Patents
Literature
88 results about "Free induction decay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
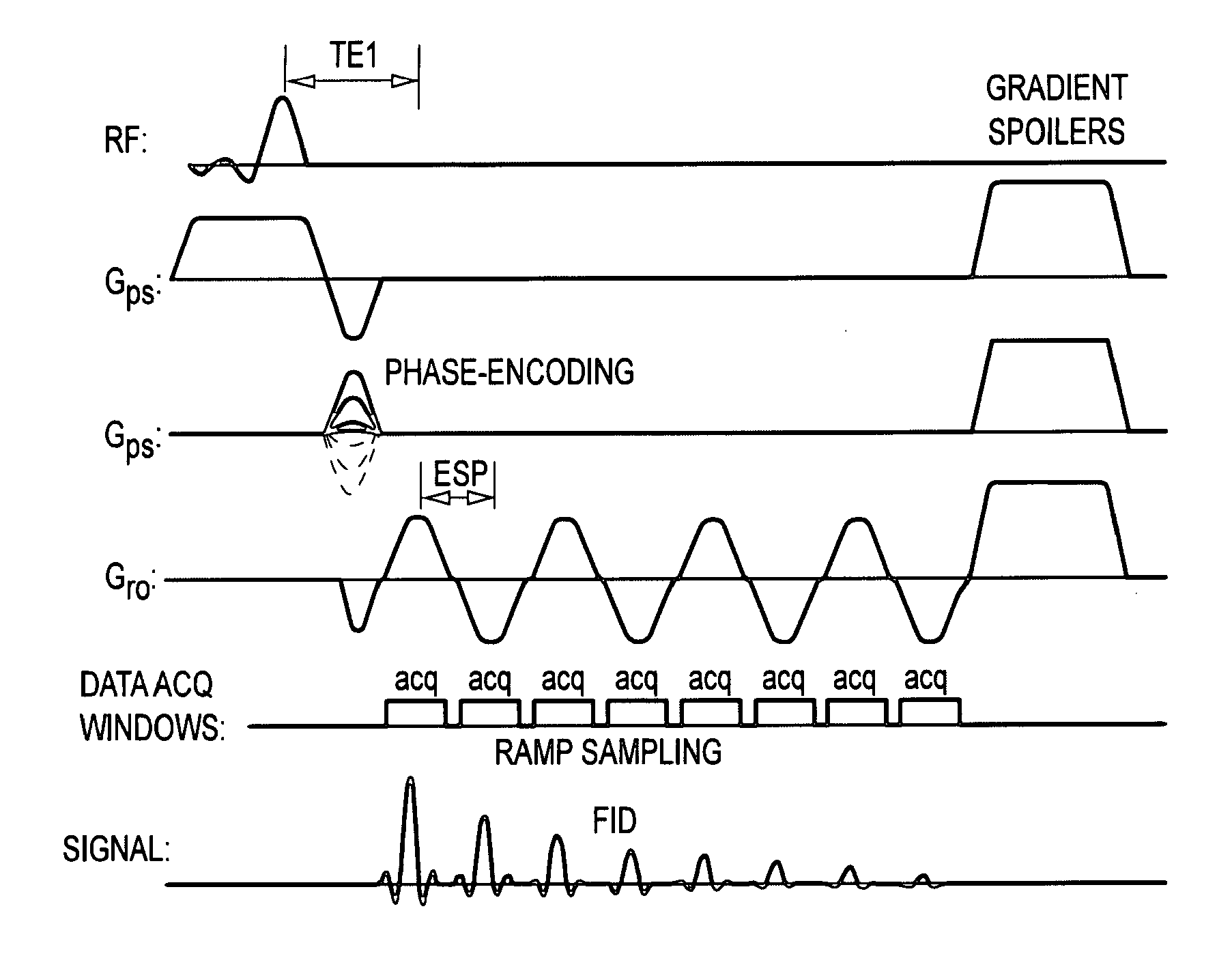
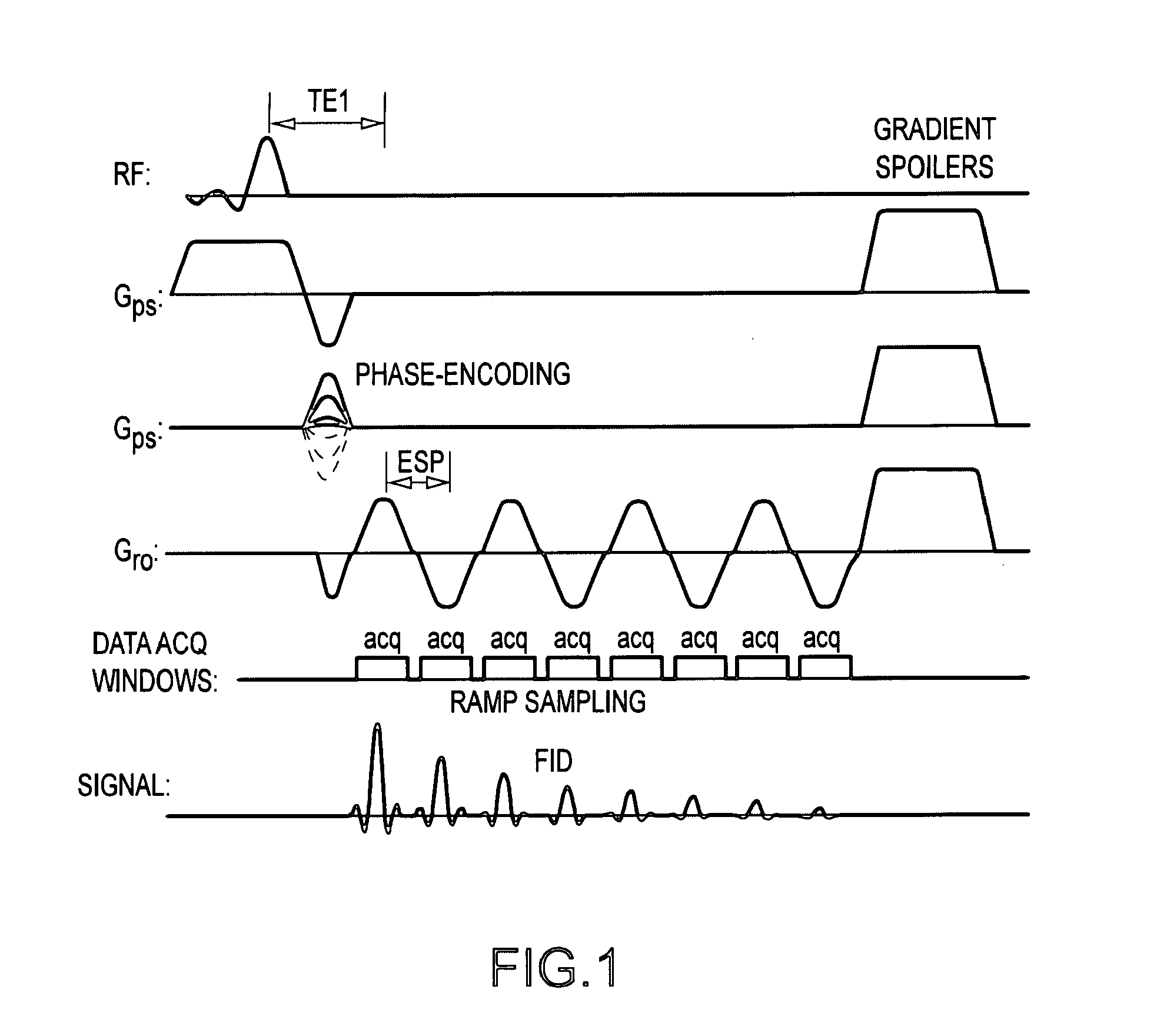
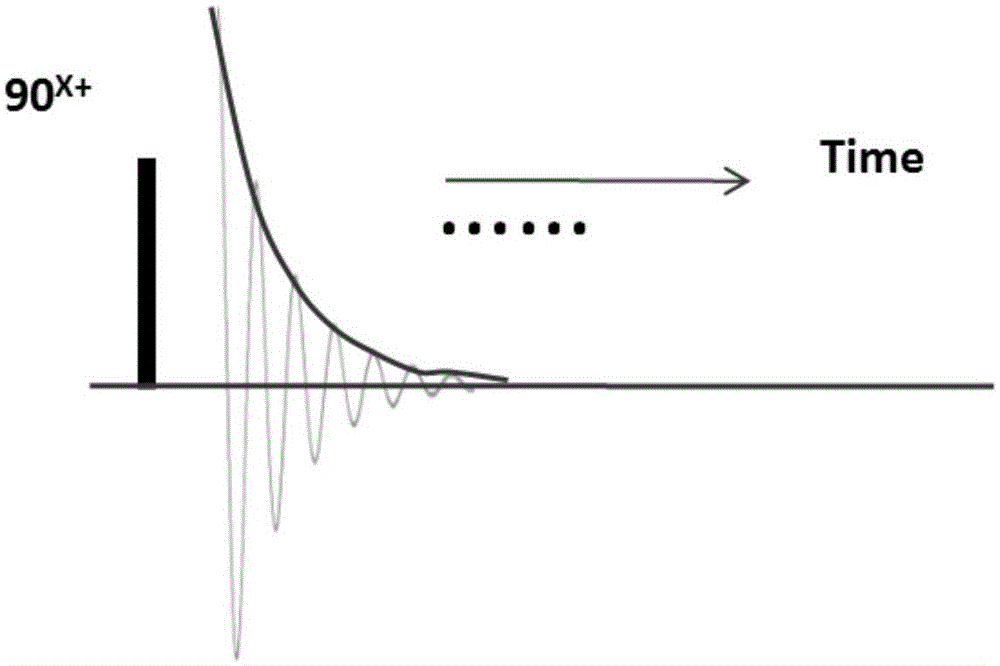
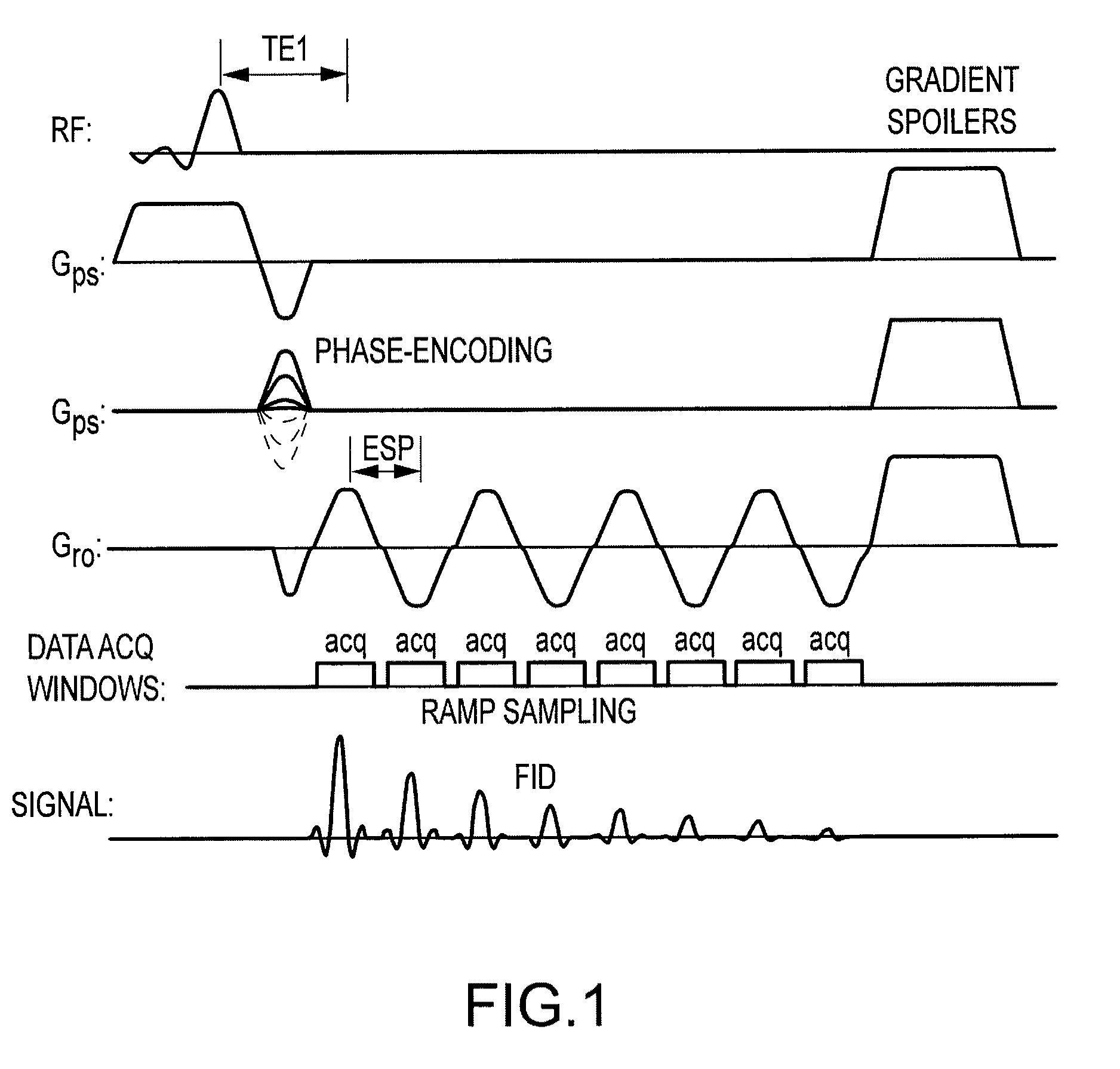
In Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, free induction decay (FID) is the observable NMR signal generated by non-equilibrium nuclear spin magnetization precessing about the magnetic field (conventionally along z). This non-equilibrium magnetization can be induced, generally by applying a pulse of resonant radio-frequency close to the Larmor frequency of the nuclear spins.
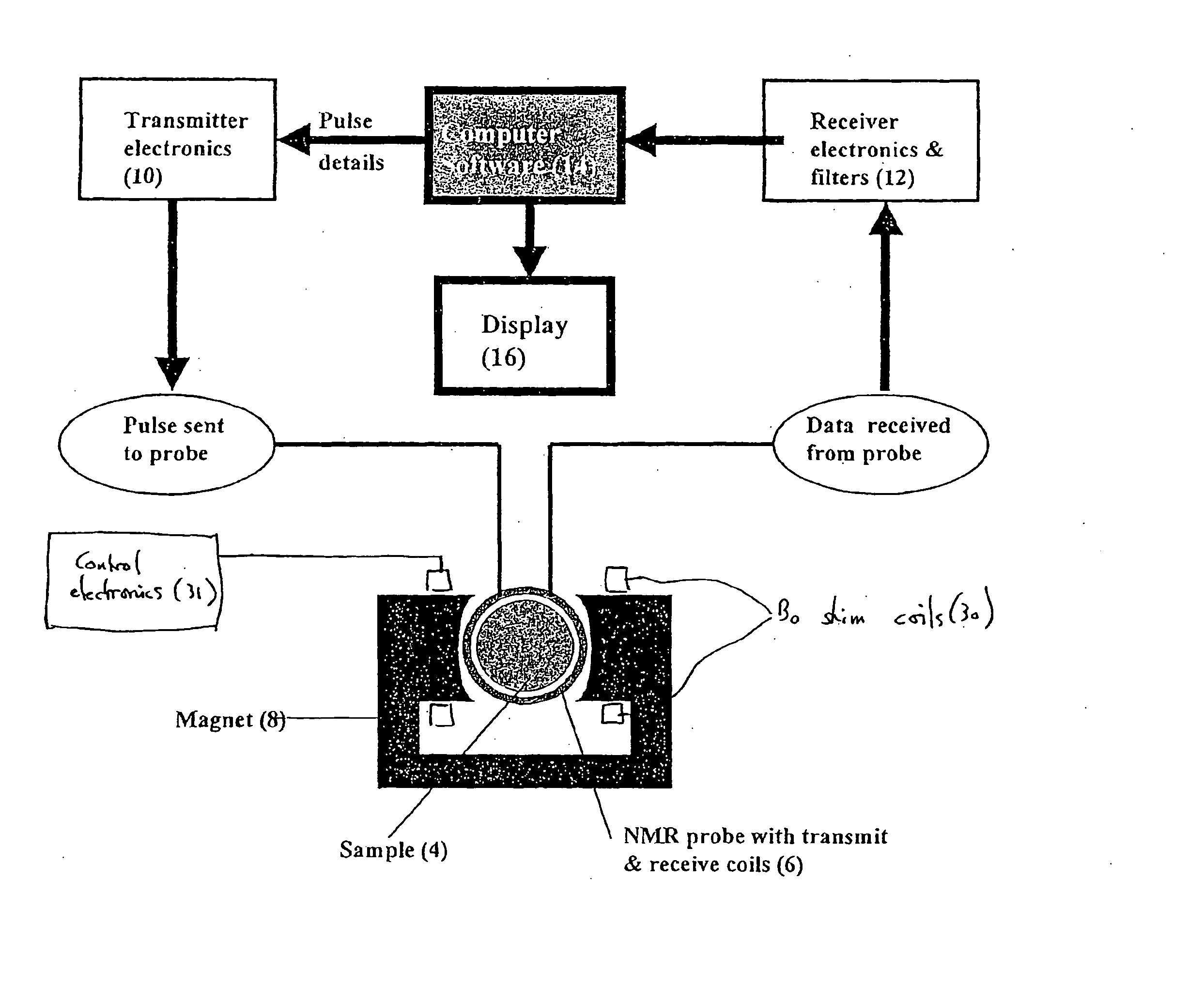
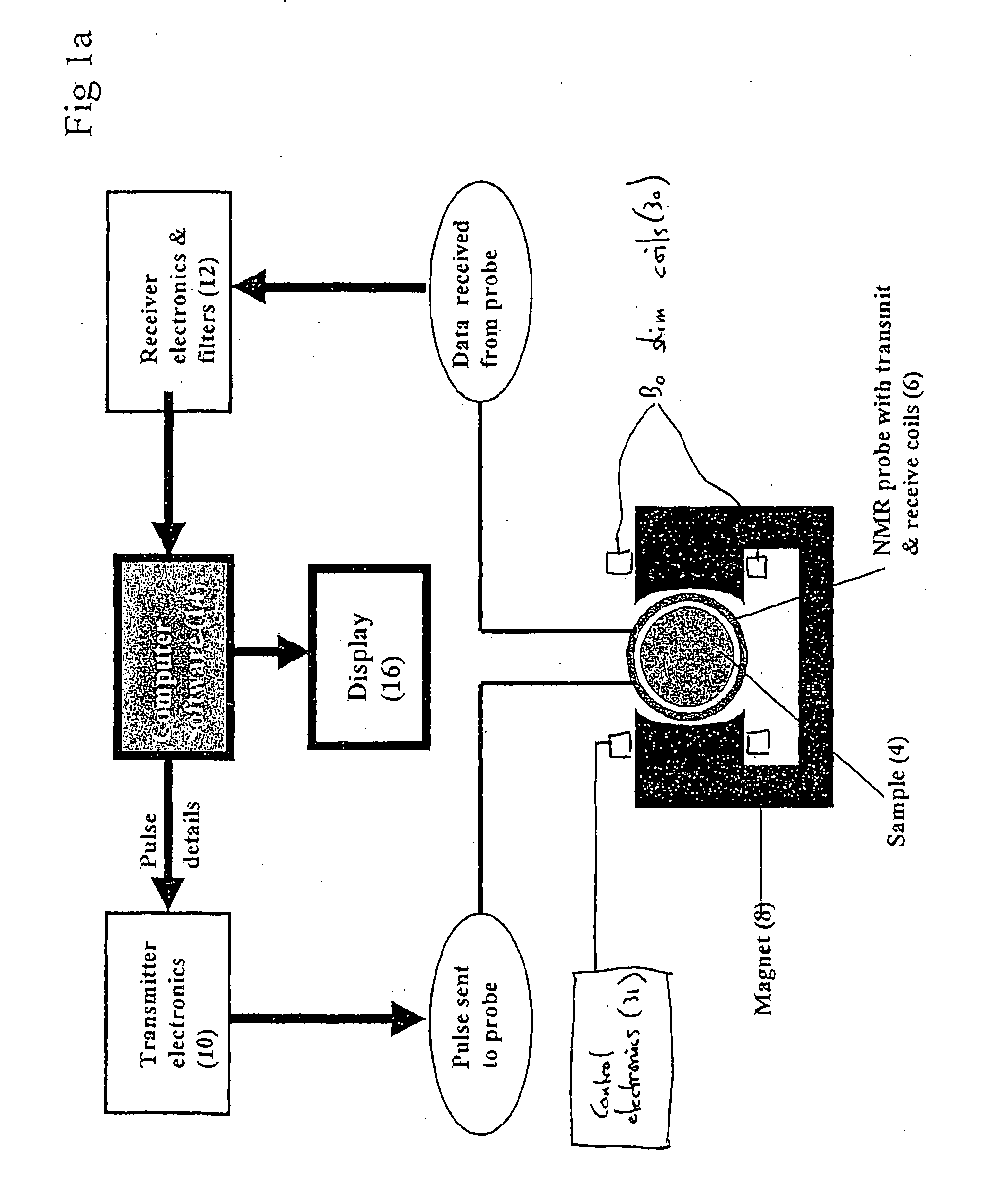
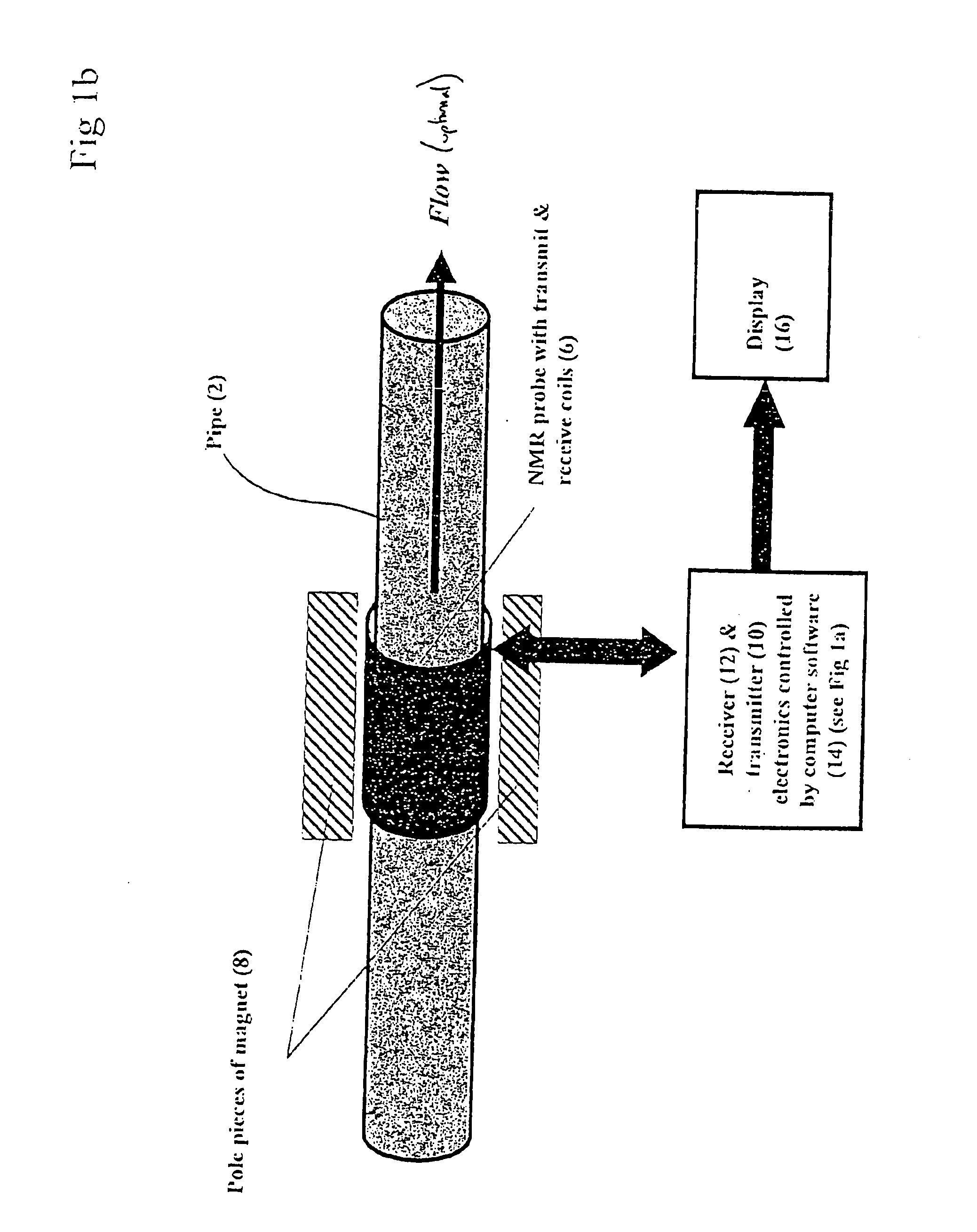
Nuclear magnetic resonance equipment
InactiveUS6958608B2High sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceSpectroscopy
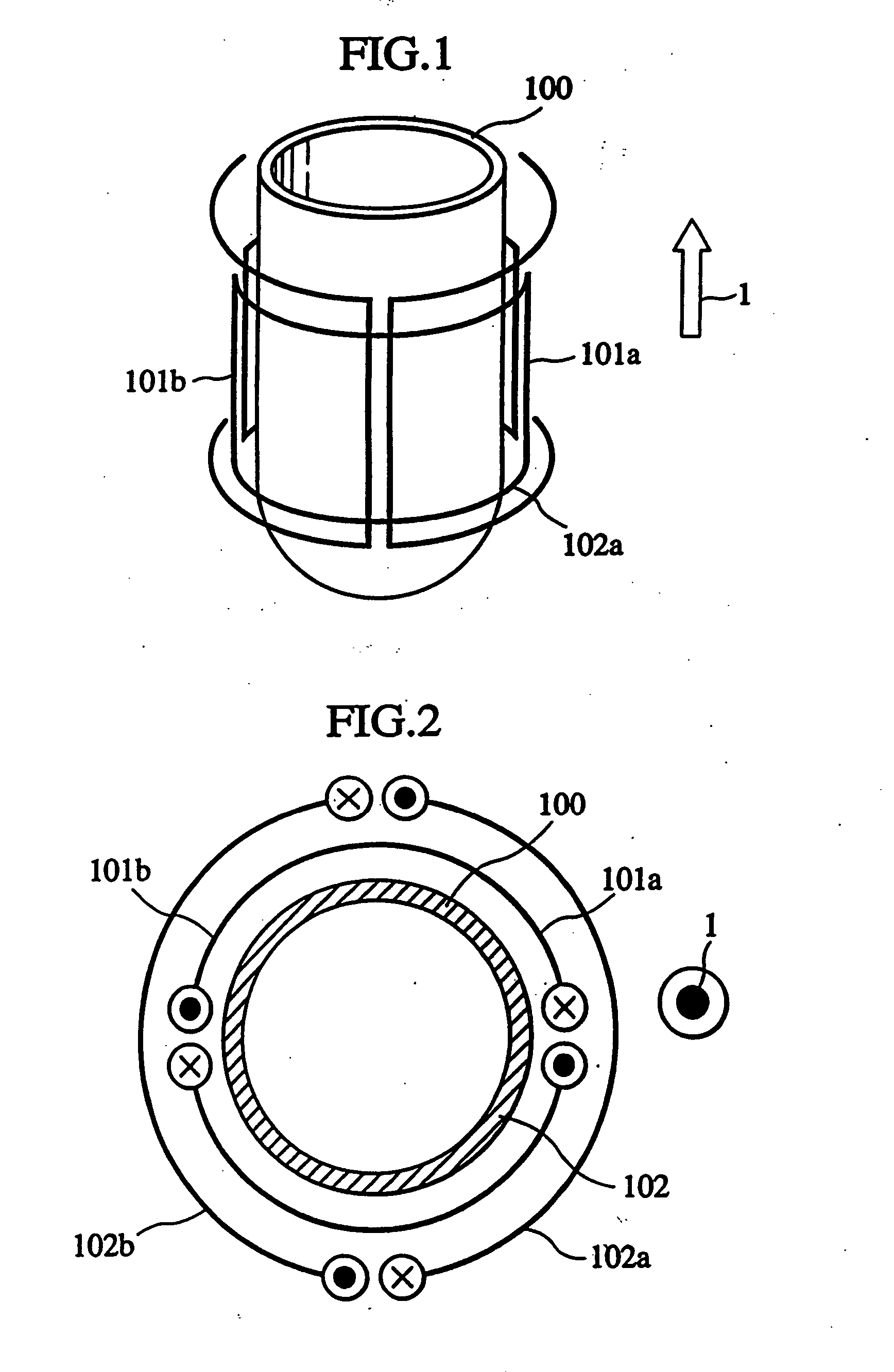
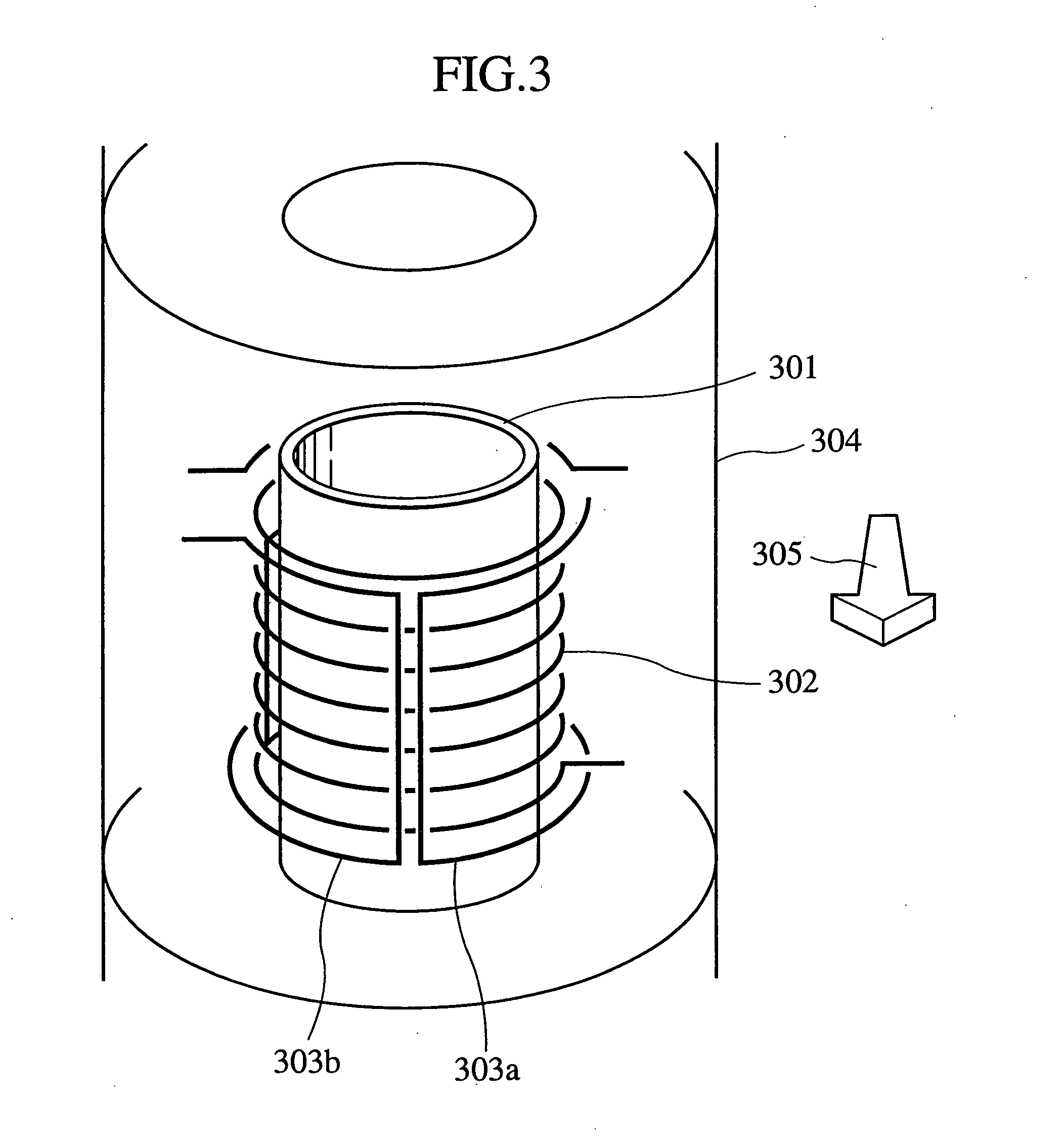
The invention provides nuclear magnetic resonance equipment realizing improved sensitivity of a probe for receiving a free induction decay (FID) signal in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in a high frequency band of 600 MHz or higher. By manufacturing a solenoid coil of a higher filling factor by using a superconductor of extremely low resistance to high frequency current, sensitivity is increased. A superconducting thin film made of magnesium diboride (MgB2) formed on a donut plate-type substrate is disposed so that the film surface becomes parallel with the uniform magnetic field. The object is realized by a probe made by a solenoid coil formed by connecting a plurality of coil parts by capacitive coupling via a normal metal lead.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
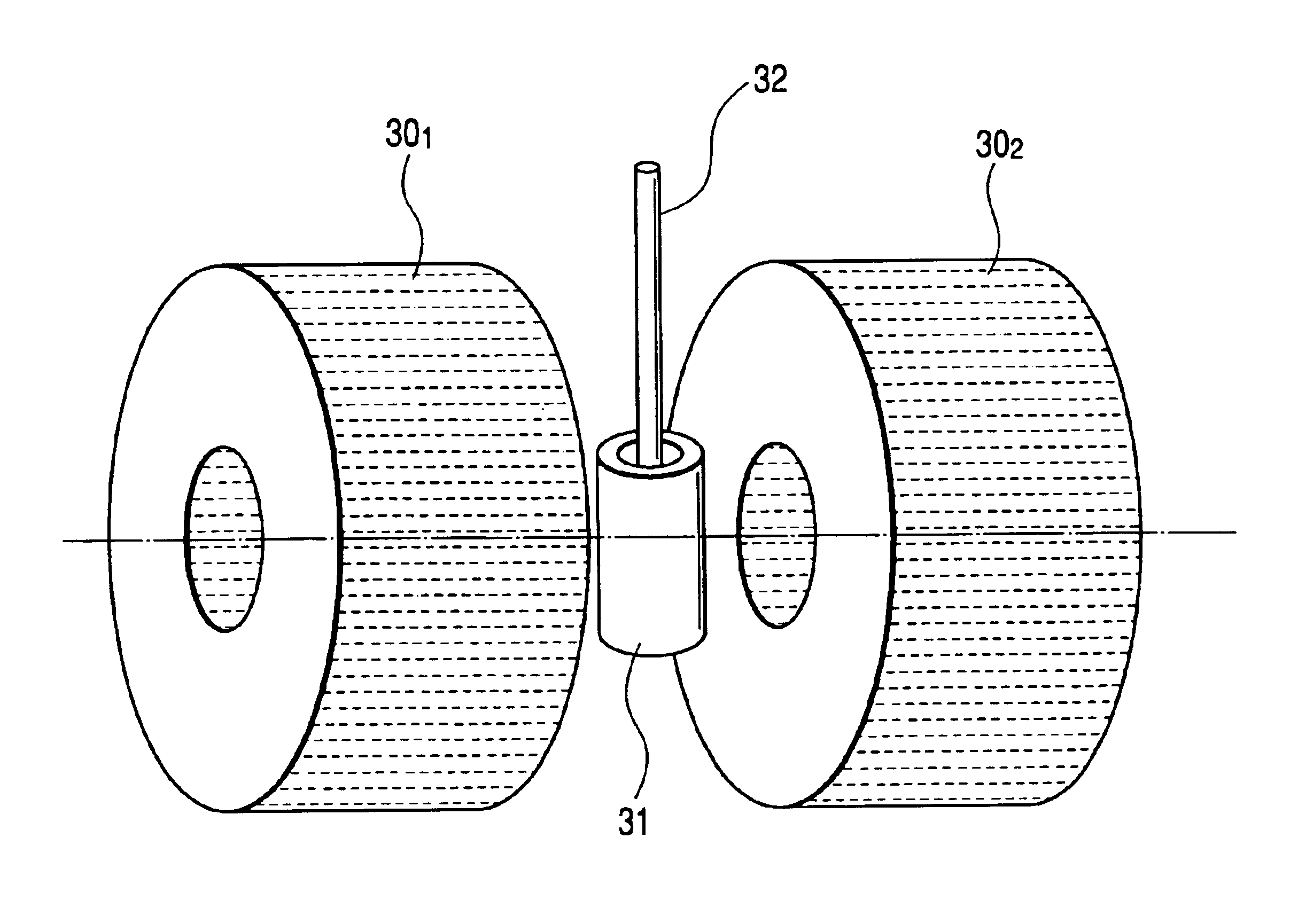
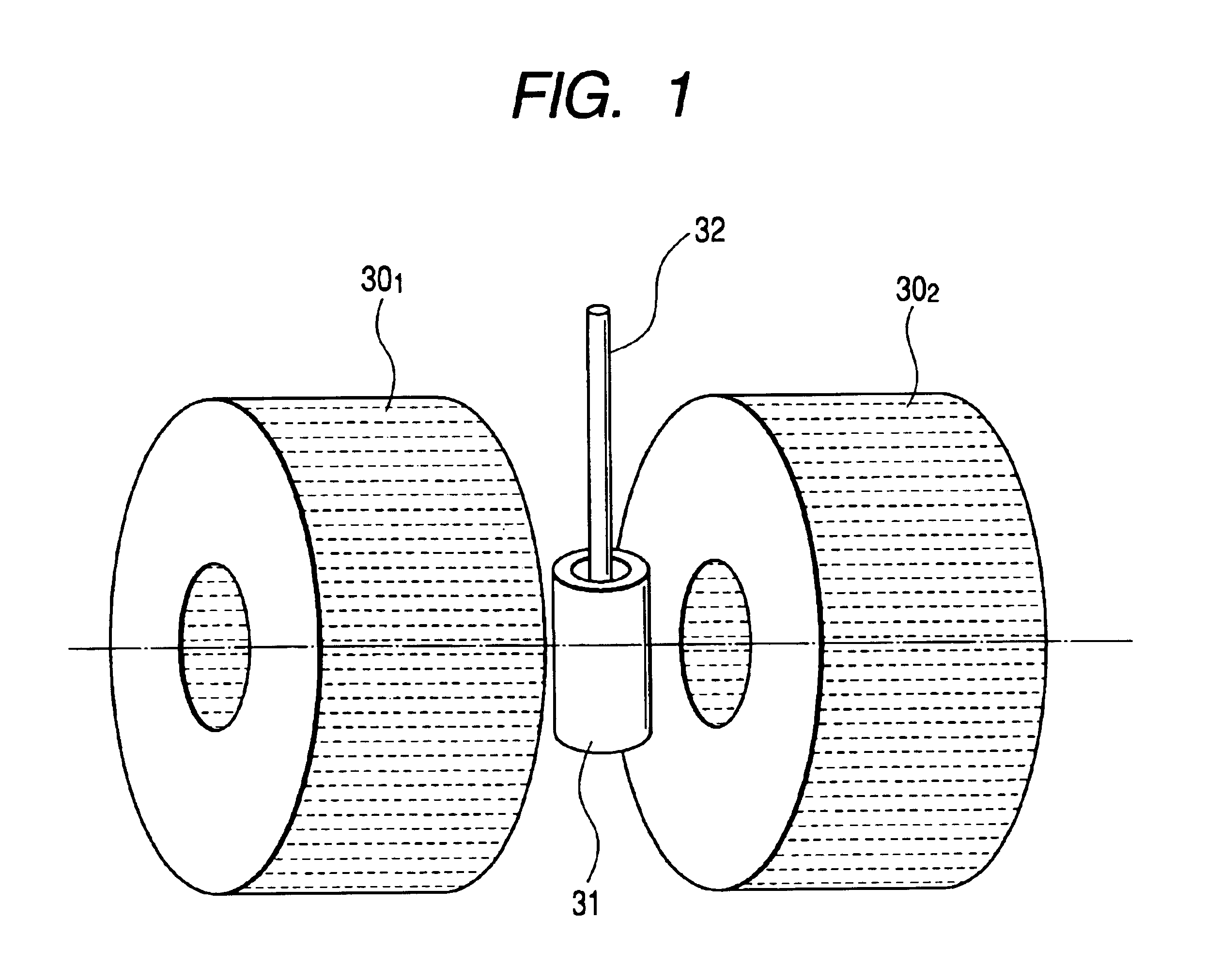
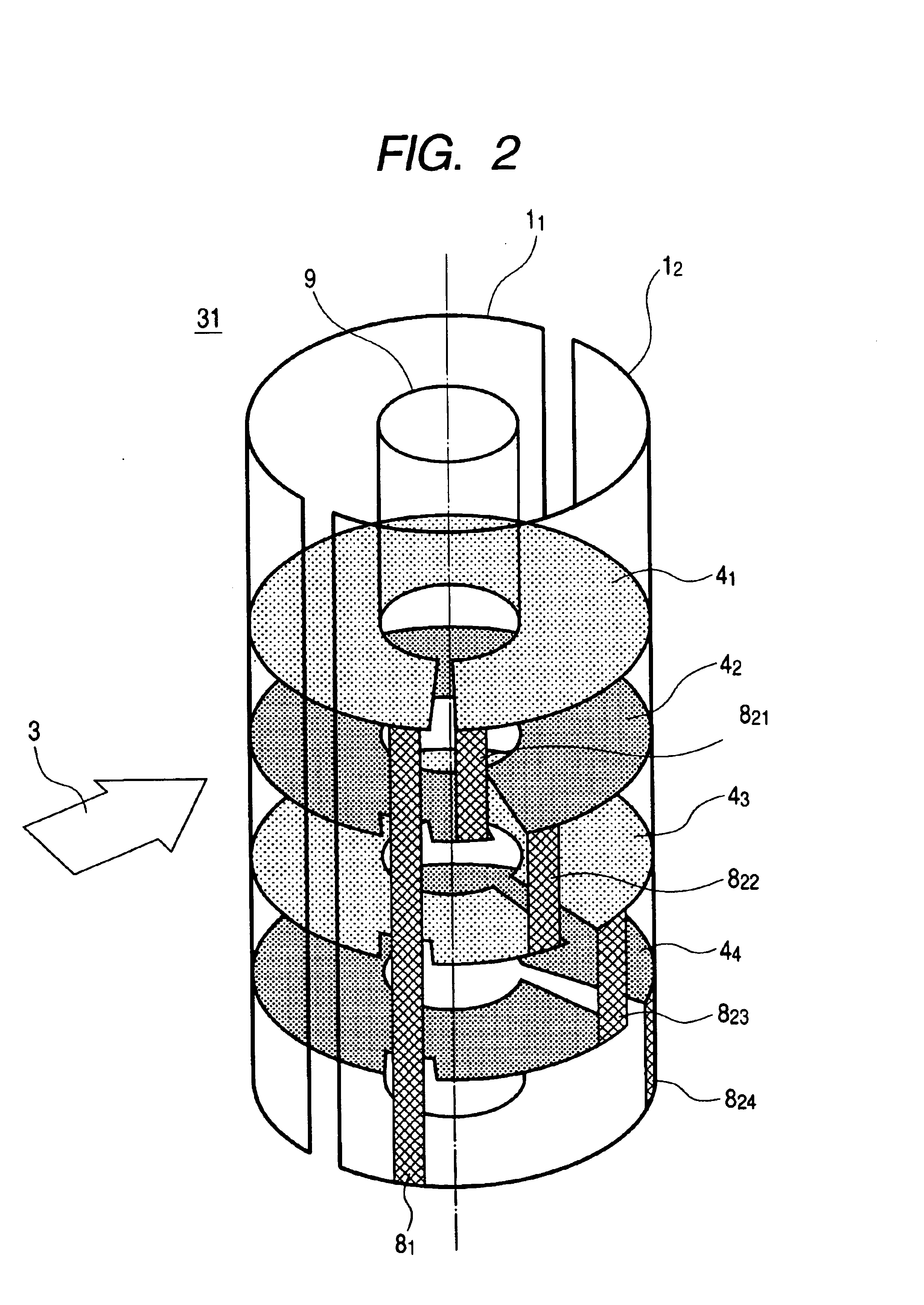
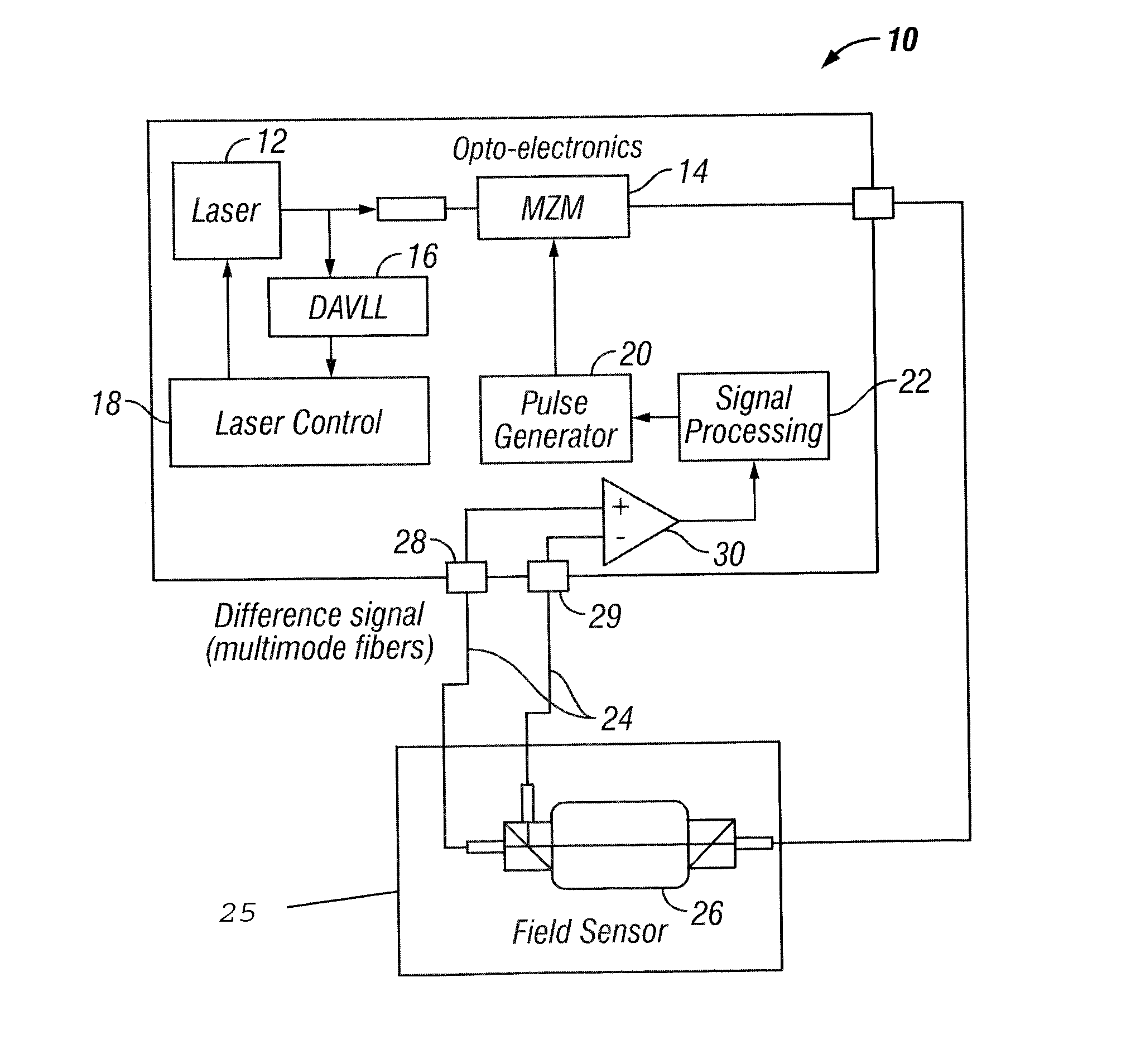
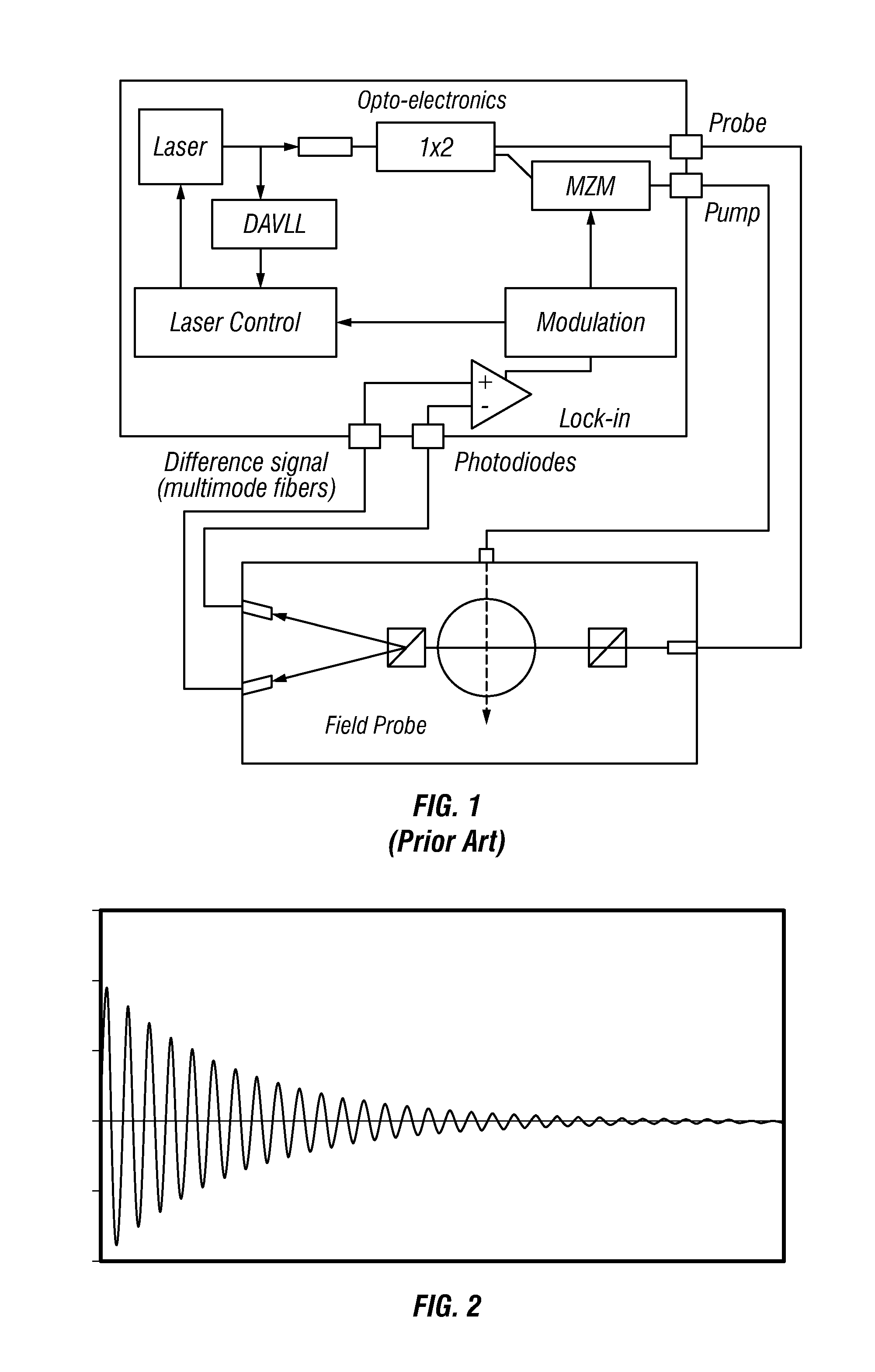
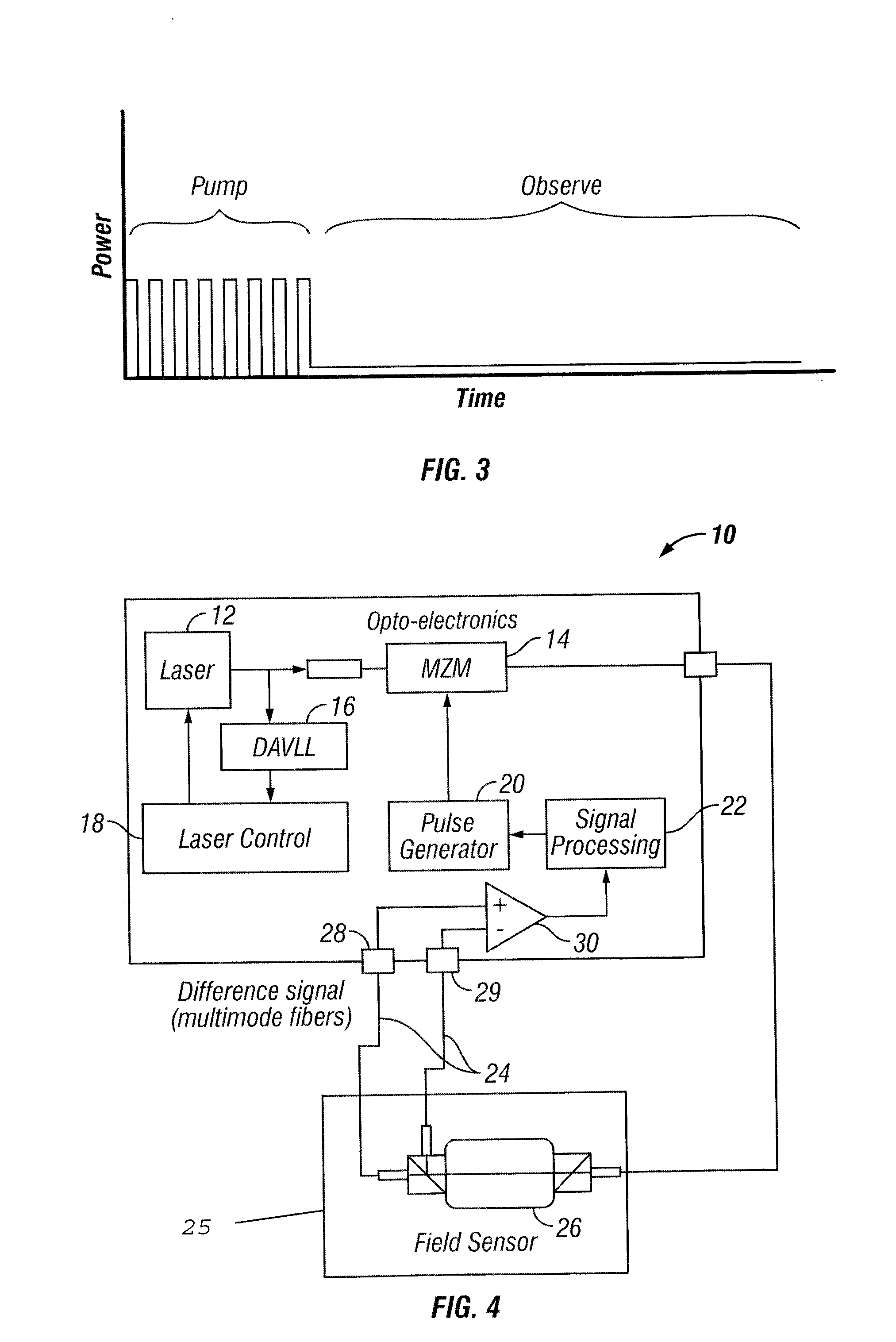
Pulsed free induction decay nonlinear magneto-optical rotation apparatus
ActiveUS8421455B1Electrodynamic magnetometersElectric/magnetic detectionOptoelectronicsSignal processing
A magnetometer and concomitant magnetometry method comprising emitting light from a light source, via a pulse generator pulsing light from the light source, directing the pulsed light to an atomic chamber, employing a field sensor in the atomic chamber, and via a signal processing module receiving a signal from the field sensor.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI +1
Method for fast multi-slice mapping of myelin water fraction
InactiveUS20090312625A1Increasing volume coverageShorten the construction periodMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseMulti slice
Mapping of myelin water content in white matter may provide important information for early diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and the detection of white matter abnormality in other diseases. It is disclosed here that free induction decay (FID) of each voxel at multiple slice locations is acquired in the brain using an echo-planar spectroscopic imaging (EPSI) pulse sequence. The multi-slice EPSI acquisition is designed to have a short first echo time (˜2 ms) and echo-spacing (˜1 ms) in order to acquire multiple sampling points during the fast decay of the myelin water signal. Multi-compartment analysis is then applied to the FID in each pixel using a 3-pool model of white matter to obtain quantitative maps of the myelin water fraction. Using this technique, the MR data for whole brain mapping of the myelin water can be acquired in less than 10 minutes, making this technique feasible for routine clinical applications.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy pulse sequence, acquisition, and processing system and method
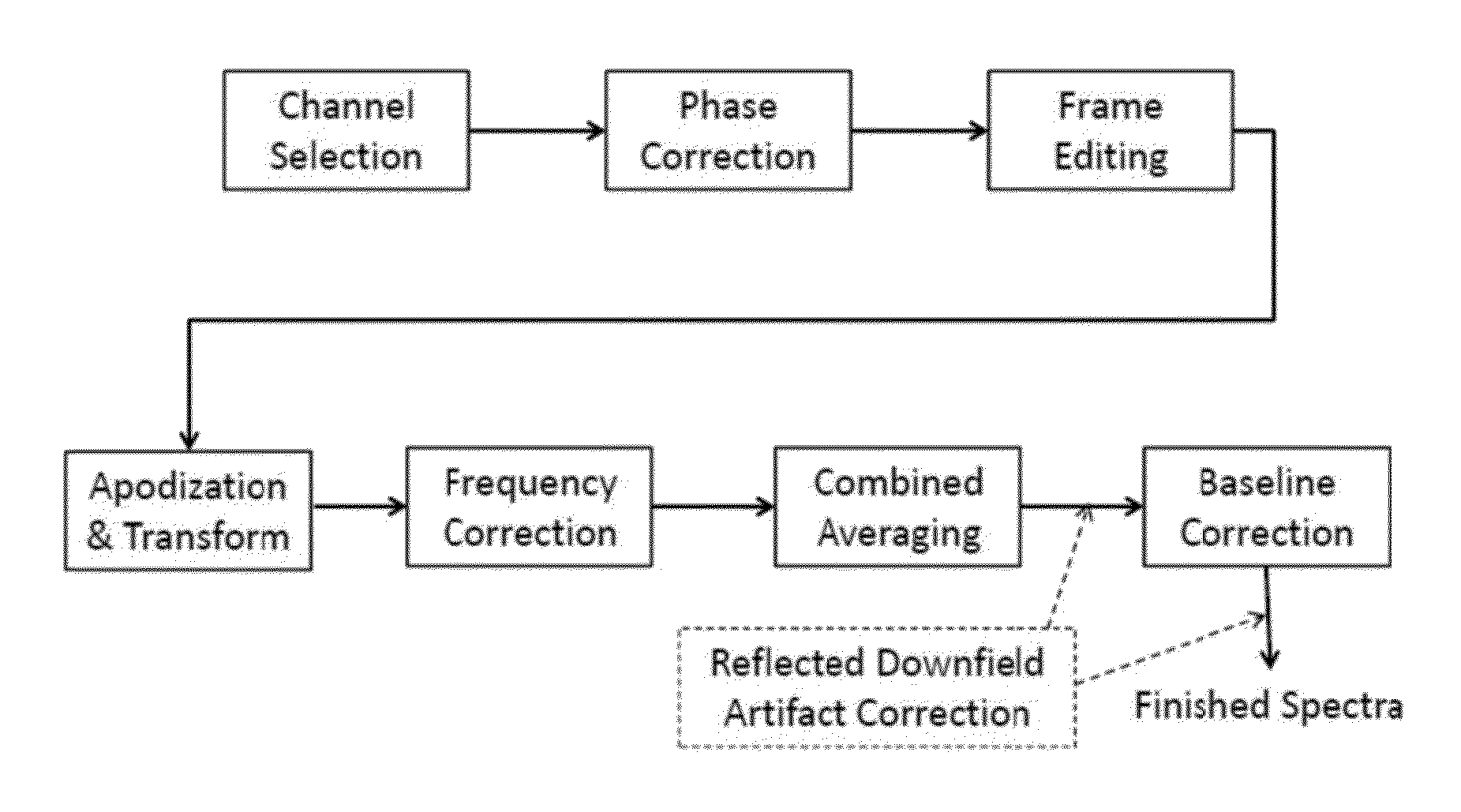
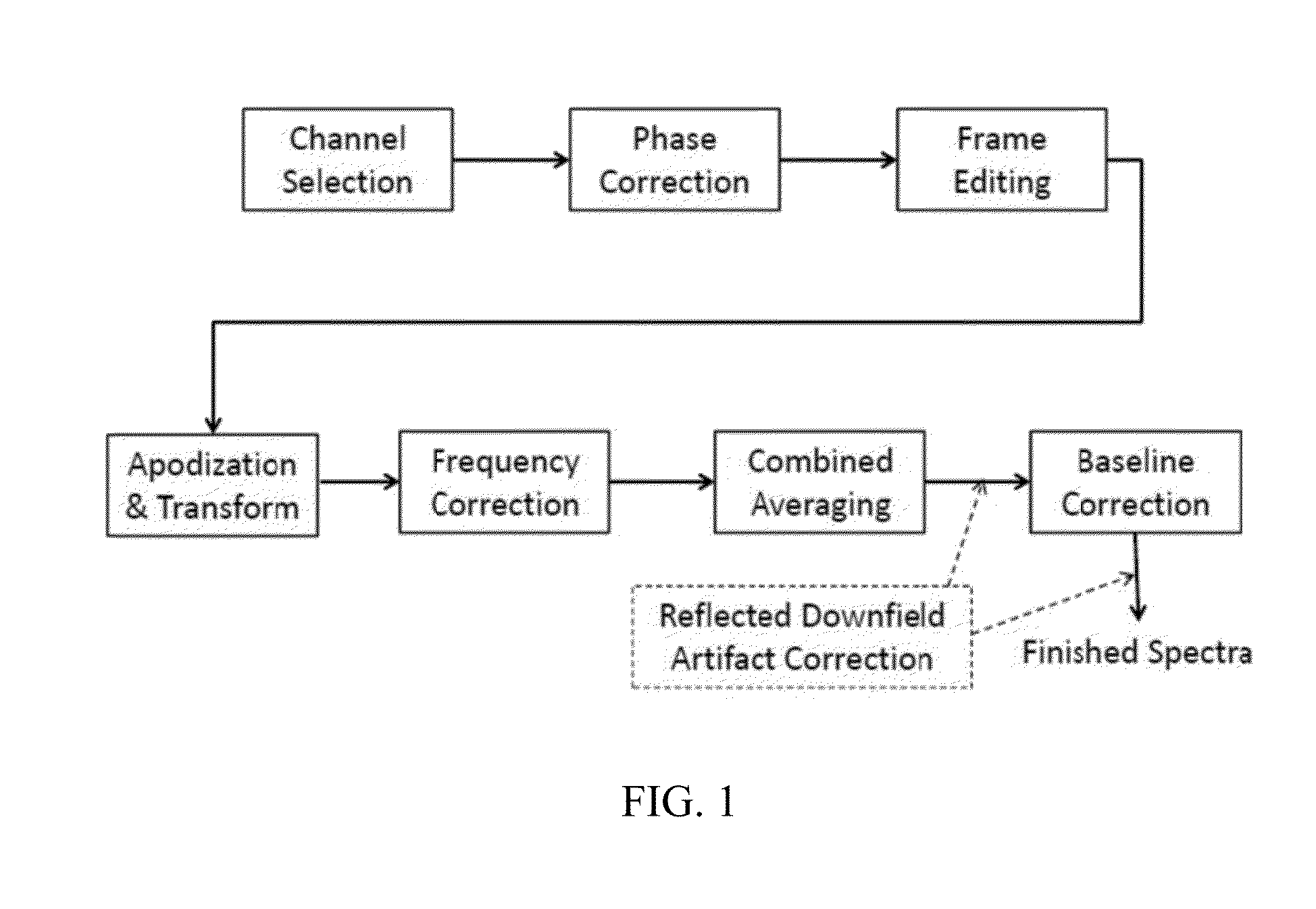
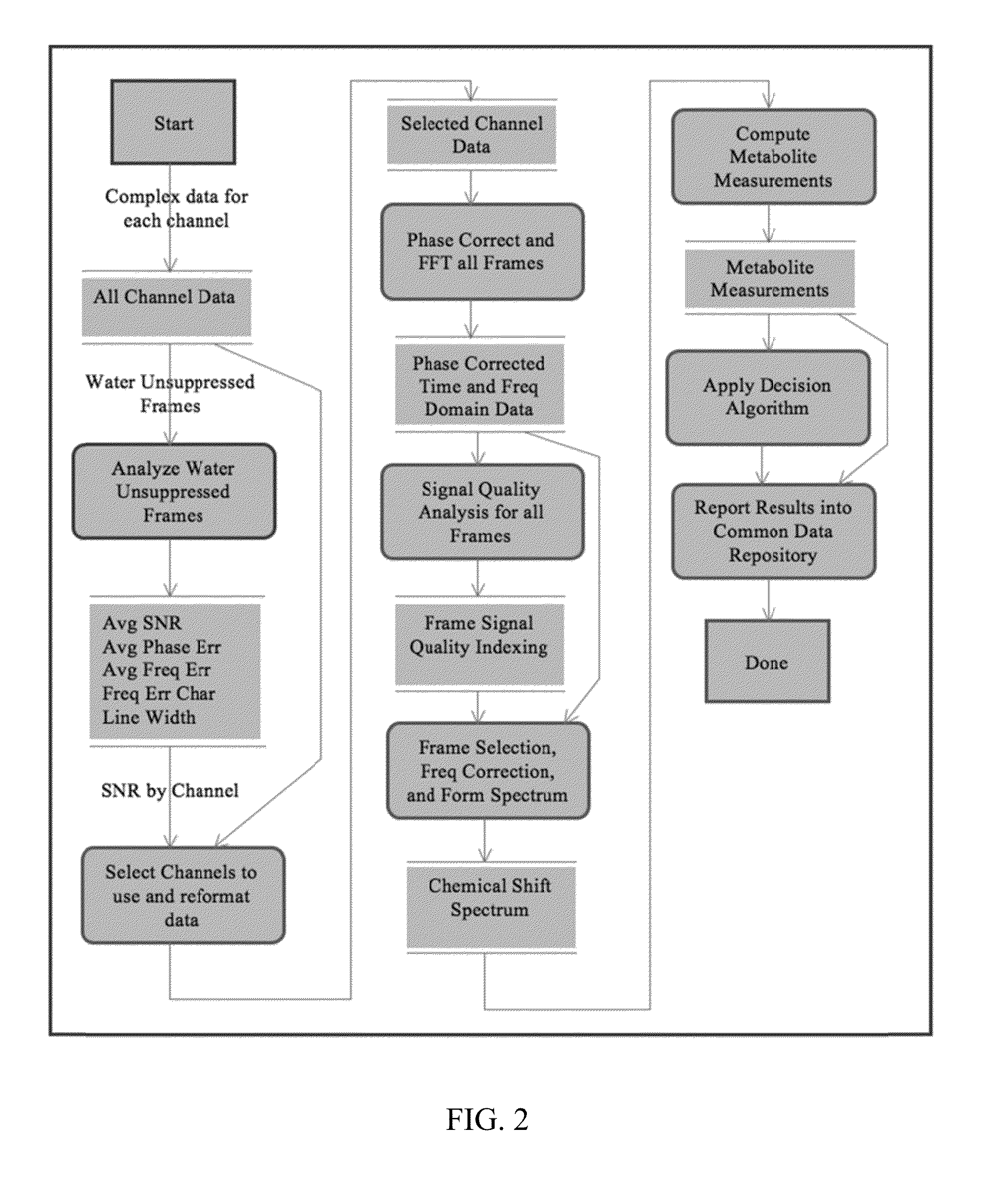
ActiveUS8965094B2Enhanced frequency shift artifact correctionEliminate the effects ofImage analysisDiagnostics using spectroscopyMagnetic resonance spectroscopicMultiple frame
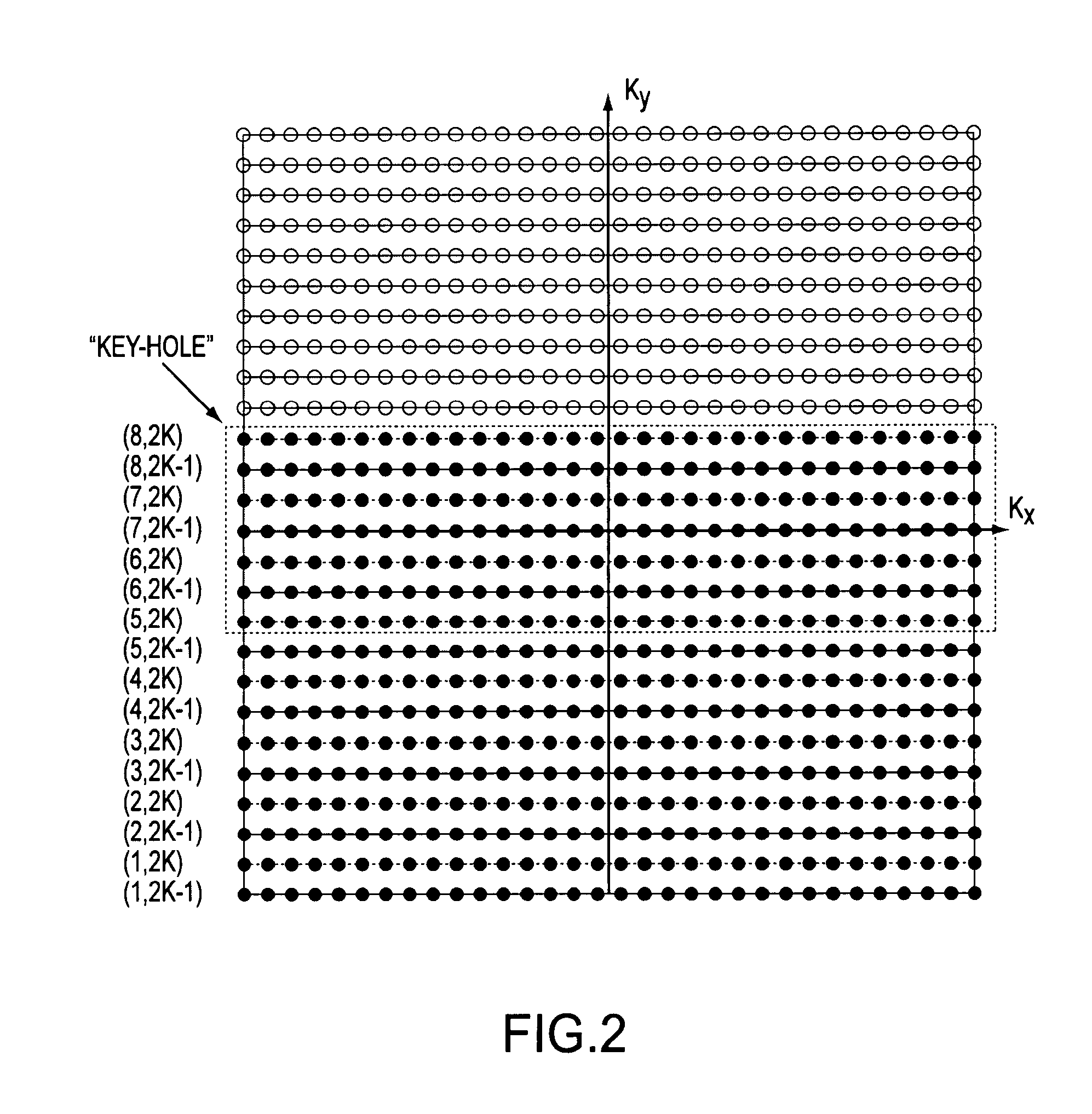
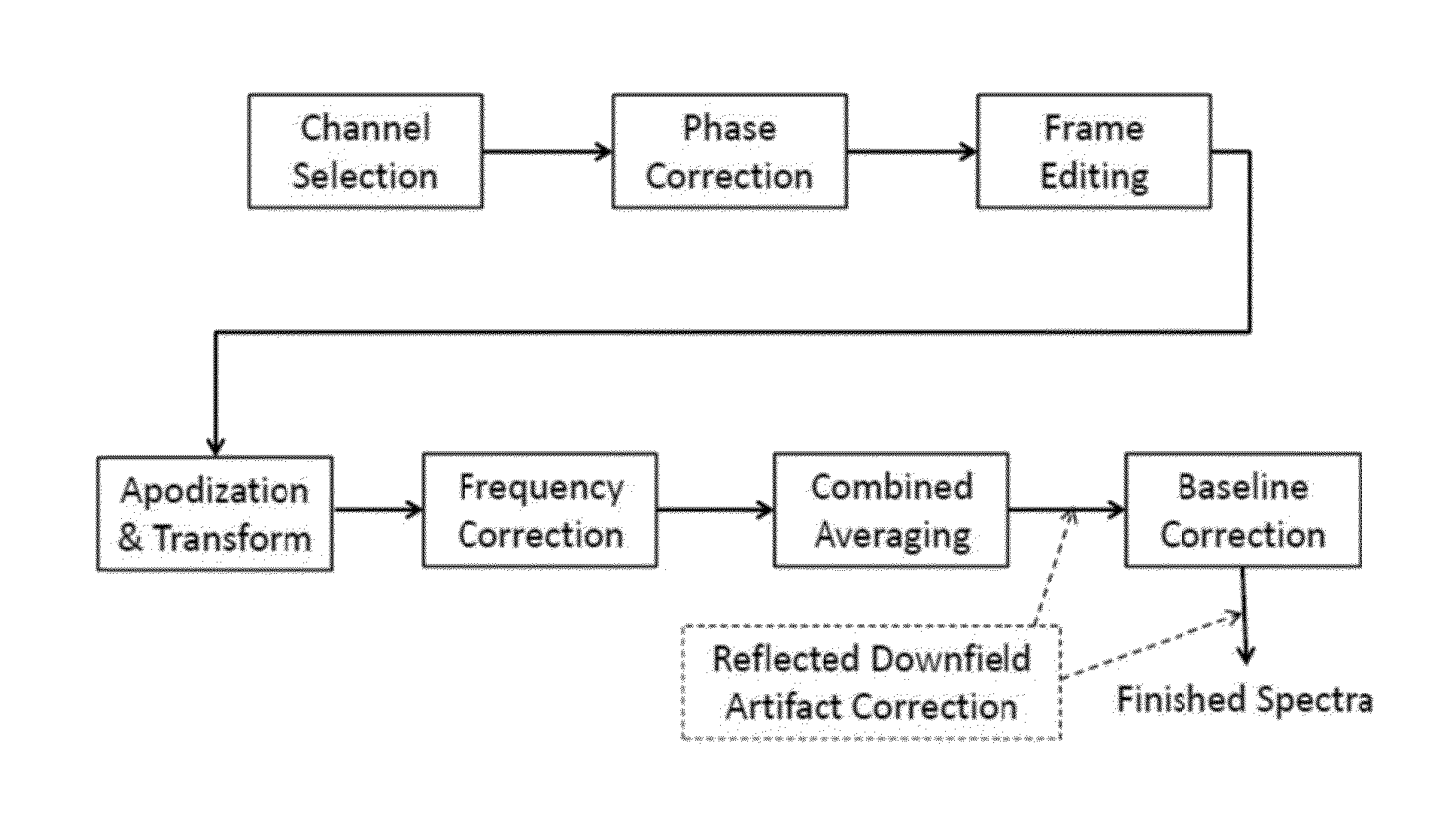
