Patents
Literature
89 results about "Adaptive antenna array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
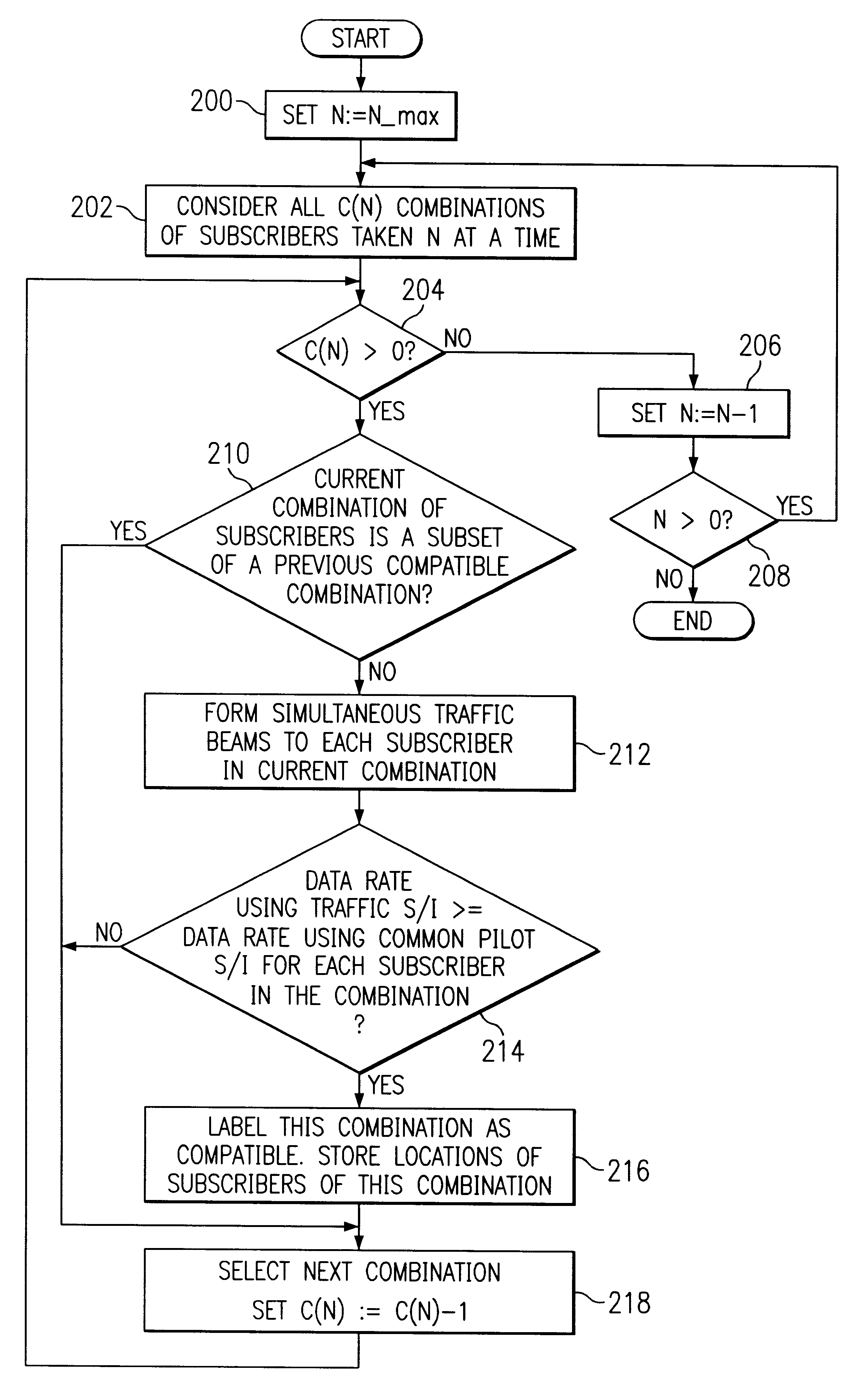
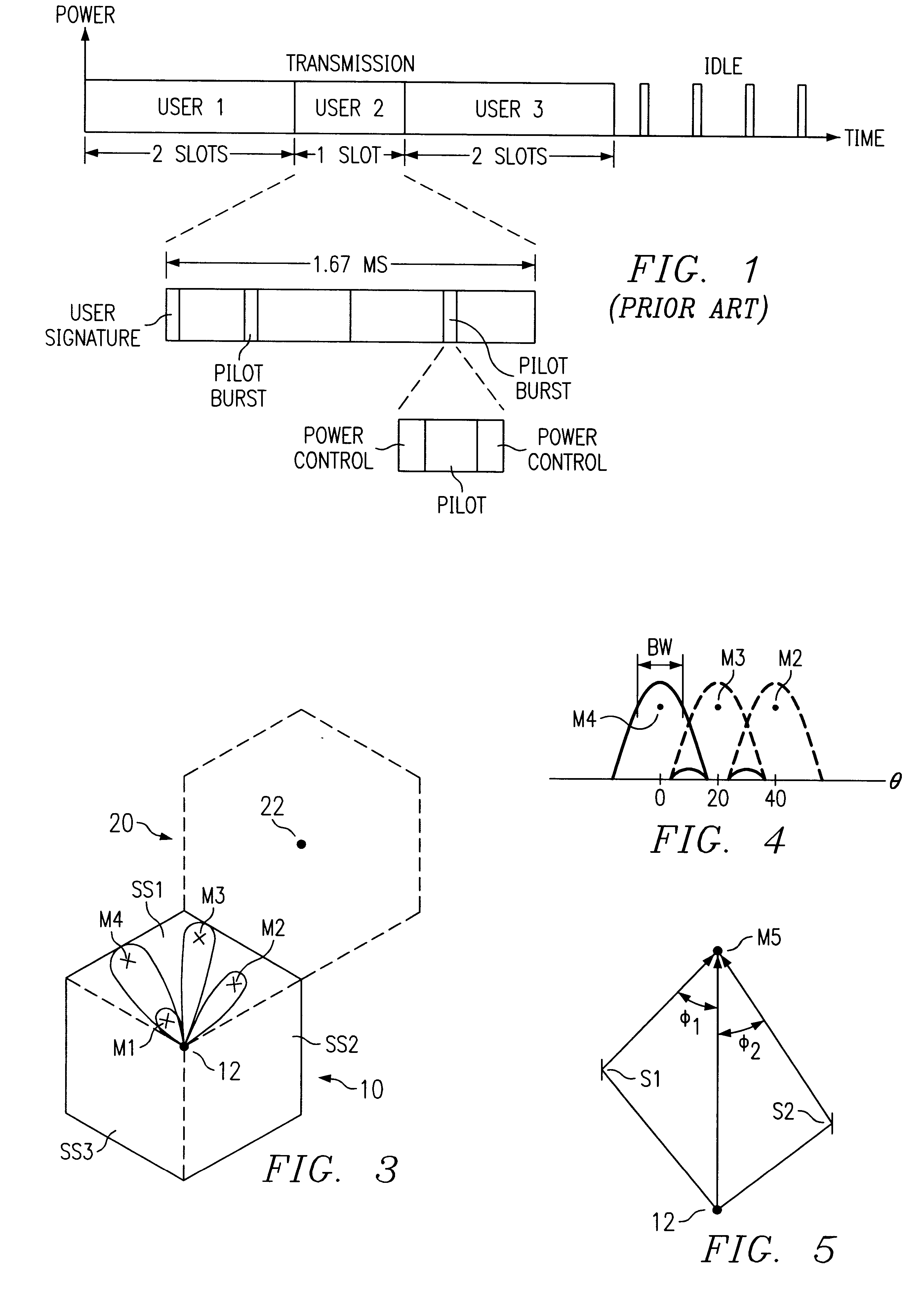
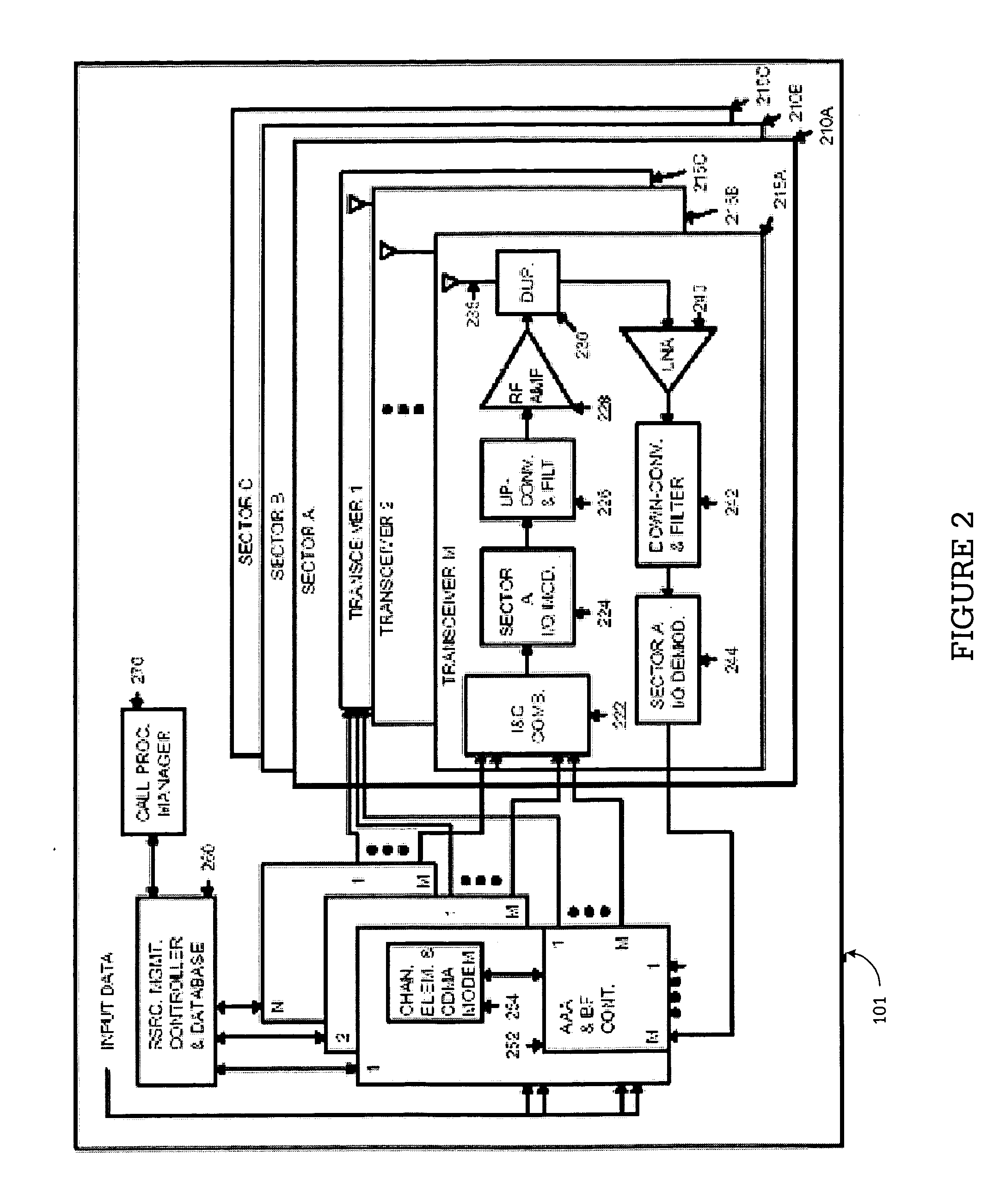
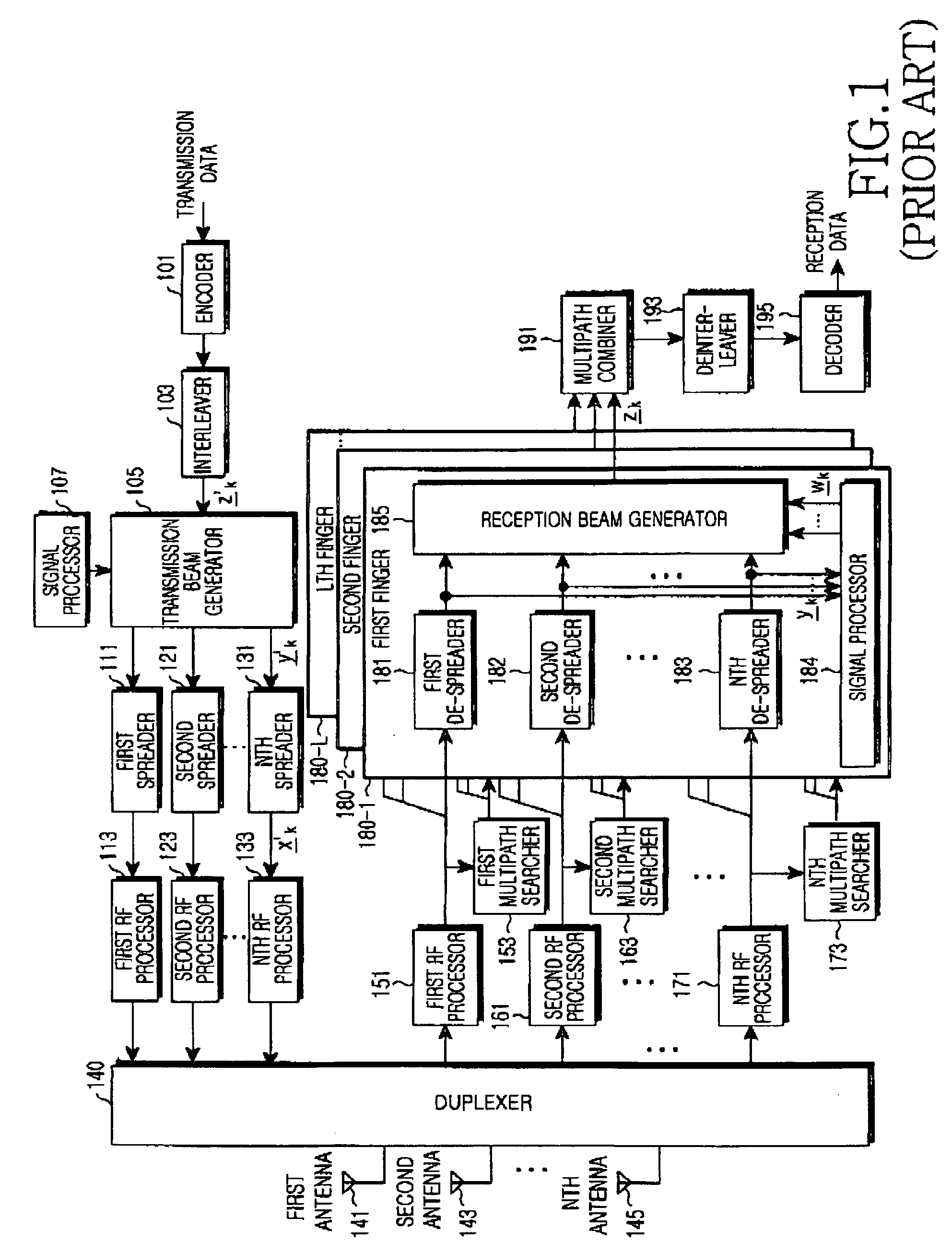
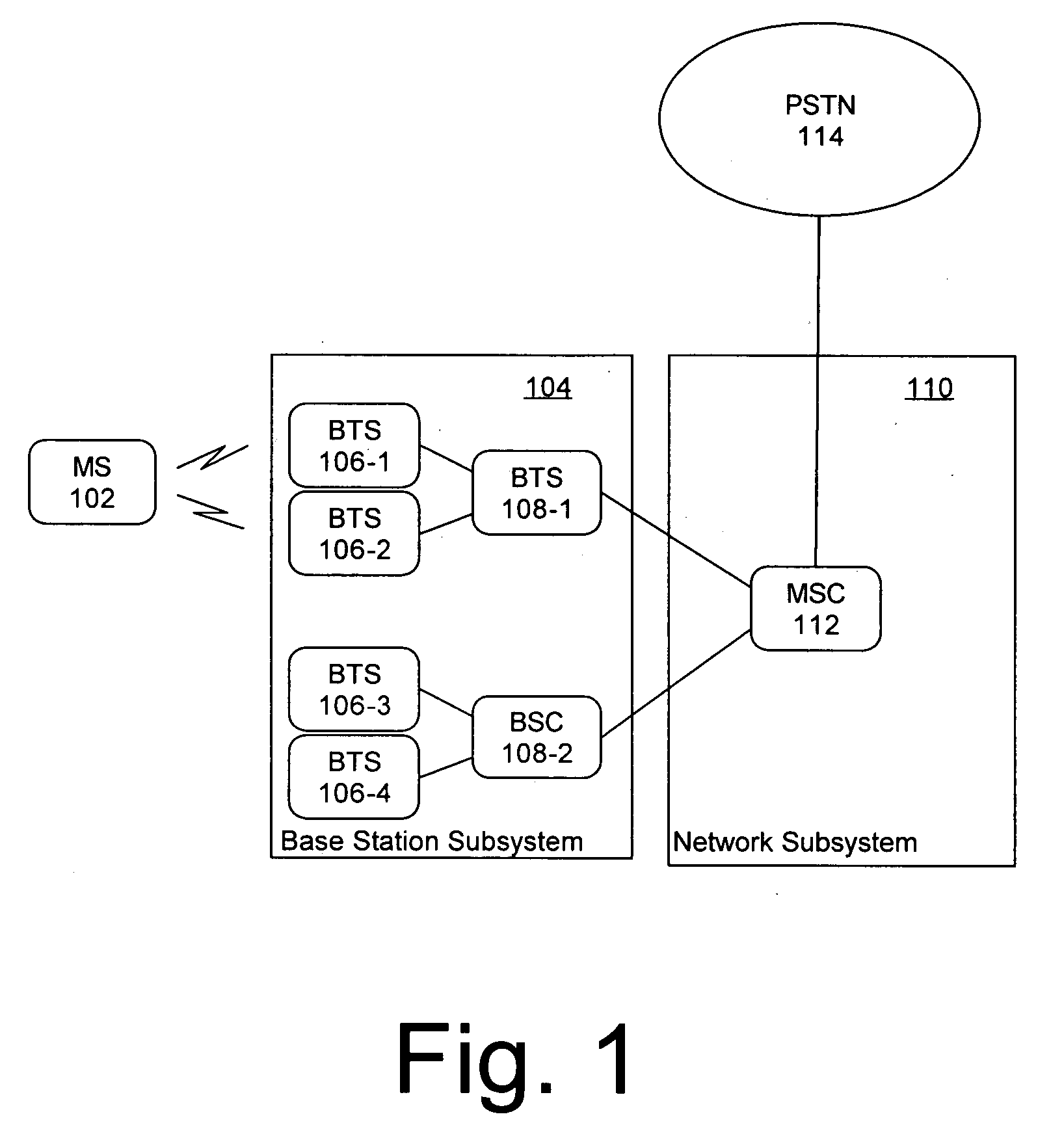
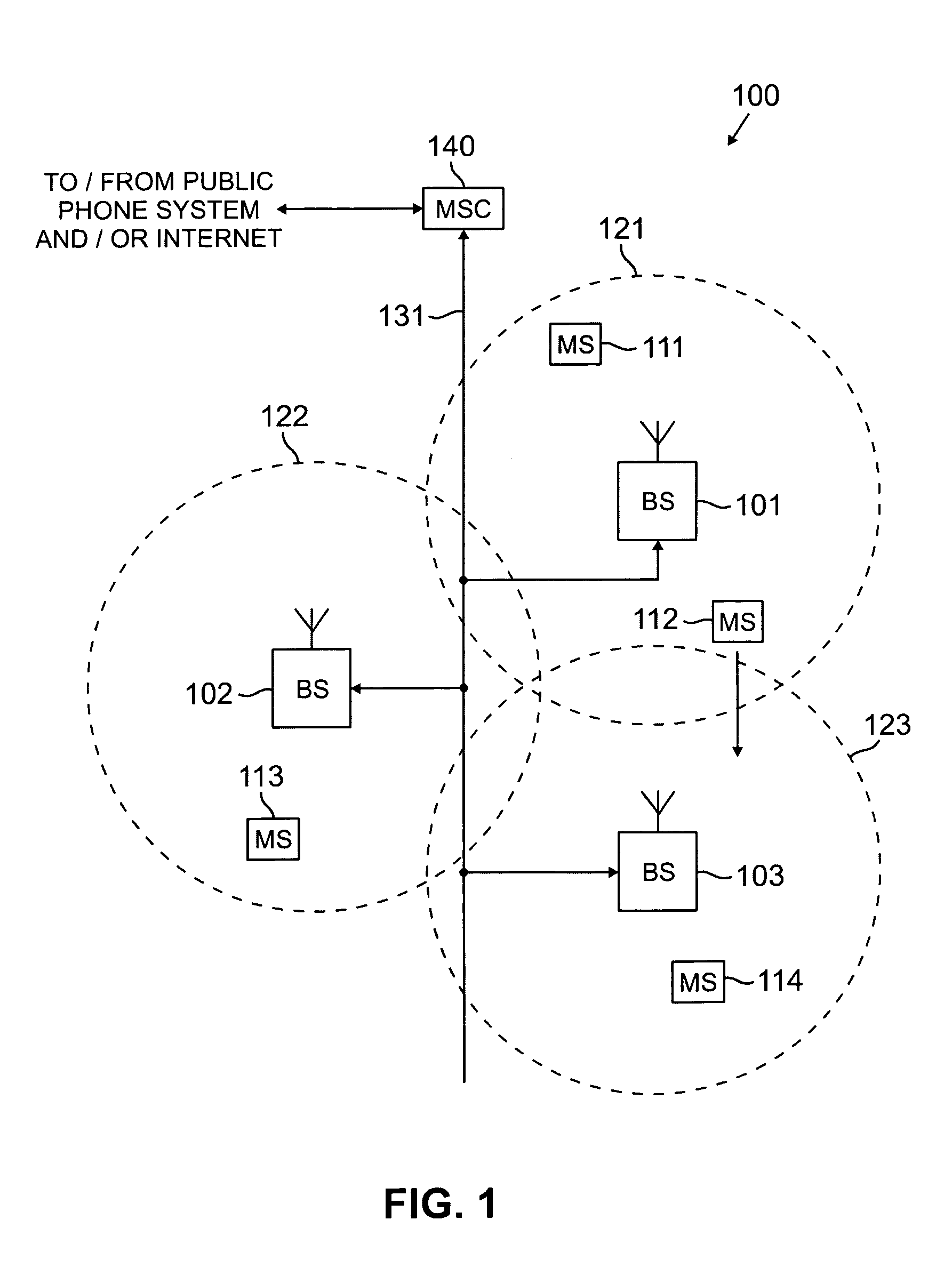
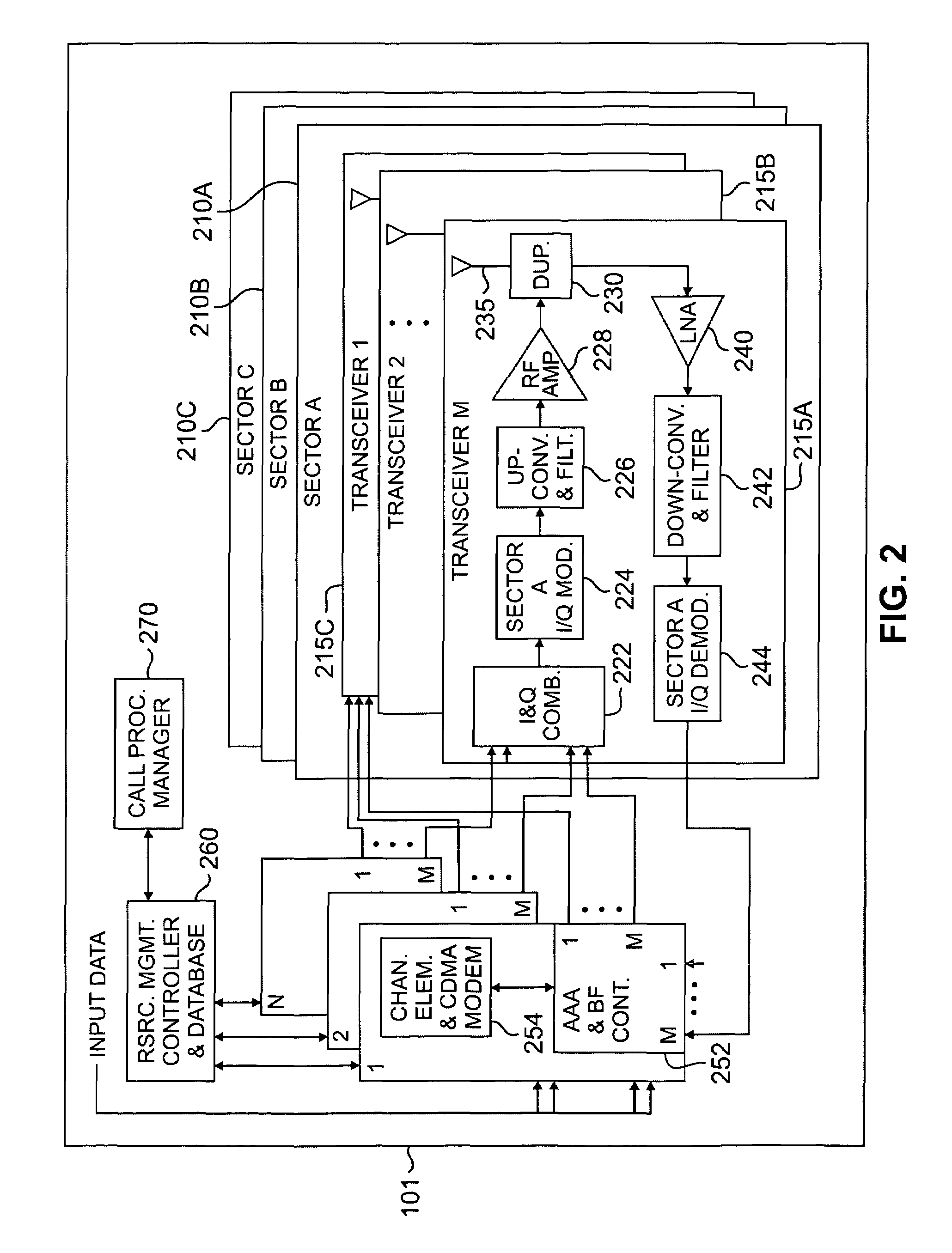
Simultaneous forward link beam forming and learning method for mobile high rate data traffic
InactiveUS6330460B1Increase aggregate digital data packet throughputImprove data transfer ratePower managementSpatial transmit diversityHigh rateCommunications system
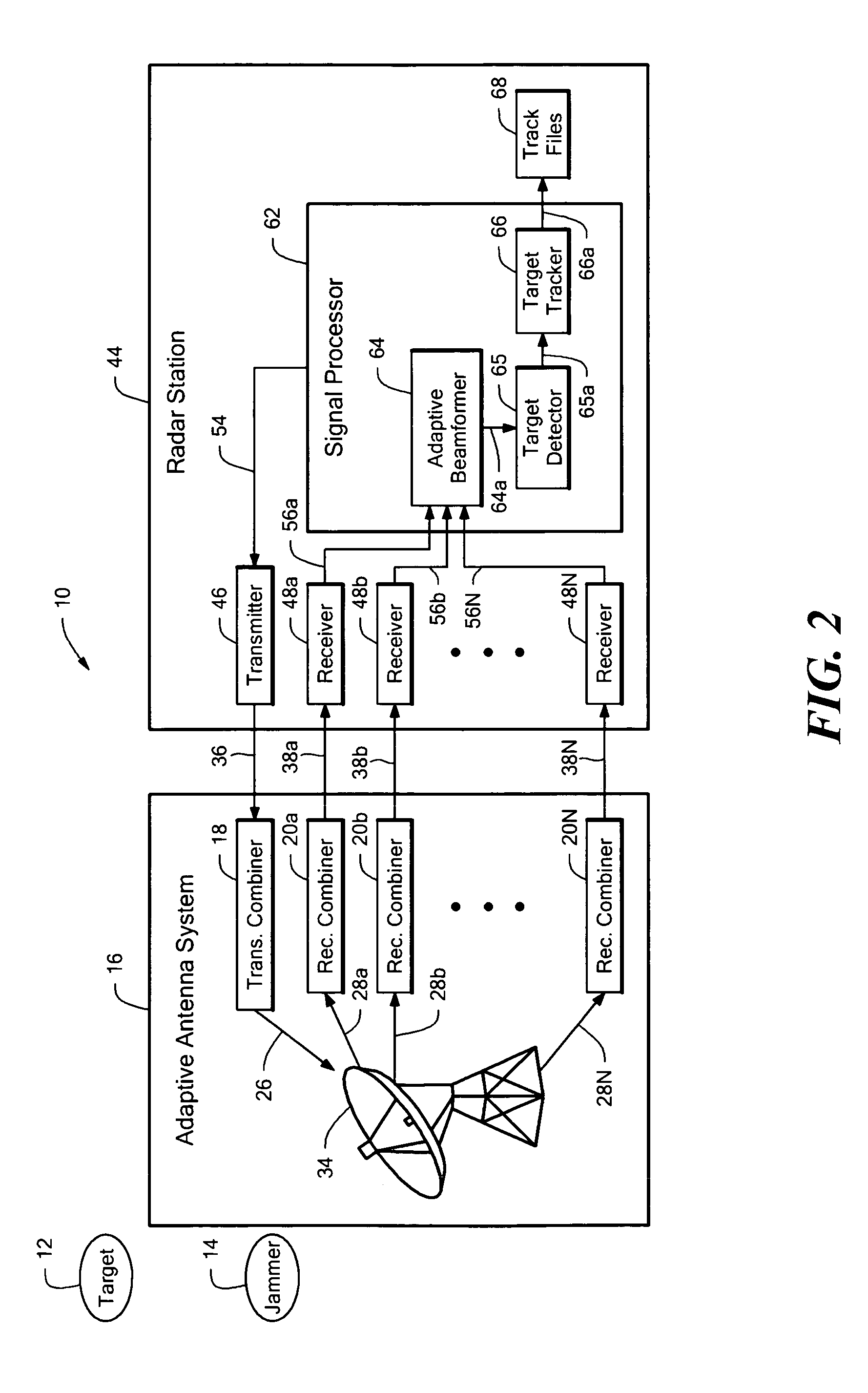
Disclosed is a base station of a wireless communications system including an adaptive antenna array and beam forming means for forming simultaneous multiple forward link beams. Preferably mobile stations are separated into groups of mobile stations corresponding to a maximum number of simultaneous forward link beams for determining which of said groups can be served by compatible simultaneous forward link beams. Preferably, if mobiles remain outside of a compatible group, the number of simultaneous forward link beams is increased and grouping of the mobile stations is repeated until all the mobile stations are included in compatible groups. Preferably simultaneous data beams are formed to mobiles of a said group during a time interval accorded to said group, such that every mobile station receives service data during a full cycle of said time intervals at a rate equal to or in excess of a target service data rate for that mobile.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
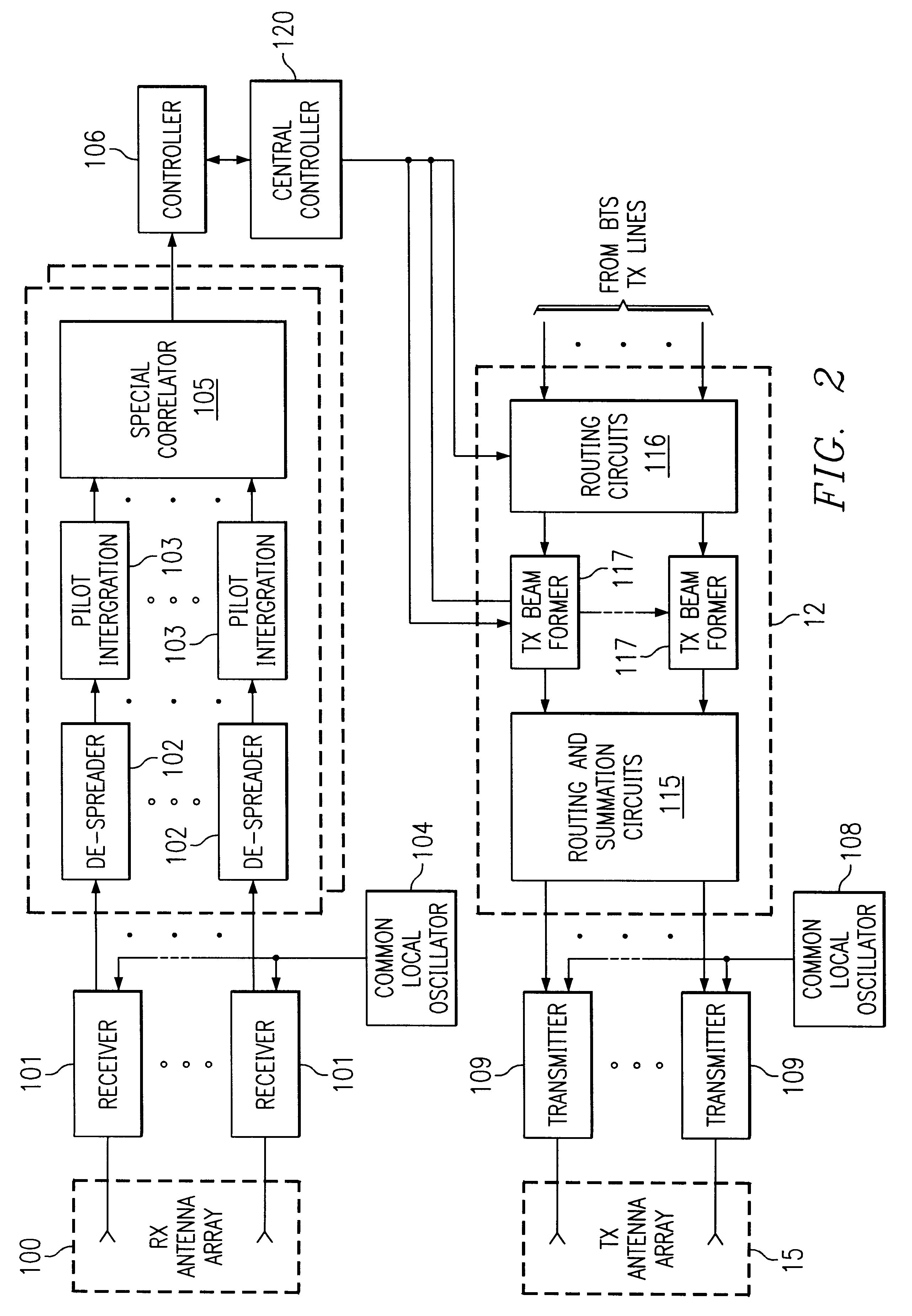
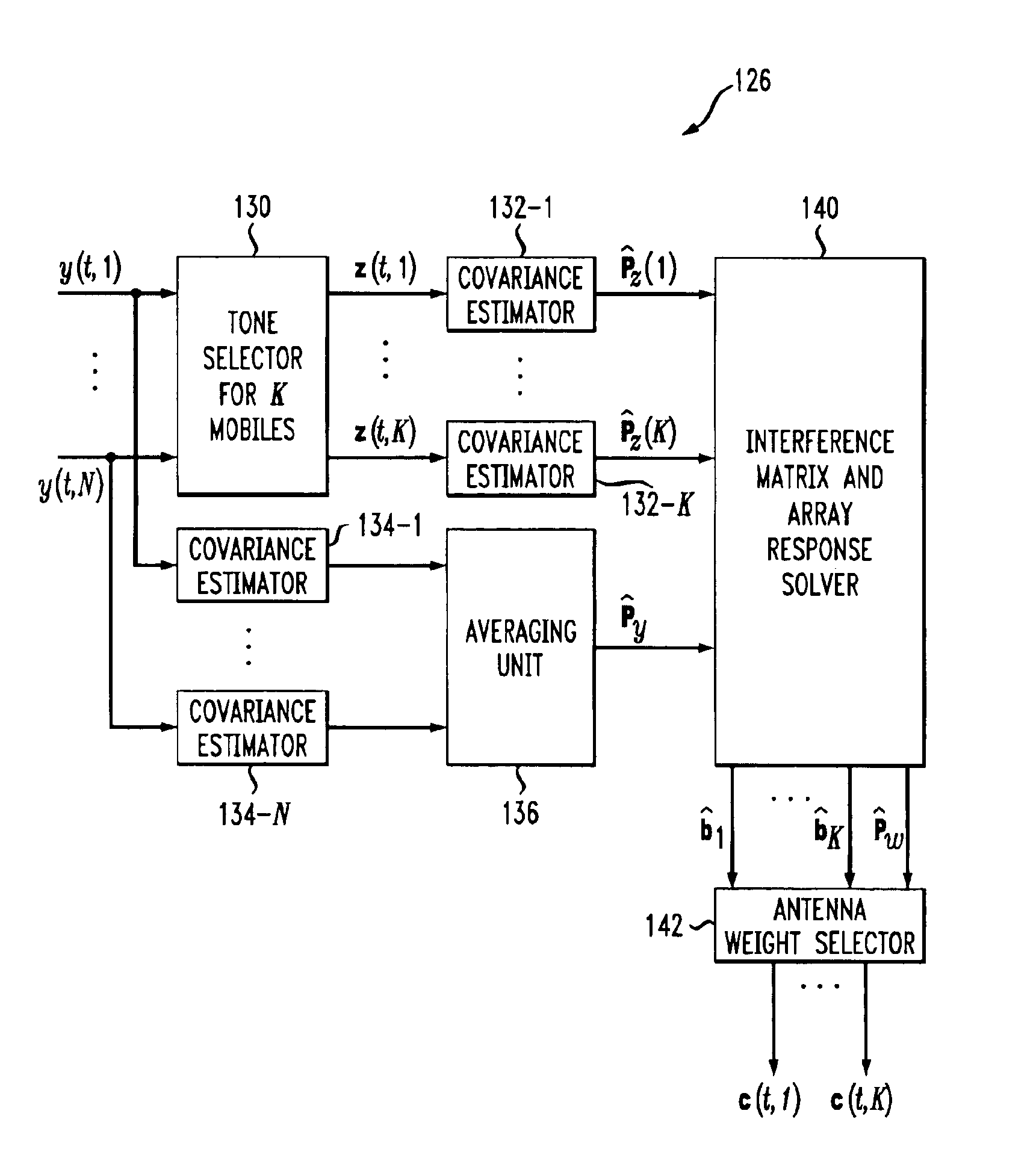
Adaptive antenna array methods and apparatus for use in a multi-access wireless communication system
InactiveUS6920192B1Fast convergenceReduce computing costSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityInterference (communication)Communications system
Adaptive antenna array techniques for use in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed spread-spectrum multi-access (OFDM-SSMA) cellular wireless system or other type of wireless communication system. A base station of the system includes an antenna array and a base station receiver. The base station receiver implements an adaptive antenna gain algorithm which estimates a spatial covariance matrix for each of K mobile stations communicating with the base station. The spatial covariance matrix for a given one of the mobile stations is determined at least in part based on a unique hopping sequence of the mobile station, and provides a correlation between signals received from the mobile station at different antenna elements within the antenna array. An average spatial covariance matrix for a set of received signals is also generated. The