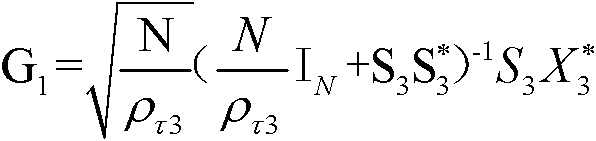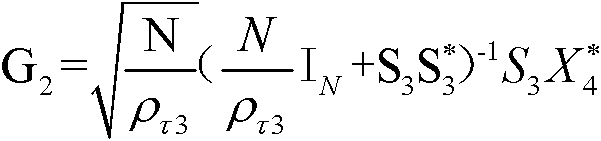Patents
Literature
419results about How to "Increase channel capacity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
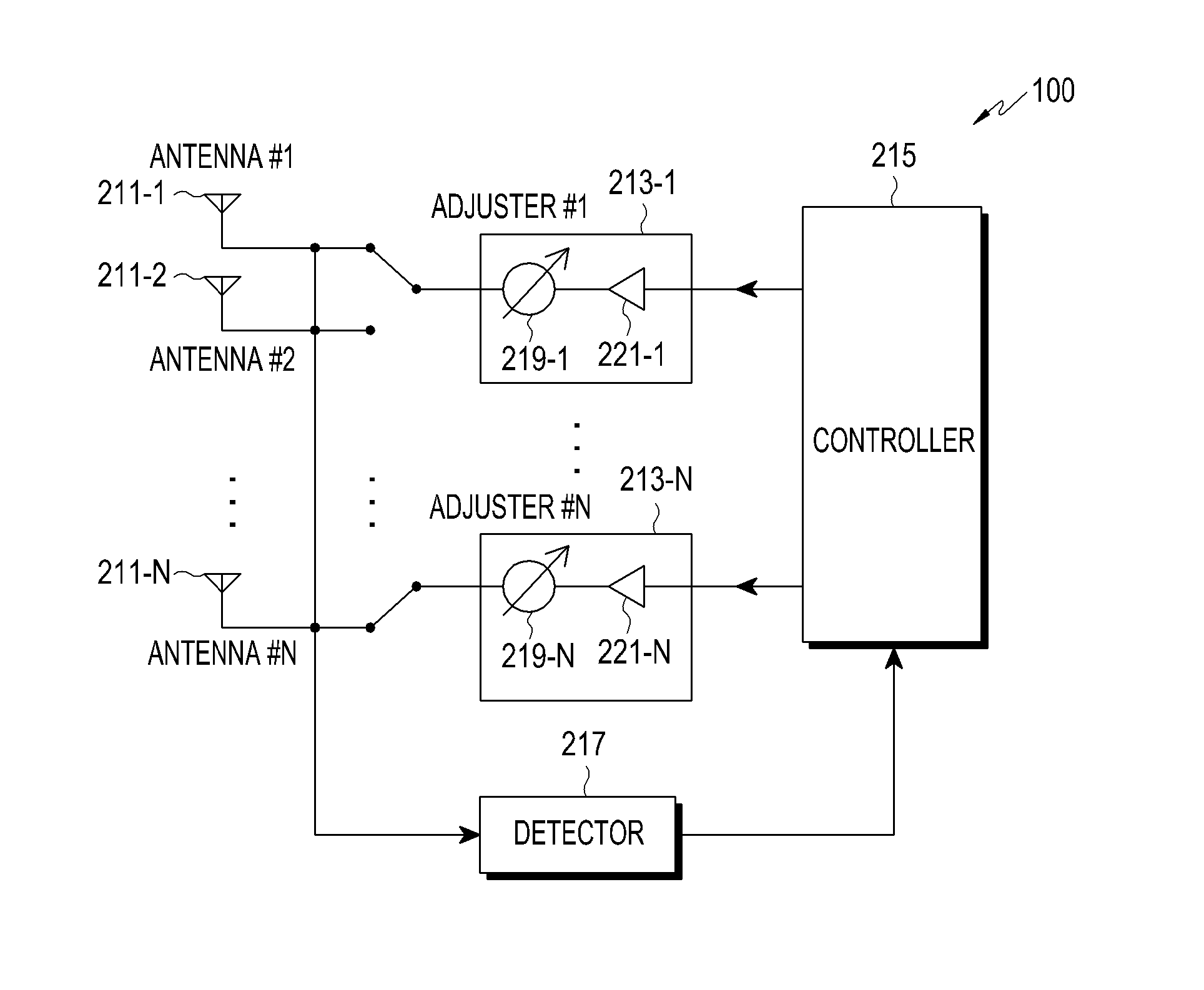
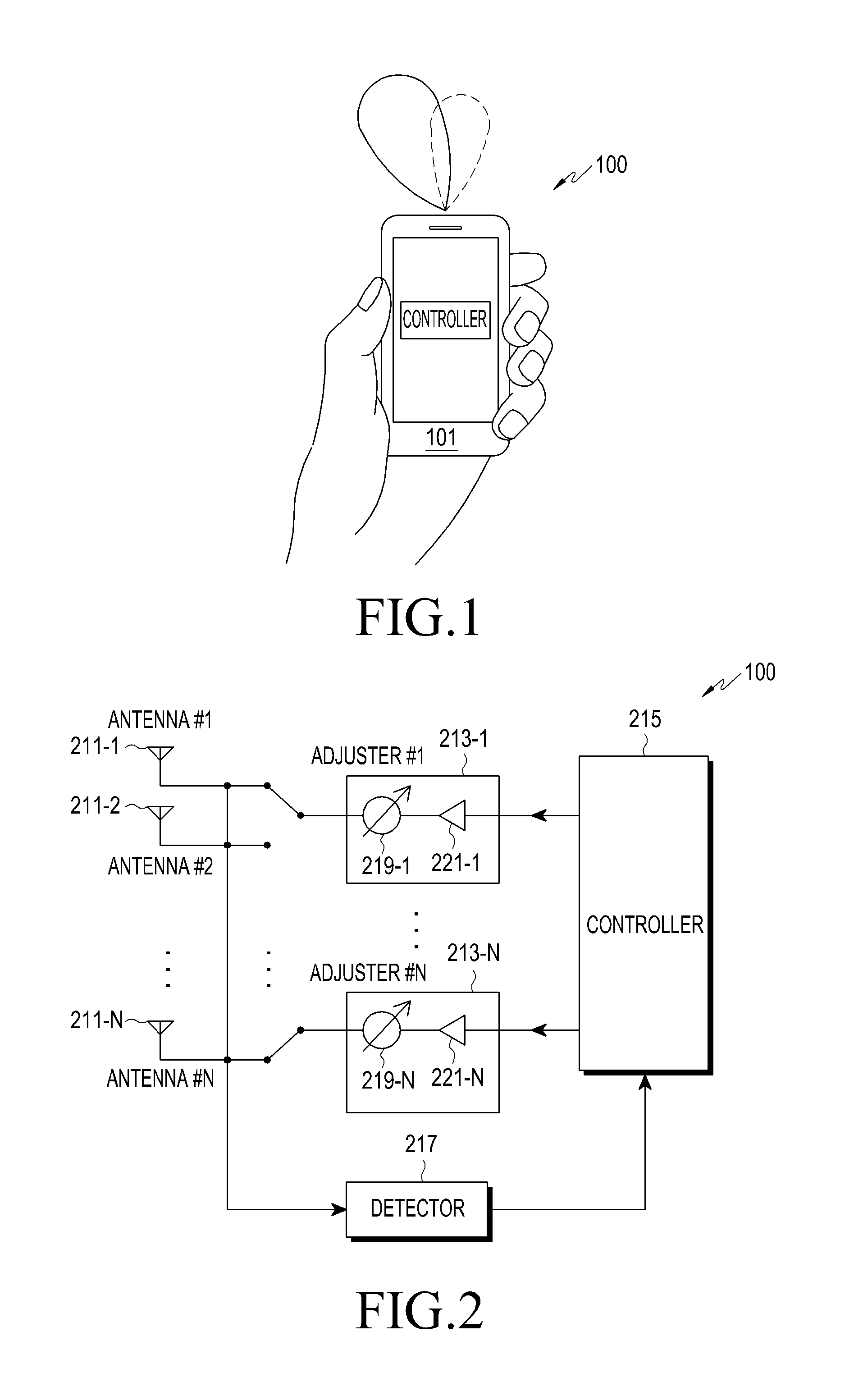
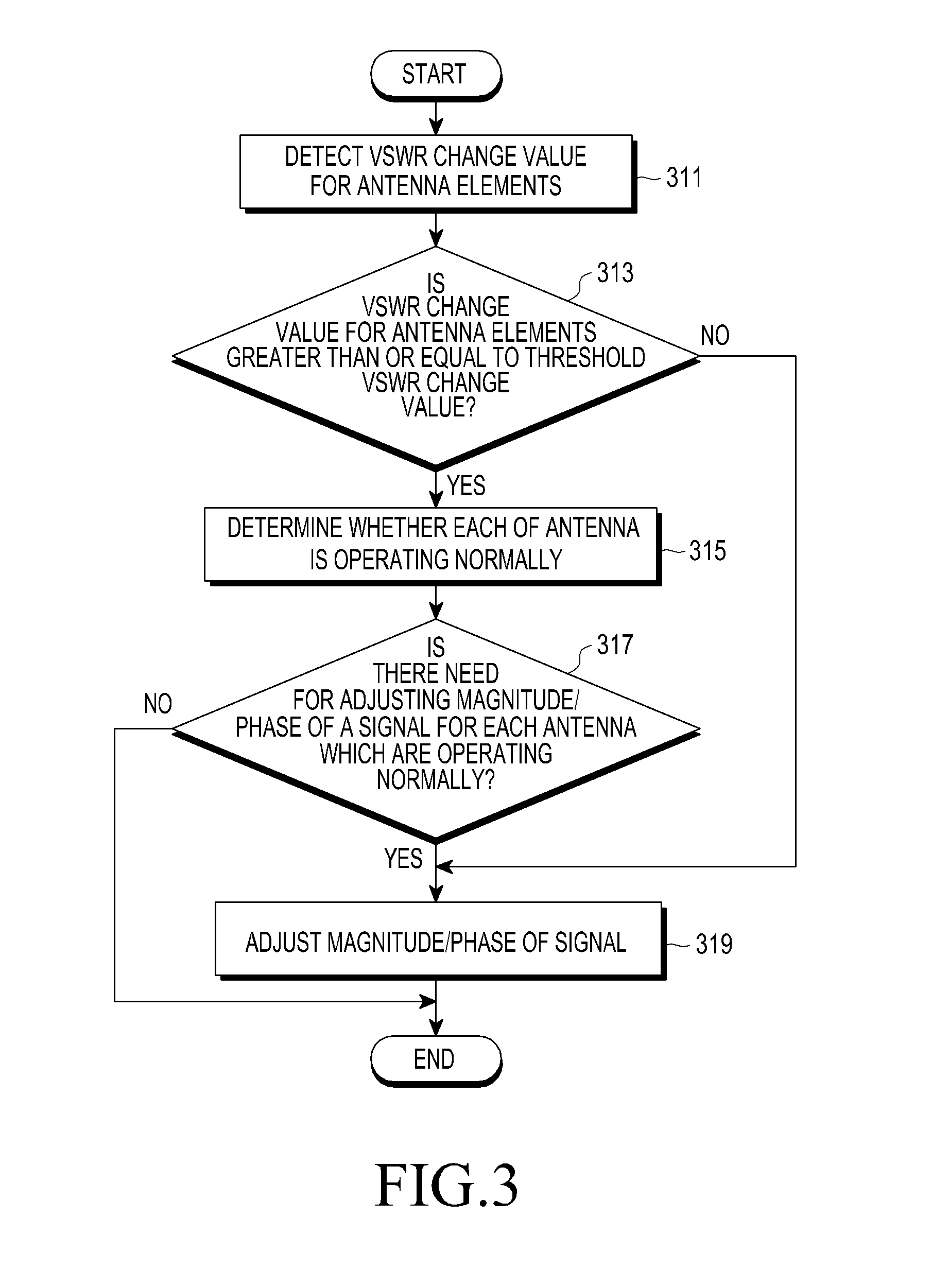
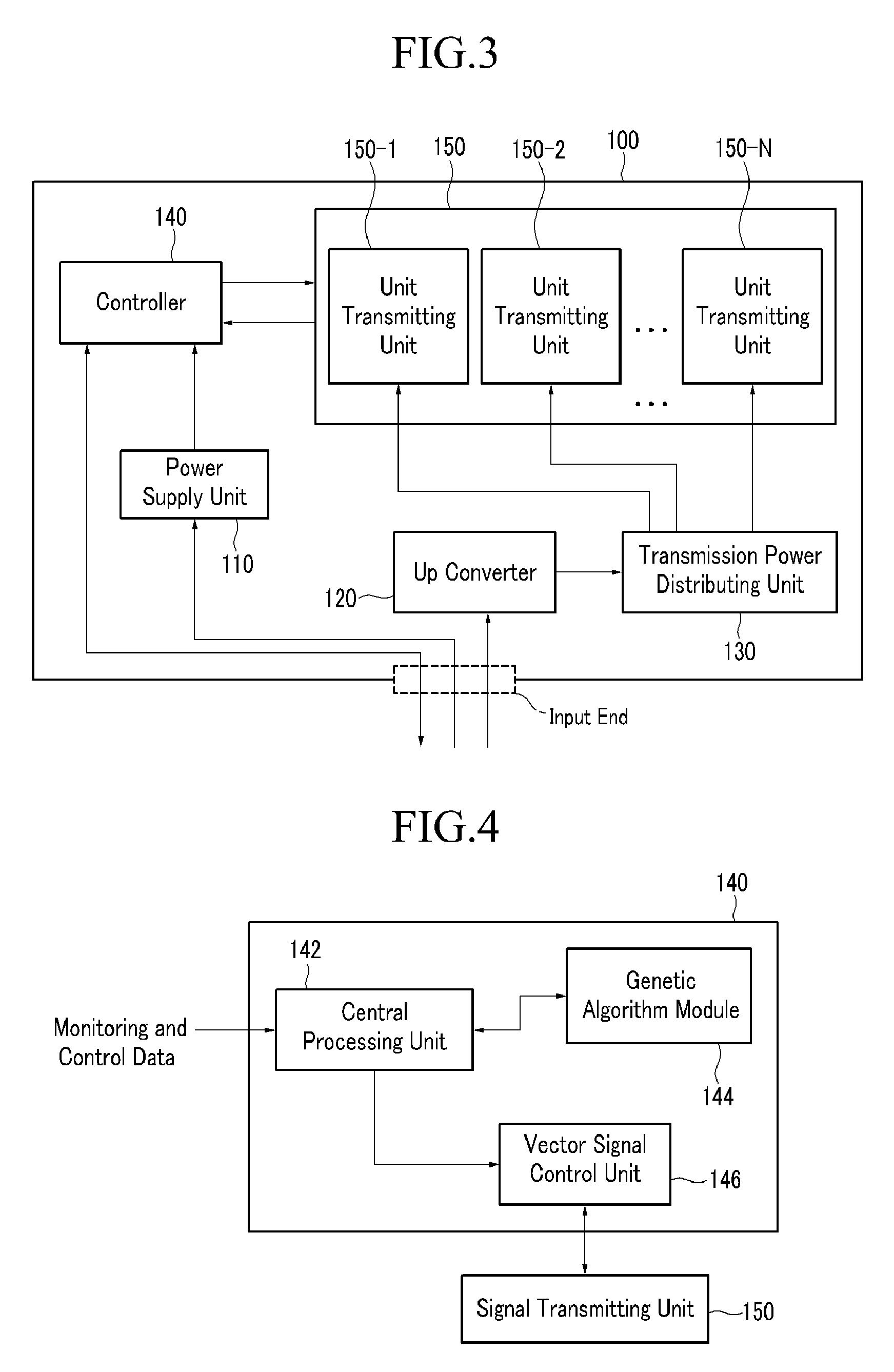
Apparatus and method for adjusting beam pattern in communication system supporting beam division multipile access scheme
ActiveUS20150318610A1Reduce degradationImprove communication system performanceTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemBeam pattern
A method for adjusting a beam pattern in a beam pattern adjusting apparatus in a communication system supporting a Beam Division Multiple Access (BDMA) scheme is provided. The method includes determining whether a Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) value for each antenna included in an antenna array included in the beam pattern adjusting apparatus is greater than or equal to a threshold VSWR value, if it is determined that an antenna of the antenna array has a VSWR value that is greater than or equal to the threshold VSWR, detecting whether each of the antenna elements is operable, and if it is determined that at least one of the antennas is inoperable, adjusting a beam pattern of at least one of the antennas that is operable.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
System and Method for Synchronized and Coordinated Beam Switching and Scheduling in a Wireless Communications System
ActiveUS20100033374A1Increase channel capacityEasy to findError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemBeam pattern
A system and method for synchronized and coordinated beam switching and scheduling in a wireless communications system is provided. A method for controller operation includes determining a beam cycle pattern, sharing the beam cycle pattern with neighboring controllers, receiving beam information from a communications device, generating scheduling information from the beam cycle pattern and beam cycle patterns from other controllers, receiving a transmission intended for the communications device, and causing the transmission to be transmitted to the communications device. The beam cycle pattern includes a list of beam patterns transmitted by the controller, and the transmission is transmitted using the scheduling information and the received beam information.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
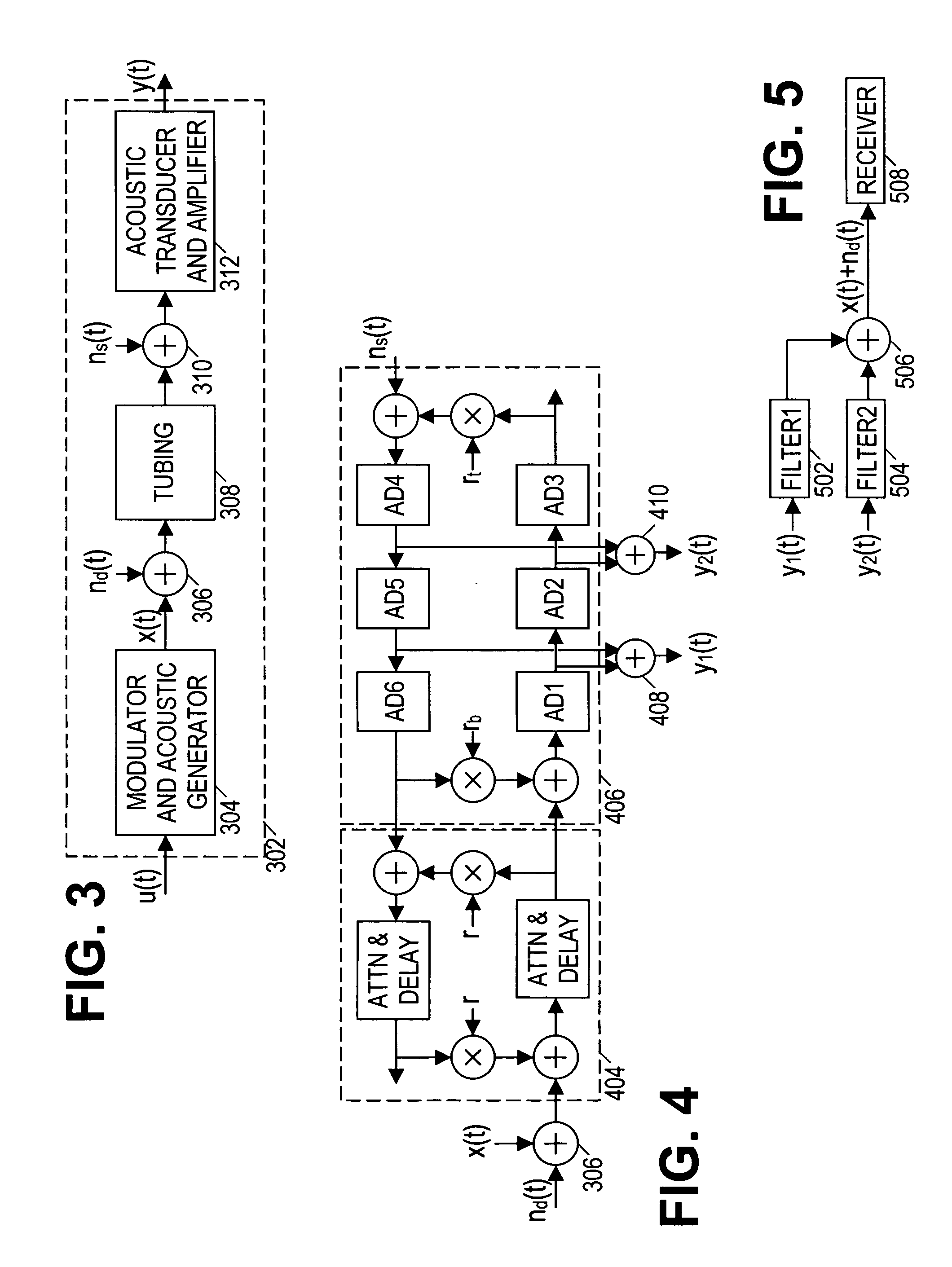
Directional acoustic telemetry receiver
ActiveUS20050024232A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioIncrease channel capacitySurveyNon-electrical signal transmission systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Computer module
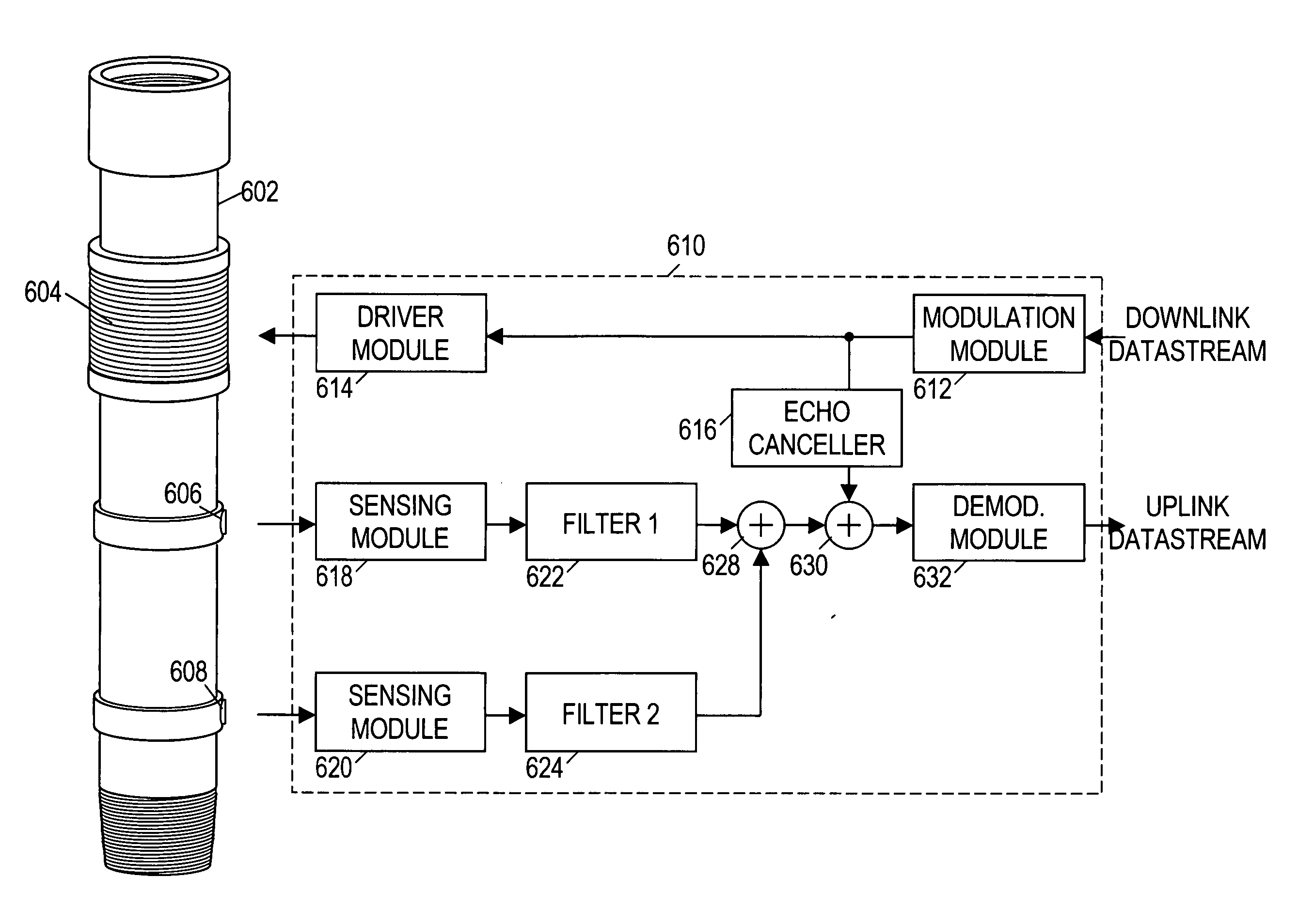
Acoustic telemetry devices and methods that provide directional detection. In one embodiment, a disclosed acoustic telemetry device comprises at least two acoustic sensors and an electronics module. A first of the acoustic sensors detects a communication signal that propagates along a tubing string in a first direction. A second of the acoustic sensors is configured to detect the communication signal before the first acoustic sensor. The electronics module combines the detection signals from the acoustic sensors to obtain a combined signal that substantially excludes signals propagating in a direction opposite to the communication signal. Such signal suppression may significantly enhance the communication signal's signal-to-noise ratio, thereby increasing channel capacity. The acoustic telemetry device may be configured to support logging while drilling and / or full-duplex communication.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
