Patents
Literature
705 results about "Image alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
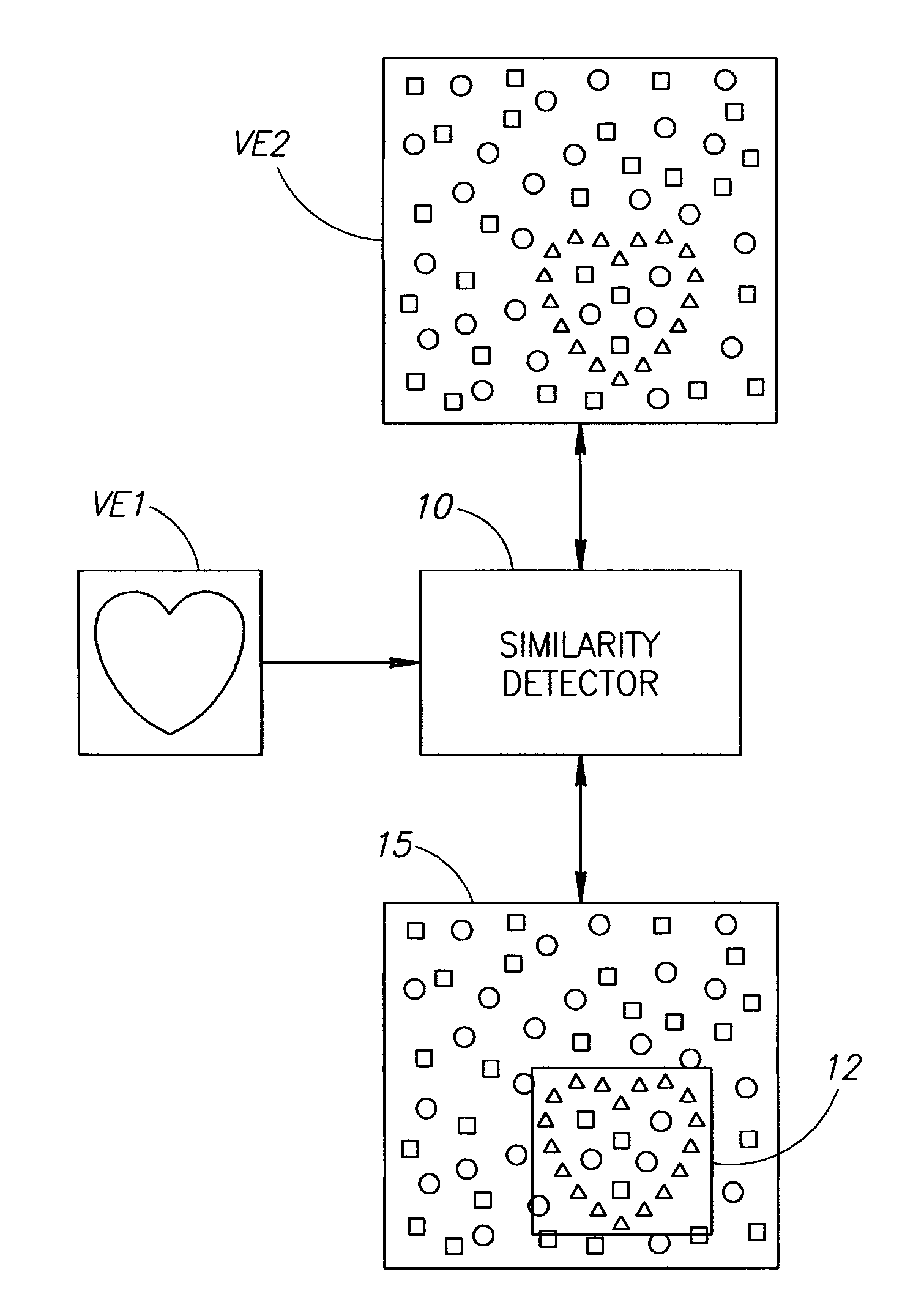
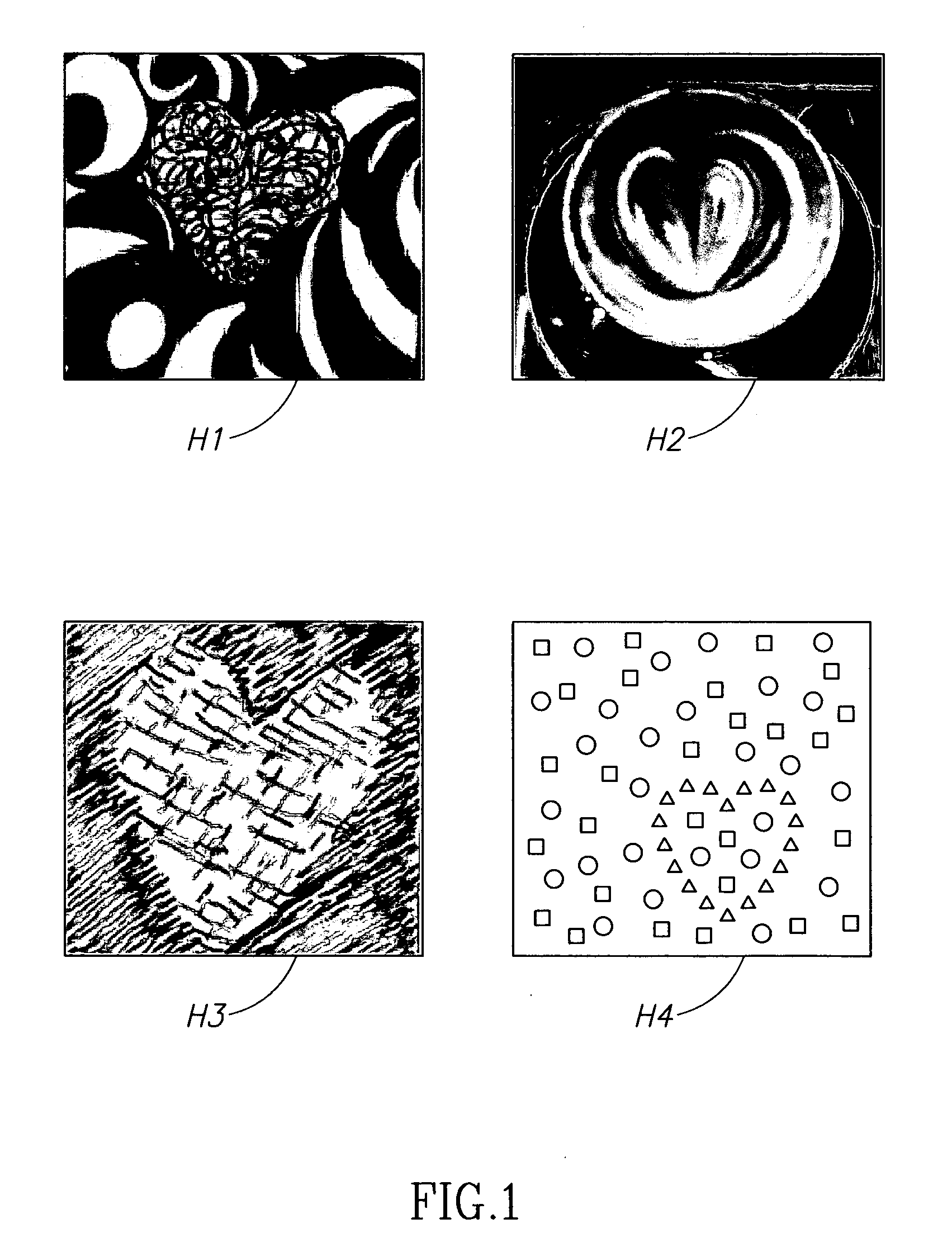
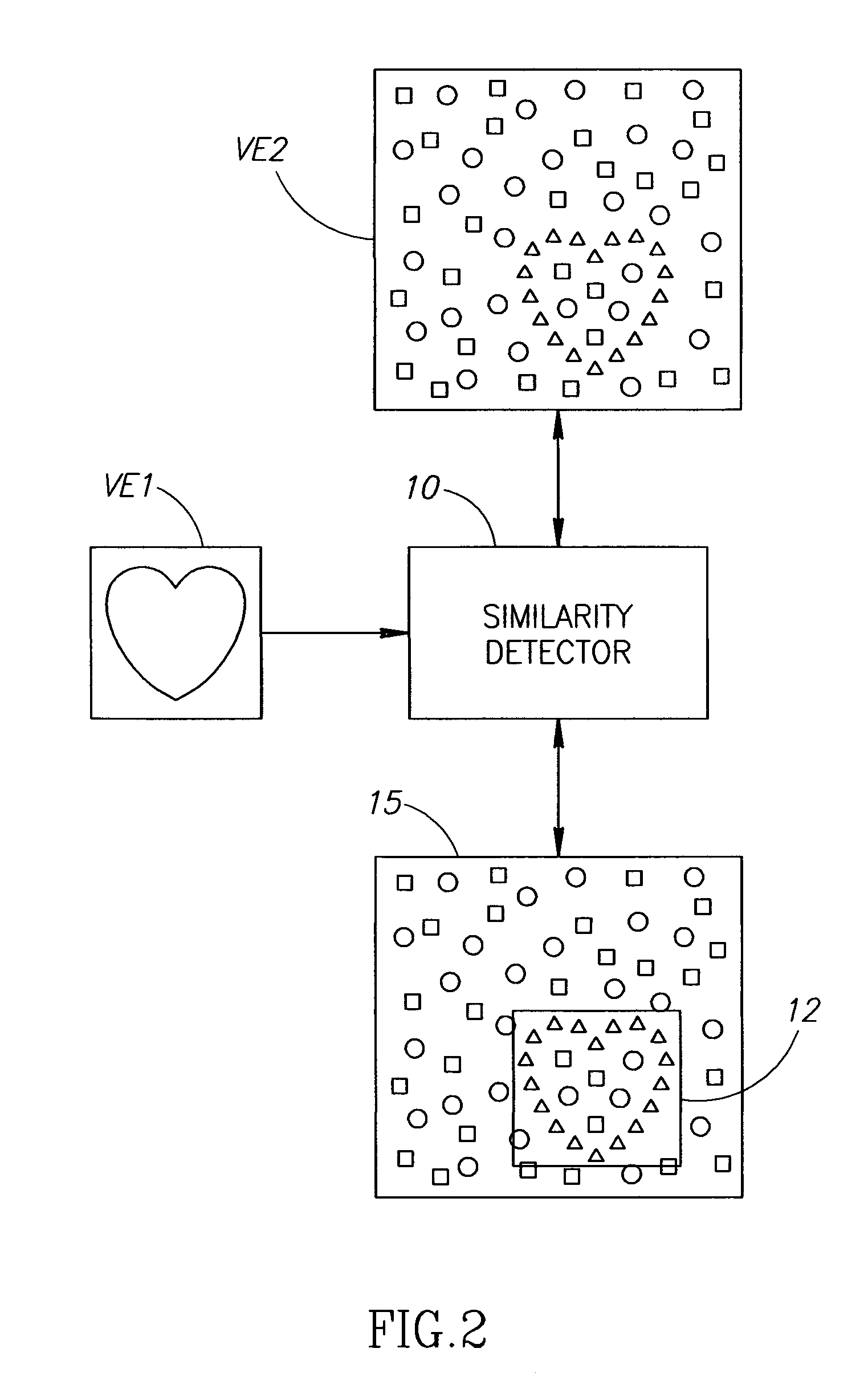
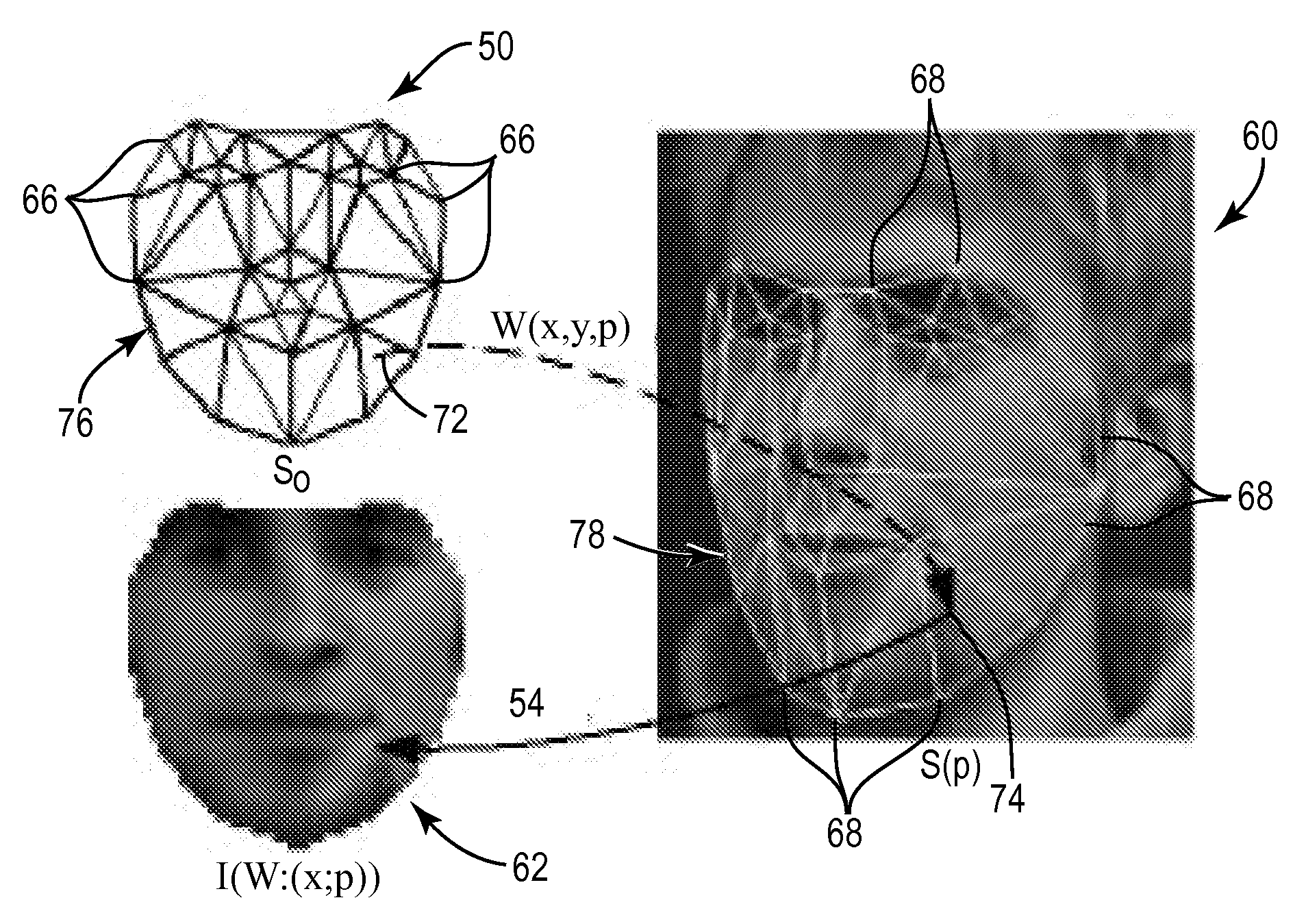
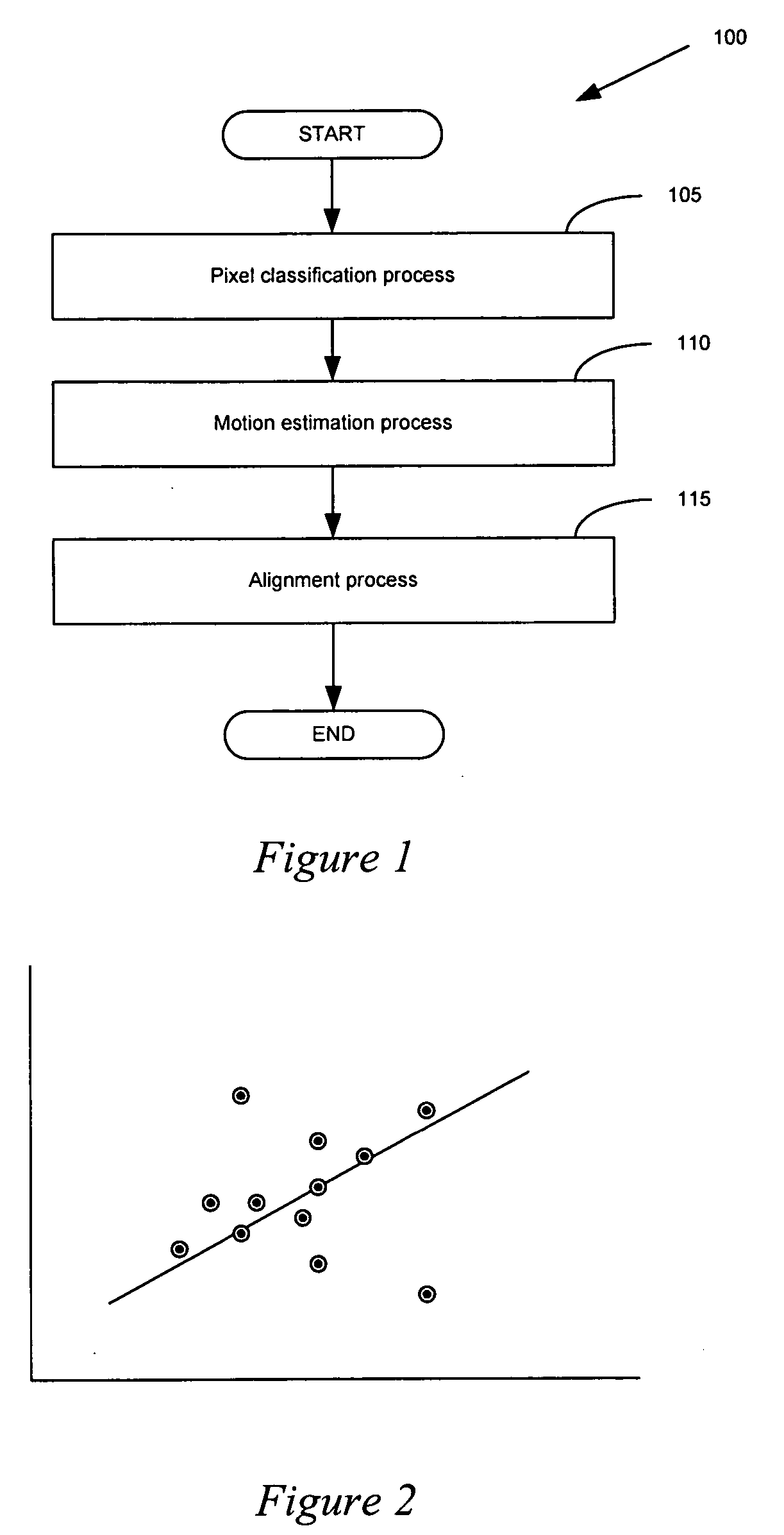
Image alignment is the process of matching one image called template (let's denote it as T) with another image, I (see the above figure). There are many applications for image alignment, such as tracking objects on video, motion analysis, and many other tasks of computer vision.
