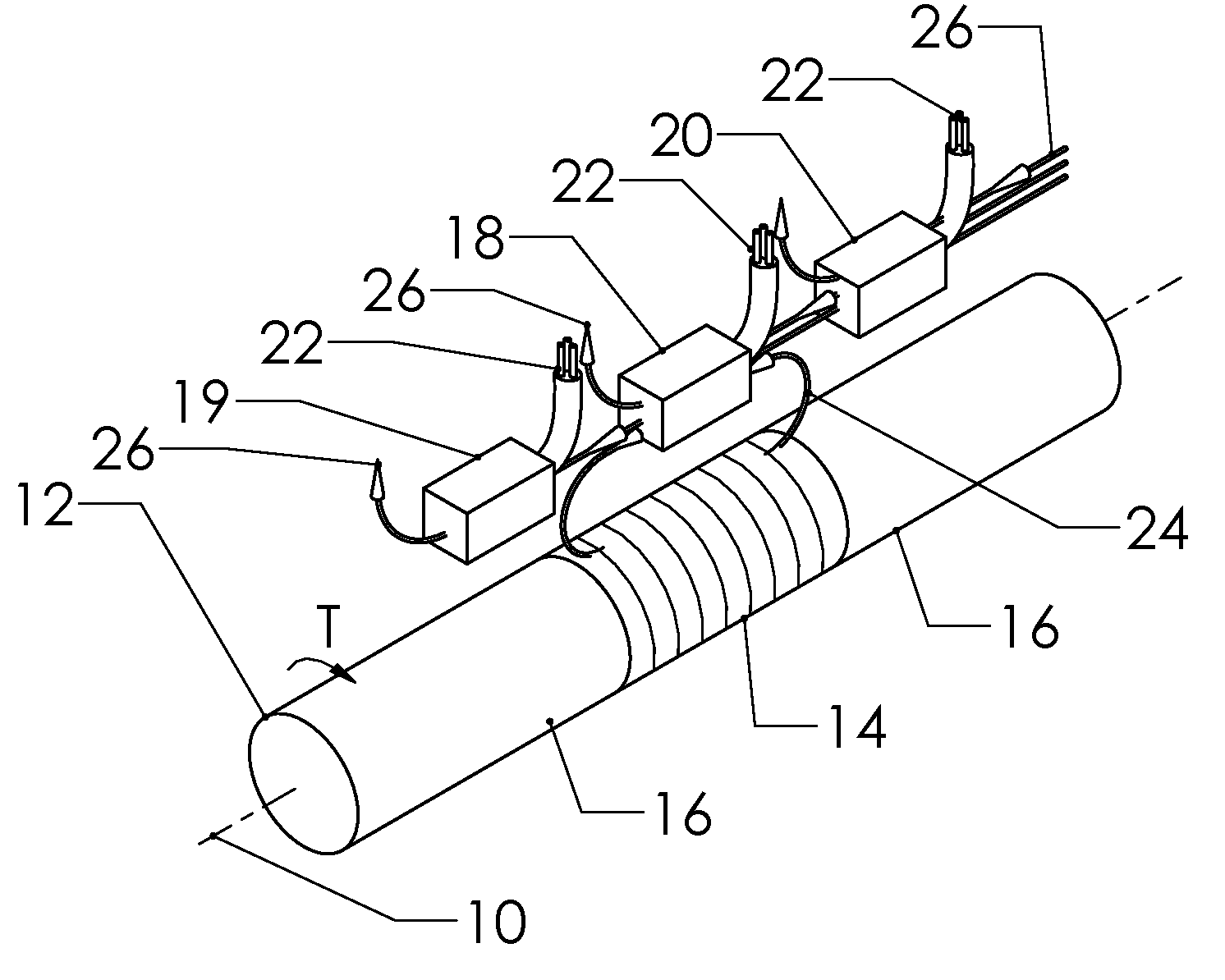
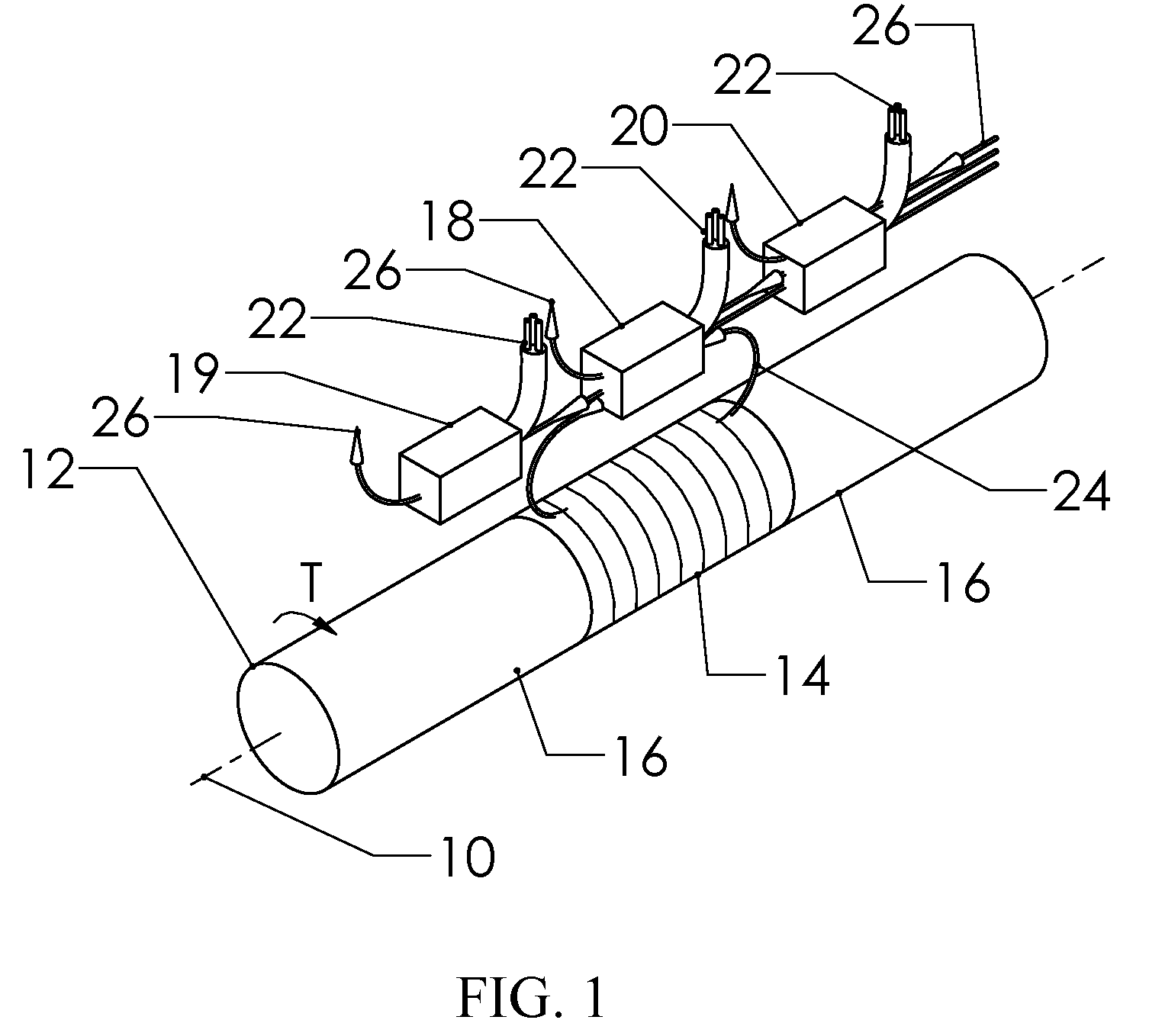
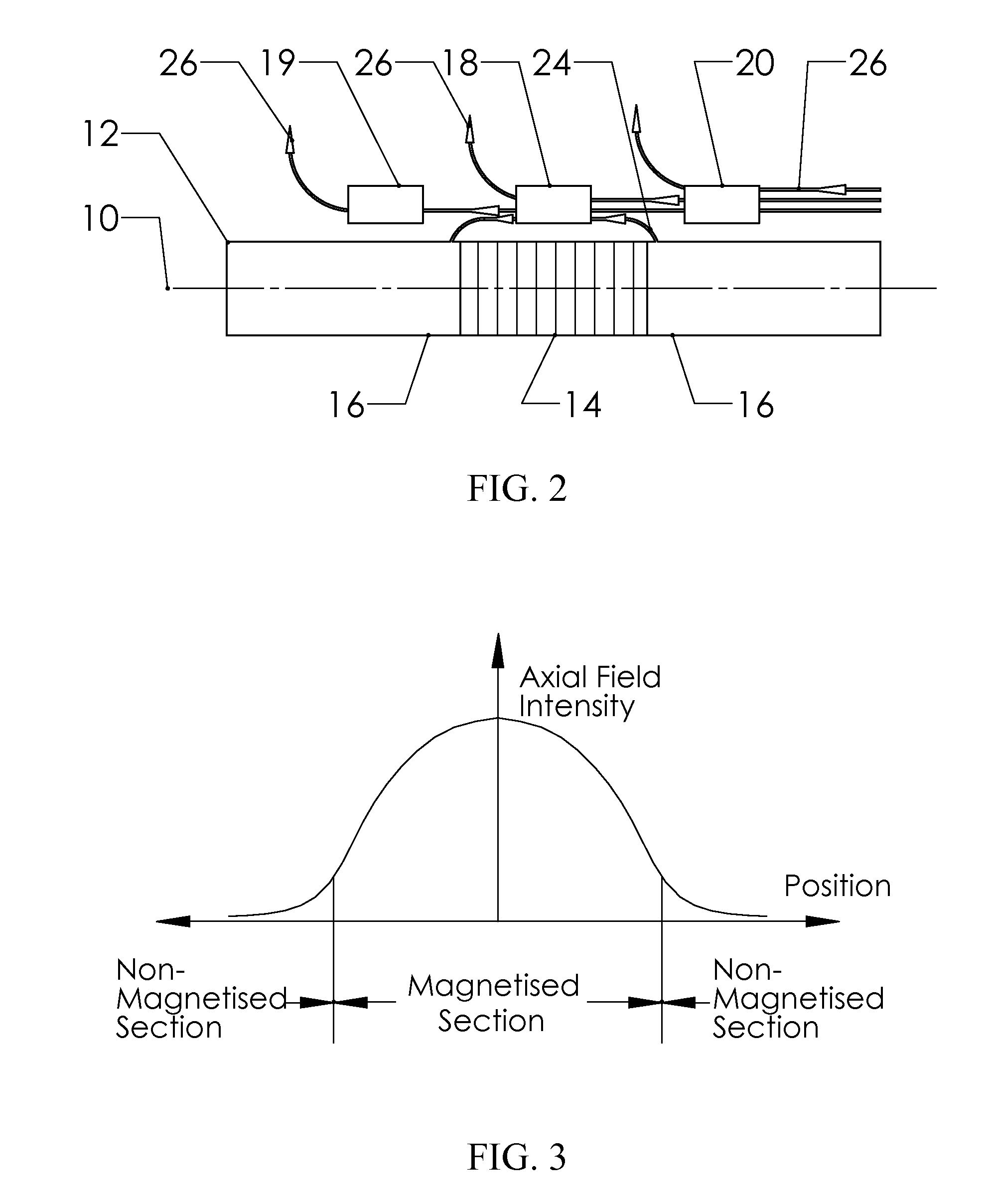
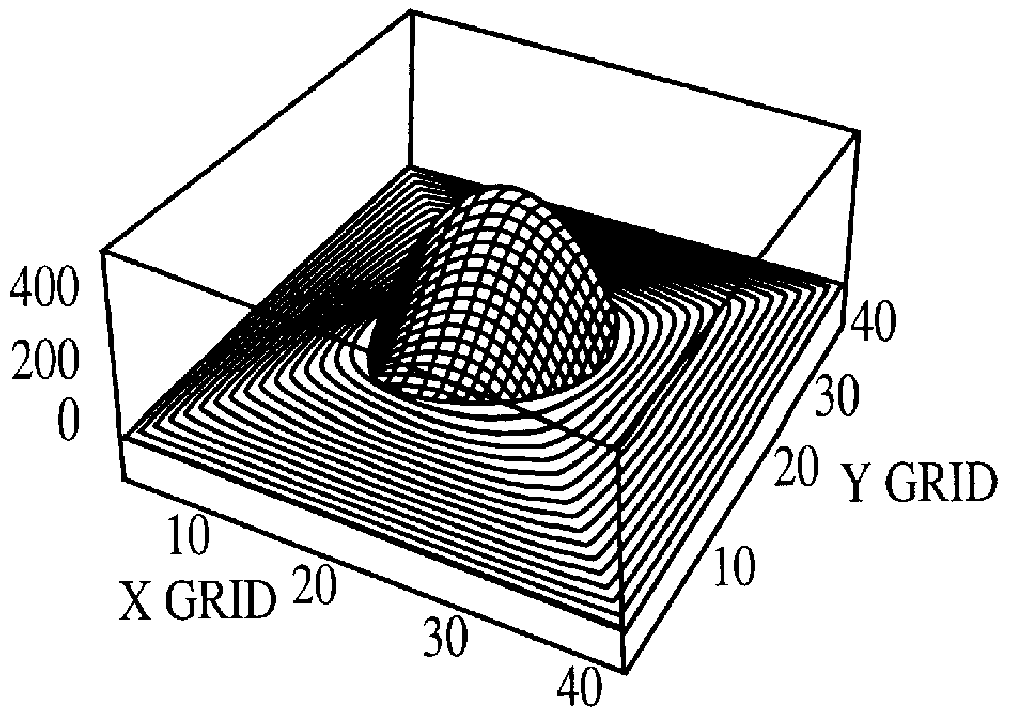
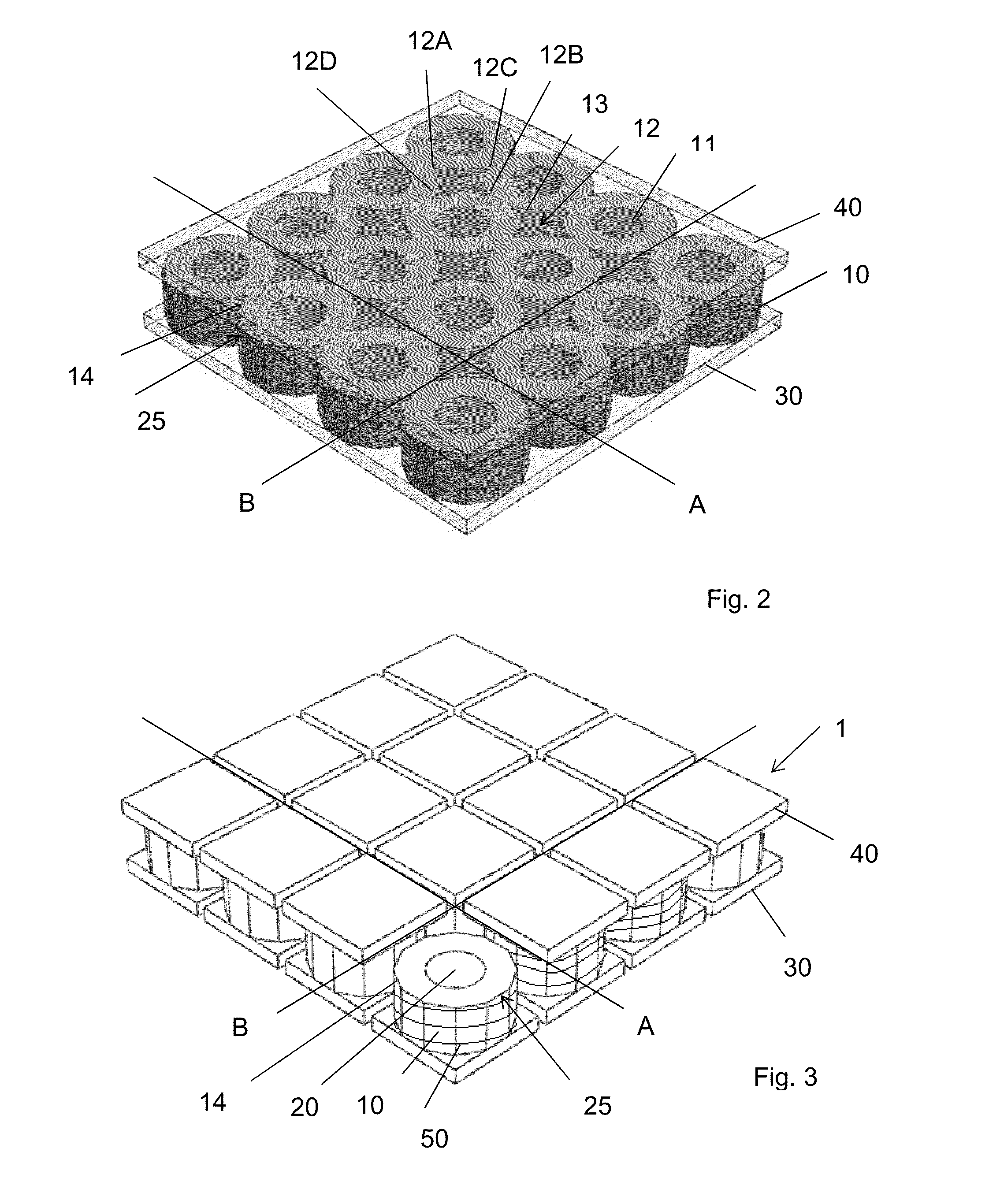
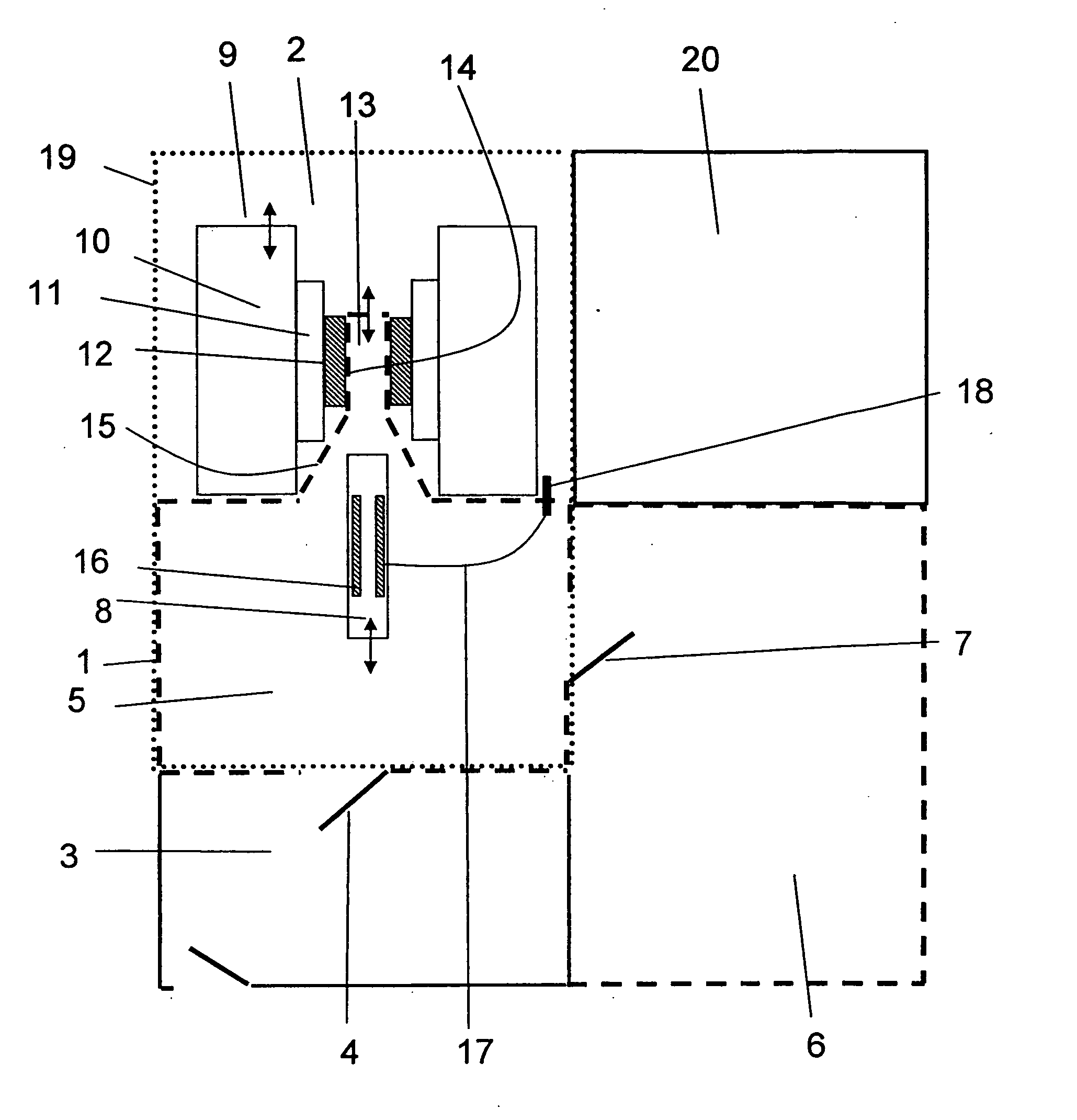
Patents
Literature
601 results about "Homogeneous magnetic field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
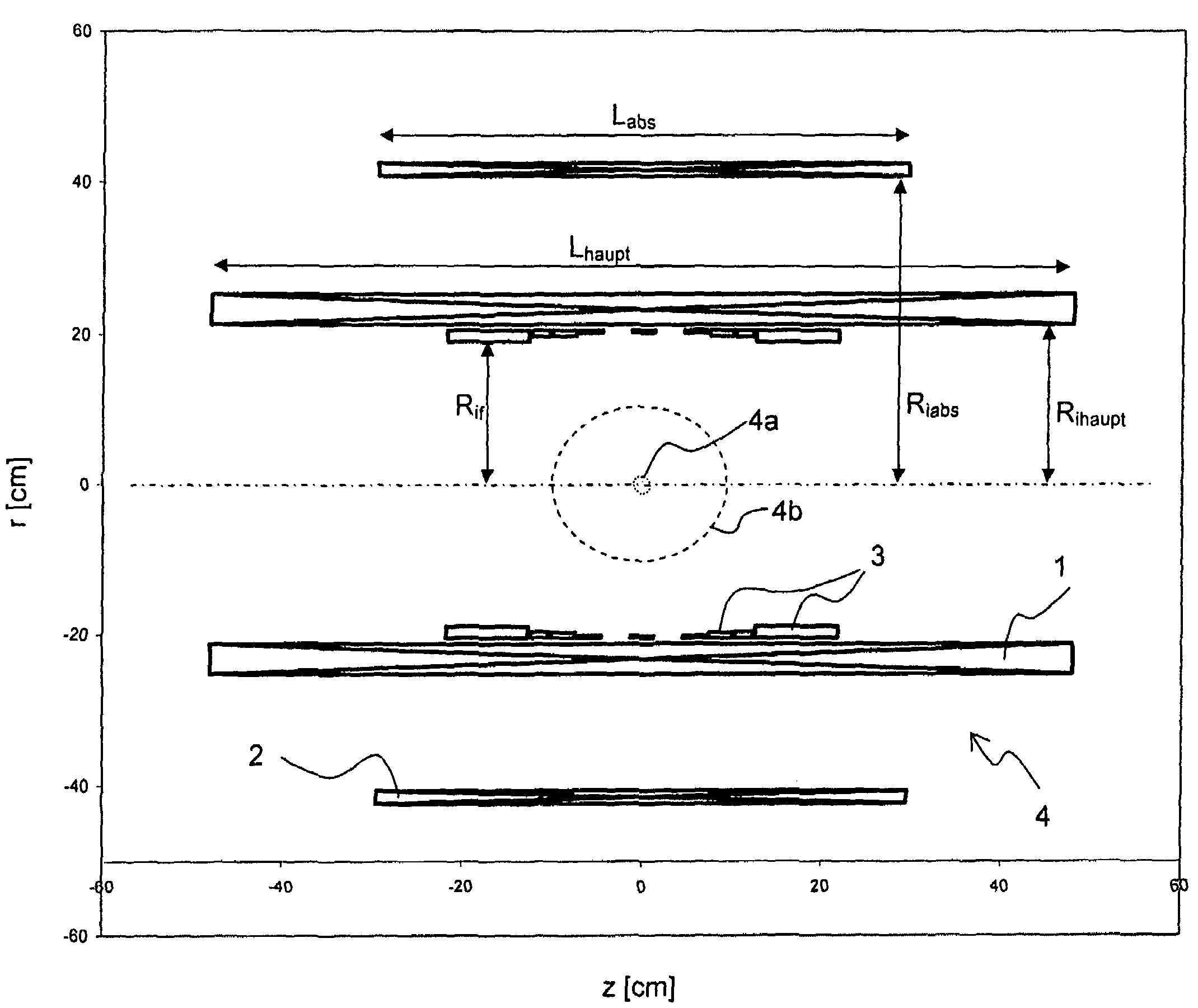
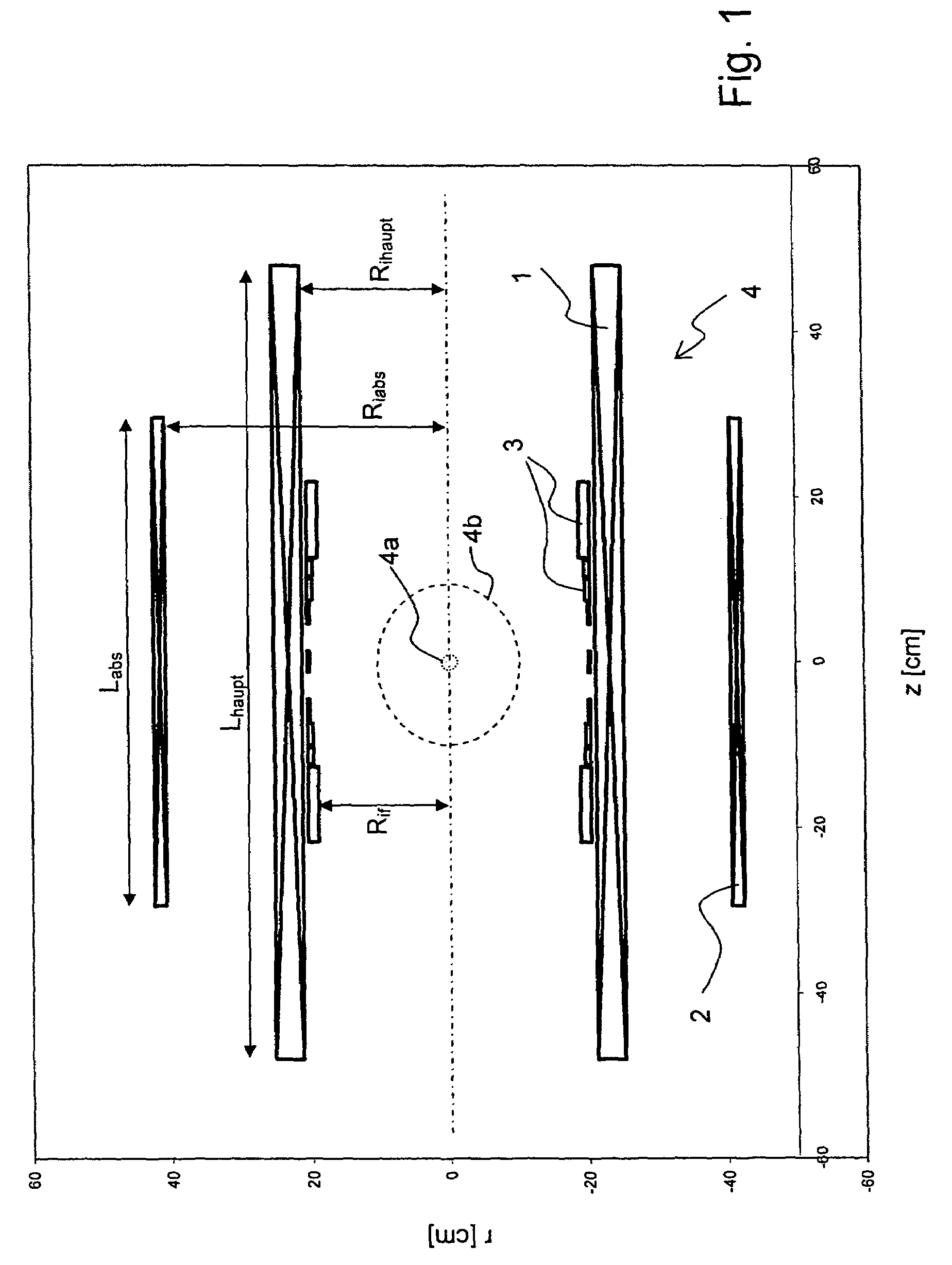
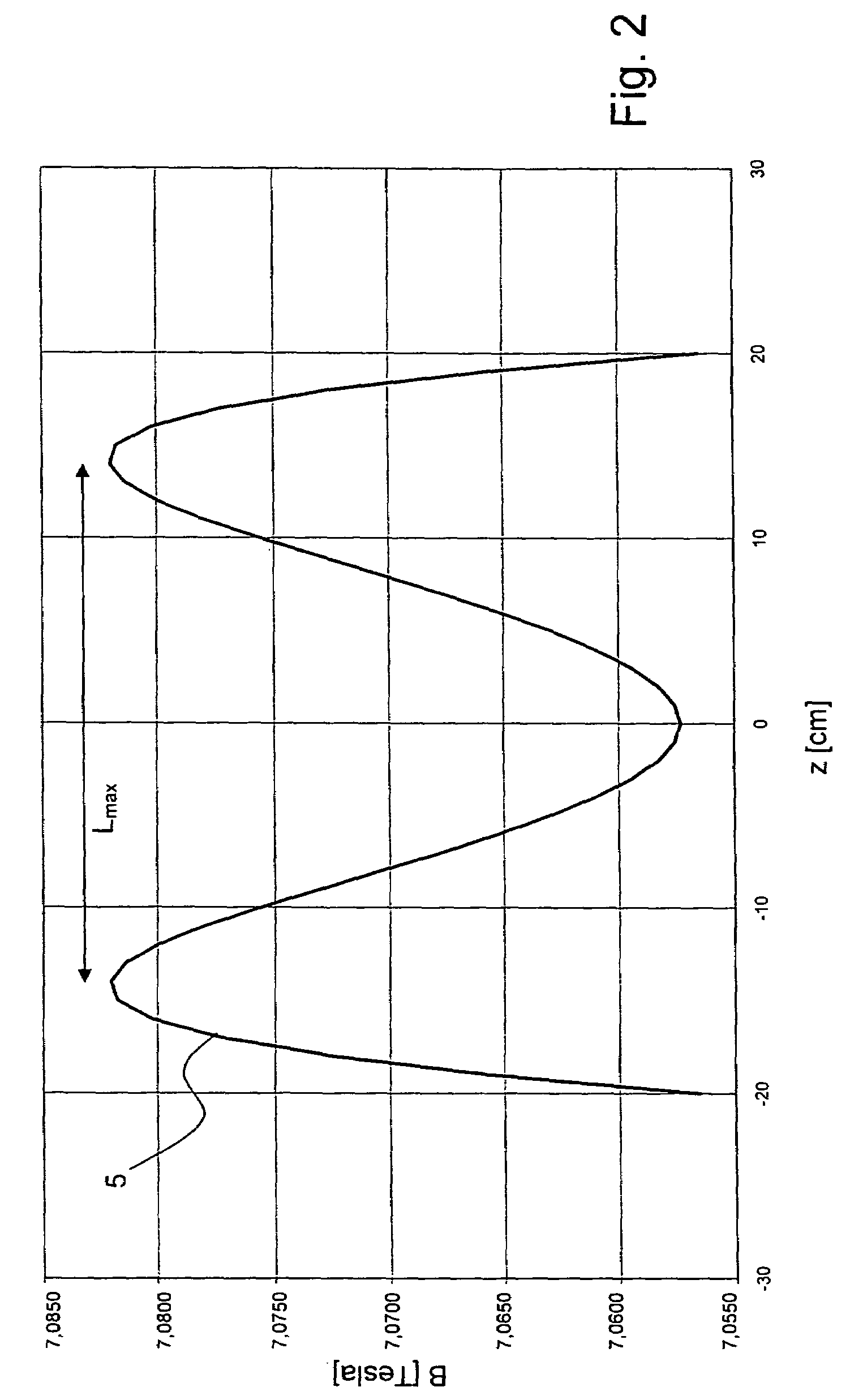
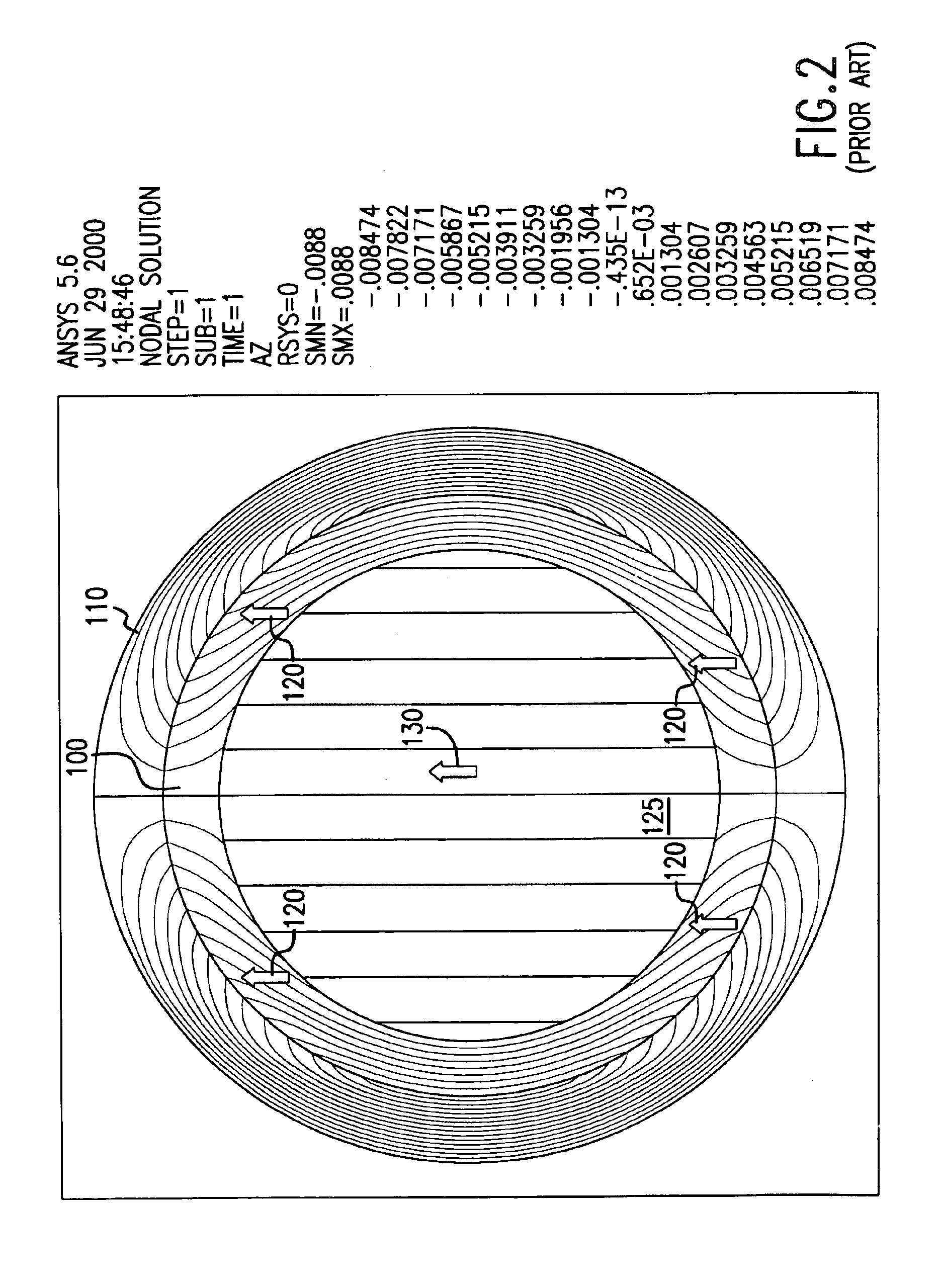
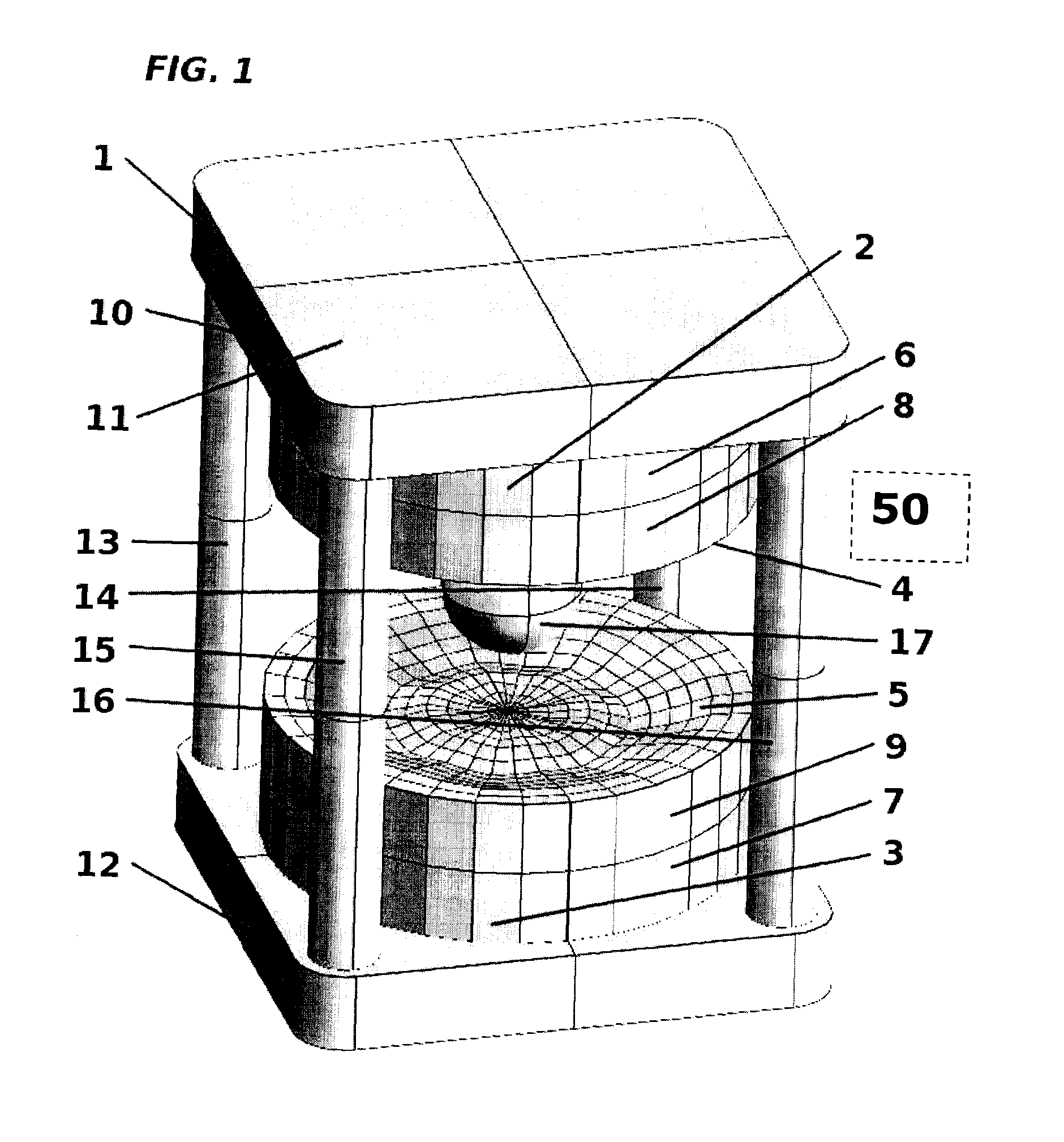
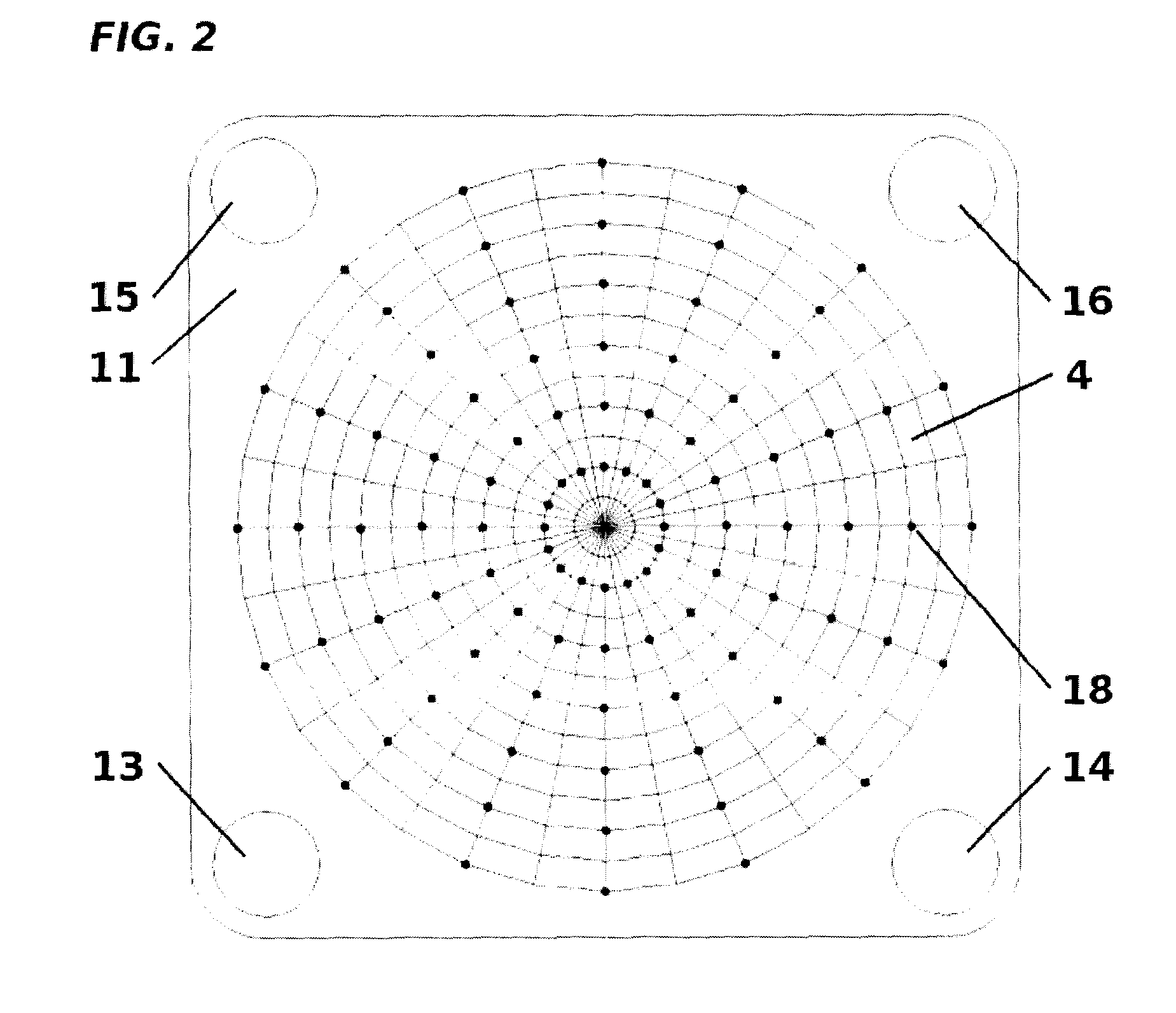
In a homogeneous magnetic field, the lines of force are parallel and the magnetic field is equally strong in all places. To create a magnetic field that is as homogeneous as possible, it is recommended to place two large magnets close to each other and to connect the back sides with an iron yoke.
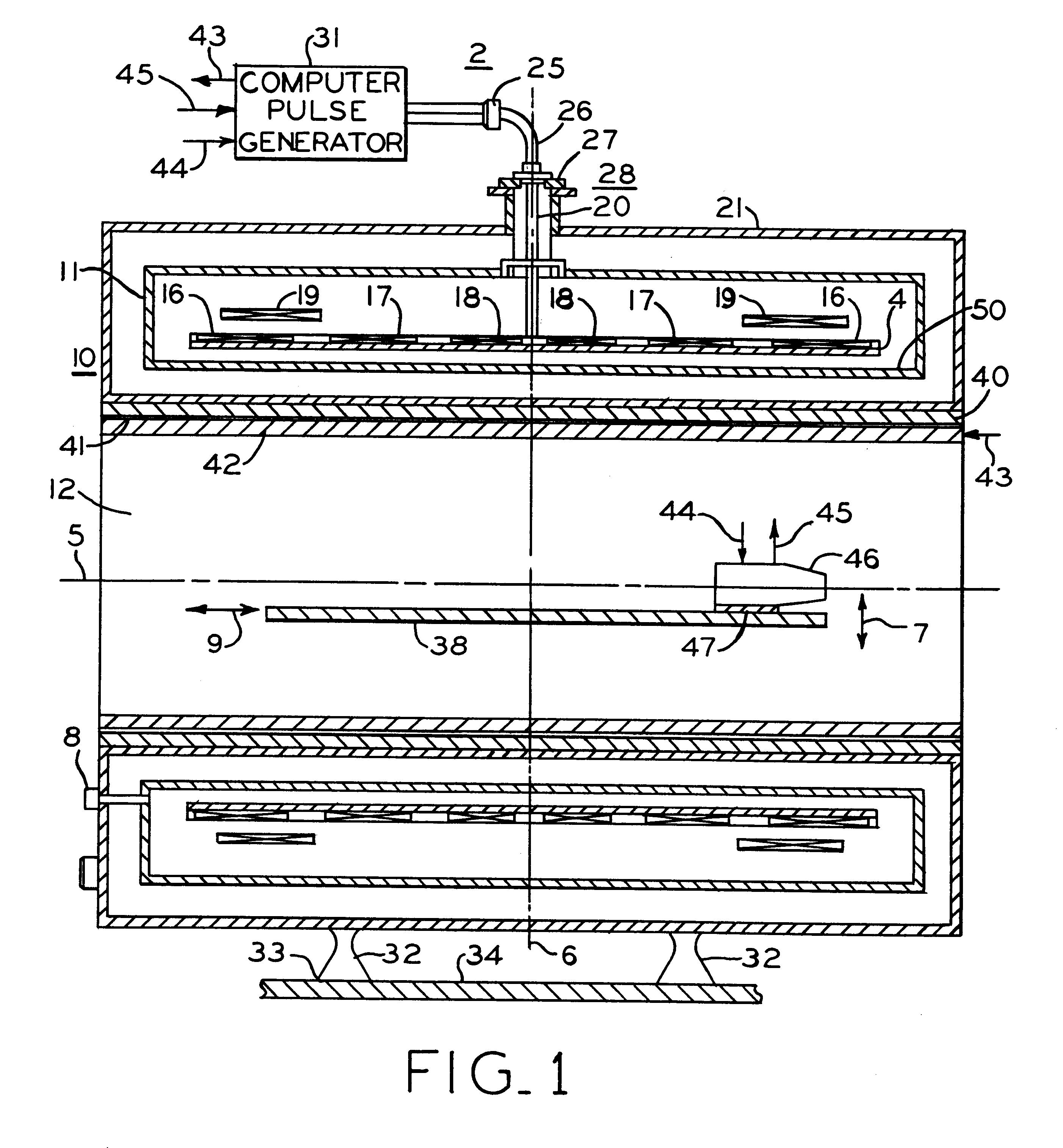
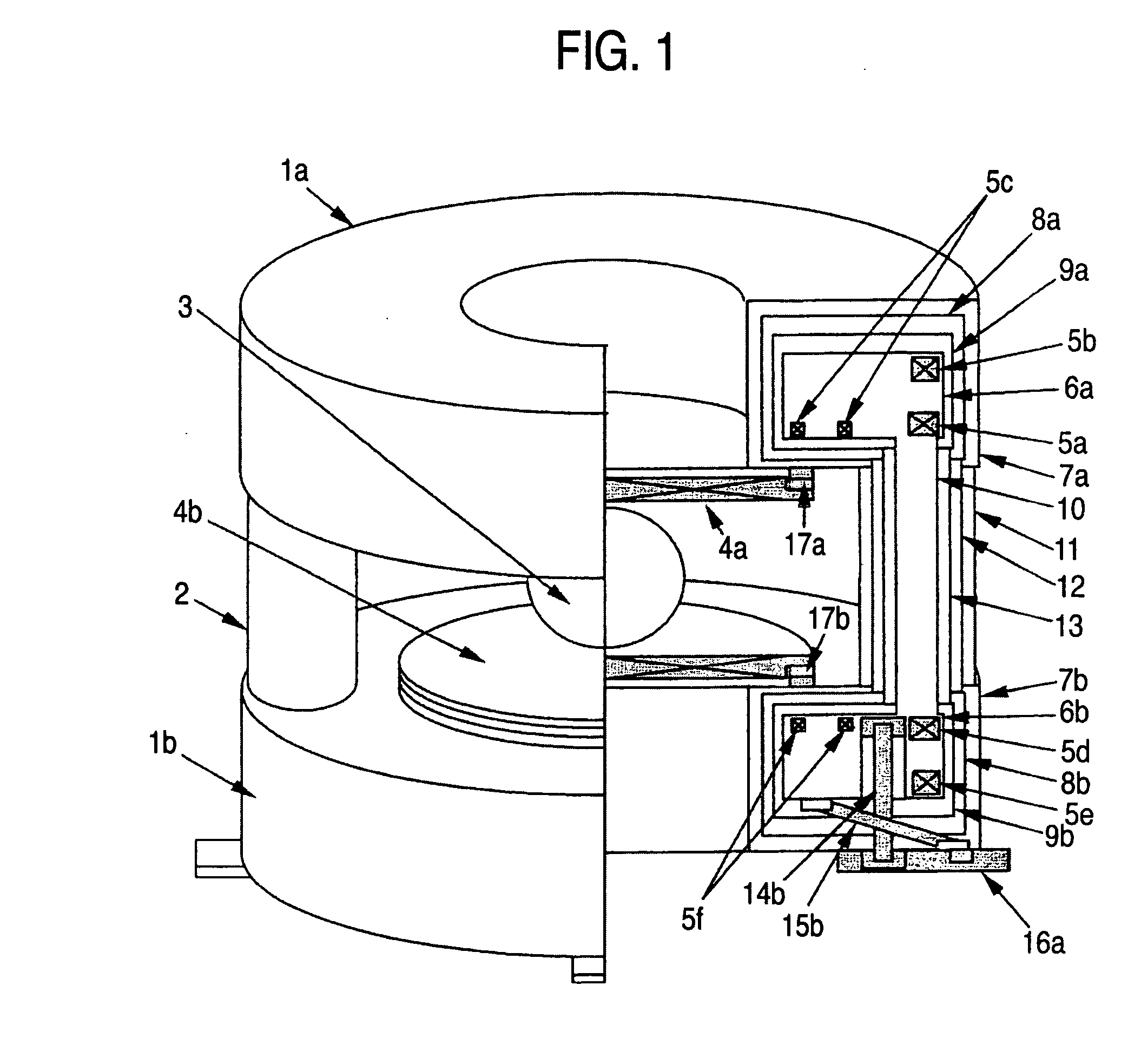
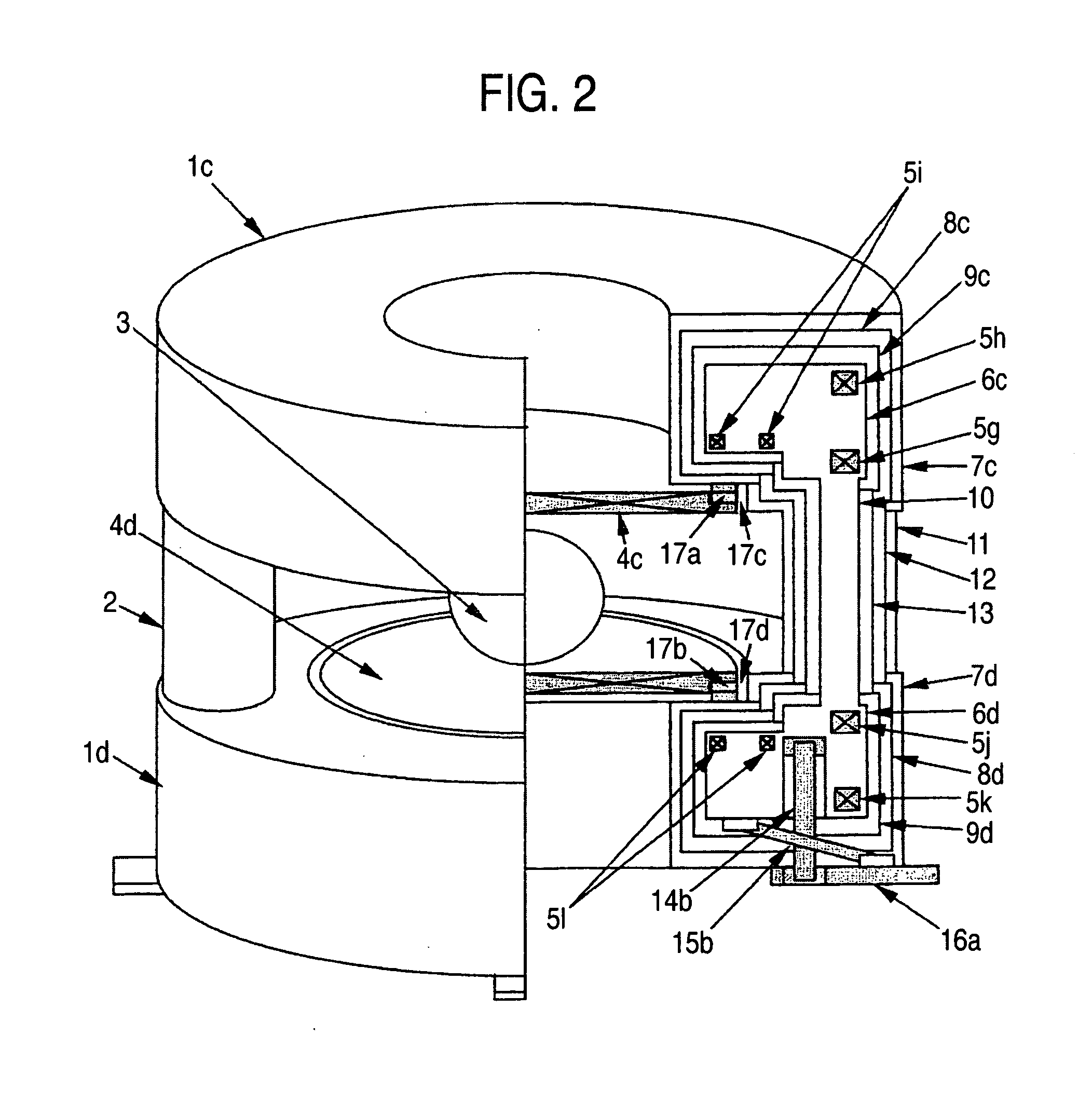
Nuclear magnetic resonance equipment
InactiveUS6958608B2High sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceSpectroscopy
The invention provides nuclear magnetic resonance equipment realizing improved sensitivity of a probe for receiving a free induction decay (FID) signal in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in a high frequency band of 600 MHz or higher. By manufacturing a solenoid coil of a higher filling factor by using a superconductor of extremely low resistance to high frequency current, sensitivity is increased. A superconducting thin film made of magnesium diboride (MgB2) formed on a donut plate-type substrate is disposed so that the film surface becomes parallel with the uniform magnetic field. The object is realized by a probe made by a solenoid coil formed by connecting a plurality of coil parts by capacitive coupling via a normal metal lead.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and nuclear magnetic resonance measuring method
ActiveCN102519999AAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and a nuclear magnetic resonance measuring method. The analyzer comprises a radio frequency circuit, a magnet, a glass tube, a first coil and a second coil, wherein a sample to be measured is placed in the glass tube; the glass tube is fixedly arranged at a position opposite to the magnet and is placed in a magnetic field produced by the magnet; the first coil and the second coil are wound on the outer surface of the glass tube respectively and are connected with the radio frequency circuit; the first coil is placed at a uniform magnetic field produced by the magnet; and the second coil is placed at a gradient magnetic field produced by the magnet. Through the analyzer, distribution data of transverse relaxation time and longitudinal relaxation time of substances in the sample to be measured can be obtained, and distribution data of diffusion coefficients of the substances in the sample can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method and apparatus for increasing the detection sensitivity in a high resolution NMR analysis
InactiveUS7205764B1Enhancing NMR signal sensitivityImprove polarizationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionOptical radiationMicrowave
