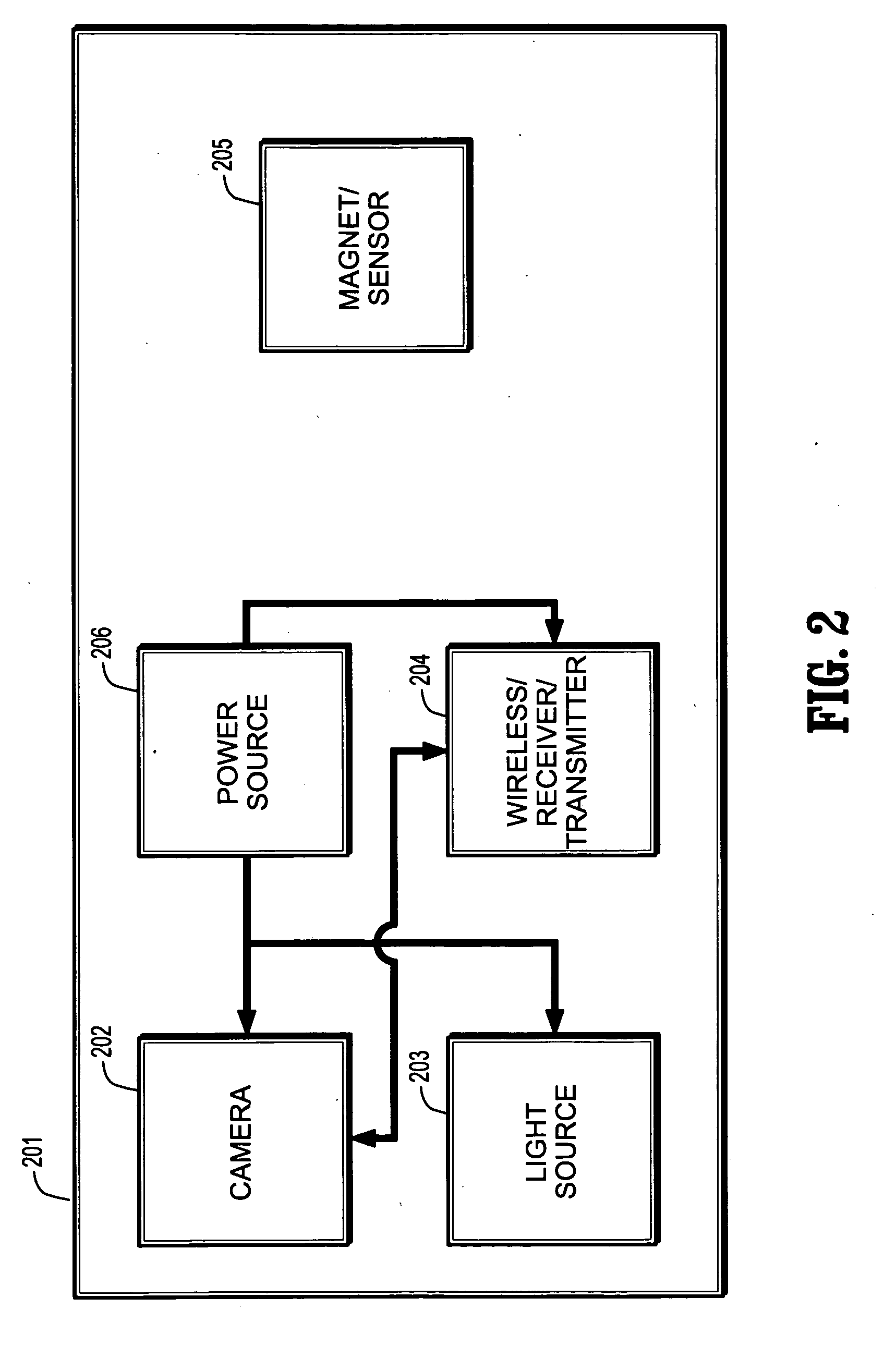
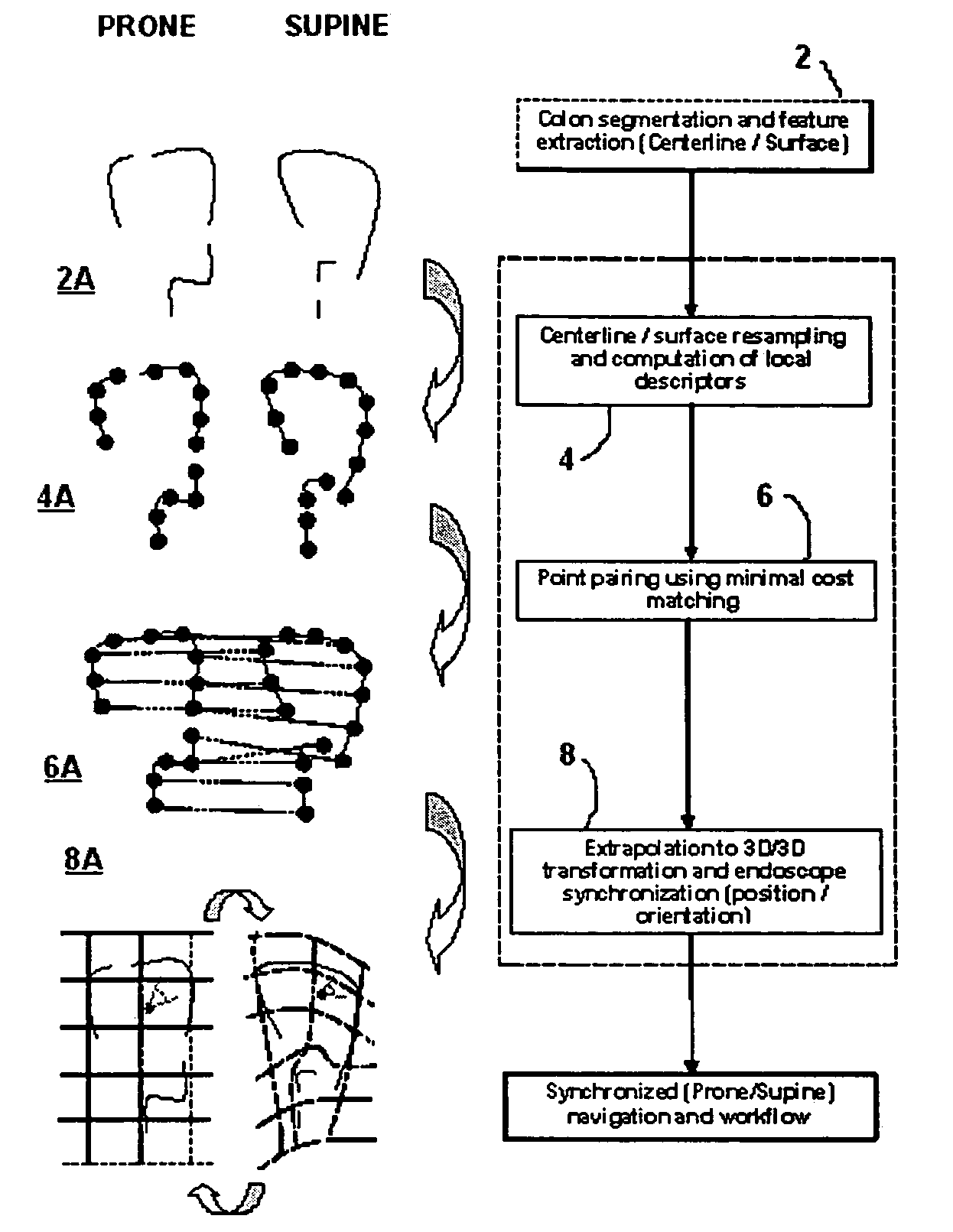
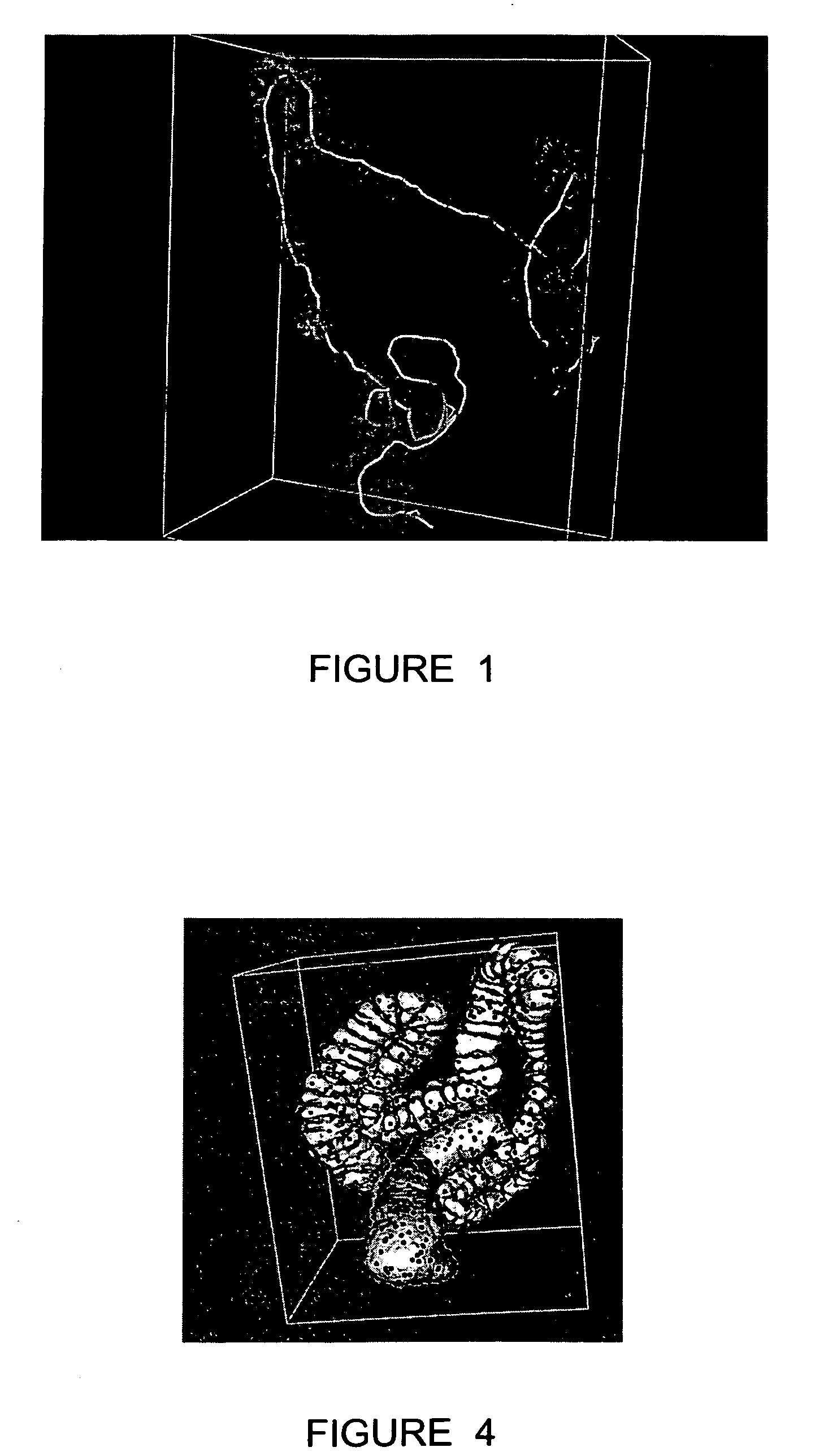
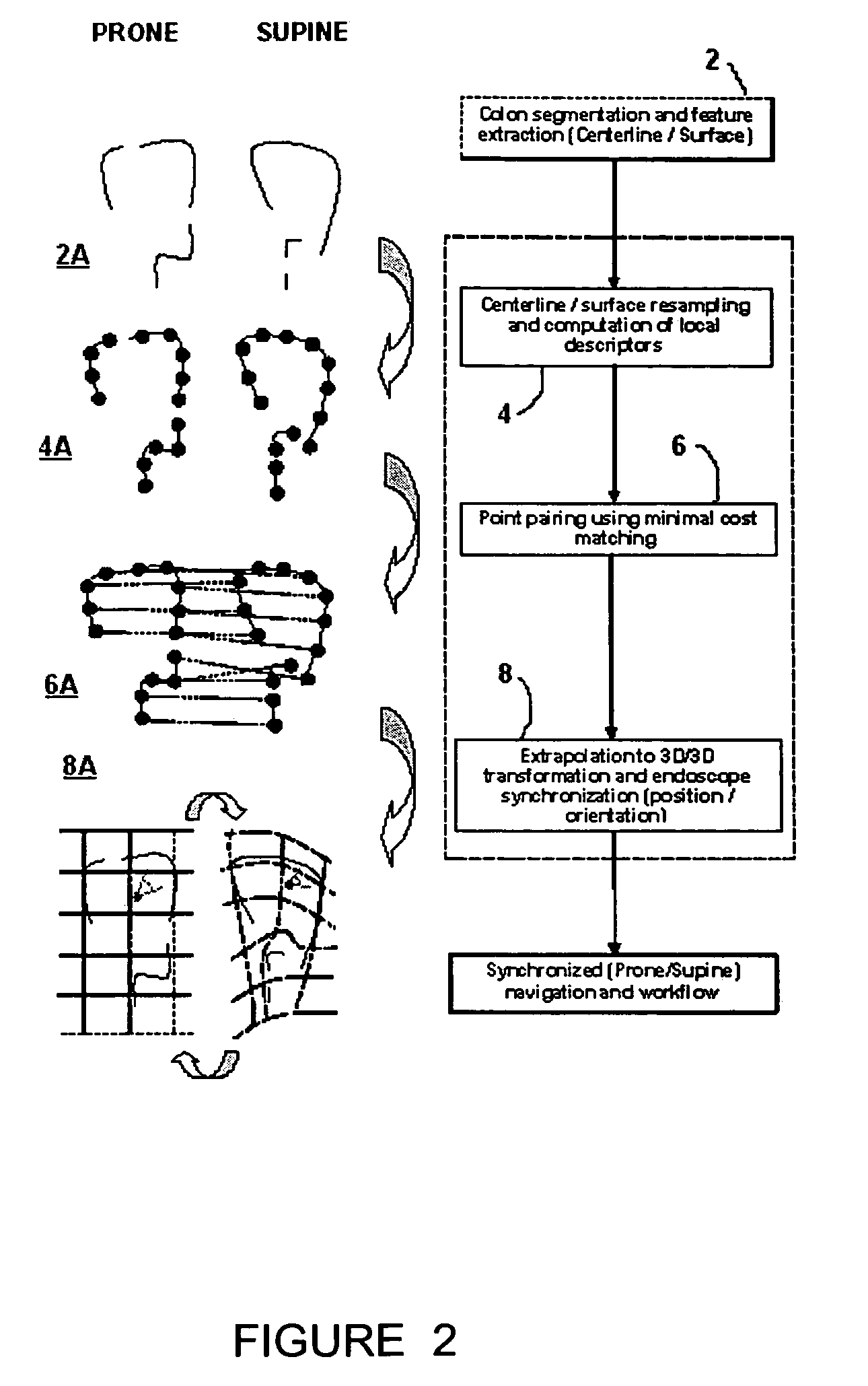
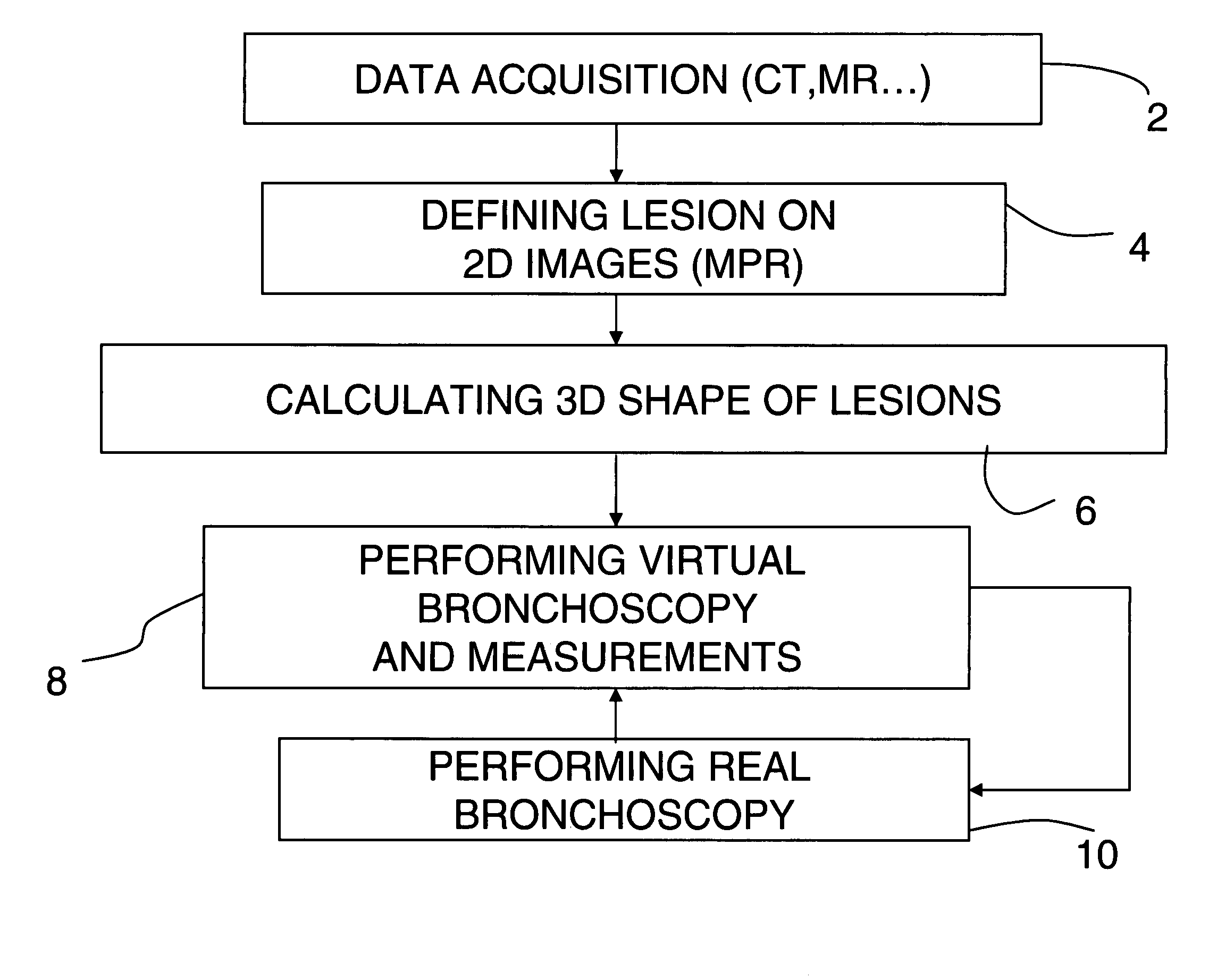
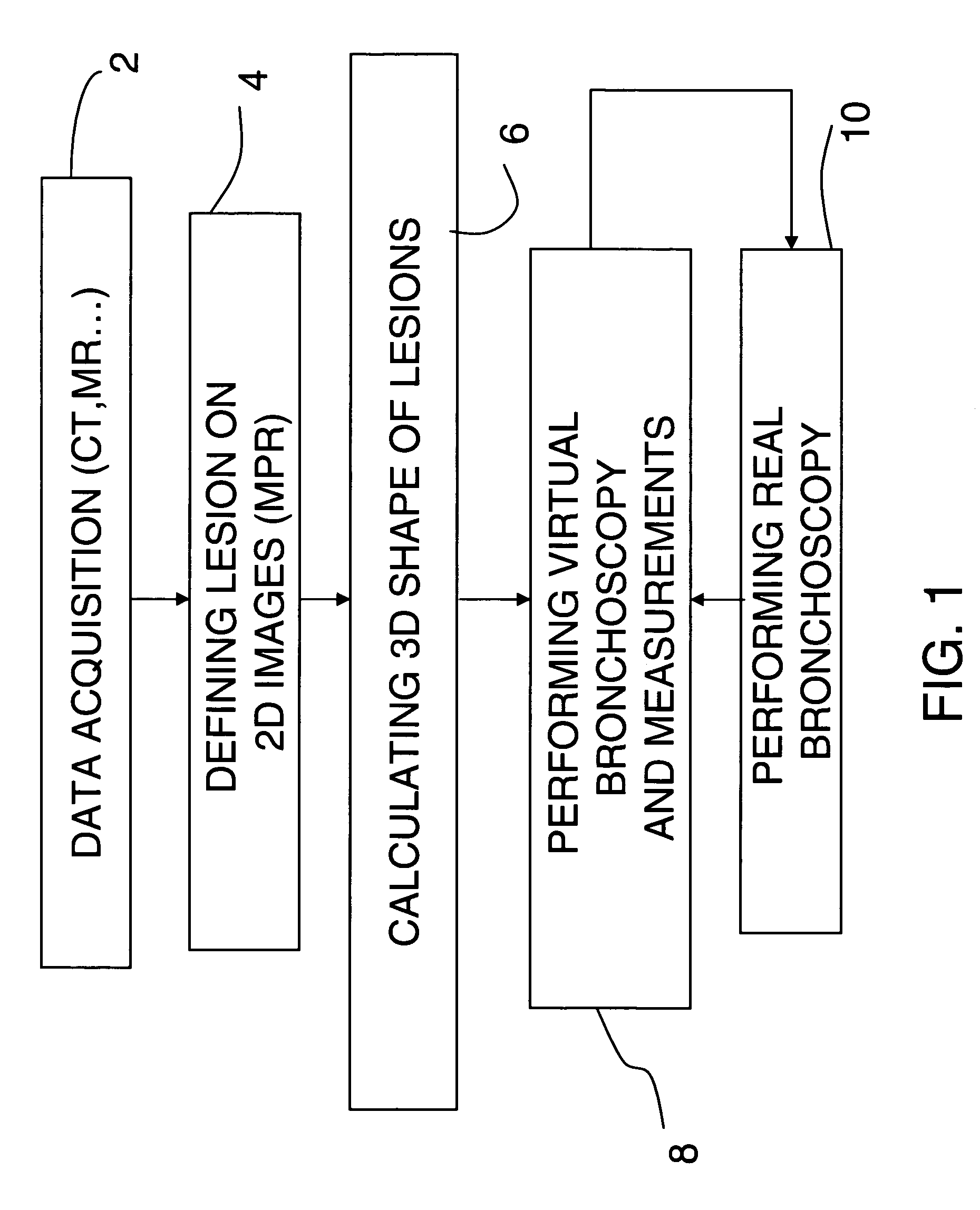
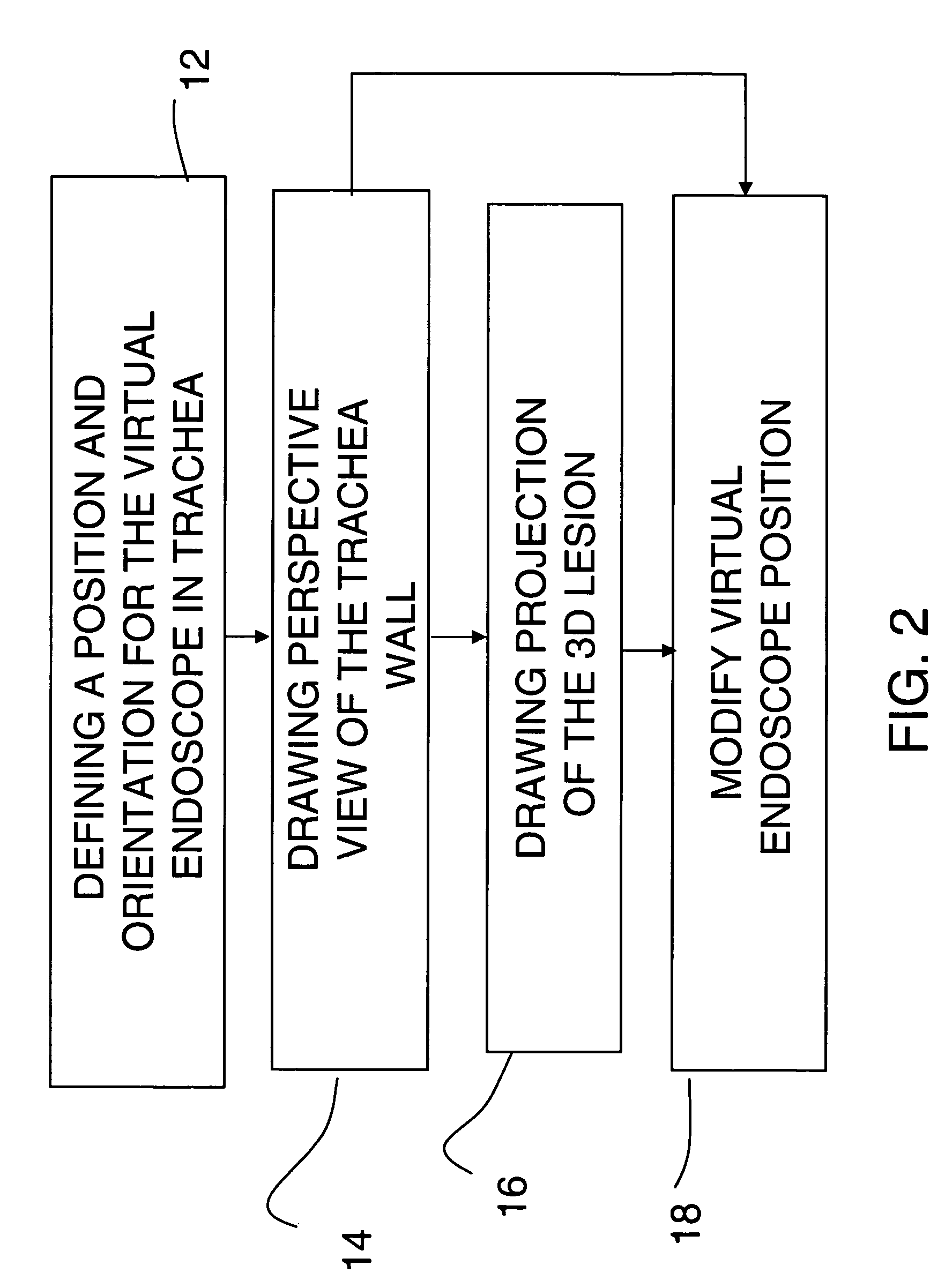
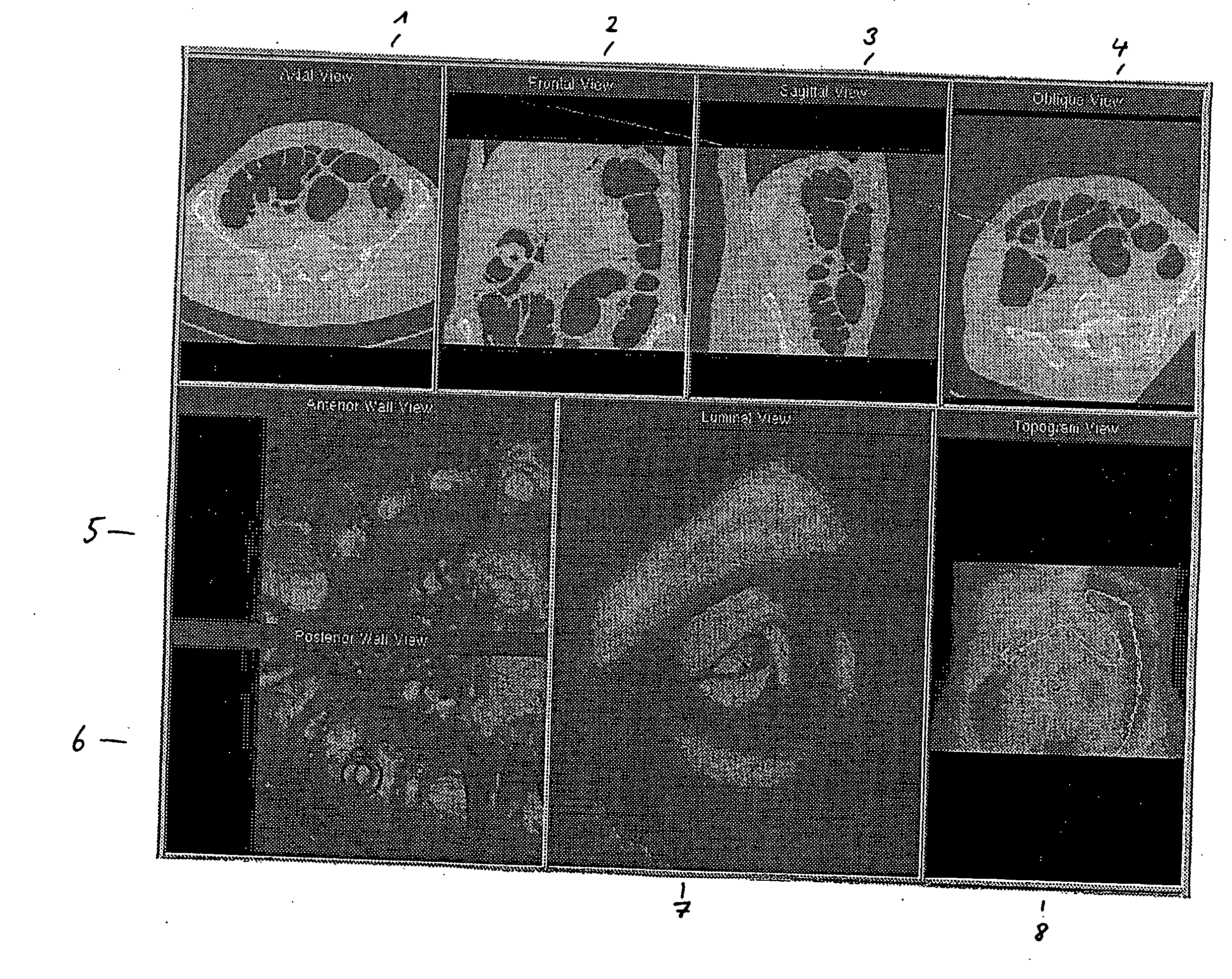
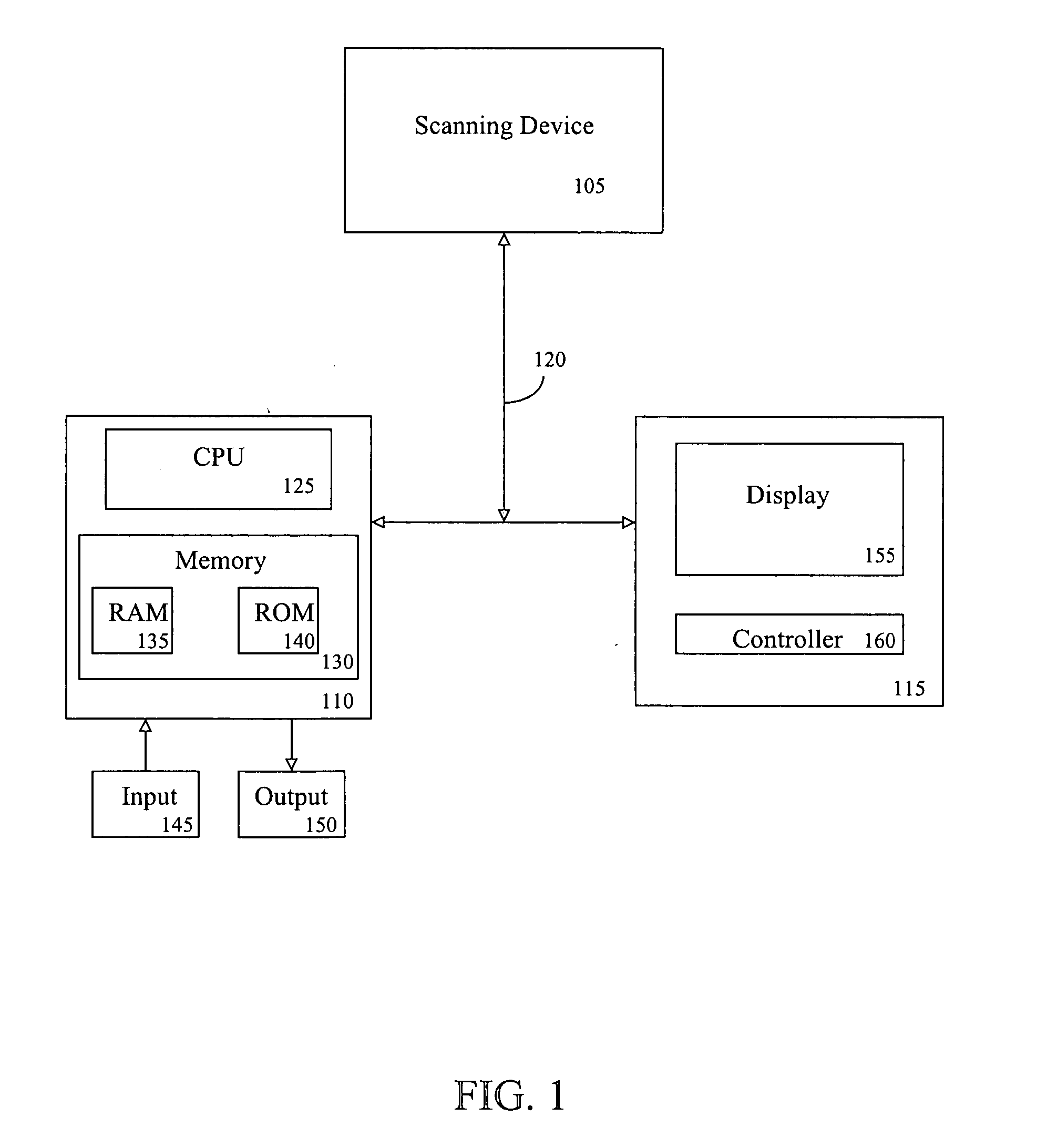
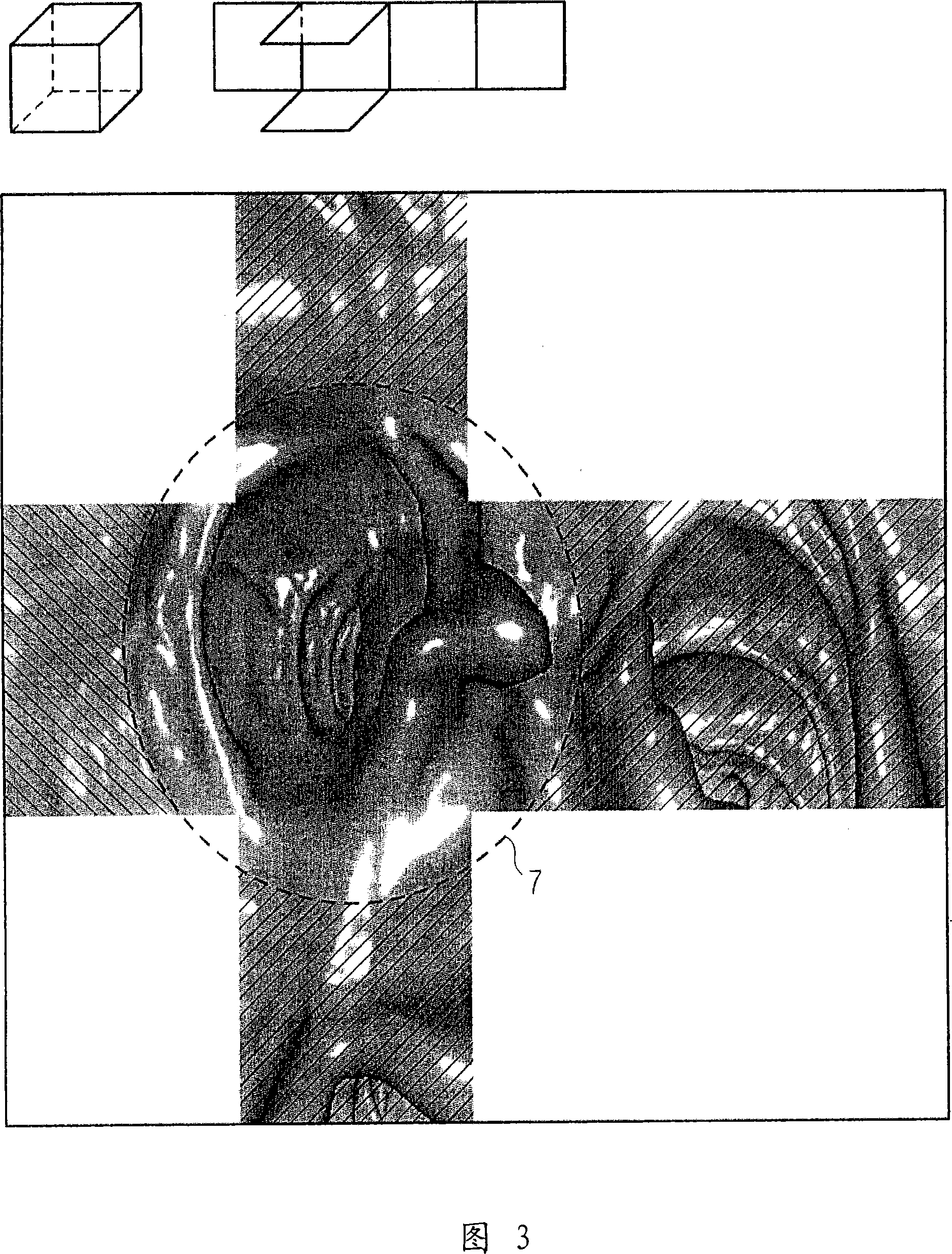Patents
Literature
53 results about "Virtual endoscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
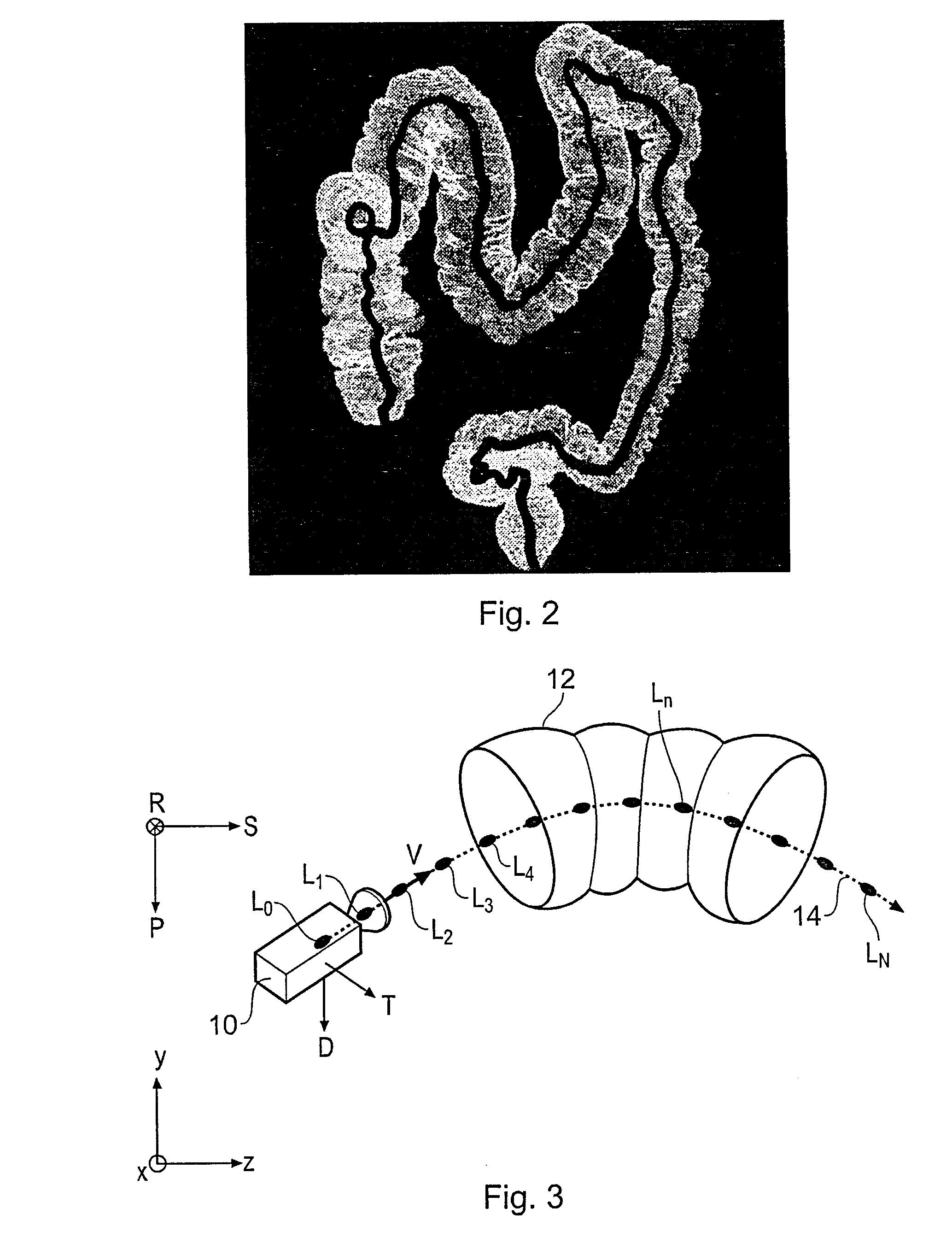
Virtual endoscopy. an imaging technique in which cross-sectional images acquired by computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are processed by computer to reconstruct a three-dimensional display similar to that seen through an endoscope.
