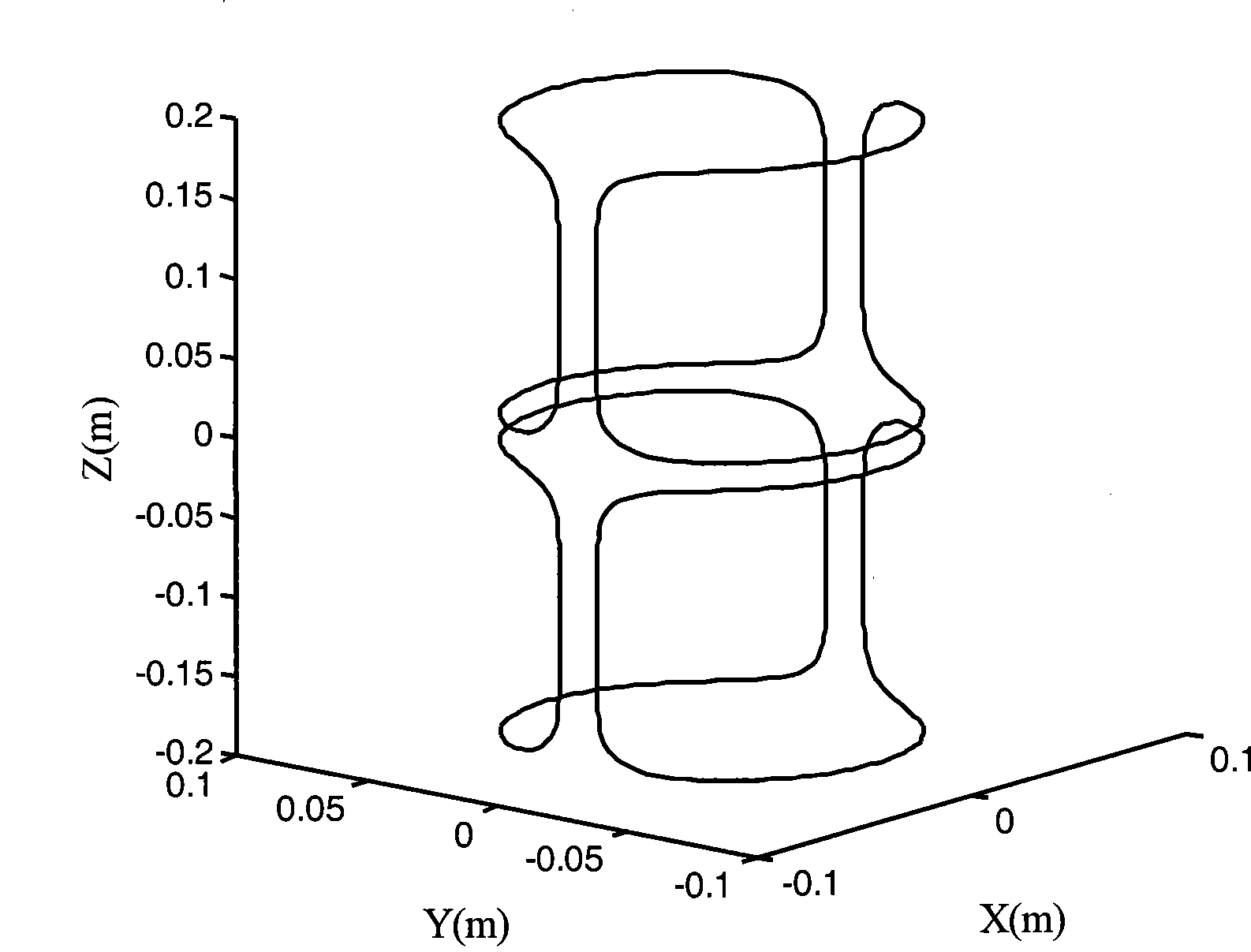Patents
Literature
47 results about "Gradient strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Loss of Strength Gradient. The Loss of Strength Gradient (LSG) is a military concept devised by Kenneth E. Boulding in his 1962 book Conflict and Defense: A General Theory. He argued that the amount of a nation’s military power that could be brought to bear in any part of the world depended on geographic distance.
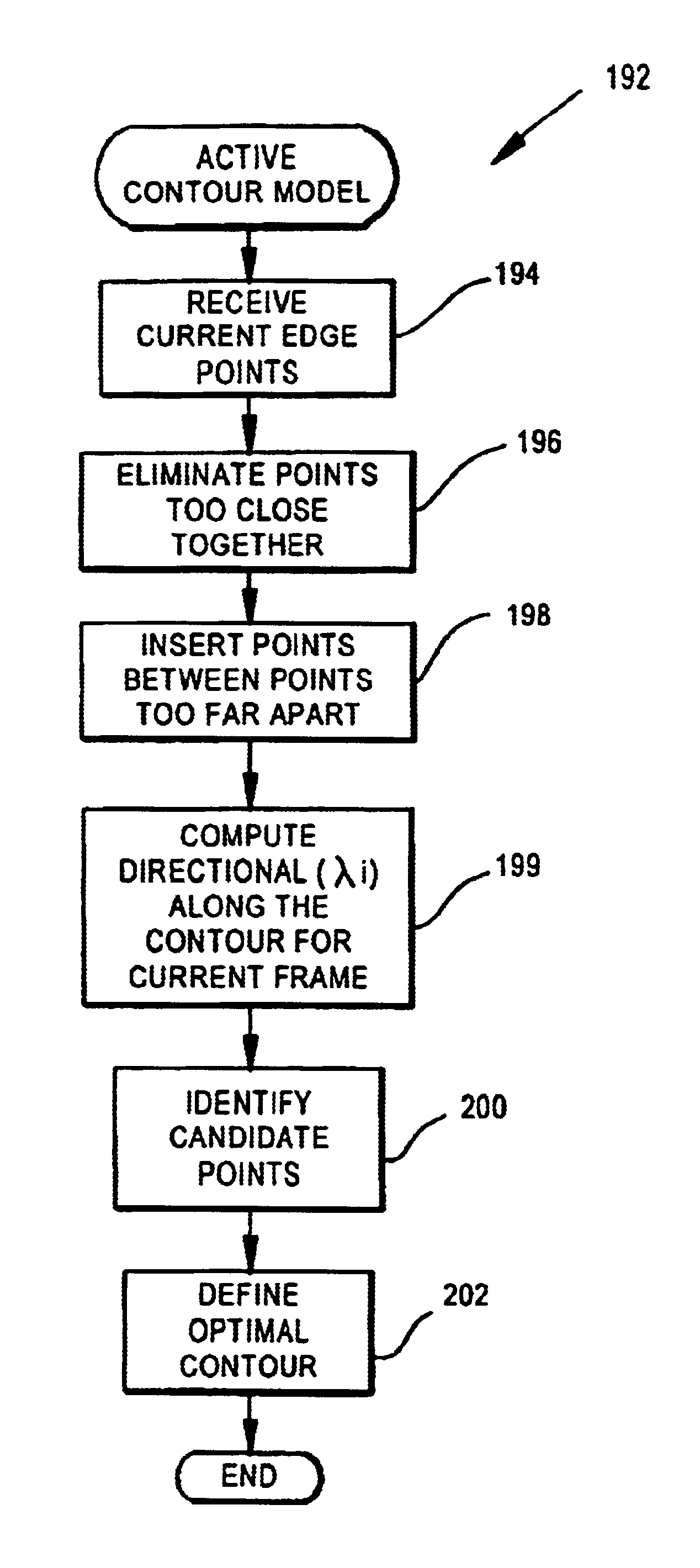
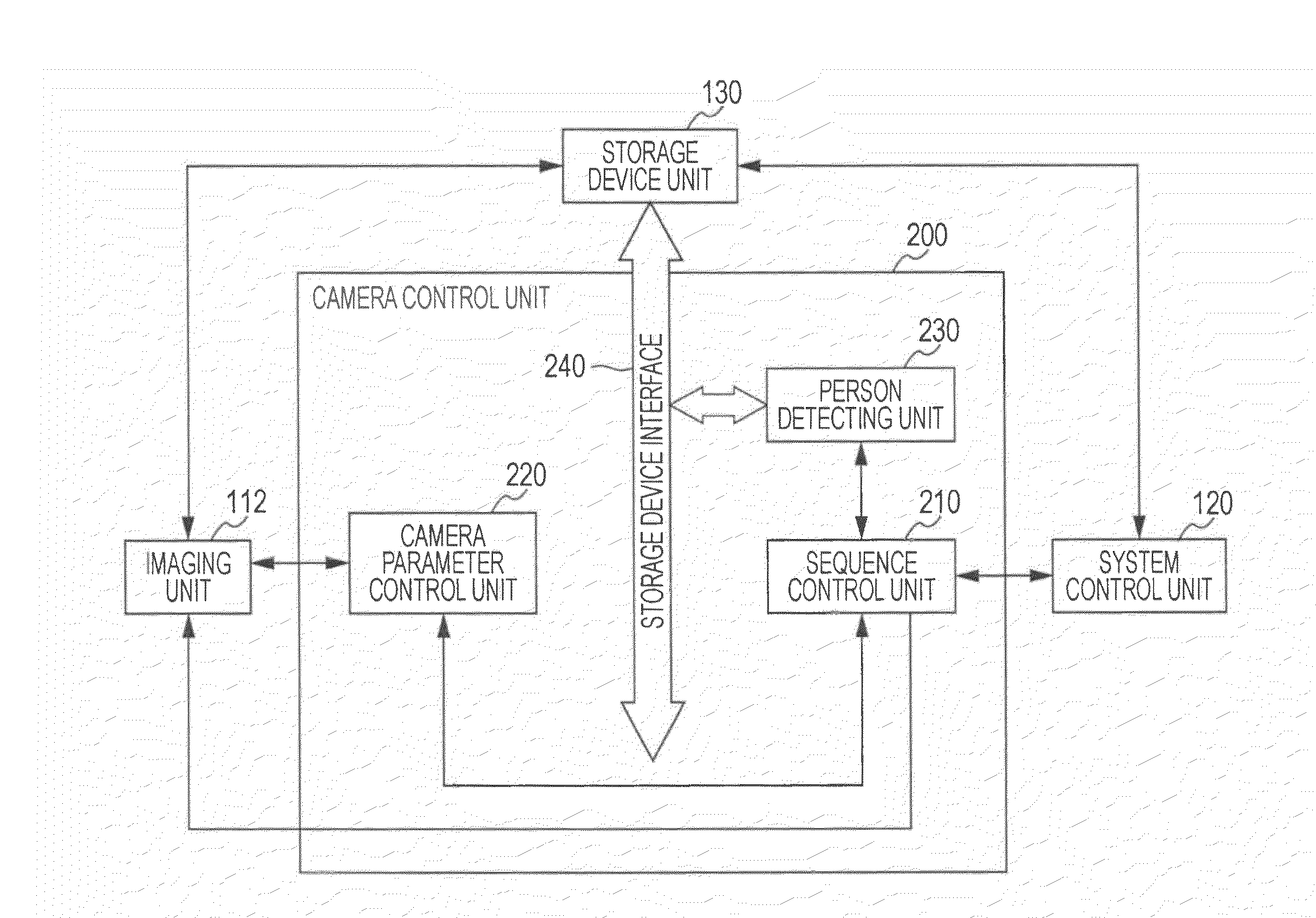
Video object segmentation using active contour model with directional information
InactiveUS6912310B1Improve segmentationAccurate segmentationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionGradient strengthEnergy minimization
Object segmentation and tracking are improved by including directional information to guide the placement of an active contour (i.e., the elastic curve or ‘snake’) in estimating the object boundary. In estimating an object boundary the active contour deforms from an initial shape to adjust to image features using an energy minimizing function. The function is guided by external constraint forces and image forces to achieve a minimal total energy of the active contour. Both gradient strength and gradient direction of the image are analyzed in minimizing contour energy for an active contour model.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
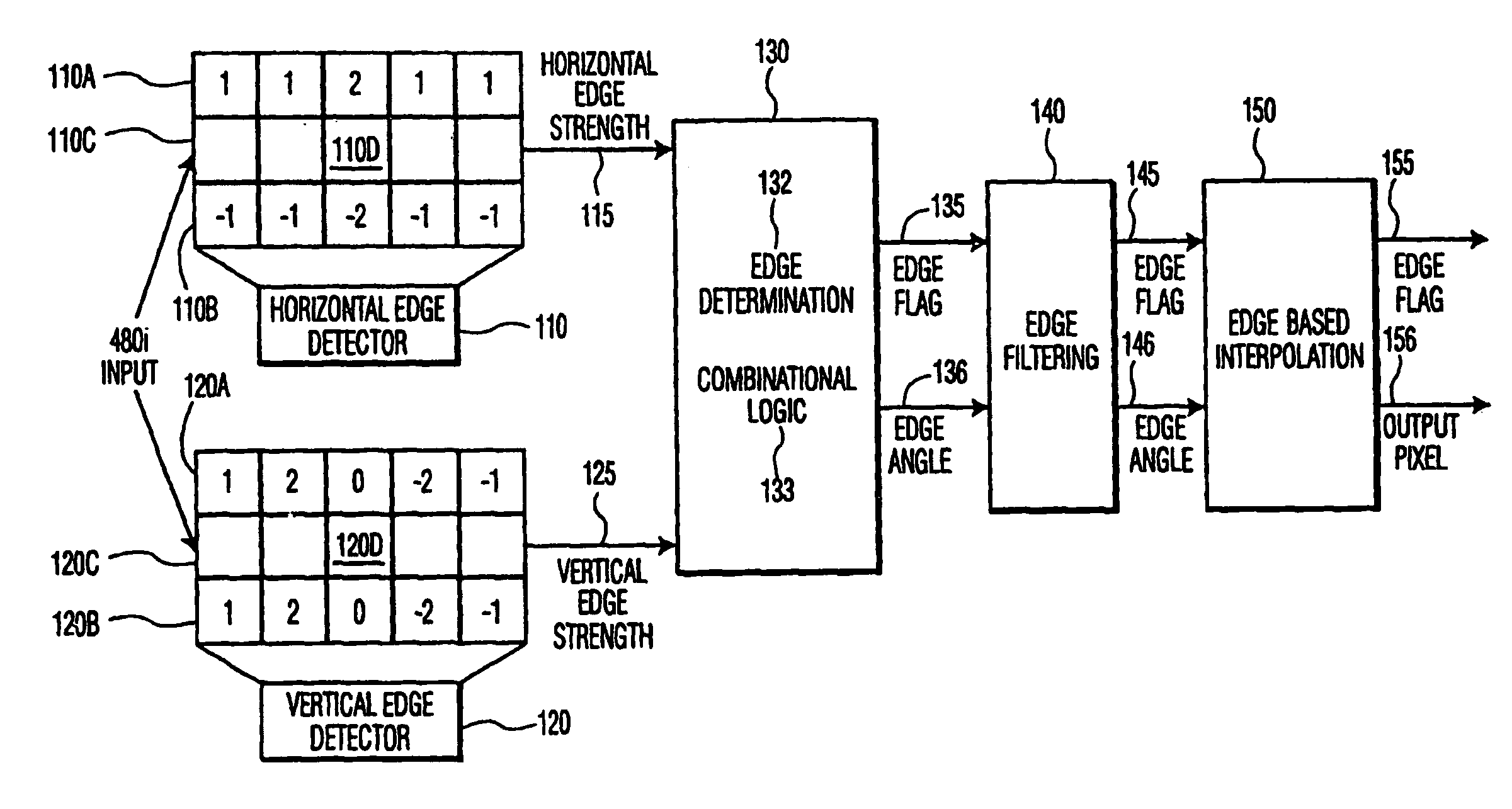
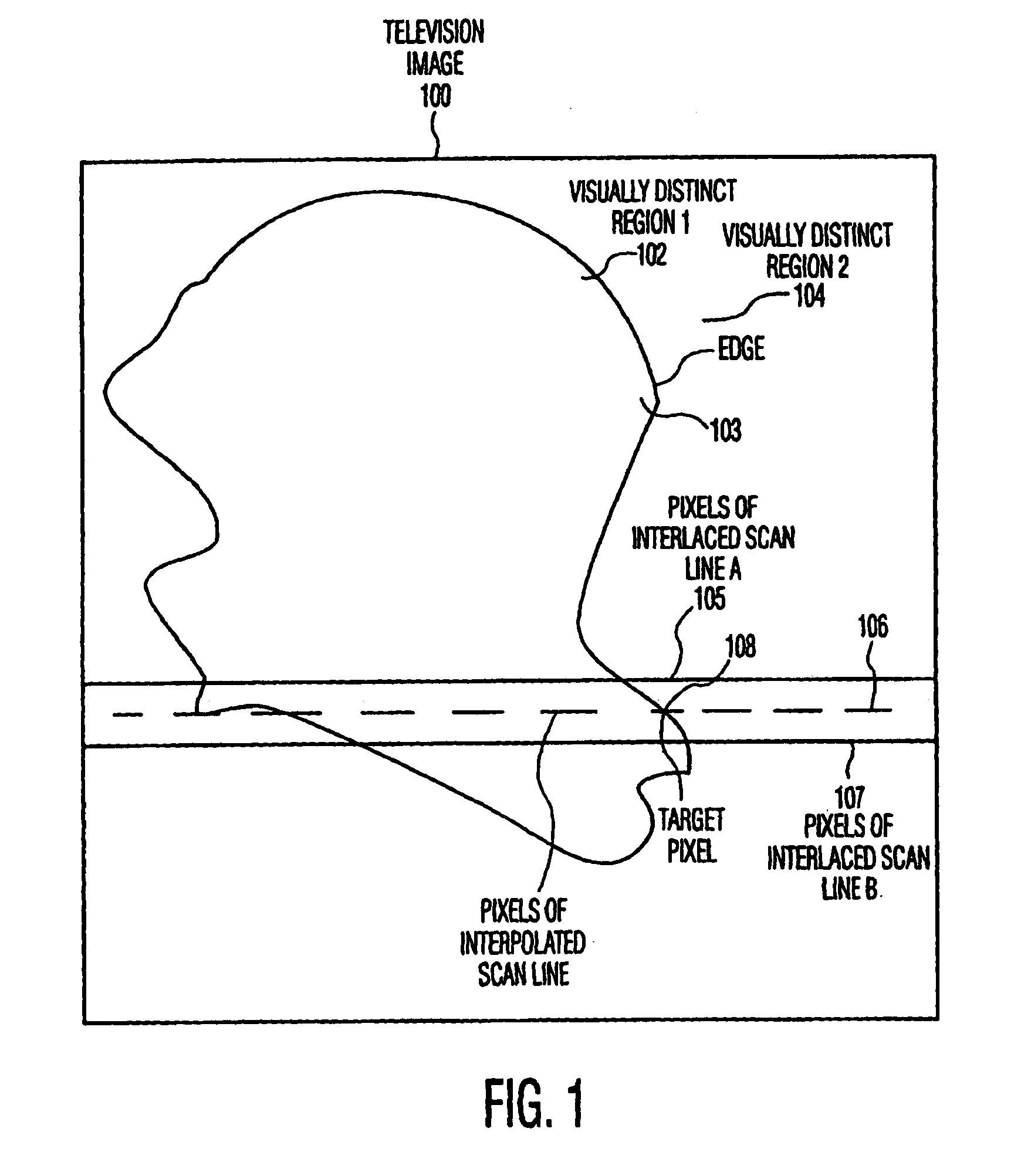
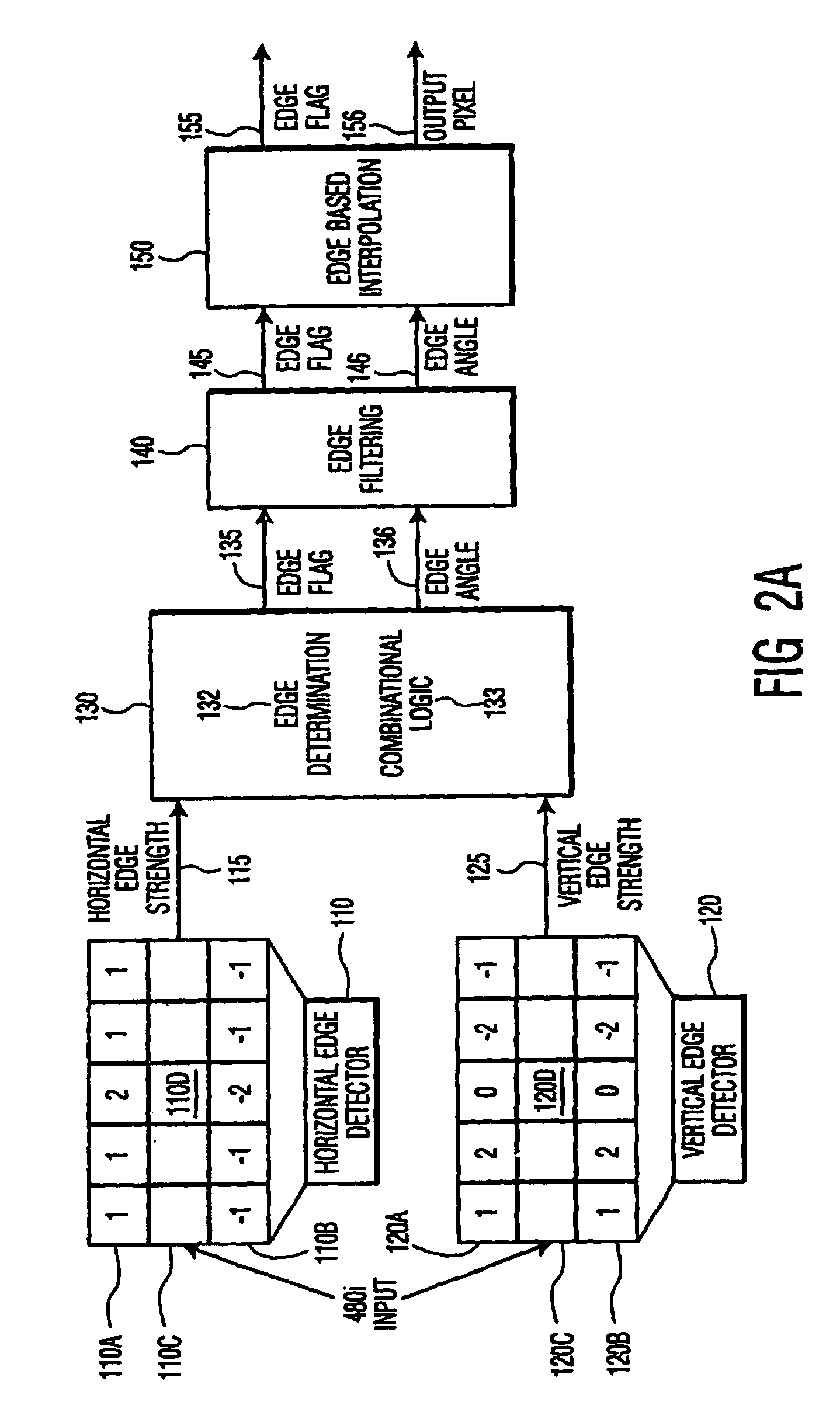
Method of edge based interpolation
InactiveUS7245326B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGradient strengthEdge based
A method for detecting an edge and generating an interpolated edge pixel at a target pixel position between two lines of an interlace scan image first determines gradient intensities in the horizontal and vertical directions and then calculates the angle of the edge by comparing the gradient intensities. The interpolated pixel value is calculated from samples in the interlace scan image that lie along the identified angle and are proximate to the target pixel position. The method represents the gradient strengths and the difference between them as bit strings; locates the most significant non-zero bit in the larger gradient value; divides the value of the corresponding bit position in the difference string, and a predetermined number of following positions, by increasing powers of 2; sums the results; subtracts the sum from 1.0 and uses the inverse tangent function to calculate the angle of the edge.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
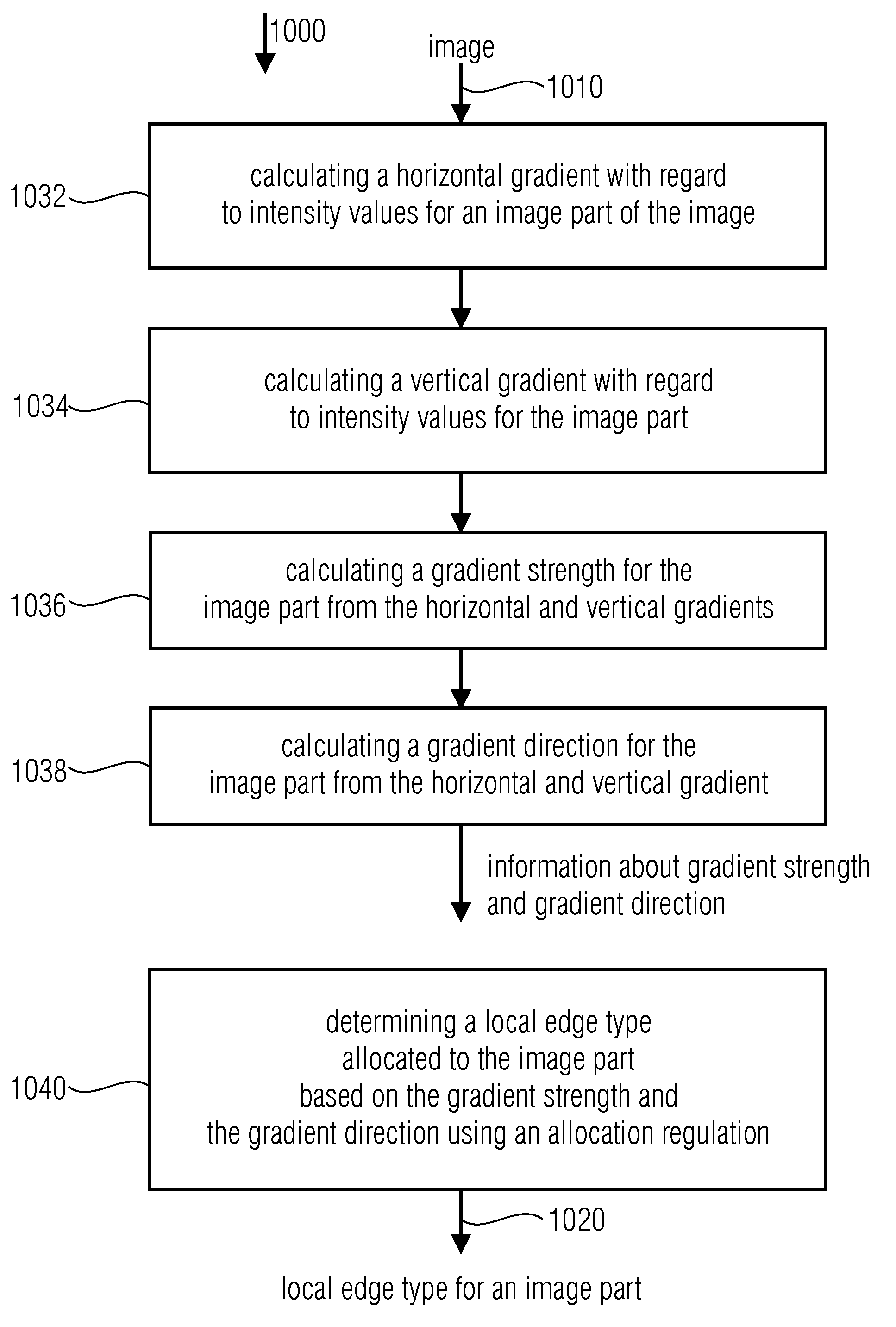
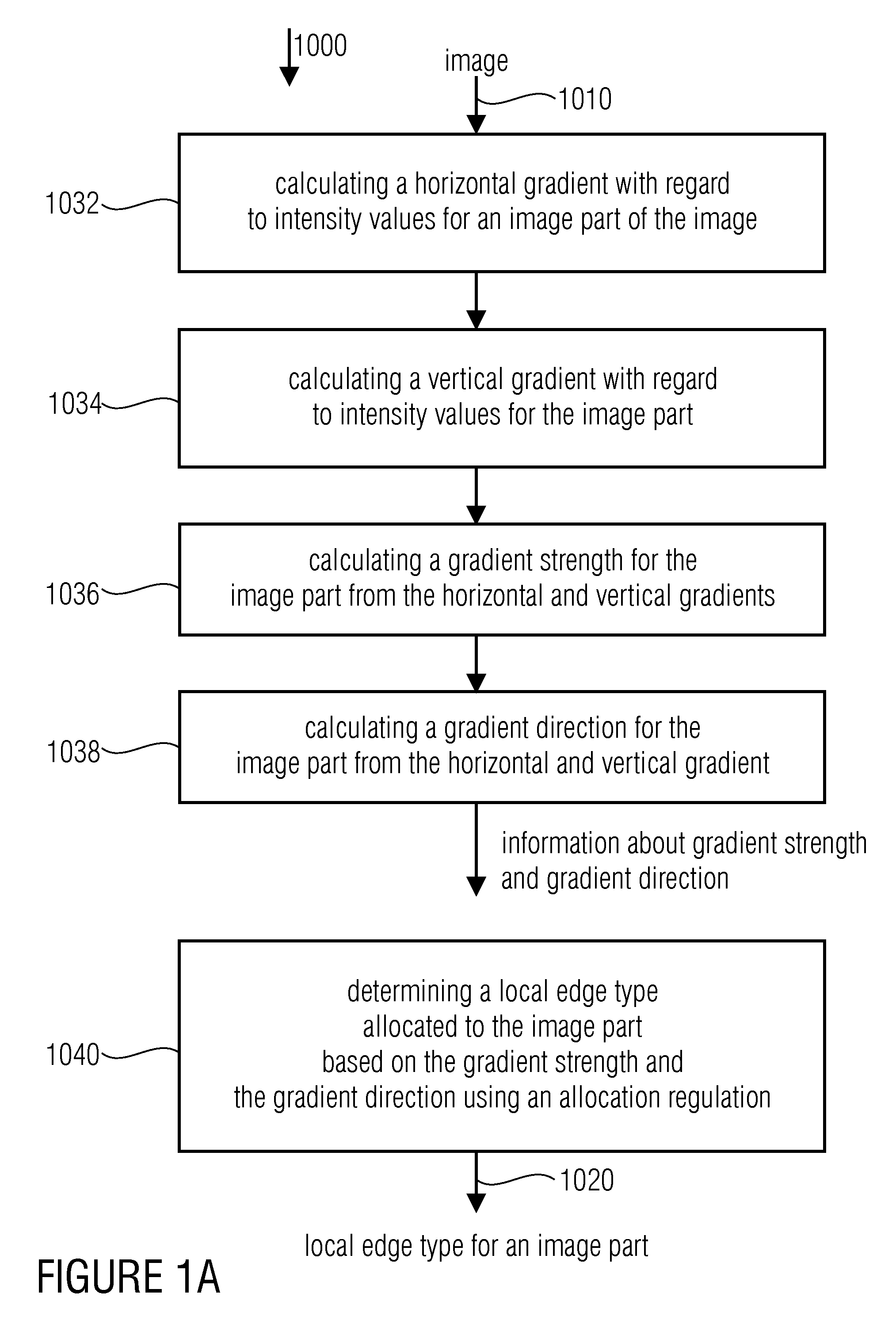
Device and method for determining an edge histogram, device and method for storing an image in an image database, device and method for finding two similar images and computer program
InactiveUS20100111416A1Reduce distortion problemsReliable edge histogramImage analysisDigital data information retrievalGradient strengthEdge type
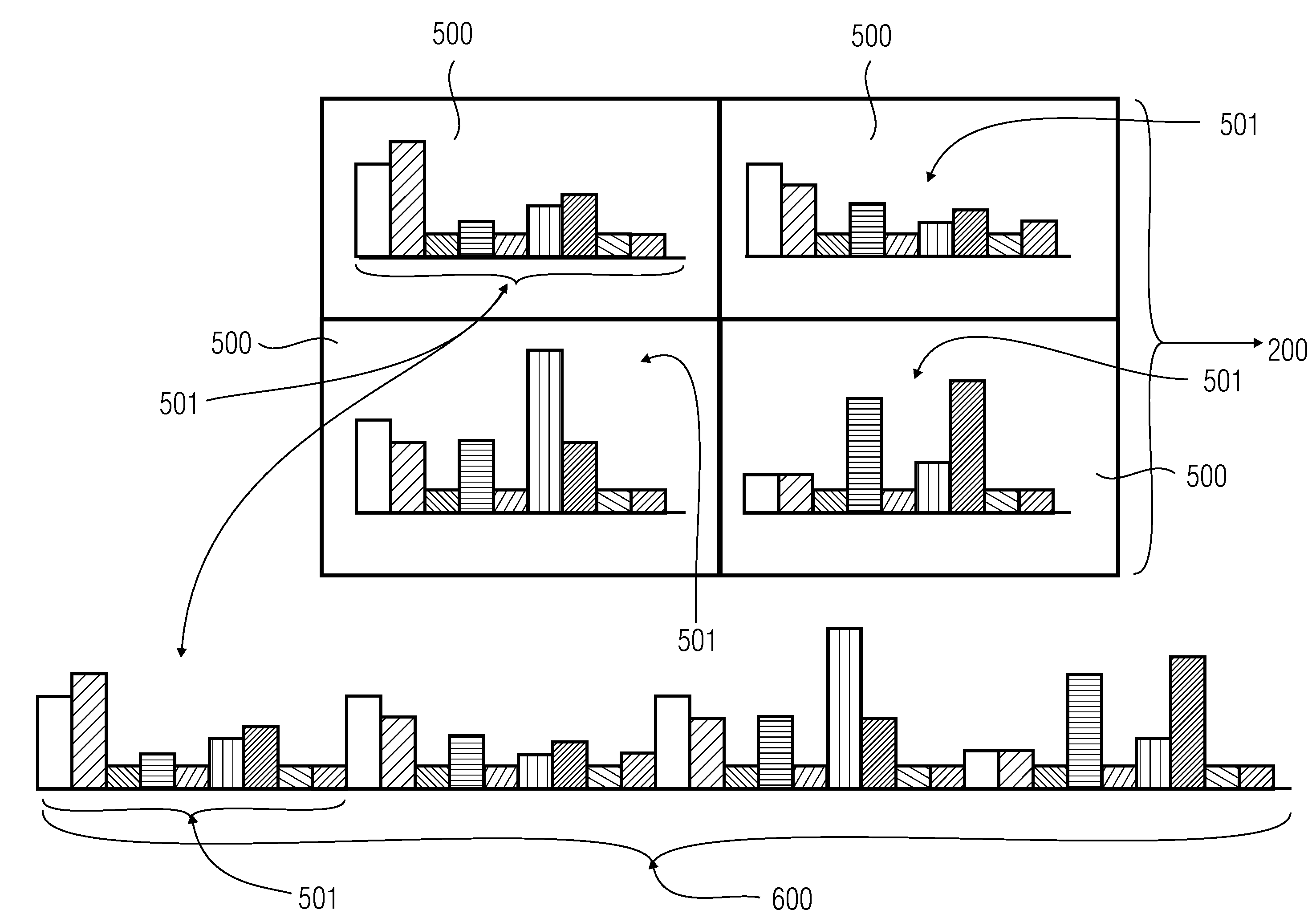
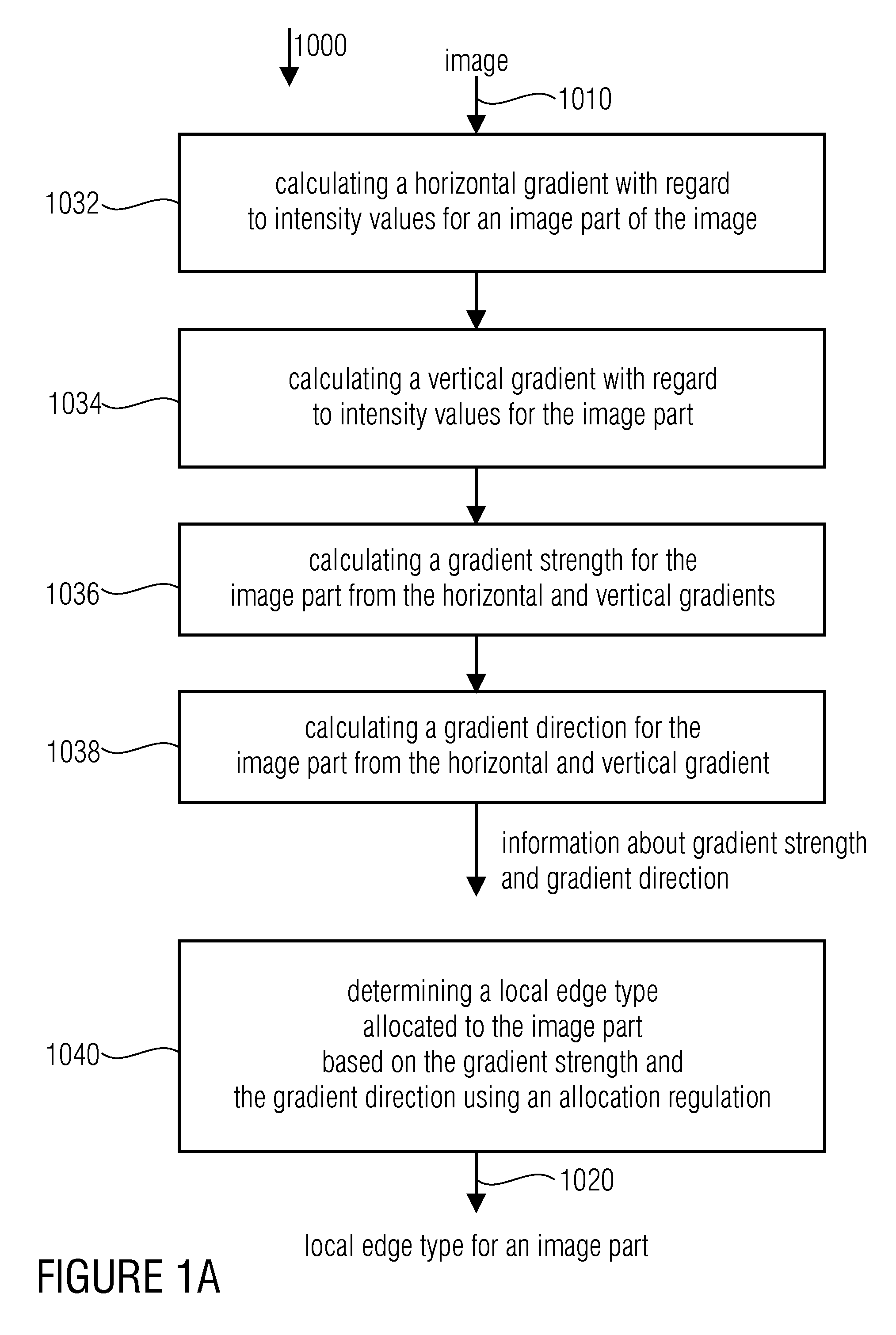
A device for determining an edge histogram of an image based on information about a gradient strength and a gradient direction of a local gradient in an image content of a partial image of the image includes an allocator which is implemented to allocate the information about the gradient strength and the gradient direction based on an allocation regulation to an edge image in order to obtain edge type information. The allocation regulation is selected such that with a predetermined gradient direction at least three different allocated edge types exist mirroring the different gradient strengths. The device further includes an edge histogram determiner which is implemented to determine the edge histogram based on the edge type information so that in the edge type histogram at least three edge types having different allocated gradient strengths may be differentiated.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Object detecting device, imaging apparatus, object detecting method, and program
InactiveUS20100067742A1Great advantageHigh precisionTelevision system detailsImage analysisPattern recognitionGradient strength
Owner:SONY CORP
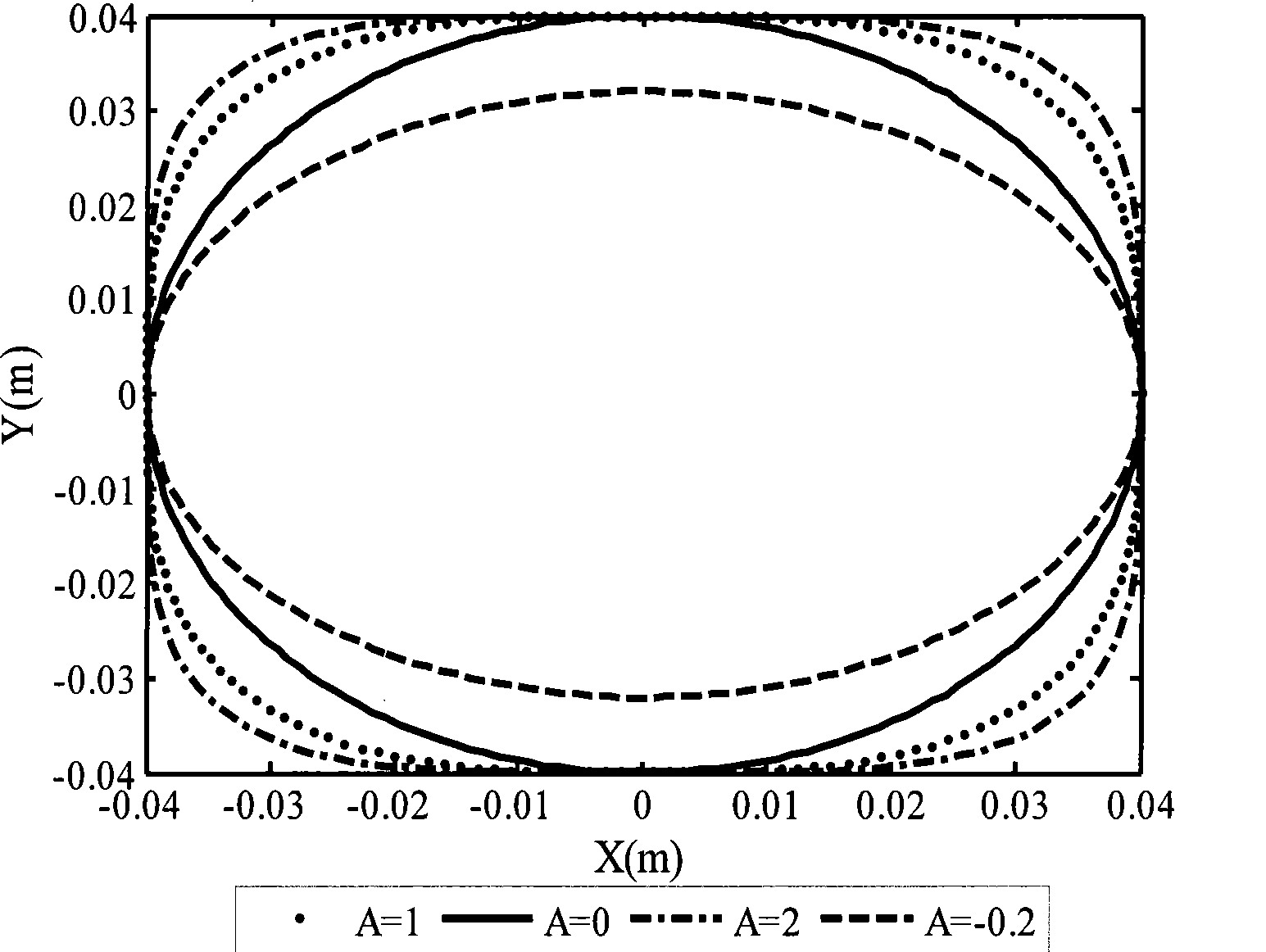
Computer aided design method for magnetic resonance imaging transverse gradient coil
InactiveCN101464924ALinearity dropImprove linearitySpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignGradient strength
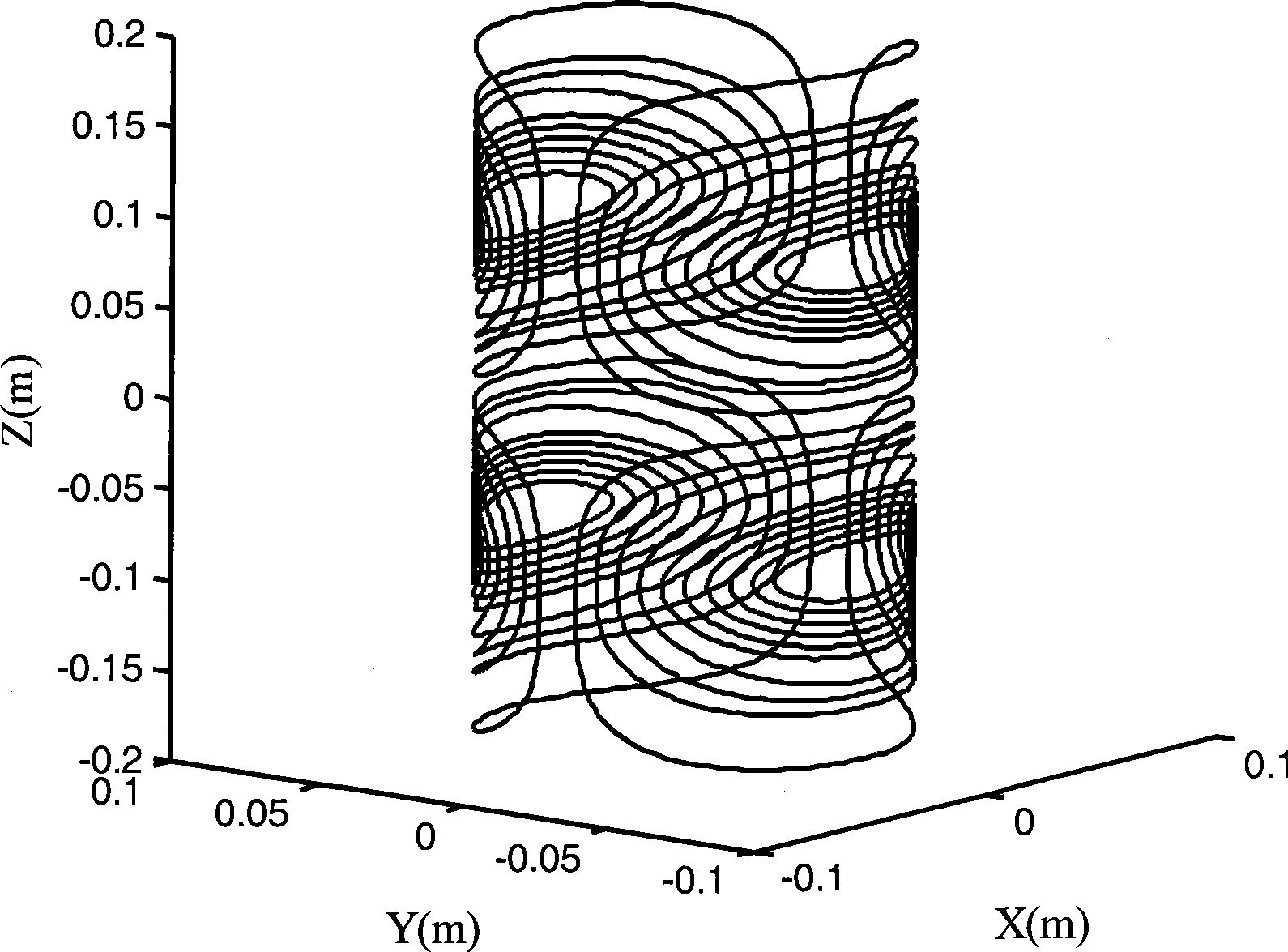
