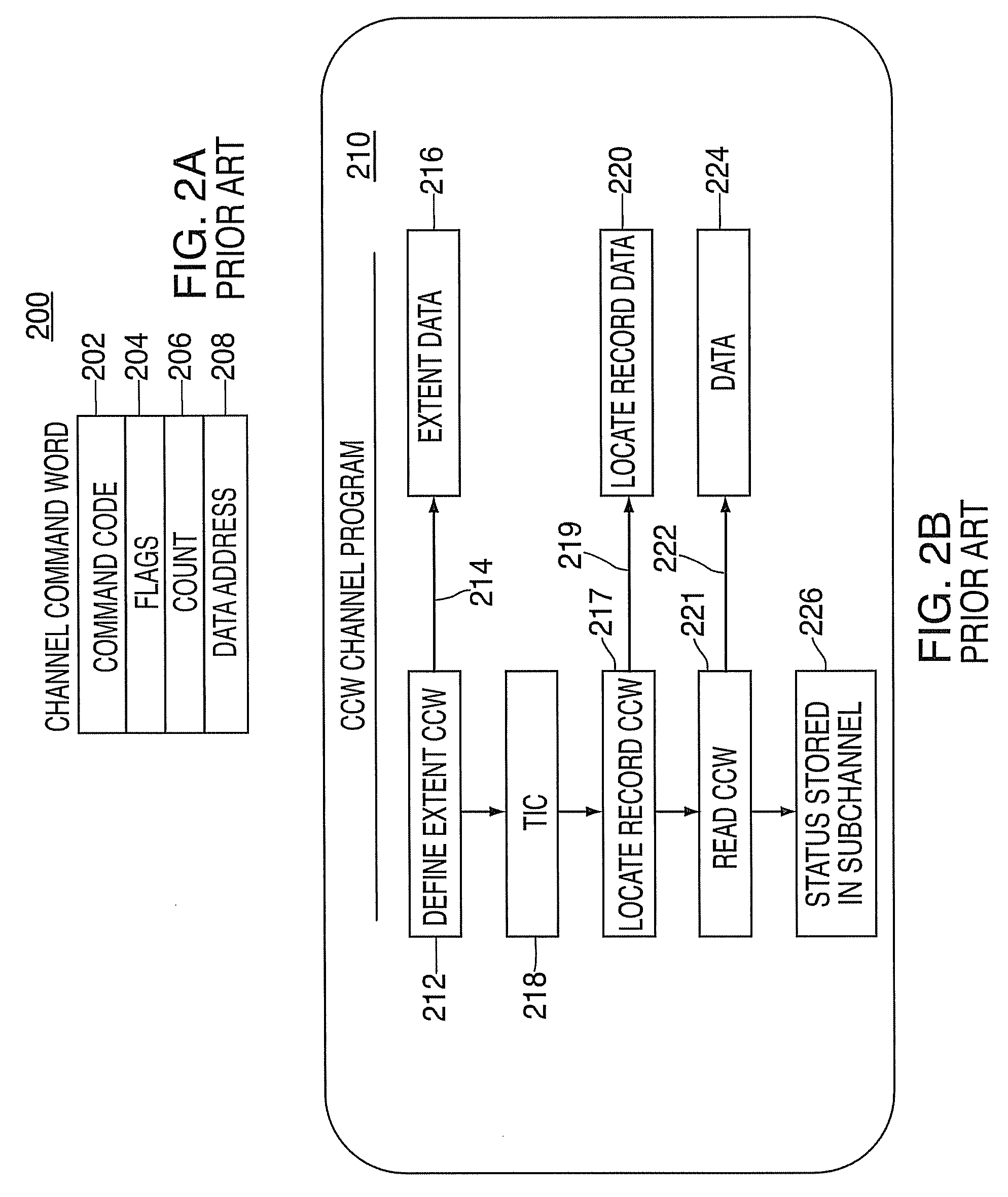
Patents
Literature
168results about How to "Reduce contention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
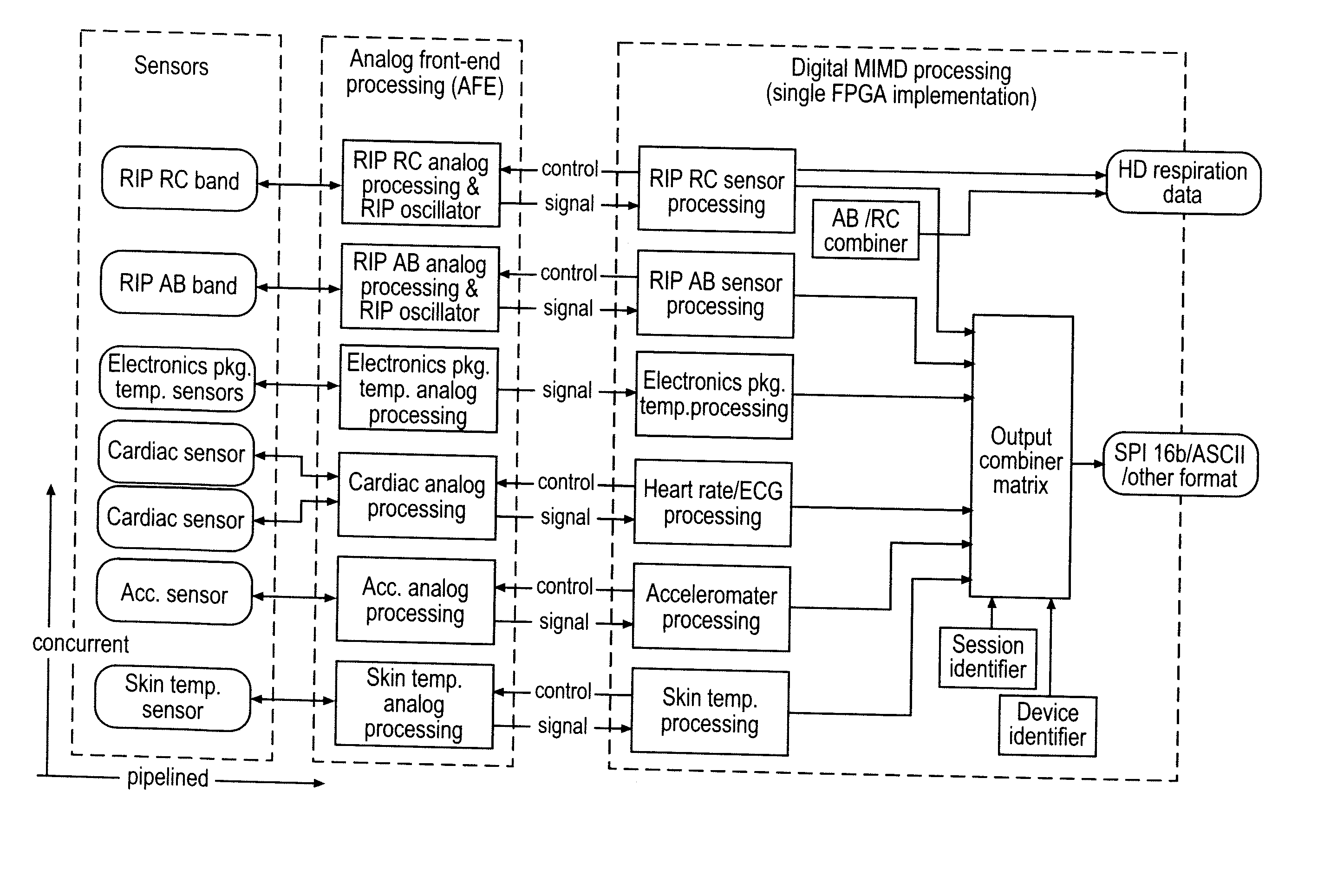
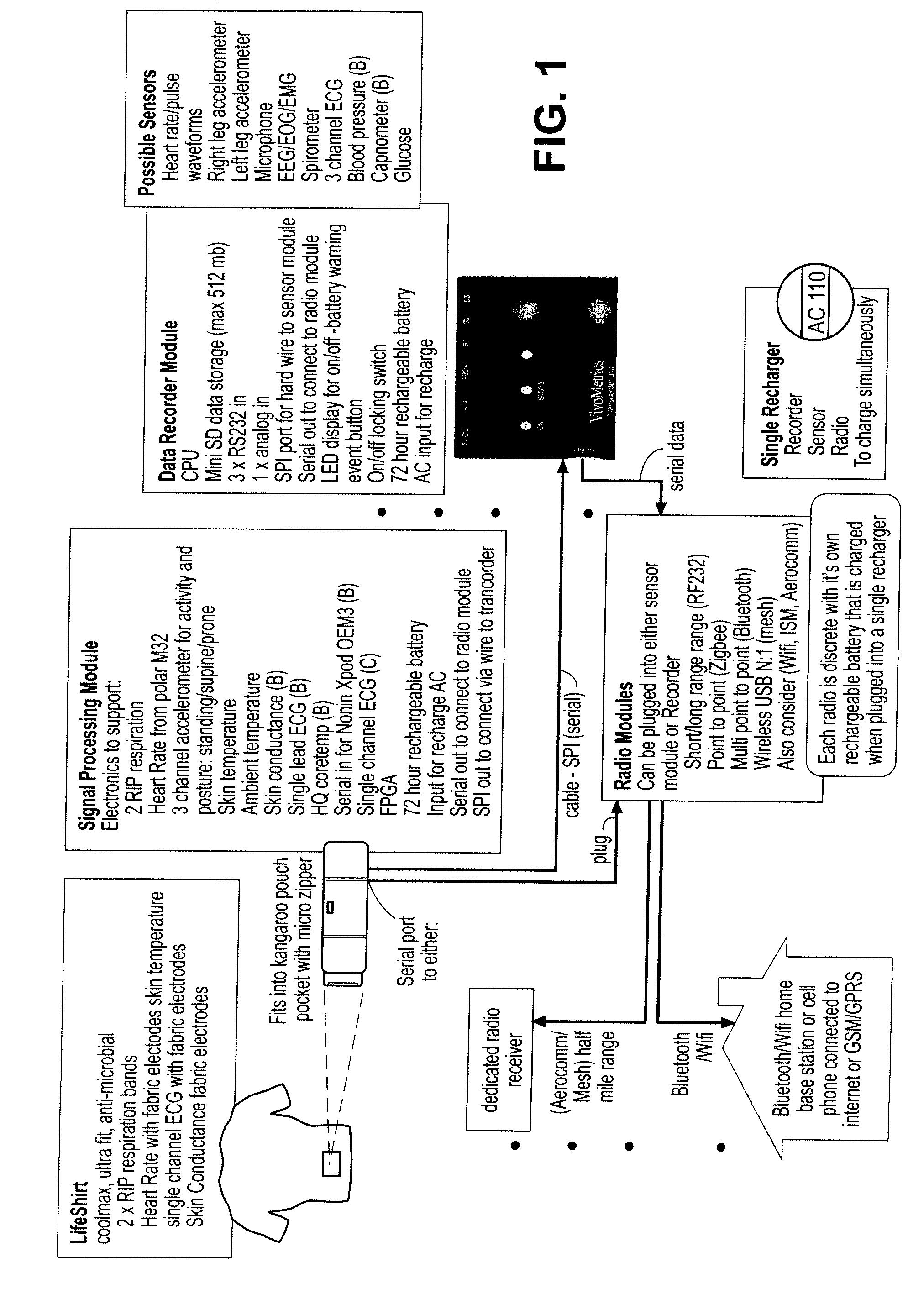
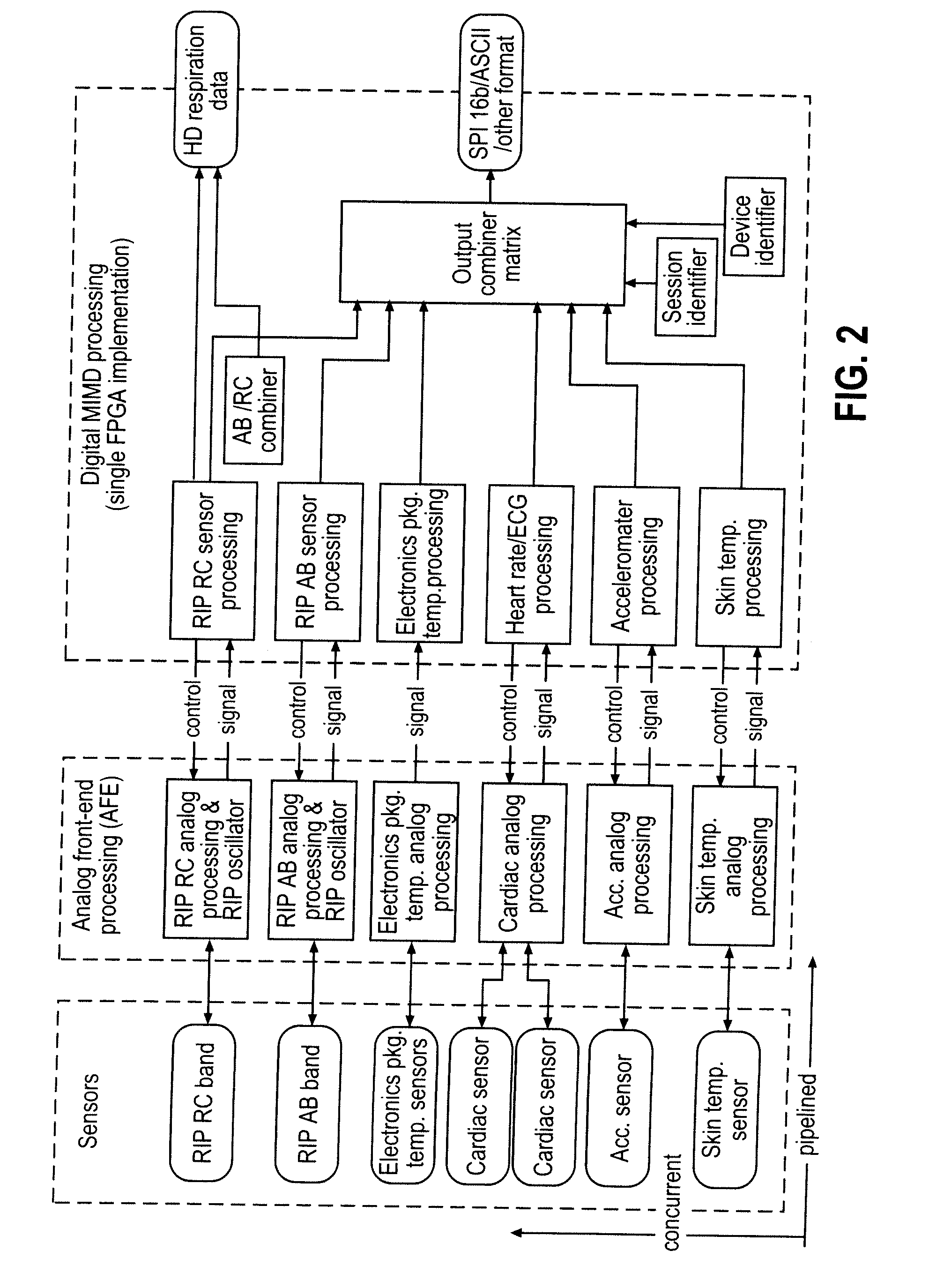
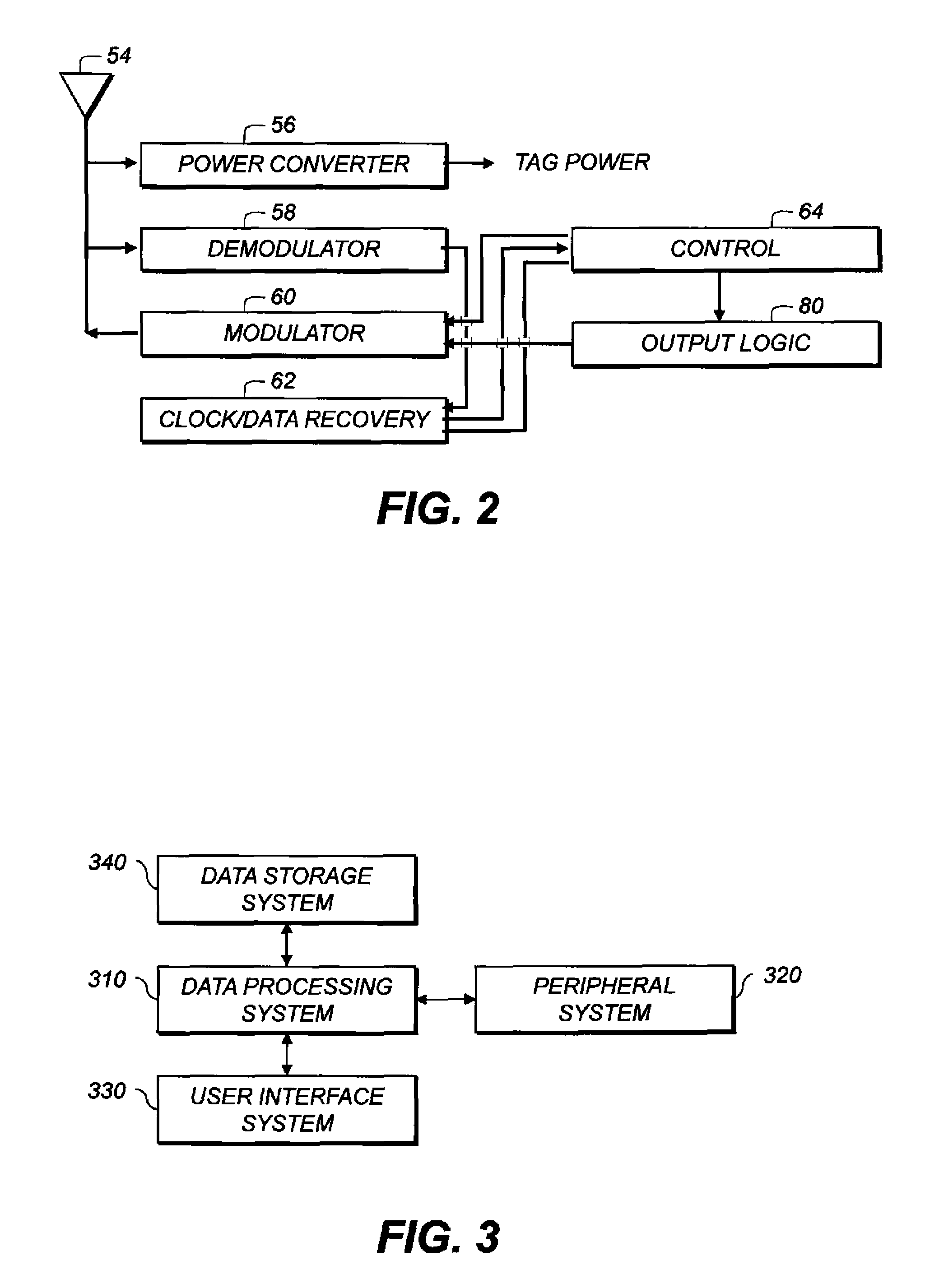
Physiological signal processing devices and associated processing methods
InactiveUS20070270671A1Speed up the processEasy to integrateSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringPhysiological monitoringParallel processing
The invention provides improved devices for processing data from one or more physiological sensors based on parallel processing. The provided devices are small, low power, and readily configurable for use in most physiological monitoring applications. In a preferred embodiment, the provided devices are used for ambulatory monitoring of a subject's cardio-respiratory systems, and in particular, process data from one or more respiratory inductive plethysmographic sensors.
Owner:ADIDAS
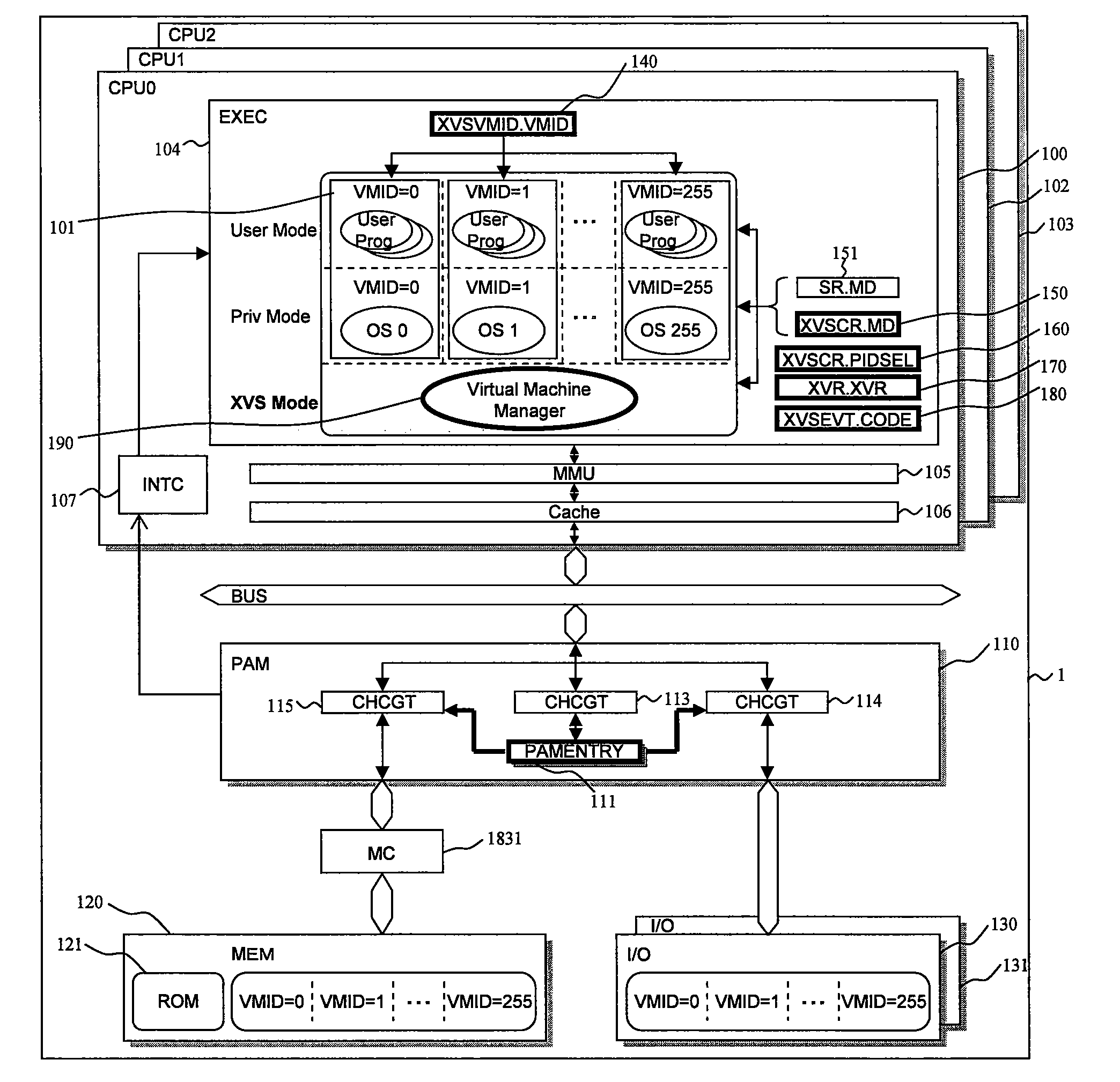
Data processor
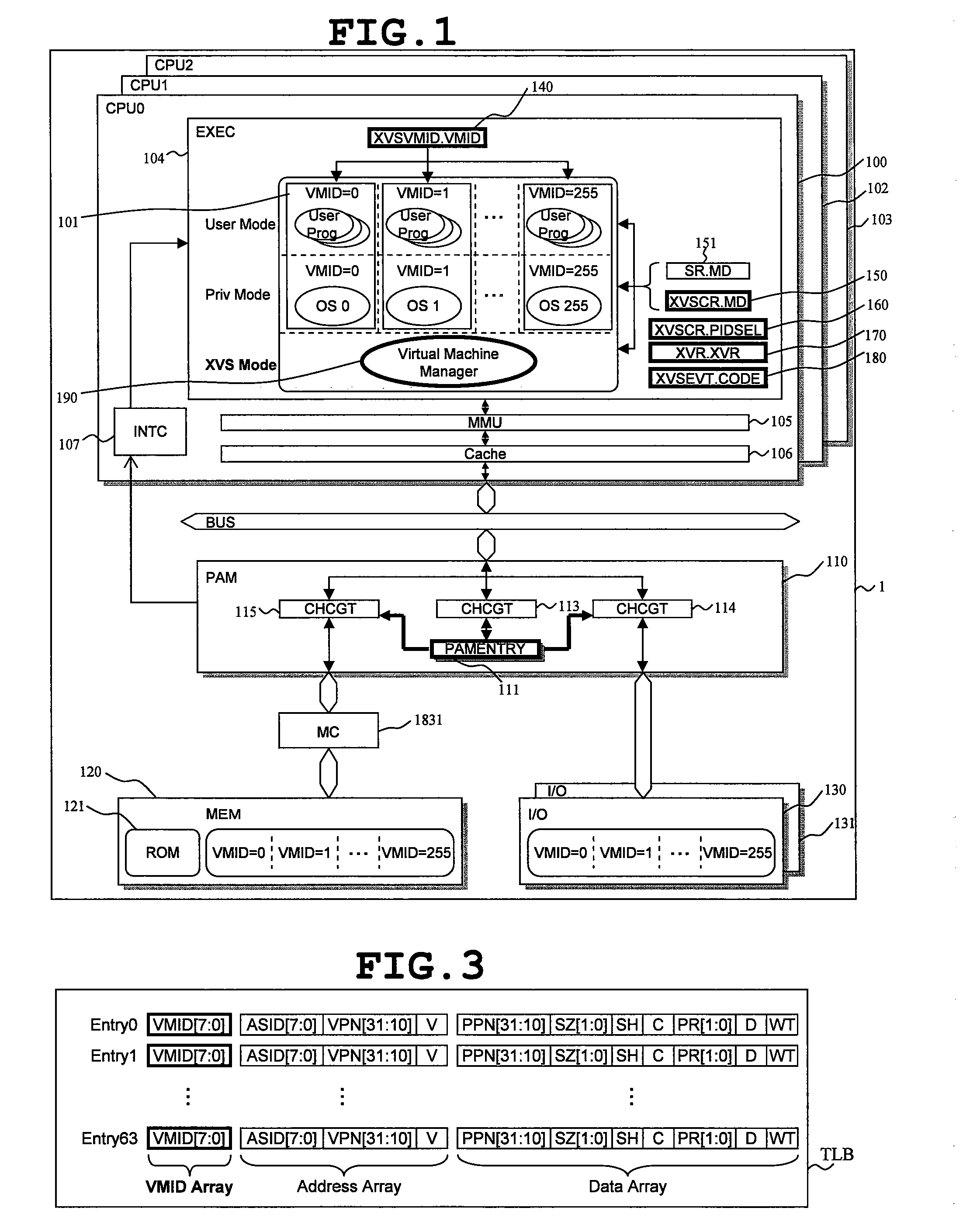
ActiveUS20080086729A1Reduce needImprove system reliabilityResource allocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationOperational systemControl register
A data processor includes: a central processing unit (CPU), in which a plurality of virtual machines (101), each running an application program under controls of different operating systems, and a virtual machine manager (190) for controlling the plurality of virtual machines are selectively arranged according to information set in mode registers (140, 150, 151); and a resource access management module (110) for managing access to hardware resource available for the plurality of virtual machines. The resource access management module accepts, as inputs, the information set in the mode registers and access control information of the central processing unit to the hardware resource, compares the information thus input with information set in a control register, and controls whether or not to permit access to the hardware resource in response to the access control information. As a result, redesign involved in changes in system specifications can be reduced, and a malfunction owing to resource contention can be prevented. The invention contributes to increase of security.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Methods and architecture for enhanced computer performance
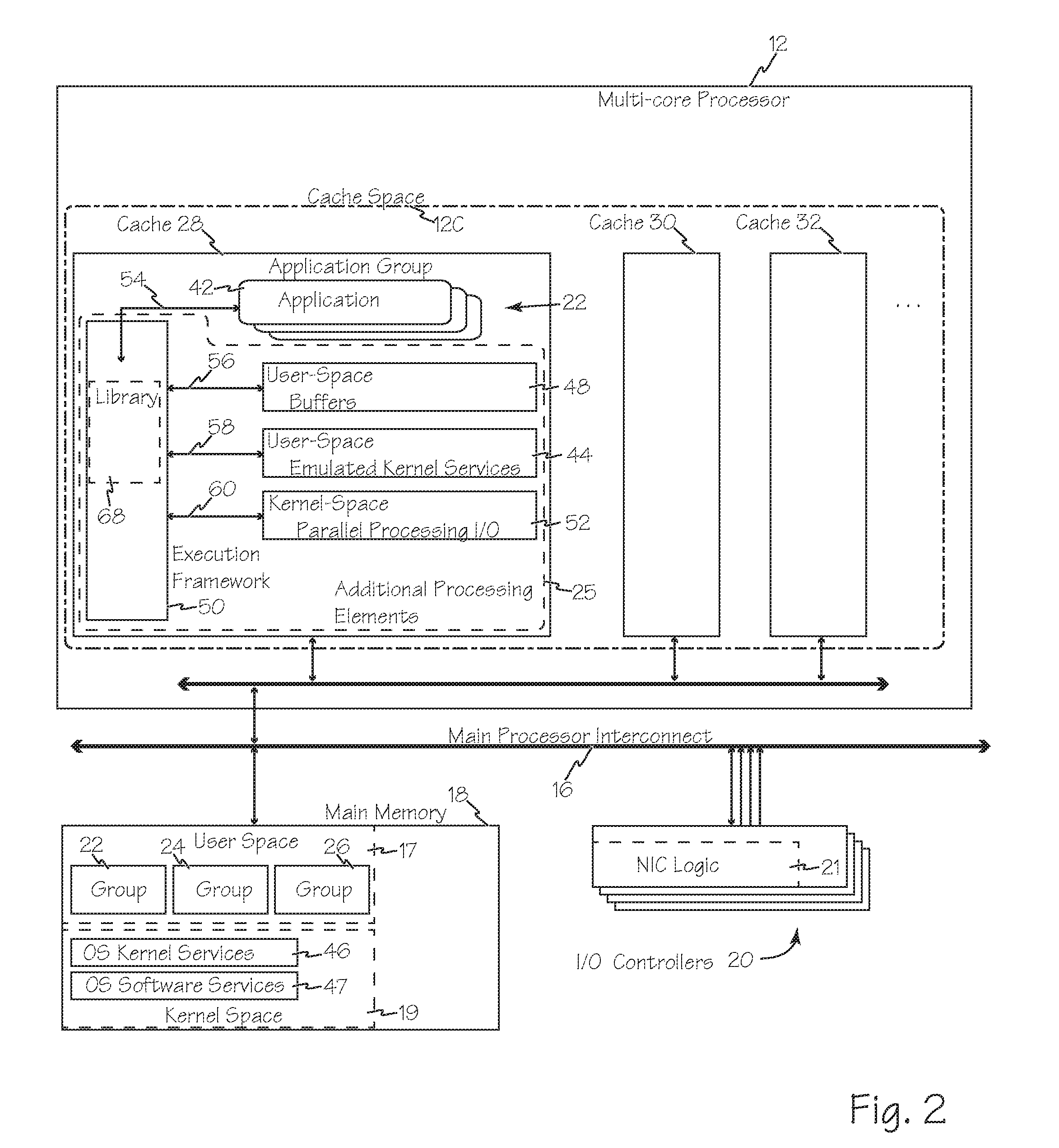
InactiveUS20160378545A1Reducing mode switchingReduce limitationsProgram initiation/switchingHardware monitoringOperational systemComputer performance
Methods and systems for enhanced computer performance improve software application execution in a computer system using, for example, a symmetrical multi-processing operating system including OS kernel services in kernel space of main memory, by using groups of related applications isolated areas in user space, such as containers, and using a reduced set of application group specific set of resource management services stored with each application group in user space, rather than the OS kernel facilities in kernel space, to manage shared resources during execution of an application, process or thread from that group. The reduced sets of resource management services may be optimized for the group stored therewith. Execution of each group may be exclusive to a different core of a multi-core processor and multiple groups may therefore execute separately and simultaneously on the different cores.
