Patents
Literature
32 results about "Self field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
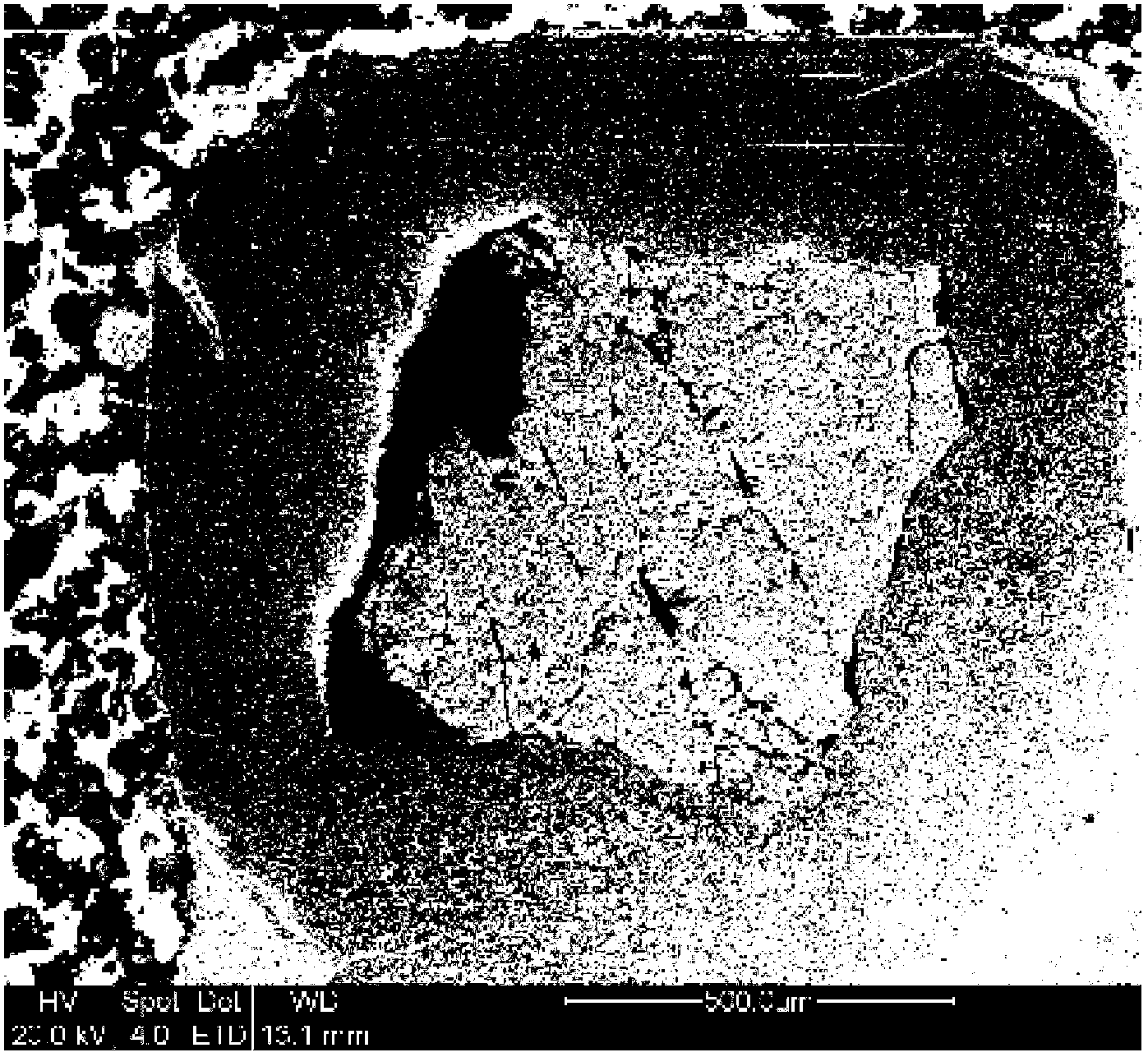
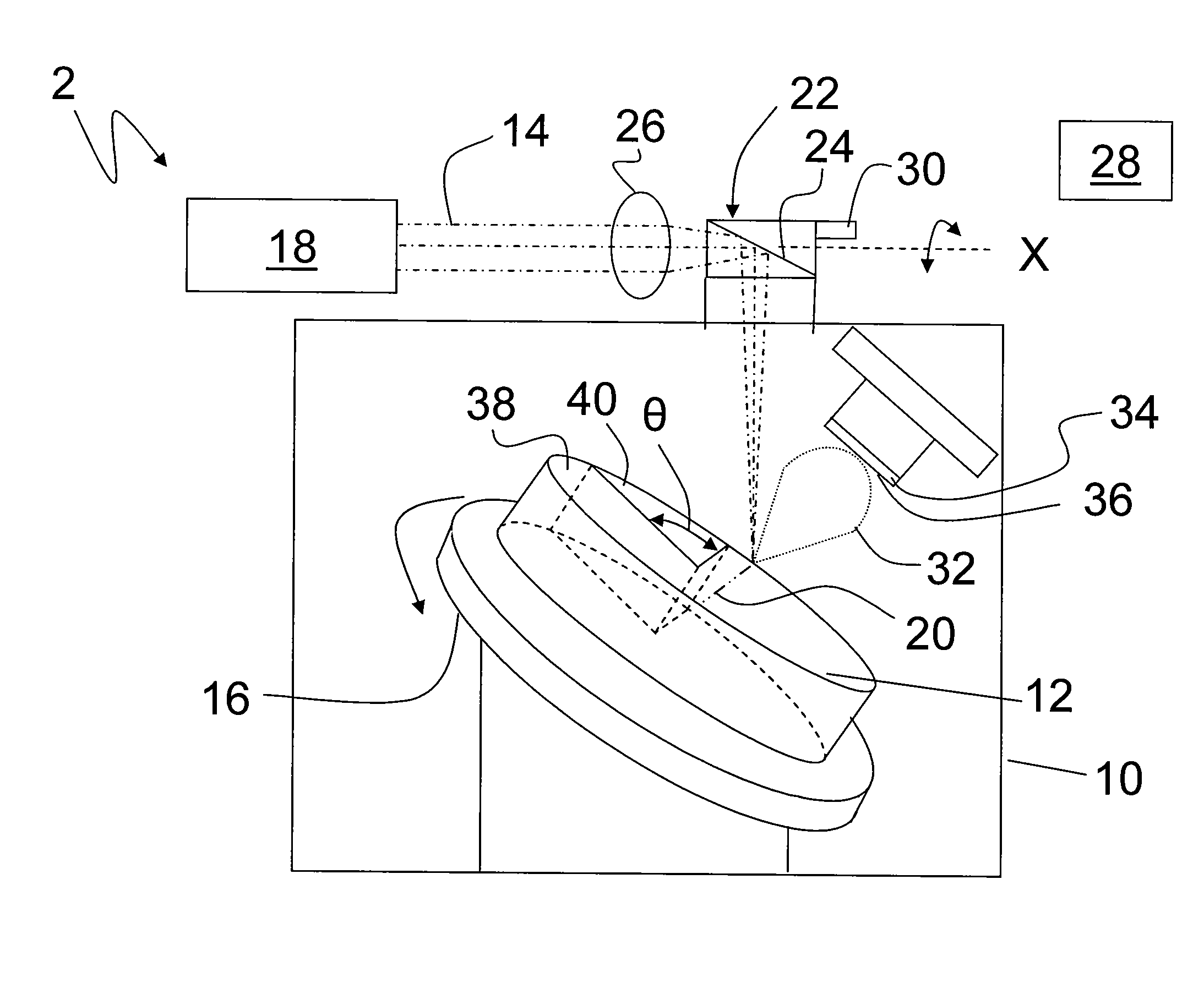
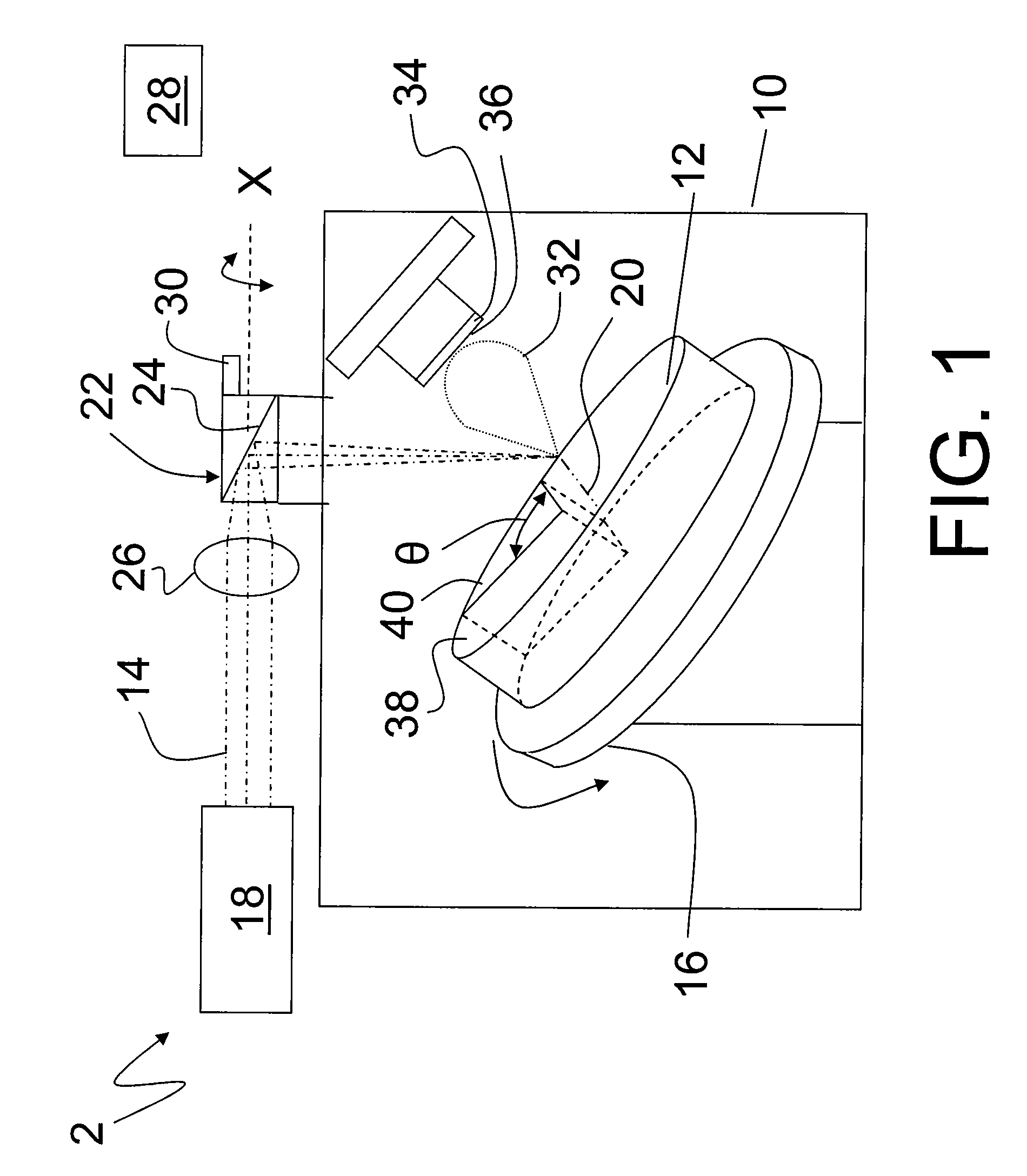
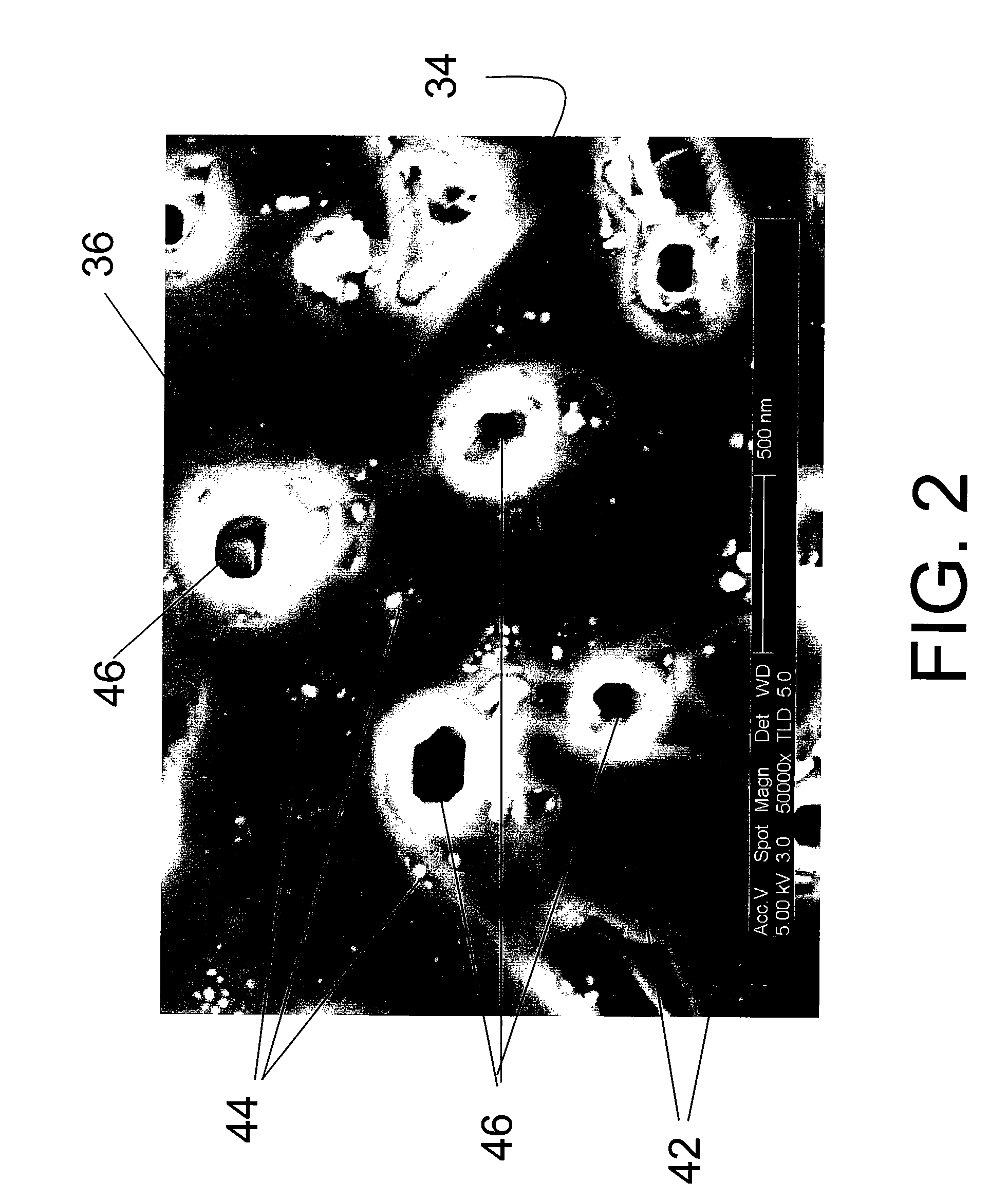
FLUX PINNING ENHANCEMENTS IN SUPERCONDUCTIVE REBa2CU3O7-x (REBCO) FILMS AND METHOD OF FORMING THEREOF
ActiveUS20070129255A1Avoid adverse reactionsSeparationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingParticulatesFlux pinning
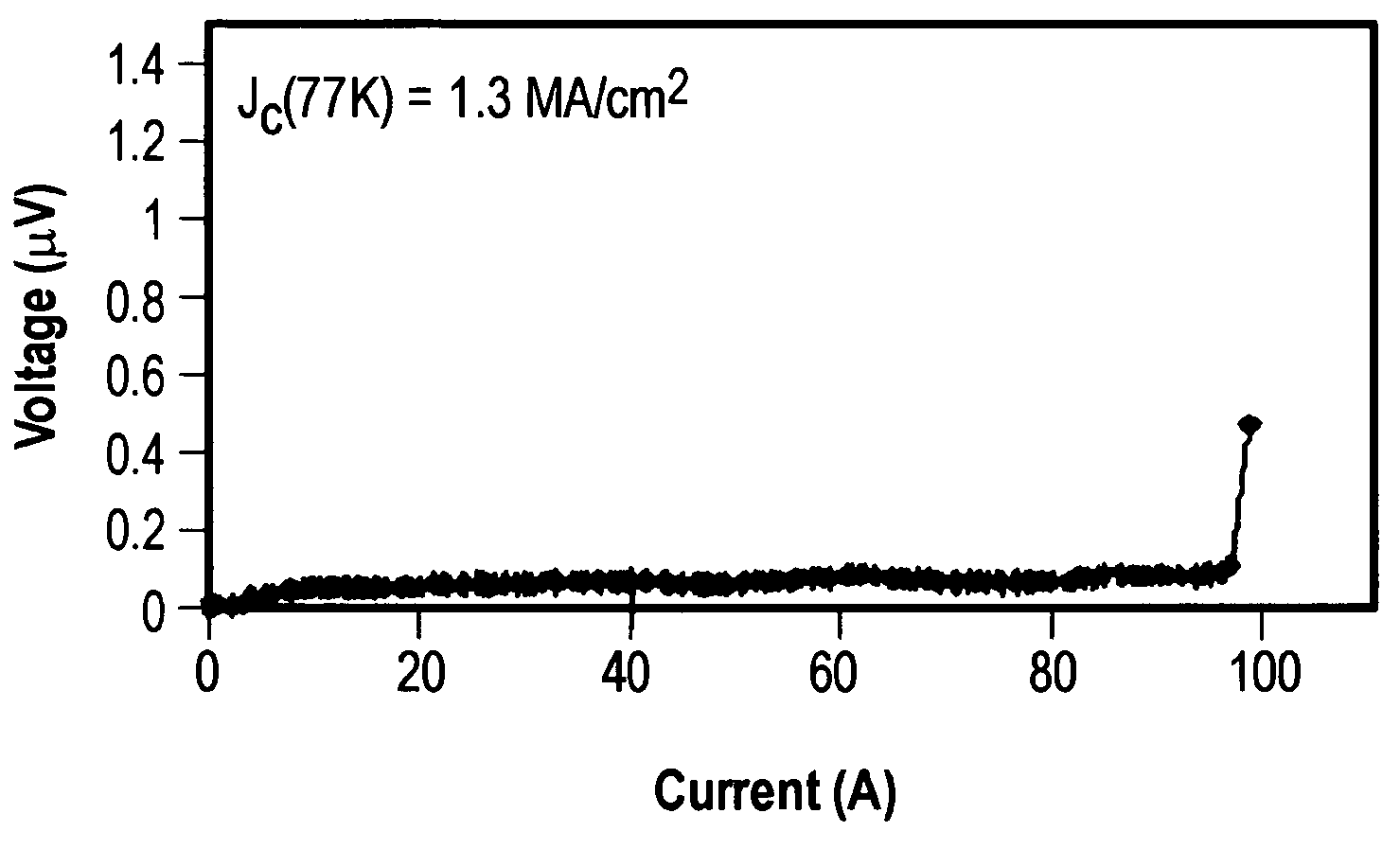
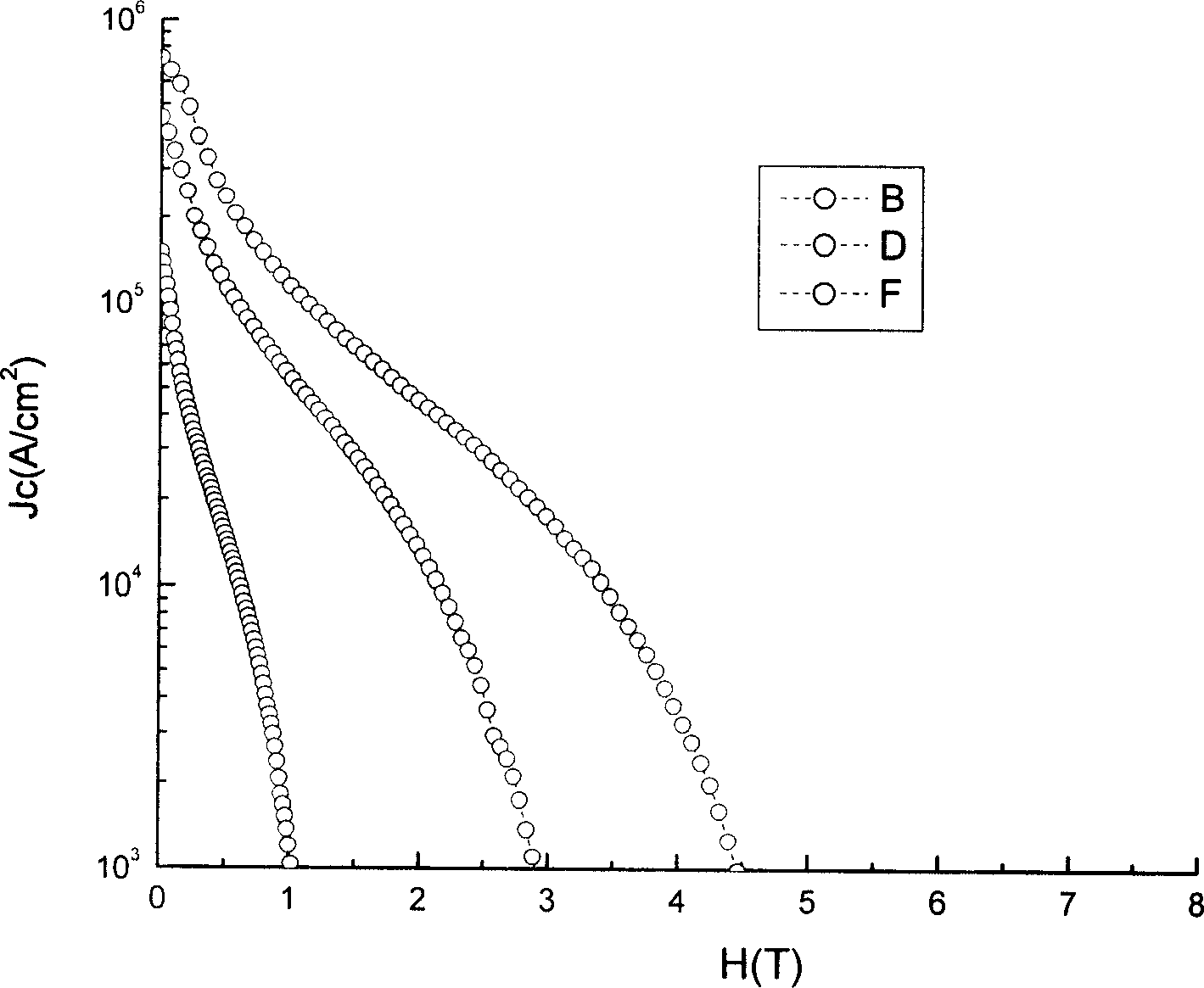
Nanometer-sized non-superconducting particulates in superconductive REBCO films, where RE is a rare earth metal, for flux pinning enhancement and a method of forming are disclosed. A target with a second phase material sector portion and a superconductive material portion is used in a pulse laser deposition process to form films on substrates according to the present invention. The films consist of 10-20 nm-sized precipitates. In a 0.5 μm thick film, a transport critical current density (Jc)>3 MA / cm2 at 77K in self-field was measured. In one embodiment, magnetization Jc at 77 K and 65K showed significant improvements in a composite YBCO films with fine precipitates produced according to the present invention as compared to non-doped (standard) YBCO films (>10 times increase at 9 T, 65 K).