A computer aided design method for magnetic resonance imaging transverse gradient coil, which belongs to the application of superconducting technology. The method is characterized in that parametric description for space trace of the transverse gradient coil is realized through introducing the basic shape of an ellipse-like double-saddle shaped coil, then space tracking parameter of the coil serves as optimization variable, and the mean square deviation of the gradient strength value and the gradient set value of each target point on an imaging space surface serves as an objective function for realizing the optimum design of the gradient linearity of the transverse gradient coil. The method is used for designing the transverse gradient coil, and has the advantages that the counting is simple and direct, the linearity of the design result is high, and the processing and the manufacturing are convenient.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
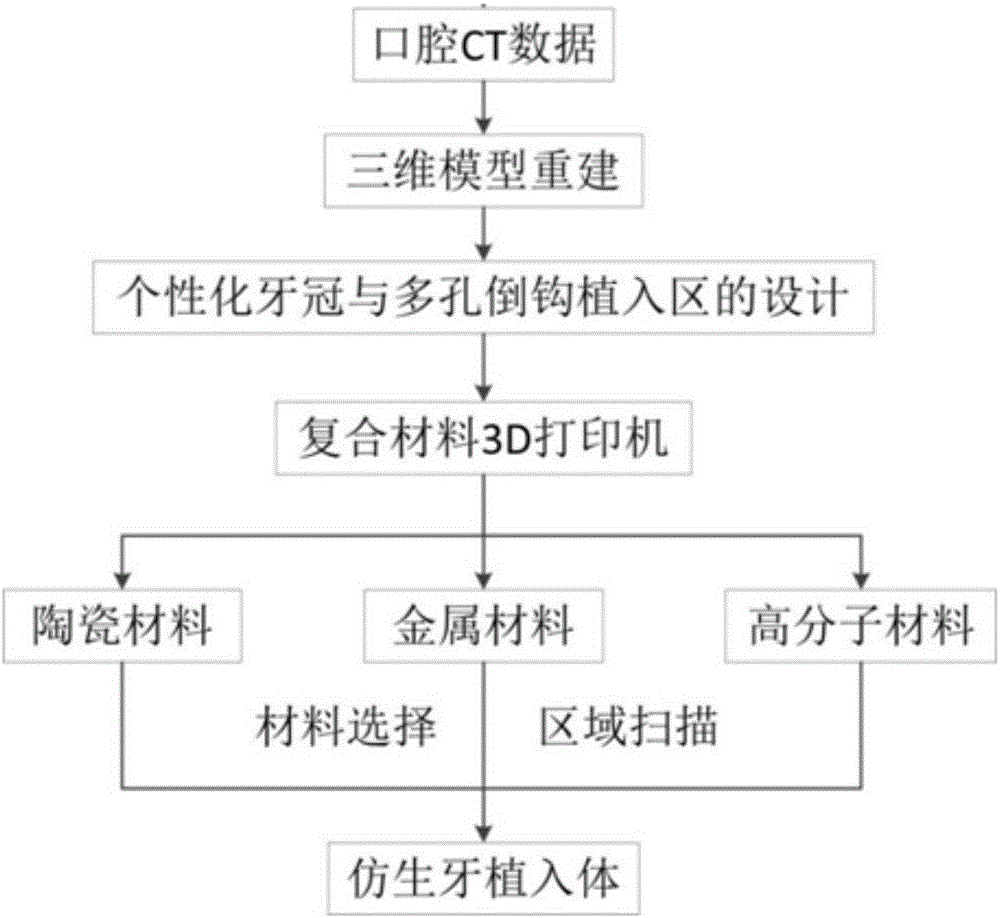
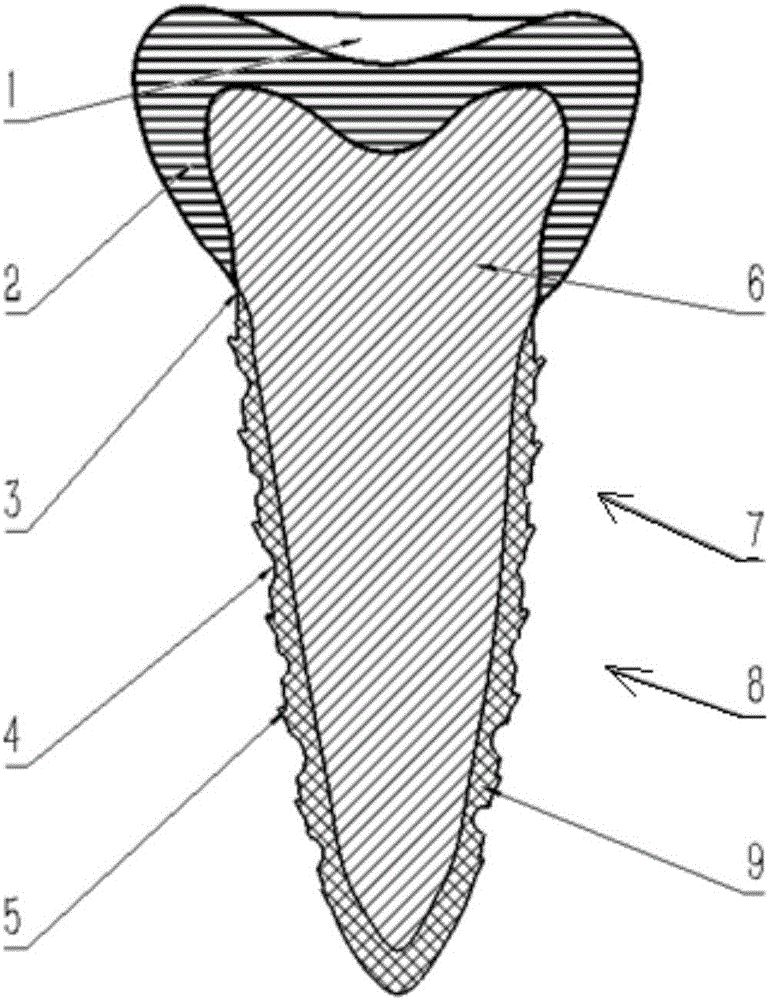
3D printing-based bionic artificial tooth and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105919683AStrong toughnessHigh strengthDental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusCell adhesionFall risk
The invention discloses a 3D printing-based bionic artificial tooth and a manufacturing method thereof. The 3D printing-based bionic artificial tooth comprises a bionic dentin main body, a bionic enamel layer coating the upper end surface of the bionic dentin main body and a bionic cementum layer coating the bionic dentin main body, the bionic enamel layer is connected to the bionic cementum layer through a transition region, the outer surface of the bionic cementum layer is covered with a microstructure layer, and the microstructure layer comprises porous structures and barb structures staggered or irregularly distributed on the bionic cementum layer. According to bionic characteristics, solids with different gradient strength are molded in different implantation material areas so that stress interference between an implantation material and an alveolar bone is reduced. Through combination with a high freedom degree molding capability of the 3D printing technology, a completely personalized bionic dental implant is directly molded so that wearing comfort is improved. The barb structures and the porous structures are conducive to cell adhesion, growth and fixation, improve a bonding capacity of an implant and an alveolar bone and reduce adverse effects such as a dental implant falling risk after an operation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A Strain field subarea dynamic selection methodmethod for dynamically selecting strain field sub-region in digital image correlation method
InactiveCN110188759AGood precisionImprove accuracyForce measurement by measuring optical property variationCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurement precisionDigital image correlation
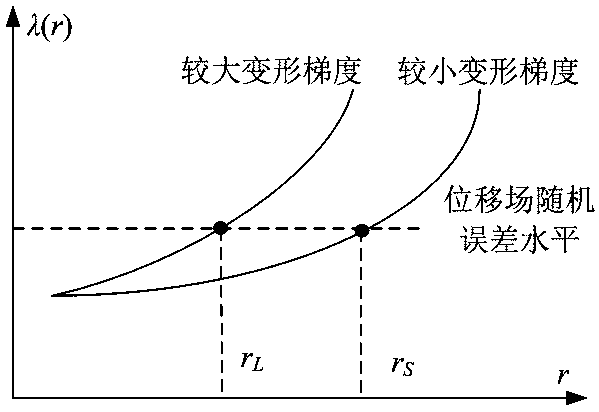
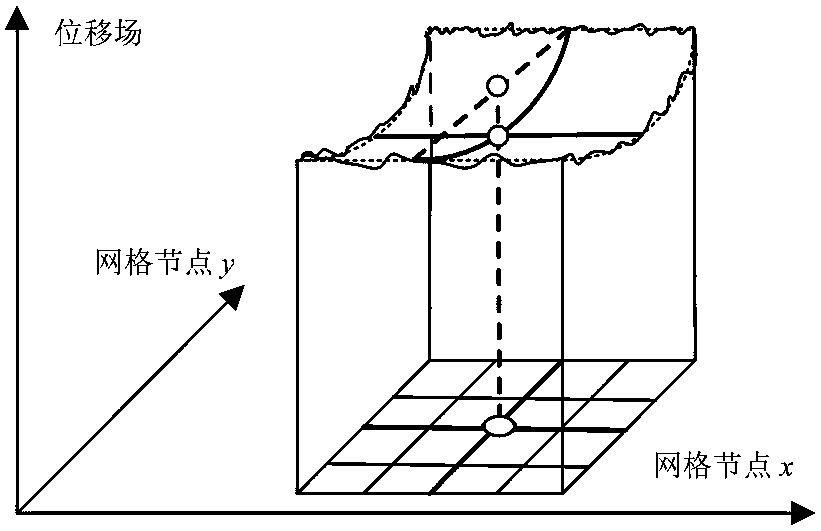
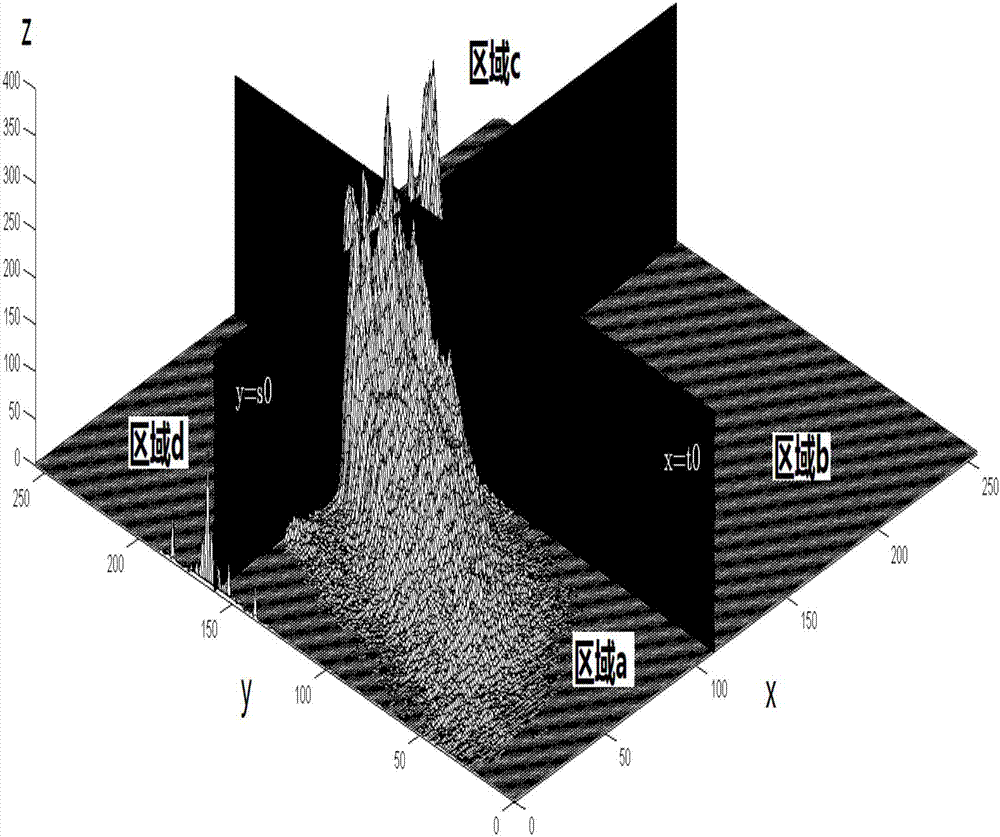
The invention discloses a strain field subarea dynamic selection method in a digital image correlation method, and provides evaluation parameters based on displacement field local gradient intensity for describing intensity of local non-uniform deformation. By balancing the noise intensity of the displacement field and the local non-uniform deformation intensity, a large strain calculation sub-region is selected at a place with relatively low non-uniform deformation gradient intensity, so that the noise of the displacement field is effectively suppressed; and a small strain calculation sub-region is selected in a place with relatively high non-uniform deformation gradient strength, so that the local deformation characteristic is reserved. And dynamic selection of the size of the strain field calculation subarea is realized, so that local deformation characteristics are reserved to the greatest extent while noise is effectively suppressed. The dynamic selection process of the size of the subarea based on the characteristics of the displacement field is different from the traditional dynamic selection process of calculating the size of the subarea based on the speckle gray level gradient information, and the measurement precision of the strain field of the digital image correlation method in the non-uniform deformation can be effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGSU OPEN UNIV
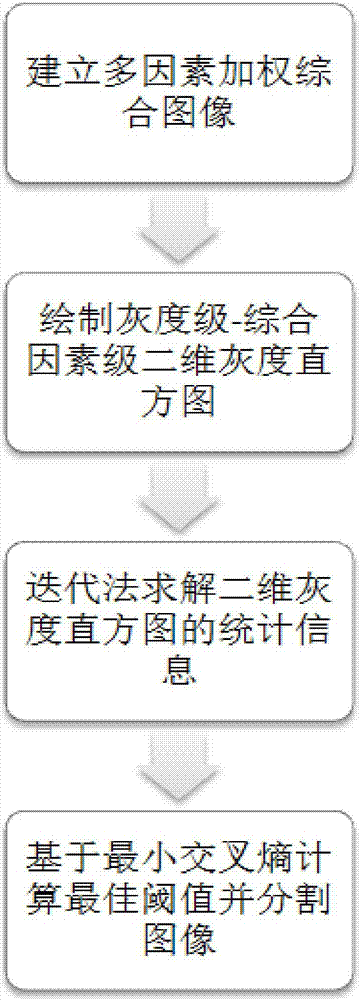
Multi-factor two-dimension grey level histogram based threshold segmentation method
InactiveCN107369159ASolve the problem of losing key information of imagesGuaranteed credibilityImage analysisOptical measurementsIterative method
