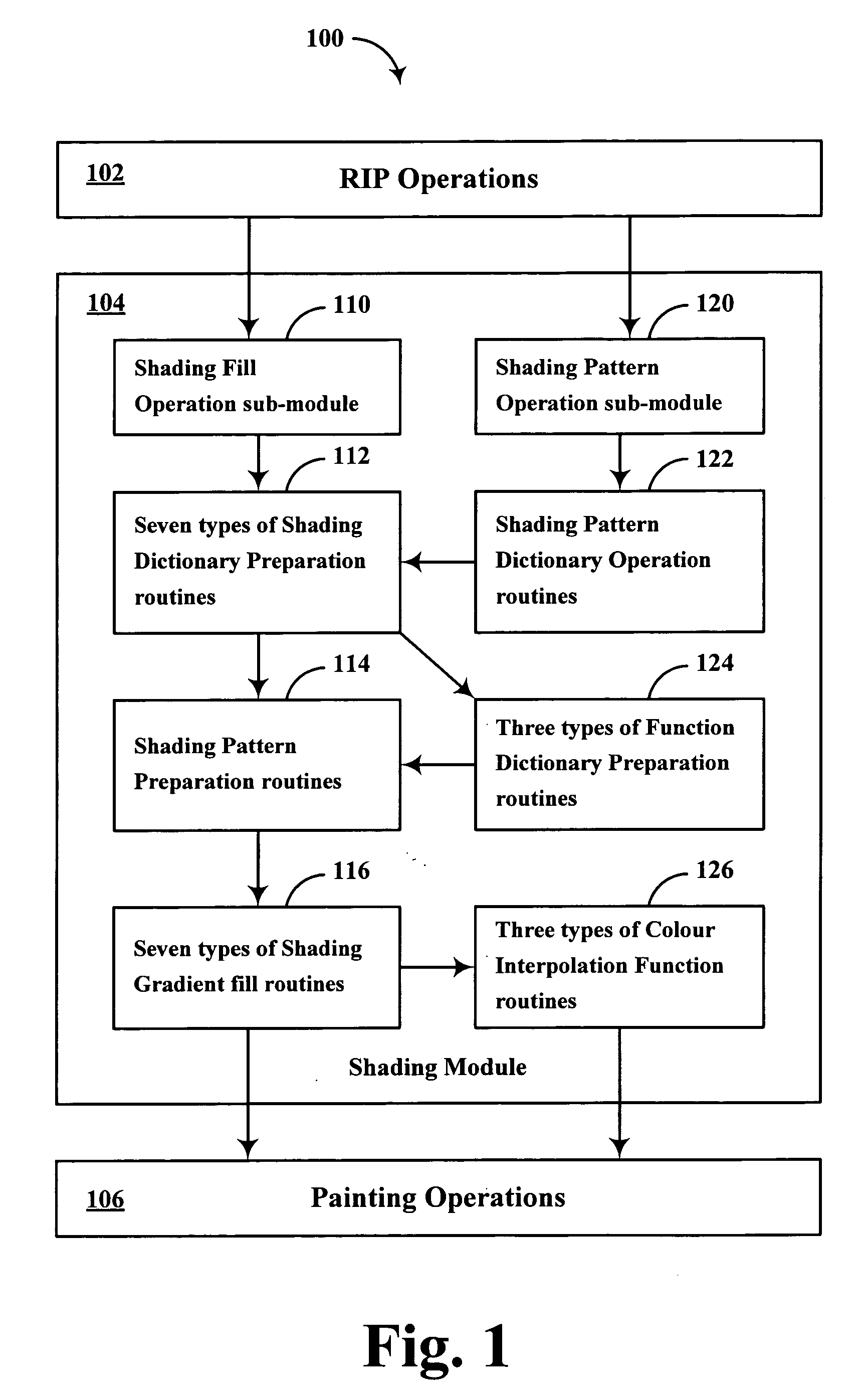
Patents
Literature
152 results about "Raster image processor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
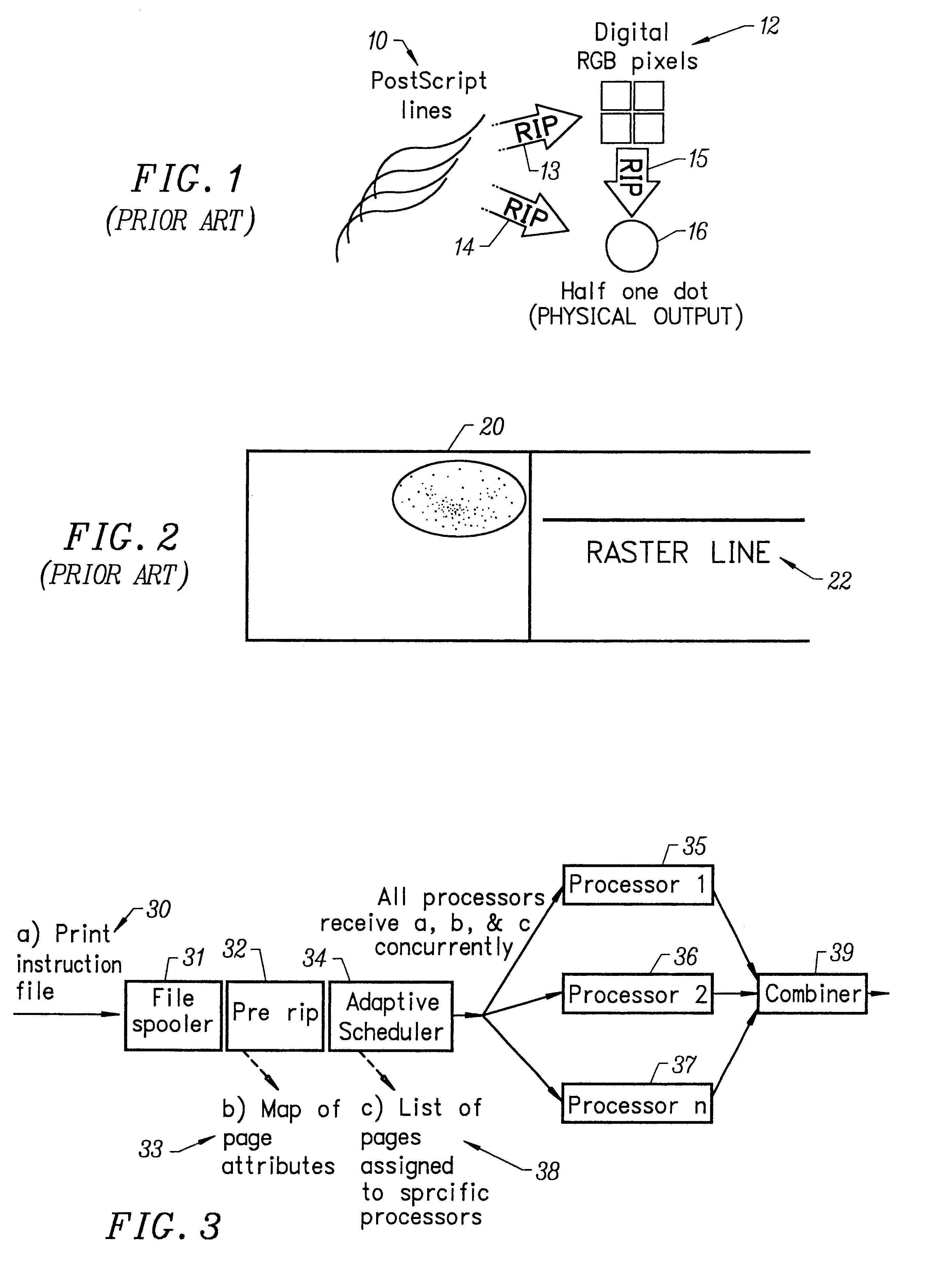
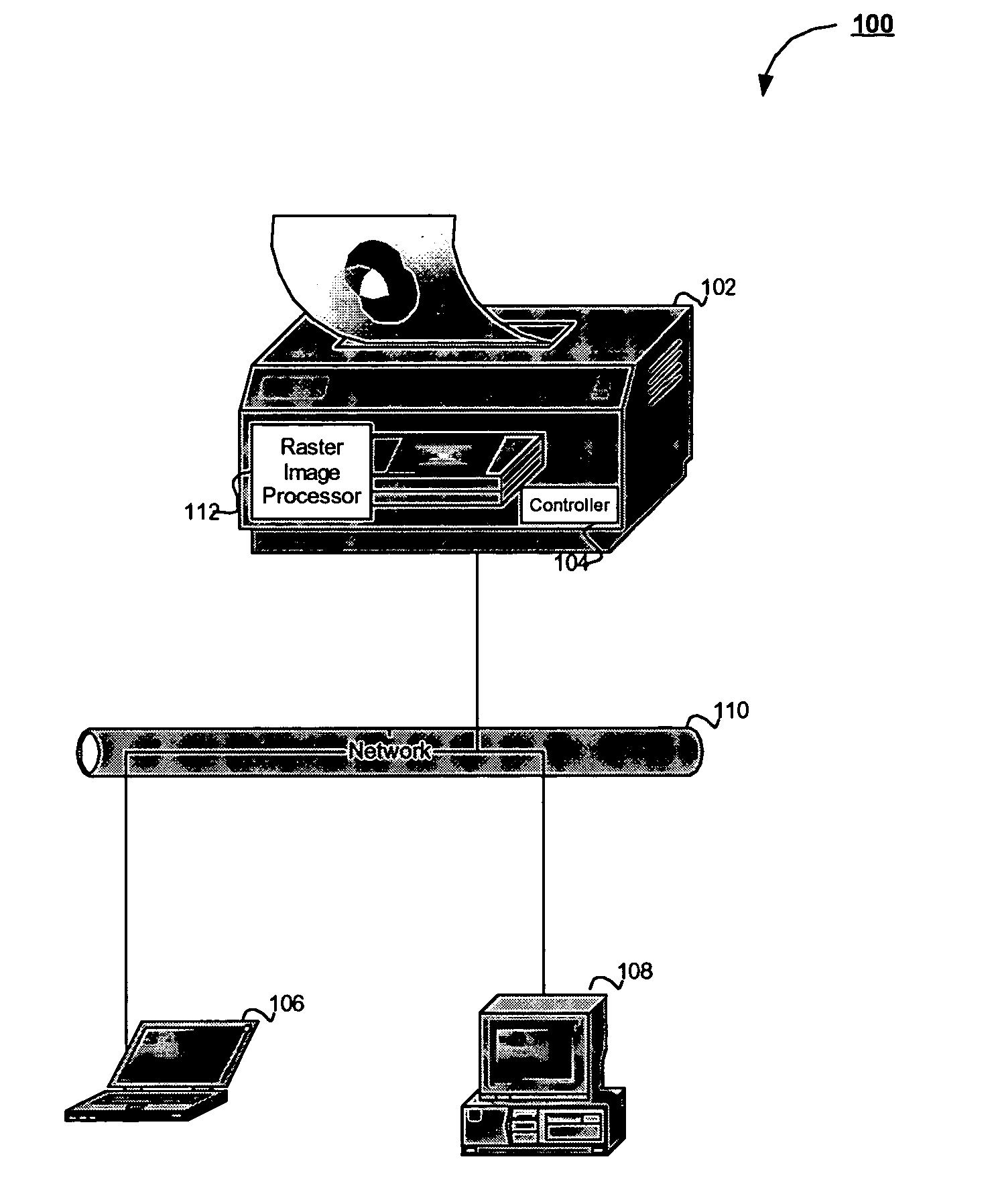
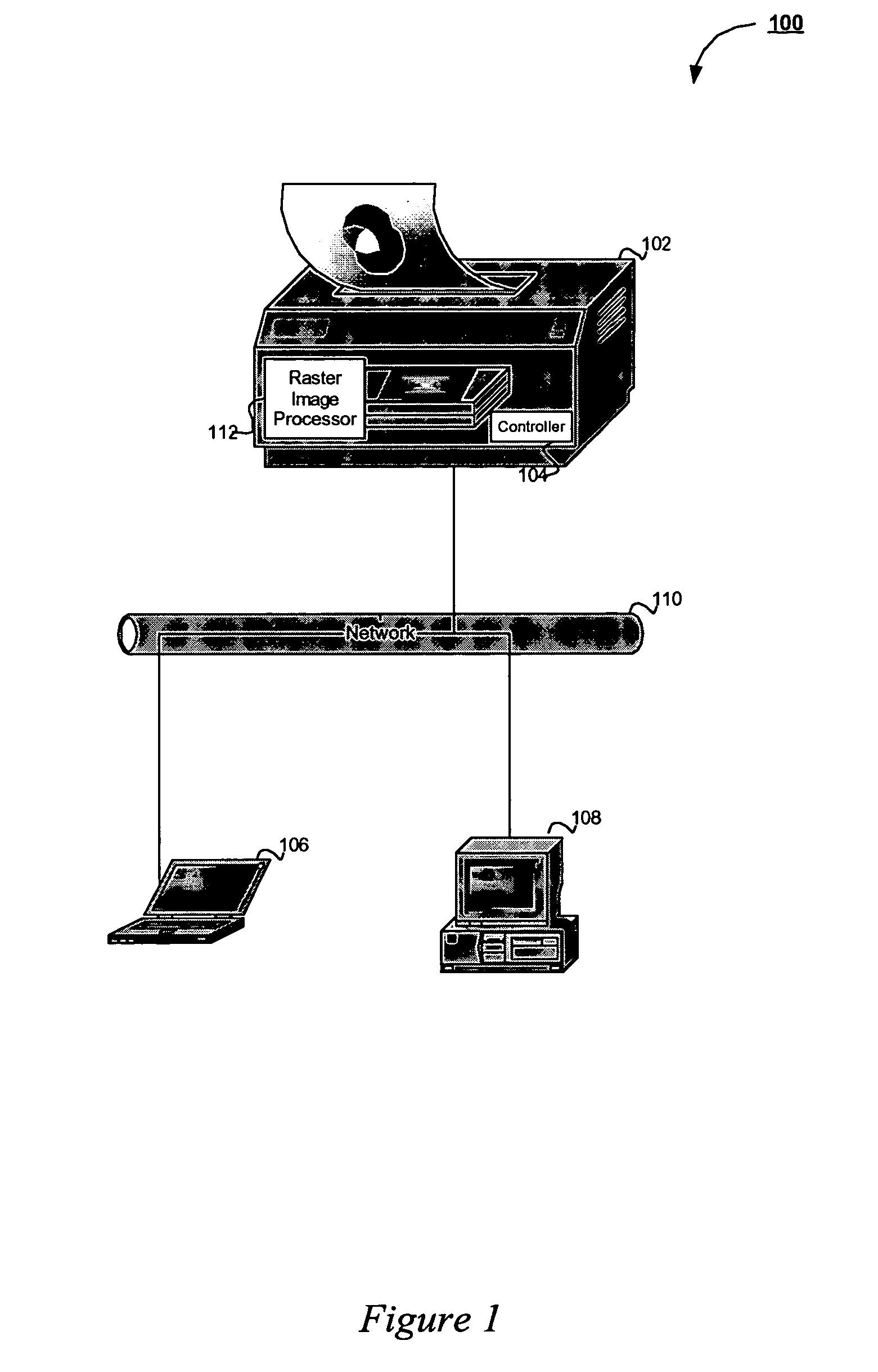
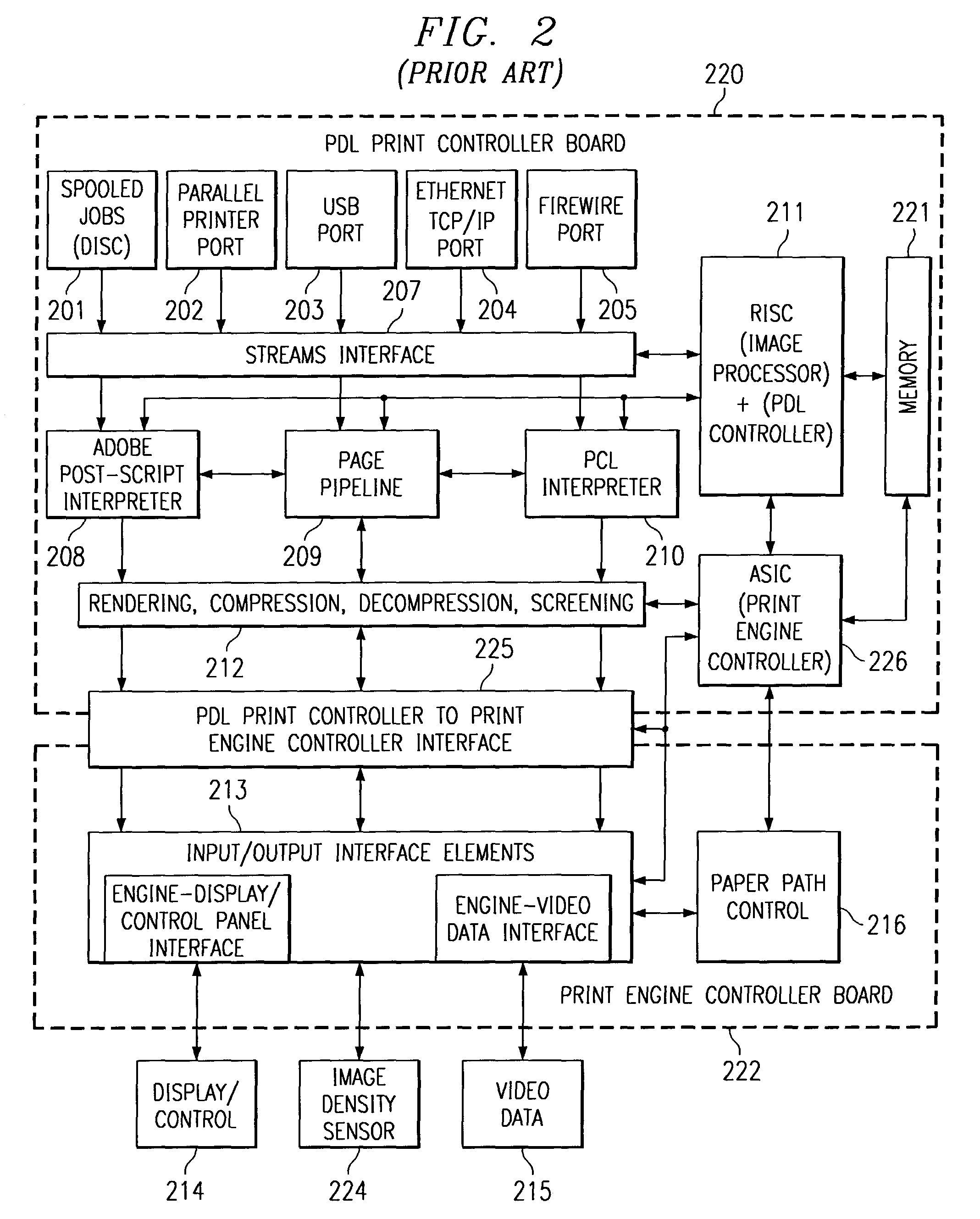
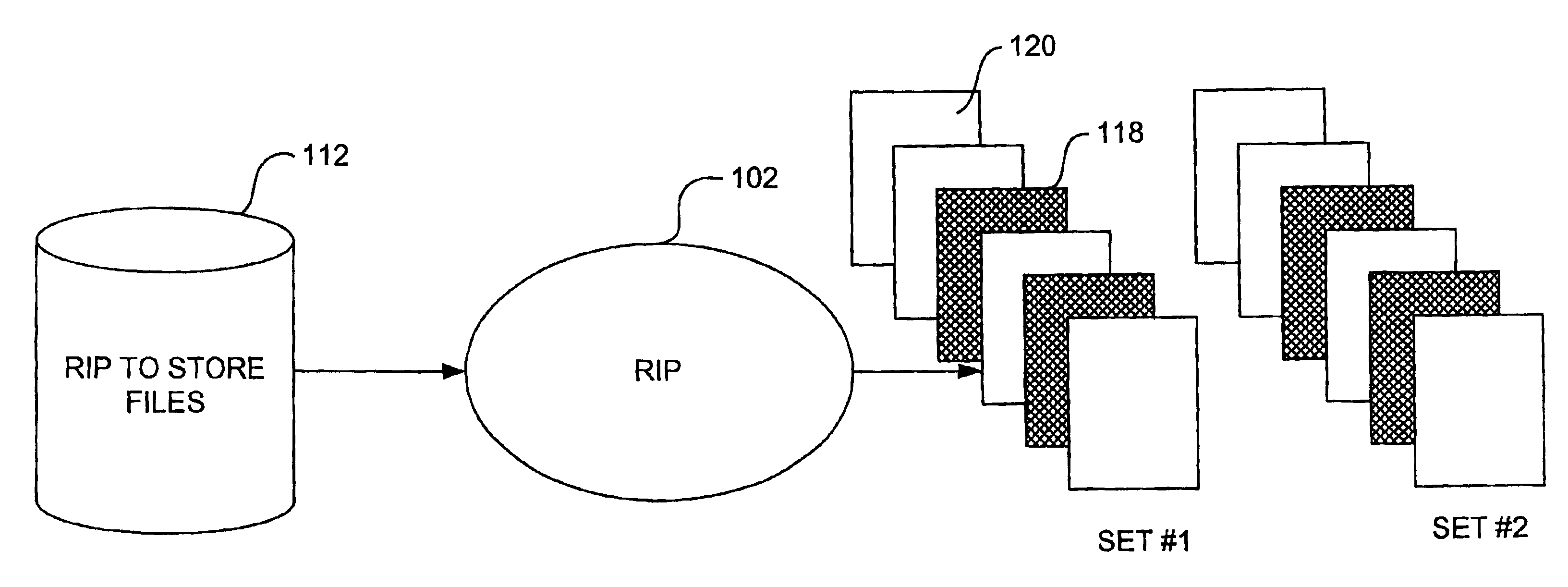
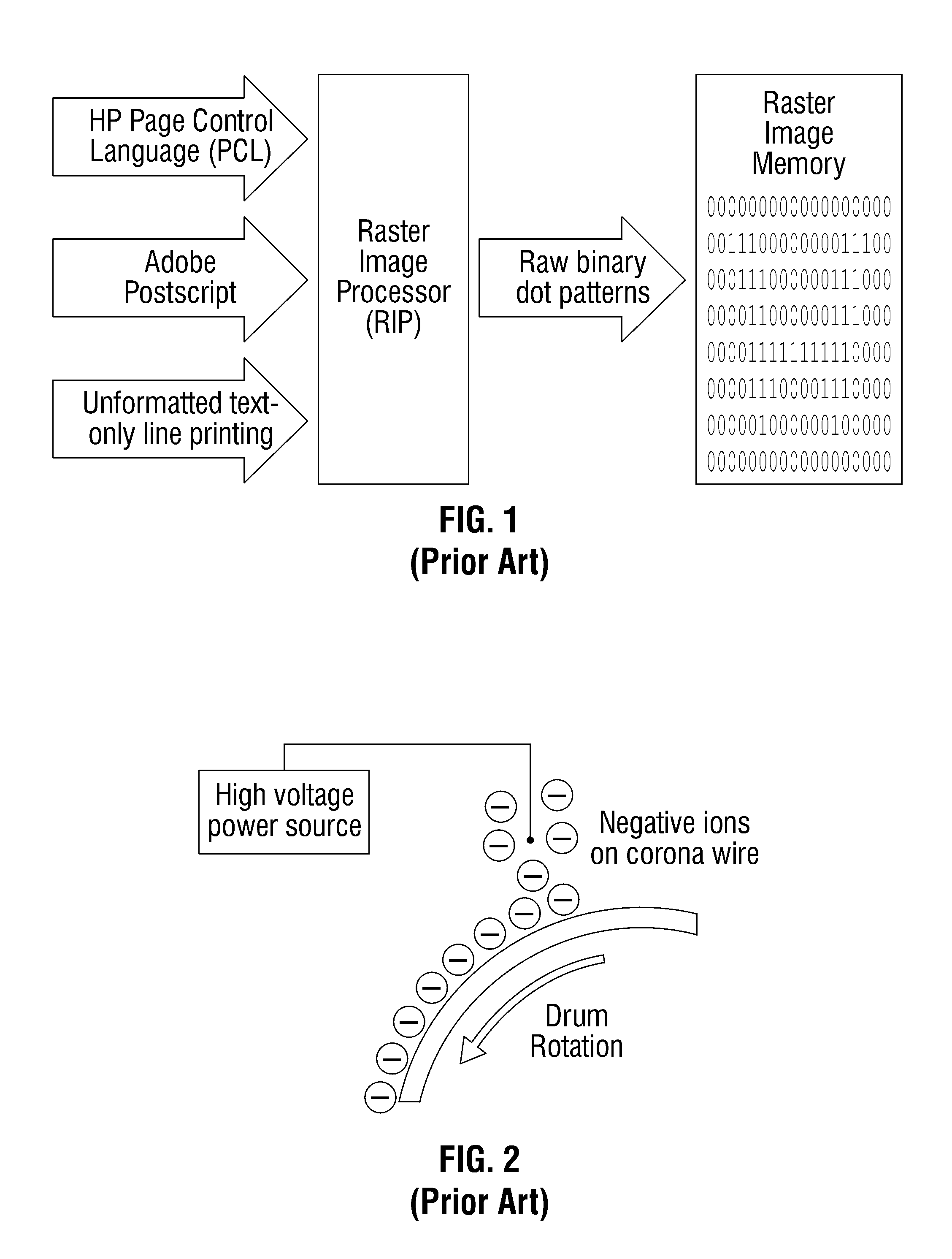
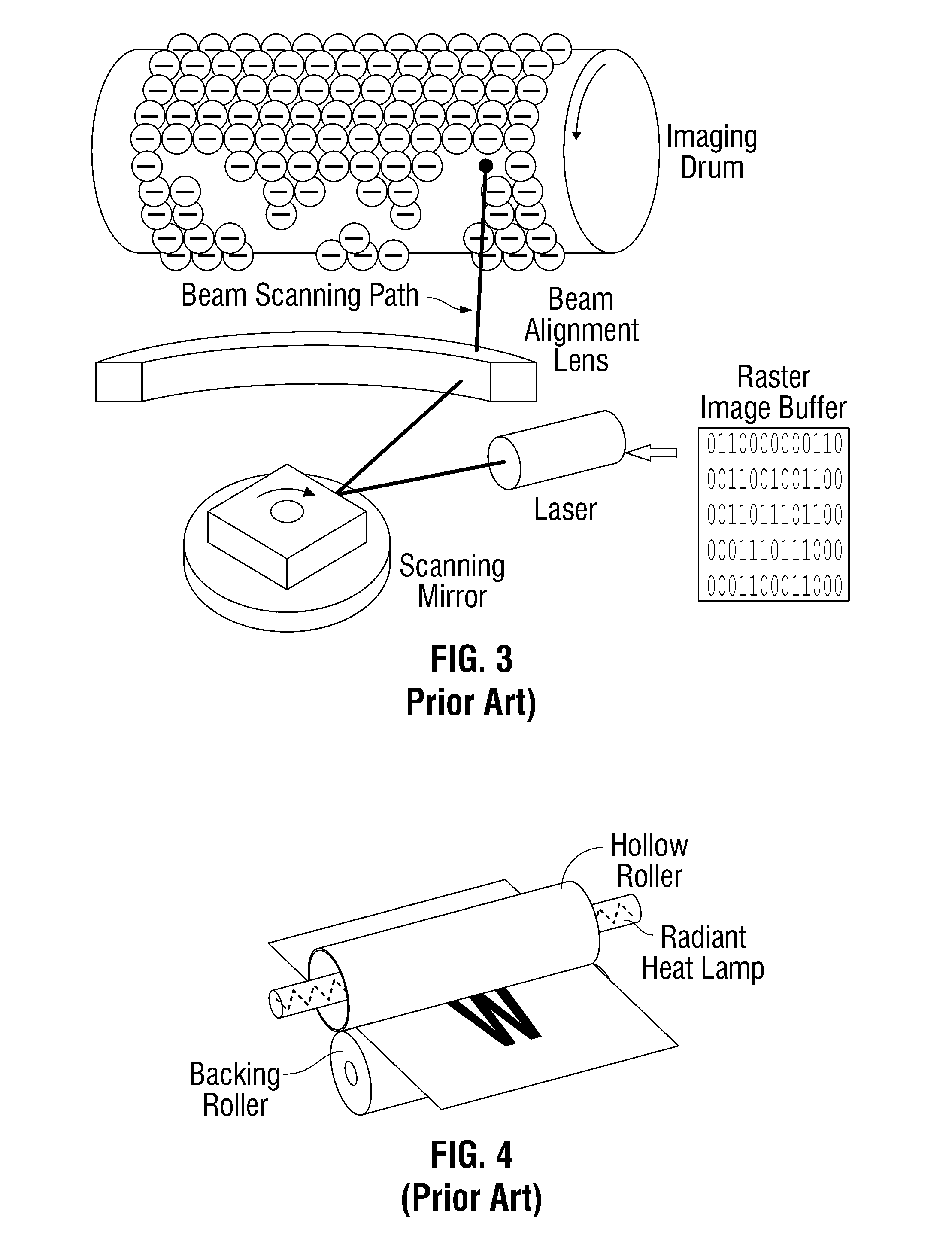
A raster image processor (RIP) is a component used in a printing system which produces a raster image also known as a bitmap. Such a bitmap is used by a later stage of the printing system to produce the printed output. The input may be a page description in a high-level page description language such as PostScript, PDF, or XPS. The input can be or include bitmaps of higher or lower resolution than the output device, which the RIP resizes using an image scaling algorithm.