Owner:APL SOFTWARE INC
System and Method for Peer to Peer Communications in Cellular Communications Systems
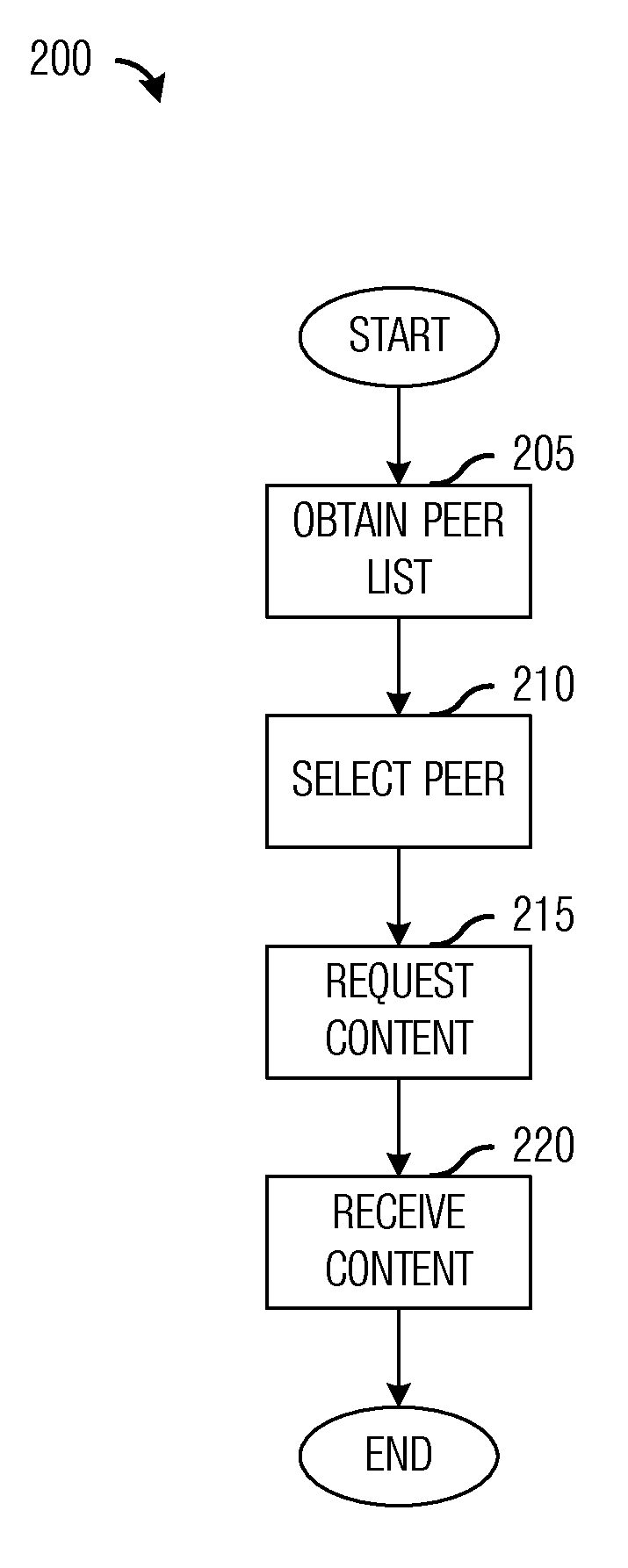
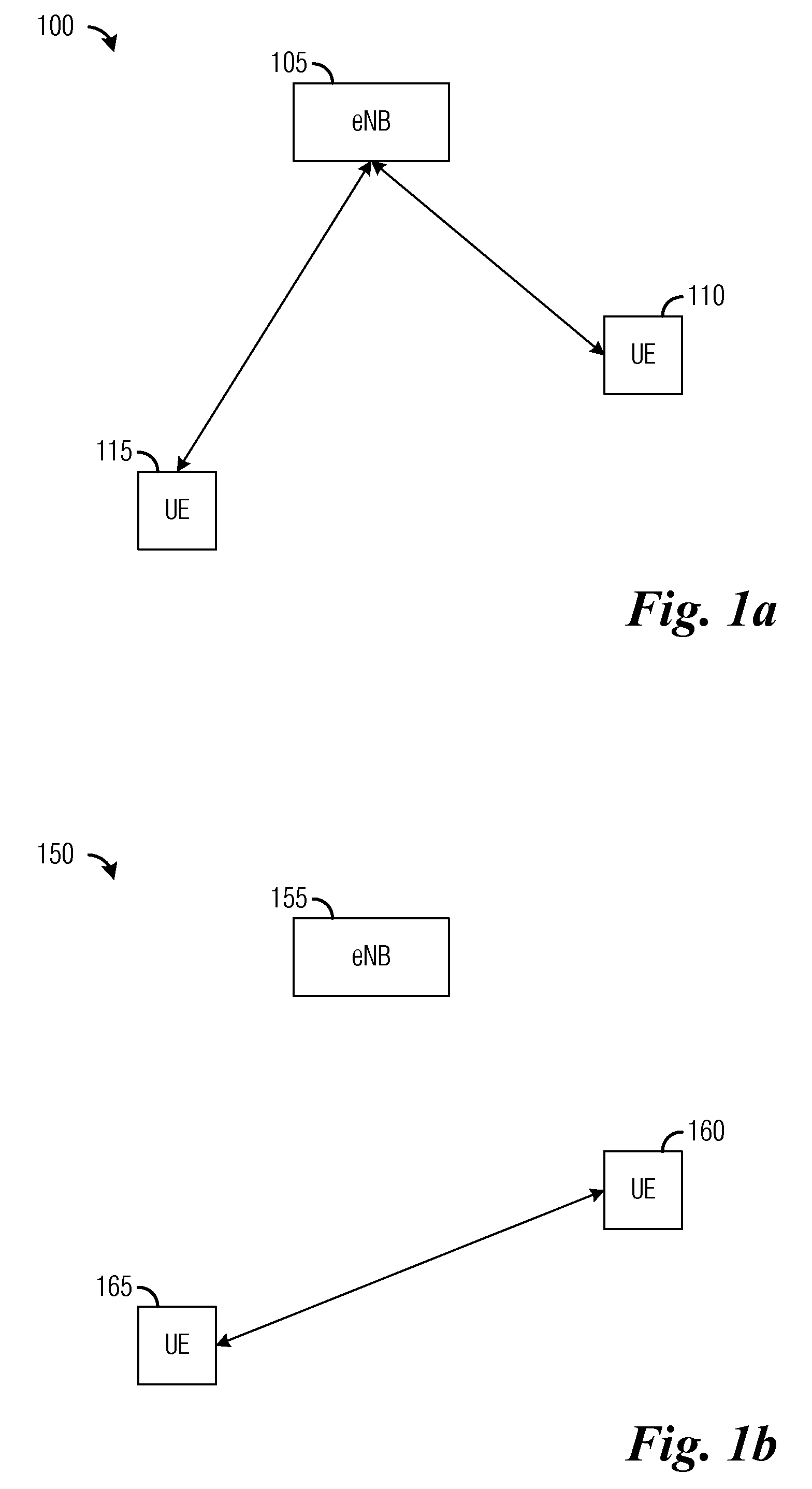
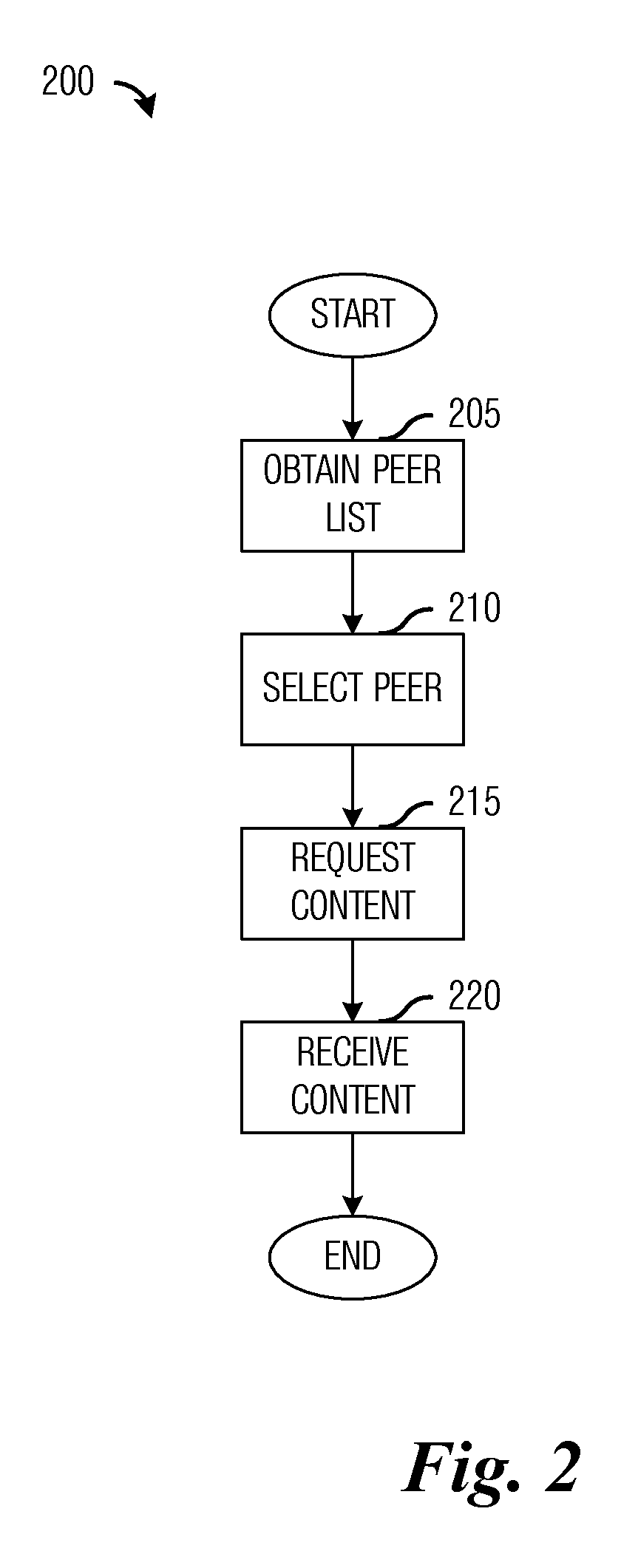
InactiveUS20120290650A1Reduce spectrum loadReduce contentionAssess restrictionConnection managementCellular communication systemsCommunication control
A system and method for peer-to-peer communications in cellular communications systems are provided. A method for communications device operations includes receiving a peer list at a communications device, where the peer list includes a list of reachable communications devices and device-to-device (D2D) capability information of the reachable communications devices, selecting a peer from the peer list, sending a content request comprising an indication of a content to a communications controller serving the communications device, and receiving the content from the peer over a channel established by the communications controller.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Printing method and apparatus having multiple raster image processors
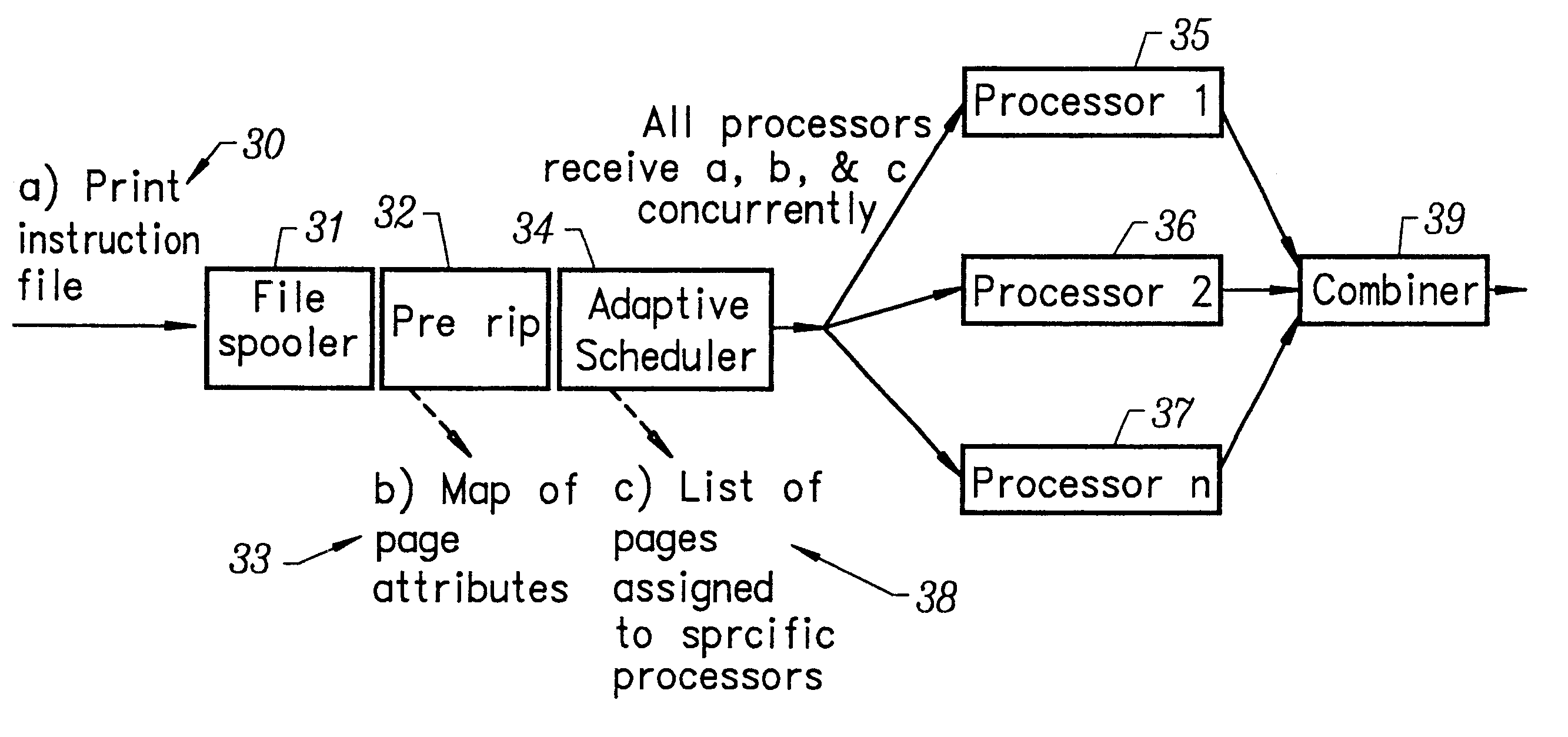
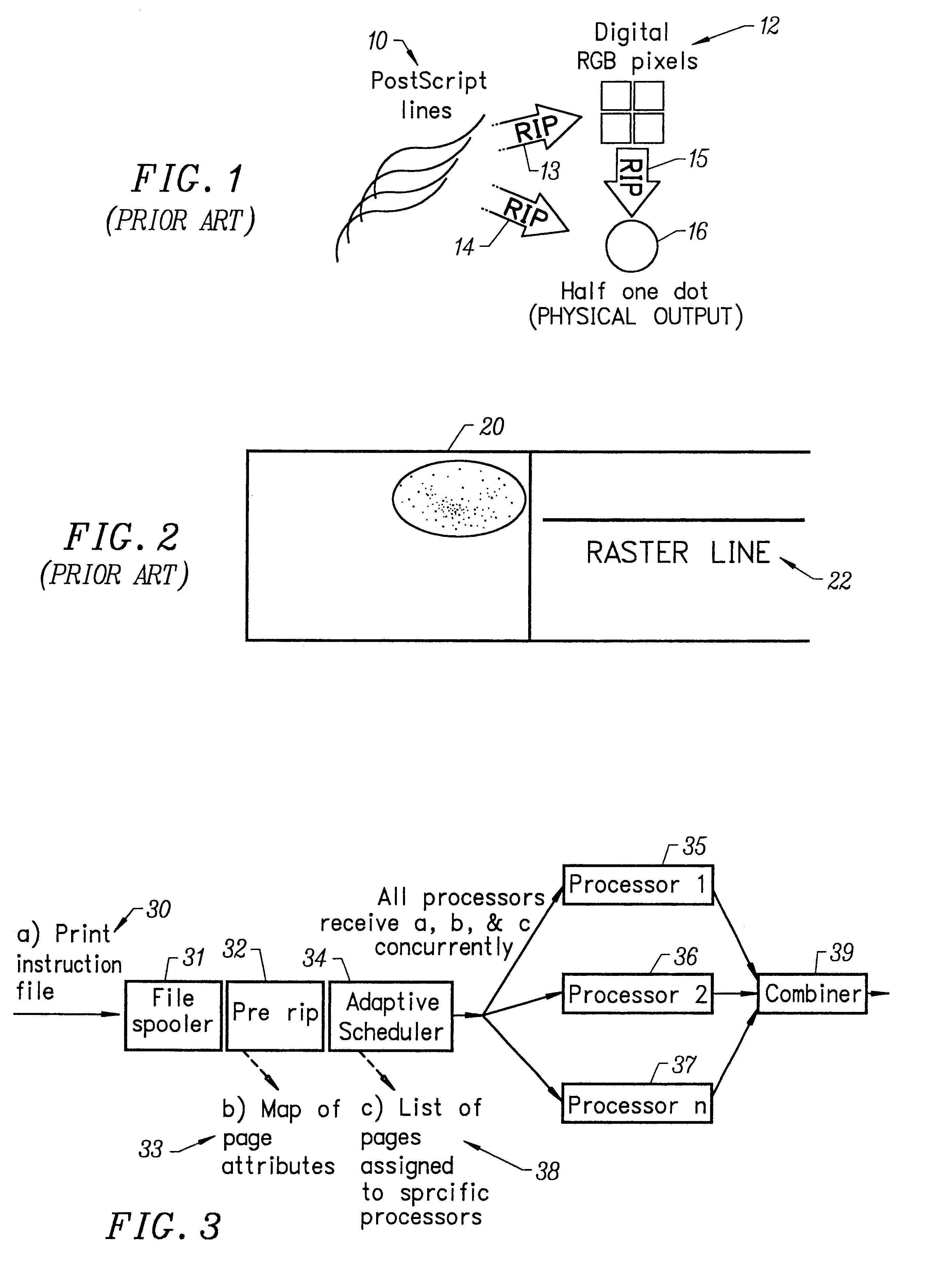
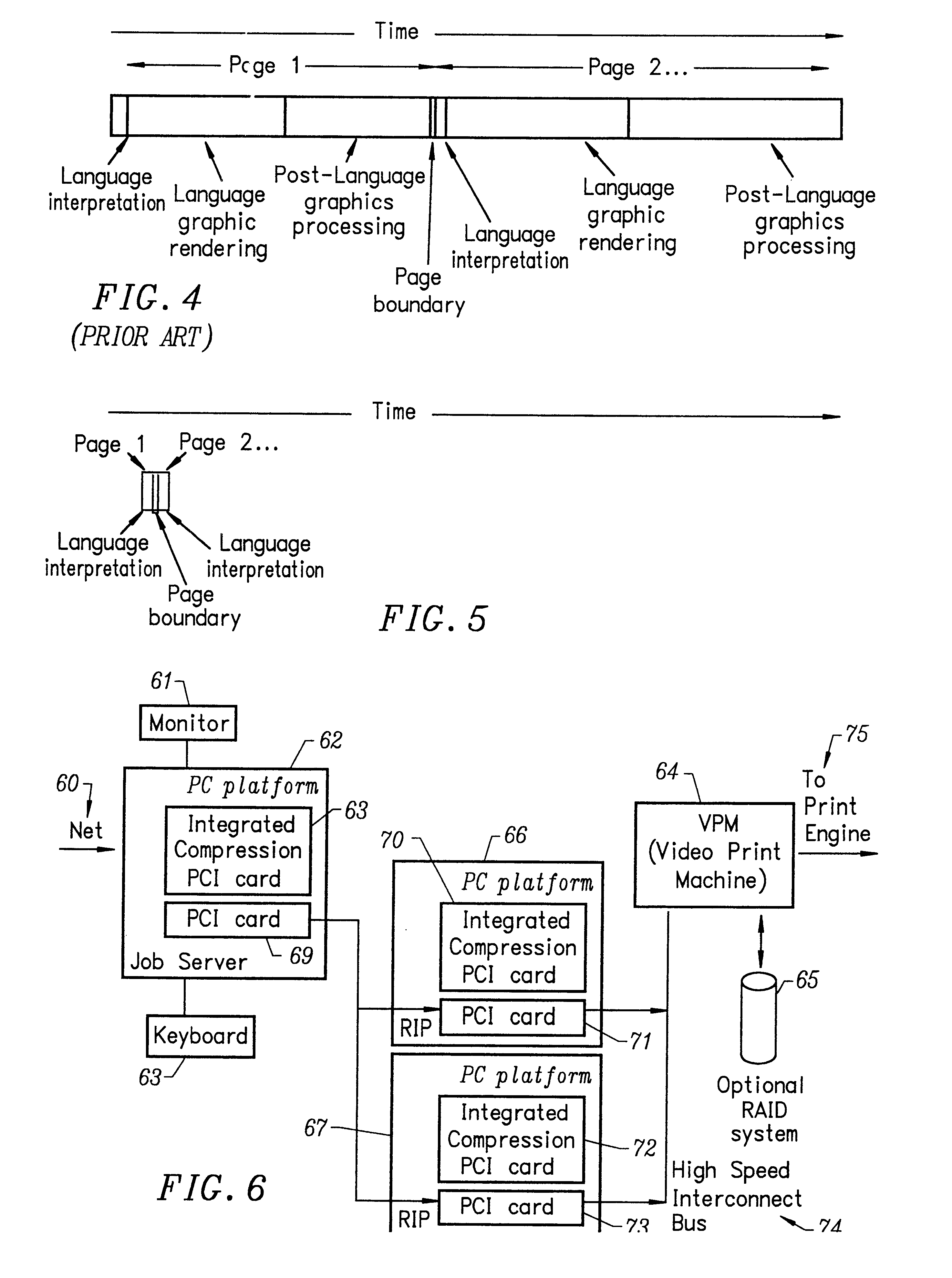
InactiveUS6559958B2Reduce contentionReduce overheadDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsRaster image processor
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING INC
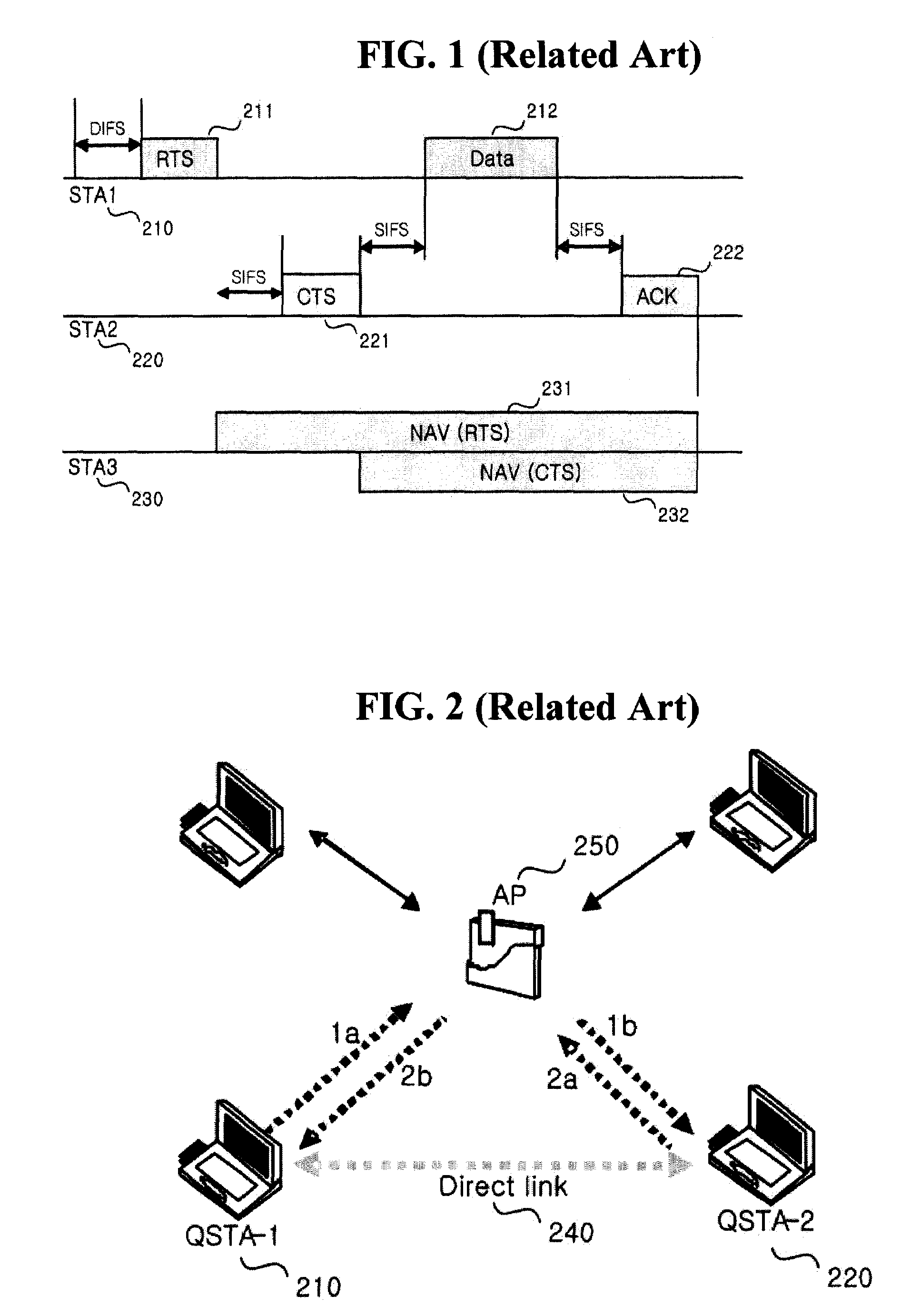
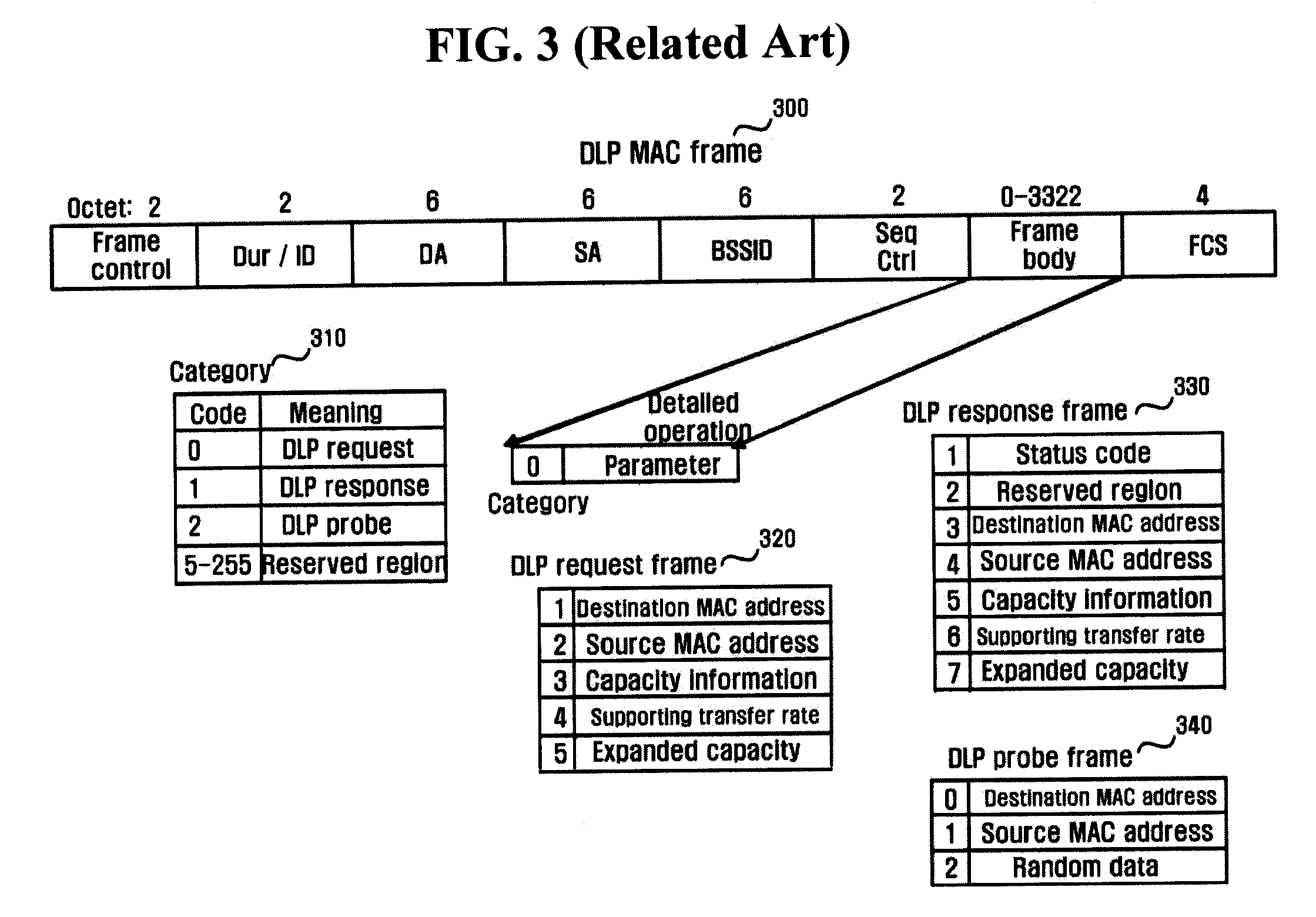
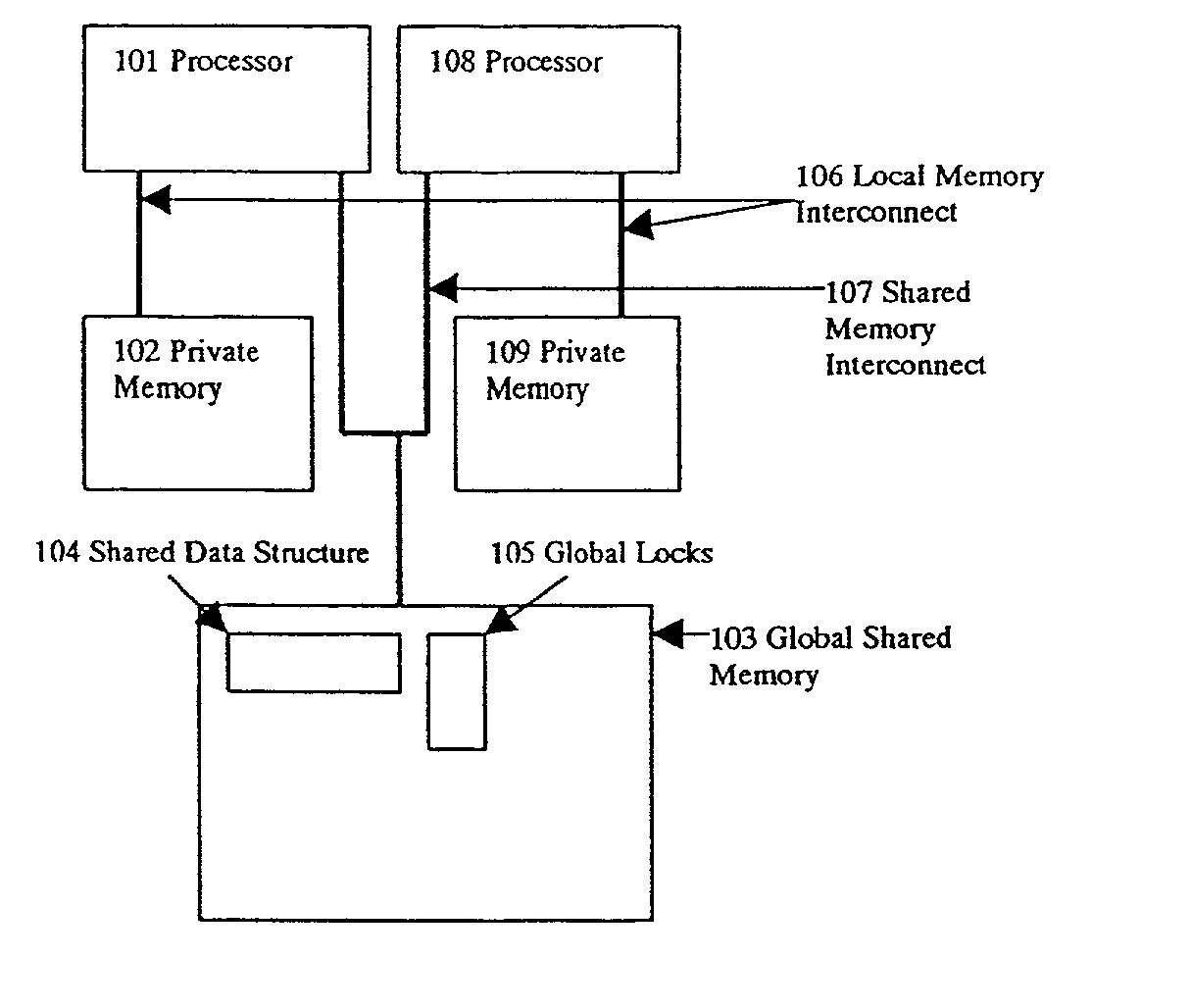
Method and apparatus for enhancing transfer rate using DLP and multi channels in wireless LAN using PCF and DCF
InactiveUS20050053015A1Reduce contentionData switching by path configurationWireless communicationWireless lanPrimary channel
A wireless network communication method and apparatus for enhancing a data transfer rate by using a direct link protocol (DLP) and multi channels during a point coordination function (PCF) period in wireless network communications in which an access point is employed in an infrastructure mode using both a contention-free period and a contention period. The wireless network communication method of the present invention including transmitting / receiving data among stations supporting a direct link, during a given duration, through the direct link using an independent channel; transmitting / receiving data among stations other than the stations supporting the direct link, during the