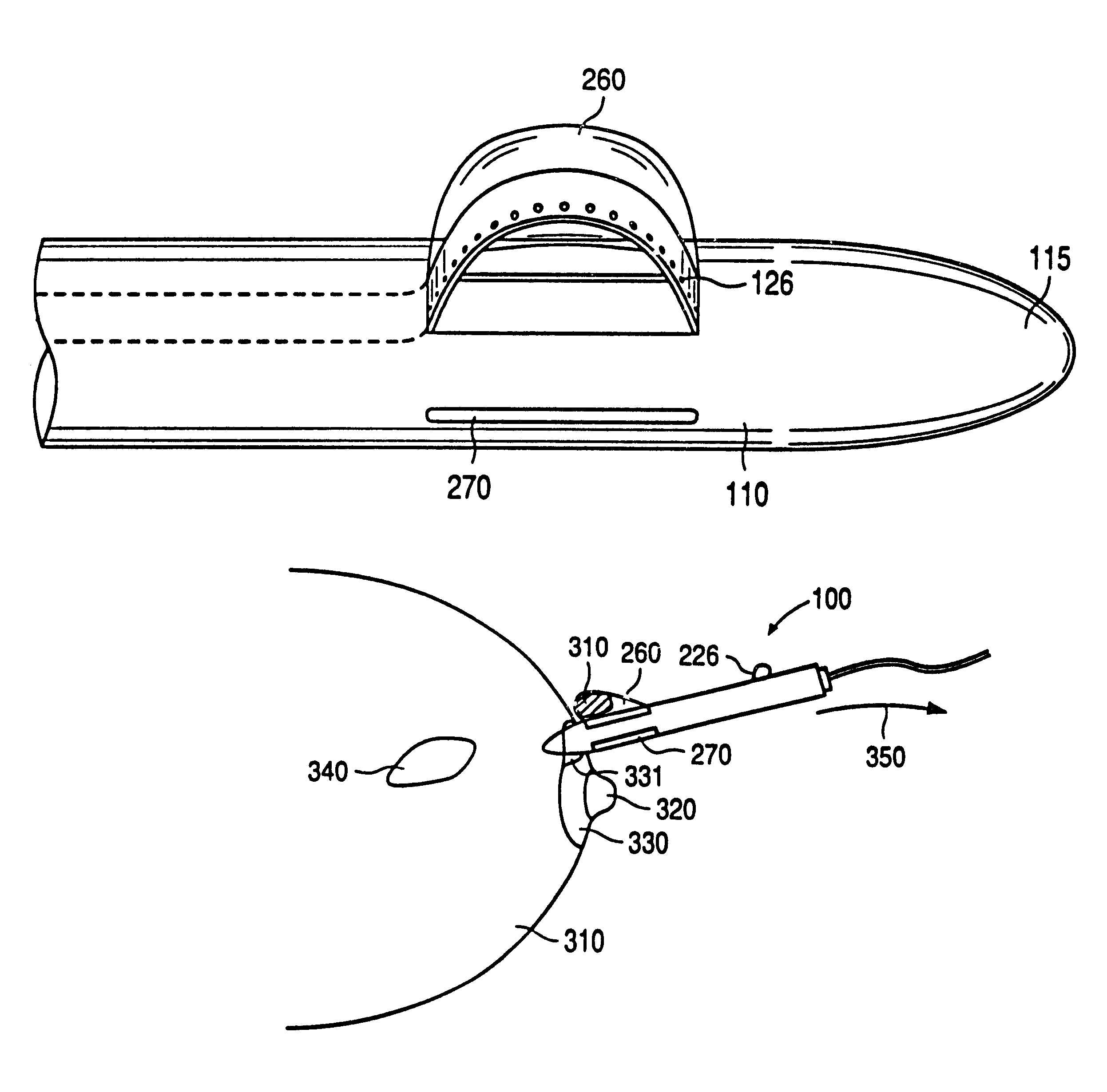
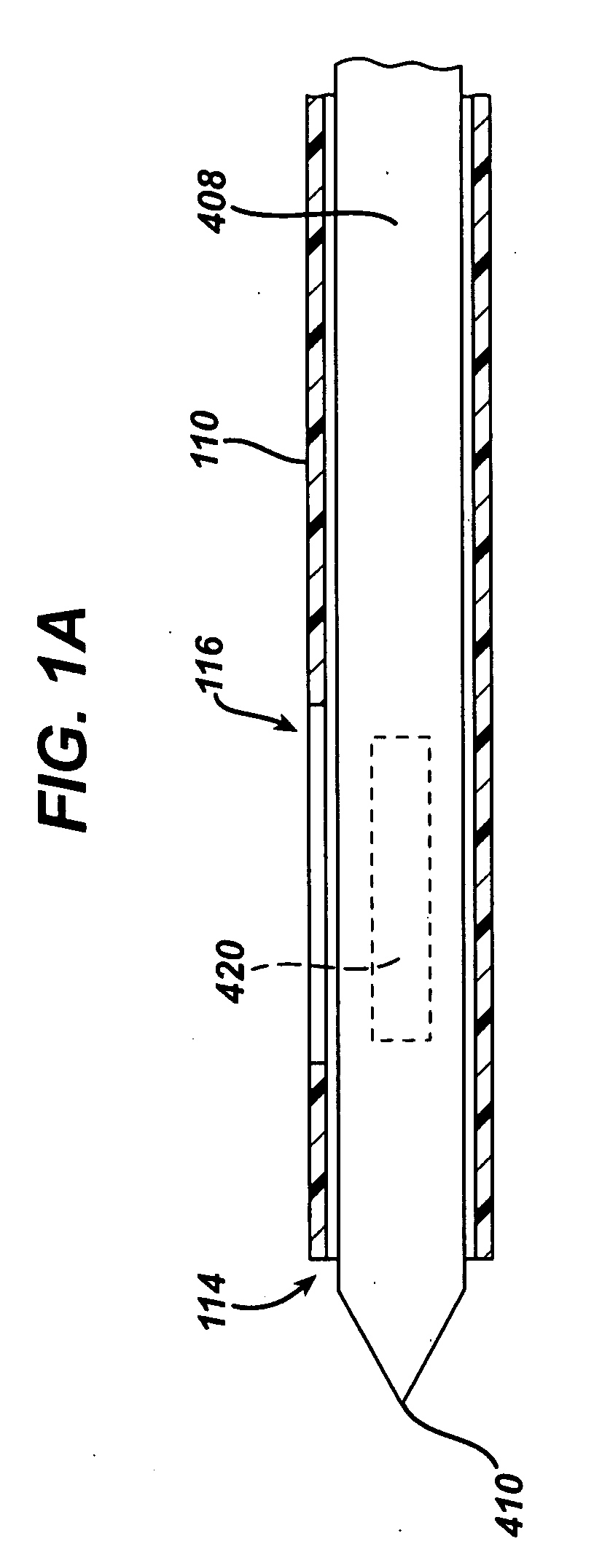
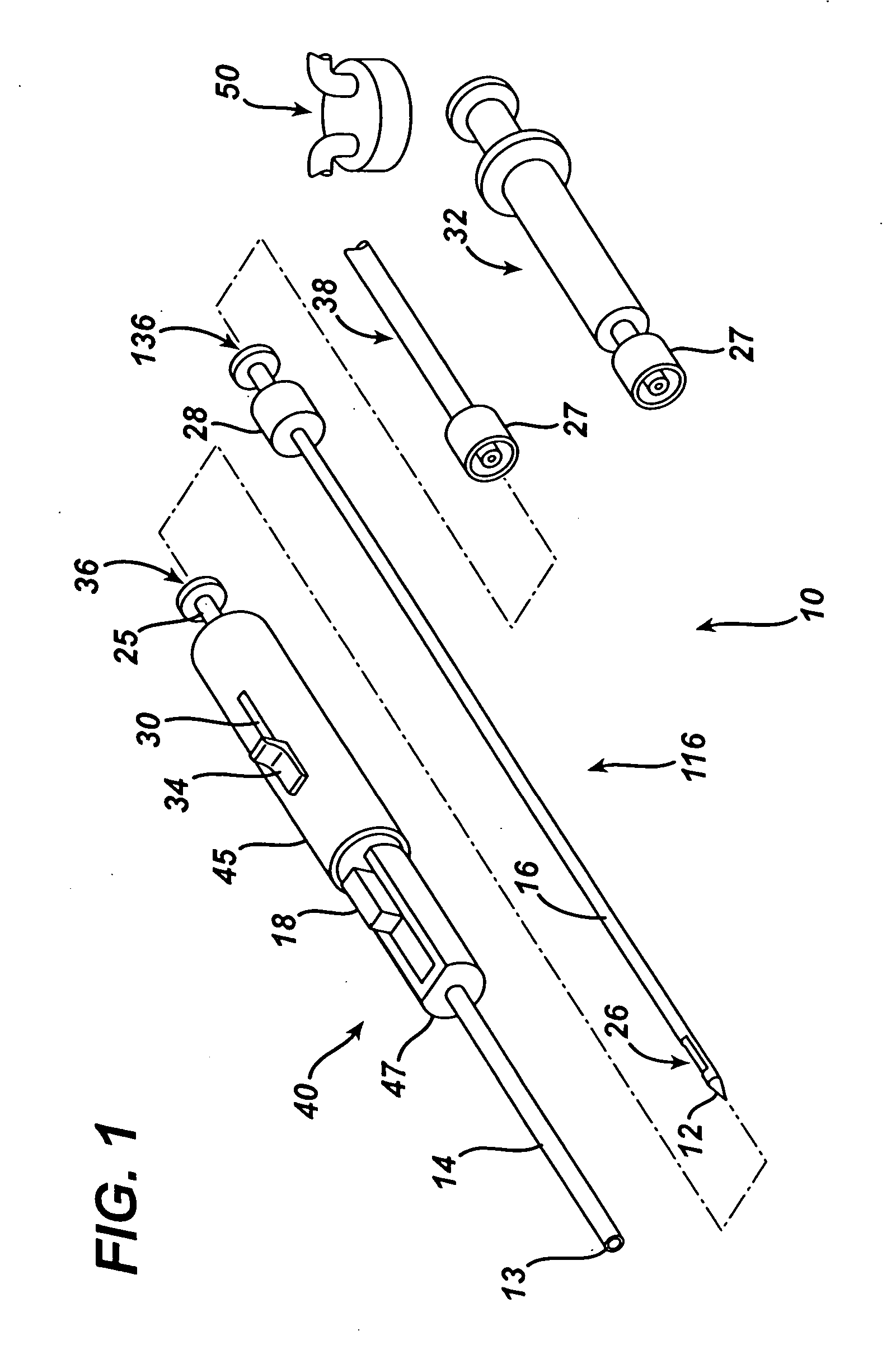
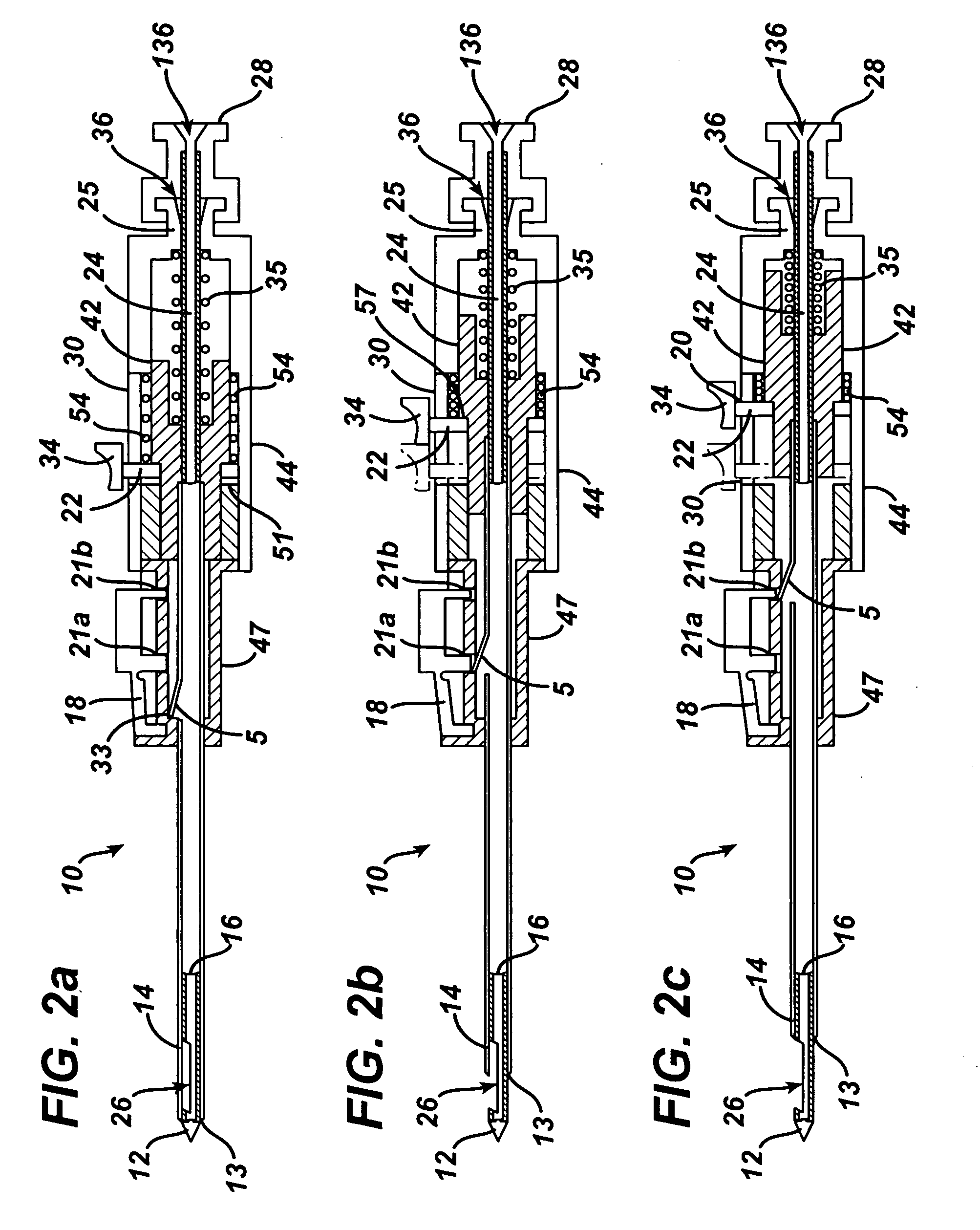
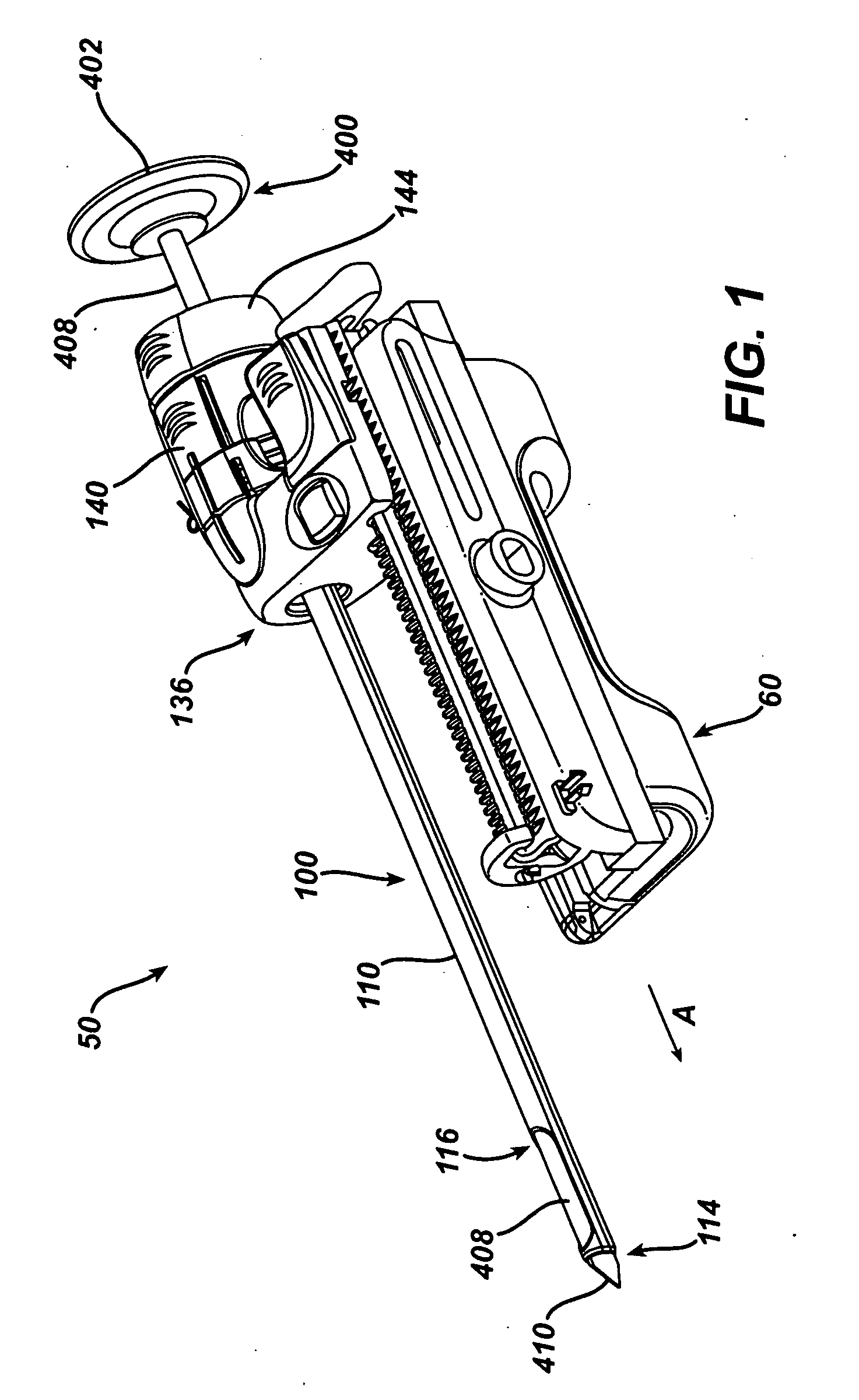
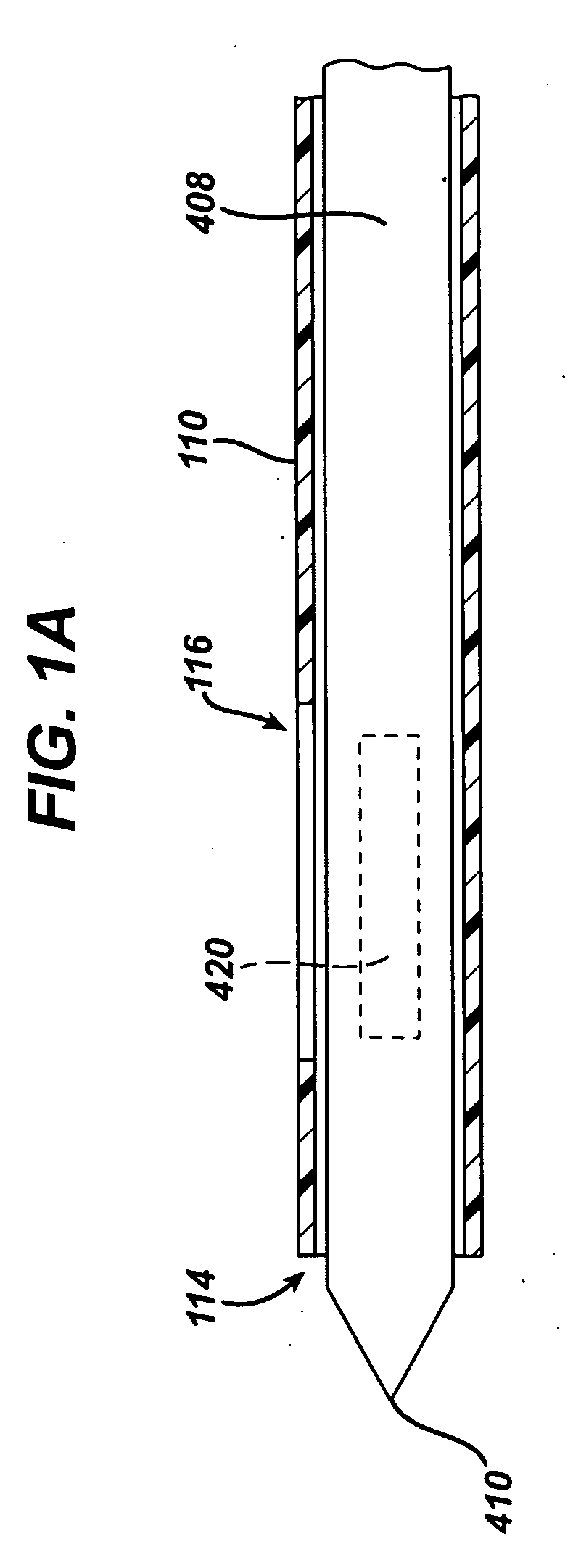
An excisional biopsy device includes a tubular member having a window near a distal tip thereof; a cutting tool, a distal end of the cutting tool being attached near the distal tip of the tubular member, at least a distal portion of the cutting tool being configured to selectively bow out of the window and to retract within the window; and a tissue collection device externally attached at least to the tubular member, the tissue collection device collecting tissue excised by the cutting tool as the biopsy device is rotated and the cutting tool is bowed. An excision al biopsy method for soft tissue includes the steps of inserting a generally tubular member into the tissue, the tubular member including a cutting tool adapted to selectively bow away from the tubular member and an external tissue collection device near a distal tip of the tubular member; rotating the tubular member; selectively varying a degree of bowing of the cutting tool; collecting tissue severed by the cutting tool in the tissue collection device; and retracting the tubular member from the soft tissue. The tubular member may include an imaging transducer and the method may include the step of displaying information received from the transducer on a display device and the step of varying the degree of bowing of the cutting tool based upon the displayed information from the imaging transducer. Alternatively, the imaging transducer may be disposed within a removable transducer core adapted to fit within the tubular member.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
Excisional biopsy device and methods
InactiveUS6849080B2Efficiently and safely exciseMinimize complicationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasBiopsy methodsDistal portion