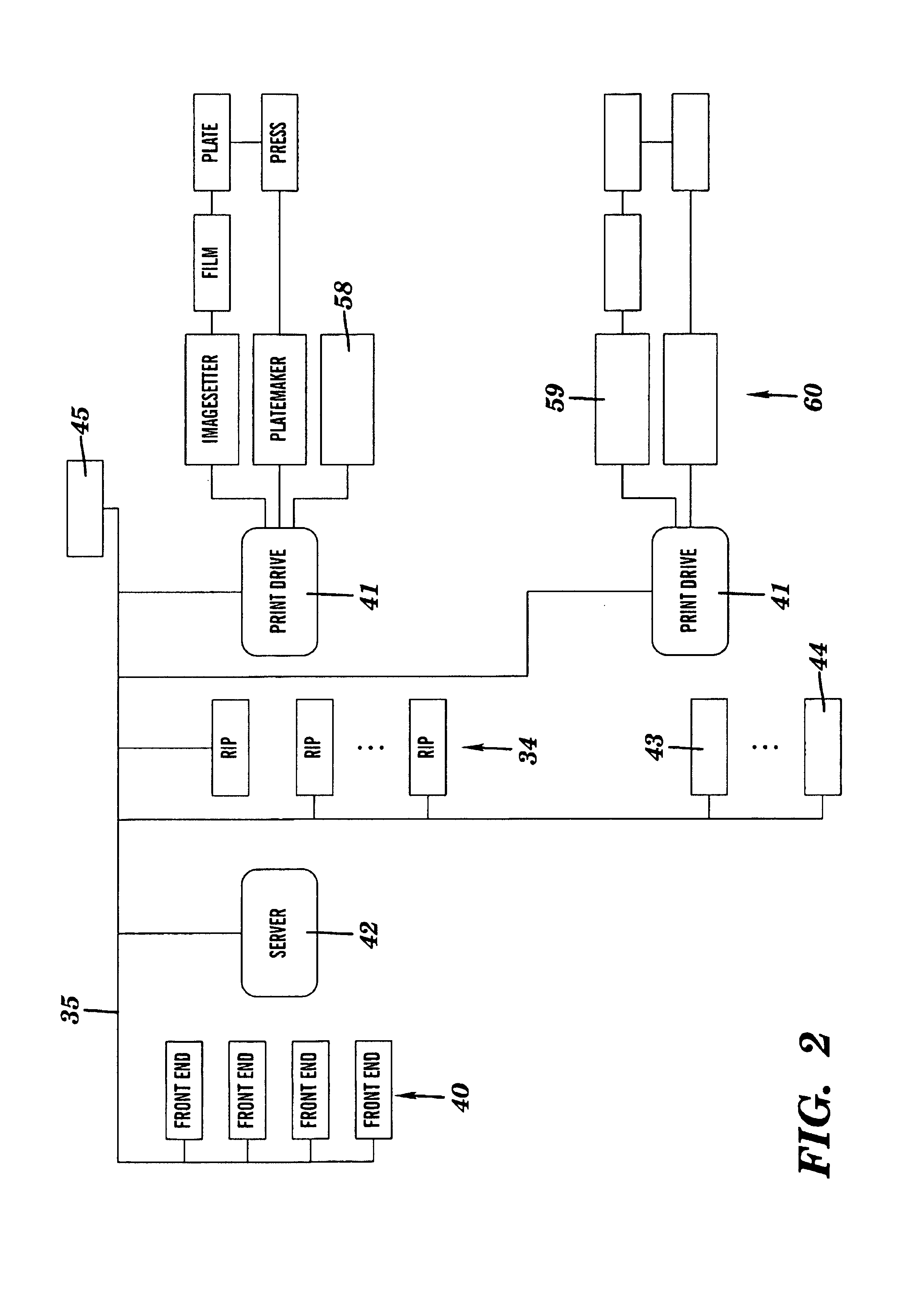
Printing method and apparatus having multiple raster image processors
InactiveUS6559958B2Reduce contentionReduce overheadDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsRaster image processor
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING INC
Printing method and apparatus having multiple raster image processors
InactiveUS20020060801A1Reduction in concurrent bus contentionReduce overheadDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsImage resolution
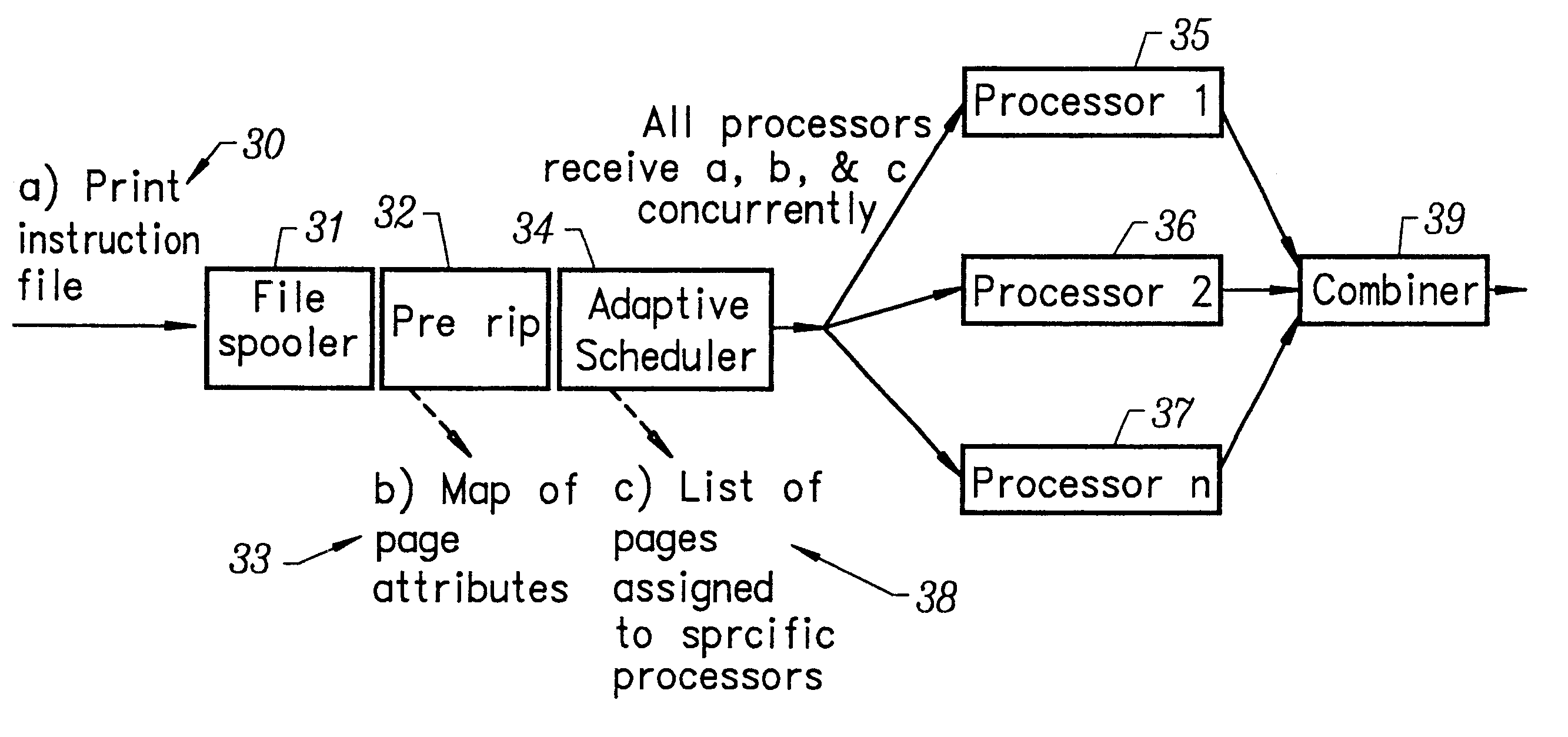
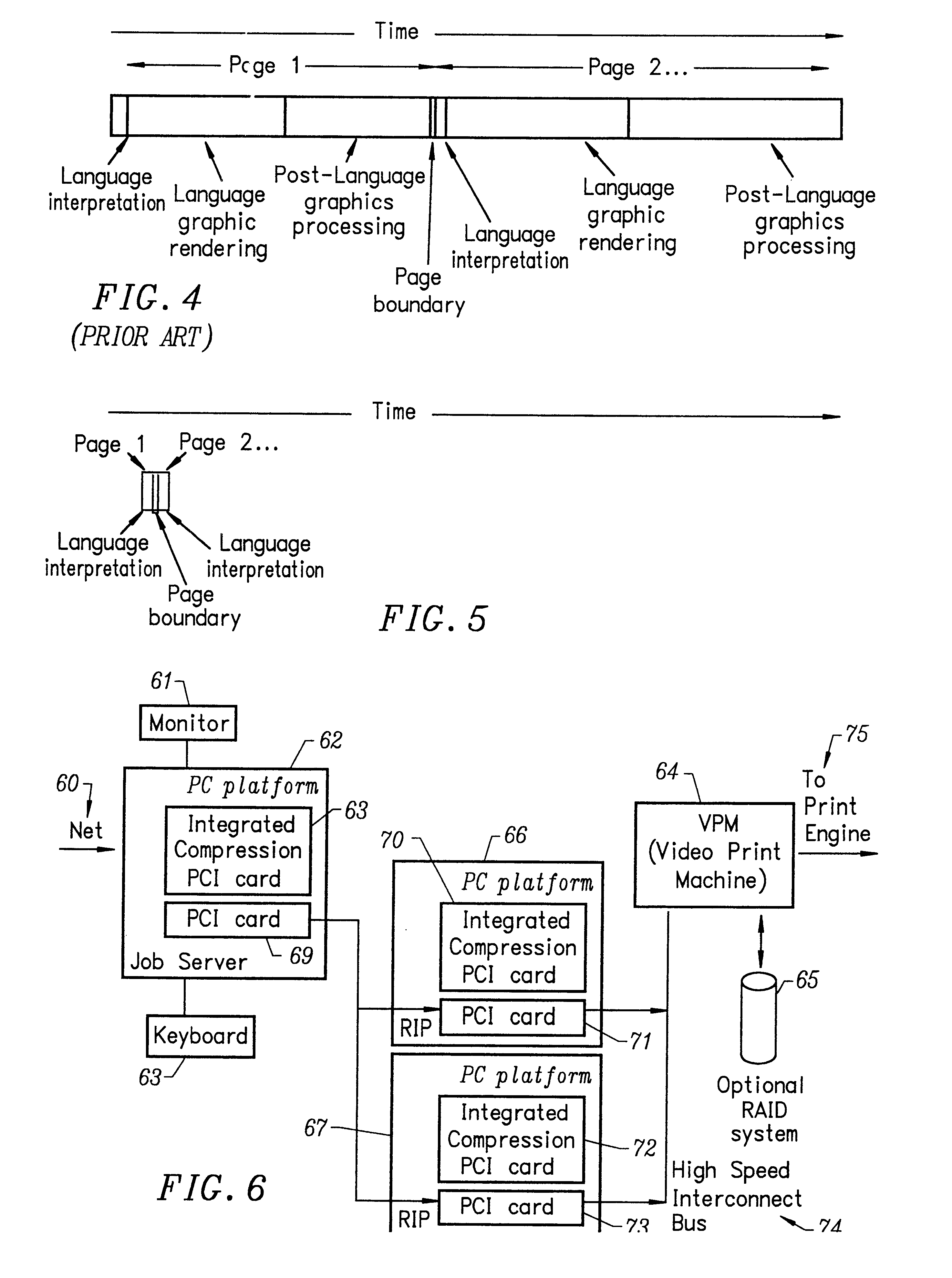
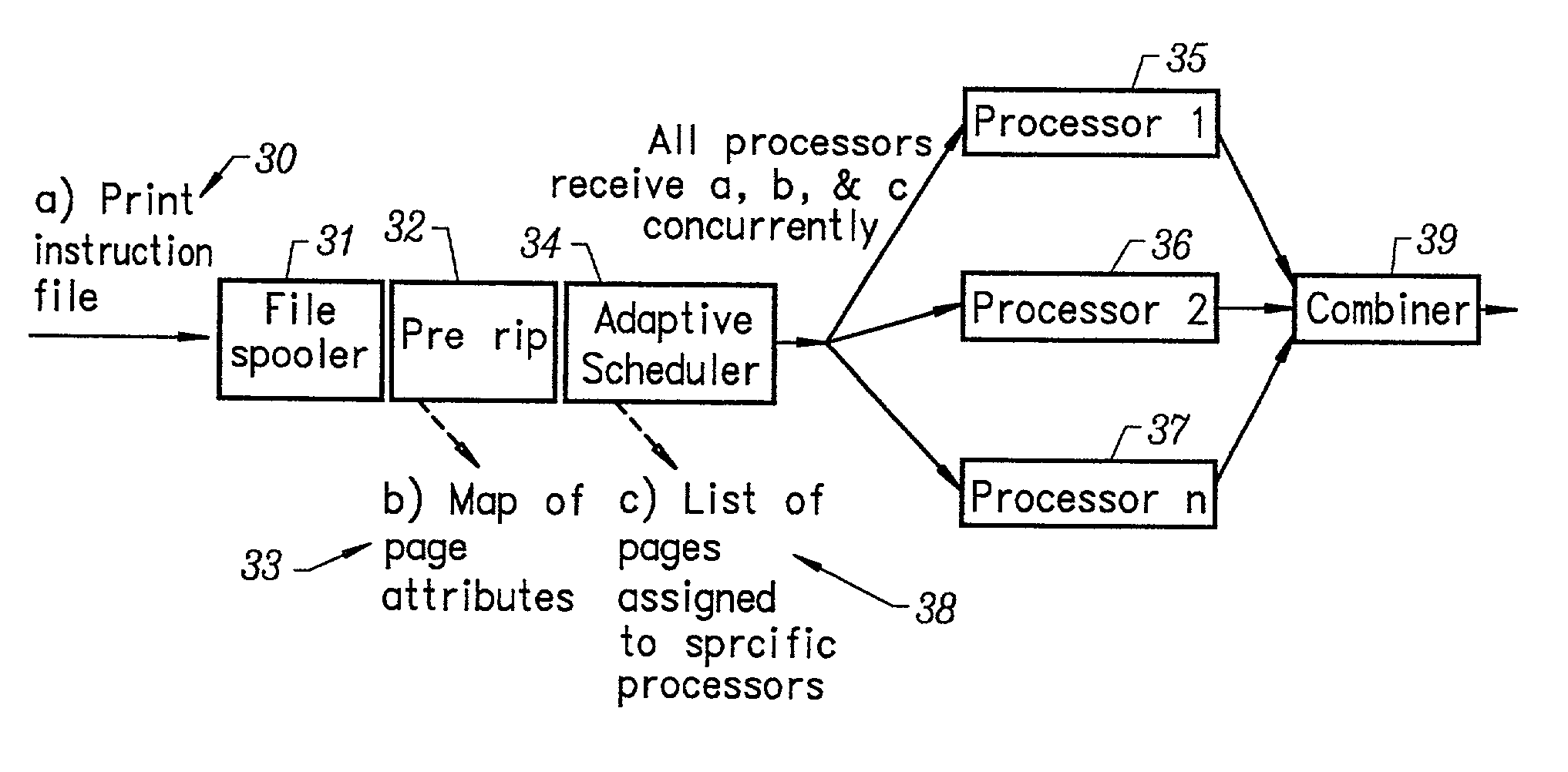
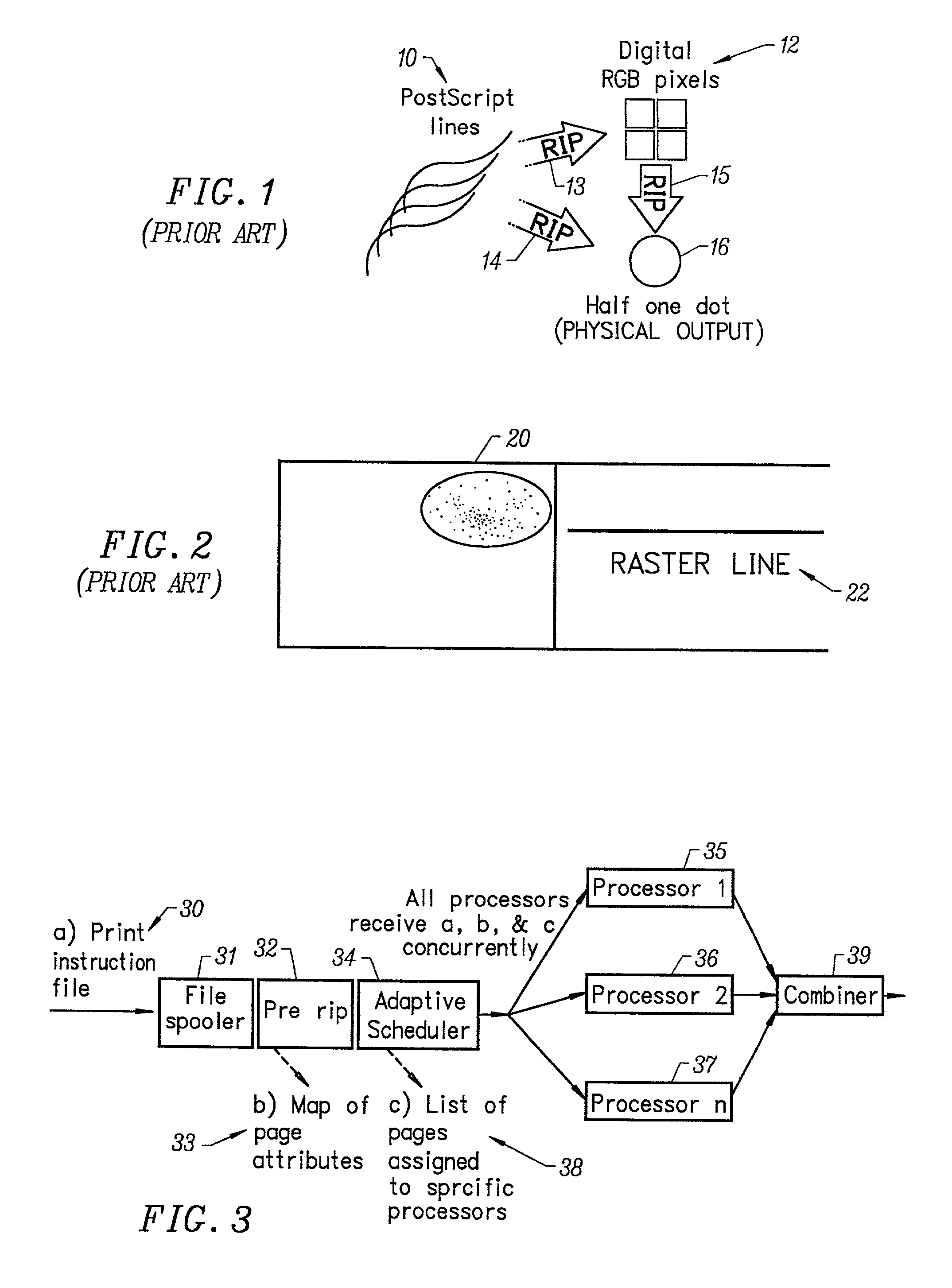
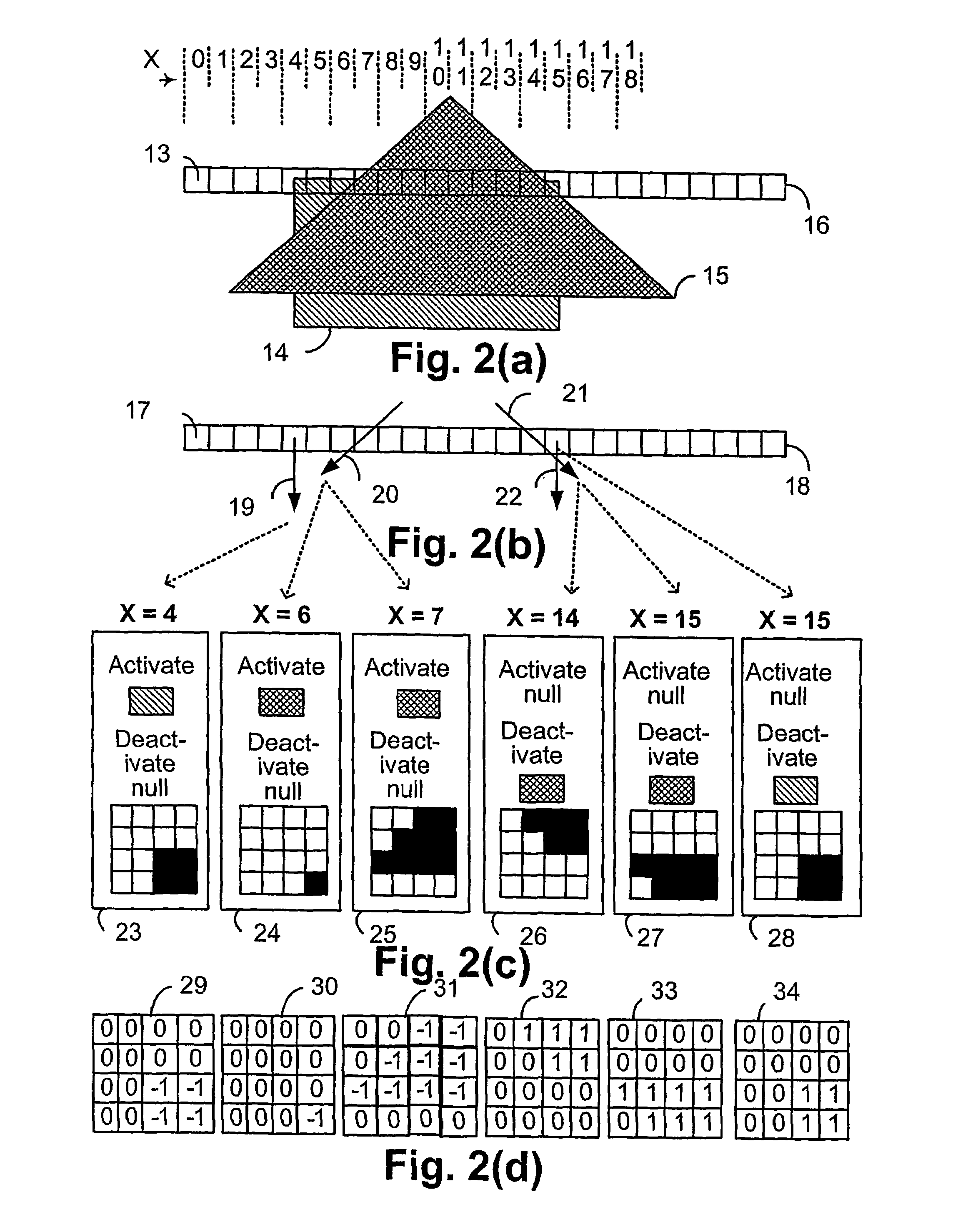
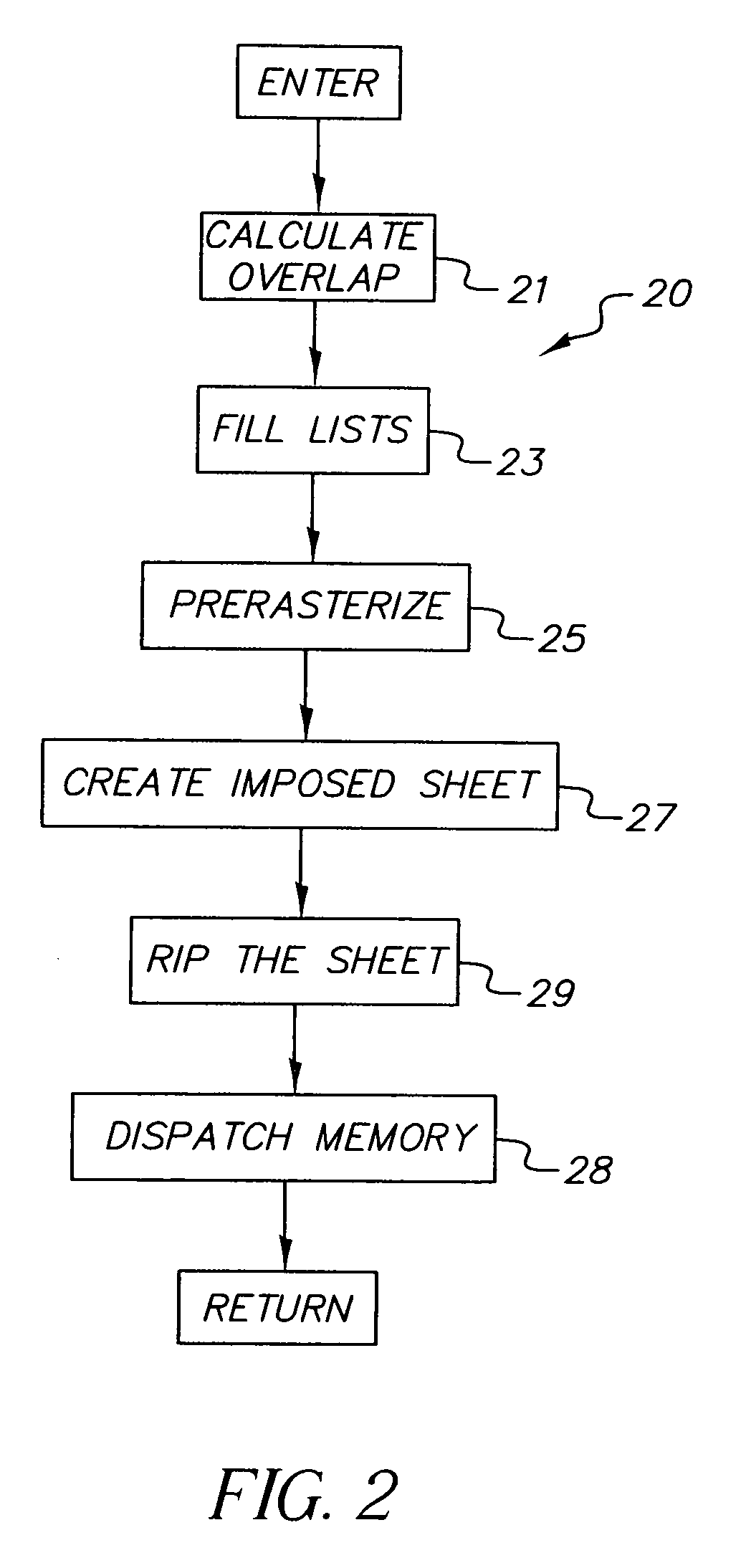
A multiple raster image processor (RIP) system which enables faster system performance over multiple processors includes a zero RIP feature consisting of a language interpreter sub-RIP that interprets a print instruction file but does not process the graphics rendering steps or the post-language processing operators. The zero RIP discovers page related attributes for individual pages within a multipage job and reports any potential errors or warnings with the file. A thumb RIP consists of a very low resolution RIP that is used specifically for the creation of thumbnail images. A skip RIP interprets selected pages in a way that skips all or most of the processing for that page. Pages to be skipped are scheduled for a different processor, thereby saving processing time and enabling the provision of a multiple processor RIP. A rules based scheduler on an page / face or machine characteristic basis supports a dynamic assignment and assessment algorithm. Scheduling results in optimum use of available resources and requested print constraints (e.g. constrained time window) and optimum use of system bandwidth (e.g. bandwidth control). Archiving and editing capability enables tagged archiving of jobs or parts of jobs in a post RIPed (i.e. raster) format in a special cache located with in the multiRIP system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
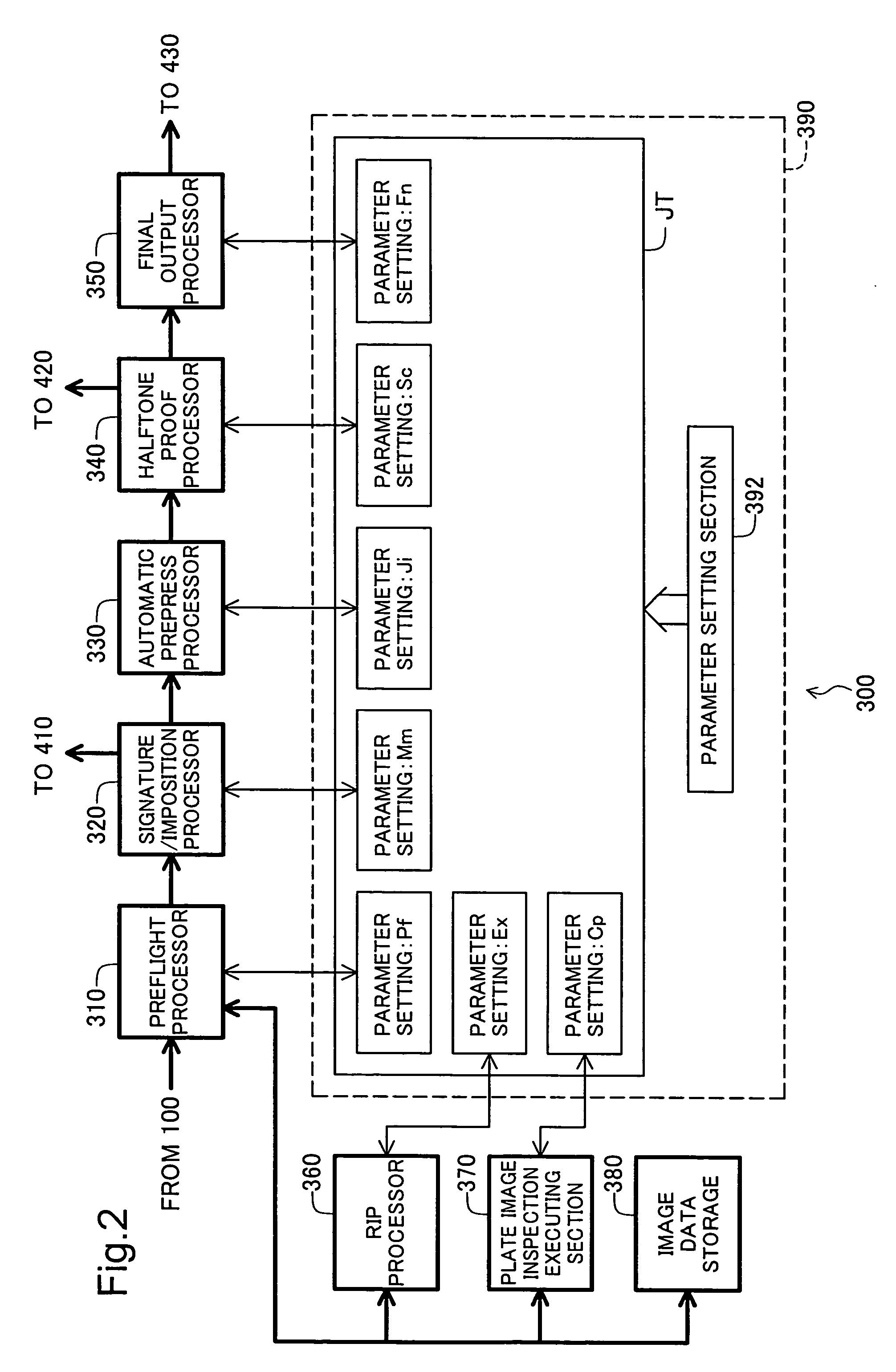
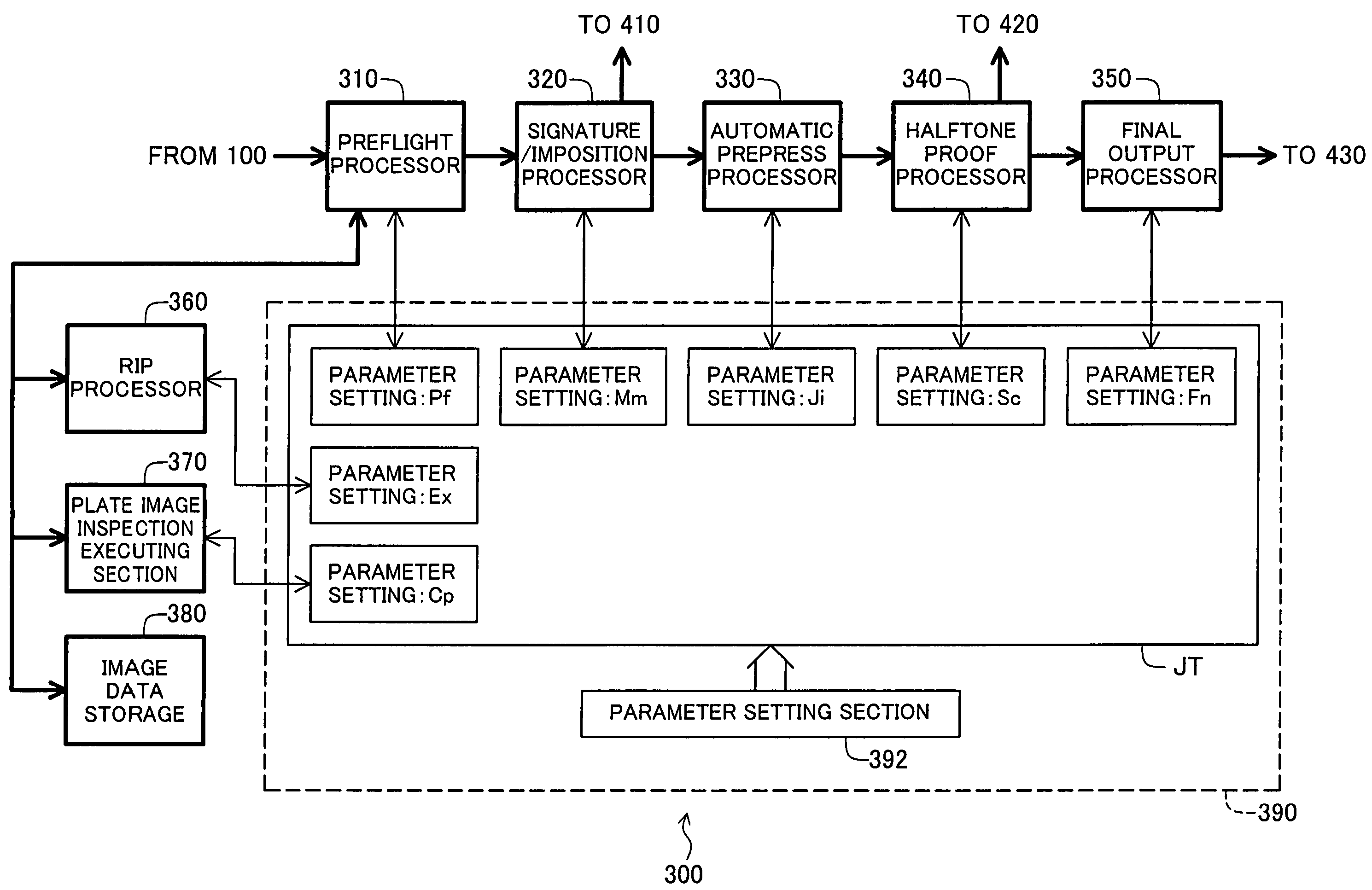
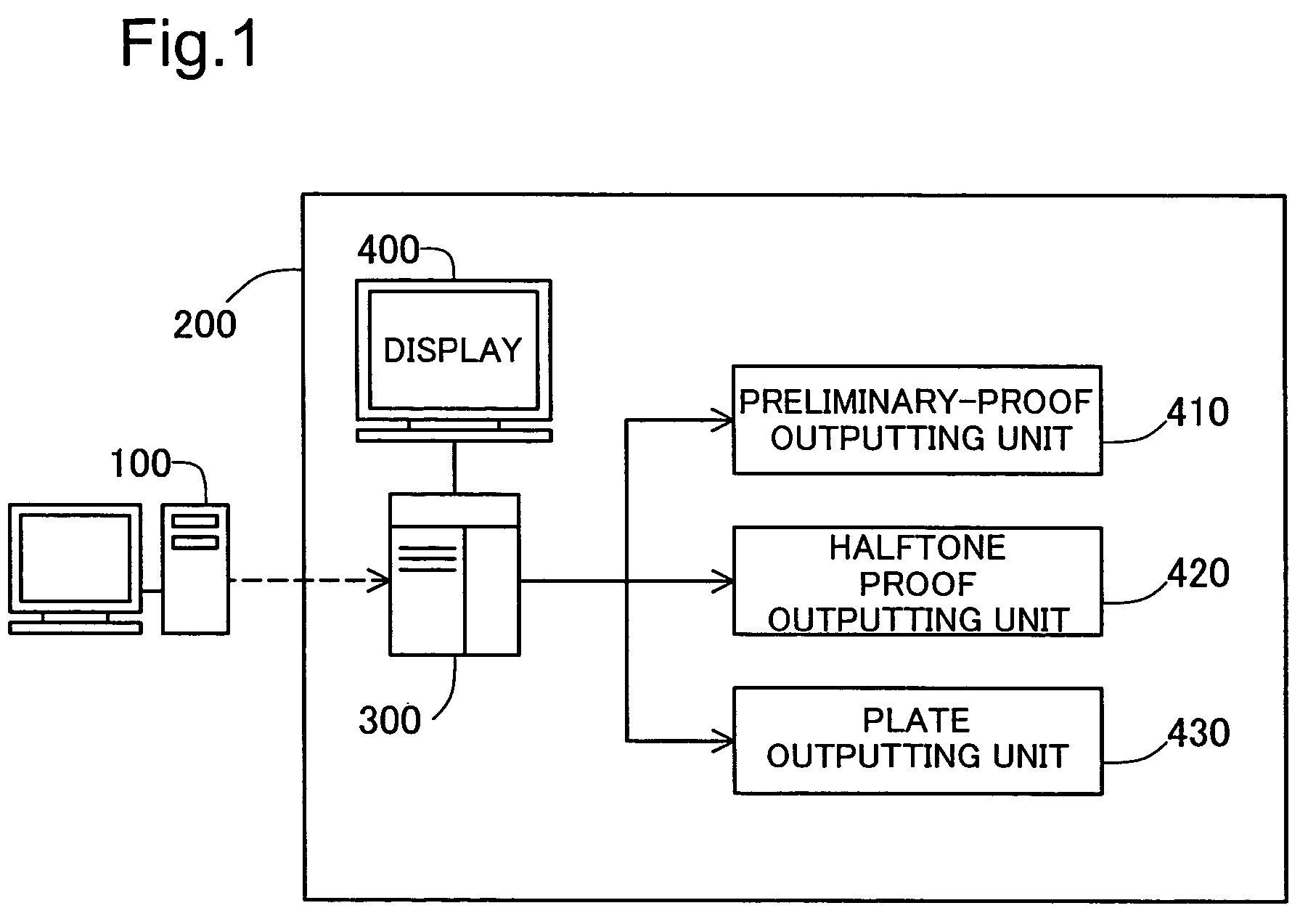
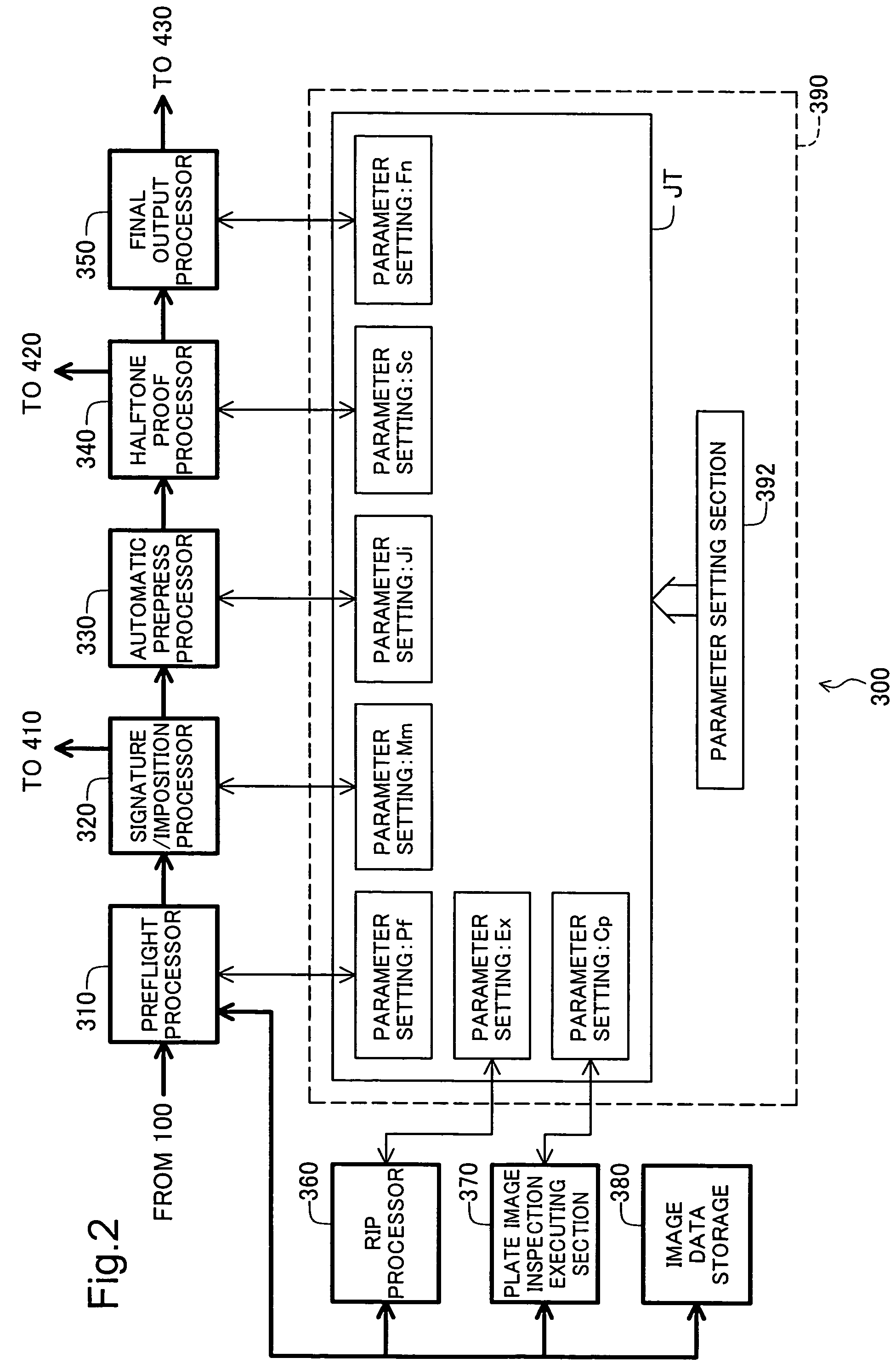
Plate image inspection for printing prepress
InactiveUS20040086156A1Addressing slow performanceImage enhancementImage analysisImage InspectionGrating
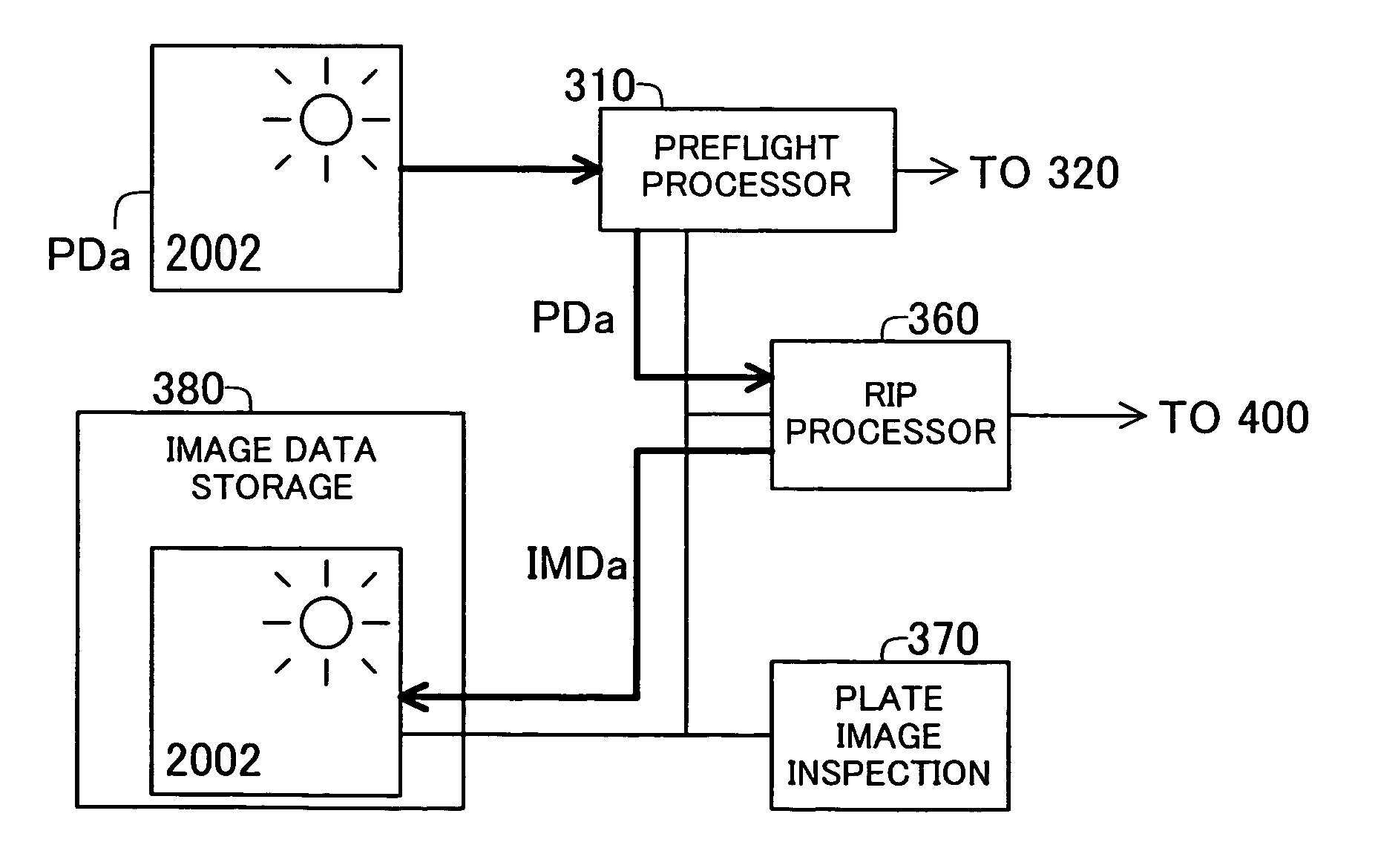
A prepress system comprises a raster image processor for developing first print image data to display resolution to create first raster image data, and for developing second print image data to the display resolution to create second raster image data. A plate image inspection processor executes a plate image inspection process by comparing the first and second raster image data, and displays on a display device the result of the plate image inspection process.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