Method for virtual endoscopic visualization of the colon by shape-scale signatures, centerlining, and computerized detection of masses
InactiveUS20050152588A1Enhancing endoscopic visualizationEasy detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionData set
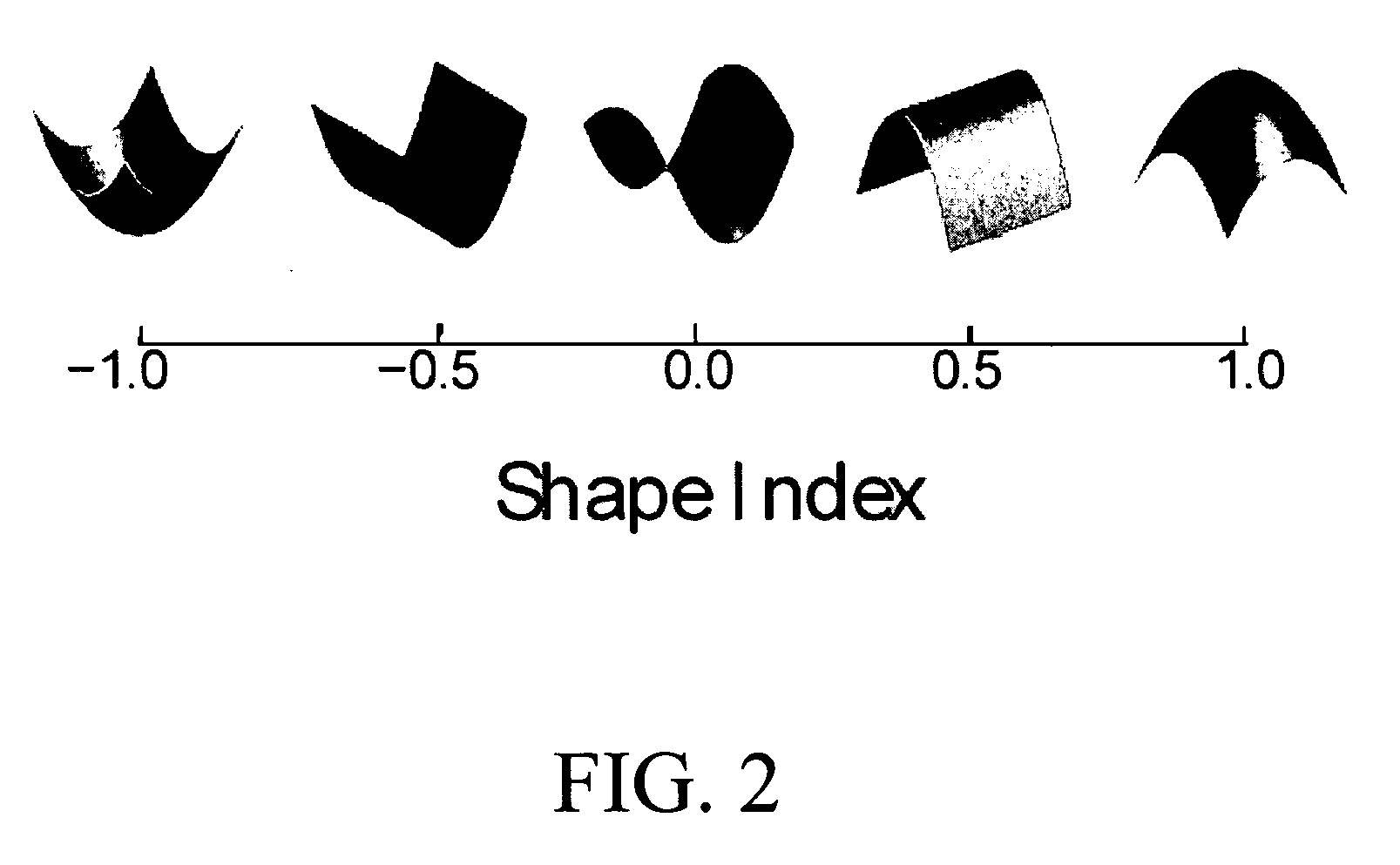
A visualization method and system for virtual endoscopic examination of CT colonographic data by use of shape-scale analysis. The method provides each colonic structure of interest with a unique color, thereby facilitating rapid diagnosis of the colon. Two shape features, called the local shape index and curvedness, are used for defining the shape-scale spectrum. The shape index and curvedness values within CT colonographic data are mapped to the shape-scale spectrum in which specific types of colonic structures are represented by unique characteristic signatures in the spectrum. The characteristic signatures of specific types of lesions can be determined by use of computer-simulated lesions or by use of clinical data sets subjected to a computerized detection scheme. The signatures are used for defining a 2-D color map by assignment of a unique color to each signature region.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Virtual endoscopy with improved image segmentation and lesion detection
InactiveUS7747055B1Exact matchAccurate representationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementBody organsLesion detection
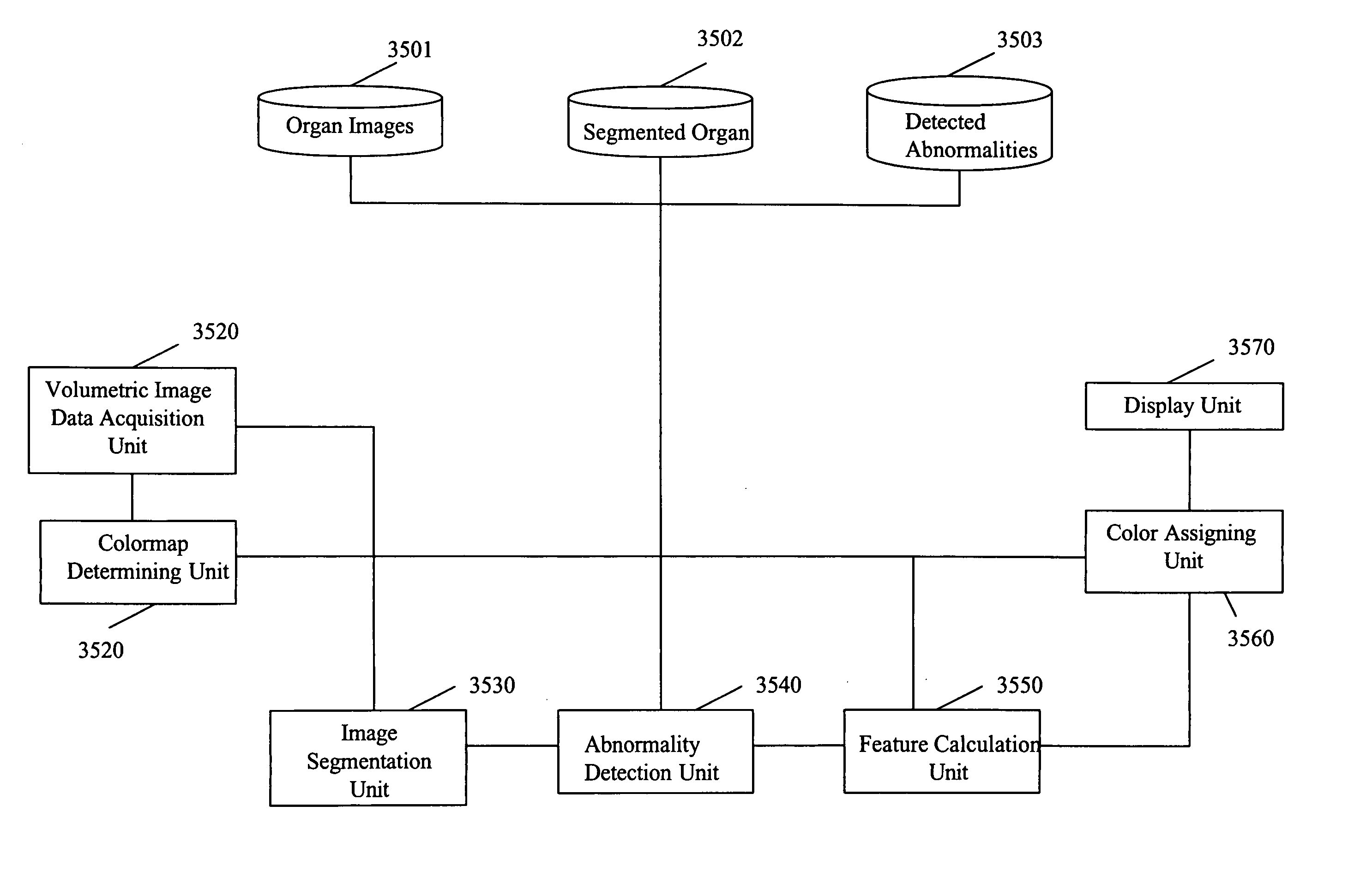
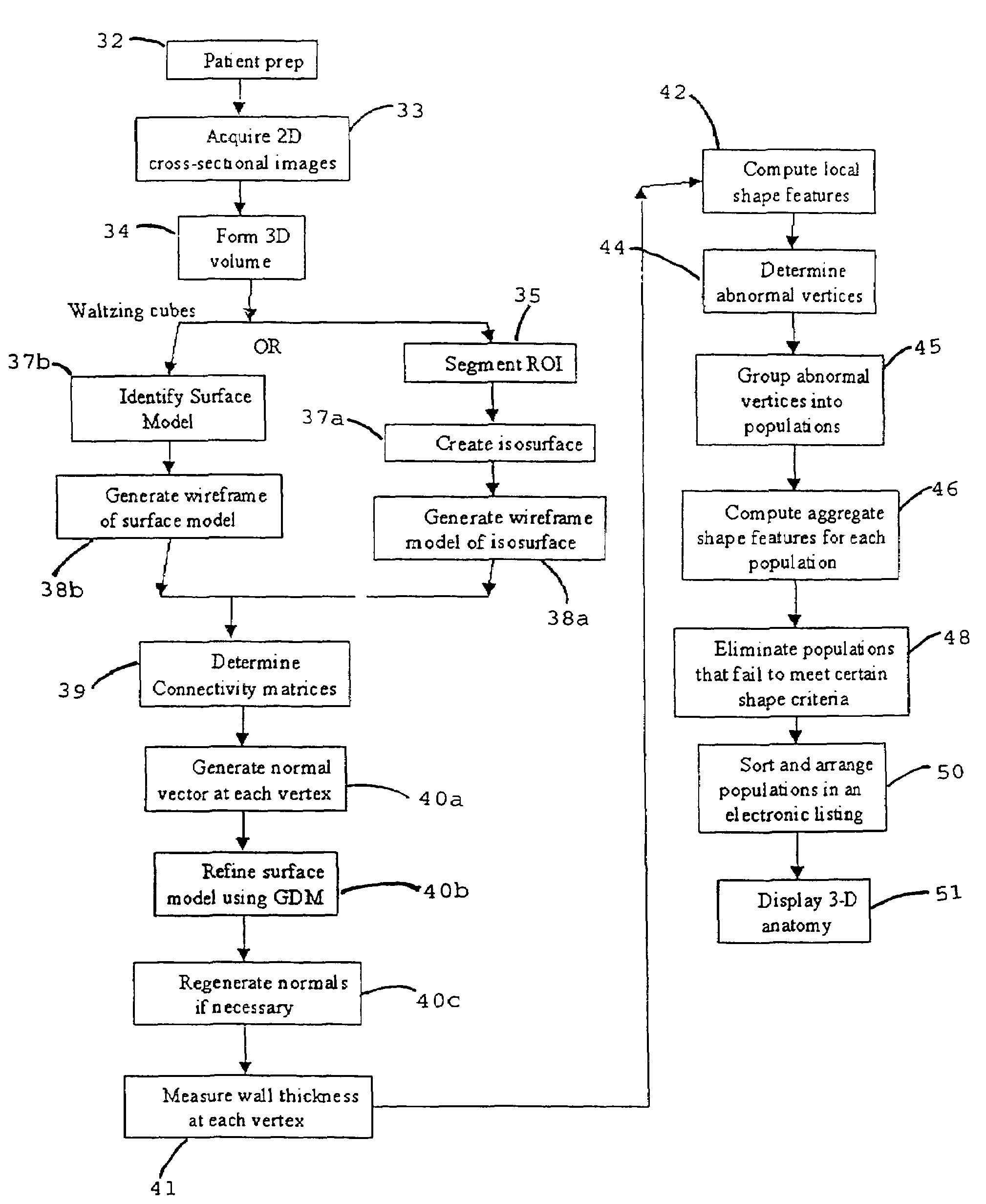
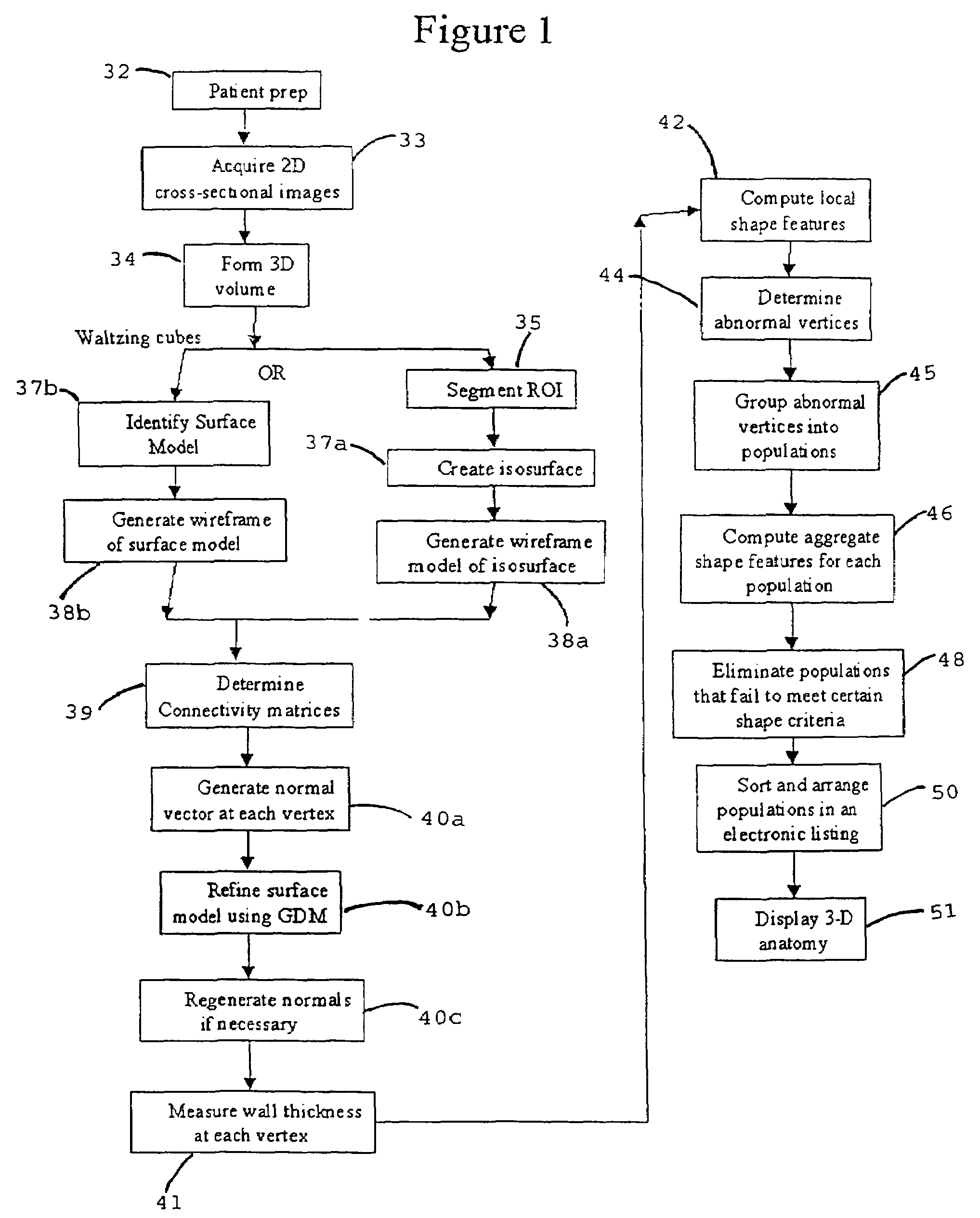
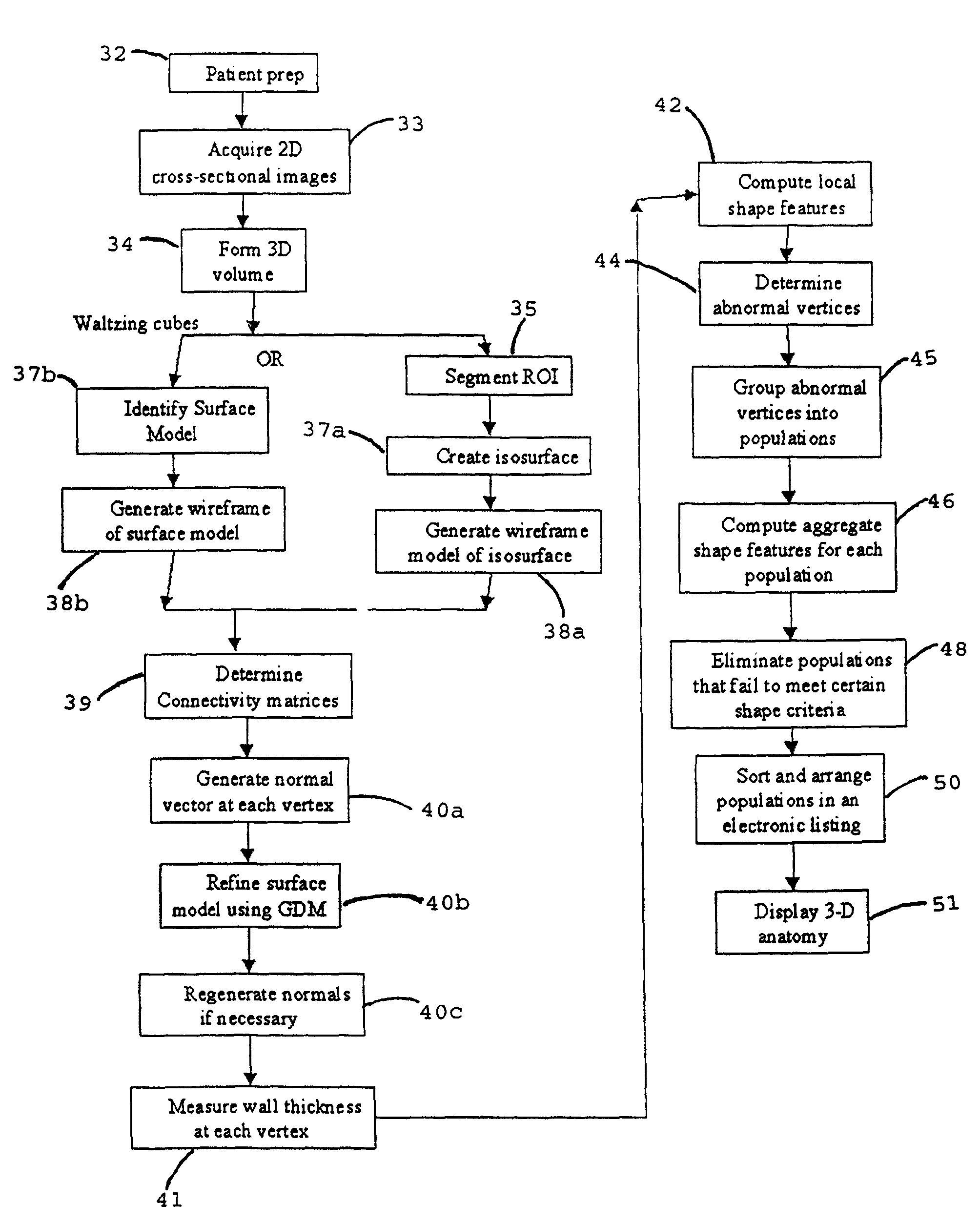
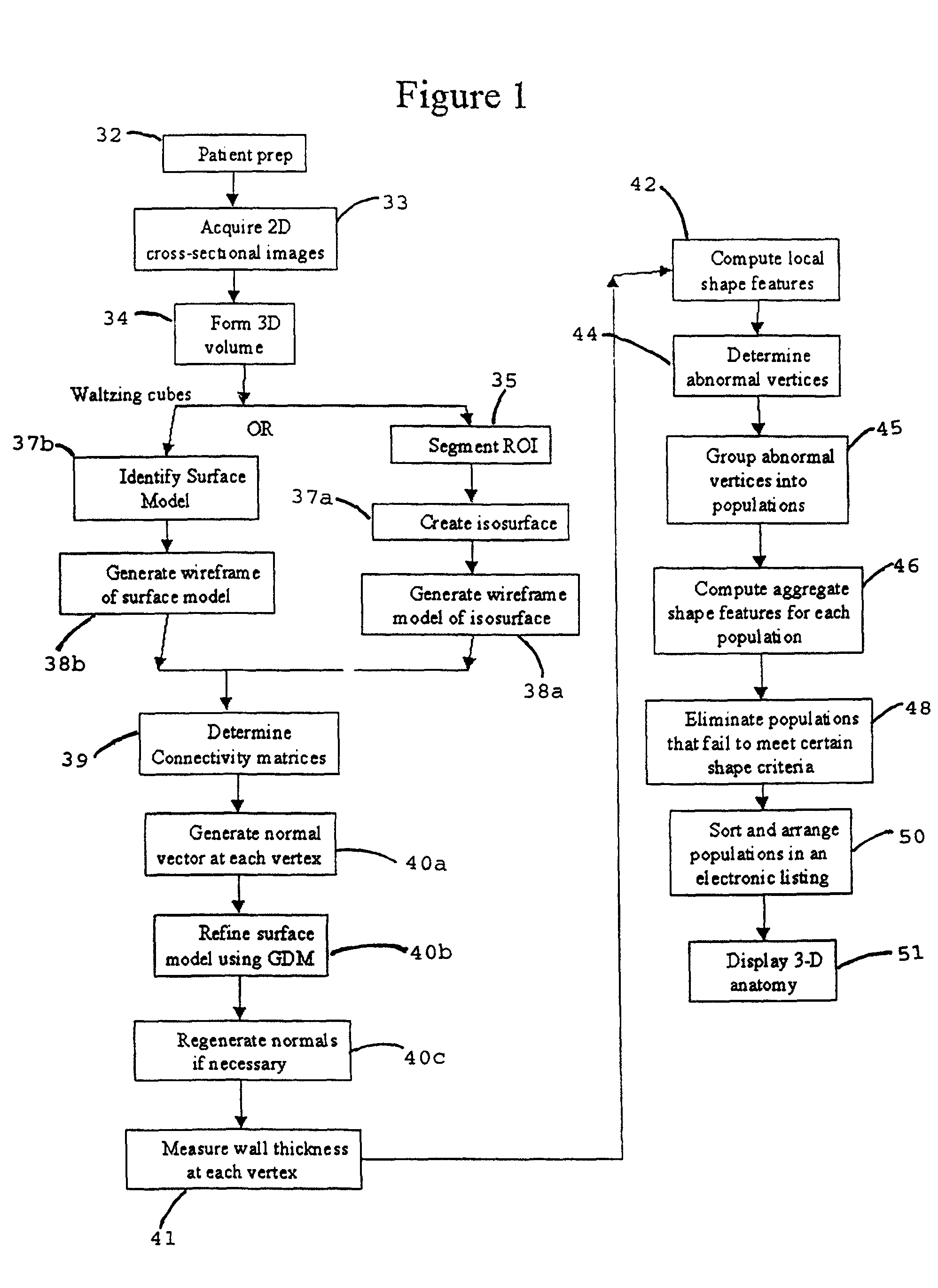
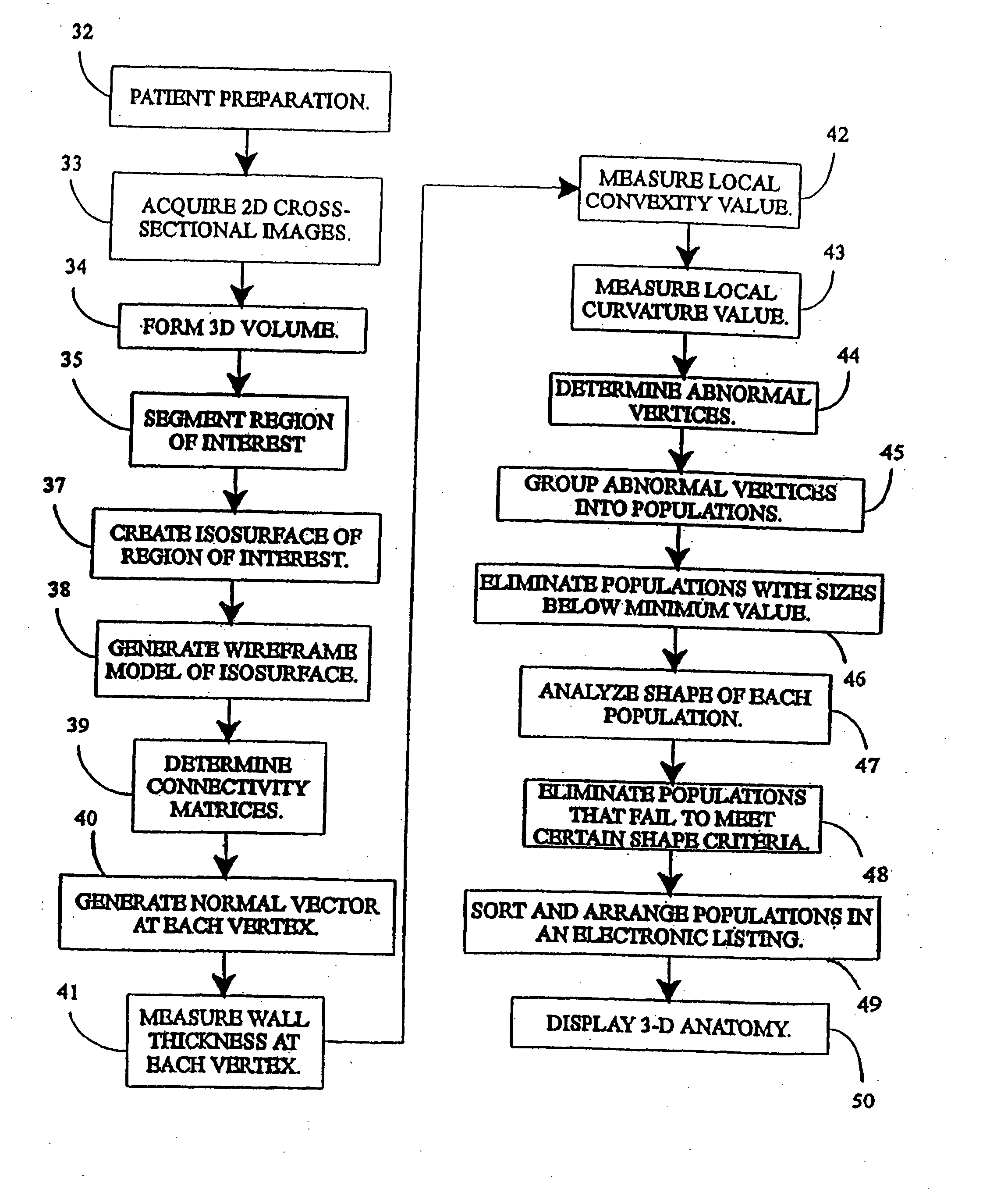
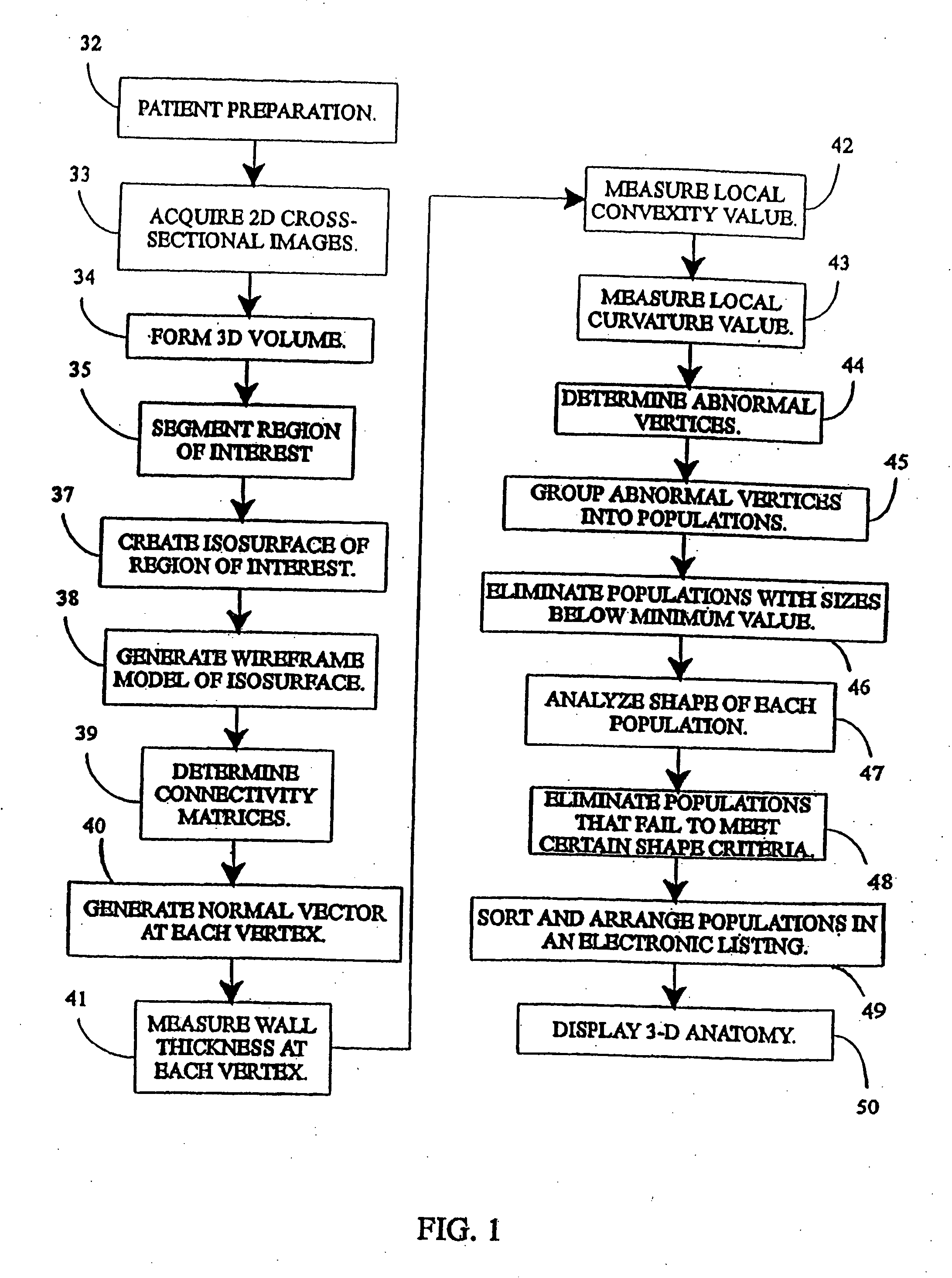
A system, and computer implemented method are provided for interactively displaying three-dimensional structures. Three-dimensional volume data (34) is formed from a series of two-dimensional images (33) representing at least one physical property associated with the three-dimensional structure, such as a body organ having a lumen. A wire frame model of a selected region of interest is generated (38b). The wireframe model is then deformed or reshaped to more accurately represent the region of interest (40b). Vertices of the wire frame model may be grouped into regions having a characteristic indicating abnormal structure, such as a lesion. Finally, the deformed wire frame model may be rendered in an interactive three-dimensional display.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Virtual endoscopy
InactiveUS20080118117A1Full effectImproved angular separationSurgeryEndoscopesData setVirtual camera
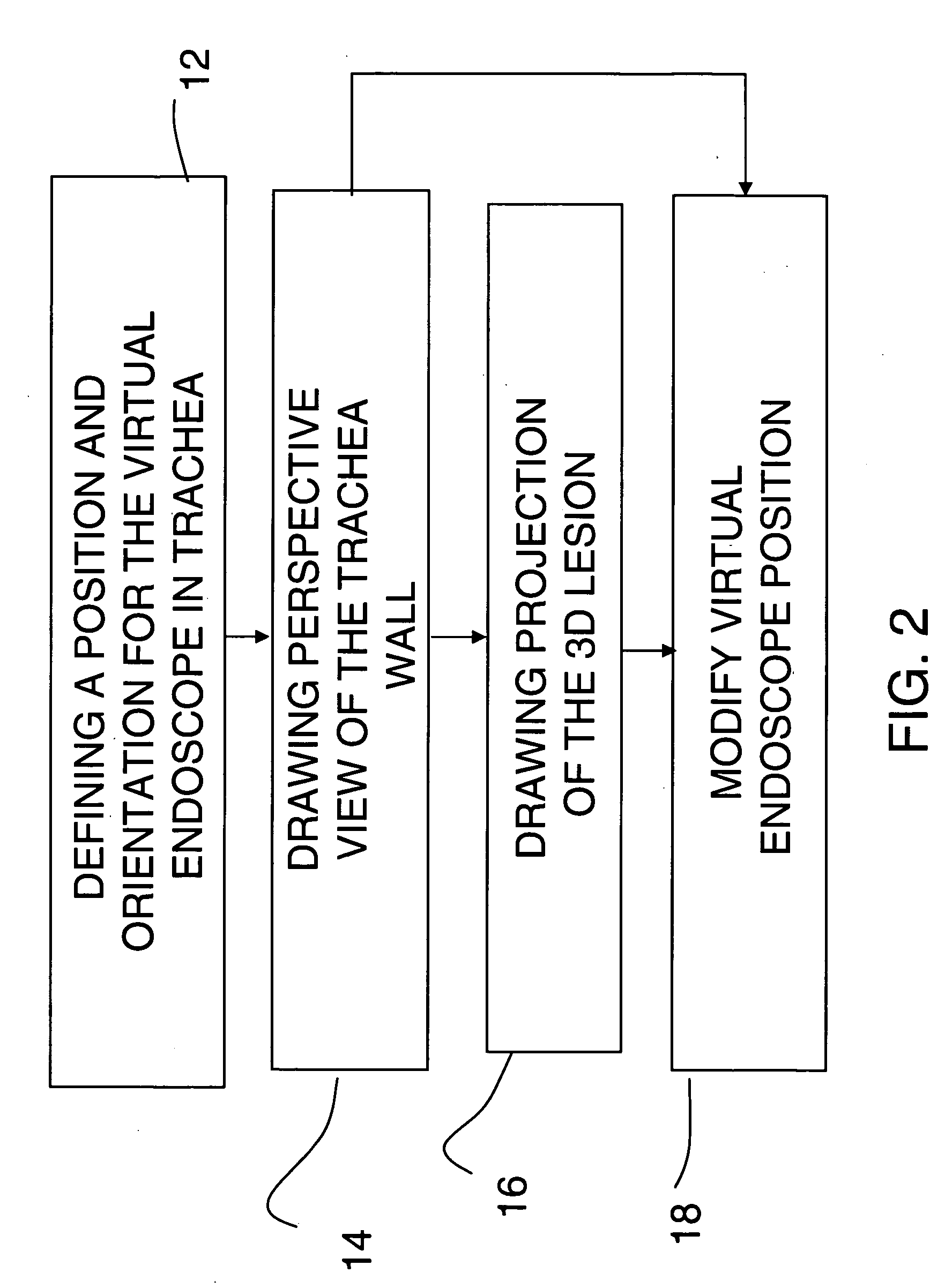
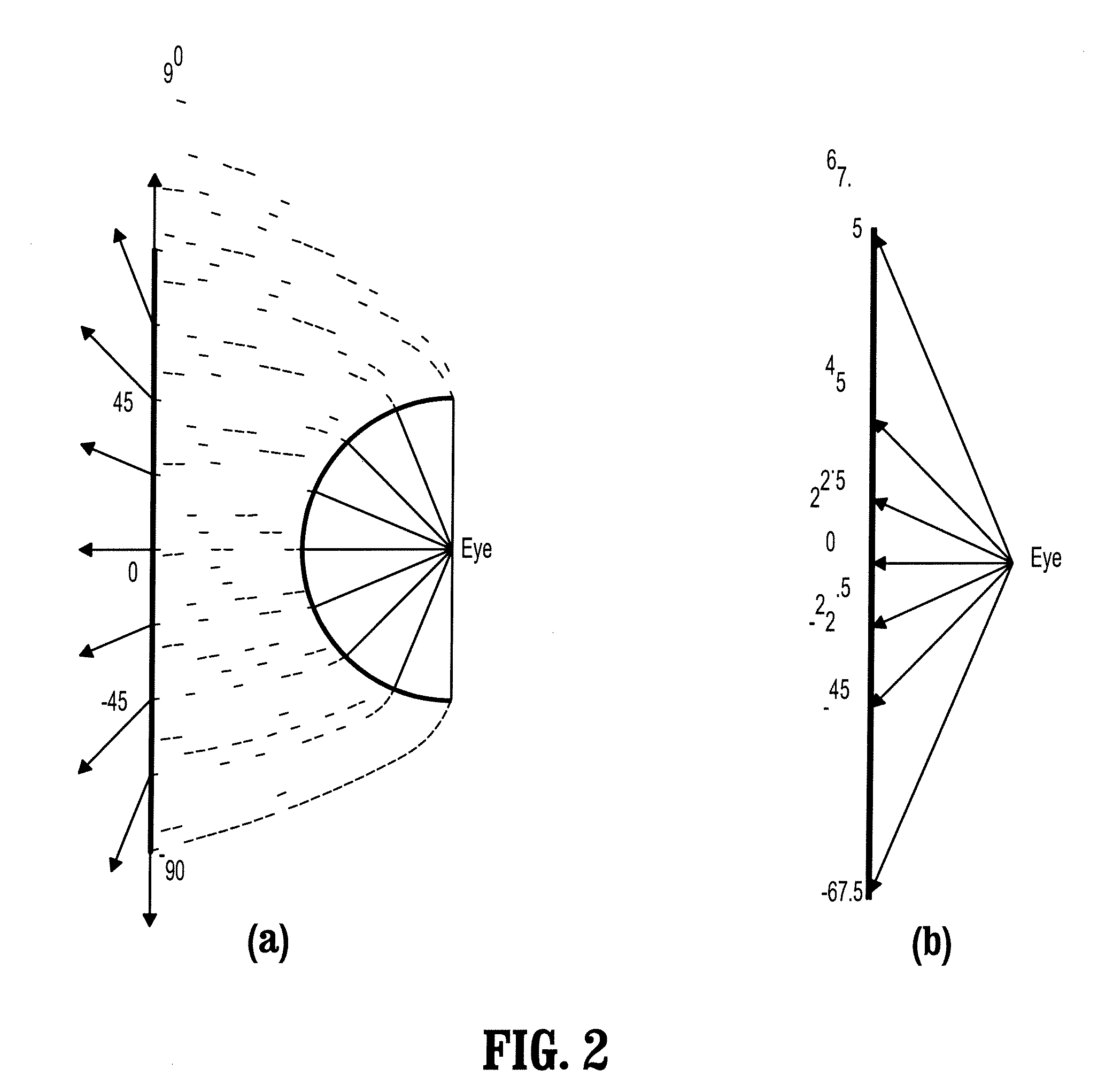
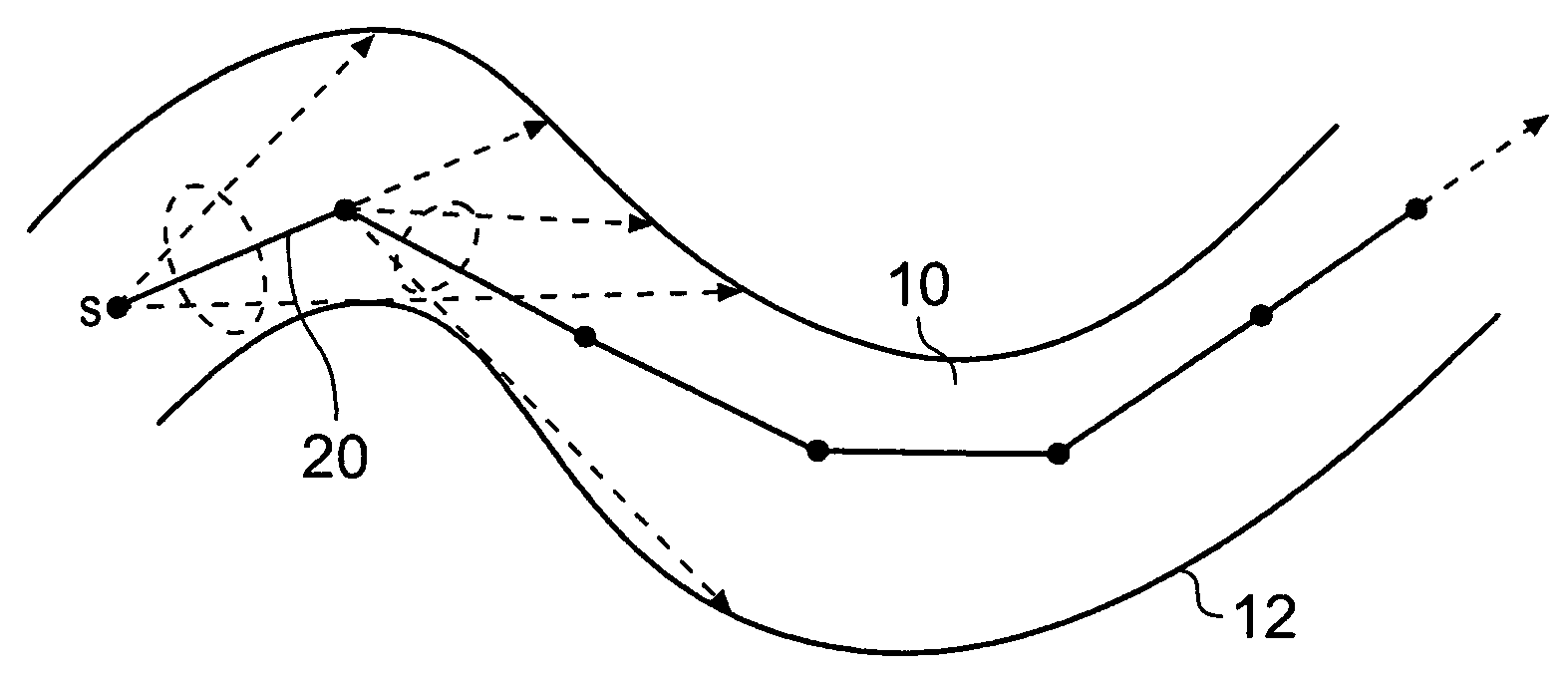
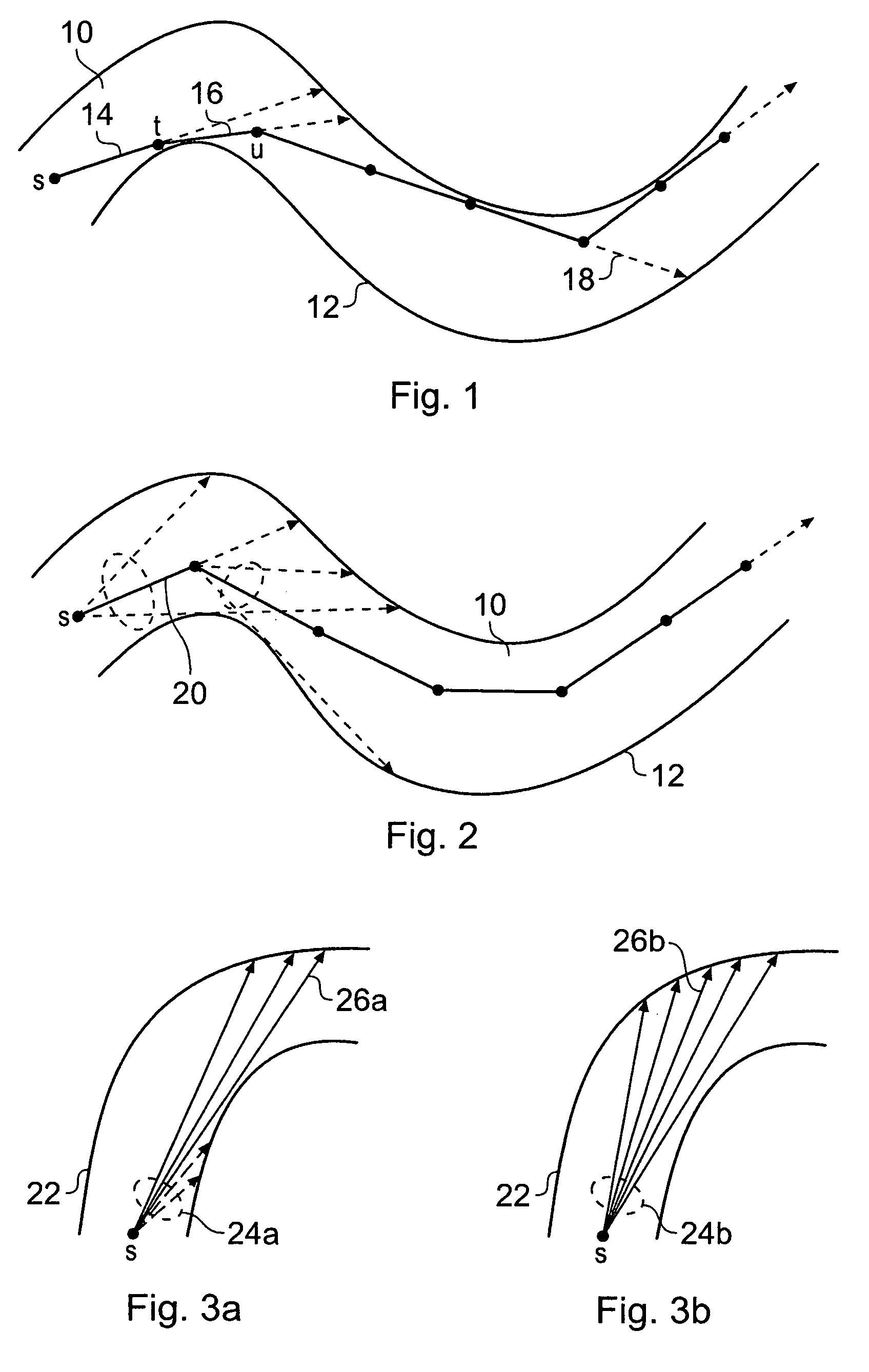
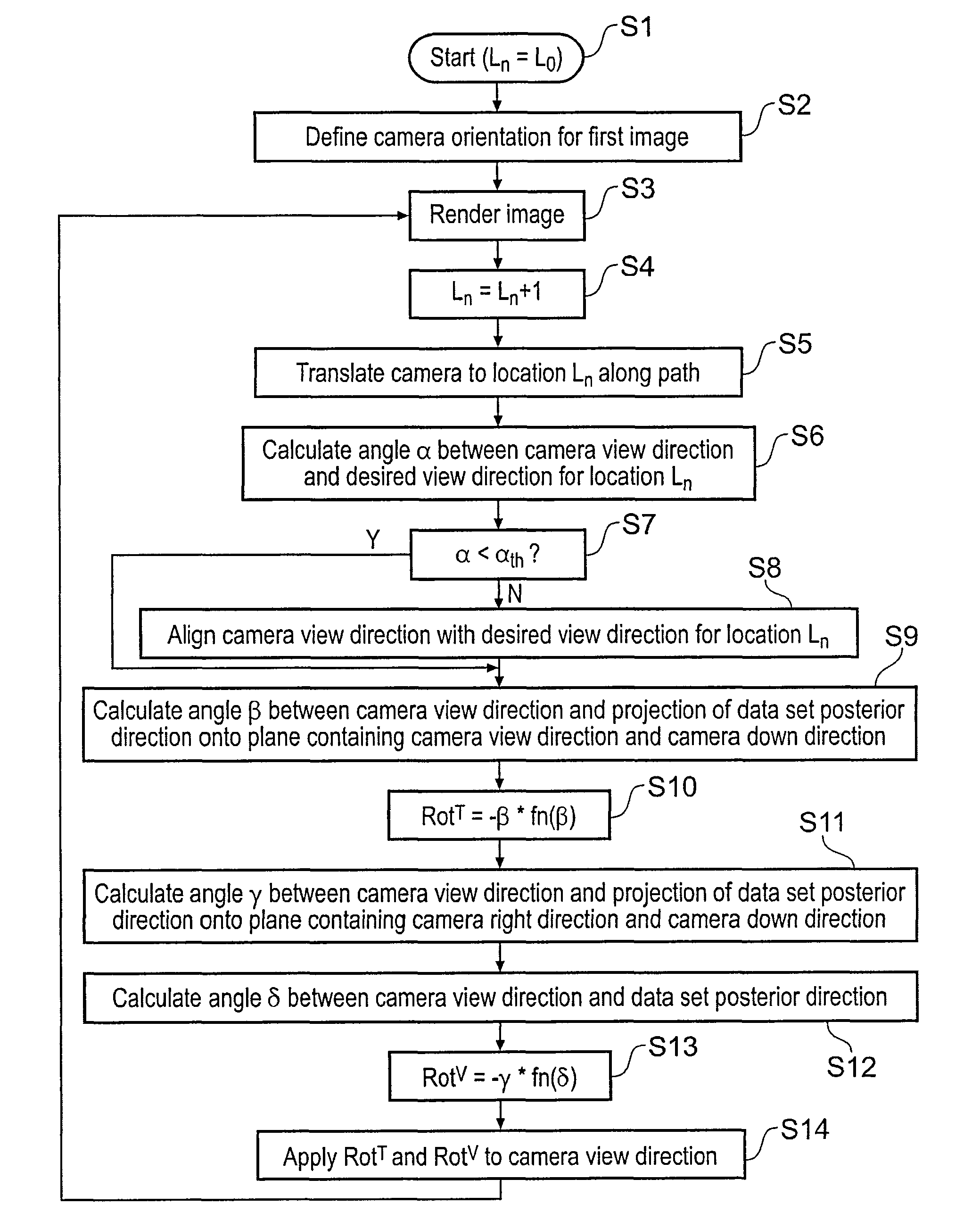