Enhanced nuclear polarization of a magnetic resonance sample provides greater detection sensitivity over conventional NMR spectroscopy due to a method and an apparatus of increasing the detection sensitivity. Molecules capable of forming photo-excited triplet states are combined in a solution with a NMR sample. While in a uniform magnetic field the solution is frozen, optical radiation is applied to produce photo-excited triplet states molecules and a microwave radiation is applied to stimulate transitions of one of the triplet lines producing dynamic polarization of the nuclei in the magnetic resonance sample. The frozen sample is then rapidly melted and a NMR analysis is performed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Particle radiation therapy equipment
InactiveUS7960710B2Material analysis by optical meansMagnetic discharge controlTherapeutic DevicesParticle beam
Particle radiation therapy equipment arranged to apply a charged particle beam in a predetermined direction to a region of application within an imaging volume, comprising a charged particle beam source arranged to direct a charged particle beam in the predetermined direction, further comprising magnetic field generation means for generating a magnetic field in the region of application at the same time that the charged particle beam is applied, wherein the magnetic field generation means is arranged to provide access to the region of application for the charged particle beam, and to provide a homogeneous magnetic field in the region of application of the charged particle beam, said magnetic field being directed substantially in the predetermined direction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE LTD
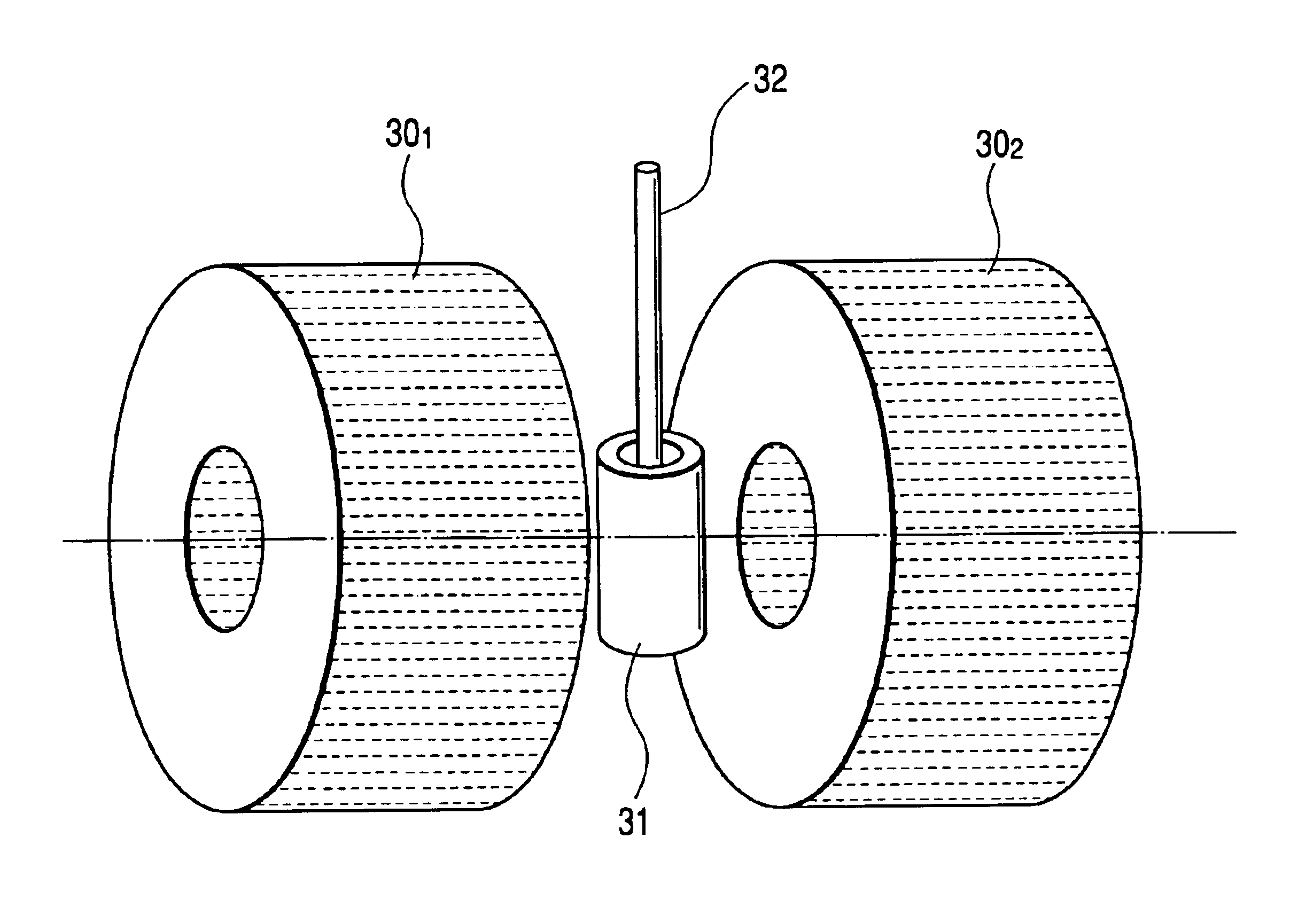
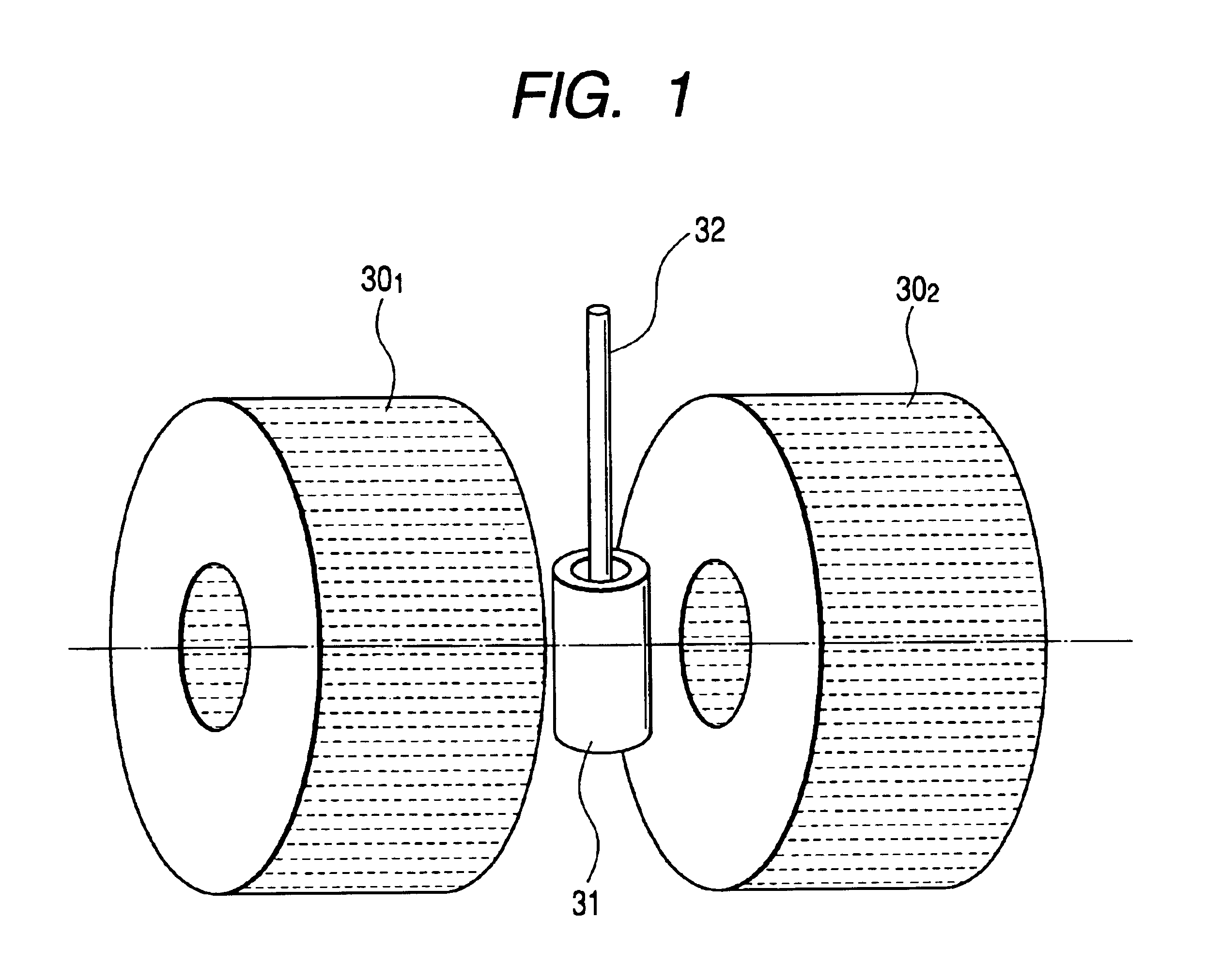
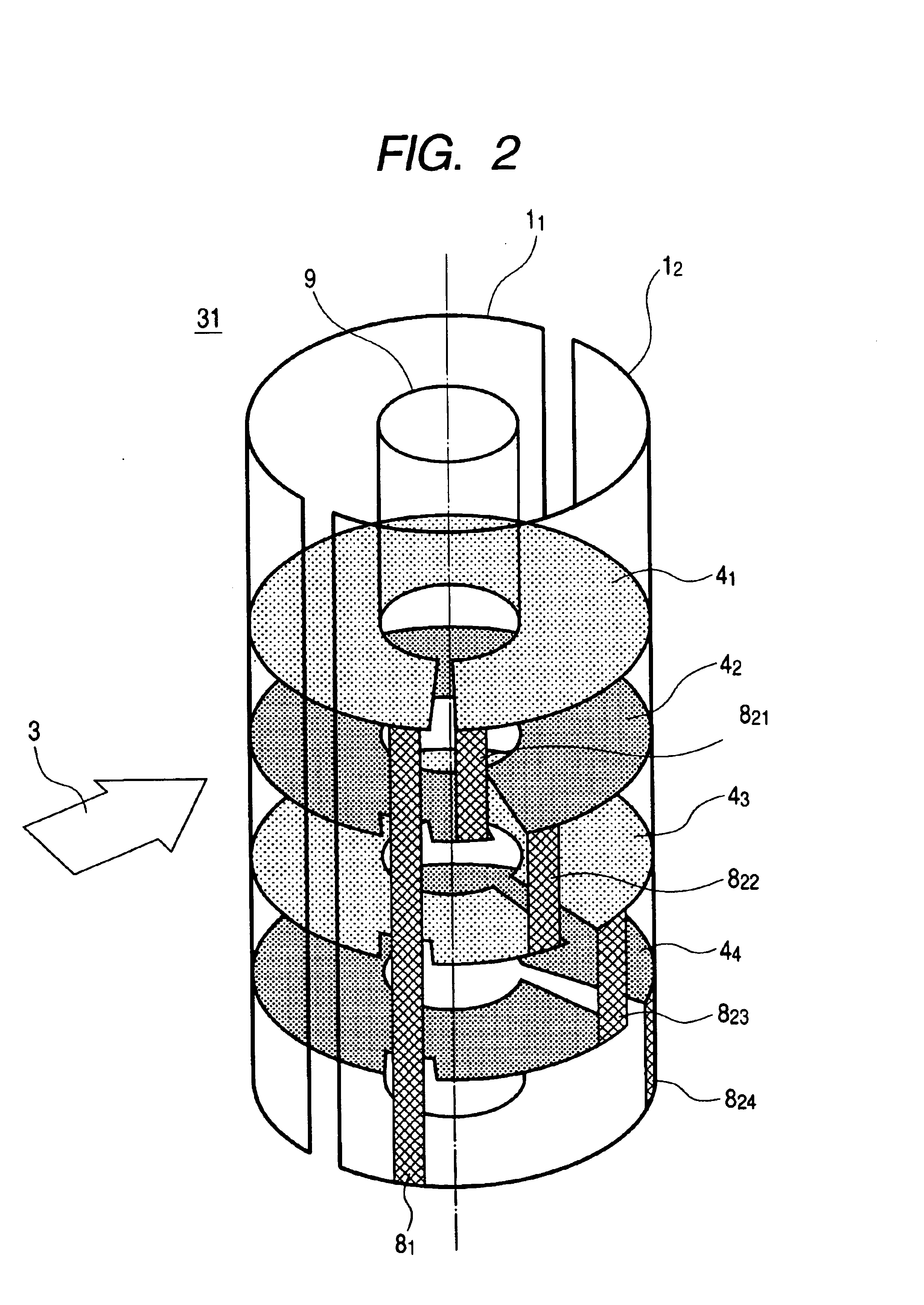
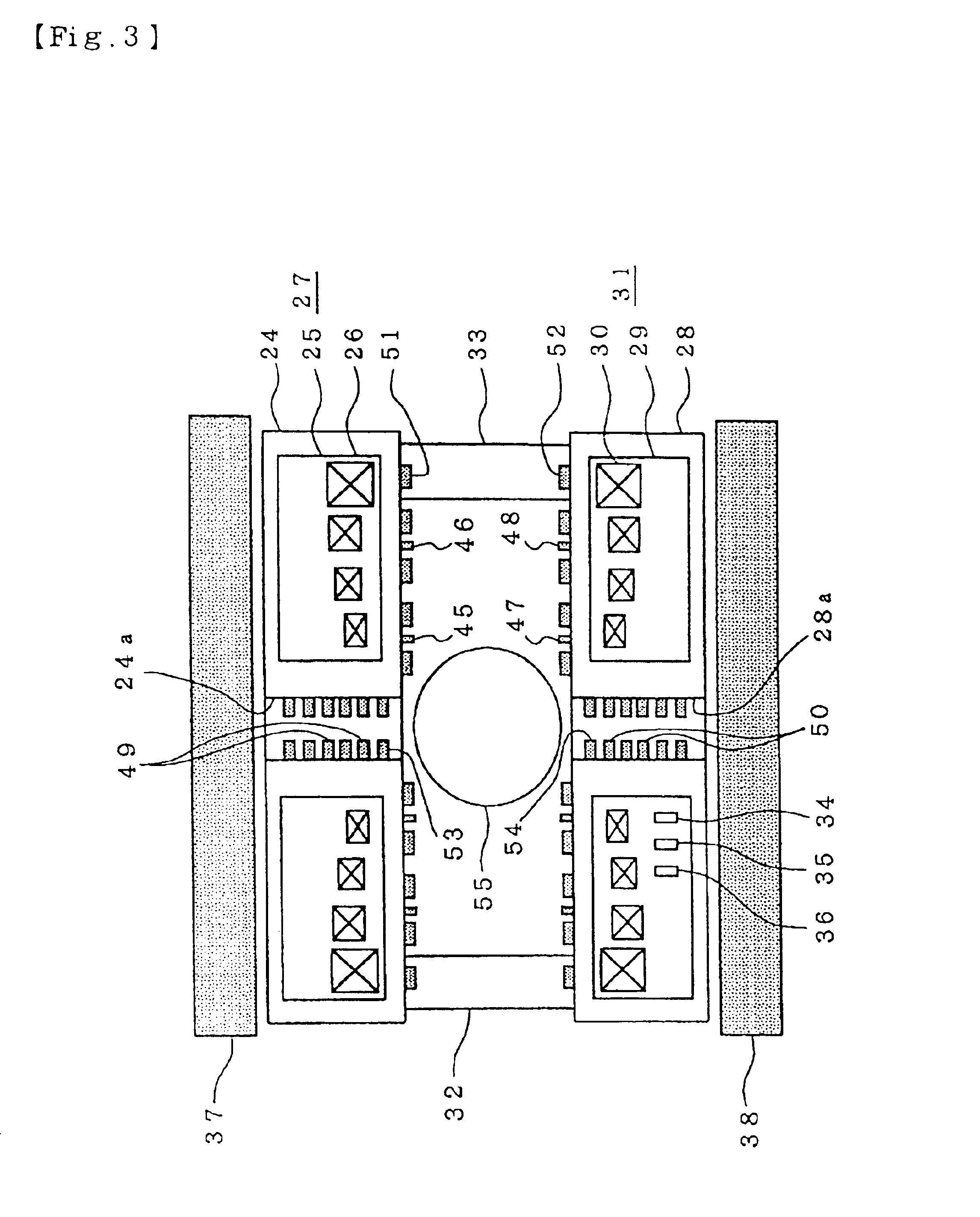
Nuclear magnetic resonance module
ActiveUS20080150524A1Low cost designSufficient signal to noise ratioElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus that may be used in connection with a variety of different tools, including a down-hole side-wall coring tool as well as with manufacturing process controllers. In one embodiment, the nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus may include a magnet assembly constructed around a sample chamber. The magnet assembly is constructed and arranged to provide a non-uniform magnetic field having a known magnetic field gradient inside the sample chamber. The use of gradient fields may allow for a more flexible and robust magnet assembly design that may be suitable for a variety of different applications.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Superconductor Magnetic Resonance Imaging System and Method (SUPER-MRI)
ActiveUS20100231215A1Improve conductivityMachines/enginesSuperconductor devicesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic resonance spectrometry