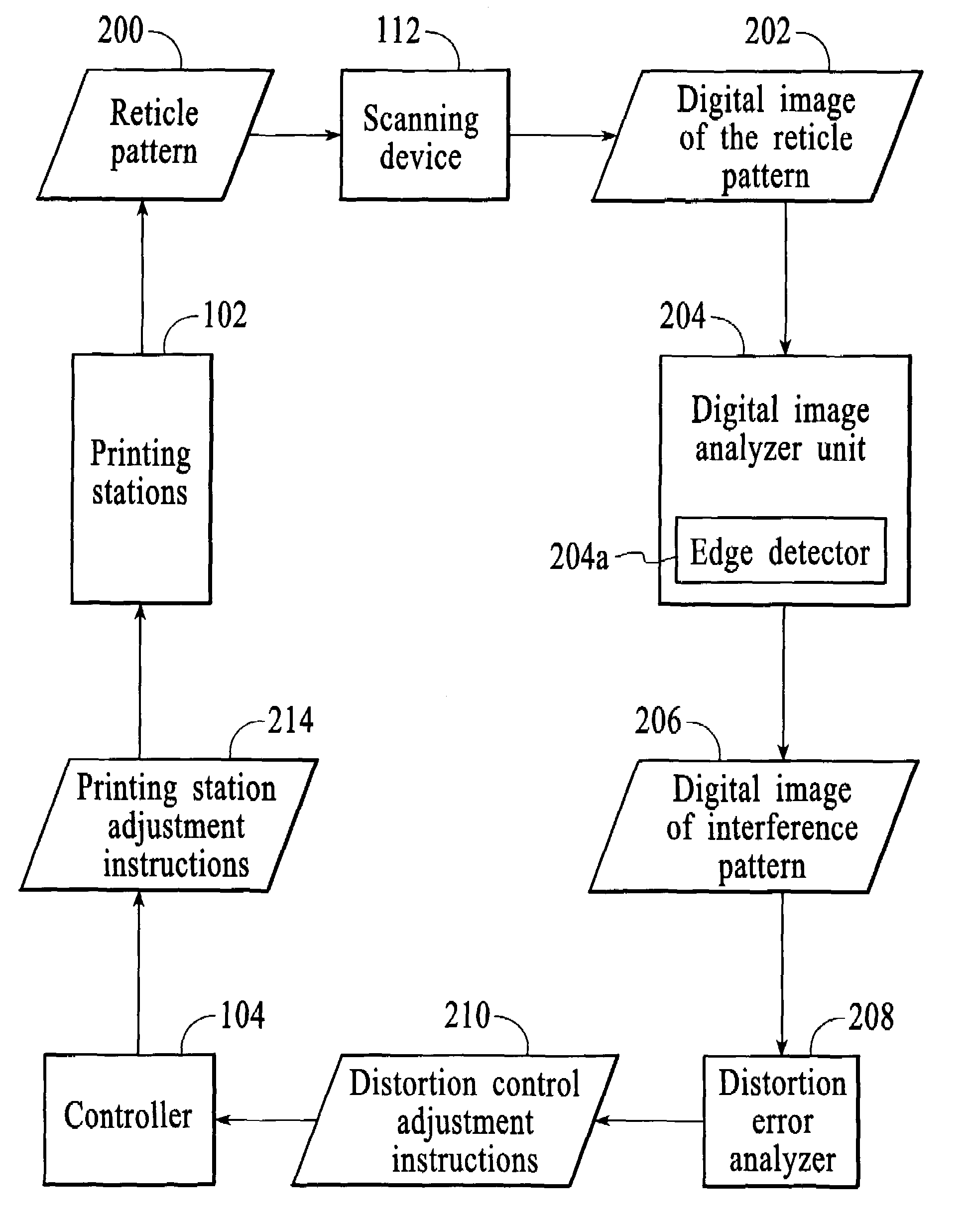
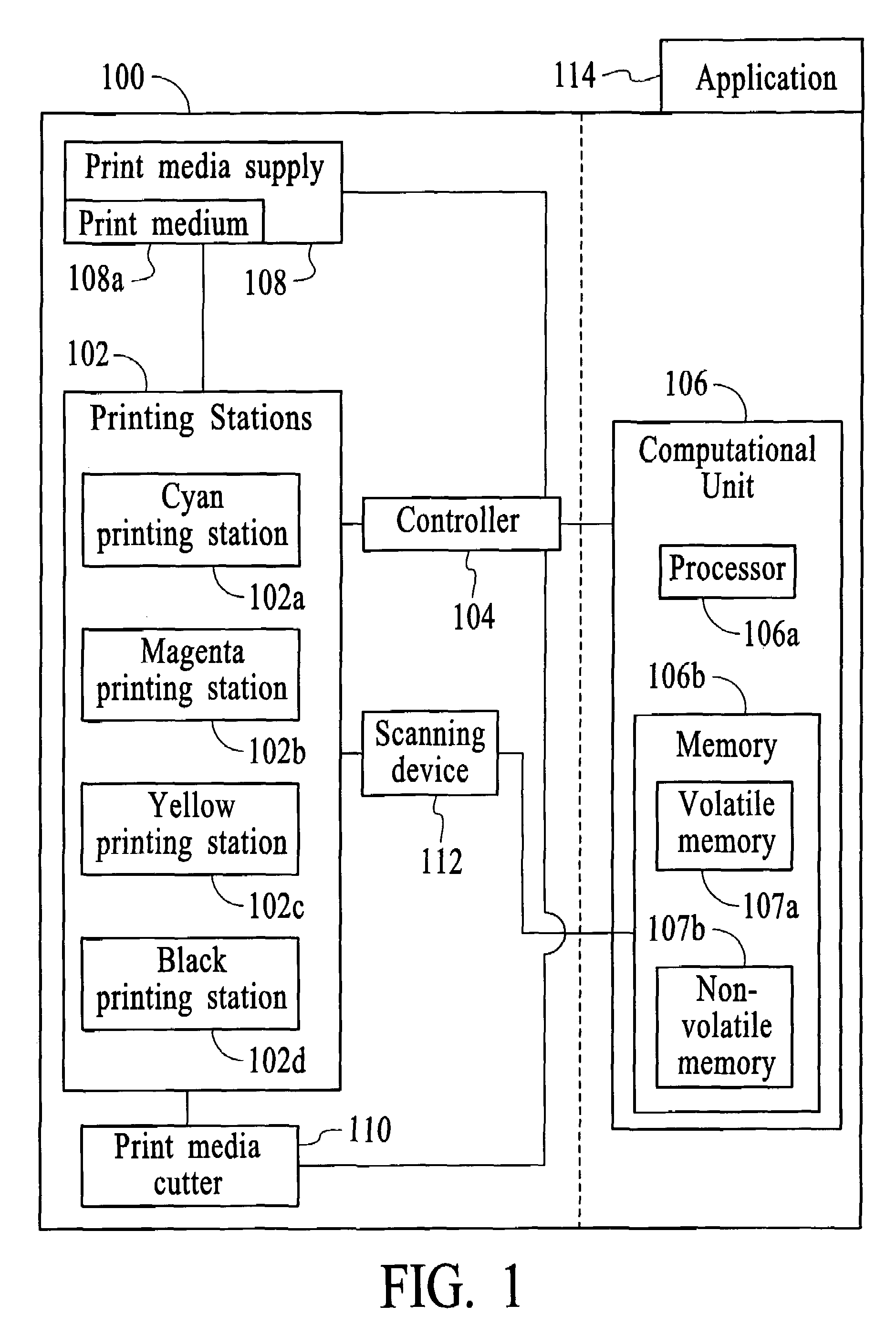
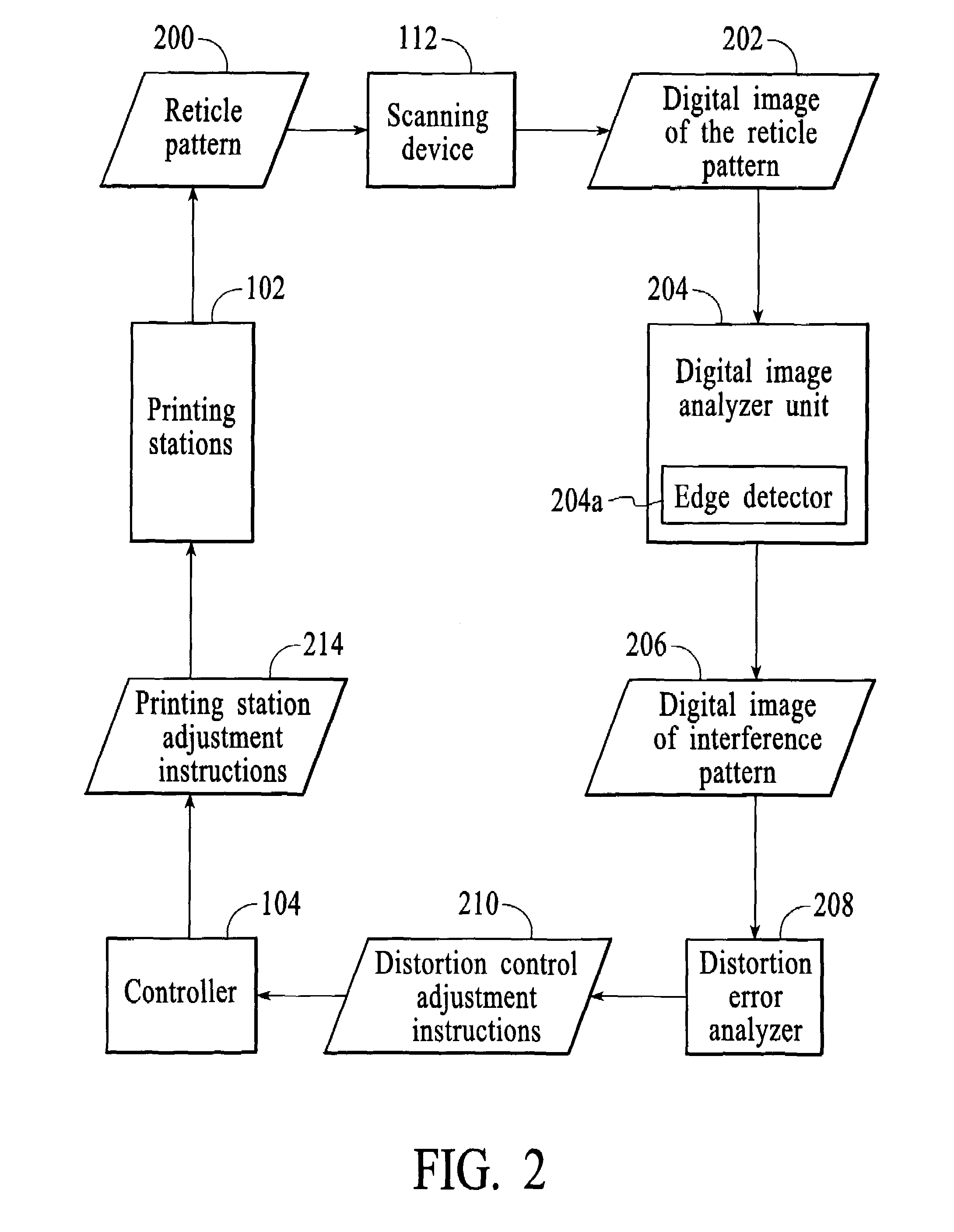
Method and system for minimizing the appearance of image distortion in a high speed inkjet paper printing system
ActiveUS6966712B2True colorPrecise registrationAddressographsPlaten pressesColor printingEngineering
A method and system for a printing device is disclosed. The method and system comprise printing a test pattern on a print medium and generating a digital image of the printed test pattern by an imaging device. The method and system include analyzing an interference pattern to measure for distortion of the print medium and calibrating the printing device based upon the measured distortion.In a preferred embodiment, the present invention utilizes the reticle patterns, which are printed in the margins of the paper, which are measured real-time during printing. The interference or Moiré patterns created by superimposed reticles may be used to measure image distortion, process direction misalignment, and misregistration caused by web distortion. The advantage of this invention is that image distortion compensation, RIP (Raster Image Processor) parameters, timing, or other printer characteristics may be adjusted on-the-fly in a closed feedback system, for high-speed textile or paper color printing, utilizing on-the-fly distortion or stretch measurement for accurate color and / or duplex images registration. In a duplex printer, automatic images alignment front-to-back is obtained by combining optically or logically the two images for the evaluation of interference patterns and amount of distortion in the process and scan direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
Printing method and apparatus having multiple raster image processors
InactiveUS6930795B1Faster system performanceAddressing slow performanceDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersGratingComputer graphics (images)
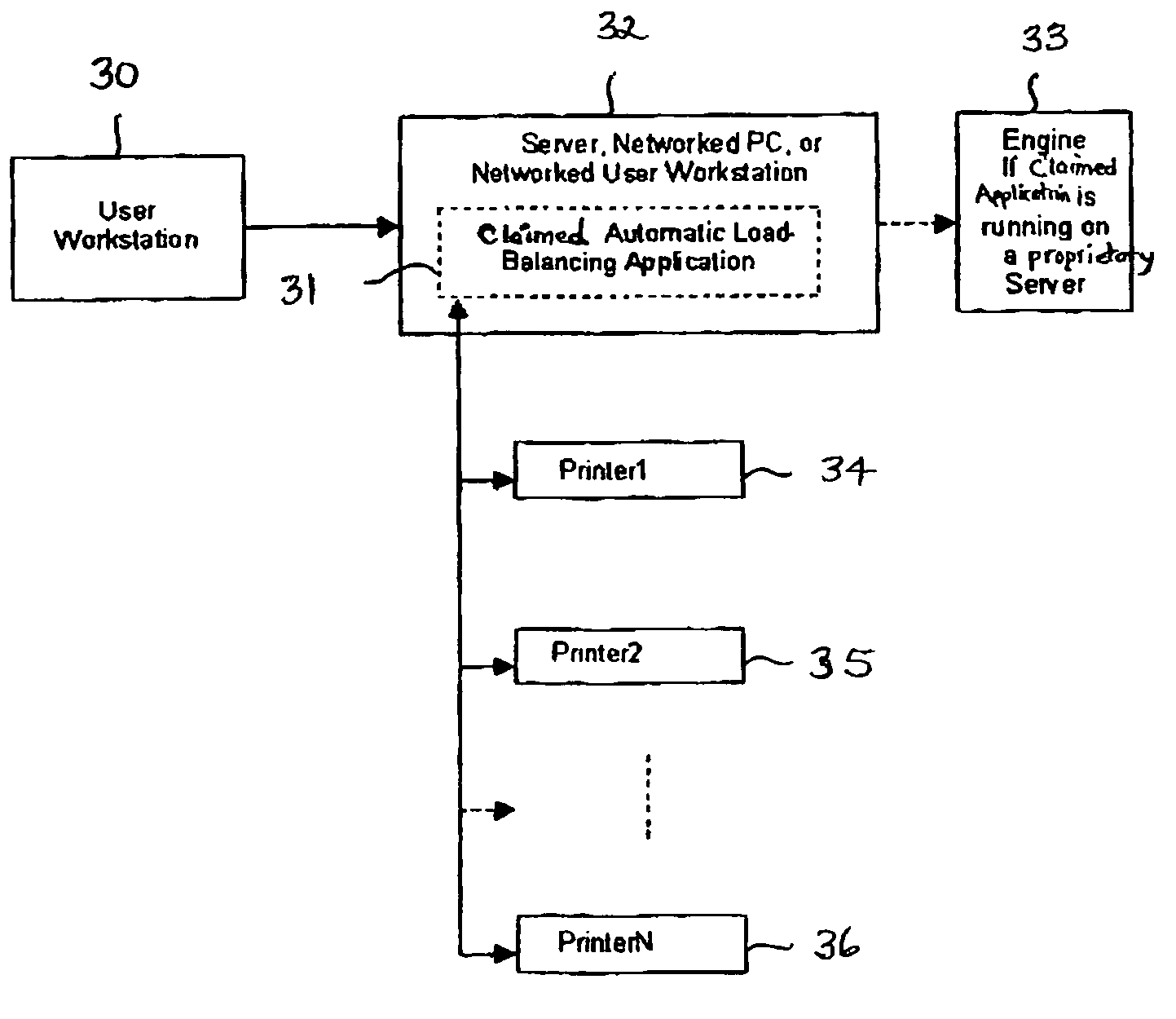
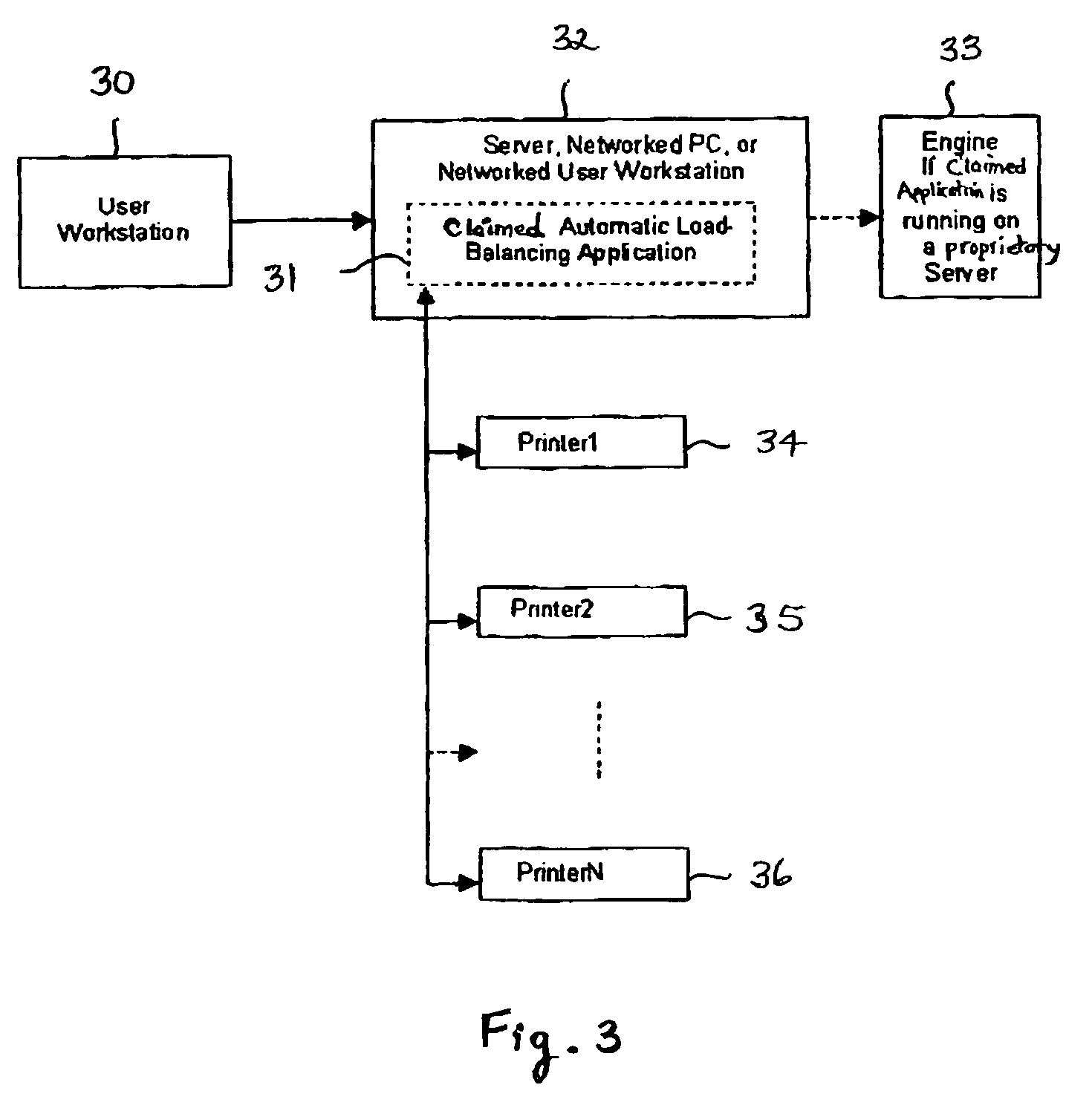
The invention provides a printing method and apparatus, comprising a software application that works with proprietary printing utilities, and that may include one or more additional software components for adding additional printing technology. The invention also comprises an automatic print load-balancing component in a centralized or distributed raster image processing (RIP) printing environment that enables faster system performance over single or multiple processors.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
Proxied printing services
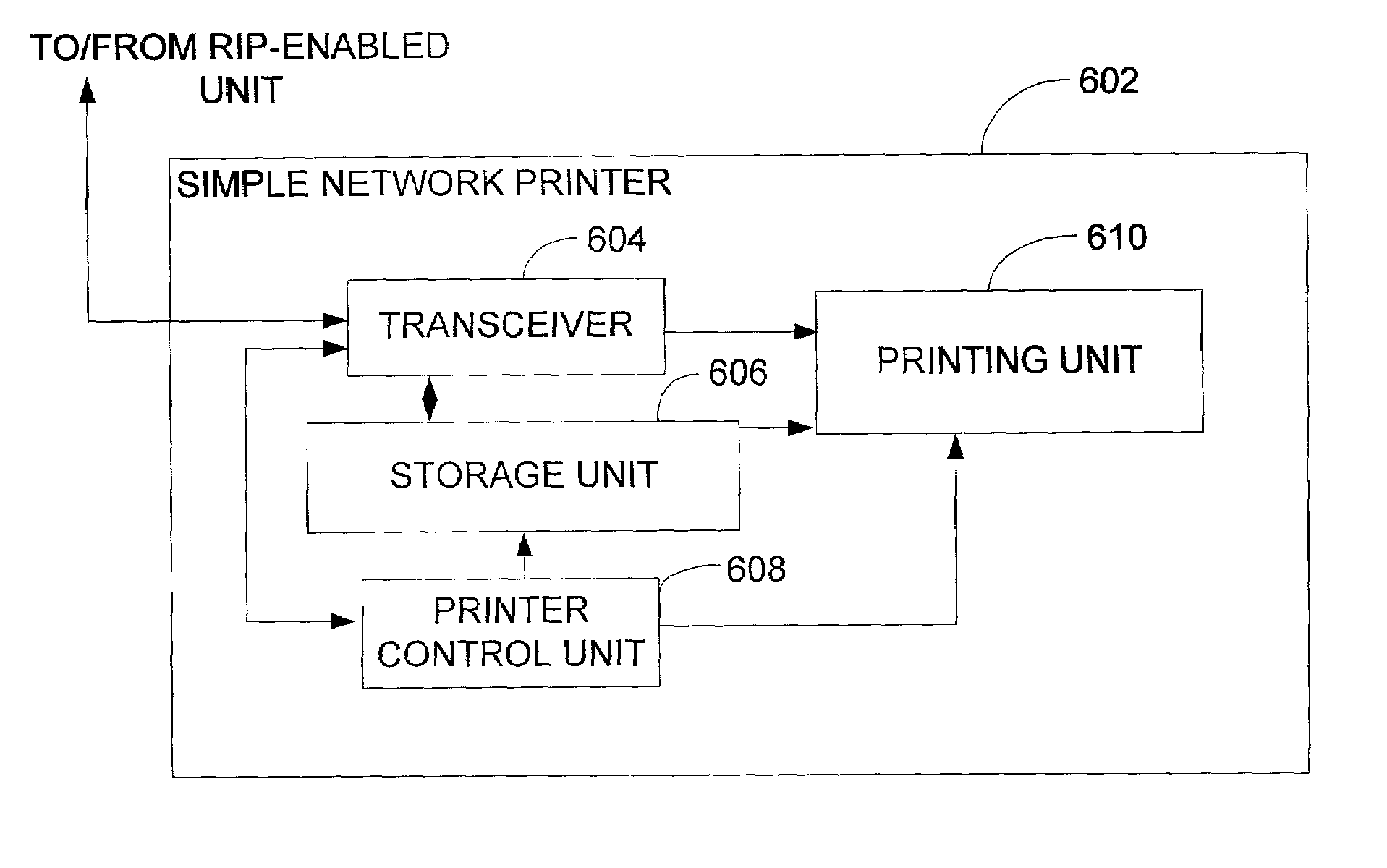
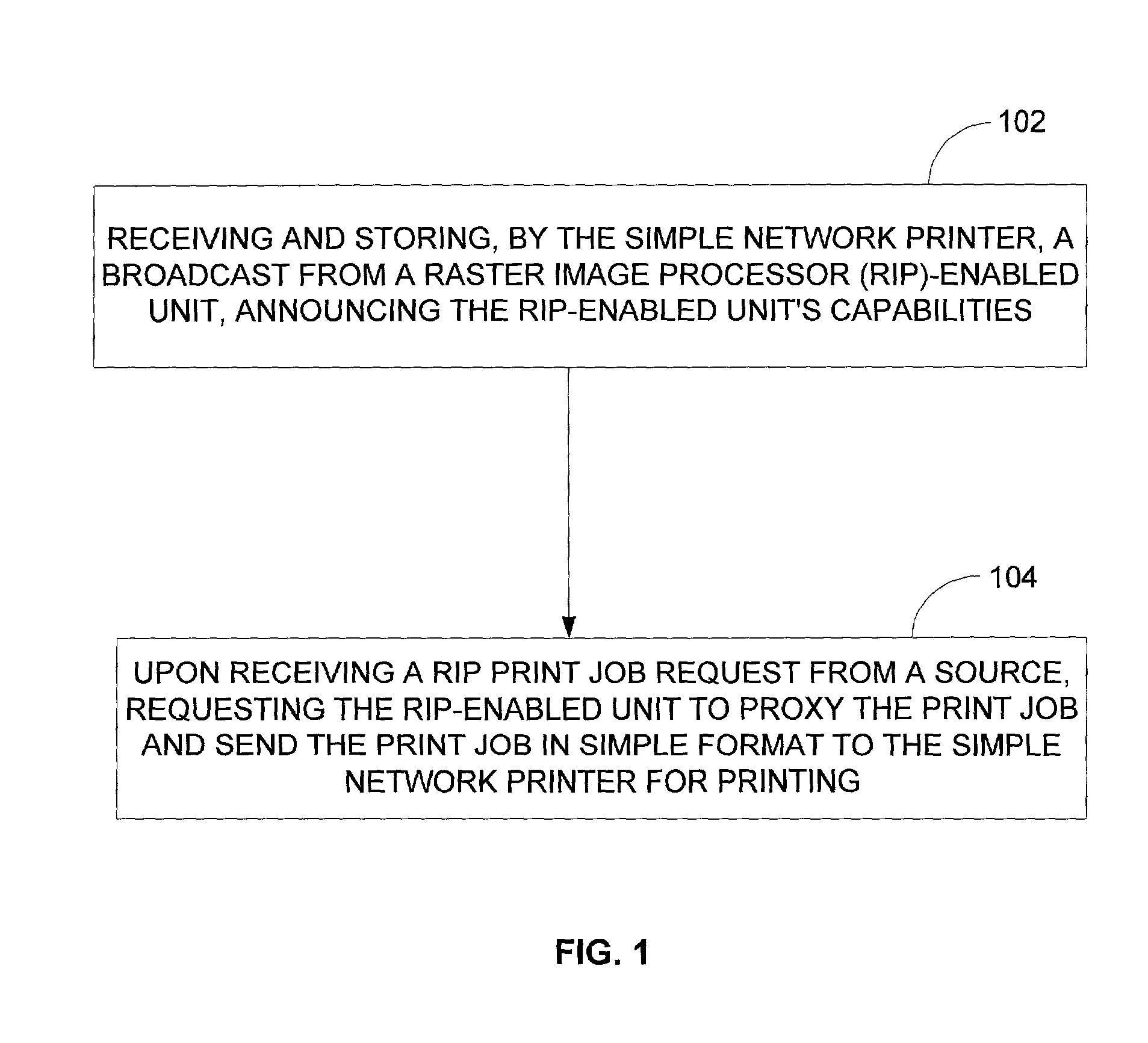
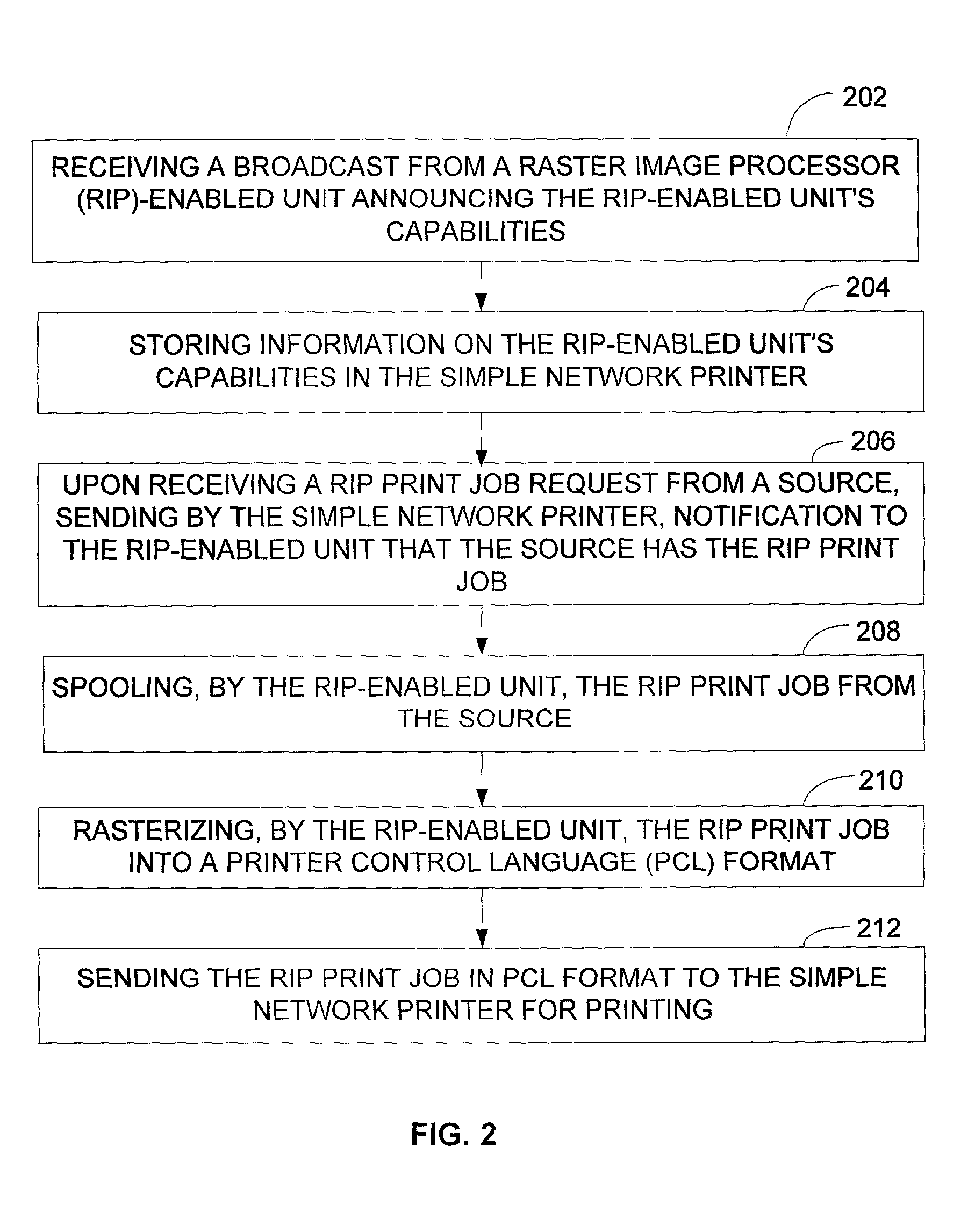
ActiveUS7242492B2Simple formatEasy networkingVisual presentationPictoral communicationImaging processingRaster image processor