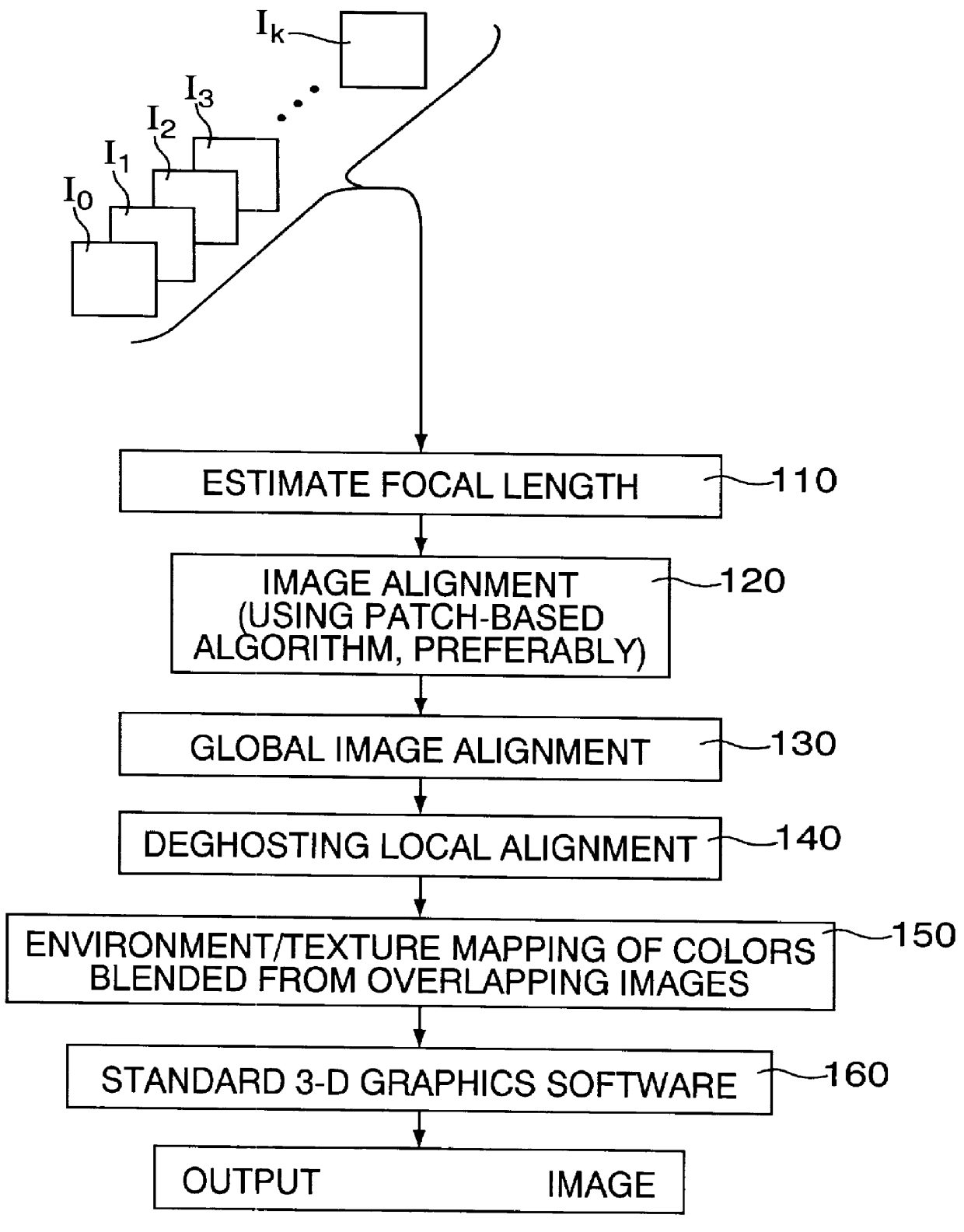
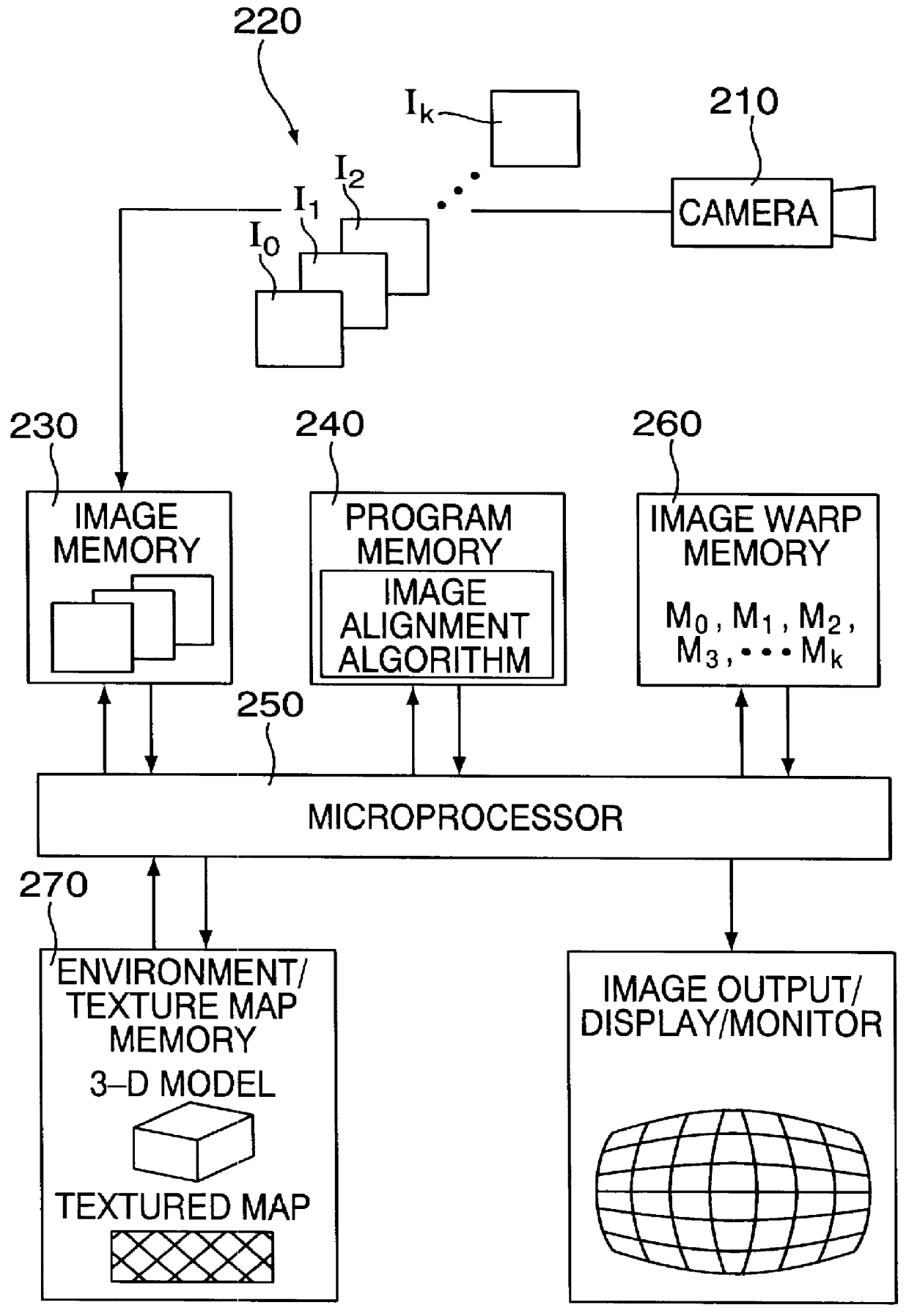
3-dimensional image rotation method and apparatus for producing image mosaics
InactiveUS6157747AQuality improvementEfficient solutionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention aligns a set of plural images to construct a mosaic image. At least different pairs of the images overlap partially (or fully), and typically are images captured by a camera looking at the same scene but oriented at different angles from approximately the same location or similar locations. In order to align one of the images with another one of the images, the following steps are carried out: (a) determining a difference error between the one image and the other image; (b) computing an incremental rotation of the one image relative to a 3-dimensional coordinate system through an incremental angle which tends to reduce the difference error; and (c) rotating the one image in accordance with the incremental rotation to produce an incrementally warped version of the one image. As long as the difference error remains significant, the method continues by re-performing the foregoing determining, computing and rotating steps but this time with the incrementally warped version of the one image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for use in camera and systems employing same
ActiveUS20070002159A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesControl signalImage resolution
There are many inventions described herein. Some aspects are directed to methods and / or apparatus to provide relative movement between optics, or portion(s) thereof, and sensors, or portion(s) thereof, in a digital camera. The relative movement may be in any of various directions. In some aspects, relative movement between an optics portion, or portion(s) thereof, and a sensor portion, or portion(s) thereof, are used in providing any of various features and / or in the various applications disclosed herein, including, for example, but not limited to, increasing resolution, optical and electronic zoom, image stabilization, channel alignment, channel-channel alignment, image alignment, lens alignment, masking, image discrimination, range finding, 3D imaging, auto focus, mechanical shutter, mechanical iris, multi and hyperspectral imaging, and / or combinations thereof. In some aspects, movement is provided by actuators, for example, but not limited to MEMS actuators, and by applying appropriate control signal thereto.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Method and system for automated production of autostereoscopic and animated prints and transparencies from digital and non-digital media
InactiveUS20060023197A1Correct keystone distortionStereoscopic photographyPhotographic printingComputer printingDisplay device
A method and system for automated production of stereoscopic and animated images and hardcopies can utilize a light-sensitive lenticular material employing a conventional or non-conventional photographic emulsion or an instant-developing material. An automated printer can produce autostereoscopic and animated hardcopies in multiple formats from digital and non-digital sources, including single images, stereopairs, and multiple-image sets of negatives, transparencies, or prints. The printer, which includes a projection device and a material plate that can rotate around two perpendicular axes, can utilize software to automate viewing angle calculation, printer control, multiple-image alignment, distortion correction, and image processing and conversion. A digital camera can capture stereoscopic and animated images and record them digitally or on photographic film. A non-digital camera can record stereoscopic and animated images directly onto light-sensitive lenticular material employing a conventional or non-conventional photographic emulsion or an instant-developing material. The printer and cameras can utilize autostereoscopic monitors to preview parallax.
Owner:VOLUGRAPHICS
Methods and Systems for Image Data Processing
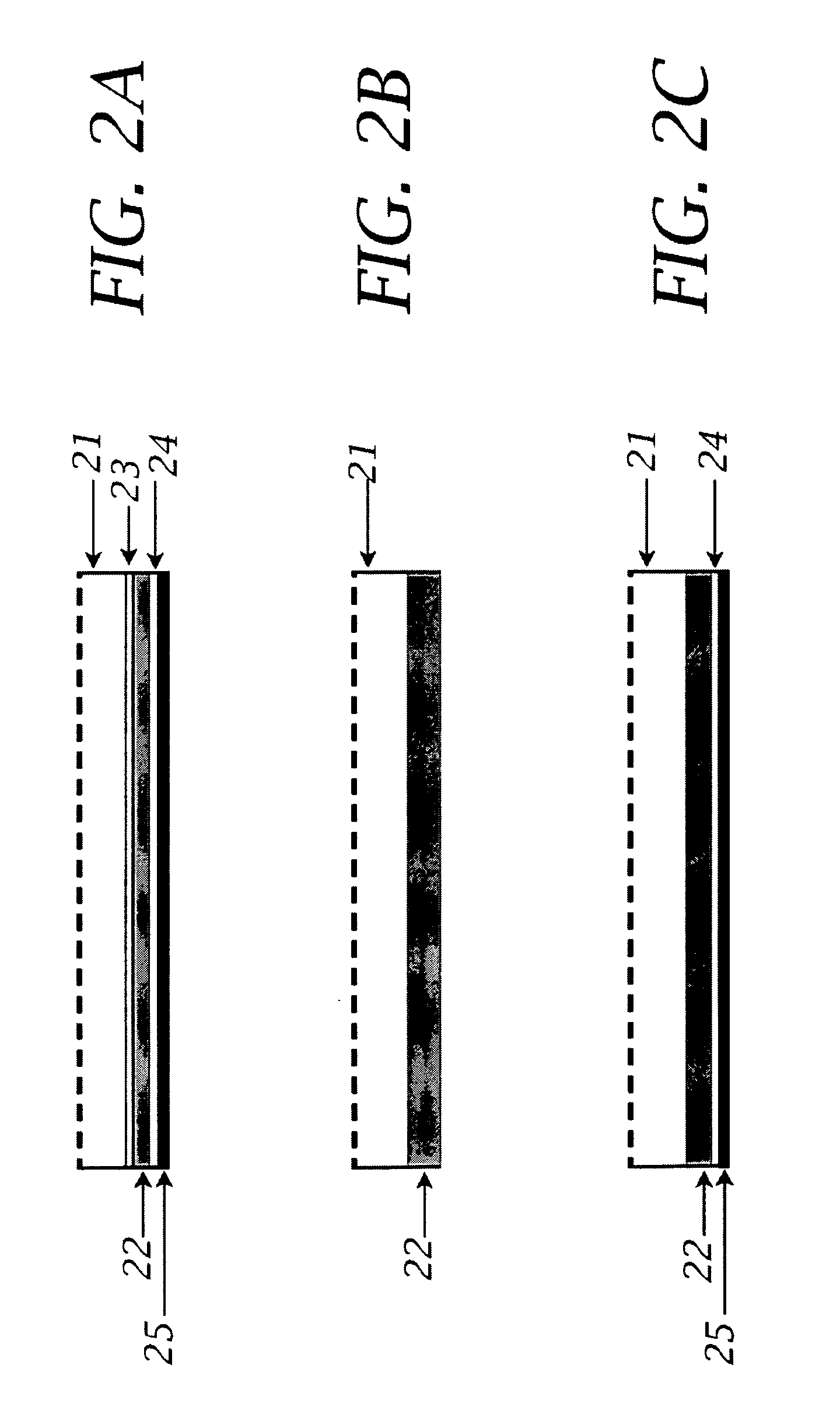
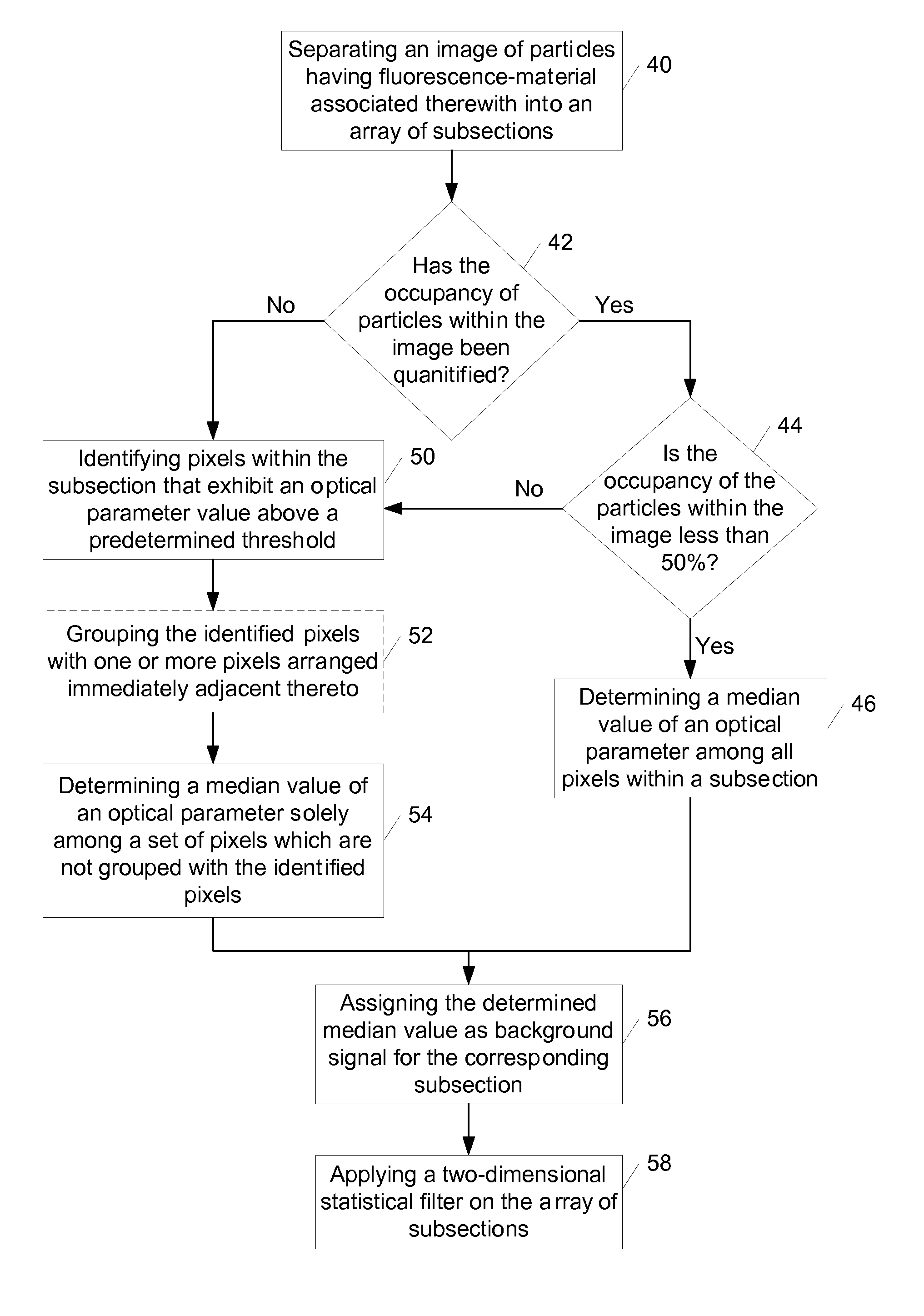
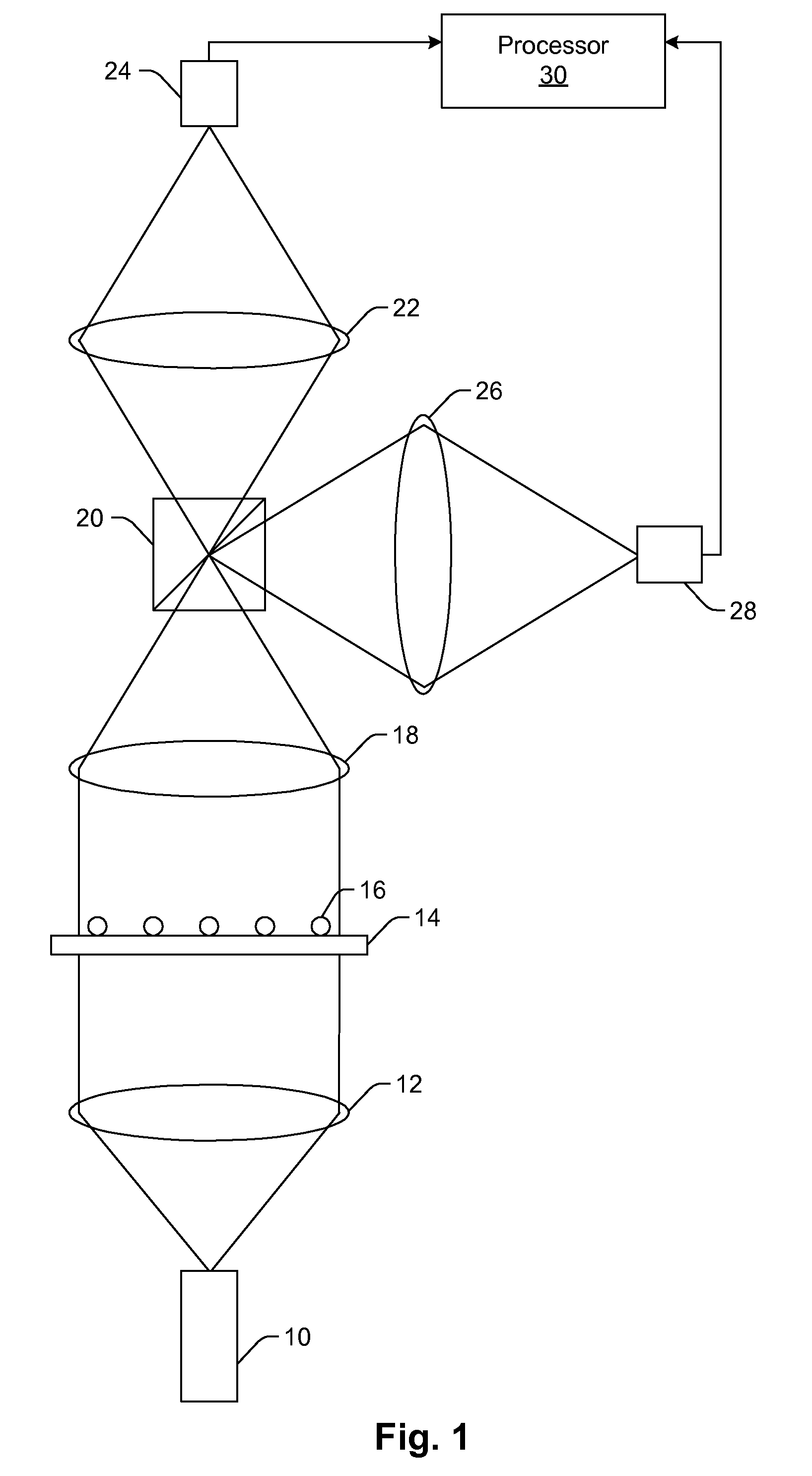
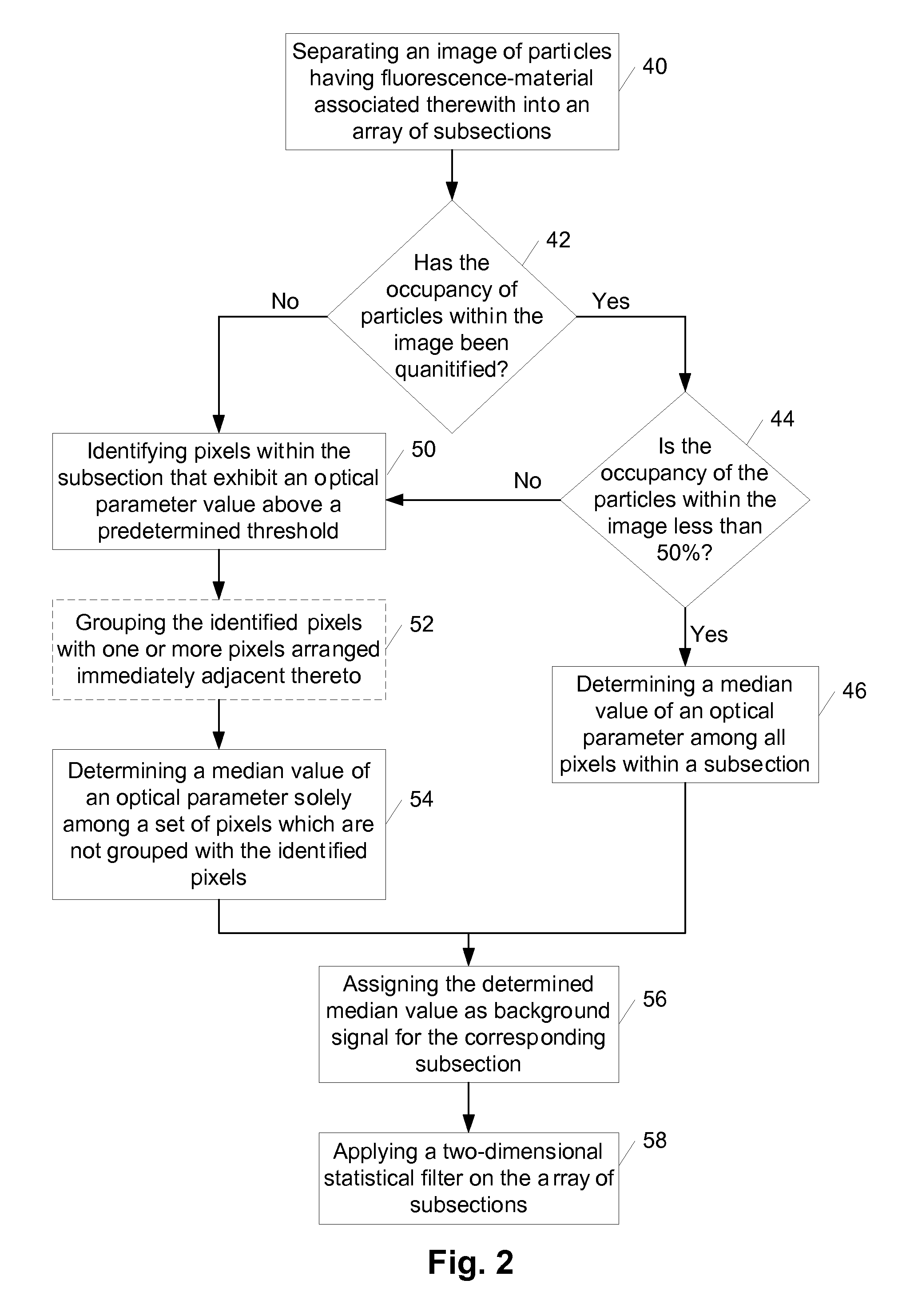
Methods, storage mediums, and systems for image data processing are provided. Embodiments for the methods, storage mediums, and systems include configurations to perform one or more of the following steps: background signal measurement, particle identification using classification dye emission and cluster rejection, inter-image alignment, inter-image particle correlation, fluorescence integration of reporter emission, and image plane normalization.