The invention provides a multi-factor two-dimension grey level histogram based threshold segmentation method belonging to the technical field of computer optical measurement. According to the invention, a multi-factor weight integrating image is created, a two-dimension grey level histogram is drawn and cross entropy is used for calculating the threshold value for segmenting the image. First, the weight integrating image based on three factors including neighborhood average gray level, gradient strength and gradient direction level. Further, a gray level image is combined and a gray level-integrated factor level two-dimension gray level histogram is drawn. Then an iteration method is adopted for solving gray level average values of foreground and background pixels. Finally, based on the minimum cross entropy, the optimal threshold value is calculated and the optimal threshold value is used for segmenting the image. The method provided by the invention solves a problem of image key information loss of a prior two-dimension gray level histogram; data accuracy and method reliability are ensured. The credibility of the threshold value and the image segmenting effect are improved. The whole threshold value segmenting algorithm is good in adaptability and high in validity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
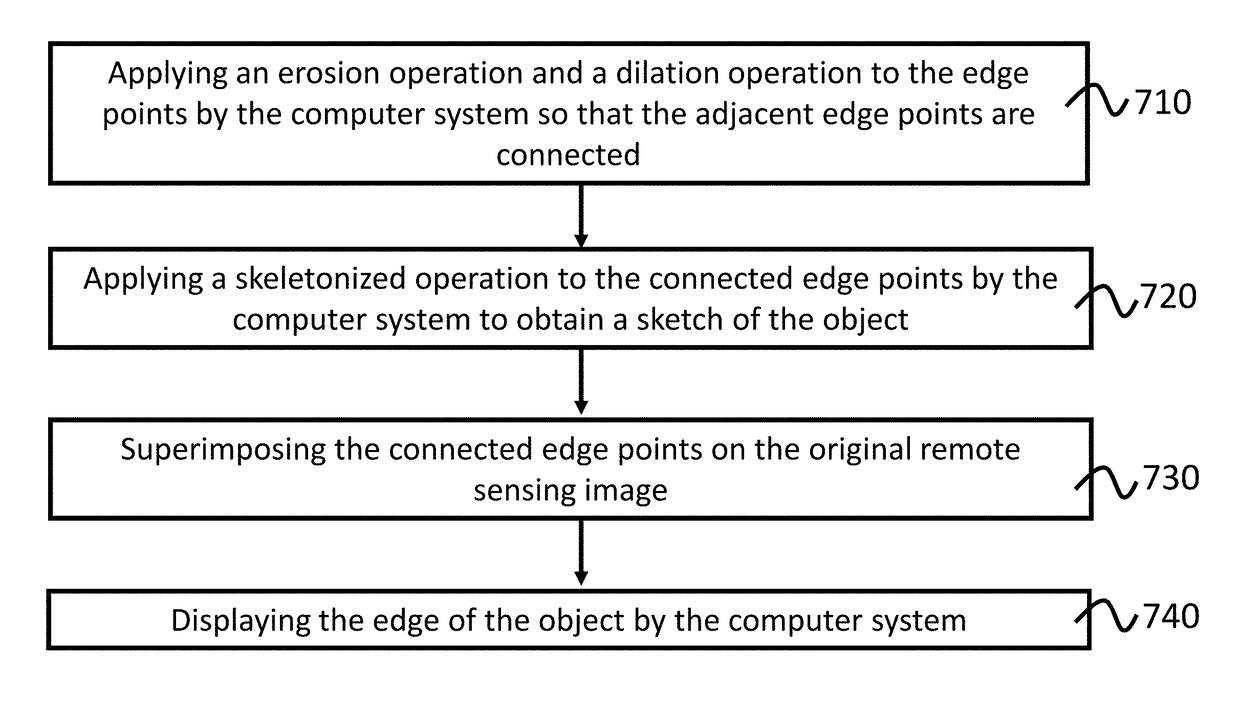
Method for edge detection
A computer system executes a method that detects an edge of an object with a Canny operator. The method calculates a gradient strength of pixels of the image and applies non-maximum suppression to the image to avoid spurious responses to edge detection. The image is divided into multiple partitions based on a brightness distribution of the pixels in the image and a set of dynamic threshold values. Multiple images for the partitions are superimposed to detect an edge of the object.
Owner:MACAU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Indoor scene flame detection method
ActiveCN106203334AImprove recognition rateImprove reliabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionYcbcr color spaceFalse alarm
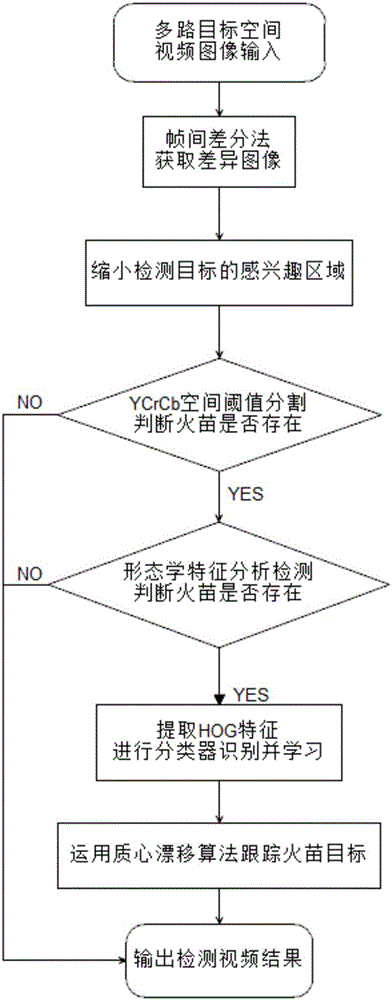
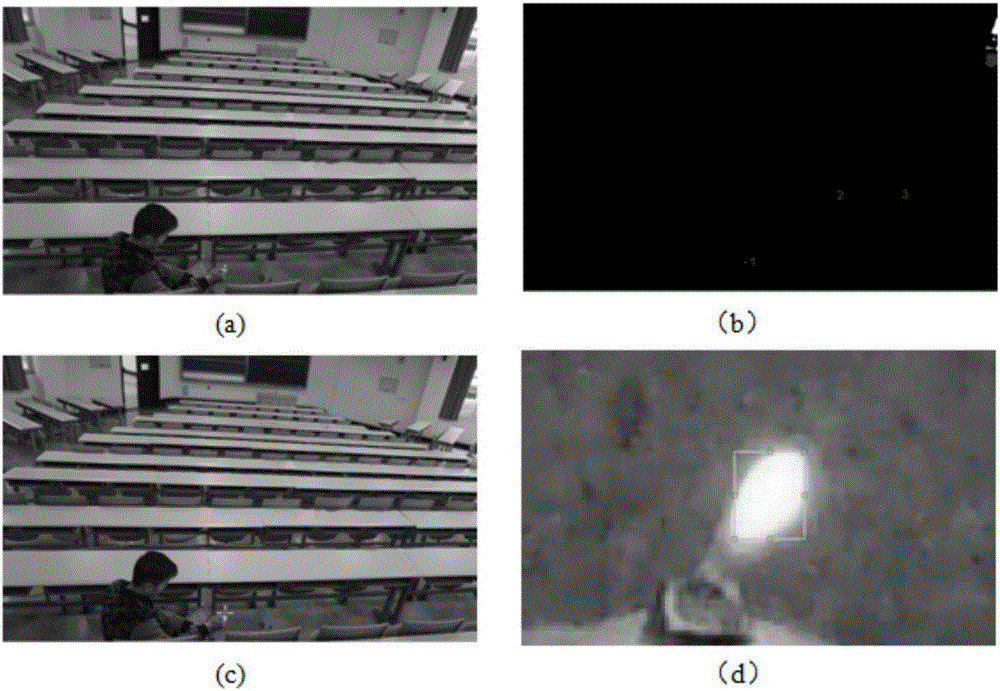
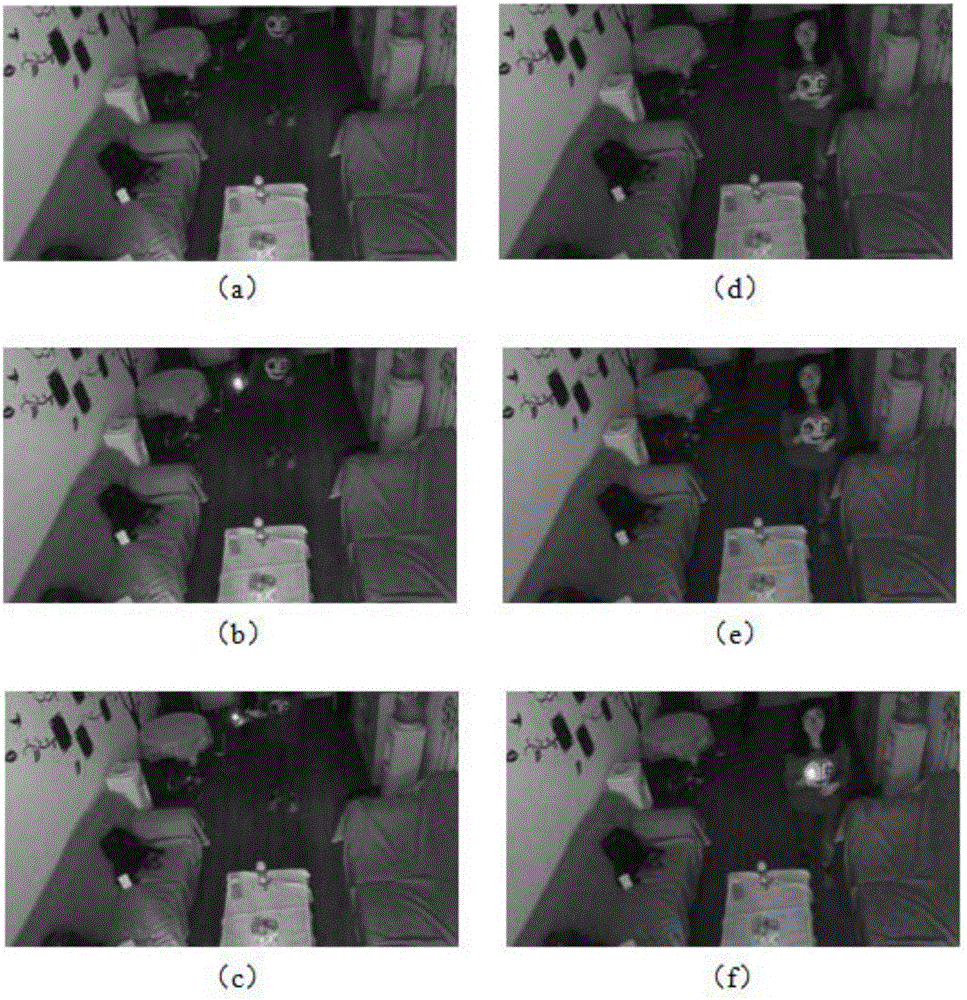
The invention discloses an indoor scene flame detection method and belongs to the application fields of a visible light image, video processing and the like. In the prior art, whether an initial stage flame and a small flame which may cause a fire hazard exist is difficult to accurately detect and track. By using the method of the invention, the above problem is solved. In the invention, color space conversion and segmentation of the visible light image are taken as a basis, and a morphological characteristic of the flame is combined so as to carry out distinguishing. Because a component channel of the flame image in a YCbCr color space possesses obvious gradient intensity and gradient distribution characteristics, a support vector machine is used to learn and identify an HOG characteristic, and in a dynamic video, through a transient frame difference and a center of mass drift algorithm, tracking of a flame target is realized. A lot of indoor flame image and video sample tests show that the method has advantages that an identification rate is high; a detection speed is fast; a false alarm rate is low and reliability is high compared to a traditional method. The method aims at detection and tracking of the initial stage flame, the small flame and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Mixed organization image full-automatic partition method of virtual colonoscope
InactiveCN101295404AAchieve segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationGradient strength
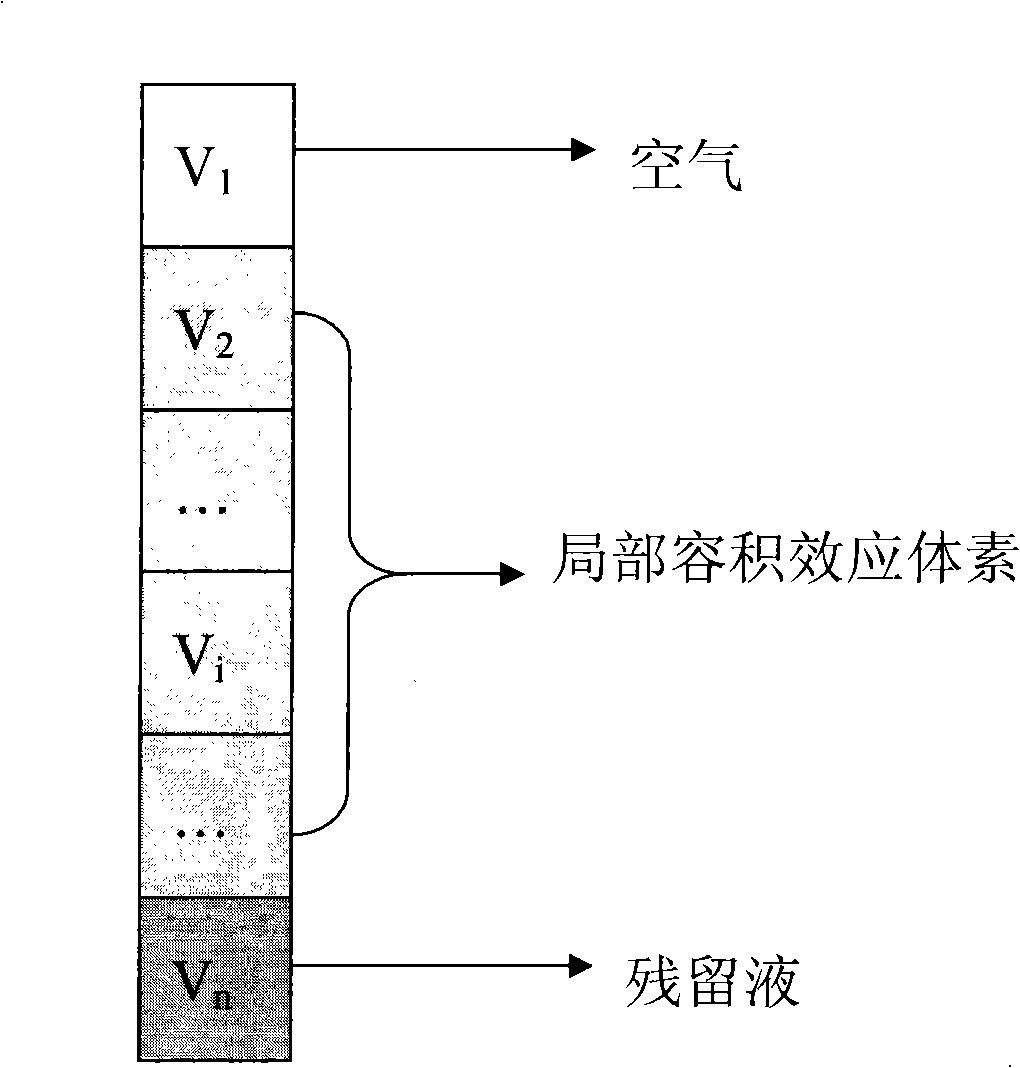
The invention provides a full-automatic segmentation method for a mixed tissue image of a simulated colonoscopy, comprising the following steps of: selecting a suitable threshold value of the air and of the enteral residual liquid; carrying out an initial segmentation for the enteral area through a traditional threshold method; wiping a local volume effect between the air and the enteral residual liquid through a vertical filter; conducting an enteral segmentation through a region growing method; enhancing the boundaries of the colon and other issues through a gradient intensity region growing method; repeating a wiping of the local volume effect between the air and the enteral residual liquid through the vertical filter for the inner part of the colon with enhanced boundaries. The full-automatic segmentation method for the mixed tissue image of a simulated colonoscopy overcomes the problems of the traditional threshold segmentation, eliminates the impacts from the local volume effect, and renders the segmentation results better in conformity with the actual conditions.
