Patents
Literature
111results about How to "Maximize signal to noise ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
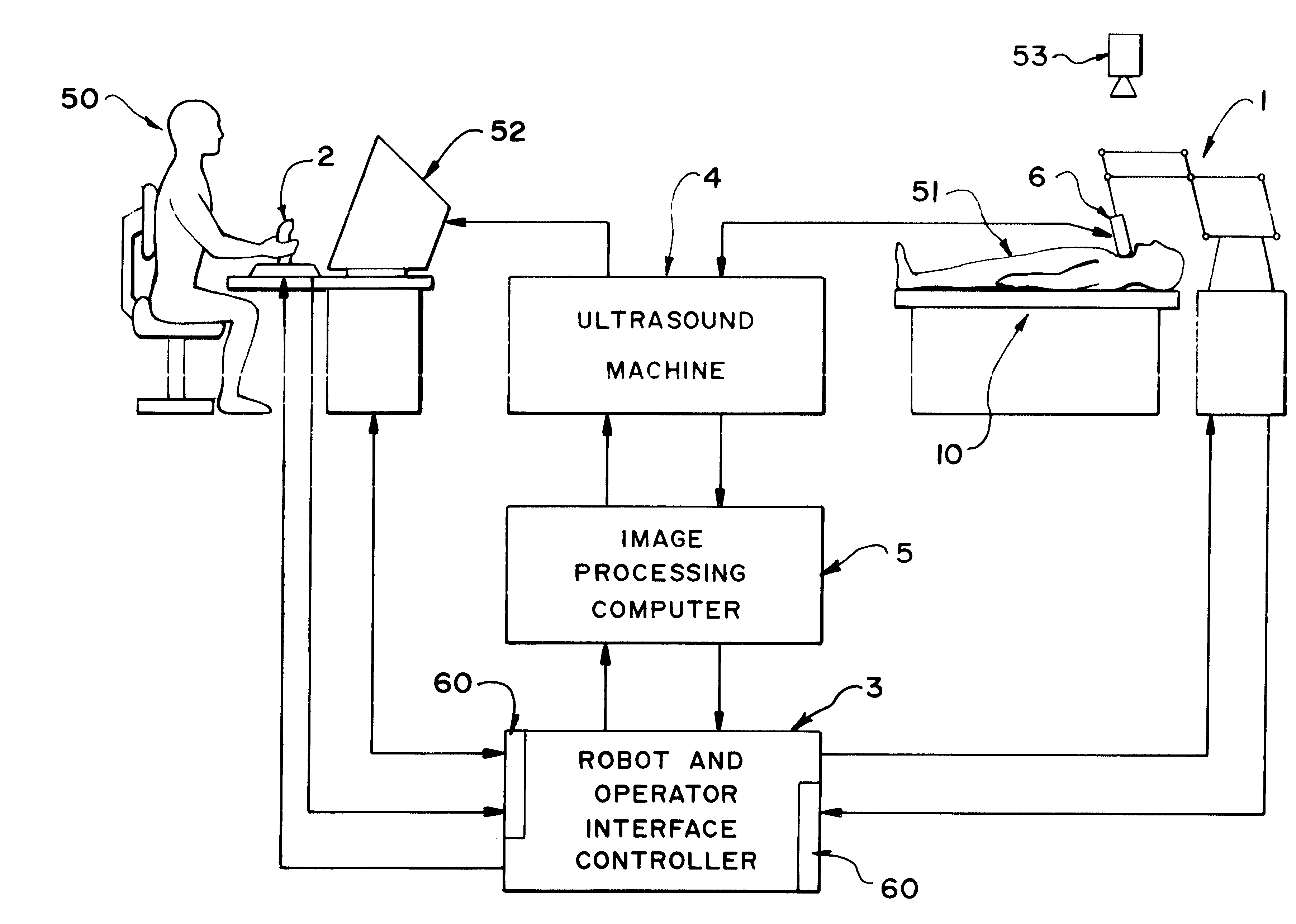
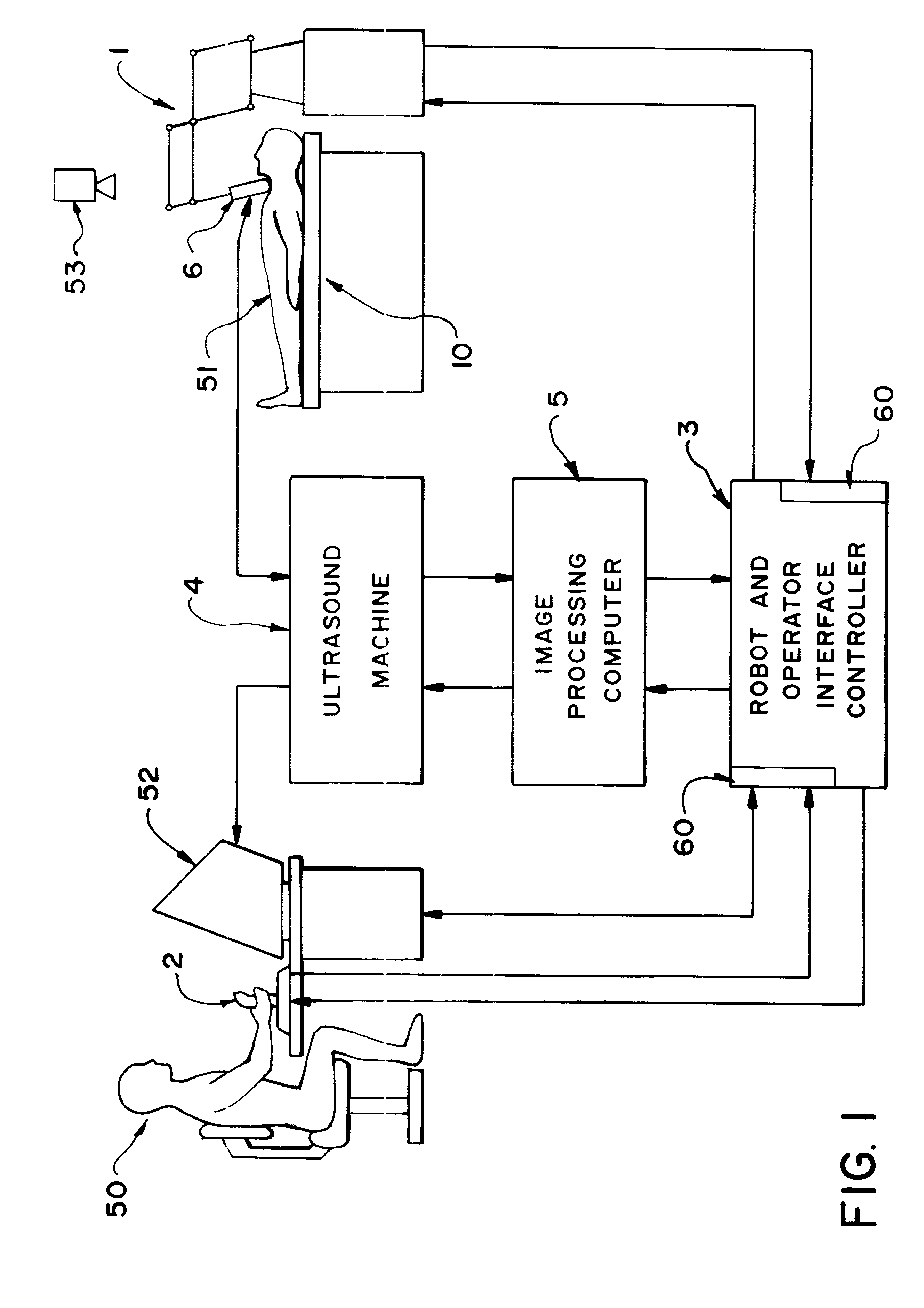
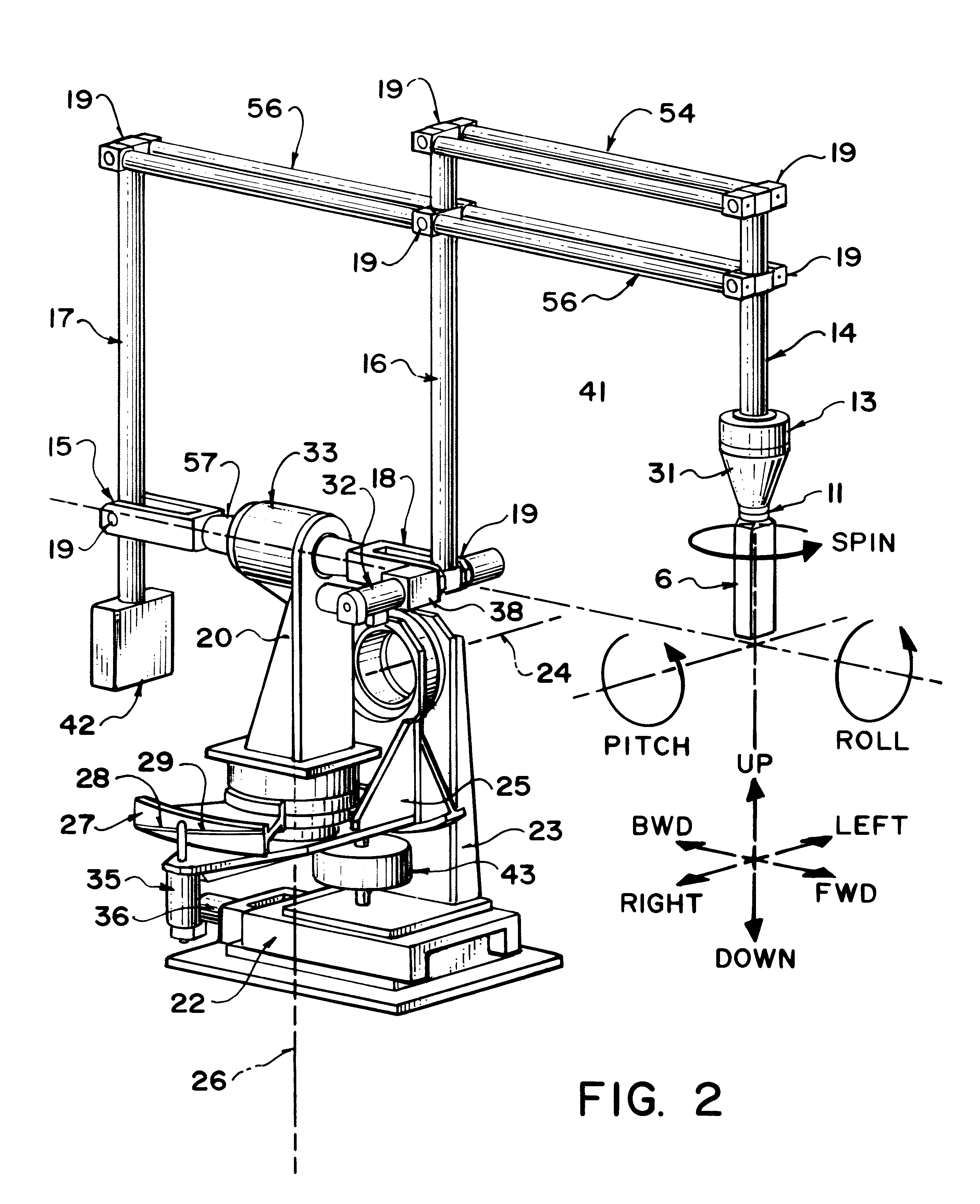
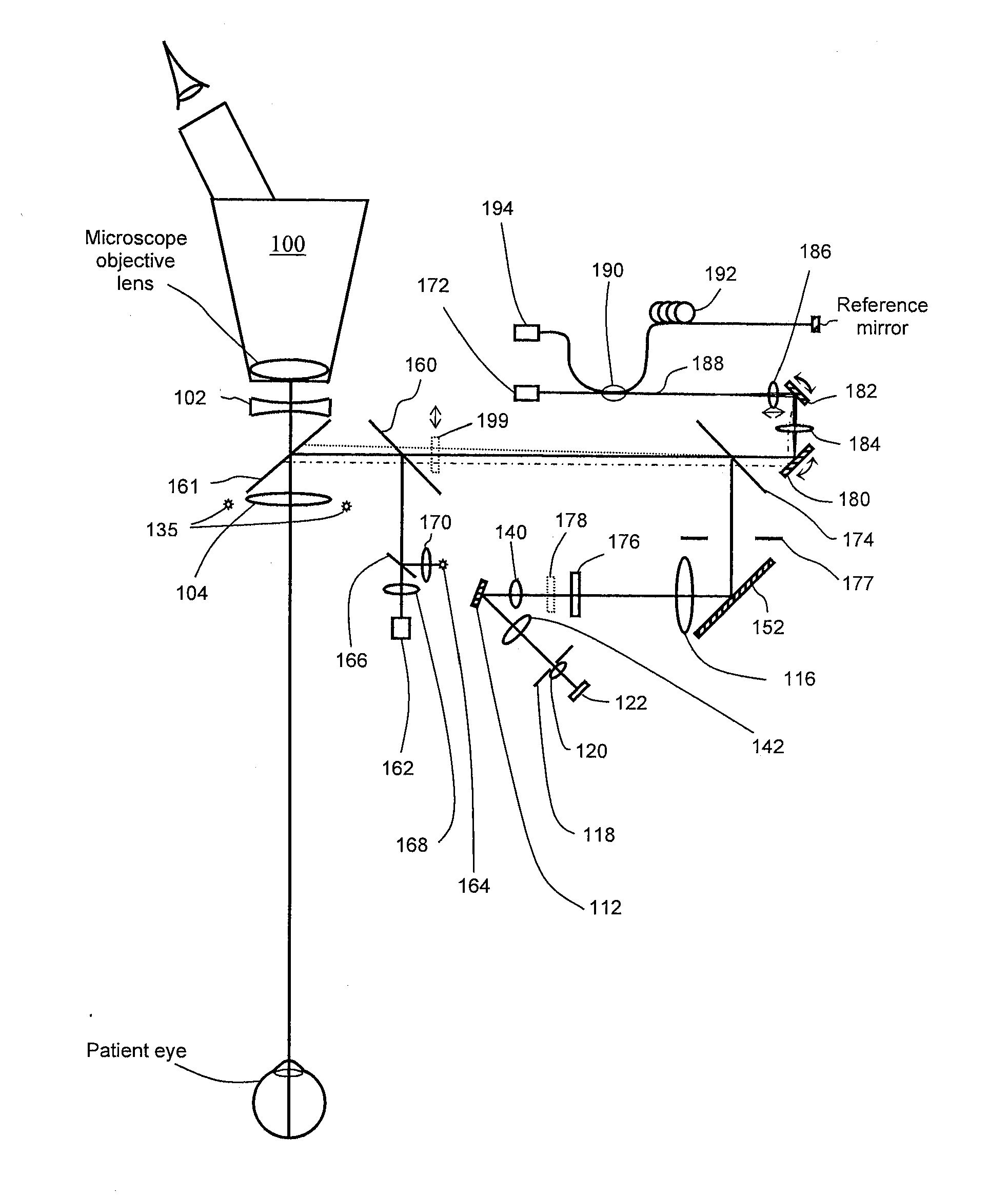
Robotically assisted medical ultrasound
InactiveUS6425865B1Maximize image signal-to-noise ratioMaximize signal to noise ratioBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionCo ordinateUltrasound image
A system for medical ultrasound in which the ultrasound probe is positioned by a robot arm under the shared control of the ultrasound operator and the computer is proposed. The system comprises a robot arm design suitable for diagnostic ultrasound, a passive or active hand-controller, and a computer system to co-ordinate the motion and forces of the robot and hand-controller as a function of operator input, sensed parameters and ultrasound images.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
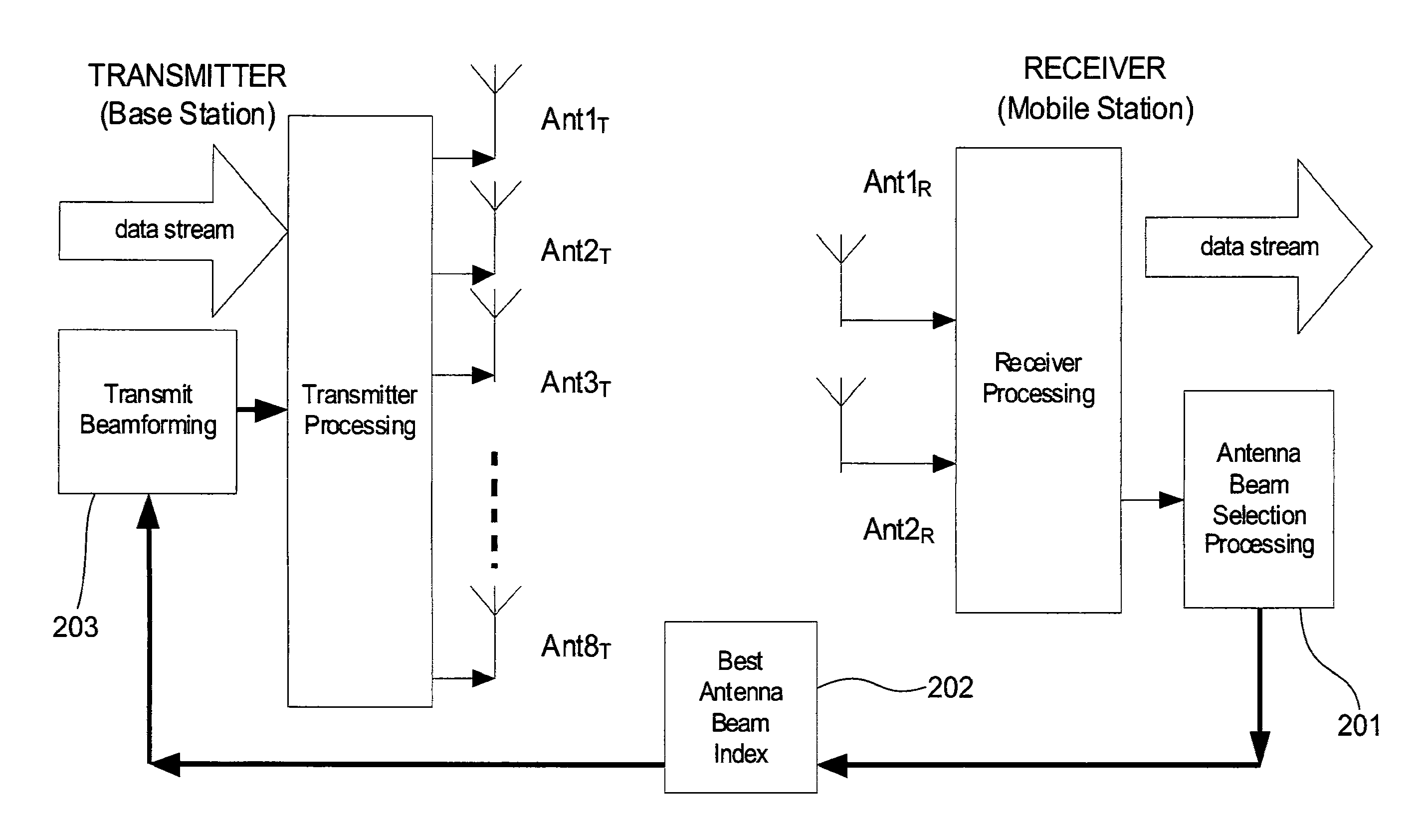
Method and apparatus of codebook-based single-user closed-loop transmit beamforming (SU-CLTB) for OFDM wireless systems
ActiveUS20090041150A1Improve throughputMaximize signal to noise ratioMultiple-port networksAntenna arraysCommunications systemClosed loop
A method includes broadcasting, at a transmitter, messages comprising antenna configuration, antenna spacing and a number of antenna of the transmitter and reference signals; generating, at a receiver, a codebook comprising a plurality of antenna beams based on the broadcasted messages; receiving, at the receiver, the broadcasted reference signals; selecting, at the receiver, an antenna beam among the plurality of antenna beams within the codebook in dependence upon a predetermined performance criteria of a data communication system and in dependence upon the broadcasted reference signals; feedbacking to the transmitter, at the receiver, information comprising the antenna beam selected by the receiver; optimizing, at the transmitter, a beamforming process by utilizing the feedback information from the receiver; transmitting, at the transmitter, data signals by utilizing the optimized beamforming process; and receiving and processing, at the receiver, the data signals in dependence upon the selected antenna beams within the codebook.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for locating/sizing contaminants on a polished planar surface of a dielectric or semiconductor material
ActiveUS7002675B2Simple and compact and portableMaximizes capturePolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsSemiconductor materialsHigh numerical aperture
To locate / size contaminants at the surface of a dielectric or semiconductor material, a P-polarized beam of light from a monochromatic solid-state source is disposed specifically at Brewster's angle and focused to form an illuminated quasi-elliptical spot on the surface that produces effectively no reflected or scattered light from the surface. The spot is scanned over the entire surface so as to assure multiple passes of any contaminant through the spot. On each pass through the spot a contaminant will produce scattered light. A novel high numerical aperture reflective or refractive system is disposed above the surface to always view the spot and to collect / redirect the bulk of the contaminant scattered light to a detector. Illumination at Brewster's angle combined with the high numerical aperture scattered light collector / redirector maximizes the signal-to-noise ratio from the detector. These core components are packaged with support subsystems as a uniquely compact and portable apparatus.
Owner:SYNETICS SOLUTIONS +2
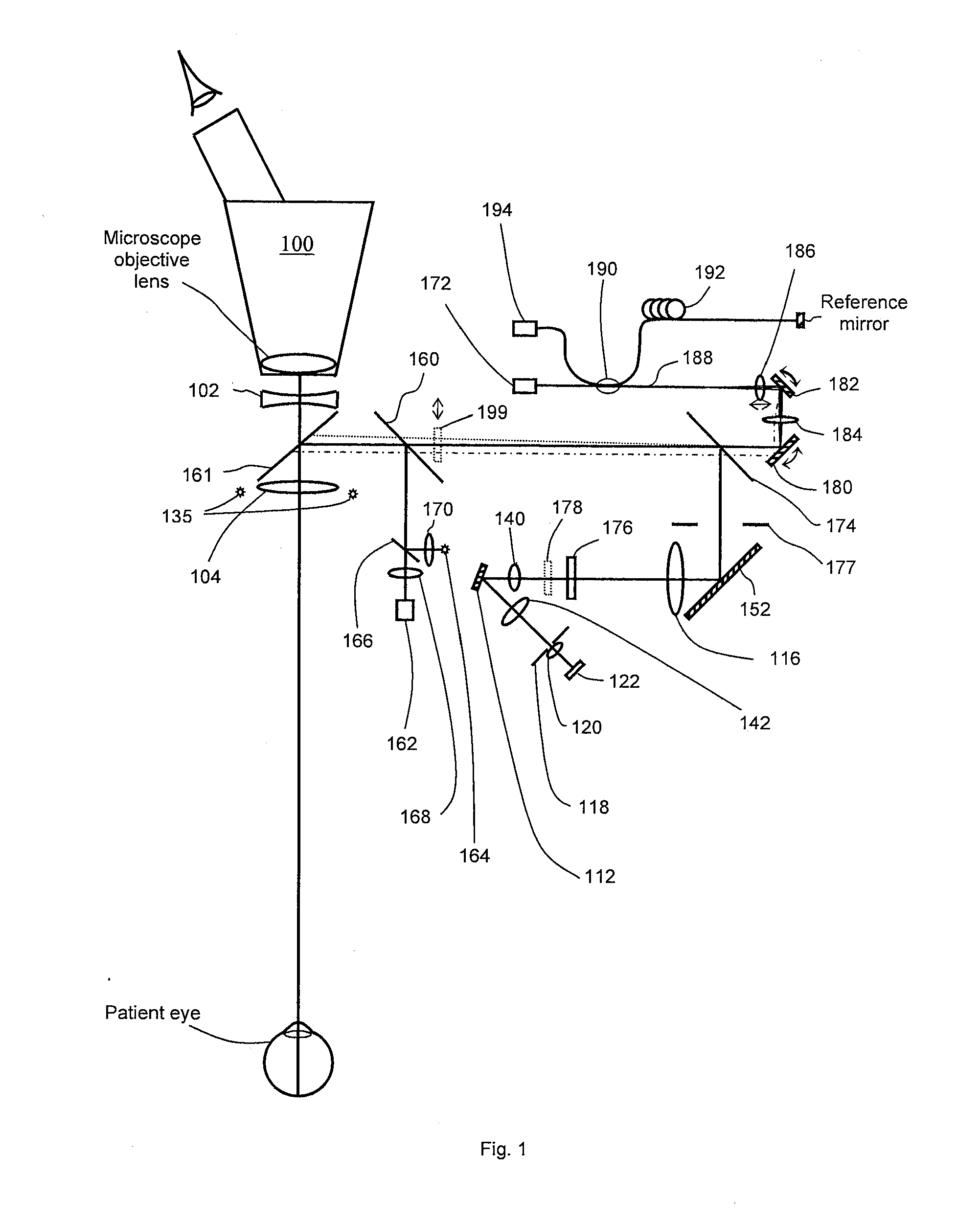
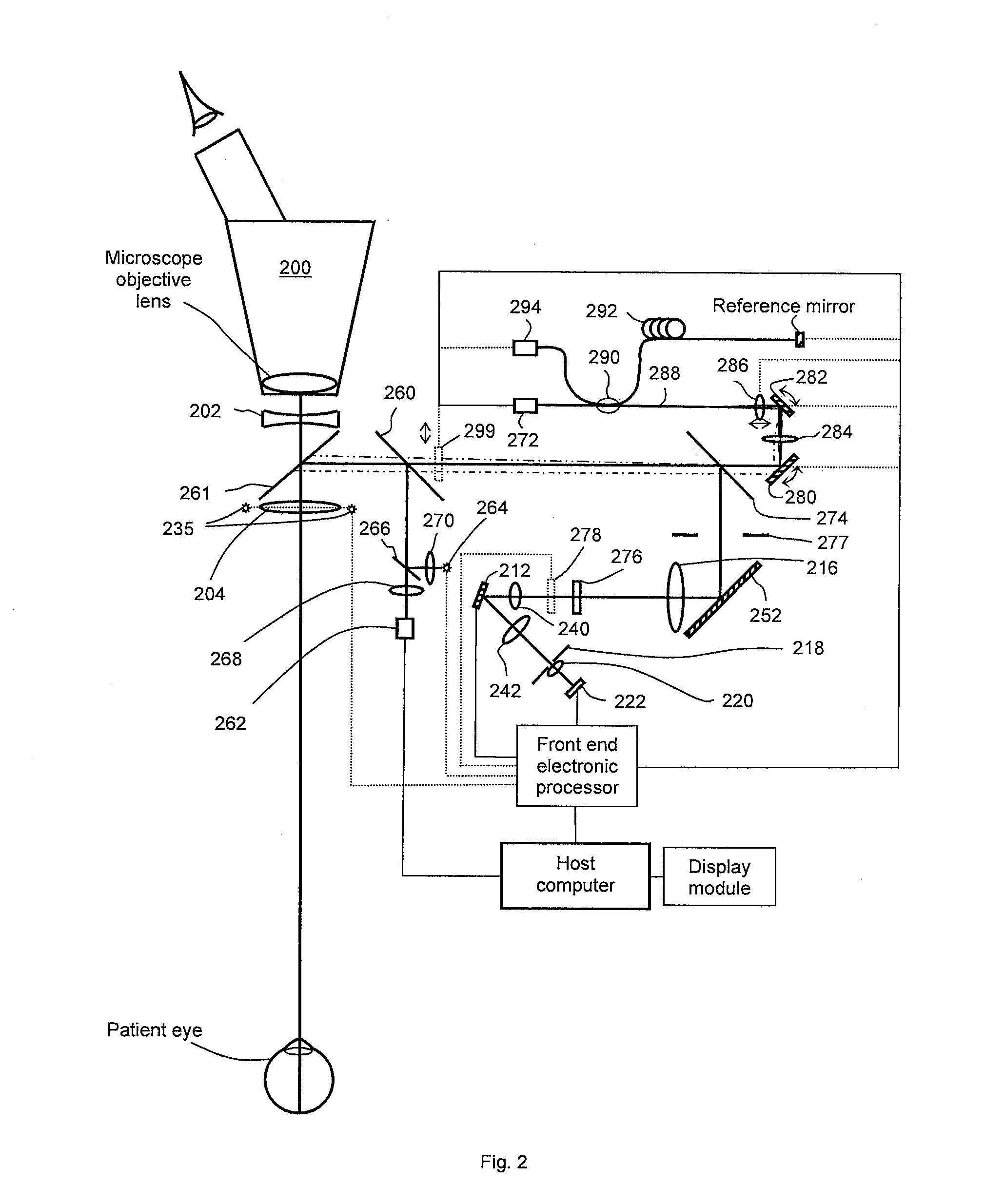
Optical mapping apparatus with optimized OCT configuration
InactiveUS6927860B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce the amount of solutionInterferometersScattering properties measurementsFace scanningBeam splitter
OCT apparatus includes an interferometer, having an input beam splitter and a 50 / 50 output splitter. The splitting ratio of the input splitter may be optimized depending on the source power of light source and on the mismatch of the balanced receiver. The input splitter is a plate beam-splitter to minimize the stray reflected light in the interferometer and allow sequential operation of the apparatus in the OCT or in the confocal regime. The switching between the two regimes may be at will, or synchronous with the en-face scanning which results in quasi-simultaneous OCT / confocal imaging or in alternatives frames, confocal and OCT. By using polarization sensitive elements, two channels are provided in each regime, OCT and confocal. The two confocal polarization sensitive channels may allow adjustments of compensators prior to OCT measurements or OCT imaging.