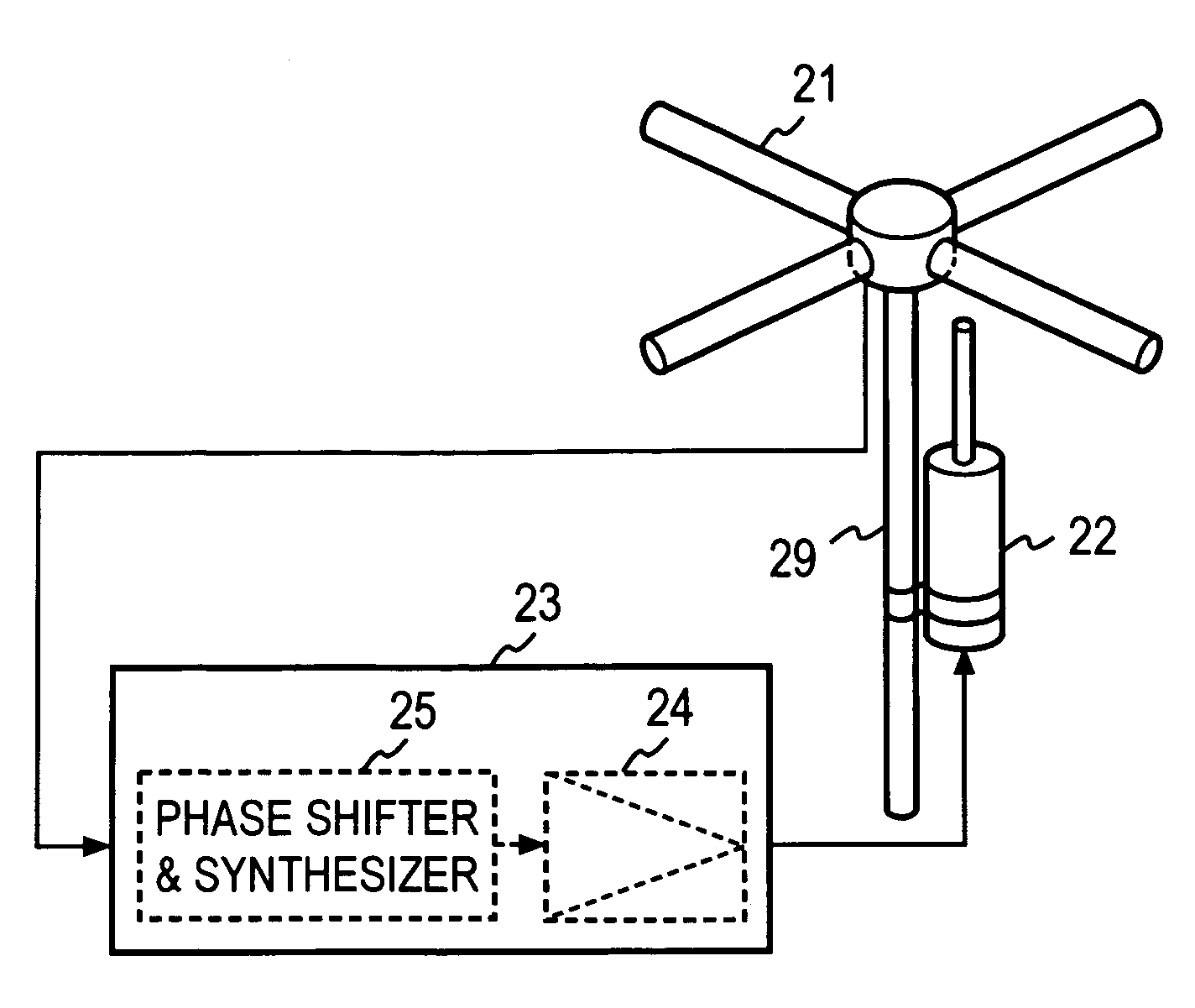
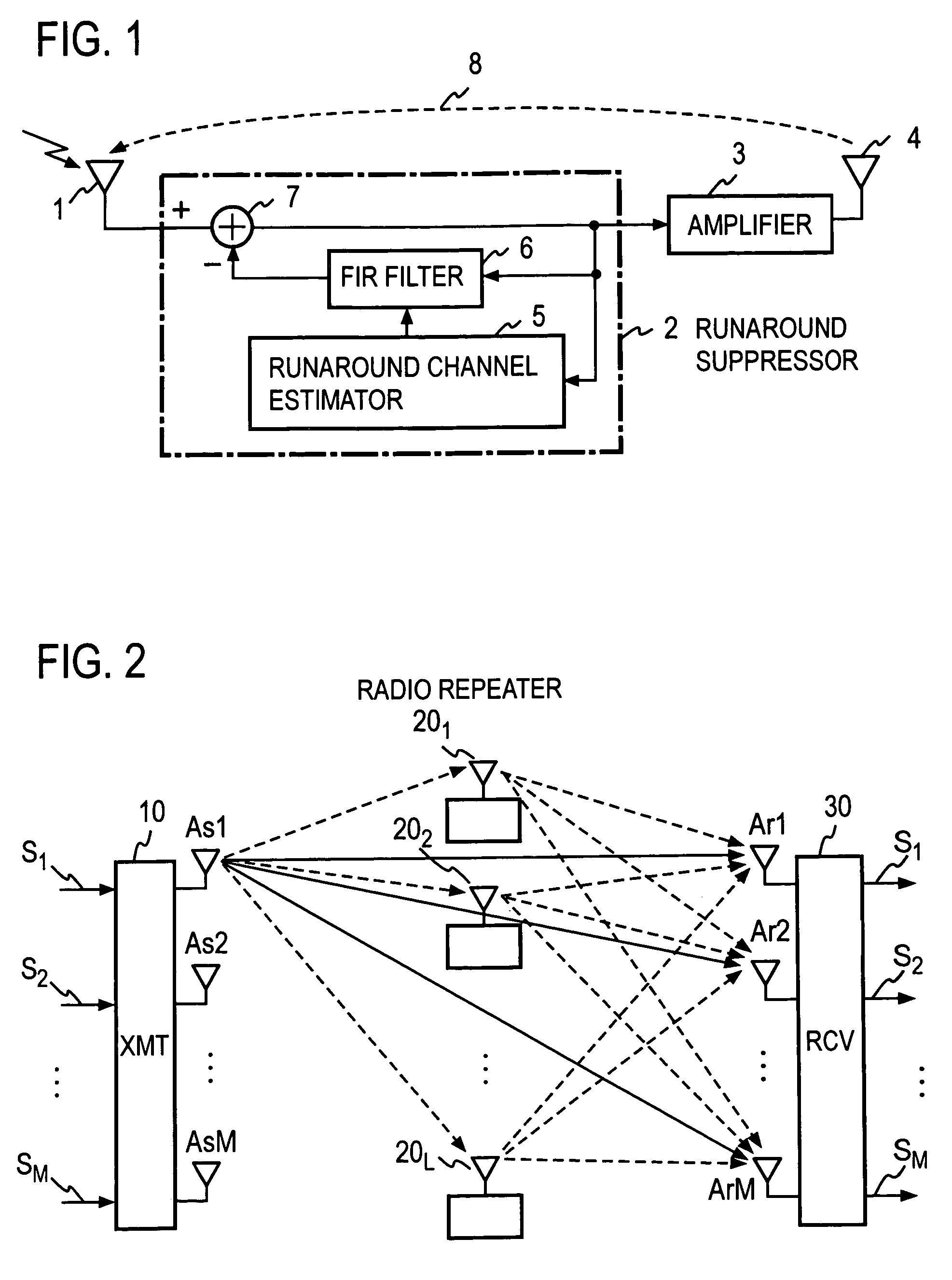
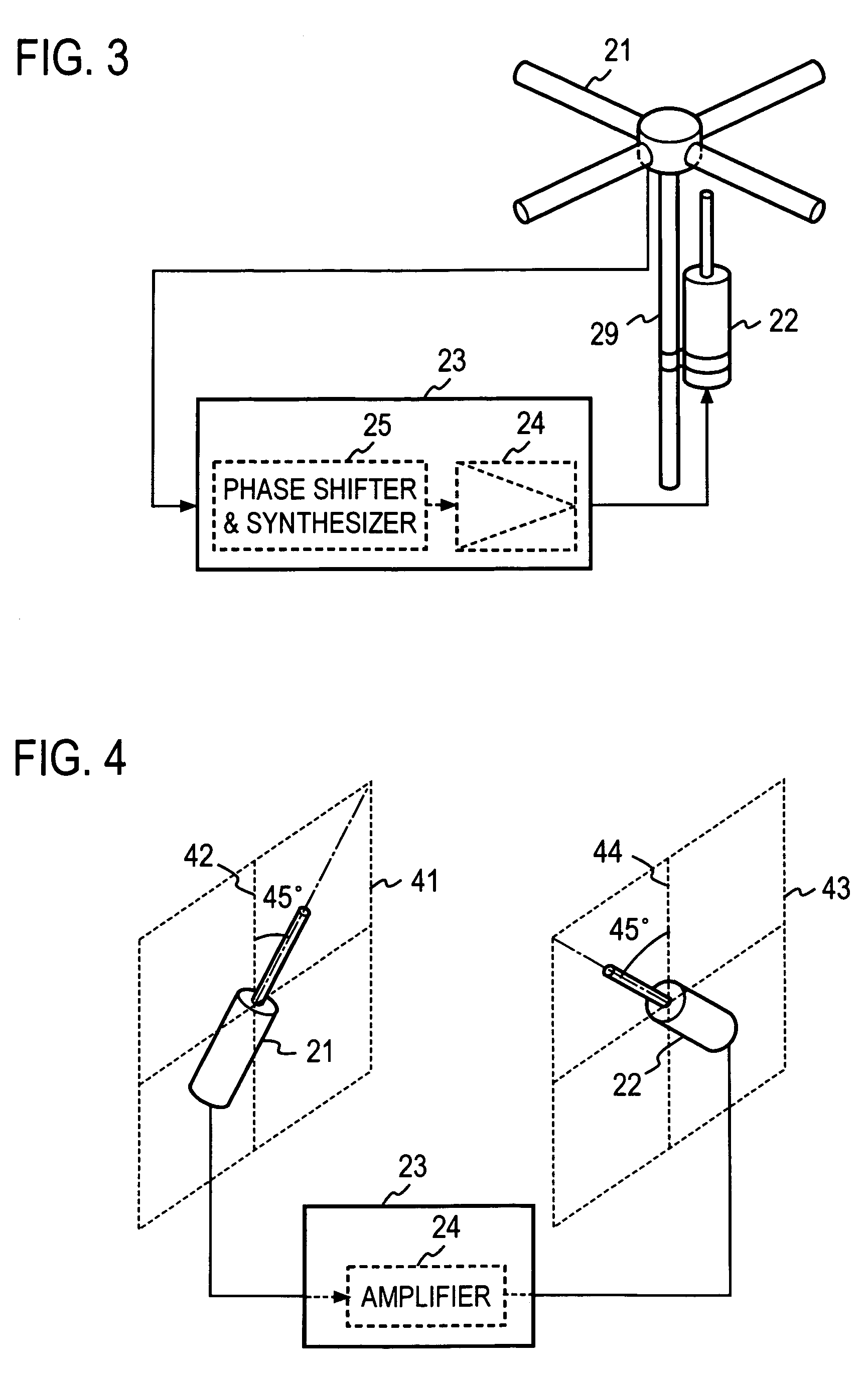
Radio repeater and radio relay transmission method
InactiveUS7430397B2Reduce couplingIncrease the number ofAntenna arraysModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierRadio relay
A radio repeater including at least first and second relay systems, each including a reception antenna configured to receive a radio signal, a loop interference suppressor, connected to the reception antenna, configured to suppress a loop interference signal in the received radio signal from said reception antenna, an amplifier configured to amplify the loop interference-suppressed radio signal from the loop interference suppressors, and a transmission antenna having a polarization characteristic, which is orthogonal to a polarization characteristic of said reception antenna, configured to transmit the output of said amplifier.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
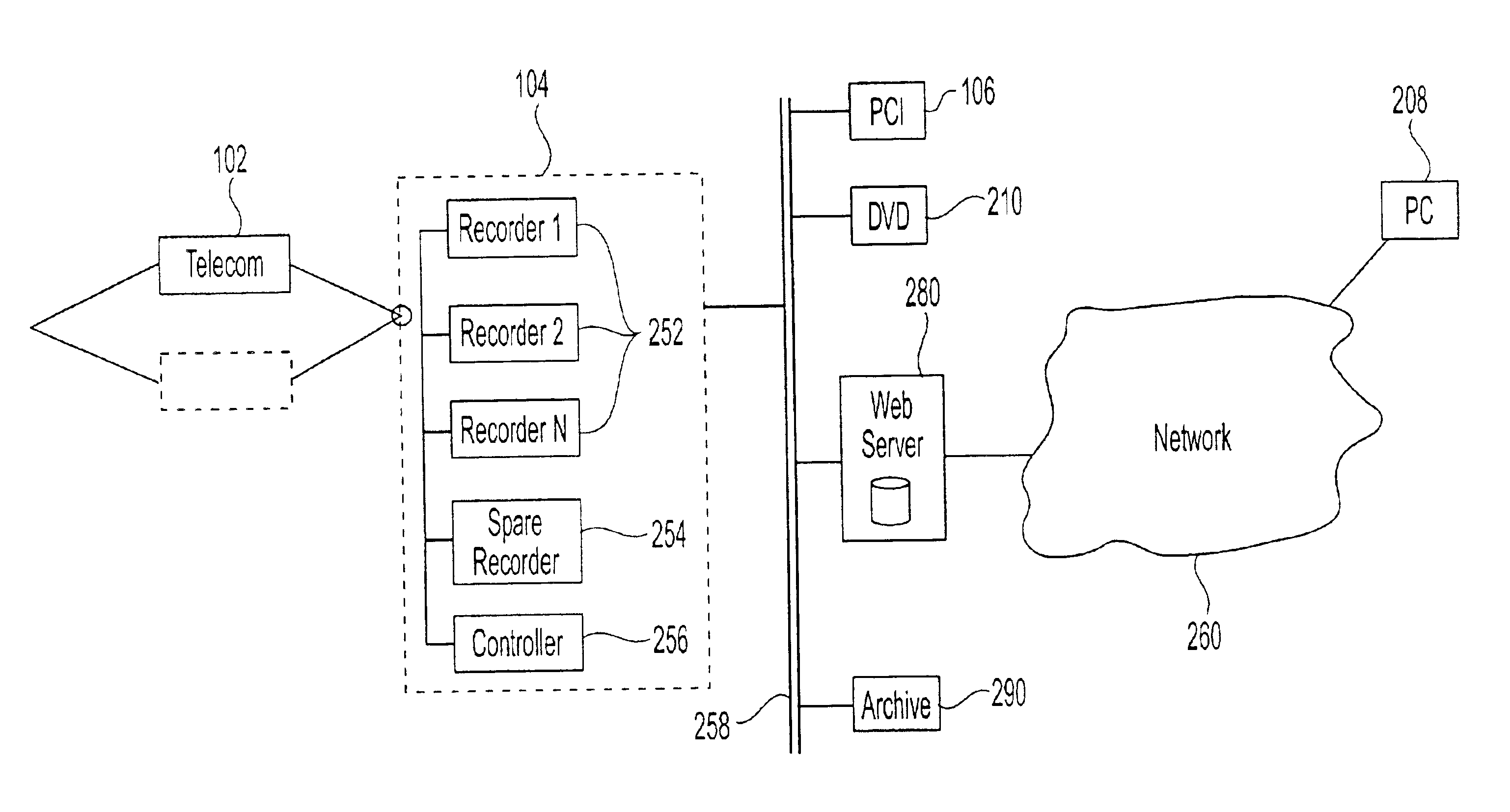
System and method for multi-stage data logging
InactiveUS6870920B2Improve input abilityHigh distribution flexibilityInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersFault toleranceThree stage
A multi-stage data logging system comprising a telecommunications stage for receiving, processing, and compressing data from one or more input channels, a recorder stage for storing said data to a memory device, a distribution stage for retrieving said stored data and distributing said data to one or more output channels, and a plurality of interface paths linking said three stages to one another. Different stages of the system can be located wide distances apart and the interface paths linking the three stages can be automatically switched to achieve fault tolerance of the system.
Owner:NICE SYSTEMS +1
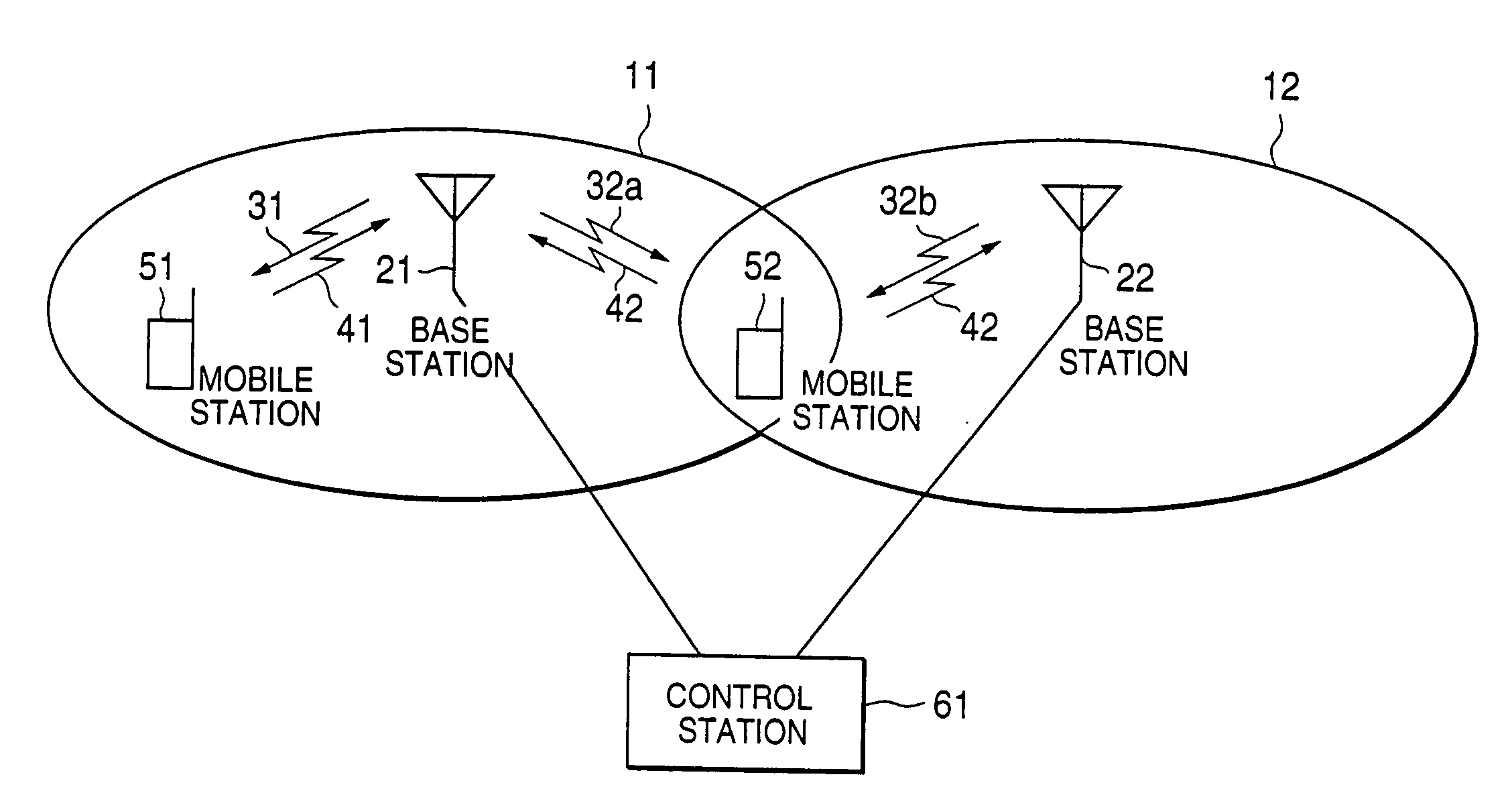
Transmission power control method and transmission power control apparatus in mobile communication system
InactiveUS6963753B1Keep the quality constantConstantPower managementSite diversityControl objectiveMobile station
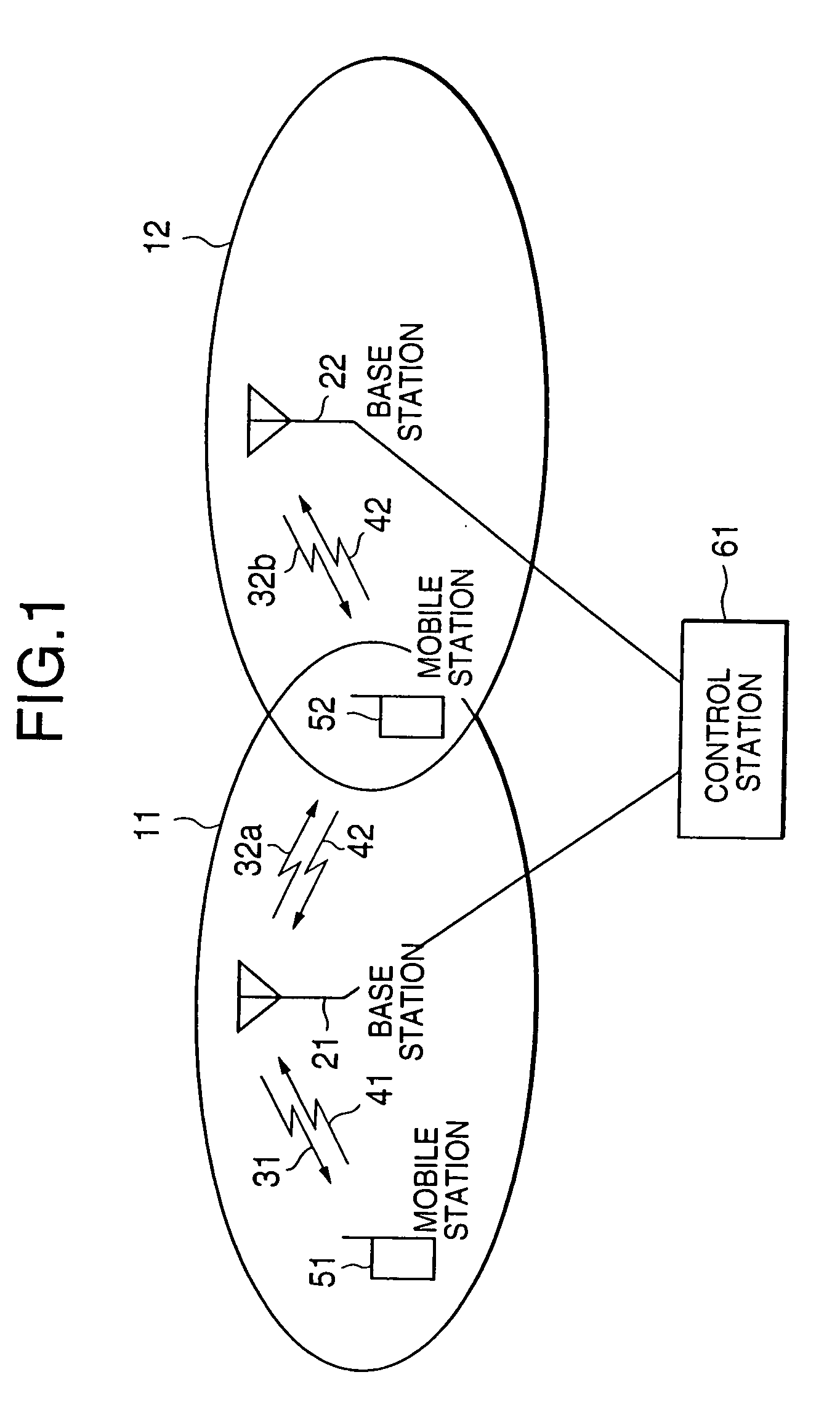
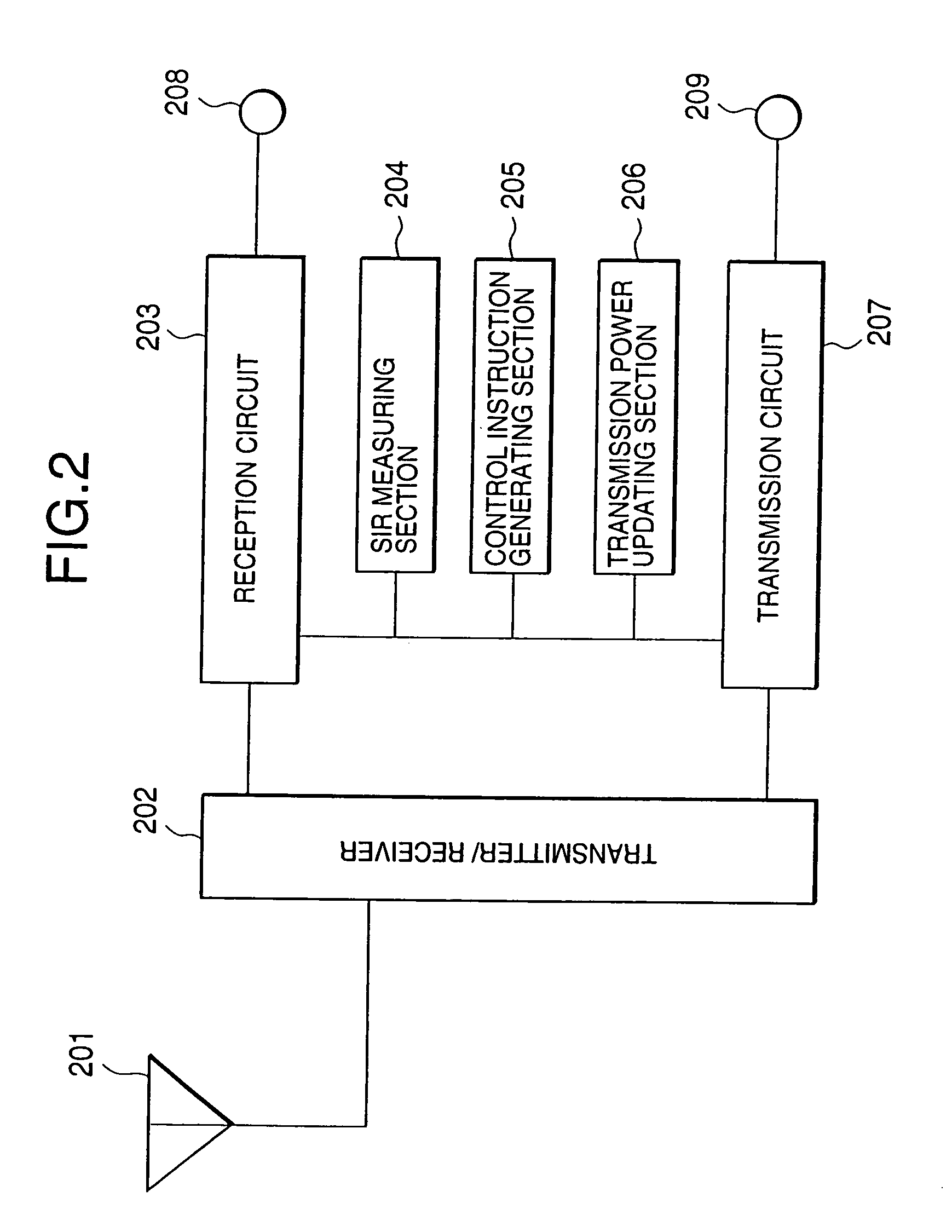
This invention relates to a transmission power control method and transmission power control apparatus in a mobile communication system. The reception quality of a signal (31, 32a, 32b, 41, or 42) transmitted from another mobile station (51 or 52) or base station (21 or 22) is compared with a predetermined control target value such as a signal-to-interference ratio. The comparison result is used for transmission power control on a remote station. If a frame error is detected in a transmitted signal, the control target value is increased by SIRinc. If no frame error is detected, the control target value is decreased by SIRdec. As SIRdec, the product of a target value of a frame error rate and SIRinc is set. With this operation, when a propagation environment such as multibus or moving speed changes, the control target value for transmission power control is changed within a short period of time, and channel quality is maintained constant, thus realizing desired channel quality.