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON THE
Super-conduction stacking brazing method and mold for high-temperature supercurrent down-lead
InactiveCN101409129AThe brazing process is correctQuality improvementWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesAmpereAlloy
The invention discloses a superconducting stack soldering method for a high-temperature superconducting current lead wire and a mold thereof; superconducting tapes to be soldered and soldering ribbons are alternately arranged in a mold cavity which is made of metal materials with good thermal conductivity; a mold core and a counterweight are pressed on the superconducting tapes, the mold is heated to the soldering temperature under the vacuum condition, the temperature is kept for 10-15 minutes, and then the mold is rapidly cooled to the solidification point of soldering filler metals to complete the soldering. The critical current of the low-heat conductivity high-temperature superconducting tapes under a 77K self-field is only 100-120A which is much less than the thousands to tens of thousands of amperes of operating current of a large superconducting magnet, so that the superconducting tapes can be used by soldering into a stack. The price of the bismuth-based superconducting tape which takes Ag-5.3wt% Au alloy as a substrate is 5-6 times than the price of the ordinary bismuth-based superconducting tape; while the offer of a superconducting stack of foreign high-temperature superconducting companies is almost doubled again. The method and the mold for soldering the superconducting stack can ensure that the current carrying performance is not deteriorated, the longitudinal heat leakage is not increased, the soldering among the superconducting tapes is uniform and the requirements on the resistance performance in a low layer can be met.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound winding made of Bi-based and Y-based high-temperature superconducting tapes
InactiveCN103035353ACost-effectiveSuperconducting magnets/coilsBobbinHigh-temperature superconductivity
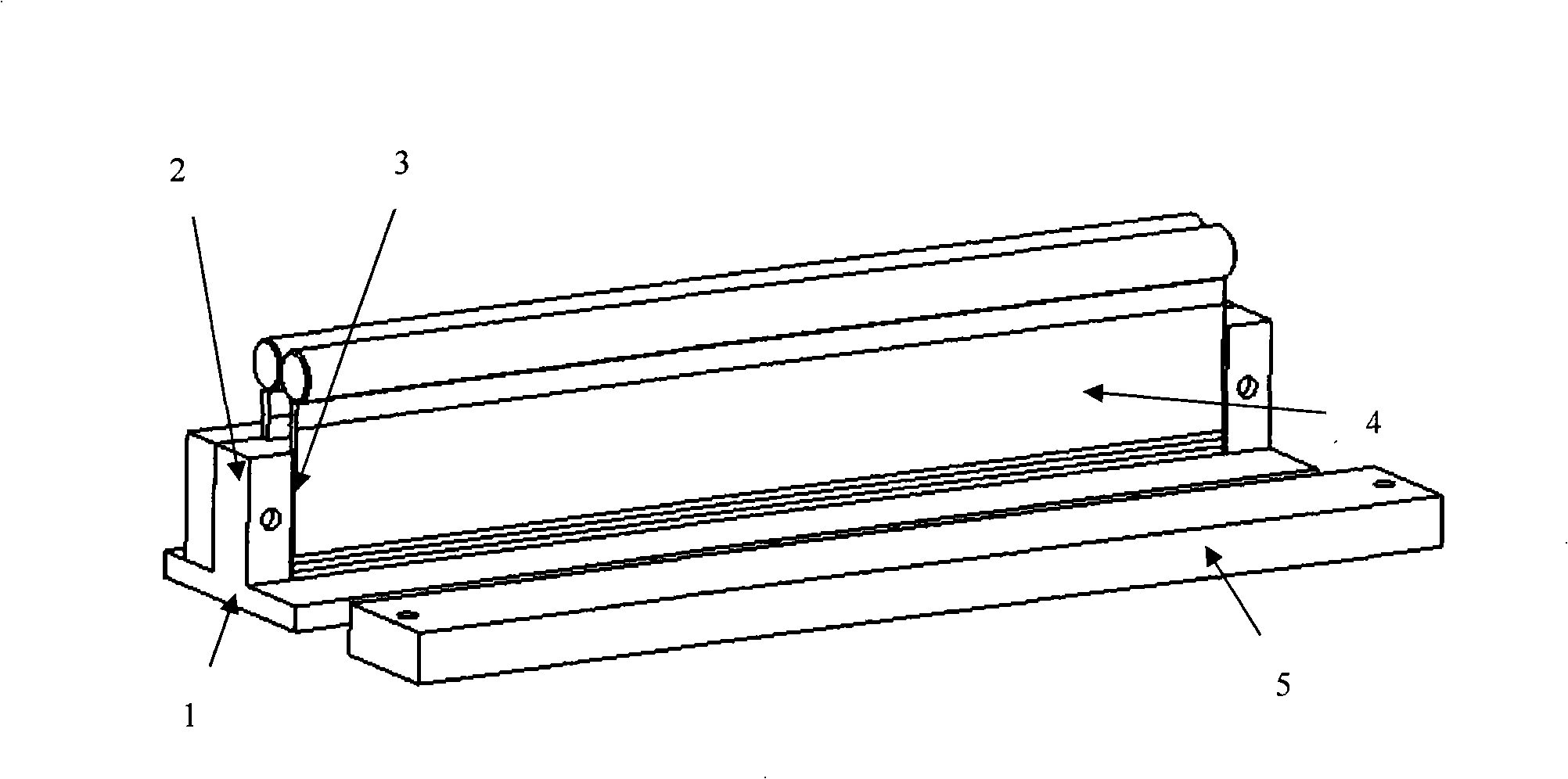
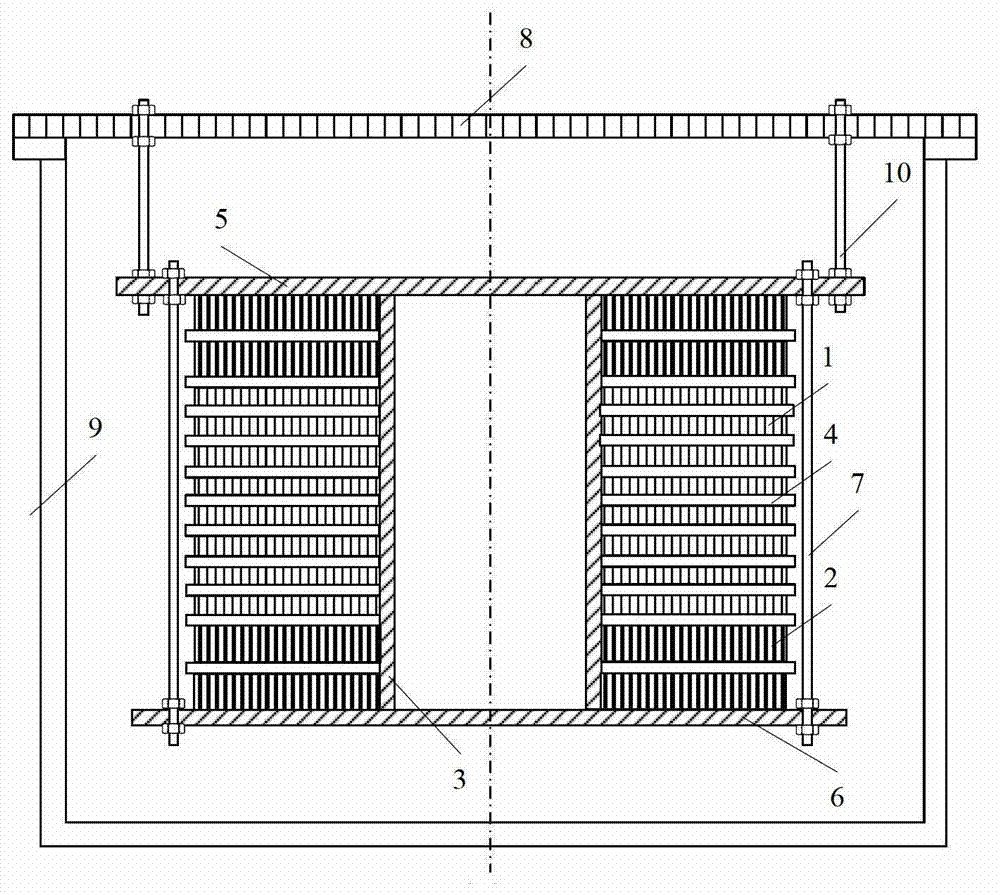
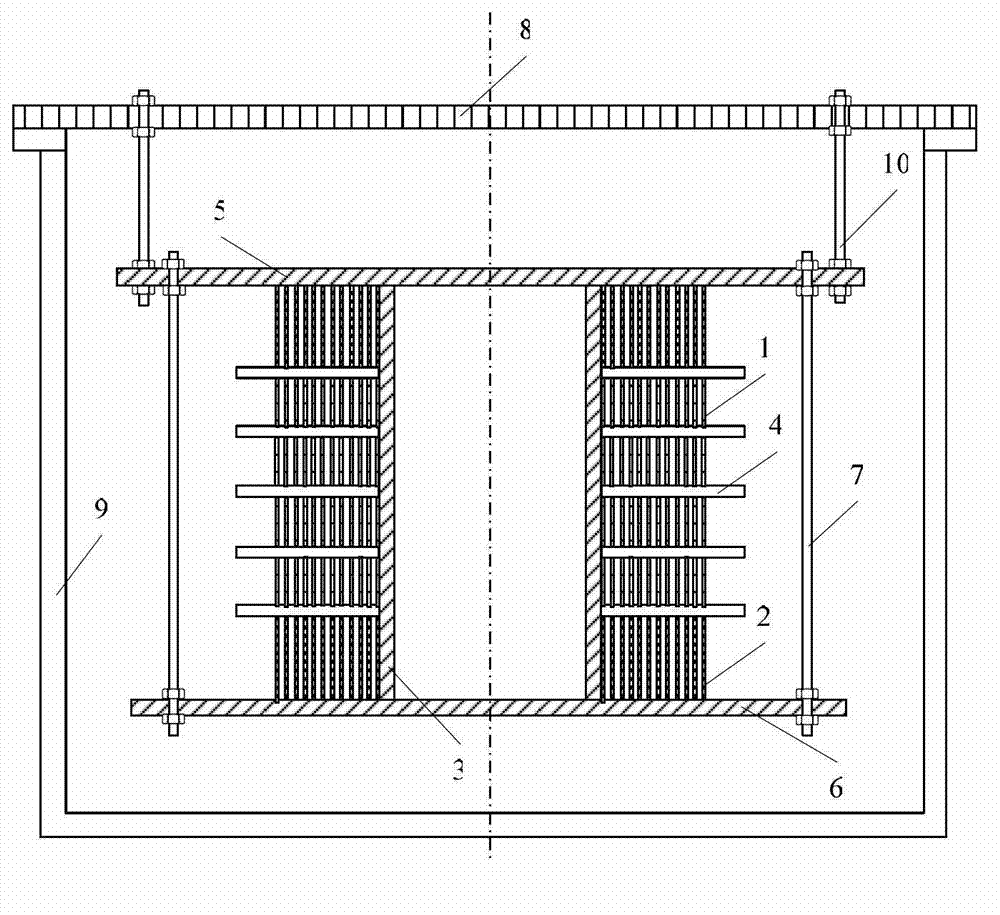
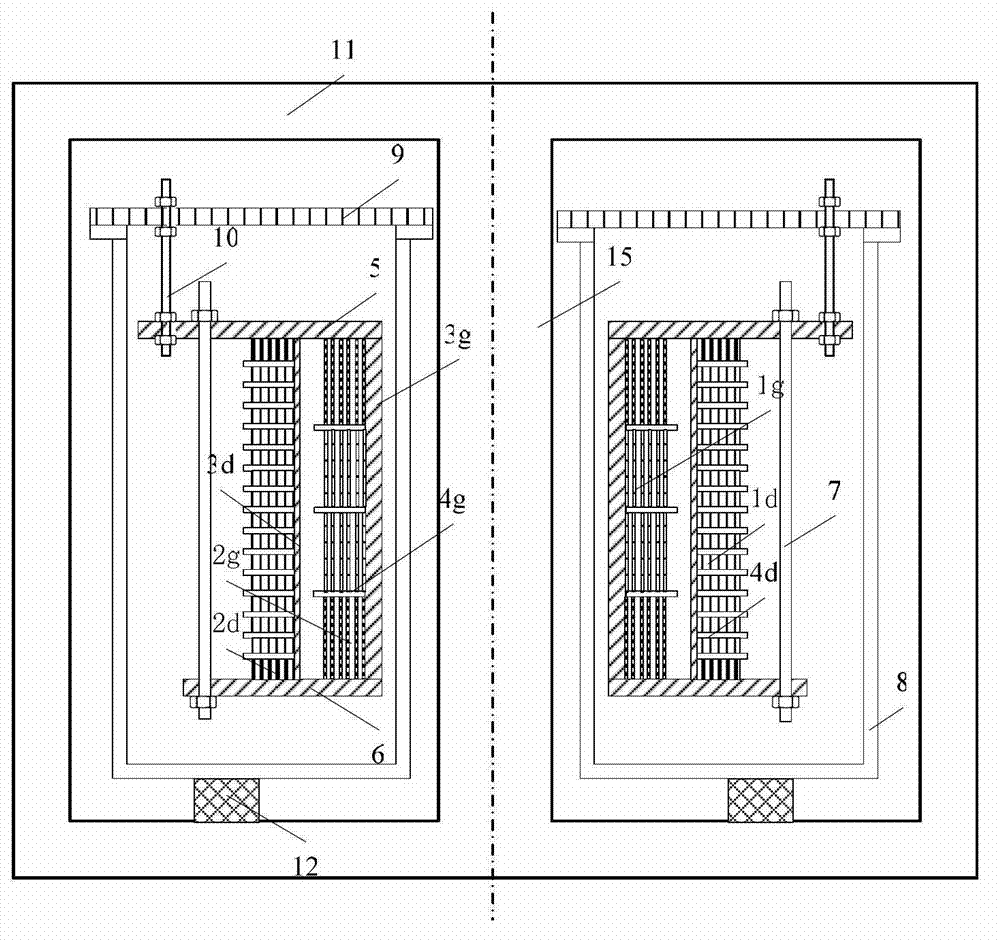
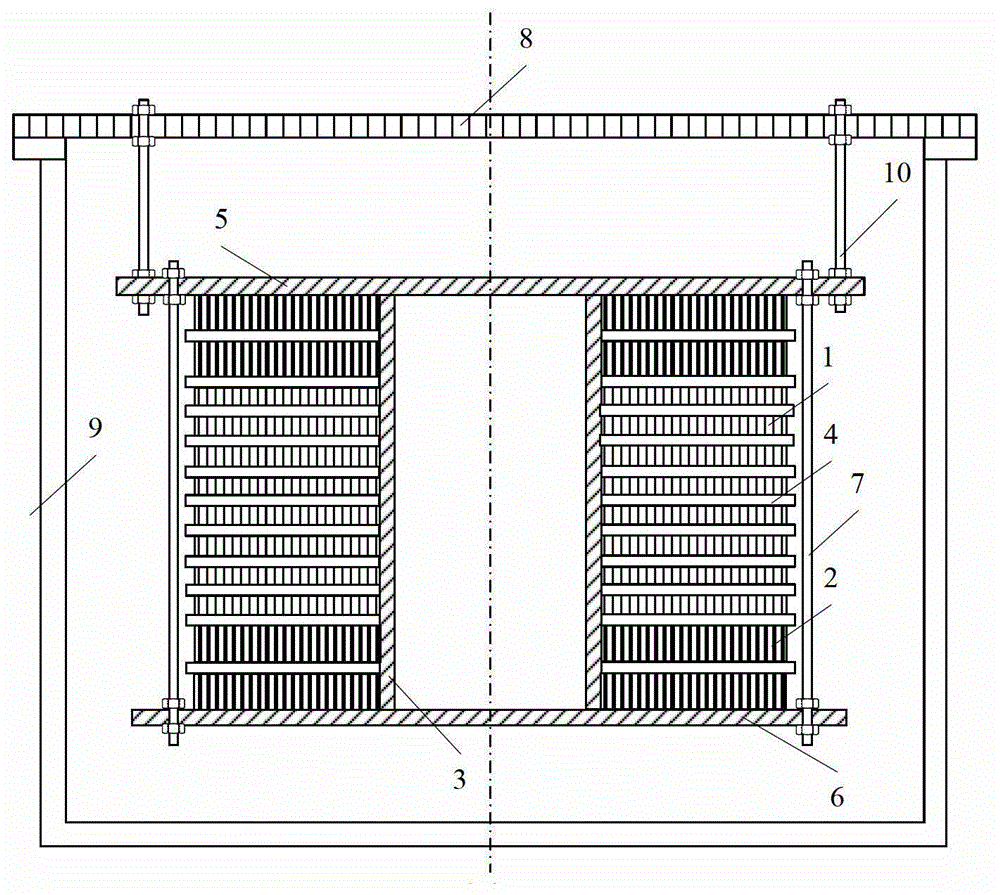
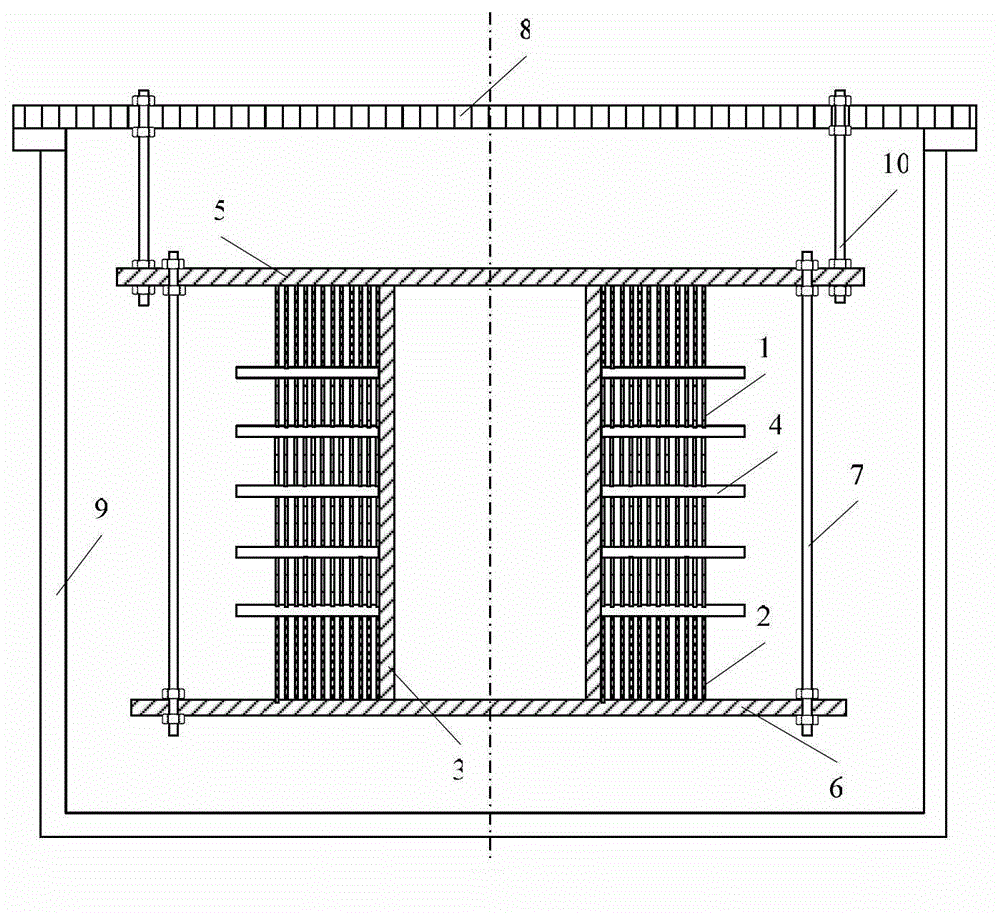
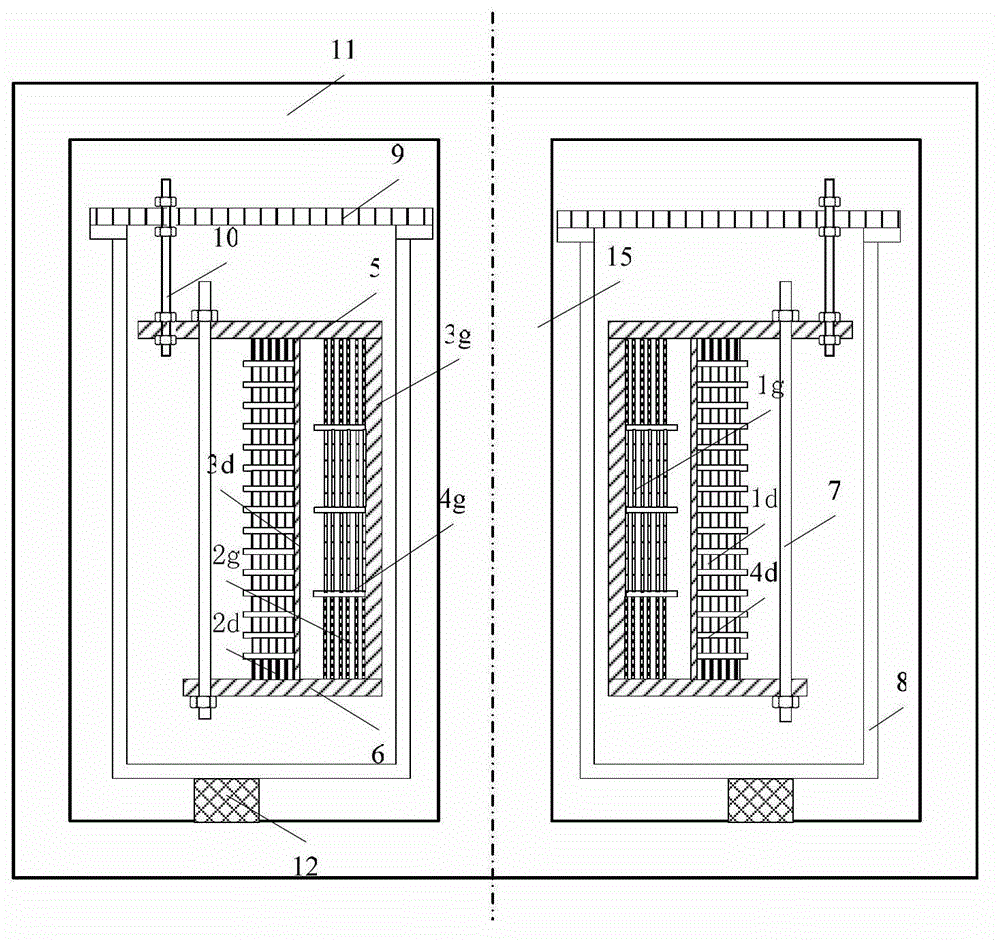
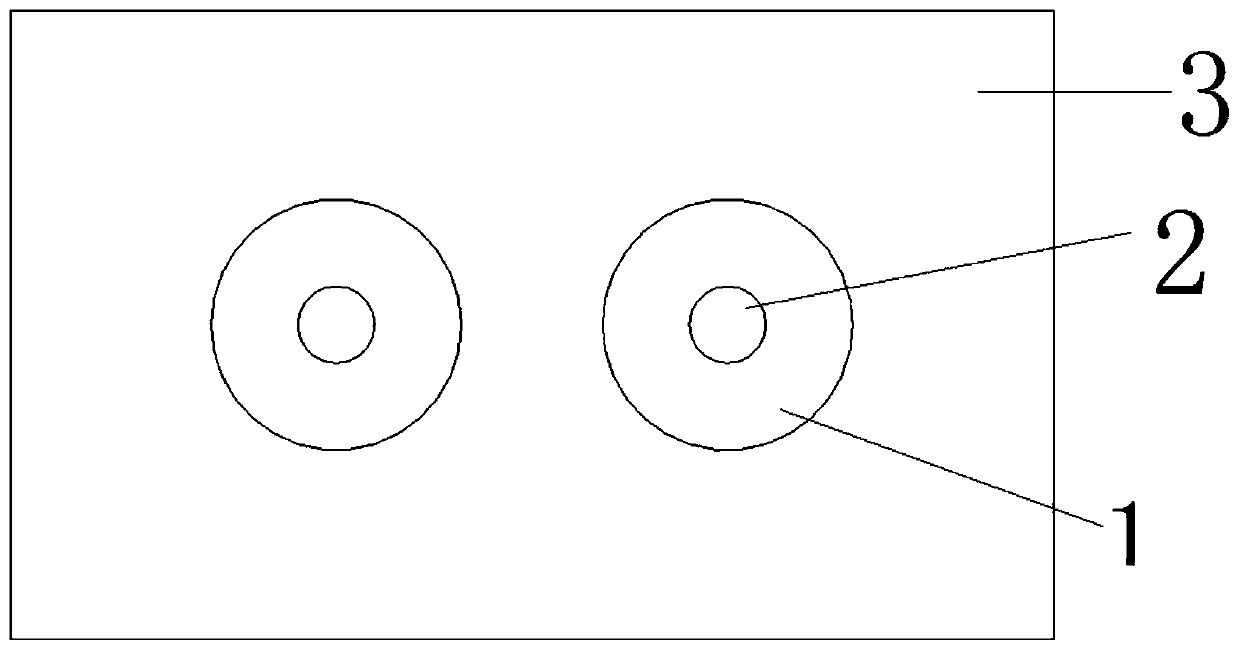
A compound winding made of Bi-based and Y-based high-temperature superconducting tapes comprises a Bi-based superconducting coil (1), a Y-based superconducting coil (2), a superconducting coil bobbin (3), axial superconducting coil partitions (4), an upper coil support board (5), a lower coil support board (6) and coil-fixing screws (7). The Bi-based superconducting coil (1) is located in the middle of the compound winding, and the Y-based superconducting coil (2) is located on the end of the compound winding; and the compound winding is mounted in a low-temperature dewar comprising a low-temperature dewar barrel (8) and a low-temperature dewar top cover board (9), and is cooled by directly evaporated liquid nitrogen or the forced flow circulation of liquid nitrogen coupled with a refrigerator. The compound winding is mounted on the low-temperature dewar top cover board (9) through tie rods (10). The compound winding utilizes the characteristics of the Bi-based high-temperature superconducting tape, such as high self-field critical current, and the characteristics of the Y-based high-temperature superconducting tape, such as little critical current decrease in the external field, and can be made into an alternating-current winding and a direct-current winding.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coated high temperature superconducting tapes, articles, and processes for forming same
A superconducting article is disclosed, including a substrate and a chemical vapor deposited thin film superconducting layer overlying the substrate, the superconducting layer having a critical current not less than about 100 A / cm width at 77K and self field. The superconducting article may be a tape, multiple tapes, or a power device, such as a power cable, power generator, or power transformer. Also disclosed are methods for manufacturing same and methods for using same.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
Flux pinning enhancements in superconductive REBa2CU3O7-x (REBCO) films and method of forming thereof
ActiveUS7687436B2Avoid adverse reactionsSeparationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingParticulatesMagnetization
Nanometer-sized non-superconducting particulates in superconductive REBCO films, where RE is a rare earth metal, for flux pinning enhancement and a method of forming are disclosed. A target with a second phase material sector portion and a superconductive material portion is used in a pulse laser deposition process to form films on substrates according to the present invention. The films consist of 10-20 nm-sized precipitates. In a 0.5 μm thick film, a transport critical current density (Jc)>3 MA / cm2 at 77K in self-field was measured. In one embodiment, magnetization Jc at 77 K and 65K showed significant improvements in a composite YBCO films with fine precipitates produced according to the present invention as compared to non-doped (standard) YBCO films (>10 times increase at 9 T, 65 K).