Methods and apparatuses for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and / or magnetic resonance spectroscopy comprising a superconducting main magnet operable to generate a uniform magnetic field in an examination region, at least one superconducting gradient field coil operable to apply a respective at least one magnetic field gradient within the examination region, and at least one RF coil that is operable to transmit and receive radio frequency signals to and from the examination region, and that is configured for cooling and comprises at least one of (i) a non-superconducting material that when cooled to a temperature below room temperature has a conductivity higher than that of copper at that temperature and (ii) a superconducting material. The main magnet, the gradient coils, and each of the at least one RF coil of a given system may each be implemented as high temperature superconductor materials.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
Improved techniques for magnetic particle imaging
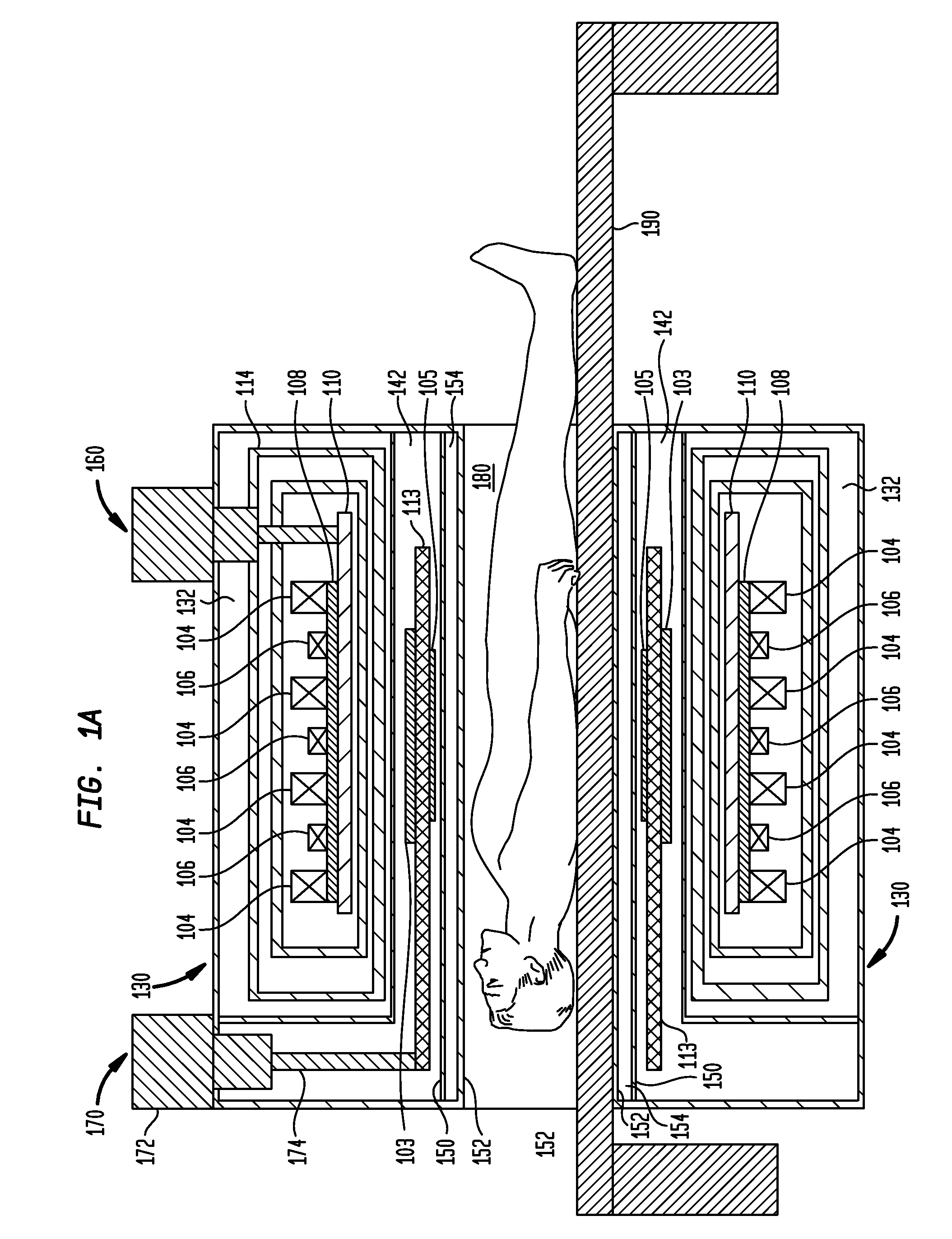
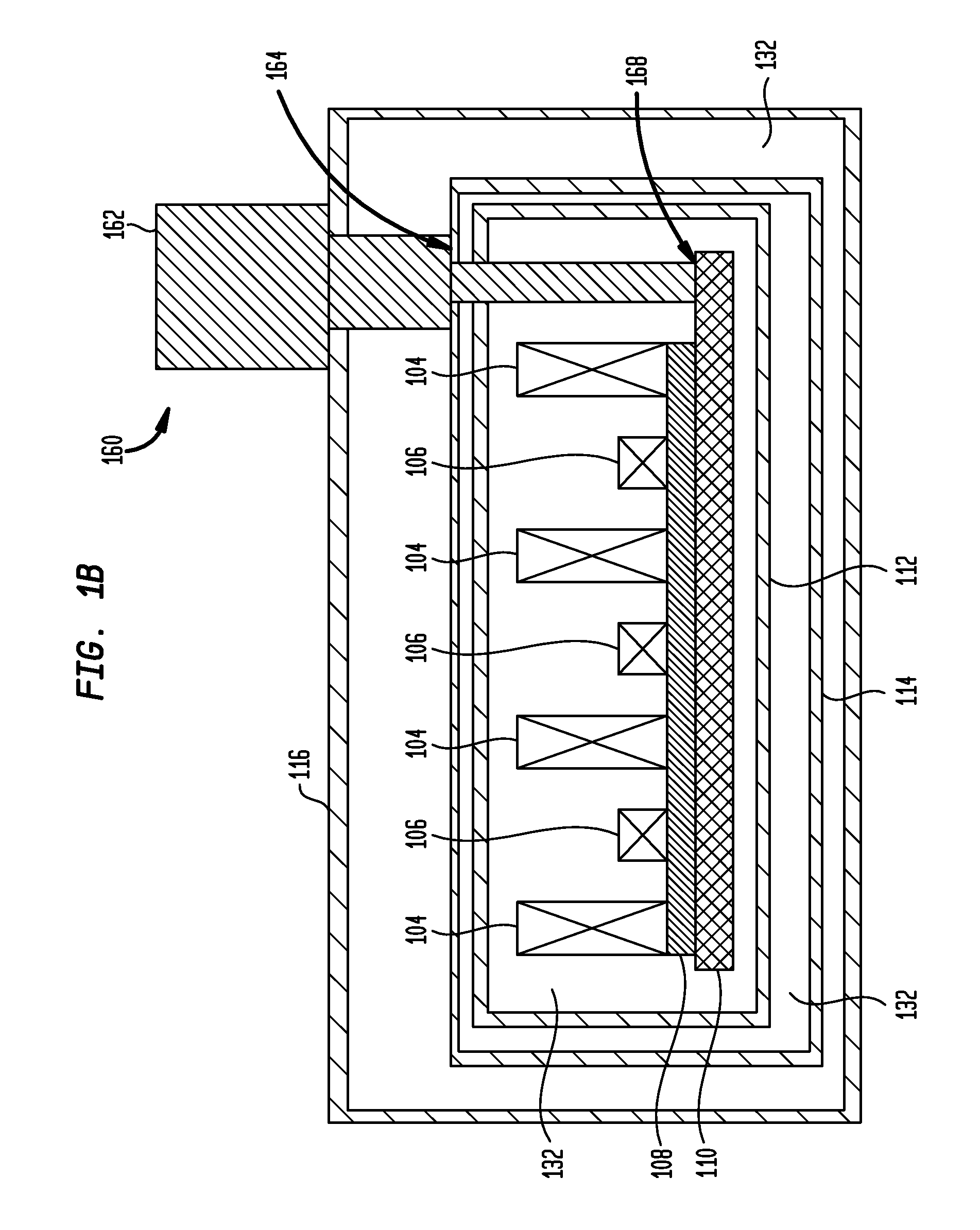
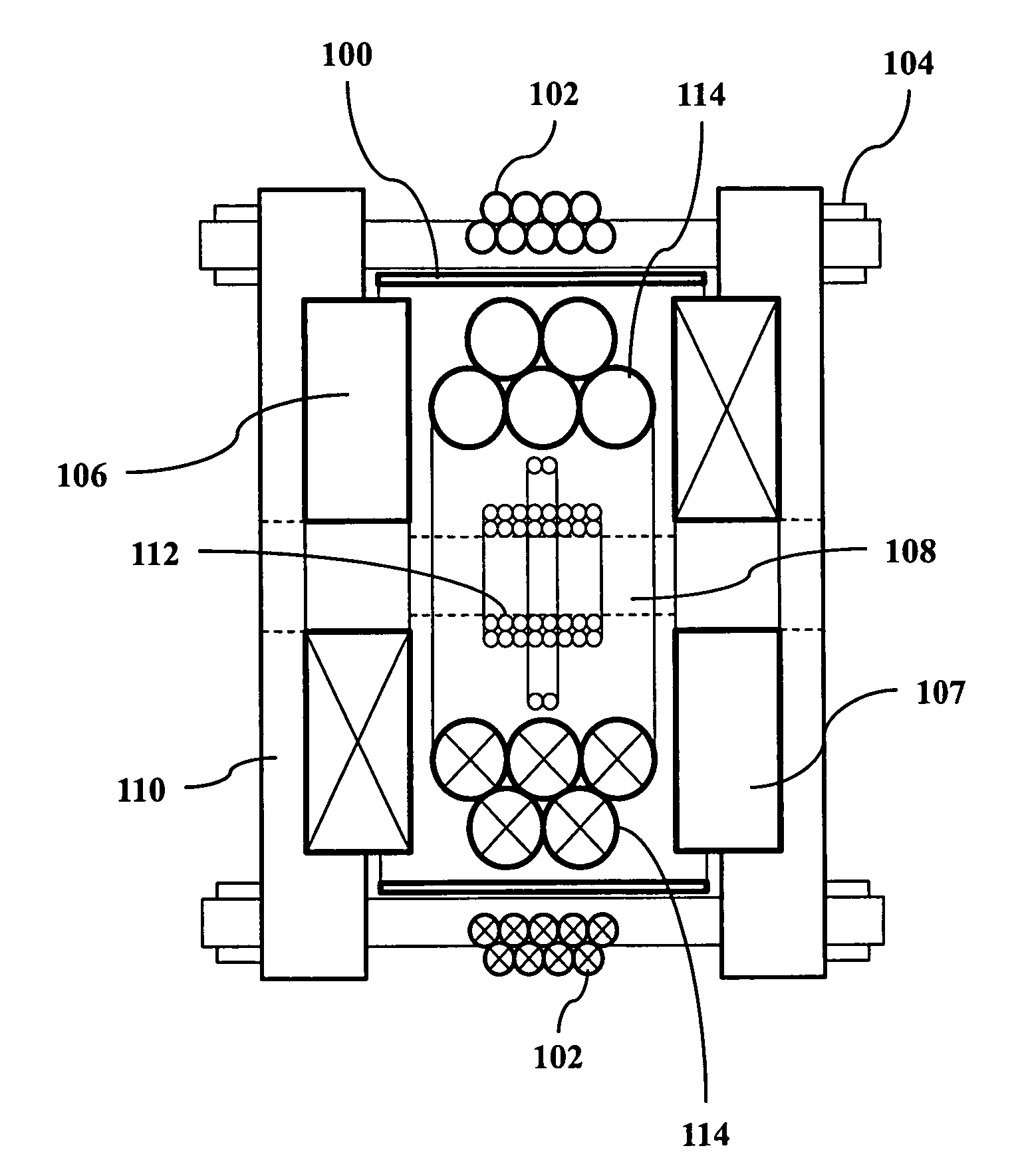
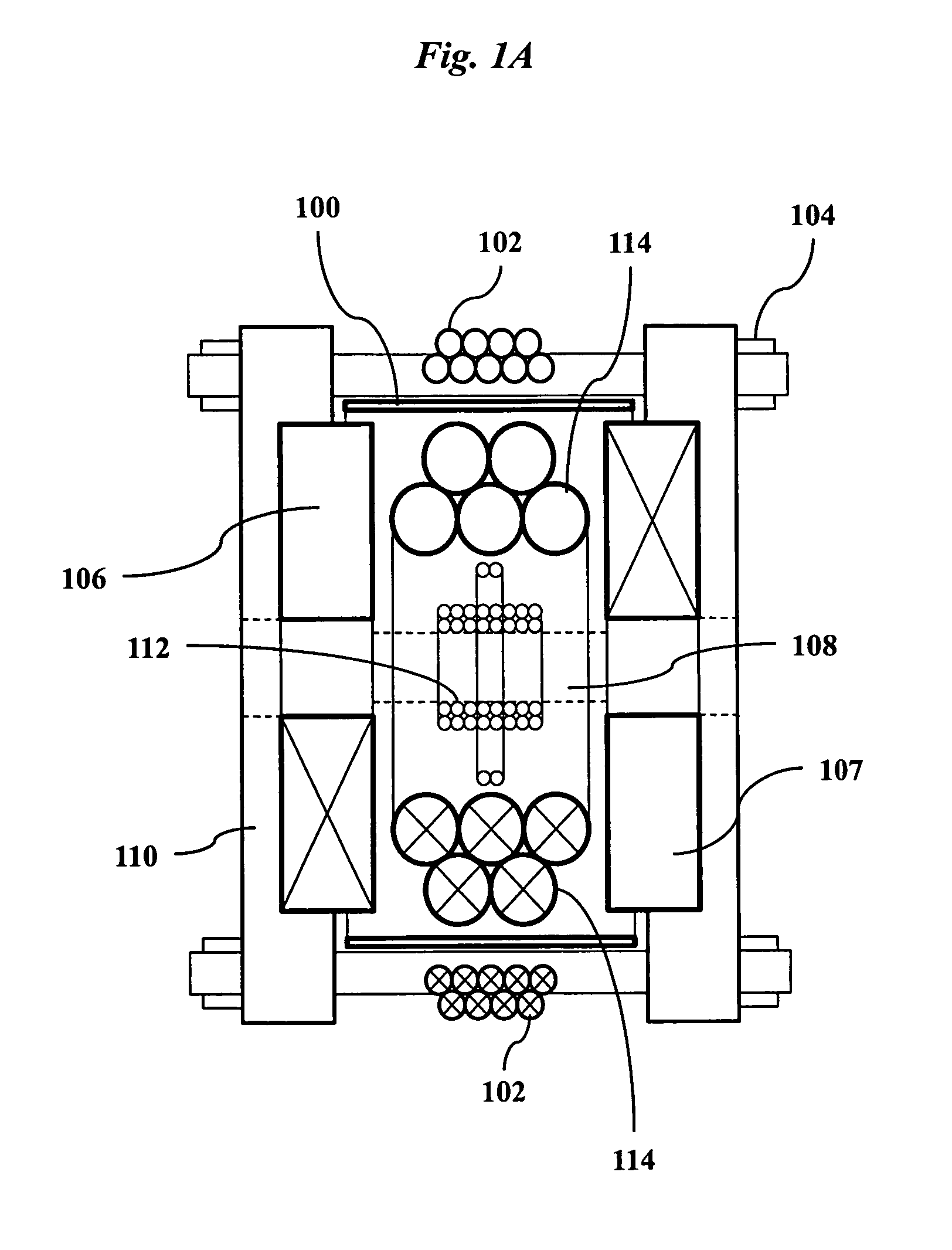
ActiveUS20110089942A1Prevents phaseHarmonic suppressionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic particle imagingMagnetite Nanoparticles
A magnetic particle imaging apparatus includes magnets [106,107] that produce a gradient magnetic field having a field free region (FFR), excitation field electromagnets [102,114] that produce a radiofrequency magnetic field within the field free region, high-Q receiving coils [112] that detect a response of magnetic particles in the field free region to the excitation field. Field translation electromagnets create a homogeneous magnetic field displacing the field-free region through the field of view (FOV) allowing the imaging region to be scanned to optimize scan time, scanning power, amplifier heating, SAR, dB / dt, and / or slew rate. Efficient multi-resolution scanning techniques are also provided. Intermodulated low and radio-frequency excitation signals are processed to produce an image of a distribution of the magnetic nanoparticles within the imaging region. A single composite image is computed using deconvolution of multiple signals at different harmonics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
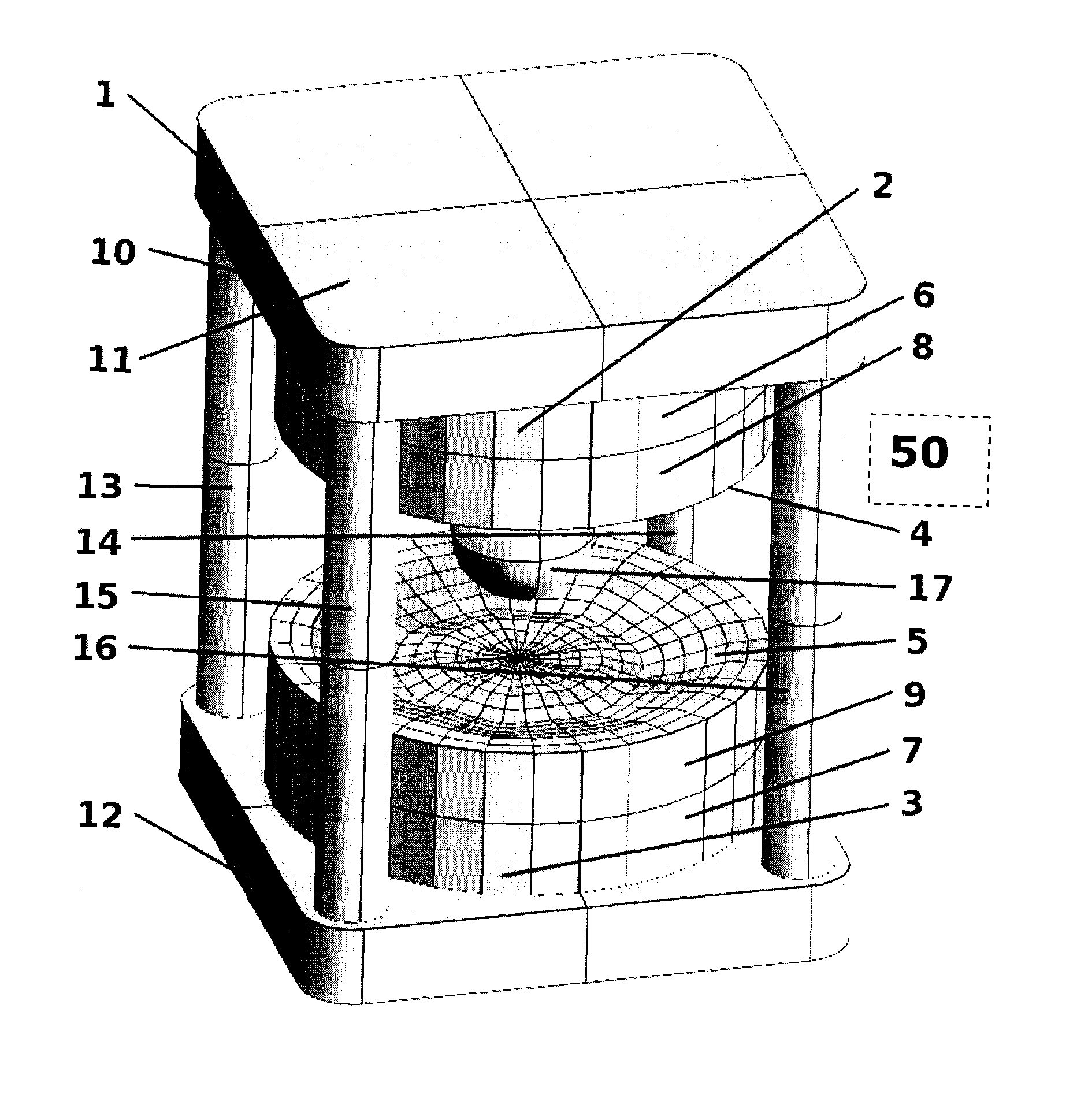
Compact superconducting magnet configuration with active shielding having a shielding coil contributing to field formation
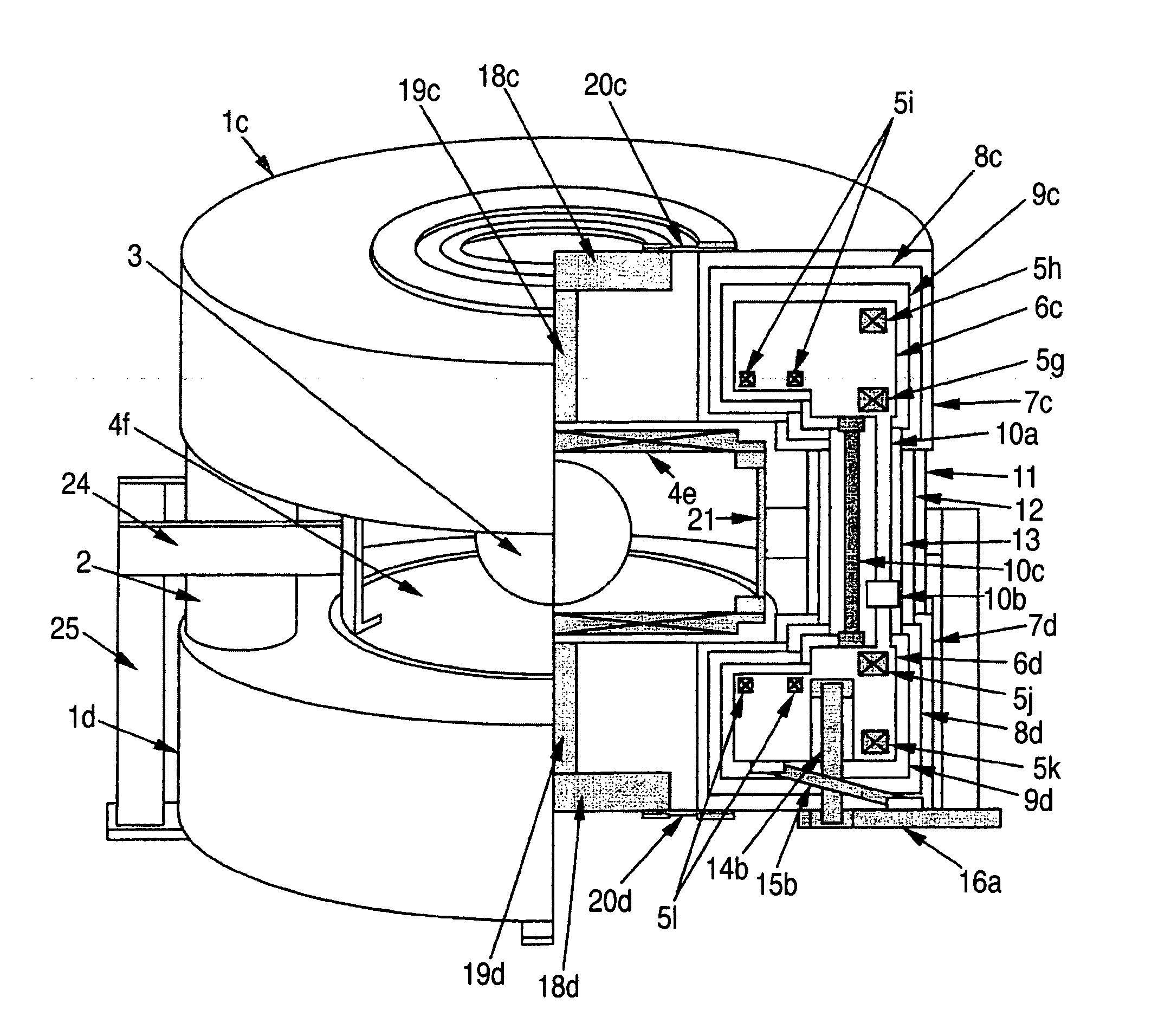
ActiveUS7898258B2Sizable impactImprove field uniformityMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting CoilsHomogeneous magnetic field
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
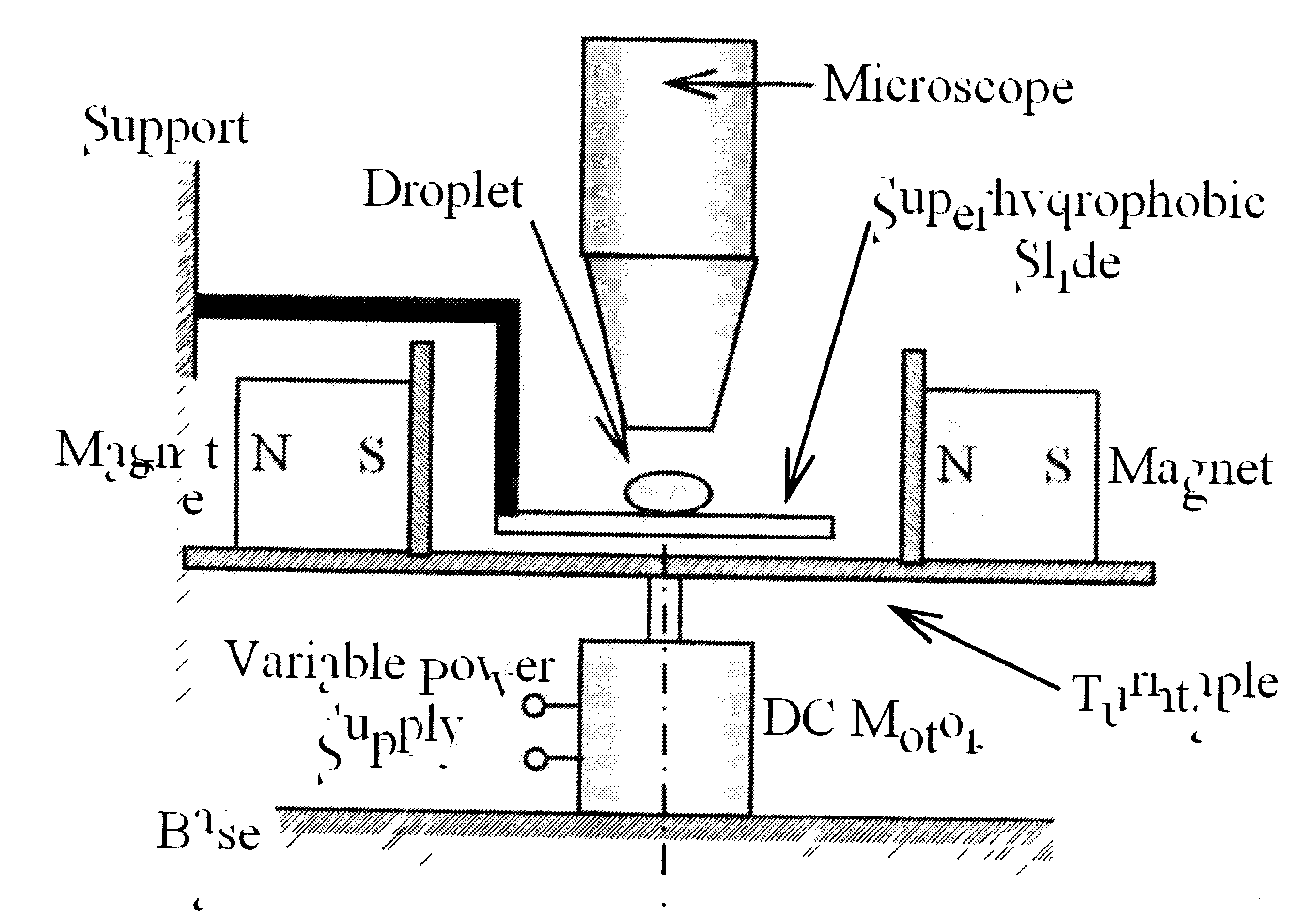
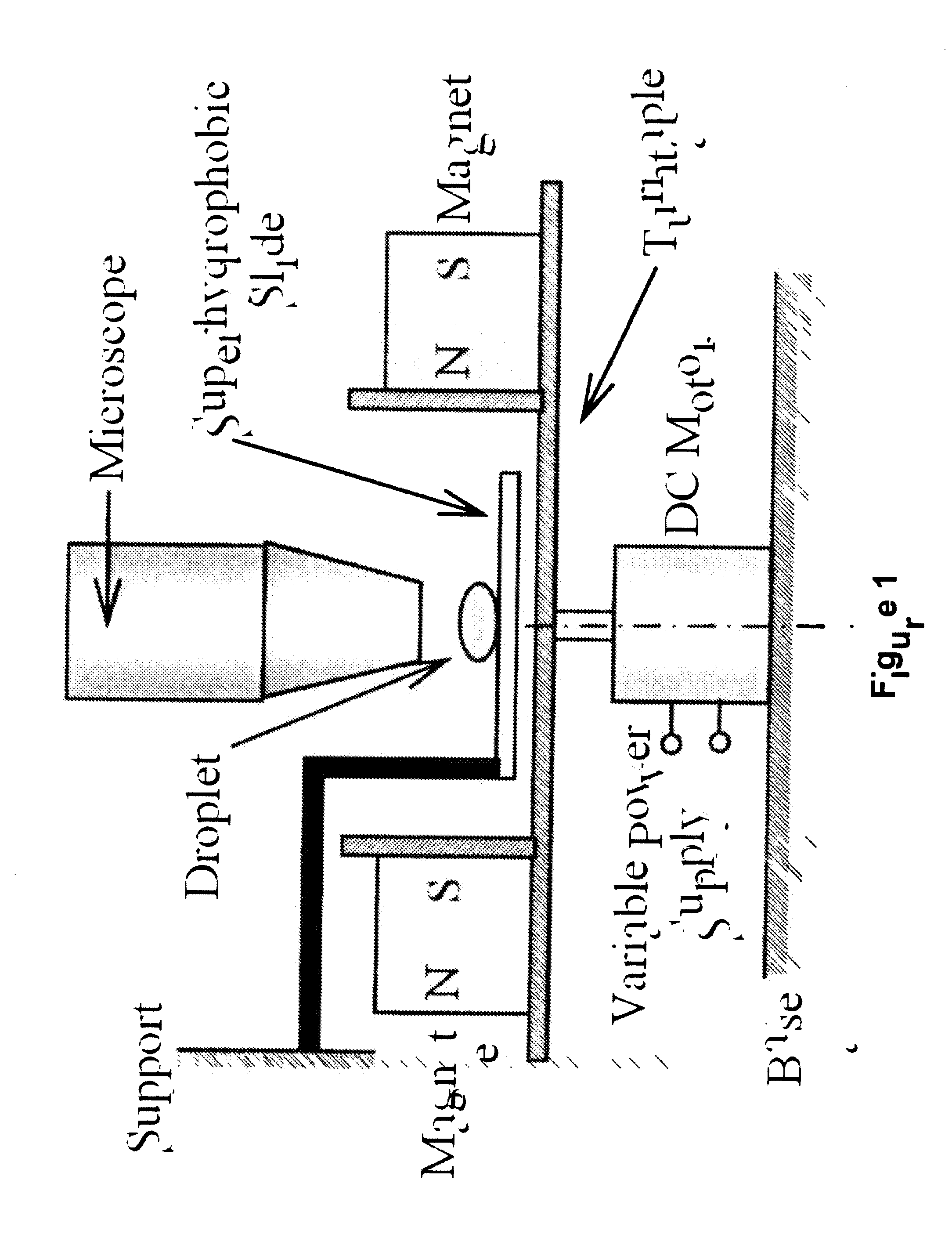
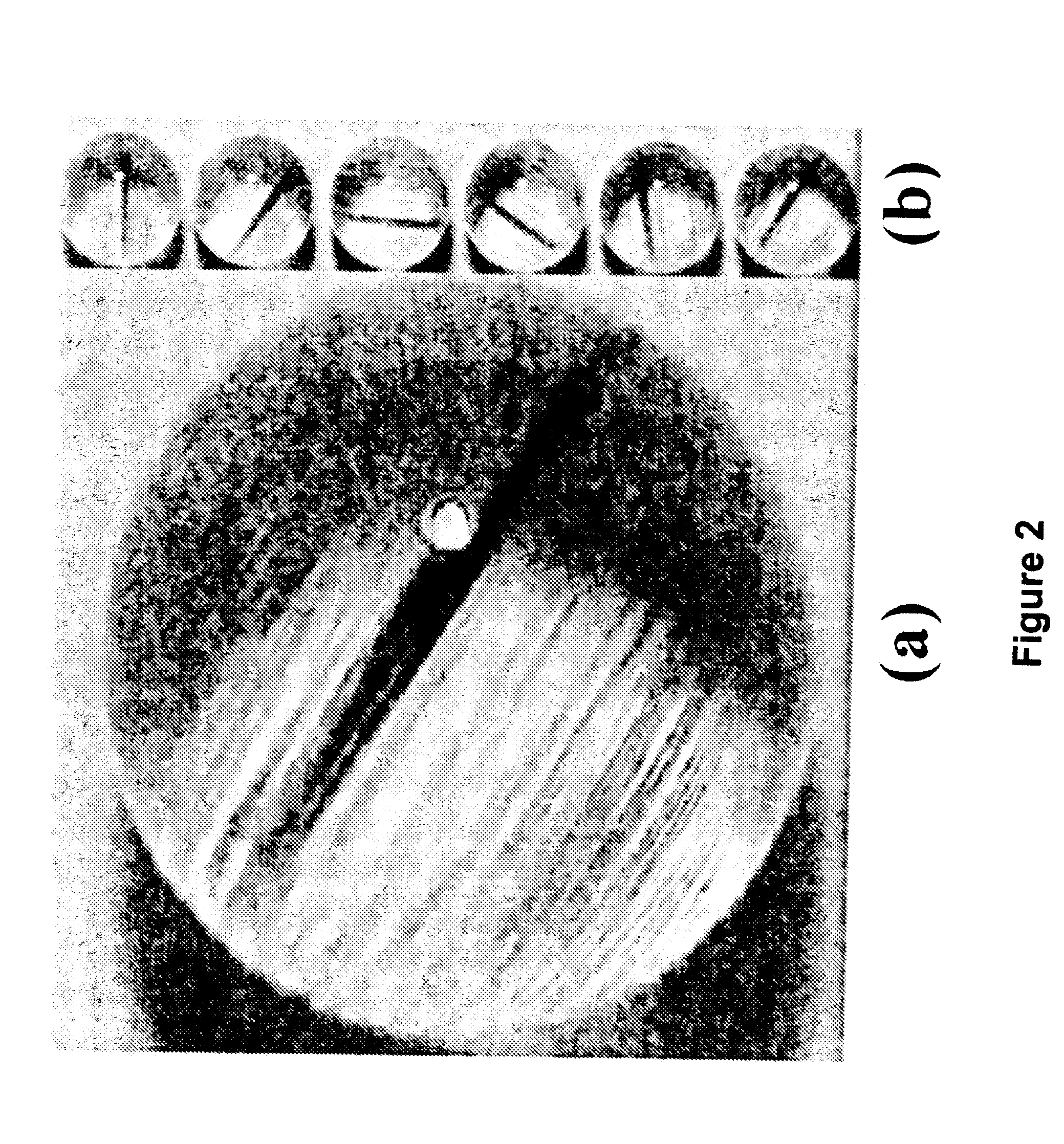
Method and apparatus for magnetic mixing in micron size droplets
InactiveUS20070207272A1Increase fluid-particle interactionEfficient productionMixersPretreated surfacesDiffusionMicrosphere
Active mixing by magnetic stirring is demonstrated inside a picoliter-size liquid droplet. Magnetic microspheres are added to the droplet, which form aligned chains under the influence of a homogeneous magnetic field. When the magnetic field is rotated, the chains also rotate synchronously. Viscous interaction between the particle-chains and the liquid induces advective motion inside the droplet thereby enhancing mixing which is otherwise diffusion-limited. The concept can be effectively used to create a lab-in-a-droplet for MEMS (Micro-Electrical-Mechanical Systems) and Bio-MEMS applications.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