individual spatial covariance matrices and the average spatial covariance matrix are processed to generate an estimate of an interference matrix for the K mobile stations, and the estimate of the interference matrix is further processed to generate array responses for each of the mobile stations. The array response for a given mobile station is processed to determine an antenna weighting which is applied to a signal received from the given mobile station in order to facilitate detection of a corresponding transmitted symbol.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
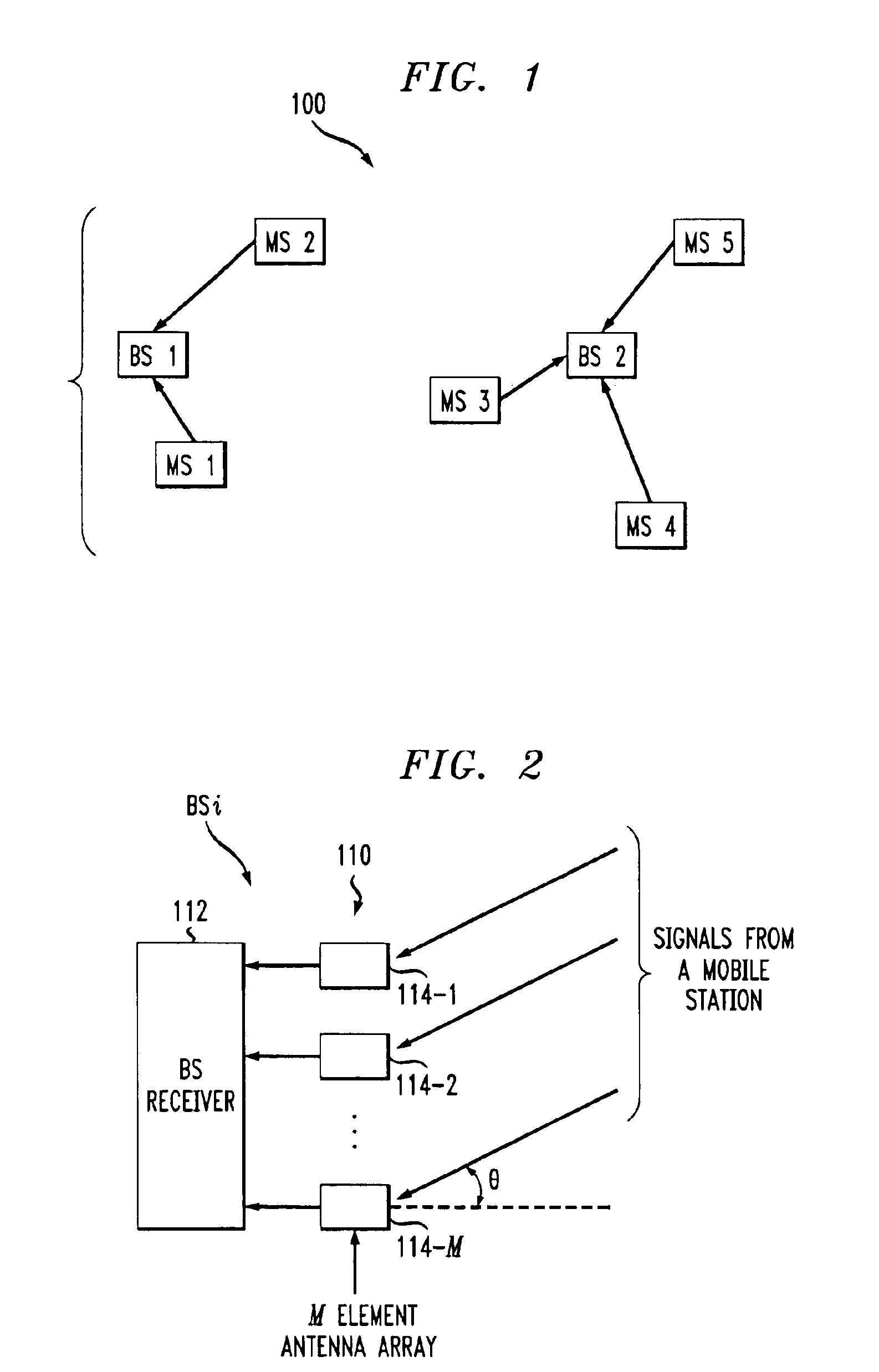
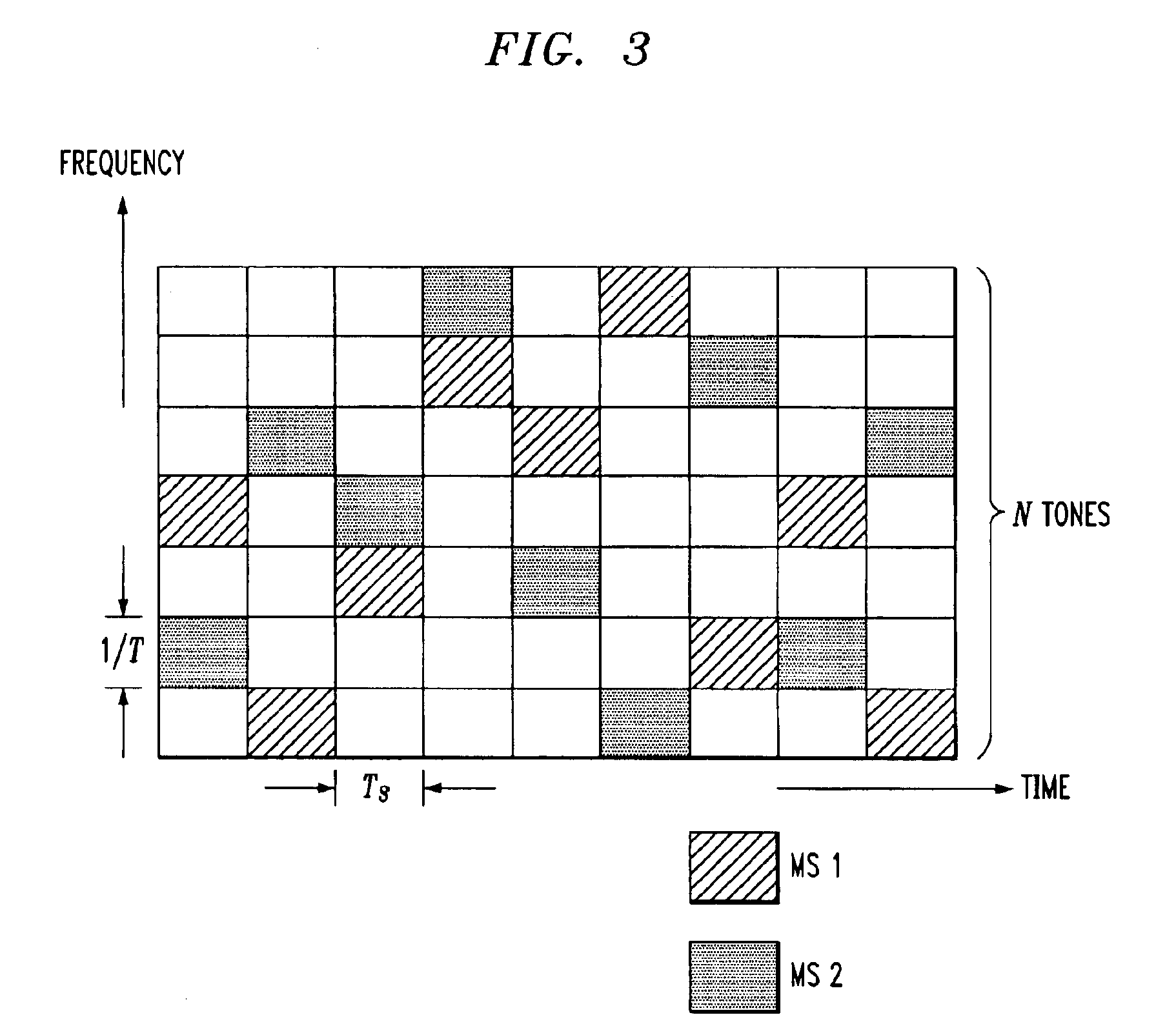
Coordinated hopping in wireless networks using adaptive antenna arrays
InactiveUS7054301B1Time-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemDiversity scheme
The present invention allows many of the benefits of spatial diversity to be realized in a hopping radio communications system. One embodiment of the invention includes transmitting signals from a first radio using a first hopping sequence and transmitting signals from a second radio using spatial processing and a second hopping sequence. The second hopping sequence is coordinated with the first hopping sequence. In another embodiment, the invention includes selecting a set of spatial processing parameters based, at least in part, on a determination whether a third radio using a first frequency resource during a first time interval uses a second frequency resource during a second time interval and transmitting a signal from a first radio to a second radio during the second time interval using the second frequency resource and the selected set of spatial processing parameters.
Owner:INTEL CORP
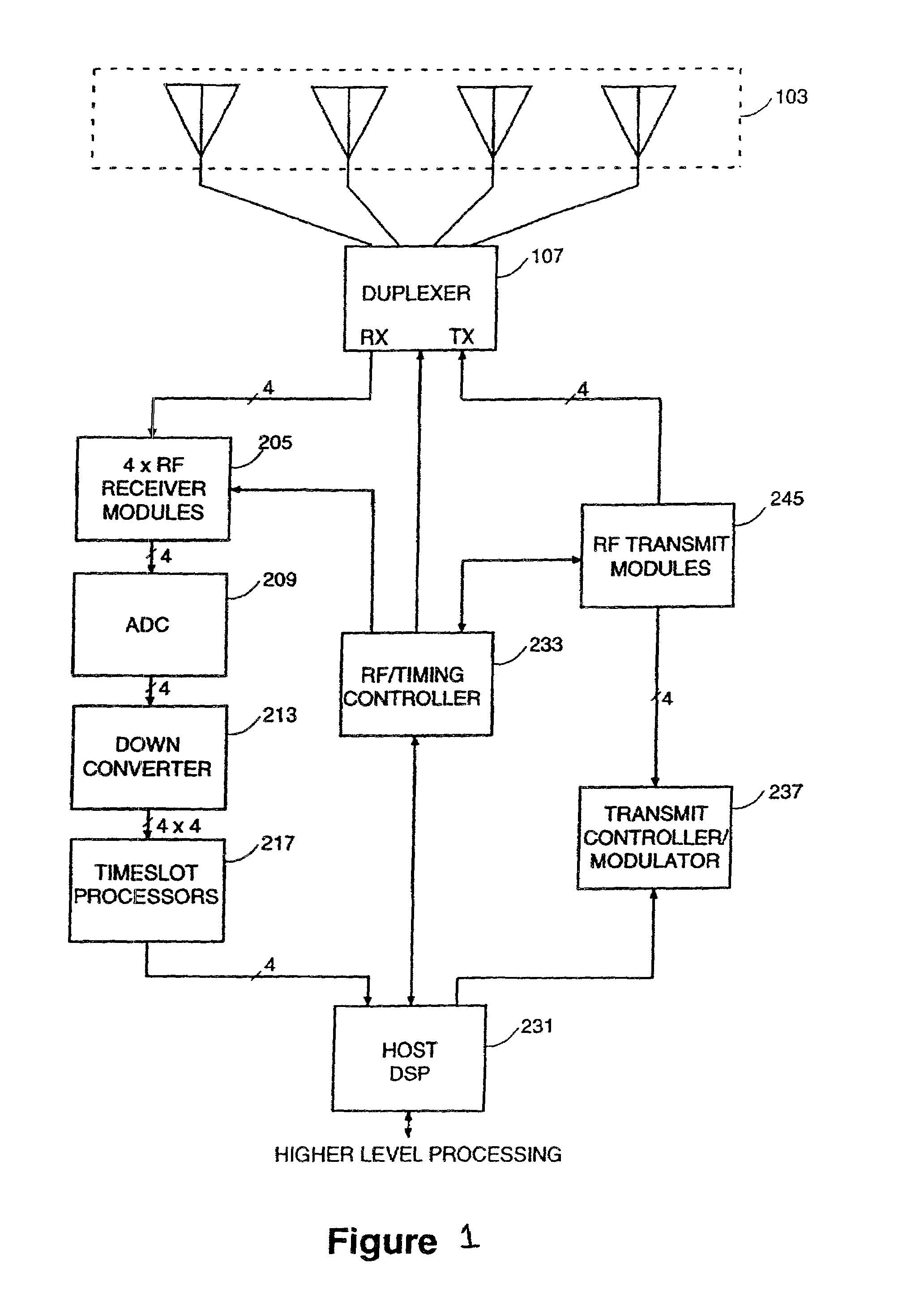
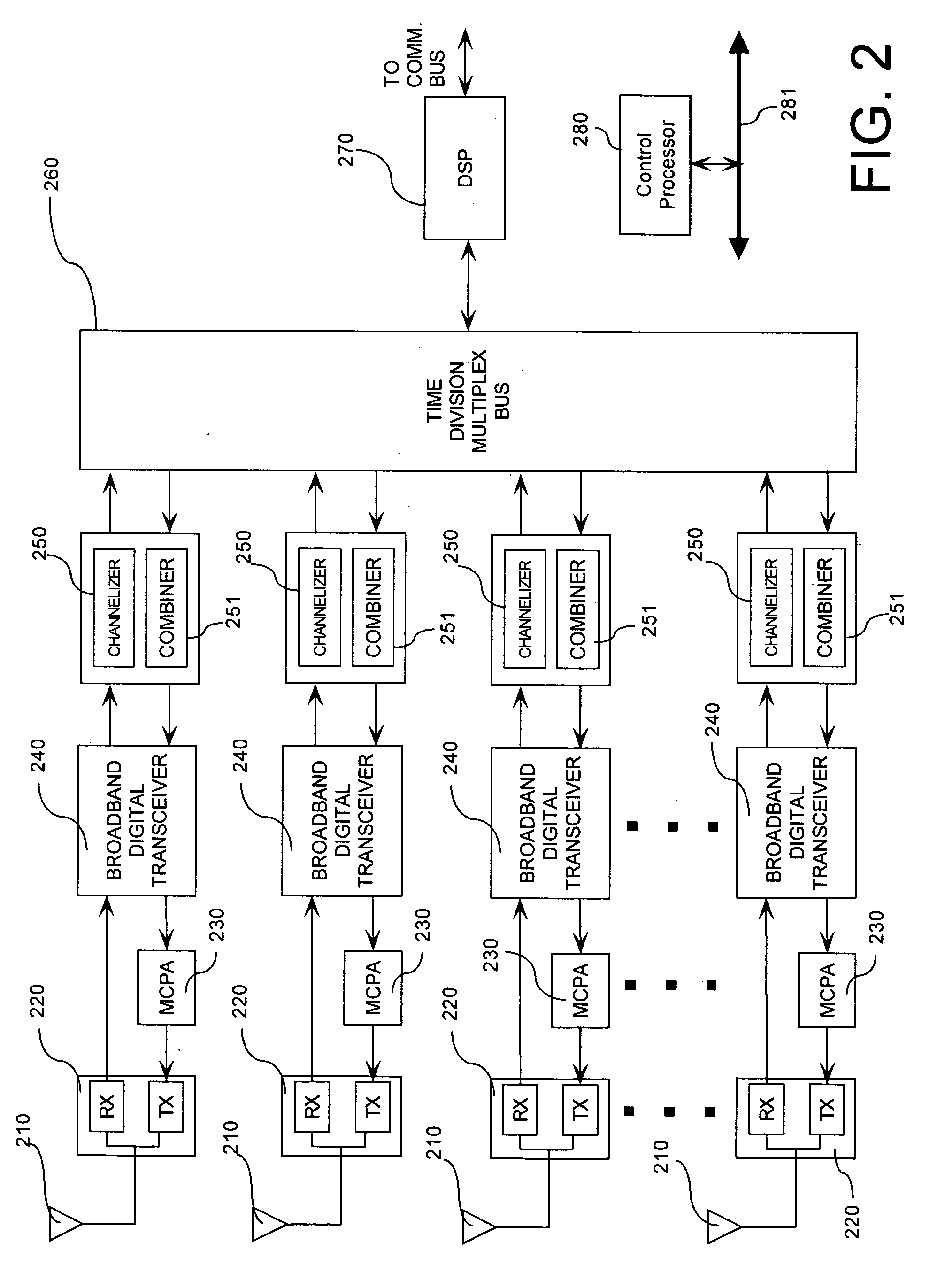
Method and apparatus for high rate data communication utilizing an adaptive antenna array
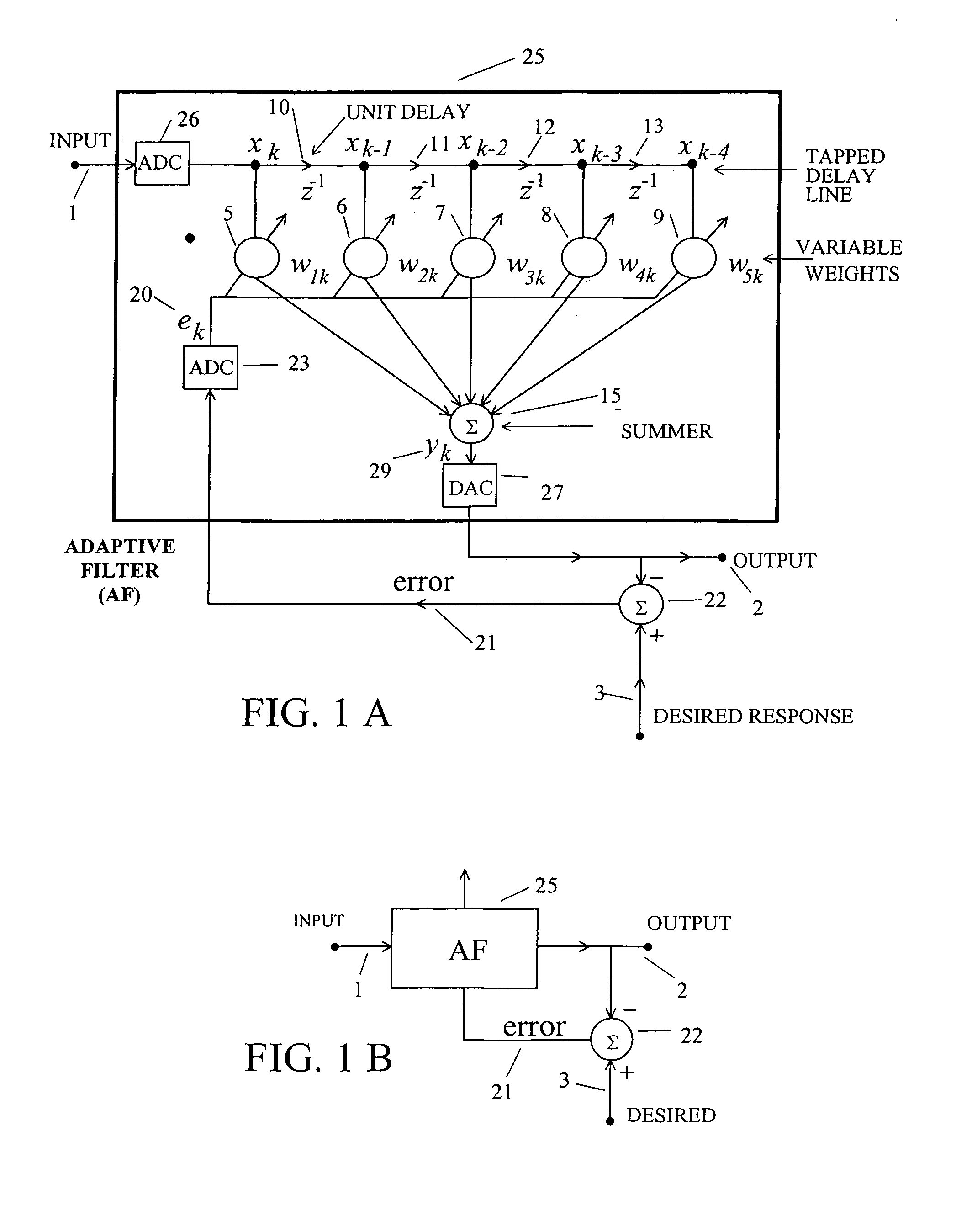
In a wideband Personal Communication Services system, a method and system are proposed for suppressing co-channel interference and reducing inter-symbol interference generated during the transfer of a data packet through a selected radio frequency channel. The system includes a weight controller utilizing recursive least squares algorithm to generate a plurality of appropriate weights to be integrated into received signals in order to maximize signal-to-noise ratio. A detected signal or a training sequence is intelligently switched in as a reference sequence in order to generate a plurality of appropriate weights. To further enhance the adaptive array system and take advantage of the multi-path radio frequency communication environment, two multi-path diversity schemes are included. One embodiment includes an adaptive array system with parallel array processors and another embodiment includes a system with tapped delay line processors.