A method of orienting a virtual camera for rendering a virtual endoscopy image of a lumen in a biological structure represented by a medical image data set, e.g., a colon. The method comprises selecting a location from which to render an image, determining an initial orientation for the virtual camera relative to the data set for the selected location based on the geometry of the lumen, determining an offset angle between the initial orientation and a bias direction; and orienting the virtual camera in accordance with a rotation from the initial orientation towards the bias direction by a fractional amount of the offset angle which varies according to the initial orientation. The fractional amount may vary according to the offset angle and / or a separation between a predetermined direction in the data set and a view direction of the virtual camera for the initial orientation. Thus the camera orientation can be configured to tend towards a preferred direction in the data set, while maintaining a good view of the lumen and avoiding barrel rolling effects.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
Virtual Endoscopy with Improved Image Segmentation and Lesion Detection
InactiveUS20100265251A1Exact matchAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisBody organsLesion detection
A system, and computer implemented method are provided for interactively displaying three-dimensional structures. Three-dimensional volume data (34) is formed from a series of two-dimensional images (33) representing at least one physical property associated with the three-dimensional structure, such as a body organ having a lumen. A wire frame model of a selected region of interest is generated (38b). The wireframe model is then deformed or reshaped to more accurately represent the region of interest (40b). Vertices of the wire frame model may be grouped into regions having a characteristic indicating abnormal structure, such as a lesion. Finally, the deformed wire frame model may be rendered in an interactive three-dimensional display.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
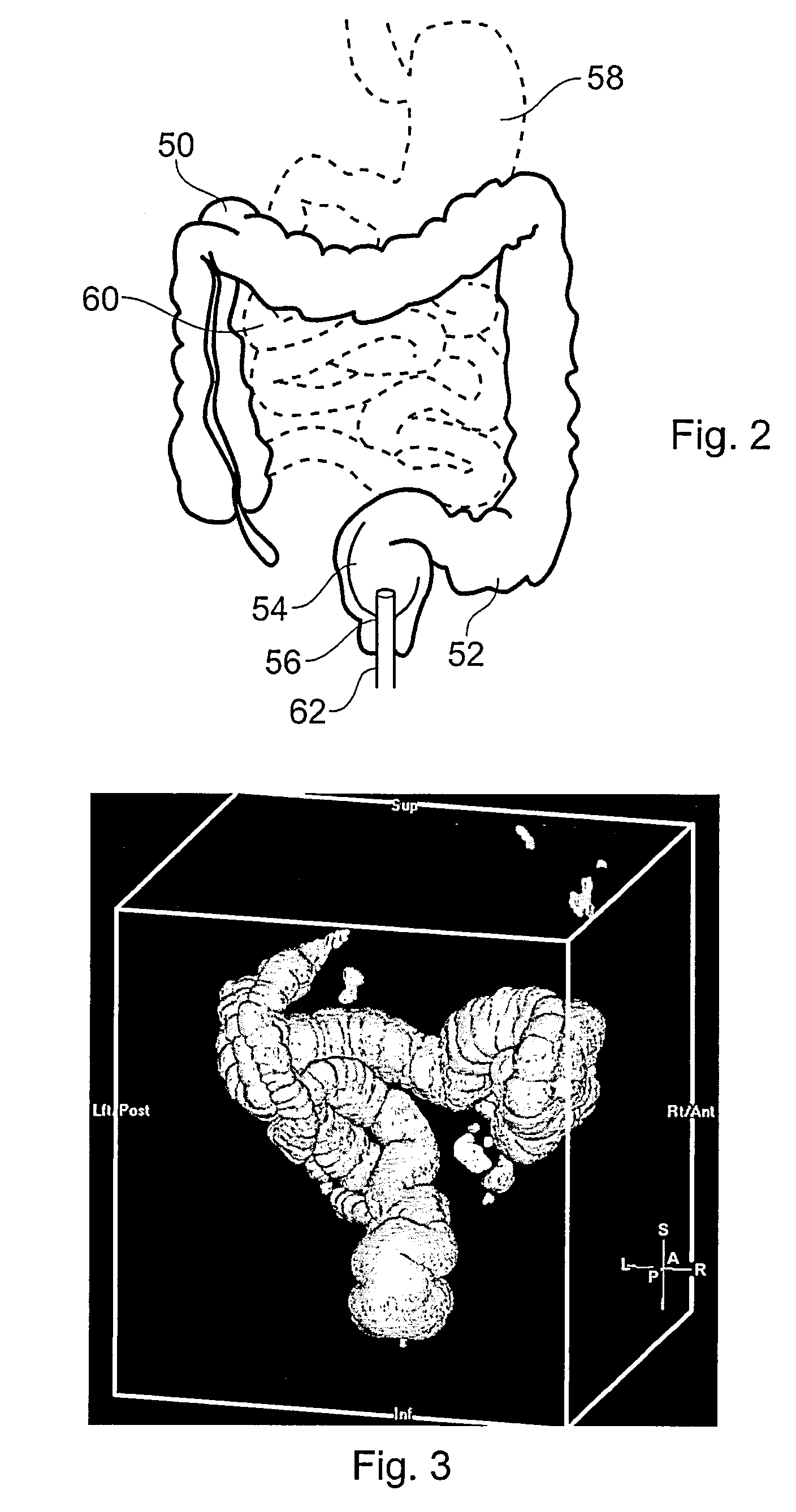
Method and system for virtual endoscopy with guidance for biopsy
InactiveUS20060084860A1Increase choiceHigh sensitivityStatic indicating devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsData setInsertion point
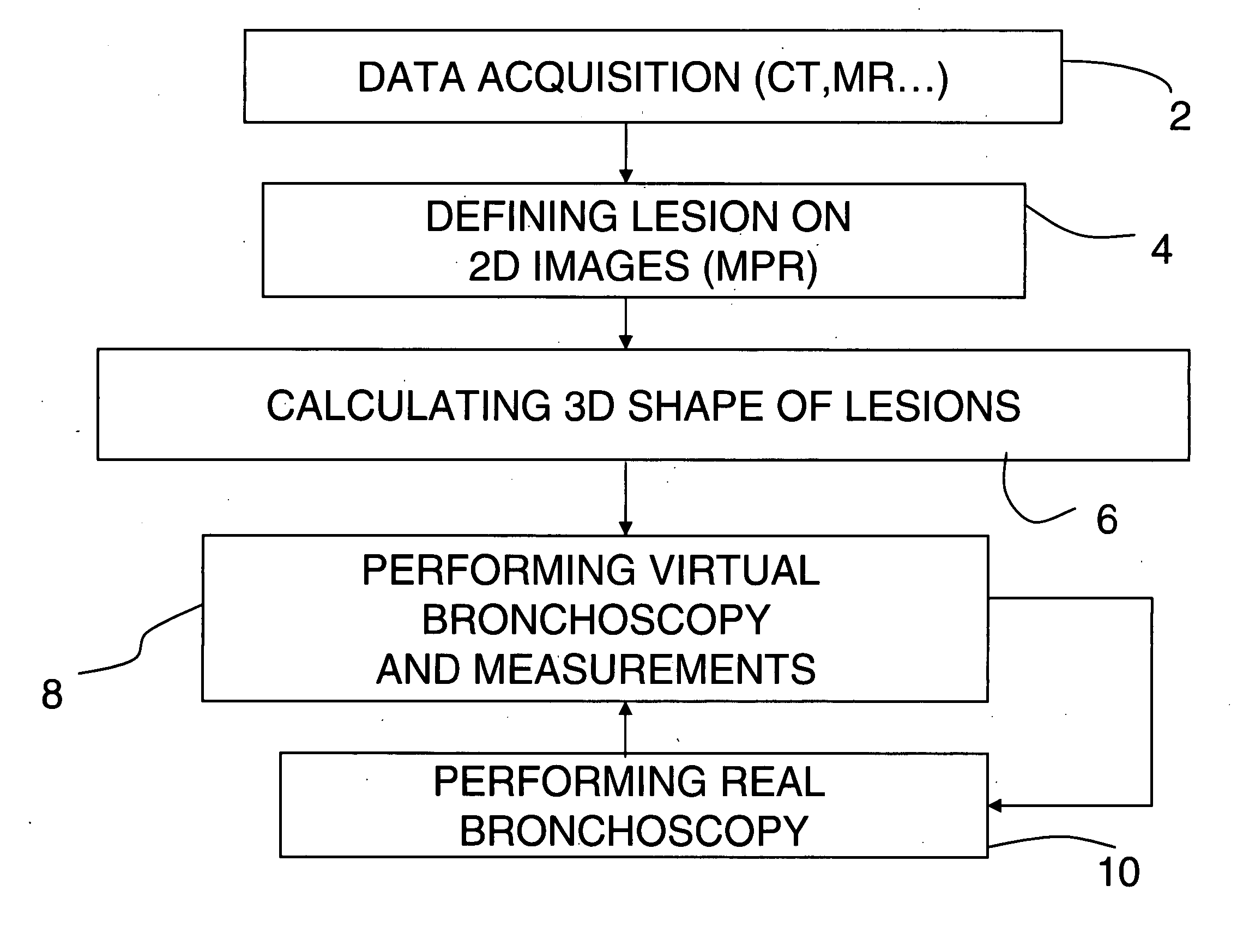
A method for virtual endoscopy in a lumen includes acquiring from a patient an imaging dataset exhibiting a lesion external to a lumen wall; deriving a three-dimensional (3-D) volume of the lesion; obtaining data on maximum bend characteristics for a given endoscope; and deriving projection criteria, based on the 3-D volume and the maximum bend, for projecting an endoluminal image of said lesion, indicating an optimal biopsy insertion point.
