Patents
Literature
98 results about "Longitudinal Relaxation Time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
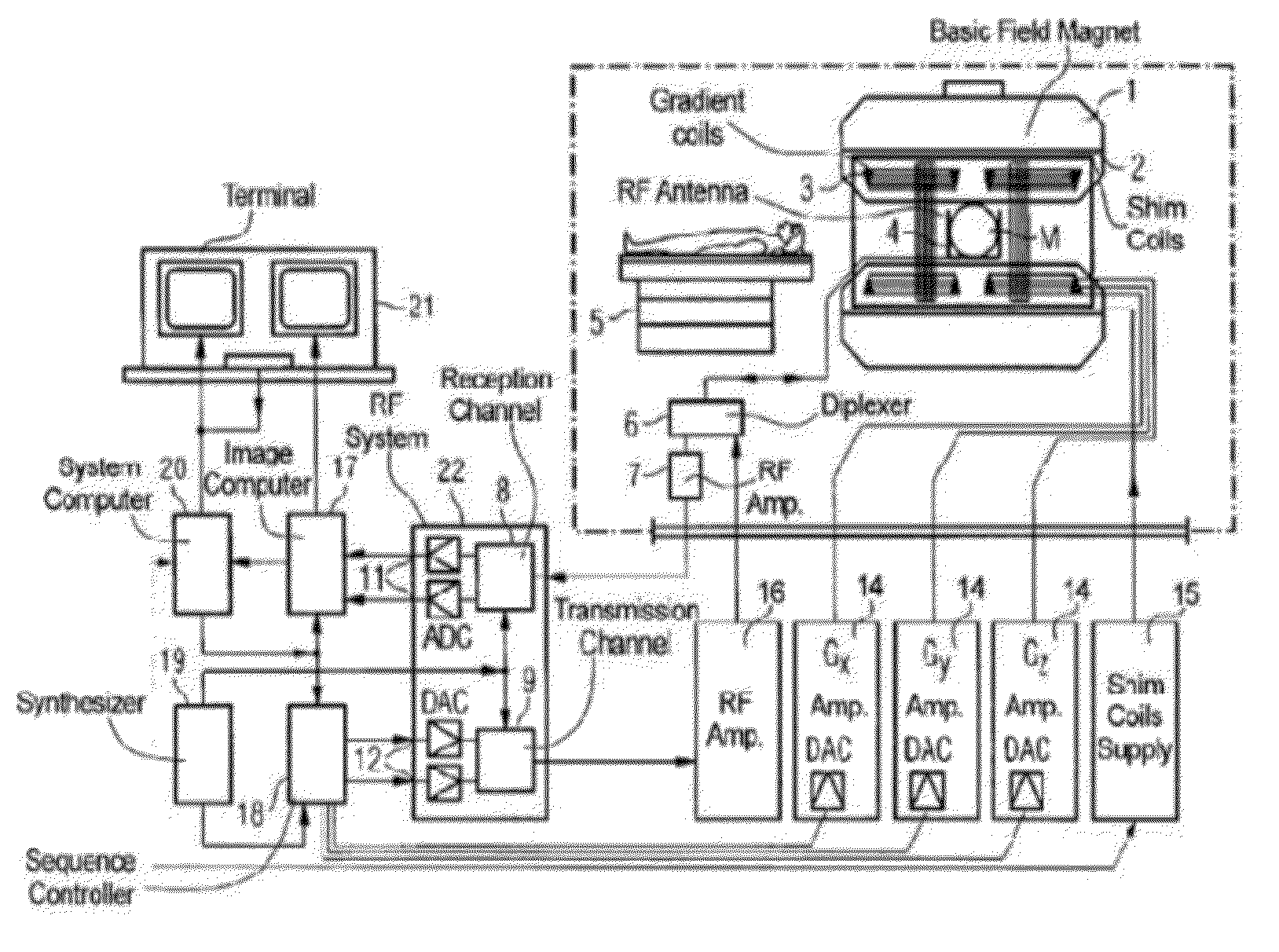
Nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and nuclear magnetic resonance measuring method
ActiveCN102519999AAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and a nuclear magnetic resonance measuring method. The analyzer comprises a radio frequency circuit, a magnet, a glass tube, a first coil and a second coil, wherein a sample to be measured is placed in the glass tube; the glass tube is fixedly arranged at a position opposite to the magnet and is placed in a magnetic field produced by the magnet; the first coil and the second coil are wound on the outer surface of the glass tube respectively and are connected with the radio frequency circuit; the first coil is placed at a uniform magnetic field produced by the magnet; and the second coil is placed at a gradient magnetic field produced by the magnet. Through the analyzer, distribution data of transverse relaxation time and longitudinal relaxation time of substances in the sample to be measured can be obtained, and distribution data of diffusion coefficients of the substances in the sample can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method and apparatus for reservoir fluid characterization in nuclear magnetic resonance logging
ActiveUS20060290350A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWell logging
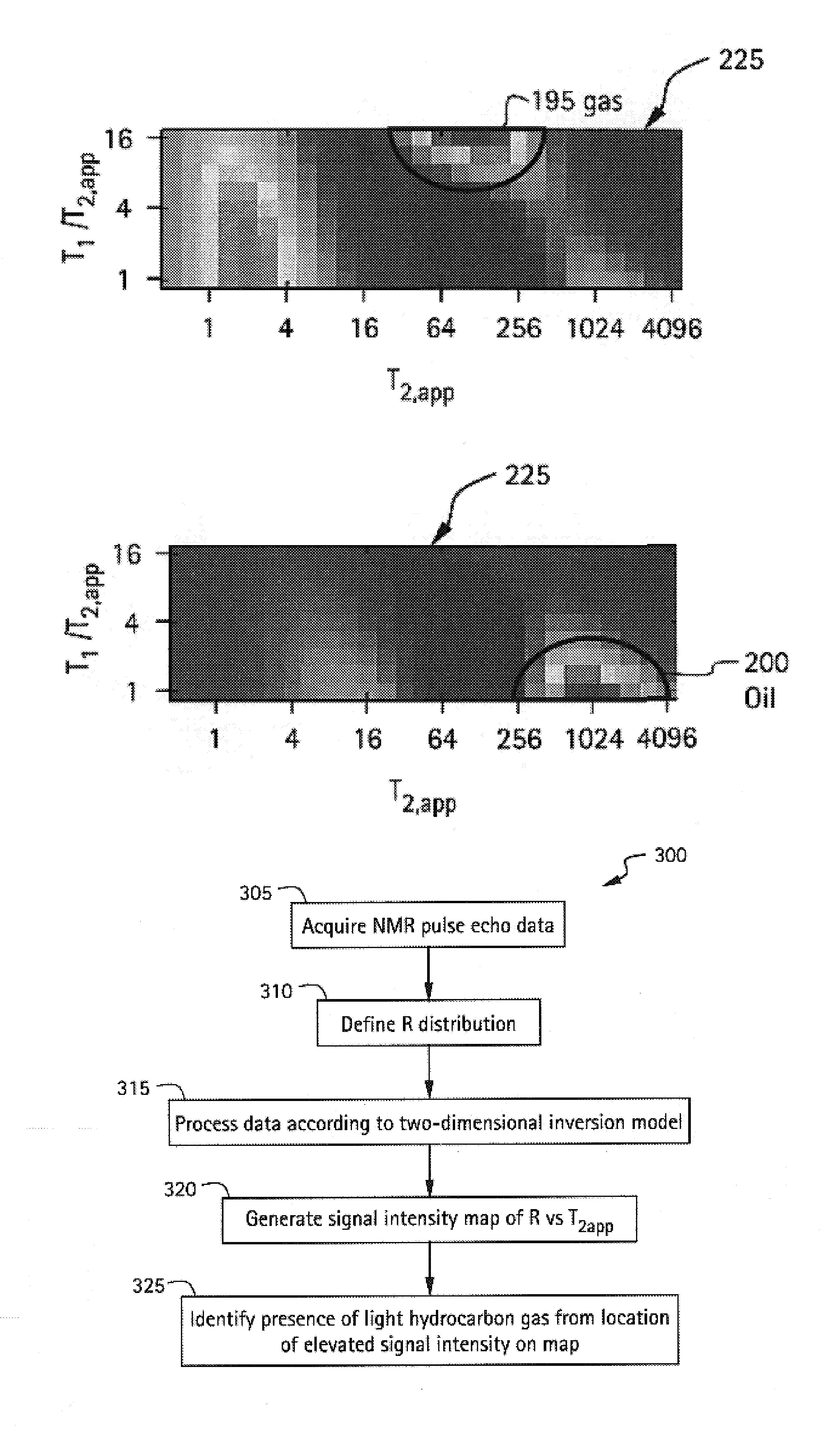
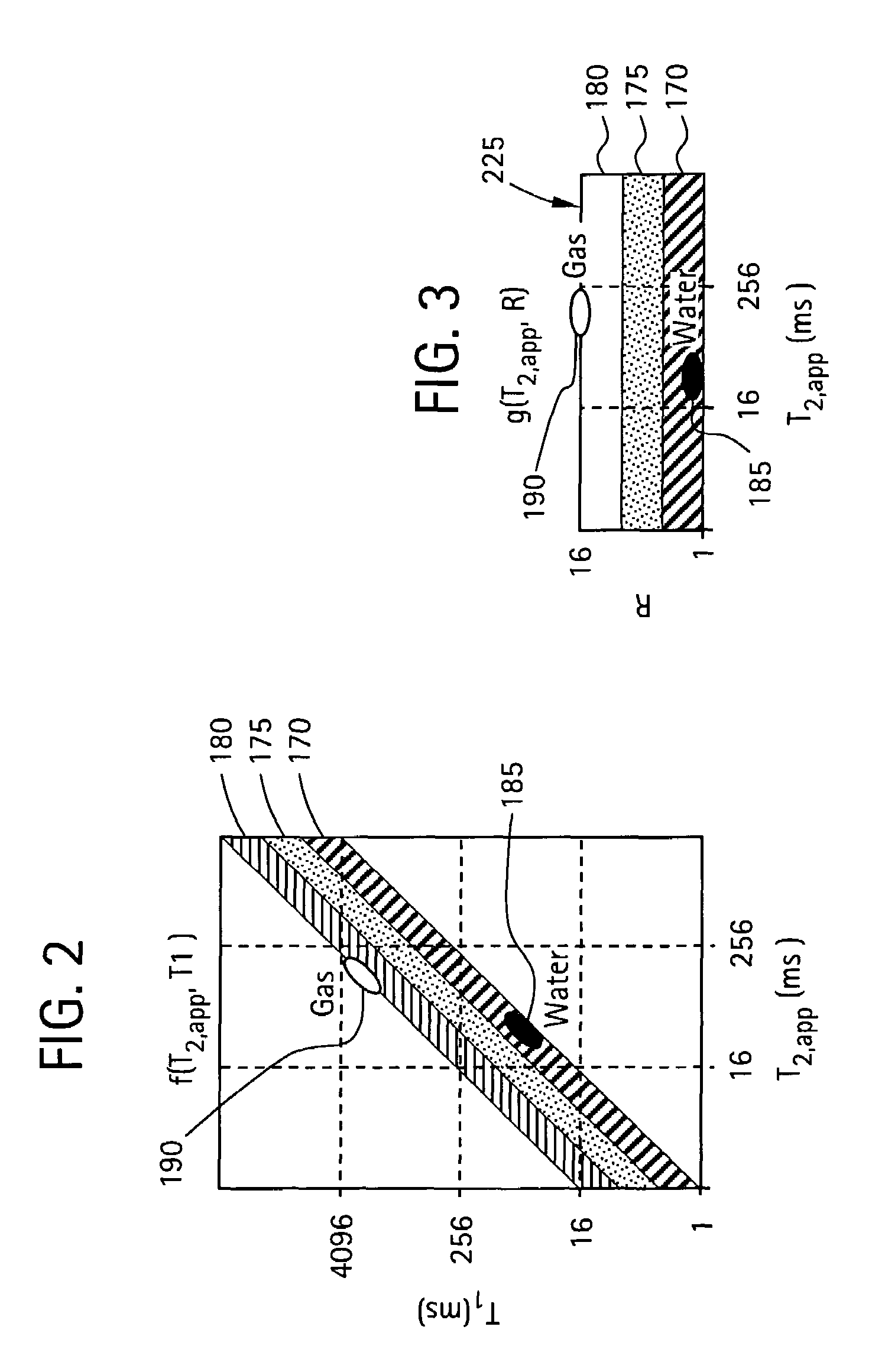
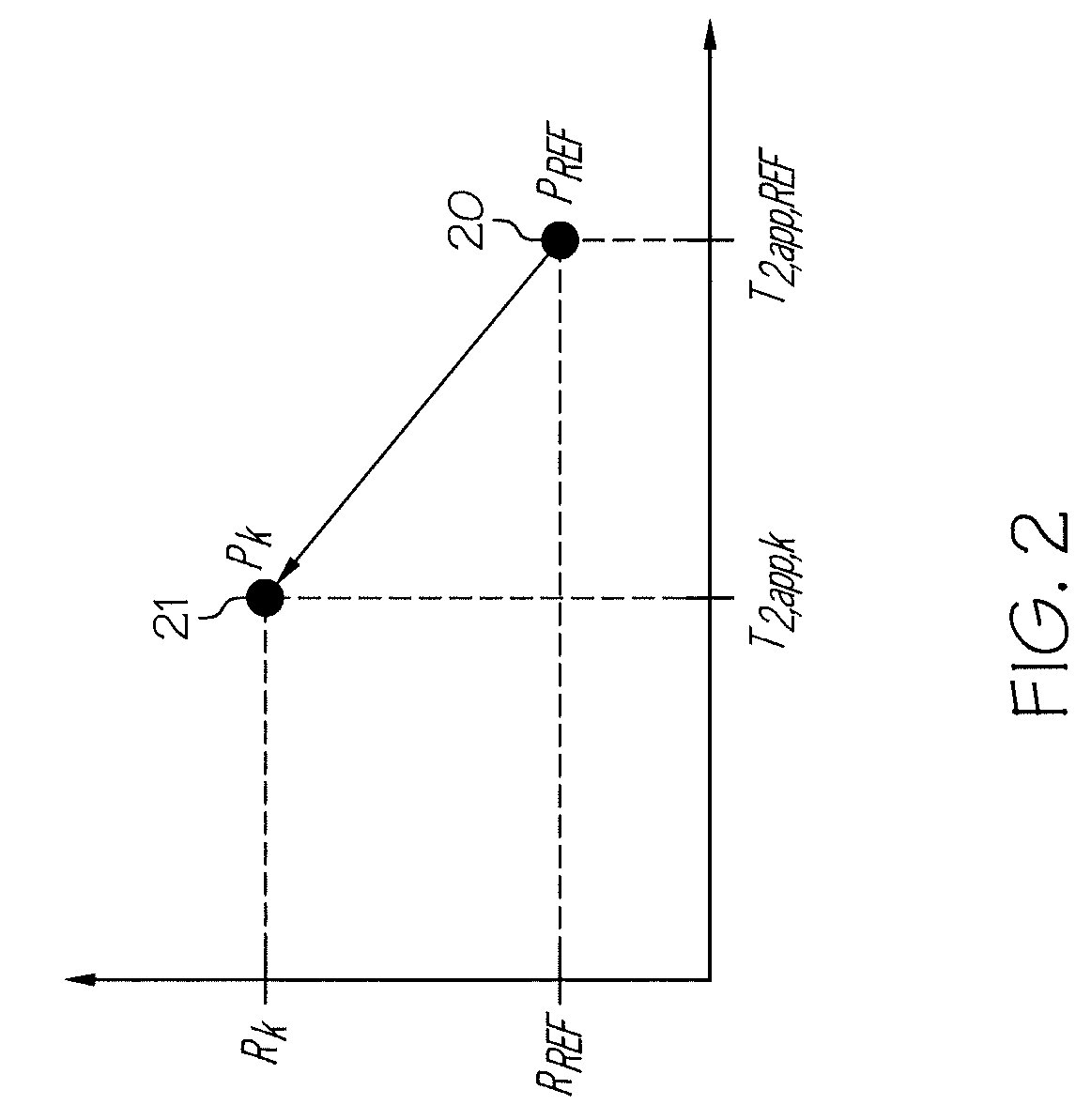
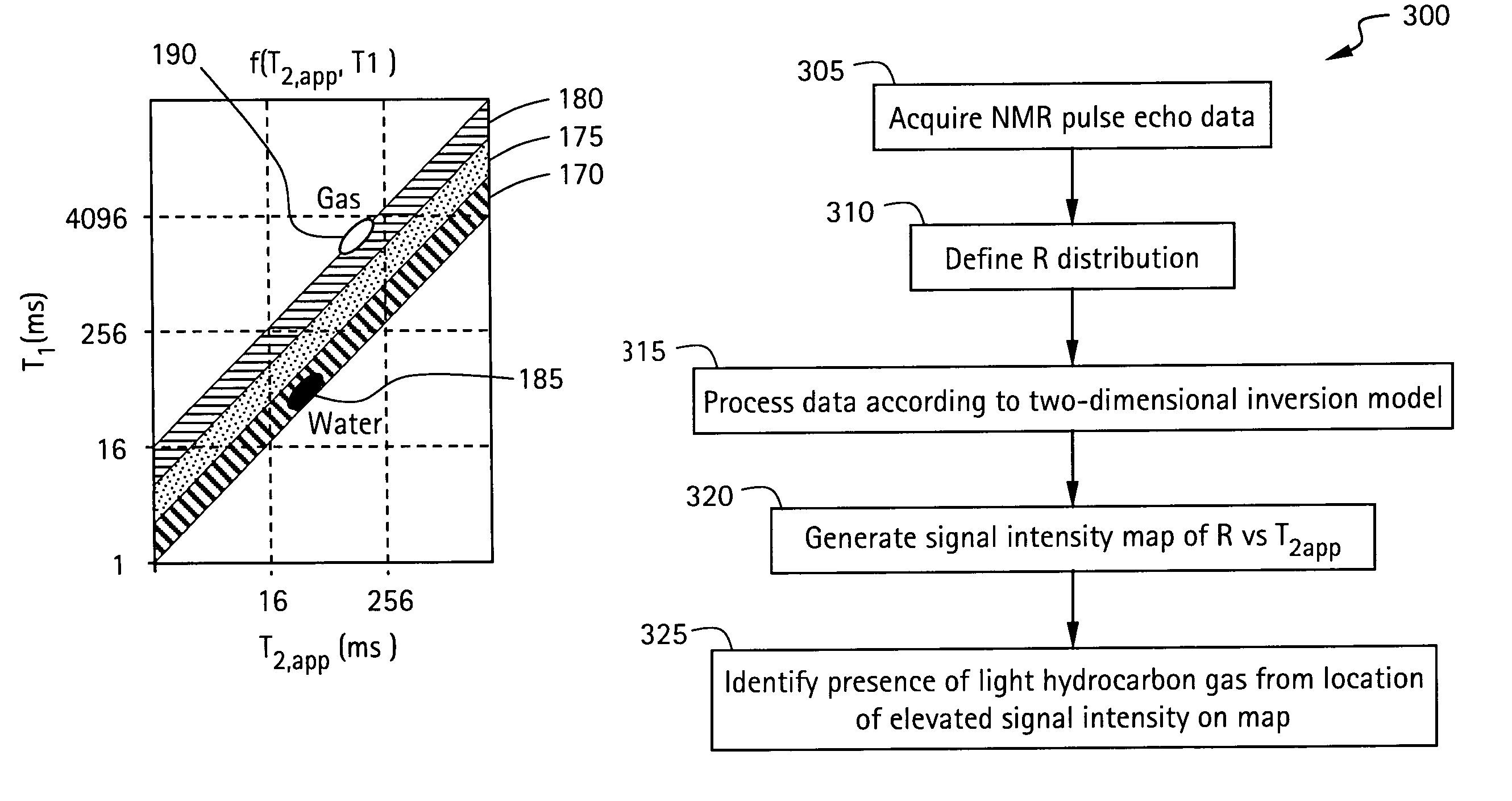
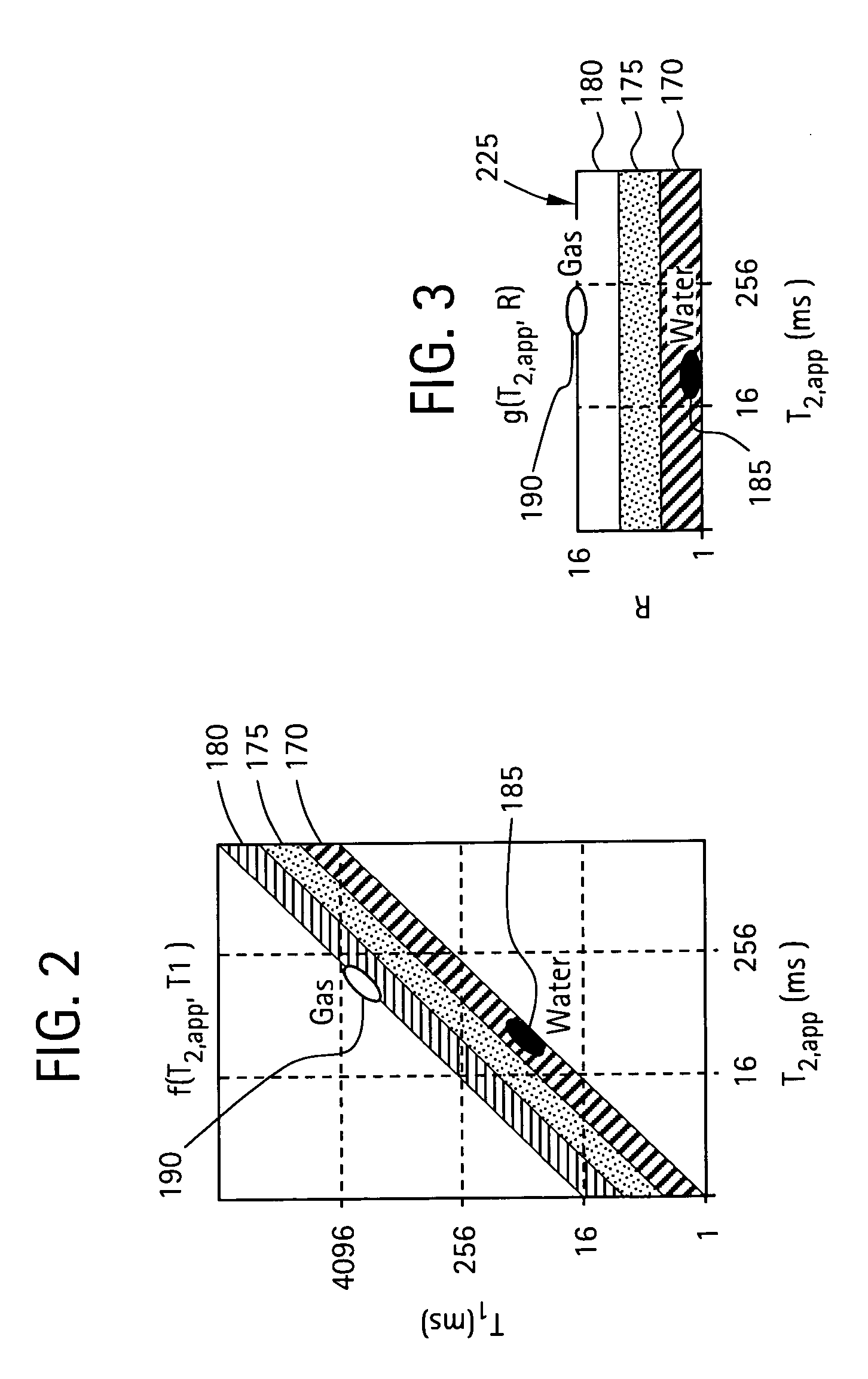
A method and apparatus for obtaining a parameter of interest relating to a region proximate a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging tool suitable for subterranean well logging is disclosed. The nuclei of the region are subjected to a pulsed NMR technique and are productive of NMR logging data, the nuclei of the region characteristically having a longitudinal relaxation time T1 distribution and an apparent transverse relaxation time T2app distribution. In response to the NMR logging data, an R distribution is defined as R=T1 / T2app, the T2app and R distributions are processed as separate bins, along with the NMR logging data, according to a two-dimensional inversion model, and a signal intensity map of R versus T2app is provided that is representative of the parameter of interest relating to the region. In response to a high-intensity signal on the map being within a first range of T2app values and a first range of R values, the presence of a light hydrocarbon within the region is identified.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
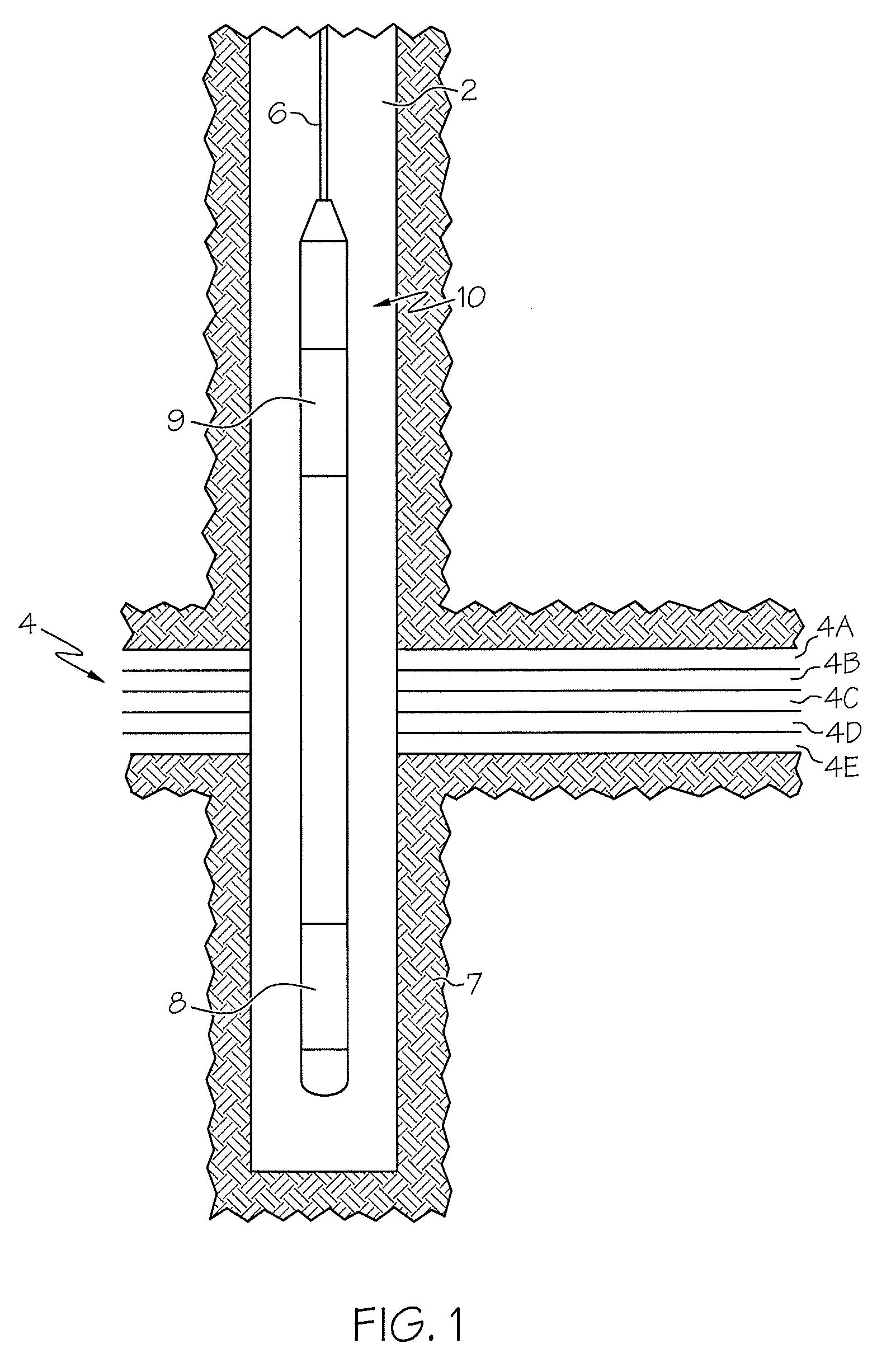
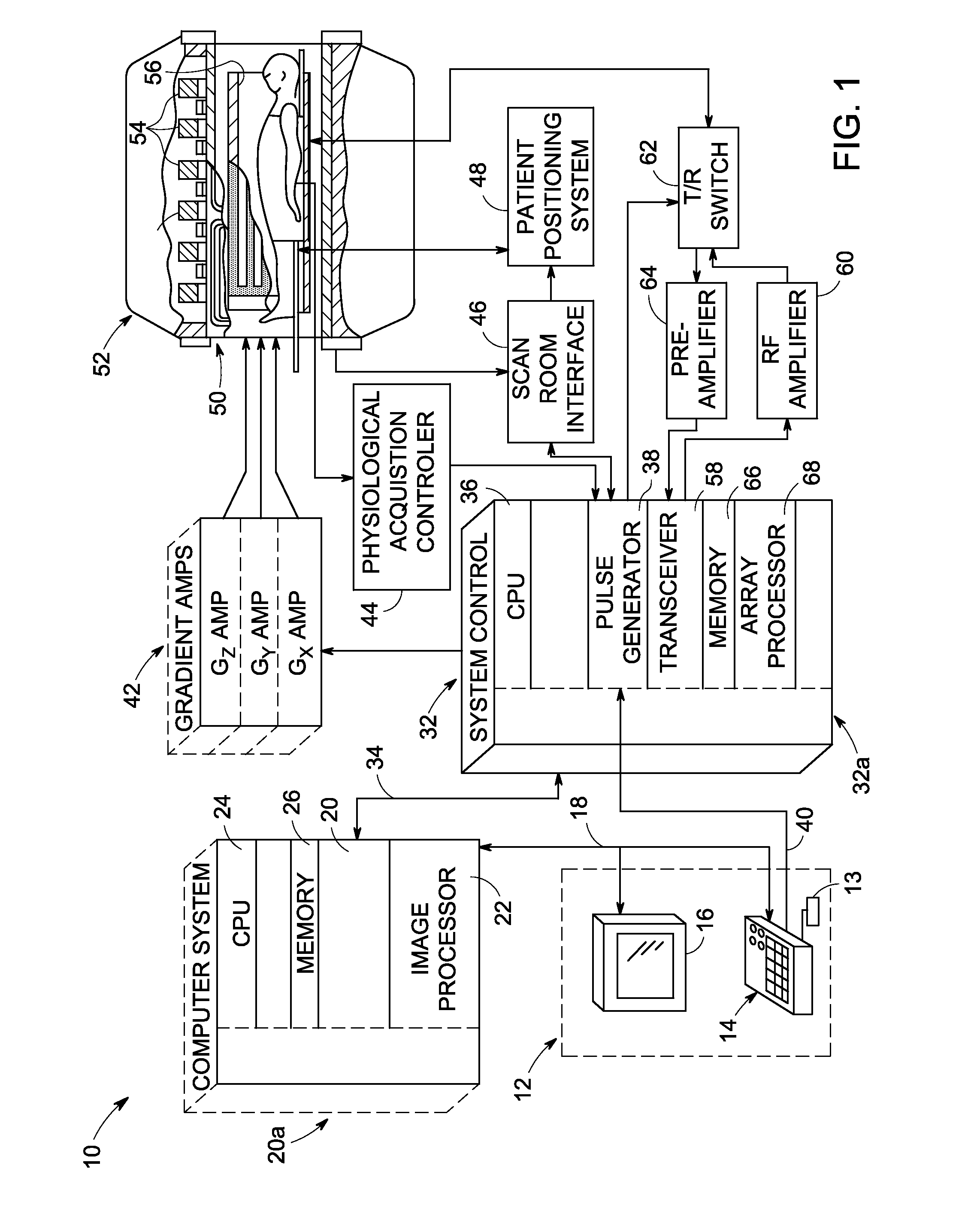
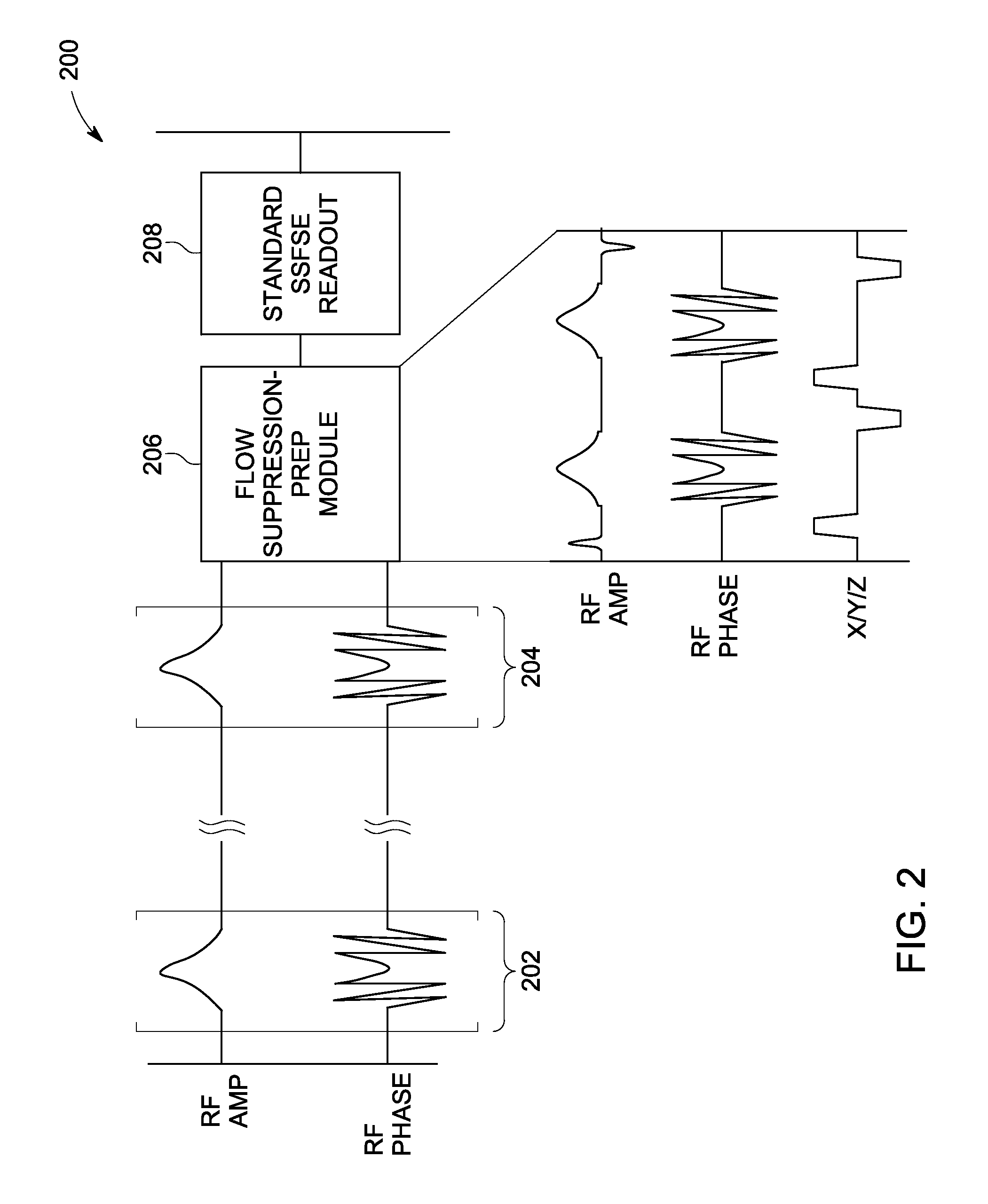
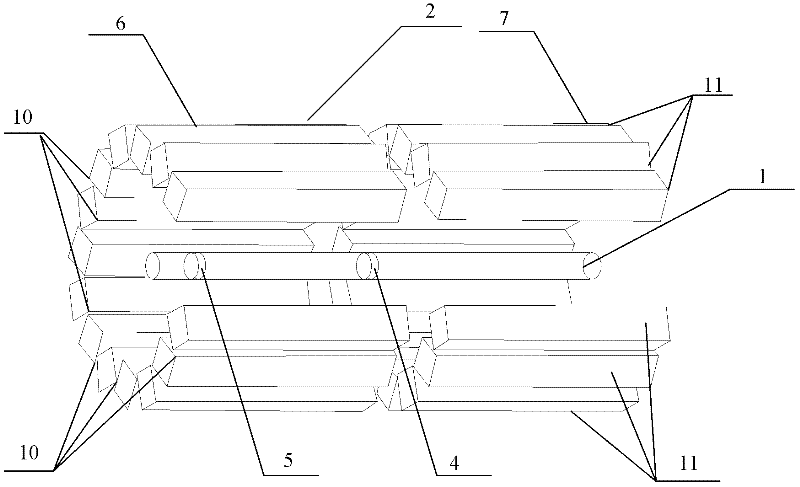