Owner:OPTOS PLC
Implantable Systemic Blood Pressure Measurement Systems and Methods
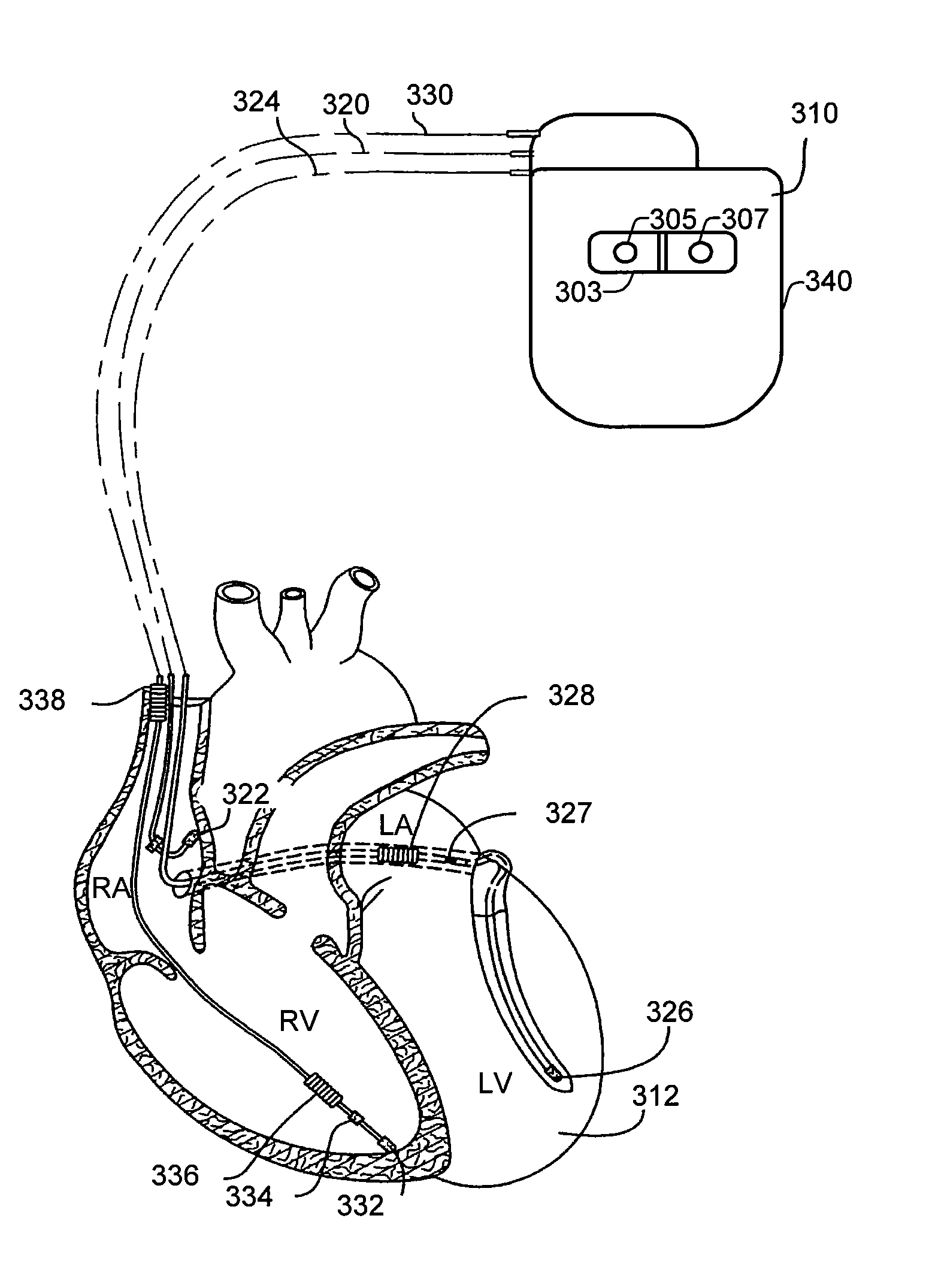
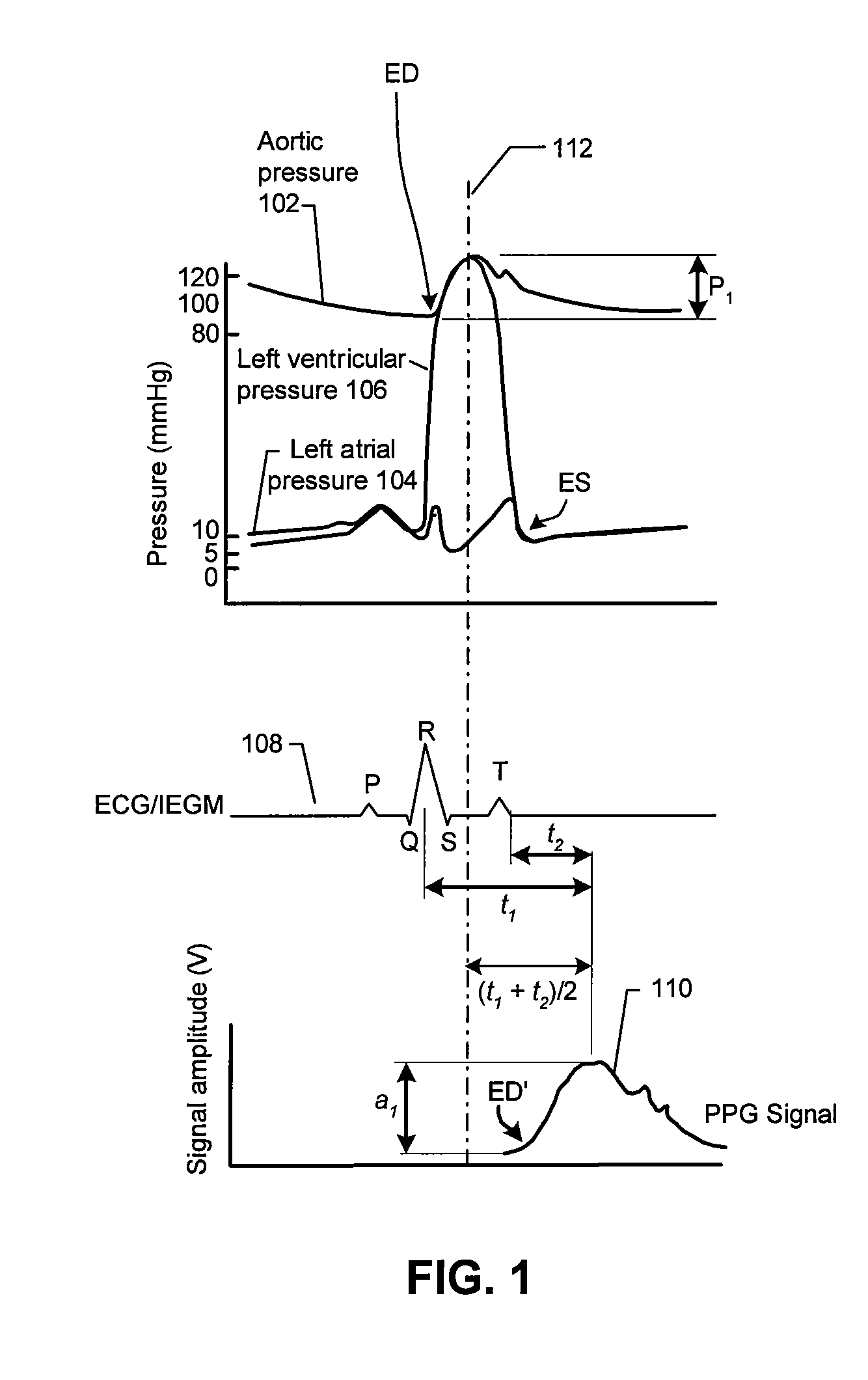
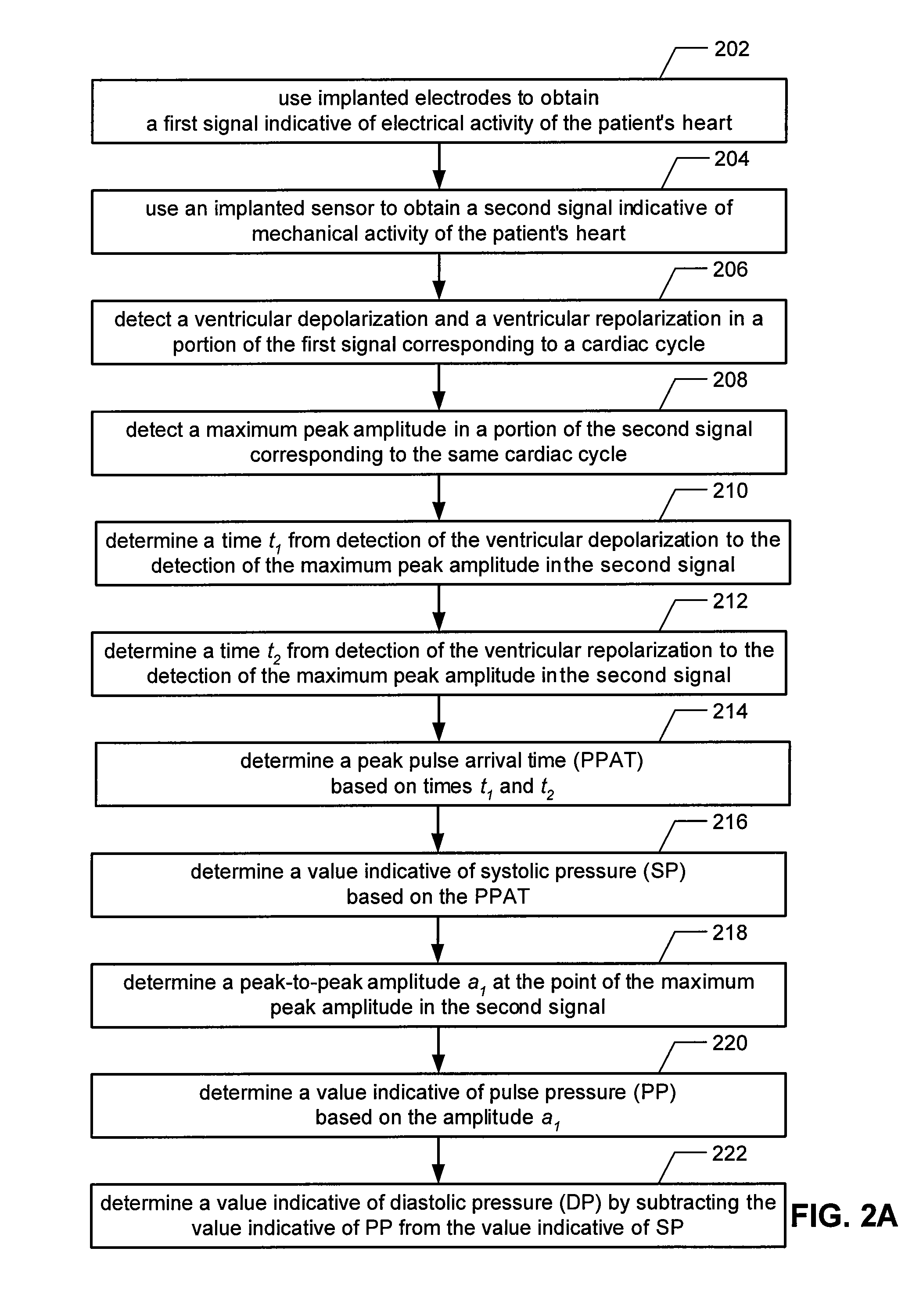
ActiveUS20090062667A1Maximize signal to noise ratioIncreased susceptibilityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyElectricityBlood arterial
Implantable systems, and methods for use therewith, for monitoring arterial blood pressure on a chronic basis are provided herein. A first signal indicative of electrical activity of a patient's heart, and a second signal indicative of mechanical activity of the patient's heart, are obtained using implanted electrodes and an implanted sensor. By measuring the times between various features of the first signal relative to features of the second signal, values indicative of systolic pressure and diastolic pressure can be determined. In specific embodiments, such features are used to determine a peak pulse arrival time (PPAT), which is used to determine the value indicative of systolic pressure. Additionally, a peak-to-peak amplitude at the maximum peak of the second signal, and the value indicative of systolic pressure, can be used to determine the value indicative of diastolic pressure.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Wafer inspection
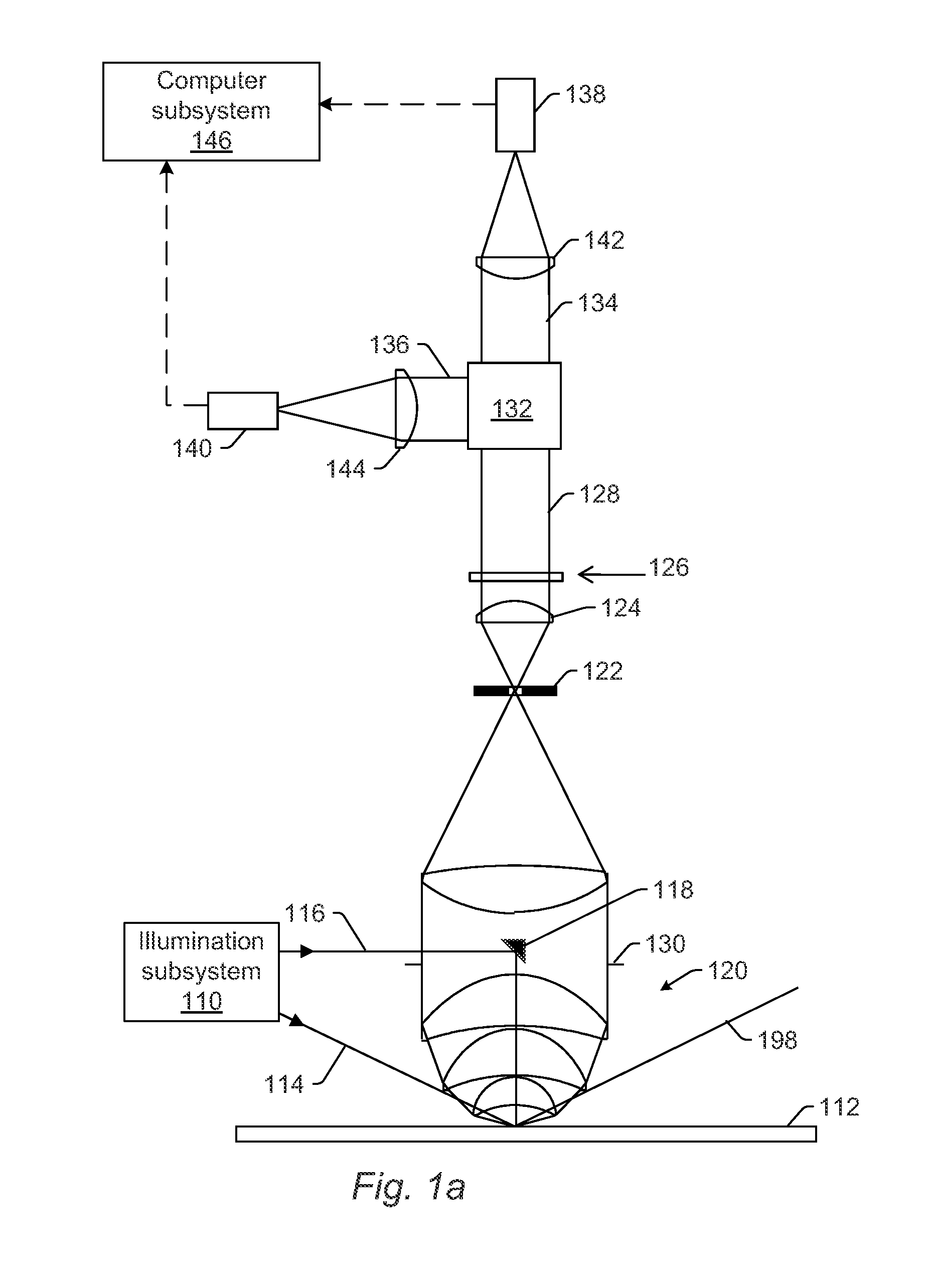
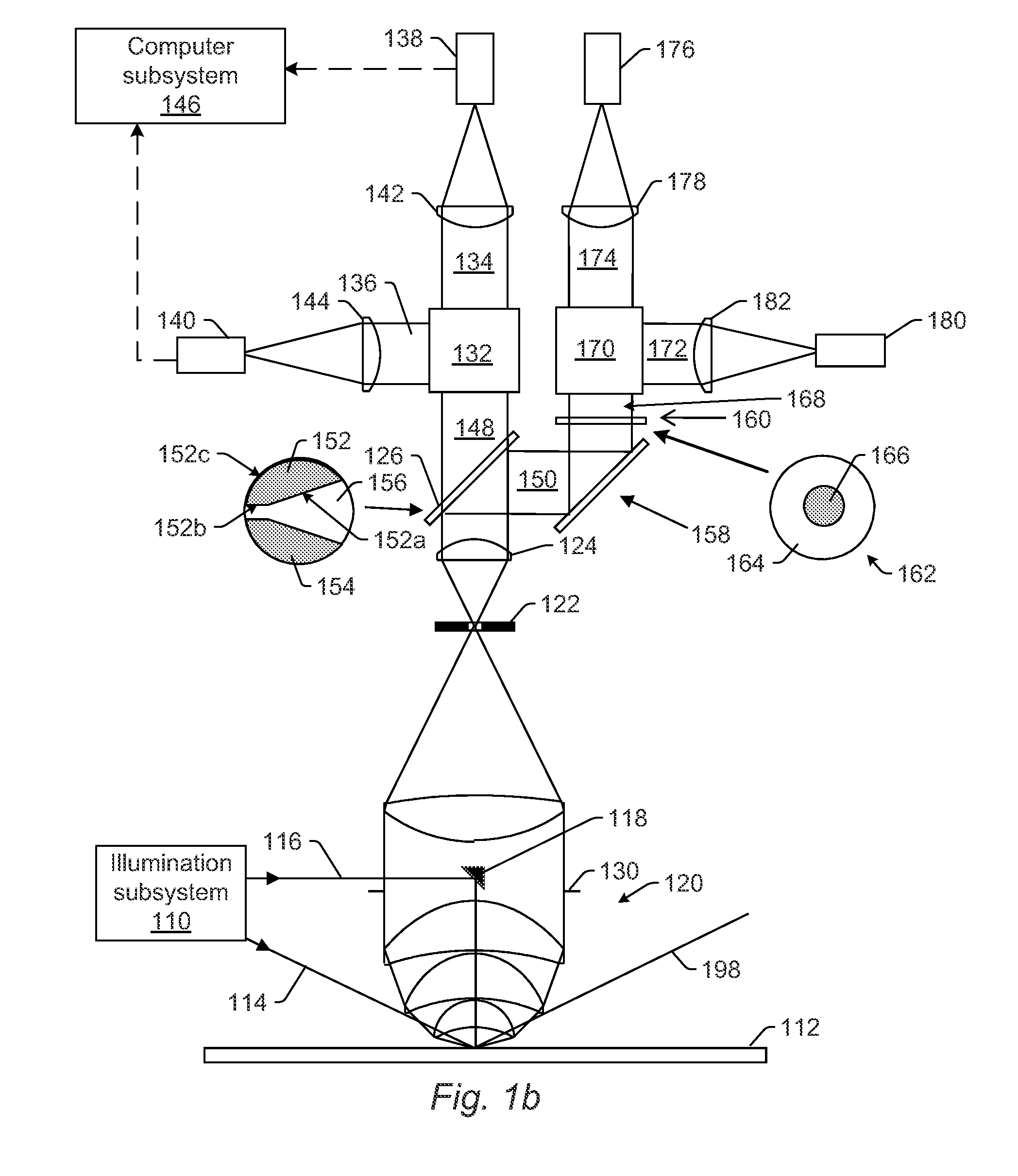
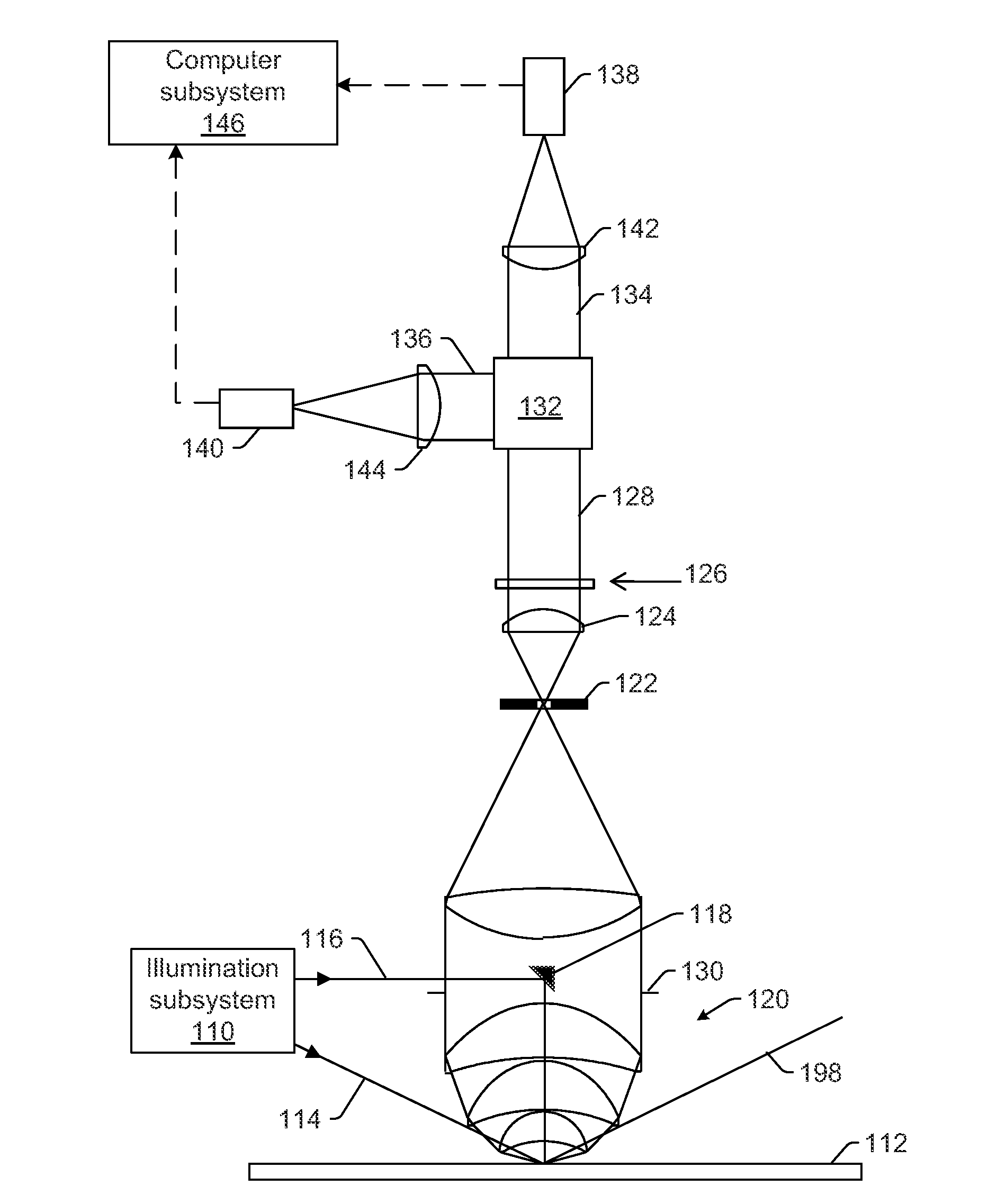
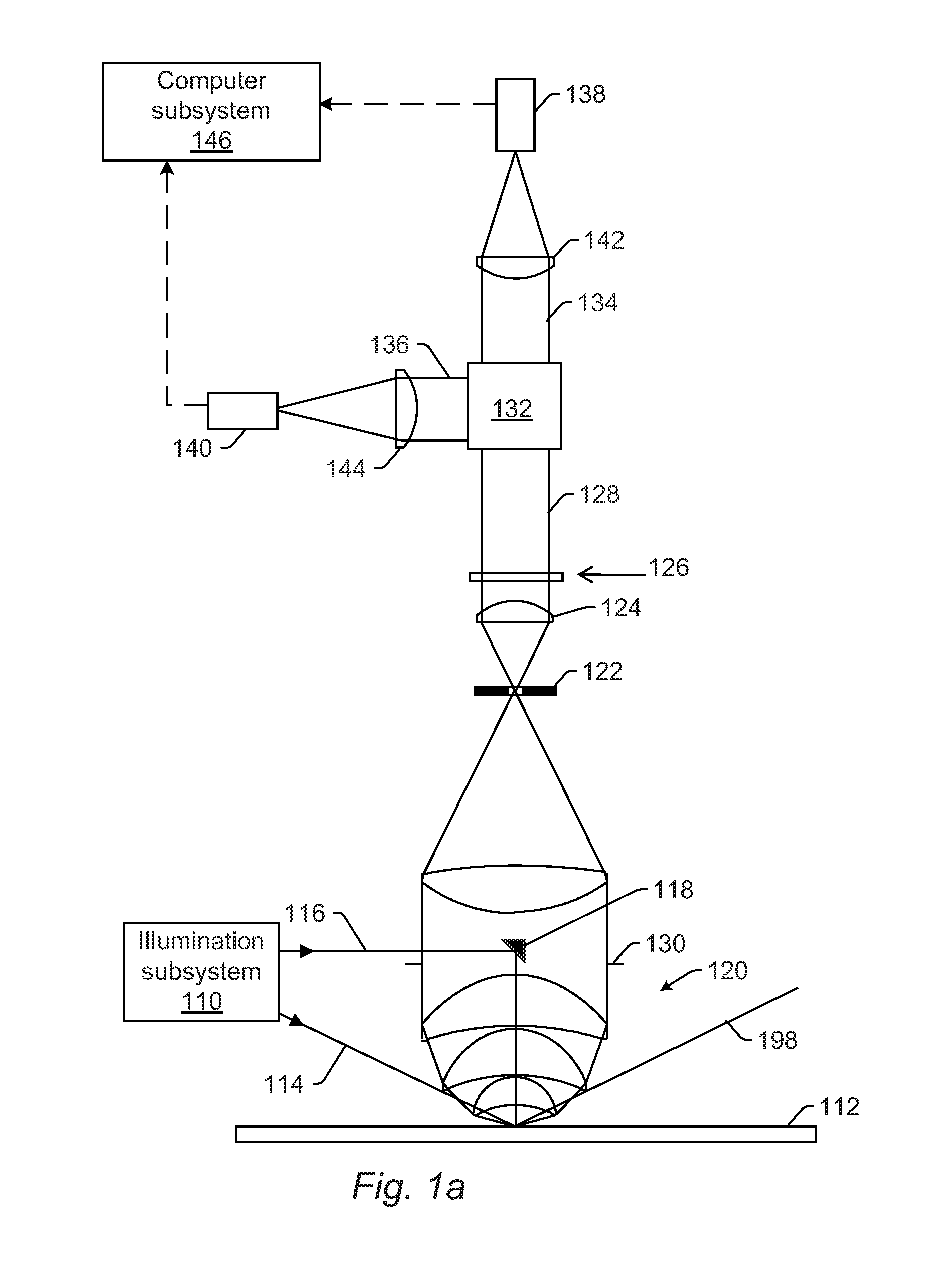
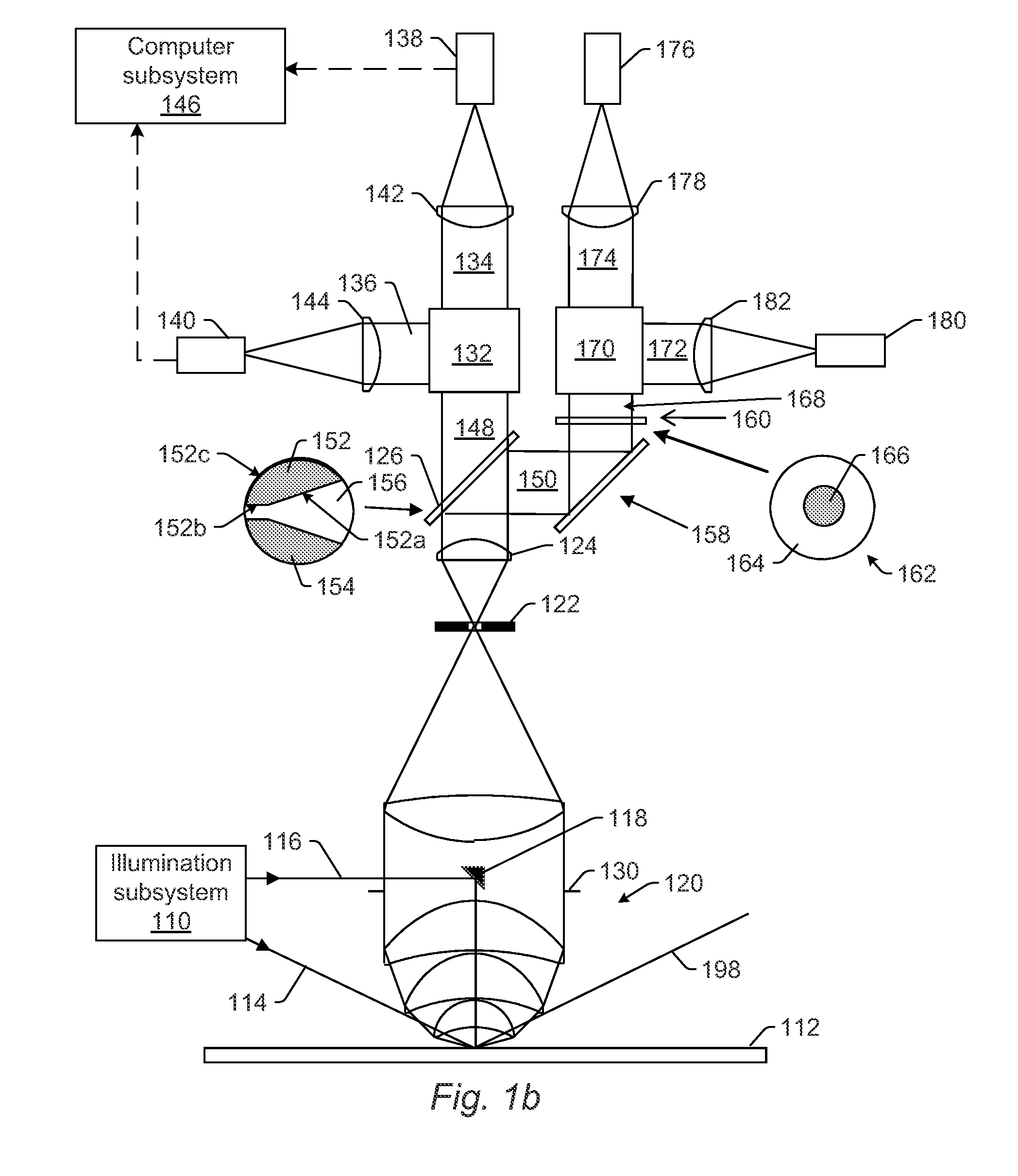
ActiveUS8891079B2High sensitivityMaximize signal to noise ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesOptical polarizationNumerical aperture
Owner:KLA CORP
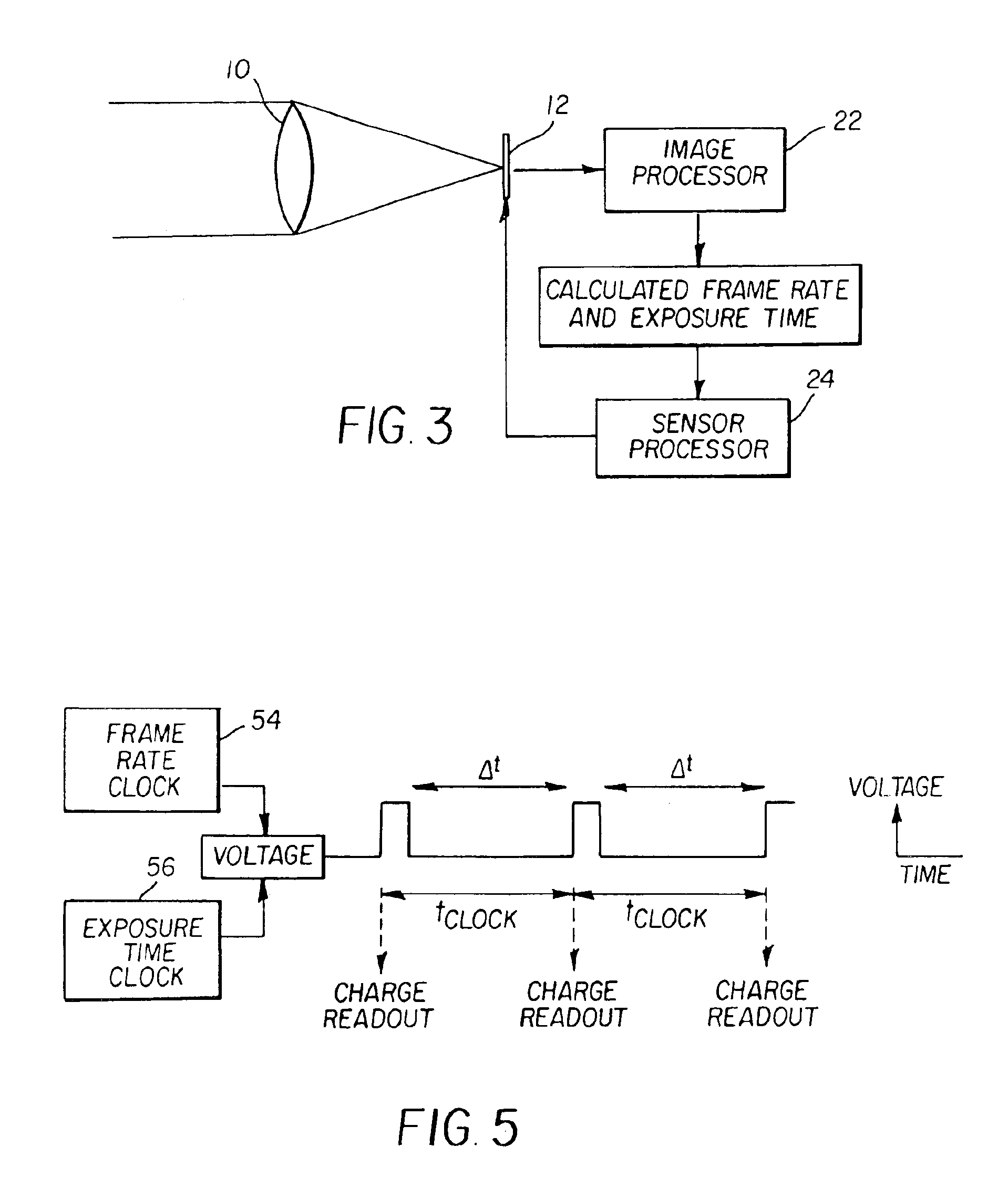
Method and adaptively deriving exposure time and frame rate from image motion
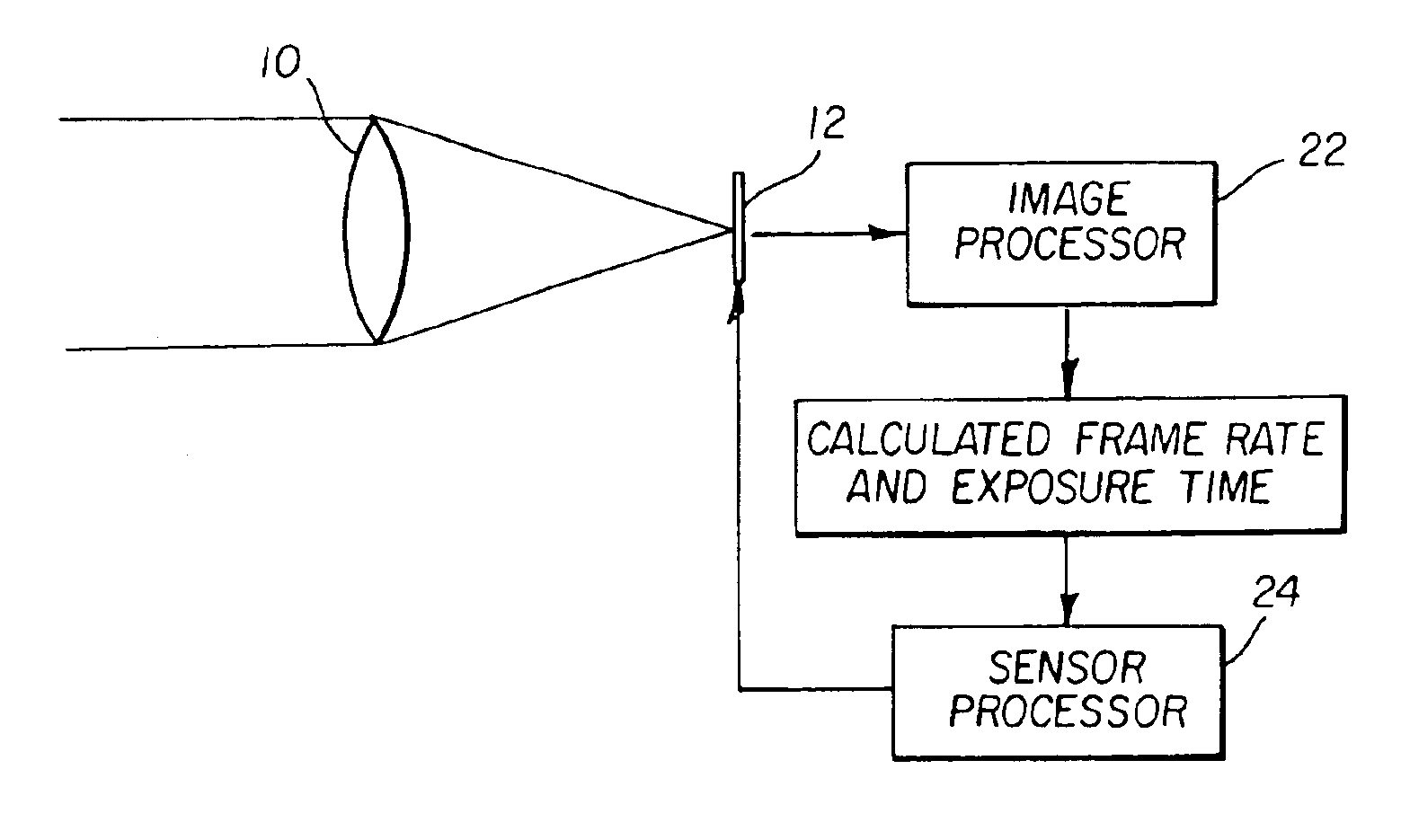
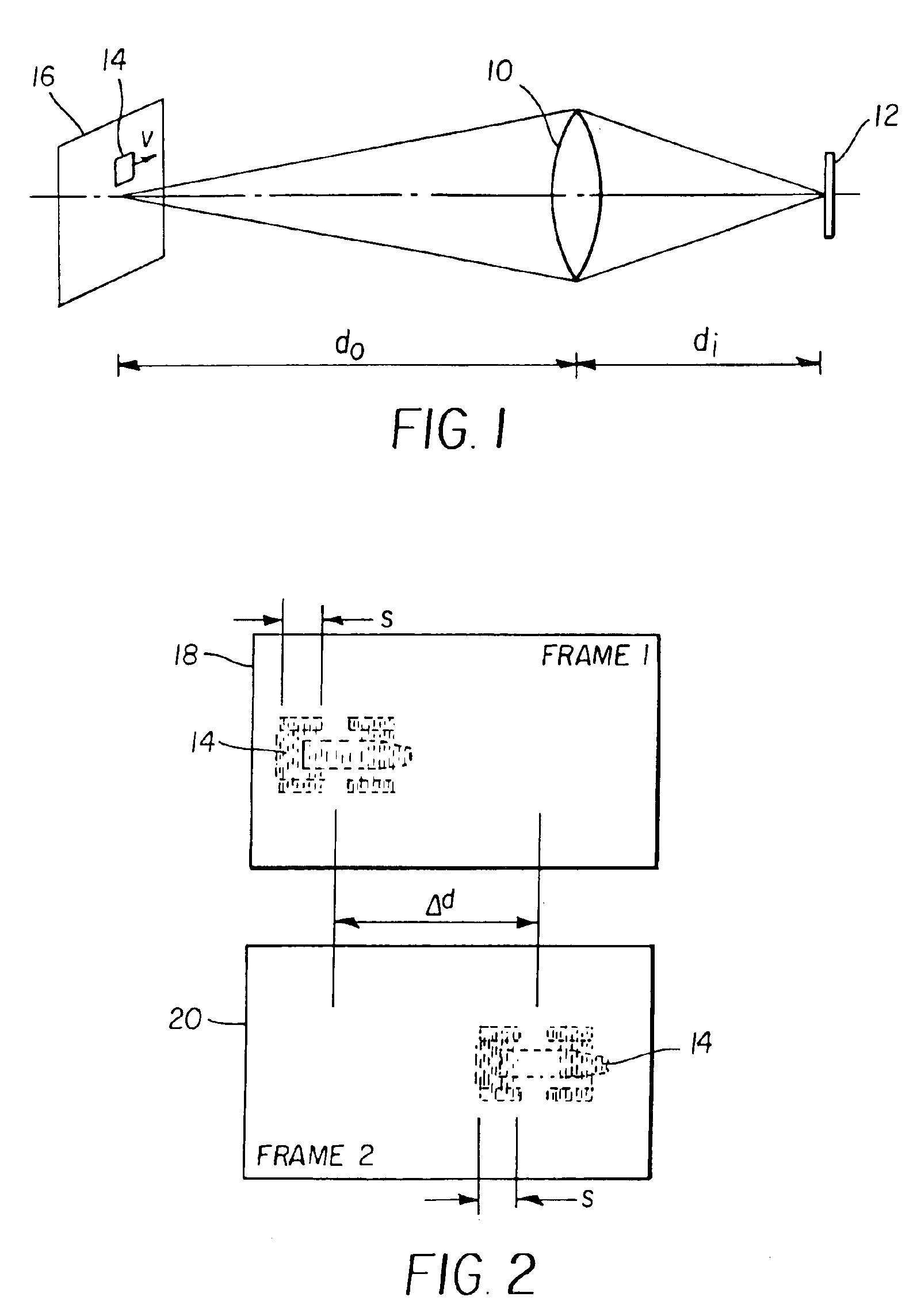
InactiveUS6891570B2Maximize signal to noise ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
In a method for determining the frame rate and exposure time for each frame of a video collection, an image capture system acquires at least two successive frames of a scene, separated in time. The two images are compared to determine if objects in the scene are in motion. If motion is detected, then the speed and displacement of the objects that are moving is determined. If the speed of the fastest moving object creates an unacceptable amount of image displacement, then the frame rate for the next frame is changed to one that produces an acceptable amount of image displacement. Also, if the speed of the fastest moving object creates an unacceptable amount of motion blur, then the exposure time for the next frame is changed to one that produces an acceptable amount of motion blur.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
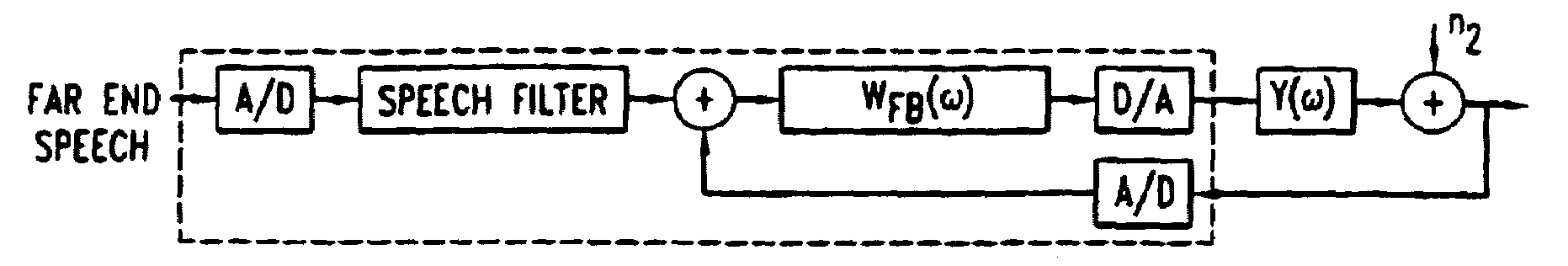
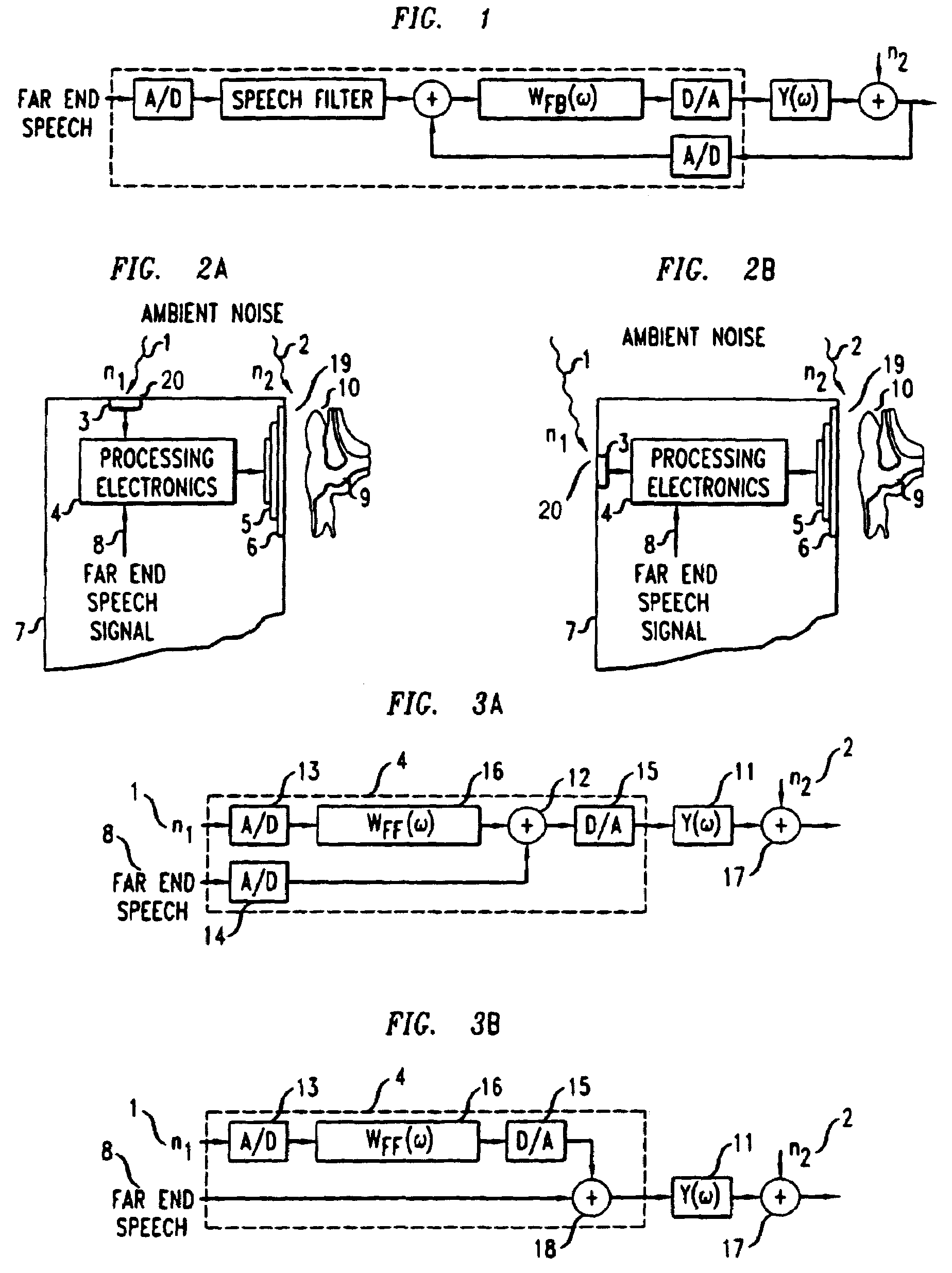
Telephonic handset employing feed-forward noise cancellation
InactiveUS7031460B1Effective noise cancellationRobust against inter-user variabilityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsEar treatmentNoise fieldIir filtering
A telephonic handset comprises an active noise reduction (ANR) system. The ANR system comprises a reference microphone and an IIR filter. The IIR filter is receivingly coupled to the reference microphone with respect to noise reference signals, and it is transmittingly coupled to the receiver transducing element of the handset. The ANR system is configured as a fixed feed-forward noise cancellation system. Preferably, the IIR filter has a transfer function derived, in part, from the open-loop gain of a feedback noise cancellation system.In specific embodiments of the invention, the noise reference microphone is situated so as to sample the ambient noise field near the front face of the receiver, but without directly sampling the noise field on the front face.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
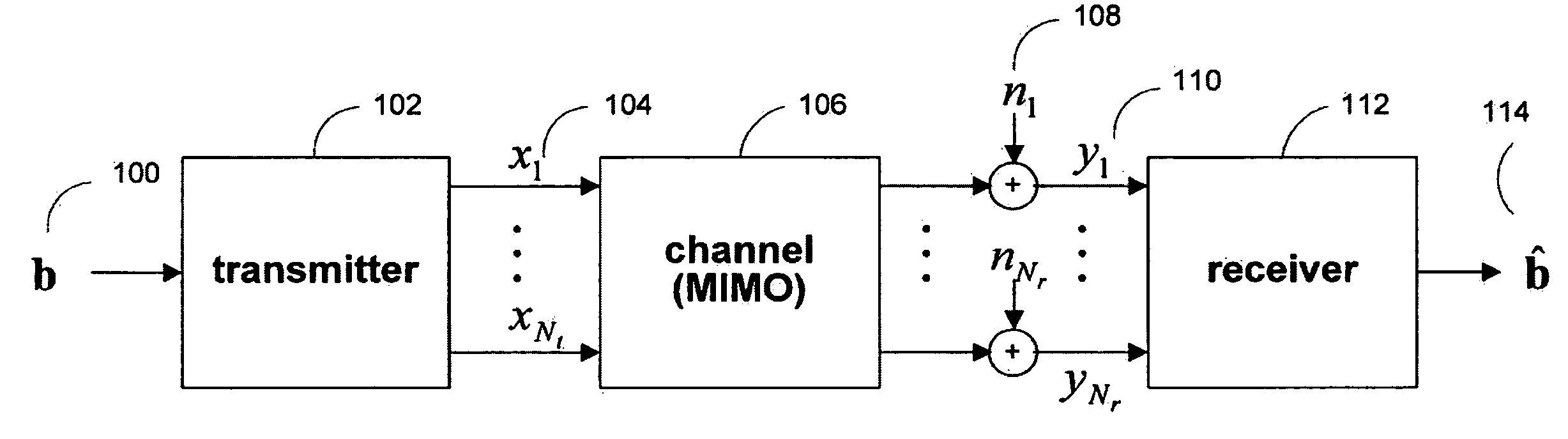
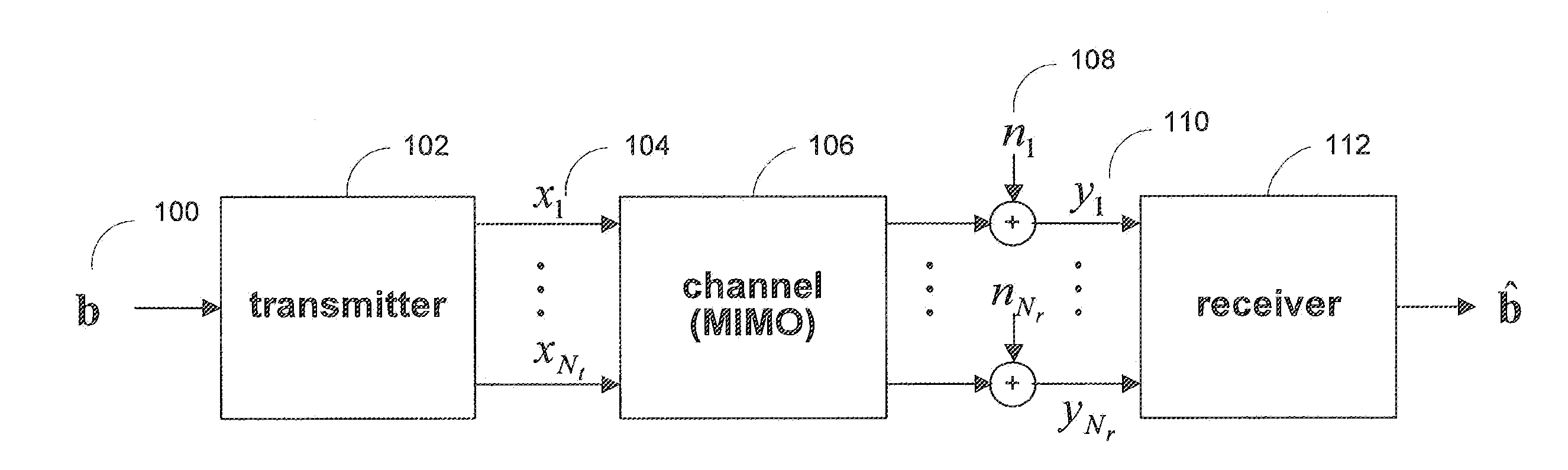
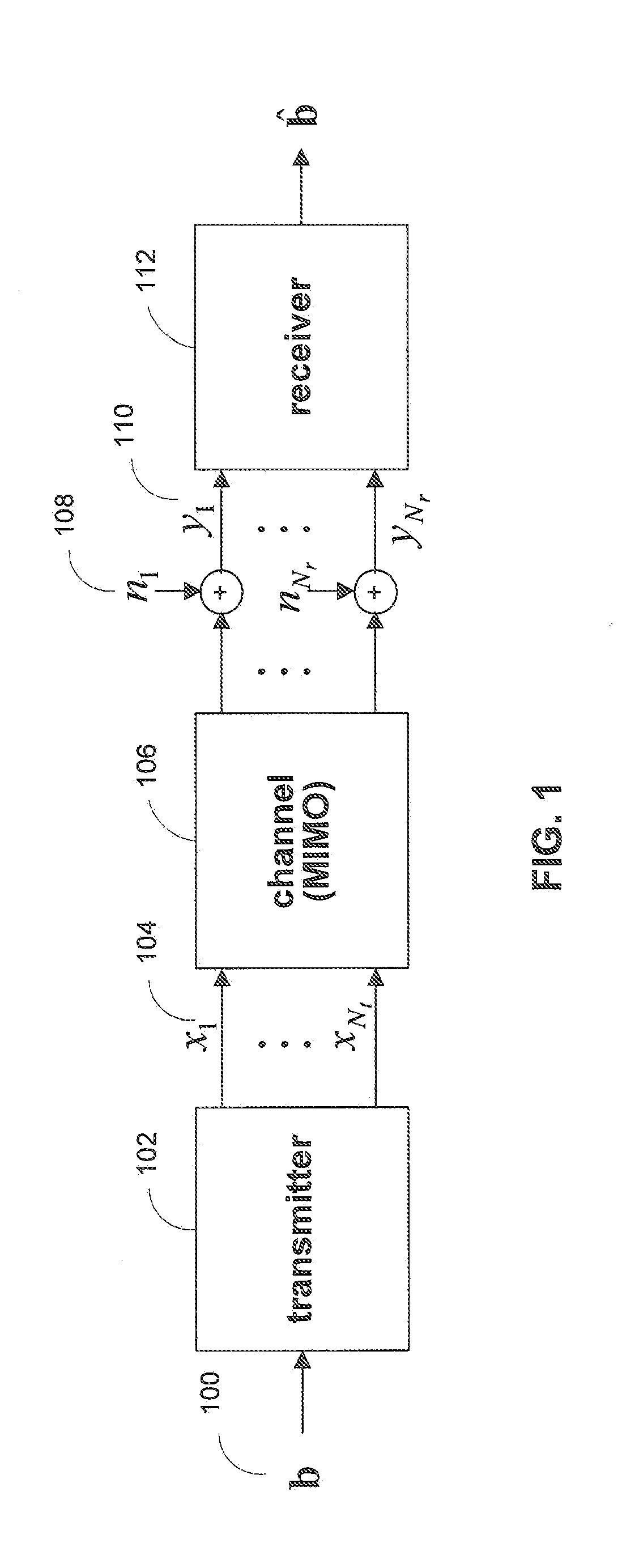