Owner:CHARITE UNIVS MEDIZIN BERLIN +1
Method for navigating a virtual camera along a biological object with a lumen
ActiveUS20070052724A1Shorten the lengthEasy to viewSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionData setVirtual camera
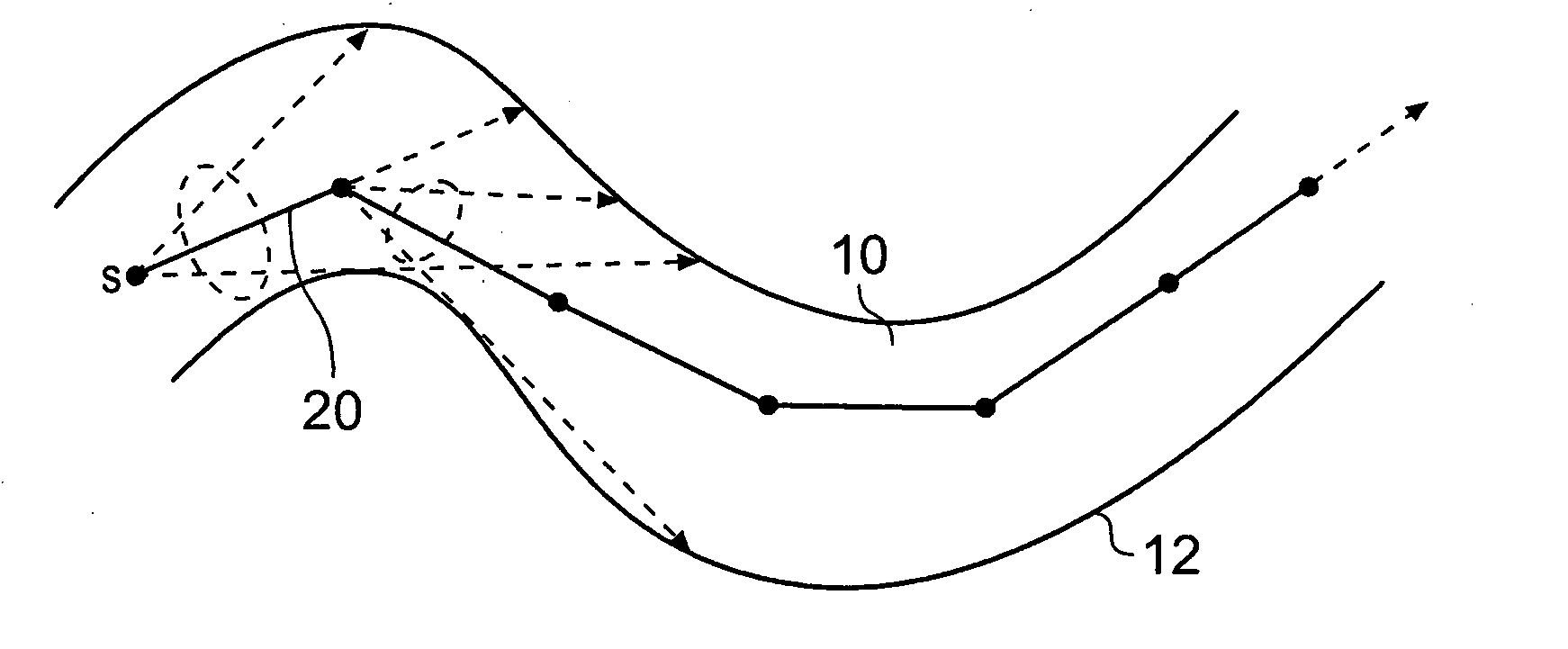
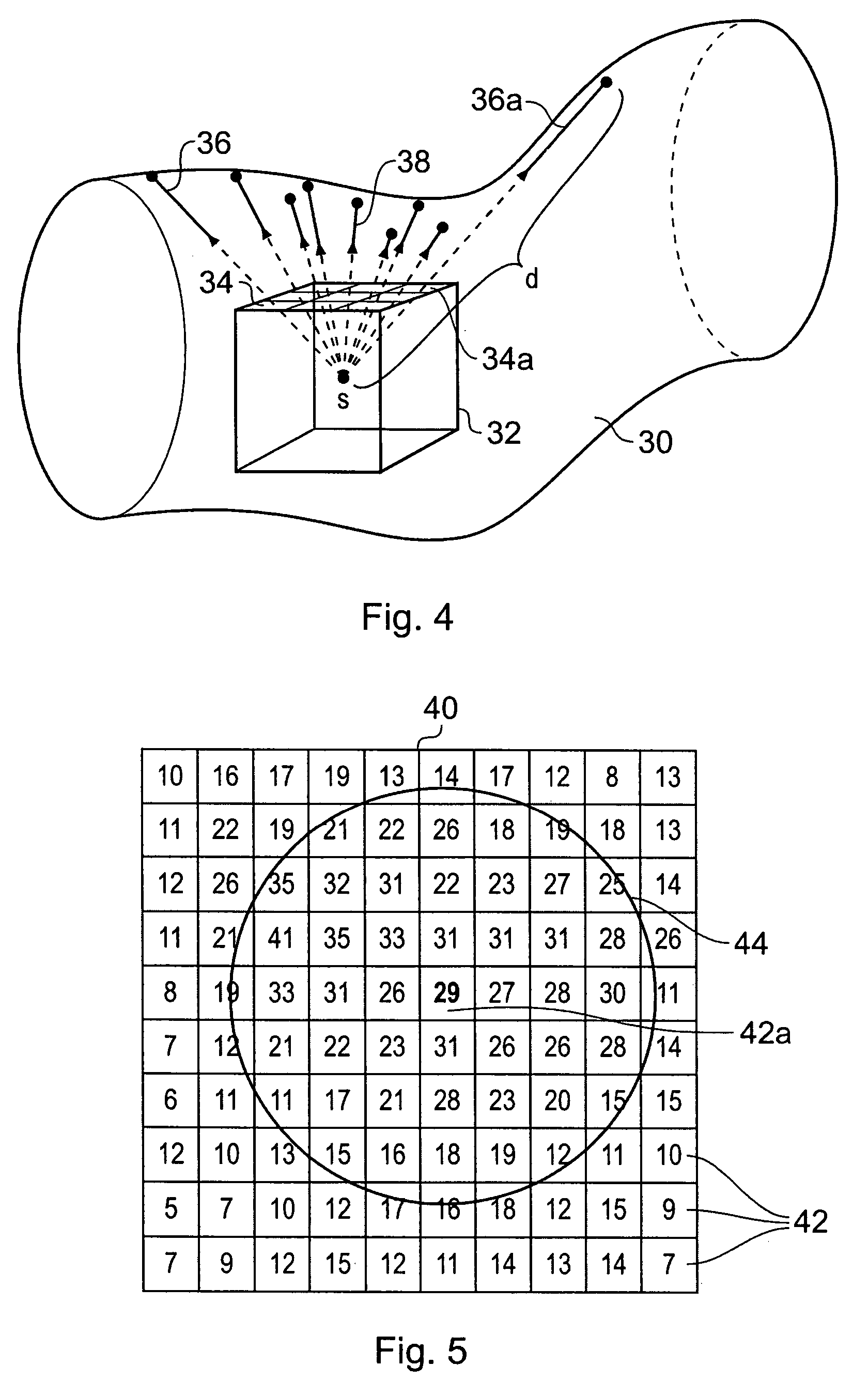
A method of navigating along a biological object with a lumen represented by a three-dimensional volume data set comprises generating a plurality of navigation segments connectable in a sequence, each segment having a start point within the lumen, a direction and a length. The navigation may be used for a camera in a virtual endoscopic examination, for example. The direction of each segment is determined by casting groups of rays outwards from the start point of the segment to the object wall, and calculating an average ray length for each group. The group having the largest average ray length is selected, and the axial direction of this group is used as the direction for the segment. The average ray lengths of the groups may be weighted using the direction of the previous segments to bias the navigation generally forward, or may be weighted using a view direction of the camera to allow a user to turn the camera into a chosen branch in the object.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
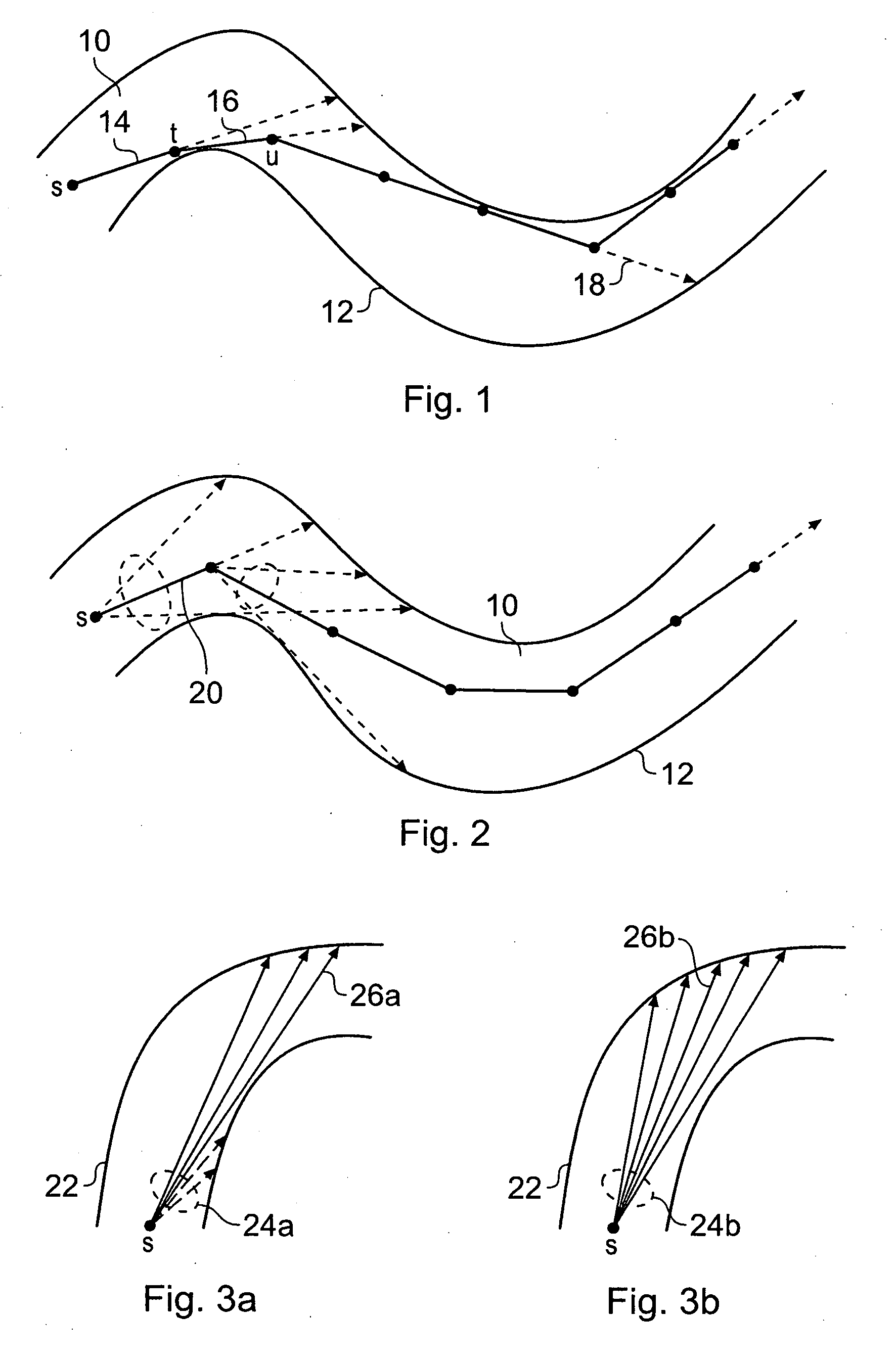
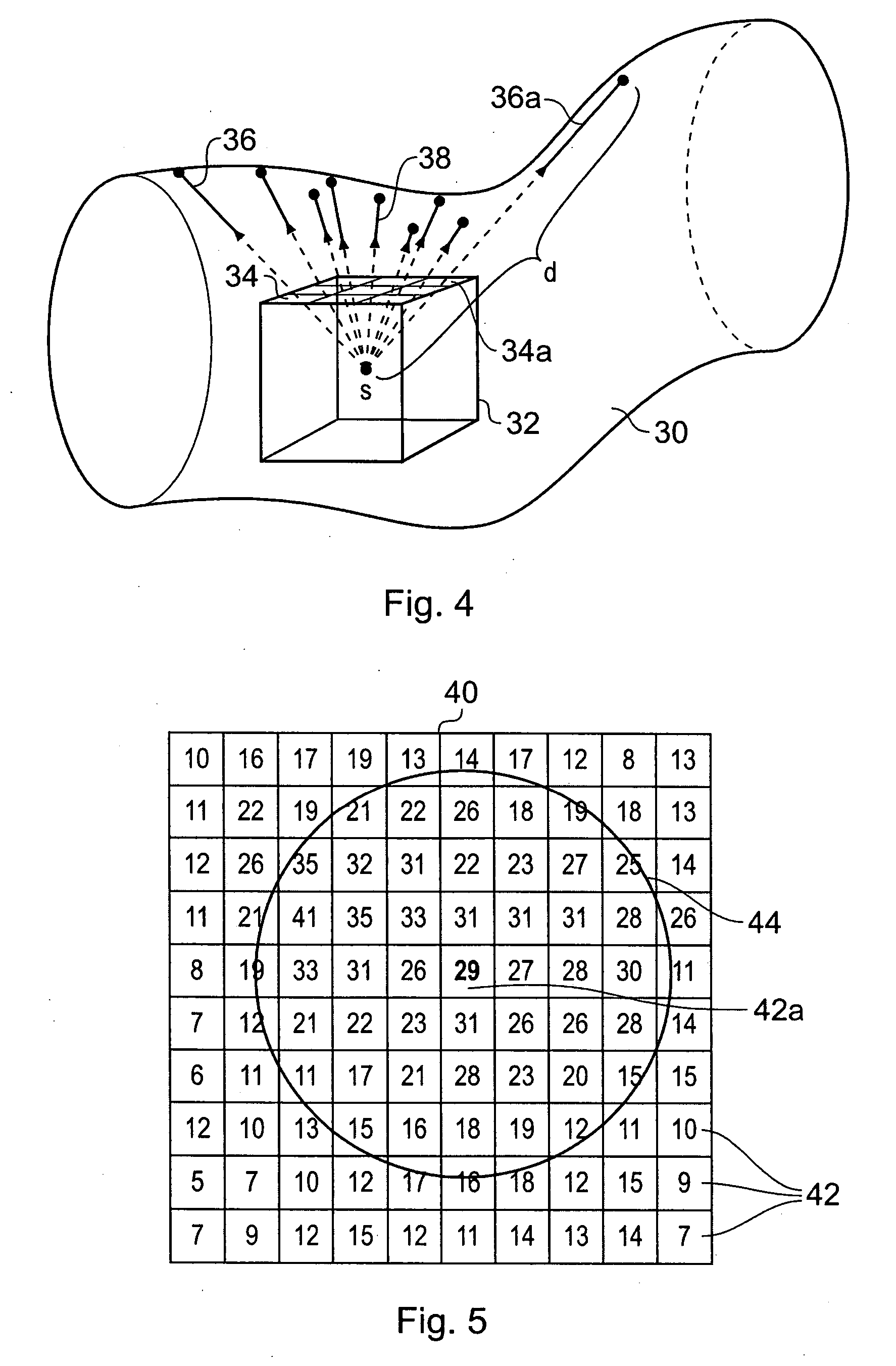
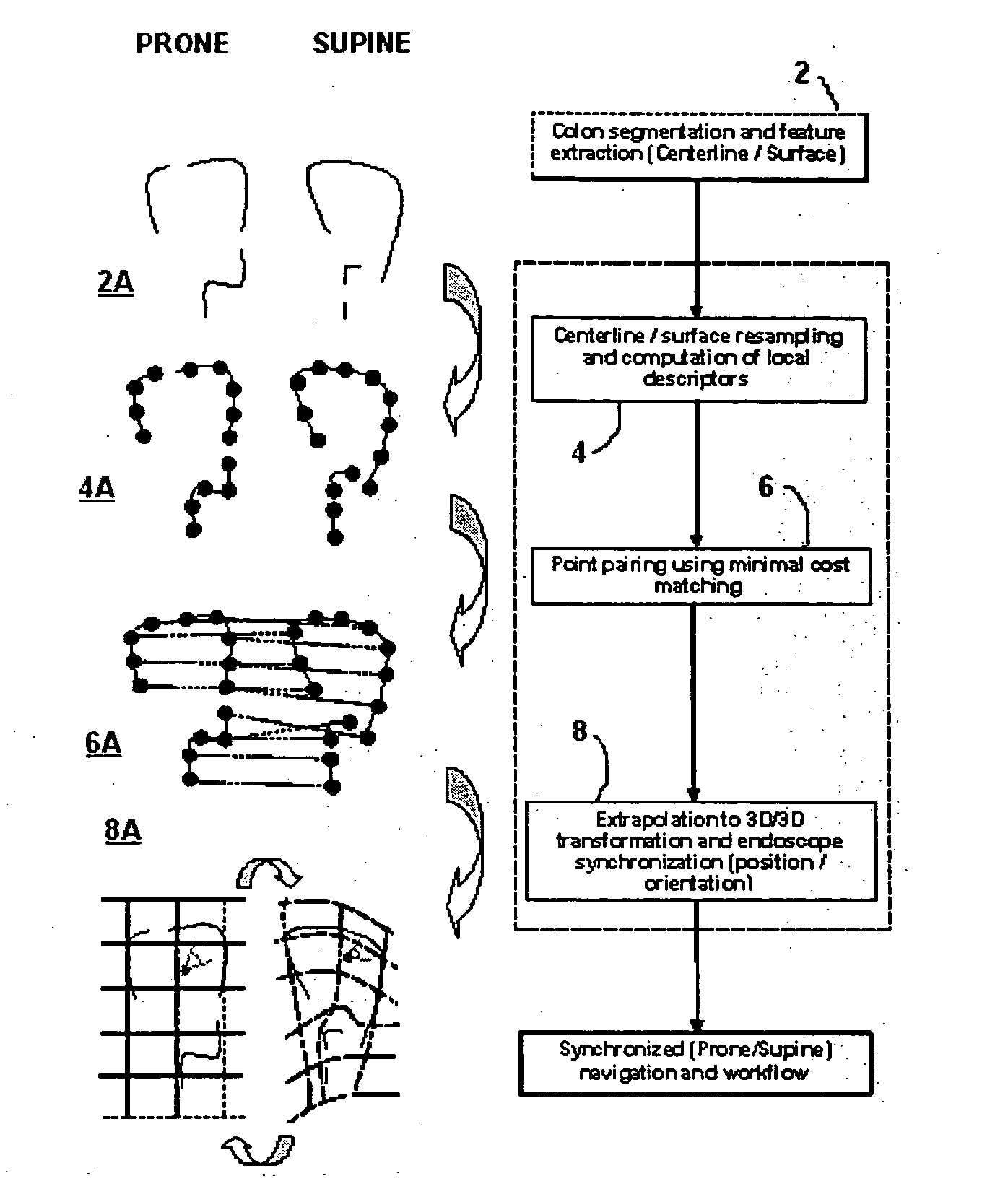
Method and apparatus for registration of virtual endoscopic images
InactiveUS20050048456A1Minimal cost matchingImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionReference frame
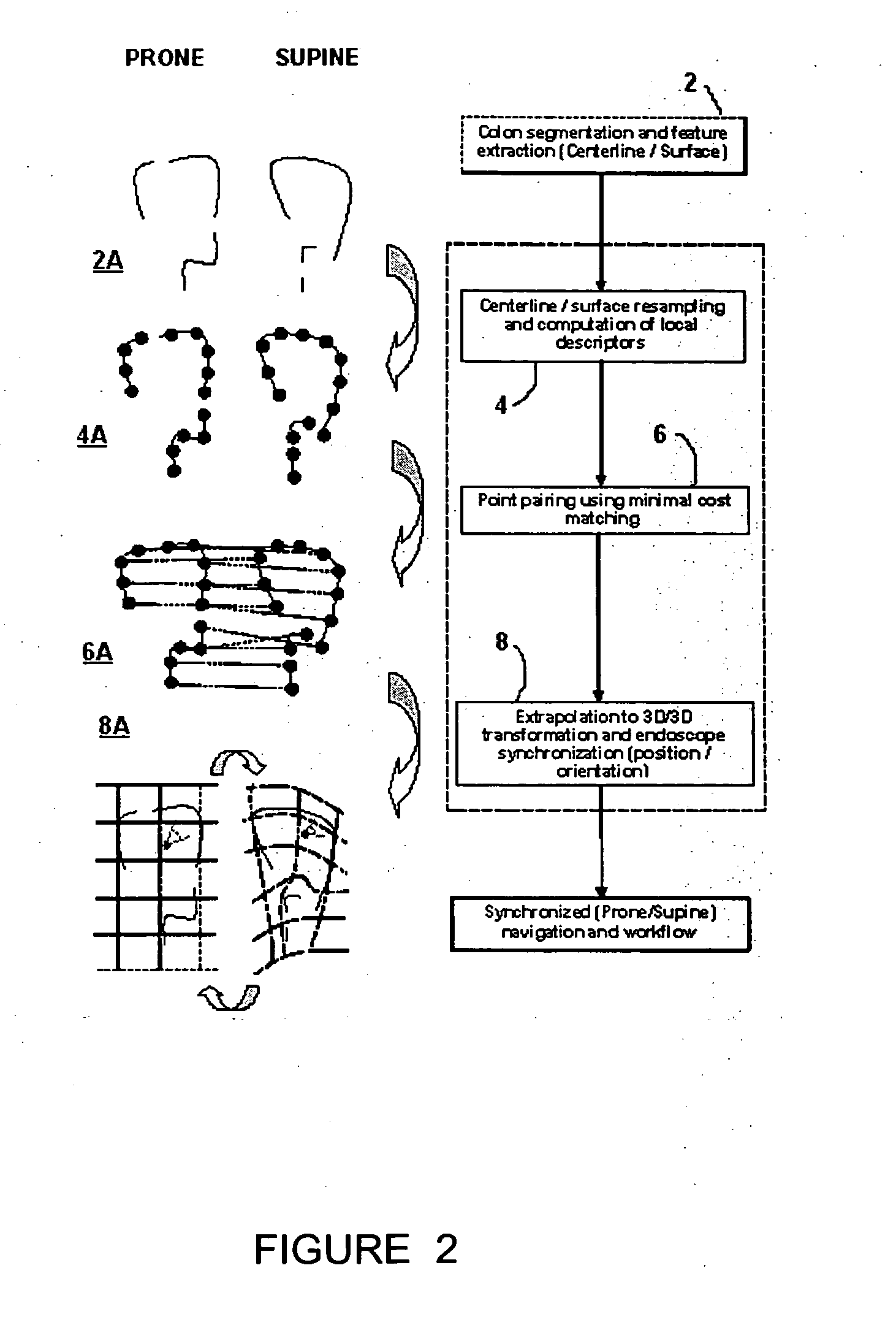
A method for registration of virtual endoscopy images in first and second patient positions comprises performing colon segmentation and feature extraction, including centerline and colon surface data for each of the images; resampling the centerline and colon surface data; computing respective local descriptors; pairing point correspondences on the centerlines between the first and second images by minimal cost matching; extrapolating the centerline point correspondences to a 3-dimensional / 3-dimensional (3D / 3D) transformation between the first and second images. The method also includes selecting a position for a virtual endoscope in one of the images; associating an orthogonal reference frame with the virtual endoscope; and applying the 3D / 3D transformation to the orthogonal reference frame so as to derive a corresponding transformed reference frame for the virtual endoscope in the other of the images.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Virtual endoscopy with improved image segmentation and lesion detection
A system, and computer implemented method are provided for interactively displaying three-dimensional structures. Three-dimensional volume data (34) is formed from a series of two-dimensional images (33) representing at least one physical property associated with the three-dimensional structure, such as a body organ having a lumen. A wire frame model of a selected region of interest is generated (38b). The wireframe model is then deformed or reshaped to more accurately represent the region of interest (40b). Vertices of the wire frame model may be grouped into regions having a characteristic indicating abnormal structure, such as a lesion. Finally, the deformed wire frame model may be rendered in an interactive three-dimensional display.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
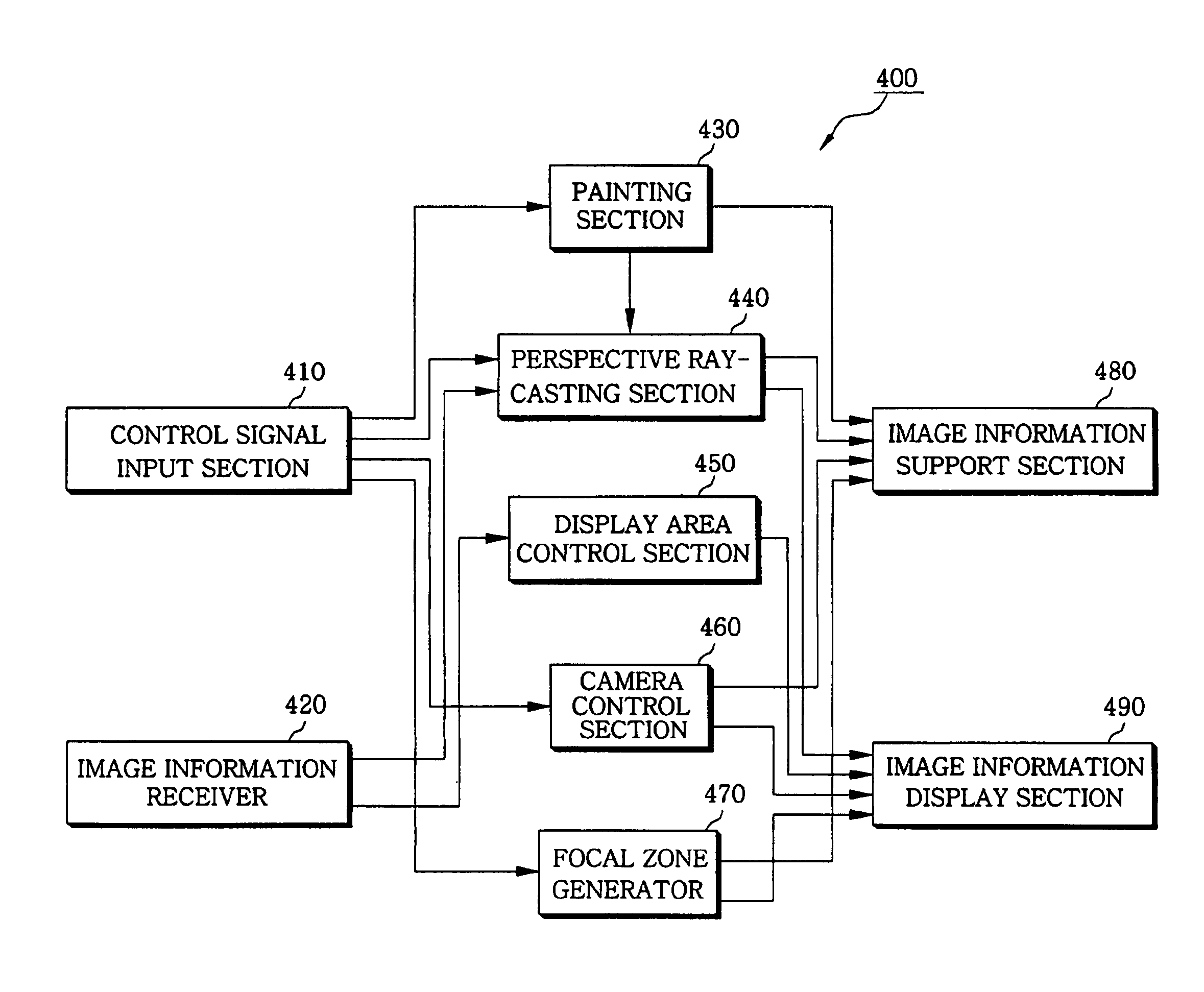
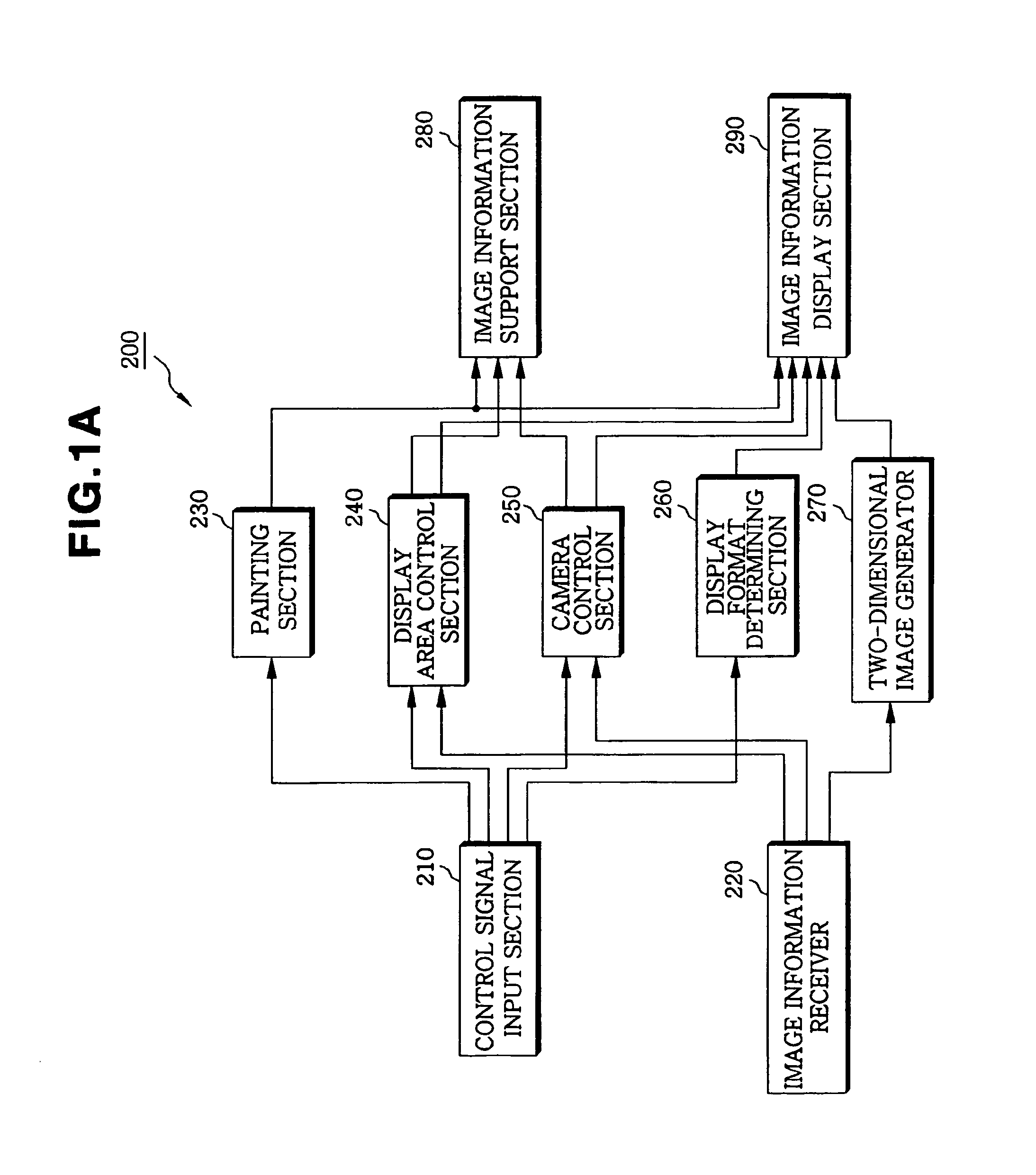
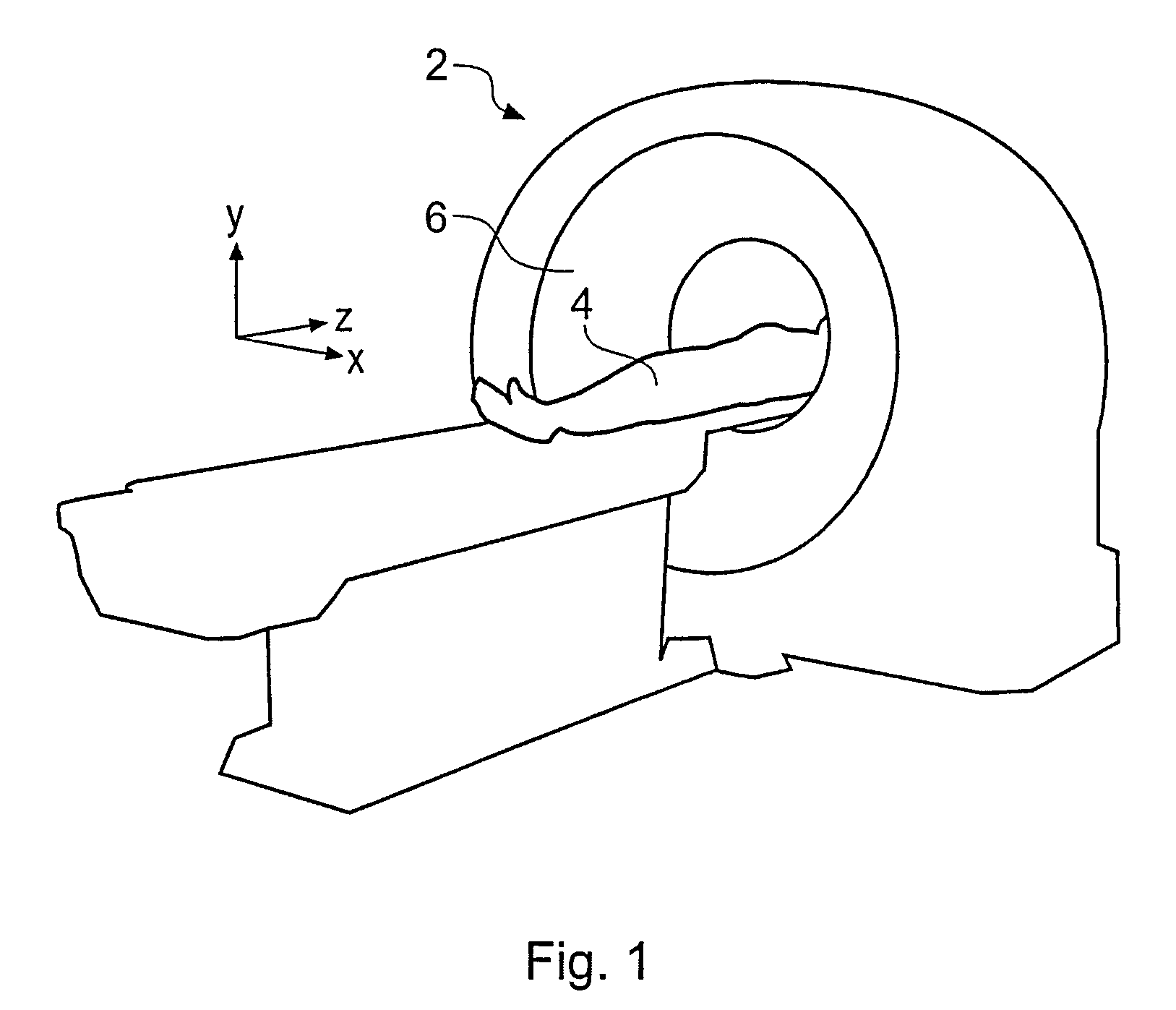
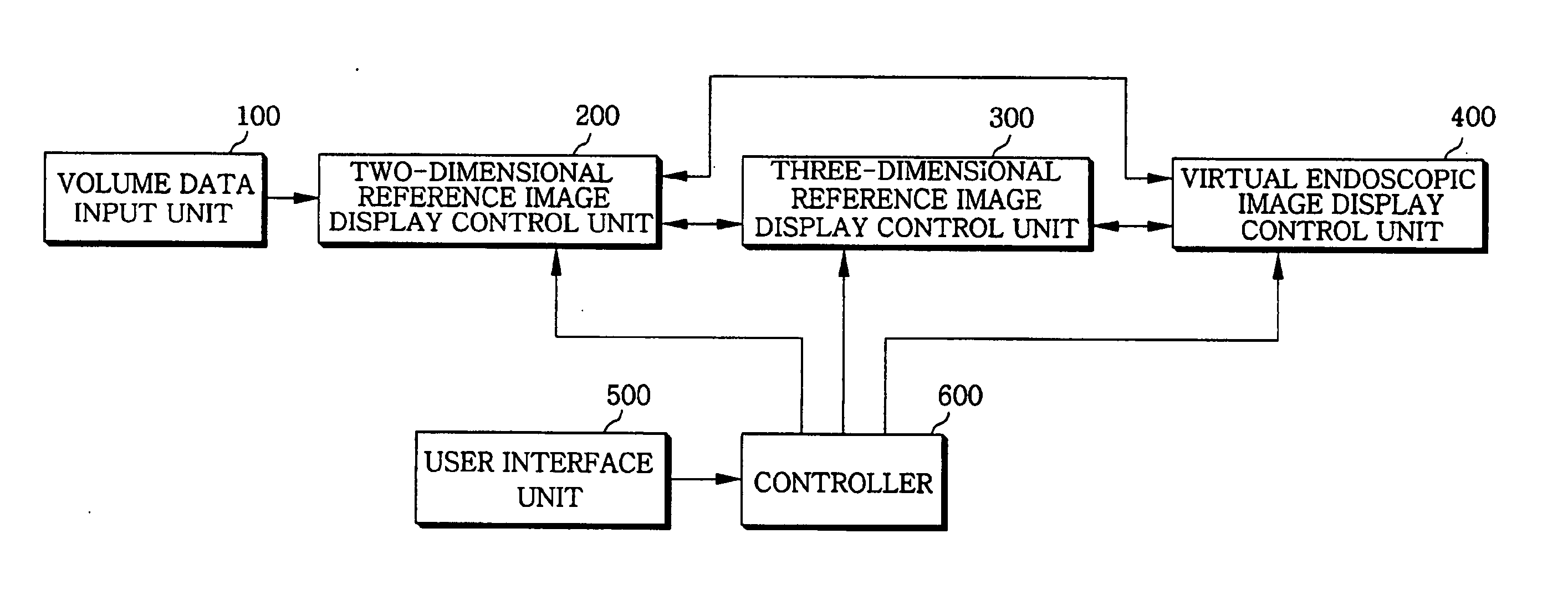
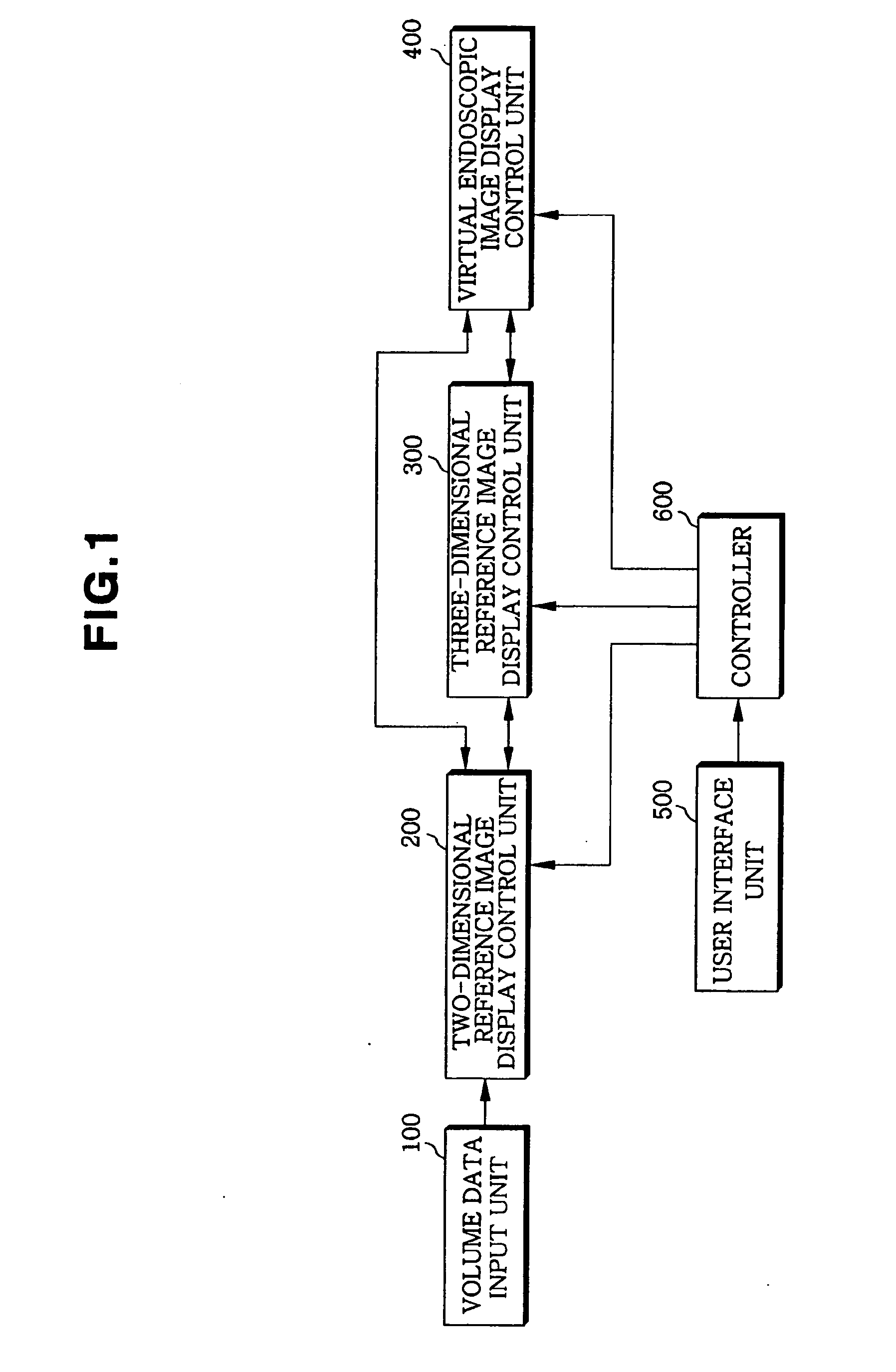
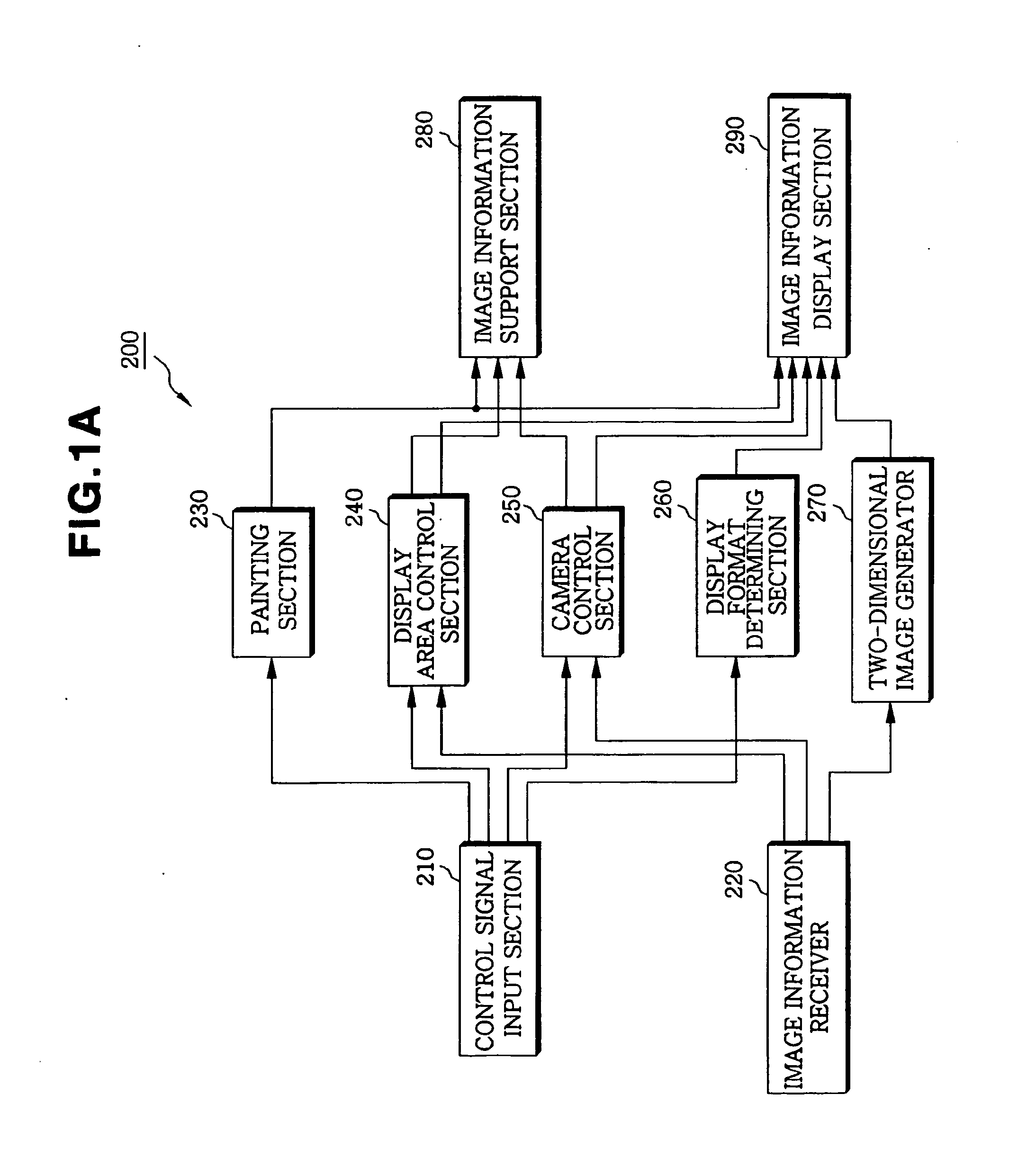
Apparatus and method for displaying virtual endoscopy display
InactiveUS7102634B2Easy to operateSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionReference imageComputer science
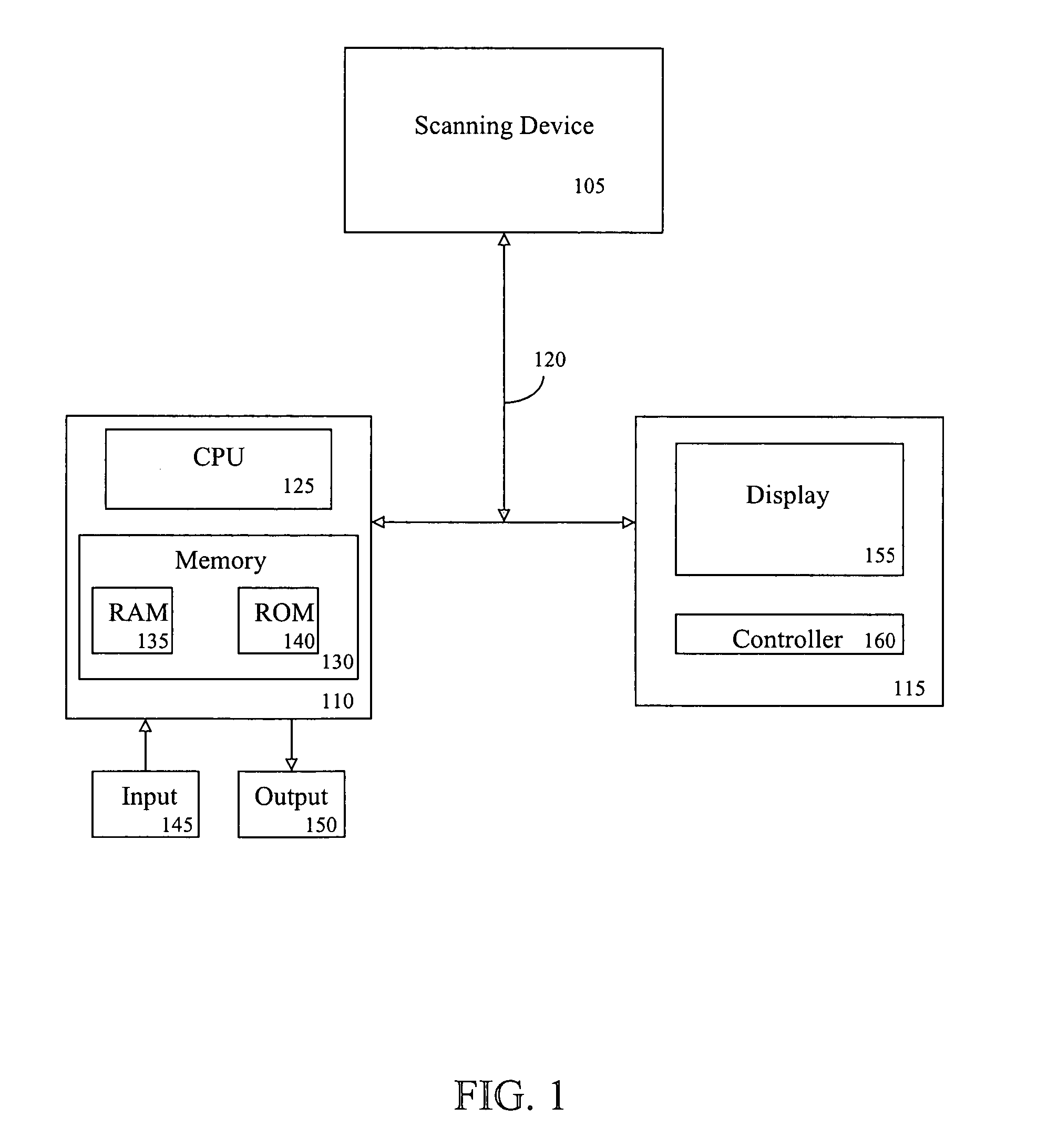
