Patents
Literature
252 results about "Superconducting thin films" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nuclear magnetic resonance equipment
InactiveUS6958608B2High sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceSpectroscopy
The invention provides nuclear magnetic resonance equipment realizing improved sensitivity of a probe for receiving a free induction decay (FID) signal in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in a high frequency band of 600 MHz or higher. By manufacturing a solenoid coil of a higher filling factor by using a superconductor of extremely low resistance to high frequency current, sensitivity is increased. A superconducting thin film made of magnesium diboride (MgB2) formed on a donut plate-type substrate is disposed so that the film surface becomes parallel with the uniform magnetic field. The object is realized by a probe made by a solenoid coil formed by connecting a plurality of coil parts by capacitive coupling via a normal metal lead.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
High power superconductive circuits and method of construction thereof
InactiveUS6041245AReduce current densityHigh Power Handling CapabilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesMicrowaveHigh-temperature superconductivity
A high power high temperature superconductive circuit for use in various microwave devices including filters, dielectric resonator filters, multiplexers, transmission lines, delay lines, hybrids and beam-forming networks has thin gold films deposited either on a substrate or on top of the high temperature superconductive film. Alternatively, other metal films can be used or a plurality of dielectric films can be used or a dielectric constant gradient substrate can be used. The use of these materials in a part or parts of a microwave circuit reduces the current density in those parts compared to the level of current density if only high temperature superconductive film is used. This increases the power handling capability of the circuit.
Owner:COM DEV LTD
High-throughput ex-situ method for rare-earth-barium-copper-oxide (REBCO) film growth
ActiveUS20050127133A1Limit reaction kineticsInhibit REBCO film growthCooking-vessel materialsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsHigh fluxWater vapor
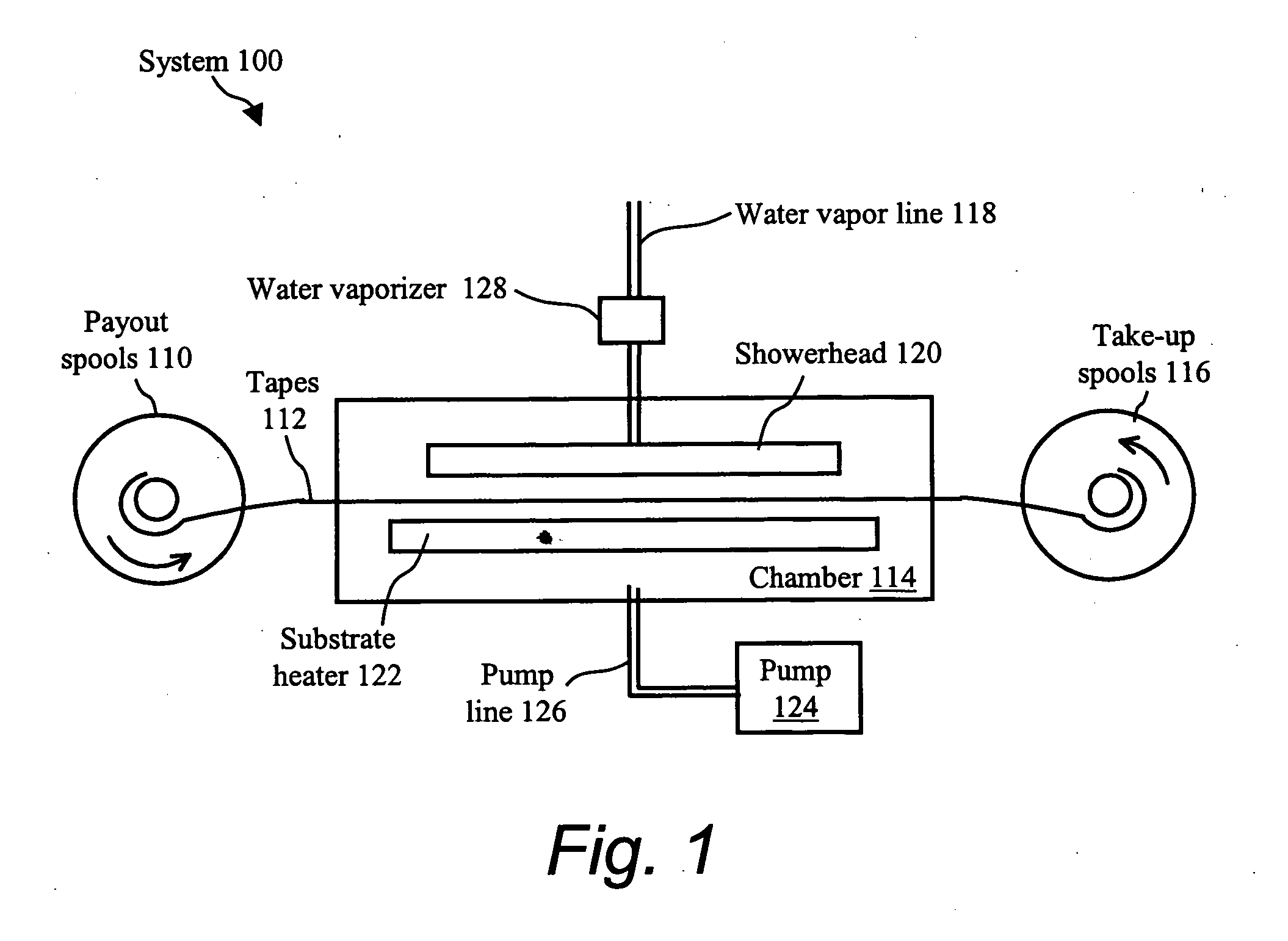
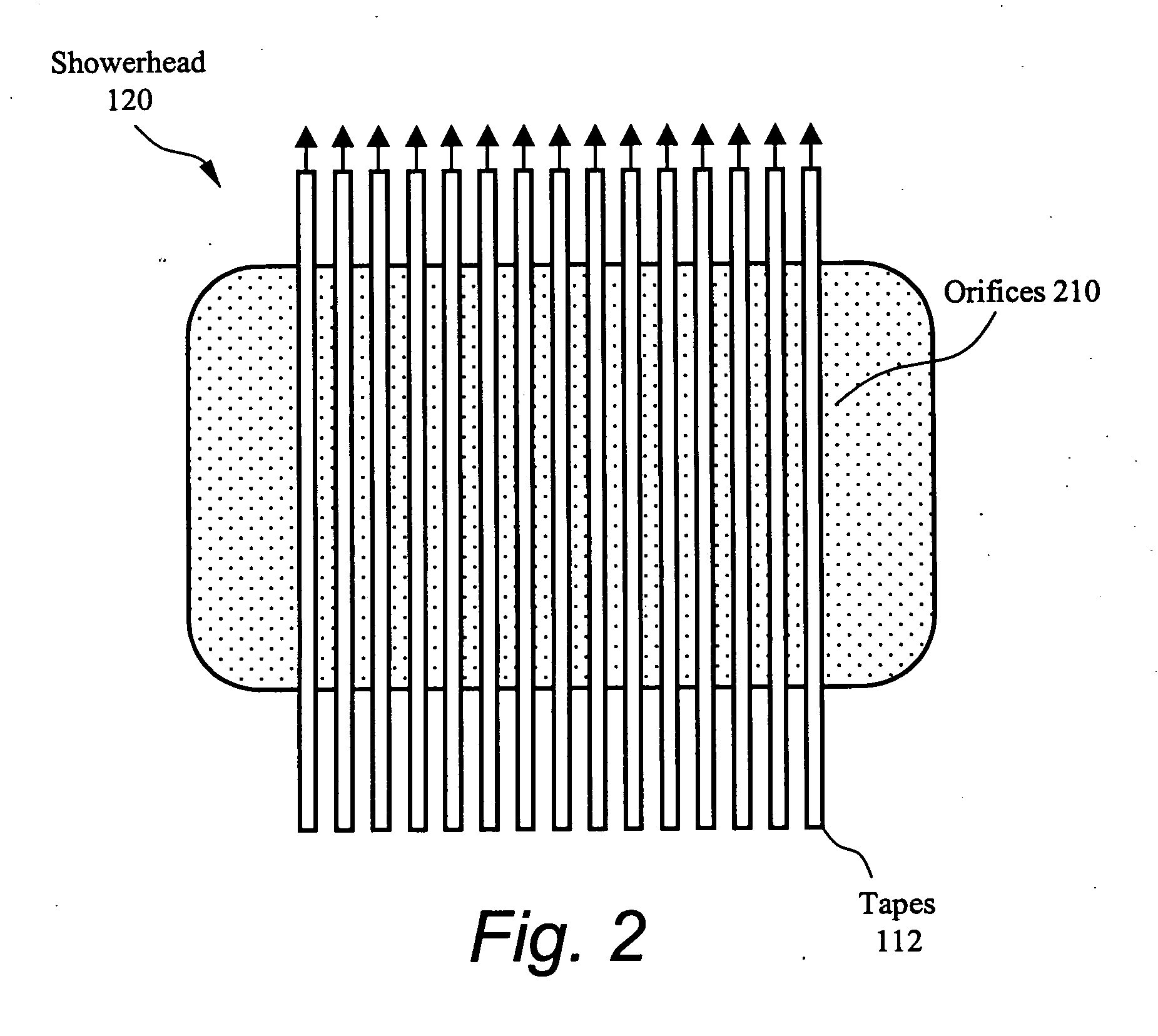
The present invention provides a high-throughput system for the ex-situ formation of a superconducting thin film, such as rare-earth-barium-copper-oxide (REBCO), atop a continuous length of buffered metal substrate tape by heating a buffered metal substrate tape coated with precursors of REBCO These precursors, when heated and introduced to water vapor within a process chamber, decompose to form a functional superconducting thin film epitaxial to the buffer layer. A chamber such as a metalorganic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) reactor having showerhead and substrate heater assemblies designed for the creation of a long and wide deposition zone is well suited for use in the process the system. The chamber could be of cold-wall type where the walls are not heated or could of hot-wall type where the walls are heated.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
Method for producing microstructured templates and their use in providing pinning enhancements in superconducting films deposited thereon
ActiveUS20110160066A1Increased flux pinningReduce AC-lossVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhase splittingThin membrane
The present invention relates to a method for producing a phase-separated layer useful as a flux pinning substrate for a superconducting film, wherein the method includes subjecting at least a first and a second target material to a sputtering deposition technique in order that a phase-separated layer is deposited epitaxially on a primary substrate containing an ordered surface layer. The invention is also directed to a method for producing a superconducting tape containing pinning defects therein by depositing a superconducting film on a phase-separated layer produced by the method described above.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
High-speed SNSPD with high-absorption structure and preparation method of high-speed SNSPD
ActiveCN103579405AHigh quality growthImprove absorption rateMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureCounting rateQuantum efficiency
The invention discloses high-speed SNSPD with a high-absorption structure and a preparation method of the high-speed SNSPD. The SNSPD is based on a high-refraction-index incident medium and an air cavity structure, and can further improve the photon absorption rate of superconducting nanowire, and compared with the prior art, the SNSPD can achieves approximate 100 percent absorption rate with lower duty ratio in the condition of nanowire made of superconducting ultrathin membrane made of the same material and having the same thickness, so that the difficulty in electron beam lithography steps is greatly lowered, the SNSPD is beneficial to the preparation of superfine nanowire, the high-quality growth of superconducting films can be guaranteed through the adoption of an SOI substrate, the intrinsic quantum efficiency of a detector is not affected; moreover, the highest counting rate of the detector can be enhanced as the total length of the required nanowire is obviously reduced in the condition that the same effective detection area is guaranteed, and the probability of defect occurrence during the preparation process is obviously reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for manufacturing soft superconducting thin film
ActiveCN102867907AControl thicknessSimple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNiobiumOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a soft superconducting thin film. The method includes following steps: cleaning a substrate and removing organic pollutants on the surface of the substrate; coating a polyimide film on the substrate and curing the polyimide film; direct-current sputtering a nitriding niobium superconducting thin film on the substrate coated with the polyimide film; removing the substrate; and stripping the substrate and the polyimide film. By the aid of the method, the soft superconducting thin film with a controllable thickness (micron dimension) can be manufactured, and application occasions and scope of the superconducting thin film and devices are widened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
YBCO high-temperature superconductive film band connection technology and special-purpose auxiliary clamp thereof
ActiveCN104710186AFirmly connectedLow joint resistanceSuperconductor elements usageEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an YBCO high-temperature superconductive film band connection technology and a special-purpose auxiliary clamp thereof. Through the specific connection clamp and its technological parameter, two high-temperature superconductive film bands are rapidly connected by a low temperature solder in short time, and low joint resistance value and good mechanical strength are provided. The whole technological parameter can be accurately optimized, for the solder with melting point lower than 140 DEG C, the welding temperature approaches to 155 DEG C, heating time is 20 minutes, and the clamp temperature is cooled to 129 DEG C and is placed on a steel plate for rapidly cooling. Through the above parameters, joint resistance magnitude order can reach 10<-7> omega even connection length is 1cm, and the resistance value can be lower if the connection length is greater than 1cm. The connection technology of the YBCO high-temperature superconductive film band has the advantages of rapid, convenient operation, high efficiency, low temperature during the connection process and short time, and is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation method of high-temperature superconducting thin film
ActiveCN103184513AGuaranteed 2D epitaxial growthAtomic level flatteningPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesCrystal structureCondensed matter physics
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-temperature superconducting thin film. The method specifically comprises steps as follows: providing an SrTiO3 substrate and placing the SrTiO3 substrate in a super-high vacuum system, growing an FeSe monocrystal layer on the surface of the SrTiO3 substrate by adopting a molecular beam epitaxy growing technology, and growing a protective layer with a layered crystal structure by adopting the molecular beam epitaxy growing technology and covering the surface of the FeSe monocrystal layer with the protective layer. By means of the method, the high-quality and ultrathin high-temperature superconducting thin film can be prepared, the starting temperature of superconducting transition of the thin film is above 54K, and the critical current density is higher than 106A / cm<2> when the starting temperature of superconducting transition of the thin film is 12K.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Mounting structure for semiconductor device
InactiveUS6323426B1Superconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
A mounting structure for a high temperature superconductor device, such as a filter, housed in a closed vacuum chamber and operated at a low temperature. The filter has dielectric substrate having: first and second surfaces; a circuit portion made of a superconducting thin film formed on the first surface of the dielectric substrate; and a ground layer consisting of a superconducting thin film formed on second surface of the dielectric substrate and a metal film deposited on the superconducting thin film. The mounting structure comprises: a device holder for holding the filter thereon; a conductive layer intervening between the ground layer of the filter and the device holder; urging parts for resiliently urging the filter toward the device holder. The conductive layer is made of a metal selected from among the group consisting of gold, silver, copper, aluminum and an alloy made of at least one of gold, silver, copper, and aluminum.The mounting structure can securely ground the ground layer of the filter enough to have an extremely low contact resistance as well as can have the amount of the released gas restricted.
Owner:ADVANCED MOBIL TELECOMM TECH
Device and method for testing superconductivity of three-dimensional low-temperature superconducting thin film coil
The invention relates to a device and method for testing the superconductivity of a three-dimensional low-temperature superconducting thin film coil, belonging to the field of a low-temperature superconductivity technology and high-accuracy measurement. Particularly, the superconductivity test is carried out on the three-dimensional low-temperature superconducting thin film coil, the superconductivity of the three-dimensional low-temperature superconducting thin film coil is tested and researched by means of a vacuum and low-temperature environment provided by a low-temperature environmental system and a vacuum environmental system provided by the invention, and further the three-dimensional superconducting thin film coil is designed in an auxiliary manner. The invention designs a low-temperature system for testing the superconductivity of the three-dimensional low-temperature superconducting thin film coil, therefore, a low-temperature environment needs to be provided for superconducting coils, as described in the background technology, in the low-temperature environment provided by the invention, liquid helium is utilized as a refrigerant, and the working temperature of a testing system is ensure to reach 4.2K, namely minus 269 DEG C. Therefore, as the tested three-dimensional low-temperature superconducting thin film coil is a core part in payloads of an STEP (satellite test of the equivalence principle) jointly developed by the NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) and the ESA (European Space Agency), the device and method provided by the invention belong to applied aerospace science and technology in terms of technology application.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Process for producing YBCO superconducting thin film target material
InactiveCN101492291AQuality improvementGuaranteed compactnessSuperconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingHigh densityHigh volume manufacturing
The invention provides a method for preparing YBCO superconducting film target materials. The method comprises the following: A, a step of preparing YBCO superconducting-phase powder; B, a step of preforming, which is to put the powder prepared in a step A in a die, compress the powder by use of the pressure of between 20 and 30 MPa on a press so as to manufacture a sheet, put the sheet obtained through compression in a rubber sleeve, perform cold isostatic pressing under the pressure of between 150 and 200 MPa and obtain a superconducting sheet; C, a step of sintering the sheet, which is to sinter the superconducting sheet obtained in a step B in a box-type furnace for 20 to 30 hours at a sintering temperature of between 850 and 960 DEG C; and D, a step of performing oxygen permeation, which is to put the superconducting sheet sintered in a step C in a tubular furnace, perform oxygen permeation treatment for 2 to 3 hours at a temperature of between 450 and 500 DEG C and obtain the target material. The target material prepared by the method has the advantages of uniformity, good shape, high density and good superconducting performance. In addition, the method is low in cost and suitable for the mass production of the target material.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Processing method for improving second generation high-temperature super-conducting strip interlayer binding force
ActiveCN107103957AImprove bindingReduced current carrying capacitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsApparatus for manufacturing conducting/semi-conducting layersState of artUltrasound attenuation
The invention provides a processing method for improving second generation high-temperature super-conducting strip interlayer binding force. The processing method comprises the following steps of taking a textured flexible strip as the base material, performing etching on an oxide layer on the surface of the strip, and controlling etching depth, width and patterns; and adopting the etched textured flexible strip to perform superconducting thin film deposition. Compared with the prior art, the processing method has the following beneficial effects: 1, the interlayer binding force of the second generation high-temperature super-conducting strip obtained by the preparation method is improved by more than one time, while the current-carrying capability attenuation is less than 20%; and 2, the second generation high-temperature super-conducting strip prepared by the preparation method has no influence to the structure and the preparation process of the subsequently prepared superconducting thin film.