Method and apparatus for determining speed and properties of flowing fluids using NMR measurements
ActiveUS6952096B2Free from pollutionReduce decreaseElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic measurements
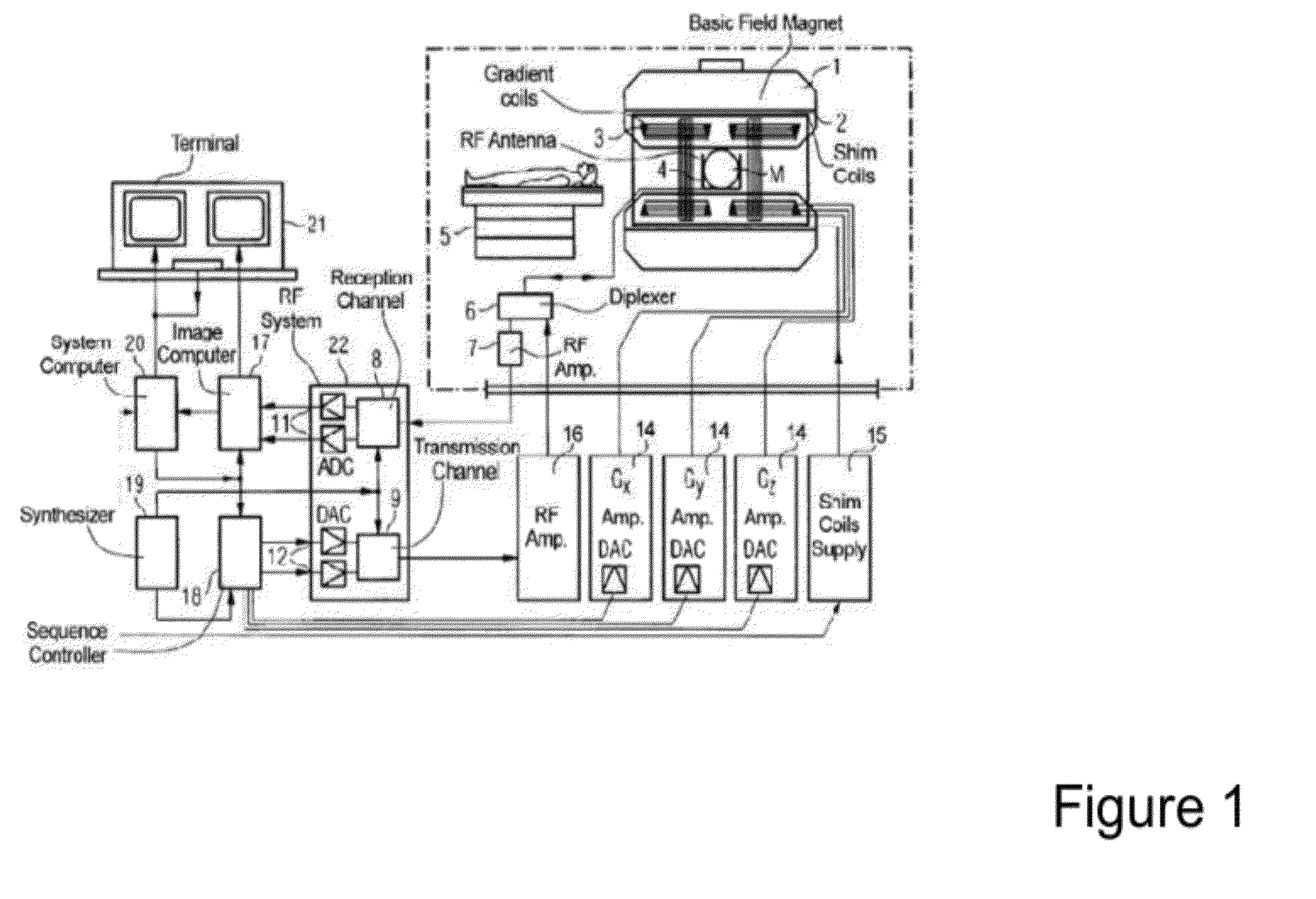
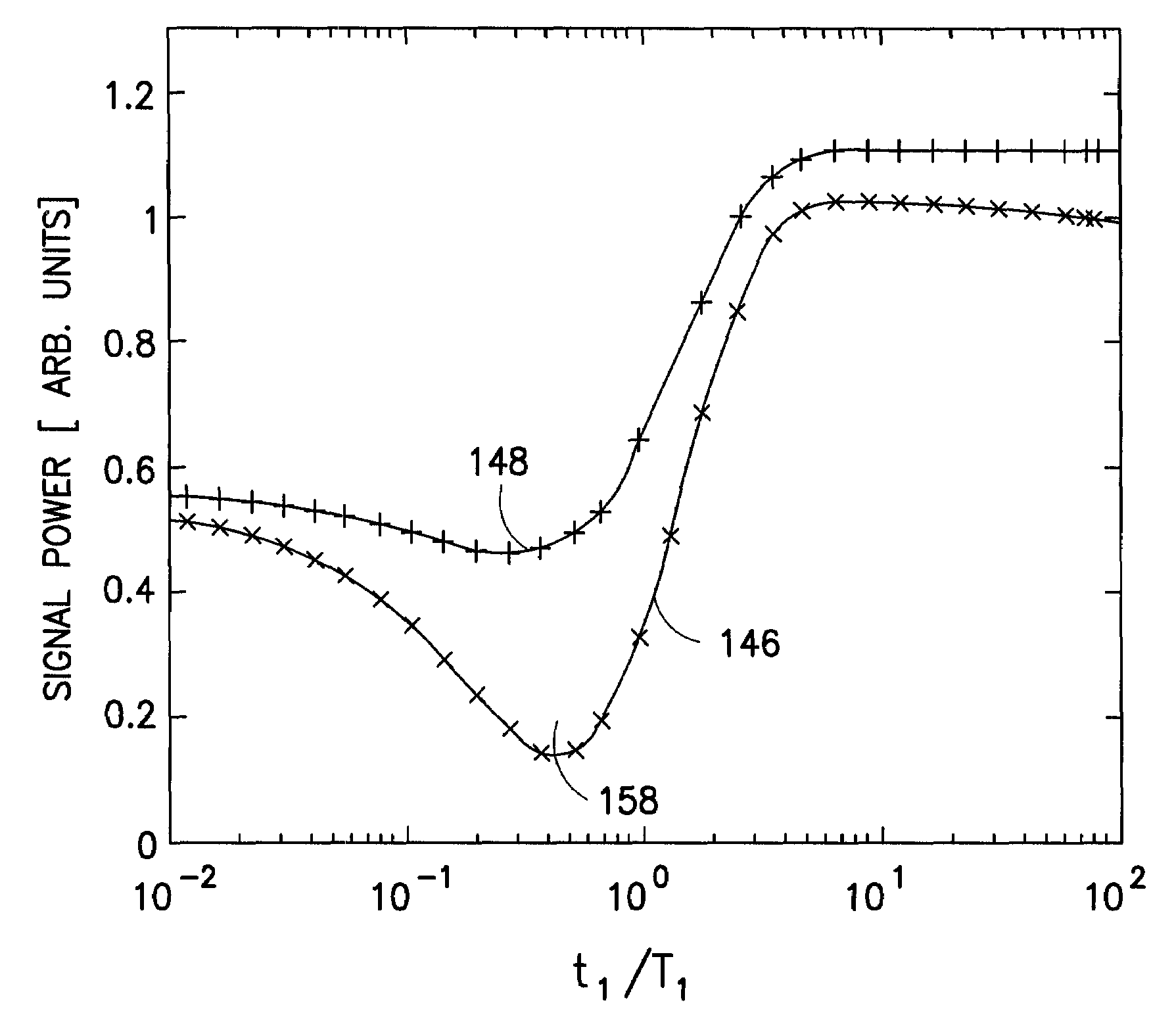
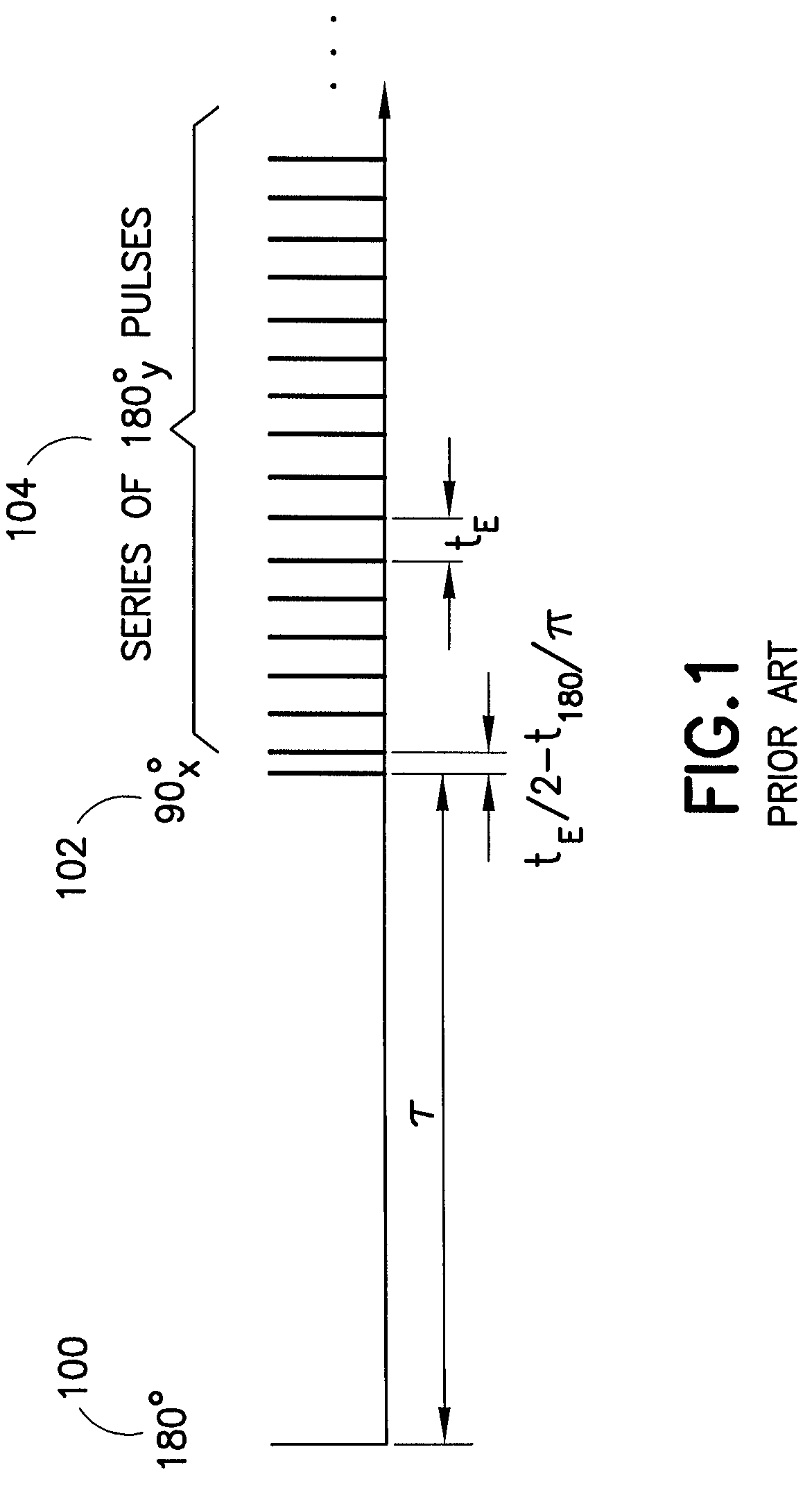
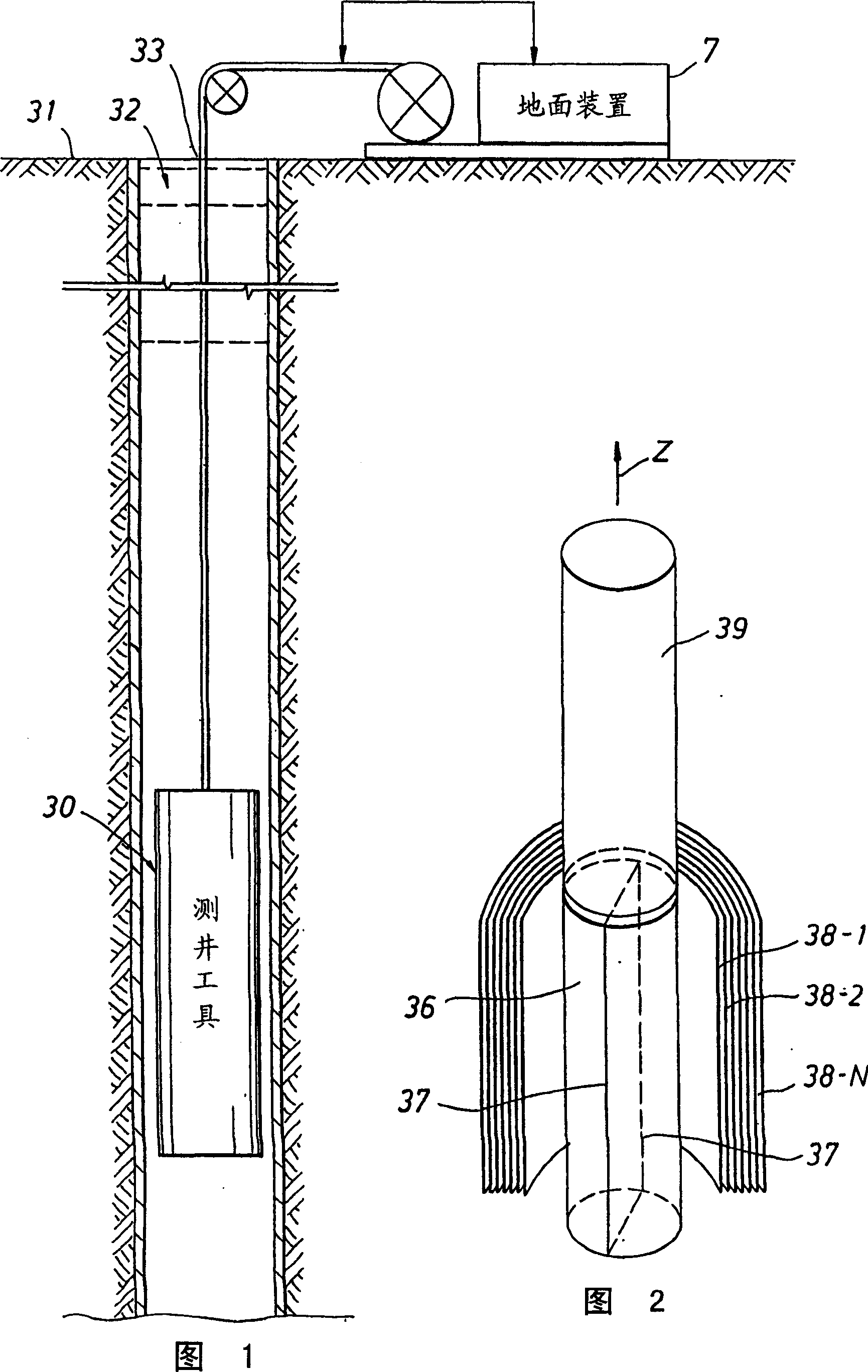
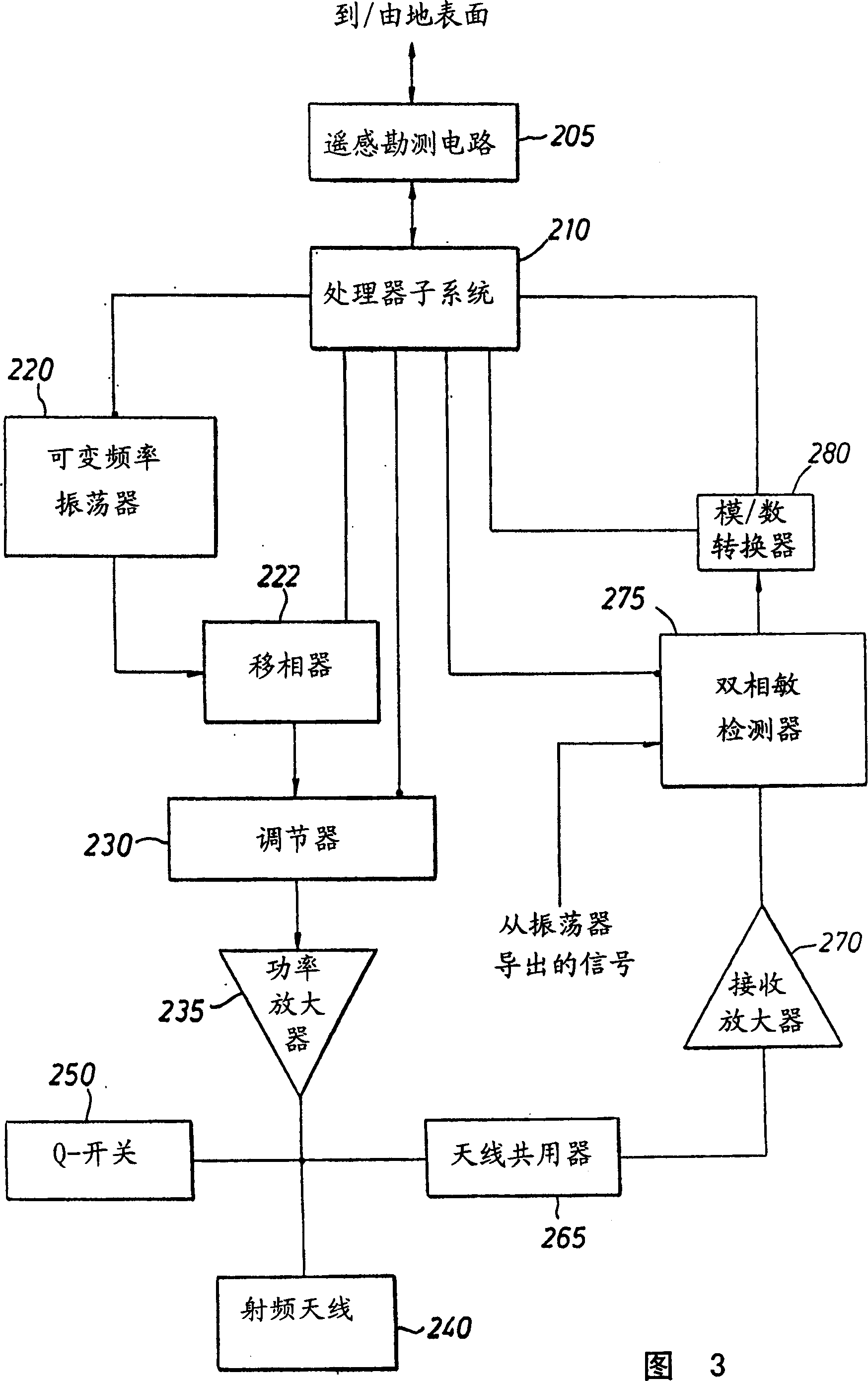
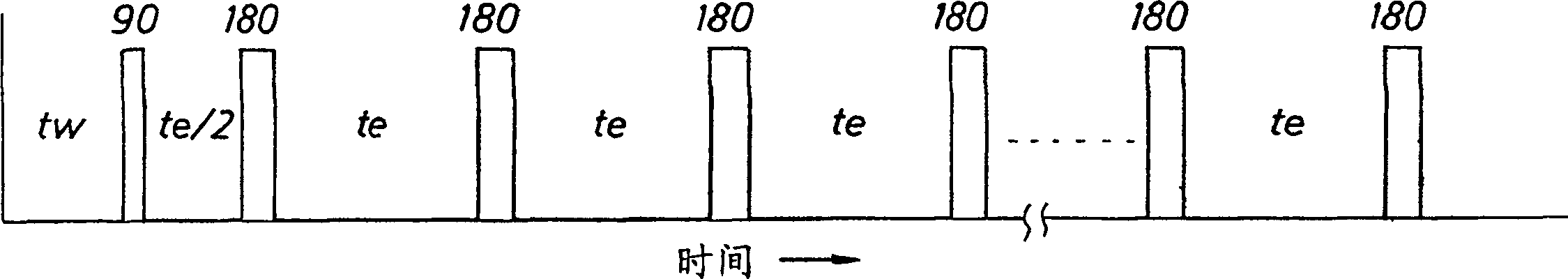
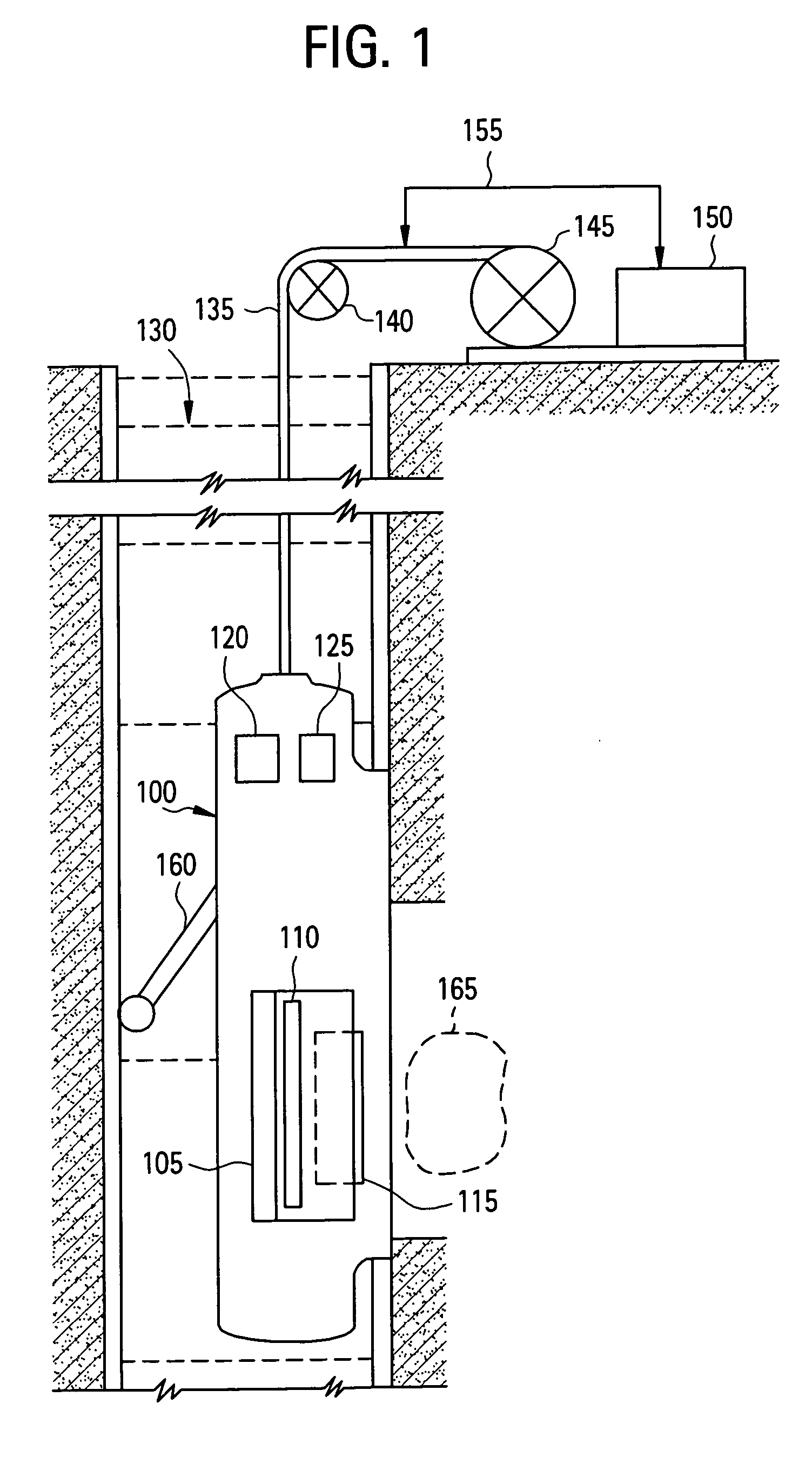
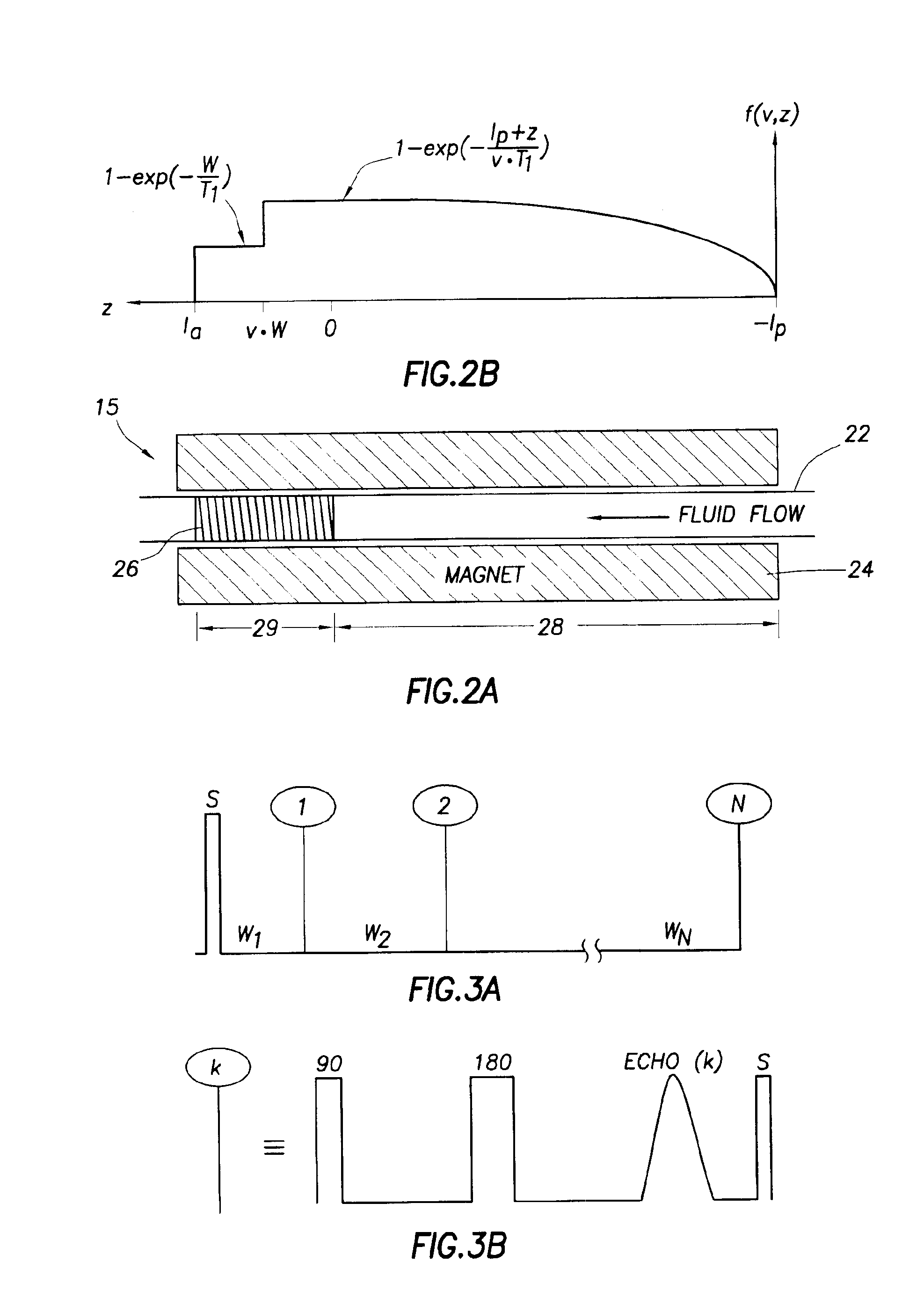
A method for determining a property of a flowing fluid by nuclear magnetic resonance includes applying a static magnetic field to the flowing fluid; acquiring a suite of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements on the flowing fluid using a pulse sequence comprising a spoiling pulse, a wait time, and an acquisition pulse sequence, wherein the suite of nuclear magnetic measurements have different values for the wait time; and fitting the suite of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements to a forward model for responses of the flowing fluid to derive a parameter selected from a flow speed, longitudinal relaxation times of the flowing fluid, and a combination thereof.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
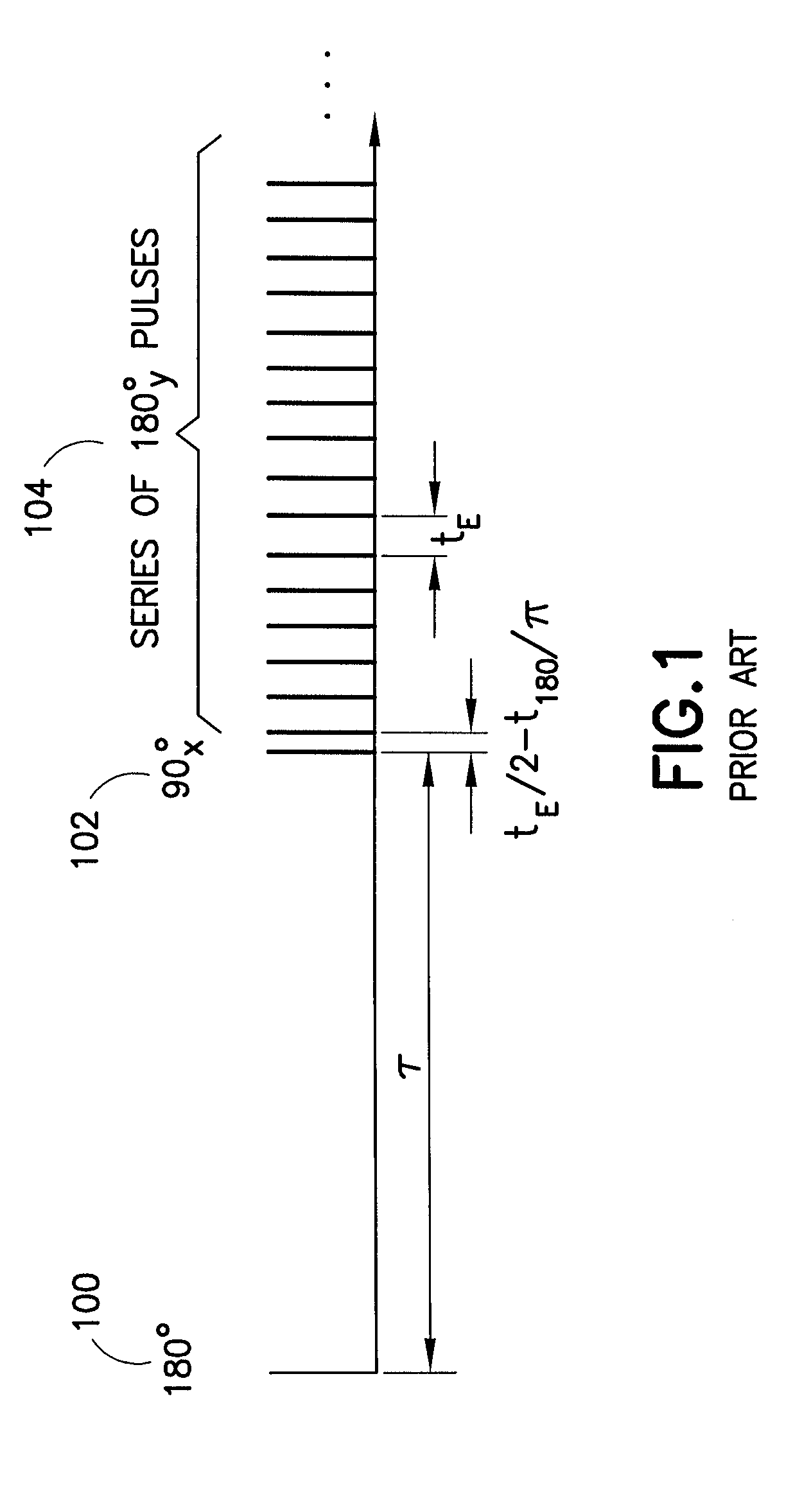
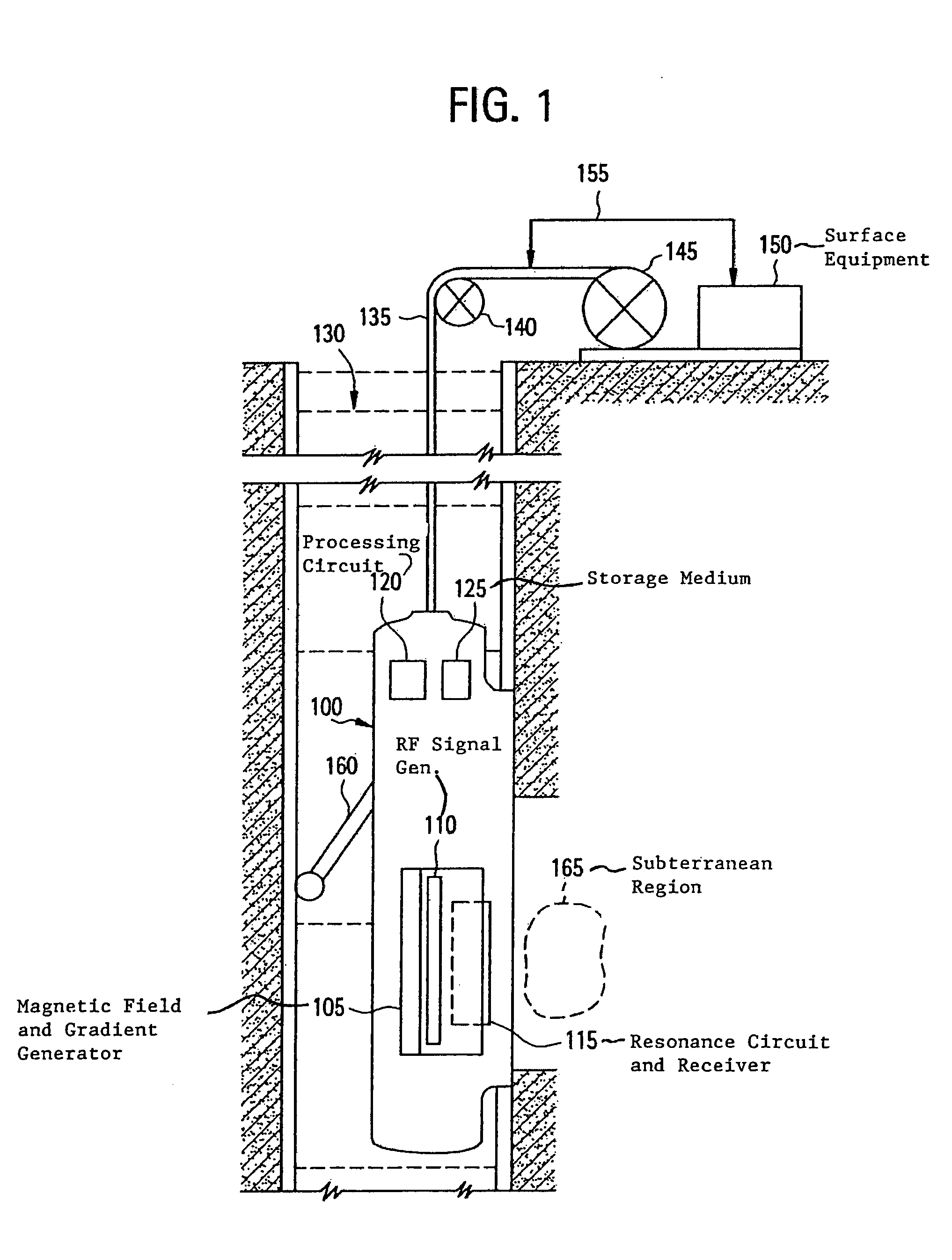
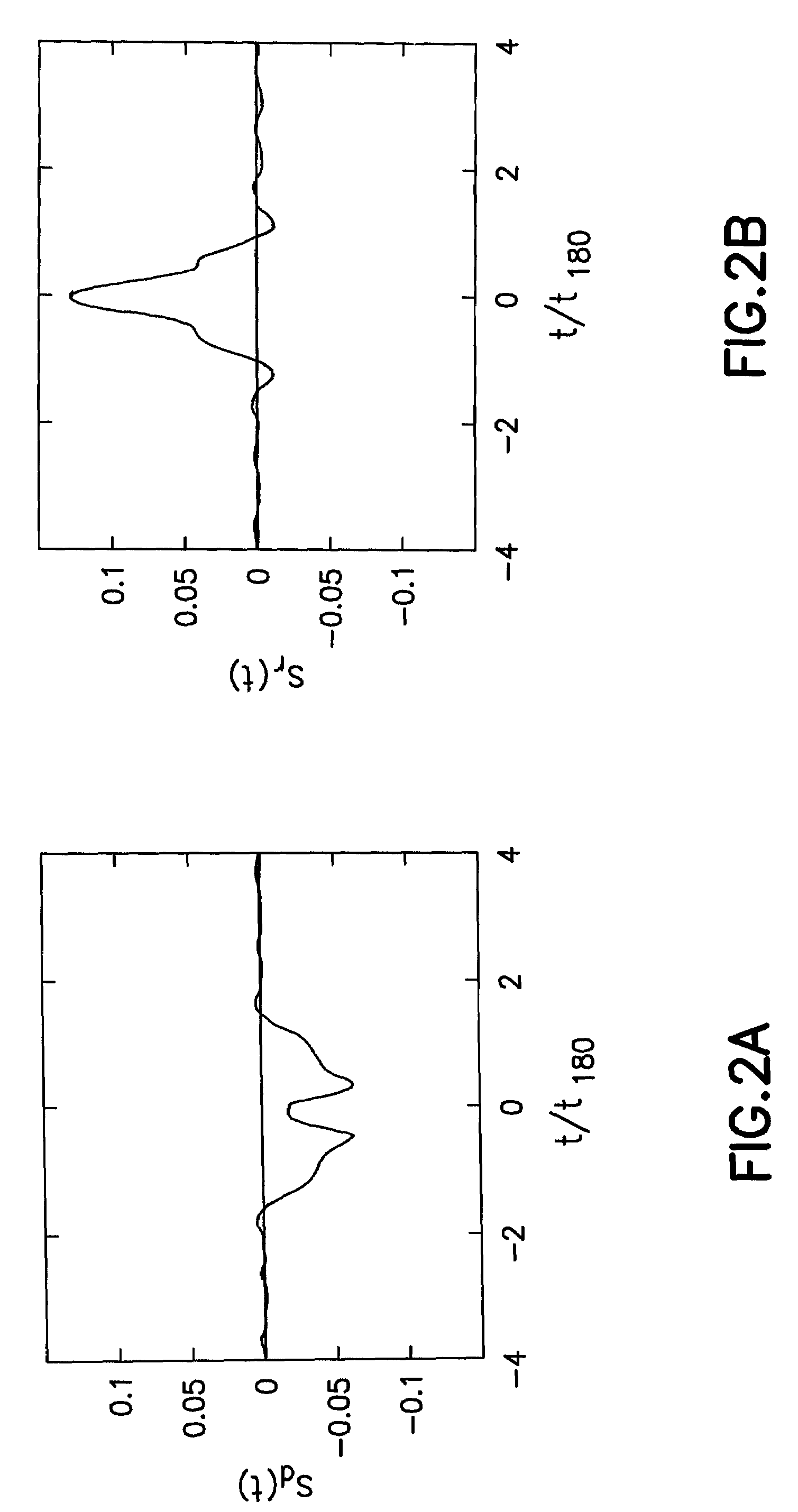
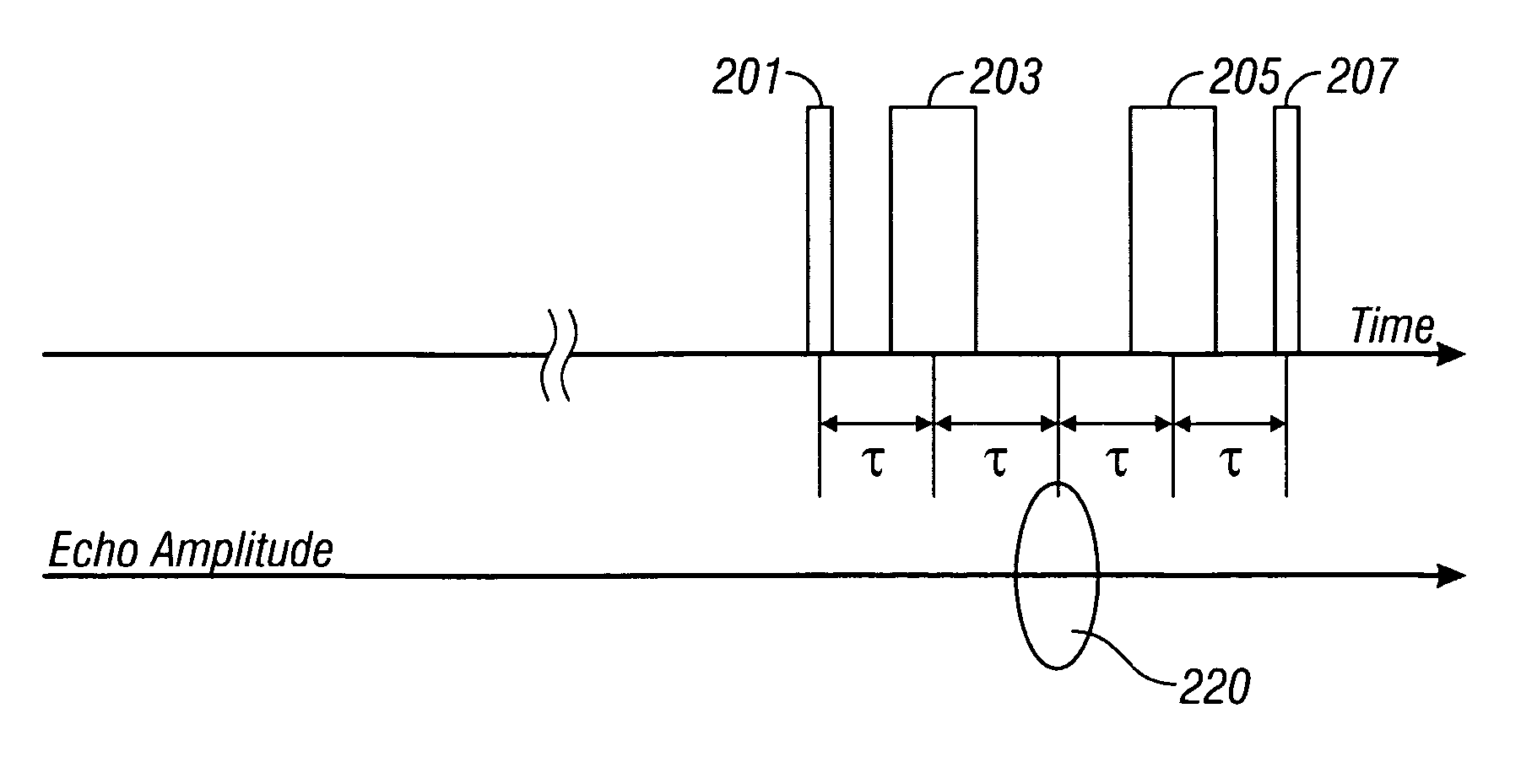
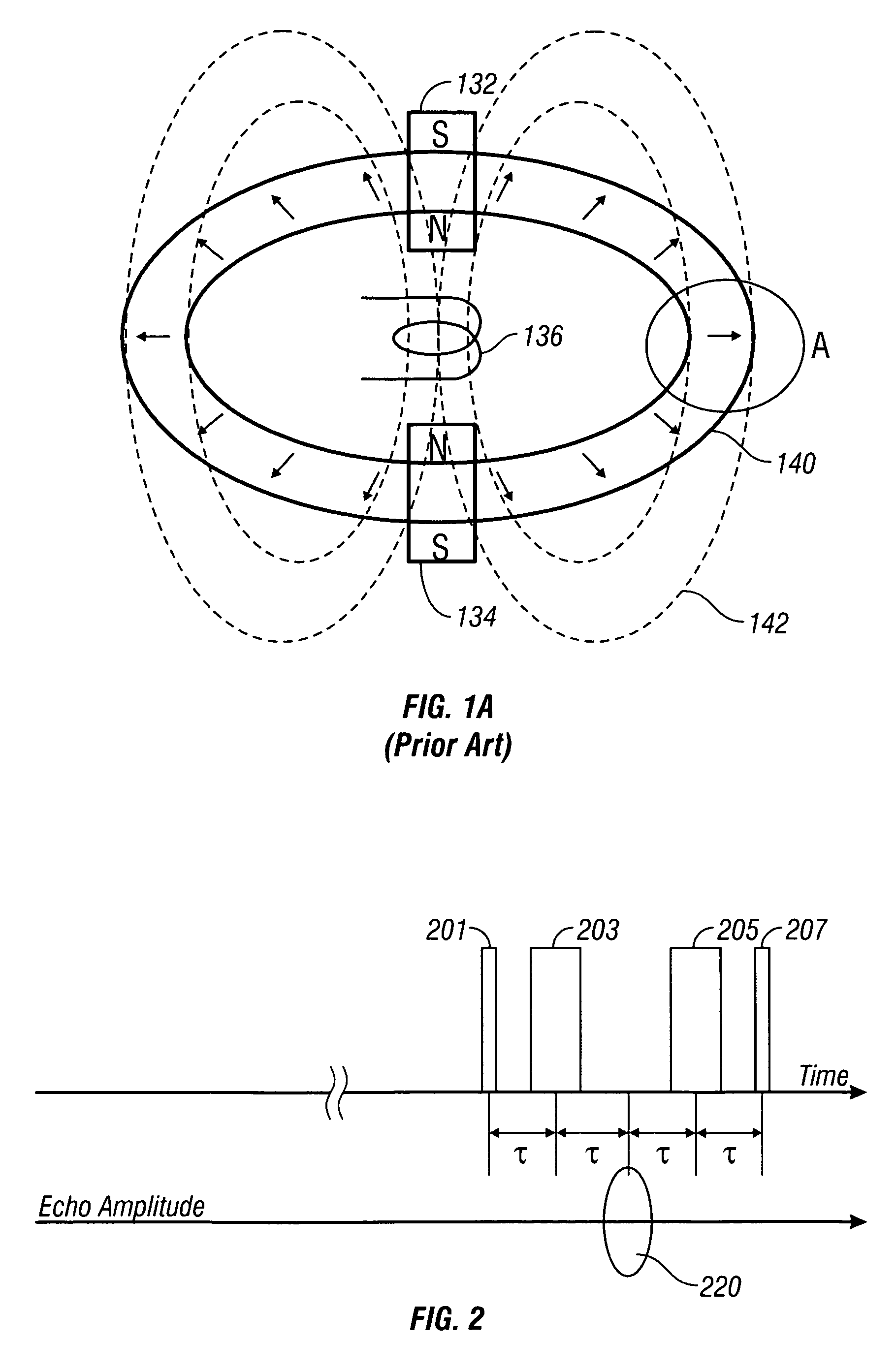
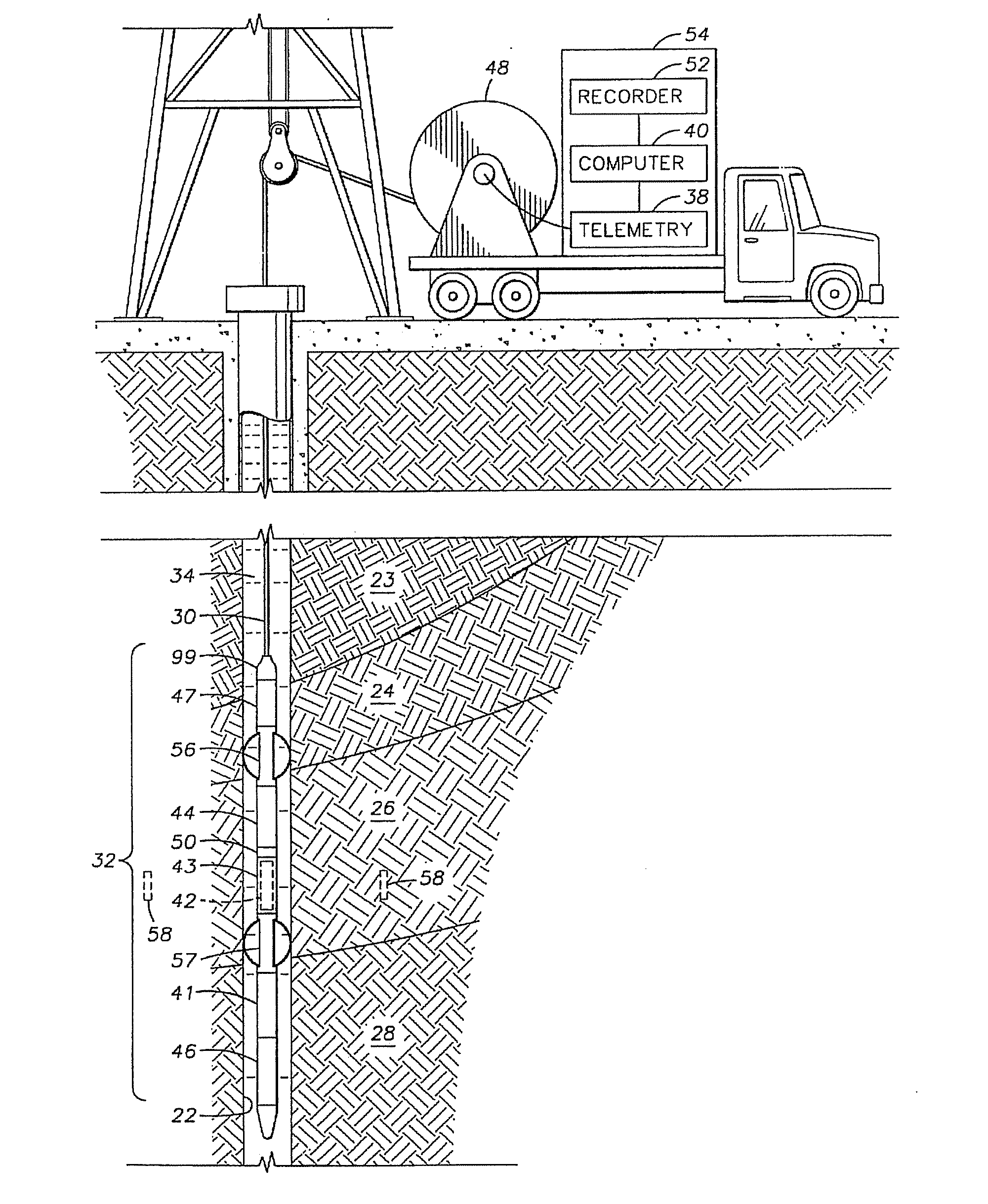
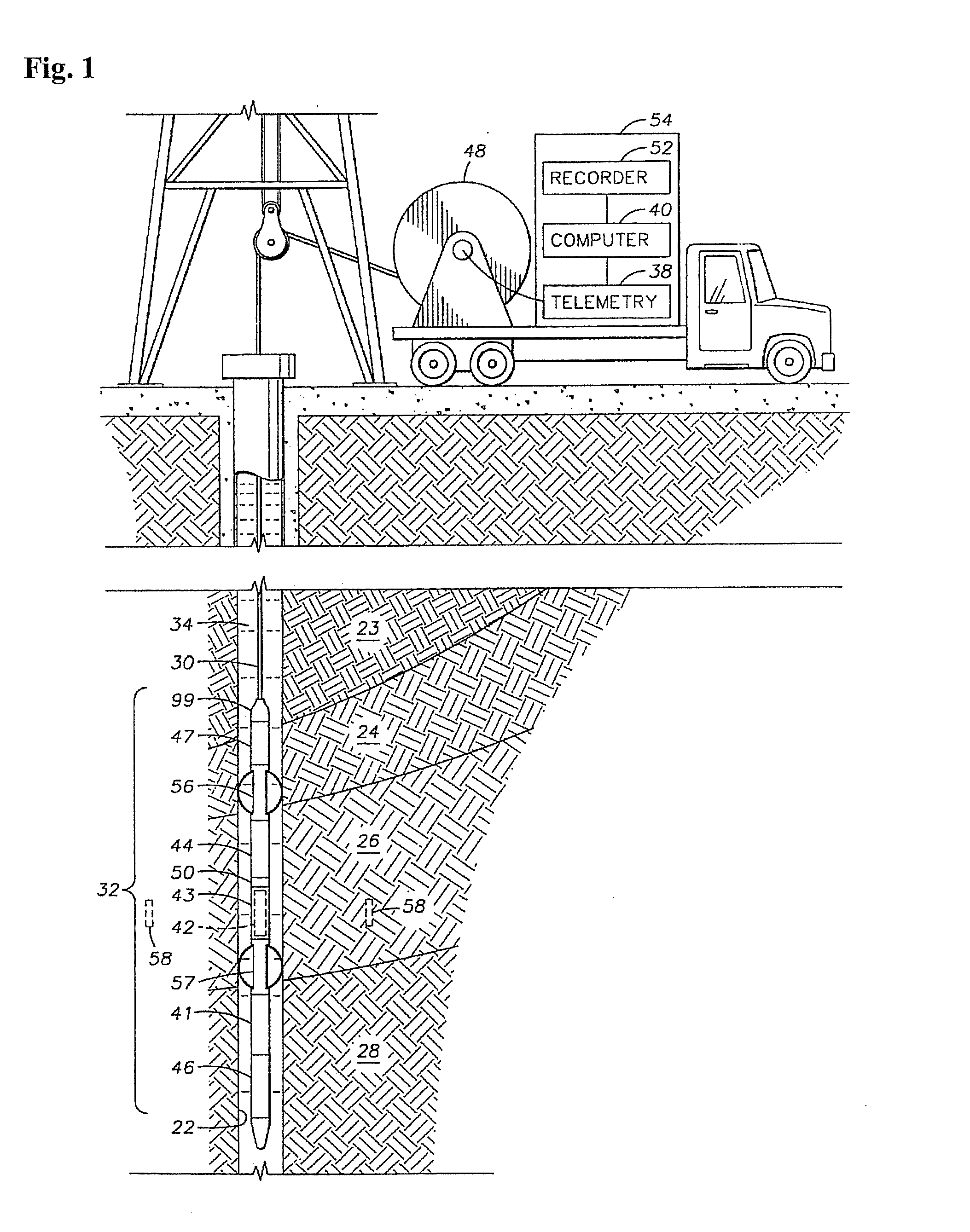
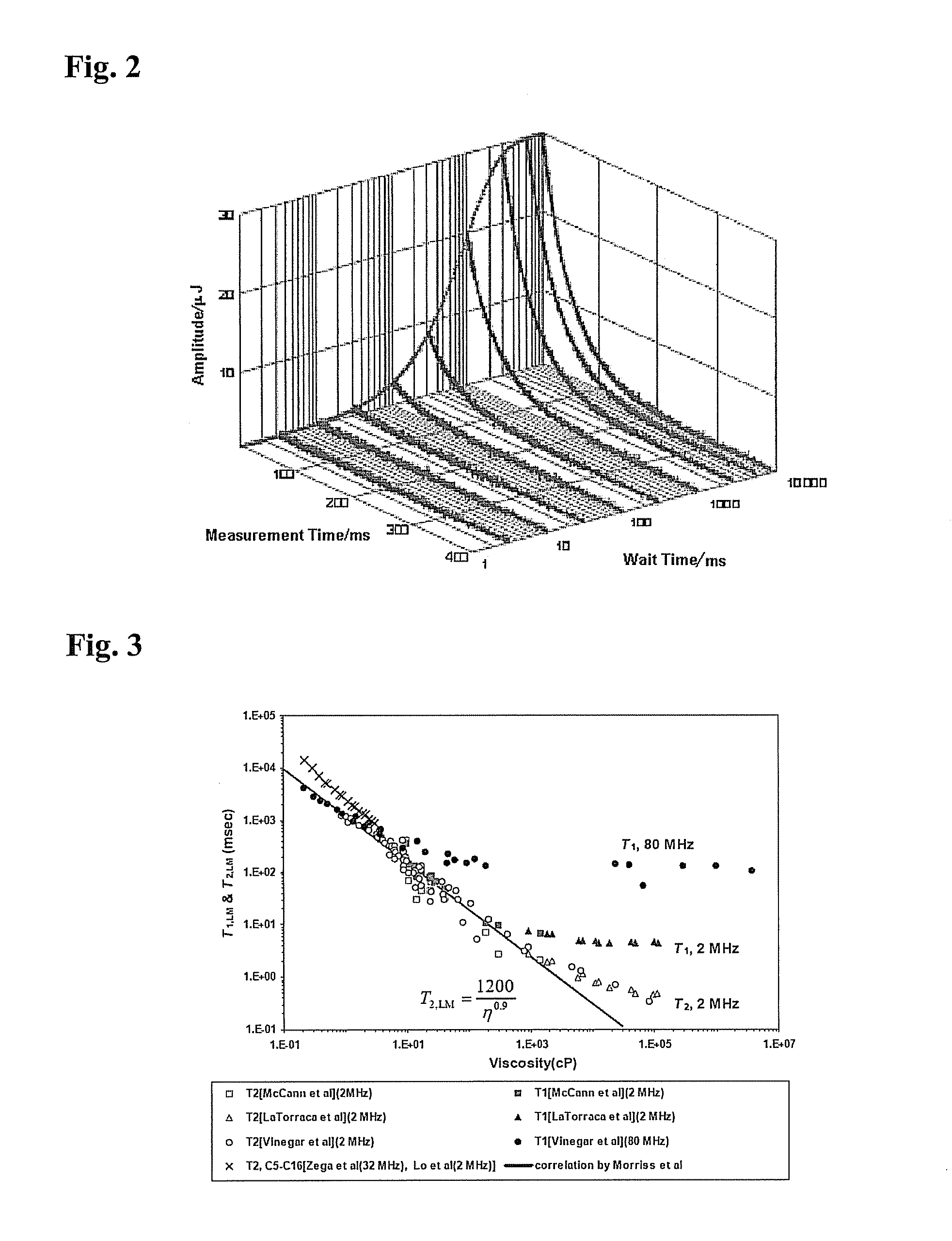
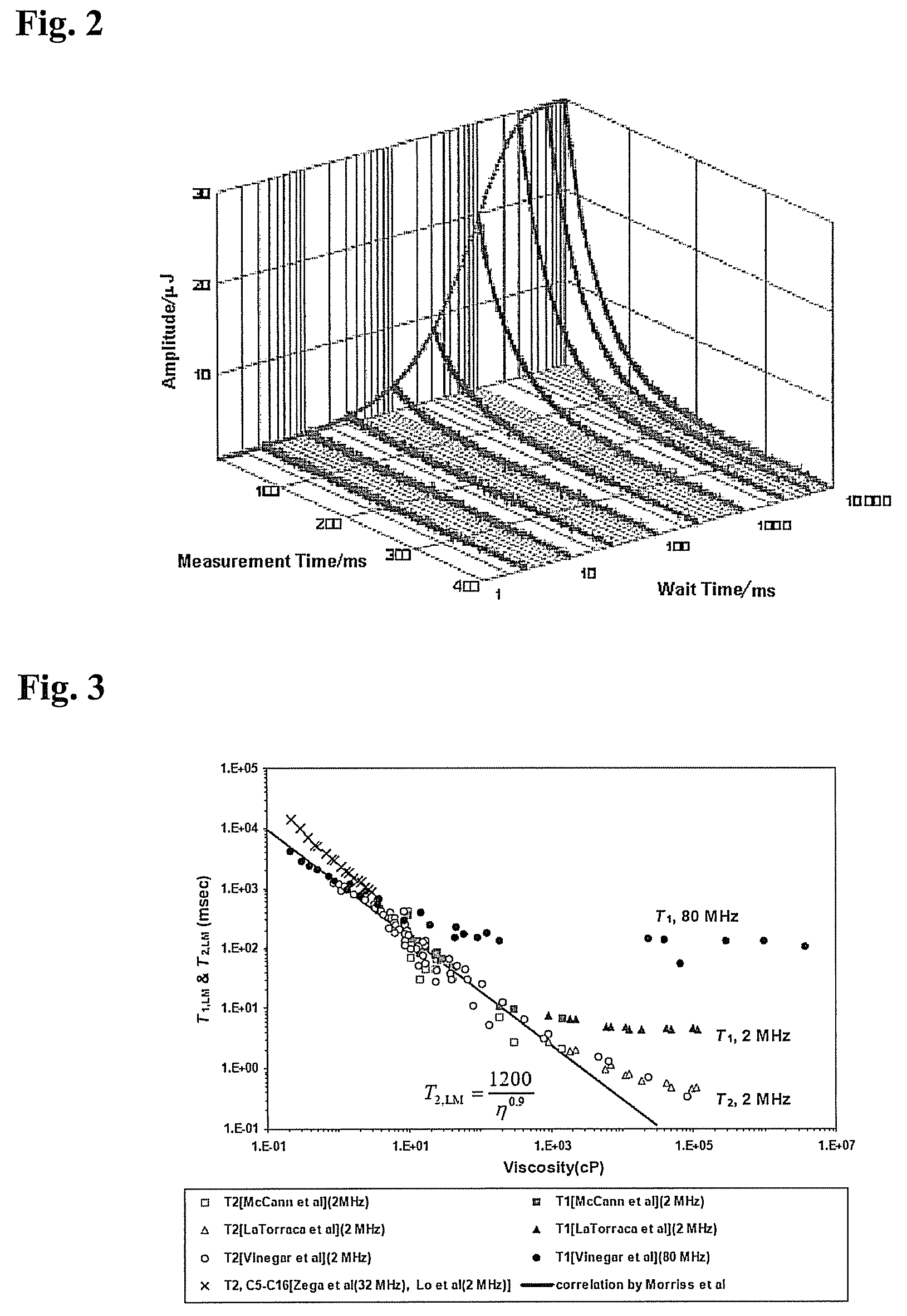
[method and apparatus for determining speed and properties of flowing fluids using nmr measurements]
ActiveUS20050140368A1Free from pollutionReduce decreaseElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsMagnetic measurementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for determining a property of a flowing fluid by nuclear magnetic resonance includes applying a static magnetic field to the flowing fluid; acquiring a suite of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements on the flowing fluid using a pulse sequence comprising a spoiling pulse, a wait time, and an acquisition pulse sequence, wherein the suite of nuclear magnetic measurements have different values for the wait time; and fitting the suite of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements to a forward model for responses of the flowing fluid to derive a parameter selected from a flow speed, longitudinal relaxation times of the flowing fluid, and a combination thereof.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for measuring atomic transverse relaxation time based on electron resonance phase frequency analysis
InactiveCN106597338ASuppression of the effects of common coefficient fluctuationsExact transverse relaxation timeMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceFrequency spectrumTransverse magnetic field