Owner:APPLE INC
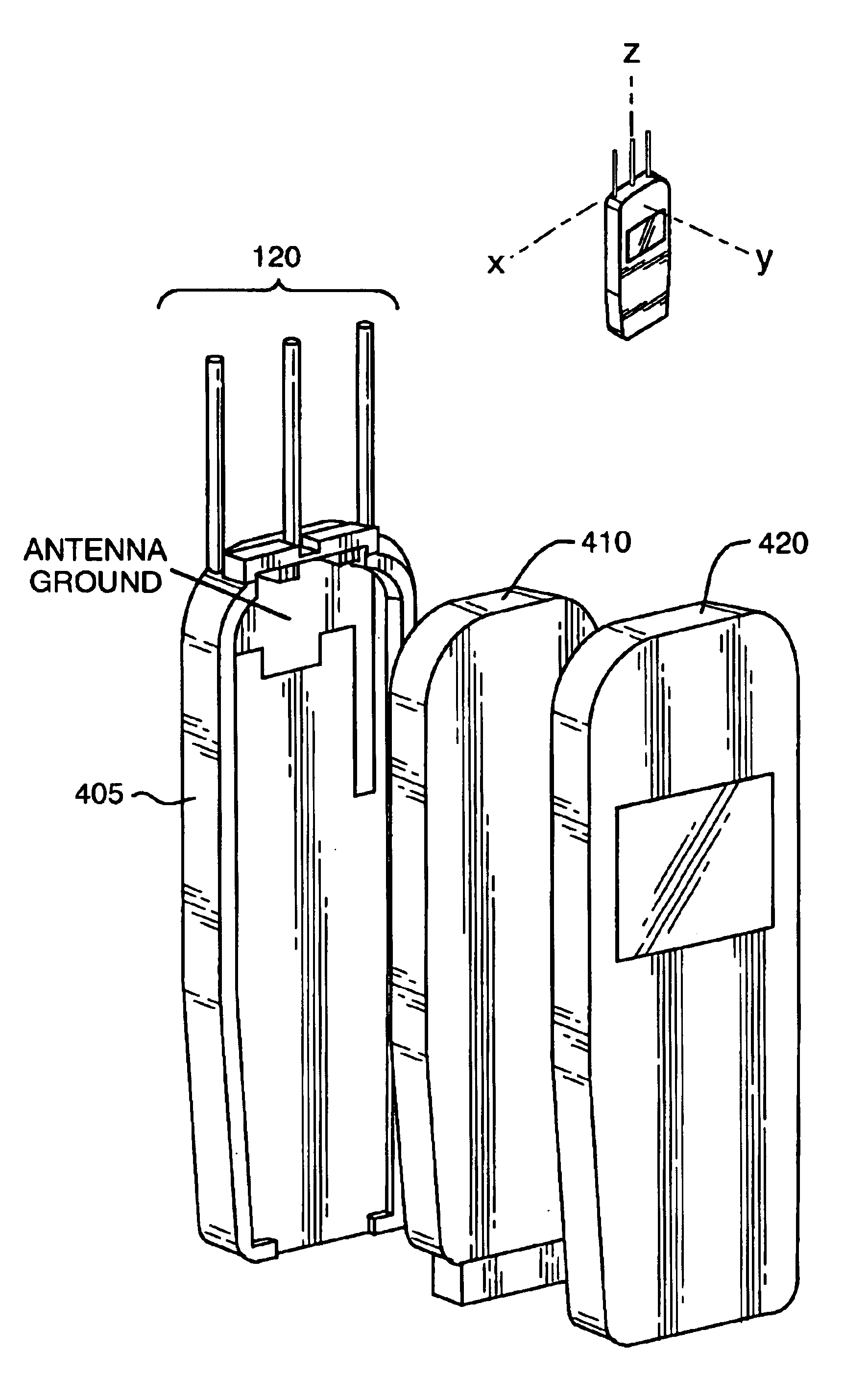
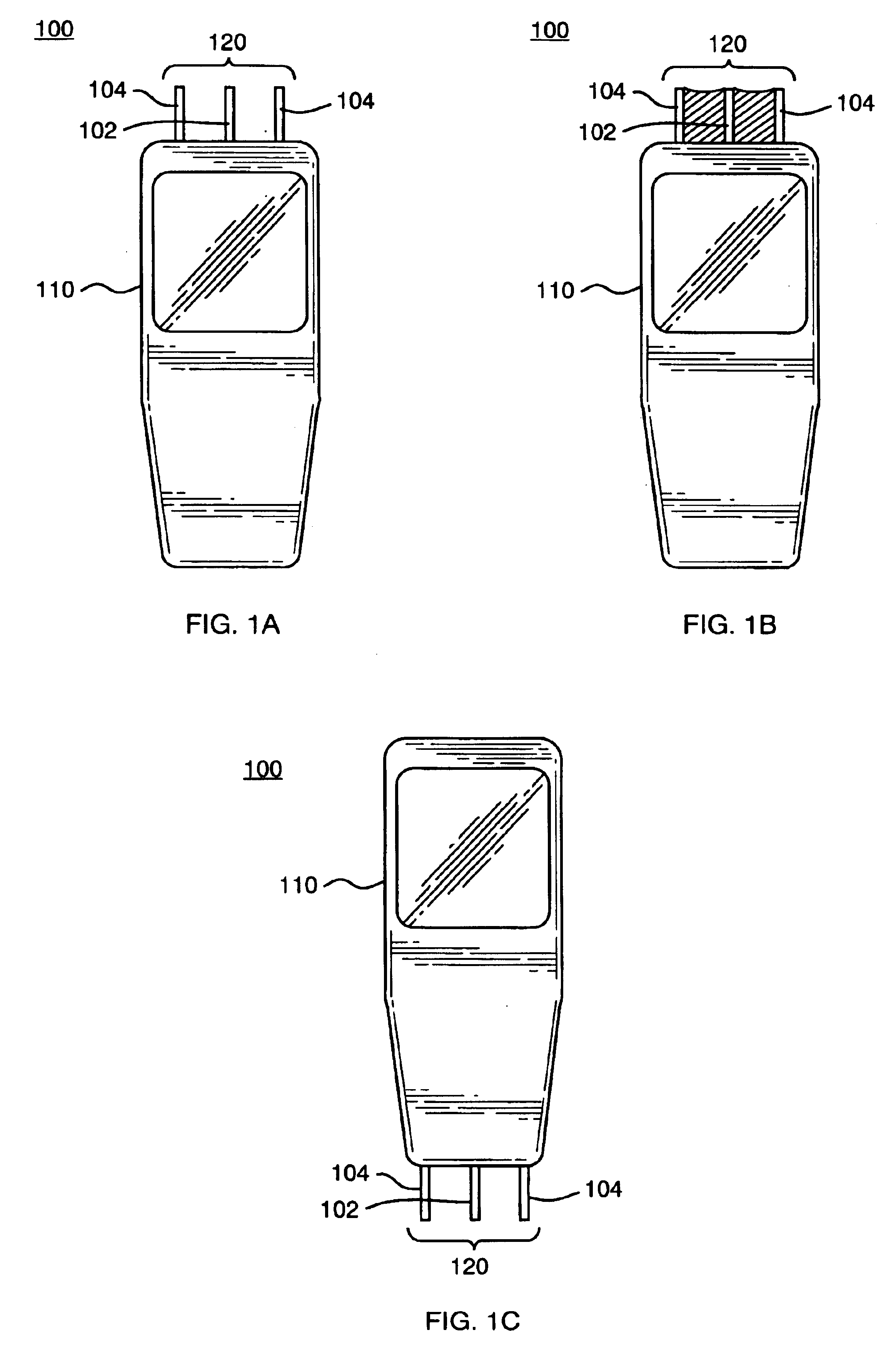
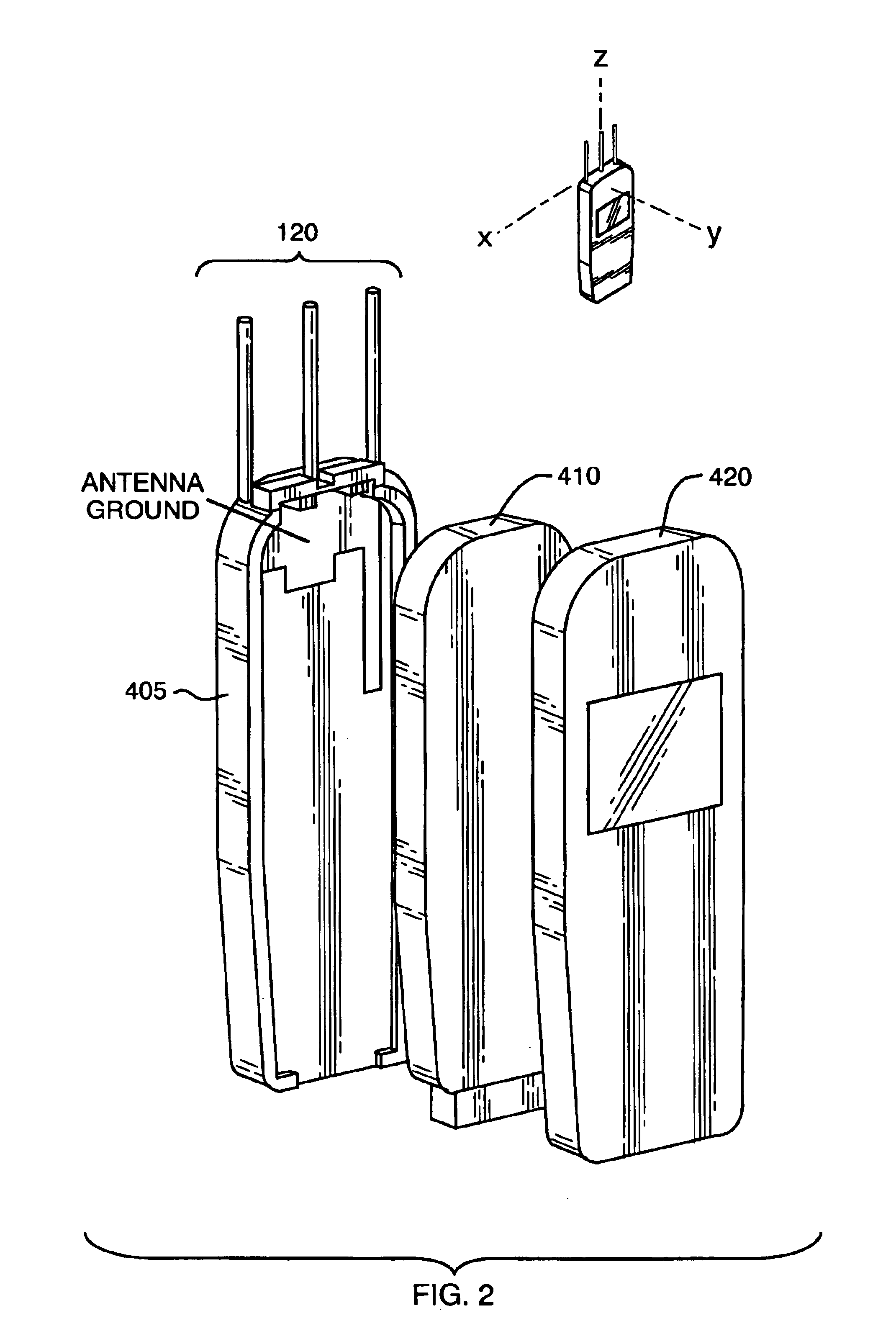
Mobile communication handset with adaptive antenna array
InactiveUS6876331B2Increase power levelReduced signal powerPolarisation/directional diversityAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna elementCommunication circuits
A mobile communication handset includes at least one passive antenna element and an active antenna element adjacent to the passive antenna elements protruding from a housing. The active element is coupled to electronic radio communication circuits and the passive antenna elements are coupled to circuit elements that affect the directivity of communication signals coupled to the antenna elements.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
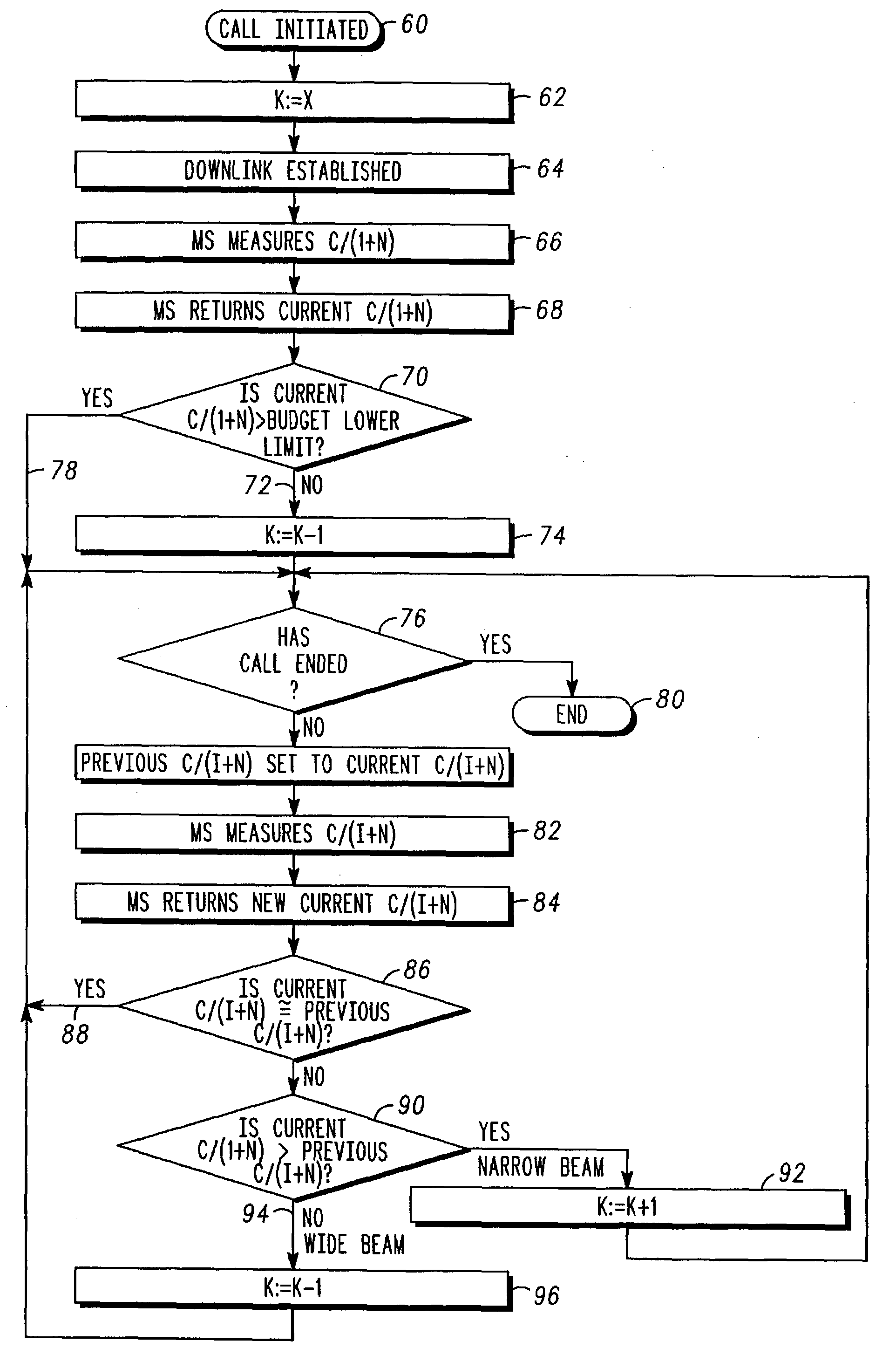
Adaptive antenna array and method of controlling operation thereof
InactiveUS7062246B2Improve translationSimple trackSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityWide areaQuality of service
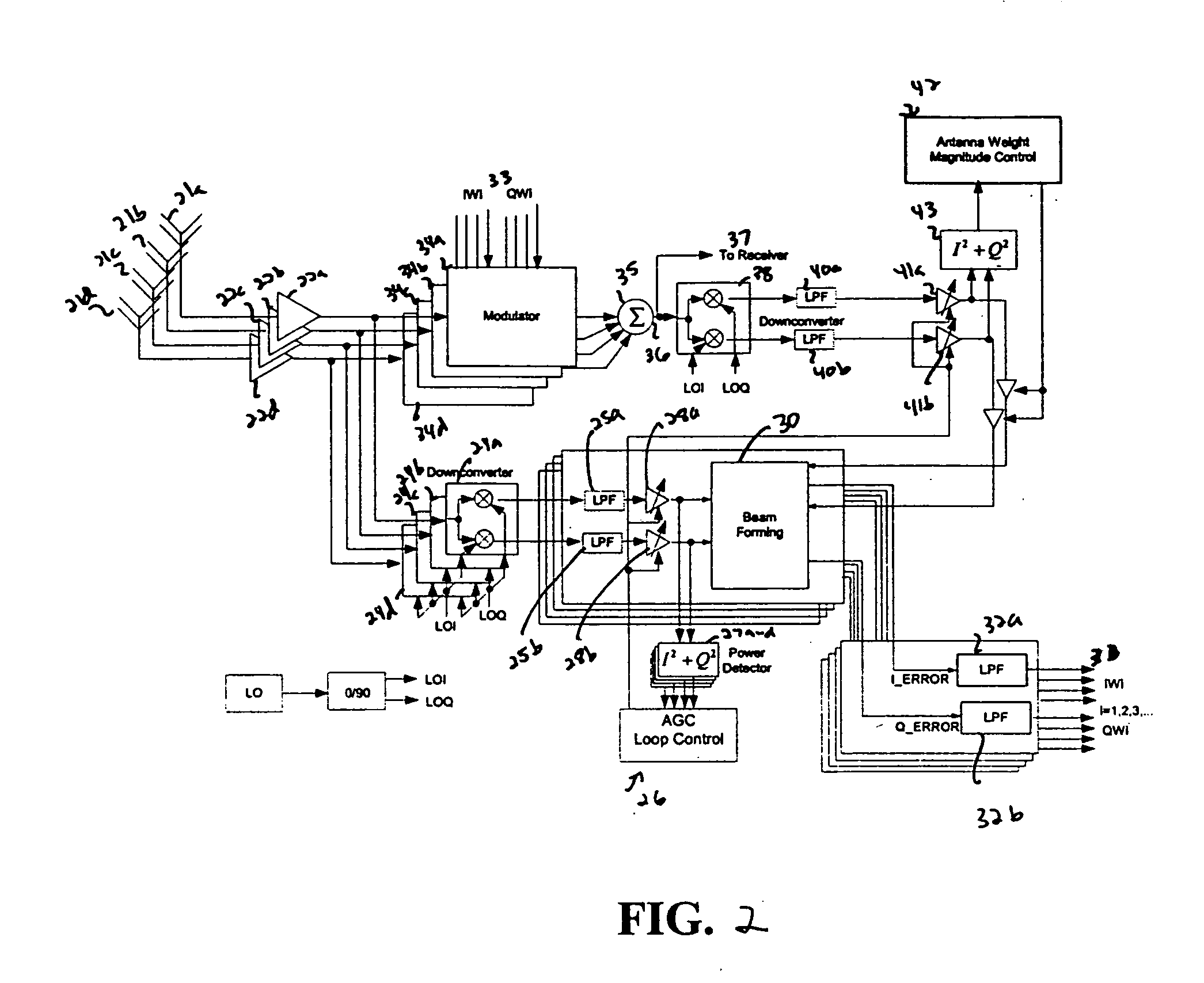
An adaptive antenna array (14) includes a muliplicity of antenna elements (12a–12k, 48a–48k) responsive to uplink communications (16a–16k) and arranged to support directional-orientated downlink communication to subscriber units (18). The adaptive antenna array (14) is operationally responsive to a signal processor (28) that co-operates with direction of arrival estimation logic (36) to assess an angle of arrival of uplink communications incident to the array. To avoid inter-cell interference, especially during early stages of a call, the signal processor operates to ensure that a wide area downlink beam (108) is provided for a downlink path to an addressed subscriber unit. With time and / or with reported (68,84) downlink quality of service (QoS) metrics, the signal processor (28) regulates (74, 92, 96) a width of the downlink beam by altering the number of antenna elements used to support the downlink beam, thereby altering the downlink beam aperture. Generally, with time, more antenna elements (92) are used and so the beam is narrowed, although in-call fluctuations in downlink quality of service are dynamically addressed by the signal processor (28) by either narrowing or broadening the width of the downlink beam by respectively switching antenna elements (12a–12k, 48a–48k) into (92) or out (96) of the adaptive antenna array (14), as shown in FIG. 3.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Vertical adaptive antenna array for a discrete multitone spread spectrum communication system
InactiveUS7061969B2Maximized the overall signal-to-interference level of a base station's coverage areaImprove performancePolarisation/directional diversityMultiplex code allocationCommunications systemAntenna element
Two or more antenna elements are arranged in the vertical direction to give vertical spatial adaptivity to a wireless discrete multitone spread spectrum communications system. The system is based on a combination of Discrete Multitone Spread Spectrum (DMT-SS) and multi-element adaptive antenna array technologies. This enables the automatic positioning of a beam in the vertical direction to position nulls where interferers are located on the same azimuth but are separated in elevation.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
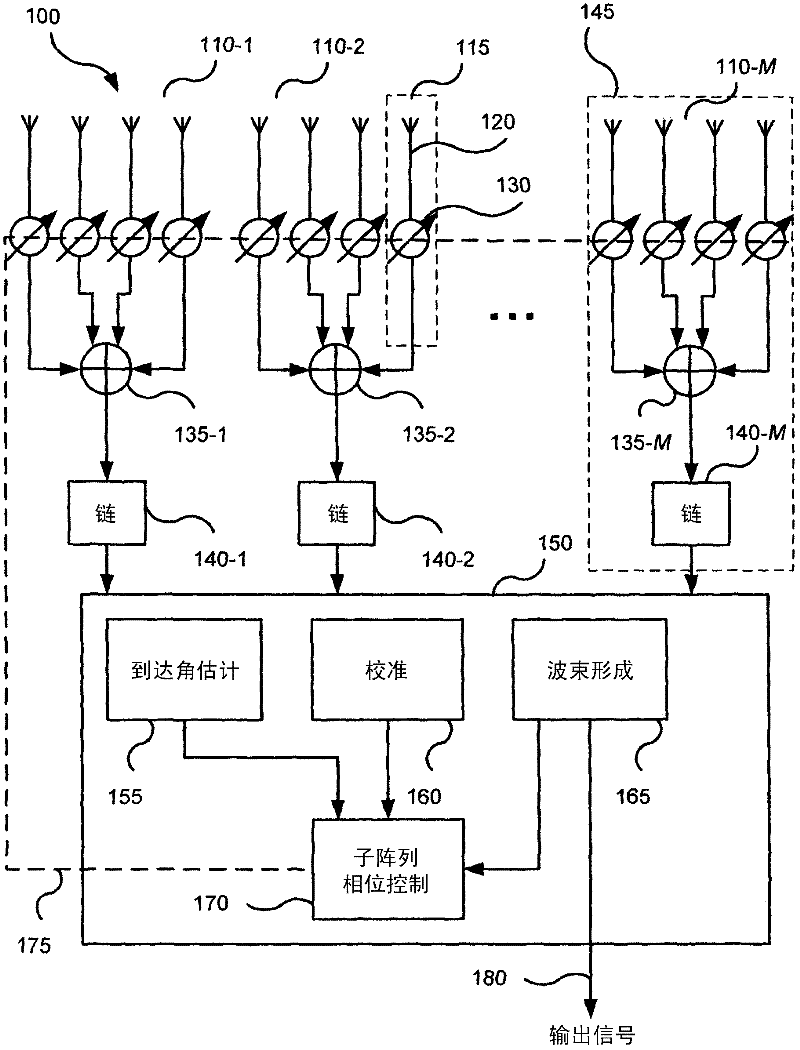
Hybrid adaptive antenna array
Disclosed is a hybrid antenna array (100) comprising a plurality of digital branches (145), each digital branch including an analogue beamforming sub-array (e.g. 110-1), each sub- array having a plurality of antenna elements (120), a phase shifter (130) adapted to apply a phase shift to the signal from each antenna element, and a combiner (e.g. 135-1) adapted to combine the phase-shifted signals. Each digital branch also includes a signal chain (e.g.140-1) adapted to convert the output of the sub-array to baseband. The hybrid antenna array also comprises a digital processing module (150), including: an angle of arrival estimation sub-module (155) adapted to estimate an angle of arrival of a signal at the antenna elements; a phase control sub-module (170) adapted to control the phase shift applied by each phase shifter depending on the estimated angle of arrival; and a digital beamformer (165) adapted to combine the baseband signals from the digital branches using a weight vector to form an output signal (180).
