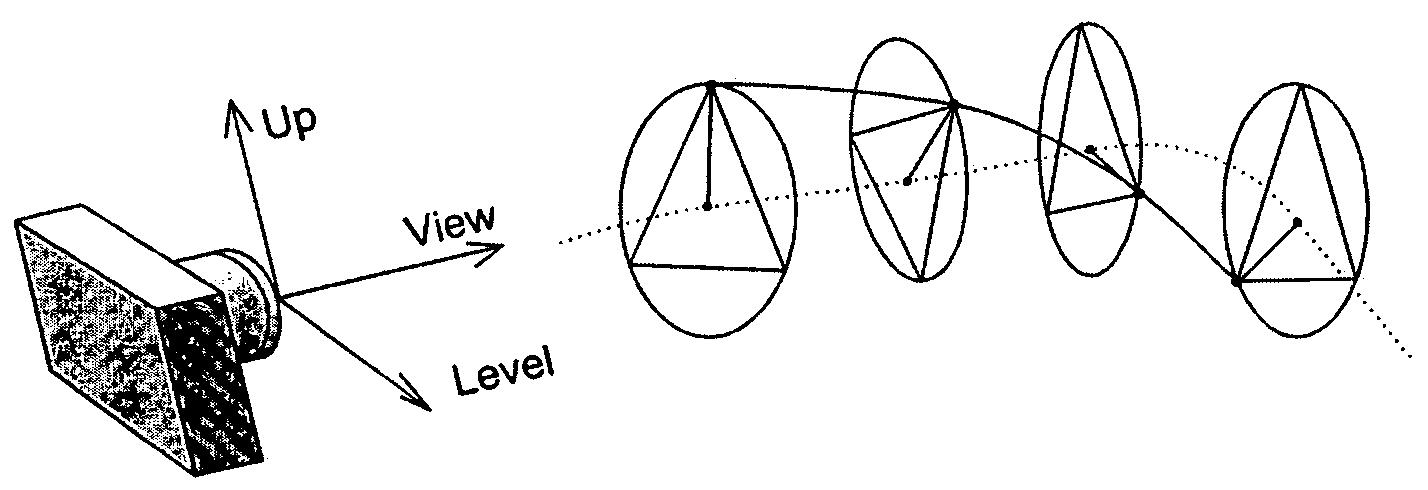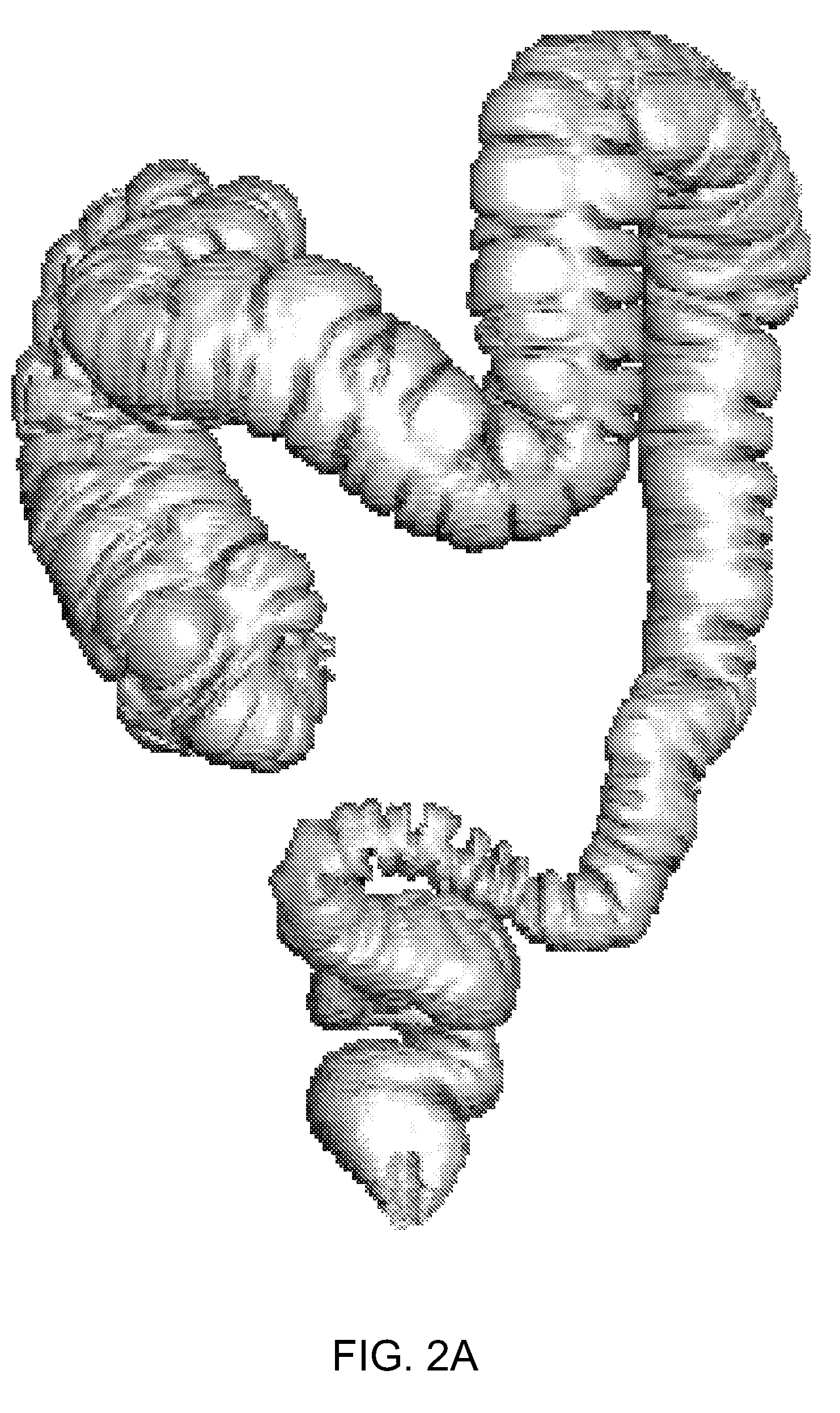Patents
Literature
39 results about "Virtual CT colonoscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
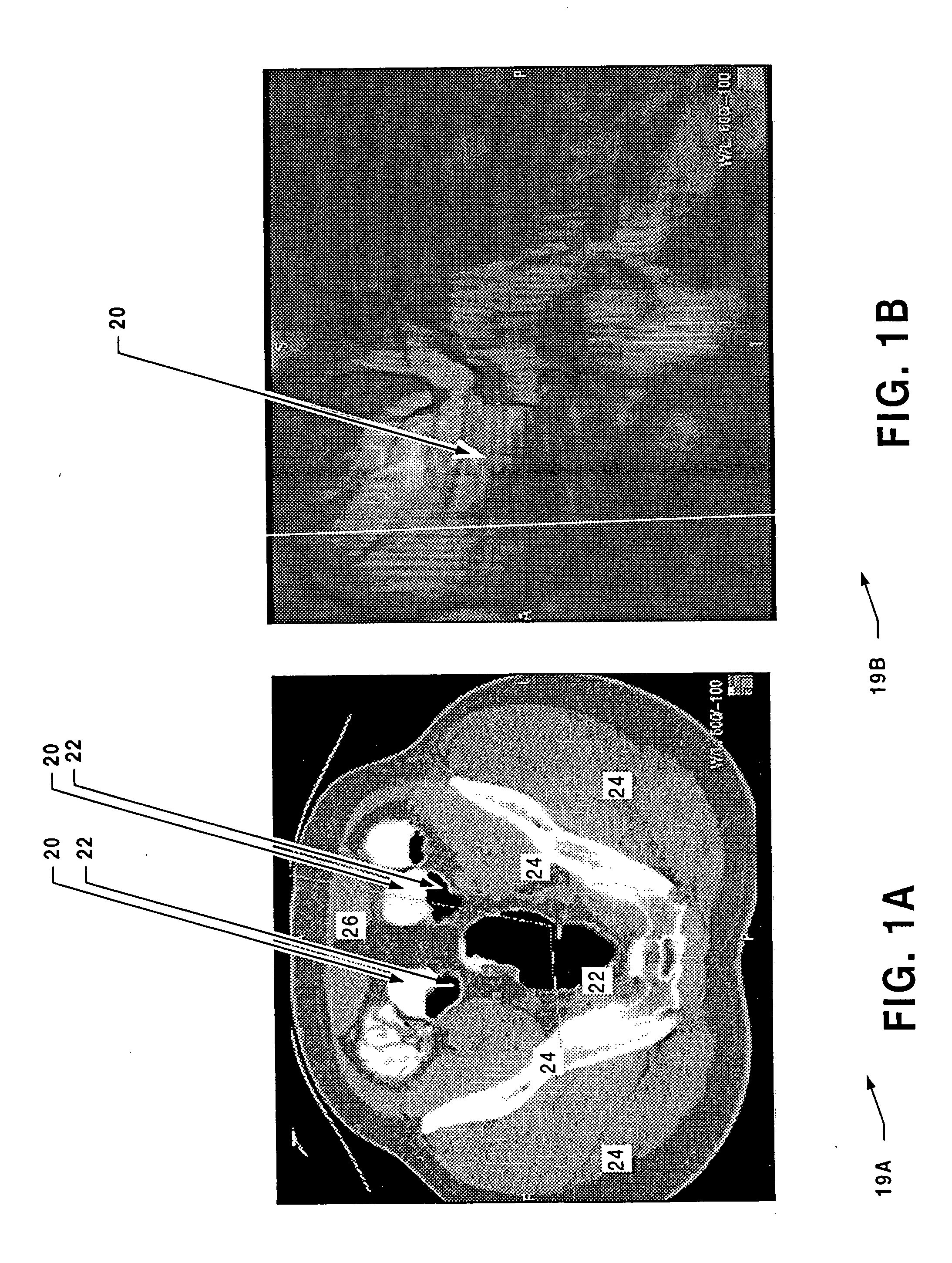
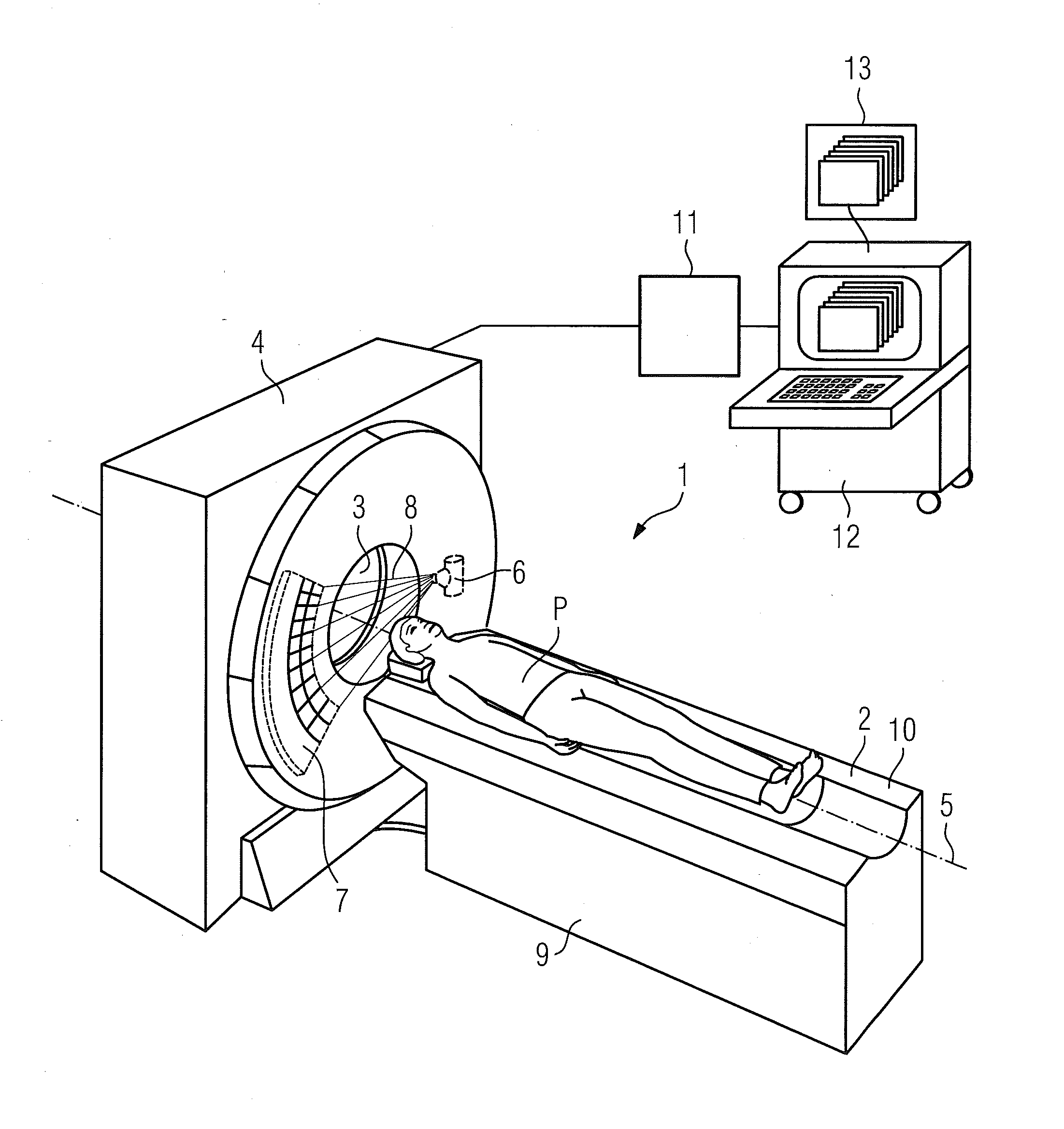
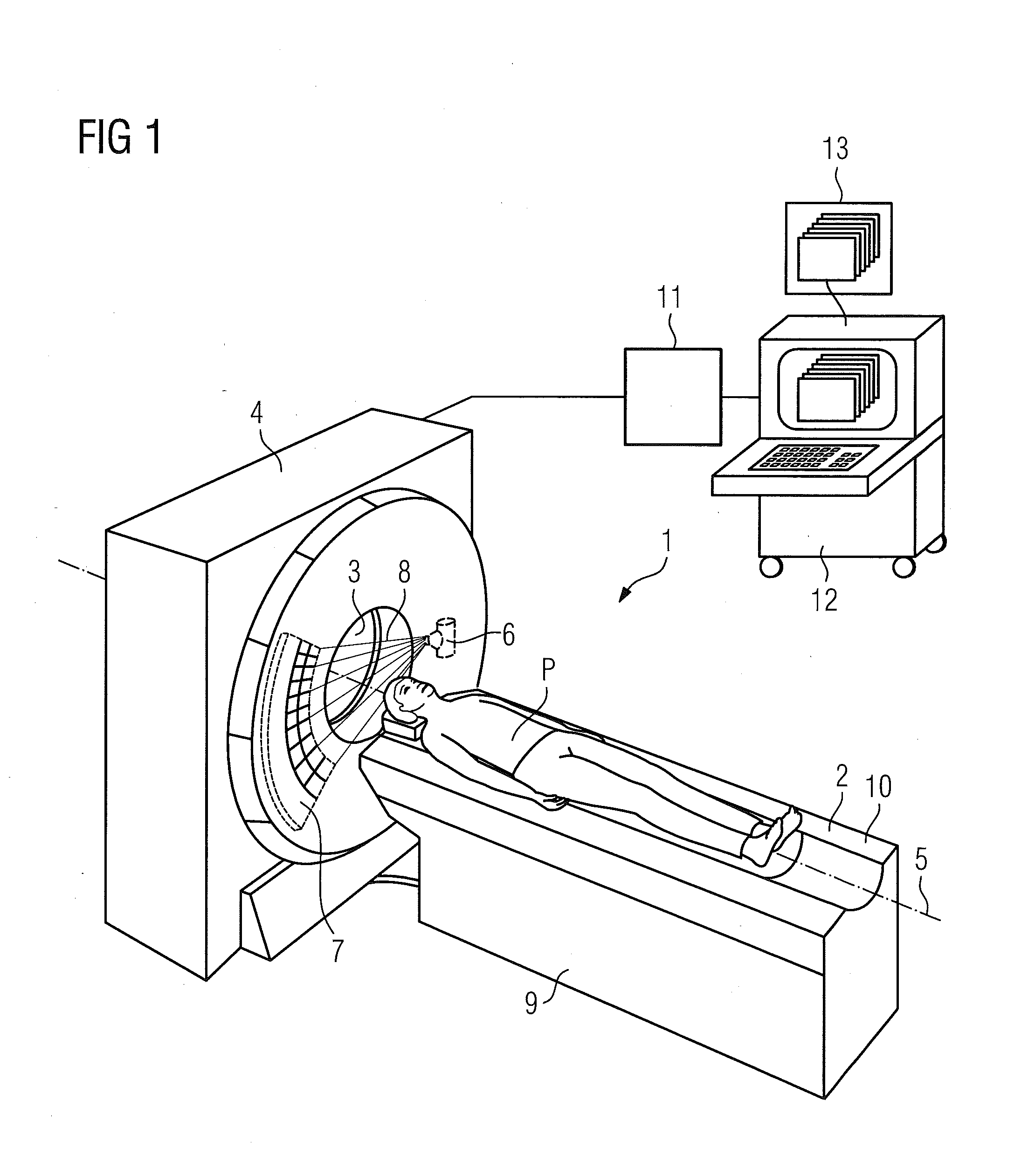
Virtual colonoscopy (VC, also called CT Colonography or CT Pneumocolon) is a medical imaging procedure which uses x-rays and computers to produce two- and three-dimensional images of the colon (large intestine) from the lowest part, the rectum, all the way to the lower end of the small intestine and display them on a screen.
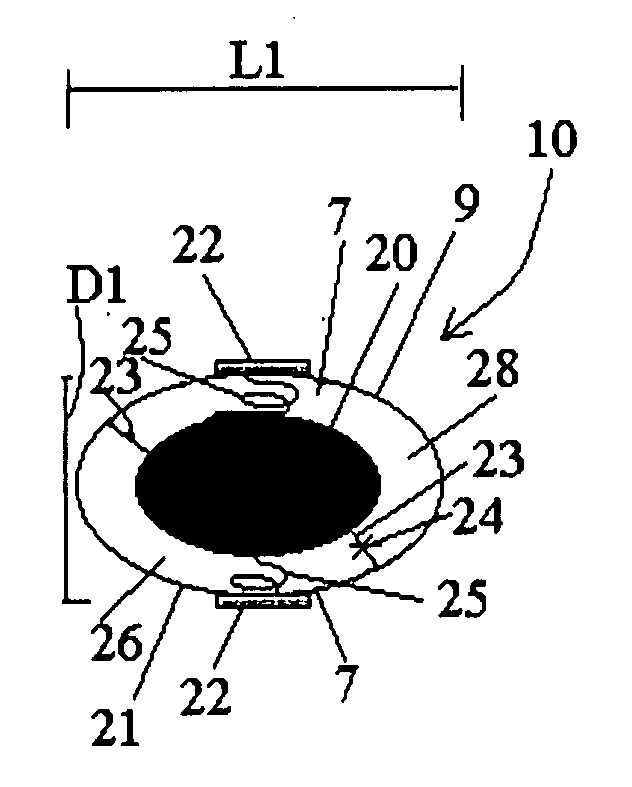
Ingestible device platform for the colon
ActiveUS20050266074A1Enhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryAbnormal tissue growthOptical fluorescence
An ingestible pill platform for colon imaging is provided, designed to recognize its entry to the colon and expand in the colon, for improved imaging of the colon walls. On approaching the external anal sphincter muscle, the ingestible pill may contract or deform, for elimination. Colon recognition may be based on a structural image, based on the differences in diameters between the small intestine and the colon, and particularly, based on the semilunar fold structure, which is unique to the colon. Additionally or alternatively, colon recognition may be based on a functional image, based on the generally inflammatory state of the vermiform appendix. Additionally or alternatively, pH, flora, enzymes and (or) chemical analyses may be used to recognize the colon. The imaging of the colon walls may be functional, by nuclear-radiation imaging of radionuclide-labeled antibodies, or by optical-fluorescence-spectroscopy imaging of fluorescence-labeled antibodies. Additionally or alternatively, it may be structural, for example, by visual, ultrasound or MRI means. Due to the proximity to the colon walls, the imaging in accordance with the present invention is advantageous to colonoscopy or virtual colonoscopy, as it is designed to distinguish malignant from benign tumors and detect tumors even at their incipient stage, and overcome blood-pool background radioactivity.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
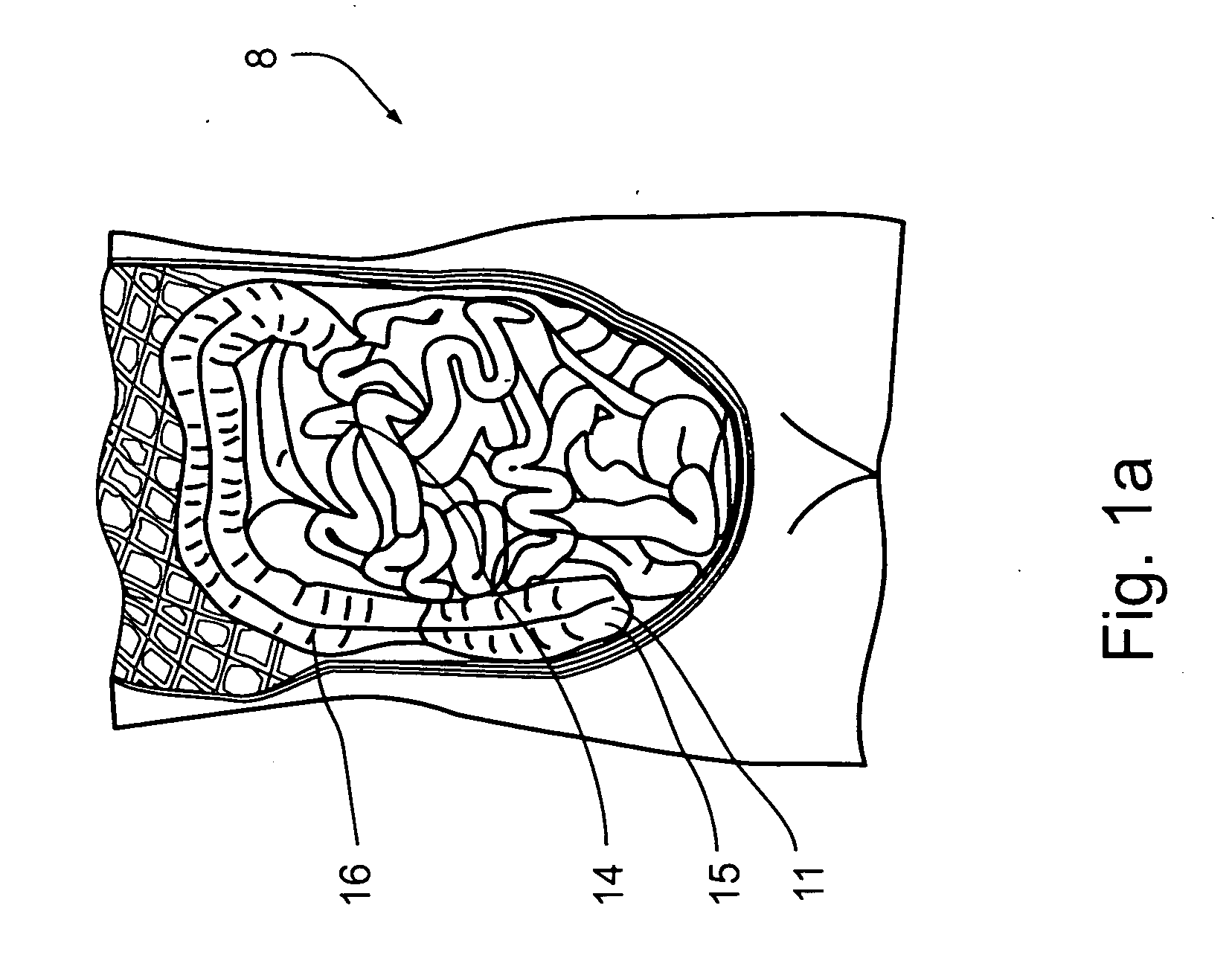
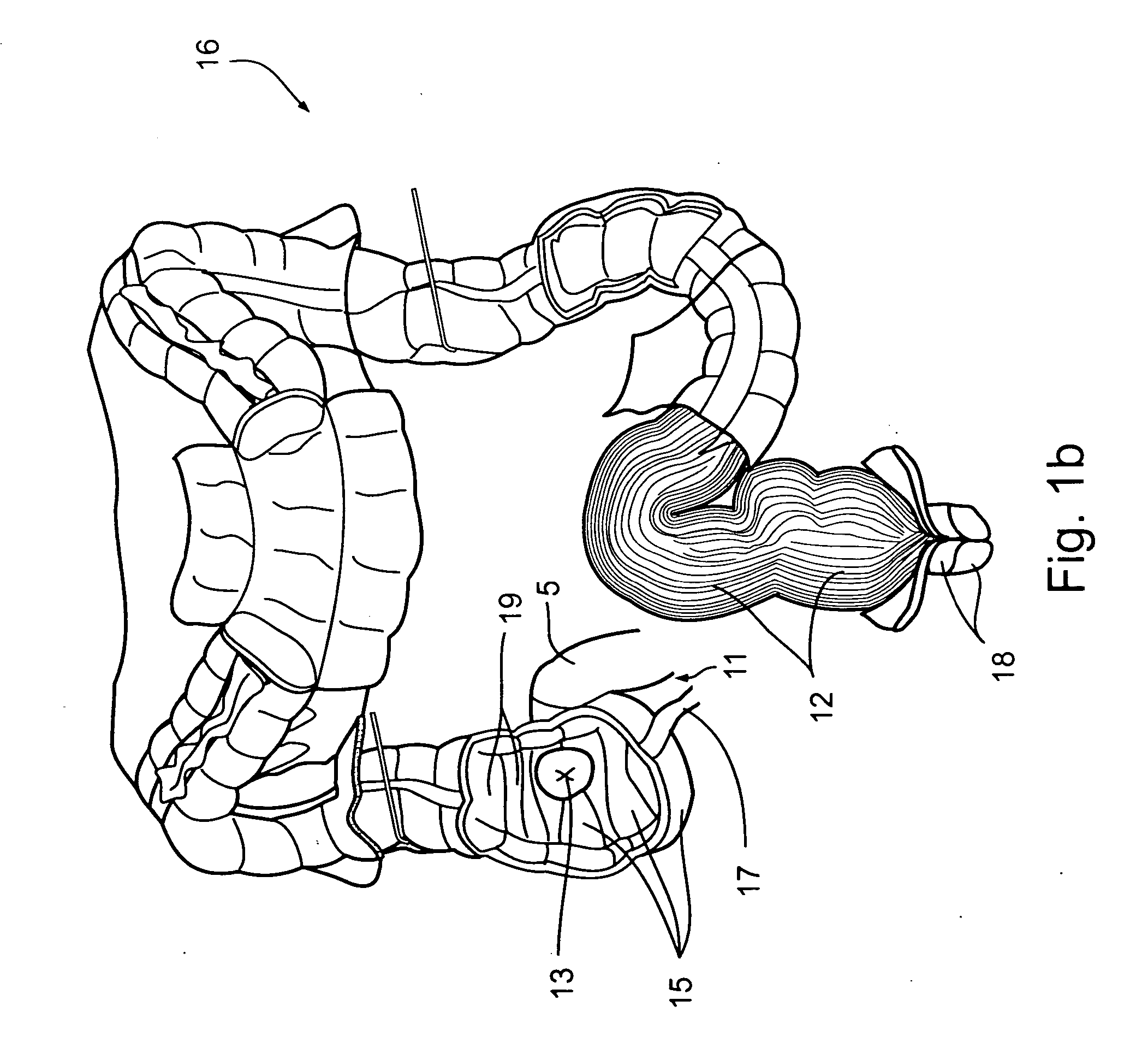
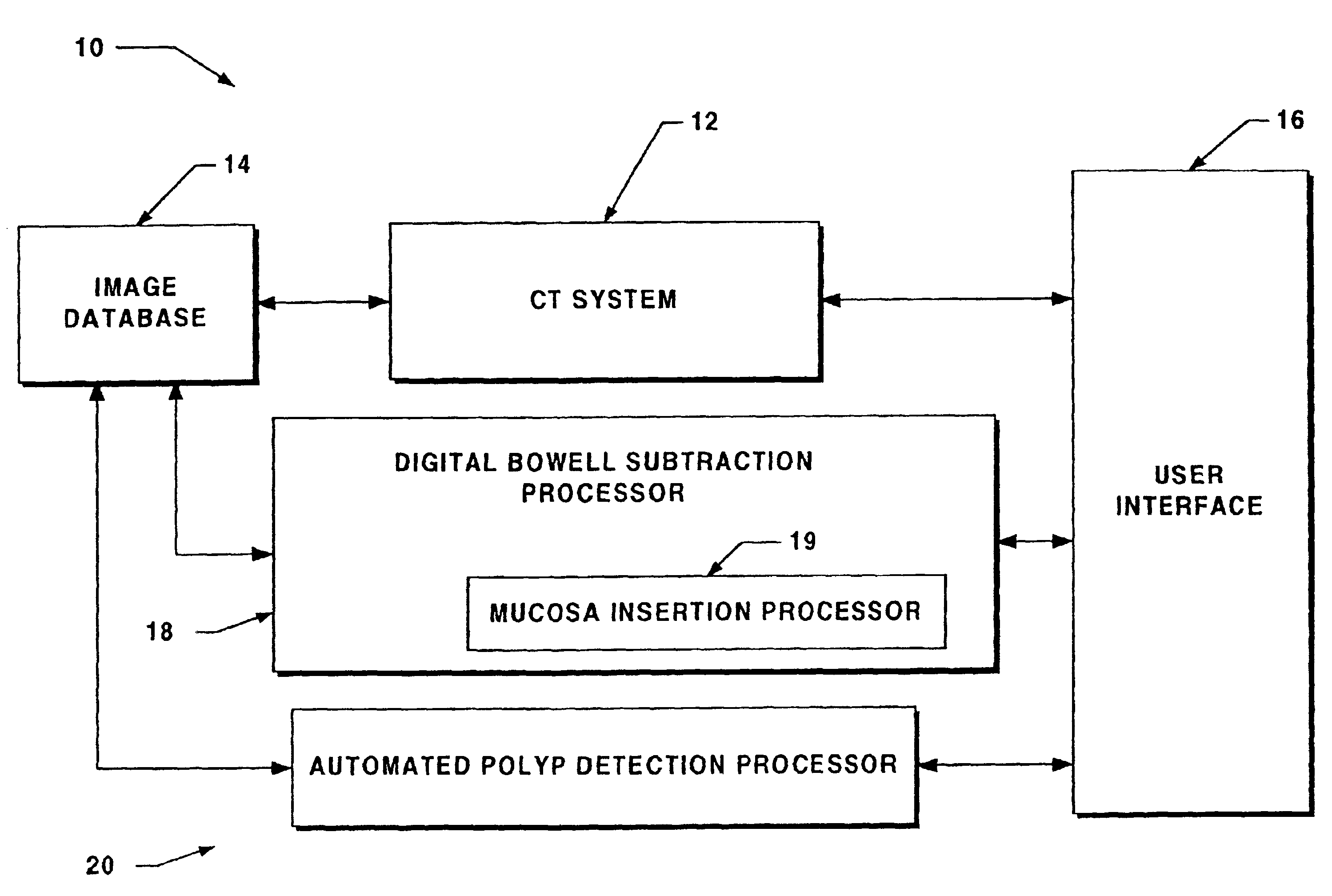