The invention discloses a method for measuring atomic transverse relaxation time based on an electron resonance phase frequency analysis. In a strong-background magnetic field with almost neglected residual magnetization in a magnetic shielding barrel, a swept-frequency signal that has a bandwidth covering a resonance curve and has an amplitude enabling the resonance curve to have a clear curve under low polarizability is applied in a horizontal direction; an optical swing angle signal of a magnetometer is detected and a spectral analysis is carried out on an outputted signal in a polar coordinate system to obtain a phase frequency response function of the magnetometer; the phase frequency response function is fitted to a corresponding theoretical phase frequency curve of the magnetometer to obtain atomic spinning transverse relaxation time. Because the phase angle is a result obtained by quotient processing of a spinning transverse component, the influence of common coefficient fluctuation is suppressed, so that the phase frequency signal expression is more stable by being compared with amplitude-frequency signal expression. Besides, the theoretical phase frequency curve is not affected by the magnetic induction intensity of the transverse magnetic field and the atomic spinning longitudinal relaxation time, so that complexity of data processing can be reduced. Moreover, a lorenz curve widening risk caused by the transverse magnetic field can be eliminated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance measurement techniques in non-uniform fields
InactiveUS20080024128A1Easy to optimizeAccurate measurementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsUniform fieldDiffusion
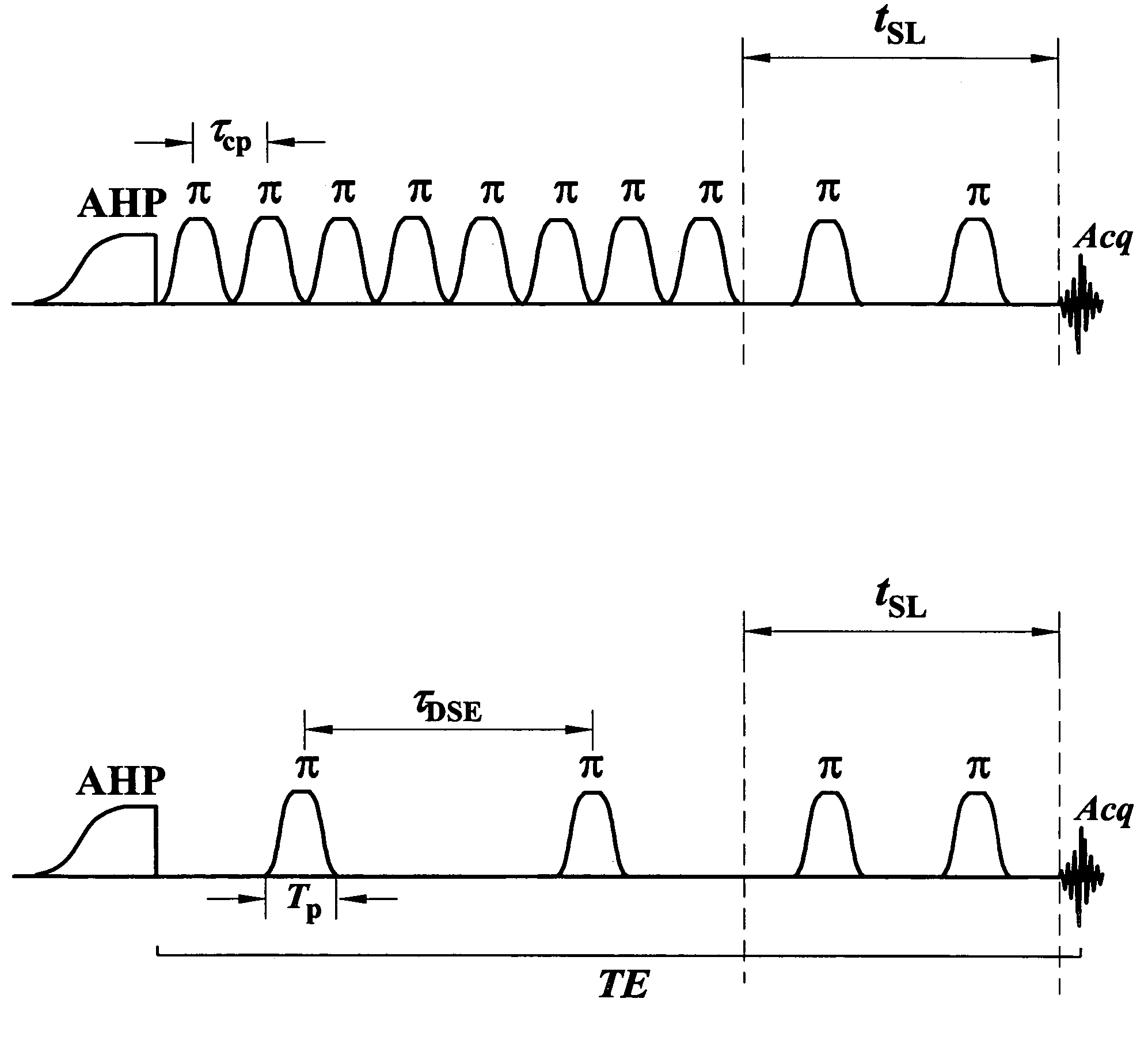
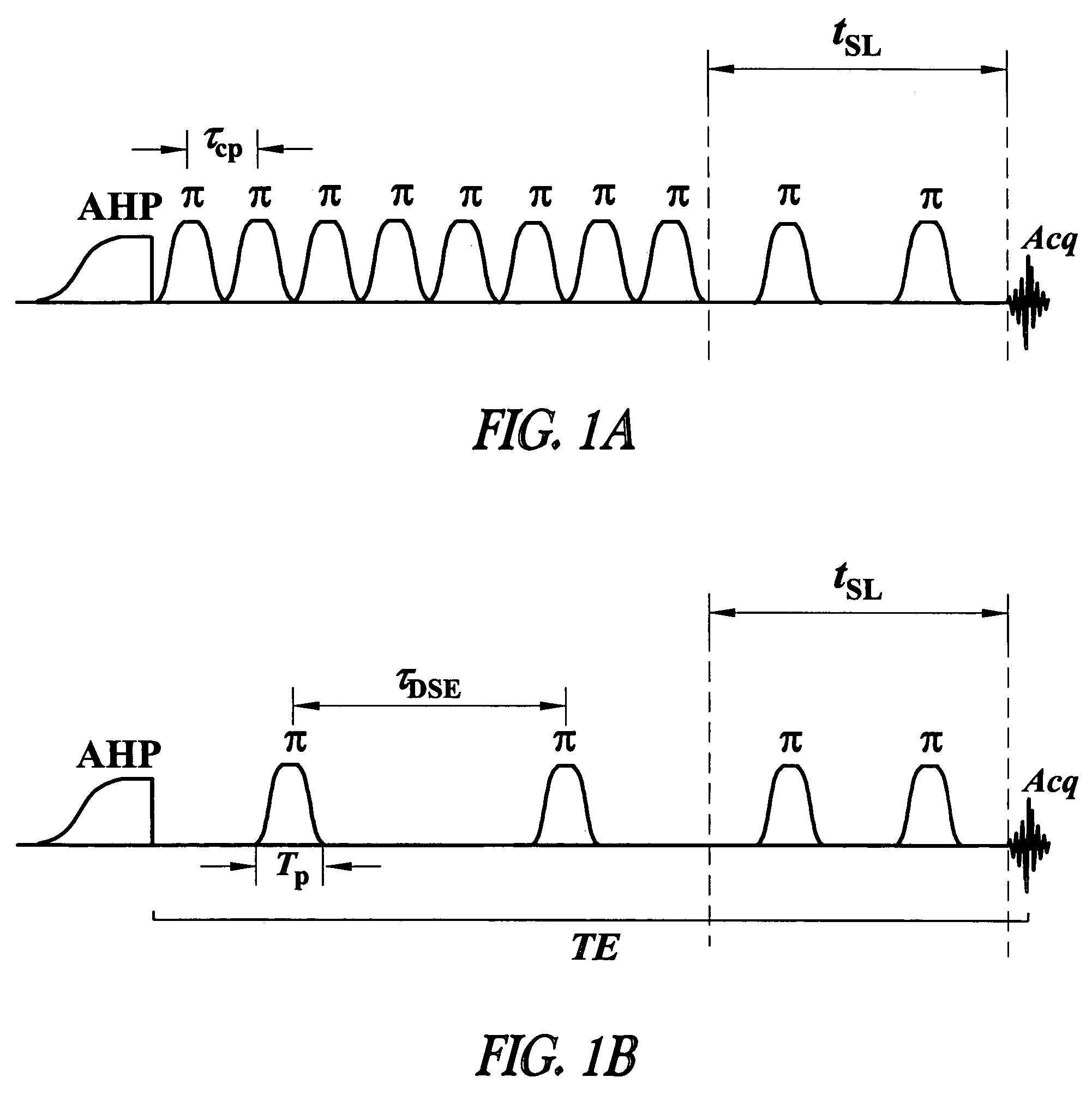
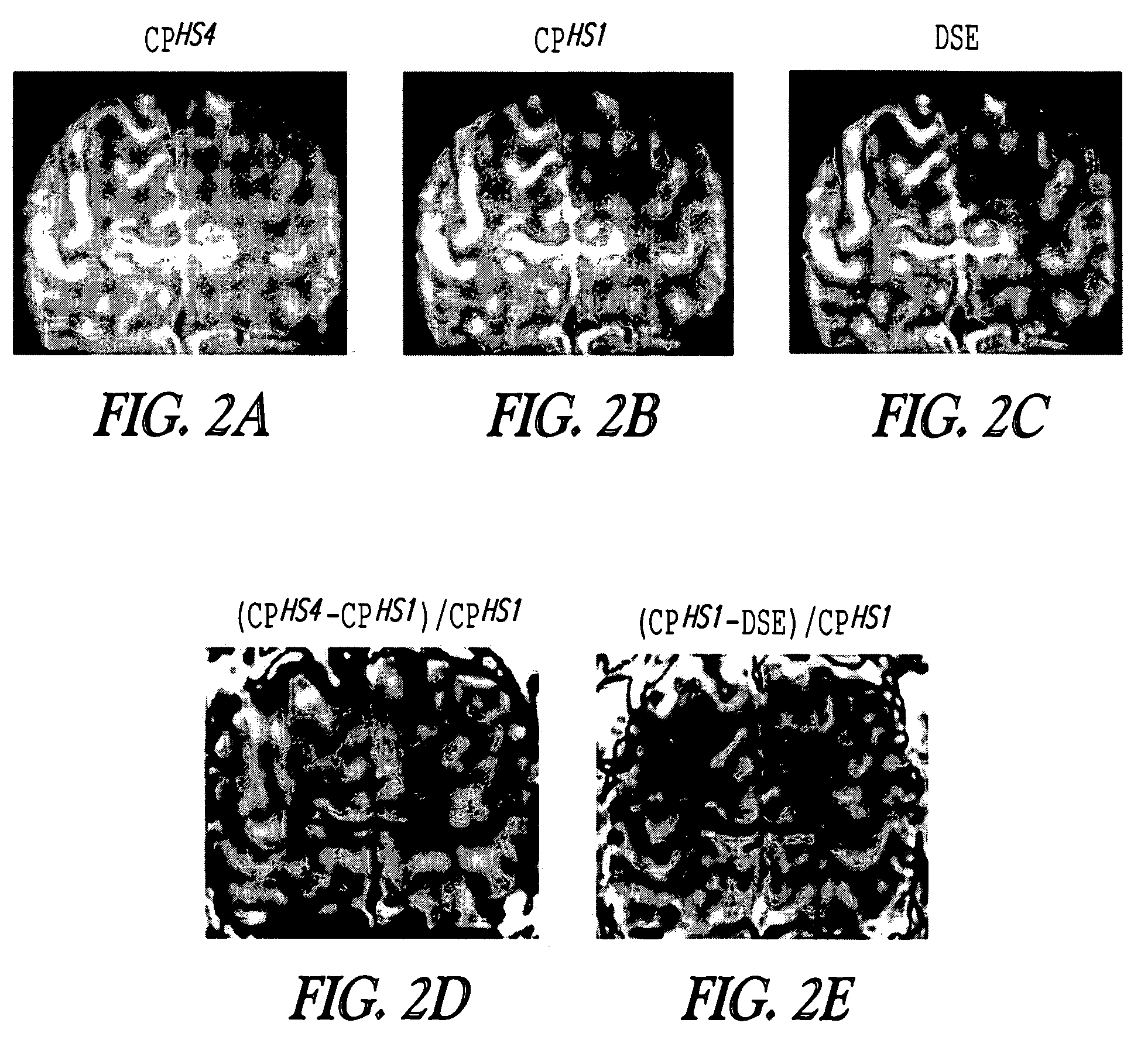
Methods and pulse sequences for facilitating nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements in grossly inhomogeneous fields. Methods and pulse sequences according to the invention may be used to accurately measure variables such as transverse relaxation time, longitudinal relaxation time, and diffusion, without the need for data at long recovery time, thereby allowing for faster measurements. In addition, methods and pulse sequences according to embodiment of the invention may allow simultaneous encoding of information in both the amplitude and the shape of echoes, so as to allow a single-shot measurement of multiple variables, e.g., both transverse relaxation time (from the decay of echo amplitudes) and longitudinal relaxation time (from the echo shape). CPMG detection may be used to overcome the often limited signal-to-noise ratio in grossly inhomogeneous fields.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for reservoir fluid characterization in nuclear magnetic resonance logging