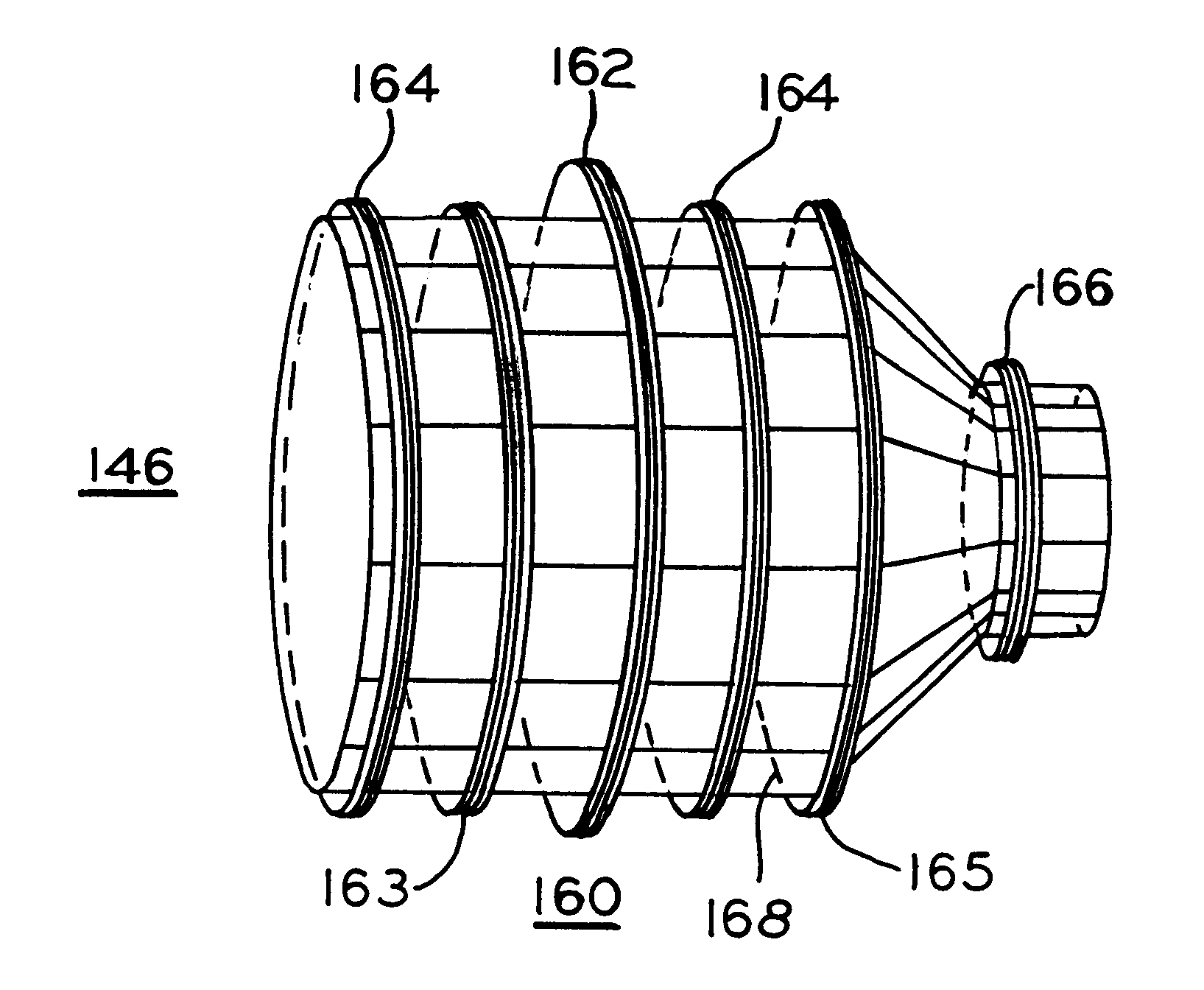
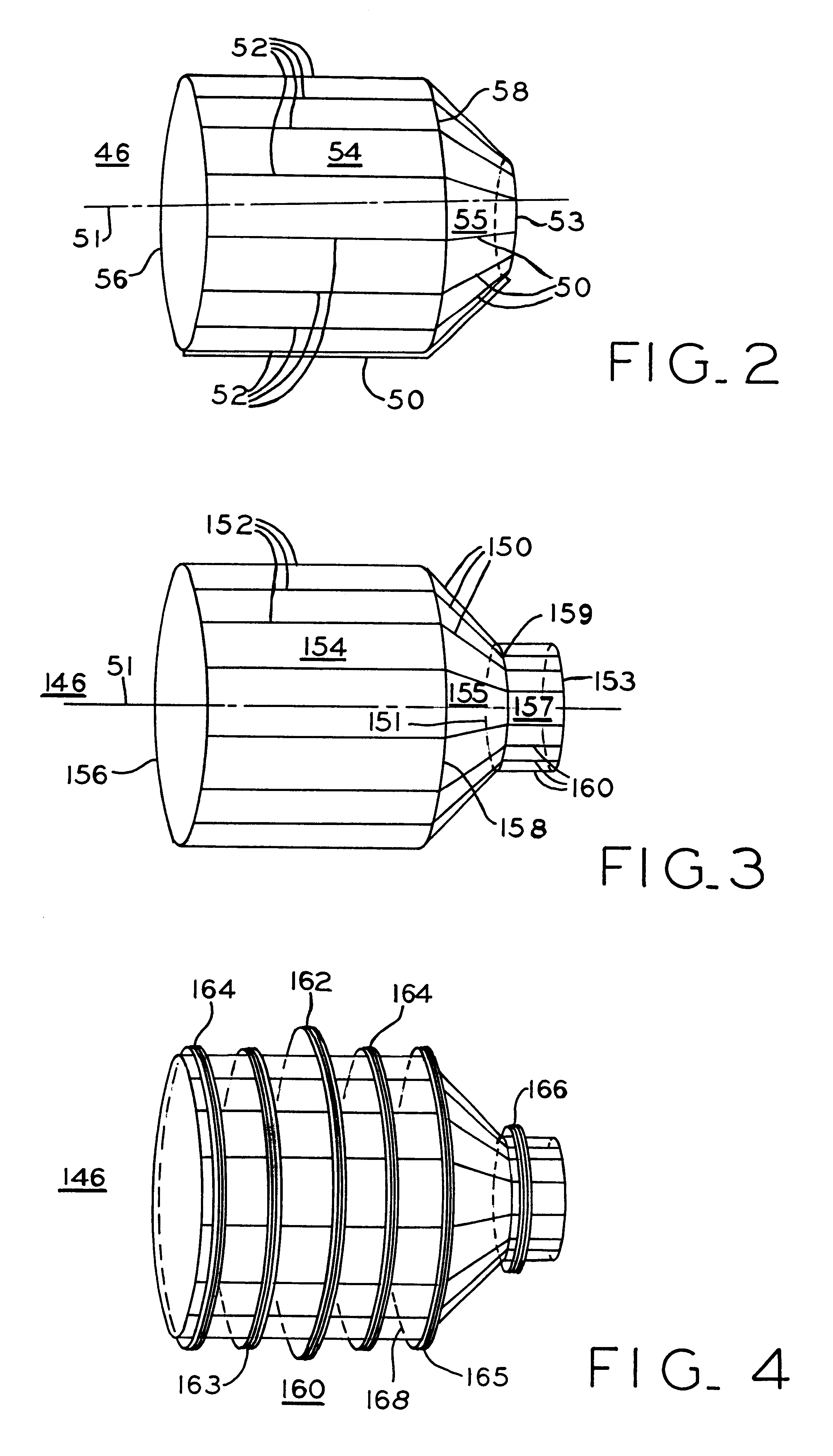
Magnetic resonance imaging head coil
InactiveUS6313633B1Improve homogeneityImprove image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical conductorHomogeneous magnetic field
A short radio frequency coil for magnetic resonance imaging of the head to provide a homogeneous magnetic field including parallel conductors forming a first cylindrical portion with end rings supporting the conductors which then continue at an angle to form the frustum of a cone and further continuing to form a reduced diameter second cylindrical portion. A third conductive end ring of reduced diameter positioned at the open end of the second cylindrical portion supports the end of the conductors and provides a reduced diameter opening. An asymmetrical coil surrounds portions of the radio frequency coil including the first cylindrical and frustum of a cone portions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for magnetic resonance measurements in an interior volume
InactiveUS6940378B2Desirable measurement flexibilityDesirable flexibilityPermanent magnetsMagnetic materialsResonance measurementMagnetization
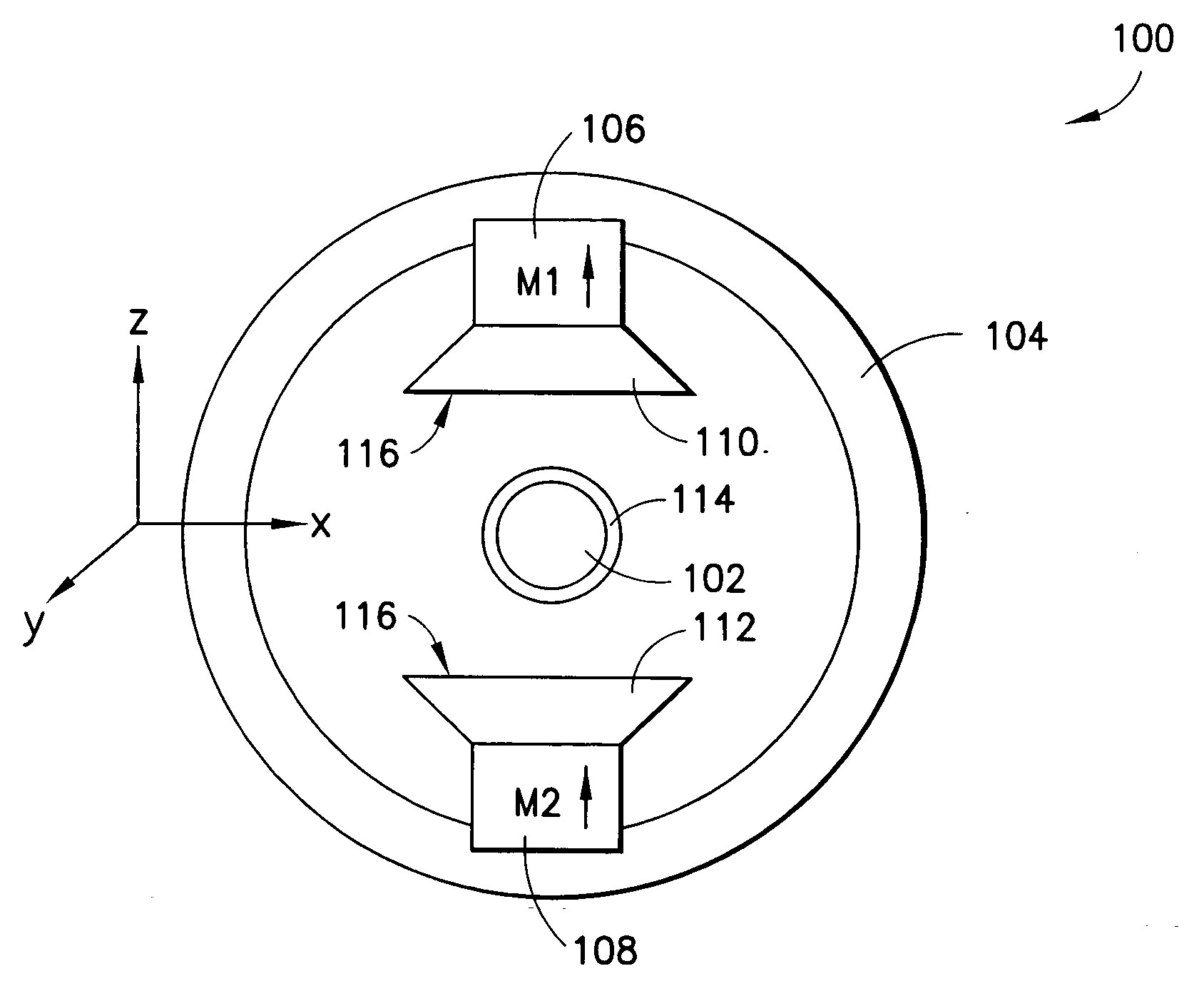
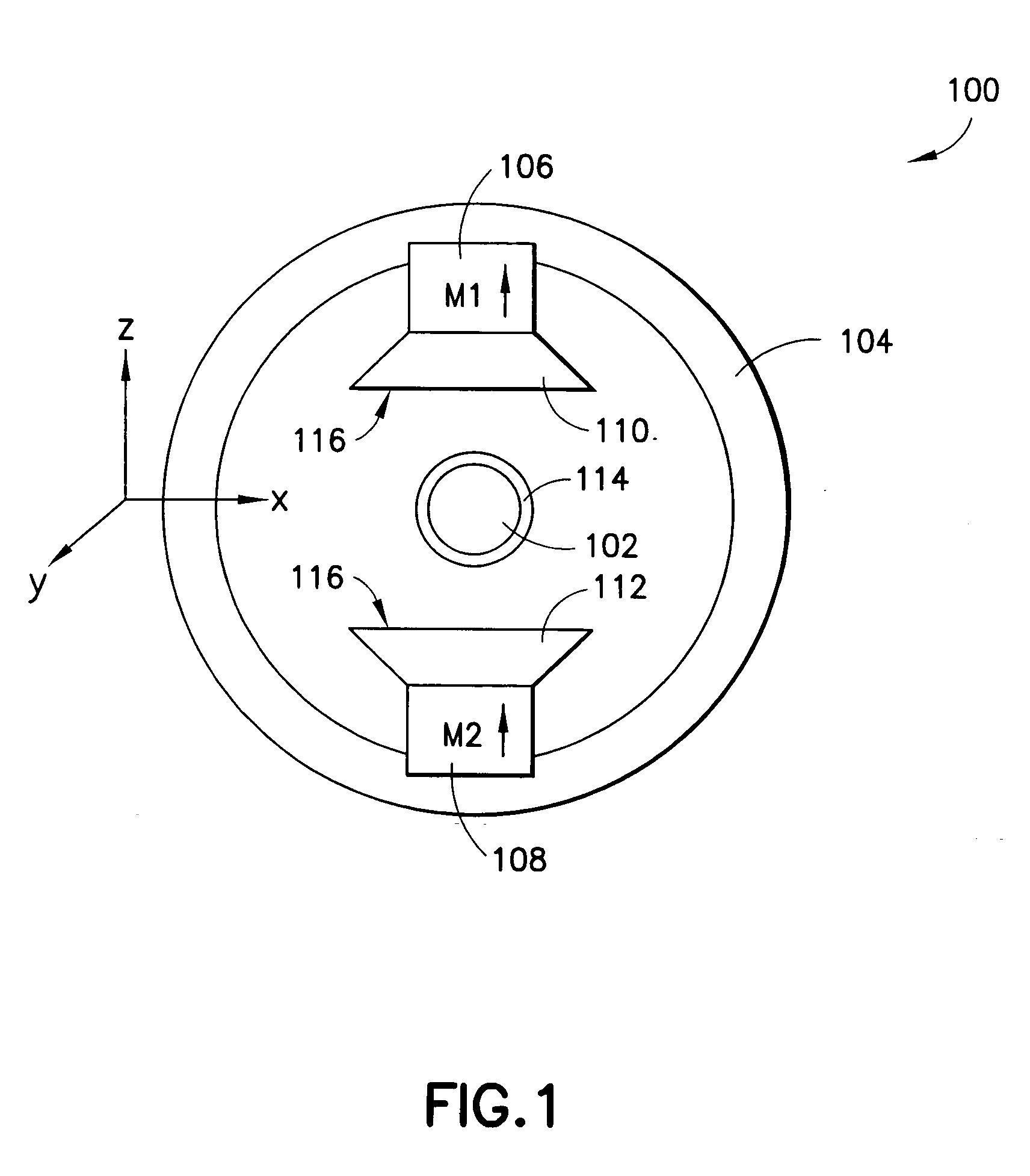
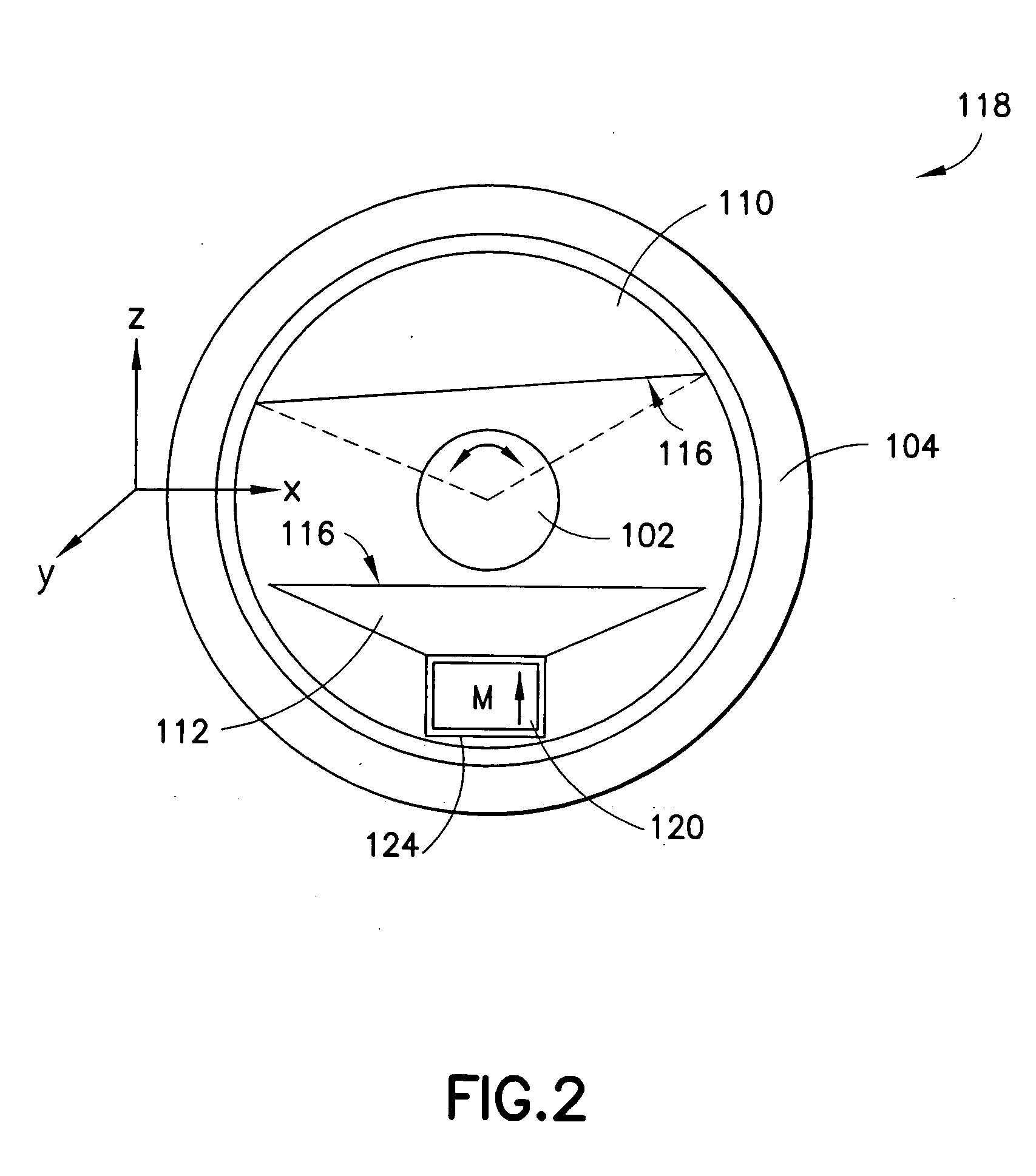
A magnet assembly and a magnetic field configuration are disclosed for the generation of a magnetic field in a defined volume, with the field being homogeneous over a pre-determined portion of the volume and not homogeneous over the rest. The disclosed magnetic assembly has a plurality of spaced-apart magnets arranged in pairs. The magnets of each pair are be positioned diametrically opposite each other with respect to an enclosed volume. In different embodiments magnets may all be arranged such that their magnetization directions are substantially aligned, or could alternatively be arranged to have magnetizations pointing in different directions. The angular spacing between the magnets is selected in the range of approximately 13°-17° and could be as large as the size of the magnets. The assembly generates a homogeneous magnetic field within an inner portion of the defined volume, and a second magnetic field, substantially different from the homogeneous magnetic field throughout the remainder, i.e., in the periphery of the defined volume.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy in non-uniform magnetic field
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Self-fastening cage surrounding a magnetic resonance device and methods thereof
ActiveUS7400147B2High strengthPrevent leakageMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementHomogeneous magnetic field
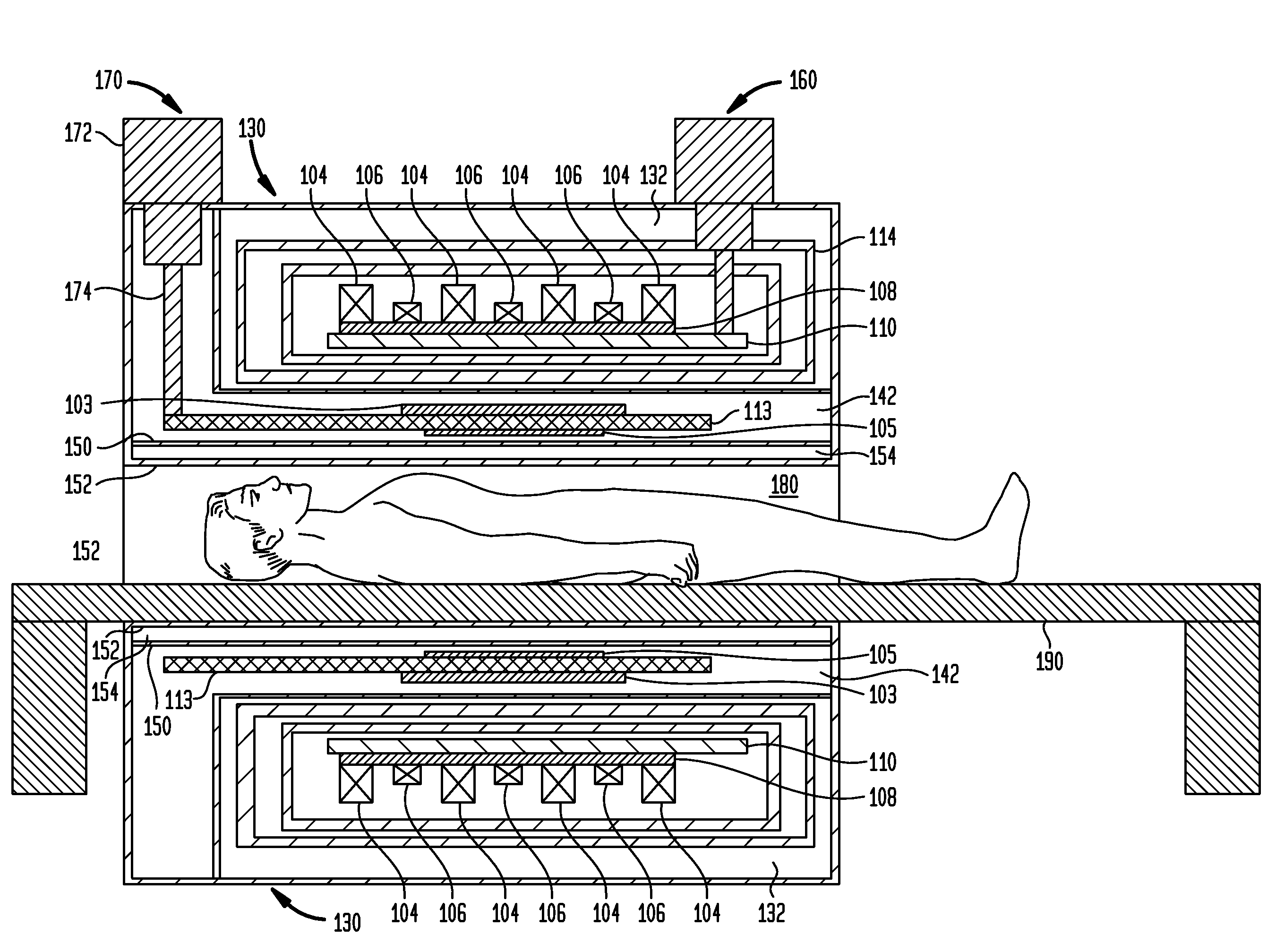