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods, an image processing device, a computer network and a simple network printer wherein a simple network printer without RIP capability is enabled to print a print job that includes raster image processor instructions. In one embodiment of the method of the present invention, the steps include receiving and storing, by the simple network printer, a broadcast from a raster image processor (RIP)-enabled unit announcing the RIP-enabled unit's capabilities and, upon receiving a RIP print job request from a source, requesting the RIP-enabled unit to proxy the print job and send the print job in simple format to the simple network printer for printing.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
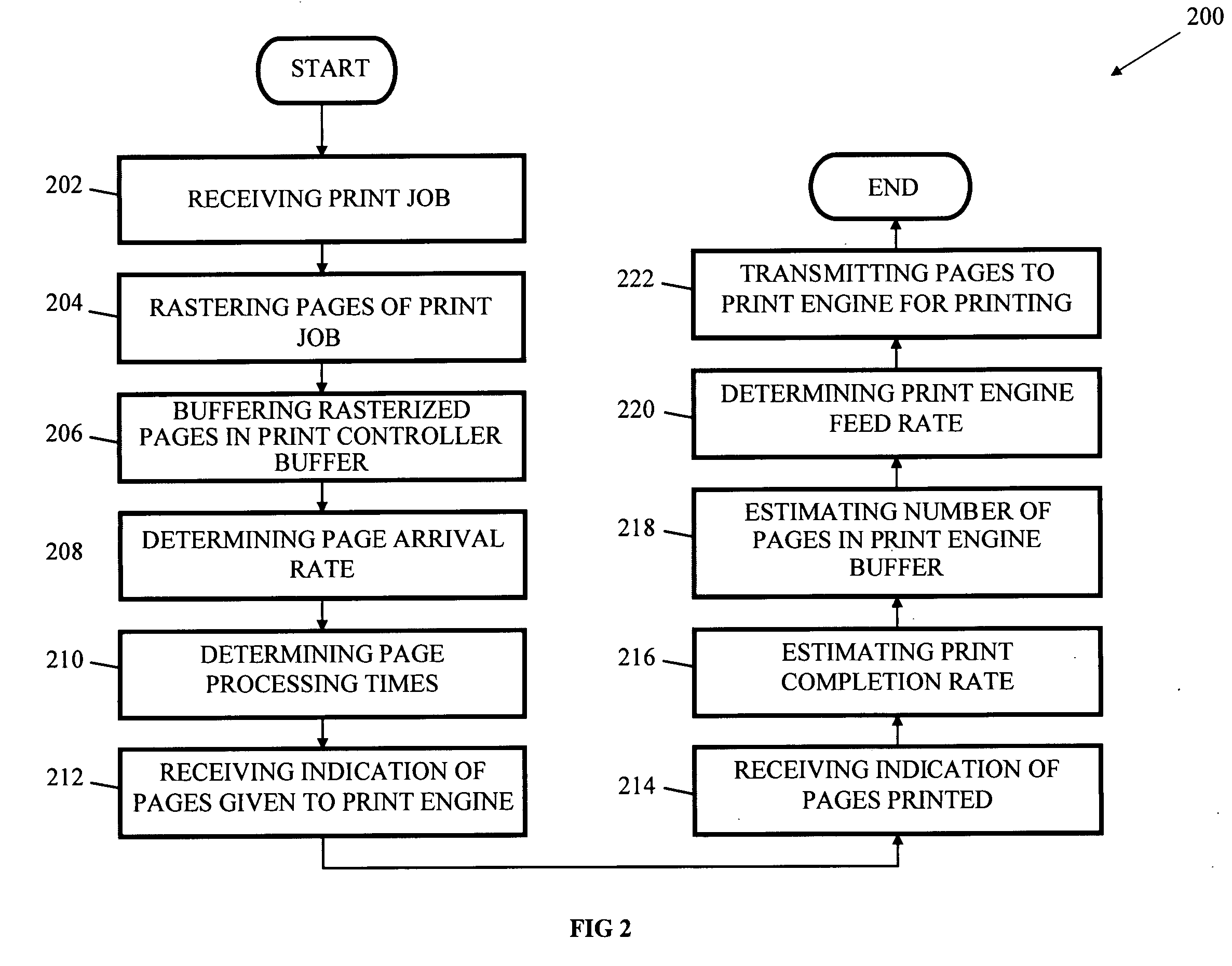
Systems, methods, media for managing the print speed of a variable speed printer
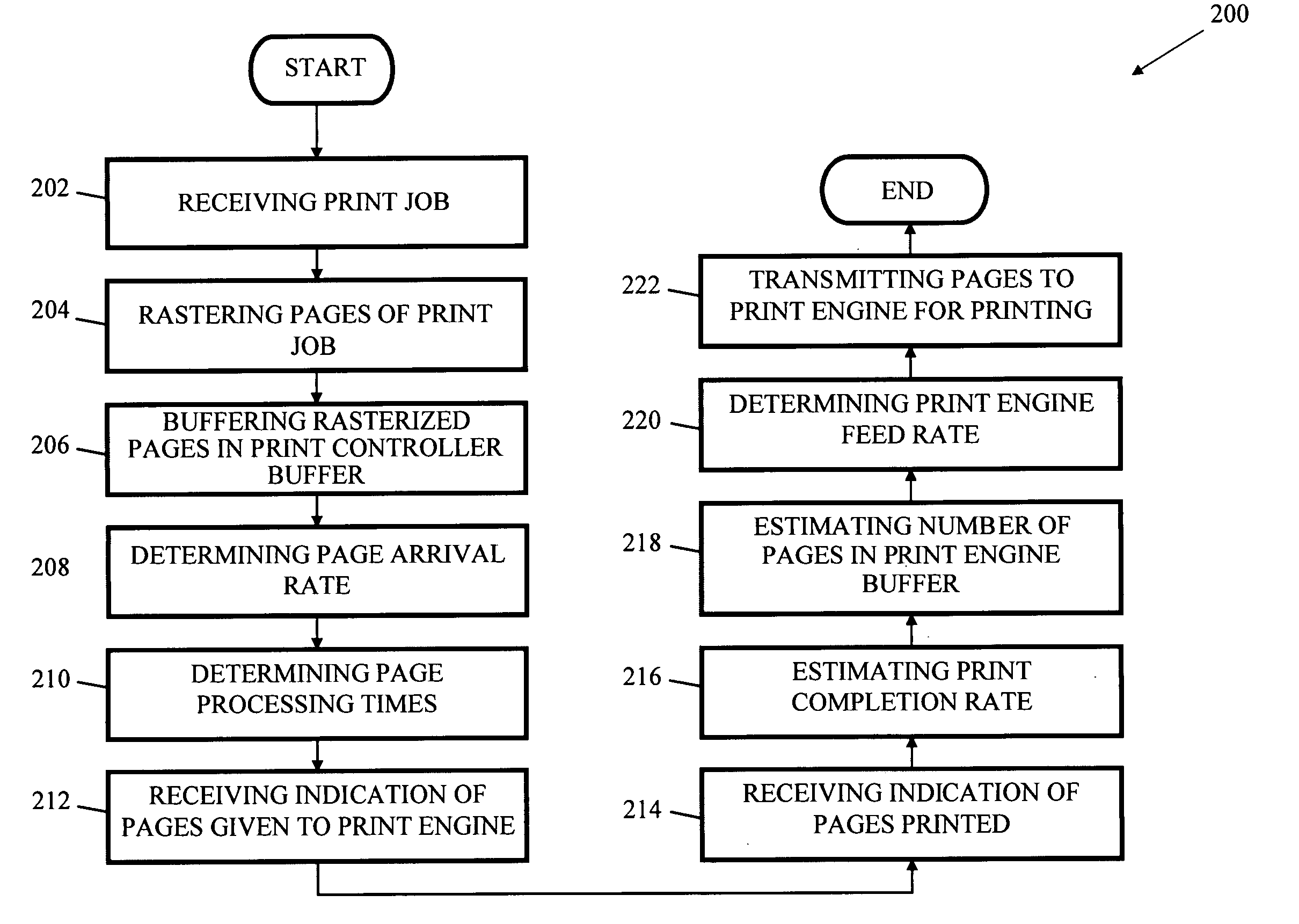
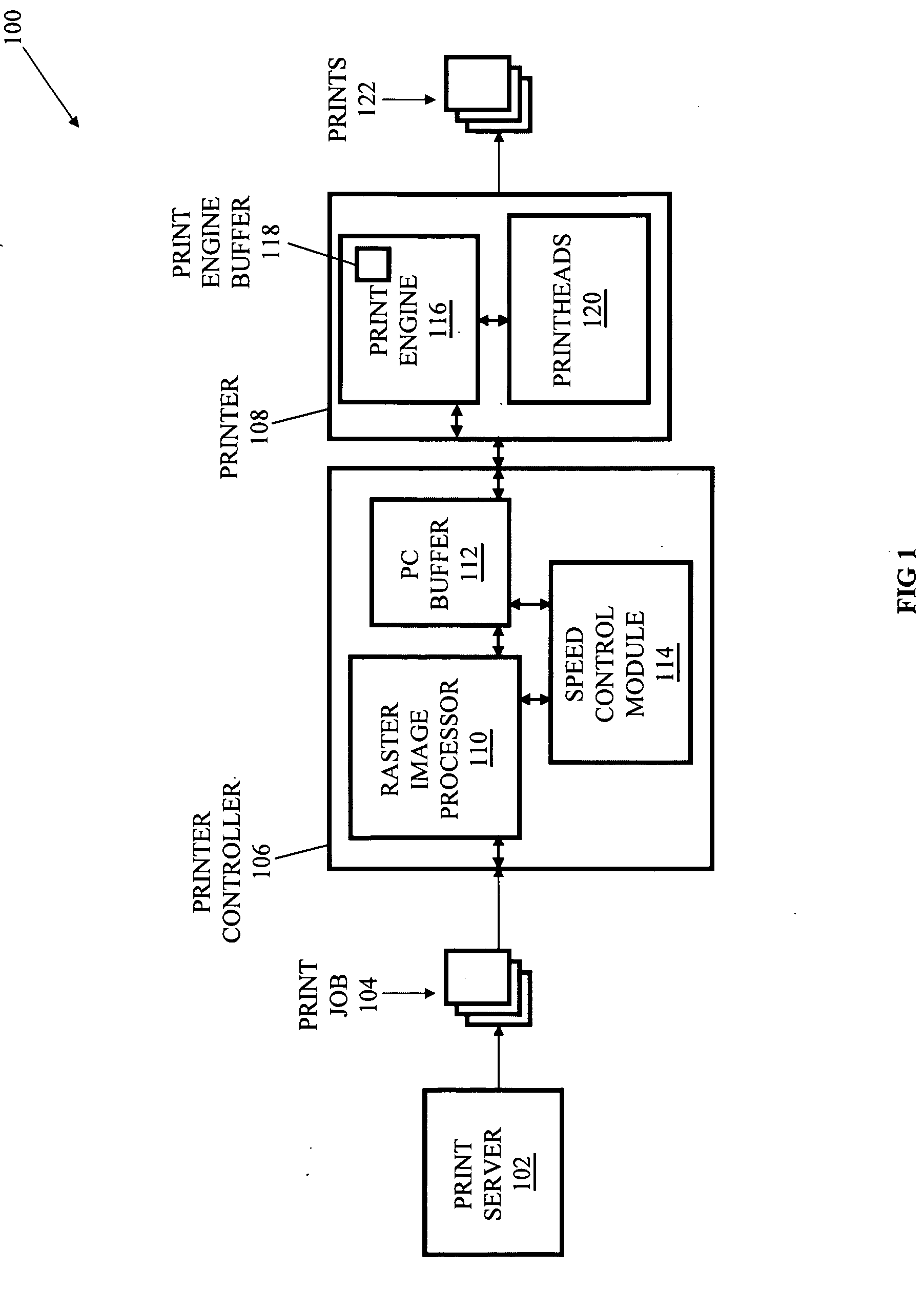
InactiveUS20060262335A1Reducing print engine feed rateIncrease feed rateDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsSystems approachesComputer science
Systems, methods, and media for managing the print speed of a variable speed printer are disclosed. Embodiments include a print controller system having a raster image processor for rasterizing a print job to create a plurality of rasterized pages and a printer controller buffer for storing one or more of the rasterized pages. The printer controller buffer may also transmit at a print engine feed rate the one or more rasterized pages to a print engine. Embodiments may also include a speed control module in communication with the printer controller buffer for determining the print engine feed rate. Further embodiments may include the speed control module determining the print engine feed rate based on one or more of page processing times, page arrival rates, estimated print completion rates, and the number of pages in a print engine buffer.
Owner:RICOH KK
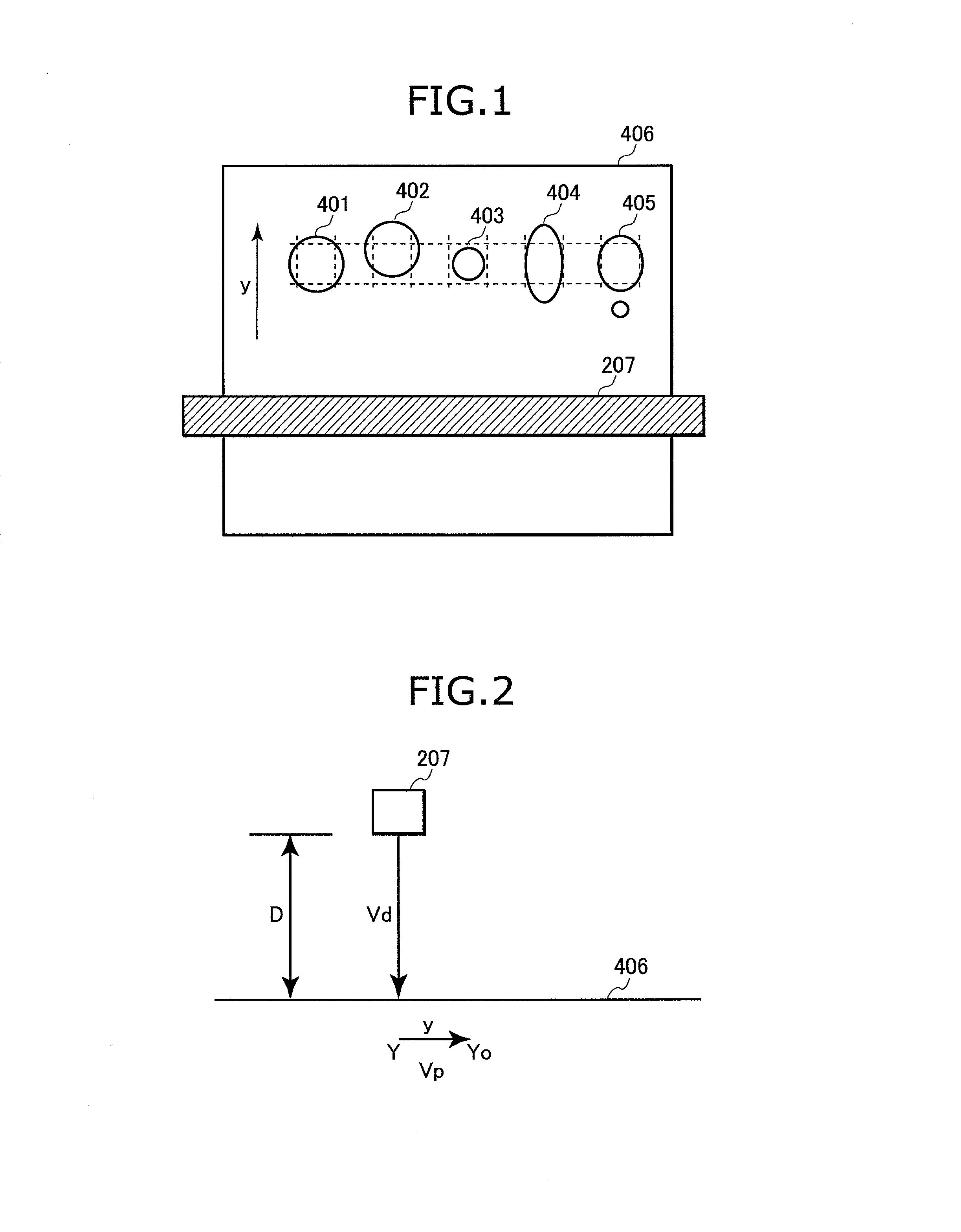
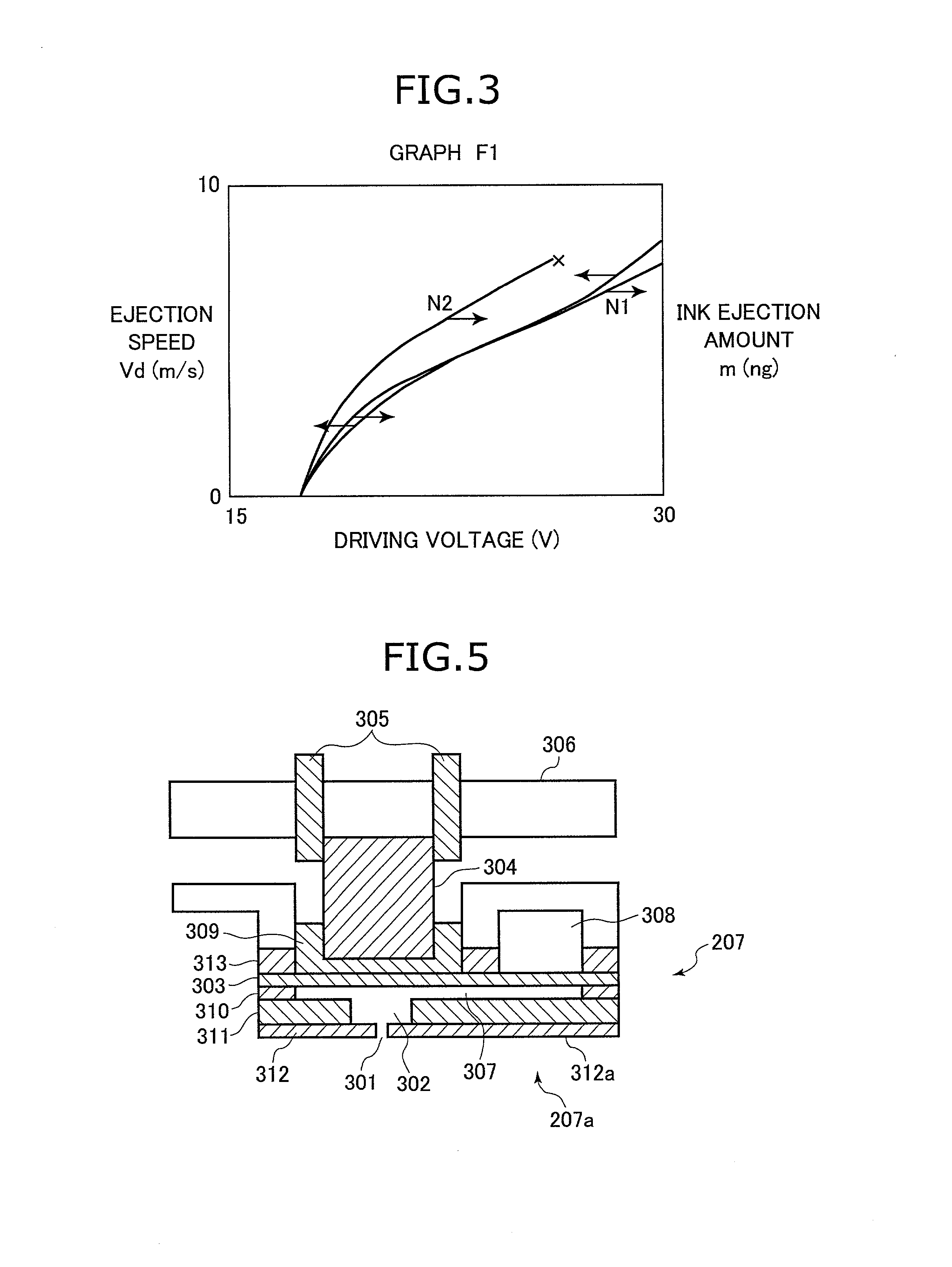
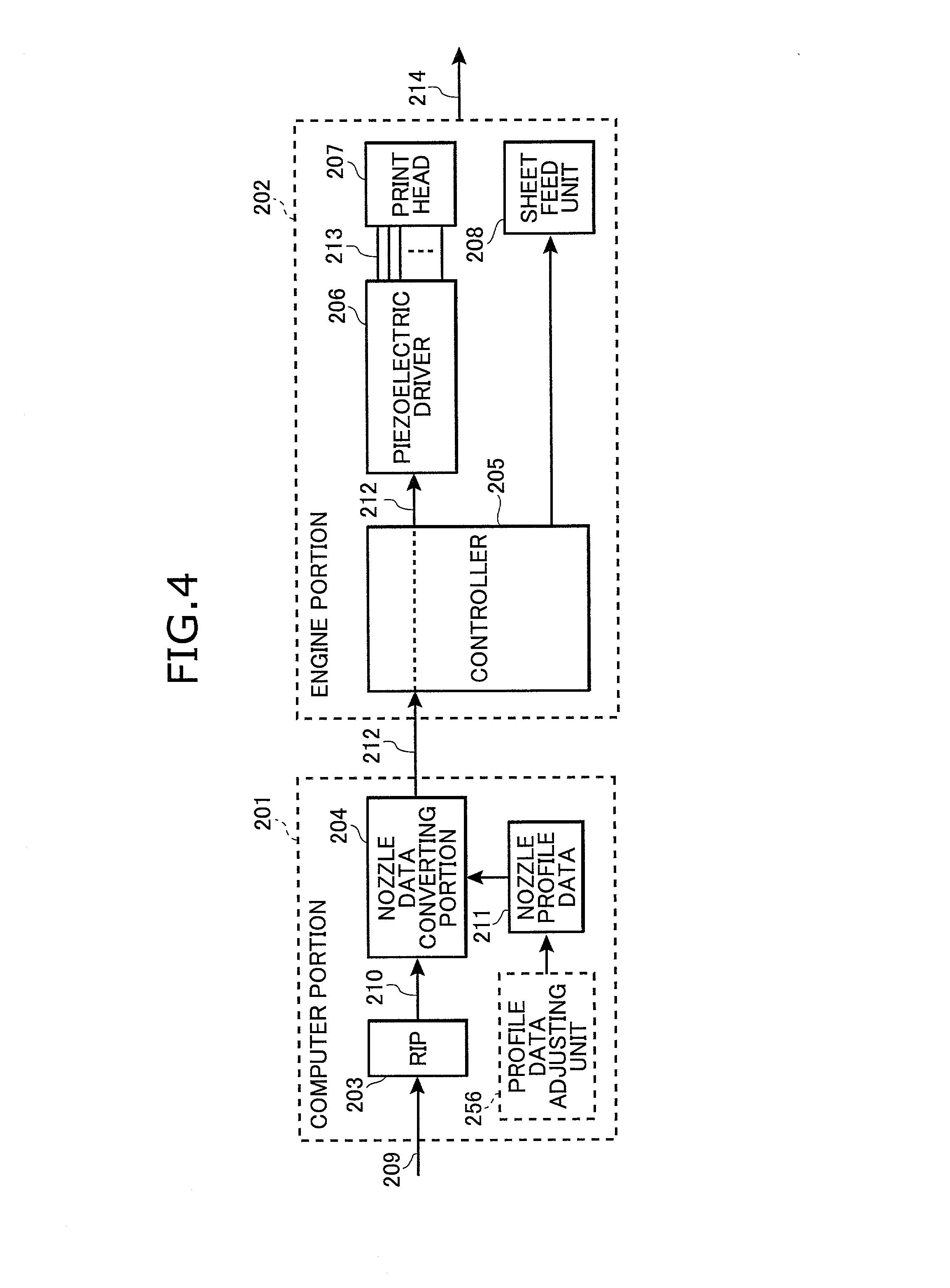
Line scanning type ink jet recording device capable of finely and individually controlling ink ejection from each nozzle
A computer portion 201 of a printer includes a memory storing a printer driver software 201a and nozzle profile data 211. The printer driver software 201a includes a raster image processor (RIP) 203. When the RIP 203 receives document data 209, the RIP 203 converts the document data 209 into bitmap data 210 which is one dot / one bit data for 300 data / inch. Then, the nozzle data converting portion 204 converts the bitmap data 210 into driving data 212 based on the nozzle profile data 211. At this time, each bit of the bitmap data 210 is replaced by 16 bits. That is, the data amount is increased to 16 times of the bitmap data 210. Accordingly, fine control of ink ejection can be achieved.