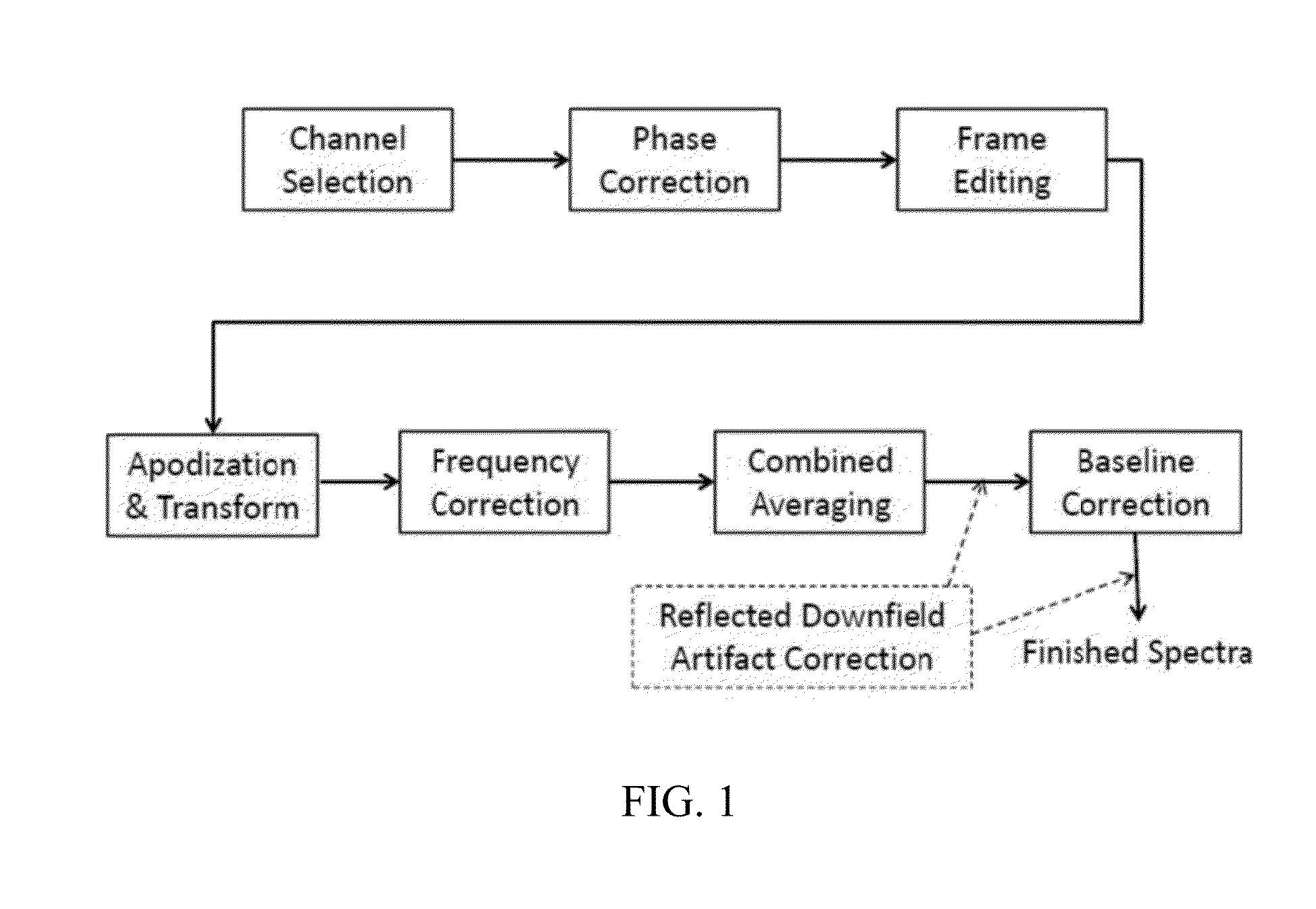
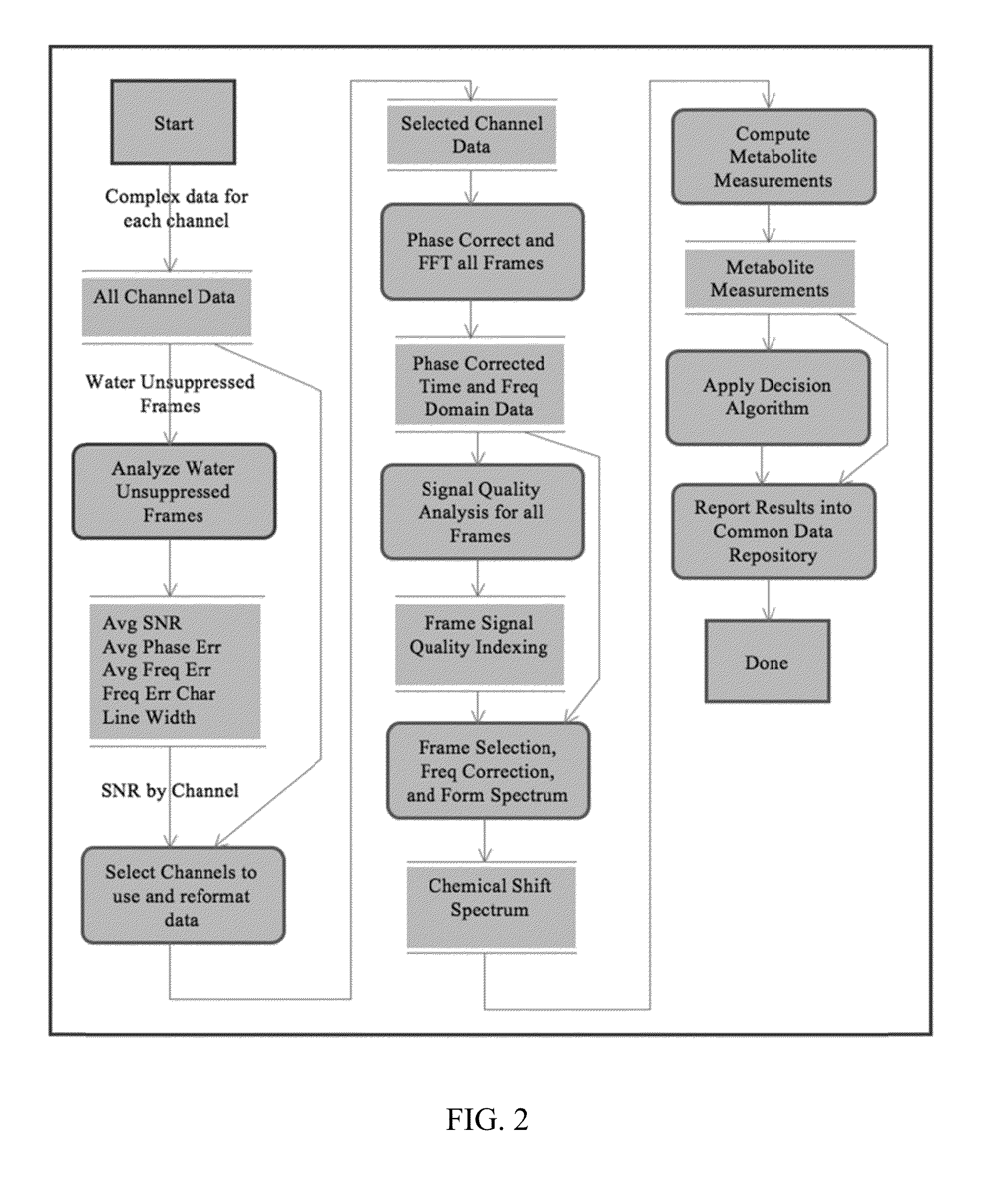
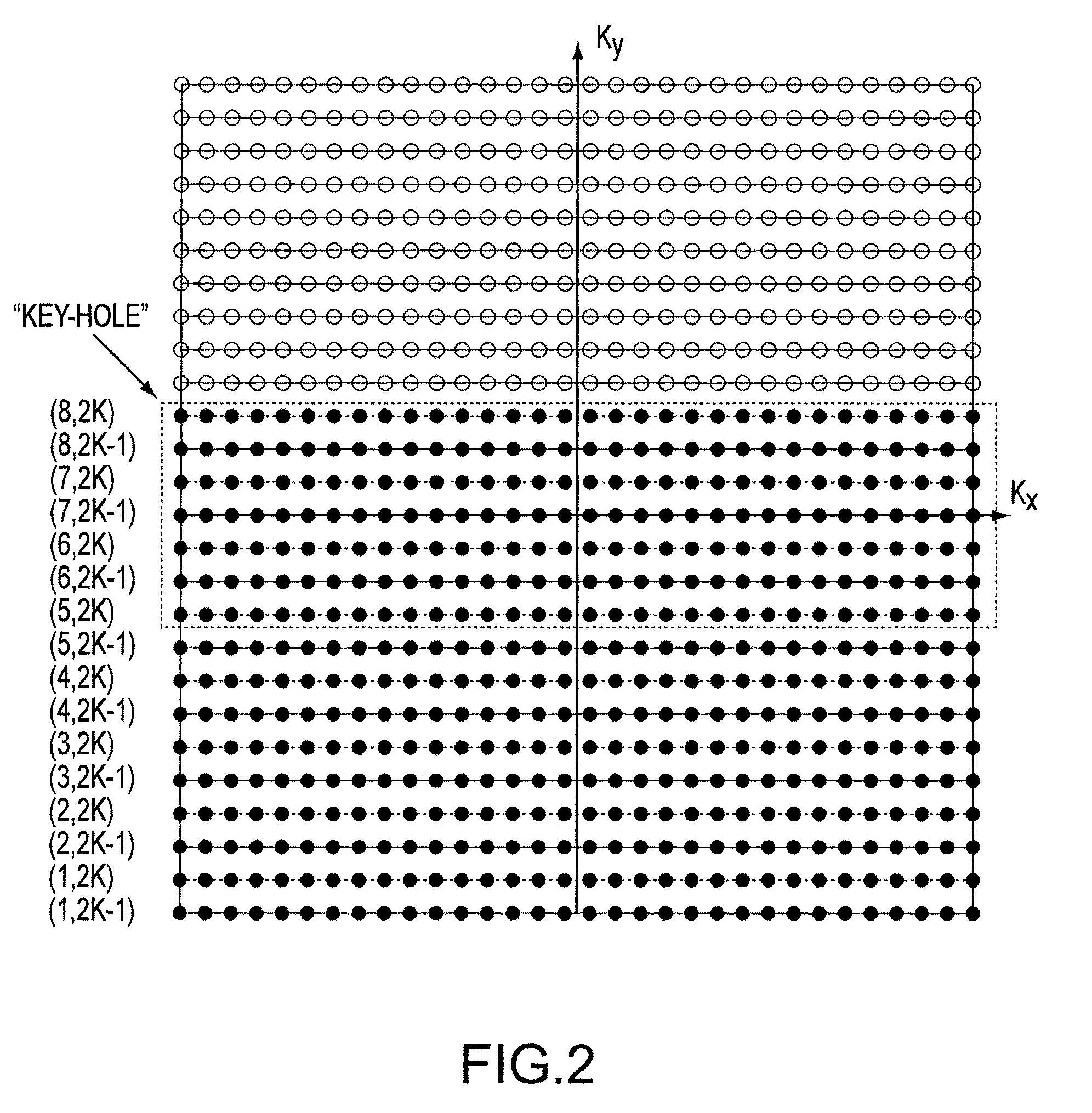
Systems and methods are provided for processing a set of multiple serially acquired magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) free induction decay (FID) frames from a multi-frame MRS acquisition series from a region of interest (ROI) in a subject, and for providing a post-processed MRS spectrum. Processing parameters are dynamically varied while measuring results to determine the optimal post-processed results. Spectral regions opposite water from chemical regions of interest are evaluated and used in at least one processing operation. Frequency shift error is estimated via spectral correlation between free induction decay (FID) frames and a reference spectrum. Multiple groups of FID frames within the acquired set are identified to different phases corresponding with a phase step cycle of the acquisition. Baseline correction is also performed via rank order filter (ROF) estimate and a polynomial fit. Sections of the ROF may be excluded from the polynomial fit, such as for example sections determined to be associated with relevant spectral peaks.
Owner:ACLARION INC
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy pulse sequence, acquisition, and processing system and method
ActiveUS20140064586A1Enhanced frequency shift artifact correctionEliminate the effects ofImage analysisDiagnostics using spectroscopyPulse sequenceHandling system
Systems and methods are provided for processing a set of multiple serially acquired magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) free induction decay (FID) frames from a multi-frame MRS acquisition series from a region of interest (ROI) in a subject, and for providing a post-processed MRS spectrum. Processing parameters are dynamically varied while measuring results to determine the optimal post-processed results. Spectral regions opposite water from chemical regions of interest are evaluated and used in at least one processing operation. Frequency shift error is estimated via spectral correlation between free induction decay (FID) frames and a reference spectrum. Multiple groups of FID frames within the acquired set are identified to different phases corresponding with a phase step cycle of the acquisition. Baseline correction is also performed via rank order filter (ROF) estimate and a polynomial fit. Sections of the ROF may be excluded from the polynomial fit, such as for example sections determined to be associated with relevant spectral peaks.
Owner:ACLARION INC
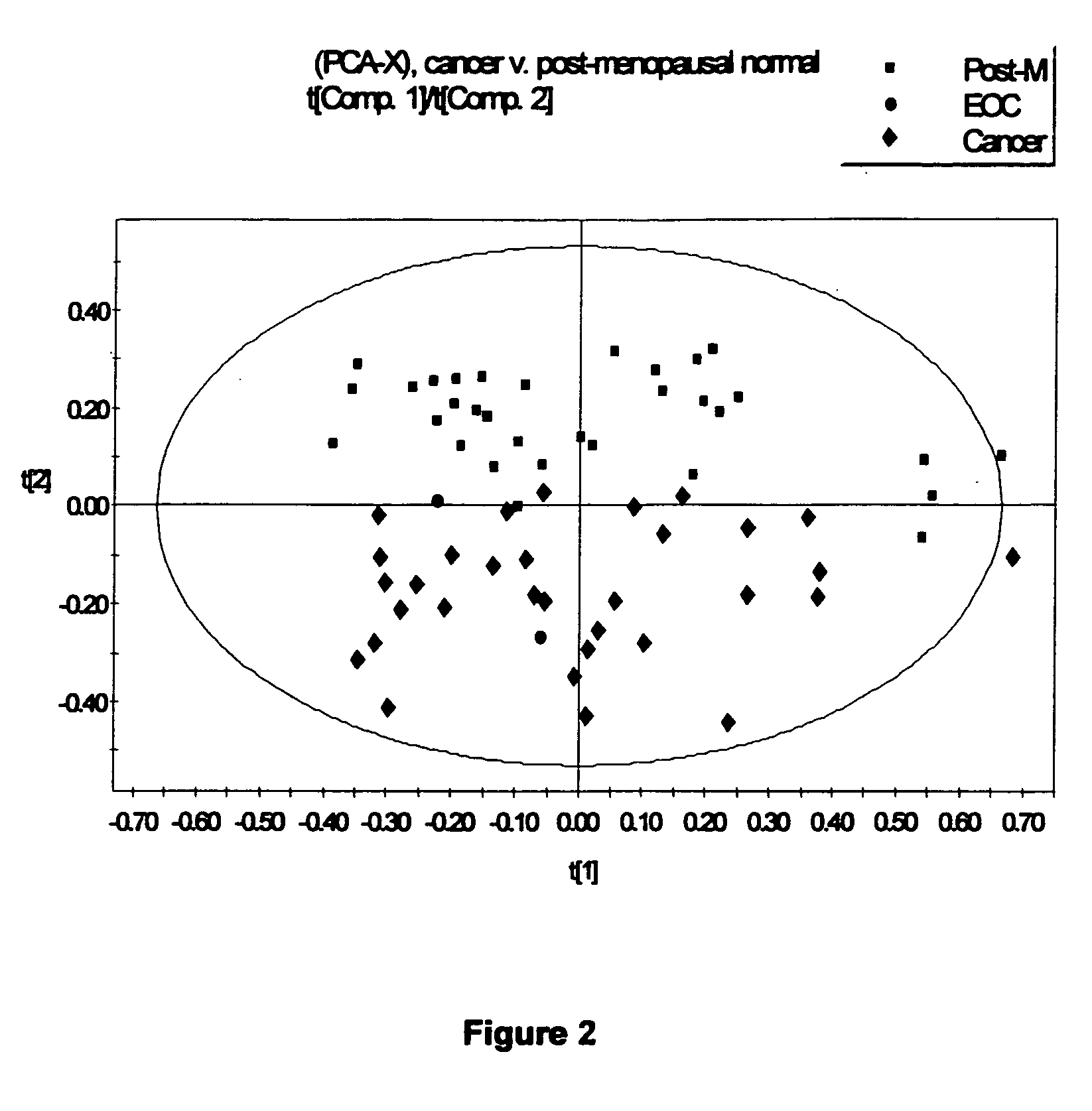
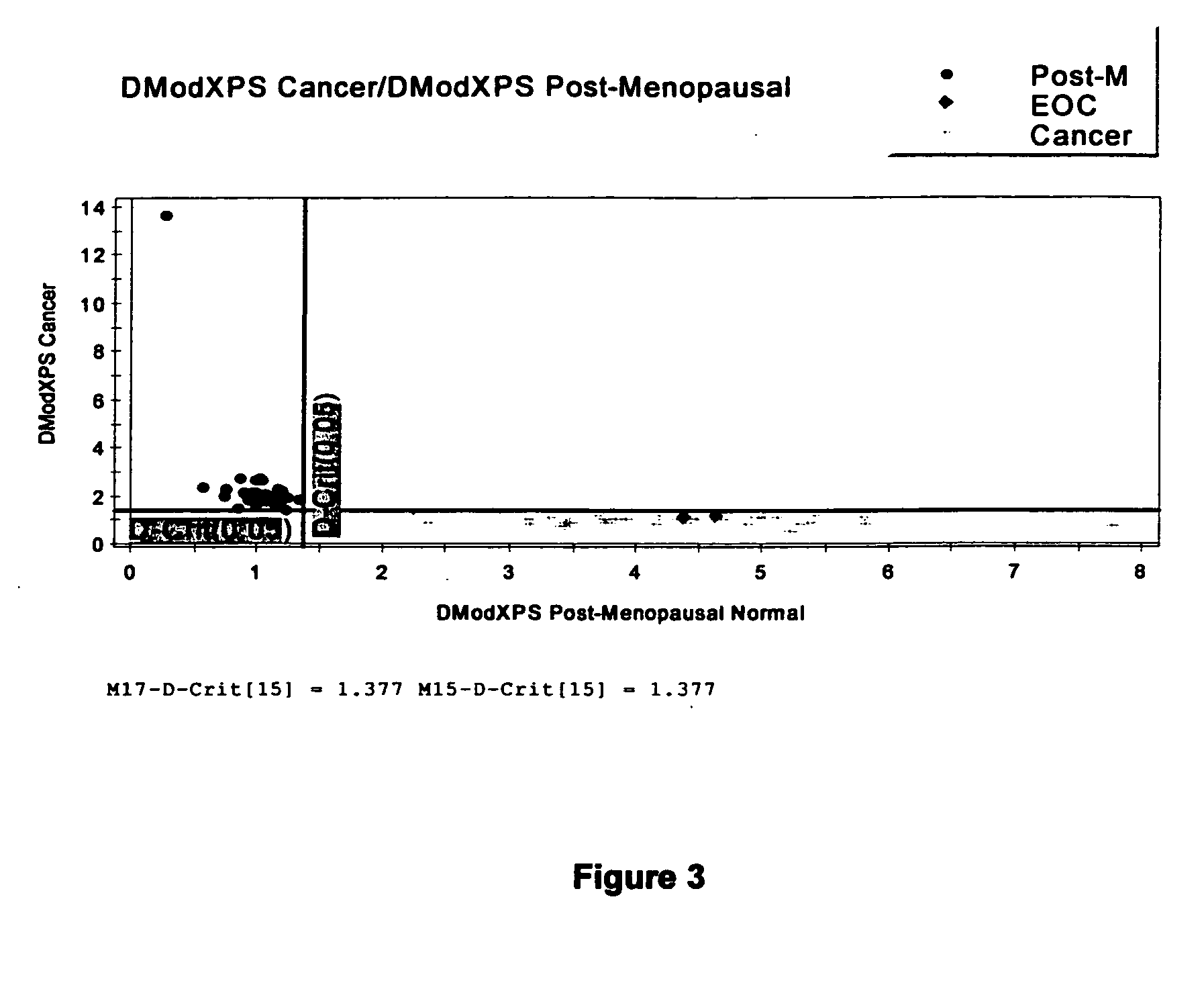
Early detection of cancer of specific type using 1HNMR metabonomics
InactiveUS20050170441A1Biological testingSpecial data processing applicationsPrincipal component analysisAbnormal cell
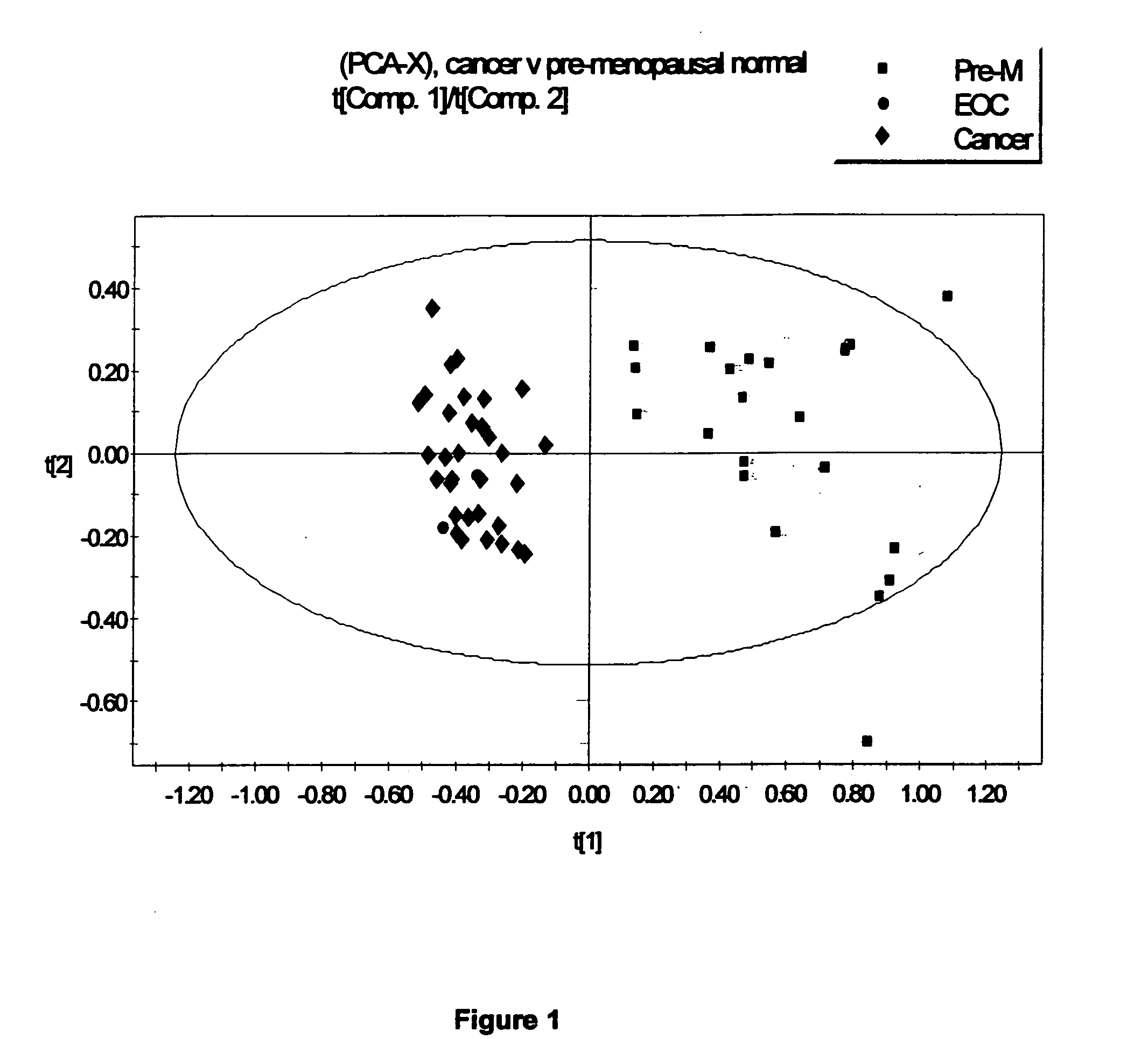
A method for determining whether a patient has a particular type of cancer which comprises: a. obtaining an ascites, abnormal cell cellular fluid or serum sample from the patient; b. diluting the sample with D2O; c. subjecting the sample to 1HNMR to obtain a series of free induction decay outputs (FID's); d. mathematically modifying the data to obtain 1HNMR spectra; e. correcting the 1HNMR spectra for phase and baseline distortions; f. data reducing the corrected 1HNMR spectra to obtain a plurality of integral spectral segments; g. compensating for effects of variation in suppression of water resonance; h. normalizing the resulting data to total spectral area to obtain normalized 1HNMR spectra; i. subjecting the normalized 1HNMR spectra to principal component analysis to obtain normalized data; and j. plotting and comparing the normalized data with corresponding control data indicating the presence of the particular type of cancer to determine whether the sample indicates that the patient has the particular type of cancer.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
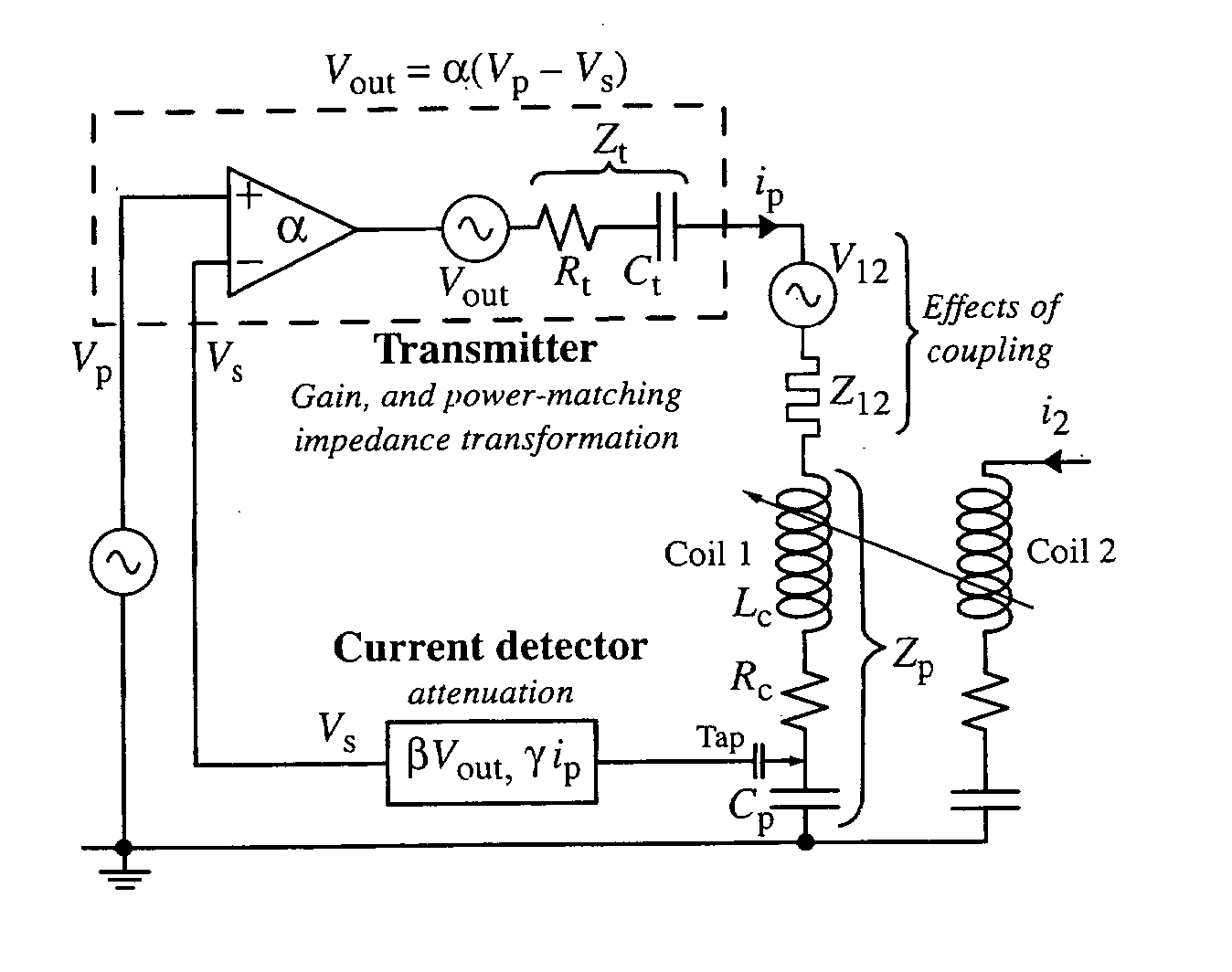
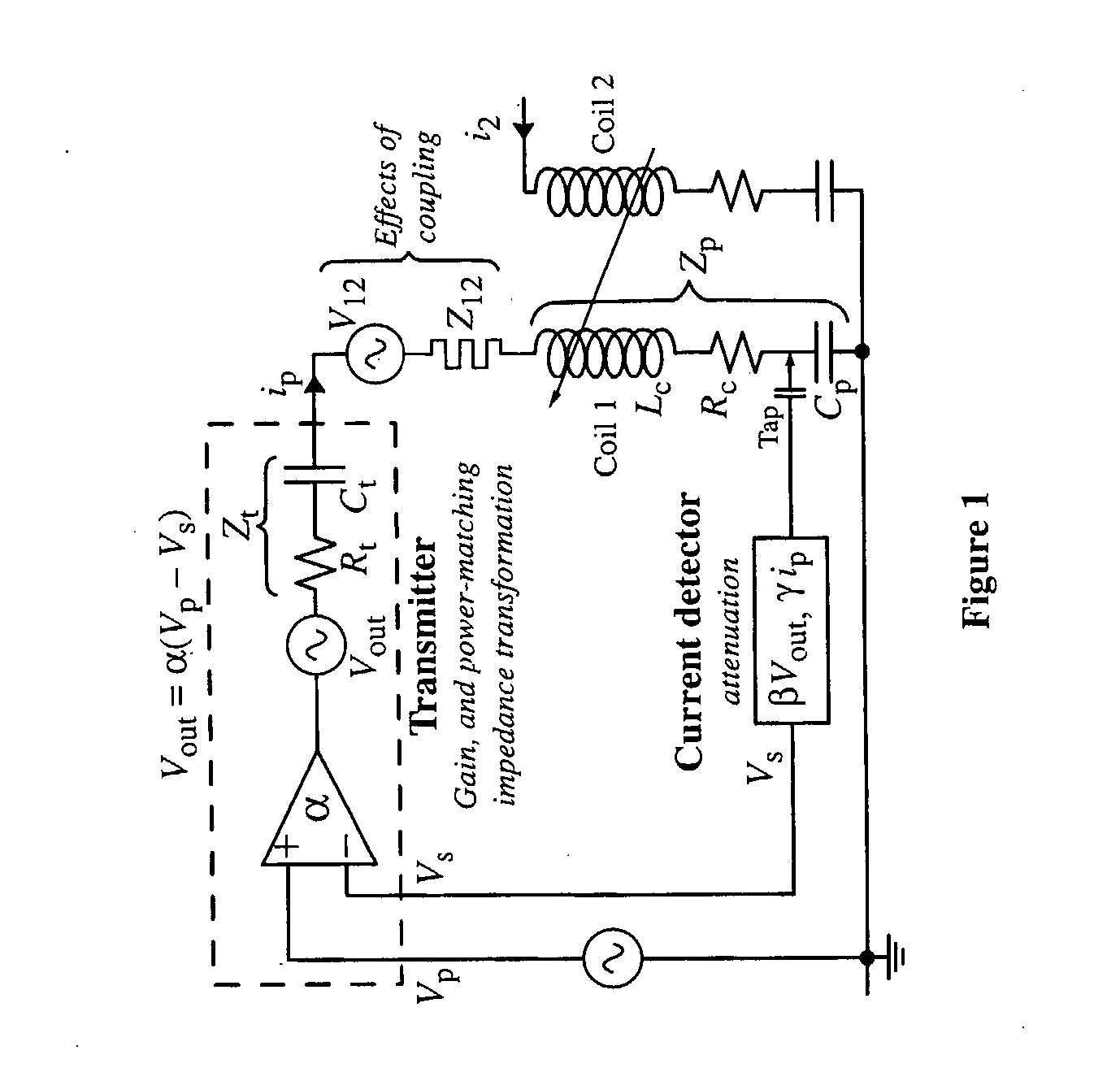
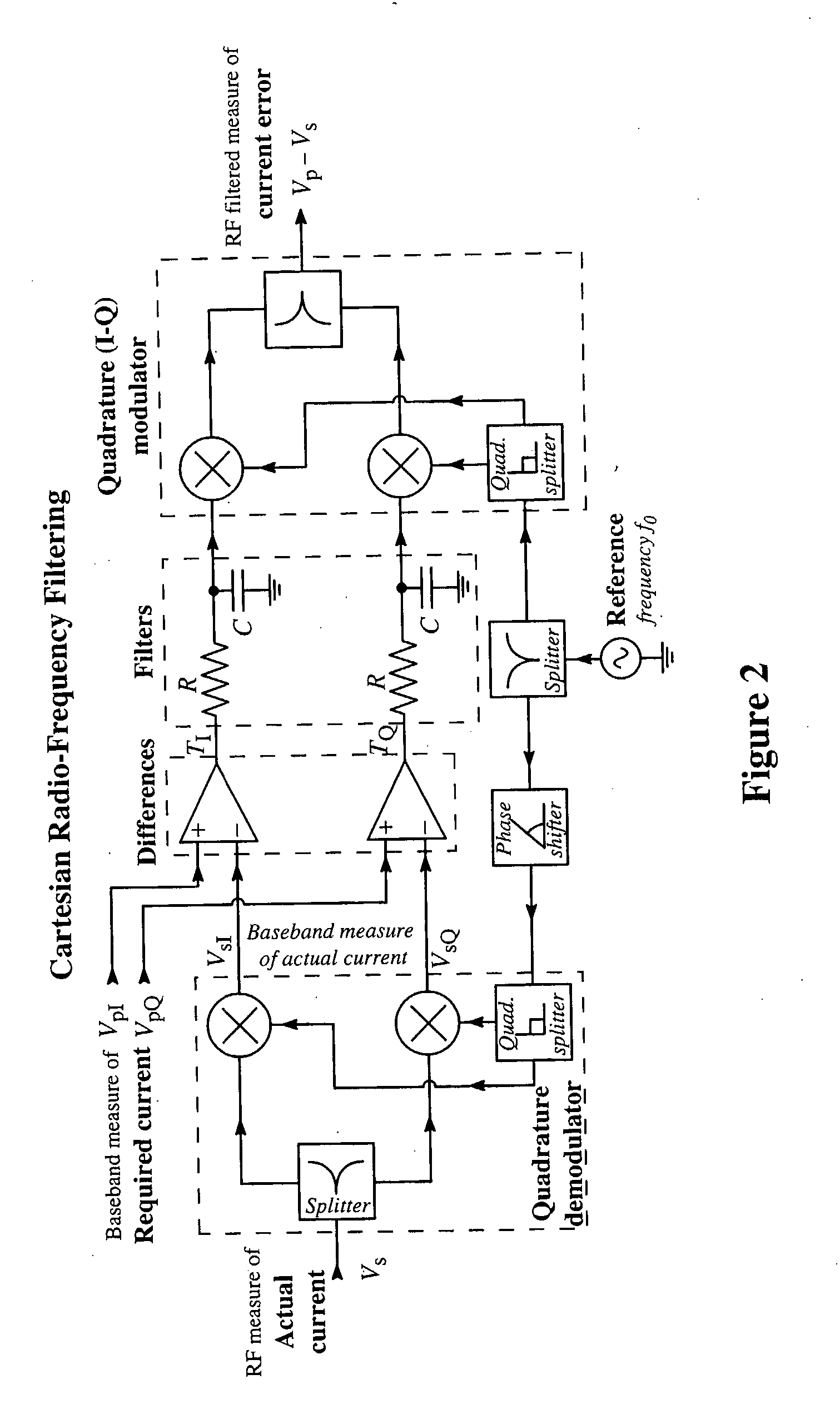
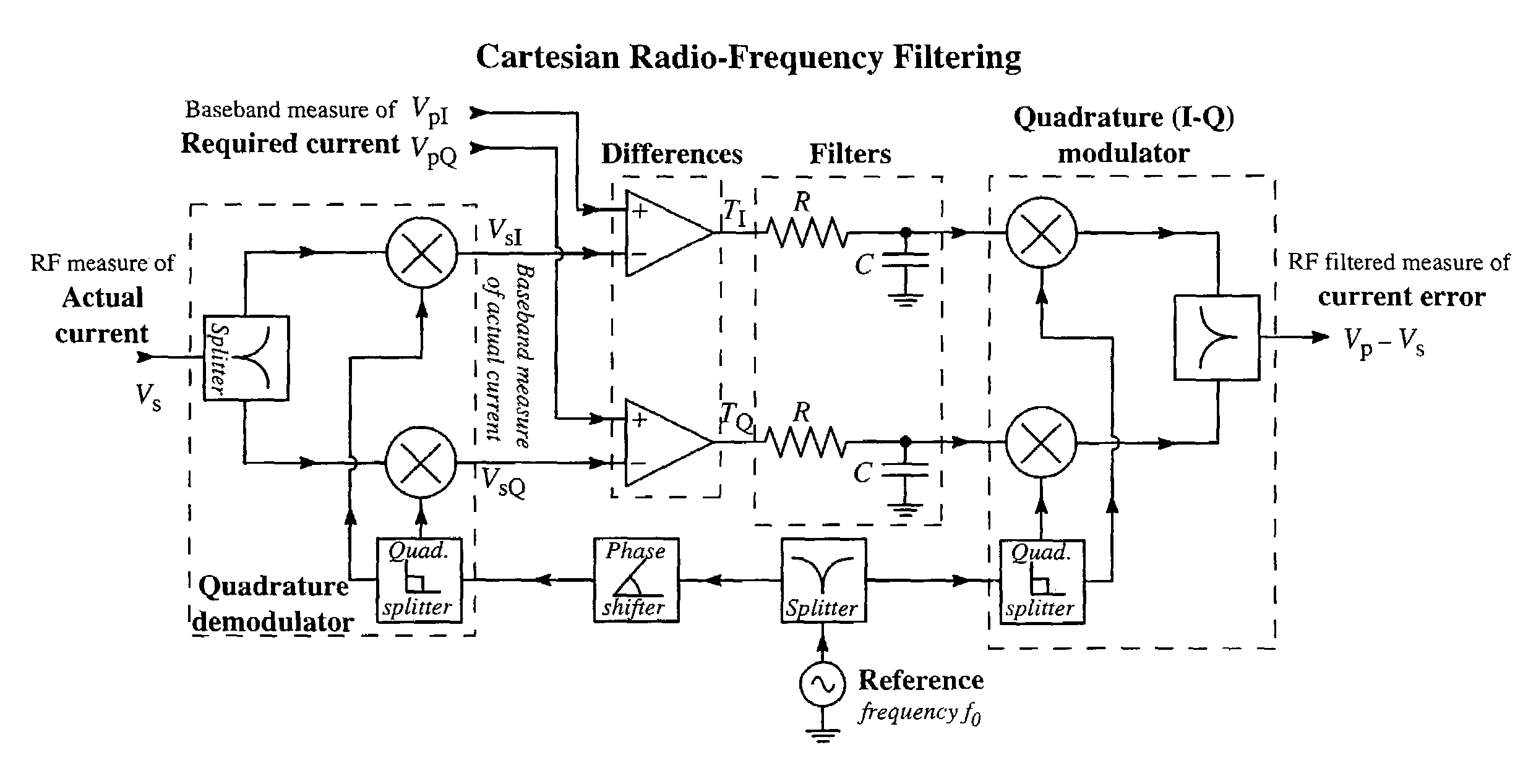
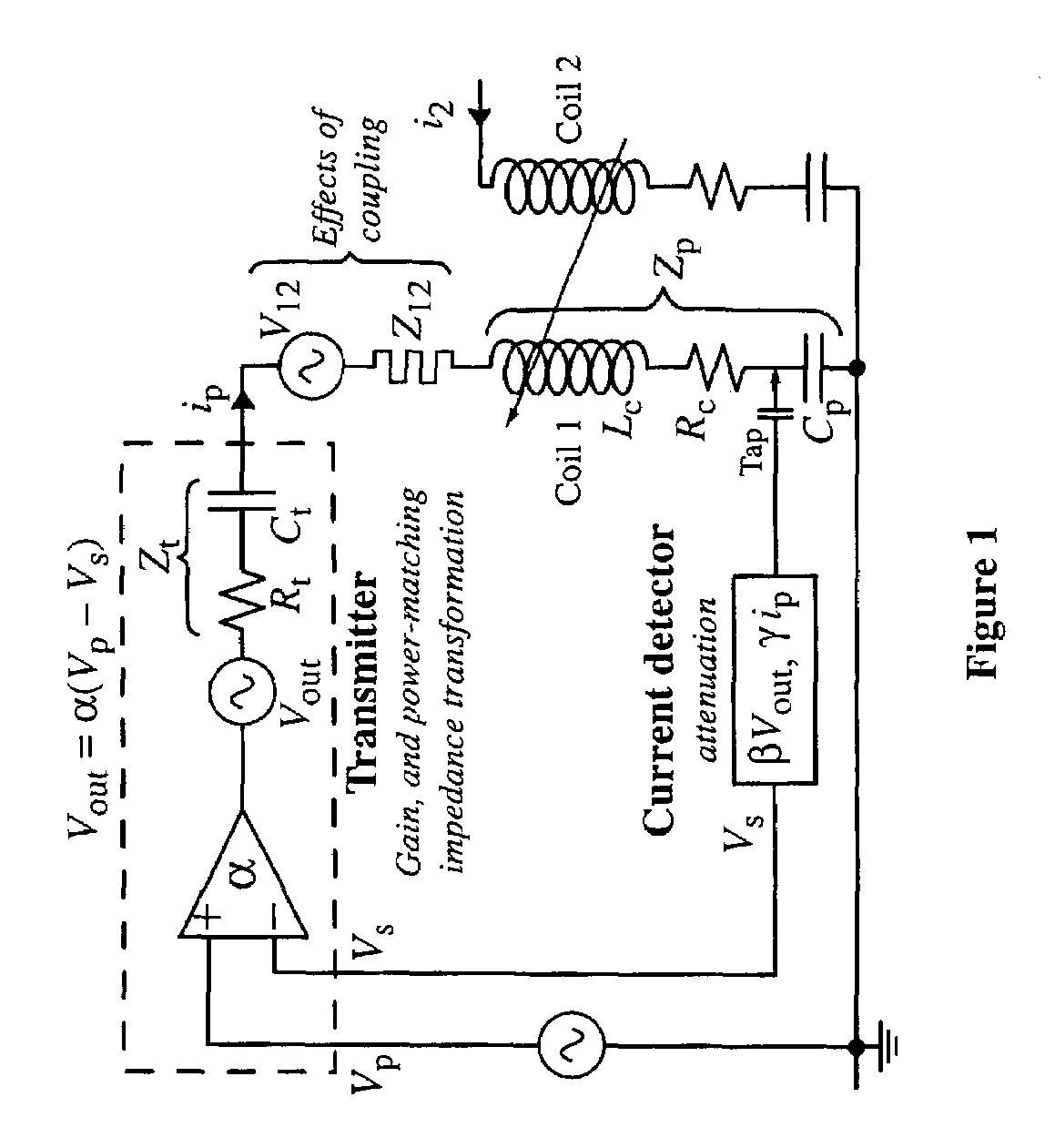
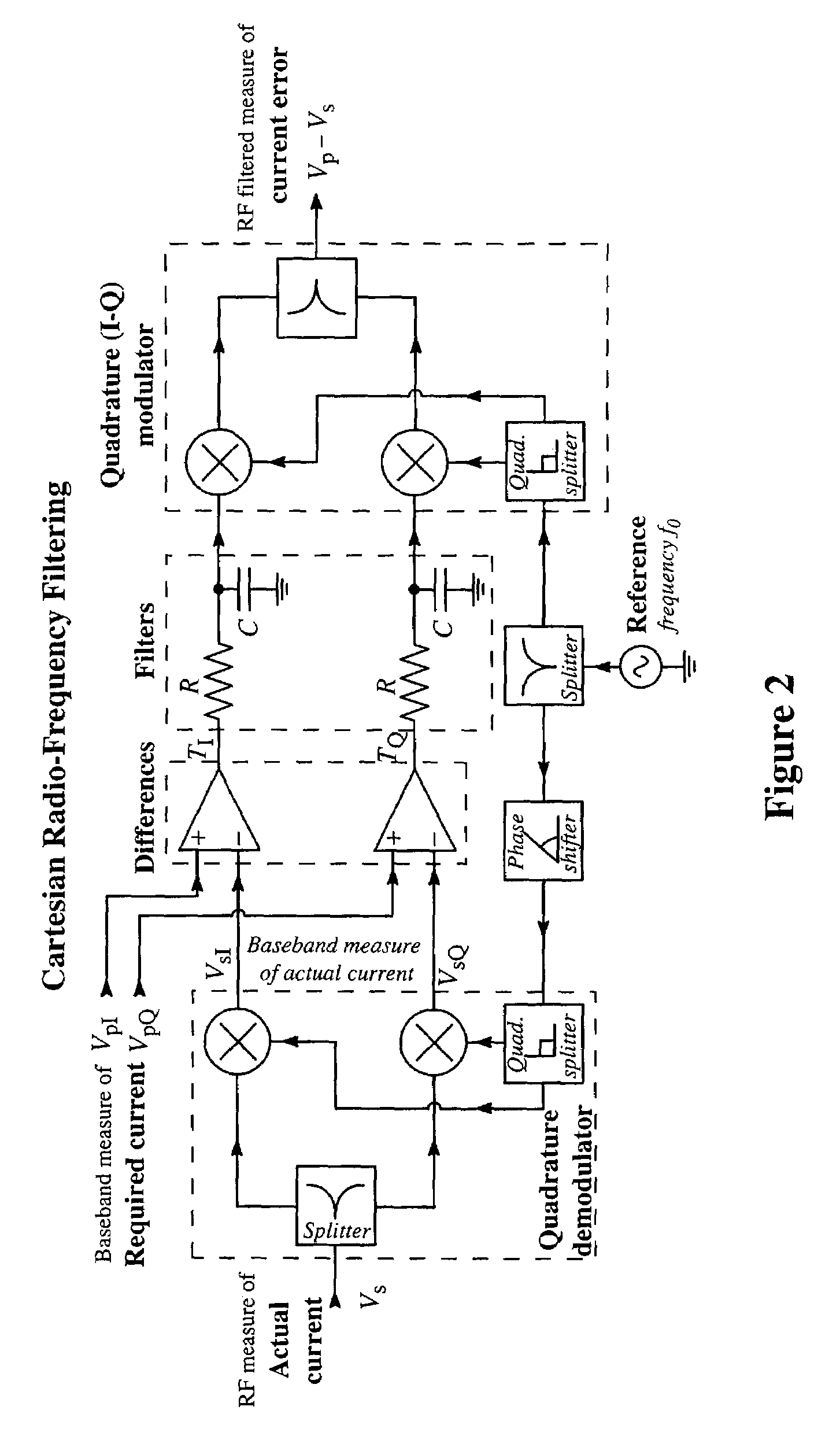
Method of Effecting Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Experiments Using Cartesian Feedback
