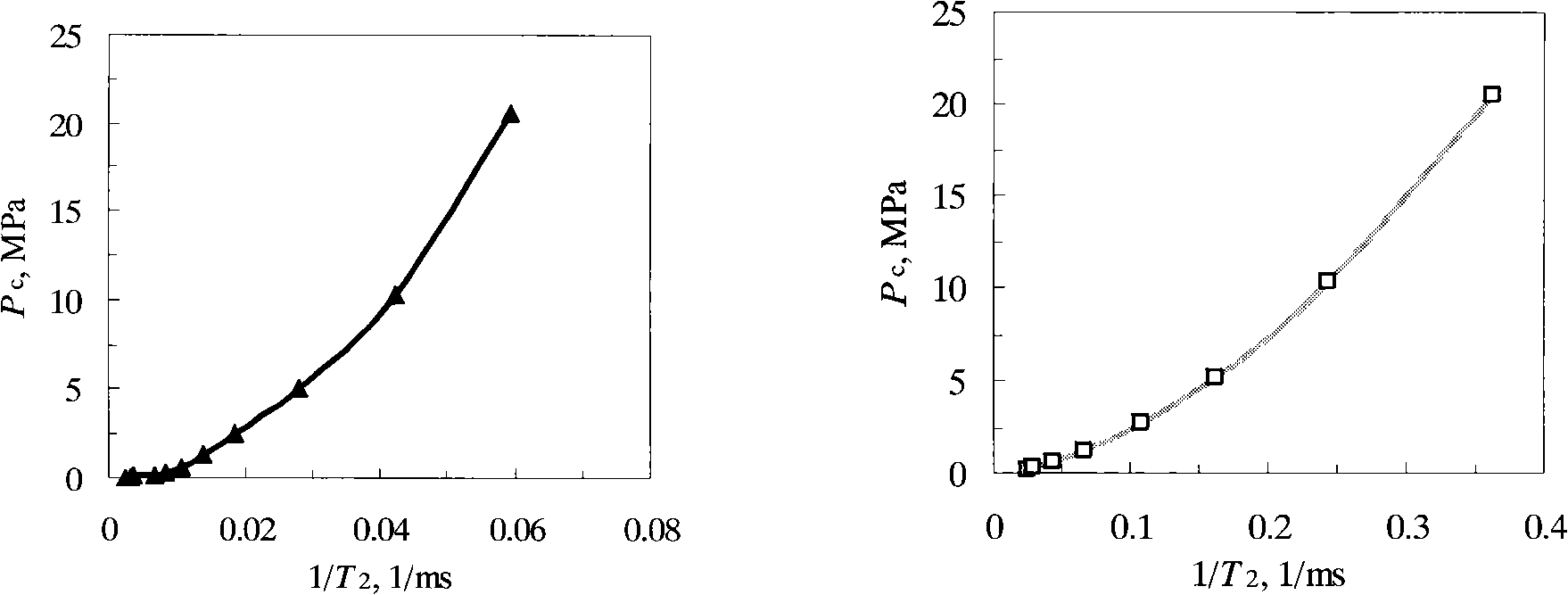Patents
Literature
628 results about "Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
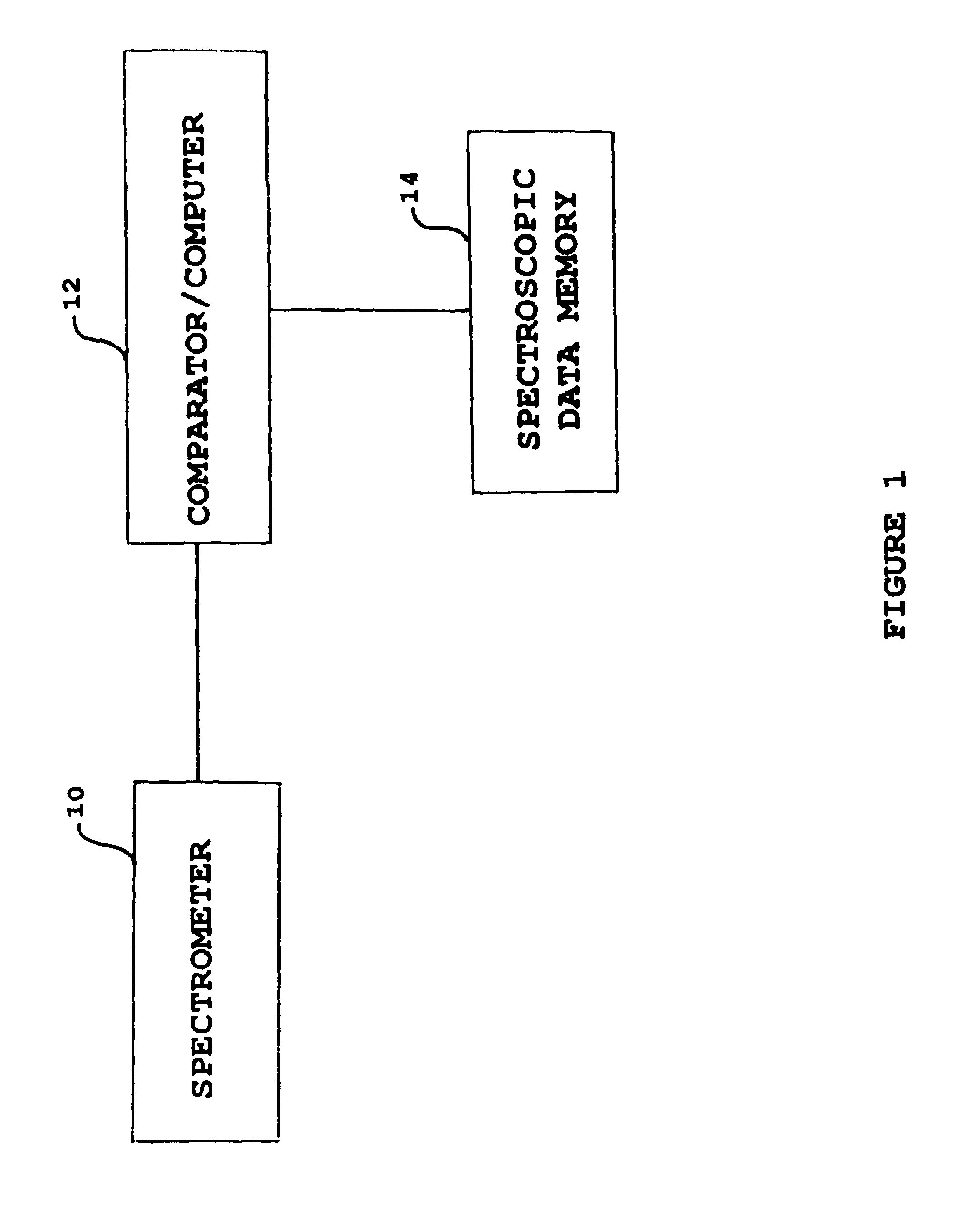
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic field and the NMR signal is produced by excitation of the nuclei sample with radio waves into nuclear magnetic resonance, which is detected with sensitive radio receivers. The intramolecular magnetic field around an atom in a molecule changes the resonance frequency, thus giving access to details of the electronic structure of a molecule and its individual functional groups. As the fields are unique or highly characteristic to individual compounds, in modern organic chemistry practice, NMR spectroscopy is the definitive method to identify monomolecular organic compounds. Similarly, biochemists use NMR to identify proteins and other complex molecules. Besides identification, NMR spectroscopy provides detailed information about the structure, dynamics, reaction state, and chemical environment of molecules. The most common types of NMR are proton and carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy, but it is applicable to any kind of sample that contains nuclei possessing spin.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) fingerprinting
ActiveUS20120235678A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMR
Apparatus, methods, and other embodiments associated with NMR fingerprinting are described. One example NMR apparatus includes an NMR logic configured to repetitively and variably sample a (k, t, E) space associated with an object to acquire a set of NMR signals. Members of the set of NMR signals are associated with different points in the (k, t, E) space. Sampling is performed with t and / or E varying in a non-constant way. The varying parameters may include flip angle, echo time, RF amplitude, and other parameters. The NMR apparatus may also include a signal logic configured to produce an NMR signal evolution from the NMR signals, a matching logic configured to compare a signal evolution to a known, simulated or predicted signal evolution, and a characterization logic configured to characterize a resonant species in the object as a result of the signal evolution comparisons.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
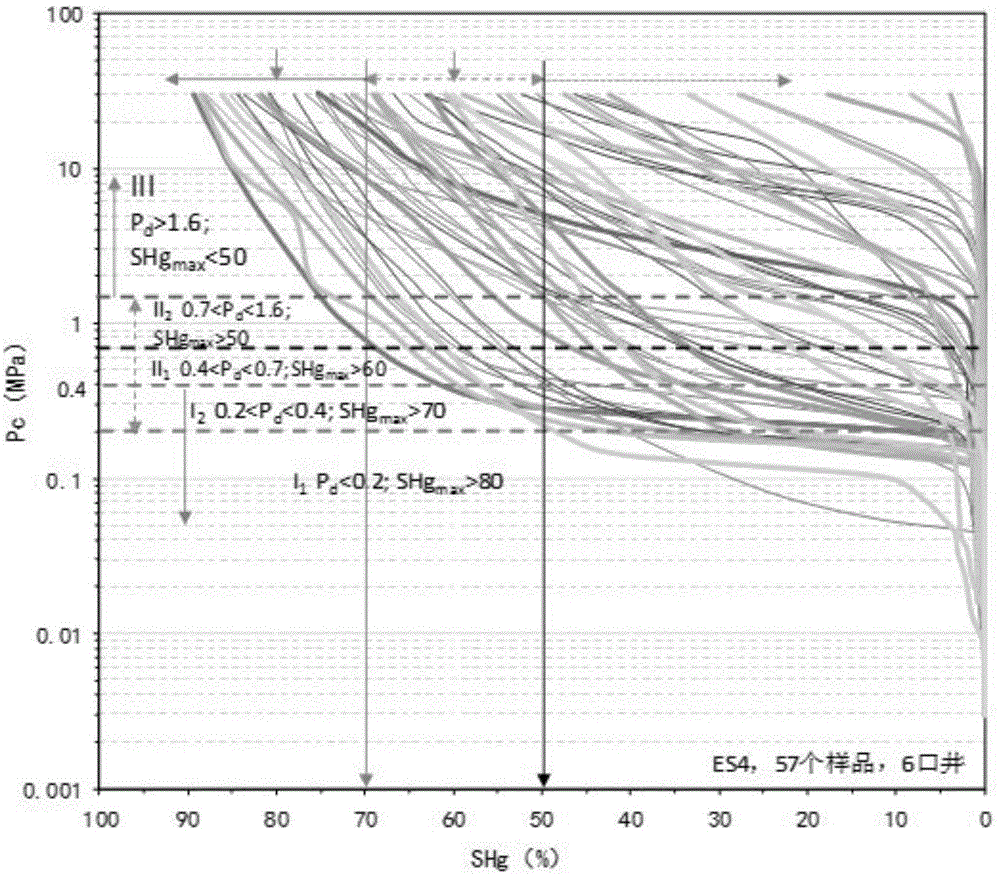
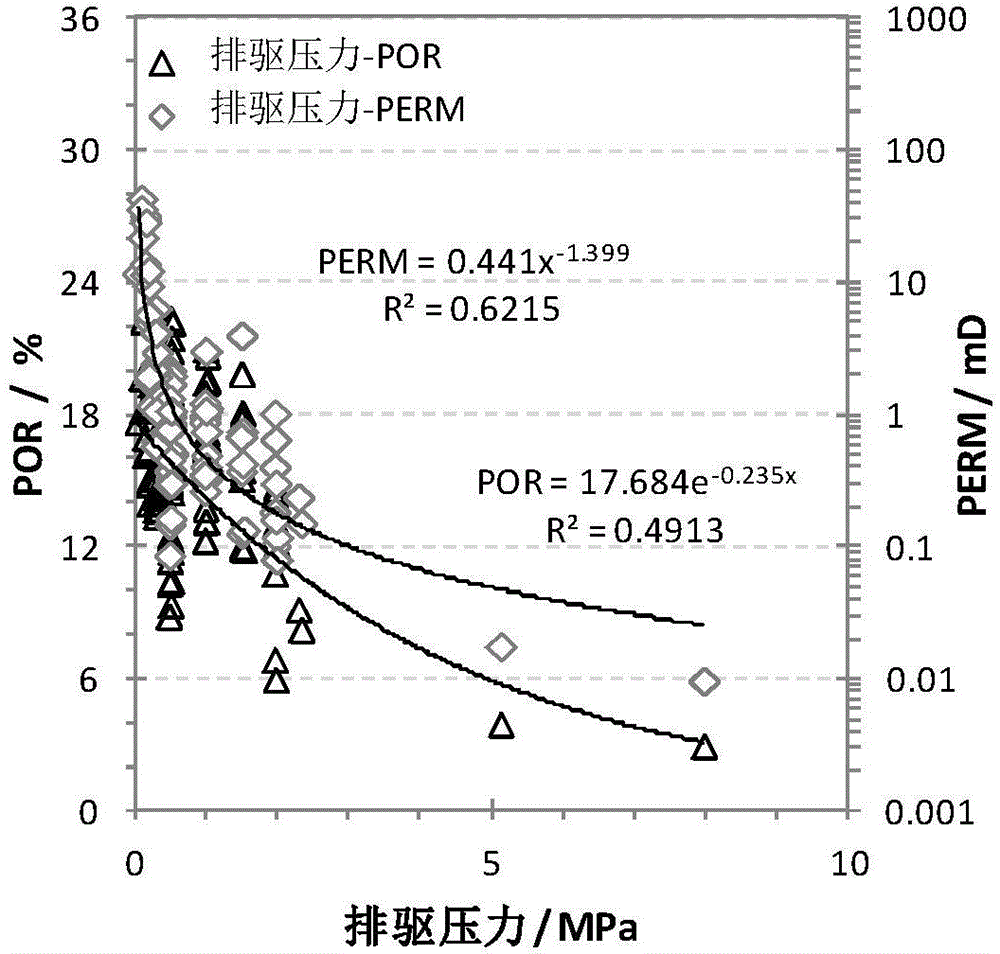
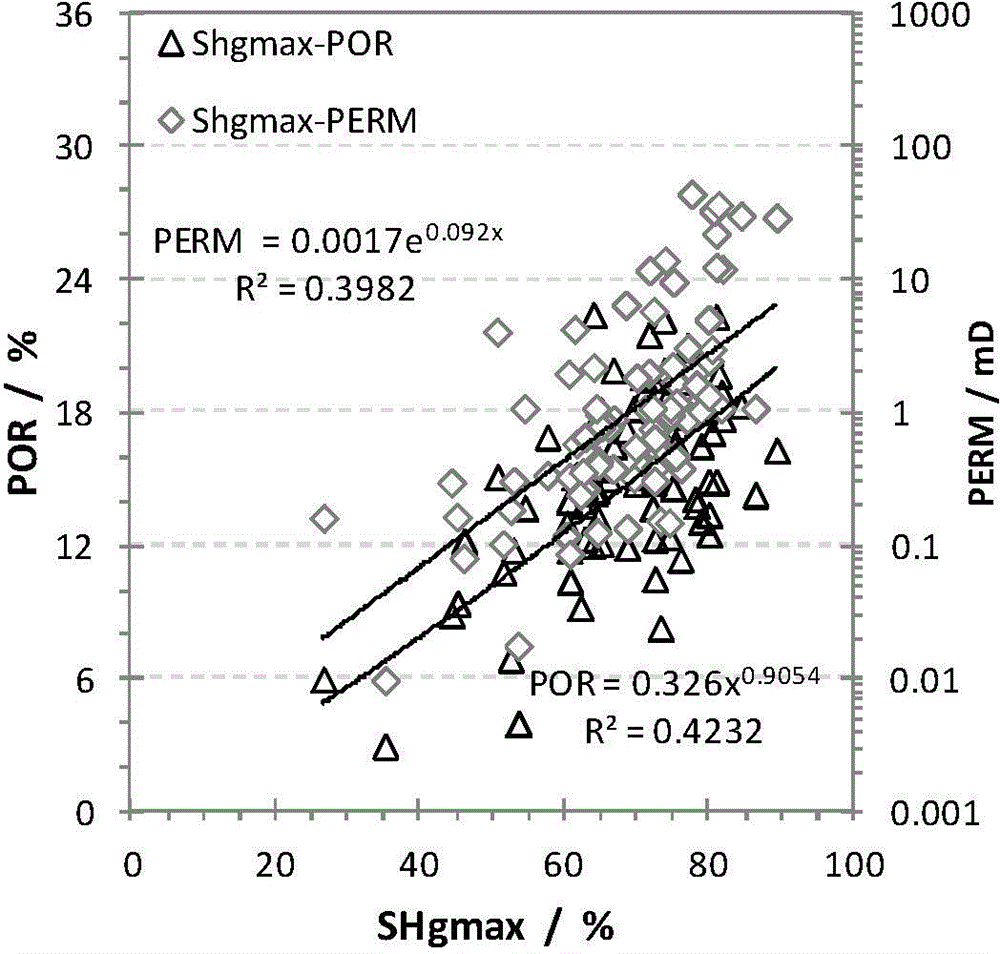
Method for continuously quantitative evaluation of pore structures of reservoir strata by utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data
ActiveCN102141637ATo achieve the purpose of classificationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingBorehole/well accessoriesThroatPressure curve
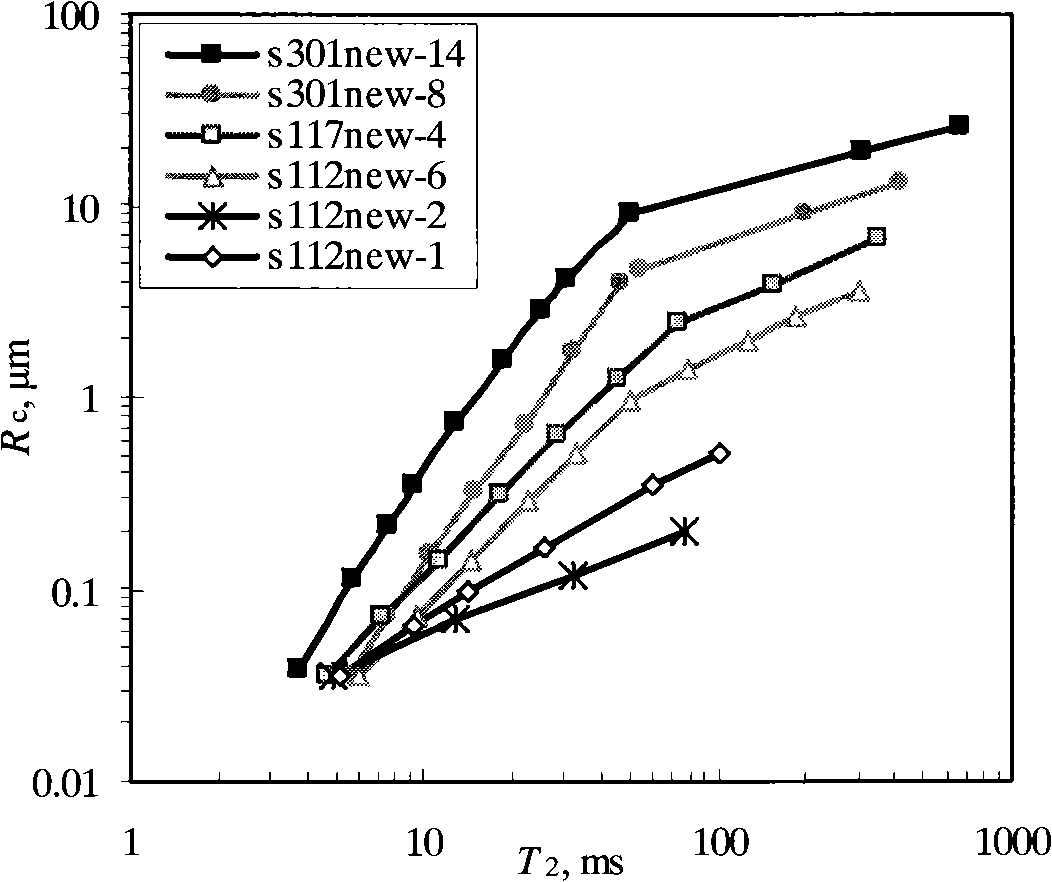
The invention relates to a method for continuously quantitative evaluation of pore structures of reservoir strata by utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data, so as to divide types of the reservoir strata. The method comprises the following steps of: classifying T2 spectrums according to parameters reflecting differences of reservoir strata, and carrying out a nonlinear calibration method on different T2 spectrums to obtain a continuously distributed capillary pressure curve of the reservoir strata; obtaining continuous reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and pore structure parameters by utilizing the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve; and evaluating the pore structure of each reservoir stratum on the basis of the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve, the features of the reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and the pore structure parameters, and dividing types of the reservoir strata. Through the adoption of the method, the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve on each depth point can be continuously obtained by utilizing the nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data, the pore structure of each reservoir stratum can be quantitatively evaluated according to the reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and the pore structure parameters of the reservoir stratum, and the types of the reservoir strata are classified, therefore, the exploitation and development efficiency of complicated oil-gas reservoir is improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Nuclear magnetic resonance method and logging apparatus for fluid analysis