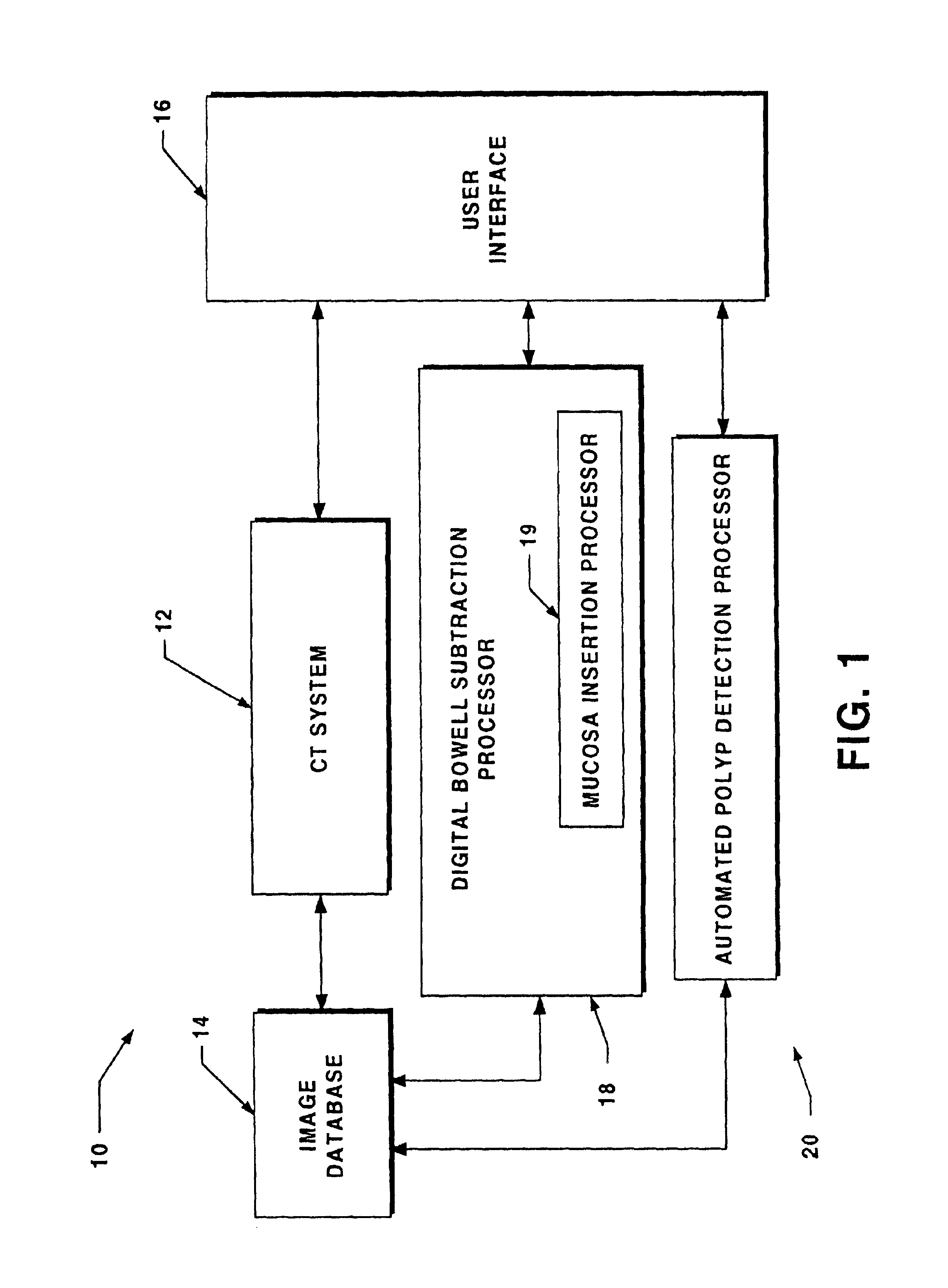
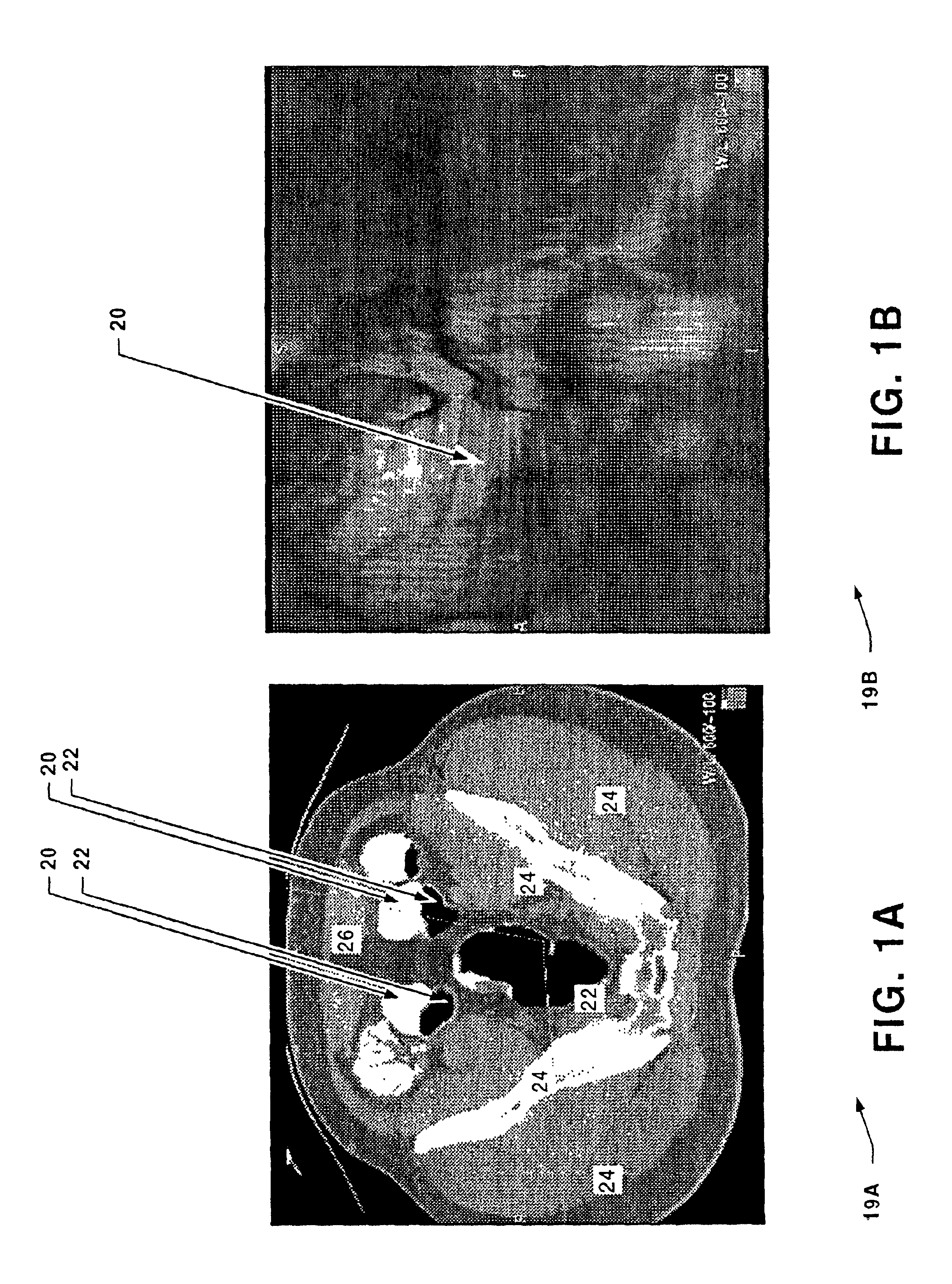
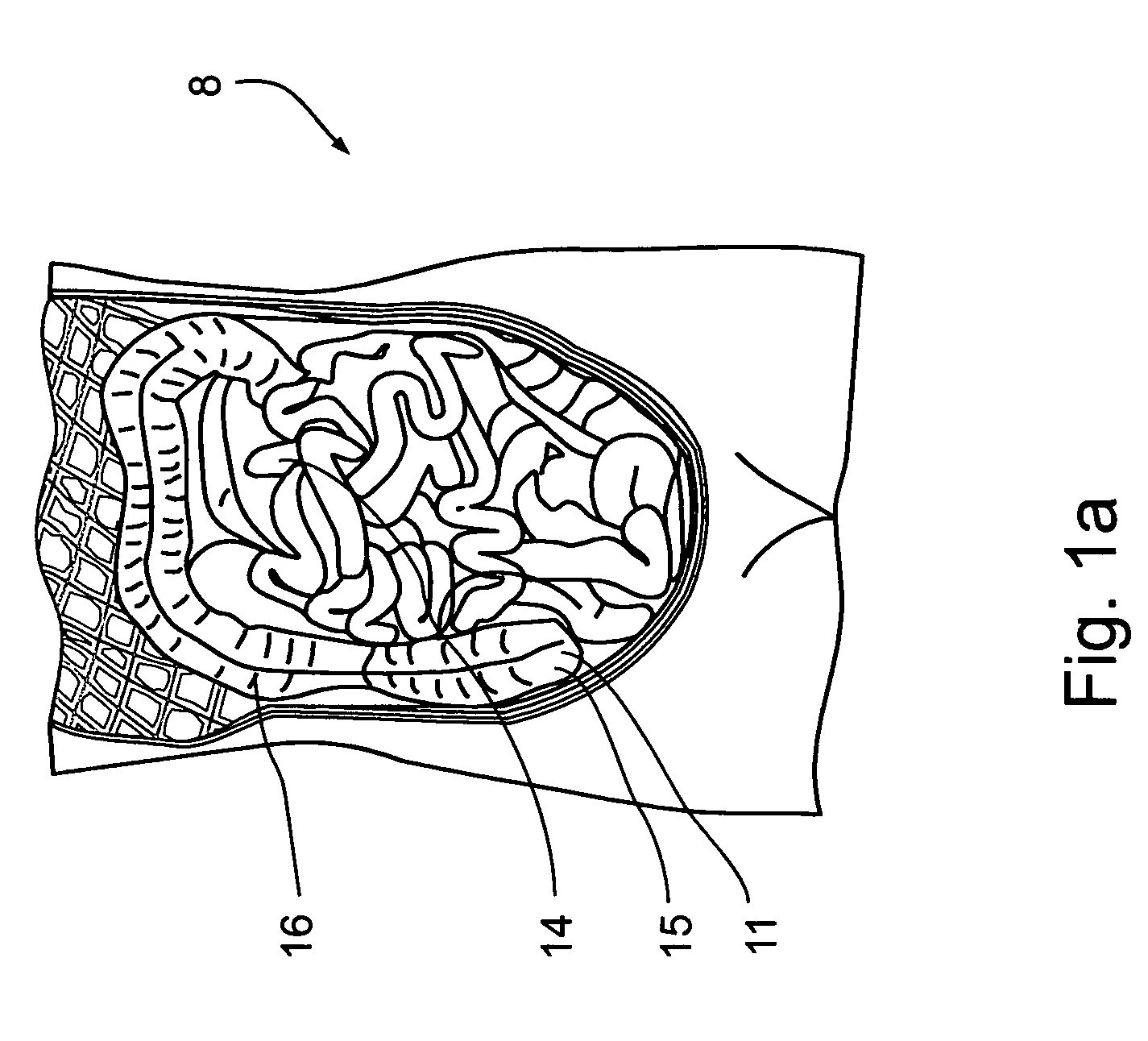
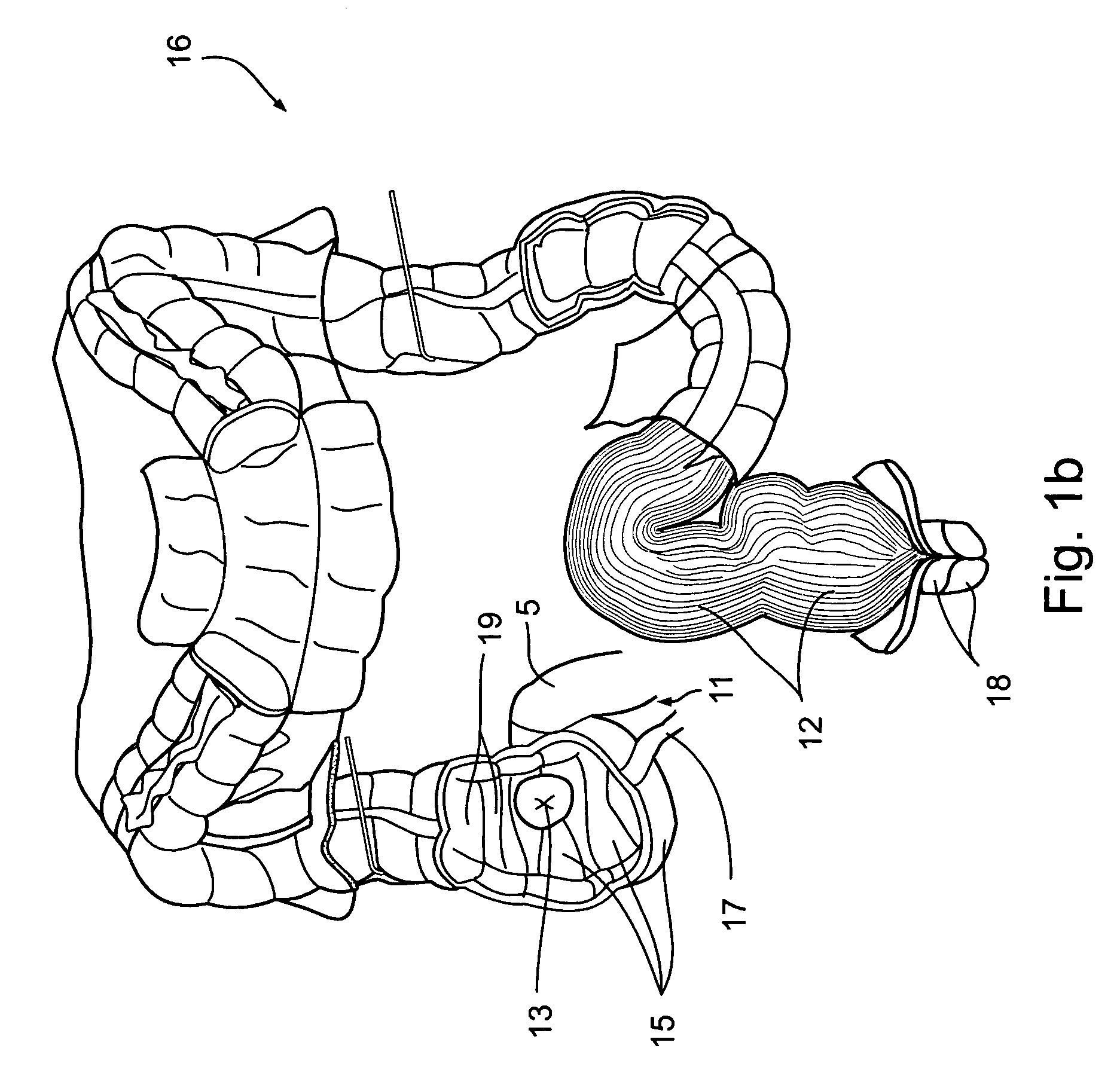
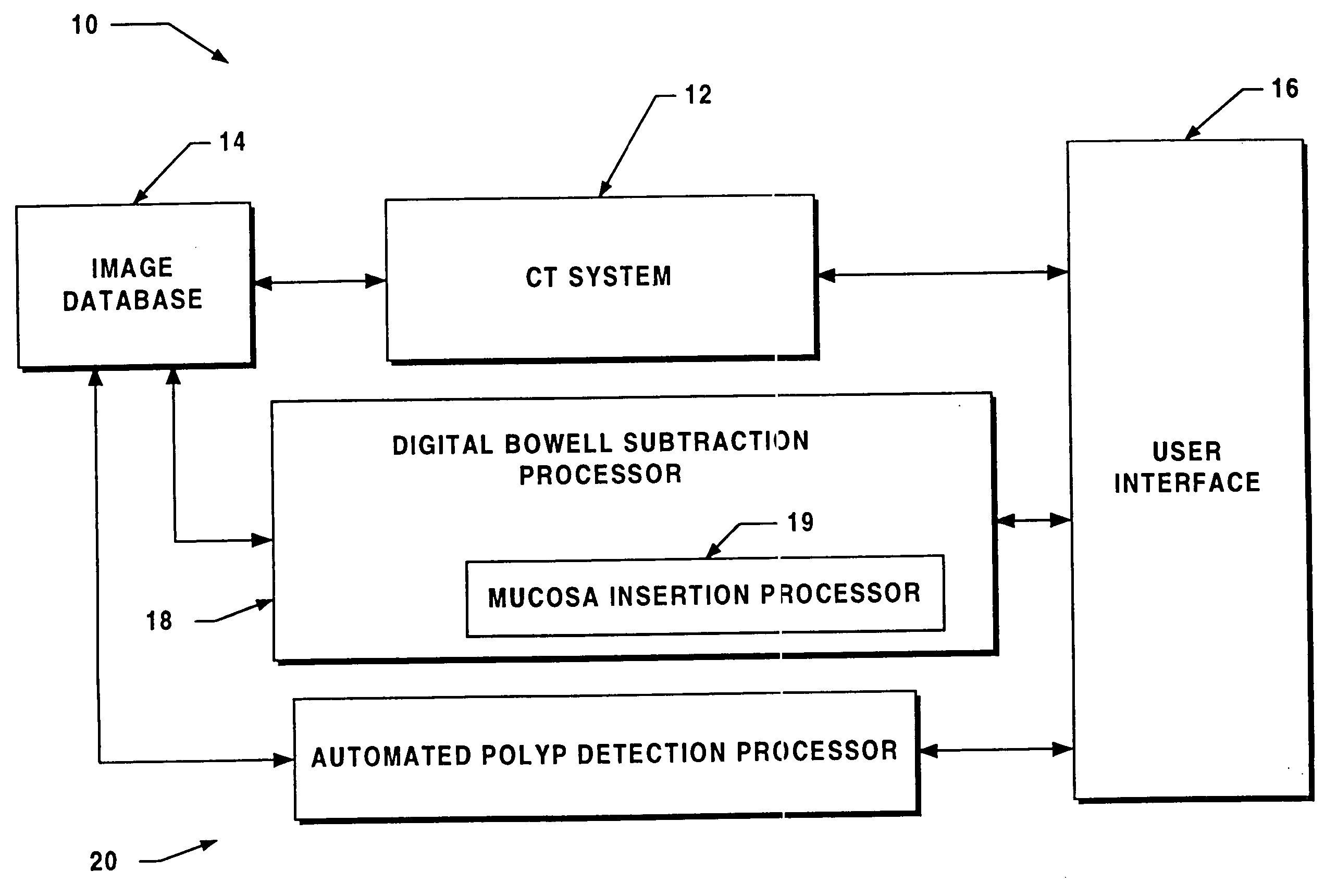
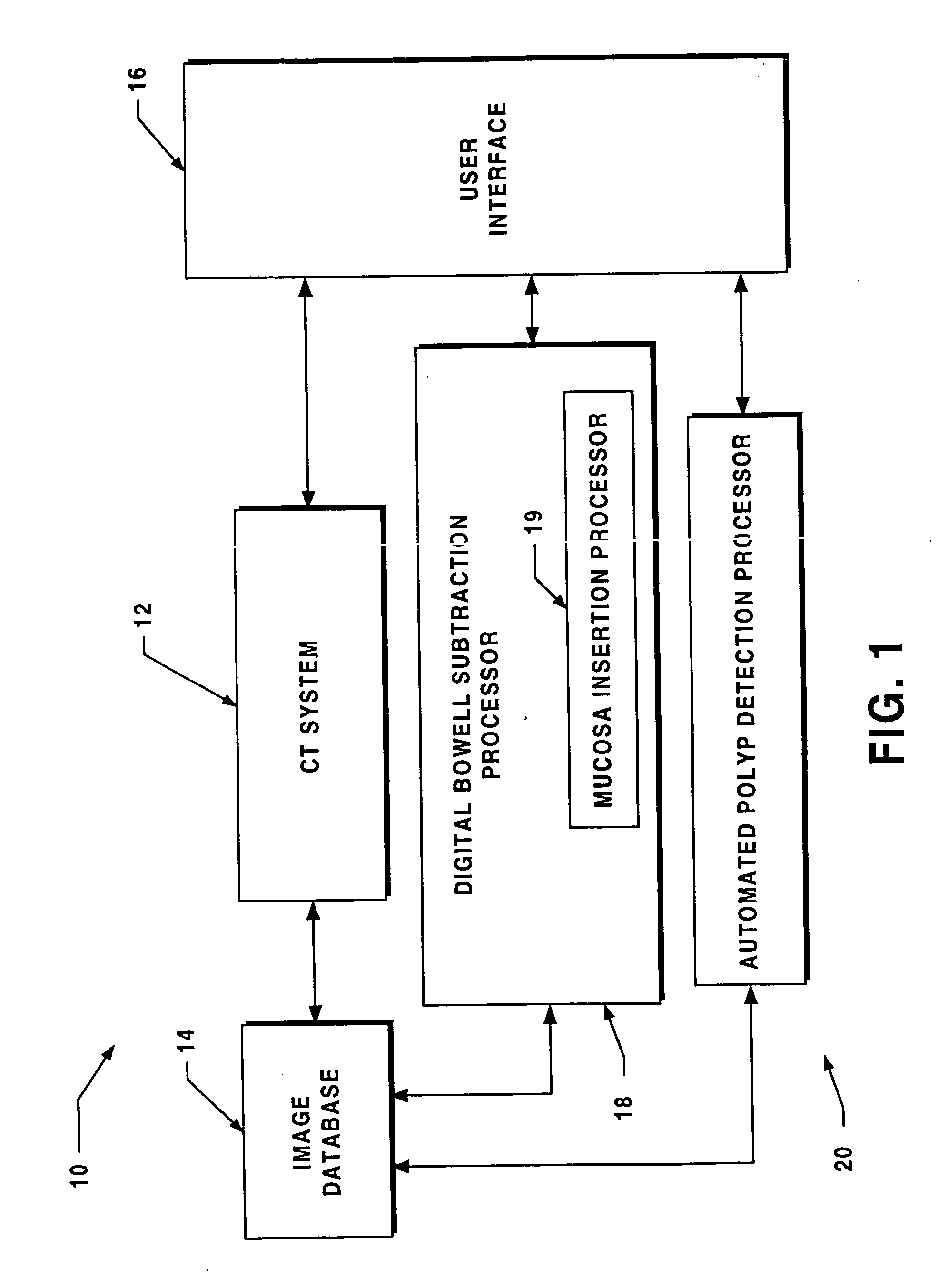
System for digital bowel subtraction and polyp detection and related techniques
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Structure-analysis system, method, software arrangement and computer-accessible medium for digital cleansing of computed tomography colonography images
ActiveUS9299156B2Reduce needAccurately abnormalitiesMedical simulationImage enhancementBowel cleansingStructure analysis
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
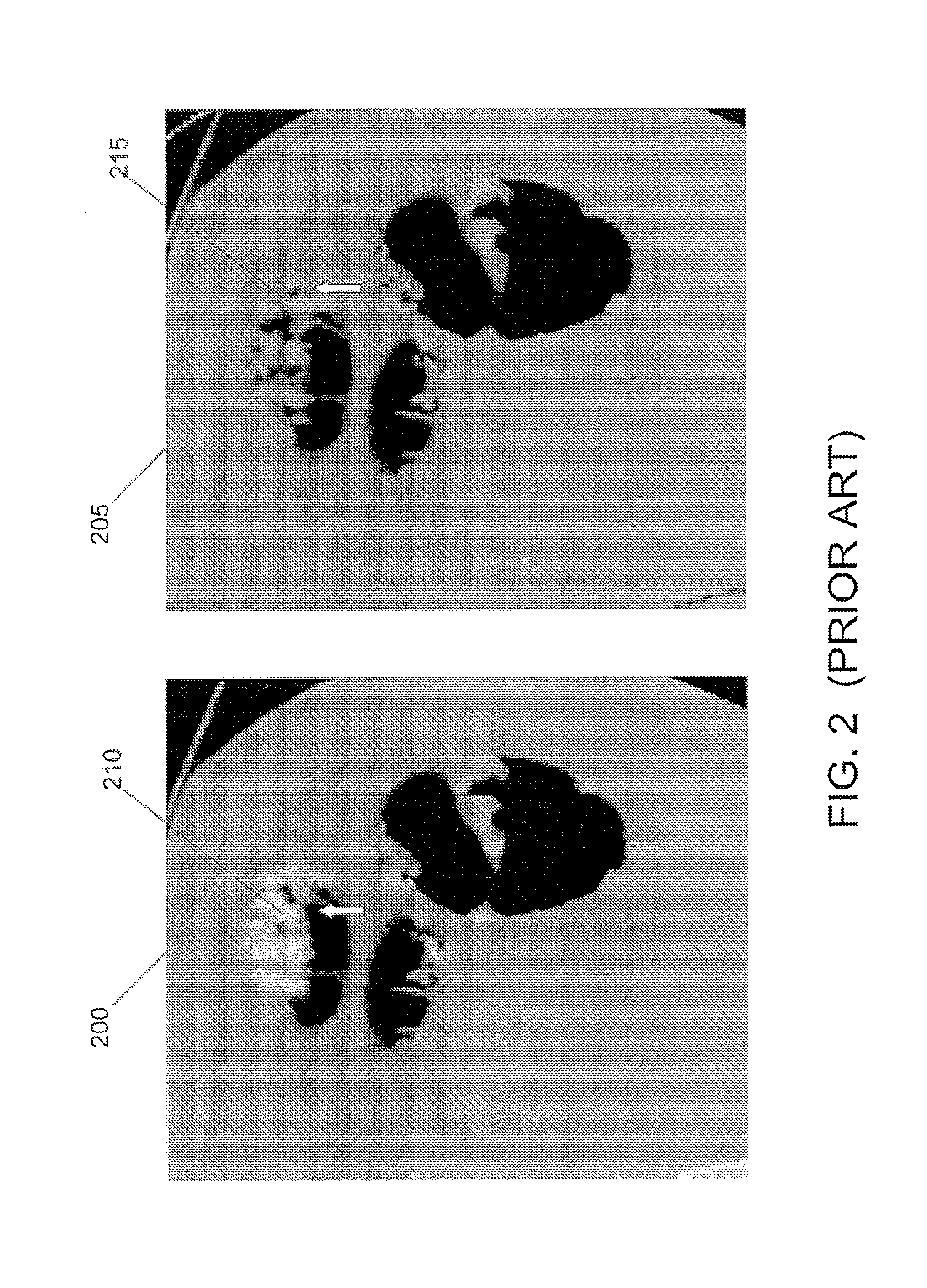
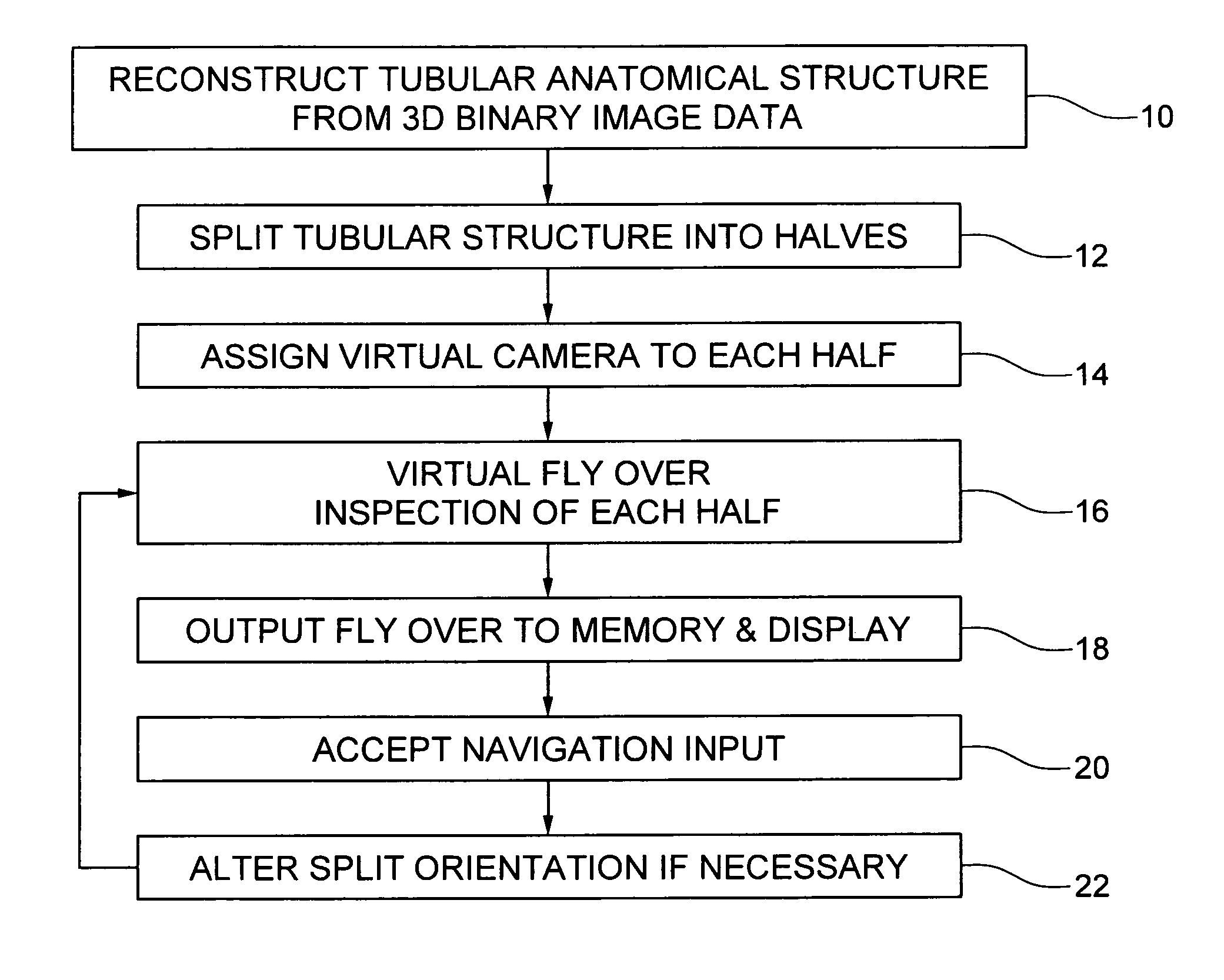
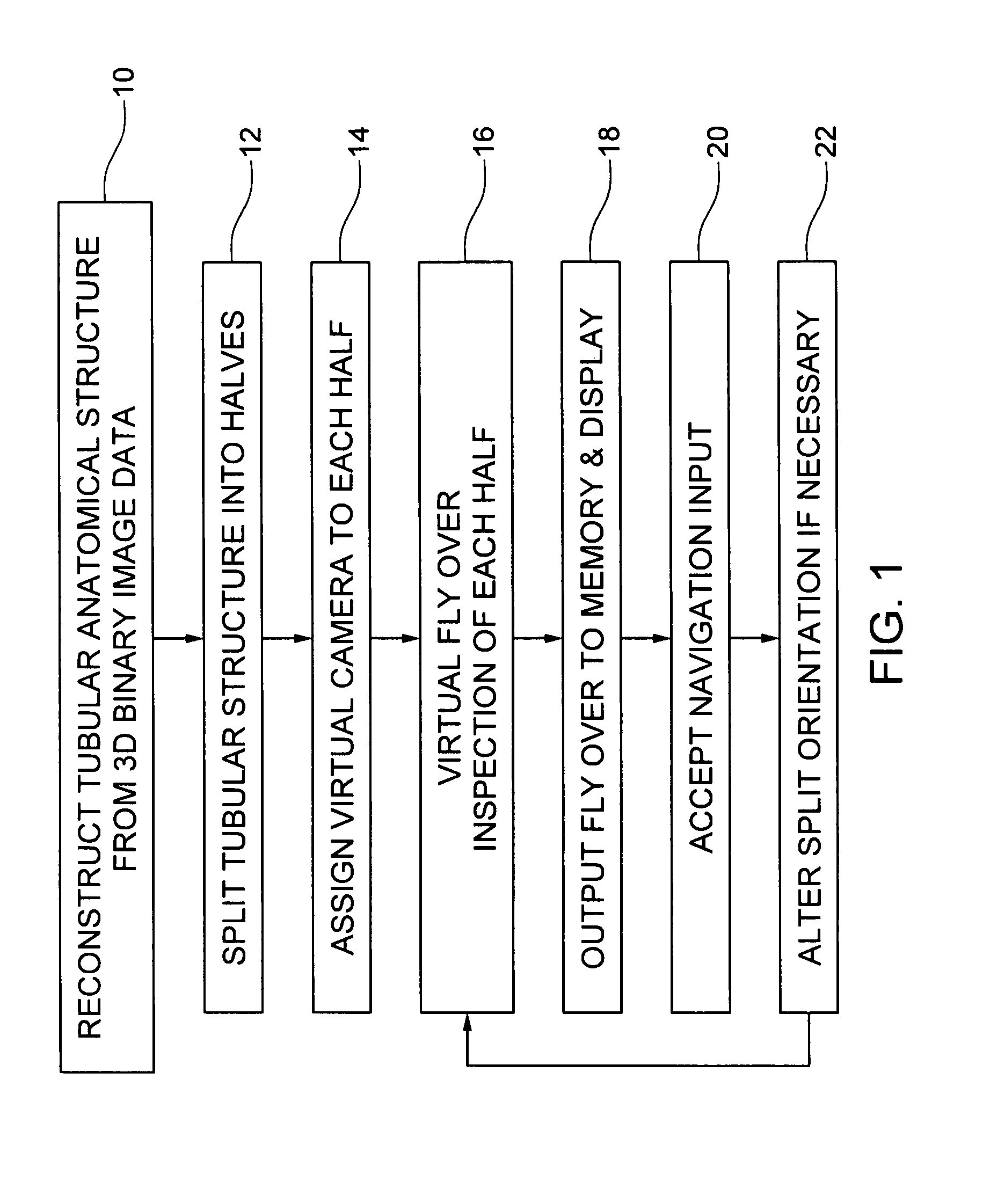
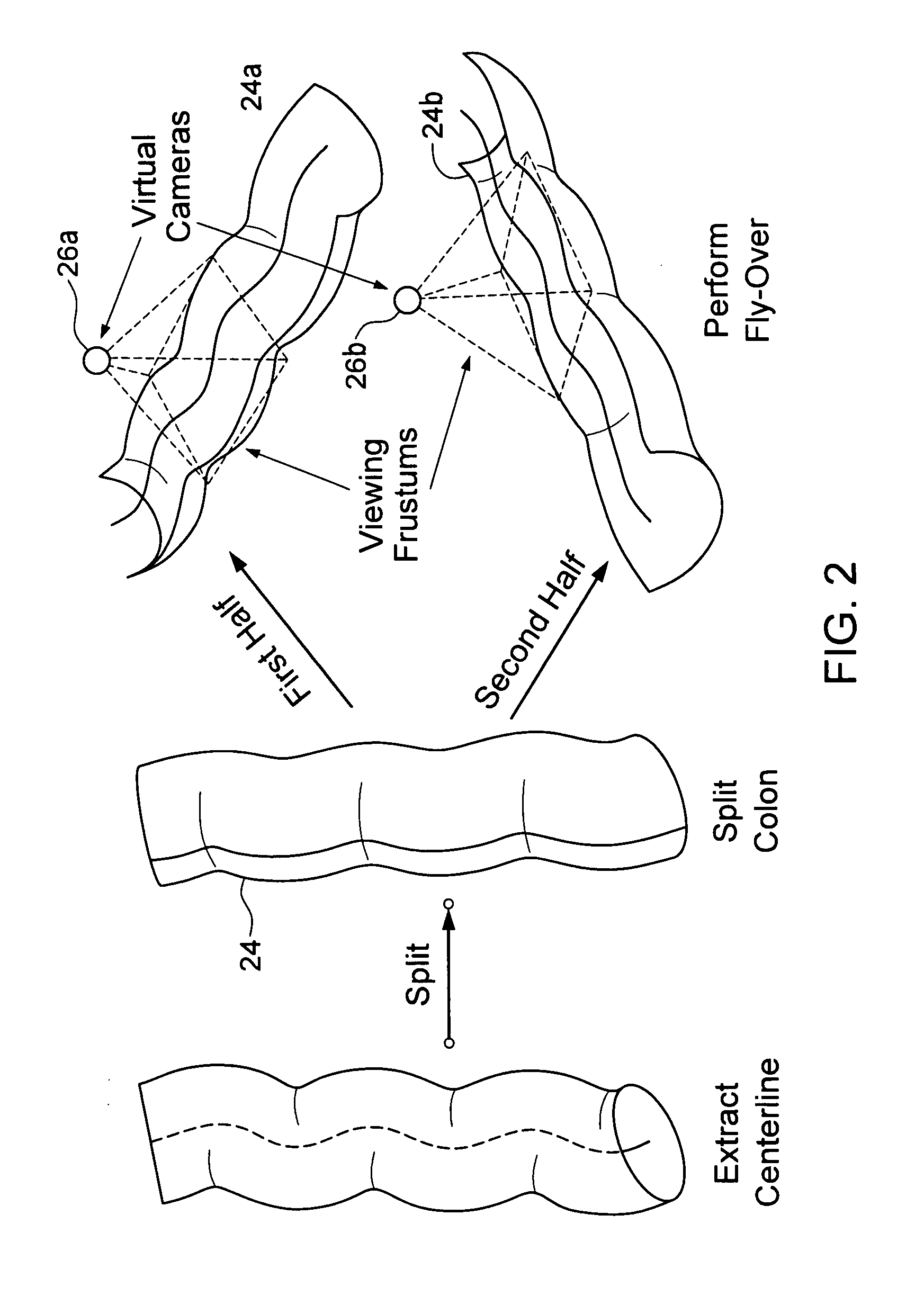
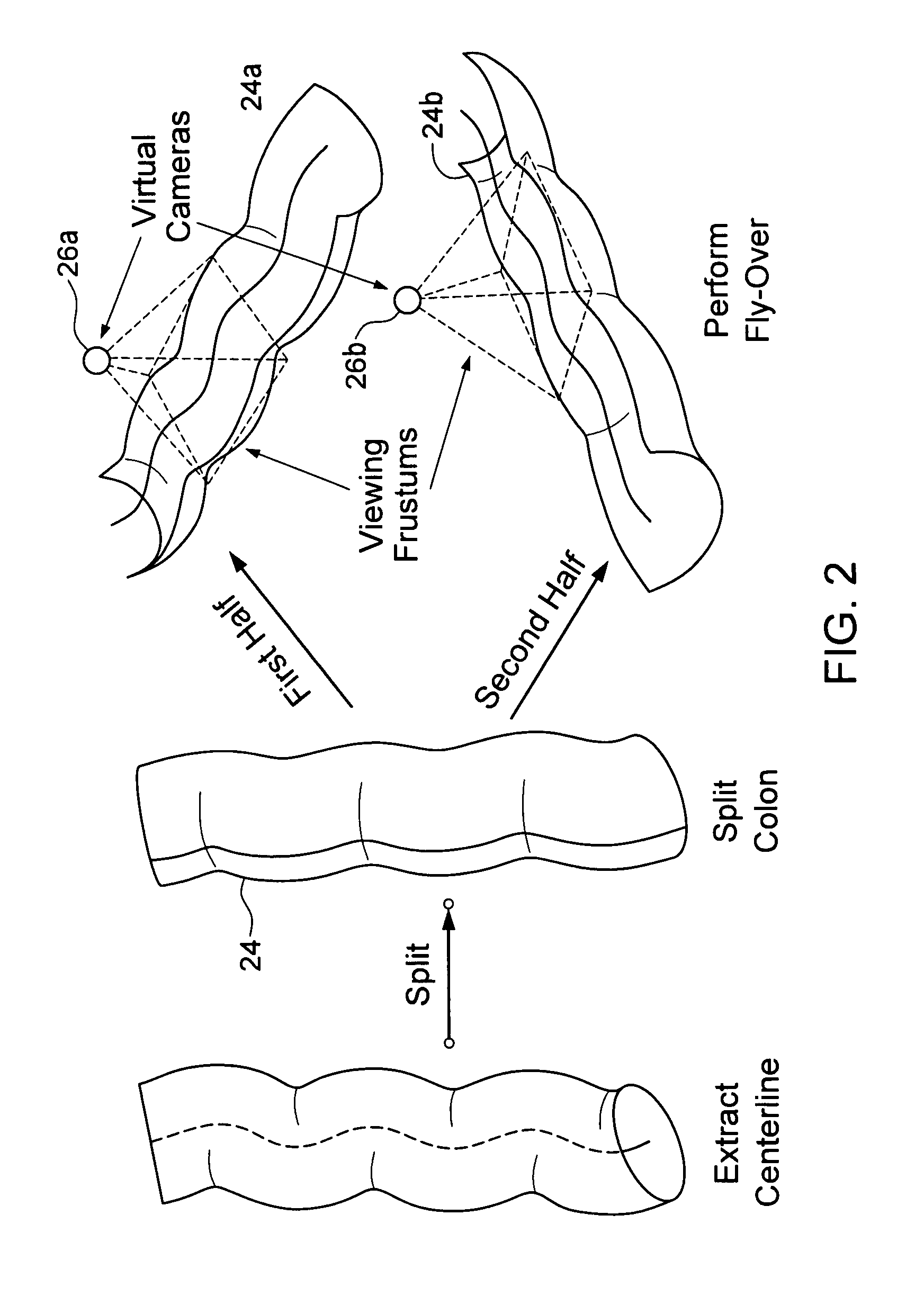
Virtual fly over of complex tubular anatomical structures
InactiveUS20080069419A1Avoid possibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical simulationAnatomical structuresData set
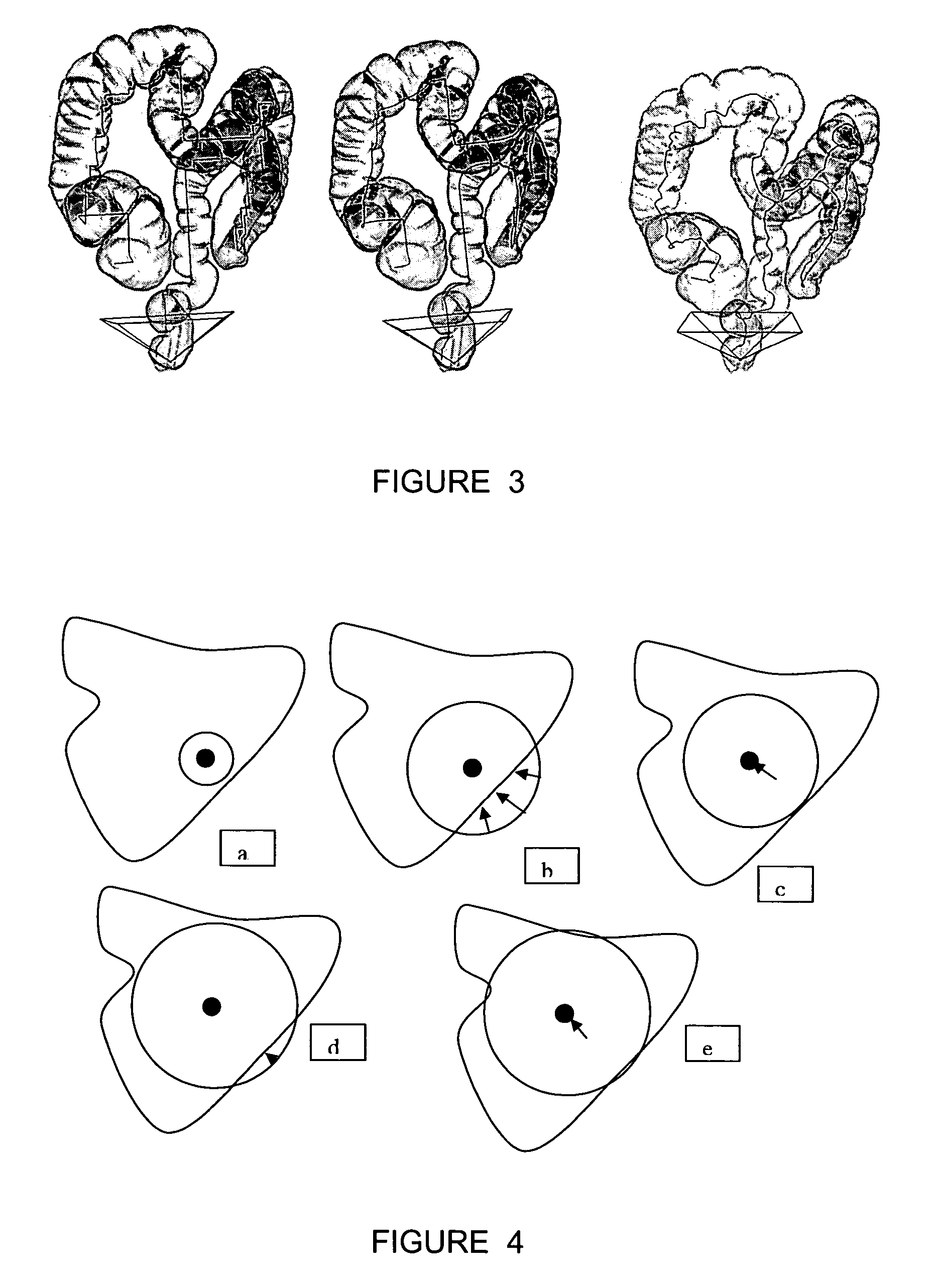
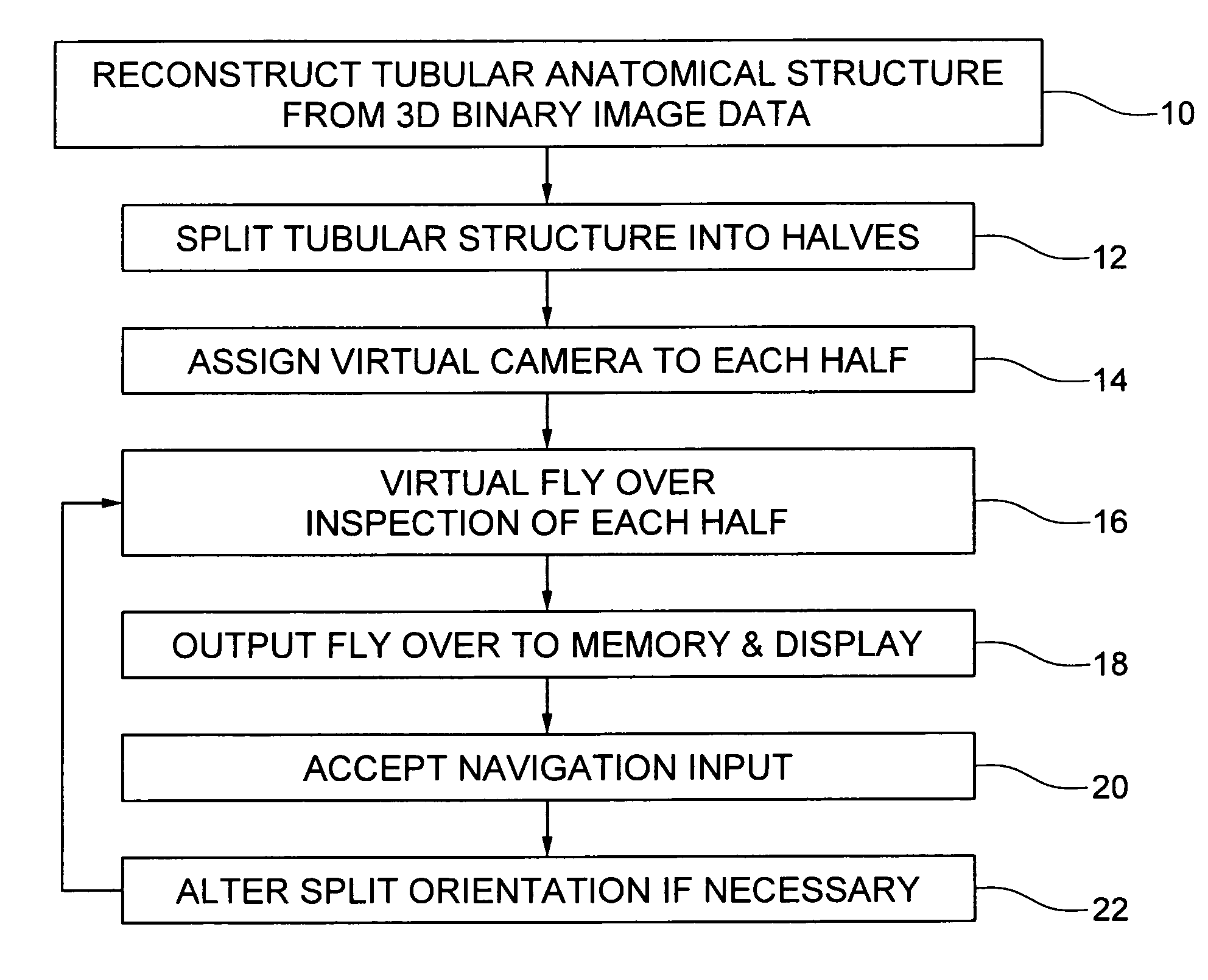
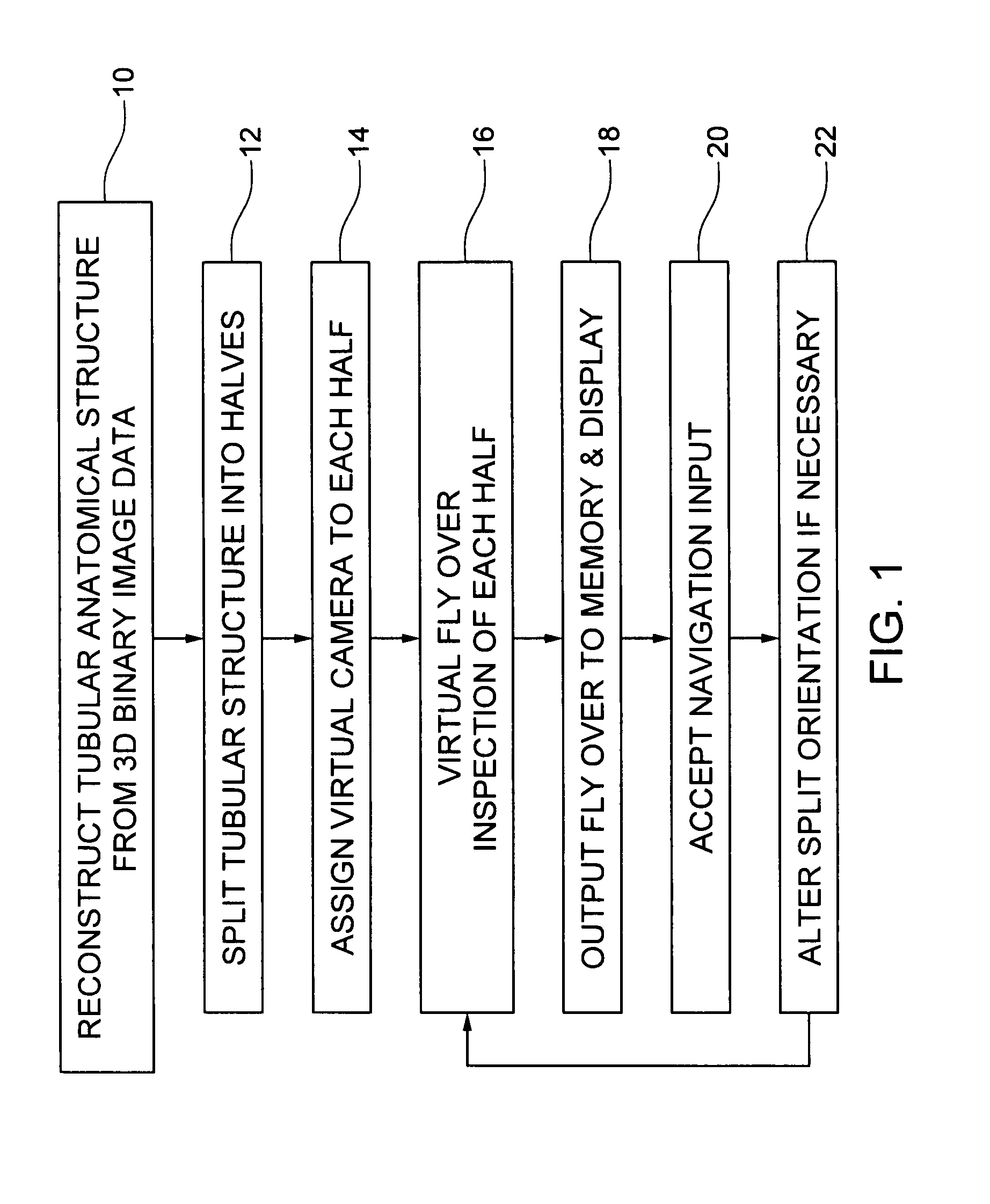
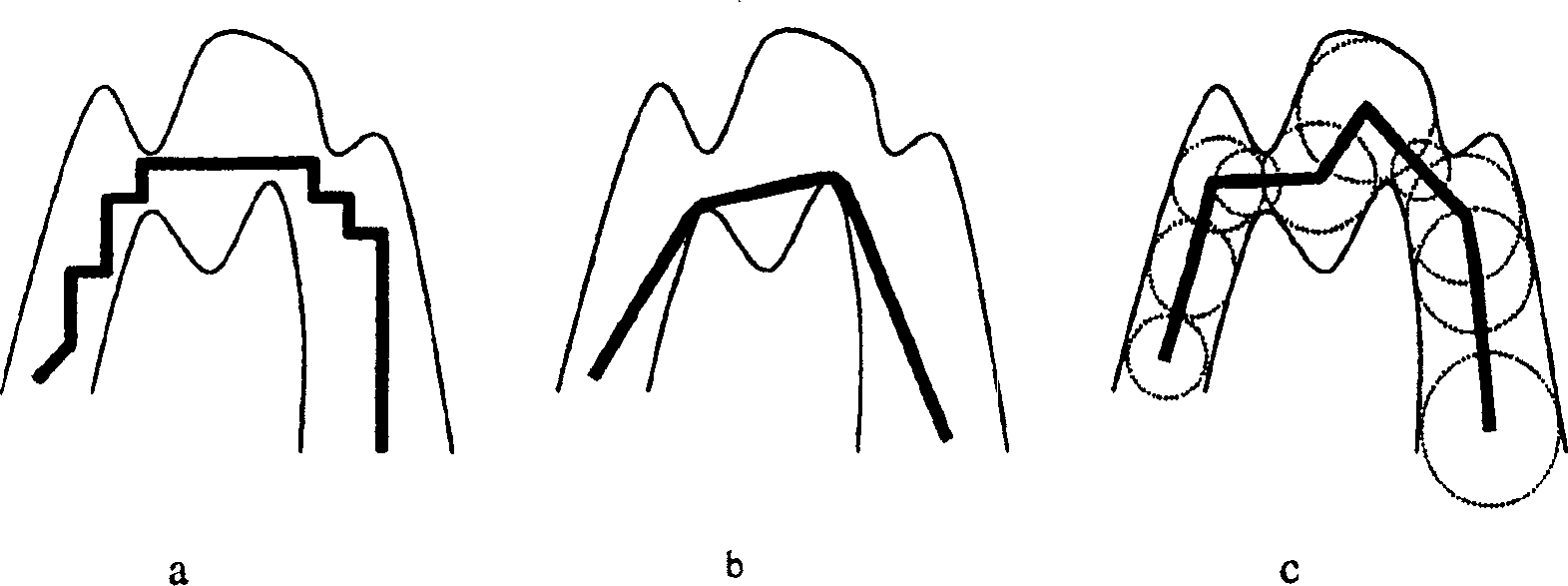
An embodiment of the invention is method, which can be implemented in software, firmware, hardware, etc., for virtual fly over inspection of complex anatomical tubular structures. In a preferred embodiment, the method is implemented in software, and the software reconstructs the tubular anatomical structure from a binary imaging data that is originally acquired from computer aided tomography scan or comparable biological imaging system. The software of the invention splits the entire tubular anatomy into exactly two halves. The software assigns a virtual camera to each half to perform fly-over navigation. Through controlling the elevation of the virtual camera, there is no restriction on its field of view (FOV) angle, which can be greater than 90 degrees, for example. The camera viewing volume is perpendicular to each half of the tubular anatomical structure, so potential structures of interest, e.g., polyps hidden behind haustral folds in a colon are easily found. The orientation of the splitting surface is controllable, the navigation can be repeated at another or a plurality of another split orientations. This avoids the