Owner:SHAANXI HI TECH MEDICAL INFORMATION
Image processing apparatus and method
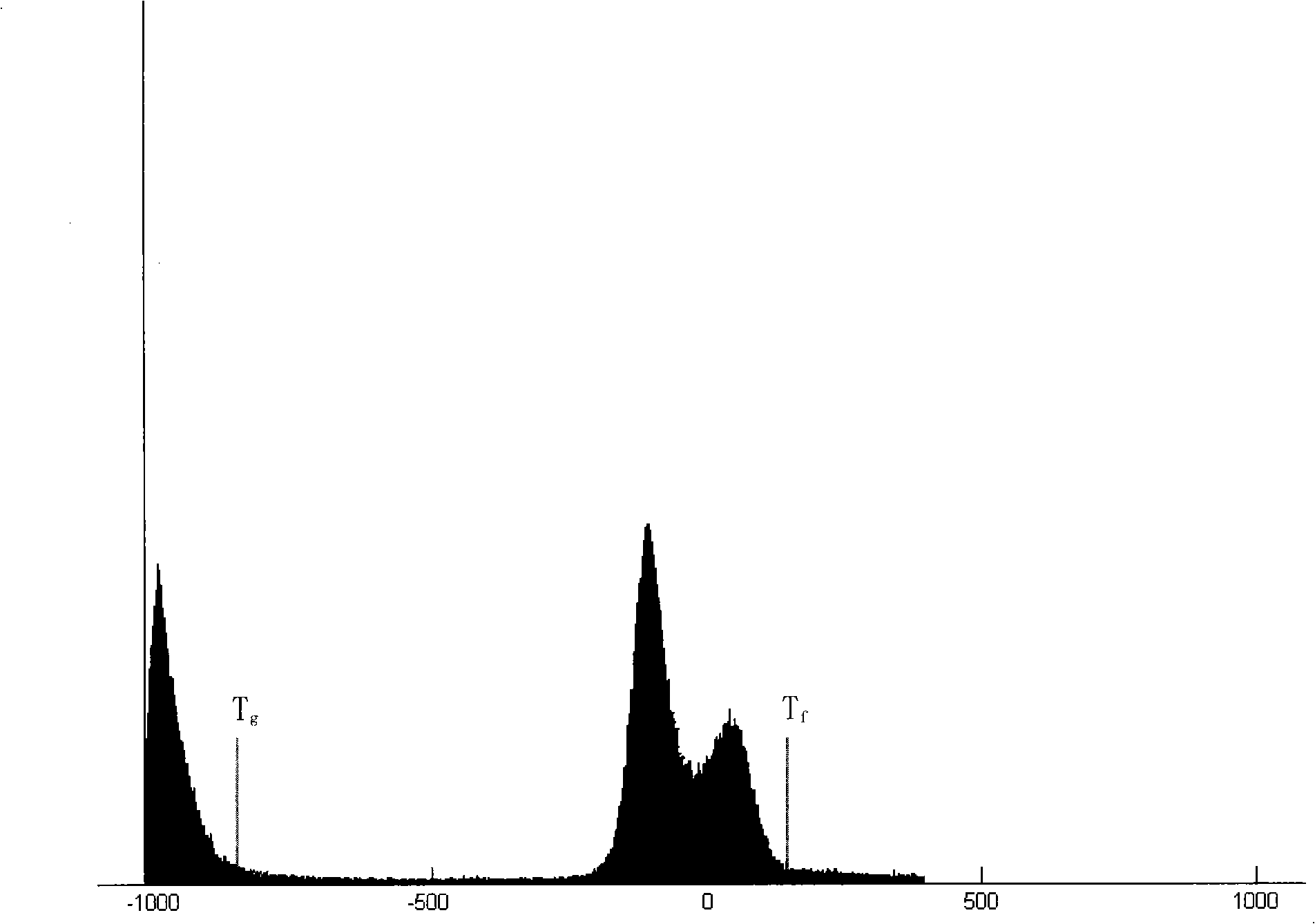
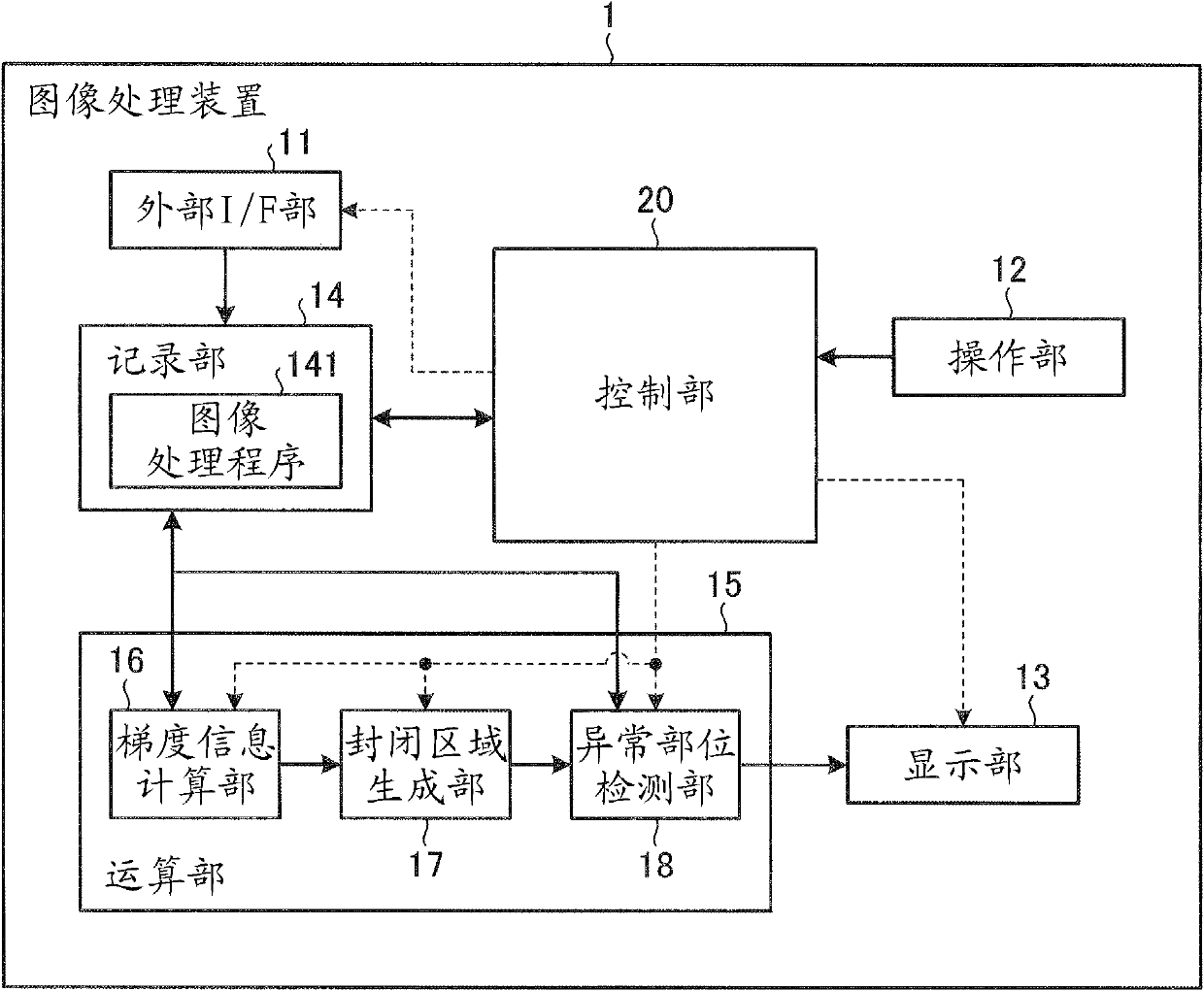
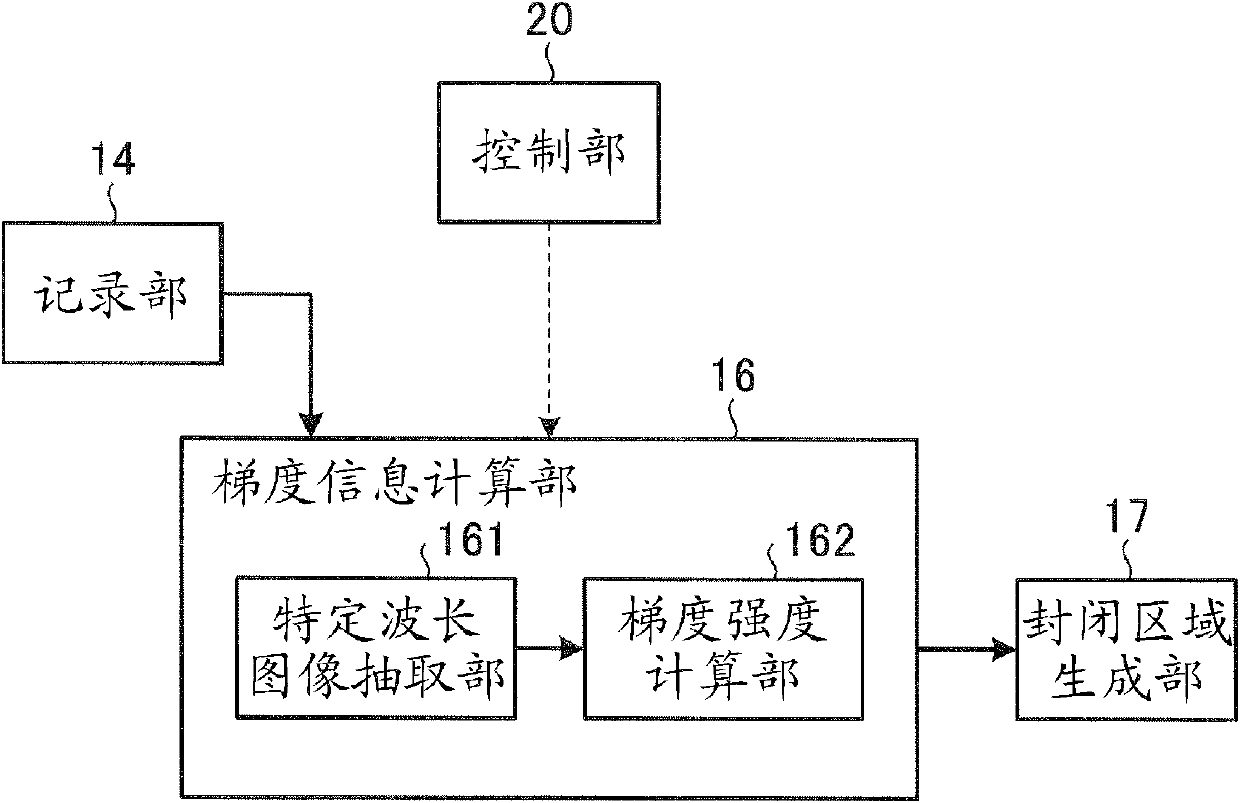
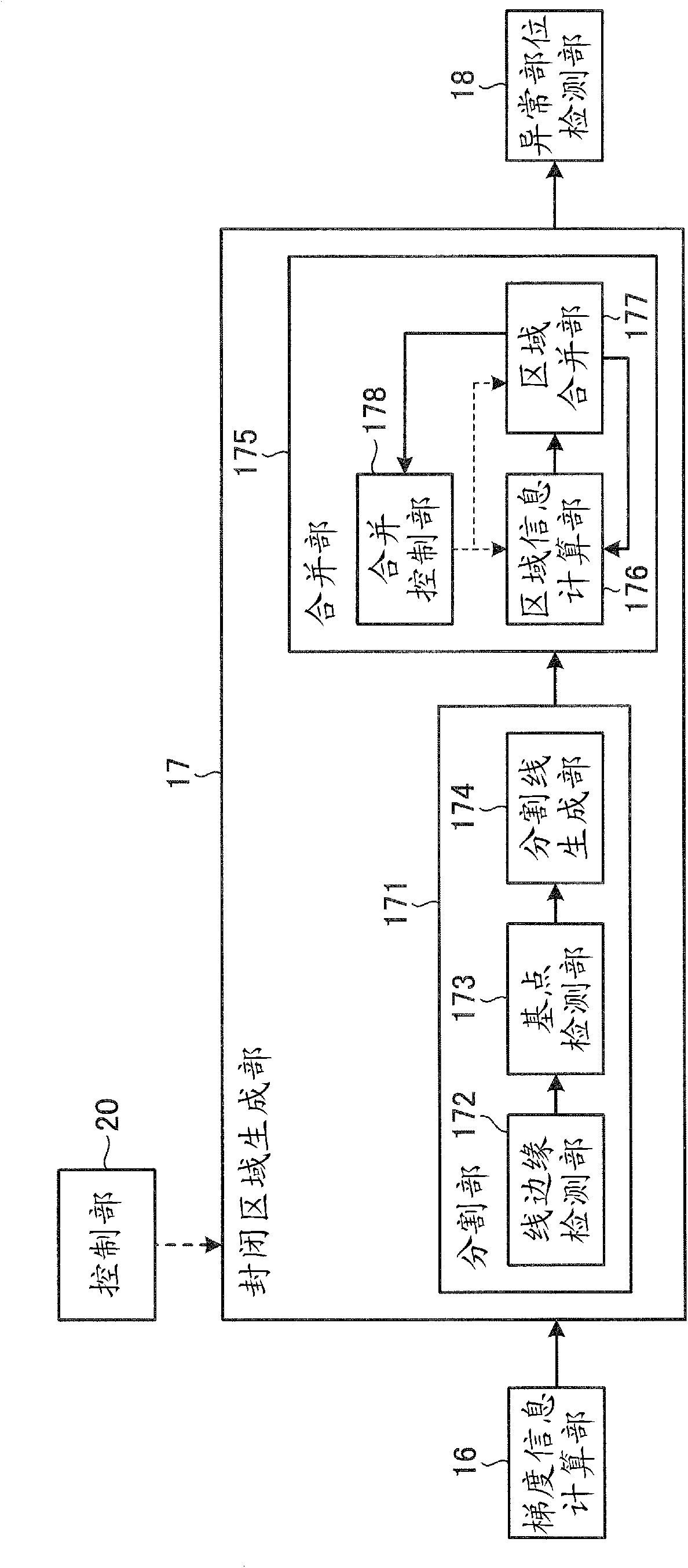
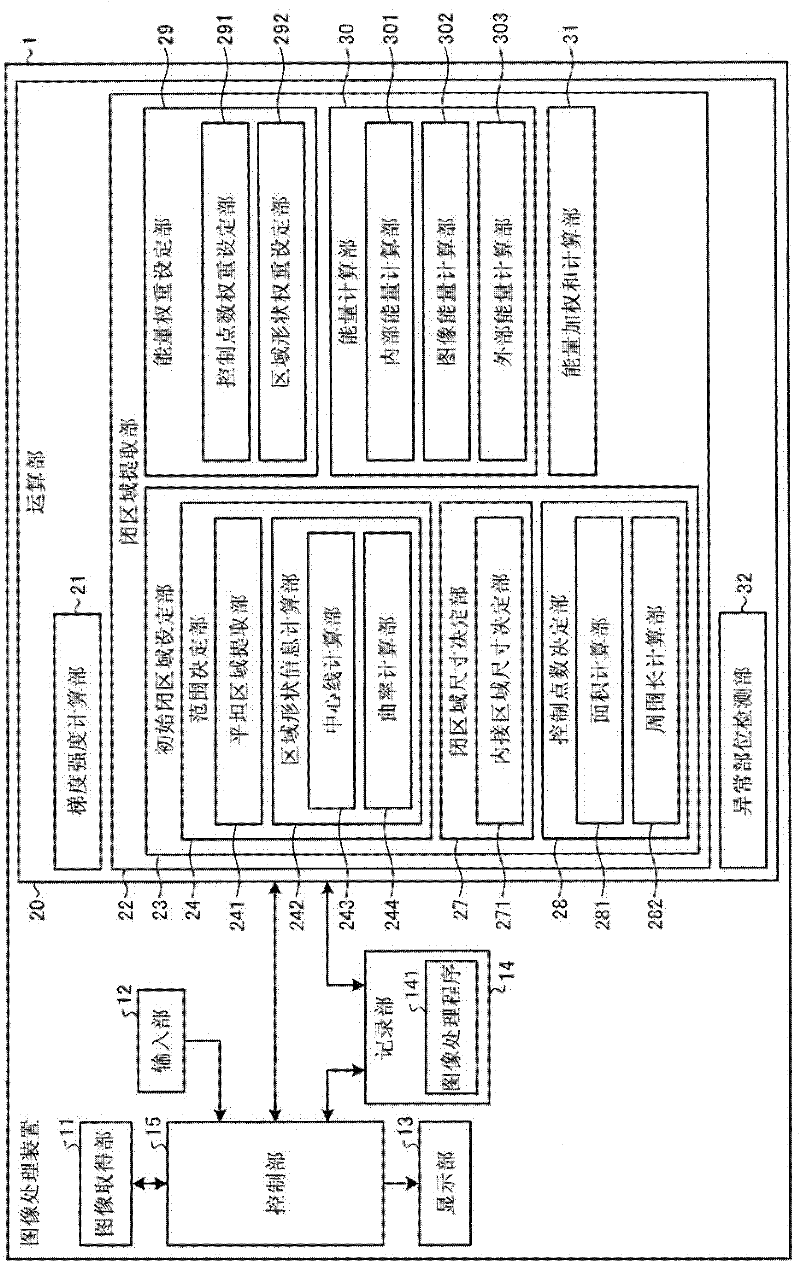
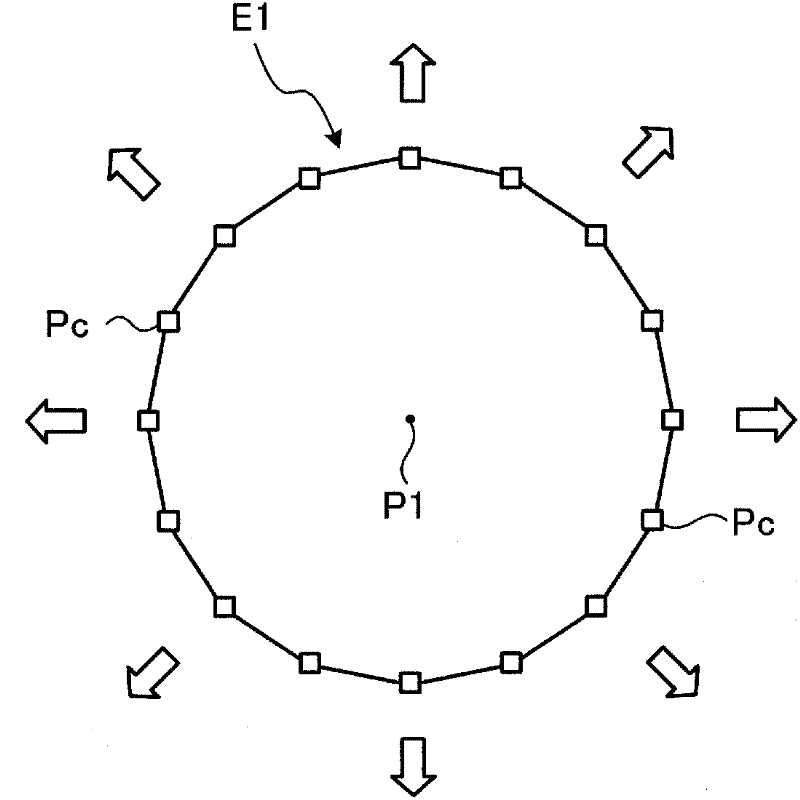
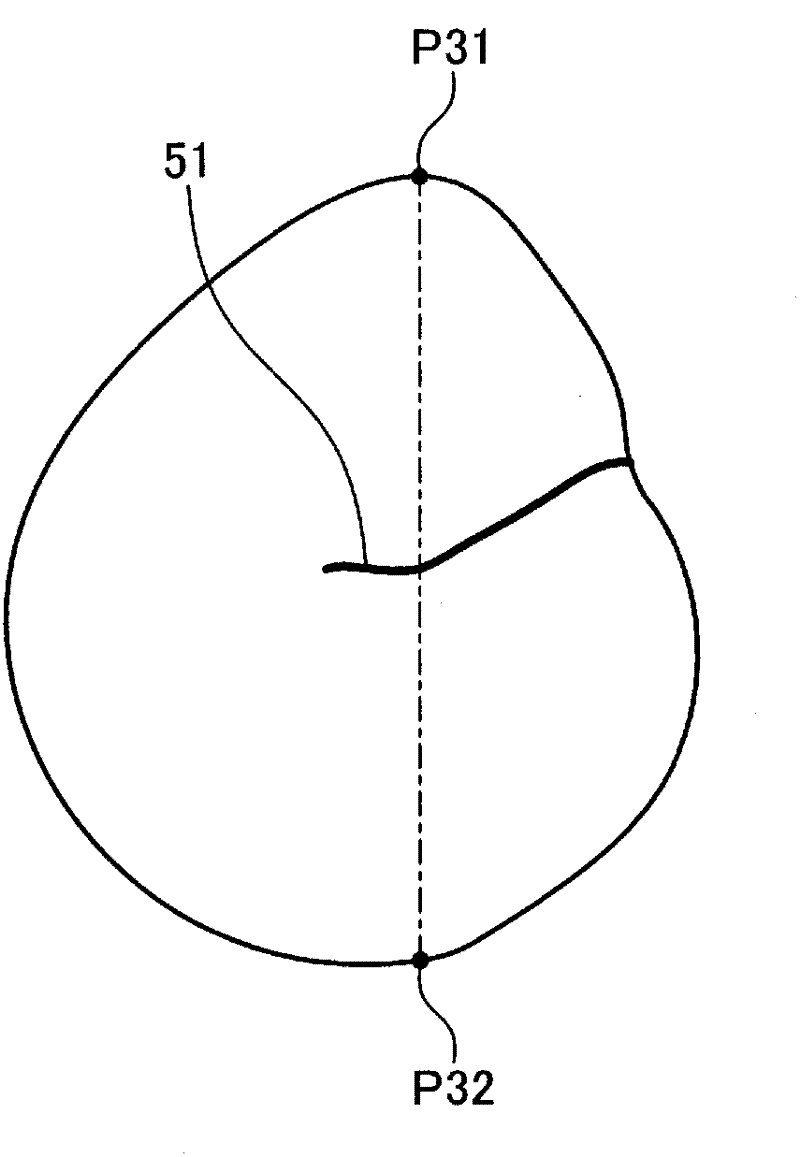
An image processing apparatus includes: a gradient information calculating unit that calculates gradient information of each of pixels, based on pixel values of an intraluminal image; a closed region creating unit that, based on the gradient information, creates a closed region satisfying a condition where the closed region does not include, on the inside thereof, any pixel of which the gradient strength is equal to or higher than a predetermined value, and also, the boundary of the closed region does not curve toward the interior of the closed region, with a curvature equal to or larger than a predetermined value; and an abnormal part detecting unit that detects an abnormal part from the inside of the closed region.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Arrangement with variable selection field orientation for magnetic particle imaging
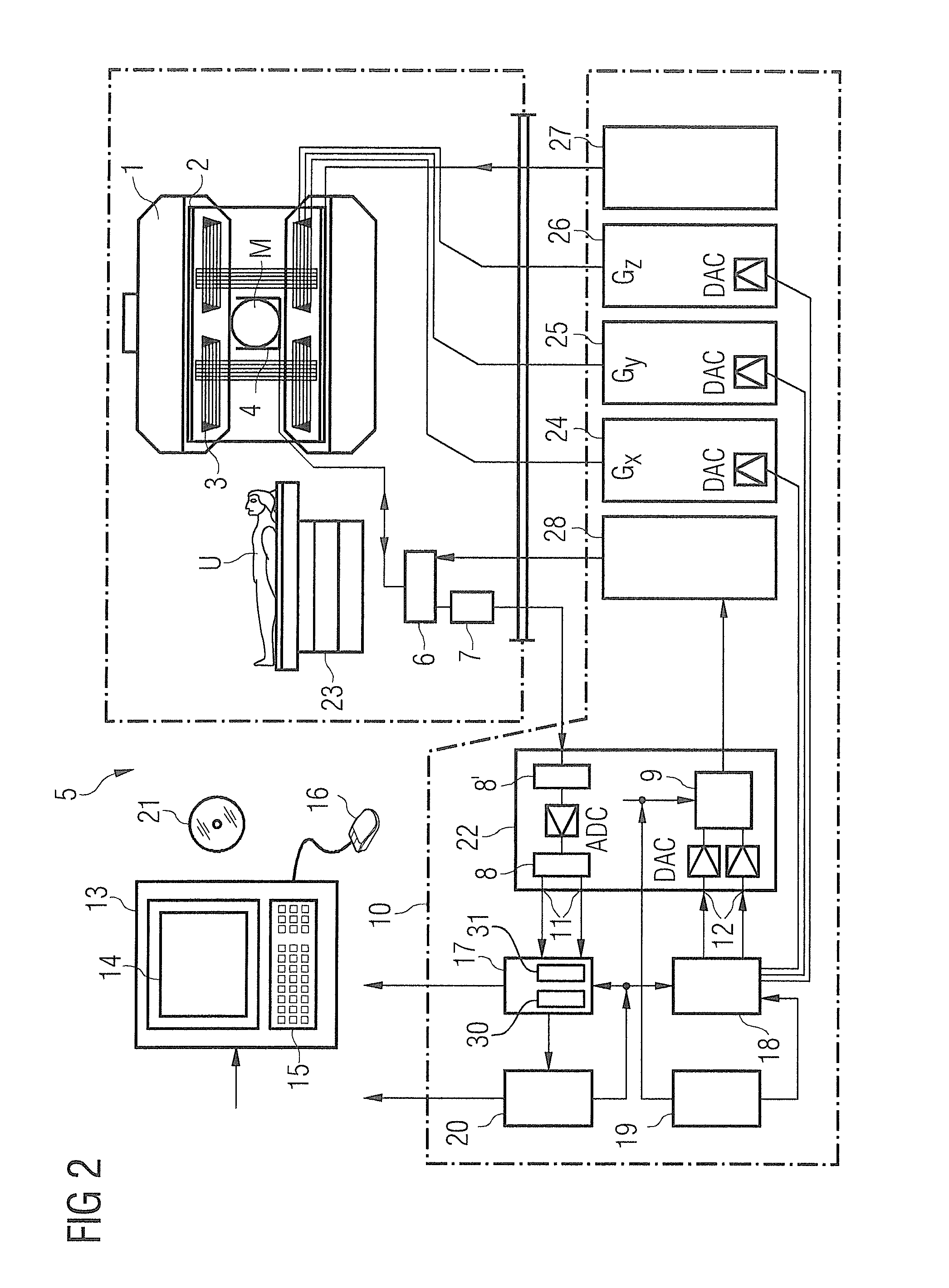
ActiveUS20110234217A1Improve imaging resolutionSpatial selectivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic gradient
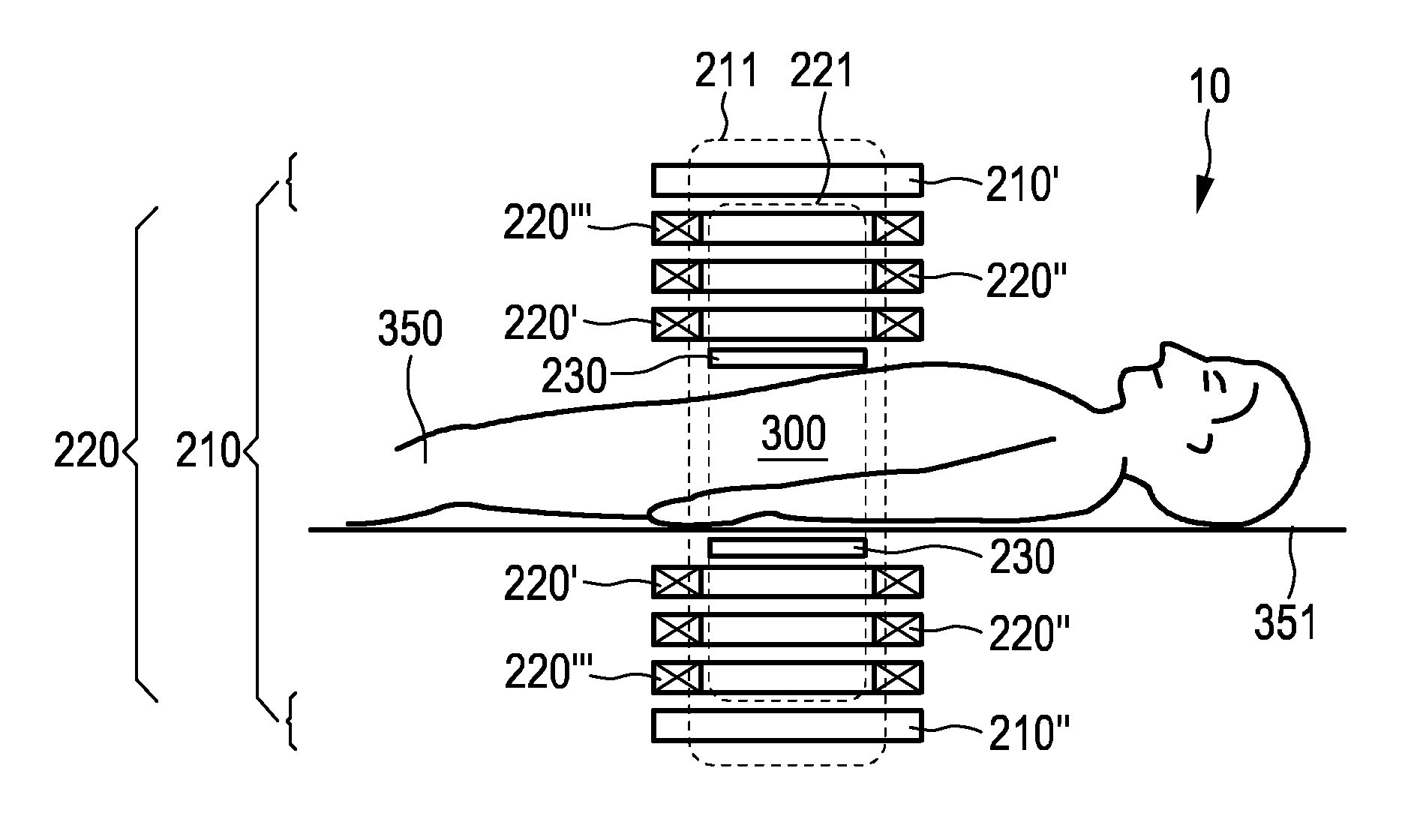
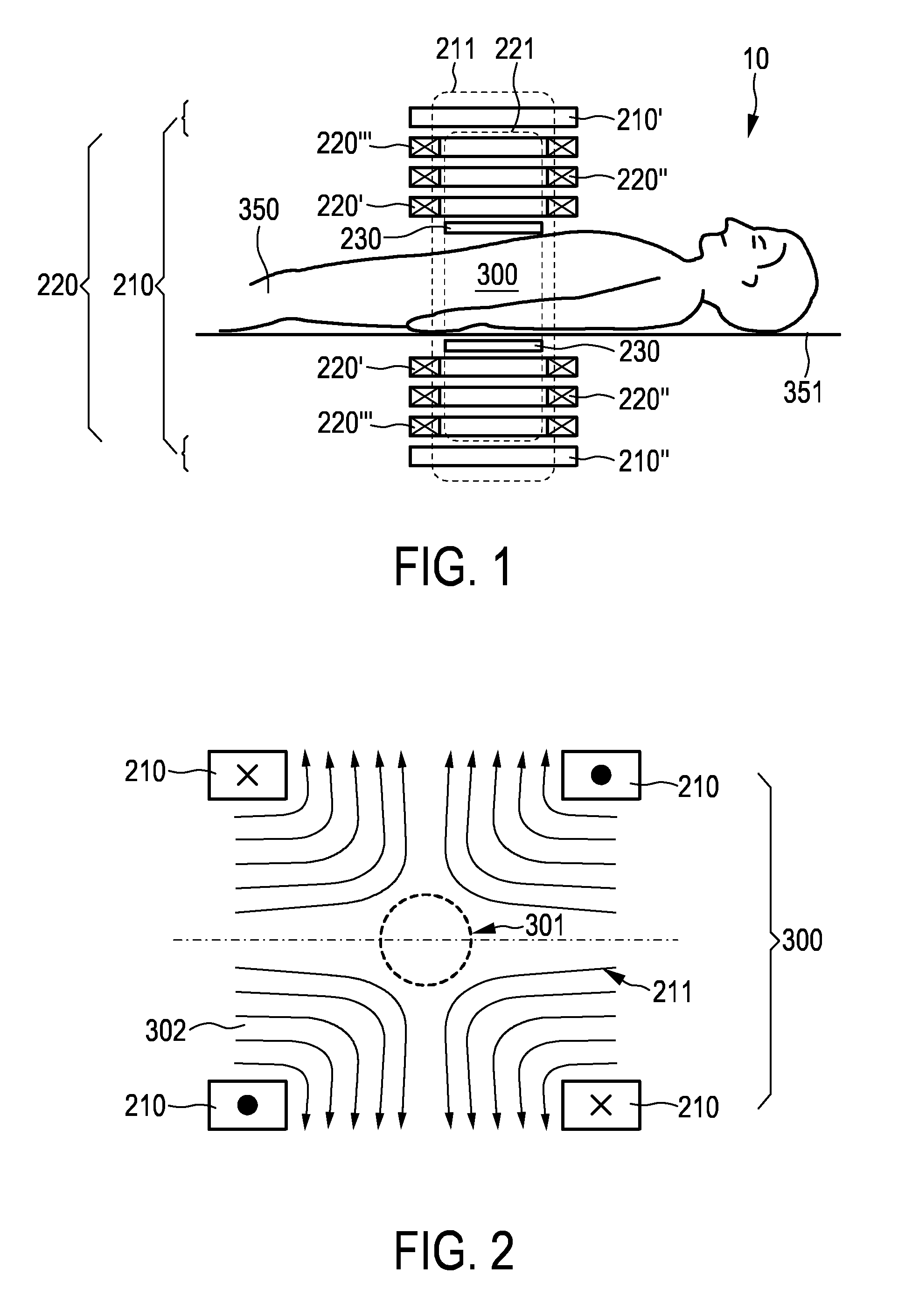
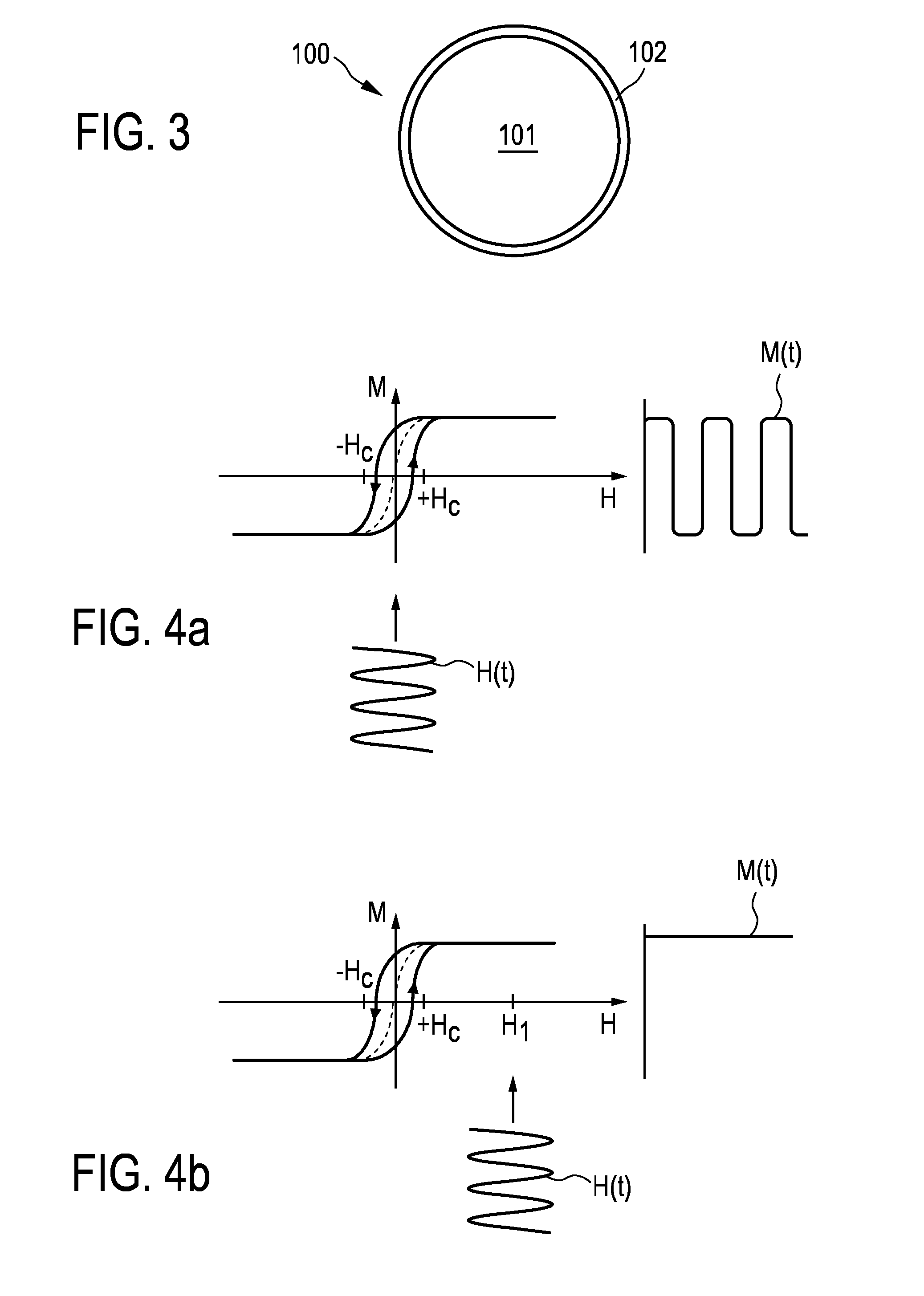
The present invention relates to an arrangement (10) for influencing and / or detecting magnetic particles (100) in a region of action (300), which comprises selection means (210) for generating a magnetic selection field (211) having a pattern in space of its magnetic field strength such that a first sub-zone (301) having a low magnetic field strength and a second sub-zone (302) having a higher magnetic field strength are formed in the region of action (300). The arrangement further comprises drive means (220) for changing the position in space of the two sub-zones (301, 302) in the region of action (300) by means of a magnetic drive field (221) so that the magnetization of the magnetic material changes locally. The arrangement further comprises receiving means (230) for acquiring detection signals, which detection signals depend on the magnetization in the region of action (300), which magnetization is influenced by the change in the position in space of the first and second sub-zone (301, 302). Control means (76) are further introduced for controlling the selection means (210) to individually set the gradient strength of at least one of the static magnetic gradient fields (211) in a desired direction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
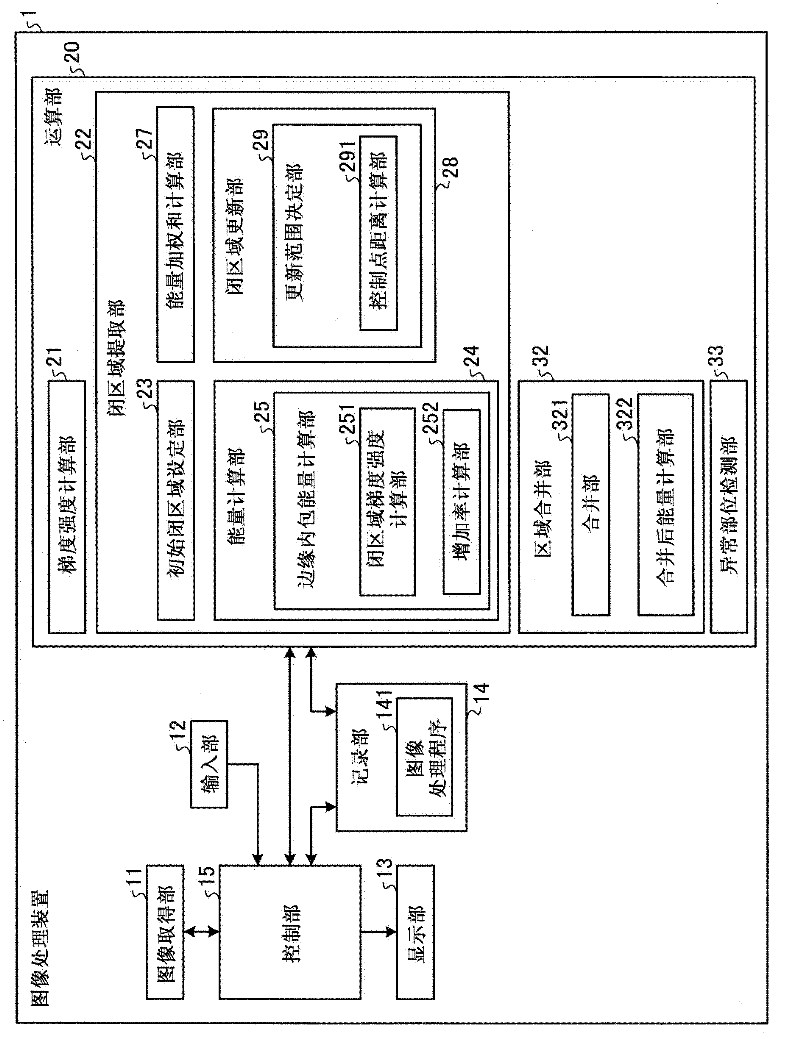
The invention provides an image processing apparatus and an image processing method. The image processing apparatus includes a gradient strength calculating unit that calculates a gradient strength of a pixel value of each pixel based on an intraluminal image that is a captured image of an intralumen; a closed region extracting unit that extracts a closed region from the intraluminal image, the closed region satisfying conditions that the pixel of which gradient strength is a predetermined value or more is not included in the closed region and a boundary