Owner:上海翌曦科技发展有限公司
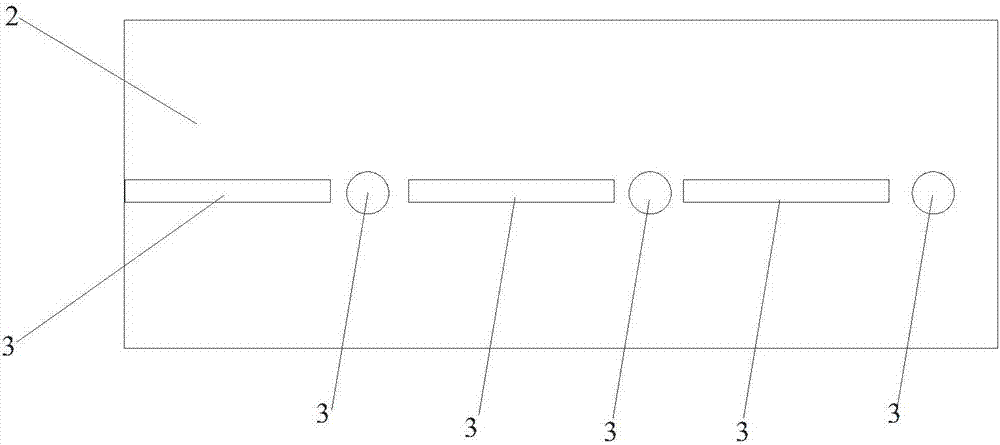
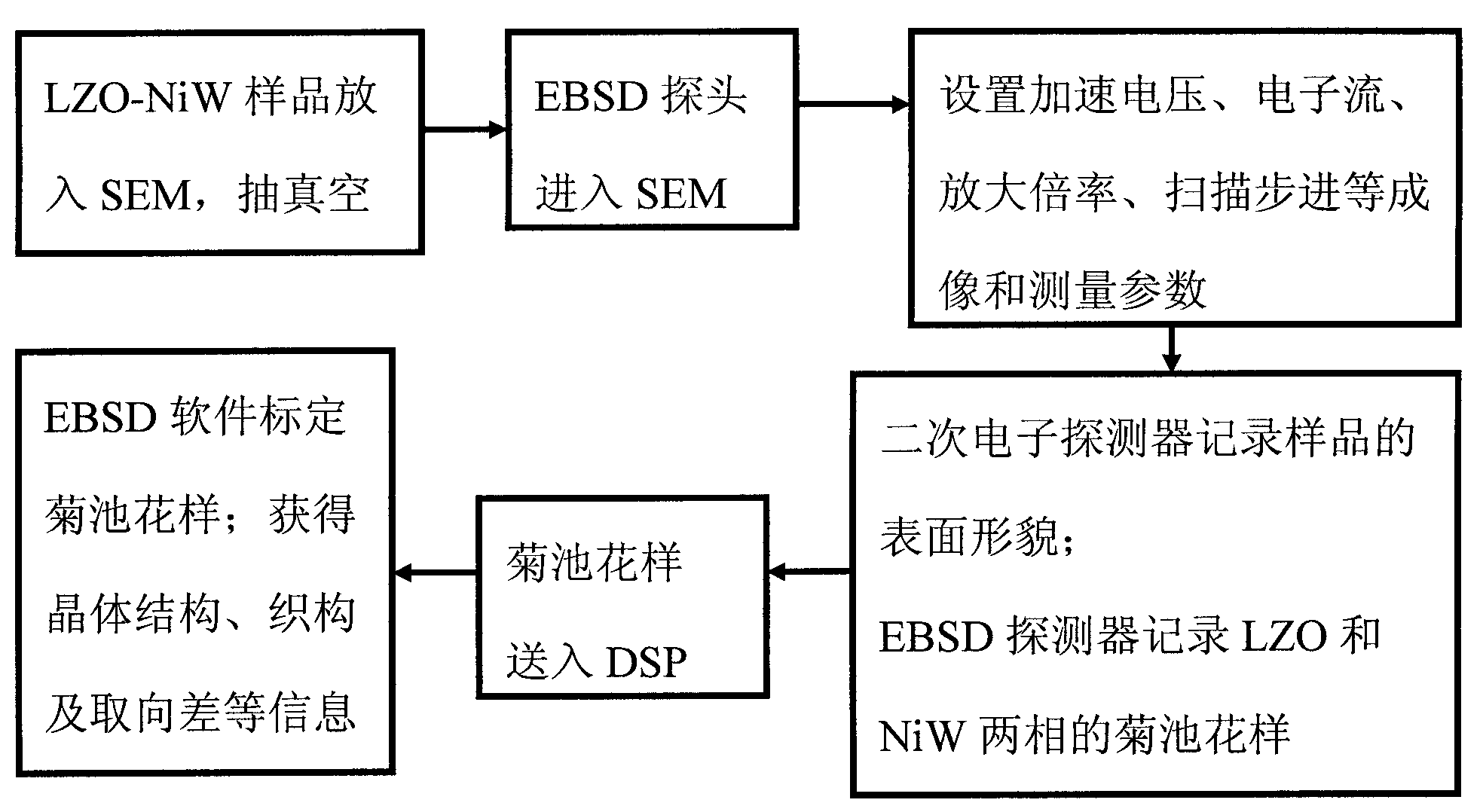
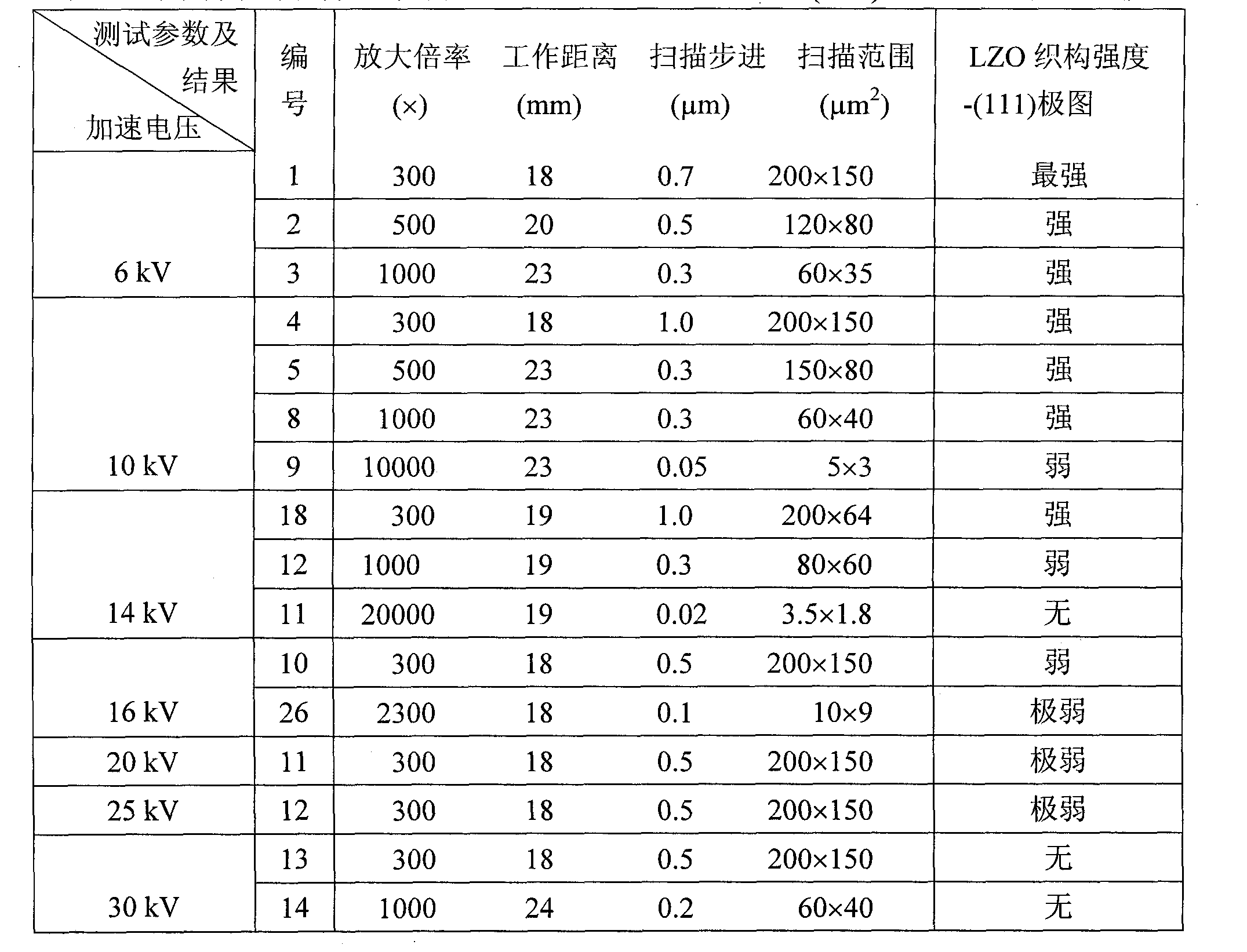
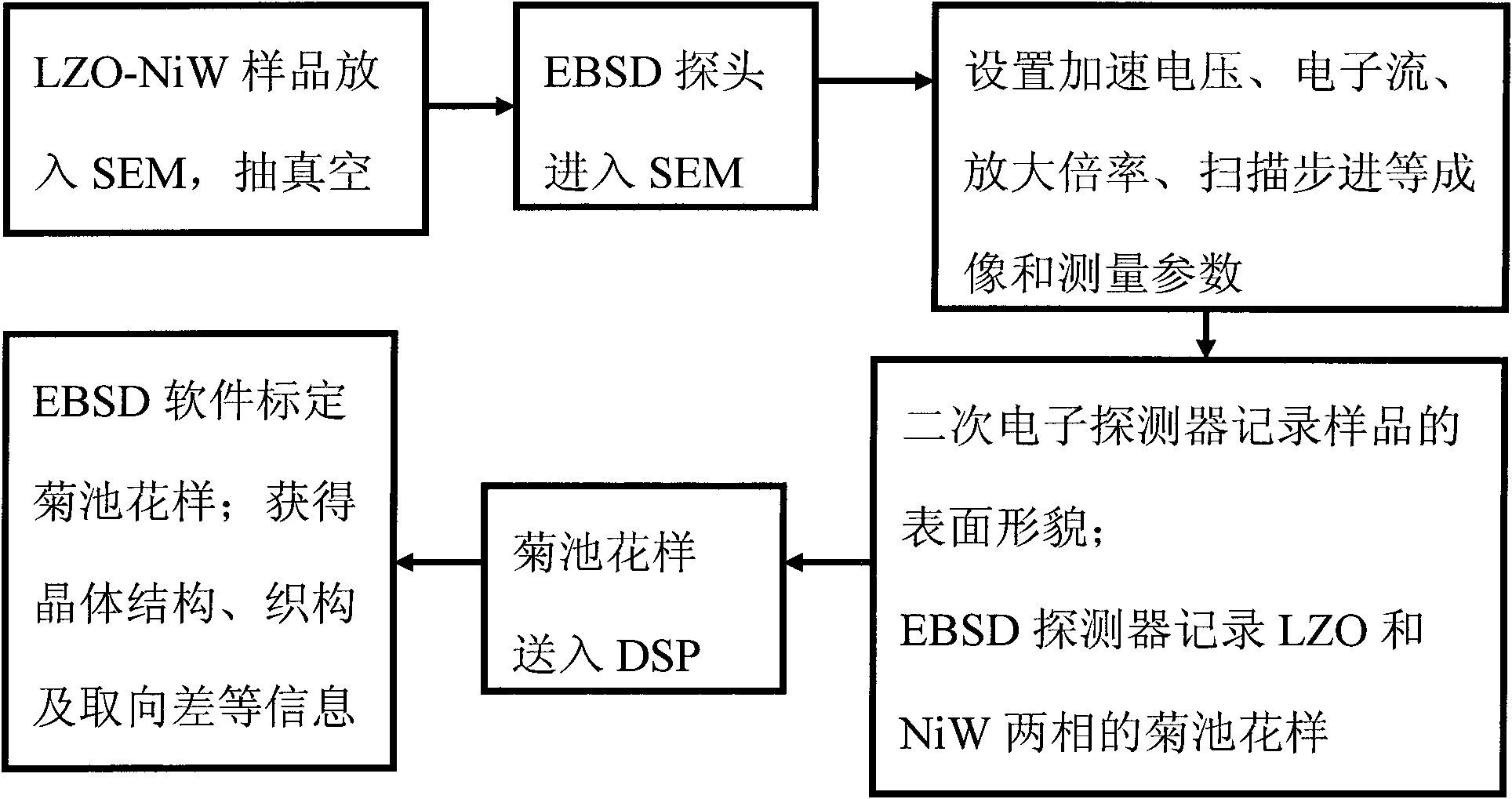
Electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) test method of crystal orientation matching relationship of nanometer zirconic acid lanthanum epitaxial layer and Ni-W substrate
InactiveCN101813645AIncrease collection rateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIn planeDouble phase
The invention discloses a test method of crystal orientation matching relationship of nanometer zirconic acid lanthanum epitaxial layer and Ni-W substrate, belonging to the technical field of superconducting thin film performance tests. The test method is characterized in that secondary electronic amplification factor is adjusted and stepping distance is scanned in a system of thermal field emission scanning electron microscope SEM-electron backscattered diffractometer (EBSD), so that 5nA incidence election current can realize that the zirconic acid lanthanum epitaxial layer and Ni-W substrate texture are simultaneously displayed in one polar diagram under the condition that the lowest accelerating voltage is 6kV; one Kikuchi pattern comprises a zirconic acid lanthanum epitaxial layer and Ni-W substrate double phases; on the basis, commercial EBSD analysis software is adopted to measure the crystal orientation matching relationship of the zirconic acid lanthanum epitaxial layer and the Ni-W substrate in the growth directions of in-plane and epitaxial (c-axis). The method is visual and simple, does not need to perform surface pretreatment on the zirconic acid lanthanum and is suitable for other epitaxial material systems.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Superconducting Fault-Current Limiting Element and the Process for Producing the Same
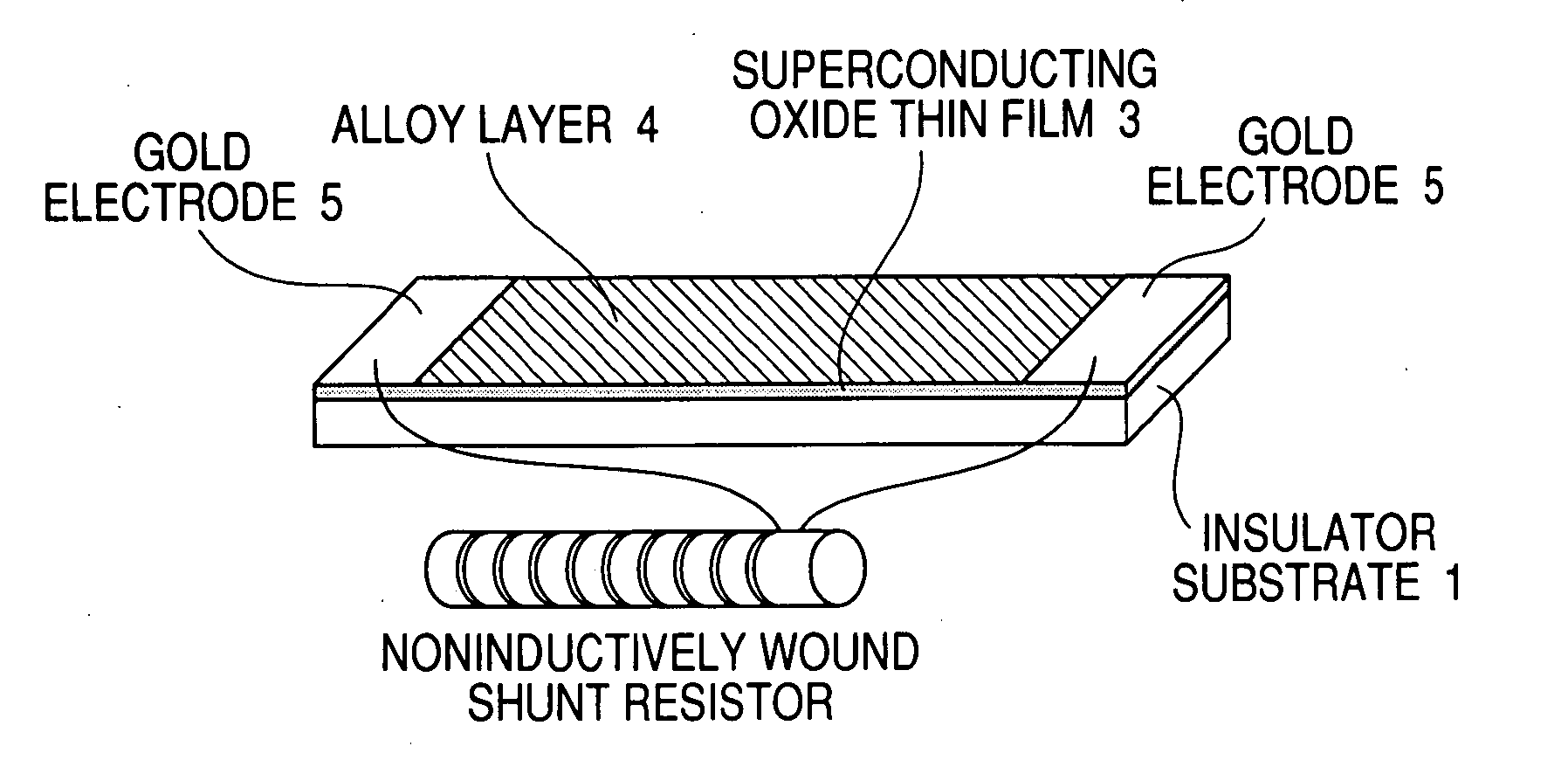
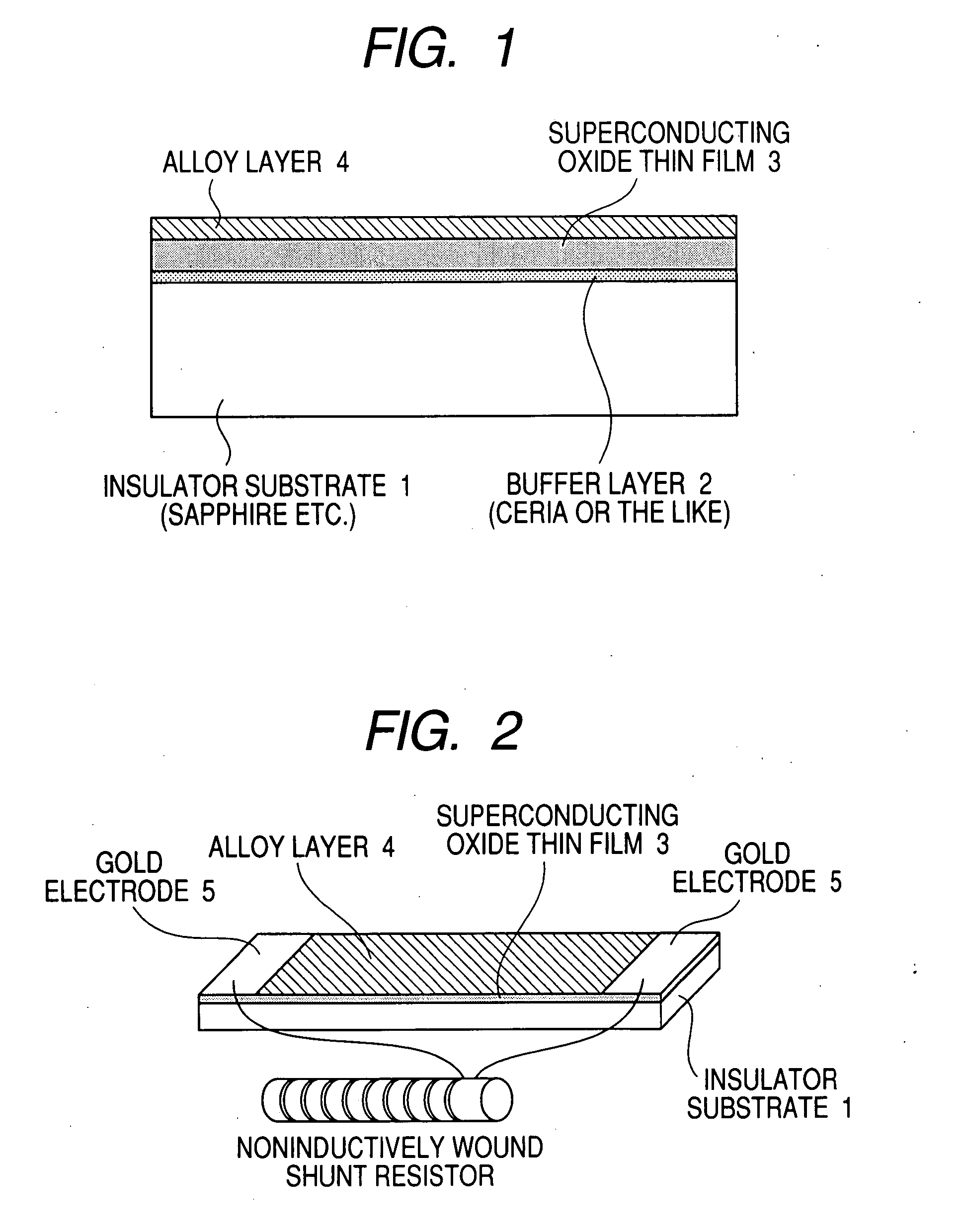
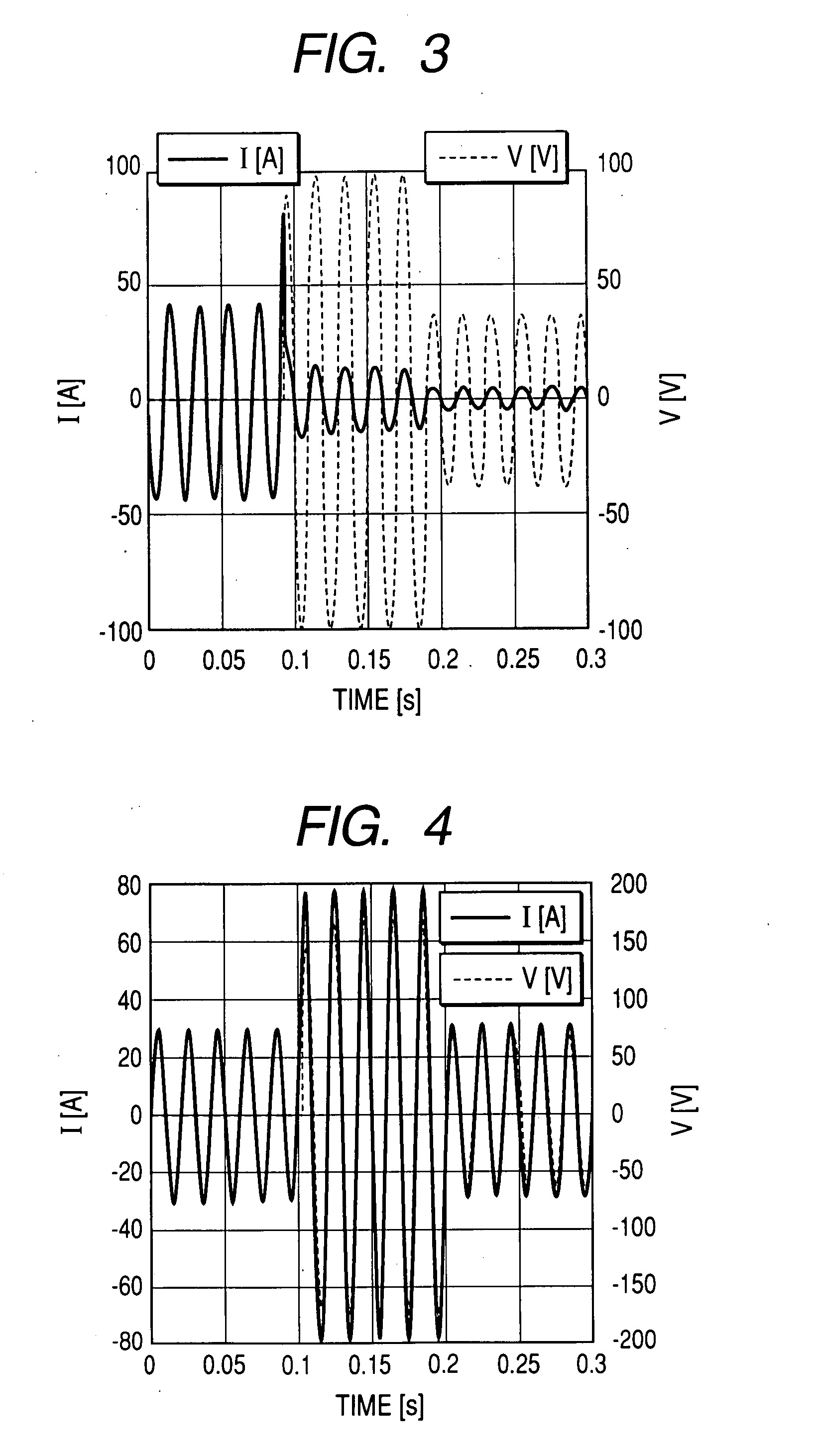
InactiveUS20080026946A1Low costResistance of alloy can be increasedSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAlloyMaterials science
[Problem] To prepare a superconducting fault-current limiting element having a high sharing electric field at low cost. [Means for Resolution] A superconducting fault-current limiting element including an insulator substrate; a superconductive thin film 3 formed on the insulator substrate; and an alloy layer 4 formed on the superconducting thin film 3, said alloy layer having a room-temperature resistivity higher by twice or more than the room-temperature resistivity of a pure metal, in which, when the superconducting thin film 3 goes into a normal conductive state by an overcurrent, the overcurrent flowing through the superconducting thin film 3 is transferred only to the alloy layer 4.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Device for sensing a magnetic field
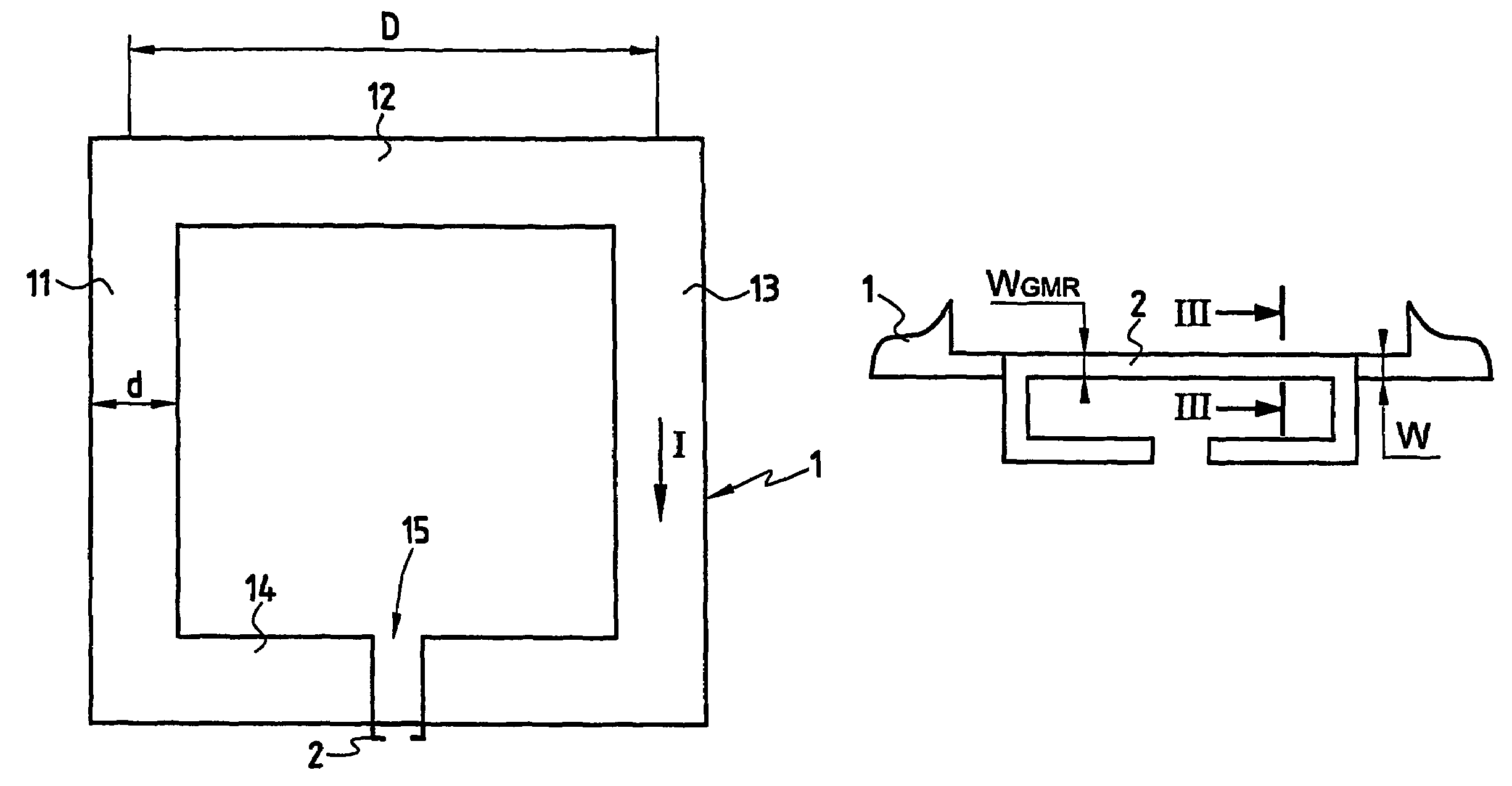
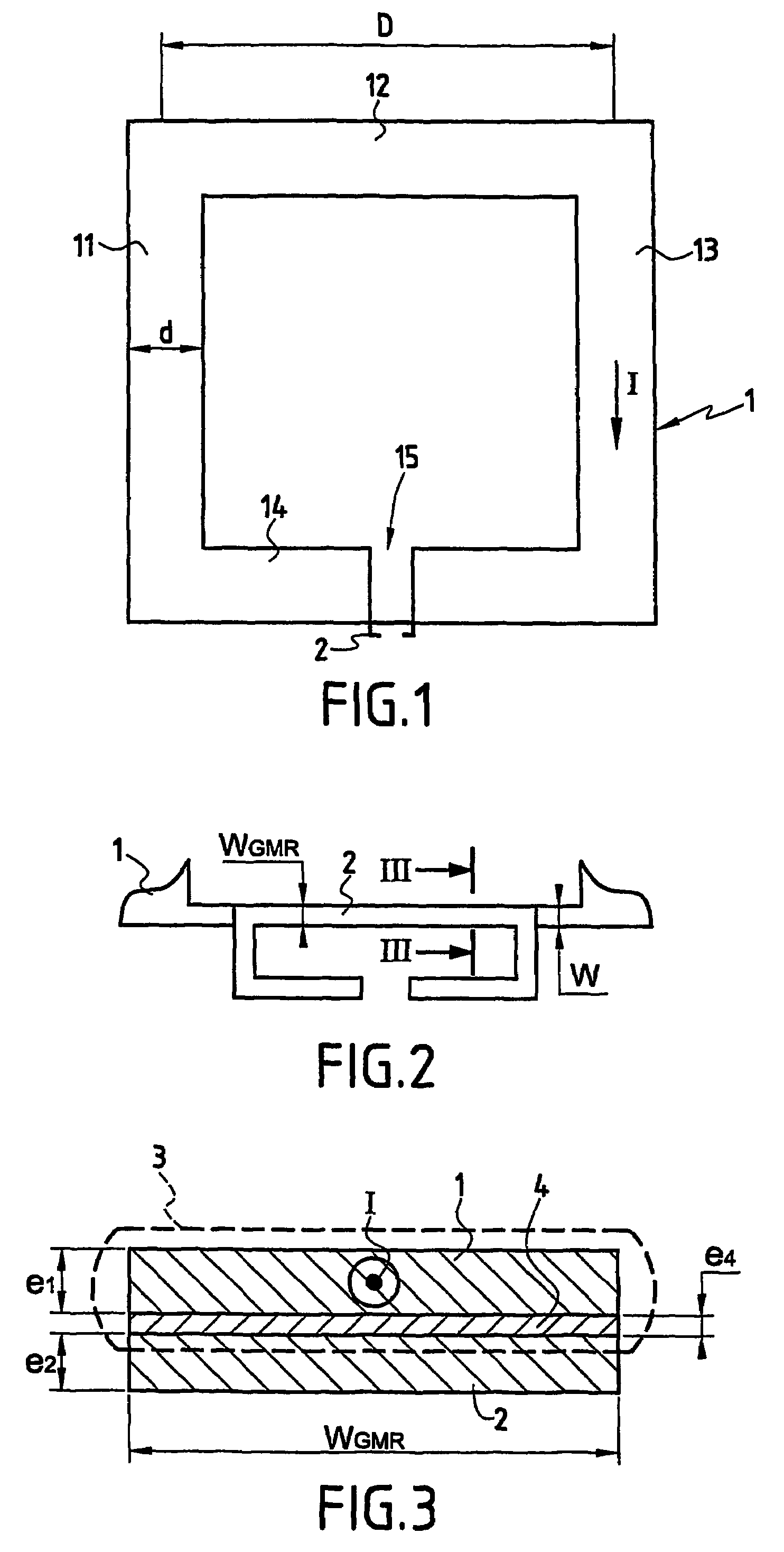
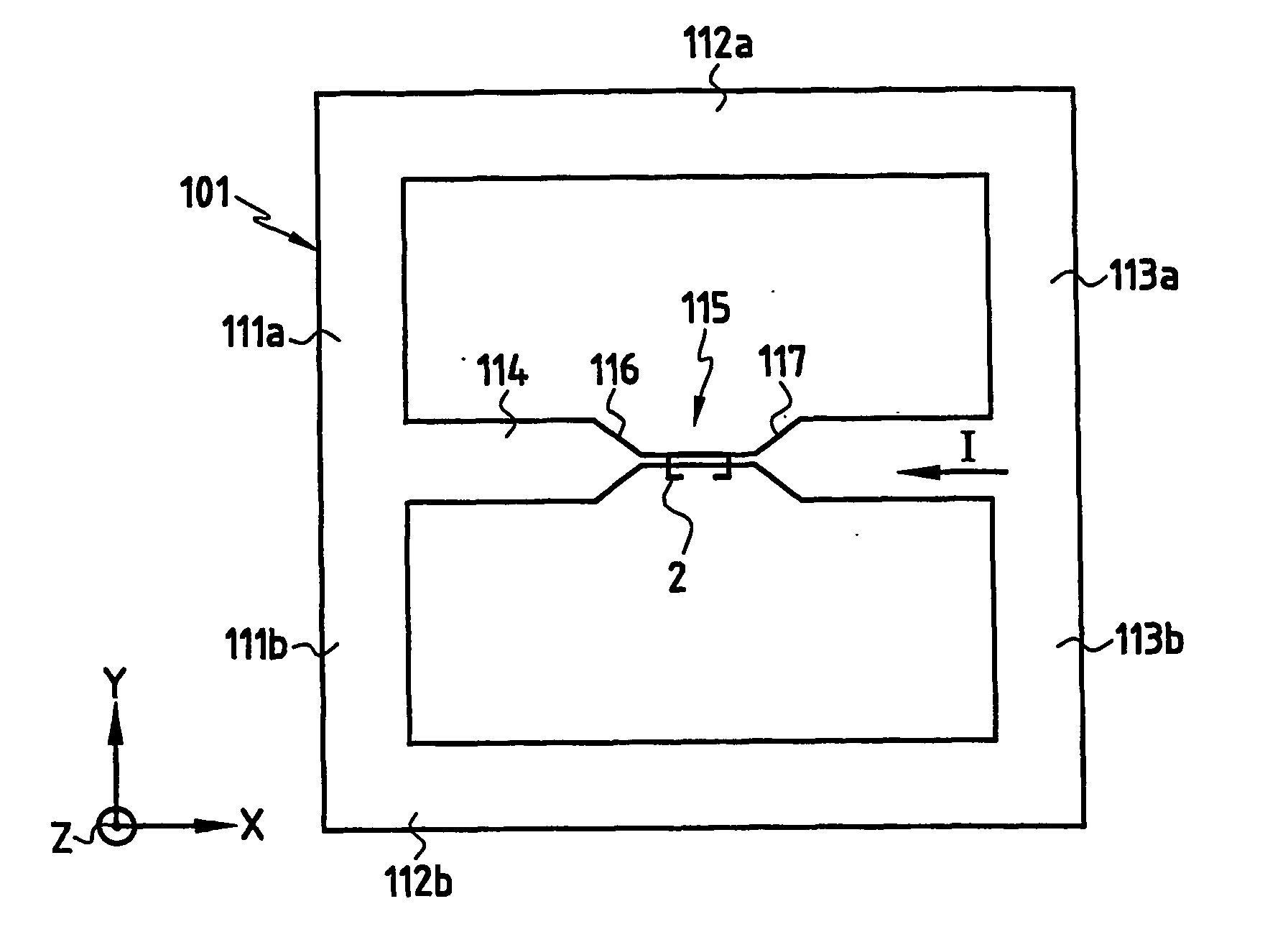
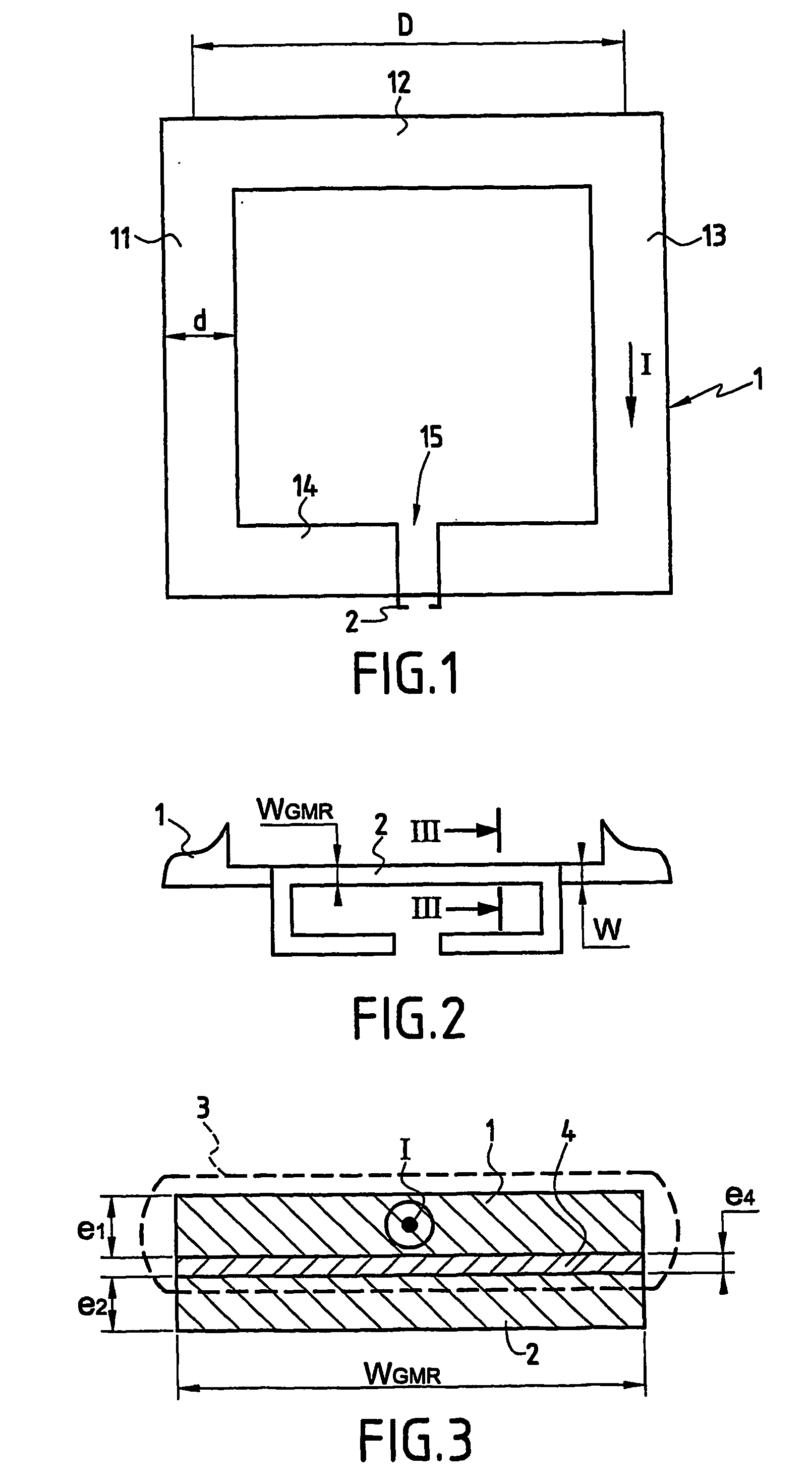
InactiveUS20060220641A1Comparable and good performanceEasy to produceMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectrical currentPath width