InactiveUS20070222449A1Easy to controlReduce delaysElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetizationElectronic feedback
In nuclear magnetic resonance experiments, Cartesian electronic feedback is used to reduce substantially in transmission and / or reception the deleterious effects of sample-mediated and direct interactions between coils in an array of transmitting and / or receiving coils. The feedback is also used with single or multiple coils to maintain at essentially constant values the relationship between an input transmitter voltage and the magnetic resonance flip angle, and the relationship between transverse nuclear magnetisation and the strength of the free induction decay signal presented by a receiver for analysis, regardless of factors such as sample electrical conductivity.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
NMR methods for measuring fluid flow rates
InactiveUS20060213283A1Loss of resolutionReduce resolutionVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersElectric/magnetic detectionUltimate tensile strengthFree induction decay
A method for measuring fluid flow rates comprises the steps of: (a) creating a non-oscillating magnetic field of a predetermined strength across a flowing fluid; (b) performing the sub-steps of: (i) exposing the flowing fluid to an oscillating magnetic field pulse orthogonal to the non-oscillating magnetic field to generate an NMR signal, and (ii) detecting the NMR signal from the flowing fluid in the form of a free induction decay; and (c) determining the fluid flow rate from the initial magnitude of the free induction decay.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Method of effecting nuclear magnetic resonance experiments using Cartesian feedback
InactiveUS7358737B2Easy to controlReduce delaysElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance
In nuclear magnetic resonance experiments, Cartesian electronic feedback is used to reduce substantially in transmission and / or reception the deleterious effects of sample-mediated and direct interactions between coils in an array of transmitting and / or receiving coils. The feedback is also used with single or multiple coils to maintain at essentially constant values the relationship between an input transmitter voltage and the magnetic resonance flip angle, and the relationship between transverse nuclear magnetisation and the strength of the free induction decay signal presented by a receiver for analysis, regardless of factors such as sample electrical conductivity.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
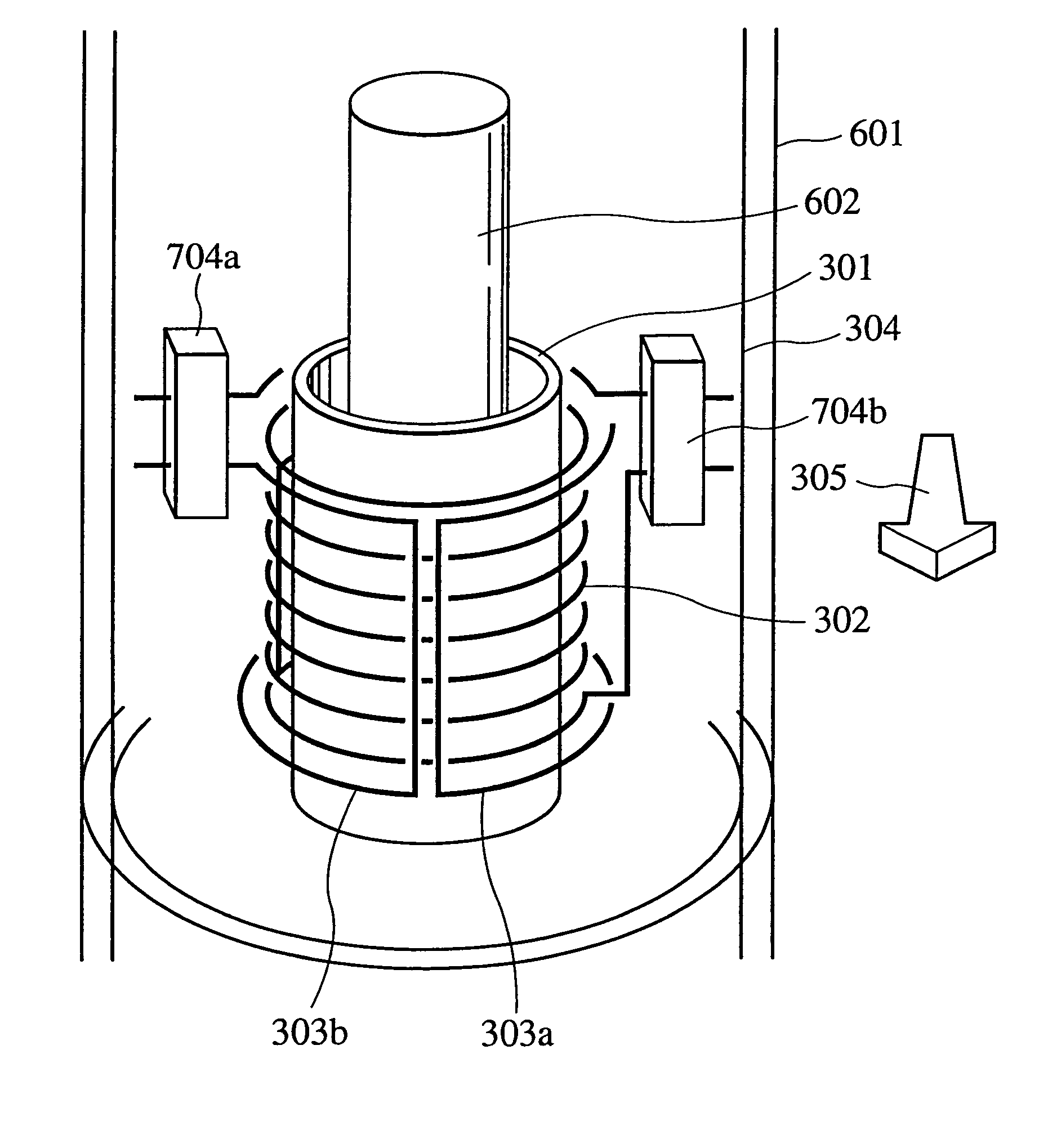
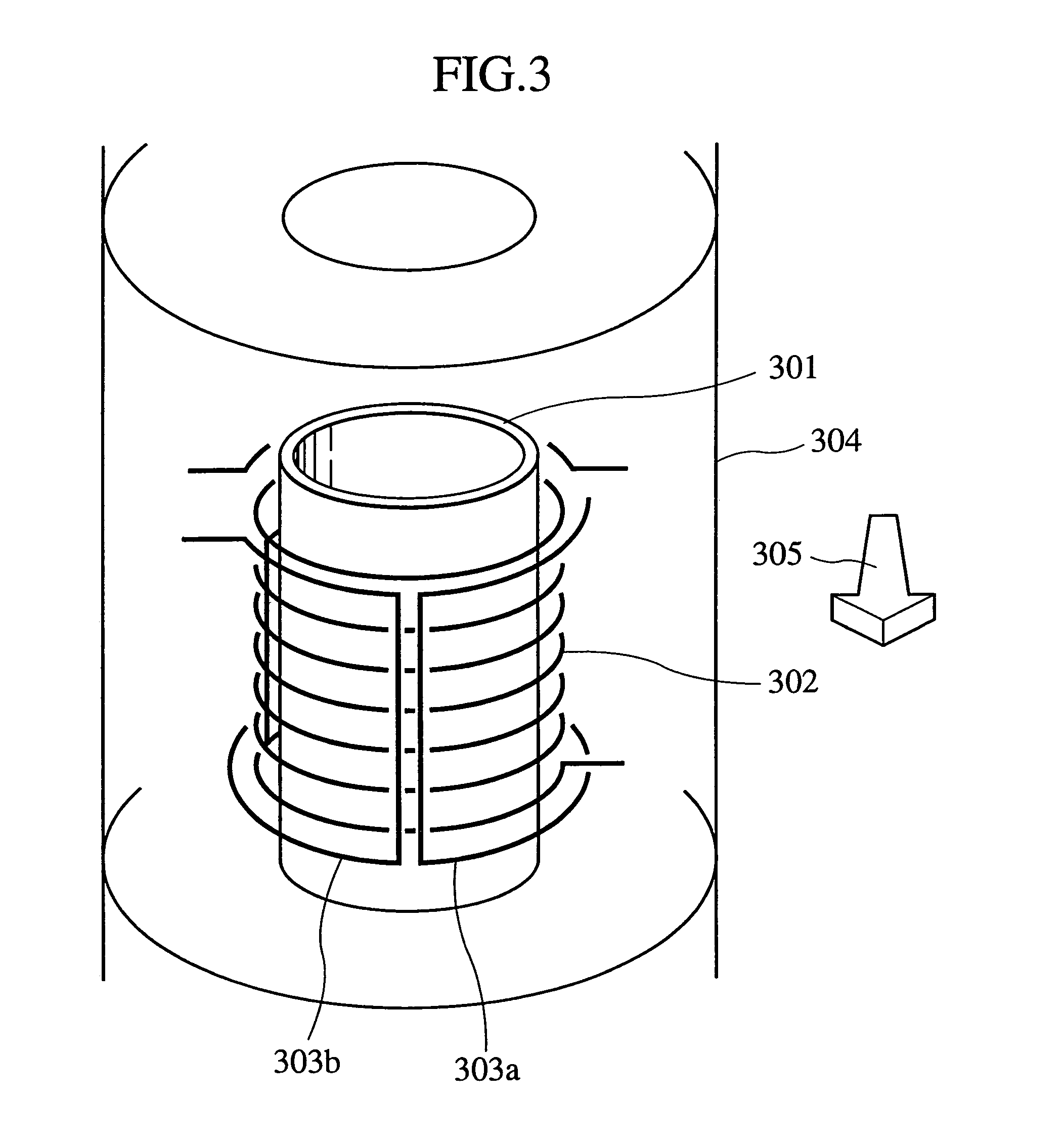
Nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus probe
InactiveUS20050083059A1High sensitivityLittle resistanceElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceAudio power amplifier
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus comprises a superconducting magnet that produces a static magnetic field, a probe having a probe coil that irradiates an RF pulse magnetic field and receives a free induction decay signal (FID signal) emitted therefrom, an RF power source that supplies the probe with an RF current, an amplifier that amplifies the FID signal, a detector that detects a signal, and an analyzer that analyzes the signal detected by the detector, wherein the probe coil includes a solenoid coil and a saddle type coil.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Nuclear magnetic resonance radio-frequency micro-coil and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101650412AHigh Q valueHigh magnetic field distribution uniformityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMicro coil
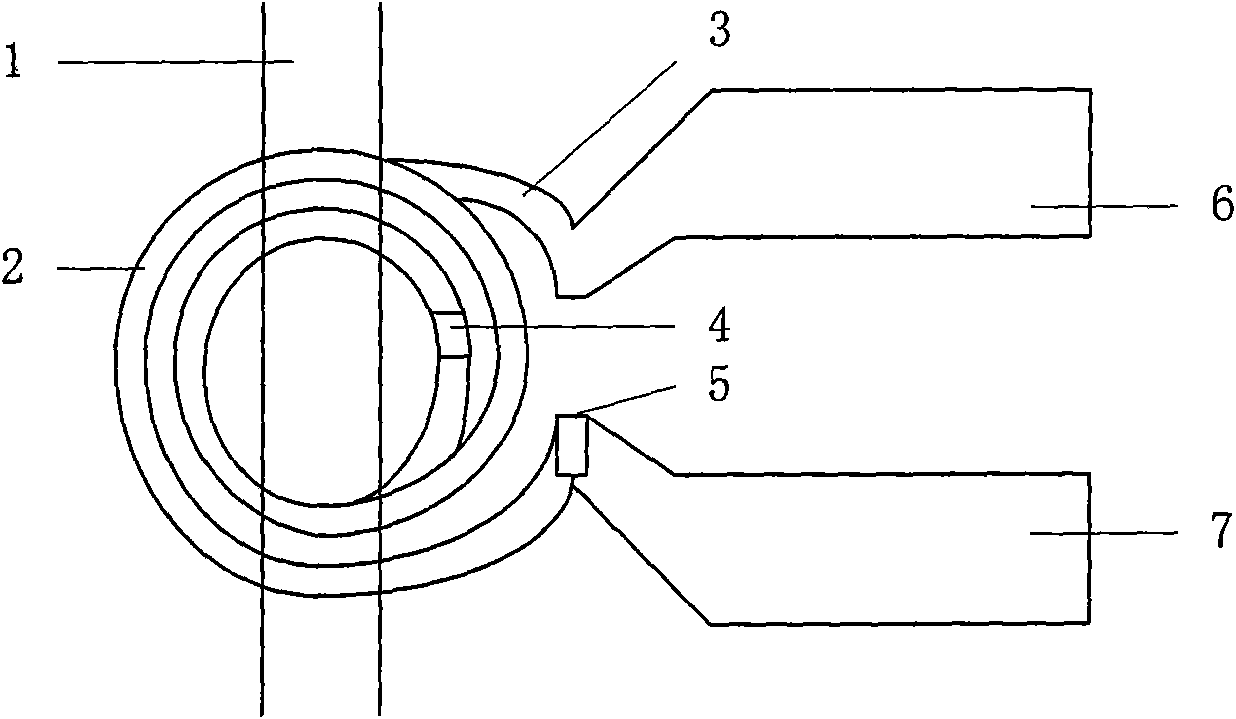