InactiveUS6891369B2Different sensitivityReadily apparentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
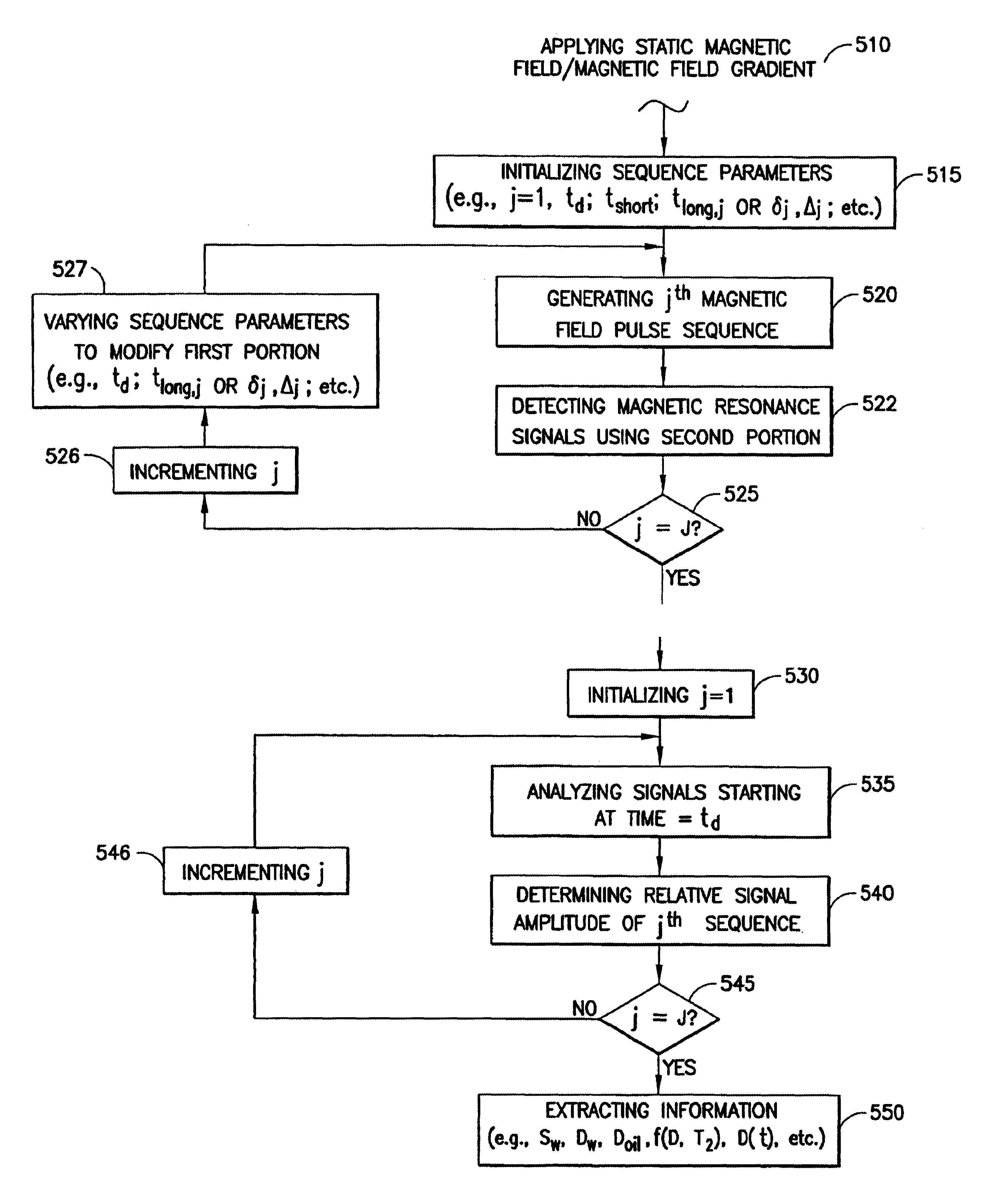
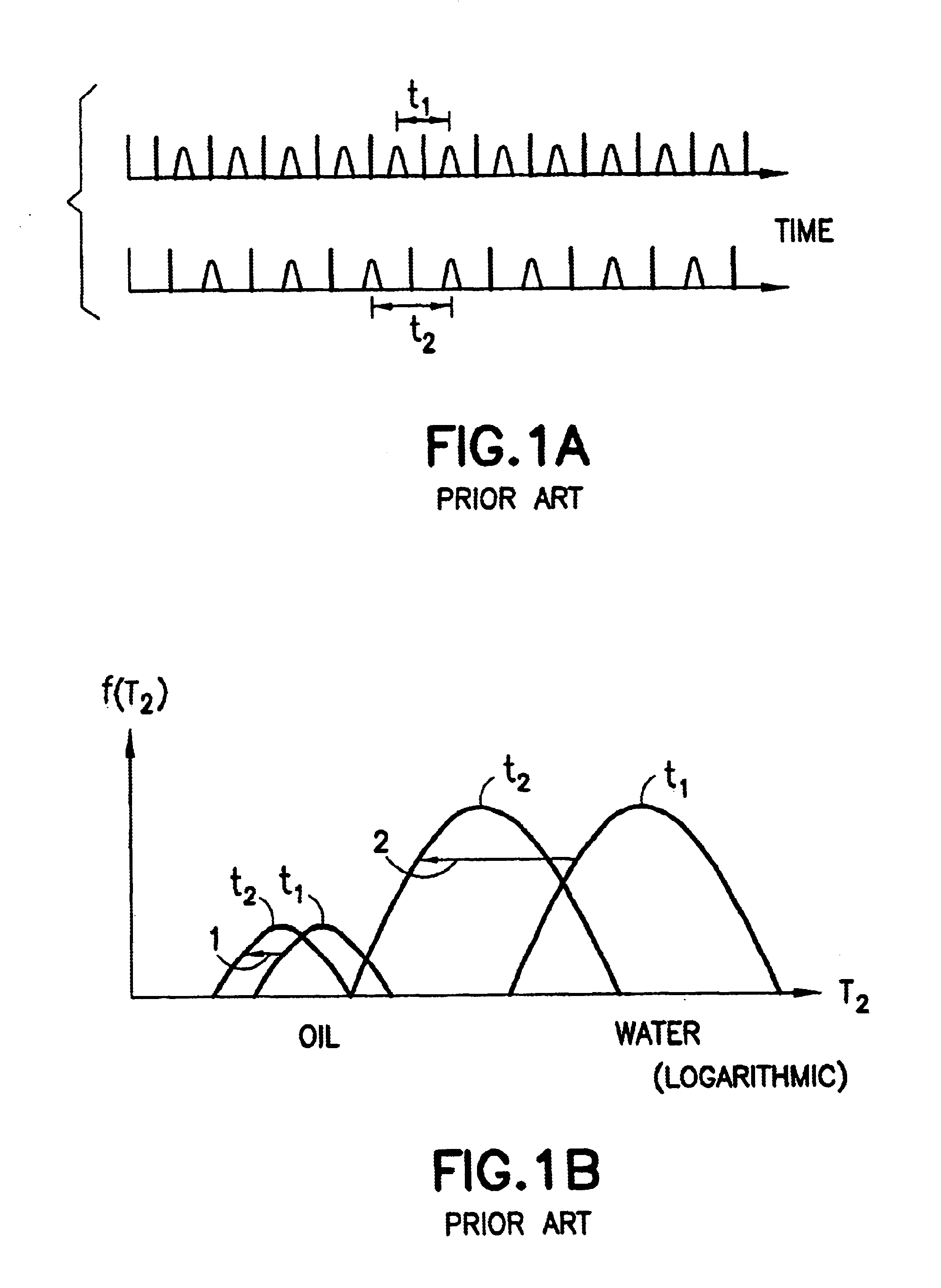
The present invention discloses a diffusion edited pulse technique that allows information about a fluid to be extracted, comprising: a) obtaining a fluid sample; b) generating a sequence of magnetic field pulses in the fluid, the sequence comprising an initial magnetic field pulse, a first portion that follows the initial magnetic field pulse, and a second portion that follows the first portion; c) detecting magnetic resonance signals using the second portion of the sequence; d) modifying the first portion of the sequence, and repeating steps (b) and (c); and e) extracting information about the fluid by determining relaxation and diffusion characteristics and their correlation based on the signals detected in steps (c) and (d). Also disclosed is a logging tool equipped with a processor to implement the diffusion edited pulse technique.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
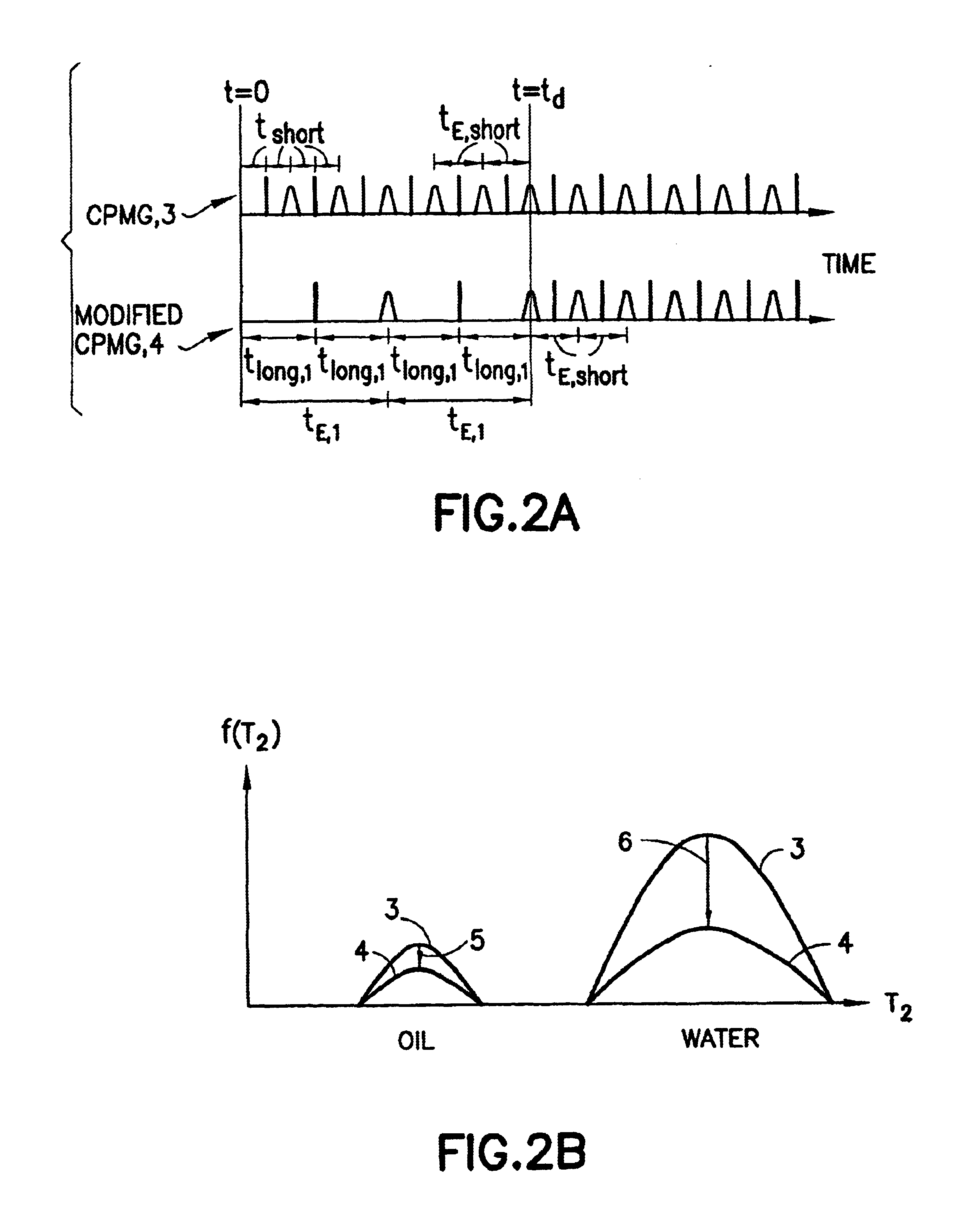
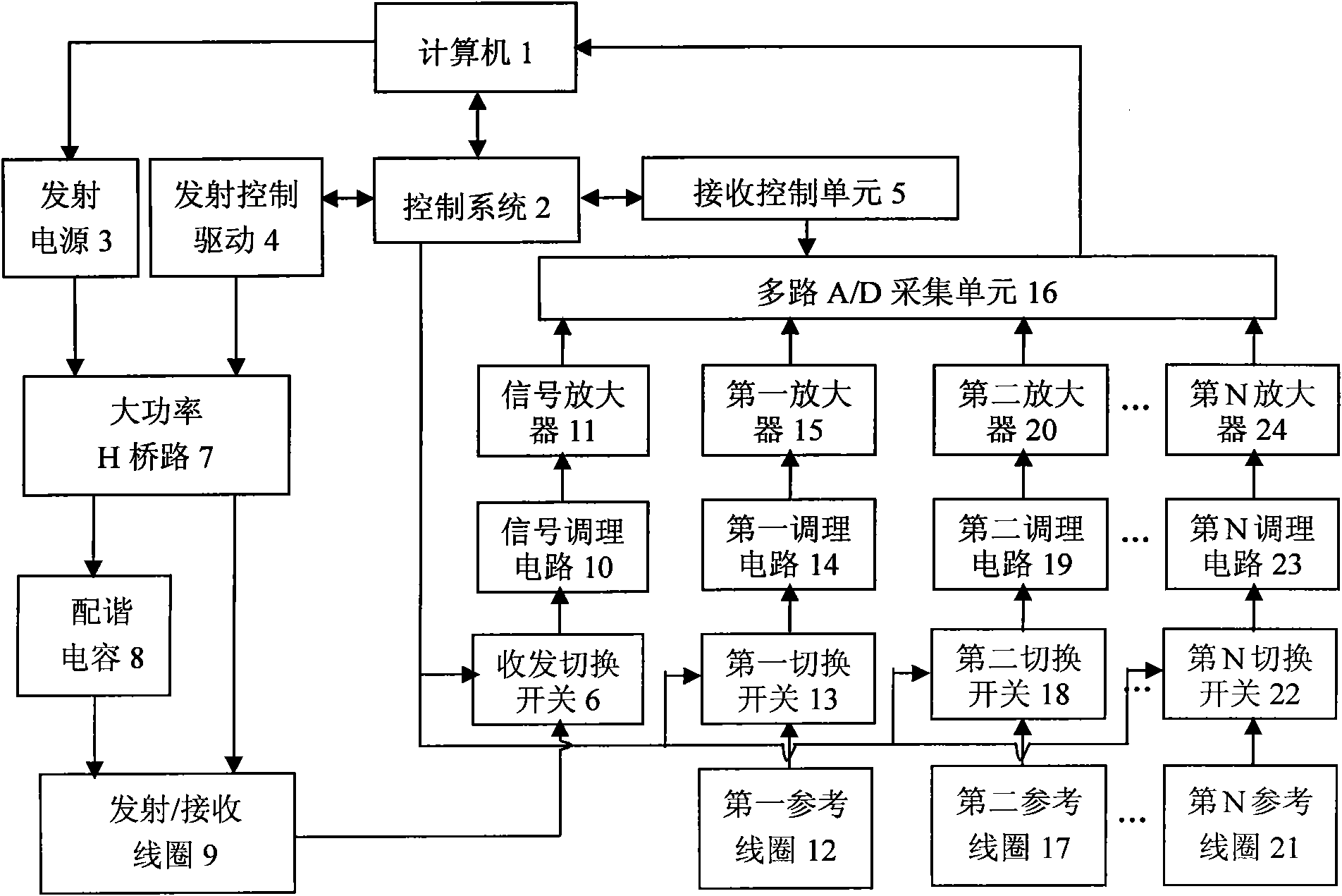
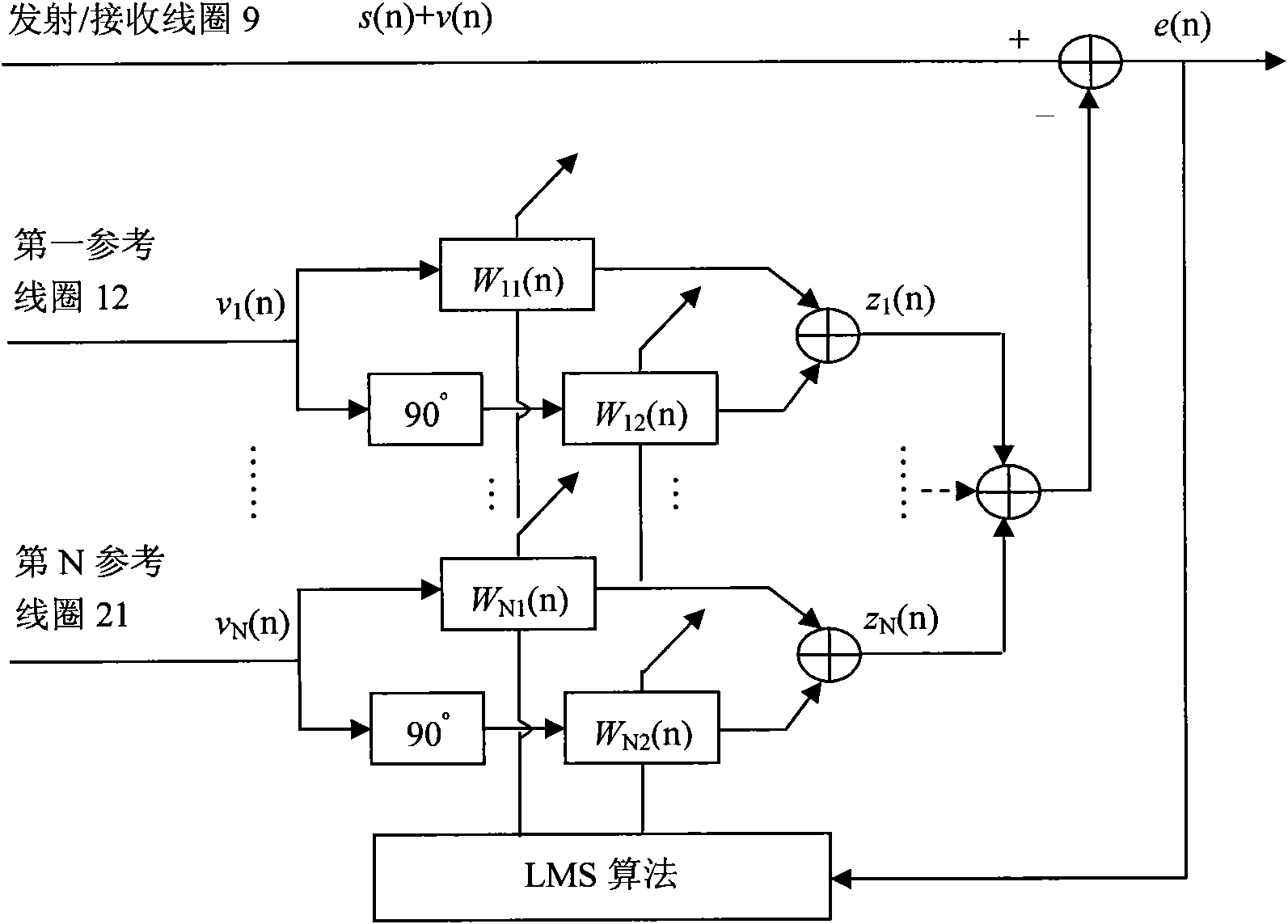
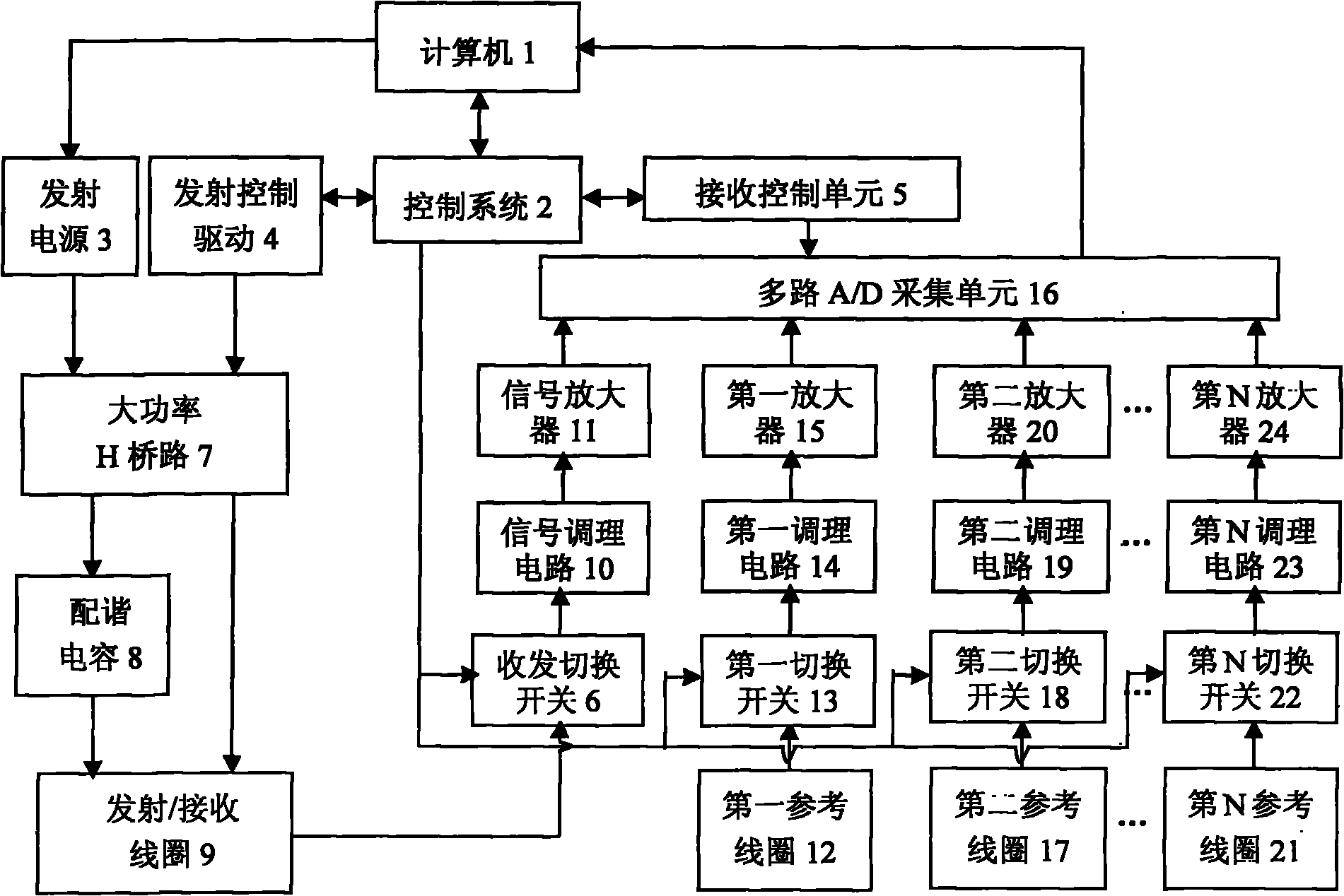
Nuclear magnetic resonance ground water detection system with reference coils and detection method
InactiveCN102053280AEfficient extractionImplement extractionWater resource assessmentDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceInterference resistance
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance ground water detection system with reference coils and a detection method. All-waveform data of nuclear magnetic resonance signals in a transmitting / receiving coil and noise signals in the reference coils are synchronously acquired through a plurality of paths of A / D acquiring units; the distribution of optimal positions and quantity of the reference coils is realized through calculating the maximum correlation of the noise signals and the nuclear magnetic resonance signals, which are acquired by the reference coils; and under the condition of unknown signal and noise statistical properties, noise in the nuclear magnetic resonance signals obtained by the transmitting / receiving coil is maximally offset by adopting a variable step adaptive algorithm, the nuclear magnetic resonance signals are extracted under the interference of multi-field source complex strong noise, thus the problems of multiple interferences of nuclear magnetic resonance detection near villages and in neighboring regions of cities and difficulty of separating multiple kinds of interference noise data are effectively solved, the interference resistance of instruments is improved, and a reliable detection device and method are provided for searching underground water near villages and in neighboring regions of cities.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
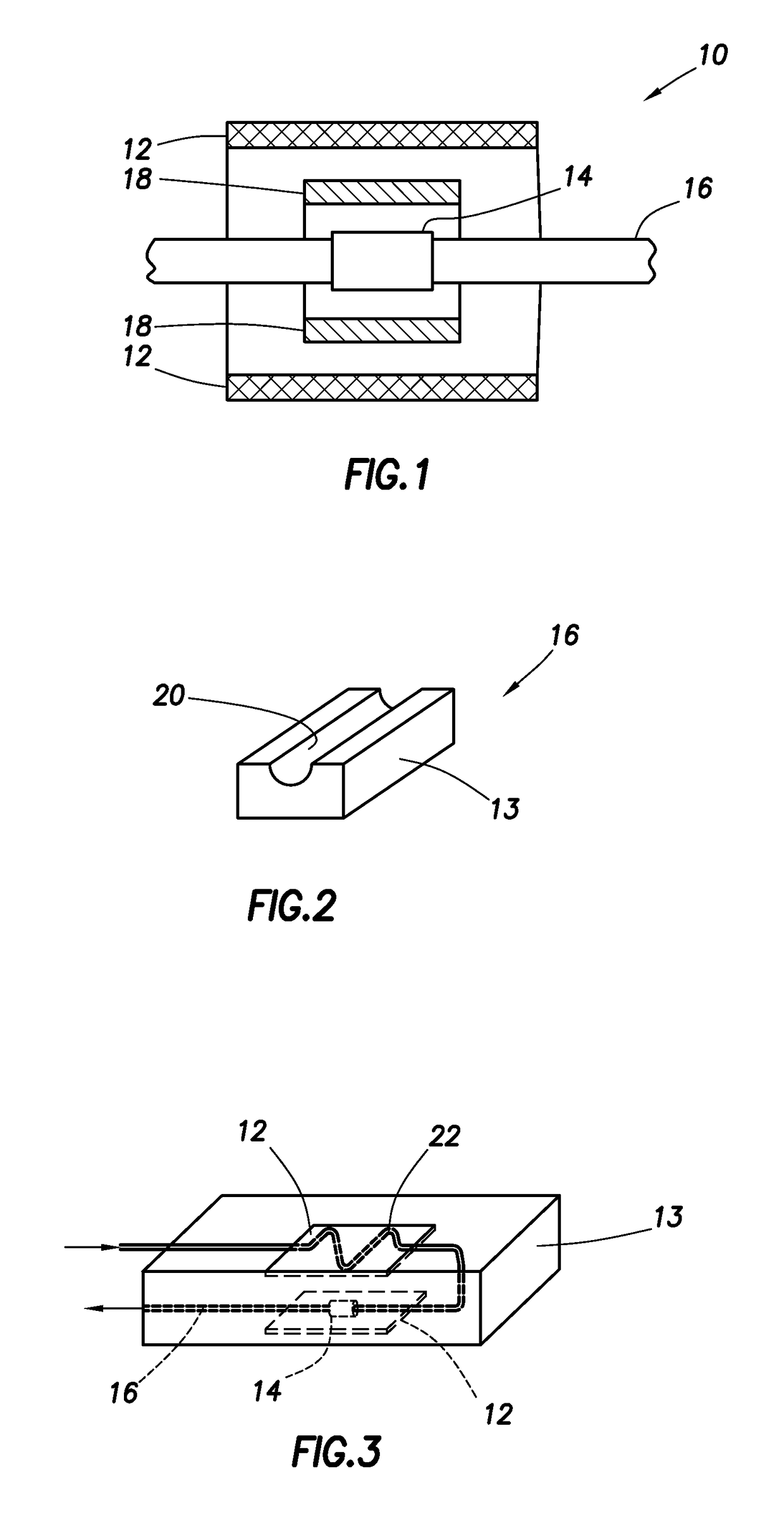
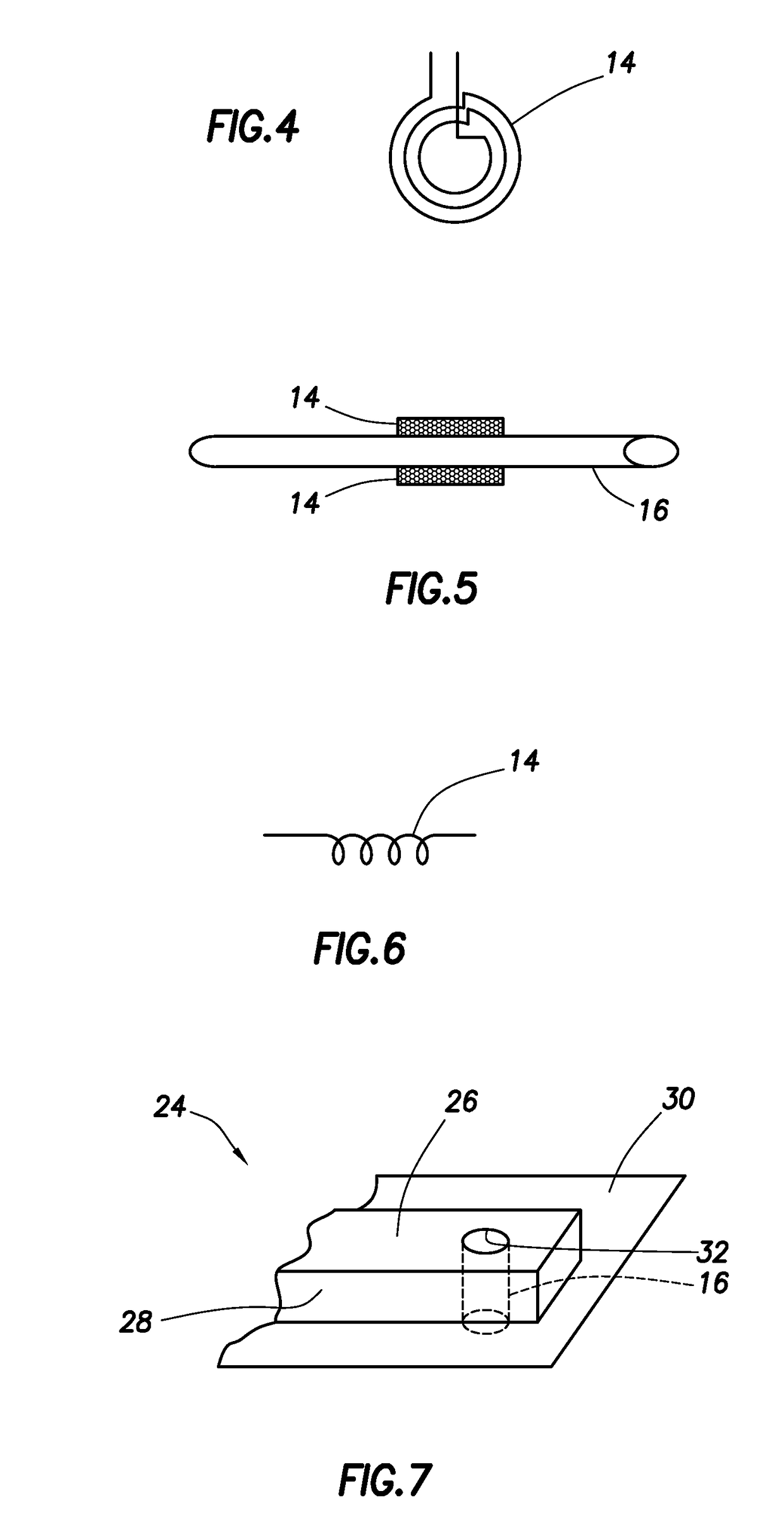
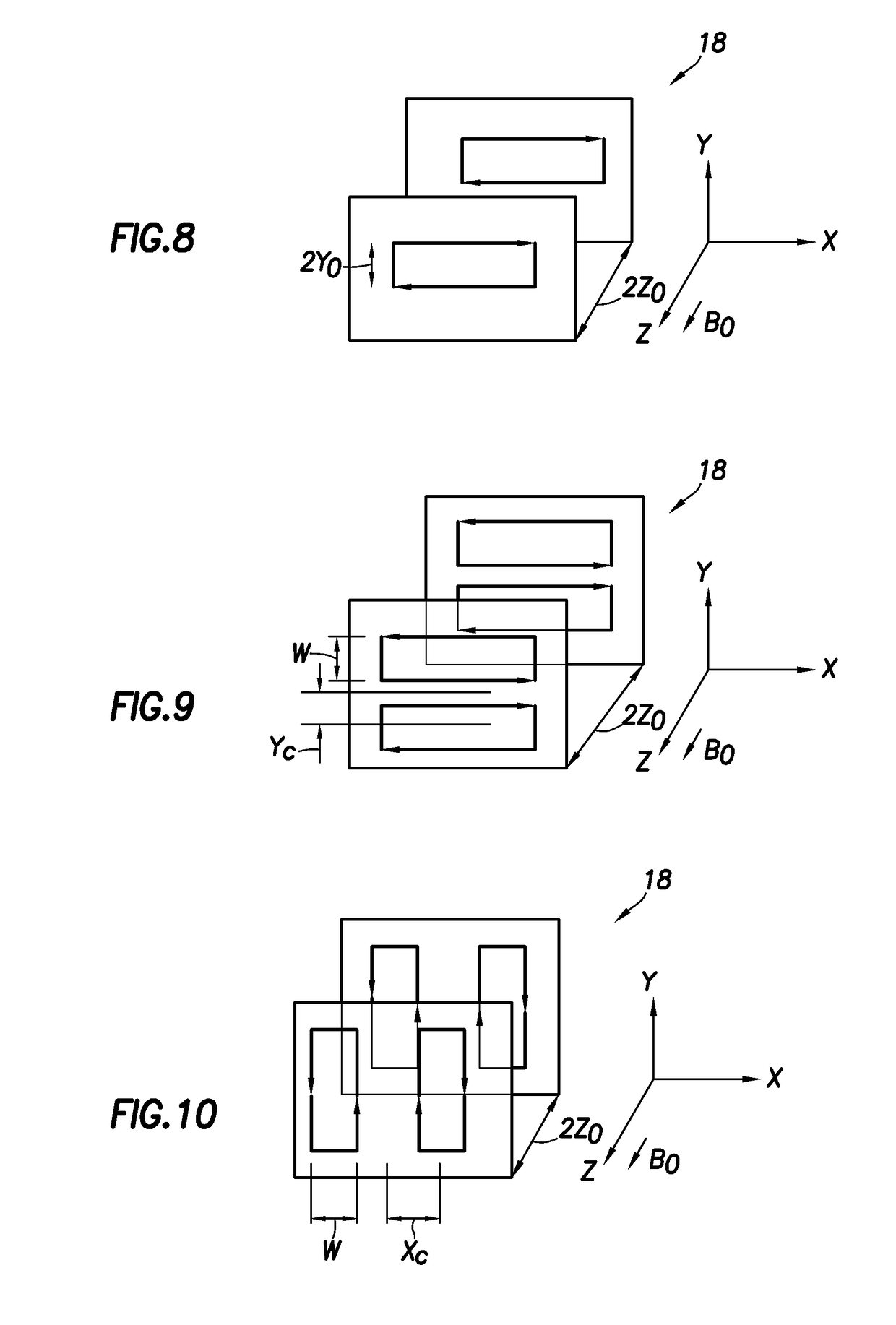
Nuclear magnetic resonance equipment
InactiveUS6958608B2High sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceSpectroscopy
The invention provides nuclear magnetic resonance equipment realizing improved sensitivity of a probe for receiving a free induction decay (FID) signal in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in a high frequency band of 600 MHz or higher. By manufacturing a solenoid coil of a higher filling factor by using a superconductor of extremely low resistance to high frequency current, sensitivity is increased. A superconducting thin film made of magnesium diboride (MgB2) formed on a donut plate-type substrate is disposed so that the film surface becomes parallel with the uniform magnetic field. The object is realized by a probe made by a solenoid coil formed by connecting a plurality of coil parts by capacitive coupling via a normal metal lead.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
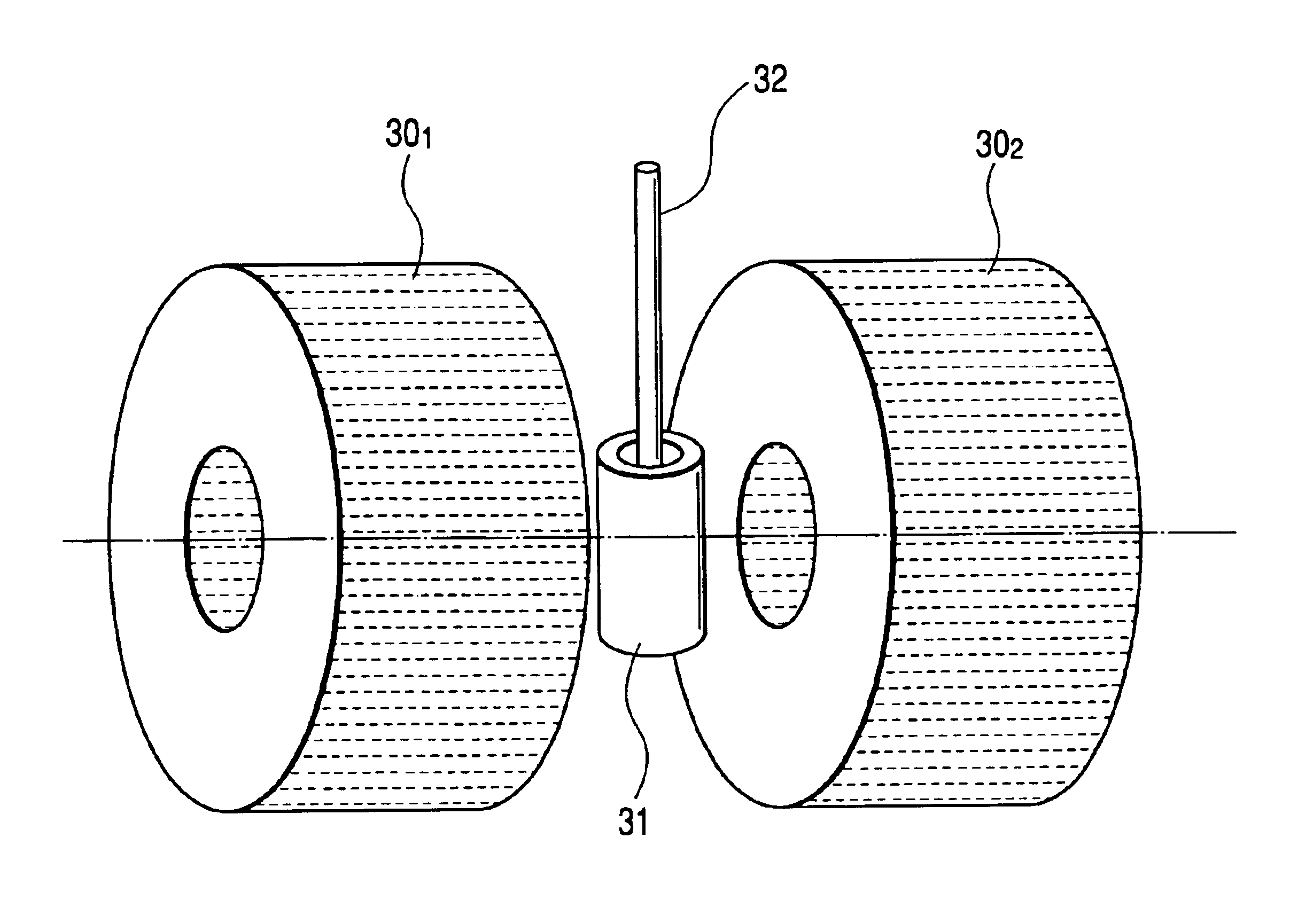
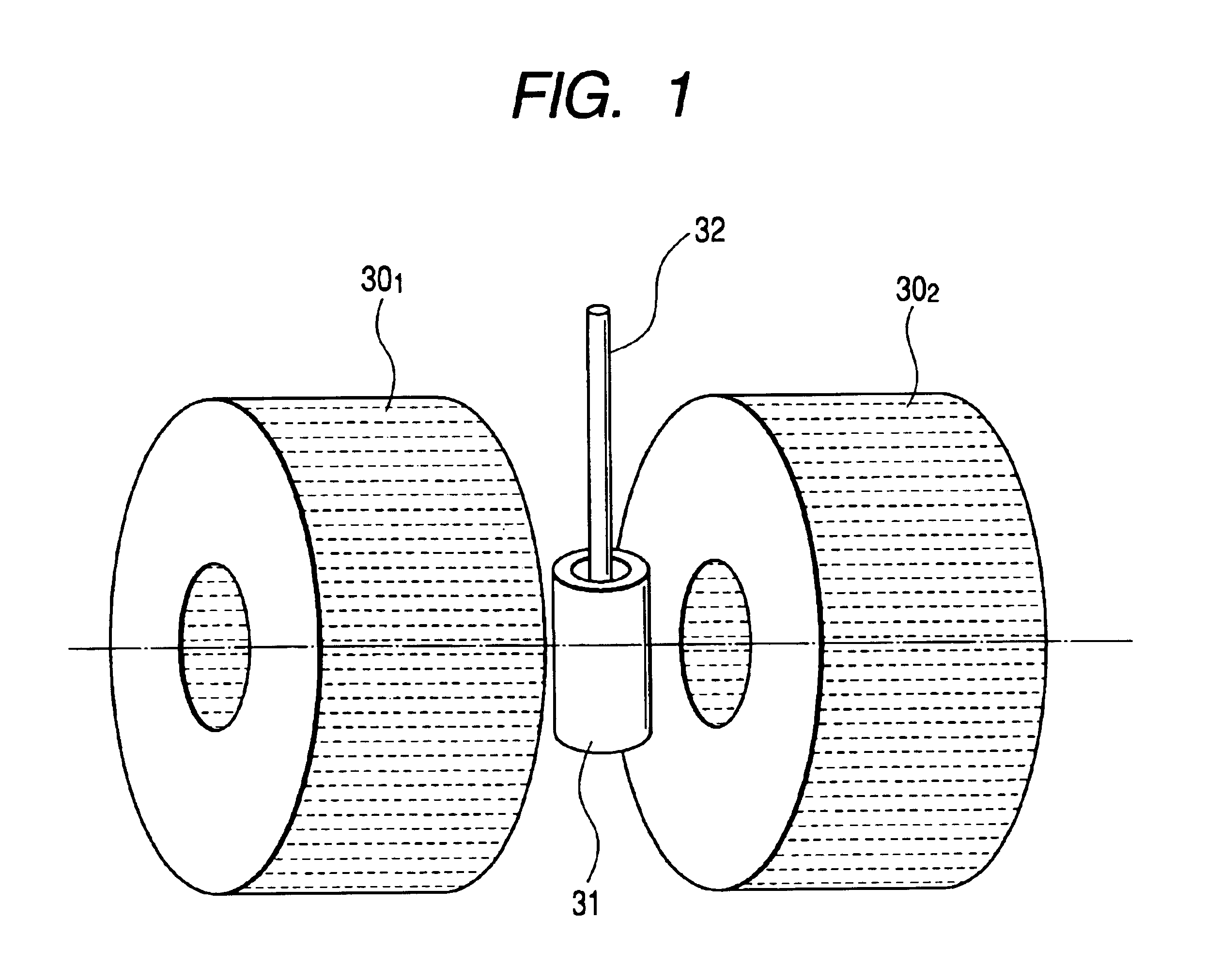