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
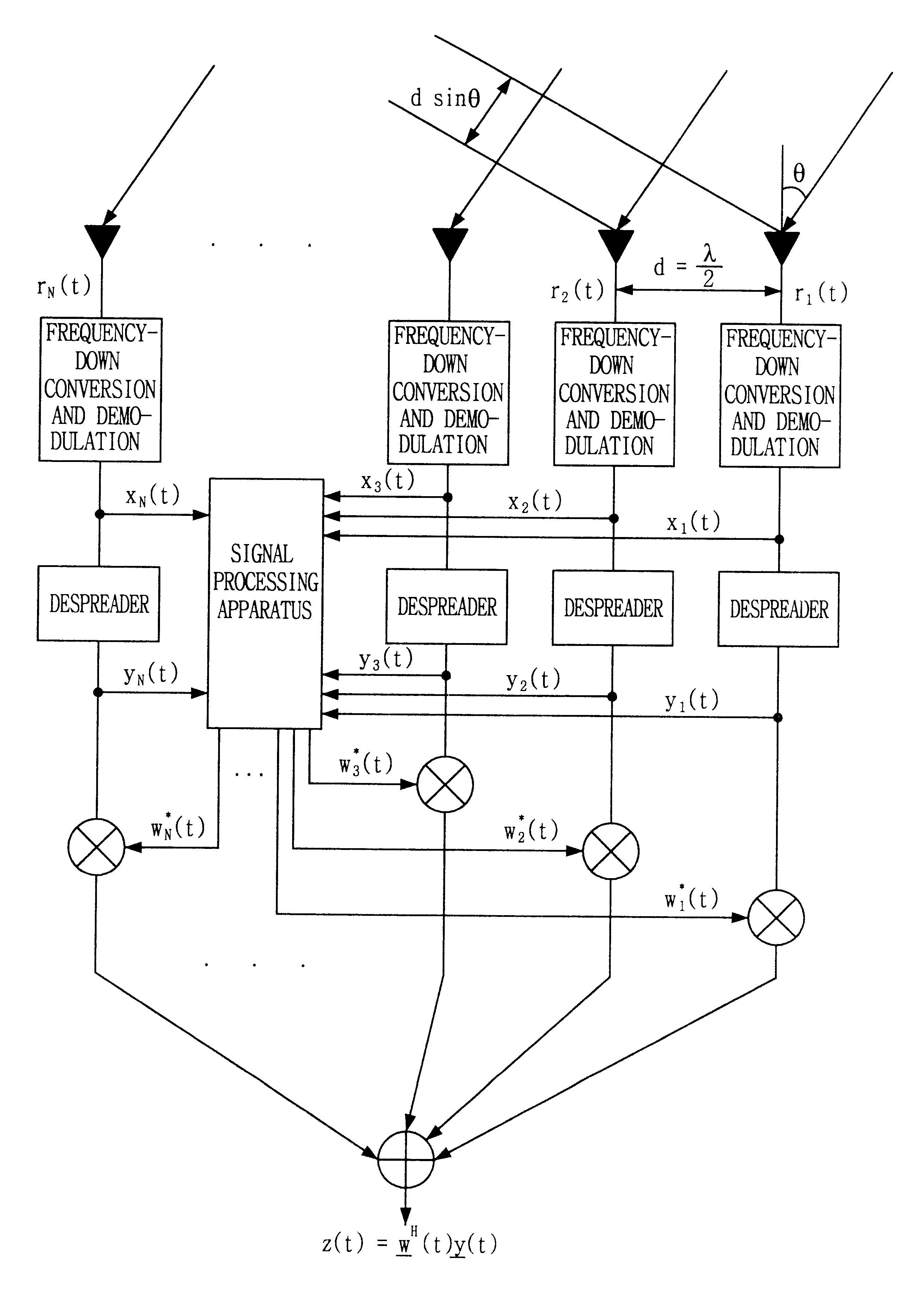
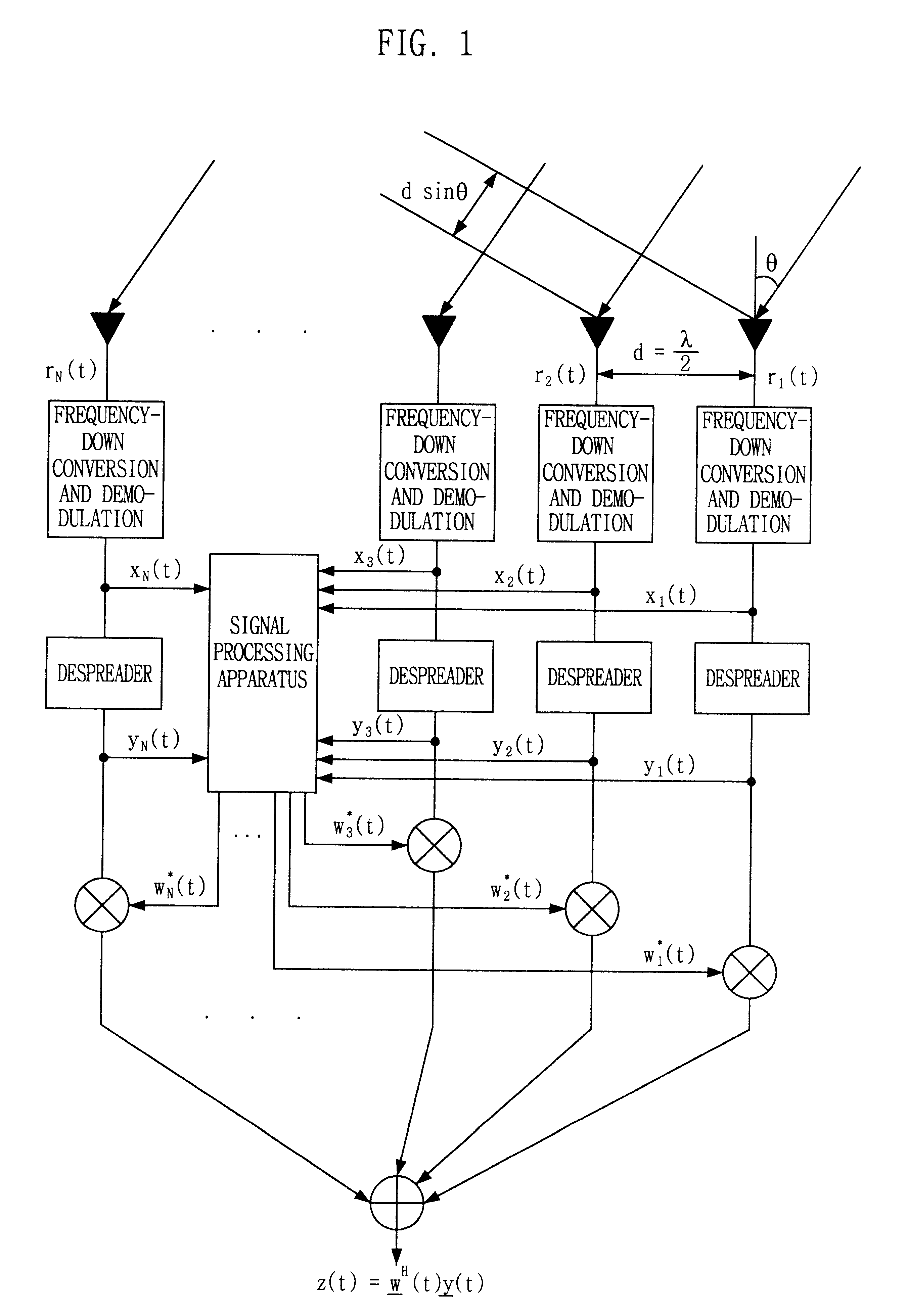
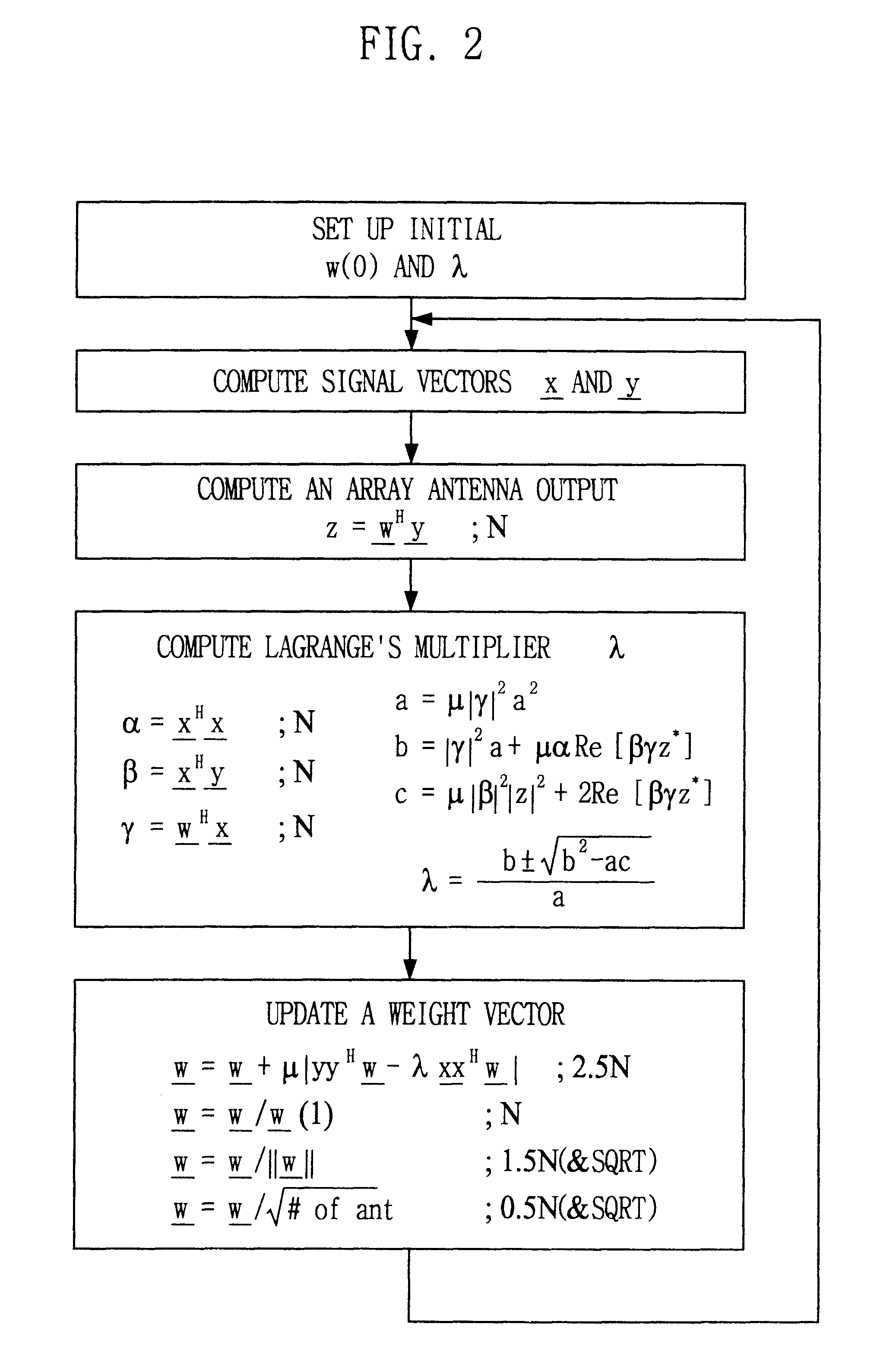
Signal processing method and apparatus for computing an optimal weight vector of an adaptive antenna array system
InactiveUS6462709B1Simple and accurate wayMaximizes the signal to interference plus noise ratioSpatial transmit diversityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsOff the shelfTarget signal
This invention relates to a signal processing method and apparatus for an adaptive array antenna. The objective is to suggest an adaptive procedure of computing the suboptimal weight vector for an array antenna system that provides a beampattern having its maximum gain along the direction of the mobile target signal source in a blind signal environment, where the transmitted data are not known (or not to be estimated) at the receiver. It is the ultimate goal of this invention to suggest a practical way of enhancing both the communication quality and communication capacity through the optimal weight vector of the array system that maximizes SINR(Signal to Interference+Noise Ratio). In order to achieve this goal, the method of Lagrange multiplier is modified in such a way that the suboptimal weight vector is produced with the computational load of about O(8N), which has been found to be small enough for the real-time processing of signals in most land mobile communications with the digital signal processor (DSP) off the shelf, where N denotes the number of antenna elements of the array.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
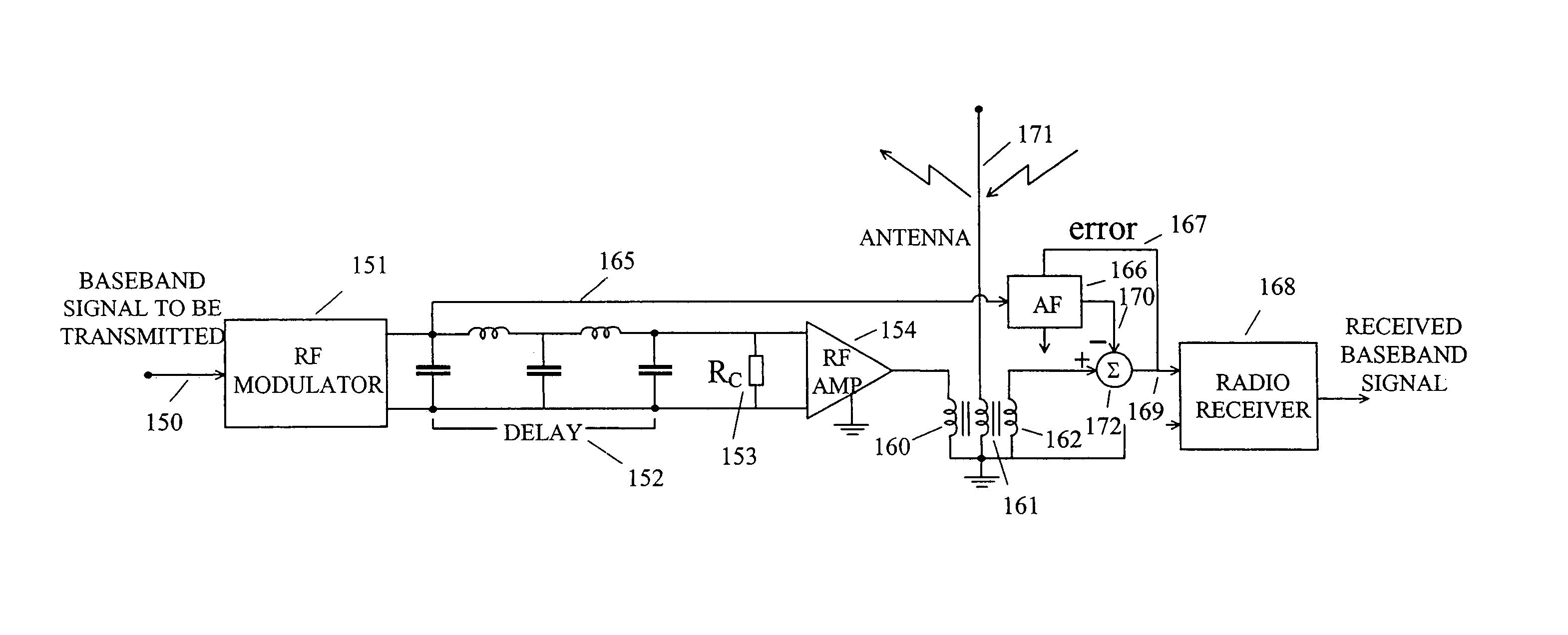
Simultaneous two-way transmission of information signals in the same frequency band
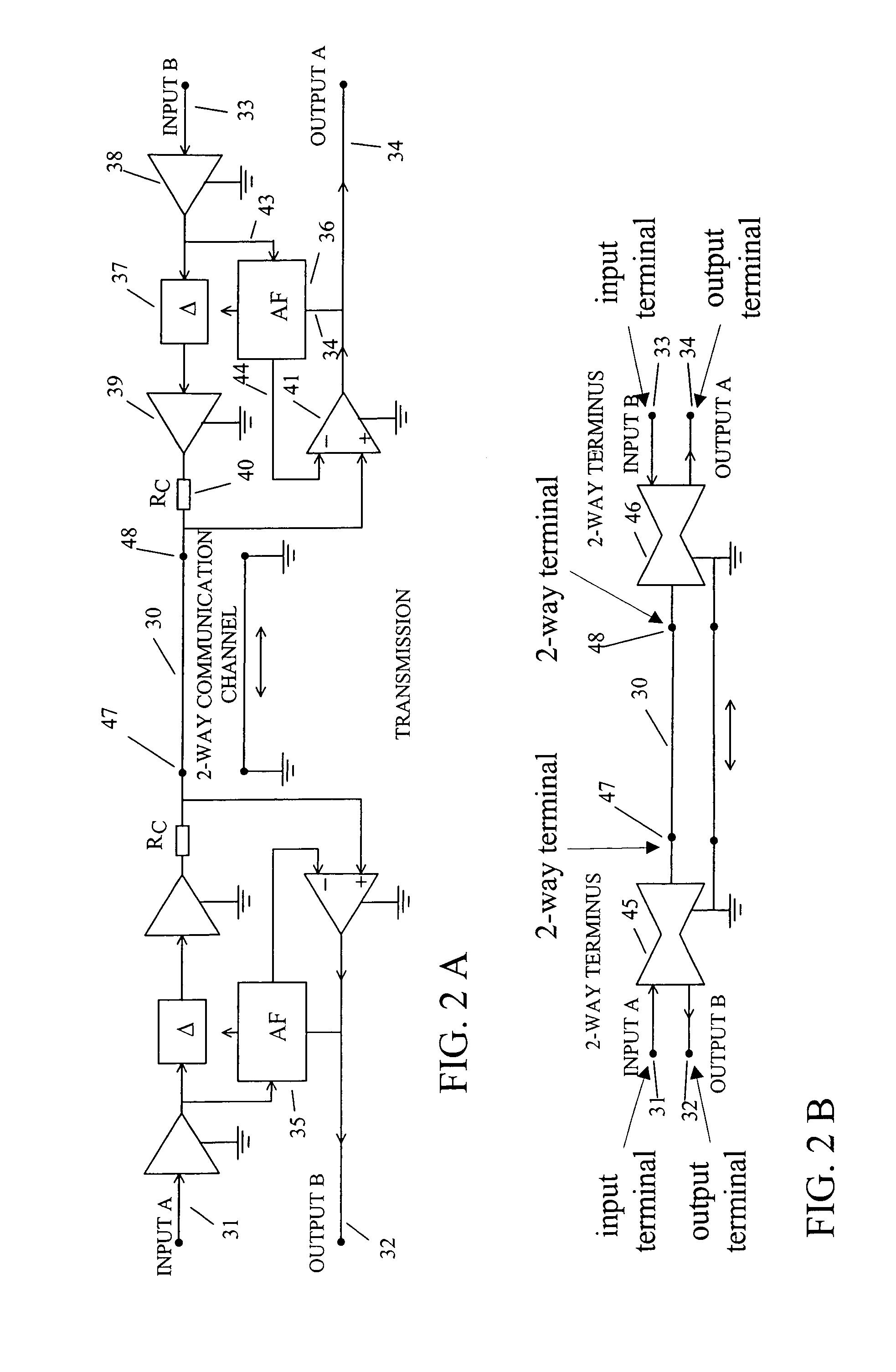
InactiveUS7187907B2Increase channel capacityPower distribution line transmissionBroadcast transmission systemsFiberAdaptive filter
This invention provides designs for communication systems that use adaptive filters in circuits whose purpose is to enable two-way transmission of information signals in the same frequency band at the same time over twisted pair channels, coaxial cable channels, fiber optic channels, or wireless channels. The methodology allows two-way DSL transmission over telephone lines, making use of existing DSL hardware and signal standards, so that the upload speed is increased by an approximate factor of ten. Applied to wireless systems with single antennas at the two ends of the channel, a doubling of the data rate is achieved for a given bandwidth. Applied to wireless systems with 2-way adaptive antenna arrays at a central location and a 2-way adaptive antenna array at each of a plurality of subscriber locations, the data rate for a given bandwidth is increased by a large factor.
Owner:WIDROW BERNARD
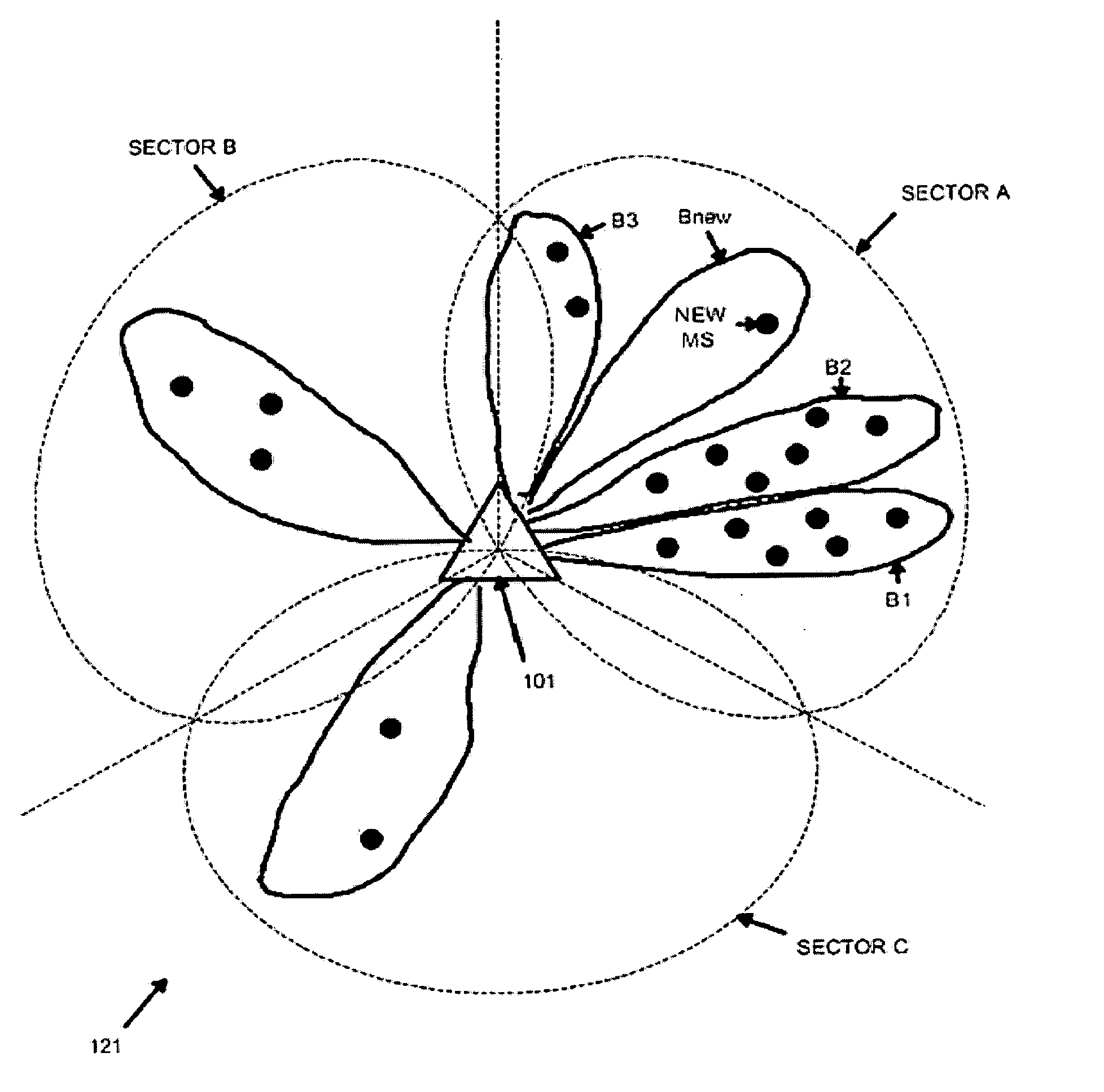
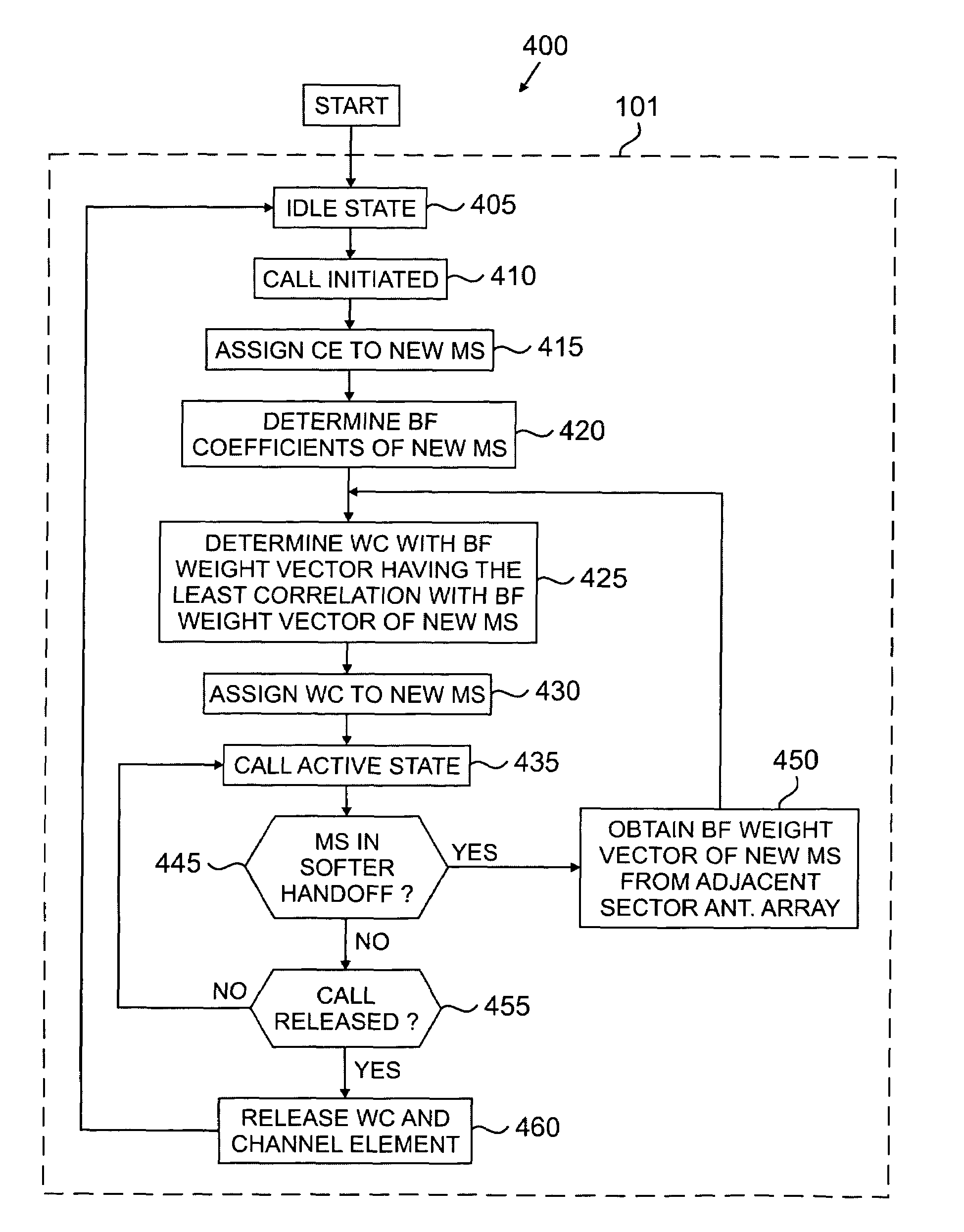
Apparatus and method for allocating walsh codes to mobile stations in an adaptive antenna array wireless network
ActiveUS20050105485A1Spatial transmit diversityCode division multiplexDownlink beamformingMobile station
An apparatus for allocating orthogonal codes to mobile stations for use in a CDMA base station that transmits using an adaptive antenna array. The apparatus comprises a database for storing R records. Each record is associated with an active mobile station and comprises an active orthogonal code associated with the active mobile station, corresponding downlink beamforming coefficients associated with the active mobile station, and mobility information associated with the active mobile station. The apparatus further comprises a controller for comparing estimated downlink beamforming coefficients associated with a new mobile station to the R records. The controller selects a first active orthogonal code associated with a first active mobile station to communicate with the new mobile station. The selection is based on the degree of correlation between the estimated downlink beamforming coefficients and first corresponding downlink beamforming coefficients, and 2) first mobility information associated with the first active mobile station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
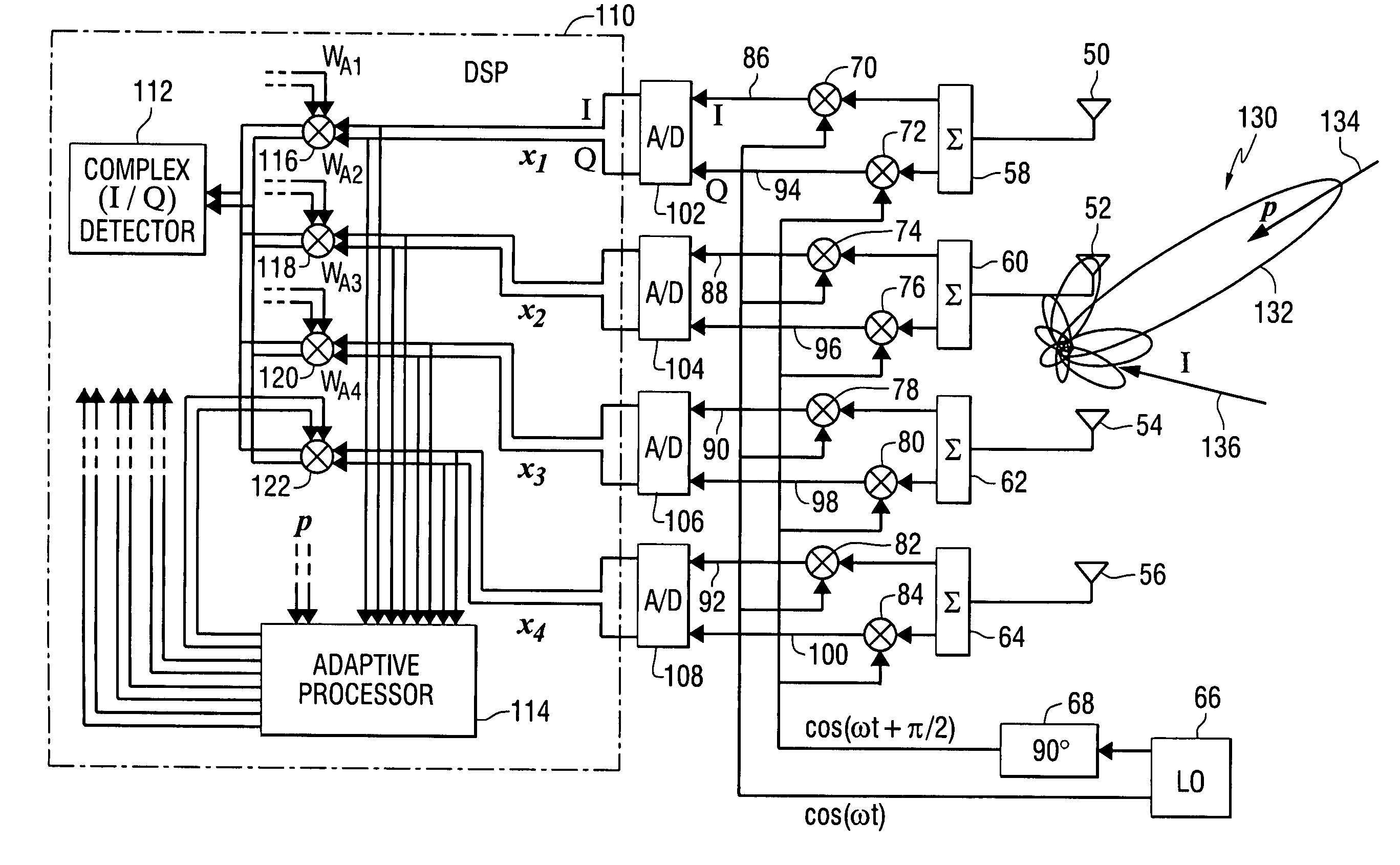
Distributed conformal adaptive antenna array for SATCOM using decision direction
ActiveUS7606528B2Antenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDirect feedbackIn-phase and quadrature components
An apparatus comprises a distributed array of antenna elements for receiving a radio frequency signal on a satellite communications link, wherein the radio frequency signal includes a known preamble; a plurality of mixers for translating the radio frequency signal to a plurality of baseband signals having in-phase and quadrature components; a processor for applying weights to the baseband signals, wherein the weights are found adaptively in response to the preamble in combination with decision-directed feedback when the preamble is not present; and a receiver for processing the weighted baseband signals. A pre-processor can be used to create sub-arrays of the antenna elements using maximal-ratio weighting. A method performed by the apparatus is also provided.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