Owner:NEC CORP
Systems and methods for wireless communication
InactiveUS20070274256A1Improve wireless resource utilization efficiencyImprove communication stabilityNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplex communicationQuality of serviceCommunications system
In a wireless communication system for communicating with a plurality of stations at the same point of time with the same frequency using a Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA), wireless resources are allocated by a first decision unit which evaluates performance of each station obtained when the SDMA is used and which determines periods of time to be allocated to groups of stations formed according to the SDMA technique. Using a first evaluation unit and a second evaluation unit to evaluate performance required by each station and each application, the first decision unit allocates the wireless resources to the stations. It is therefore possible that the wireless resources are efficiently allocated to the stations while preventing an event in which the wireless resources are excessive or insufficient for required quality of service.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Collapsible bag for dispensing liquids and method
InactiveUS6851579B2Increase channel capacityHigh trafficLarge containersDischarging meansBiomedical engineeringFlange
Owner:SCHOLLE CORP
Method and apparatus for optimization of channel capacity in multi-line communication systems using spectrum management techniques
InactiveUS7356049B1Increase channel capacityReduce contentionModulated-carrier systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsSpectrum managementChannel capacity
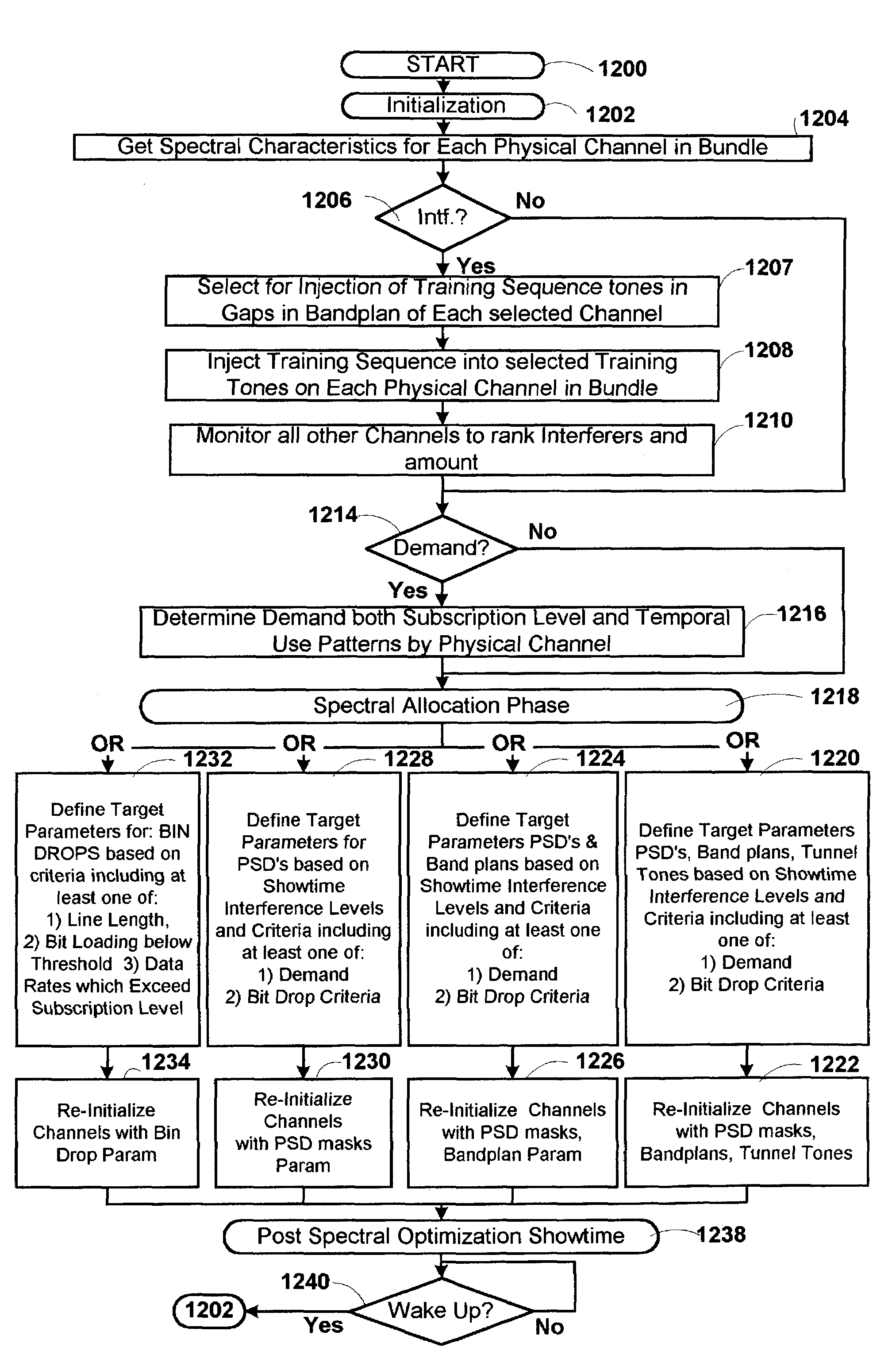
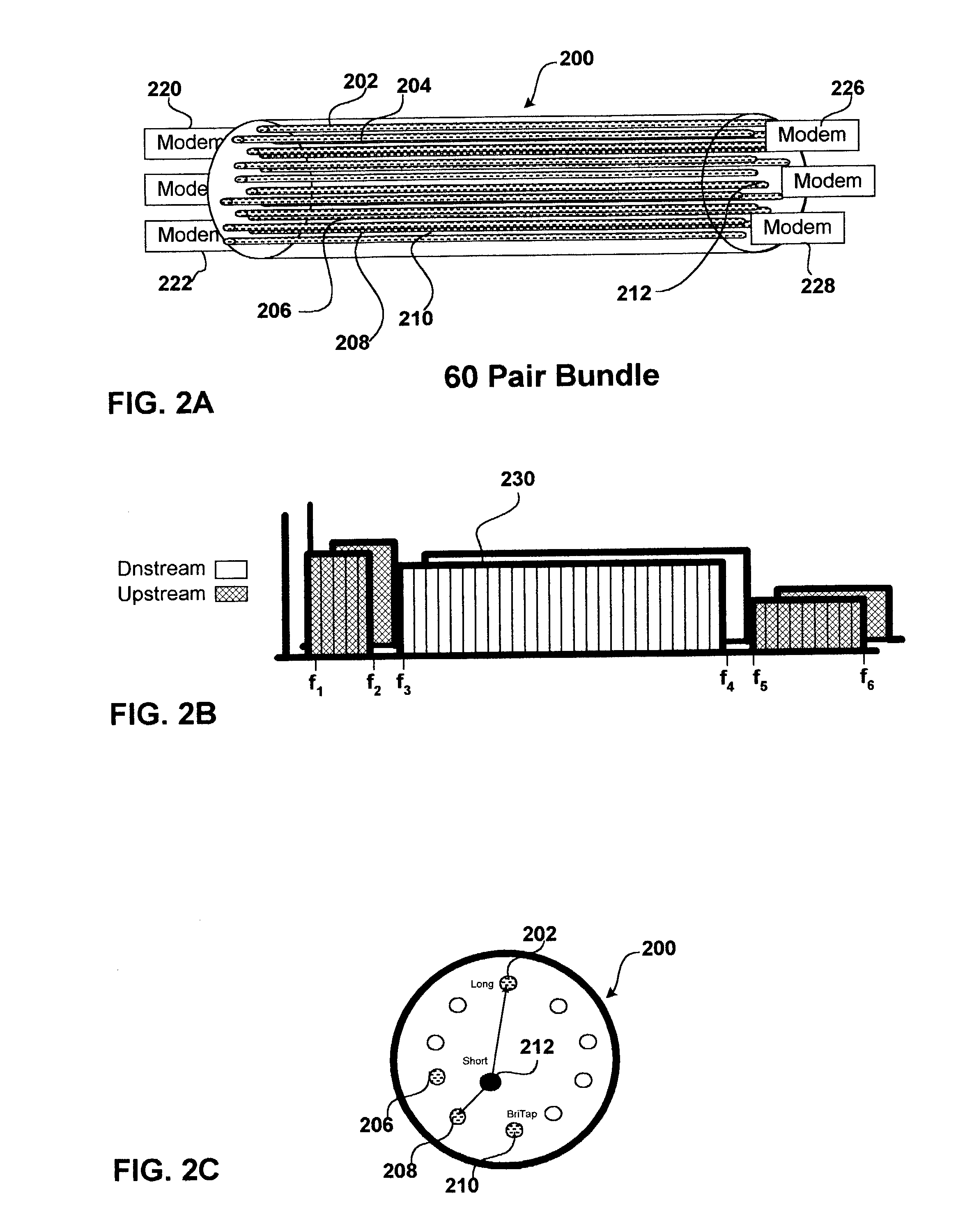
The present invention advantageously provides a method and apparatus for optimization of channel capacity in multi-line multi-tone communications such as X-DSL among subscriber lines which are bundled with one another. In an embodiment of the invention an apparatus for optimizing channel capacity of multi-tone communications effected by opposing sets of modems coupled to one another by a plurality of subscriber lines is disclosed. The apparatus includes a spectrum manager coupled to at least one of the opposing sets of modems. The spectrum manager includes: a profiler, a demand module and an optimizer. The profiler obtains from the at least one of the opposing sets of modems the spectral characteristics of each of the plurality of subscriber lines. The demand module determines for each of the plurality of subscriber lines the subscriber demand profile. The optimizer defines target parameters for at least one of bit loading, and power spectral density (PSD) for selected tones of the multi-tone communications based on the spectral characteristics from the profile module and the demand profiles from the demand module and downloads the target parameters to the at least one of the opposing sets of modems.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Multiple access system and method for multibeam digital radio systems
InactiveUS7072410B1Increase channel capacityImprove qualityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationMultiple antennaTelecommunications link
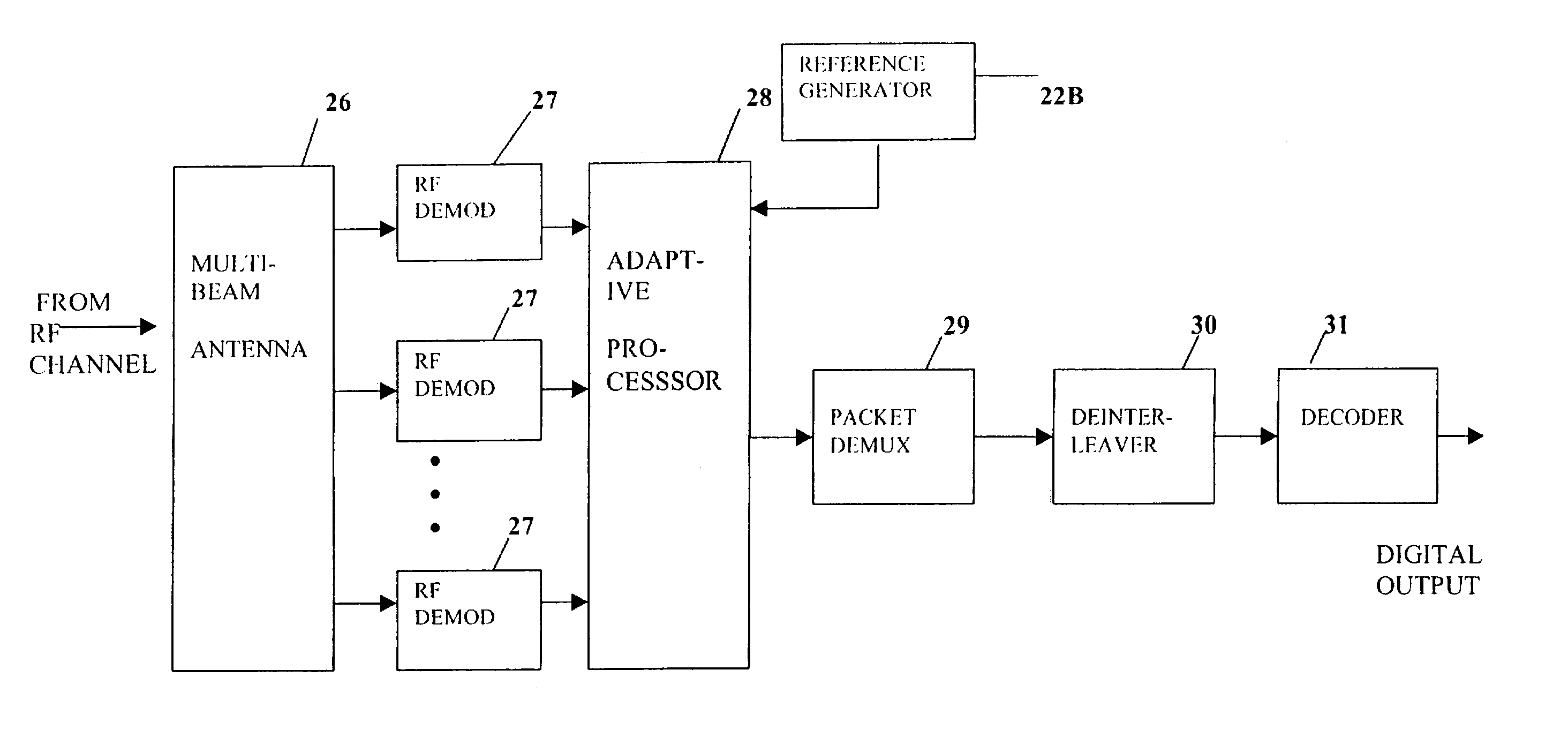
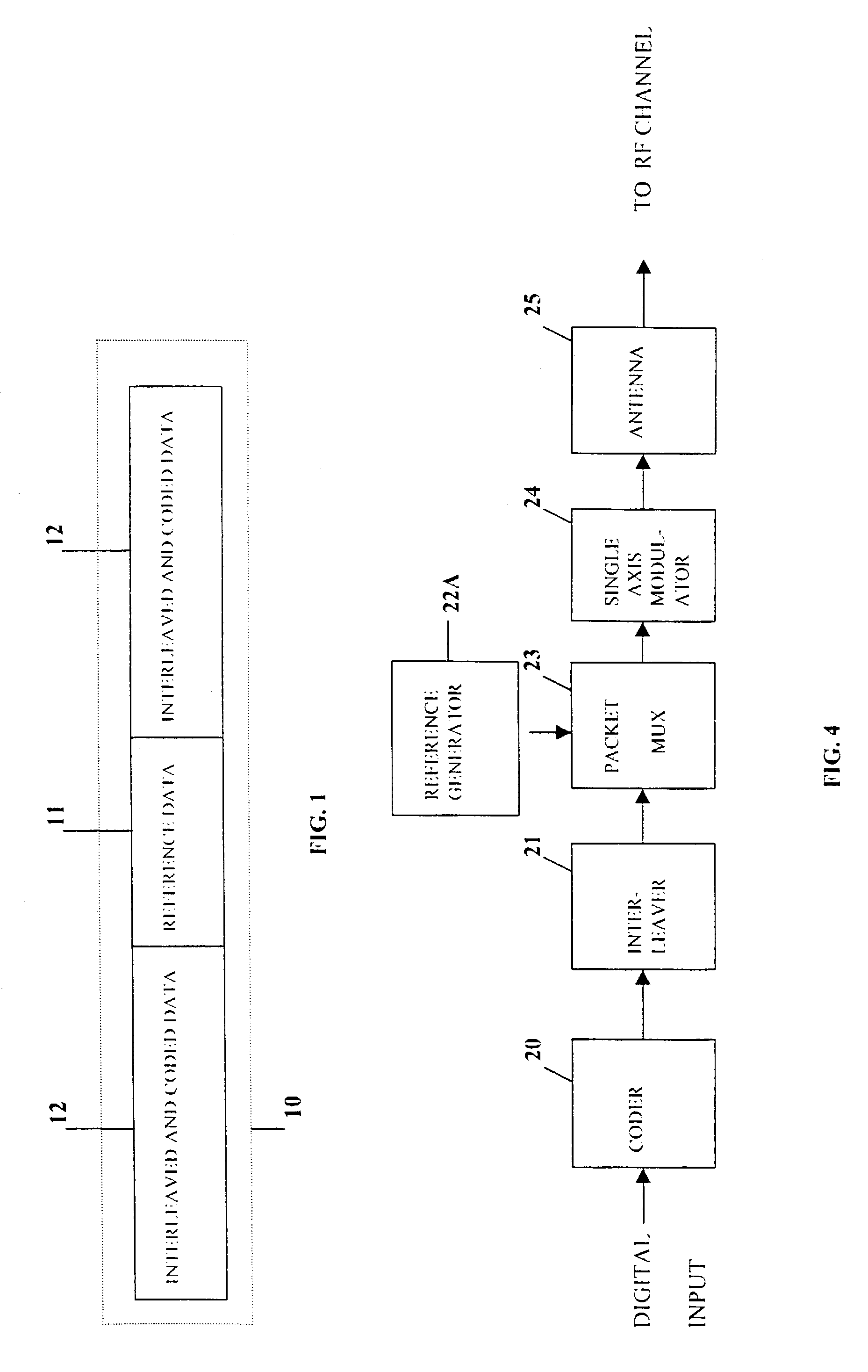
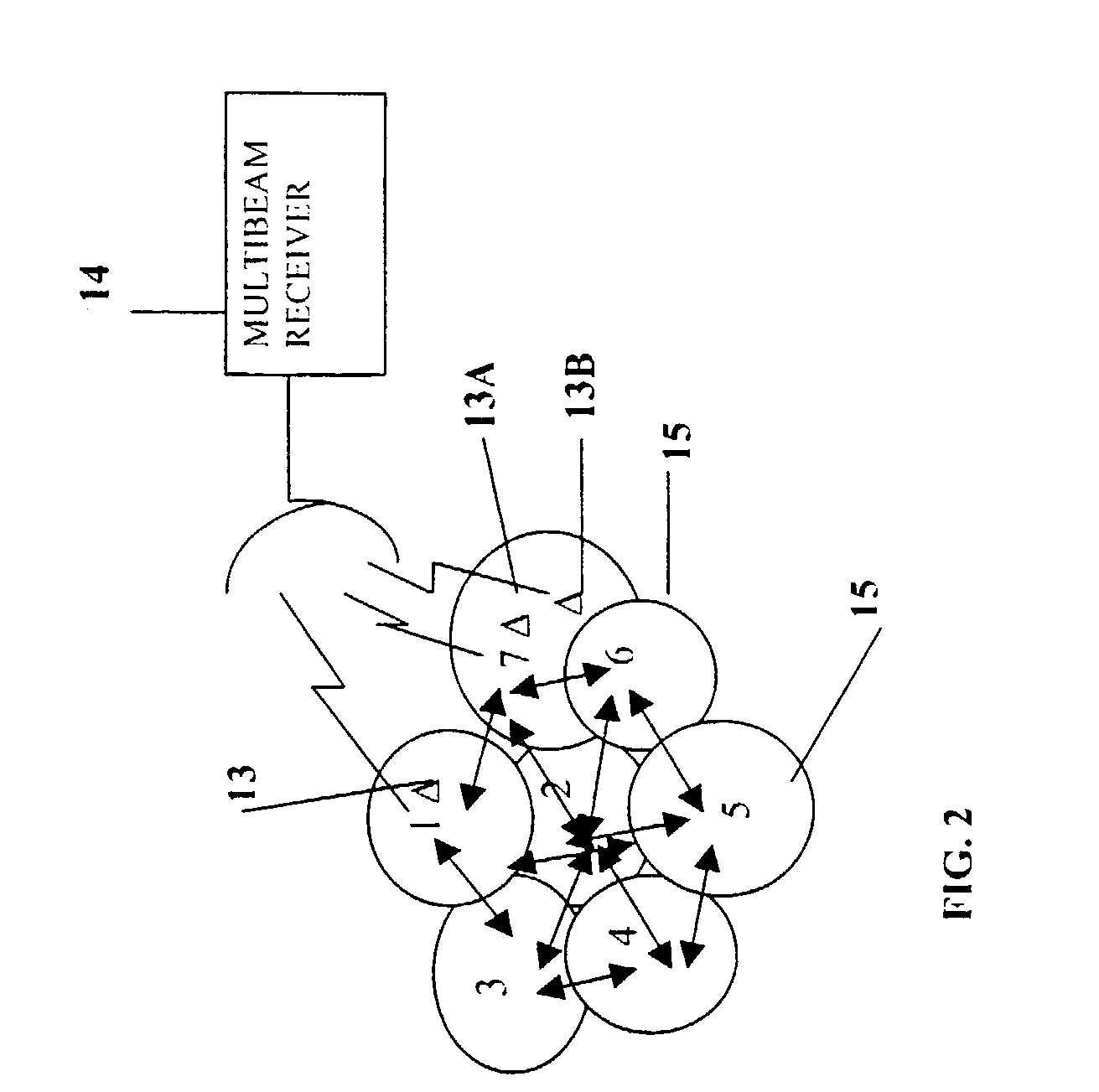
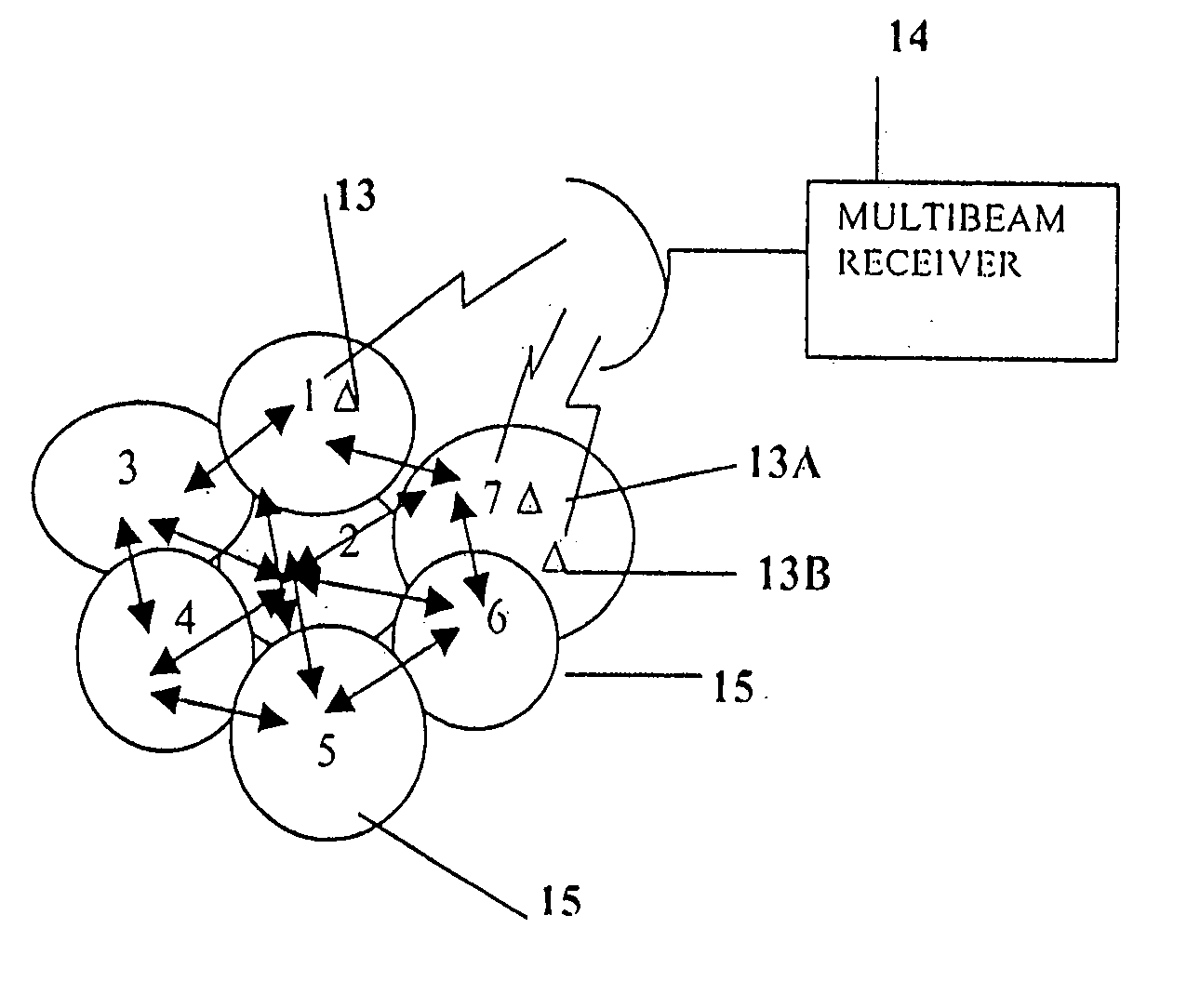
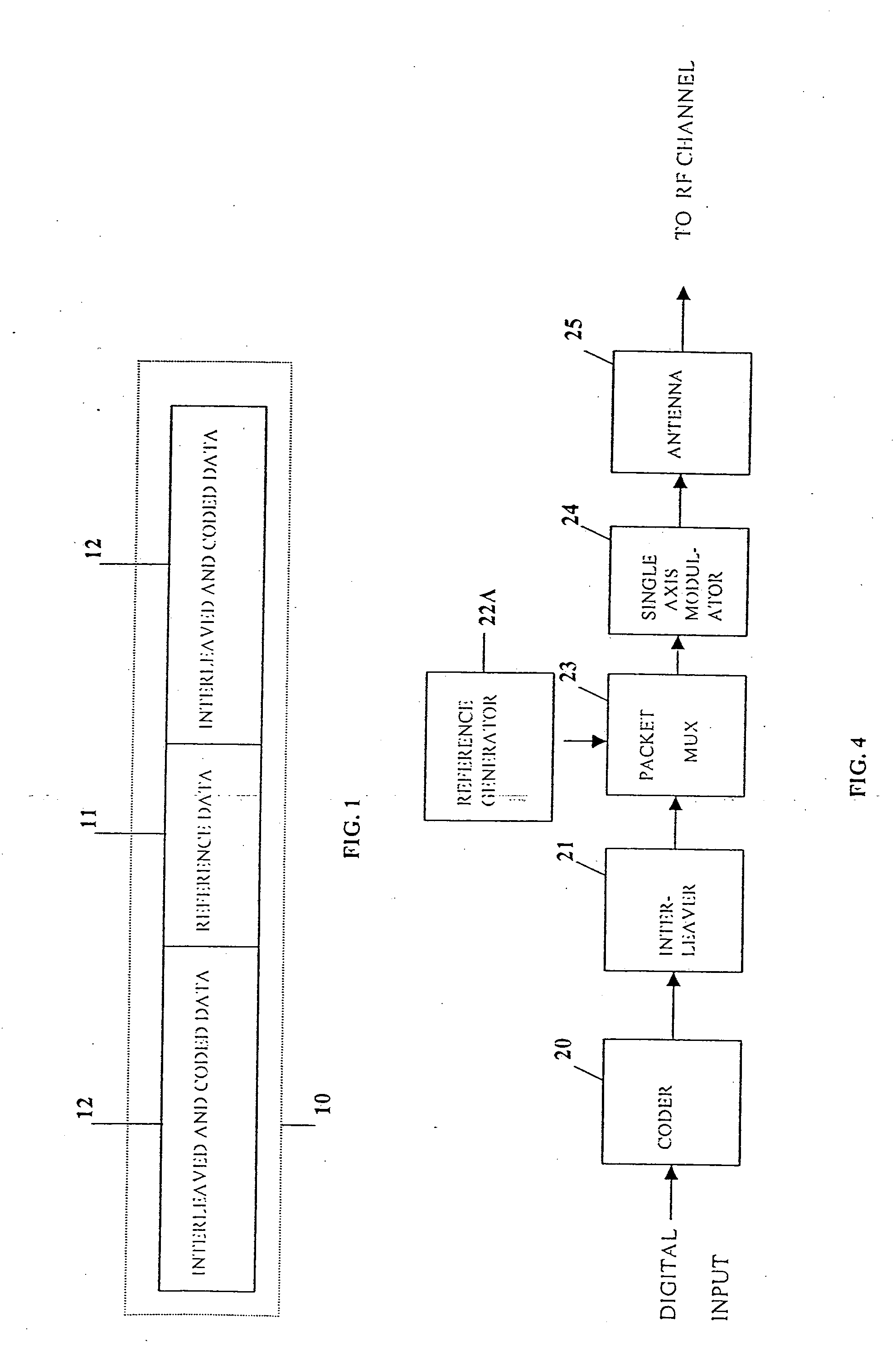
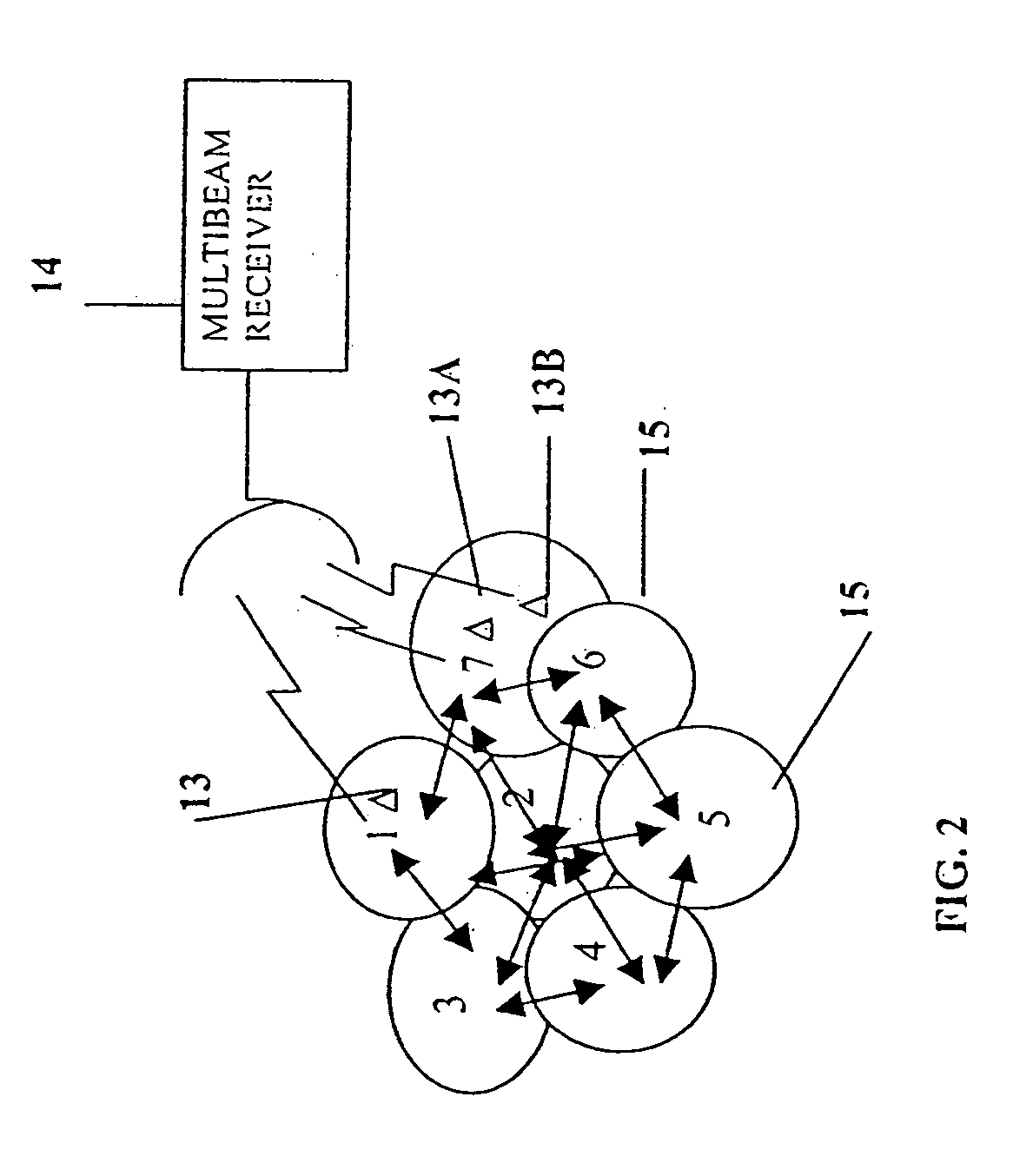
A multiple-access digital radio communication system and method with communication links between user terminal transmitters and central node with a receiver system including a multibeam antenna. User terminal transmitters assigned to one beam coverage region use mltiple access channels that are mutually orthogonal for transmitting digital message information. These multiple access channels are reused in adjacent and other beam coverage regions. Error-correction coding (20), interleaving (21), and a single-axis modulator (24) are used in the user transmitter to increase resistance to potential interference from user terminal transmitters in other coverage regions. At the receiver, an adaptive processor (28) such as an equalizer or sequence estimator is used to combine multiple antenna beam signals (27) to produce a combined signal associated with each user. Deinterleaving (30) and error-correction decoding (31) of the combined signal is used to complete the recovery of the digital message information.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
Multiple access system and method for multibeam digital radio systems
InactiveUS20050220057A1Increase channel capacityImprove qualityError preventionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMultiple antennaRandom assignment