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
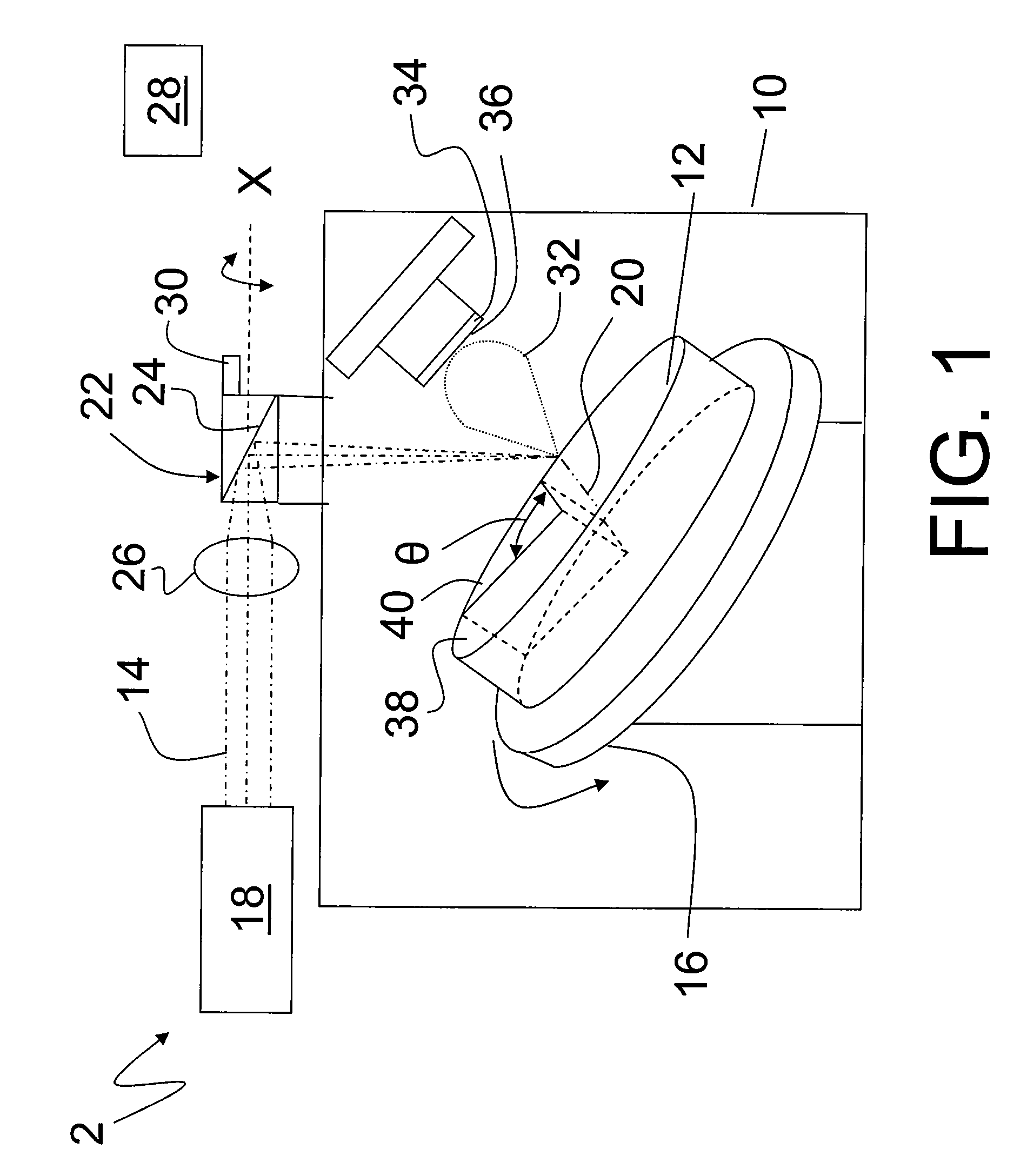
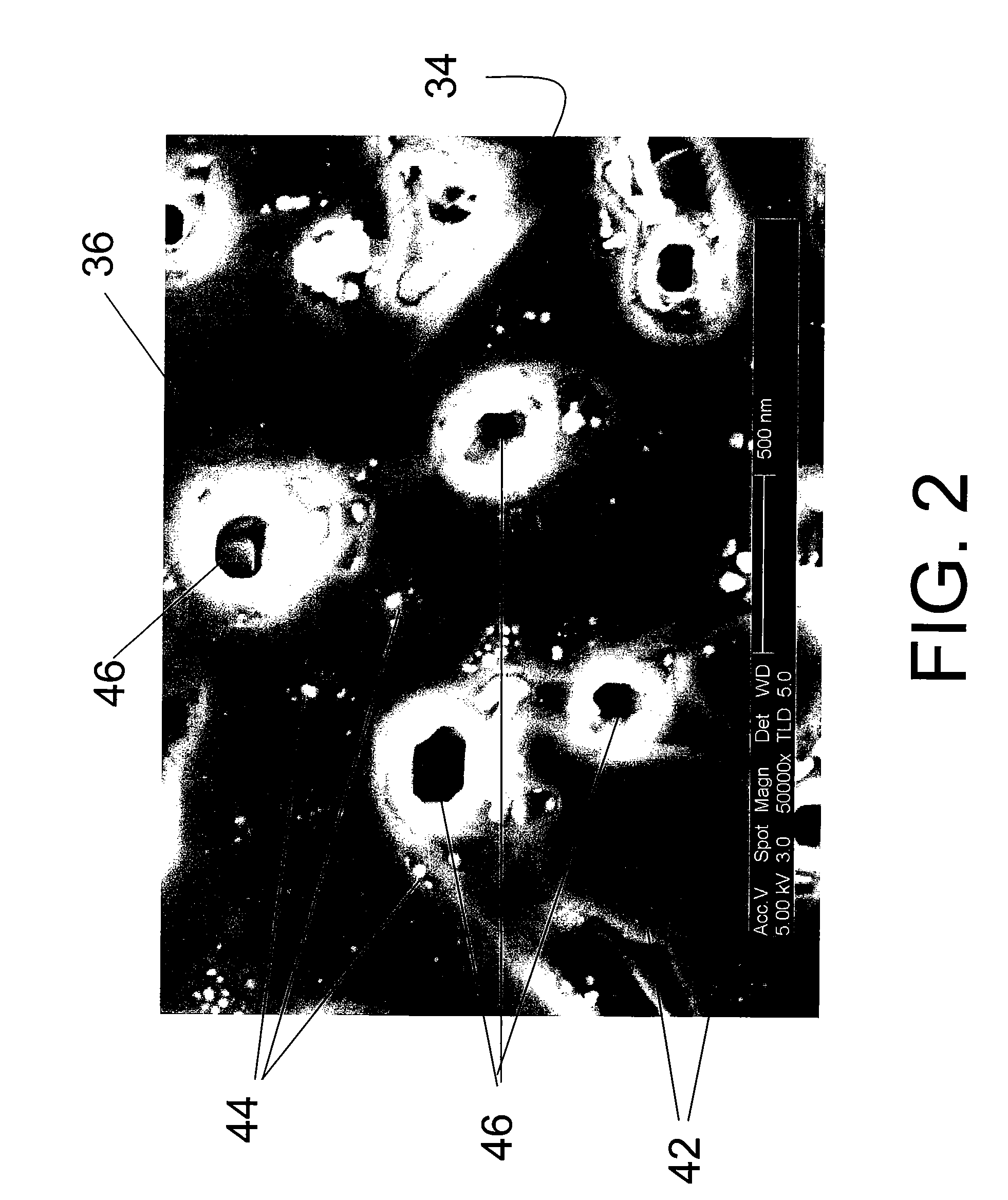
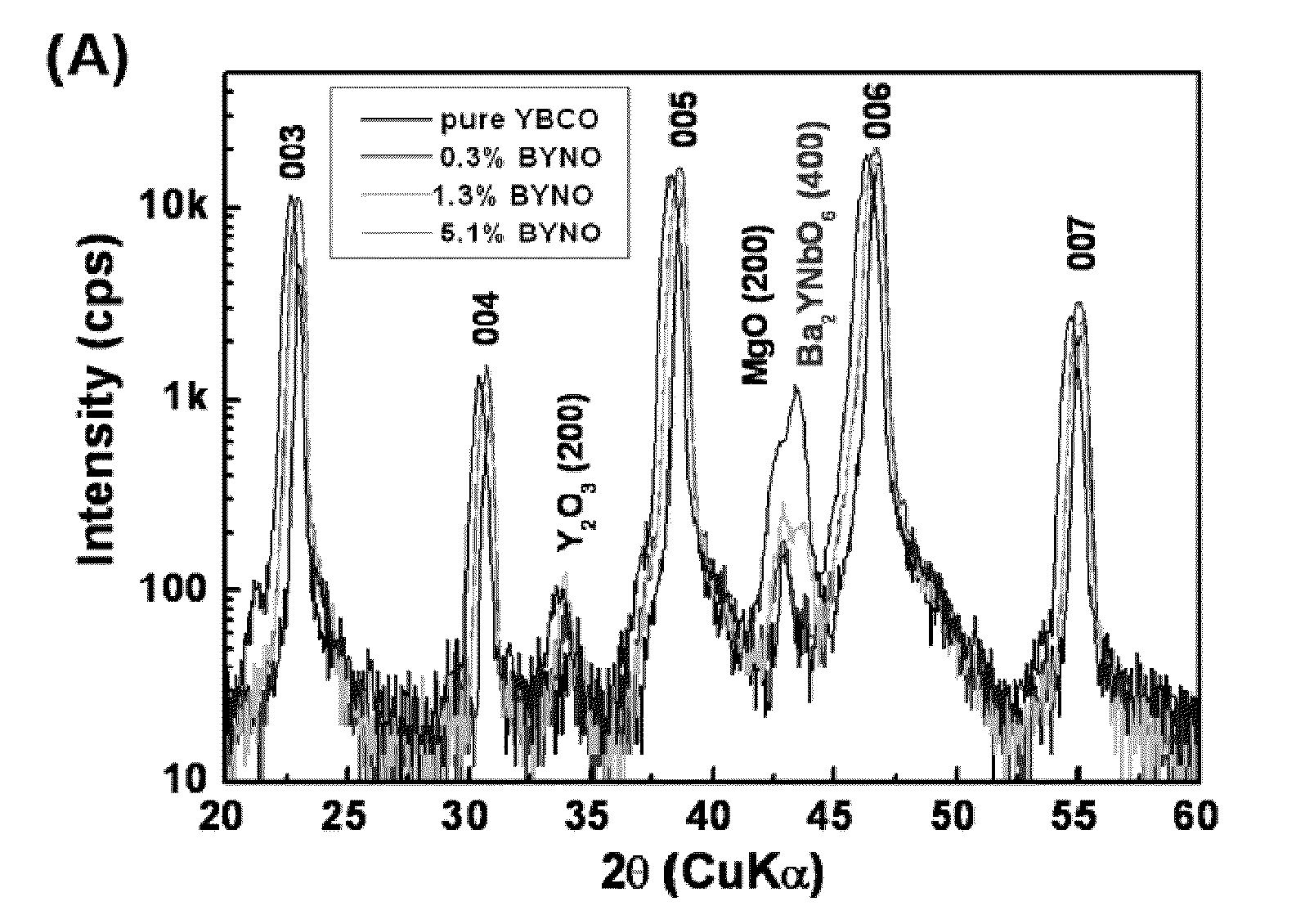
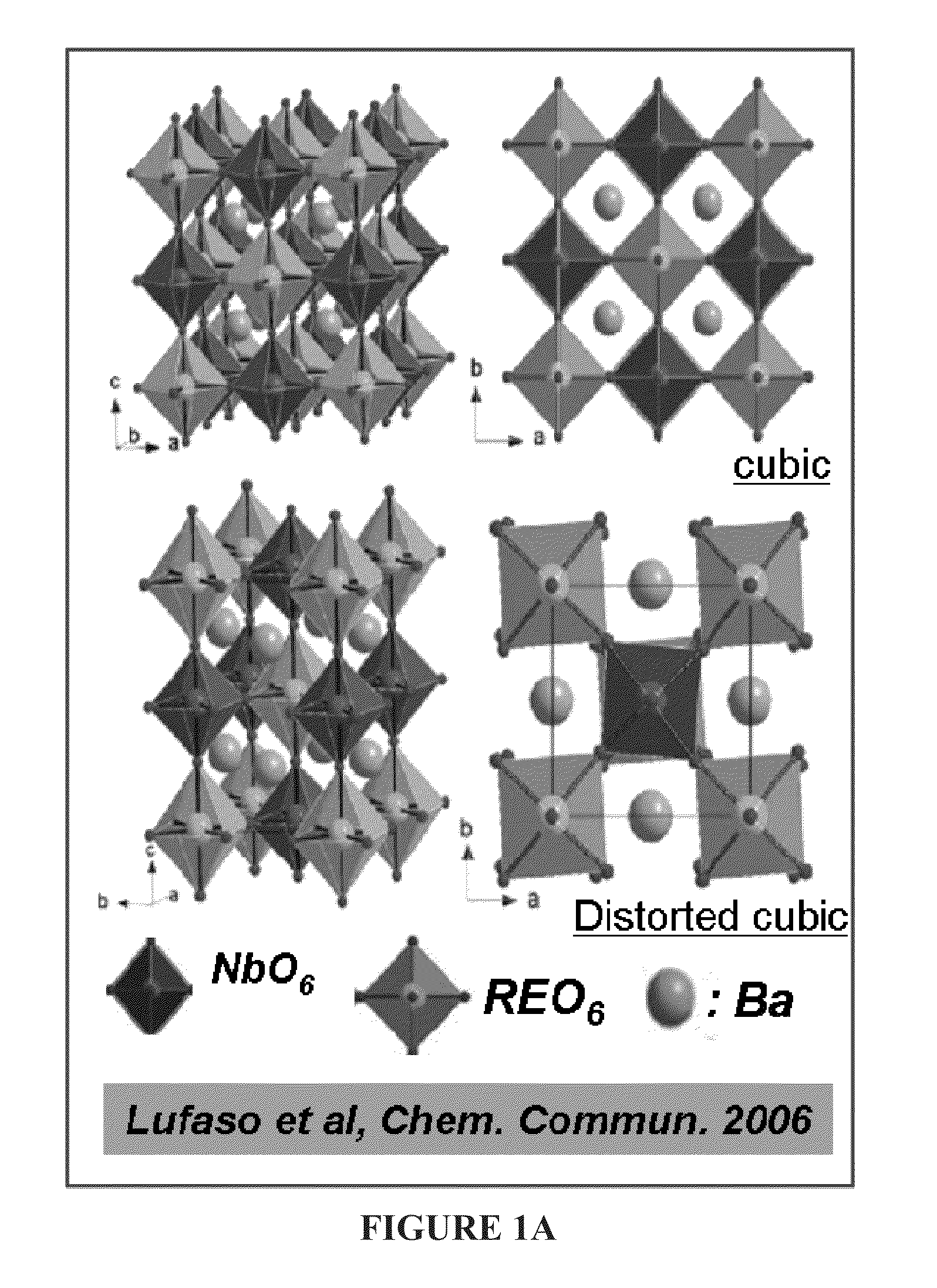
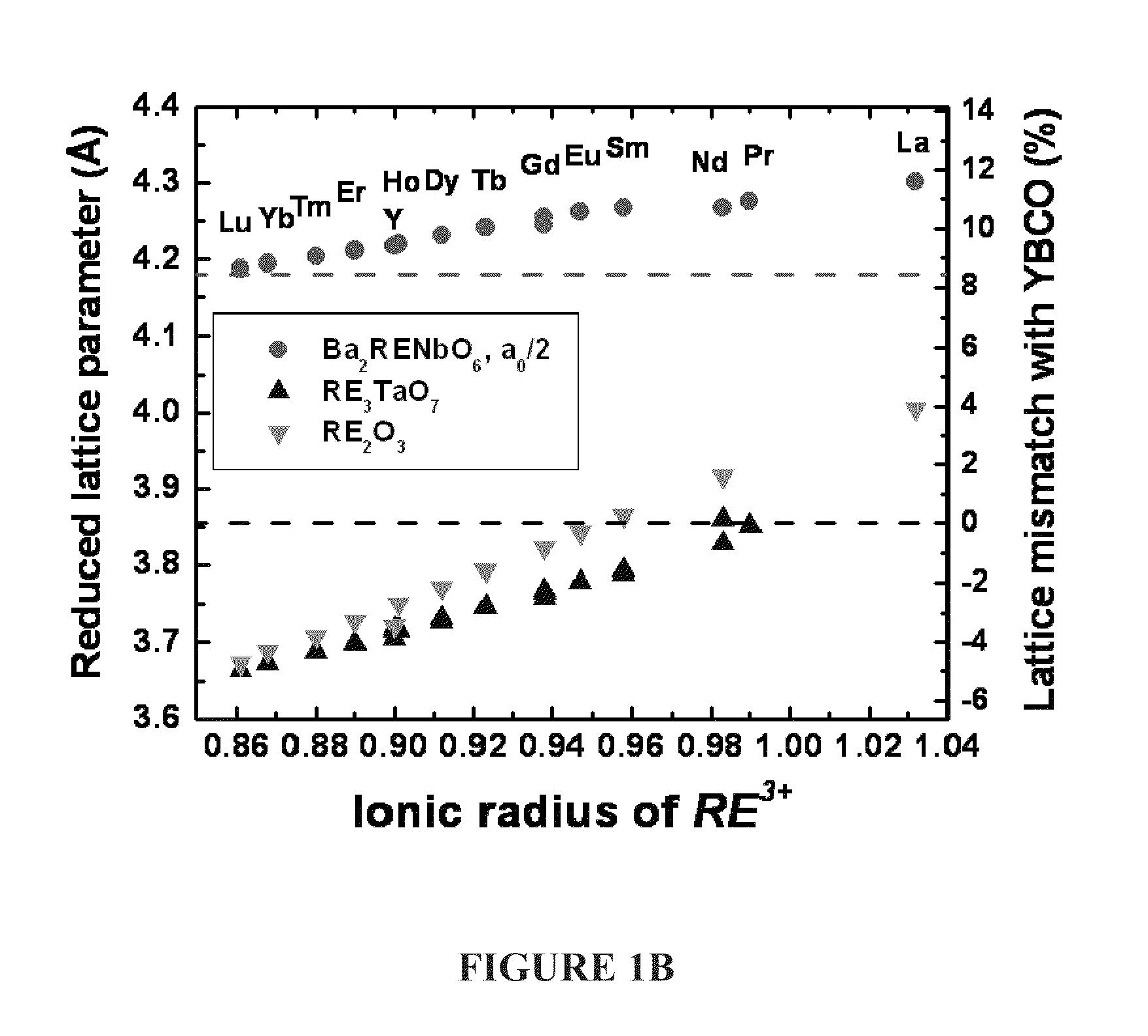
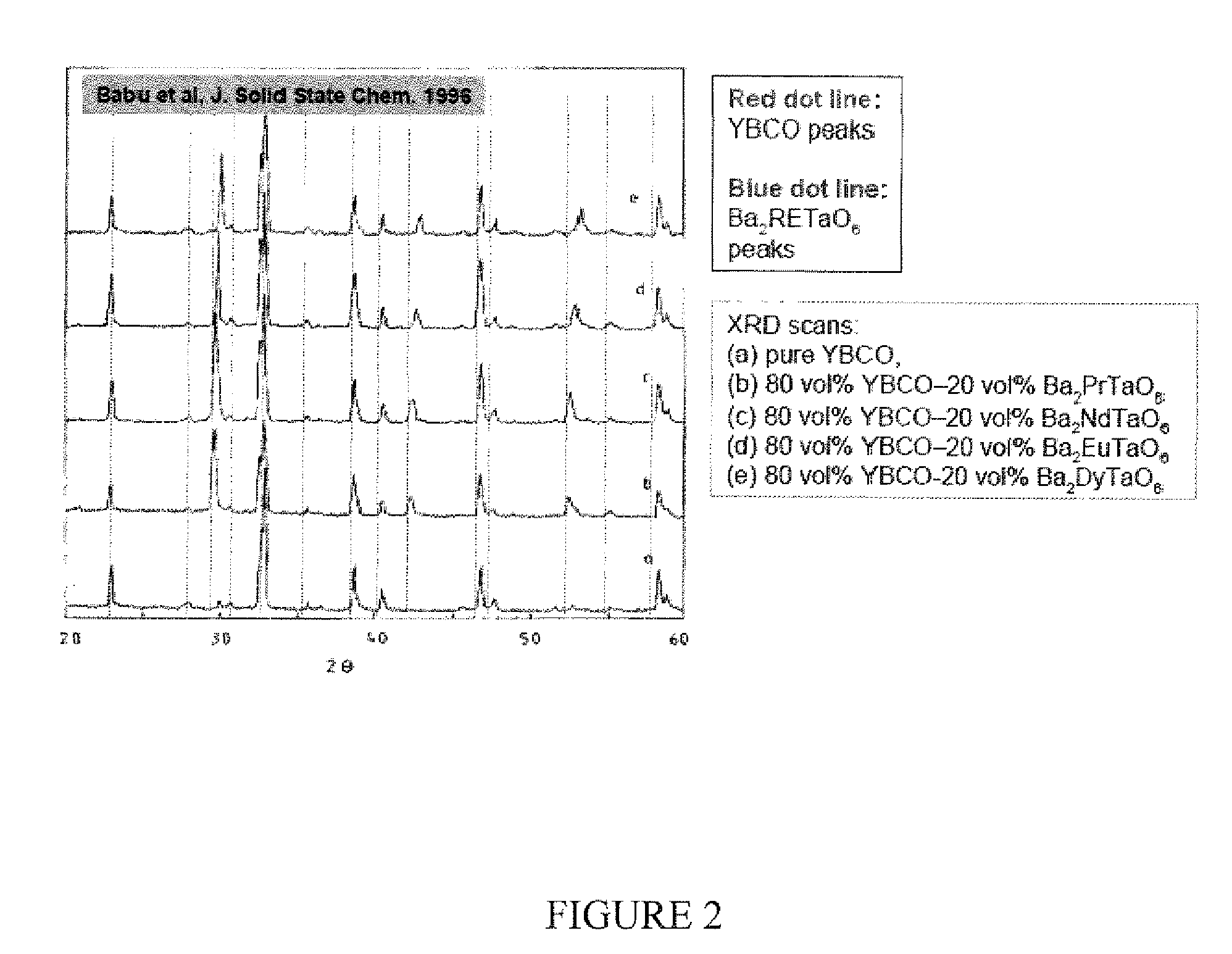
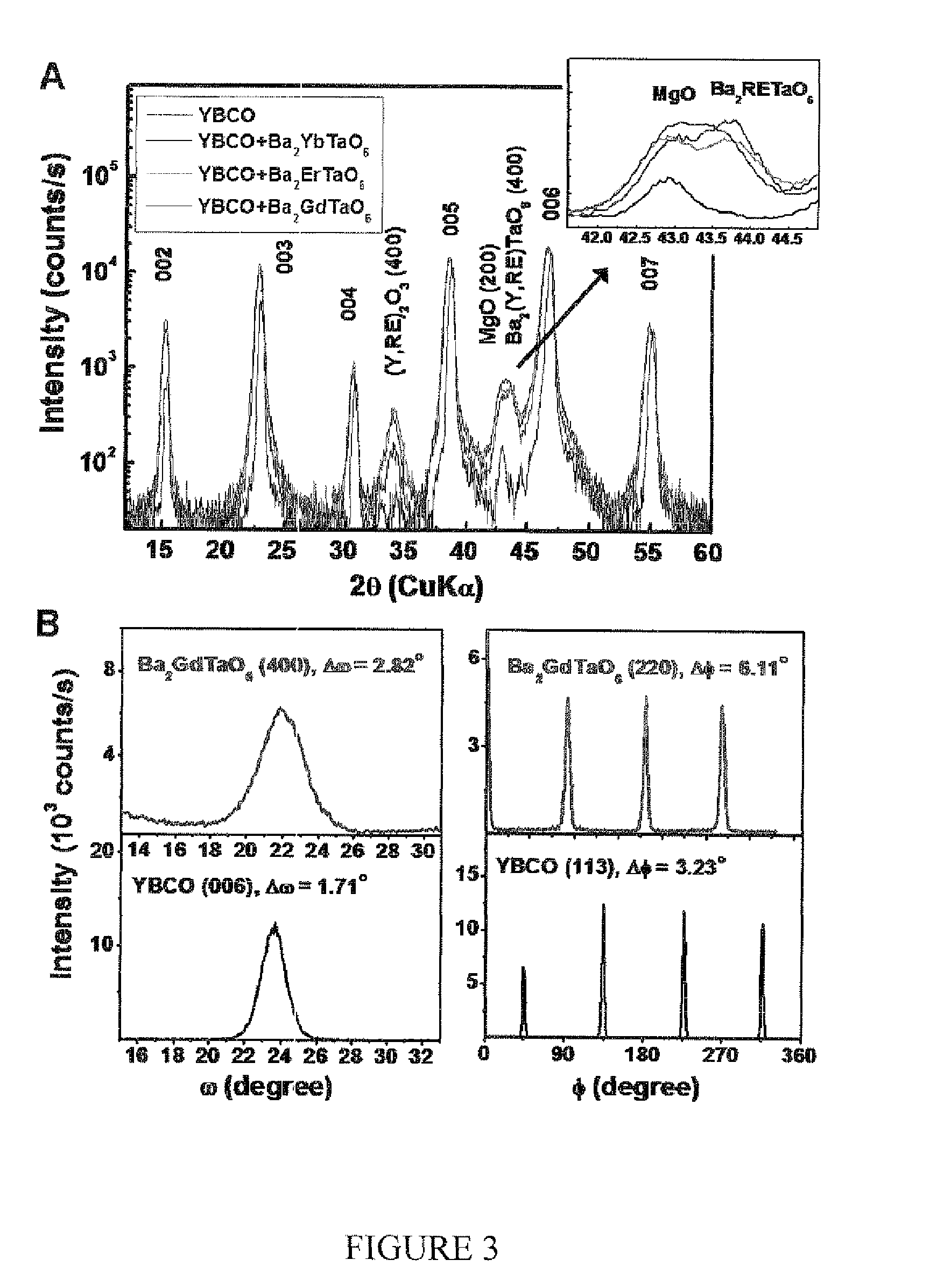
CRITICAL CURRENT DENSITY ENHANCEMENT VIA INCORPORATION OF NANOSCALE Ba2(Y,RE)NbO6 IN REBCO FILMS
A superconducting article includes a substrate having a biaxially textured surface, and an epitaxial biaxially textured superconducting film supported by the substrate. The epitaxial superconducting film includes particles of Ba2RENbO6 and is characterized by a critical current density higher than 1 MA / cm2 at 77K, self-field. In one embodiment the particles are assembled into columns. The particles and nanocolumns of Ba2RENbO6 defects enhance flux pinning which results in improved critical current densities of the superconducting films. Methods of making superconducting films with Ba2RENbO6 defects are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Vacuum welding device and welding method for superconducting stack of high-temperature superconducting current lead
ActiveCN103071874ACut off the power supplyImprove cooling effectSoldering apparatusElectrical conductorVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses a vacuum welding device and a method for a high-temperature superconducting stack used for a large-sized magnet current lead. The vacuum welding device comprises an independent heating vacuum chamber, a cold base and a hot base, wherein the cold base and the hot base are arranged in the vacuum chamber. The interior of the vacuum chamber also comprises a movable welding die and a moving part which can be used for enabling the die to move in the vacuum chamber. After the welding die is contacted with the hot base through the moving part and heated to specified temperature, the welding die is separated from the hot base and is contacted with the cold base to realize rapid cooling. According to the vacuum welding device and the welding method, the superconducting stack is high in density, welding effect and current-carrying capability; and 7-stacked critical current measured under self-fields at 77K can reach 70 percent of the critical current of an original strip, and 4-stacked critical current exceeds the 80 percent critical current of the original strip. The superconducting stack can be applied to the large-sized magnet current lead as a discharge current conductor, and therefore, the effect of reducing heat emission and heat transfer of the lead is achieved, the cooling power is saved, and the operating environment of a magnet is improved.
Owner:INNOVA SUPERCONDUCTOR TECH
Apparatus and method for interfering with pathological cells survival processes
InactiveUS8192969B2Increase probabilityHeart defibrillatorsMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsNormal cellWorking environment
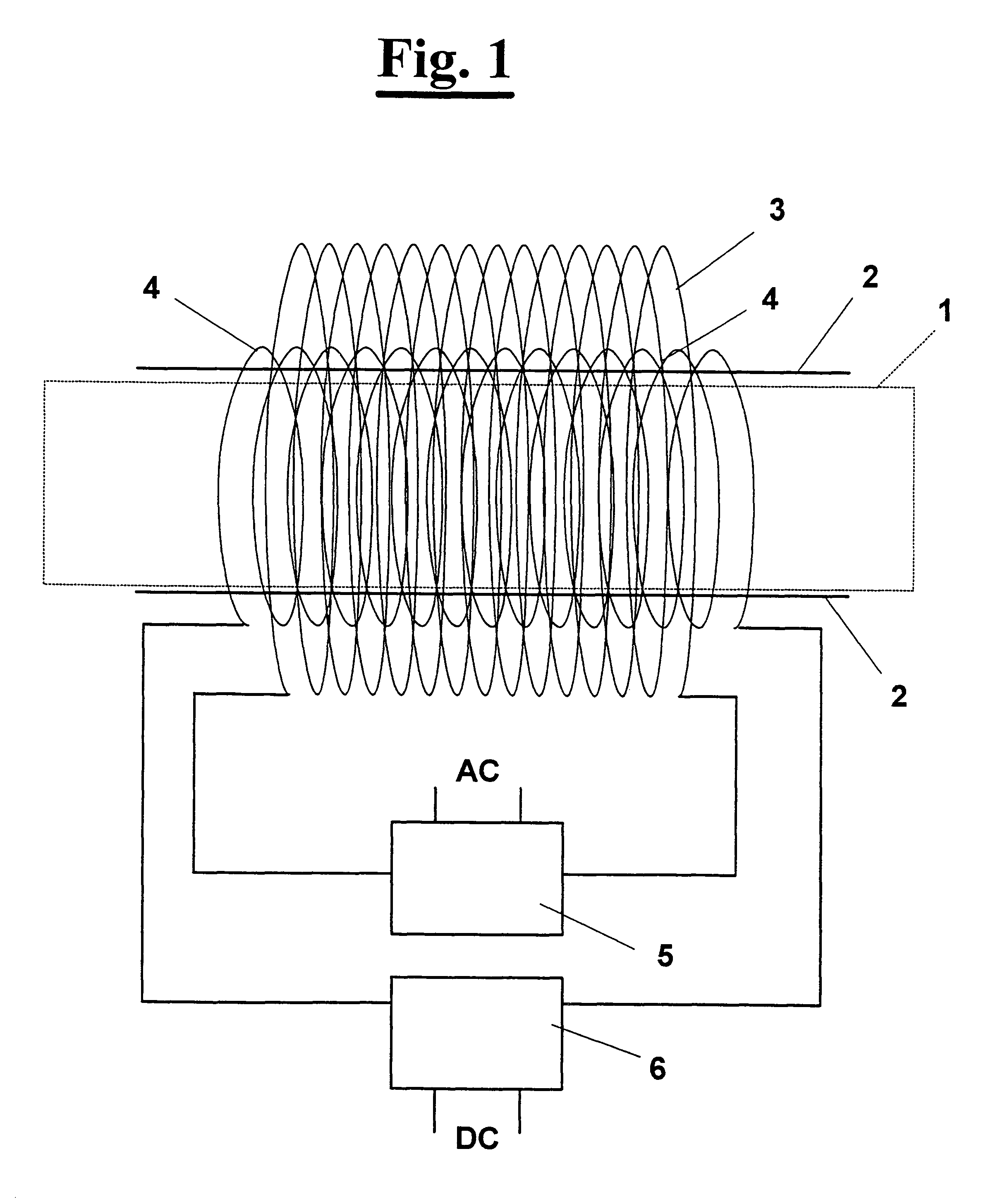
A method and an apparatus for interfering with pathological cells survival processes, i.e. inducing directly or indirectly apoptosis, on living pathological cells, by using magnetic fields without adversely affecting normal cells. Static (S) and extremely low frequency (ELF) magnetic fields are used having low intensity comprised between 1 and 100 mT, preferably comprised between 1 and 30 mT. In particular SELF fields are used which are different sequences of S and / or ELF fields, i.e. S fields followed by ELF fields, ELF fields followed by S fields, S and ELF field together, as well as the presence of S or ELF fields alone, said ELF fields having a field frequency comprised between 1 and 1000 Hz. An apparatus for carrying out the method comprises means for generating static magnetic (S) fields crossing a working environment and / or means for generating electromagnetic extremely low frequency (ELF) fields over the working environment in addition to the S fields. Means are provided for modulating the S fields associated to the S fields generating means and varying the intensity of the S fields from 1 to 100 mT, preferably between 1 to 30 mT according to a predetermined function. Means may also be provided for modulating the ELF fields associated to the ELF fields generating means and imposing to the ELF fields a frequency between 1 and 1000 Hz with intensity comprised between 1 to 100 mT, preferably between 1 and 30 mT according to a predetermined function.