The device for sensing a magnetic field comprises a closed superconducting pick-up loop (1) having a path width (d) etched out of a single layer superconducting thin film and provided with a constriction (15) having a width (w) of narrow dimension smaller than the path width (d). The closed superconducting pick-up loop (1) constitutes a flux-to-field transformer (FFDT). At least one magnetoresistive element (2) is placed on top of or below the superconducting thin film, is isolated from the superconducting thin film by a thin insulating layer and is located so that an active part of the magnetoresistive element (2) is at the location of the constriction (15) and has a width equal to or less than the width of the constriction (15). The active part of the magnetoresistive element (2) is oriented so that the bias current in this active part is directed essentially along the constriction (15), orthogonally to the width of narrow dimension.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
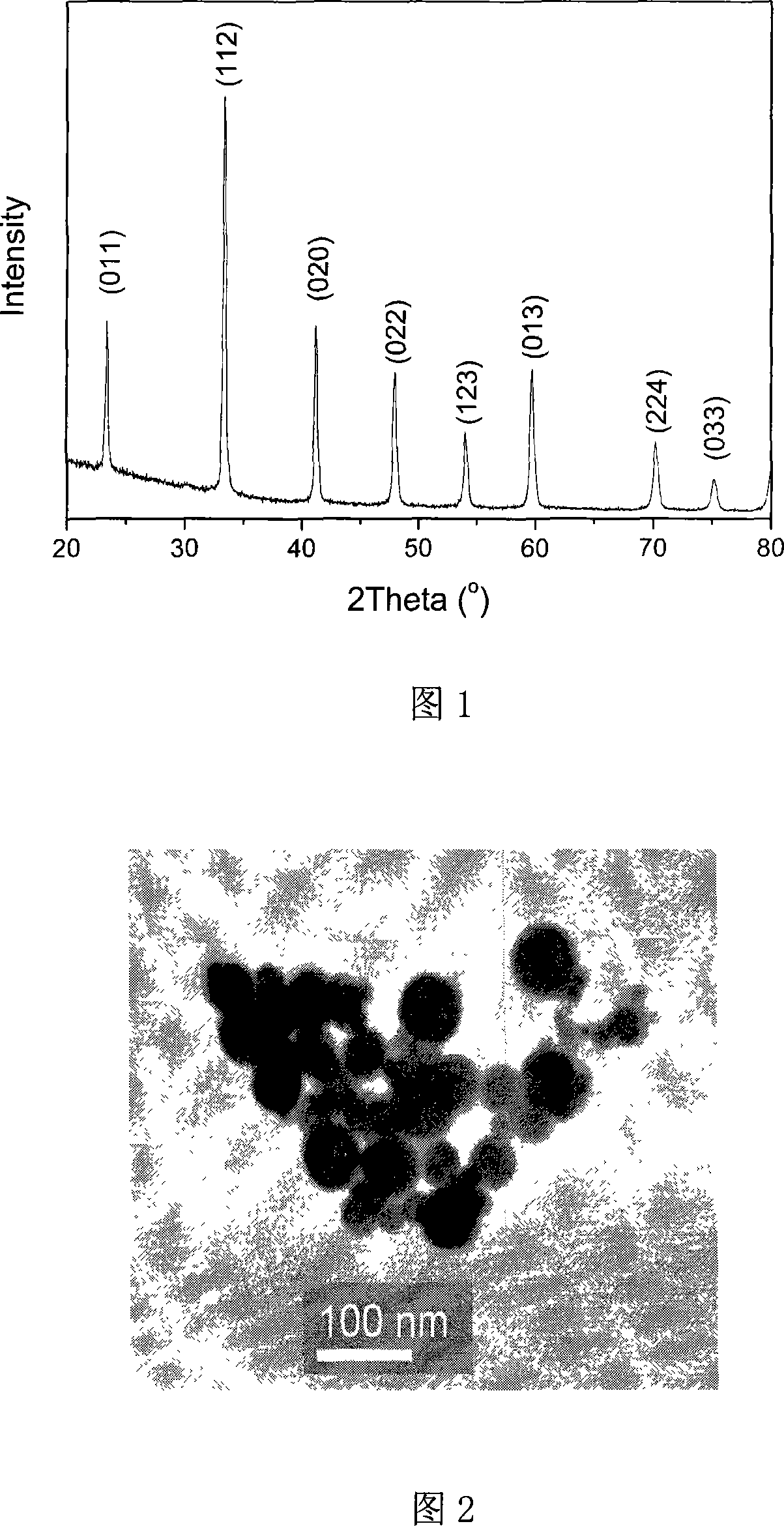
Yttrium barium copper oxide superconducting thin film mixed with samarium and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN102491740AGood c-axis textureGood in-plane and out-of-plane textureYttrium barium copper oxideChemical composition
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
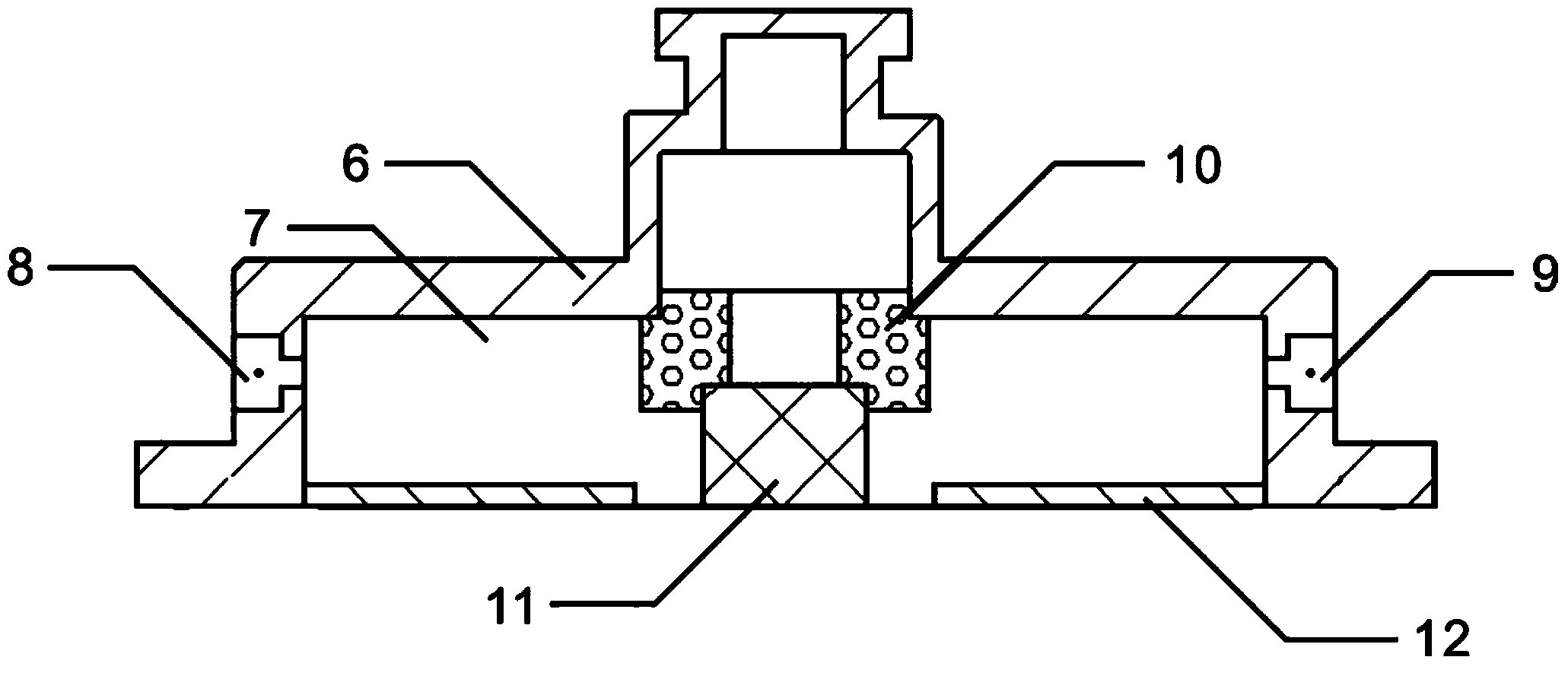
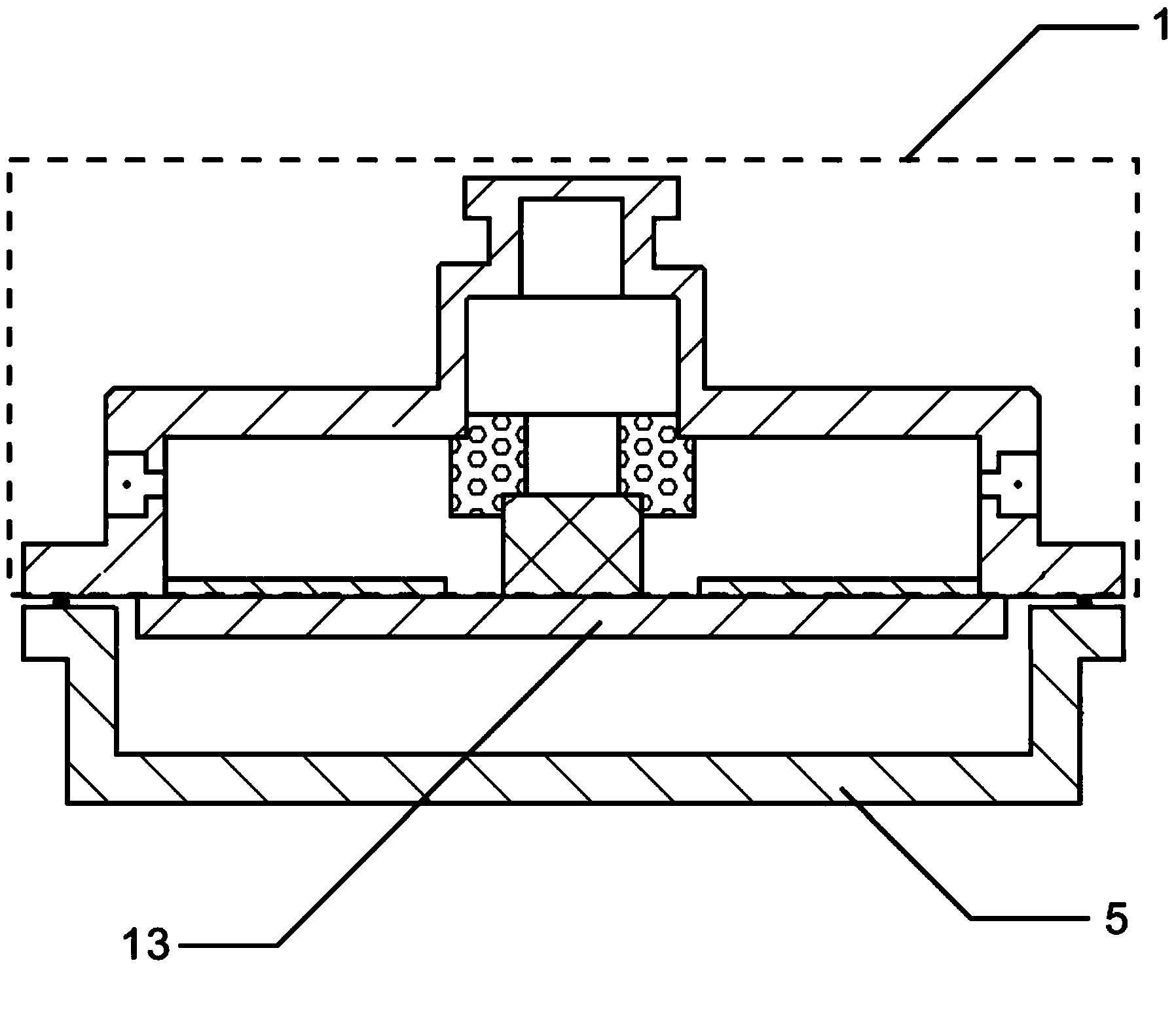
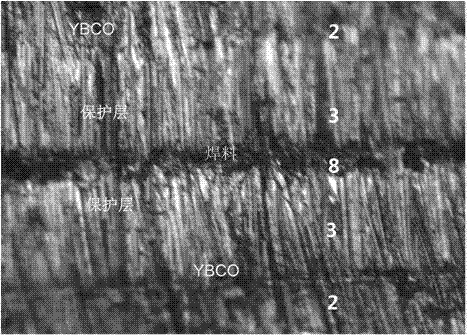
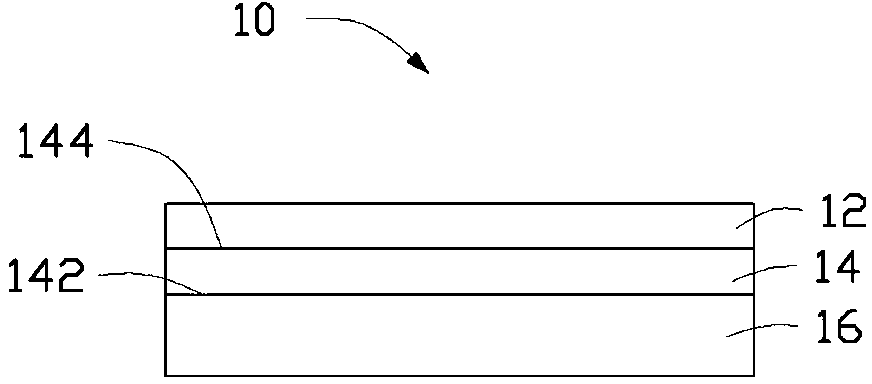
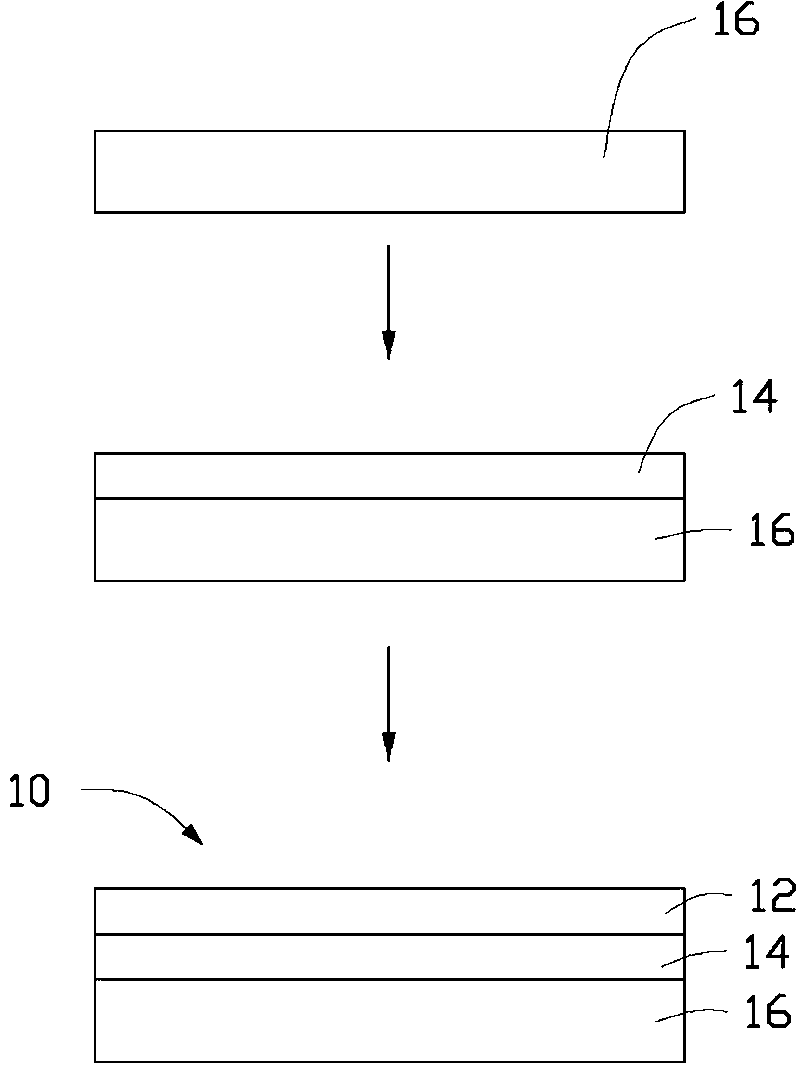
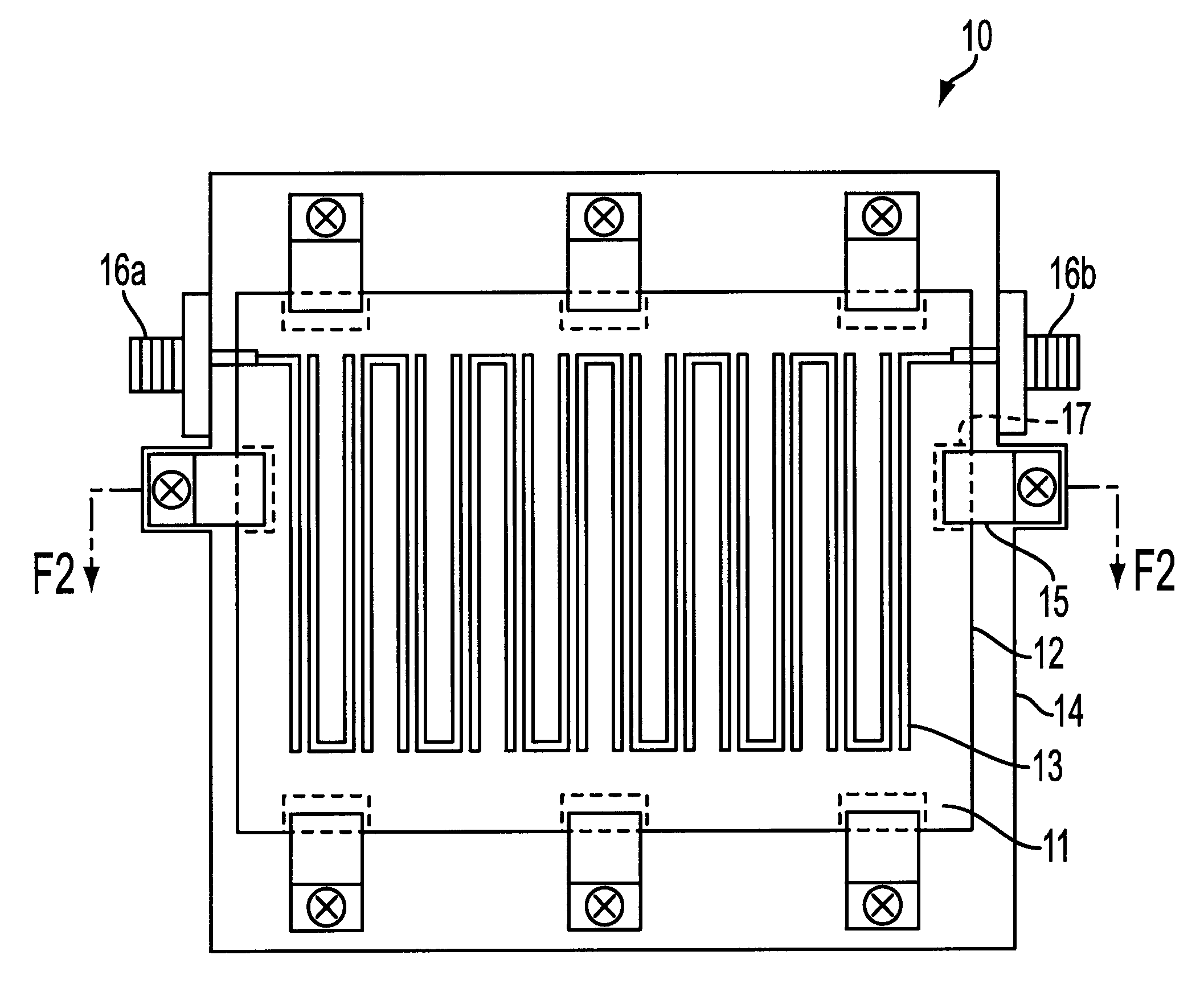
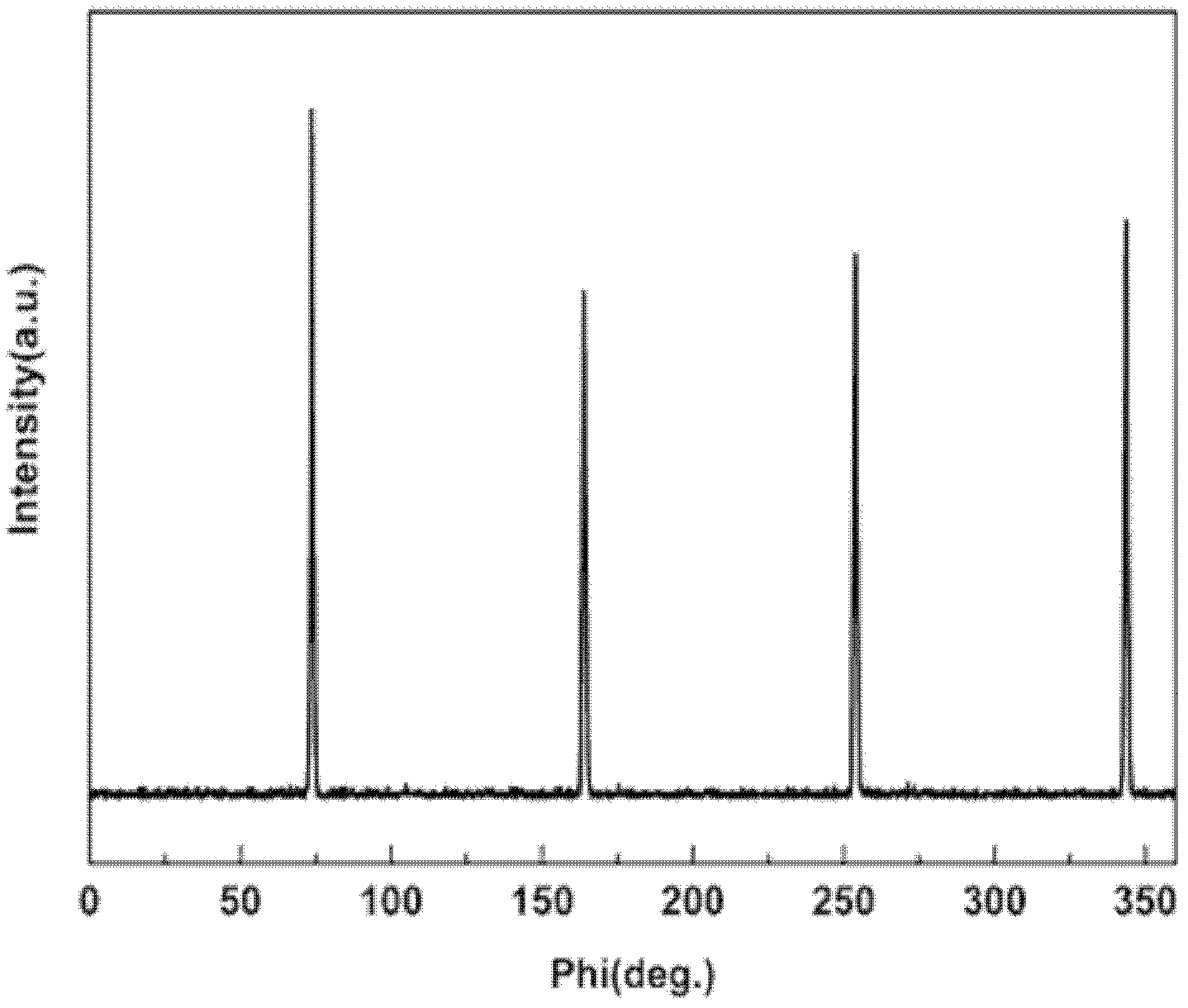
ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and pressure heating system thereof
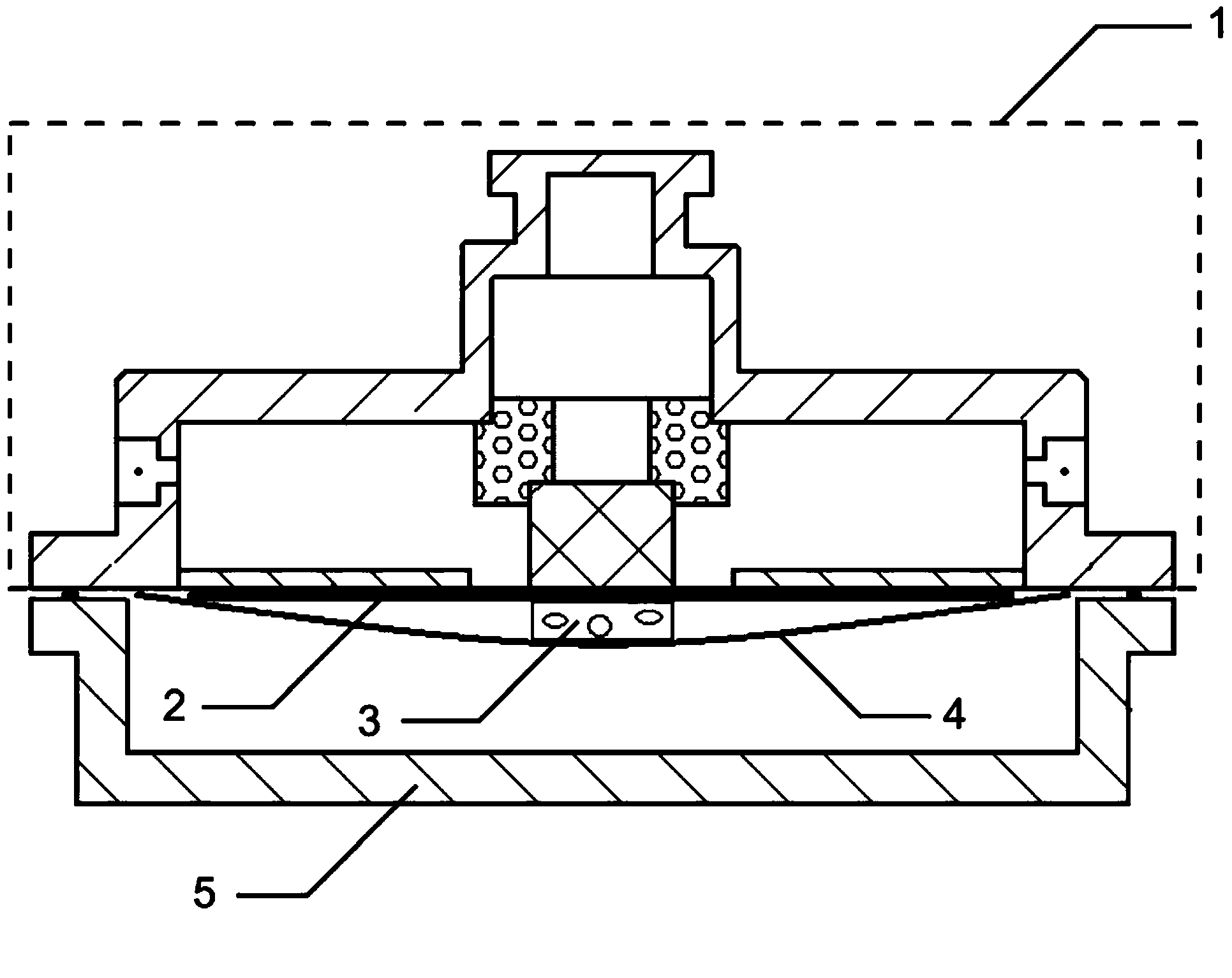
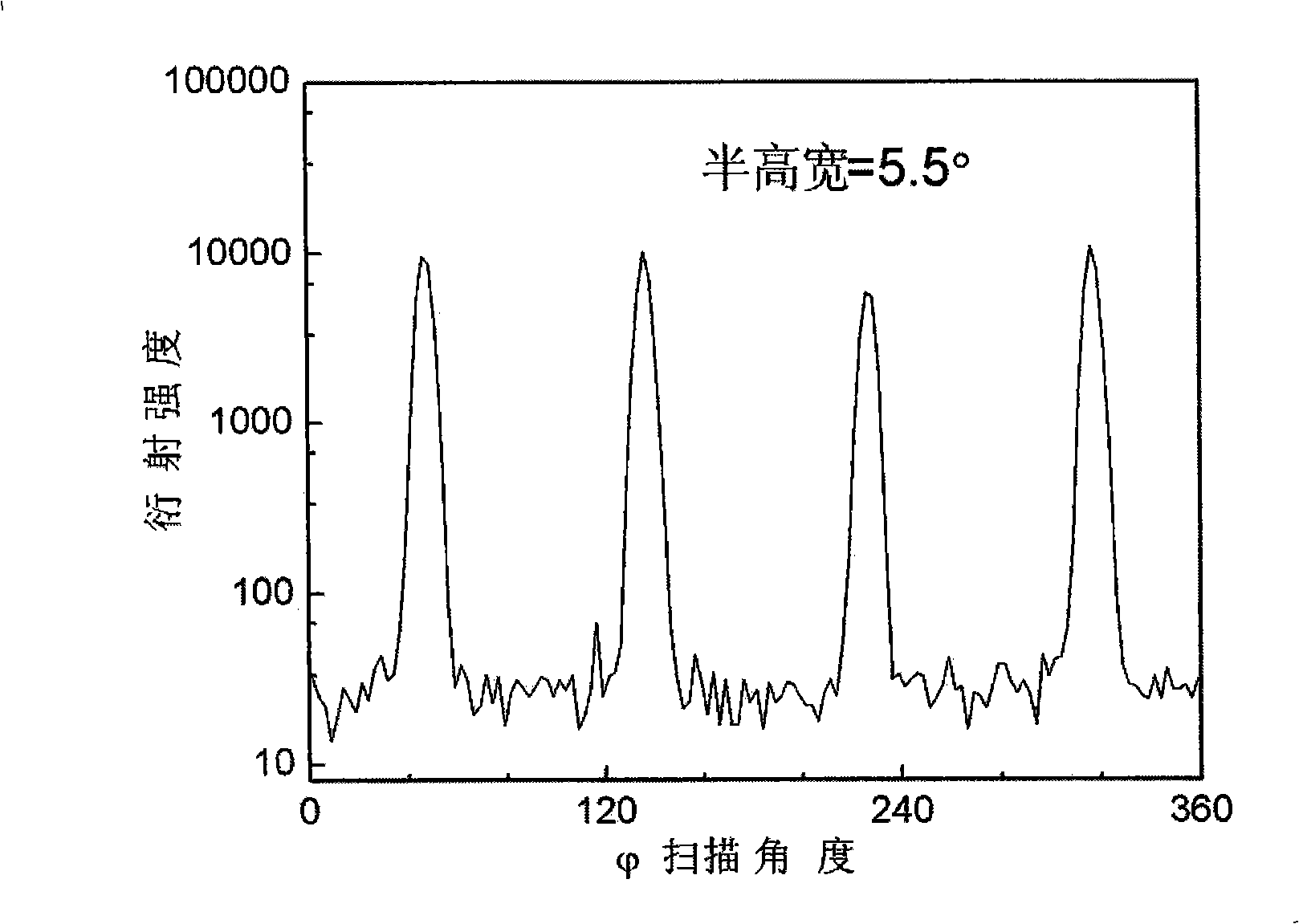
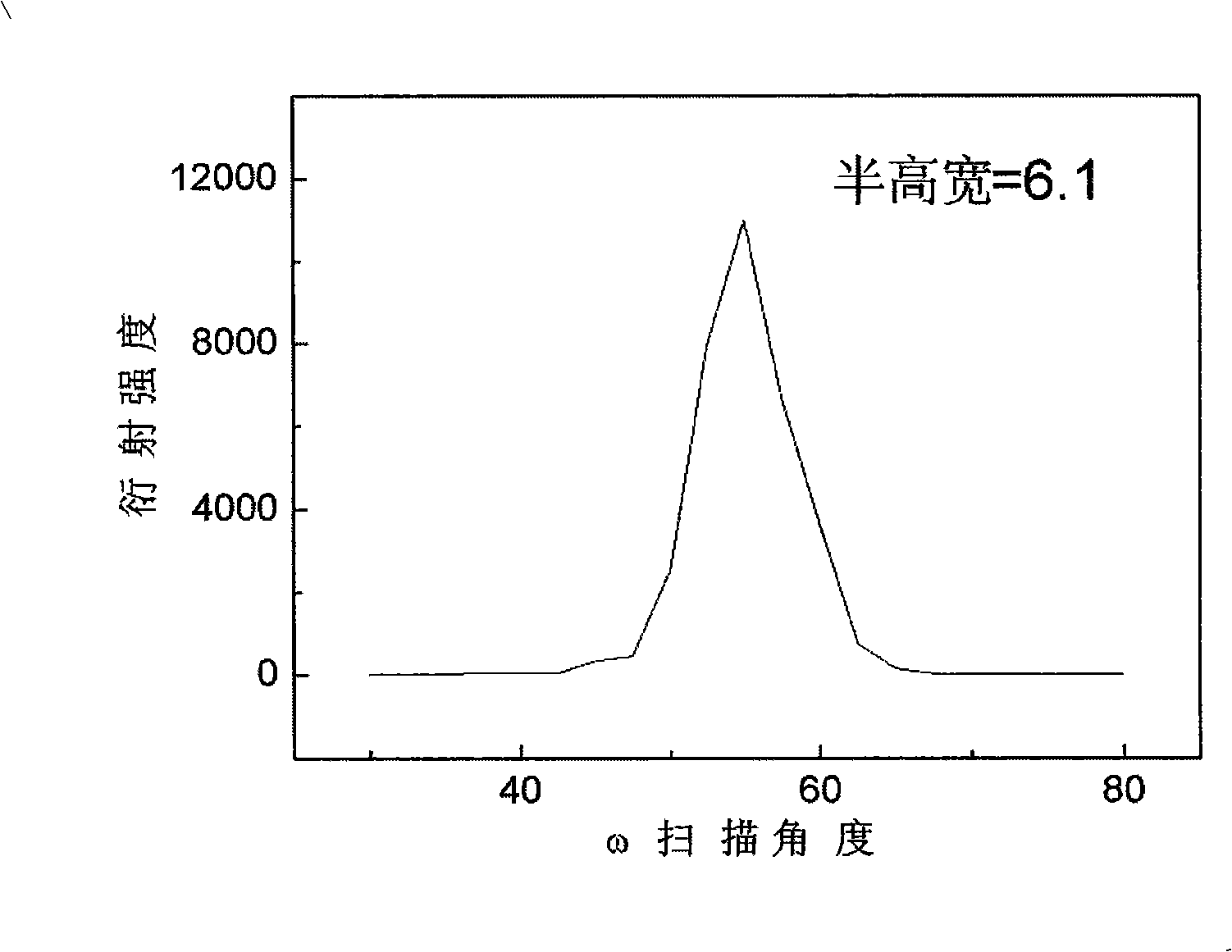
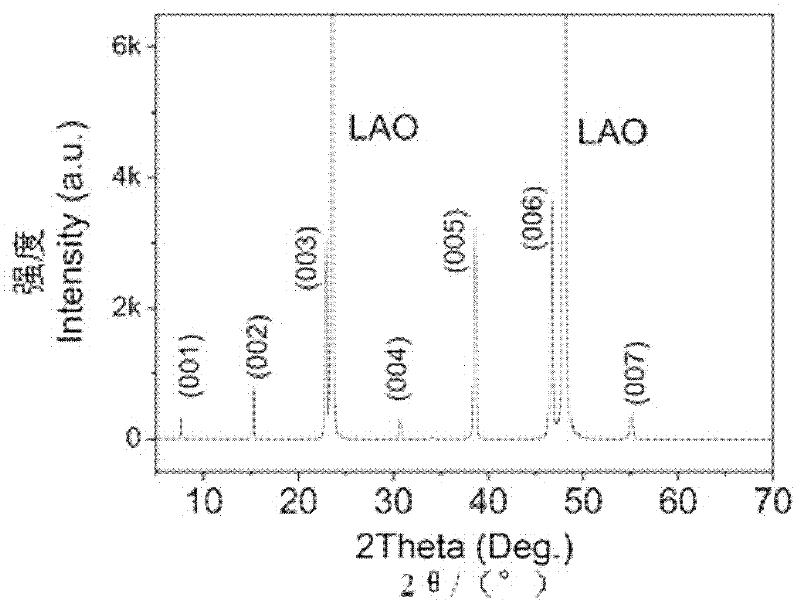
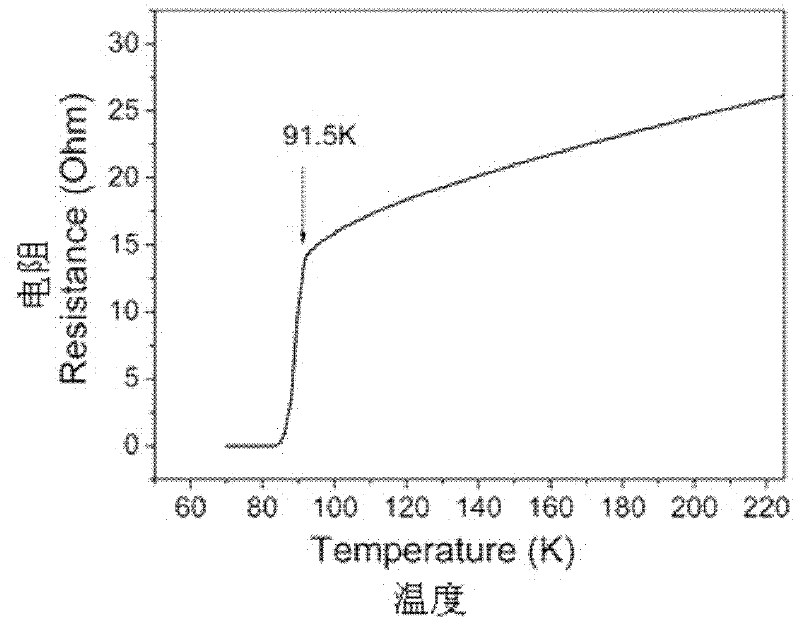
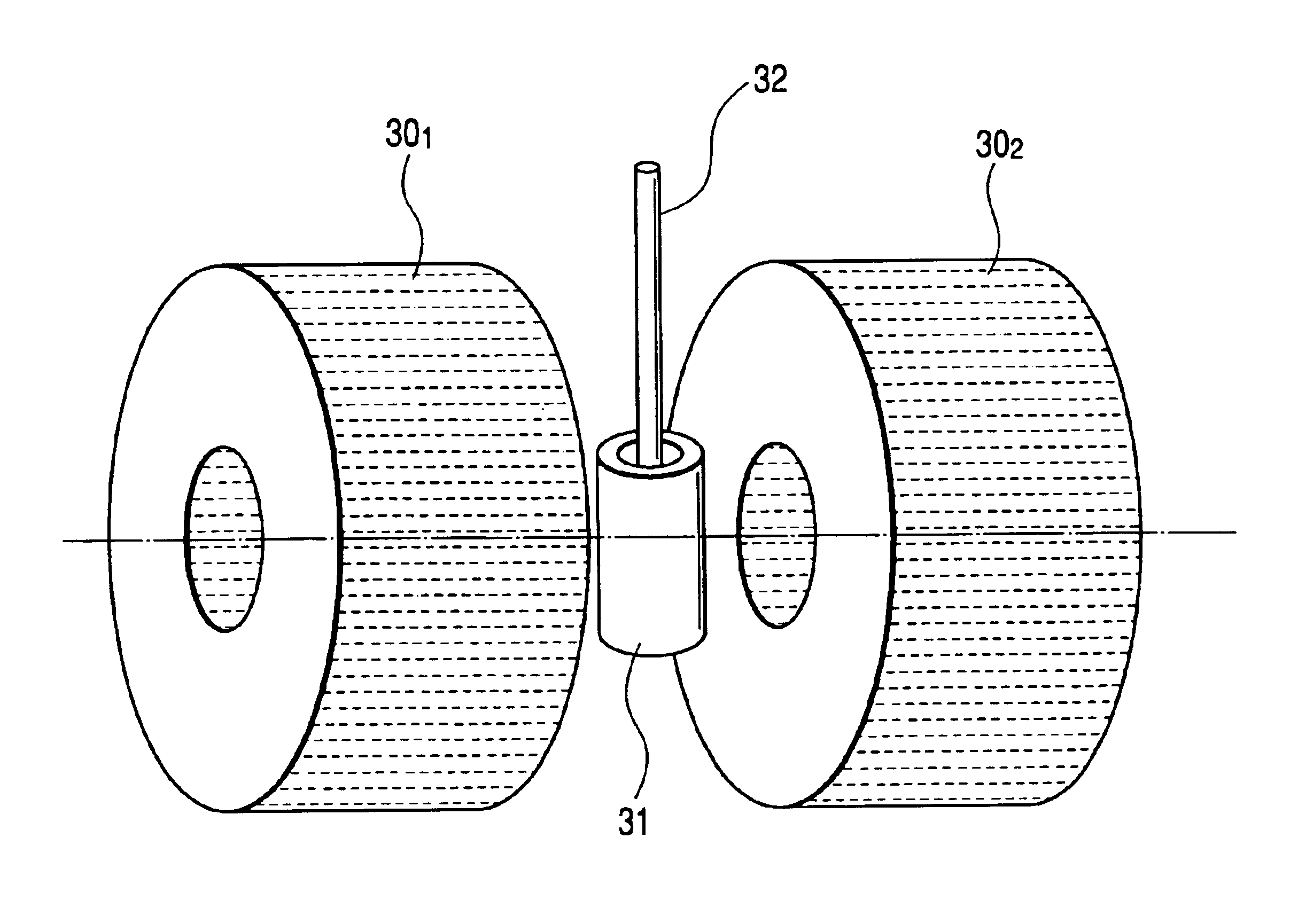
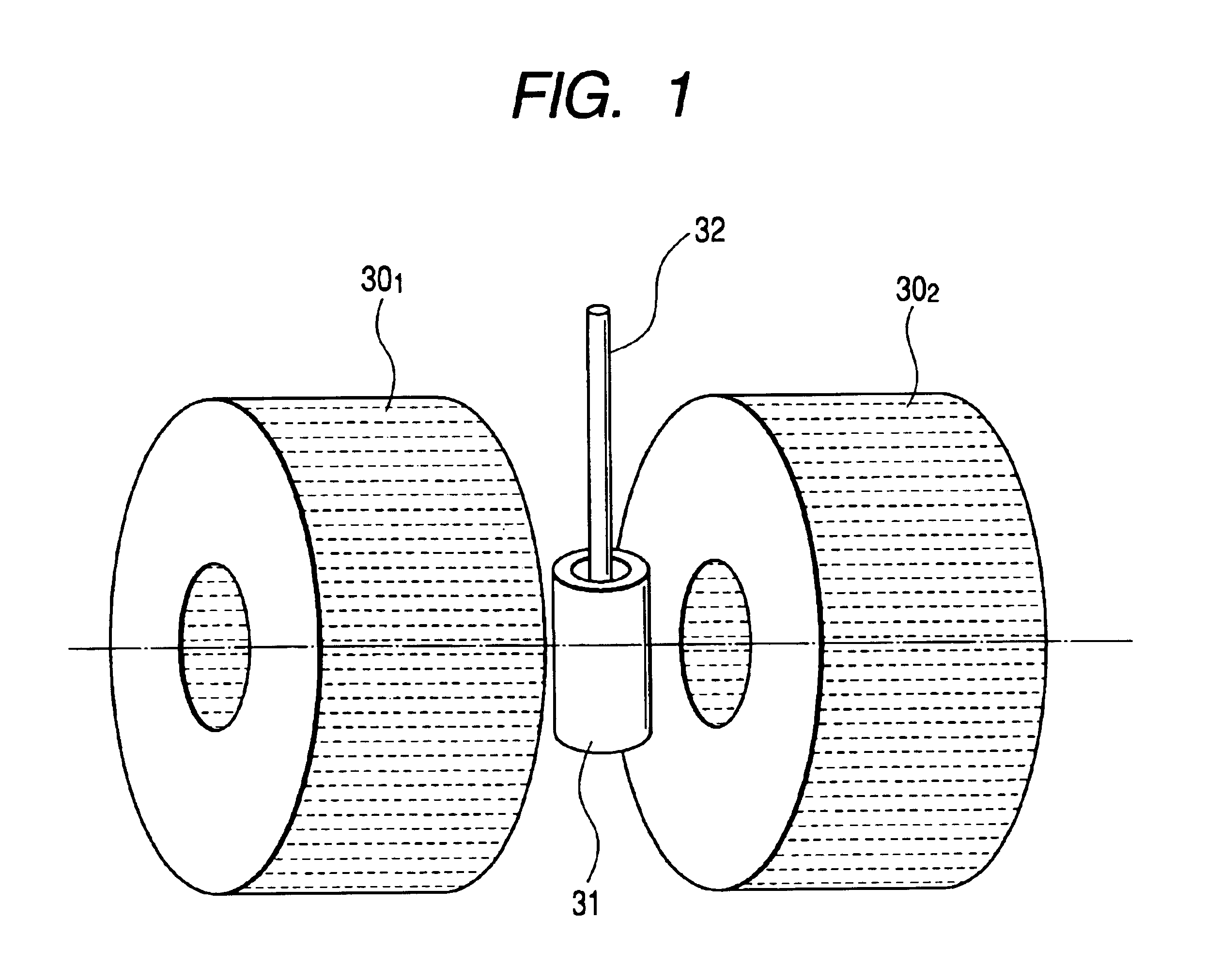
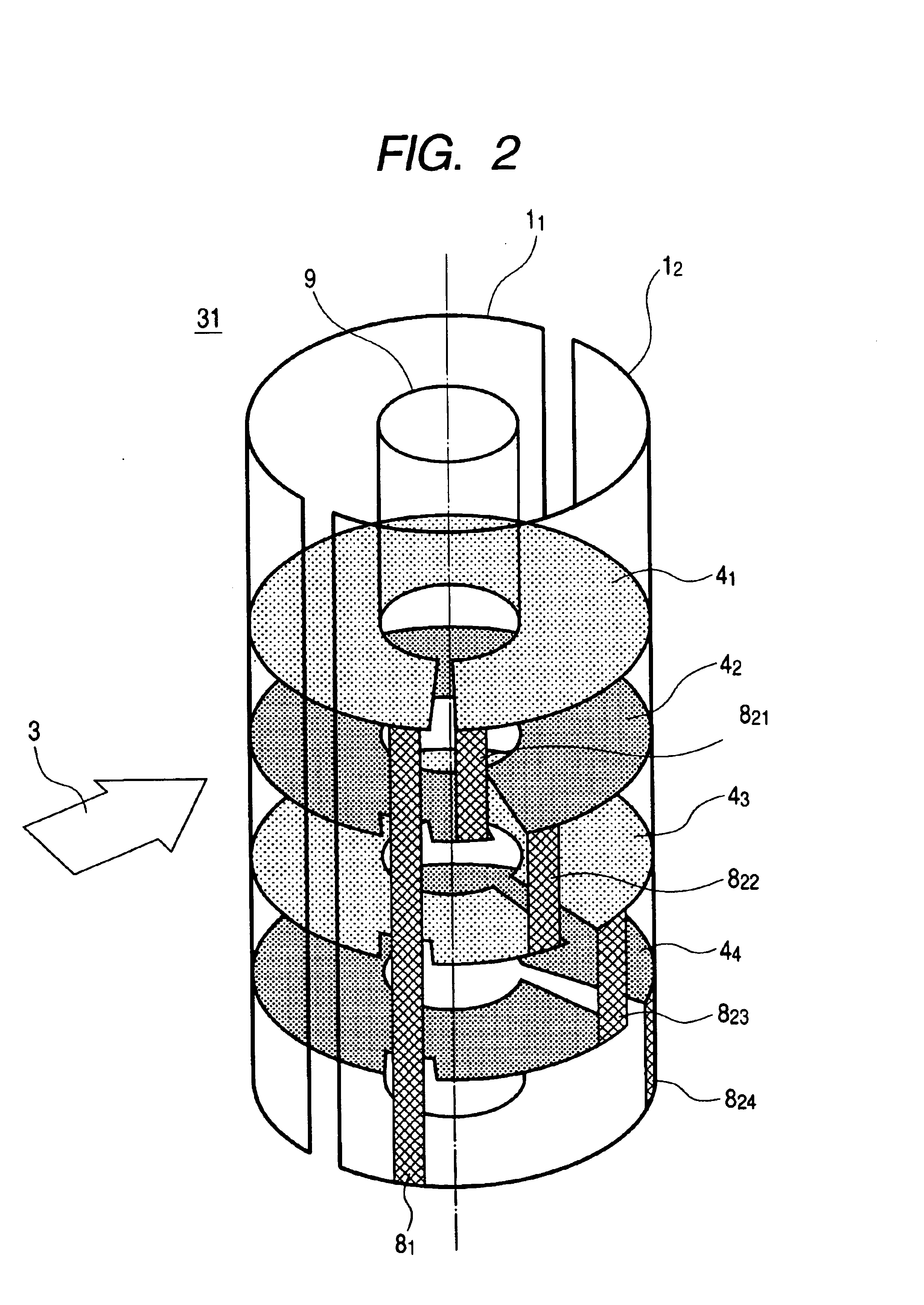
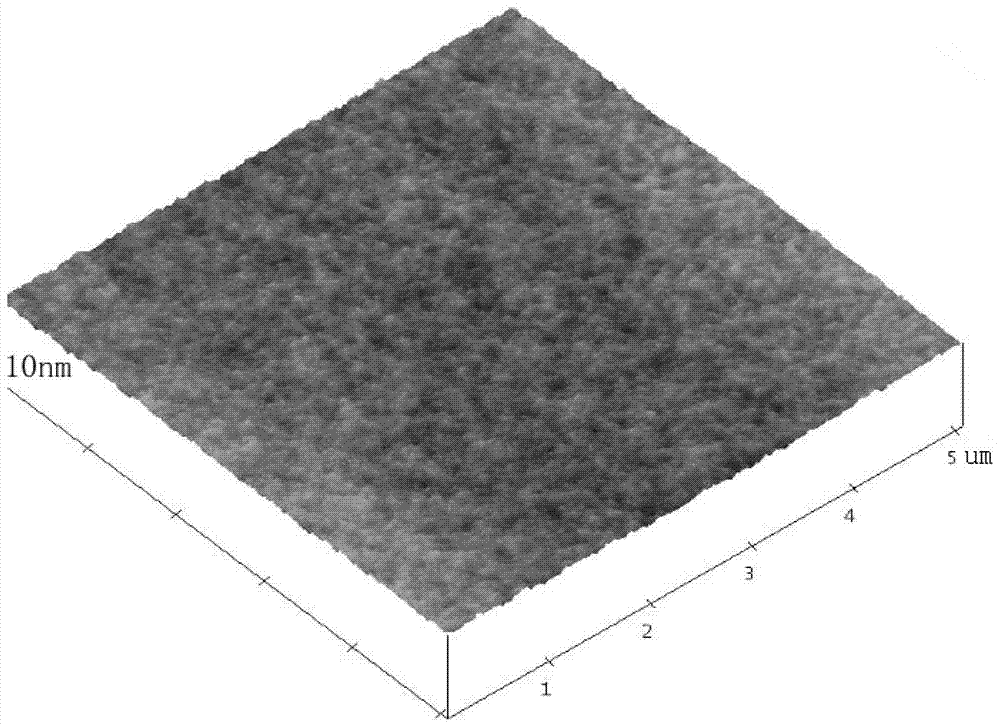
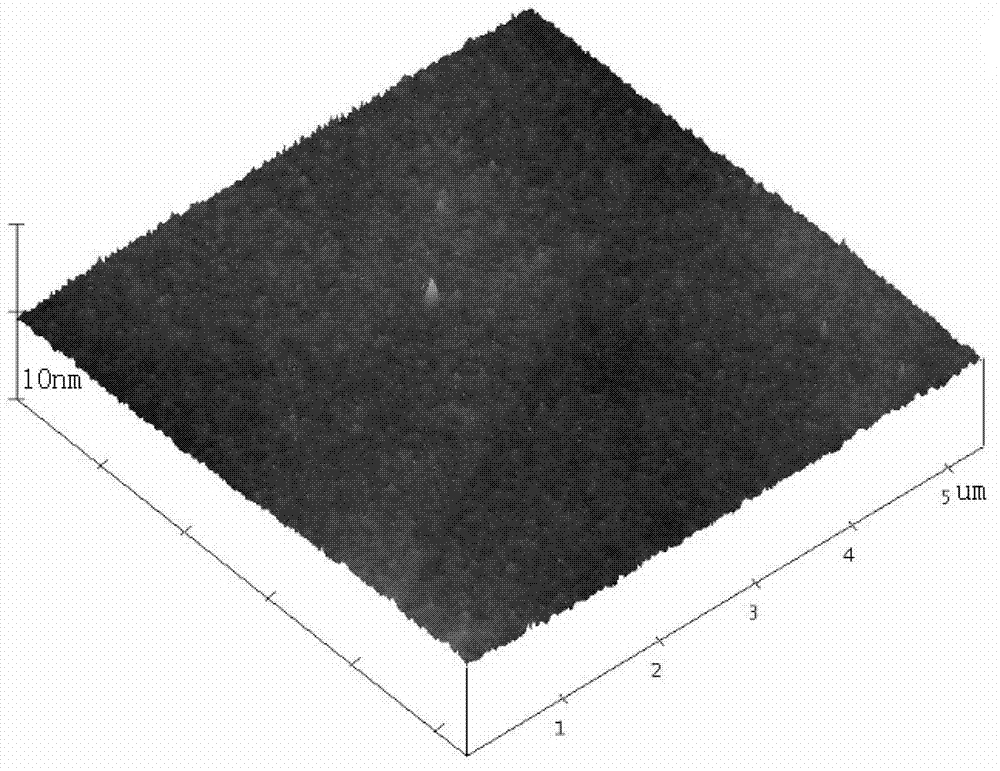
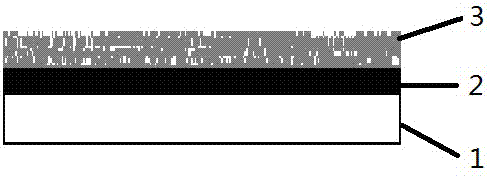
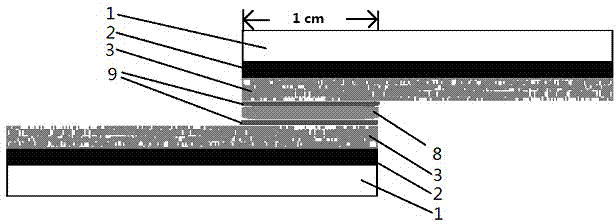
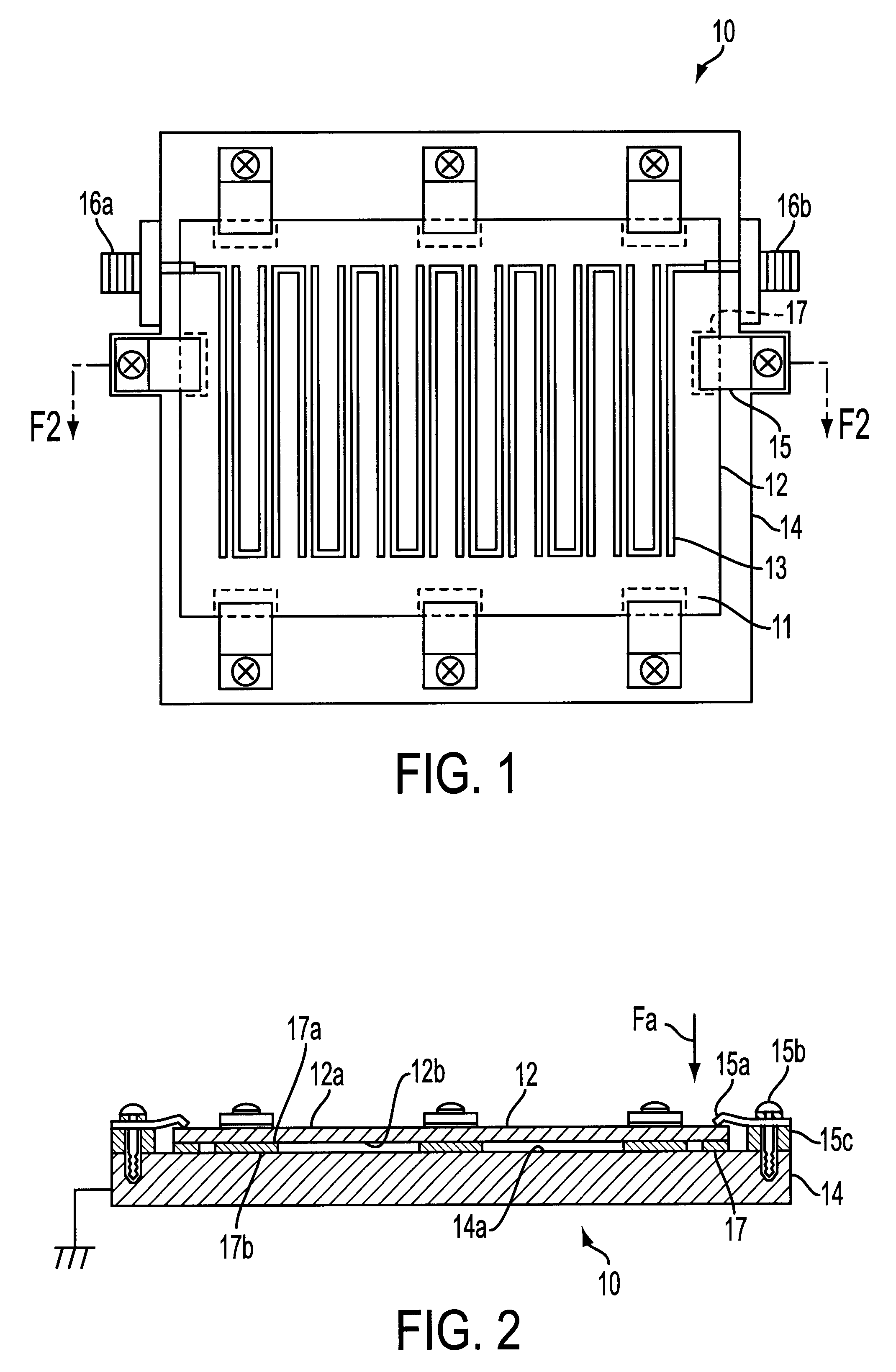
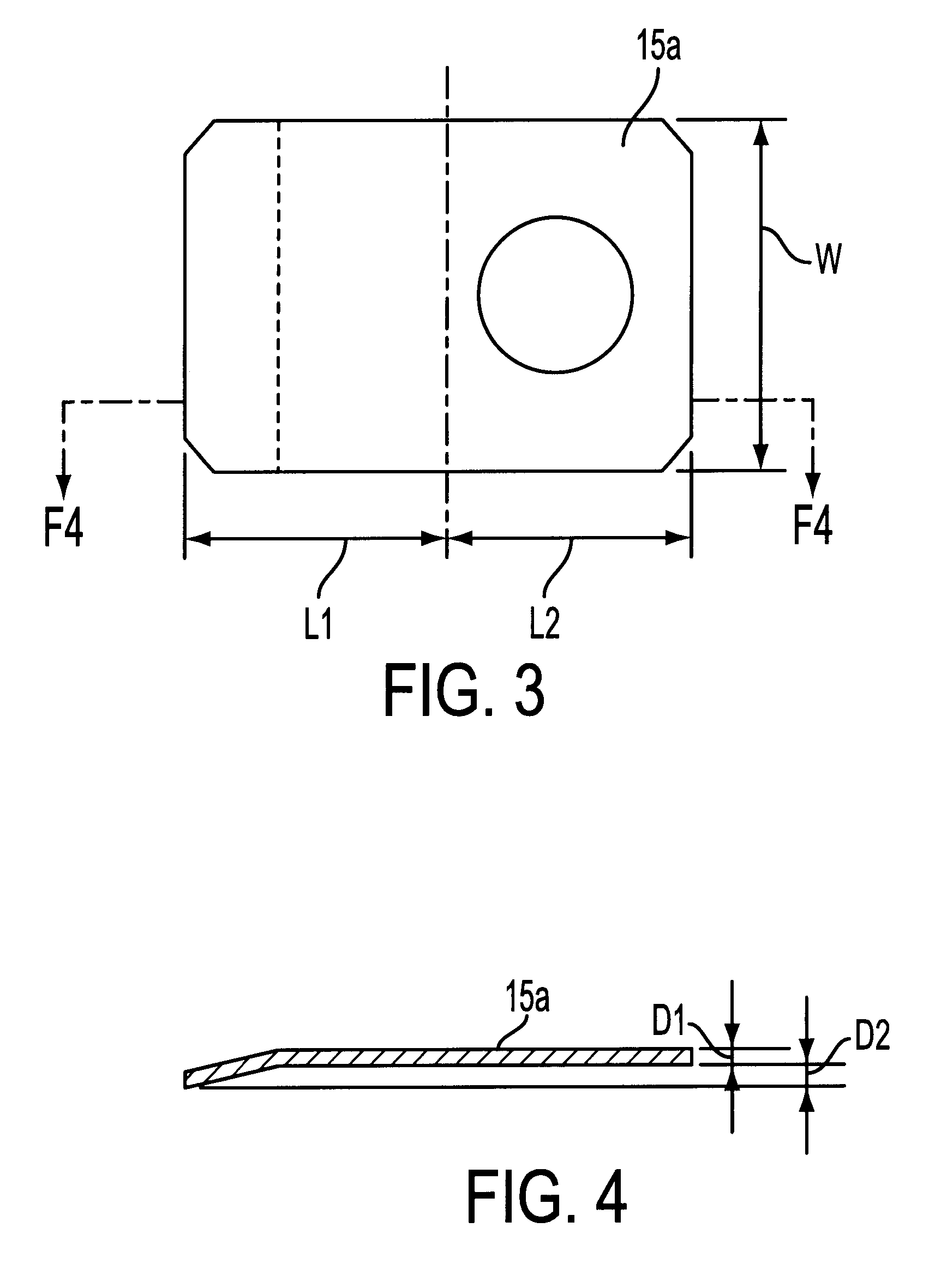
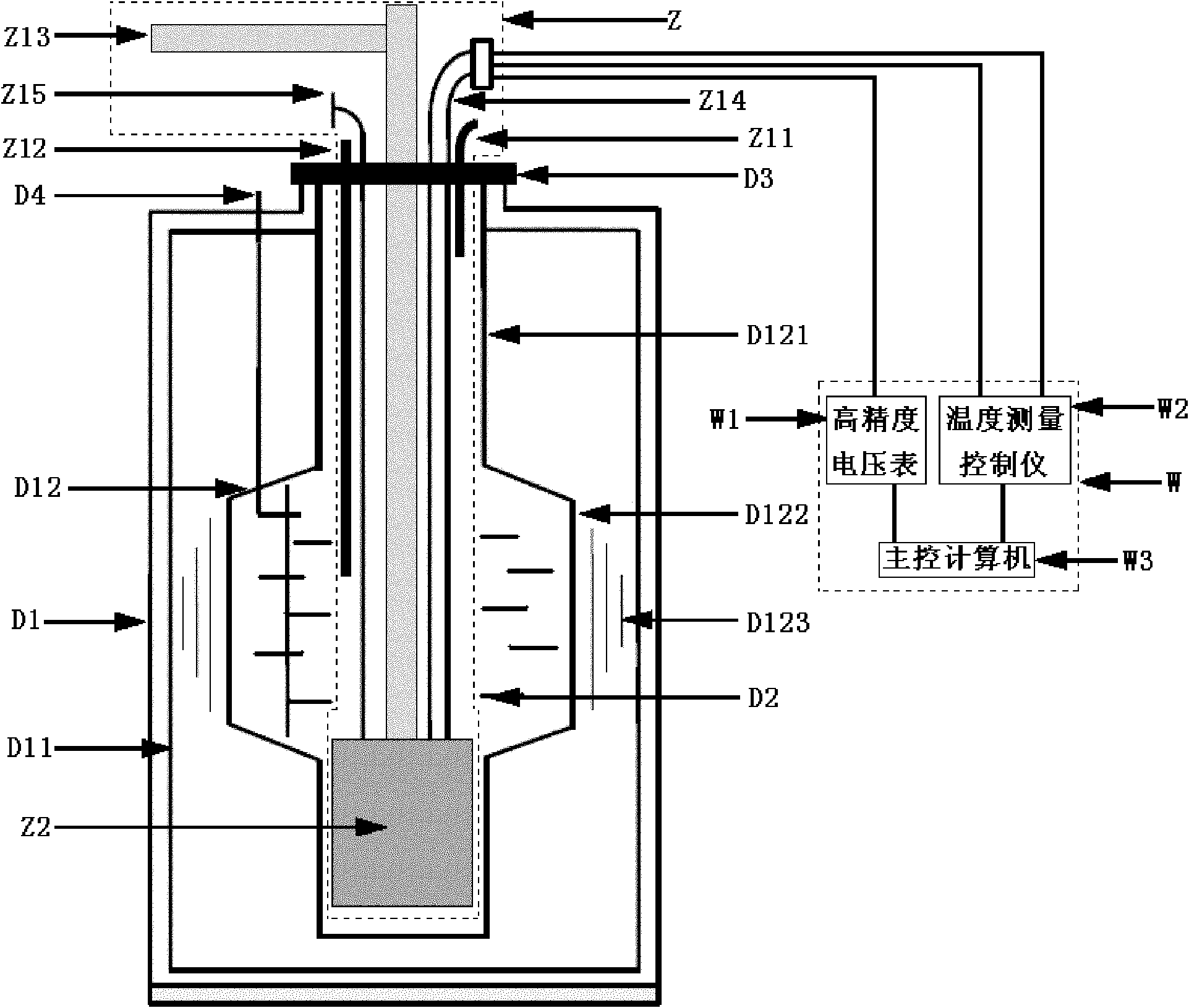
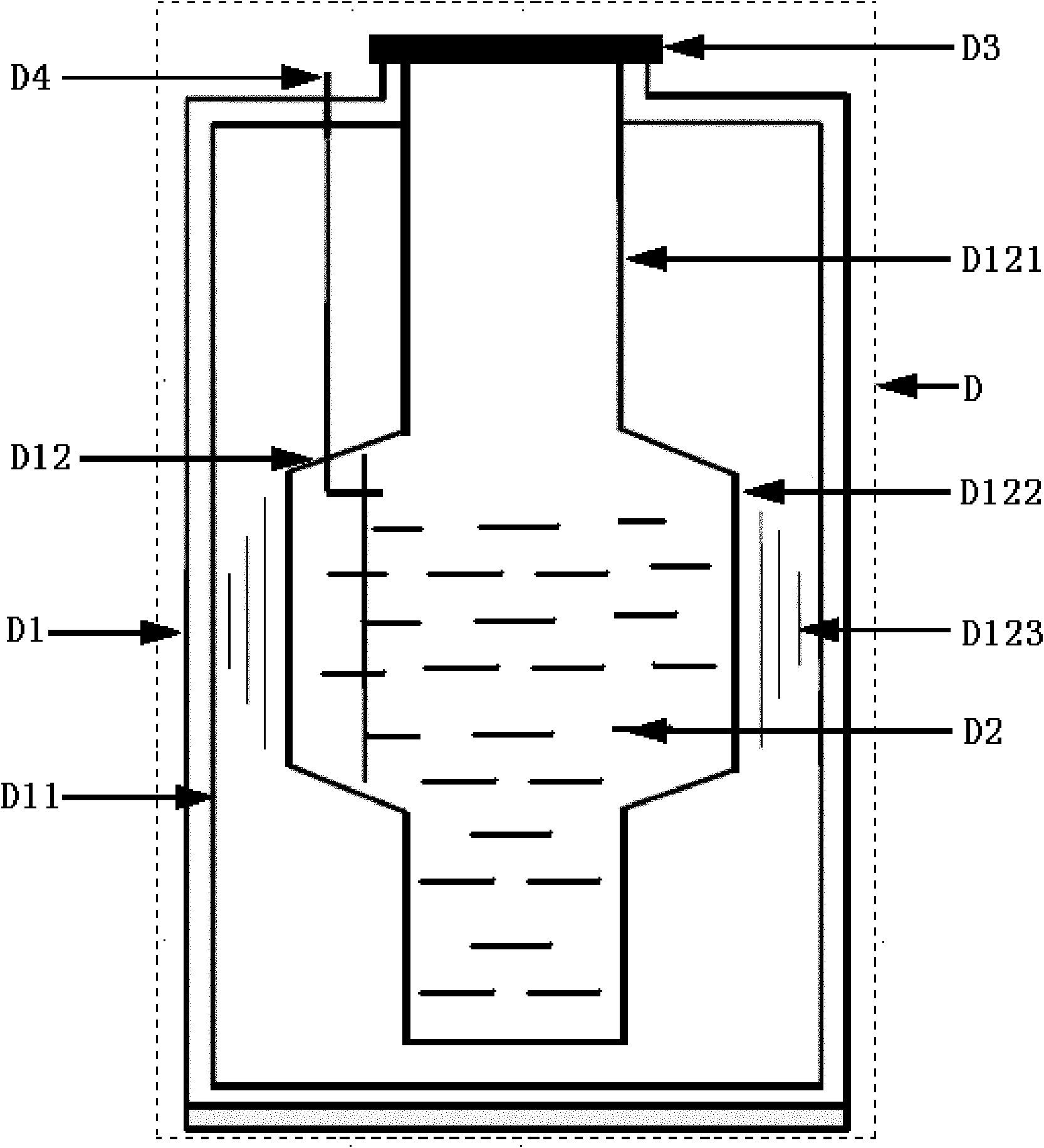
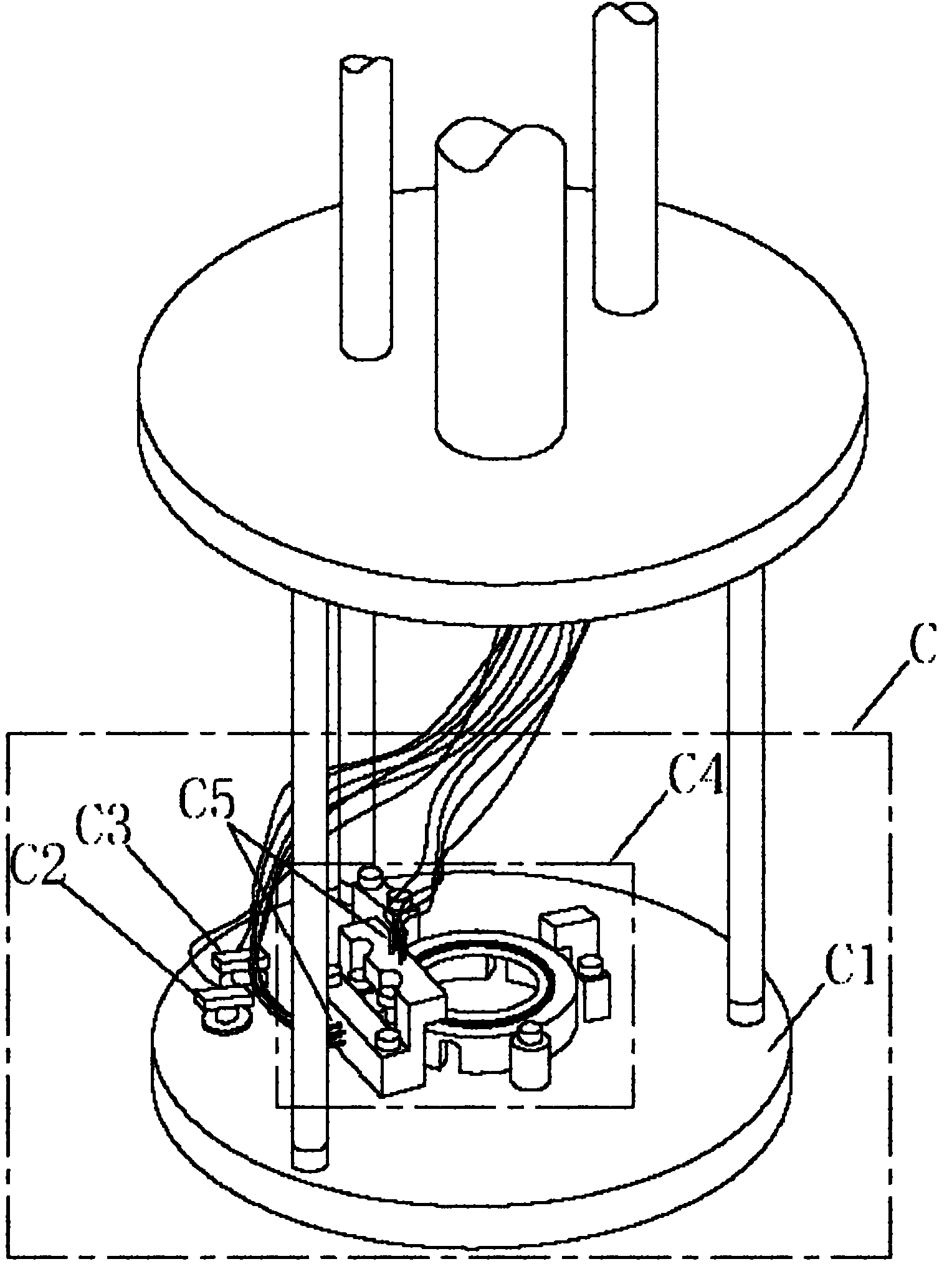
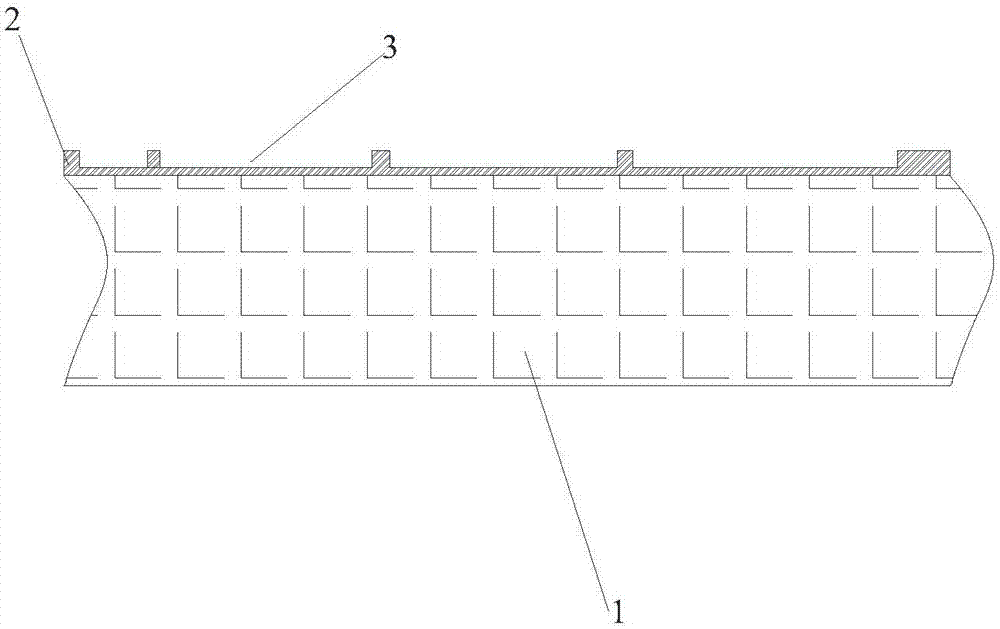
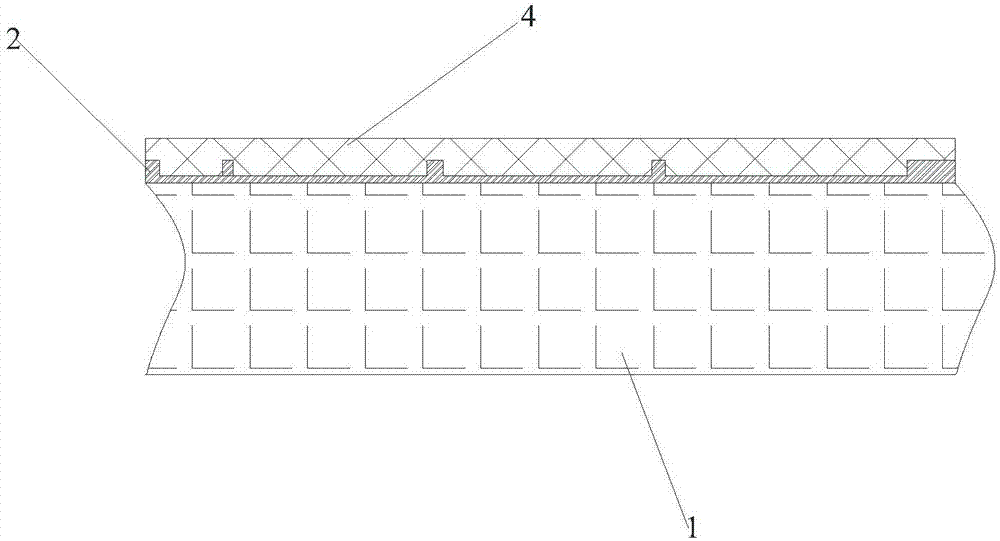
InactiveCN105826789AQuick connectionHigh mechanical strengthLine/current collector detailsConnection contact member materialElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh temperature superconducting
The present invention discloses a ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and a pressure heating system thereof. The ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and the pressure heating system thereof are able to conveniently and rapidly connect two ReBCO high-temperature superconducting-thin film strips together to obtain a connection strip with low resistance of a joint resistor, good mechanical property, good strip superconductivity and mostly unchanged connection. Low-temperature welding flux is employed in the connection process, is heated for 5 to 30mins at the temperature in the range of 150-300 DEG C, is pressed and reinforced once again at the temperature in the range of 150-200 DEG C, and is rapidly cooled while being subjected to natural cooling at the temperature in the range of 100-160 DEG C. The ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and the pressure heating system thereof are able to easily realize the joint resistance with 10-8 [Omega] magnitude when the splicing length is 1-5cm, when the splicing length is further increased, the joint resistance is continuously reduced, and when the splicing length is increased to 5-10cm, the resistance with n[Omega] magnitude is successfully realized. The ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology is rapid, efficient, easy to operate and good in splicing effect, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