ActiveUS7298142B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic property measurementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWell logging
A method and apparatus for obtaining a parameter of interest relating to a region proximate a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging tool suitable for subterranean well logging is disclosed. The nuclei of the region are subjected to a pulsed NMR technique and are productive of NMR logging data, the nuclei of the region characteristically having a longitudinal relaxation time T1 distribution and an apparent transverse relaxation time T2app distribution. In response to the NMR logging data, an R distribution is defined as R=T1 / T2app, the T2app and R distributions are processed as separate bins, along with the NMR logging data, according to a two-dimensional inversion model, and a signal intensity map of R versus T2app is provided that is representative of the parameter of interest relating to the region. In response to a high-intensity signal on the map being within a first range of T2app values and a first range of R values, the presence of a light hydrocarbon within the region is identified.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
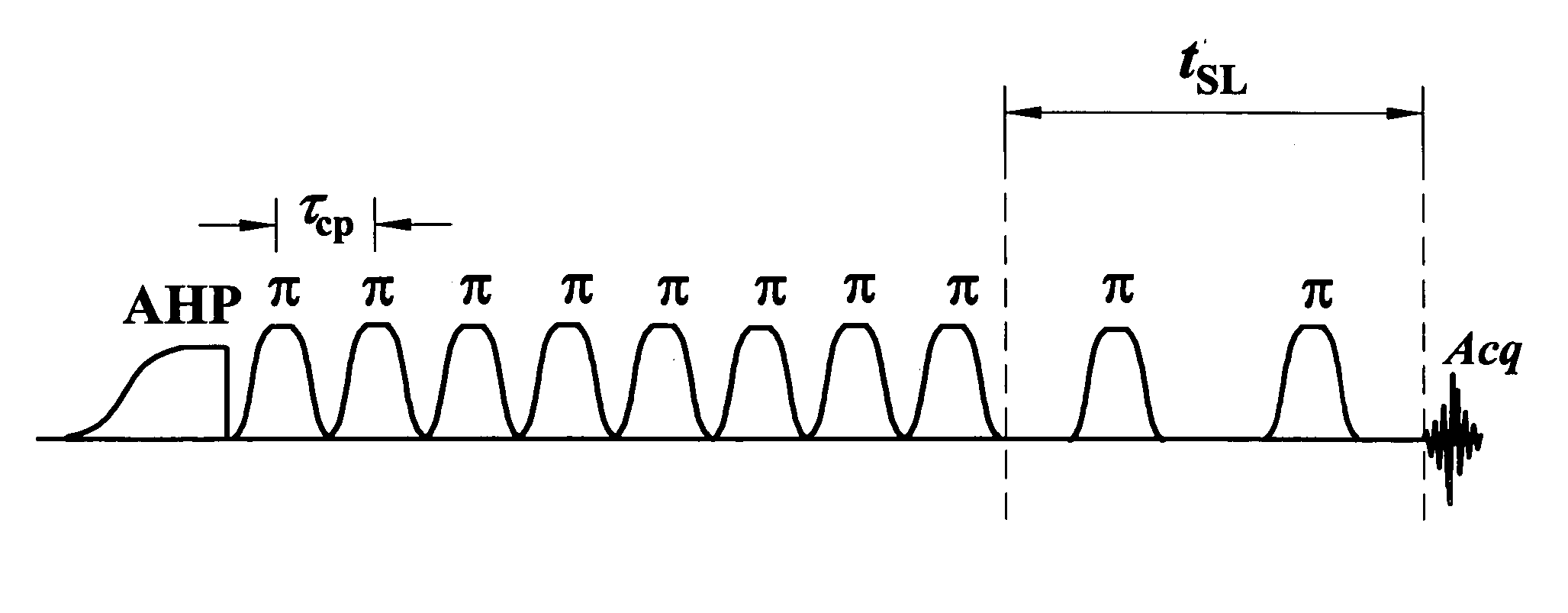
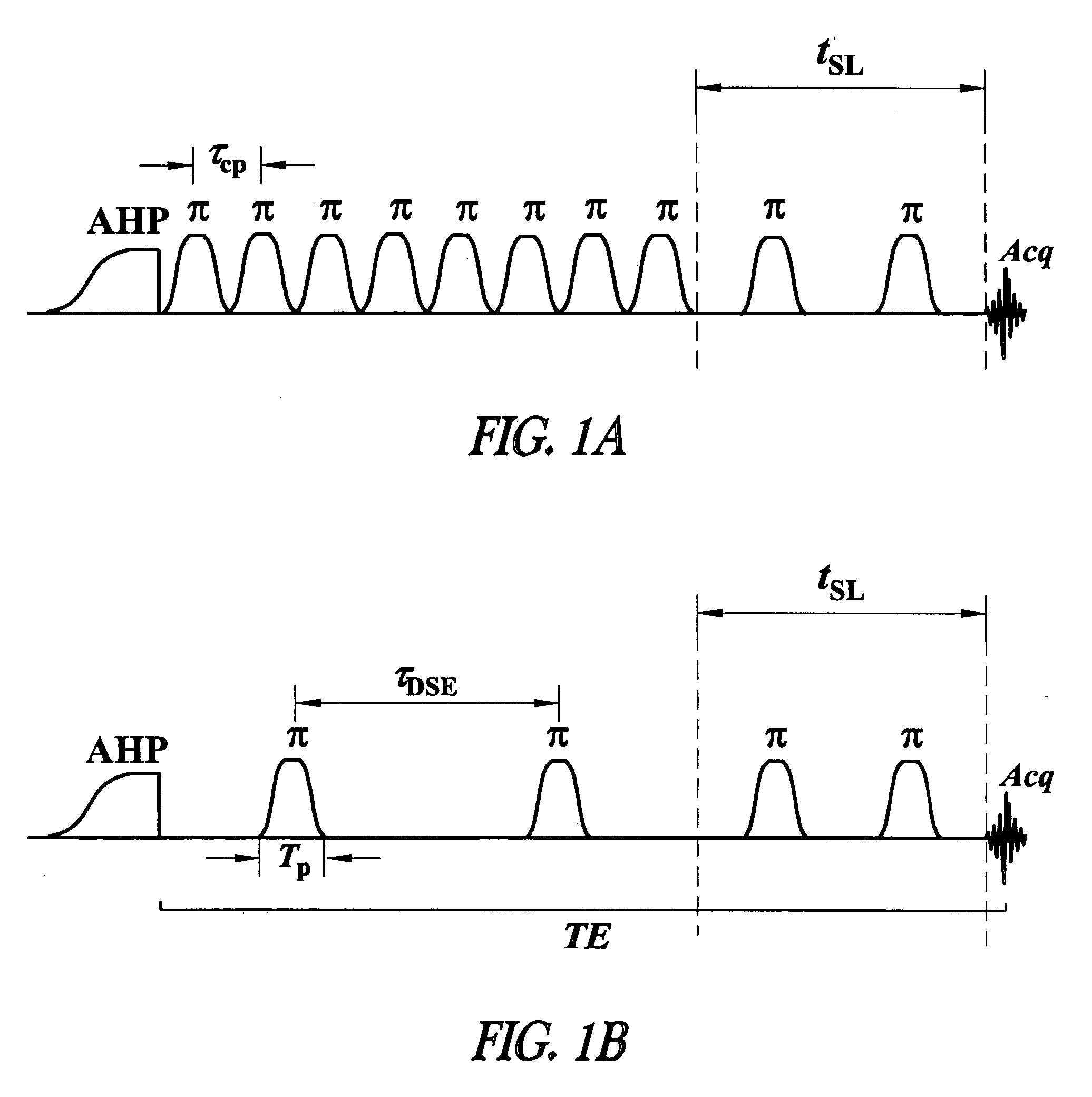
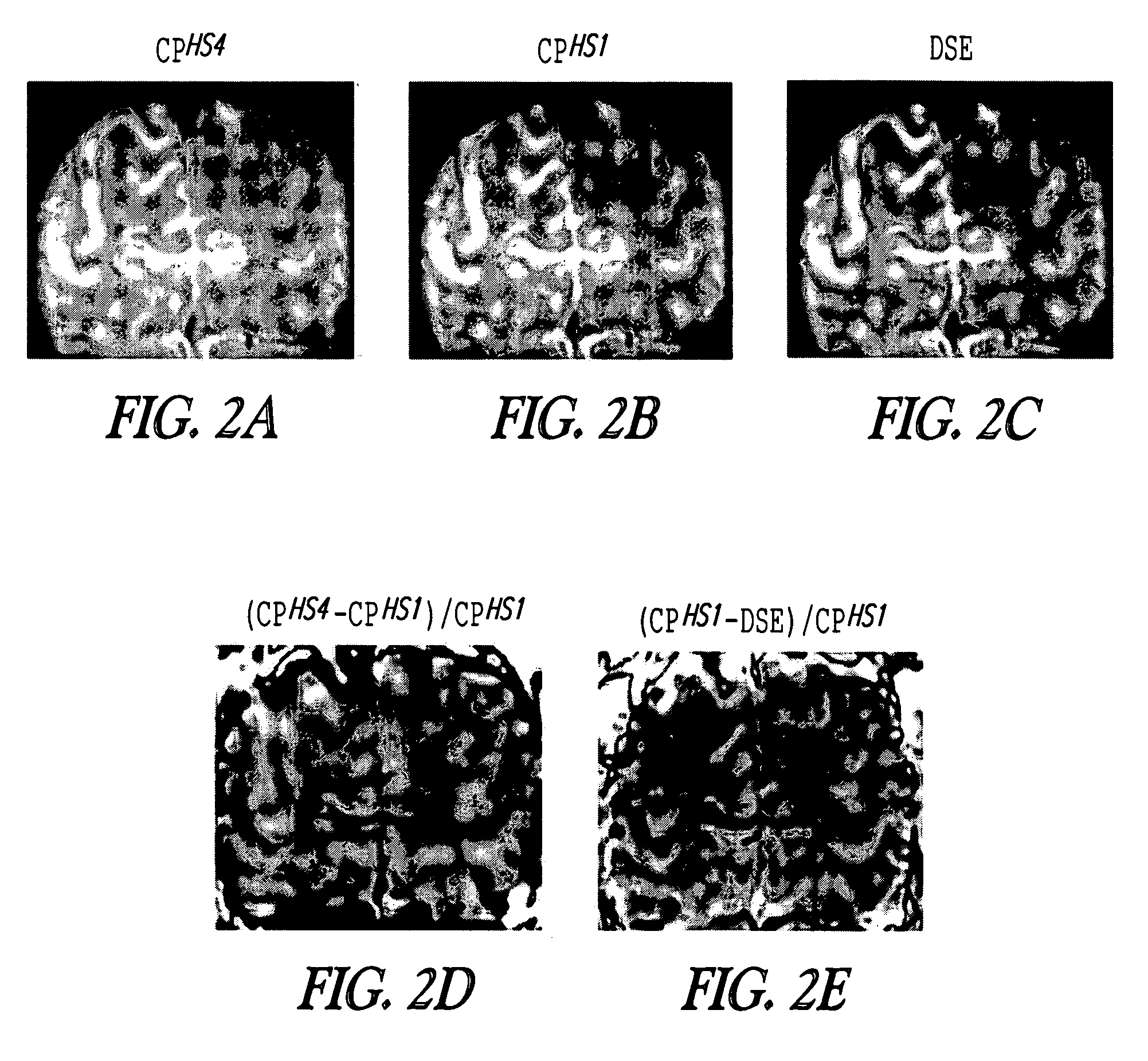
Contrast from rotating frame relaxation by adiabatic pulses
ActiveUS7279899B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFrame basedEngineering
This document discusses, among other things, a system and method for modulating transverse and longitudinal relaxation time contrast in a rotating frame based on a train of radio frequency pulses.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Contrast from rotating frame relaxation by adiabatic pulses
ActiveUS20060244447A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFrame basedEngineering
This document discusses, among other things, a system and method for modulating transverse and longitudinal relaxation time contrast in a rotating frame based on a train of radio frequency pulses.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
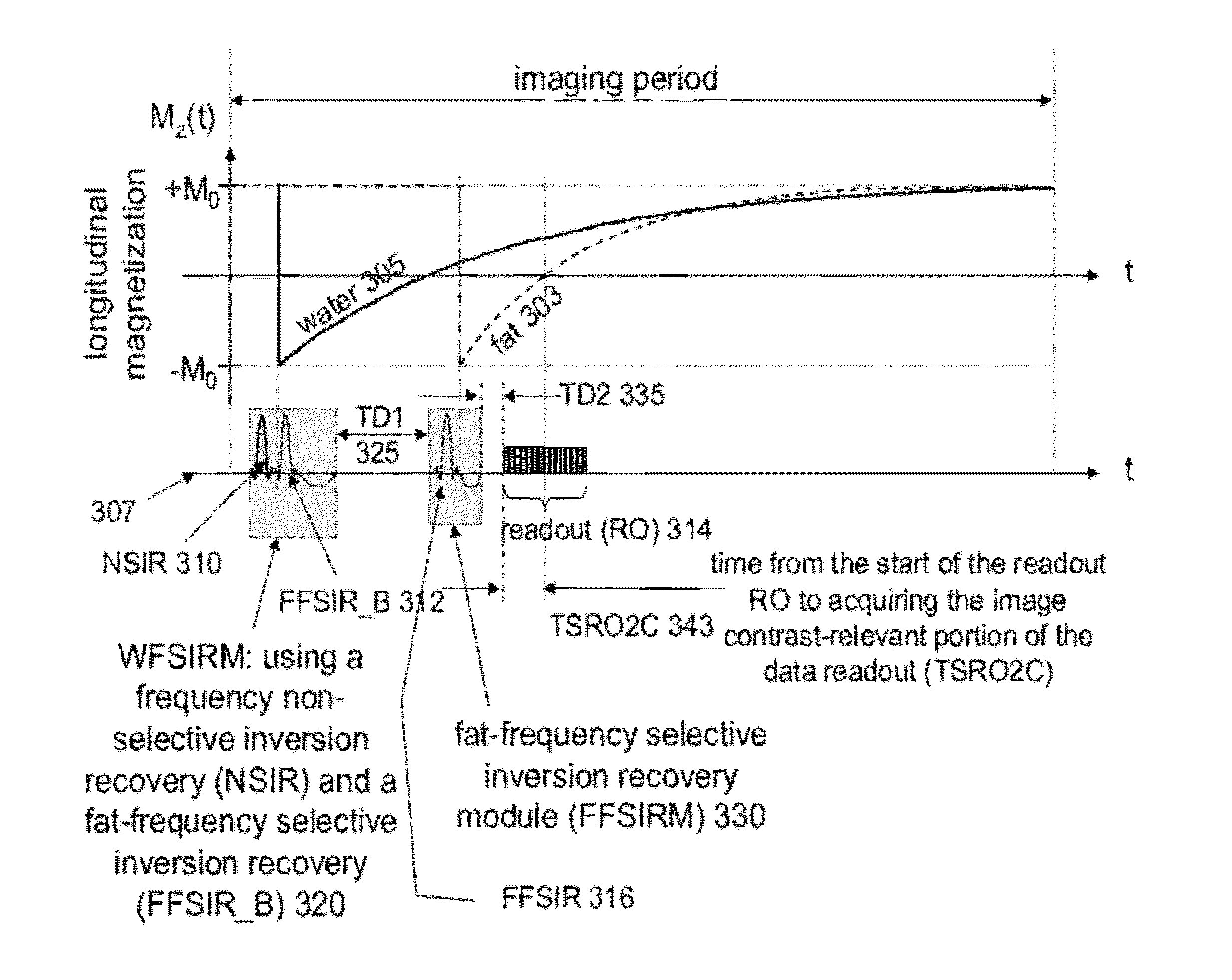
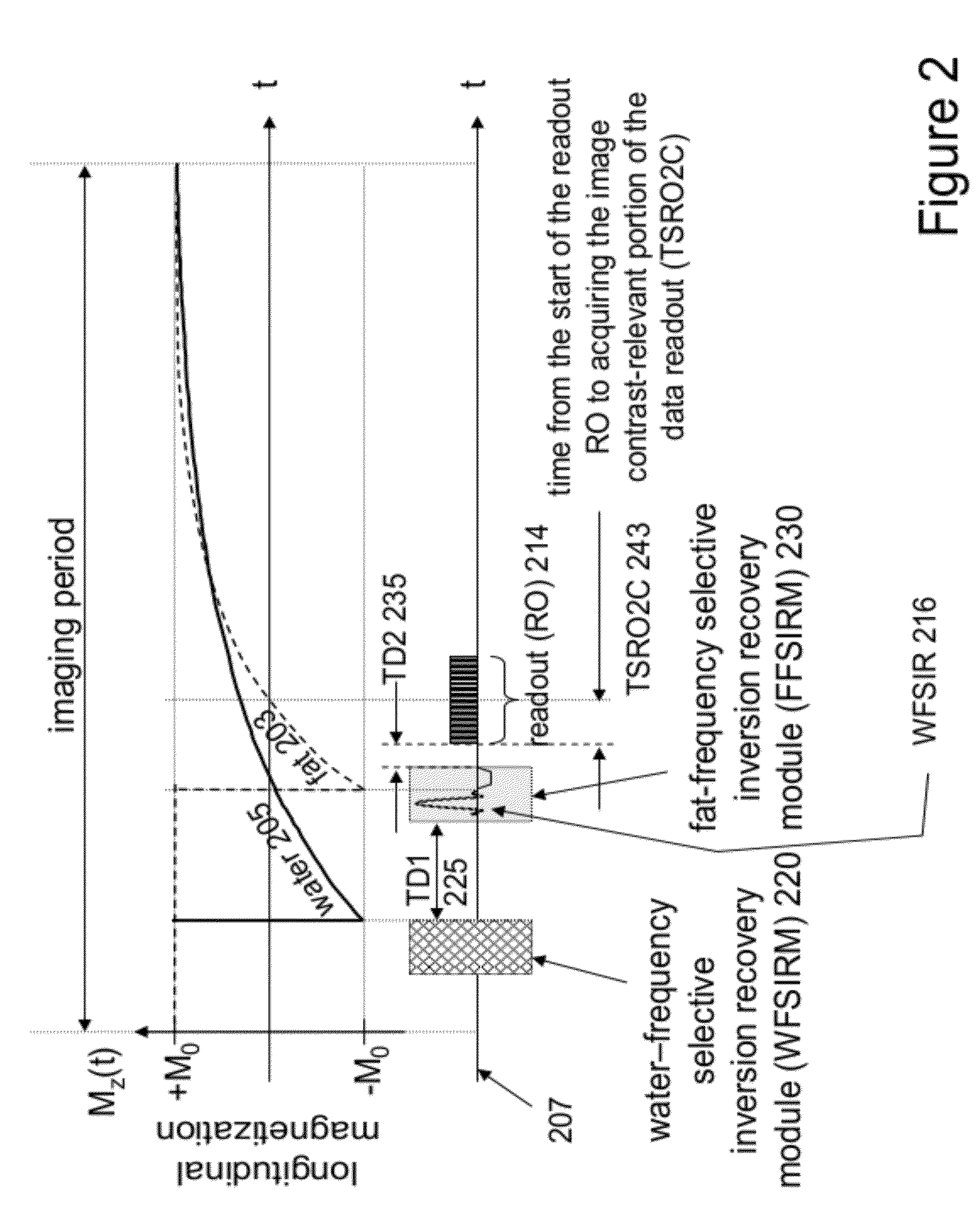
Method for independent manipulation of a fat and a water component in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
ActiveUS20120194193A1Suppresses fat signalImprove visualizationElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientObject based
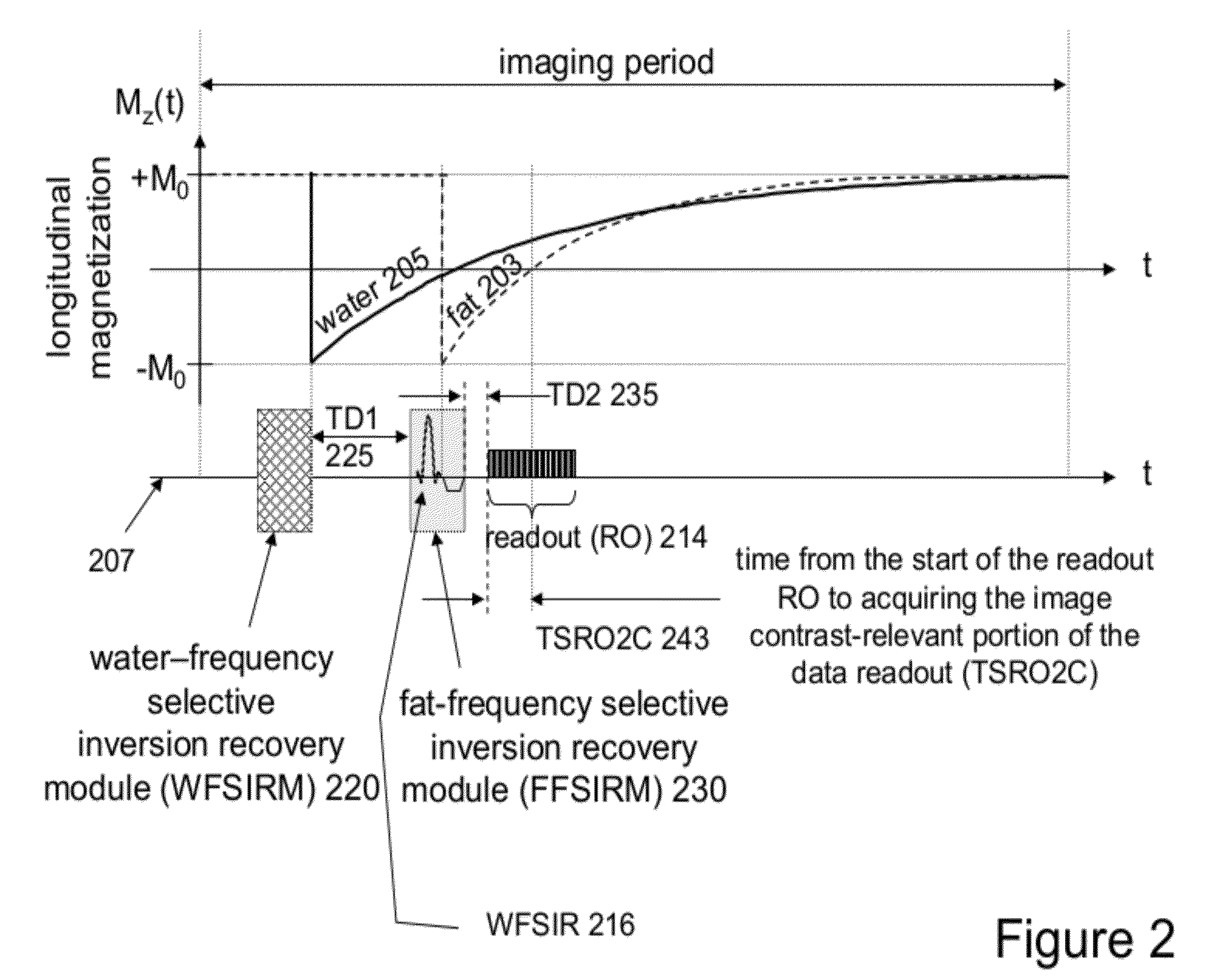
An MR imaging system independently manipulates a fat and a water component of MR signals used for generating image data. An RF signal generator and a magnetic field gradient generator provide an RF pulse and magnetic field gradient sequence for acquisition of an MR signal discriminating between anatomical objects based on longitudinal relaxation time (T1). The sequence comprises, a first pulse sequence for selectively inverting a water component of the MR signal substantially exclusively of fat, a first time delay adjustable to discriminate between different anatomical elements, a second pulse sequence having a resonant frequency selected to invert a fat component of the MR signal substantially exclusively of water and a data acquisition magnetic field gradient for acquisition of the MR signal. An image shows enhanced visualization of discriminated anatomical elements.