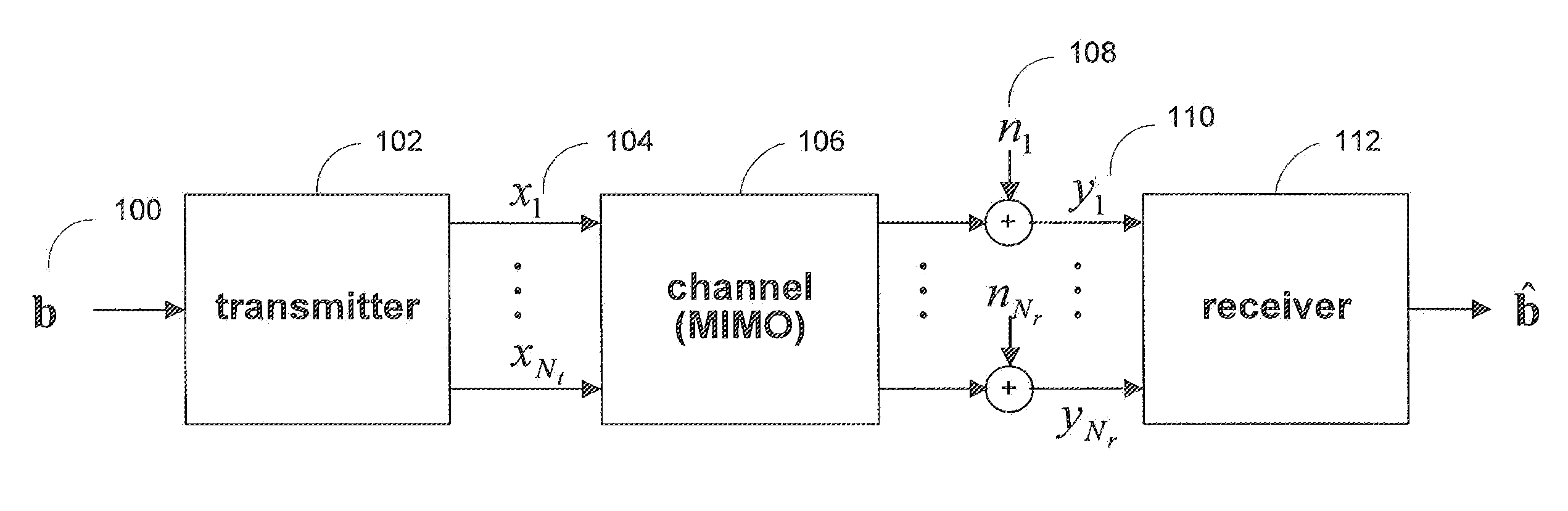
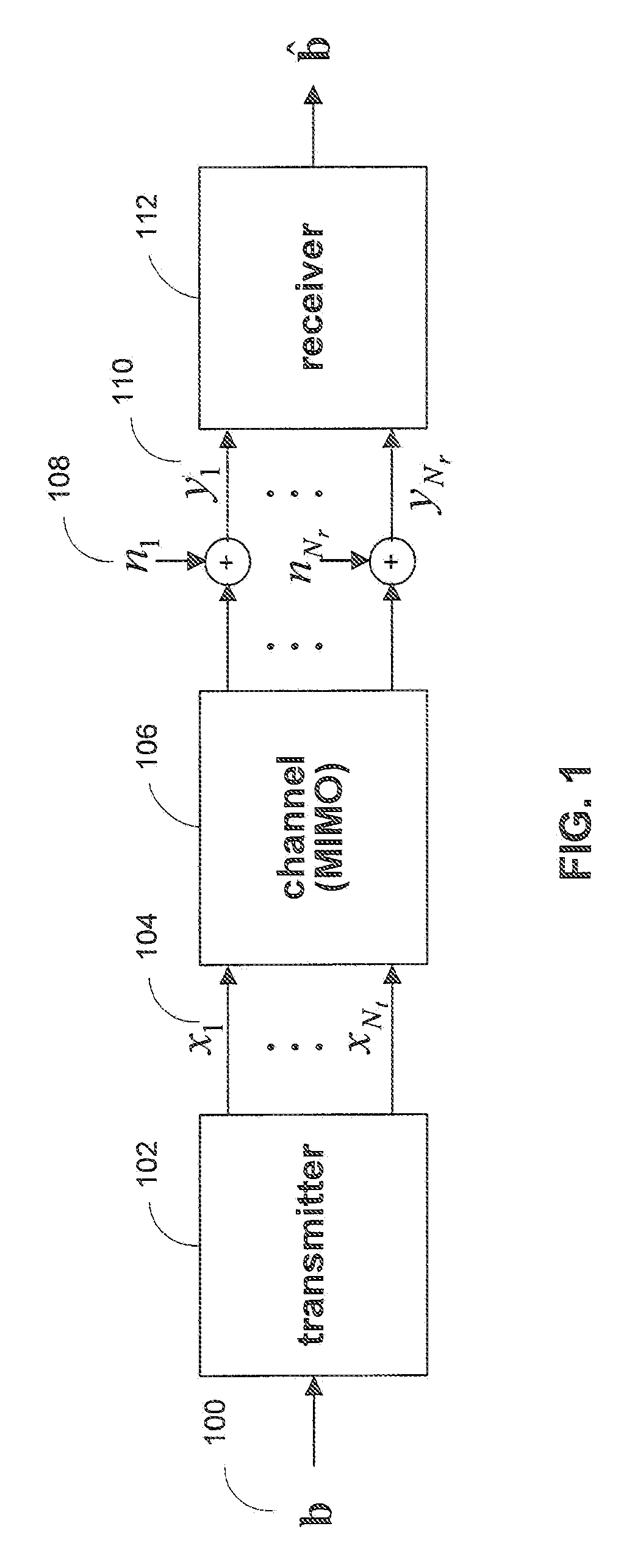
Maximal ratio combining of equalized symbols for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS20080037670A1Maximize signal to noise ratioPrevent magnitudeEqualisersSecret communicationLinearizationMimo systems
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors based on the same transmitted vector. The receiver linearizes each received signal vector using one or more zero-forcing, MMSE, or other suitable linear equalizers. The components of the equalized signal vectors may be combined using maximum-ratio combining to form the components of a combined equalized signal vector. The components of the combined equalized signal vector may then be decoded individually using a linear decoder.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Apparatus and method for operating a real time large diopter range sequential wavefront sensor
InactiveUS20140055749A1Easy maintenanceMaximize signal to noise ratioLaser surgeryOptical measurementsWavefront sensorLight beam
A sequential wavefront sensor includes a light source, a beam deflecting element, a position sensing detector configured to output a plurality of output signals and a plurality of composite transimpedance amplifiers each coupled to receive an output signal. The output of each composite transimpedance amplifier is phase-locked to a light source drive signal and a beam deflecting element drive signal.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Nanoscale probes for electrophysiological applications
InactiveUS20070187840A1Improve spatial resolutionMaximize signal to noise ratioMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice formEngineering
A device comprising a planar integrated circuit that includes an array of electrodes and at least one nanostructure, having a major axis, in electrical contact with at least one electrode. The device forms an interface between an integrated circuit platform and electro-physiologically active cells and is used in manipulate the same.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
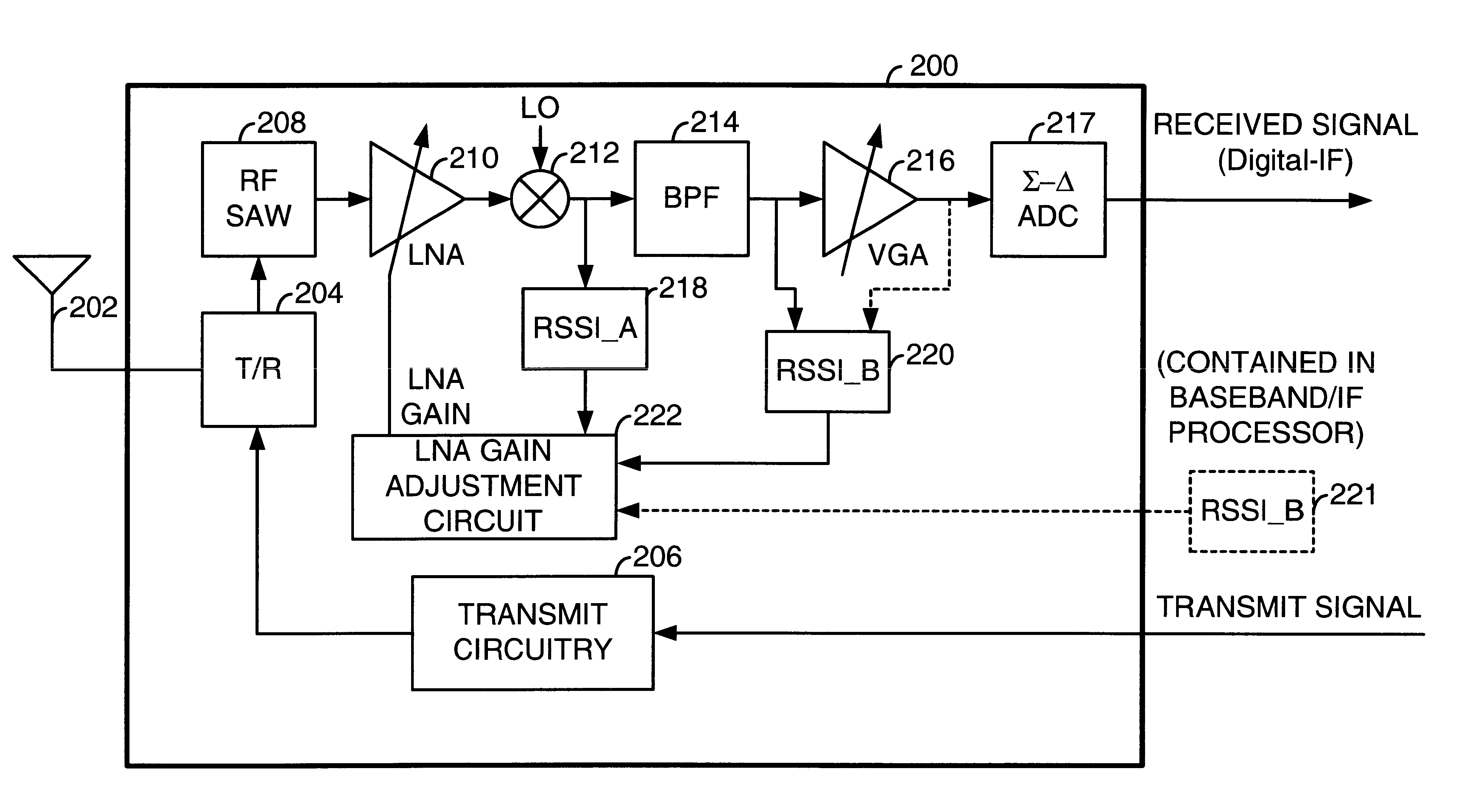
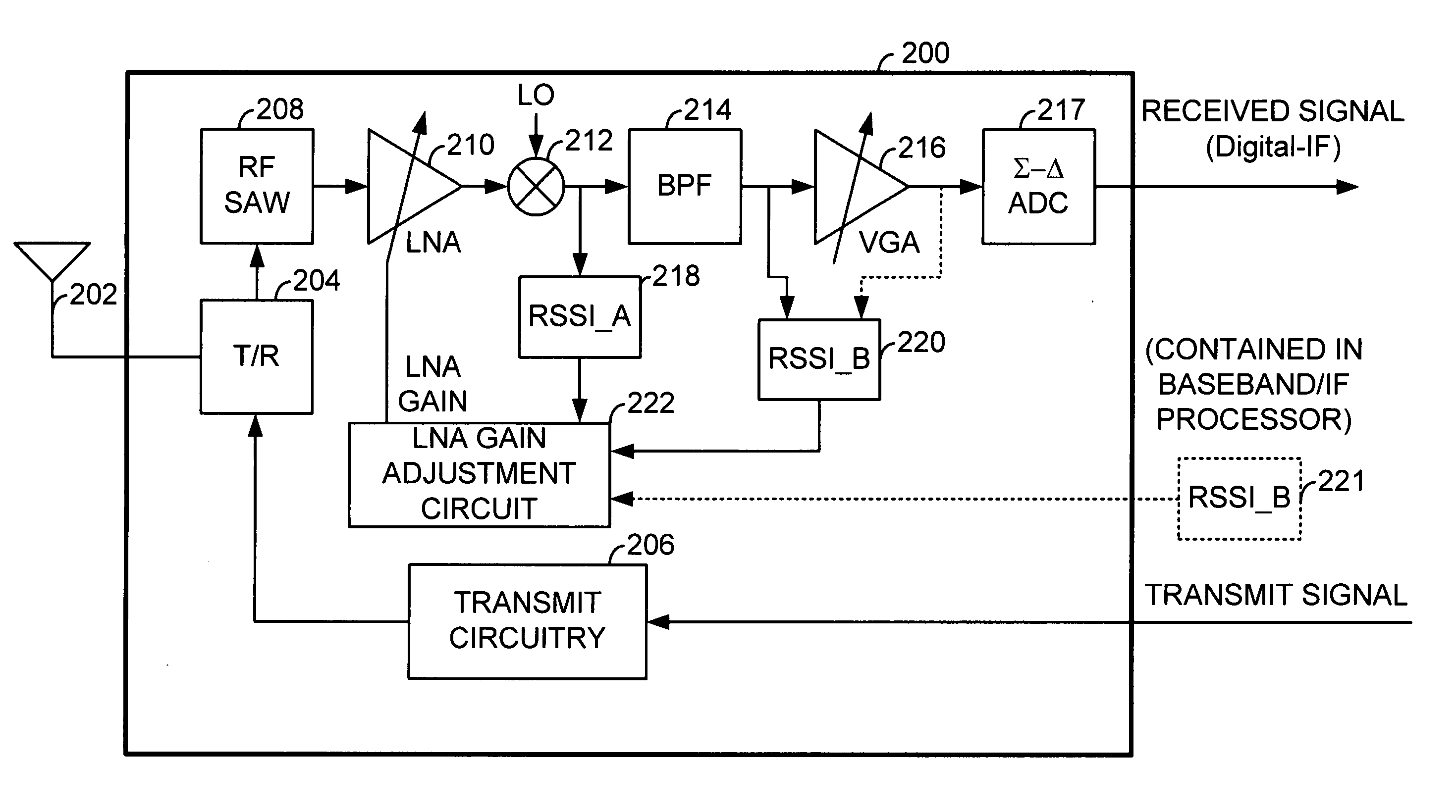
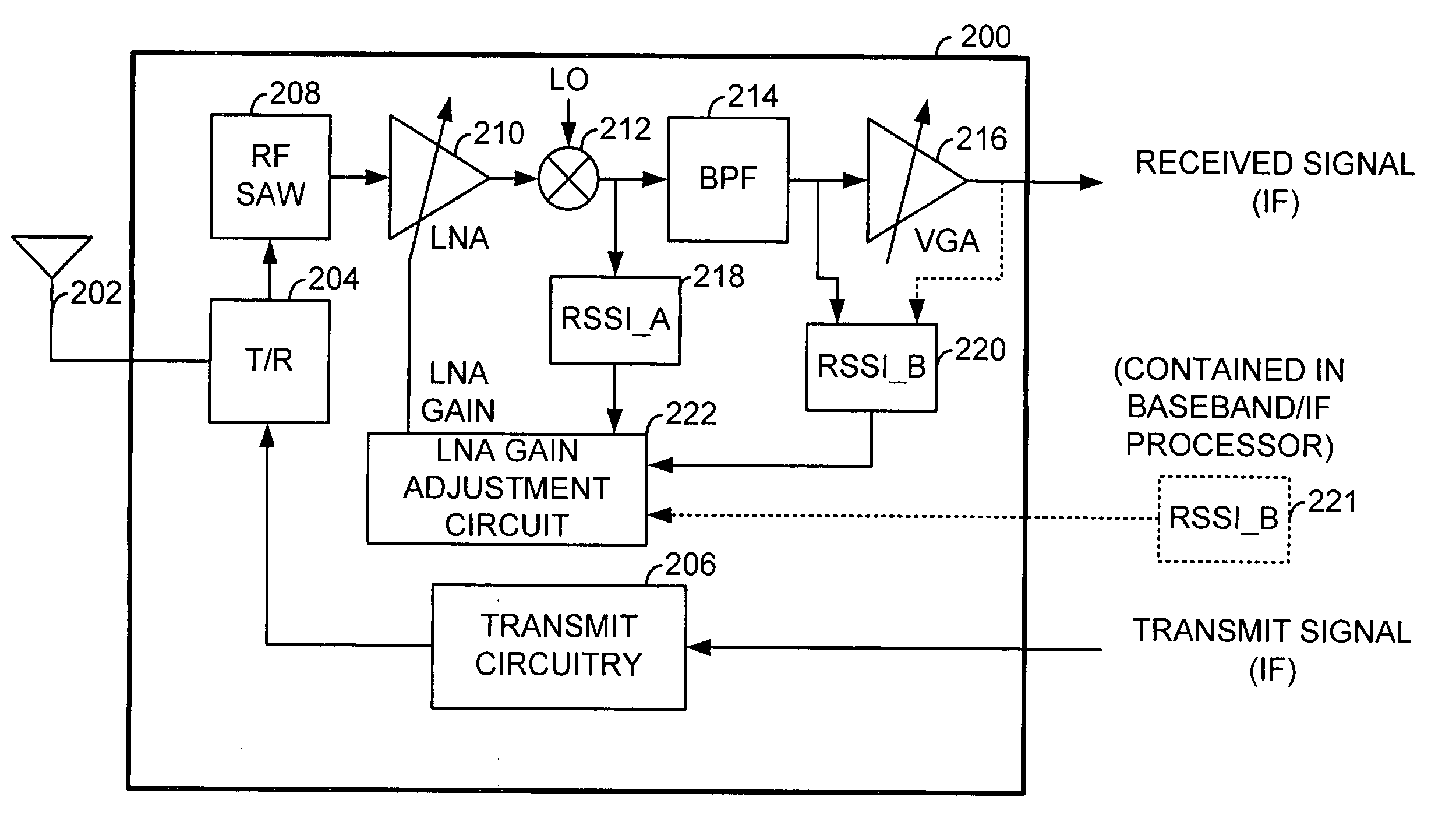
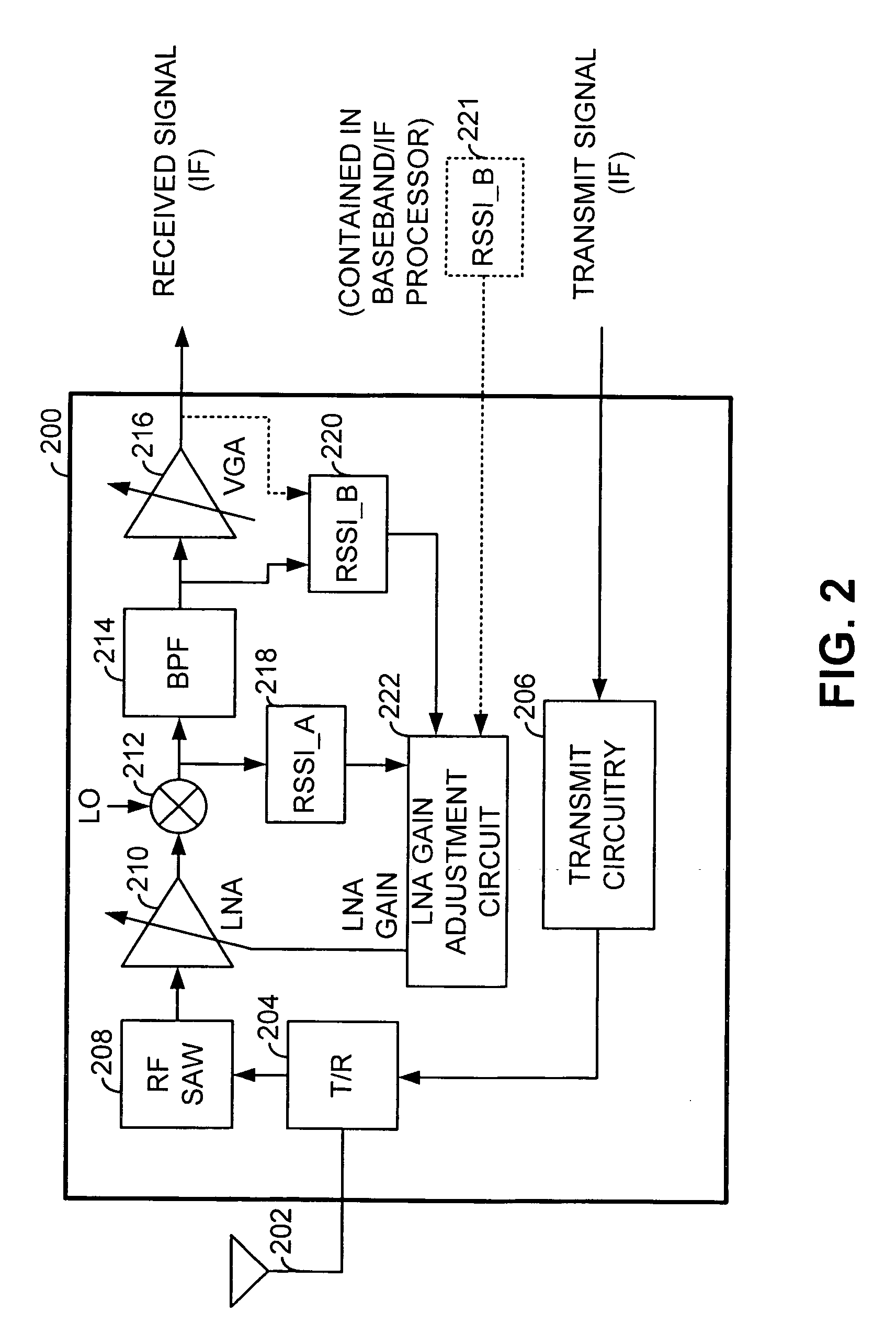
Timing based LNA gain adjustment in an RF receiver to compensate for intermodulation interference
InactiveUS6873832B2Keep linearMaximize signal to noise ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlLinear regionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A Radio Frequency (RF) receiver includes a low noise amplifier (LNA) and a mixer coupled to the output of the LNA. The gain of the LNA is adjusted to maximize signal-to-noise ratio of the mixer and to force the mixer to operate well within its linear region when an intermodulation interference component is present. The RF receiver includes a first received signal strength indicator (RSSI_A) coupled to the output of the mixer that measures the strength of the wideband signal at that point. A second received signal strength indicator (RSSI_B) couples after the BPF and measures the strength of the narrowband signal. The LNA gain is set based upon these signal strengths. LNA gain is determined during a guard period preceding an intended time slot of a current frame and during a guard period following an intended time slot of a prior frame. The lesser of these two LNA gains is used for the intended time slot of the current frame.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
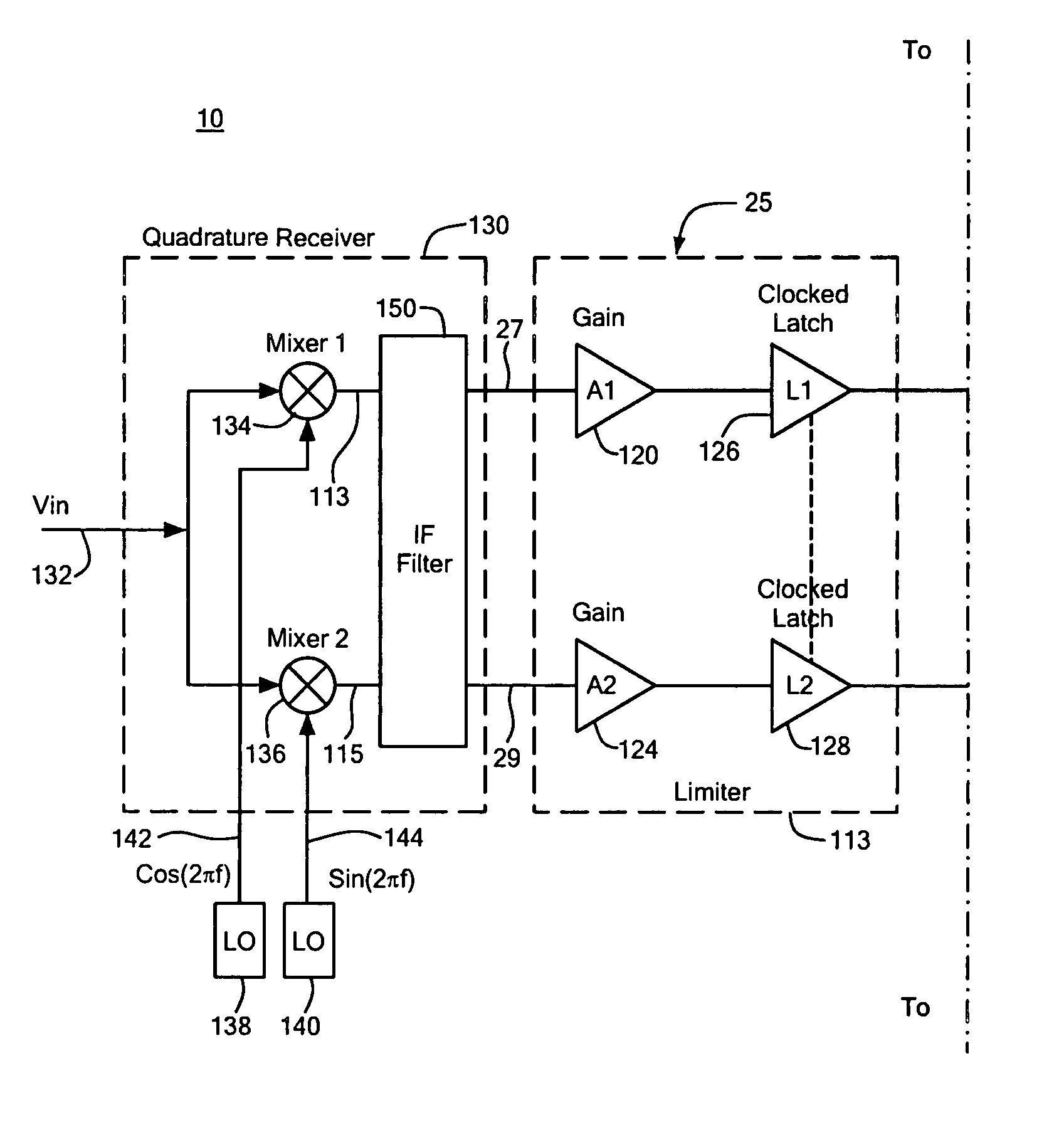
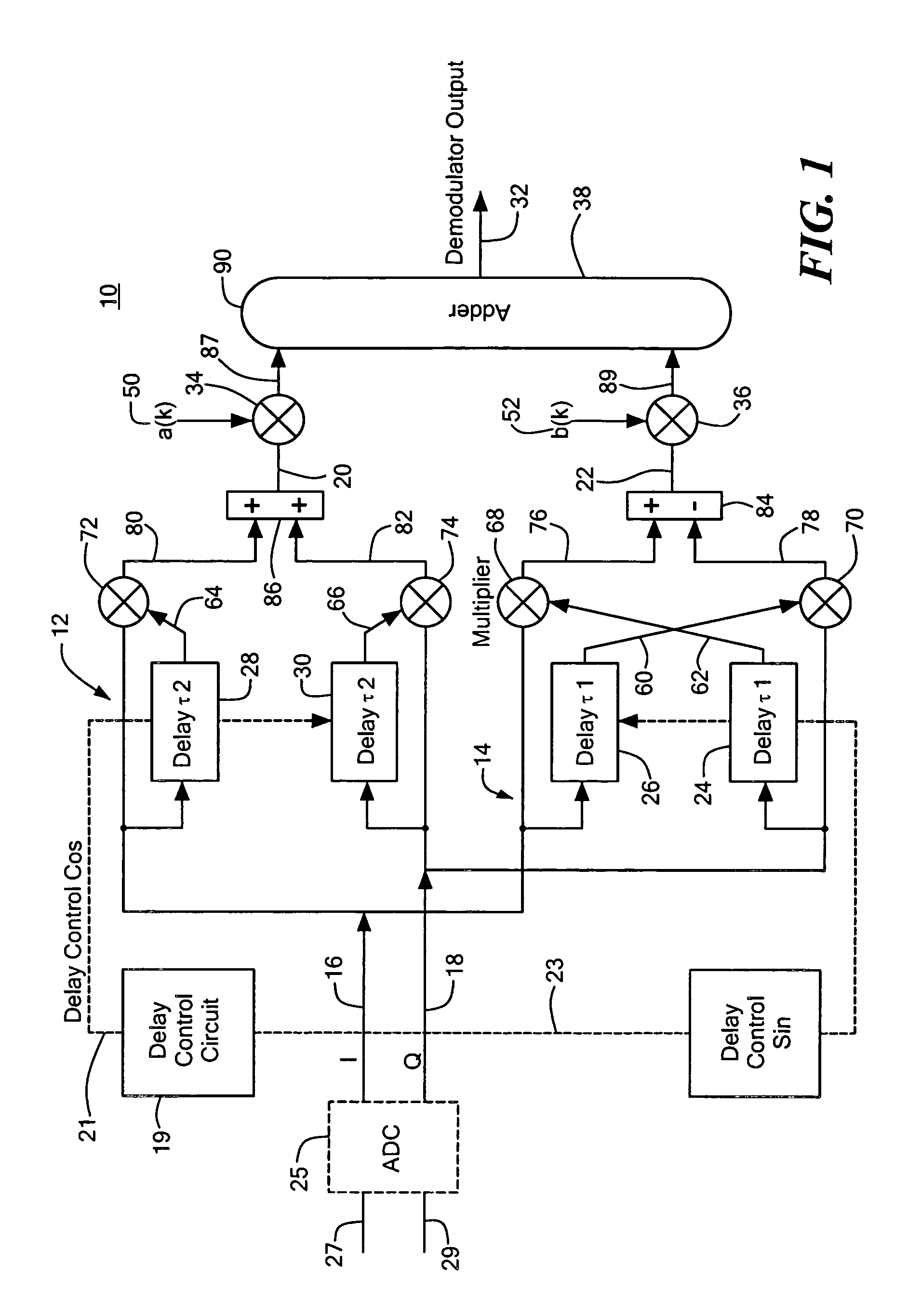
FSK demodulator system and method
ActiveUS20050089120A1Cancel noiseMaximize signal to noise ratioFrequency analysisAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumSpectral response