A multiple-access digital radio communication system and method with communication links between user terminal transmitters and a central node with a receiver system including a multibeam antenna. User terminal transmitters assigned to one beam coverage region use multiple access channels that are mutually orthogonal for transmitting digital message information that is included in a data group. Assignments are random and are changed for successive data groups. The same multiple access channels are reused in adjacent and other beam coverage regions each with an independent random assignment algorithm. Error-correction coding and interleaving are used in the user transmitter and an adaptive processor is used in the receiver. A reference sequence unique to either each user or each beam coverage region is multiplexed into user data groups for transmission. At the receiver the adaptive processor such as an equalizer or sequence estimator is used to combine multiple antenna beam signals to produce a combined signal associated with each user. The combining in the adaptive processor reduces interference from user terminal transmitters associated with different beam coverage regions but with the same multiple access channel. Deinterleaving and error-correction decoding of the combined signal are used to protect against channel assignments with larege mutual interference levels. The communication system can reuse each orthogonal multiple access channel in all of the other beams, i.e., a reuse factor of unity for each multiple access channel.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
Simultaneous two-way transmission of information signals in the same frequency band
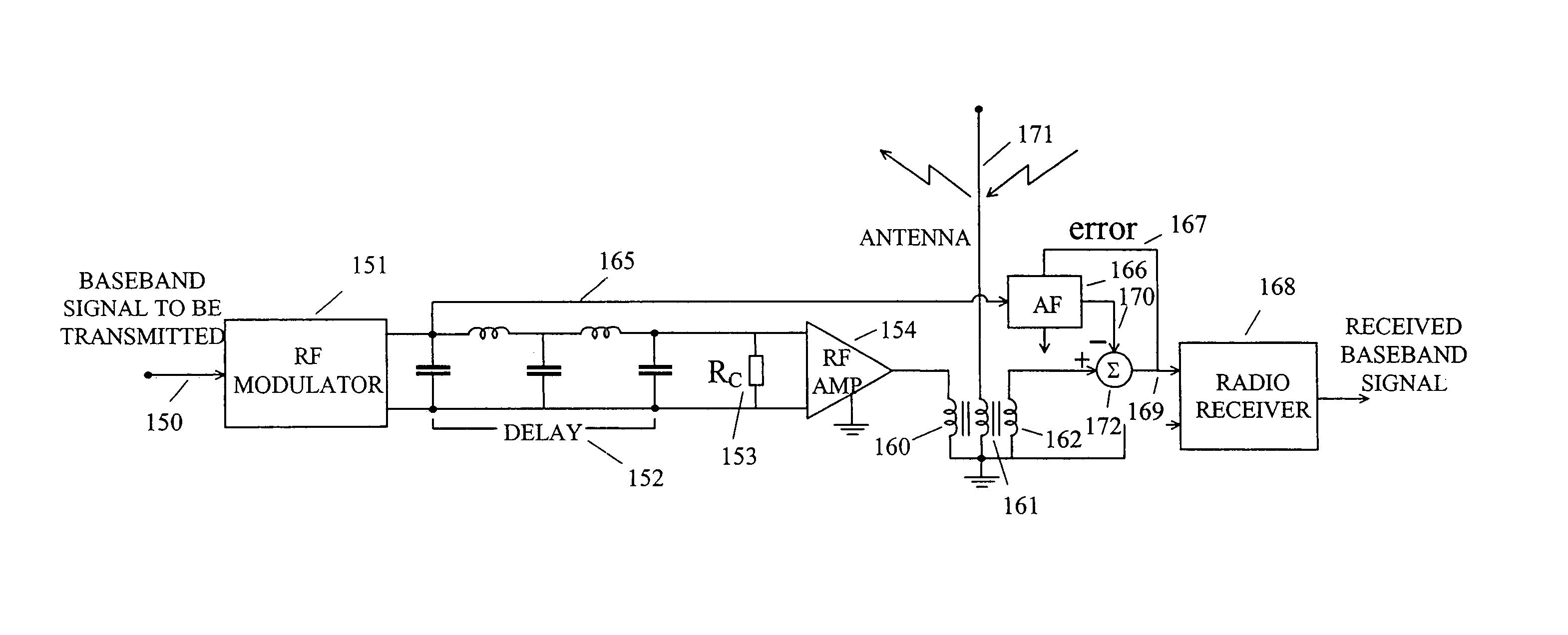
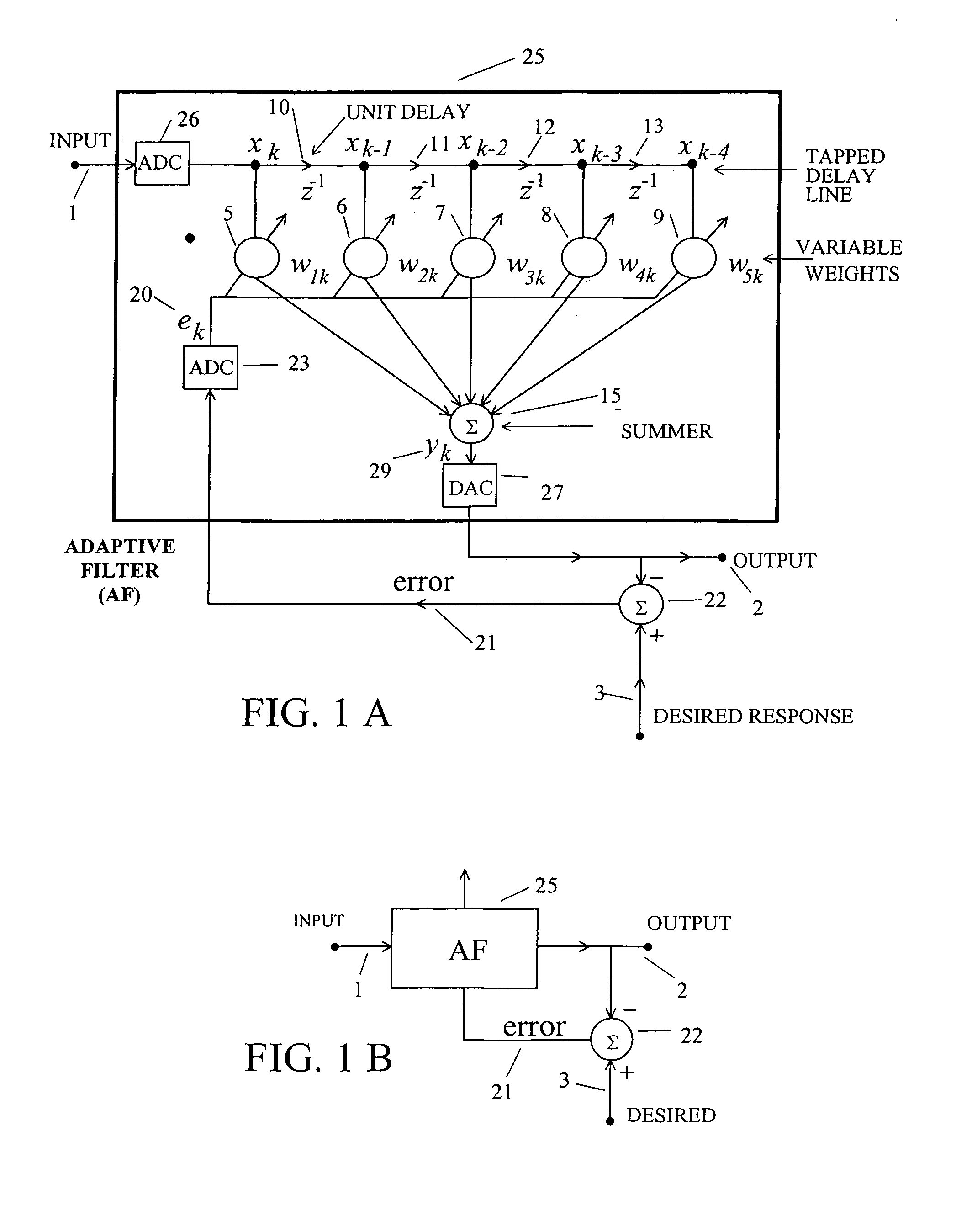
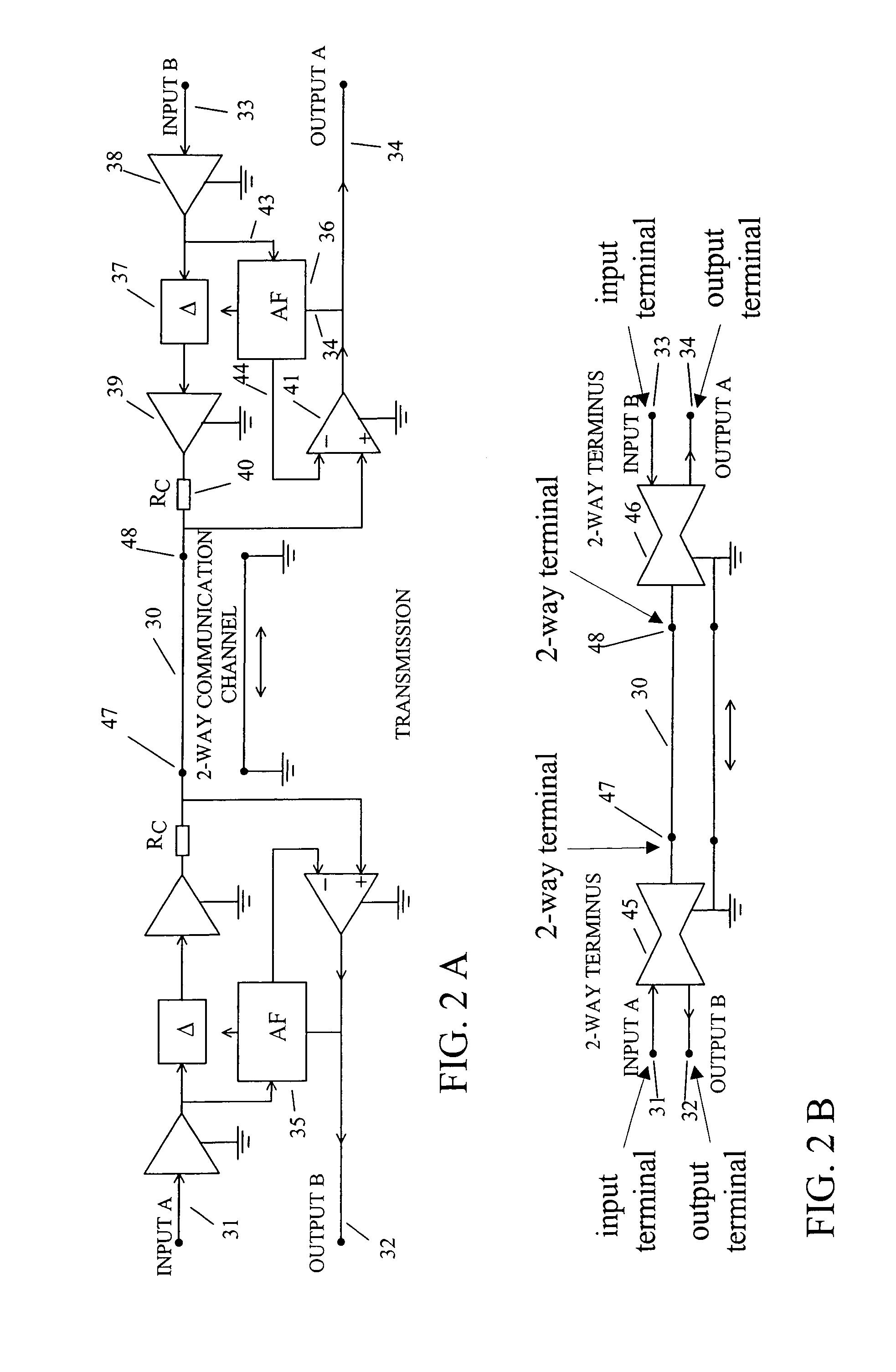
InactiveUS7187907B2Increase channel capacityPower distribution line transmissionBroadcast transmission systemsFiberAdaptive filter
This invention provides designs for communication systems that use adaptive filters in circuits whose purpose is to enable two-way transmission of information signals in the same frequency band at the same time over twisted pair channels, coaxial cable channels, fiber optic channels, or wireless channels. The methodology allows two-way DSL transmission over telephone lines, making use of existing DSL hardware and signal standards, so that the upload speed is increased by an approximate factor of ten. Applied to wireless systems with single antennas at the two ends of the channel, a doubling of the data rate is achieved for a given bandwidth. Applied to wireless systems with 2-way adaptive antenna arrays at a central location and a 2-way adaptive antenna array at each of a plurality of subscriber locations, the data rate for a given bandwidth is increased by a large factor.
Owner:WIDROW BERNARD
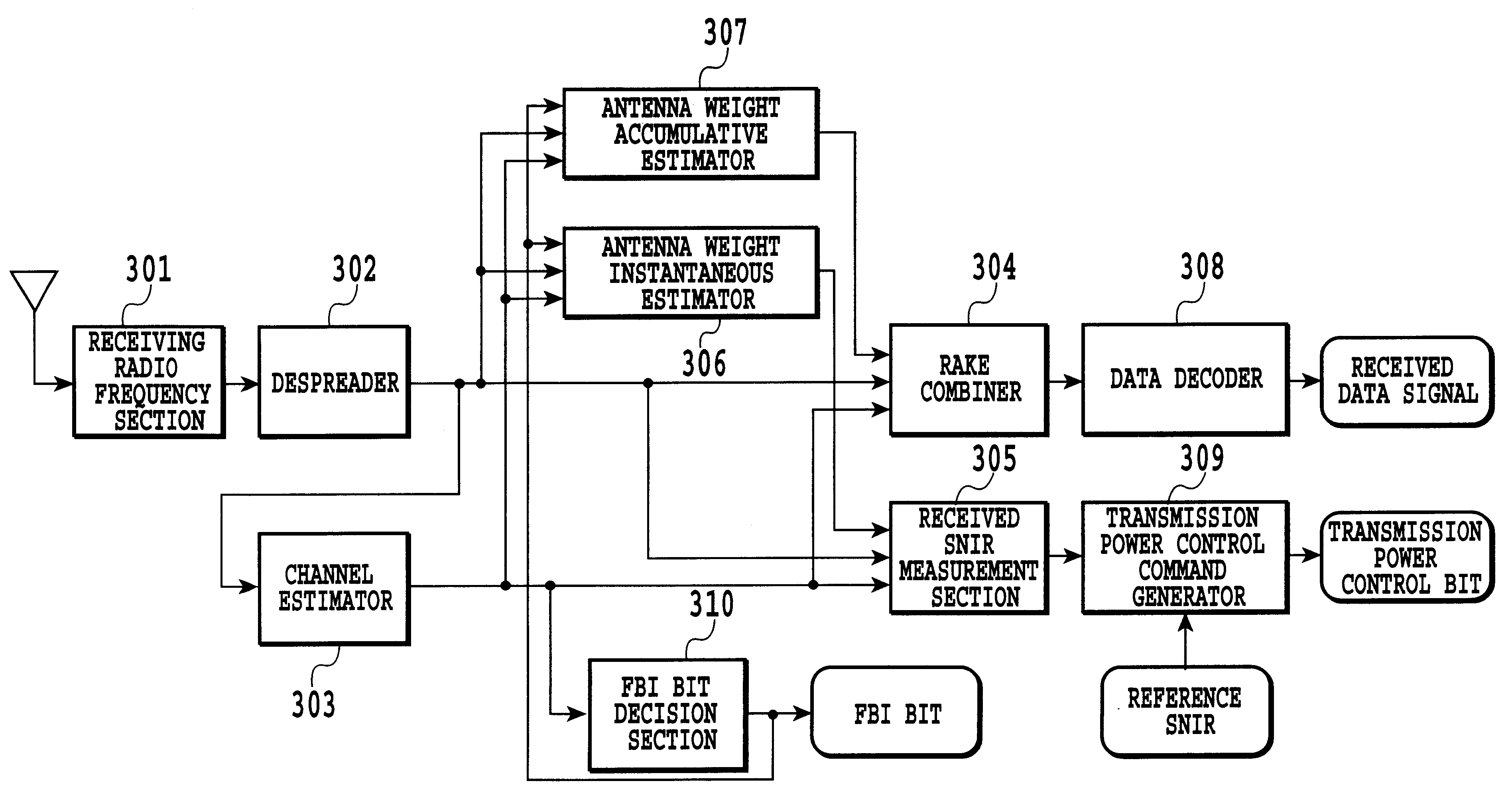
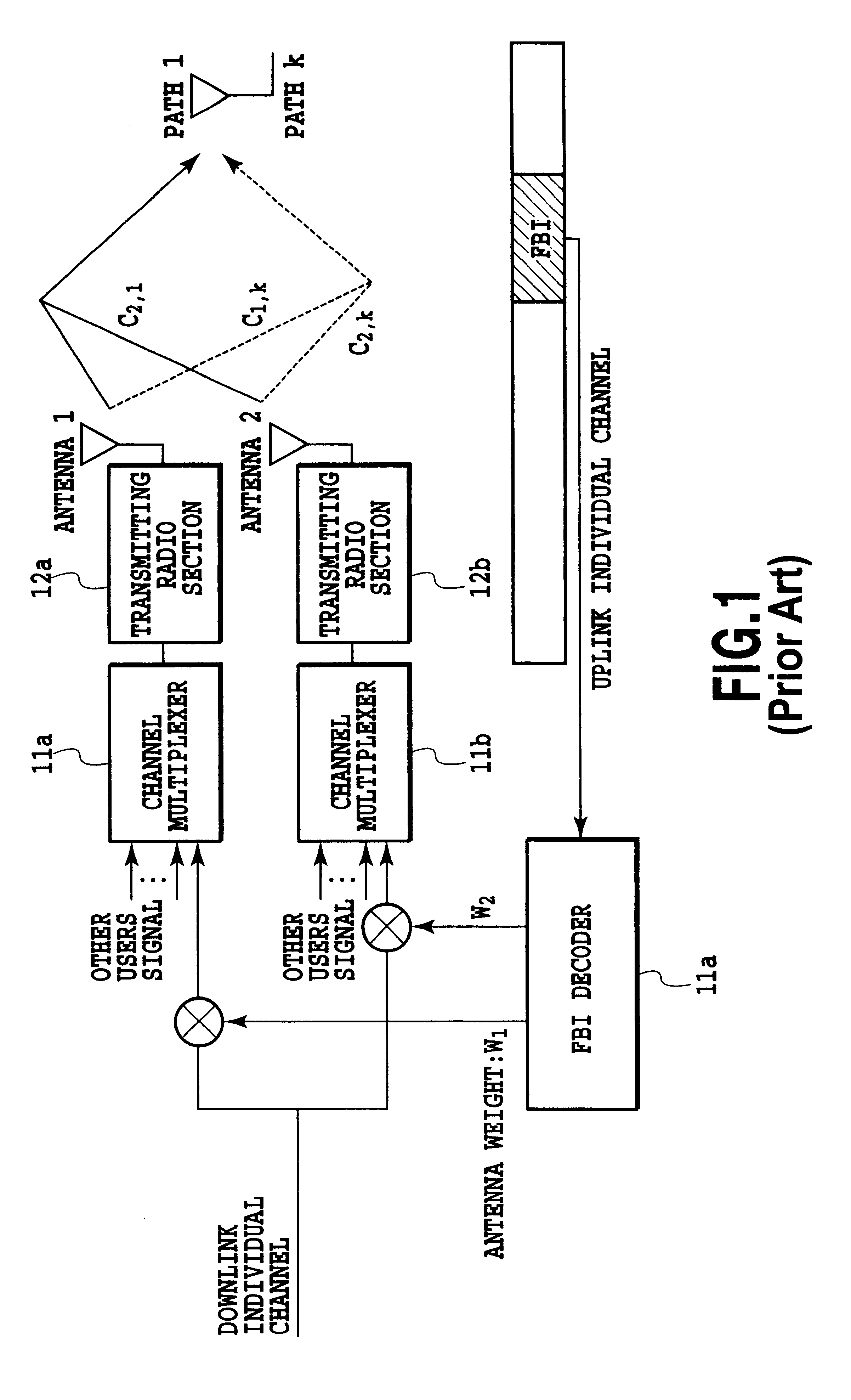
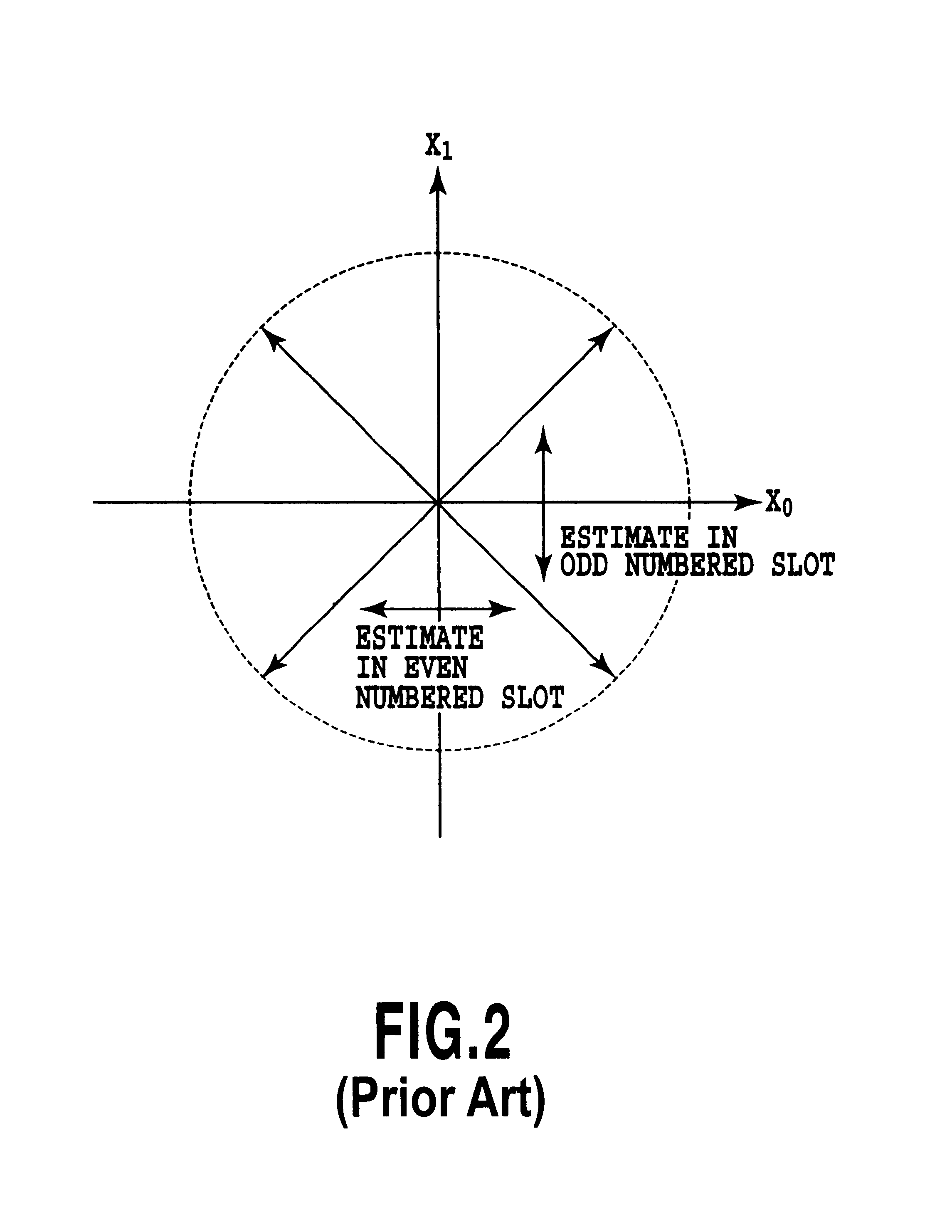
Method of antenna-weight estimation and mobile communication terminal
InactiveUS6853839B2Improve communication qualityIncrease radio channel capacityPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunication qualityRadio channel
An antenna weight estimation method in a mobile communication system is capable of improving the accuracy of antenna weight estimation values, thereby improving communication quality and increasing radio channel capacity. It operates instantaneous estimation and accumulative estimation in parallel, in which the former is made for estimating the antenna weight used for received SNIR estimation for transmission power control, and the latter is made for demodulating the received data. Thus, it can obtain the antenna weight for the received SNIR measurement with a minimum delay, and at the same time, it can improve the reliability of the antenna weight for the data demodulation.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
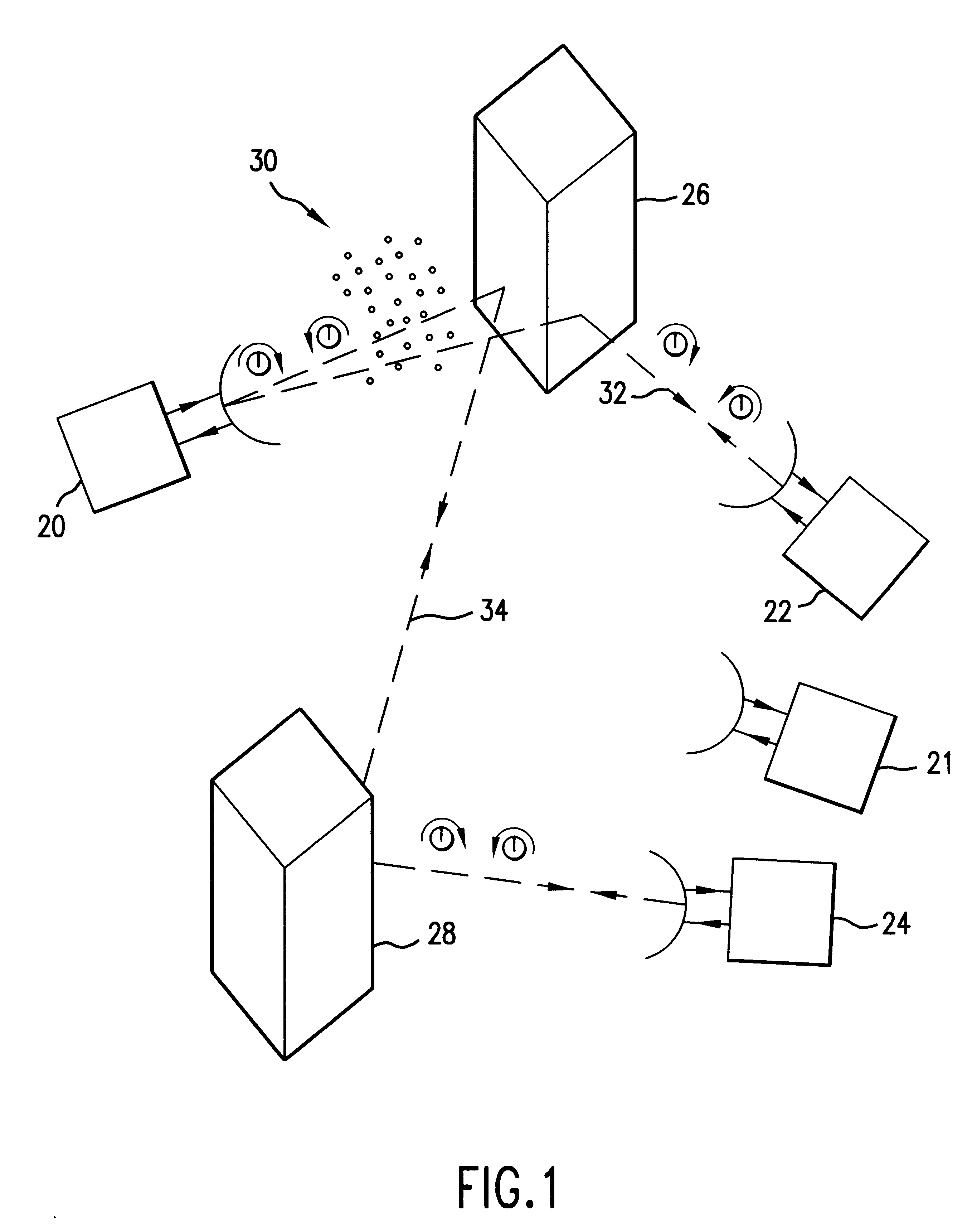
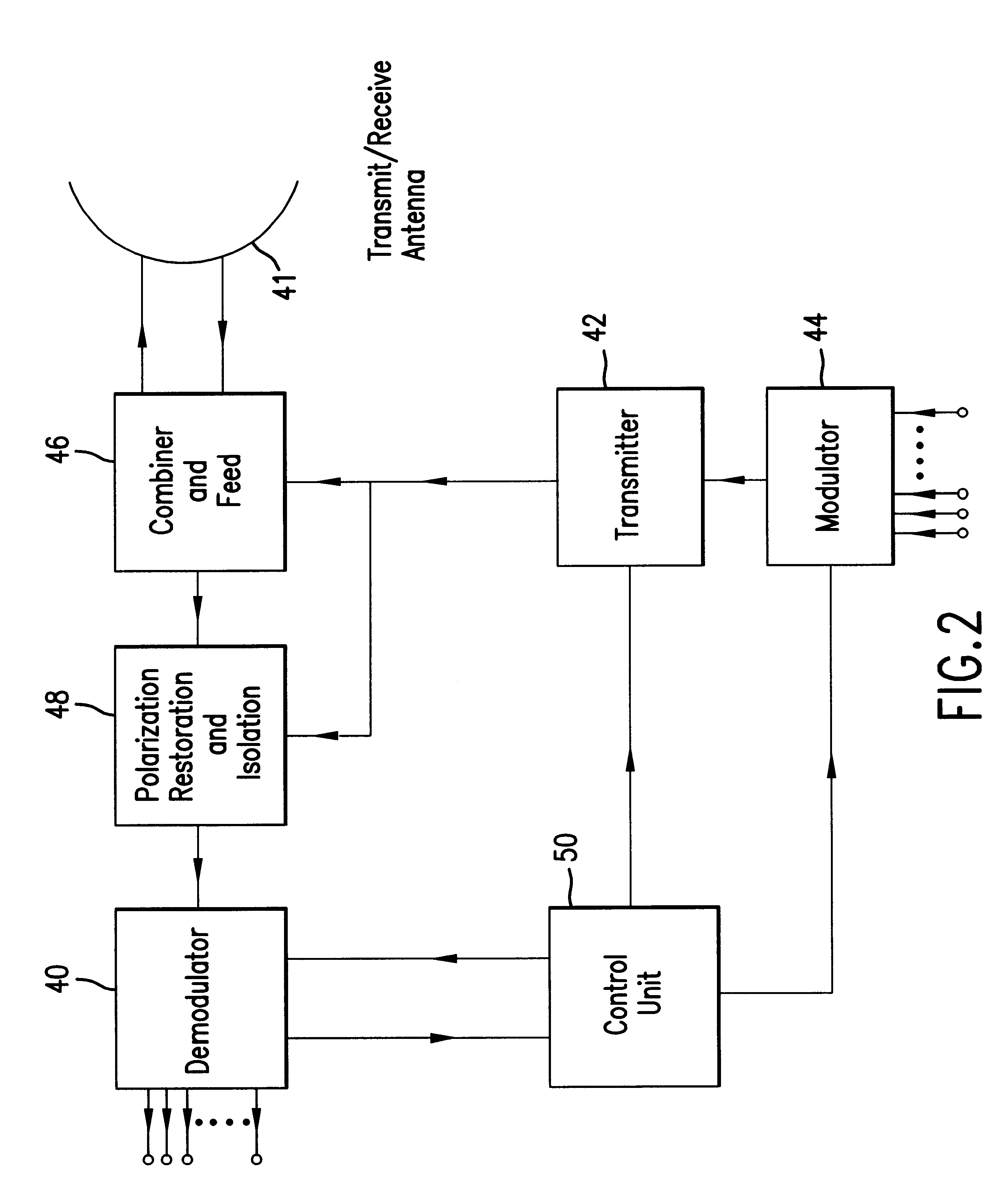
Multi-function interactive communications system with circularly/elliptically polarized signal transmission and reception
InactiveUS6233435B1Increase channel capacityNegligible effectPolarisation/directional diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPolarization diversityTransceiver
A communications system that uses electromagnetic waves. The communications system preferably operates in the millimeter-wave frequencies, and provides relatively high signal restoration and isolation. The communications system can use polarization diversity to increase the capacity of a channel. Isolation and restoration features in the transceivers eliminate or reduce the effects of precipitation and / or reflection and diffraction from objects, and thus is well-suited for an urban environment.The transceiver will select the proper antenna and signal path for optimal information throughput as the conditions in the propagation medium of the network vary.