The present invention discloses a novel self-fastening cage of a magnetic resonance device (MRD) (100) for providing a homogeneous, stable and uniform magnetic field therein, characterized by an outside shell comprising at least three flexi-jointed superimposed walls (1). In a technology of self-fastening cage, the invention teaches an effective multi-streamed MRD comprising a cage including a closed magnetic circuit constructed from strong permanent magnets; and an optional shimming mechanism selected from an array of active shim coils, passive shimming elements or any combination thereof; a contained cavity within which the magnetic field strength is approximately uniform; and a means, such as a plurality of conveyor belts, pipes or any other transportation means by which a plurality of samples are introduced into the region of uniform magnetic field; such that magnetic resonance measurements are made on a plurality of samples within the region of uniform magnetic field. The invention depicts a cost effective method for obtaining a self-fastening cage of a MRD (100) characterized by an outside shell comprising superimposing at least three flexi-jointed walls (1) so that a homogeneous, stable and uniform magnetic field is provided therein.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
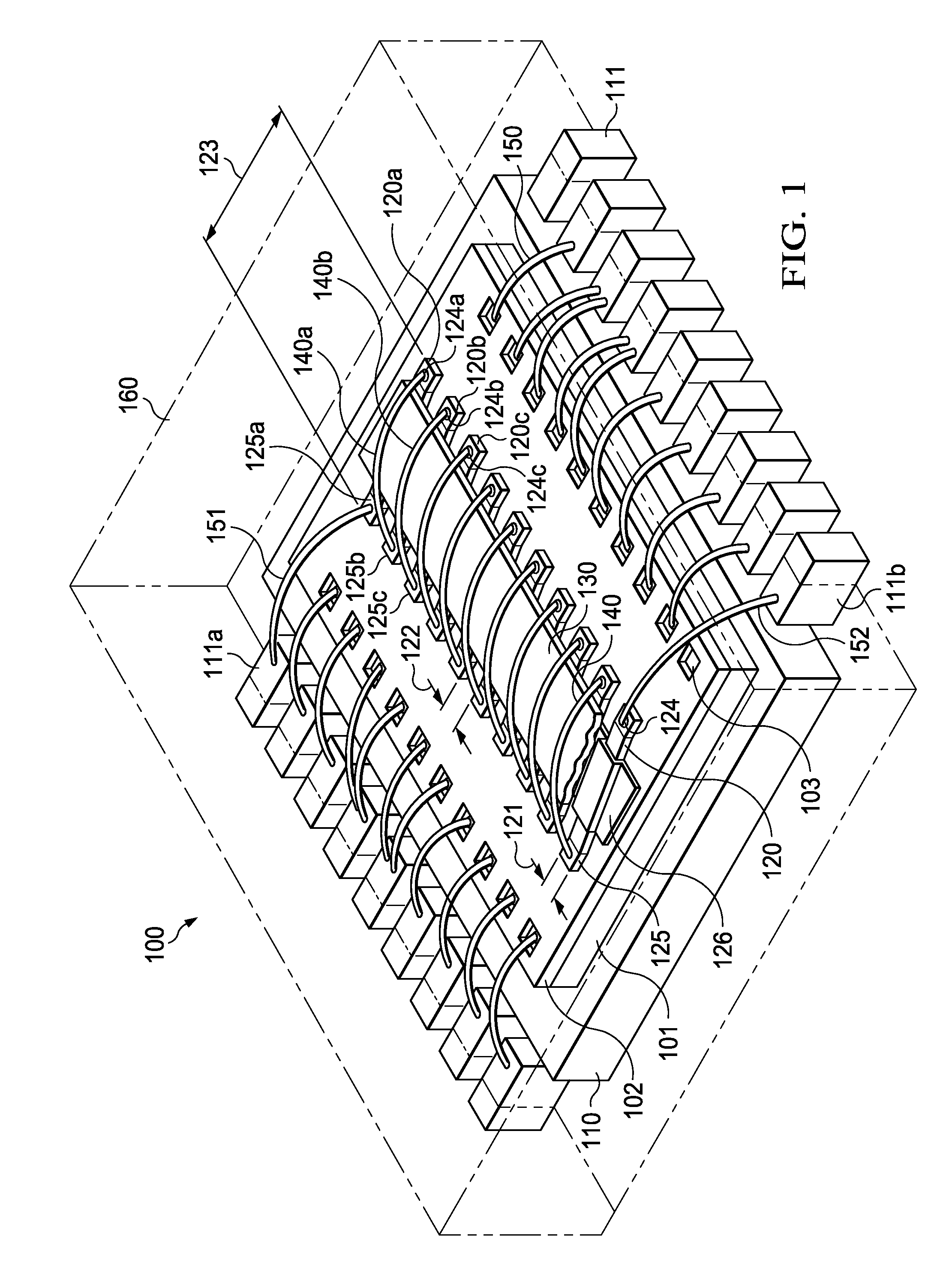
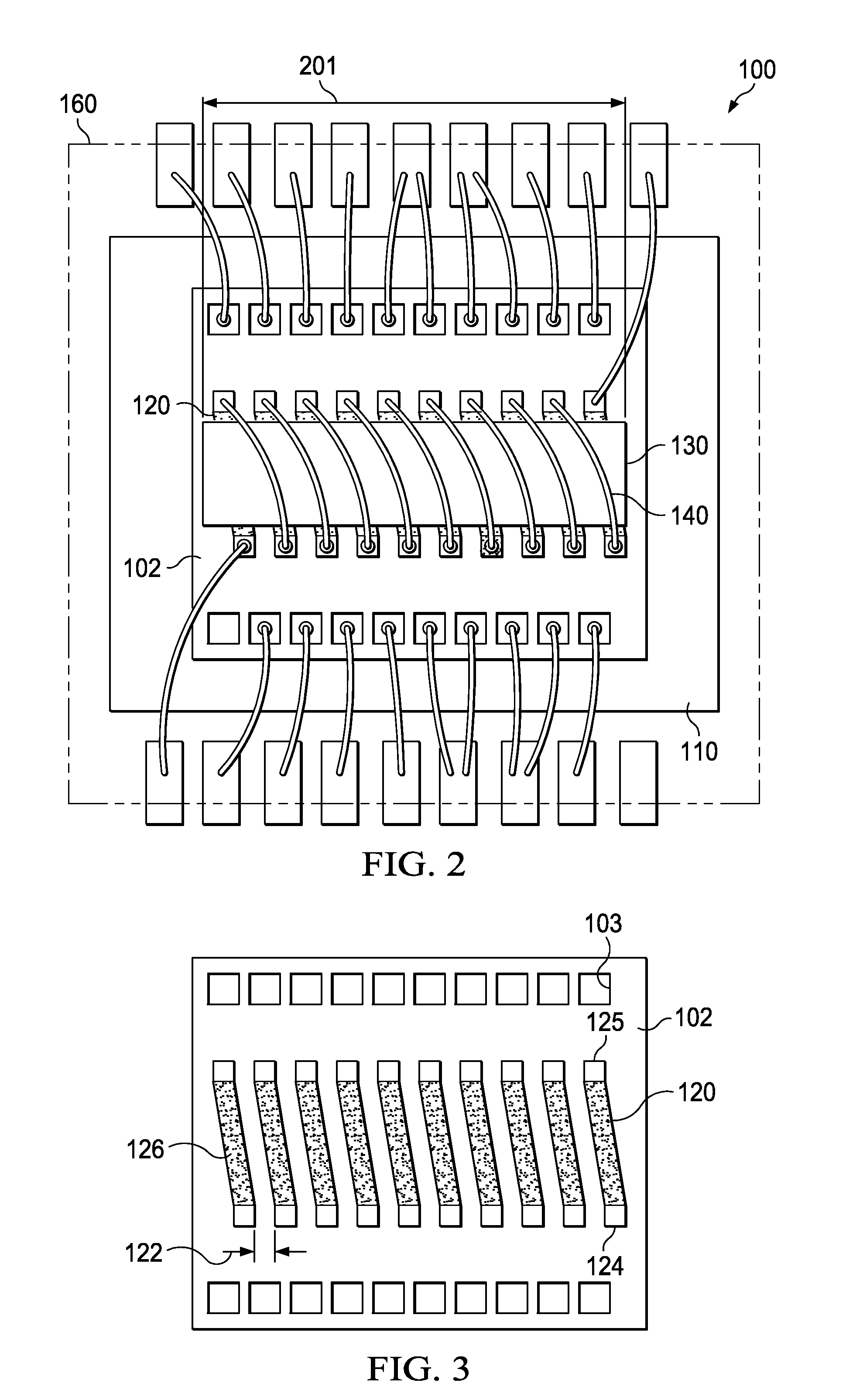
Structure and Method for Inductors Integrated into Semiconductor Device Packages
InactiveUS20130307117A1Low costSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageInductor
A thin-contour semiconductor device with a solenoid and iron core integrated into the device package. The solenoid windings are constructed by a stripe-shaped layer portion, deposited on the chip surface, and an arced wire portion welded to the layer portion by low-cost standard wire bonding technique. The stripes are arrayed parallel to each other, spaced apart respective insulating gaps. The arced wires span from one stripe to the adjacent next stripe by bridging the gap and keeping the clock direction constant. The arced solenoid windings are then integrated into the encapsulating device package. The ferromagnetic core may be shaped as a ring to allow the formation of a strong and nearly homogeneous magnetic field inside the solenoid, providing reliable energy storage for power supply circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
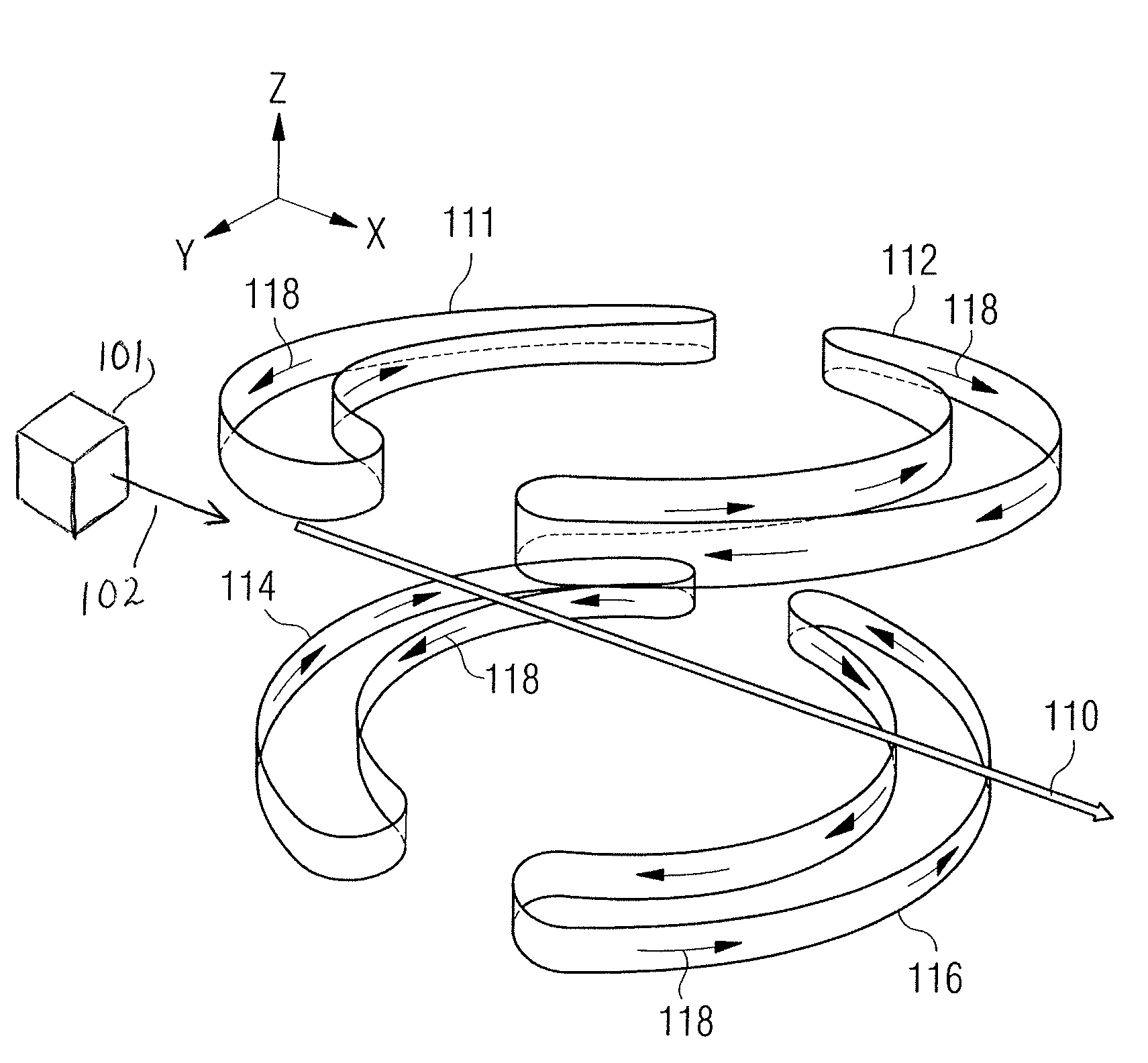
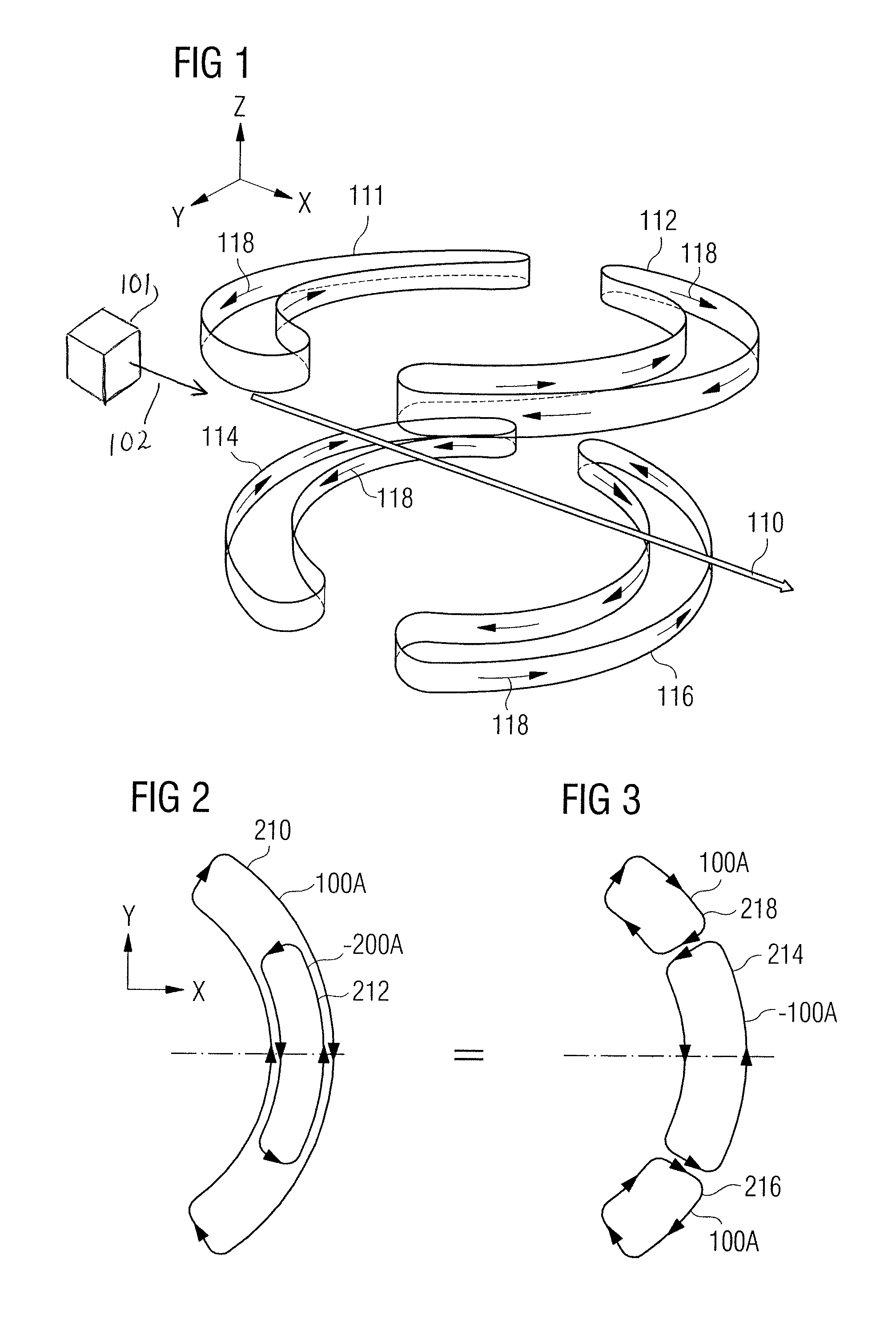
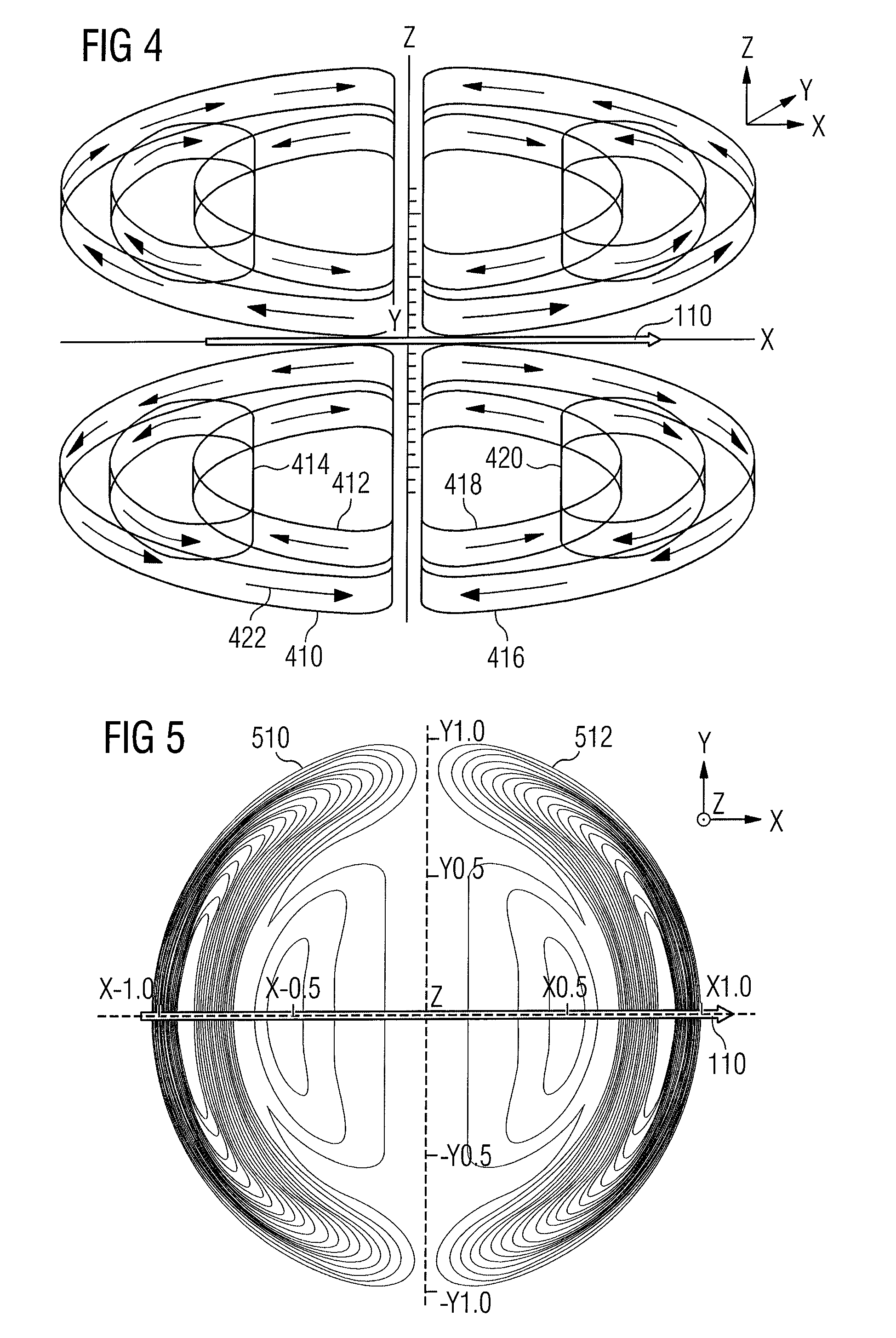
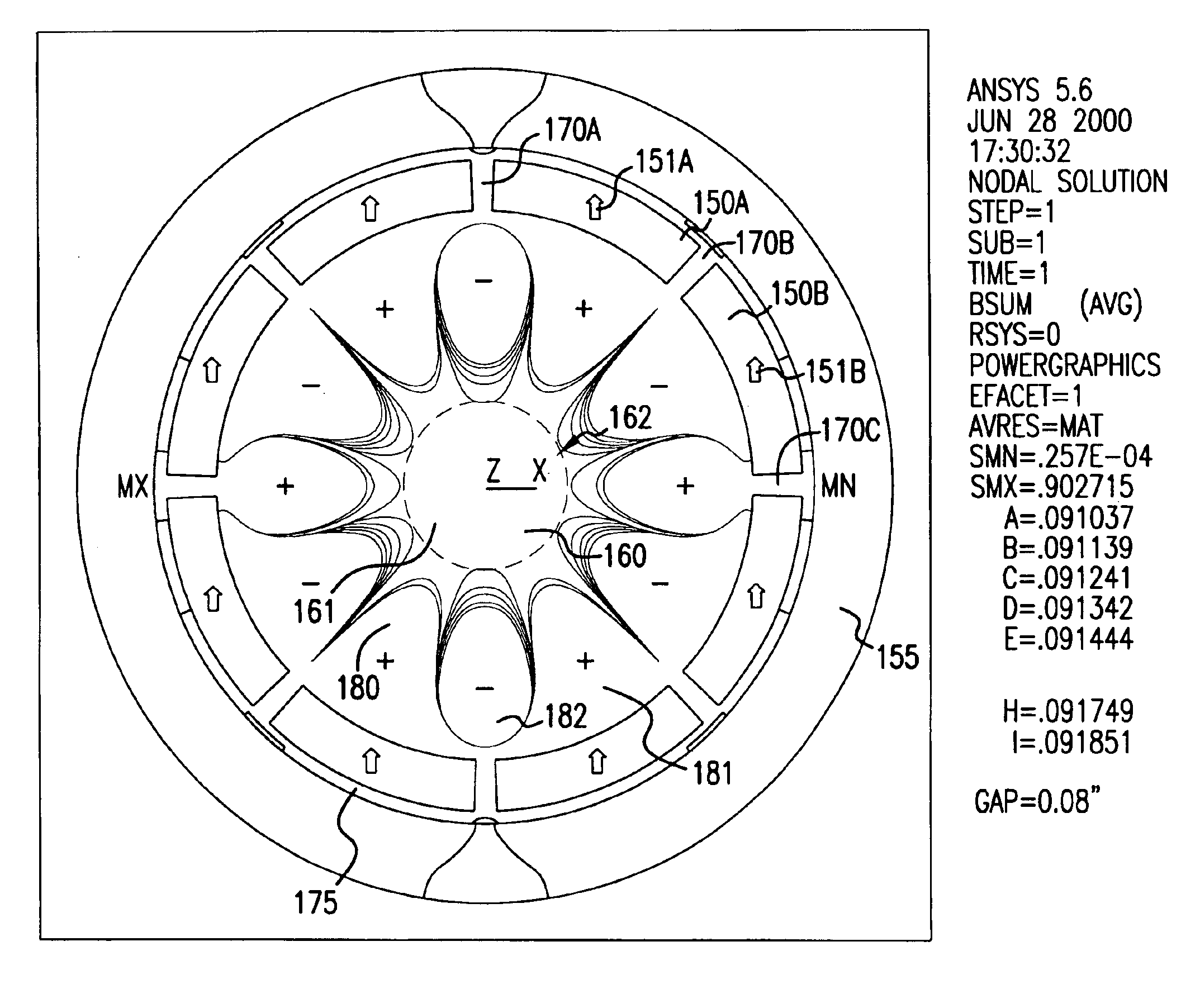
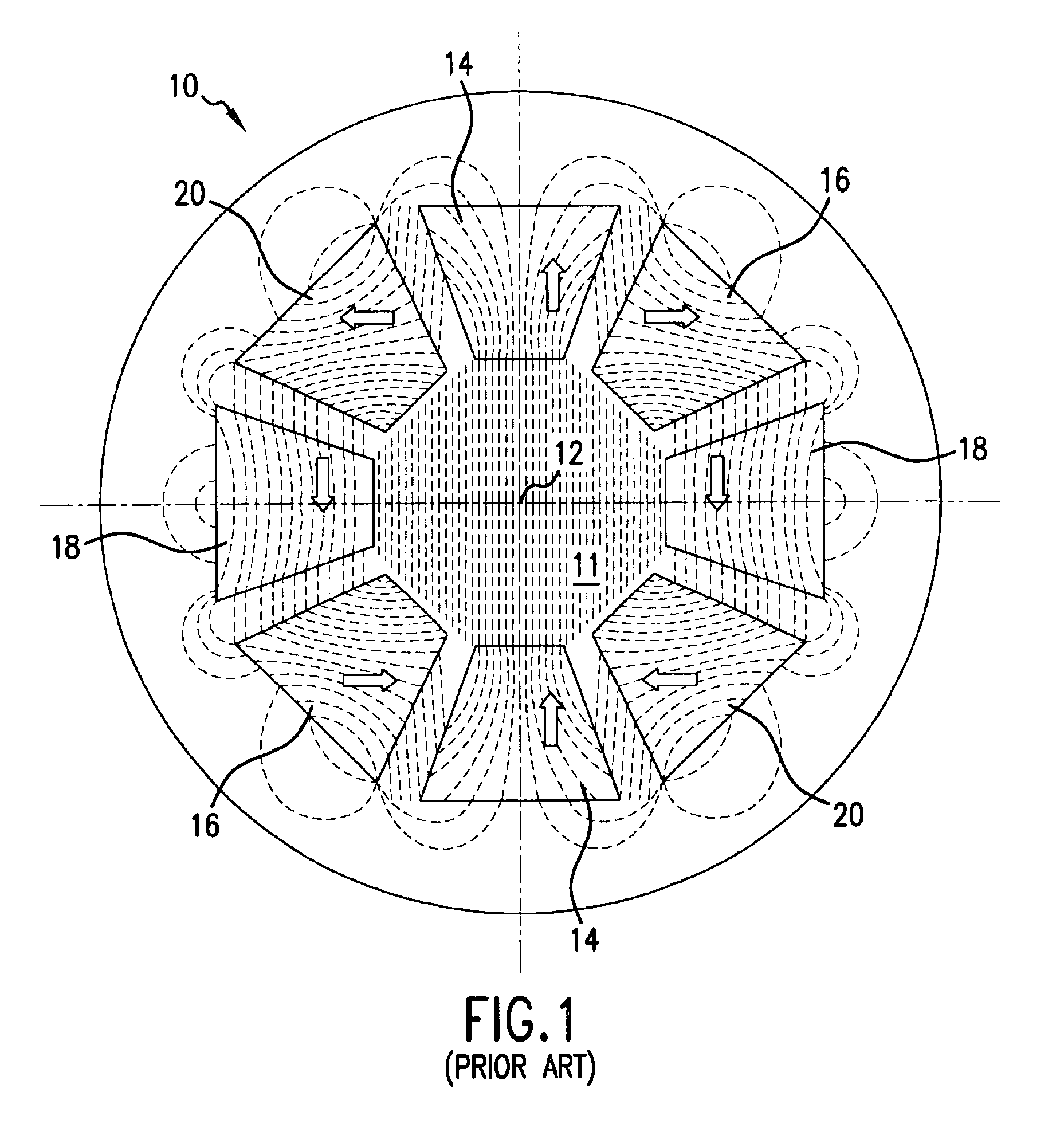
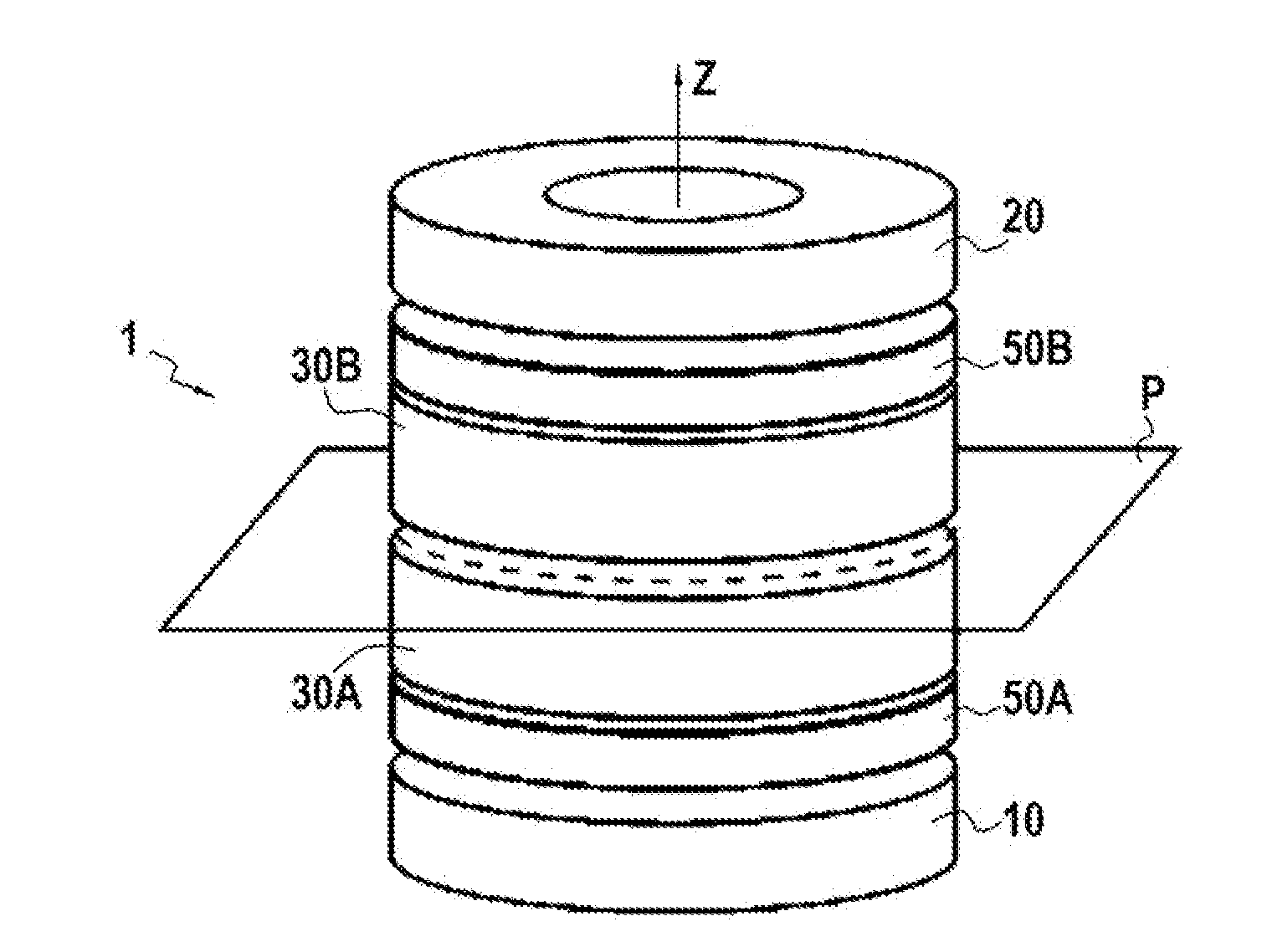
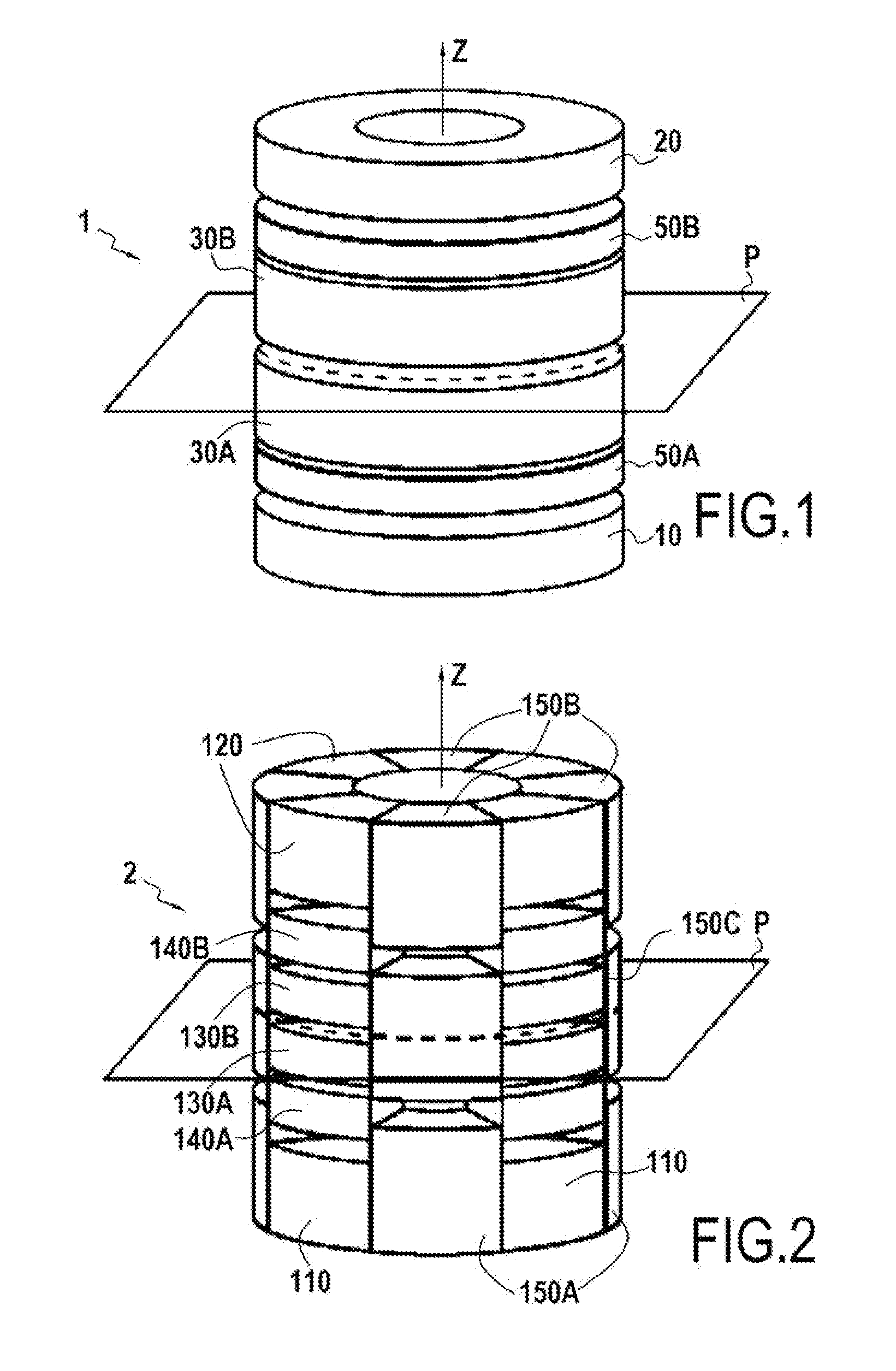
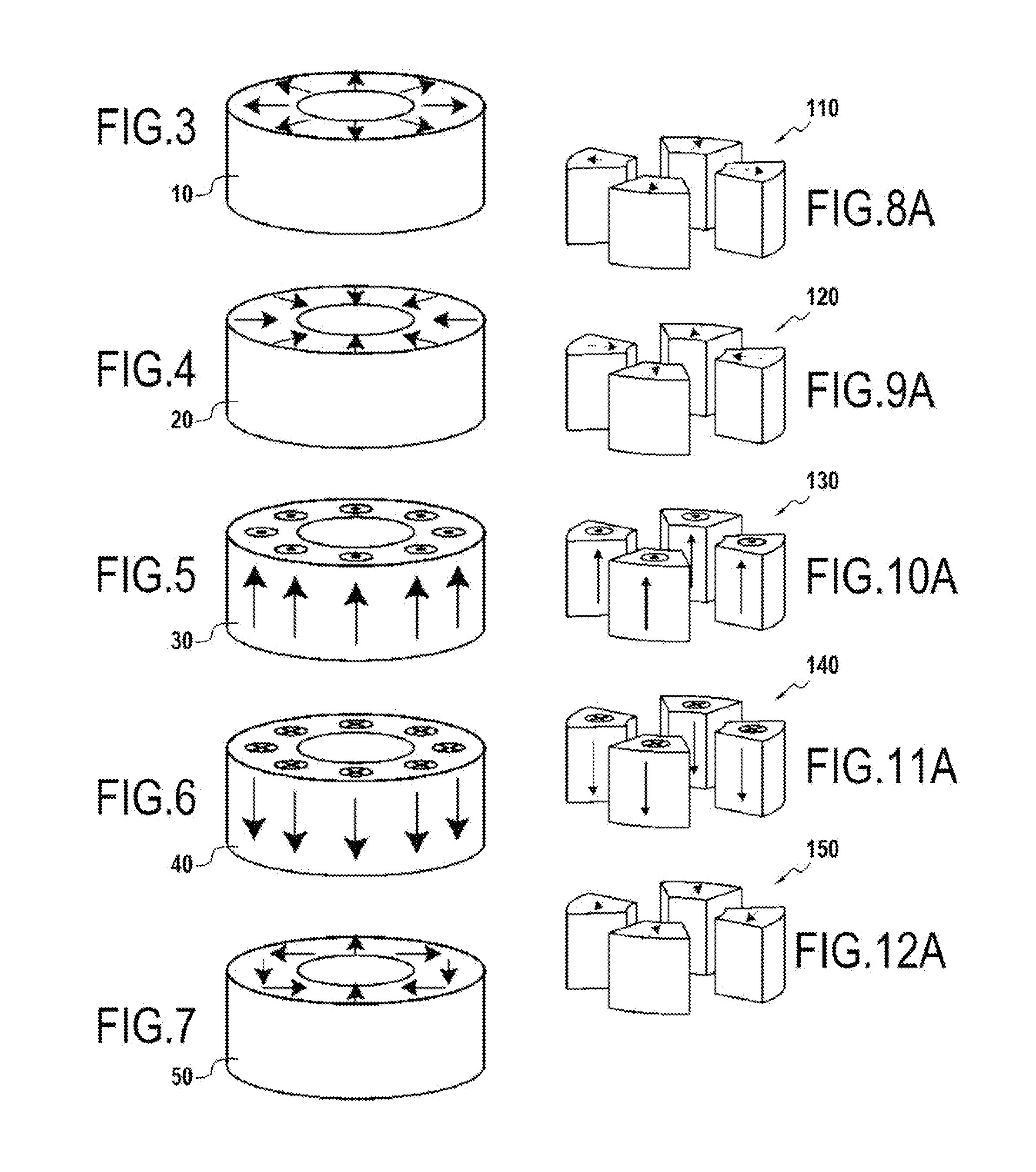
Magnetised structure inducing a homogeneous field, in the centre thereof, with a pre-determined orientation
A magnetized structure that induces in a central area of interest a homogeneous magnetic field of predetermined orientation relative to a longitudinal axis (z) of the structure comprises at least two magnetized rings (110, 120) disposed symmetrically relative to a plane (P) that is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis (z) and that contains the central area of interest, and at least one median annular magnetized structure disposed at least partly between the two magnetized rings (110, 120) and also disposed symmetrically relative to the plane (P) of symmetry, one of the two magnetized rings (110) being magnetized radially relative to the longitudinal axis (z) with divergent magnetization and the other of the two magnetized rings (120) being magnetized radially relative to the