Method for preparing nano aluminate lanthanum powder
InactiveCN101157474AReunion slightRegular shapeRare earth metal compoundsAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminatePtru catalyst
The invention relates to a method for preparing nanometer lanthanum aluminate powders. The method comprises the following steps: mixing and stirring microemulsion with the composite of Span80 and Tween80 as the surfactant, with n-butanol as the assistant surfactant and respectively with water solution of lanthanum nitrate and aluminum nitrate and ammonia water as the aqueous phase; after separation, washing and drying, incinerating the product at 750-1000 DEG C to obtain globular lanthanum aluminate powders with high purity, light agglomeration and particle diameter range of 20-60mm. The method of the invention solves problems of the traditional nanometer lanthanum aluminate powder preparing method, including high temperature, large lanthanum aluminate powder size, morphological irregularity and serious agglomeration. The product can be used as key materials for microwave devices such as wave filters, harmonic oscillators, superconductive films, etc., and can also be applied as the catalyst for oxidative coupling of methane as well as hydrogenization and hydrogenolysis of hydrocarbons.
Owner:重庆工学院
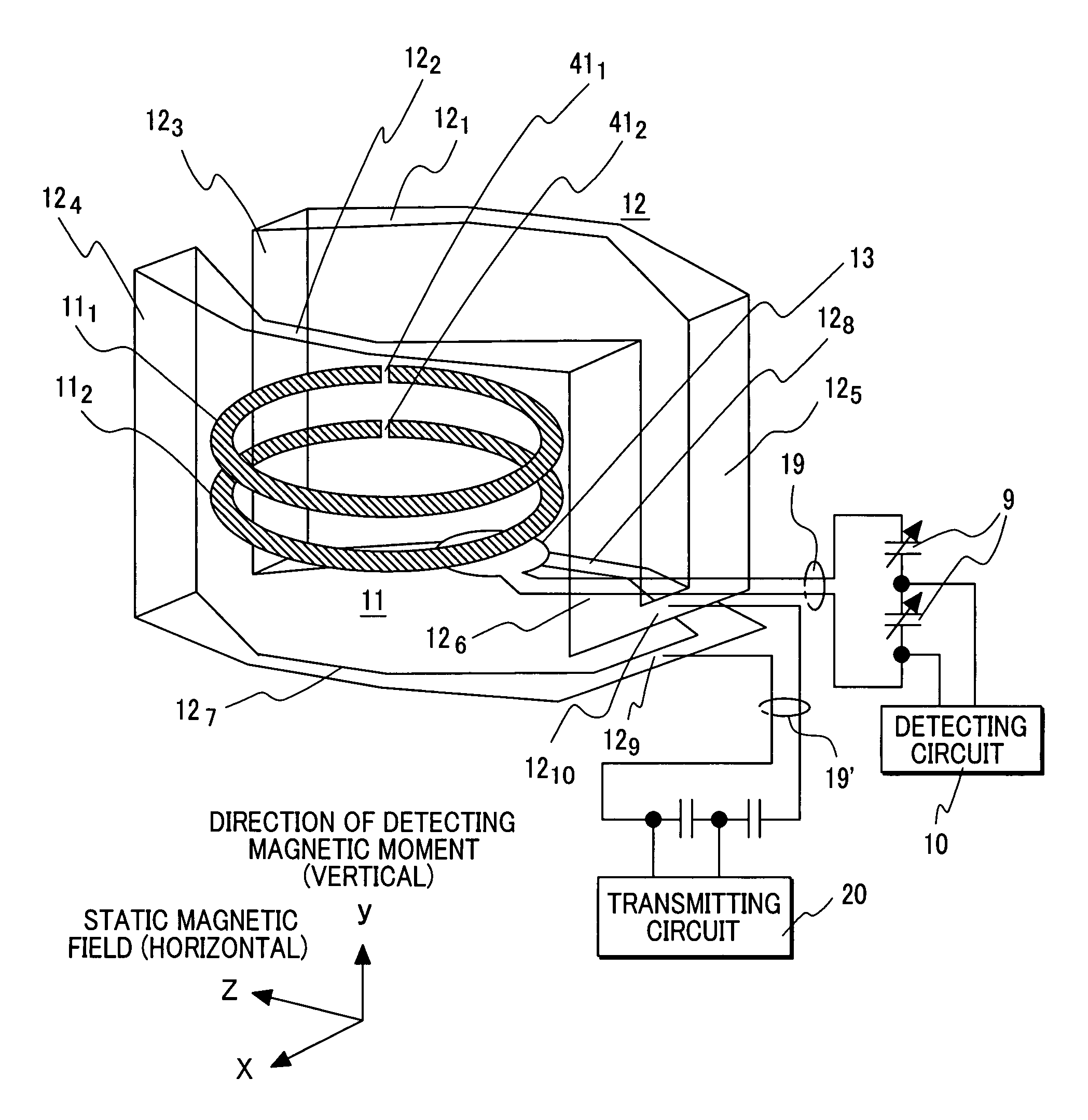
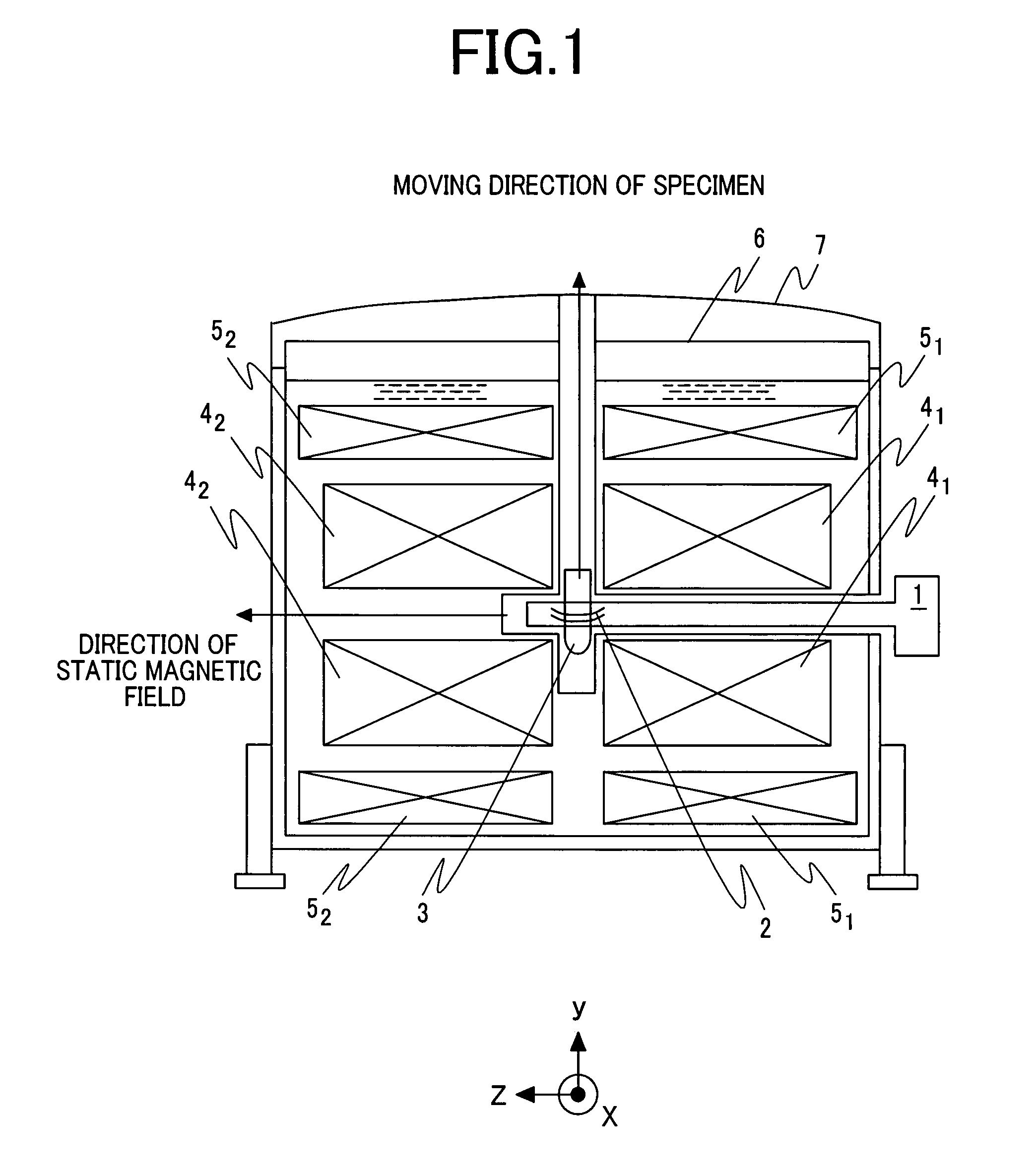
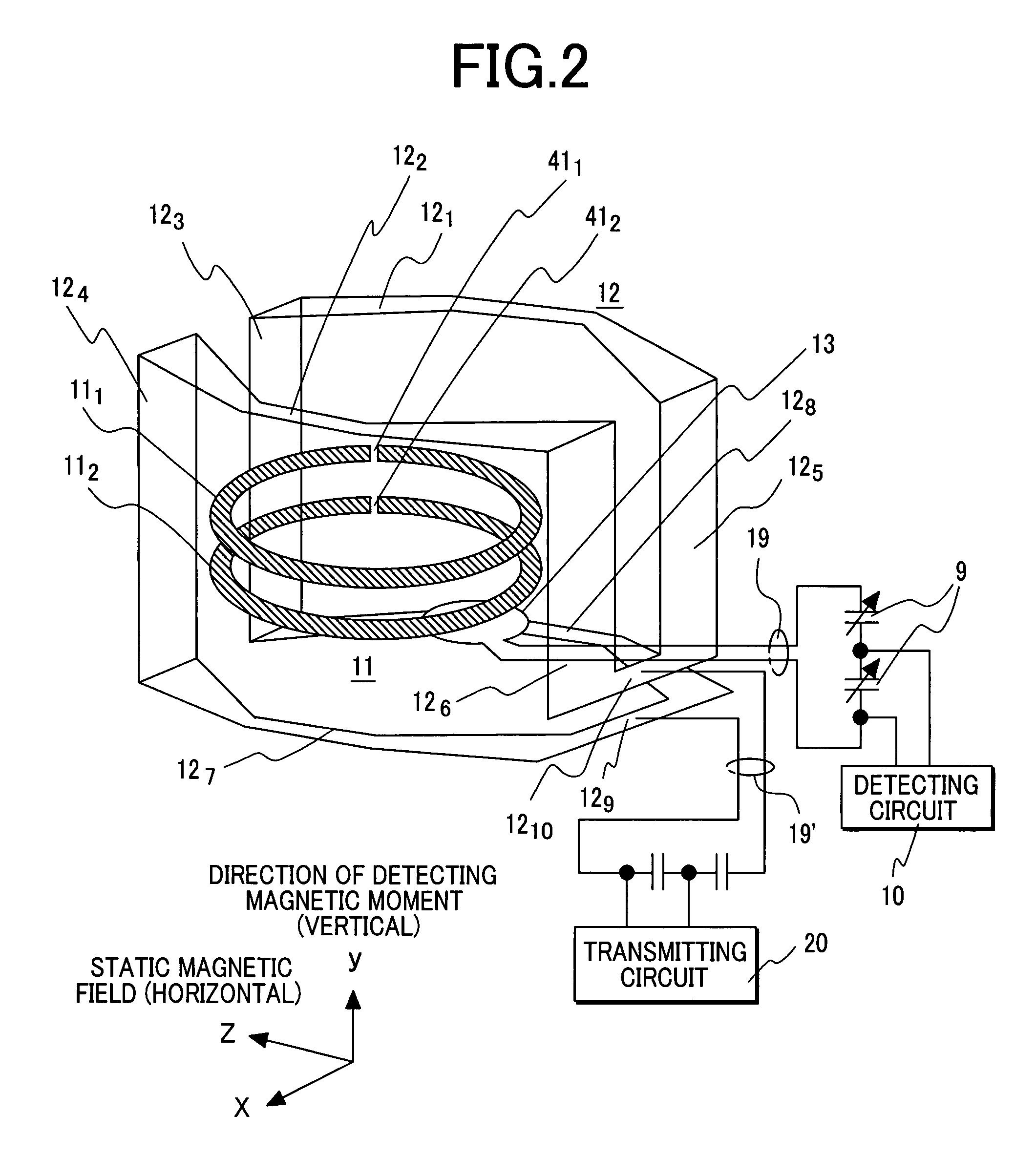
Nuclear magnetic resonance probe coil
InactiveUS7352186B2Readily measuring multiple nuclear specieMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSuperconducting thin films
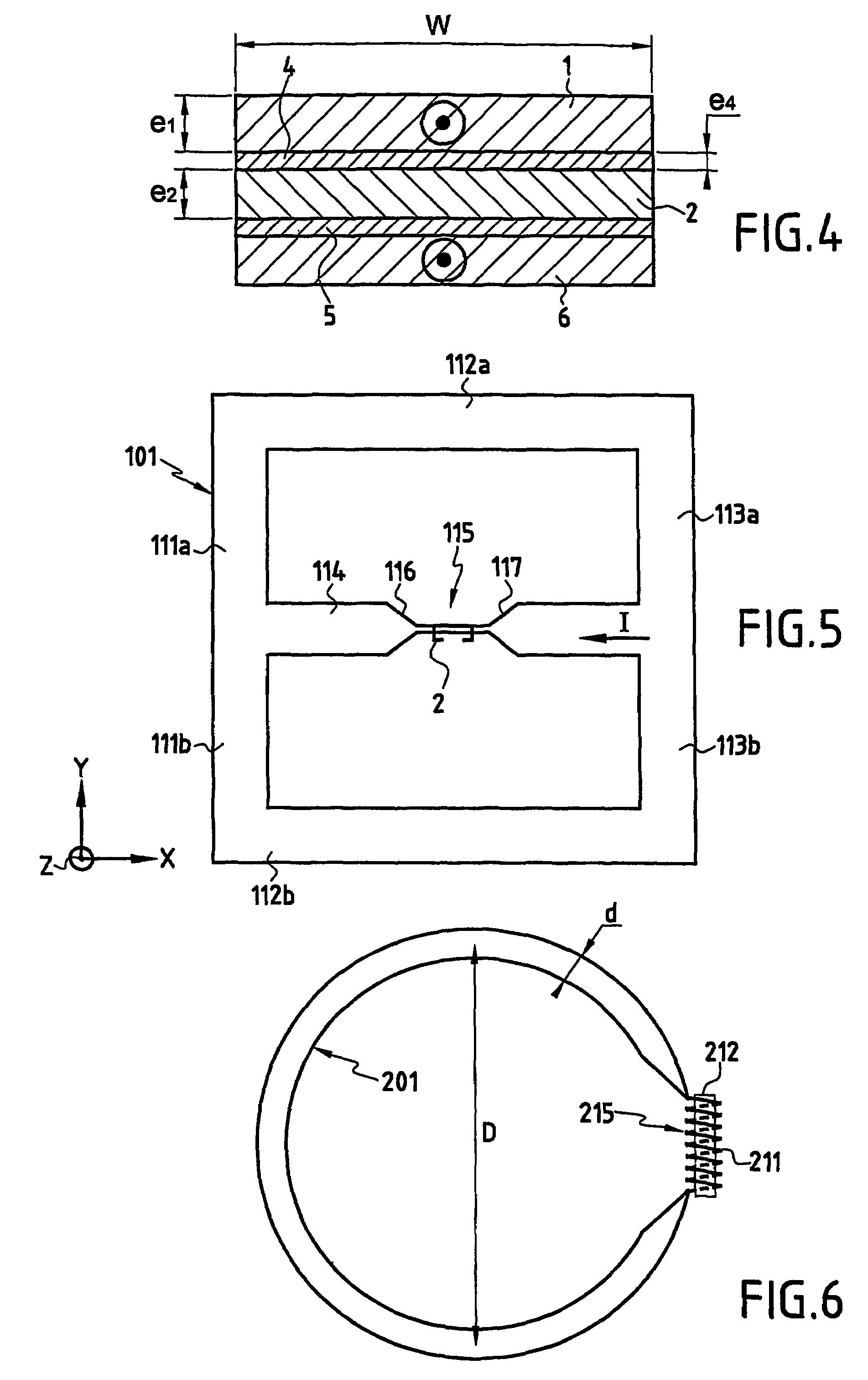
Provided is a nuclear magnetic resonance probe coil that is included in a nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus in which the direction of a static magnetic field is horizontal and that can highly sensitively measure multiple nuclear species. A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus includes a unit that horizontally applies a static magnetic field, a unit that vertically moves a specimen to a predetermined position in the apparatus, and a probe including in the distal part thereof a probe coil that applies a radiofrequency signal to the specimen and that detects a signal produced by the specimen. The probe coil includes multiple pairs of superconducting thin-film rings formed on respective substrates that are disposed in parallel with the static magnetic field while being separated from each other by a predetermined distance, a detection loop that detects a signal received by the superconducting thin-film rings, and a transmission coil that applies the radiofrequency signal to the specimen and that has the normal thereto extended horizontally.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Device for sensing a magnetic field
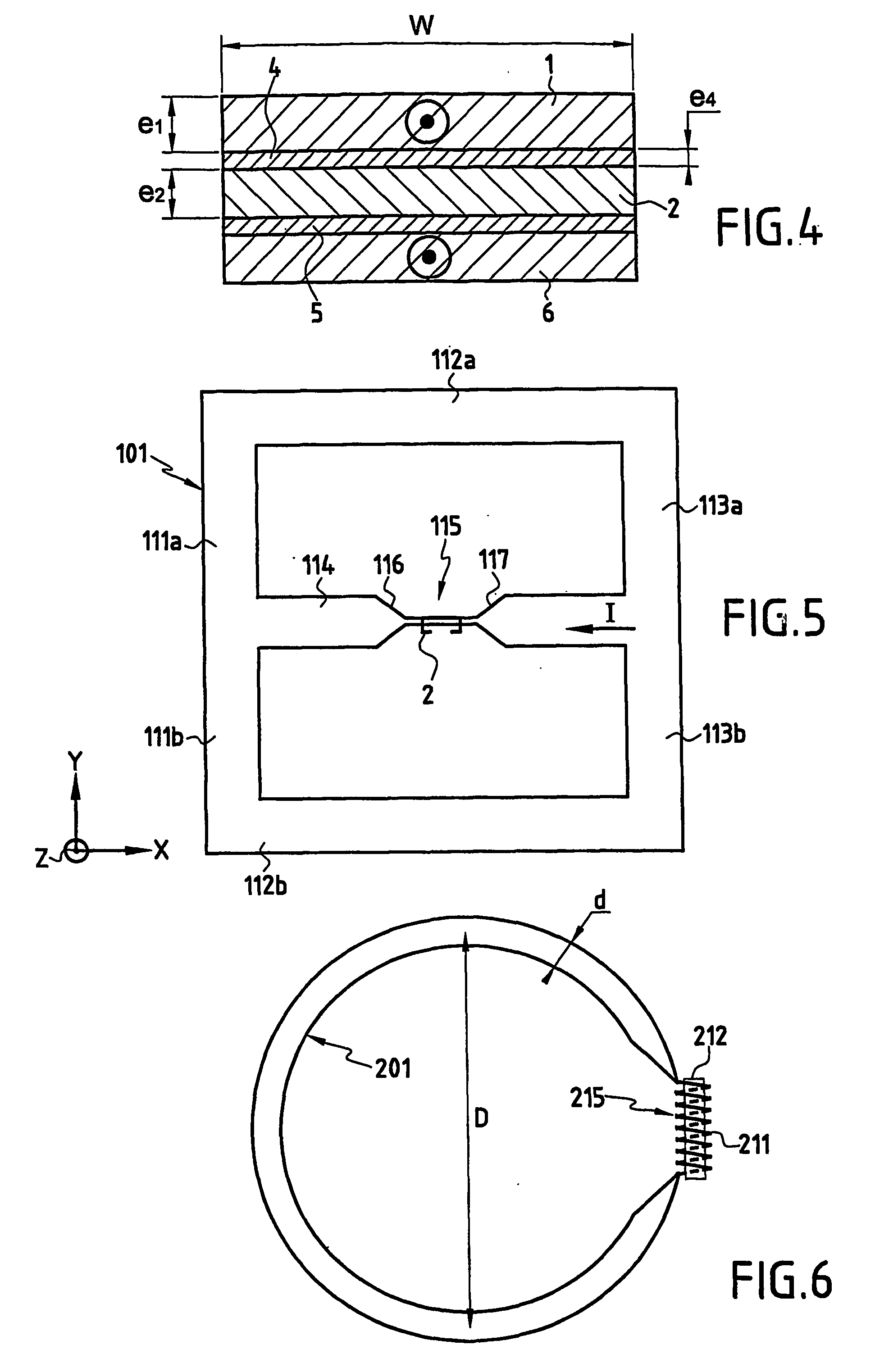
InactiveUS7342396B2Comparable and good performanceEasy to produceMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectrical currentSuperconducting thin films