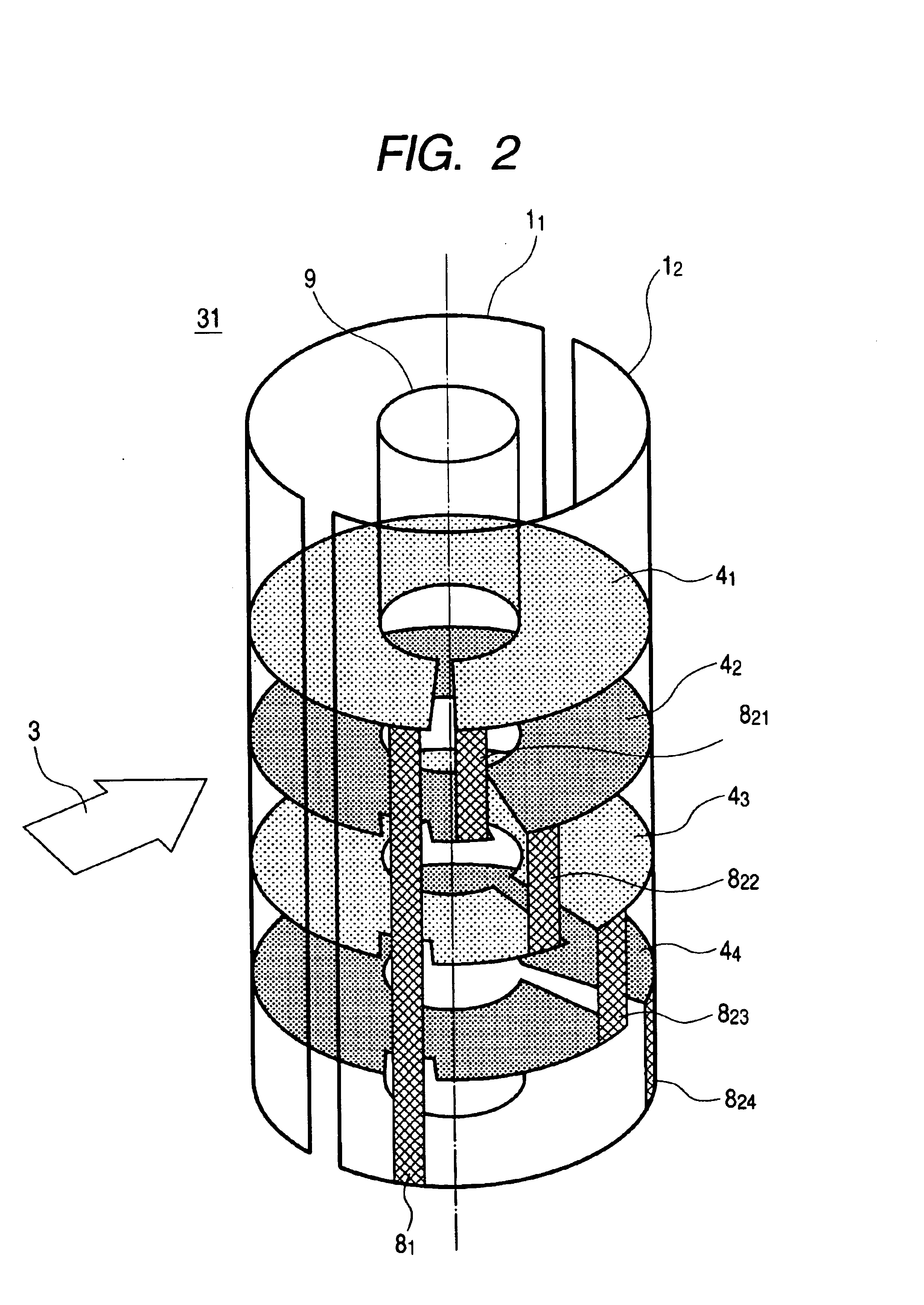
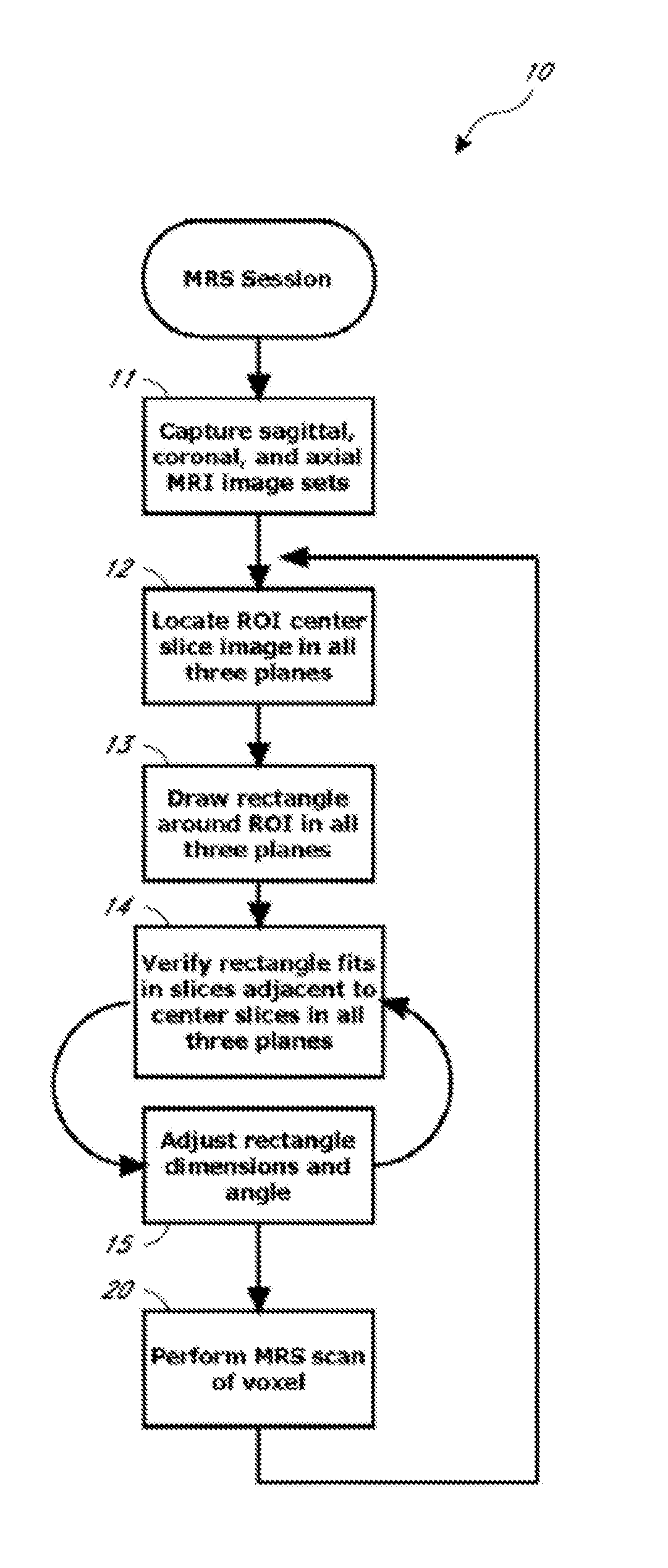
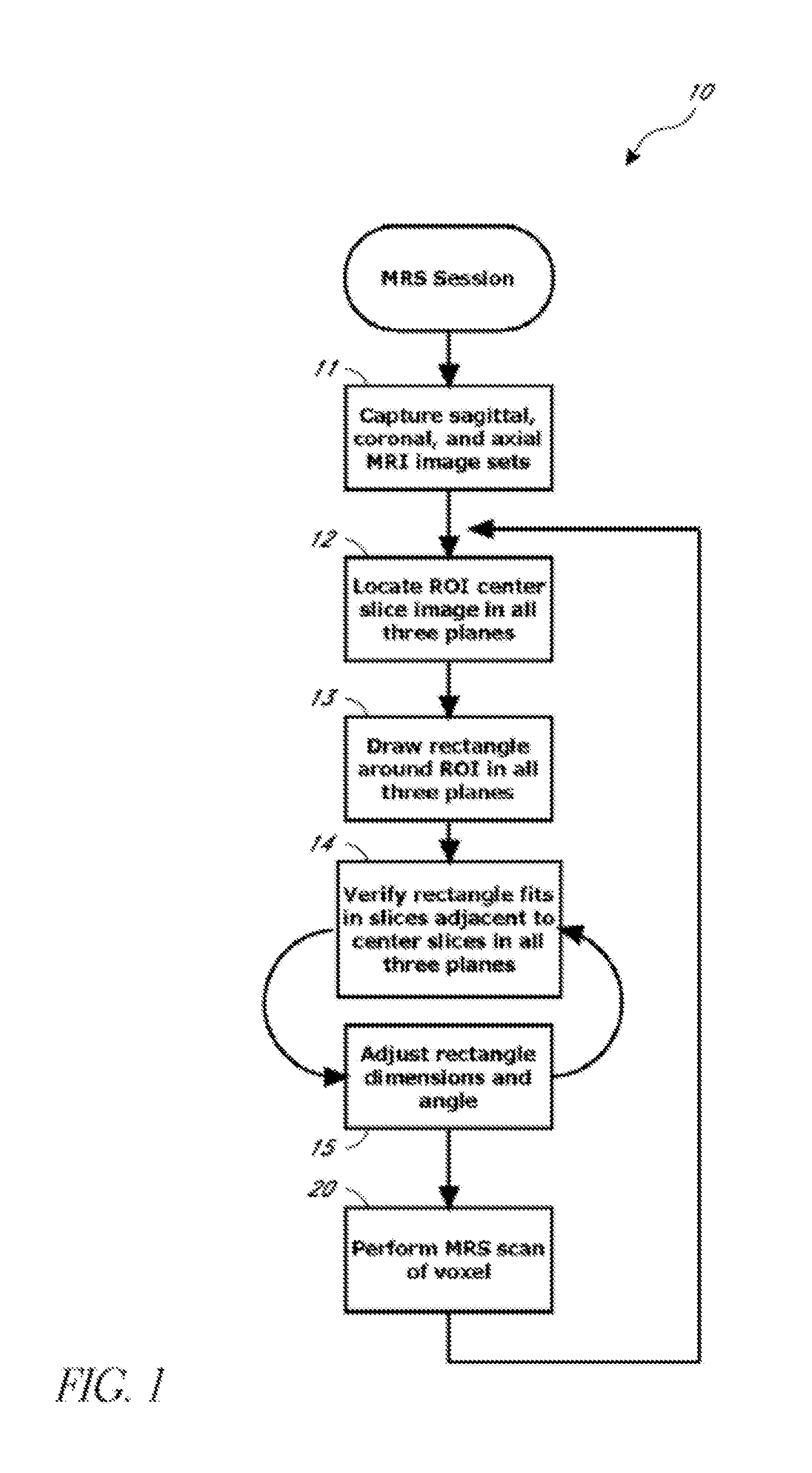
Systems and methods for automated voxelation of regions of interest for magnetic resonance spectroscopy
A system and method for automating an appropriate voxel prescription in a uniquely definable region of interest (ROI) in a tissue of a patient is provided, such as for purpose of conducting magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in the ROI. The dimensions and coordinates of a single three dimensional rectilinear volume (voxel) within a single region of interest (ROI) are automatically identified. This is done, in some embodiments by: (1) applying statistically identified ROI search areas within a field of view (FOV); (2) image processing an MRI image to smooth the background and enhance a particular structure useful to define the ROI; (3) identifying a population of pixels that define the particular structure; (4) performing a statistical analysis of the pixel population to fit a 2D model such as an ellipsoid to the population and subsequently fit a rectilinear shape within the model; (5) repetiting elements (1) through (4) using multiple images that encompass the 3D ROI to create a 3D rectilinear shape; (6) a repetition of elements (1) through (5) for multiple ROIs with a common FOV. A manual interface may also be provided, allowing for override to replace by manual prescription, assistance to identify structures (e.g. clicking on disc levels), or modifying the automated voxel (e.g. modify location, shape, or one or more dimensions).
Owner:ACLARION INC
Transceiver apparatus, system and methodology for superior In-Vivo imaging of human anatomy
ActiveUS20120112748A1Maximize efficiencyElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRHuman anatomyDisease
The inventive subject matter as a whole is an improved transceiver apparatus and system for diagnostic evaluations of living subject, human or animal; and is particularly effective as a clinical tool for the spectroscopic scanning or magnetic resonance imaging of humans suspected of being afflicted with a particular disease, disorder, or pathology. The improved transceiver apparatus is used as an essential component in a computer controlled system suitable for magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”), or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (“MRS”), and / or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (“MRSI”); and the present improvement of these electromagnetic signaling systems will provide far more accurate and precise visual images and accumulated data for the clinician or surgeon, as well as serve as a basis upon which to make a diagnosis and decide upon a mode of therapeutic treatment for that individual.
Owner:HETHERINGTON HOBY P +2
Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20130082701A1Avoid sensitivityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceIn plane
The present invention has an object to provide a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus or the like that avoids a region with zero sensitivity of an optical magnetometer and allows imaging by strong magnetic resonance when a common magnetic field is used as a bias field of an optical magnetometer and as a magnetostatic field to be applied to a sample. When a direction of a magnetostatic field application unit applying a magnetostatic field to a sample is a z direction, alkali metal cells of a plurality of scalar magnetometers are arranged so as not to overlap a region to be imaged in a z direction, and so as not to intersect the region to be imaged in an in-plane direction perpendicular to the z direction.
Owner:CANON KK
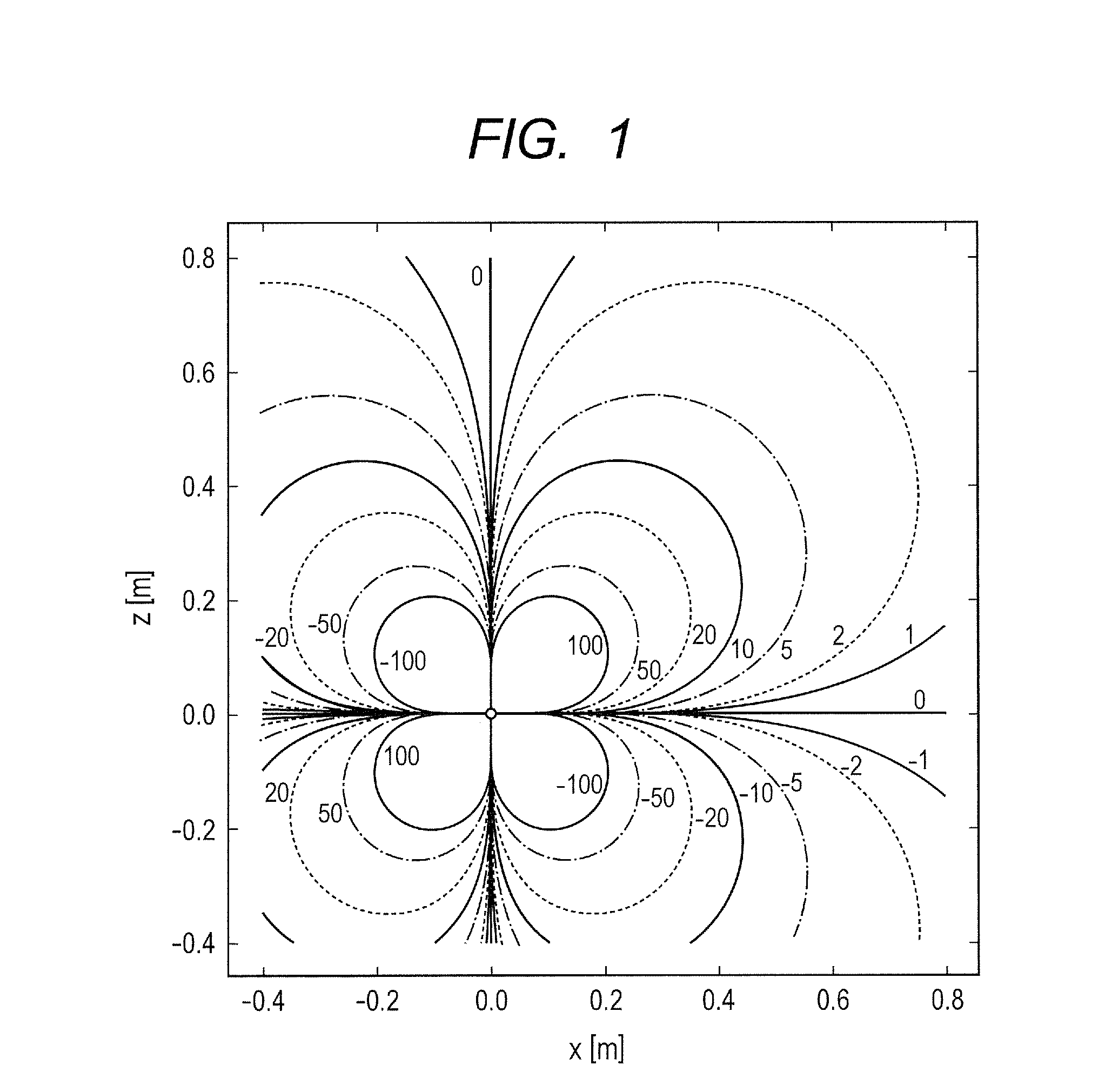
Atomic magnetic gradiometer for room temperature high sensitivity magnetic field detection
InactiveUS7573264B2Reduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceProton NMRSingle polarization
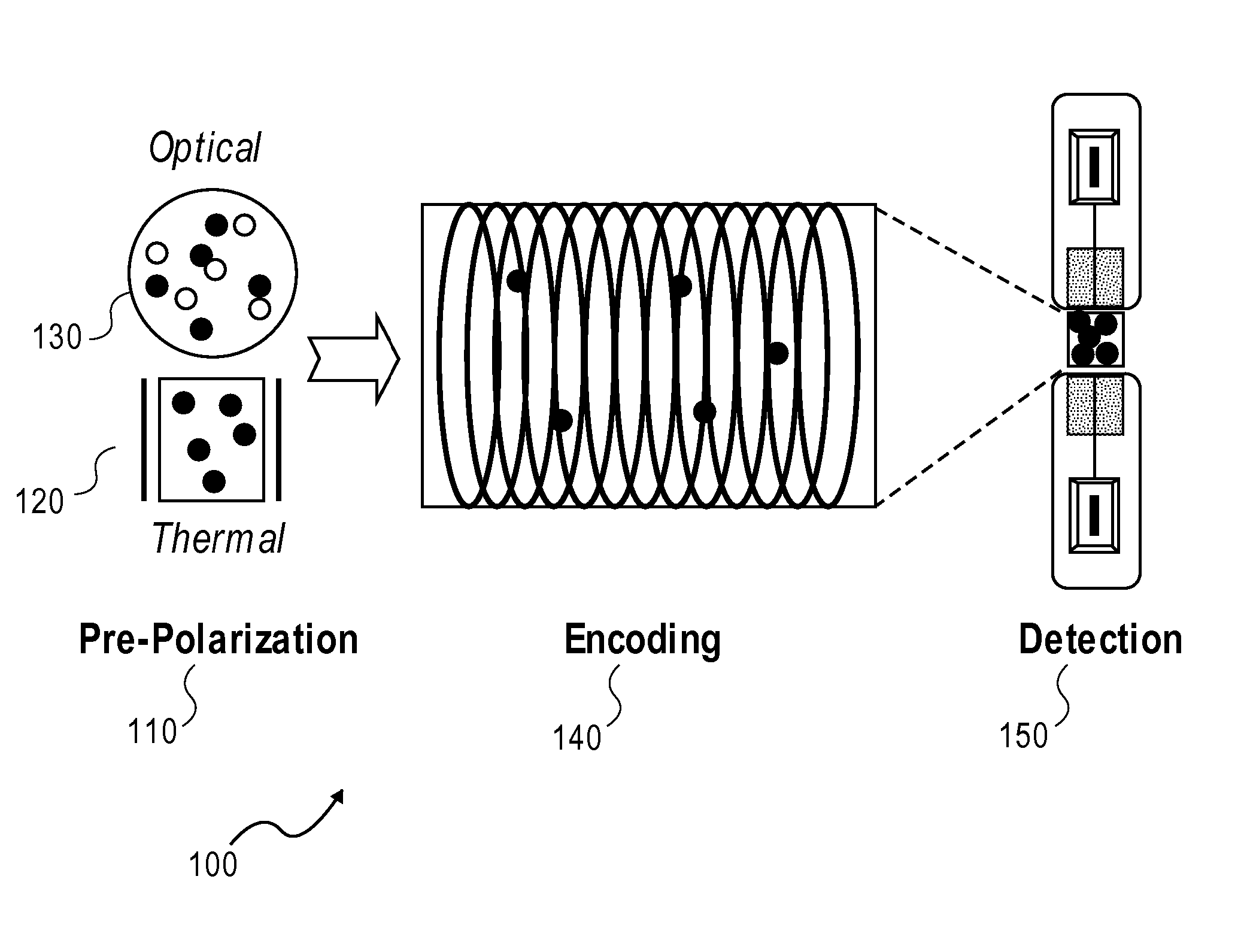
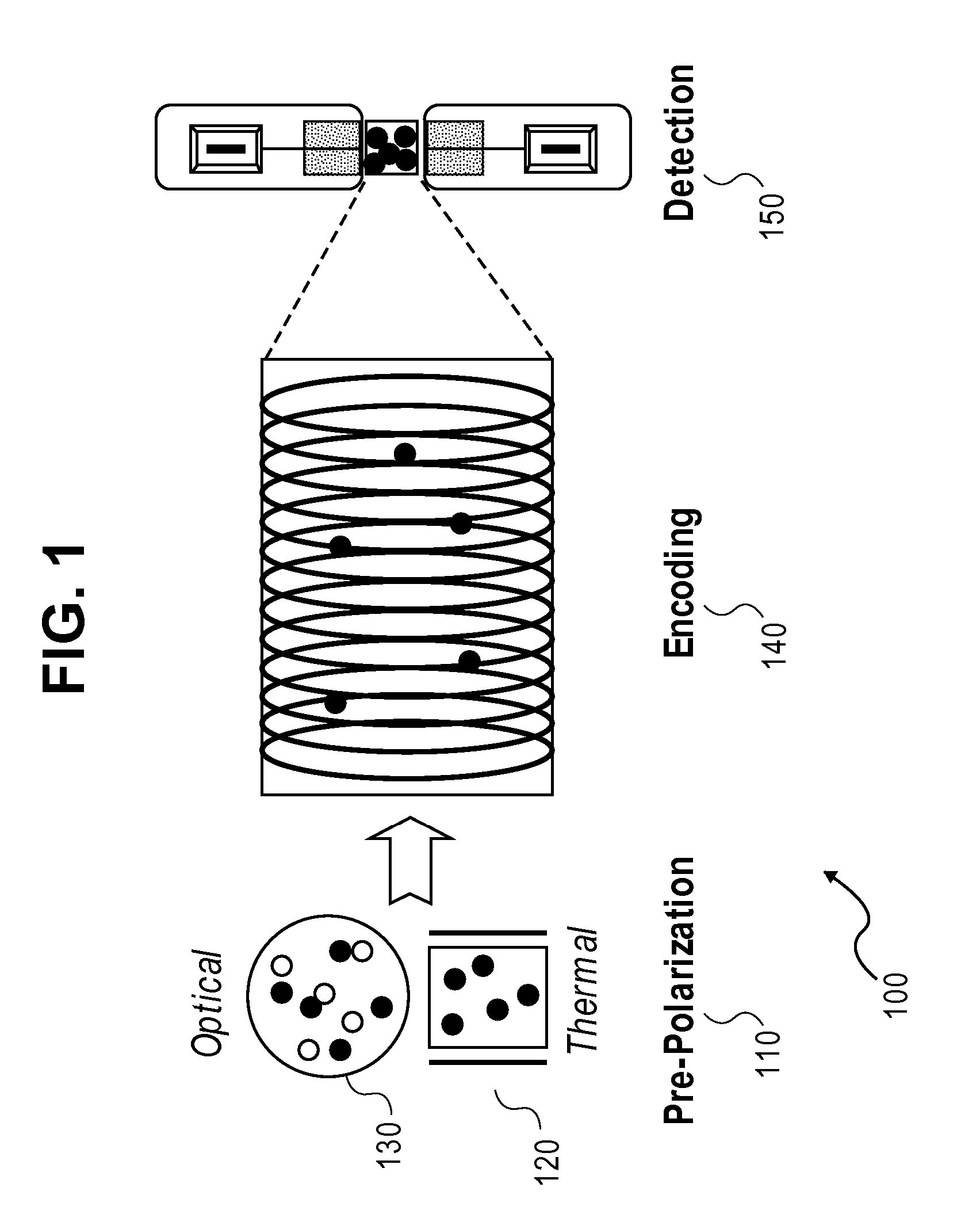