of the closed region does not bend with a predetermined curvature or higher toward an inner side of the closed region; and an abnormal portion detecting unit that detects an abnormal portion inside the closed region. The closed region extracting unit includes an initial closed region setting unit that sets an initial shape of the closed region; an energy calculating unit that calculates values of a plurality of types of energy including at least energy determined by an outer shape of the closed region and energy determined by the gradient strength in the closed region; an energy-weighted sum calculating unit that calculates a weighted sum of the plurality of types of energy; and a closed region updating unit that updates a shape of the closed region within an update range based on the weighted sum. The closed region updating unit includes an update range determining unit that determines the update range in which the shape of the closed region is updated based on any one of the values of the plurality of types of energy.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method and apparatus for correction of artifacts in magnetic resonance images
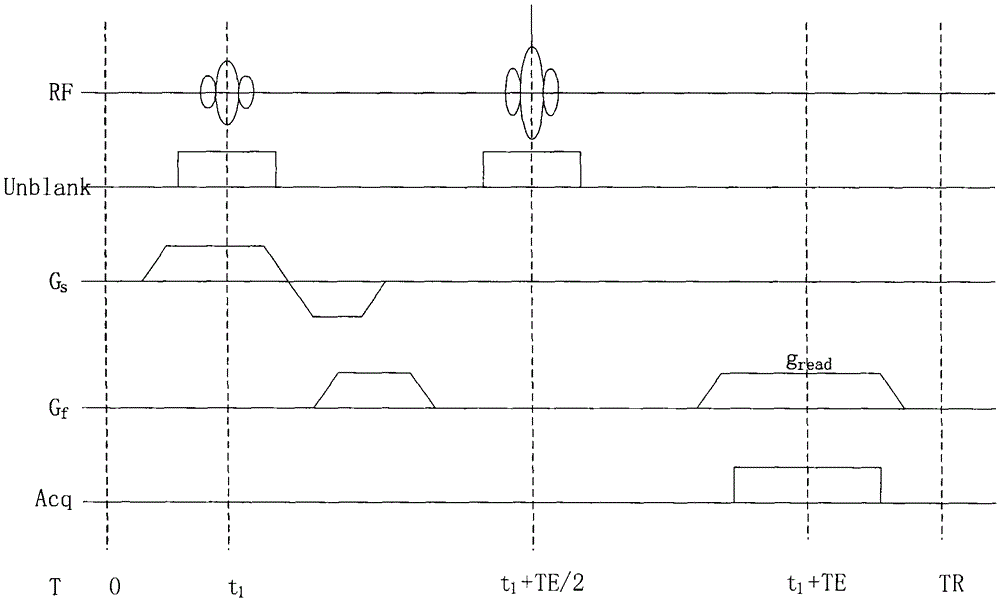
ActiveUS20140086468A1Reduce artifactsReduce computing costMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGradient strengthSelective excitation
In a method for the calculation of individual elements of a matrix to correct artifacts in magnetic resonance images that are reconstructed from measurement data acquired using an MR pulse sequence, in which gradients are switched simultaneously during the radiation of at least one non-selective excitation pulse, at least one excitation profile of an excitation pulse used to acquire measurement data is loaded into a process, the profile depending on the measured location x and the measured k-space point k and the gradient strength applied in the measurement. From each loaded excitation profile, an element of a transposed, inverted disturbance matrix is calculated which corresponds to the location x and the measured k-space point k. Instead of a Fourier back-transformation, matrix inversion is used for the image reconstruction of a corrected image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
Provided is an image processing apparatus and an image processing method. The apparatus includes a calculating unit that calculates gradient strength of respective pixel values based on an intraluminal image, an extracting unit that extracts a closed region from the image, and a detecting unit that detects an abnormal portion of the closed region. The closed region satisfies conditions that the pixel of which gradient strength is a predetermined value or more is not included in the closed region and a boundary of the closed region does not bend with predetermined curvature or higher toward an inner side of the closed region. The extracting unit includes a setting unit that sets an initial closed region based on the gradient strength, an energy calculating unit that calculates values of types of energies based on an outer shape of the closed region and the gradient strength, and an energy weighted-sum calculating unit that calculates a weighted sum of the types of energy.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
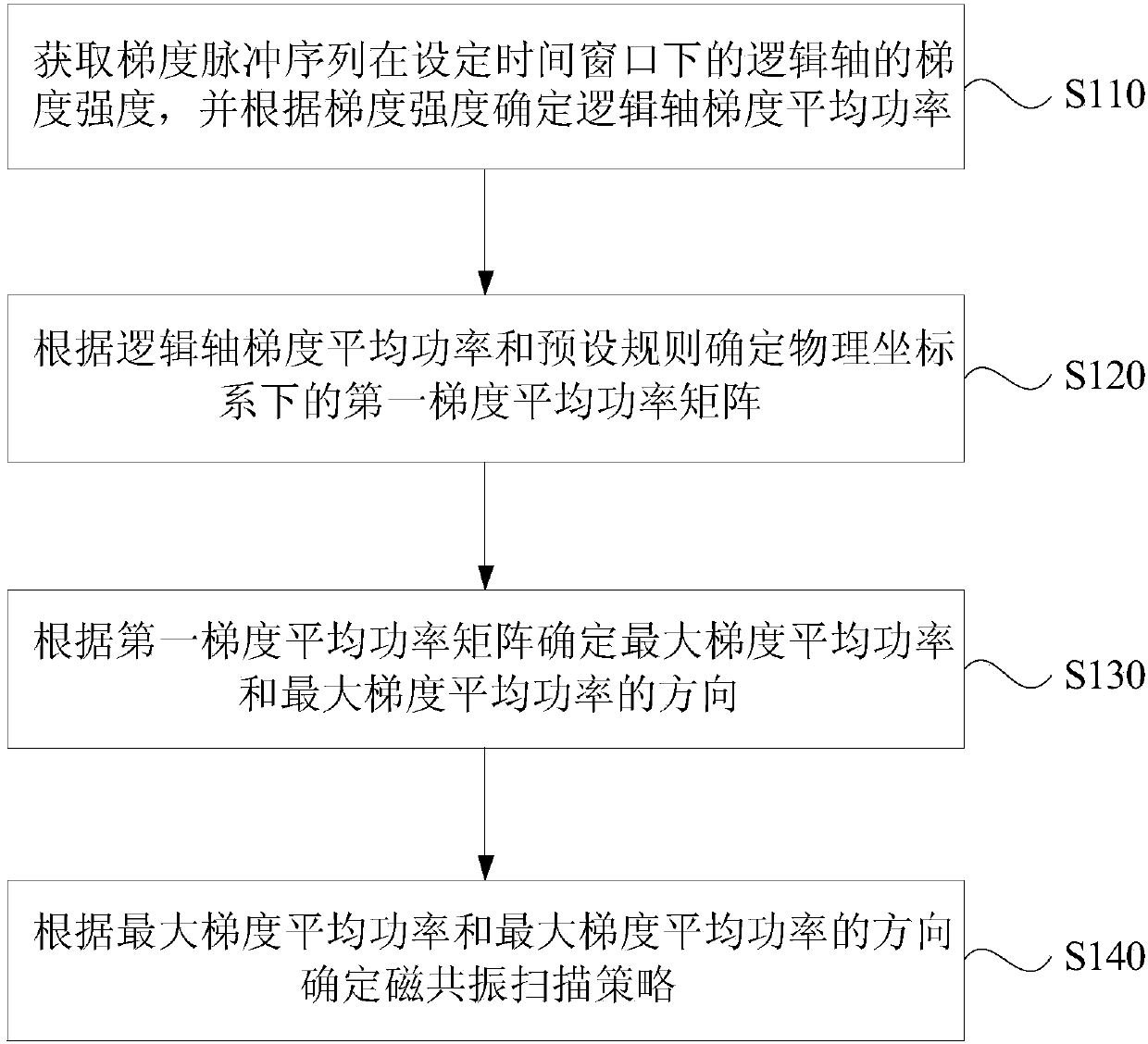
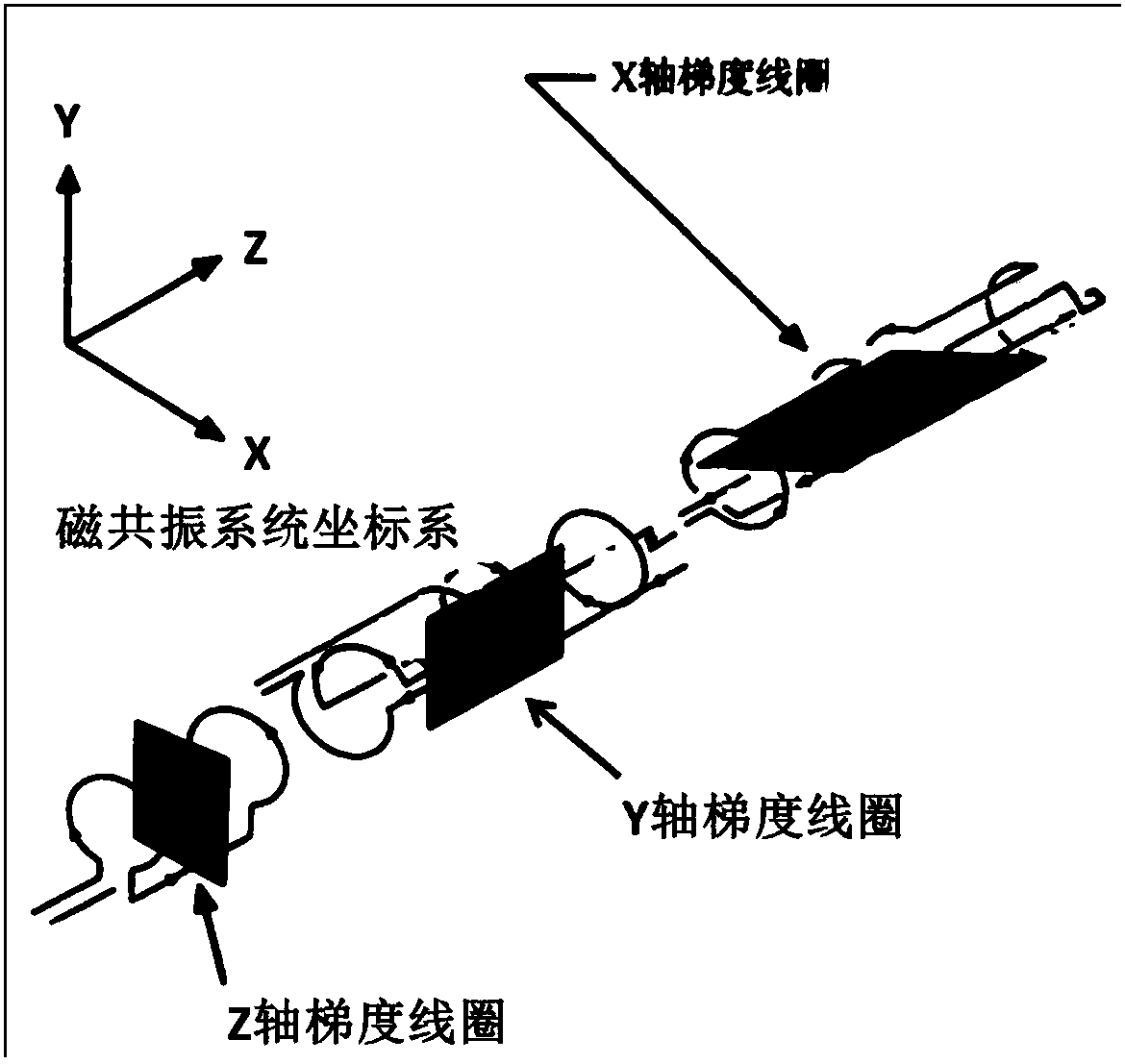