An FSK demodulator system with tunable spectral shaping including a pair of quadri-correlators responsive to first and second quadrature signals, one of the pair deriving first and second signals representative of the frequency deviation of the quadrature signals at even integer multiples of the frequency deviation and for resolving the modulated FSK data represented by the quadrature signals and the other of the pair deriving first and second signals representative of the frequency deviation of the quadrature signals at odd integer multiples of the deviation frequency and for resolving the modulated FSK data represented by the quadrature signals, and a delay control circuit for setting a delay to each of the pair of quadri-correlators to control the first and second signals representative of the frequency deviation of the quadrature signals derived by each of the pair of quadri-correlators and generate a tuned spectral response at both even and odd integer multiples of the frequency deviation.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Symbol-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS20080025443A1Reduced system complexityWhiten noiseSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsMimo systemsCritical path method
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from the same transmitted vector. The symbols of the received signal vectors are combined, forming a combined received signal vector that may be treated as a single received signal vector. The combined signal vector is then decoded using a maximum-likelihood decoder. In some embodiments, the combined received signal vector may be processed prior to decoding. Systems and methods are also provided for computing soft information from a combined signal vector based on a decoding metric. Computationally intensive calculations can be extracted from the critical path and implemented in preprocessors and / or postprocessors.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Symbol-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS20080025427A1Reduce decoding complexityWhitens noiseSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCritical path methodMimo systems
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from the same transmitted vector. The symbols of the received signal vectors are combined, forming a combined received signal vector that may be treated as a single received signal vector. The combined signal vector is then decoded using a maximum-likelihood decoder. In some embodiments, the combined received signal vector may be processed prior to decoding. Systems and methods are also provided for computing soft information from a combined signal vector based on a decoding metric. Computationally intensive calculations can be extracted from the critical path and implemented in preprocessors and / or postprocessors.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Wafer Inspection
ActiveUS20140009759A1High sensitivityMaximize signal to noise ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesNumerical apertureOptical polarization
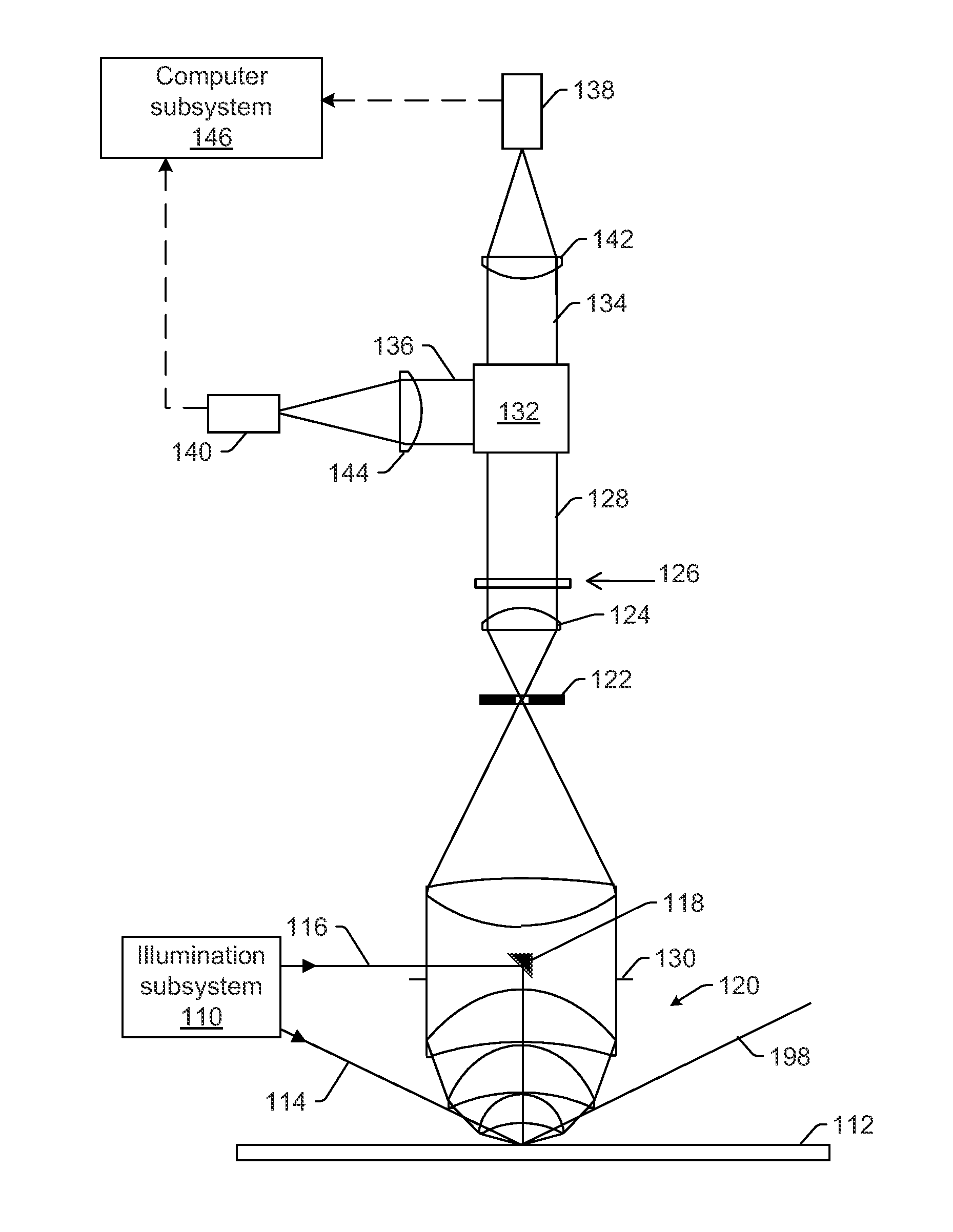
Systems and methods for inspecting a wafer are provided. One system includes an illumination subsystem configured to illuminate the wafer; a collection subsystem configured to collect light scattered from the wafer and to preserve the polarization of the scattered light; an optical element configured to separate the scattered light collected in different segments of the collection numerical aperture of the collection subsystem, where the optical element is positioned at a Fourier plane or a conjugate of the Fourier plane of the collection subsystem; a polarizing element configured to separate the scattered light in one of the different segments into different portions of the scattered light based on polarization; and a detector configured to detect one of the different. portions of the scattered light and to generate output responsive to the detected light, which is used to detect defects on the wafer.
Owner:KLA CORP
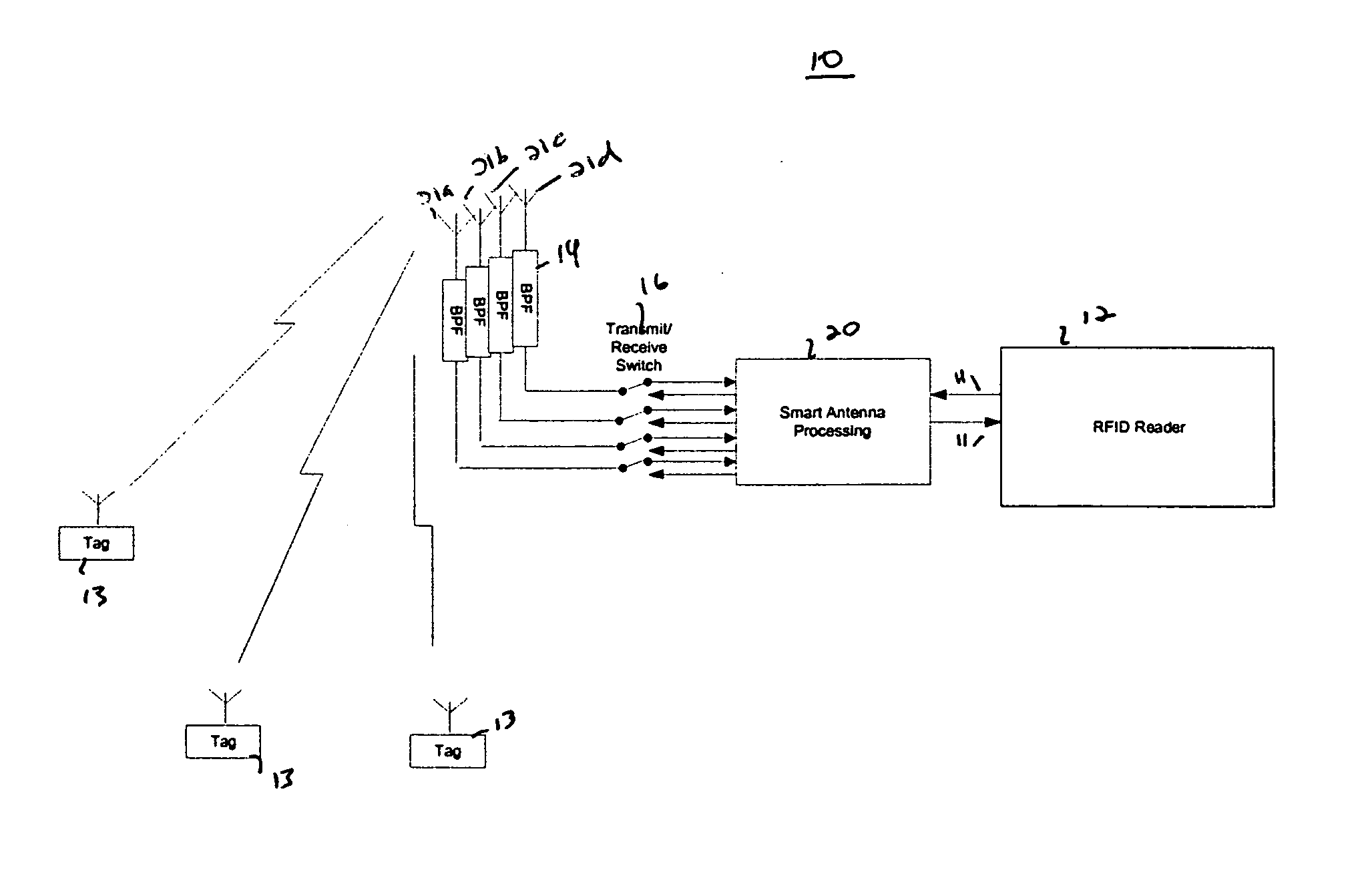
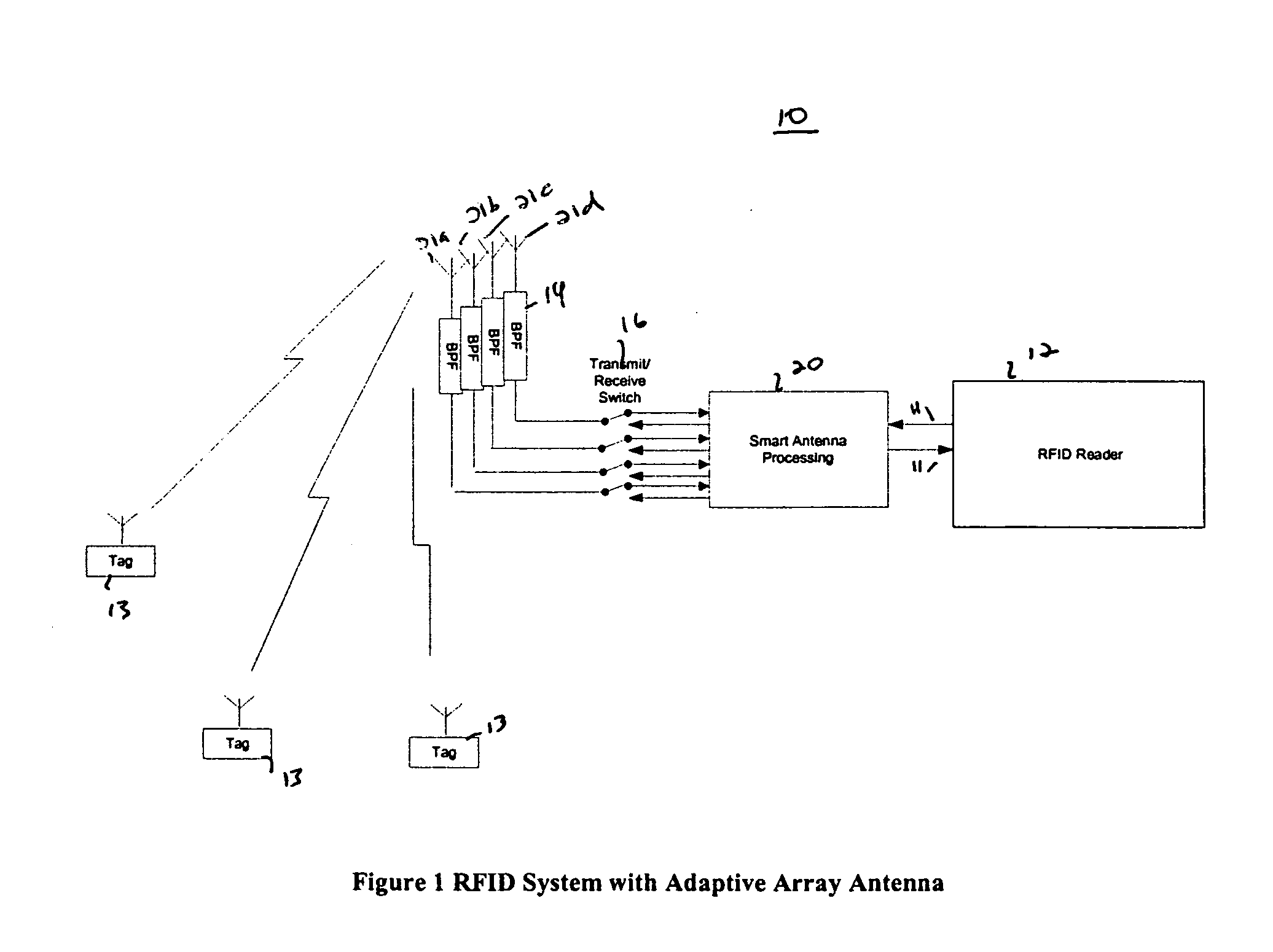
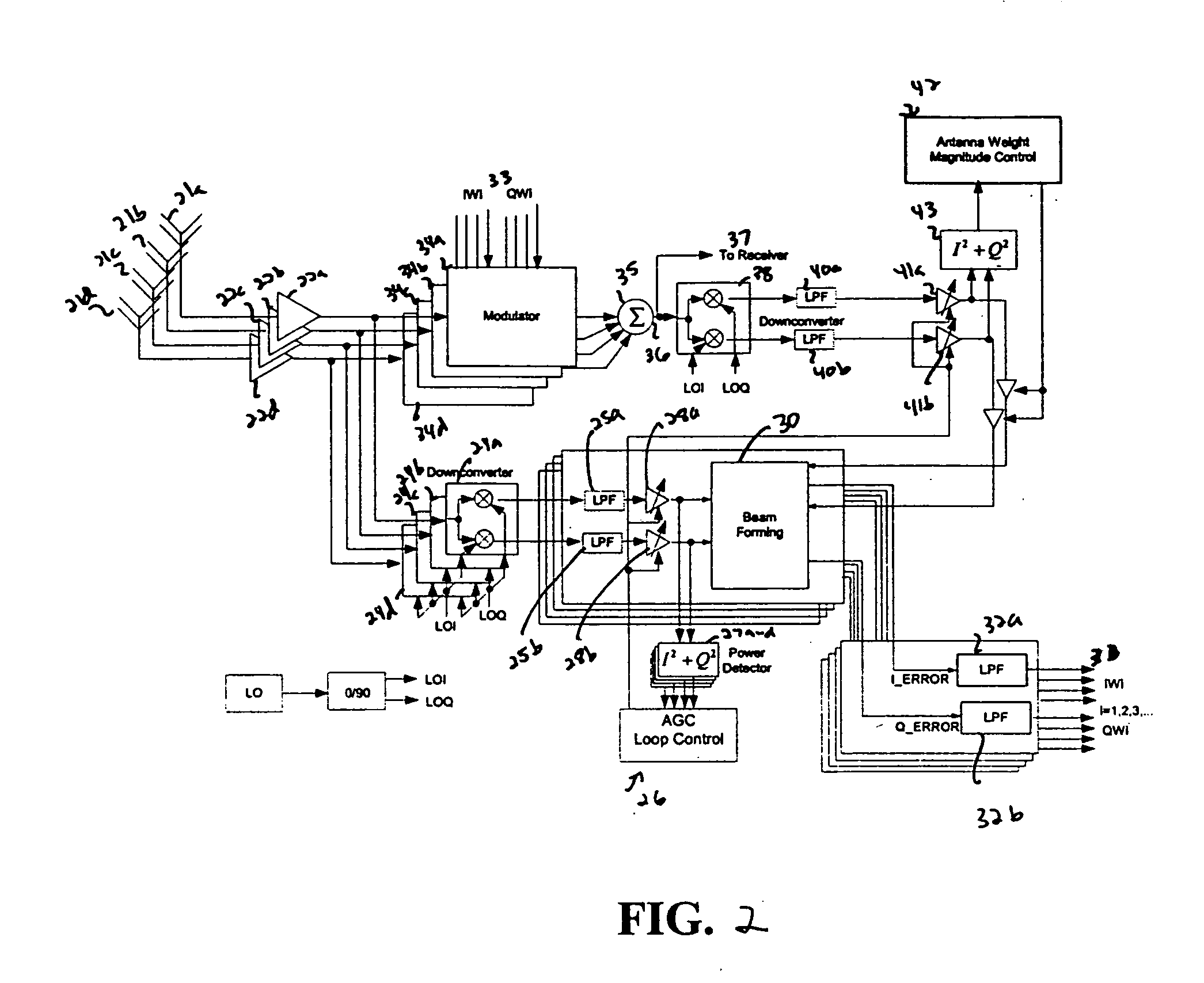
RFID system with an adaptive array antenna
InactiveUS20050128159A1Expand the scope of operationImprove the receiving signal-to-noise ratioSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysSignal qualityPhase shifted