Owner:TELECOMM EQUIP
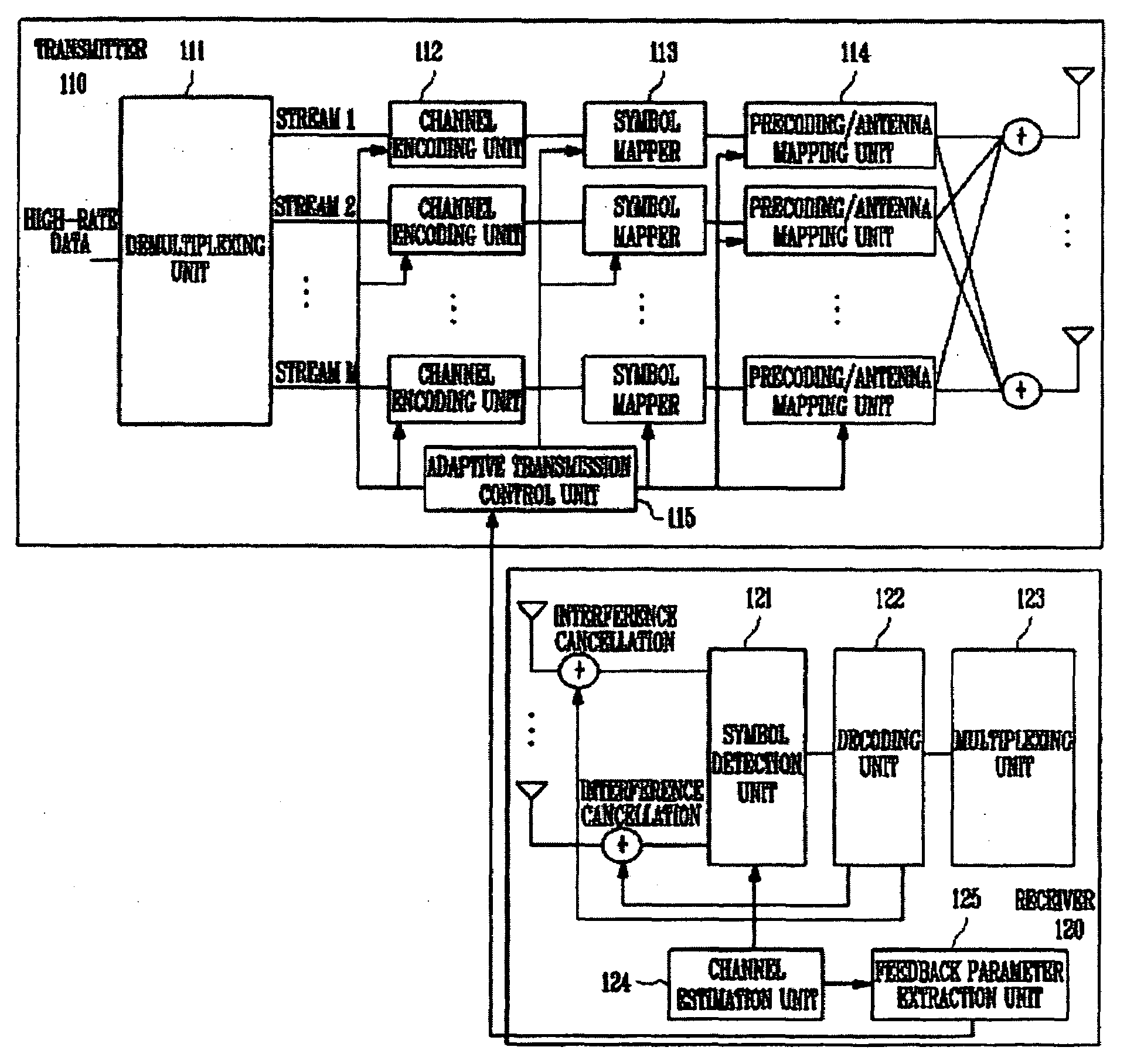
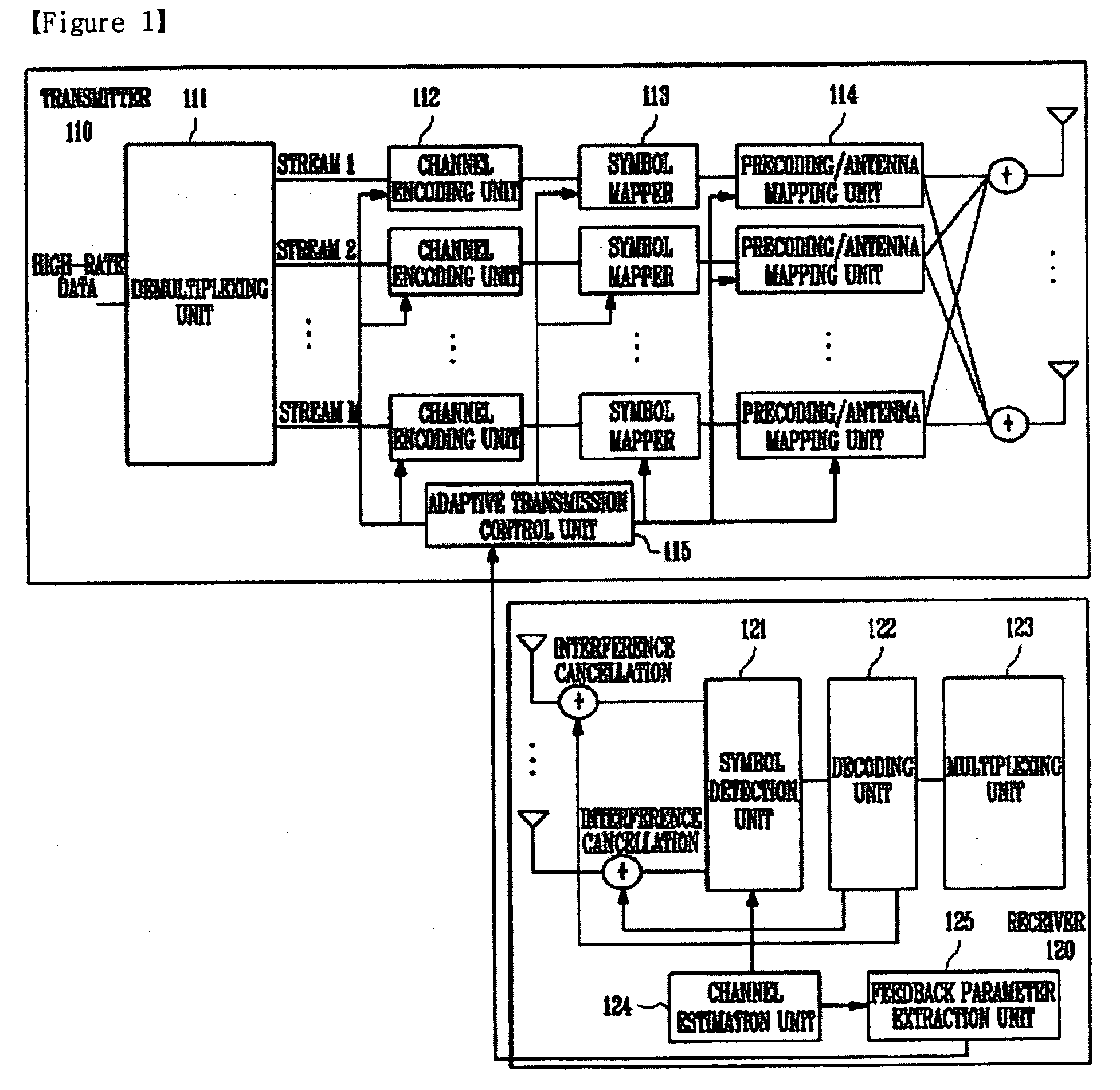
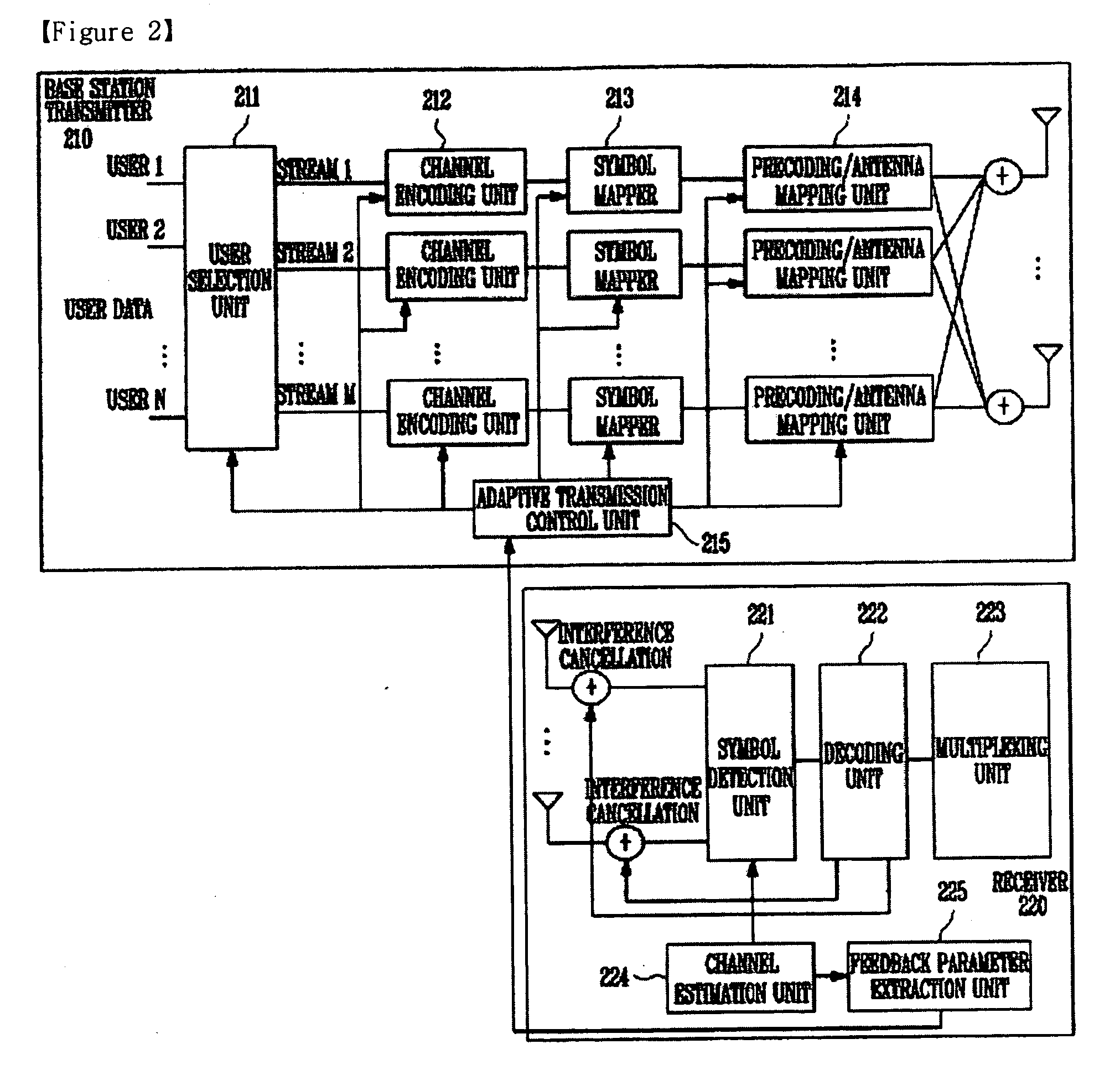
Transmitter, receiver and method for controlling multiple input multiple output system
InactiveUS20090252247A1Increase channel capacitySuperior performancePower managementMultiplex communicationData transmissionTransmission rate
Provided is a method of controlling a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) system. One embodiment of the method includes the steps of: estimating, at a receiver, a MIMO channel and detecting data streams using a successive interference cancellation scheme; calculating, at the receiver, S and P using the estimated channel and then feeding back information corresponding to (P1, P2, . . . , PM-1, SINR5M) to a transmitter, and determining, at the transmitter, a transfer rate and transmission power perstream using the fed-back information. Another embodiment of the method includes the steps of: estimating, at a receiver, a MIMO channel and detecting data streams using a signal received from an antenna; extracting, at the receiver, a feedback parameter to be fed back to the transmitter using the estimated channel, and feeding back the feedback parameter to the transmitter, and determining, at the transmitter, a stream to be allocated to the receiver from among the streams of the transmitter using the fed-back parameter and a data transfer rate per stream, wherein the feedback parameter is information corresponding to a successive interference cancellation order and a signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) per stream reflecting successive interference cancellation.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
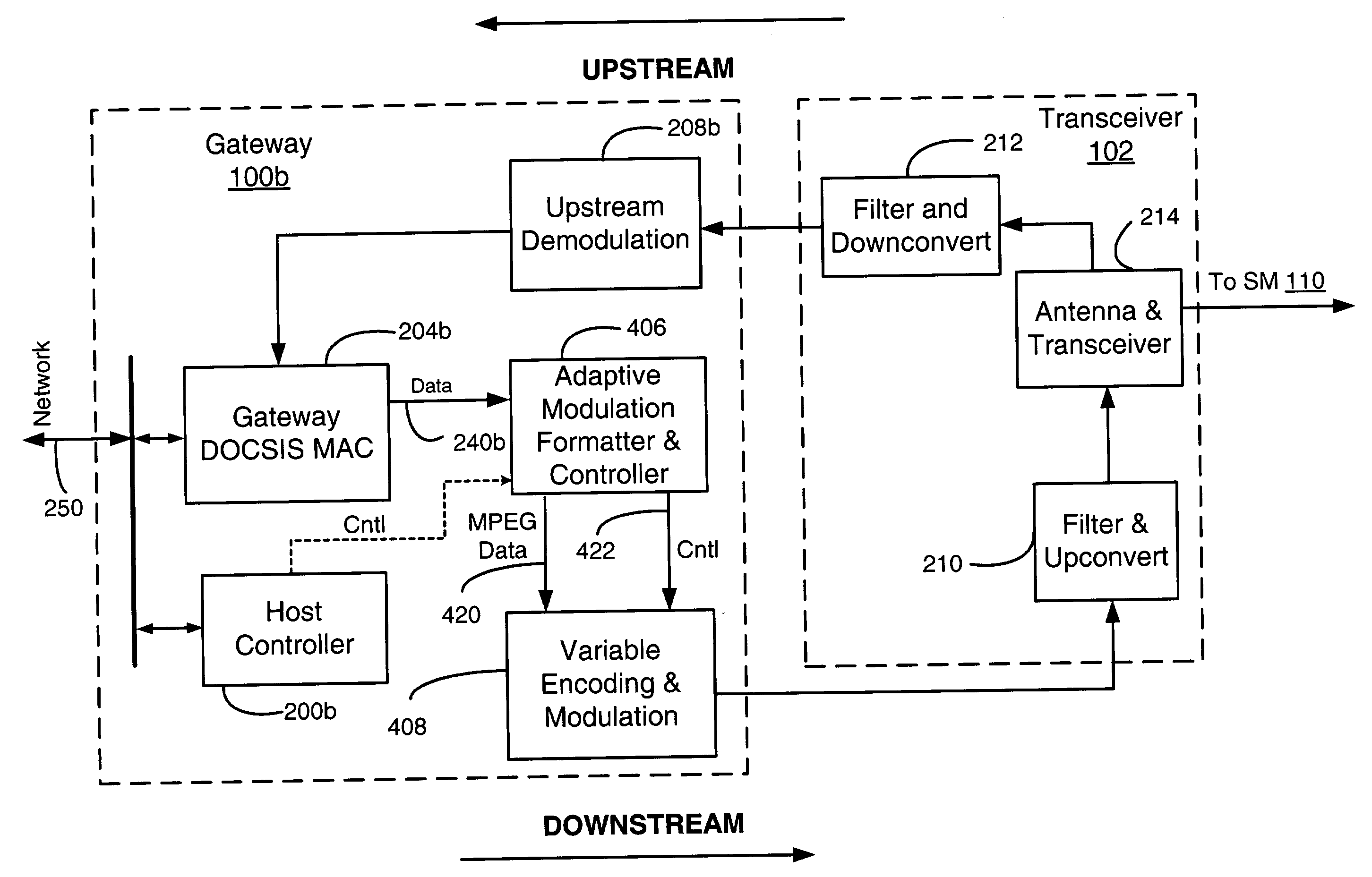
Downstream time domain based adaptive modulation for DOCSIS based applications
InactiveUS7508785B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove bandwidth efficiencyBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexTime domainSignal quality
In a DOCSIS based satellite gateway data is transmitted over a single downstream channel, at different throughput rates. Data destined for each subscriber / receiver is assigned a throughput rate depending upon the downstream signal quality of that subscriber / receiver. To accomplish this, the downstream DOCSIS MAC data is parsed to extract DOCSIS packets. The DOCSIS packets are then loaded into packet queues based on an identifier within such packets such as the MAC destination address or SID. Each of the queues represents a bandwidth efficiency or throughput rate that can be currently tolerated by specific subscribers based on the current signal quality being experienced at the subscriber location. A PHY-MAP describing the downstream data structure to be transmitted and inserted into the downstream data. Data is extracted from the packet queues in queue blocks as defined by the PHY-MAP. The queue blocks are modulated with transmission parameters appropriate for each queue block and transmitted to the DOCSIS based satellite modems. The satellite modems extract the PHY-MAP from the downstream data and use the information contained in it to demodulate and decode the queue for which they have sufficient downstream signal quality. Satellite modems measure and transmit downstream signal quality to the satellite gateway to be used to assigned traffic to the appropriate queues.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Mobile communication system, channel synchronization establishing method, and mobile station
InactiveUS7315566B2Increase the number ofIncrease channel capacityPower managementSynchronisation arrangementPhase differenceCarrier signal
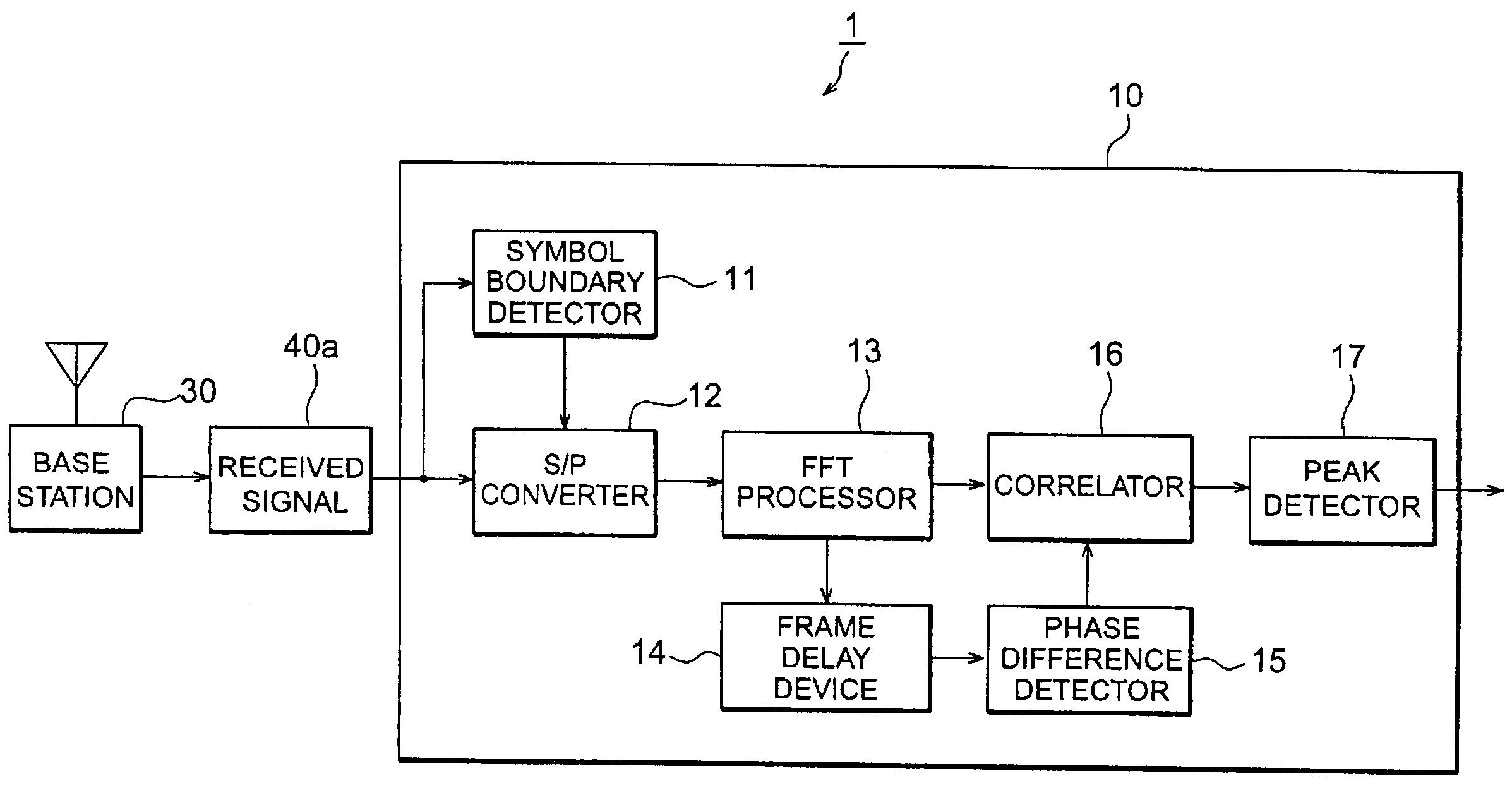
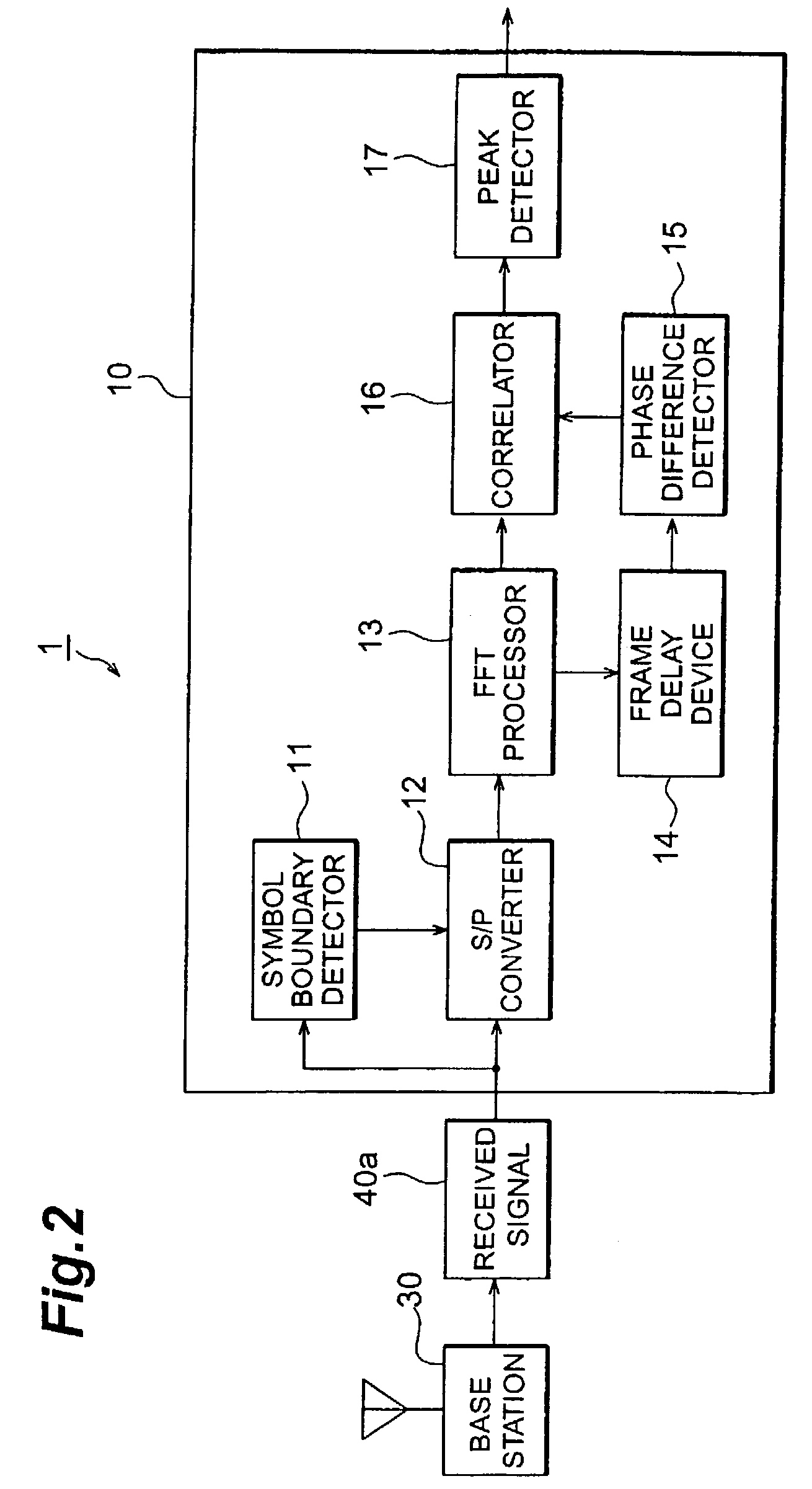
A mobile communication system 1 according to the present invention comprises base station 30 and mobile station 10. The base station 30 sends a pilot symbol sequence known to the mobile station 10, to the mobile station 10, using a plurality of carriers for downward channels, and performs communication with the mobile station 10 while multiplying the channels by frequencywise same scrambling codes every symbol period. The mobile station 10 is provided with a peak detector 17 for calculating cross correlation allowing for a phase difference of the scrambling codes, between frequencywise pilot symbol sequences received from the base station 30, thereby detecting a radio frame boundary.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method for selecting full-duplex antenna in multiple-in multiple-out (MIMO) system