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Nuclear magnetic resonance measurement techniques in non-uniform fields
InactiveUS7622919B2Accurate measurementEasy to measureElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsUniform fieldDiffusion
Methods and pulse sequences for facilitating nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements in grossly inhomogeneous fields. Methods and pulse sequences according to the invention may be used to accurately measure variables such as transverse relaxation time, longitudinal relaxation time, and diffusion, without the need for data at long recovery time, thereby allowing for faster measurements. In addition, methods and pulse sequences according to embodiment of the invention may allow simultaneous encoding of information in both the amplitude and the shape of echoes, so as to allow a single-shot measurement of multiple variables, e.g., both transverse relaxation time (from the decay of echo amplitudes) and longitudinal relaxation time (from the echo shape). CPMG detection may be used to overcome the often limited signal-to-noise ratio in grossly inhomogeneous fields.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
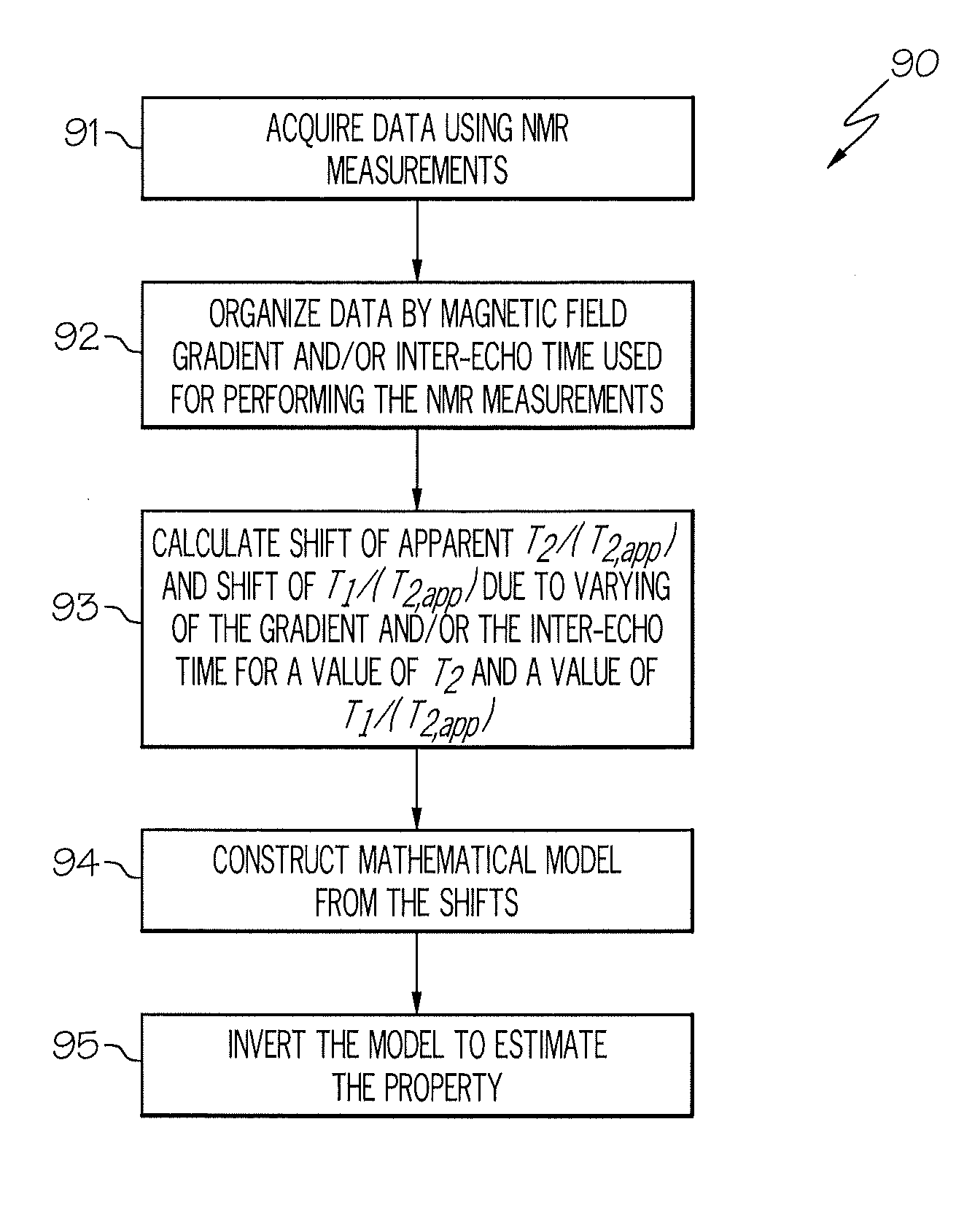
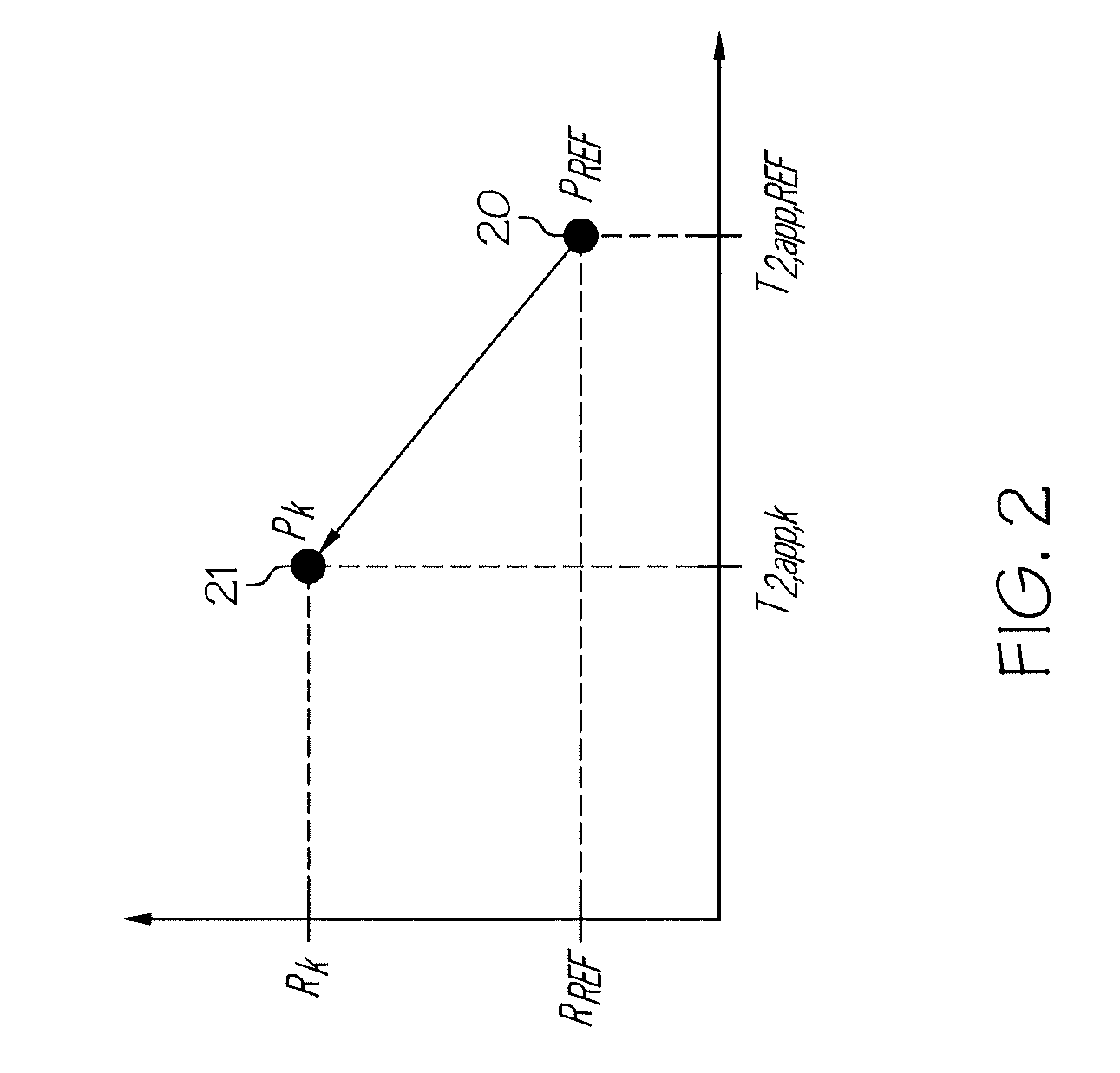
Two dimensional t1/t2app-t2app processing of multi-gradient nmr data
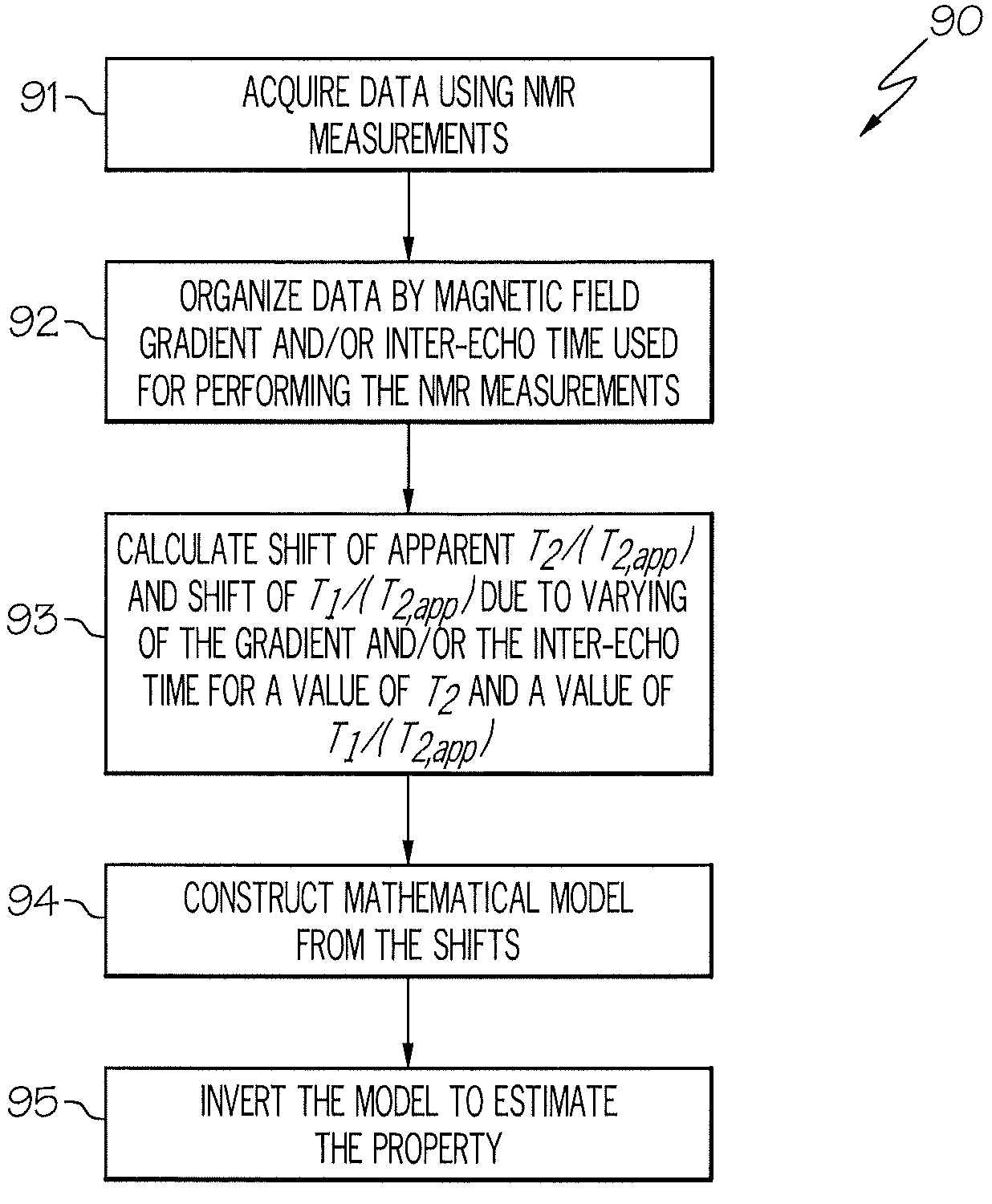
ActiveUS20090198446A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for estimating a property of a material, the method including: acquiring data using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements, the measurements performed by varying at least one of a magnetic field gradient (G) and an inter-echo time (TE); organizing the data according to at least one of magnetic field gradients (G) and inter-echo times (TE) used in the NMR measurements; calculating a shift of apparent transverse relaxation time (T2,app) and (longitudinal relaxation time T1) / (apparent transverse relaxation time T2,app) due to a variation of the product of G and TE; constructing a mathematical model of the NMR measurements from the shifts; and inverting the mathematical model to estimate the property.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
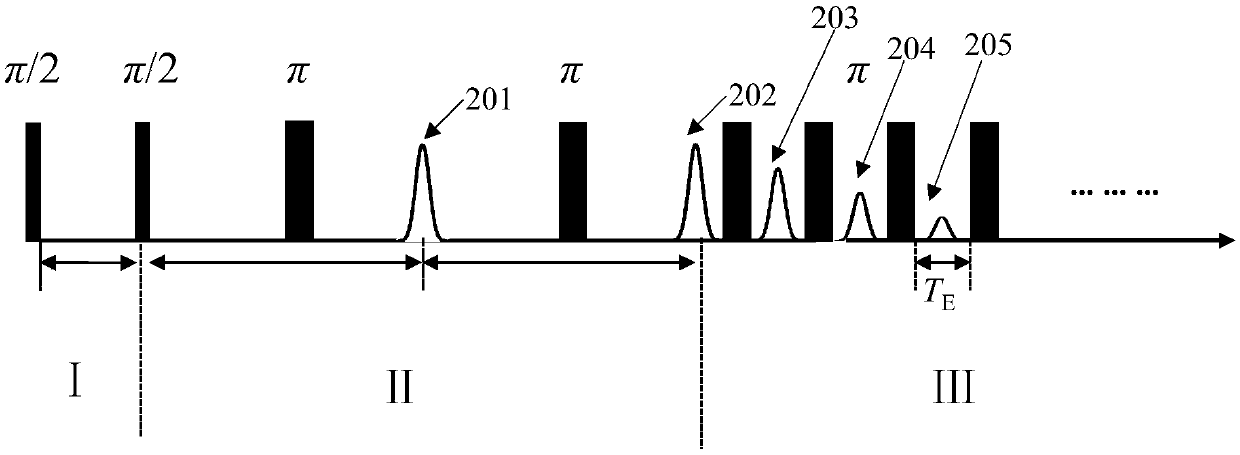
Fast T1 measurement by using driven equilibrium
InactiveUS20070032956A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingFast measurementLongitudinal Relaxation Time