The device for sensing a magnetic field comprises a closed superconducting pick-up loop (1) having a path width (d) etched out of a single layer superconducting thin film and provided with a constriction (15) having a width (w) of narrow dimension smaller than the path width (d). The closed superconducting pick-up loop (1) constitutes a flux-to-field transformer (FFDT). At least one magnetoresistive element (2) is placed on top of or below the superconducting thin film, is isolated from the superconducting thin film by a thin insulating layer and is located so that an active part of the magnetoresistive element (2) is at the location of the constriction (15) and has a width equal to or less than the width of the constriction (15). The active part of the magnetoresistive element (2) is oriented so that the bias current in this active part is directed essentially along the constriction (15), orthogonally to the width of narrow dimension.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Device and method for testing microwave surface resistance distribution of high-temperature superconducting thin film
ActiveCN104316769AResolve resolutionResolve SensitivityResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceMicrowave
The invention discloses a device and method for testing the microwave surface resistance distribution of a high-temperature superconducting thin film. The testing device comprises a testing seat, a fixing assembly, a calibration assembly and a sealing cover, and the working resonant mode is TE012. The testing seat comprises a shielding shell, an input coupling structure, an output coupling structure, a supporting ring, a dielectric cylinder and a metal circular ring. The testing seat is loaded with the tested superconducting thin film to constitute a resonator. The fixing assembly is used for fixing the tested superconducting thin film, and the sealing cover is used for isolating the inside and the outside of the resonator. The device and method for testing the microwave surface resistance distribution of the high-temperature superconducting thin film have the advantages that the contradiction among the resolution ratio, the sensitivity and the universality of the testing device in the microwave surface resistance distribution test of the superconducting thin film is solved; the tested superconducting thin film can be effectively prevented from being pressed to be damaged; direct coupling can be effectively avoided, and high testing precision is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
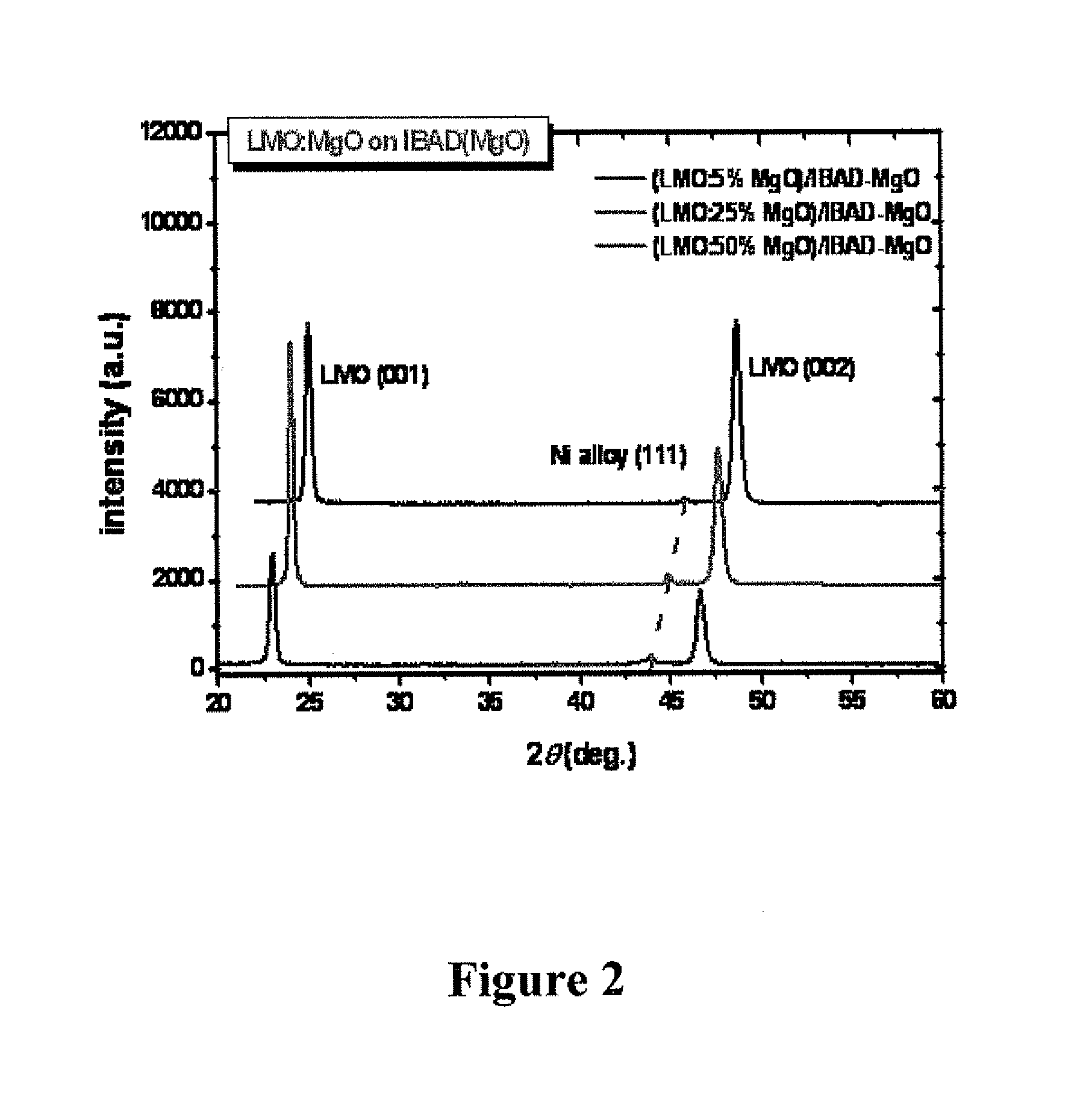
Substrate for fabricating superconductive film, superconductive wires and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110218113A1Excellent characteristicsImprove reliabilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsPretreated surfacesThin membraneMetal substrate
Provided is a substrate for superconductive film formation, which includes a metal substrate, and an oxide layer formed directly on the metal substrate, containing chromium oxide as a major component and having a thickness of 10-300 nm and an arithmetic average roughness Ra of not more than 50 nm. A method of manufacturing a substrate for superconductive film formation, which includes forming an oxide layer directly on a metal substrate, the oxide layer containing chromium oxide as a major component and having a thickness of 10-300 nm and an arithmetic average roughness Ra of not more than 50 nm.
Owner:JAPAN FINE CERAMICS CENT +1
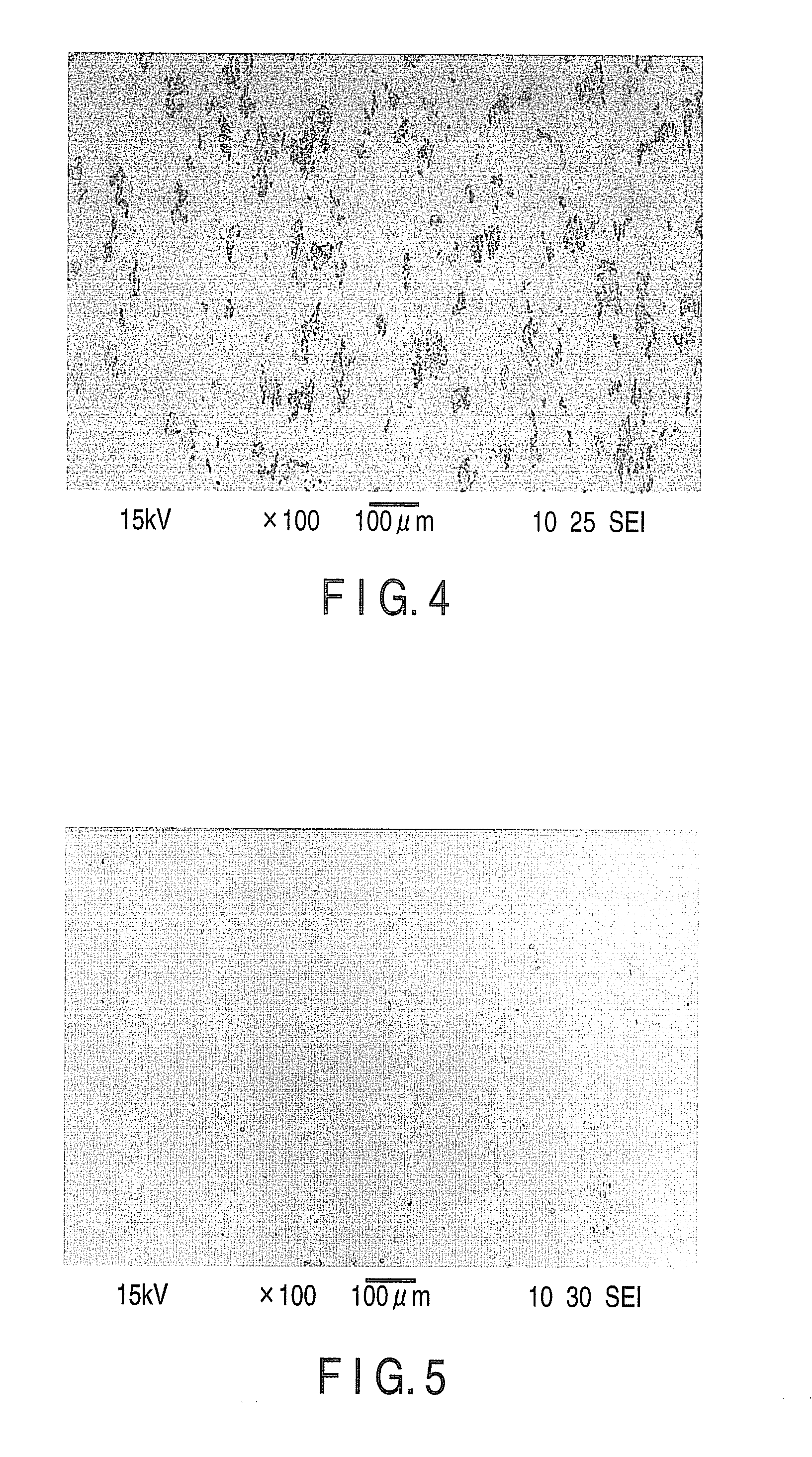
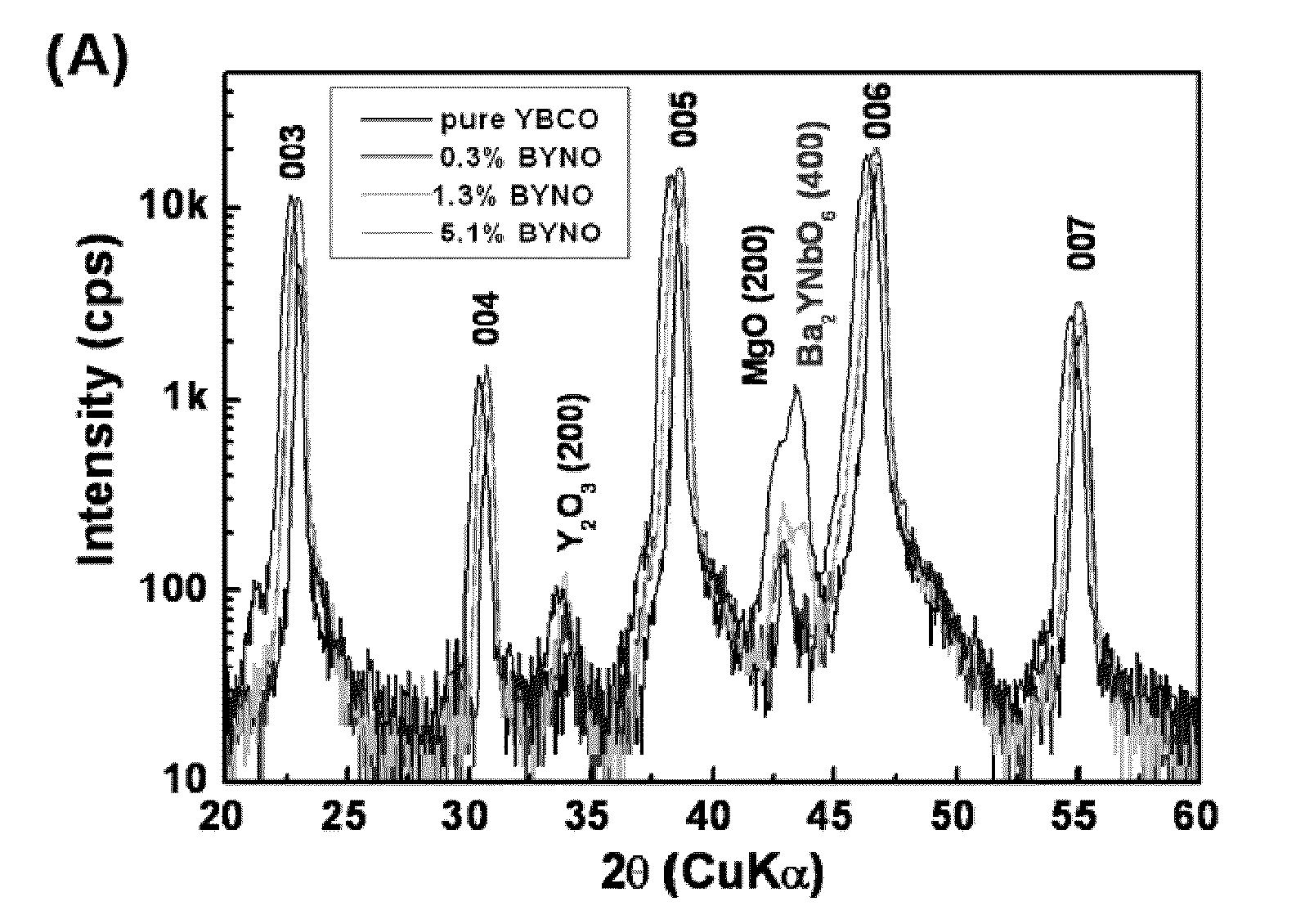
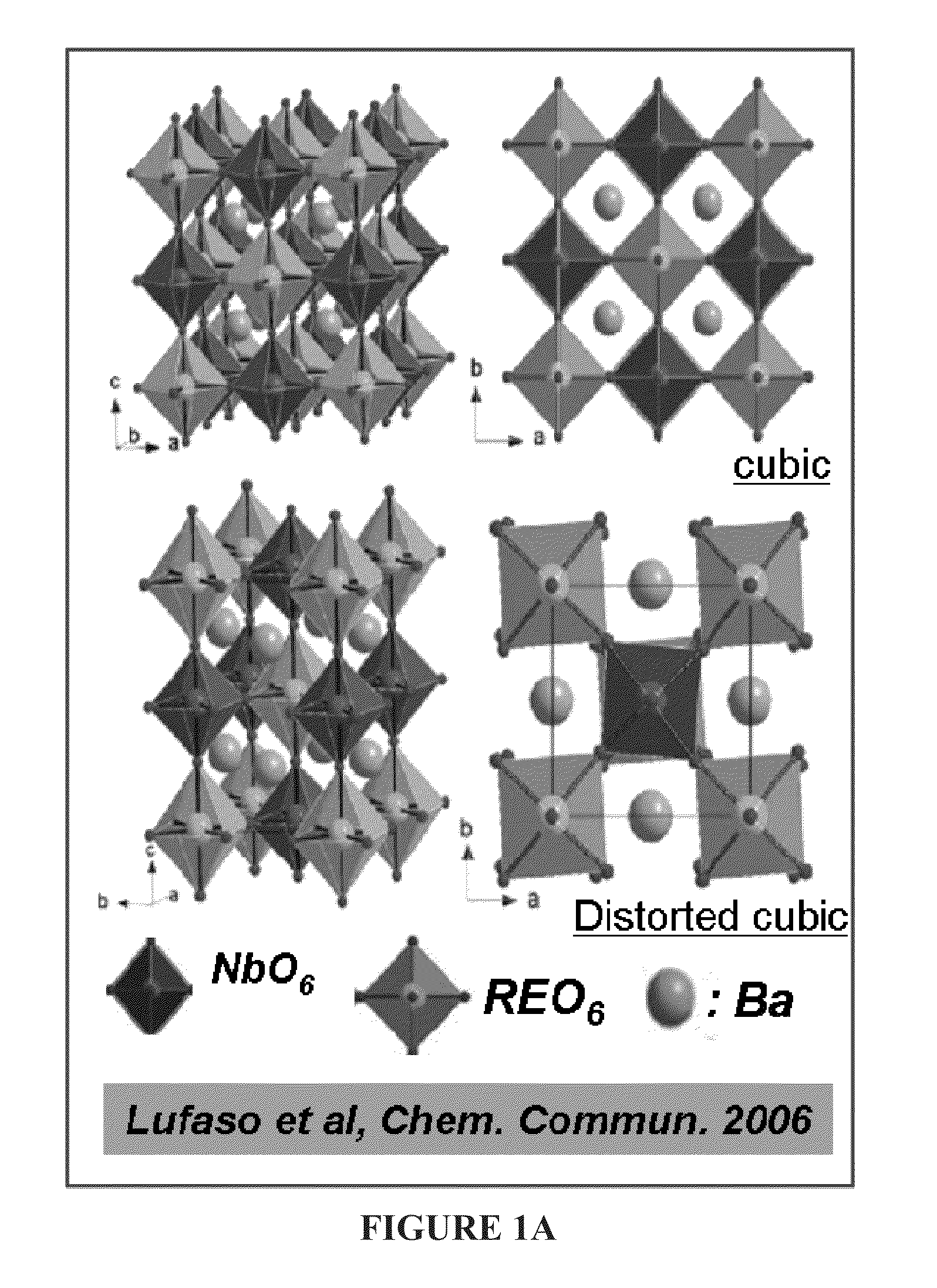
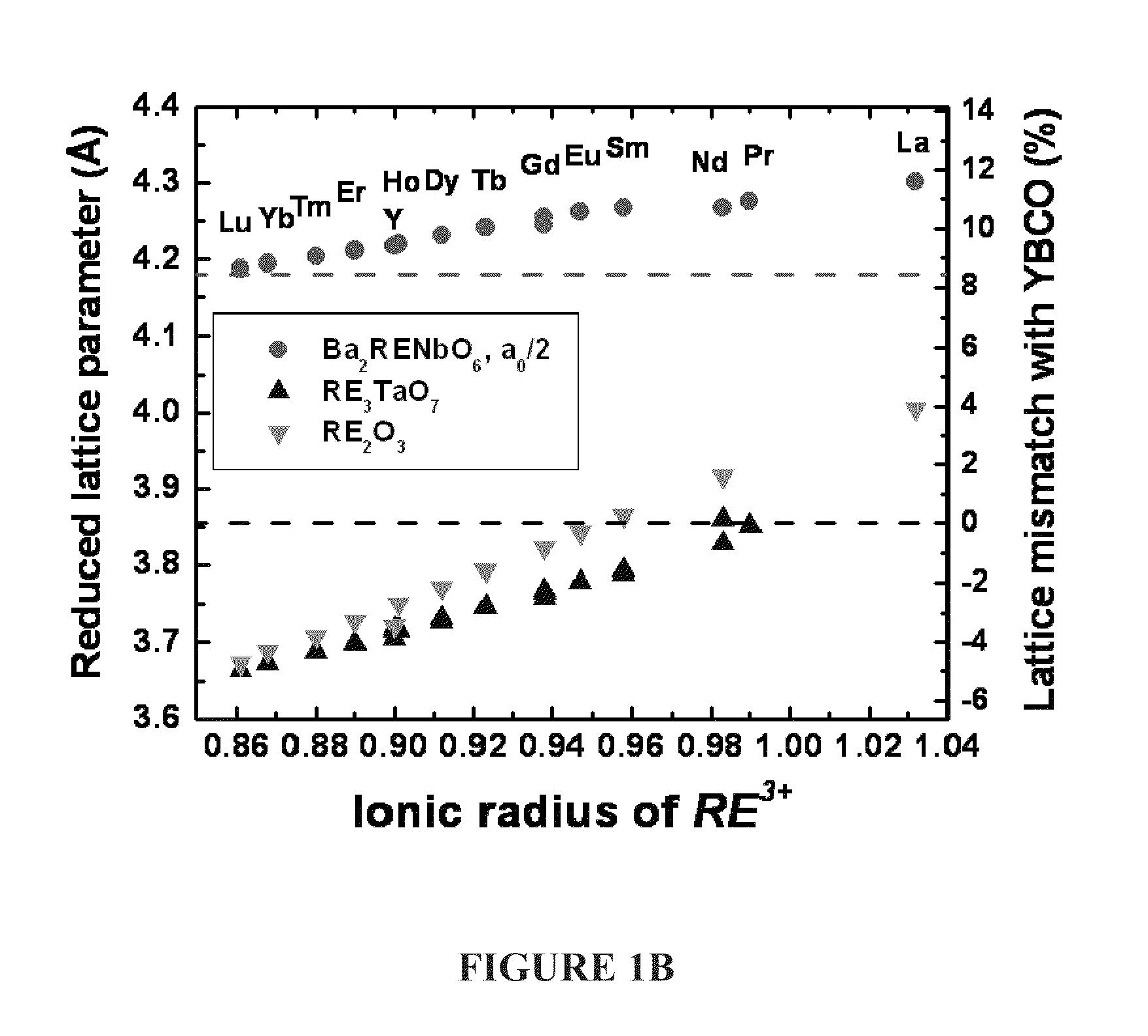
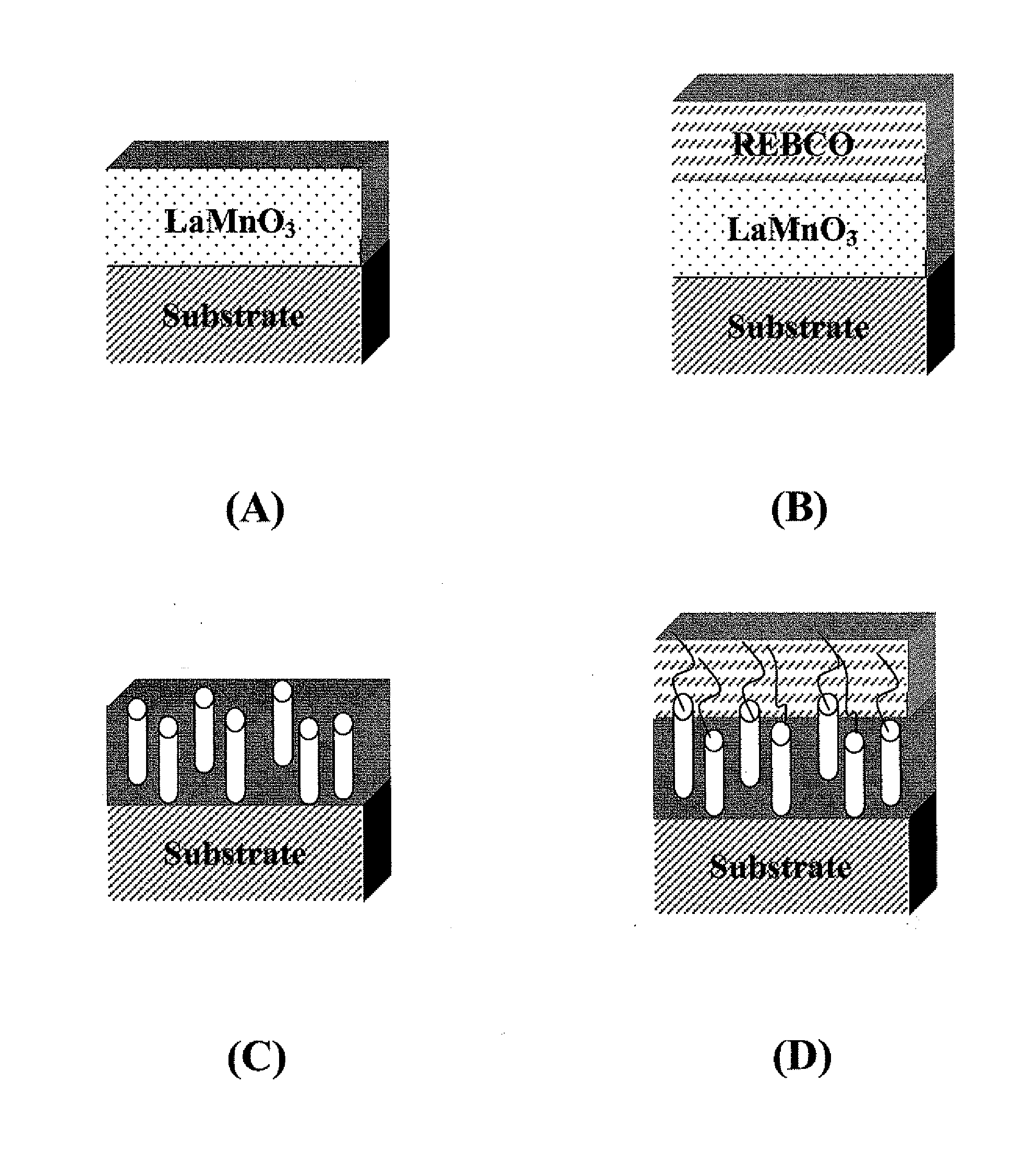
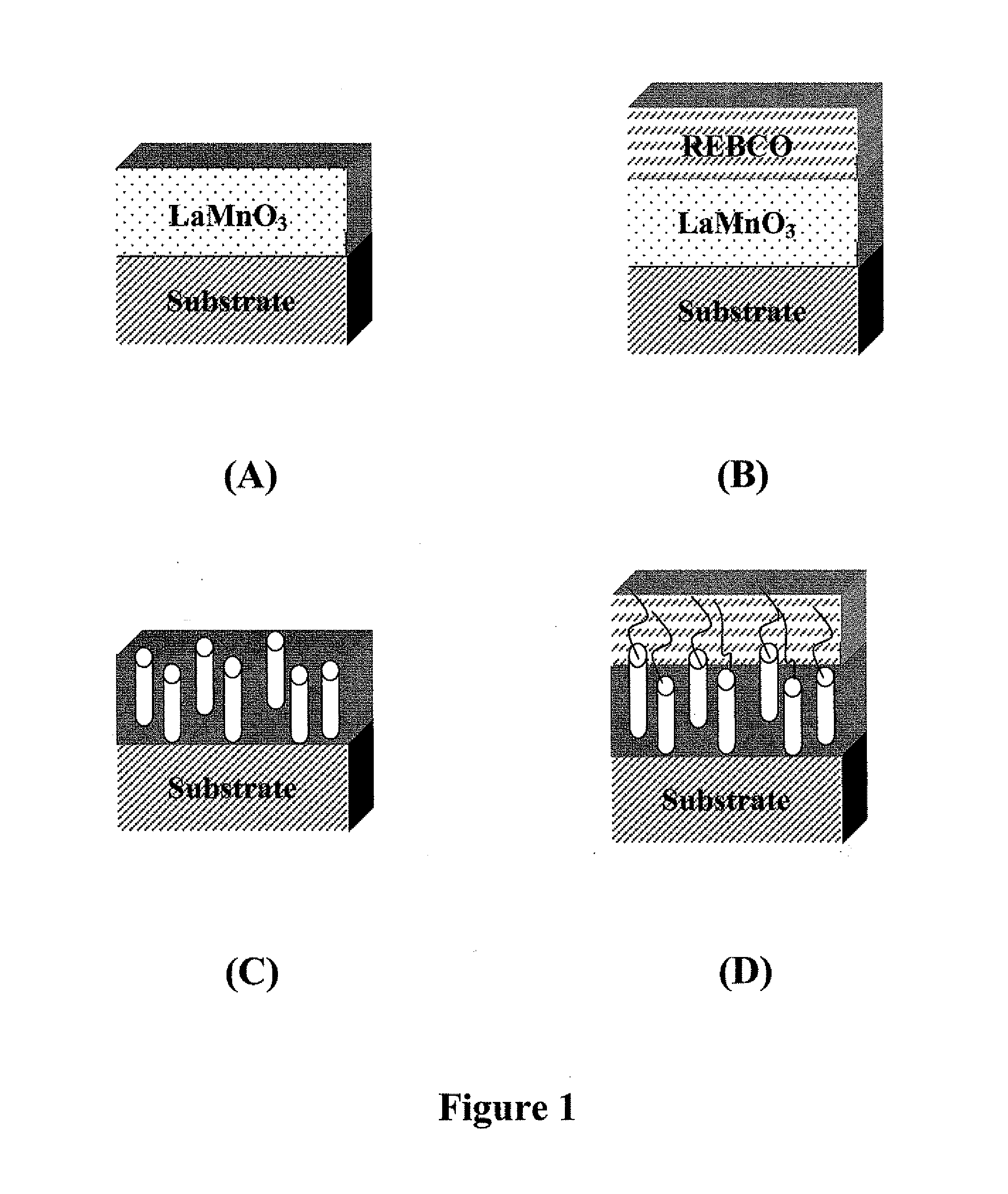
CRITICAL CURRENT DENSITY ENHANCEMENT VIA INCORPORATION OF NANOSCALE Ba2(Y,RE)NbO6 IN REBCO FILMS