possibility that a structure of interest, e.g., a polyp that is divided between the two halves of the anatomical structure in a first fly over is missed during a virtual inspection. Preferred embodiment software conducts virtual colonoscopy fly over. Experimental virtual fly over colonoscopy software of the invention that performed virtual fly over on 15 clinical datasets demonstrated average surface visibility coverage is 99.59+ / −0.2%.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
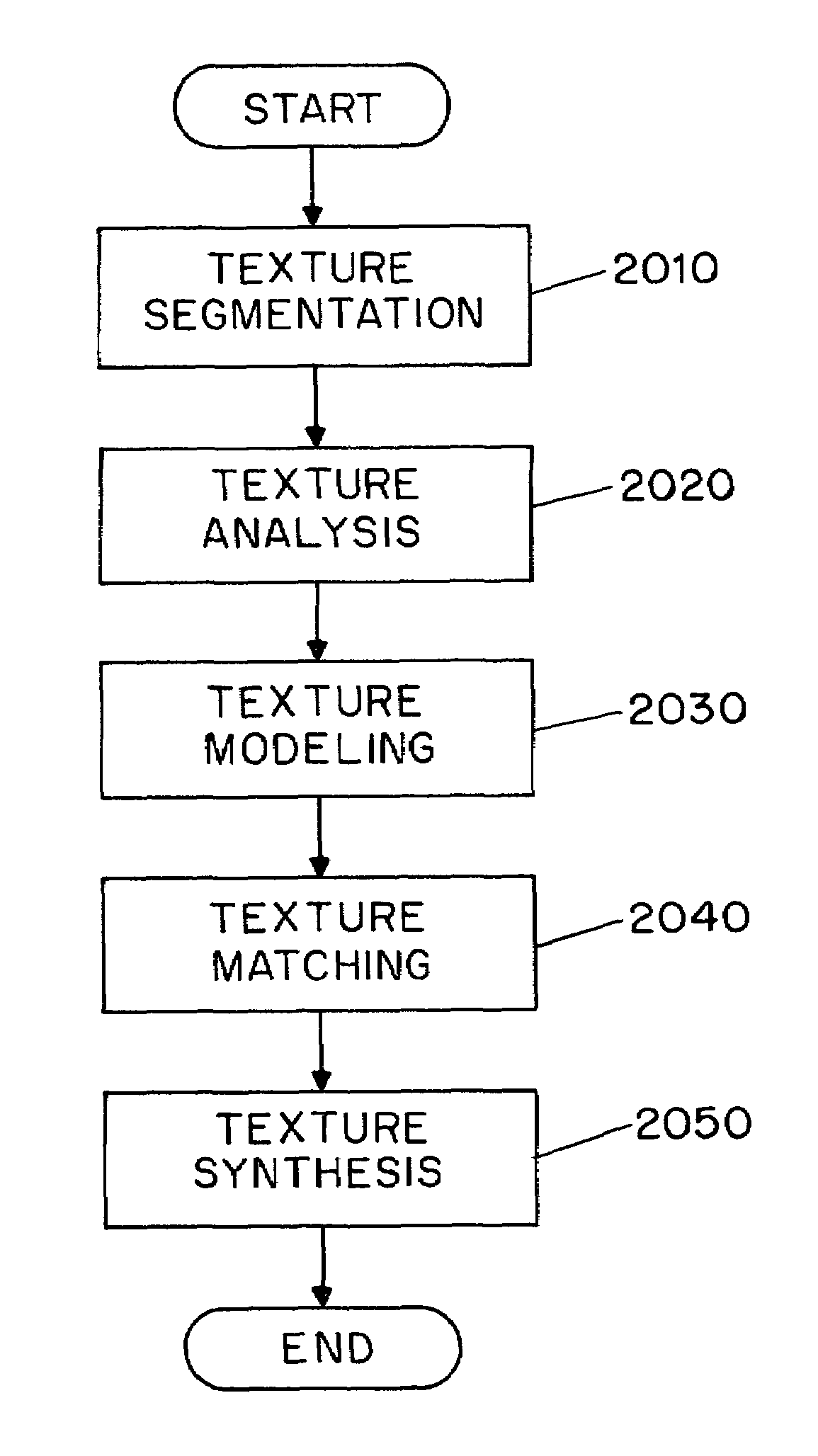
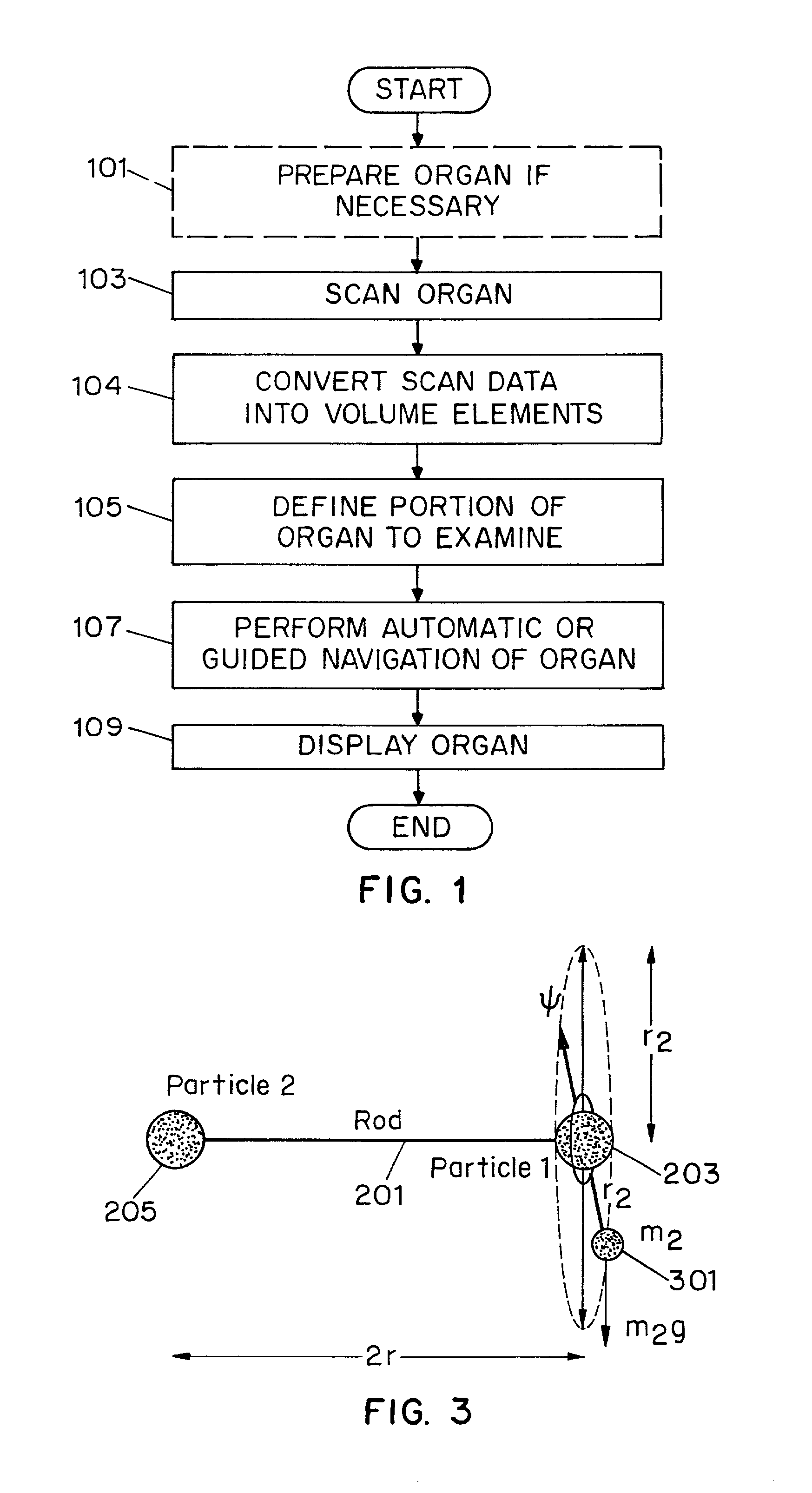
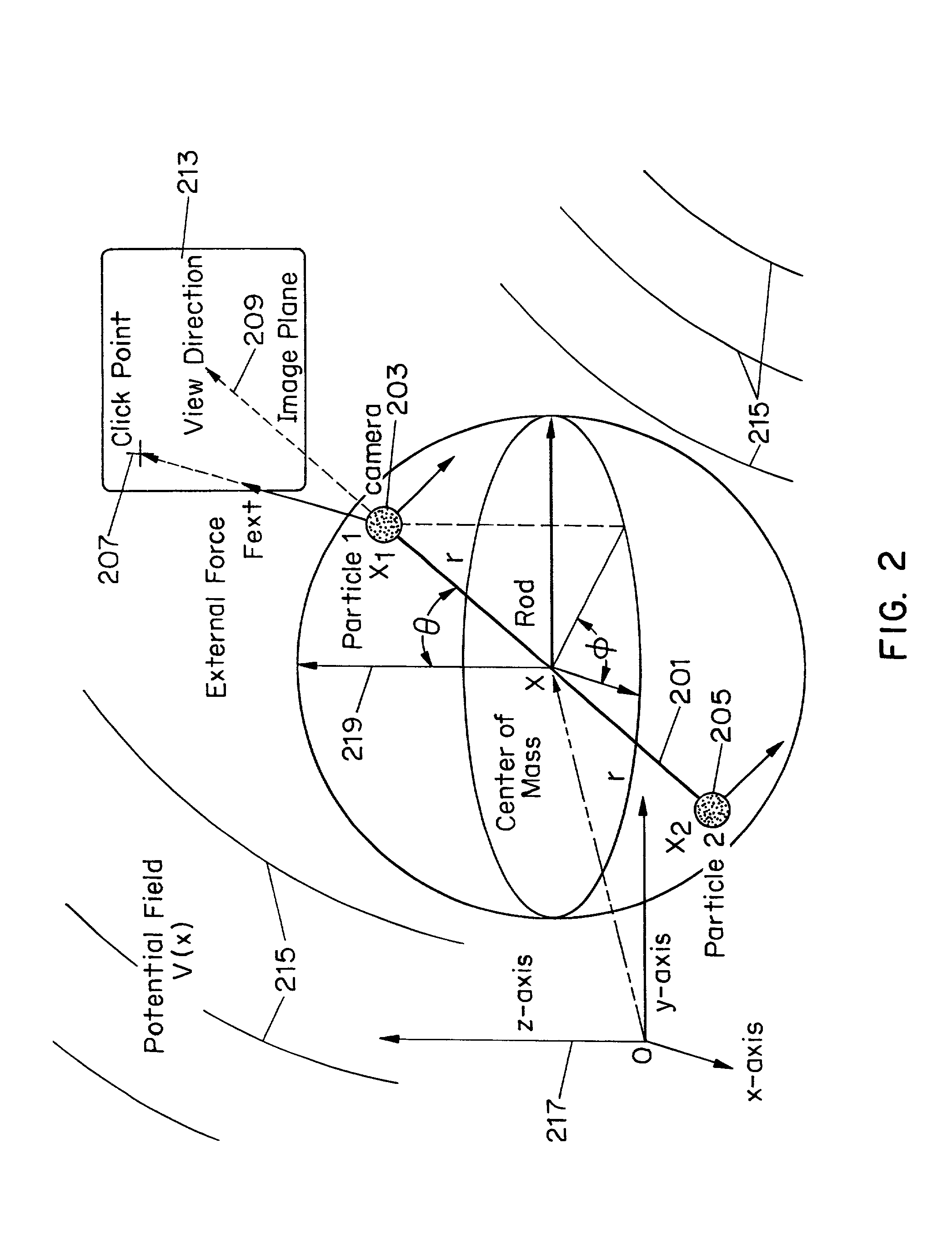
System and method for performing a three-dimensional virtual segmentation and examination with optical texture mapping
A system and method for generating a three-dimensional visualization image of an object such as an organ using volume visualization techniques and exploring the image using a guided navigation system which allows the operator to travel along a flight path and to adjust the view to a particular portion of the image of interest in order, for example, to identify polyps, cysts or other abnormal features in the visualized organ. An electronic biopsy can also be performed on an identified growth or mass in the visualized object. Virtual colonoscopy can be enhanced by electronically removing residual stool, fluid and non-colonic tissue from the image of the colon, by employing bowel preparation followed by image segmentation operations. Methods are also employed for virtually expanding regions of colon collapse using image segmentation results.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Ingestible device platform for the colon
ActiveUS7970455B2Enhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySphincterSpectroscopy
An ingestible pill platform for colon imaging is provided, designed to recognize its entry to the colon and expand in the colon, for improved imaging of the colon walls. On approaching the external anal sphincter muscle, the ingestible pill may contract or deform, for elimination. Colon recognition may be based on a structural image, based on the differences in diameters between the small intestine and the colon, and particularly, based on the semilunar fold structure, which is unique to the colon. Additionally or alternatively, colon recognition may be based on a functional image, based on the generally inflammatory state