An amplitude of an echo signal in a driven equilibrium (DE) pulse group is used for determination of a longitudinal relaxation time T1 of an earth formation. DE pulse groups followed by a CPMG sequence can be used for estimating both T1 and a transverse relaxation time T2 within one fast measurement.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System and method of high signal-to-noise ratio magnetic resonance imaging screening
ActiveUS20120262175A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionTransceiver
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
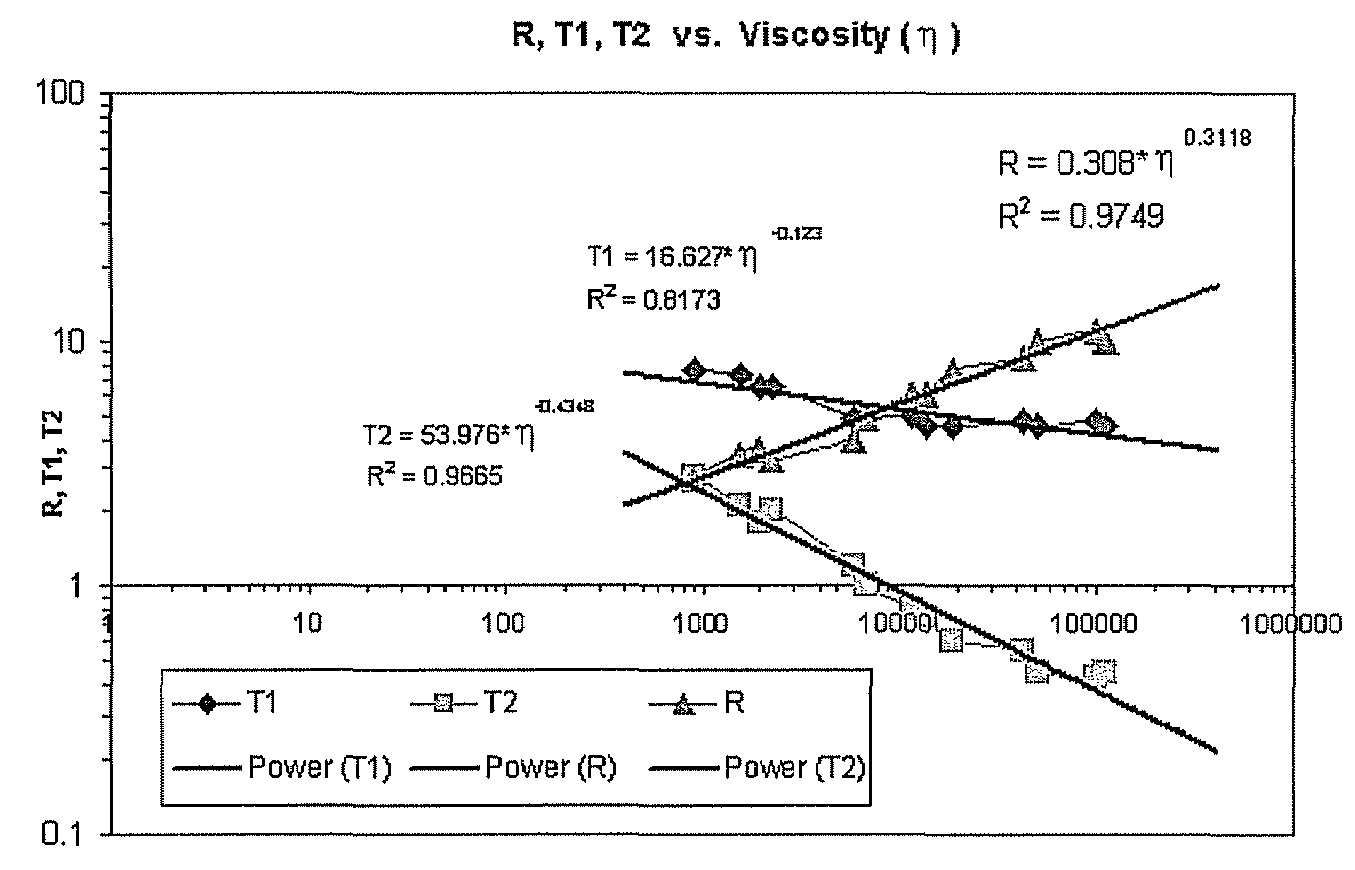
Viscosity determination from logarithmic mean ratio of relaxation times
ActiveUS20080272773A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic measurementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceViscosity
A method for determining viscosity, η, of a fluid downhole, calls for performing a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) survey of the fluid; determining a longitudinal relaxation time, T1, and an apparent transverse relaxation time, T2app, for the fluid; forming a ratio R of T1 / T2app for the fluid; and determining the viscosity, η, according to the ratio, R. A computer program product for implementing the method is provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Viscosity determination from logarithmic mean ratio of relaxation times
ActiveUS7511488B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceViscosity
A method for determining viscosity, η, of a fluid downhole, calls for performing a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) survey of the fluid; determining a longitudinal relaxation time, T1, and an apparent transverse relaxation time, T2app, for the fluid; forming a ratio R of T1 / T2app for the fluid; and determining the viscosity, η, according to the ratio, R. A computer program product for implementing the method is provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Magnetic resonance method for quantification of transverse relaxation times
ActiveUS8314618B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionRapid imagingTransverse relaxation
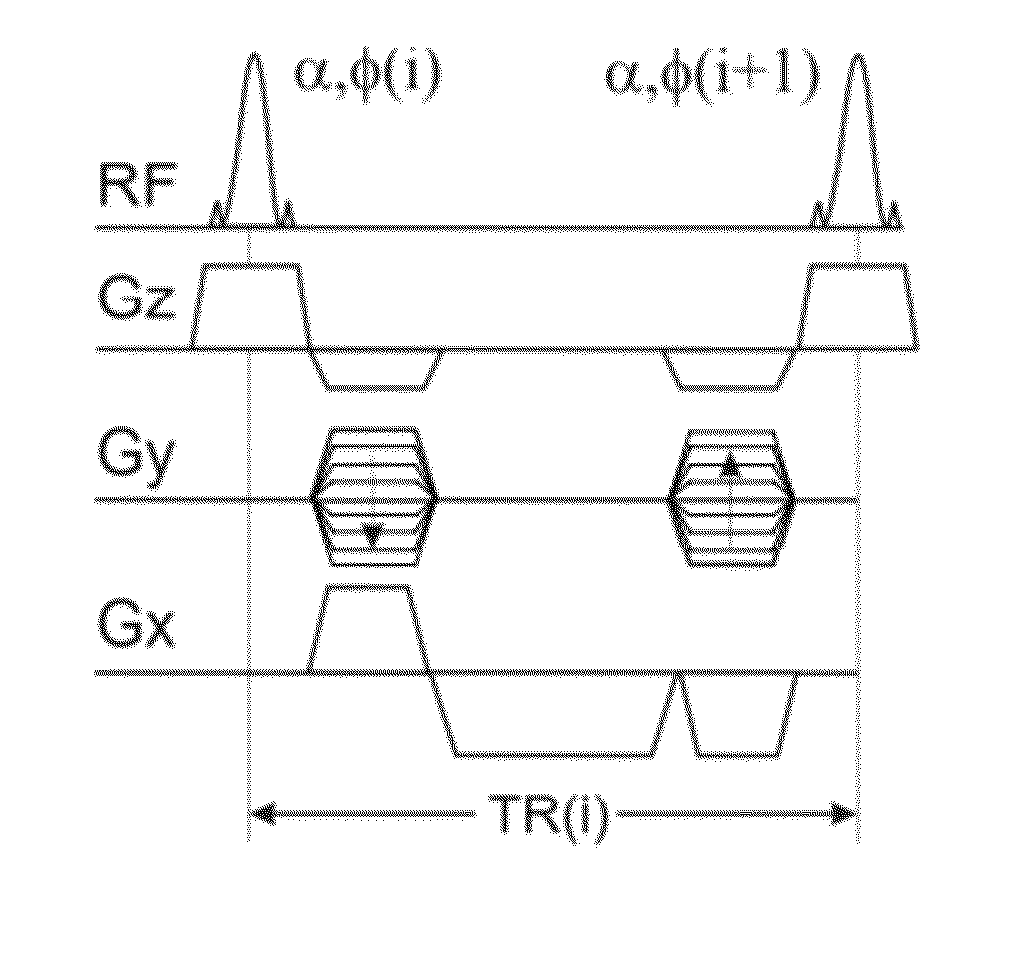
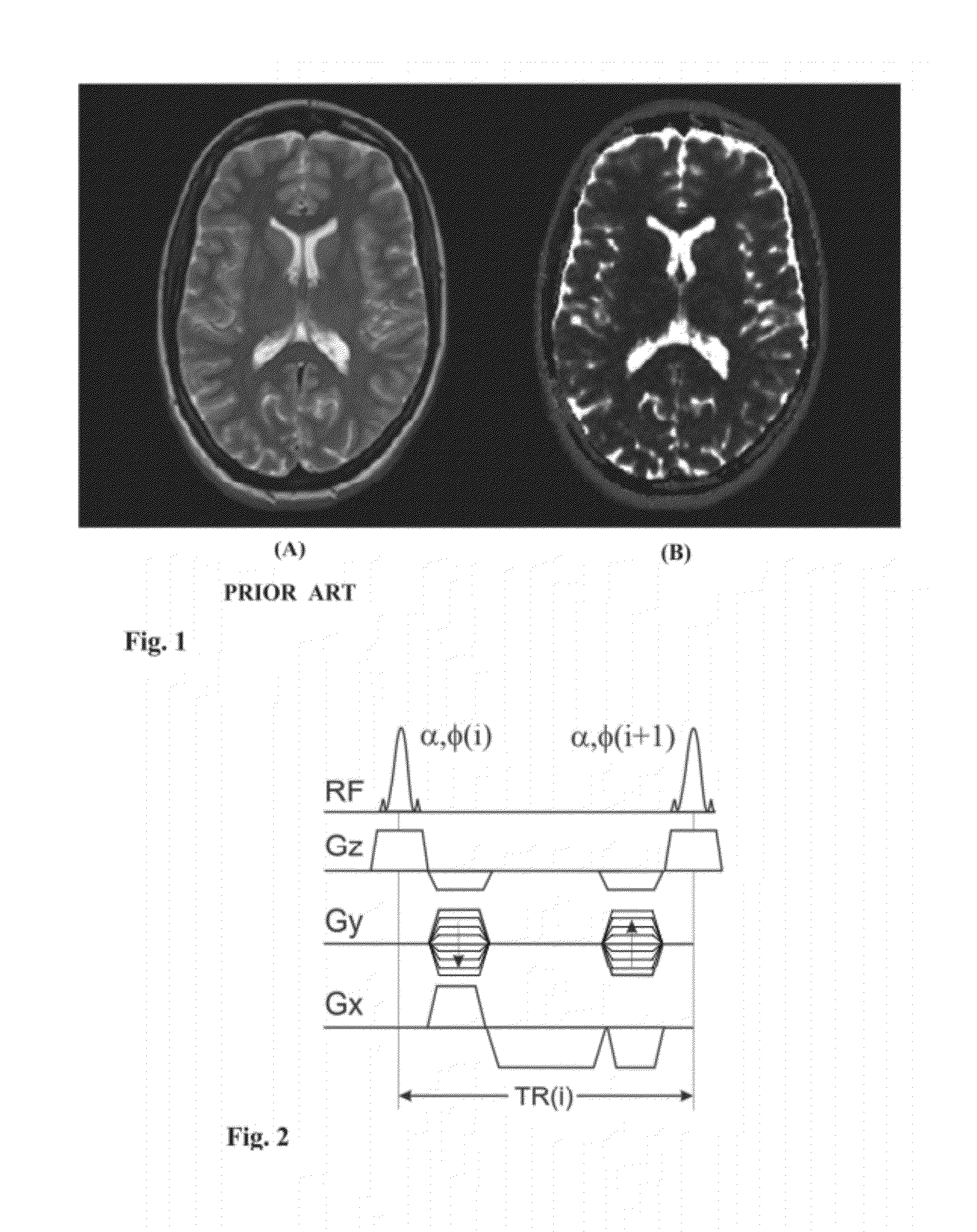
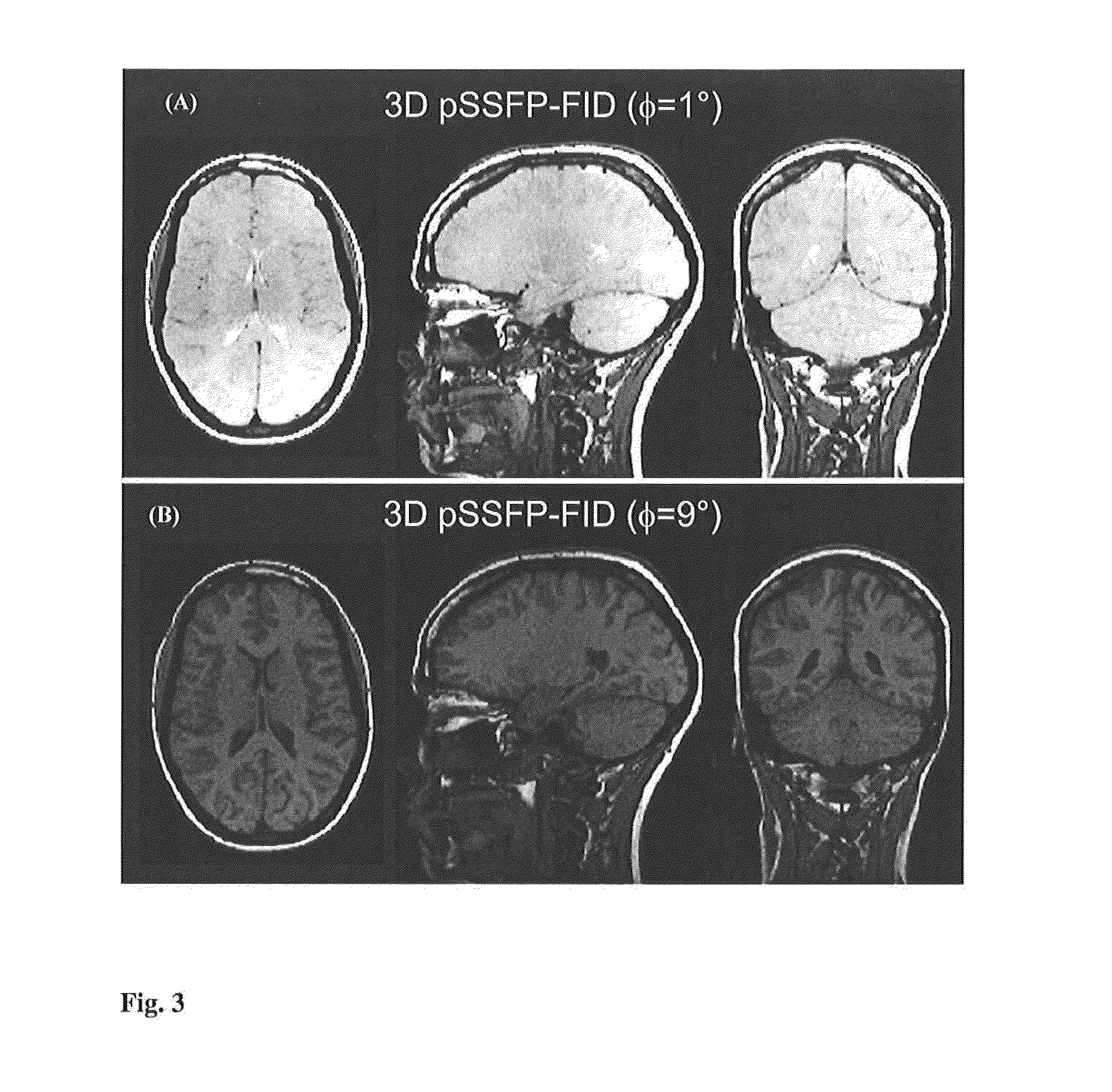
Apparatus and methods for quantification of transverse relaxation times (T2) using steady-state free precession sequences (generally known as fast imaging sequences) and their sensitivity to a quadratic increase of the RF pulse phase, also known as RF spoiling. Using at least two image acquisitions with different partial RF spoiling increments, T2 can be assessed with high precision and with short acquisition times in the limit of large excitation angles being independent on the longitudinal relaxation time (T1) and magnetization transfer effects as compared to other SSFP based quantitative T2 methods. This invention is not restricted to any kind of target and may be applied in 3D as well as in 2D.