An excisional biopsy device includes a tubular member having a window near a distal tip thereof; a cutting tool, a distal end of the cutting tool being attached near the distal tip of the tubular member, at least a distal portion of the cutting tool being configured to selectively bow out of the window and to retract within the window; and a tissue collection device externally attached at least to the tubular member, the tissue collection device collecting tissue excised by the cutting tool as the biopsy device is rotated and the cutting tool is bowed. An excisional biopsy method for soft tissue includes the steps of inserting a generally tubular member into the tissue, the tubular member including a cutting tool adapted to selectively bow away from the tubular member and an external tissue collection device near a distal tip of the tubular member; rotating the tubular member; selectively varying a degree of bowing of the cutting tool; collecting tissue severed by the cutting tool in the tissue collection device; and retracting the tubular member from the soft tissue. The tubular member may include an imaging transducer and the method may include the step of displaying information received from the transducer on a display device and the step of varying the degree of bowing of the cutting tool based upon the displayed information from the imaging transducer. Alternatively, the imaging transducer may be disposed within a removable transducer core adapted to fit within the tubular member.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
Devices Useful In Imaging
InactiveUS20090270725A1Convenient amountSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy methodsGamma imaging
Biopsy devices and methods useful with Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Breast Specific Gamma Imaging (BSGI) are disclosed. A biopsy device including a flexible tube having a side aperture, and a PET or BSGI imageable material disposed within the flexible tube is disclosed. A biopsy method is disclosed that includes advancing a flexible tube having a PET or BSGI imageable material distally through the biopsy device. Various other embodiments and applications are disclosed.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biopsy method for use in human face identification
InactiveCN101908140AGuaranteed concealmentImprove recognition ratePerson identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionEyelidBiopsy methods