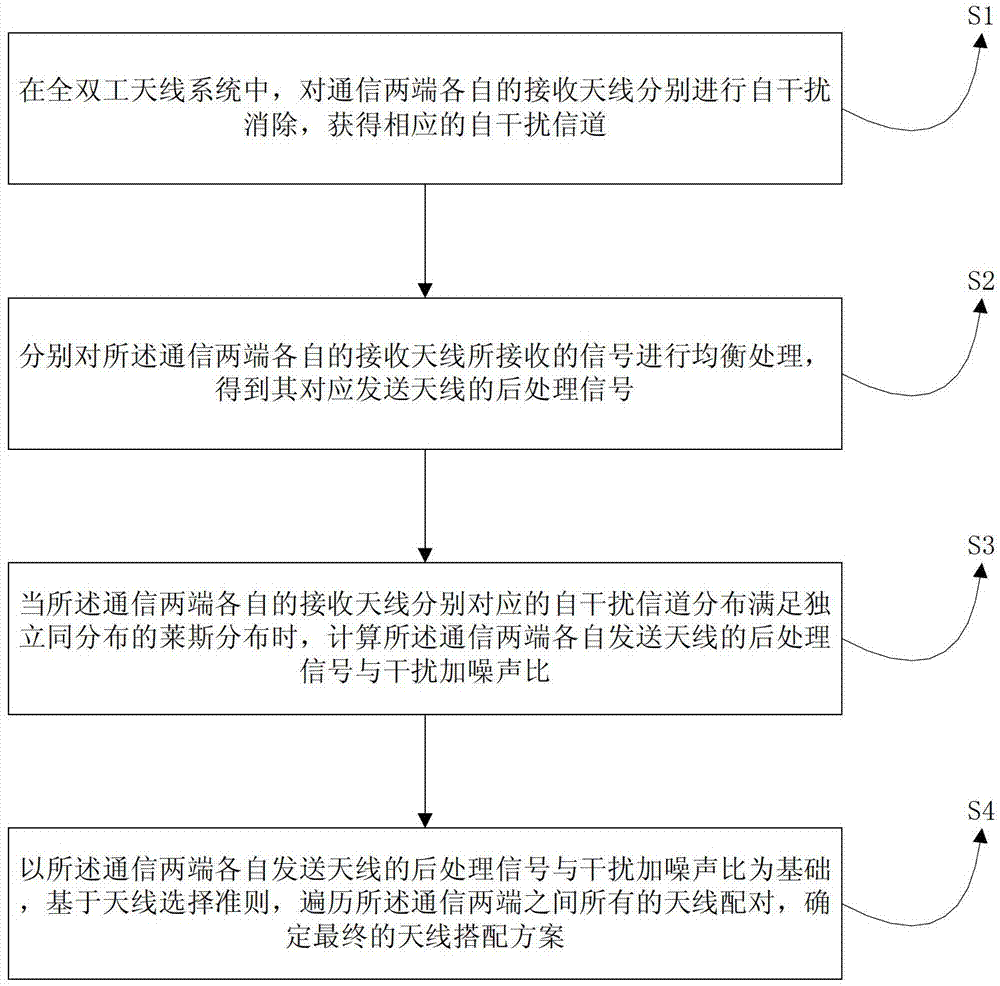
InactiveCN103117970AIncrease channel capacityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSelf interferenceSelection criterion
The invention provides a method for selecting a full-duplex antenna in a multiple-in multiple-out (MIMO) system. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, performing self-interference elimination on receiving antennae at two communication ports in a full-duplex antenna system to acquire corresponding self-interference channels; 2, performing equalization processing on signals received by the receiving antennae at the two communication ports to acquire postprocessing signals of corresponding transmitting antennae; 3, when distribution of the self-interference channels corresponding to the receiving antennae at the two communication ports accords with independent identically distributed Rice distribution, calculating the postprocessing signal to interference and noise ratio of the receiving antennae at the two communication ports; and 4, traversing all antenna pairs between the two communication ports based on antenna selection criteria to determine a final antenna matching scheme. The advantages of a full-duplex antenna technology and an MIMO technology are combined, a scheme with gain is selected from all possible antenna matching schemes, channel capacity is improved, and the whole performance of the system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
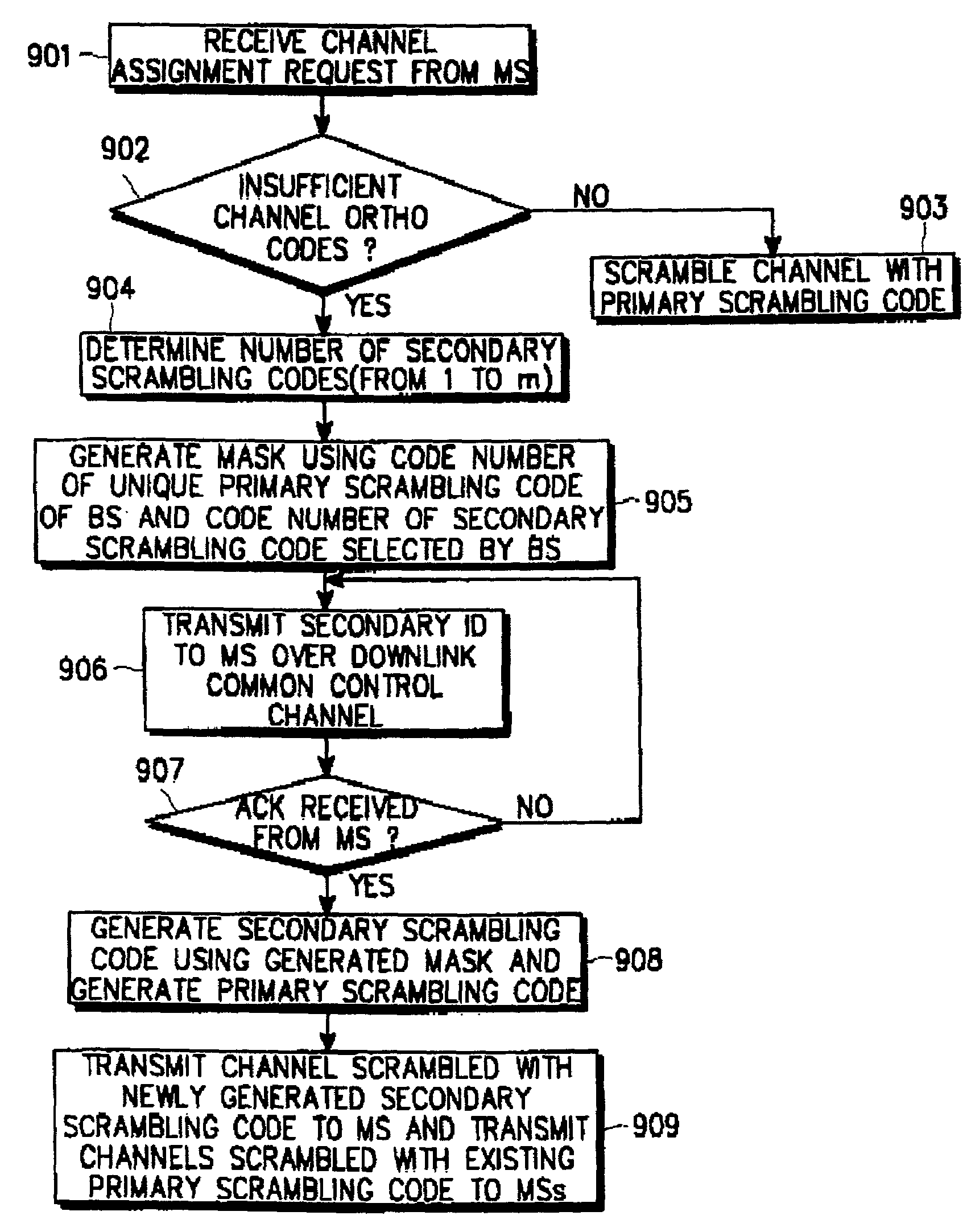
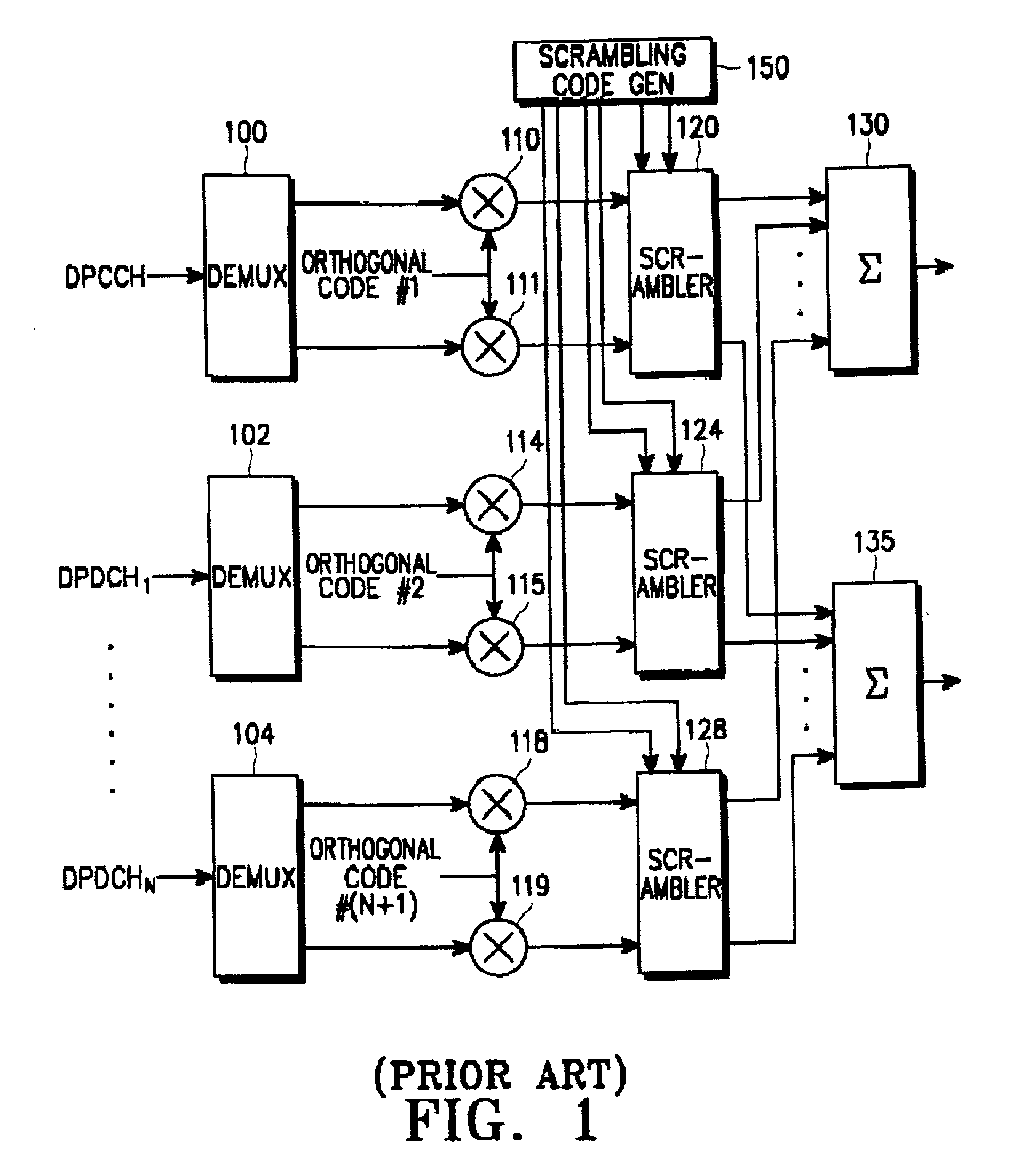
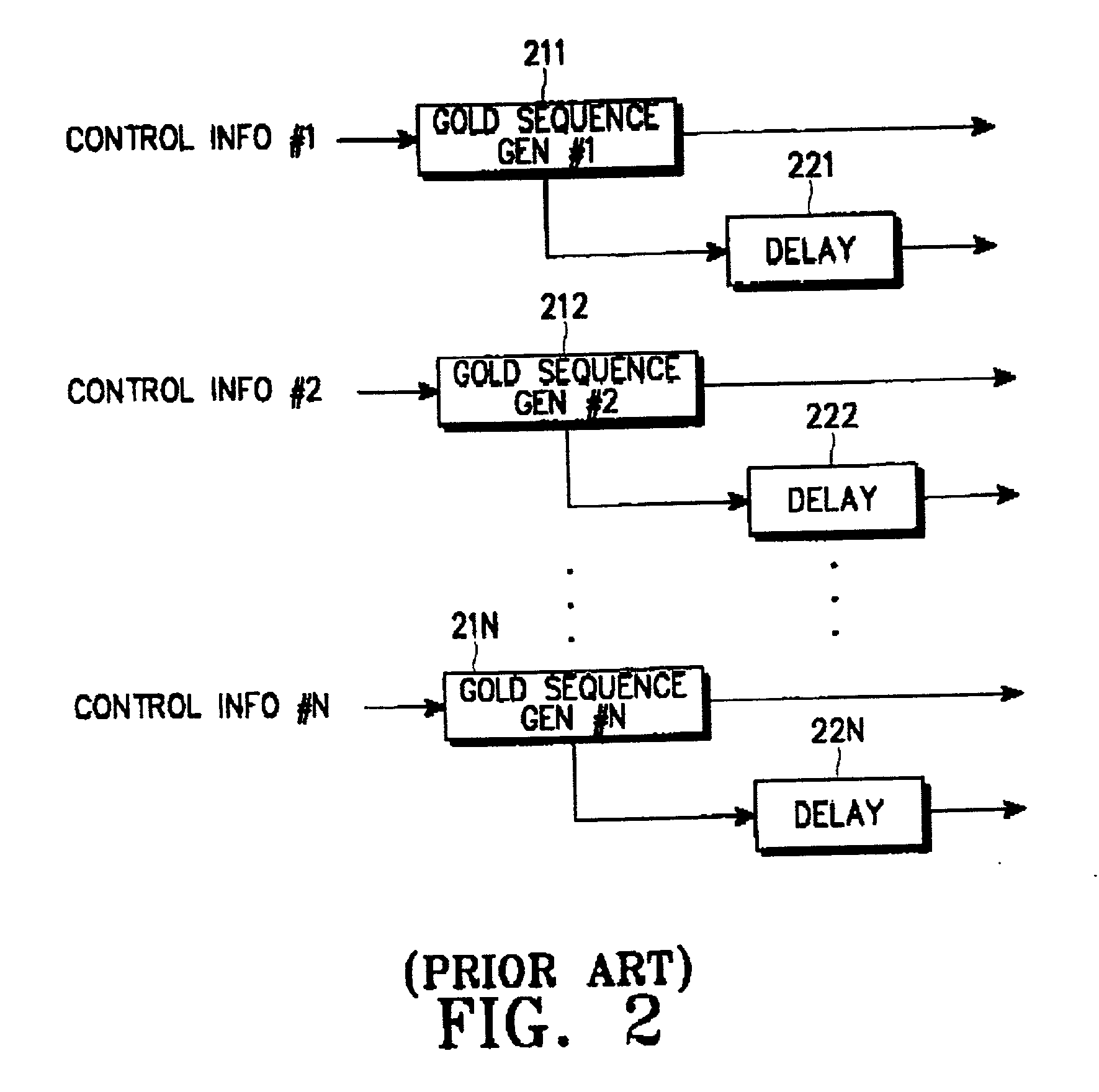
Method for communicating scrambling code ID in mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050169349A1Efficient communicationIncrease channel capacityNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementMobile stationMobile communication systems
Disclosed is a method for transmitting a channel signal in a base station of a mobile communication system which scrambles a common channel signal using a primary scrambling code for identifying the base station. The method comprises determining an identifier (ID) of a secondary scrambling code, upon receipt of a dedicated channel assignment request from a mobile station; transmitting the determined ID of the secondary scrambling code to the mobile station and awaiting a response; upon receipt of a response message from the mobile station, generating a primary scrambling code and a secondary scrambling code using an ID of the primary scrambling code and said ID of the secondary scrambling code; and scrambling a common channel signal using the primary scrambling code, scrambling a dedicated channel signal using the secondary scrambling code, and transmitting the scrambled channel signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-input and multi-output selectivity OFDM underwater sound communication system and method
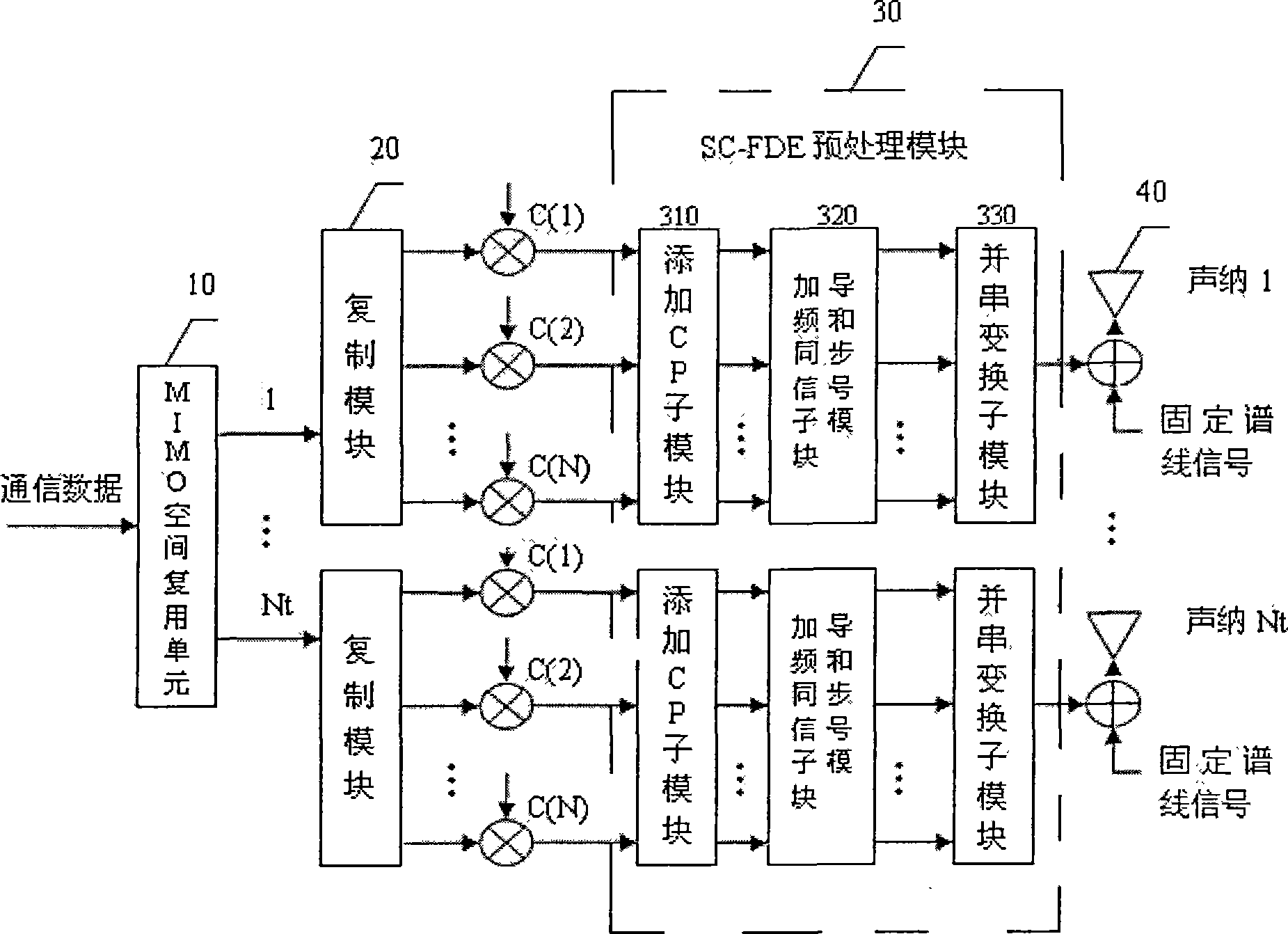
InactiveCN101631099AIncrease channel capacityIncrease transfer rateSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsSubcarrierFrequency domain
The invention relates to a multi-input and multi-output selectivity OFDM underwater sound communication system and a method thereof, having the advantages of resisting multi-path interference, resisting frequency selectivity deep fading, improving the transmission rate of information and the like. The transmitter of the system comprises a space multiplexing unit, a plurality of spectrum spreading units, a subcarrier zero setting unit, a plurality of OFDM modulation units, a multiple sonar transmitting unit and a communication channel estimation unit, wherein, the spectrum spreading units are connected between the space multiplexing unit and the subcarrier zero setting unit; the OFDM modulation units are connected between the subcarrier zero setting unit and the multiple sonar transmitting unit. A receiver comprises a multiple sonar receiving unit, a plurality of OFDM demodulation units, a communication channel frequency domain balancing unit, a plurality of dispreading units and space demultiplexing units, the OFDM demodulation units are connected between the multiple sonar receiving unit and the communication channel frequency domain balancing unit, the dispreading units are connected between the communication channel frequency domain balancing unit and the space demultiplexing unit, and the communication channel estimation unit is respectively connected with the subcarrier zero setting unit and the communication channel frequency domain balancing unit.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