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance radio-frequency micro-coil, comprising an upper flat subcoil and a lower flat subcoil which are mutually parallel, i.e. a top layer subcoil (2) and a bottom layer subcoil (3). The two flat subcoils have the same shape, and the distance between the subcoils is larger than or equal to the inside radius of the subcoils; the two flat subcoils are connected through a wire; a micro channel (1) used for containing a sample is positioned between and parallel with the top layer subcoil (2) and the bottom layer subcoil (3). An inner through hole (4)is positioned at the joint between the bottom layer subcoil (3) and the top layer subcoil (2); and an outer through hole (5) is positioned at the joint between the top layer subcoil (2) an a second bonding pad (7). The invention can emit radio-frequency pulse signal and (or) receive free induction decay echo signals coming from a tested object. The micro-coil is manufactured based on SU-8 photoresist by utilizing a micro-electro-mechanical system process on a Pyrex substrate (12). The invention can be used for nuclear magnetic resonance test of a nano-liter bio-chemical sample.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus probe
InactiveUS7084634B2Reduce sensitivityHigh sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceAudio power amplifier
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus comprises a superconducting magnet that produces a static magnetic field, a probe having a probe coil that irradiates an RF pulse magnetic field and receives a free induction decay signal (FID signal) emitted therefrom, an RF power source that supplies the probe with an RF current, an amplifier that amplifies the FID signal, a detector that detects a signal, and an analyzer that analyzes the signal detected by the detector, wherein the probe coil includes a solenoid coil and a saddle type coil.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and device for determining asphaltene content by low field nuclear magnetic resonance
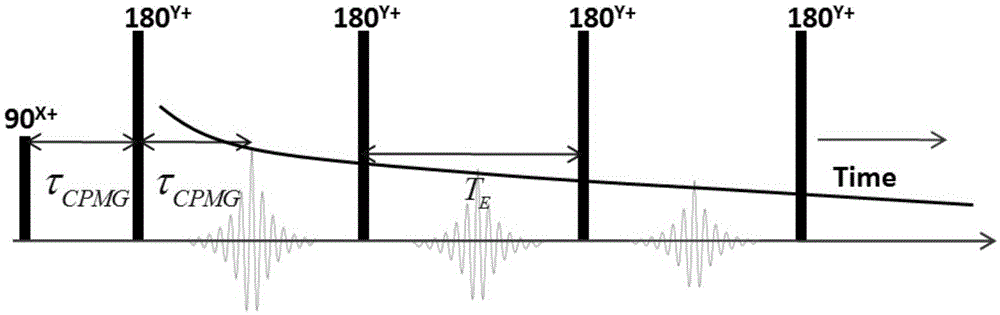
ActiveCN105136836AQuick checkShort test cycleAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceEcho intensity
The invention provides a method and a device for determining the asphaltene content by low field nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out low field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on a crude oil sample by adopting FID (free induction decay) pulse sequence to obtain a crude oil sample FID signal intensity curve of the crude oil sample; carrying out low field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement according to a preset CPMG (Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill) echo interval to obtain a CPMG echo intensity curve of the crude oil sample; analyzing the FID signal intensity curve of the crude oil sample and the CPMG echo intensity curve of the crude oil sample to obtain signal intensity difference data of the crude oil sample; and determining the asphaltene content in the crude oil sample according to the signal intensity difference data of the crude oil sample. Therefore, the method and the device provided by the invention can be used for obtaining the asphaltene content on line and realizing fast and accurate asphaltene content detection which is short in testing period, and free of damage to the crude oil sample and consumption of chemical reagents.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Tuning device and method for magnetic resonance imaging system radio frequency coil
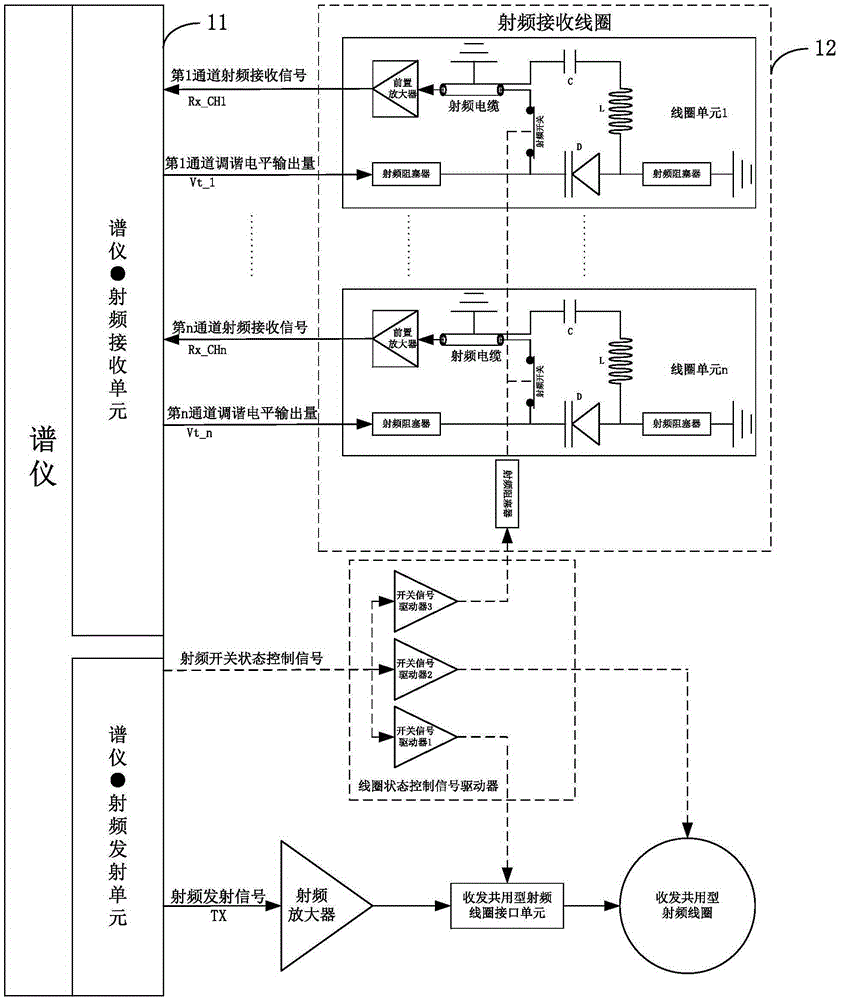
ActiveCN105388435AAchieve frequency tuningChange terminal voltageMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceResonance
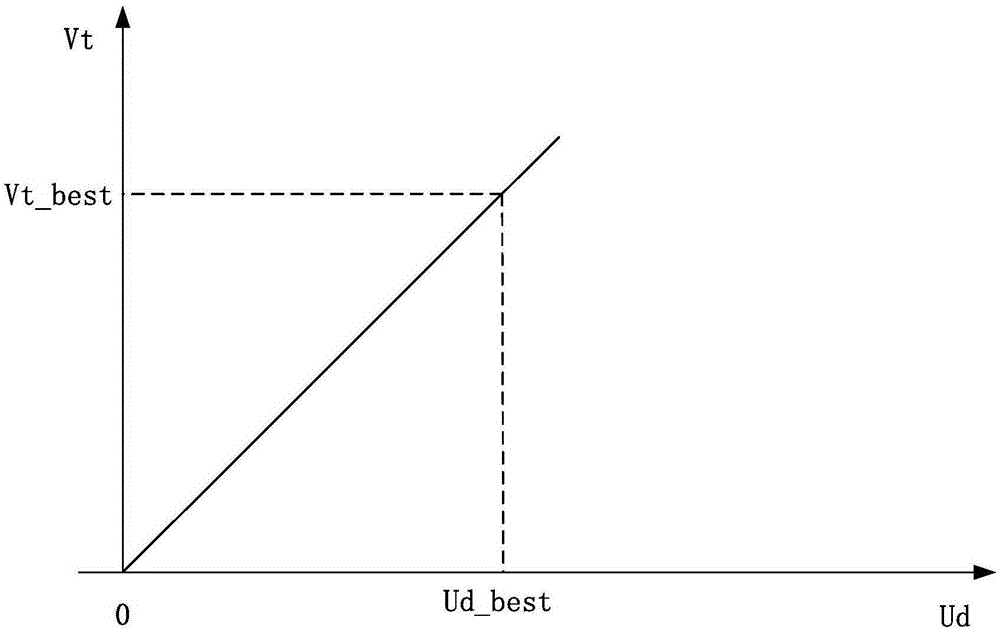
The invention provides a tuning device and method for a magnetic resonance imaging system radio frequency coil. The device comprises a spectrometer and a radio frequency receiving coil, wherein the radio frequency receiving coil comprises multiple coil units, each coil unit of the multiple coil units comprises a variable capacitive reactance device and a radio frequency obturator, each variable capacitive reactance device is bunched into a resonance circuit of the corresponding coil unit, and coil tuning level input to each coil unit by the spectrometer is applied to the corresponding variable capacitive reactance device through the corresponding radio frequency obturator, so as to regulate the capacitance of the corresponding resonance circuit; the spectrometer is used for receiving a free induction decay signal generated by each coil unit in the radio frequency receiving coil due to magnetic resonance, finding maximum values of the free induction decay signals on the basis of iteration traversal of a tuning evaluation function, and applying the tuning level corresponding to the maximum values to two ends of the variable capacitive reactance devices in the resonance circuits. By adopting the technical scheme, tuning of the magnetic resonance imaging oil can be quickly realized.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