The present invention relates to use of a smart antenna for a RF reader on a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system to significantly increase the operating range of the RFID system. The smart antenna can be an adaptive antenna array. The smart antenna comprises a plurality of antenna elements and, by combining the signals from multiple antenna elements, significantly increases the received signal-to-noise ratio. In a noise limited environment, combining the signals to maximize the received signal-to-noise ratio can be based on the maximal ratio combining (MRC) principle. To achieve the best signal quality, the received signal from each antenna can be phase-shifted such that the resultant signals from all antennas are in phase. In addition, the signal from each antenna can be scaled in amplitude based on the square root of its received signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
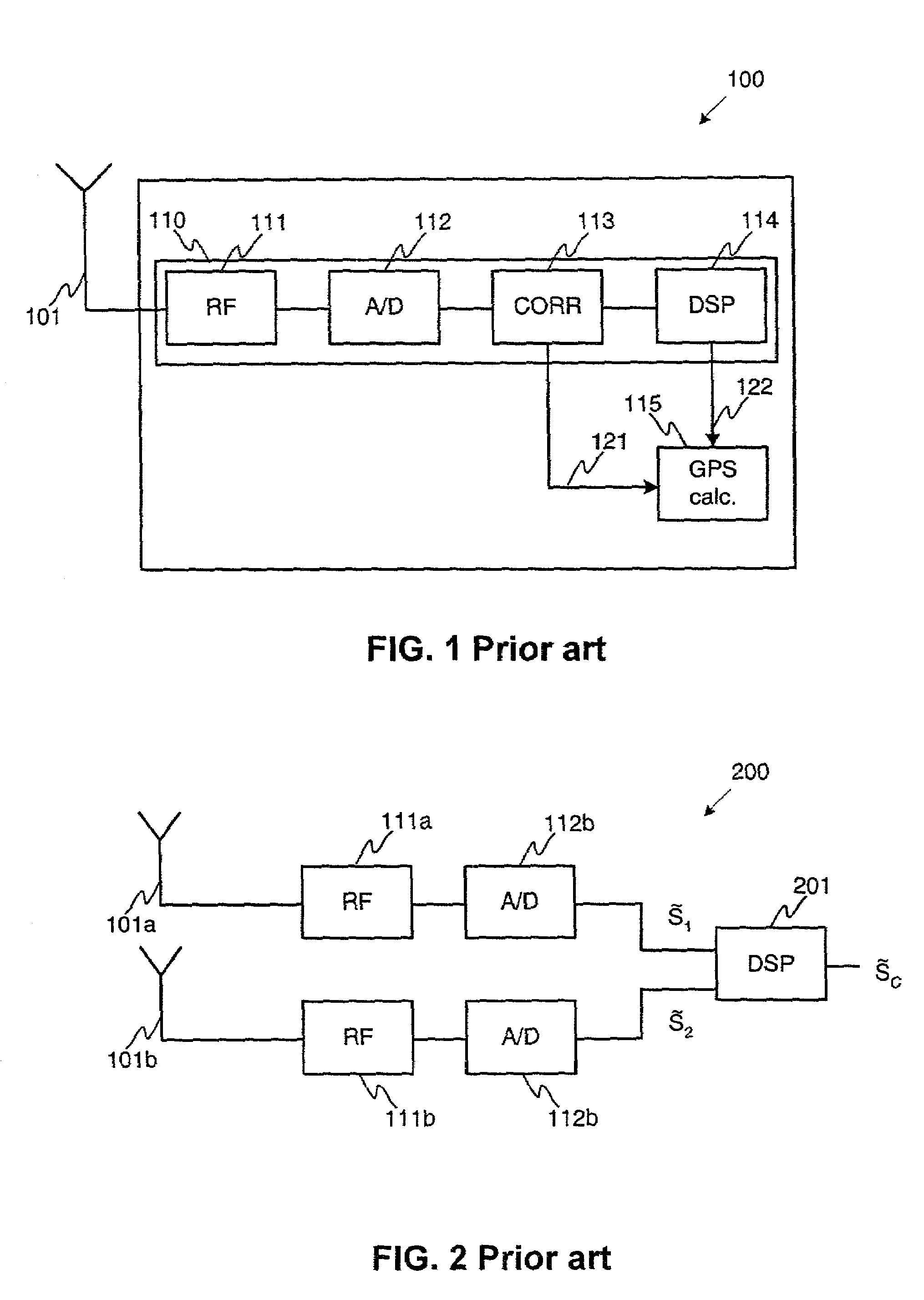
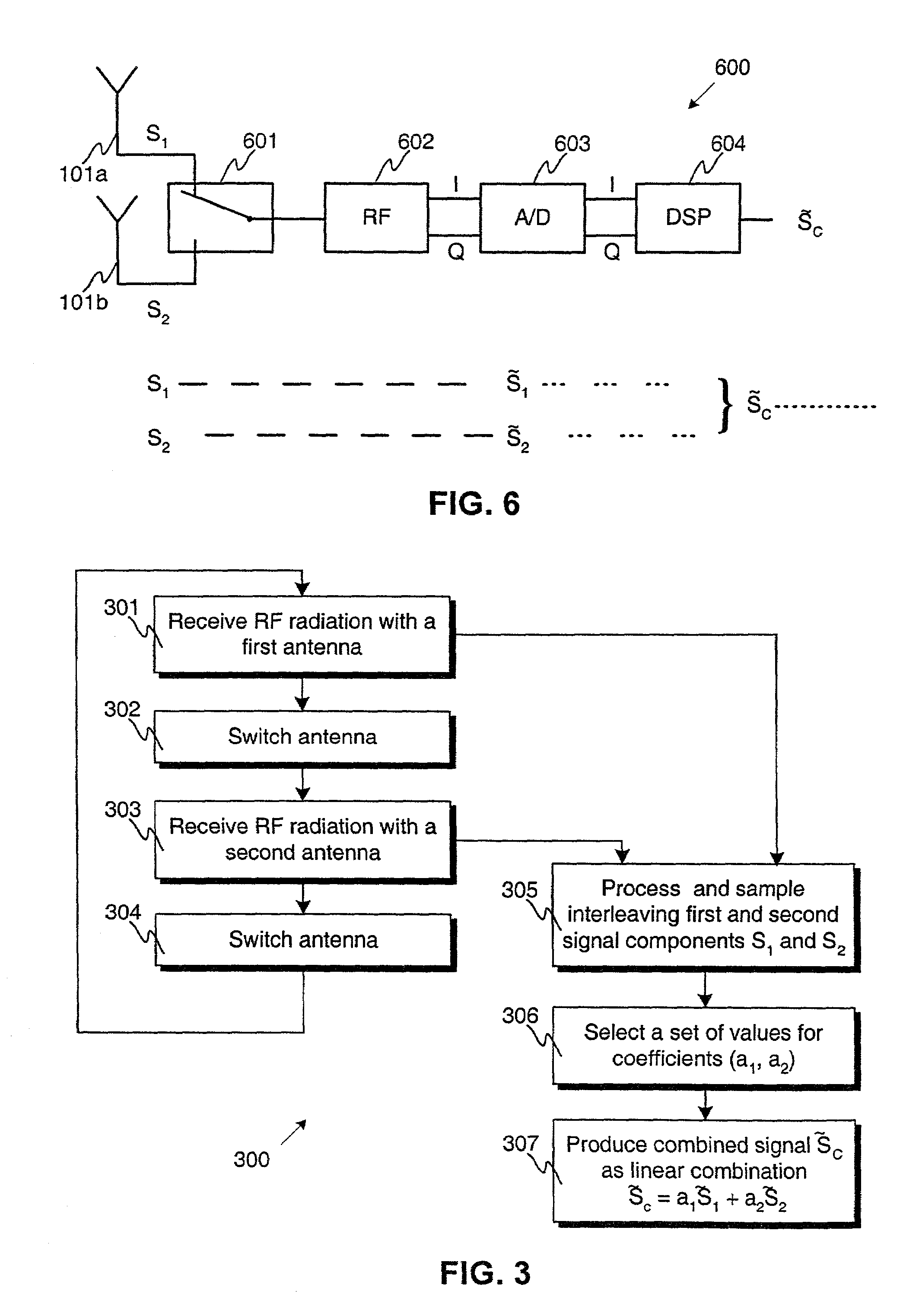
Method for receiving radio frequency signal and a receiver device
ActiveUS7171175B2Maintain good propertiesEasy to produceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityRadio frequency signalComplex valued
In a method (300) for receiving a radio signal, there are steps of: receiving (301, 303) first and second received signal components by use of first and second antennas having different properties; processing (305) a received signal component to produce a sampled signal component; producing (307) at least one combined signal, which is a linear combination of at least two sampled signal components; and selecting (306) at least one set of complex values for coefficients of the linear combination so that a quality of a combined signal is at least equal to the quality of that sampled signal component having the best quality. Furthermore, the antennas are alternately connected (302, 304) via a switching element to radio frequency means so that received signal components are interleaving and so that first and second parts of a certain piece of transmitted information are received with the first and second antennas, respectively. A corresponding receiver device is also presented.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for mapping the underground soil
InactiveUS20160187524A1Maximize signal-to-noise ratioIncrease distanceElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electromagnetic wavesUltrasound attenuationSoil science
The invention describes a method and system, for mapping non-magnetic soils in terms of their local permittivity and velocity of the traversing electromagnetic waves, by measuring the straight-line attenuation and elapsed time between transmitters and receivers located within tubes inserted into the soil.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
Adaptive blind start-up receiver architecture with fractional baud rate sampling for full-duplex multi-level PAM systems
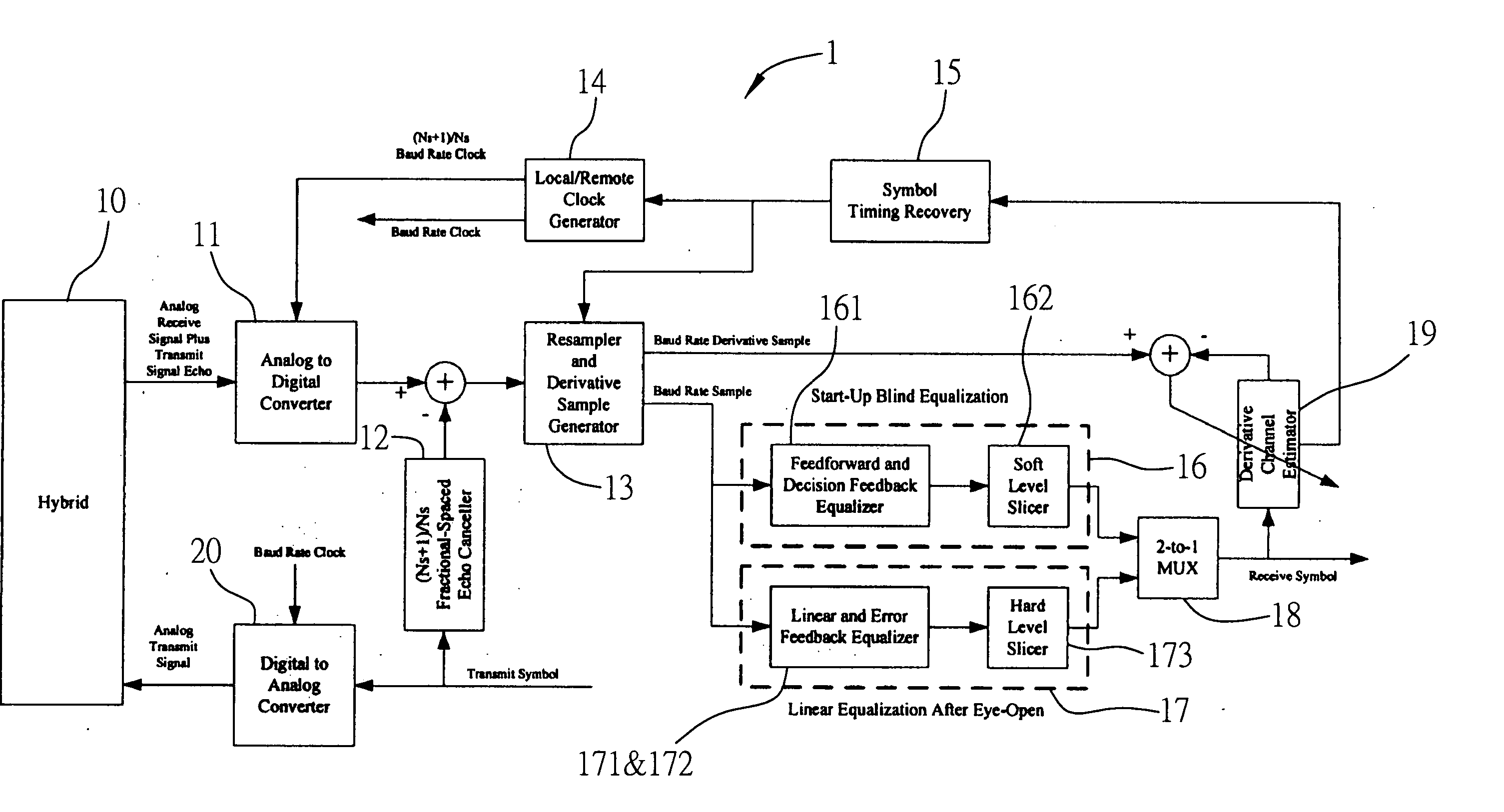
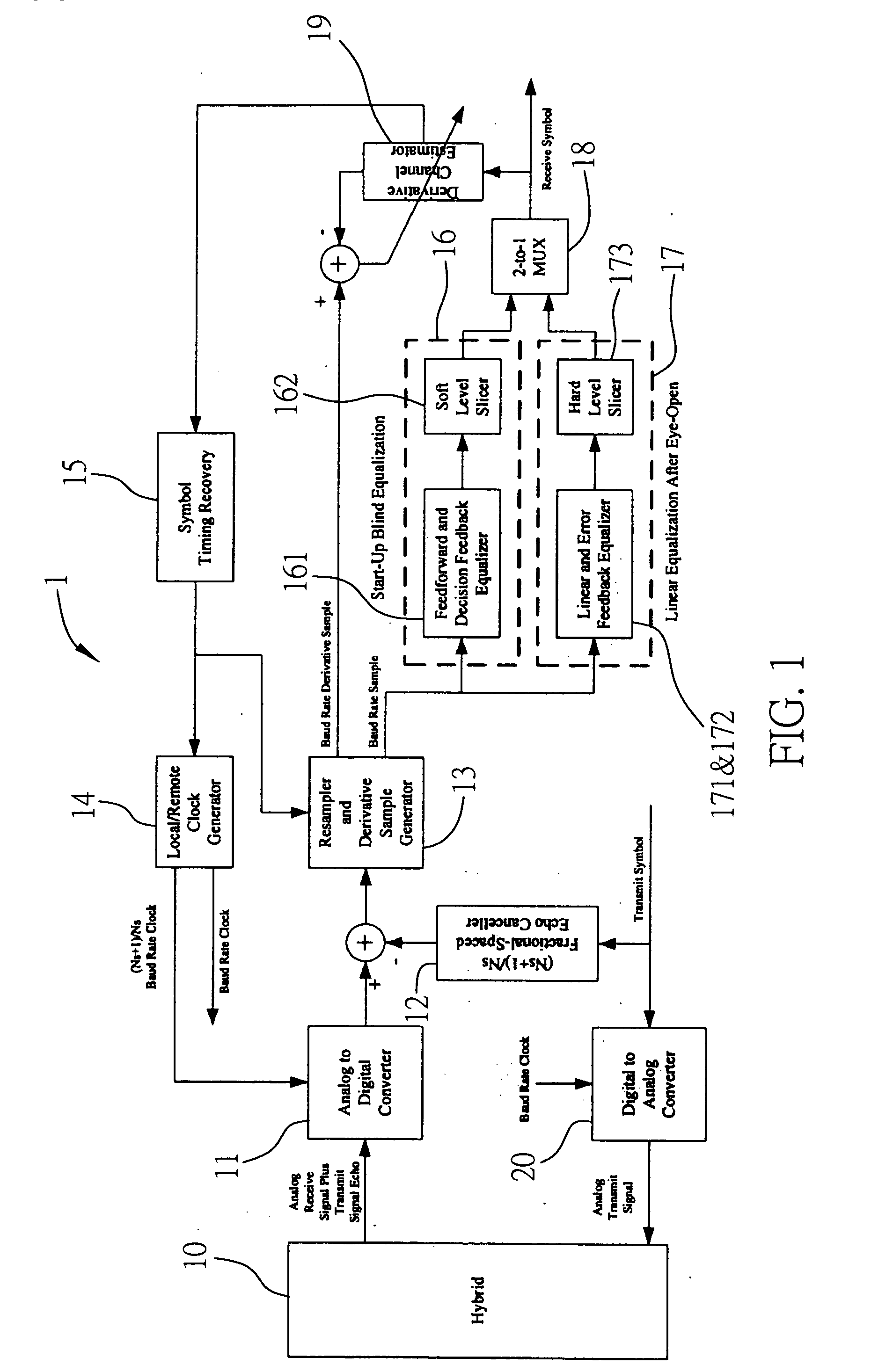
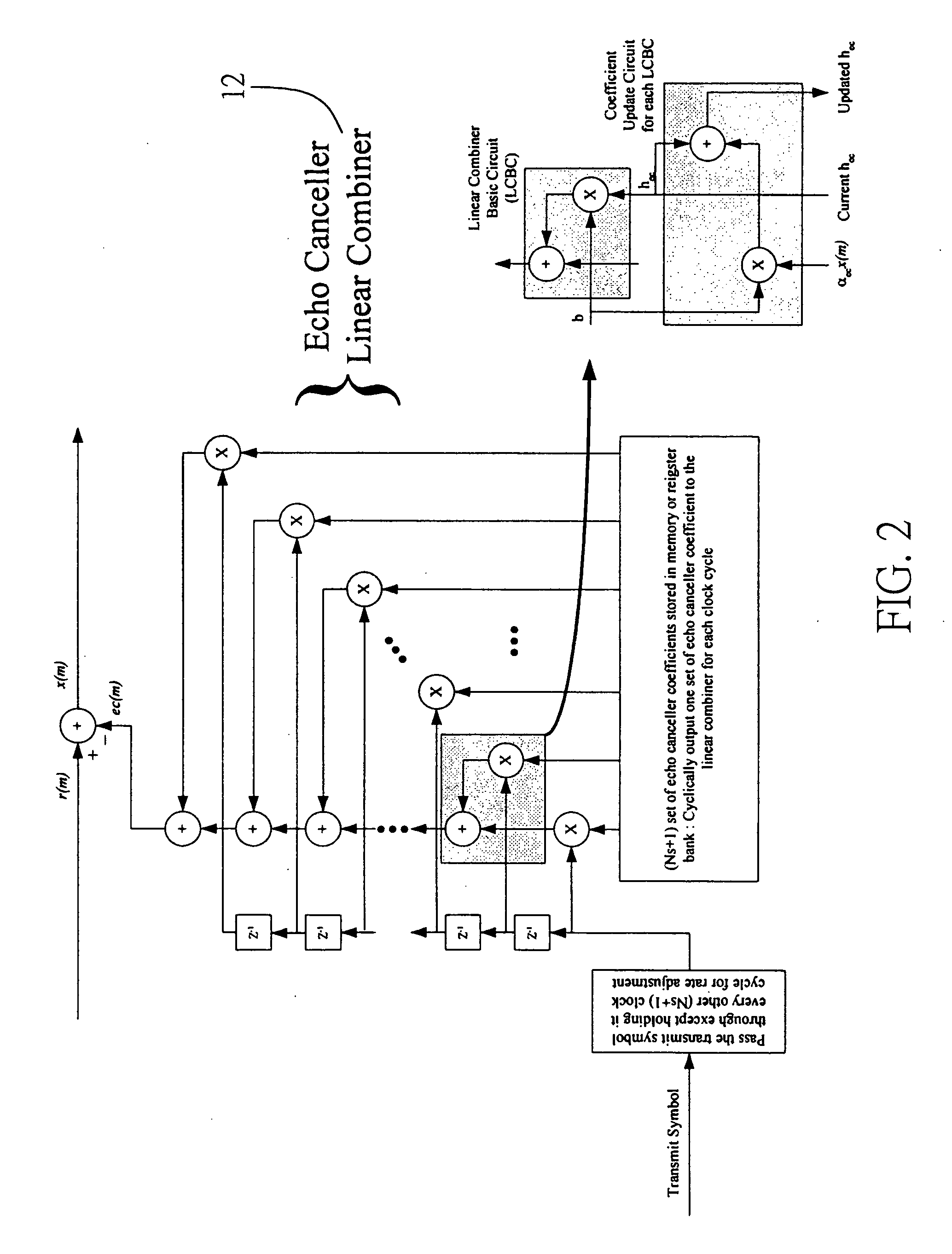
ActiveUS20060256849A1Maximize signal to noise ratioEasy to useMultiple-port networksError preventionA d converterEqualization
This invention presents a novel receiver architecture for full-duplex multi-level PAM systems. The receiver employs an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) that has a sample rate flexibly specified as (Ns+1) / Ns baud rate where Ns is an integer equal or greater than 1. A fractional-spaced echo canceller is used to cancel the echo at the ADC output. The use of a fractional sampling rate higher than the baud rate also enables the timing recovery function be implemented in the digital domain and hence eliminates the need of using the complex analog phase selection circuit. The receiver is also capable of fast, blind start-up by use of a decision feedback equalizer with unity main tap and a soft level slicer. The timing phase can be optimally located using a derivative channel estimator. Once the “eye-open” condition is achieved, the channel equalization is switched to the use of linear equalizer coupled with an error feedback equalizer to alleviate the error propagation problem associated with the decision feedback equalizer.