Owner:LUMINEX
Process for roll-to-roll manufacture of a display by synchronized photolithographic exposure on a substrate web
InactiveUS20020182544A1High aspect ratioWell-defined shapePhoto-taking processesPhotomechanical apparatusDisplay deviceRefractive index
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> This invention relates to an electrophoretic display or a liquid crystal display and novel processes for its manufacture. The electrophoretic display (EPD) of the present invention comprises microcups of well-defined shape, size and aspect ratio and the microcups are filled with charged pigment particles dispersed in an optically contrasting dielectric solvent. The liquid crystal display (LCD) of this invention comprises well-defined microcups filled with at least a liquid crystal composition having its ordinary refractive index matched to that of the isotropic cup material. A novel roll-to-roll process and apparatus of the invention permits the display manufacture to be carried out continuously by a synchronized photo-lithographic process. The synchronized roll-to-roll process and apparatus permits a pre-patterned photomask, formed as a continuous loop, to be rolled in a synchronized motion in close parallel alignment to a web which has been pre-coated with a radiation sensitive material, so as to maintain image alignment during exposure to a radiation source. The radiation sensitive material may be a radiation curable material, in which the exposed and cured portions form the microcup structure. In an additional process step, the radiation sensitive material may be a positively working photoresist which temporarily seals the microcups. Exposure of a selected subset of the microcups via the photomask image permits selective re-opening, filling and sealing of the microcup subset. Repetition with additional colors permits the continuous assembly of a multicolor EPD or LCD display.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Methods and apparatuses for image guided medical procedures
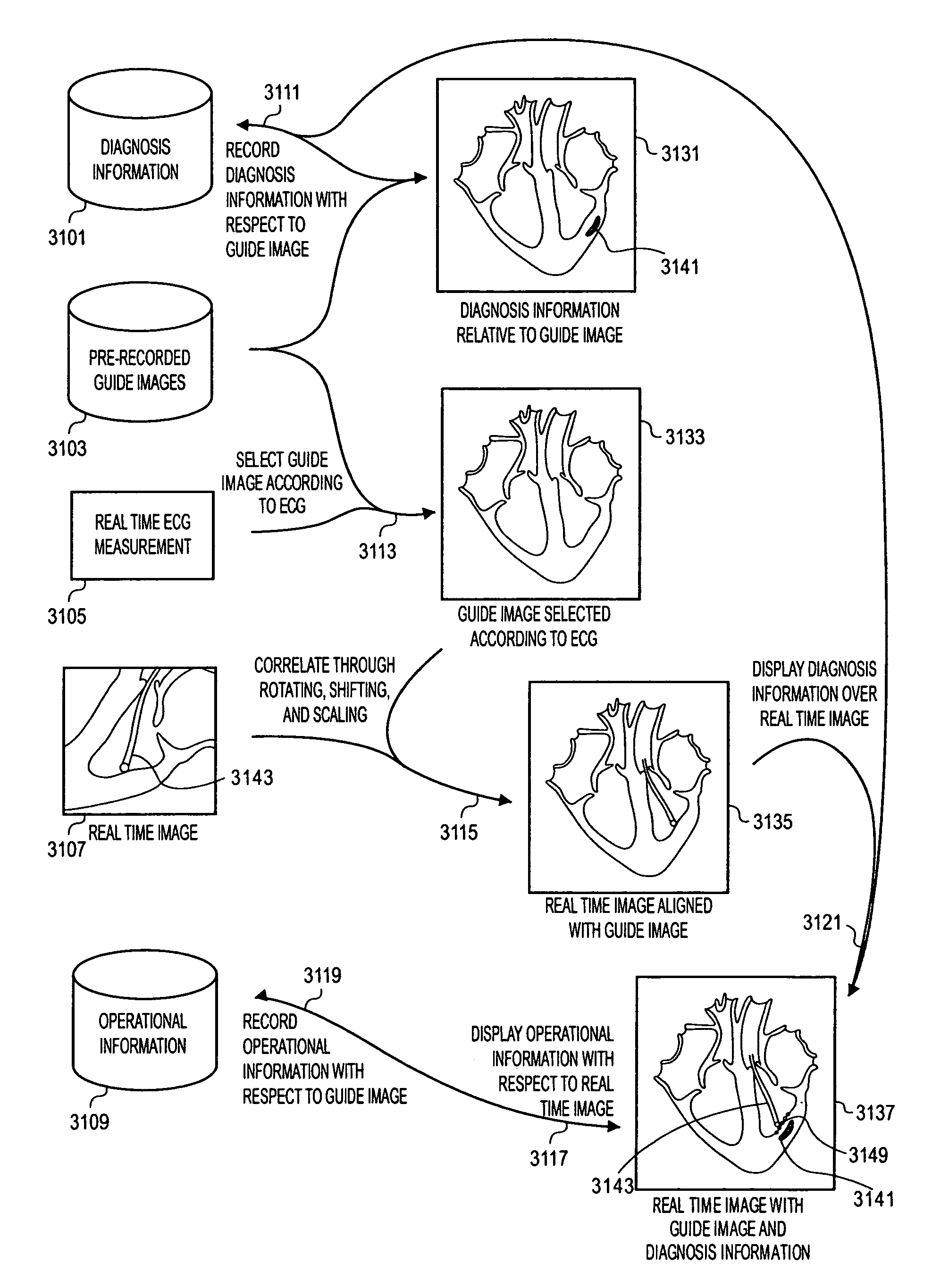
ActiveUS8303505B2Uncertainty errorLocation uncertaintyMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTime informationImaging data