A laser-based atomic magnetometer (LBAM) apparatus measures magnetic fields, comprising: a plurality of polarization detector cells to detect magnetic fields; a laser source optically coupled to the polarization detector cells; and a signal detector that measures the laser source after being coupled to the polarization detector cells, which may be alkali cells. A single polarization cell may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) by prepolarizing the nuclear spins of an analyte, encoding spectroscopic and / or spatial information, and detecting NMR signals from the analyte with a laser-based atomic magnetometer to form NMR spectra and / or magnetic resonance images (MRI). There is no need of a magnetic field or cryogenics in the detection step, as it is detected through the LBAM.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
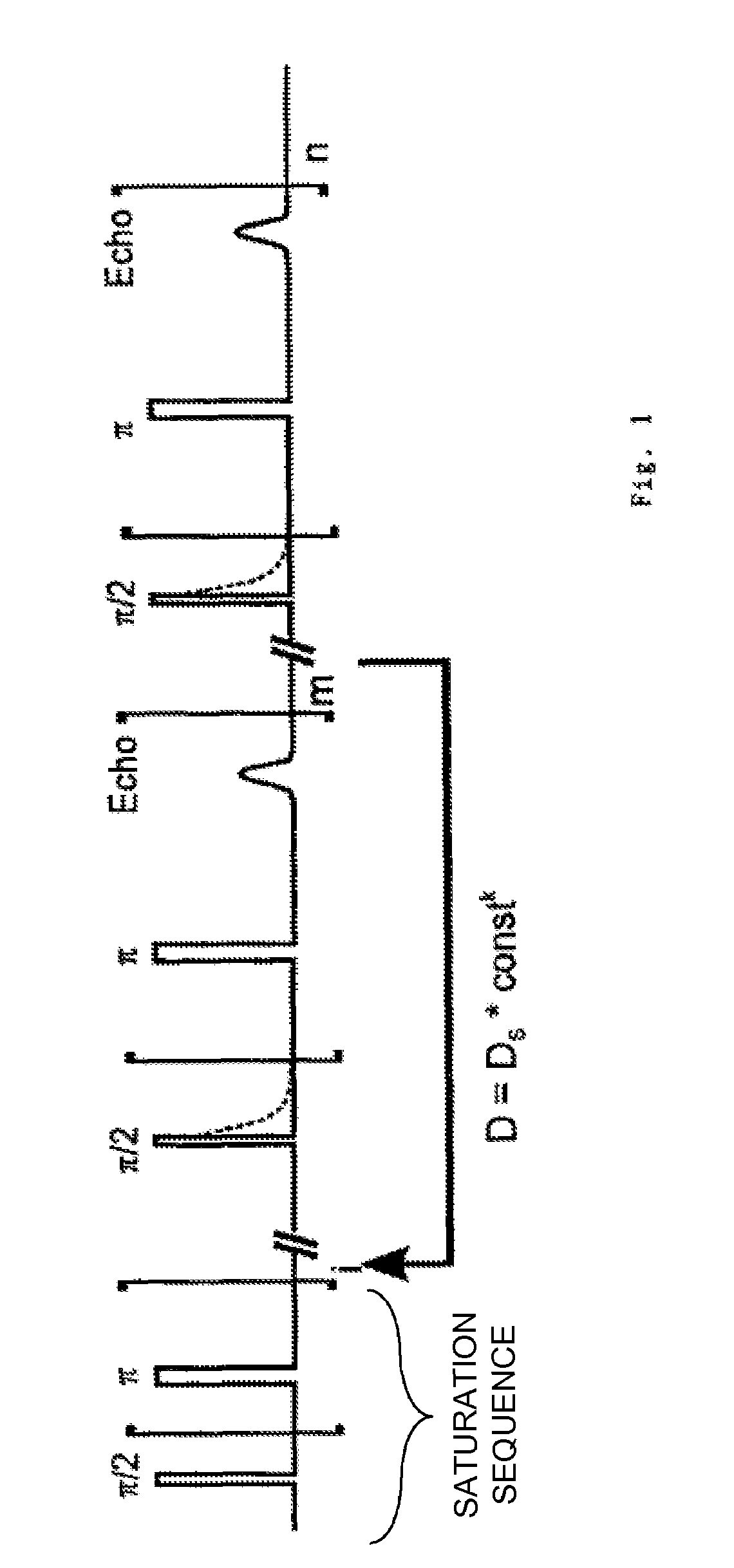
Method for determining the content of at least one component of a sample by means of a nuclear magnetic resonance pulse spectrometer
ActiveUS7397241B2Reliable measurementShort timeMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceTransverse relaxation
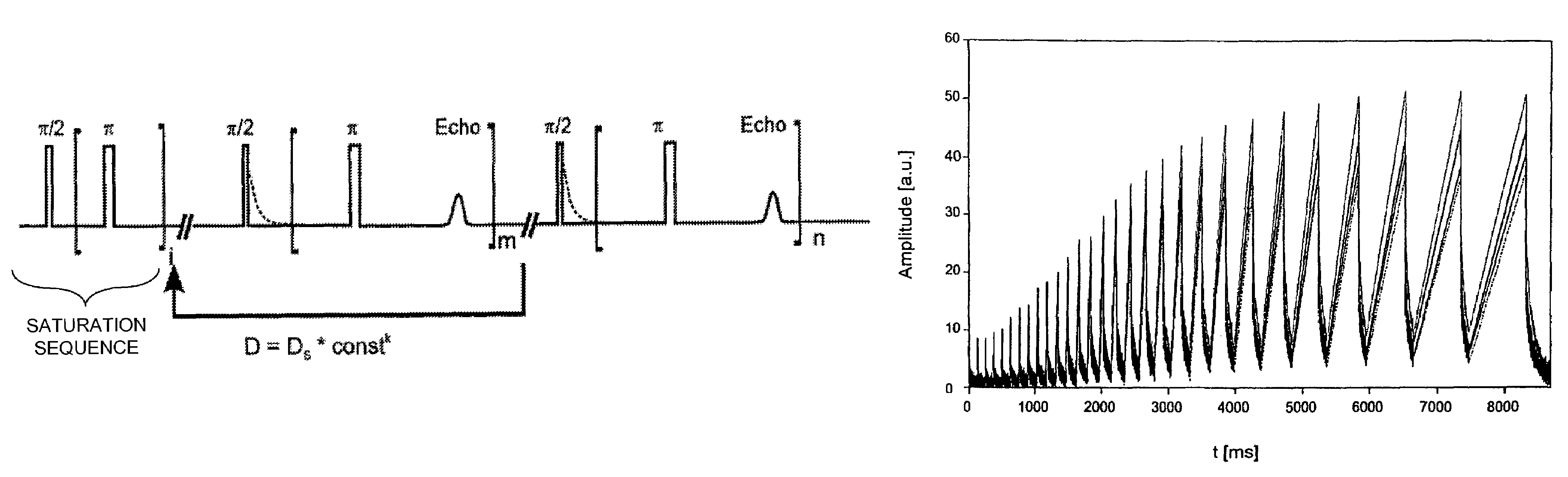
A method is described for determination of the content of at least one component of a sample by means of a nuclear magnetic resonance pulse spectrometer, with the magnetization of the sample being influenced by a sequence of radio-frequency pulses such that the signal amplitudes to be observed can be determined. The magnetization of the sample is initially saturated, and the signal amplitudes which are determined at each time by the longitudinal and transverse relaxation times T1 and T2 and / or T2* and / or T1p, from which a value for the content of the at least one component is determined, are measured at the same time in a cohesive experimental procedure.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Method and apparatus of using soft non-ferritic magnetic material in a nuclear magnetic resonance probe
InactiveUS6452388B1Optimization of RF antenna efficiencyLow efficiencyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceStructural geometry
The present invention provides a novel use of a powdered high saturation flux density soft magnetic material as a NMR probe core material. The probe structural geometry facilitates the use of powdered material, which has a relatively low magnetic permeability.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System and method for emulating nuclear magnetic resonance well logging tool diffusion editing measurements on a bench-top nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for laboratory-scale rock core analysis
InactiveUS20110234220A1Increase displacementPromote recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWell loggingLaboratory scale
A laboratory NMR methodology (and corresponding laboratory apparatus) defines a sample volume. The method stores downhole tool data corresponding to a hydrocarbon-bearing sample collected from a given subsurface formation. The downhole tool data includes parameters pertaining to magnetic fields used by a downhole tool during a suite of NMR measurements of the given subsurface formation. The sample is positioned in the sample volume of the laboratory apparatus, which applies a static magnetic field in the sample volume. Furthermore, the laboratory apparatus applies a suite of NMR measurements to the sample volume to thereby determine a property of the sample. The NMR measurements of the suite each include a pulse sequence of oscillating magnetic field in conjunction with a pulsed-mode gradient field. The pulsed-mode gradient field is based on the stored downhole tool data corresponding to the sample. A laboratory NMR methodology for optimizing downhole NMR measurements is also described.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Organic silicon micro-pore zeolite and synthesizing method thereof
ActiveCN101121523AImprove technical effectMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesAlkaneSorbent