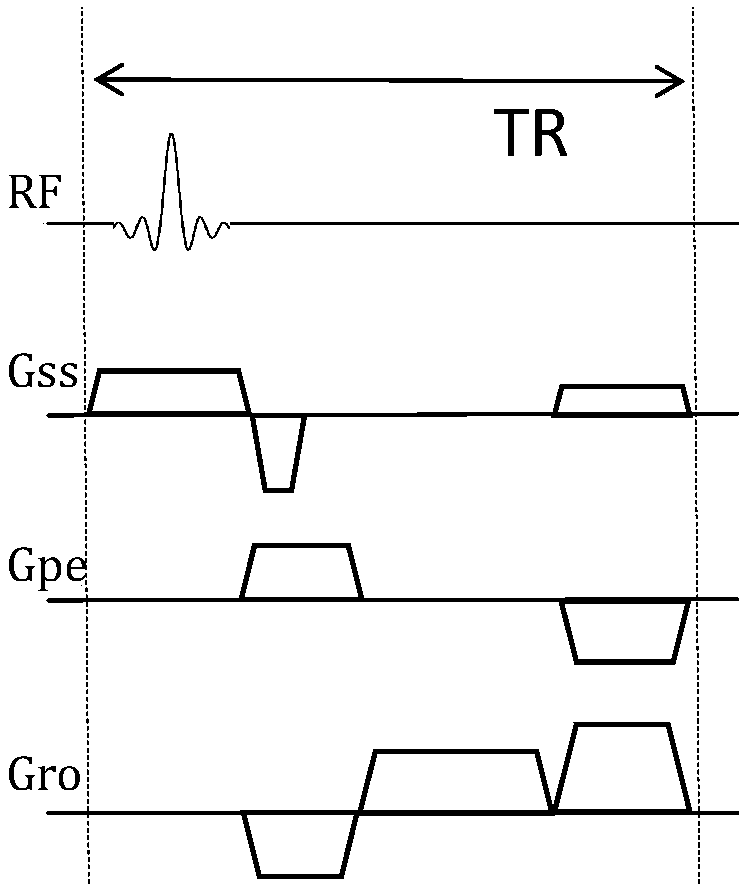
Magnetic resonance scanning strategy determination method and magnetic resonance scanning system
ActiveCN107656222AQuick fixClinical scan went wellMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringGradient strengthResonance
The embodiment of the invention provides a magnetic resonance scanning strategy determination method and a magnetic resonance scanning system. The magnetic resonance scanning strategy determination method comprises the steps of acquiring the gradient strength of a logic axis of a gradient pulse sequence in a set time window, and determining the gradient average power of the logic axis according tothe gradient strength; determining a first gradient average power matrix in a physical coordinate system according to the gradient average power of the logic axis and preset rules; determining the maximum gradient average power and a direction of the maximum gradient average power according to the first gradient average power matrix; and determining a magnetic resonance scanning strategy according to the maximum gradient average power and the direction of the maximum gradient average power. The embodiment of the invention solves problems that the calculation for the maximum average power is great in calculation amount, the operation is complex, and the time spent on determining the magnetic resonance scanning strategy is long, a scanning strategy can be quickly determined according to thecalculation result, and clinical scanning is ensured to be performed smoothly.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Field Strength Test Devices and Methods for Installed Engineered Material Arresting Systems
Embodiments of the present invention provide field test devices and methods for testing the compressive gradient strength of installed vehicle arresting systems, such as those installed on airport runways. Current methods of testing such arresting systems are conducted on sample materials in-house, and these methods are not applicable or useful when tests need to be conducted on currently-installed systems in the field.
Owner:RUNWAY SAFE IPR AB
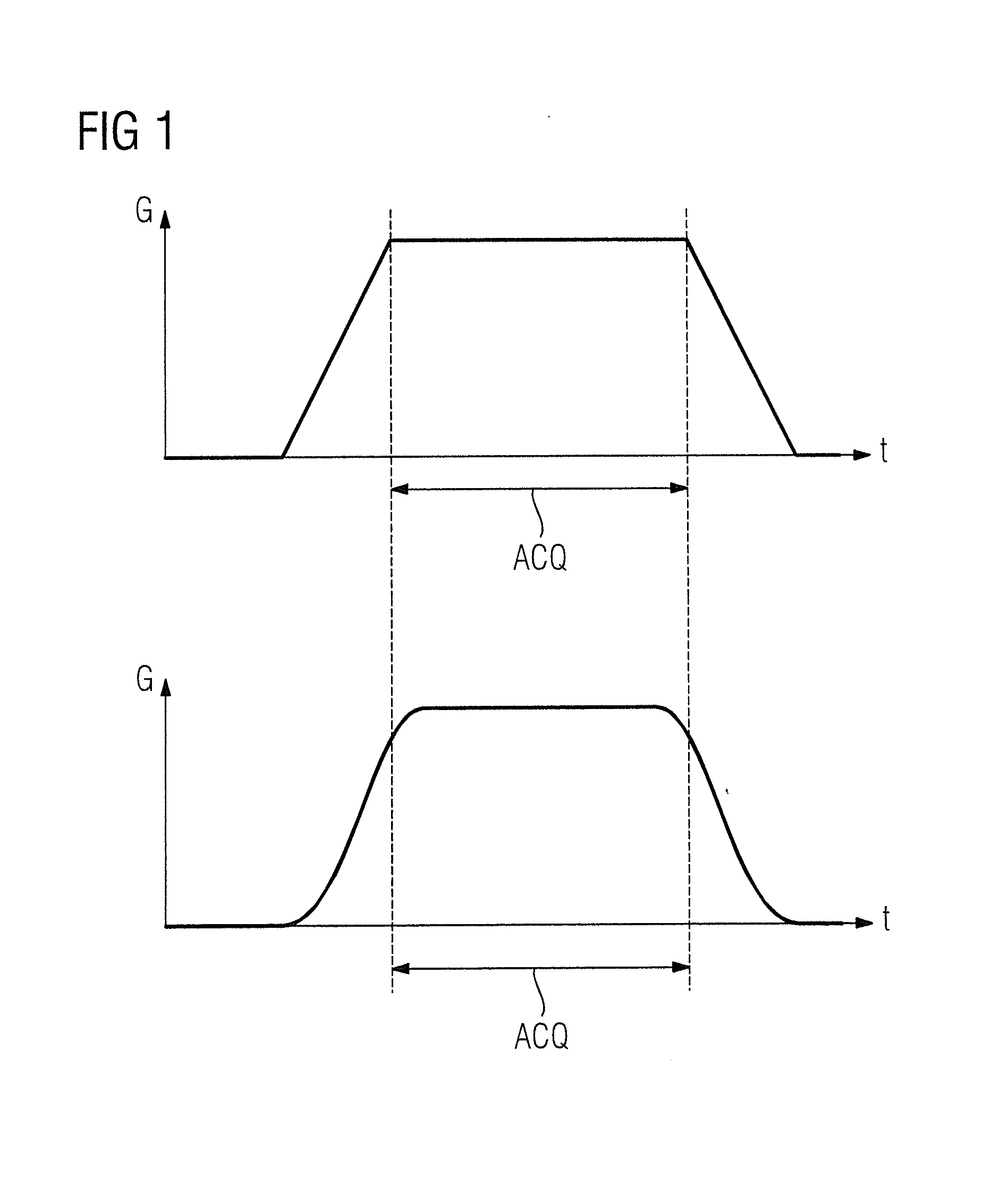
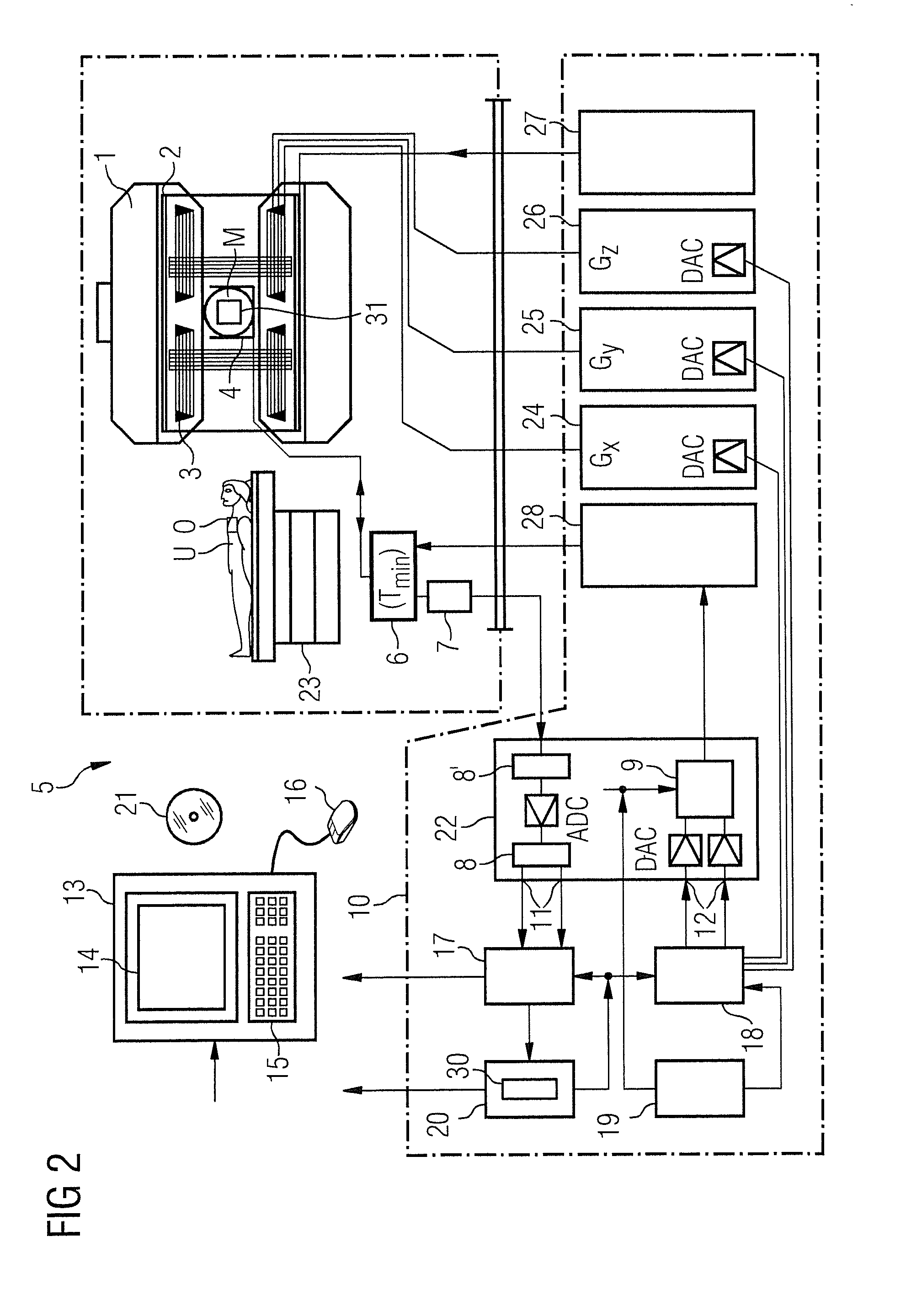
Gradient system for an NMR tomograph
InactiveUSRE36881E1The production process is simpleImprove performanceMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical conductorLinearity
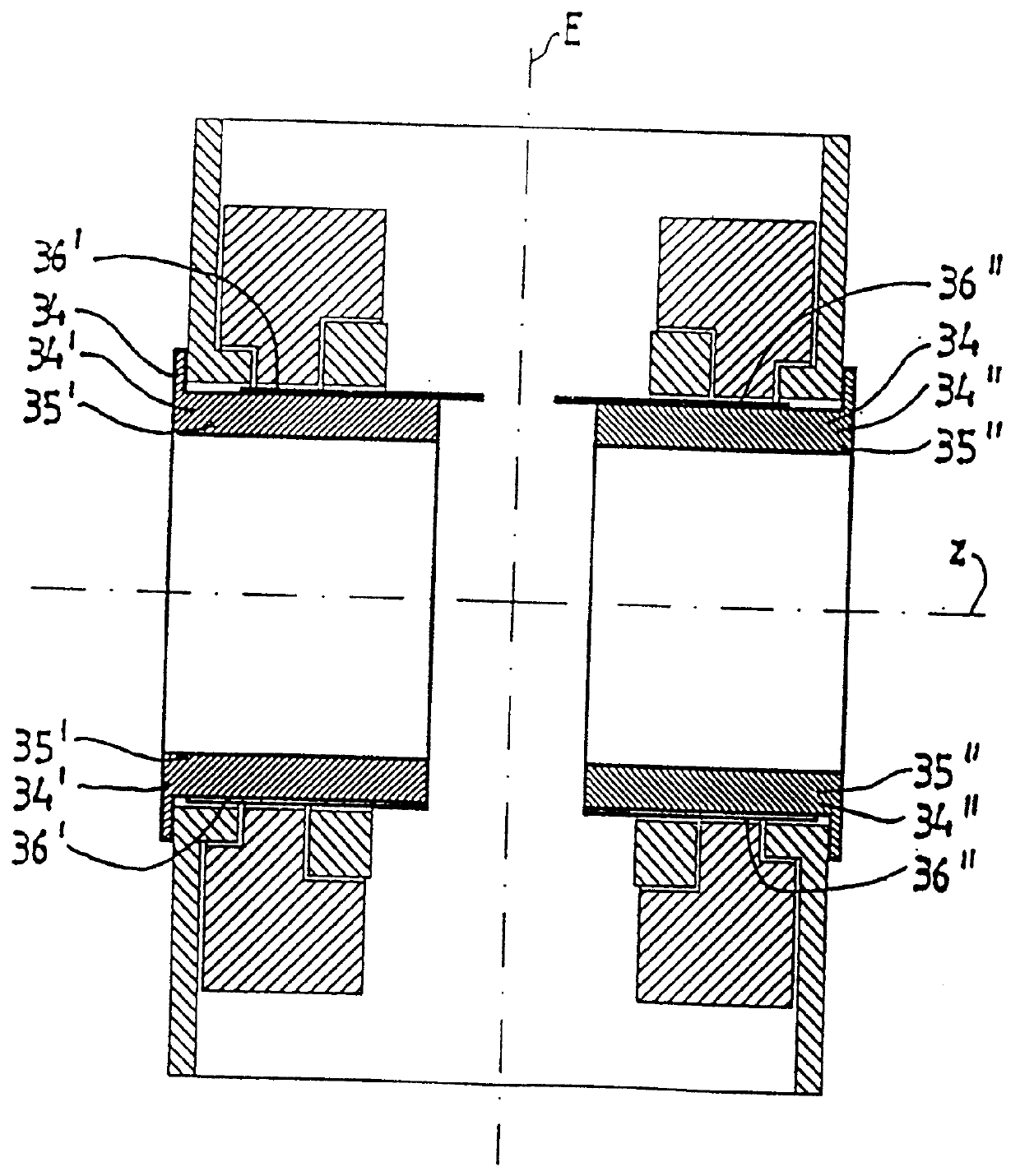
A gradient system for a nuclear spin resonance (NMR) tomograph with a main magnet system producing a homogeneous magnetic field directed along a z-axis inside a measuring volume, wherein the main magnet system provides access to the measuring volume along the z-axis and transversely to the z-axis, and wherein the gradient system comprises two first partial gradient systems which are located at opposite sides of a central plane perpendicular to the z-axis, across the measuring volume. At least one of the two partial gradient systems is movable between at least two positions along the z-axis. In this way, with a small constructional size and with a simple manufacturing procedure, a gradient system is obtained with high performance capability with respect to generated gradient strength for given ampere turns, high linearity of the generated gradient fields, minimum inductance and minimum electrical resistance of the conductor segments.