Methods and apparatuses for the image guidance and documentation of medical procedures. One embodiment includes combining small field of view images into a recorded image of with a large field of view and aligning the small field of view real time image with the recorded image through correlation of imaging data. A location and orientation determination system may be used to track the imaging system and provide a starting set of image alignment parameters and / or provide change updates to a set of image alignment parameters, which is then further improved through correlating imaging data. The recorded image may be selected according to real time measurement of a cardiac parameter during an image guided cardiac procedure. Image manipulations planned based on the recorded image can be stored and applied to the real time information. The position of the medical device may be determined and recorded through manipulating a cursor in a 3-D image space shown in two non-parallel views.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
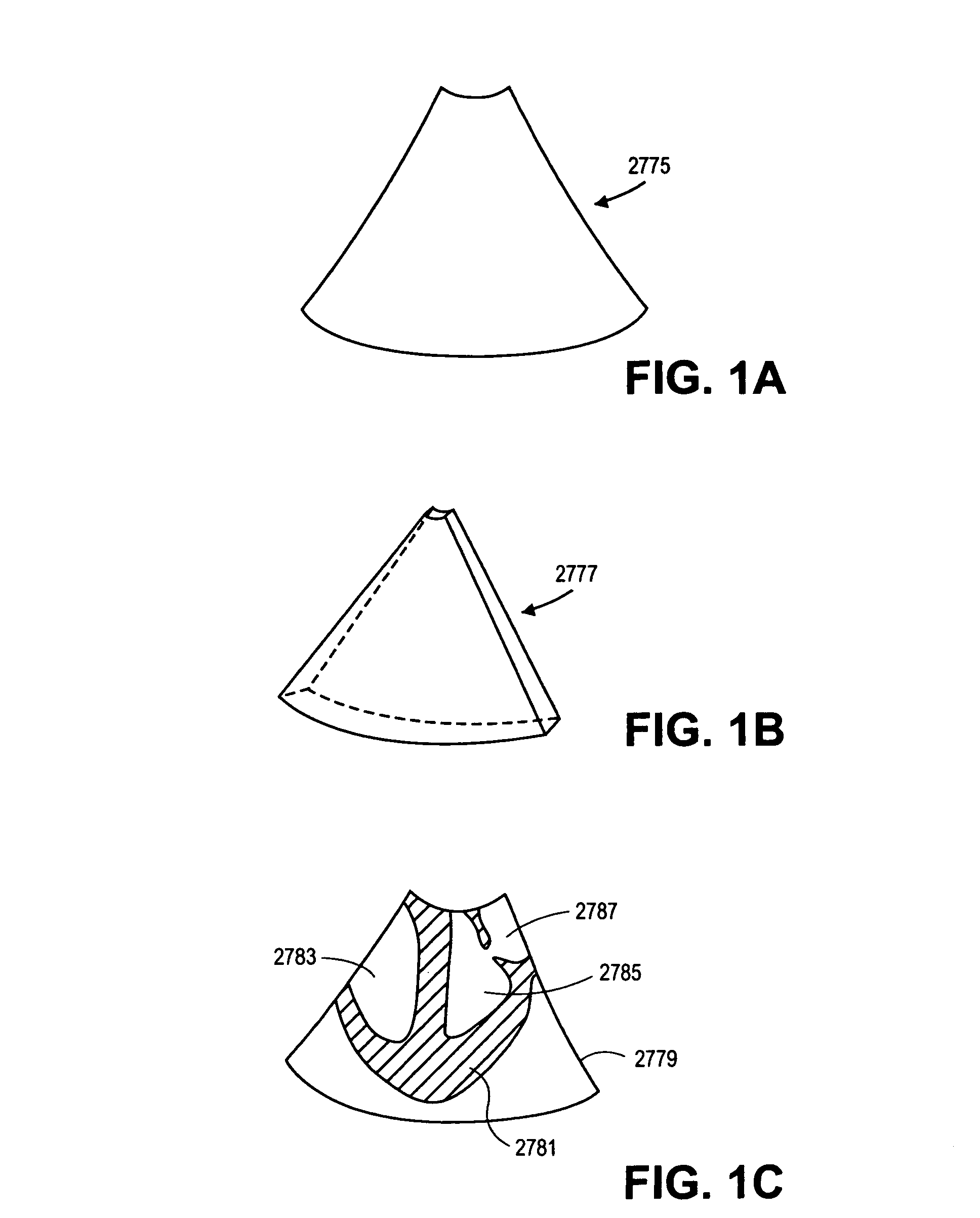
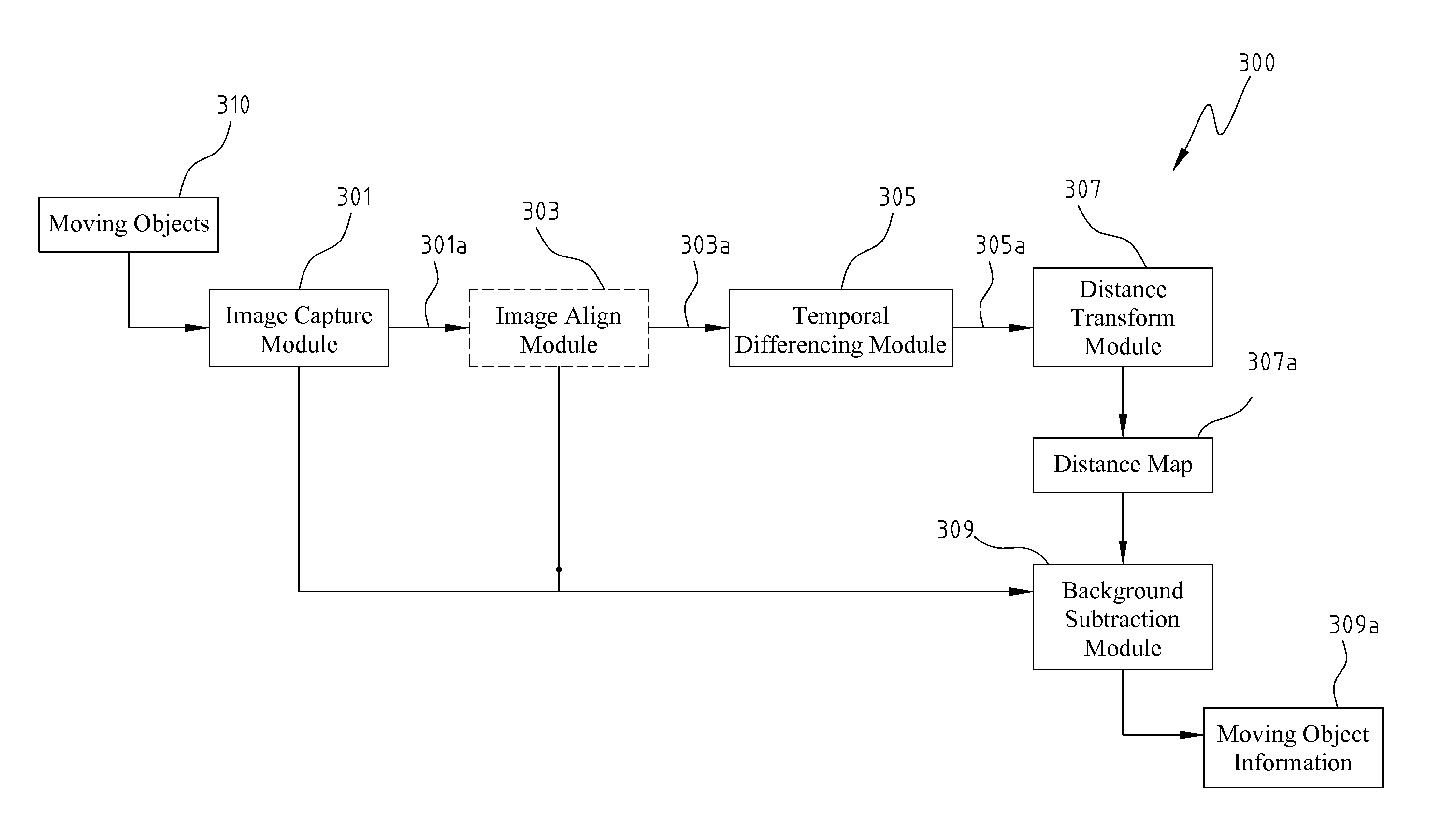
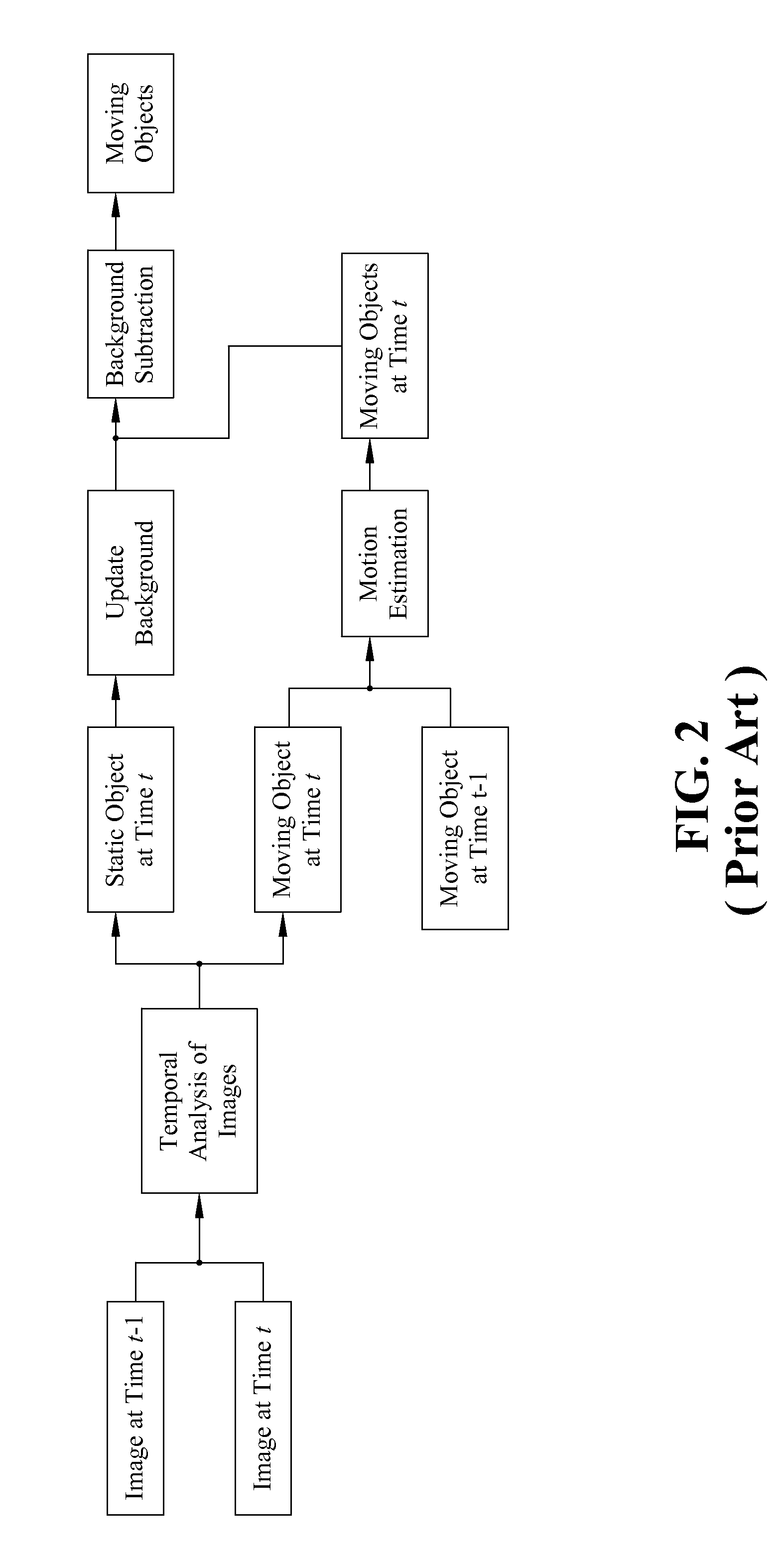
Moving object detection apparatus and method
InactiveUS8000498B2Improve reliabilityEnhancing subtractionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage alignmentImage capture
Disclosed is directed to a moving object detection apparatus and method. The apparatus comprises an image capture module, an image alignment module, a temporal differencing module, a distance transform module, and a background subtraction module. The image capture module derives a plurality of images in a time series. The image alignment module aligns the images if the image capture module is situated on a movable platform. The temporal differencing module performs temporal differencing on the captured images or the aligned images, and generates a difference image. The distance transform module transforms the difference image into a distance map. The background subtraction module applies the distance map to background subtraction technology and compares the results with the current captured image, so as to obtain the information for moving objects.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
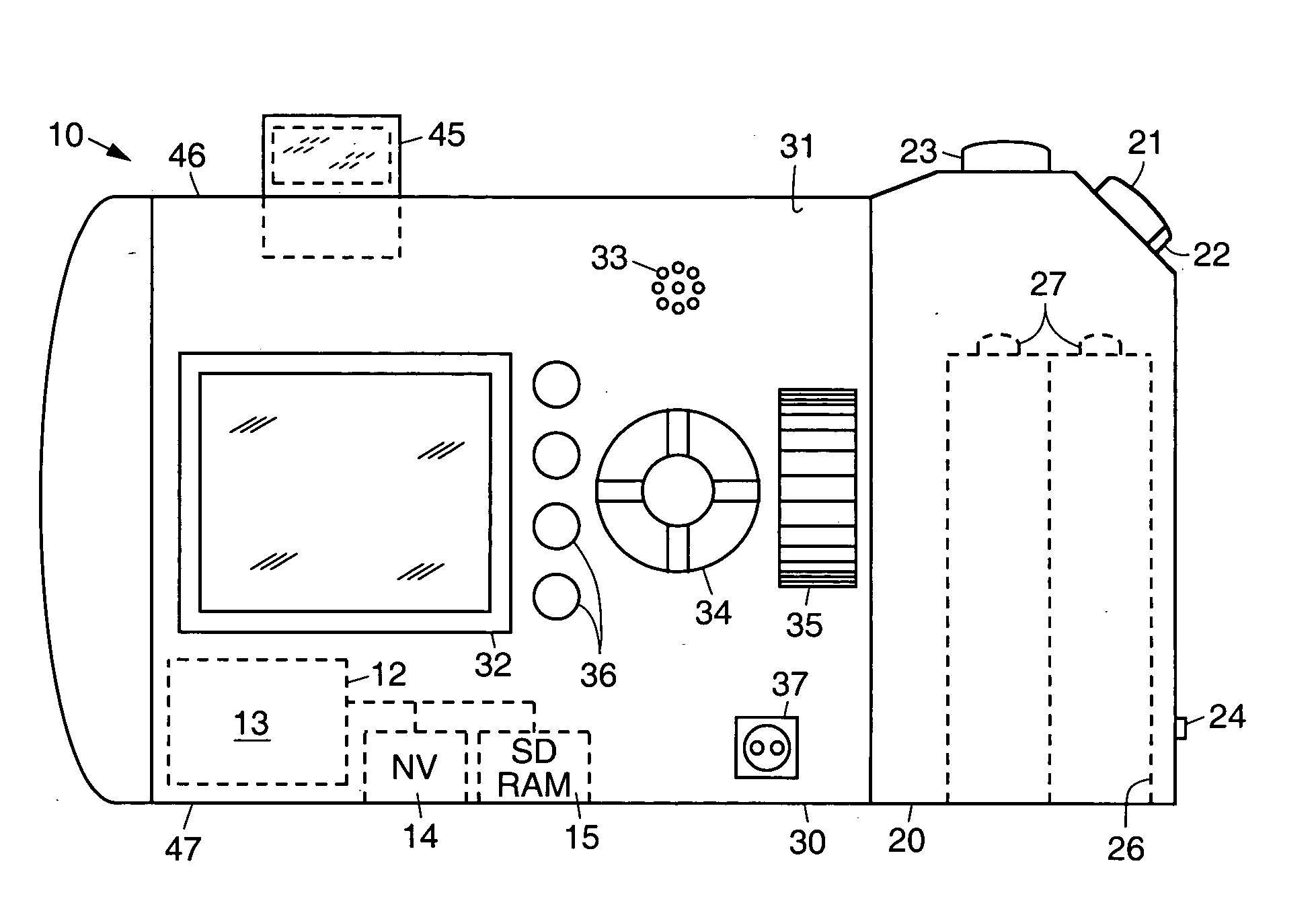
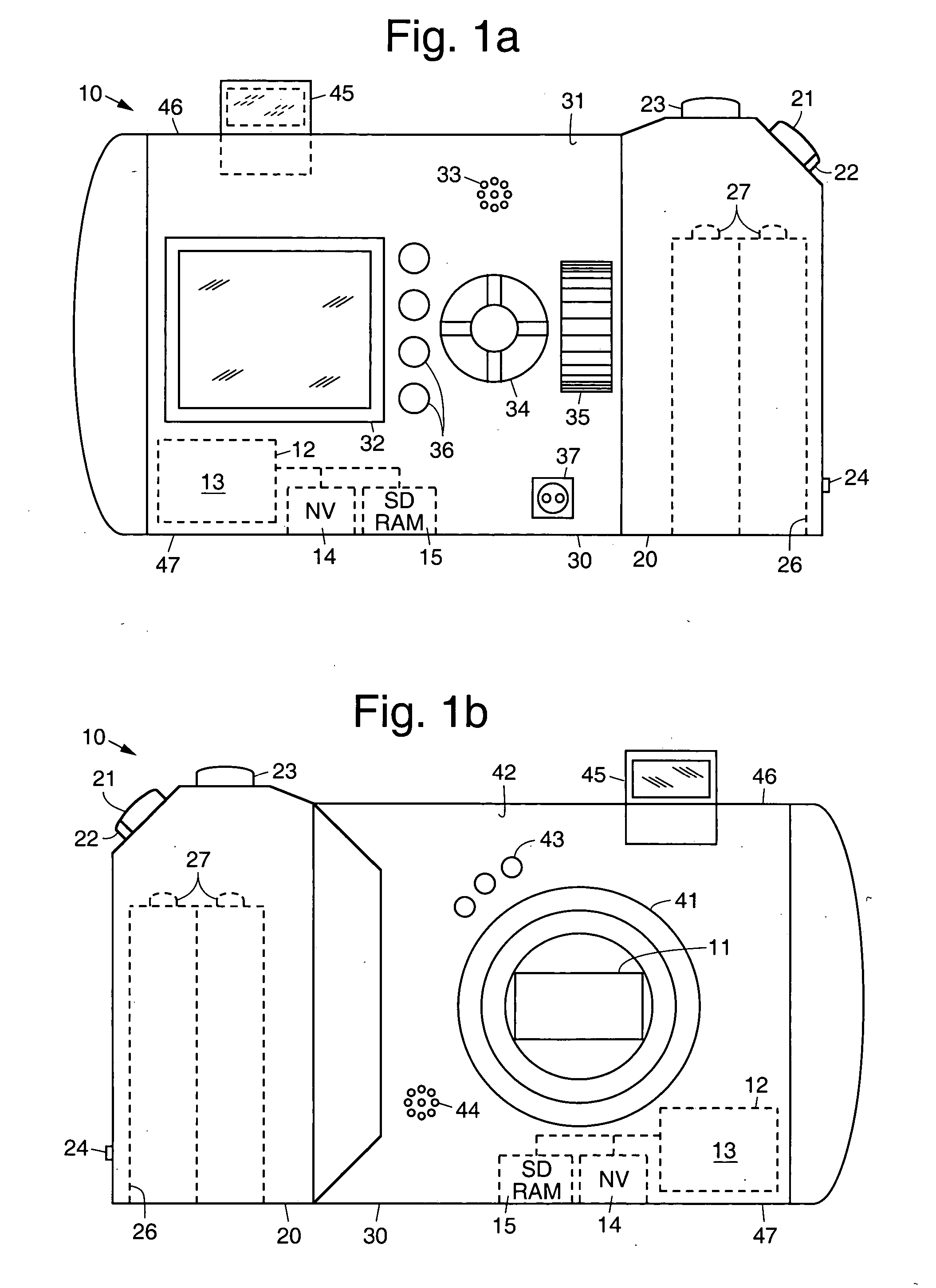
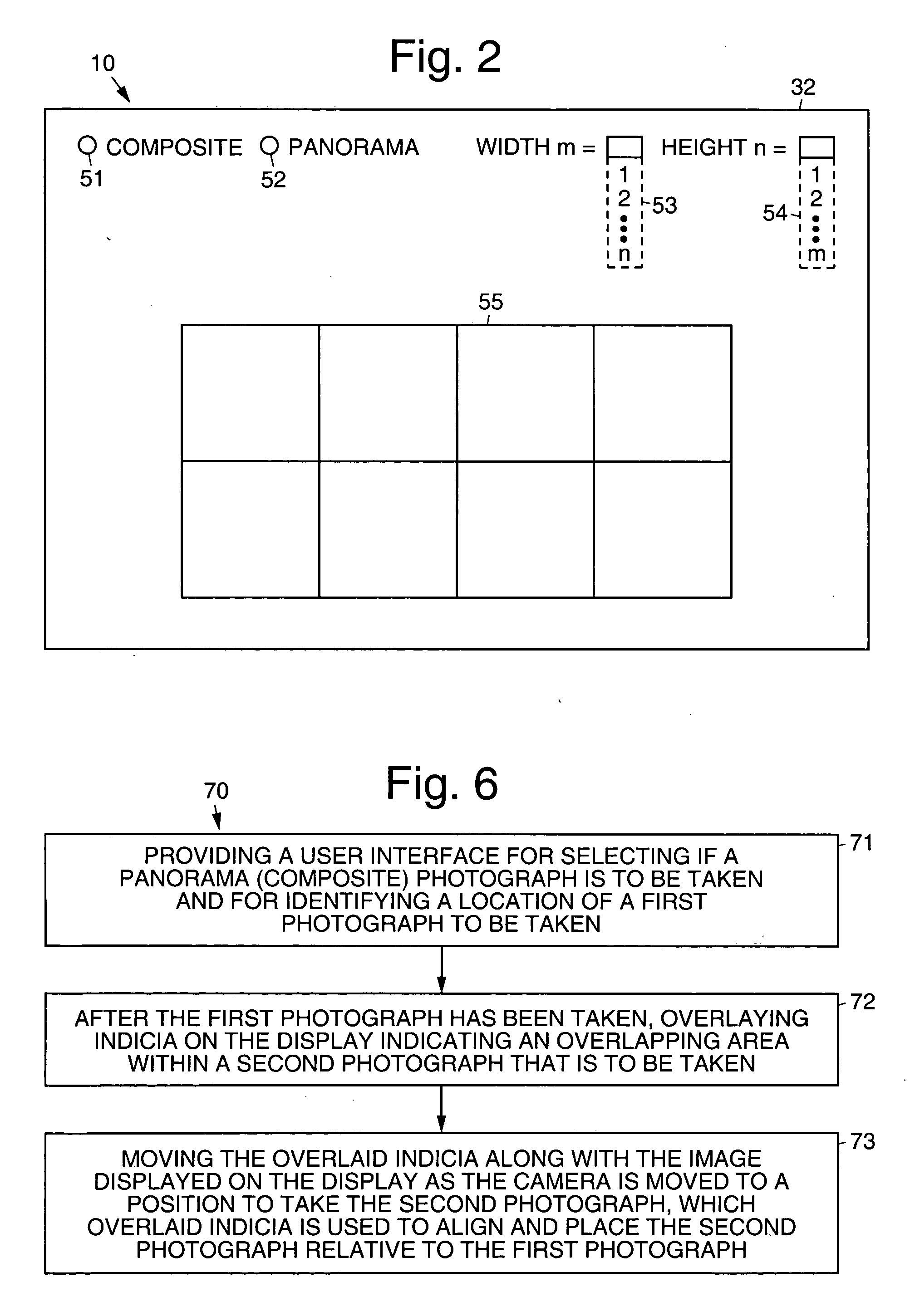
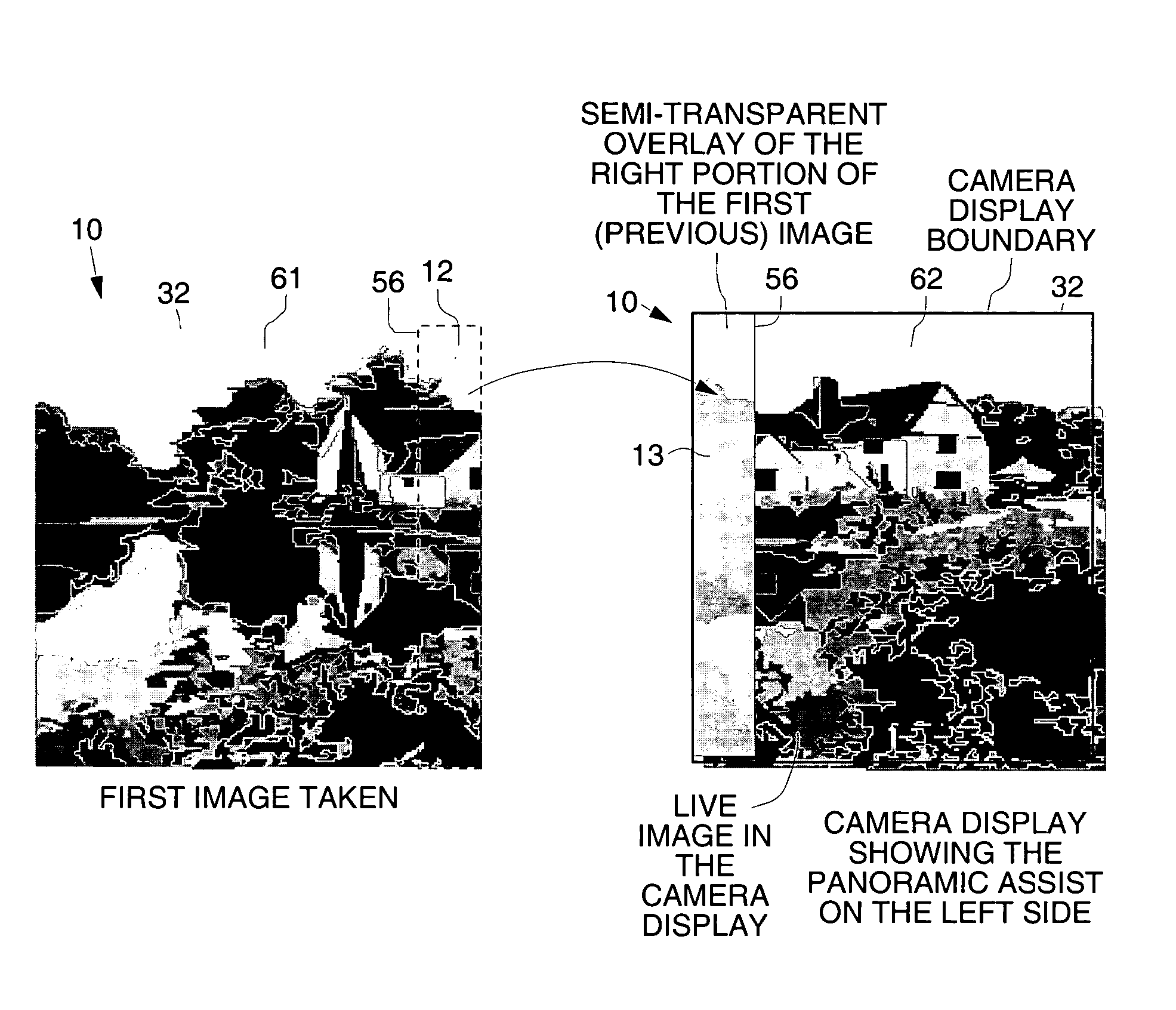
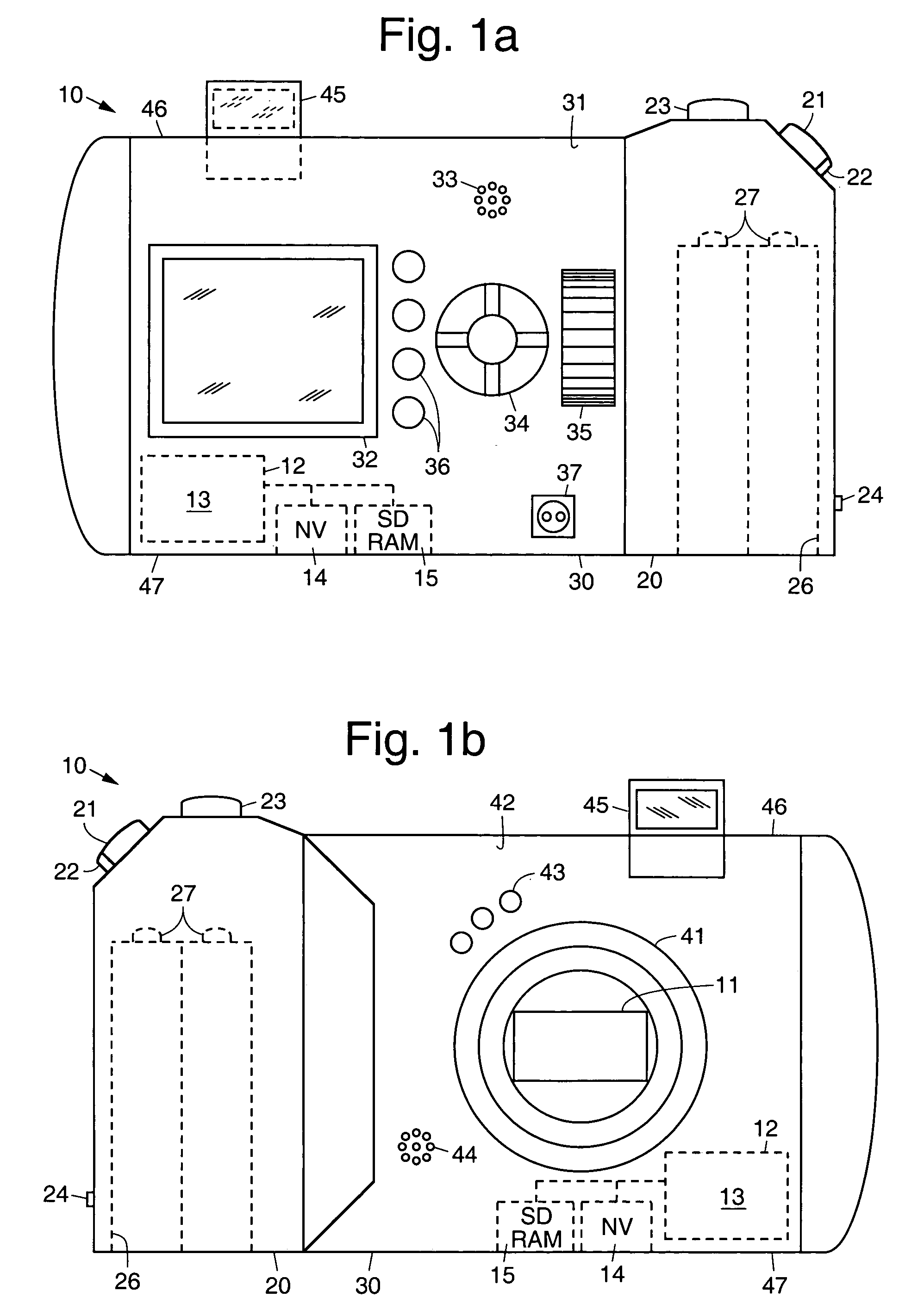
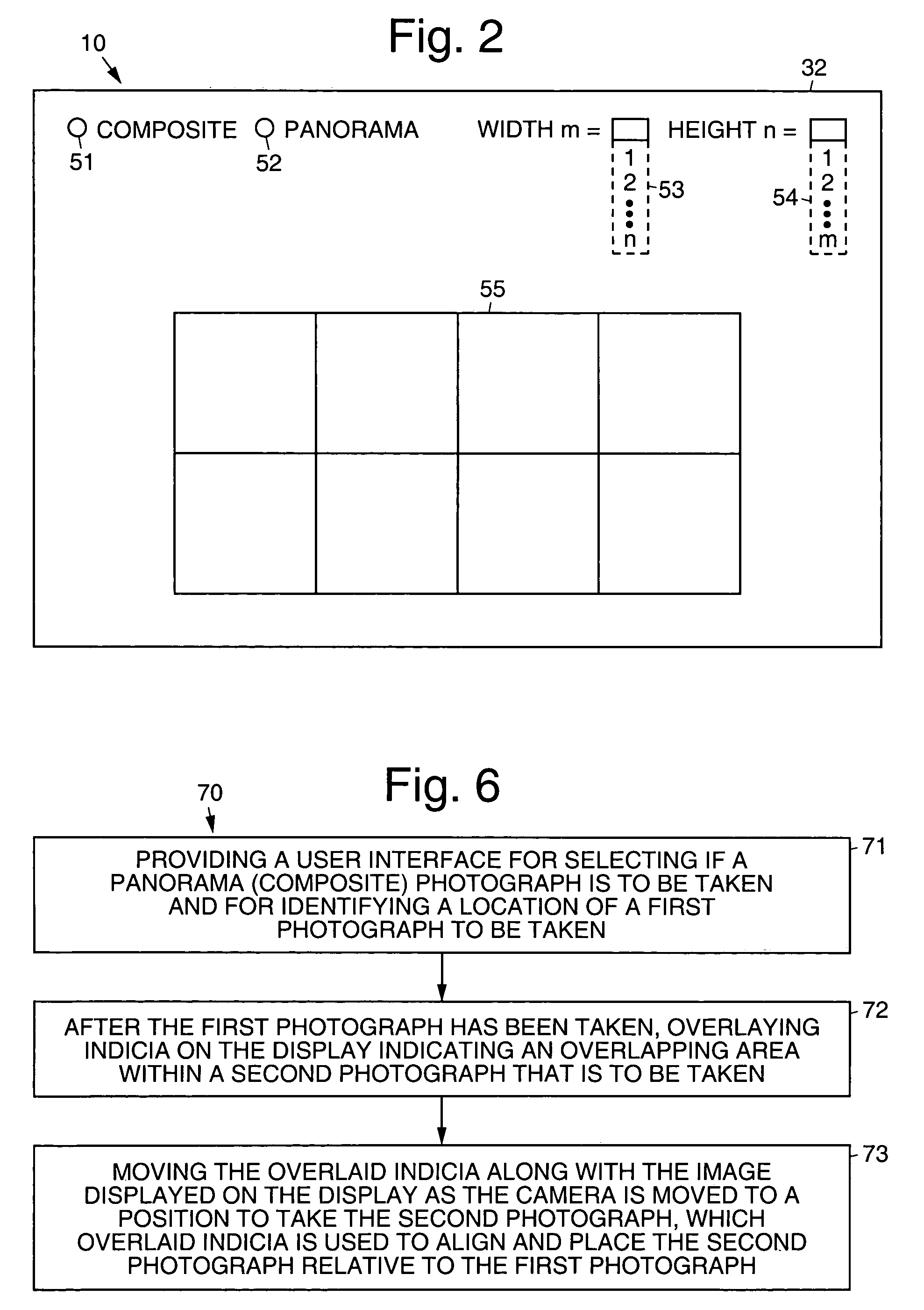
Digital camera and method for in creating still panoramas and composite photographs
ActiveUS20050168594A1High resolutionPrecise alignmentTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