Owner:TOFANI SANTI
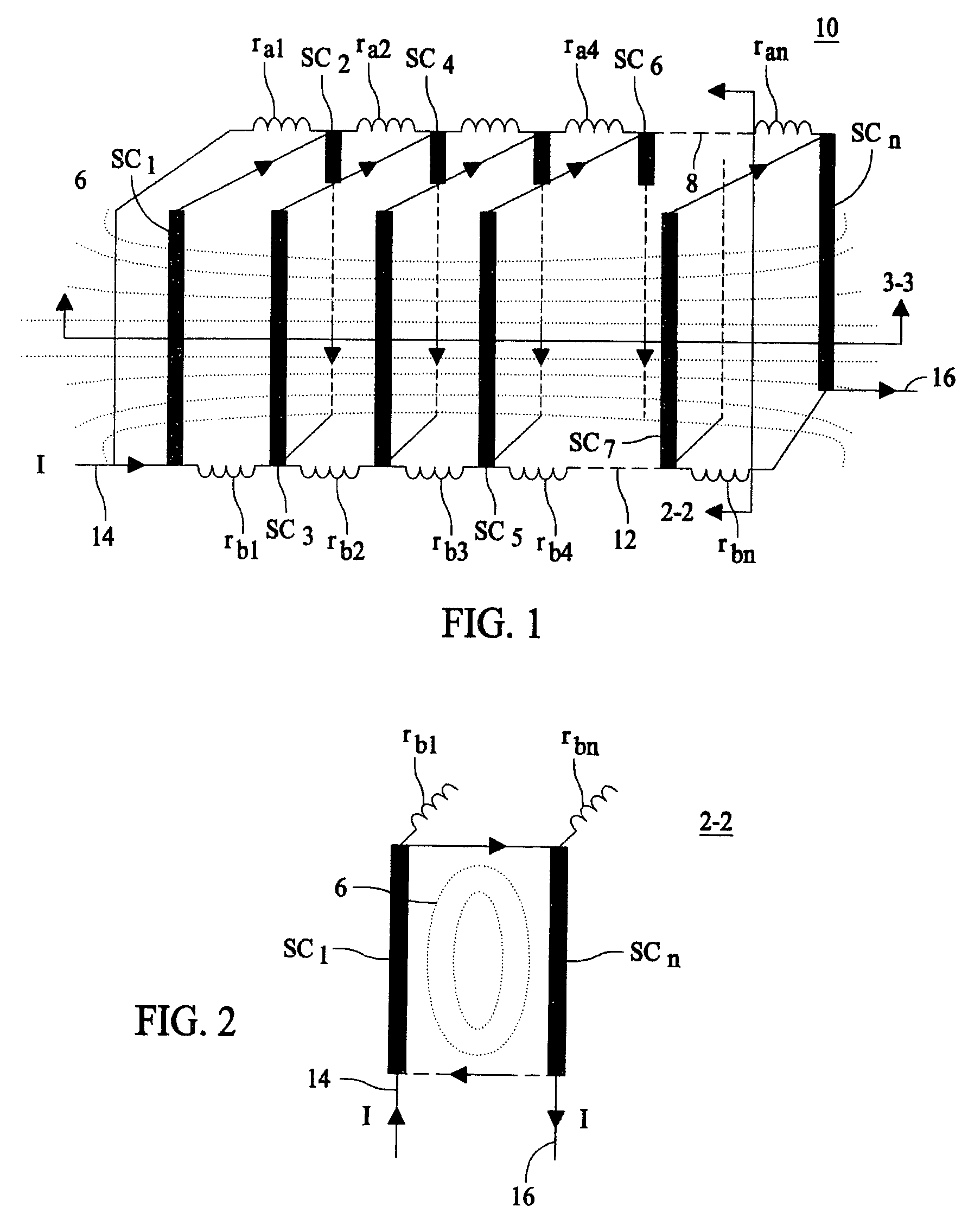
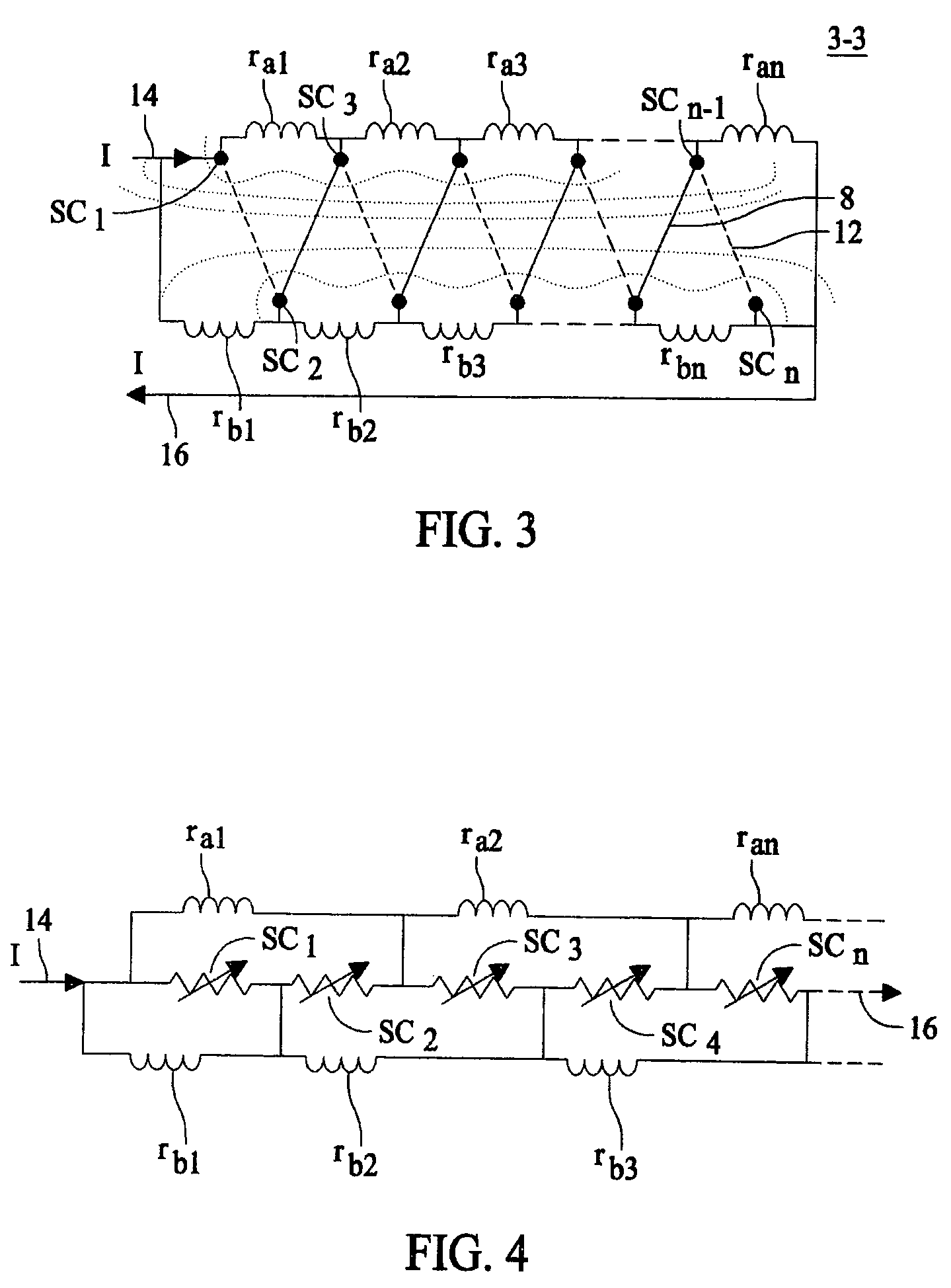
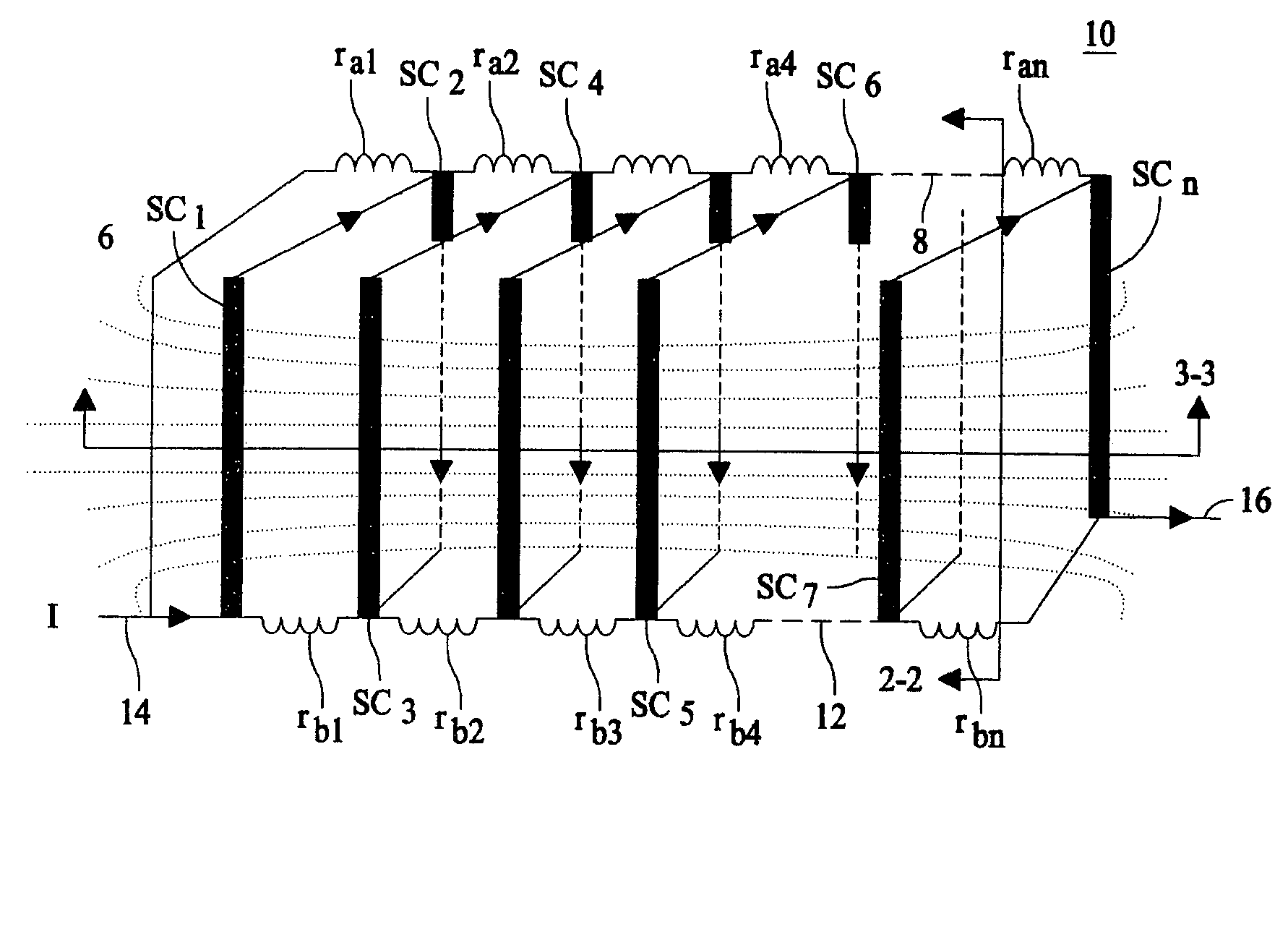
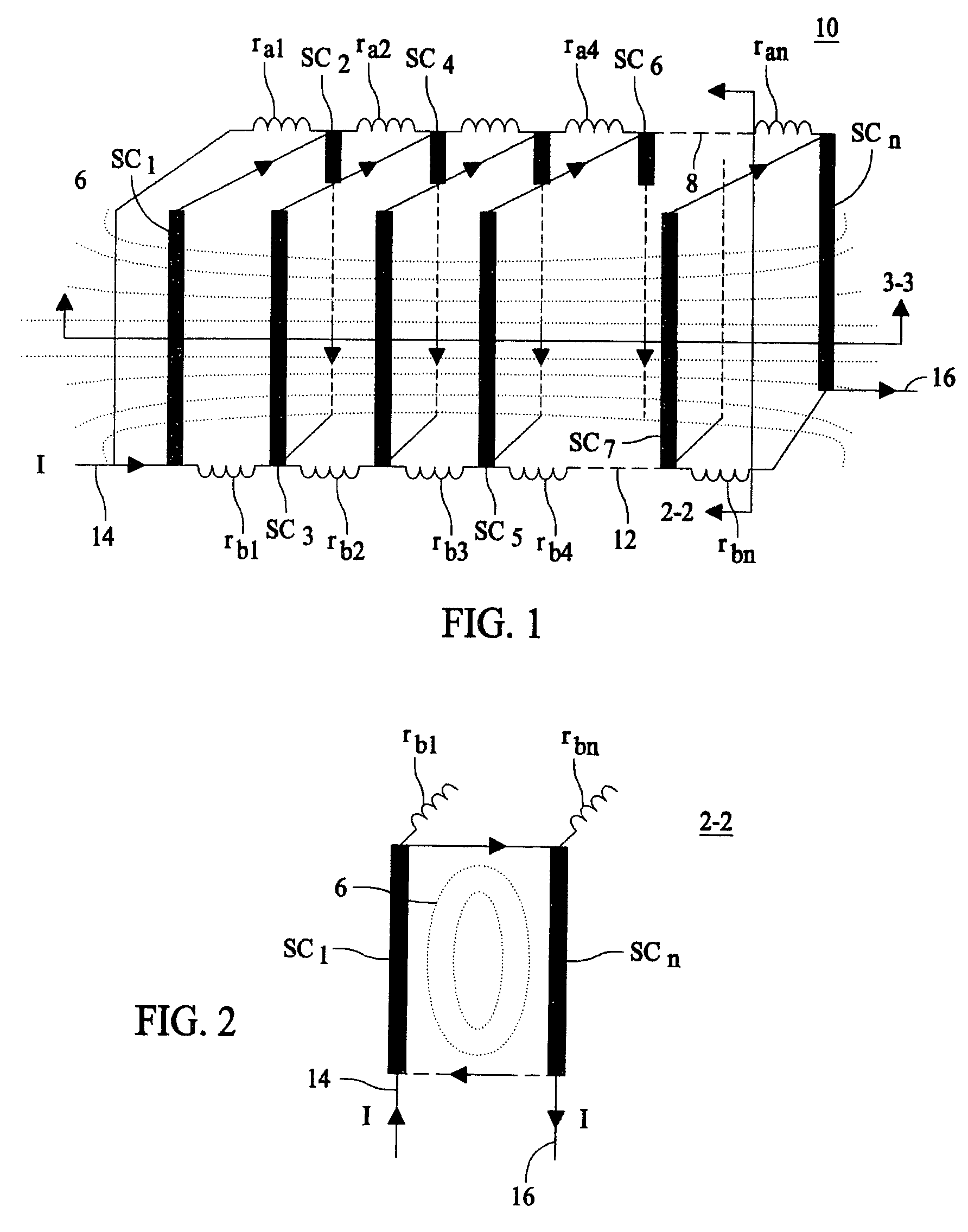
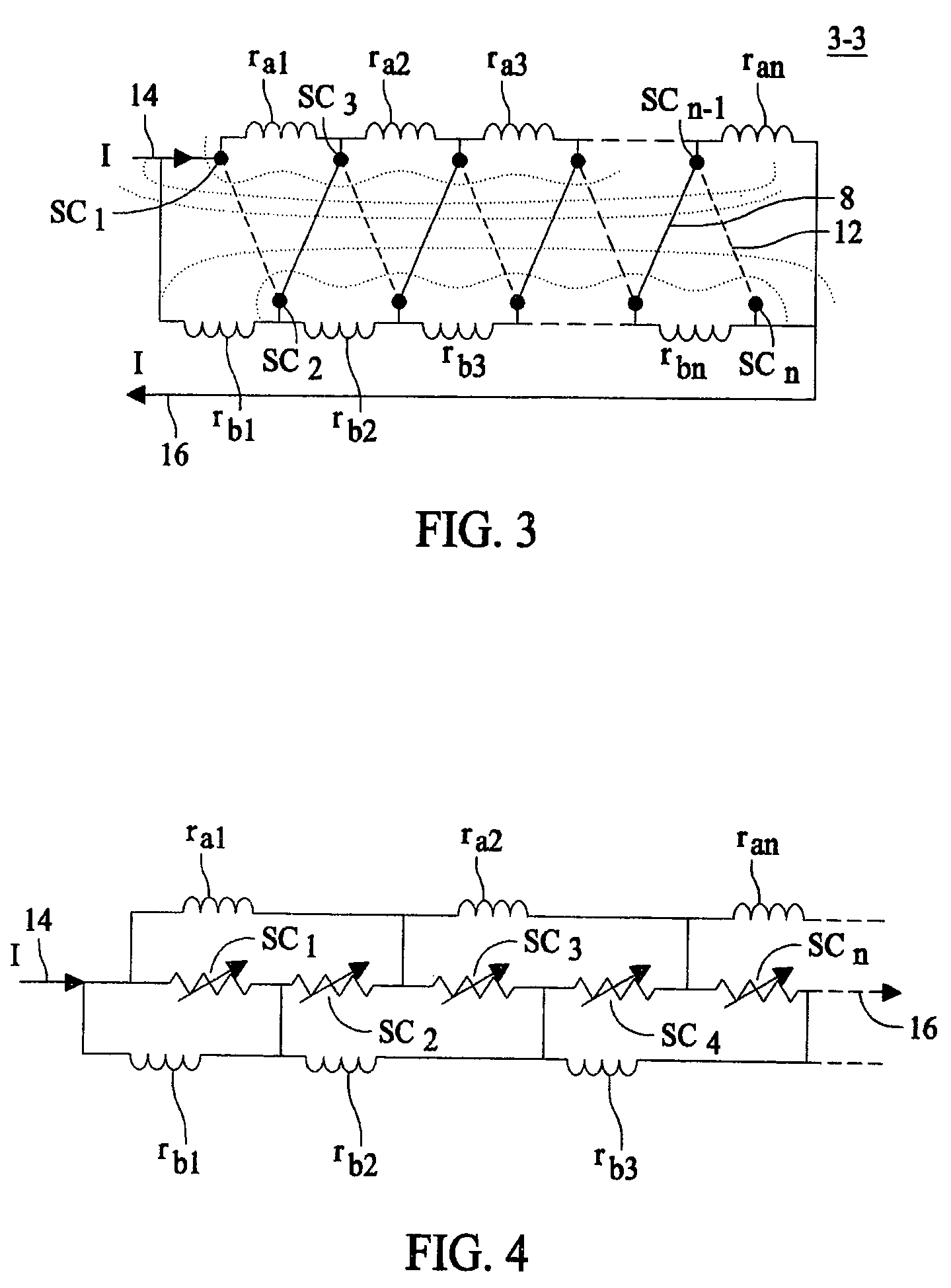
Self field triggered superconducting fault current limiter
InactiveUS20060279388A1Improve equipment reliabilityIncreased complexityMagnetsMagnetic materialsElectrical conductorSuperconducting fault current limiters
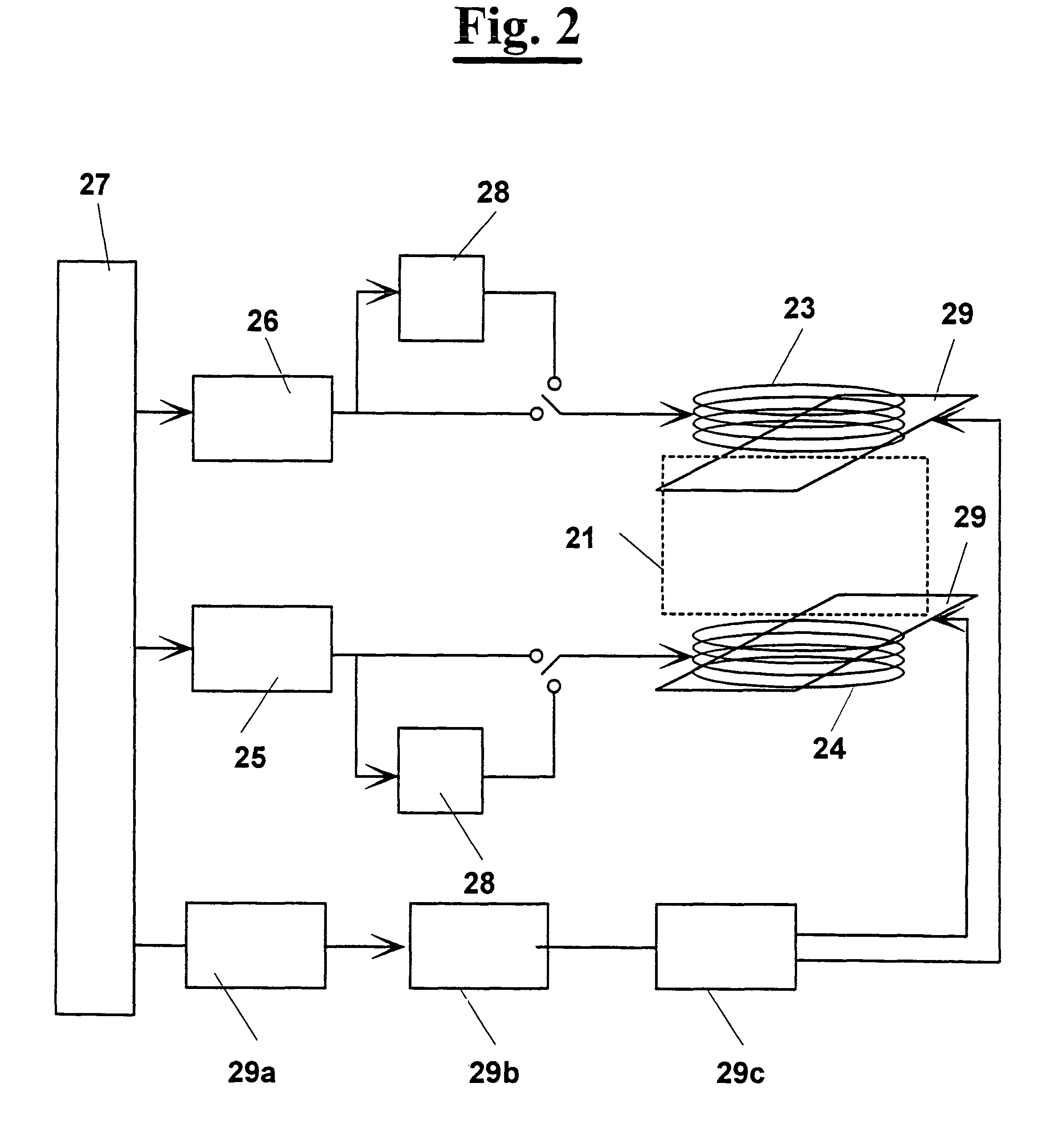
A superconducting fault current limiter array with a plurality of superconductor elements arranged in a meanding array having an even number of supconductors parallel to each other and arranged in a plane that is parallel to an odd number of the plurality of superconductors, where the odd number of supconductors are parallel to each other and arranged in a plane that is parallel to the even number of the plurality of superconductors, when viewed from a top view. The even number of superconductors are coupled at the upper end to the upper end of the odd number of superconductors. A plurality of lower shunt coils each coupled to the lower end of each of the even number of superconductors and a plurality of upper shunt coils each coupled to the upper end of each of the odd number of superconductors so as to generate a generally orthoganal uniform magnetic field during quenching using only the magenetic field generated by the superconductors.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
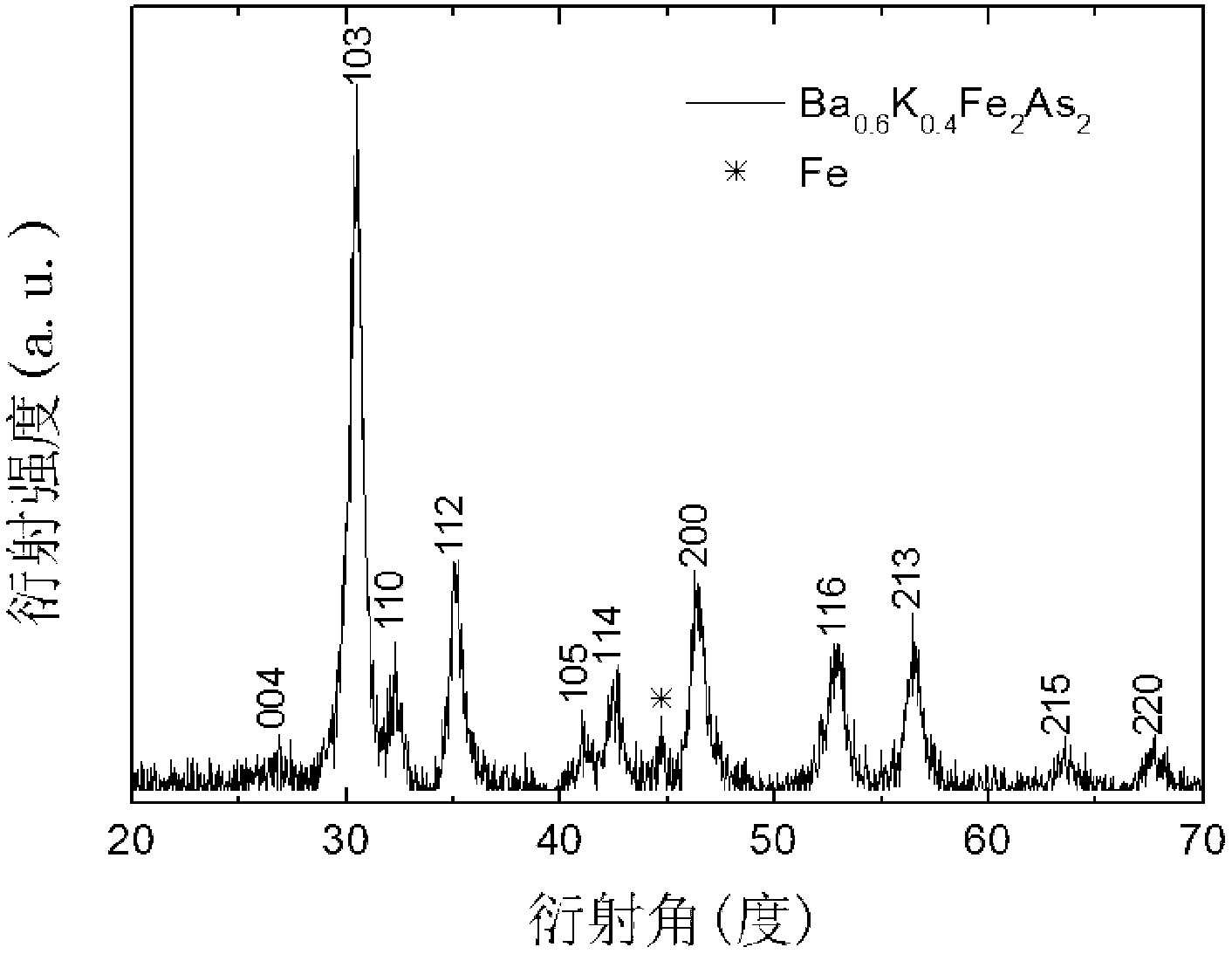
Method for preparing and conducting cold high pressure densifying on Cu wrapped Ba0.6K0.4Fe2As2 superconducting wire
InactiveCN102938270AThe sintering method is safe and reliableSimple processSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesPower flowHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for preparing and conducting cold high pressure densifying on a Cu wrapped Ba0.6K0.4Fe2As2 superconducting wire. The method is used for improving critical current density of the wire. Based on a traditional powder in tube (PIT) method and a high-energy ball milling powder alloying method, the method adopts a high-energy ball mill to directly prepare simple substance raw materials into superconducting powder, filling mixed powder into a copper tube and rolling the powder into the wire. The rolled wire is sintered in vacuum or under protection of inert gas, or the wire is subjected to cold high pressure densifying processing and then is sintered. The preparation method includes conducting high-energy ball milling on simple substances of Ba, K, Fe and As with the stoichiometric ratio of 0.6: 0.4: 2: 2 to obtain precursor powder, filling the completely mixed powder into the copper tube, and tightly pressing two ends of the copper tube to prepare the wire in pulling and rolling mode. The prepared wire is sintered in vacuum or under protection of inert gas, or the wire is subjected to cold high pressure densifying processing and then is sintered. The critical current density of the Ba0.6K0.4Fe2As2 superconducting wire prepared by the method under a 4.2K self field reaches 1.5*104A / cm<2> to 2.8*104A / cm<2>.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
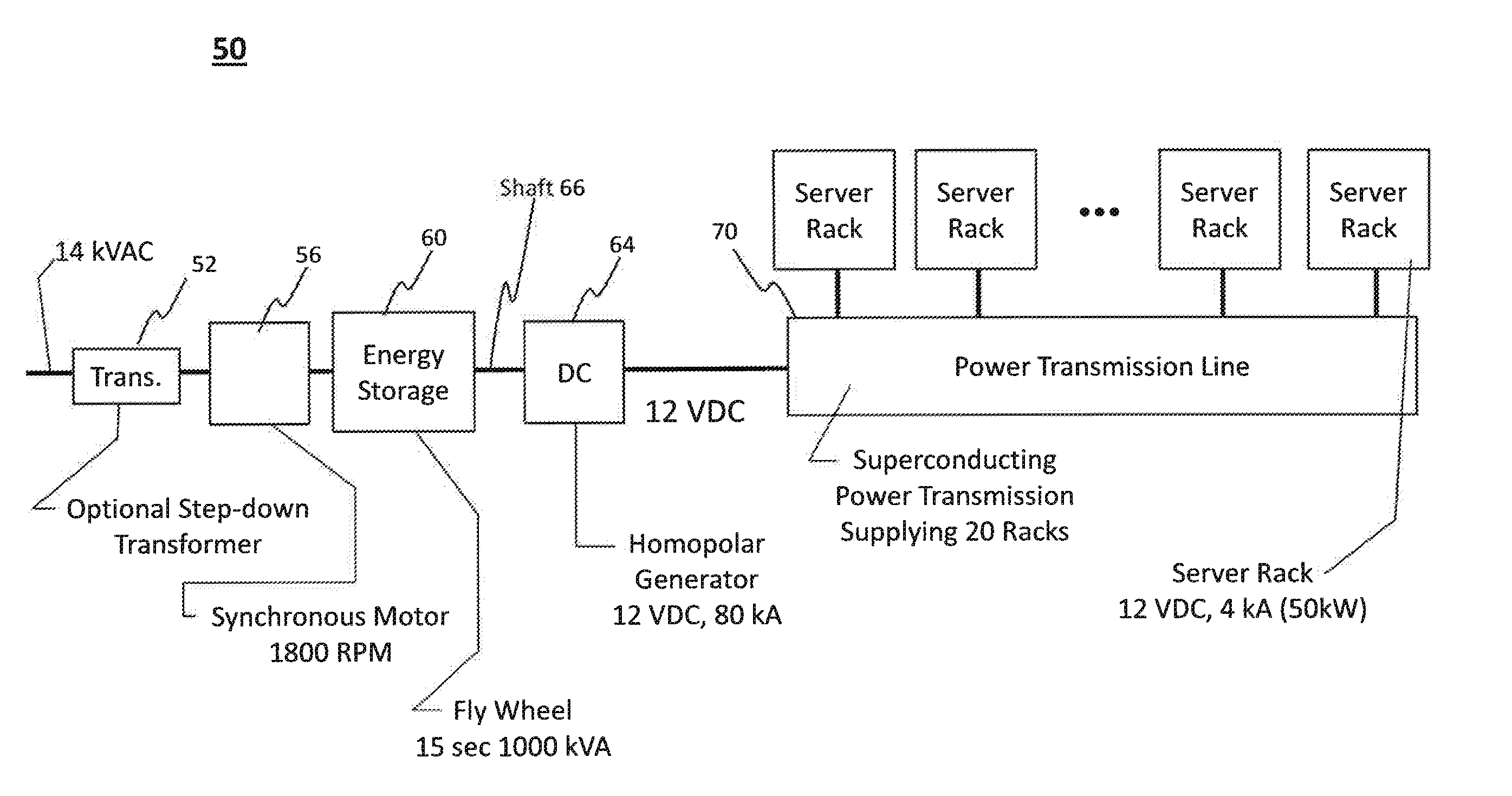
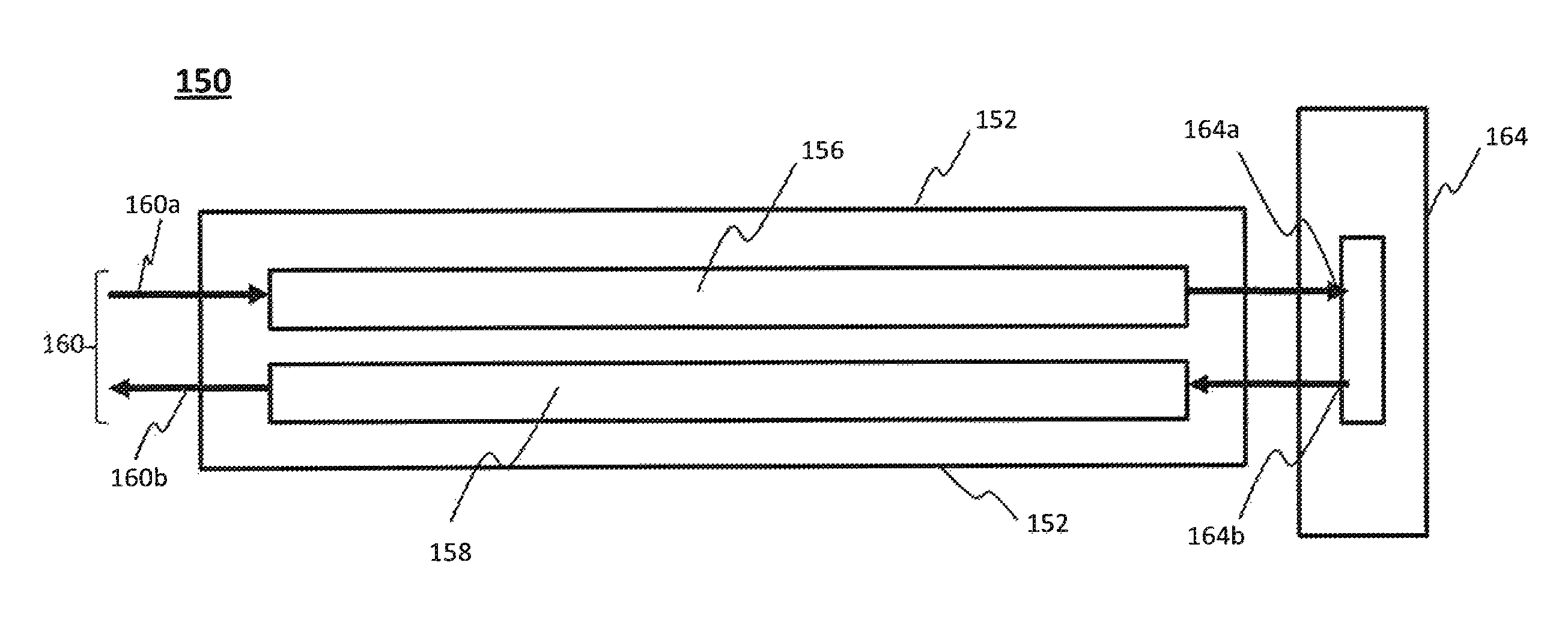
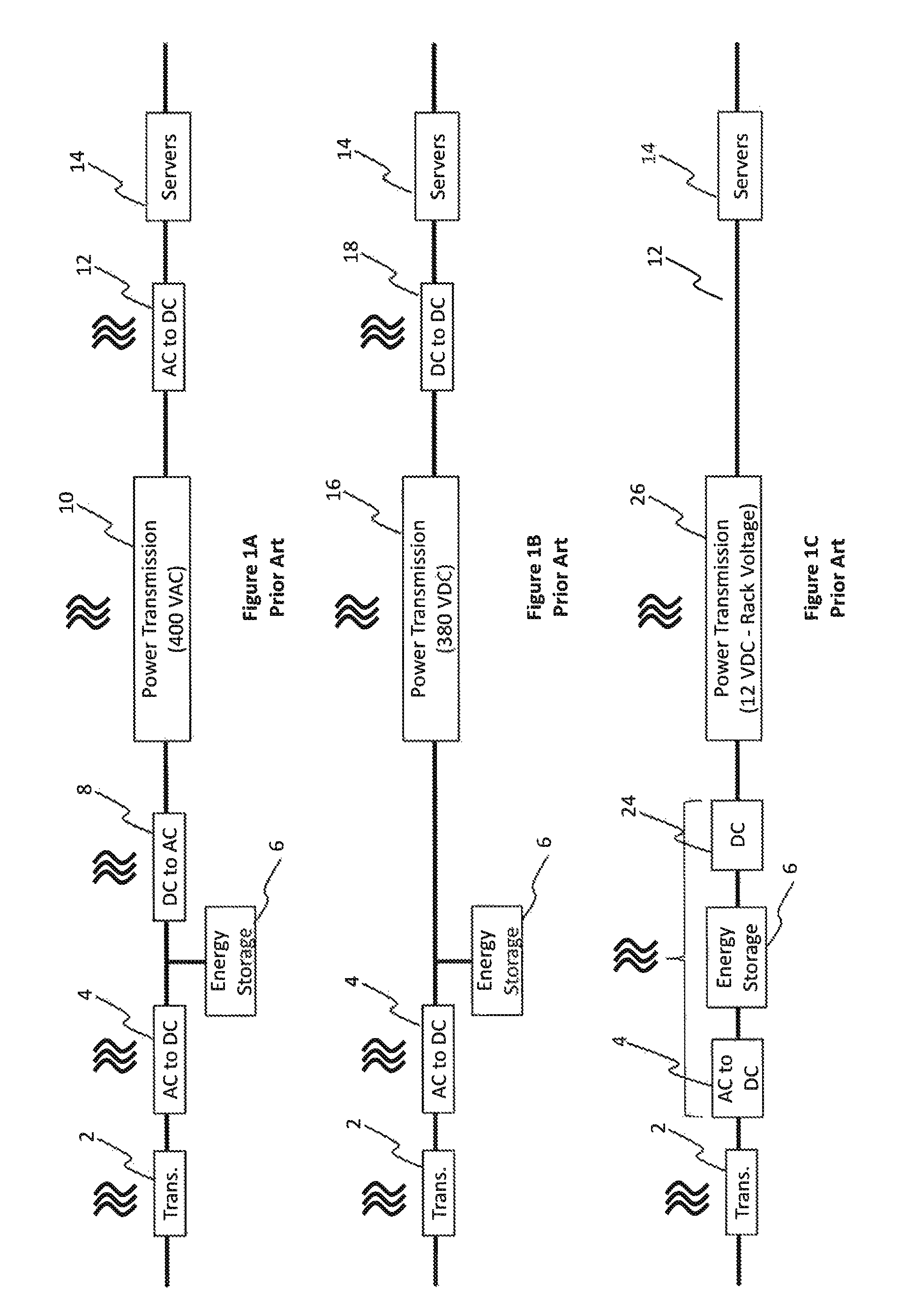
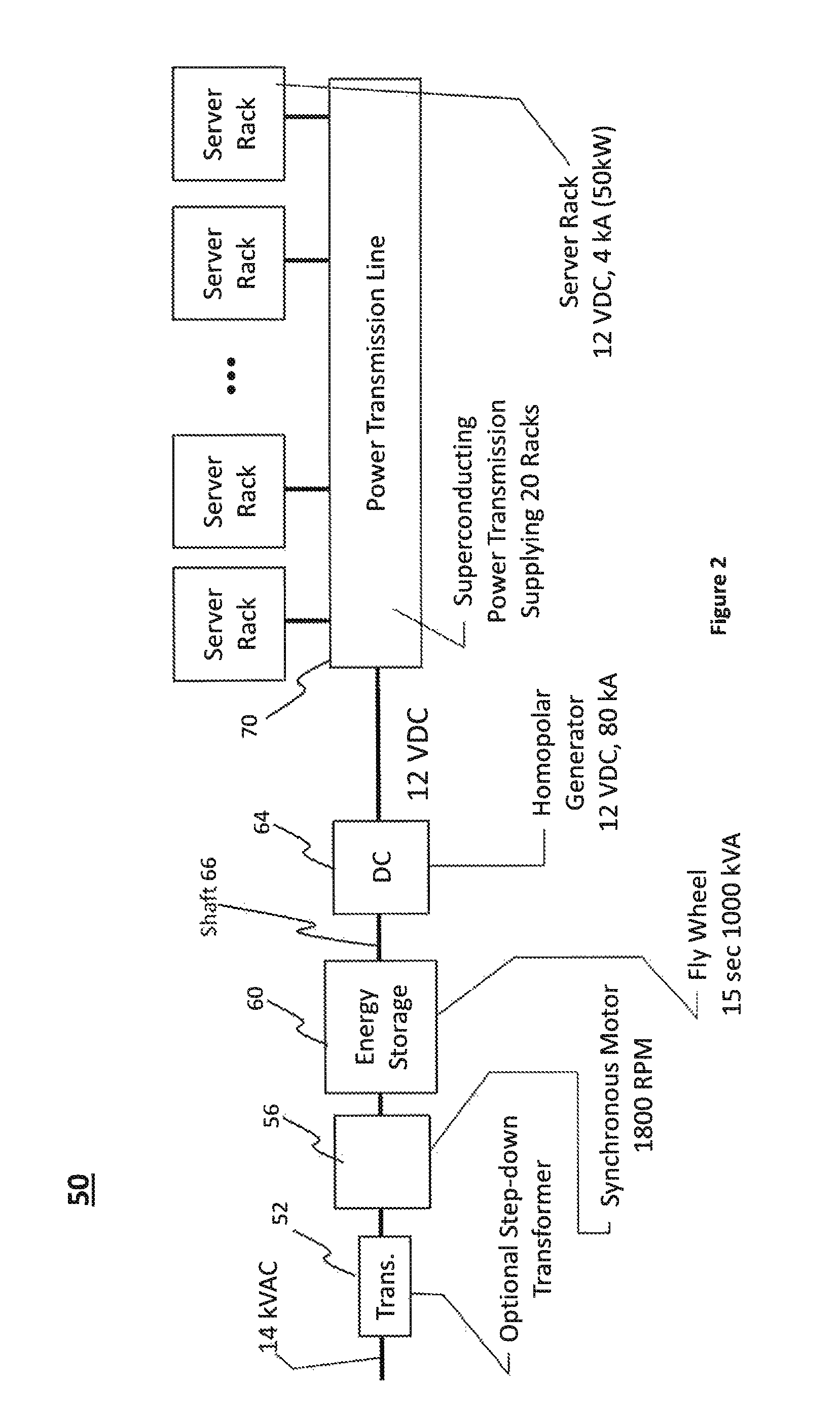
Power Transmission Systems and Components For Direct Current Applications
InactiveUS20130221748A1Electrically conductive connectionsAC/DC convertorsElectric power transmissionDrivetrain