Owner:RICOH PRINTING SYST
Super resolution encoded microprinting through postscript
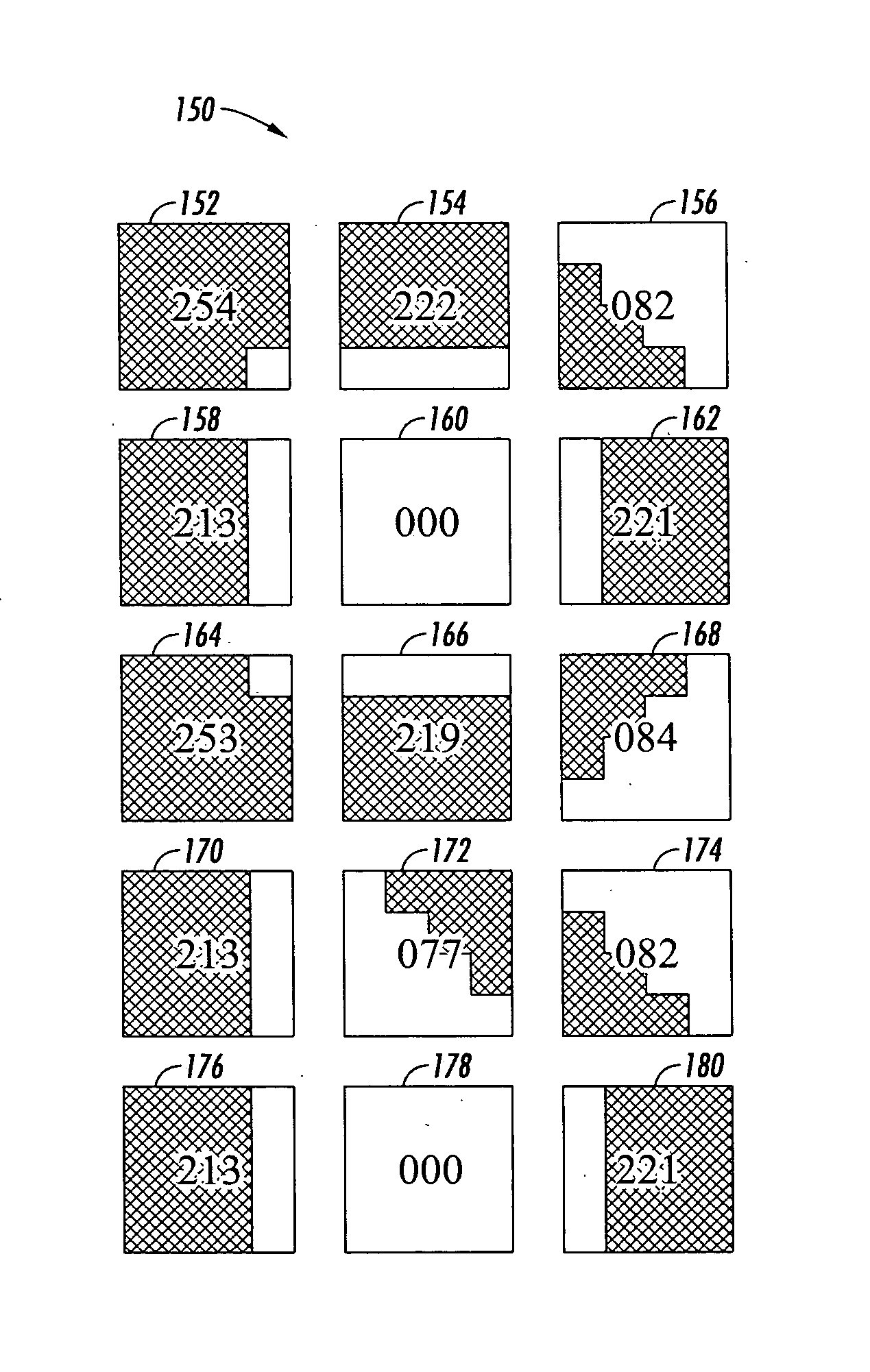
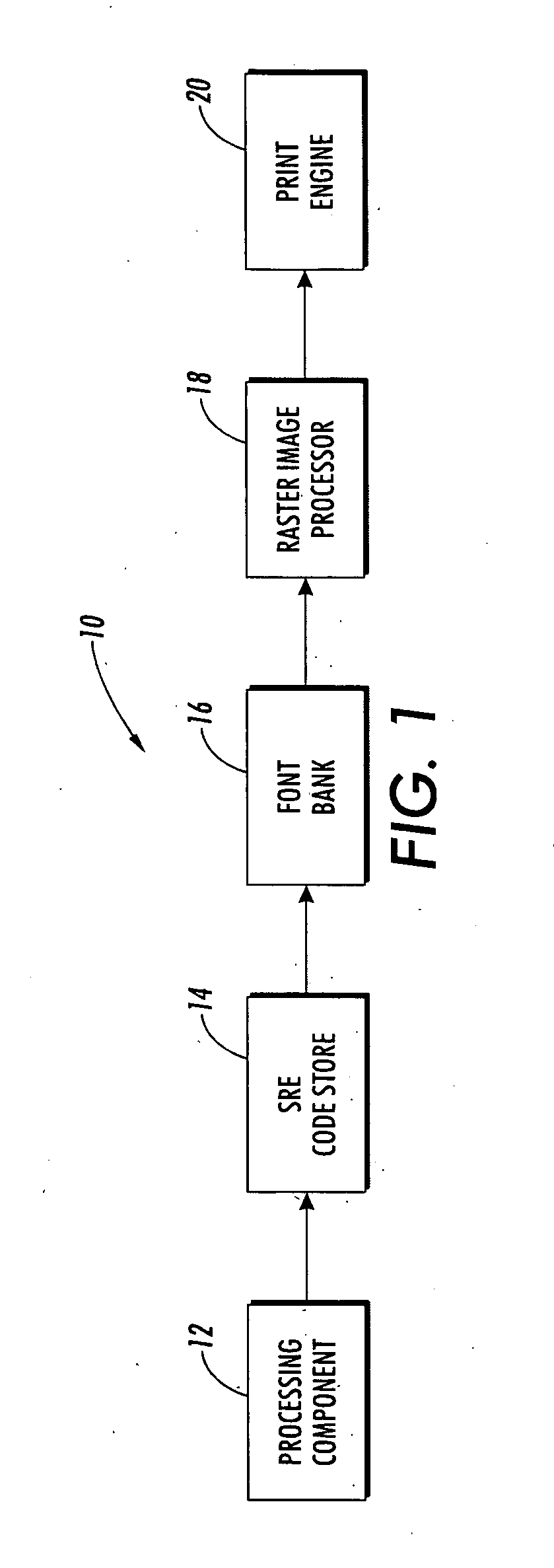
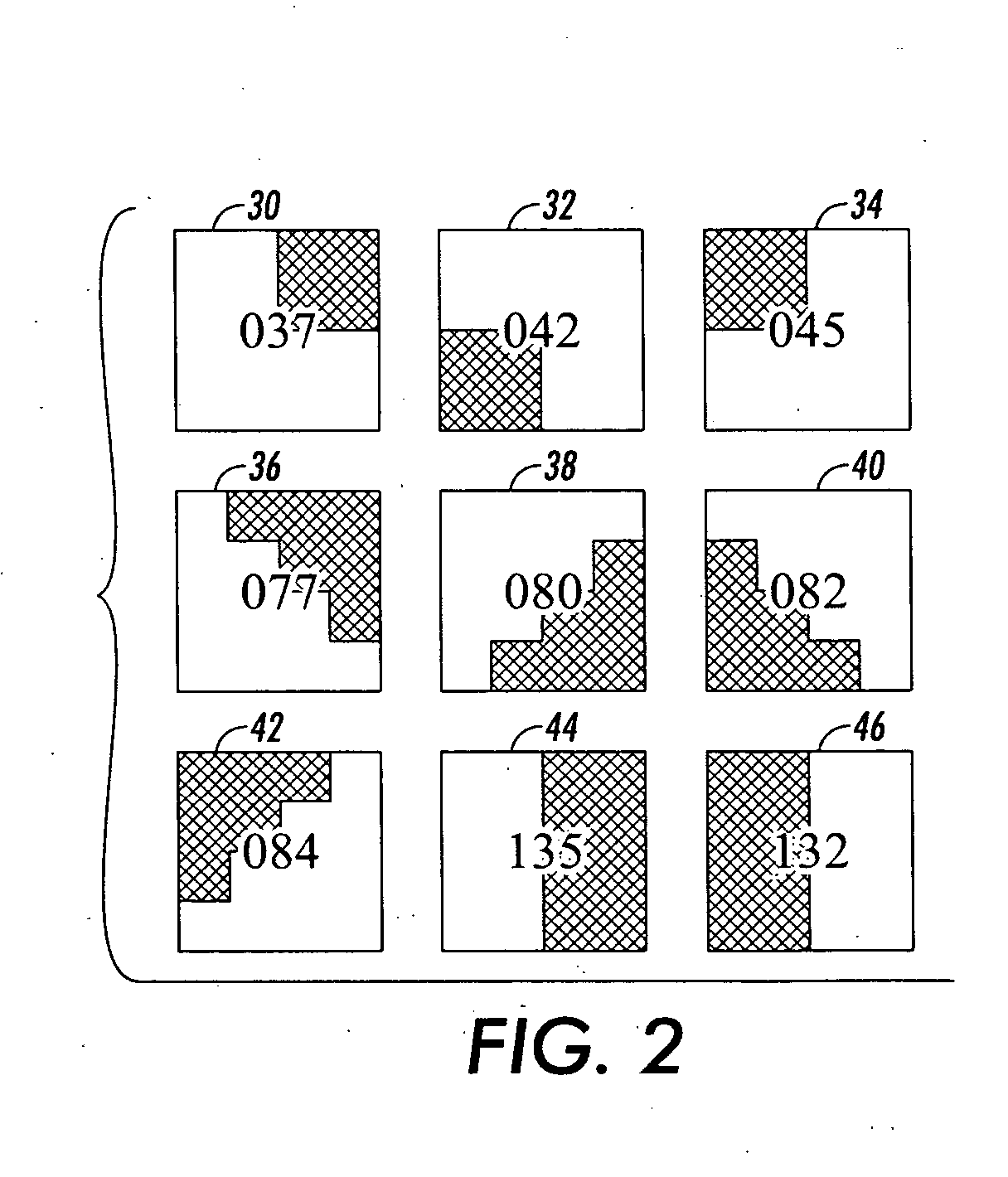
InactiveUS20070252838A1Easy to printDigitally marking record carriers2D-image generationData packGrating
A system facilitates printing of microtext. A processing component allows a user to create one or more microtext characters, wherein the characters are output as a data packet. An SRE code store receives and associates one or more SRE codes with the data packet, each SRE code is representative of a bit pattern, wherein the bit pattern is a grid of bits that are filled to create a particular pattern. A font bank receives the one or more SRE codes from the SRE code store and defines such codes via a font. A raster image processor receives the font from the font bank, decodes the font and outputs instructions to print the microtext.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Colorful picture six color separation printing method
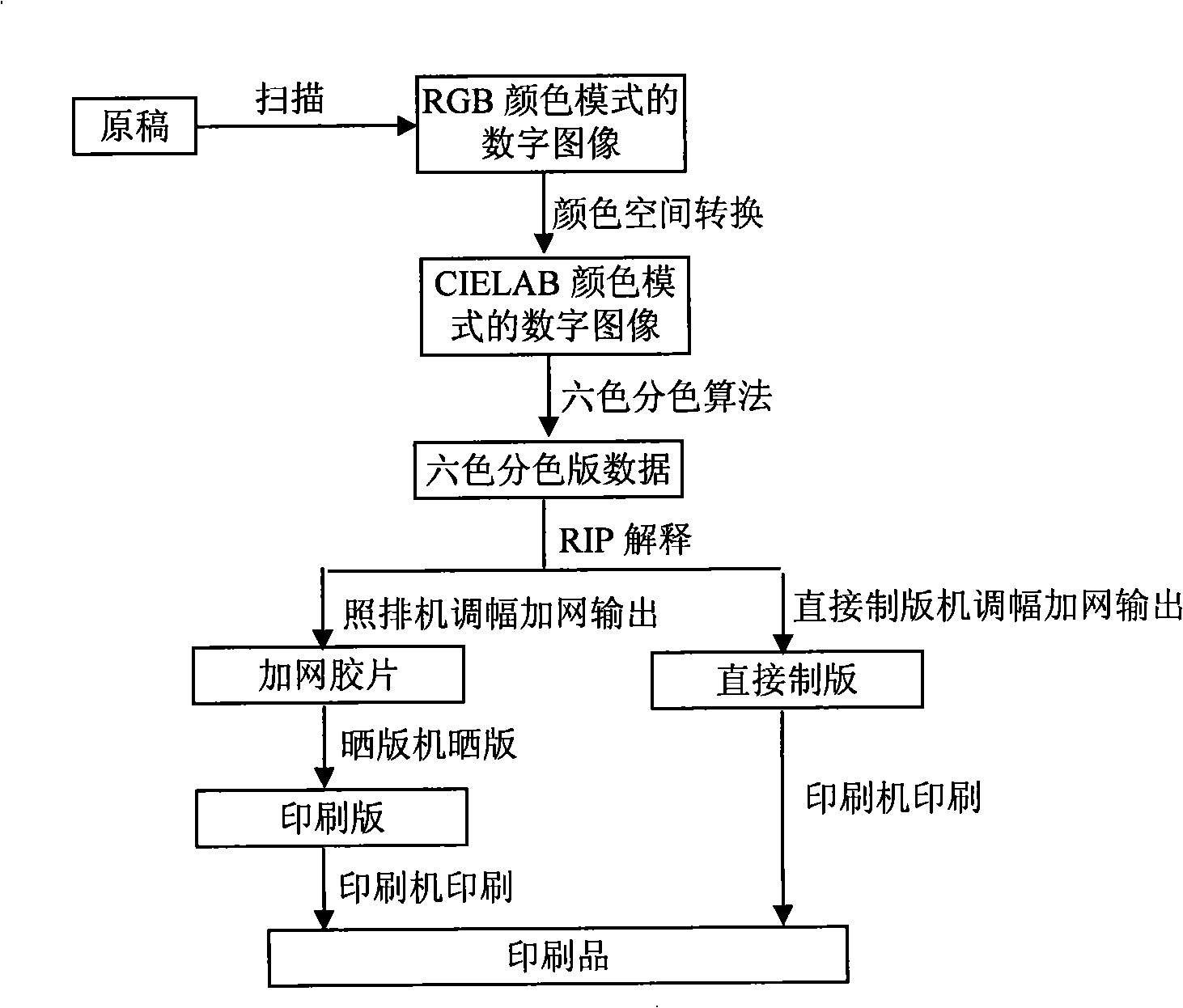
InactiveCN101276142AThe phenomenon of collision does not occurQuality improvementColour-separation/tonal-correctionGratingCell separation
The present invention provides a six-color separation printing method of a color chart, effectively resolving the problems that the color of the prints is not bright and full, and each color version is easy to generate bumping net phenomenon under the prior equipment and technical condition, the technical solution includes following steps: the manuscript is scanned to a digital image of red, green and blue mode, changed to a digital image of CIELAB color mode after the color space conversion, divided into a six-color separation version data of yellow, magenta, cyan, black, orange and green by an algorithm of six-color separation, the data is outputted to a screening film by amplitude modulation and screening of a camera after explained of a raster image processor, burnt to a printing plate by a copyboard, printing by a printer, or outputted by amplitude modulation and screening of a direct platemaker, the prints is printed by the printer, the invention greatly improves the quality of the prints, the prints have bright and full color, each color version does not produce bumping net phenomenon, especially for printing high exquisite articles.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
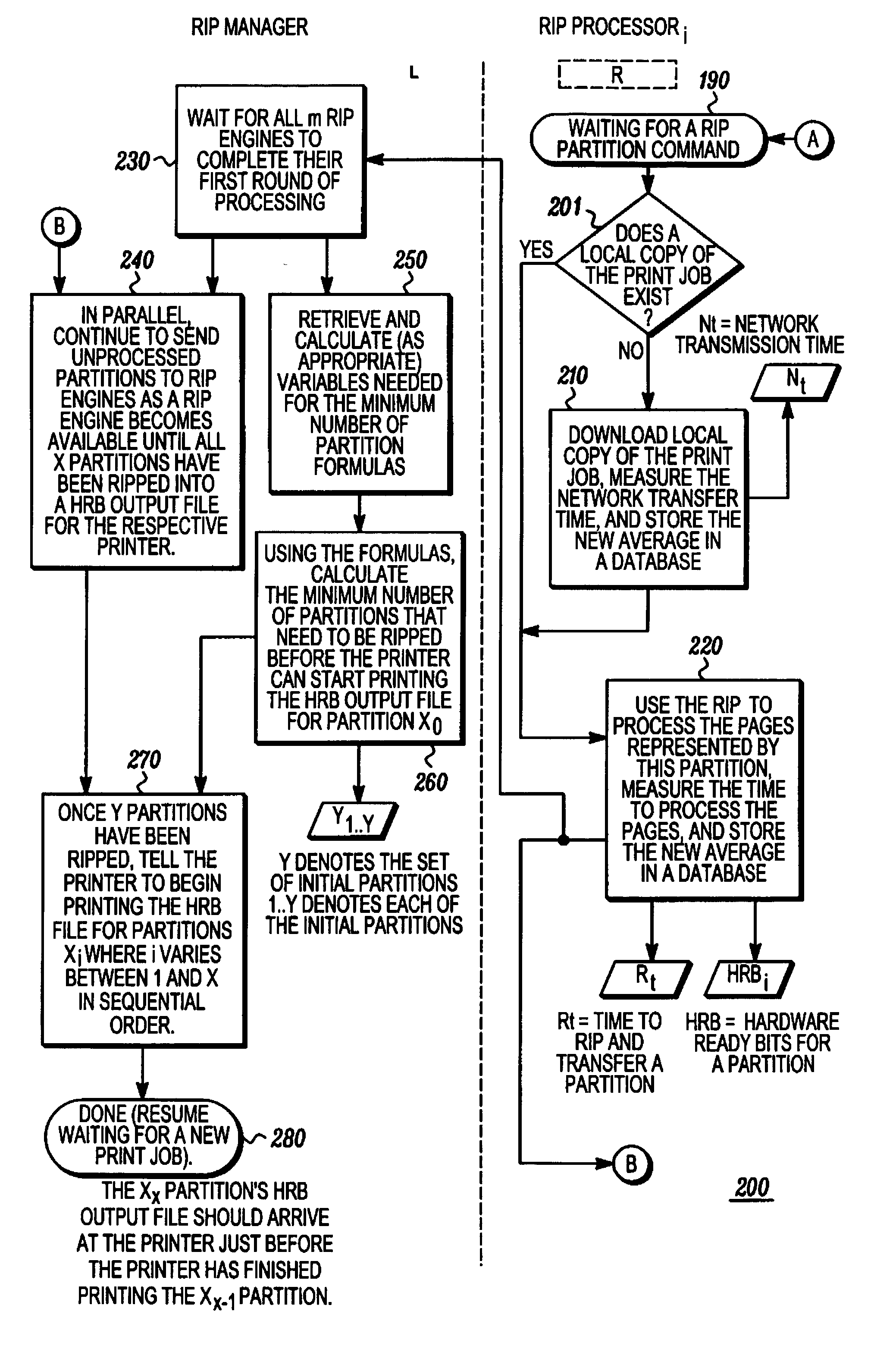
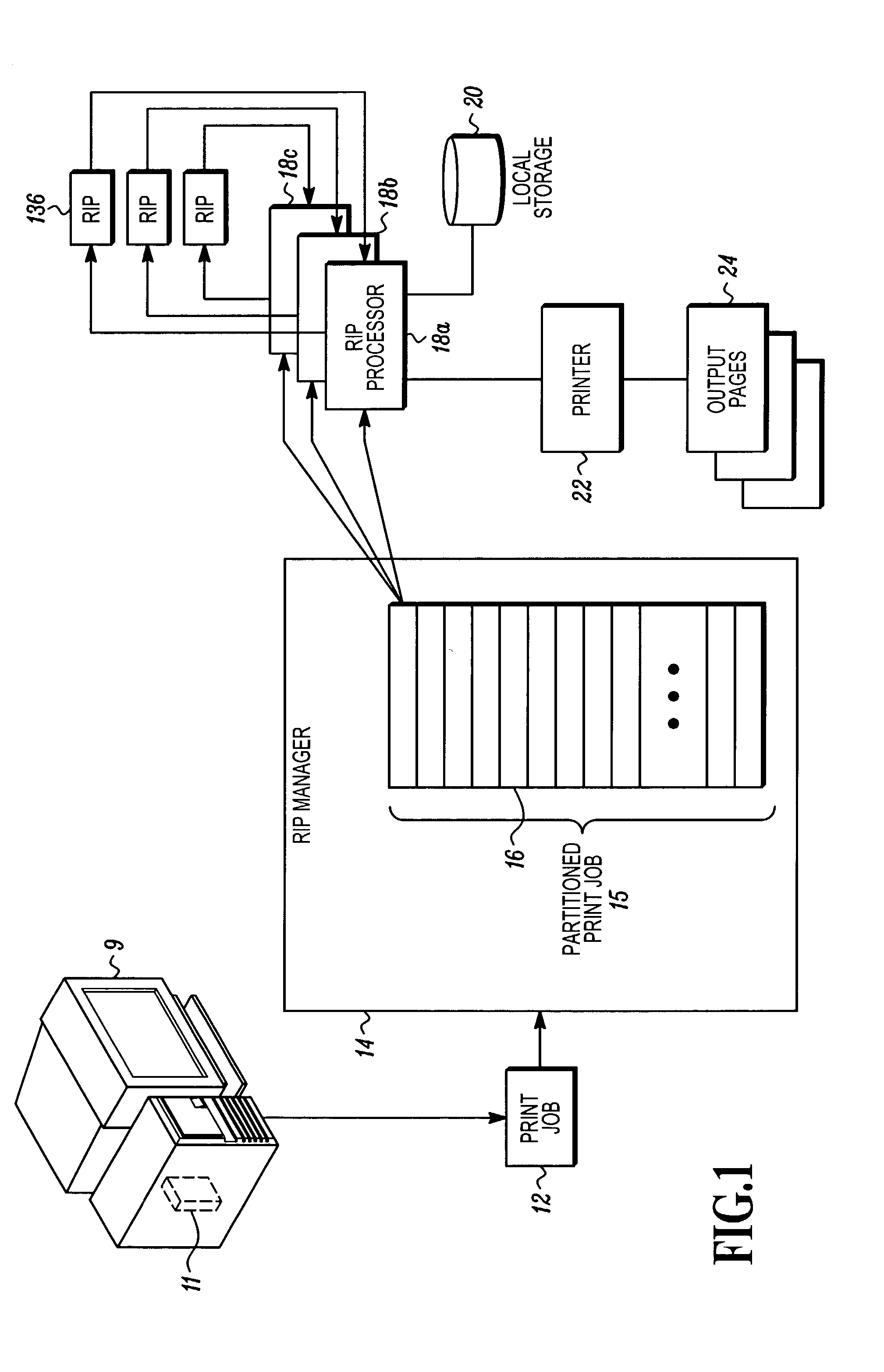
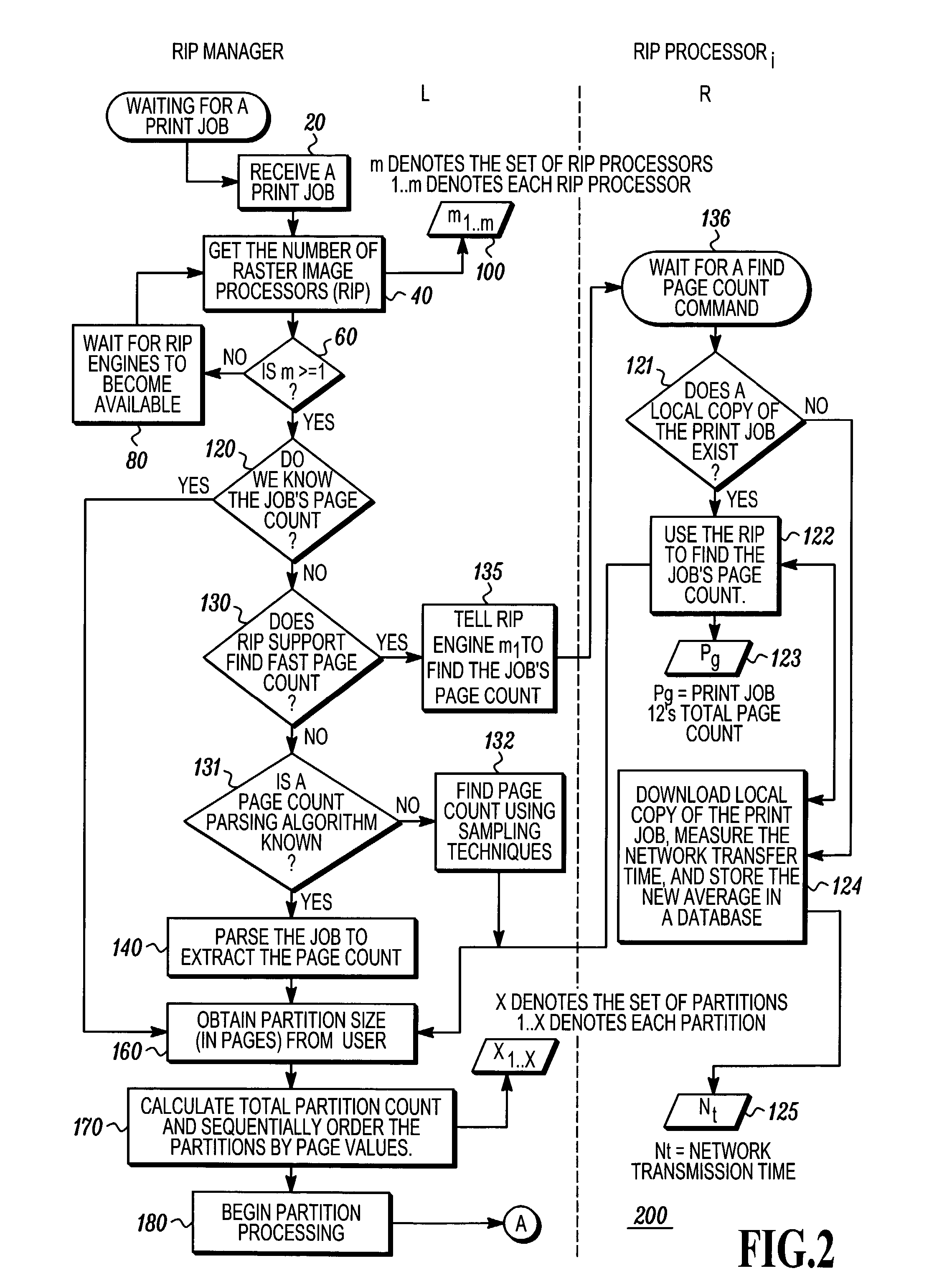
Determining raster image processor cycle count to fully utilize a printer
Commercial printers operate more efficiently when they run continuously after being started on a print job. Print job image data is processed by a predetermined number of raster image processors (RIP engines) before starting a printer so as to be able to operate a printer continuously for the duration of the print job. Print job partitions are determined and counted. A predetermined number of partitions are processed into hardware ready bit (HRB) output files which are transferred to the printer. Using a predetermined formula, the total number of partitions to process is calculated before sending resultant HRB output files to said printer. Remaining partitions are processed into HRB files by at least one of the RIP engines until all partitions have been processed.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
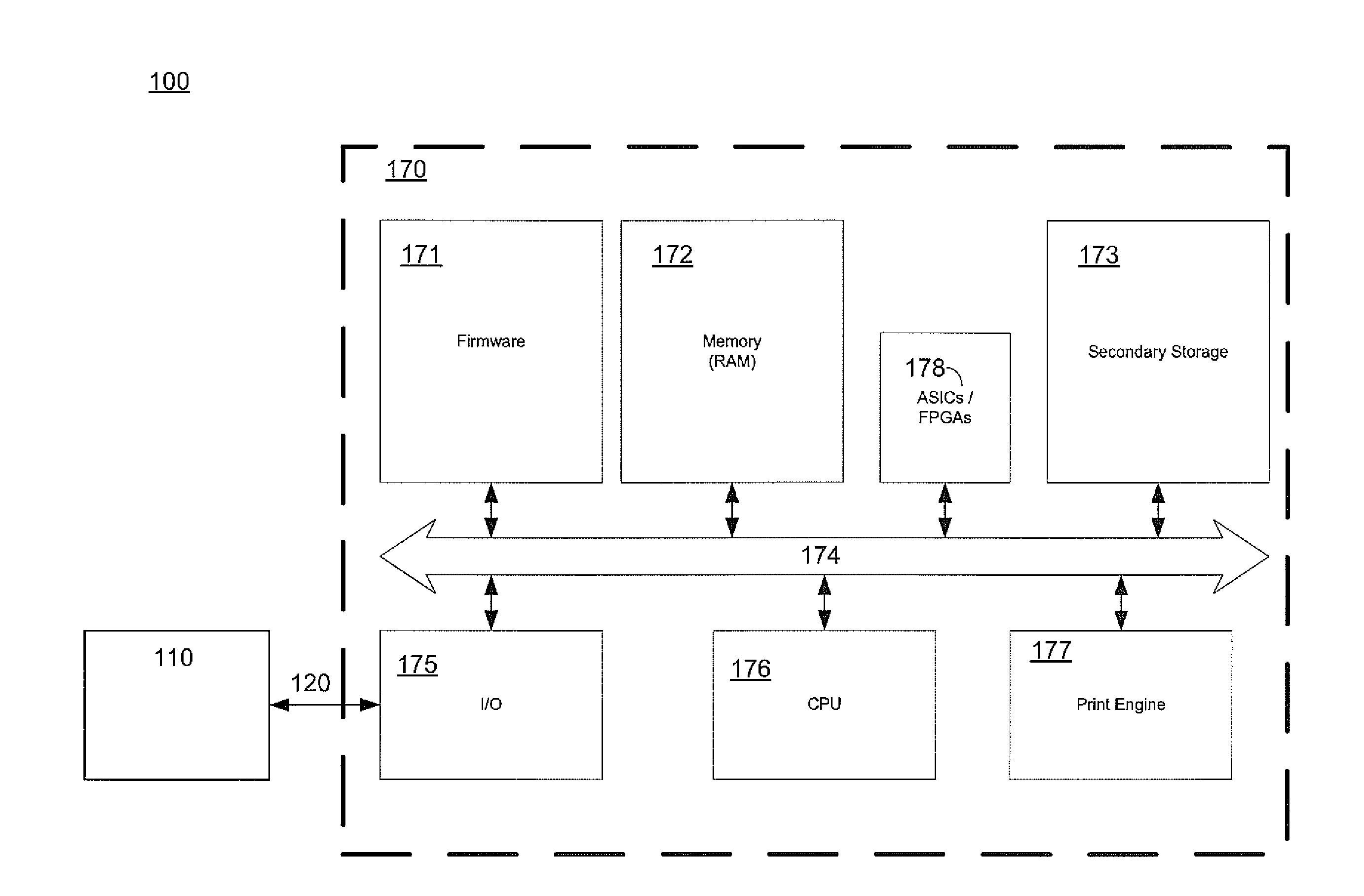
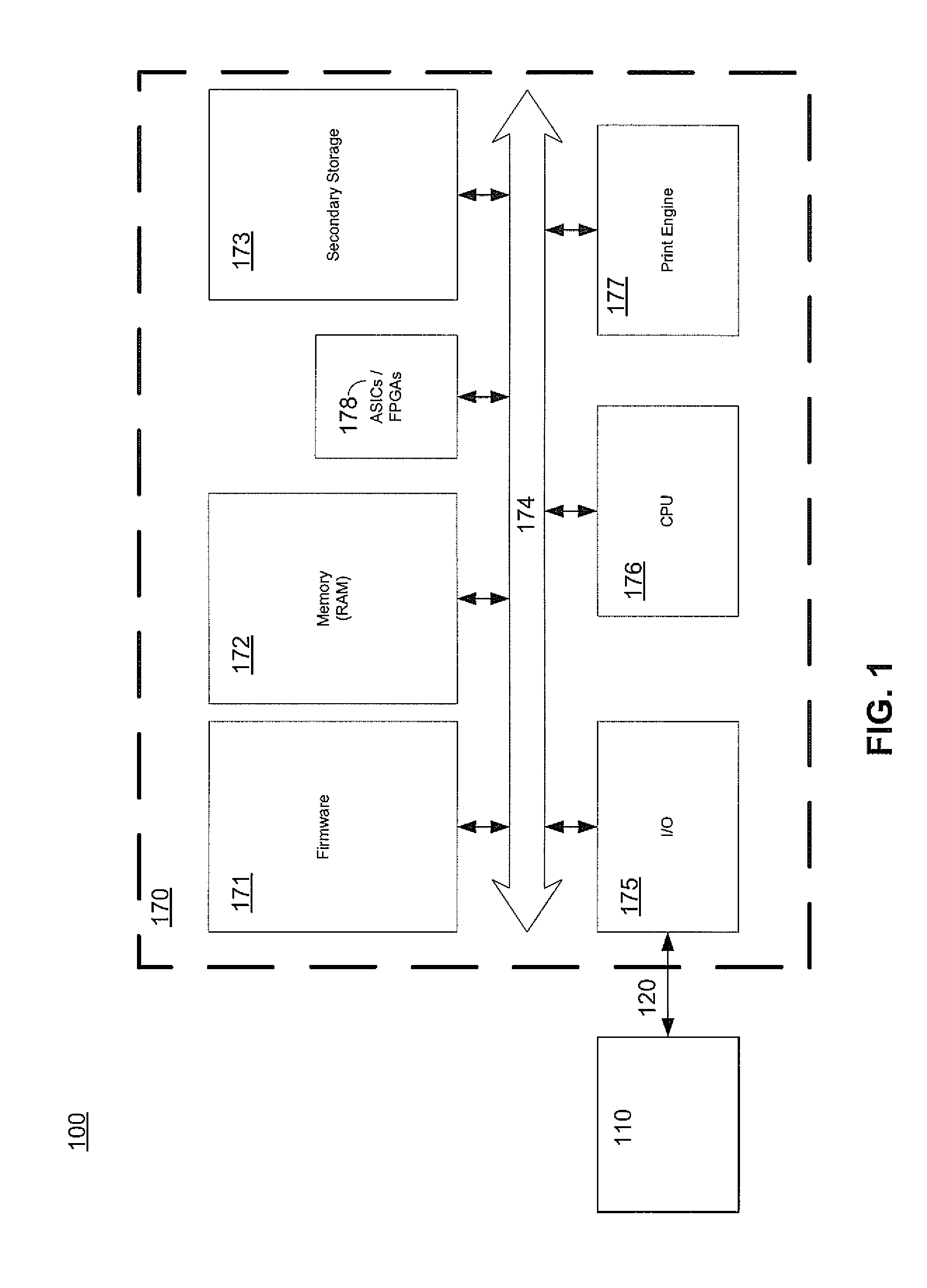
Image processor for high-speed printing applications
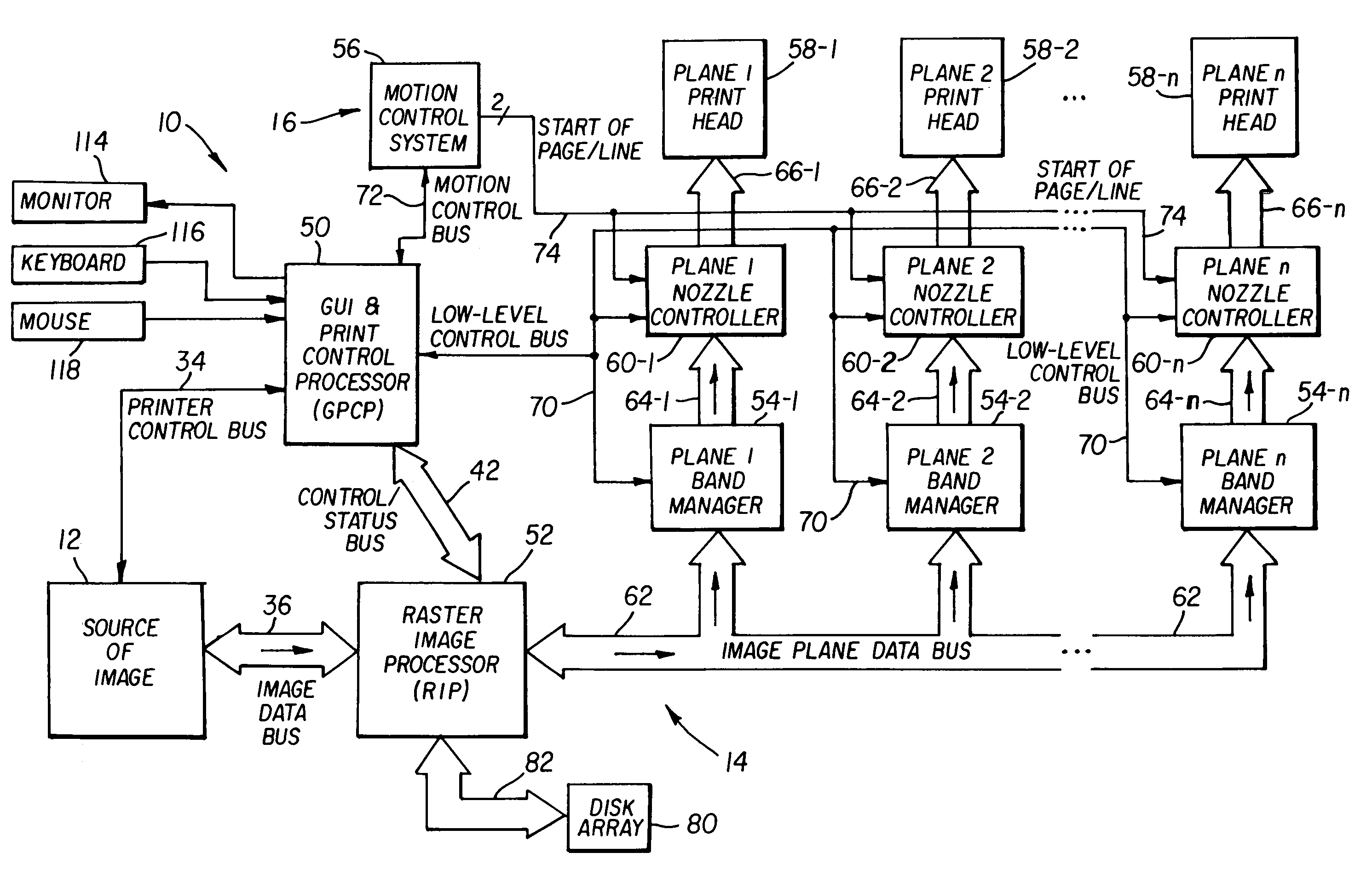
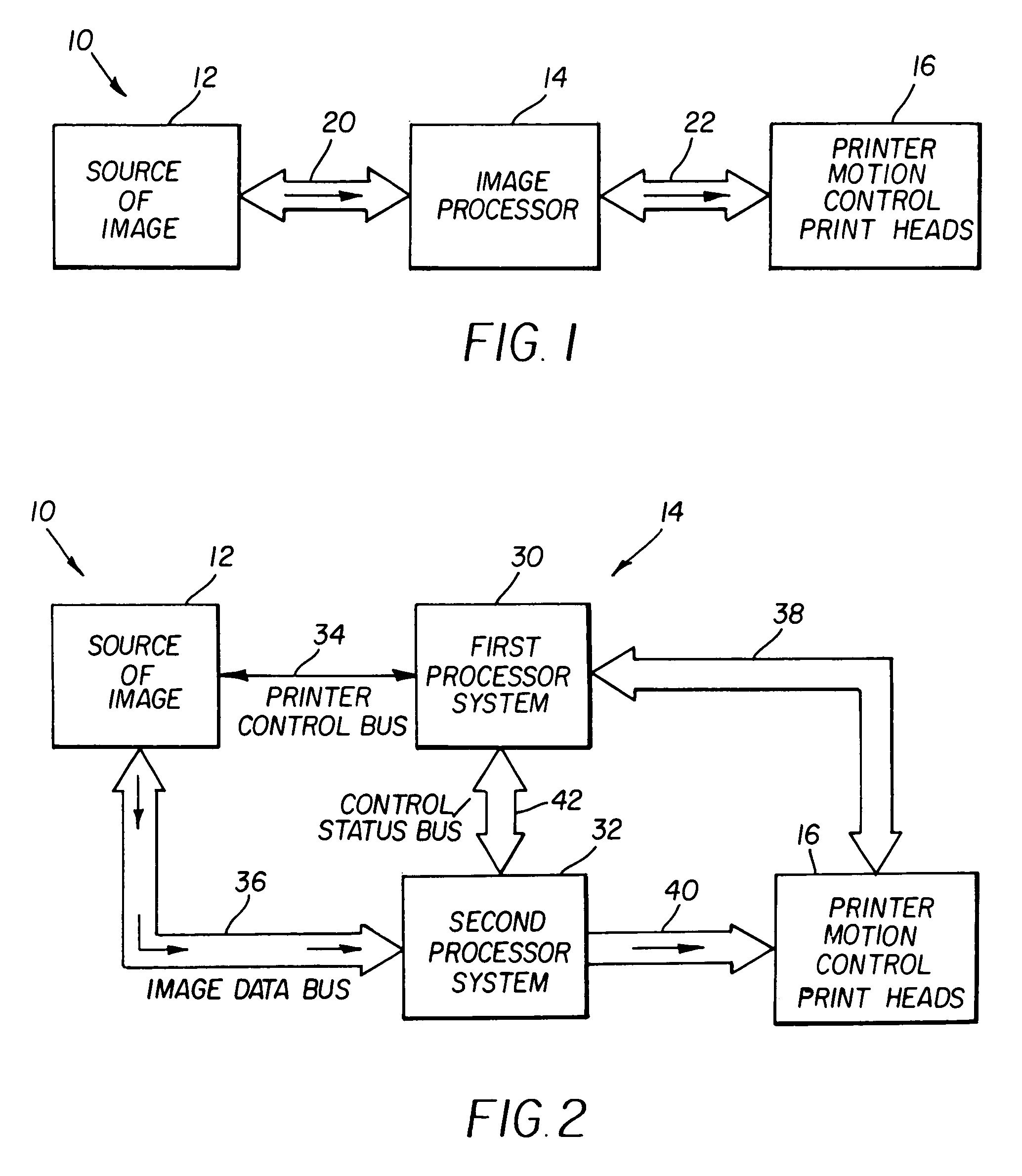
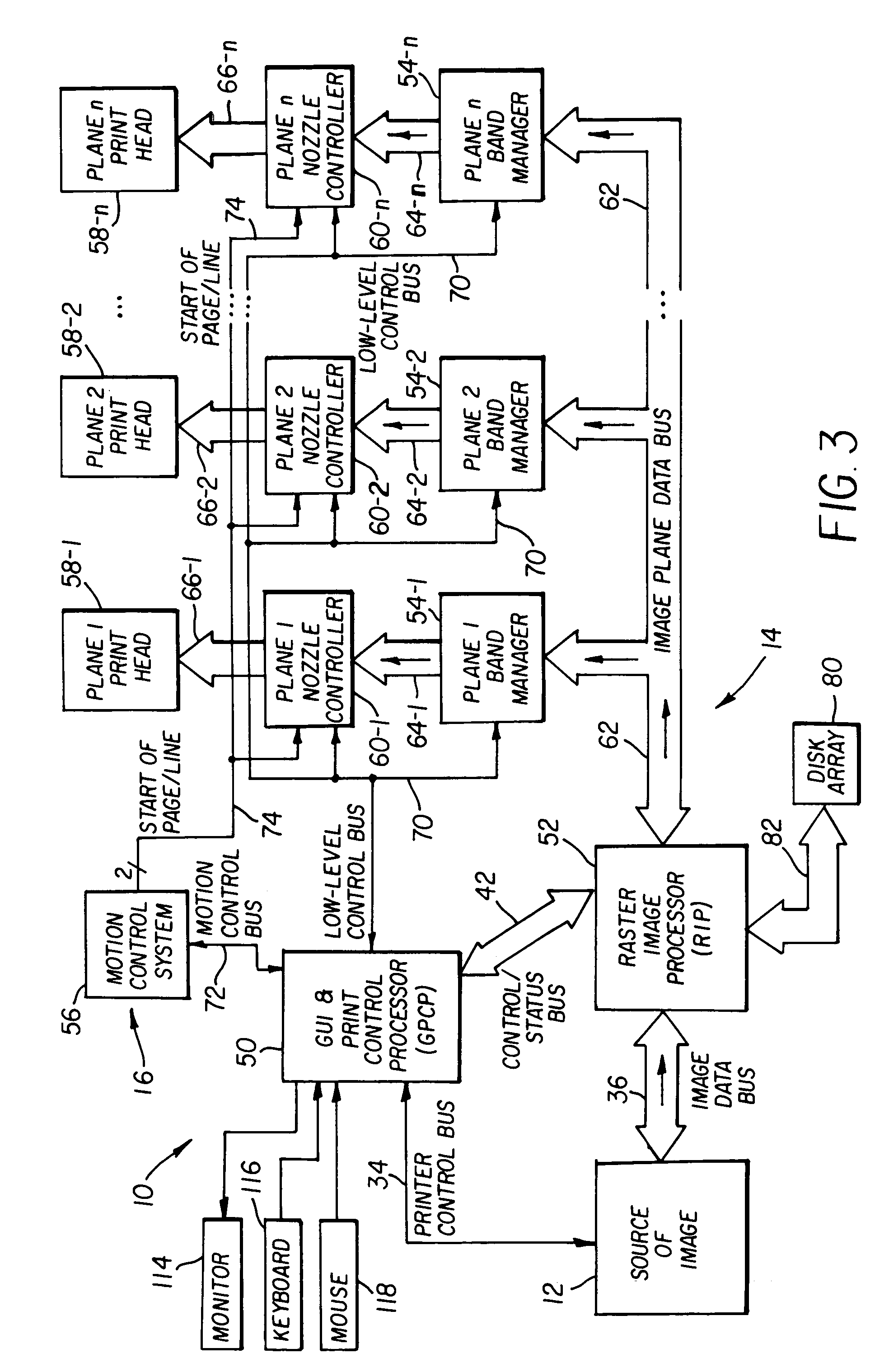
ActiveUS7050197B1High-speed image processingDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer details24-bitTagged Image File Format
An image processor (14) supporting very high-speed printing. The image processor (14) preferably has two separate connections to a source (12) of the image being printed, e.g., a printer control bus (34) and an image data bus (36). The image processor (14) preferably accepts images from the image source (12) in commonly known graphics file formats, such as the well-known 24-bit, uncompressed TIFF file format. The image processor (14) is a multiprocessor implementation. Preferably, one processor (30) coordinates or “orchestrates” control of the printing system and handshaking with the image source via the printer control bus (34) and the other processor (32) functions as a raster image processor (RIP) processor (52) and accepts and stores images into the printer environment from the image source (12) via the image data bus (36). The RIP processor (52) preferably performs color separation on the image into color planes and transmits each color plane to a separate processing path from that point on in the imaging chain. Each color plane preferably has a separate imaging path out from a shared image data bus (62). This separate path for each color plane preferably includes a band manager (54), a print engine or nozzle controller (60), and a print head (58).