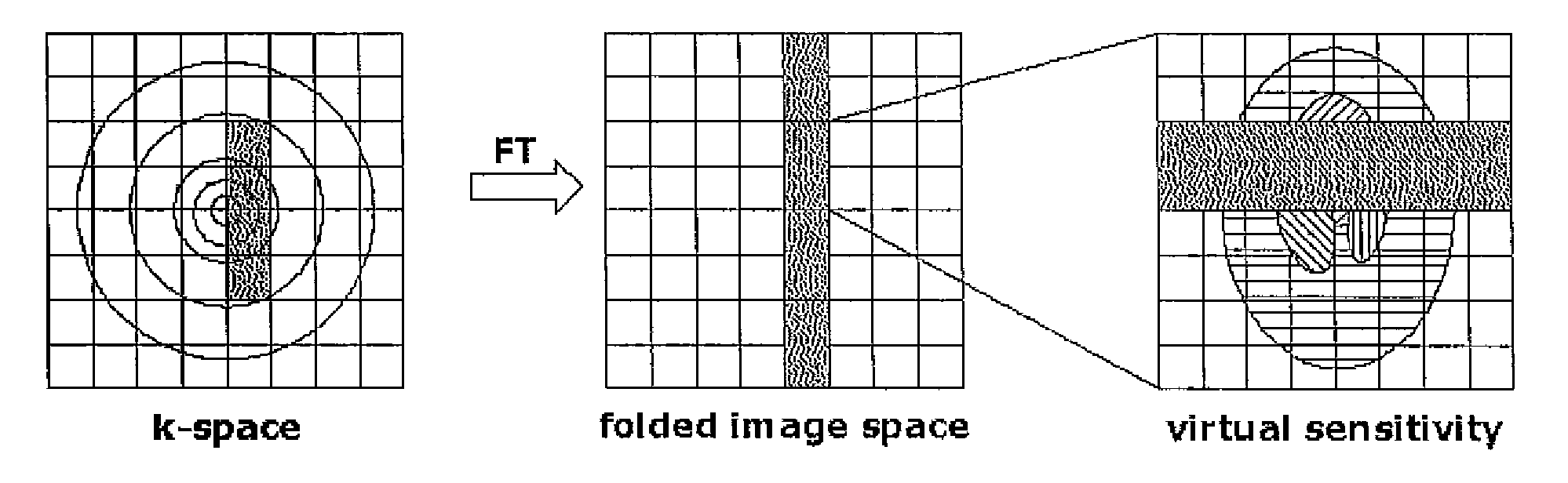
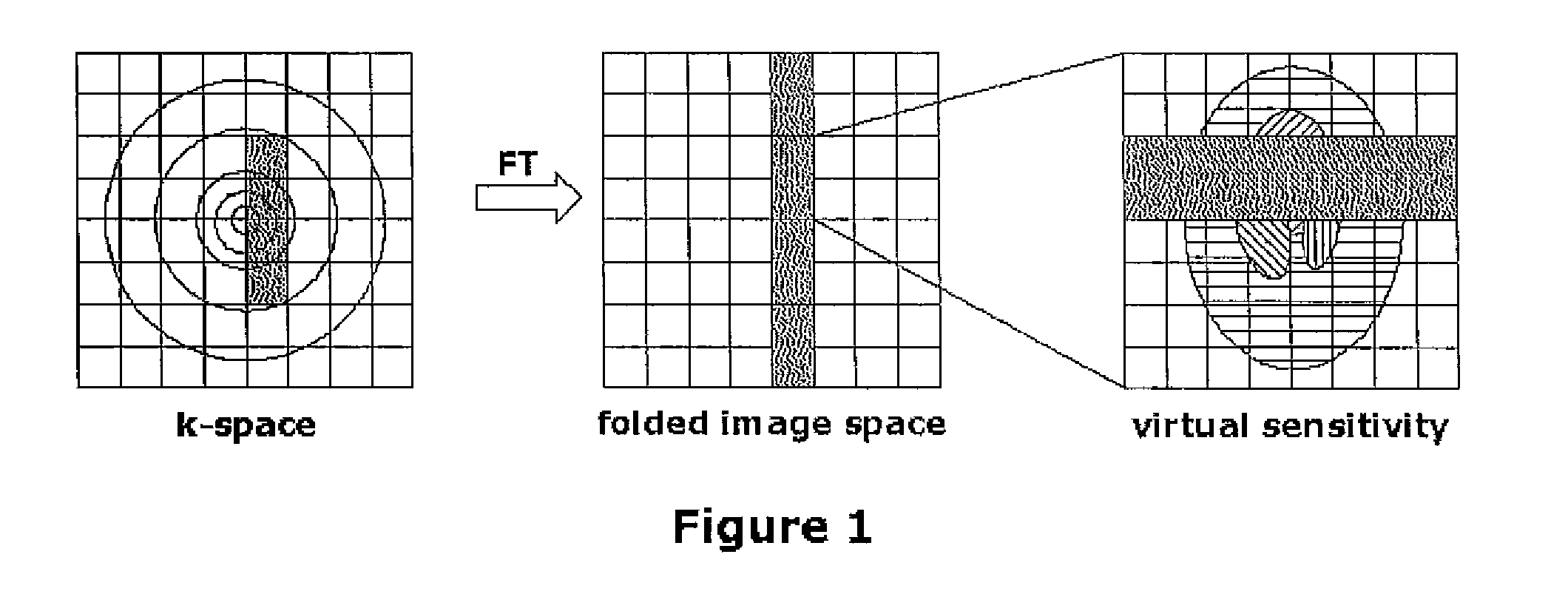
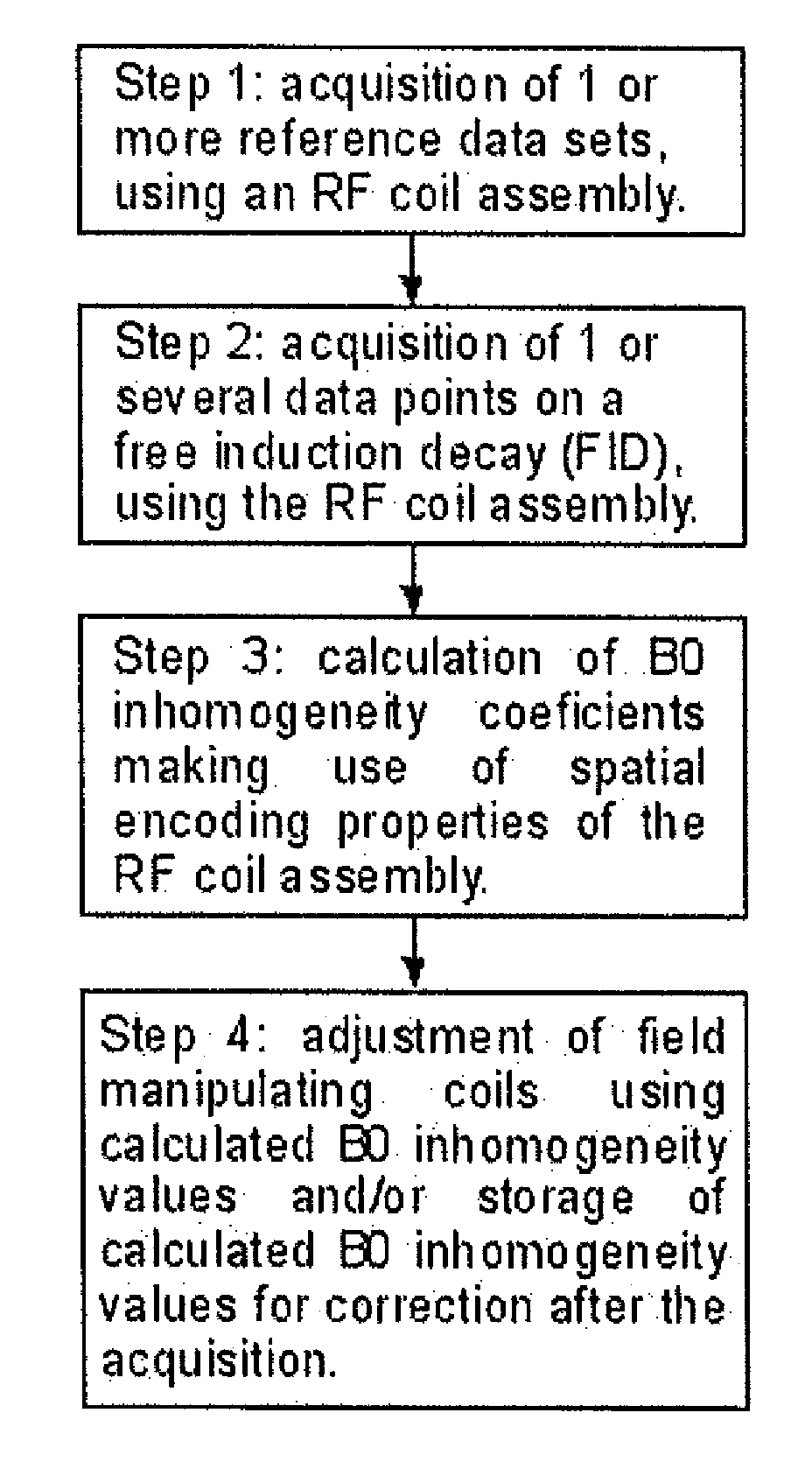
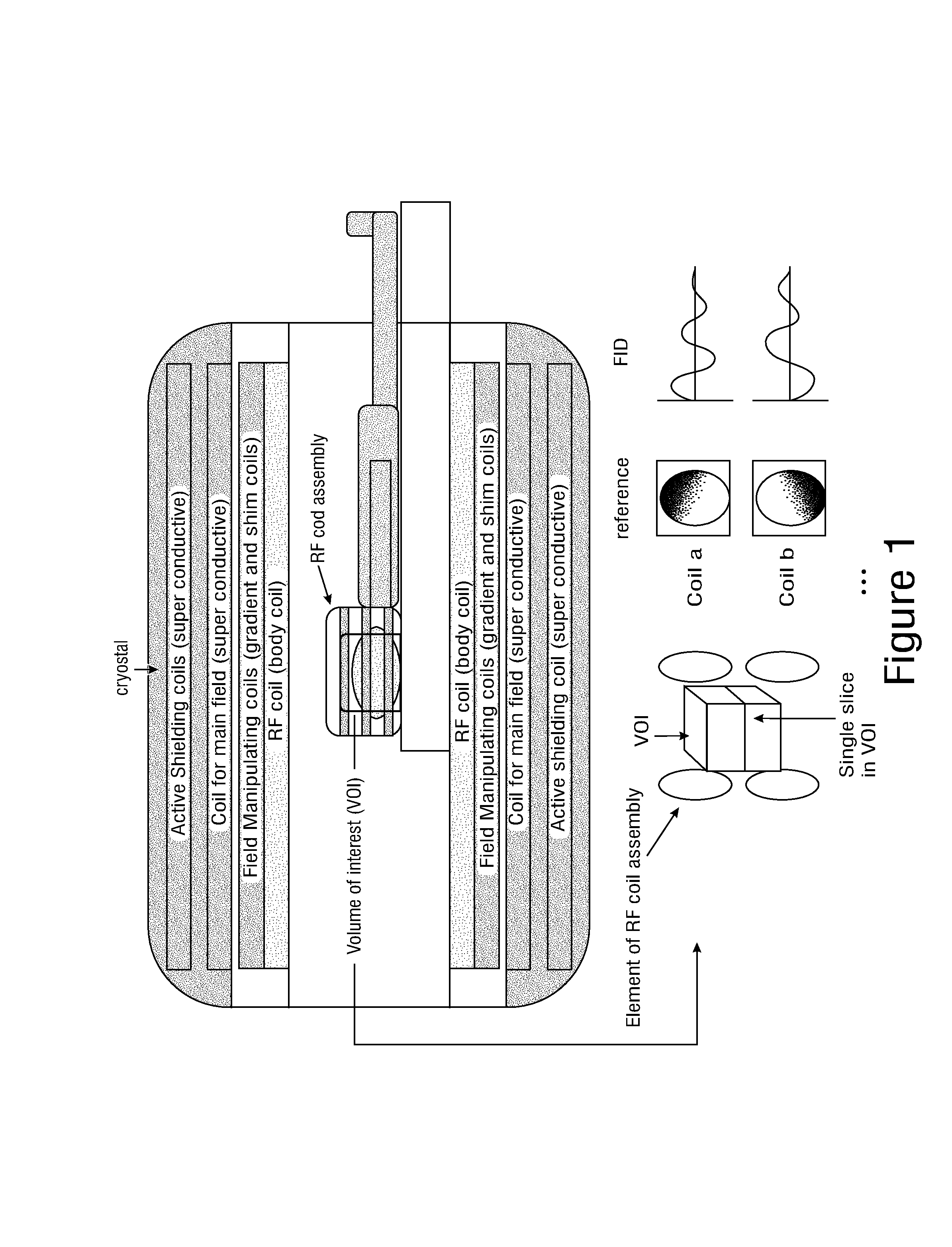
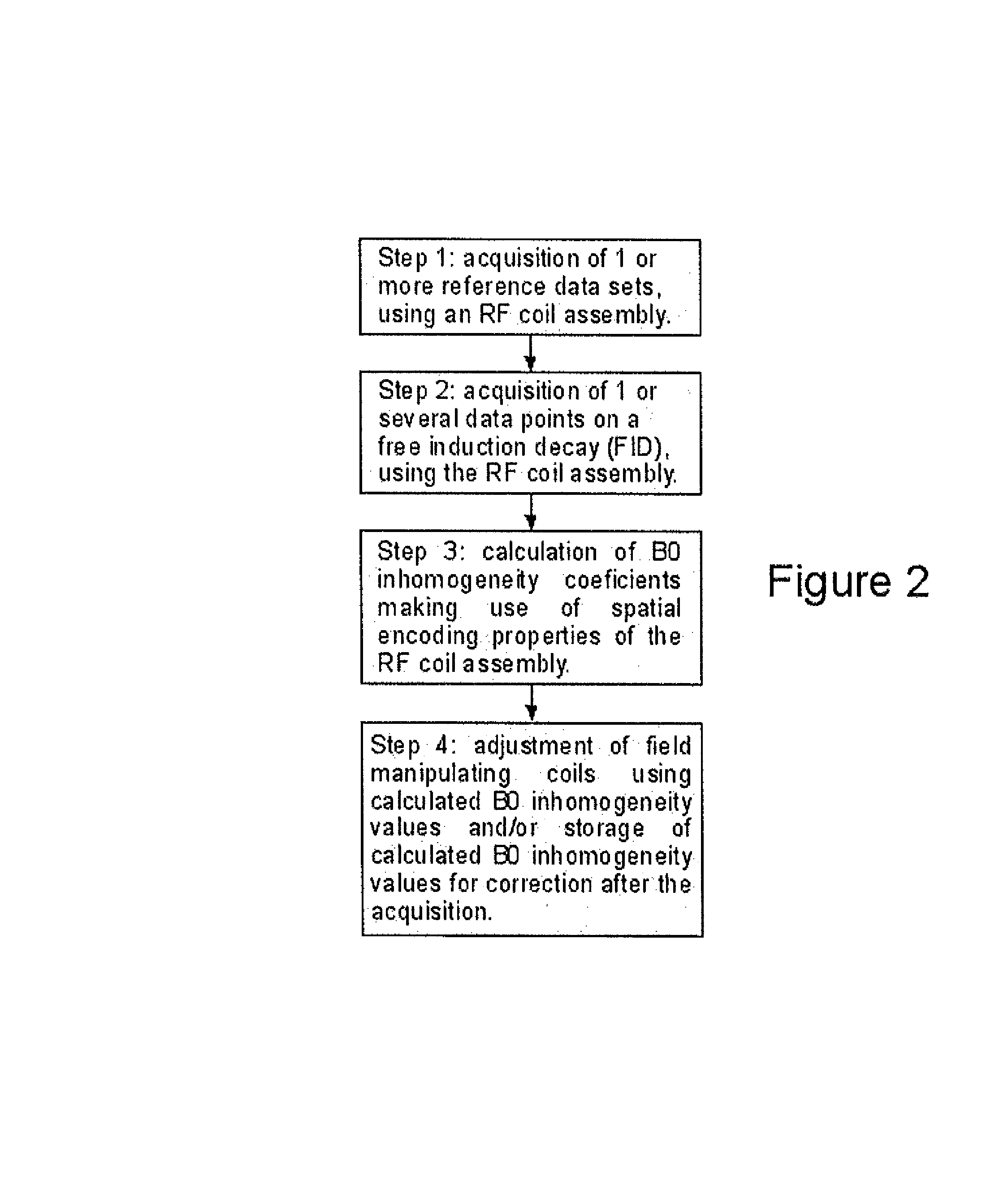
Sense Shimming (SSH): a fast approach for determining B0 field inhomogeneities using sensitivity encoding
InactiveUS20100102819A1Quick checkQuick correctionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionCoil arrayData acquisition
The pursuit for ever higher field strengths and faster data acquisitions has led to the construction of coil arrays with high numbers of elements. With the SENSE technique it has been shown, how the sensitivity of those elements can be used for spatial image encoding. A method in accordance with the present invention, largely abstains from using encoding gradients. The resulting sensitivity encoded free induction decay (FID) data is then not used for imaging, but for determining field inhomogeneity distribution. The method has therefore been termed SSH for Sense SHimming.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Method for analysis by nuclear magnetic resonance of a sample including a species to be characterized and a reference species
InactiveUS20150362571A1Well representedSignal obtained can be enhancedMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
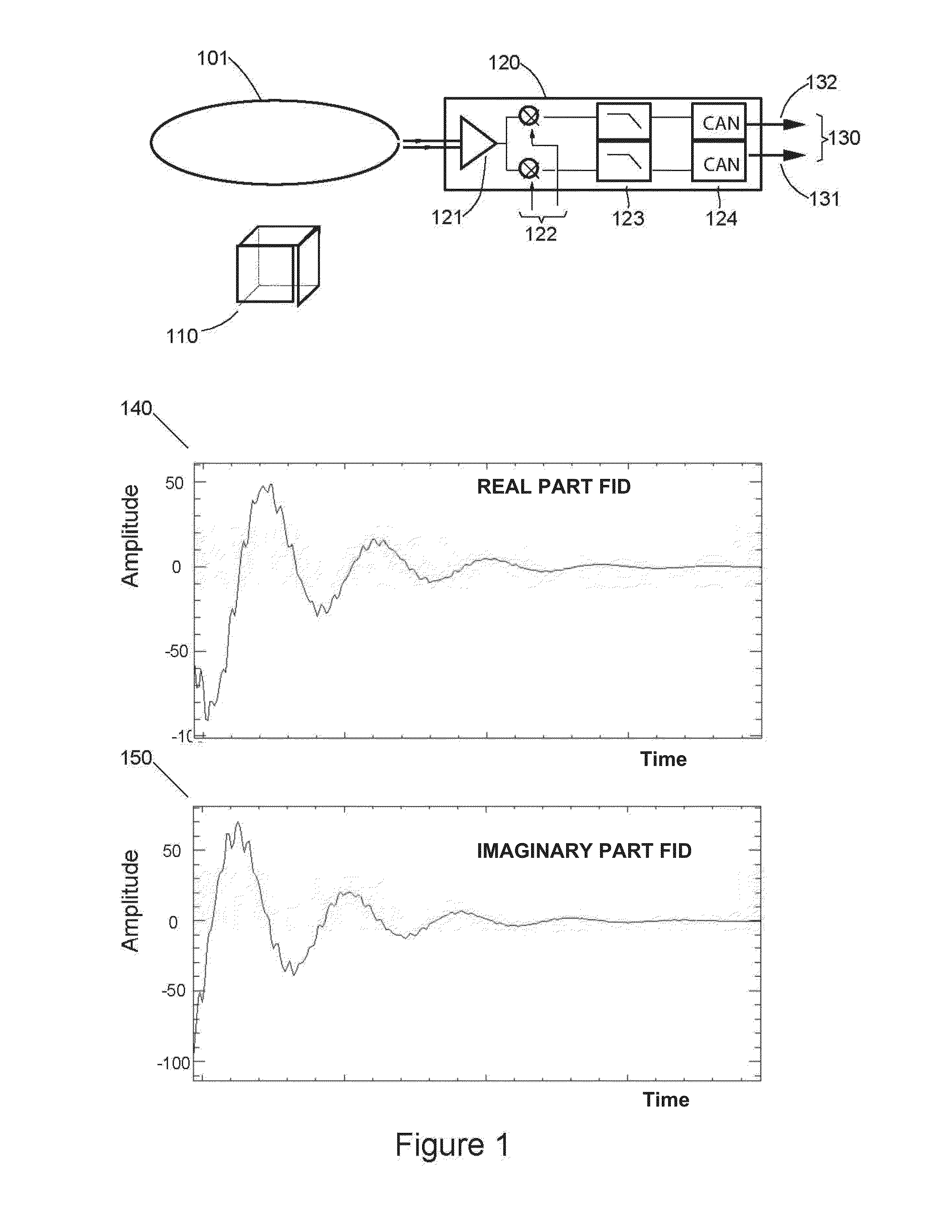
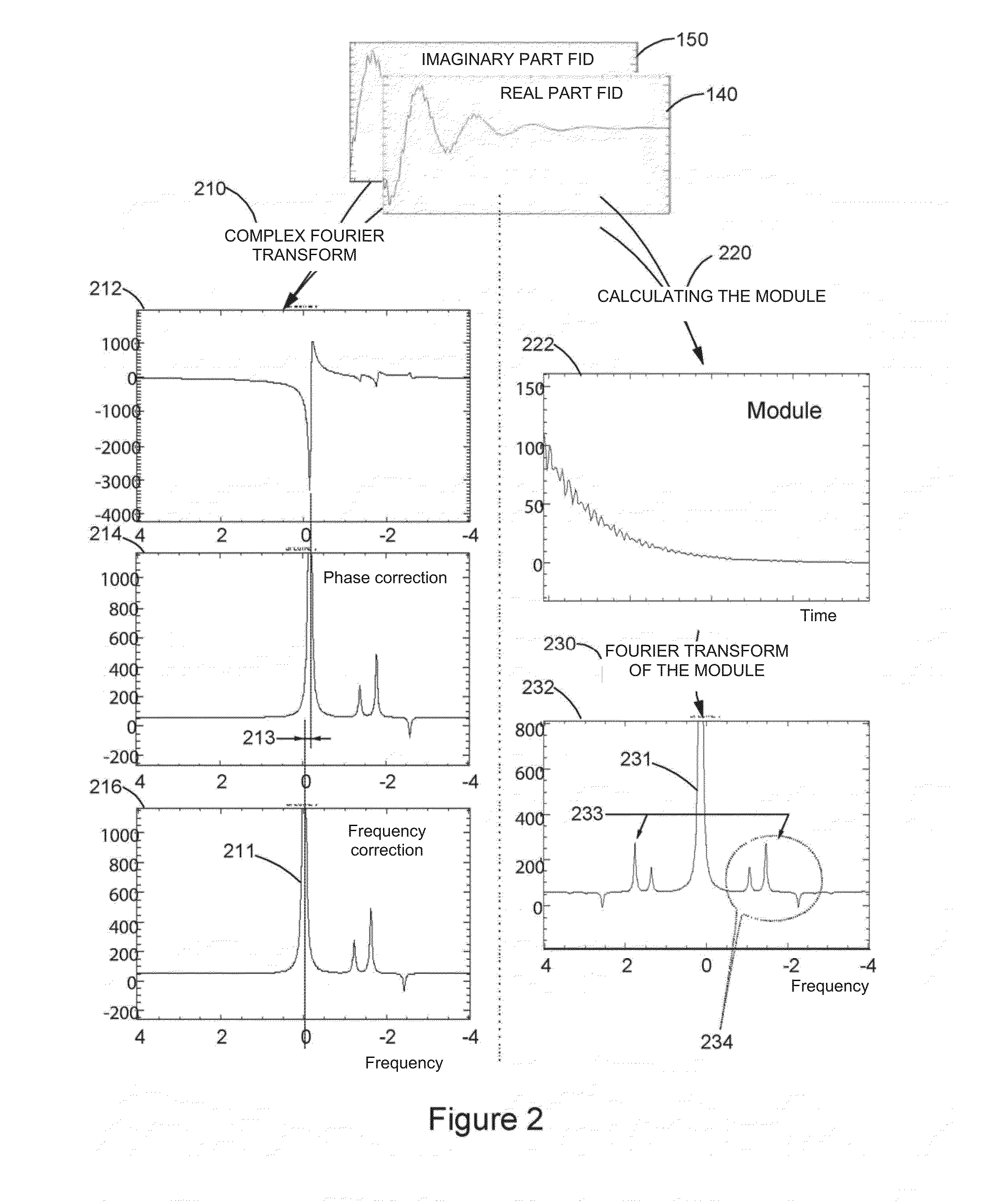
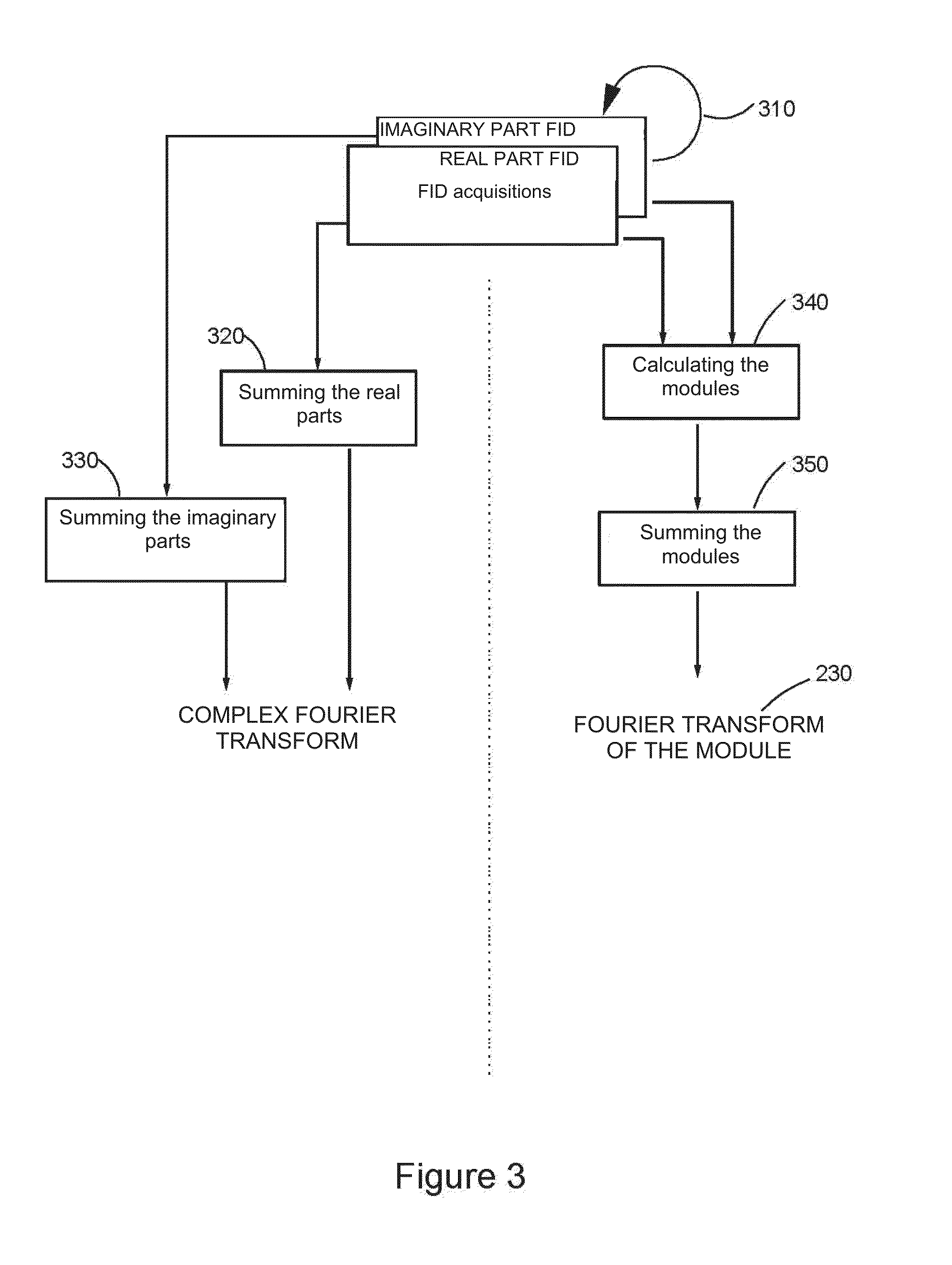
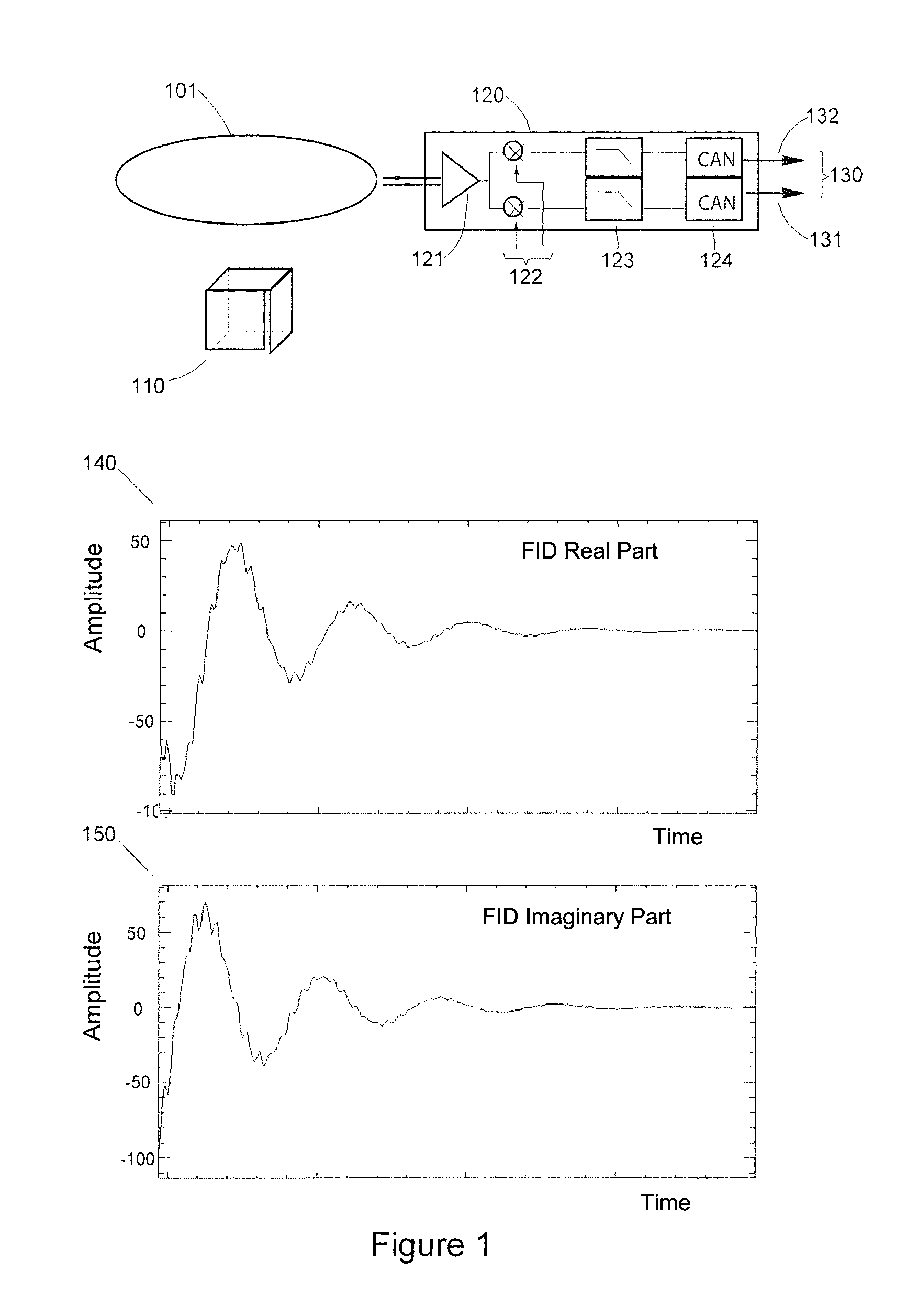
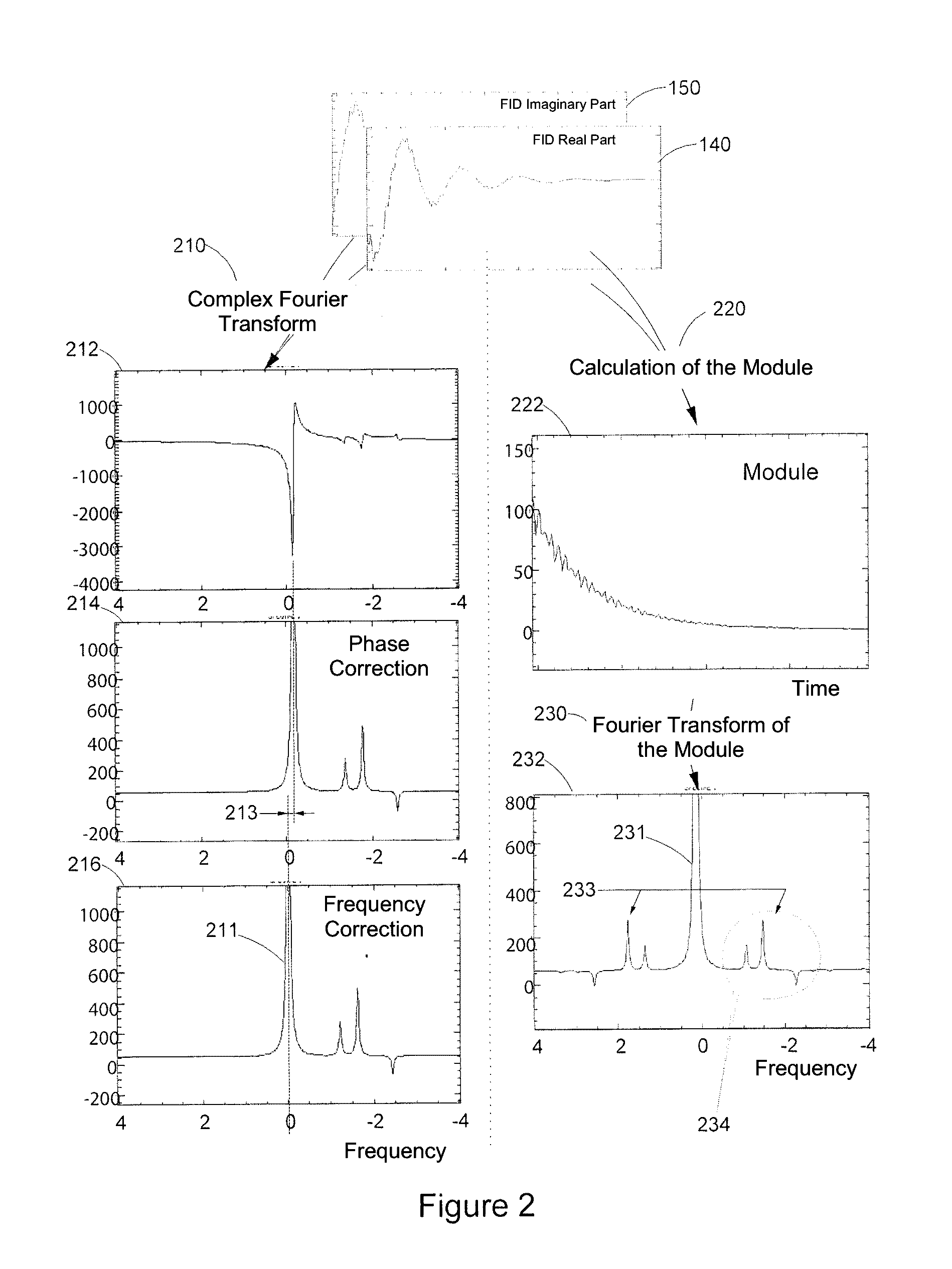
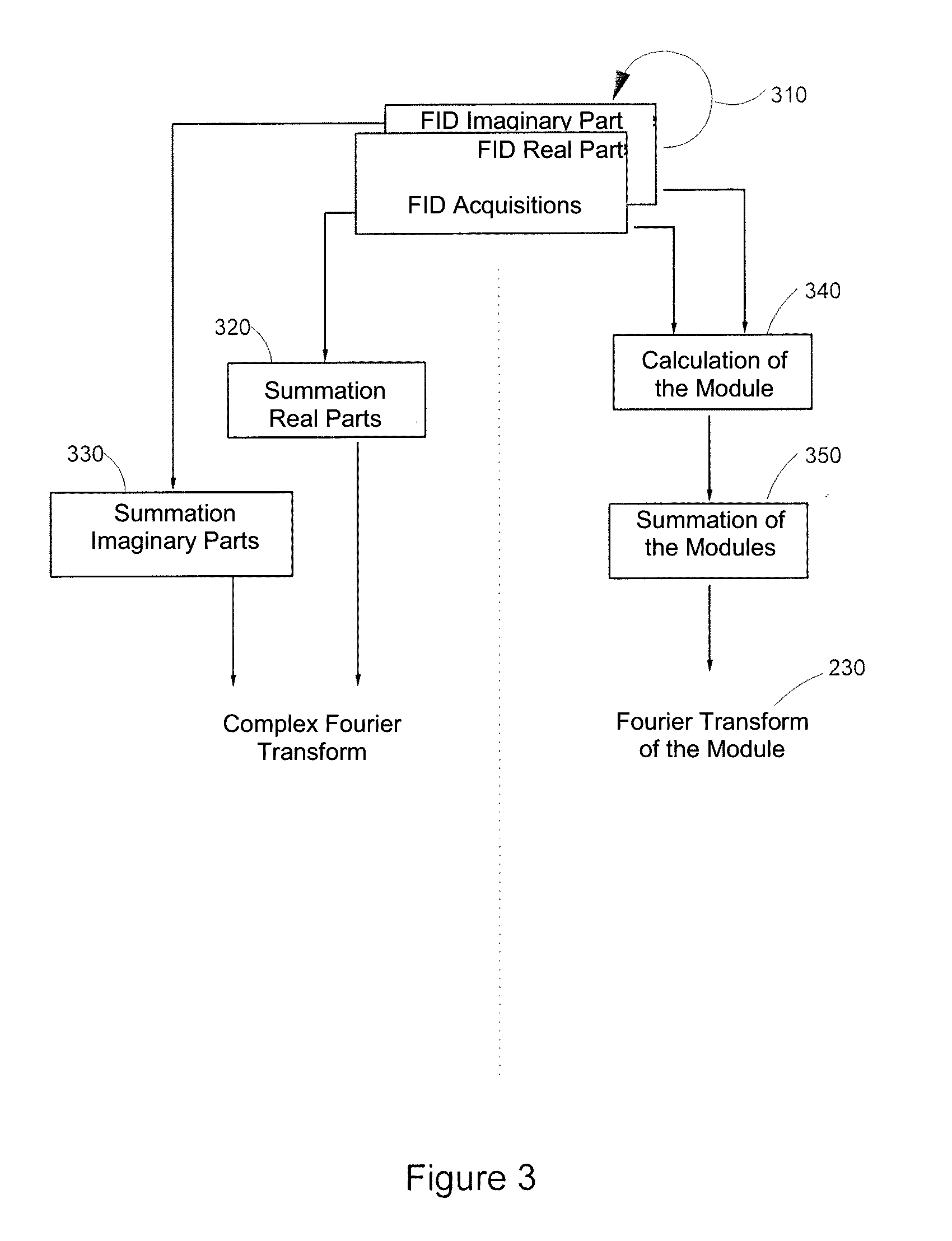
Method for analyzing, using nuclear magnetic resonance, at least one sample including at least one species to be characterized and a reference species having a content, in the sample, that is more than twice greater than the content of the species to be characterized, the method includes:applying at least one constant field B0 to the at least one sample;acquiring, using one or more antenna(s), one or more complex free induction decay (FID) signal(s) S(t), with each complex FID signal S(t) including a real part and an imaginary part; with the acquisition step being carried out such that, in each complex FID signal S(t), the amplitude of the signal of the reference species is at least twice greater than the amplitude of the signal of the at least one species to be characterized; andfor each complex FID signal S(t), calculating the module of each complex FID signal S(t).
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
MRI RF encoding using multiple transmit coils
InactiveUS20100016708A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringOperational systemLinearity
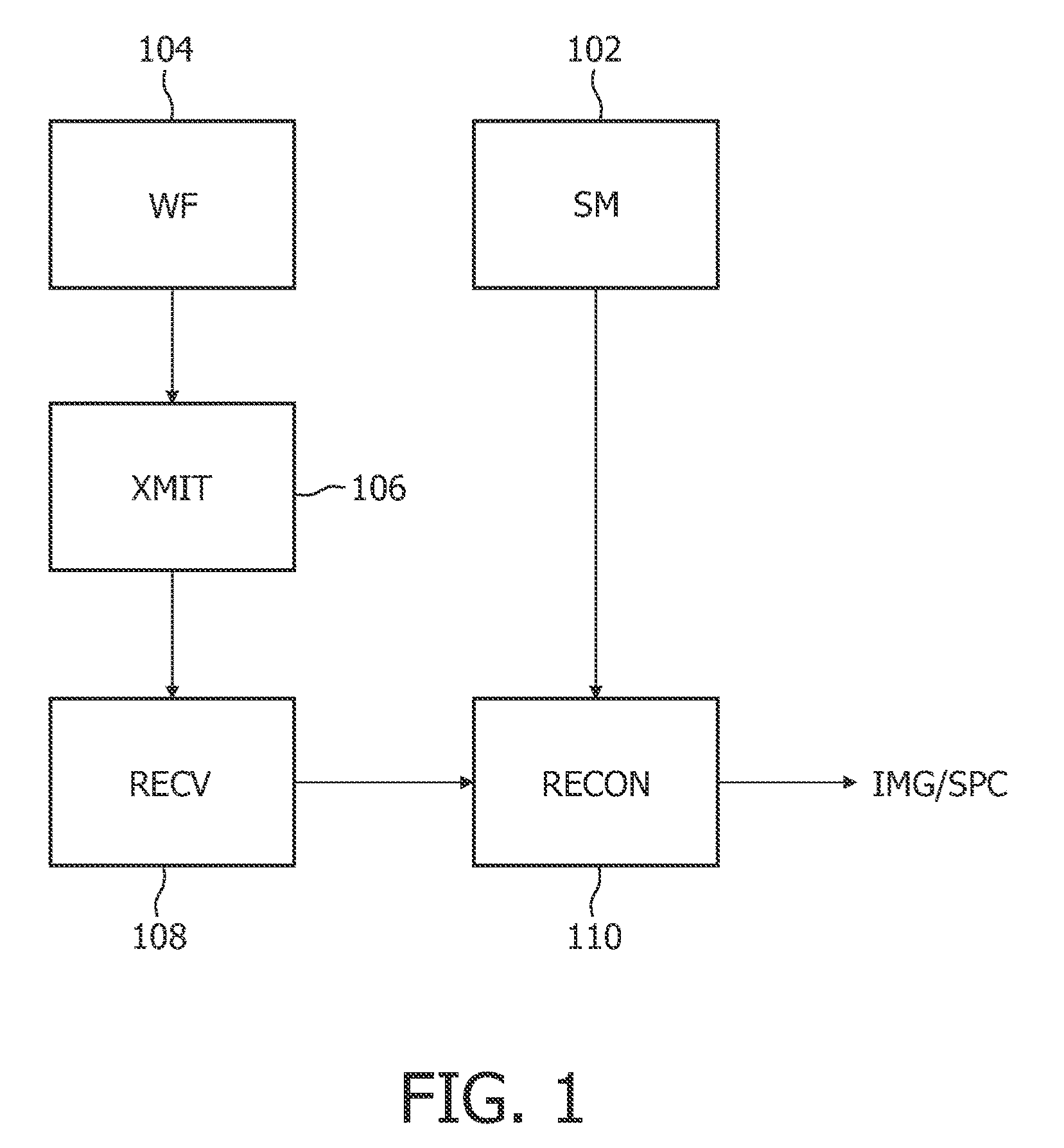
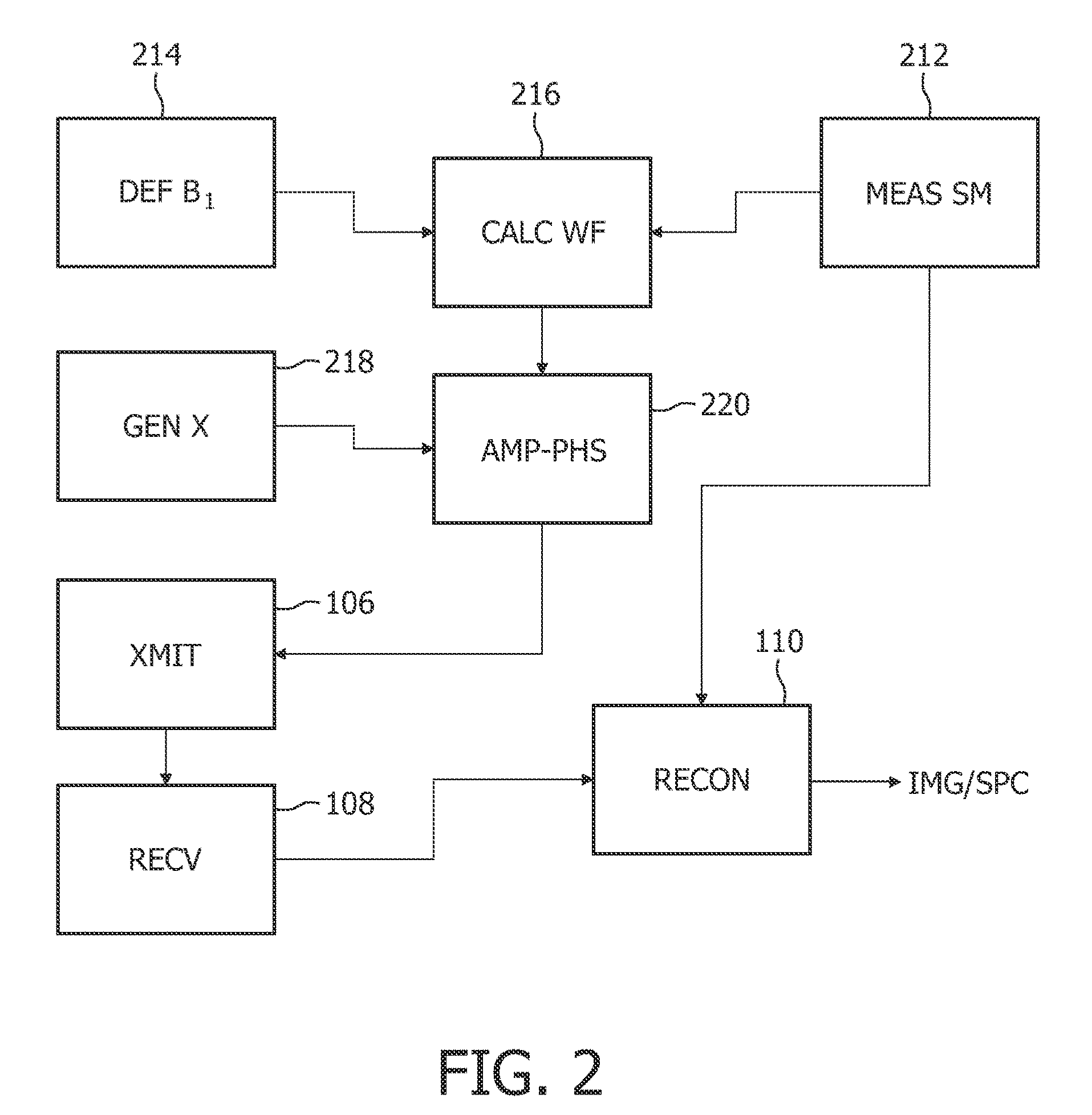
A common method of RF encoding assumes that the Bi field generated by the RF coils is linear, which is likely not the case in many situations. It is therefore desirable to have a method of operating an MR system to reconstruct an image of a subject, wherein the method is capable of also handling arbitrary Bi fields used for RF encoding. Accordingly, such an MR system employing one or more RF coils is disclosed herein. The method comprises obtaining transmit sensitivities and weighting factors for individual RF coils. Each RF coil is activated based on its respective weighting factor to apply RF excitation to a subject under examination in the MR system. MR signals—such as free induction decays (FID) signals or echo signals—generated from the subject in response to the RF excitation are received and processed based on the transmit sensitivities to generate an MR image or spectrum representative of the subject.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
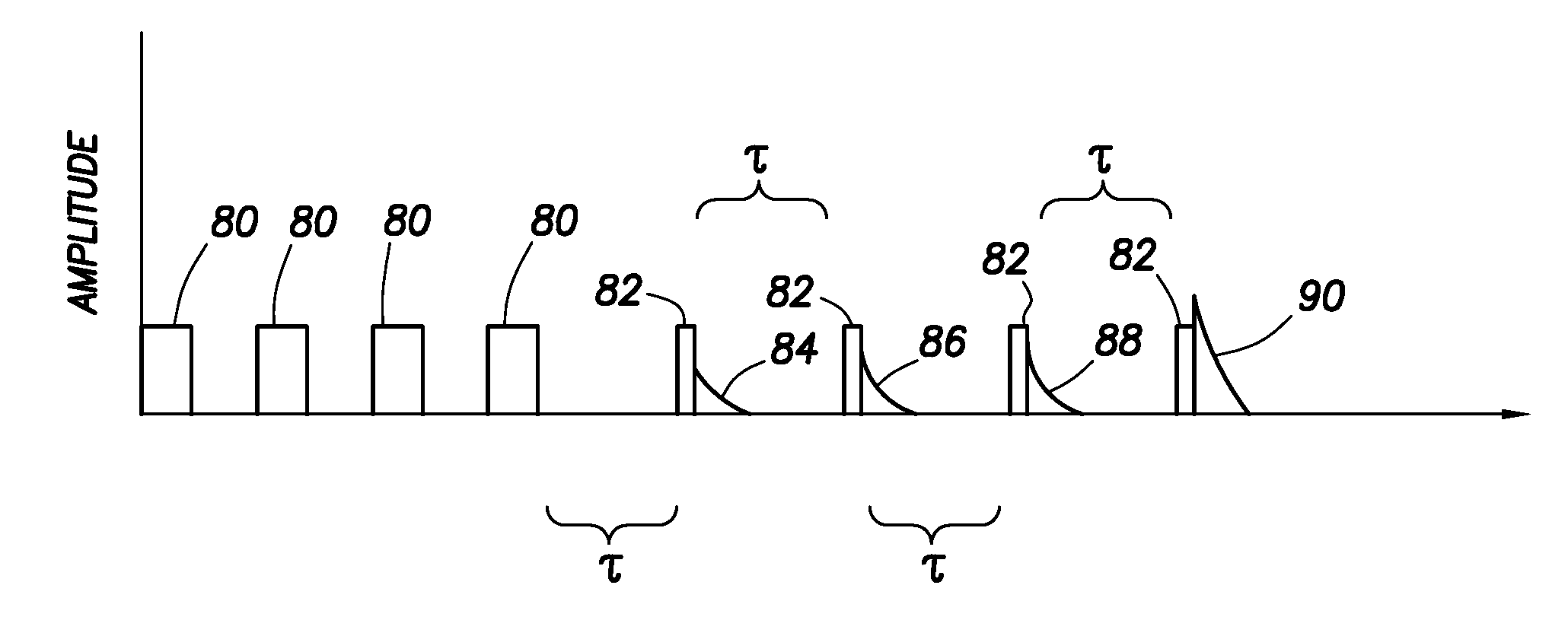
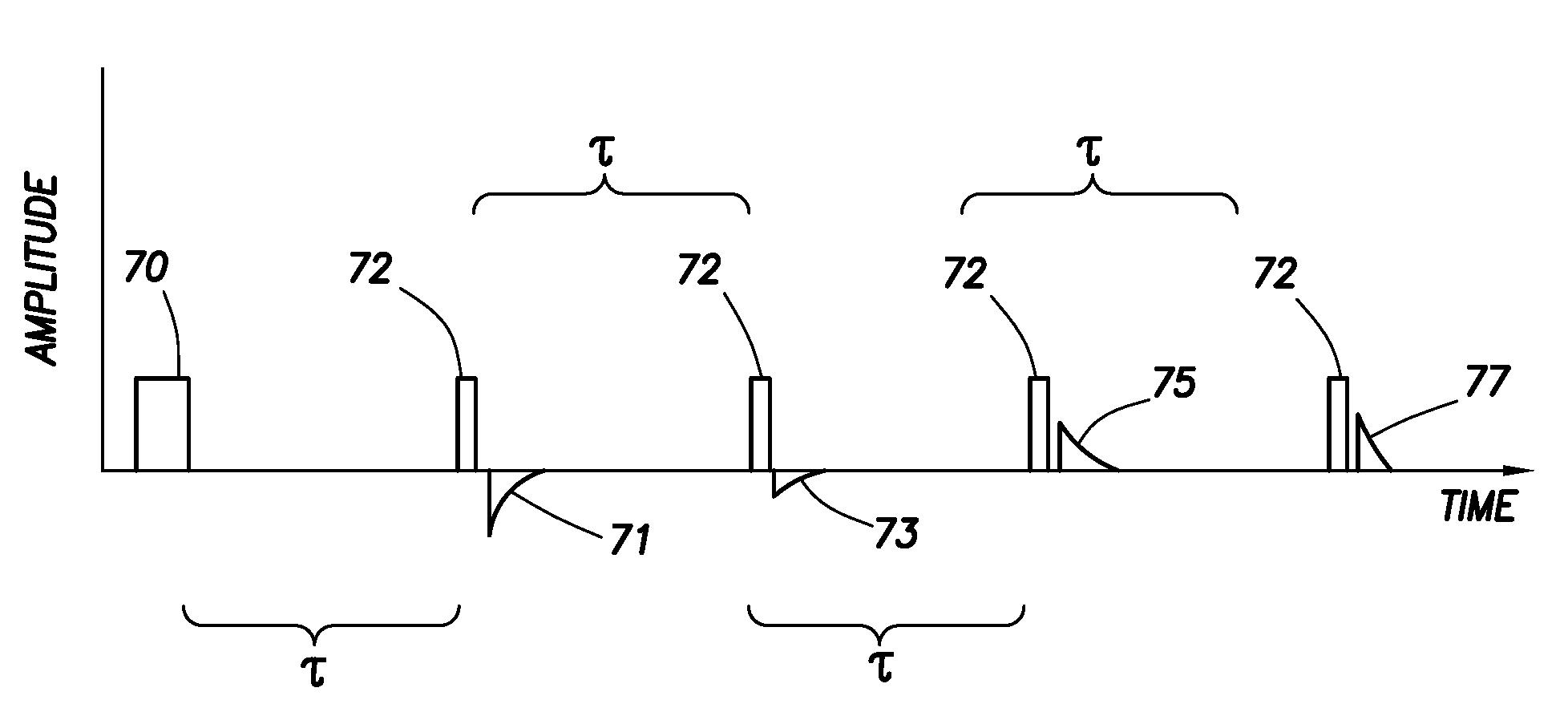
Method and apparatus for measuring free induction decay signal and its application to composition analysis