A power conversion and distribution system. In one embodiment low voltage source components convert a high voltage AC power source to a relatively low voltage supply and provide a direct current output. First superconductor wires carry current from the low voltage source components to a load, and second superconductor wires carry current from the load to the low voltage source components. Individual ones of the first wires are grouped with individual ones of the second wires so that wires connected to carry current in opposite directions are in such sufficiently close proximity that additives of self-fields generated by individual ones of the wires during power transmission result in reduction of the magnetic fringe field generated, thereby increasing the current carrying capacity of the wires.
Owner:ADVANCED MAGNET LAB
CRITICAL CURRENT DENSITY ENHANCEMENT VIA INCORPORATION OF NANOSCALE Ba2(Y,RE)TaO6 IN REBCO FILMS
A superconducting article includes a substrate having a biaxially textured surface, and an epitaxial biaxially textured superconducting film supported by the substrate. The epitaxial superconducting film includes particles of Ba2RETaO6 and is characterized by a critical current density higher than 1 MA / cm2 at 77K, self-field. In one embodiment the particles are assembled into columns. The particles and nanocolumns of Ba2RETaO6 defects enhance flux pinning which results in improved critical current densities of the superconducting films. Methods of making superconducting films with Ba2RETaO6 defects are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Self-magnetic field accelerated ultra-high enthalpy arc heater
ActiveCN106508113BLong test timeIncrease enthalpyElectric discharge heatingPlasma techniqueLow voltageOperation mode
A self-magnetic field accelerated ultra-high enthalpy arc heater, including: a cathode, a nozzle and an anode, the cathode and the anode are separated by a supersonic nozzle, the cathode is placed upstream of the supersonic nozzle, 6-30 anode terminals along the The circumferential direction is evenly placed at the outlet of the supersonic nozzle, and the supersonic nozzle is composed of 5-10 mutually insulated metal rings. The upstream end of the plasma arc is attached to the cathode terminal, and the downstream end is evenly distributed on the anode terminal. Using high current and low voltage operation mode, the high current of the arc itself generates a strong magnetic field, which compresses the arc to the central area and accelerates the plasma. The structure of the supersonic nozzle makes the air flow disturbed upstream. These reasons make the air flow and arc fully Mixing increases airflow enthalpy. The self-magnetic field accelerated ultra-high enthalpy arc heater can be applied to simulate the high-altitude thermal environment of the aerospace vehicle when it returns from deep space exploration, and provide a thermal environment for the screening experiment of the thermal-proof material of the aerospace vehicle.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
IP group similarity calculation method
ActiveCN107645493AHigh precisionPersuasive similarityCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmissionFeature vectorSelf field
The invention relates to an IP group similarity calculation method which includes the steps of taking any IP, and obtaining the high-dimensional feature vectors of self field attribute, the regional information attribute, the alarm time attribute and the alarm type attribute of the IP, obtaining the combined feature vector of the current IP through weighted combination, further obtaining the combined feature vectors of IPs to be grouped, clustering to obtain an IP group, and measuring the similarity of each IP group through the root-mean-square error (RMSE). According to the method, the multi-dimensional attributes of an IP are considered, and a field, a regional characteristic and a behavior mode of the IP are combined, so that the similarity of the IP group is more persuasive, and the precision is higher.