The invention provides a biopsy method for use in human face identification and belongs to the technical field of mode identification. The algorithm provided by the invention comprises: firstly, giving a 'please-face-the-camera-with-face' prompt to a user logging in regardless of the current posture of the user, finding the face and eye socket areas by using an Adaboost human face sorter during the posture correction of the user, determining upper and low eyelids and left and right eye corners by using differential projection and precisely framing the positions of the eye sockets; secondly, computing optical flow field of two adjacent frames in an input video sequence by using an LK algorithm; and thirdly, further processing obtained optical flow data to obtain an optical flow amplitude, acquiring the number of the pixels with high amplitude, computing the specific gravity of the pixels with high amplitude, and determining eye movement if the proportion is big. Experiments show that for a real human face, eye movement can be detected easily due to a heavy optical flow generated on the eyes in a posture correction and eye twinkling process, while for a picture, eyes only perform a micro movement no matter how the picture moves or translations. When the method is used for biopsy, a better effect can be obtained.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Biopsy Devices
InactiveUS20090270760A1Convenient amountSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy methodsGamma imaging
Biopsy devices and methods useful with Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Breast Specific Gamma Imaging (BSGI) are disclosed. A biopsy device including a flexible tube having a side aperture, and a PET or BSGI imageable material disposed within the flexible tube is disclosed. A biopsy method is disclosed that includes advancing a flexible tube having a PET or BSGI imageable material distally through the biopsy device. Various other embodiments and applications are disclosed.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biopsy method
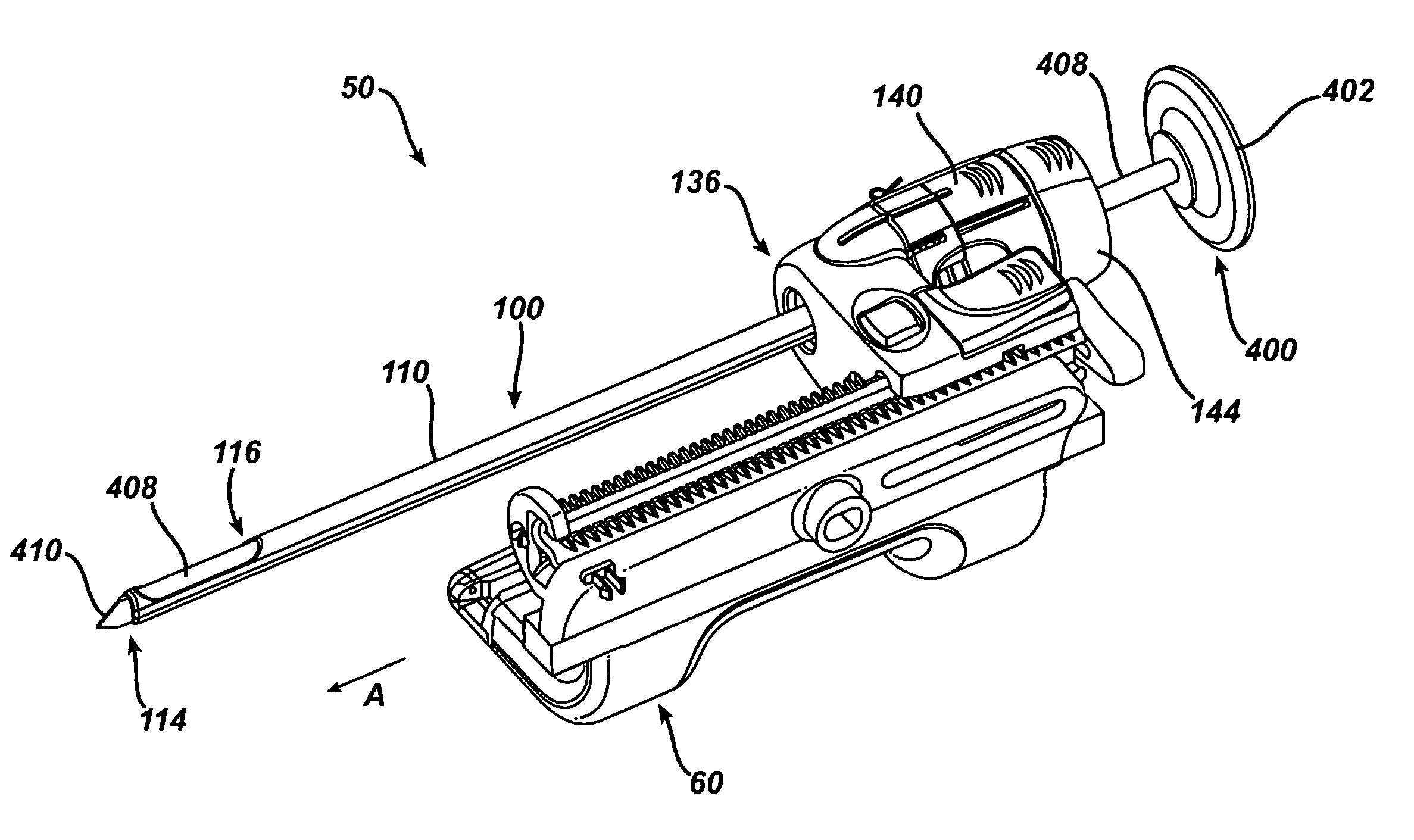
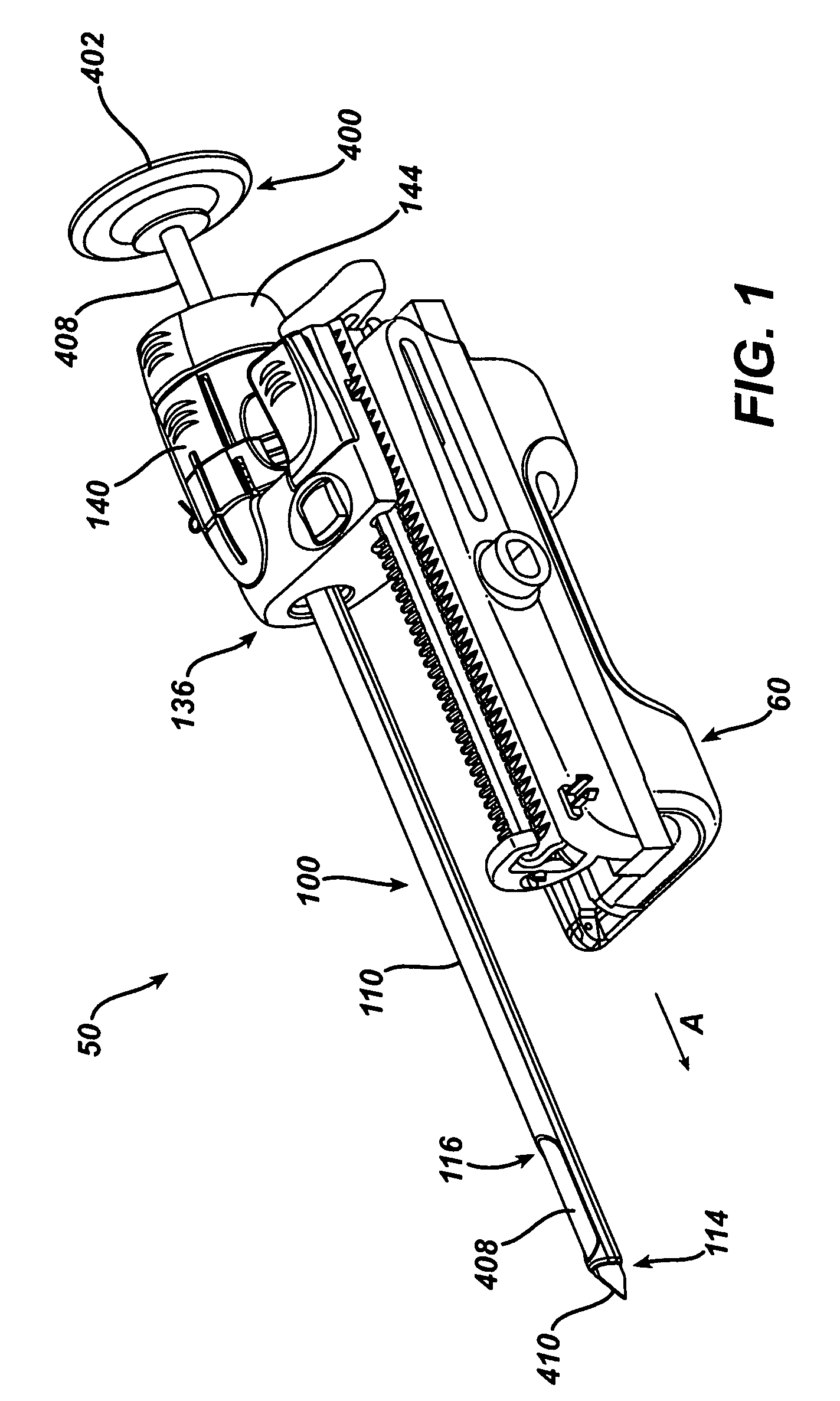
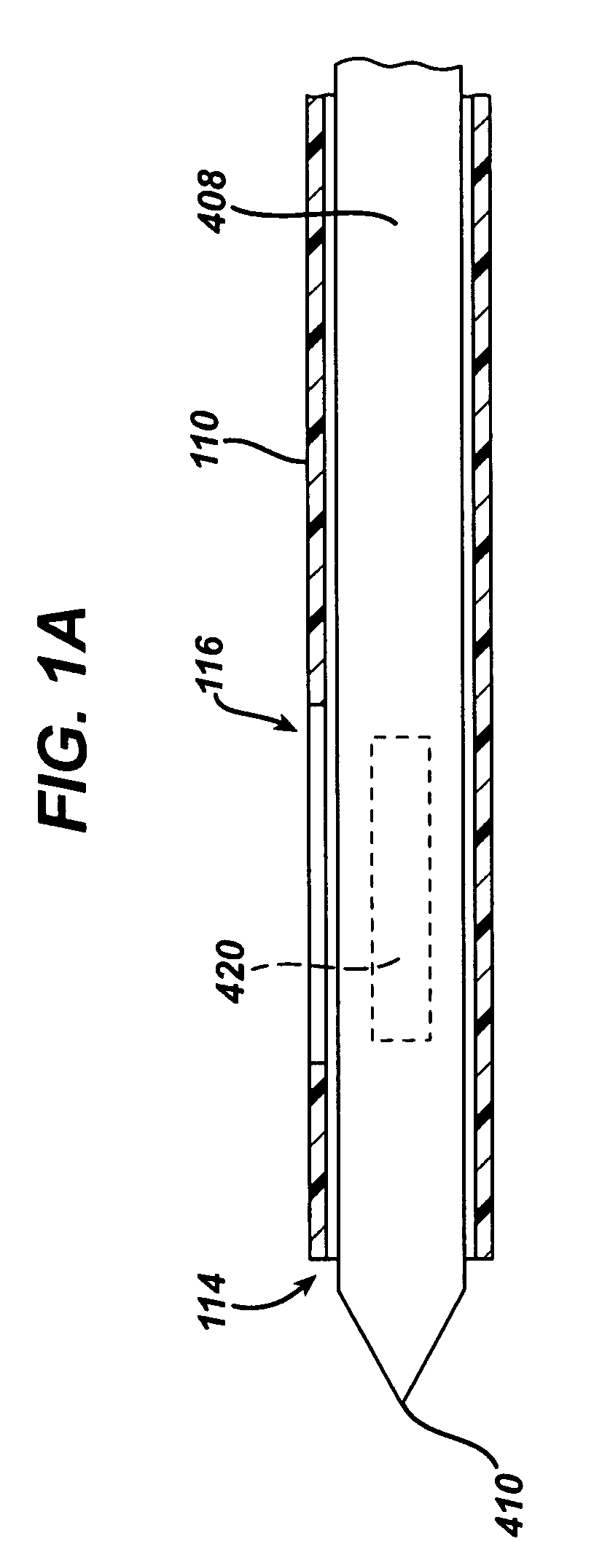
A biopsy method is disclosed. The biopsy method can be used to provide a fine needle aspiration sample and a core biopsy sample. The biopsy method can include adjusting a sample port length without removing the biopsy device from the patient.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