Digital cameras and methods that help a user accurately align sequential photographs to create large panoramas and composite photographs derived from a sequence of smaller photographs. This effectively creates a higher resolution, or larger, photograph from a zigzag series of photographs using a low resolution camera. An algorithm running on the camera guides a user through the image-taking procedure, allowing him or her to select if a panoramic or composite photograph is to be taken, and optionally the number of images (width and height) needed to create the final image. The algorithm displays indicia, such as marks or a shadow (transparent) image, that are overlaid and moved over the live image during the image-taking process to help align the subsequent image to be taken with the previously recorded image.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and apparatus for matching local self-similarities
A method includes matching at least portions of first, second signals using local self-similarity descriptors of the signals. The matching includes computing a local self-similarity descriptor for each one of at least a portion of points in the first signal, forming a query ensemble of the descriptors for the first signal and seeking an ensemble of descriptors of the second signal which matches the query ensemble of descriptors. This matching can be used for image categorization, object classification, object recognition, image segmentation, image alignment, video categorization, action recognition, action classification, video segmentation, video alignment, signal alignment, multi-sensor signal alignment, multi-sensor signal matching, optical character recognition, image and video synthesis, correspondence estimation, signal registration and change detection. It may also be used to synthesize a new signal with elements similar to those of a guiding signal synthesized from portions of the reference signal. Apparatus is also included.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Auto-image alignment system and method based on identified anomalies
InactiveUS20050111757A1Facilitate pagingEffective imagingImage enhancementImage analysisCritical positionComputer-aided
The present invention provides a novel technique and is particularly useful in medical imaging, although a number of fields may benefit from its application. In one aspect of the technique, a user identifies anomalies or, more generally, features in at least two different comparable images either by computer aided techniques or by manual identification. Once the features are identified they are numbered, sized, and a key location for the feature, such as the middle of an anomaly, may be estimated. Once this location is determined, a location marker is used to perform registration of the images. When comparisons are to be conducted, then, the registration is used to effectively anchor the images with respect to one another to facilitate paging between the images and reduction of eye movement.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