duration, in a specific mode corresponding to the contention-free or contention period; switching the DLP stations to a primary channel after the given duration; and transmitting / receiving data among all stations including the DLP stations, during the remaining duration, in a specific mode corresponding to the contention-free or contention period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for parallelizing database requests
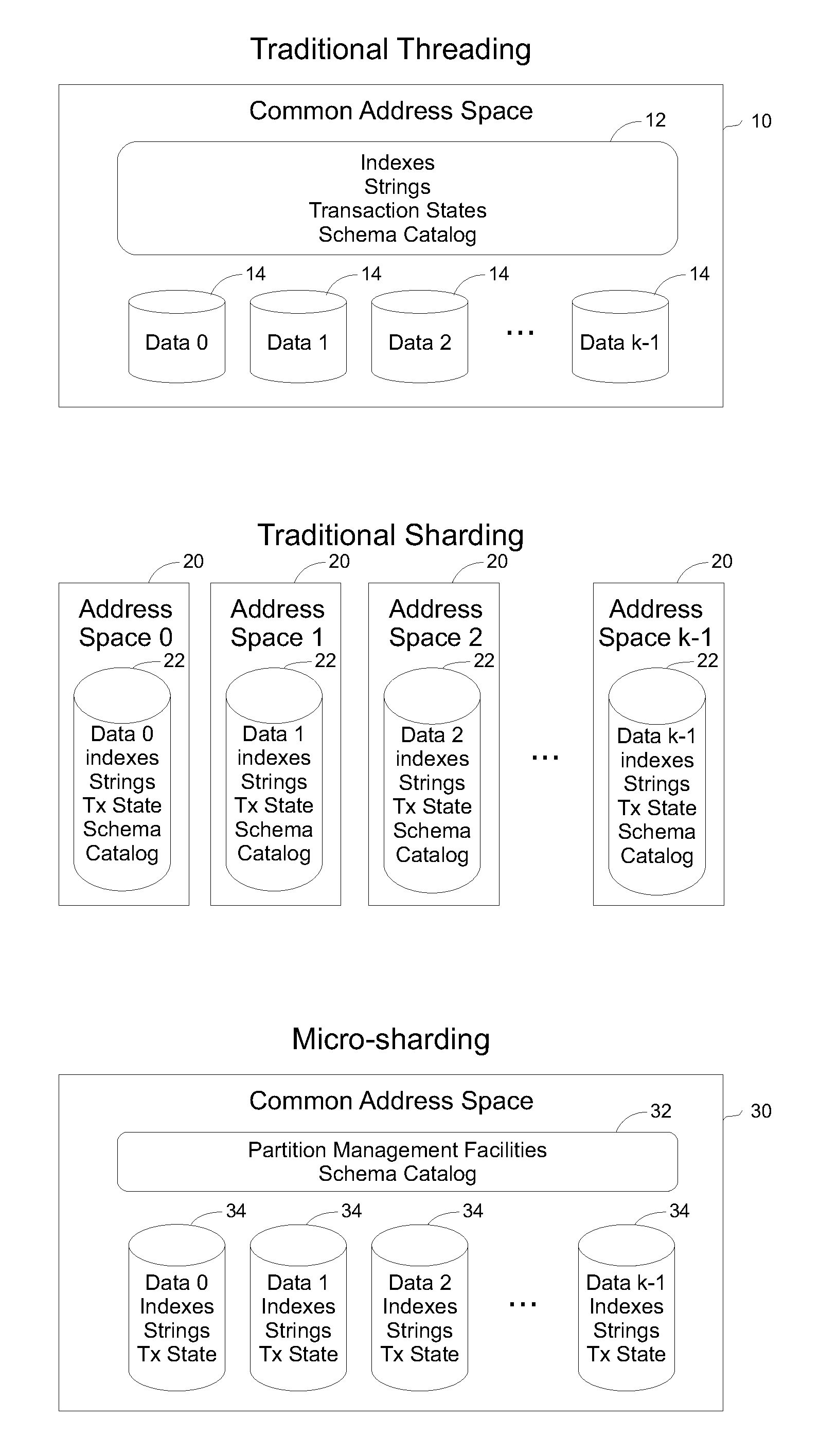
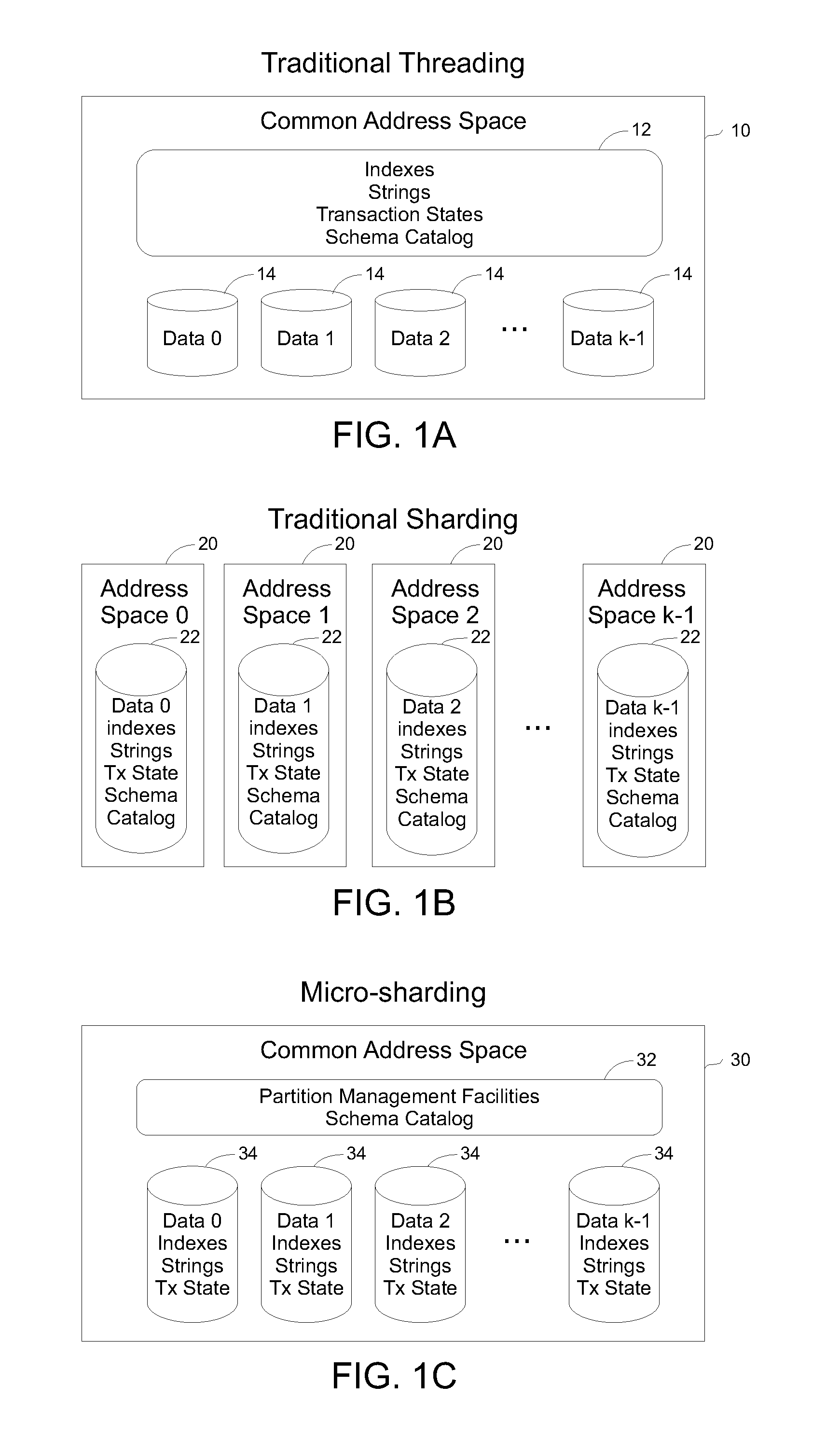
ActiveUS20110202929A1Reduce communication overheadReduced response timeDigital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsClient-sideSingle process
Methods and systems are described for applying the use of shards within a single memory address space. A database request is processed by providing the request from a client to a processor, the processor then distributing the request to multiple threads within a single process but executing in a shared memory address environment, wherein each thread performs the request on a distinct shard, and aggregating the results of the multiple threads being aggregated and returning a final result to the client. By parallelizing operations in this way, the request response time can be reduced and the total amount of communication overhead can be reduced.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
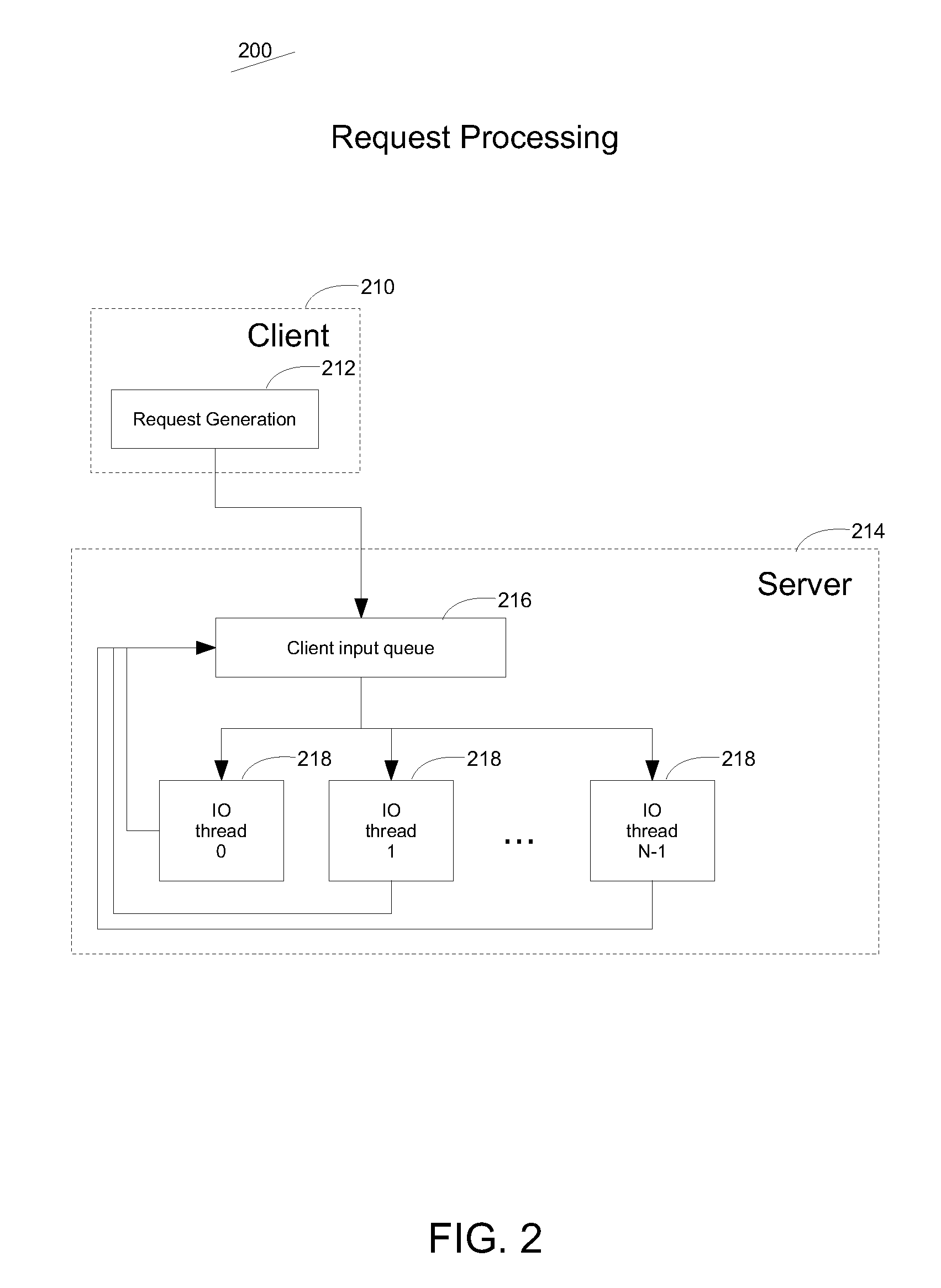
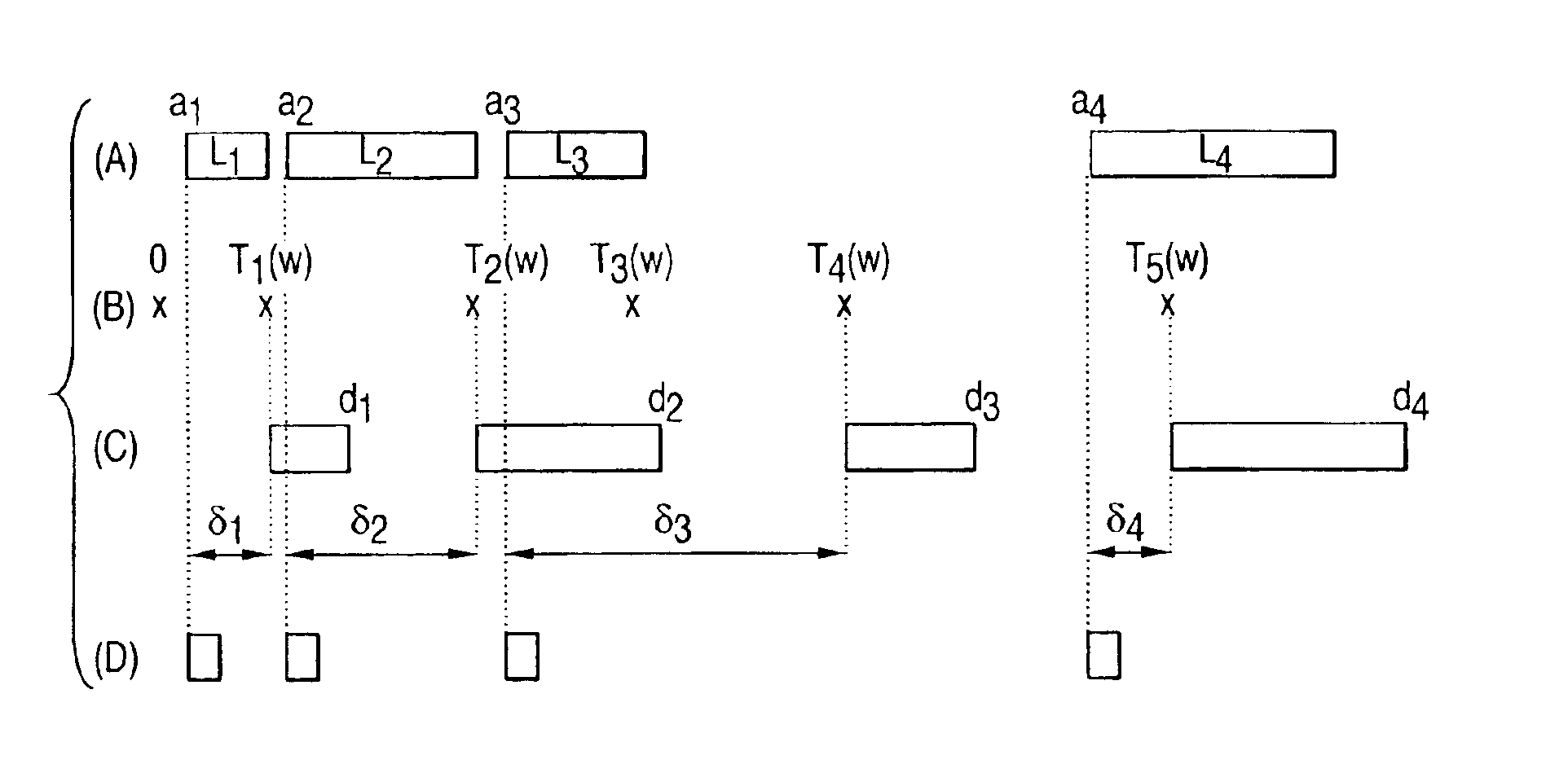
Robust transport of IP traffic over wdm using optical burst switching
InactiveUS6898205B1Reduce contentionImprove performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTraffic volumeTraffic capacity
A technique for selecting the offset between data bursts and their respective control packets in an optical burst switching arrangement includes: randomly generating a plurality of tokens; receiving a plurality of sequentially generated data bursts; and receiving a plurality of control packets, each control packet corresponding to a respective one of the plurality of data bursts. One of the plurality of control packets is first outputted and its corresponding respective data burst is then outputted at a time corresponding to the generation of the first of the plurality of tokens which occurs at a time in which no data burst is being outputted, the outputting of the data burst being offset from the output of its corresponding respective control packet by a time period. The average rate at which the plurality of data bursts are outputted may be equal to the reciprocal of the mean of the probability distribution used to generate the plurality of tokens. The plurality of tokens may be randomly generated according to a Poisson process.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Access method for periodic contention-free sessions