An apparatus and method for displaying a three-dimensional virtual endoscopic image are provided. In the method, information on a virtual endoscopic image is input in the form of volume data expressed as a function of three-dimensional position. A two-dimensional reference image, a three-dimensional reference image, and a virtual endoscopic image are detected from the volume data. The detected images are displayed on one screen. Virtual cameras are respectively displayed on areas, in which the two and three-dimensional reference images are respectively displayed. Here, a camera display sphere and a camera display circle are defined on the basis of a current position of each virtual camera. When information regarding to one image, among the two and three-dimensional reference images and the virtual endoscopic image on one screen, is changed by a user's operation, information regarding to the other images is changed based on the information changed by the user's operation.
Owner:INFINITT HEALTHCARE CO LTD
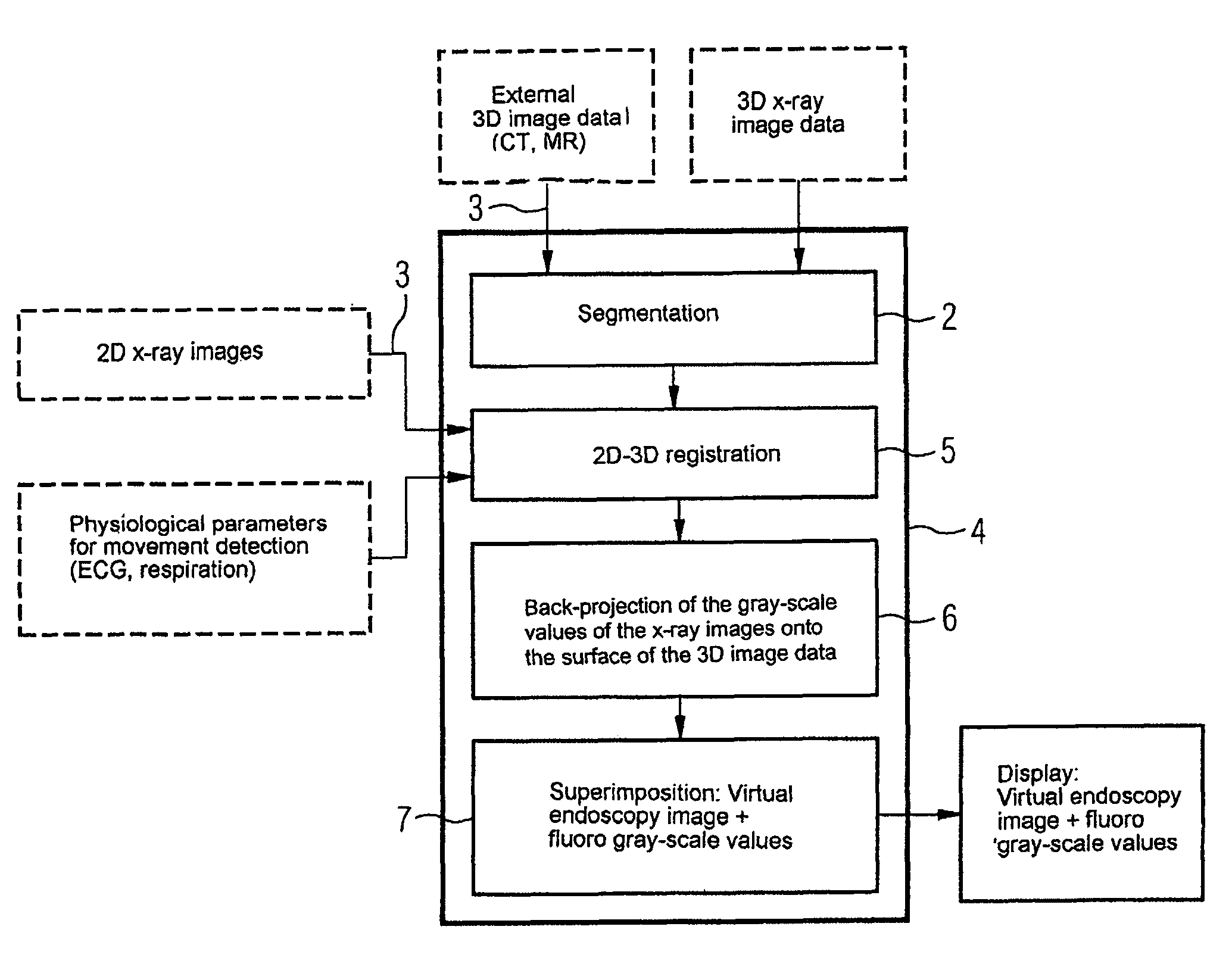
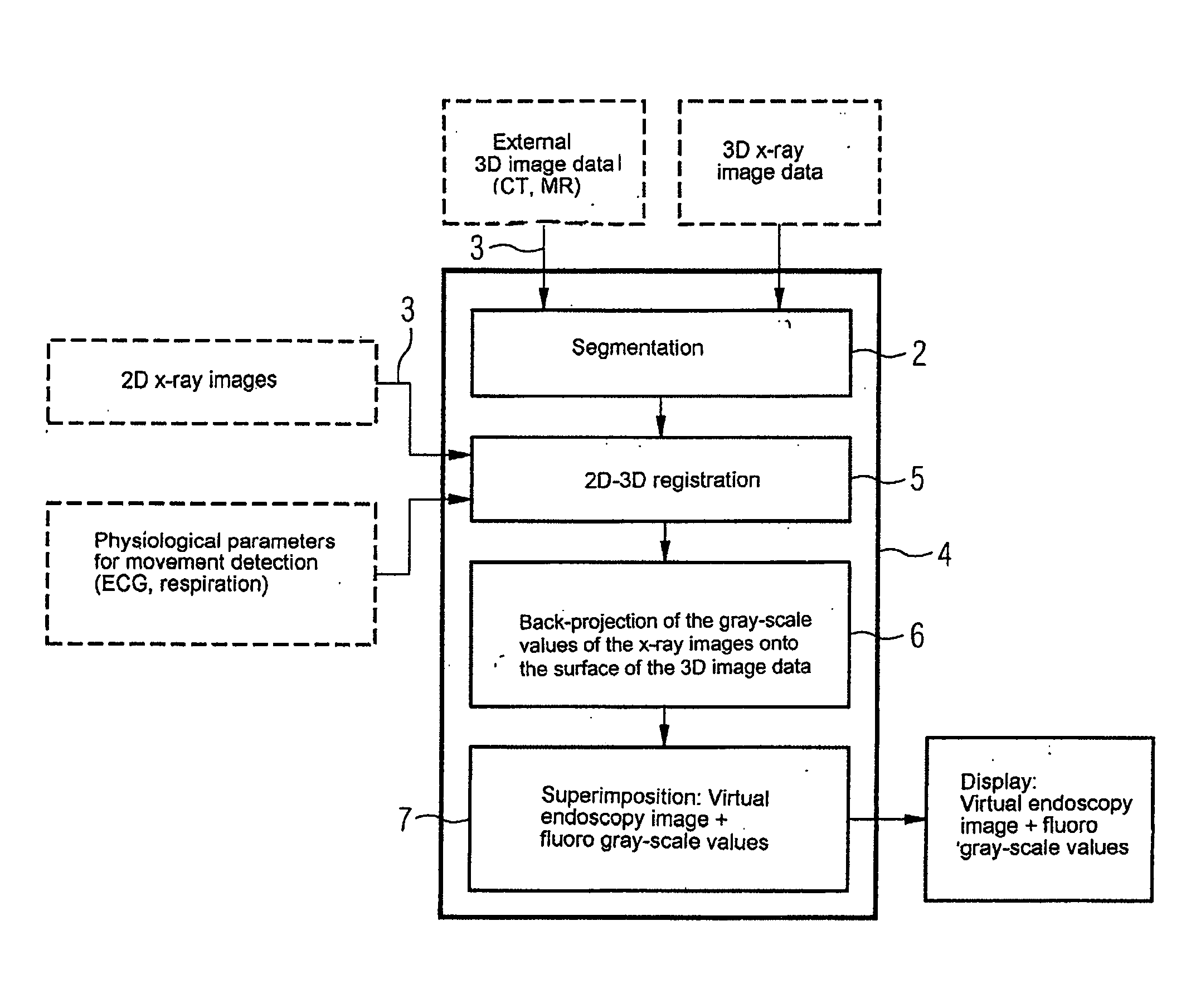
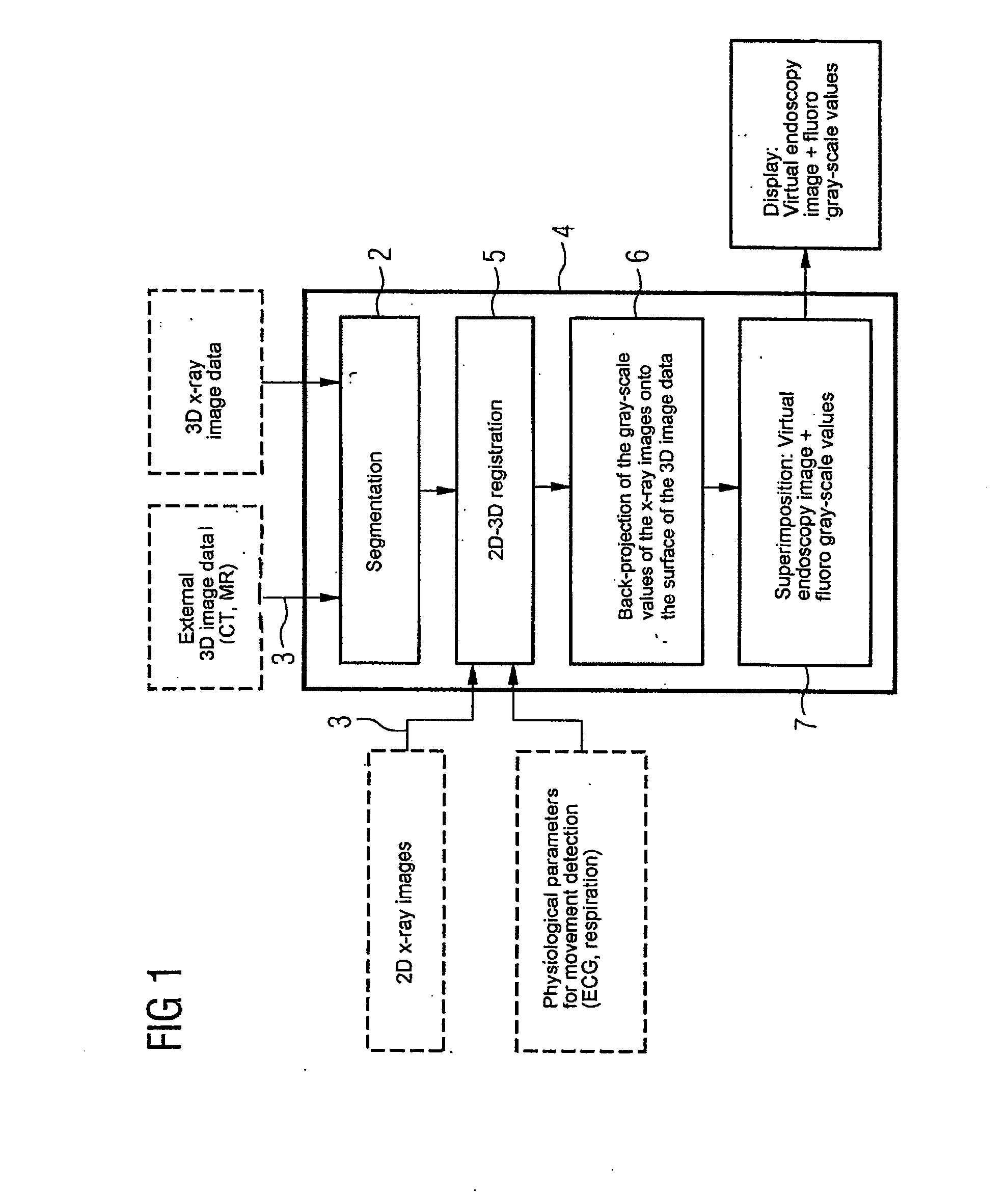
Device for merging a 2D radioscopy image with an image from a 3D image data record
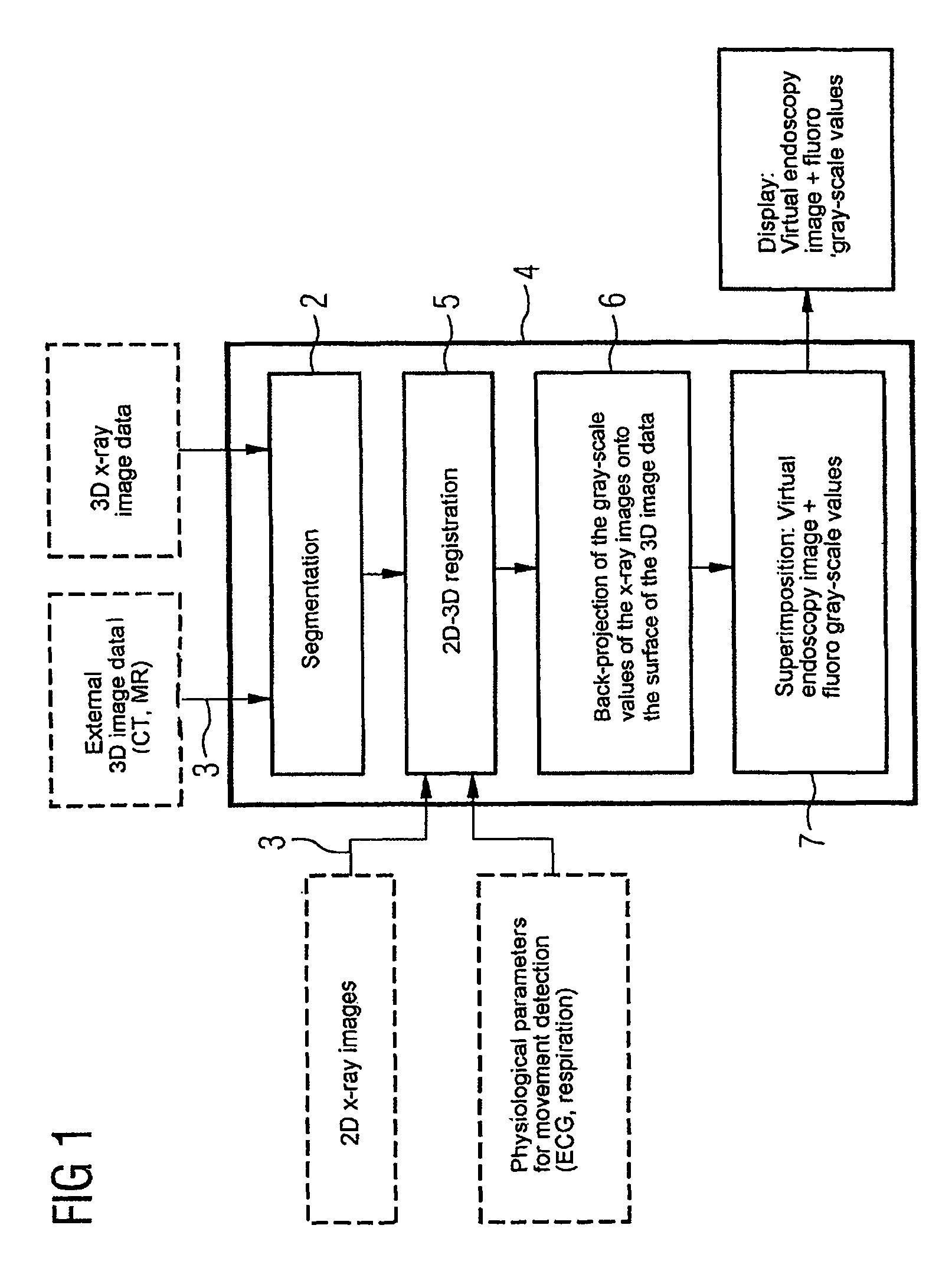
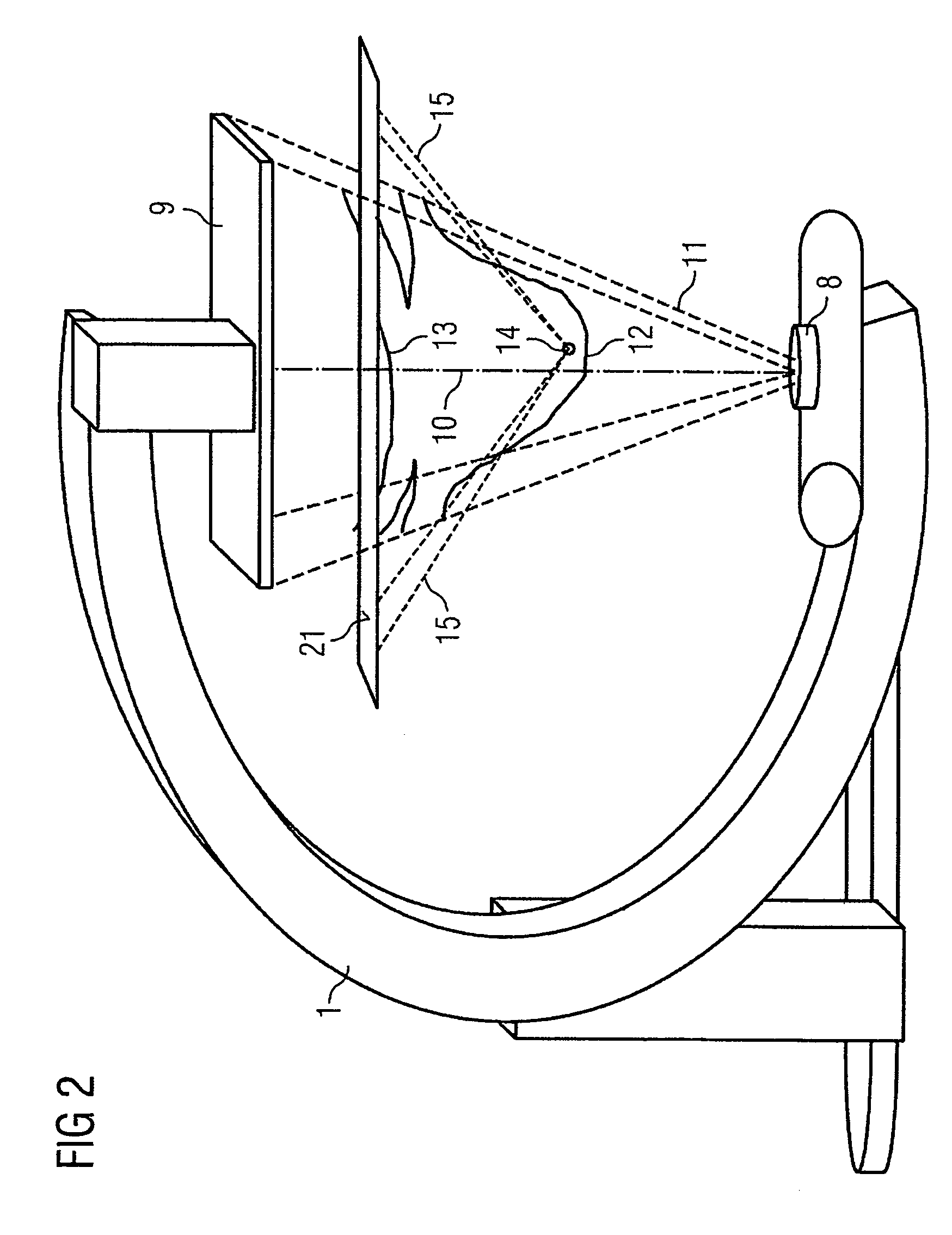
ActiveUS8045780B2Reduce total usageImprove bindingImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionBack projectionDisplay device
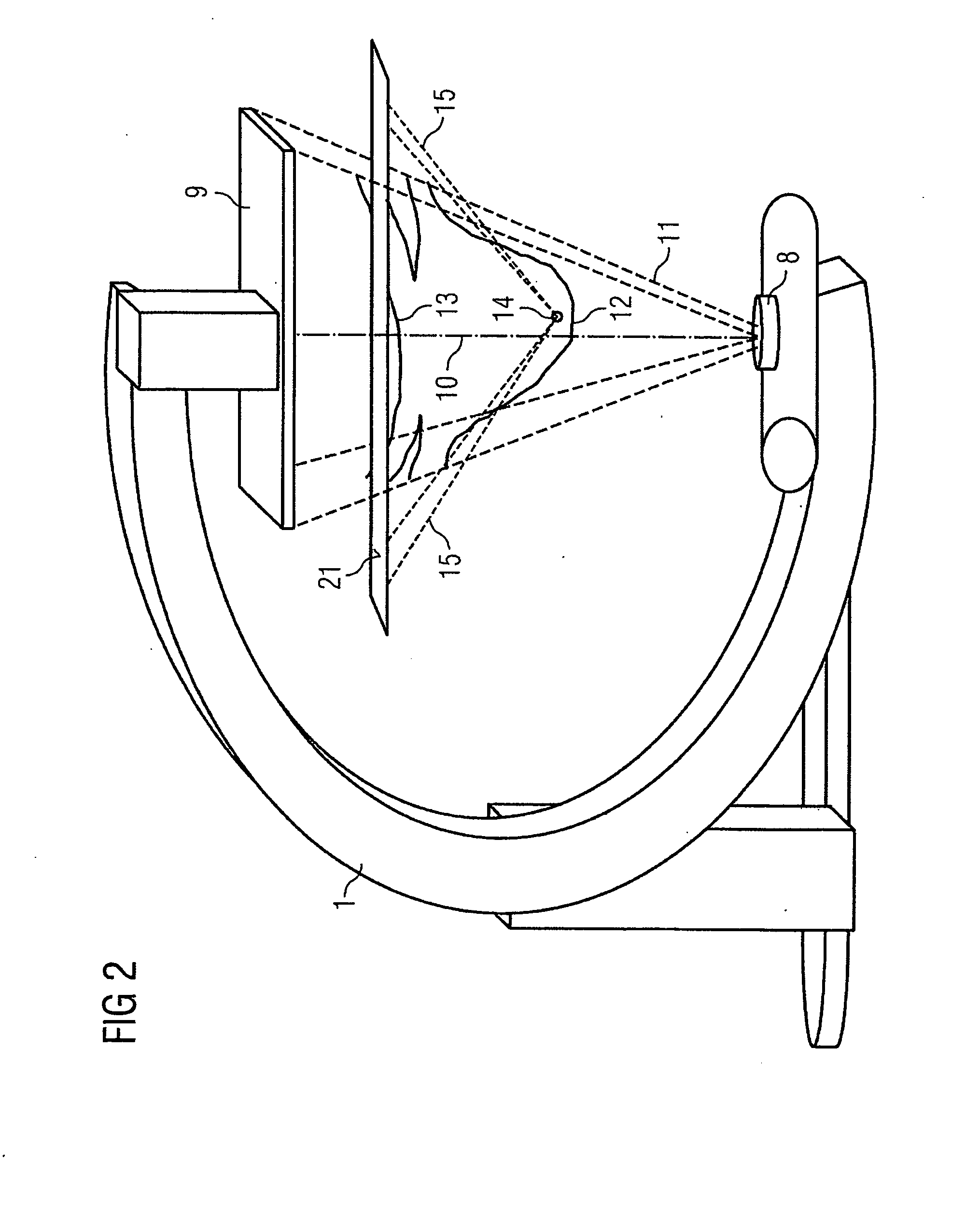
The invention relates to a device for merging a 2D radioscopy image with an image obtained from a 3D image data record, having a memory unit that stores the 2D radioscopy image and the 3D image data record, a segmentation unit that segments an inner surface of a hollow organ from the 3D image data record, a registration unit that registers the 2D radioscopy image with the 3D image data record, a back-projection unit that back-projects the pixels of the 2D radioscopy image onto the segmented surface, taking account of the projection geometry of the 2D radioscopy image and the registration, and an image merger unit that generates a virtual endoscopy view of the surface from the segmented surface using the back-projected pixels. The device primarily allows 2D radioscopy images to be superimposed during interventional procedures with a fly display of the interior of an interesting organ.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method registered video endoscopy and virtual endoscopy
ActiveUS20050251017A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementImage captureRegion of interest
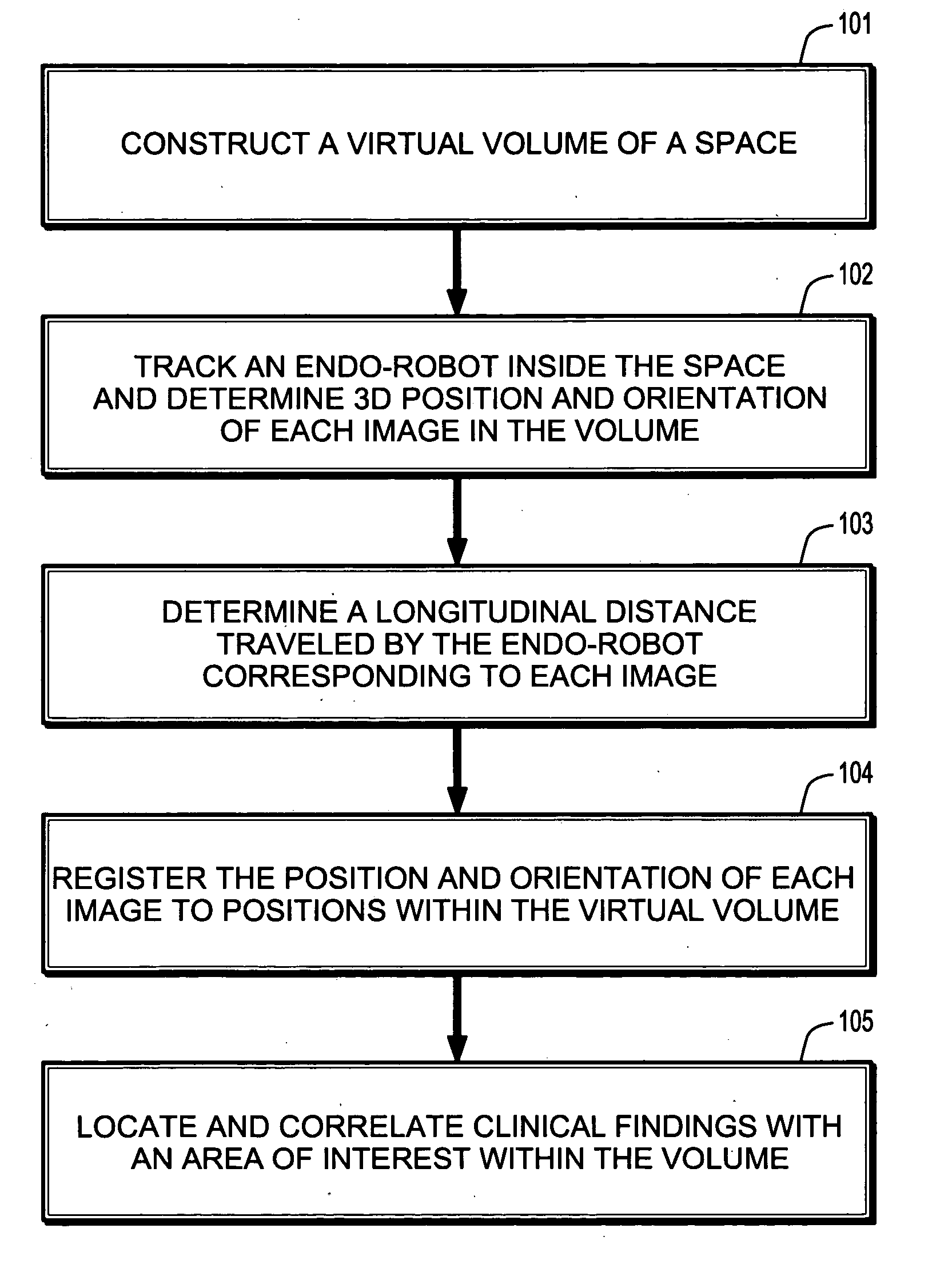
An endo-robot can be tracked and a reconstructed 3D volume of data can be created for virtual endoscopy. The 3D position and orientation of each image captured by the endo-robot is determined. The longitudinal distance traveled inside the structure of interest is determined. The position, orientation and longitudinal distance are used to register the position of the endo-robot to a corresponding position inside the 3D volume of data. Virtual endoscopy can be used to locate areas of interest and correlate clinical findings with the images of the areas of interest.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for registration of virtual endoscopic images
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Automatic analysis in virtual endoscopy
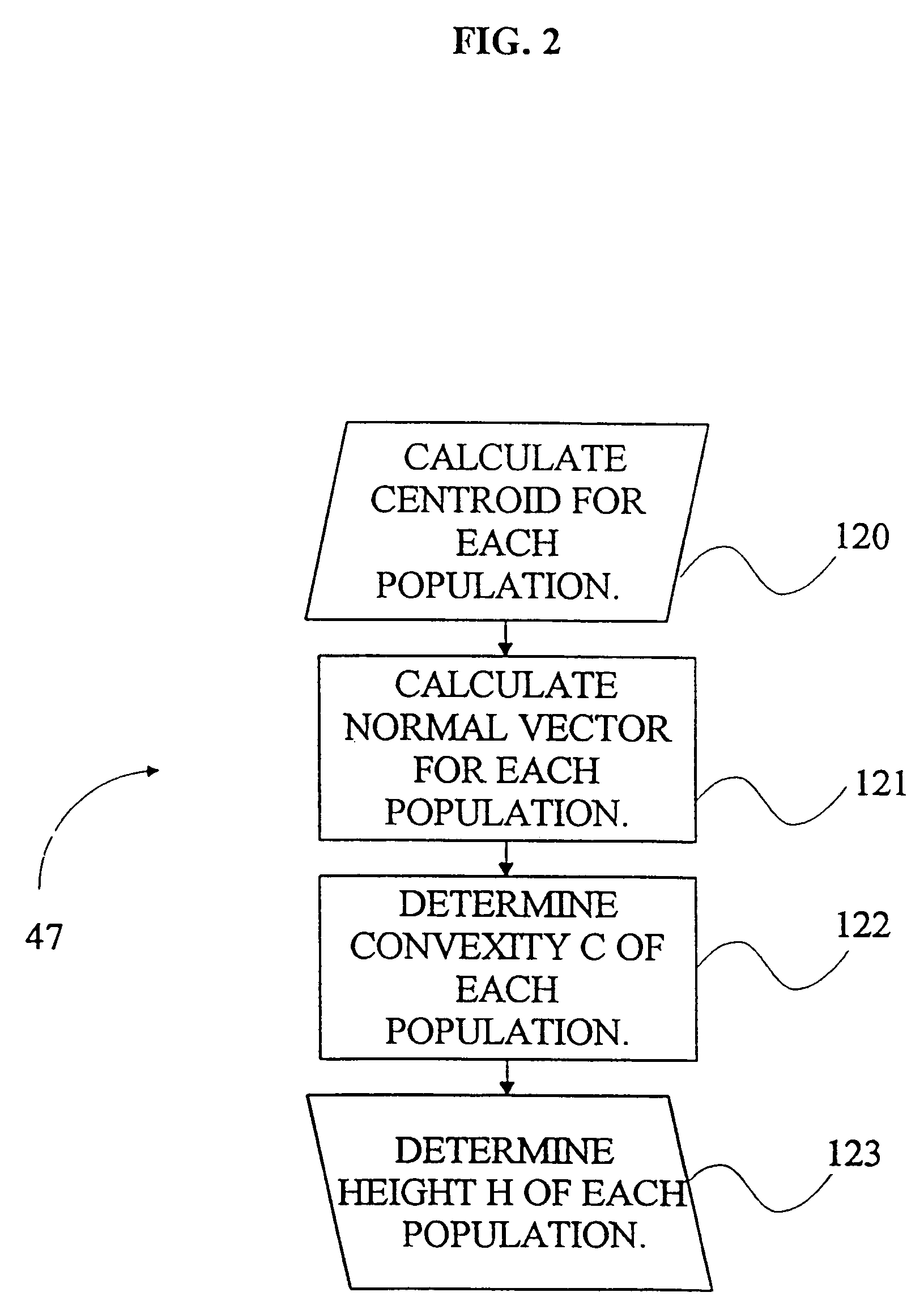
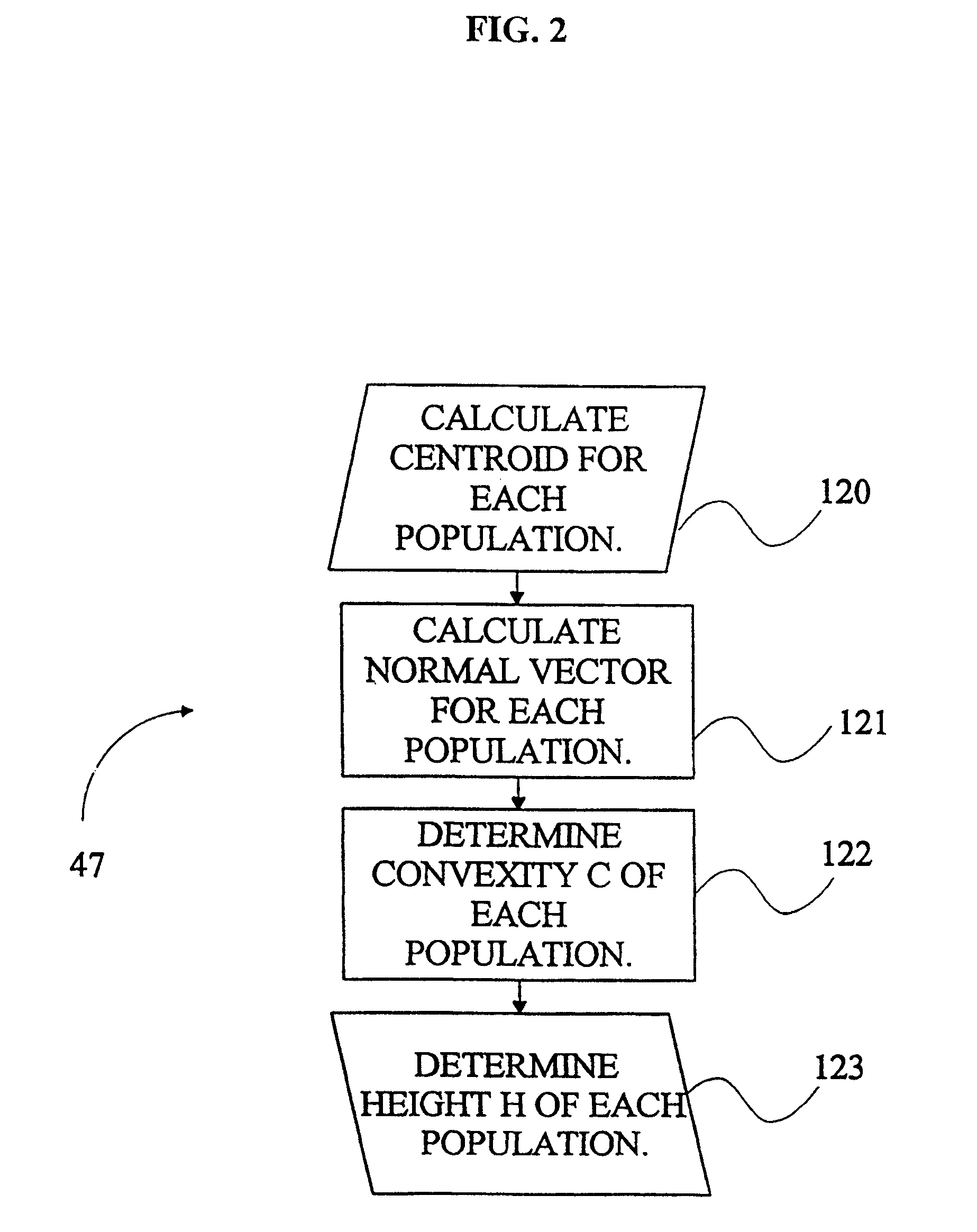
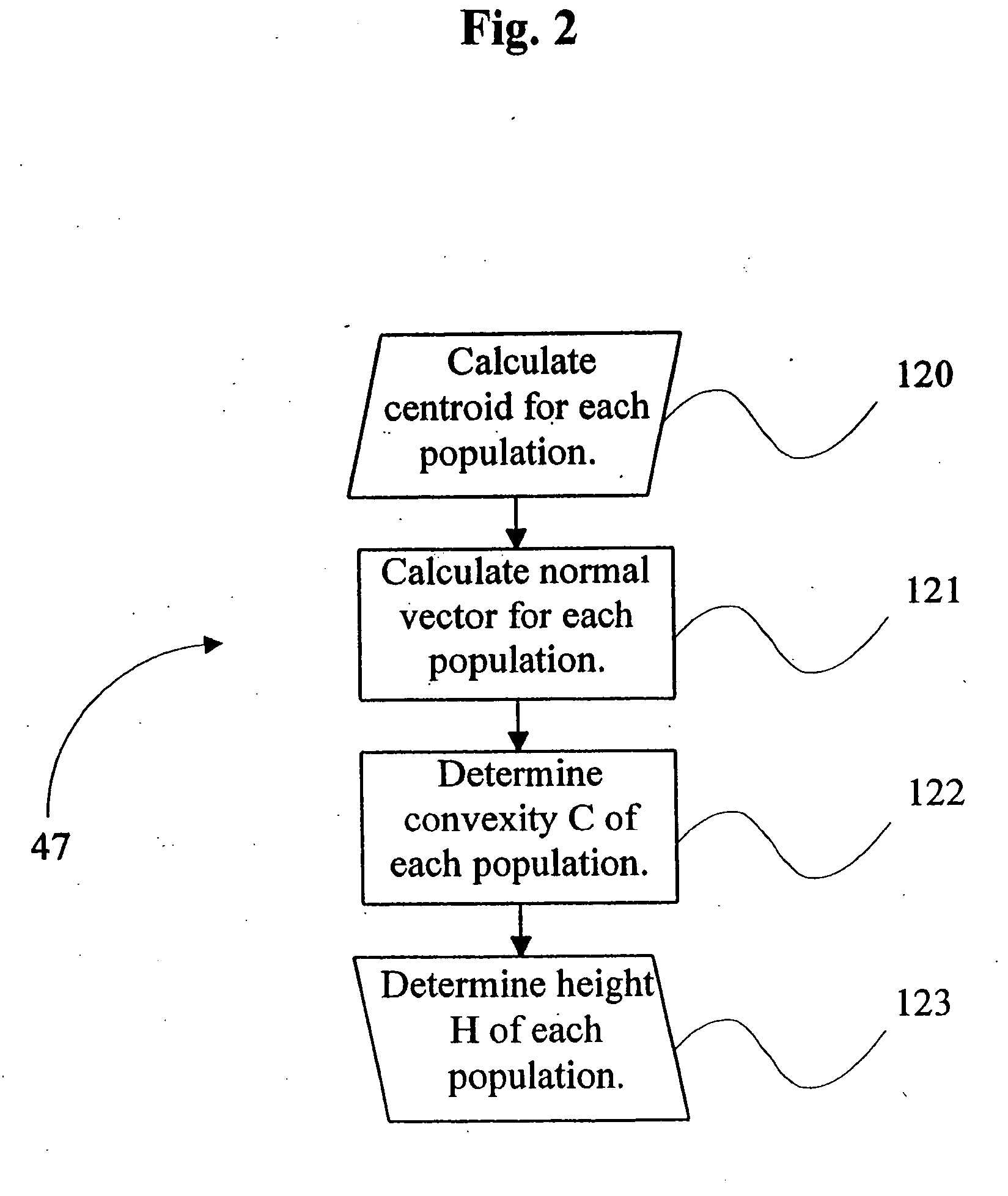
A computer system and a computer-implemented method are provided for interactively displaying a three-dimensional rendering of a structure having a lumen and for indicating regions of abnormal wall structure. A three-dimensional volume of data is formed from a series of two-dimensional images representing at least one physical property associated with the three-dimensional structure. An isosurface of a selected region of interest is created by a computer from the volume of data based on a selected value or values of a physical property representing the selected region of interest. A wireframe model of the isosurface is generated by the computer wherein the wireframe model includes a plurality of vertices. The vertices are then grouped into populations of contiguous vertices having a characteristic indicating abnormal wall structure by the computer. The wireframe model is then rendered by the computer in an interactive three-dimensional display to indicate the populations of abnormal wall structure.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Virtual endoscopy