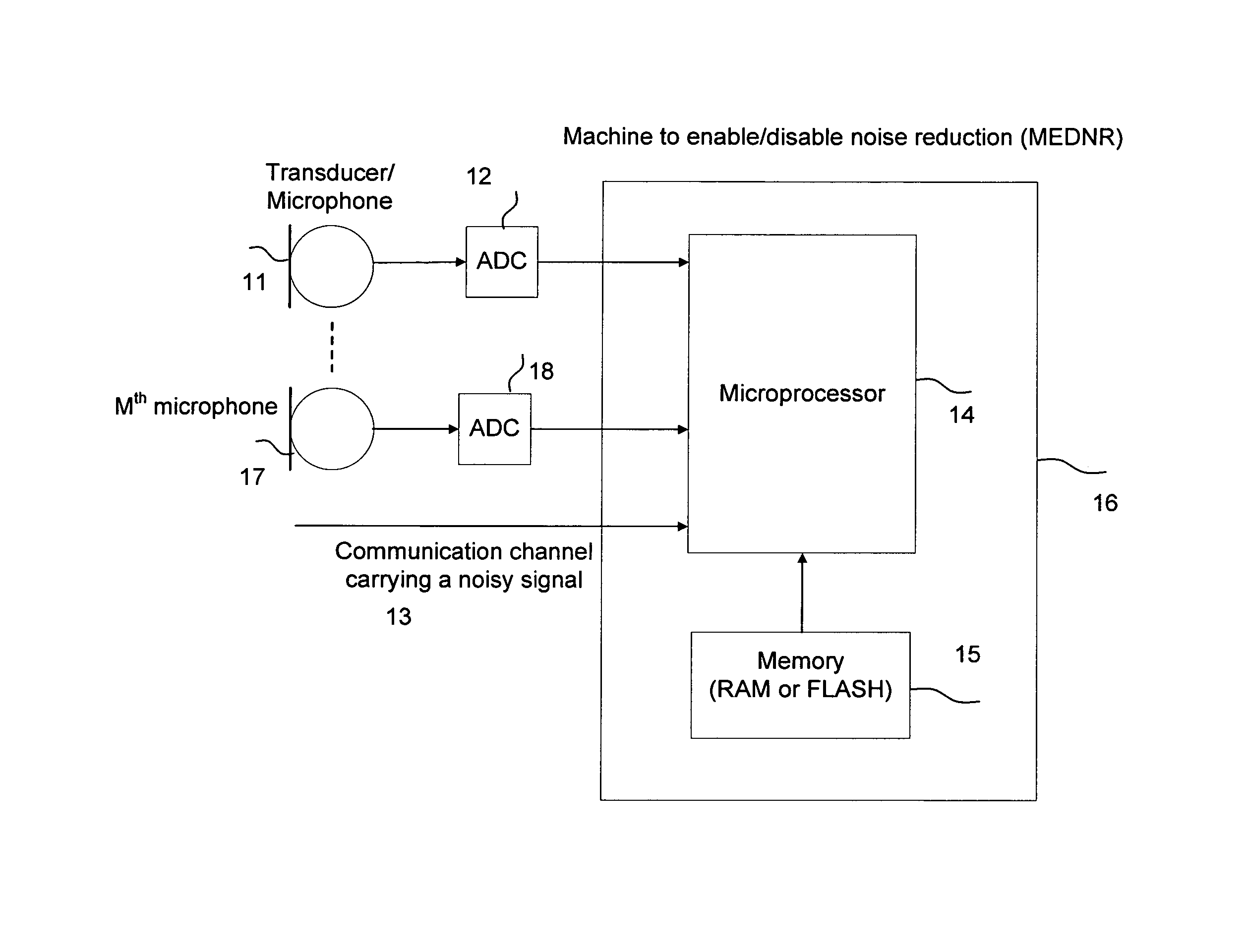
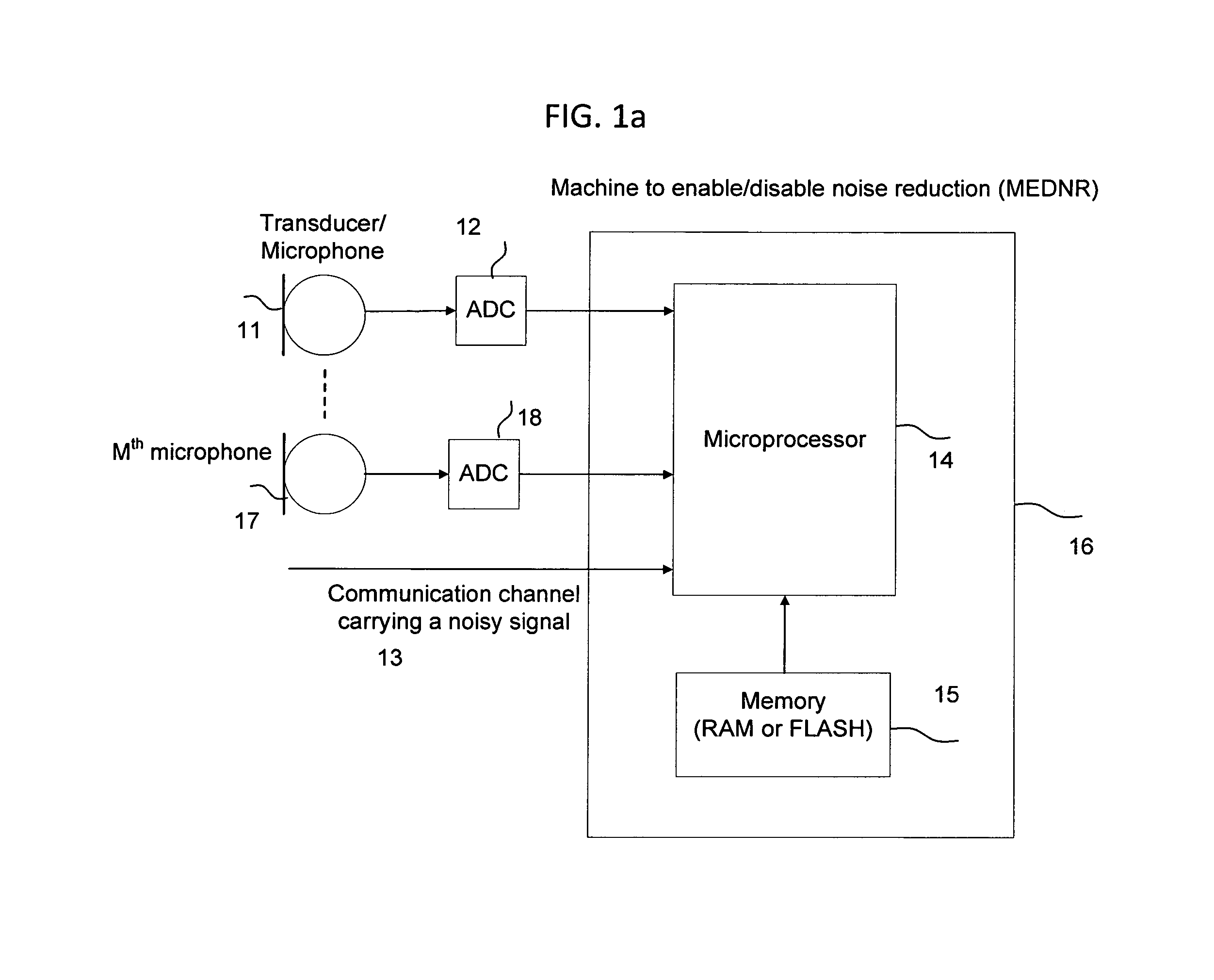
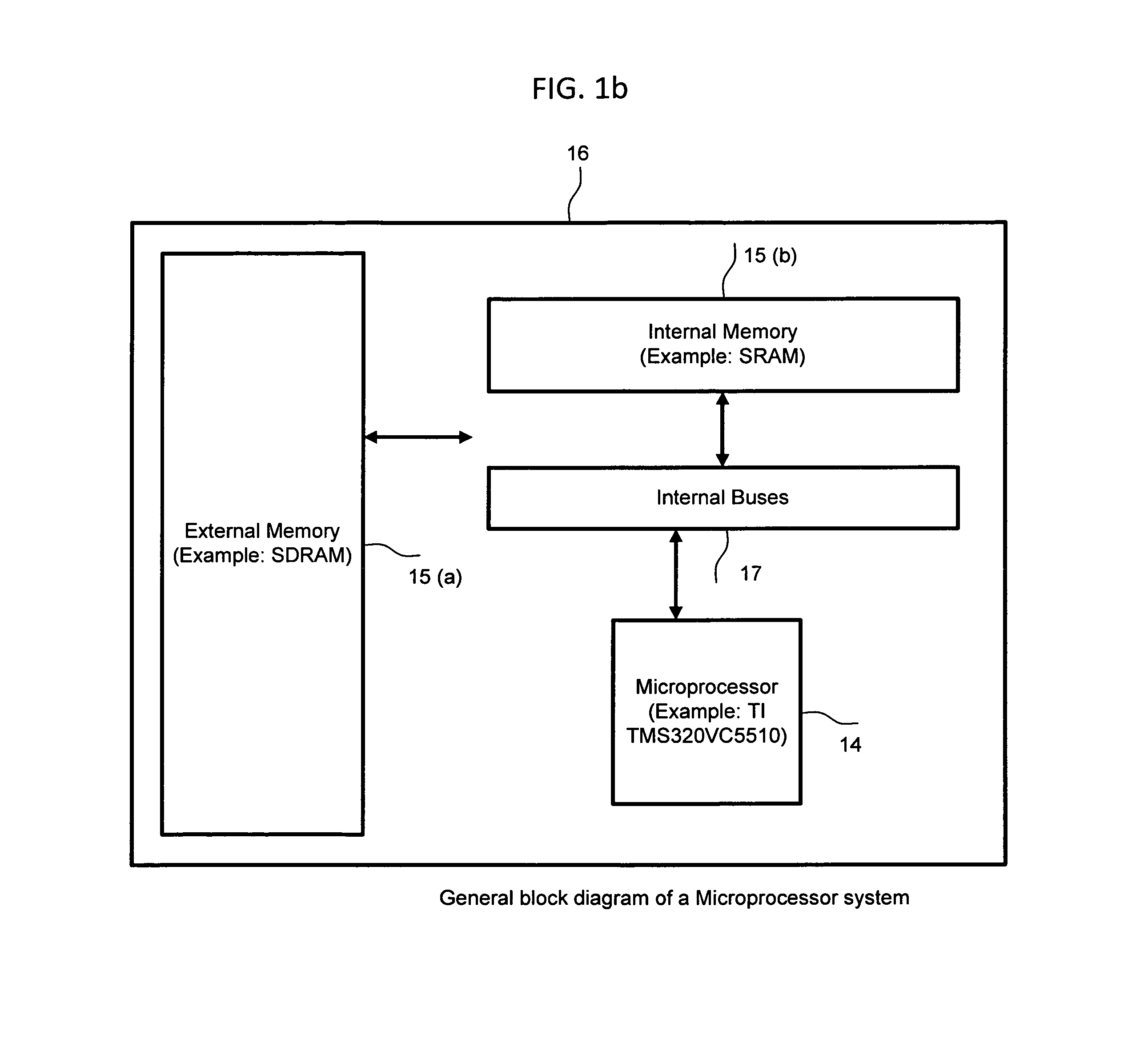
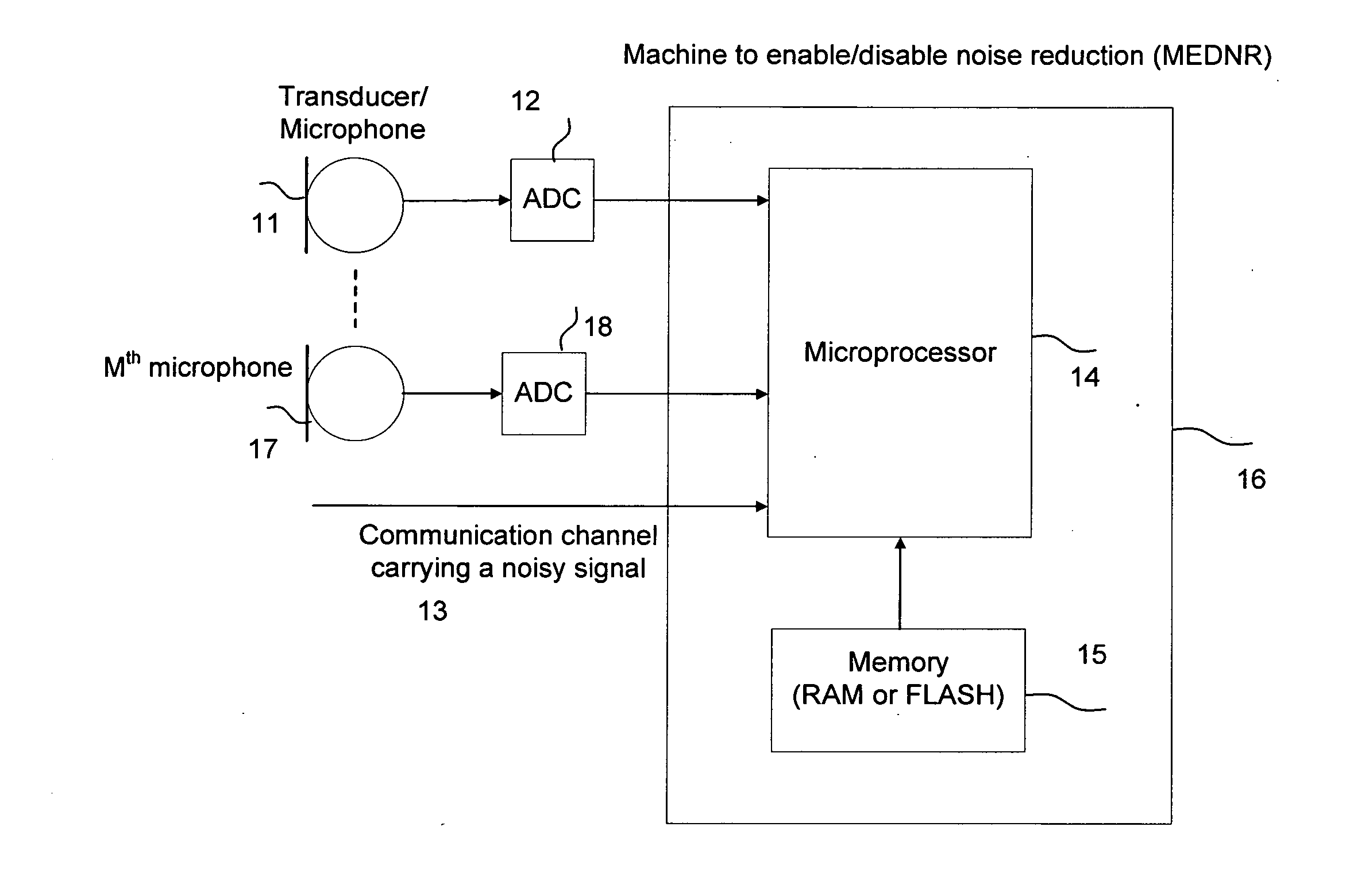
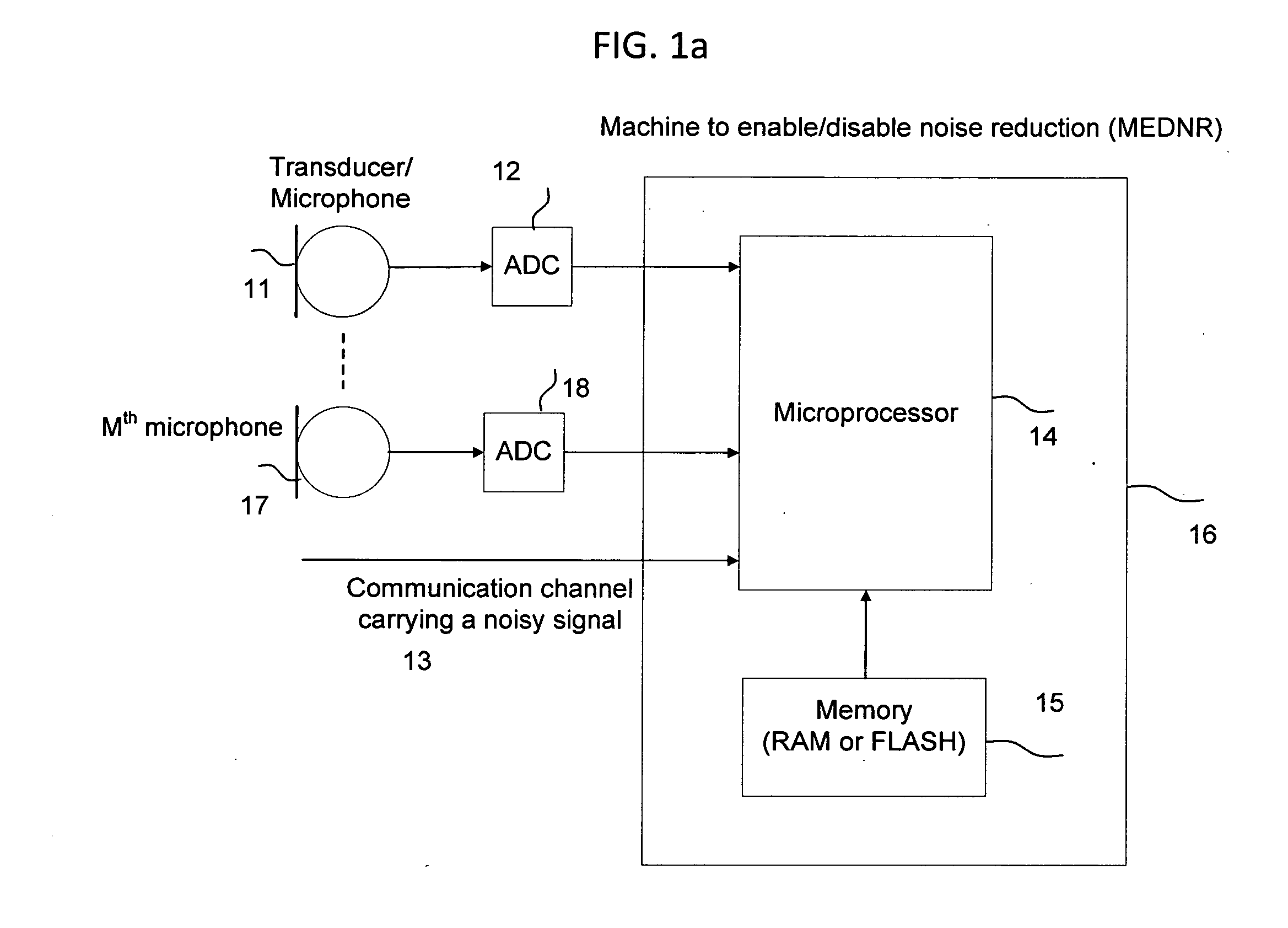
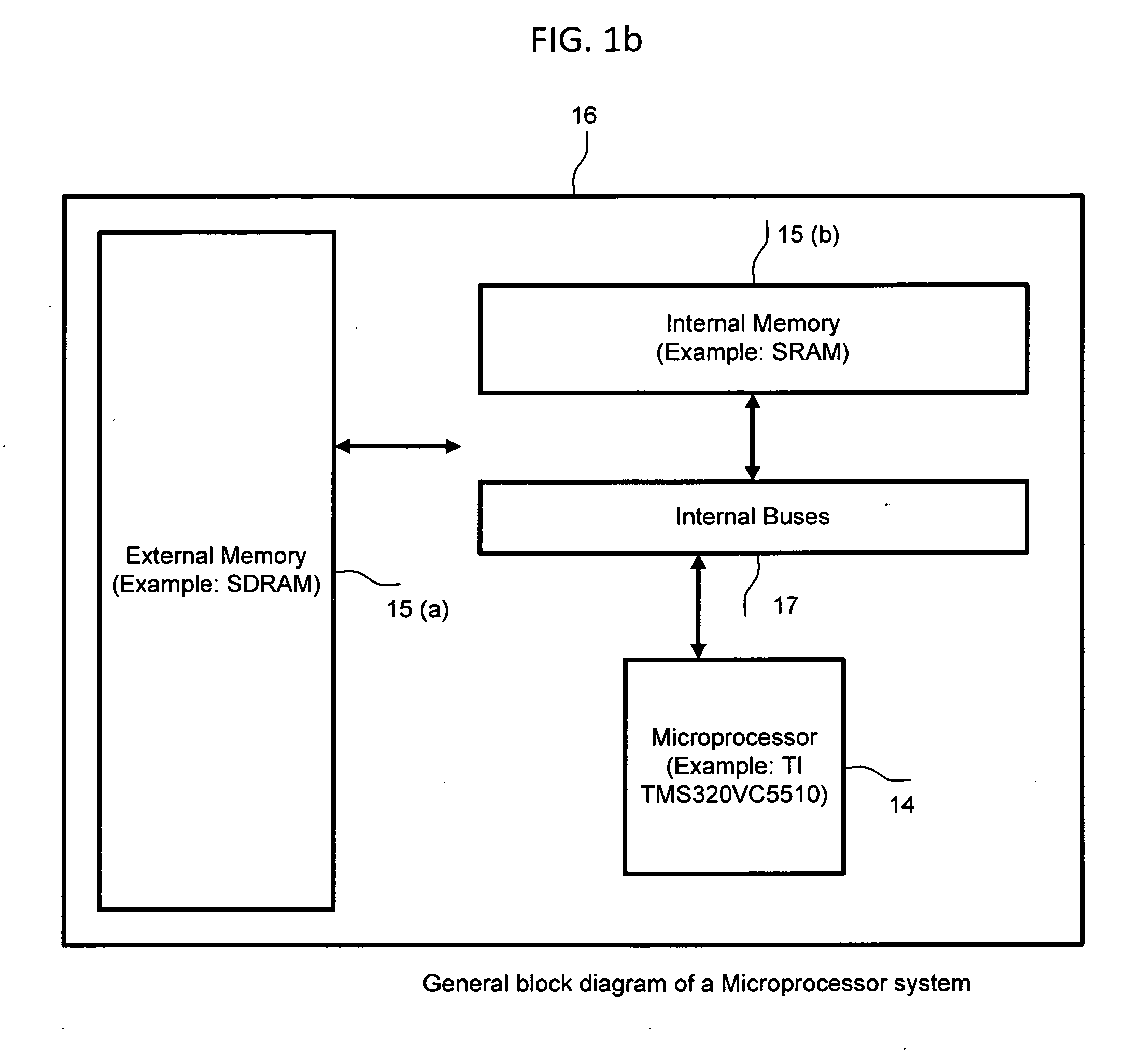
Machine for enabling and disabling noise reduction (MEDNR) based on a threshold
InactiveUS8775172B2Reduce noiseIncrease channel capacityHearing device energy consumption reductionSpeech analysisNoise reductionCommunication device
Owner:NOISE FREE WIRELESS
Four-color LED light mixing method based on visible light communication
ActiveCN104053278ASpectrum richColor temperature adjustablePoint-like light sourceElectric lightingColor rendering indexSpectrograph
The invention discloses a four-color LED light mixing method based on visible light communication. The method comprises the steps that spectral power distribution of all monochromatic light is obtained through a spectrograph, and the tristimulus value of each corresponding monochromatic light is calculated; the target color temperature of mixed light is determined, and a corresponding reference light source is selected and used for obtaining the tristimulus value of a mixed color; according to the color addition principle, the sum of the tristimulus values of all the monochromatic light should be equal to the tristimulus value of the mixed color, and a color mixing equation set is obtained; the spectral power distribution of the mixed light can be obtained according to the light mixing coefficient of all the monochromatic light in the color mixing equation set, and the color rendering index Ra of the mixed light is calculated according to the spectral power distribution of the mixed light, wherein Ra is larger than or equal to epsilon; the range of the channel capacity C of the mixed light is calculated, and the maximum capacity Cmax is solved within the range; the ratio of all the colored light with the maximum capacity is output.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for communicating scrambling code ID in mobile communication system
InactiveUS7221695B1Efficient communicationIncrease channel capacityNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementMobile communication systemsMobile station
Disclosed is a method for transmitting a channel signal in a base station of a mobile communication system which scrambles a common channel signal using a primary scrambling code for identifying the base station. The method comprises determining an identifier (ID) of a secondary scrambling code, upon receipt of a dedicated channel assignment request from a mobile station; transmitting the determined ID of the secondary scrambling code to the mobile station and awaiting a response; upon receipt of a response message from the mobile station, generating a primary scrambling code and a secondary scrambling code using an ID of the primary scrambling code and said ID of the secondary scrambling code; and scrambling a common channel signal using the primary scrambling code, scrambling a dedicated channel signal using the secondary scrambling code, and transmitting the scrambled channel signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Machine for Enabling and Disabling Noise Reduction (MEDNR) Based on a Threshold
InactiveUS20120084080A1Reduce noiseIncrease channel capacityHearing device energy consumption reductionSpeech analysisNoise reductionAudio frequency
The present invention provides a novel system and method for monitoring the audio signals, analyze selected audio signal components, compare the results of analysis with a threshold value, and enable or disable noise reduction capability of a communication device.