Owner:HANGZHOU ANHENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
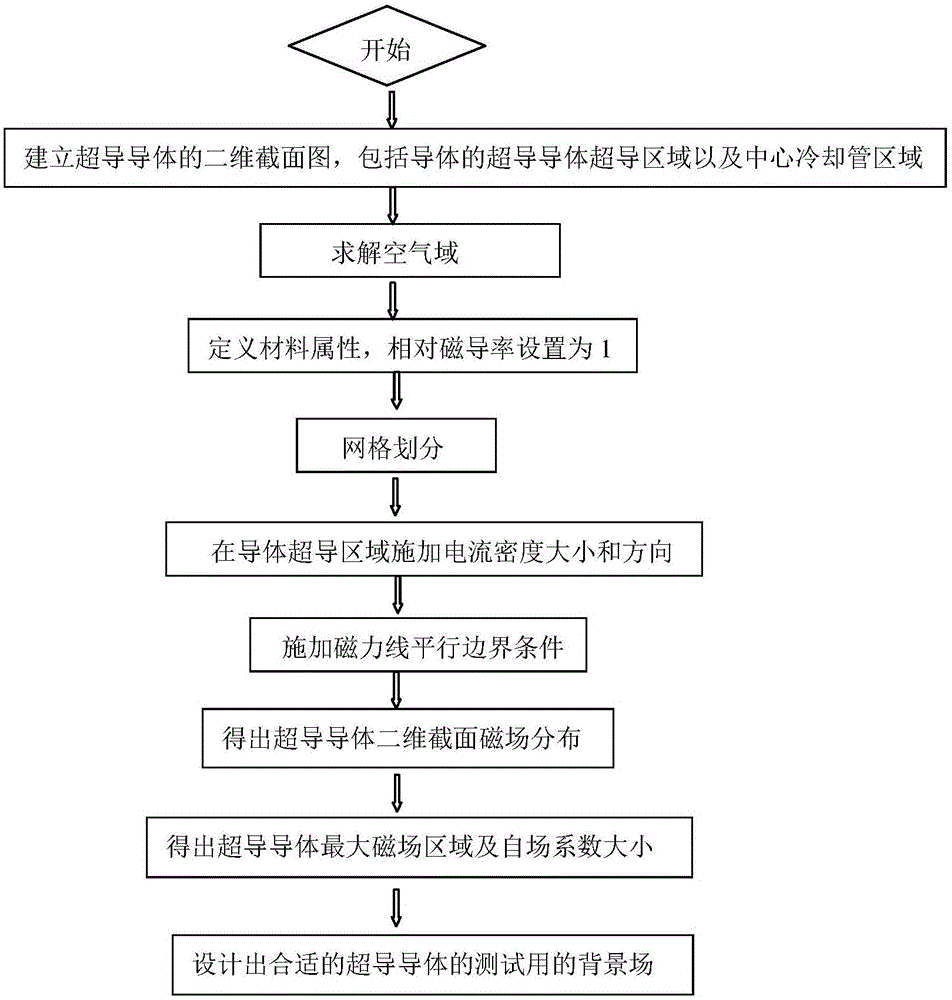
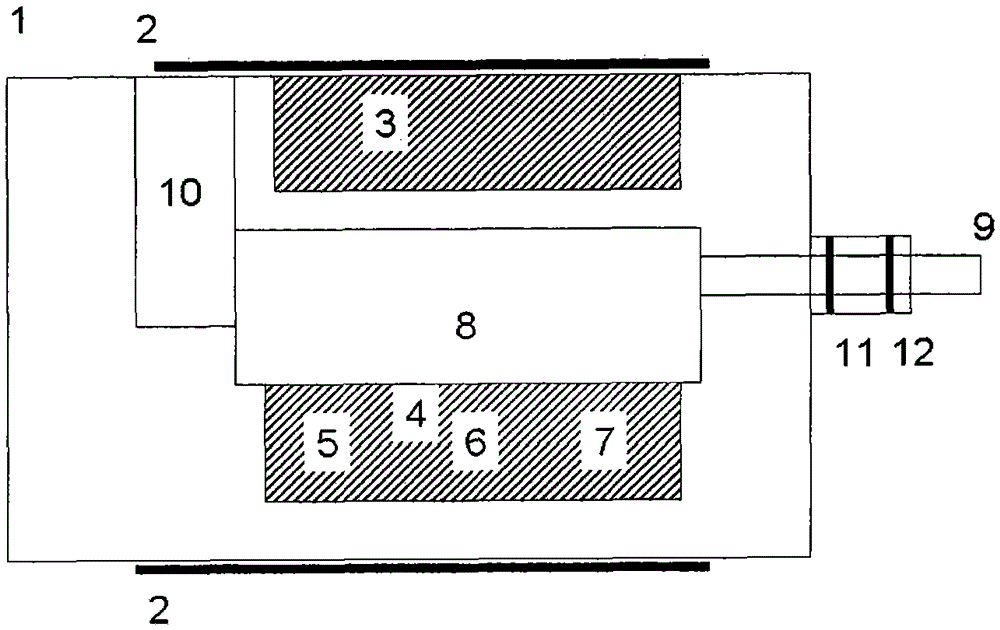
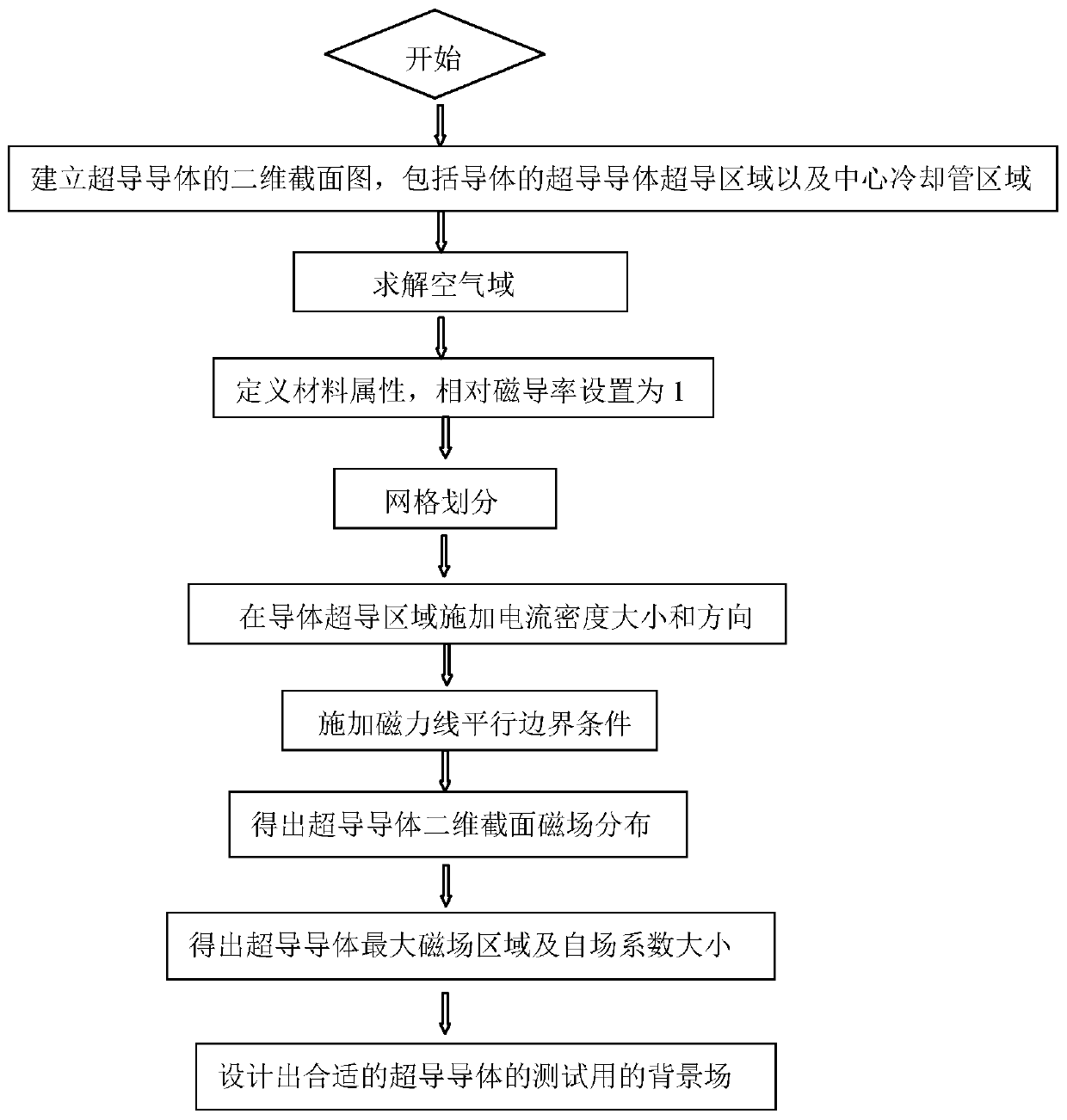
Large-current superconductor self-field finite element analysis method
ActiveCN106446483AAccurate and intuitive self-field 2D distributionDetermine the self-field coefficientDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorElement analysis
The invention provides a large-current superconductor self-field finite element analysis method. The method comprises the steps that a two-dimensional section of a superconductor is built, the finite element method is adopted for performing finite element magnetic field analyzing on the superconductor under the large-current testing condition, magnetic field distribution of the superconductor generated under the large-current operation condition is obtained, the self-field coefficient and position where the maximum magnetic field is generated on the superconductor are obtained, and therefore the appropriate magnitude of a background field for testing of the superconductor is determined and designed. Superconductor self-field analysis under the large-current testing condition is carried out by adopting the finite element method, the self-field two-dimensional distribution of the superconductor can be obtained through more accurate and visual analysis compared with an analysis method, the maximum magnetic field region of the superconductor can be obtained through visual analysis, the self-field coefficient of the conductor is determined, and therefore the reasonable magnitude of the background field for large-current testing of the superchanductor can be designed on the basis of the self-field coefficient.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH QINGDAO NEW ENERGY MATERIALS TECH RES INST CO LTD
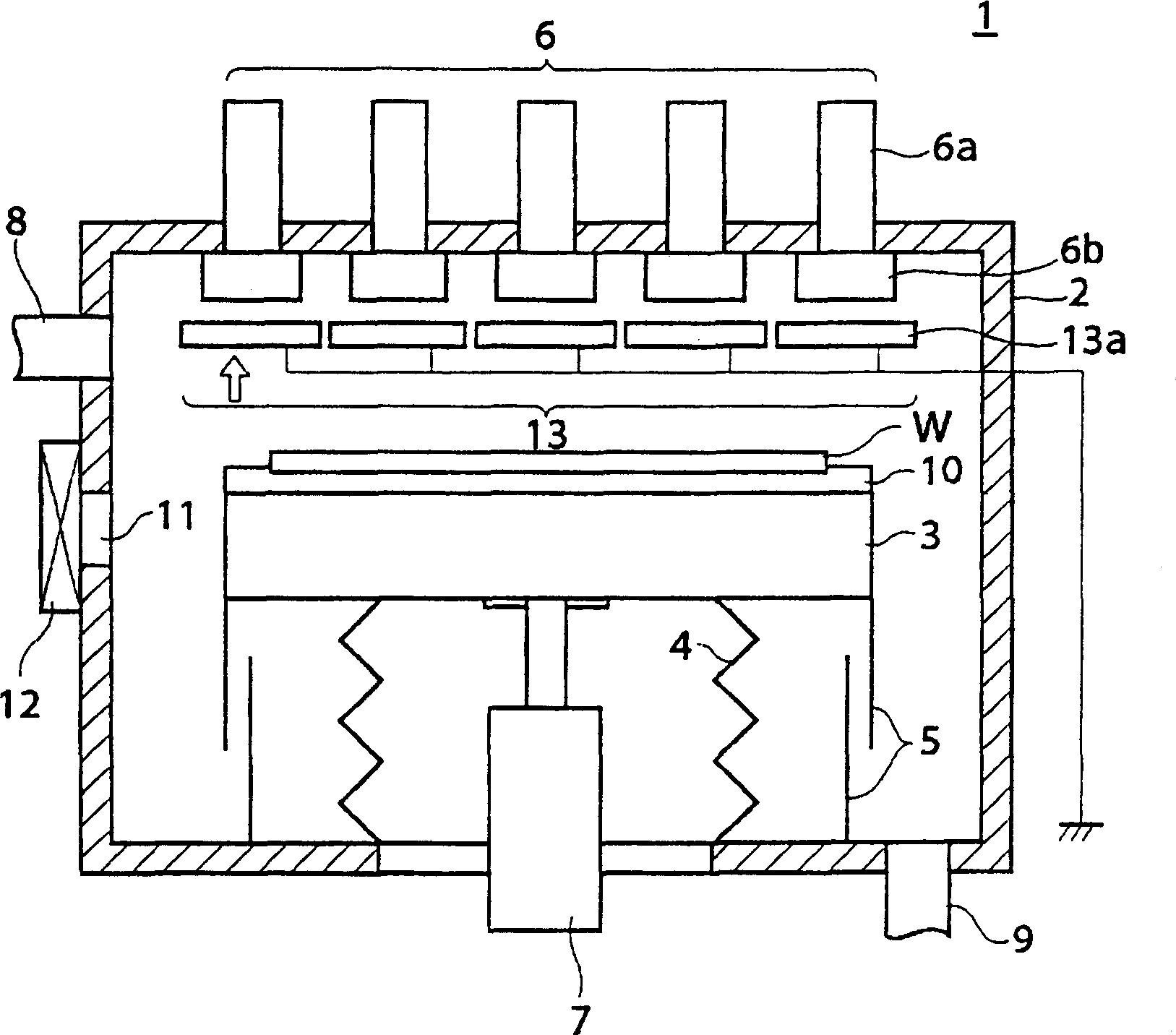
Surface processing apparatus
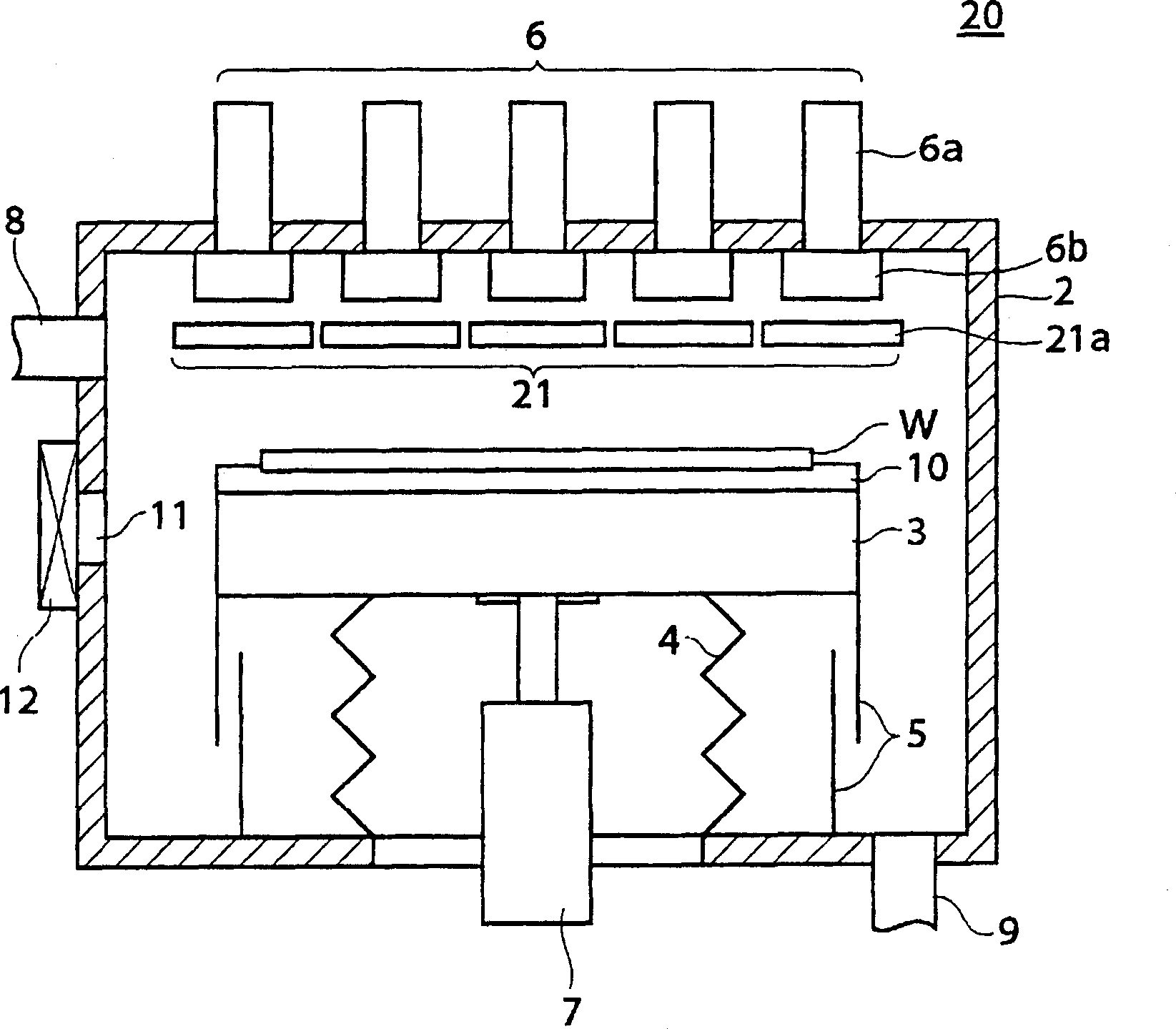
InactiveCN1550903ALow costElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorSelf field
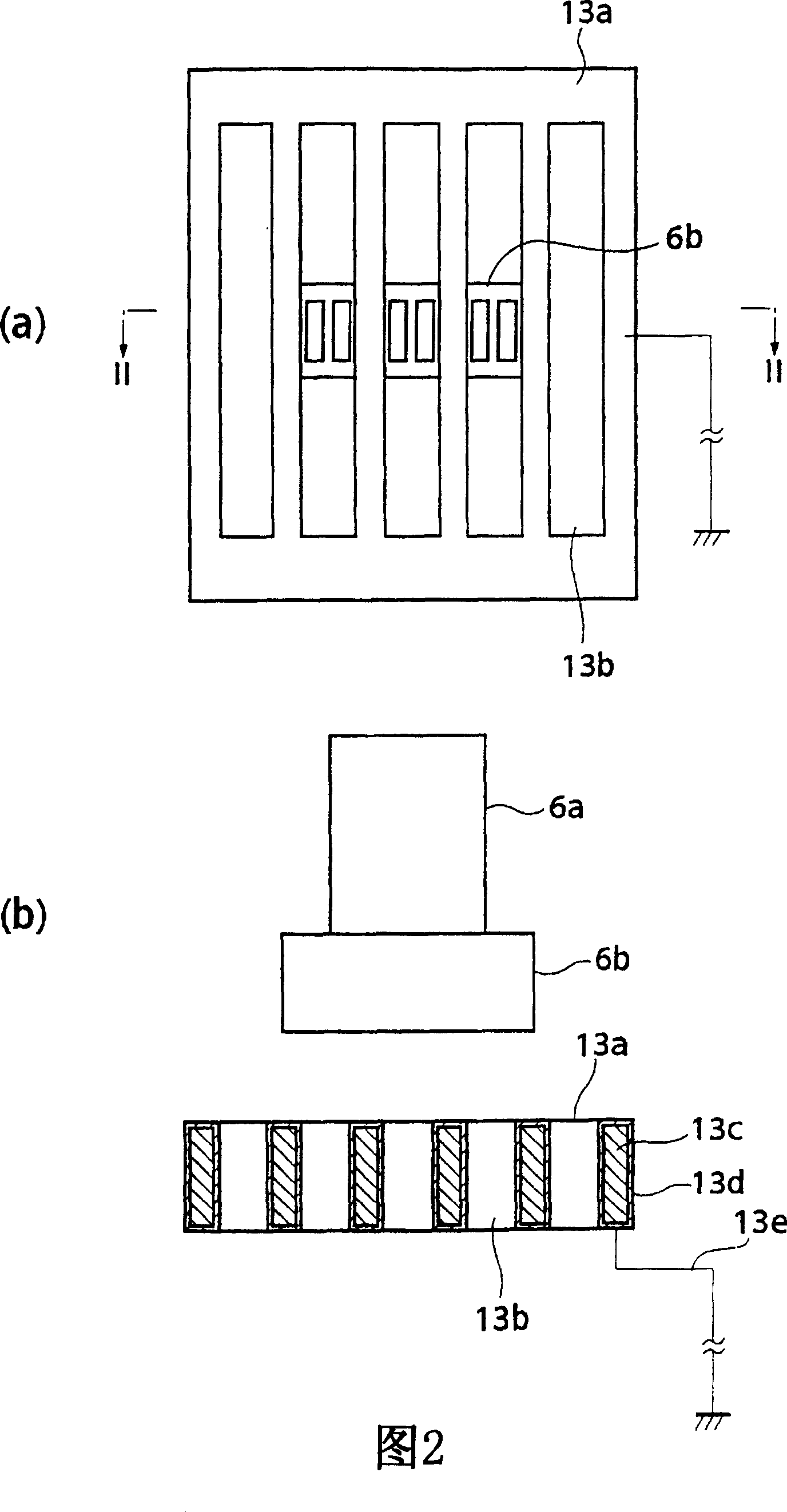
Provided is a surface treatment apparatus which can reduce the energy of an electron beam and simplify a constitution. The surface treatment apparatus 1 is equipped with a mounting stand 3 for mounting almost horizontally a semiconductor wafer W in a vacuum chamber 2, an electron beam irradiation mechanism 6 which is arranged at a ceiling of the vacuum chamber 2 and irradiates the semiconductor wafer W with an electron beam, and a self-field generator 13 arranged between the mounting stand 3 and the electron beam irradiation mechanism 6. The self-field generator 13 is constituted of a plurality of electro static charge boards 13a which are arranged in face to face with each of irradiation windows 6b in the electron beam irradiation mechanism 6. The electro static charge board 13a is a plate-like object, has five slits 13b which passes the electron beam on the facing surface which faces the irradiation windows 6b, and is provided with an internal component 13c constituted of a conductor, an external component 13d constituted of an insulator covering the internal component 13c, and a wire 13e which grounds the internal component 13c.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Apparatus and method for interfering with pathological cells survival processes
InactiveUS20050267535A1Increase probabilityHeart defibrillatorsMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsApoptosisCell survival
A method and an apparatus for interfering with pathological cells survival processes, i.e. inducing directly or indirectly apoptosis, on living pathological cells, by using magnetic fields without adversely affecting normal cells. Static (S) and extremely low frequency (ELF) magnetic fields are used having low intensity comprised between 1 and 100 mT, preferably comprised between 1 and 30 mT. In particular SELF fields are used which are different sequences of S and / or ELF fields, i.e. S fields followed by ELF fields, ELF fields followed by S fields, S and ELF field together, as well as the presence of S or ELF fields alone, said ELF fields having a field frequency comprised between 1 and 1000 Hz. An apparatus for carrying out the method comprises means for generating static magnetic (S) fields crossing a working environment and / or means for generating electromagnetic extremely low frequency (ELF) fields over the working environment in addition to the S fields. Means are provided for modulating the S fields associated to the S fields generating means and varying the intensity of the S fields from 1 to 100 mT, preferably between 1 to 30 mT according to a predetermined function. Means may also be provided for modulating the ELF fields associated to the ELF fields generating means and imposing to the ELF fields a frequency between 1 and 1000 Hz with intensity comprised between 1 to 100 mT, preferably between 1 and 30 mT according to a predetermined function.
Owner:TOFANI SANTI
Self field triggered superconducting fault current limiter
InactiveUS7333309B2Uniform quenchingMagnetsMagnetic materialsSuperconducting fault current limitersSelf field
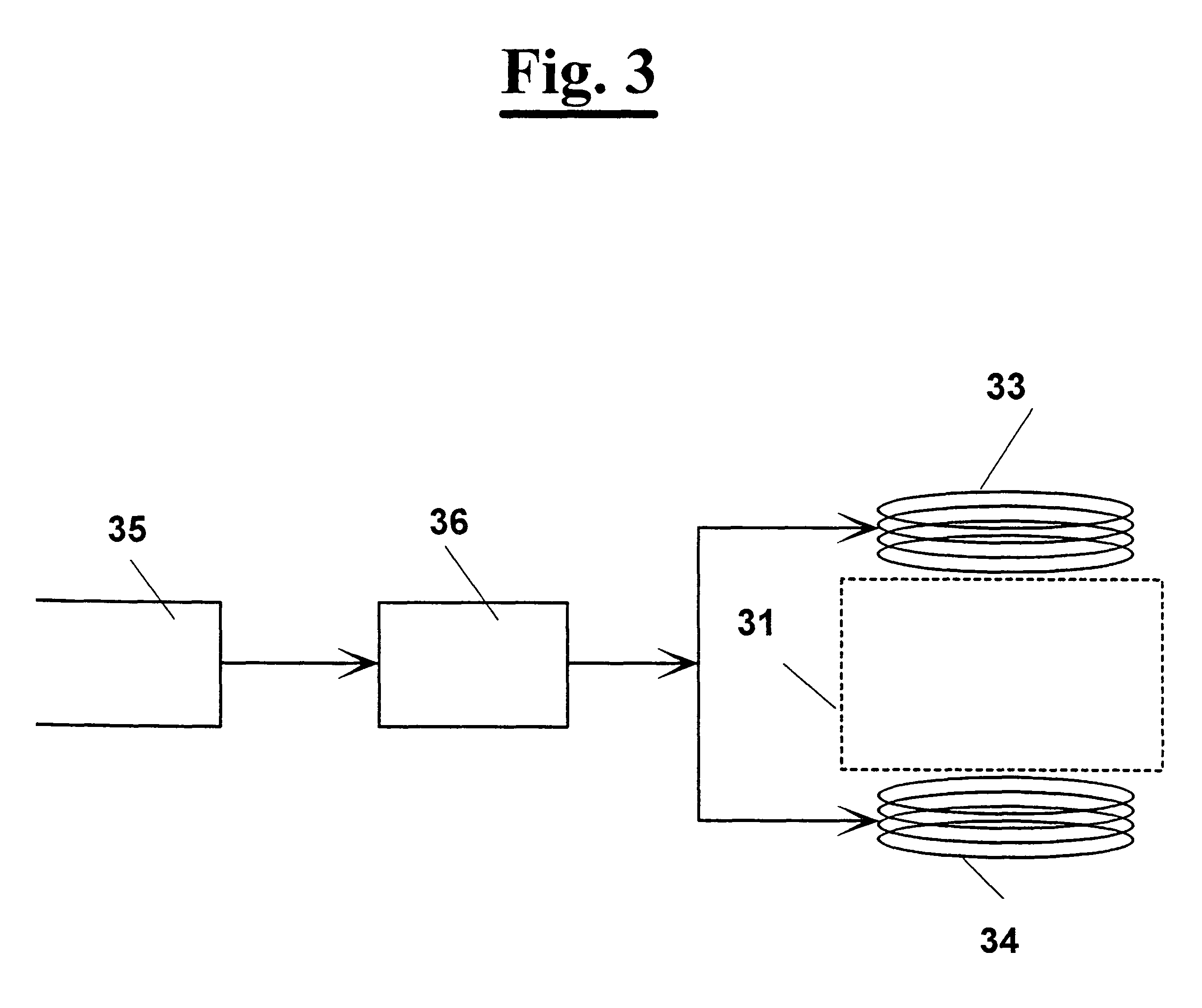
A superconducting fault current limiter array with a plurality of superconductor elements arranged in a meanding array having an even number of supconductors parallel to each other and arranged in a plane that is parallel to an odd number of the plurality of superconductors, where the odd number of supconductors are parallel to each other and arranged in a plane that is parallel to the even number of the plurality of superconductors, when viewed from a top view. The even number of superconductors are coupled at the upper end to the upper end of the odd number of superconductors. A plurality of lower shunt coils each coupled to the lower end of each of the even number of superconductors and a plurality of upper shunt coils each coupled to the upper end of each of the odd number of superconductors so as to generate a generally orthoganal uniform magnetic field during quenching using only the magenetic field generated by the superconductors.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
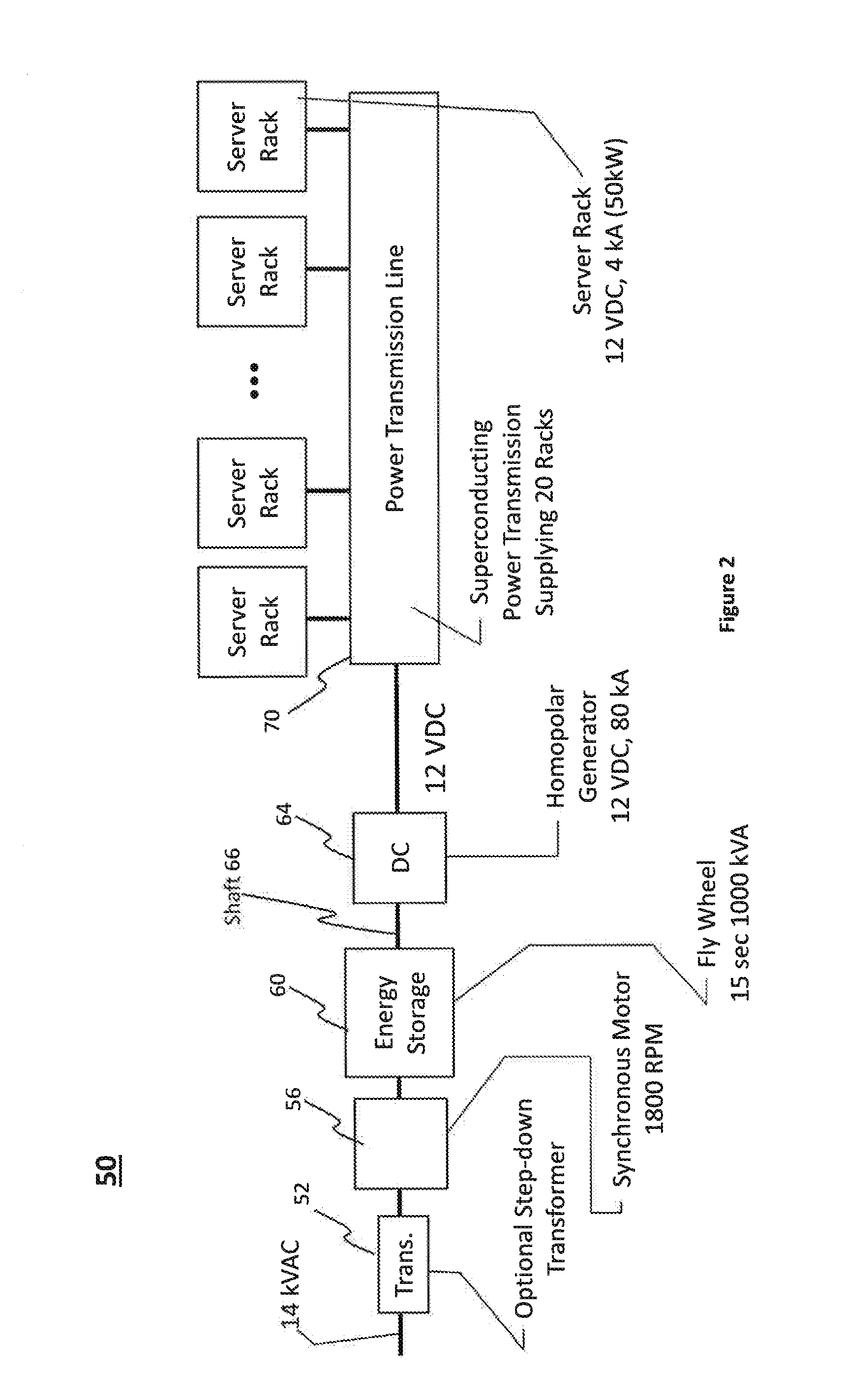
Power transmission systems and components for direct current applications
InactiveUS9525214B2Electric signal transmission systemsElectrically conductive connectionsElectric power transmissionDrivetrain
A power conversion and distribution system. In one embodiment low voltage source components convert a high voltage AC power source to a relatively low voltage supply and provide a direct current output. First superconductor wires carry current from the low voltage source components to a load, and second superconductor wires carry current from the load to the low voltage source components. Individual ones of the first wires are grouped with individual ones of the second wires so that wires connected to carry current in opposite directions are in such sufficiently close proximity that additives of self-fields generated by individual ones of the wires during power transmission result in reduction of the magnetic fringe field generated, thereby increasing the current carrying capacity of the wires.