Owner:RDC SEMICON CO LTD
Method and apparatus of codebook-based single-user closed-loop transmit beamforming (SU-CLTB) for OFDM wireless systems
ActiveUS8254487B2Improve throughputMaximize signal to noise ratioMultiple-port networksAntenna arraysCommunications systemClosed loop
A method includes broadcasting, at a transmitter, messages comprising antenna configuration, antenna spacing and a number of antenna of the transmitter and reference signals; generating, at a receiver, a codebook comprising a plurality of antenna beams based on the broadcasted messages; receiving, at the receiver, the broadcasted reference signals; selecting, at the receiver, an antenna beam among the plurality of antenna beams within the codebook in dependence upon a predetermined performance criteria of a data communication system and in dependence upon the broadcasted reference signals; feedbacking to the transmitter, at the receiver, information comprising the antenna beam selected by the receiver; optimizing, at the transmitter, a beamforming process by utilizing the feedback information from the receiver; transmitting, at the transmitter, data signals by utilizing the optimized beamforming process; and receiving and processing, at the receiver, the data signals in dependence upon the selected antenna beams within the codebook.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Sorting System Using Narrow-Band Electromagnetic Radiation
InactiveUS20070158245A1Minimize the numberQuick switchRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesControl systemEngineering
Owner:KABUSHIKI KAISHA MSS
Timing based LNA gain adjustment in an RF receiver to compensate for intermodulation interference
InactiveUS20050079842A1Keep linearMaximize signal to noise ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasLinear regionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A Radio Frequency (RF) receiver includes a low noise amplifier (LNA) and a mixer coupled to the output of the LNA. The gain of the LNA is adjusted to maximize signal-to-noise ratio of the mixer and to force the mixer to operate well within its linear region when an intermodulation interference component is present. The RF receiver includes a first received signal strength indicator (RSSI_A) coupled to the output of the mixer that measures the strength of the wideband signal at that point. A second received signal strength indicator (RSSI_B) couples after the BPF and measures the strength of the narrowband signal. The LNA gain is set based upon these signal strengths. LNA gain is determined during a guard period preceding an intended time slot of a current frame and during a guard period following an intended time slot of a prior frame. The lesser of these two LNA gains is used for the intended time slot of the current frame.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multi-touch panel capacitance sensing circuit
InactiveUS20120092297A1Reduce power consumptionImprove toleranceTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceEngineering
Disclosed herein is a multi-touch panel capacitance sensing circuit. The multi-touch panel capacitance sensing circuit includes a touch panel, a transmission circuit unit, and a reception circuit unit. The touch panel includes transmission electrodes and reception electrodes. The transmission circuit unit applies a transmission signal, having a predetermined period, to the transmission electrodes in a time division manner. The reception circuit unit for detecting a difference in capacitance components, generated between the transmission electrode and the reception electrode, based on the reception electrode when a touch is generated by the human body of a user. The reception circuit unit includes a current mirror-based charge integration circuit, and detects whether a touch is generated or not.