of the vermiform appendix. Additionally or alternatively, pH, flora, enzymes and (or) chemical analyses may be used to recognize the colon. The imaging of the colon walls may be functional, by nuclear-radiation imaging of radionuclide-labeled antibodies, or by optical-fluorescence-spectroscopy imaging of fluorescence-labeled antibodies. Additionally or alternatively, it may be structural, for example, by visual, ultrasound or MRI means. Due to the proximity to the colon walls, the imaging in accordance with the present invention is advantageous to colonoscopy or virtual colonoscopy, as it is designed to distinguish malignant from benign tumors and detect tumors even at their incipient stage, and overcome blood-pool background radioactivity.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
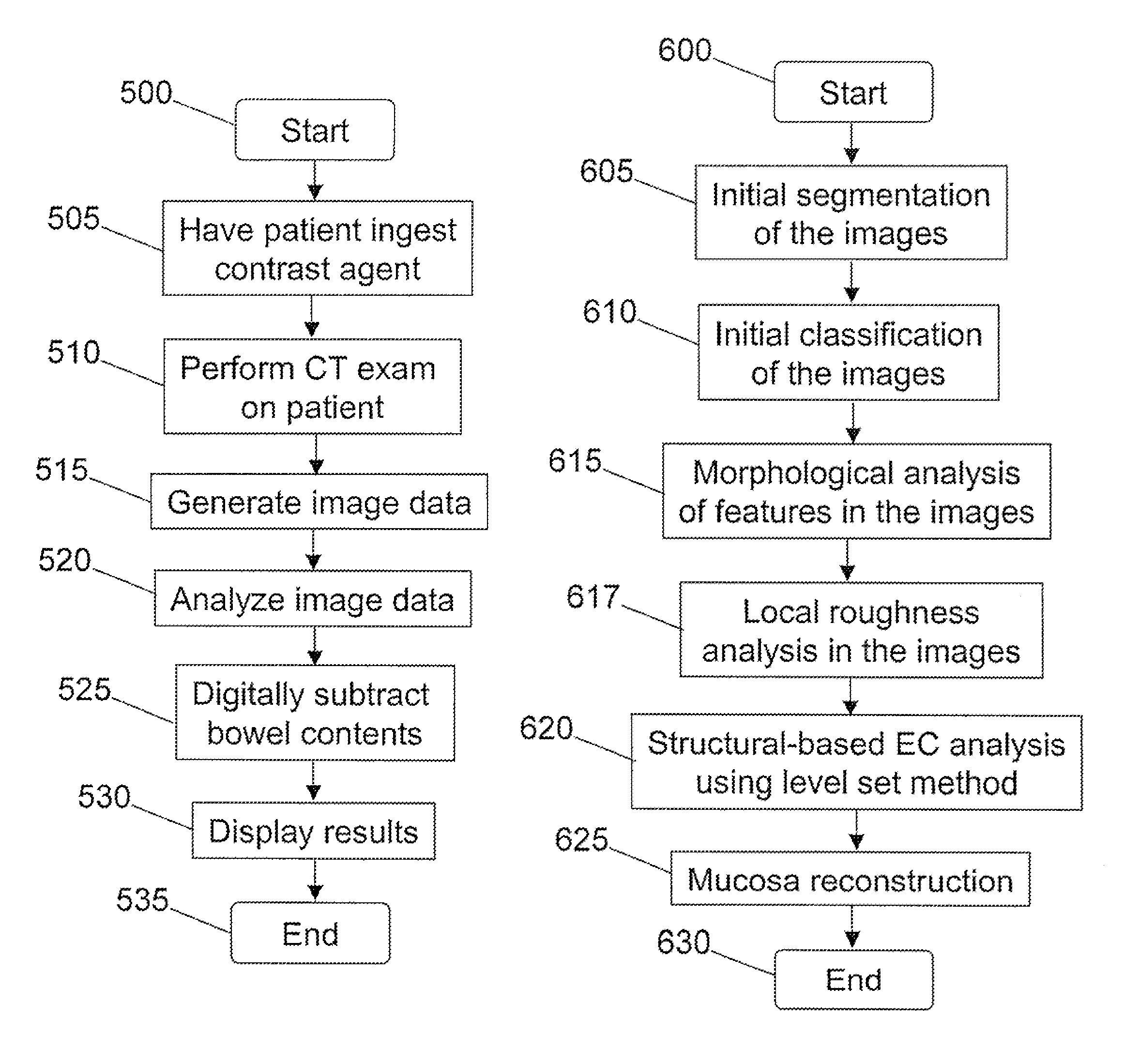
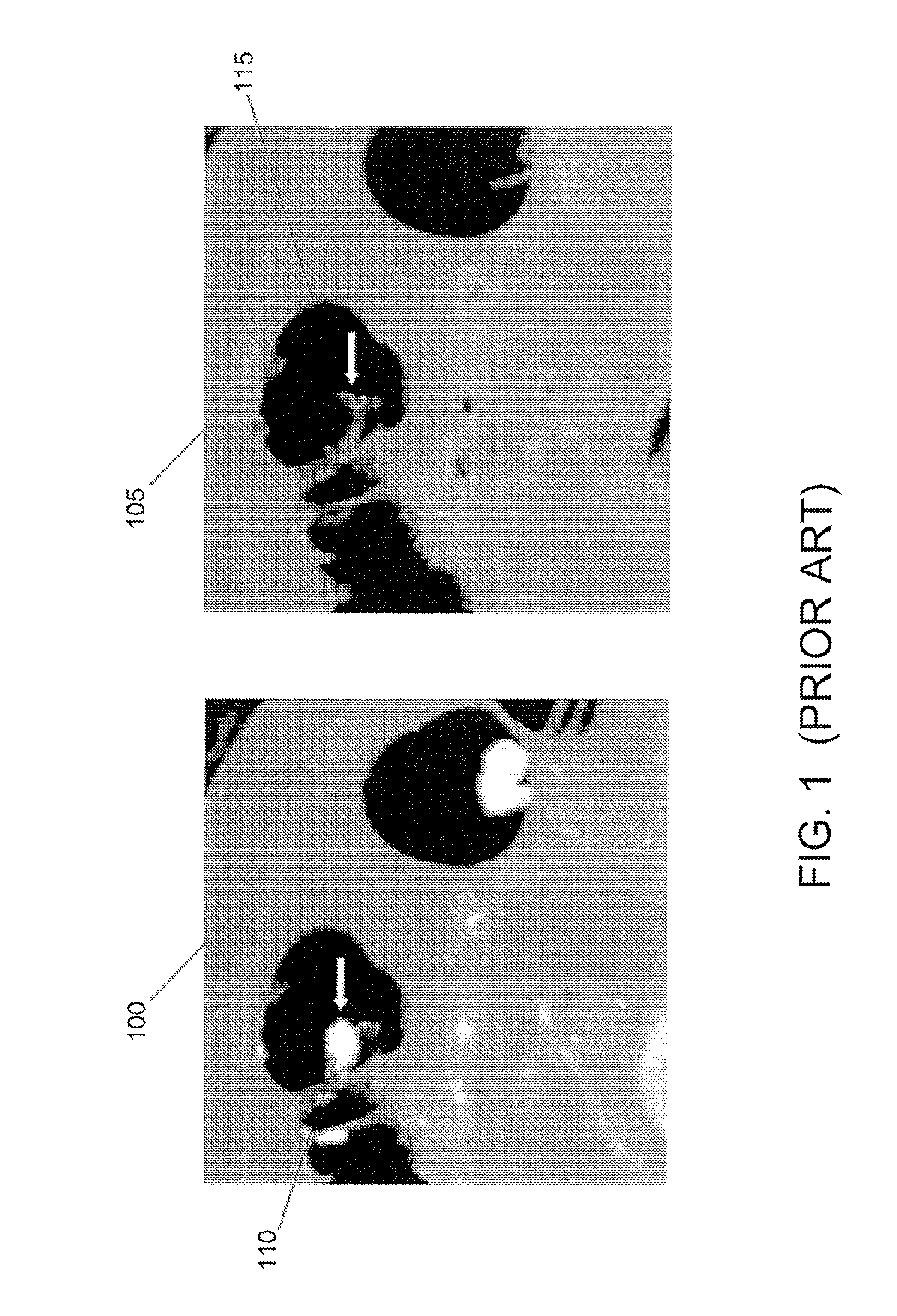
Methods for digital bowel subtraction and polyp detection
InactiveUS20050107691A1Heavy calculationMany timesImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionDigital image
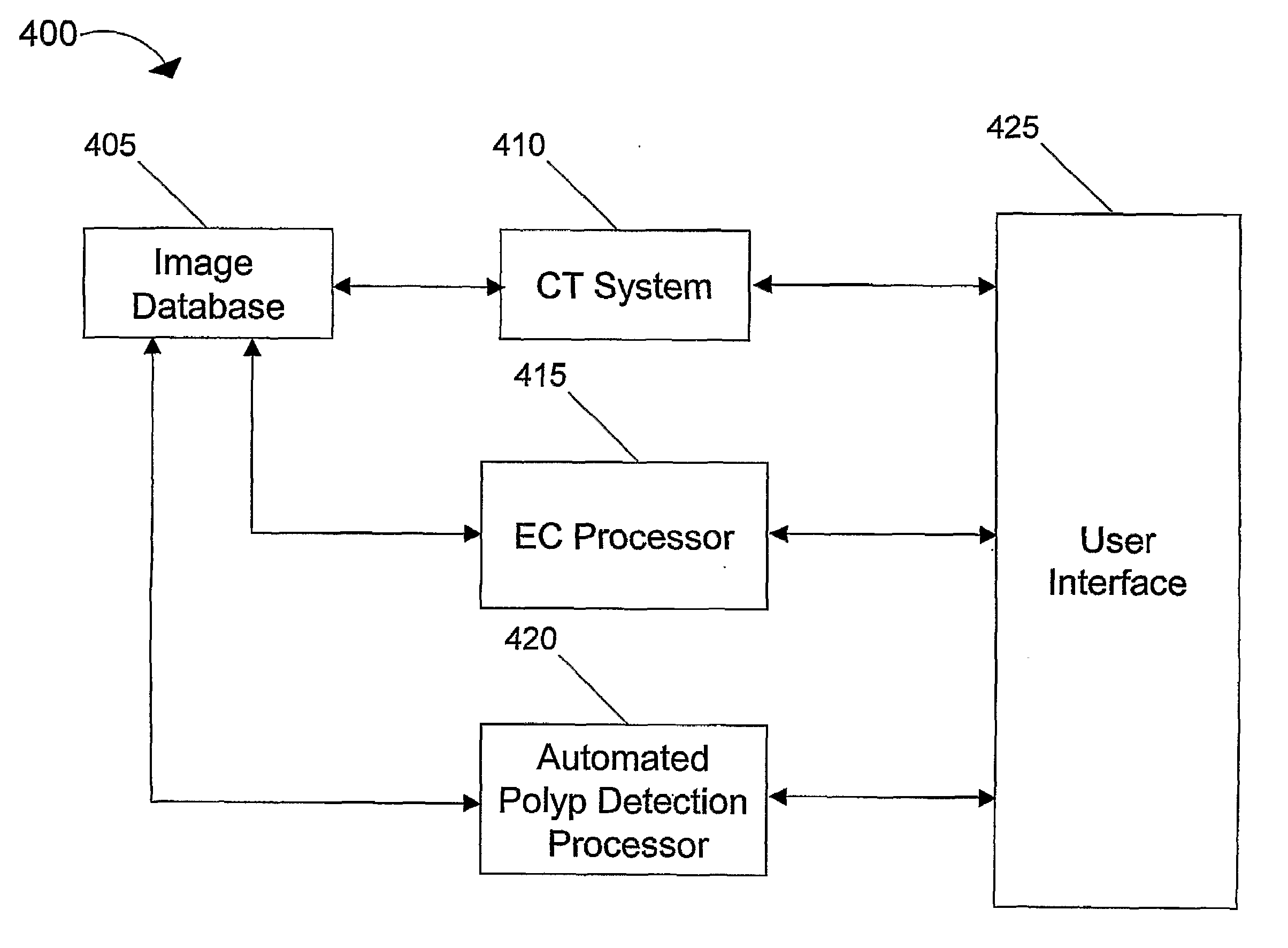
A system for performing a virtual colonoscopy includes a system for generating digital images, a storage device for storing the digital images, a digital bowel subtraction processor coupled to receive images of a colon from the storage device and for removing the contents of the colon from the image and an automated polyp detection processor coupled to receive images of a colon from the storage device and for detecting polyps in the colon image.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
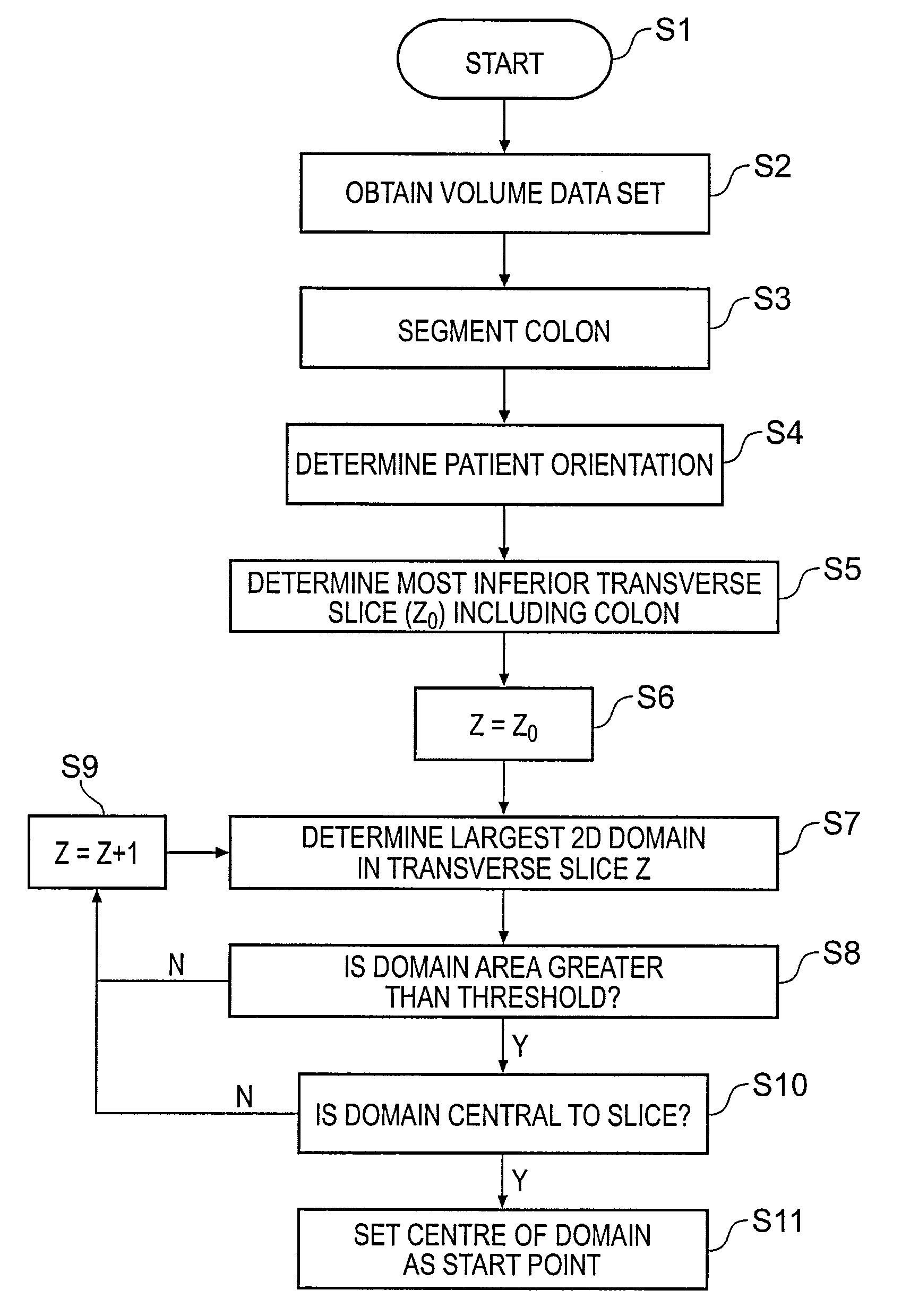
Method and apparatus for automatic local path planning for virtual colonoscopy
InactiveUS7081088B2Increase in sizeMedical simulationImage enhancementComputer graphics (images)Computer vision
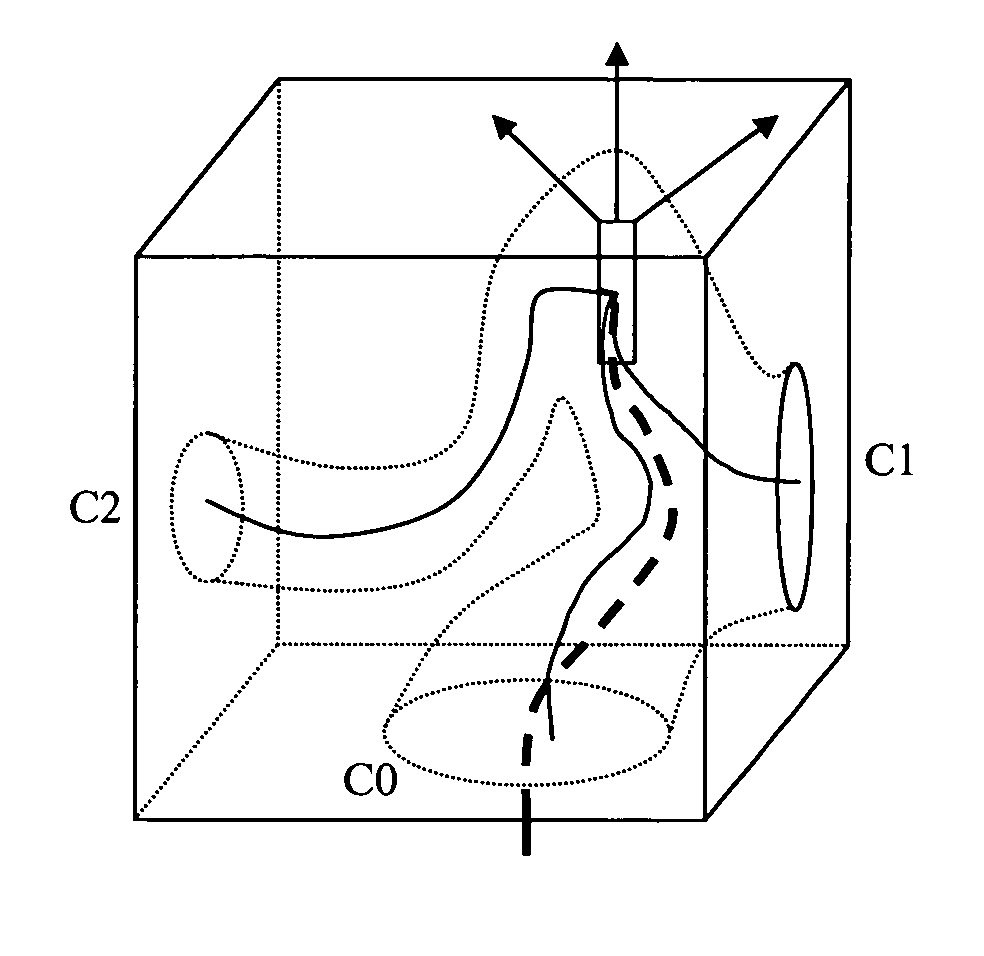
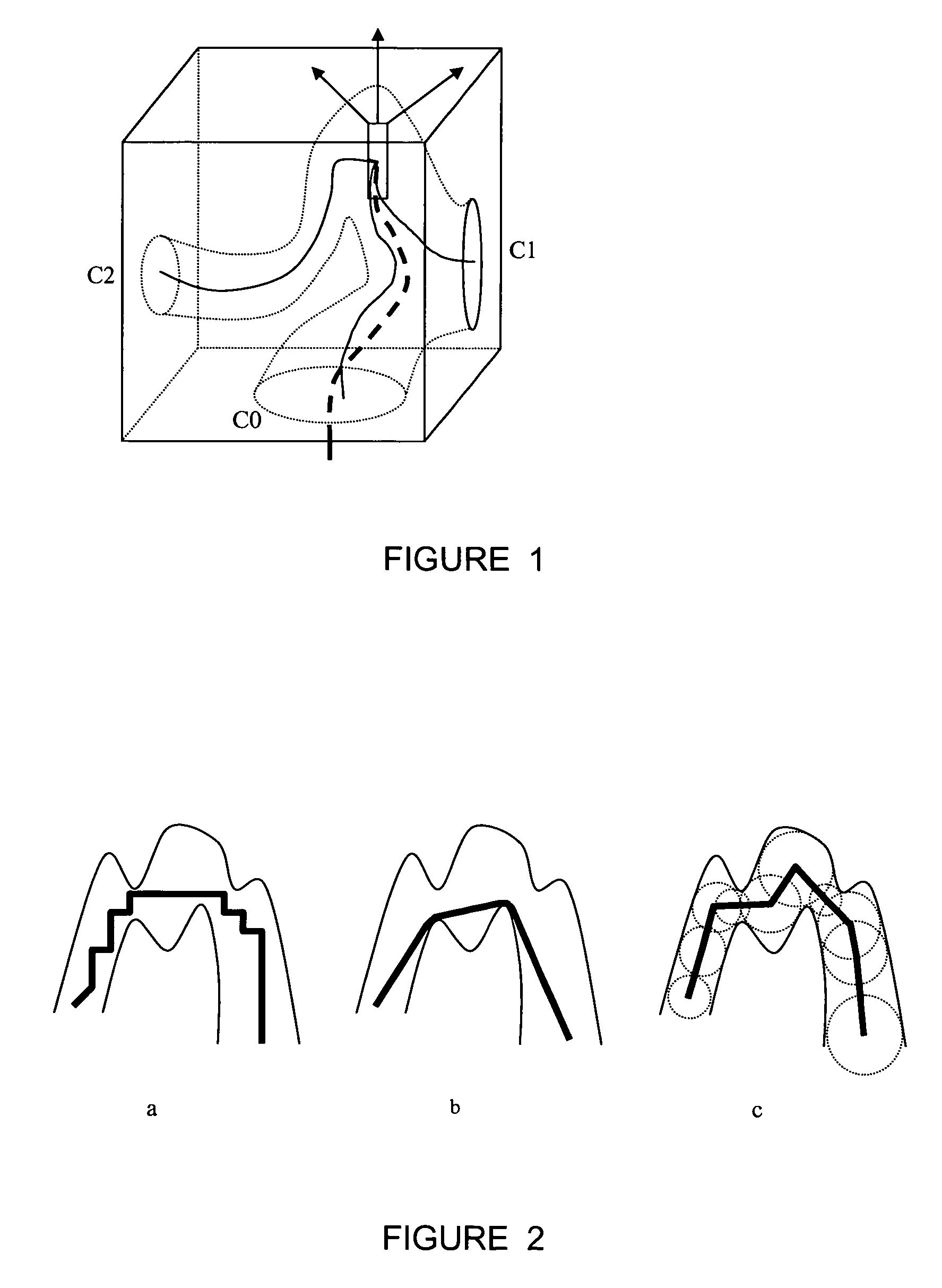
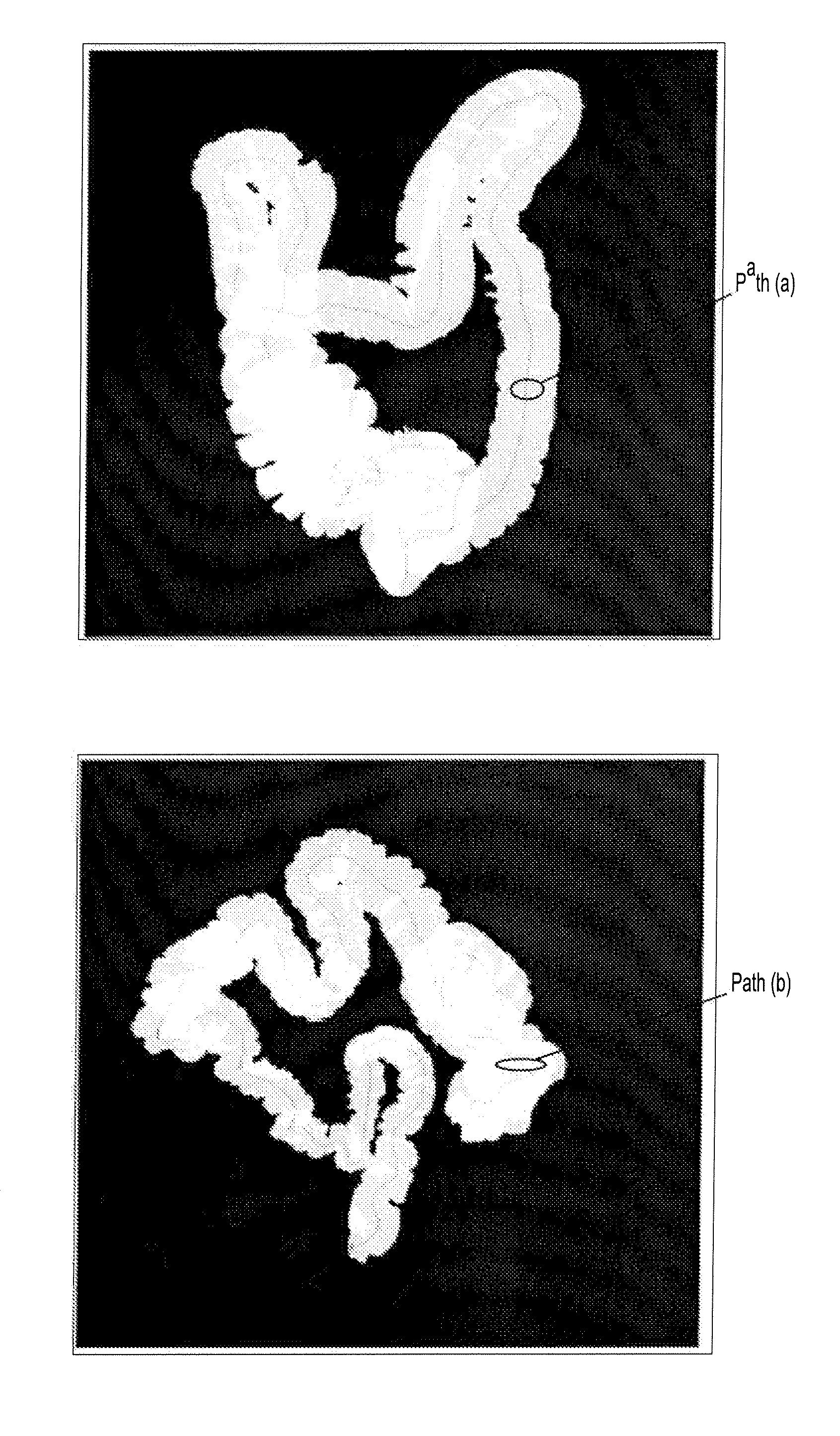
A method for automatic local path planning for a virtual endoscope comprises the steps of defining a sub volume around a current endoscope position in a lumen; performing a region growing inside the lumen, starting from the current endoscope position; calculating and clustering the intersection of the region with the faces of a cube circumscribing the sub volume; calculating approximated centerline paths from the current endoscope position to the center of each cluster formed in the preceding step; comparing each of the centerline paths with a current path exhibited by the endoscope; and selecting an optimal centerline path based on the comparison.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