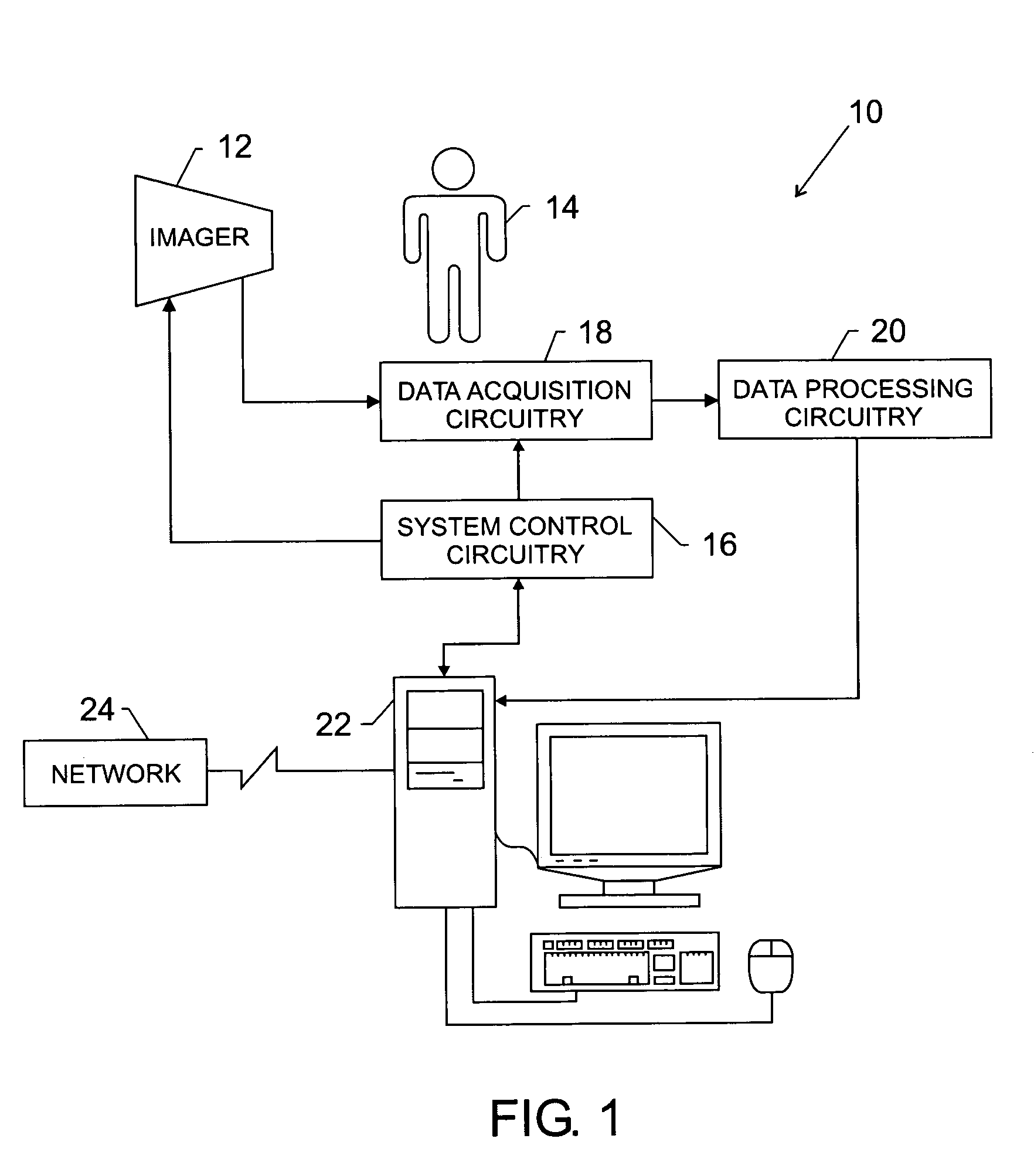
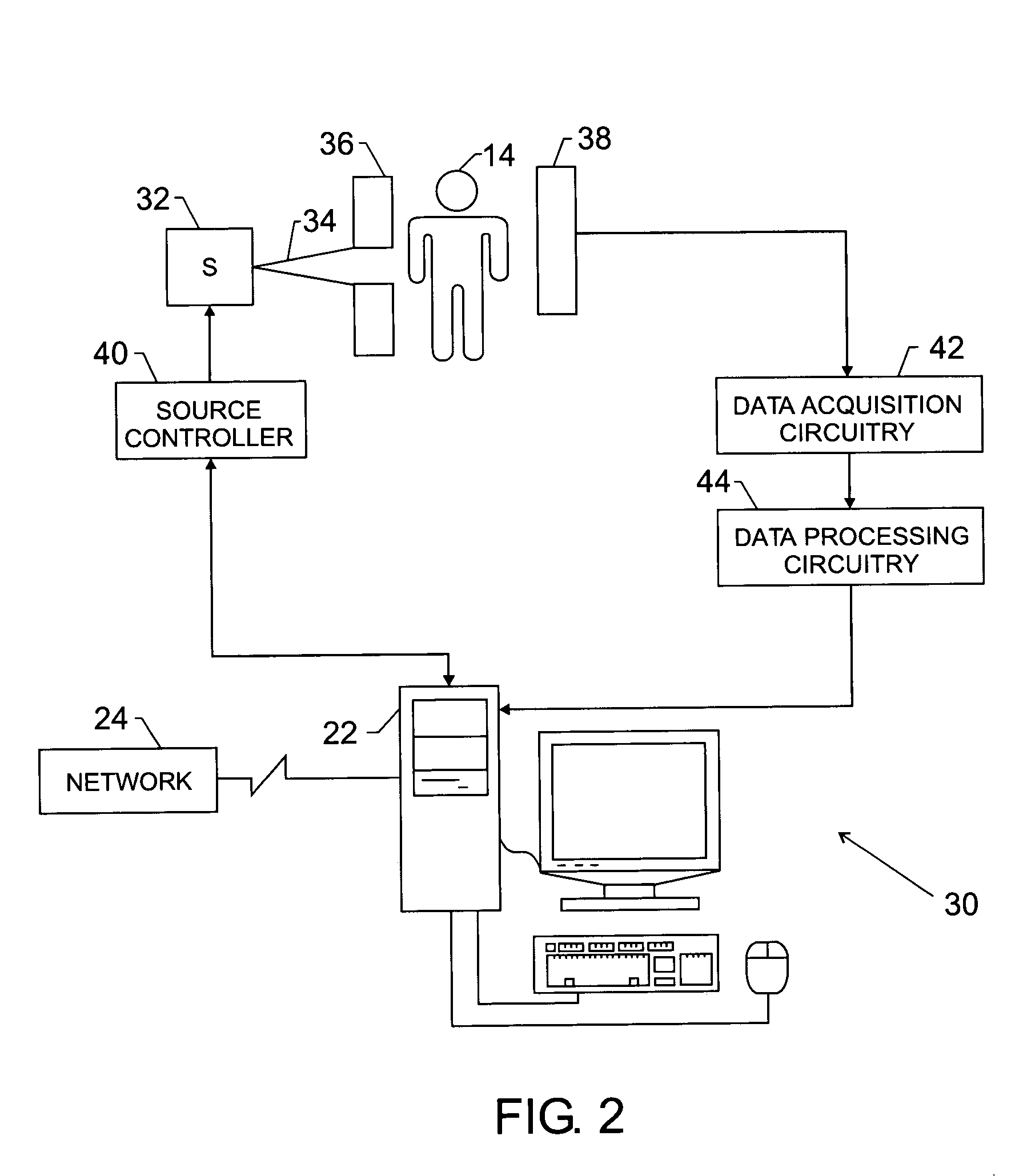
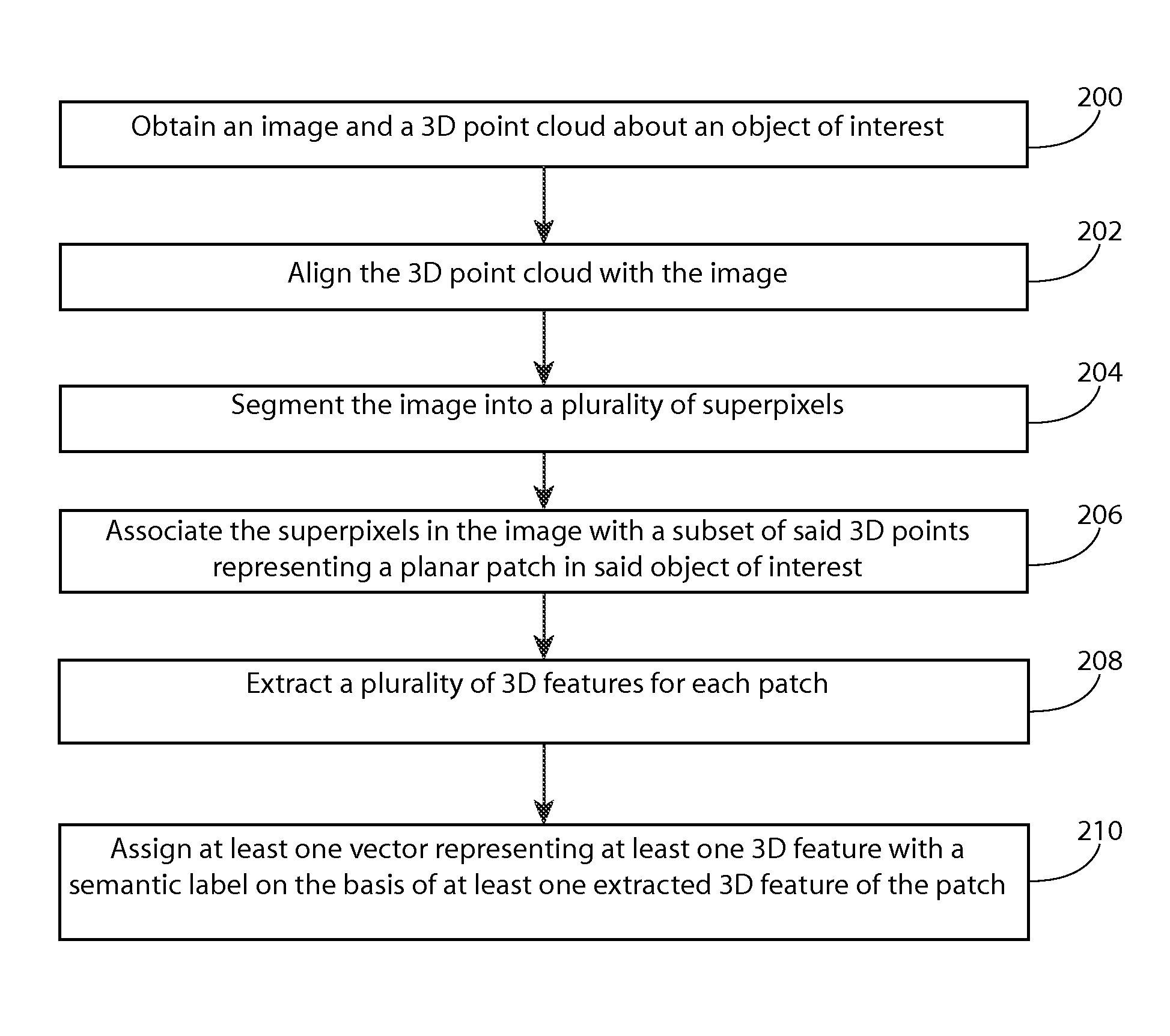
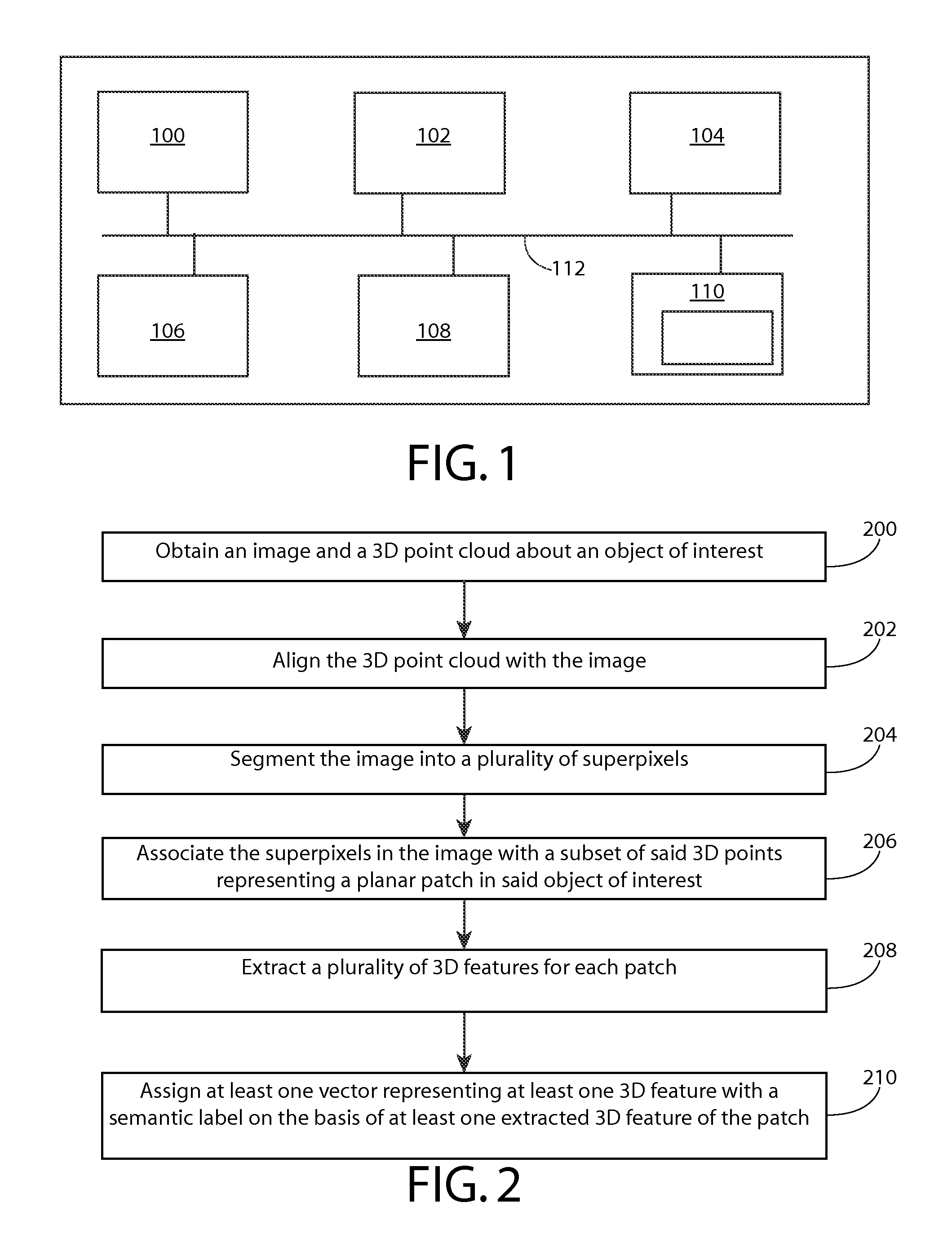
Automatic scene parsing
A method comprising: obtaining an image about an at least one object of interest and a three-dimensional (3D) point cloud about said object of interest; aligning the 3D point cloud with the image; segmenting the image into a plurality of superpixels preserving a graph structure and spatial neighbourhood of pixel data of the image; associating the superpixels in the image with a subset of said 3D points, said subset of 3D points representing a planar patch in said object of interest; extracting a plurality of 3D features for each patch; and assigning at least one vector representing at least one 3D feature with a semantic label on the basis of at least one extracted 3D feature of the patch.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
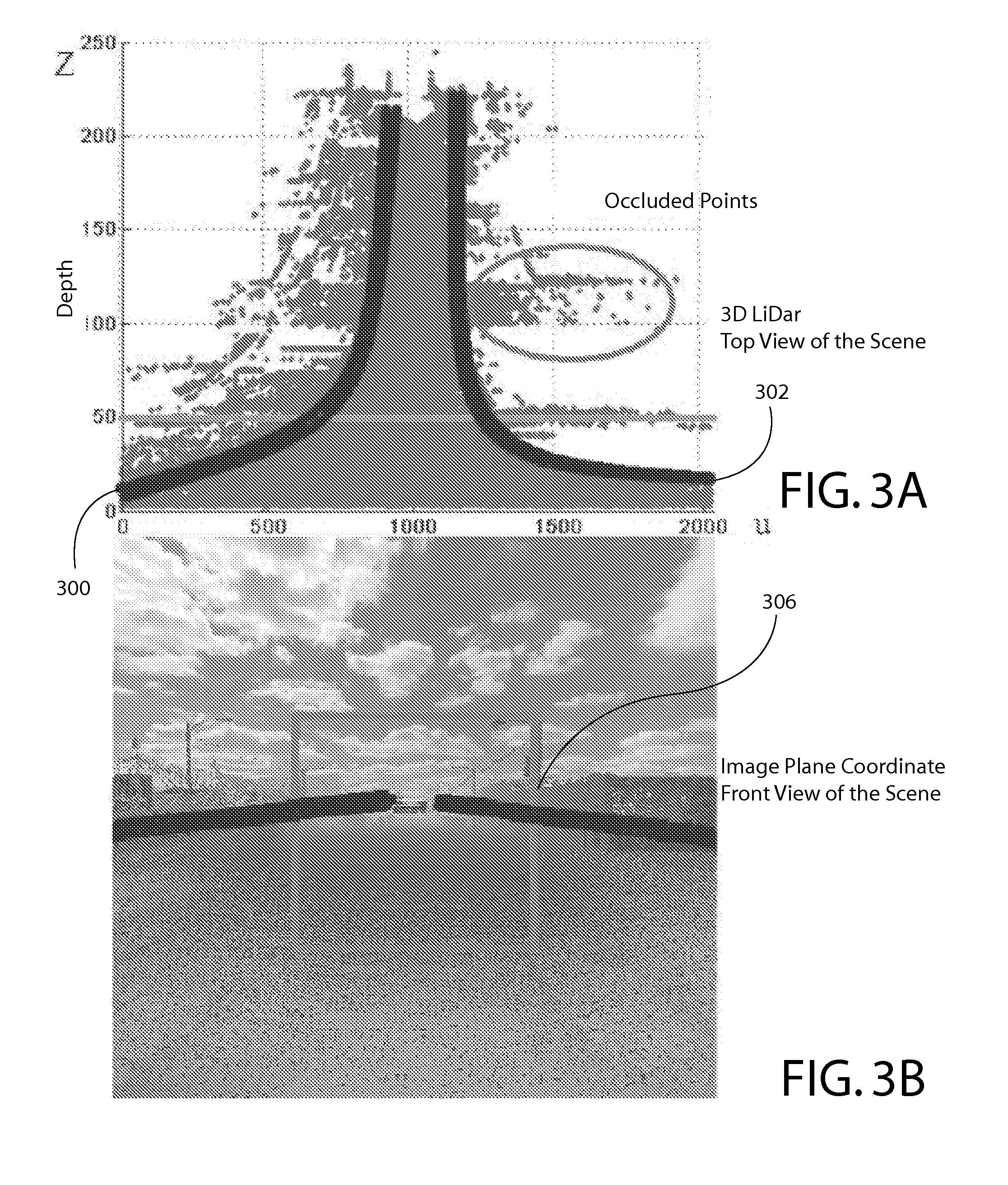
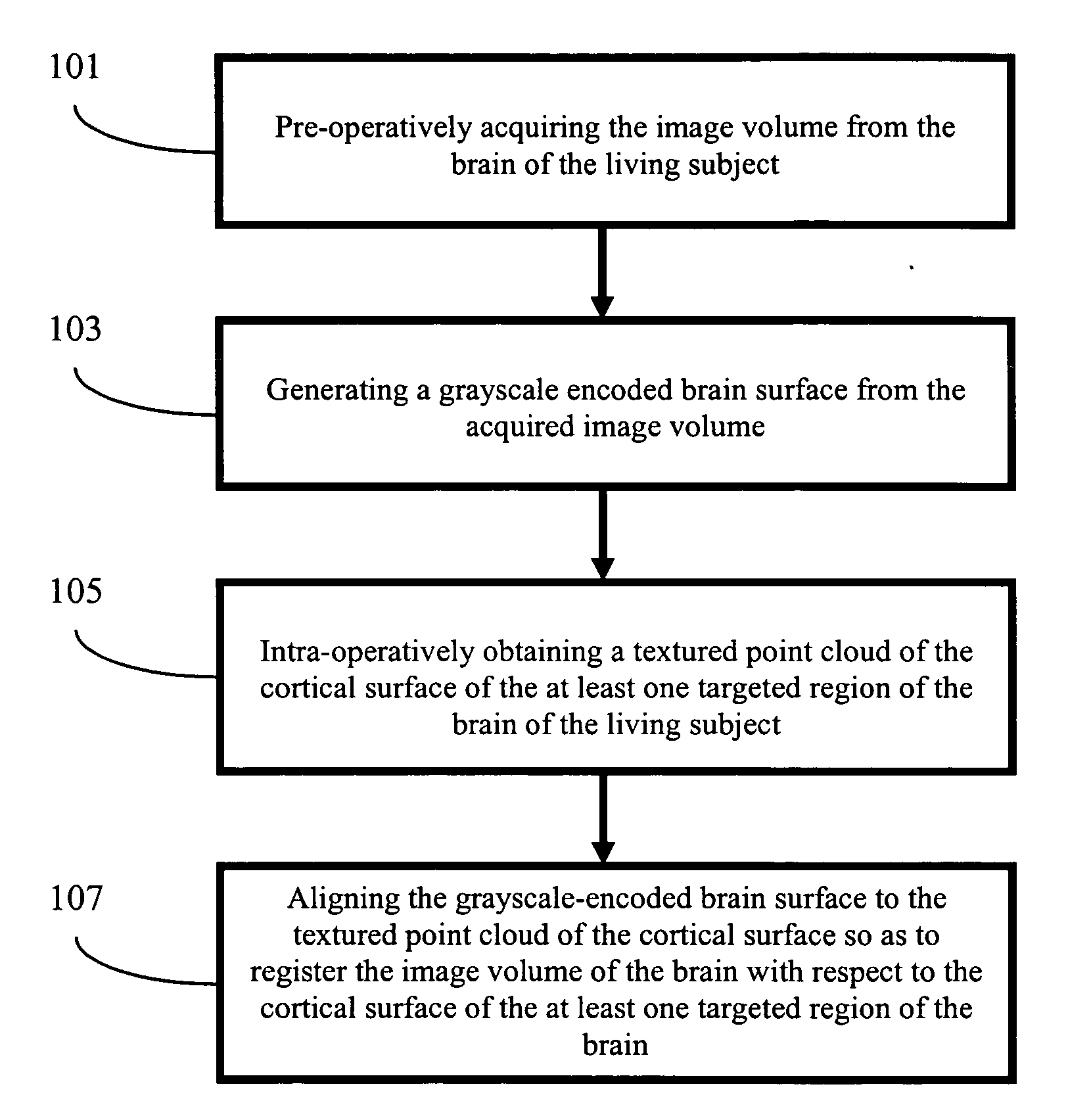
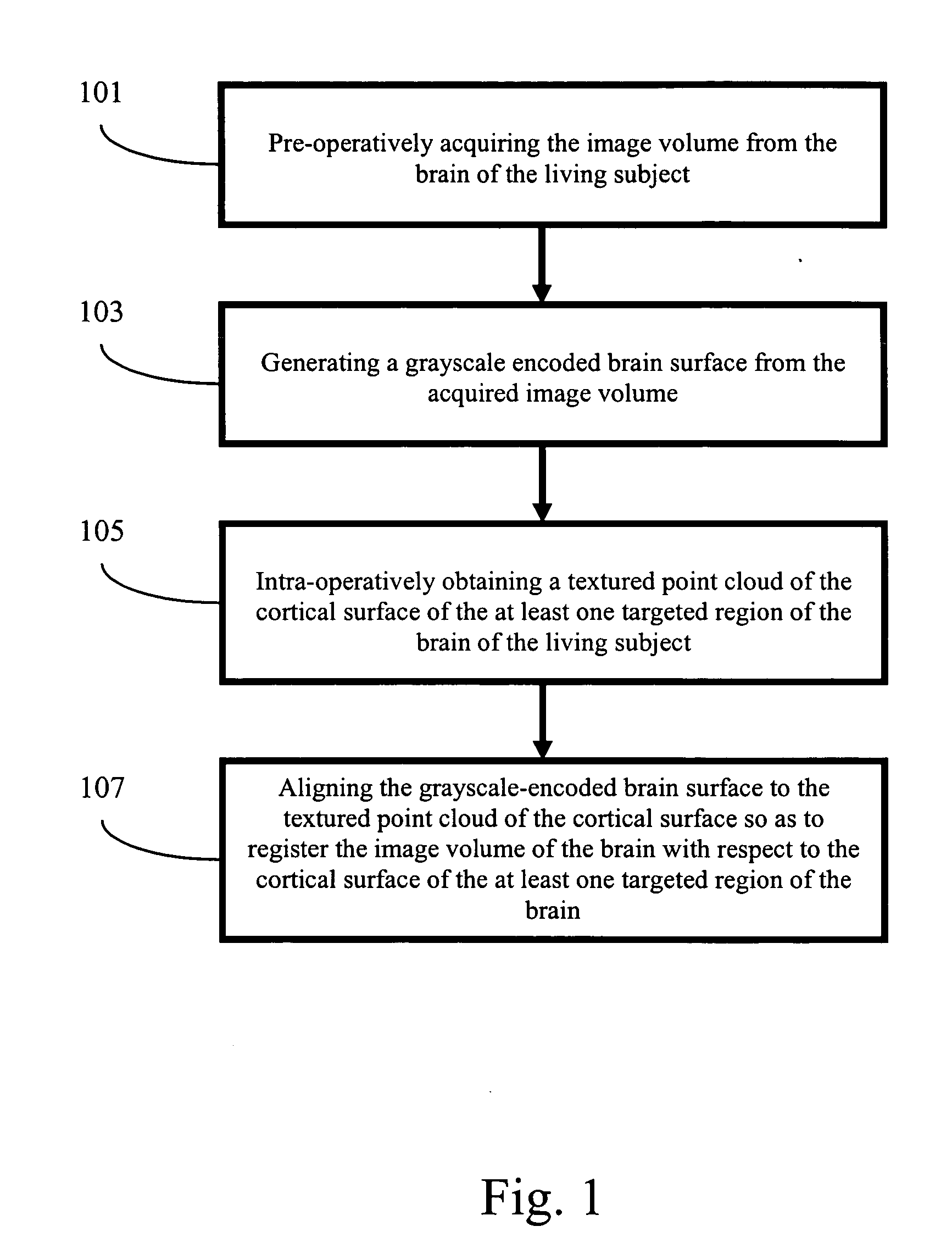
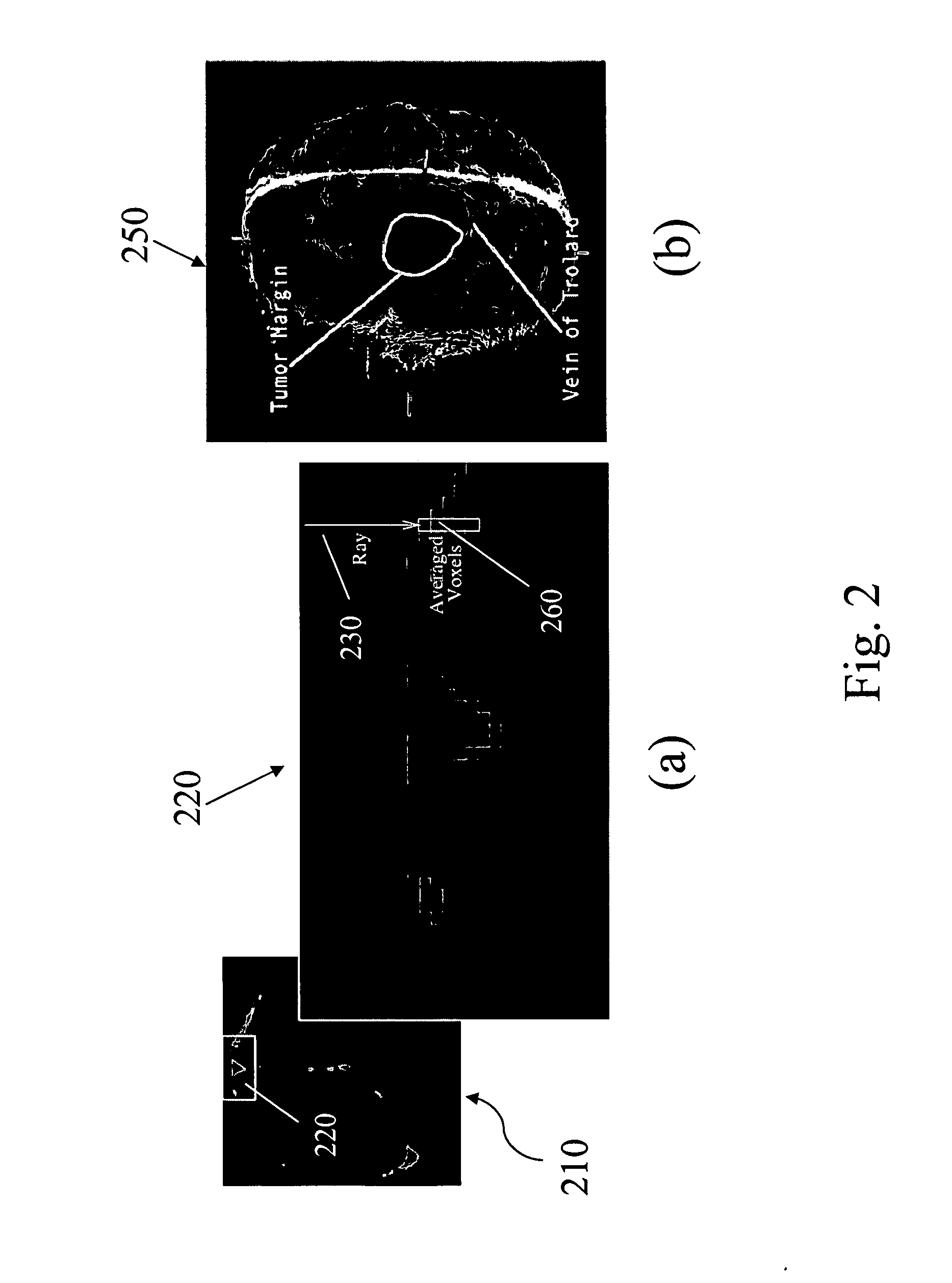
Apparatus and methods of cortical surface registration and deformation tracking for patient-to-image alignment in relation to image-guided surgery
ActiveUS20050148859A1Facilitate surgical procedureImage analysisSurgical navigation systemsPoint cloudMedicine
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Sequential image alignment
InactiveUS20110182486A1Easy to useLower requirementCharacter and pattern recognitionImage alignmentComputer science
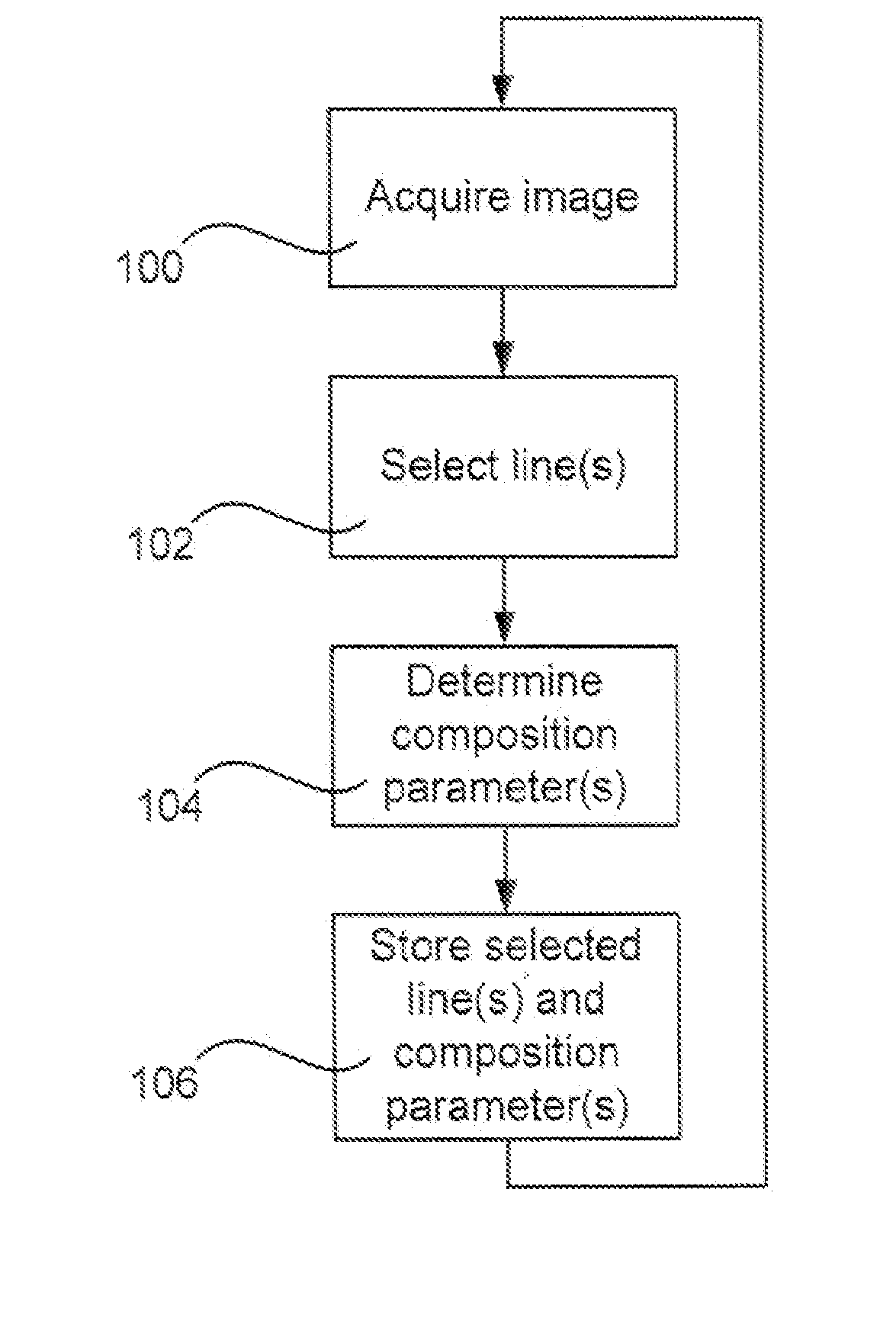
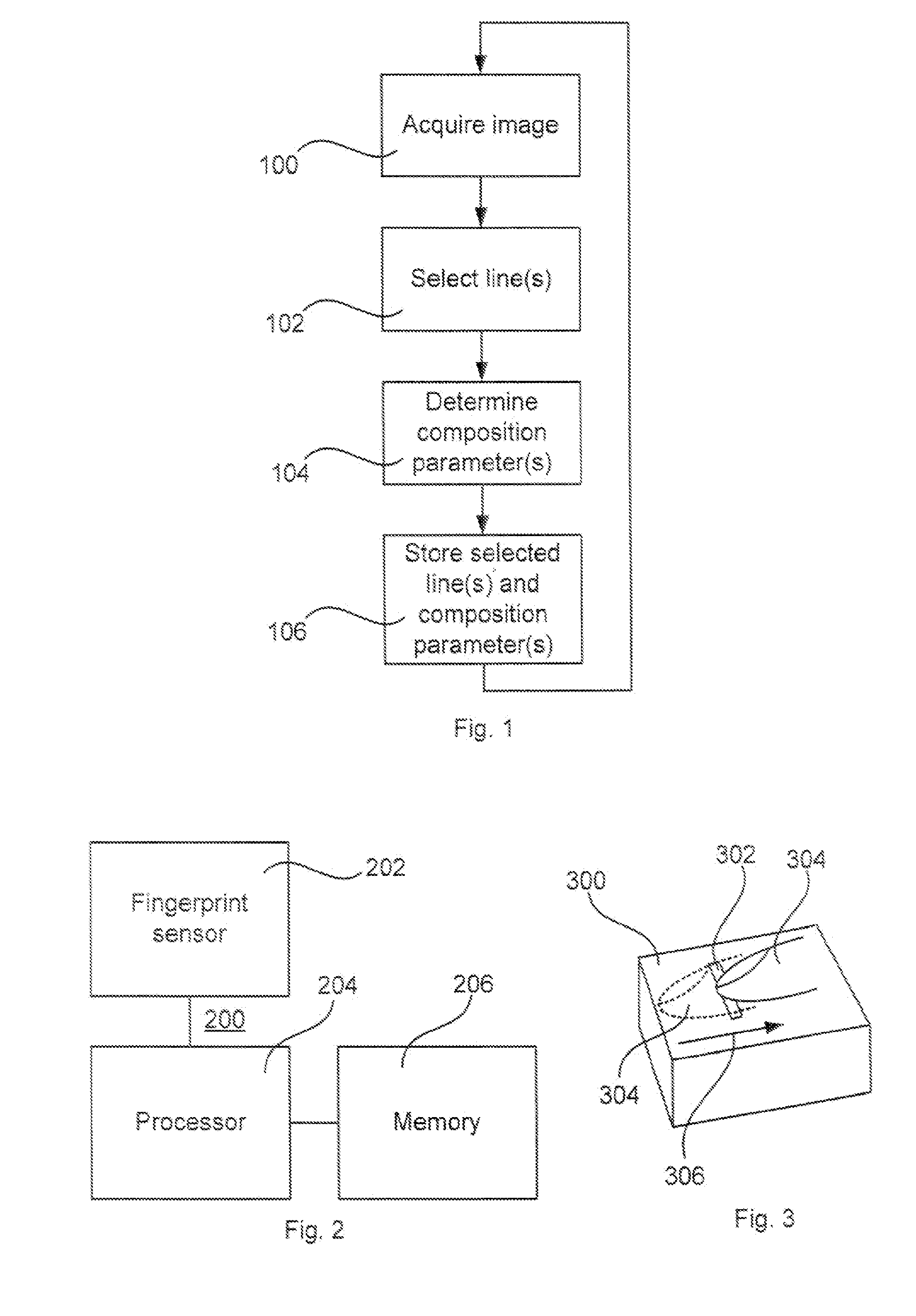
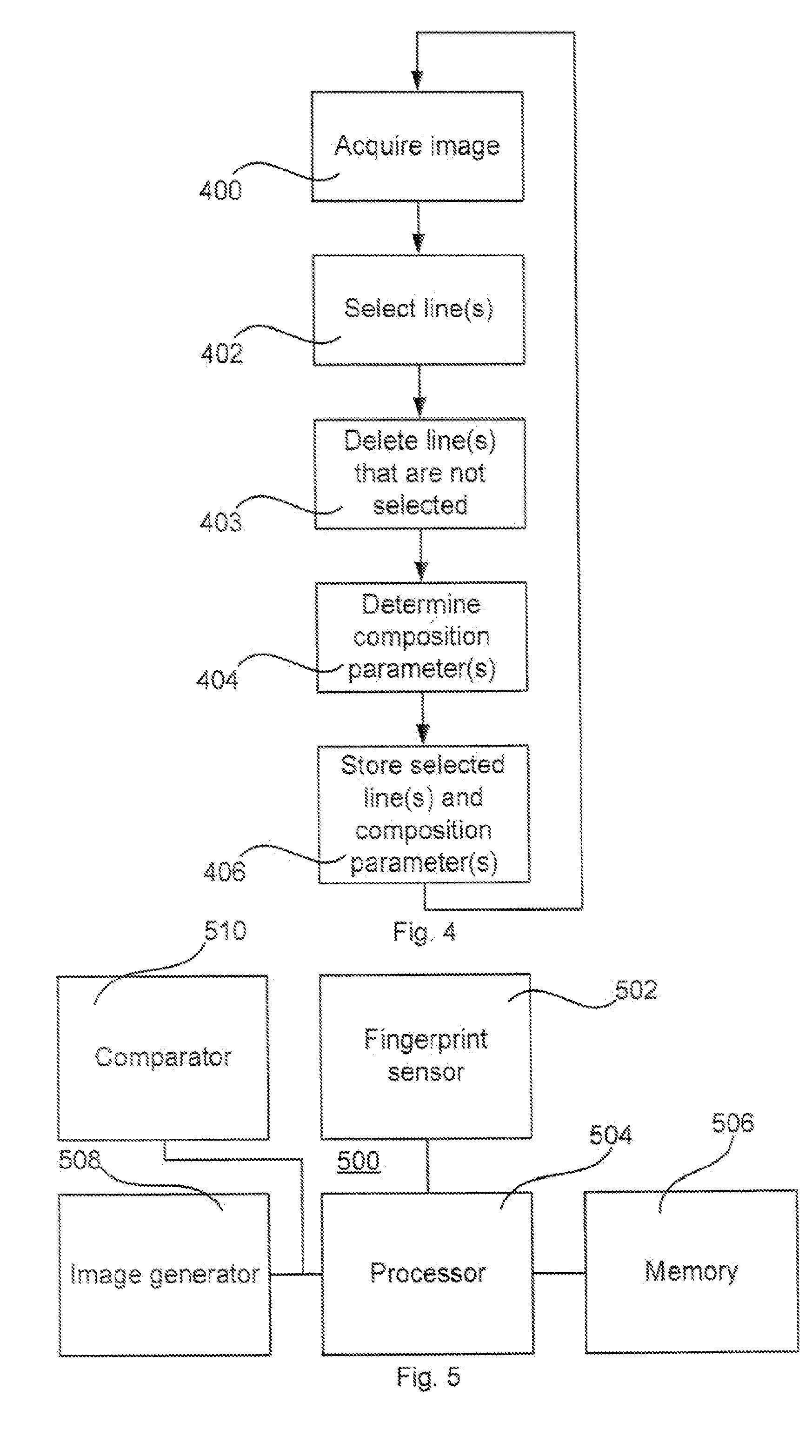
A method for reading fingerprints is disclosed. The method comprises acquiring images of a fingerprint from a finger upon relative movement between the finger and an image sensor; selecting lines from said acquired images representing a new area of said fingerprint; determining composition parameters for each selected line: and storing said composition parameters and said selected lines such that a composite image comprising said selected lines is composabte. A corresponding fingerprint reading apparatus, a device, and a computer program are also disclosed.