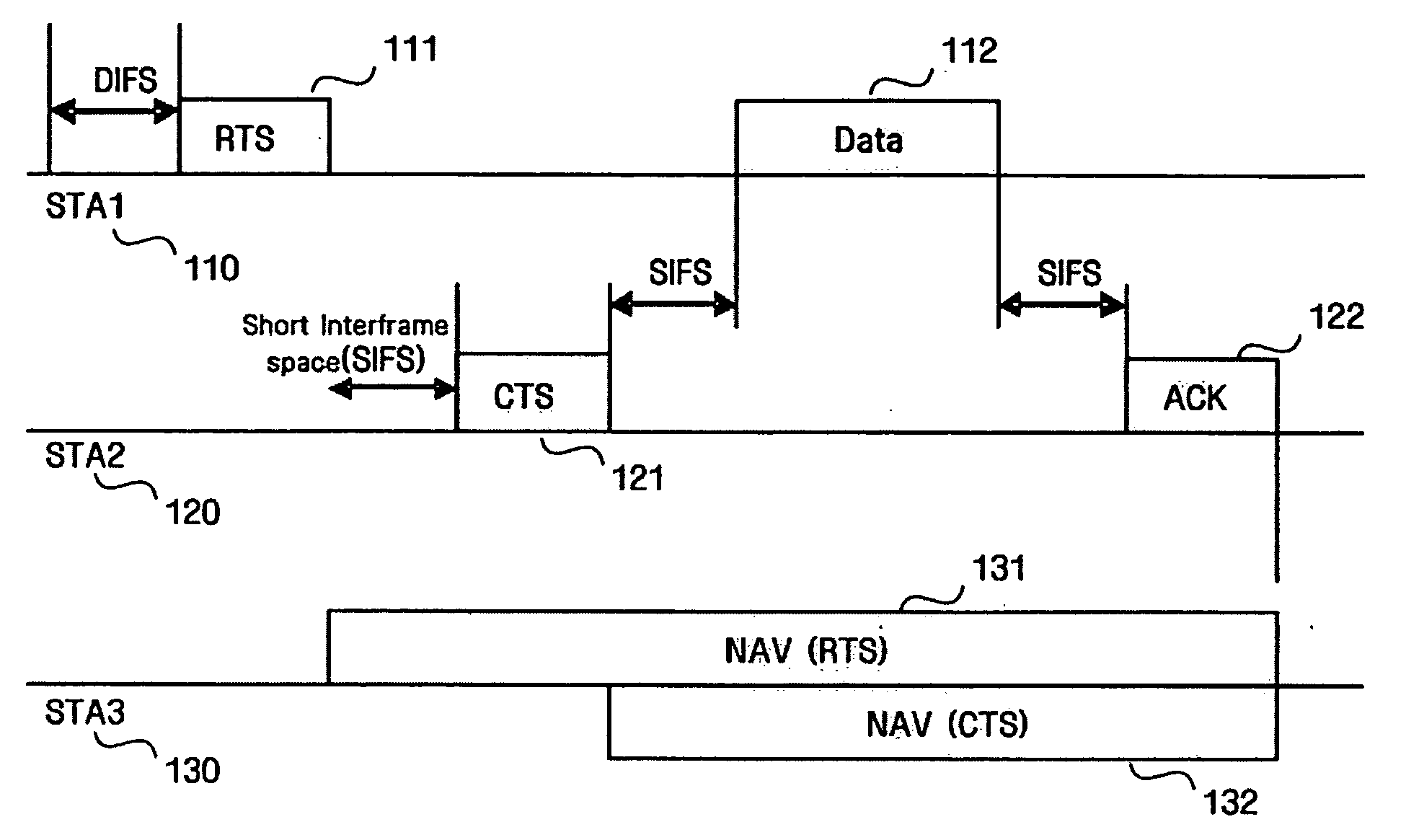
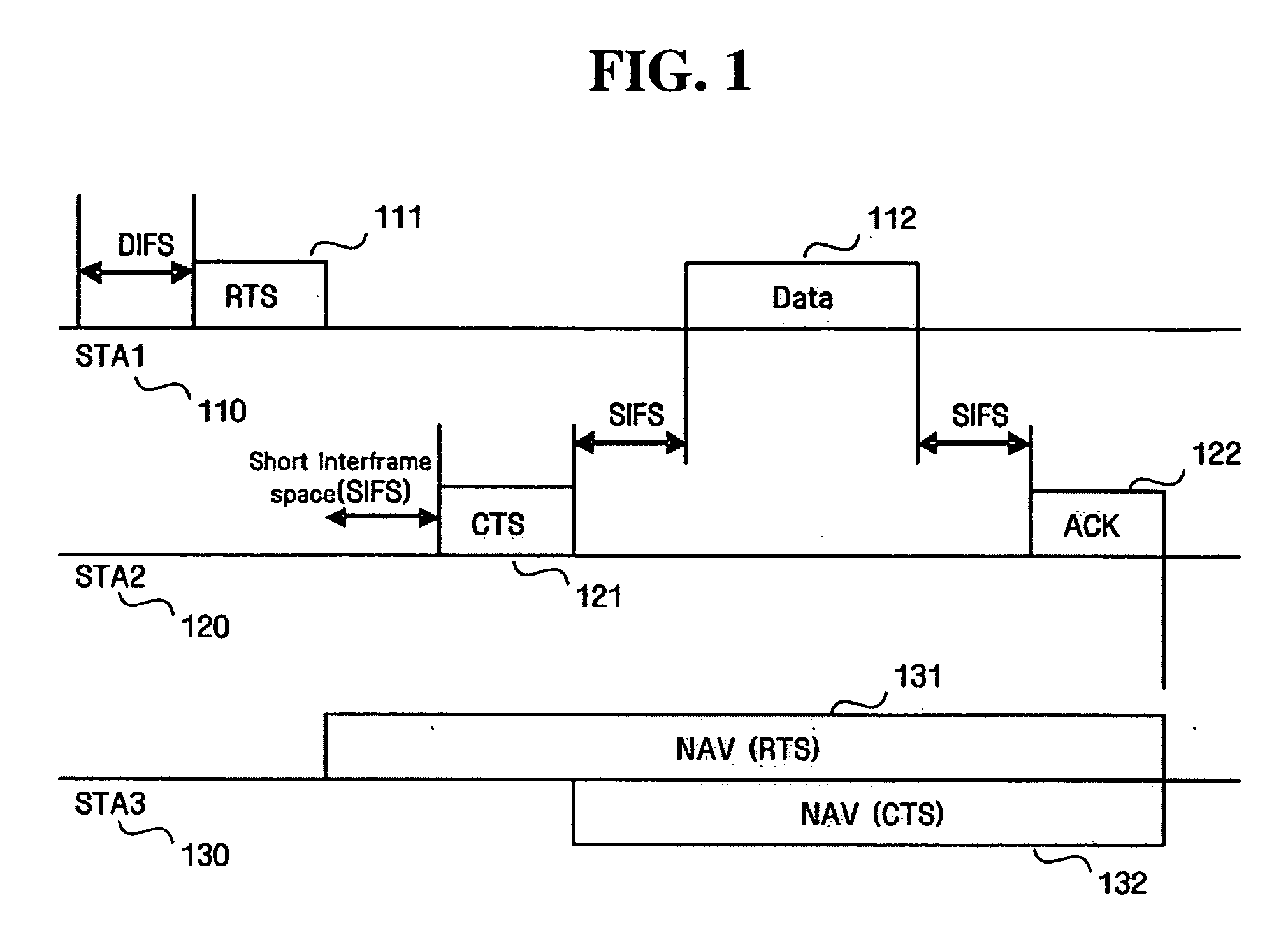
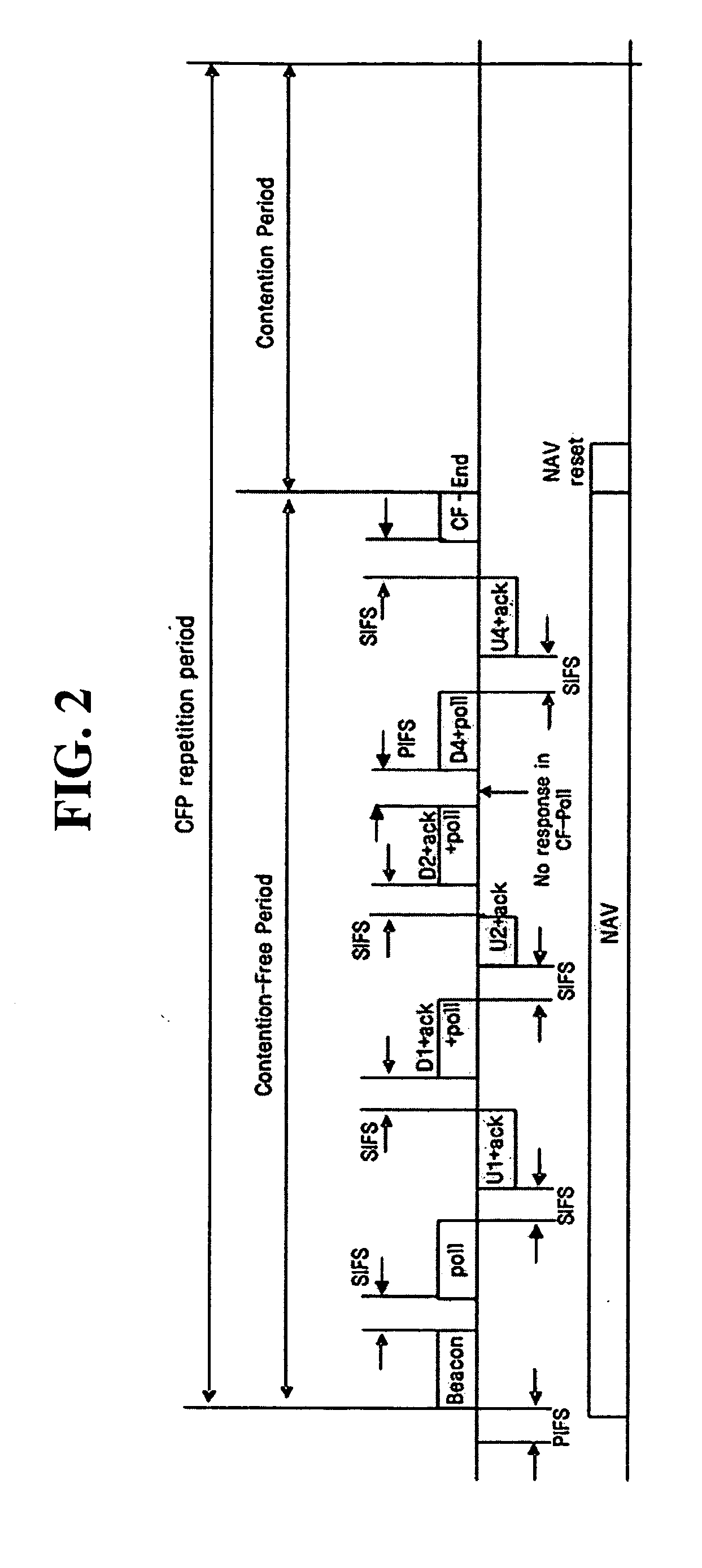
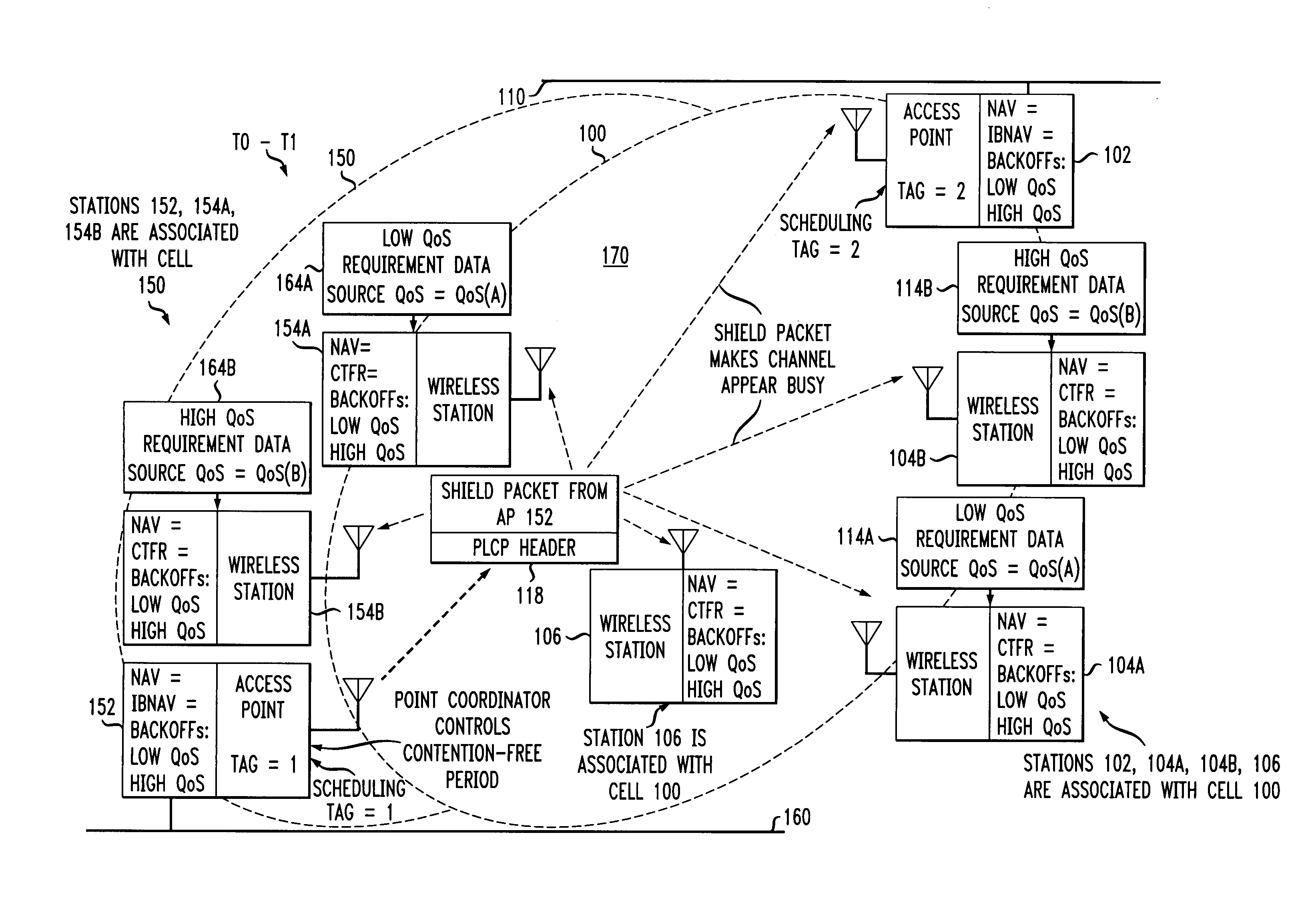
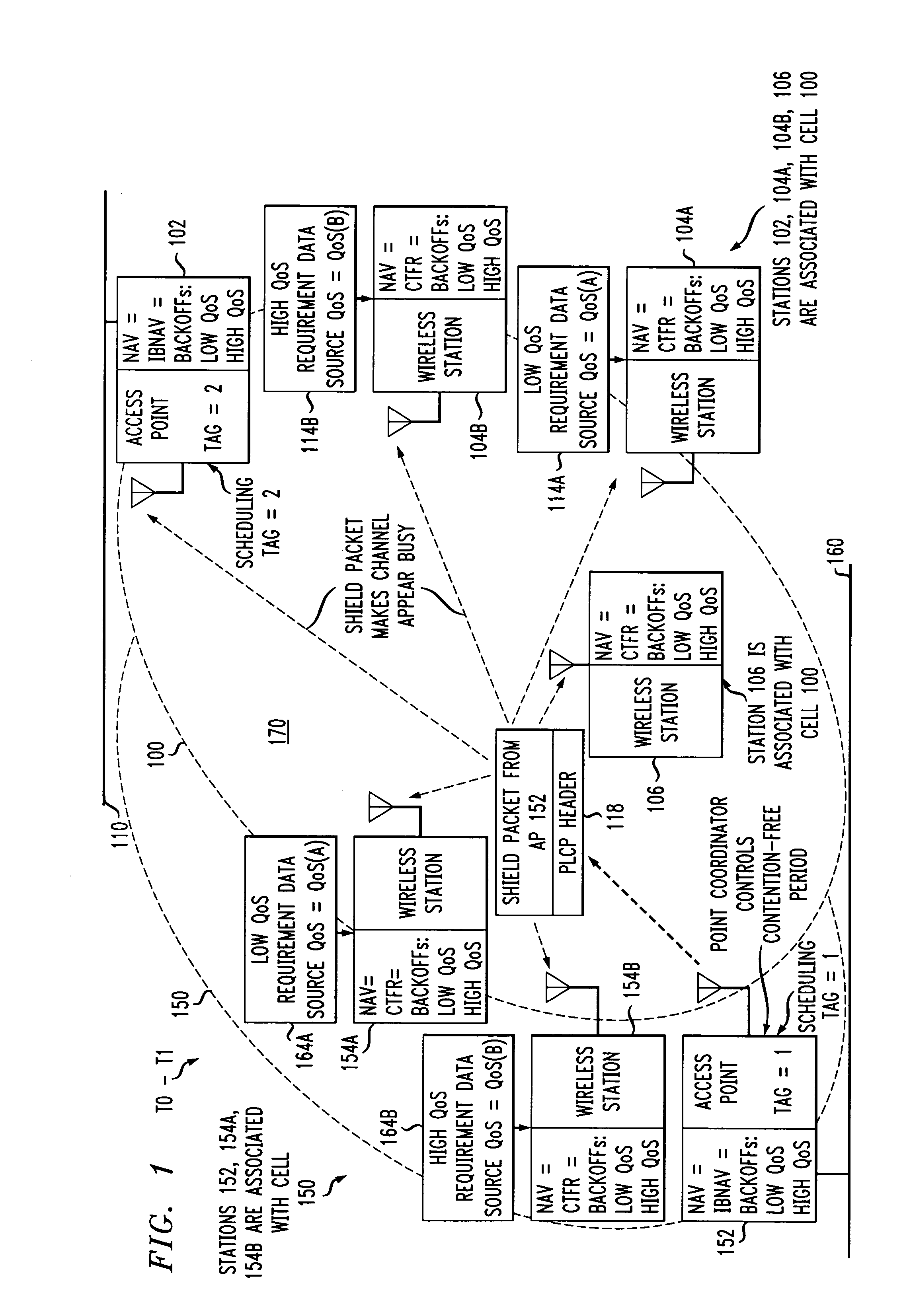
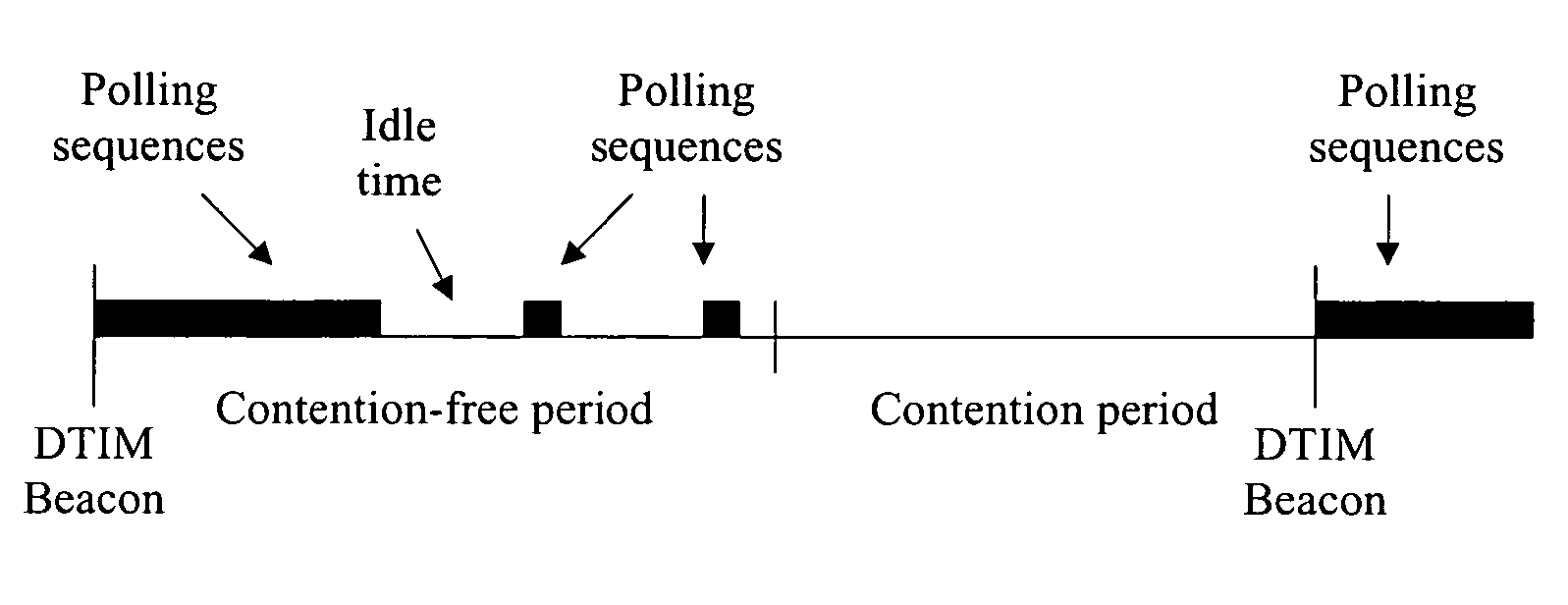
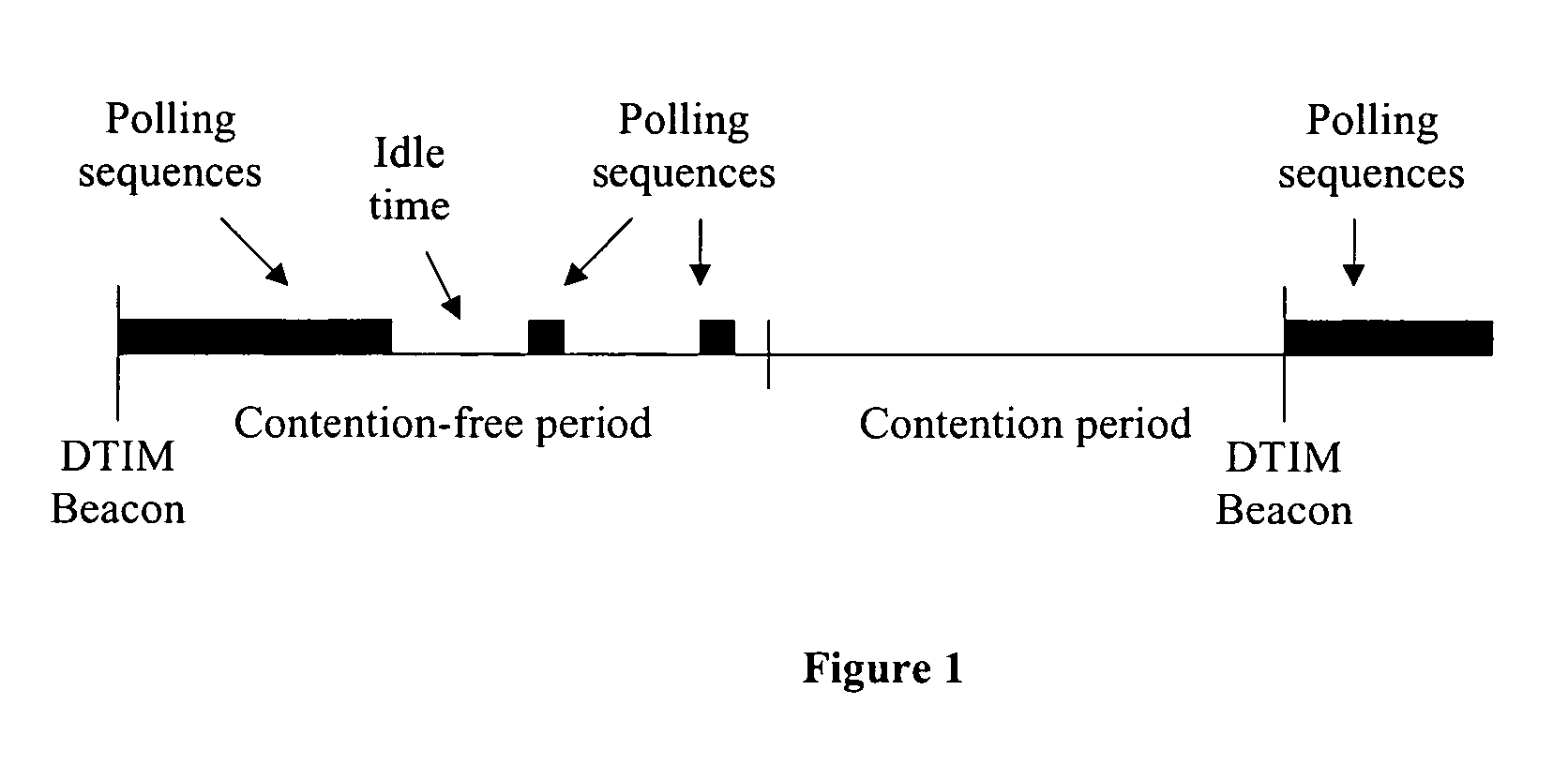
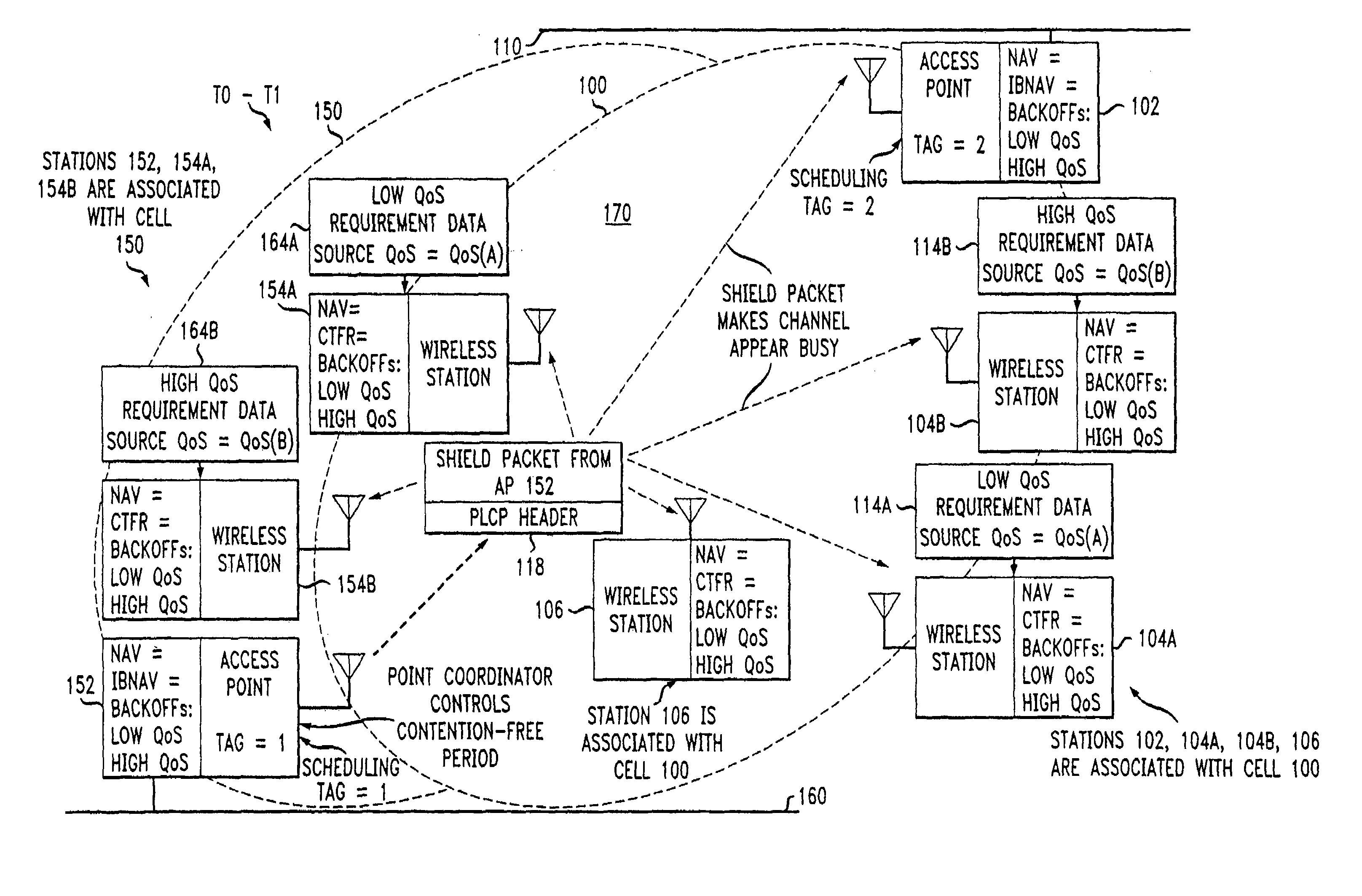
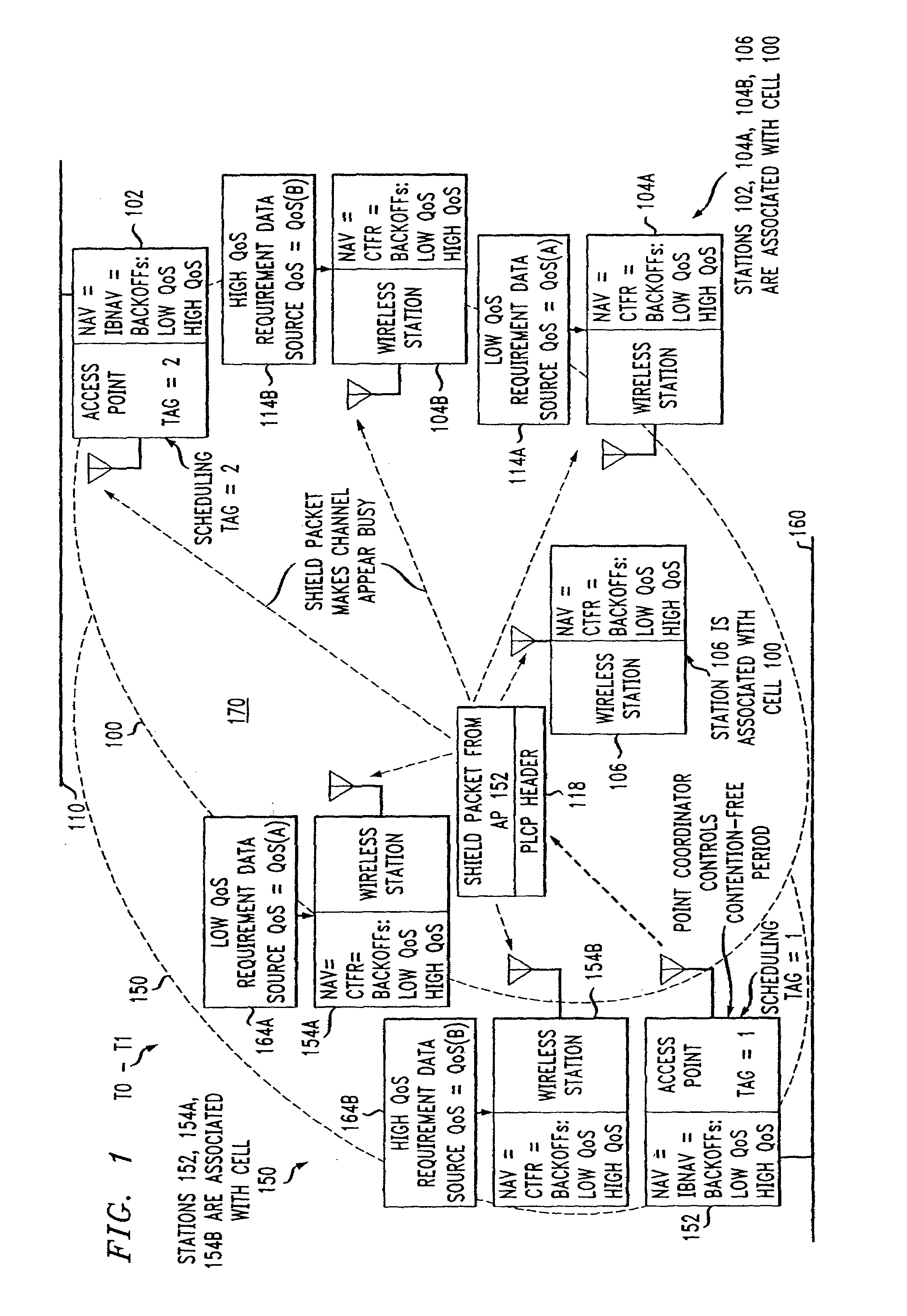
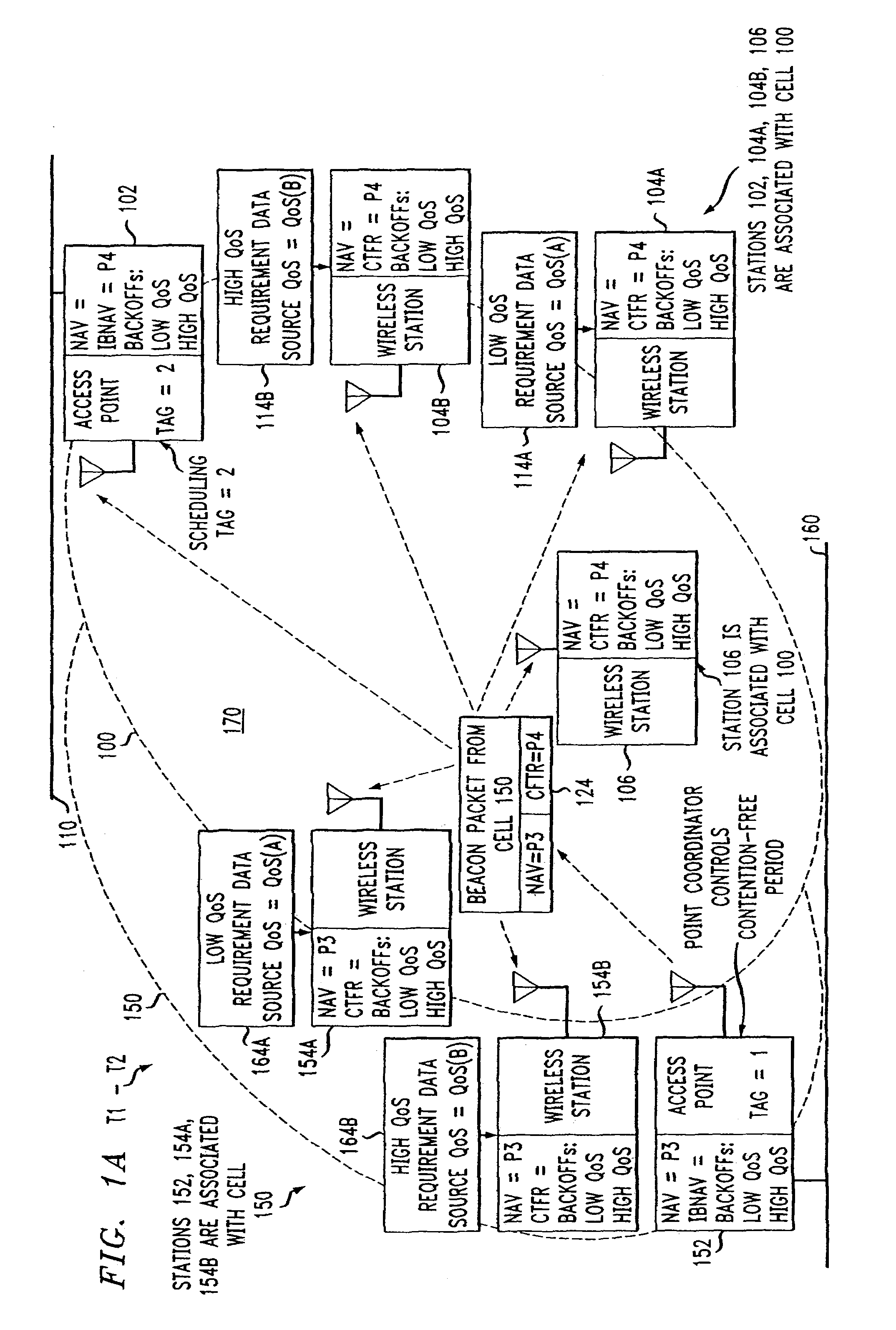
ActiveUS7180905B2Reduce distractionsReduce conflictSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceAccess method
An access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) reduces interference between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations and an access point (AP) station. The access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) includes a fixed cycle time that reduces conflicts with PCFS from other cells. The PCFS from several cells are repeated in cycles of cycle period (CP), which is the contention-free period (CFP) of an access point times a factor that is a function of the number of overlapping cells. Periodic contention-free sessions (PCFSs) are generated, one from each overlapping cell. PCFS transmission attempts occur at the fixed specified time spacing following the start of the previous cycle. Each active AP sets a timer at CP and a PCFS is initiated when the timer expires. The timer is then reset to CP and this starts a new cycle. Contention transmissions are attempted by stations based on their assigned priority. If a channel is busy at the designated start time for transmitting a PCFS, the PCFS is shortened by the time lost. Interleaving PCFSs and CFSs reduces conflicts with CFSs from other cells. To lessen the contention between APs of different cells, each station's Network Allocation Vector (NAV) and Inter-BSS Network Allocation Vector (IBNAV) is updated by an increased value of the next CFS length, the increment being the inter-BSS contention period (IBCP). APs will attempt to access the channel during the IBCP only for transmitting a PCFS, while they will wait for the NAV and IBNAV expirations before attempting to transmit a CFS. Interleaving PCFSs and CFSs also enables maintaining quality of service (QoS).