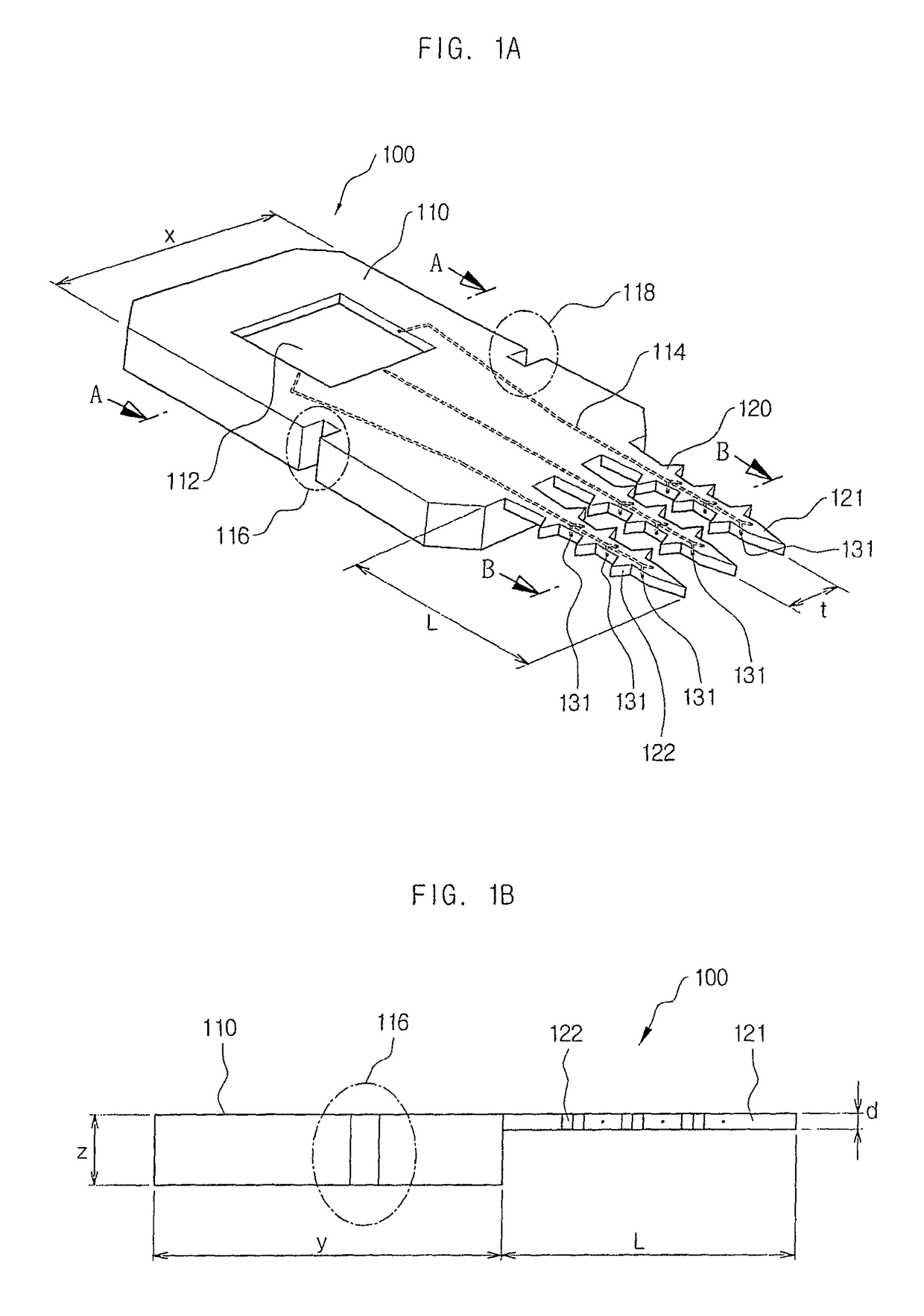
Barb-wired micro needle made of single crystalline silicon and biopsy method and medicine injecting method using the same
InactiveUS20070060837A1Minimizing invasionSimple procedureMicroneedlesSurgeryBiopsy procedureBiopsy methods
Disclosed are a barb-wired single crystalline silicon micro needle and a biopsy method and a medicine injecting method using the same. The micro needle comprises a main body part, at least one extension part formed on a side surface of the main body part, and a protrusion part protruded from both side surfaces of the extension part. A medicine storage is formed on a surface of the main body part. A fluid passage is formed in the extension part and the main body part. It is easy to pick the tissue sample with the protrusion part just by inserting and extracting the extension part of the micro needle into and from the tissue for a biopsy. Therefore, the biopsy procedures can be simplified. In addition, the medicine in the storage can be injected into the tissue via the fluid passage.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Biopsy method
A biopsy method is disclosed. The biopsy method can be used to provide a fine needle aspiration sample and a core biopsy sample. The biopsy method can include adjusting a sample port length without removing the biopsy device from the patient.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
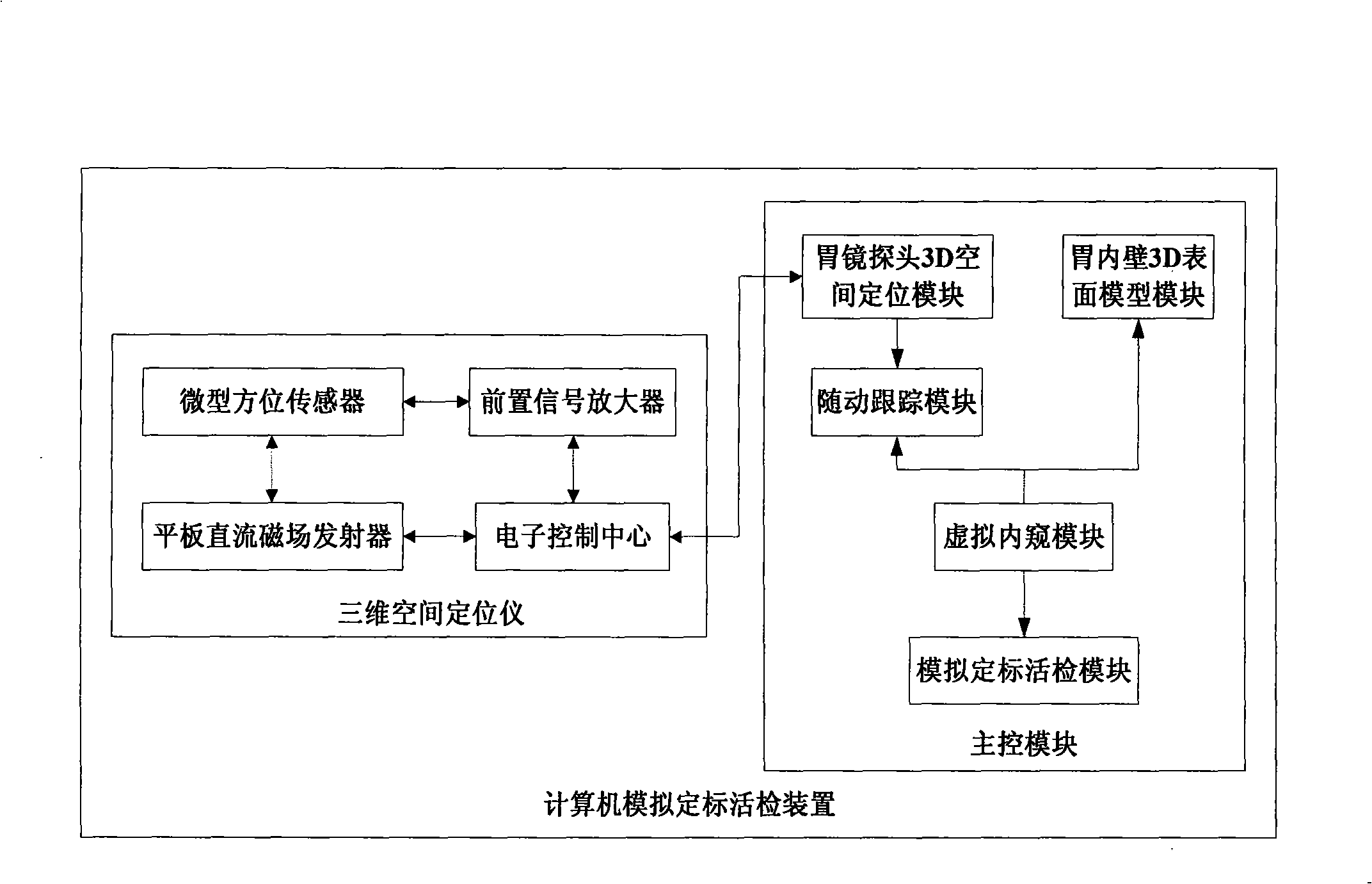
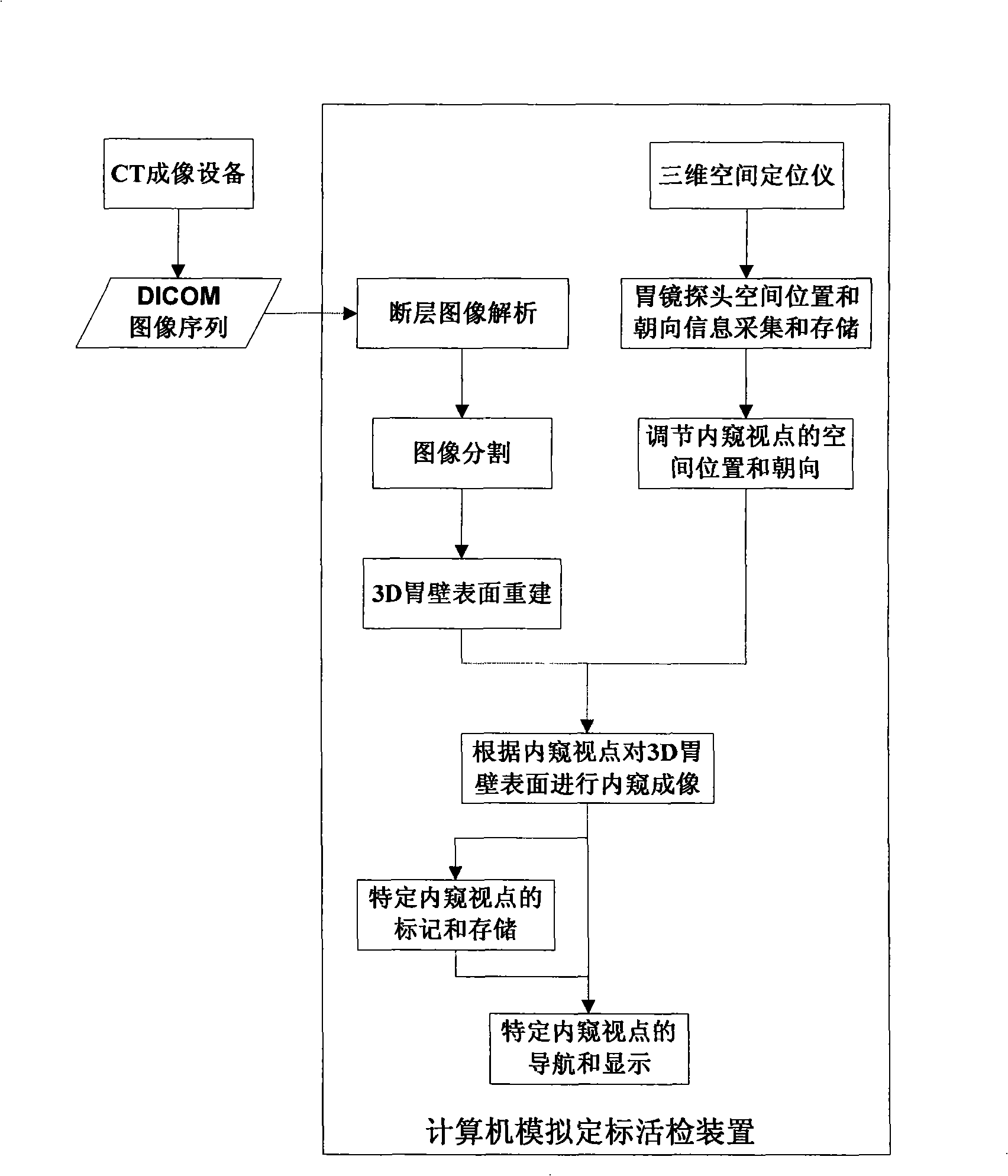
Computer simulation scaling biopsy method and apparatus
InactiveCN101322652ARelieve painReduce workloadSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDiseaseBiopsy methods
The invention discloses a method which can carry out follow-up tracing and virtual endoscopy to a gastroscope probe in gastroscopy process to implement analogue scaling biopsy on the focus in the stomach and provides a device for computer analogue scaling biopsy; the device comprises a main control module and a three-dimensional space locator used for acquiring spatial location and orientating information of the gastroscope probe, wherein, the main control module comprises a three-dimensional surface