Owner:ADVANCED MAGNET LAB
Method for preparing Mg0.8CUO.2B2 superconduct bulk material
InactiveCN1722313AReduce volatilityThe synthesis reaction process is rapidSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentFree coolingSelf field
This invention relates to a method for preparing Mg0.8CU0.2B2 superconductive block material, which comprises the following steps: mixing the powder stock evenly in the ball grinder, compressing it into blank, heating the blank in the vacuum furnace protected with inactive gas to certain temperature, using arc ignition, activating the reaction, then, cooling it naturally to the ambient temperature to get the production with its critical temperature Tc=36.9K, when T=5K, at self field, critical current density Ic=6.8X105A / cm2. Compared with other methods, the Mg0.8CU0.2B2 superconductive material prepared by this method has the advantages of simpler process, shorter time, less energy consumption, higher production efficiency, even product component and being suitable for batch production.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of rare earth barium copper oxygen high-temperature superconducting film
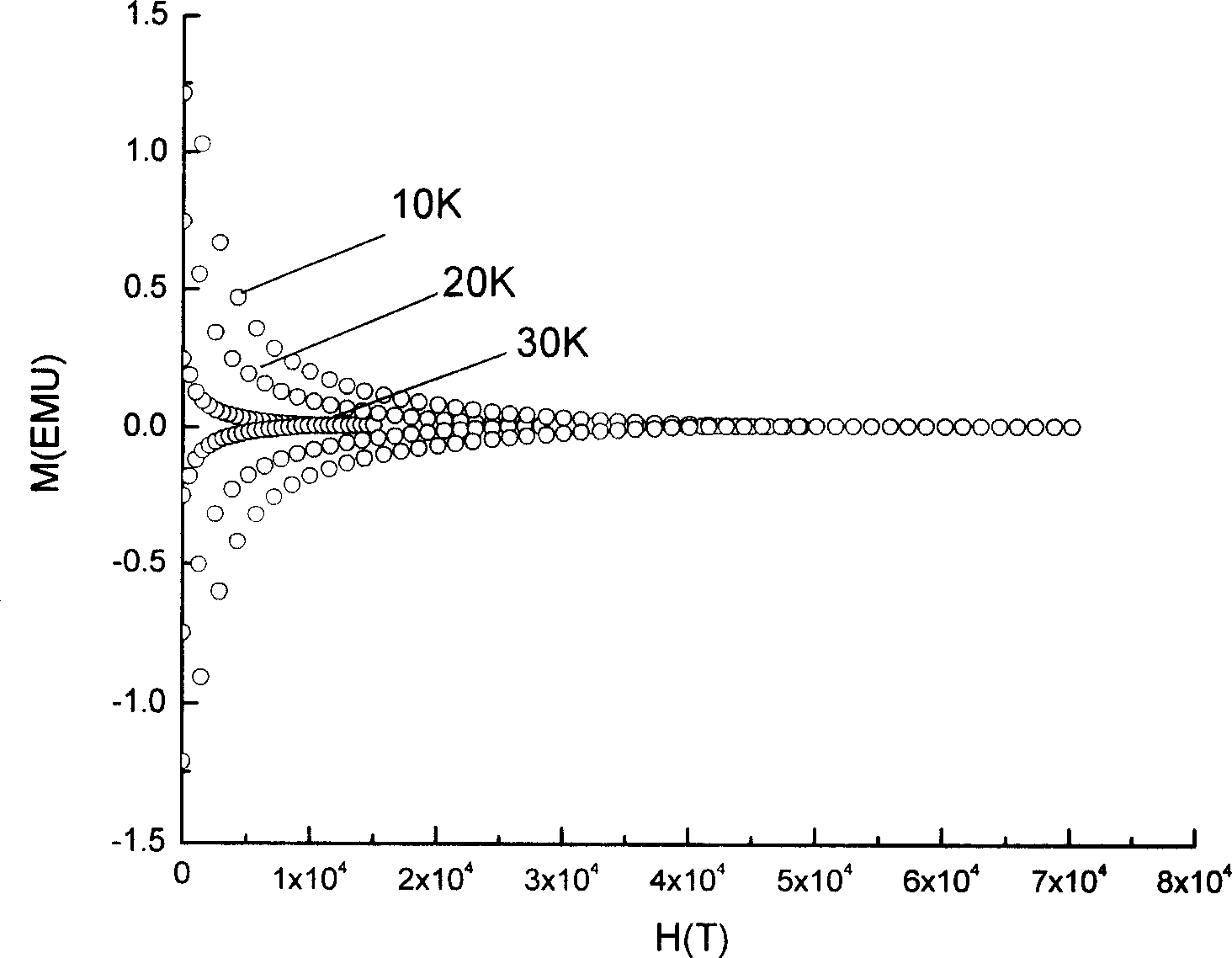
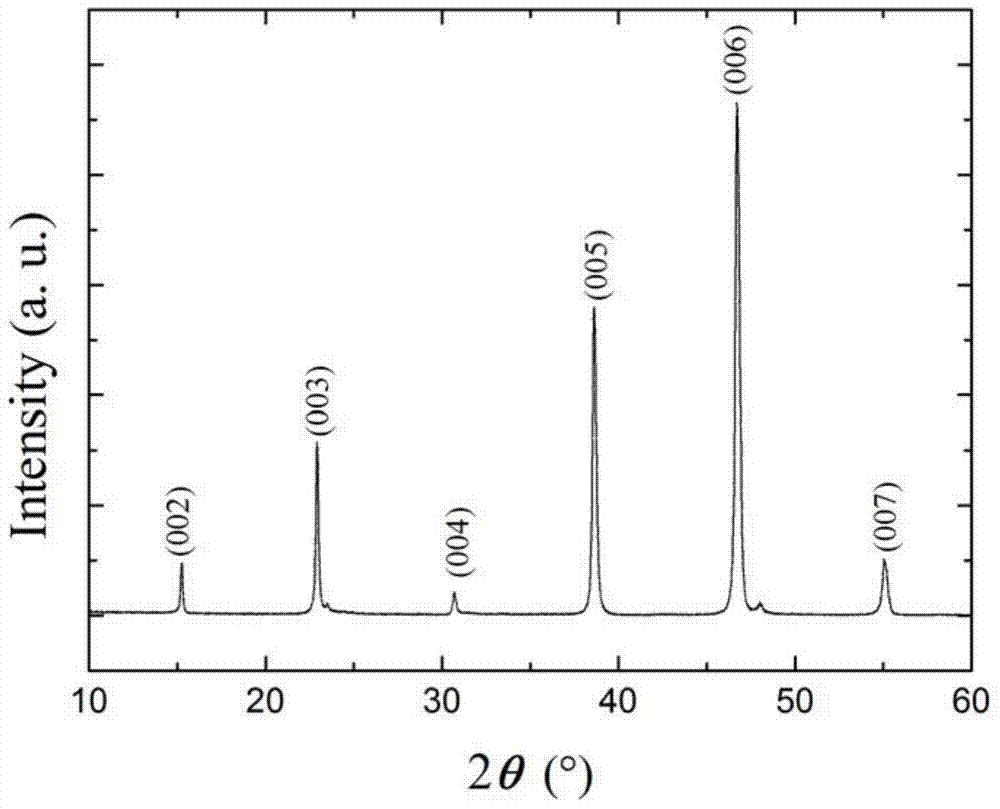
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rare earth barium copper oxygen high-temperature superconducting film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a) weighing rare earth metal salt, barium salt, copper salt and a doping element compound according to a ratio, and dispersing the earth metal salt, the barium salt, the copper salt and the doping element compound into a solvent to obtain a precursor, wherein the doping element compound can generate doping element oxide at 300 to 650 DEG C and under the oxygen atmosphere; b) coating the precursor on a substrate to form a precursor film; c) placing the precursor film into a heat treatment furnace, introducing oxygen, heating the furnace to 300 to 650 DEG C, preserving heat for 0 to 5 hours, and introducing water vapor when the furnace temperature reaches 80 to 120 DEG C until thermal decomposition is finished; d) introducing oxygen nitrogen mixed gas and water vapor, heating the furnace to 700 to 825 DEC C, preserving heat for 20 to 250 DEG C, and stopping introducing the water vapor at the last 1 to 30 percent of time of heat preservation; and e) cooling the furnace to 400 to 500 DEG C and preserving heat for 0 to 240 minutes to obtain a product. According to the rare earth barium copper oxygen high-temperature superconducting film obtained by the preparation method, the thickness is more than 300 nm, the superconduction critical temperature is more than 90 K, and the critical current density at the temperature of 77 K and under the self-field condition is more than 1 mA / cm<2>.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film and preparation method and application thereof
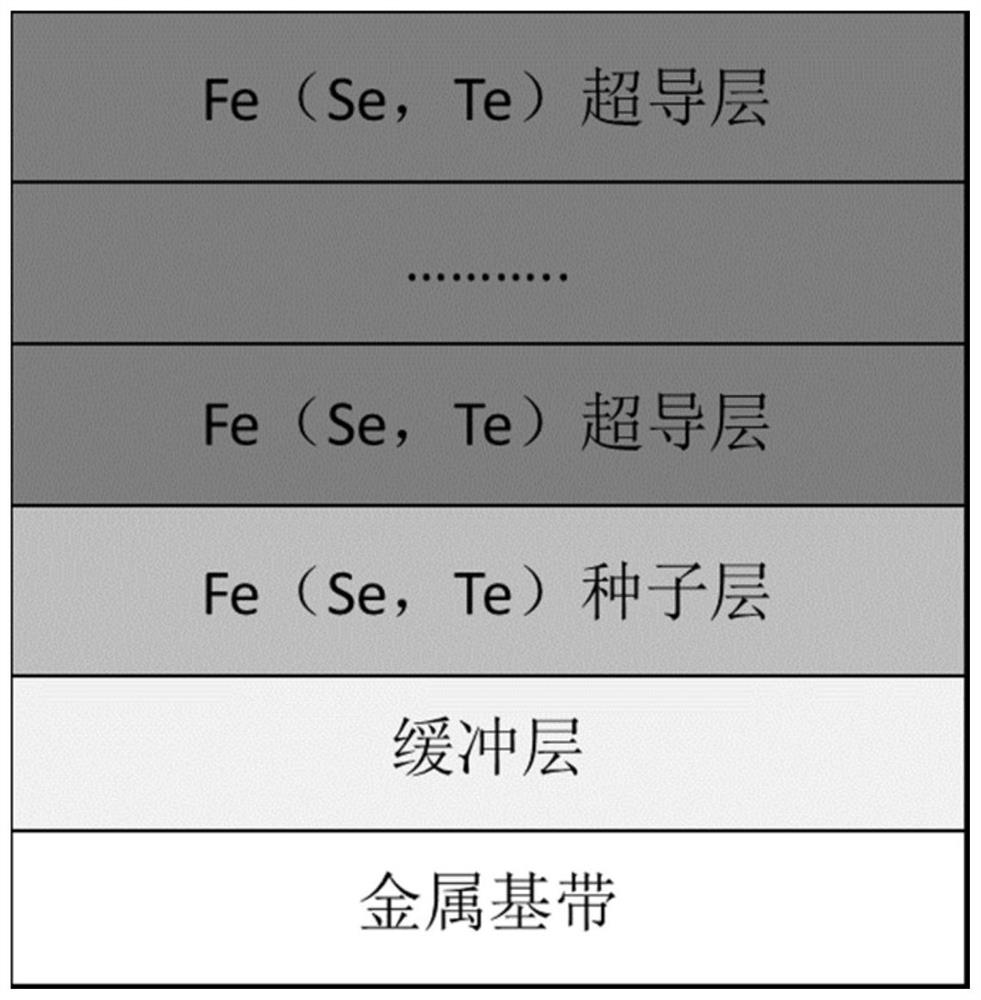
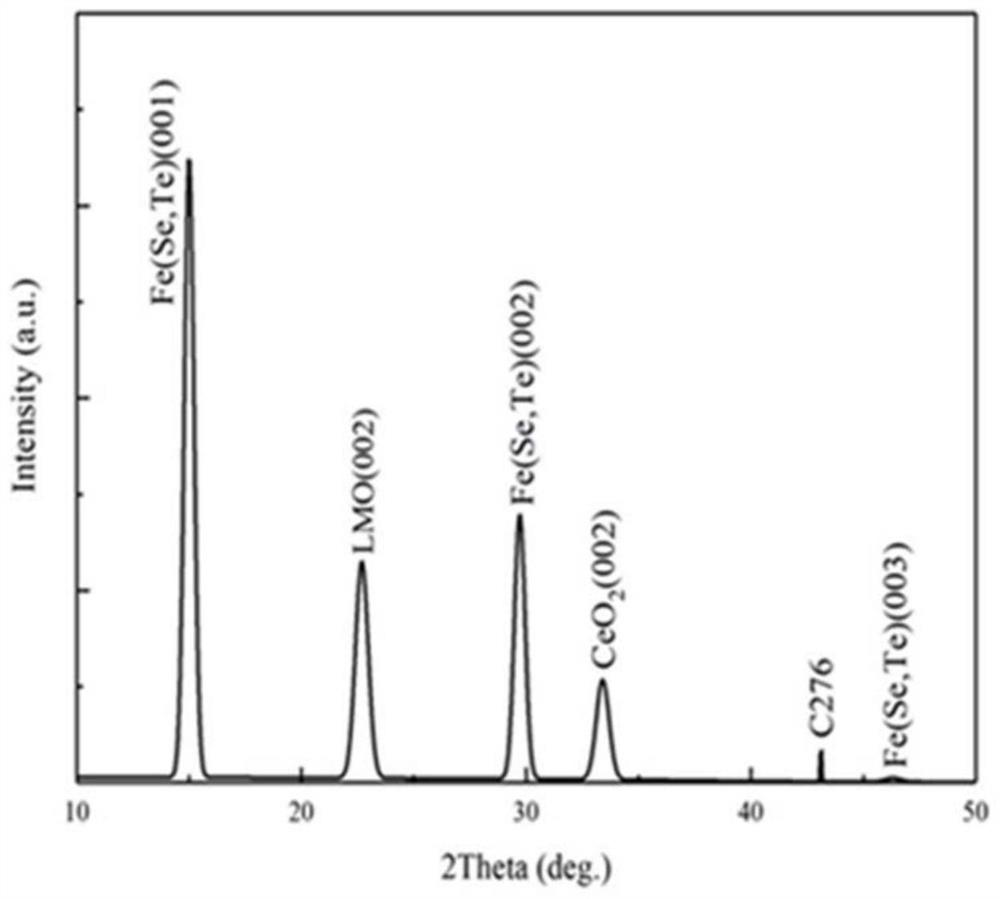
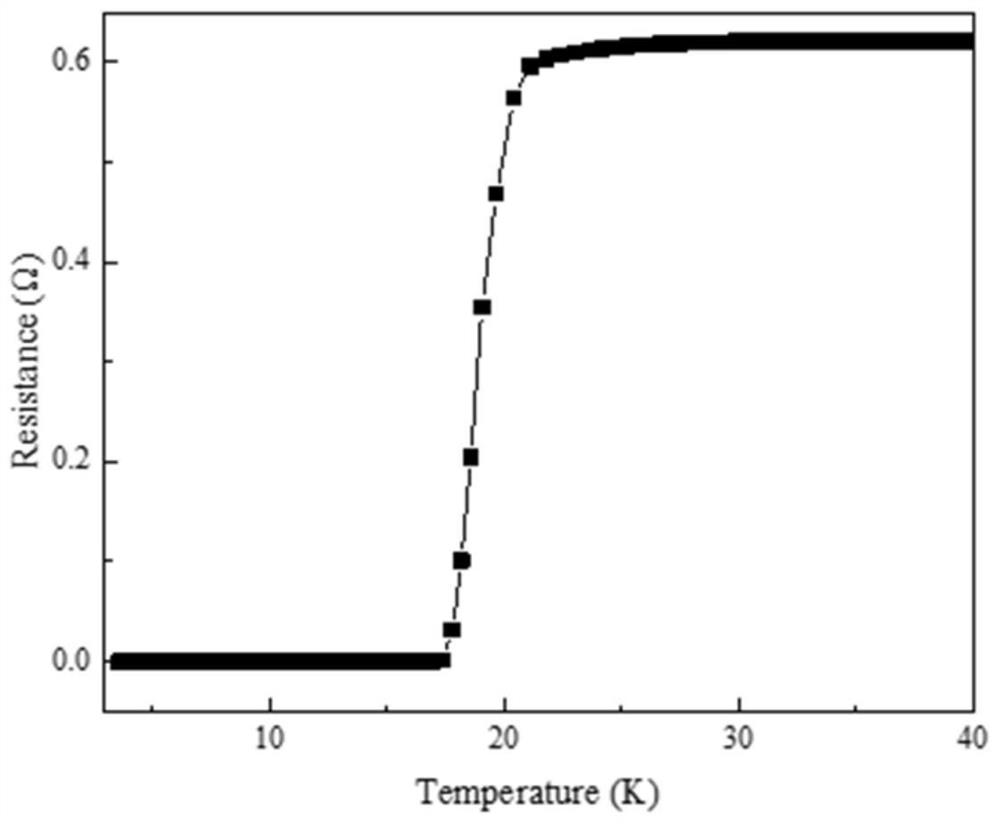
ActiveCN114318242AIncrease the critical currentRaise the superconducting transition temperatureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSelf fieldSuperconducting transition temperature
The invention relates to a Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film and a preparation method and application thereof, and the preparation method of the Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film comprises the following steps: depositing a Fe (Se, Te) seed layer on a metal base band plated with a buffer layer by adopting a multi-channel pulse laser deposition method, and then depositing a plurality of Fe (Se, Te) superconducting layers on the Fe (Se, Te) seed layer. Compared with the prior art, the Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film prepared by the method has pure C-axis orientation, high superconducting transition temperature, high critical current and high critical current density, and under 4.2 K and self field, the critical current is greater than 300A, and the critical current density is as high as 2.3 MA / cm < 2 >; the Fe (Se, Te) superconducting thick film provided by the invention has high critical current and critical current density in a self field and a magnetic field, can meet high-intensity magnetic field application, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
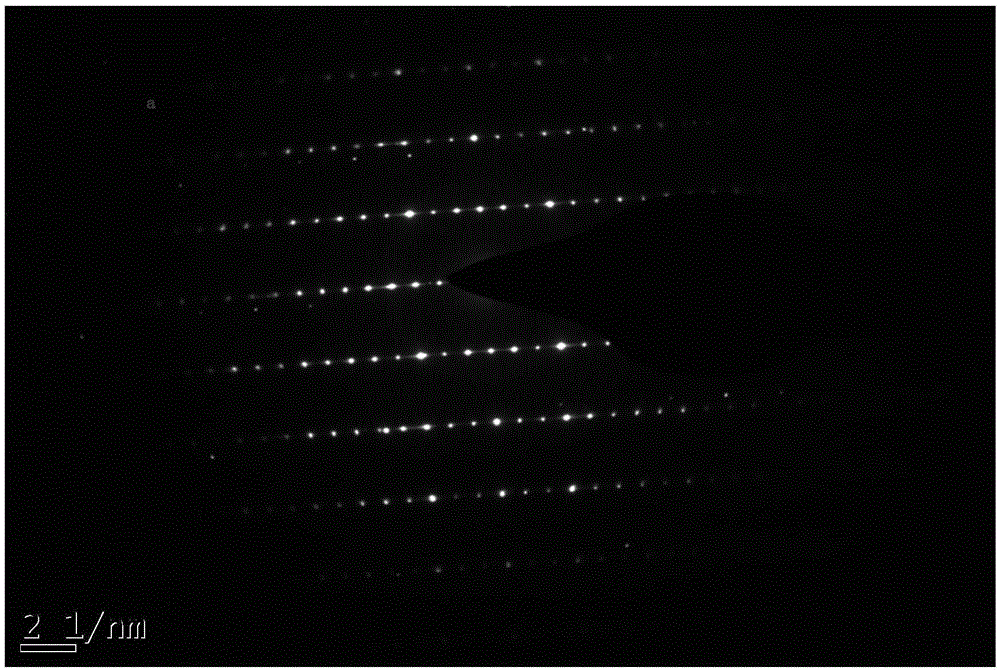
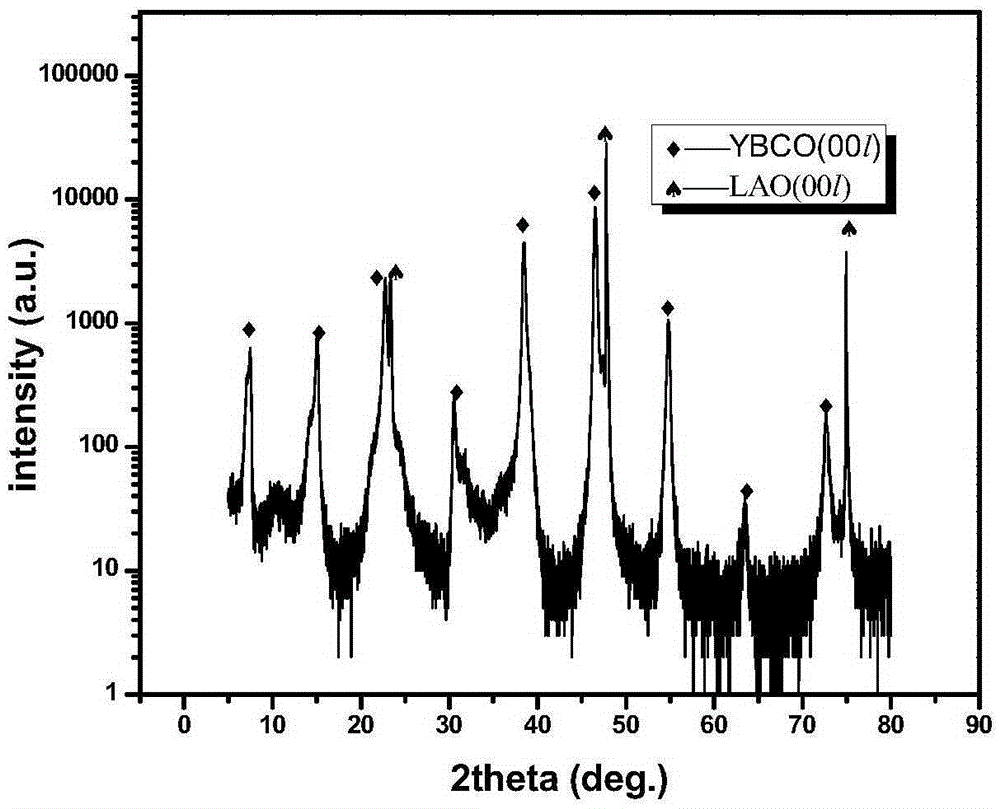
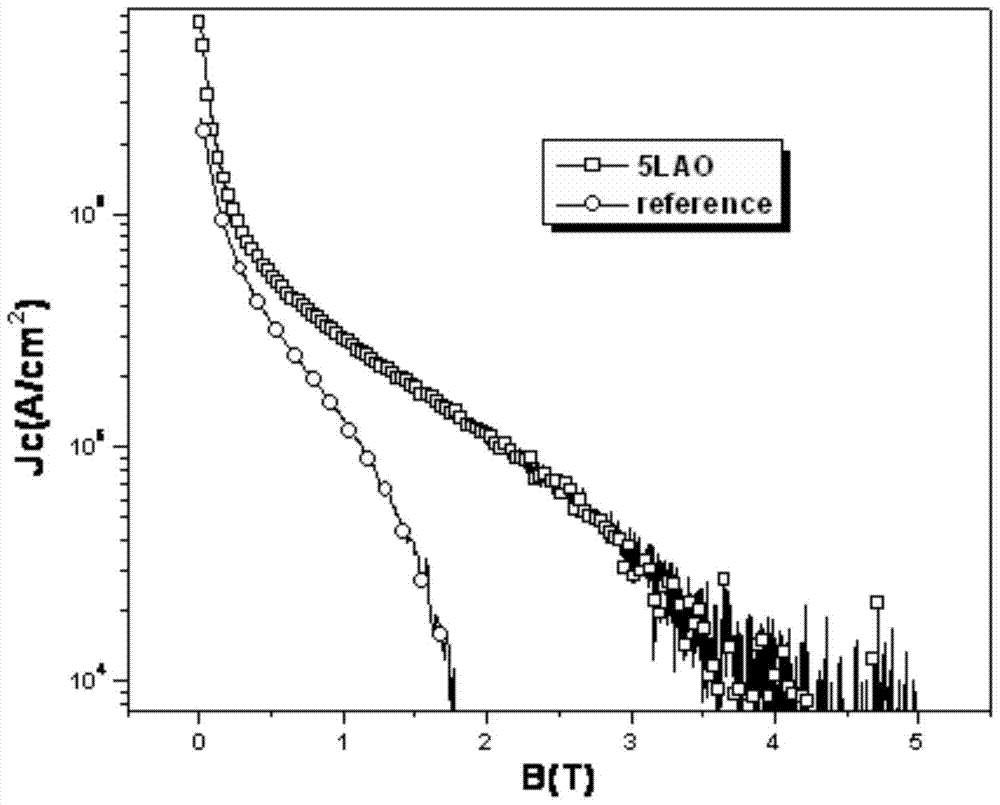
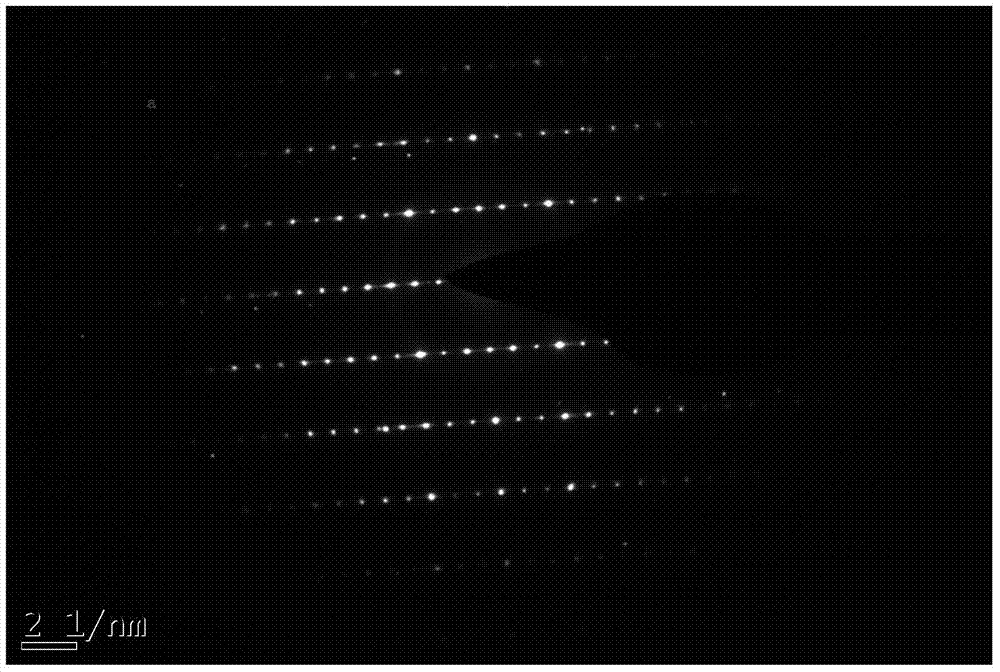
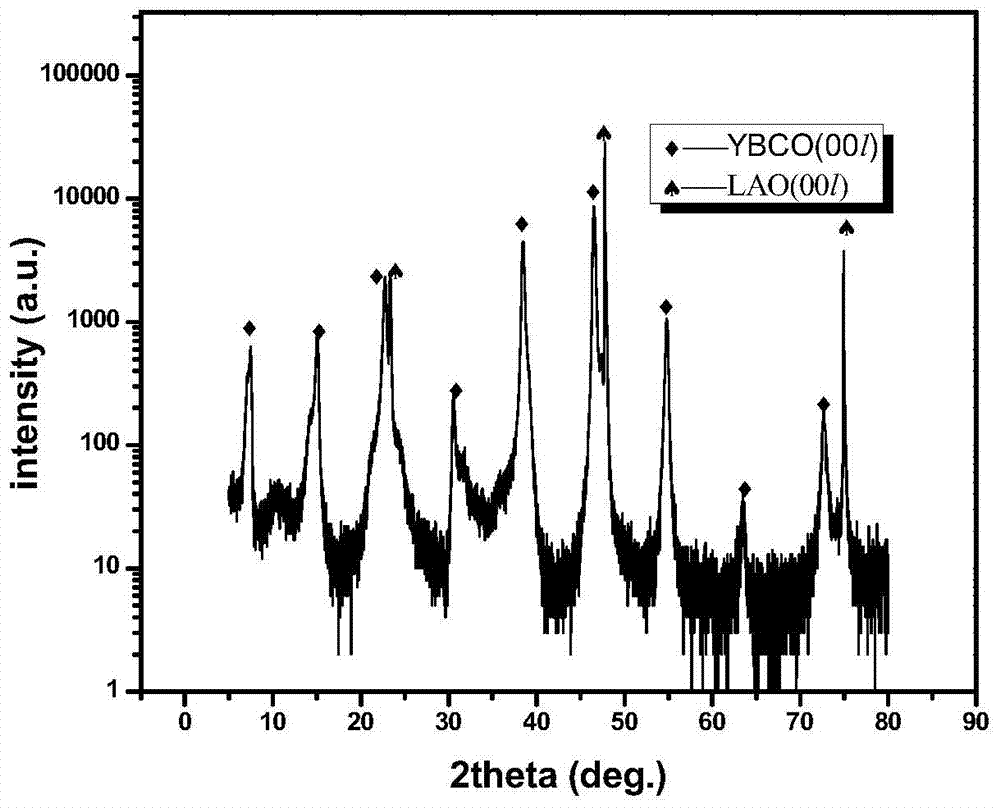
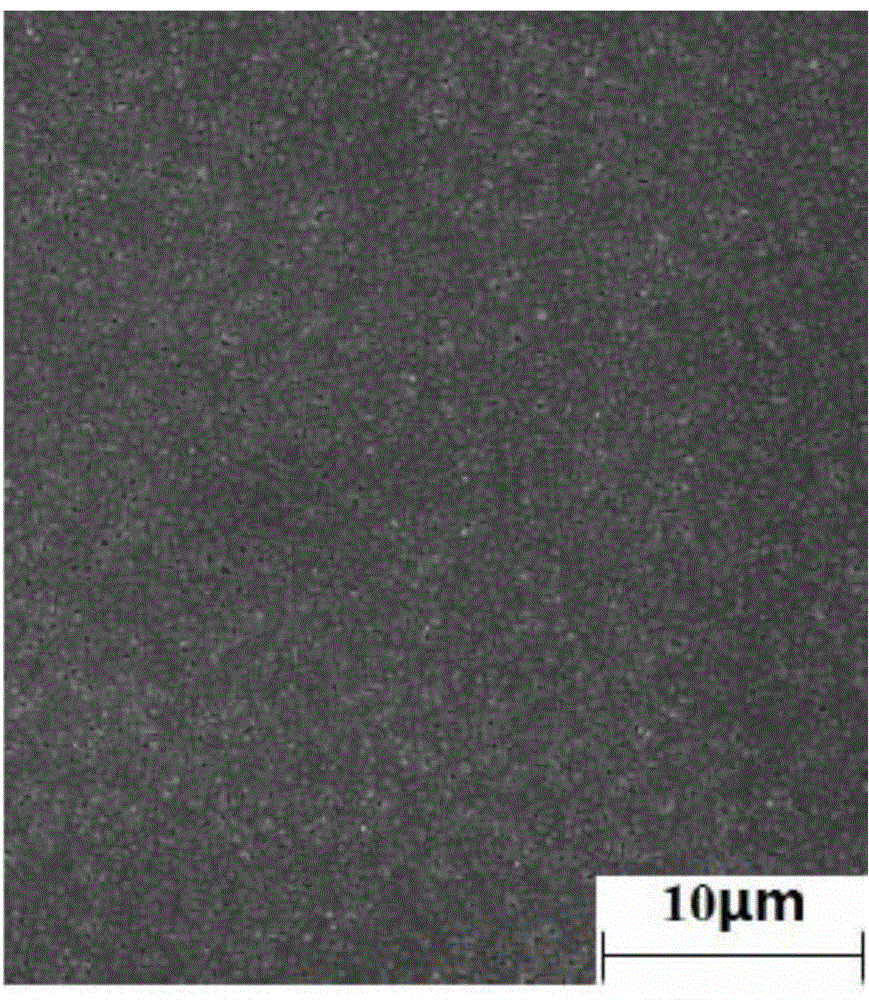
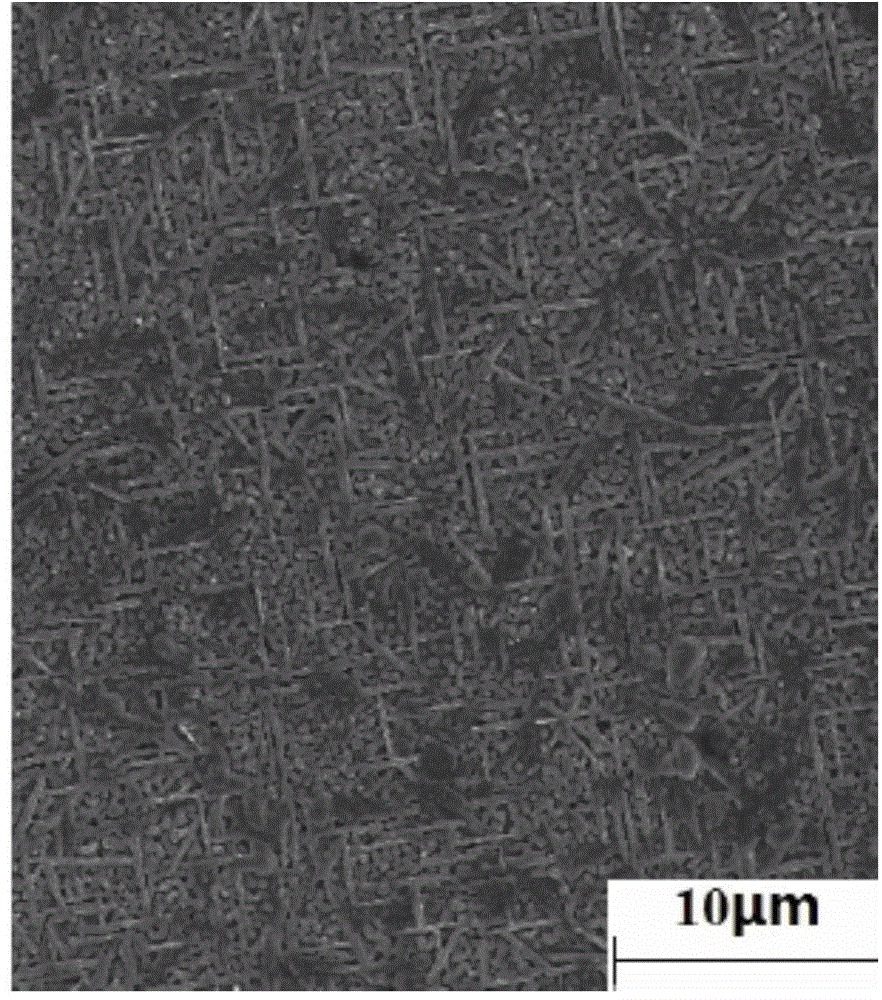
Preparation method of LAO (LaAlO3) doped composite YBCO film
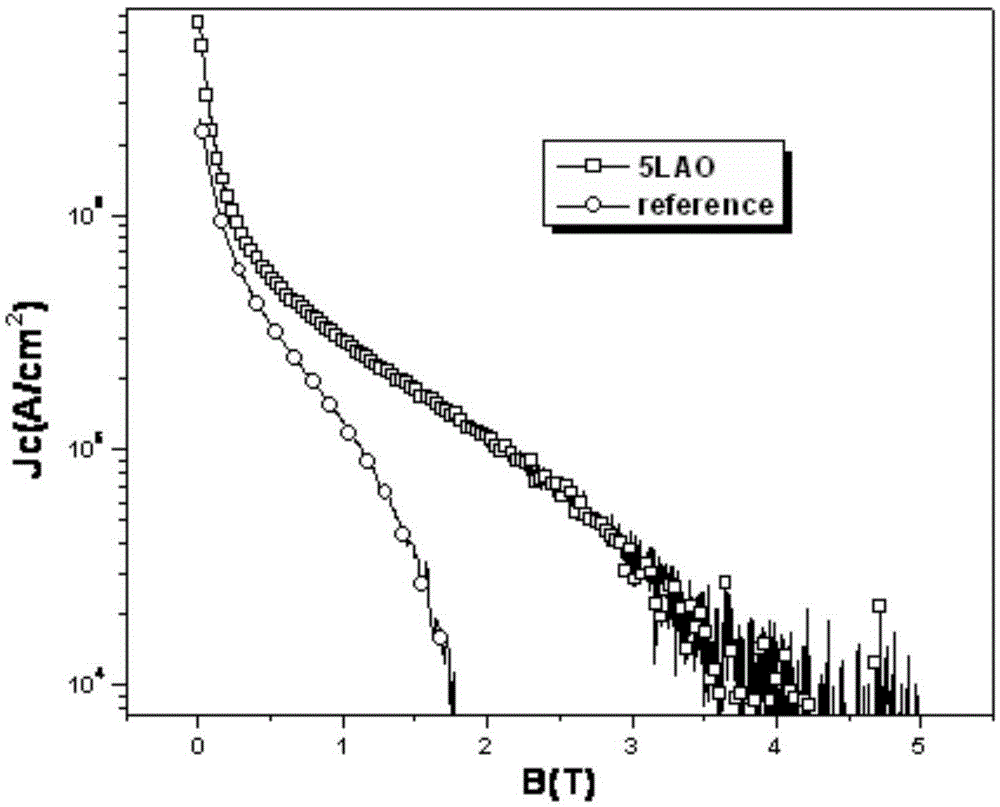
ActiveCN105272203ANot destroyedPlay a pinning roleSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesChemical solutionComposite film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a LAO (LaAlO3) doped composite YBCO film and belongs to the technical field of preparation of high-temperature superconducting materials. According to the method, organic La salt and Al salt are taken as precursor salts, a precursor solution is prepared with a chemical solution method and then applied to an LAO single crystal substrate with a spin coating method, and then a film is composited to the single crystal surface with a heating processing technology. According to the provided LAO doped composite film, the doping phase LAO can have a coherent boundary with YBCO, and the YBCO structure is not damaged while a pinning defect is introduced. An external solvent is not added, a system is simple, cost-saving, time for a sintering technology is shorter, and epitaxial growth of YBCO is not hindered while the LAO phase is formed. Je of a sample, doped with 5% of LAO, of the composite film under self-field is about 3 times of that of a pure YBCO film and is about 6 times of that of the pure YBCO film under an external field with 77 K and 1.5 T.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
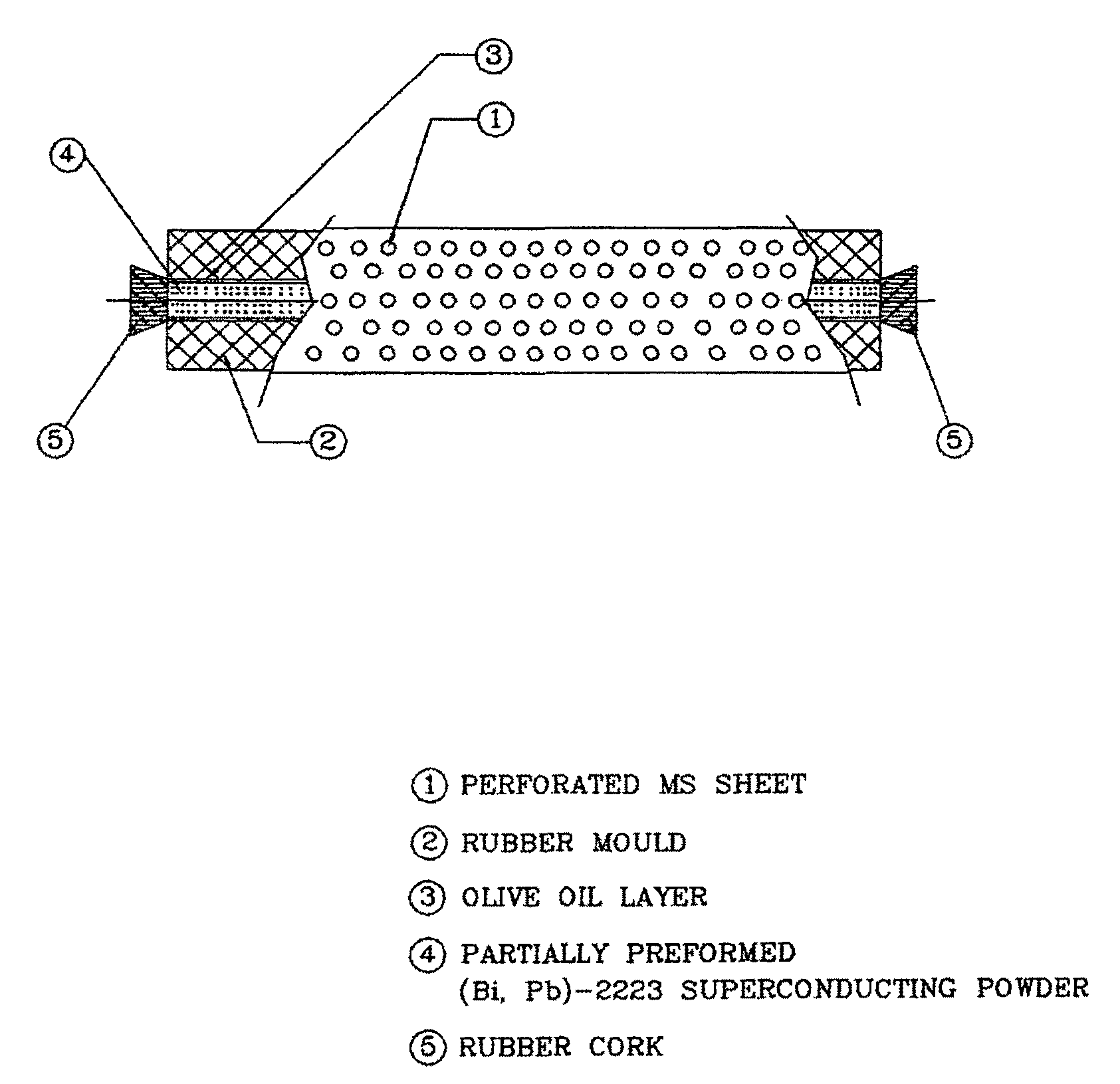
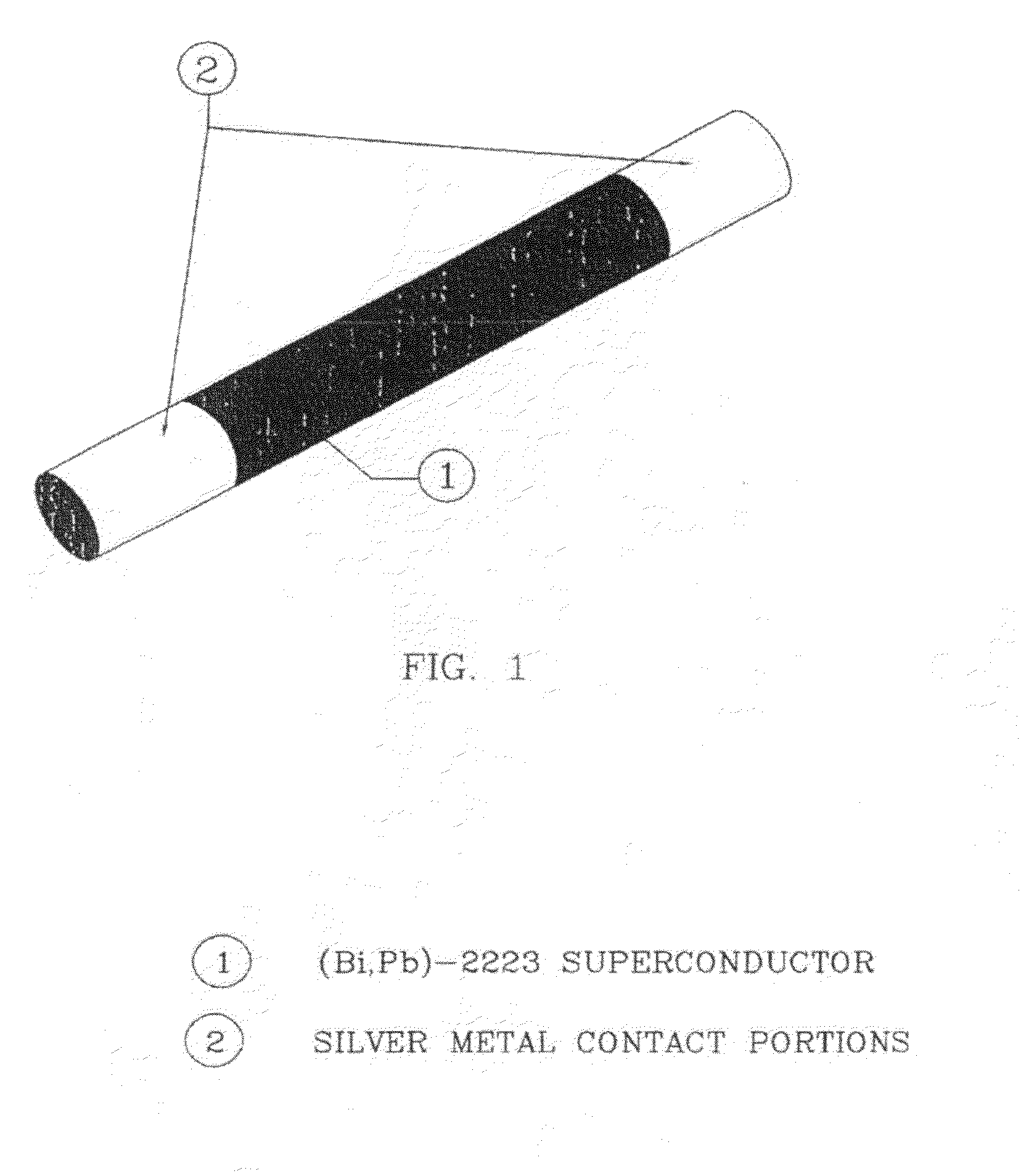
Process for the preparation of oxide superconducting rods
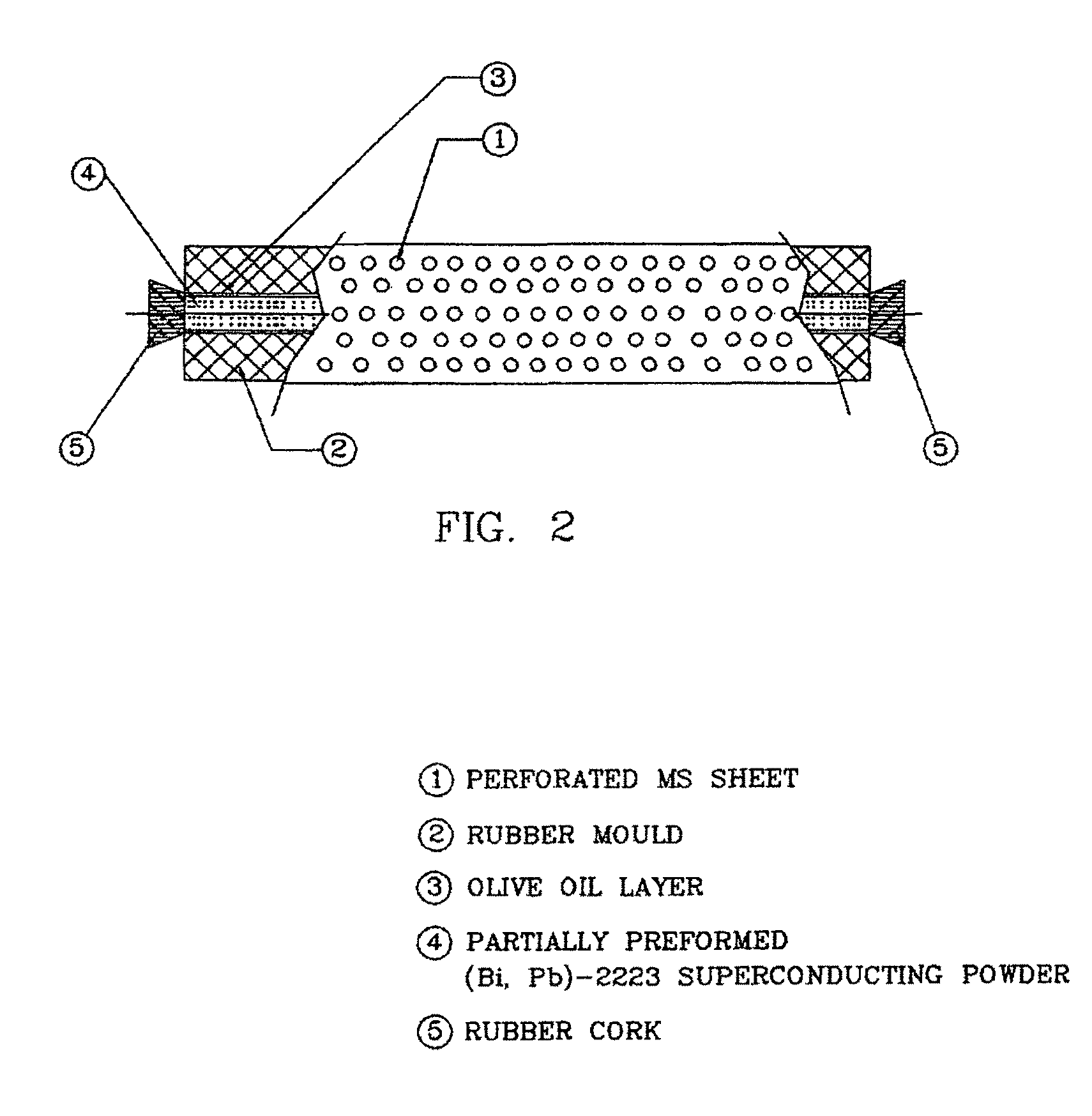
InactiveUS8530389B2Simple methodImprove environmental resistanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsApparatus for heat treatmentSelf fieldNatural field
An improved process for the preparation of oxide superconducting rods. The present invention provides a process for the preparation of oxide superconducting rods. The process includes the steps of a cold isopressing process without addition of binder, particularly thin and those based on Ag-added (Bi,Pb)2 Sr2 Ca2 Cu3 O10+x is disclosed. The main features of the process are the packing of partially preformed oxide superconducting powder obtained from spray drying a nitrate solution of Bi,Pb,Sr,Ca,Cu and Ag in a flexible rubber mould wrapped with a perforated metal sheet and whose inner surface is coated with olive oil, evacuating the packed partially preformed powder to remove trapped air and thereby reduces the defects and improves the subsequent cold isopressing to form rods; immediate cleaning the surface of the said rods so that no trace of olive oil is left; sintering initially the said rod in a silver tube / alumina sager, making silver metal contacts at both ends of the initially sintered rod; finally sintering the assembly of the said rod and both end silver metal contacts. The rods obtained according to these aspects show desired and consistent values of transport current not less than 36 Amp, contact resistance not more than 0.015 μOhm-cm2 at 77K in self field and fracture strength not less than 140 MPa.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Compound winding made of Bi-based and Y-based high-temperature superconducting tapes
InactiveCN103035353BCost-effectiveSuperconducting magnets/coilsBobbinHigh-temperature superconductivity