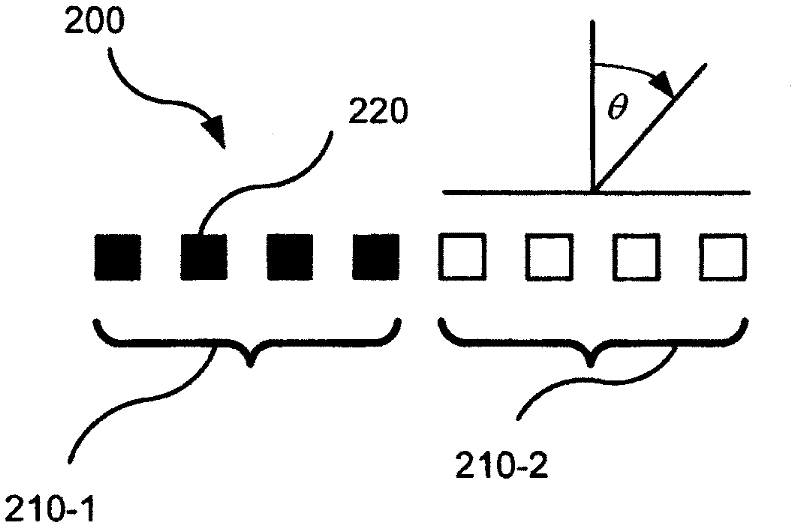
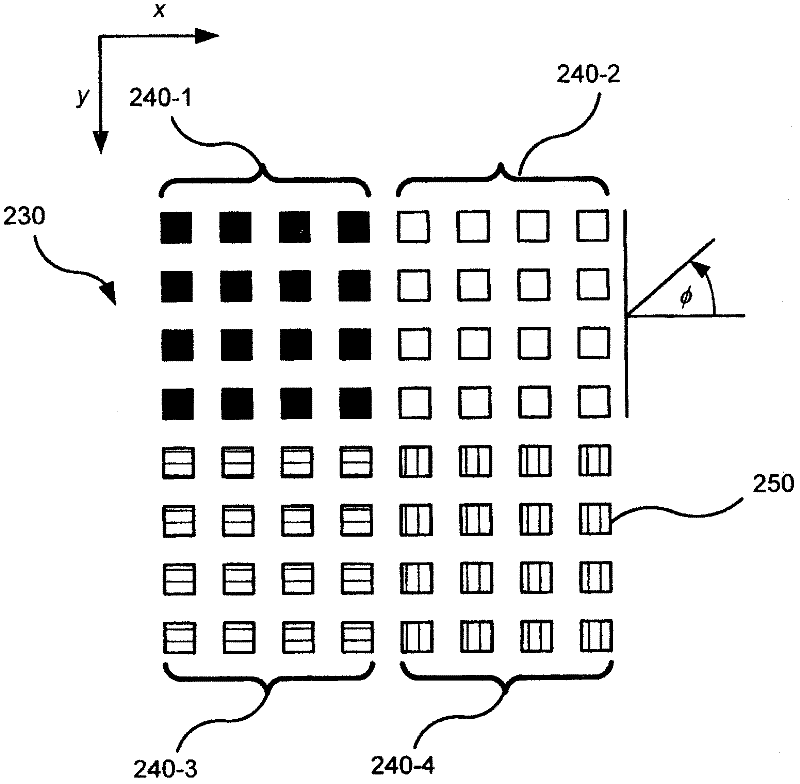
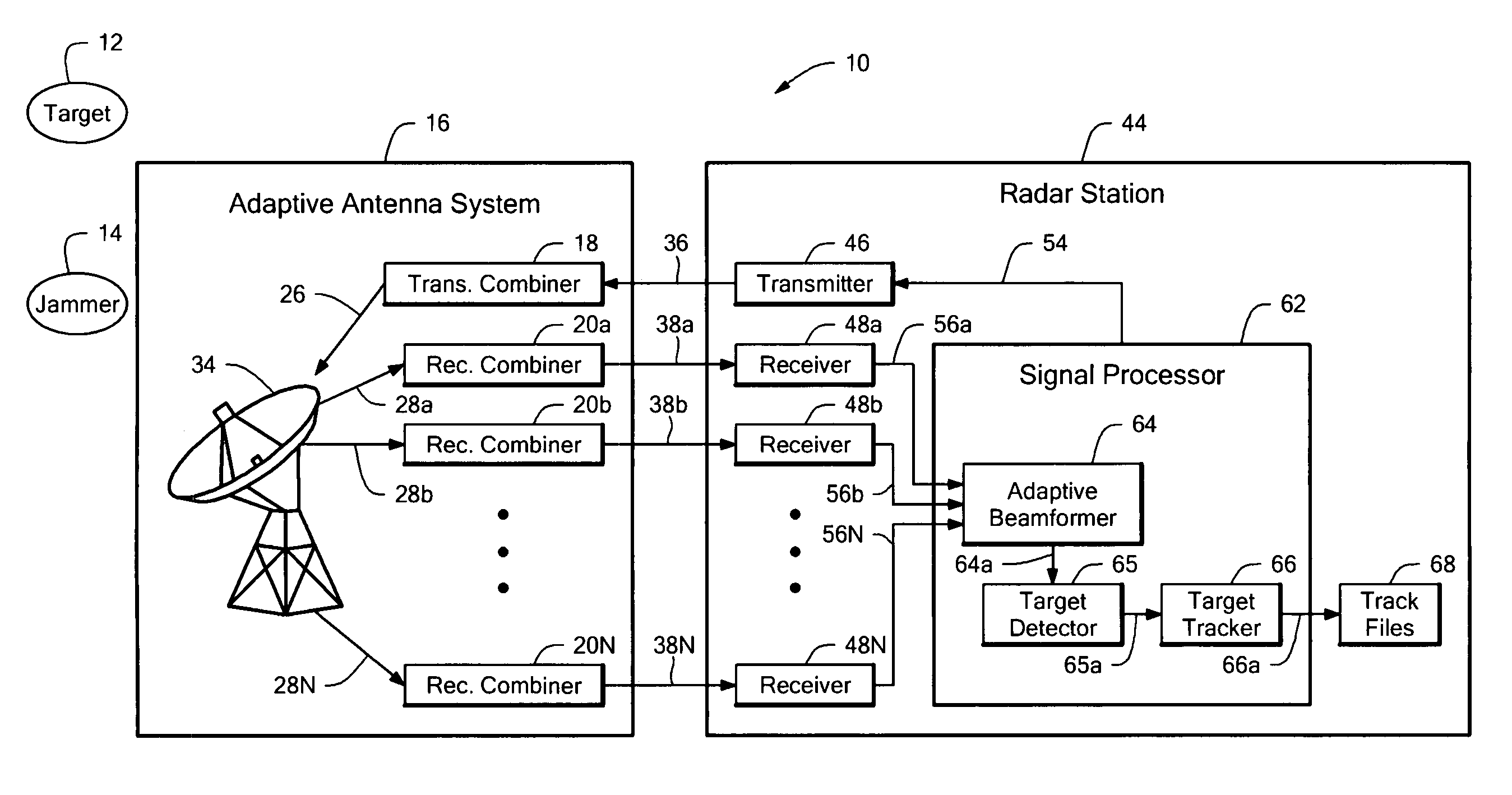
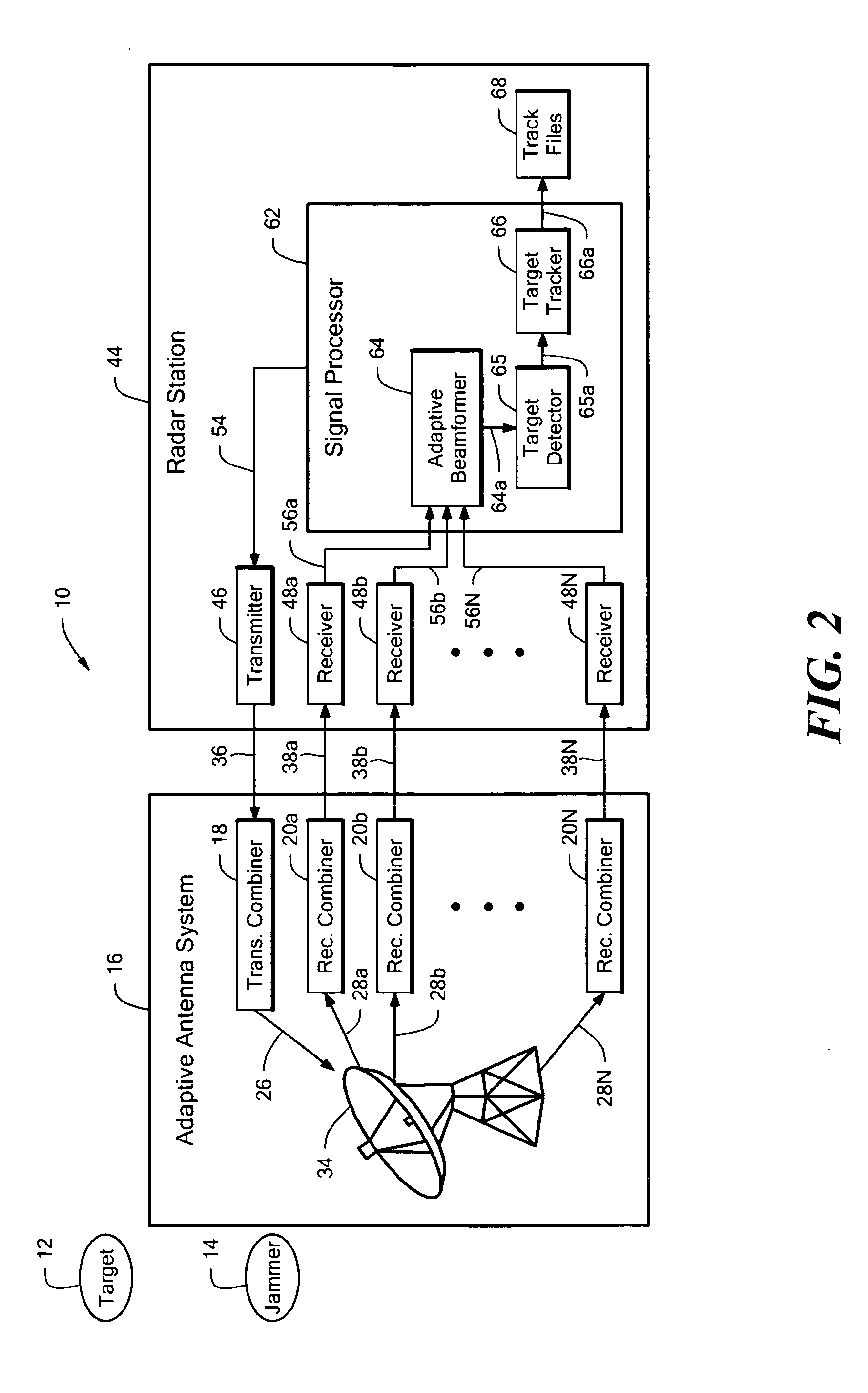
Adaptive array
ActiveUS20060164284A1Easy to detectImprove tracking performanceCommunication jammingIndividually energised antenna arraysRadar systemsArray element
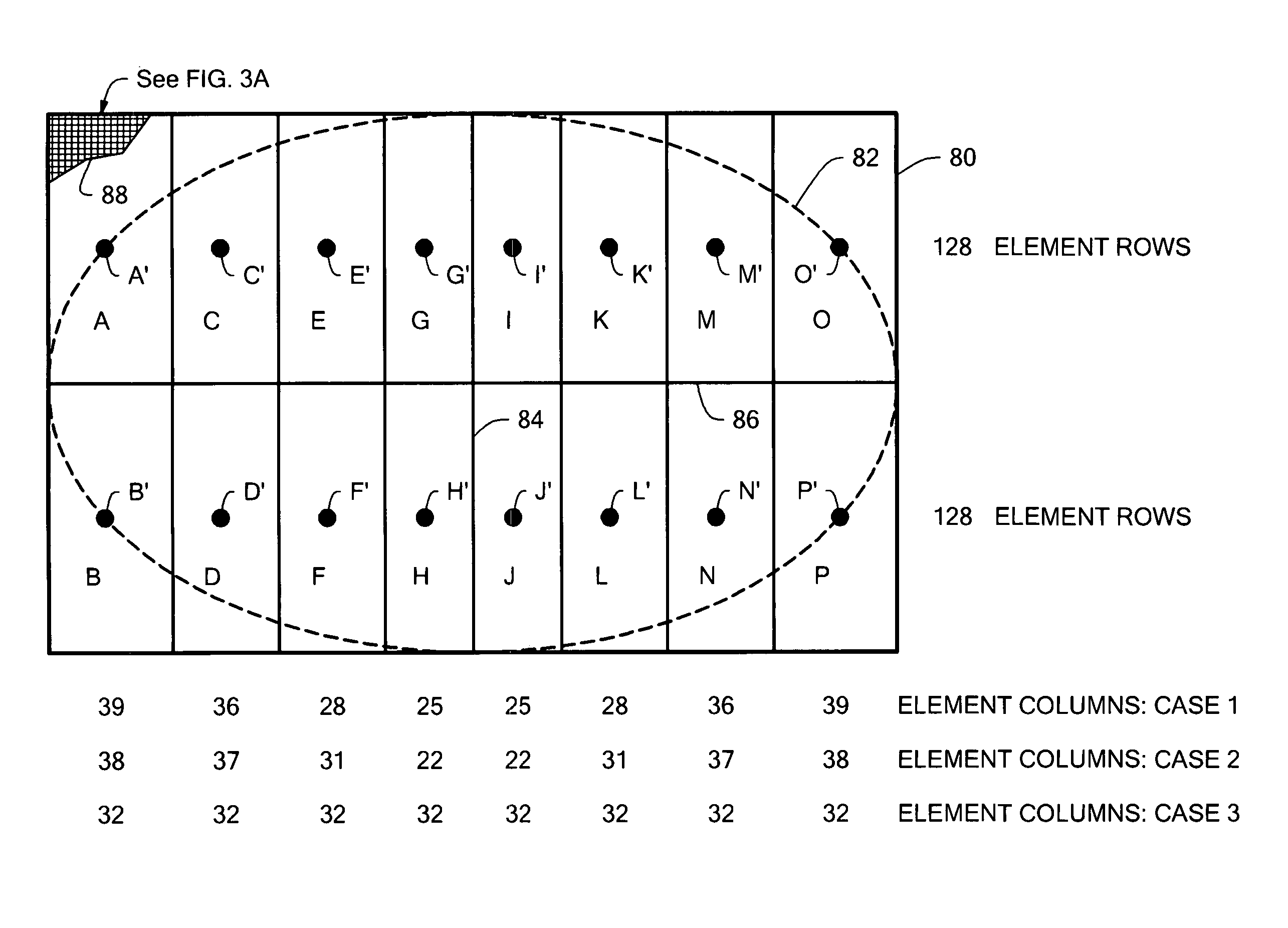
An adaptive antenna array has array elements arranged in element rows and element columns and subarrays arranged in subarray rows and subarray columns, for which the subarray phase centers have non-uniform spacing. The adaptive antenna array provides good detection and tracking performance when used in a radar system, while being inexpensive and easy to manufacture. A radar system and a method of adapting a radar array both employ the above described adaptive antenna array.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
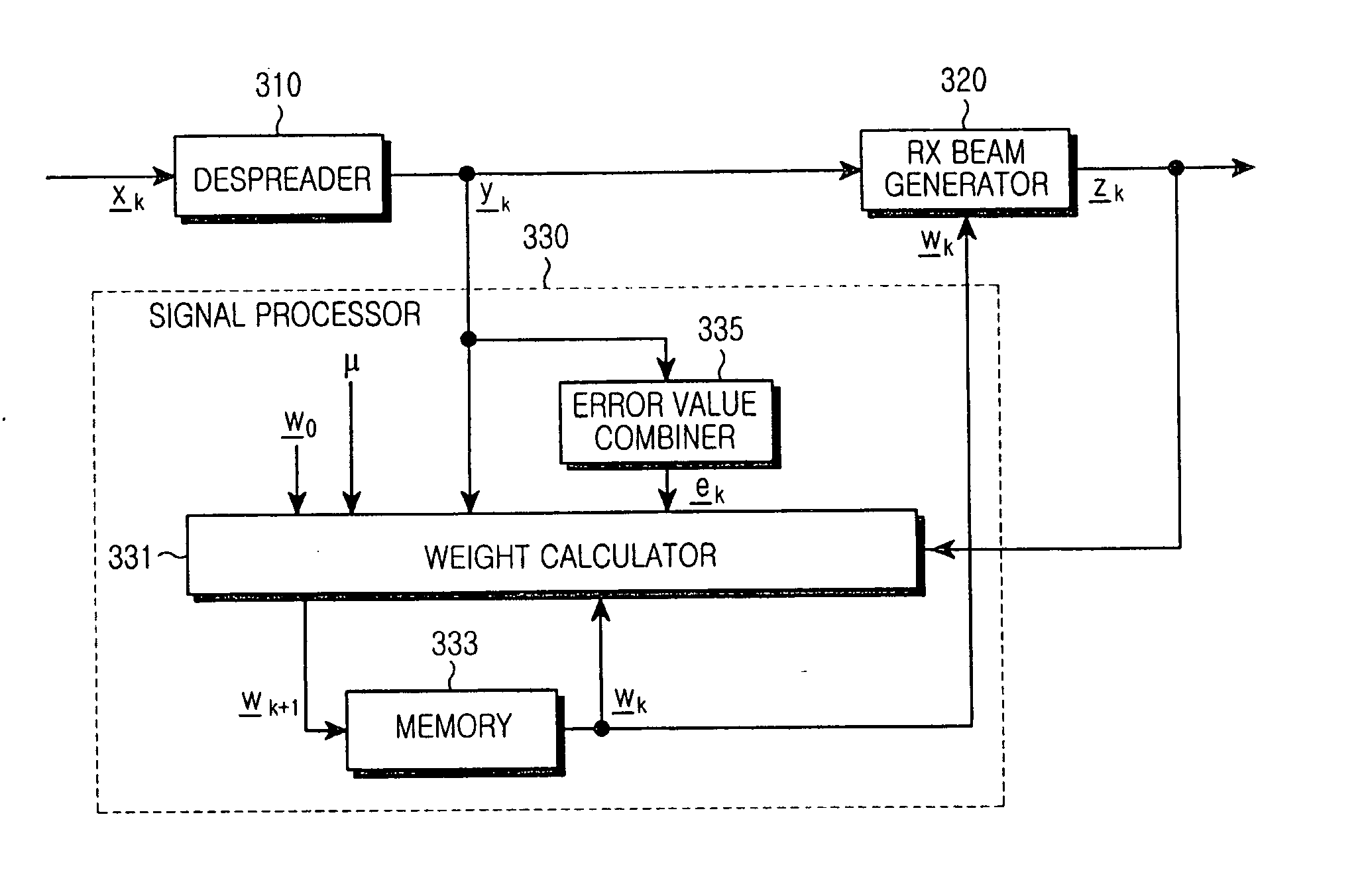
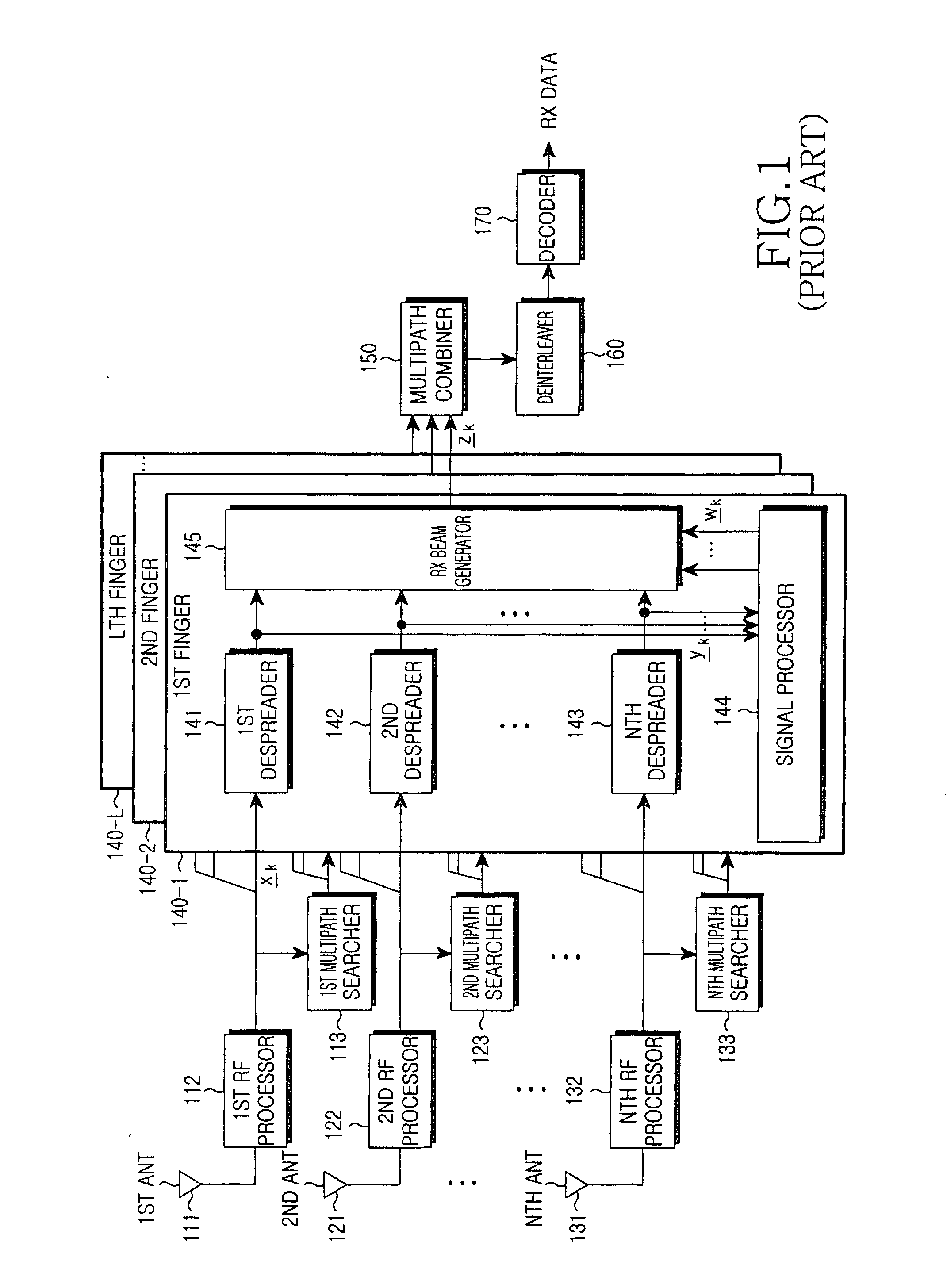
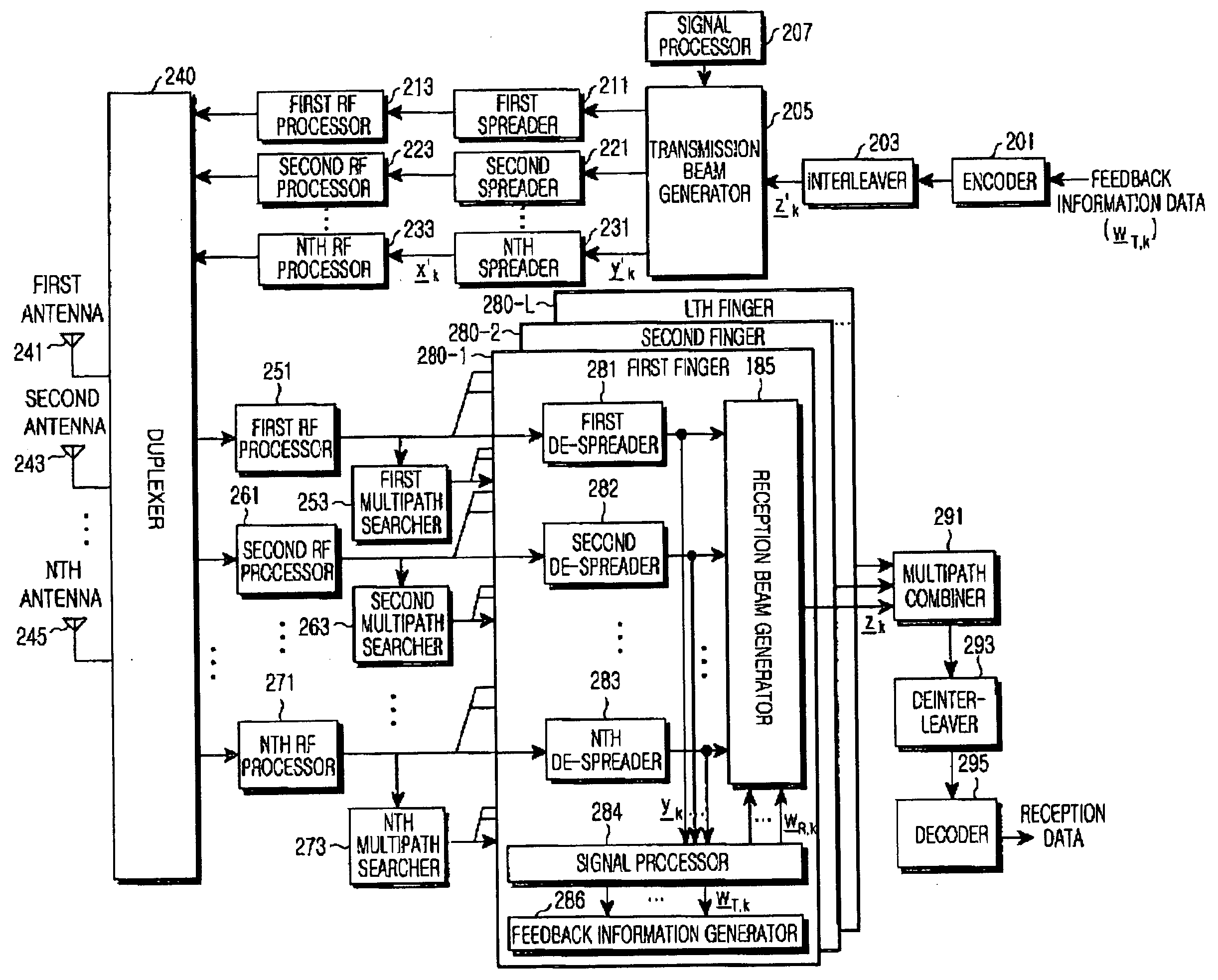
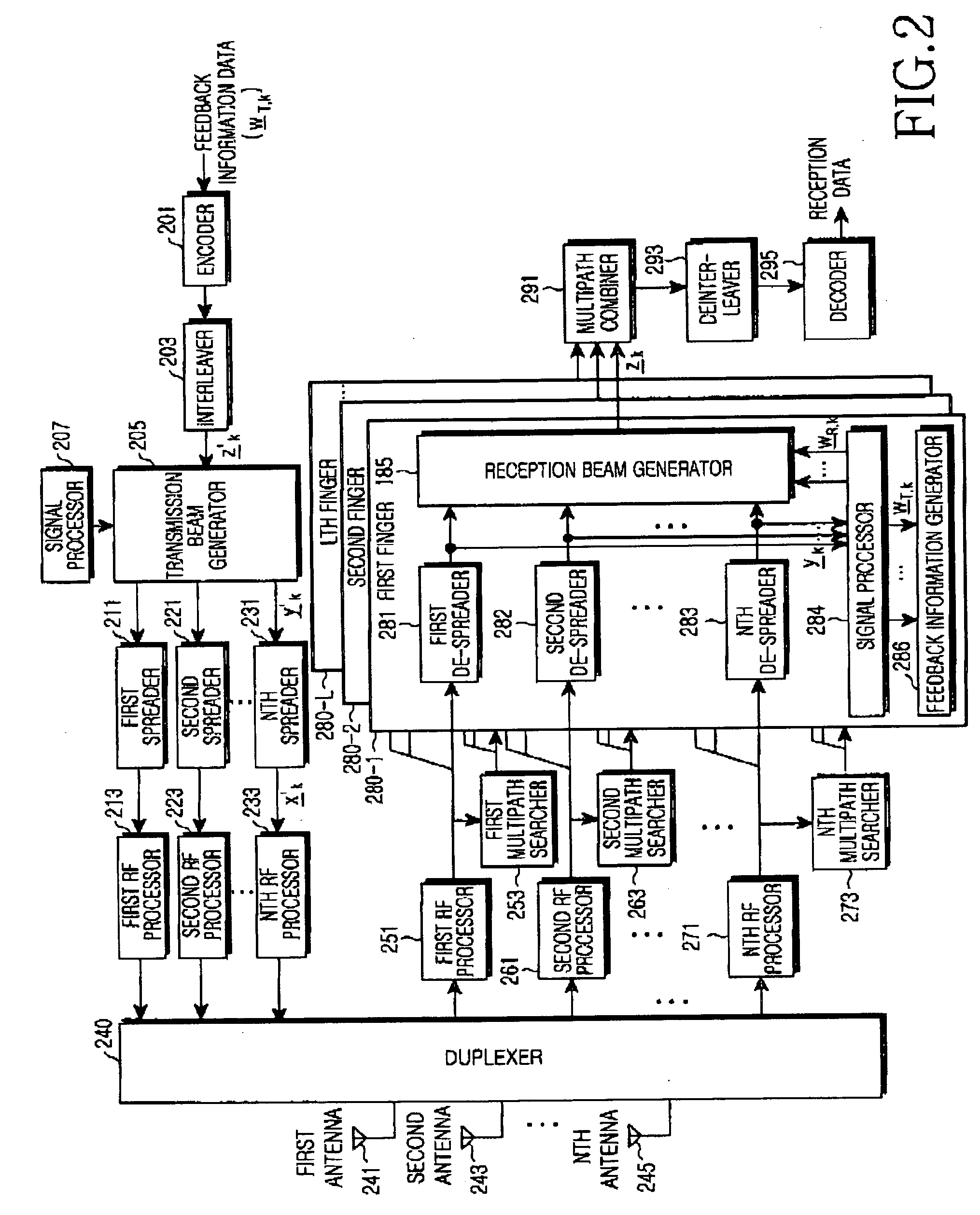
Apparatus and method for receiving data in a mobile communication system using an adaptive antenna array scheme
ActiveUS20050013349A1Inaccurate valueSpatial transmit diversityError preventionCommunications systemMobile communication systems
A mobile communication system receives a despread signal of a reception signal, and determines a first error value by using a first scheme at a timing point, and a second error value by using a second scheme different from the first scheme at the timing point, and determines a first scheme application weight according to a difference between the first error value and the second error value, and a second scheme application weight according to the difference between the first error value and the second error value, and generates a third error value using a scheme that combines the first scheme to which the first scheme application weight is applied and the second scheme to which the second scheme application weight is applied, and determines a reception beam weight using the despread reception signal, the third error value, and an output signal generated by applying the reception beam to the despread reception signal, wherein the reception beam weight is used for generating the reception beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
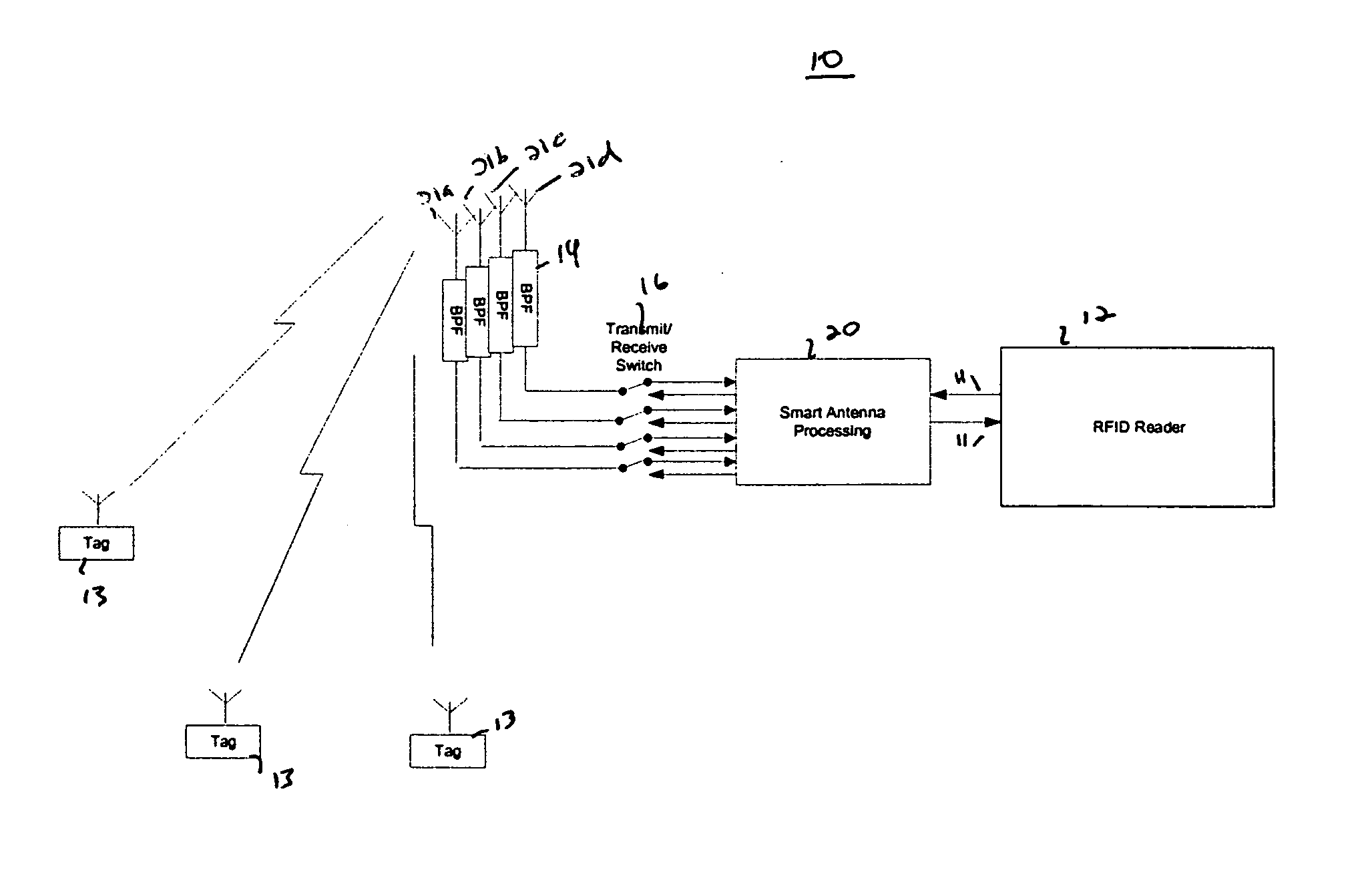
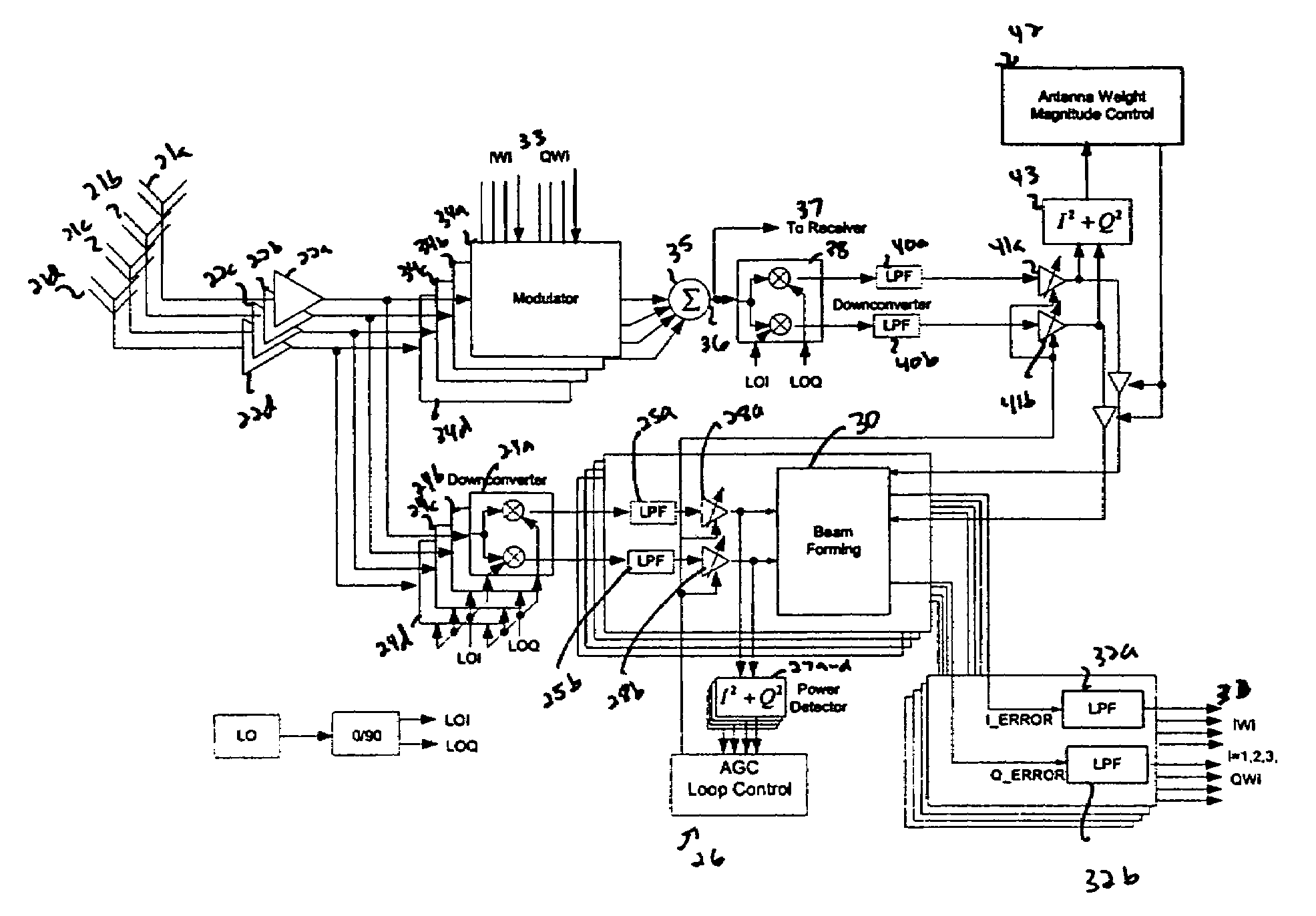
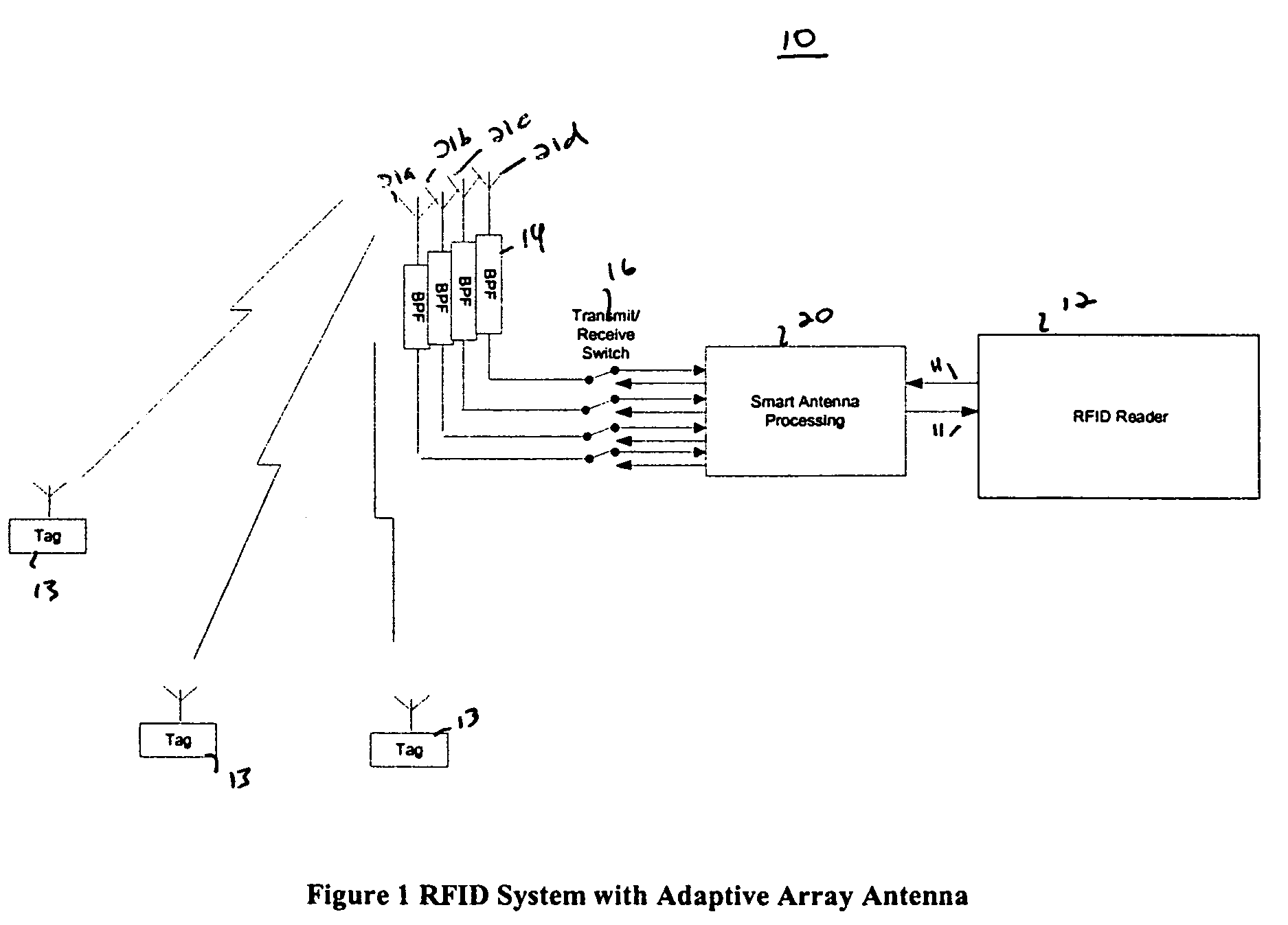
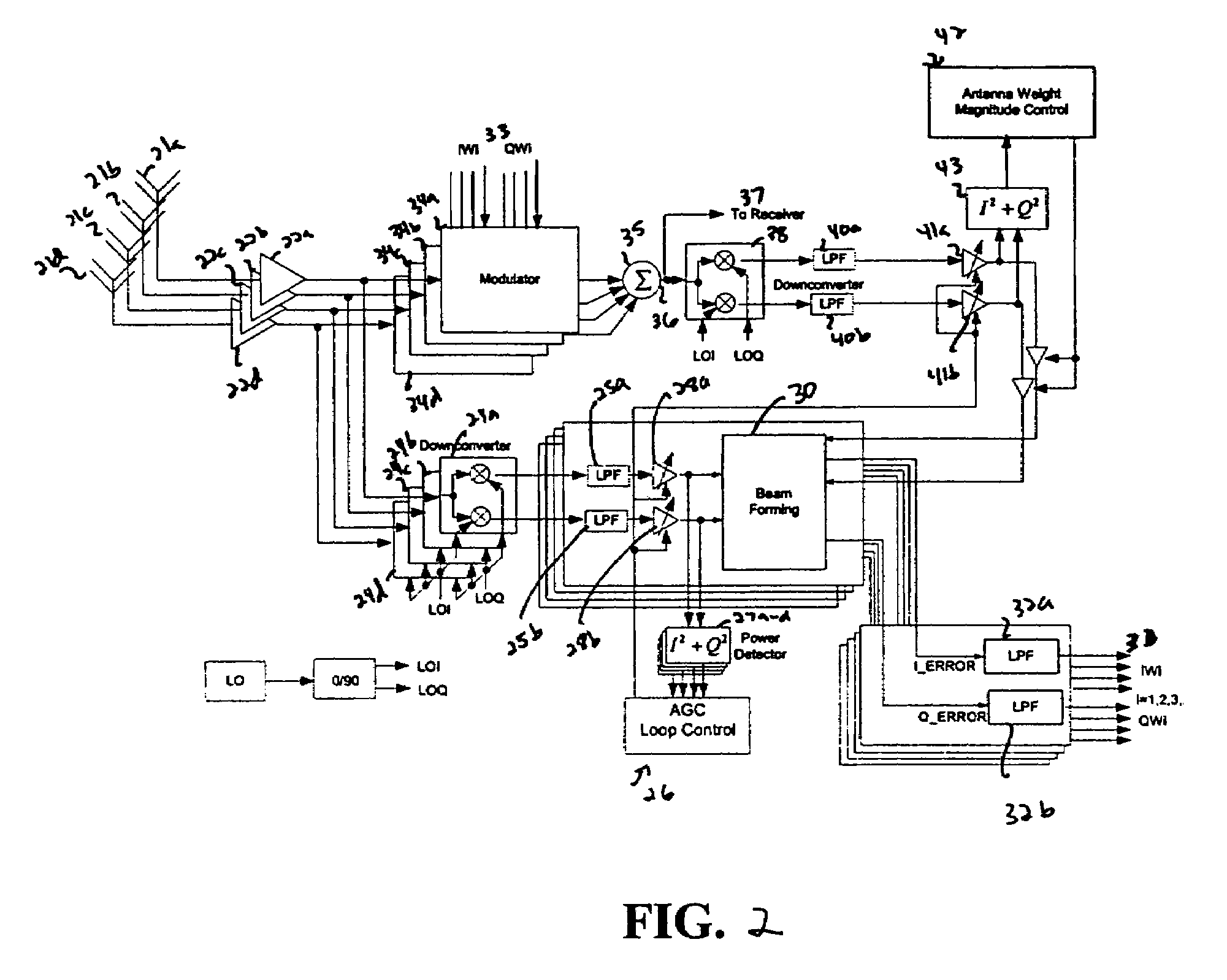
RFID system with an adaptive array antenna
InactiveUS20050128159A1Expand the scope of operationImprove the receiving signal-to-noise ratioSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysSignal qualityPhase shifted
The present invention relates to use of a smart antenna for a RF reader on a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system to significantly increase the operating range of the RFID system. The smart antenna can be an adaptive antenna array. The smart antenna comprises a plurality of antenna elements and, by combining the signals from multiple antenna elements, significantly increases the received signal-to-noise ratio. In a noise limited environment, combining the signals to maximize the received signal-to-noise ratio can be based on the maximal ratio combining (MRC) principle. To achieve the best signal quality, the received signal from each antenna can be phase-shifted such that the resultant signals from all antennas are in phase. In addition, the signal from each antenna can be scaled in amplitude based on the square root of its received signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
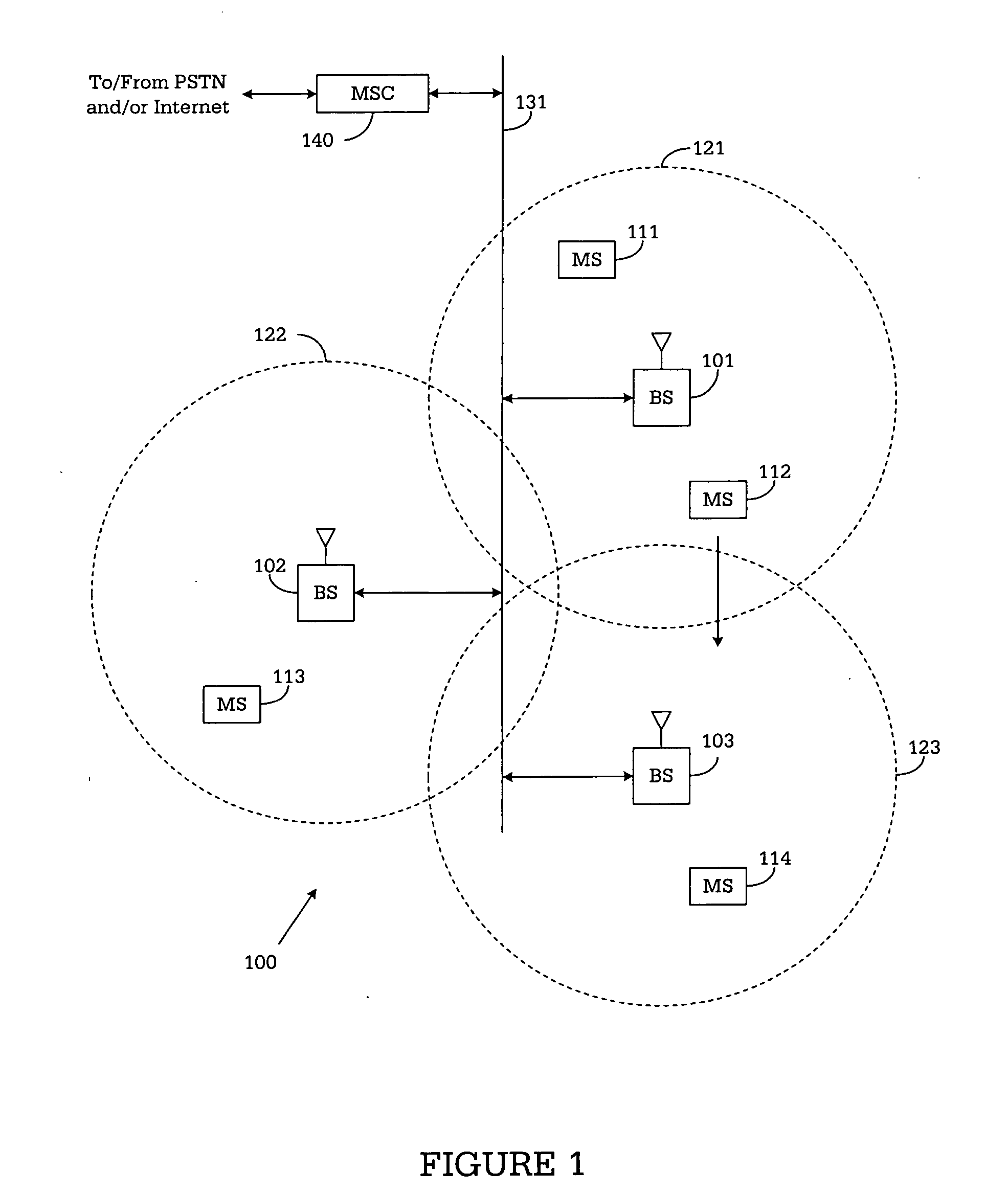
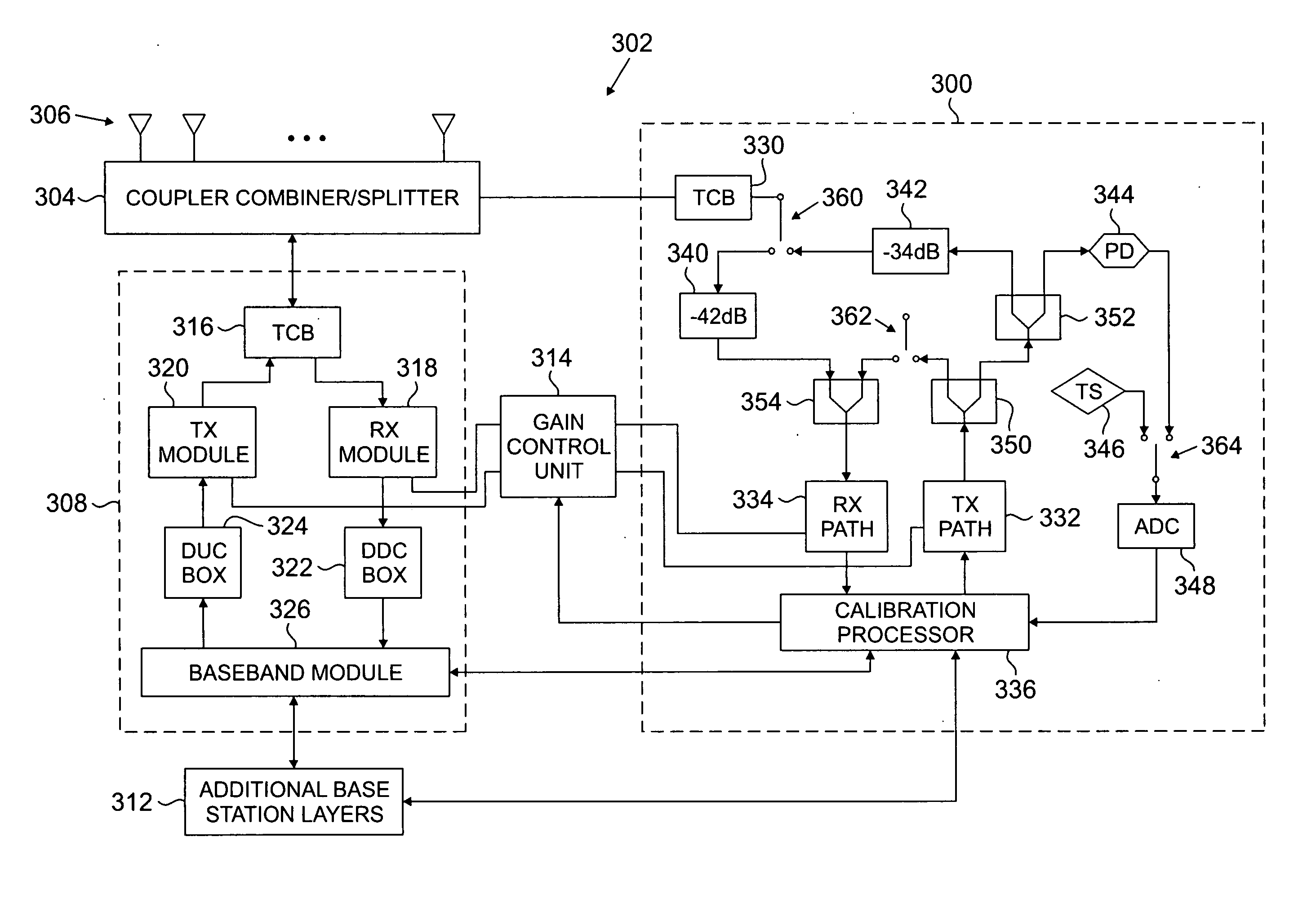
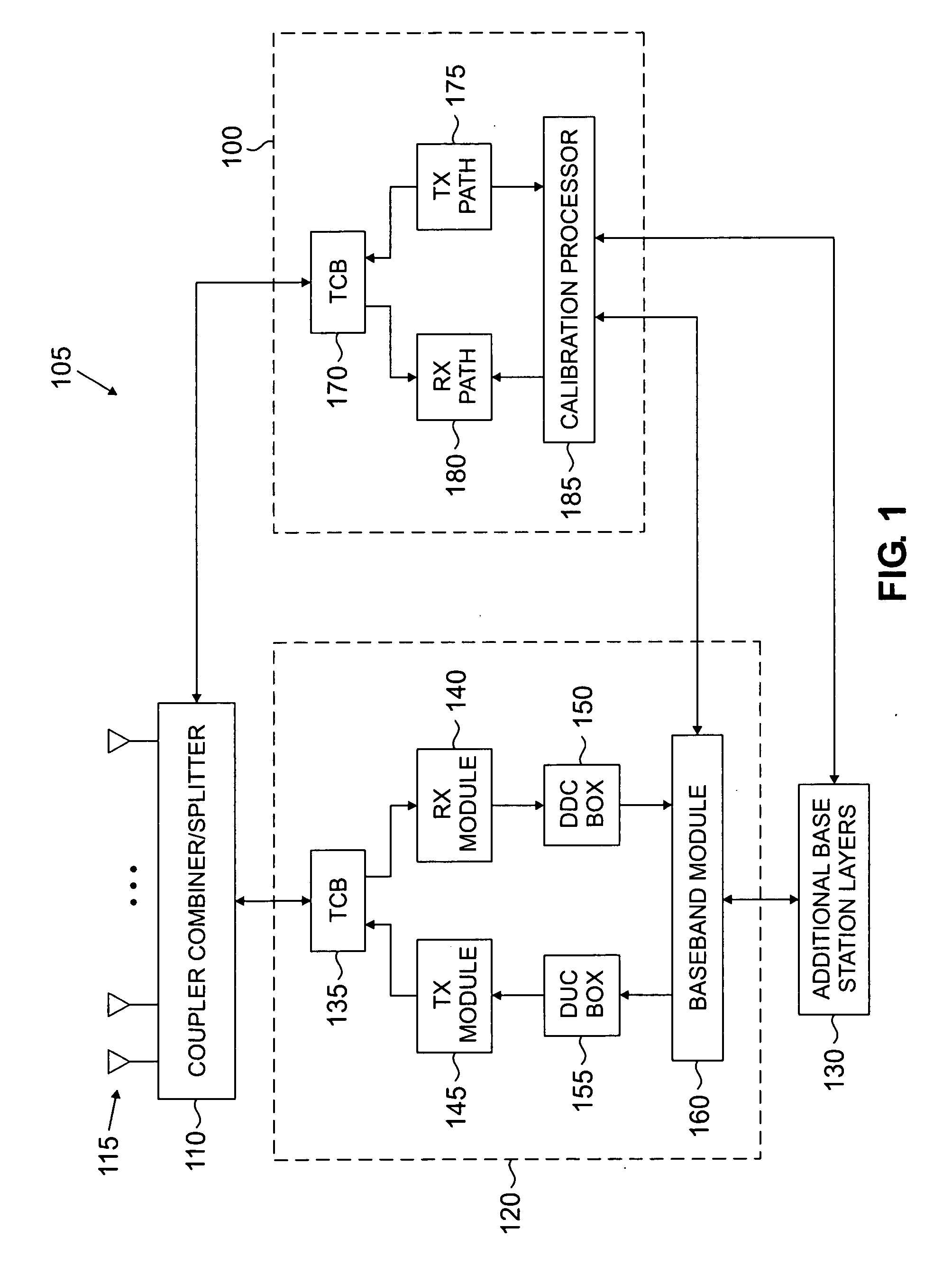
Method and system for calibrating multiple types of base stations in a wireless network
A method of calibrating multiple types of base stations is provided. The method includes selecting one of a plurality of technology types for the wireless base station. The wireless base station has an adaptive antenna array. A calibration is performed for the wireless base station based on the selected technology type.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for transmitting and receiving a signal in a mobile communication system using a multiple input multiple output adaptive antenna array scheme
ActiveUS20050020313A1Error minimizationWeight controlSpatial transmit diversityError preventionEngineeringMobile communication systems