Owner:PRECISE BIOMETRICS AB
Video stabilizing method based on matching and tracking of characteristic
InactiveCN101009021AGuaranteed stabilityOvercoming the smoothness problemImage enhancementTelevision system detailsCurve matchingCurve fitting
This invention relates to one visual frequency stable method based on property matching in the computer image visual frequency process technique field, which comprises the following steps: finding out each frame of visual SIFT property points; adopting simulation module as parameters estimation module for total estimation; adopting Gauss filter and curve matching method to process visual sequence process to fill unknown area.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
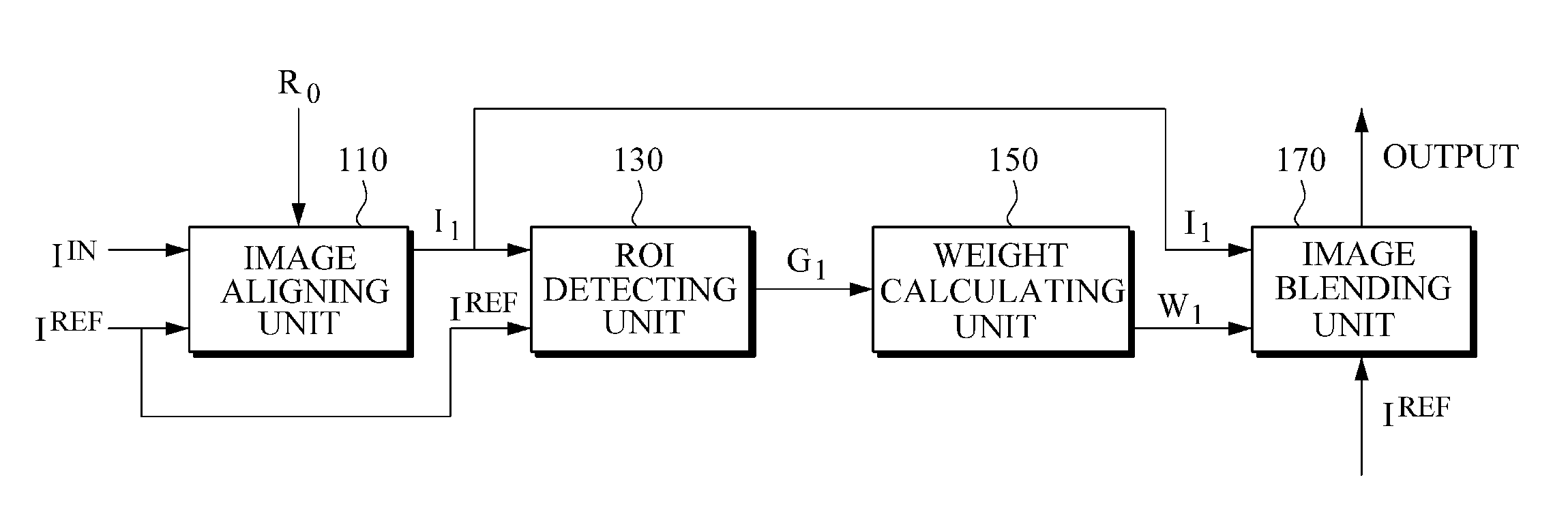
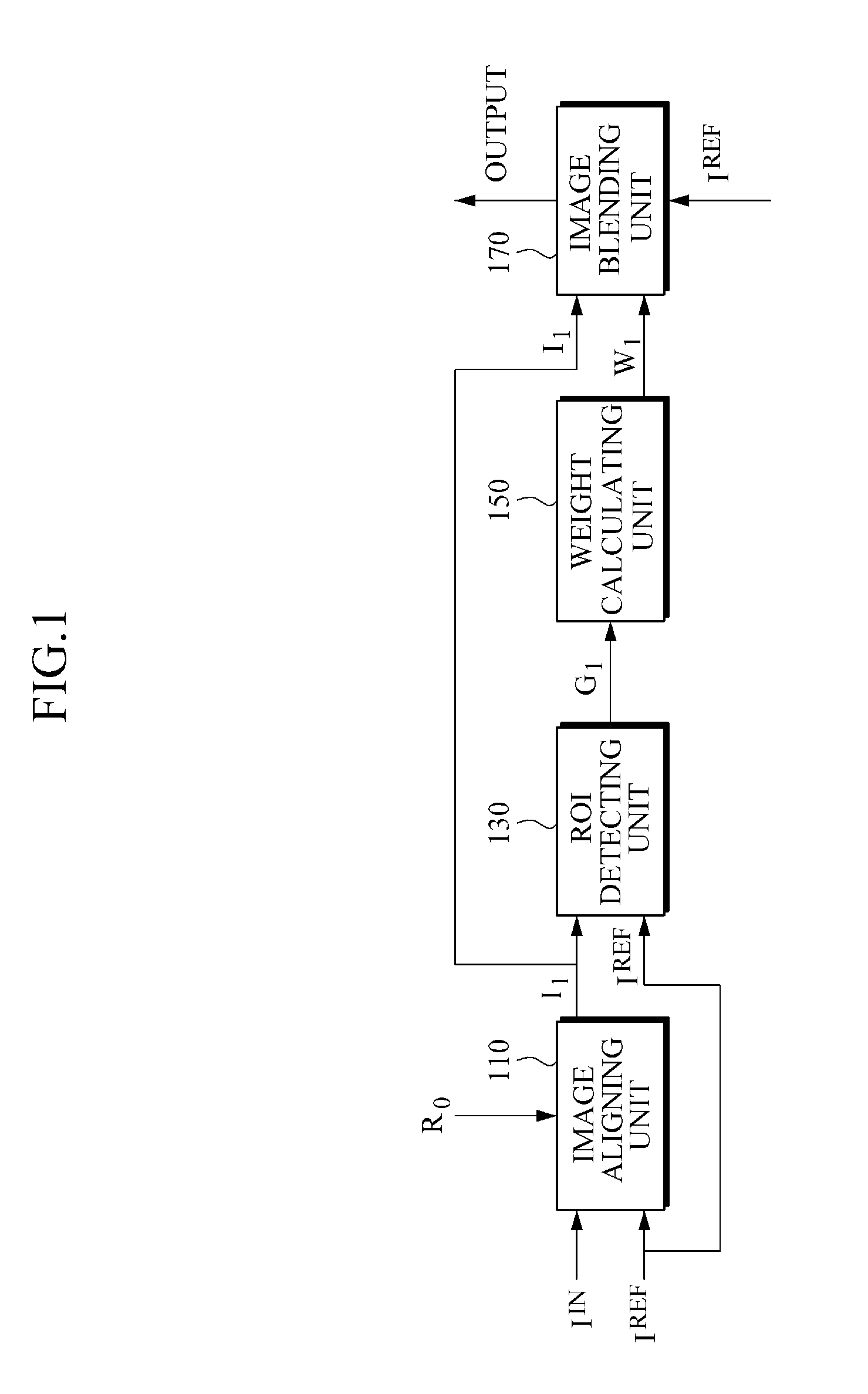
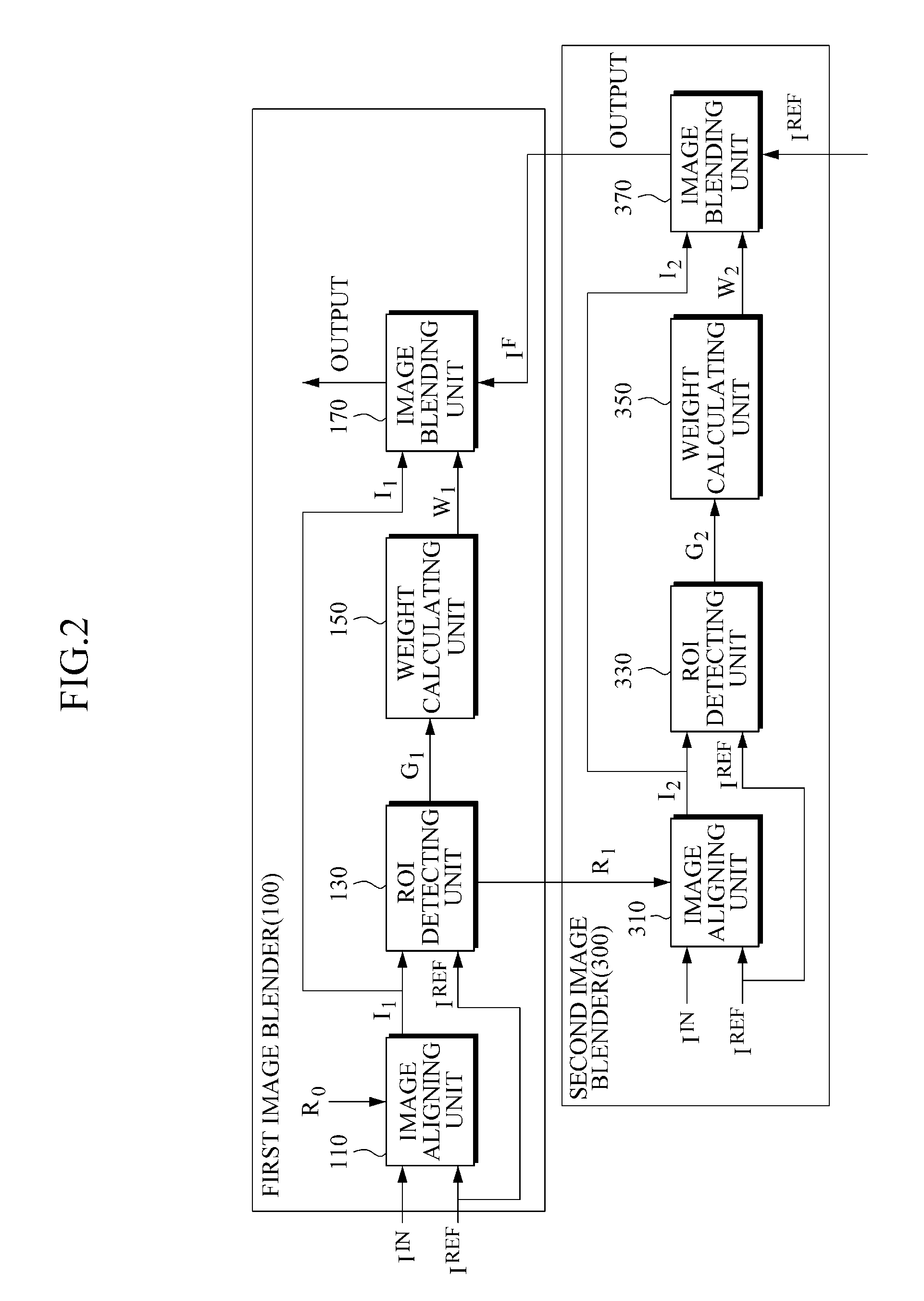
Method and apparatus for blending images
A method and apparatus may include aligning a reference image and an input image through ROI-based image alignment; detecting an ROI associated with an incompletely aligned region in the aligned image; and blending the aligned reference image and input image by using a plurality of weights which are attenuated according to a spatial distance from a boundary of the detected ROI. In addition, the method and apparatus may include aligning a reference image and an input image through image alignment based on an nth region of interest (ROI) which is detected at a previous stage; detecting another ROI associated with an incompletely aligned region in the aligned image; and blending the aligned image in the other ROI and an (n+1)th blended image, which is input from a next stage, in a region outside the other ROI, and outputting the last blended image to the previous stage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
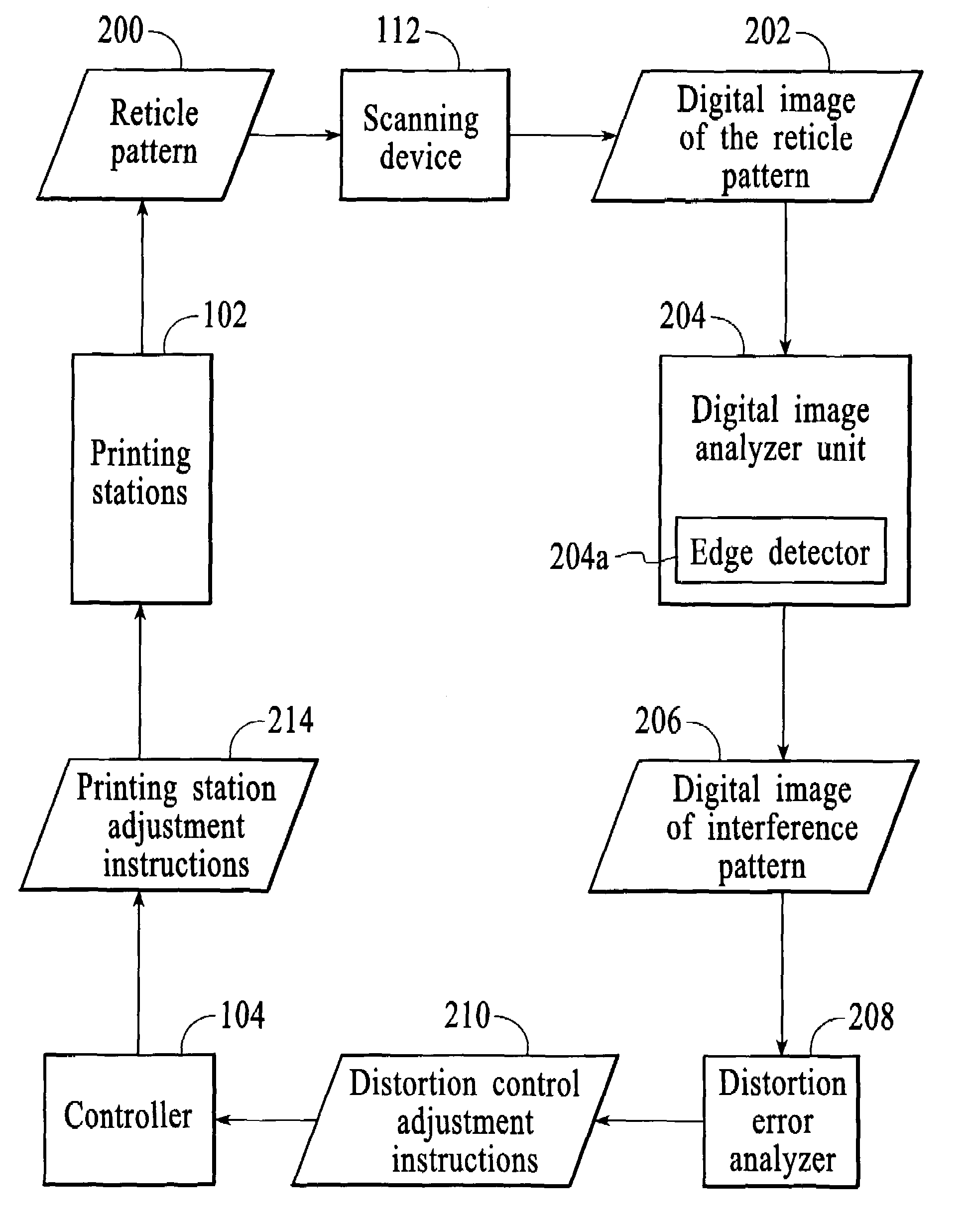
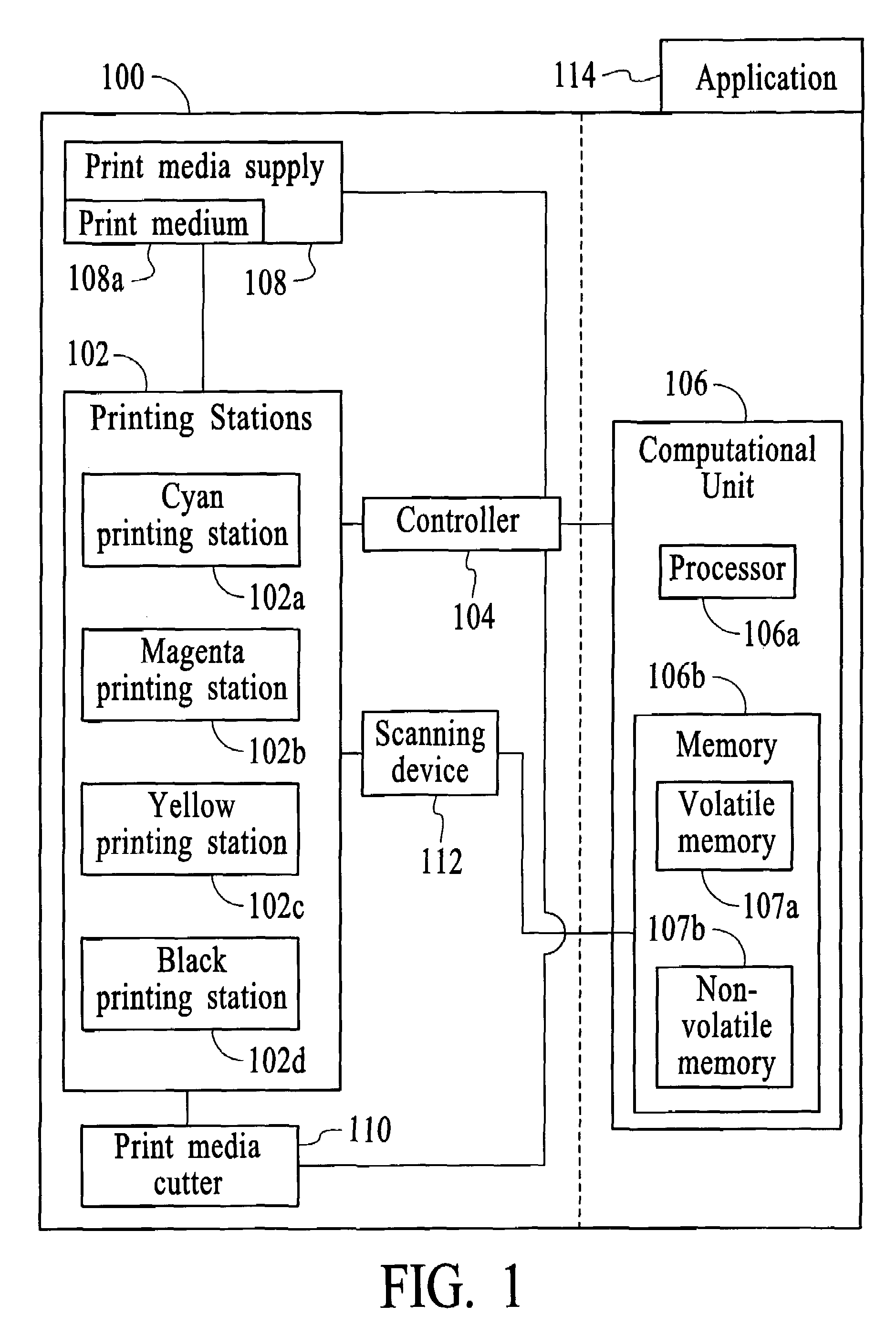
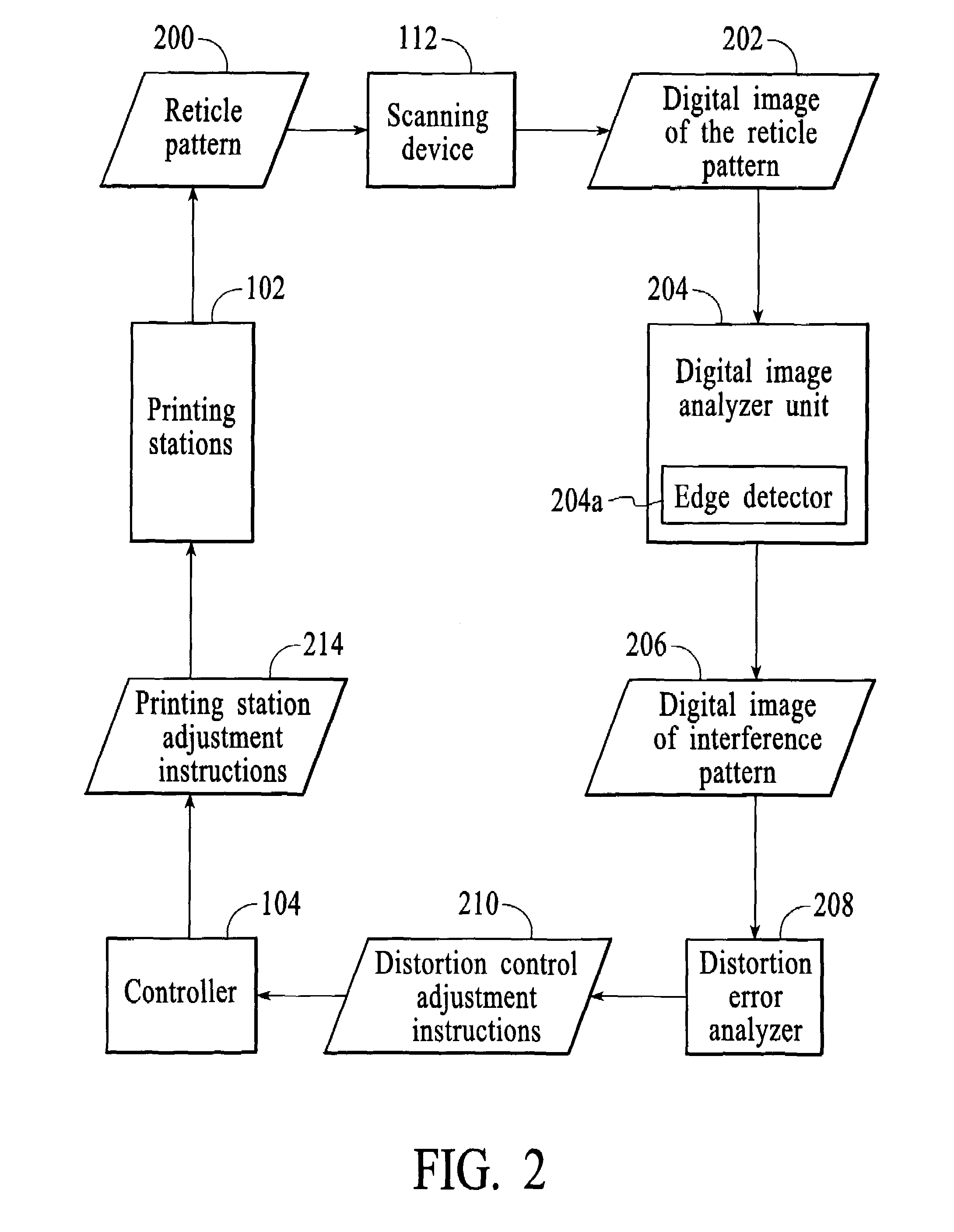
Method and system for minimizing the appearance of image distortion in a high speed inkjet paper printing system
ActiveUS6966712B2True colorPrecise registrationAddressographsPlaten pressesColor printingEngineering
A method and system for a printing device is disclosed. The method and system comprise printing a test pattern on a print medium and generating a digital image of the printed test pattern by an imaging device. The method and system include analyzing an interference pattern to measure for distortion of the print medium and calibrating the printing device based upon the measured distortion.In a preferred embodiment, the present invention utilizes the reticle patterns, which are printed in the margins of the paper, which are measured real-time during printing. The interference or Moiré patterns created by superimposed reticles may be used to measure image distortion, process direction misalignment, and misregistration caused by web distortion. The advantage of this invention is that image distortion compensation, RIP (Raster Image Processor) parameters, timing, or other printer characteristics may be adjusted on-the-fly in a closed feedback system, for high-speed textile or paper color printing, utilizing on-the-fly distortion or stretch measurement for accurate color and / or duplex images registration. In a duplex printer, automatic images alignment front-to-back is obtained by combining optically or logically the two images for the evaluation of interference patterns and amount of distortion in the process and scan direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