Owner:NOISE FREE WIRELESS
Method, apparatus and equipment for sending and receiving data of MIMO system
InactiveCN101437007AImprove performanceEasy to detectDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsMulti inputSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
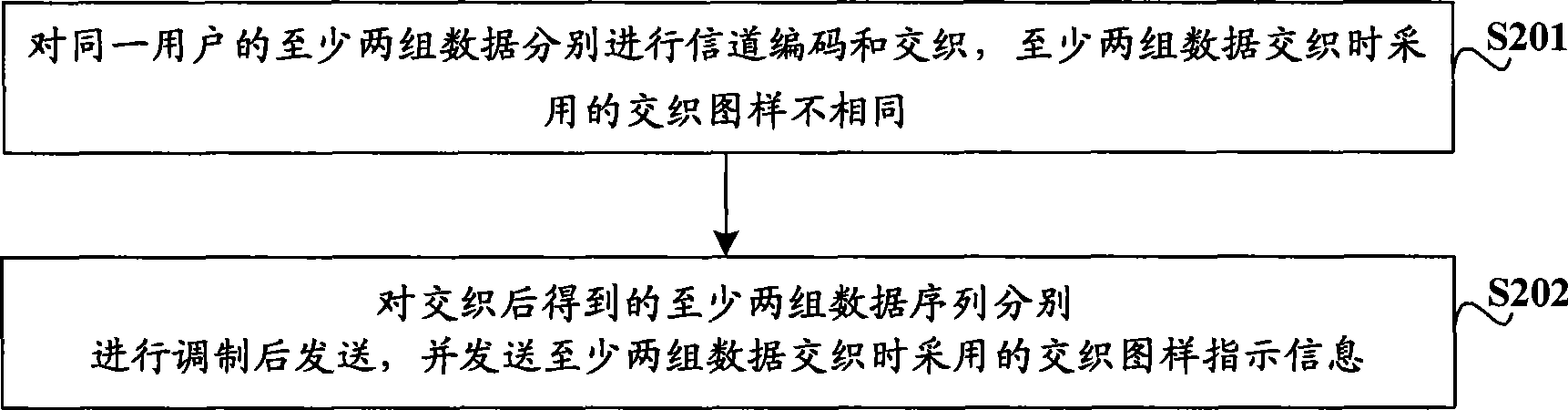
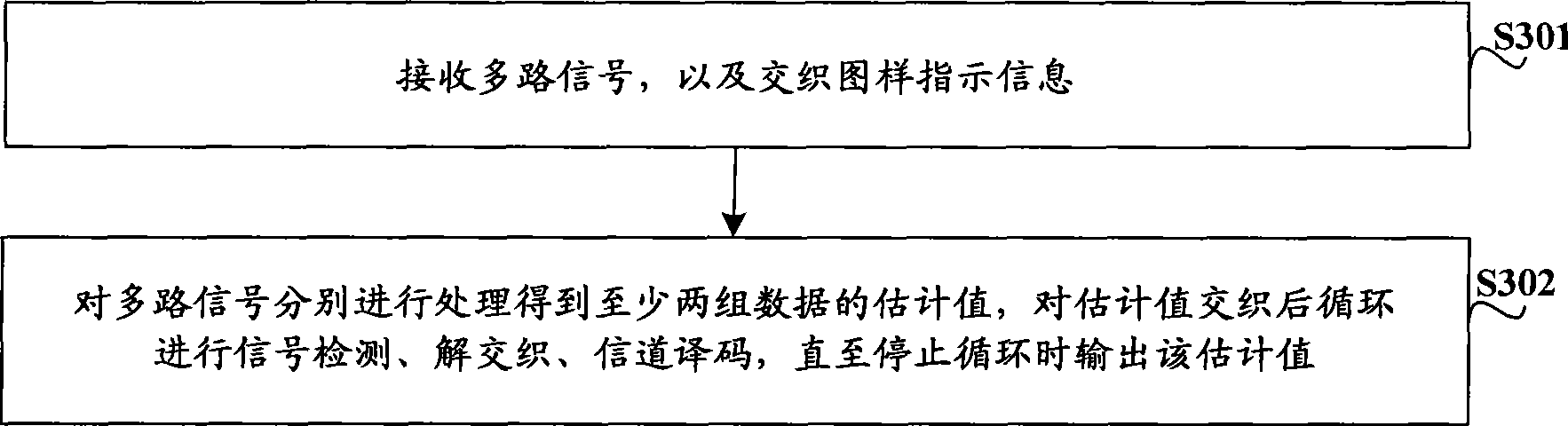
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile communication, in particular to data sending technology for a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) system and corresponding data receiving technology. The embodiment of the invention provides a data sending method, a corresponding data receiving method, a corresponding data receiving device and corresponding data receiving equipment for the MIMO system, and is used for increasing the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio of received signals of the MIMO system and improving the performance of the system. The data sending method for the MIMO system comprises the following steps: at least two groups of data of the same user are subjected to channel coding and interweaving respectively, and interweaving patterns adopted when the data are interwoven are not same; two data sequences obtained after the interweaving are modulated respectively and then are sent, and interweaving pattern indication information adopted when the data are interwoven is sent.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Base station transmitting and receiving antenna and control method thereof
InactiveUS20090061921A1Increase channel capacityLow costPower managementSubstation equipmentAntenna radiation patternsBeam pattern
The present invention relates to base station transmitting and receiving antennas and control methods thereof. For this purpose, the present invention provides a control method of a base station transmitting antenna. The control method includes collecting positional information and transmission level values of all terminals in a cell; analyzing statistics of cell traffic using the positional information and transmission level values, and generating antenna radiation patterns on the basis of the analyzed statistics result; optimizing the antenna radiation patterns by synthesizing beam patterns; and changing antenna beam patterns according to the optimized antenna radiation patterns. According to embodiments of the present invention, it is possible to increase a channel capacity in a cell, ensure the QoS in all terminals in the cell, and reduce installation and operation costs of a base station system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
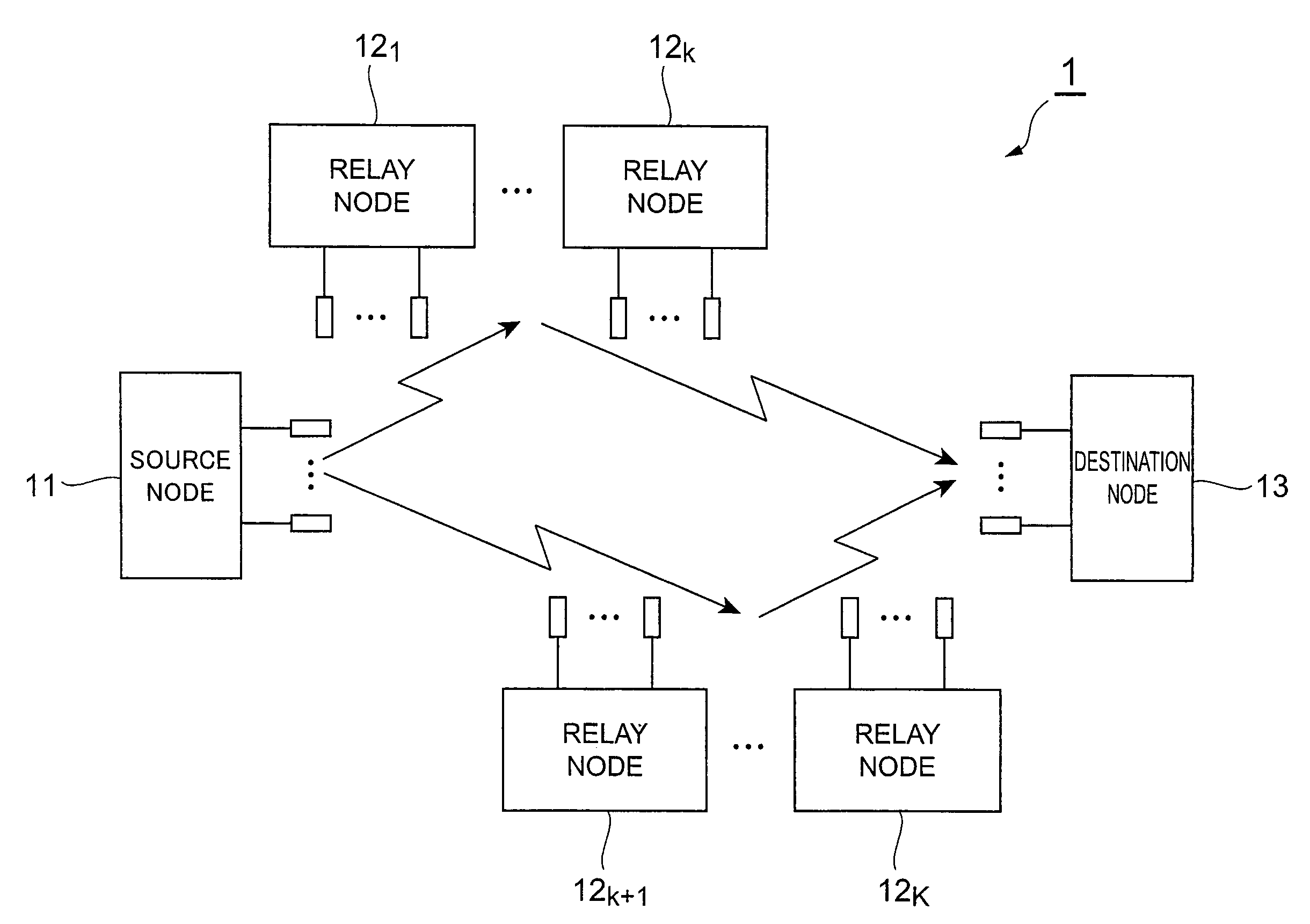
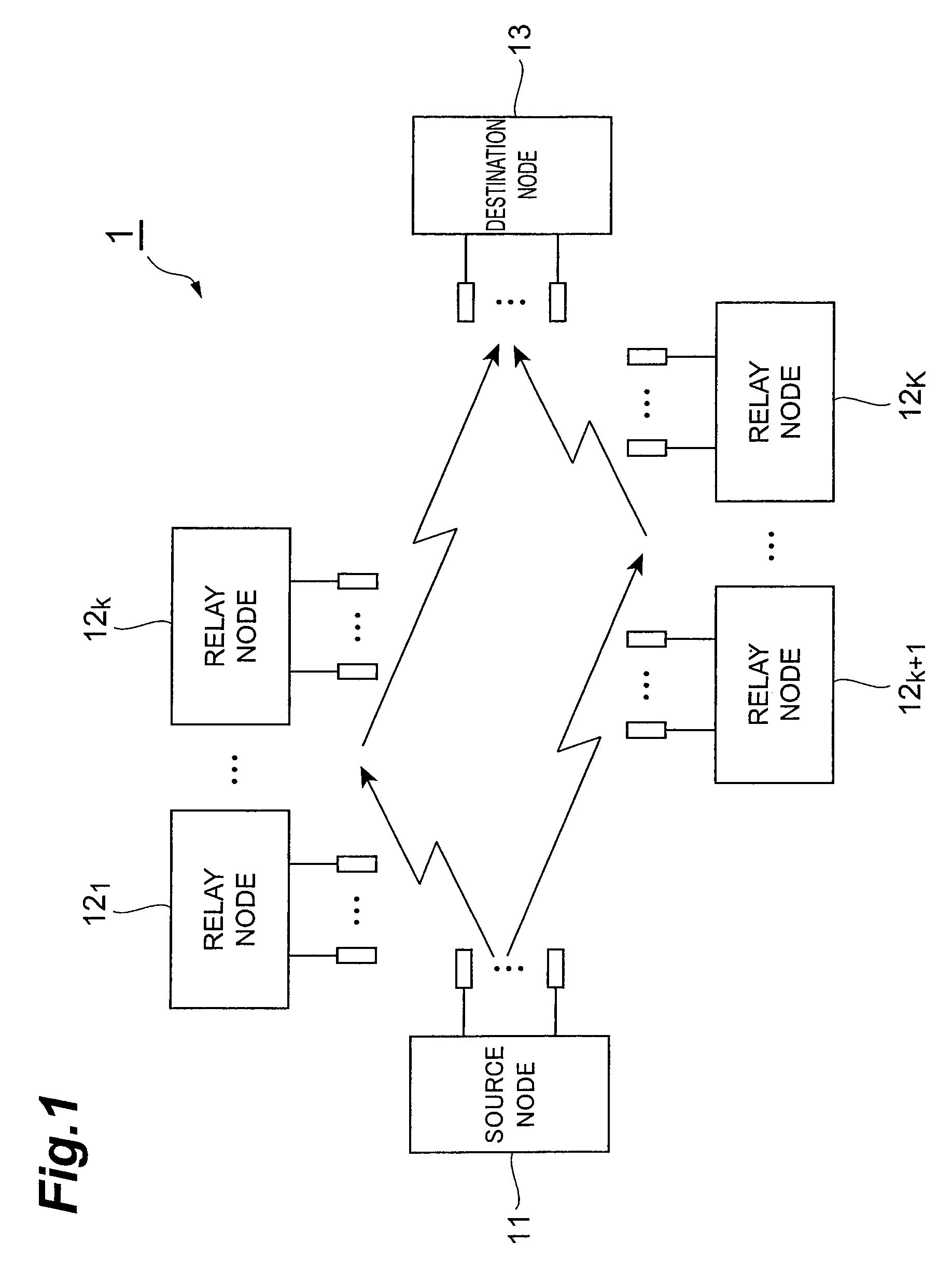
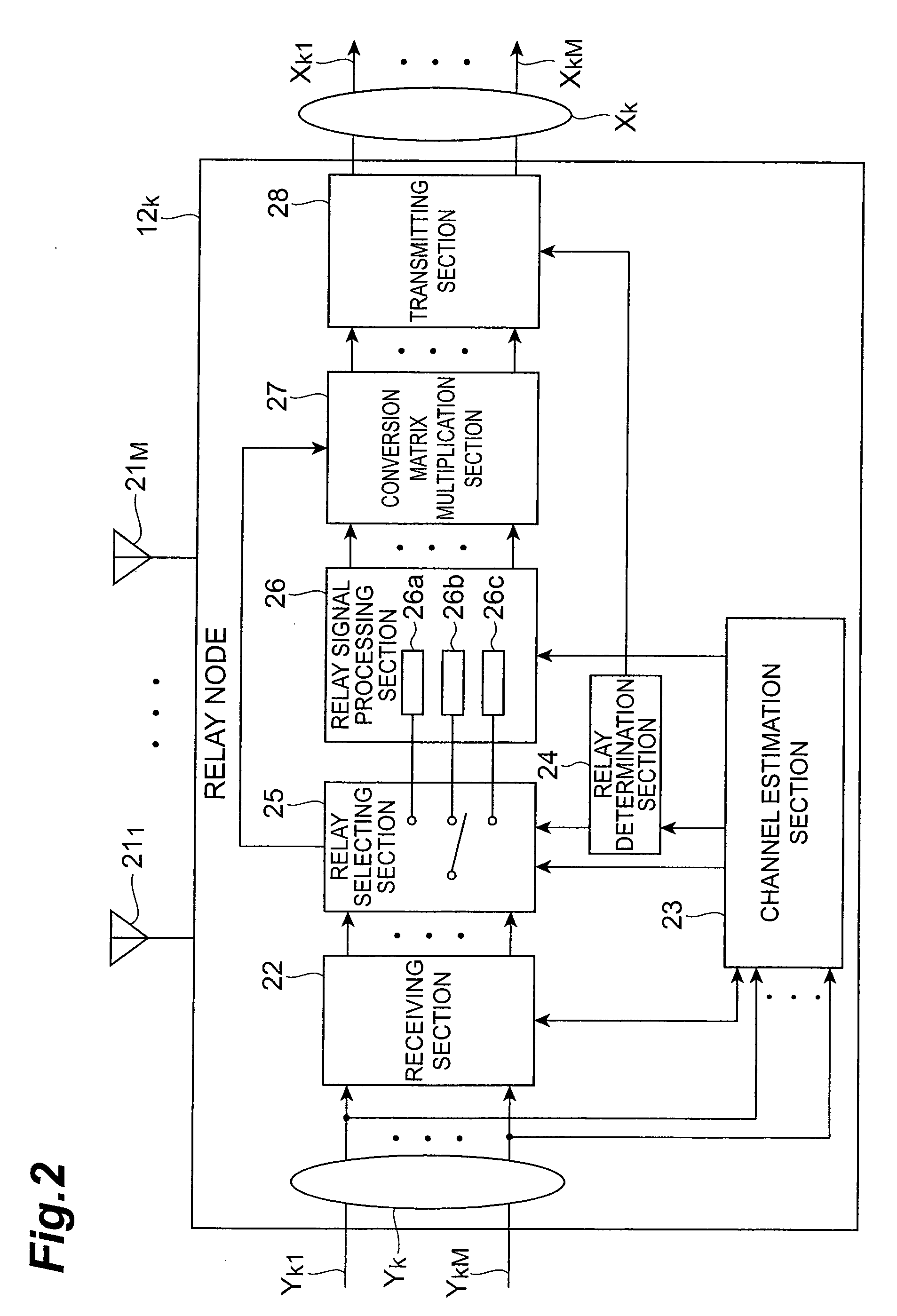
Relay node and relay method
InactiveUS20080049658A1Increase channel capacityUnwanted signalSite diversityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemTransmission quality
To improve the channel capacity of an entire communication system in accordance with transmission quality of the channels of each node. A relay node has: a receiving section that receives a received signal from a source node; a channel estimation section that measures SNR of a backward channel between the source node and the relay node, and SNR of a forward channel between the relay node and a destination node; a relay selecting section that selects, from among a QR-P-ZF method, a QR-P-QR method and a ZF-P-QR method, a relay method of the relay node in accordance with the ratio between the SNRs of the backward and forward channels; a relay signal processing section that multiplies the received signal by a transmission weight matrix corresponding to the selected relay method, and thereby converts the received signal to a relay signal; and a transmitting section that transmits the relay signal to the destination node.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Underwater sound communication system
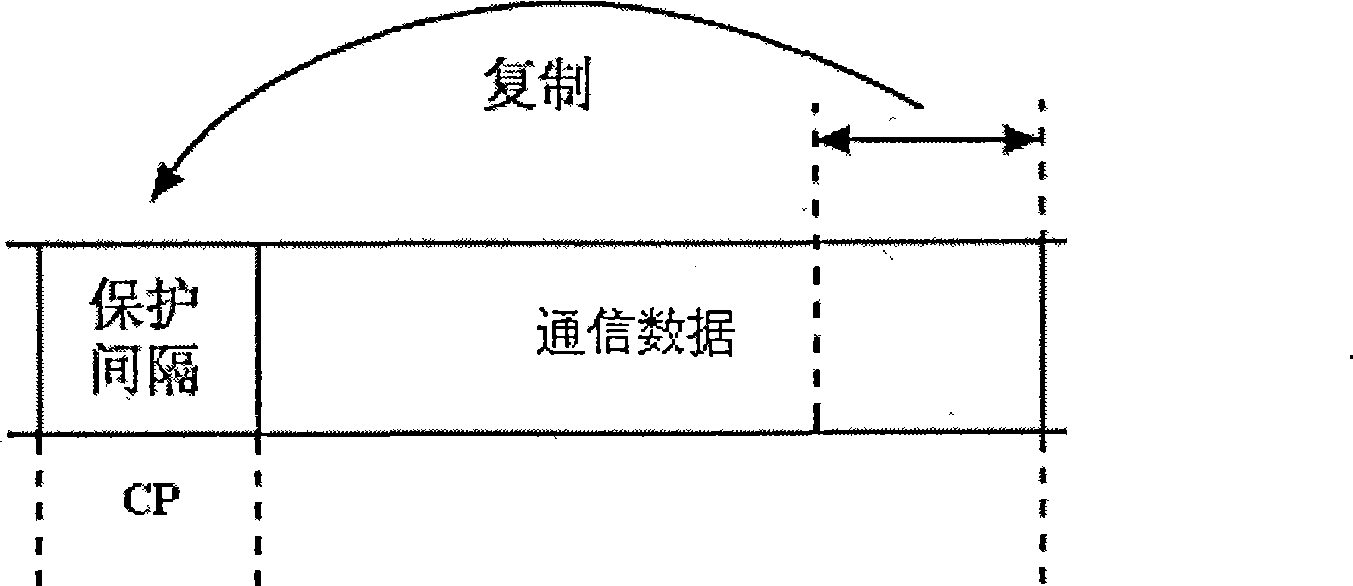
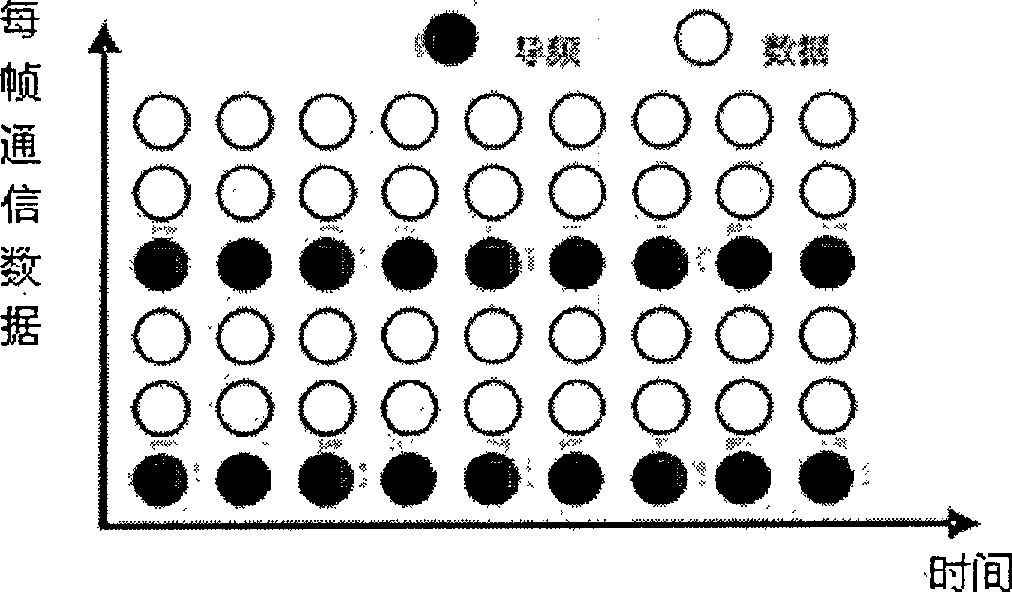
InactiveCN101534269AIncrease channel capacityIncrease transfer rateMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Channel capacity
The invention discloses an underwater sound communication system, wherein a transmitter comprises an MIMO space multiplexing unit, a plurality of spectrum spreading units, a plurality of SC-FDE pretreatment modules and a plurality of transmitting sonars; a plurality of output ends of the MIMO space multiplexing unit are in one-to-one connection with the plurality of the spectrum spreading units; each spectrum spreading unit is connected to one SC-FDE pretreatment module; each SC-FDE pretreatment module is connected to one transmitting sonar; a receiver comprises a plurality of receiving sonars, a plurality of filtering detecting units, a plurality of SC-FDE modules, a plurality of dispreading units, and an MIMO demultiplexing unit; each receiving sonar is connected with one filtering detecting unit; each filtering detecting unit is connected to one SC-FDE module; each SC-FDE module is connected to one dispreading unit; and the plurality of the dispreading units are in one-to-one connection with a plurality of input ends of the MIMO demultiplexing unit. The system can resist multipath interface, improve frequency spectrum utilization ratio, channel capacity, information transmission rate and confidentiality, compensate Doppler frequency shift and reduce signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Combined signal processing method for source end and relay end in bidirectional relay system
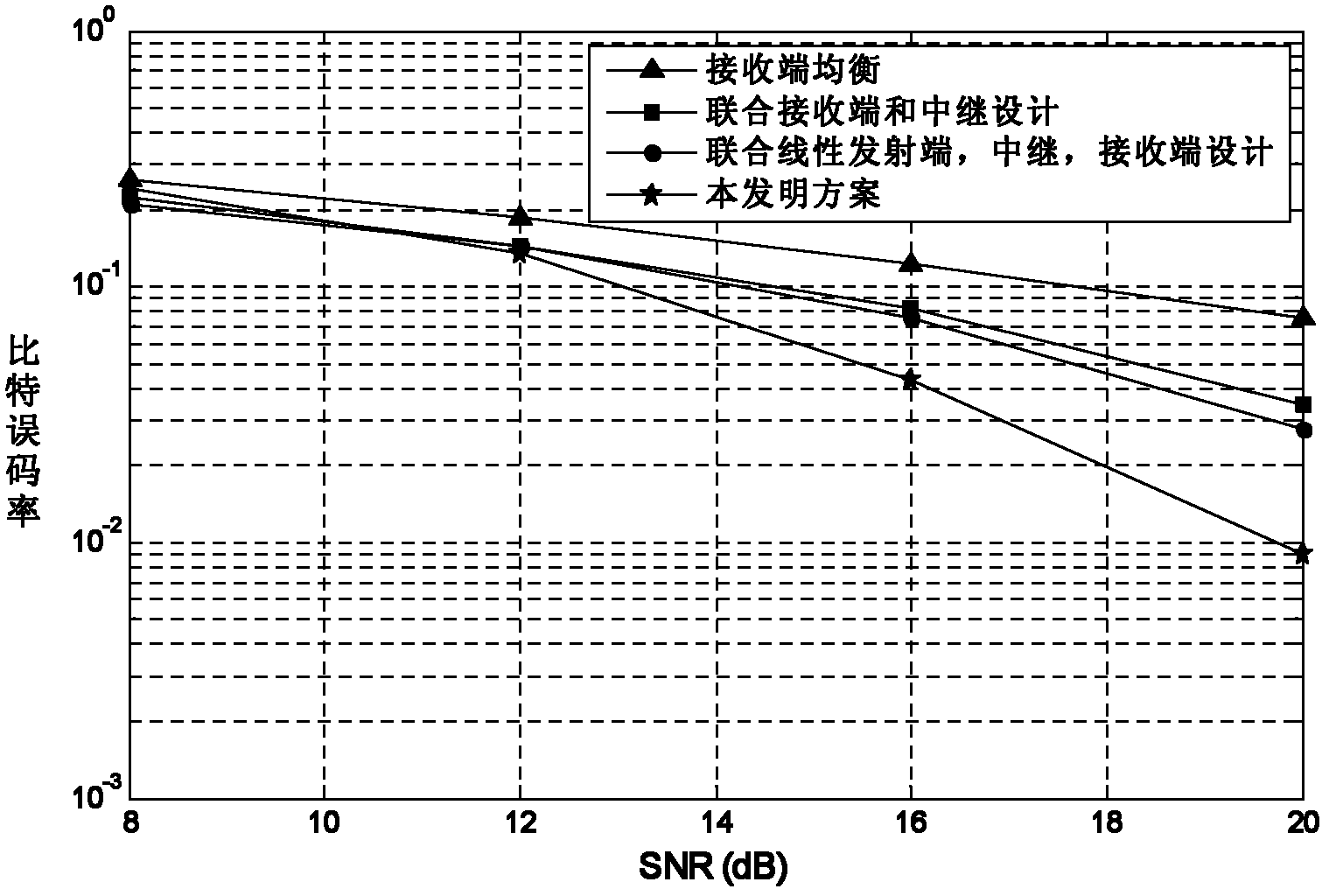
InactiveCN102571279AIncrease channel capacityImprove bit error rate performanceBaseband system detailsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionInformation transmissionEqualization
A combined signal processing method for a source end and a relay end in a bidirectional relay system comprises the following steps: the source end emits a training sequence to a relay, and the relay performs backward channel estimation to obtain an estimation channel between the source end and the relay; the relay emits a training sequence to the source end, and the source end performs forward channel estimation to obtain an estimation channel between the relay and a user; the source end feed forward channel information back to the relay, the relay performs iterative computation to source end nonlinear pre-coding matrixes, relay linear pre-coding matrixes and source end receiving equalization matrixes; the relay feeds the information of the source end back to the source end; emitting signals are subjected to nonlinear pre-treatment through the source end and then emitted to the relay; the signals received by the relay are subjected to linear pre-treatment through the relay and then broadcasted to the source end; and the source end detects the received signals to obtain information required to be transmitted therebetween. According to the invention, the bidirectional relay information transmission mode is adopted to improve the channel capacity, and the nonlinear signal processing method is adopted at the source end, so that the bit error rate performance of the system is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Tripolar magneto-dipole MIMO (multiple input multiple output) antenna system
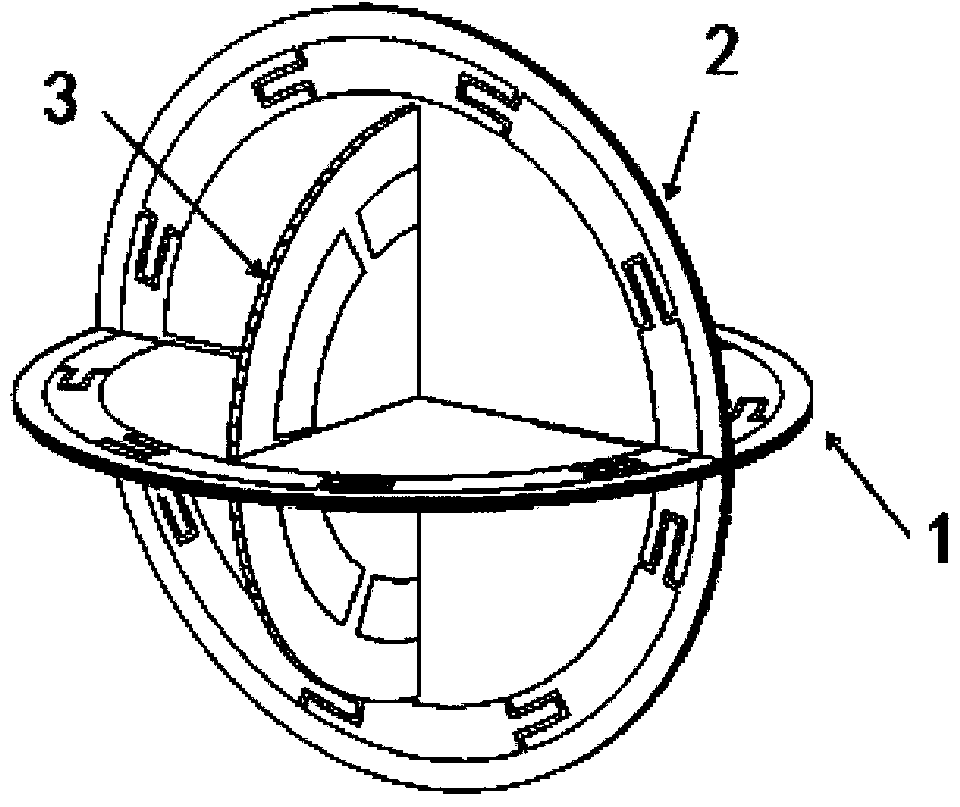
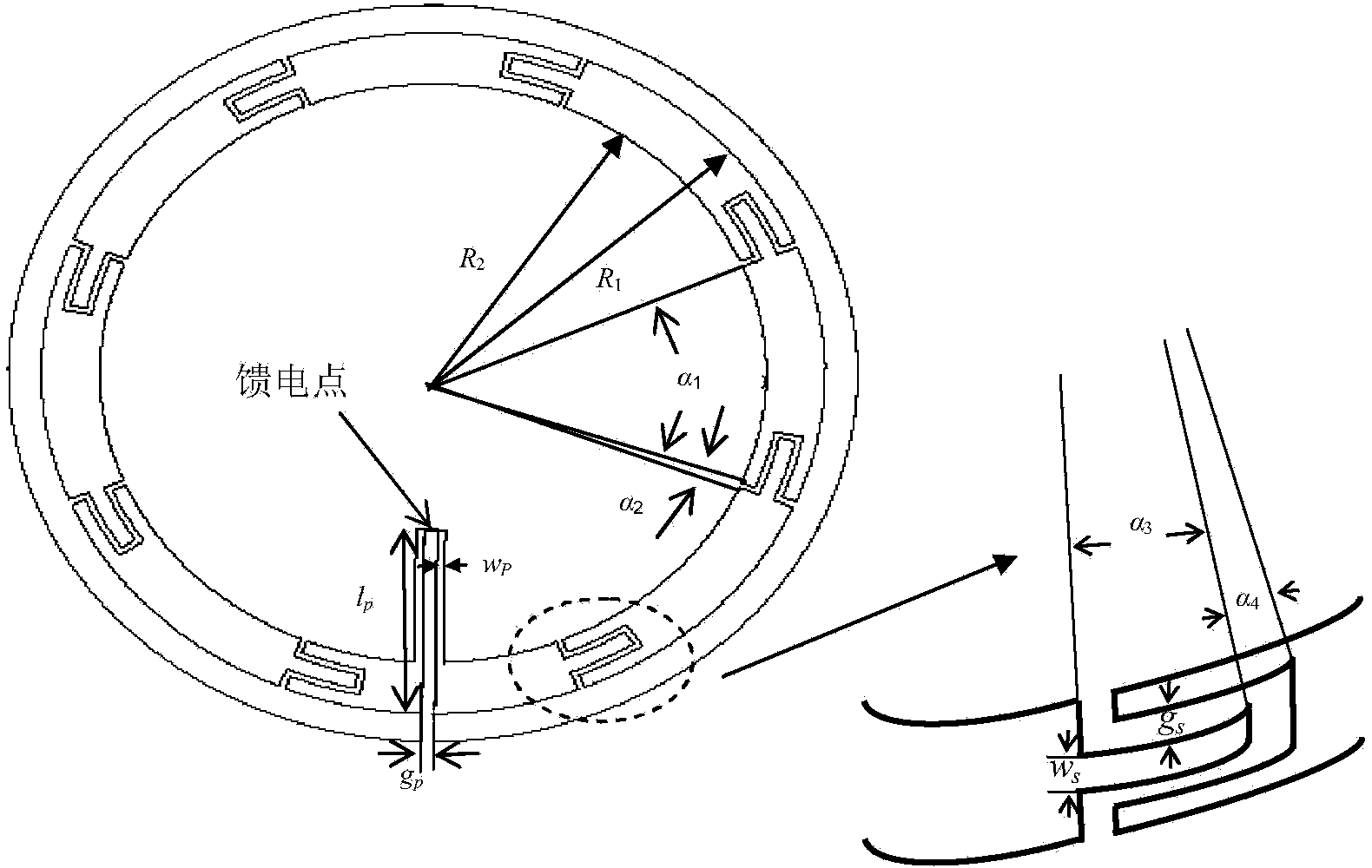
InactiveCN104218320AIncrease channel capacitySmall sizeRadiating elements structural formsLoop antennasChannel capacityDipole
The invention relates to a tripolar magneto-dipole MIMO (multiple input multiple output) antenna system and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication systems. A tripolar magneto-dipole MIMO antenna is composed of a first loop antenna, a second loop antenna and a third loop antenna which are mutually orthogonal. Geometric centers of the first, the second and the third loop antennas are located at one spatial point and feed respectively. Each loop antenna has evenly distributed current; meanwhile, the first, the second and the third loop antennas are low in coupling; MIMO channel capacity is high accordingly. The compact MIMO antenna with high channel capacity is composed of the coincident low-coupled tripolar magneto-dipoles. Extraction and utilization of three magnetic field polarization components are achieved, and three polarization degrees of freedom of the magnetic field components can be acquired accordingly.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com