A method for transmitting and receiving weight information for creating transmission / reception beams in a mobile communication system using a multiple input multiple output adaptive antenna array scheme. The method includes a receiver receiving a predetermined signal, and differentially providing weights to a first scheme and a second scheme for minimizing an error between the received signal and a predetermined reference signal, thereby obtaining a minimum error value. The receiver generates a despread signal by despreading the received signal, produces a reception weight for creation of a reception beam by the receiver through calculation using the despread signal and the minimum error value, and produces a transmission weight for creation of a transmission beam by a counterpart transmitter through calculation using the reception weight and the minimum error value. The receiver generates predetermined feedback information including the transmission weight and a transmitter transmits the feedback information to a counterpart receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
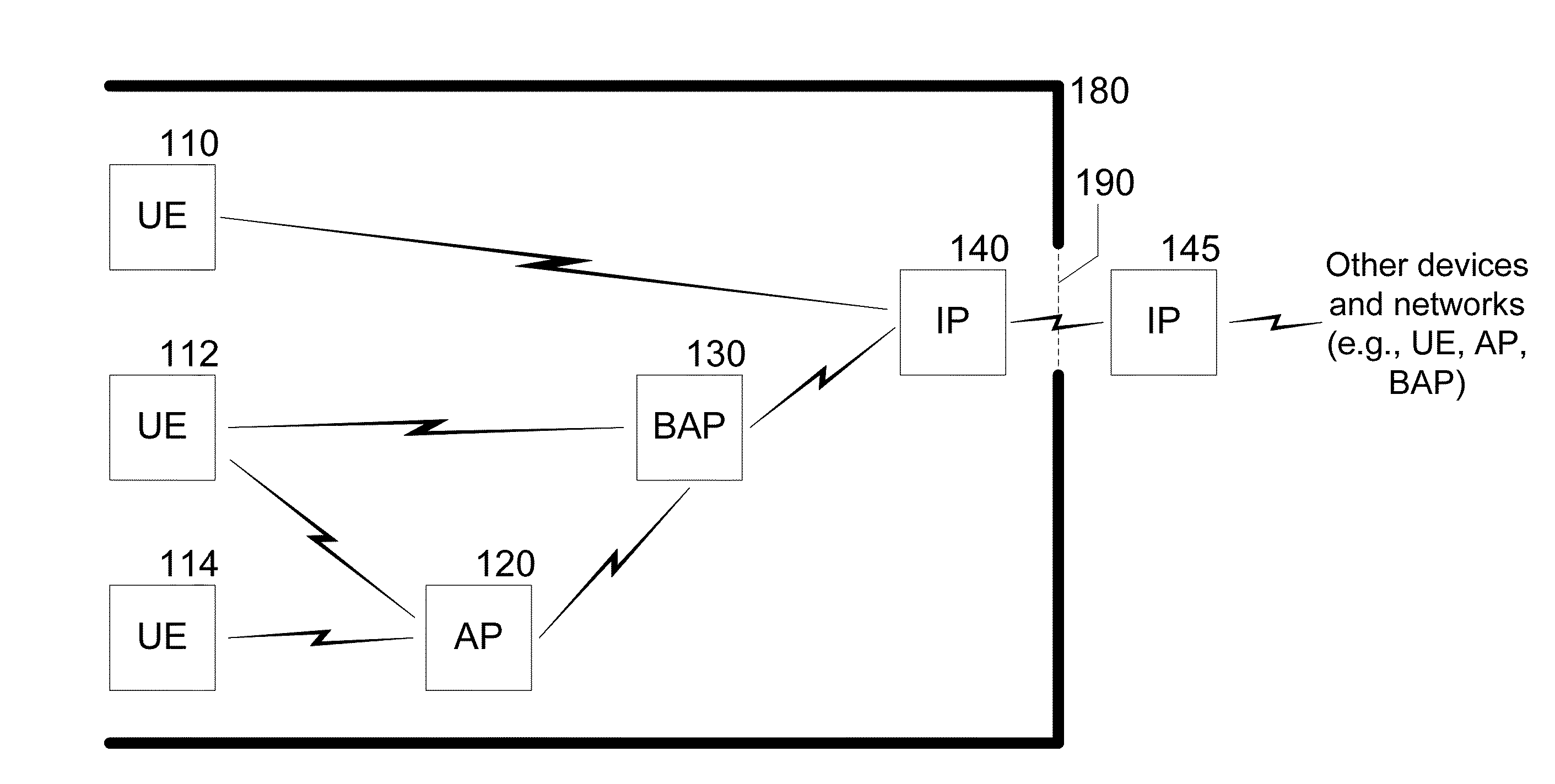
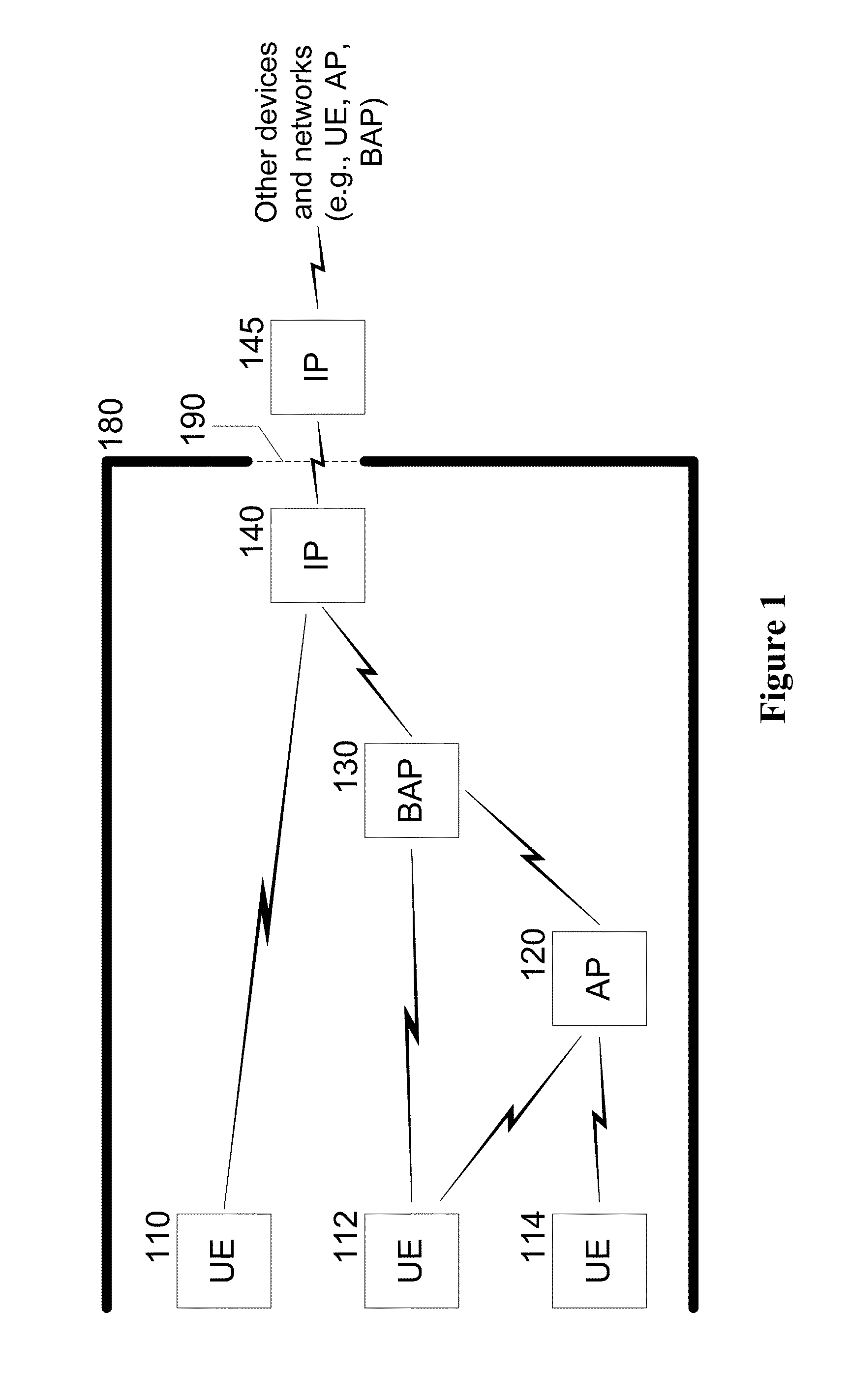
System, device, and method for high-frequency millimeter-wave wireless communication using interface points
ActiveUS20160134356A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsActive radio relay systemsComputer hardwareCommunications system
Exemplary embodiments include a communication system comprising a portal between radio-frequency propagation environments; one or more of interface points disposed in the plurality of propagation environment and configured to communicate with each other via the portal; and one or more access points disposed in one of the propagation environments, at least a portion being configured to communicate with a particular interface point. Other embodiments include apparatus for communicating across radio-frequency propagation environments comprising at least one antenna array, a computer arrangement, and a non-transitory, computer-readable medium comprising computer-executable instructions that configure an adaptive antenna array to receive expected signals from a device or system disposed in a first propagation environment and to reject interfering signals originating in the same environment; and transmit the received expected signals to a compatible apparatus in a second propagation environment via a portal that is relatively permeable with respect to a particular frequency.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
System and method for improving performance of an adaptive antenna array in a vehicular environment
InactiveUS7139593B2Improve adaptabilitySpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentMobile antennasDownlink beamforming
A system and method is disclosed for improving downlink performance of an adaptive antenna array in a vehicular environment. The system comprises a mobile station that has a first mobile antenna and a second mobile antenna. A spatial signature estimator associated with a base transceiver station obtains spatial signatures from signals from the first mobile antenna and from the second mobile antenna within an uplink interval. Correlation circuitry uses the spatial signatures to identify a least changing spatial signature to obtain an optimal downlink beamforming weight vector to be used in the transmission of a signal to the mobile station in the next downlink interval.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
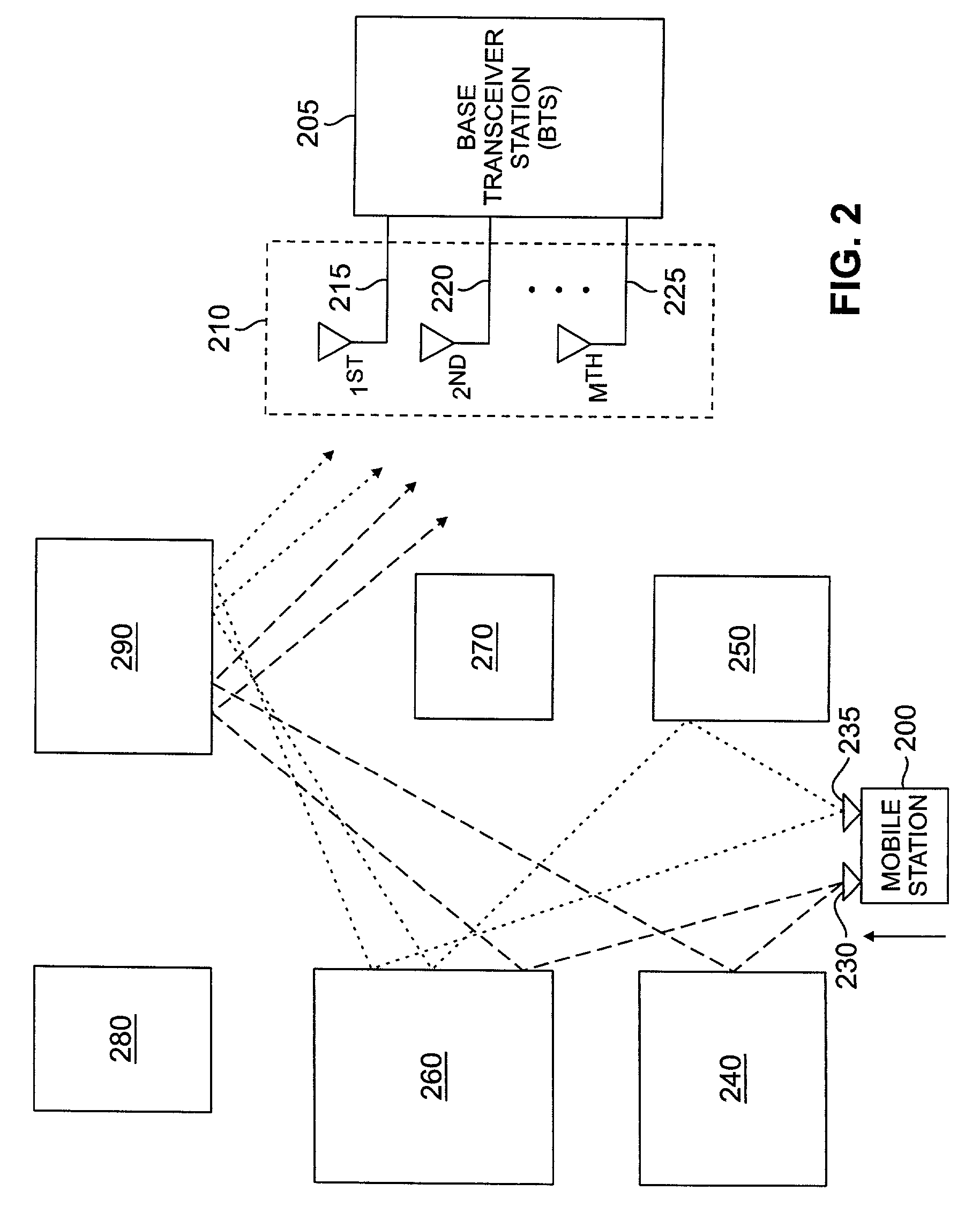
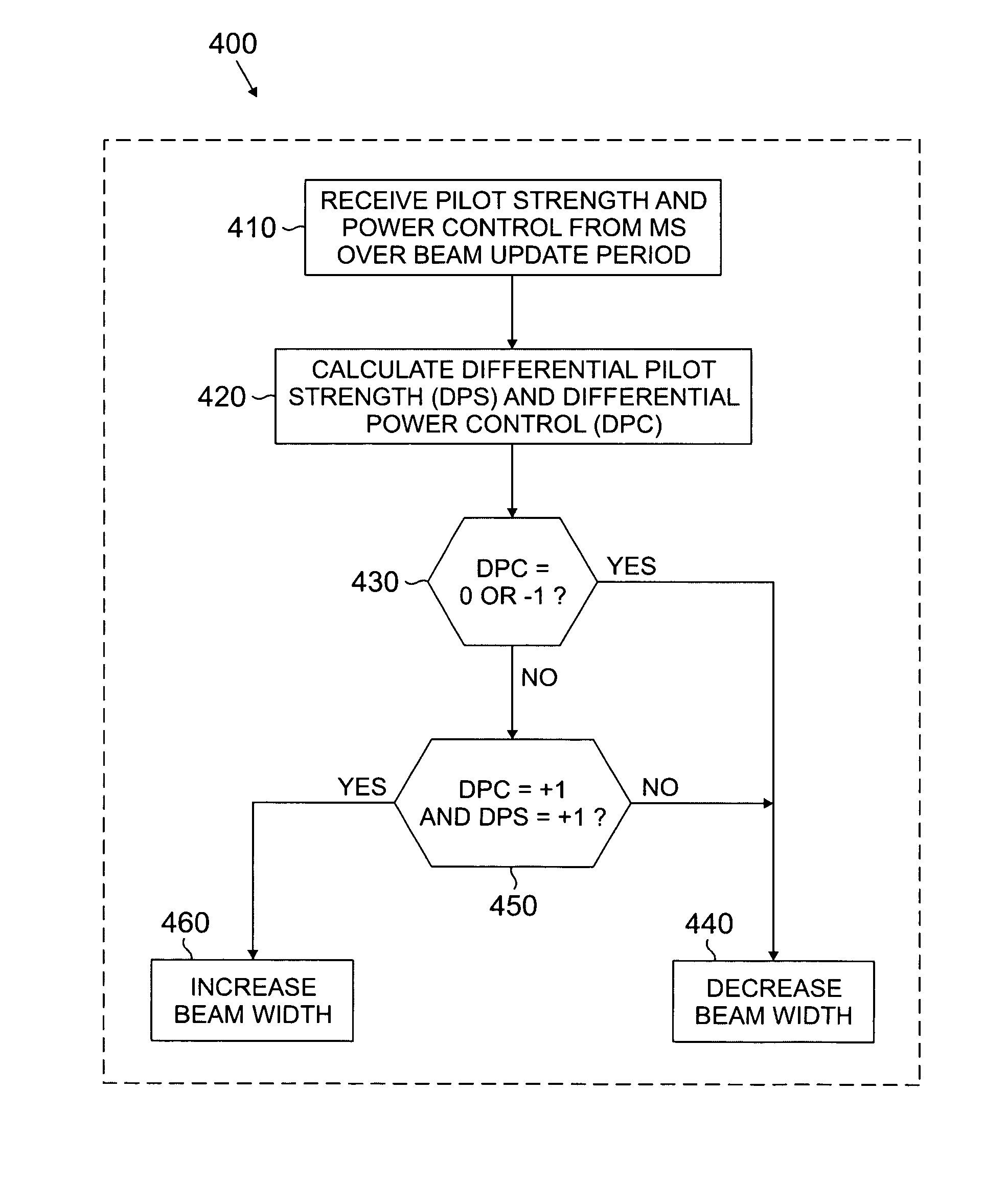
Apparatus and method for dynamic control of downlink beam width of an adaptive antenna array in a wireless network
InactiveUS20050215289A1Easy to shapeReduced beam widthPower managementReceivers monitoringTransceiverEngineering
A wireless network base station for optimizing the beam width of a downlink traffic beam in real time is provided. The base station includes a transceiver for receiving a pilot strength signal and a power control signal from a mobile station. The base station further includes beam forming circuitry operable to form a downlink traffic beam spatially directed to serve the mobile station having a beam width set as a function of the received pilot strength signal and power control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Radio transmission method for multiple self adaption antenna array
InactiveCN1988410AImprove communication performanceSpatial transmit diversityFiberWireless transmission
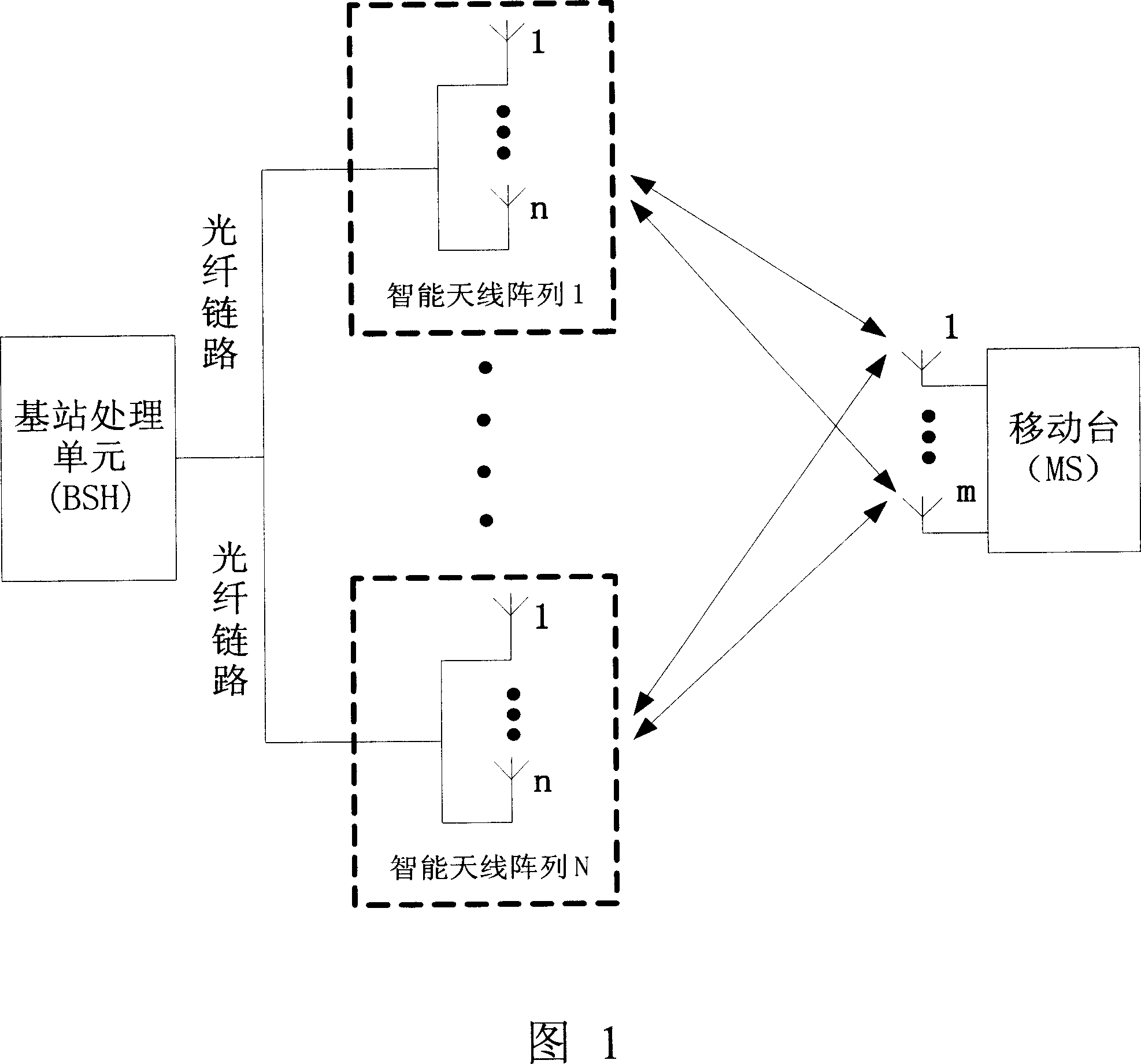
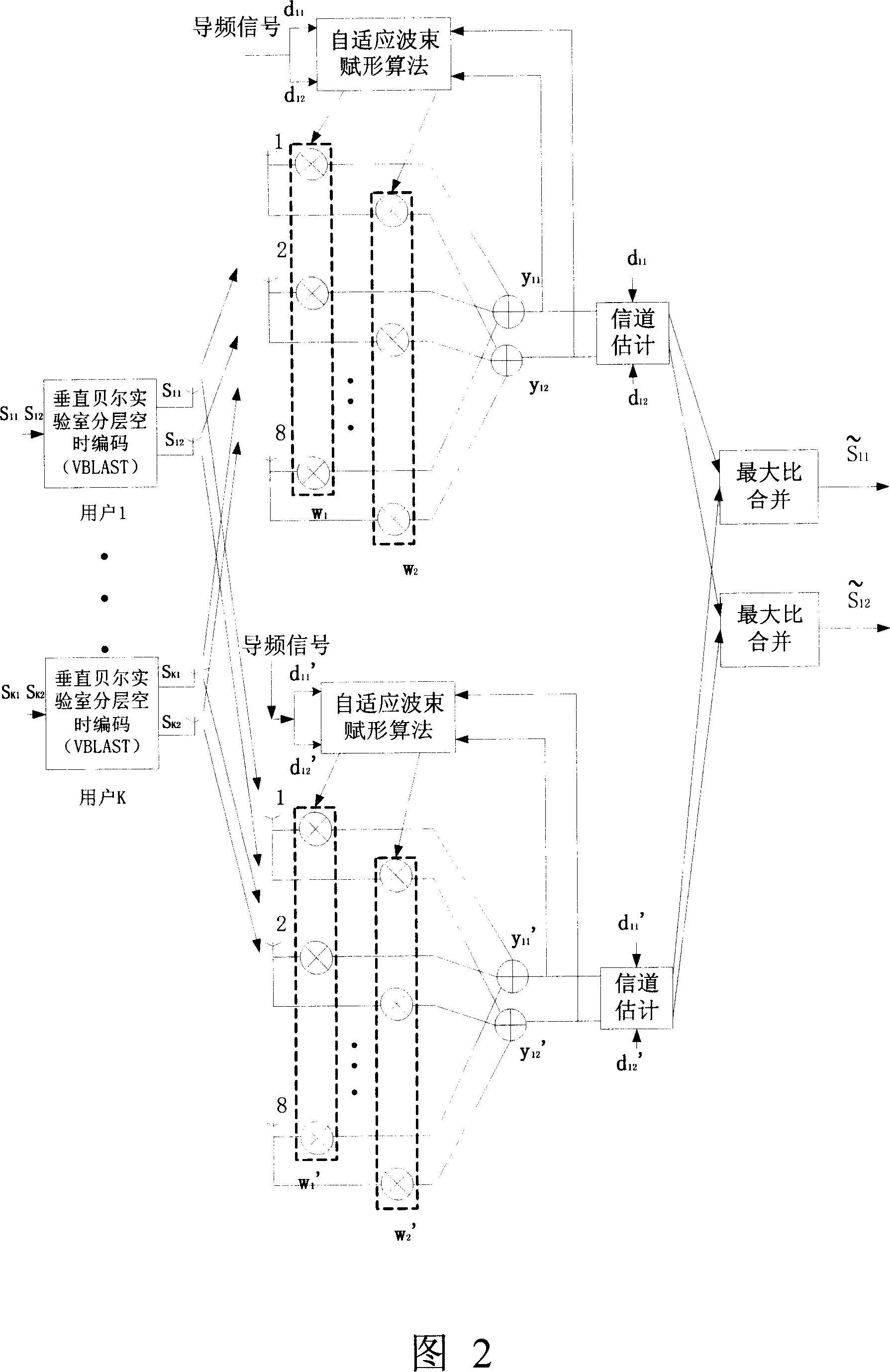
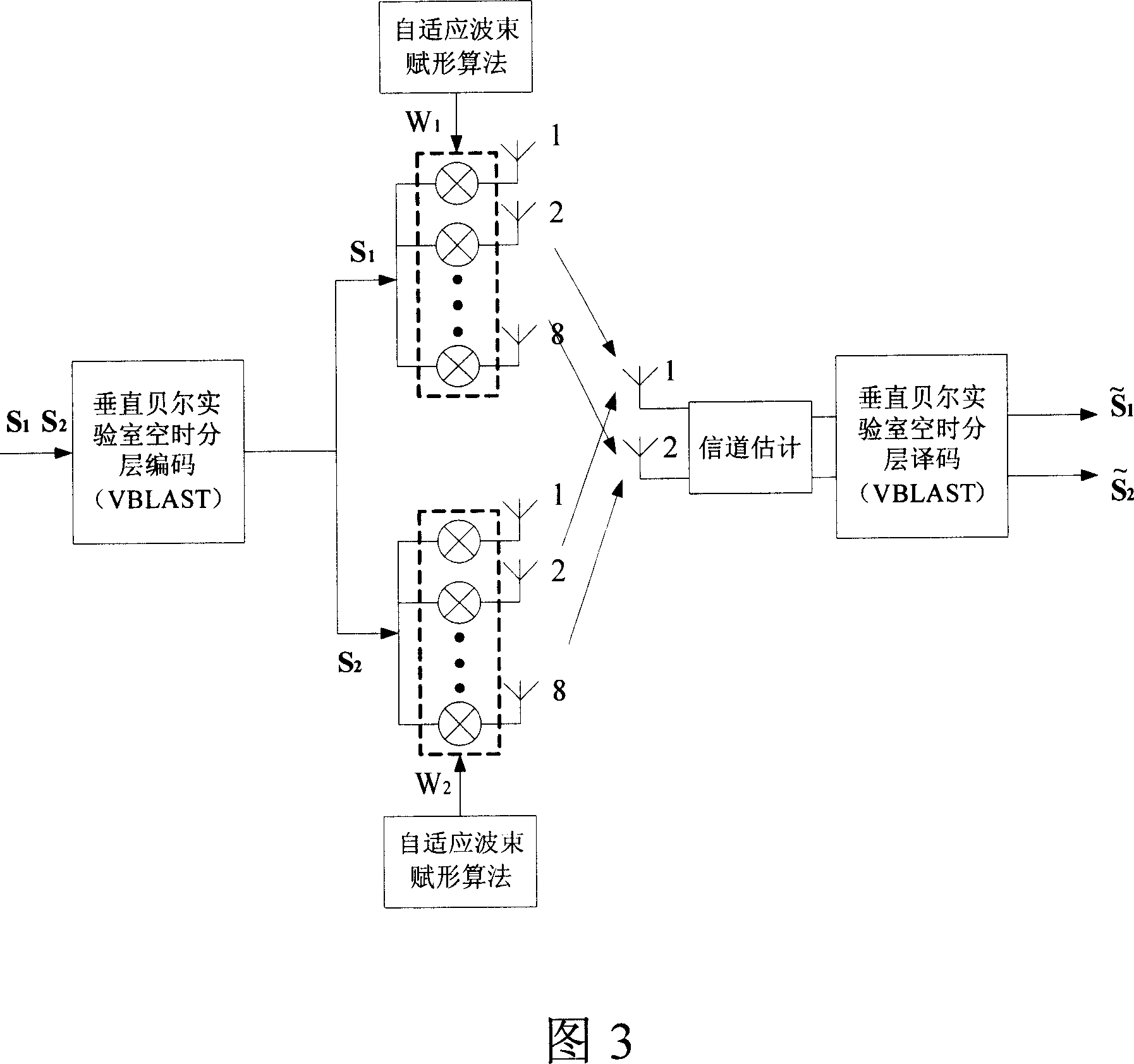
This invention relates to a radio transmission method for multiple adaptive antenna arrays, in which, a mobile station utilizes MIMO empty time process technology to send signals from multiple antennas simultaneously when the mobile station transmits signals and the base station receives them, multiple intelligent antenna arrays receive signals simultaneously and transmit them to a base station process unit (BSH) via fiber links, which first of all carries out adaptive wave beam shaping process to the received signals of each intelligent antenna array then utilizes the MIMO technology to diversify and merge signals of the array, when the base station transmits signals and the mobile station receives them, the BSH divides the signals into multiple signals by MIMO empty time process then carries out adaptive wavebeam shaping to the multiple signals to be transmitted by multiple intelligent antennas at the same time, and the mobile station gets signals by related empty time process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Mobile station handover for base stations with adaptive antenna system