longitudinal axis (z) with convergent magnetization, and the median annular magnetized structure being magnetized with an orientation different from that of the magnetization of the two magnetized rings (110, 120). The median annular magnetized structure comprises at least one magnetized ring (150) having a magnetization distribution of orientation that varies as in Halbach dipoles and the first two magnetized rings (110, 120) and the median annular magnetized structure are each divided into individual components in the form of regularly distributed identical sectors.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Measuring device and method of non-orthogonal angle between magnetic coil X and Y axes of atom magnetometer
The invention aims to provides a measuring device and method suitable for a non-orthogonal angle between saddle-shaped coil X and Y axes of an SERF atom magnetometer, and belongs to the technical fields of optical detection, weak magnetic detection and uniform magnetic field coils. Aimed at the problem that non-orthogonality of three-dimensional magnetic coils influences the sensitivity of the SERF atom spin magnetometer, the measuring method and device of the non-orthogonal angle between the saddle-shaped coil X and Y axes, which are based on Bloch kinetic equations, are provided. The invention fills in the blanks of the measuring method and device of the non-orthogonal angle between the saddle-shaped coil X and Y axes of the atom magnetometer, effective references are provided for the atom magnetometer to estimate and compensate a magnetic field deviation value, and the improvement of the sensitivity of the SERF atom magnetometer is ensured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Self-compensating magnetoelastic torque sensor system
InactiveUS20100242626A1Improve reliabilityWork measurementMagnetostrictive property measurementsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic source
An improved magnetic torque transducer arrangement for self-compensating effects of external magnetic sources and temperature offset comprises a shaft with at least one magnetized zone, at least one active magnetic field sensor and at least one passive magnetic field sensor disposed in such a way that active field sensor always in a position with higher magnetic field strength arise from applied torque than that of passive sensor. Passive field sensors may also be placed in both sides of the active field sensor, or on one side of active field sensor only. The transducer output is obtained by subtract the output of passive field sensors from that of active field sensor thus cancel out the effect of interfering magnetic field flux and temperature offset on the torque transducer, and partially filter out temperature sensitivity drift and rotational dependant signal. The sensitivity of active and passive field sensors can also be electrically matched by calibrating them in a uniform magnetic field, thus a completely common mode rejection can be achieved. The sensor arrangements may also be utilized in other type of sensors that extract changes in magnetic fields to indirectly detect direction, speed, presence, force, linear position, or angle to cancel out interfering magnetic field and temperature offset effect.