model module of an inner gastric wall, a three-dimensional space locating module of the gastroscope probe, a follow-up tracing module, a virtual endoscopy module and an analogue scaling biopsy module. The method can help to carry out callback and follow-up examination to stomach diseases, can realize noninvasive analogue scaling biopsy of stomach focus and can support doctors to make completely non-invasive focus image analysis in vitro.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Barb-wired micro needle made of single crystalline silicon and biopsy method and medicine injecting method using the same
ActiveUS8118753B2Minimizing invasionSimple procedureMicroneedlesSurgeryBiopsy methodsBiopsy procedure
Disclosed are a barb-wired single crystalline silicon micro needle and a biopsy method and a medicine injecting method using the same. The micro needle comprises a main body part, at least one extension part formed on a side surface of the main body part, and a protrusion part protruded from both side surfaces of the extension part. A medicine storage is formed on a surface of the main body part. A fluid passage is formed in the extension part and the main body part. It is easy to pick the tissue sample with the protrusion part just by inserting and extracting the extension part of the micro needle into and from the tissue for a biopsy. Therefore, the biopsy procedures can be simplified. In addition, the medicine in the storage can be injected into the tissue via the fluid passage.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
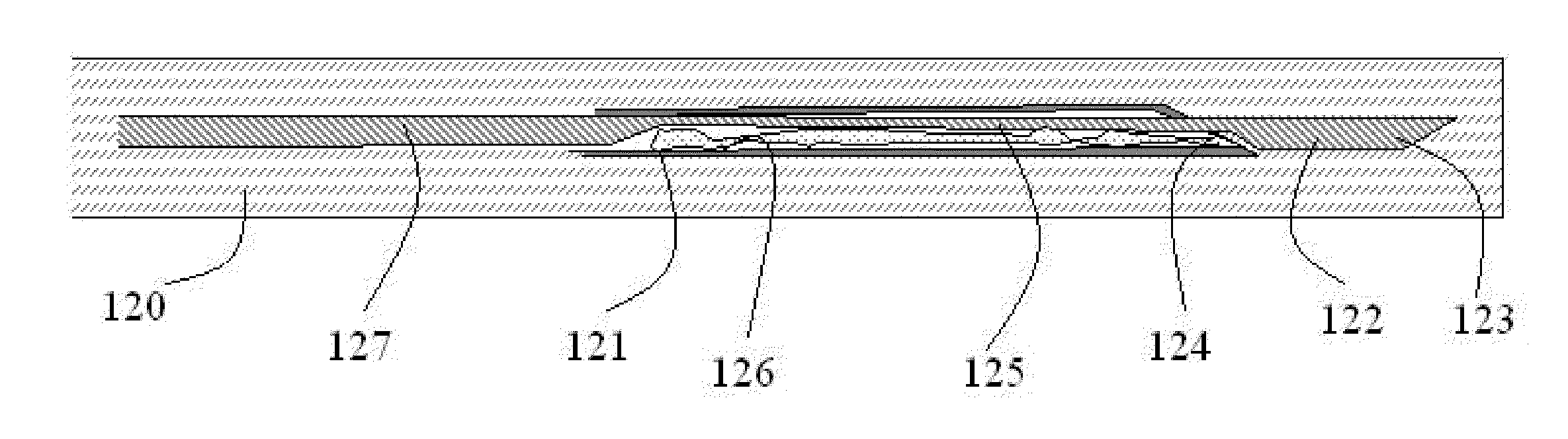
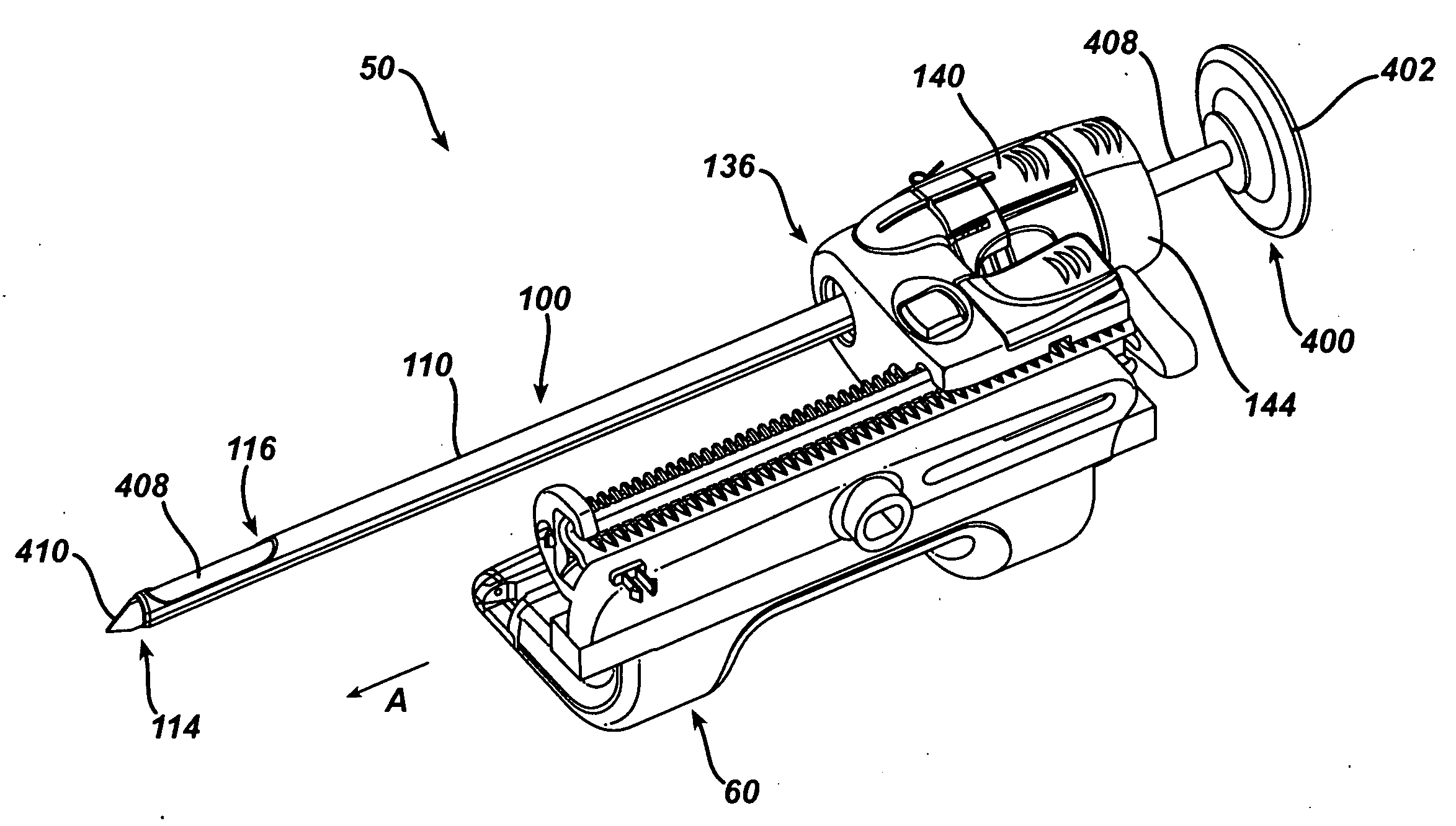
Biopsy method and device
InactiveUS6176835B1Minimize shadowsSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy methodsSkin surface
This invention relates to a method of performing accurate biopsies, particularly core breast biopsies, and a device for facilitating the accuracy of the taking of biopsies. The device involves the provision of guiding members or wing-type projections on at least two sides of the barrel of a biopsy gun. Each guiding member is parallel to the axis of a biopsy needle attached to the gun and there are at least two guiding members projecting from the barrel of the gun substantially perpendicular to one