A superconducting article includes a substrate having a biaxially textured surface, and an epitaxial biaxially textured superconducting film supported by the substrate. The epitaxial superconducting film includes particles of Ba2RENbO6 and is characterized by a critical current density higher than 1 MA / cm2 at 77K, self-field. In one embodiment the particles are assembled into columns. The particles and nanocolumns of Ba2RENbO6 defects enhance flux pinning which results in improved critical current densities of the superconducting films. Methods of making superconducting films with Ba2RENbO6 defects are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Method for manufacturing magnesium diboride superconducting thin film micro-structure through annealing
InactiveCN103500793AAvoid contactDoes not lead to deterioration of superconducting propertiesSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentMicro structureChemical reaction
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a magnesium diboride superconducting thin film micro-structure through annealing. According to the method, electron beams are used for annealing a magnesium diboride precursor film with micro-structure patterns in a vacuum. The magnesium diboride precursor film with the micro-structure patterns is an Mg / B multi-layer film manufactured with a film masking method. Elementary substances of magnesium and boron in the precursor film undergo a chemical reaction in annealing time of a second order of magnitude, and finally, the magnesium diboride superconducting thin film micro-structure with the conversion temperature higher than 35K is generated.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Konstantan alloy baseband for high-temperature superconduction coating conductor
InactiveCN101302590ALow resistivityGood electrical conductivityRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsTemperature controlMaterials preparation
The invention relates to a konstantan alloy baseband used for a high-temperature superconducting coated conductor without magnetism and with high conductance and a method for preparing the same, belonging to the high conducting metal alloy material preparation process technical field. The compositions by weight percentage of the konstantan alloy baseband used for the high-temperature superconducting coated conductor are: 50 to 60 percent of Cu, 38 to 48 percent of Ni, and 1 to 5 percent of Mn. The alloy baseband can form a biaxially texture through each step in the technical process via annealing under a mixed atmosphere of Ar plus 4 percent Hz with an annealing temperature controlled to be between 700 and 1000 DEG C and the annealing time controlled for 30 to 90 minutes. The structure is advantageous to the coating of a YBCO superconducting thin film layer of the konstantan alloy baseband.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Low-fluorine solution deposition and heat treatment process of YBCO (Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide) superconducting thin film
InactiveCN102443792AIncrease the critical current densityAvoid crackingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSolid/suspension decomposition chemical coatingFurnace temperatureMoisture