Owner:BRUKER ANALYTISCHE MESSTECHN
Gradient coil for magnetic resonance imaging and processing method thereof
ActiveCN109917312AImprove efficiencyHigh strengthMagnetic measurementsGradient strengthImaging quality
Owner:RAY PLUS MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Device and method for determining an edge histogram, device and method for storing an image in an image database, device and method for finding two similar images and computer program
InactiveUS8437547B2Promote resultsClear separationImage analysisDigital data information retrievalGradient strengthEdge type
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Image boundary extraction method and system
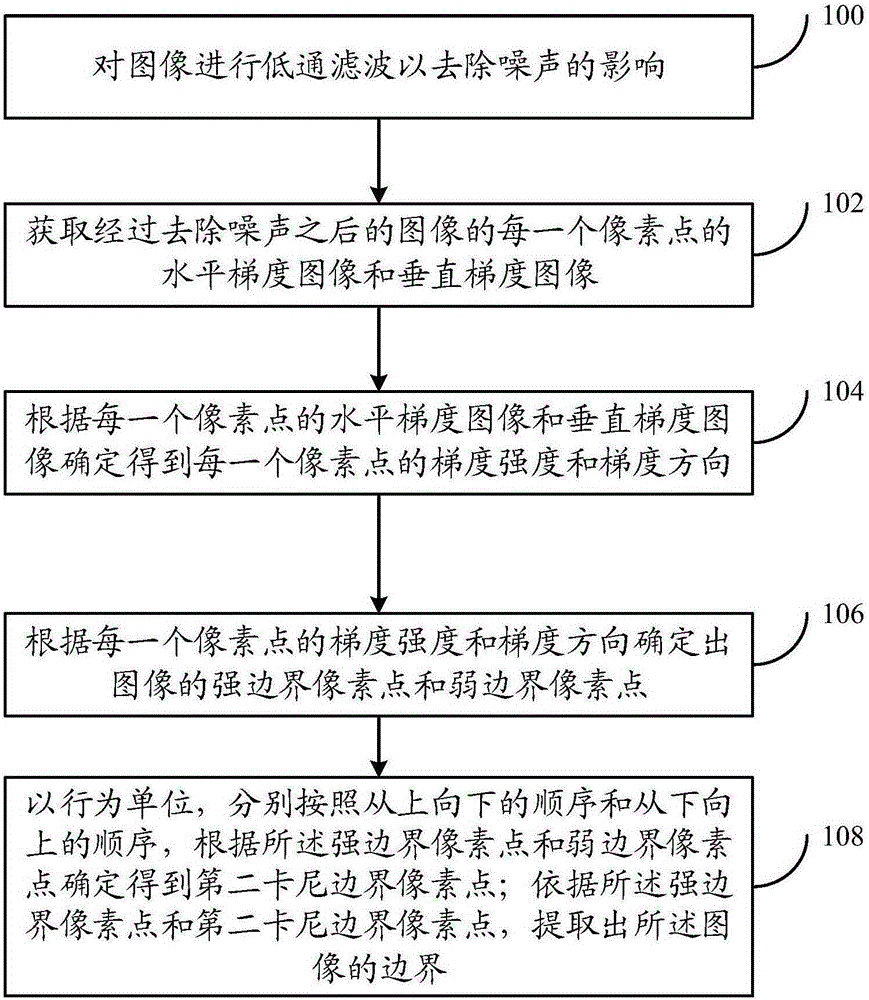
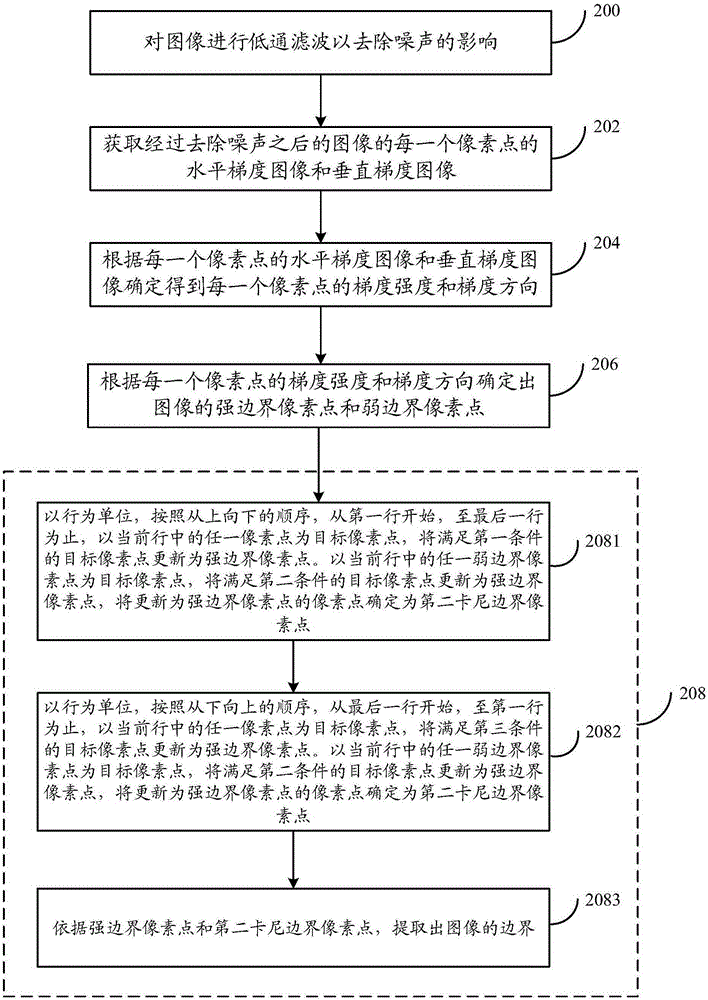
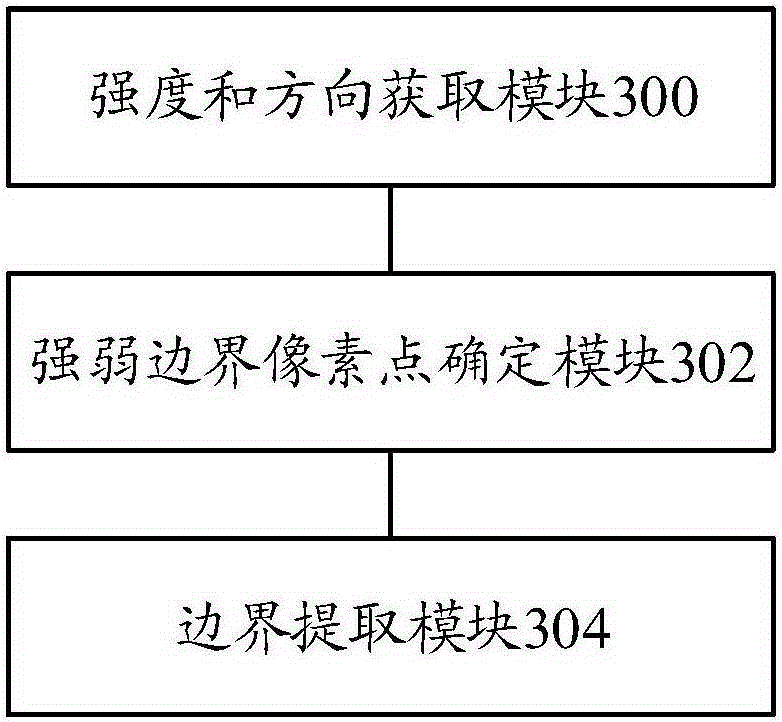
ActiveCN105354843AHigh speedAchieve parallelizationImage analysisGradient strengthExtraction methods
The present invention provides an image boundary extraction method and system. The method comprises: acquiring gradient strength and a gradient direction of each pixel point of an image; according to the gradient strengthen and the gradient direction of each pixel point, determining strong boundary pixel points and weak boundary pixel points of the image; using row as the unit, and according to the strong boundary pixel points and the weak boundary pixel points, determining and obtaining second canny boundary pixel points respectively in order from top to bottom and in order from bottom to top; and according to the strong boundary pixel points and the second canny boundary pixel points, extracting a boundary of the image. According to the image boundary extraction method and system provided by the present invention, parallelization of boundary connection is realized and the speed of canny boundary connection is improved.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method and device to determine distortion correction data
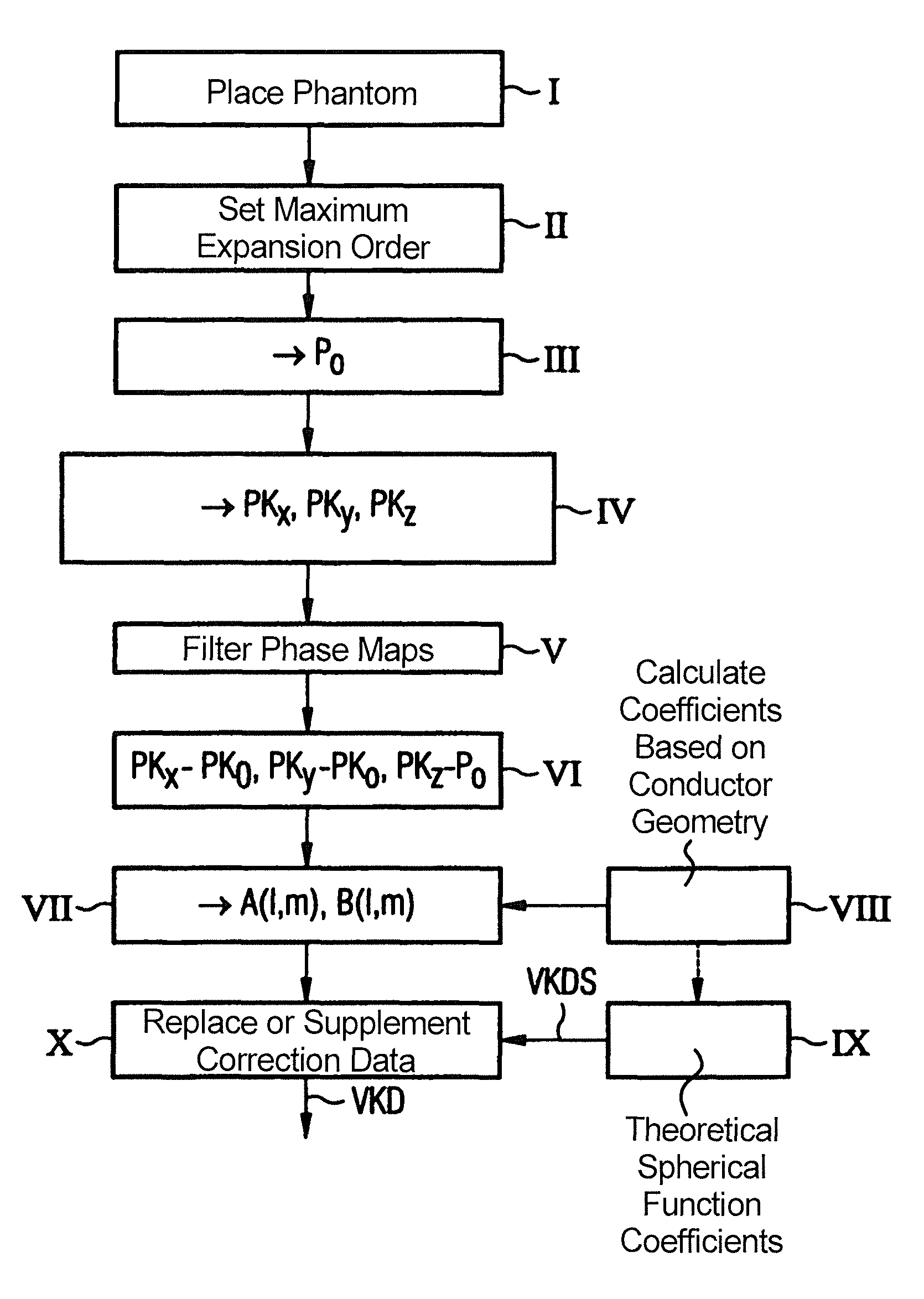
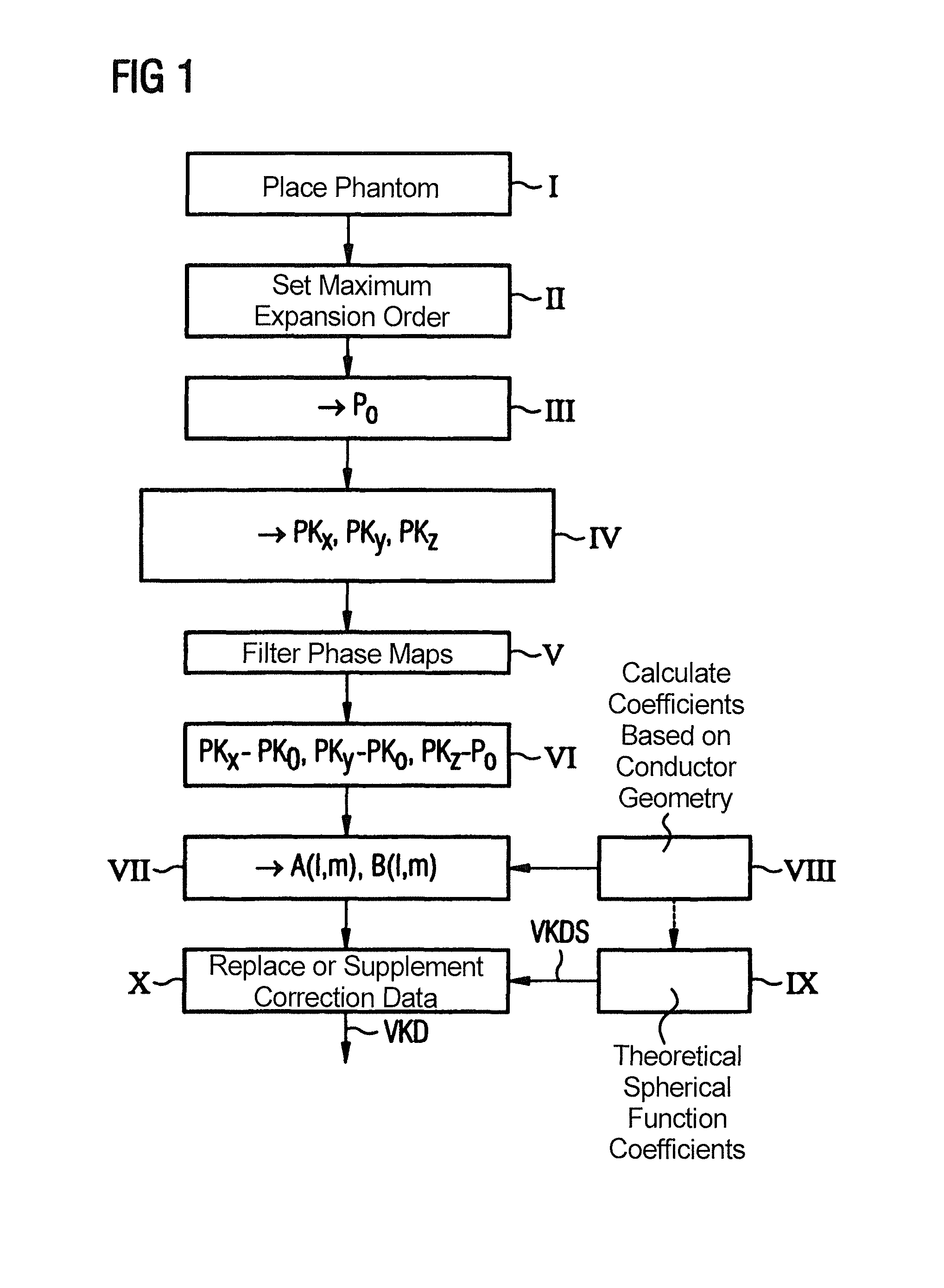
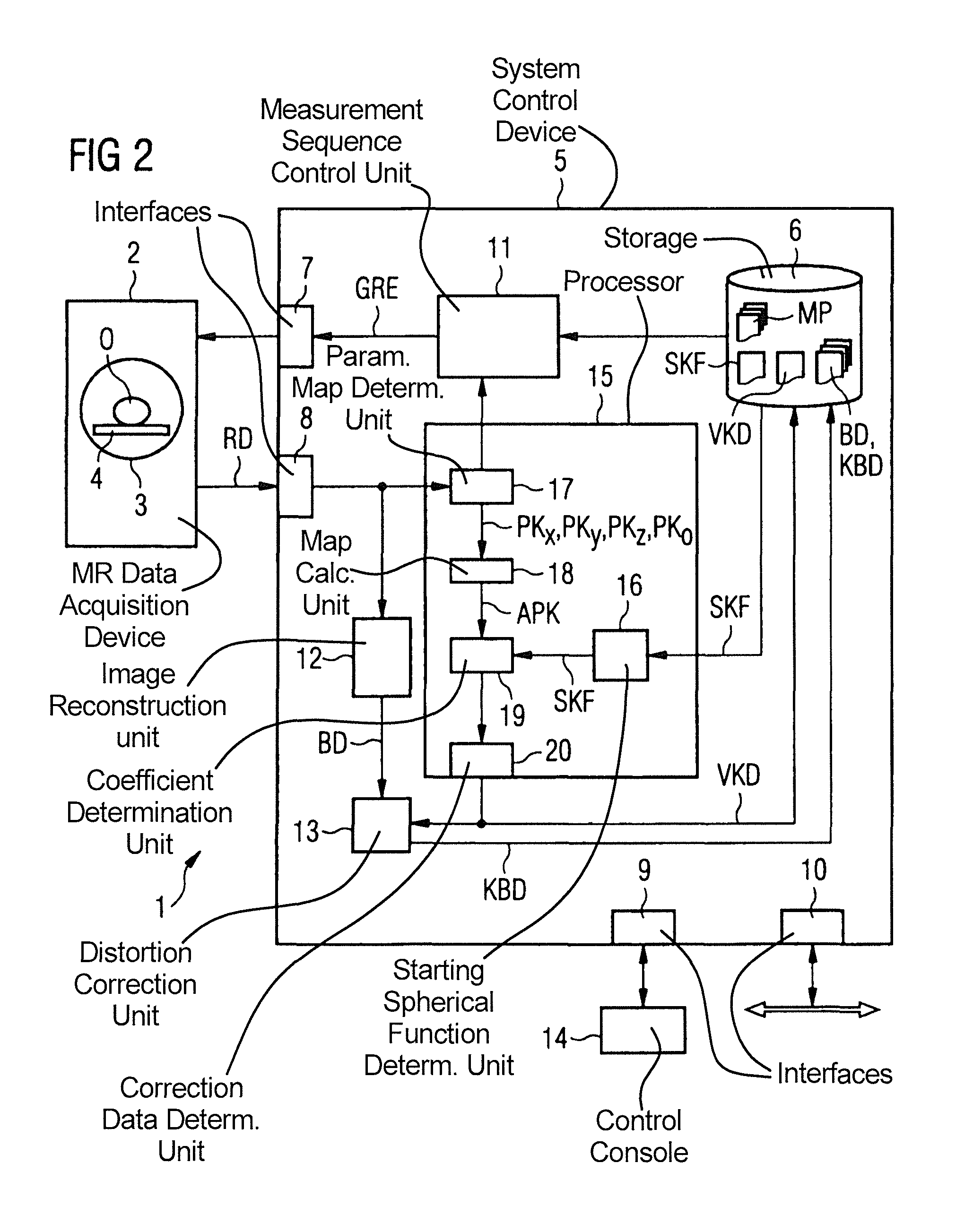
InactiveUS8755582B2Faster and precise determinationEasy to modifyMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGradient strengthElectrical conductor
In a method and device to determine distortion correction data for distortion correction of magnetic resonance images acquired with a magnetic resonance system, a starting spherical function is calculated represents the magnetic field of a gradient coil of the magnetic resonance system on the basis of the conductor geometry of the gradient coil. A three-dimensional parameter map is determined that represents a magnetic field generated by the gradient coil using a defined measurement subject, with a defined gradient strength being set for the appertaining gradient coil. A deviation parameter map is generated on the basis of the parameter map and on the basis of a reference parameter map which was determined with deactivated gradient coil. Spherical function coefficients of the gradient magnetic field are determined by fitting a spherical function representing the magnetic field of the gradient coil to the deviation parameter map using the starting spherical function. The distortion correction data are determined on the basis of the spherical function coefficients of the fitted spherical function.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance apparatus and operating method
InactiveUS20140091794A1Short acquisition timeMinimize timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGradient strengthResonance
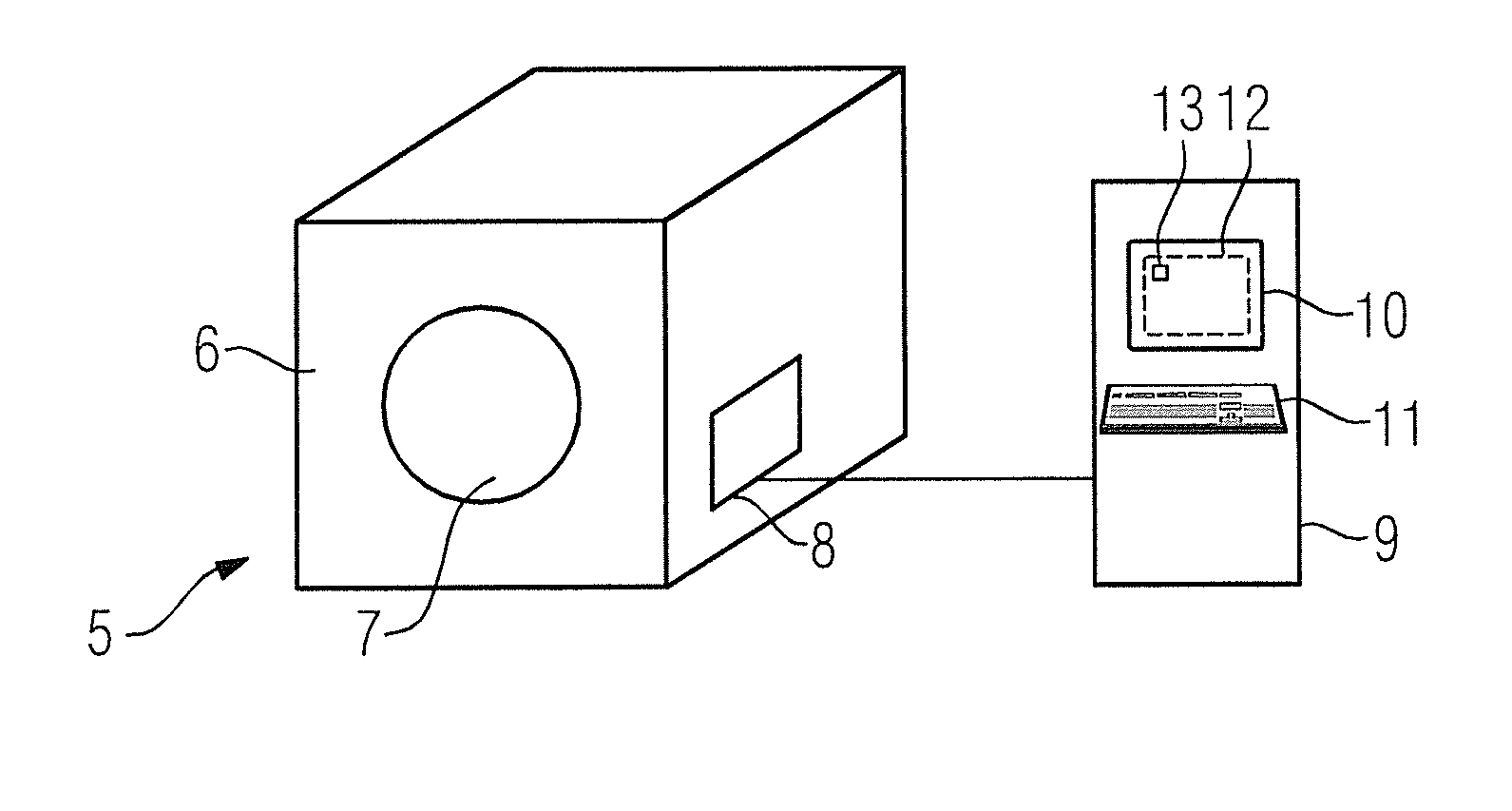
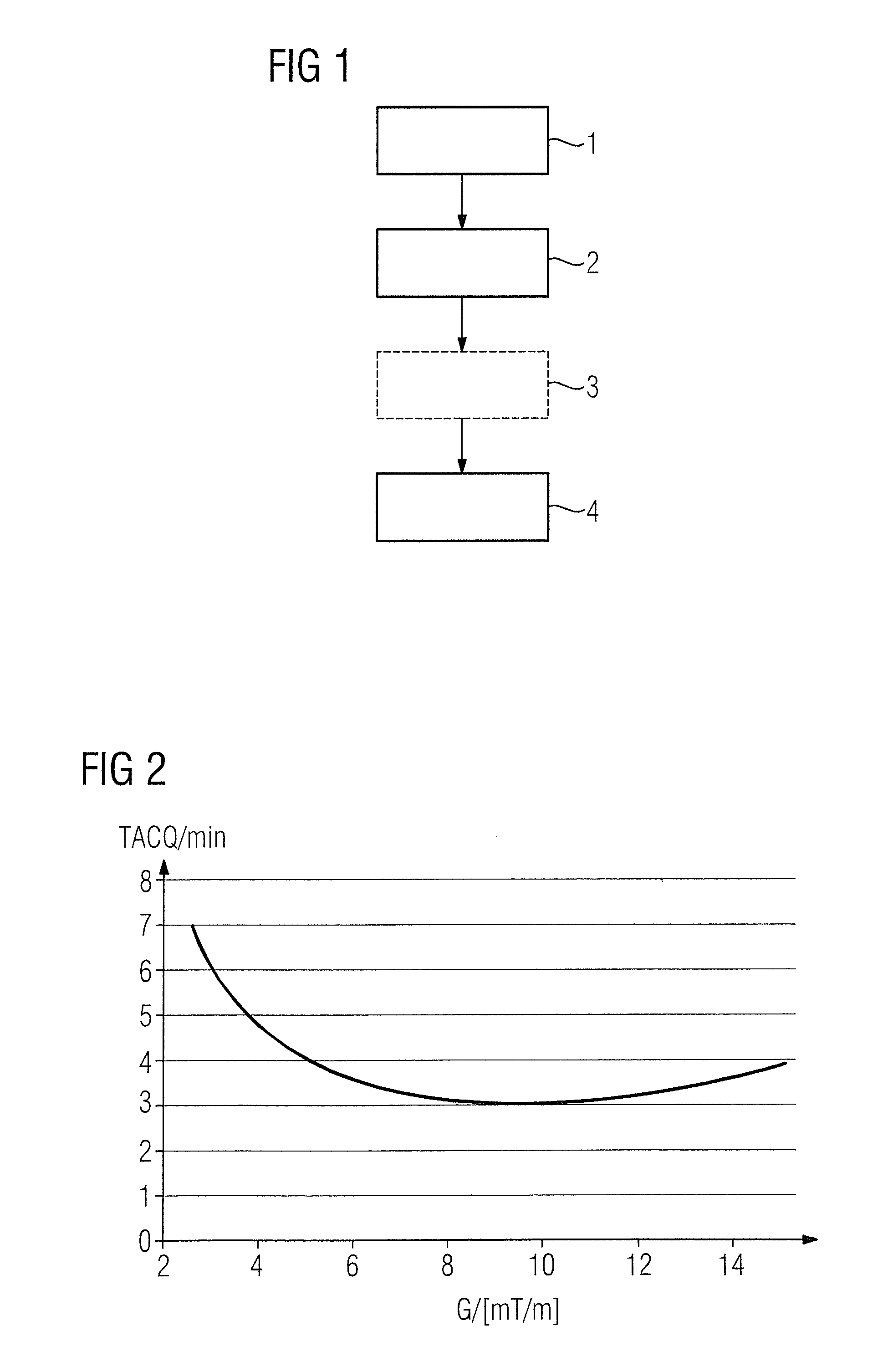
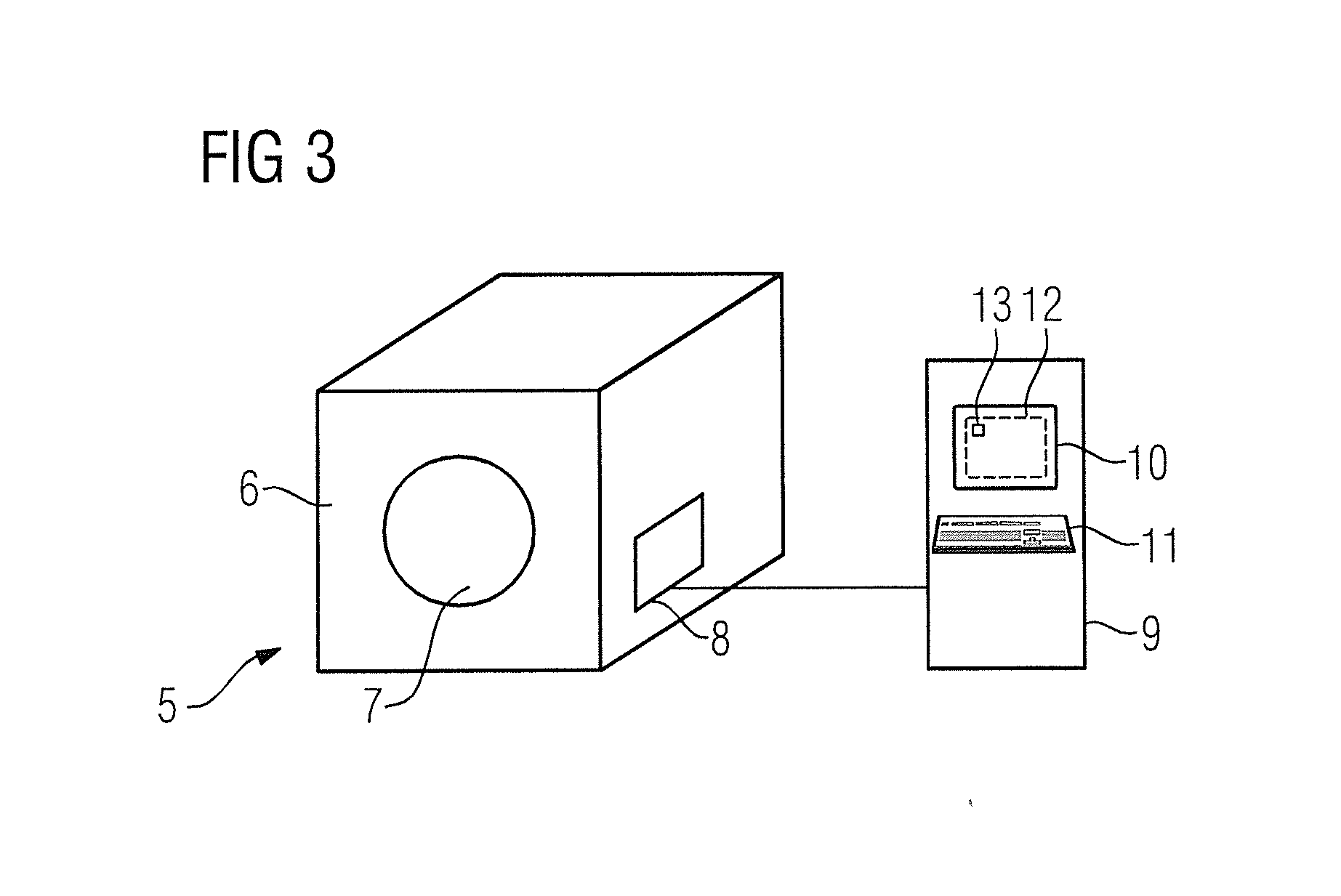
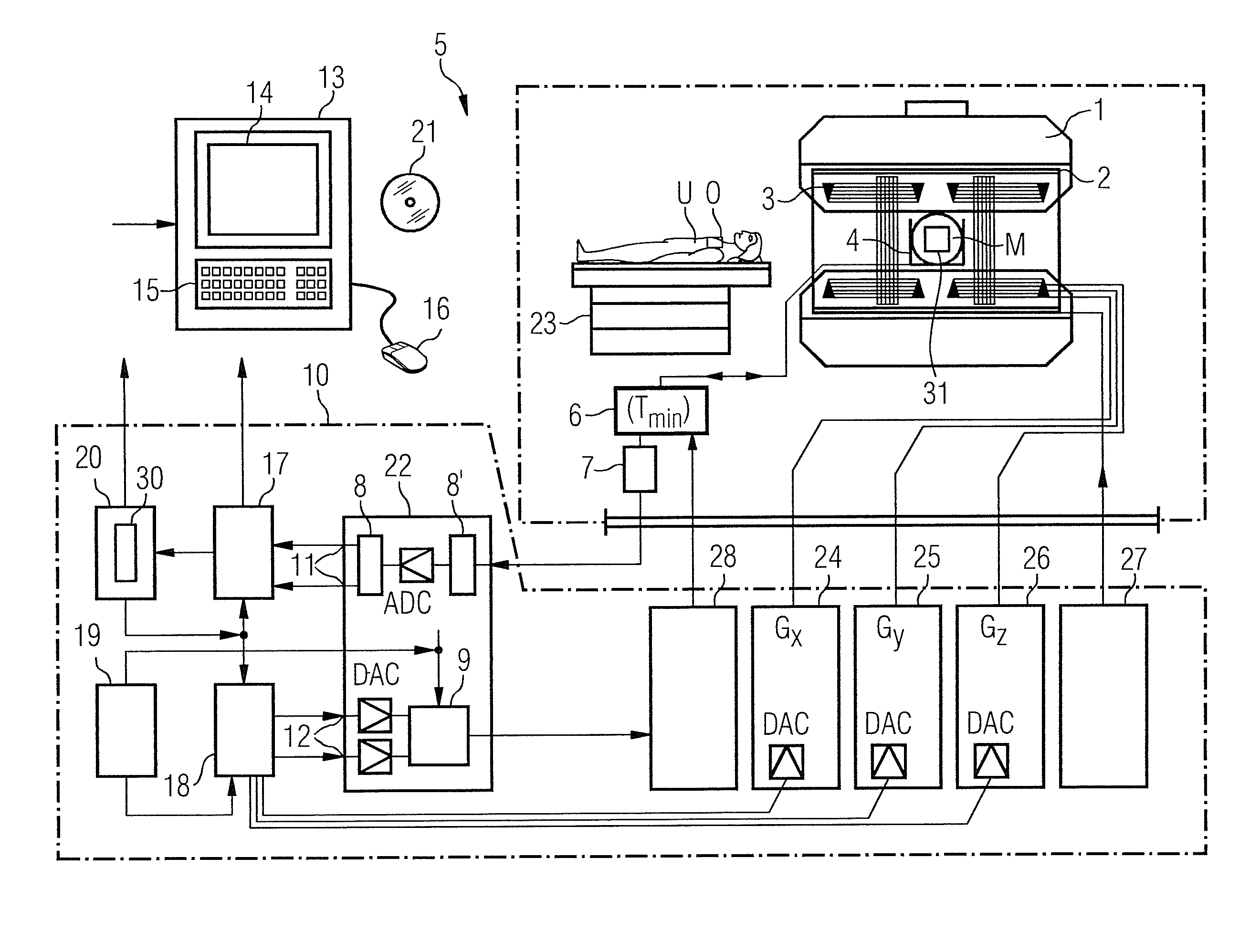
In a method to operate a magnetic resonance apparatus with a magnetic resonance sequence—in particular a PETRA sequence—in which k-space is radially scanned for an image acquisition in a first region of k-space that does not include the center of k-space, and in which an excitation pulse is radiated as the full strength of at least two phase coding gradients is reached, and in which k-space is scanned in a Cartesian manner—in particular by single point imaging—in a second region of k-space remaining without the first region, the gradient strength corresponding to a shortest total acquisition time is determined automatically from predetermined sequence parameters and / or sequence parameters defined by a user. The sequence parameters parameterize the magnetic resonance sequence and describe the number of acquisitions for the regions of k-space and the repetition time, and the gradient strength is indicated to a user as a recommendation and / or is set automatically in the implementation of the magnetic resonance sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
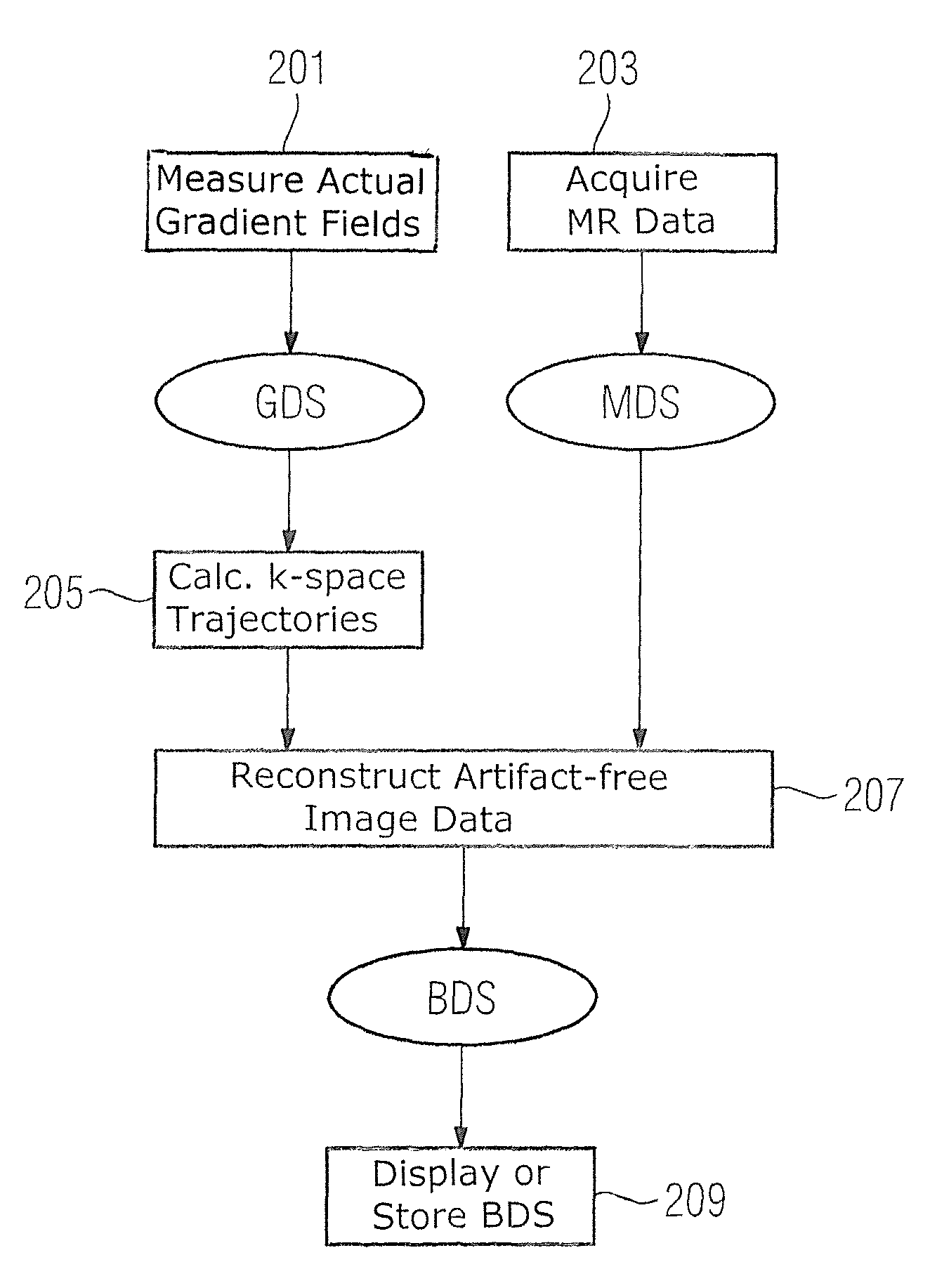
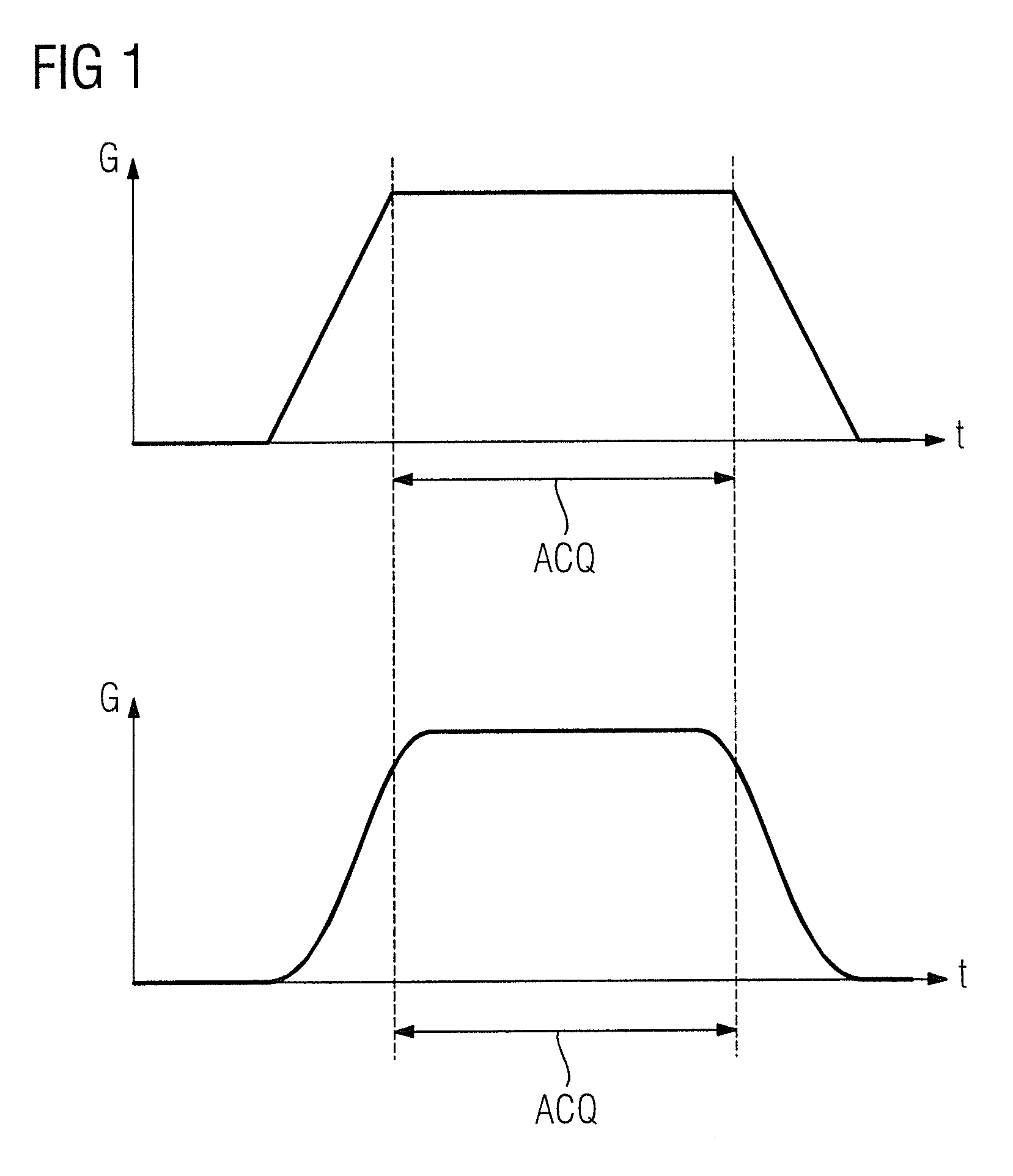
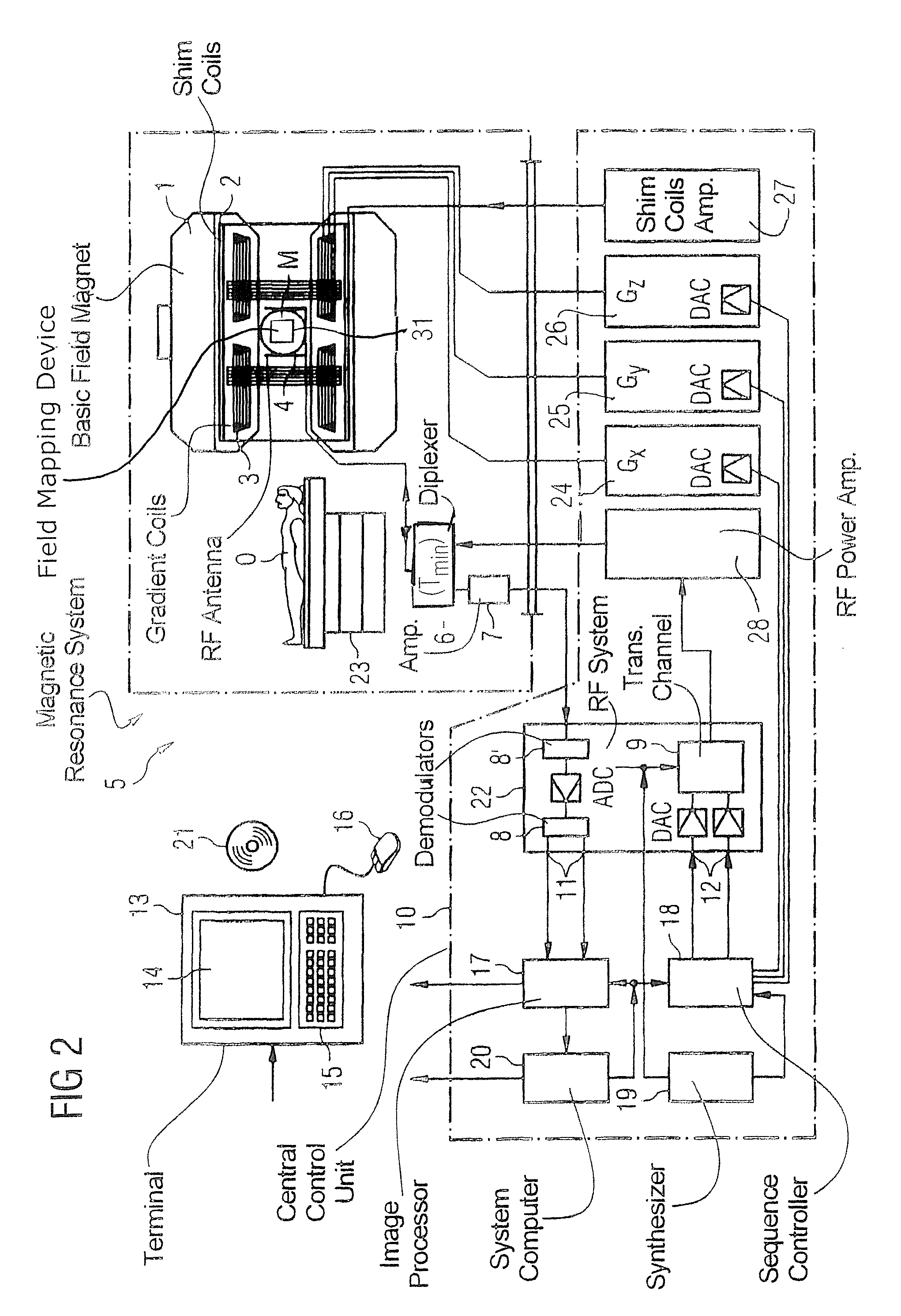
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus to generate an artifact-free magnetic resonance image data set
ActiveUS20140091796A1Set evenlyElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceData setGradient strength
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) system for the creation of an artifact-free image data set of an imaging area located in a measurement volume of the MR system, measurement data are acquired from which an image data is to be reconstructed, with gradients for spatially coding of the measurement data are ramped continuously over time to a strength desired for the acquisition of the measurement data, without abrupt changes in the gradient strength. The actual gradients present in the measurement volume are measured by a field mapping device in the measurement volume of the MR system. The trajectories along which k-space is scanned during the acquisition of the measurement data are calculated on the basis of the measured actual gradients. An artifact-free image data set is reconstructed from the acquired measurement data under consideration of the calculated trajectories, and is displayed and / or stored.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Double-gradient-strength passenger car stand column structure