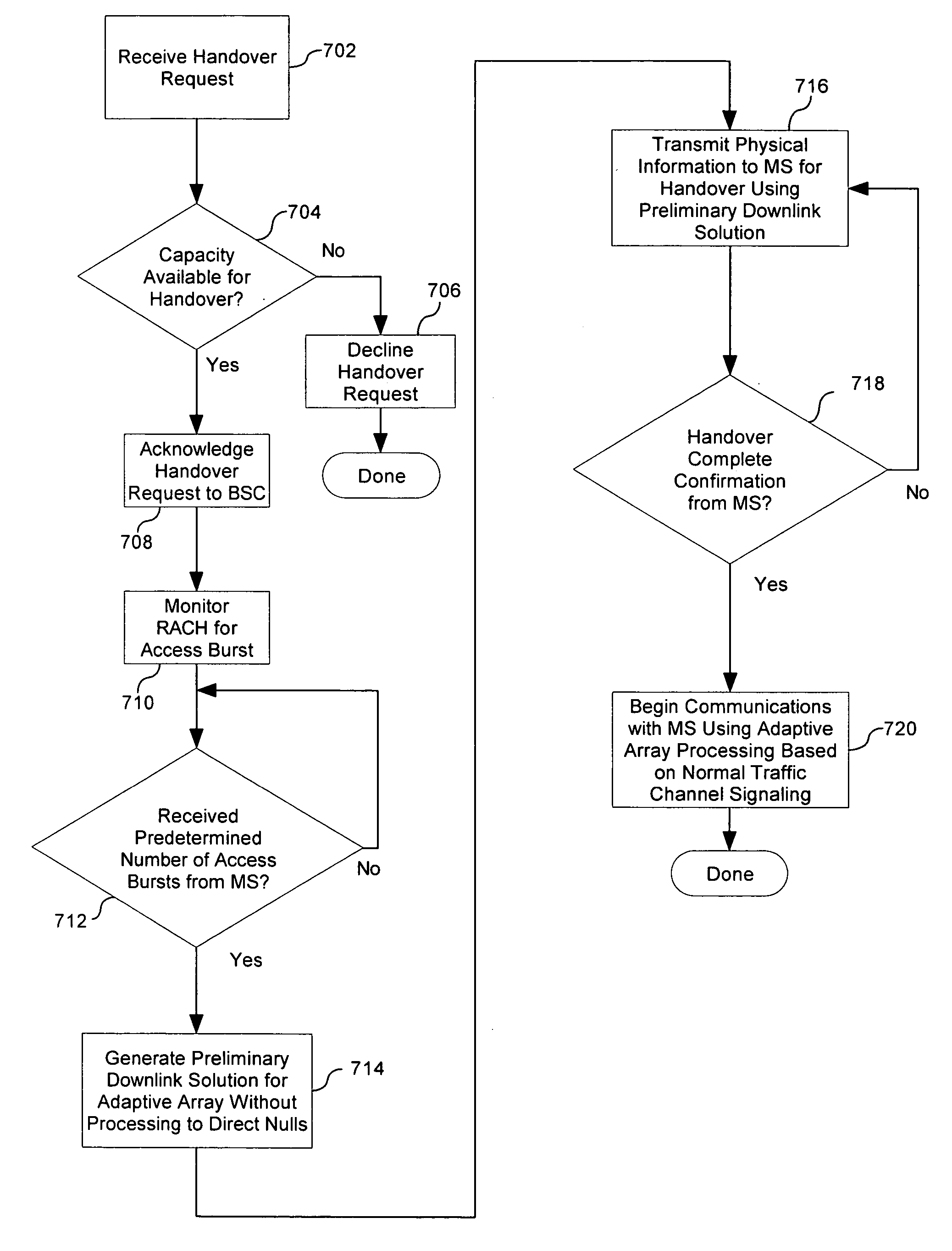
InactiveUS20070123257A1Reduce co-channel interferenceReduce gainRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentMobile stationSelf adaptive
Method for transferring service for a mobile station call signal from a first base transceiver station to a second base transceiver station in a wireless mobile telecommunication system, while a call is in progress. The method can include receiving at a base transceiver station an access burst from a mobile station with a call already in progress and requiring service from the base transceiver station. Based on the received access burst, the base transceiver station can electronically steer a beam of an adaptive antenna array of the base transceiver station toward a location of the mobile station.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC
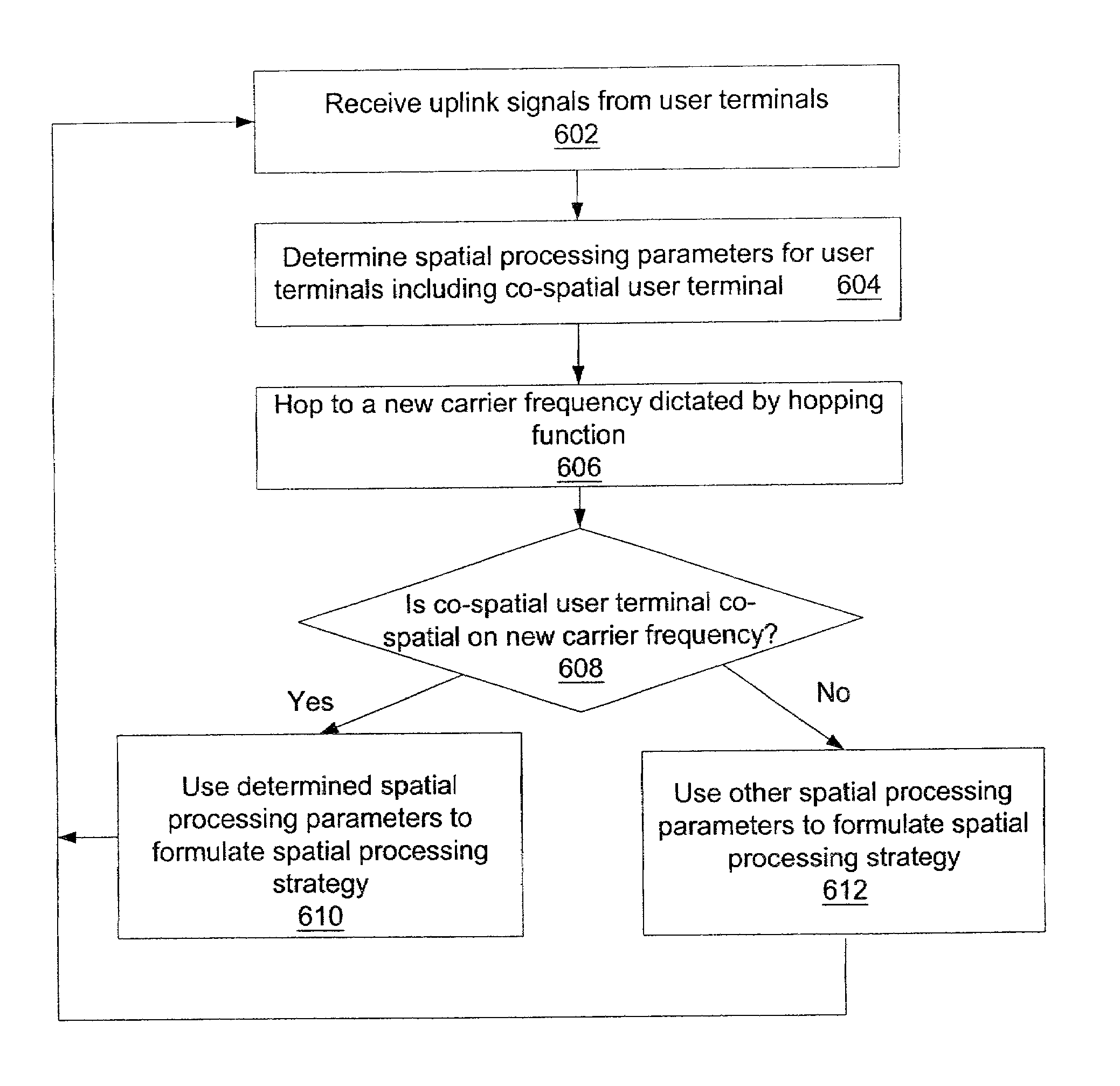
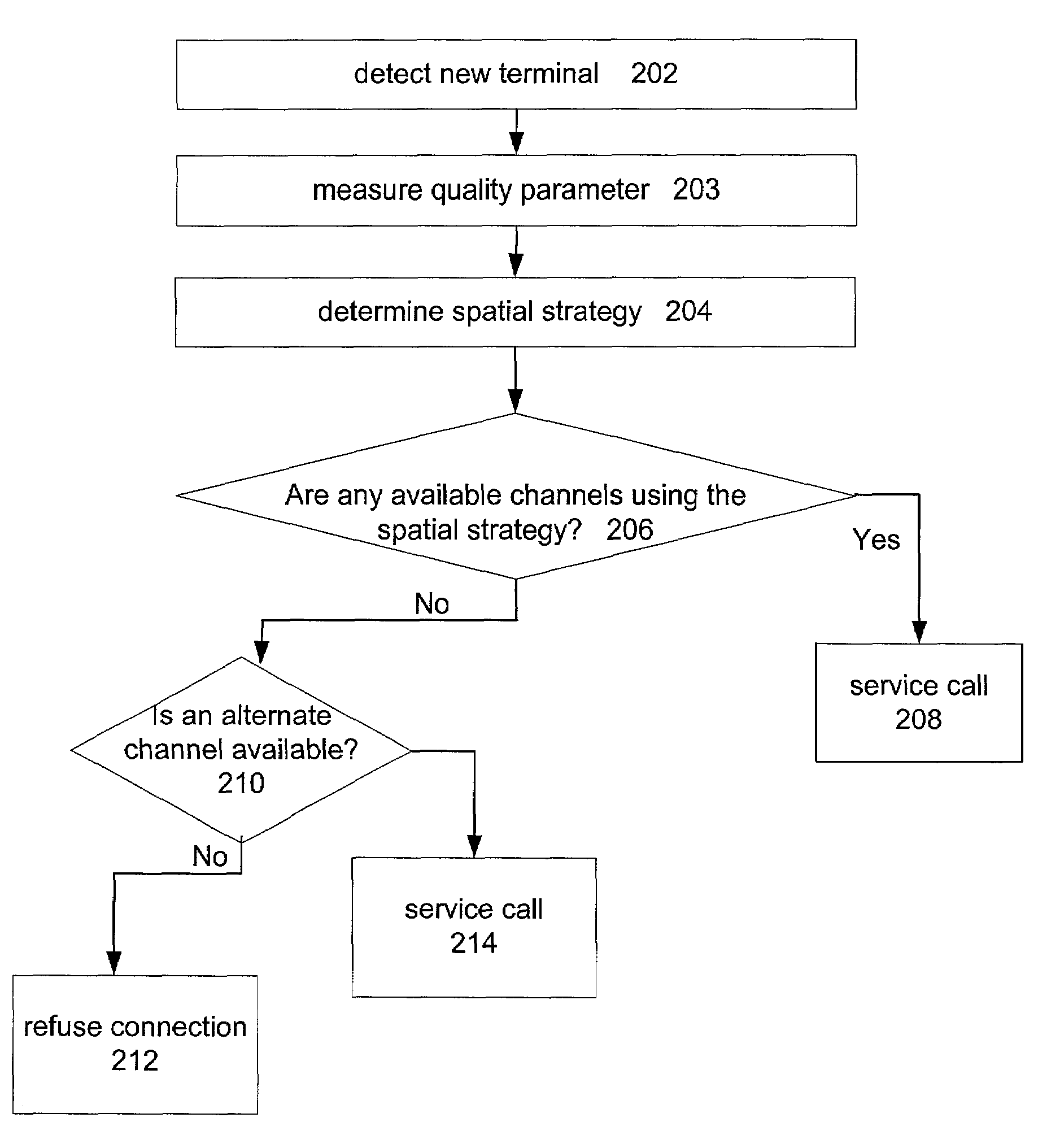
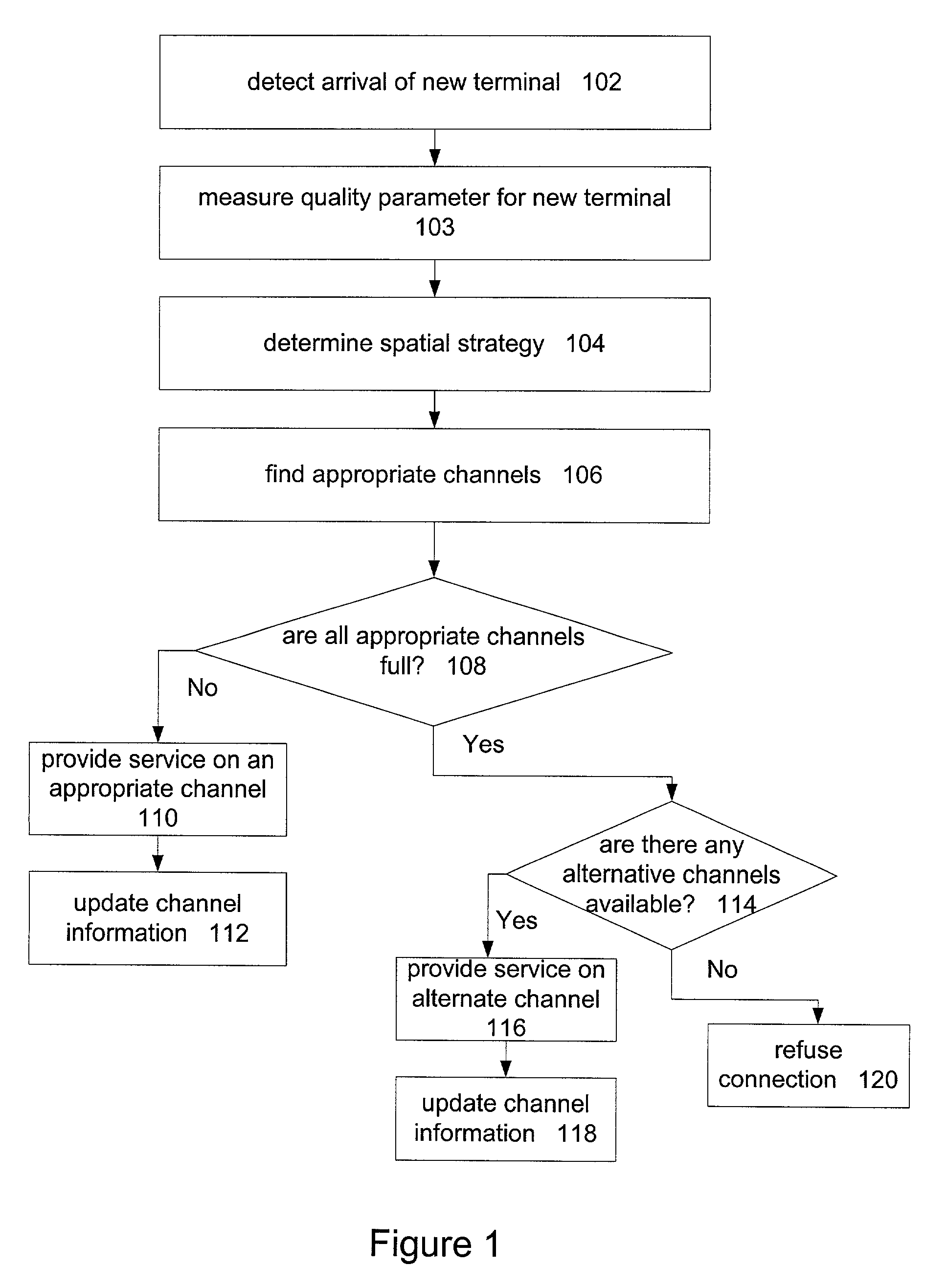
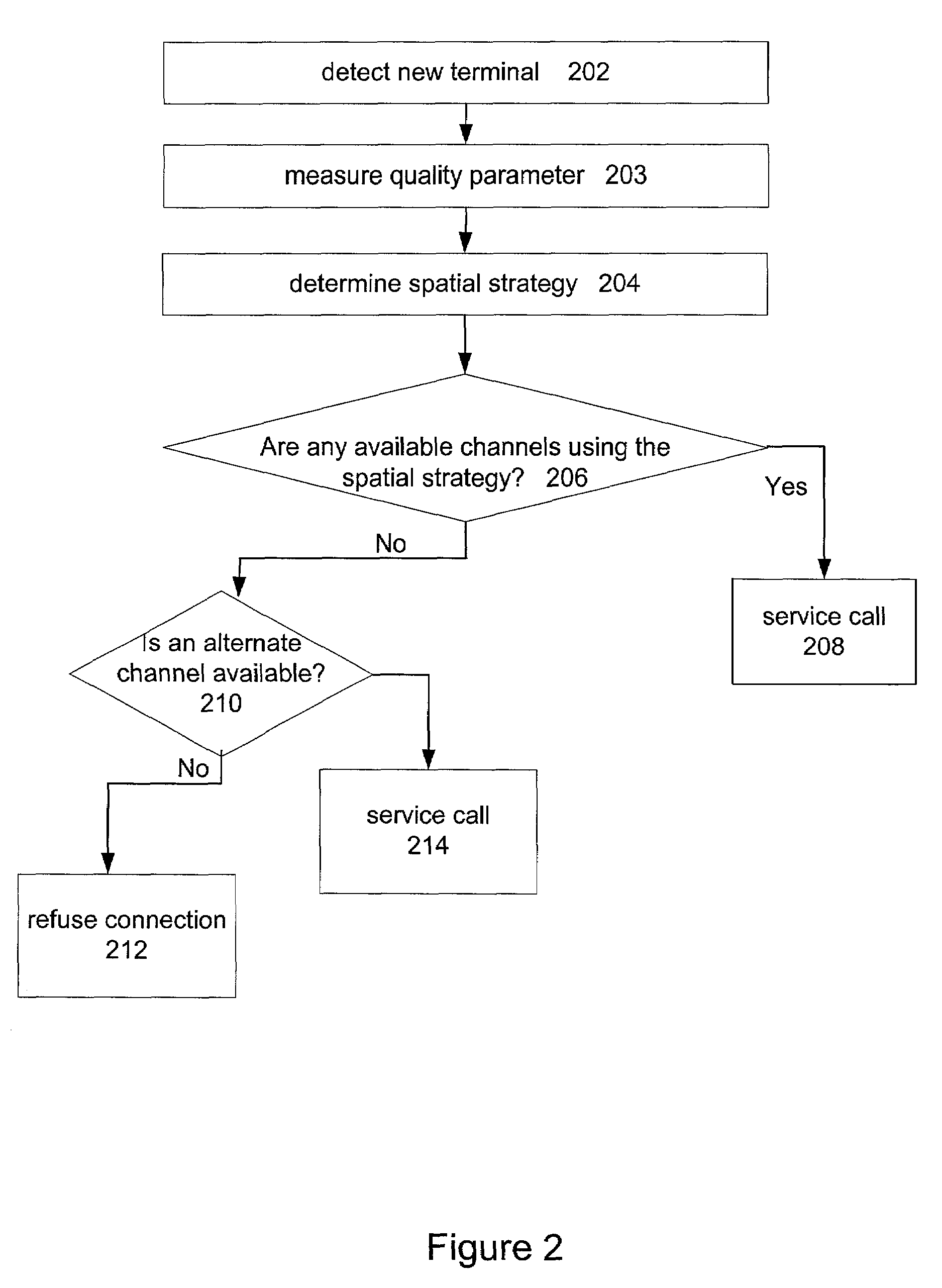
Channel assignment based on spatial strategies in a wireless network using adaptive antenna arrays
InactiveUS7539496B1Improve efficiencyRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringRadio networksWireless mesh network
The present invention can improve efficiency in wireless radio networks using spatial division multiple access (SDMA) strategies. One embodiment of the invention includes determining a quality parameter of a user terminal based on a signal received from the user terminal at a base station. One embodiment further includes determining a co-spatial constraint on the user terminal based on the quality parameter, the co-spatial constraint comprising a limitation on the quantity of additional user terminals with which the user terminal can share a conventional communications channel.
Owner:INTEL CORP
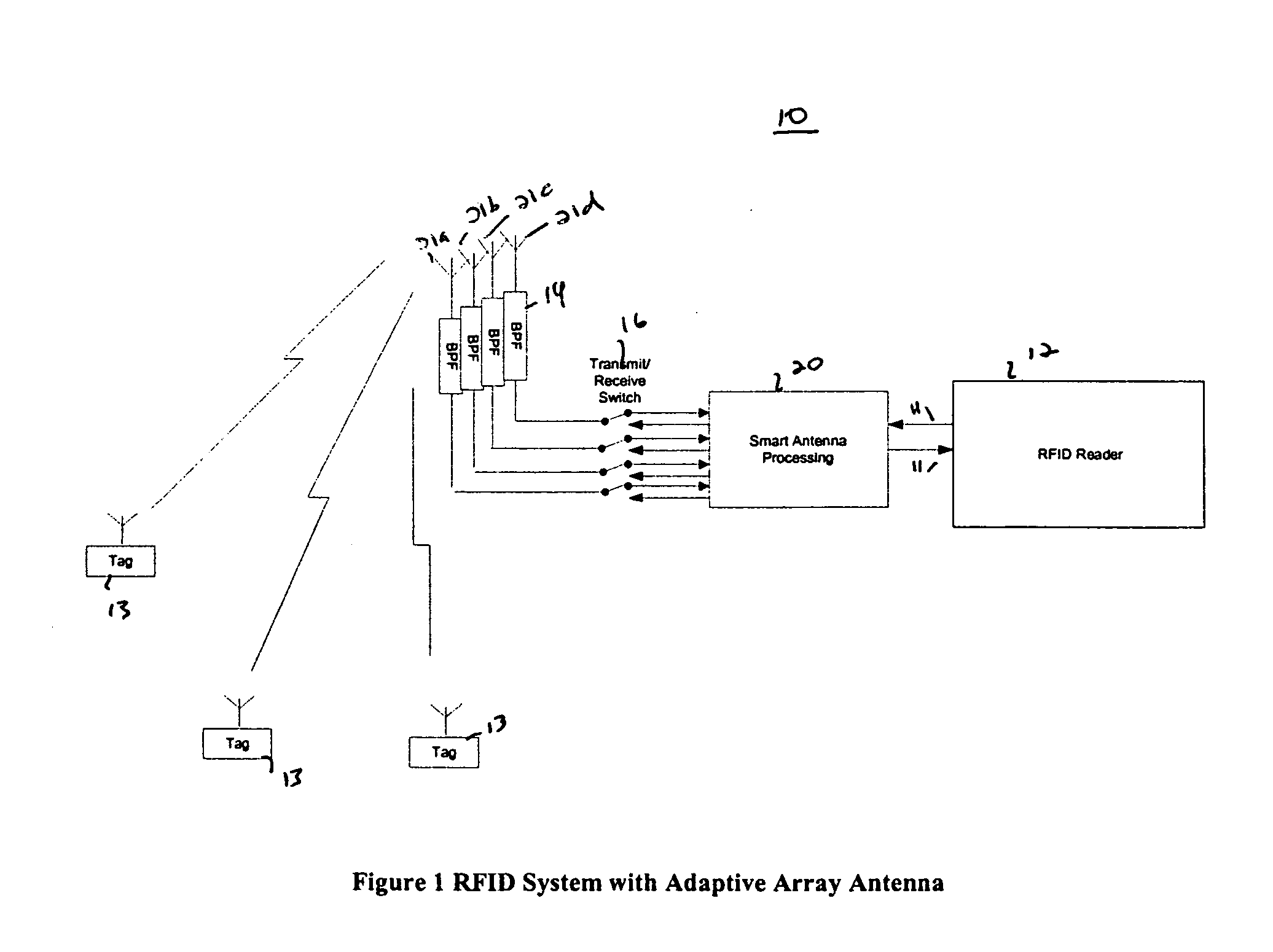
RFID system with an adaptive array antenna
InactiveUS7212116B2Expand the scope of operationImprove signal-to-noise ratioSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysSignal qualityPhase shifted
The present invention relates to use of a smart antenna for a RF reader on a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system to significantly increase the operating range of the RFID system. The smart antenna can be an adaptive antenna array. The smart antenna comprises a plurality of antenna elements and, by combining the signals from multiple antenna elements, significantly increases the received signal-to-noise ratio. In a noise limited environment, combining the signals to maximize the received signal-to-noise ratio can be based on the maximal ratio combining (MRC) principle. To achieve the best signal quality, the received signal from each antenna can be phase-shifted such that the resultant signals from all antennas are in phase. In addition, the signal from each antenna can be scaled in amplitude based on the square root of its received signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Adaptive array
ActiveUS7317427B2Easy to detectImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsArray data structureRadar systems
An adaptive antenna array has array elements arranged in element rows and element columns and subarrays arranged in subarray rows and subarray columns, for which the subarray phase centers have non-uniform spacing. The adaptive antenna array provides good detection and tracking performance when used in a radar system, while being inexpensive and easy to manufacture. A radar system and a method of adapting a radar array both employ the above described adaptive antenna array.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Geo-Directed Adaptive Antenna Array
ActiveUS20120021687A1Dramatically relax the phase and/or amplitude calibration requirements of an antenna elementRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringTarget signalAmplitude response
Systems and methods for on-the-fly characterization of an arbitrary array of antenna elements are provided. An array of arbitrary antenna elements and a reference receiver is provided. A location for a target source of signals is provided or assumed. Cross ambiguity functions are computed between the signal received by the reference receiver and the signal received by each antenna element. The cross ambiguity functions are analyzed to determine the phase and amplitude response of the antenna array to signals originating from the location of the target source of signals.
Owner:RINCON RES CORP
Geo-directed adaptive antenna array
ActiveUS8565798B2Dramatically relax the phase and/or amplitude calibration requirements of an antenna elementRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringTarget signalAmplitude response