another. Each guiding member is preferably in line with the needle, so that in use the biopsy needle is in the plane of each guiding member. The device may be in the form of a biopsy gun with the guiding members integrally formed or affixed, or it may be in the form of an attachment for attaching to a conventional biopsy gun. The method of the invention involves a means of guiding a biopsy needle to a calculated site of a target lesion; identifying a location on the skin surface directly between the calculated site and a source of electromagnetic radiation, including a light source; positioning a biopsy needle tip at that location; monitoring shadows on the skin surface created by guiding members on a biopsy gun to which the biopsy needle is attached, each guiding member projecting from a side of the biopsy gun, in a parallel axis to the needle attached or held by the gun, and at least two of the guiding members substantially perpendicular to one another; and guiding the biopsy needle to the calculated site by minimizing the shadows so that the needle remains substantially parallel to the electromagnetic radiation beam.
Owner:MURRAY PACHAL FAMILY TRUST TRUSTEES MURRAY PACHAL JAN PACHAL ROBERT PARKINSON
Biopsy method and gun set devices
InactiveUS20140228661A1Reduce transmissionCut evenlySurgical needlesDiagnostics using spectroscopyBiopsy methodsDensitometry
A novel set of biopsy-gun related tools are developed in order to make a better safer sampling and diagnosis, comprising a set of tools that takes the sample, releases a drug impregnated plug and additionally may inject drugs, measure pH and the molecular content of the penetrated tissues.A novel technology aiming to minimize the penetrated tissue damage, using a small diameter needle with capabilities for immediate spectroscopic analysis of the tissue, and followed by sampling and plugging of the tissue when needed.The invention describes a set of variable diameter thin tubes used to guide and insulate the penetrated organs, and a final operation of plugging the wounds with absorbable substances, impregnated with drugs.The supplementary low intensity radiation sources could increase the processes' accuracy and safety, offering the opportunity of gathering supplementary x-densitometry information.