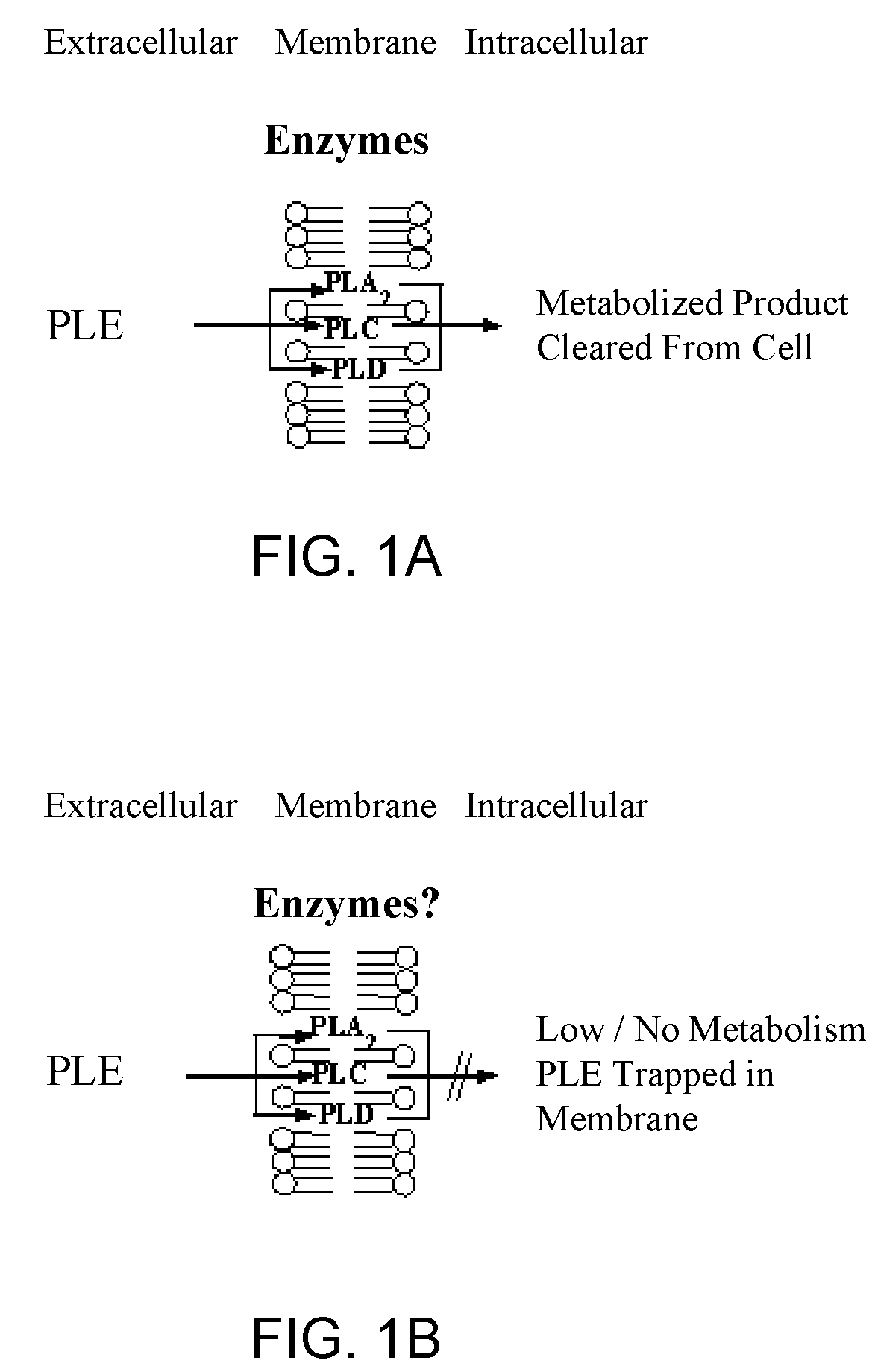
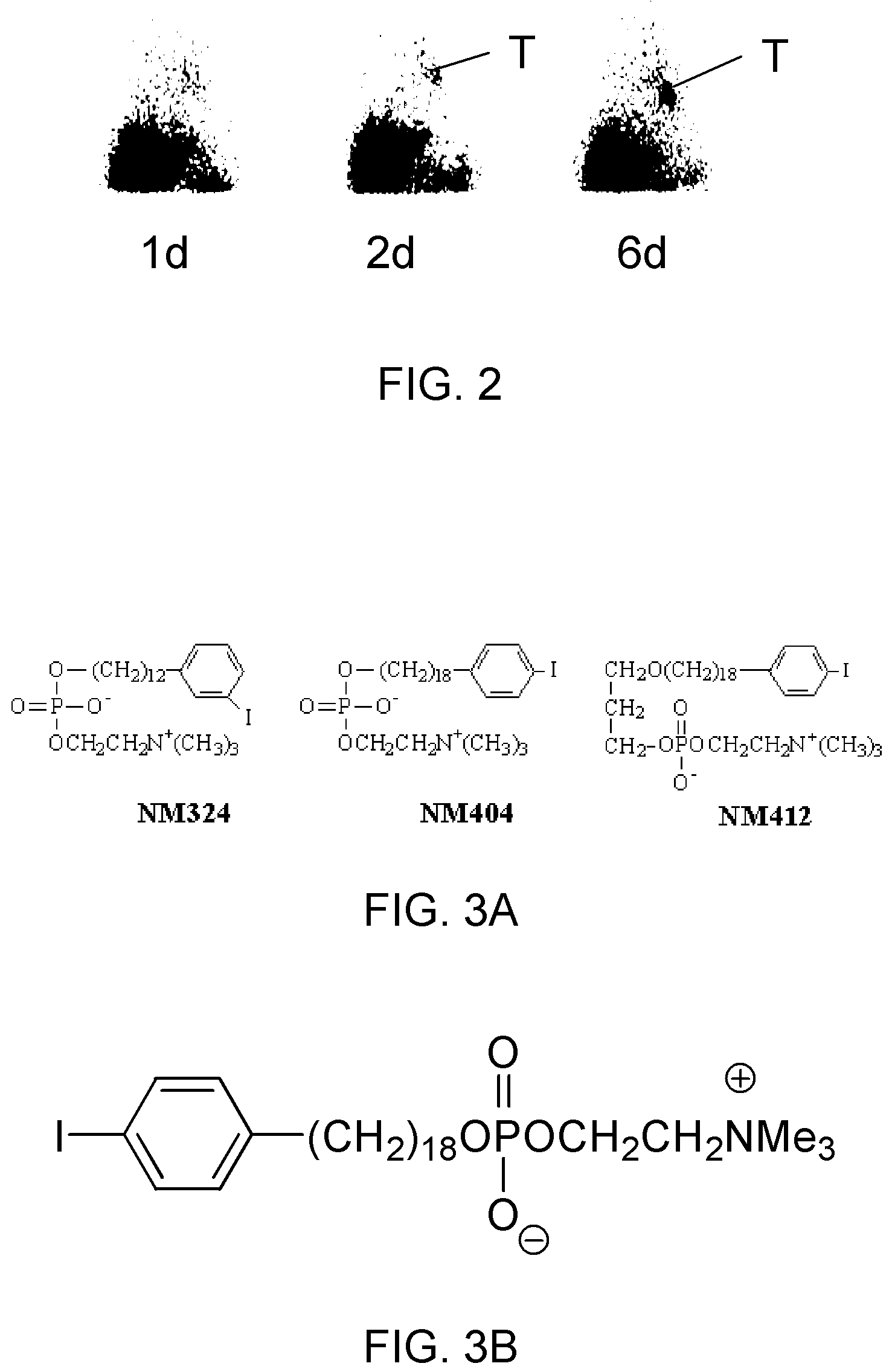
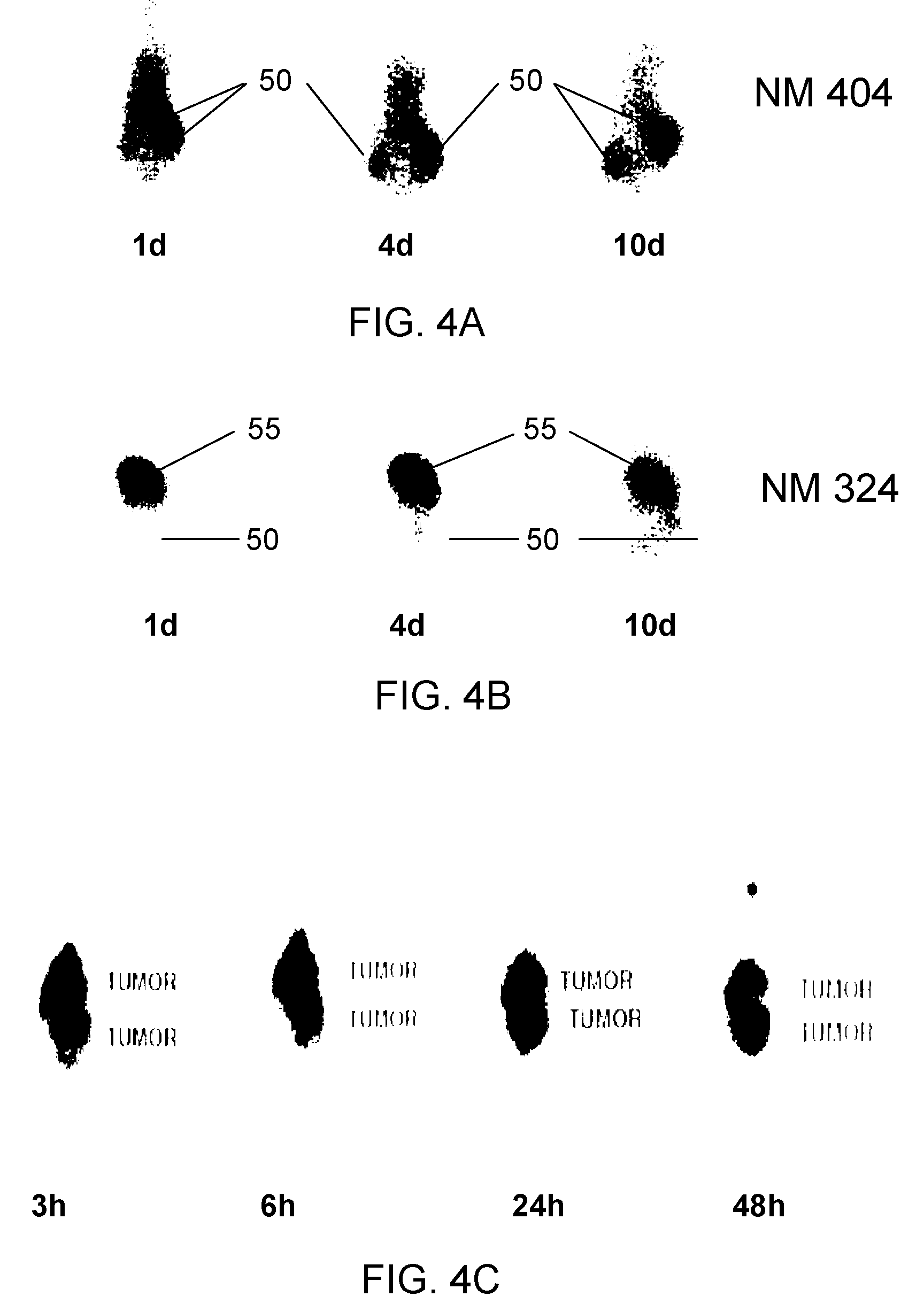
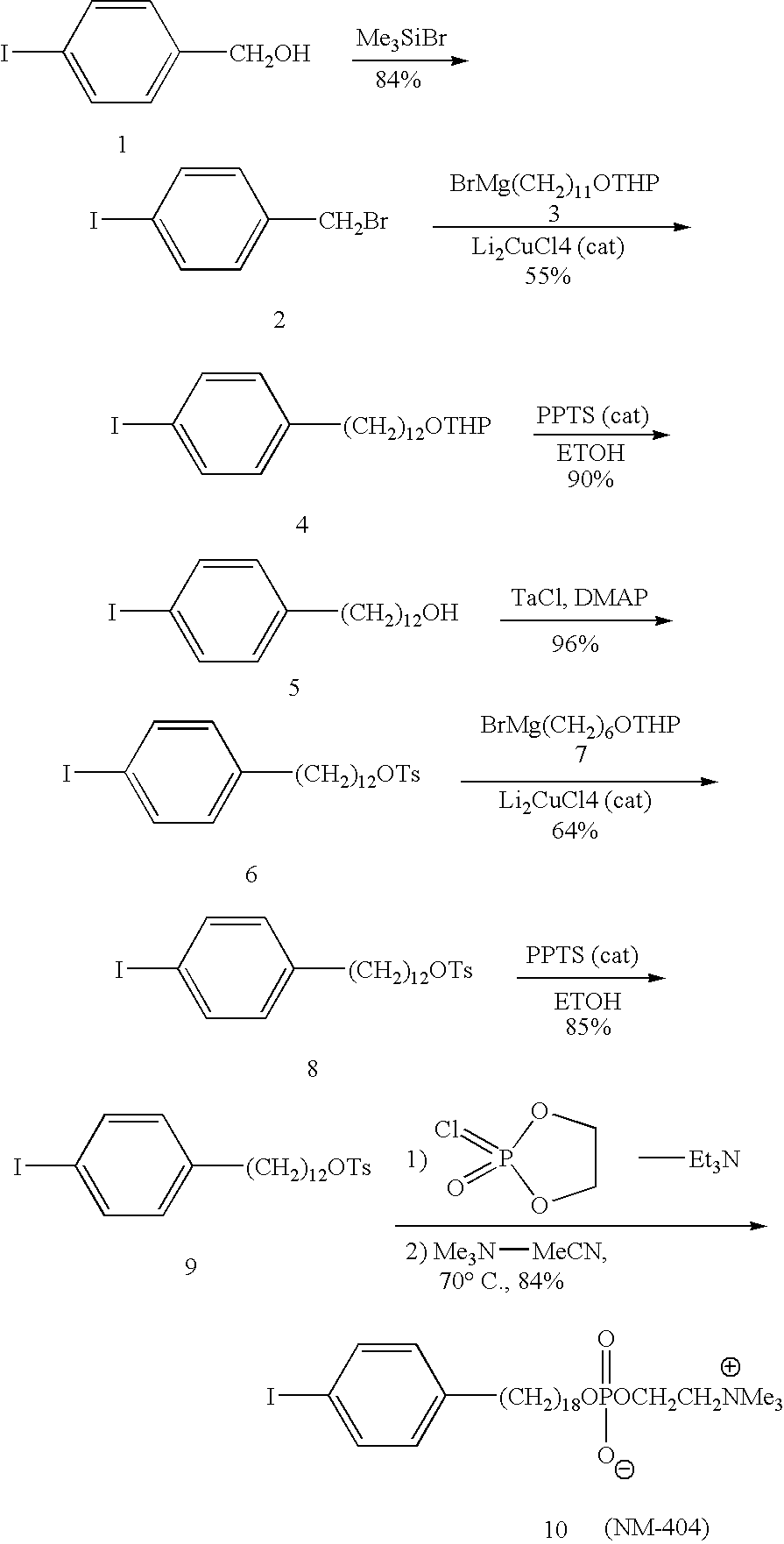
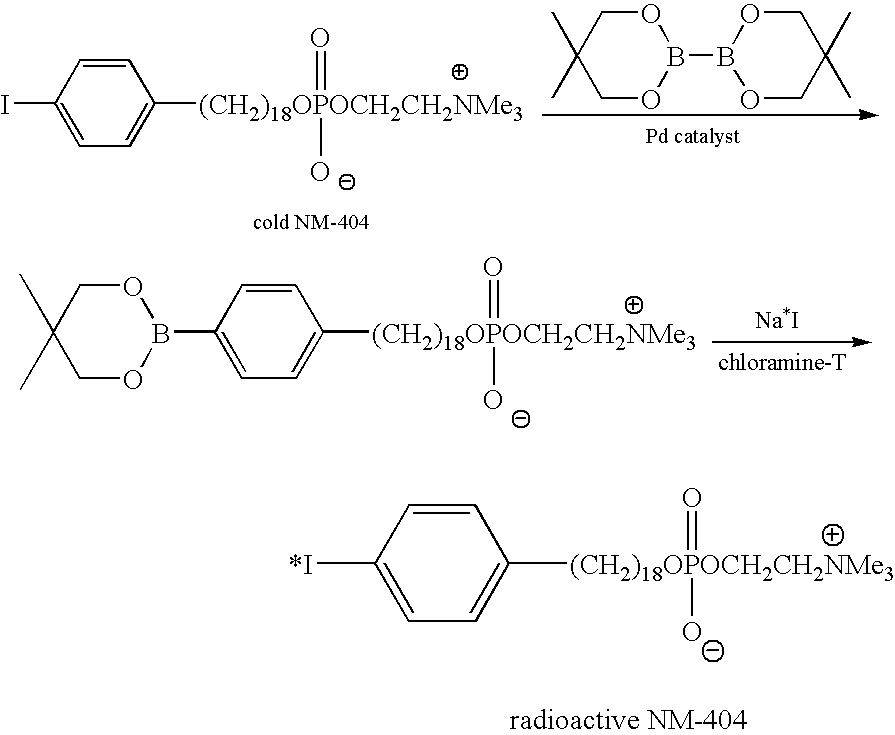
Virtual colonoscopy with radiolabeled phospholipid ether analogs
ActiveUS7700075B2X-ray constrast preparationsRadioactive preparation carriersRadiologyPhospholipid Ethers
The present invention provides agents and methods for dual modality virtual colonoscopy that gives both anatomical and functional information using hybrid CT / PET scanning. In preferred embodiments, the present invention provides radiolabeled tumor-specific agents and methods for distinguishing benign polyps from malignant tumors. In further embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods useful for distinguishing morphological and functional subregions of a selected region of tissue based on relative levels of phospholipid metabolism. Preferred radiolabeled tumor-specific agents are phospholipid ether analogs labeled with a halogen radioisotope. In certain preferred embodiments, the compositions including radiolabeled phospholipid ether analogs have therapeutic actions in addition to functionally identifying malignant tissue.
Owner:CELLECTAR LLC
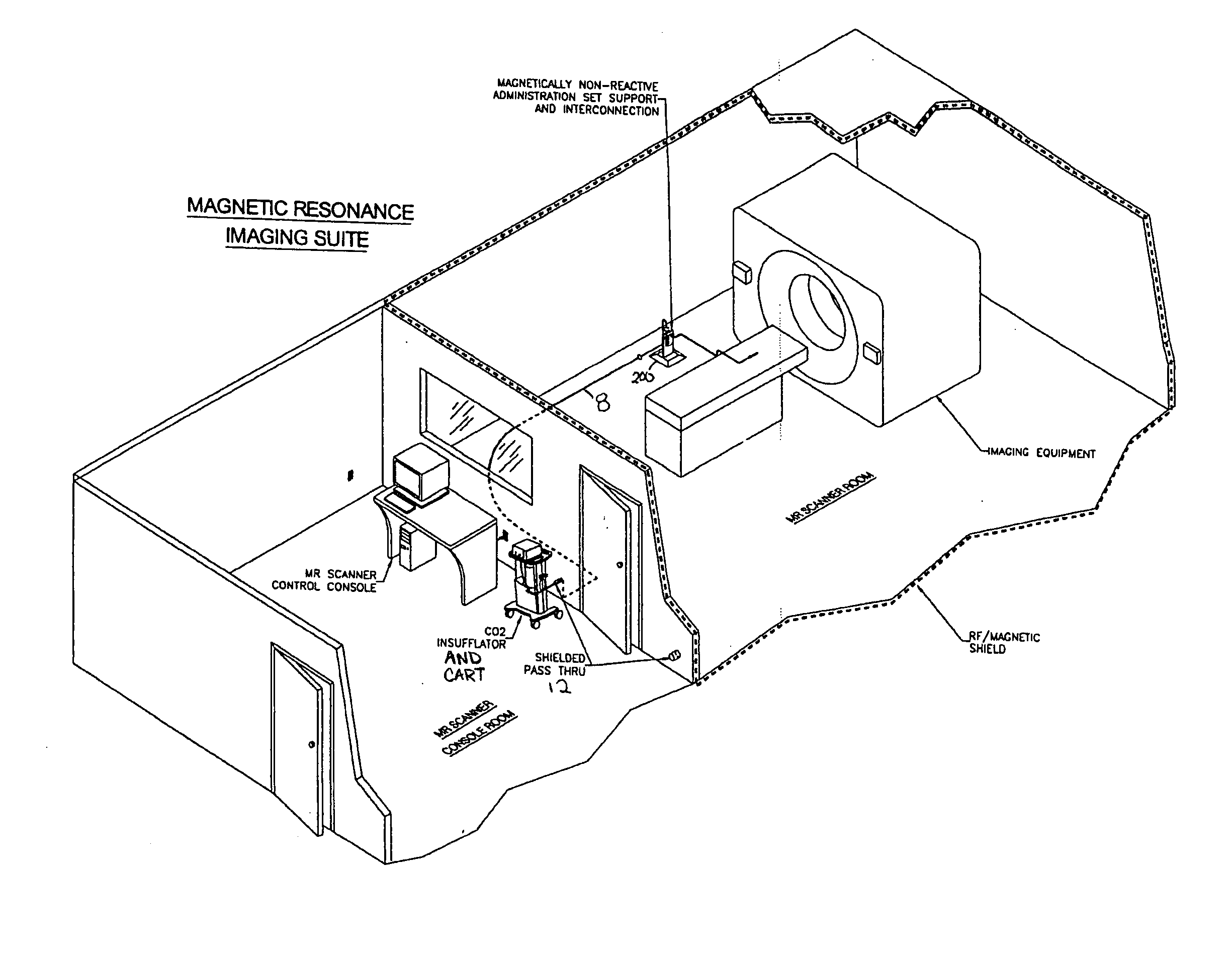
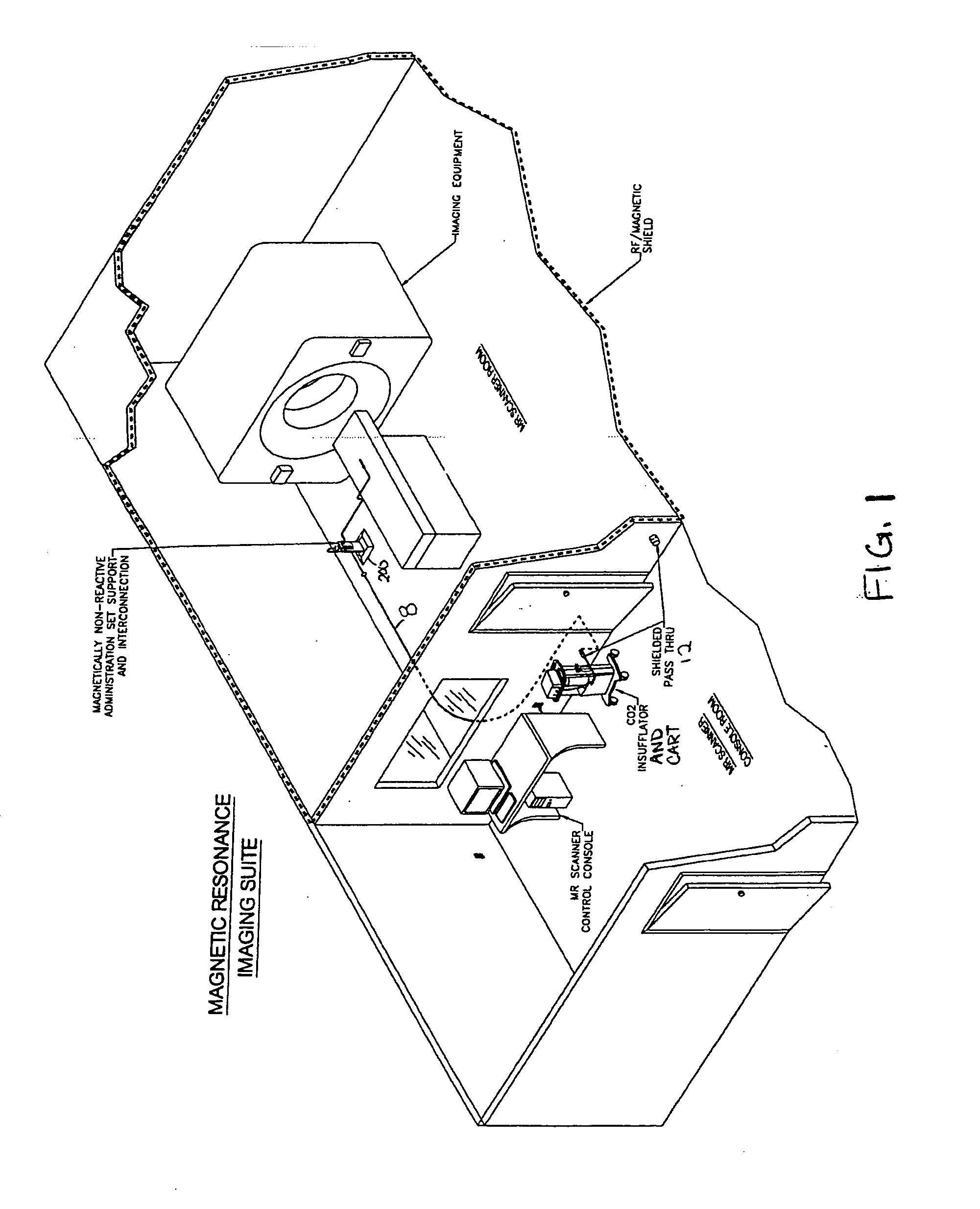
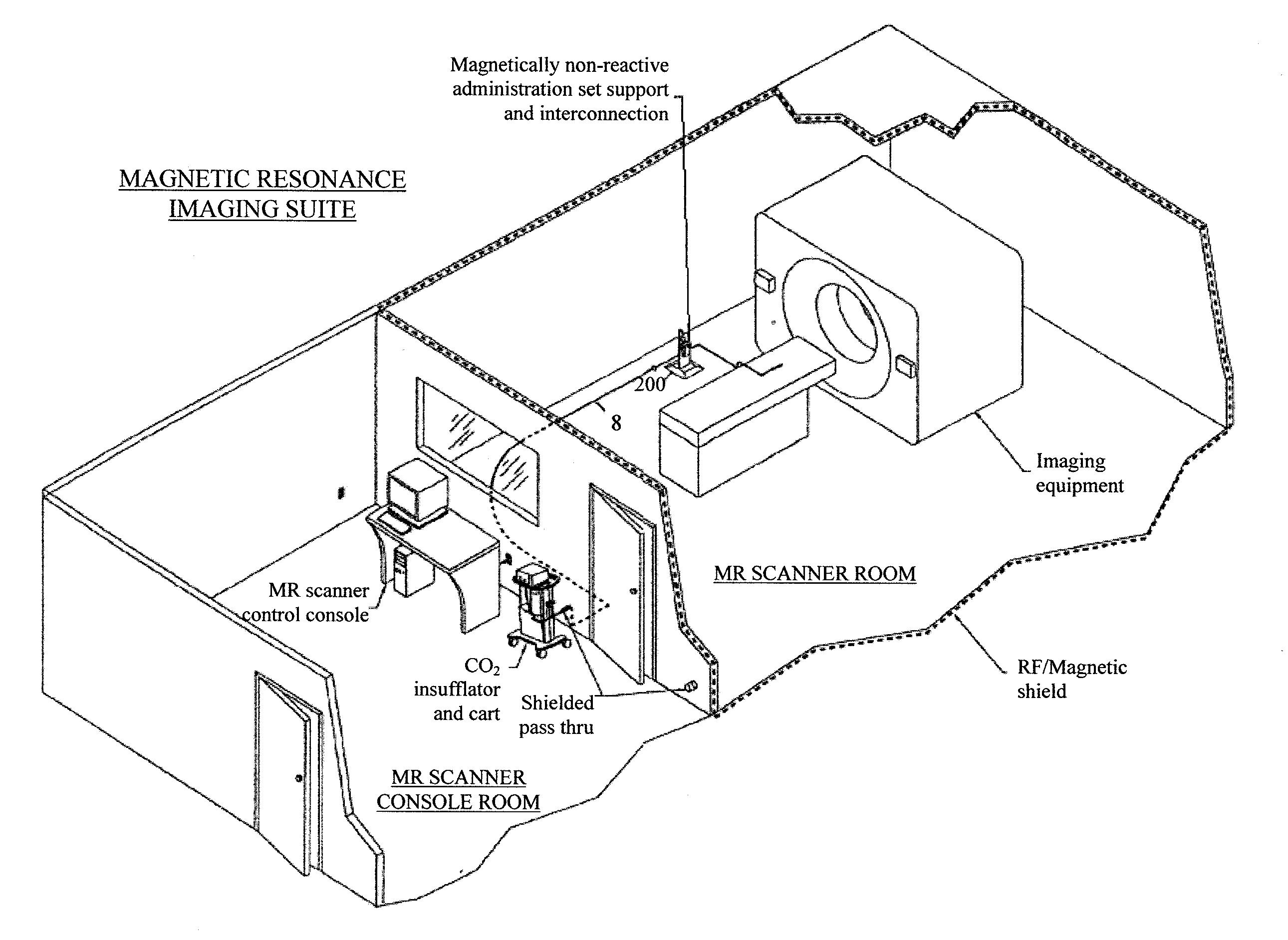
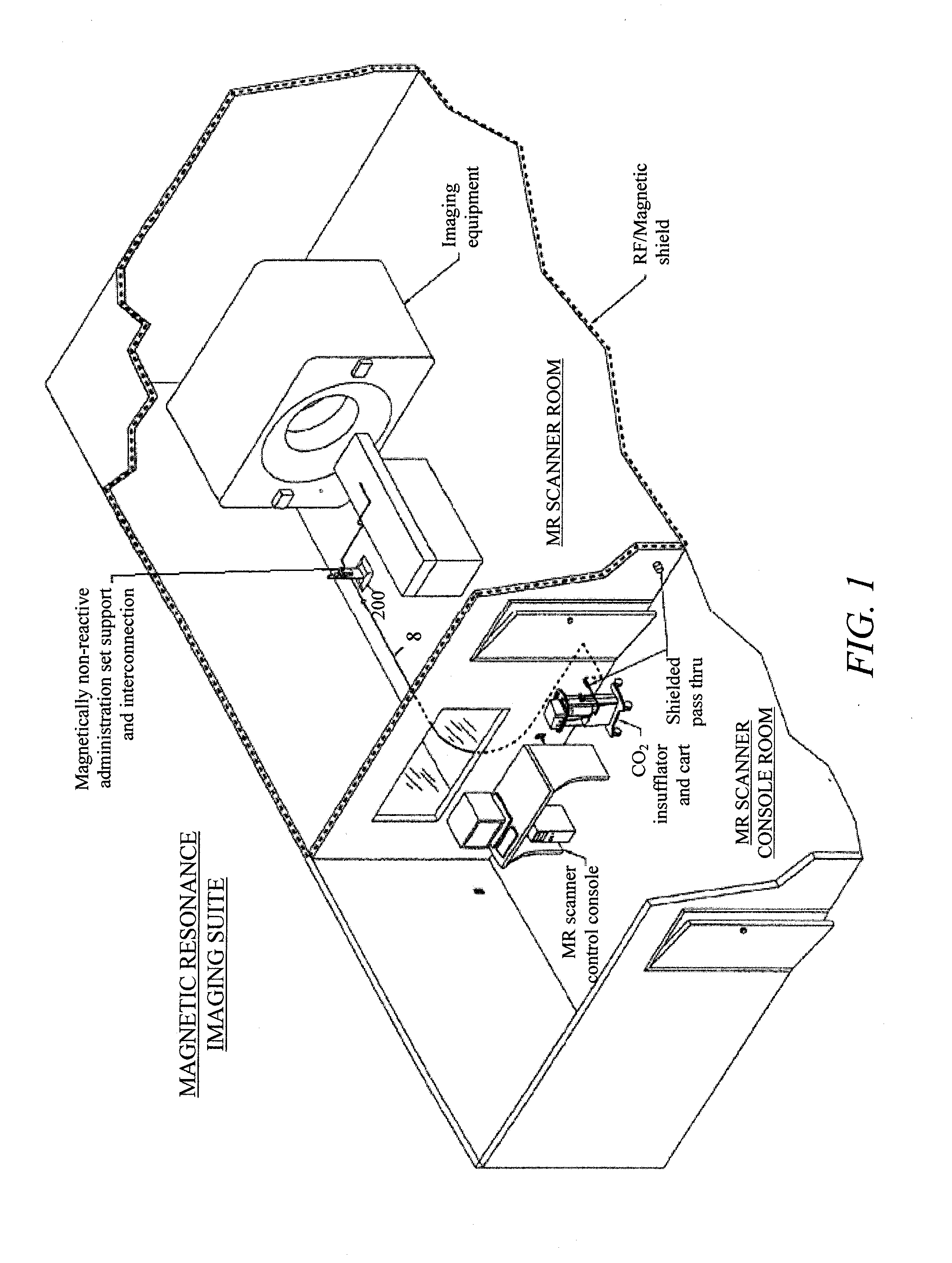
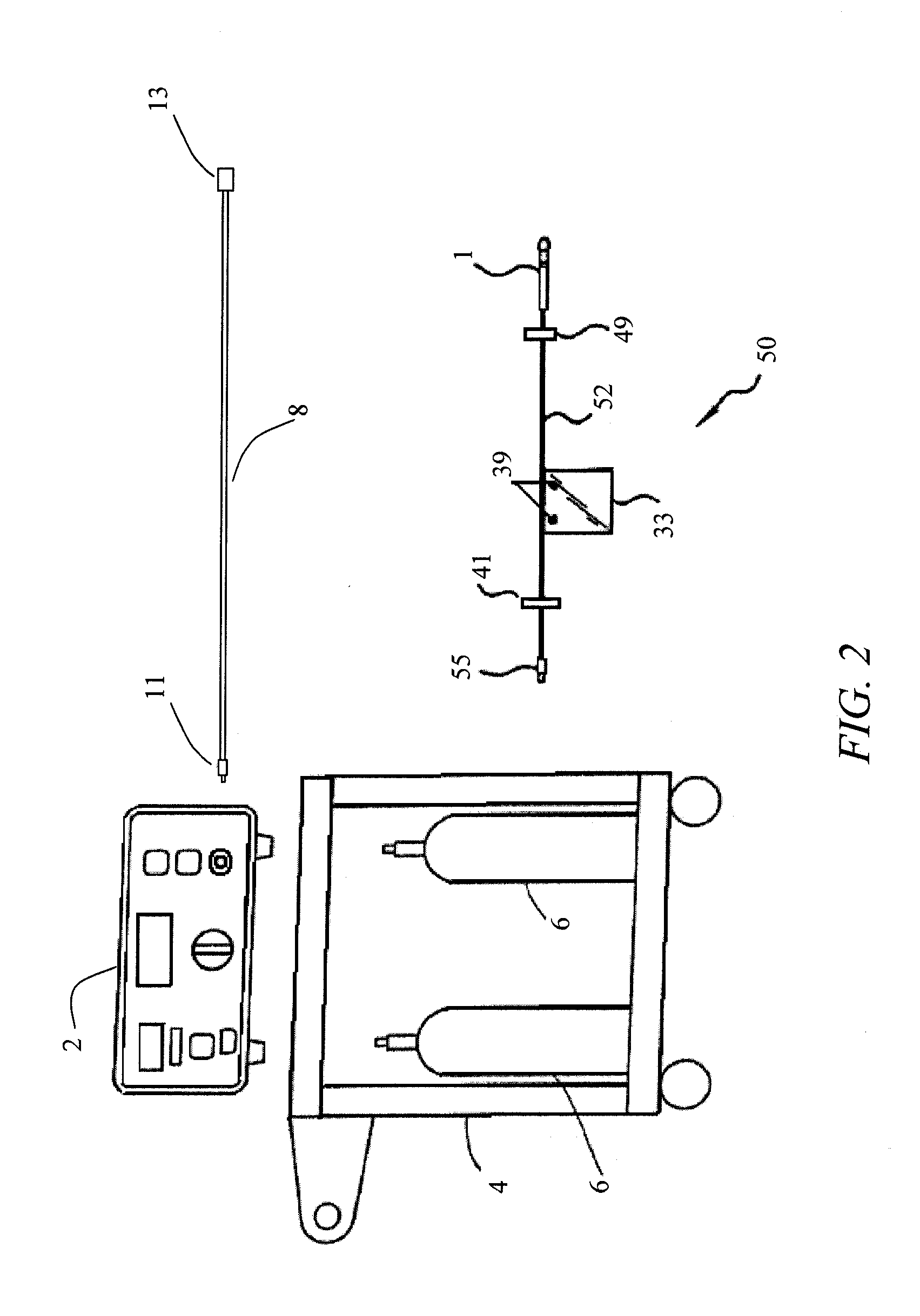
System, imaging suite, and method for using an electro-pneumatic insufflator for magnetic resonance imaging
Embodiments of the invention provide a system and method for using an electro-pneumatic insufflator for magnetic resonance imaging, such as for virtual colonoscopy. Embodiments of the invention further provide a MRI imaging suite and a method for distension of a body part to be imaged. As an alternative to the complete redesign of an electromagnetic insufflator, embodiments of the current invention utilize a standard electro-pneumatic insufflator that operates in a location impervious to electromagnetic radiation using an electromagnetically inactive connection tube.