Owner:POINTCHIPS CO LTD
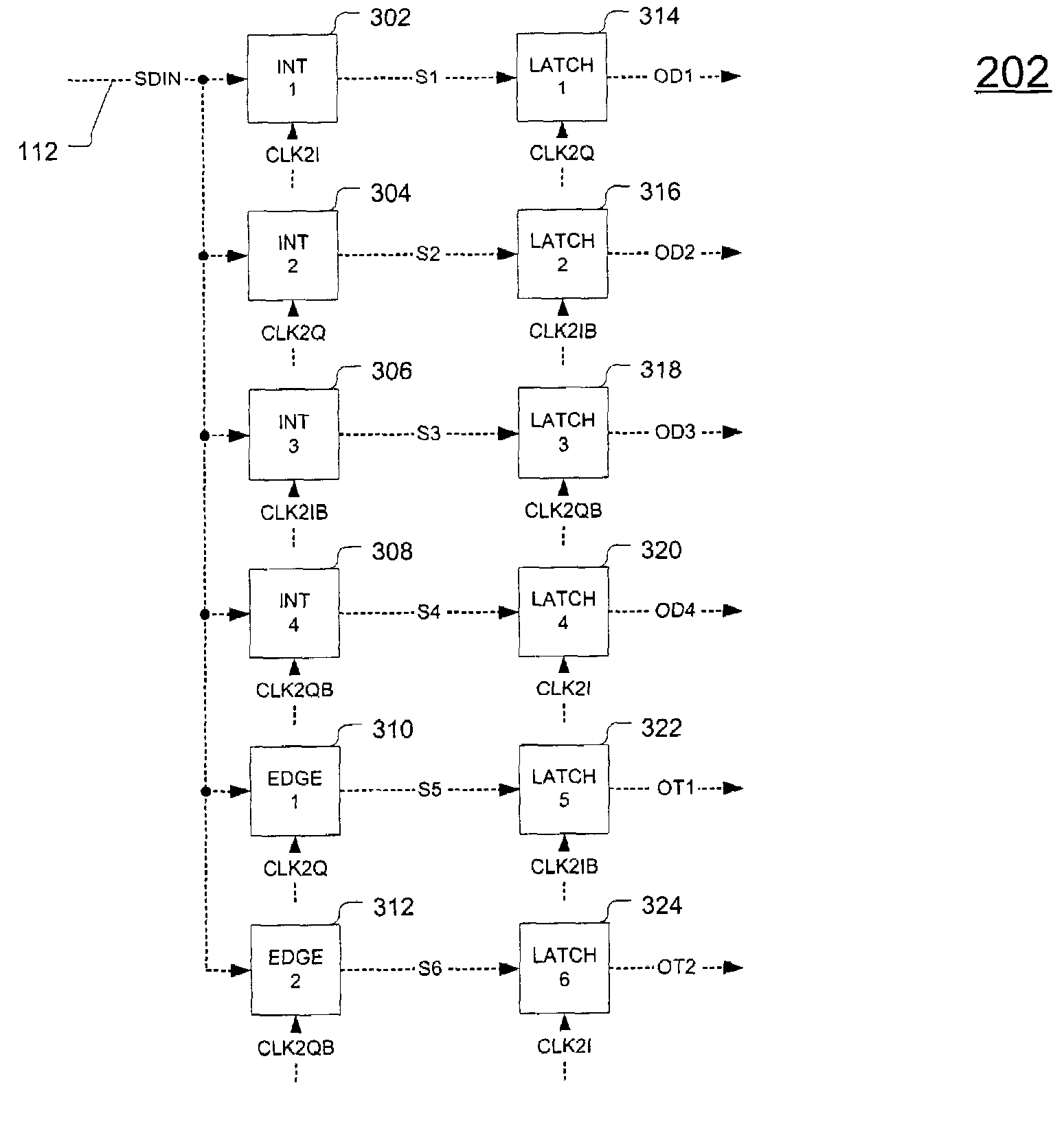
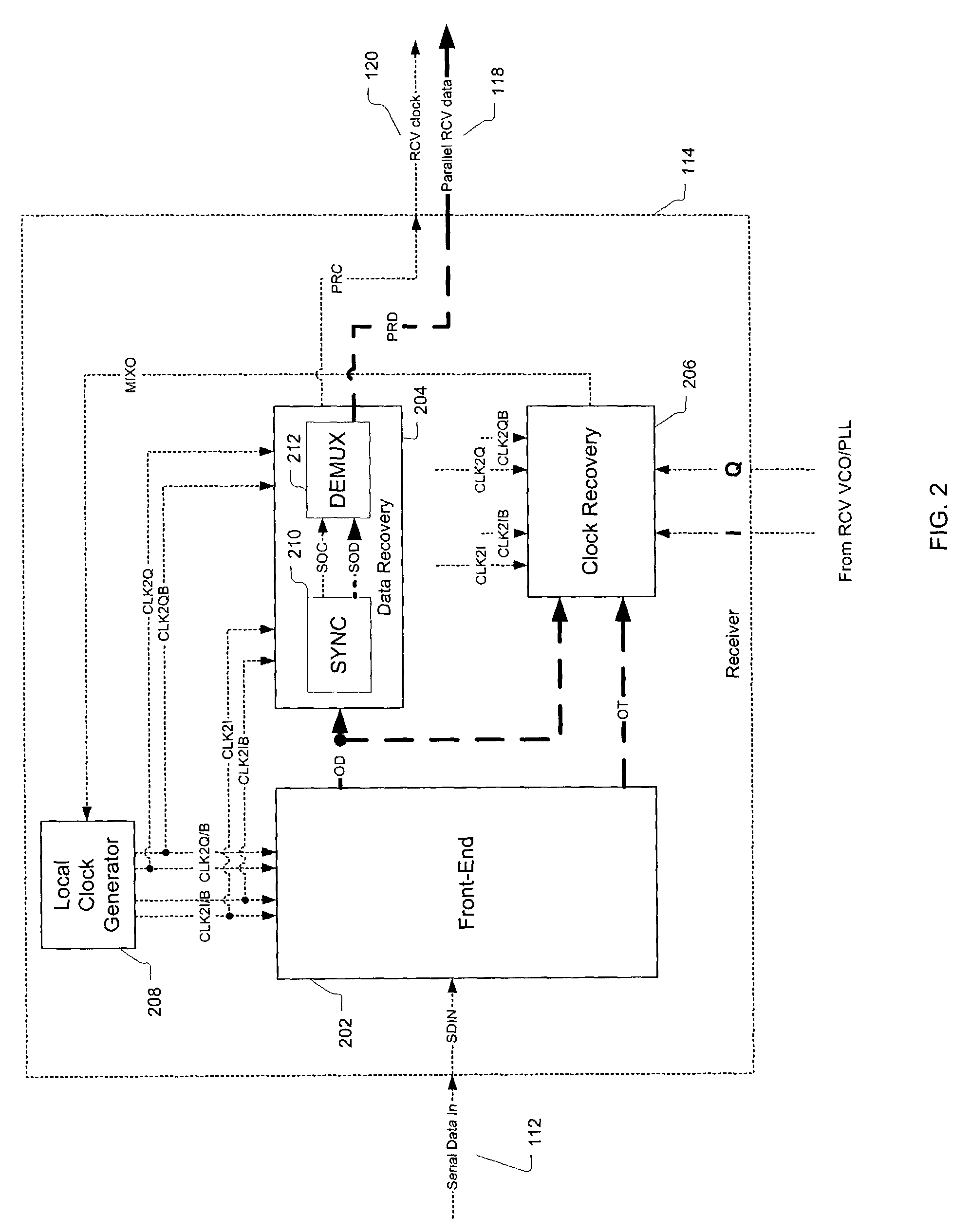
Clock and data recovery with extended integration cycles
InactiveUS7209525B2Small possibilityHigh sensitivityPulse automatic controlModulated-carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Integrator
Clock and data recovery circuitry includes an interleaved sampler having multiple integrators, where at least one of the integrators integrates the input data for at least two unit intervals (UIs). One embodiment includes a four-way interleaved sampler, where each integrator in the sampler integrates the input data for two UIs, where each integrator is sampled at or near the middle of its two-UI integration cycle. In an exemplary 10-GHz system, the reset cycle of each integrator may begin many tens of picoseconds after the data is sampled. Since the signal is sampled near the center of the integration cycle and is not highly proximate to the time of the integrator reset, the latch signal has a window of uncertainty extending into the length of a data bit cell with little possibility of latching erroneous data. The sensitivity of the clock recovery circuitry may be optimized by centering the latch function over the time of highest signal level, thereby maximizing signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
LNA gain adjustment in an RF receiver to compensate for intermodulation interference
InactiveUS20070010224A1Keep linearMaximize signal to noise ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlLinear regionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A Radio Frequency (RF) receiver includes a low noise amplifier (LNA) and a mixer coupled to the output of the LNA. The gain of the LNA is adjusted to maximize signal-to-noise ratio of the mixer and to force the mixer to operate well within its linear region when an intermodulation interference component is present. The RF receiver includes a first received signal strength indicator (RSSI_A) coupled to the output of the mixer that measures the strength of the wideband signal at that point. A second received signal strength indicator (RSSI_B) couples after the BPF and measures the strength of the narrowband signal. The LNA gain is set based upon these signal strengths. By altering the gain of the LNA by one step and measuring the difference between a prior RSSI_B reading and a subsequent RSSI_B′ reading will indicate whether intermodulation interference is present.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
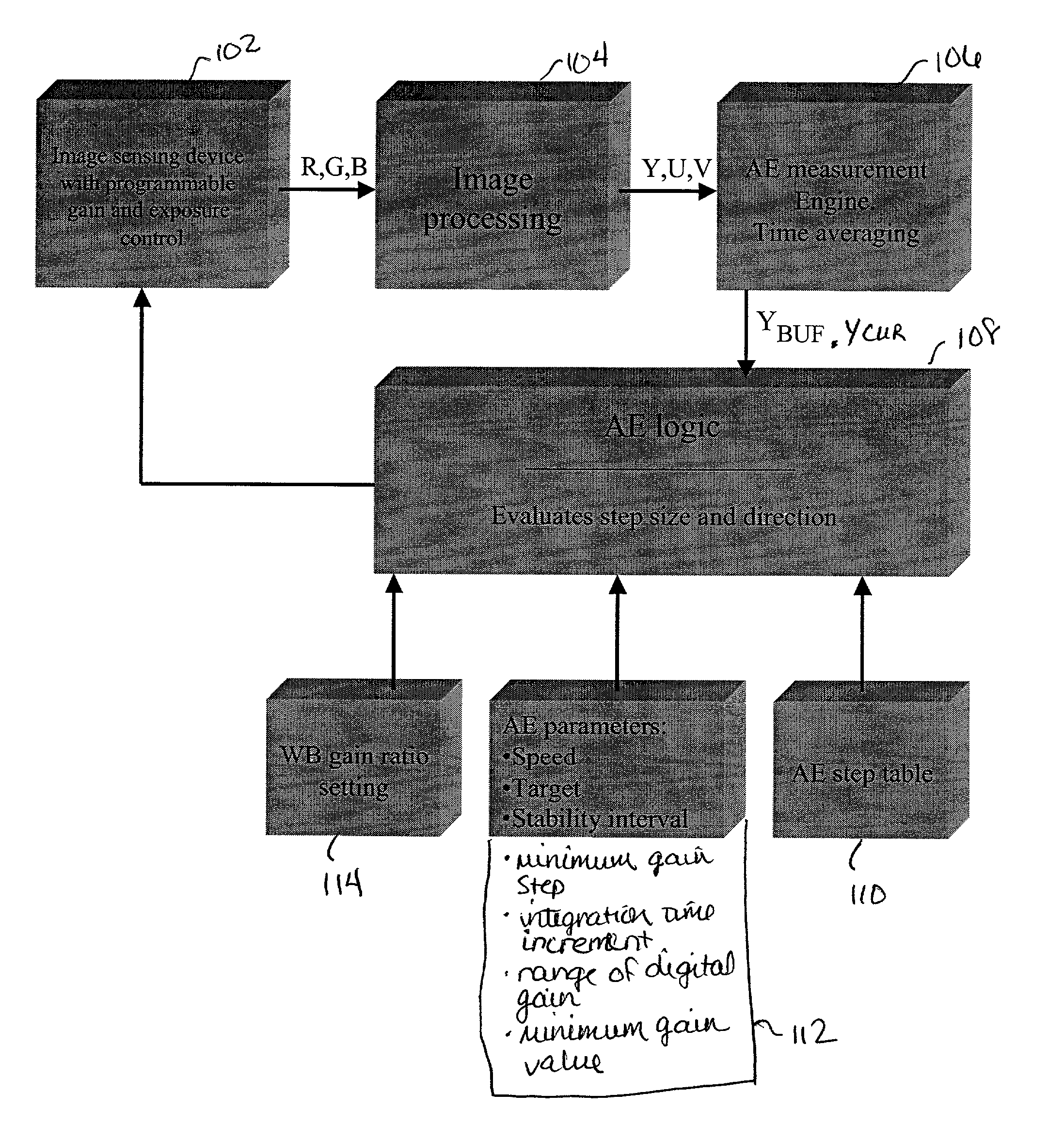
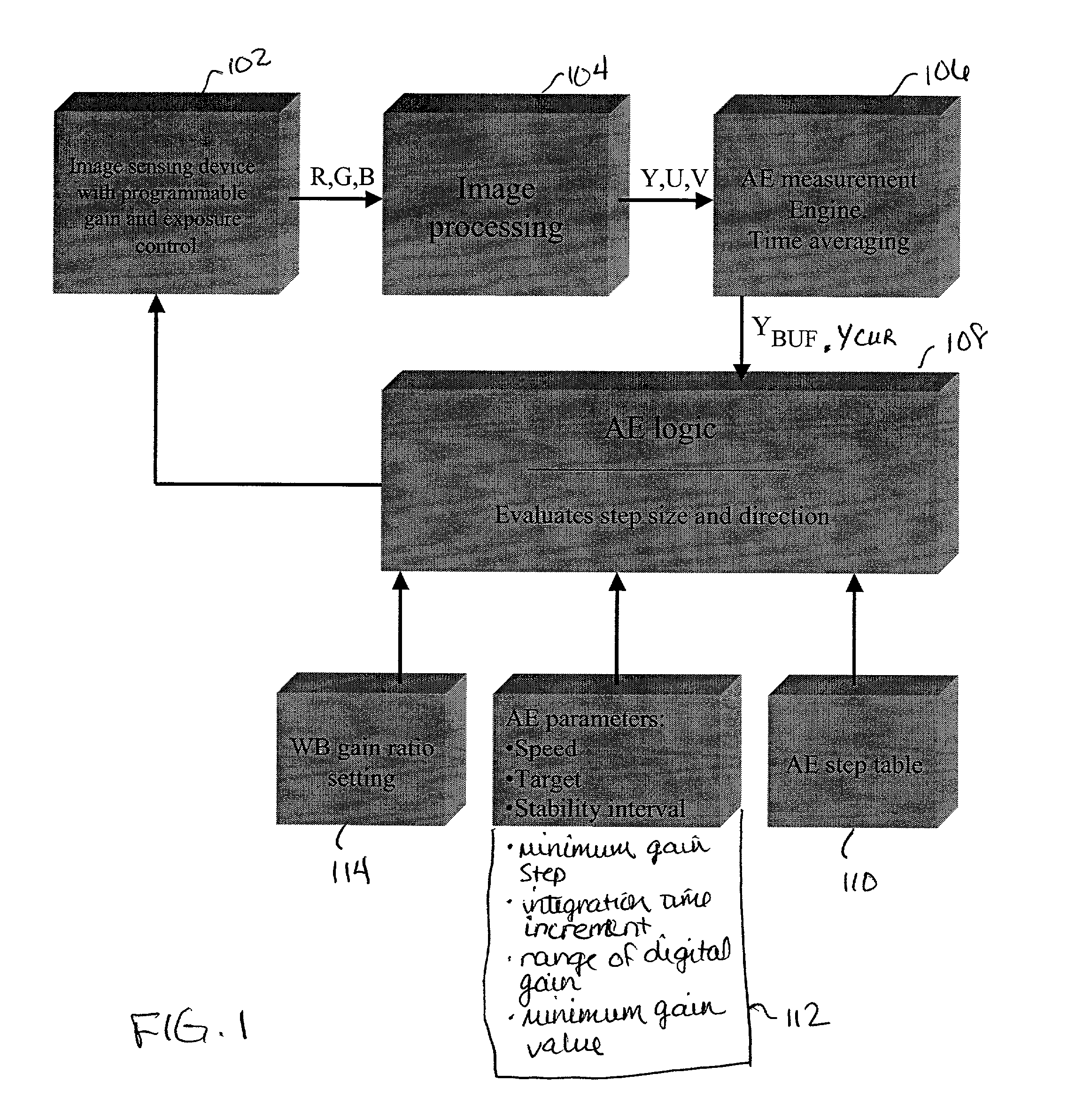
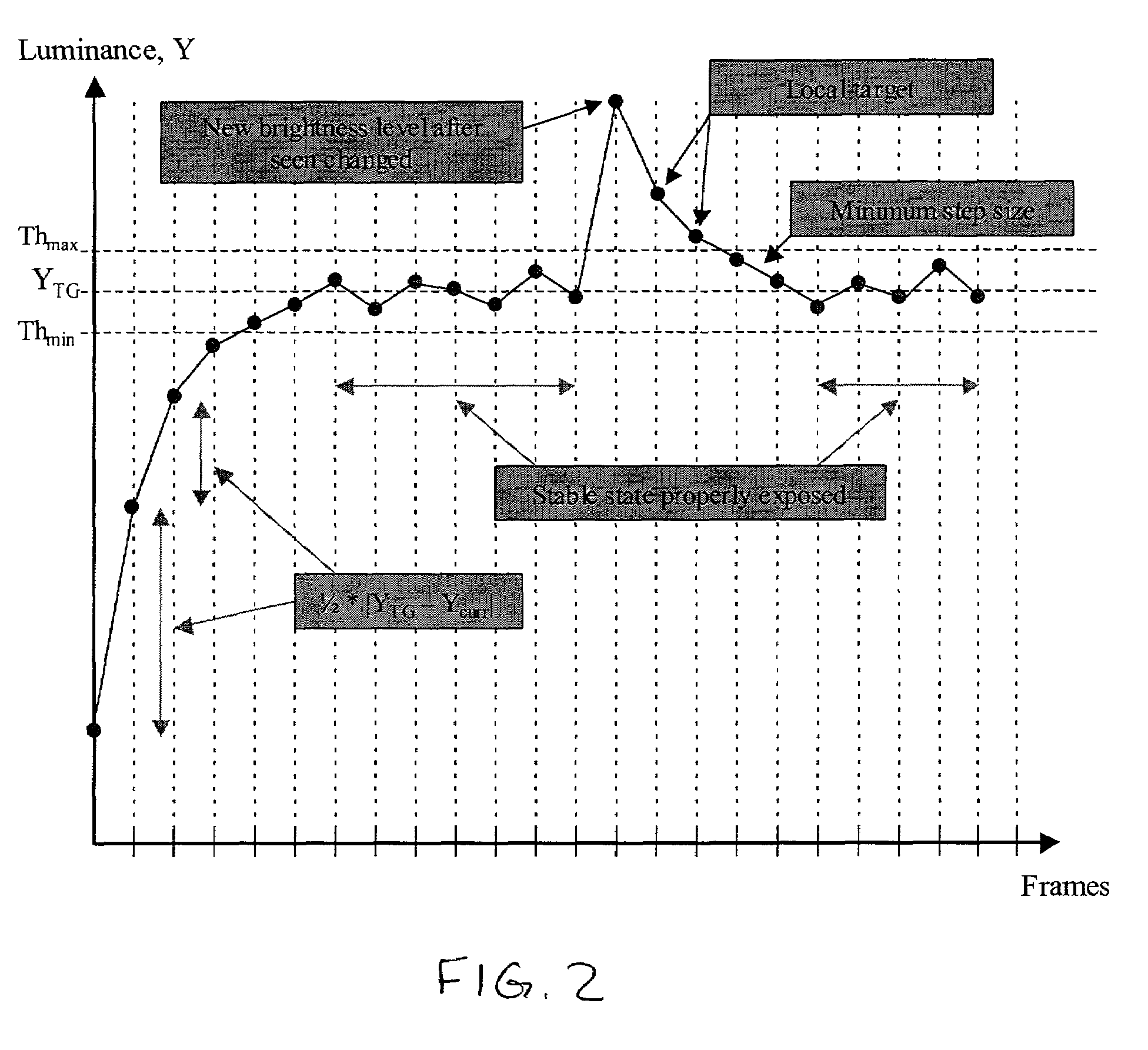
Method and apparatus for automatic gain and exposure control for maintaining target image brightness in video imager systems
ActiveUS7245320B2Maximize signal to noise ratioEfficiently maintaining a target image brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Imaging processing
In an image processing system, the imager gain and the exposure time are adjusted based on a predefined stepping sequence using a stepping table designed to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio in the image. This is achieved by providing a stepping sequence with each step having the largest suitable integration time (exposure) and an appropriate amplifier and digital gain setting, while achieving an equal relative percentage change in image brightness between adjacent sequence steps. The size of the executed AE steps is proportional to the distance between a current image luminance and the target luminance. This is achieved by the capability to skip one or more steps in the stepping sequence, if appropriate, for each relevant executed step, with the number of skipped steps, if any, being proportional to the magnitude of the deviation from the target brightness.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