The present invention relates to a silicone microporous zeolite and the synthesis method of the silicone microporous zeolite, used to solve the problem that a frame structure of the microporous zeolite synthesized by the prior technology does not contain the silicone and to provide the microporous zeolite, in which the frame structure contains the silicone. The present invention contains the following mol relation: In the formula of (1 / n) Al2O3: SiO2: (m / n) R, n is equal to 5-1000 and m is equal to 0.01-300. R is an alkyl, an alkane alkenyl or a phenyl. A solid nuclear magnetic map of Si29NMR is between -80ppm and +50ppm and includes at least one nuclear magnetic resonance spectral peak of Si29. A diffraction pattern of x-ray has a d-spacing maximum at the position of 11.14 plus or minus 0.05, 9.99 plus or minus 0.05, 9.74 plus or minus 0.05, 6.36 plus or minus 0.05, 5.99 plus or minus 0.05, 5.70 plus or minus 0.05, 5.57 plus or minus 0.05, 4.98 plus or minus 0.05, 4.26 plus or minus 0.05, 3.83 plus or minus 0.05, 3.75 plus or minus 0.05, 3.72 plus or minus 0.05, 3.65 plus or minus 0.05, 3.44 plus or minus 0.05, 3.32 plus or minus 0.05 angstrom and 3.05 plus or minus 0.05 angstrom. The microporous zeolite can serve as a sorbent or an activator component used in the transformation of the organic compounds.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Inversion method of nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional spectrum
InactiveCN103116148AHigh-resolutionImprove execution efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSingular value decompositionData compression
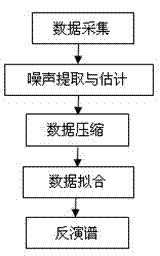
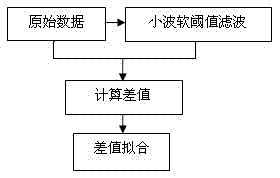
The invention relates to an inversion method of nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional spectrum. The method includes firstly, extracting and estimating noise, namely extracting noise in CPMG (Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill) echo string of acquired data and estimating standard deviation of the noise; secondly, compressing data, namely generating an inversion kernel and performing truncated singular value decomposition and reconstruction by sequence of a nuclear matrix to complete data compression; and thirdly, fitting the data, namely subjecting fitting problem of the compressed data to regularization, performing iterative solution to regularization factors and inversion spectrum by newton method with non-exact one-dimensional search so as to obtain the inversion spectrum. Execution efficiency of two-dimensional inversion algorithm and resolution of two-dimensional spectrum are increased greatly, and the inversion method is well robust.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus and methods for analyzing fluids extracted from earth formation
InactiveUS6841996B2Readily apparentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWaiting time
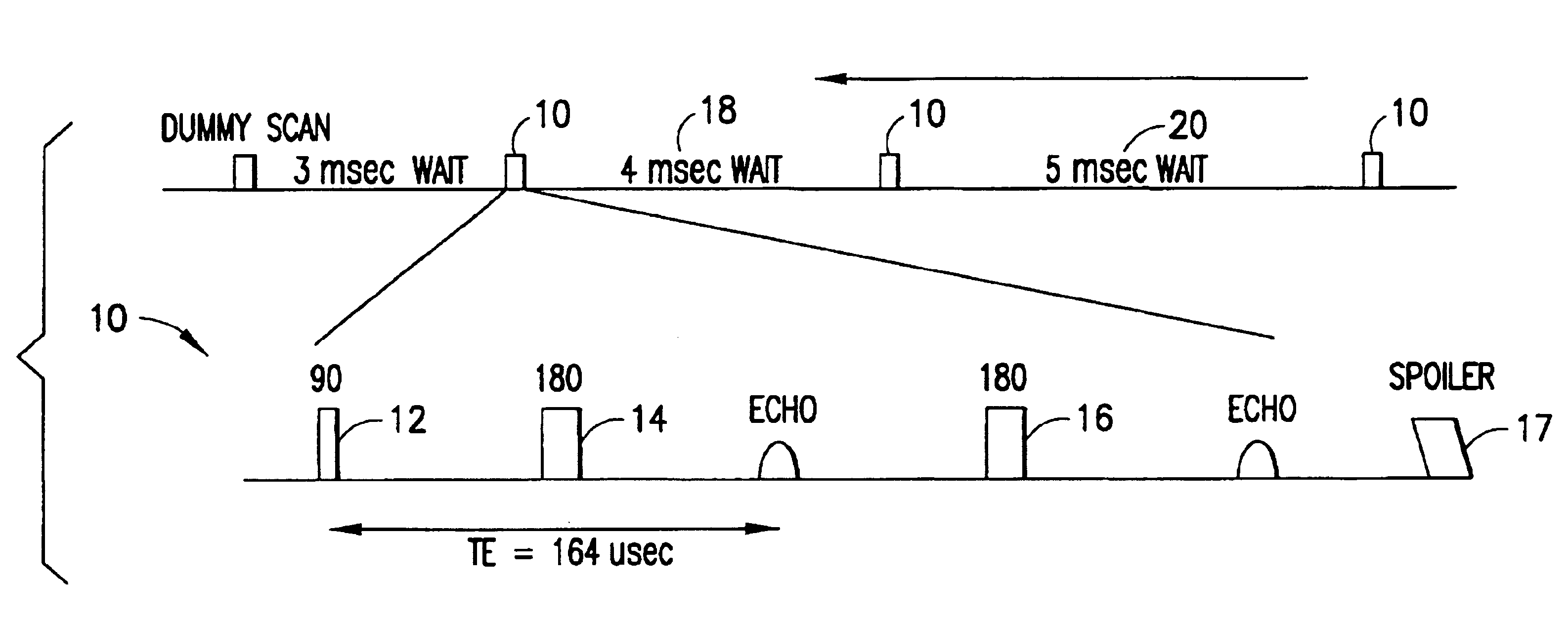
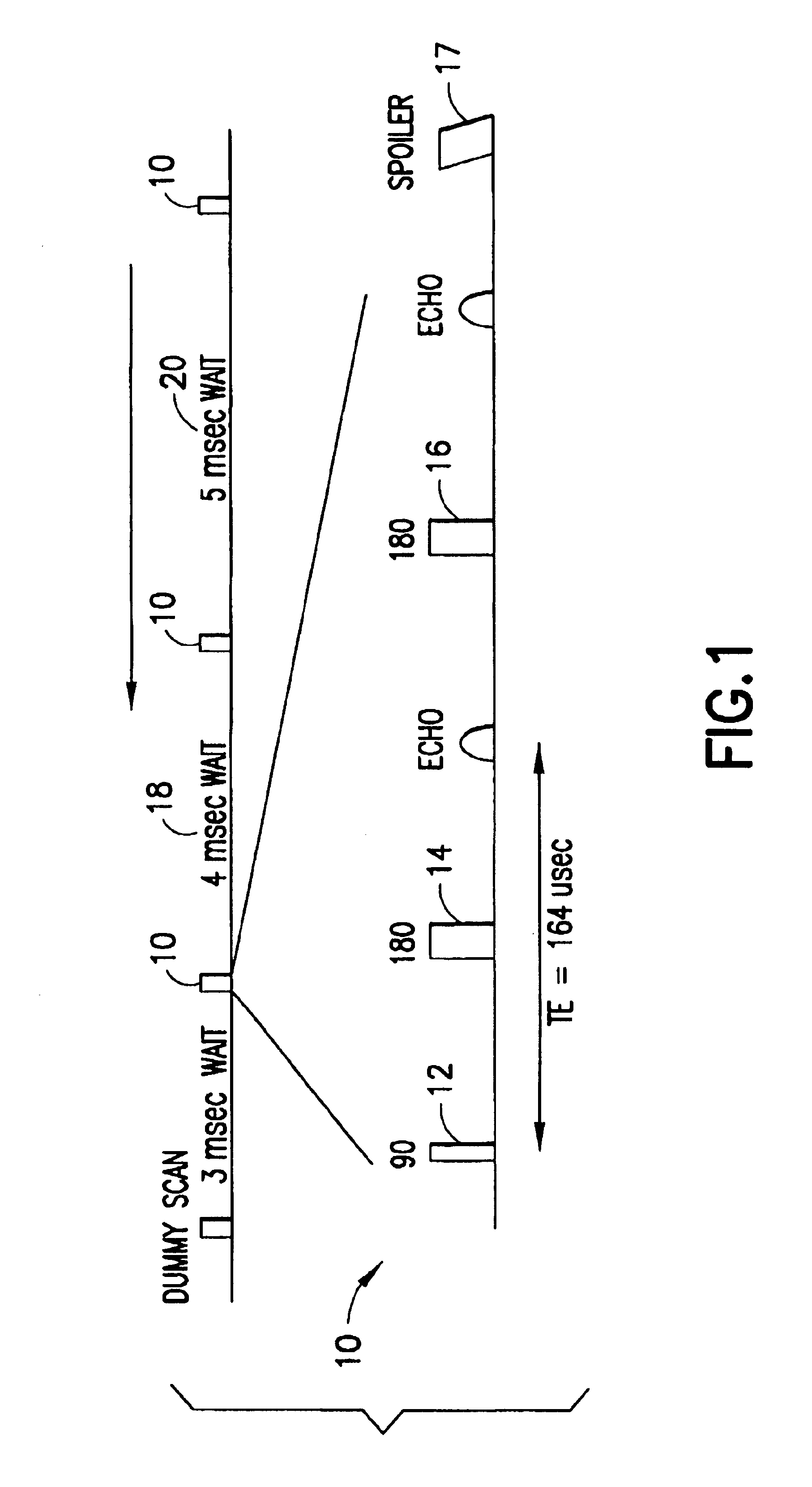
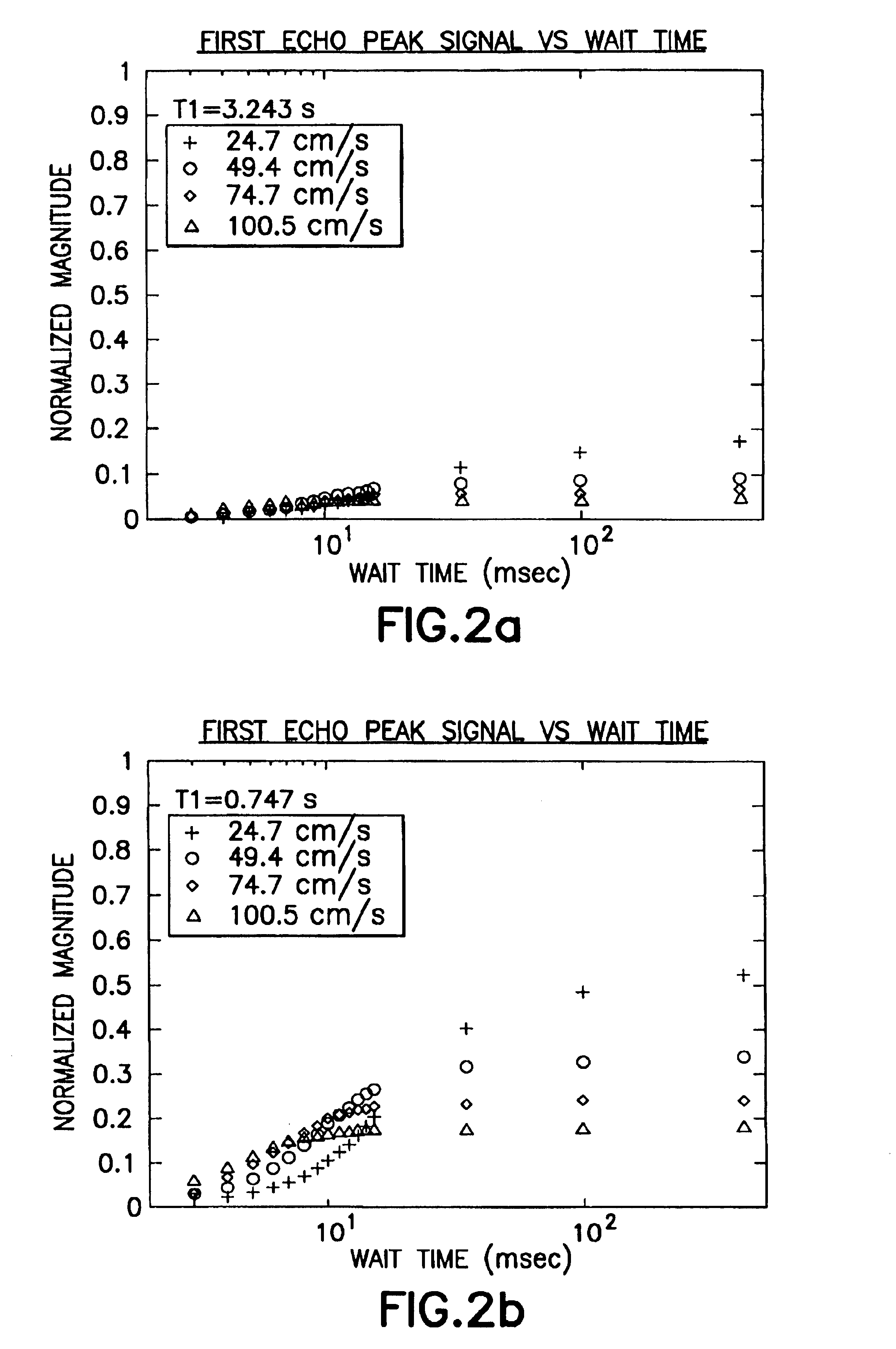
The present invention discloses a method and apparatus to make a nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on a flowing fluid using varied wait times. In one method, NMR measurements are made by: a) flowing the fluid through a static magnetic field; b) applying a group of oscillating magnetic field pulses to the flowing fluid, wherein the group of pulses is comprised of an initial pulse and one or more refocusing pulses; c) detecting magnetic resonance signals from the flowing fluid; d) after a wait time, repeating (b) and (c) one or more times, wherein at least two of the repetitions have varied wait times; and e) analyzing the detected magnetic resonance signals to extract information about the flowing fluid. Further, varied wait time measurements may be useful in determining the flow rate of the sample.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20130082700A1Avoid sensitivityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceIn plane
The present invention has an object to provide a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus or the like that avoids a region with zero sensitivity of an optical magnetometer and allows imaging by strong magnetic resonance when a common magnetic field is used as a bias field of an optical magnetometer and as a magnetostatic field to be applied to a sample. When a direction of a magnetostatic field application unit applying a magnetostatic field to a sample is a z direction, alkali metal cell of a scalar magnetometer is arranged so as not to overlap a region to be imaged in a z direction, and so as not to intersect the region to be imaged in an in-plane direction perpendicular to the z direction.