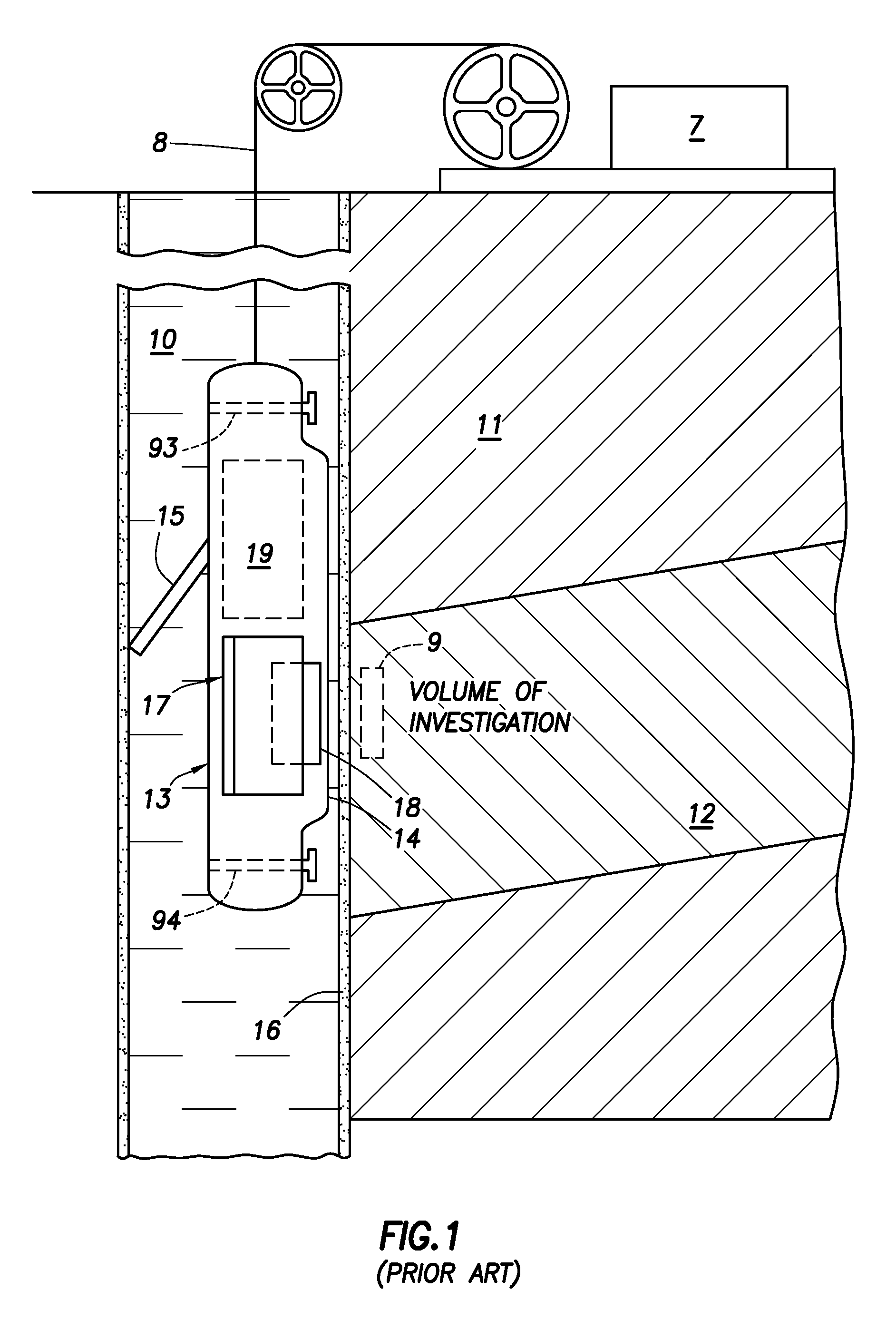
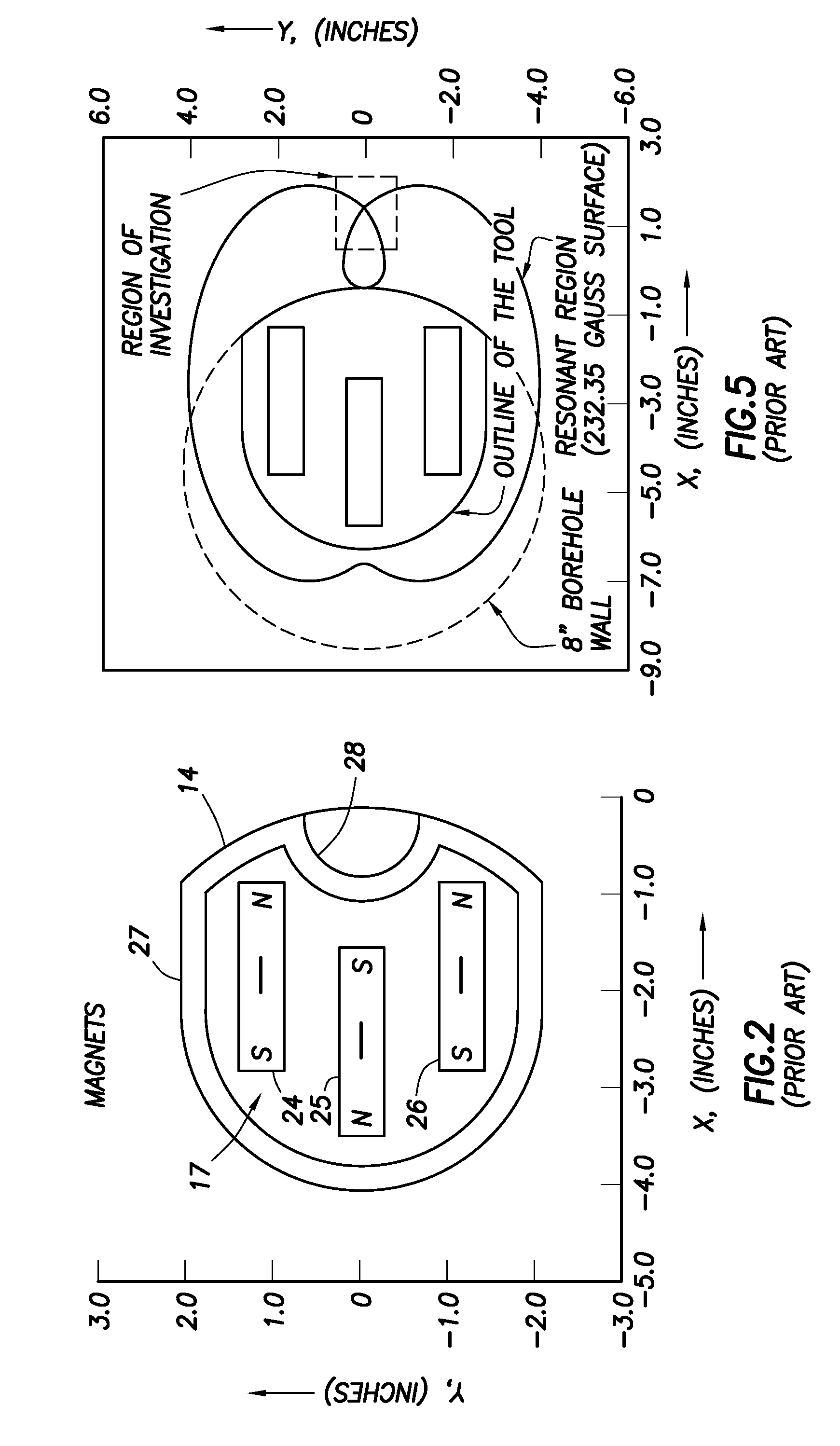
ActiveUS7564240B2Minimize contribution of inhomogeneityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic measurementsSpinsComposition analysis
A method to obtain a free induction decay signal using includes inducing a static magnetic field in a sample volume. A radio frequency (RF) magnetic field is then induced in the sample volume. The RF magnetic field has parameters selected to minimize the contribution of inhomogeneity in the static magnetic field to a free induction decay time. The free induction decay signal is then detected from the sample volume. In one example, prior to inducing the RF magnetic field, a reorienting radio frequency magnetic field is induced in the sample volume to reorient magnetic spins by a first selected angle. The inducing the RF magnetic field in this example has parameters selected to reorient spins by a second angle. The inducing the RF magnetic field and detecting the free induction decay signal are repeated until nuclear magnetic equilibrium is substantially attained.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
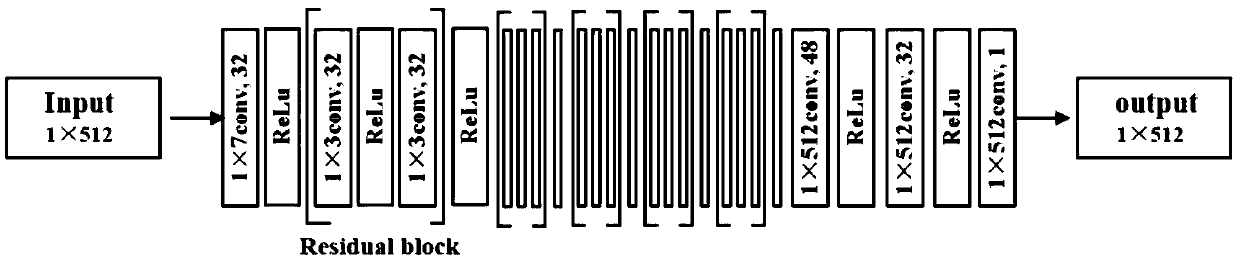
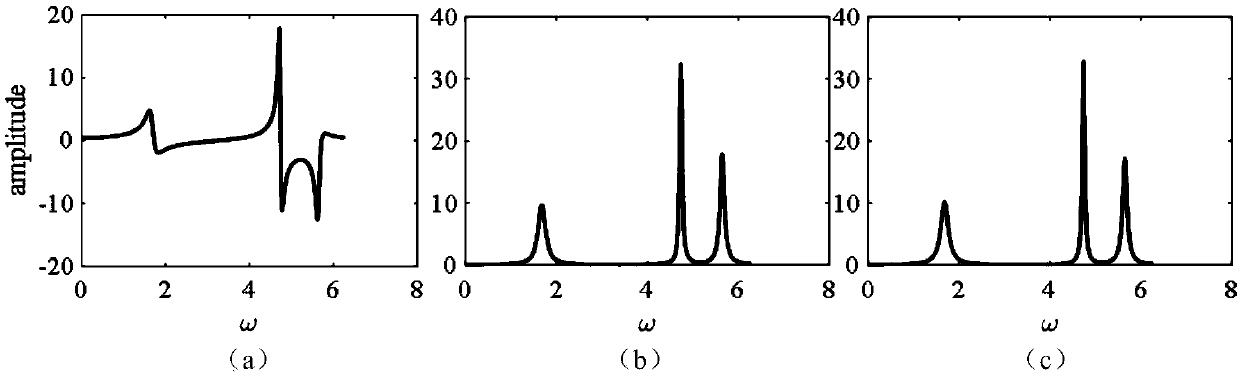
Time-frequency transform and phase correction method of magnetic resonance signal based on residual network
InactiveCN109557487AIdeal absorption spectrumMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyNeural architecturesFrequency spectrumMathematical model
The invention discloses a time-frequency transform and phase correction method of a magnetic resonance signal based on a residual network, related to time-frequency transform methods of magnetic resonance signals. The time-frequency transform and phase correction method of the magnetic resonance signal based on the residual network comprises the following steps: constructing a mathematical model of a free-sensing attenuation time-domain signal having zero-order phase imbalance and first-order phase imbalance simultaneously and an ideal absorption spectrum according to the characteristics of aFID signal, that is, constructing a mathematical model of the spectrum real part without phase imbalance, and generating a simulation signal by means of the mathematical model to construct training set data and test set data; constructing a residual network model and setting relevant training parameters; performing network training; and performing network testing. The free-sensing attenuation signal in the time domain is automatically transformed into the ideal absorption spectrum by using the residual neural network in deep learning, that is, the spectrum real part with the phase imbalance does not exist. In the process, the automatic conversion from the time domain to the frequency domain and the automatic correction of the phase imbalance are completed, so that the ideal absorption spectrum can be obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for fast multi-slice mapping of myelin water fraction
InactiveUS8170644B2Increase the number ofExpand coverageMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseMulti slice
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis method
ActiveUS20170052238A1Simple correctionEfficient simple correctionMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFrequency spectrum
Method for analyzing a sample including a species to be characterized and a reference species, includes:acquiring one or more complex free induction decay (FID) signal(s) (S(t)),obtaining a FID spectrum S(ω) by applying a Fourier transform to the signal S(t), with the FID spectrum obtained including two portions, each extending from the resonance frequency of the reference species (F0ref) and respectively on either side of F0Ref, with the frequency of the species to be characterized located on a portion of the spectrum;modeling the signal of the reference species from the real and complex parts of the at least one complex FID signal;obtaining a spectrum Sref(ω) of the reference species including the reference species only,obtaining a modified FID {tilde over (S)}(ω) spectrum;applying a reverse Fourier transform to {tilde over (S)}(ω) to obtain a modified signal {tilde over (s)}(t);calculating the module of the {tilde over (s)}(t) modified FID signal.