Owner:VARIABLE GAUGE CATHETER INC
Devices useful in imaging
Biopsy devices and methods useful with Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Breast Specific Gamma Imaging (BSGI) are disclosed. A biopsy device including a flexible tube having a side aperture, and a PET or BSGI imageable material disposed within the flexible tube is disclosed. A biopsy method is disclosed that includes advancing a flexible tube having a PET or BSGI imageable material distally through the biopsy device. Various other embodiments and applications are disclosed.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Liver cancer image feature extraction and pathological classification method and device based on imaging omics
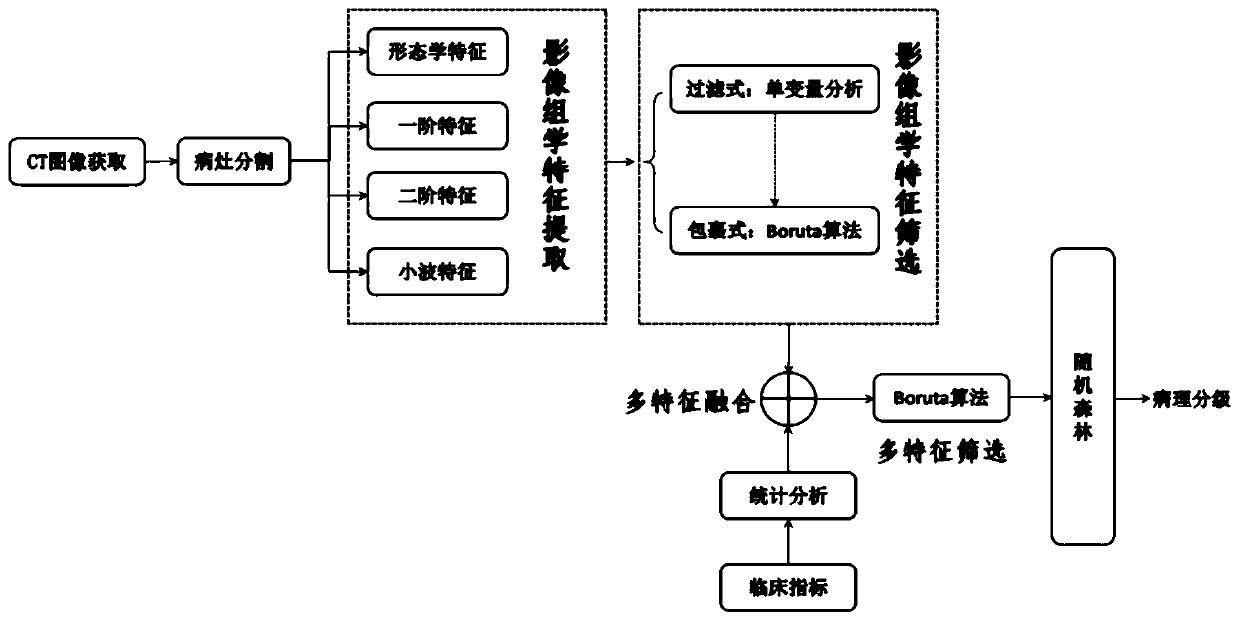
ActiveCN111242174AEfficient use ofExcellent performance for distinguishing subtle differencesImage enhancementImage analysisBiopsy methodsStatistical analysis
The invention discloses a liver cancer image feature extraction and pathological classification method and device based on imaging omics. The method comprises the following steps: 1) collecting a patient clinical image meeting the standard, and sketching a liver cancer lesion area of the collected image by adopting a Growcut semi-automatic segmentation method; 2) performing different levels of image omics feature extraction on the segmented lesion area; 3) feature screening: starting from a filtering method, extracting non-redundant features strongly related to the classification targets by adopting a filtering Boruta algorithm; 4) in combination with clinical indexes of the patient, filtering out significant and undifferentiated features through preliminary statistical analysis, and thenfusing the image omics features to perform next Boruta screening; and 5) training on a random forest by using the finally screened features to obtain classification labels, and completing prediction of pathological classification of liver cancer. Compared with a clinically traditional biopsy method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of non-invasion, safety and stability,and is expected to become an effective preoperative evaluation tool for clinic.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Endoscopic system for lung biopsy and biopsy method of insufflating gas to collapse a lung
InactiveUS20090124927A1Reduce riskIncrease surface areaSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsThoracic structureBiopsy methods
An endoscopic biopsy system comprising a means for drawing a sample to be sealed, separated, and / or collected towards an instrument, such as a structure that includes one or more of: an extendable wire, an extendable mast, an extruded tube with at least one opening and a vacuum therein, a pivot point, a hinge, and a mounting block. The system should have a means to transfer energy to a sample after a sample is grasped, such as a conducting wire or an anvil. The system should also have an airtight means to remove a separated sample from a biopsy site for analysis, such as a collection bag or an internal vacuum suction system. The endoscopic biopsy system can be used in a method of obtaining a biopsy from the thoracic cavity that includes a step of insufflating gas to induce pneumothorax and collapse a lung.
Owner:CHEST INNOVATIONS
Radiographic image capturing apparatus, biopsy apparatus, radiographic image capturing method, and biopsy method
InactiveUS20100249647A1Unwanted radiationAvoid exposureSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy methodsImage capture
A radiographic image capturing apparatus includes a radiation source for applying a radiation to an object to be examined, a radiation detector for detecting the radiation which has passed through the object and converting the detected radiation into a radiographic image, a positional information acquiring unit for acquiring positional information of the object, and an image capturing angle changer for changing an image capturing angle of the radiation source with respect to the radiation detector based on the positional information in a stereographic image capturing process for capturing at least two radiographic images of the object by applying the radiation to the object from directions which are different from each other.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Prawn white spot syndrome virus nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection reagent kit and detecting method
InactiveCN101372714AEfficient detectionEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementBiopsy methodsNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to a detection kit for isothermal amplification of nucleic acid for the white spot syndrome virus and a detecting method thereof. The kit is designed by using a set of LAMP primers as the main body designed according to the gene conserved sequence of the white spot syndrome virus. The kit is provided with eleven agents needed by WSSV detection including SEMP lapping liquid, nucleic acid extract, UNG enzyme, TE buffer solution, enzymolysis buffer solution, LAMP reaction solution and on the like, thus realizing a programmed and standardized detection; therefore, the invention has the advantages of the highest sensitivity, simplicity, rapidity, safety, good specificity and low cost, and the amount of the copies detected with virus can be as low as 26. Only one water-bath is needed to correctly detect the white spot syndrome virus in prawns and aquaculture water within 2 hours by the kit and the detecting method. Moreover, the problem that the detection is subject to interference in the LAMP technology is also solved. The detecting method of the invention is expected to substitute the previous related detecting methods of the white spot syndrome virus, such as the electron microscope method, the TE staining method, the biopsy method, the antibody detecting method, the nucleic acid probe hybridization method and the PCR detecting method.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Biopsy apparatus and biopsy method
ActiveUS20100249648A1Reduce in quantityShorten the timeX-ray/infra-red processesSurgical needlesBiopsy methodsRadiography
A biopsy apparatus has a biopsy needle, which faces a radiation reception surface of a radiation detector and is held obliquely to the radiation reception surface by a biopsy needle holding mechanism. The biopsy apparatus includes a radiographic image capturing apparatus for capturing two radiographic images. One of the two radiographic images is produced according to a scout image capturing mode or a stereographic image capturing mode, and the other is produced according to the stereographic image capturing mode.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Detection Panel and kit for pan-cancerous detection or targeted medication based on second generation sequencing and application
PendingCN111424087AImprove uniformityReduce data volumeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiopsy methodsGenetic Change
The invention discloses a detection Panel and kit for pan-cancerous detection or targeted medication based on second generation sequencing and application of the detection Panel and kit. The detectionPanel comprises a target gene region used for detecting pan-cancerous mutation burden and mutation sites related to targeted medication, and an exon region related to pan-cancerous mutation sites. According to the invention, a liquid (blood) biopsy method is adopted, and a combined determination method is used for carrying out genetic change and protein biomarkers; the detection Panel not only can identify the existence of relatively early cancers, but also can locate origin organs of the cancers, has higher sensitivity, can better carry out combined detection, and provides more accurate support for treatment diagnosis of targeting drugs, chemotherapeutic drugs or immune drugs; and by designing and integrating common areas of different mutation-type information, the uniformity of the Panel is improved, the overall data volume of the Panel is reduced, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:合肥诺为尔基因科技服务有限公司
Methods For Imaging
InactiveUS20090270726A1Convenient amountSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy methodsGamma imaging
Biopsy devices and methods useful with Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Breast Specific Gamma Imaging (BSGI) are disclosed. A biopsy device including a flexible tube having a side aperture, and a PET or BSGI imageable material disposed within the flexible tube is disclosed. A biopsy method is disclosed that includes advancing a flexible tube having a PET or BSGI imageable material distally through the biopsy device. Various other embodiments and applications are disclosed.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Marker for identifying benign and malignant pulmonary nodules by using exosome protein and application of marker
The invention belongs to the technical field of cancer molecular diagnosis technique, in particular to a marker for identifying benign and malignant pulmonary nodules by using an exosome protein and an application of the marker. The marker comprises the following steps: S1, looking for differentially expressed proteins of exosomes in plasmas of patients suffering from benign and malignant pulmonary nodules; S2, screening the differential proteins; S3, verifying the differential diagnosis effect of FGB on the benign and malignant pulmonary nodules; and S4, analyzing the relative transcript level. The non-invasive liquid-state biopsy method is used to search out the molecular marker for identifying the benign and malignant pulmonary nodules, and the mass spectrometric detection and the subsequent bio-information analysis show that the molecular marker FGB provides a novel molecular target for the diagnosis of the pulmonary nodules and the observation of clinical effects.