Systems and methods for on-the-fly characterization of an arbitrary array of antenna elements are provided. An array of arbitrary antenna elements and a reference receiver is provided. A location for a target source of signals is provided or assumed. Cross ambiguity functions are computed between the signal received by the reference receiver and the signal received by each antenna element. The cross ambiguity functions are analyzed to determine the phase and amplitude response of the antenna array to signals originating from the location of the target source of signals.
Owner:RINCON RES CORP
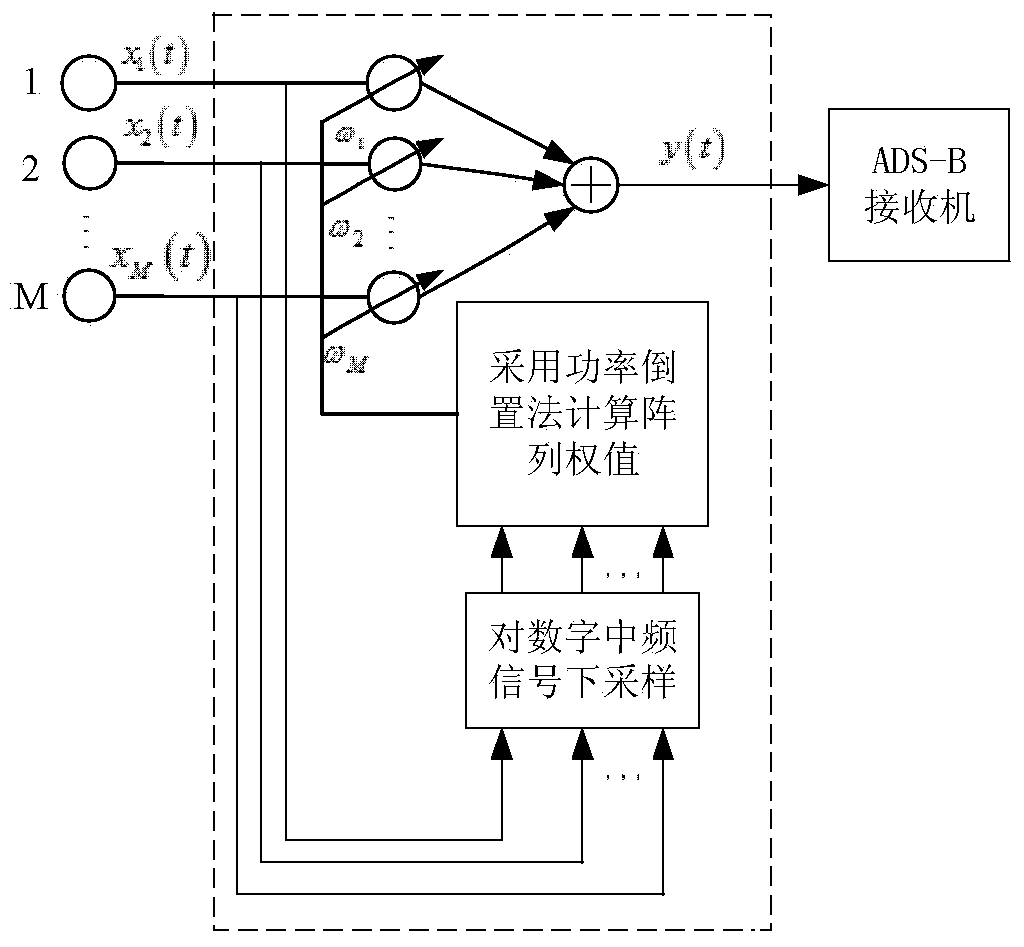
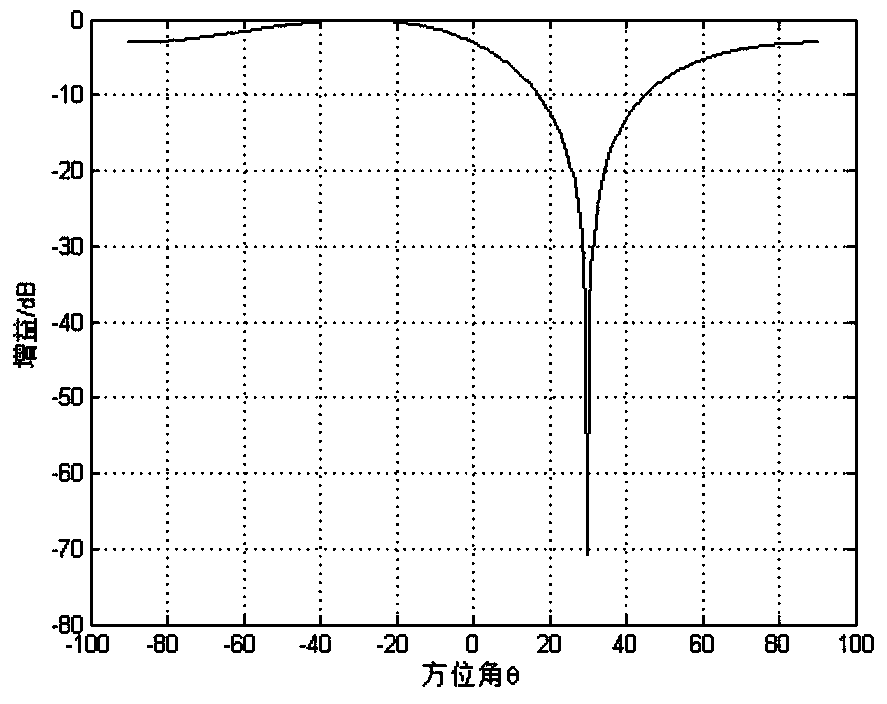
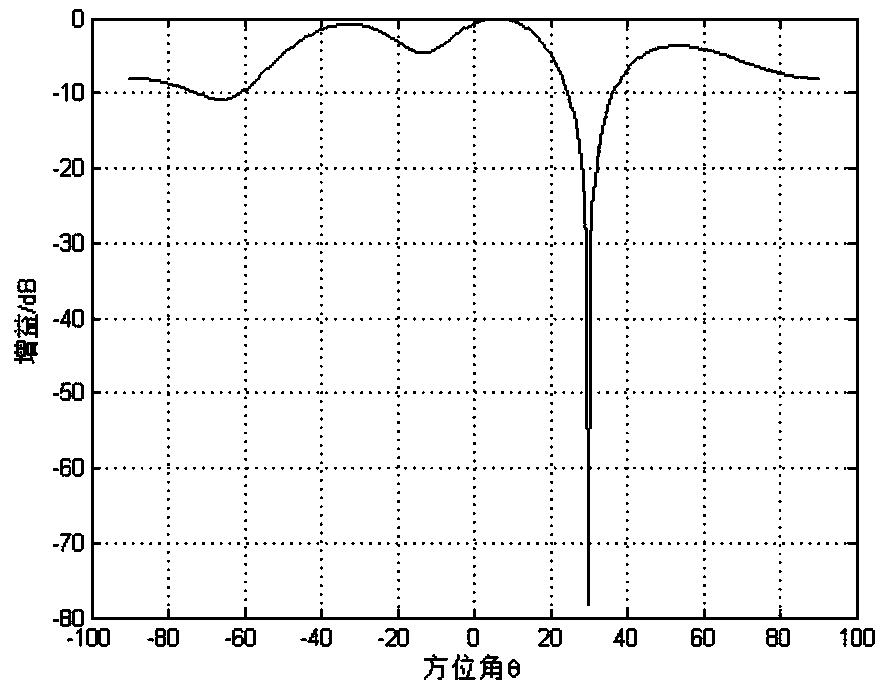
ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) blanket jamming suppression method based on improved power inversion method
InactiveCN104393883AImprove SINRSuppressive Interference SuppressionSpatial transmit diversityRadio frequency signalEngineering
The invention discloses an ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) blanket jamming suppression method based on an improved power inversion method. The ADS-B blanket jamming suppression method comprises the following steps of converting a radio frequency signal received by an array antenna to a digital intermediate frequency signal; carrying out down-sampling on the digital intermediate frequency signal; estimating a covariance matrix of a receiving signal by utilizing a signal sample after down-sampling; and computing an adaptive antenna array weighting vector based on the improved power inversion method by utilizing the covariance matrix. According to the ADS-B blanket jamming suppression method, the characteristics of short duration and intermittence of an ADS-B signal and persistence of blanket jamming are combined, through carrying out down-sampling on the digital intermediate frequency signal and estimating the covariance matrix by utilizing the signal sample after down-sampling, the influence of the ADS-B signal on the covariance matrix of the receiving signal is weakened; the array weighting vector is computed by utilizing the covariance matrix, so that beam forming is carried out, and thus the blanket jamming is suppressed. By adopting the ADS-B blanket jamming suppression method, an antenna pattern can form null in a jamming suppression direction and keeps gain unchanged basically, so that the blanket jamming is suppressed.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Signal transmitting method (variants) and device for carrying out said method
InactiveUS20070189148A1Improve efficiencyMaximize signal reception qualitySpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationPresent methodFrequency spectrum
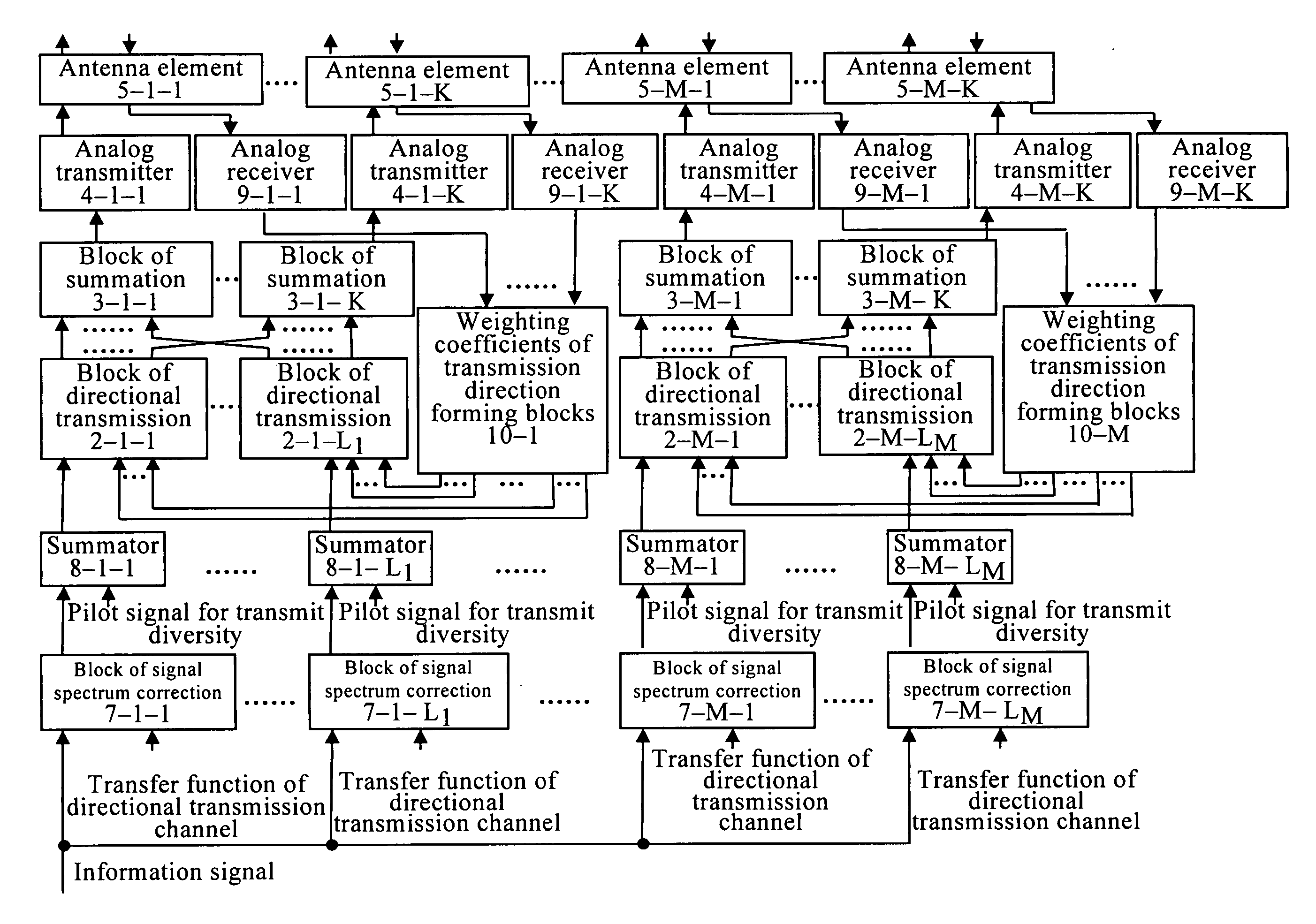
A group of inventions relate generally to radio engineering, and more particularly to a method of data transmission (embodiments) and apparatus of data transmission (embodiments) to be used, for example, in cellular communications systems when transmitting an information signal over the downlink from base station to mobile station. The goal of the present method of data transmission (embodiments) and the apparatus of data transmission (embodiments) is to increase the efficiency of the information signal transmission in the downlink and, thus, maximize the information signal reception quality at the mobile station. The claimed solution also reduces the feedback channel (from mobile to base station) load. The object of the invention is attained by correcting the spectrum of the transmitted information signal copies, transmitting the information signal copies from each adaptive antenna array in each efficient transmission direction, estimating the transfer functions of the directional transmission channels using the pilot signals transmitted from each antenna element, pilot signals for transmit diversity, transmitted from each adaptive antenna array in each efficient transmission direction, combining these two estimates, and by estimating the efficient transmission directions at the base station using the mobile station signal.
Owner:JSC KODOFON
Apparatus and method for allocating walsh codes to access terminals in an adaptive antenna array CDMA wireless network
InactiveUS7411899B2Maximizing re-useSpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationDownlink beamformingWireless network
An apparatus having: 1) a database for storing R active wireless terminal records, each of the R active wireless terminal records containing: a) an active orthogonal code and b) corresponding downlink beamforming coefficients used to communicate with one of the wireless access terminals; and 2) a controller associated with the database that receives a notification that a new wireless access terminal is accessing the base station and, in response to the notification, compares each of the R active wireless terminal records to new downlink beamforming coefficients associated with the new wireless access terminal. The controller determines at least one active wireless terminal record containing corresponding downlink beamforming coefficients that have the least correlation with the new downlink beamforming coefficients.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com