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
Apparatus and method for displaying virtual endoscopy display
InactiveUS20050024724A1Effectively show correlationEasy to operateSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionReference imageVirtual camera
An apparatus and method for displaying a three-dimensional virtual endoscopic image are provided. In the method, information on a virtual endoscopic image is input in the form of volume data expressed as a function of three-dimensional position. A two-dimensional reference image, a three-dimensional reference image, and a virtual endoscopic image are detected from the volume data. The detected images are displayed on one screen. Virtual cameras are respectively displayed on areas, in which the two and three-dimensional reference images are respectively displayed. Here, a camera display sphere and a camera display circle are defined on the basis of a current position of each virtual camera. When information regarding to one image, among the two and three-dimensional reference images and the virtual endoscopic image on one screen, is changed by a user's operation, information regarding to the other images is changed based on the information changed by the user's operation.
Owner:INFINITT HEALTHCARE CO LTD
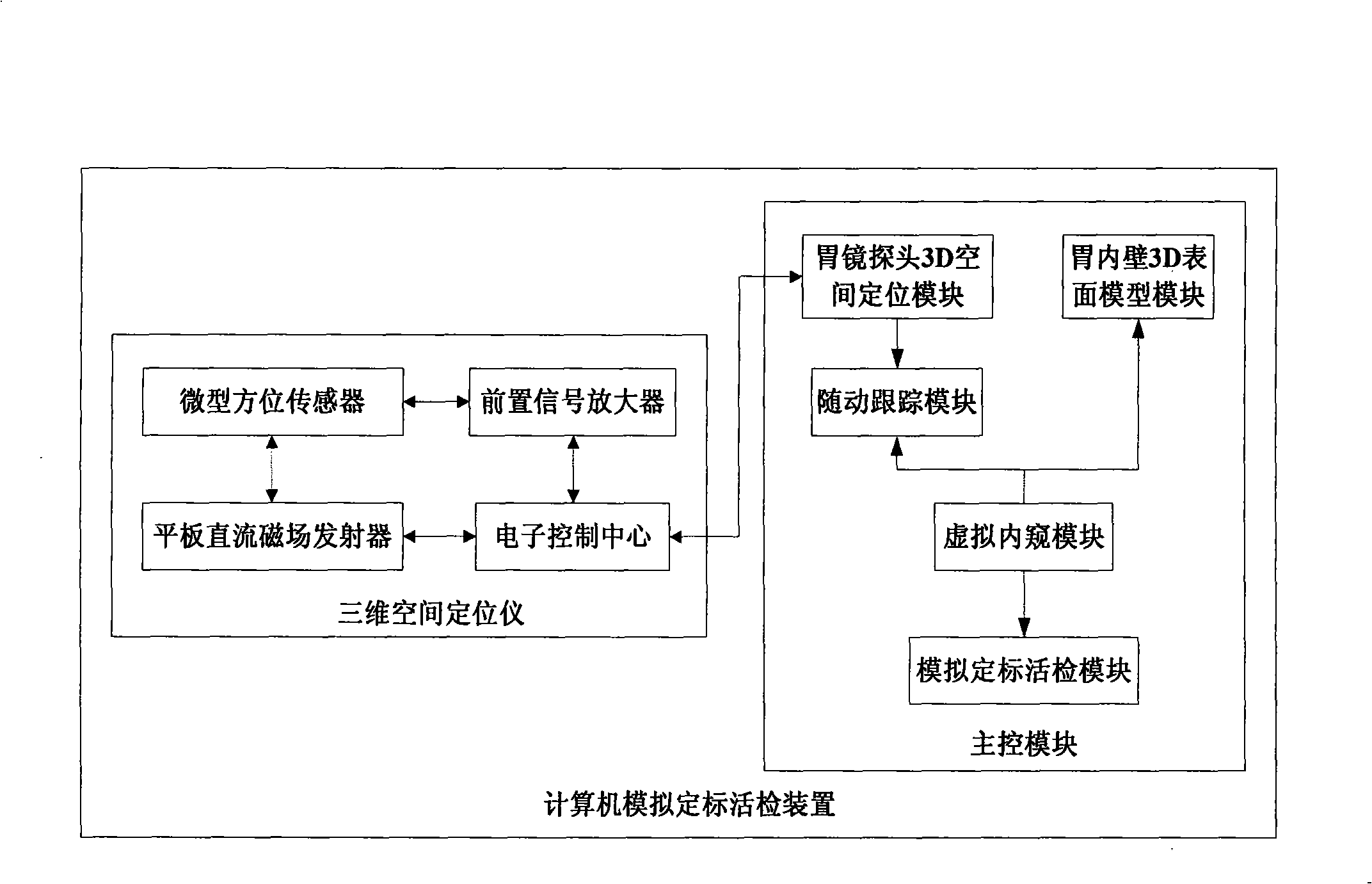
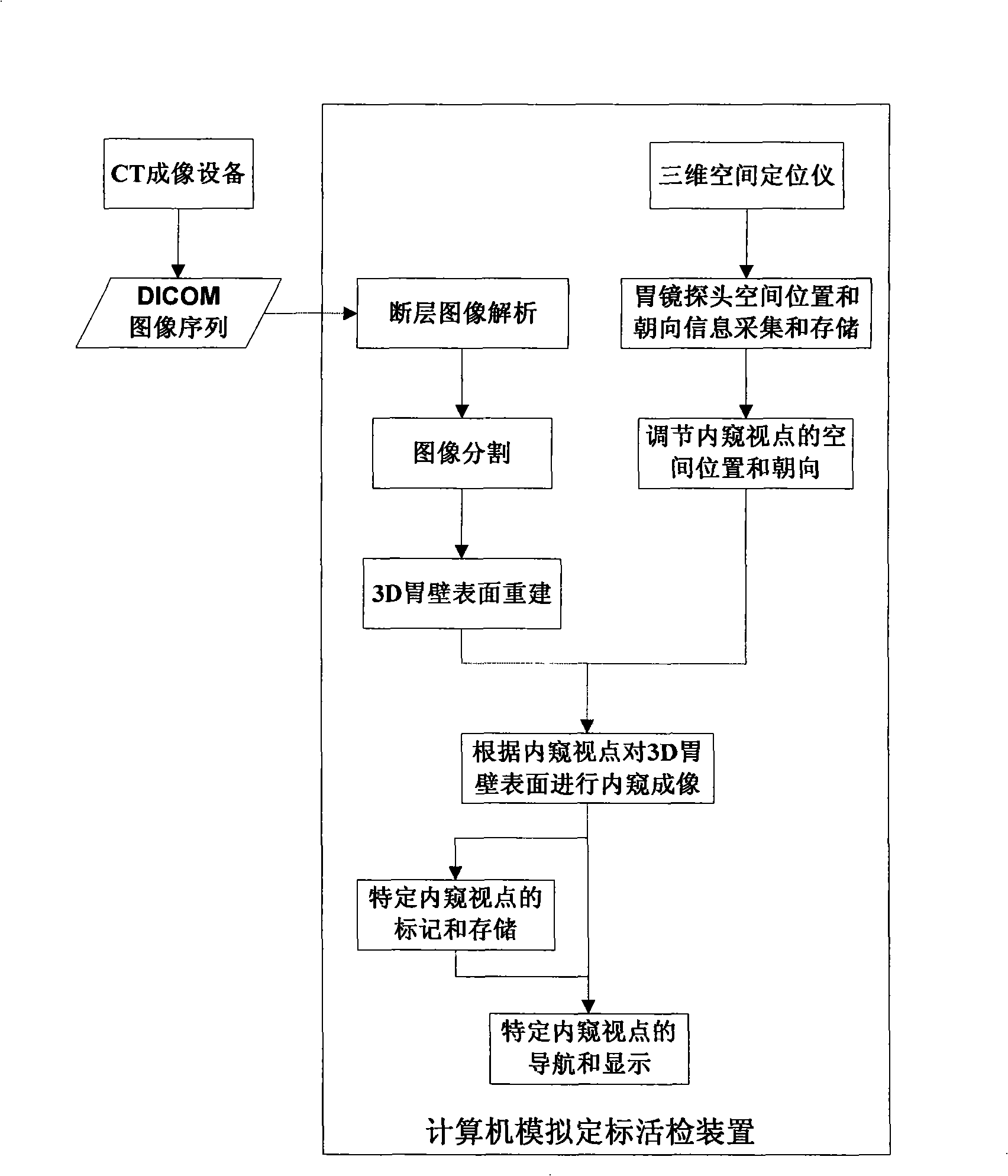
Computer simulation scaling biopsy method and apparatus
InactiveCN101322652ARelieve painReduce workloadSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDiseaseBiopsy methods
The invention discloses a method which can carry out follow-up tracing and virtual endoscopy to a gastroscope probe in gastroscopy process to implement analogue scaling biopsy on the focus in the stomach and provides a device for computer analogue scaling biopsy; the device comprises a main control module and a three-dimensional space locator used for acquiring spatial location and orientating information of the gastroscope probe, wherein, the main control module comprises a three-dimensional surface model module of an inner gastric wall, a three-dimensional space locating module of the gastroscope probe, a follow-up tracing module, a virtual endoscopy module and an analogue scaling biopsy module. The method can help to carry out callback and follow-up examination to stomach diseases, can realize noninvasive analogue scaling biopsy of stomach focus and can support doctors to make completely non-invasive focus image analysis in vitro.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method and system for virtual endoscopy with guidance for biopsy
InactiveUS7536216B2Increase choiceHigh sensitivityStatic indicating devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsData setInsertion point
A method for virtual endoscopy in a lumen includes acquiring from a patient an imaging dataset exhibiting a lesion external to a lumen wall; deriving a three-dimensional (3-D) volume of the lesion; obtaining data on maximum bend characteristics for a given endoscope; and deriving projection criteria, based on the 3-D volume and the maximum bend, for projecting an endoluminal image of said lesion, indicating an optimal biopsy insertion point.
Owner:CHARITE UNIVS MEDIZIN BERLIN +1
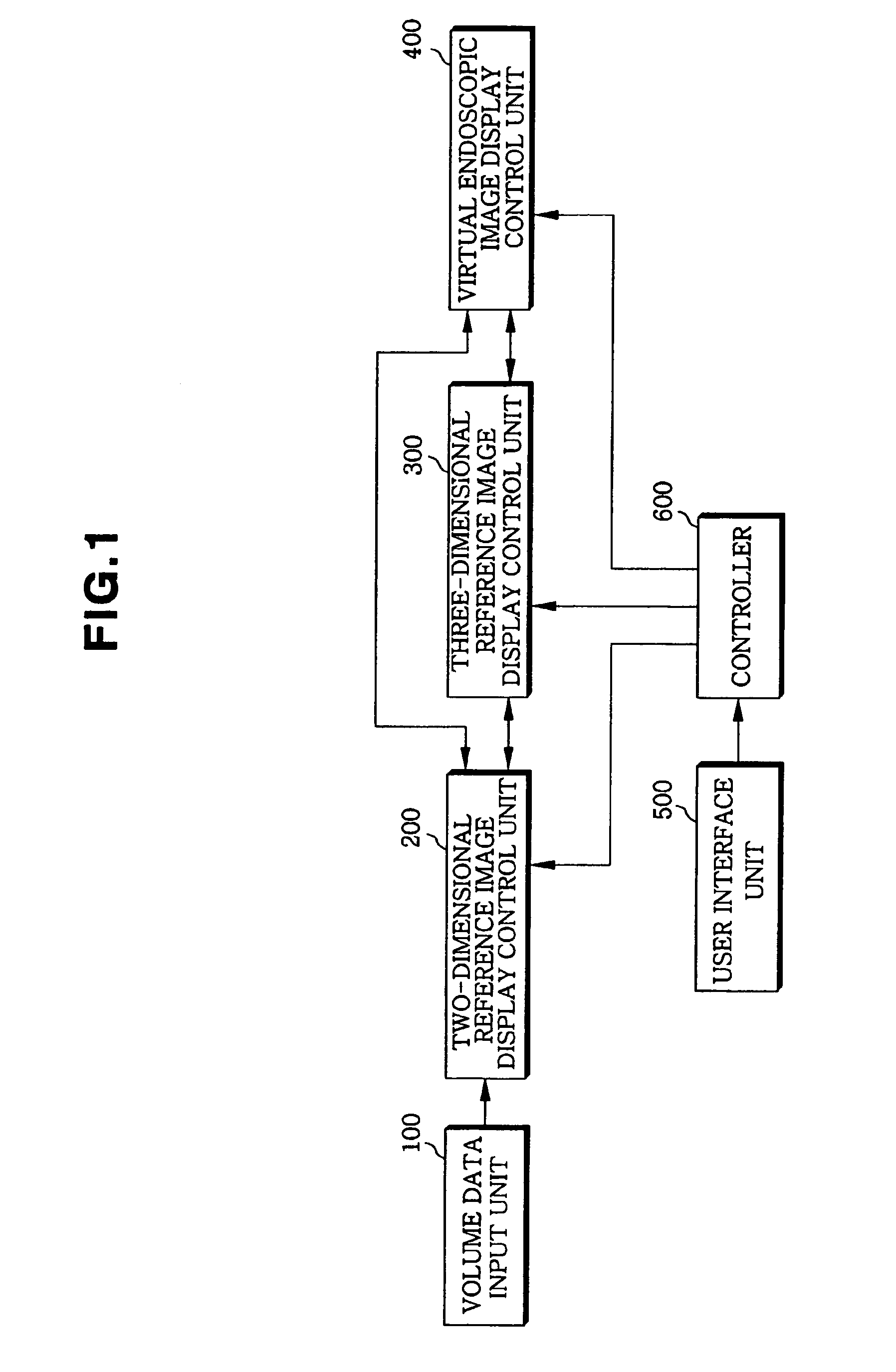
Interactive virtual endoscopy
The invention relates to a method for processing of a three-dimensional image data set, wherein the three-dimensional image data set is converted to a data set suitable for a two-dimensional image reproduction. The invention further relates to apparatuses for performing the required calculations and / or for reproduction of the data representations. The invention is particularly appropriate for medical applications of endoscopy, in particular, coloscopy.