Owner:UNIV DE PROVENCE D AIX MARSEILLE I +1
Analysis method of high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance FID signal
InactiveCN102023174AFrequency Accurate EstimationThe result is accurateMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
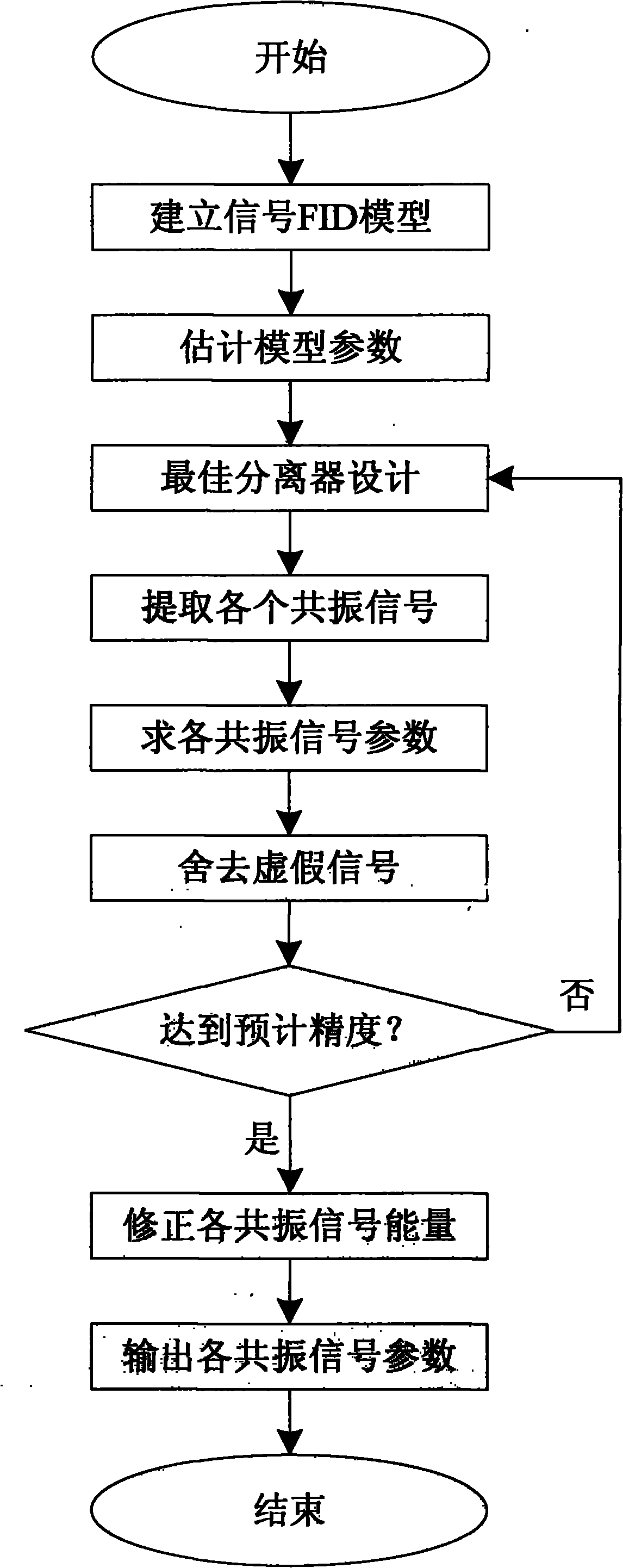
The present invention relates to analysis and treatment of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) time-domain free induction decay signal (FID). The resonance signal parameters of FID signal are measured by pre-estimate of parameters, iterative separation and accurate estimate of parameters, and calculation of final result. Compared with traditional Fourier transform method, the method can estimate resonance frequency and peak area of FID signal in high resolution and appear transverse relaxation time, further to achieve correct results at a low ratio of signal to noise.
Owner:吴雪梅
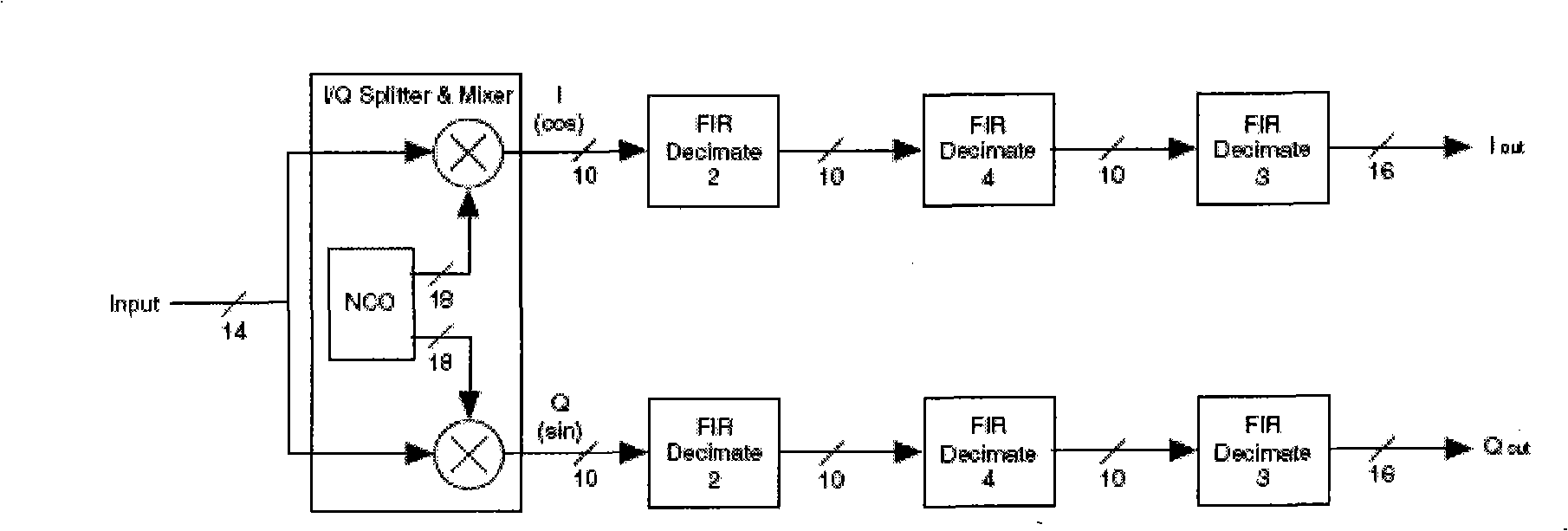
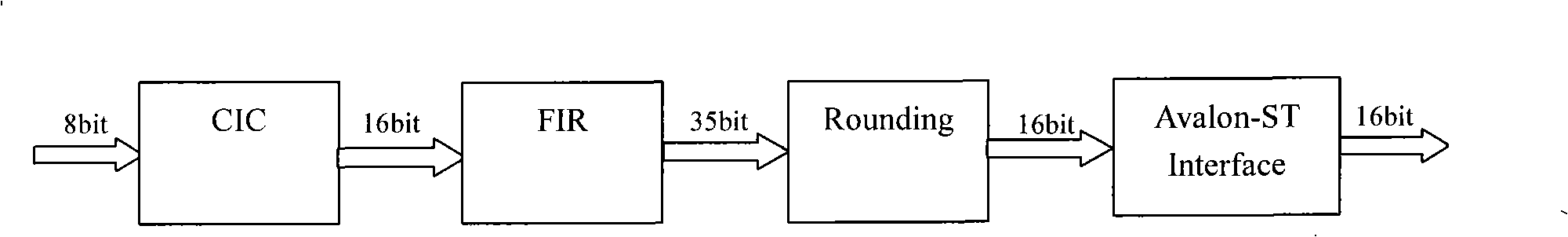
Magnetic nuclear resonance radio frequency receiving signal digital downward conversion implementing device and method
InactiveCN101334456AChange the decimation rate in real timeSave resourcesDigital technique networkMeasurements using NMRDigital signal processingNumerical control
The invention relates to a device and a method for realizing the nuclear magnetic resonance radio frequency received signal digital down conversion, which are realized on the basis of the FPGA technology, the device comprises a DC-offset suppressor, a command decoder, a numerical controlled oscillator, a real part channel, an imaginary part channel and an output control interface, wherein, the DC-offset suppressor suppresses the DC-offset which is generated during the digital signal processing process; the command decoder decodes control words of the numerical controlled oscillator, the related control words of a CIC comb filter and the control words of a DDC output in a real-time manner; the numerical controlled oscillator decodes the control words of the numerical controlled oscillator in the real-time manner; the real part channel and the imaginary part channel complete the orthogonal detection operation of a digital nuclear magnetic resonance free induction decay signal from the radio frequency signal to the baseband signal; and the output control interface realizes the data communication with a follow-up digital signal processing module or a data memory. The device has strong practicability and can be flexibly updated according to user needs, thereby avoiding the crises that the whole product can not be continued or the production of the whole product is stopped due to the termination of the life cycle of key components, etc.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD +1
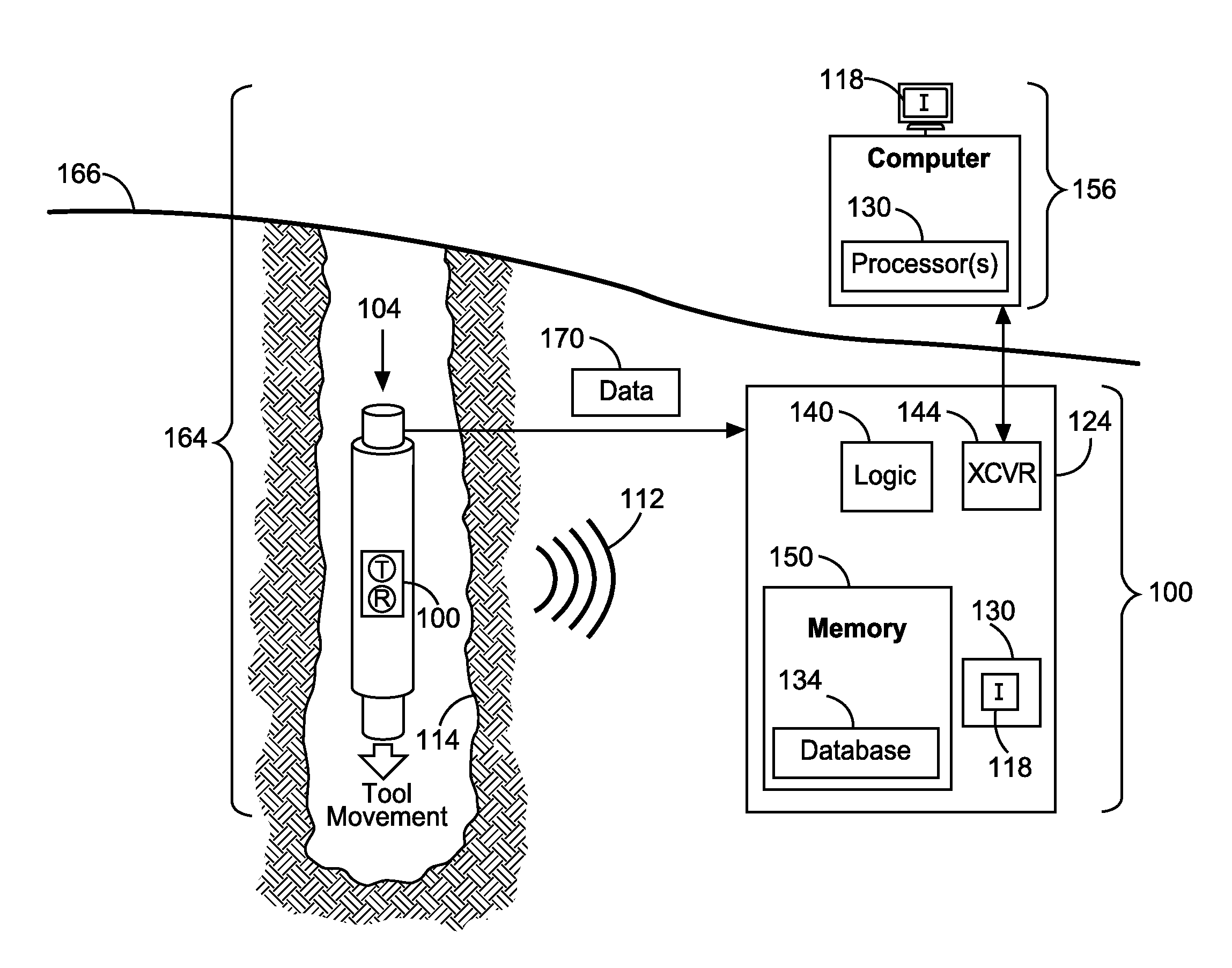
Frequency location apparatus, methods, and systems
ActiveUS20150204186A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceDecomposition
In some embodiments, an ex-situ apparatus and a system, as well as a method and an article, operate to transmit wideband modulated pulses to generate an externally-projected oscillating magnetic field in a material body, to record one or more raw echo free induction decay (REFID) signals during echo acquisition periods following some of the second modulated pulses, and to transform the acquired REFID signals via frequency decomposition to determine a preferred nuclear magnetic resonance frequency associated with a maximum amplitude of decomposed frequency components. Additional apparatus, systems, and methods are described.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
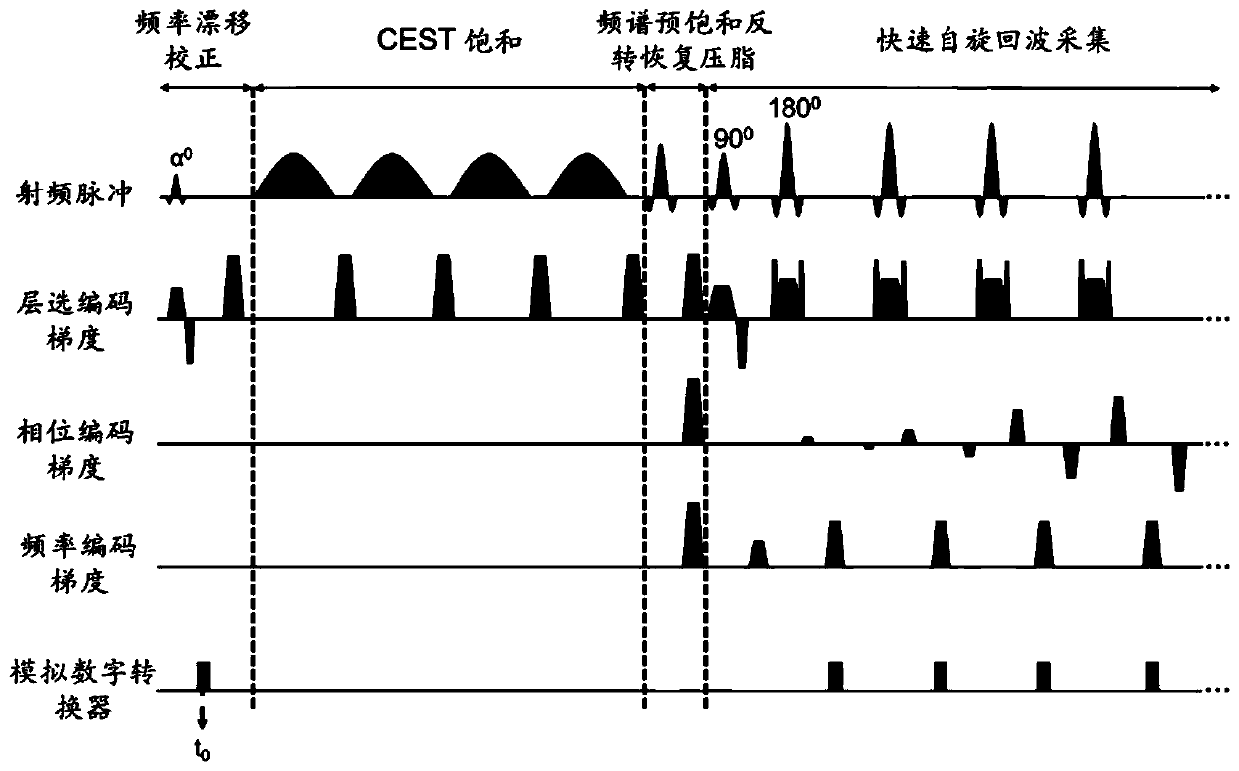
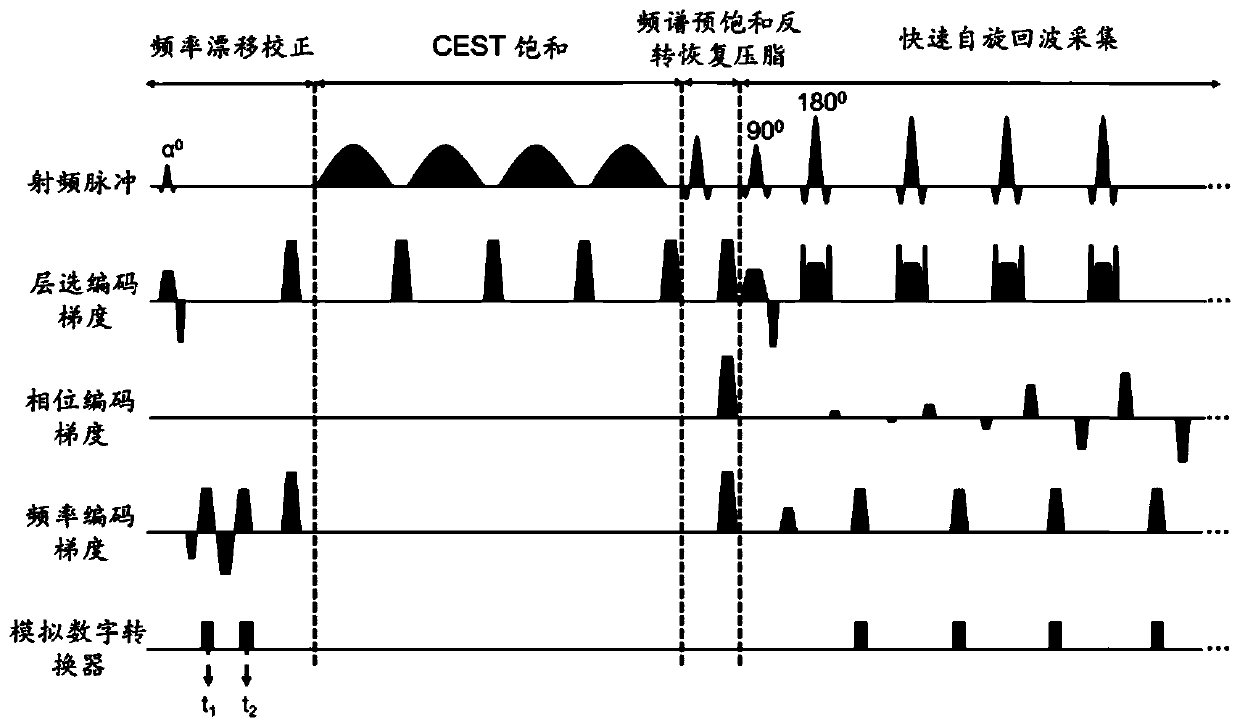
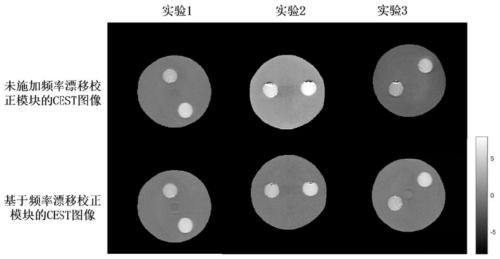
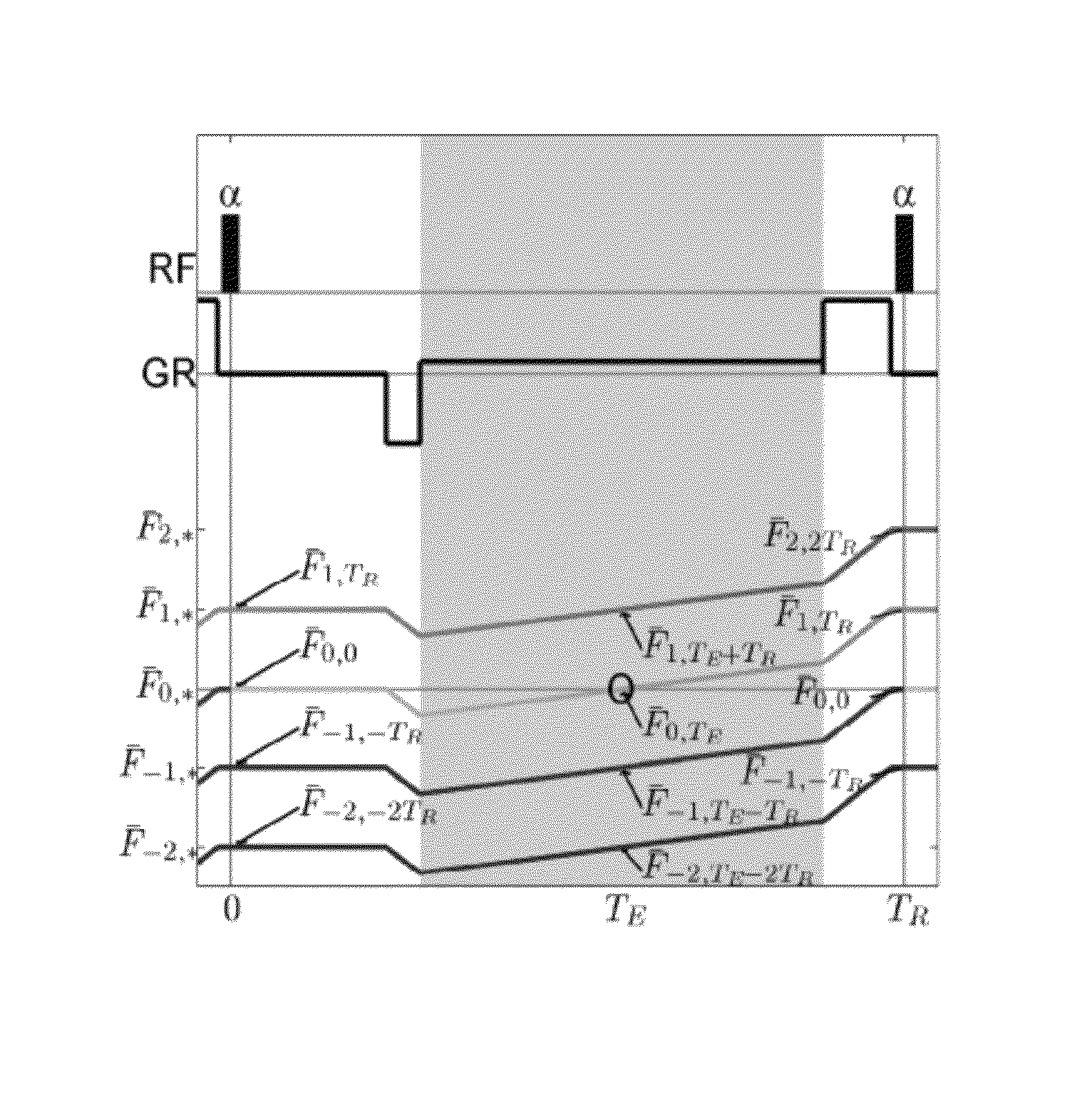
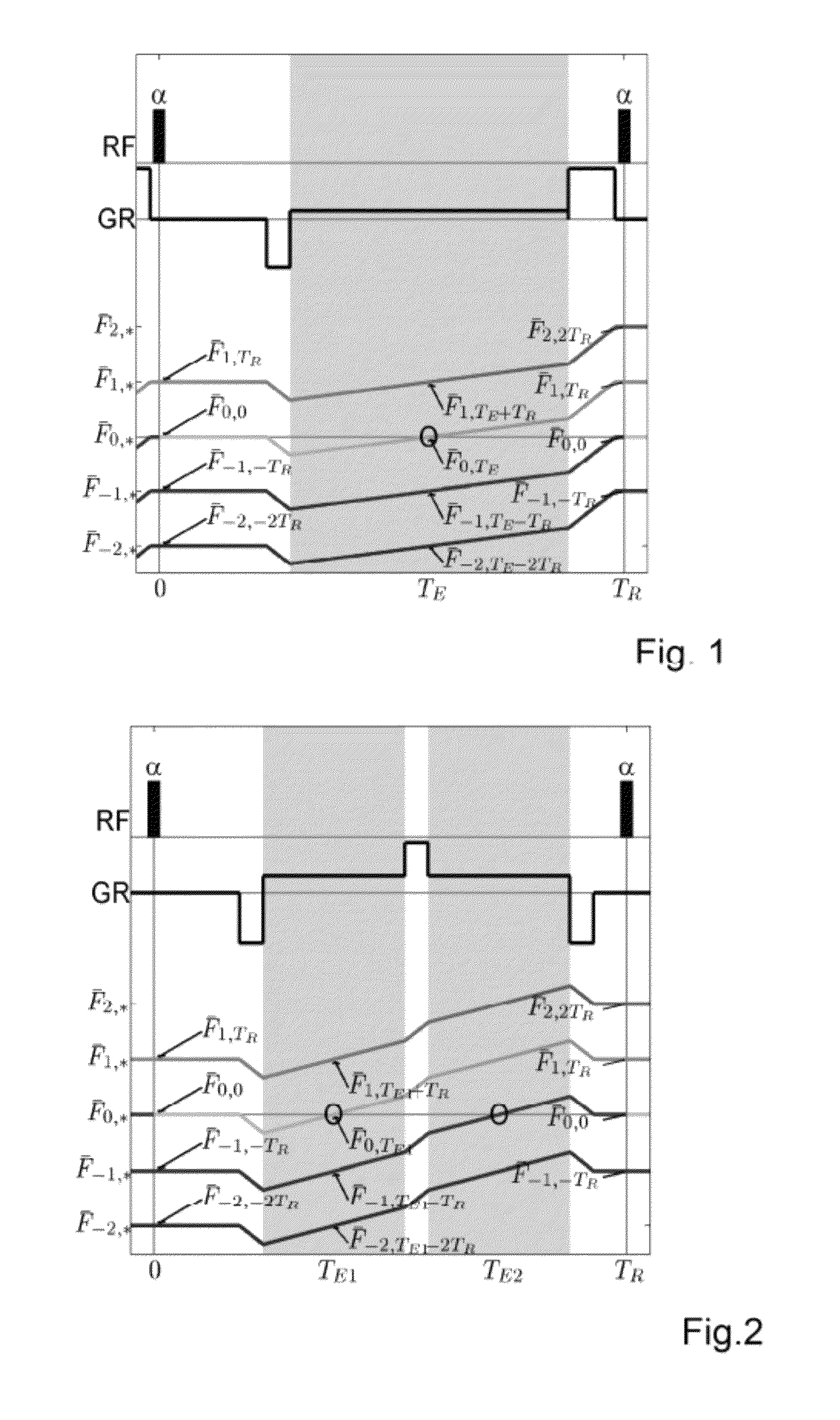
Magnetic resonance CEST imaging frequency drift correction method and device, medium and imaging equipment
ActiveCN111413655AImprove robustnessGood repeatabilityMagnetic measurementsImaging equipmentRadio frequency
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance CEST imaging frequency drift correction method and device, a medium and imaging equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, in a frequency drift correction module, exciting a target layer by using a small-flip-angle radio frequency pulse, and acquiring a single-row free induction attenuation signal or two-row non-phase encoding gradient echo signals; secondly, according to the phase information and the acquisition time of a single-row free induction attenuation signal or two-row non-phase coding gradient echo signals, calculating main magnetic field frequency drift values respectively; adjusting the center frequency of the magnetic resonance equipment in real time according to the main magnetic field frequency drift calculation value to realize real-time correction of the main magnetic field frequency drift; carrying out CEST imaging. Aiming at the problem of main magnetic field frequency drift in magnetic resonance CESTimaging, the invention provides a frequency drift correction module for correcting frequency drift in real time based on acquisition of a free induction attenuation signal or a non-phase encoding gradient echo signal, and therefore the robustness and repeatability of magnetic resonance CEST imaging are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of generating 2D or 3D maps of MRI T1 and T22 relaxation times
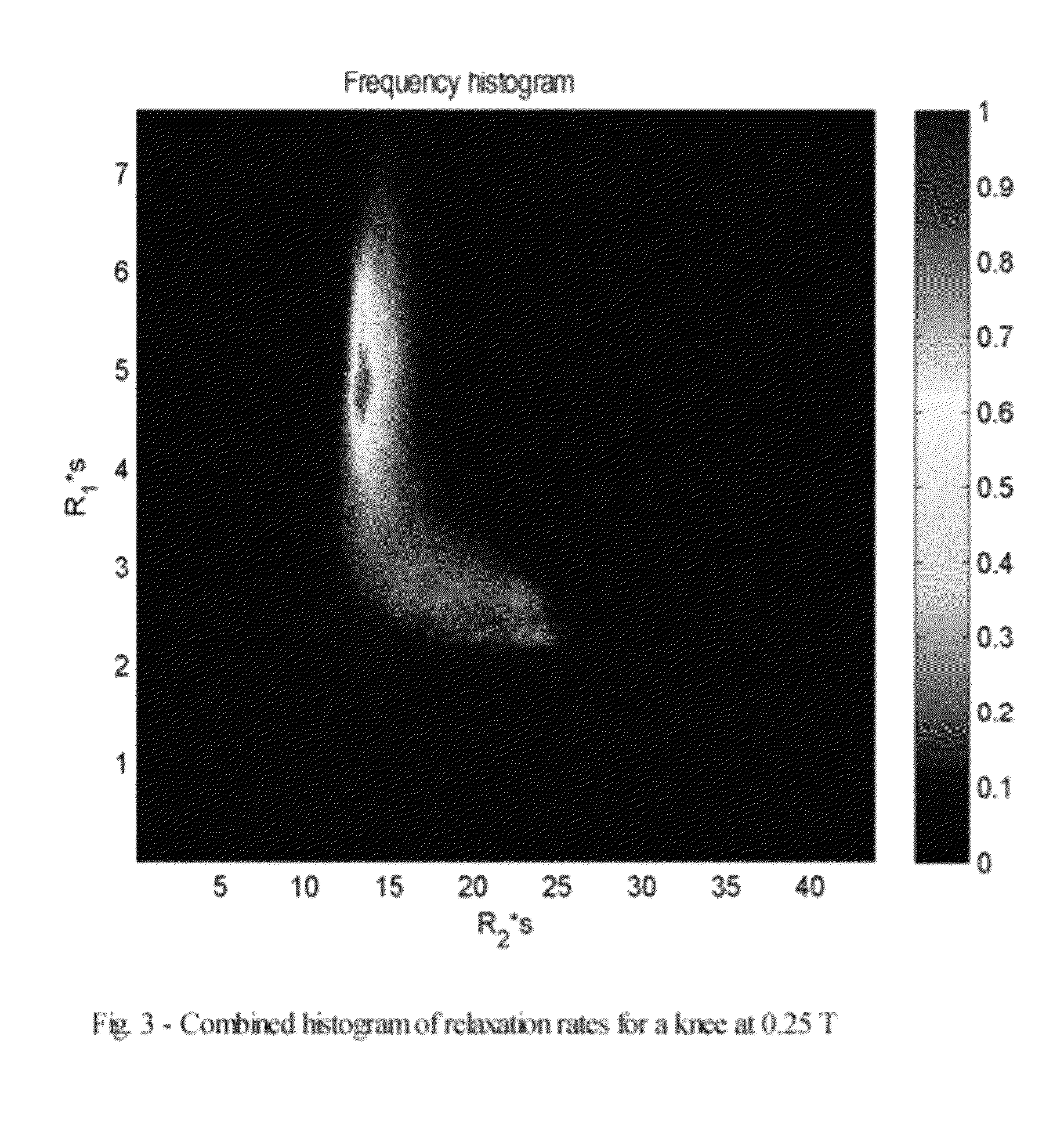
ActiveUS9052372B2Eliminate dependenciesMaximize signal to noise ratioMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionVoxelMri image
A method of generating 2D or 3D maps of MRI T1 and T2 relaxation times by acquiring 2D or 3D MRI gradient-echo images and extracting the T1 and T2 values from the images, wherein MRI images are acquired using a combination of gradient-echo sequences, including a first MRI image acquired using a SSFP-FID (Steady State Free Precession-Free Induction Decay) acquisition sequence; two further images acquired using a Dual-Echo SSFP acquisition sequence; and the T1 and T2 values are extracted for each image pixel or voxel from the corresponding MRI signals.