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
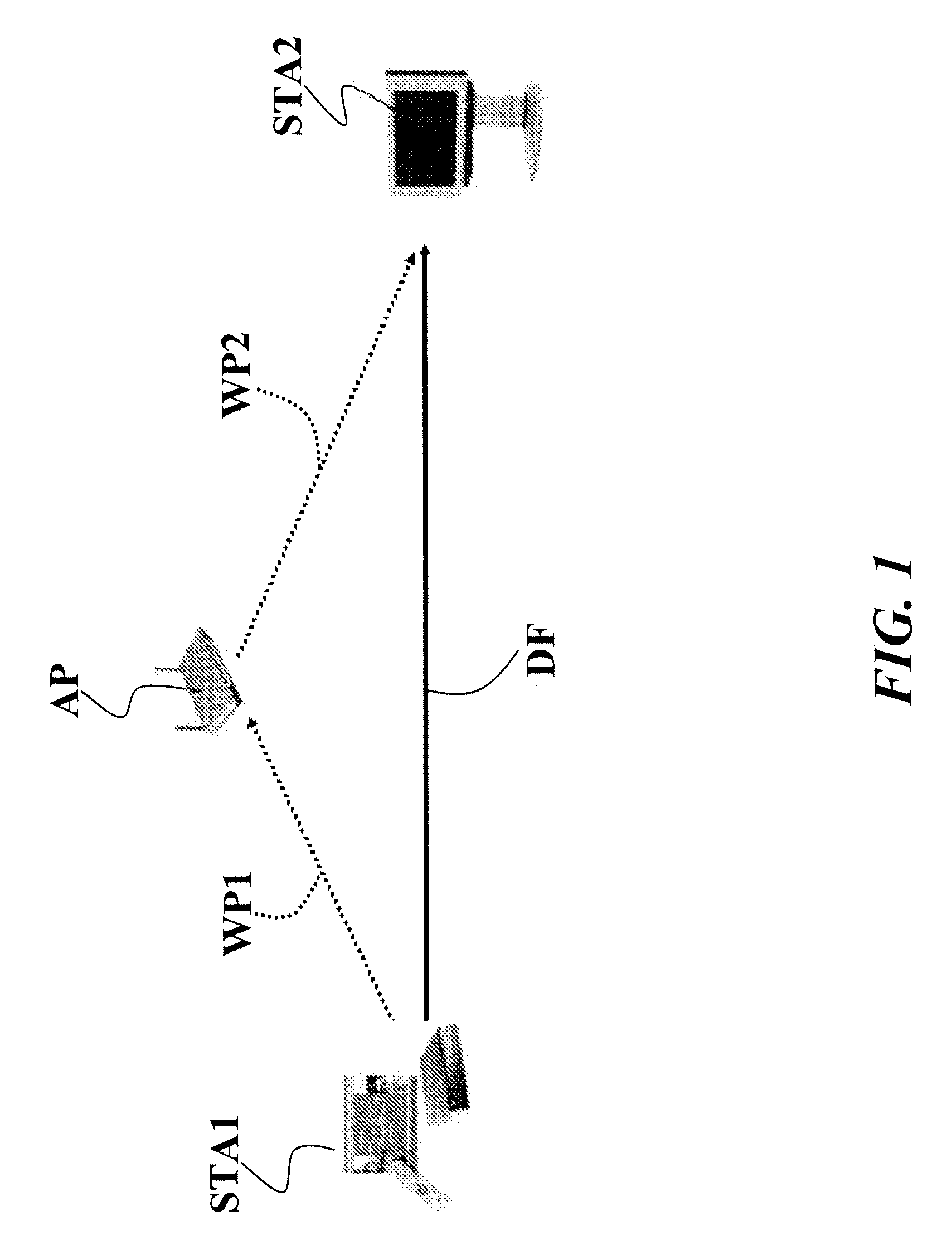
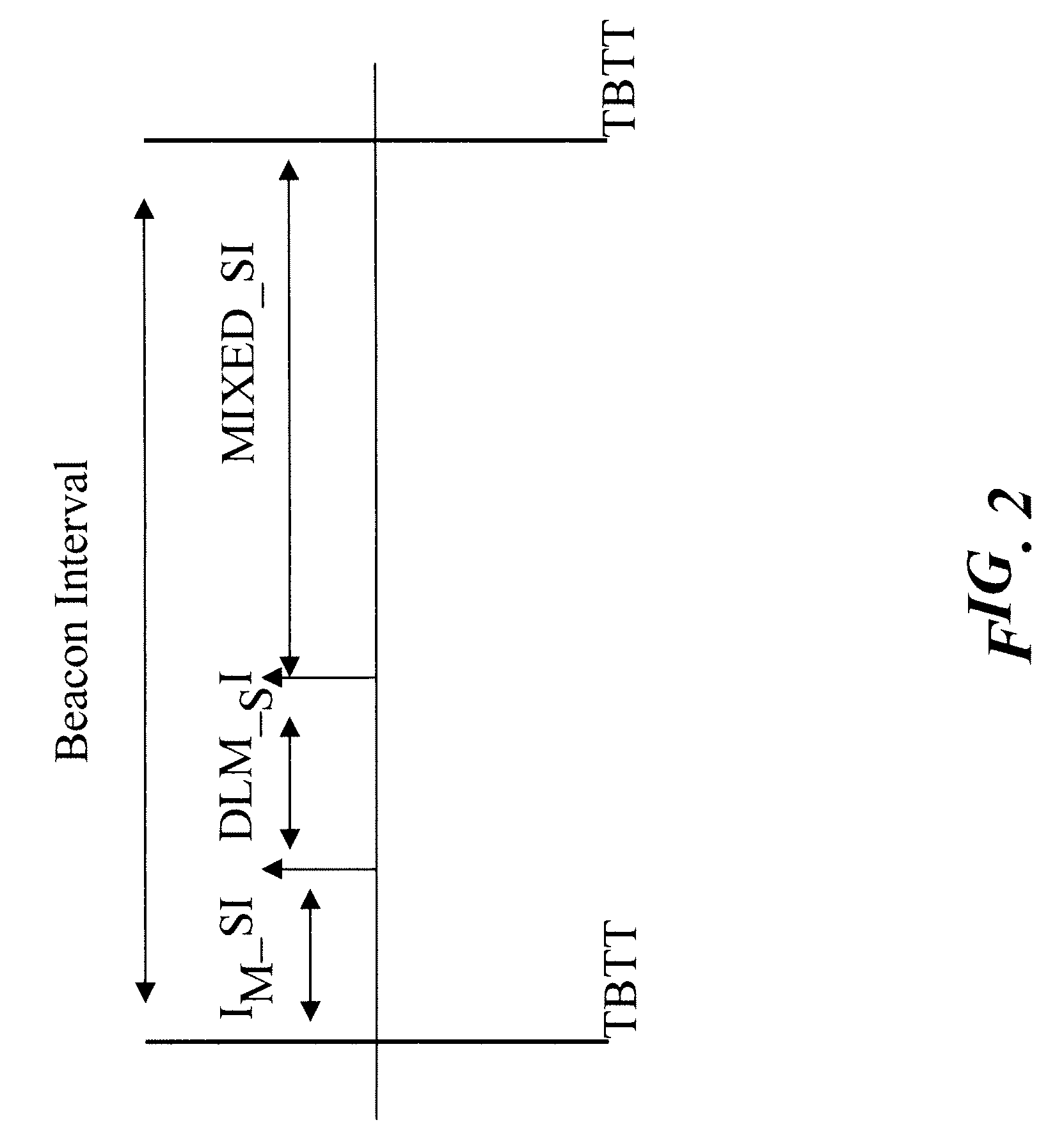
Method and system for enabling multi-channel direct link connection in a communication network, related network and computer program product
ActiveUS20090310578A1Reduce contentionPerformance maximizationNetwork topologiesConnection managementTime frameComputer program
A wireless communication network includes an access point and a plurality of stations. The access point sends towards the stations periodic information arranged in time frames or beacon intervals. The stations in the network are configured to in a first mode through the access point, and in a second mode directly with each other. The time frames are partitioned into a first time interval wherein the stations communicate in the first mode over a first channel; a second time interval wherein the stations communicate in the second mode over a second channel, and a third time interval wherein the stations communicate in either of the first or the second mode.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
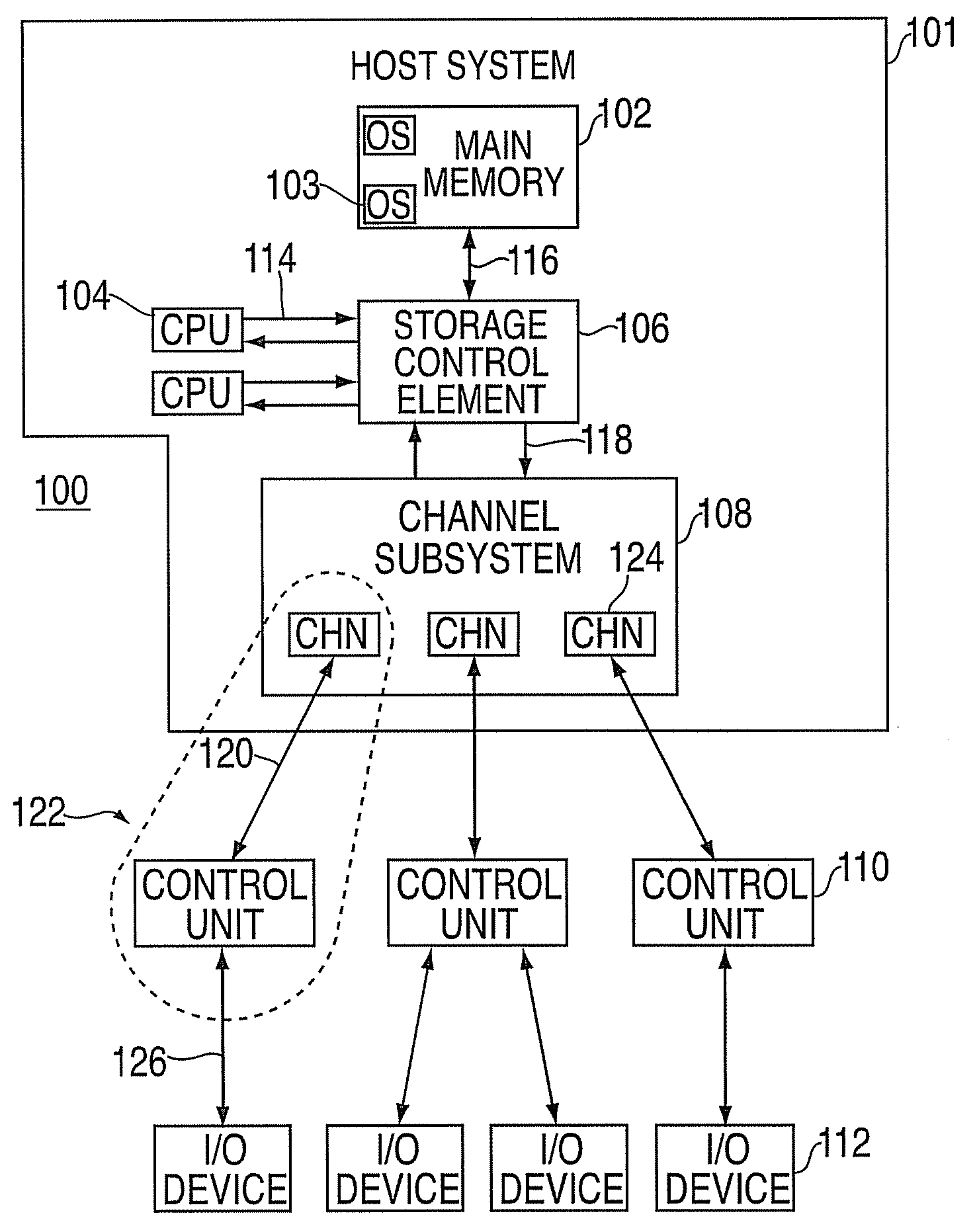
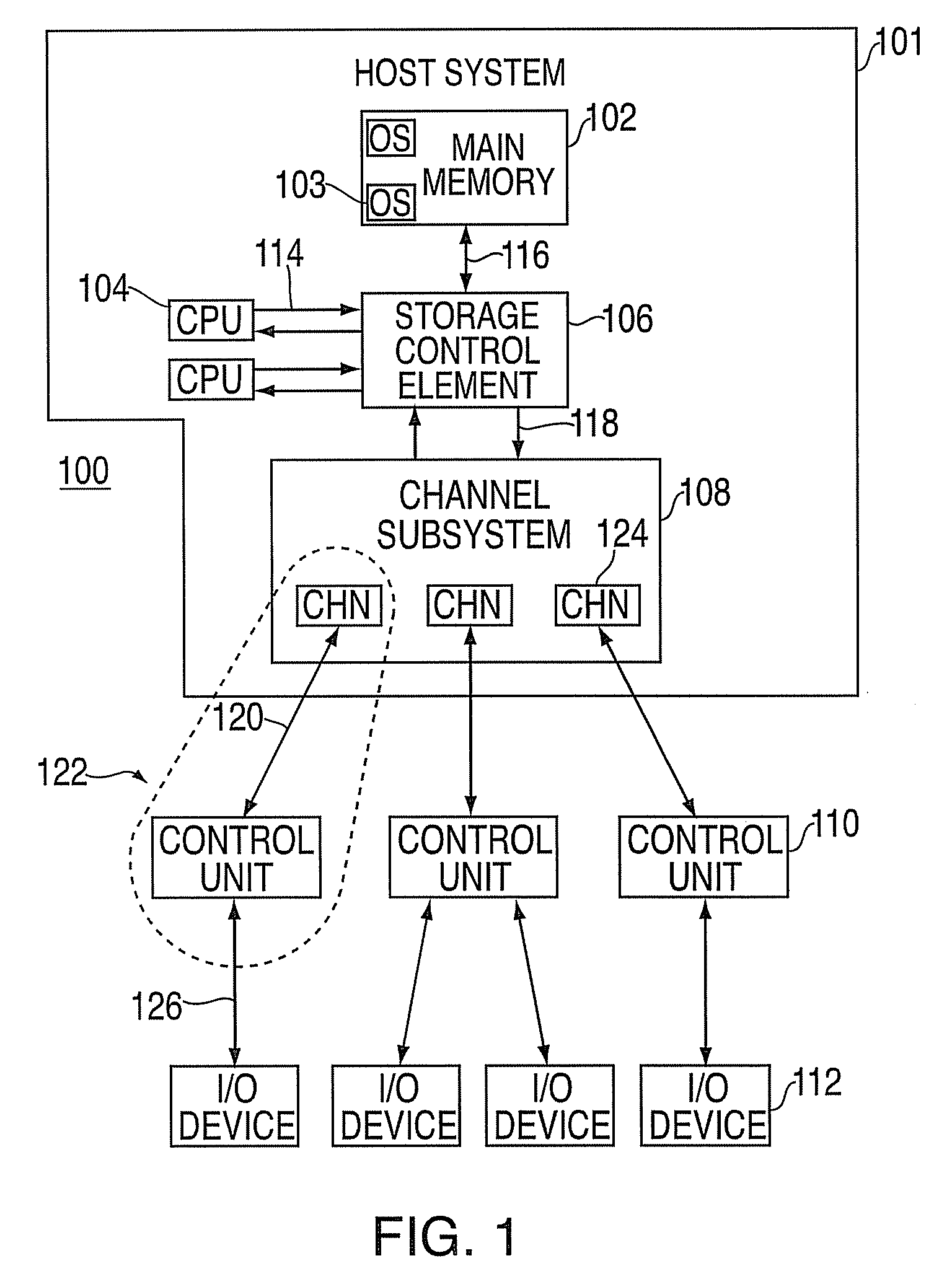
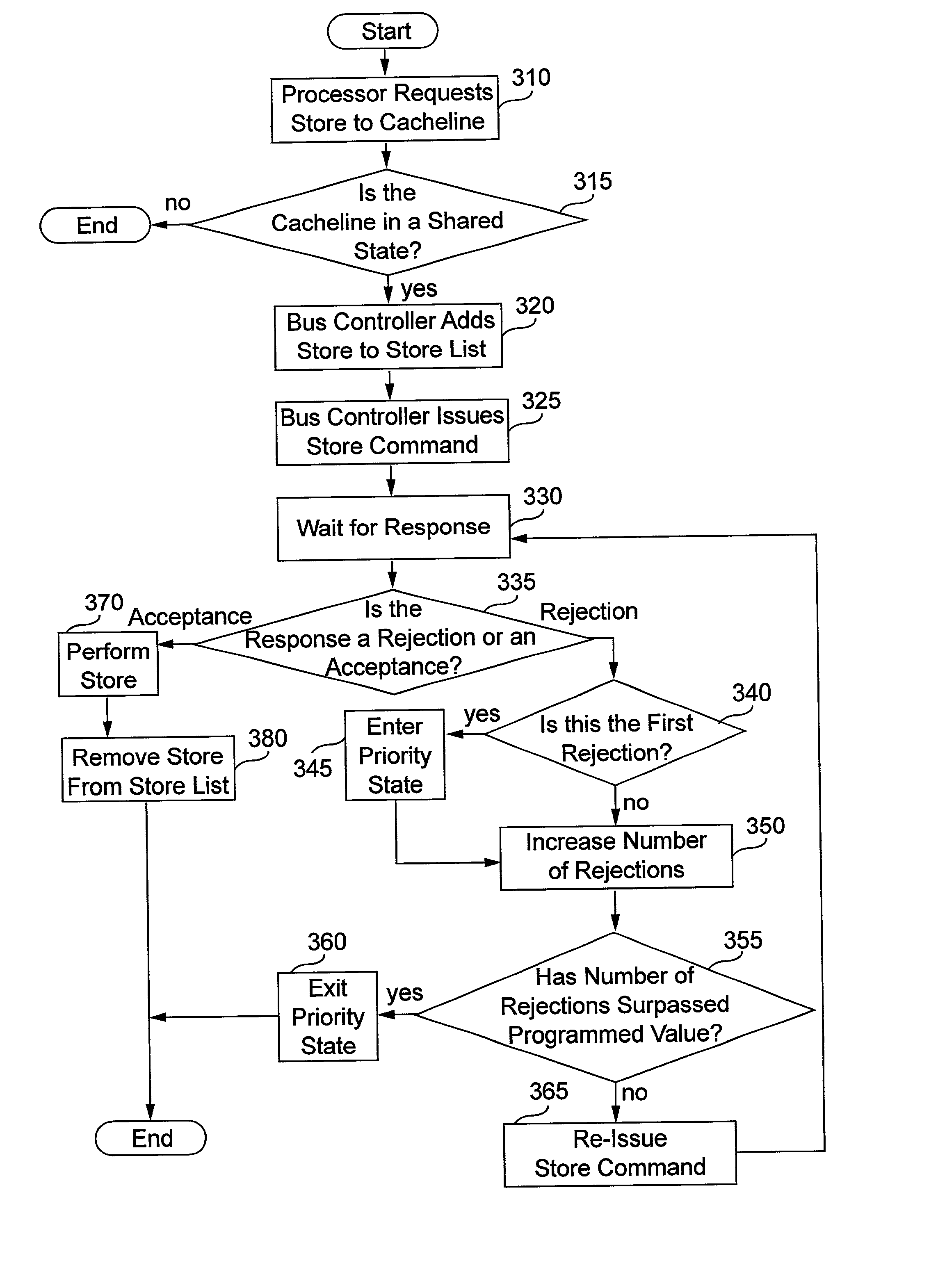
Reserved device access contention reduction
ActiveUS20090210583A1Reducing access contentionReduce contentionResource allocationInput/output processes for data processingOperational systemStore instruction
A computer program product, an apparatus, and a method for reducing reserved device access contention at a control unit in communication with a plurality of operating systems via one or more channels are provided. The computer program product includes a tangible storage medium readable by a processing circuit and storing instructions for execution by the processing circuit for performing a method that includes receiving a command message at the control unit from a first operating system, including an I / O operation command for a device. A device busy indicator is received, indicating that a second operating system has reserved the device. The command message is queued on a device busy queue in response to the device busy indicator. The control unit monitors for a device end indicator. The device busy queue is serviced to perform the I / O operation command in response to the device end indicator.
Owner:IBM CORP
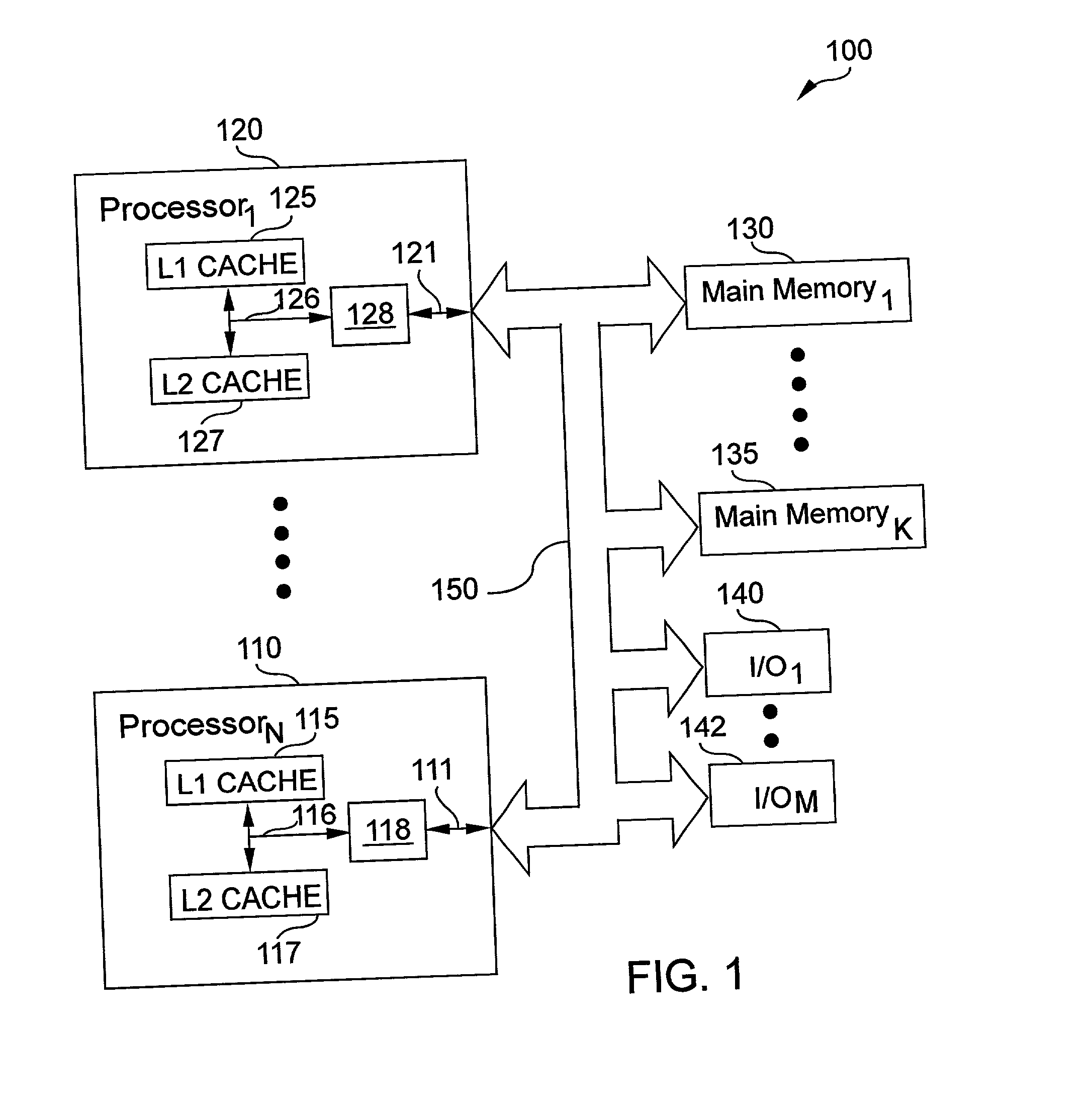
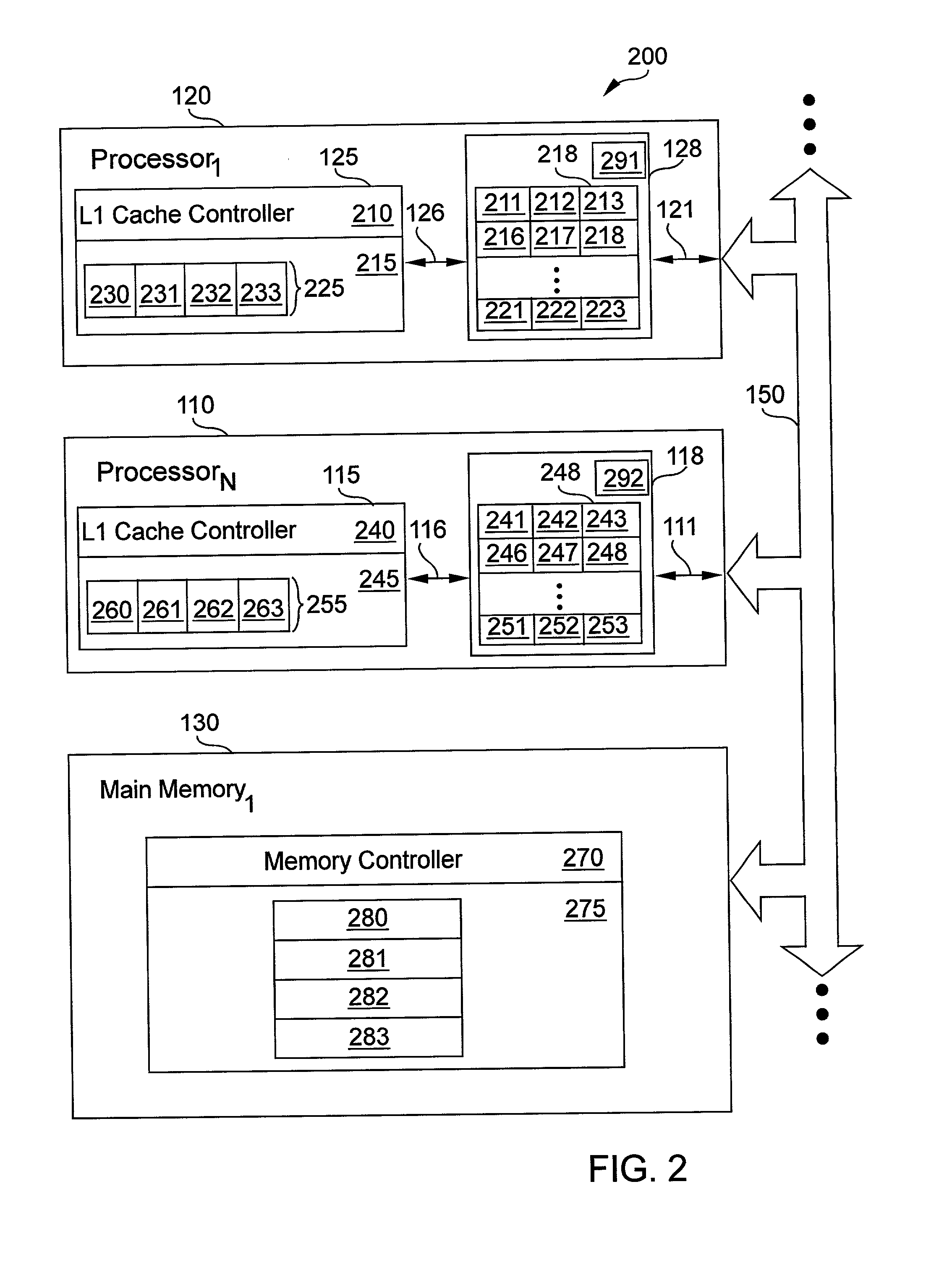
Apparatus and method to improve performance of reads from and writes to shared memory locations
InactiveUS6557084B2Easy to readShorten the timeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingShared memoryReal-time computing
According to the present invention, an apparatus and method for improving reads from and writes to shared memory locations is disclosed. By giving writes priority over reads, the current invention can decrease the time associated with certain sequences of reads from and writes to shared memory locations. In particular, load-invalidate-load sequences are changed to load-load sequences with the current invention. Furthermore, contention for a shared memory location will be reduced in particular situations when using the current invention.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
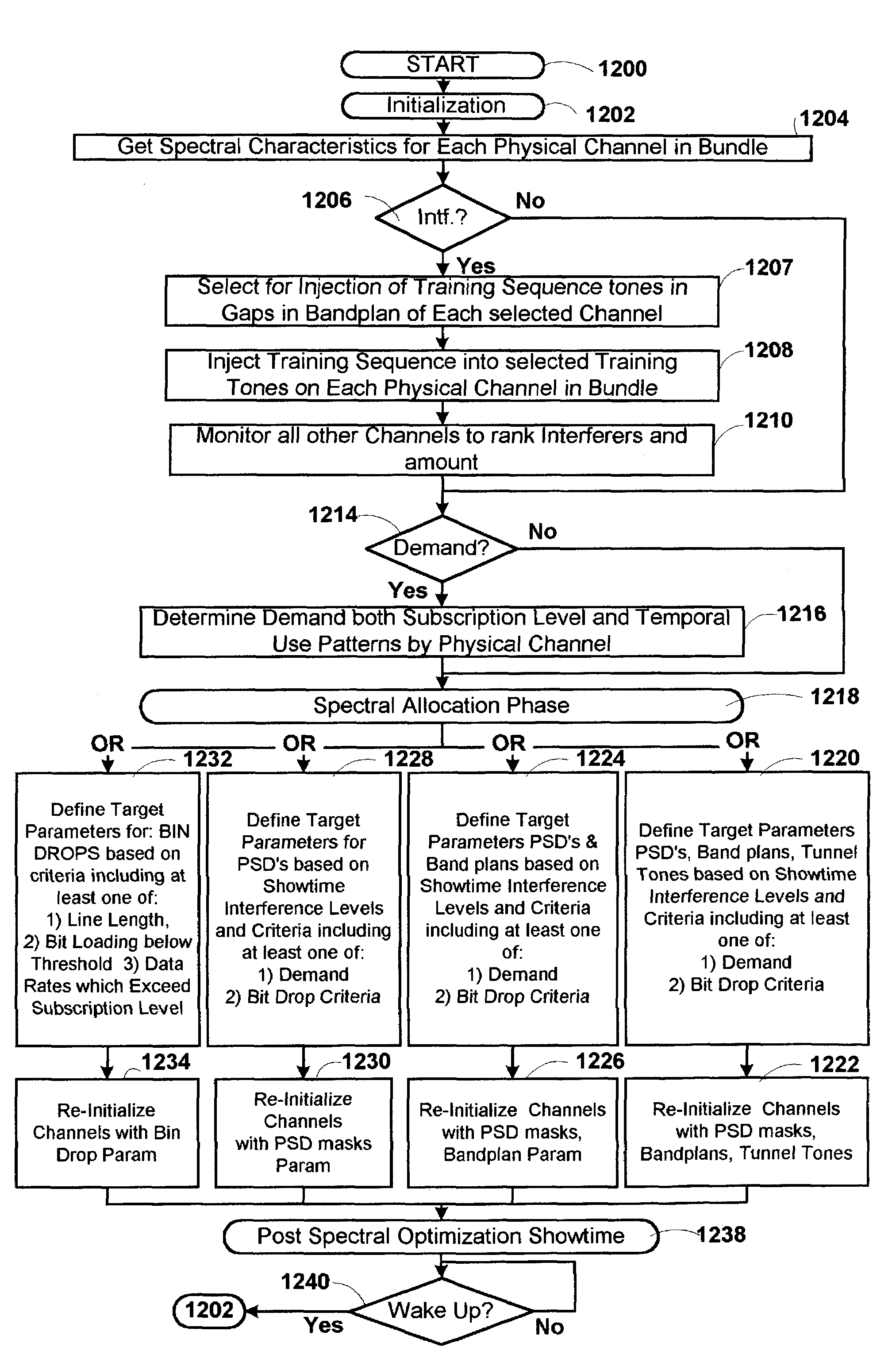
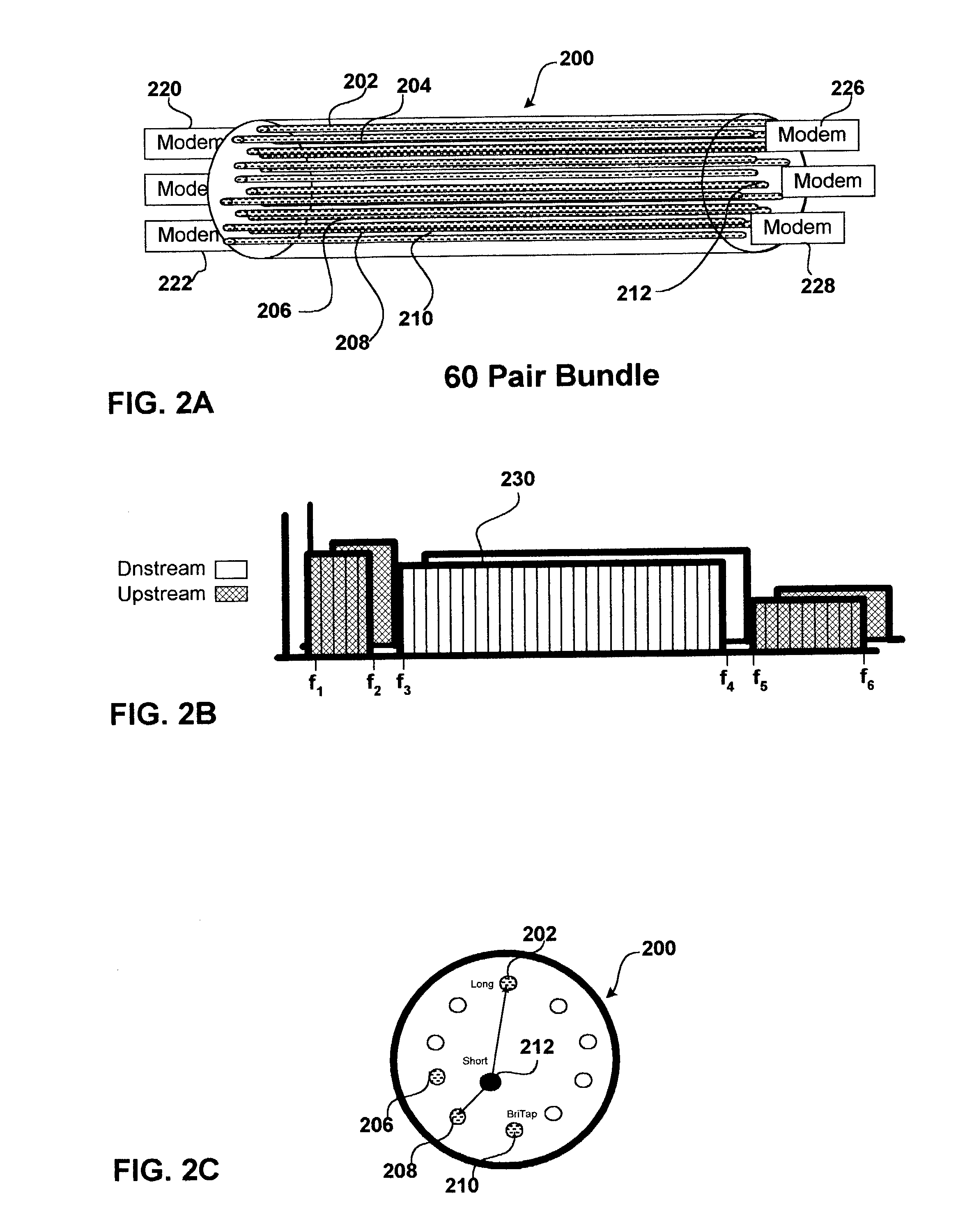
Method and apparatus for optimization of channel capacity in multi-line communication systems using spectrum management techniques
InactiveUS7356049B1Increase channel capacityReduce contentionModulated-carrier systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsSpectrum managementChannel capacity
The present invention advantageously provides a method and apparatus for optimization of channel capacity in multi-line multi-tone communications such as X-DSL among subscriber lines which are bundled with one another. In an embodiment of the invention an apparatus for optimizing channel capacity of multi-tone communications effected by opposing sets of modems coupled to one another by a plurality of subscriber lines is disclosed. The apparatus includes a spectrum manager coupled to at least one of the opposing sets of modems. The spectrum manager includes: a profiler, a demand module and an optimizer. The profiler obtains from the at least one of the opposing sets of modems the spectral characteristics of each of the plurality of subscriber lines. The demand module determines for each of the plurality of subscriber lines the subscriber demand profile. The optimizer defines target parameters for at least one of bit loading, and power spectral density (PSD) for selected tones of the multi-tone communications based on the spectral characteristics from the profile module and the demand profiles from the demand module and downloads the target parameters to the at least one of the opposing sets of modems.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Channel reservation signals for new radio interference management
ActiveUS20180167848A1Reducing access contentionReduce overheadNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork planningPriority callInterference management
Channel reservation systems and methods are disclosed herein, which schedule transmissions on a shared radio medium that is shared by a plurality of licensed network operators. In embodiments, priority access is pre-assigned to the network and the method determines whether to send a transmission based at least on the transmitter's priority class as compared to another transmitter's priority class and to which transmitter the time slot of a signal is dedicated. In embodiments, priority access may not be preassigned to the network and pre-grants may be used in conjunction with CR-Ts and CR-Rs to determine whether a transmitter transmits.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive queuing methodology for system task management
InactiveUS20120102501A1Reduce contentionIncrease pressureResource allocationMemory systemsGranularityHigh pressure
A task management methodology for system having multiple processors and task queues adapts a queuing topology by monitoring a queue pressure and adjusting the queue topology from a selection of at least two different queue topologies. The queue pressure may be periodically monitored and queues with different granularities selected. The methodology reduced contention when there is high pressure on the queues while also reducing overhead to manage queues when there is less pressure on the queues.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adjustable differential input and output drivers