The invention provides a low-fluorine solution deposition and heat treatment process of a YBCO (Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide) superconducting thin film. The low-fluorine solution deposition and heat treatment process comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a low-fluorine YBCO solution; secondly, preparing and drying a gel thin film and pre-treating the dried film; and finally, carrying out final treatment on the dry film: using mixed gas of moisture oxygen gas and inert gas and keeping the mixed gas at the furnace temperature of 790-810DEG C for 1-2 hours; switching the atmosphereinto the mixed gas of dry oxygen gas and inert gas with the same oxygen partial pressure; continuously keeping the mixed gas at the furnace temperature of 790-810DEG C for 10-30 minutes; and finally,naturally cooling the mixed gas along with the furnace, switching the atmosphere into dry O2 after the temperature is reduced to 400-500 DEG C, preserving the heat for 2-4 hours, finally naturally cooling to room temperature along with the furnace and taking out a sample. The YBCO superconducting thin film which is finally obtained in the invention has a high c-axle texture and critical current density Jc as high as (1-5)*106A / cm<2> at the liquid nitrogen temperature.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing magnesium diboride superconducting thin film by electron beam annealing
InactiveCN102214786AAchieve preparationReduce volatilitySuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentChemical reactionMagnesium diboride
The invention relates to a method for preparing a magnesium diboride superconducting thin film by electron beam annealing. The method is characterized by annealing a magnesium diboride forerunner film in vacuum by adopting an electron beam, enabling a magnesium and boron simple substance in the forerunner film in the annealing time of the order of magnitude of seconds to perform chemical reaction, and generating the magnesium diboride superconducting thin film finally; and determining electron beam parameters and annealing time according to different thicknesses of the forerunner film and annealing temperatures in annealing, and finishing the annealing of thin films of different thicknesses through controlling energy and dosage of the electron beam accurately. The magnesium diboride superconducting thin film prepared by using the method in the invention has the advantages of stable performances, flat surface, higher transformation temperature than 35k, uniform annealing, and the method for preparing the film has high efficiency, and is simple in operation and the like, and can be used for the preparation of a plurality of functional thin films.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing high temperature superconducting thin film by chemical process
ActiveCN101752035AIncrease the critical current densitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesRare-earth elementEvaporation
The invention provides a method for preparing high temperature superconducting thin film by chemical process. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing a precursor solution, by mixing Y(CH3COO)3, RE(CH3COO)3, Ba(CH3COO)2 and Cu(CH3COO)2 with ratio of (Y+RE) to Ba to Cu equaling to 1:2:3 (wherein RE is Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd and Dy) and dissolving in 20-30 mol percent aqueous trifluoroacetic acid solution; stirring to be uniform, performing vacuum drying by evaporation to the solvent to obtain gel; then adding methanol, stirring to be uniform, performing drying by evaporation to the solvent to obtain gel; then adding proper amount of methanol to prepare the precursor solution with the total concentration of metal ions of Y, RE, Ba and Cu being 0.8-3.0mol / L; then coating the precursor solution on a substrate; performing low temperature heat treatment at 400-410 DEG C to the coated thin film to decompose trifluoroacetic acid salt; and finally performing high temperature heat treatment at 800-850 DEG C and annealing process at 490-510 DEG C to form YBCO thin film doped with rare-earth element.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