InactiveCN105383569AIncrease stiffnessPlay a role in heat insulationSuperstructure subunitsGradient strengthEnergy absorption
The invention discloses a double-gradient-strength passenger car stand column structure. The double-gradient-strength passenger car stand column structure is characterized by consisting of a longitudinal gradient strength stand column and a transverse filling gradient density foam material. As the transverse filling density foam material is bonded on the inner side wall of a gradient strength L-shaped plate in the length direction of the gradient strength L-shaped plate, the collision force of the key part-stand column of a passenger car closed loop structure can be guaranteed to be matched with the strength of the corresponding position in the passenger car tilting process, the stress of each surrounding part of a passenger car is more uniform, and the unloading of external impact load is facilitated. In addition, the transverse filling gradient density foam material enhances the rigidity of the stand column, and the energy absorption is more stable in the tilting of the passenger car, so that secondary collision casualties are reduced. Meanwhile, the foam material also achieves the effects of sound isolation and heat insulation, and improves the tilting safety and the comfort of the passenger car.
Owner:XIAMEN KING LONG UNITED AUTOMOTIVE IND CO LTD
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus to generate an artifact-free magnetic resonance image data set
ActiveUS9547062B2Set evenlyMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMeasurements using magnetic resonanceData setGradient strength
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) system for the creation of an artifact-free image data set of an imaging area located in a measurement volume of the MR system, measurement data are acquired from which an image data is to be reconstructed, with gradients for spatially coding of the measurement data are ramped continuously over time to a strength desired for the acquisition of the measurement data, without abrupt changes in the gradient strength. The actual gradients present in the measurement volume are measured by a field mapping device in the measurement volume of the MR system. The trajectories along which k-space is scanned during the acquisition of the measurement data are calculated on the basis of the measured actual gradients. An artifact-free image data set is reconstructed from the acquired measurement data under consideration of the calculated trajectories, and is displayed and / or stored.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and mehtod for differential phase contrast microscopy
The invention provides a system and a method for differential phase contrast microscopy. The system comprises a light strength modulating module, a light focusing lens, an objective lens and an imageacquisition module. The light strength modulating module is used for modulating an incident light field to a detecting optical field with gradient strength distribution according to a control signal.The focusing lens is used for receiving the detecting optical field and generates an off-axis optical field for projecting to a to-be-measured object, and furthermore generates the light field of theto-be-measured object for receiving by the objective lens. The image acquisition module is used for receiving the optical field of the to-be-measured object, thereby generating an optical image with corresponding strength gradient distribution. The method further comprises the steps of controlling the light strength modulating module for generating a first gradient shield with gradually reducing light strength in a first axial direction, a second gradient shield with gradually increasing light strength in the first axial direction, a third gradient shield with gradually reducing light strengthin a second axial direction, and a fourth gradient shield with gradually increasing light strength in the second axial direction, and making the image acquisition module to acquire a first optical image, a second optical image, a third optical image and a fourth optical image which respectively correspond with the first gradient shield, the second gradient shield, the third gradient shield and the fourth gradient shield.
Owner:骆远
Test method for gradient strength and gradient switching rate of magnetic resonance system
InactiveCN103364746BEasy to operateSimplify the test operation processMeasurements using magnetic resonancePower flowGradient strength
Owner:山东汇影互联科技有限公司
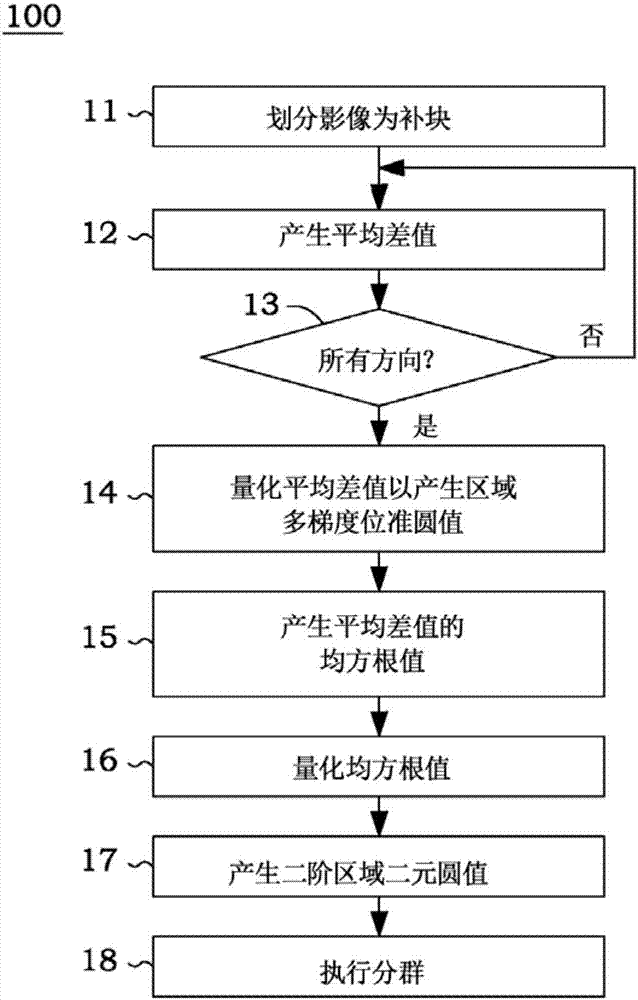
Clustering method using two-stage local binary pattern and iterative image test system
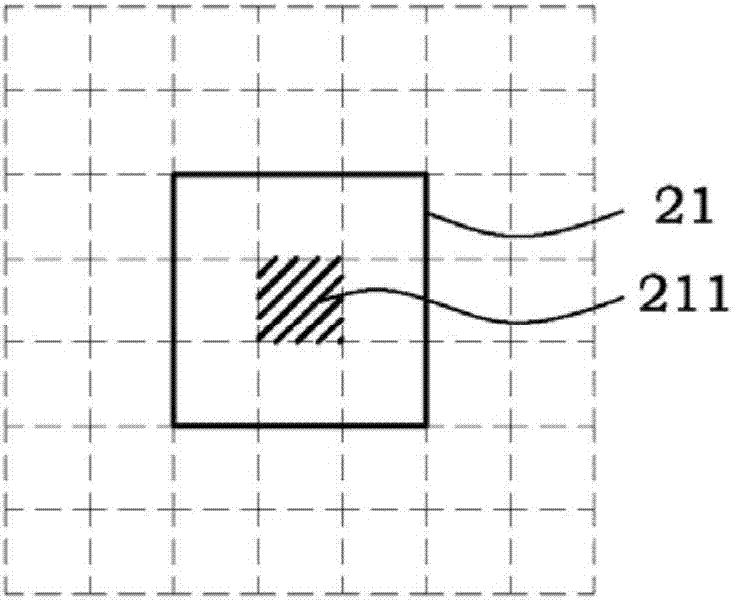
The invention relates to a clustering method using a two-stage local binary pattern (2SLBP). The method comprises the steps of generating a gradient direction value according to a central sub-block and adjacent sub-blocks of each patch of an image; quantizing each gradient direction value to generate a quantized gradient direction value; generating a gradient strength value according to each gradient direction value; quantizing each gradient strength value to generate a quantized gradient strength value; connecting the quantized gradient direction values with the quantized gradient strength values in series to generate a 2SLBP value; and using the 2SLBP value as an pointer to execute the clustering of super-resolution image processing.
Owner:NCKU RES & DEV FOUND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com