ActiveUS6864704B1Reduce resistanceIncrease currentReliability increasing modificationsBaseband system detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceTelecommunications link
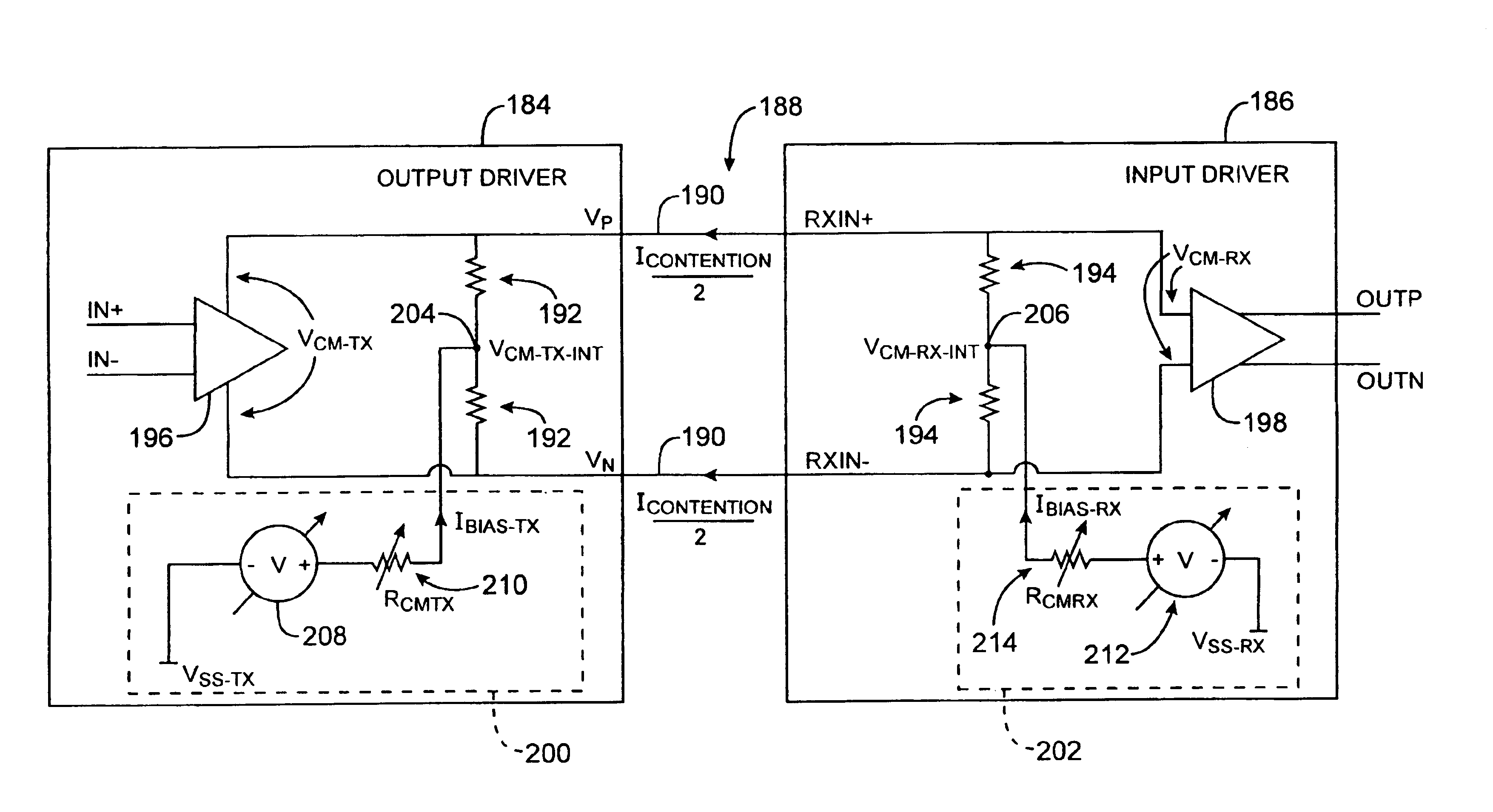
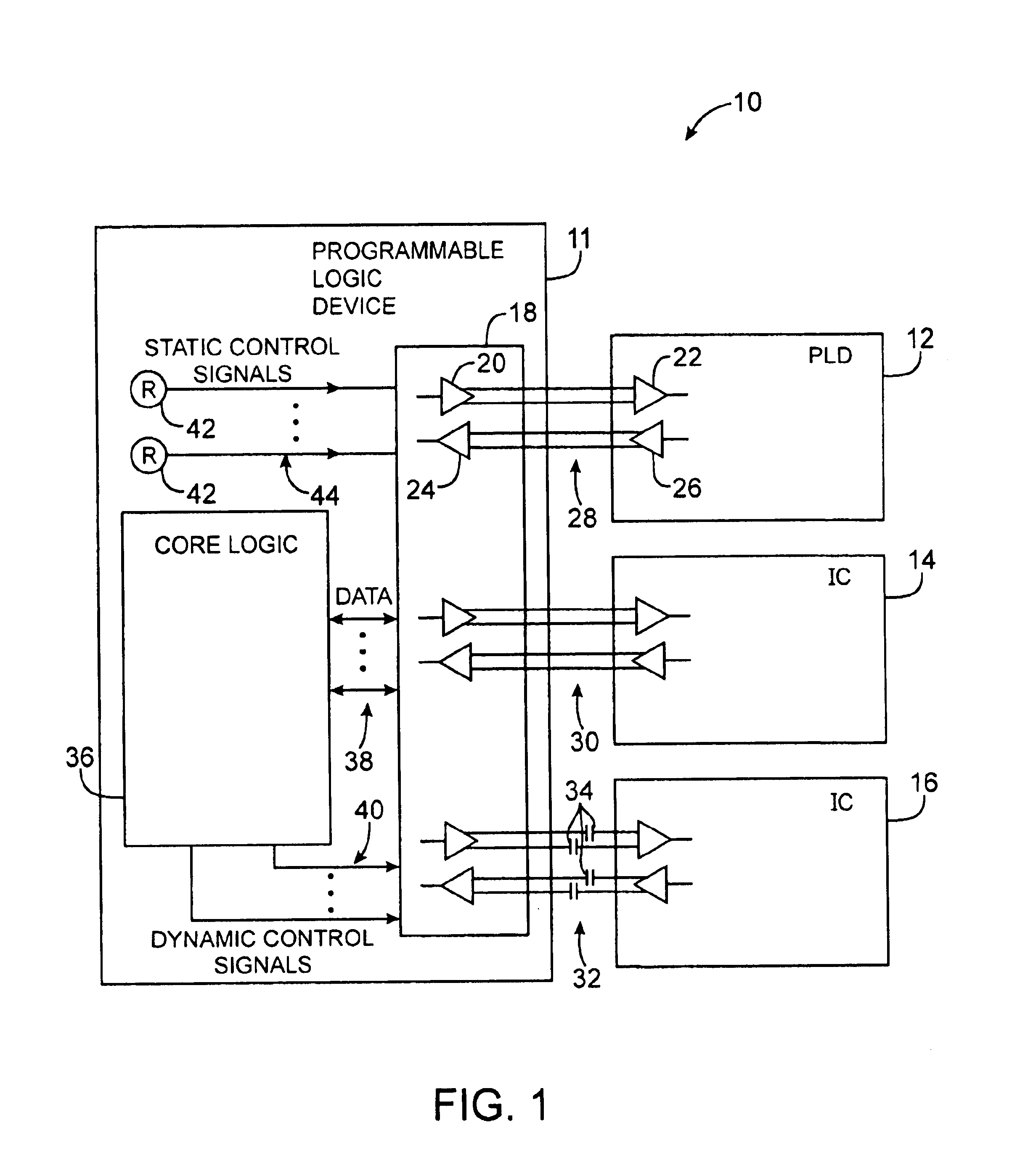
Systems and methods are provided using common-mode-voltage bias circuitry to make common-mode-voltage adjustments to differential driver circuitry in integrated circuit differential communications links. Adjustable bias circuitry may be controlled using static and dynamic control signals. Dynamic control signals can be produced by core logic on a programmable logic device or other integrated circuit. Static control signals can be produced by programmable elements. Bias circuit adjustments made at one end of a differential link can be used to improve performance at either end of the link or can be used to improve power consumption or to balance power and performance considerations. The same integrated circuit design can be used in both AC-coupled and DC-coupled environments. The bias circuitry can be formed from an adjustable current source and adjustable resistor. The current source and adjustable resistors can be controlled by the same control signals.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Method and apparatus for bandwidth provisioning in a wlan
InactiveUS20060153117A1Eliminate requirementsReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTime informationBroadcasting
The invention provides for a receiver transmitter comprising: a plurality of logical access points; for downloading a duration into a mobile terminal in accordance with an access point determination of the maximum amount of time information linked with a downlink broadcast traffic to deliver all the broadcast / multicast information in a single communication stream. The invention also provides for a method of broadcast / multicast frames “Duration” are set to values in order to deliver all the broadcast / multicast information in a single communication stream eliminating the requirement for contending for the medium for each broadcast / multicast frame transmission. This pseudo-reservation of the wireless medium can also be made periodic for enabling broadcast / multicast services.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Apparatus and method for enhancing transfer rate using a direct link protocol (DLP) and multiple channels in a wireless local area network (LAN) using a distributed coordination function (DCF)
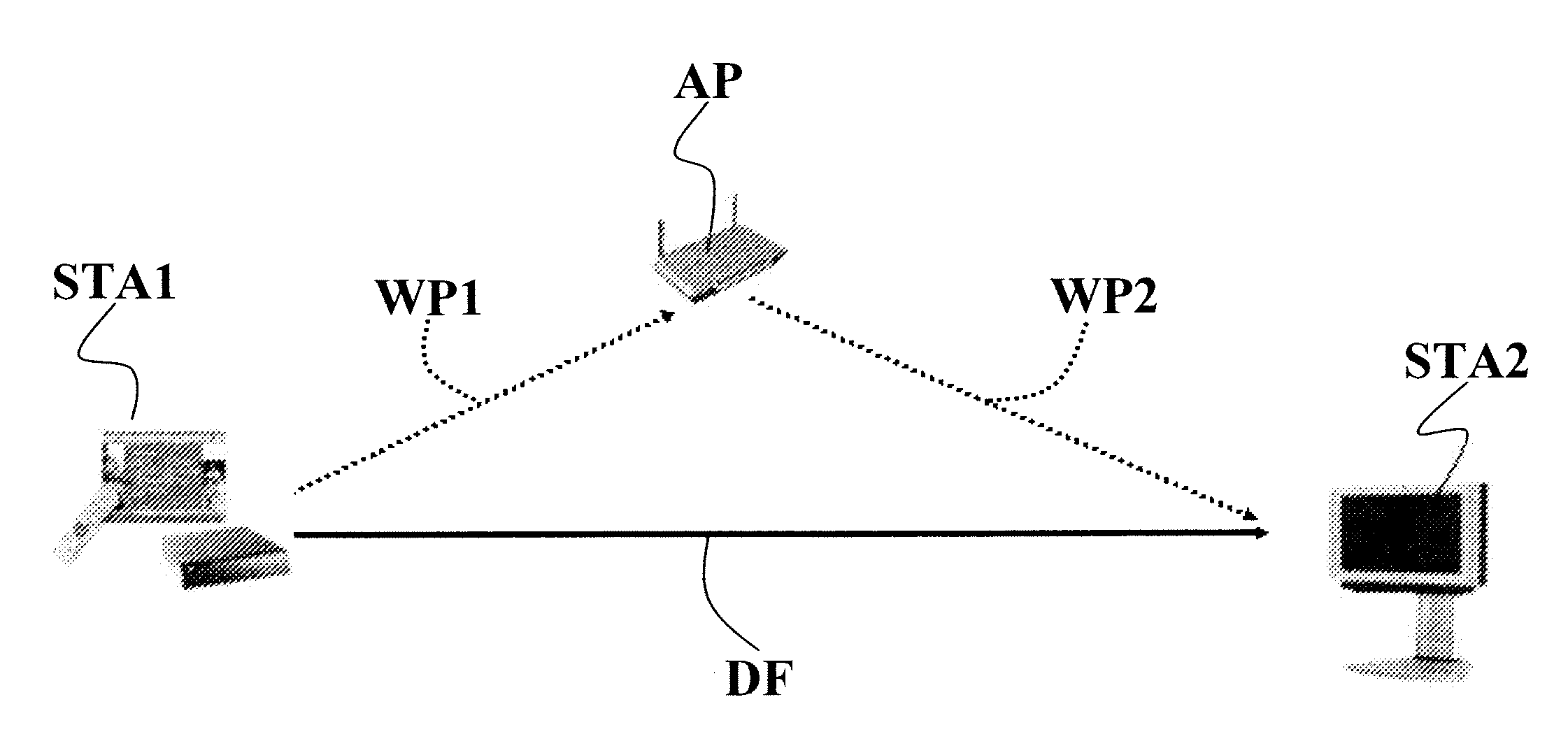
InactiveUS7450550B2Reduce contentionNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexMedia access controlLocal area network
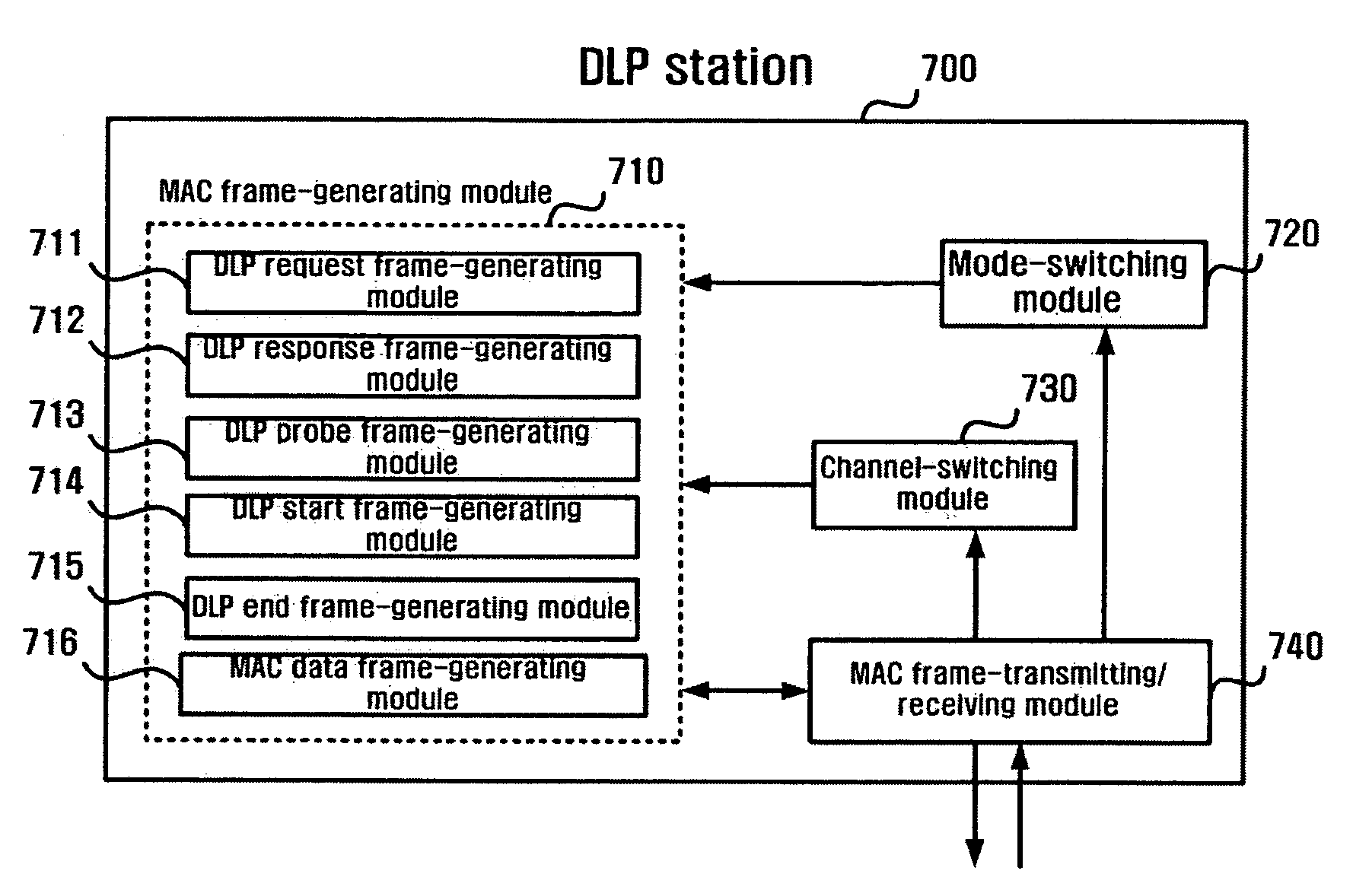
An apparatus and a method for presenting a novel format of a media access control (MAC) frame that enables the use of a direct link protocol (DLP) and multiple channels, thereby reducing contention among stations, and enhancing a transfer rate by using the MAC frame format in infrastructure-based wireless communications. A DLP station of the present invention includes a channel-switching module for switching a channel by writing a new channel number in a DLP request frame; a mode-switching module for switching a DLP mode by writing a new mode number in the DLP request frame; and a MAC frame-generating module for generating various MAC frames including the DLP request frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
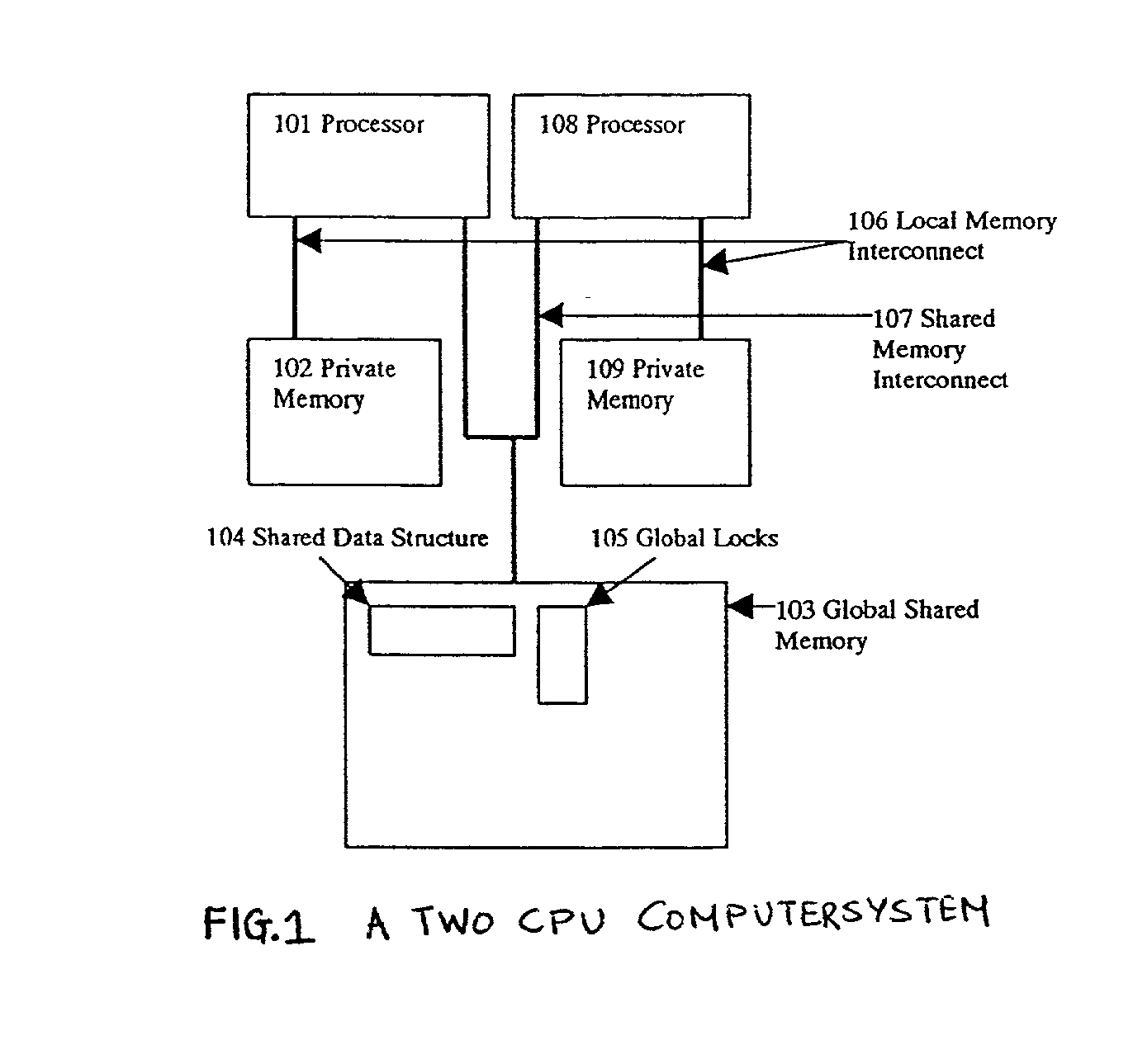
Distributed shared memory management
InactiveUS20020032844A1Reduce contentionCost effectiveResource allocationProgram synchronisationDistributed shared memoryManagement system
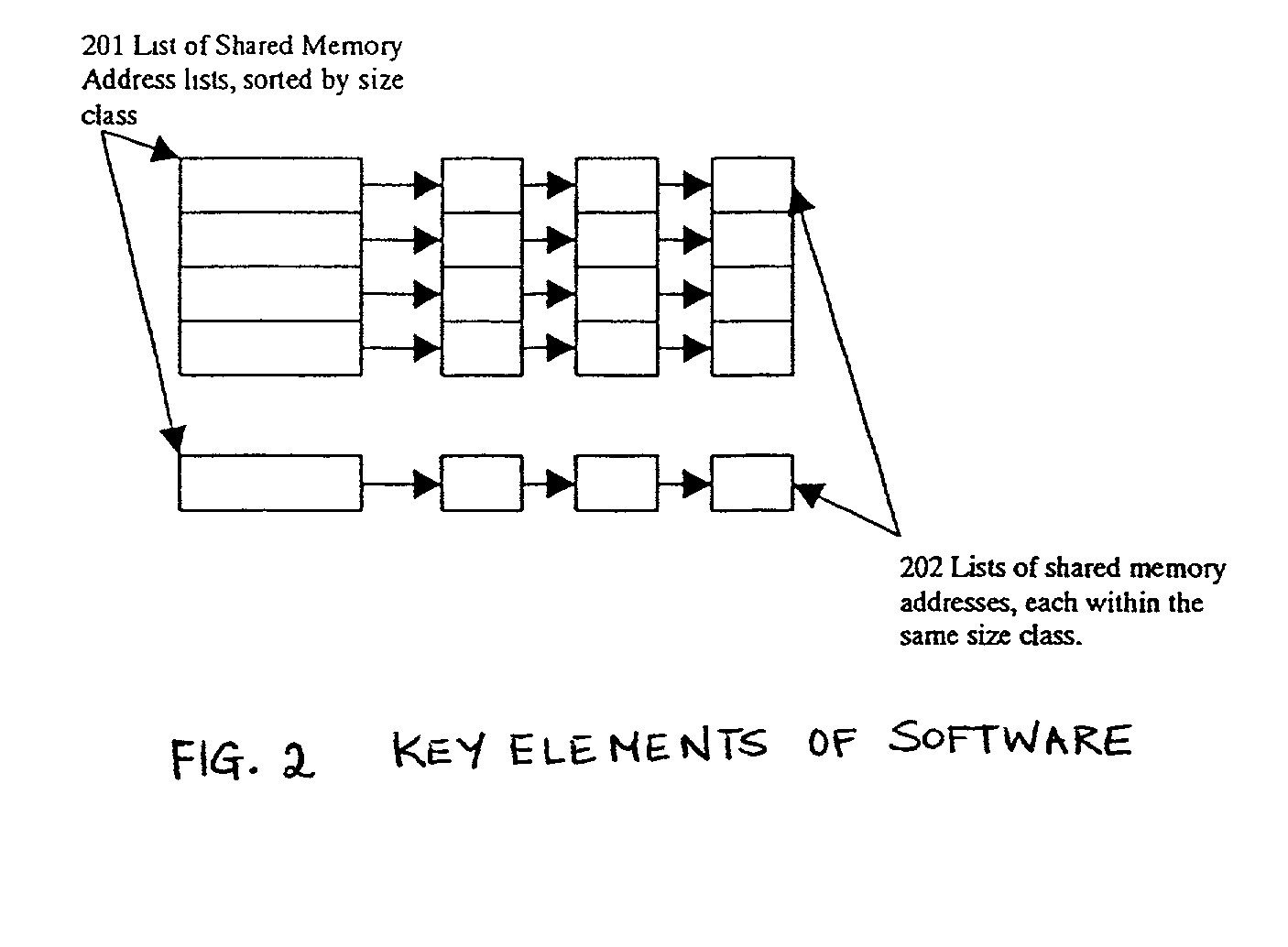
Systems and methods are described for distributed shared memory management. A method includes receiving a request from a requesting software to allocate a segment of memory; scanning a data structure for a smallest suitable class size, the data structure including a list of memory address size classes, each memory address size class having a plurality of memory addresses; determining whether the smallest suitable size class is found; if the smallest suitable size class is found, determining whether memory of the smallest suitable size class is available in the data structure; if the smallest suitable size class is found, and if memory of the smallest suitable size class is available, selecting a memory address from among those memory addresses belonging to the smallest suitable size class; and if the smallest suitable size class is found, and if memory of the smallest suitable size class is available in the data structure returning the memory address to the requesting software. An apparatus includes a processor; a private memory coupled to the processor; and a data structure stored in the private memory, the data structure including a list of memory address size classes wherein each memory address size class includes a plurality of memory addresses.
Owner:TIMES N SYST +1
Data migration with reduced contention and increased speed
InactiveUS20060155950A1ContentionReduce contentionMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingData setSpace allocation
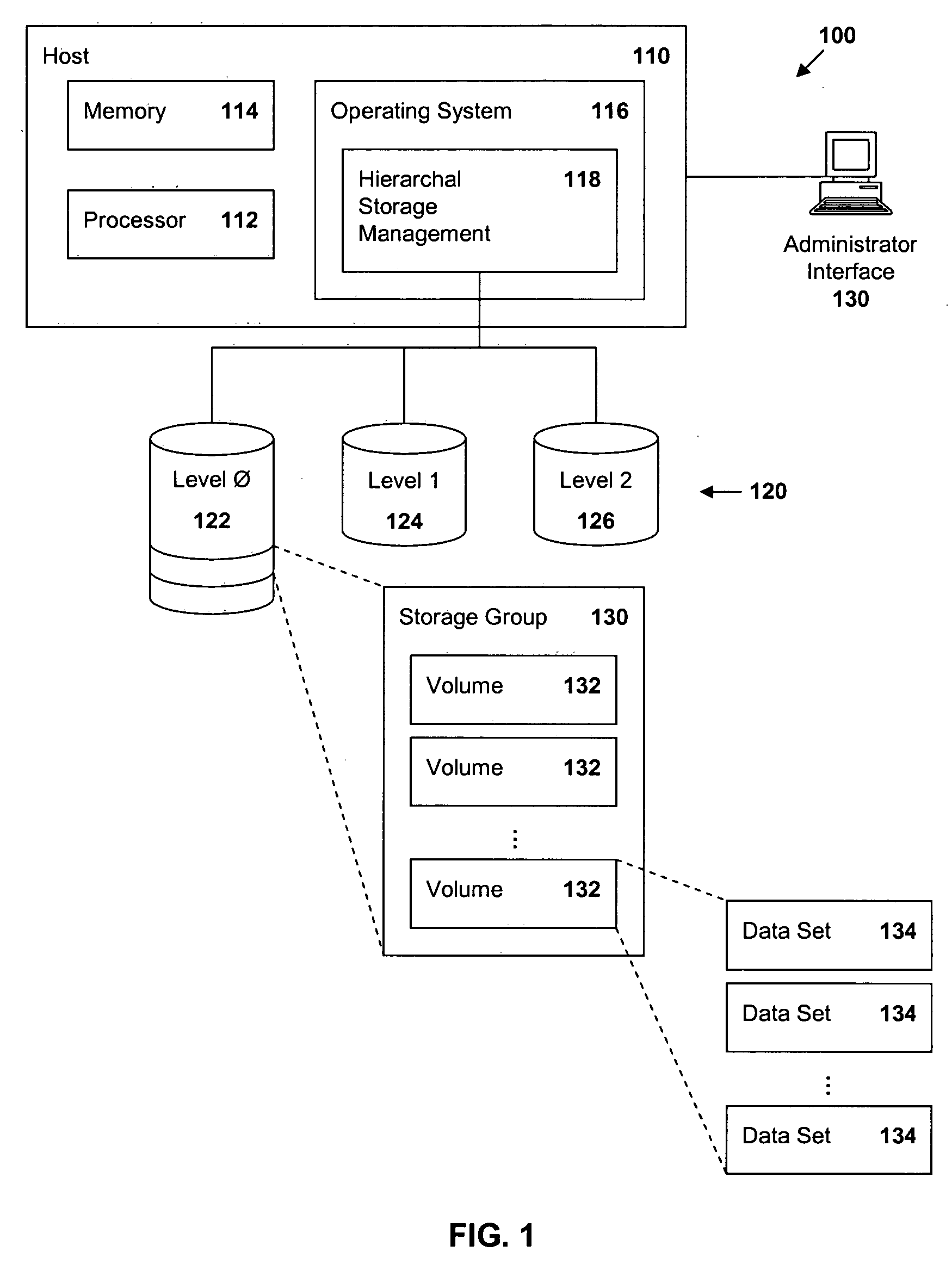
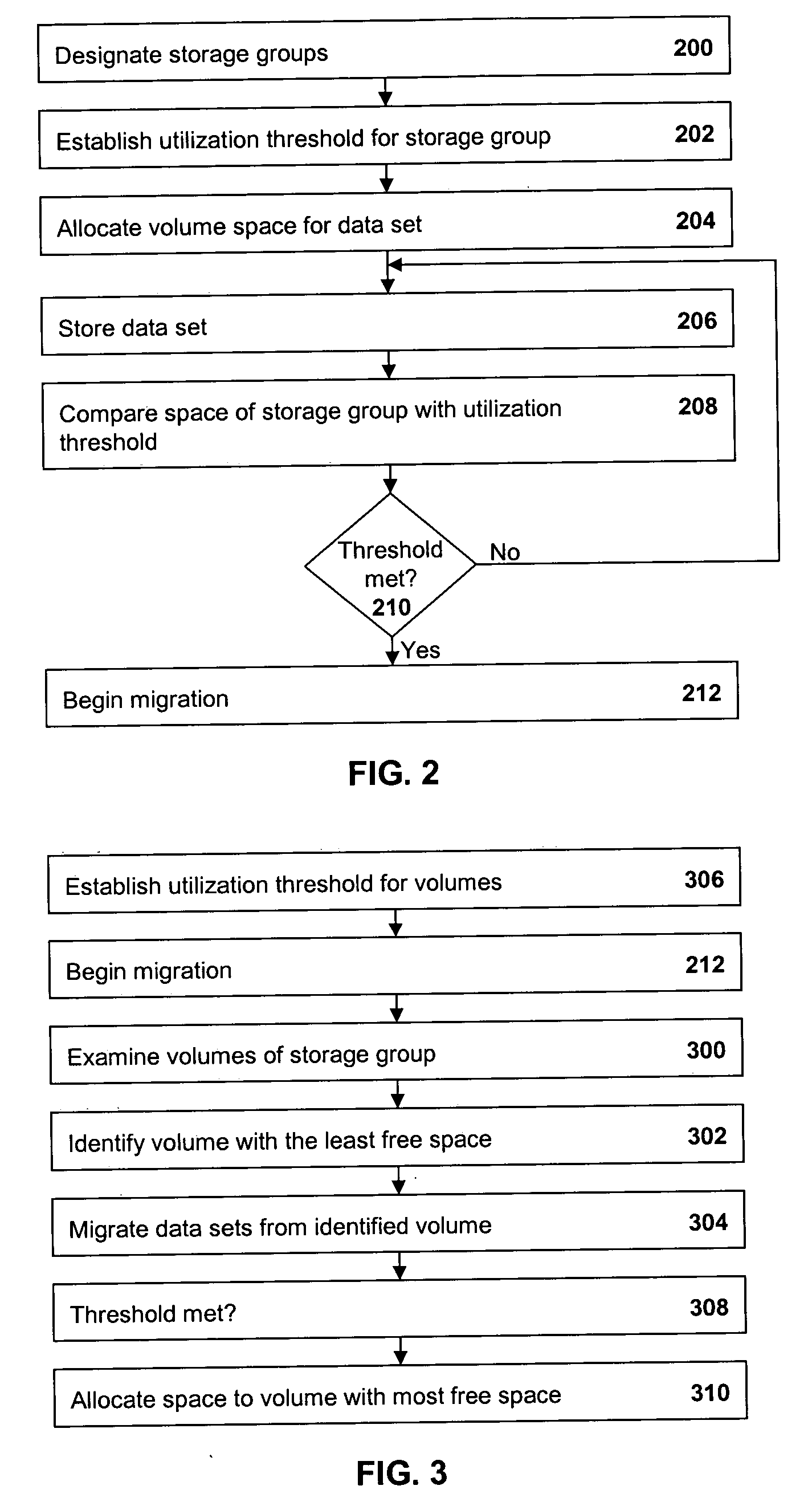
Methods and apparatus are provided for managing data in a hierarchal storage subsystem. A plurality of volumes is designated as a storage group for Level 0 storage; a high threshold is established for the storage group; space is allocated for a data set to a volume of the storage group, storing the data set to the volume; the high threshold is compared with a total amount of space consumed by all data sets stored to volumes in the storage group; and data sets are migrated from the storage group to a Level 1 storage if the high threshold is less than or equal to the total amount of space used by all of the data sets stored to volumes in the storage group. Optionally, high threshold are assigned to each storage group and, when the space used in a storage group reaches or exceeds the high threshold, migration of data will begin from volumes in the storage group, beginning with the volume having the least free space. Thus, contention between migration and space allocation is reduced. Also optionally, when a volume is selected for migration, a flag is set which prevents space in the volume from being allocated to new data sets. Upon completion of the migration, the flag is cleared and allocation is allowed. Thus, contention between migration and space allocation is avoided.