A compound winding made of Bi-based and Y-based high-temperature superconducting tapes comprises a Bi-based superconducting coil (1), a Y-based superconducting coil (2), a superconducting coil bobbin (3), axial superconducting coil partitions (4), an upper coil support board (5), a lower coil support board (6) and coil-fixing screws (7). The Bi-based superconducting coil (1) is located in the middle of the compound winding, and the Y-based superconducting coil (2) is located on the end of the compound winding; and the compound winding is mounted in a low-temperature dewar comprising a low-temperature dewar barrel (8) and a low-temperature dewar top cover board (9), and is cooled by directly evaporated liquid nitrogen or the forced flow circulation of liquid nitrogen coupled with a refrigerator. The compound winding is mounted on the low-temperature dewar top cover board (9) through tie rods (10). The compound winding utilizes the characteristics of the Bi-based high-temperature superconducting tape, such as high self-field critical current, and the characteristics of the Y-based high-temperature superconducting tape, such as little critical current decrease in the external field, and can be made into an alternating-current winding and a direct-current winding.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Superconducting stack brazing method and mold for high-temperature superconducting current leads
InactiveCN101409129BThe brazing process is correctQuality improvementSuperconducting magnets/coilsHeat conductingMetallic materials
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vacuum welding apparatus and method for superconducting stacks of high temperature superconducting current leads
ActiveCN103071874BCut off the power supplyImprove cooling effectSoldering apparatusElectrical conductorVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses a vacuum welding device and a method for a high-temperature superconducting stack used for a large-sized magnet current lead. The vacuum welding device comprises an independent heating vacuum chamber, a cold base and a hot base, wherein the cold base and the hot base are arranged in the vacuum chamber. The interior of the vacuum chamber also comprises a movable welding die and a moving part which can be used for enabling the die to move in the vacuum chamber. After the welding die is contacted with the hot base through the moving part and heated to specified temperature, the welding die is separated from the hot base and is contacted with the cold base to realize rapid cooling. According to the vacuum welding device and the welding method, the superconducting stack is high in density, welding effect and current-carrying capability; and 7-stacked critical current measured under self-fields at 77K can reach 70 percent of the critical current of an original strip, and 4-stacked critical current exceeds the 80 percent critical current of the original strip. The superconducting stack can be applied to the large-sized magnet current lead as a discharge current conductor, and therefore, the effect of reducing heat emission and heat transfer of the lead is achieved, the cooling power is saved, and the operating environment of a magnet is improved.
Owner:INNOVA SUPERCONDUCTOR TECH
A self-field finite element analysis method for high-current superconducting conductors
ActiveCN106446483BAccurate and intuitive self-field 2D distributionDetermine the self-field coefficientDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorElement analysis
The invention provides a large-current superconductor self-field finite element analysis method. The method comprises the steps that a two-dimensional section of a superconductor is built, the finite element method is adopted for performing finite element magnetic field analyzing on the superconductor under the large-current testing condition, magnetic field distribution of the superconductor generated under the large-current operation condition is obtained, the self-field coefficient and position where the maximum magnetic field is generated on the superconductor are obtained, and therefore the appropriate magnitude of a background field for testing of the superconductor is determined and designed. Superconductor self-field analysis under the large-current testing condition is carried out by adopting the finite element method, the self-field two-dimensional distribution of the superconductor can be obtained through more accurate and visual analysis compared with an analysis method, the maximum magnetic field region of the superconductor can be obtained through visual analysis, the self-field coefficient of the conductor is determined, and therefore the reasonable magnitude of the background field for large-current testing of the superchanductor can be designed on the basis of the self-field coefficient.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH QINGDAO NEW ENERGY MATERIALS TECH RES INST CO LTD
a kind of laalo <base:sub> 3</base:sub> Preparation method of doped composite ybco thin film
ActiveCN105272203BPlay a pinning roleImprove current carrying capacitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesComposite filmChemical solution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a LAO (LaAlO3) doped composite YBCO film and belongs to the technical field of preparation of high-temperature superconducting materials. According to the method, organic La salt and Al salt are taken as precursor salts, a precursor solution is prepared with a chemical solution method and then applied to an LAO single crystal substrate with a spin coating method, and then a film is composited to the single crystal surface with a heating processing technology. According to the provided LAO doped composite film, the doping phase LAO can have a coherent boundary with YBCO, and the YBCO structure is not damaged while a pinning defect is introduced. An external solvent is not added, a system is simple, cost-saving, time for a sintering technology is shorter, and epitaxial growth of YBCO is not hindered while the LAO phase is formed. Je of a sample, doped with 5% of LAO, of the composite film under self-field is about 3 times of that of a pure YBCO film and is about 6 times of that of the pure YBCO film under an external field with 77 K and 1.5 T.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of rare earth barium copper oxygen high-temperature superconducting film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rare earth barium copper oxygen high-temperature superconducting film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a) weighing rare earth metal salt, barium salt, copper salt and a doping element compound according to a ratio, and dispersing the earth metal salt, the barium salt, the copper salt and the doping element compound into a solvent to obtain a precursor, wherein the doping element compound can generate doping element oxide at 300 to 650 DEG C and under the oxygen atmosphere; b) coating the precursor on a substrate to form a precursor film; c) placing the precursor film into a heat treatment furnace, introducing oxygen, heating the furnace to 300 to 650 DEG C, preserving heat for 0 to 5 hours, and introducing water vapor when the furnace temperature reaches 80 to 120 DEG C until thermal decomposition is finished; d) introducing oxygen nitrogen mixed gas and water vapor, heating the furnace to 700 to 825 DEC C, preserving heat for 20 to 250 DEG C, and stopping introducing the water vapor at the last 1 to 30 percent of time of heat preservation; and e) cooling the furnace to 400 to 500 DEG C and preserving heat for 0 to 240 minutes to obtain a product. According to the rare earth barium copper oxygen high-temperature superconducting film obtained by the preparation method, the thickness is more than 300 nm, the superconduction critical temperature is more than 90 K, and the critical current density at the temperature of 77 K and under the self-field condition is more than 1 mA / cm<2>.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com