Owner:RUST GEORG FRIEDERMANN
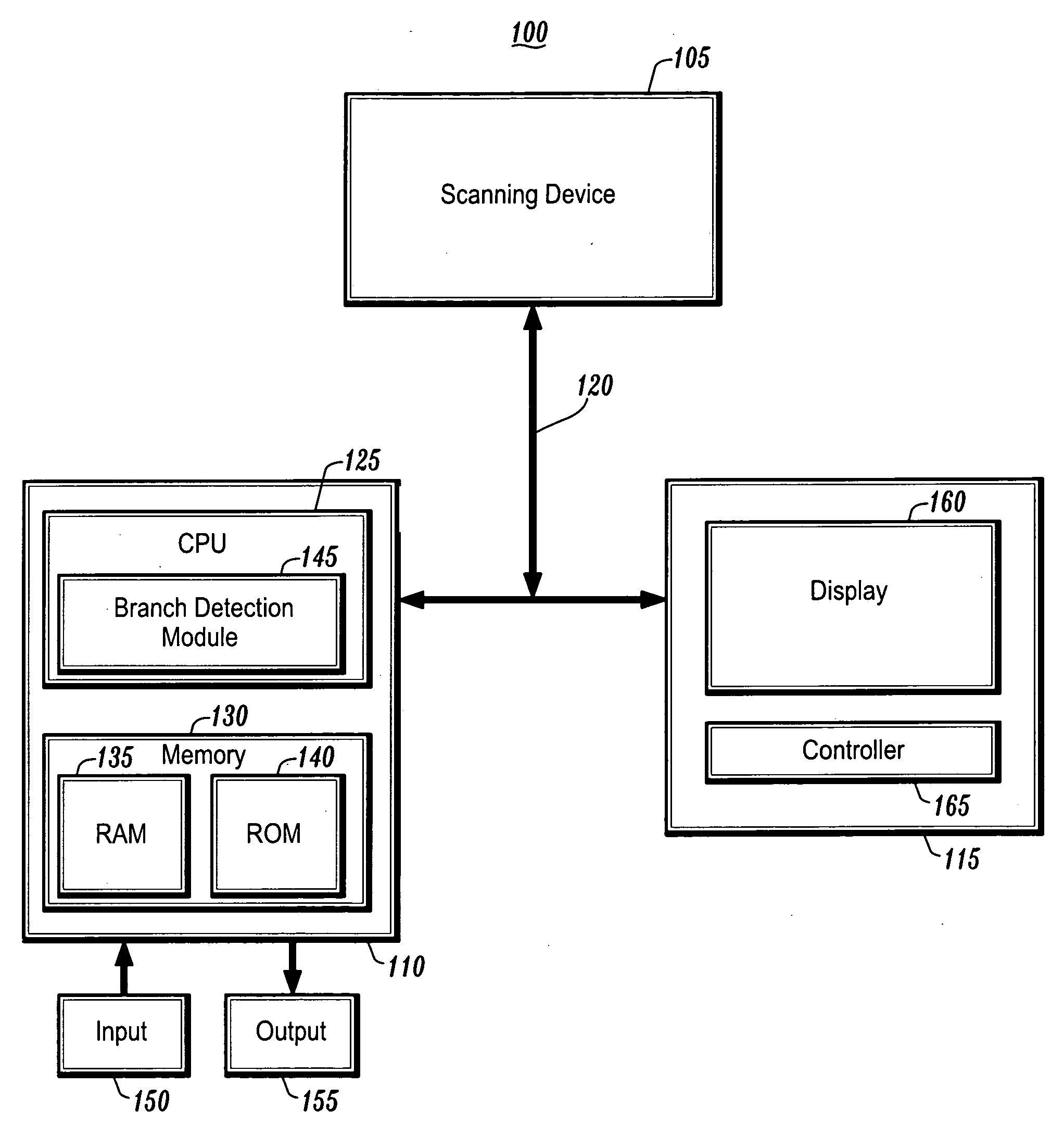
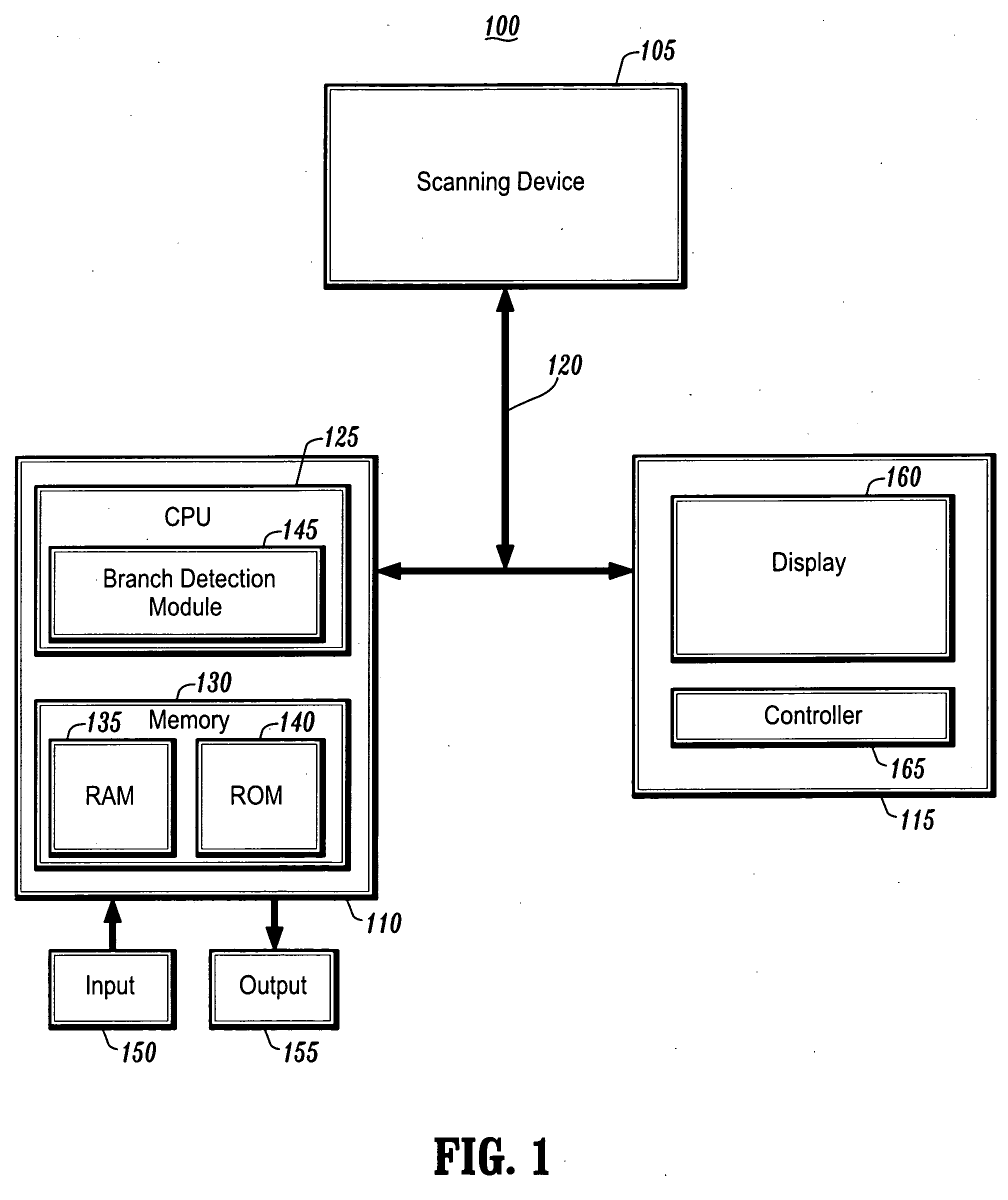
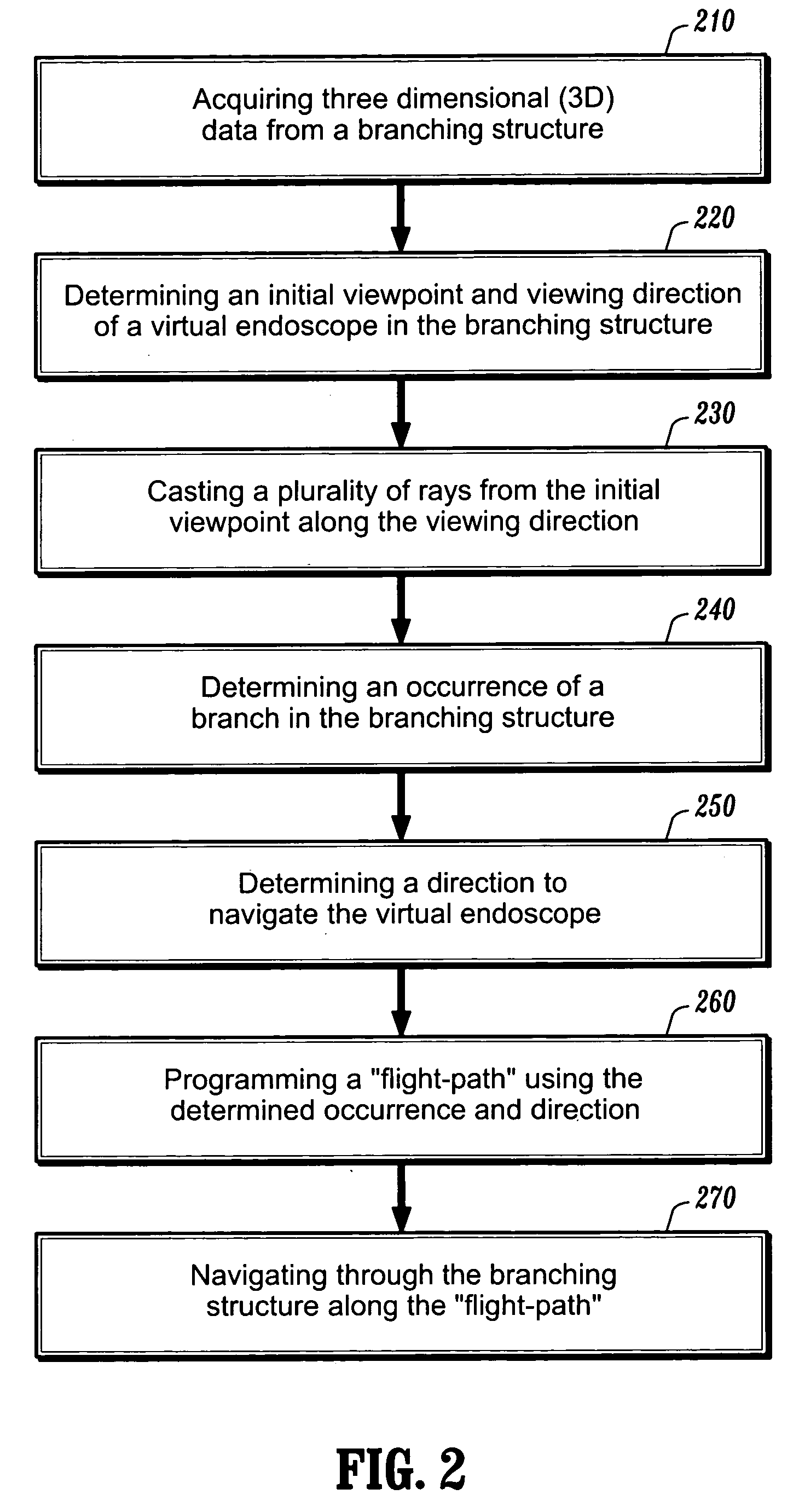
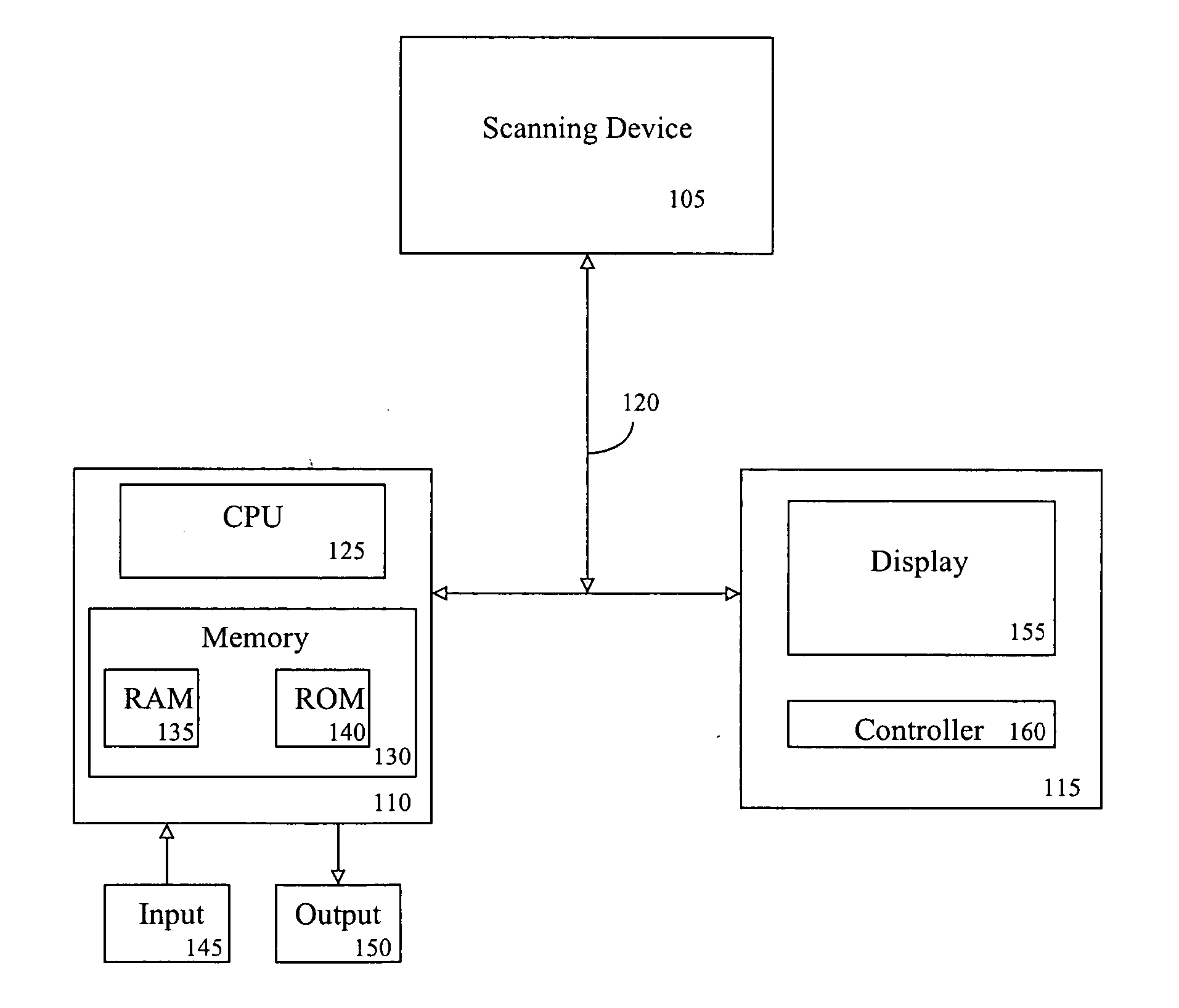
System and method for performing a virtual endoscopy in a branching structure
A system and method for performing a virtual endoscopy in a branching structure is provided. The method comprises the steps of: determining an initial viewpoint and viewing direction of a virtual endoscope in a branching structure; casting a plurality of rays from the initial viewpoint along the viewing direction; and determining an occurrence of a branch in the branching structure, wherein the occurrence is associated with a cluster that corresponds to the branch.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
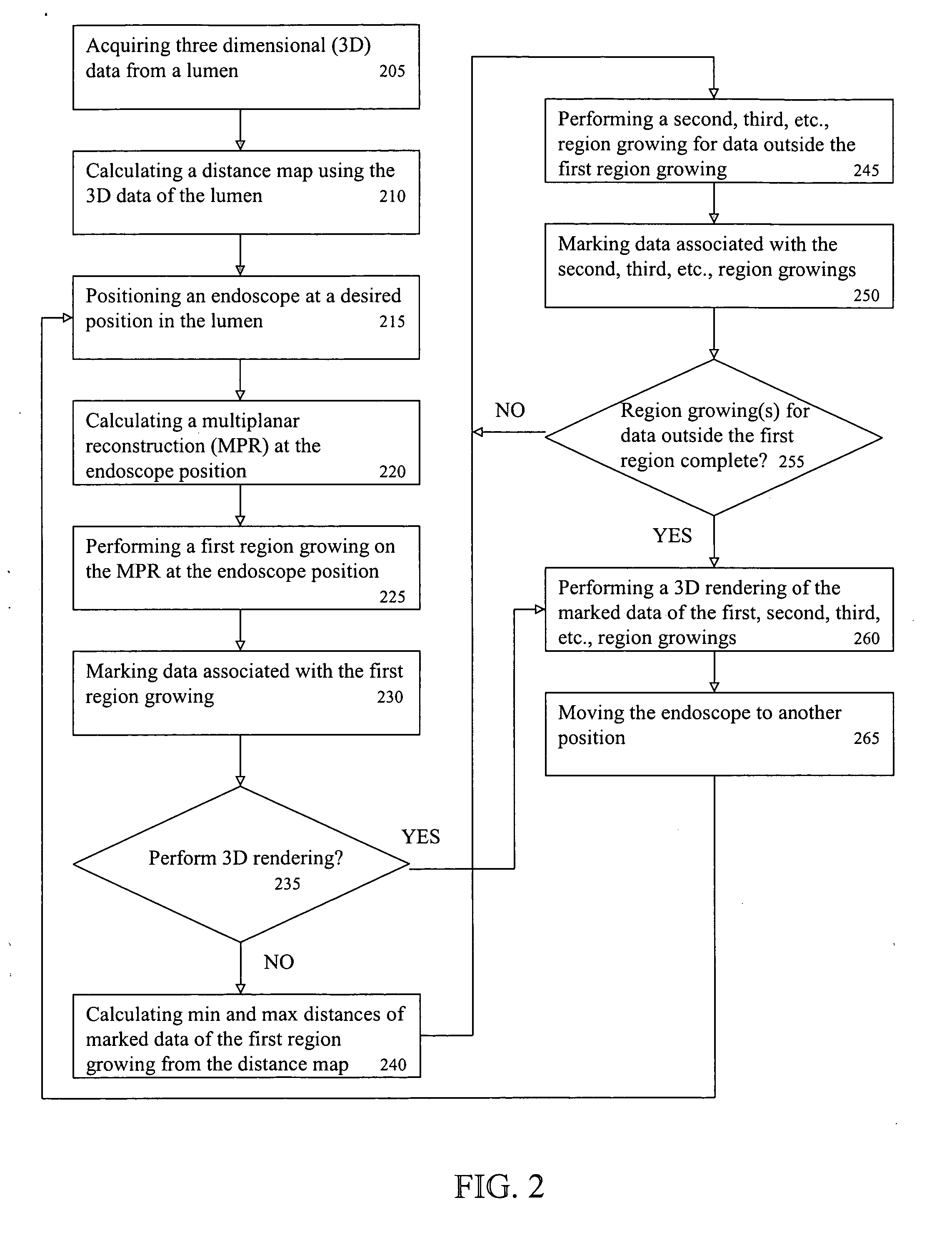
System and method for performing a virtual endoscopy
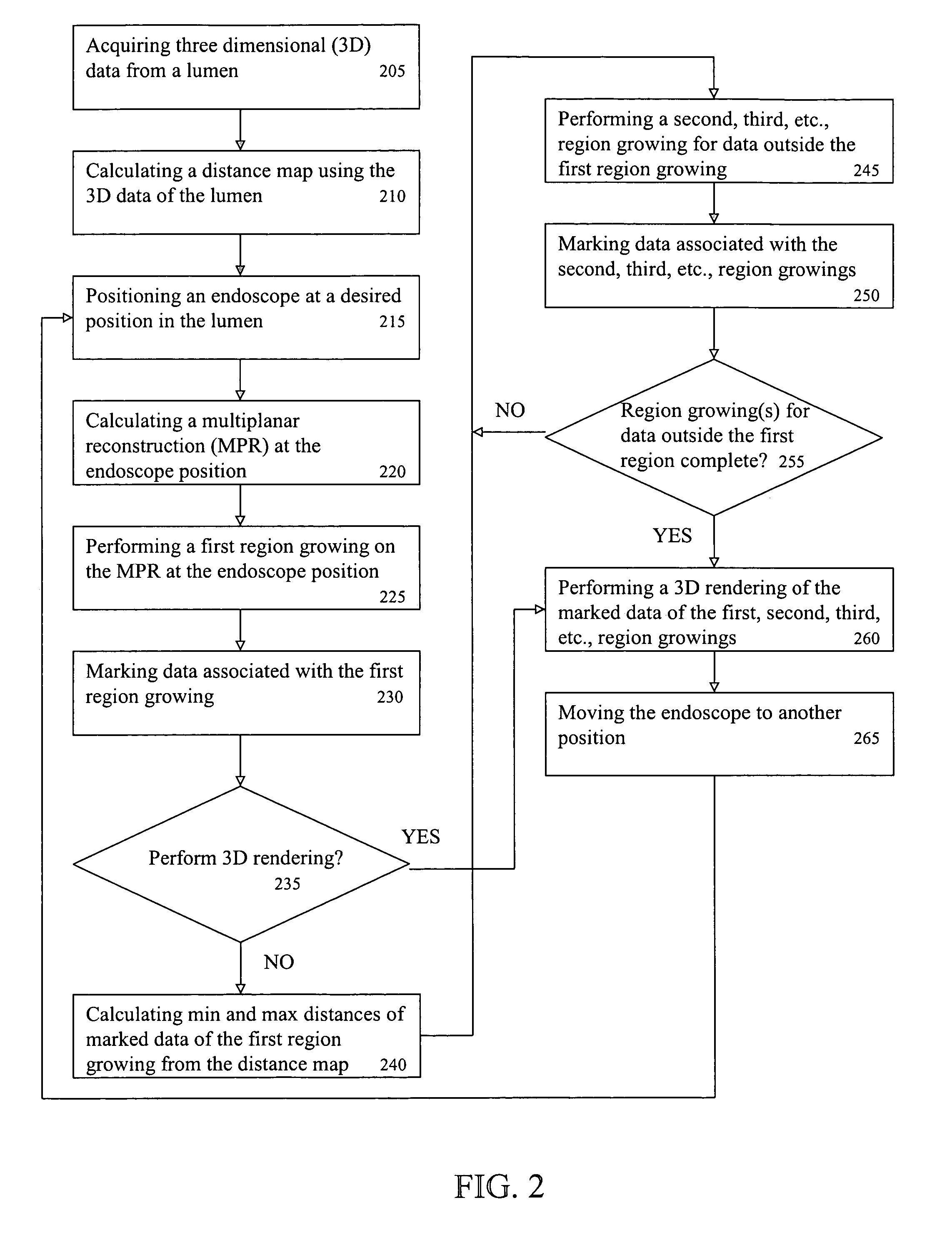
A system and method for performing a virtual endoscopy is provided. The method comprises the steps of: calculating a distance map using three-dimensional (3D) data of a lumen; calculating a multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) of the lumen, wherein the MPR is calculated orthogonal to the lumen at an endoscope position; performing a first region growing on the MPR of the lumen at the endoscope position, wherein data associated with the first region is marked; calculating a minimum distance and a maximum distance from the marked data of the first region growing using corresponding distances from the distance map; performing a second region growing on the MPR of the lumen for data outside the first region growing, wherein data associated with the second region is marked; and performing a 3D rendering of the marked data associated with the first region growing and the second region growing.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Device for merging a 2D radioscopy image with an image from a 3D image data record
ActiveUS20080137924A1Reduce total usageImprove bindingImage enhancementReconstruction from projection3d imageBack projection
The invention relates to a device for merging a 2D radioscopy image with an image obtained from a 3D image data record, having a memory unit that stores the 2D radioscopy image and the 3D image data record, a segmentation unit that segments an inner surface of a hollow organ from the 3D image data record, a registration unit that registers the 2D radioscopy image with the 3D image data record, a back-projection unit that back-projects the pixels of the 2D radioscopy image onto the segmented surface, taking account of the projection geometry of the 2D radioscopy image and the registration, and an image merger unit that generates a virtual endoscopy view of the surface from the segmented surface using the back-projected pixels. The device primarily allows 2D radioscopy images to be superimposed during interventional procedures with a fly display of the interior of an interesting organ.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Image-based Path Planning for Automated Virtual Colonoscopy Navigation
ActiveUS20090048482A1Smooth virtual endoscopy navigationSmooth navigationPrintersProjectorsVirtual CT colonoscopyVirtual colonoscopy
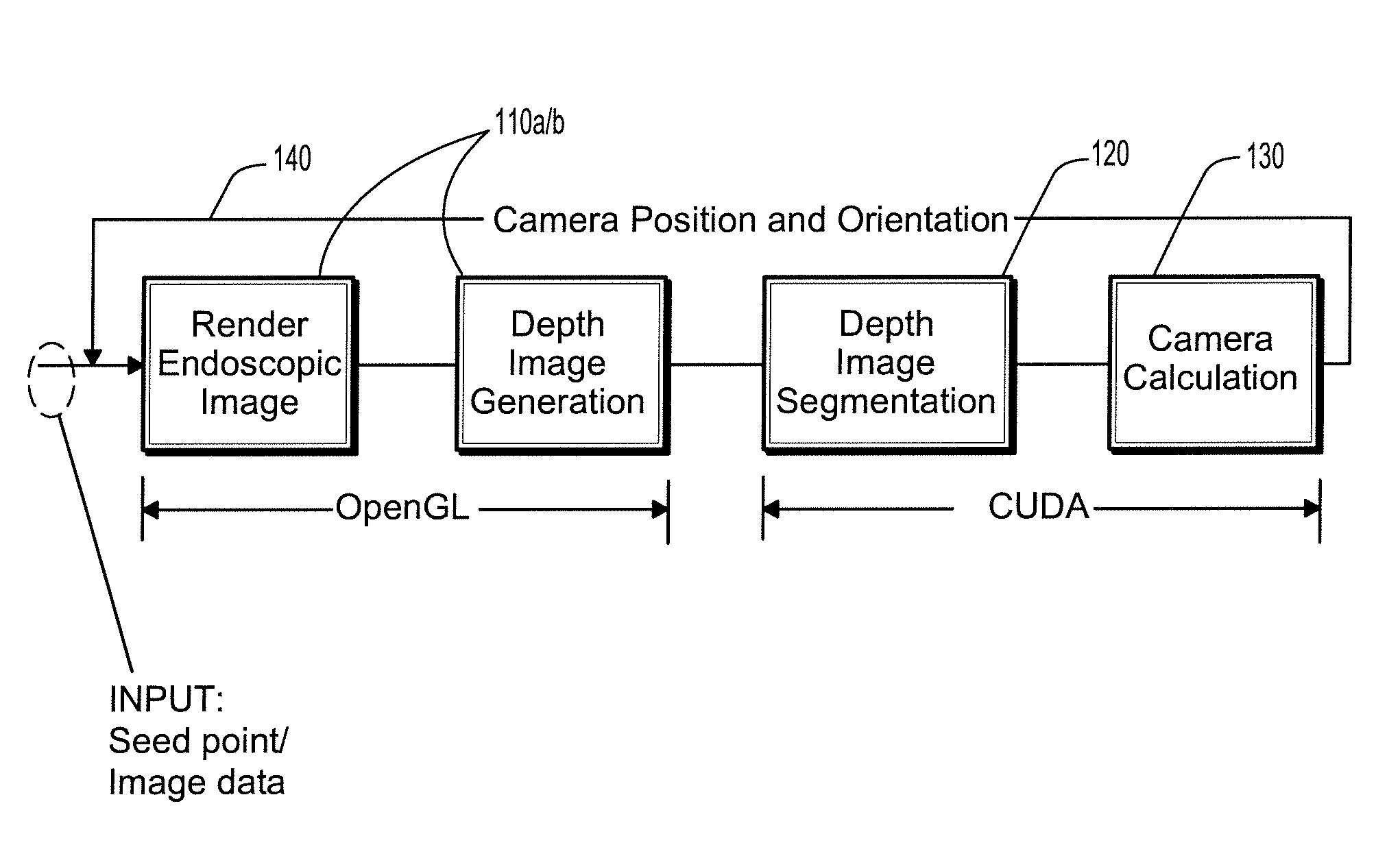
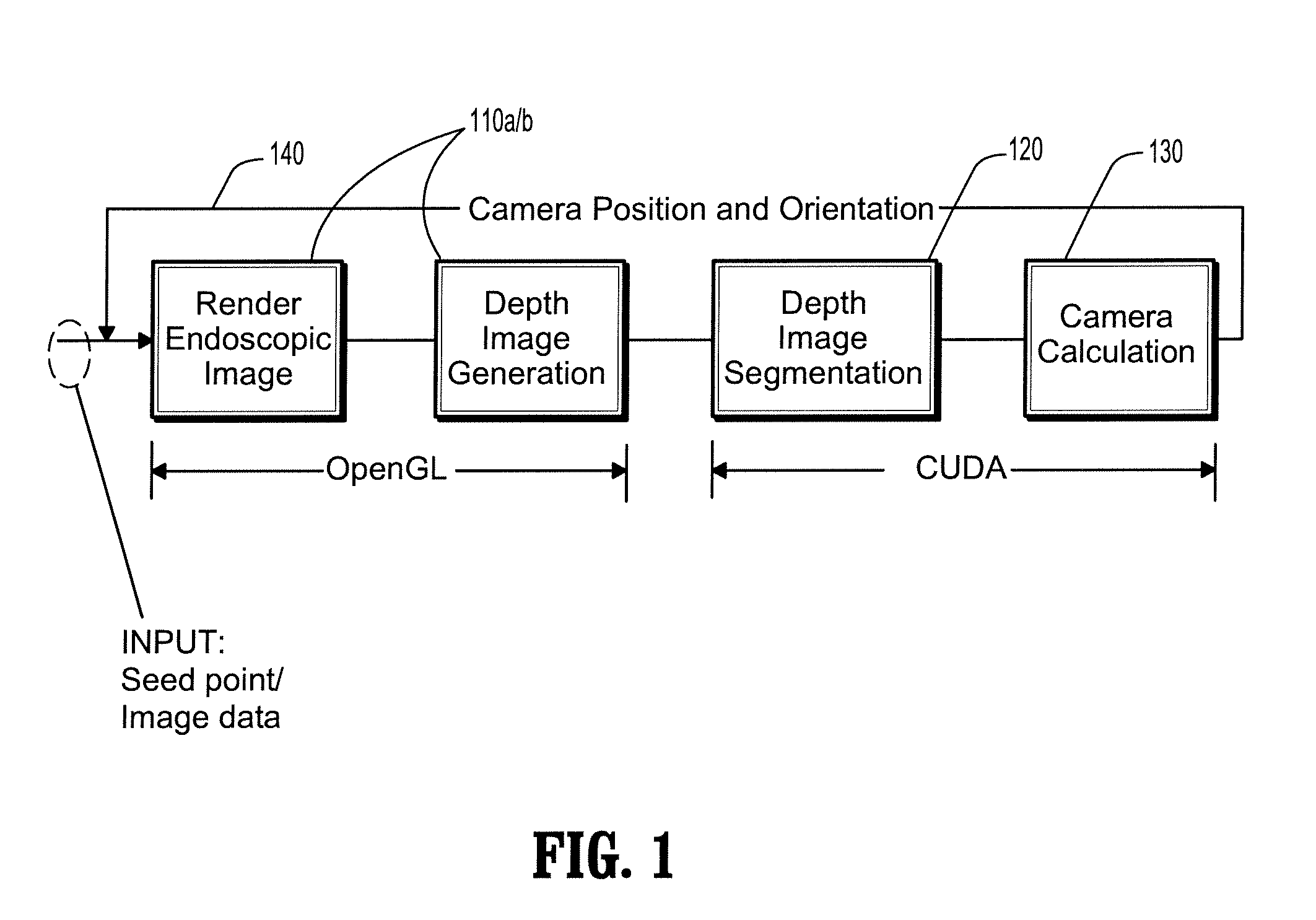
A method for automatic virtual endoscopy navigation, including: (a) using a fisheye camera to generate an endoscopic image and a depth image from a current position of the camera in lumen computed tomographic (CT) data; (b) segmenting a first region and a second region from the depth image, wherein the first region identifies a view direction of the camera and the second region is an area through which the camera can be moved without touching an inner surface of the lumen; (c) moving the camera from the current position, while pointing the camera in the view direction, to a next position in the second region; and (d) repeating steps (a-c) in sequence using the next position in step (c) as the current position in step (a).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for navigating a virtual camera along a biological object with a lumen
ActiveUS7623900B2Shorten the lengthEasy to viewSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionData setVirtual camera
A method of navigating along a biological object with a lumen represented by a three-dimensional volume data set comprises generating a plurality of navigation segments connectable in a sequence, each segment having a start point within the lumen, a direction and a length. The navigation may be used for a camera in a virtual endoscopic examination, for example. The direction of each segment is determined by casting groups of rays outwards from the start point of the segment to the object wall, and calculating an average ray length for each group. The group having the largest average ray length is selected, and the axial direction of this group is used as the direction for the segment. The average ray lengths of the groups may be weighted using the direction of the previous segments to bias the navigation generally forward, or may be weighted using a view direction of the camera to allow a user to turn the camera into a chosen branch in the object.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
Determining a viewpoint for navigating a virtual camera through a biological object with a lumen
A method of orienting a virtual camera for rendering a virtual endoscopy image of a lumen in a biological structure represented by a medical image data set, e.g., a colon. The method comprises selecting a location from which to render an image, determining an initial orientation for the virtual camera relative to the data set for the selected location based on the geometry of the lumen, determining an offset angle between the initial orientation and a bias direction; and orienting the virtual camera in accordance with a rotation from the initial orientation towards the bias direction by a fractional amount of the offset angle which varies according to the initial orientation. The fractional amount may vary according to the offset angle and / or a separation between a predetermined direction in the data set and a view direction of the virtual camera for the initial orientation. Thus the camera orientation can be configured to tend towards a preferred direction in the data set, while maintaining a good view of the lumen and avoiding barrel rolling effects.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
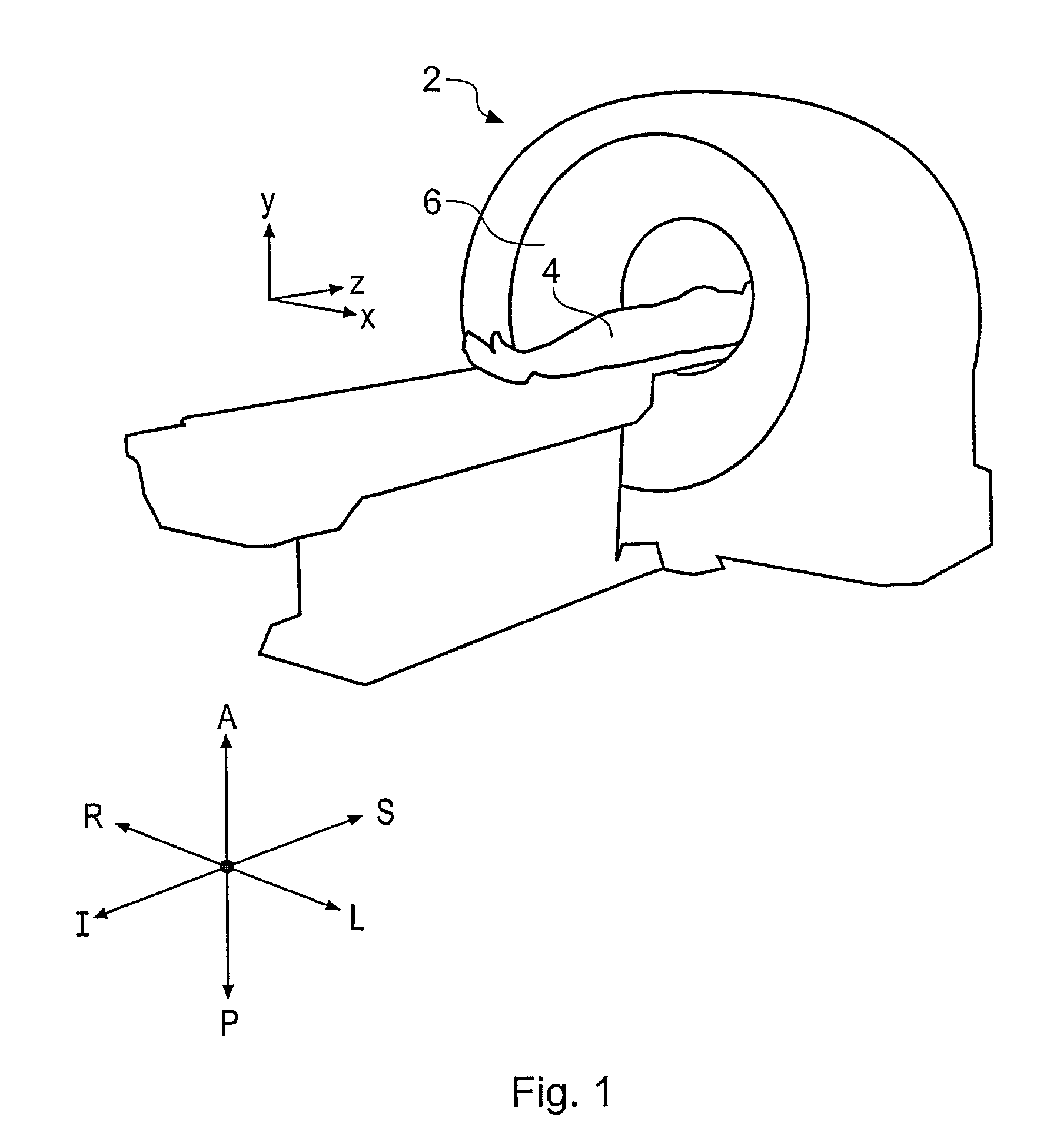
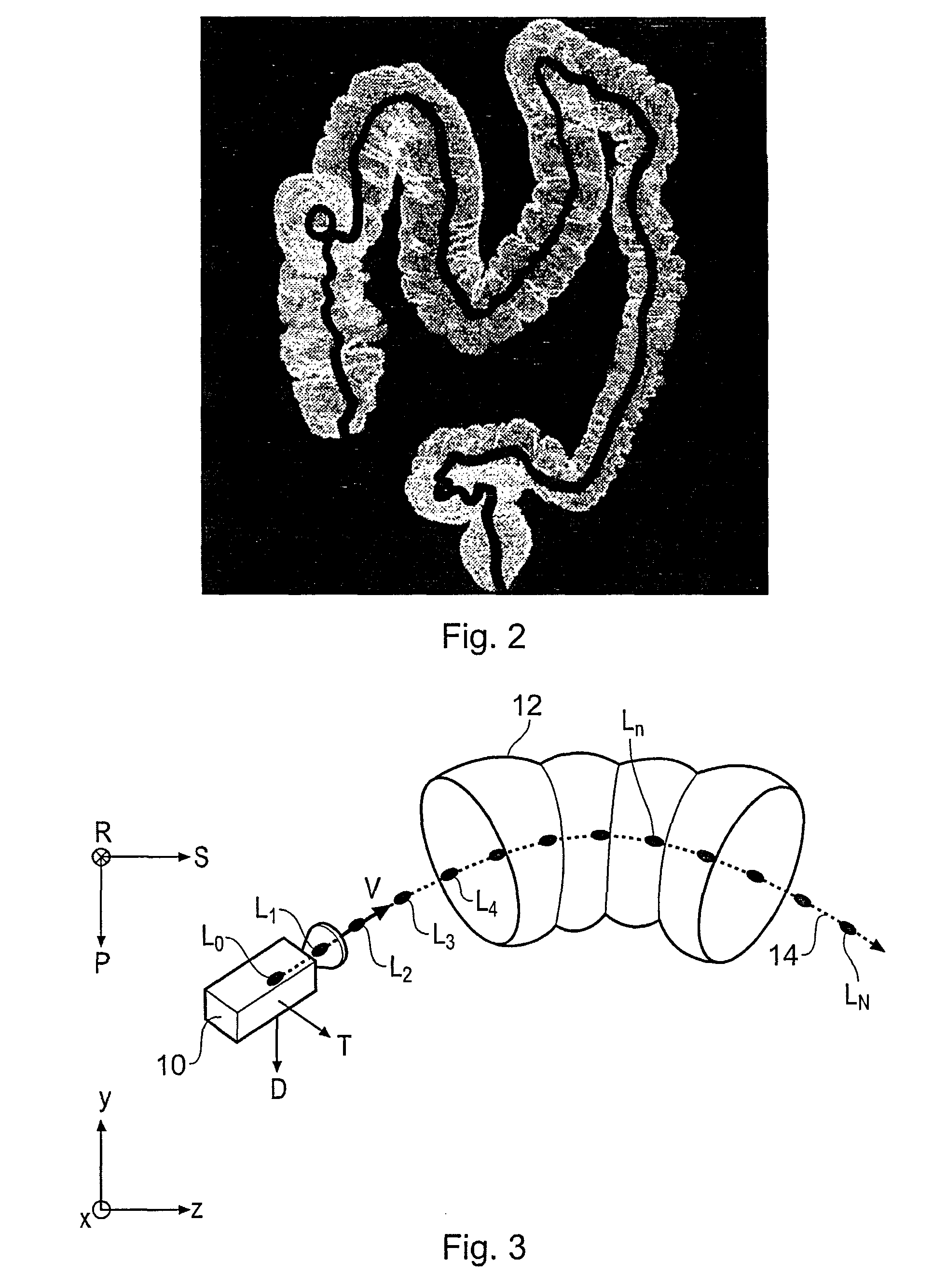
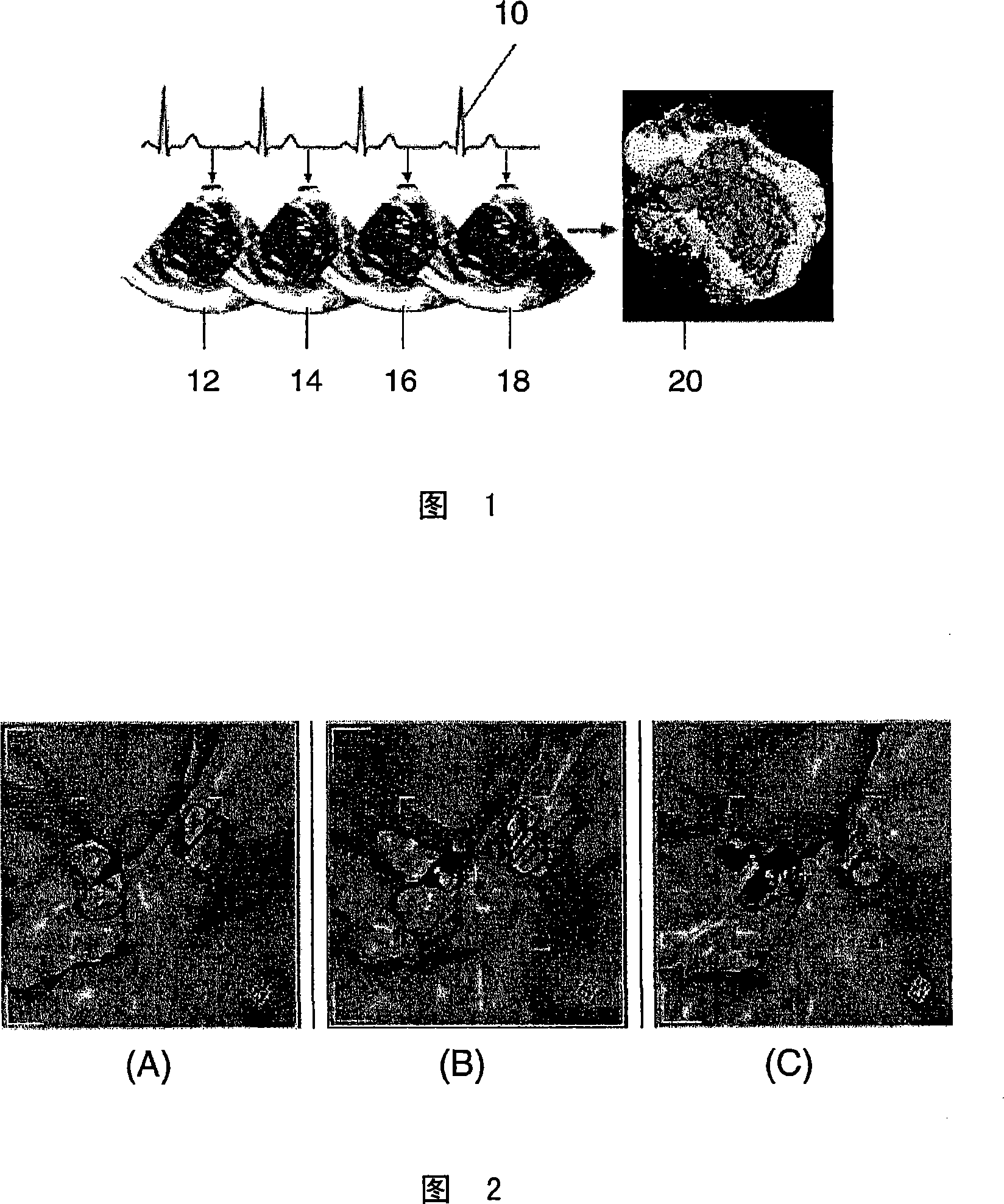
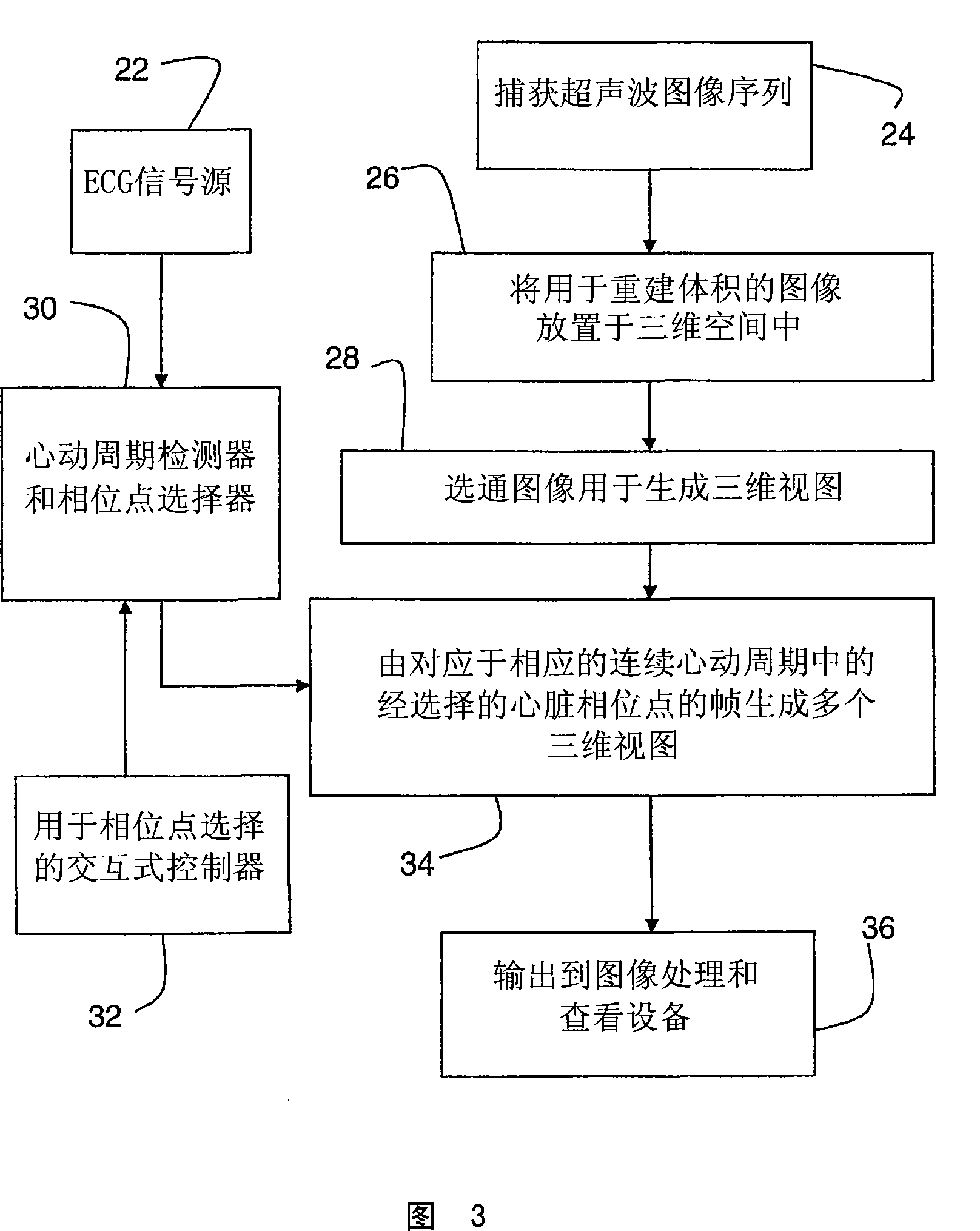
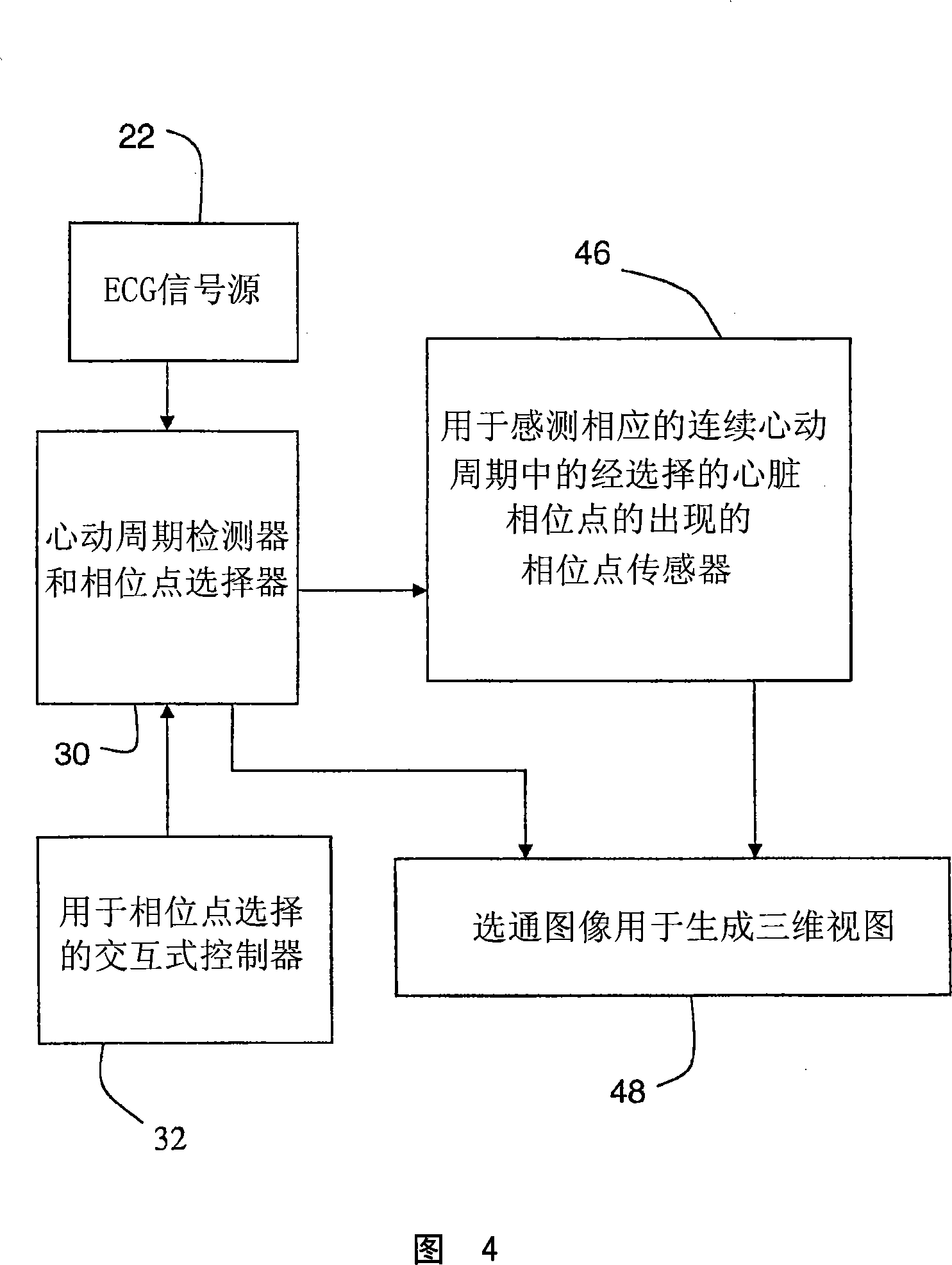
Interactive type four-dimensional dummy endoscopy method and apparatus
ActiveCN101190124ARich visual informationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFlexible endoscopeCardiac cycle