Owner:ESAOTE
Sense shimming (SSH): a fast approach for determining B0 field inhomogeneities using sensitivity encoding
InactiveUS8018230B2Reduce amountReduce acquisition timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData acquisitionSpatial image
The pursuit for ever higher field strengths and faster data acquisitions has led to the construction of coil arrays with high numbers of elements. With the SENSE technique it has been shown, how the sensitivity of those elements can be used for spatial image encoding. A method in accordance with the present invention, largely abstains from using encoding gradients. The resulting sensitivity encoded free induction decay (FID) data is then not used for imaging, but for determining field inhomogeneity distribution. The method has therefore been termed SSH for Sense SHimming.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Method and Apparatus for Measuring Free Induction Decay Signal and Its Application to Composition Analysis
ActiveUS20080315873A1Minimize contribution of inhomogeneityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic measurementsSpinsComposition analysis
A method to obtain a free induction decay signal using includes inducing a static magnetic field in a sample volume. A radio frequency (RF) magnetic field is then induced in the sample volume. The RF magnetic field has parameters selected to minimize the contribution of inhomogeneity to the static magnetic field to a free induction decay time. The free induction decay signal is then detected from the sample volume. In one example, prior to inducing the RF magnetic field, a reorienting radio frequency magnetic field is induced in the sample volume to reorient magnetic spins by a first selected angle. The inducing the RF magnetic field in this example has parameters selected to reorient spins by a second angle. The inducing the RF magnetic field and detecting the free induction decay signal are repeated until nuclear magnetic equilibrium is substantially attained.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
MRI RF encoding using multiple transmit coils
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
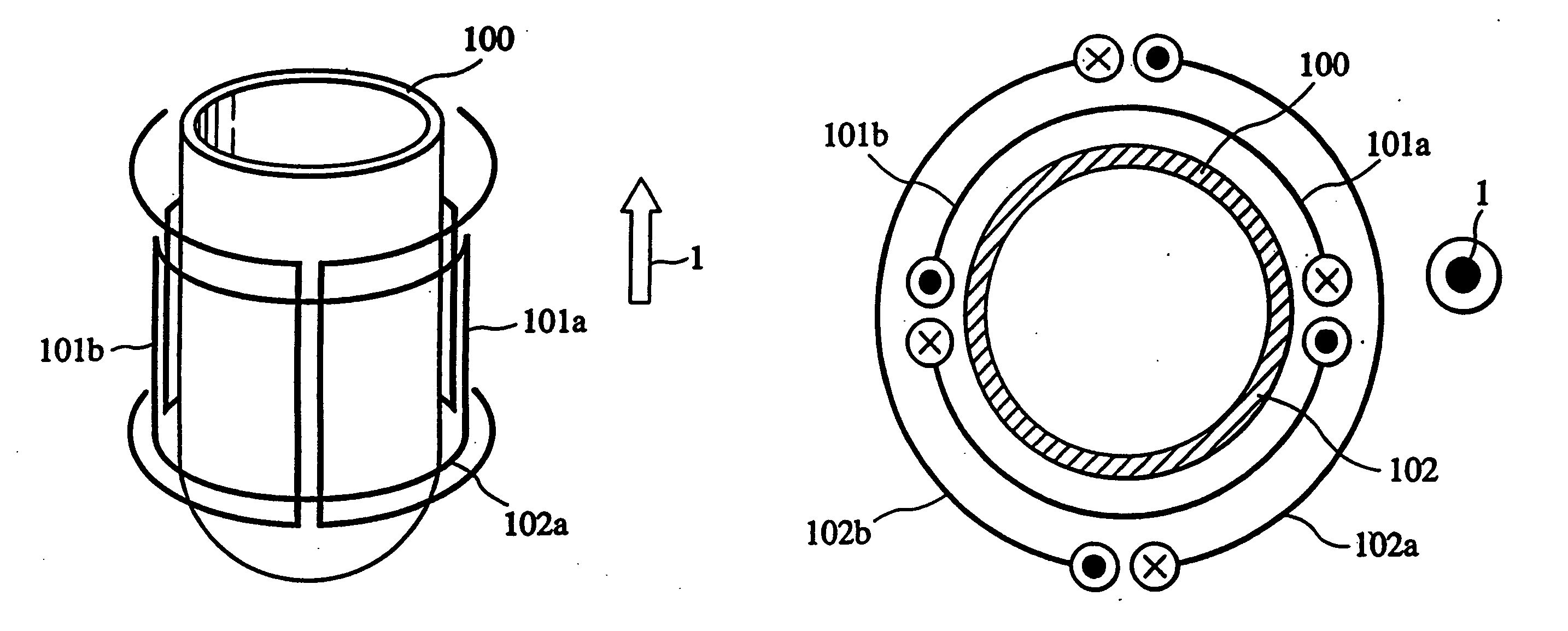
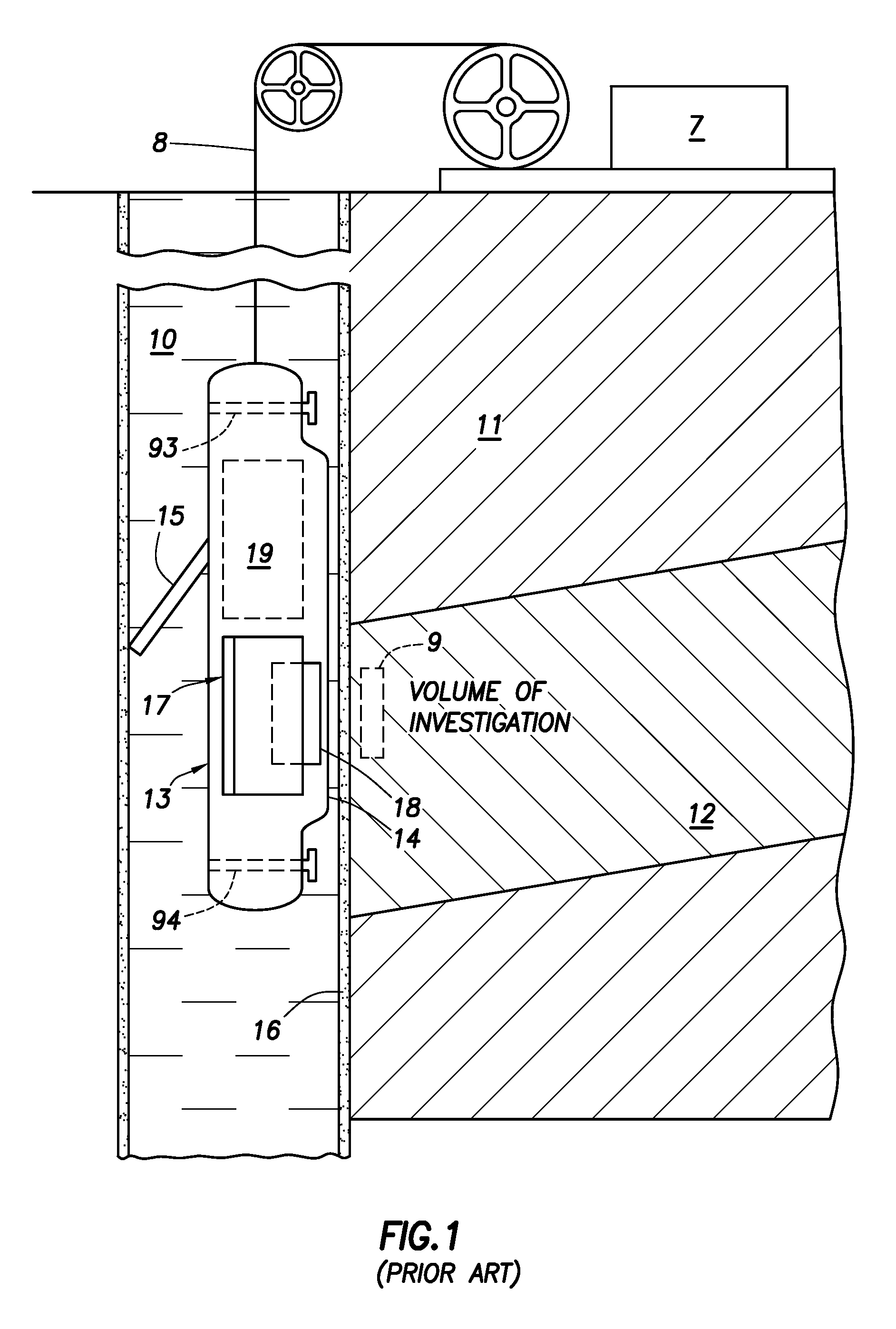
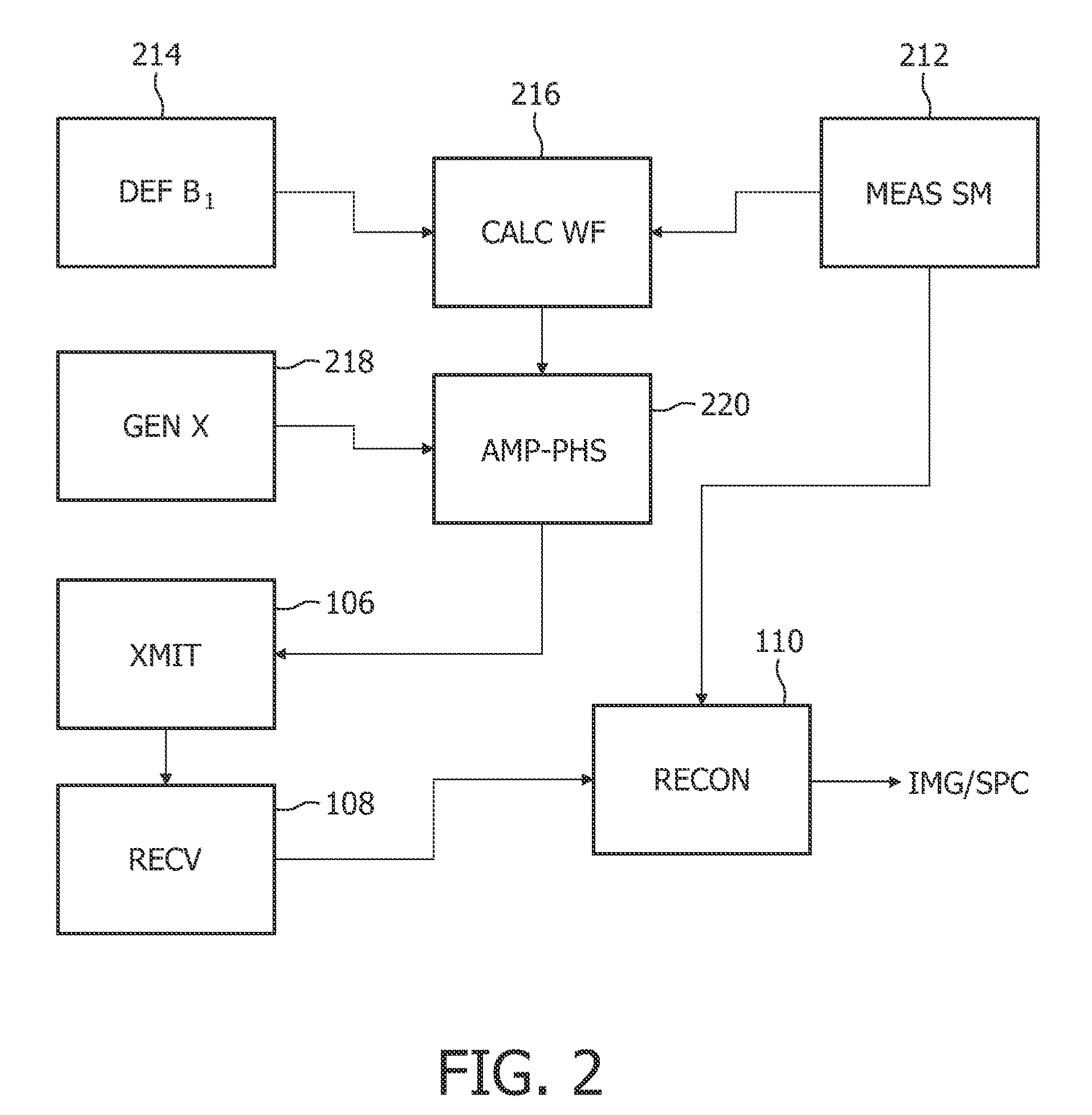
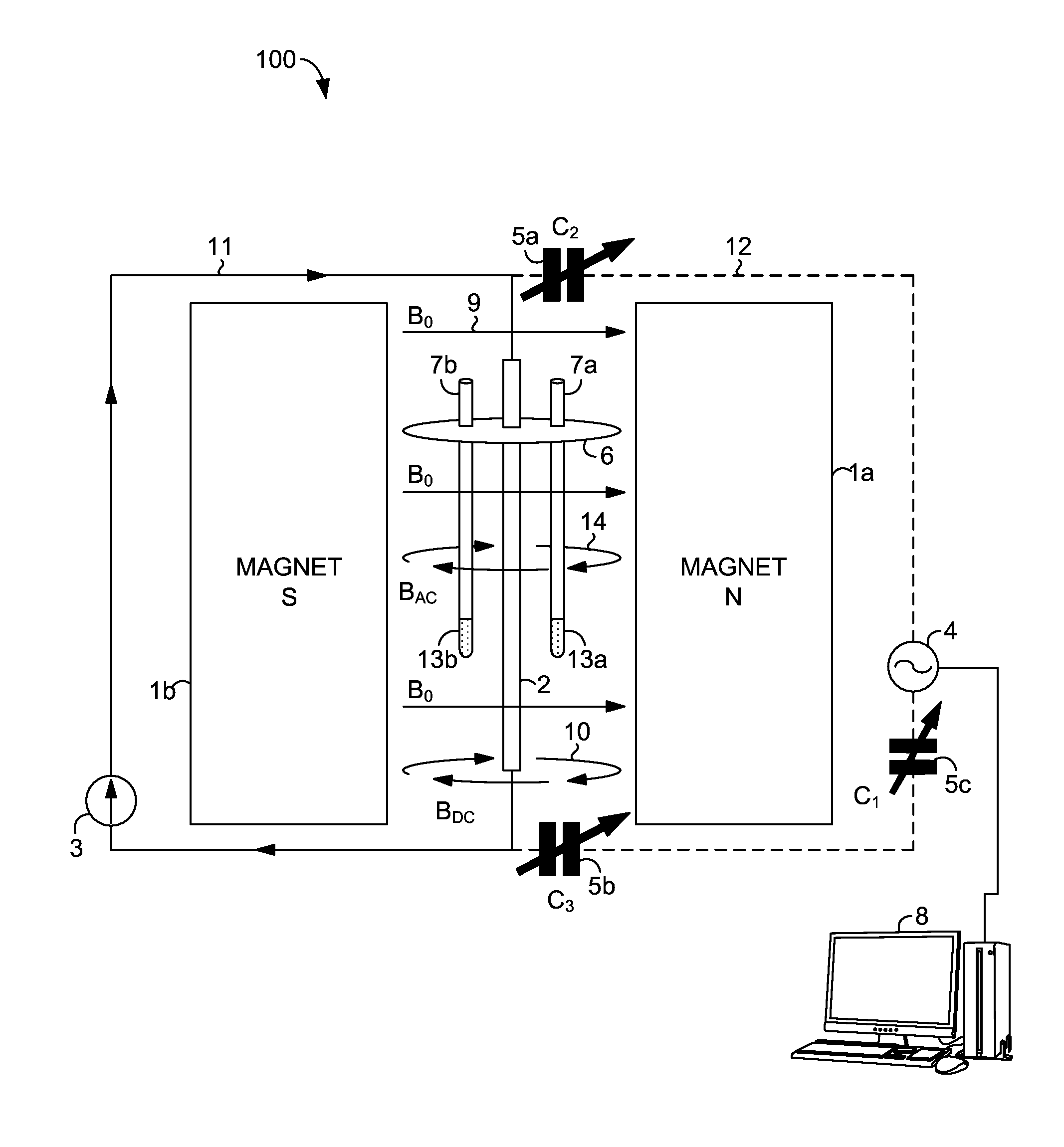
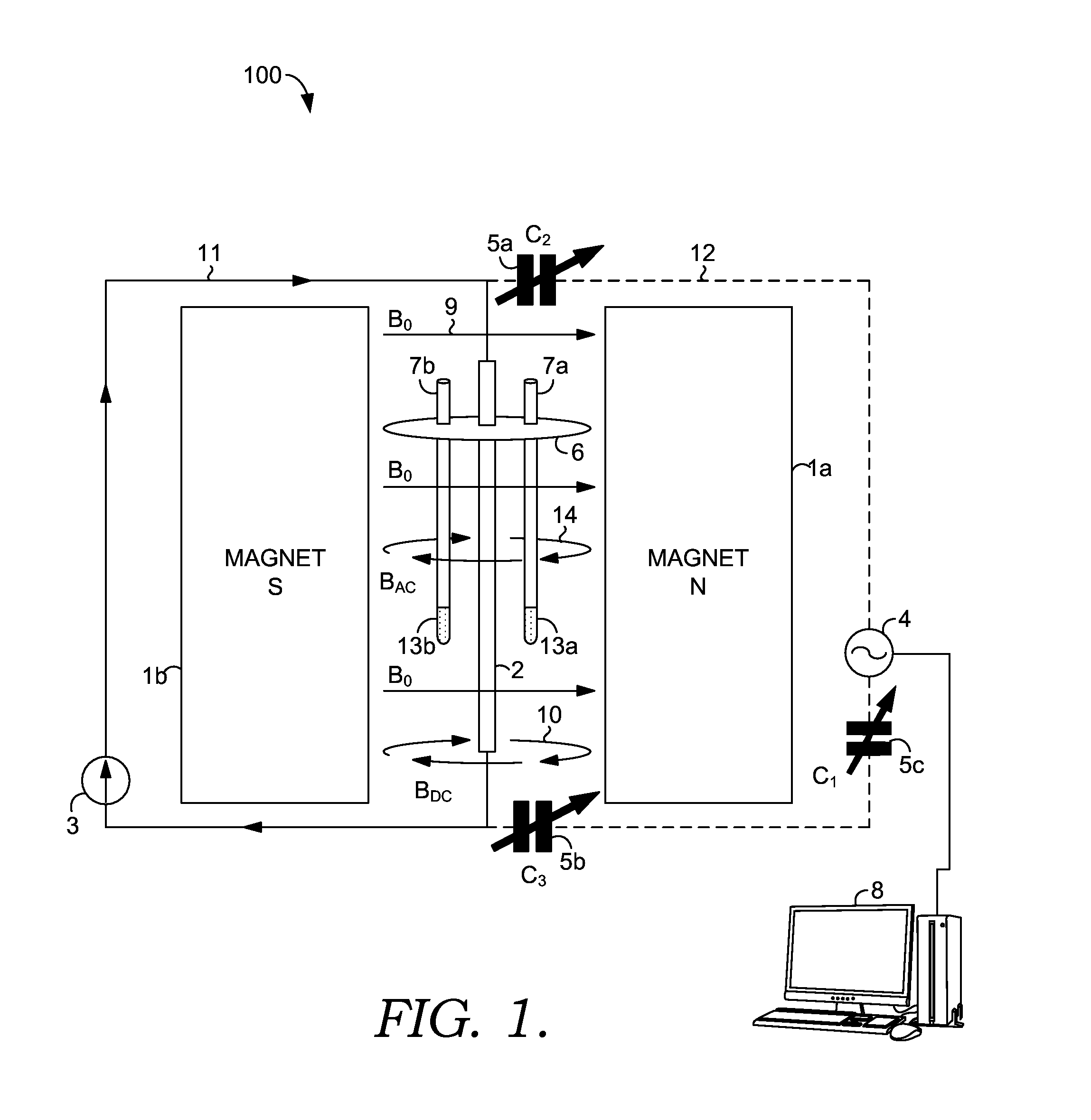
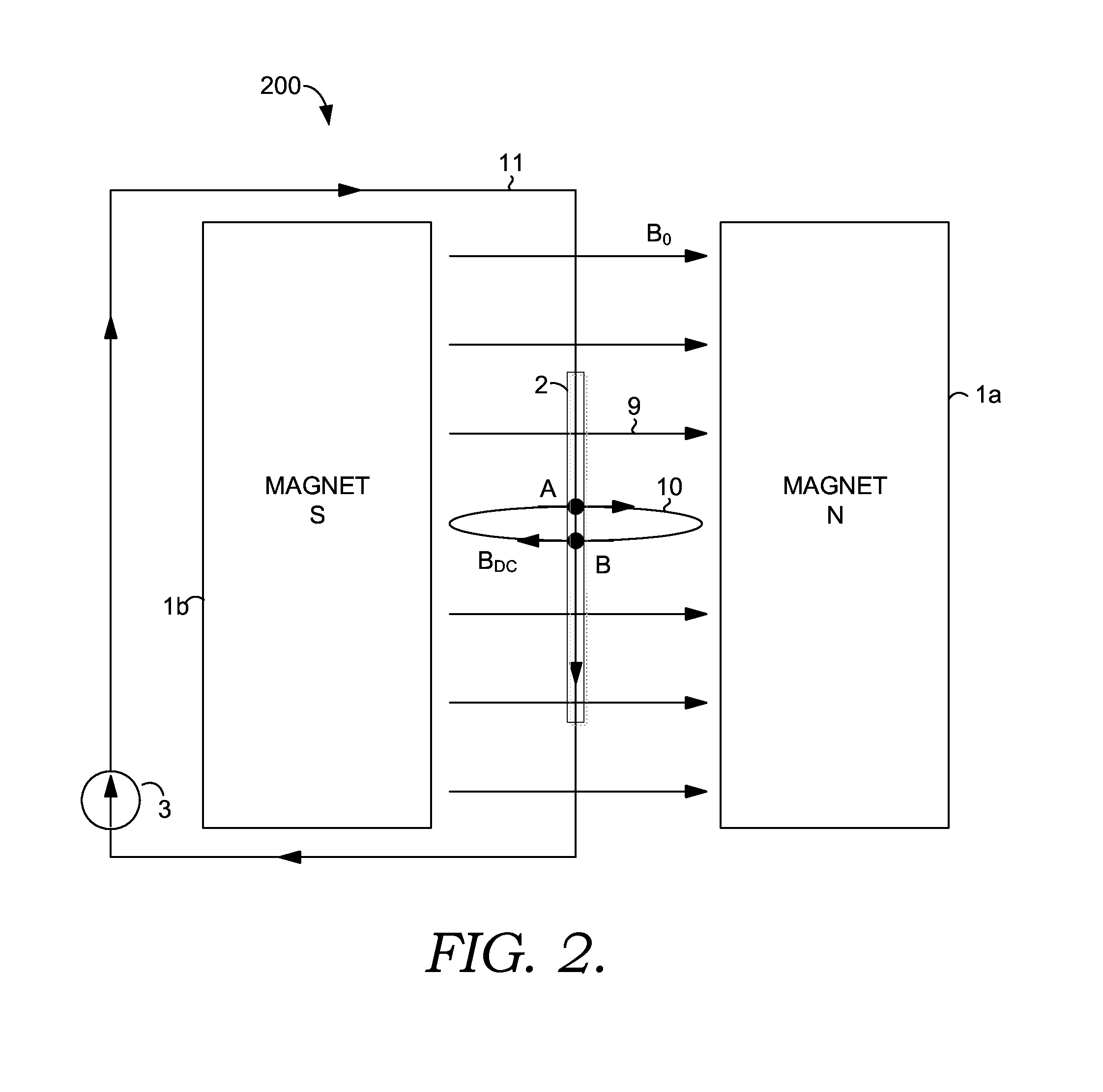
Device for Subdividing Magnetic Field and Simultaneous Detection of Magnetic Resonance Signals from Multiple Sample Compartments
InactiveUS20170030985A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectricitySpectroscopy
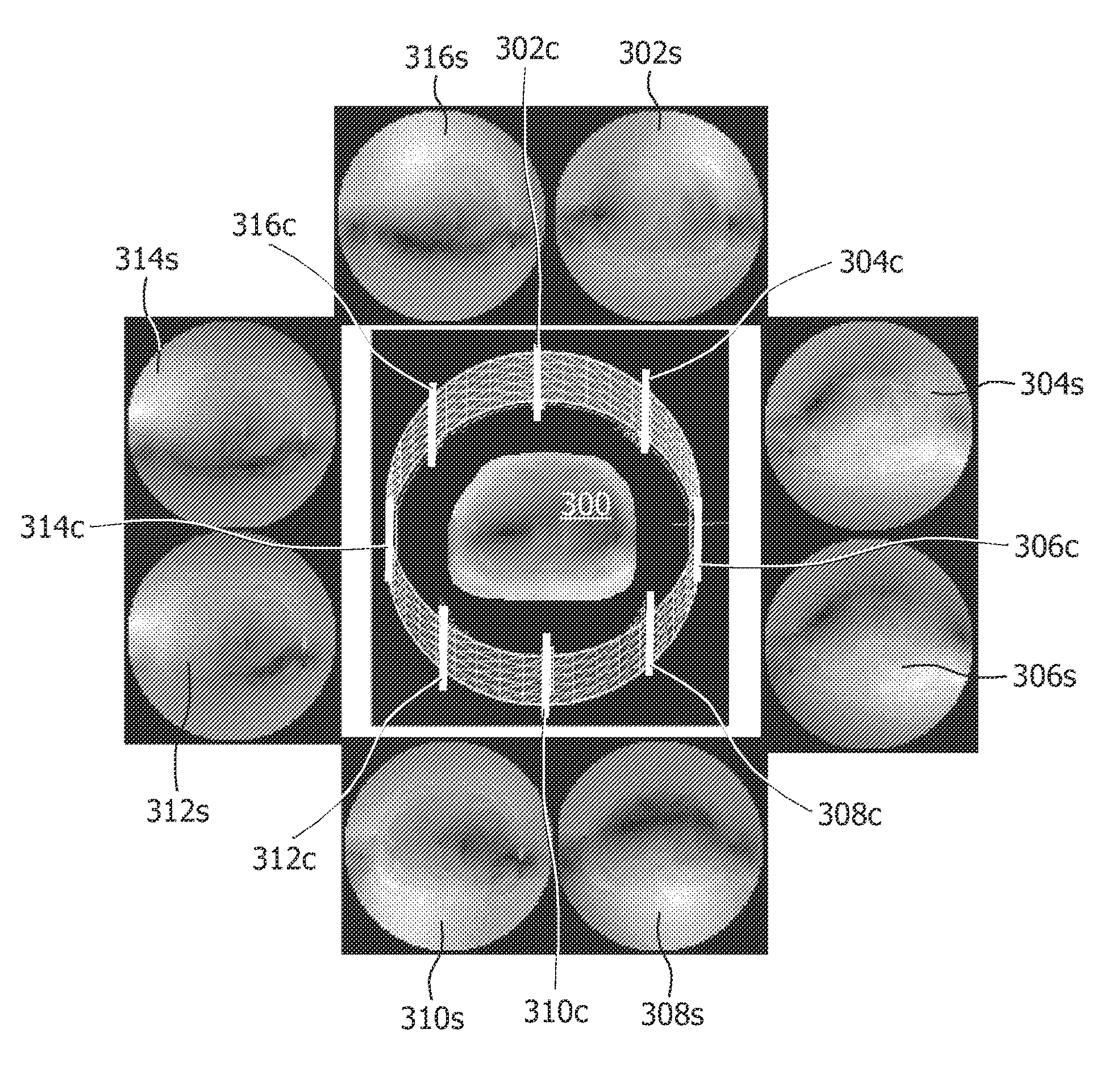
Devices and methods are provided for simultaneously interrogating multiple samples using NMR spectroscopy. A first magnetic field is induced. A flow of electricity is induced through a conductive material. The flow of electricity has a direction that is perpendicular to the first magnetic field, and the flow of electricity induces a second magnetic field. A first sample is placed in an additive magnetic field region, where a direction of the first magnetic field and a direction of the second magnetic field are aligned within the additive magnetic field region. A second sample is placed in a canceling magnetic field region, where the direction of the first magnetic field and the direction of the second magnetic field are opposed within the canceling magnetic field region. A free induction decay (FID) of at least the first and second samples is induced.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com