Owner:BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS
Virtual endoscopy
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
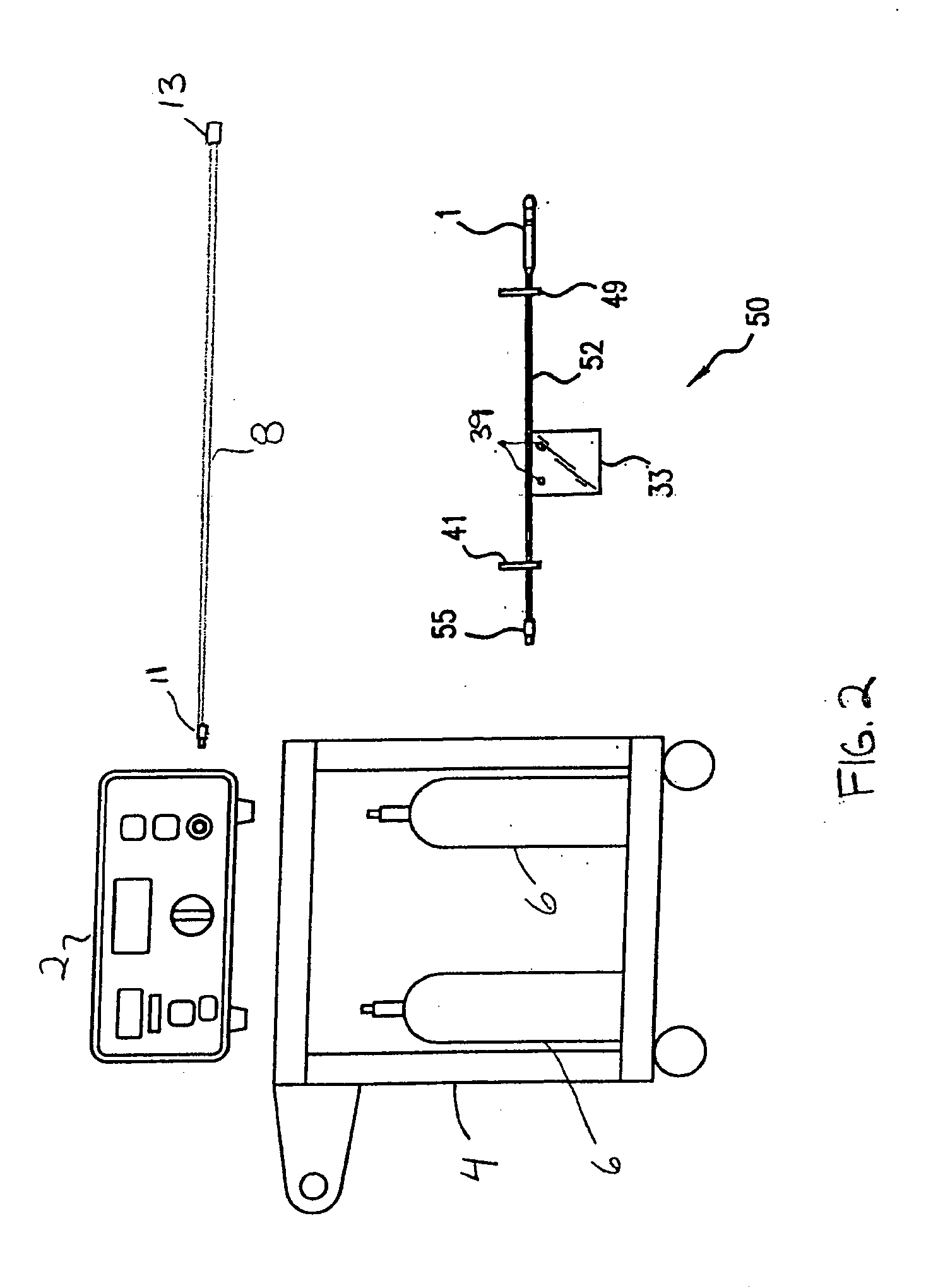
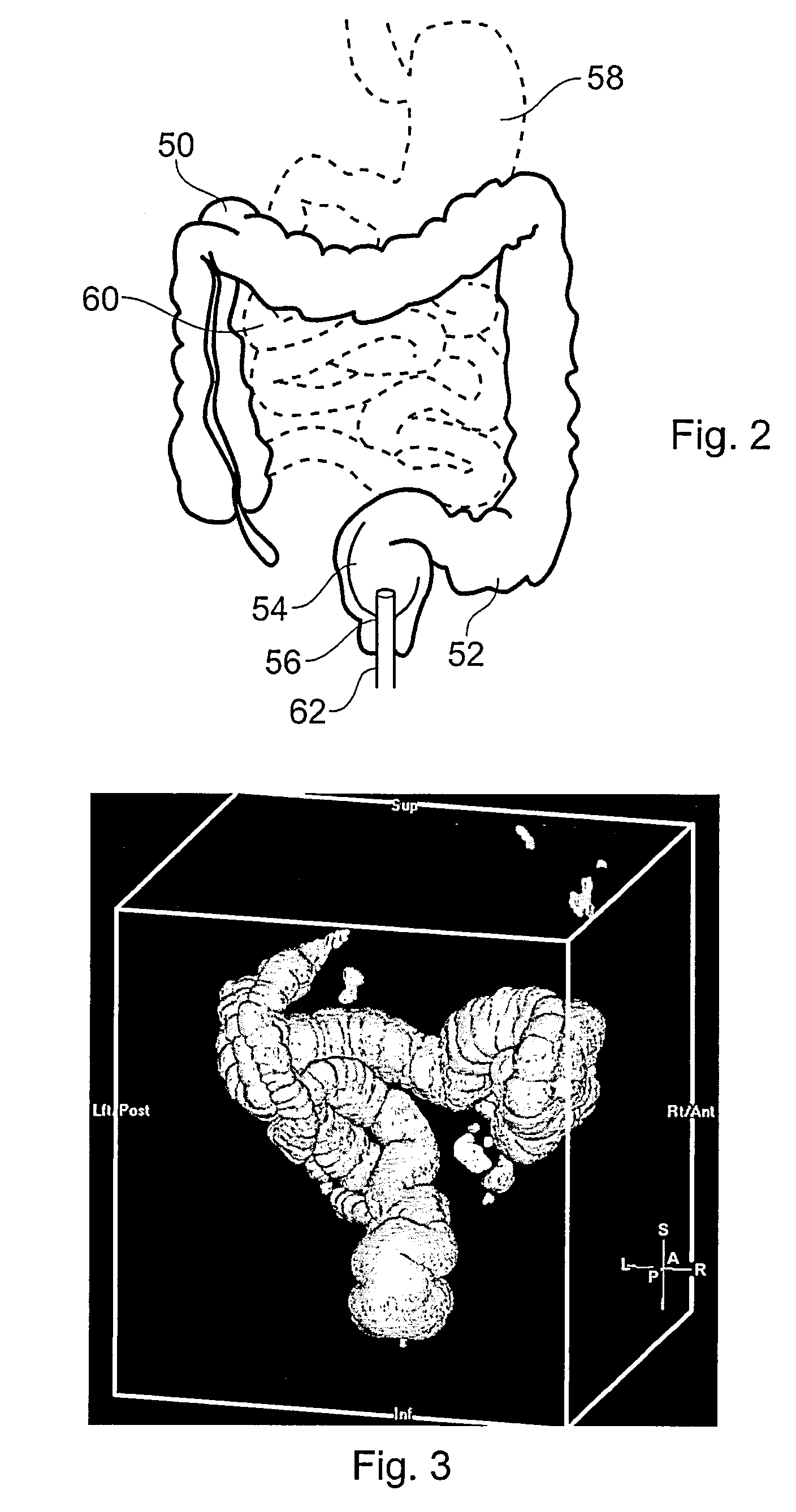
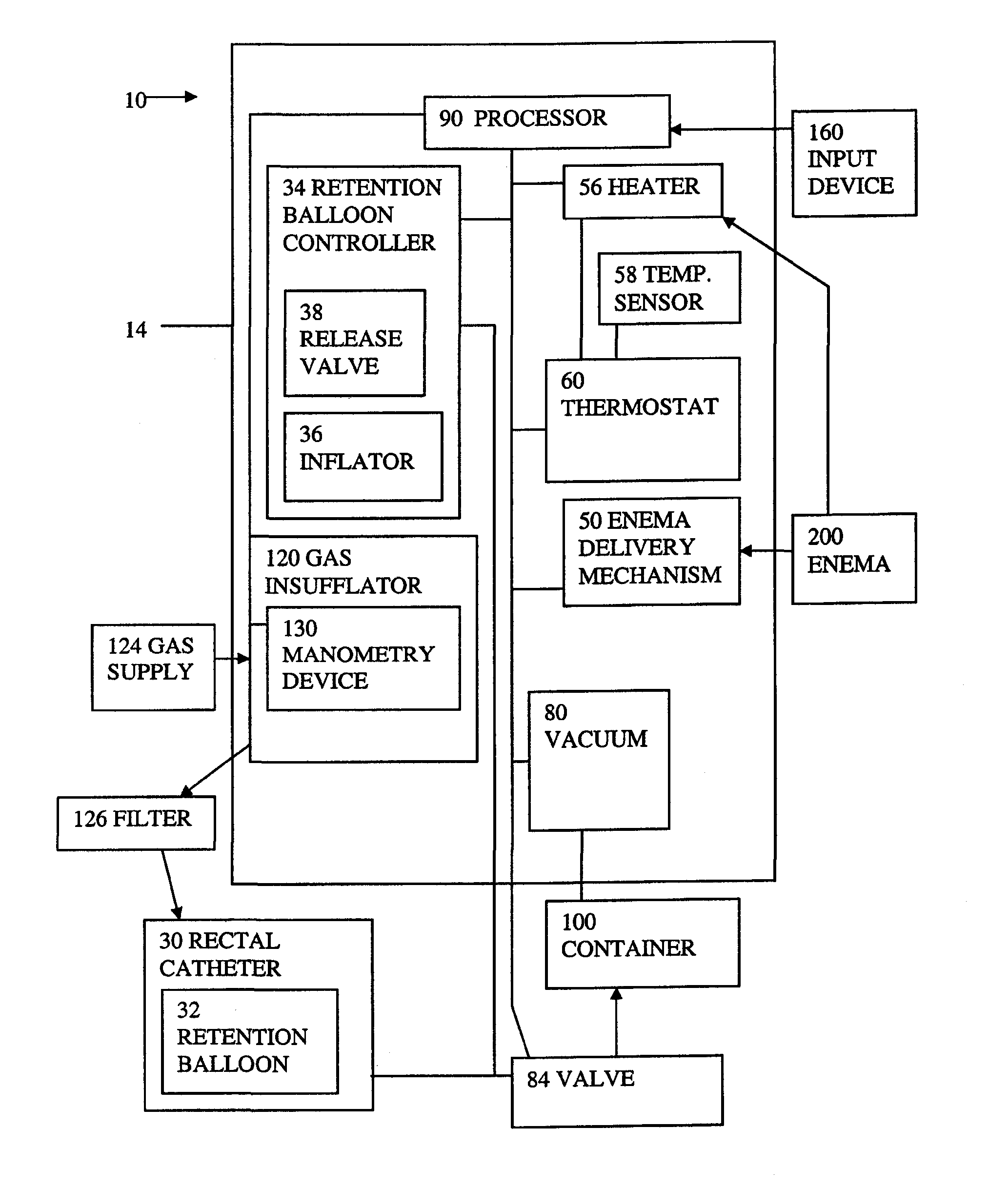
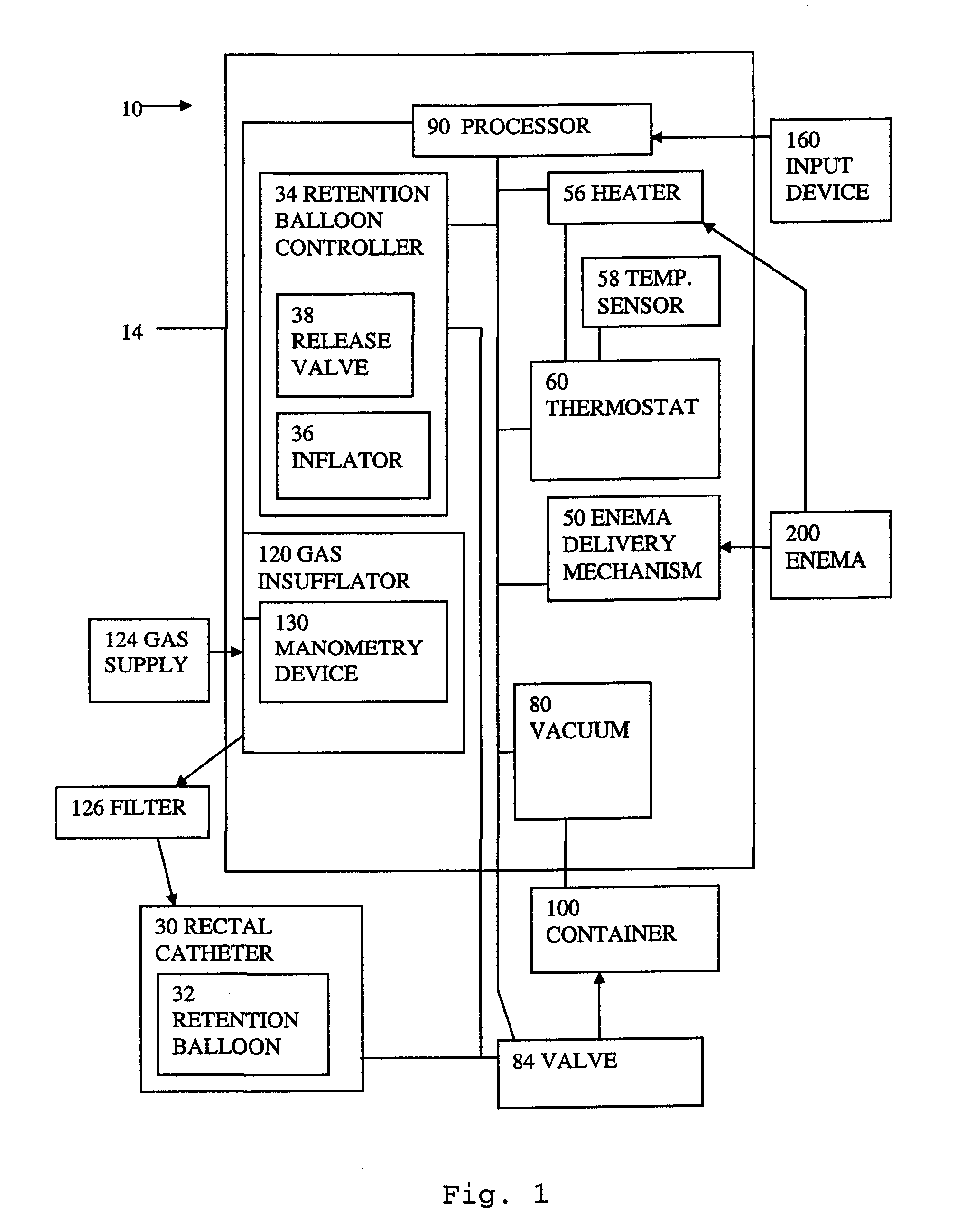
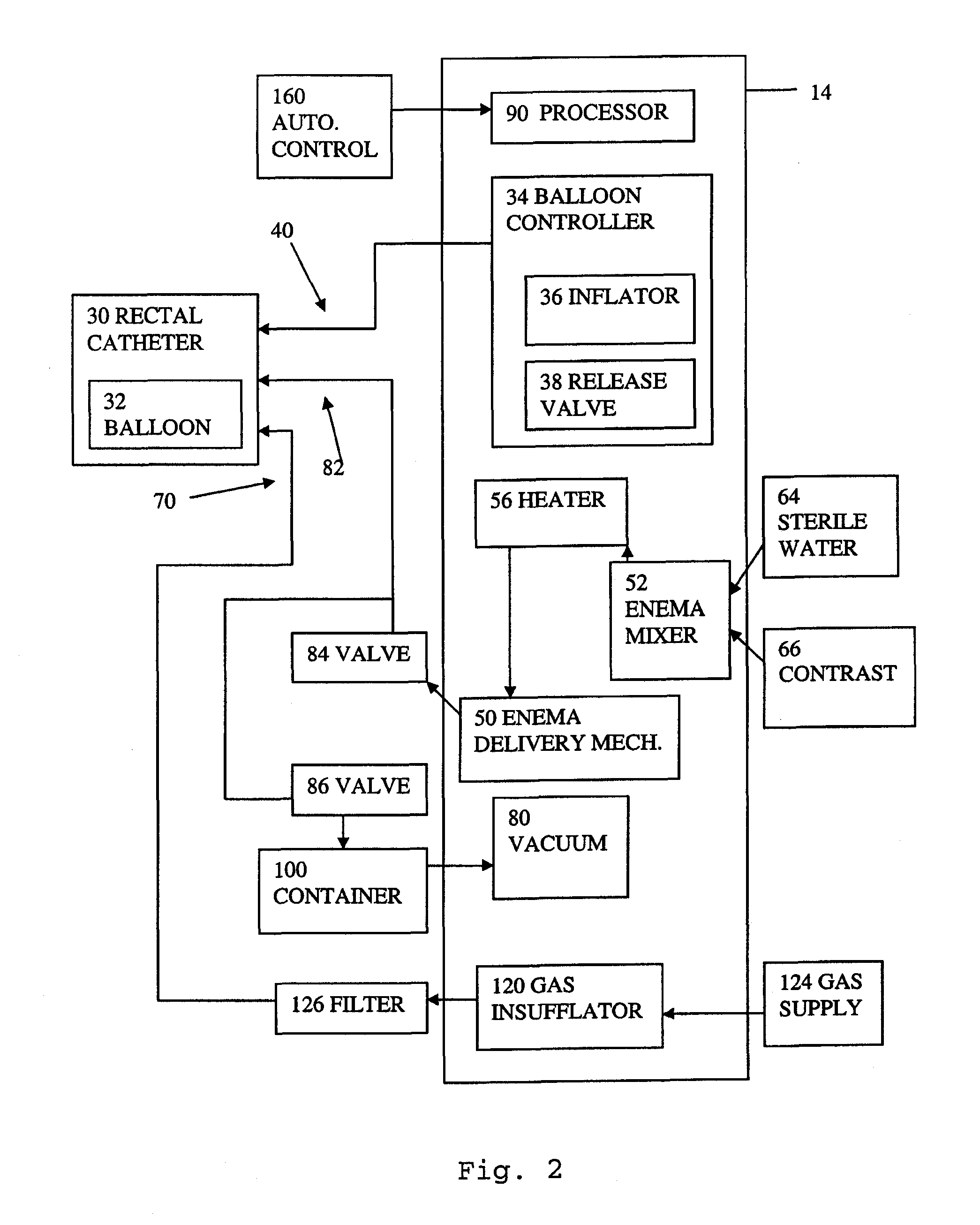
Apparatus and method for automating an enema with controlled distension
An apparatus and method are provided for use in administering a rectal contrast enema to a patient to prepare the patient for a medical procedure. A rectal catheter may be provided to facilitate administration of the enema preparation to the patient. The rectal catheter may include a retention balloon. A delivery mechanism may be provided to urge the enema preparation into the patient. A vacuum may be provided to remove waste from the patient. A gas insufflator may be provided to insufflate the patient's colon for a medical procedure such as a scan, and more specifically, a virtual colonoscopy.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Structure-analysis system, method, software arrangement and computer-accessible medium for digital cleansing of computed tomography colonography images
ActiveUS20090304248A1Easy to identifyImprove preservationMedical simulationImage enhancementBowel cleansingStructure analysis
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
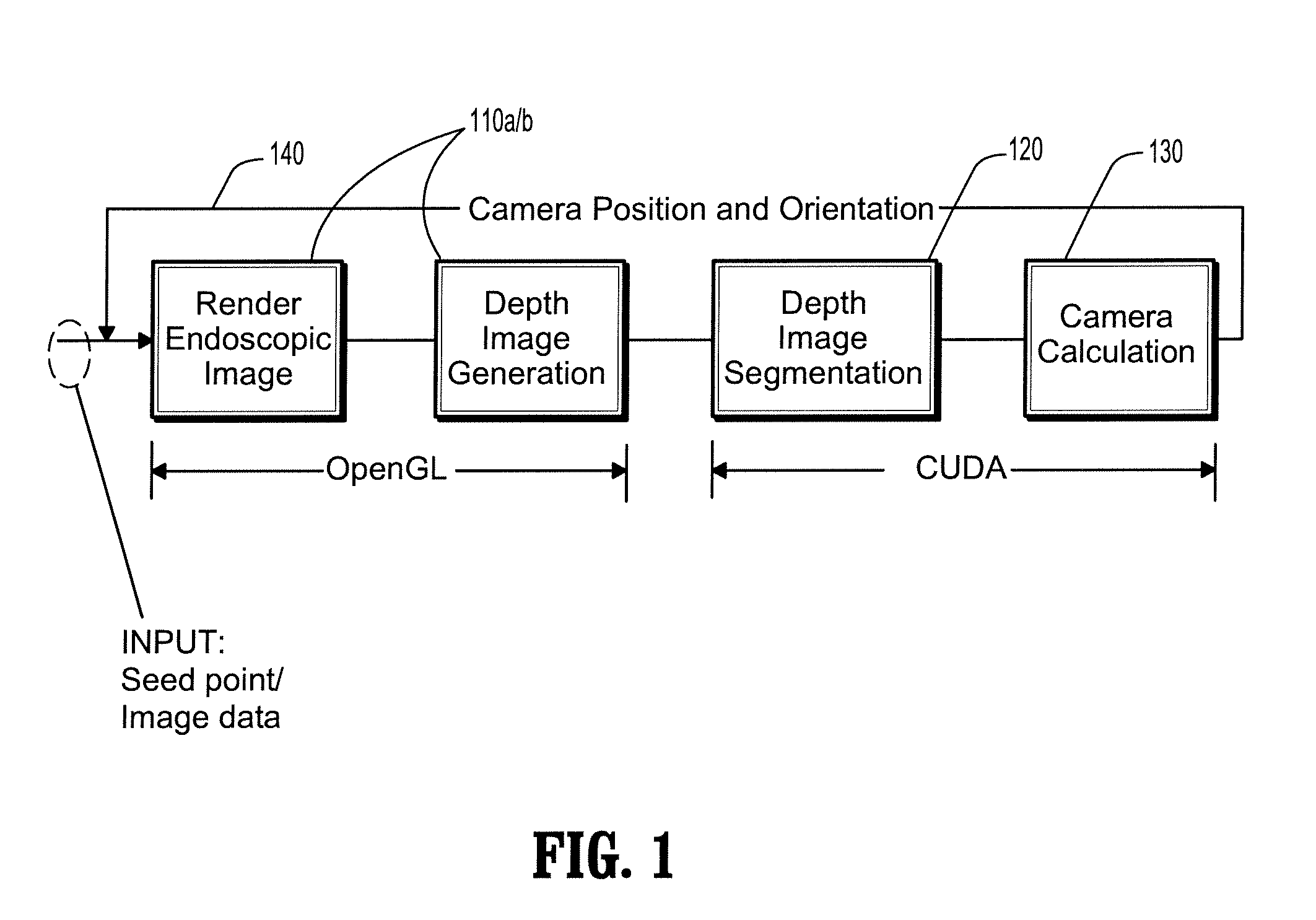
Image-based Path Planning for Automated Virtual Colonoscopy Navigation
ActiveUS20090048482A1Smooth virtual endoscopy navigationSmooth navigationPrintersProjectorsVirtual CT colonoscopyVirtual colonoscopy
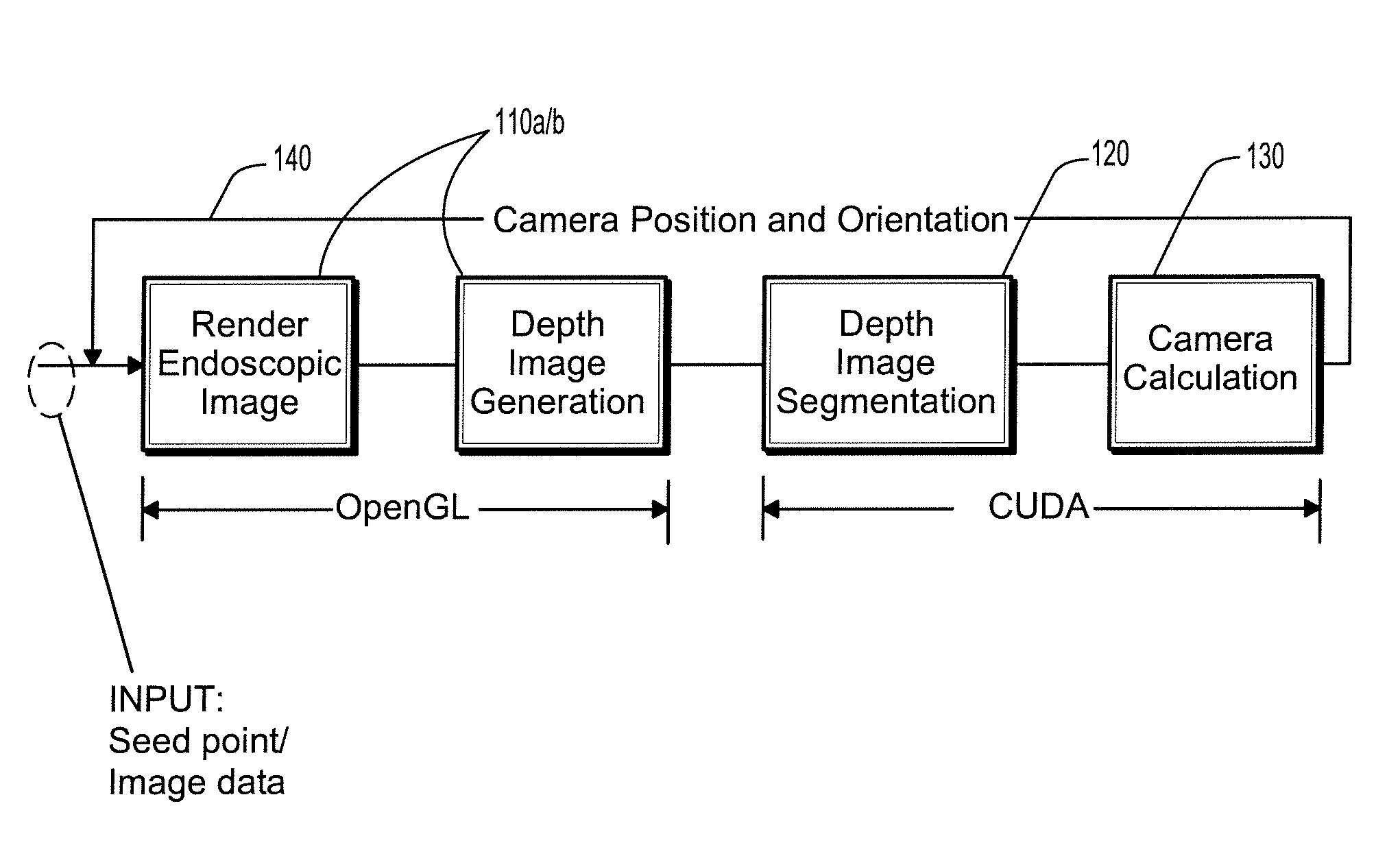
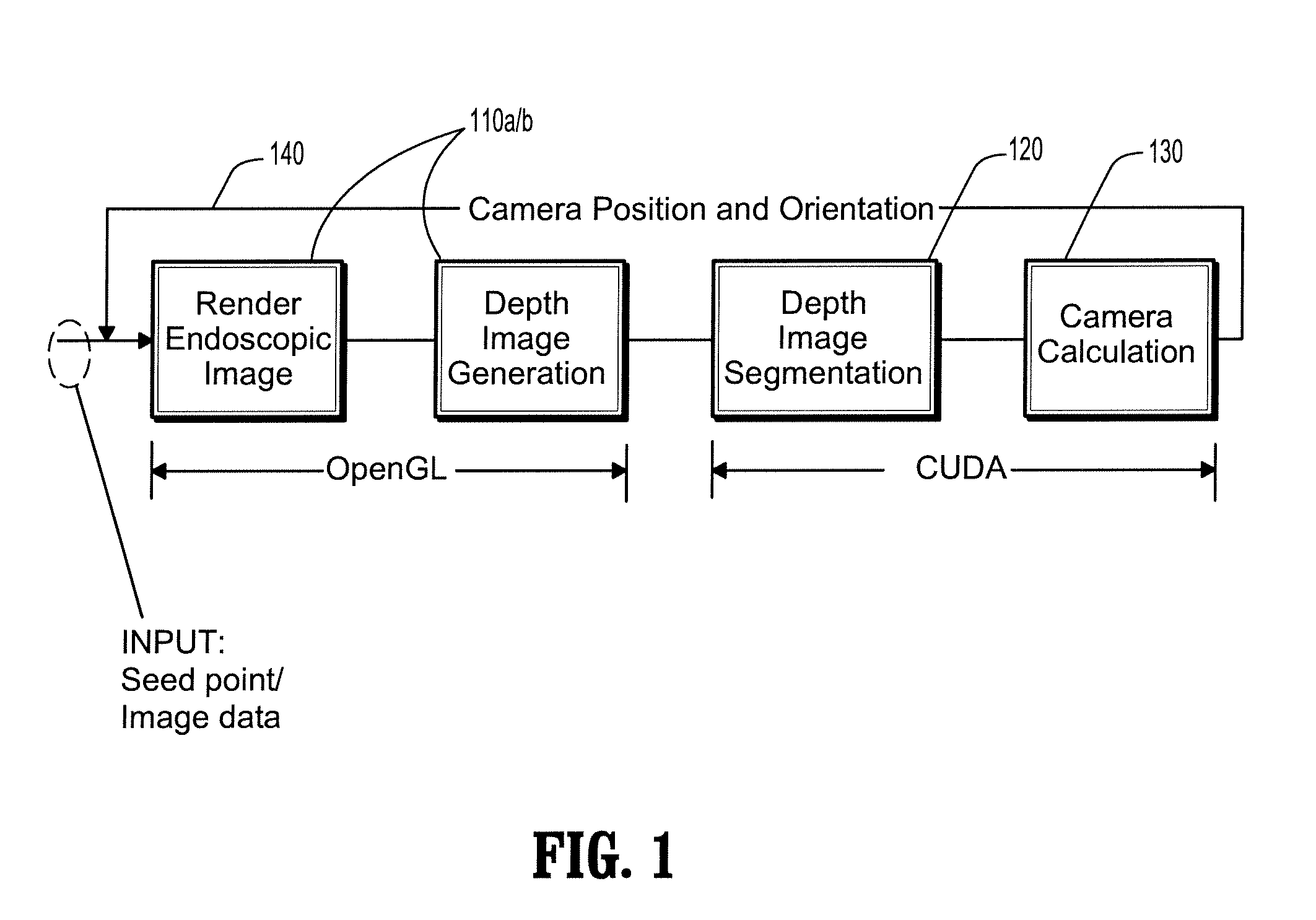
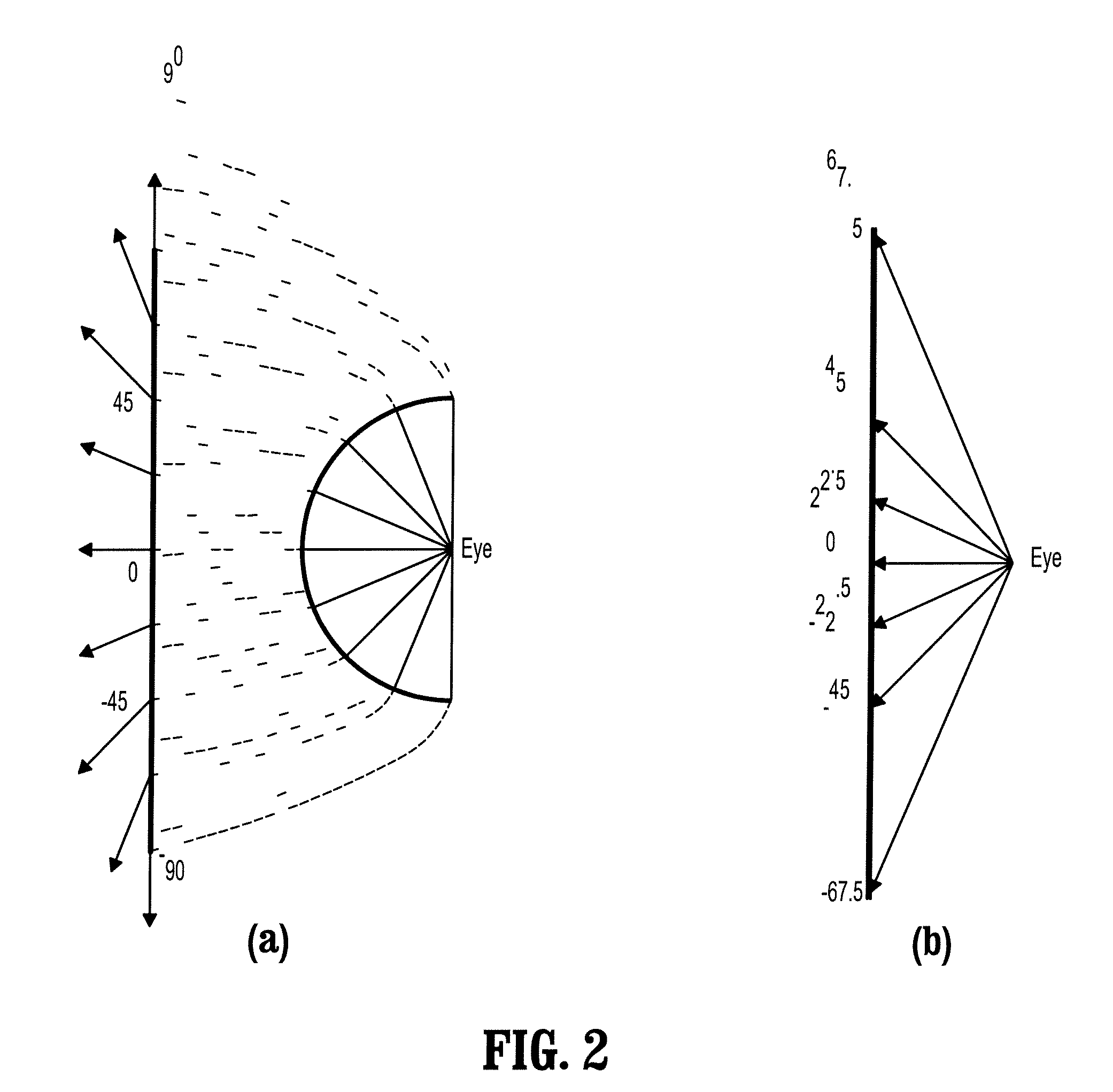
A method for automatic virtual endoscopy navigation, including: (a) using a fisheye camera to generate an endoscopic image and a depth image from a current position of the camera in lumen computed tomographic (CT) data; (b) segmenting a first region and a second region from the depth image, wherein the first region identifies a view direction of the camera and the second region is an area through which the camera can be moved without touching an inner surface of the lumen; (c) moving the camera from the current position, while pointing the camera in the view direction, to a next position in the second region; and (d) repeating steps (a-c) in sequence using the next position in step (c) as the current position in step (a).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Virtual colonoscopy with radiolabeled phospholipid ether analogs
ActiveUS20060013767A1Radioactive preparation carriersX-ray constrast preparationsAbnormal tissue growthIsotopic labeling
The present invention provides agents and methods for dual modality virtual colonoscopy that gives both anatomical and functional information using hybrid CT / PET scanning. In preferred embodiments, the present invention provides radiolabeled tumor-specific agents and methods for distinguishing benign polyps from malignant tumors. In further embodiments, the present invention provides compositions and methods useful for distinguishing morphological and functional subregions of a selected region of tissue based on relative levels of phospholipid metabolism. Preferred radiolabeled tumor-specific agents are phospholipid ether analogs labeled with a halogen radiosiotope. In certain preferred embodiments, the compositions including radiolabeled phospholipid ether analogs have therapeutic actions in addition to functionally identifying malignant tissue.