Owner:UNIV HOSPITAL OF BASEL
Petroleum reservoir rock constituent identification and quantitative evaluation method
ActiveCN105182431AAchieving identifiabilityRealize quantitative evaluationDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceAcoustic wave reradiationNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceCut off value
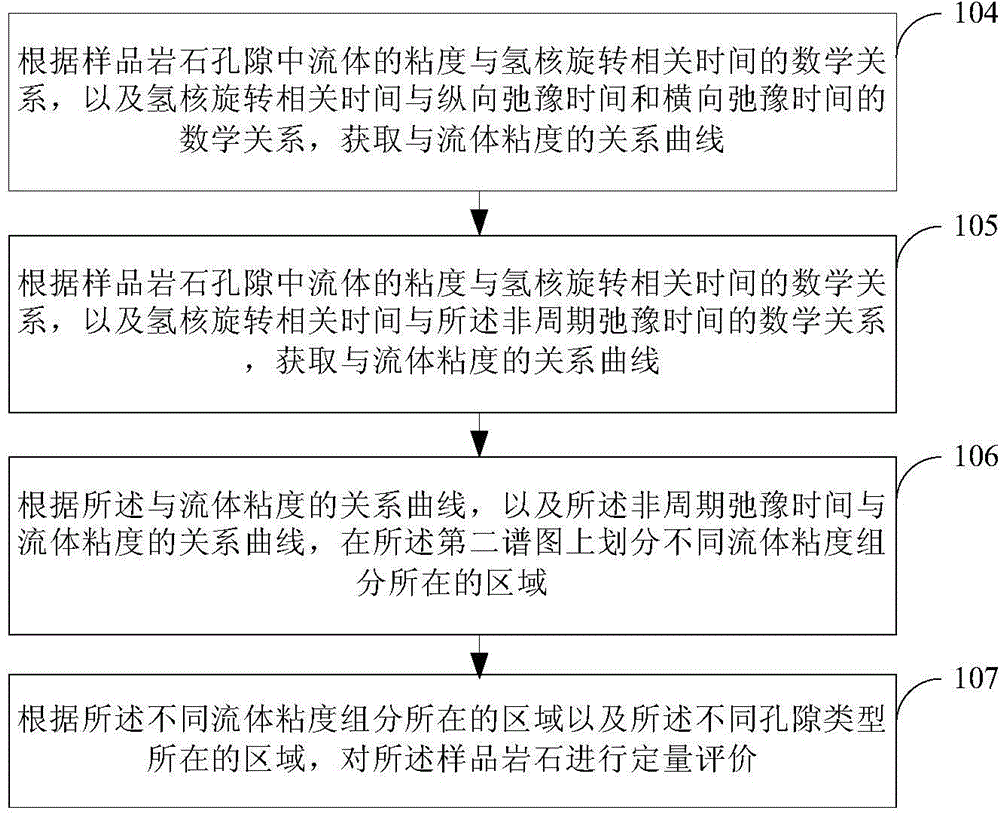
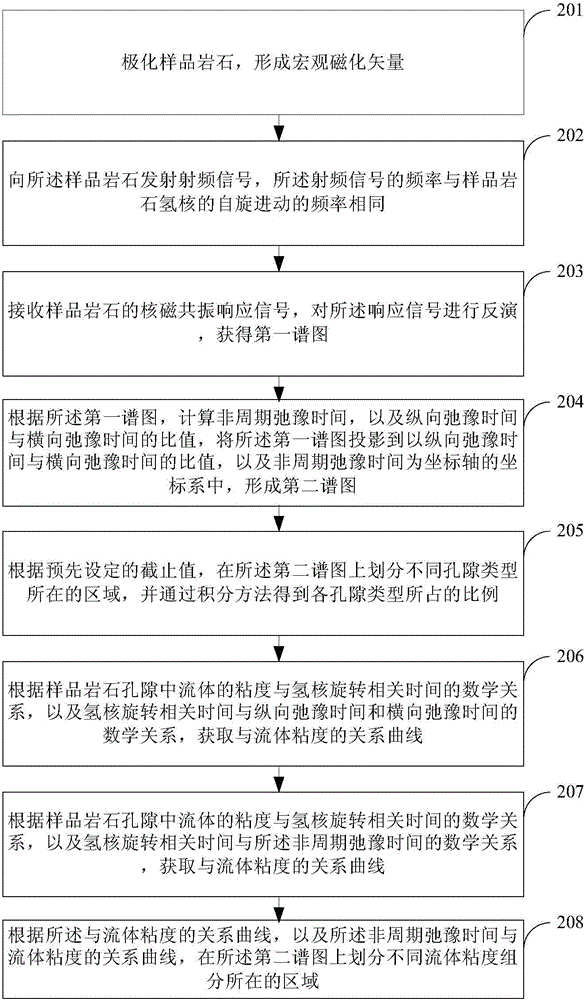
The invention provides a petroleum reservoir rock constituent identification and quantitative evaluation method. The method comprises the steps that nuclear magnetic resonance response signals of sample rocks are received, and inversion is performed on the response signals so that a first spectrogram is acquired; aperiodic relaxation time T2sec and the specific value T1 / T2 of longitudinal relaxation time T1 to transverse relaxation time T2 are calculated according to the first spectrogram, and the first spectrogram is projected to a coordinate system with the specific value T1 / T2 of longitudinal relaxation time T1 to transverse relaxation time T2 and aperiodic relaxation time T2sec acting as coordinate axes so that a second spectrogram is formed; and locating areas of different hole types are divided on the second spectrogram according to the preset cut-off value, and the proportion of each hole type is obtained via an integration method. According to the petroleum reservoir rock constituent identification and quantitative evaluation method, accuracy of reservoir rock constituent identification and reliability of the reservoir quantitative evaluation result can be enhanced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Changing method of CPMG test value increased by short waiting time test value
InactiveCN1458536AElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for determining an earth formation property from nuclear magnetic resonance measurements includes applying suppression functions to spin echoes in at least one burst measurement set to produce a modified burst data set, the suppression functions to suppress contribution of spin echoes having non-negligible polarization correction; inverting the modified burst data set and at least one standard spin echo measurement set to produce a nuclear magnetic resonance parameter distribution, the at least one standard spin echo measurement set and the at least one burst measurement set being acquired on an earth formation sample; and computing the earth formation property from the nuclear magnetic resonance parameter distribution. The nuclear magnetic resonance parameter includes at least one selected from longitudinal relaxation time, transverse relaxation time, a ratio of longitudinal relaxation time to transverse relaxation time, and diffusion constant.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER OVERSEAS SA
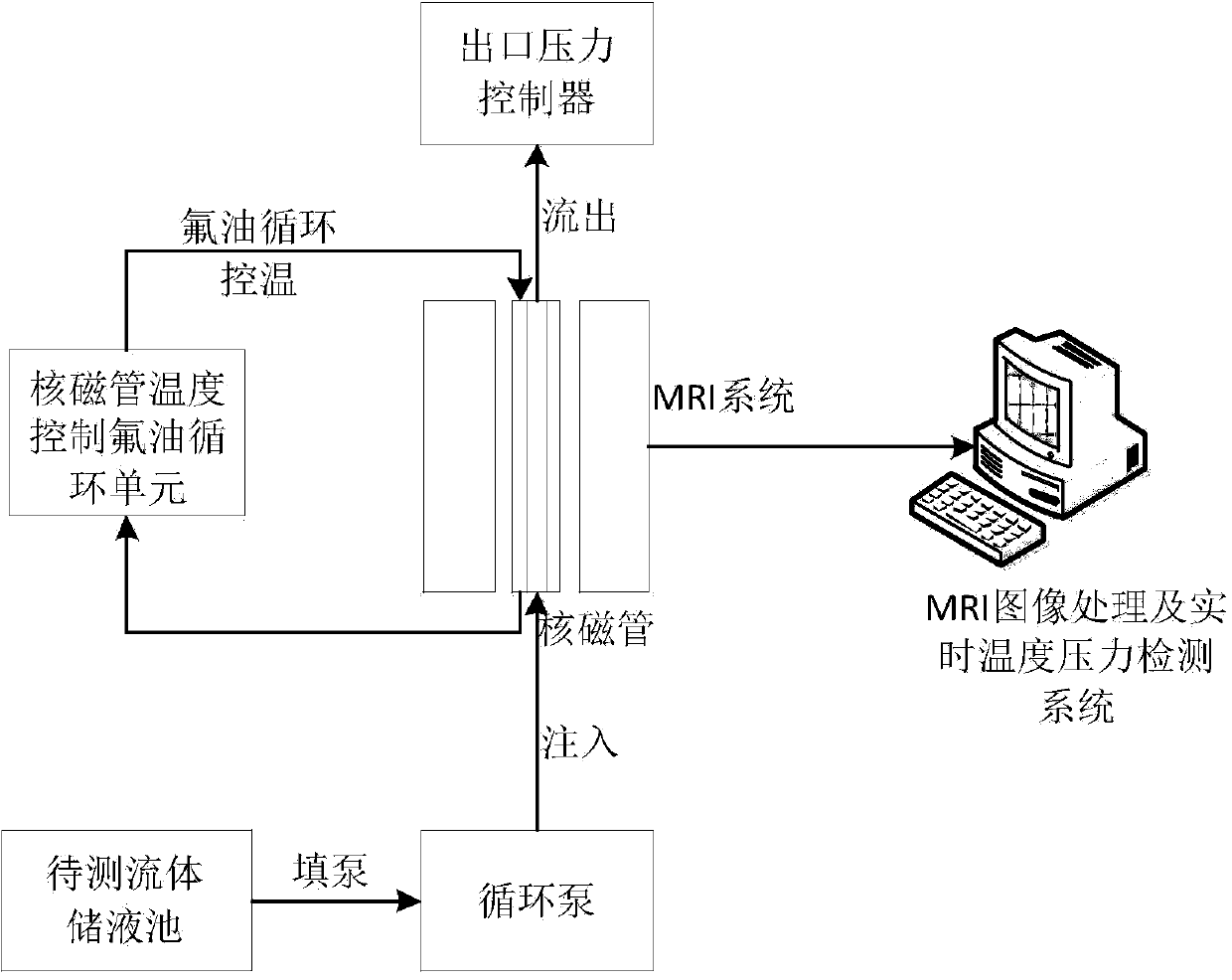
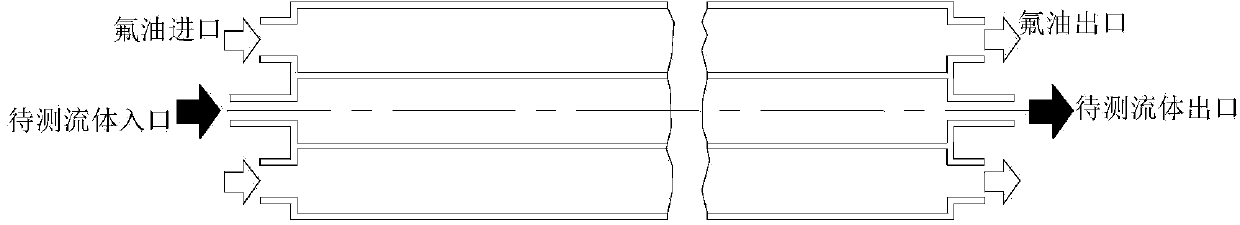
Magnetic-resonance imaging method for synchronous measurement of fluid speed and temperature in porous medium
ActiveCN103776490ANo optical requirementsCompensate for temperature deficienciesMeasurement devicesNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePorous medium
Disclosed is a magnetic-resonance imaging method for synchronous measurement of fluid speed and temperature in a porous medium and the method belongs to the field of magnetic-resonance imaging measurement. The method adopts a nuclear-magnetic-resonance overturning restoring label method: firstly a spin-echo sequence two-point method is used to measure a longitudinal relaxation time T1 of a tested fluid at a specific temperature; step 1 is repeated at different temperatures so that T1 values at different temperatures are obtained and then the relation between T1 and temperature T is obtained through fitting; an overturning restoring label sequence is used to measure the fluid at a static state and then the fluid at any temperature and flow speed is measured; a matlab is used to read an image so that image signal intensity (SI) distribution is obtained, and then the temperature T is calculated according to the relation of SI and T; label displacement within an overturning restoring time ti is solved through comparison of a label coordinate under the flow speed and a label coordinate at a static state so that a fluid flow speed is solved. The magnetic-resonance imaging method for the synchronous measurement of the fluid speed and the temperature in the porous medium is high in measurement speed and capable of compensating effectively for signal reduction resulted from flowing when a traditional overturning restoring method is used to measure flow-field temperatures.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
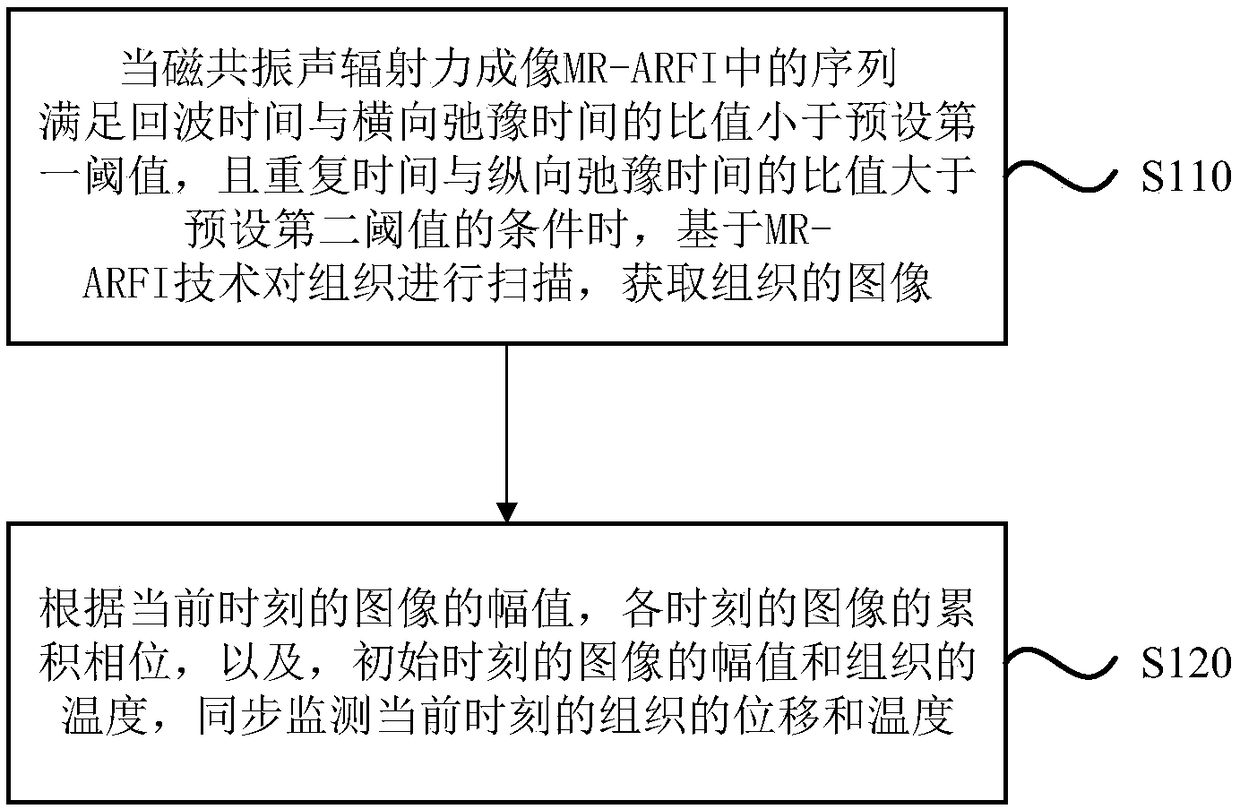
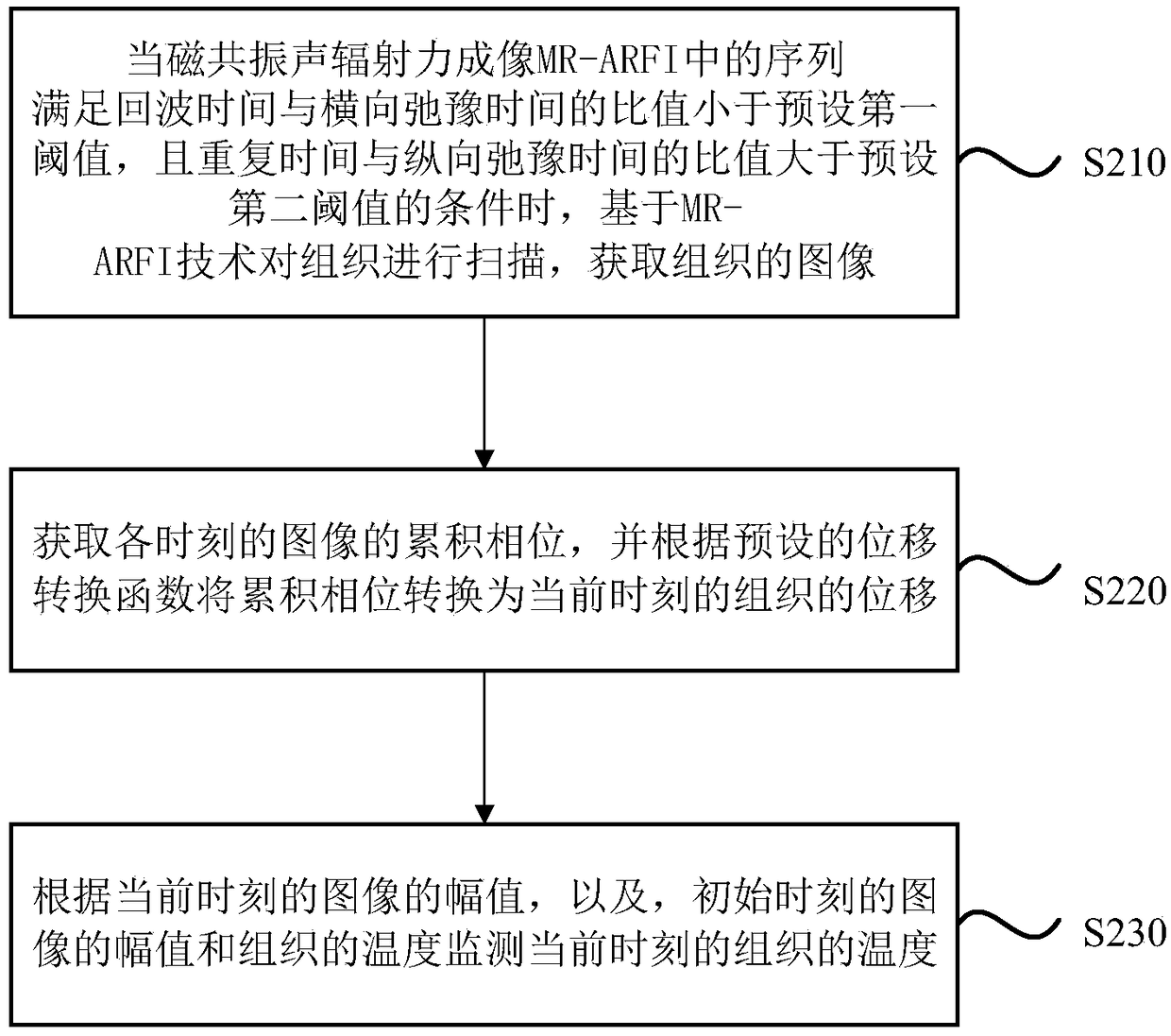
Synchronous monitoring method, apparatus and device for tissue displacement and temperature and storage medium
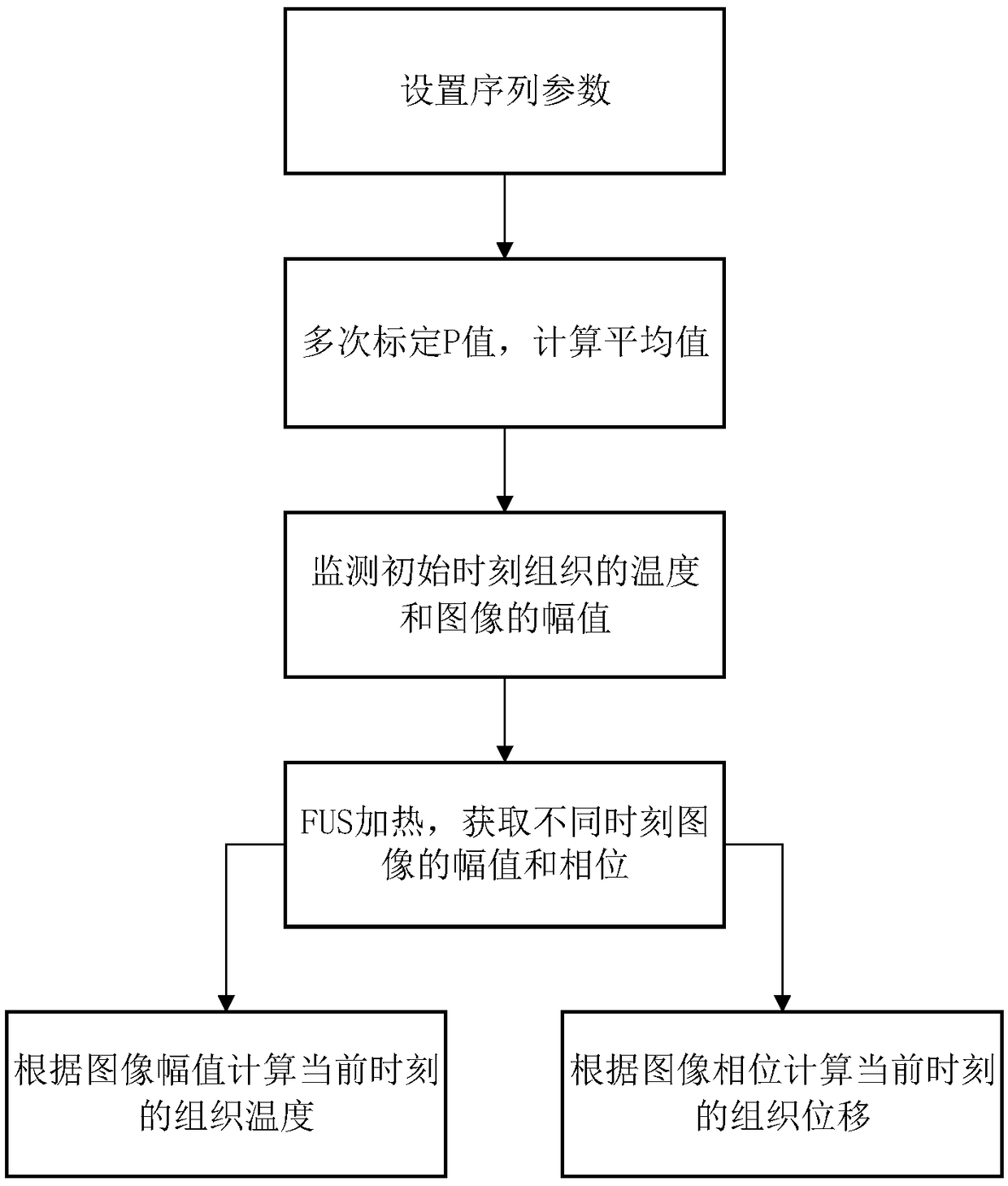
ActiveCN109480844ASimultaneous monitoring of displacementSimultaneous monitoring of temperatureImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionMagnetic resonance soundingComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses a synchronous monitoring method, apparatus and device for tissue displacement and temperature and a storage medium. The method includes the steps that when asequence in a magnetic resonance sound radiation power image MR-ARFI meets the condition that the ratio of echo time to transverse relaxation time is smaller than a preset first threshold value and the ratio of repetition time to longitudinal relaxation time is greater than a preset second threshold value, tissues are scanned based on MR-ARFI technology to obtain a tissue image; according to an image amplitude at the current moment, the accumulated phases of the image at all moments and the image amplitude at the initial moment and the tissue temperature, the tissue displacement and temperature at the current moment are monitored synchronously. By adopting the technical scheme of the embodiment of the present invention, the displacement and temperature of the tissue at the current moment can be synchronously monitored, and the safety of the FUS focusing process is ensured.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Two dimensional T1/T2APP-T2APP processing of multi-gradient NMR data
ActiveUS7705592B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Methods and systems for estimating longitudinal relaxation times in MRI
InactiveUS20110137612A1Digital computer detailsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsLinearityComputer science
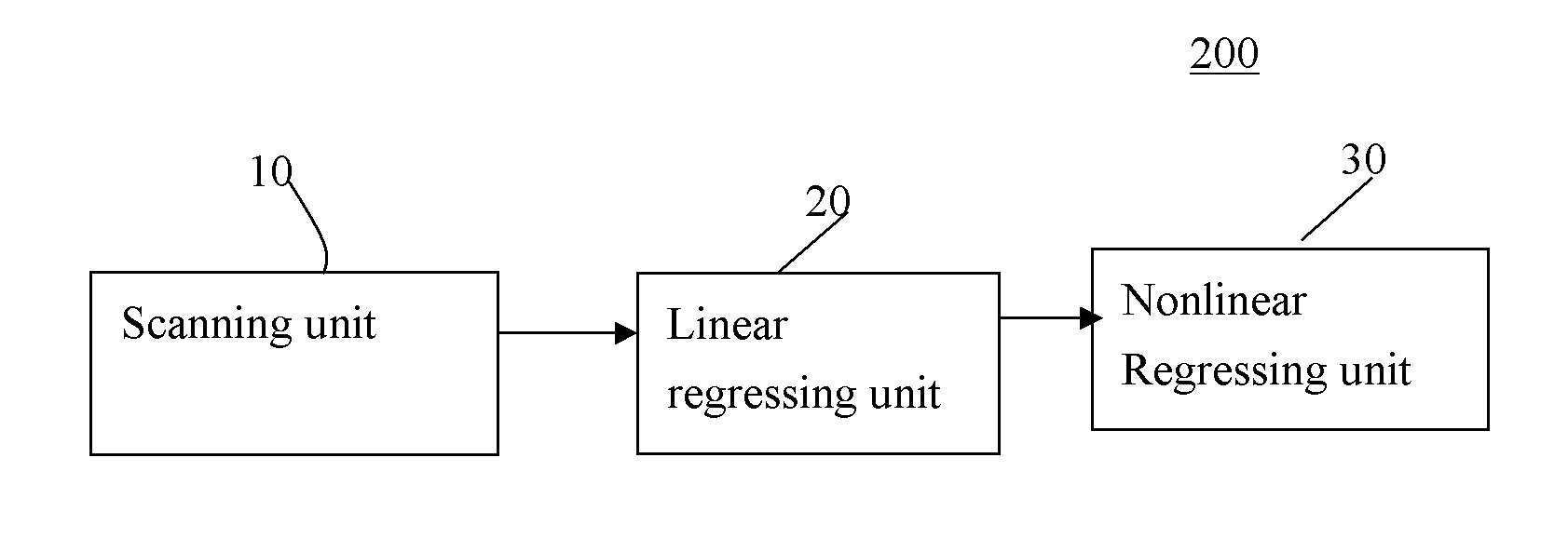
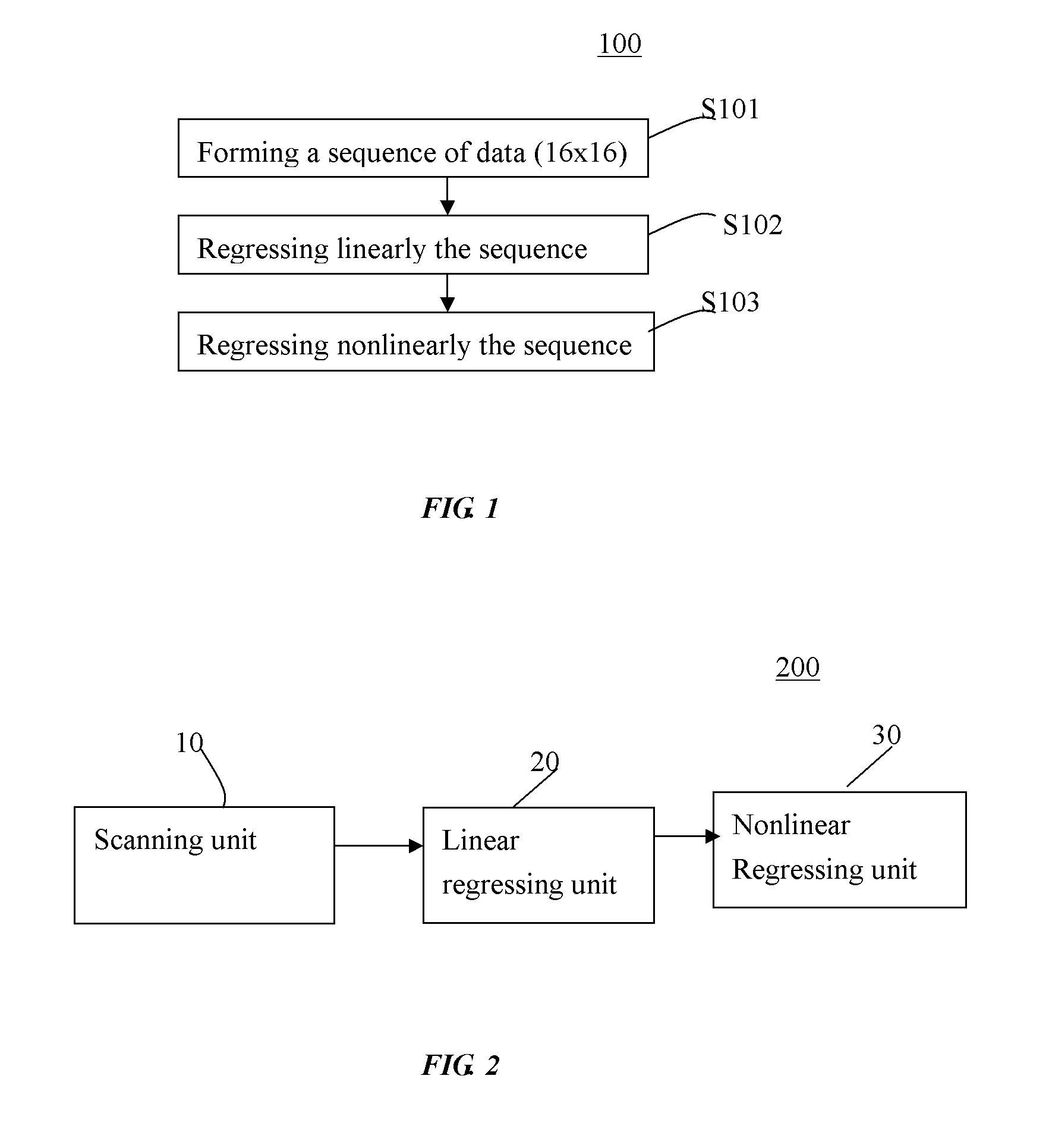
A method and a system for estimating a longitudinal relaxation time in magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes scanning at least one object to form a sequence of data with a plurality of flip angles; regressing linearly the formed sequence of data based on a first signal intensity model associated with the flip angles to obtain an initial estimation for said longitudinal relaxation time; and regressing nonlinearly the formed sequence of data based on a second signal intensity model associated with the flip angles so as to obtain a final estimation for the longitudinal relaxation time, in which the initial estimation is used as an initial guess for the longitudinal relaxation time based on the second signal intensity model.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for determining purity of daptomycin on basis of hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance
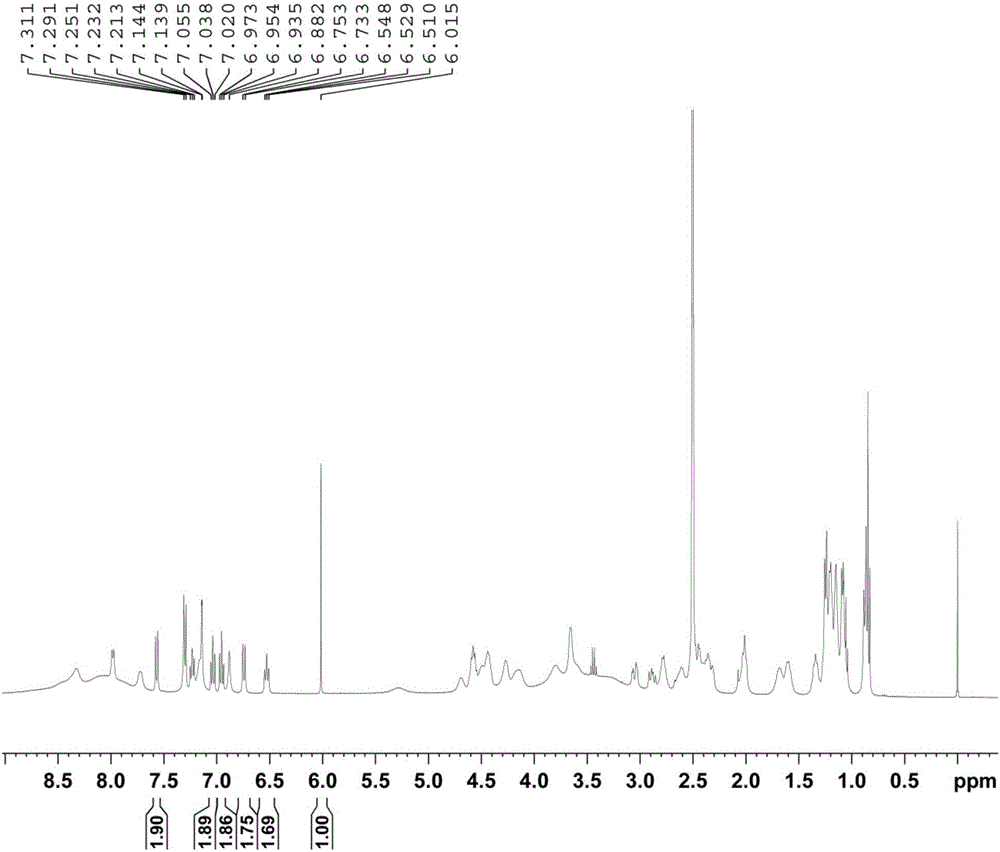
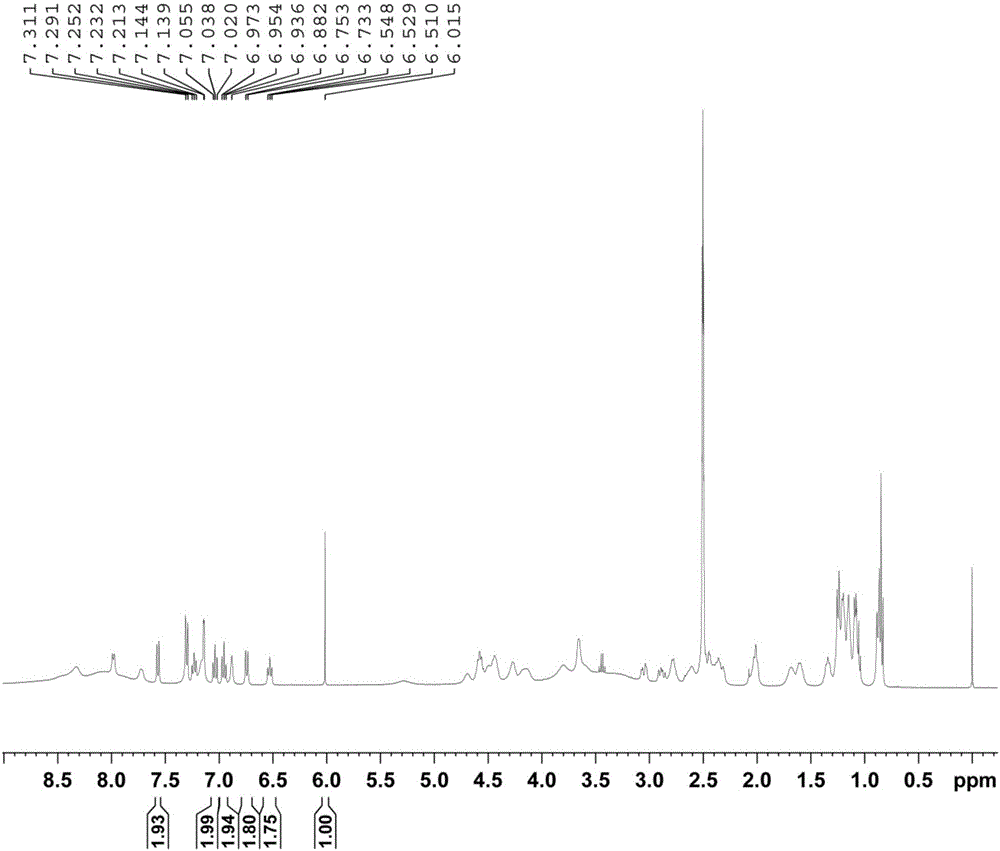
InactiveCN106018456AAccurately get the absolute contentReduce analysis costsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDelayed timeProton NMR
The invention discloses a method for determining the purity of daptomycin on the basis of hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the following steps that 1, longitudinal relaxation time (T<1>) of quantitative target peaks of daptomycin and an internal standard substance in a deuterated reagent is determined; 2, a flip angle of a nuclear magnetic resonance wave spectrometer and relaxation delay time (d<1>) are set according to the determined T<1> value; 3, integral areas of all quantitative target peaks of a daptomycin sample and the internal standard substance are determined according to the parameters set in the second step, and the molar mass ratio of daptomycin to the internal standard substance is obtained; 4, the purity of daptomycin is calculated according to the mass of the internal standard substance, and the purity of daptomycin is calculated according to the following formula of W%=(m<IS> *H<IS>*A<S>*M<S>*100%) / (M<IS>*A<IS>*m<S>*H<S>). The method has the advantages of being good in repeatability and easy and convenient to operate, can rapidly and accurately detect the purity of daptomycin and provides a novel method for strictly controlling the purity of daptomycin.