Owner:IBM CORP
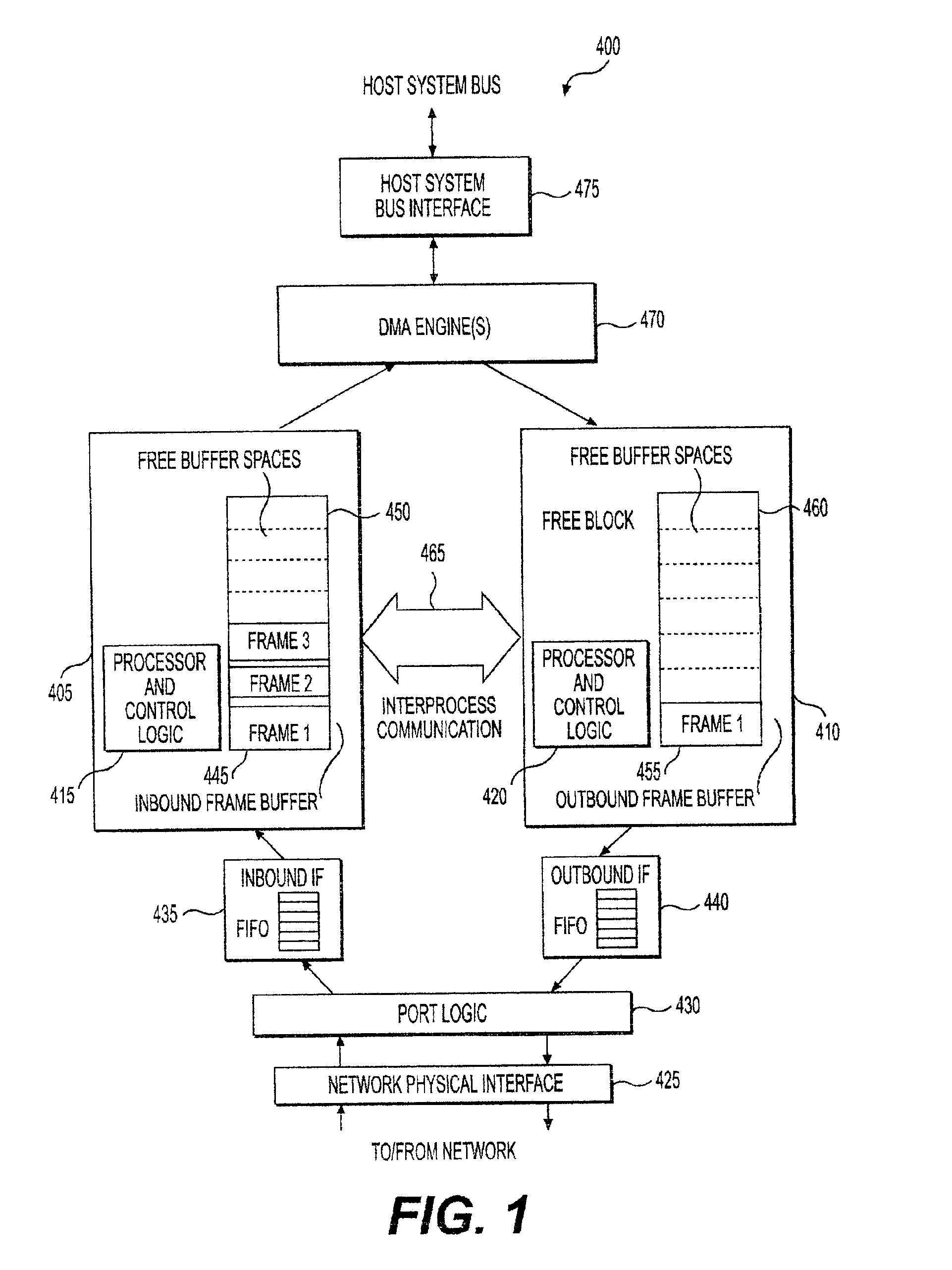
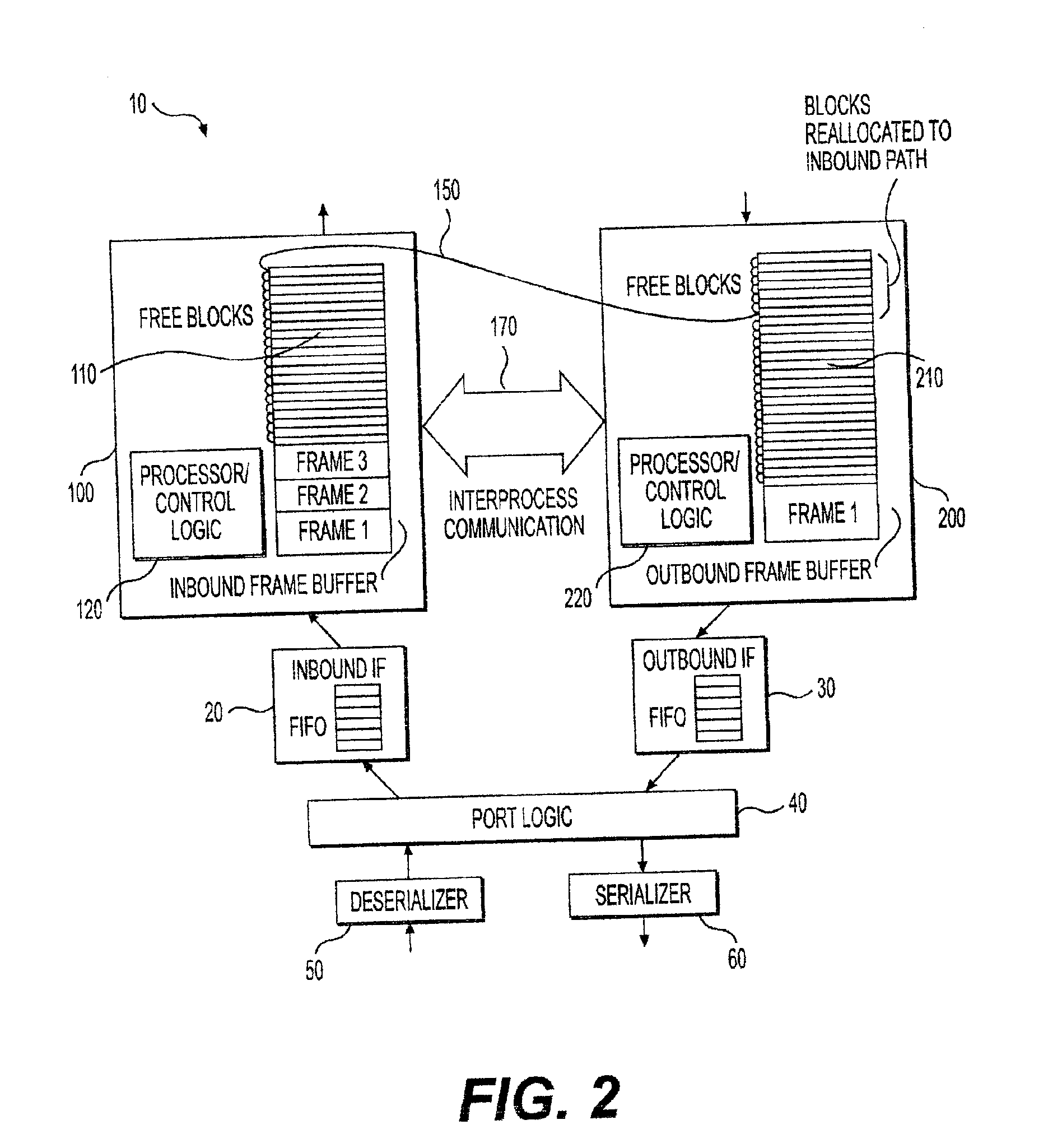
Dynamic memory allocation between inbound and outbound buffers in a protocol handler
InactiveUS6877048B2Reduce contentionSpace minimizationData switching networksInput/output processes for data processingNetworking protocolProtocol processing
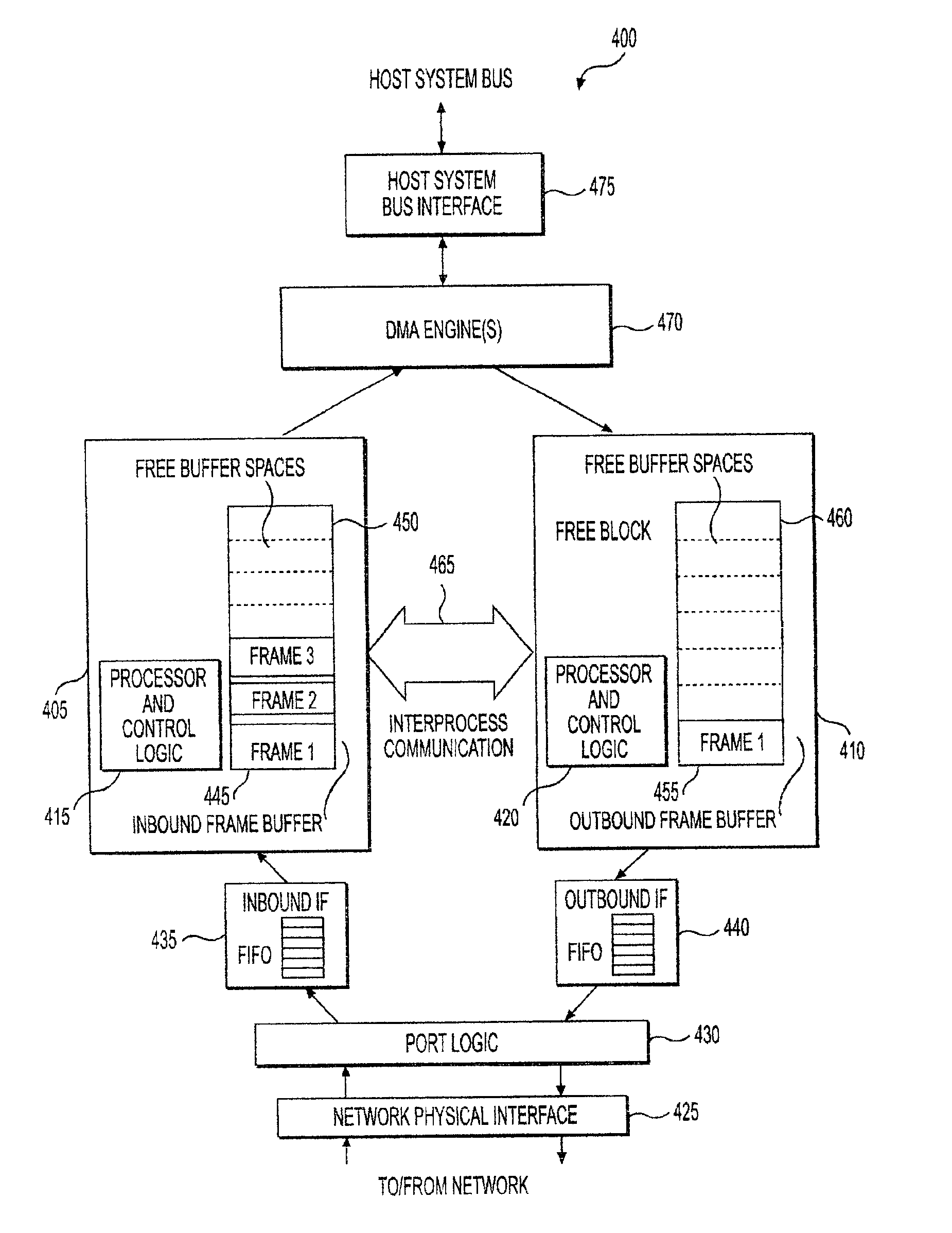
An apparatus and method for dynamically allocating memory between inbound and outbound paths of a networking protocol handler so as to optimize the ratio of a given amount of memory between the inbound and outbound buffers is presented. Dedicated but sharable buffer memory is provided for both the inbound and outbound processors of a computer network. Buffer memory is managed so as to dynamically alter what portion of memory is used to receive and store incoming data packets or to transmit outgoing data packets. Use of the present invention reduces throttling of data rate transmissions and other memory access bottlenecks associated with conventional fixed-memory network systems.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Data communications
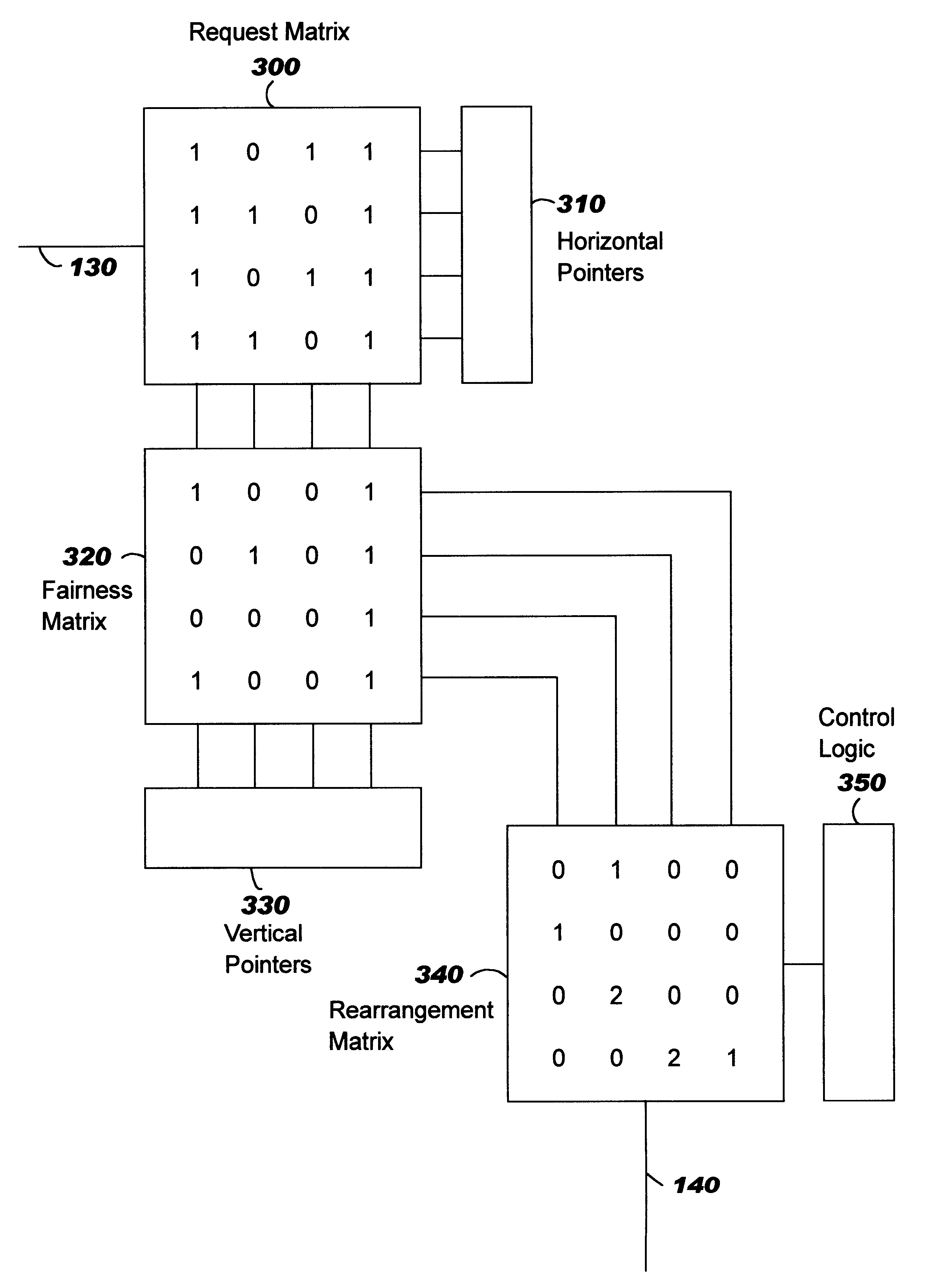
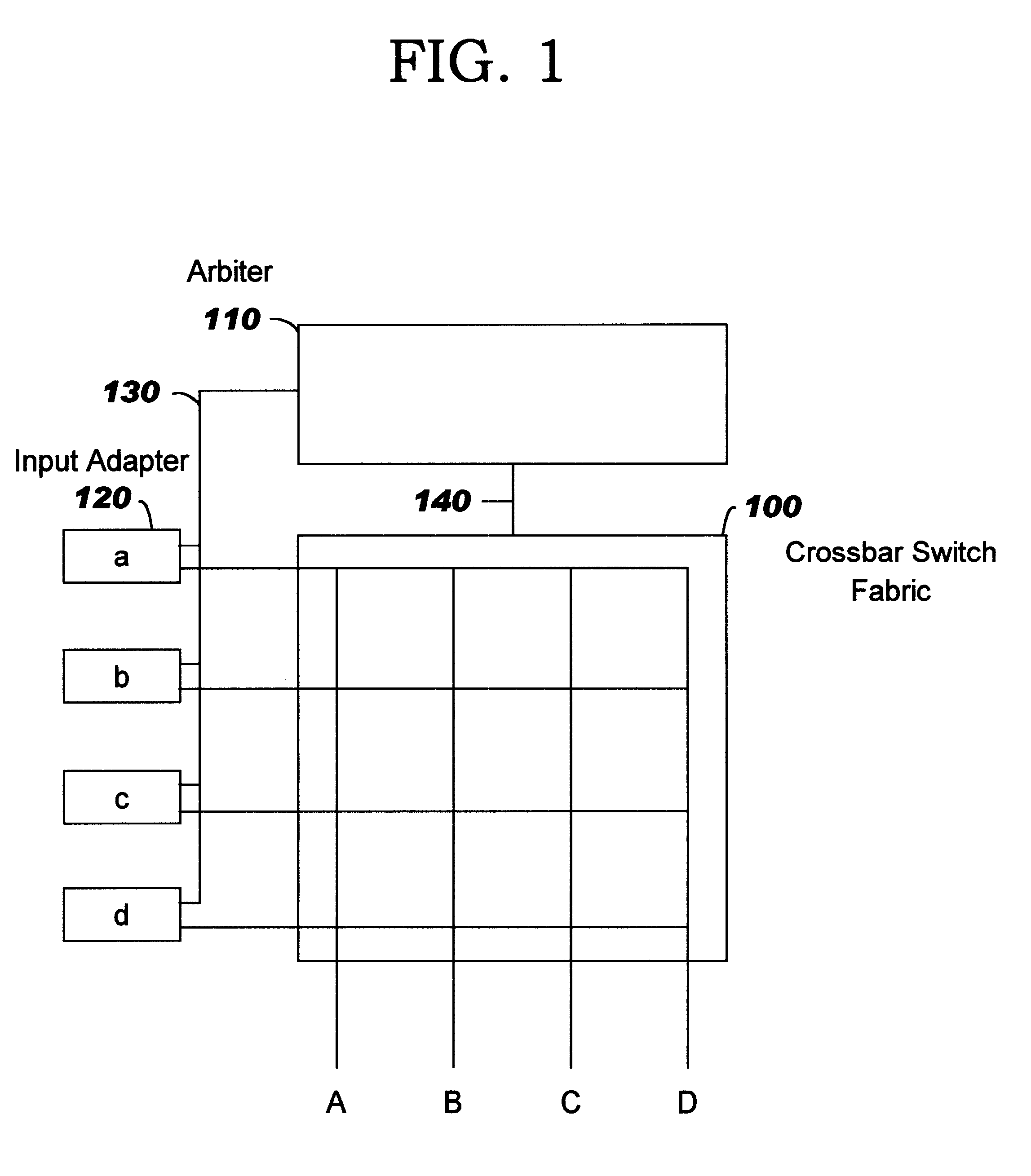
InactiveUS6370148B1High selectivityReduce impactTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData interchangeMinimum probability
An improved arbiter is described for arbitrating requests by a plurality of first data processing units for access to a plurality of second data processing units interconnected by a switching system of a type in which at any time each first unit can only access one second unit and each second unit can only be accessed by one first unit. The arbiter comprises a scheduler mechanism for repeatedly selecting access requests with a defined minimum probability of selecting a request for each first unit-second unit combination. Rearrangement storage means records requests selected by the scheduler mechanism. A rearranger is provided for repeatedly selecting a set of requests recorded in the rearrangement storage means, so that only one request per first unit and per second unit is selected, using a priority mechanism which increases the probability of selection with the length of time a request is stored in the rearrangement storage means. Finally, means are provided for communicating the grant of the selected set of requests to the switching system and for deleting the selected set of requests from the rearrangement storage means. In one embodiment, the arbiter is used for controlling switching paths in a packet data switch.
Owner:IBM CORP
Point-controlled contention arbitration in multiple access wireless LANs
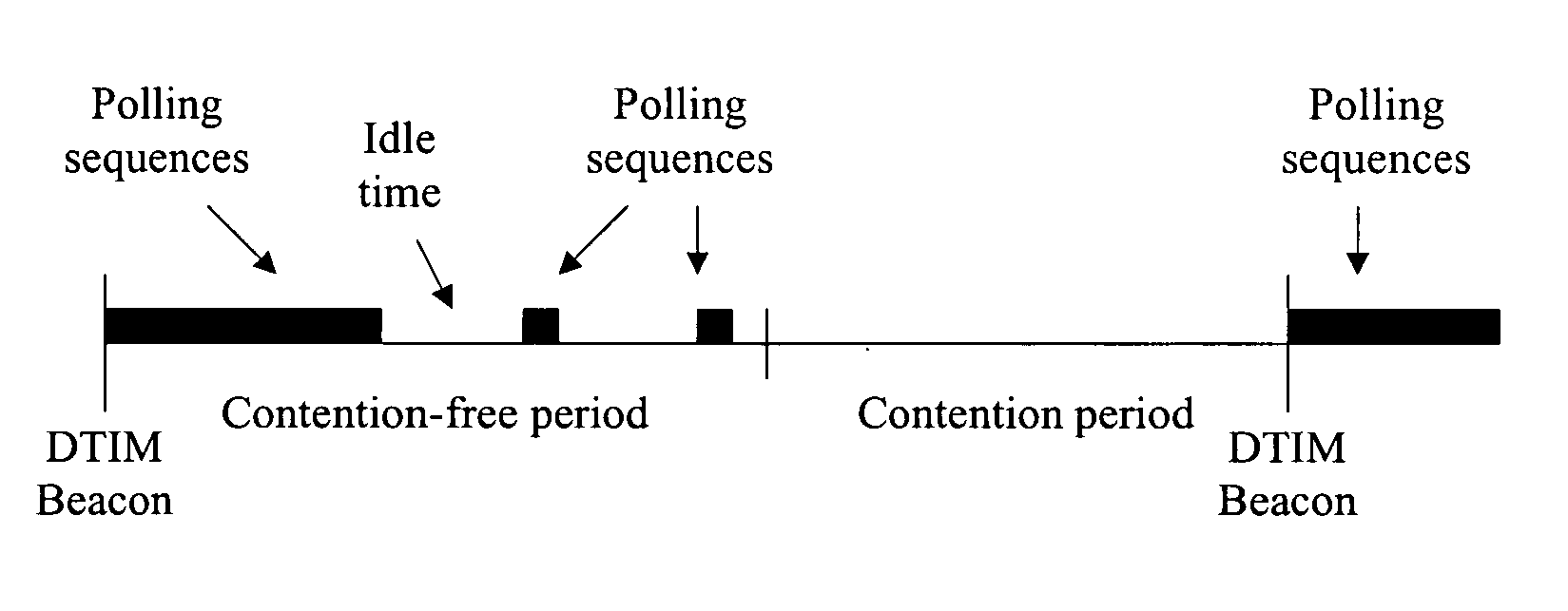
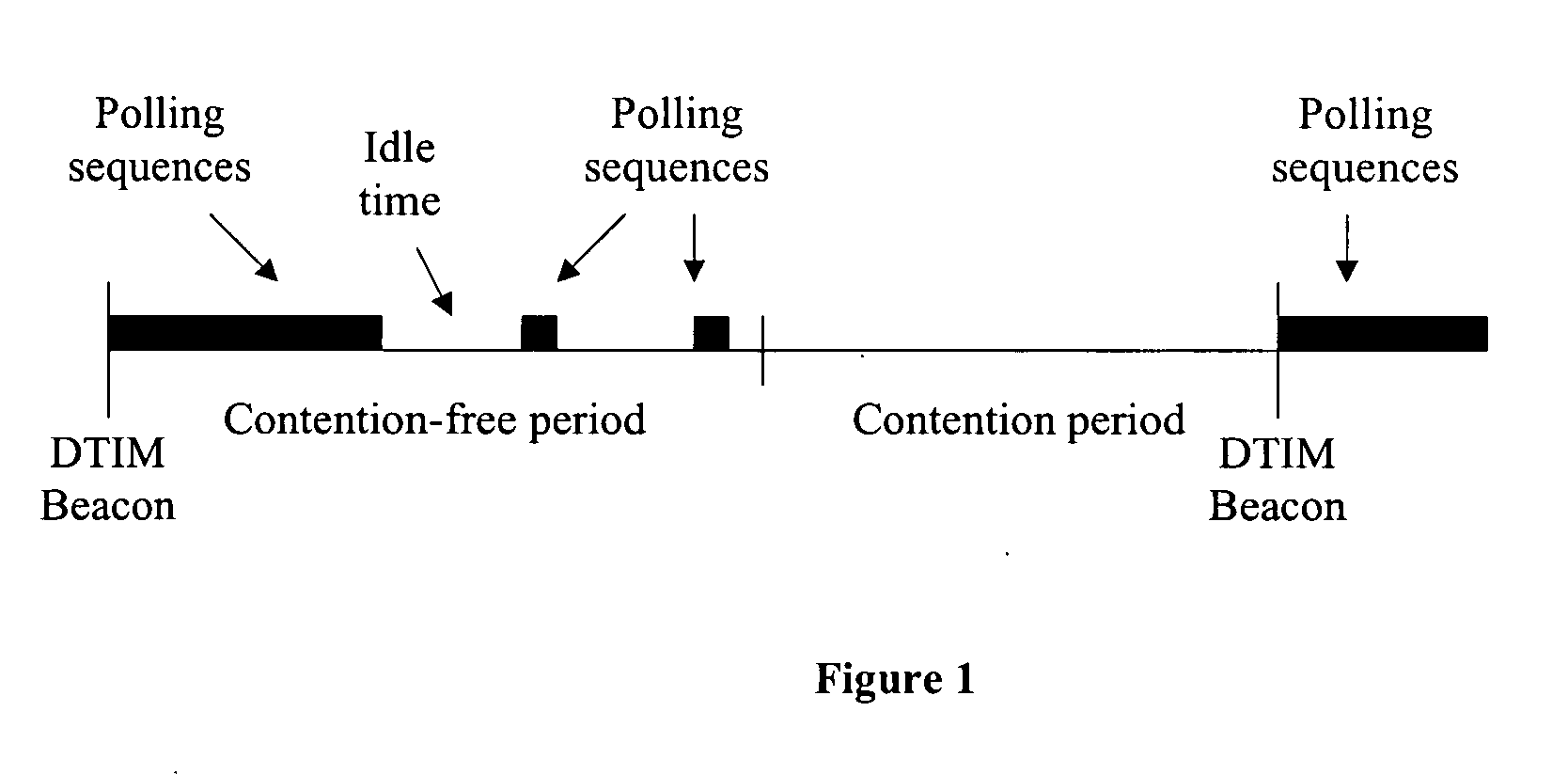
ActiveUS20060072488A1Reduce contentionIncrease powerSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast transmission systemsMulticastLocal area network
A power management method that transmits multicast frames independent of DTIM beacons. An access point associates power save stations with a multicast group. Each member of the group is signaled of a predetermined time period to operate in an active mode. During the predetermined time period the access point sends multicast frames for the group. The frames may be sent along with a poll.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Access method for periodic contention-free sessions
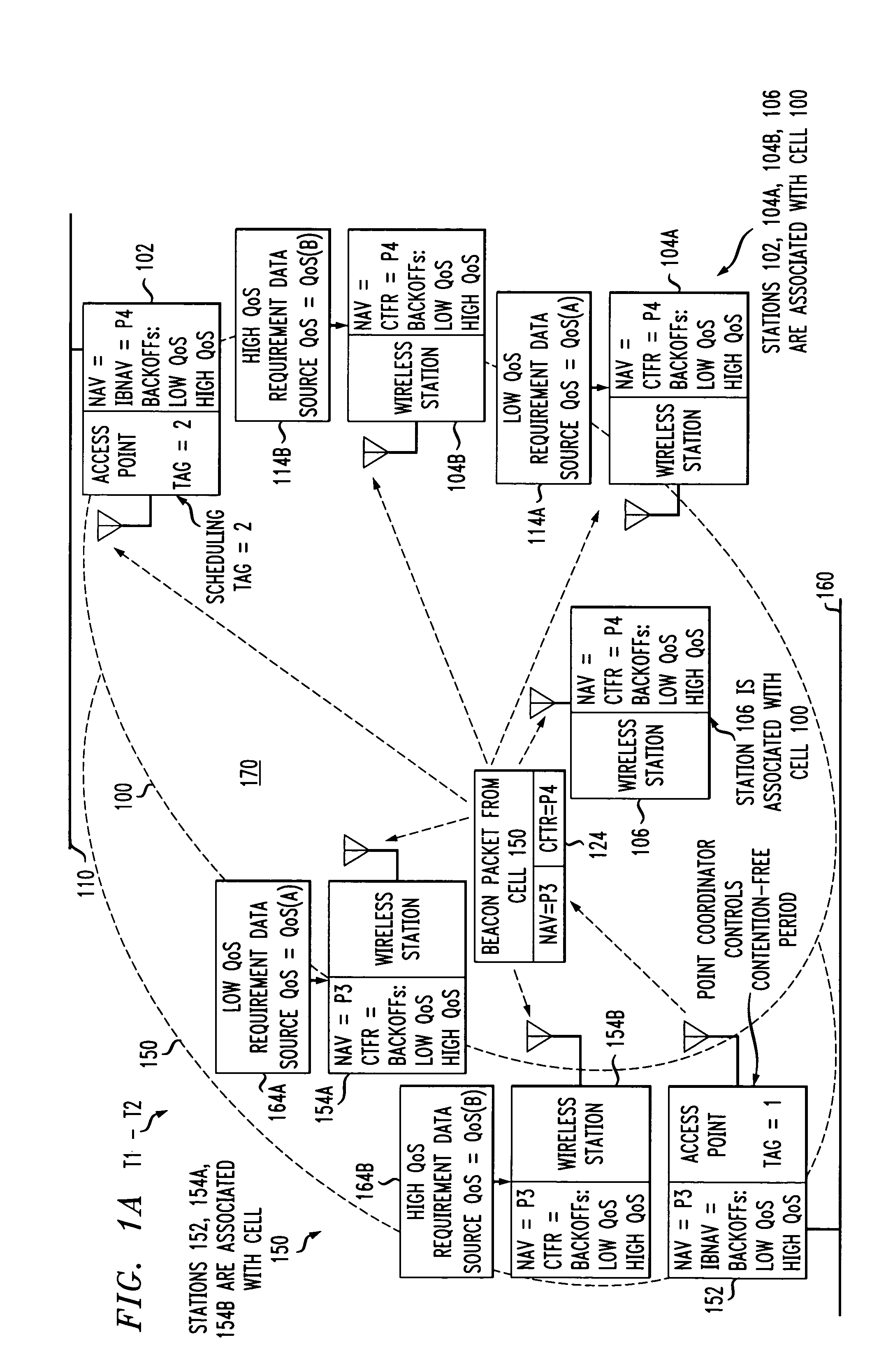
InactiveUS7773625B2Reduce conflictReduce distractionsSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess methodWireless lan
An access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) reduces interference between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations and an access point (AP) station. The access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) includes a fixed cycle time that reduces conflicts with PCFS from other cells. The PCFS from several cells are repeated in cycles of cycle period (CP), which is the contention-free period (CFP) of an access point times a factor that is a function of the number of overlapping cells. Periodic contention-free sessions (PCFSs) are generated, one from each overlapping cell. PCFS transmission attempts occur at the fixed specified time spacing following the start of the previous cycle. Each active AP sets a timer at CP and a PCFS is initiated when the timer expires. The timer is then reset and starts a new cycle.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Point-controlled contention arbitration in multiple access wireless LANs
InactiveUS20060092868A1Reduce contentionIncrease powerSpecial service provision for substationTransmission control/equalisingWireless lanActive state
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
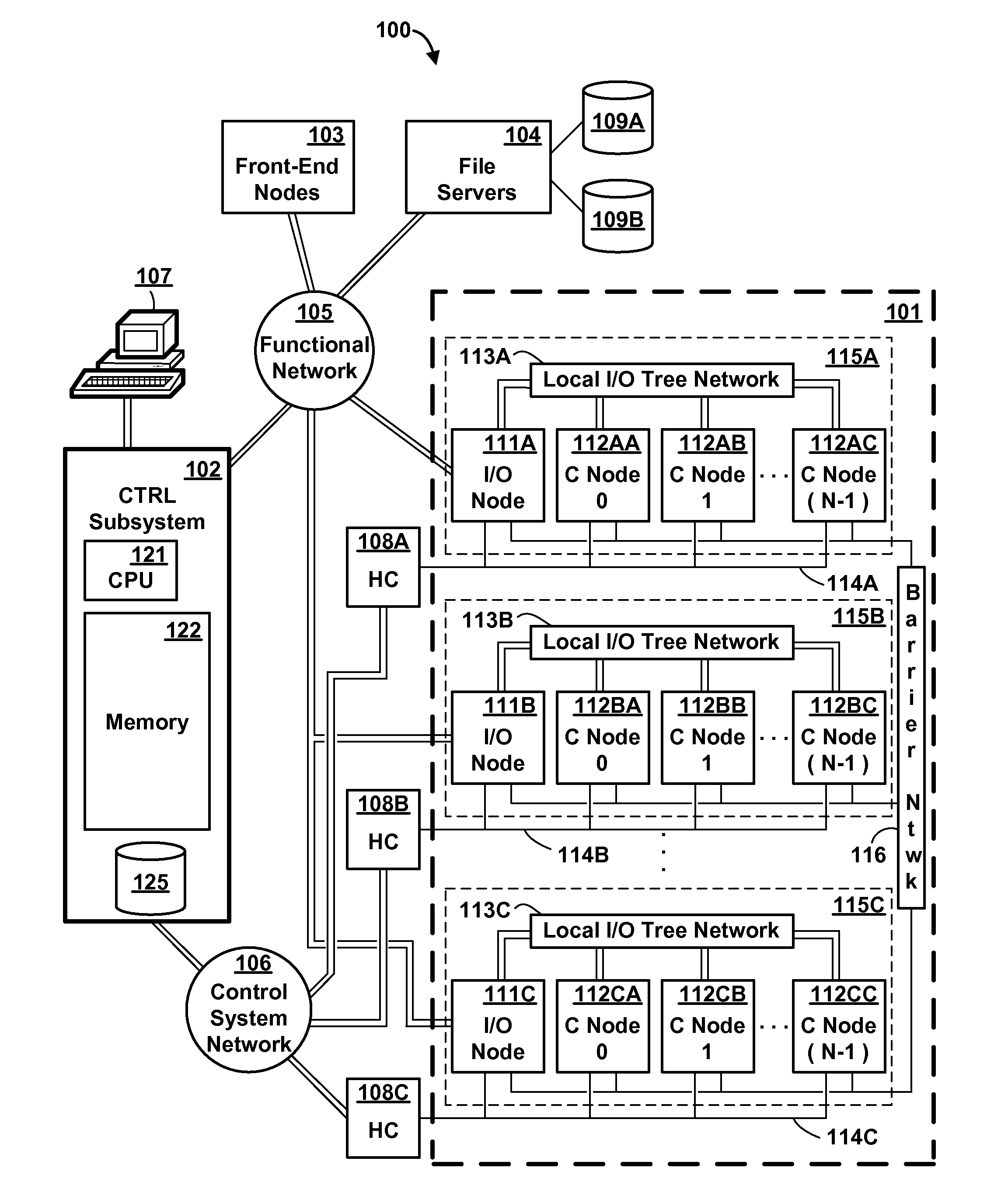
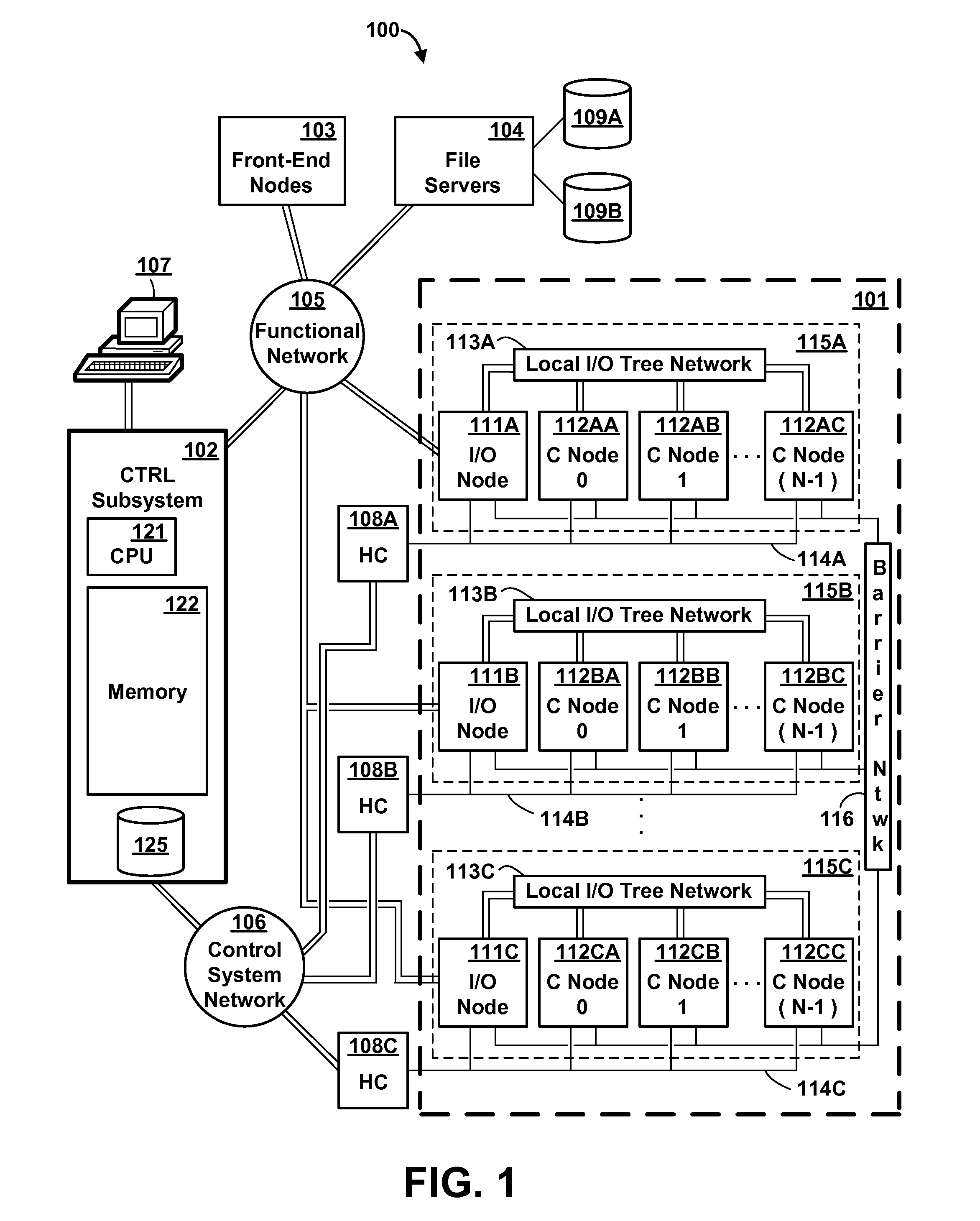
Method and apparatus for routing data in an inter-nodal communications lattice of a massively parallel computer system by employing bandwidth shells at areas of overutilization