A method for performing four-dimensional virtual endoscopy, includes capturing a heart image sequence of a patient by an imaging equipment and a electrocardiagram signal displaying a cardiac cycle of the heart. The electrocardiagram signal is used to select images to derive the corresponding three-dimensional view successively in the corresponding cardiac cycle with the corresponding heart image in the common and selected phase point of each corresponding cardiac cycle.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Pictorial Representation in Virtual Endoscopy
The invention relates to a method for the pictorial representation of a three-dimensional measured data record representing part of a hollow body, comprising the following steps: processing of a first subset of the two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional measured data record for an image reproduction in a first two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional intraluminal pictorial representation of an inner surface of the part of the hollow body, processing of a second subset of the three-dimensional measured data record for an image reproduction in a second two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional intraluminal pictorial representation of the part of the hollow body, representation of the processed first subset of the three-dimensional measured data record in the form of the first two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional intraluminal pictorial representation in a representation plane and representation of the processed second subset of three-dimensional measured data record in the form of the second two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional intraluminal pictorial representation in the representation plane. data of the second subset of the three-dimensional measured data record for one or several planes in a predetermined distance perpendicular to the surface structure represented in the first two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional intraluminal pictorial representation are represented color-coded on the surface structure of the inside of the hollow body which is represented in the entire first two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional intraluminal pictorial representation.
Owner:RUST GEORG FRIEDEMANN
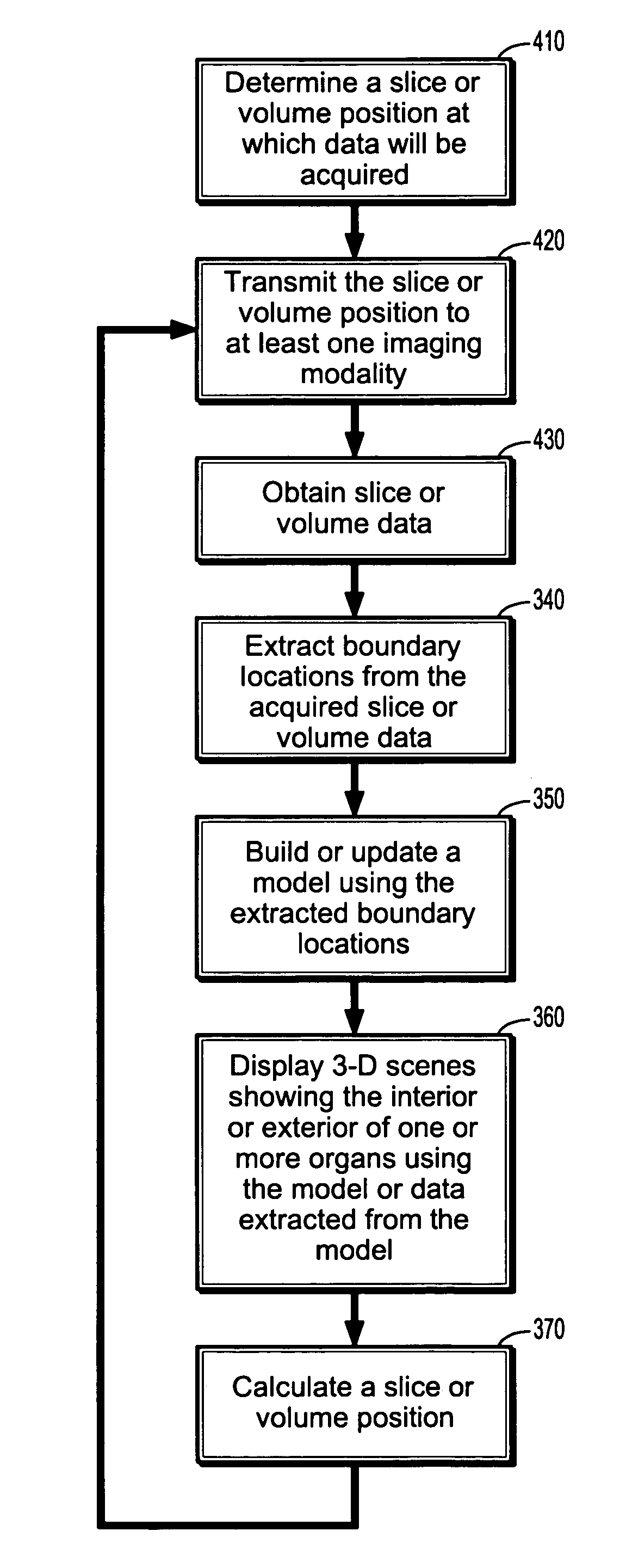
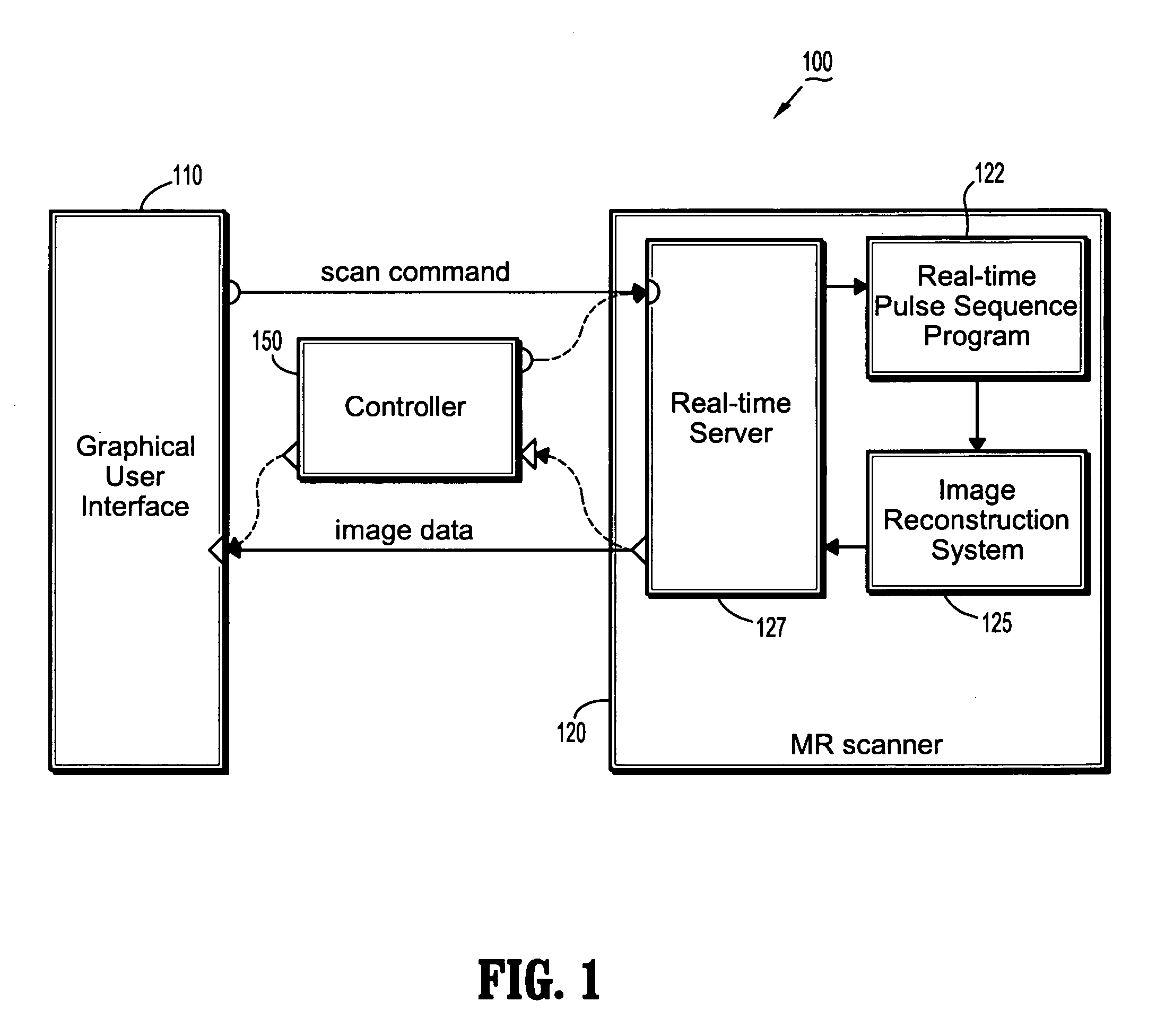
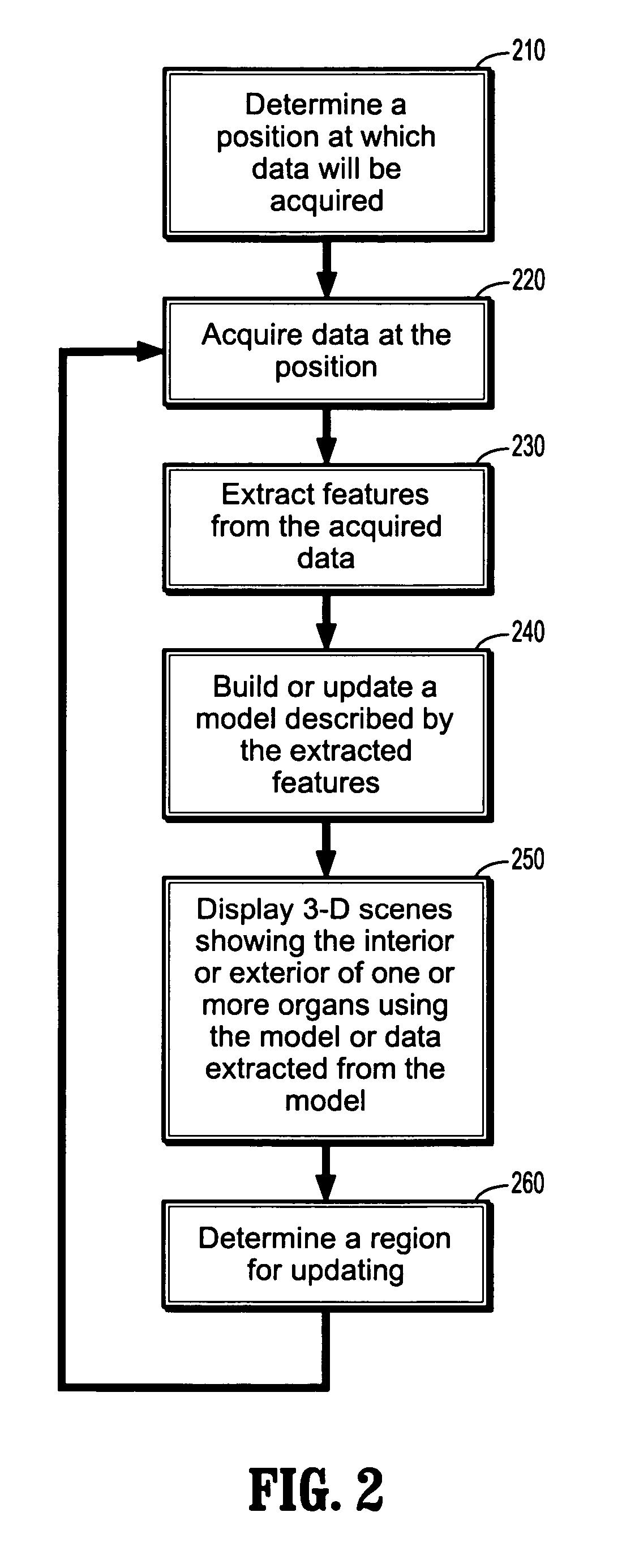
Real-time virtual endoscopy
InactiveUS8712115B2Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMarine navigation3 d visualization
In a method of real-time 3-D visualization and navigation for interventional procedures a position is determined at which data will be acquired, and data is acquired at the position. Features are extracted from the acquired data. A model described by the extracted features is built or updated, wherein updating the model includes calculating at least one acquisition parameter of a set of acquisition parameters. 3-D scenes showing the interior or exterior of one or more organs are displayed using the model or data extracted from the model. A region for updating is determined.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and method for performing a virtual endoscopy
A system and method for performing a virtual endoscopy is provided. The method comprises the steps of: calculating a distance map using three-dimensional (3D) data of a lumen; calculating a multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) of the lumen, wherein the MPR is calculated orthogonal to the lumen at an endoscope position; performing a first region growing on the MPR of the lumen at the endoscope position, wherein data associated with the first region is marked; calculating a minimum distance and a maximum distance from the marked data of the first region growing using corresponding distances from the distance map; performing a second region growing on the MPR of the lumen for data outside the first region growing, wherein data associated with the second region is marked; and performing a 3D rendering of the marked data associated with the first region growing and the second region growing.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Virtual endoscopy system based on CT image
PendingCN107204045AQuick switchIncrease authenticityImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsImaging processing
The present invention discloses a virtual endoscopy system based on a CT image. The system comprises: an image collection module configured to receive a plurality of CT images; an image processing module being in communication connection with the image collection module and configured to perform smooth processing and boundary processing of each CT image in the CT images transmitted by the image collection module; a three-dimensional conversion module being in communication connection with the image processing module and configured to perform surface reconstruction of each CT image after the processing through the image processing module to obtain a special three-dimensional image; a center line extraction module being in communication connection with the three-dimensional conversion module and configured to extract the center line of the special three-dimensional image; and a roaming module being in communication connection with the three-dimensional conversion module and the center line extraction module and configured to control the movement track of a virtual camera taking a center line as a viewpoint in the special three-dimensional image and perform roaming.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF QINGDAO UNIV
Method and apparatus for examining hollow lumen by virtual endoscope
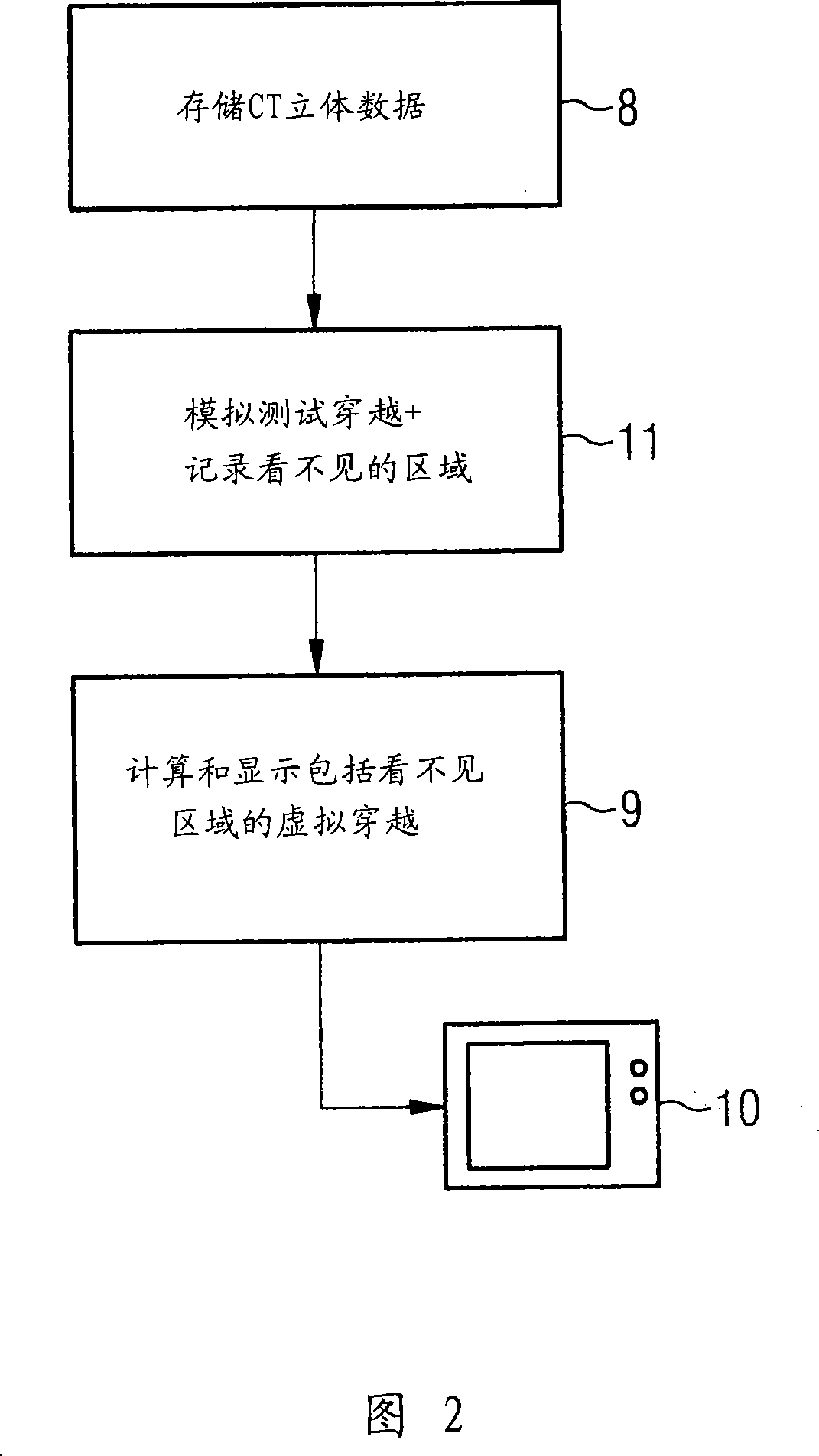
InactiveCN101069655AReduce time overheadImage enhancementData processing applicationsDisplay deviceComputer science
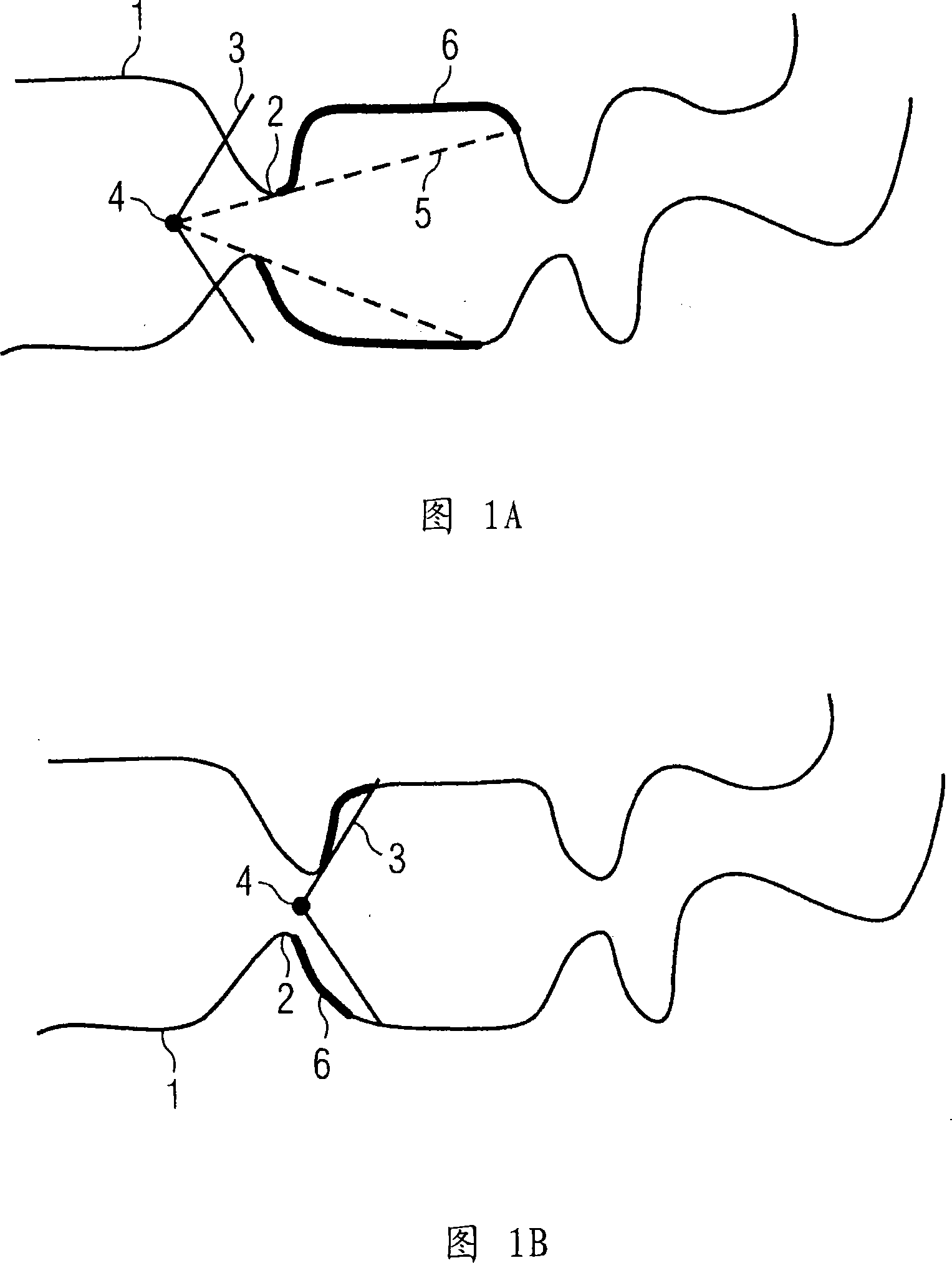
The invention relates to a method and a device for virtual endoscopy in a hollow tract, in which at least one volume record of the hollow tract (1), recorded by tomographic imaging, is provided from which a virtual flight through the hollow tract (1) in endoscopic perspective is calculated and visualized on a display device (10). In at least one embodiment, in the method and the device, before the visualization of the virtual flight, a virtual test flight without visualization is first simulated in which unobservable areas (6) of the hollow tract are detected during the test flight. Subsequently, the observer is notified of the unobservable areas (6) close to the location during the visualization of the virtual flight or the unobservable areas (6) are automatically visualized during the virtual flight. Using the present method and the associated device, in at least one embodiment, the time consumption during virtual endoscopy may be reduced for the observer without overloading him with redundant information.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com