Owner:SHANDONG ANALYSIS & TEST CENT
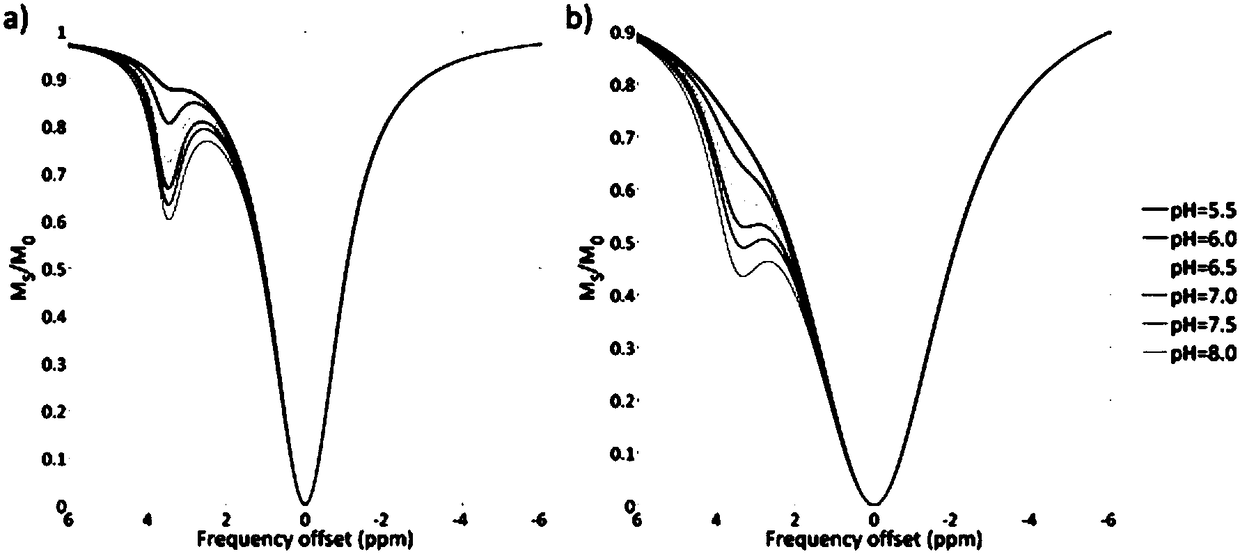
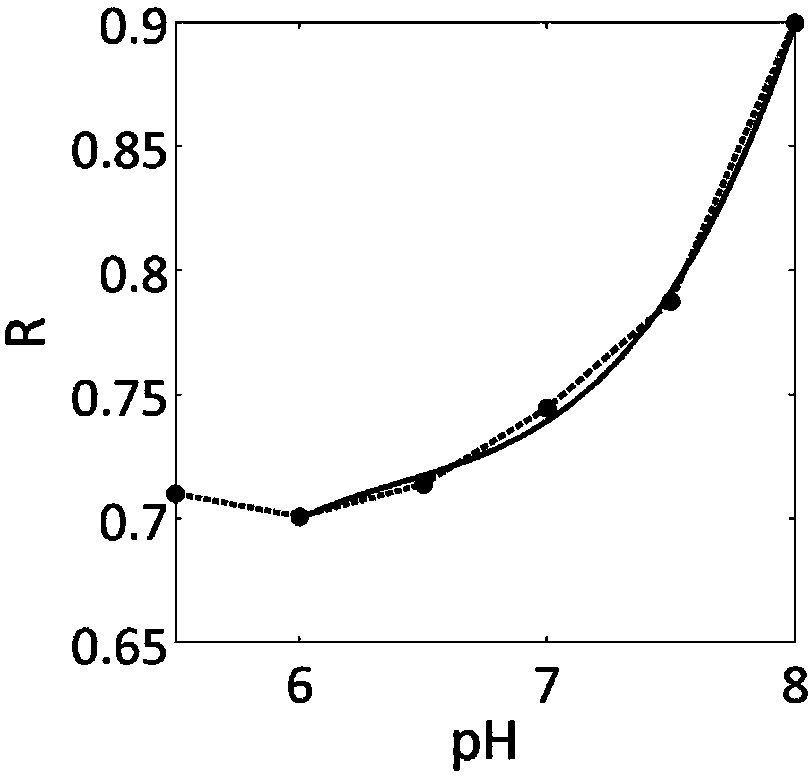
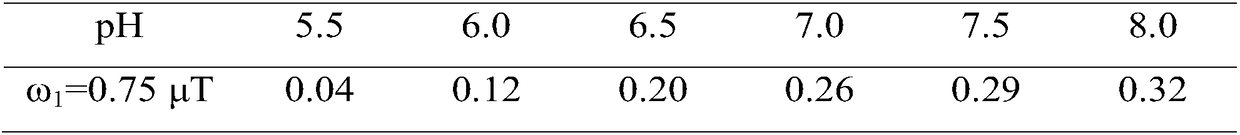
pH value testing method
ActiveCN108195867AAccurate measurementEasy to measureMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceResonanceProton
The invention relates to the field of biological medicines, in particular to a pH value testing method which comprises the following steps: with an amino proton as an endogenous contrast agent, testing corresponding chemical exchange saturated transferring effect ratios R of amino protons of known pH value amino proton source solutions under different saturated pulse intensities, establishing function relationships of pH values and the ratios R corresponding to the different known pH value amino proton source solutions according to the different known pH value amino proton source solutions andtested corresponding ratios R, and finally calculating expected pH values according to the function relationships of values Ri tested through experiments and the function relationships. By adopting the method, influence of concentrations can be eliminated, parameters such as exchangeable proton concentrations and longitudinal relaxation times of water do not need to be estimated or measured, so that pH values can be relatively accurately, conveniently and non-destructively measured. In addition, since amino is relatively low in chemical exchange velocity, stable imaging under magnetic resonance field intensity of common clinical application can be achieved, and thus the method has good application prospects.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for determining conversion rate during p-polyisobutylene phenol synthesis process through quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
ActiveCN108152318AAvoid cumbersomeImprove accuracyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyPhenol
The invention relates to a method for determining the conversion rate of polyisobutylene, in particular to a method for determining the conversion rate of the polyisobutylene during a process of generating p-polyisobutylene phenol through reaction of the polyisobutylene and excessive phenol through a quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The method comprises the steps of respectively acquiring a polyisobutylene phenol sample, and a polyisobutylene and phenol nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, obtaining chemical shift of the p-polyisobutylene phenol through spectrogram comparison and spectrogram reasoning; determining longitudinal relaxation time T1 of a p-polyisobutylene phenol sample in a deuteration reagent, setting a pulse flip angle and relaxation time of a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer according to the T1, utilizing the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for determining the nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of a solution to be tested, obtaining a peak area of each part of hydrogen through integration, and calculating to obtain the conversion rate of the polyisobutylene through the number of hydrogen actually contained in a target product and raw materials. The method provided by the invention is low in cost, can be used for quickly and accurately evaluating the type and the conversion rate of a synthetic product of the polyisobutylene and the phenol, and provides a powerful evidence for synthesis.
Owner:CHAMBROAD CHEM IND RES INST CO LTD
Prostate magnetic resonance image segmentation method based on level set
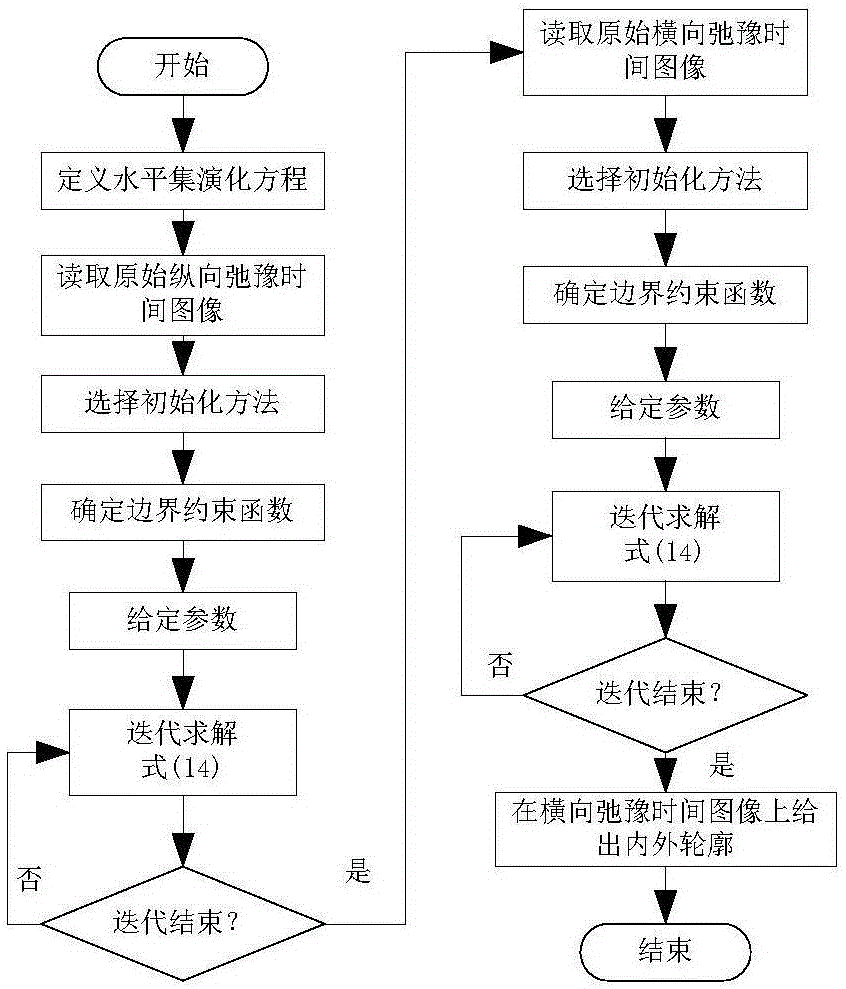
ActiveCN106846349AThe outer contour is clearly segmentedAvoid Numerical ErrorsImage enhancementImage analysisContour segmentationManual segmentation
The invention provides a prostate magnetic resonance image segmentation method based on a level set and relates to the technical field of magnetic resonance image segmentation. Based on a prostate magnetic resonance image, the invention provides a prostate magnetic resonance image segmentation method based on edge distance adjustment level set evolution for the comprehensive segmentation of the internal and external contours of the prostate. Based on the establishment of a level set evolution equation, the method achieves the segmentation of the external contour based on a prostate magnetic resonance longitudinal relaxation time image, and achieves the segmentation of the internal contour based on a prostate magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time image under an external contour constraint condition, thereby further completing the full effective segmentation of the internal and external contours of the prostate. The method can achieve the comprehensive segmentation of the internal and external contours of the prostate, is very close to the ideal result of manual segmentation of a clinical expert, and has a good reference value for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of prostate diseases.
Owner:FOSHAN BAIKANG ROBOT TECH CO LTD
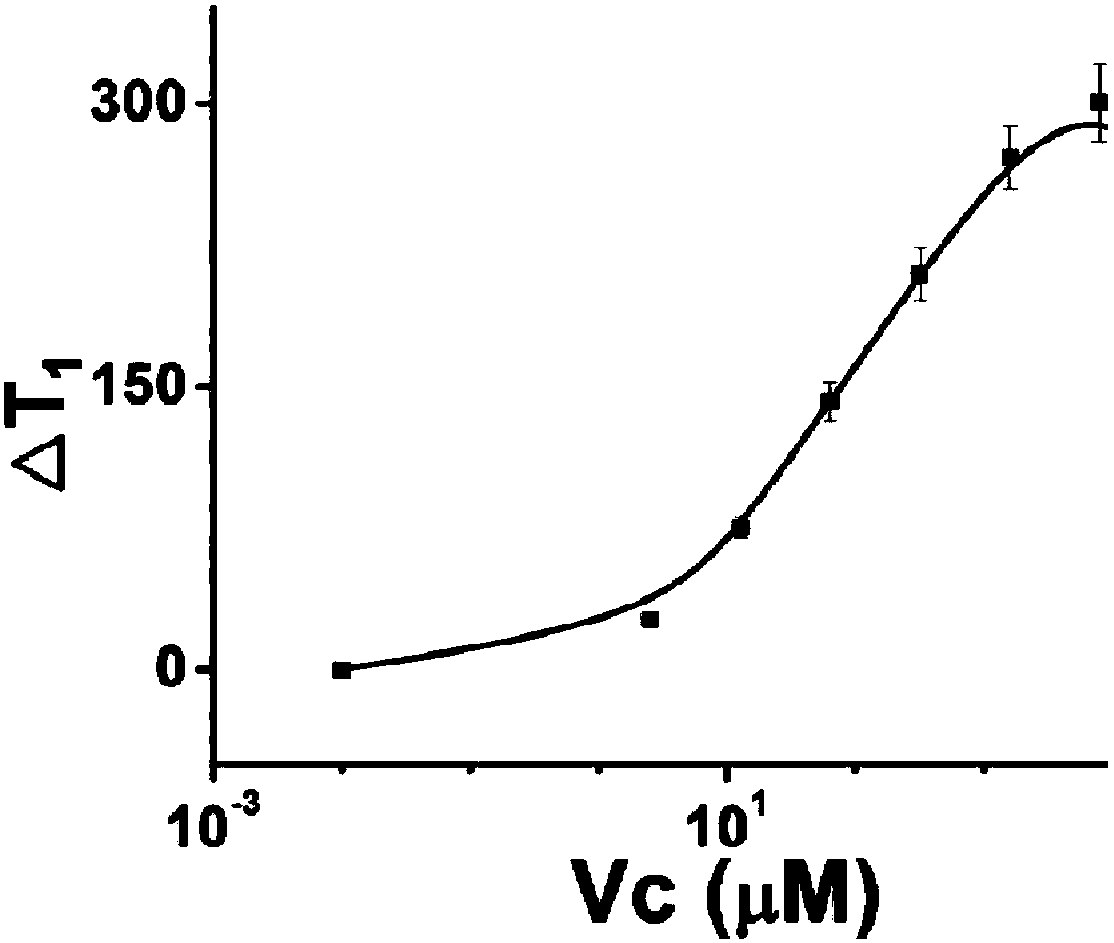
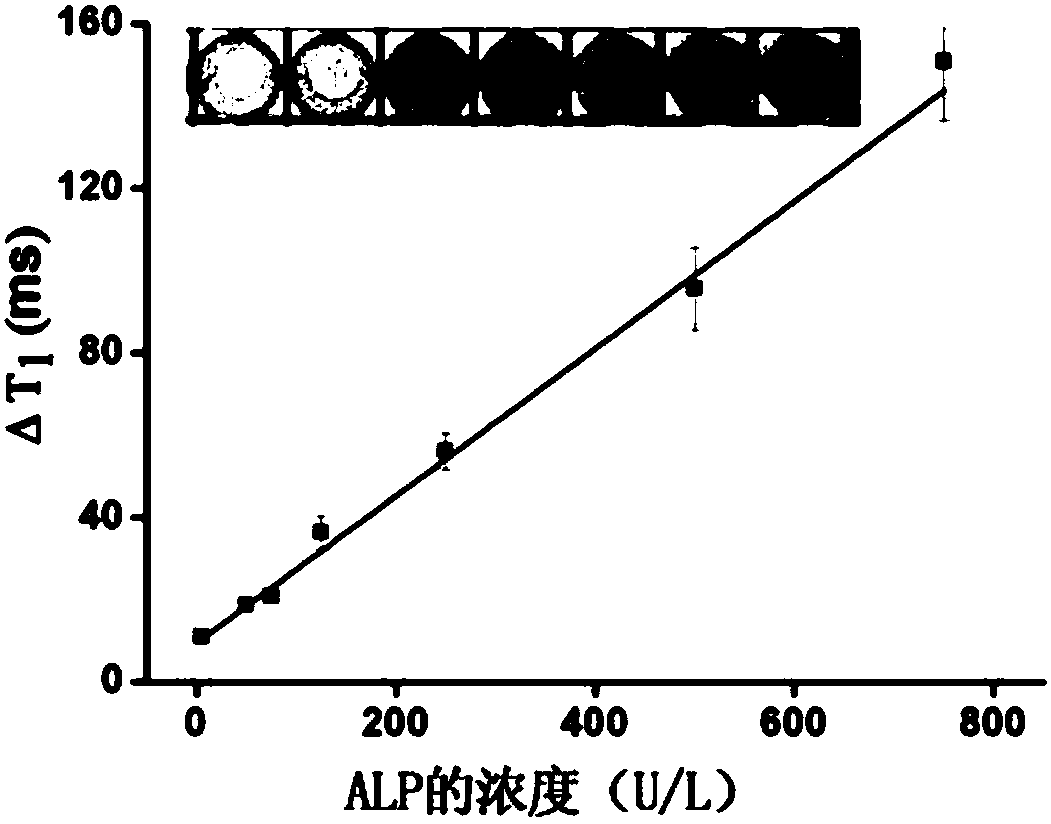
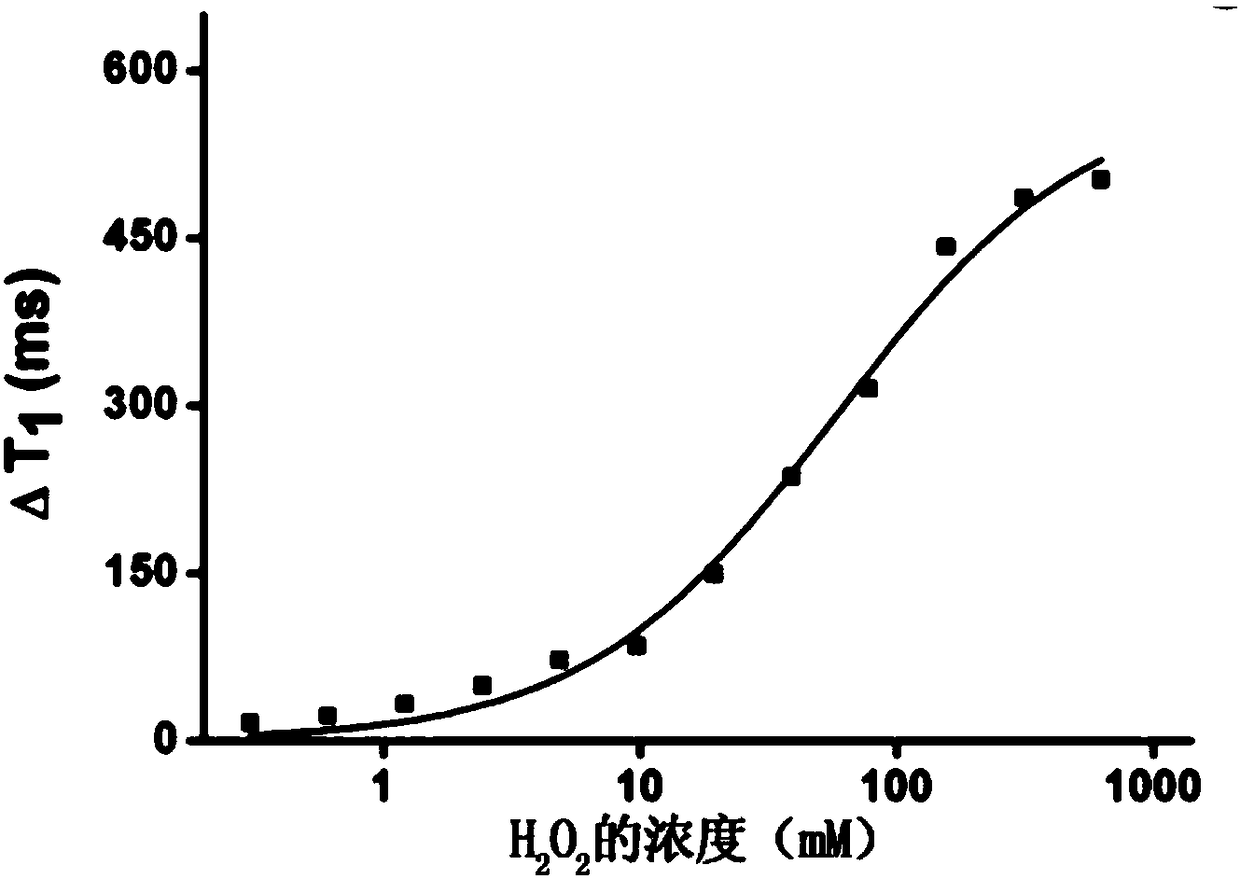
Magnetic sensor based on longitudinal relaxation time signal readout, method for constructing same and use of same
ActiveCN108333536AAchieve conversionExpand the scope of detectionMagnetic measurementsBiological testingFood safetyEngineering
The invention provides a magnetic sensor based on longitudinal relaxation time signal readout. The magnetic sensor takes a longitudinal relaxation time (T1) as a readout signal. The invention also provides a method for constructing a magnetic sensor based on longitudinal relaxation time signal readout, and the use of the magnetic sensor in the fields of biochemical analysis and immunoassay, food safety, environmental detection and the like.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
System and method for independent manipulation of a fat and a water component in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS9030201B2Improve visualizationSuppresses signalMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientObject based
An MR imaging system independently manipulates a fat and a water component of MR signals used for generating image data. An RF signal generator and a magnetic field gradient generator provide an RF pulse and magnetic field gradient sequence for acquisition of an MR signal discriminating between anatomical objects based on longitudinal relaxation time (T1). The sequence comprises, a first pulse sequence for selectively inverting a water component of the MR signal substantially exclusively of fat, a first time delay adjustable to discriminate between different anatomical elements, a second pulse sequence having a resonant frequency selected to invert a fat component of the MR signal substantially exclusively of water and a data acquisition magnetic field gradient for acquisition of the MR signal. An image shows enhanced visualization of discriminated anatomical elements.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
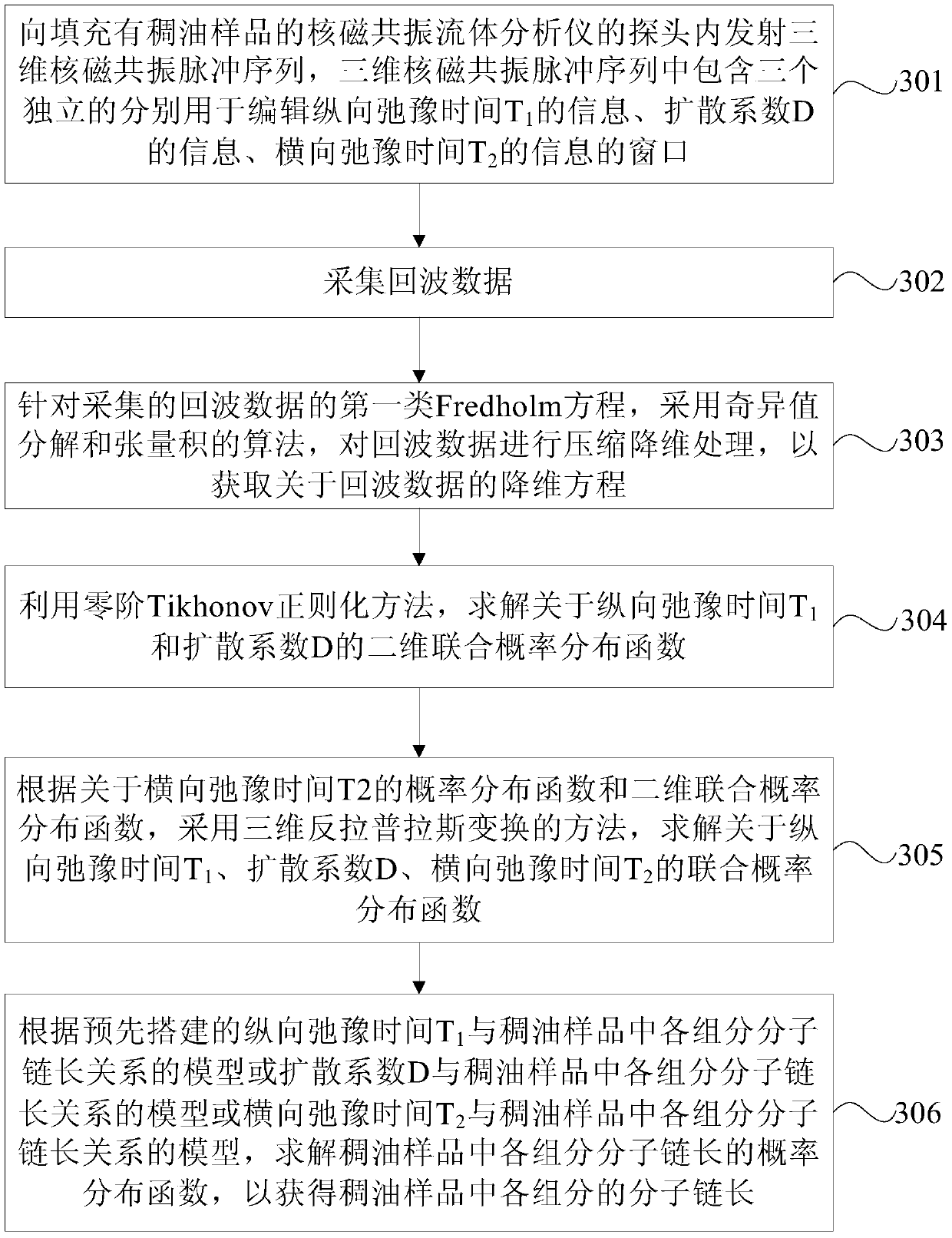
Measuring method and device for underground thick oil molecule chain length
ActiveCN105486709AProcessing speedRealize in-situ non-destructive measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention provides a measuring method and device for the underground thick oil molecule chain length. The method comprises the steps that a three-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence is emitted into a probe of a nuclear magnetic resonance fluid analyzer filled with a thick oil sample, wherein the three-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence contains three independent windows used for editing information of the longitudinal relaxation time T<1>, information of the diffusion coefficient D and information of the transverse relaxation time T<2> respectively; echo data is collected; inversion is performed on the echo data by adopting a fast inversion algorithm, and a joint probability distribution function about the longitudinal relaxation time T<1>, the diffusion coefficient D and the transverse relaxation time T<2> is calculated; a probability distribution function of the molecule chain length of all components in the thick oil sample is solved according to a pre-established model of the relation between the longitudinal relaxation time T<1> and the molecule chain length of all the components in the thick oil sample or a pre-established model of the relation between the diffusion coefficient D and the molecule chain length of all the components in the thick oil sample or a pre-established model of the relation between the transverse relaxation time T<2> and the molecule chain length of all the components in the thick oil sample.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[method and apparatus for determining speed and properties of flowing fluids using nmr measurements] [method and apparatus for determining speed and properties of flowing fluids using nmr measurements]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2f41d1bc-f391-4033-923f-4d7607c0216d/US20050140368A1-20050630-D00000.png)
![[method and apparatus for determining speed and properties of flowing fluids using nmr measurements] [method and apparatus for determining speed and properties of flowing fluids using nmr measurements]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2f41d1bc-f391-4033-923f-4d7607c0216d/US20050140368A1-20050630-D00001.png)
![[method and apparatus for determining speed and properties of flowing fluids using nmr measurements] [method and apparatus for determining speed and properties of flowing fluids using nmr measurements]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2f41d1bc-f391-4033-923f-4d7607c0216d/US20050140368A1-20050630-D00002.png)