InactiveUS20080186853A1Improve network efficiencyLower the volumeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityDistributed computing
A massively parallel computer system contains an inter-nodal communications network of node-to-node links. An automated routing strategy routes packets through one or more intermediate nodes of the network to reach a final destination. The default routing strategy is altered responsive to detection of overutilization of a particular path of one or more links, and at least some traffic is re-routed by distributing the traffic among multiple paths (which may include the default path). An alternative path may require a greater number of link traversals to reach the destination node.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hash table operations with improved cache utilization
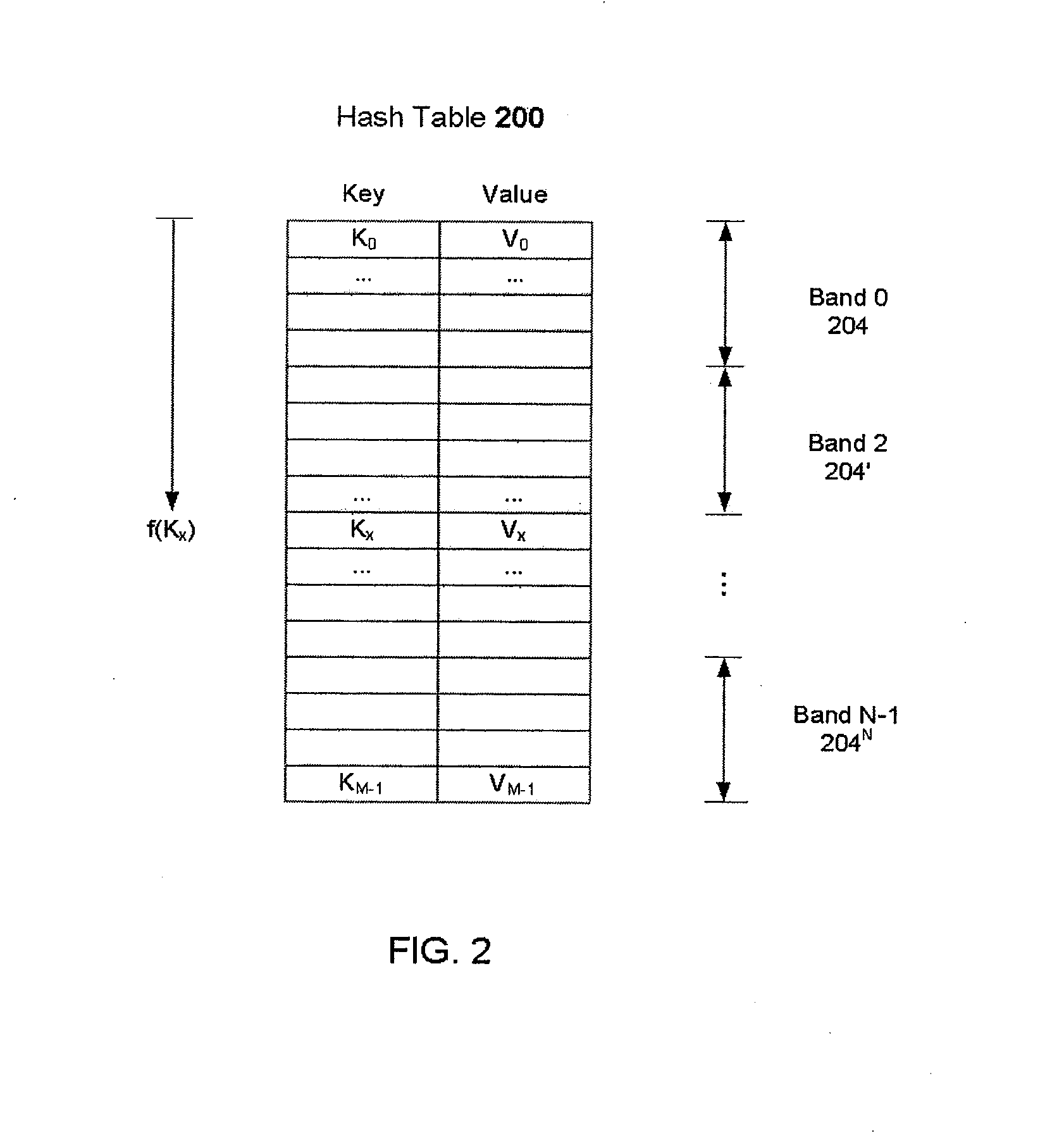
InactiveUS20080215849A1Improve cache utilizationImprove localityDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsGeneral purposeFalse sharing
Method and apparatus for building large memory-resident hash tables on general purpose processors. The hash table is broken into bands that are small enough to fit within the processor cache. A log is associated with each band and updates to the hash table are written to the appropriate memory-resident log rather than being directly applied to the hash table. When a log is sufficiently full, updates from the log are applied to the hash table insuring good cache reuse by virtue of false sharing of cache lines. Despite the increased overhead in writing and reading the logs, overall performance is improved due to improved cache line reuse.
Owner:CERTEON
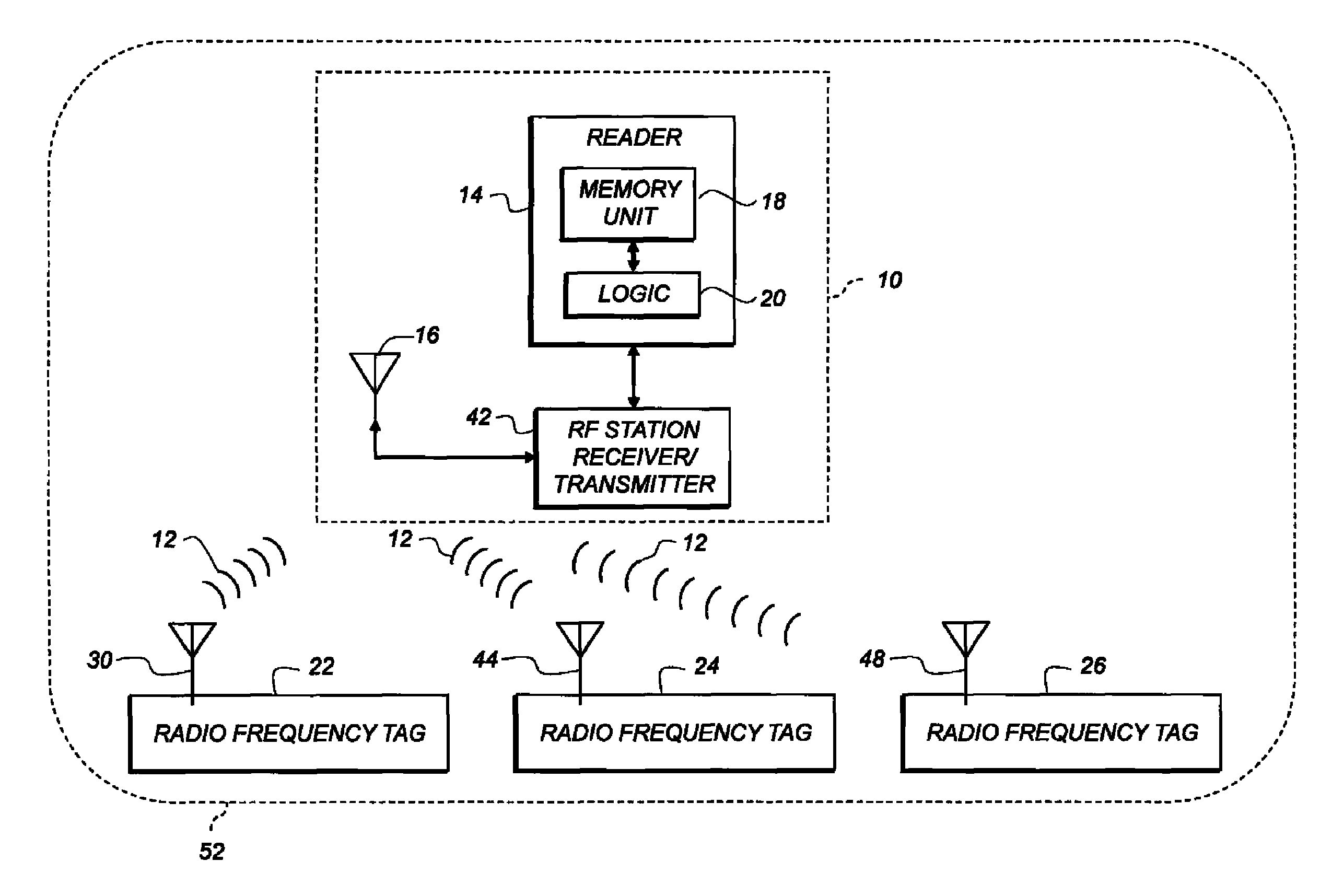
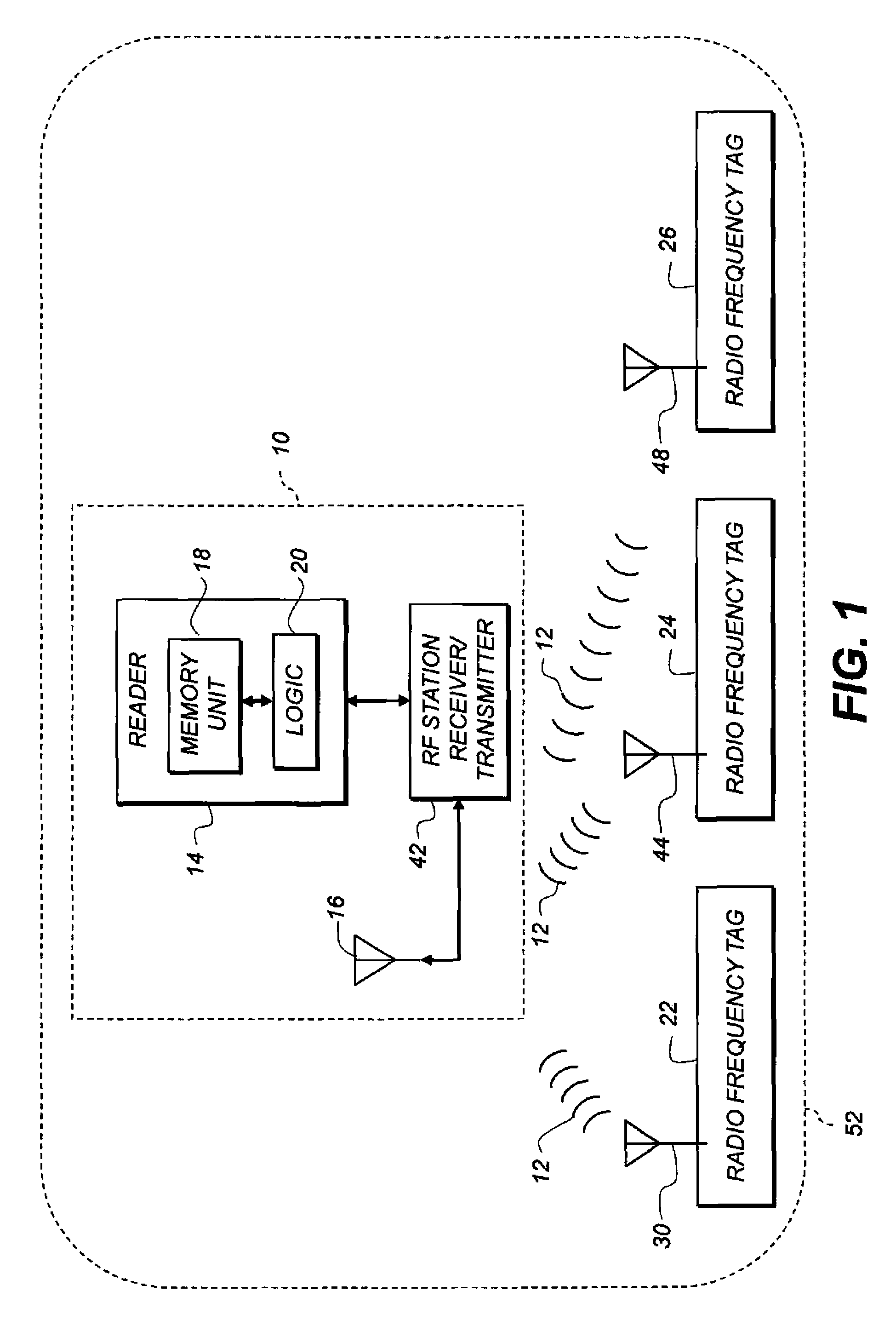
RFID system with multiple tag transmit frequencies
InactiveUS8937531B2Reduce contentionComplete banking machinesTicket-issuing apparatusLength waveElectrical and Electronics engineering
An RFID system has an active tag with one antenna inside, and one outside, an RF-blocking enclosure having a port with a selected shortest dimension. The RFID reader is located outside the enclosure and uses a selected RF read frequency range. The RFID tag simultaneously transmits on a plurality of frequencies corresponding to respective wavelengths smaller than the selected shortest dimension, so that a respective beat frequency is defined between two of the frequencies. The beat frequency is within the selected RF uplink frequency range. The tag transmits a first signal at a first one of the plurality of frequencies using the interior antenna and a second signal at a second, different one of the plurality of frequencies using the exterior antenna.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Apparatus and method to improve performance of reads from and writes to shared memory locations
InactiveUS20020035675A1Easy to readShorten the timeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingComputer architectureEngineering
According to the present invention, an apparatus and method for improving reads from and writes to shared memory locations is disclosed. By giving writes priority over reads, the current invention can decrease the time associated with certain sequences of reads from and writes to shared memory locations. In particular, load-invalidate-load sequences are changed to load-load sequences with the current invention. Furthermore, contention for a shared memory location will be reduced in particular situations when using the current invention.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multiprocessing apparatus
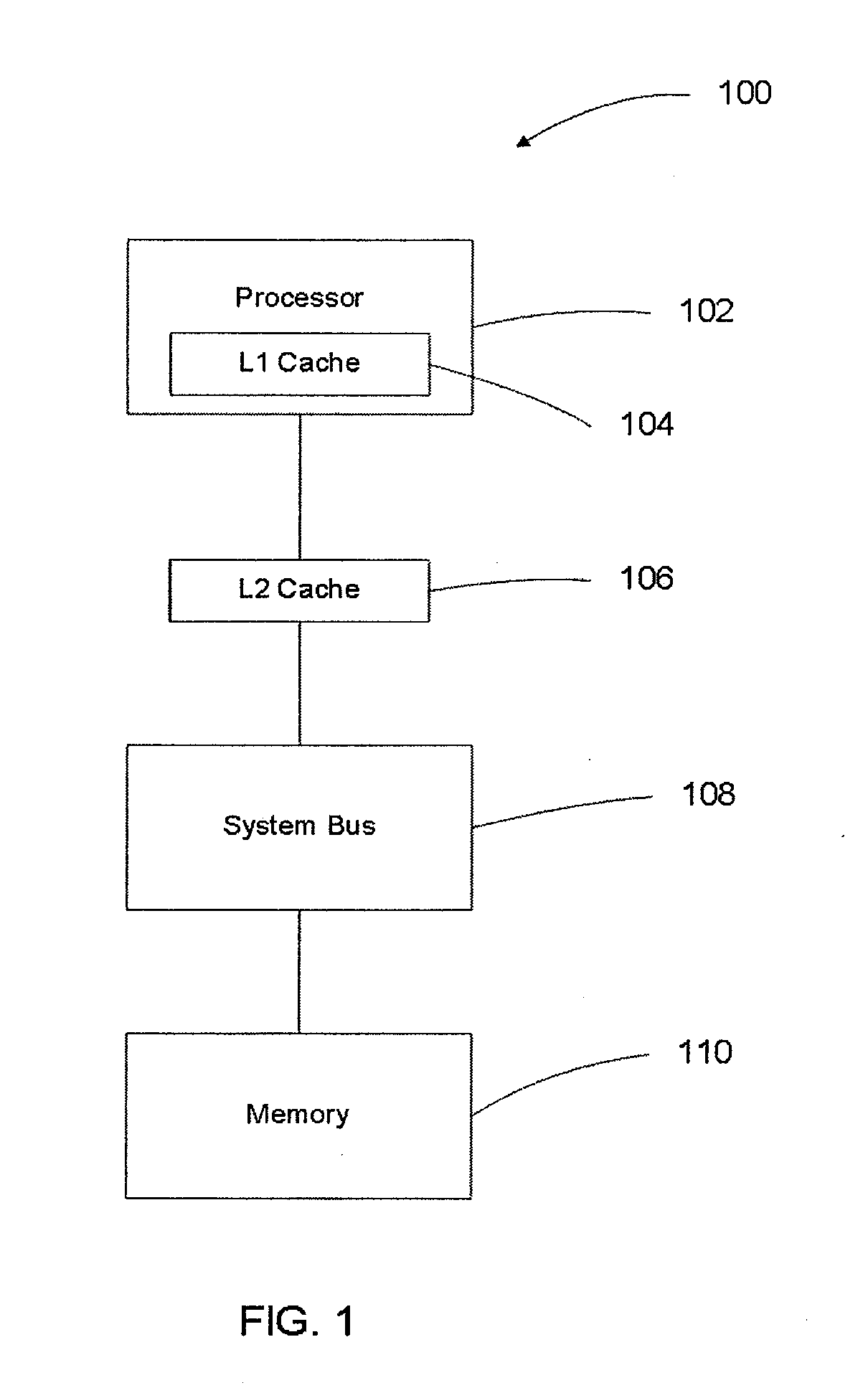
InactiveUS20060059317A1Miss occurrence ratioReducing bus contentionMemory systemsComputer architectureControl cell
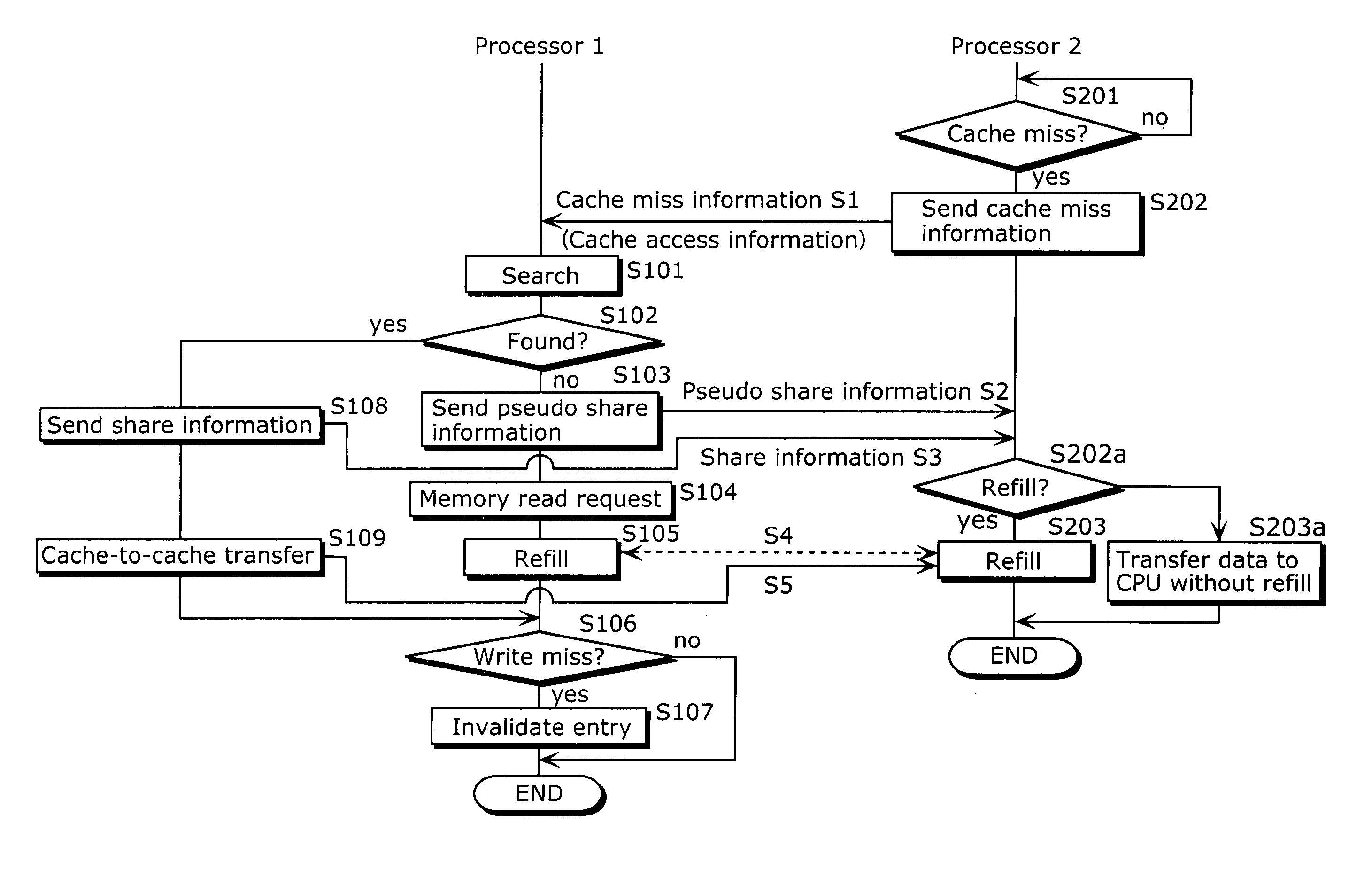
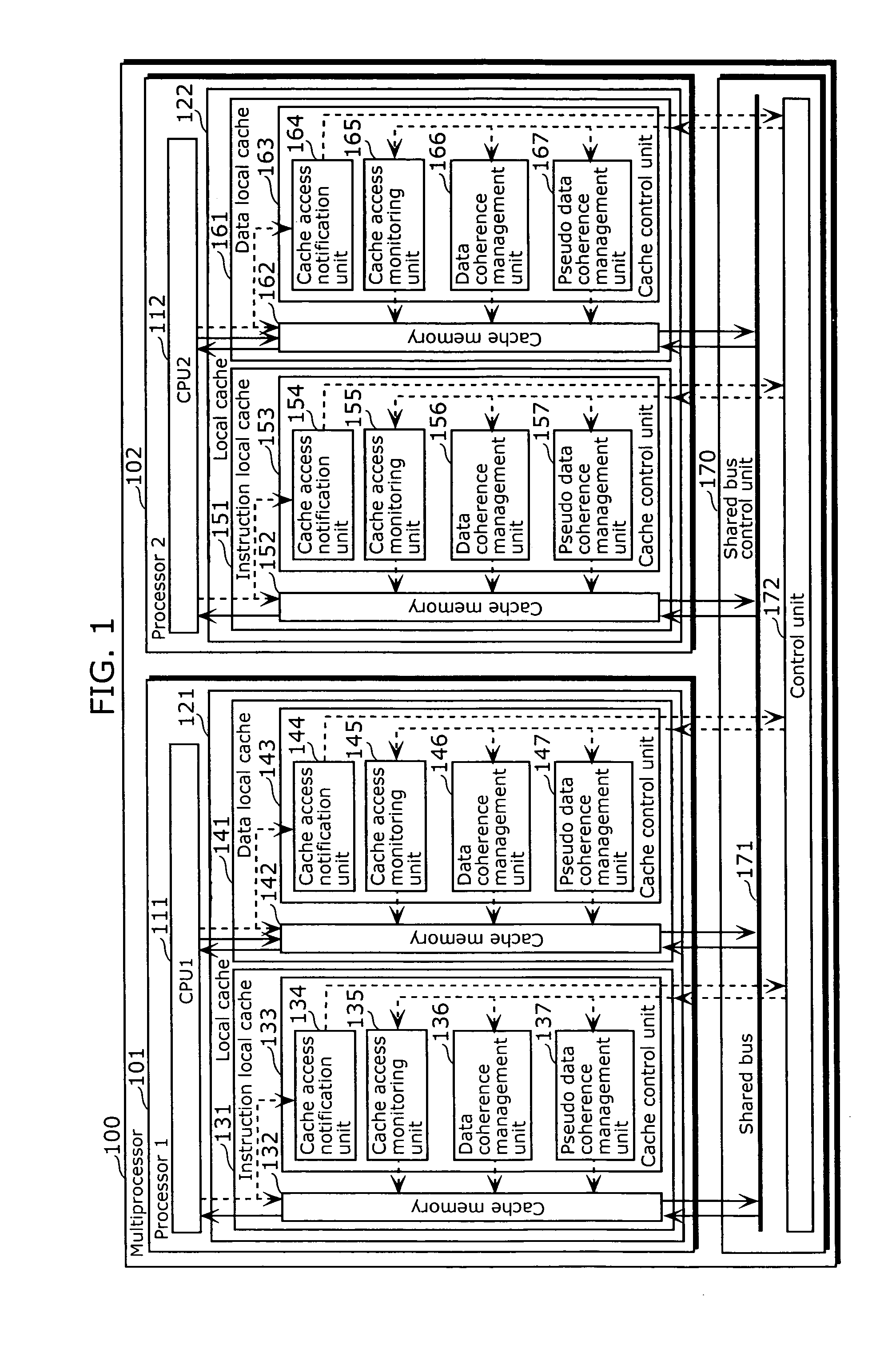
The multiprocessing apparatus of the present invention is a multiprocessing apparatus including a plurality of processors, a shared bus, and a shared bus controller, wherein each of the processors includes a central processing unit (CPU) and a local cache, each of the local caches includes a cache memory, and a cache control unit that controls the cache memory, each of the cache control units includes a data coherence management unit that manages data coherence between the local caches by controlling data transfer carried out, via the shared bus, between the local caches, wherein at least one of the cache control units (a) monitors a local cache access signal, outputted from another one of the processors, for notifying an occurrence of a cache miss, and (b) notifies pseudo information to the another one of the processors via the shared bus controller, the pseudo information indicating that data corresponding to the local cache access signal is stored in the cache memory of the local cache that includes the at least one of the cache control units, even in the case where the data corresponding to the local cache access signal is not actually stored.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com