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method and apparatus for raster image processing
InactiveUS20060017974A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsEqual and good performanceDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsDisplay listPage description language
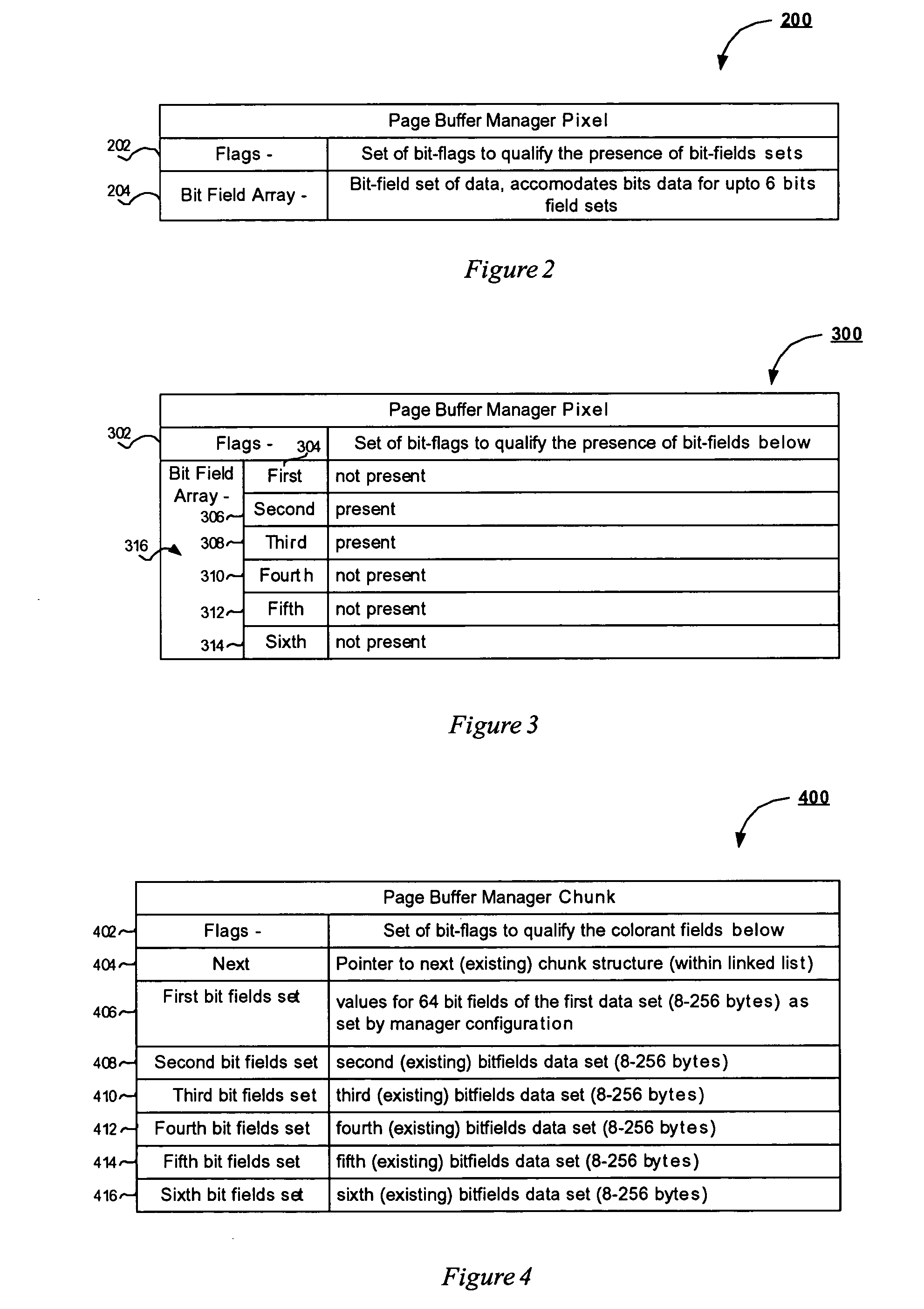
This invention is directed to a method and apparatus for raster image processing which allows access to the page buffer during raster image processing. The method and apparatus of the present invention allow for virtually every page presented to the raster image processor to be printed with available memory. In addition, the method and apparatus for raster image processing of the present invention significantly reduces the bandwidth required between the raster image processor and the raster image processor manager. In addition, the method and apparatus for raster image processing of the present invention has equal or better performance than those methods or apparatuses that use display lists. Further, the method and apparatus of the present invention support the use of tag data and multiple page description languages.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
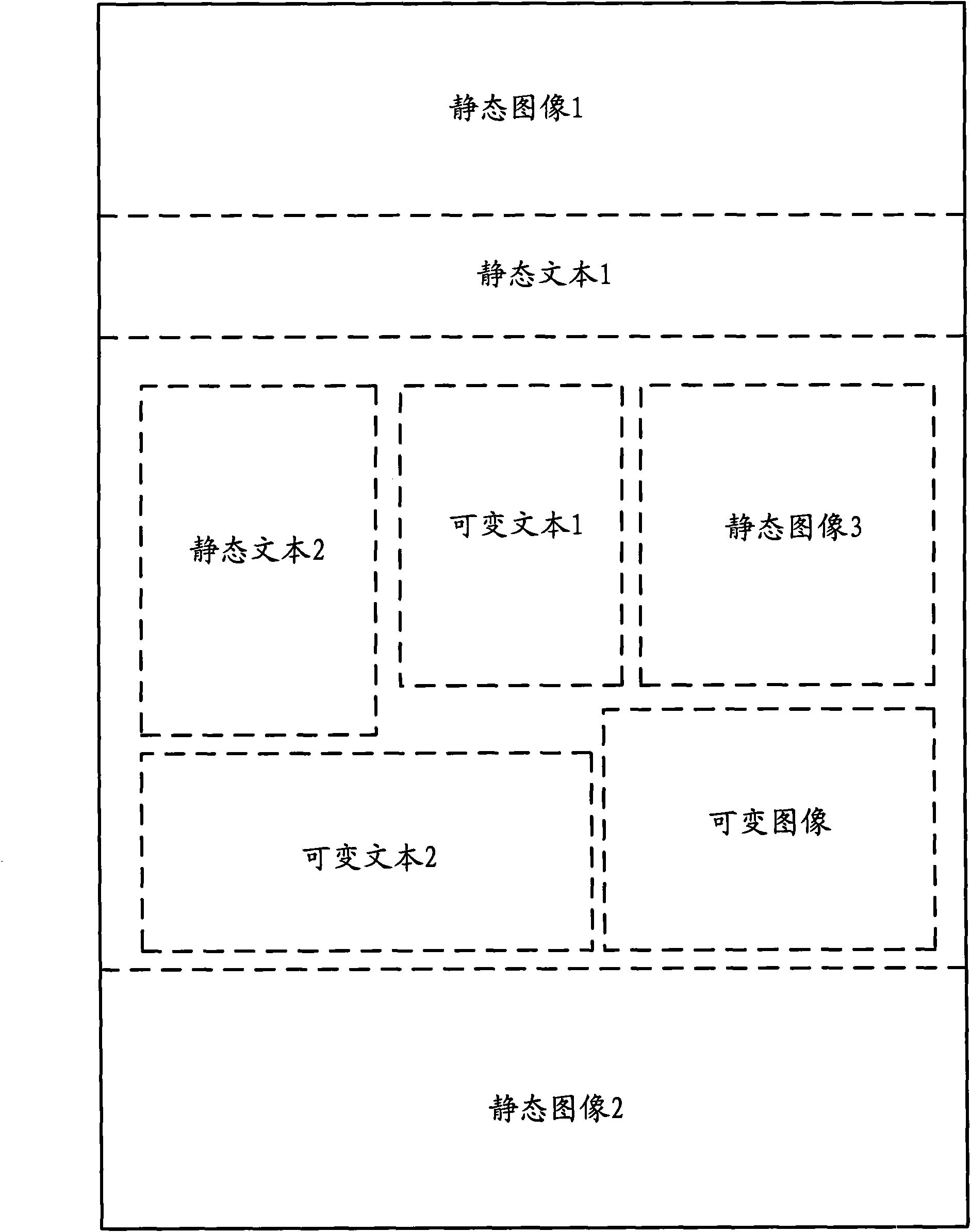
Storing method of rasterization lattice of variable data printed page
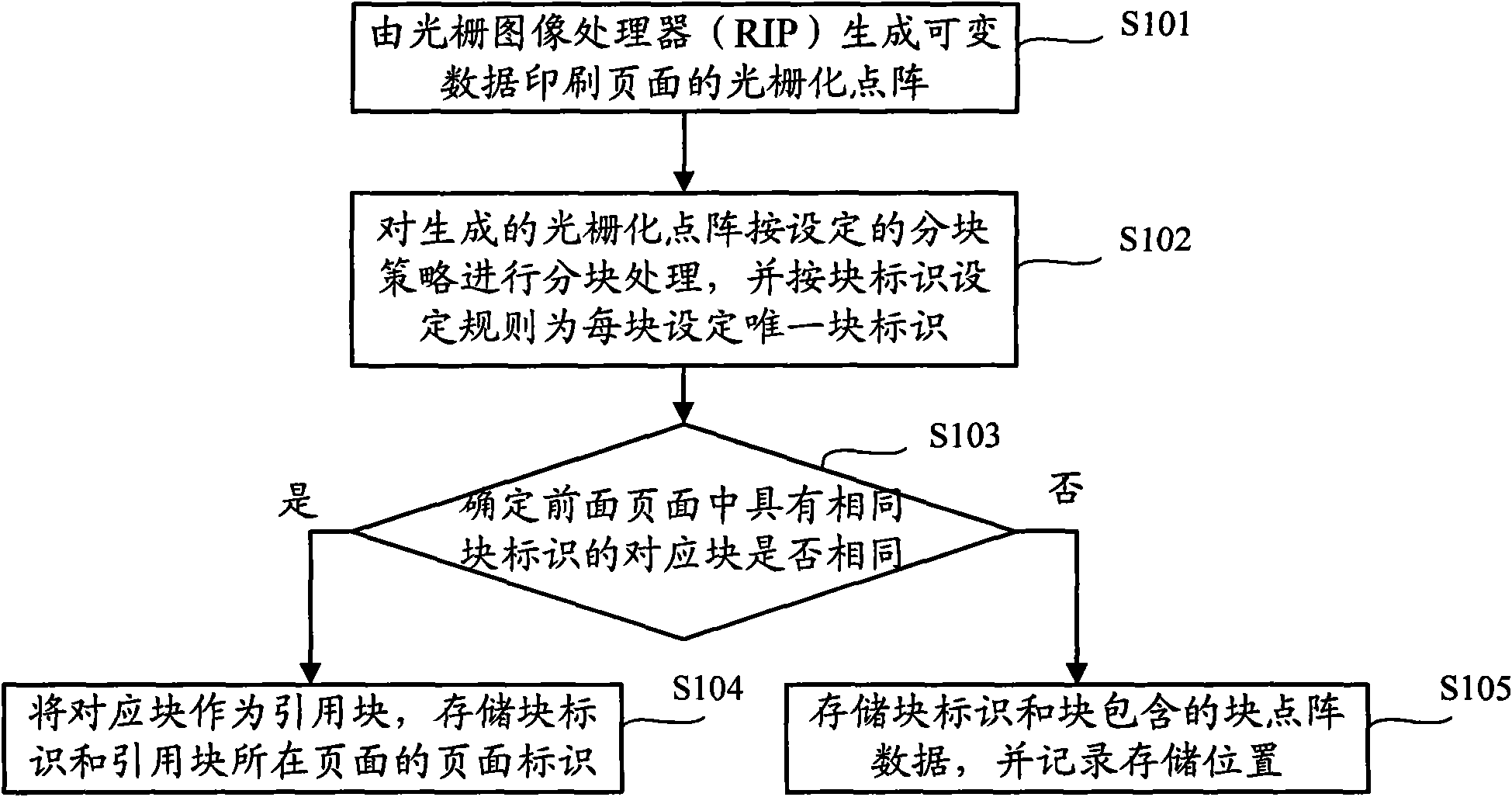
ActiveCN101576995AReduce storageImprove storage speedImage memory managementComputer hardwareGrating
The invention discloses a storing method of a rasterization lattice of a variable data printed page. The method comprises the following steps of: generating the rasterization lattice of the variable data printed page by a raster image processor RIP; carrying out block processing on the generated rasterization lattice according to a set block strategy, and setting a unique block identification for each block according to the set regulation of block identification; determining whether the blocks in the current page are same with the corresponding blocks with same block identification in the front page; if so, using the corresponding blocks as reference blocks and storing page identification of the page where the block identification and the reference block are located; if not, storing the block identification and block lattice data contained in the blocks and recording the storing positions. The storing method and the system can reduce the data storage capacity of the rasterization lattice of the variable data printed page, save storage space and cost and can improve the speed of storage and access.
Owner:NEW FOUNDER HLDG DEV LLC +2
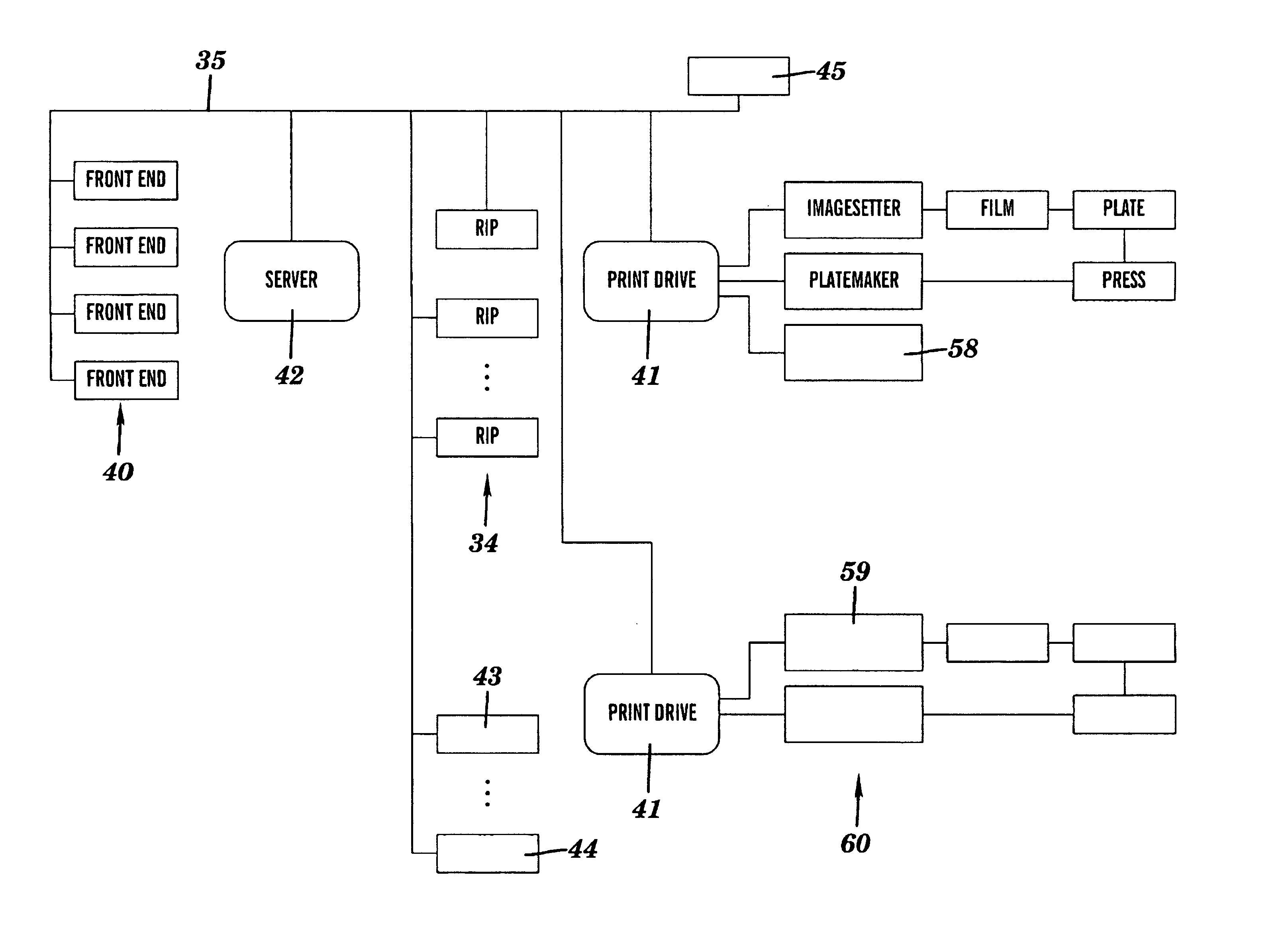
Print driver system having a user interface and a method for processing raster data
InactiveUS7242487B2Improve data transfer rateEfficient transferDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGratingComputer terminal
A system and method for processing raster data including at least one input computer terminal for creating postscript data, at least one raster image processor (RIP), for processing the postscript data into raster data, and a PrintDrive system for managing and controlling the workflow of image files containing raster image data to a plurality of user selectable output devices.
Owner:AGFA DIVISON BAYER CORP
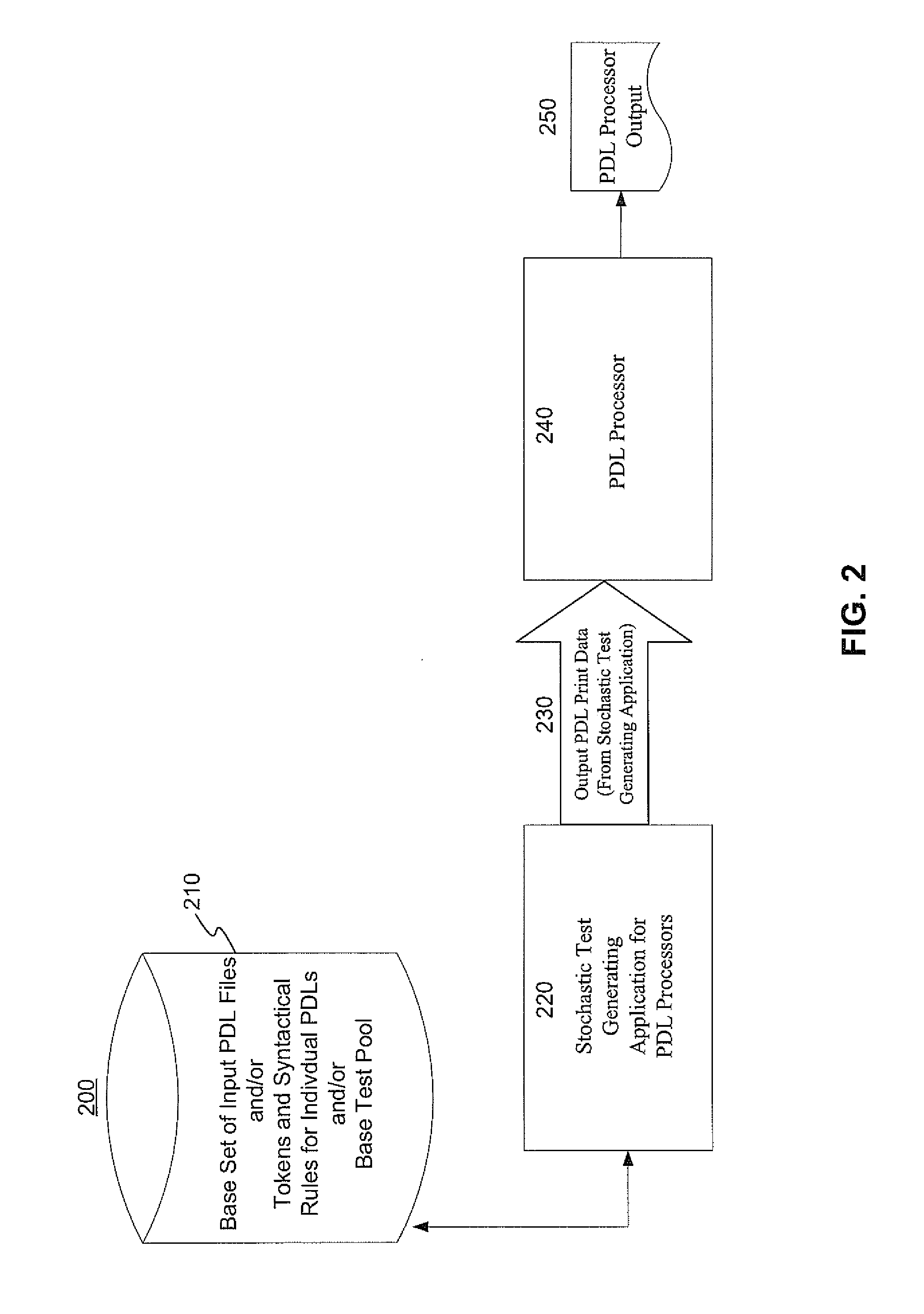
Systems and methods for stochastic regression testing of page description language processors
InactiveUS20110157620A1Error detection/correctionDigital output to print unitsRegression testingLanguage processor
Systems and methods consistent with embodiments presented pertain to the stochastic regression testing of software PDL processors. Test input for PDL processors, which include language processors and raster image processors, may be generated by randomly altering the values of one or more of text, graphical object parameters, image object parameters, graphical combination parameters in an existing PDL input file. In another embodiment, test input for PDL processors may be generated by randomly selecting a first token from a lexical token dictionary and combining the first token with at least one of a plurality of second tokens randomly selected from the lexical token dictionary, so that the combination of the first token and the plurality of second lexical tokens satisfies the syntactical rules for the PDL. In a further embodiment, existing tests in a test pool may split and recombined in a syntactically correct manner to generate new tests.
Owner:XEROX CORP +1
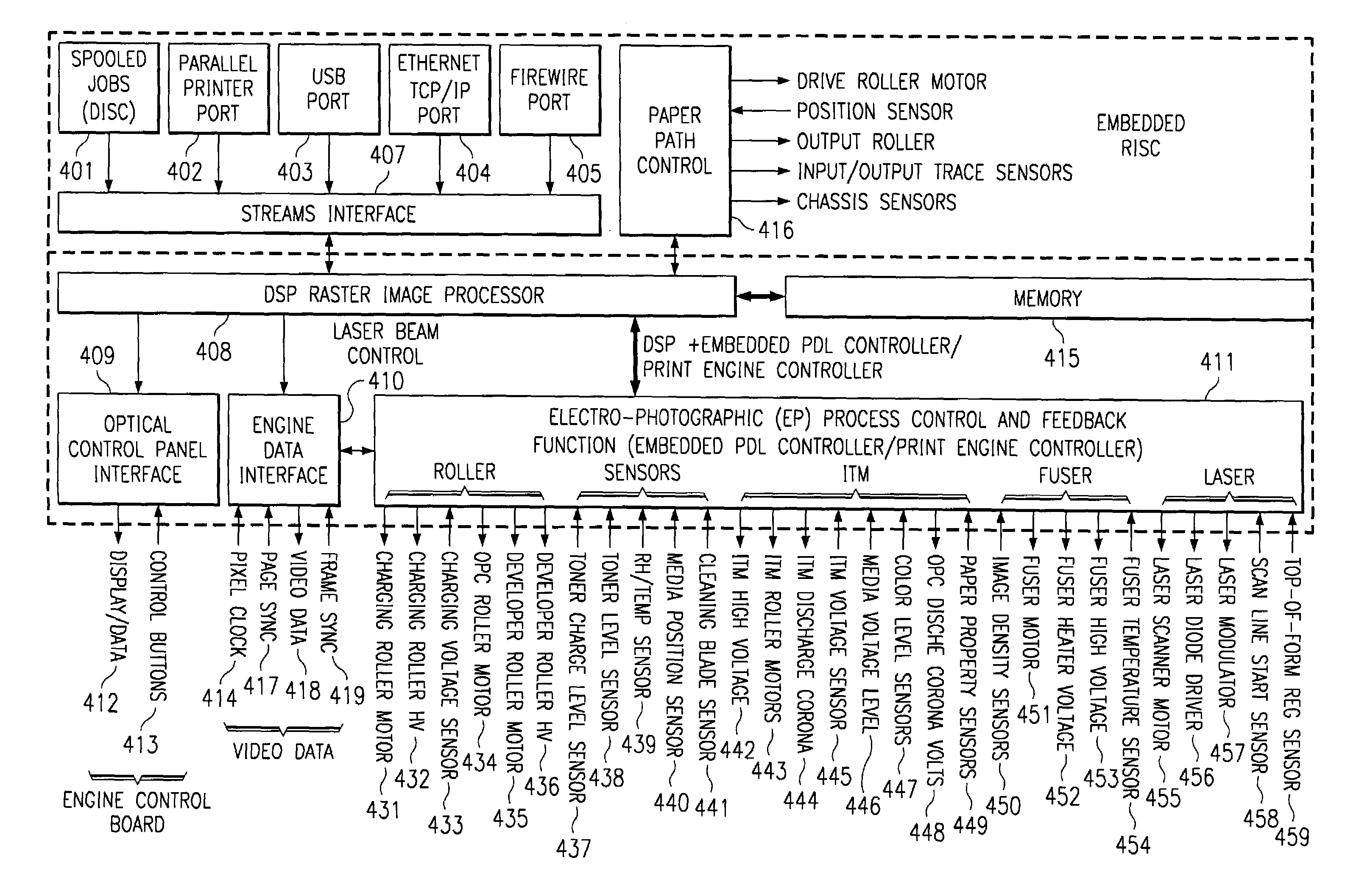
Integrated raster image processor and electro-photographic engine controller
ActiveUS7173719B2Quality improvementCostDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGratingClosed loop feedback
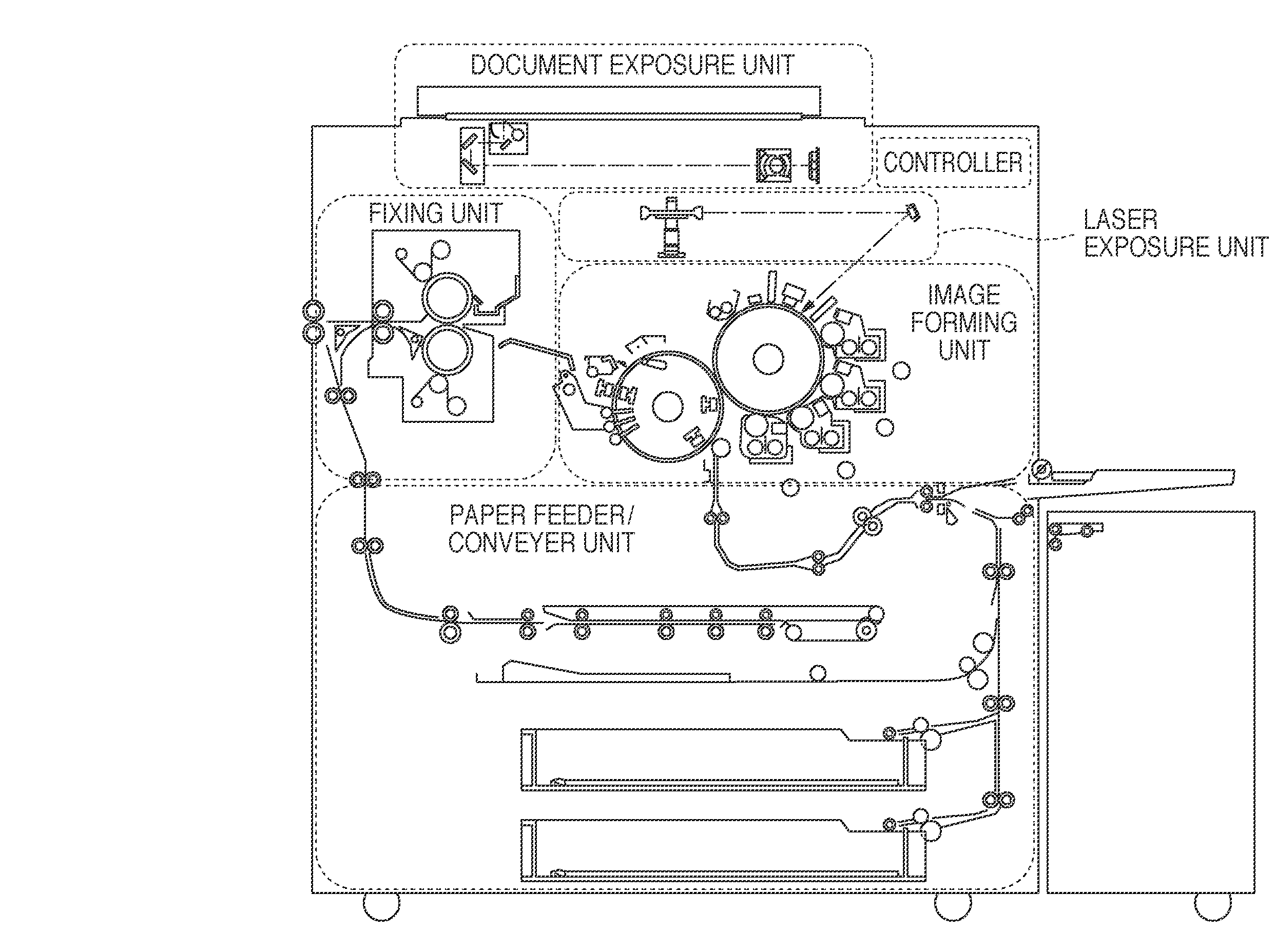
This invention comprises a converged printer architecture for controlling both electro-photographic (EP) processing and raster image processing (RIP) of data for laser modulation over a video line. By converging EP process control with image processing control, significant advantages in cost, image quality, and output stability are achieved. A digital signal processor (DSP) serves as the central processing resource of the architecture. The DSP is well suited for the dual role of image processing and real-time feedback process control. The DSP can operate in open loop motor / motion control, print process control, and in closed loop feedback control including image processing adaptations for quality and stability enhancements.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
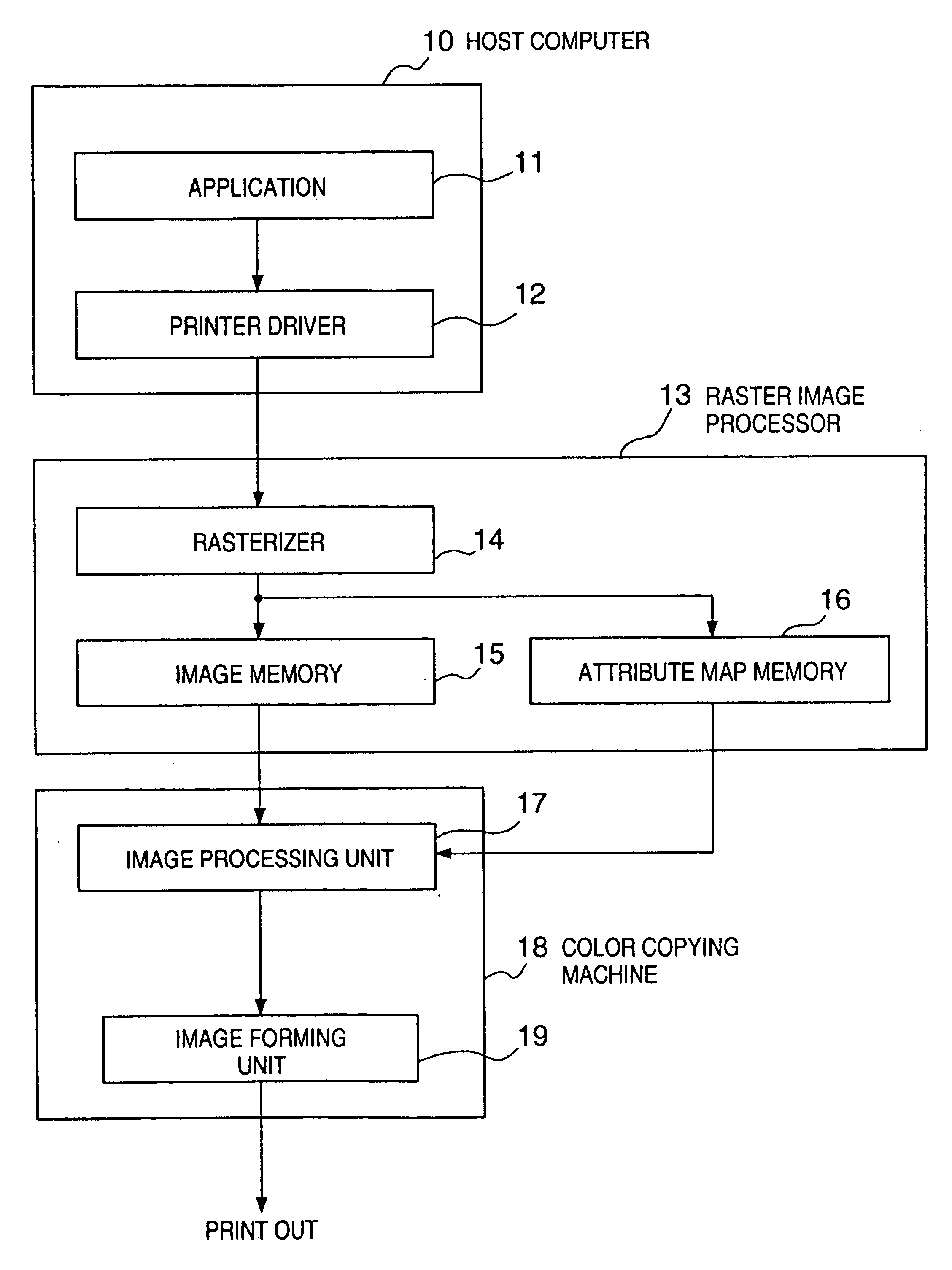
Color image processing apparatus and method, and storage medium
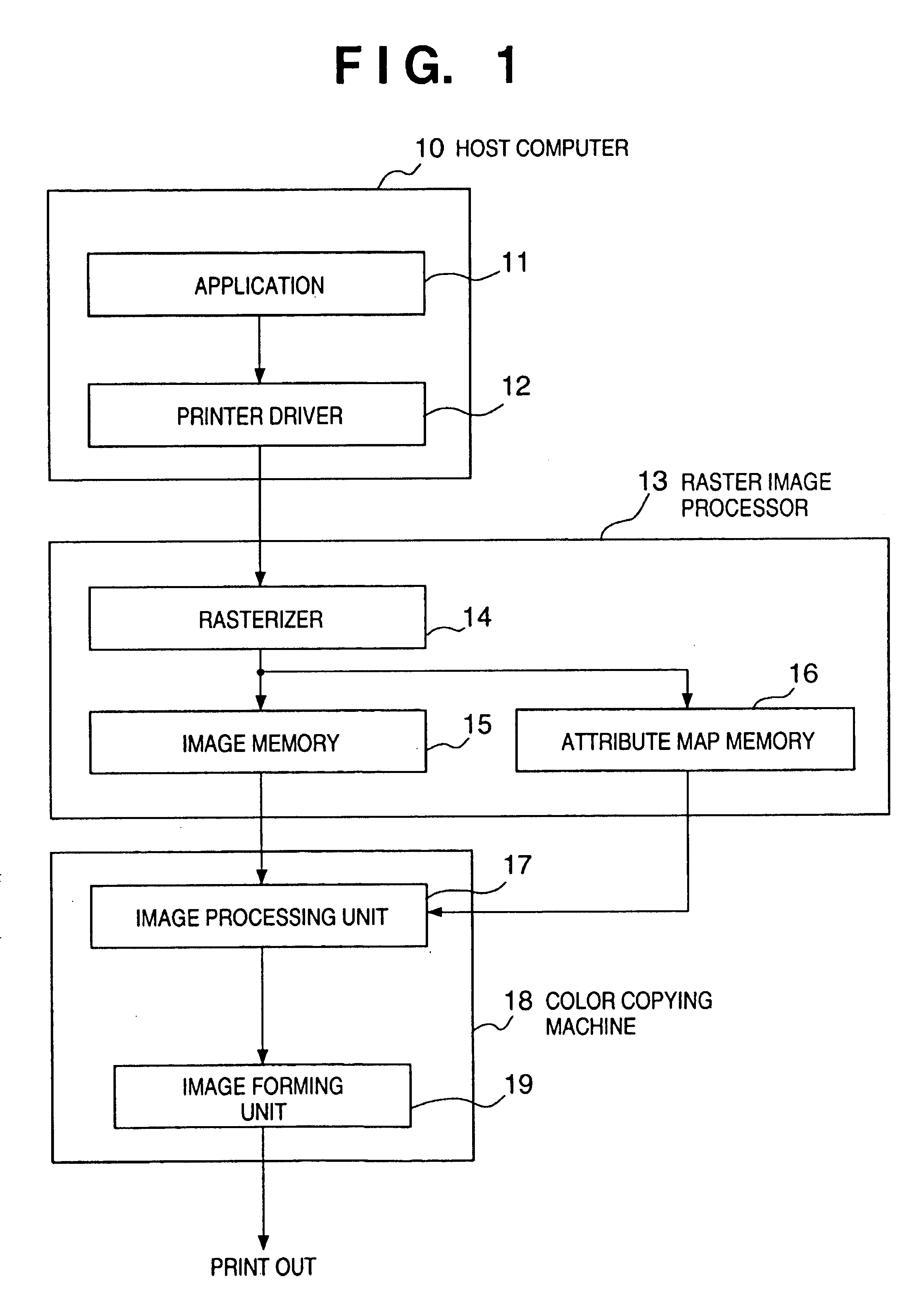
InactiveUS7057764B1Prevent image deteriorationReduce the differenceDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsRaster image processor
A full-color image input from an external apparatus can undergo an optimal adaptive process using an image area separation circuit mounted in a color copying machine main body, and also attribute map information, thus providing a higher-quality image. When a color copying machine (18) prints an image such as a computer graphics image sent from a host computer (10), a raster image processor (13) renders bitmap data of a given recording color on an image memory (15) on the basis of that print data, and stores attribute information in an attribute map memory (16) in units of pixels. The color copying machine (18) forms an image on the basis of image data of respective recording color components, which are frame-sequentially input from the raster image processor (13), and attribute information from the attribute map memory (16).