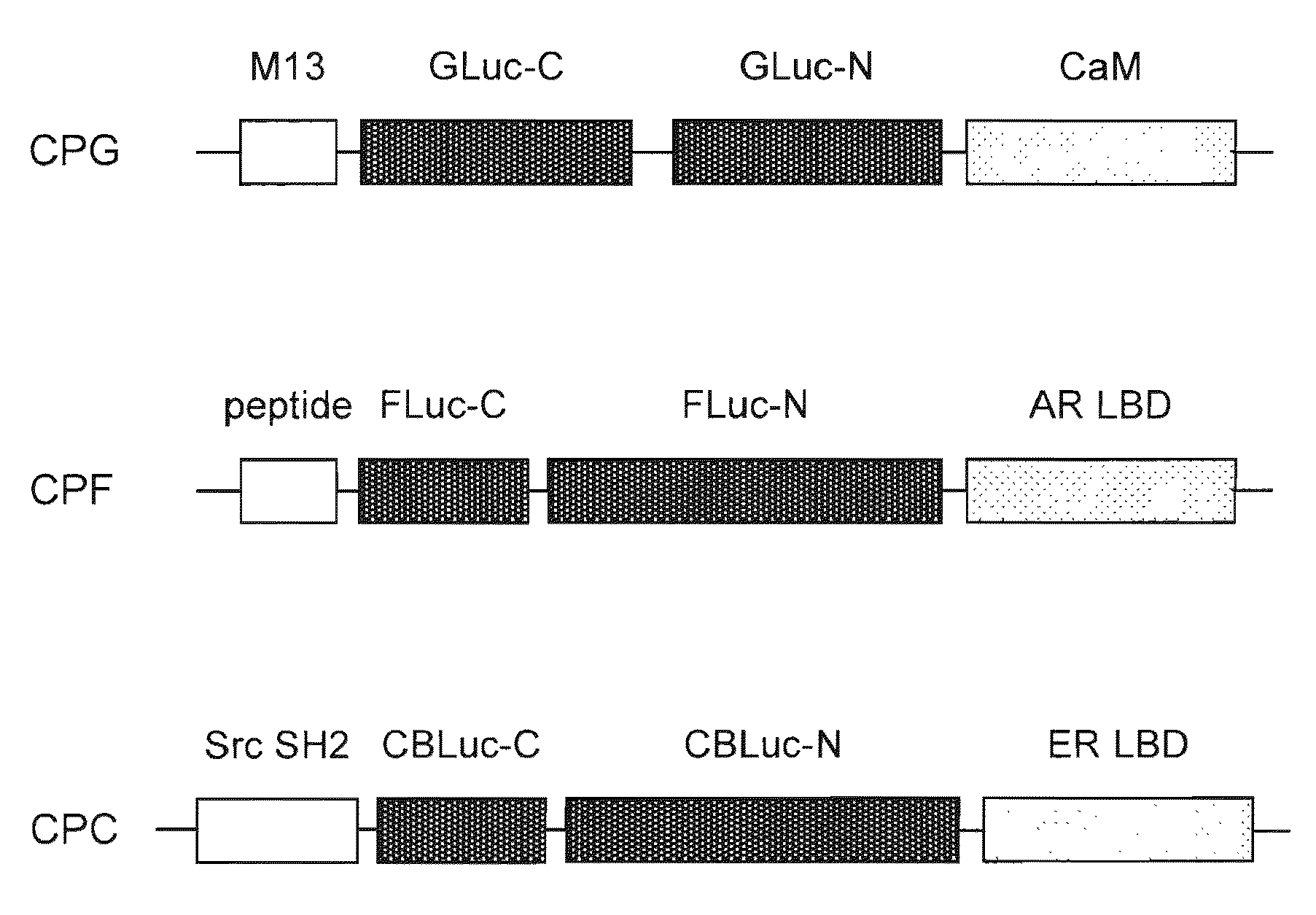
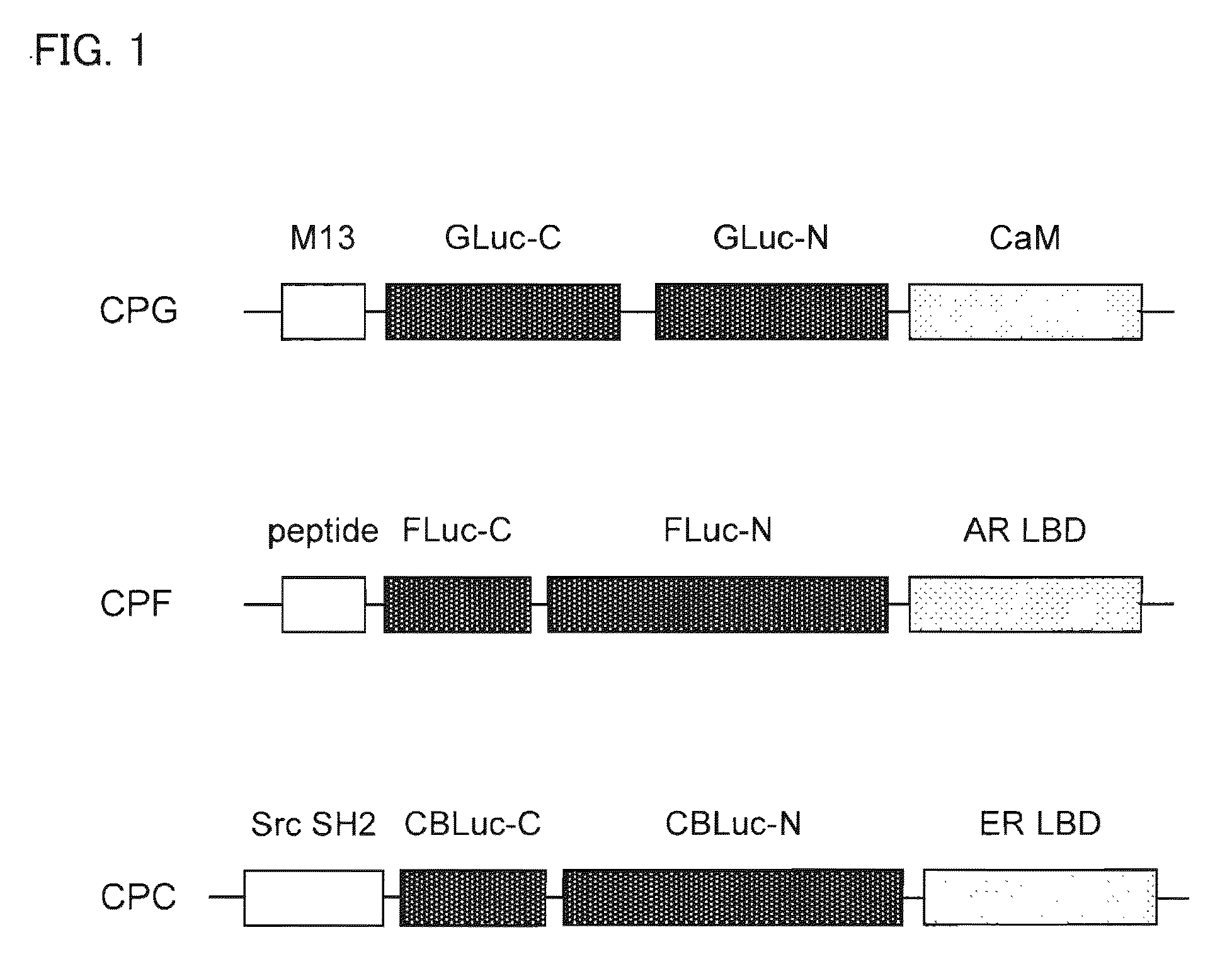
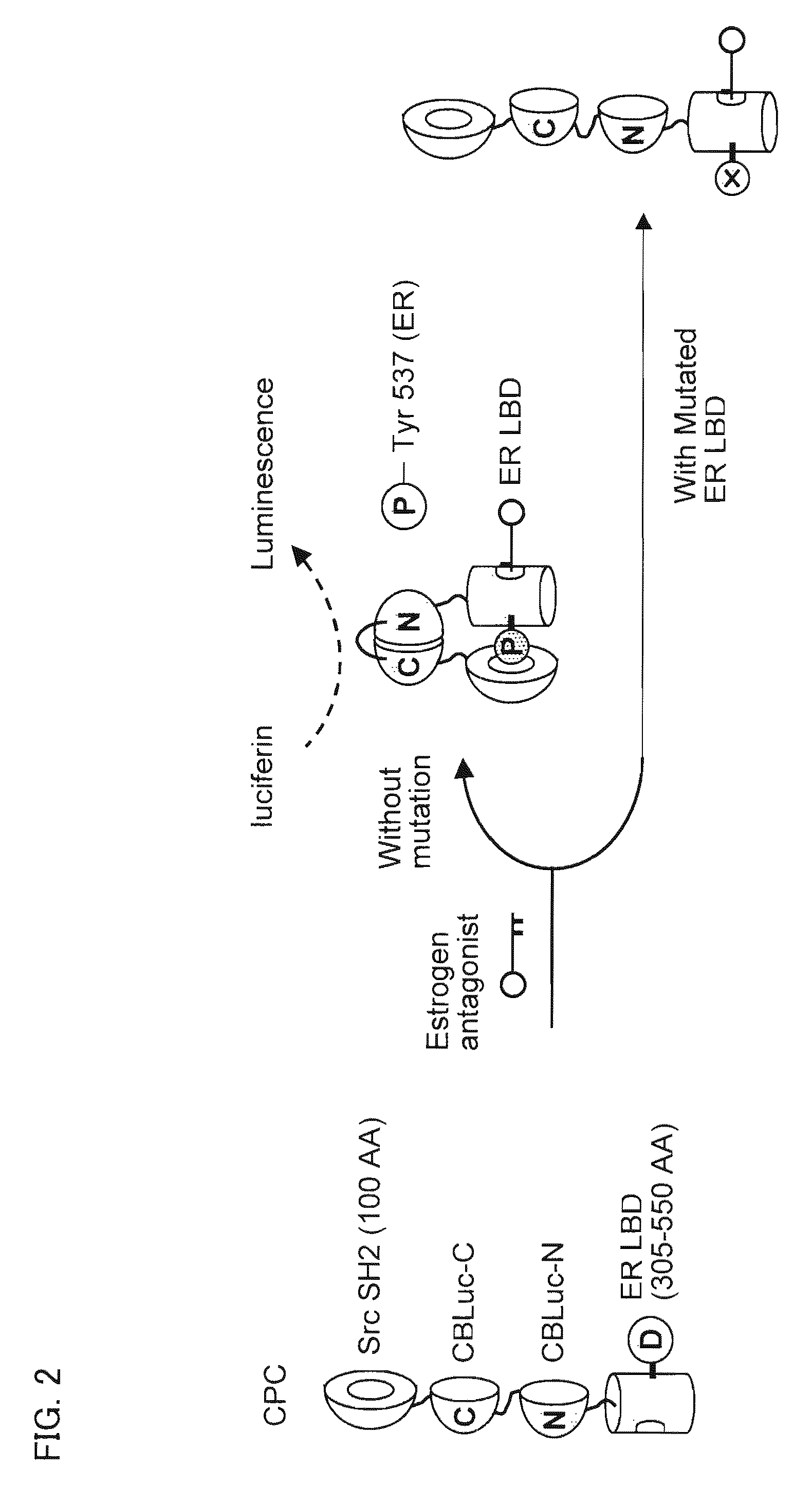
Single-Molecule-Format Probe And Utilization Thereof
InactiveUS20090269781A1High sensorial efficiencySuppresses background enzyme activityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesCrystallographyProtein target
A single-chain probe of the present invention for detecting a ligand, comprises: a ligand binding protein for binding the ligand; a recognition protein for recognizing that the ligand is bound by the ligand binding protein; and C— and N-terminal fragments, generated by dissecting an enzyme, between the ligand binding protein and the recognition protein, wherein a carboxy terminal end of the C-terminal fragment is located upstream of an amino terminal end of the N-terminal fragment, and the C— and N-terminal fragments vary the enzyme activity via complementation in case where the recognition protein recognizes that the ligand is bound by the ligand binding protein. This makes it possible to achieve detection of a target protein-specific ligand using the single chain with a high efficiency.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Iterative interference canceller for wireless multiple-access systems employing closed loop transmit diversity
ActiveUS20070110137A1Maximize signal-to-noise ratioPolarisation/directional diversityBaseband systemsTransmit diversityDiversity scheme
An interference-canceling receiver processes coded, multiple-access, spread-spectrum transmissions that propagate through frequency-selective communication channels from multiple transmit antennas to multiple receive antennas in a closed-loop transmit-diversity channel. The receiver provides for repeated use of symbol-estimate weighting, subtractive cancellation with a stabilizing step-size, and mixed-decision symbol estimation. Receivers may be designed, adapted, and implemented explicitly in software or programmed hardware, or implicitly in standard Rake-based hardware, either within a Rake receiver at the finger level or outside the Rake at the user or subchannel symbol level. The receiver may be employed in user equipment on the forward link or in a base station on the reverse link.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Iterative interference canceller for wireless multiple-access systems employing closed loop transmit diversity
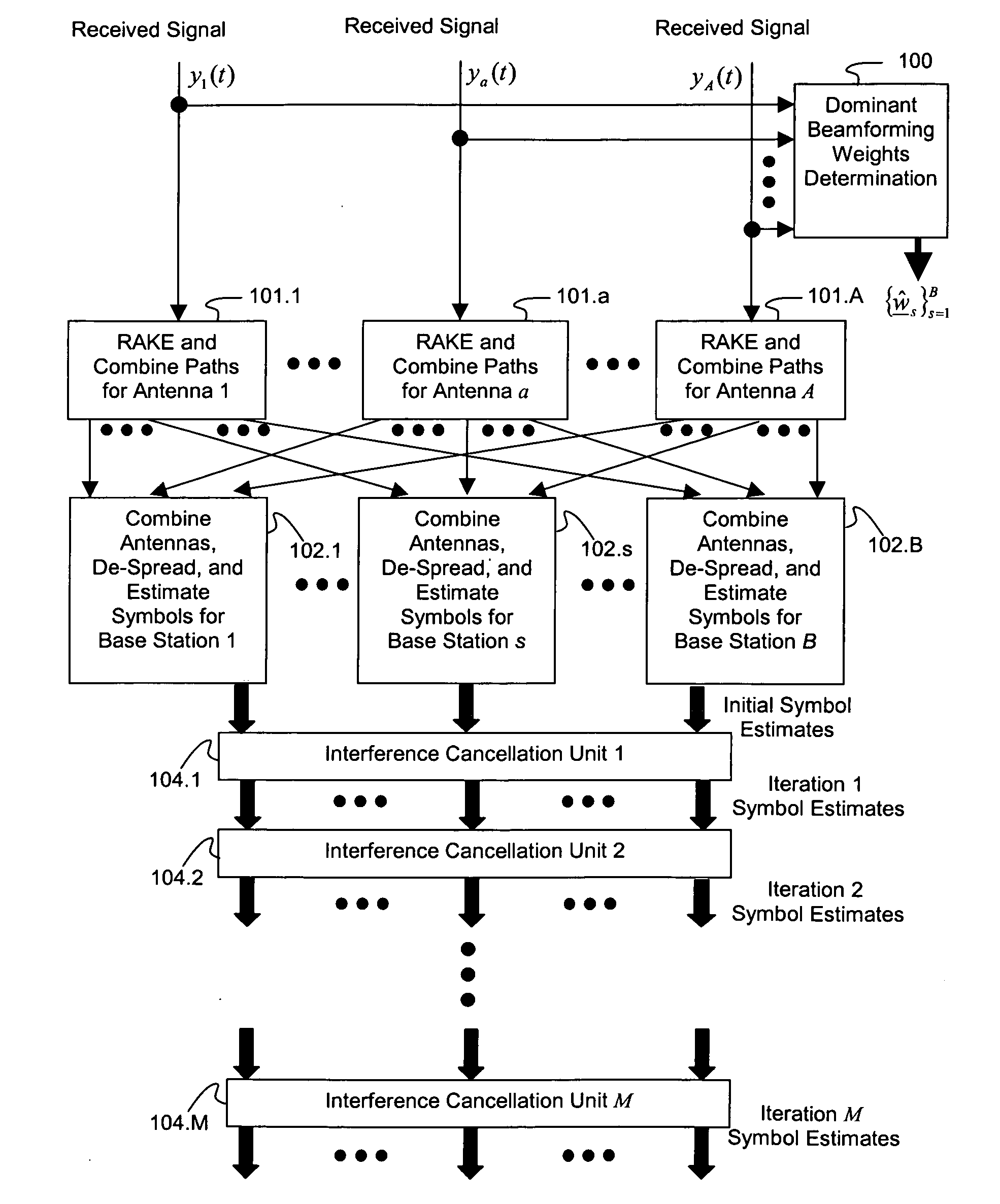
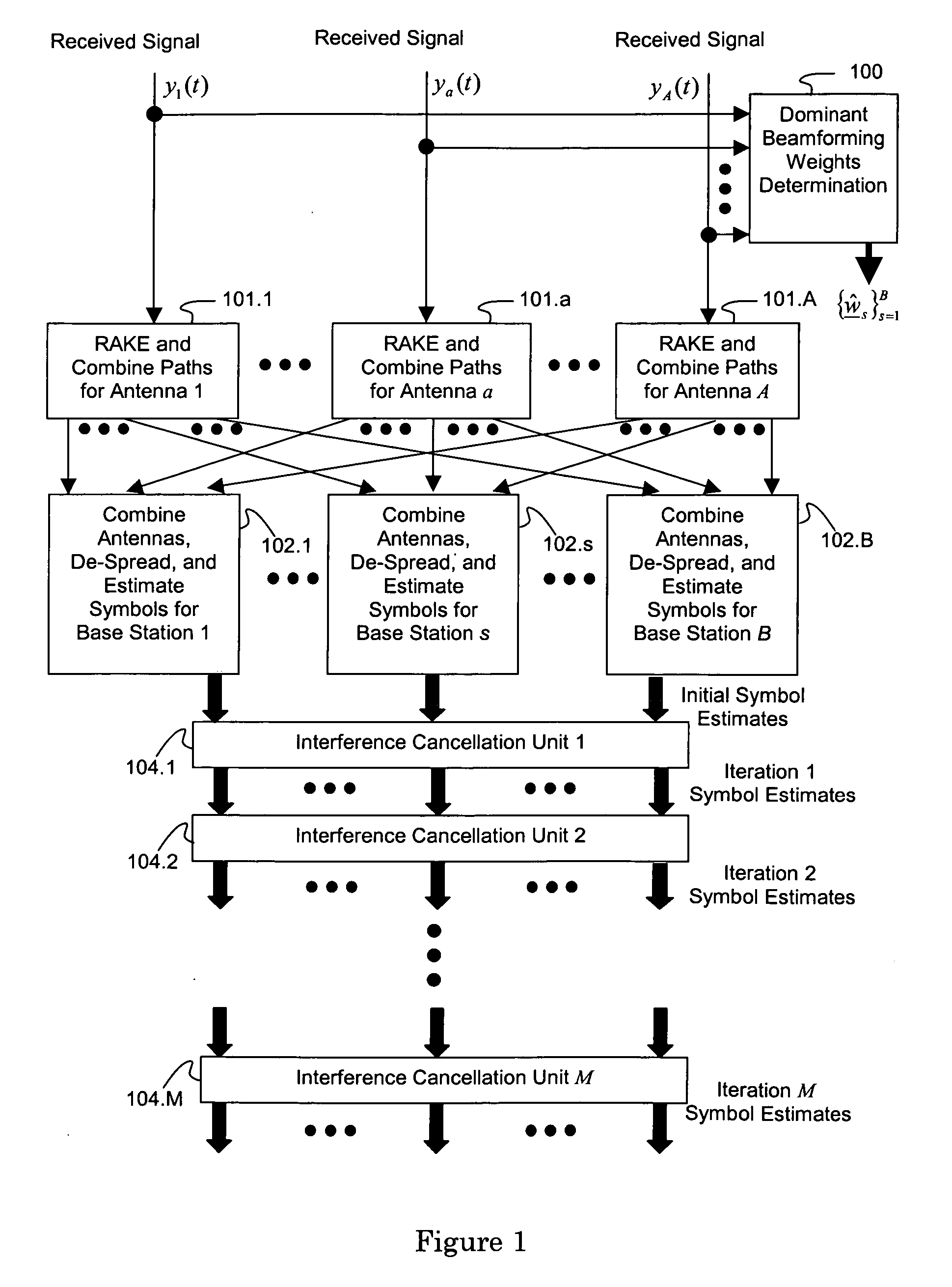
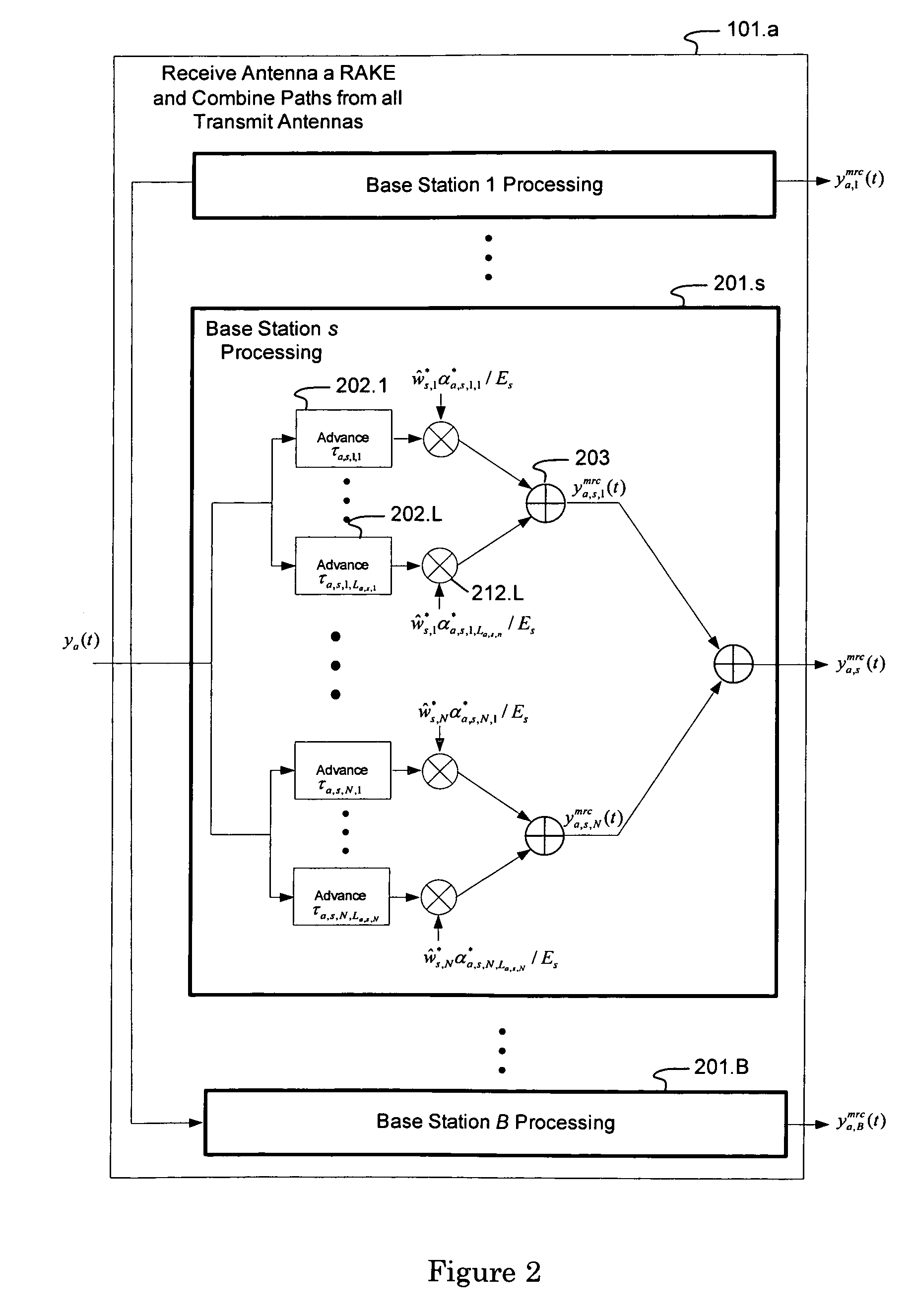
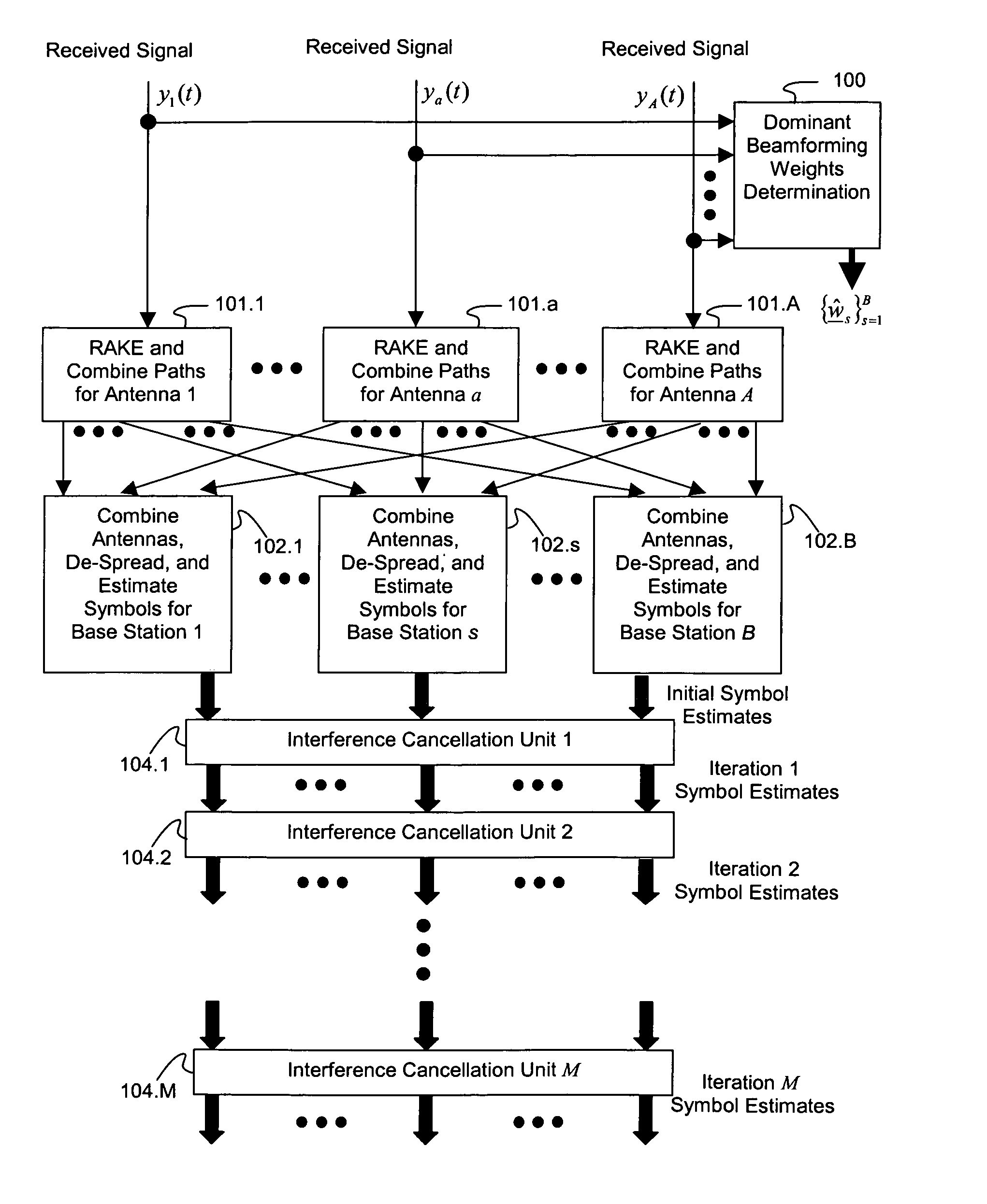
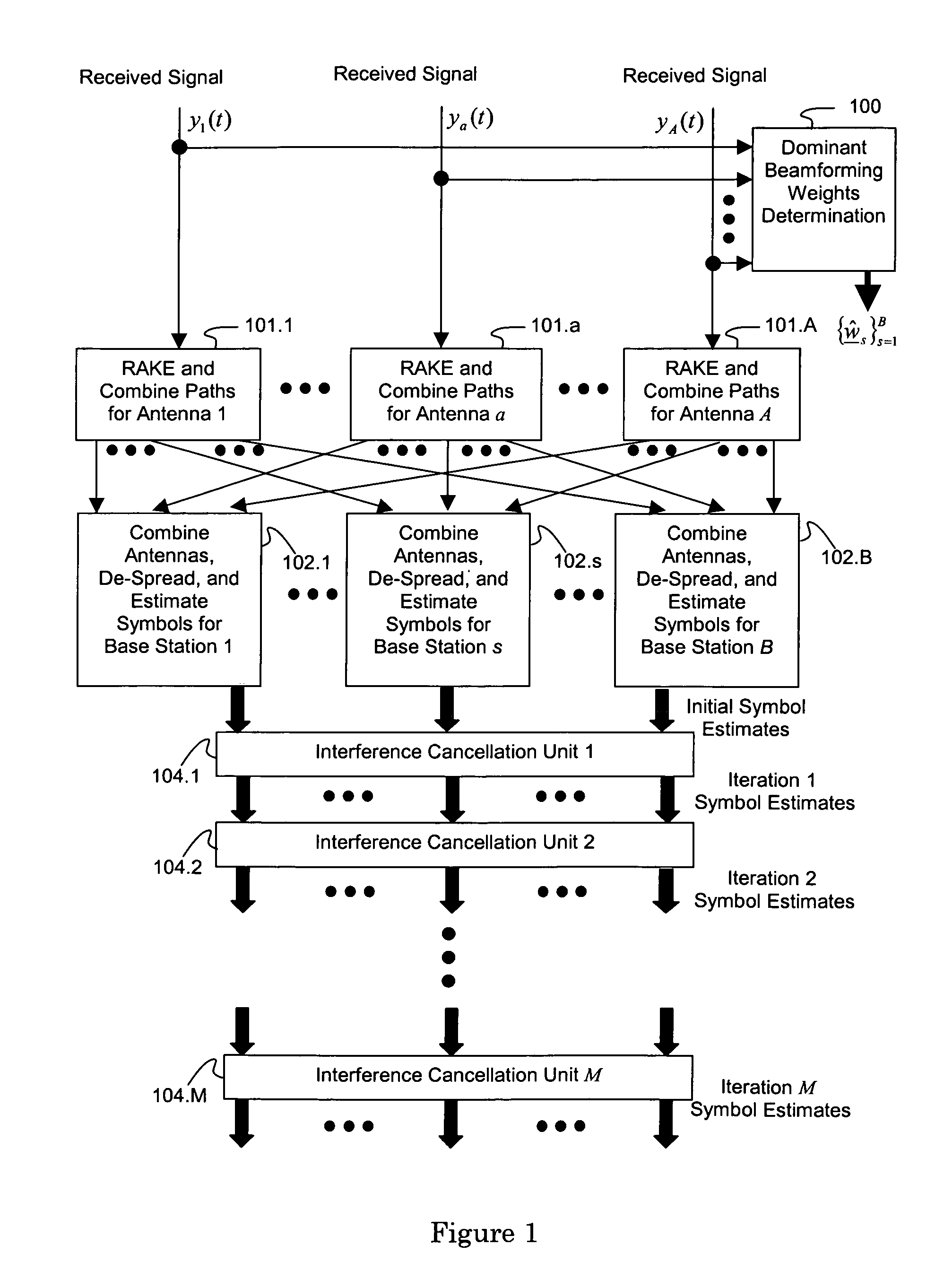
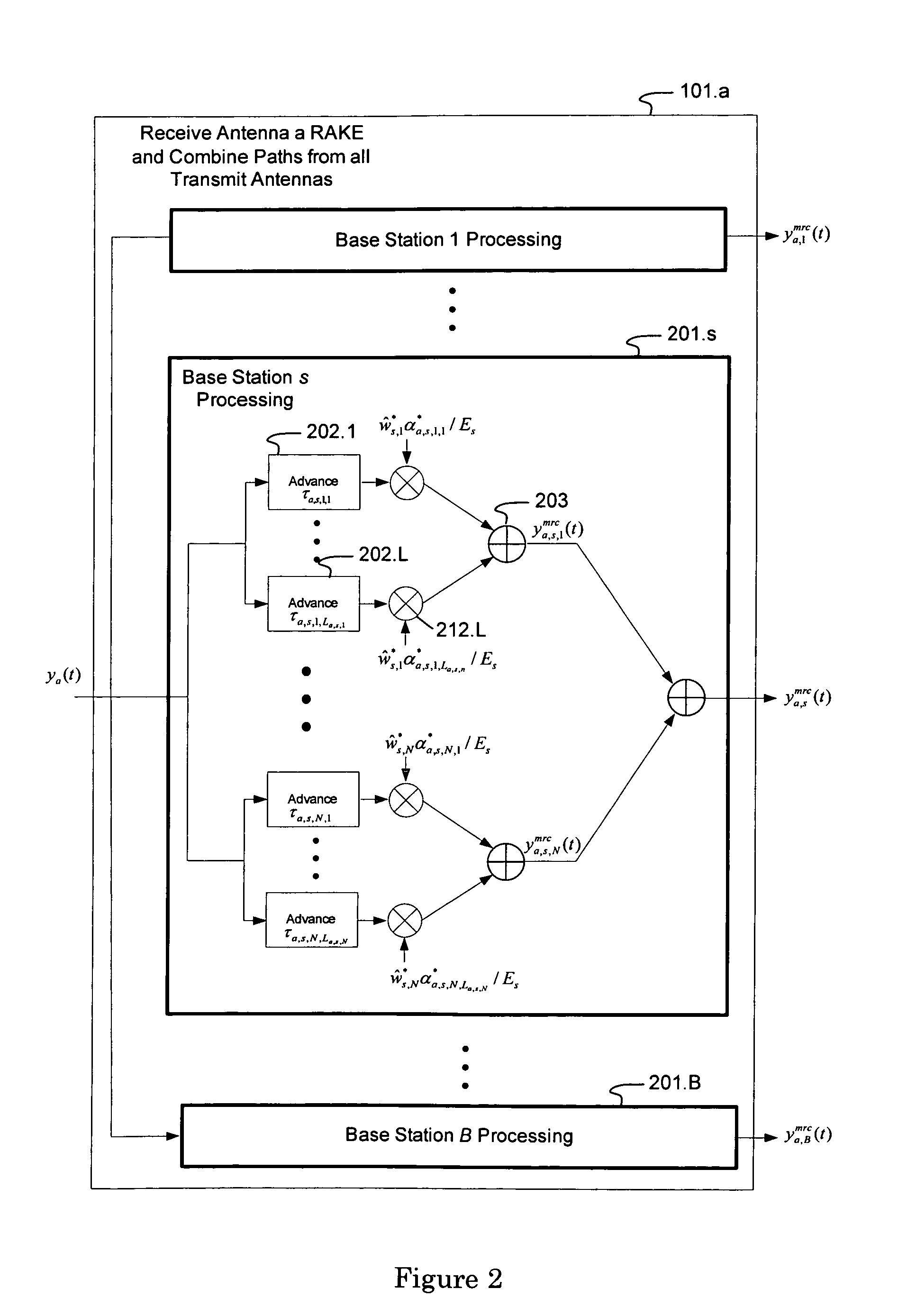
ActiveUS7623602B2Maximize signal to noise ratioPolarisation/directional diversityBaseband systemsInterference cancellerClosed loop
An interference-canceling receiver processes coded, multiple-access, spread-spectrum transmissions that propagate through frequency-selective communication channels from multiple transmit antennas to multiple receive antennas in a closed-loop transmit-diversity channel. The receiver provides for repeated use of symbol-estimate weighting, subtractive cancellation with a stabilizing step-size, and mixed-decision symbol estimation. Receivers may be designed, adapted, and implemented explicitly in software or programmed hardware, or implicitly in standard Rake-based hardware, either within a Rake receiver at the finger level or outside the Rake at the user or subchannel symbol level. The receiver may be employed in user equipment on the forward link or in a base station on the reverse link.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com