Owner:CANON KK
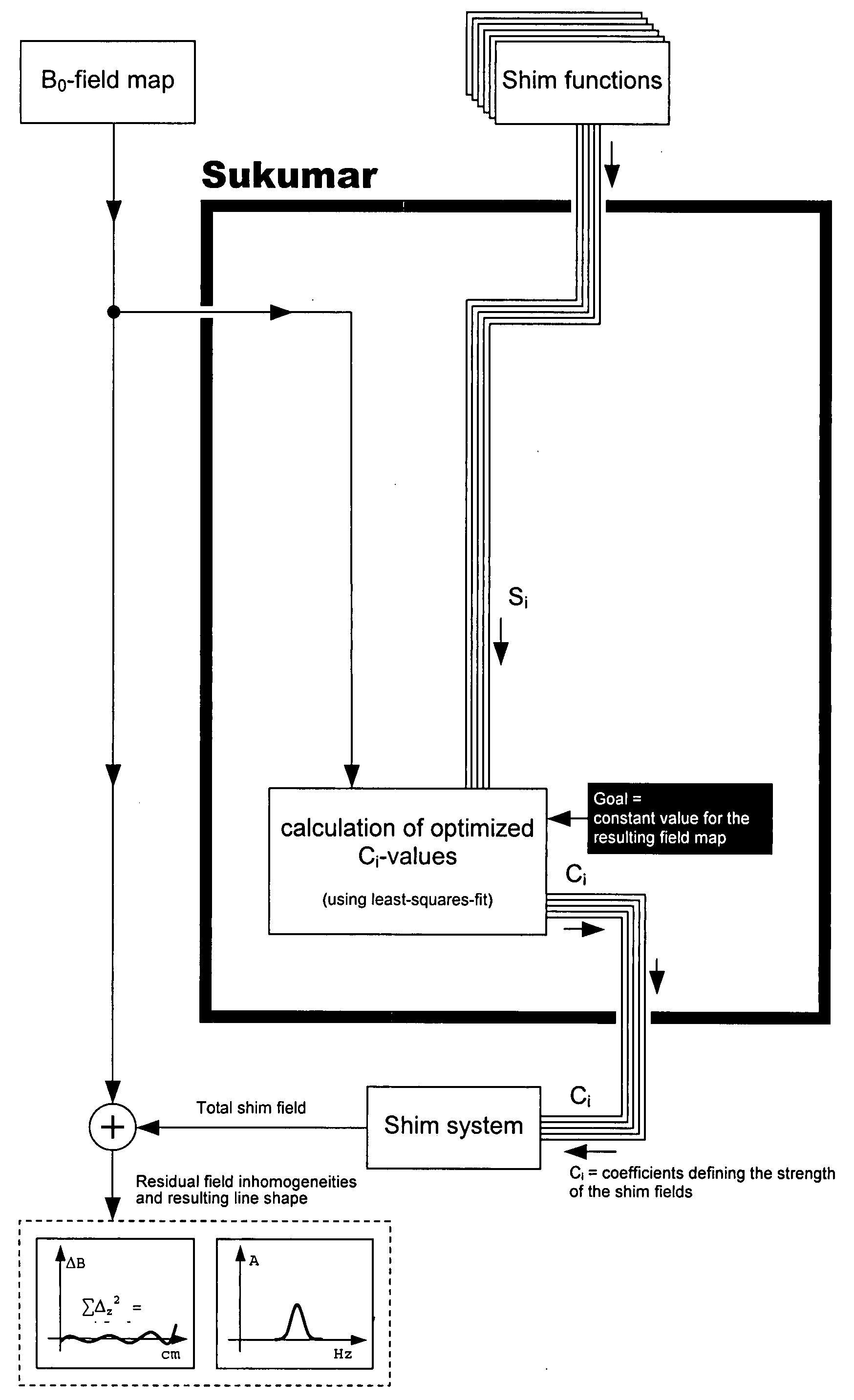
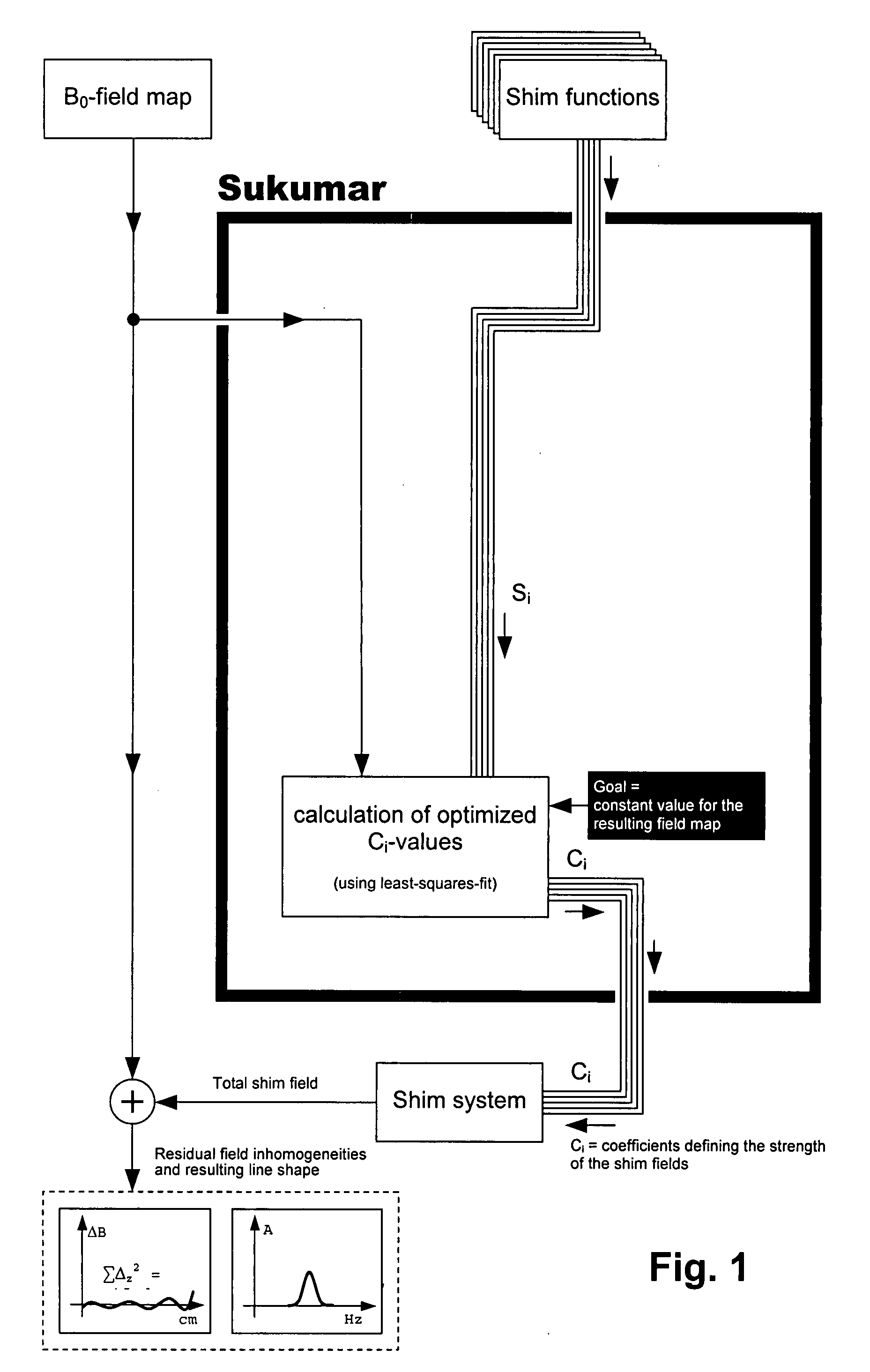
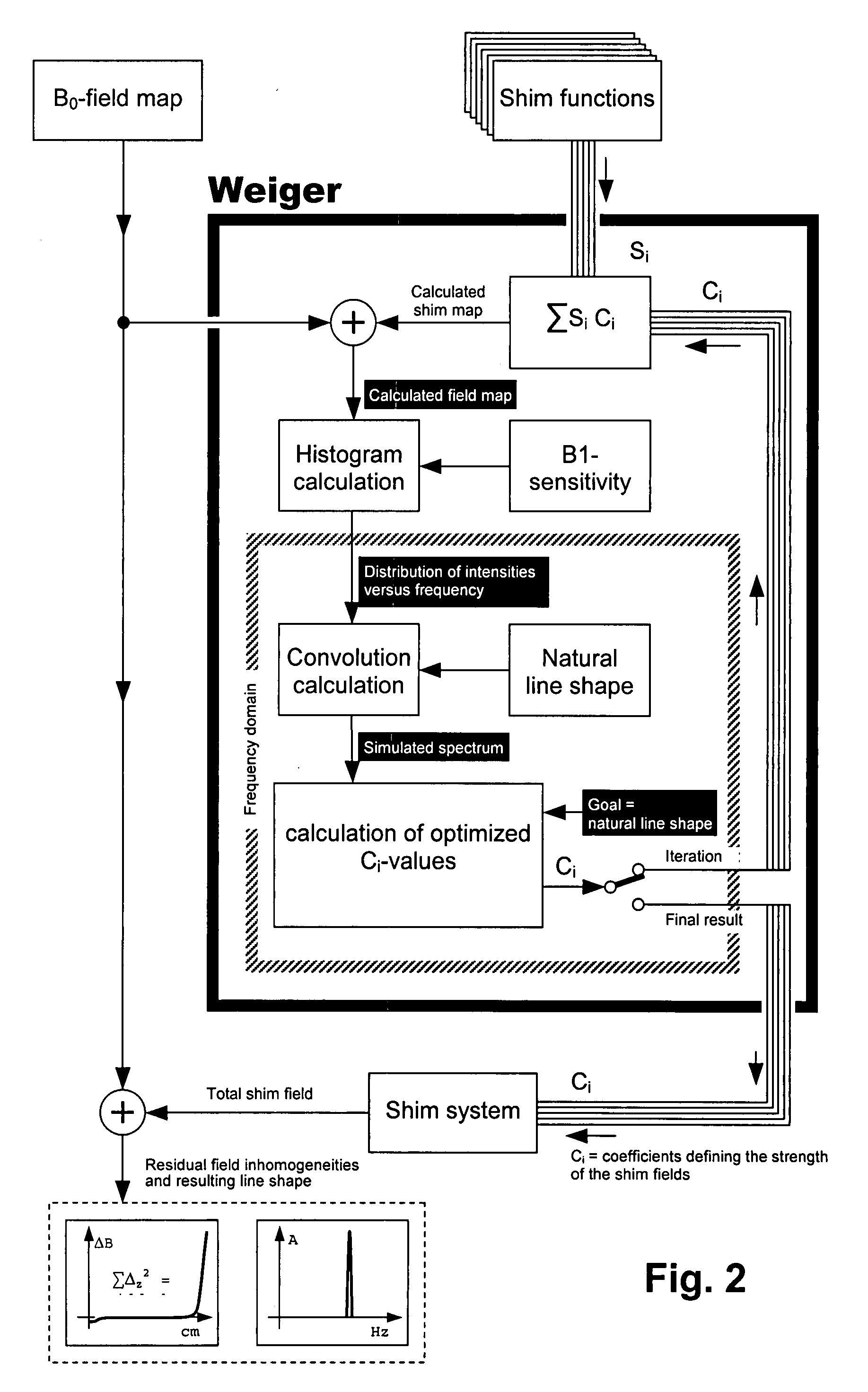
Method for automatic shimming for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20080116894A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumResonance
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Nuclear magnetic resonance sensor used for nondestructive aging resonance of umbrella skirt of composite insulator
InactiveCN102735706ARealize non-destructive testingImprove performanceAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceComposite insulatorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance sensor used for the nondestructive aging resonance of an umbrella skirt of a composite insulator. The sensor comprises a permanent magnet structure and a plane radio-frequency coil, wherein the permanent magnet structure mainly consists of two cylindrical permanent magnet sheets of same specification, the two cylindrical permanent magnet sheets are oppositely and coaxially arranged, and the permanent magnet structure is used for producing a static state main field B0; and the permanent magnet structure is provided with a slide mechanism, so that the distance between the permanent magnet sheets can be adjusted so as to adapt to umbrella skirts of different thickness. The plane radio-frequency coil is formed by two spiral coils which are connected in series on a plane according to the reverse direction of the magnetic field, and the plane radio-frequency coil is used for generating radio-frequency magnetic field B1 orthometric with the main magnetic field in a target region, and detecting return signals produced by a sample to be tested. During the aging detection of the umbrella skirt of the composite insulator, the slide mechanism is adjusted to enable the sensor to clamp the umbrella skirt to be tested, so that the transverse relaxation time T2 of the umbrella skirt can be measured, and further, the aging degree of the umbrella skirt can be judged according to the transverse relaxation time T2. The open-type nuclear magnetic resonance sensor has the advantages of small volume, light weight, and convenience in engineering field detection.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
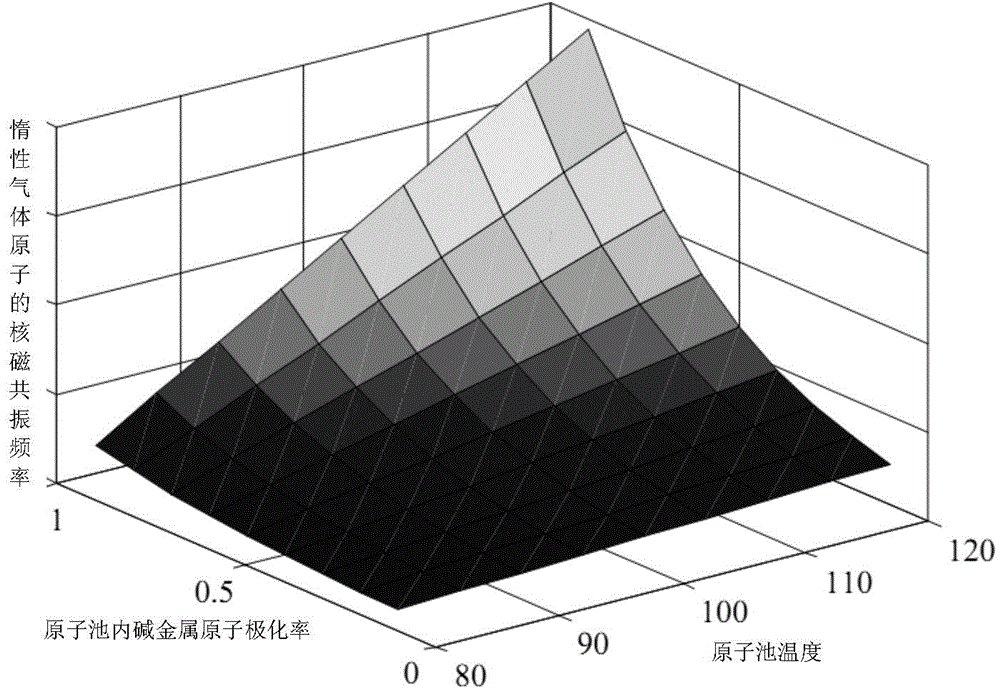
Method for measuring alkali metal atomic polarizability of nuclear magnetic resonance gyro in real time
ActiveCN104833690ADoes not affect the structureEasy to measureAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePolarizabilityProton NMR
The invention provides a method for measuring alkali metal atomic polarizability of a nuclear magnetic resonance gyro in real time and belongs to the field of atomic physics. The method includes: measuring alkali metal atomic densities of an atomic pool at different temperatures, measuring atomic nuclear magnetic resonance frequency of inert gas caused by polarization of alkali metal atoms, and thus acquiring polarizability of the alkali metal atoms in the atomic pool without changing the optical path structure of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro and the magnetic field environment; building a three-dimensional model of changes in nuclear magnetic resonance frequency of the inert gas in the atomic pool along with temperature and the alkali metal atomic polarizability, measuring the frequency shift of atomic NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) of the inert gas at any temperature point while the nuclear magnetic resonance frequency normally runs, and thus calculating the polarizability of the alkali metal atoms in the atomic pool in real time. The method has the advantages that the method is simple, no influence is caused to the optical path structure of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro and the method is of great significance to improving the performance of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
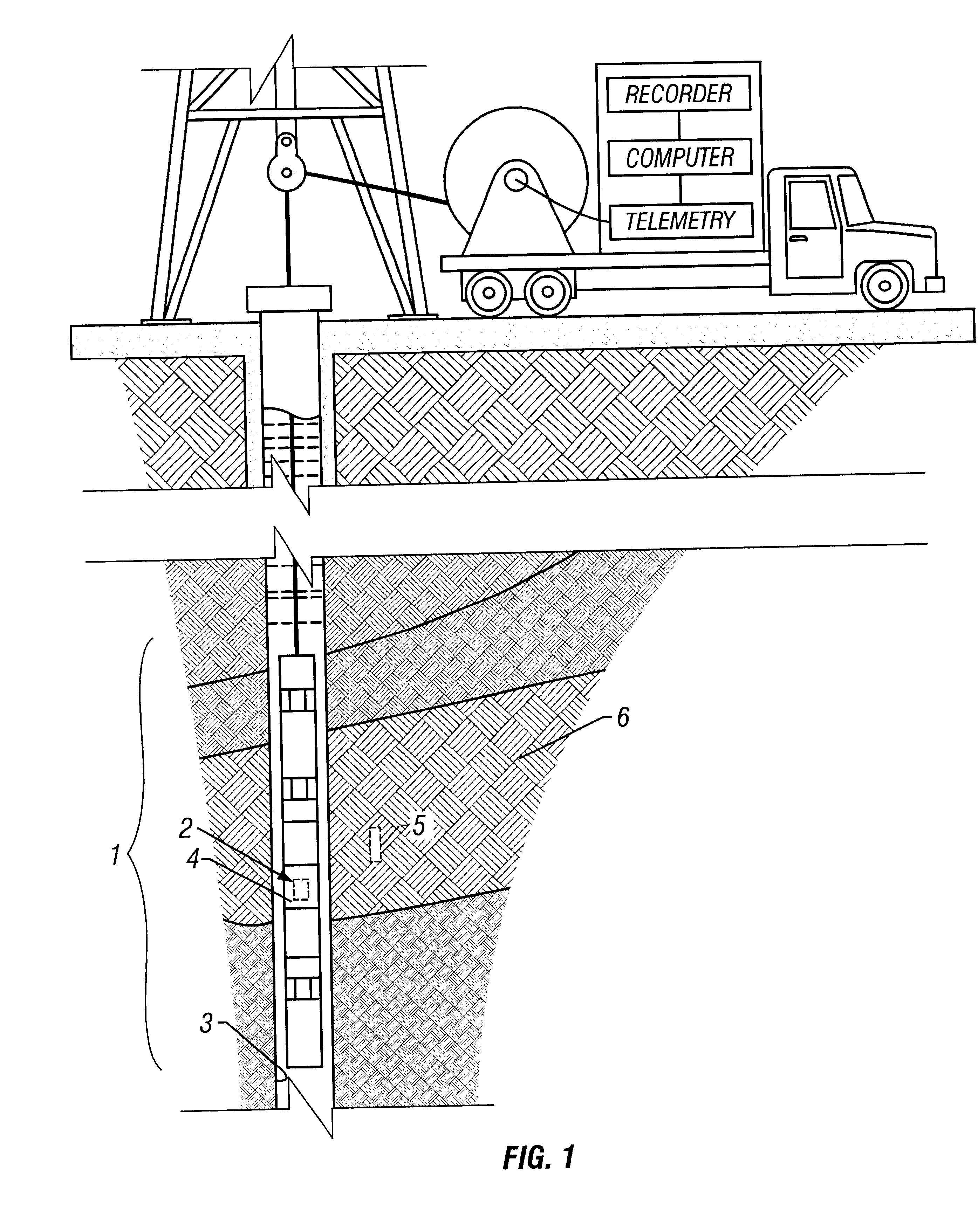
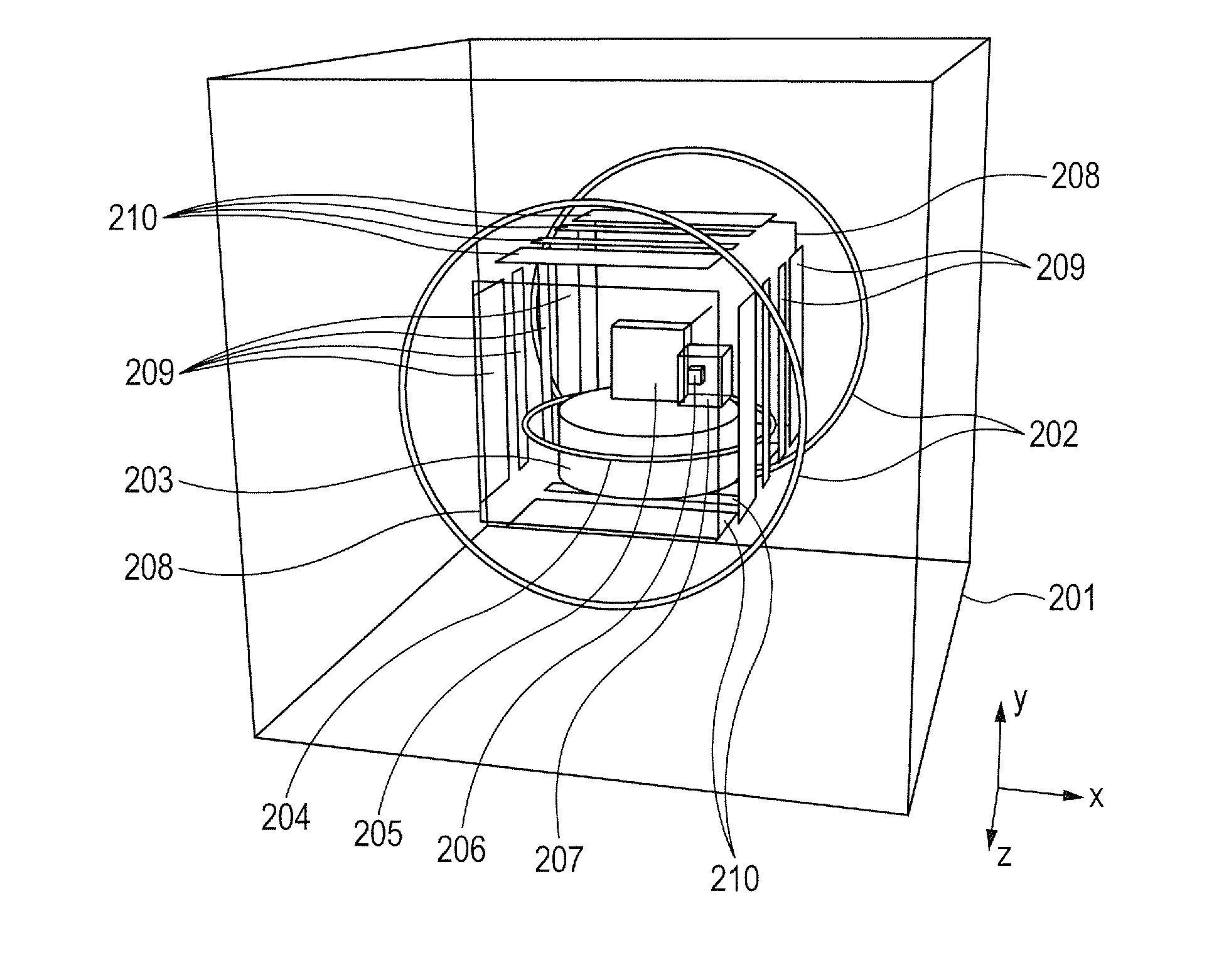
Downhole micro magnetic resonance analyzer
ActiveUS8471559B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic property measurementsSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A downhole micro MR analyzer for use in a wellbore, having a micro sample tube, a micro RF coil in close proximity to the micro sample tube, and one or more magnets disposed about the micro sample tube is disclosed. The micro MR analyzer can be used for nuclear magnetic resonance or electron spin resonance experiments to ascertain formation properties and chemical compositions.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
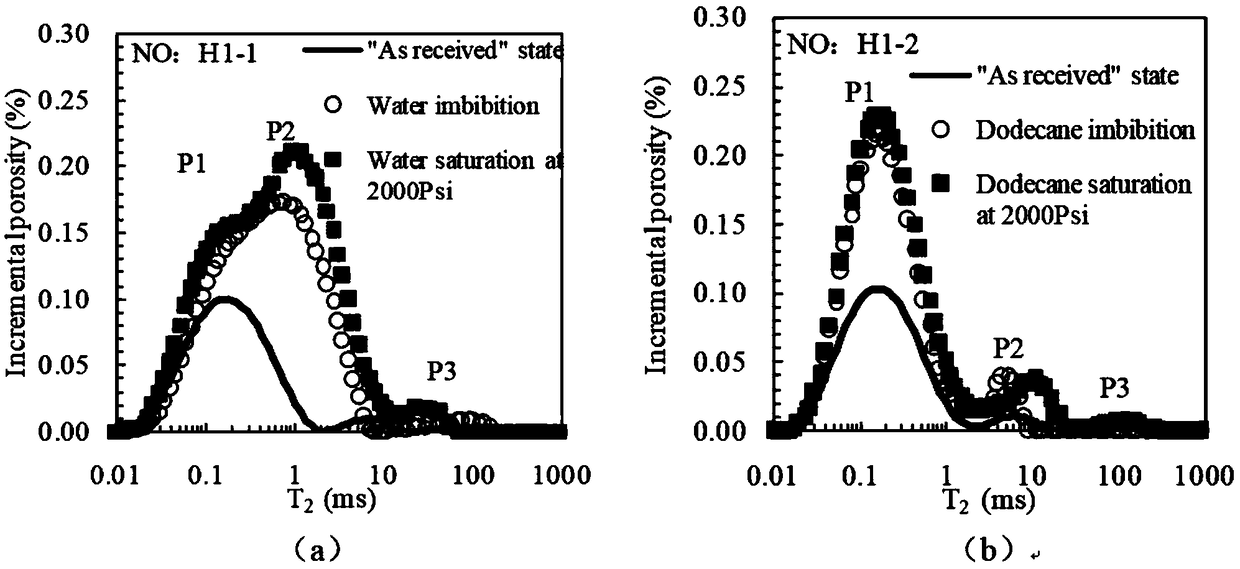
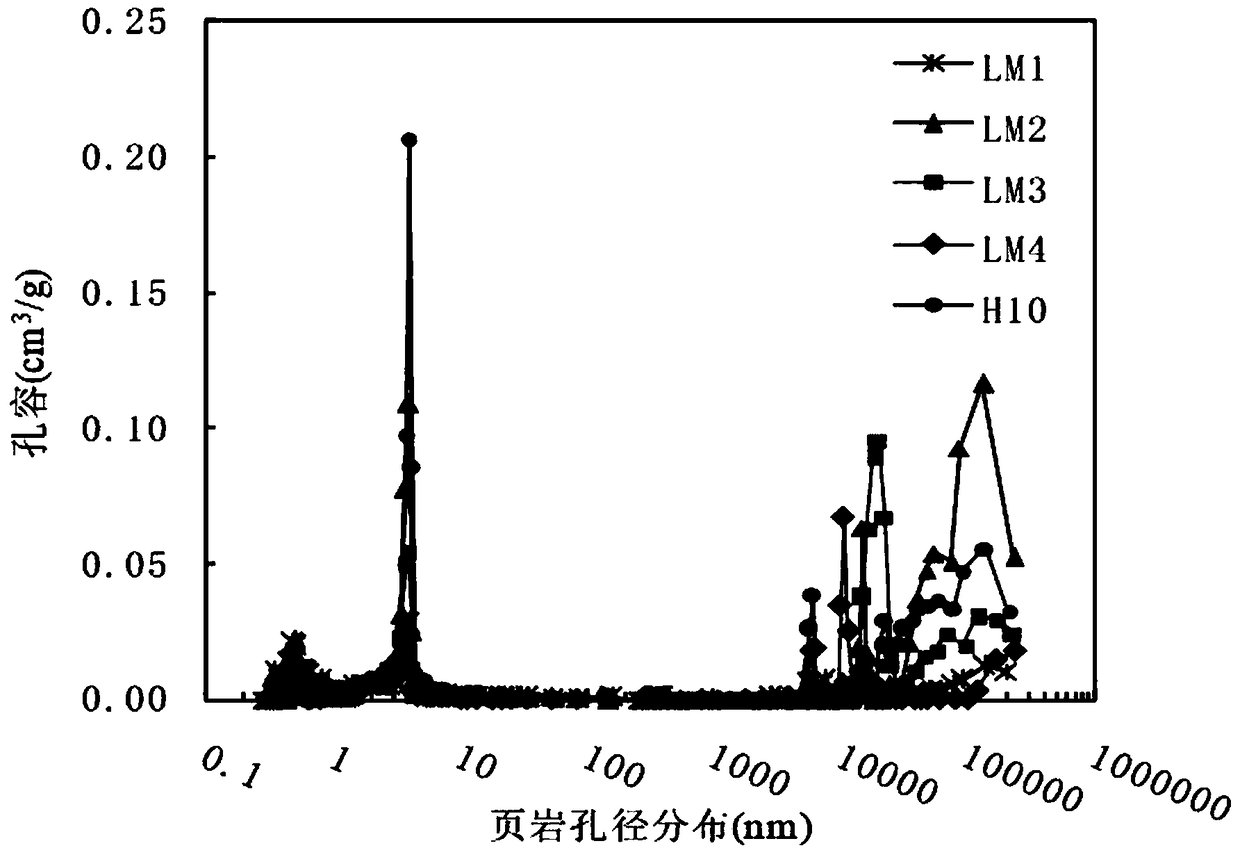
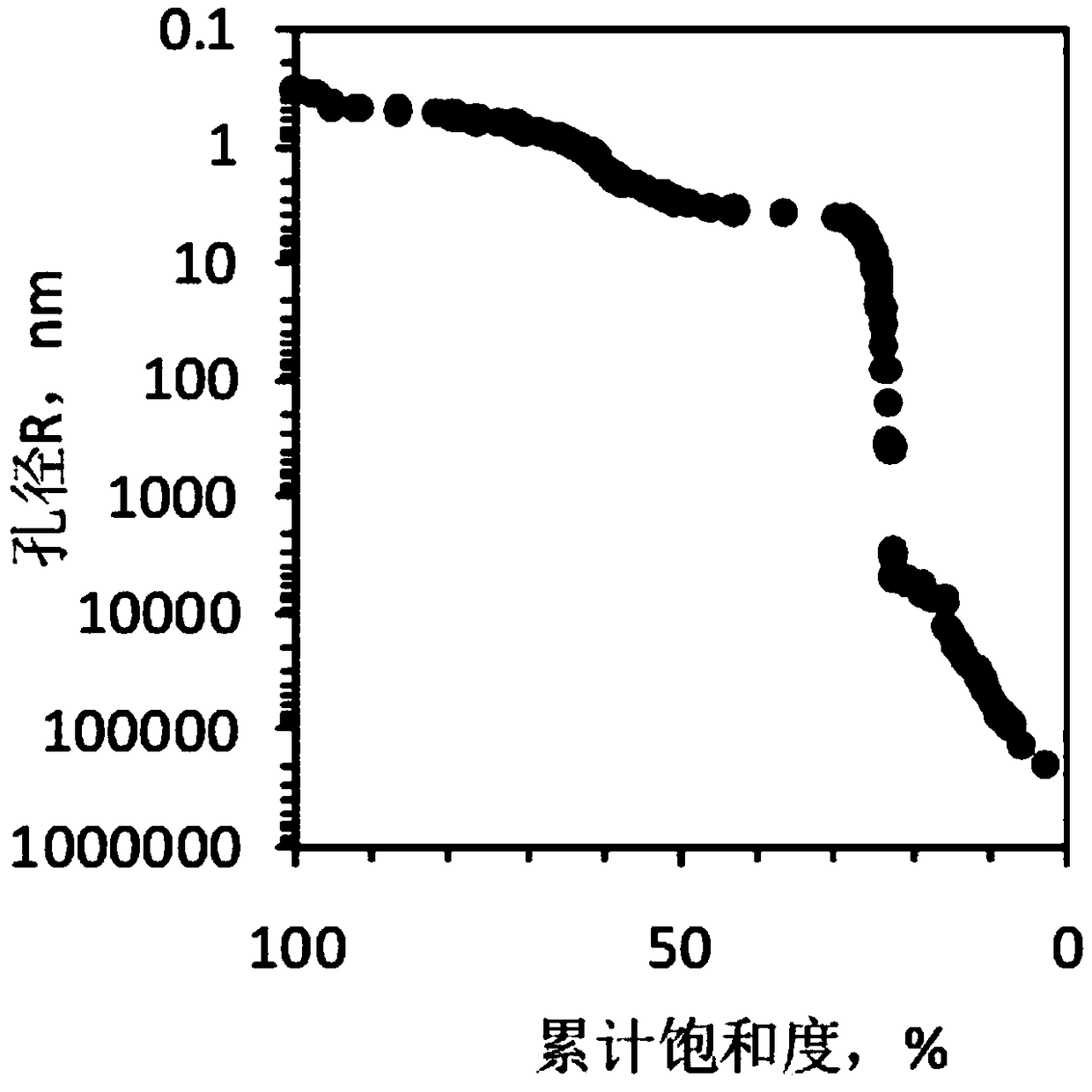
Shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation method based on nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN108169099AThe calculation result is accuratePracticalAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisPore distributionHigh pressure