Owner:WENG WENSHENG
Tailored mesh susceptors for uniform induction heating, curing and bonding of materials
Mesh susceptors for use in induction heating and bonding processes are tailored to obtain more uniform heating across the susceptor and hence, the bondline, when bonding composite parts. The susceptors are tailored by cutting and removing segments from the mesh areas where the induced current and hence, heat generation, is highest. An algorithm is employed to predict the induced current patterns throughout the mesh so that areas of high heat generation can be identified and then cut and removed. In this way, essentially uniform temperatures in metal mesh susceptors may be achieved by specifically designed cut patterns within the mesh even though the mesh susceptor is subject to non-uniform magnetic fields.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
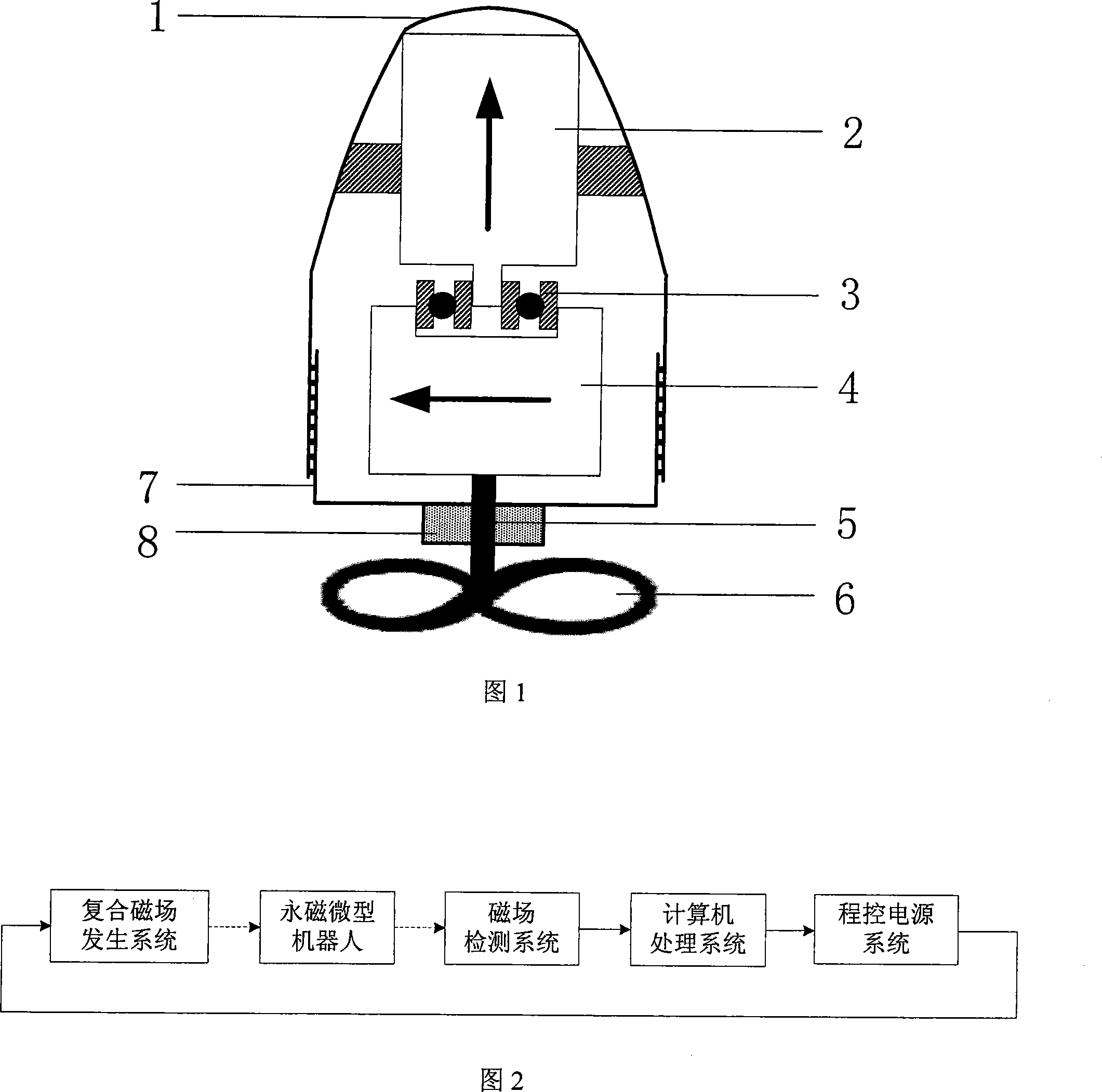
Permanent magnetism minisize robot
InactiveCN101169212ARealize external wireless driver controlReduce volumePigs/molesHelmholtz coilDc current
A permanent-magnet micro-robot consists of a casing (5), an axially magnetized permanent magnet (1), a radially magnetized permanent magnet (2), a non-magnetic miniature bearing (3) and a propeller (4), wherein, the head of the casing (5) is round and smooth, and a bottom (6) has a cavity (7) which is filled with lubricating grease; the axially magnetized permanent magnet (1) and the radially magnetized permanent magnet (2) are connected by the non-magnetic miniature bearing (3); the radially magnetized permanent magnet (2) and the propeller (4) are fixed via an axle (8) of the propeller. An outside magnetic field is generated by a rotation magnetic field device and a uniform magnetic field device, wherein, the rotation magnetic field consists of three groups of perpendicular Helmholtz coils, a sinusoidal current source and a phaser; the uniform magnetic field device consists of three groups of perpendicular Helmholtz coils and three groups of direct current sources. Under the effect of the rotation magnetic field, the robot rotates with the radially magnetized permanent magnet (2) and produces the axial driving force to drive; at the same time, under the deflecting guidance of the uniform magnetic field, the robot realizes flexible steering and moves along an expected locus.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Superconducting magnet apparatus for MRI
InactiveUS20060290351A1Avoid spreadingReduce oscillationMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting CoilsHomogeneous magnetic field
In a superconducting magnets for MRI configured to generate a homogeneous magnetic field and a gradient magnetic field in a space between a top superconducting magnet and a bottom superconducting magnet, the bottom superconducting magnet is provided with a supporting member that supports a helium vessel, and the supporting member is fixed to a vacuum vessel of the bottom superconducting magnet at one end, and is fixed to the floor surface in the vicinity of the end fixed to the vacuum vessel. A high-quality MR image can be thus obtained by preventing direct transmission of oscillation of the gradient coils to the superconducting magnet and reducing oscillation of the gradient coils while achieving a reduction of the overall superconducting magnet in size.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
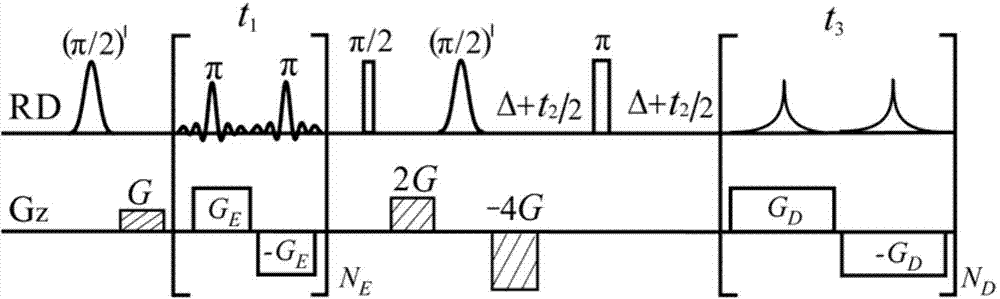
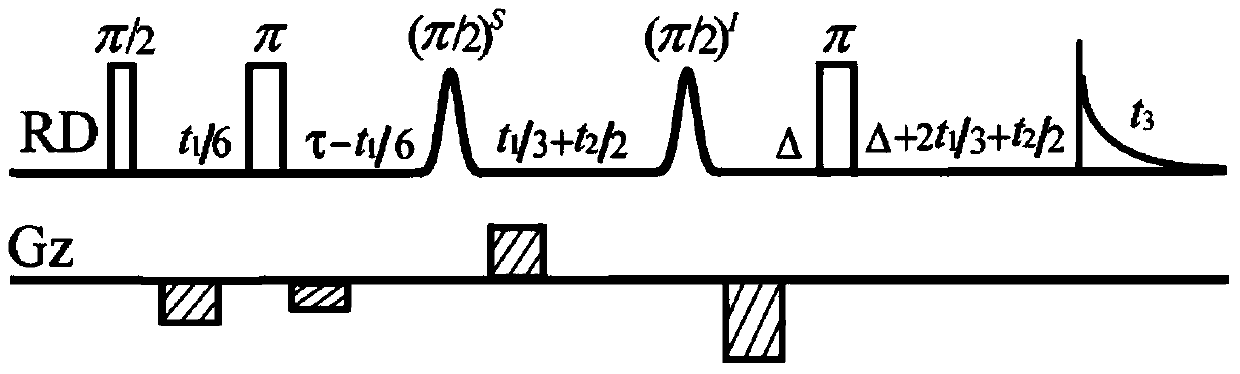
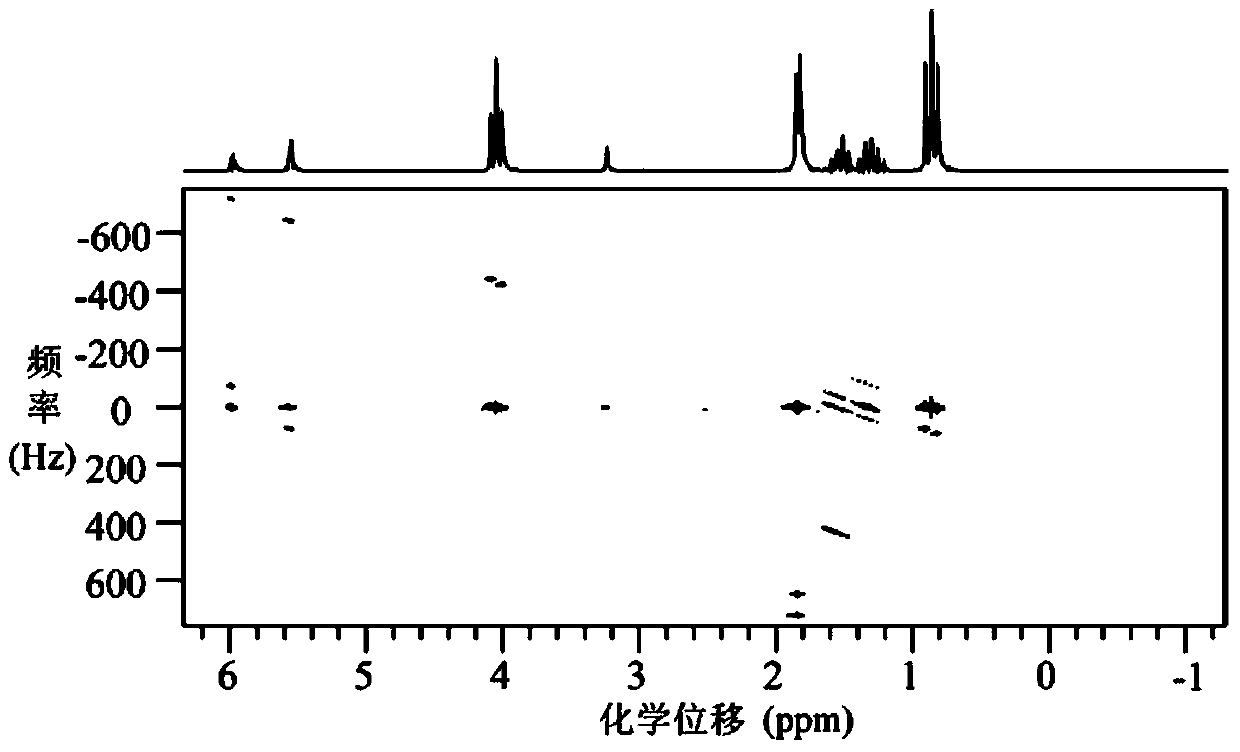
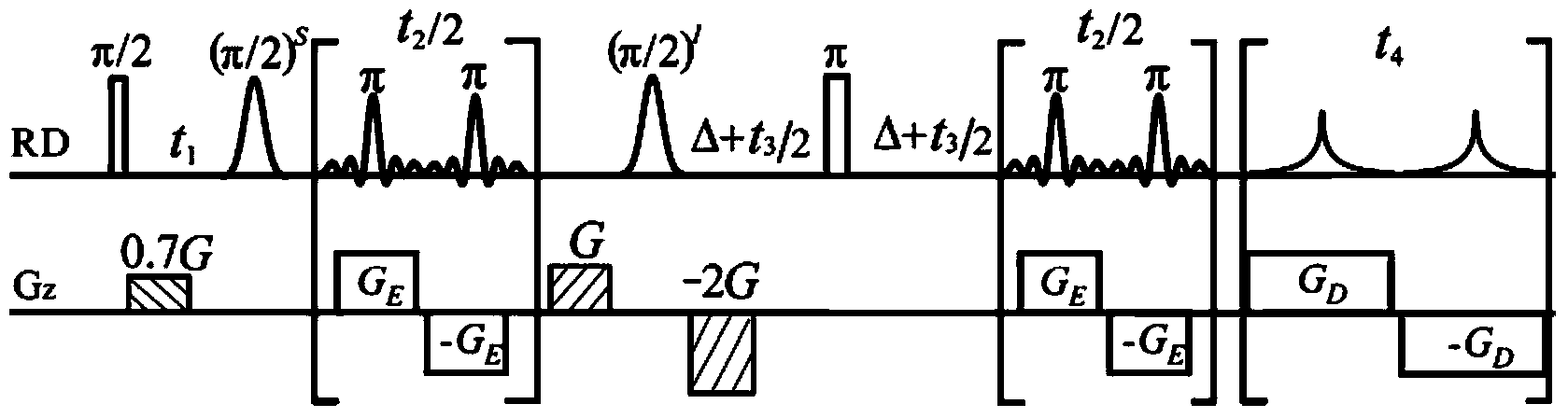
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimension spin echo related spectrum under uneven magnetic field
ActiveCN103744042AOvercoming the influence of uneven magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsLine widthPulse sequence
A method for obtaining a nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimension spin echo related spectrum under an uneven magnetic field relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance wave spectrum detection method and comprises the steps of using a normal one-dimension pulse sequence to sample a one-dimension spectrum, obtaining the line width of spectral lines, and providing a basis for spectrum width parameter setting, wherein the line width value also reflects the uniformity condition of a magnetic field; introducing well precompiled two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences onto a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; opening a multi-quantum coherent signal selection module, a three-dimension sampled indirect dimension evolution period t1 combination and indirect dimension evolution period t2 combination and an echo delay module among the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences; setting each experiment parameter of the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences; executing the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences, of which the experiment parameters are set, for data sampling; after the data sampling is finished, performing related data postprocessing to obtain the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum uninfluenced by the uneven magnetic field. The method has no need of shimming operation and is simple, convenient and effective.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
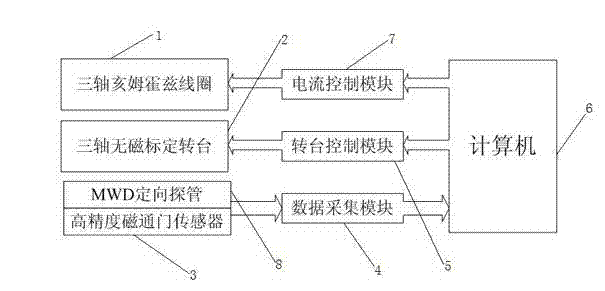
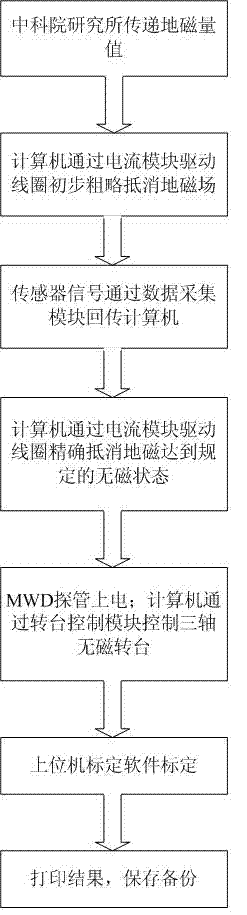
Active magnetic field calibration method for measurement while drilling (MWD) directional probe
InactiveCN103089242ASolve the problem of qualification calibrationCalibration method is fastSurveyHelmholtz coilData acquisition
The invention relates to an active magnetic field calibration method for a measurement while drilling (MWD) directional probe. According to the method, an MWD directional probe active magnetic field calibration instrument is used for calibration, and a high-accuracy fluxgate sensor and an MWD directional probe are arranged on a three-axis non-magnetic calibration rotation table; a computer controls a current module to produce current with certain power, a three-axis square Helmholtz coil is driven to produce a uniform magnetic field in a certain range in a central area to offset an earth magnetic field, and a non-magnetic space is formed in a certain range; the fluxgate sensor and the MWD directional probe detect signals, a data acquisition module acquires the signals, and the signals are transmitted to the computer; and calibration software on the computer are used for calculation and comparison to calibrate whether the current MWD directional probe has the qualification that the MWD can descend into the well to work normally. The method has the advantages of quickness, accuracy and stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Magnetic assembly and method for defining a magnetic field for an imaging volume
InactiveUS20110175694A1Small sizeCompact assemblyMagnetic measurementsRadiation/particle handlingHomogeneous magnetic fieldMagnetic field magnitude
Disclosed herein is a magnet assembly that includes at least two magnets arranged in a fixed spaced relationship with one another thereby to define a space between the magnets that encompasses an imaging volume. Each of the magnets produces a variety of magnetic field strengths across inward-facing surfaces thereof that, in combination, produce an acceptably homogeneous magnetic field in the imaging volume. Also disclosed is a method of defining a magnetic field for an imaging volume. The method comprises generating an initial model of a magnet assembly; estimating a magnetic field for the imaging volume based on the model; calculating deviation between the estimated magnetic field and a target magnetic field for the imaging volume; and updating the model to reduce the deviation by modifying the magnet assembly to produce a variety of magnetic field strengths that, in combination, produce substantially the target magnetic field in the imaging volume.