Owner:CELLECTAR
Virtual colonoscopy via wavelets
ActiveUS8023710B2Improve feature extractionMedical data miningCharacter and pattern recognitionViewpointsFeature extraction
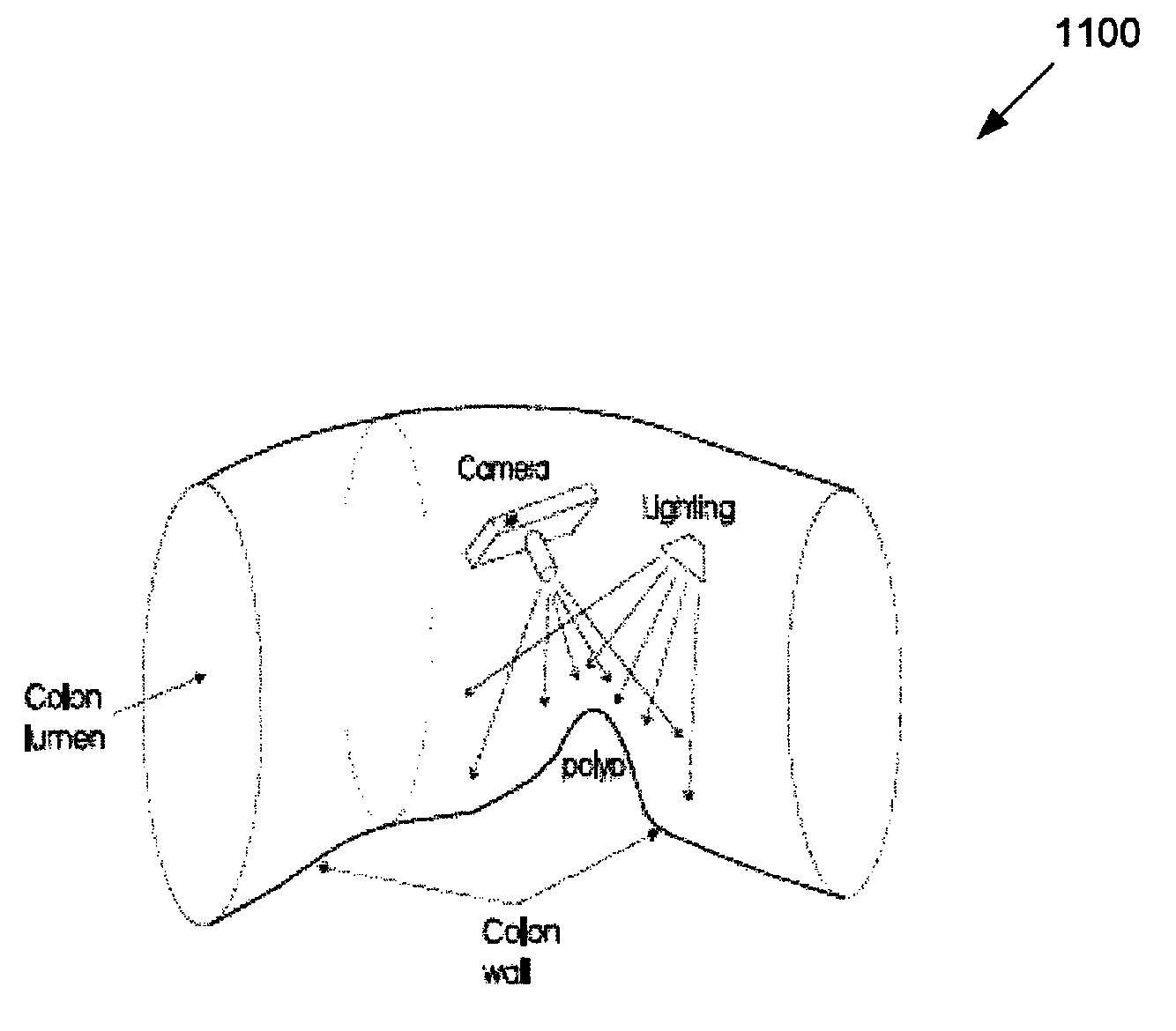
Various techniques can be used to improve classification of colon polyps candidates found via computed tomographic colonography computer aided detection (CTCCAD). A polyp candidate can be classified as a true positive or a false positive. For example, a two-dimensional projection image of the polyp can be generated from a three-dimensional representation and classified based on features of the projection image. An optimal viewpoint for the projection image can be found via techniques such as maximizing viewpoint entropy. Wavelet processing can be used to extract features from the two-dimensional projection image. Feature extraction can use a piecewise linear orthonormal floating search for locating most predictive neighbors for wavelet coefficients, and support vector machines can be employed for classification. The techniques can be useful for improving accuracy of CTCCAD techniques.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Mixed organization image full-automatic partition method of virtual colonoscope
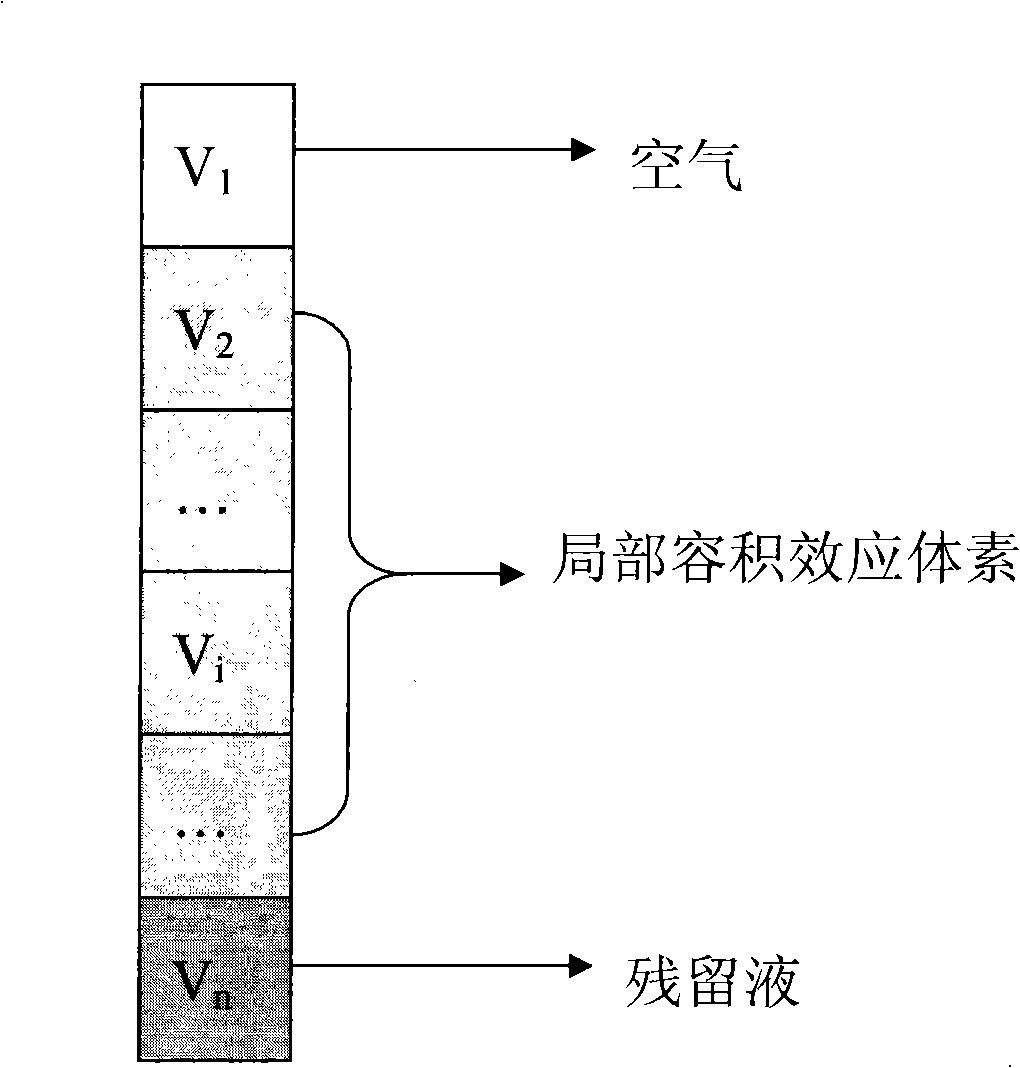
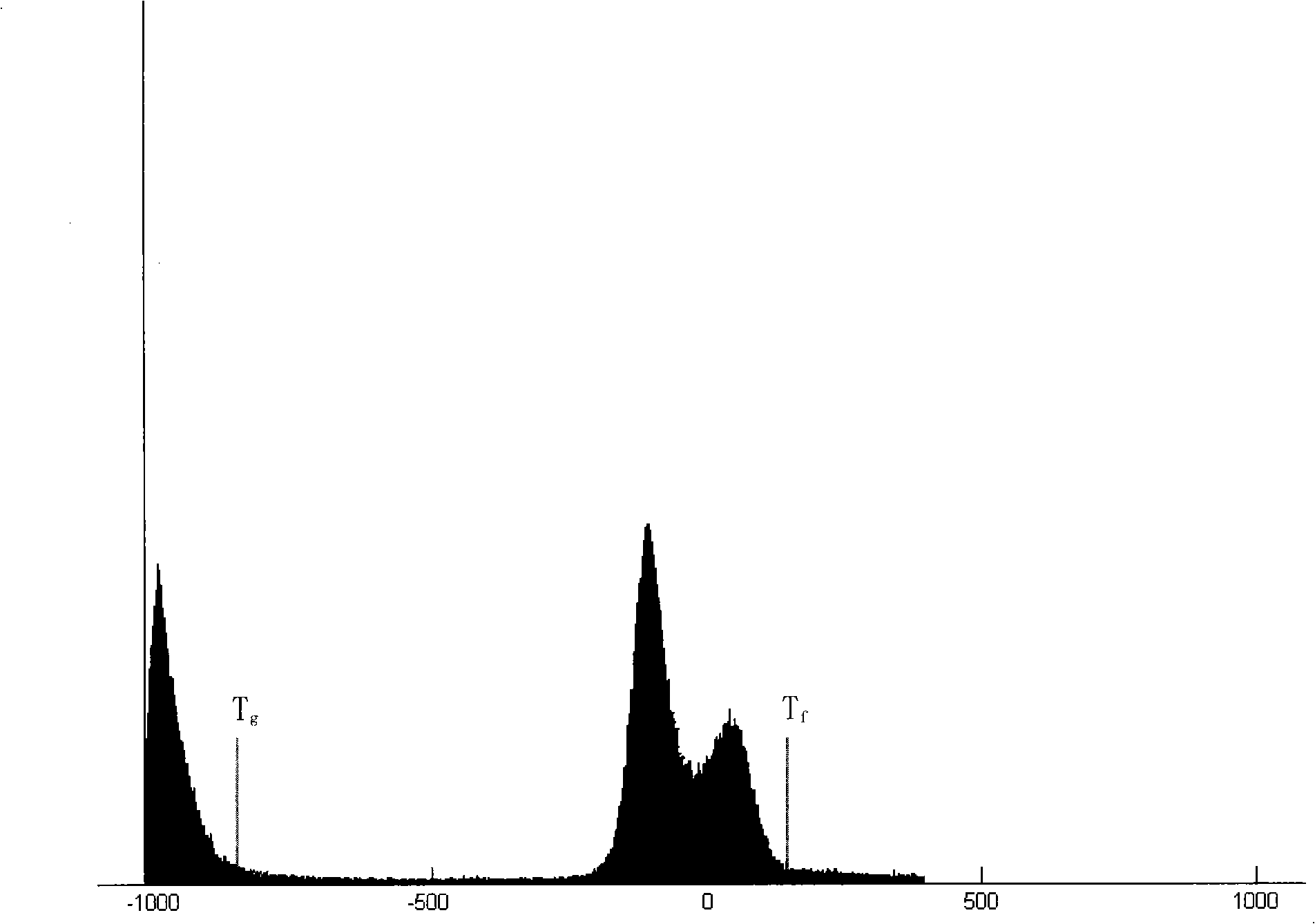
InactiveCN101295404AAchieve segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationGradient strength
The invention provides a full-automatic segmentation method for a mixed tissue image of a simulated colonoscopy, comprising the following steps of: selecting a suitable threshold value of the air and of the enteral residual liquid; carrying out an initial segmentation for the enteral area through a traditional threshold method; wiping a local volume effect between the air and the enteral residual liquid through a vertical filter; conducting an enteral segmentation through a region growing method; enhancing the boundaries of the colon and other issues through a gradient intensity region growing method; repeating a wiping of the local volume effect between the air and the enteral residual liquid through the vertical filter for the inner part of the colon with enhanced boundaries. The full-automatic segmentation method for the mixed tissue image of a simulated colonoscopy overcomes the problems of the traditional threshold segmentation, eliminates the impacts from the local volume effect, and renders the segmentation results better in conformity with the actual conditions.
Owner:SHAANXI HI TECH MEDICAL INFORMATION
Virtual fly over of complex tubular anatomical structures
InactiveUS8014561B2Avoid possibilityMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnatomical structuresData set
An embodiment of the invention is method, which can be implemented in software, firmware, hardware, etc., for virtual fly over inspection of complex anatomical tubular structures. In a preferred embodiment, the method is implemented in software, and the software reconstructs the tubular anatomical structure from a binary imaging data that is originally acquired from computer aided tomography scan or comparable biological imaging system. The software of the invention splits the entire tubular anatomy into exactly two halves. The software assigns a virtual camera to each half to perform fly-over navigation. Through controlling the elevation of the virtual camera, there is no restriction on its field of view (FOV) angle, which can be greater than 90 degrees, for example. The camera viewing volume is perpendicular to each half of the tubular anatomical structure, so potential structures of interest, e.g., polyps hidden behind haustral folds in a colon are easily found. The orientation of the splitting surface is controllable, the navigation can be repeated at another or a plurality of another split orientations. This avoids the possibility that a structure of interest, e.g., a polyp that is divided between the two halves of the anatomical structure in a first fly over is missed during a virtual inspection. Preferred embodiment software conducts virtual colonoscopy fly over. Experimental virtual fly over colonoscopy software of the invention that performed virtual fly over on 15 clinical datasets demonstrated average surface visibility coverage is 99.59+ / −0.2%.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Method and apparatus for improving a virtual colonoscopy and A CT angiography
InactiveUS20040167400A1Reduce signalingIncrease differentiationAngiographyRadiation diagnosticsUltrasound attenuationMedicine
Methods and apparatus for improving a virtual colonoscopy and a CT angiography. Embodiments of the present invention provide a contrast media into the patient's stool or blood stream so as to reduce an attenuation signal of the patient's stool or blood. Reducing the signal of the stool allows an examining physician to better differentiate the stool from polyps in the colon and allows an examining physician to better differentiate the blood from an arterial wall.
Owner:ACCUIMAGE DIAGNOSTICS CORP
System, imaging suite, and method for using an electro-pneumatic insufflator for magnetic resonance imaging
Embodiments of the invention provide a system and method for using an electro-pneumatic insufflator for magnetic resonance imaging, such as for virtual colonoscopy. Embodiments of the invention further provide a MRI imaging suite and a method for distension of a body part to be imaged. As an alternative to the complete redesign of an electro-magnetic insufflator, embodiments of the current invention utilize a standard electro-pneumatic insufflator that operates in a location impervious to electromagnetic radiation using an electromagnetically inactive connection tube.
Owner:BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS
Method and apparatus for automatic local path planning for virtual colonoscopy
A method for automatic local path planning for a virtual endoscope comprises the steps of defining a sub volume around a current endoscope position in a lumen; performing a region growing inside the lumen, starting from the current endoscope position; calculating and clustering the intersection of the region with the faces of a cube circumscribing the sub volume; calculating approximated centerline paths from the current endoscope position to the center of each cluster formed in the preceding step; comparing each of the centerline paths with a current path exhibited by the endoscope; and selecting an optimal centerline path based on the comparison.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Bowel preparation for virtual colonoscopy
InactiveUS20060024236A1Supplement cleansingBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsMedicineWater soluble
The instant invention combines three distinct components to form a single effective bowel preparation for virtual colonoscopy (VC) examination: 4) a cathartic for colonic cleansing; 5) barium sulfate for stool tagging; and 6) water soluble iodinated contrast for colonic fluid opacification. Each component has been employed previously for VC preparation with sub-optimal results. The unique bowel preparation described herein combines these components and has been proven highly effective in a large, prospective multi-center VC screening trial. In addition to being highly efficient, the packaging of these three components into a single preparation kit is much more convenient for patients and their referring physicians. The specific timing and dosage of each component can vary within an acceptable effective range.
Owner:PICKHARDT PERRY J
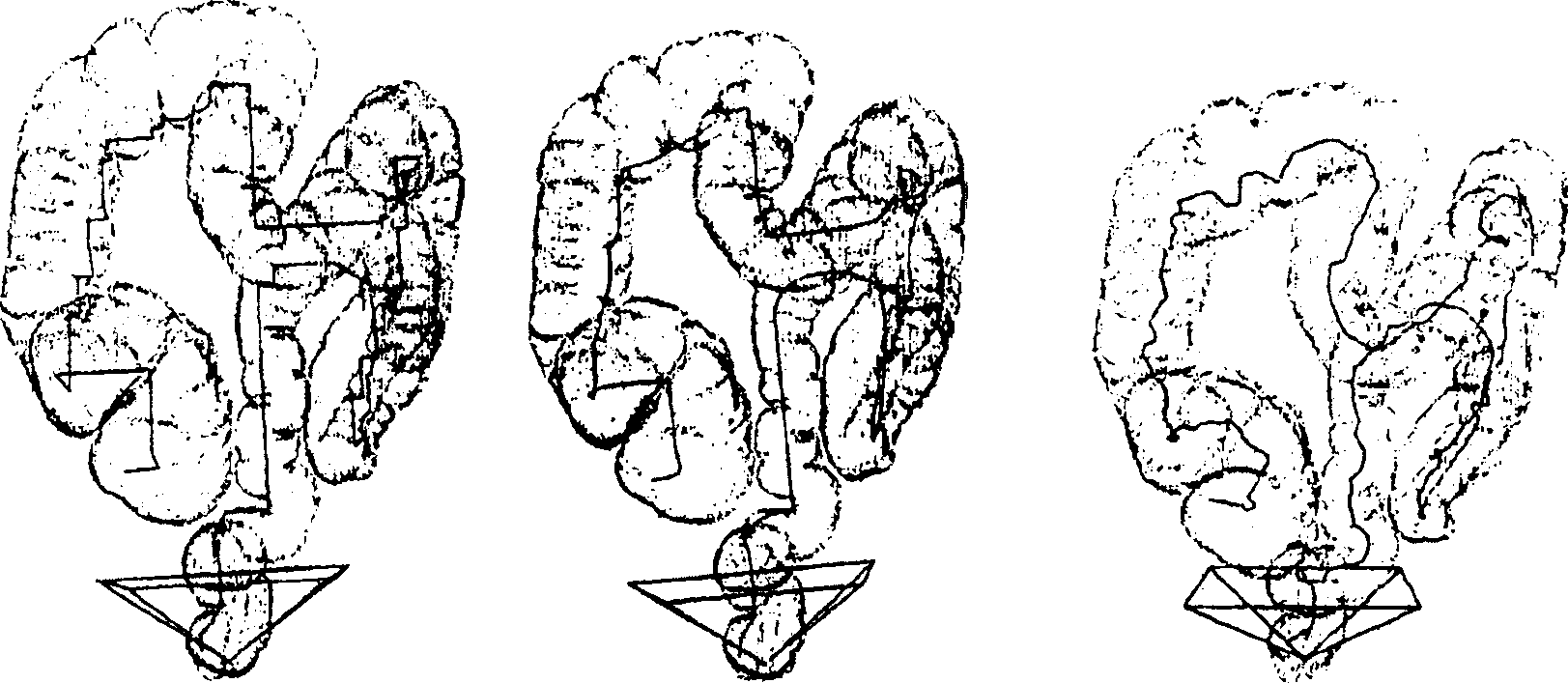
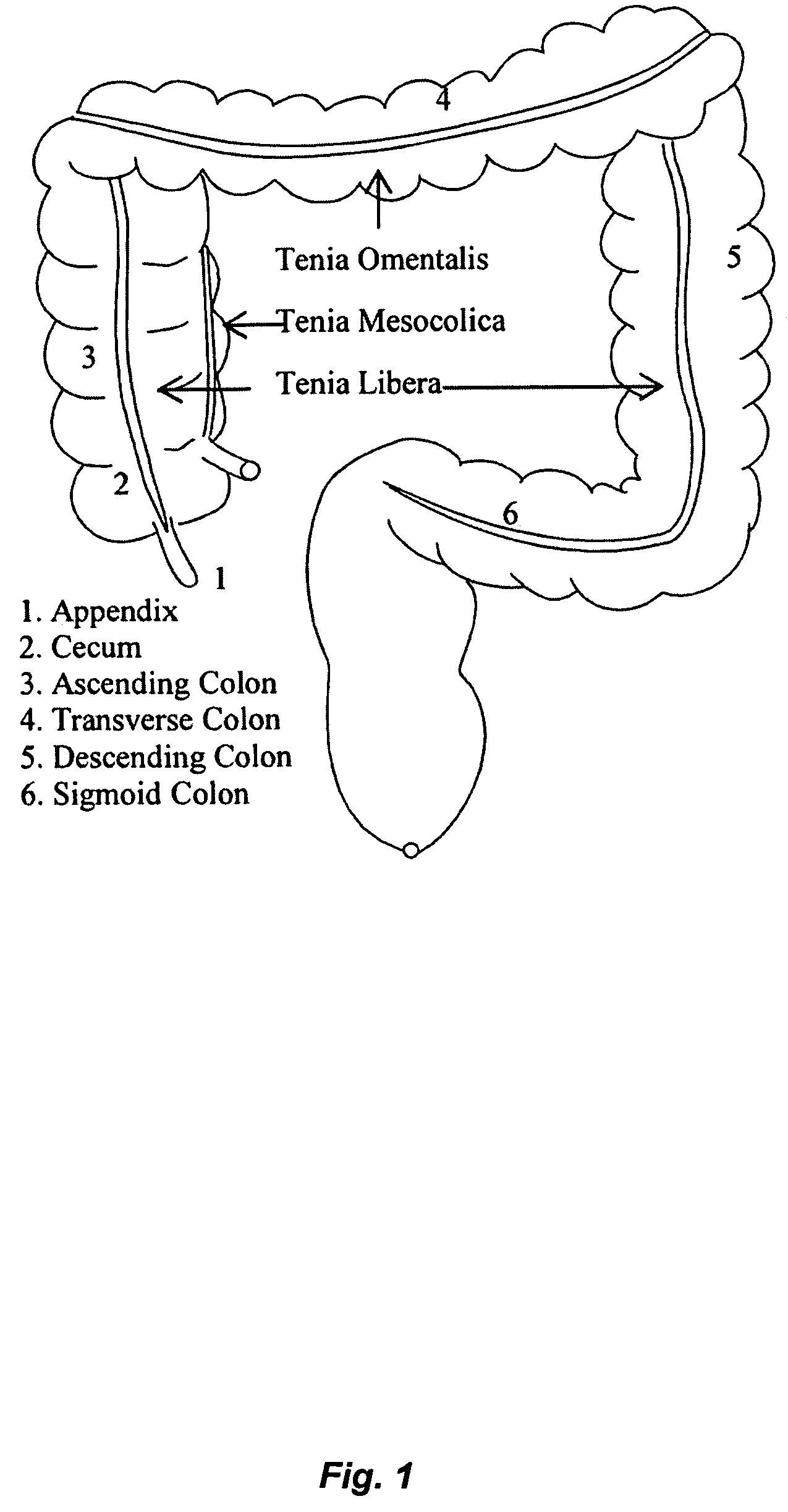
Teniae coli guided navigation and registration for virtual colonoscopy
A computer-assisted method for detecting surface features in a virtual colonoscopy. The method includes providing a three-dimensional construction of a computed tomography colonography surface; creating a path along the teniae coli from the proximal ascending colon to the distal descending colon on the colonography surface; forming an indexed computed tomography colonography surface using the created path; and registering the supine and prone scans of the computed tomography colonography surface using the indexed computed tomography colonography surface. The method also includes navigating the internal surface of the computed tomography colonography using the indexed computed tomography colonography surface.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
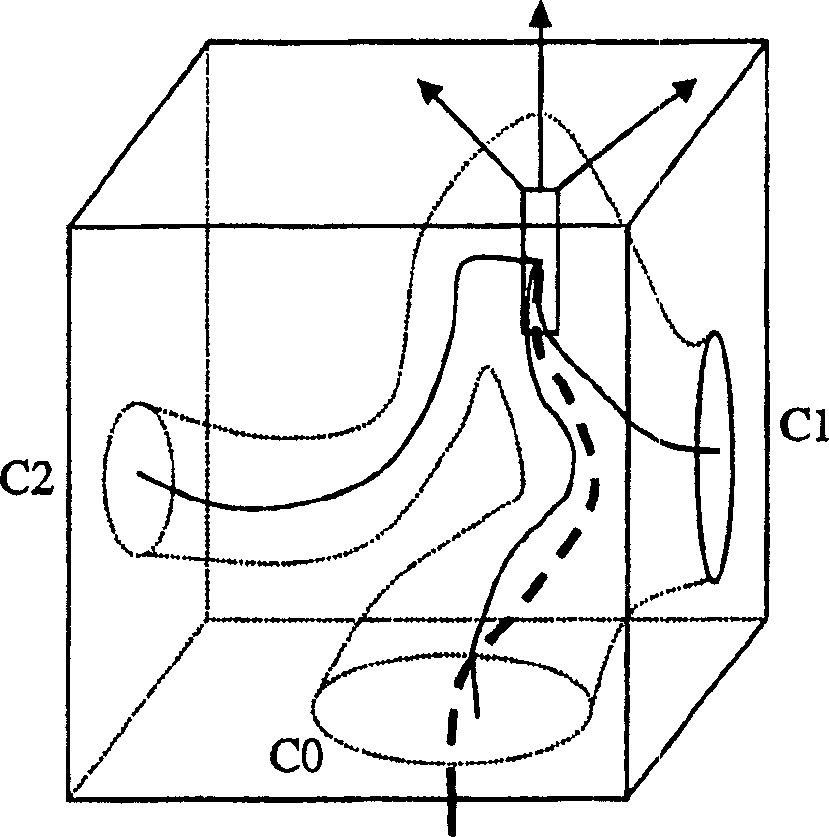
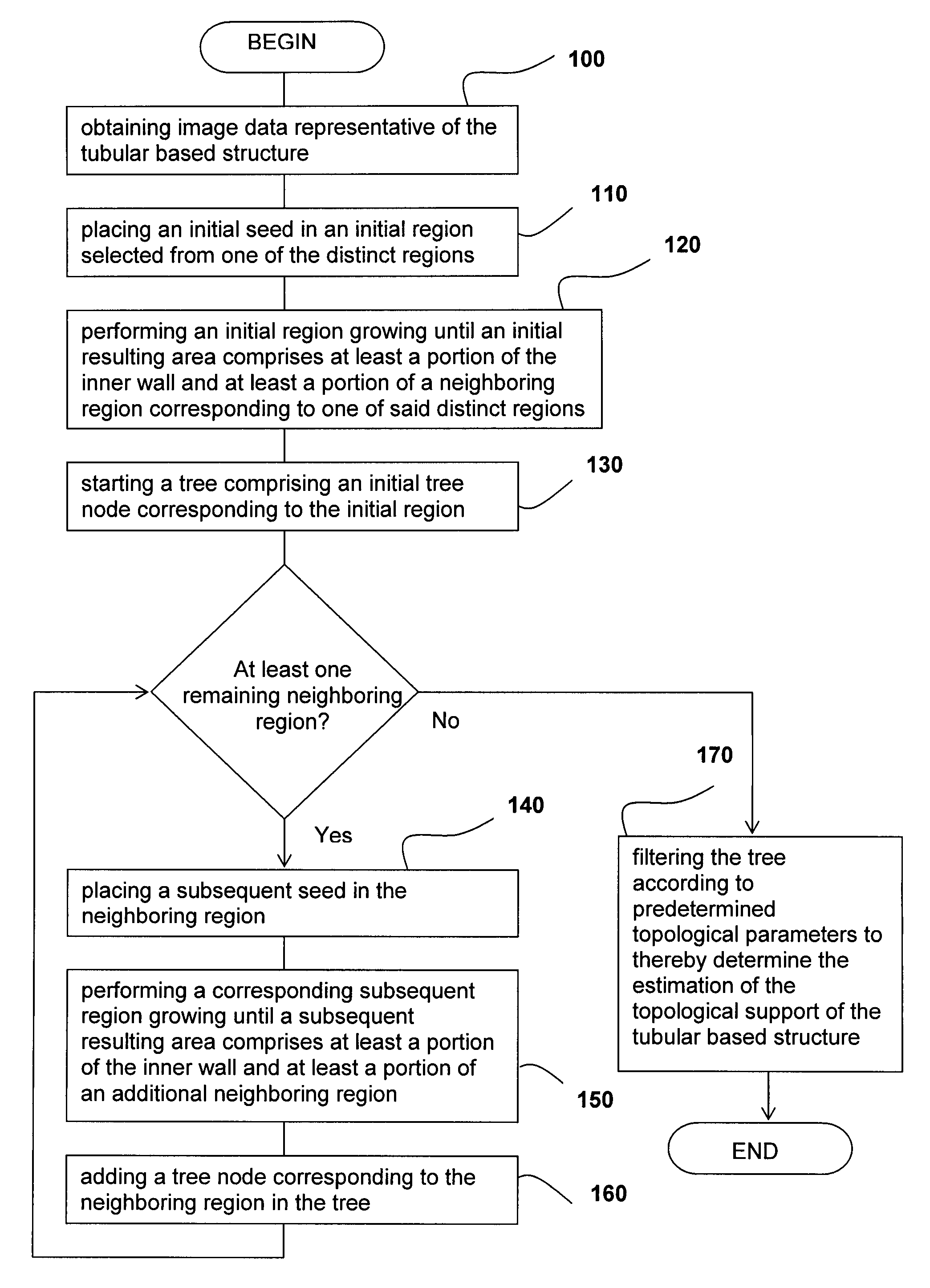
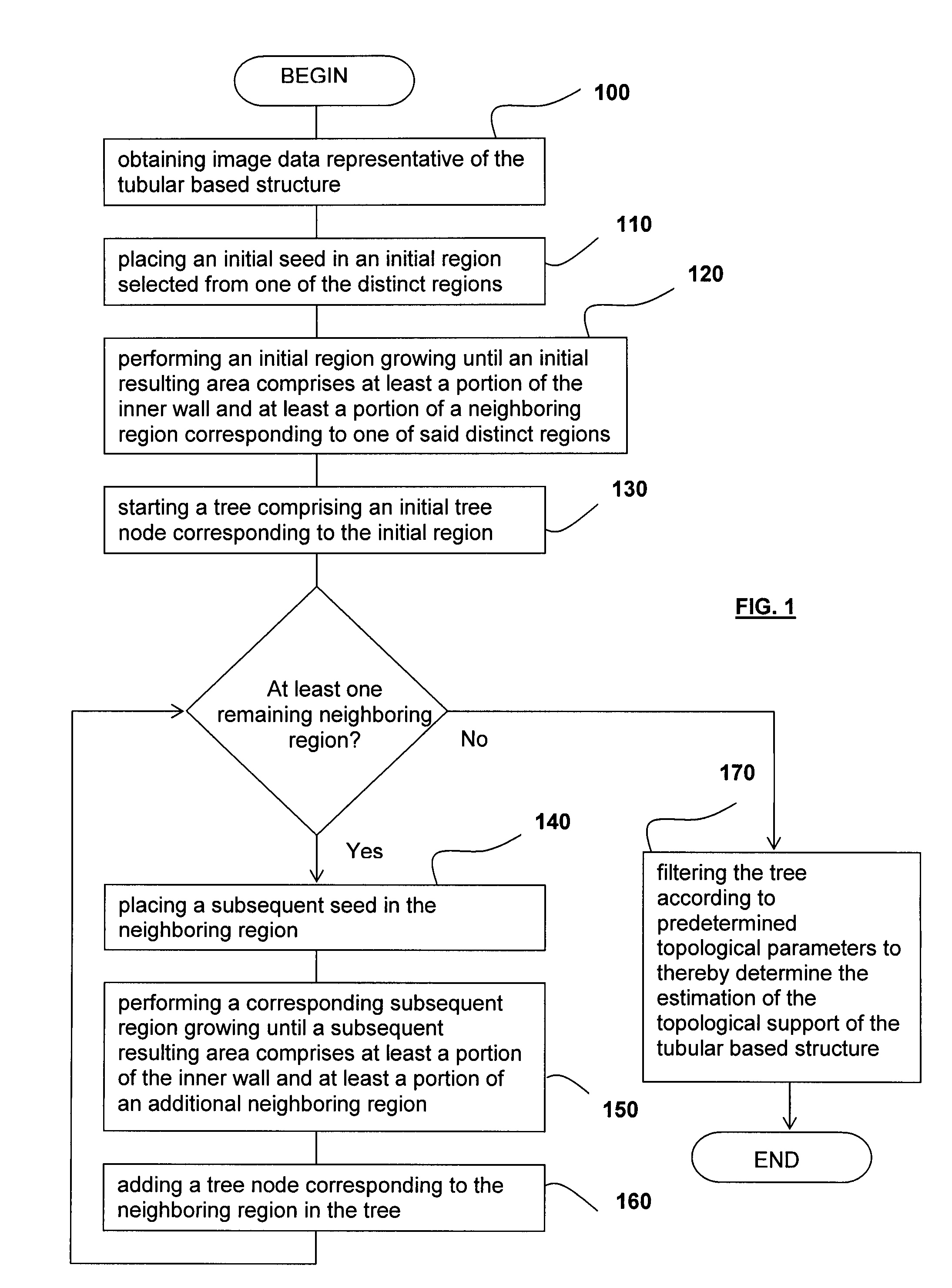
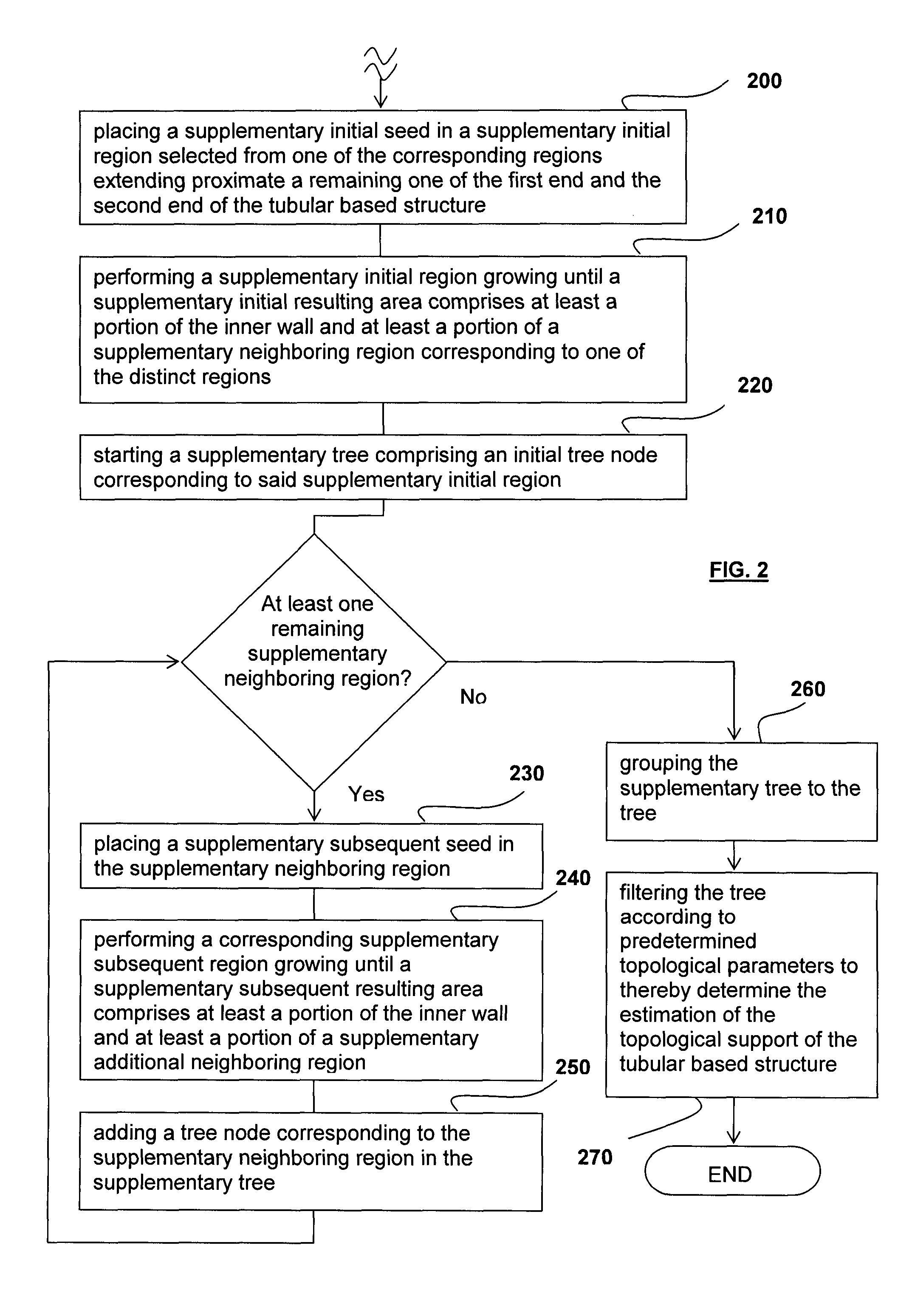
Method for determining an estimation of a topological support of a tubular structure and use thereof in virtual endoscopy
ActiveUS8611622B2Provide quicklyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementTopological insulatorTree node
A method for determining an estimation of a topological support of a tubular based structure comprising an inner wall and a plurality of distinct regions, the method comprising (a) obtaining image data representative of the tubular based structure; (b) placing an initial seed in an initial region selected from one of the distinct regions; (c) performing an initial region growing until an initial resulting area comprises at least a portion of the inner wall and at least a portion of a neighboring region corresponding to one of the distinct regions; (d) starting a tree comprising an initial tree node corresponding to the initial region; (e) for each neighboring region: placing a subsequent seed in the neighboring region; performing a corresponding subsequent region growing until a subsequent resulting area comprises at least a portion of the inner wall and at least a portion of an additional neighboring region; and adding a tree node corresponding to the neighboring region in the tree; (f) performing processing step (e) for each of the additional neighboring regions; and (g) filtering the tree according to predetermined topological parameters to thereby determine the estimation of the topological support of the tubular based structure. Applications of the method for estimating a colon topology for virtual colonoscopy are also disclosed.