The invention discloses a shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation method based on nuclear magnetic resonance. The shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation methodcomprises the following steps: collecting cores; drilling parallel samples, carrying out oil and water self-adsorption nuclear magnetic resonance experiment measurement; contrastively analyzing the difference of a parallel sample oil and water nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum, and determining the distribution of different wetting pore types on the nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum; obtaining a shale gas reservoir full-pore distribution curve according to high-pressure pressurized mercury, nitrogen adsorption and carbon dioxide adsorption; furthermore, obtaining an intersection plate of pore diameters and corresponding T2 time; and according to the intersection plate of different pore types of pore diameters and corresponding T2 time, establishing a quantitative calculation model of the pore diameters according to the pore types. The method has the advantages that a shale gas reservoir pore full-pore distribution curve can be quantitatively calculated through the technology;simultaneously, the nuclear magnetism measurement is quick, simple and loss-free, and is higher in practicability by compared with high-pressure pressurized mercury, nitrogen adsorption and carbon dioxide adsorption; and compared with a conventional method, the calculation result is more accurate.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Metabolite detection using magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20080081375A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic measurementsMetaboliteDisease cause
Methods using magnetic resonance, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are provided for detecting metabolites in a sample. The methods are useful for the diagnosis or prognosis of a disease such as cancer and can also be used to determine or monitor a treatment protocol. The methods are useful in characterizing speciation in biological samples where mixtures are often encountered and chemical shifts of the same structural group of similar molecules can produce complicated overlapping resonances.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
Computer assisted diagnosis (CAD) of cancer using multi-functional, multi-modal in-vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and imaging (MRI)
This invention relates to computer-assisted diagnostics and classification of prostate cancer. Specifically, the invention relates to segmentation of the prostate boundary on MRI images, cancer detection using multimodal multi-protocol MR data; and their integration for a computer-aided diagnosis and classification system for prostate cancer.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
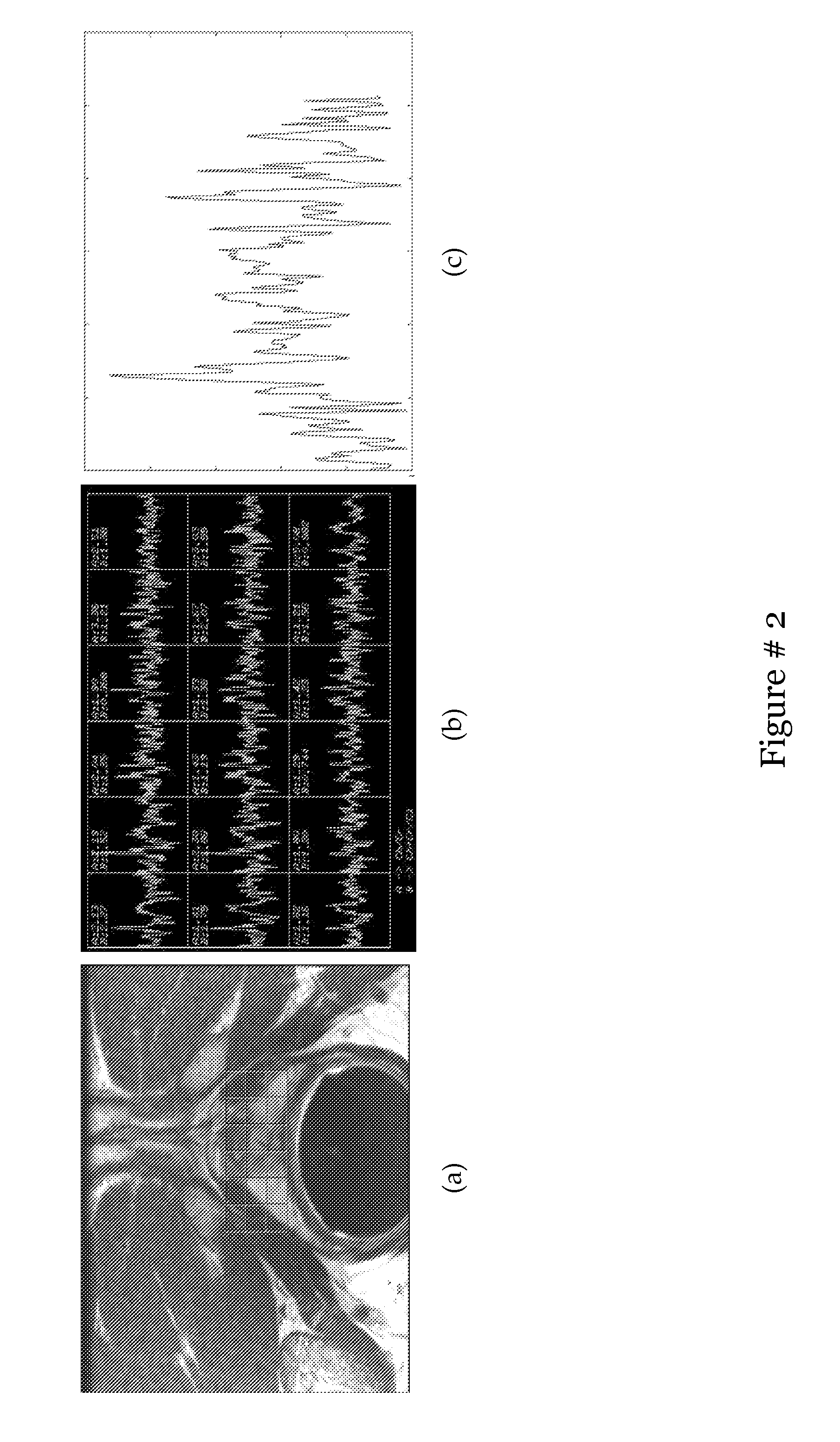
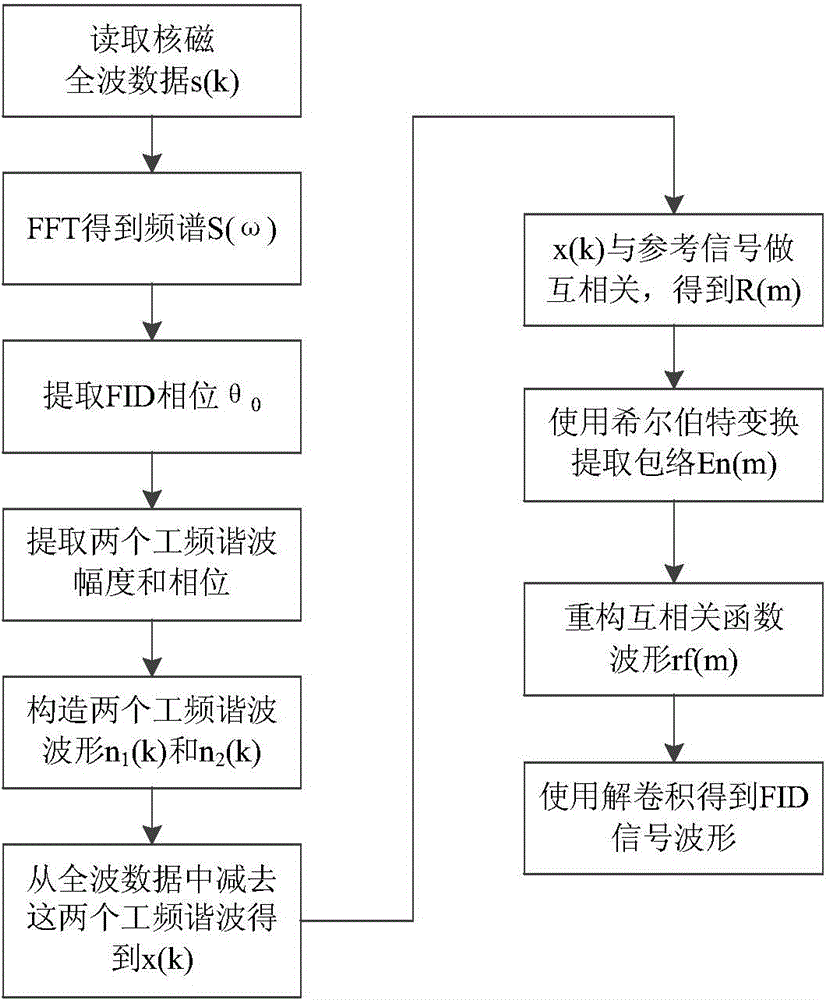
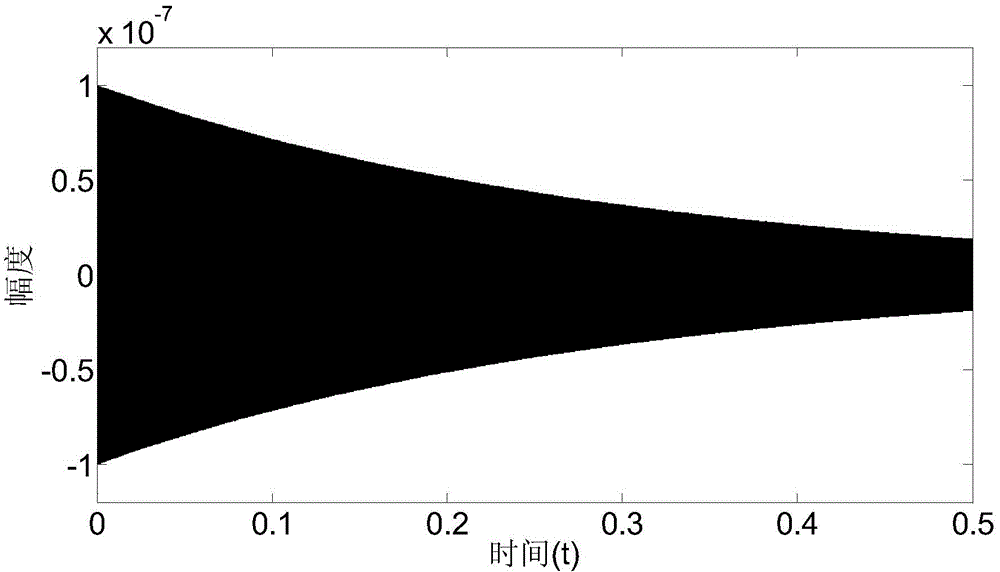
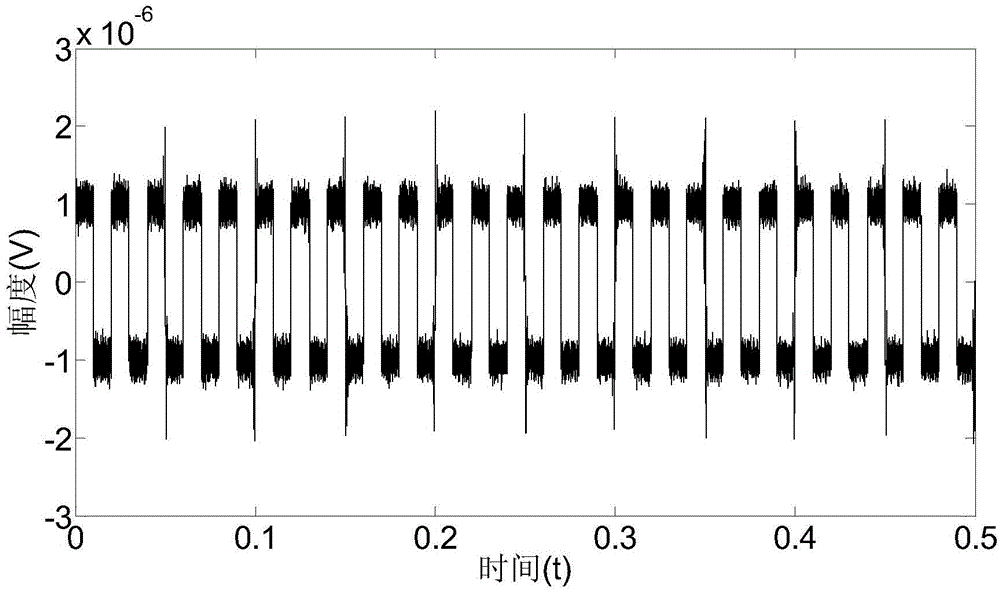
Cross-correlation-based nuclear magnetic resonance full wave signal noise filtering method
ActiveCN104898172AImprove detection depthSmall amount of calculationDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceFull waveRandom noise
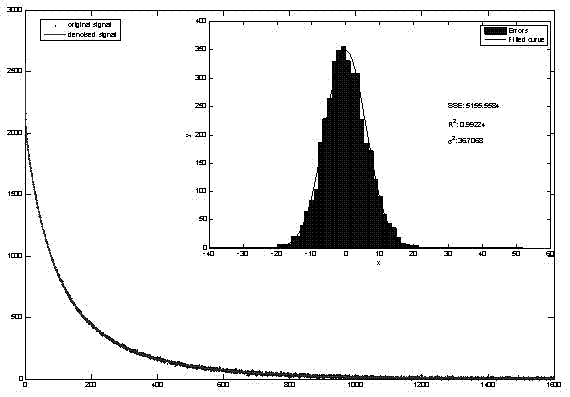
The invention relates to a cross-correlation-based nuclear magnetic resonance full wave signal noise filtering method. Based on characteristics that noise is irrelevant to the sinusoidal signals of Larmor frequency but FID amplitude attenuation sinusoidal signals are relevant to the sinusoidal signals of Larmor frequency, the method comprises steps of filtering noise via cross-correlation operation, then fitting envelope of related wave forms, reconstituting correlation wave forms without noise and at last extracting FID signals in nuclear magnetic resonance full wave data by use of the deconvolution algorithm. According to the invention, calculated amount of operation data is small; power frequency, noise of harmonic waves, random noise and peak noise can be simultaneously suppressed; signal to noise ratio of the nuclear magnetic resonance full wave data is remarkably increased, thereby facilitating application range and detection depth of a nuclear magnetic resonance water explorer; additional reference noise eliminating devices are not required, so cost is reduced; and ideal filtering effects of the full wave data which are acquired at a time can be achieved via cross correlation, so measuring time is saved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Low-permeability sandstone reservoir pore structure quantitative inversion method based on nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN104819923ABreak down research ideasImprove correspondencePermeability/surface area analysisWell loggingStructural type
The invention discloses a low-permeability sandstone reservoir pore structure quantitative inversion method based on nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the following steps: I, selecting a basic sample; II, classifying the type of a pore structure; III, establishing a well logging chart for identifying the pore structure; IV, establishing a pore throat distribution inversion formula according to the type of the pore structure; V, verifying the accuracy of the formula; VI, identifying the type of the pore structure of a shaft section by utilizing the well logging chart; VII, quantitatively inverting the distribution of free fluid pore throats by utilizing a nuclear magnetic resonance well logging T2 spectrum. The method has the following beneficial effects: a reliable method and technology are provided for quantitatively evaluating the pore structure, and the research concept of the current method can be broken through. The continuous free fluid pore throat distribution can be inverted by virtue of the nuclear magnetic resonance well logging, so that direct evidence is provided for evaluating the effectiveness of the low-permeability sandstone reservoir, application of the well logging information in the quantitative inversion of the micro pore structure of the reservoir is favorably explored, and the application and development of the nuclear magnetic well logging technology can be promoted.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