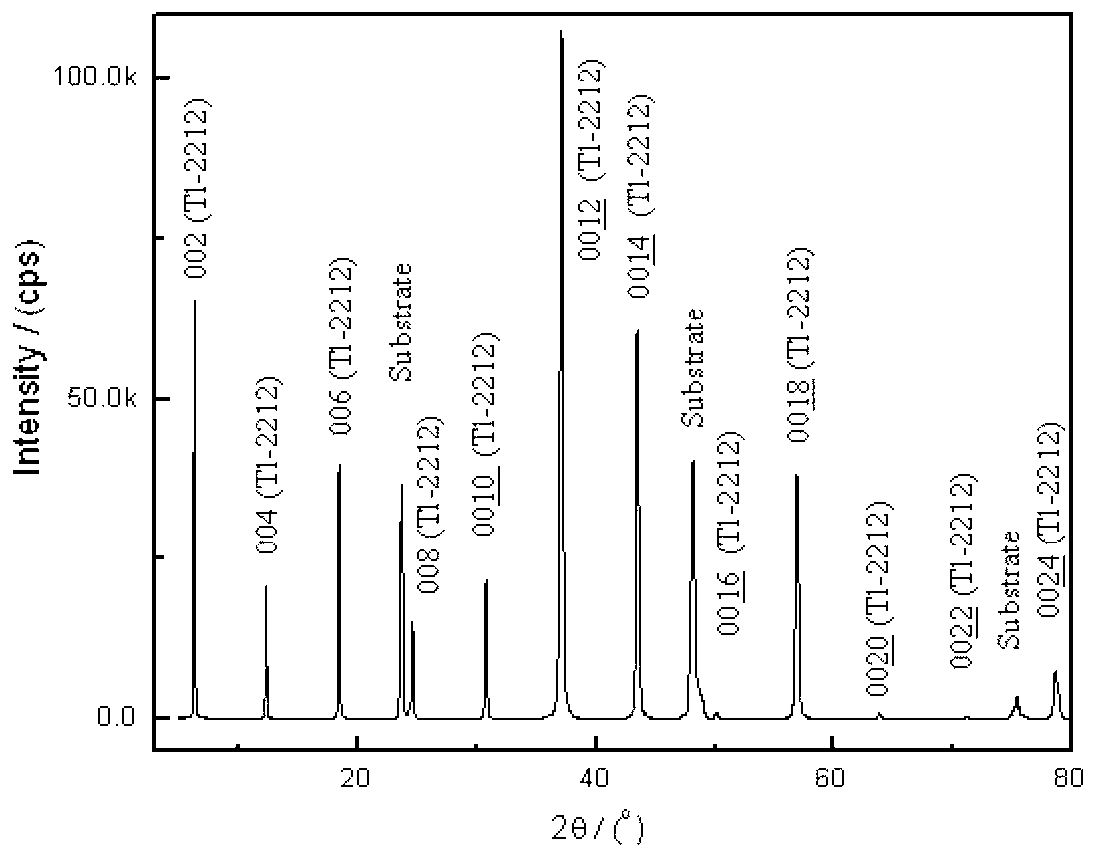
Preparation method for synthesizing T1-2212 superconducting thin film by employing sol-gel method
InactiveCN103304232ASimple processReduce manufacturing costSuperconductor elements usageDiethylenetriamineSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method for synthesizing a T1-2212 superconducting thin film by employing a sol-gel method. The method comprises the following steps: by taking thallium acetate, barium acetate, calcium acetate and copper acetate as initial raw materials, by taking lactic acid, alpha-methacrylic acid, diethylenetriamine, triethylene tetramine and methanol as complexing agents and solvents, and preparing the sol with proper viscosity. The sol has the characteristics of fewer materials, simple preparation process and easily and accurately controlled components; the T1-2212 superconducting thin film prepared by employing the sol has flat surface topography and good superconducting characteristics.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Superconducting thin film for single photon detection system and preparation method thereof
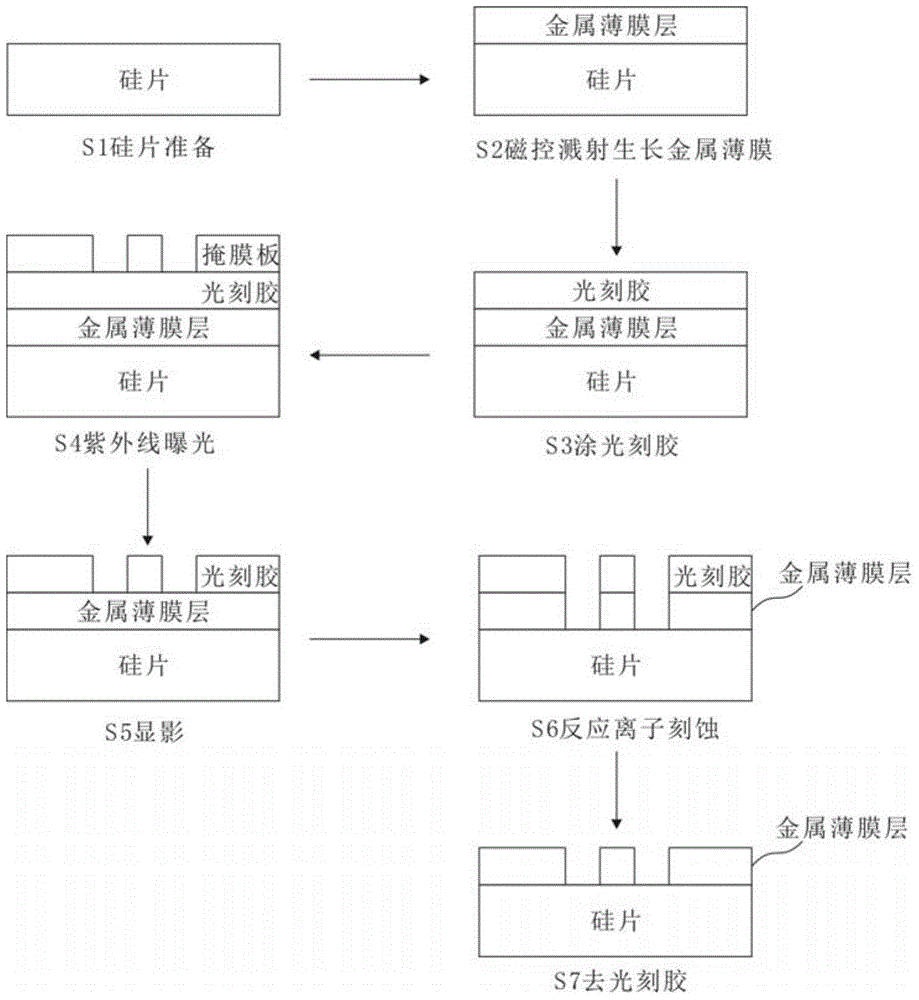
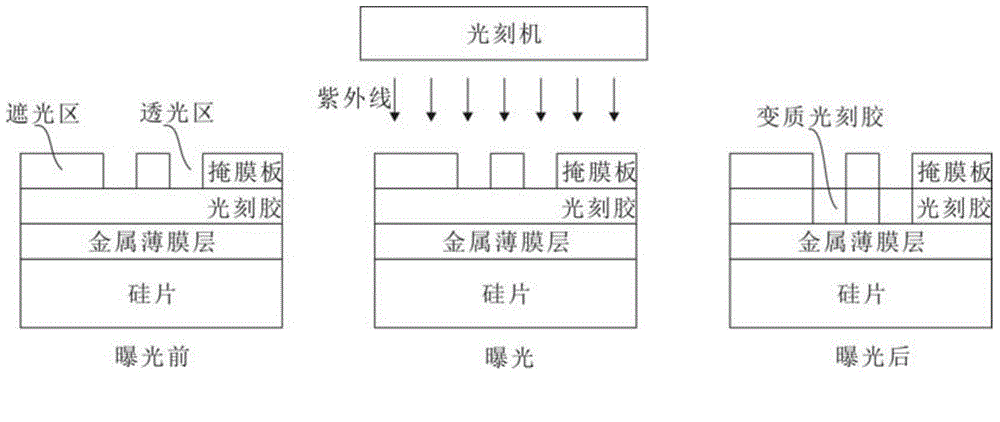
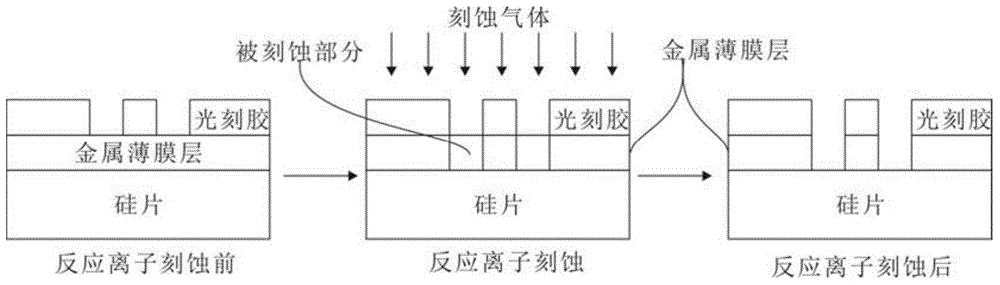
InactiveCN104617214ANot easy to fall offNo photoresist residueSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentNormal-superconductive switchable devicesCooking & bakingPhoton detection
The invention discloses a preparation method for a single photon detection system; the preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, cleaning the silicon wafer; S2, growing the metal film on the silicon wafer by magnetron sputtering operation; S3, evenly coating a layer of photoresist on the surface of the metal film, baking and sizing; S4, using the prefab mask for covering the photoresist, using the ultraviolet ray for exposing the photoresist; S5, taking off the mask, using the developing liquid for etching the exposed part of the photoresist; S6, etching the exposed metal film part from the developed film; and S7, cleaning the etched film and air drying. A superconducting thin film for a single photon detection system is further disclosed, the film takes the silicon wafer as the substrate material, the material of the thin film is metal, and the locating mark is formed on the thin film for automatically cutting the sheet. The thin film prepared by the method has flat surface and is not easy to fall off, the photoresist has no residue, and the locating mark is formed on the thin film for exactly finding the position for the following cutting operation and the automatically cutting operation can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and pressure heating system thereof ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and pressure heating system thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ae99d24-df91-4f78-b736-cd75b48a0ac2/160329083943.PNG)
![ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and pressure heating system thereof ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and pressure heating system thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ae99d24-df91-4f78-b736-cd75b48a0ac2/160329084038.PNG)
![ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and pressure heating system thereof ReBa2Cu3O7-[Delta] high-temperature superconducting-thin film strip attachment technology and pressure heating system thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ae99d24-df91-4f78-b736-cd75b48a0ac2/160329084135.PNG)