Owner:DOG MICROSYST
Method and device for providing a segmented volume data record for a virtual colonoscopy, and computer program product
InactiveUS20110013815A1Disadvantage of false and undesiredFalse and undesired subtractionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringVoxelIntestinal walls
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Visualization method based on virtual coloscope
InactiveCN1785115AVarious control methodsThe control method is convenient and effectiveComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringSimulationApplication areas
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Image-based path planning for automated virtual colonoscopy navigation
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
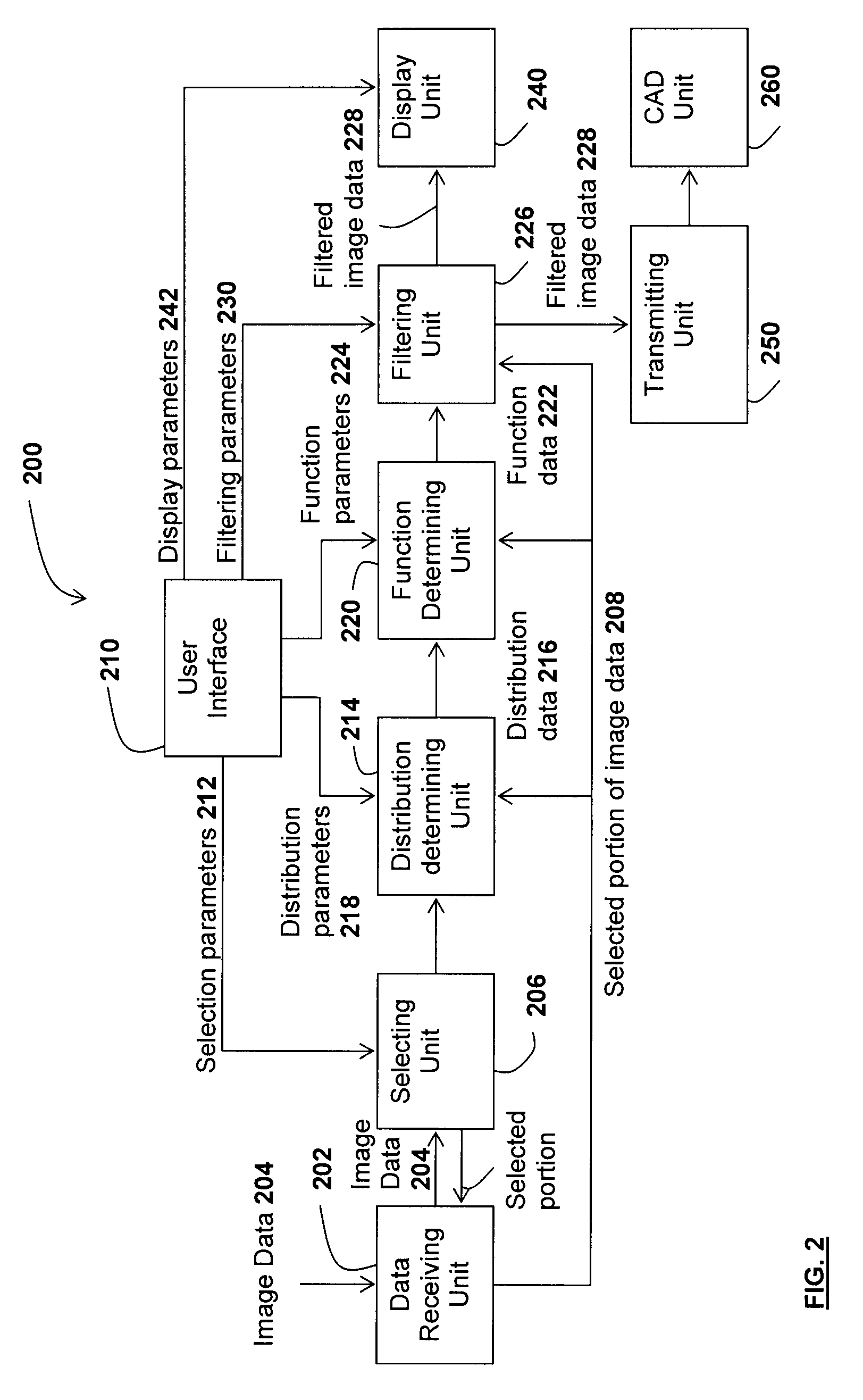
Method and system for filtering image data and use thereof in virtual endoscopy
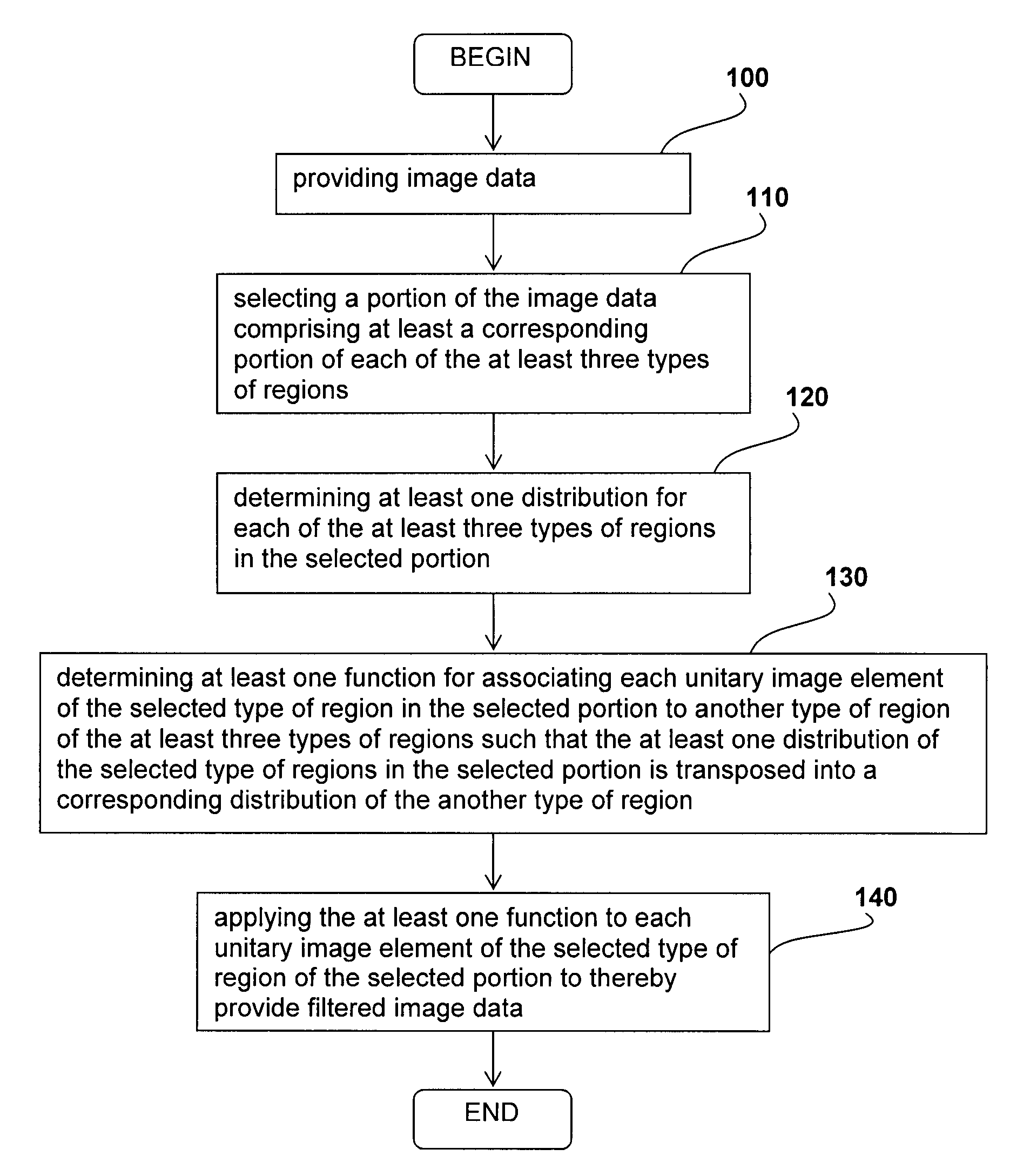
ActiveUS9161734B2Short calculation timeImage enhancementImage analysisVirtual colonoscopyVirtual CT colonoscopy
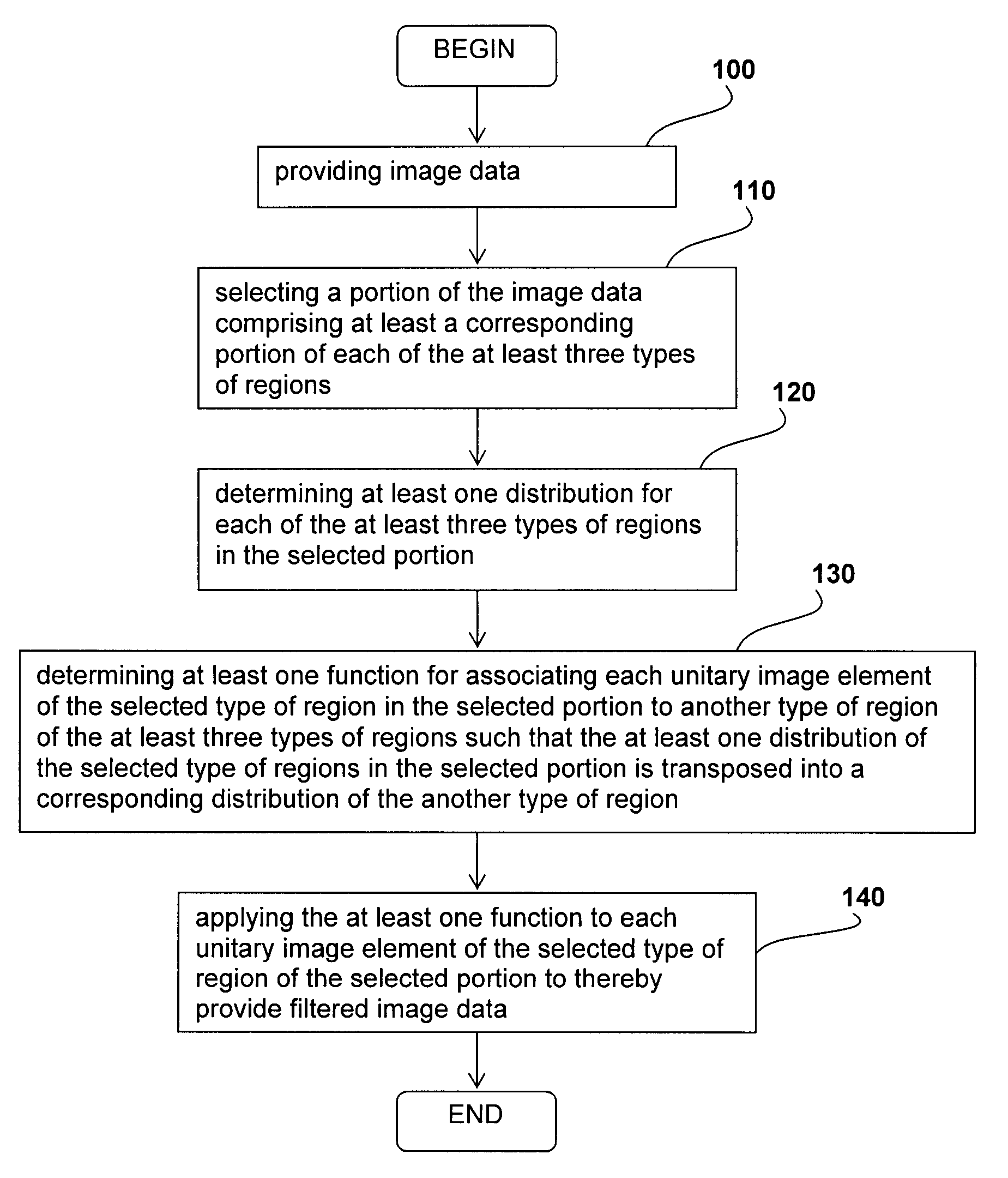
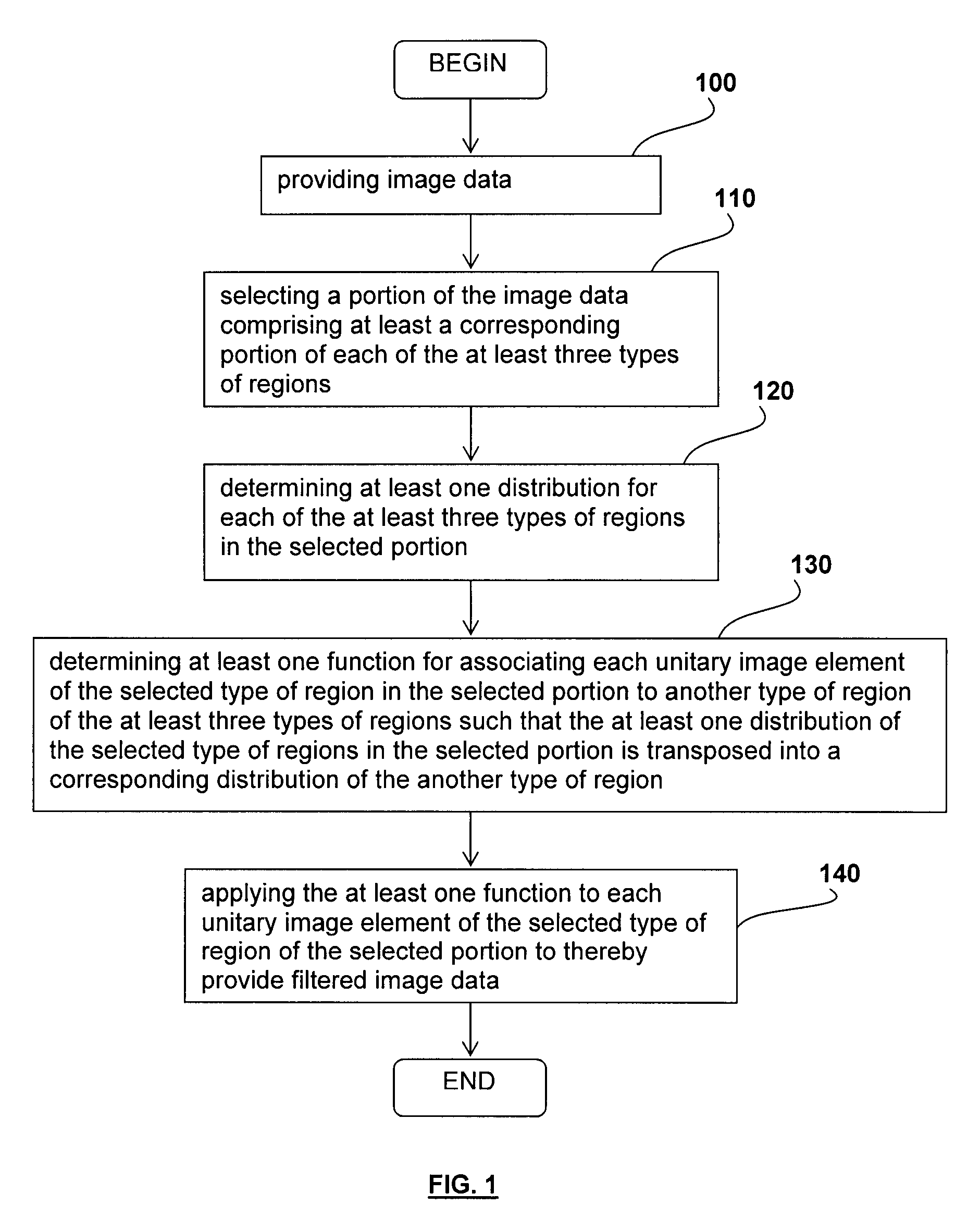
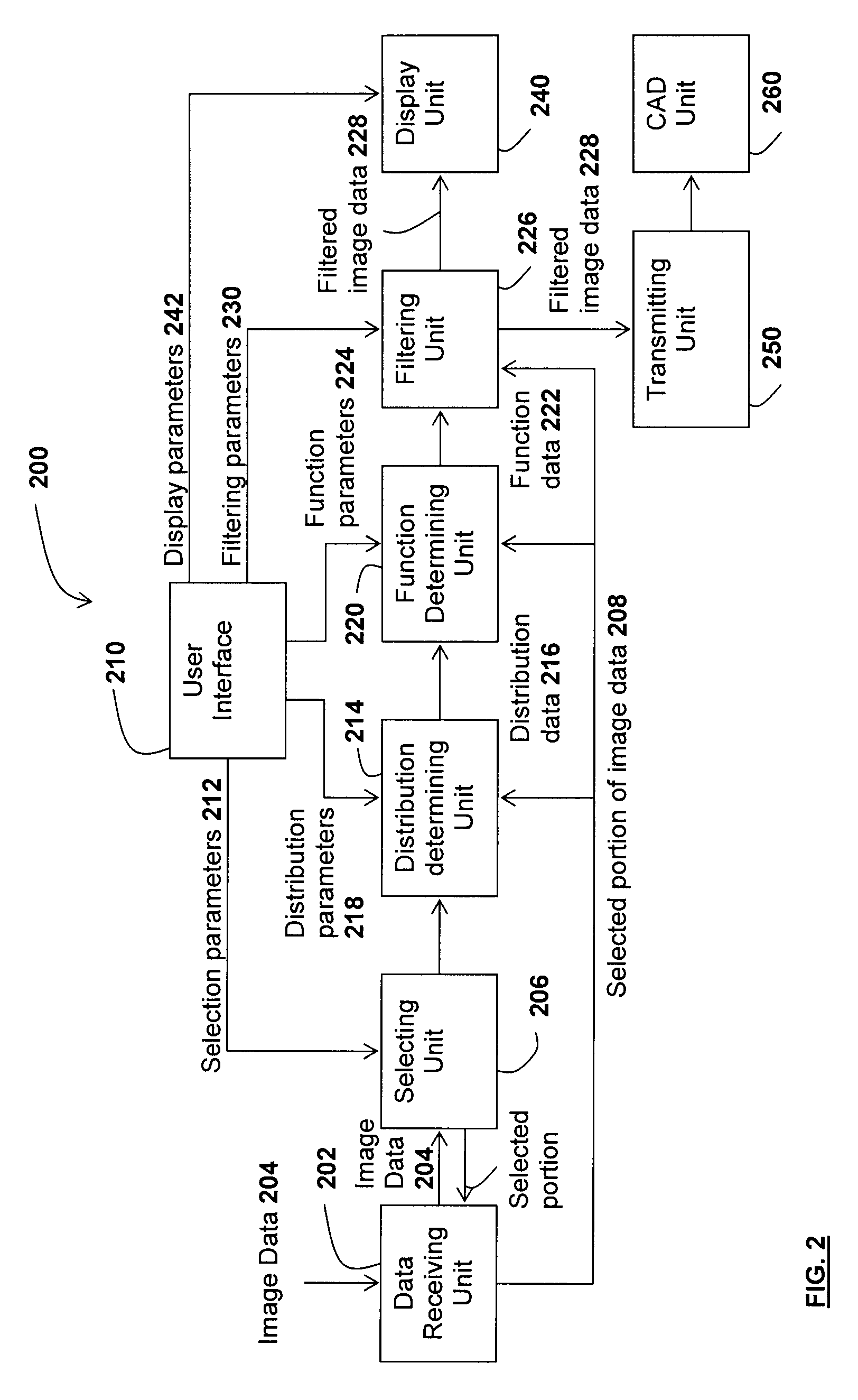
A method for filtering image data having at least three types of distinct regions from a selected type of region, each of the at least three types of distinct regions being characterized by a plurality of unitary image elements, the method comprising providing the image data; selecting a portion of the image data comprising at least a corresponding portion of each of the at least three types of regions; determining at least one distribution for each of the at least three types of regions in the selected portion; determining at least one function for associating each unitary image element of the selected type of region in the selected portion to another type of region of the at least three types of regions such that the at least one distribution of the selected type of regions in the selected portion is transposed into a corresponding distribution of the another type of region; and applying the at least one function to each unitary image element of the selected type of region of the selected portion to thereby provide filtered image data. Applications of the method for suppressing tagged material in virtual colonoscopy are also disclosed.
Owner:CADENS MEDICAL IMAGING
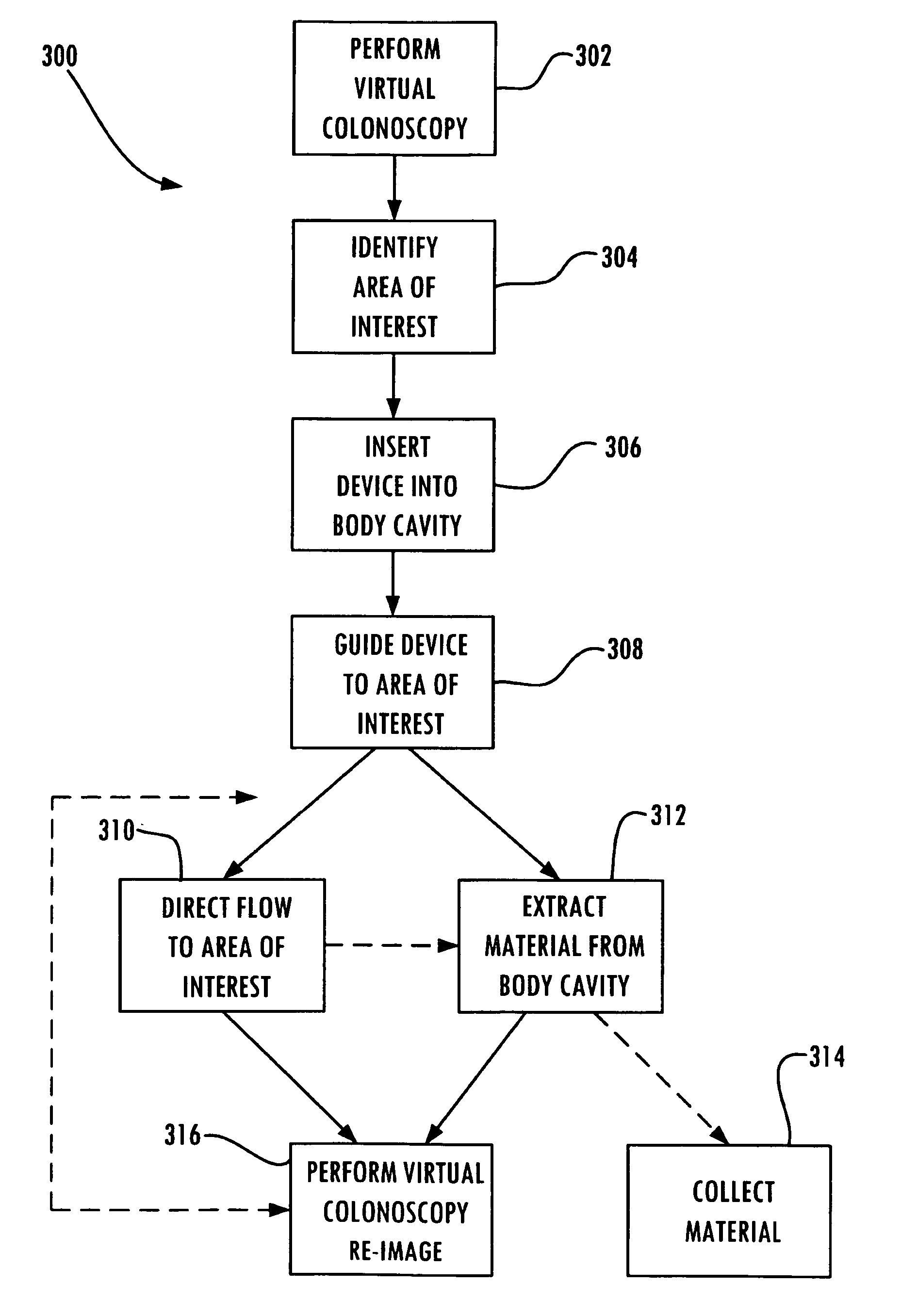
Apparatus and method for removing material from the colon
An apparatus includes an elongate body including a proximal end portion and a distal end portion and configured to be at least partially inserted into a body cavity. The elongate body defines a first passageway and a second passageway. The first passageway is configured to communicate fluid from the distal end portion in a first direction, and the second passageway is configured to communicate material from outside of the elongate body into the distal end portion in a second direction opposite the first direction and includes at least one port. An actuator is coupled to the elongate body and is configured to guide the distal end of the elongate body to an area of interest identifiable by a virtual colonoscopy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and system for filtering image data and use thereof in virtual endoscopy
ActiveUS20120296771A1Accurate colorectal cancer screeningImprove lesionImage enhancementImage analysisVirtual colonoscopyVirtual CT colonoscopy
A method for filtering image data having at least three types of distinct regions from a selected type of region, each of the at least three types of distinct regions being characterized by a plurality of unitary image elements, the method comprising providing the image data; selecting a portion of the image data comprising at least a corresponding portion of each of the at least three types of regions; determining at least one distribution for each of the at least three types of regions in the selected portion; determining at least one function for associating each unitary image element of the selected type of region in the selected portion to another type of region of the at least three types of regions such that the at least one distribution of the selected type of regions in the selected portion is transposed into a corresponding distribution of the another type of region; and applying the at least one function to each unitary image element of the selected type of region of the selected portion to thereby provide filtered image data. Applications of the method for suppressing tagged material in virtual colonoscopy are also disclosed.
Owner:CADENS MEDICAL IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com