System and method for detecting pain and its components using magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS7676254B2Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMetaboliteAssessing Pain
Owner:SYDNEY UNIV OF +2
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) device and measurement method based on laser atomic magnetometer
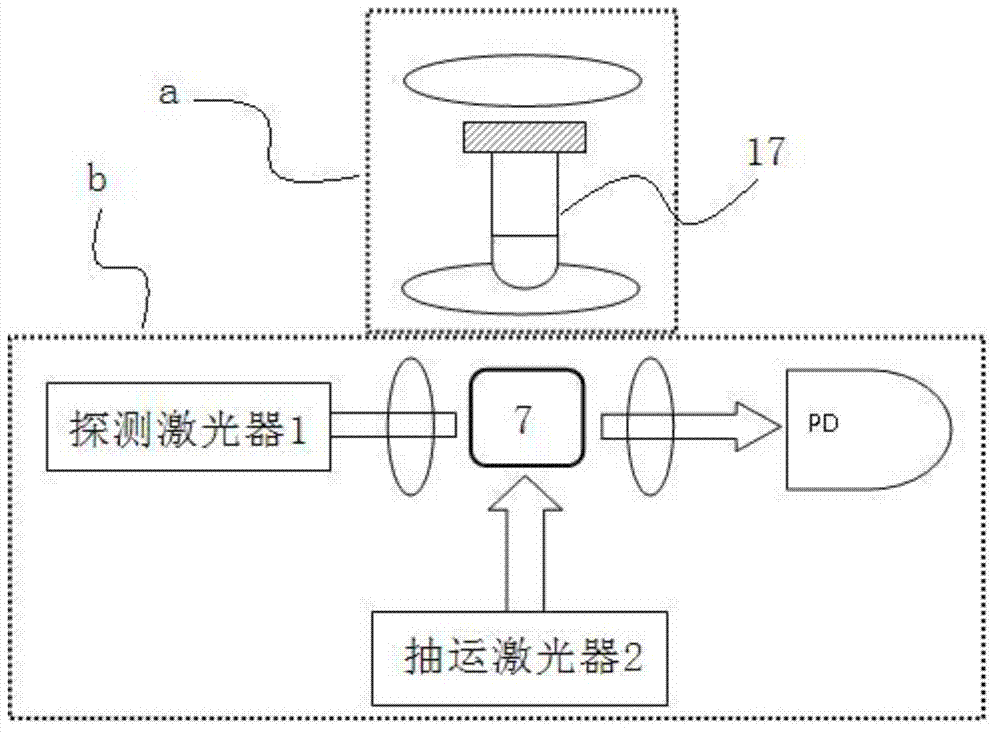
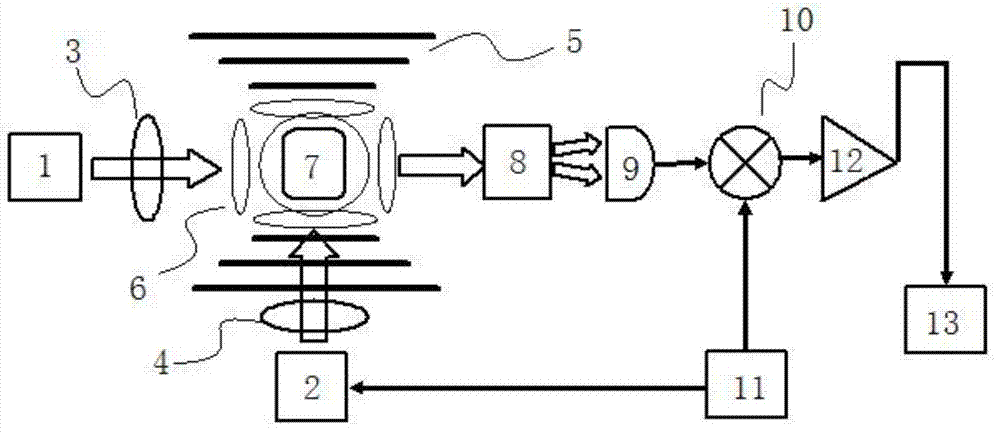
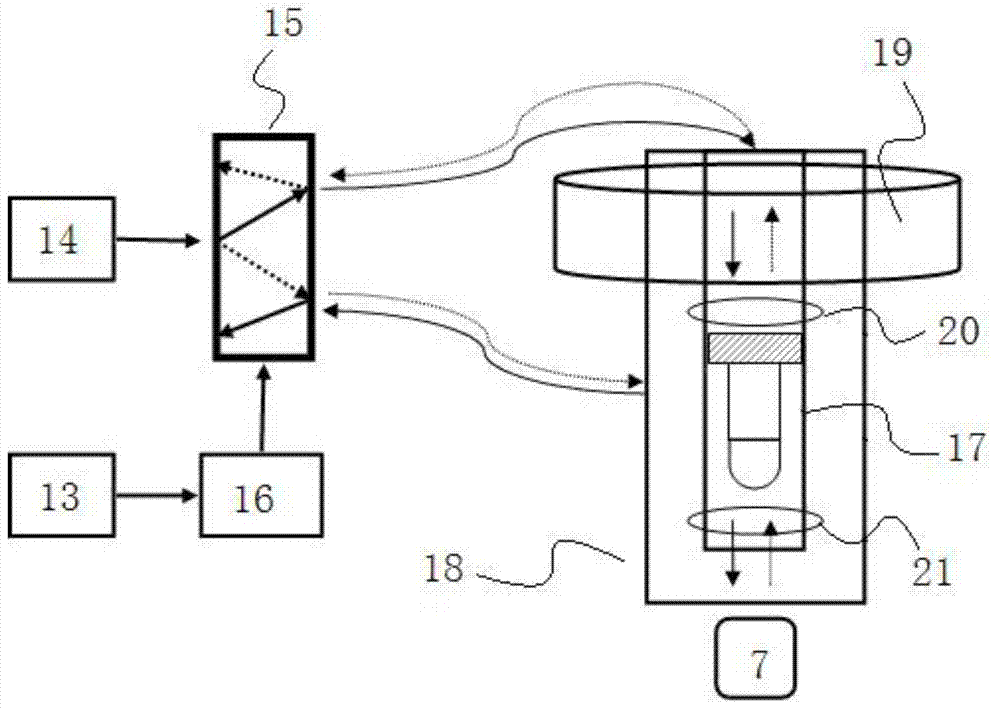
ActiveCN102830381AHigh detection sensitivityLow running costMeasurements using NMRHelmholtz coilProton NMR
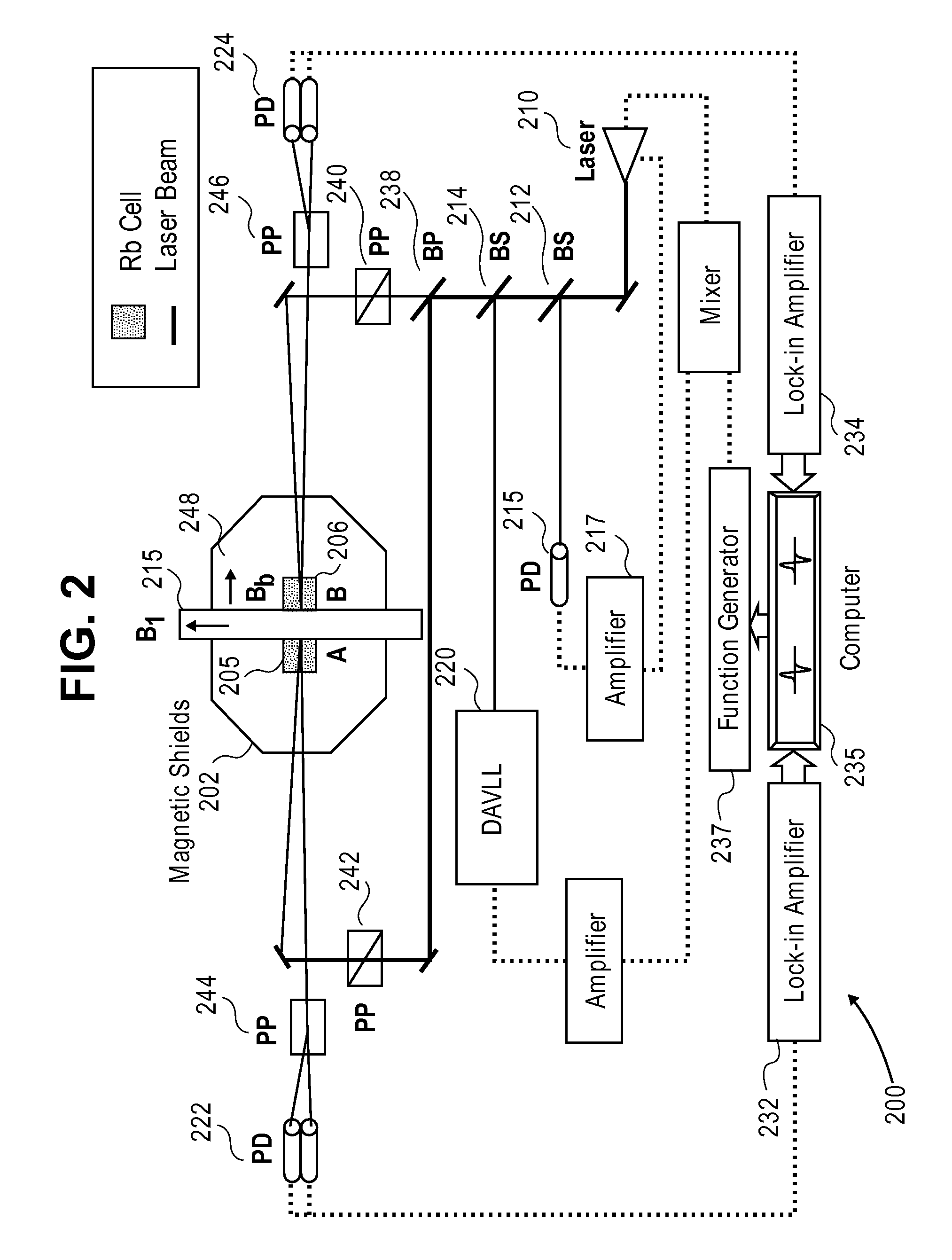
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) device based on a laser atomic magnetometer, and the NMR device comprises a cesium atom vapor bubble, a magnetic shielding bushing which is sleeved on the cesium atom vapor bubble, three groups of Helmholtz coils which are arranged inside the magnetic shielding bushing, a polarization device which is used for polarizing cesium atoms inside the cesium atom vapor bubble, a laser transmitting device which is used for transmitting detection laser to the cesium atom vapor bubble, a detection device which is used for detecting an NMR signal of the detection laser penetrating the cesium atom vapor bubble and a pneumatic sample feeding device which is used for pre-polarizing a sample to be detected and can place the pre-polarized sample on the cesium atom vapor bubble. The invention also discloses a measurement method of an NMR based on the laser atomic magnetometer. The device and the method are high in detection sensitivity, free from needing low-temperature refrigeration, low in running cost and lower in working temperature.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
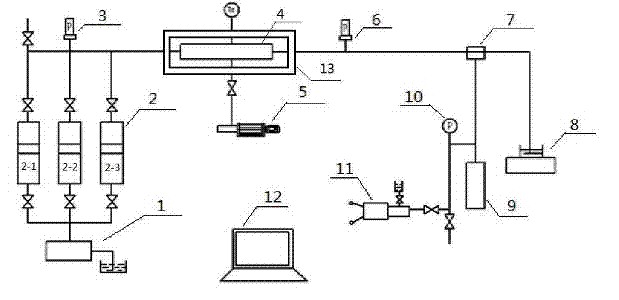
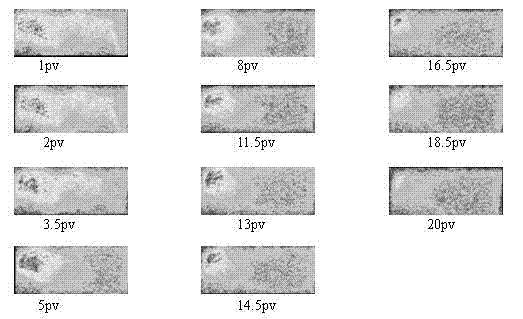
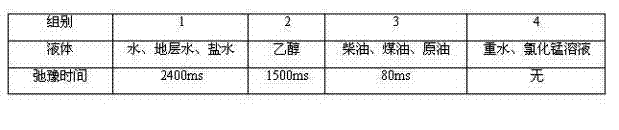
Rock core displacement effect visual evaluation method
ActiveCN103091346AWill not harmAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
The invention relates to a rock core displacement effect visual evaluation method. The distribution characteristic and effect of a solution A for displacing another solution B in the rock core are determined by using specific rock core nuclear magnetic resonance equipment, wherein the solution A and the solution B need to be selected from different groups, and are significantly different in relaxation time. The method comprises the following specific steps of: placing a rock core in a rubber tube, thermosetting, placing into an anti-magnetic holder, and placing into a nuclear magnetic resonance test coil; loading the solutions A and B into a solution container; starting nuclear magnetic resonance imaging MRI and rock core application as well as displacement software, and inputting data of the rock core and a displacement solution; adjusting the flow rate and the pressure difference between annular pressure and displacement pressure, starting a pump to displace the solution A, and reversing the process to displace the solution B when only the solution A flows from the outlet; determining and recording 2D images and T2 spectra of the rock core and fluid at different moments when the solution A is displaced by the solution B, and stopping displacement when the 2D images and T2 spectra have no changes; and processing the data to obtain the distribution cloud images of the fluid at different moments.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance evaluation using independent component analysis (ICA)-based blind source separation
InactiveUS20090072824A1Efficient and effective in separatingElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentTime domainBound water
Disclosed is a non-lineal statistical independent component (ICA) analysis methodology for calculating T2 or T1 distributions of nuclear magnetic resonance logs. In one aspect, the invention employs a classical blind source separation (BSS) approach with the input data (T2 or T1 distributions) being considered not only horizontally (in relaxation time units), but also vertically (in depth). The statistical variations are used for separating the principal independent components and their corresponding weighting matrix. The result of such ICA based BSS is an efficient separation of T2 components correlative to the presence of particular conditions (e.g., clay bound water, heavy oil, capillary bound water, free water, mud filtrate (water and oil), and noise). Individual saturation of estimated fluids can be calculated from the weighting matrix generated in accordance with the invention. In accordance with a further feature of the invention, it is contemplated that independent component analysis techniques may be applied to the underlying time domain data prior to its transformation to a T2 distribution. This advantageously results in “de-noising” of the signal, leading to more precise and accurate results following analysis of the T2 distribution.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
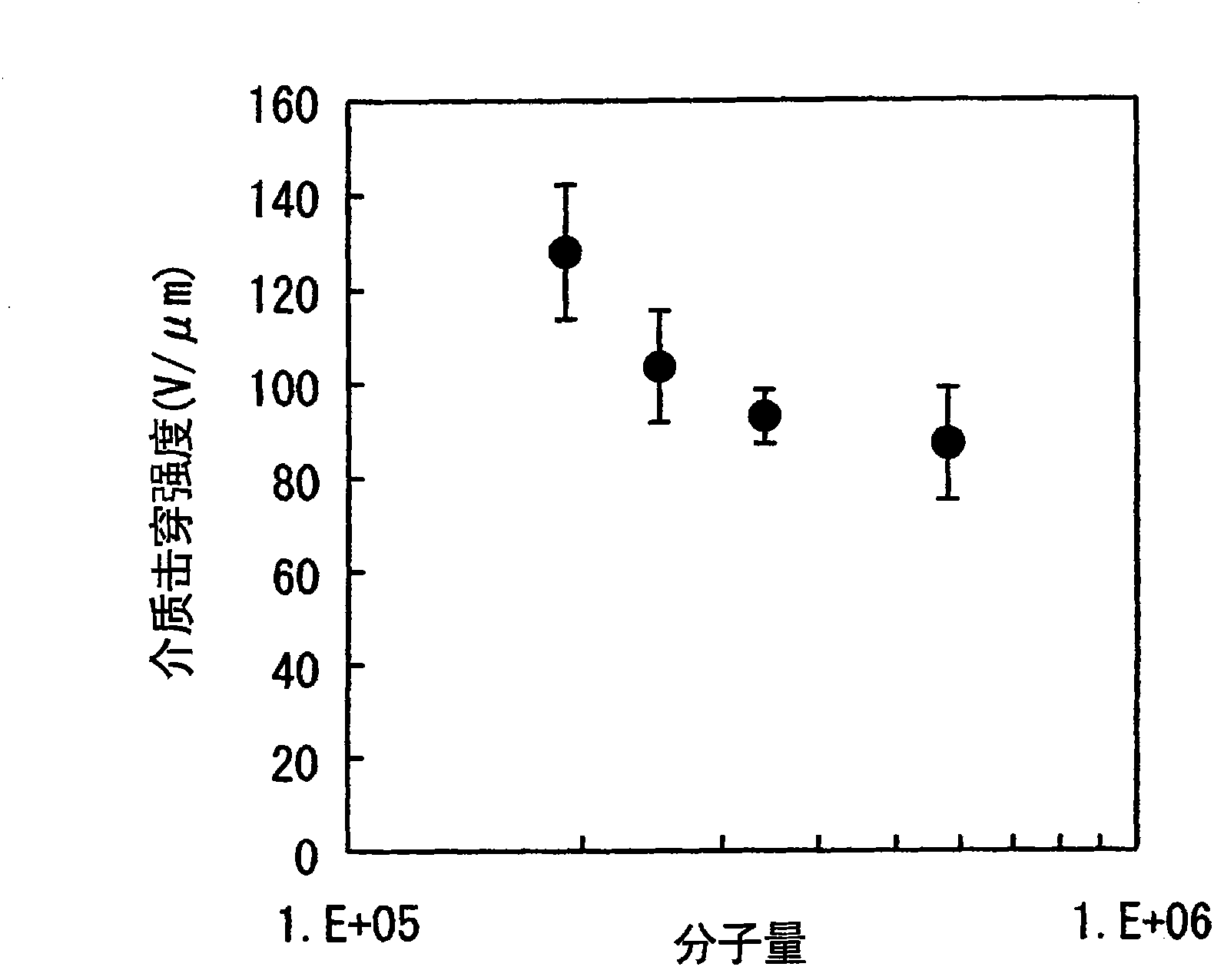
Biaxially stretched polypropylene film for capacitor, deposition-coated film obtained from the same, and capacitor employing the same
ActiveCN101848961AHigh crystallinityExcellent withstand voltage characteristicsFixed capacitor dielectricSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringPolypropylene
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com