Owner:CANON KK
Method for tracking depths in a scanline based raster image processor
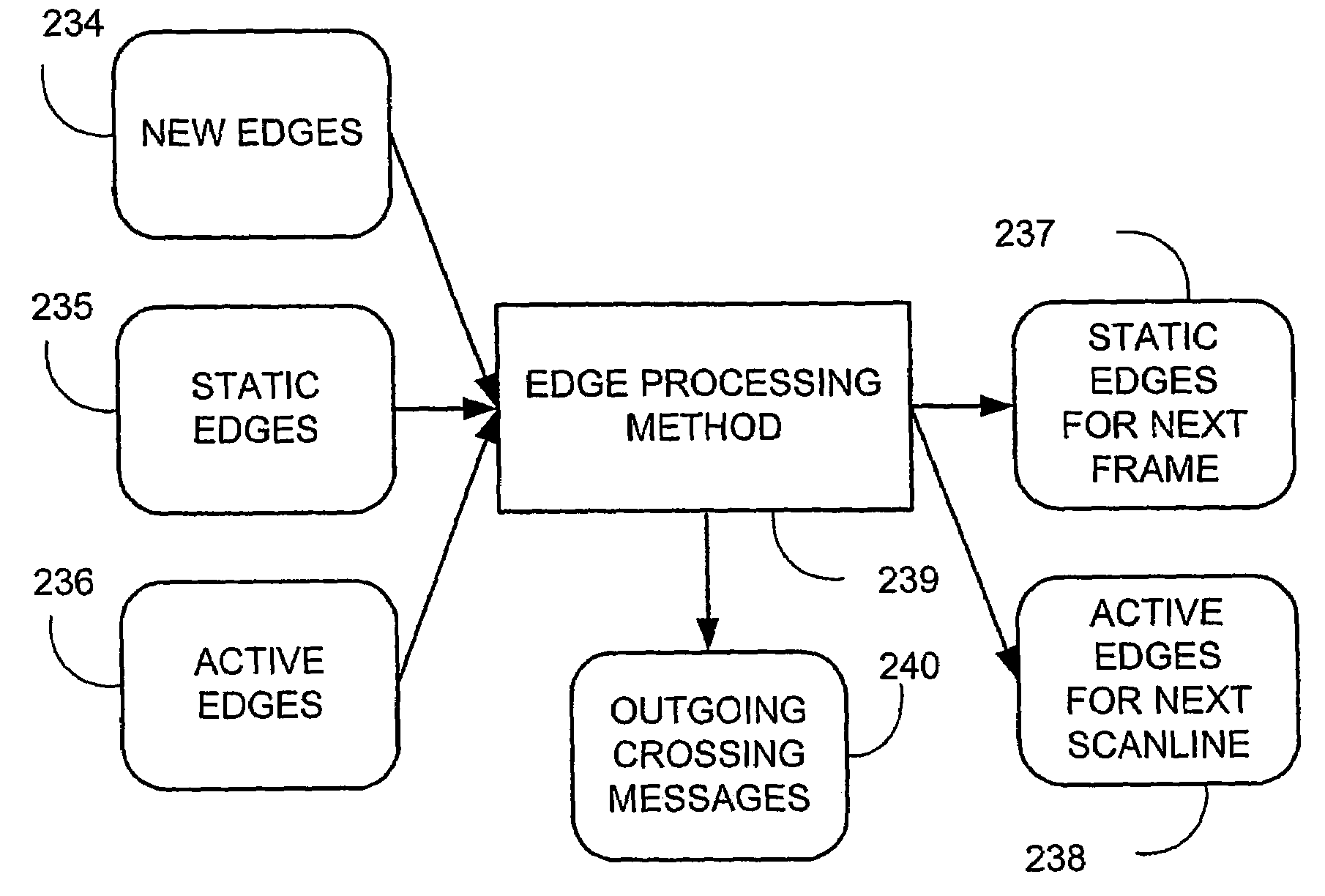
ActiveUS7425955B2More disadvantageFilling planer surface with attributes3D-image renderingGraphicsGrating
A method of rendering a scan line of a graphic object image in a scan line renderer for spans of pixels laying between consecutive x-ordered edges intersecting the scan line includes maintaining a set of depths present in the rendering of the scan line, with the set being maintained in depth order. For each span, the set contains at least those depths that are active in the span, and the set is subject to removal of at least one depth at a subsequent span on the scan line where the corresponding depth is no longer active.
Owner:CANON KK
Data transmission system and method for distributed optical grating picture processing
InactiveCN101131626AReduce occupancyAcquisition speed is fastTransmissionDigital output to print unitsGratingOutput device
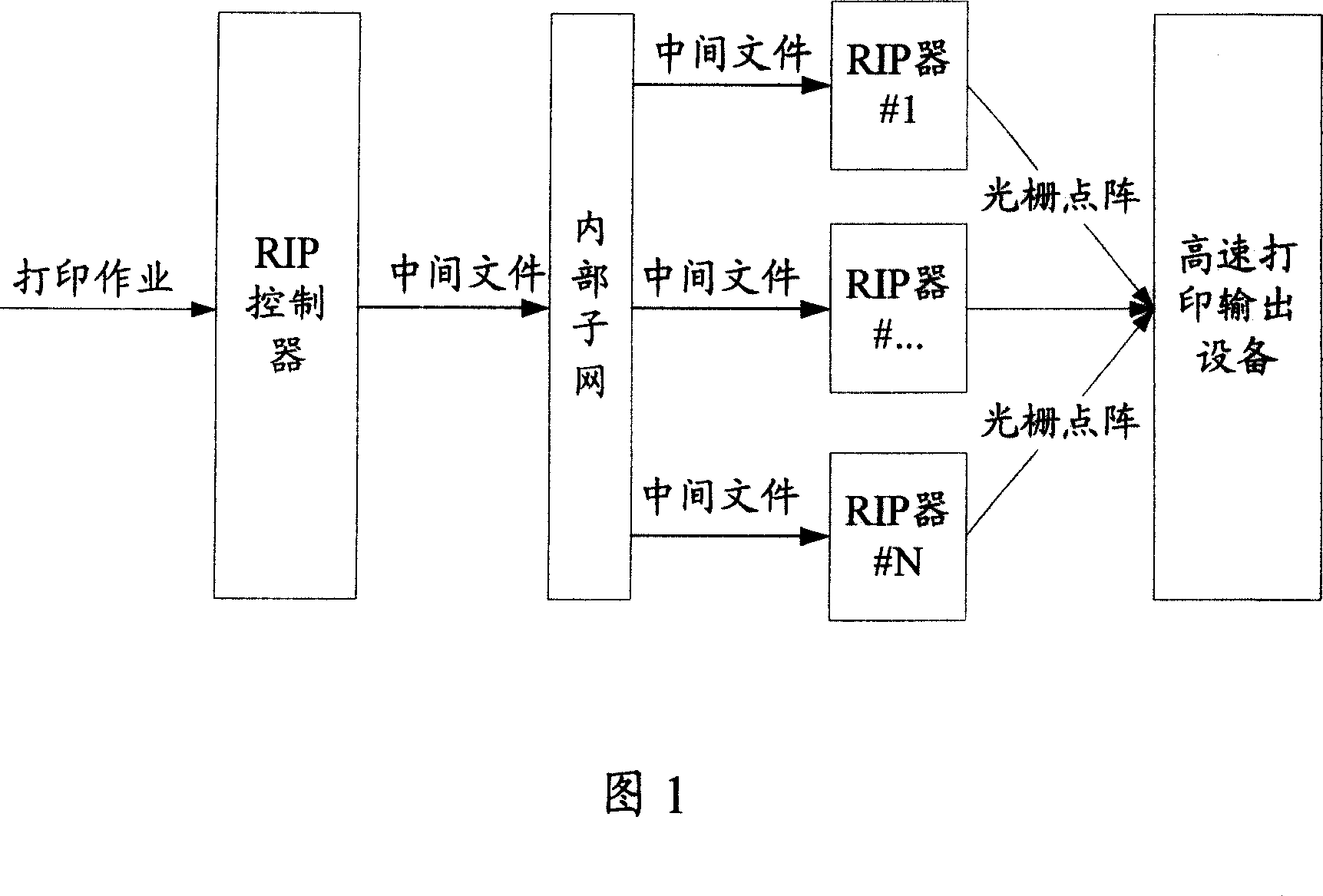
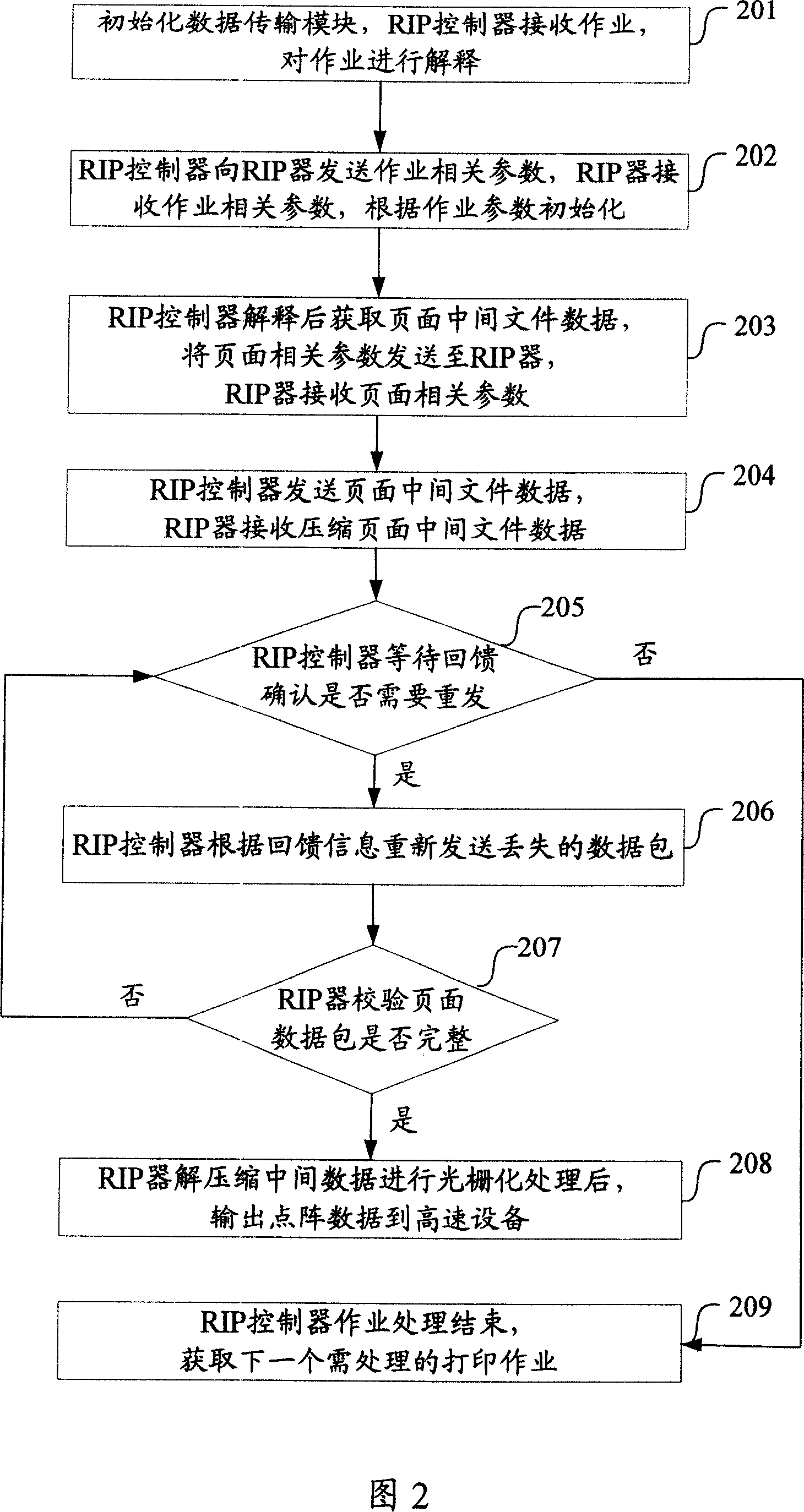
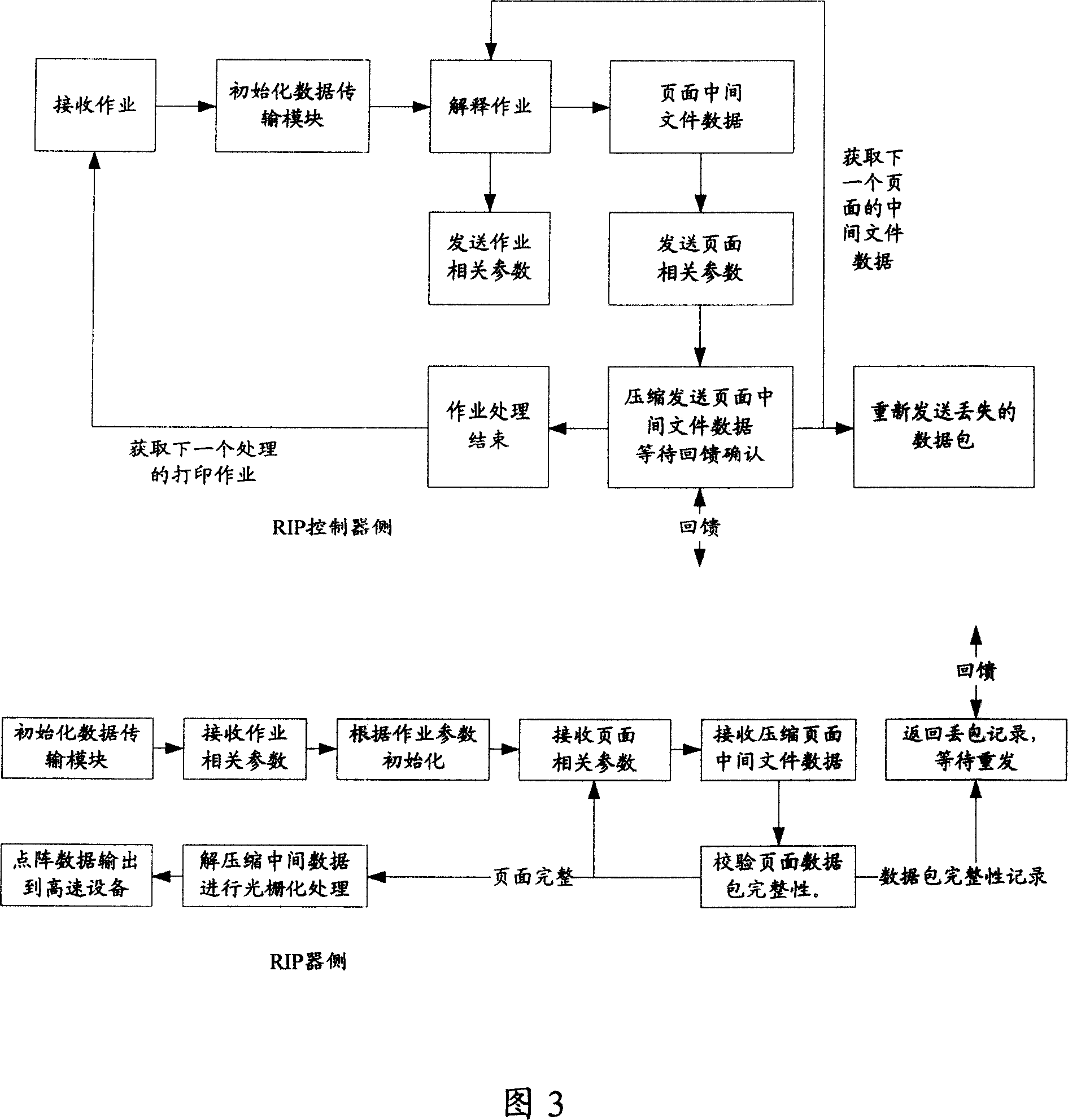
This invention discloses a kind of distributed grating image processing data transfer system of the figure and image printing treatment. In this invention method after the grating image processing controller interprets the printing describing language to the document data use the user data paper agreement to distribute it to the grating processor for grated process. In this invention system the grating image processing controller connects with the multiple grating image processor through the first data transfer module and the first transfer module is distributed to the grating image processor for grated process through the user data paper agreement after the first transfer module interprets the printing describing language to the document data in the grating image processing controller. By using this invention the transfer velocity is quicker and the occupation for the network resource is less and it improves the getting velocity of the grating image processing system for the processing work resource at the same time improves the processing velocity of the distributed grating processing system and it is satisfied for the requirement of high speed printing output device.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
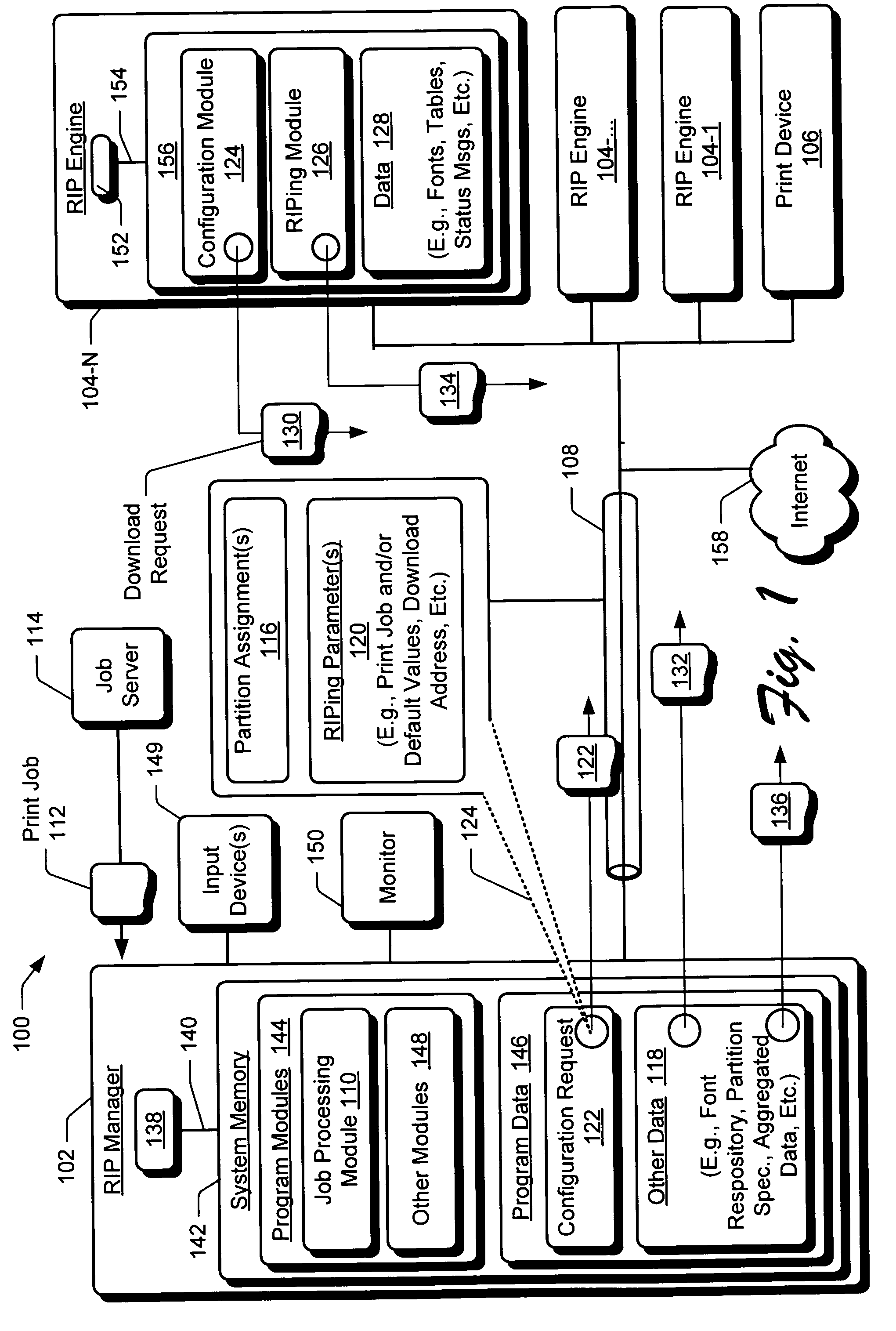
Automatically configuring a raster image processor
ActiveUS20050015779A1Multiprogramming arrangementsDigital output to print unitsAuto-configurationComputer science
Systems and methods to configure a Raster Image Processor (RIP) are described. In one aspect, a networked computing environment includes a RIP manager coupled to at least one RIP engine. A print job is received. The RIP engine is requested to dynamically configure its RIPing operations when at least one of the RIP Engine's RIPing parameters is not congruent to a RIP manager supplied processing preference. Such dynamic configuration is requested in consideration of the RIP engine RIPing a particular portion of the print job.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
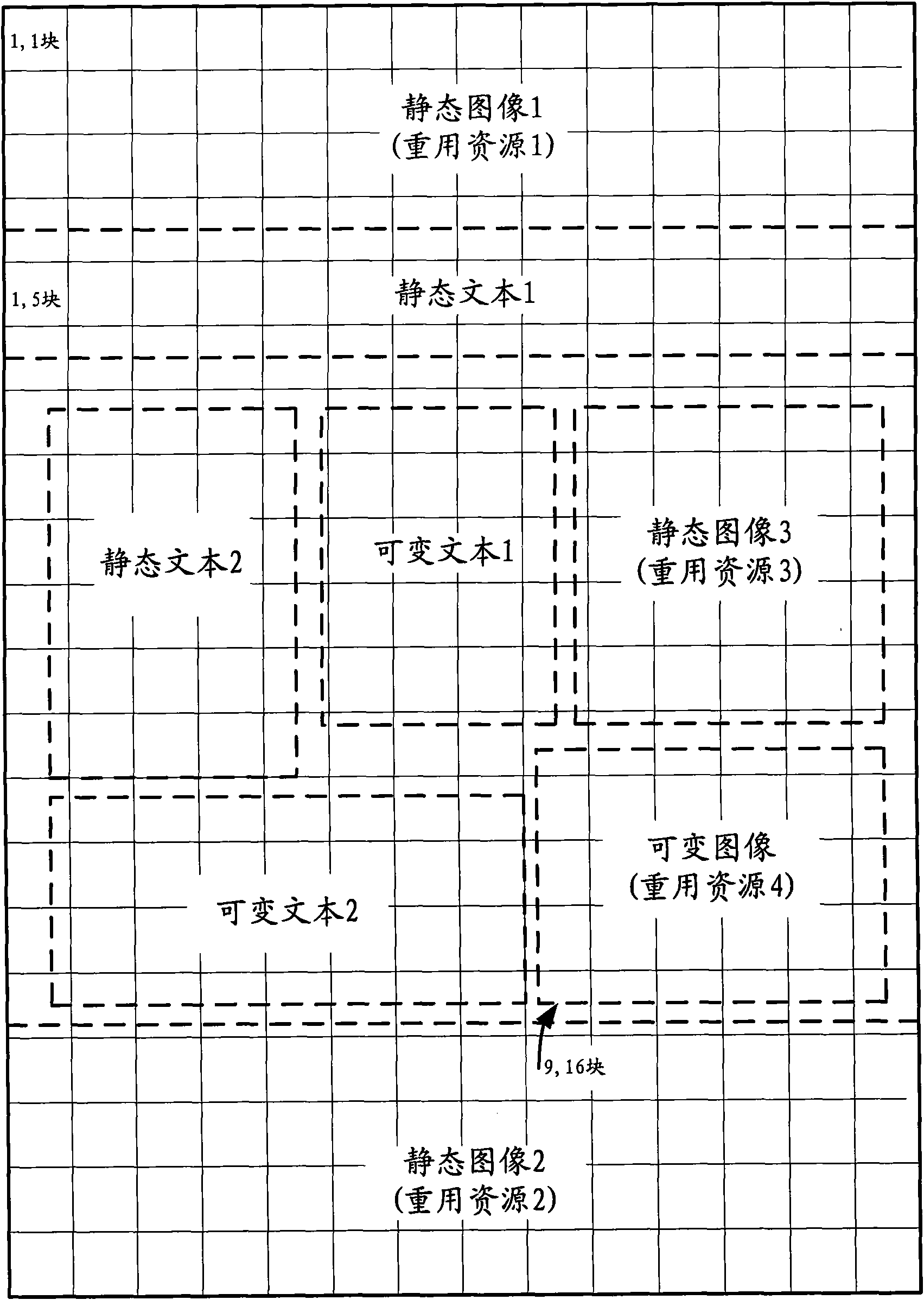
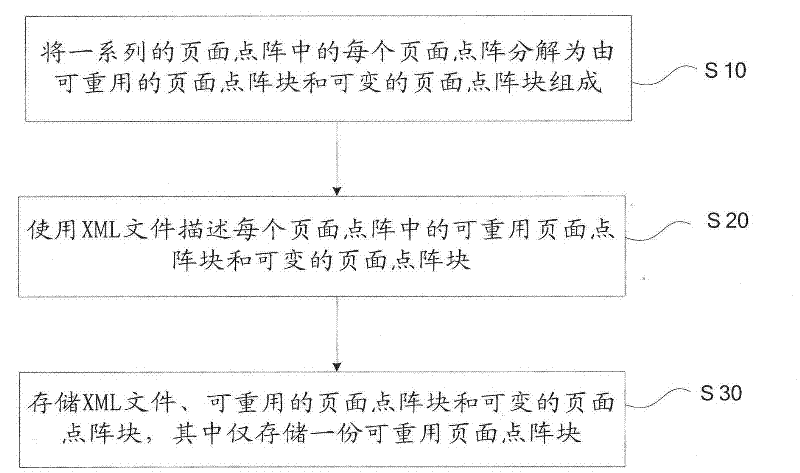
Page lattice storage method for variable data printing and device adopting same
ActiveCN102446163AReduce data volumeSolve the problem of low storage efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsDigital output to print unitsExtensible markupRaster image processor
The invention provides a page lattice storage method for variable data printing and a device adopting the same. The method comprises the following steps: each page lattice in a series of page lattices is broken down into a reusable page lattice block and a variable page lattice block, wherein the series of page lattices are formed by breaking down a variable data printing operation which is subject to rasterization of an RIP (Raster Image Processor); the reusable page lattice block and the variable page lattice block in each page lattice are described by XML (Extensible Markup Language) documents; the XML documents, one reusable page lattice block and all the variable page lattice blocks are stored. By adopting the page lattice storage method and the device adopting the same, which are provided by the invention, the storage method is flexible and easy to expand, the storage efficiency is high, and the method and the device are suitable for massive variable data printing systems.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +2
Parallel printing system
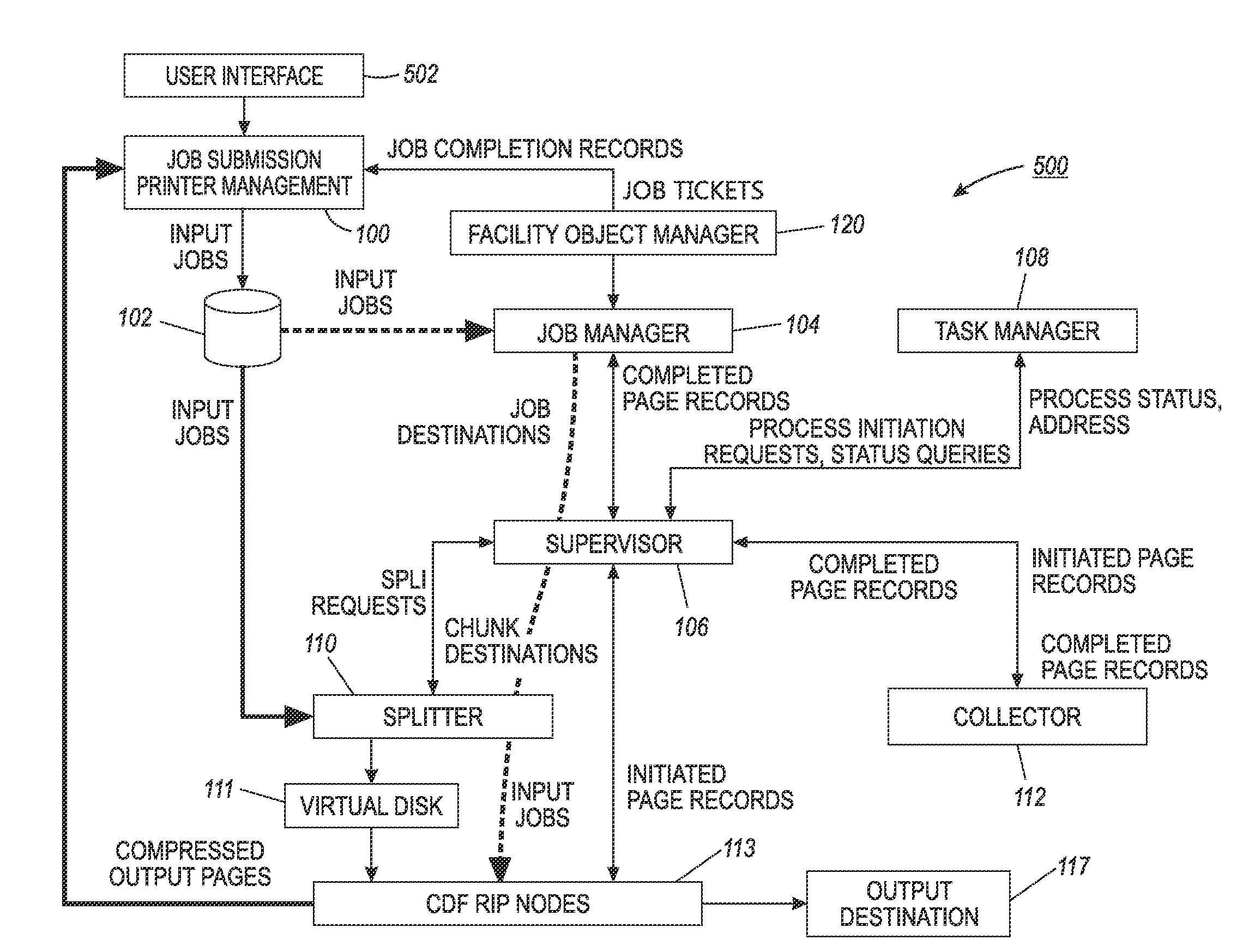
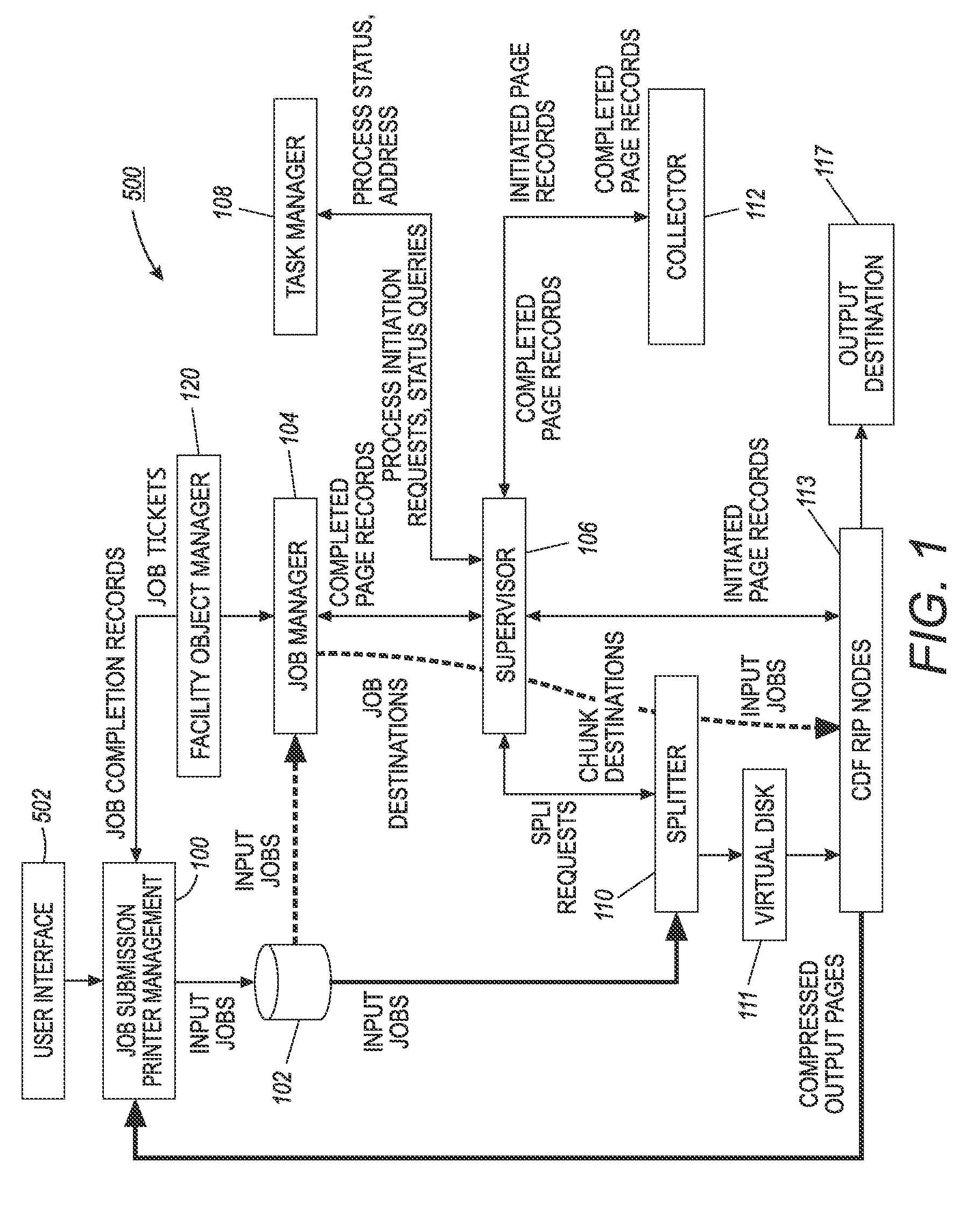
InactiveUS20130258375A1Visual presentation using printersDigital output to print unitsComputer graphics (images)Parallel processing
A parallel Raster Image Processor system that includes a plurality of Raster Image Processors (RIPs) for parallel processing of a plurality of document jobs into a printer-ready format for the printing of the document jobs and a splitter. The splitter configured to combine the plurality of document jobs to form a plurality of chunks, each chunk is sent to a respective designated RIP for processing.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Integration of color pages on a black and white printer managed by a raster imaging processor
InactiveUS6934047B2Reduce needEase of productionVisual presentationOther printing apparatusGratingComputer graphics (images)
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Image forming apparatus and control method thereof
InactiveUS20110058191A1Quality improvementSuppressing print performanceDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging qualityJPEG
The present invention provides a technique for reducing image quality deterioration and suppressing print performance reduction. A raster image processor (RIP) generates intermediate data by interpreting PDL data, and stores it in a memory. In a case where the memory area overflows in the middle of intermediate data generation and storage processing on the print data for one page, rendering is executed based on the intermediate data. In accordance with JPEG XR, tile division is performed. An encoding parameter indicative of lossless-encoding or lossy-encoding is determined in accordance with each tile, and encoding is executed. The encoded image data is stored in a background image memory area as a background image of intermediate data that will subsequently be generated. When subsequent intermediate data generation is completed, rendering is executed, the rendered image is synthesized with the image saved as a background image, then the data is outputted.