Owner:HUADONG HOSPITAL
Biopsy methods and devices
Owner:INDICATOR SYST INT
Biopsy method and associated biopsy device
ActiveUS20170202544A1Maximize safetyVariable positionSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy methodsBiopsy device
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Loading method of biopsy specimens
InactiveCN109251958AShorten the timeImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiopsy methodsBlastomere biopsy
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and discloses a loading method of biopsy specimens. The loading method comprises the followings steps: preparing for a biopsy vessel, preparingfor a biopsy washing vessel, carrying out blastomere biopsy, and carrying out blastaea biopsy. Compared with the traditional biopsy method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the intermediate transferring link is saved, the transferring time of the biopsy specimens is saved, the pollution of the specimens is reduced, meanwhile, in the specimen transferring process, the visual operation is realized under an inverted microscope, and therefore, the loss probability of the specimens due to the excessively small specimens or the adhering phenomenon is reduced. The embryogenetic materials are obtained safely and effectively for detection, and thus the diagnosis accuracy and effectiveness are improved.
Owner:大连市妇女儿童医疗中心
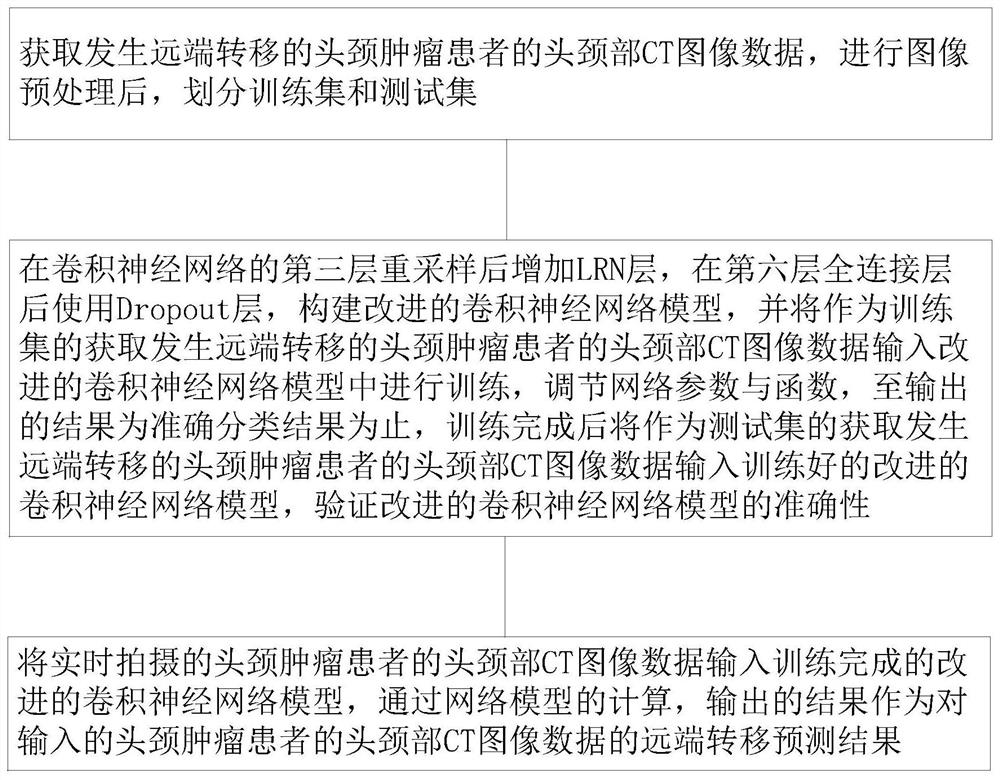
Head and neck tumor distal metastasis prediction method based on machine learning
InactiveCN113128599AAvoid painSolve few problemsImage enhancementImage analysisBiopsy methodsHead and neck tumors
The invention relates to a head and neck tumor distal metastasis prediction method based on machine learning, and the method comprises the steps: building an improved convolutional neural network, training a built network model through the head and neck CT image data of a head and neck tumor patient with distal metastasis, and predicting the distal metastasis of the head and neck tumor after the training; and inputting a head and neck CT image of a head and neck tumor patient, which is shot in real time, into the network model, and outputting a result as far-end metastasis prediction of the head and neck CT image of the head and neck tumor patient. A radiomics method is adopted to replace a biopsy method to predict far-end metastasis of head and neck cancers, the pain that a head and neck patient suffers from multiple times of biopsy is avoided, a deep learning method is adopted to supplement a feature extraction algorithm of original radiomics, and the problem that the number of head and neck medical images is small is solved.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Biopsy methods and devices
Owner:INDICATOR SYST INT
Biopsy apparatus and biopsy method
ActiveUS20120289824A1Shorten the timeReduce in quantitySurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringBiopsy methodsRadiography
A biopsy apparatus has a biopsy needle, which faces a radiation reception surface of a radiation detector and is held obliquely to the radiation reception surface by a biopsy needle holding mechanism. The biopsy apparatus includes a radiographic image capturing apparatus for capturing two radiographic images. One of the two radiographic images is produced according to a scout image capturing mode or a stereographic image capturing mode, and the other is produced according to the stereographic image capturing mode.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Biopsy needle guiding apparatus for stereotactic biopsy, imaging apparatus having the same and biopsy method using the same
InactiveUS20150126851A1Rapidly and accurately detectShorten the timeSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsNeedle guideBiopsy methods
The present invention provides a biopsy needle guiding apparatus which makes it possible to precisely and rapidly perform stereotactic biopsy, an imaging apparatus having the same and a biopsy method using the same. The biopsy needle guiding apparatus includes a needle guiding apparatus body having a biopsy needle, and at least one X-ray source provided in the needle guiding apparatus body.
Owner:RAYENCE
CD44 targeting polypeptide and application thereof for preparing affinitive probe used for screening early gastric cancer
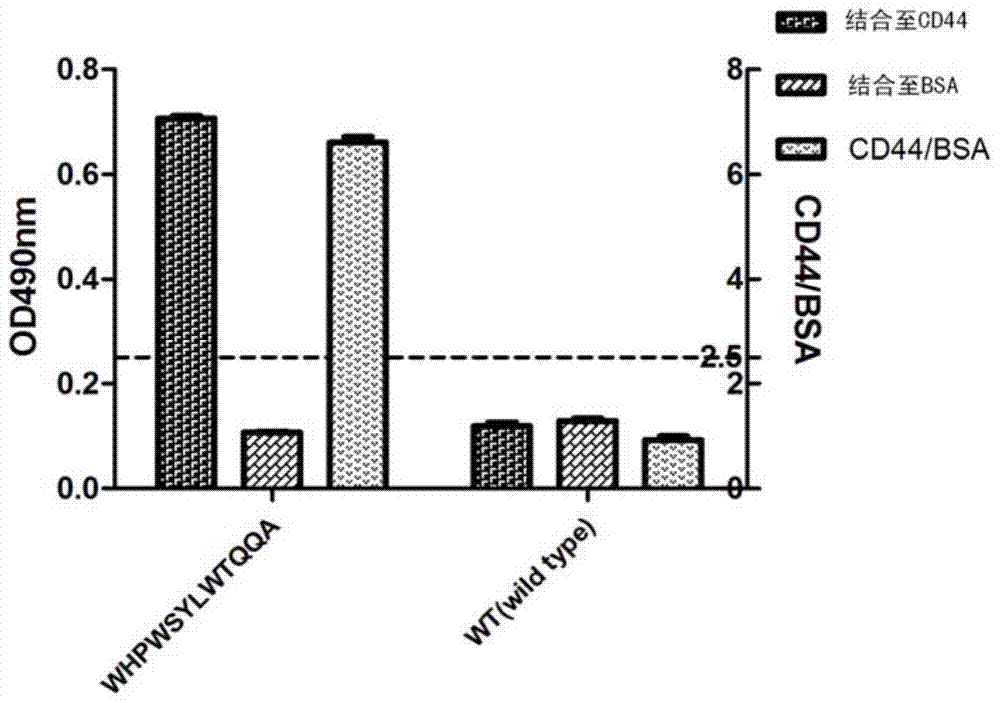
ActiveCN104327161AOvercoming suspicious lesionsHigh clinical application valuePeptidesBiological testingBiopsy methodsFluorescence
The invention provides a CD44 targeting polypeptide and an application thereof for preparing an affinitive probe used for screening early gastric cancer. The polypeptide includes an amino acid sequence of WHPWSY. The polypeptide can be specifically combined with a gastric cancer bio-labeled molecule CD44 and can be used as the affinitive probe with a common optical endoscope or a con-focal fluorescent micro-endoscope for achieving high-efficient screening of the gastric cancer. The CD44 targeting polypeptide overcomes a defect that only a random multi-point biopsy method can be employed in detection of a large-area gastric mucosa suspected lesion by a conventional optical endoscope. The CD44 targeting polypeptide can achieve early-stage, real-time and localized diagnosis in gastroscopy and is high in clinical application value.
Owner:赛特斯(海南)生物医学有限公司
Technique for heart disease external differentiation therapy by utilizing stem cells of masticatory muscles and orbicularis oculi muscles
InactiveCN102703382AArtificial cell constructsUnknown materialsCoronary artery guide catheterNon invasive
The invention belongs to the field of adult stem cells and regenerative medicine, and relates to the techniques of adult stem cell extraction, external expansion and differentiation induction as well as stem cell transplantation. The techniques are based on the theory that head and facial masticatory muscles have the same origin with cardiac progenitor cells. As shown by the analysis on the genetic expression, cardiac muscle genes Nk*2.5 and Isl1 in the masticatory muscle stem cells have expressions of different degrees. The techniques utilize that the masticatory muscle stem cells have the characteristics of the cardiac muscle stem cells, collect a masticatory muscle sample by the non-invasive biopsy method, and externally expands the masticatory muscle stem cells by the suspension culture method; and non-coding micro RNA (ribonucleic acid) is adopted to change the masticatory muscle stem cells and facilitate differentiation and purification of the masticatory muscle stem cells into the heart muscle cells. The transplantation of the purified cardiac muscle cells to a part with myocardial infarction is performed by means of the coronary artery duct injection or the cell membrane technique (the cell membrane is placed on the surface of myocardial infarction organization), so that the myocardial infarction or the ischemic heart disease can be cured.
Owner:珠海霍普金斯医药研究院股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com