Owner:ALBERTA HEALTH SERVICES
Superconductive magnet device
InactiveUS6861933B1Reduce consumptionImprove the uniformity of the magnetic fieldMagnetsElectric/magnetic detectionSuperconducting CoilsHomogeneous magnetic field
A superconductive magnet device comprises a pair of oppositely disposed superconductive bodies in which annular superconductive coils are accommodated, and fine chip-shaped ferromagnetic shims disposed on a surface of the pair of superconductive magnet bodies so as to improve uniformity of magnetic field in a uniform magnetic field in a uniform magnetic field space generated in the proximity of the center between the superconductive magnet bodies, wherein ring-shaped ferromagnetic shims are disposed concentrically with the center of annular superconductive coils on the surface of the superconductive magnet bodies.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
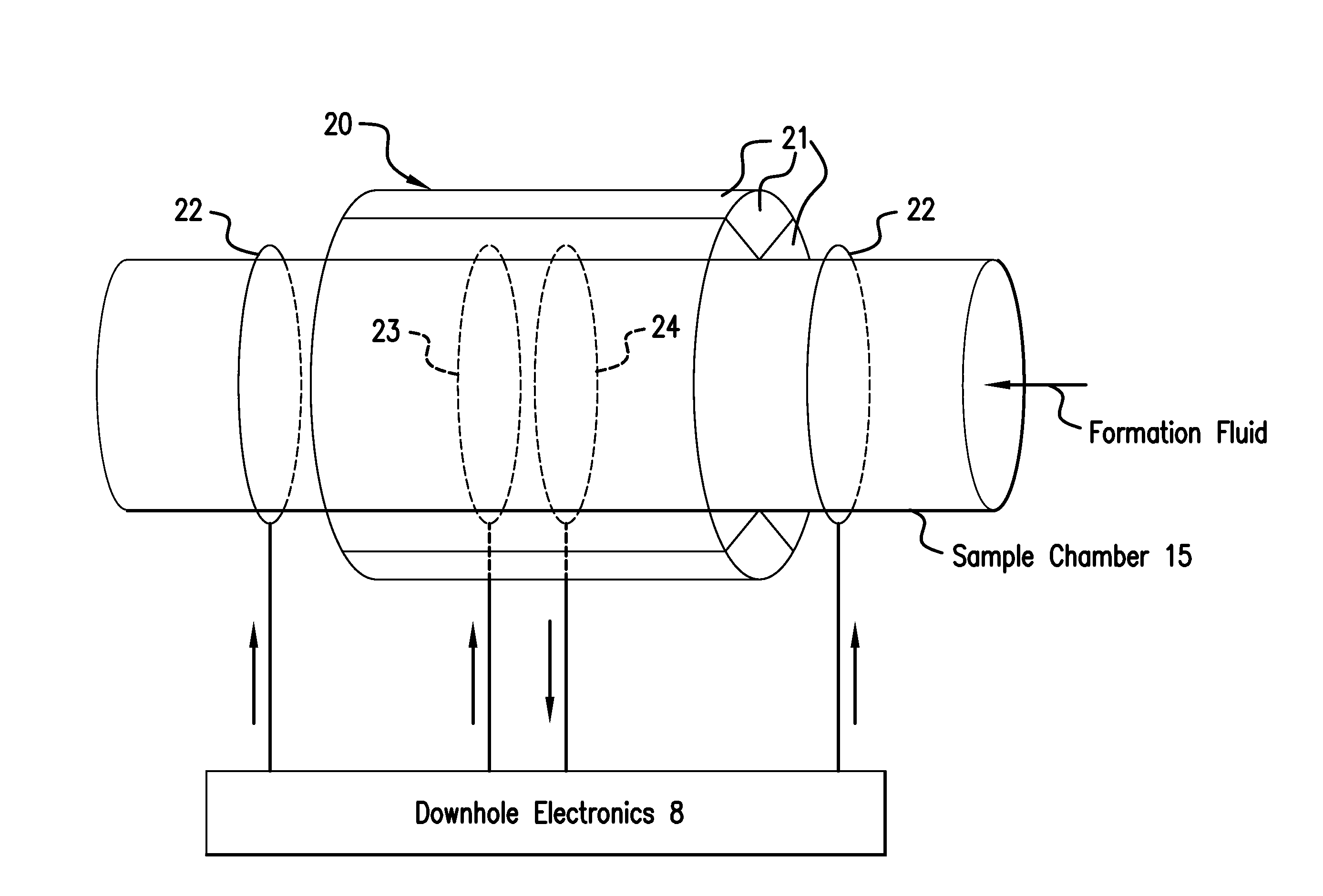
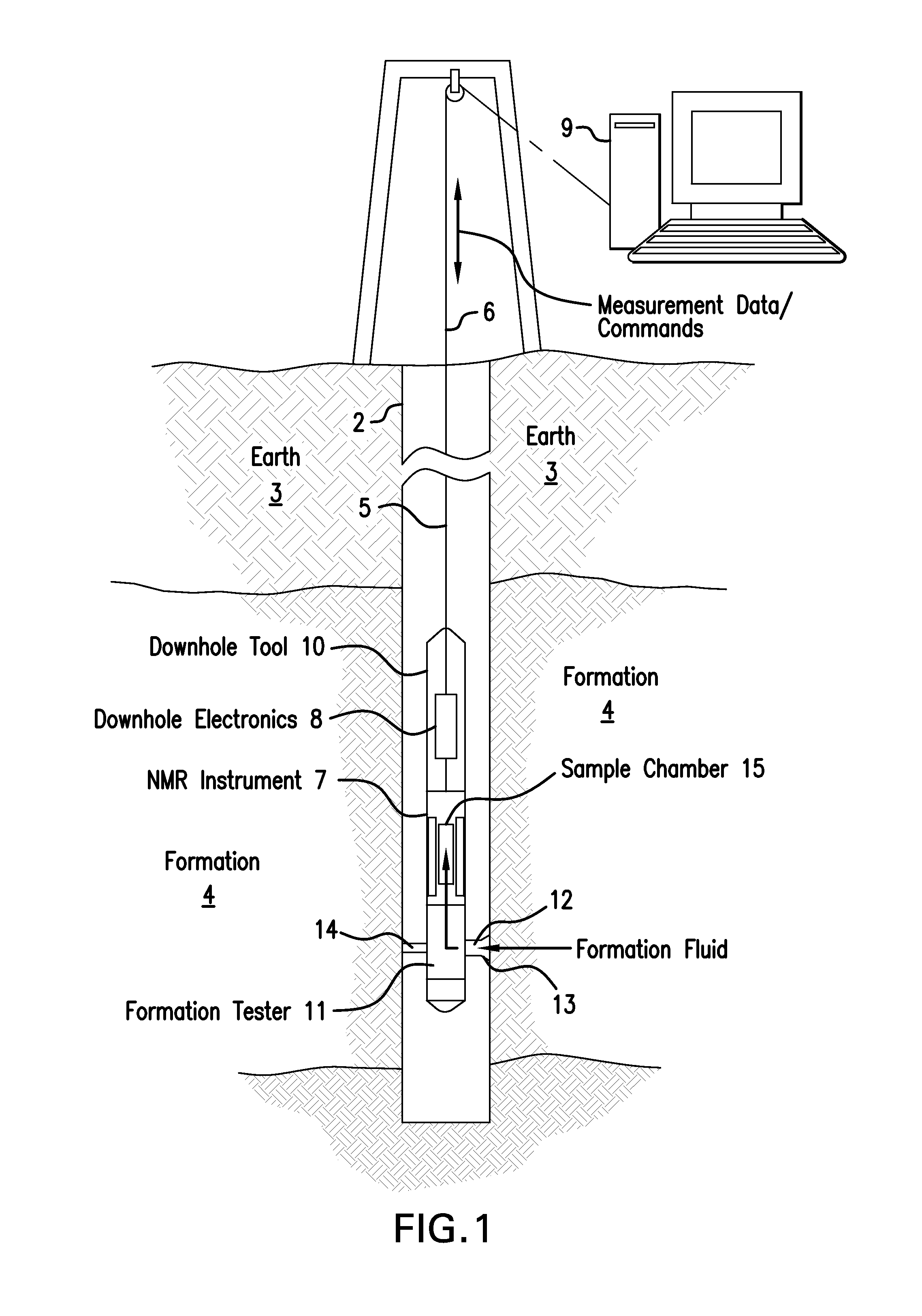
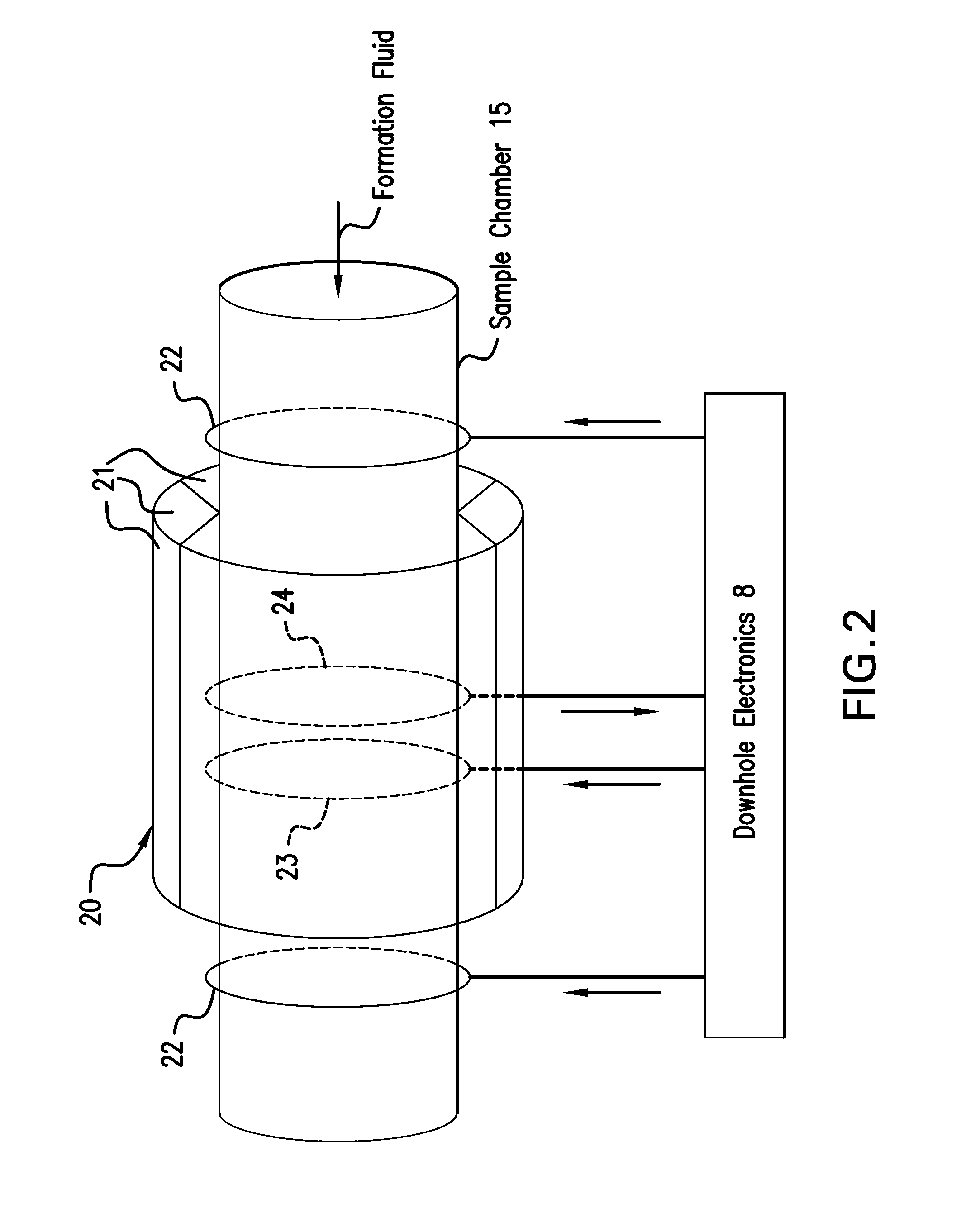
Estimating molecular size distributions in formation fluid samples using a downhole nmr fluid analyzer
ActiveUS20140225607A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceTime domainNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for estimating a property of subsurface material includes extracting a sample of the material using a downhole formation tester and performing a plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements on a sensitive volume in the sample where each measurement in the plurality is performed in a static homogeneous magnetic field with a pulsed magnetic field gradient that is different in magnitude from other NMR measurements to provide a waveform signal. The method further includes transforming each received waveform signal from a time domain into a frequency domain and comparing the frequency domain signal to a reference to provide proton chemical-shift information related to a chemical property of one or more molecules in the sample and transforming the frequency domain signals into a complex number domain that quantifies waveform signal amplitude changes to provide one or more diffusion rates with each diffusion rate being associated with a corresponding frequency.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
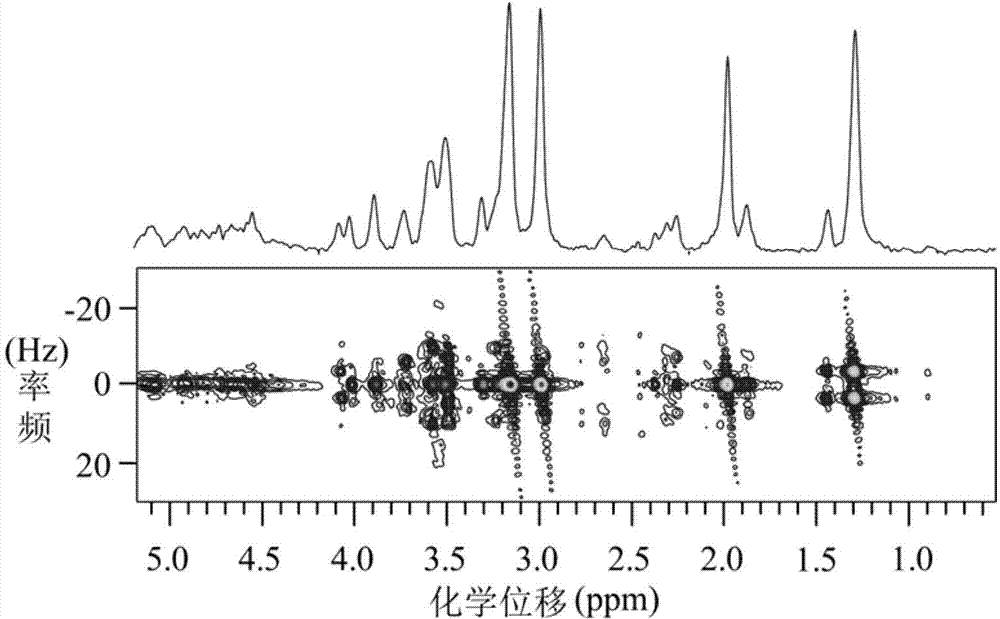
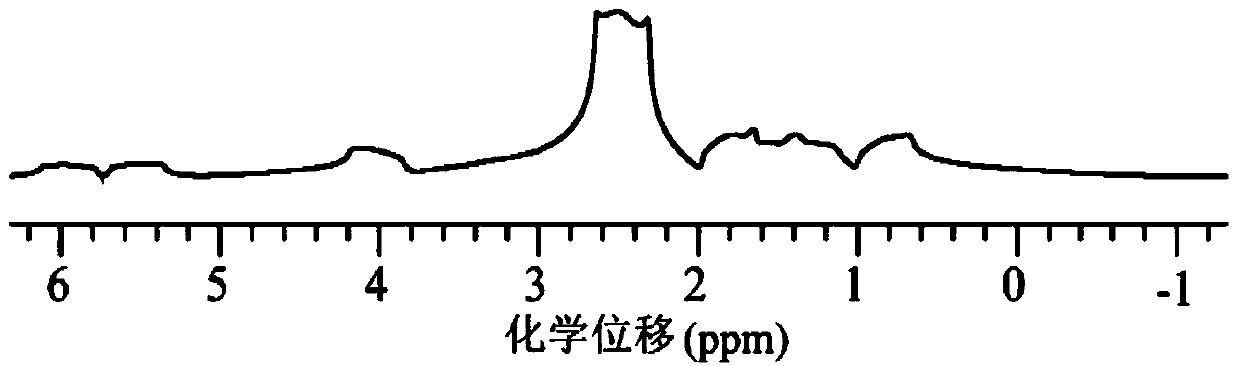
Method for obtaining high-resolution three-dimensional NMR spectrum under non-uniform magnetic field
InactiveCN103941204AMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLine widthZero quantum coherence
The invention provides a method for obtaining a high-resolution three-dimensional NMR spectrum under a non-uniform magnetic field, and relates to nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometers. The method comprises the steps that (1) a one-dimensional spectrum is sampled by using a conventional one-dimensional pulse sequence and used for analyzing the condition of the non-uniformity of the magnetic field to obtain the line width of a spectral line and provide a basis for experimental spectral width parameter settings; (2) a precompiled intermolecular zero-quantum-coherence three-dimensional spectrum pulse sequence is guided into a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; (3) an intermolecular zero-quantum-coherence signal selection module, an indirect dimension evolution period t1 module, an indirect dimension evolution period t2 module, an indirect dimension evolution period t3 module and a signal sampling period t4 module of the intermolecular zero-quantum-coherence three-dimensional spectrum pulse sequence are opened, and experiment parameters of all the modules of the pulse sequence are set; (4) the intermolecular zero-quantum-coherence three-dimensional spectrum pulse sequence in the step (3) after experimental parameter setting is executed, and data sampling is performed; (5) after data sampling is completed, relevant data post-processing is performed, so that the high-resolution three-dimensional NMR spectrum free of influence by the non-uniform magnetic field is obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
System and method for externally calibrated parallel imaging in the presence of an inhomogeneous magnetic field
ActiveUS20160154080A1Efficient measurementReduce acquisition timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceParallel imaging
A system and method for accelerated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) includes controlling an RF system of an MRI system to acquire coil calibration data from a subject including a material causing inhomogeneities in a static magnetic field of the MRI system when arranged in the bore of the MRI system. After acquiring the coil calibration data, the RF system is controlled to acquire imaging data from the subject at multiple different resonance frequency offsets. The spectral bin images relate specific resonance frequencies to distinct spatial locations in the static magnetic field of the MRI system. An image of the subject is reconstructed from the imaging data using coil calibration data and the spectral bin data to provide spatial encoding of the image.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Micro-machined vapor cell
ActiveUS20160218726A1Low resistivityIncrease volumePulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksMiniaturizationHomogeneous magnetic field
The invention concerns a micro-machined vapor cell comprising a central silicon element forming a cavity containing vapor cell reactants such as alkali metal or alkali metal azide, buffer gas(es), and / or anti relaxation coating(s); a first and a second glass caps sealing the cavity; and a solenoid arranged to provide a homogeneous magnetic field to said vapor cell. The solenoid is coiled directly on the central silicon element of the vapor cell. This invention is an improvement for the highly miniaturized atomic clocks developments.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
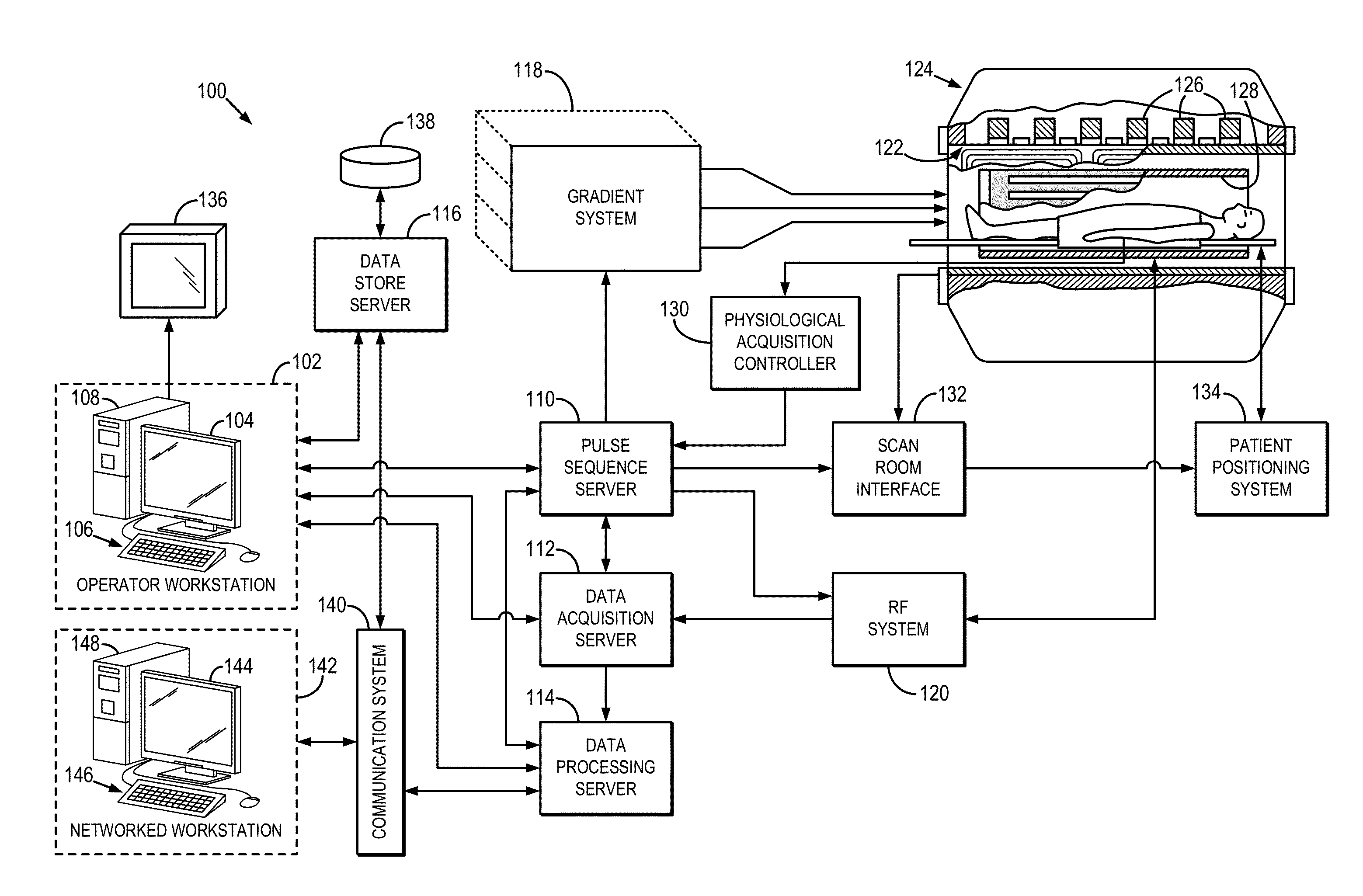
Installation for investigating objects using magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20050200360A1Reduce in quantityInhibit transferAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceEngineering
An installation for the investigation of objects by means of magnetic resonance has a magnet system for the production of a homogenous magnetic field in an investigational volume and is characterized in that the magnet system is disposed in a magnet room and the investigational volume, in a first operational mode of the installation, is disposed in a safety room which is decoupled in a gas-tight fashion from the magnet room. The installation in accordance with the invention facilitates the investigation of contaminated objects by means of magnetic resonance, wherein the measurement apparatus is not contaminated and simultaneously allows for simple maintenance of the system external to the safety room as well as a simple positioning of the object under investigation.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
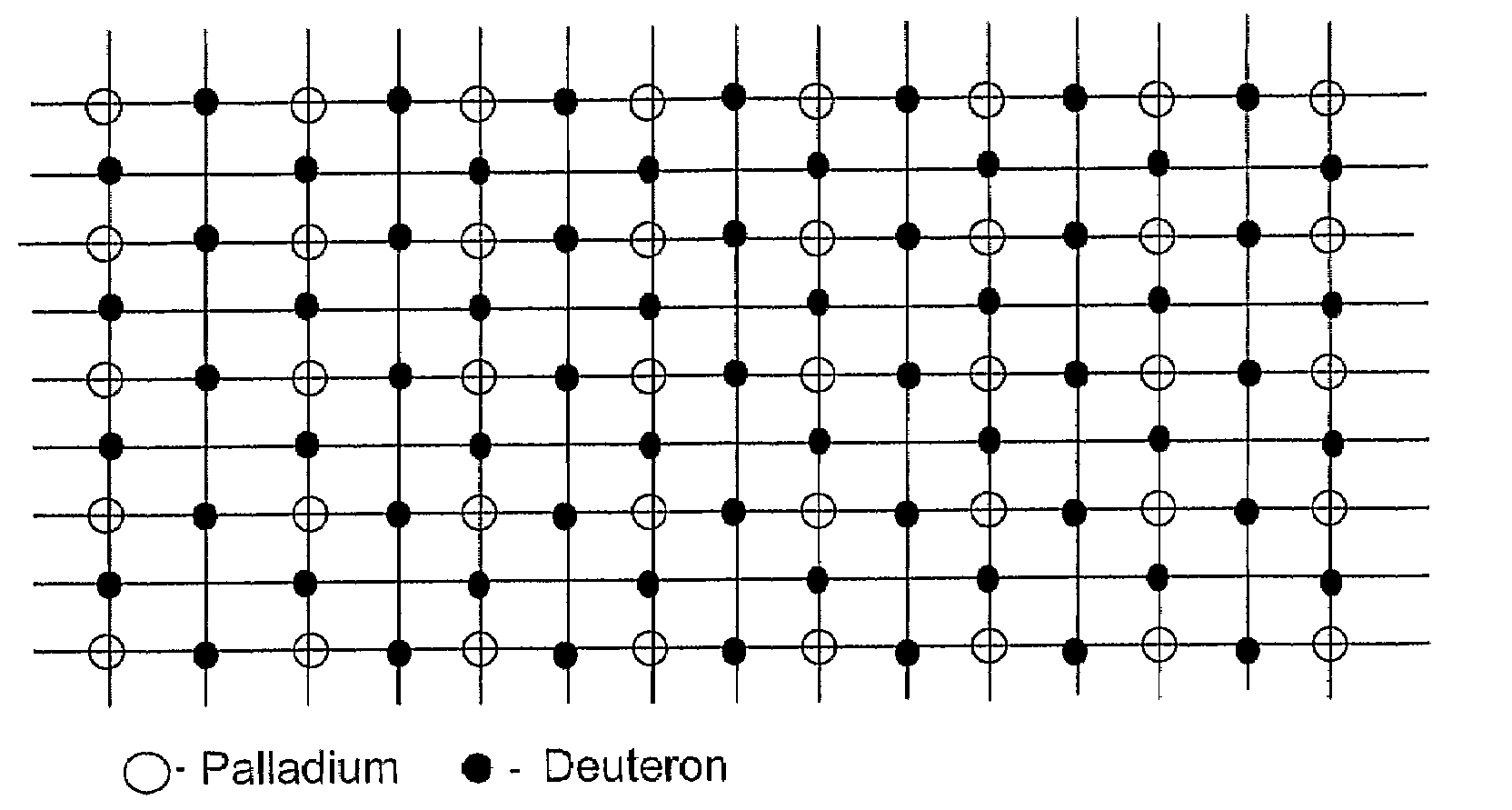
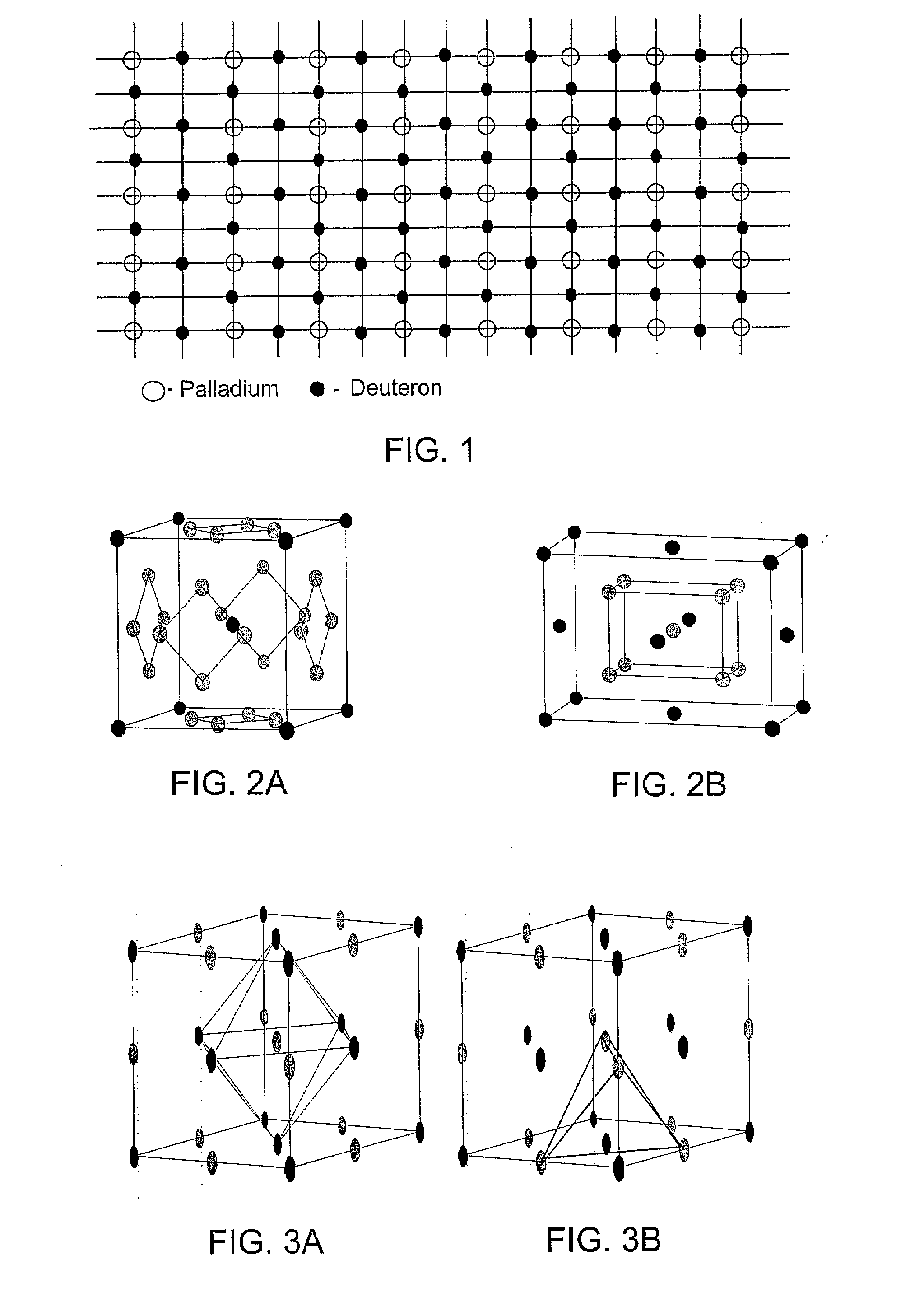
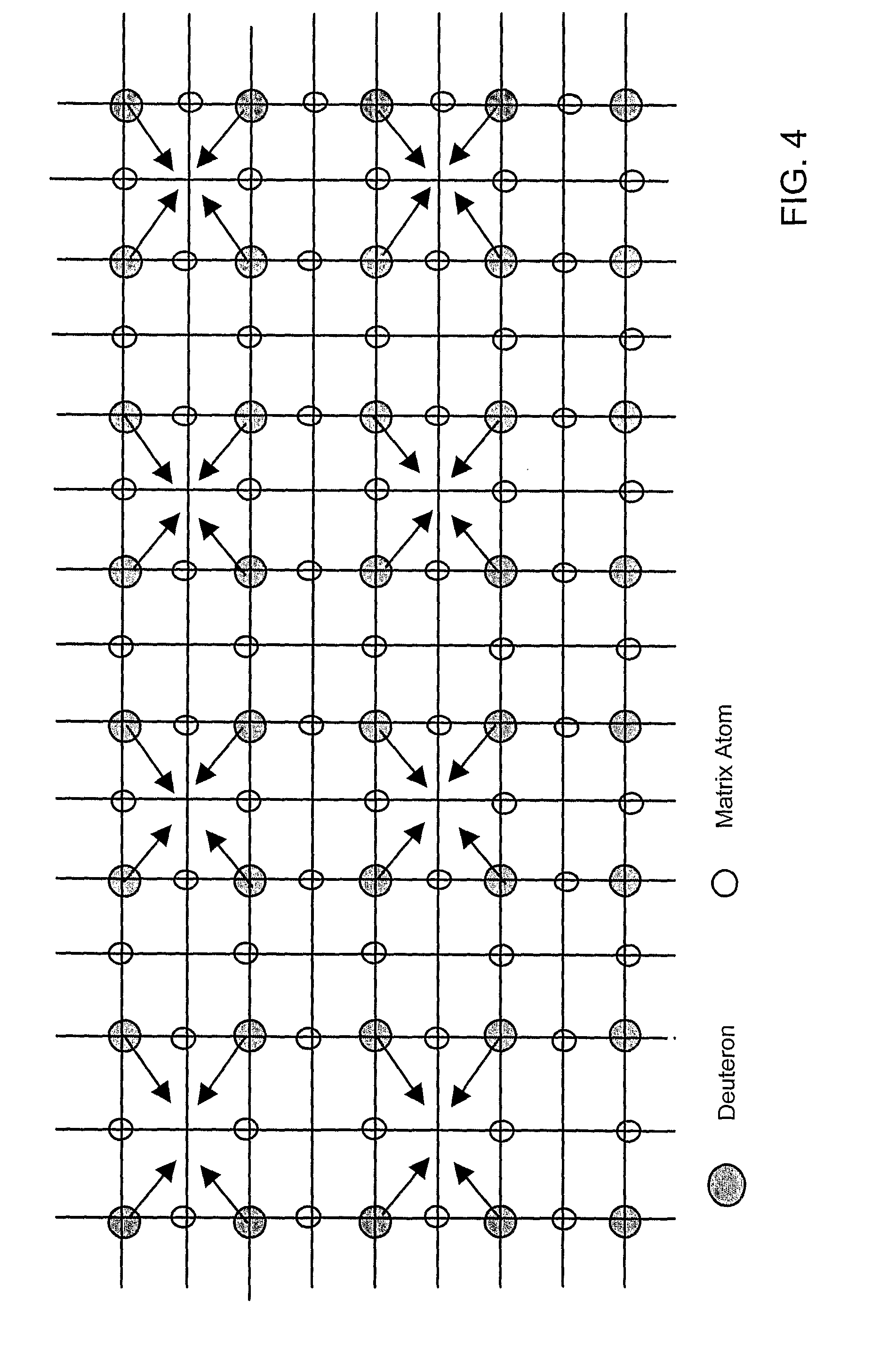
Low temperature fusion
InactiveUS20090122940A1Nuclear energy generationLow temperature fusion reactorOptical radiationScreening effect
Methods for low-temperature fusion are disclosed. In one embodiment, a symmetrical crystal lattice including a plurality of deuterons either absorbed or embedded in a heavy-electron material is selected. The method provides alternatives for initiating a vibration mode involving the deuterons on the crystal lattice that induces them to converge. The oscillating convergence of the deuterons is enhanced by the charge screening effect of electrons. The electron screening effect is in turn enhanced by the high effective-mass associated with the selected materials. The vibration modes are excited, for example, by applying an electrical stress, a uniform magnetic field, mechanical stress, non-uniform stress, acoustic waves, the de Haas van Alphen effect, electrical resistivity, infrared optical radiation, Raman scattering, or any combination thereof to the crystal lattice.
Owner:CONE PARTNERS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com