Owner:CANON KK
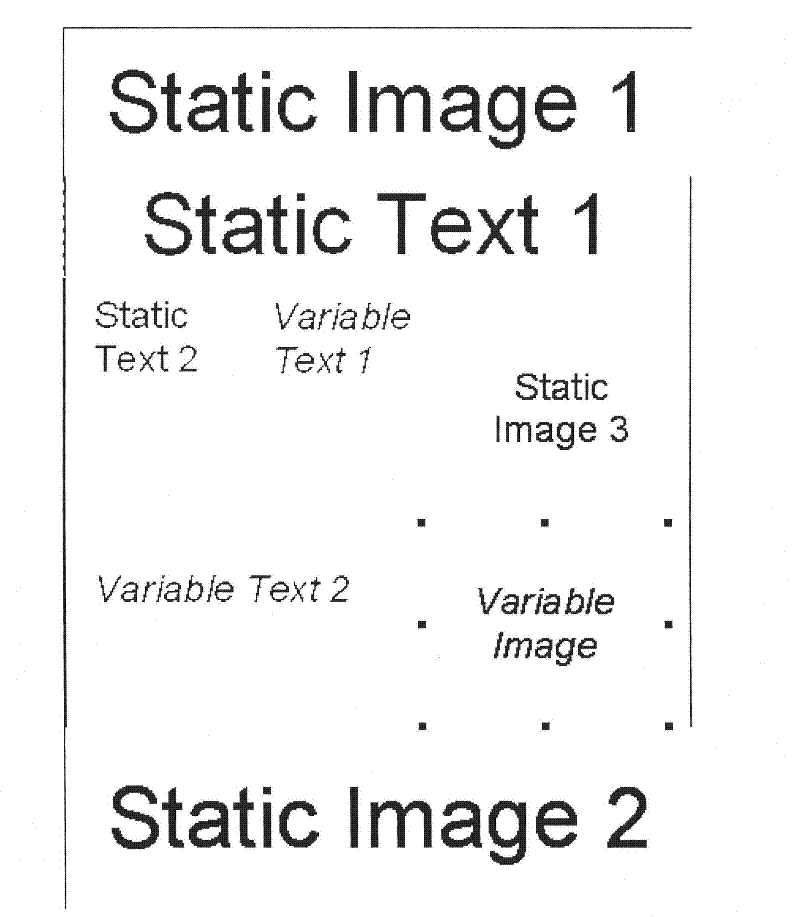
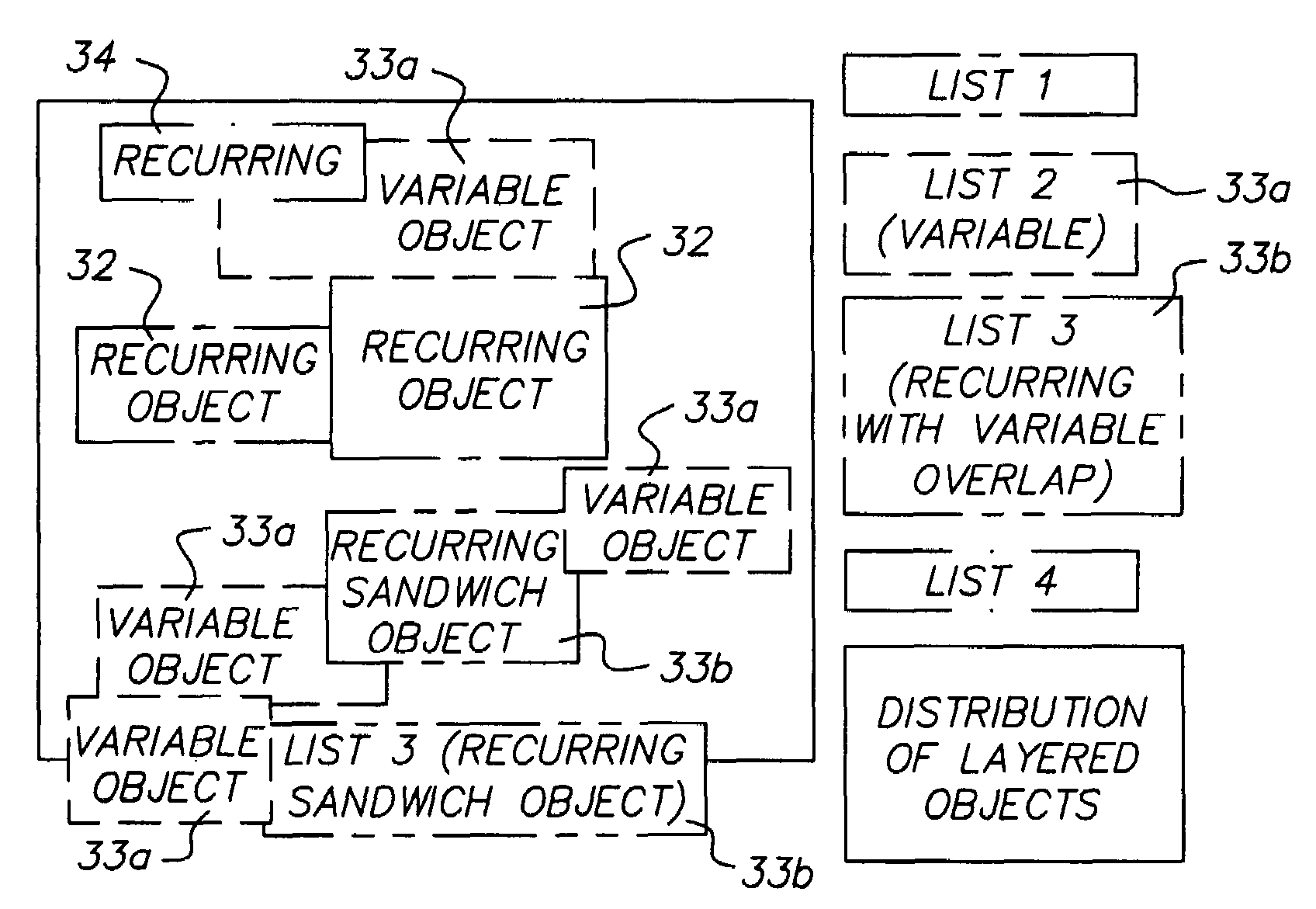
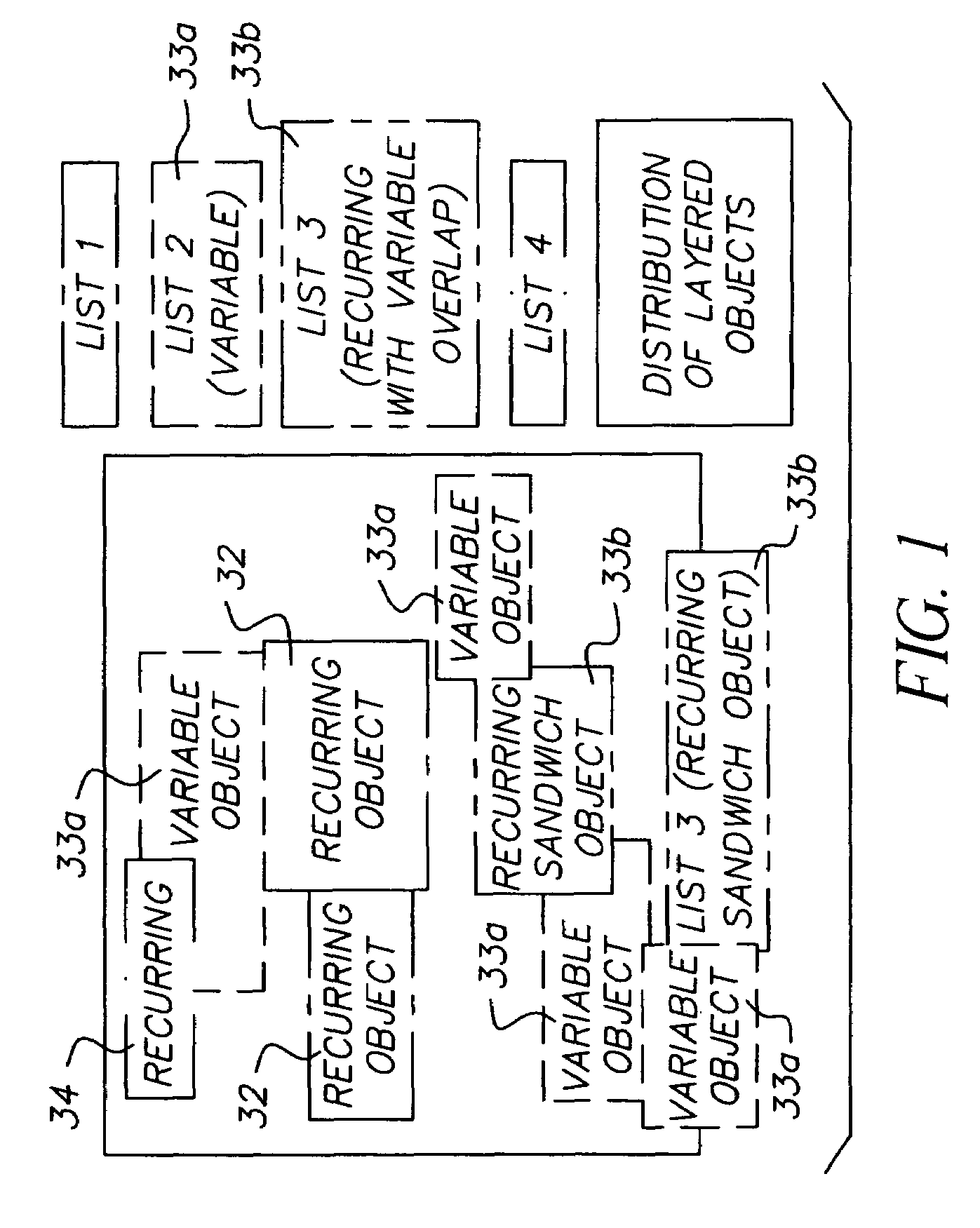
Banded compositor for variable data
A method and apparatus for Variable Data Printing that adds performance requirements to a raster image processor (RIP) memory optimization that employs memory bands within the page composition process. Documents containing both recurring elements as well as non-recurring elements are sorted into element lists depending on their frequency of recurrence and their layering position. The recurring elements are retained in rasterized form, while the non-recurring elements are rasterized as they are used in output memory. One pass assembly in raster image processing of the elements occurs when the recurring elements are blitted into memory and the variable elements are RIPped on the fly.
Owner:NEXPRESS SOLTUIONS LLC +1
Methods for positioning a print integrity image capture device
InactiveUS20030133139A1Reduce operating costsPrint operatorDigital computer detailsTypewritersElectronic documentGrating
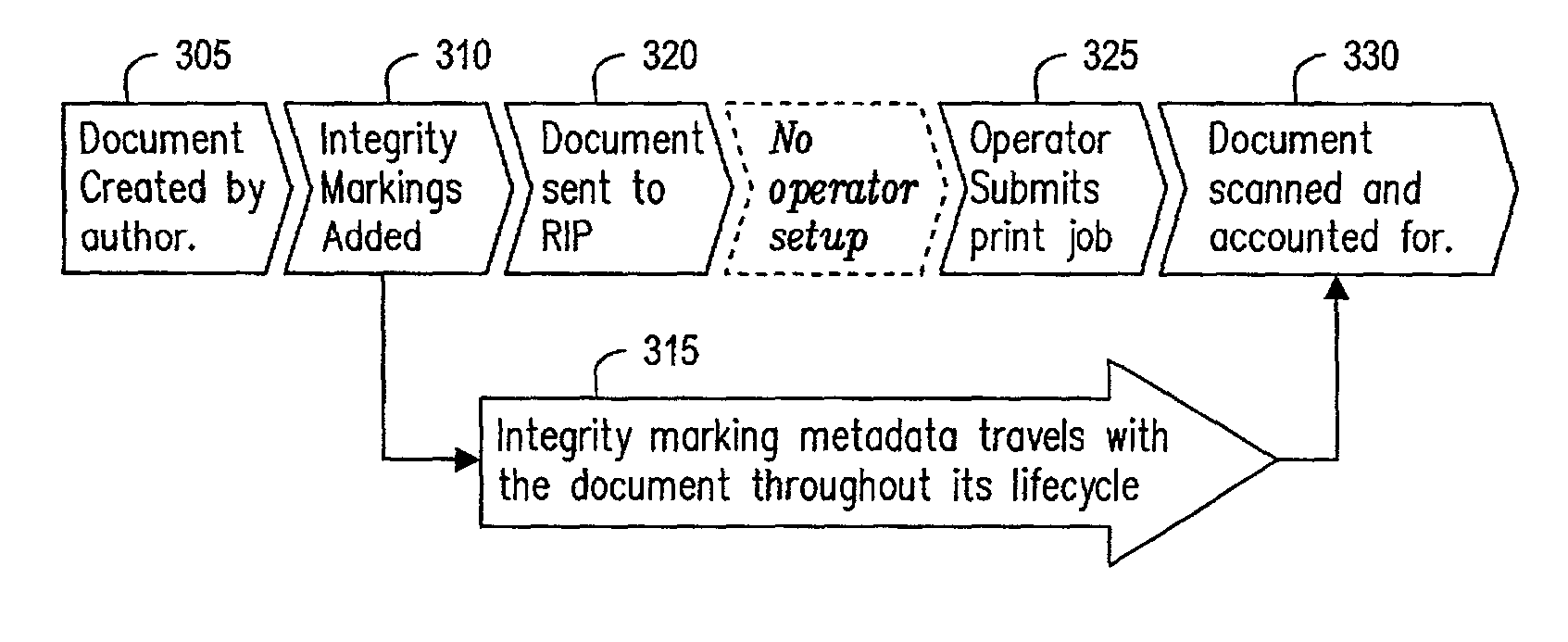
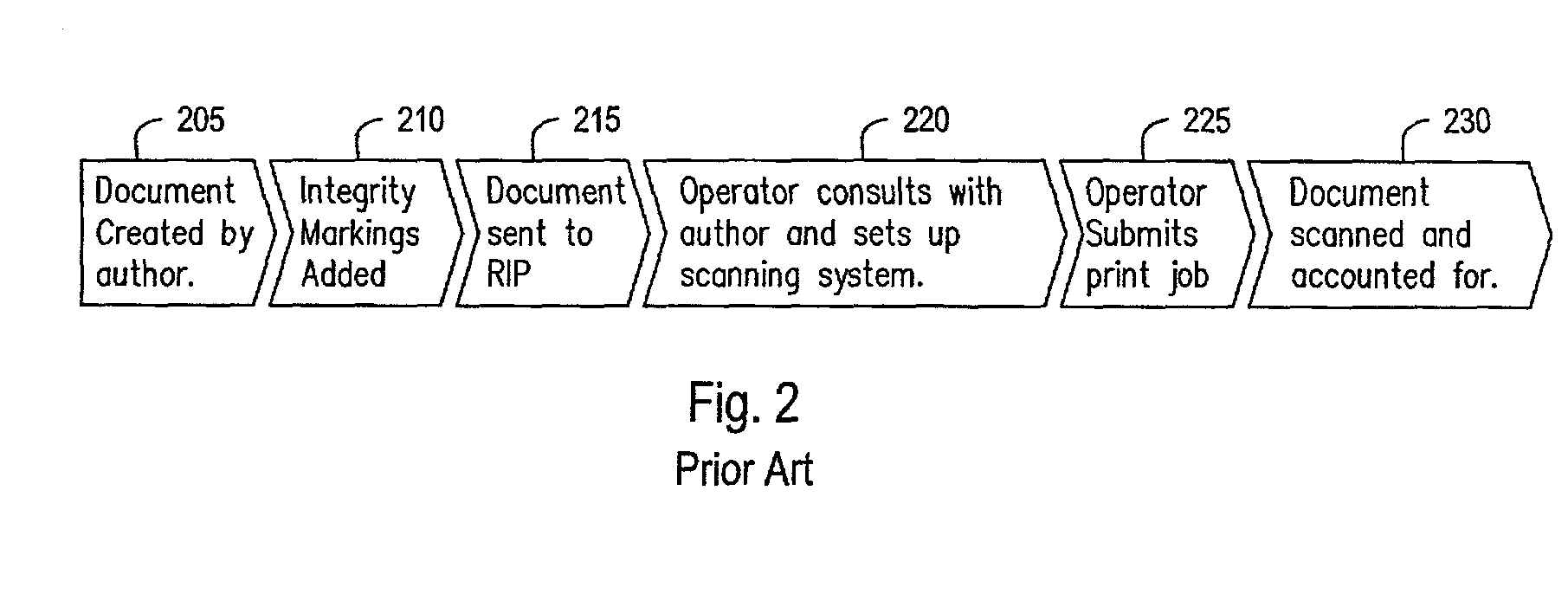
A method for positioning a print integrity image capture device comprises the steps of creating electronic document data; adding print integrity markings to the electronic document data; sending the electronic document data to a raster image processor; determining the location of integrity markings for a tangible print of electronic document data; automatically adjusting an image capture device location based on integrity marking location information; providing necessary scheduling information to a feeding device and / or a sorting device; printing a tangible print of electronic document data; scanning a tangible print of electronic document data based on a determined image capture location; analyzing an image to determine which integrity marking is located on the tangible print of electronic document data; relaying an integrity marking number to a production management algorithm; determining whether all tangible prints of electronic document data have been printed; and determining whether all documents have been printed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
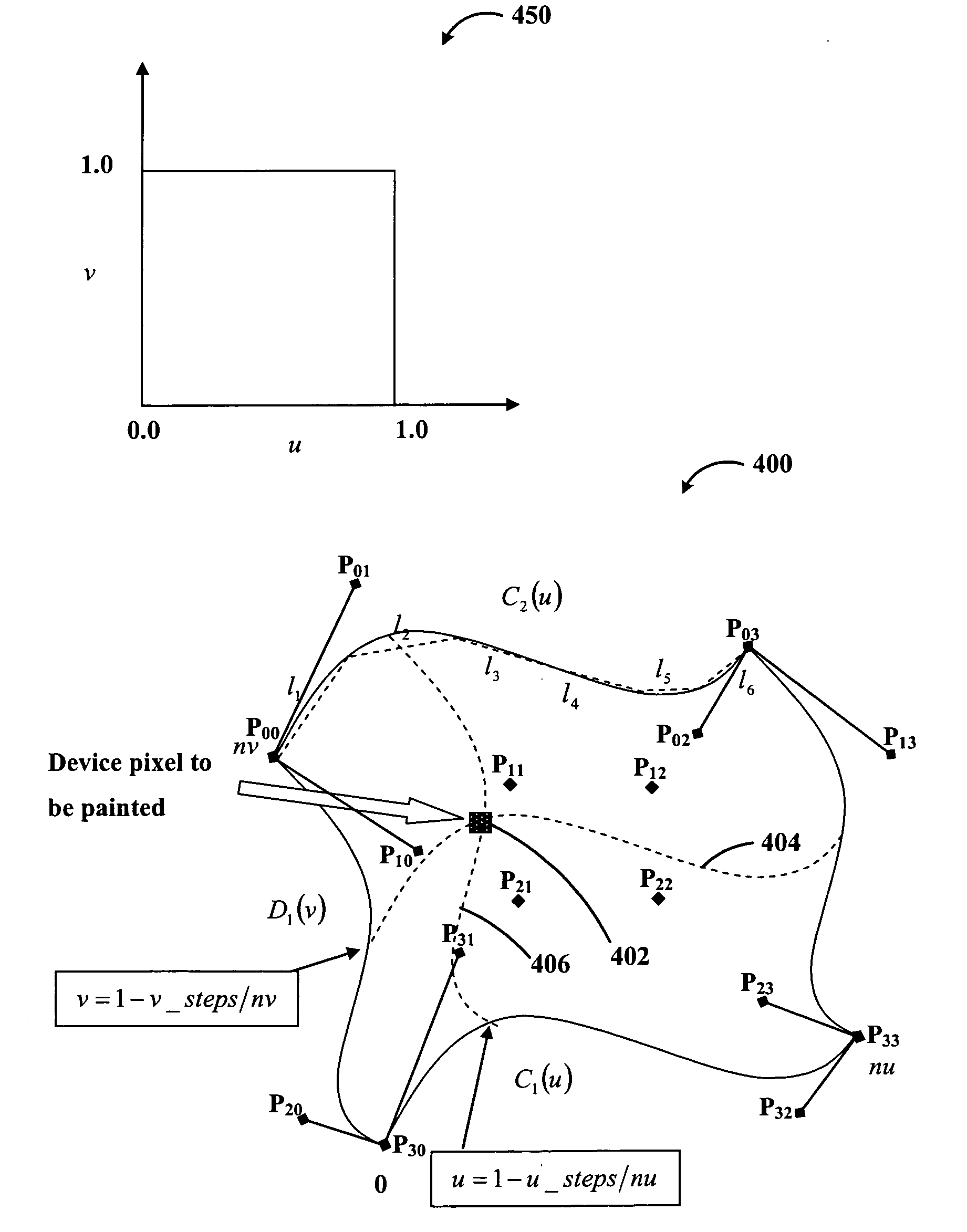
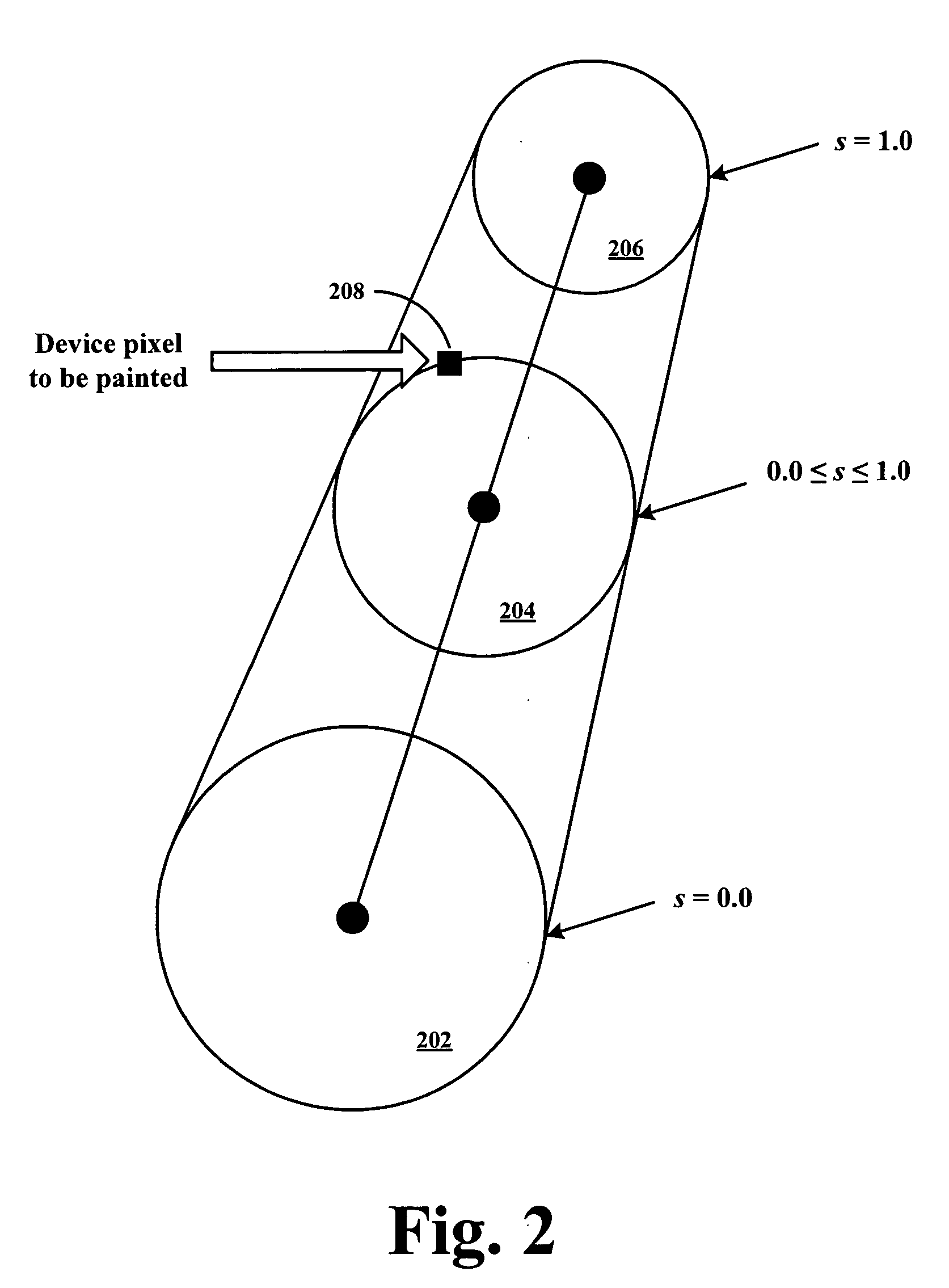
Method and apparatus for rapid shading in a raster image processor
InactiveUS20060176304A1Correct and fast shading colour computationCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingGratingComputer graphics (images)
Methods of mapping the shading dictionary parameters provided by a postscript language interpreter into device space coordinates and performing shading in the device space is disclosed. For radial shading, the shading transformation matrix representing the coordinate conversion from the shading space to device space is embedded within the shading mechanism parameters to directly compute the shading colour for a particular device space pixel, avoiding device coordinate transformations to the shading space. For triangle meshes based shading, the vertexes of the defined triangles are converted to device domain prior to performing interpolation for determining device pixel shading colour. For patch based shading, comprising of patches bounded by four Bezier curves, the Bezier curves are converted to the device domain to directly compute the corresponding shading parameter variables for a particular device pixel.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Print Engine Page Streamlining
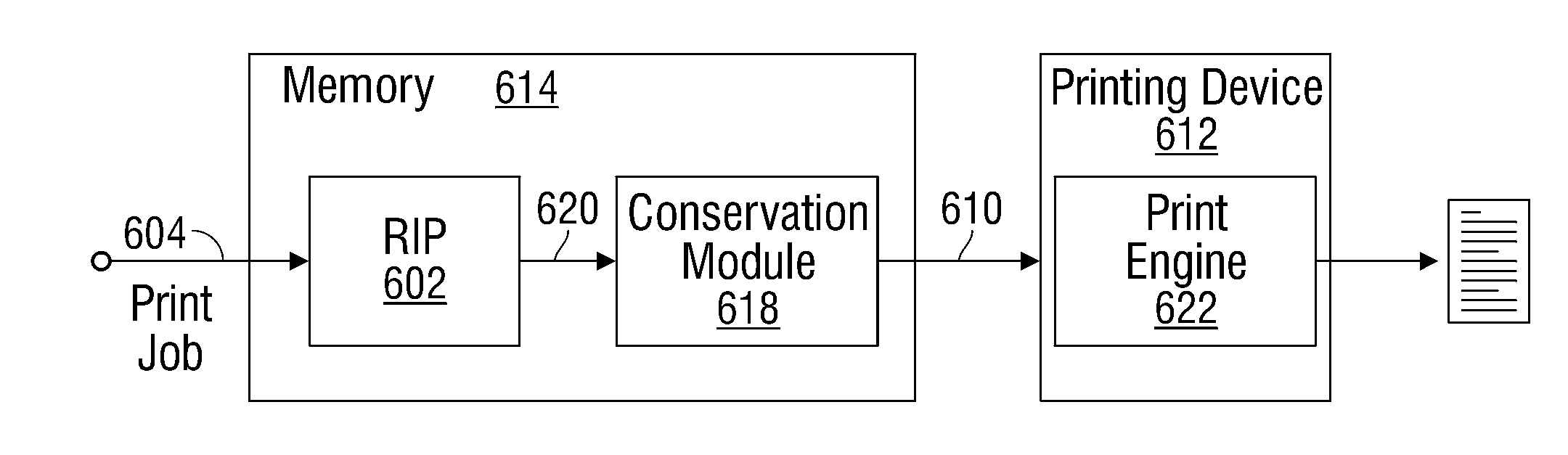
InactiveUS20110242575A1Optimize energy useAvoid delayDigitally marking record carriersElectrographic process apparatusGraphicsRaster image processor
A system and method are provided for economically printing a physical media, such as paper. The method receives a print job with a plurality of logical pages, formatted as graphics commands. A raster image processor (RIP) renders the print job into a rasterized image. The rasterized image is accumulated as logical pages in a memory, as the print job is being rendered. The RIP sends the accumulated rasterized image logical pages to a printing device print engine. The print engine is warmed to an operating temperature in response to receiving the accumulated rasterized image logical pages. In one aspect, a printing device fuser roller is warmed to a temperature sufficient to melt toner on the physical medium. To conserve energy, the rasterized image logical pages are printed on a physical medium, while maintaining the print engine at the operating temperature between the printing of each logical page.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
Plate image inspection for printing prepress
InactiveUS7224821B2Raise checkAddressing slow performanceImage enhancementImage analysisImage InspectionGrating
A prepress system comprises a raster image processor for developing first print image data to display resolution to create first raster image data, and for developing second print image data to the display resolution to create second raster image data. A plate image inspection processor executes a plate image inspection process by comparing the first and second raster image data, and displays on a display device the result of the plate image inspection process.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com