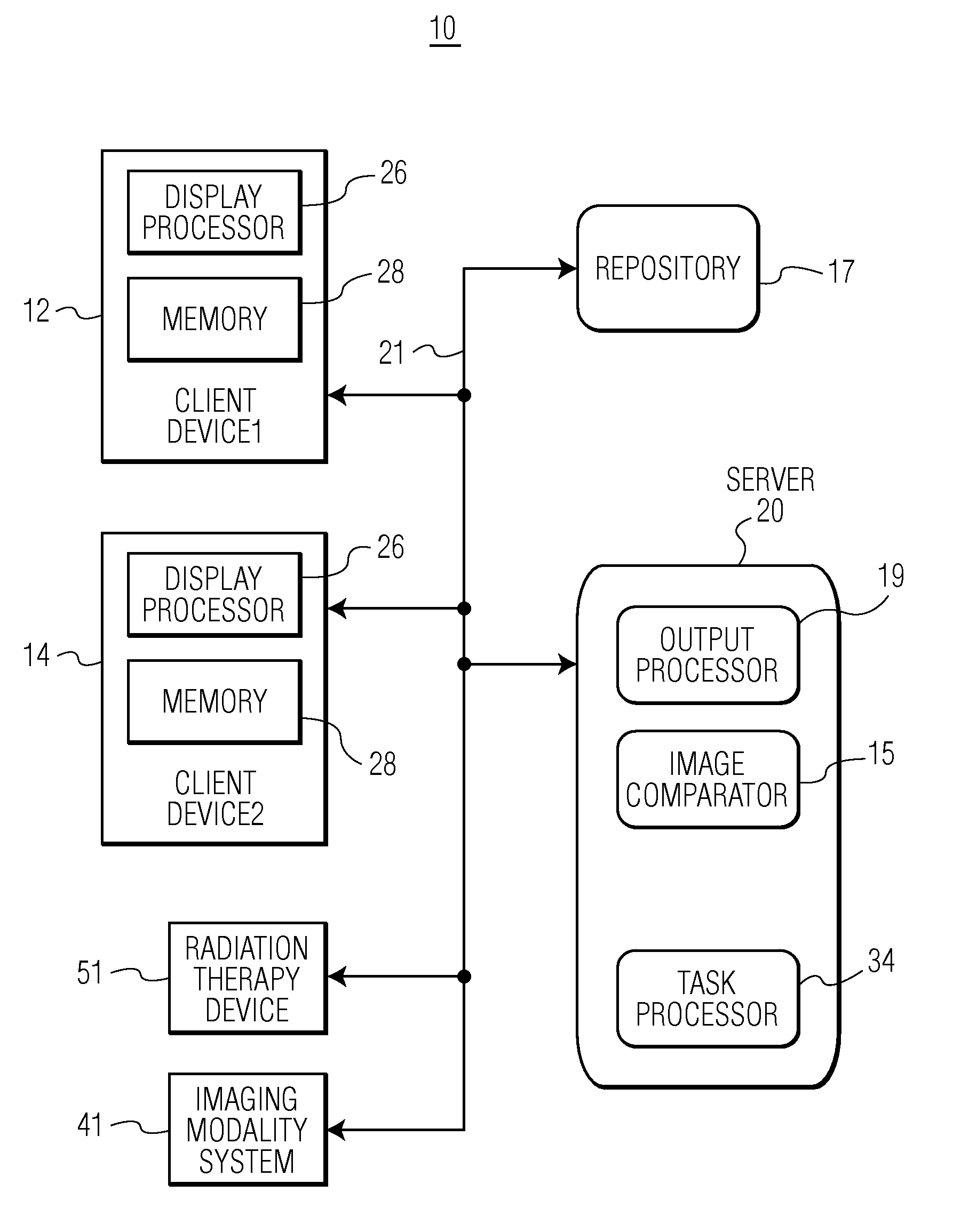
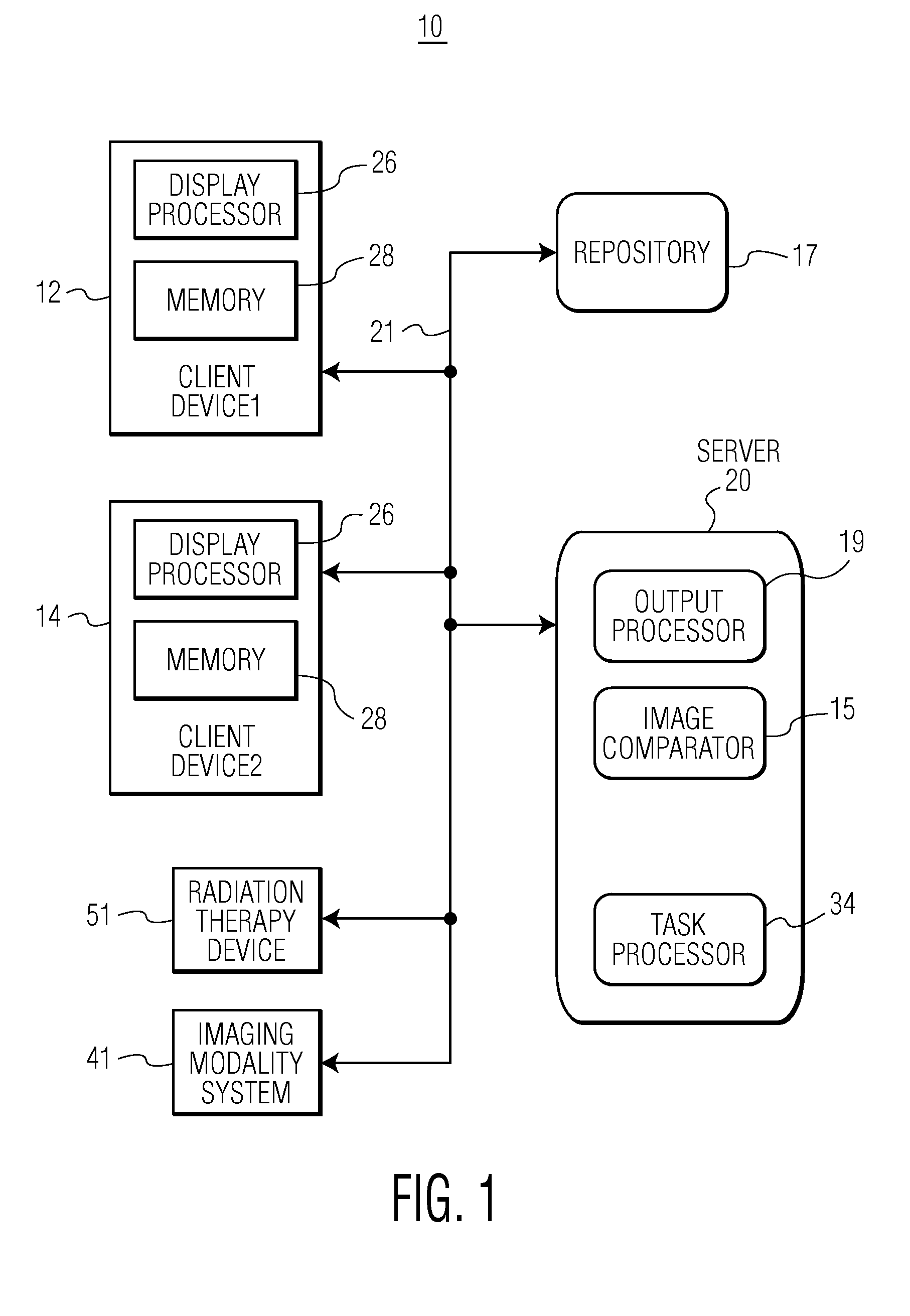
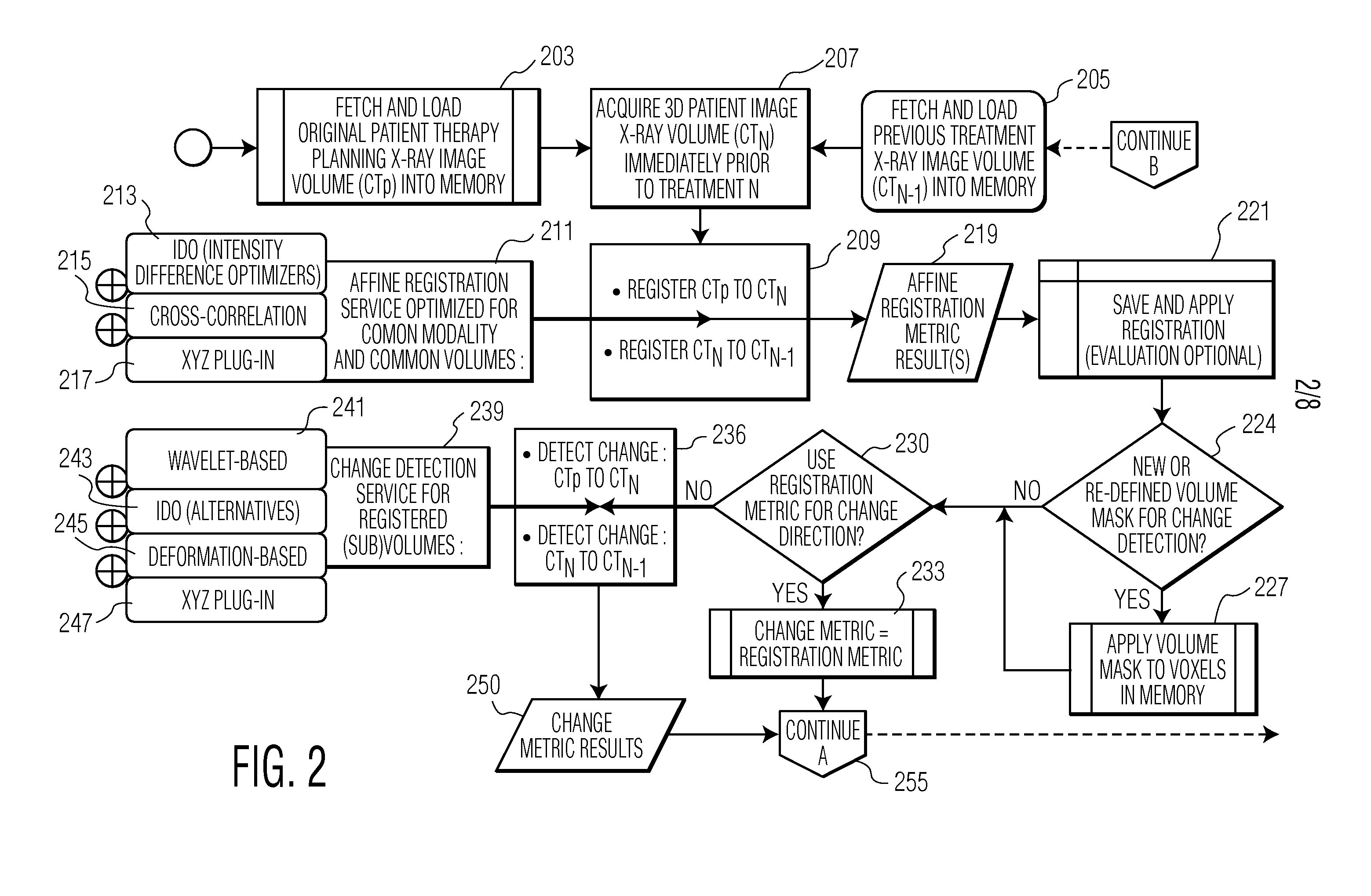
Medical Imaging Processing and Care Planning System
ActiveUS20090262894A1Accurate detectionAccurate treatmentImage enhancementImage analysisMedical imagingImage alignment
A system automatically compares radiotherapy 3D X-Ray images and subsequent images for update and re-planning of treatment and for verification of correct patient and image association. A medical radiation therapy system and workflow includes a task processor for providing task management data for initiating image comparison tasks prior to performing a session of radiotherapy. An image comparator, coupled to the task processor, in response to the task management data, compares a first image of an anatomical portion of a particular patient used for planning radiotherapy for the particular patient, with a second image of the anatomical portion of the particular patient obtained on a subsequent date, by image alignment and comparison of image element representative data of aligned first and second images to determine an image difference representative remainder value and determines whether the image difference representative remainder value exceeds a first predetermined threshold. An output processor, coupled to the image comparator, initiates generation of an alert message indicating a need to review planned radiotherapy treatment for communication to a user in response to a determination the image difference representative remainder value exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
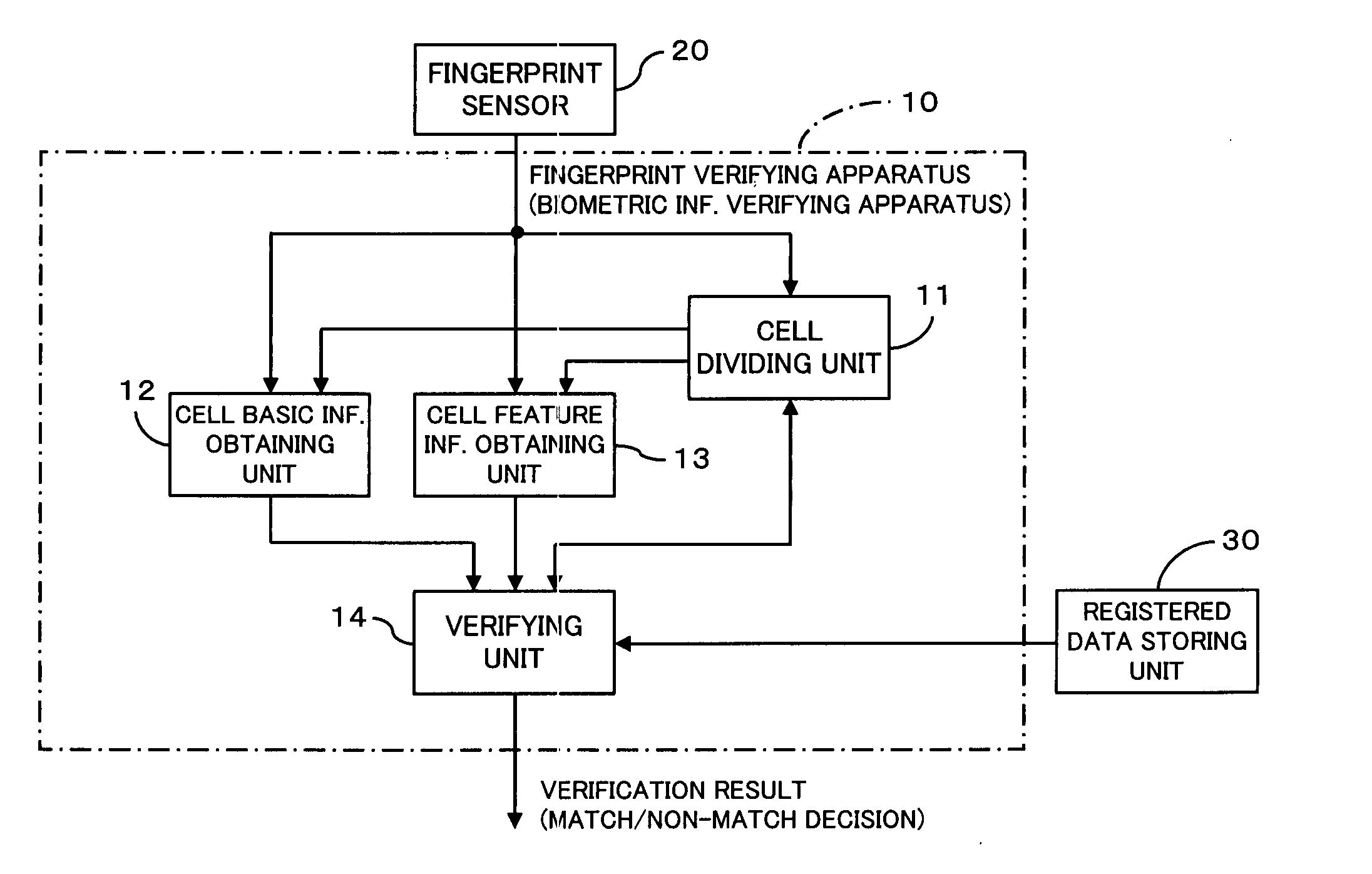
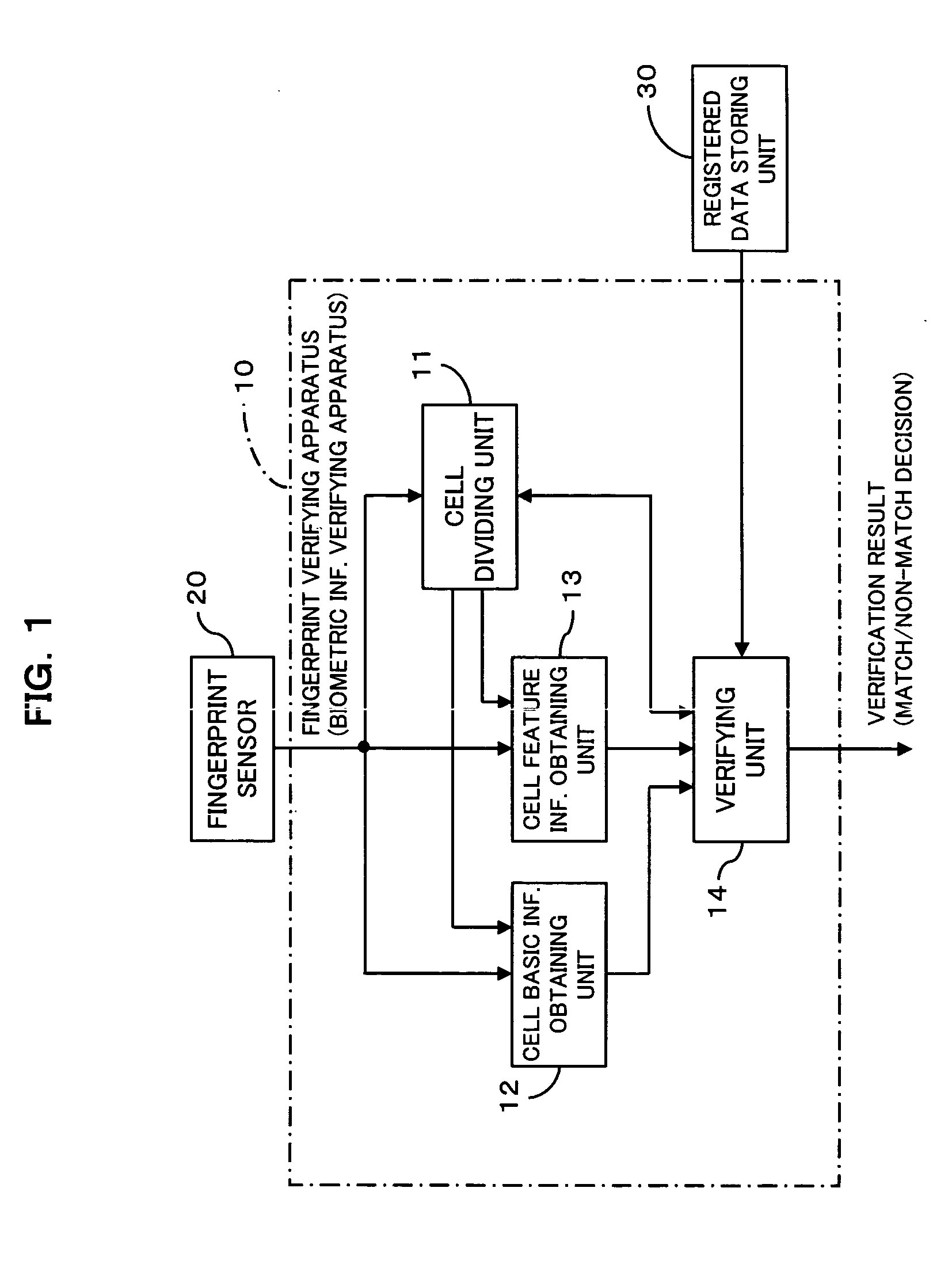
Biometric information verifying apparatus
InactiveUS20050175225A1Decreases false verification rateReduce data volumeImage analysisPerson identificationUser verificationPalm print
The apparatus greatly reduces the registered data amount and the verification computation amount required for user verification, in comparison with the verification using image information itself, and also decreases the false verification rate. The apparatus divides a biometric information image into cells, and extracts minutia information as well as cell basic information from the individual cells. After comparison of direction information of the individual cells of the registered data with direction information of the individual cells of the to-be-verified data, thereby aligning the registered fingerprint image and the to-be-verified fingerprint image, the apparatus compares the minutia information of corresponding cells between the registered data and the to-be-verified data to make a match / non-match decision. Such an apparatus is applicable to systems that employ pattern matching type image verification to perform user verification utilizing biometric information such as fingerprints, palm prints, blood vessel patterns, iris patterns, and facial images.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Generic face alignment via boosting
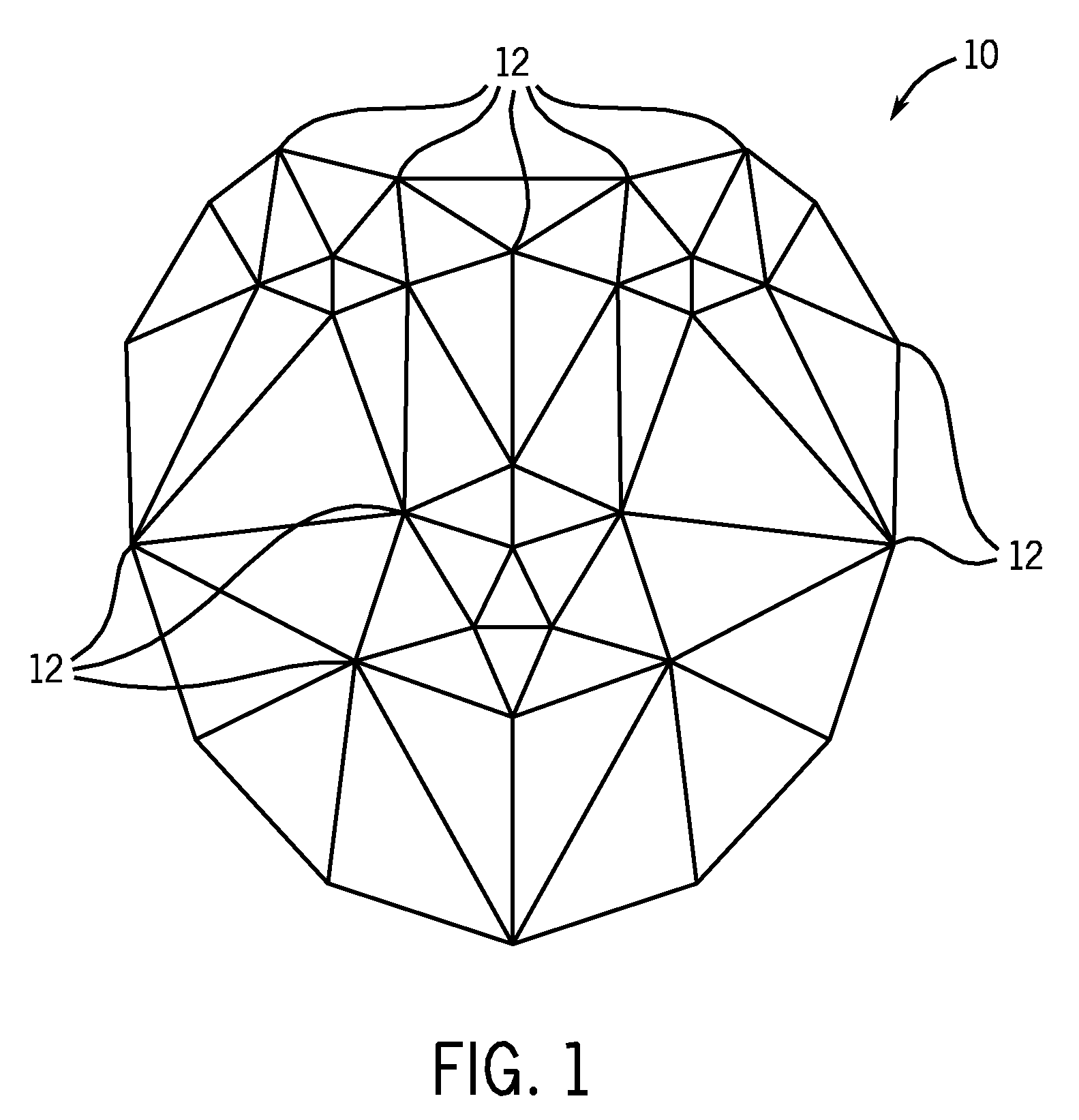
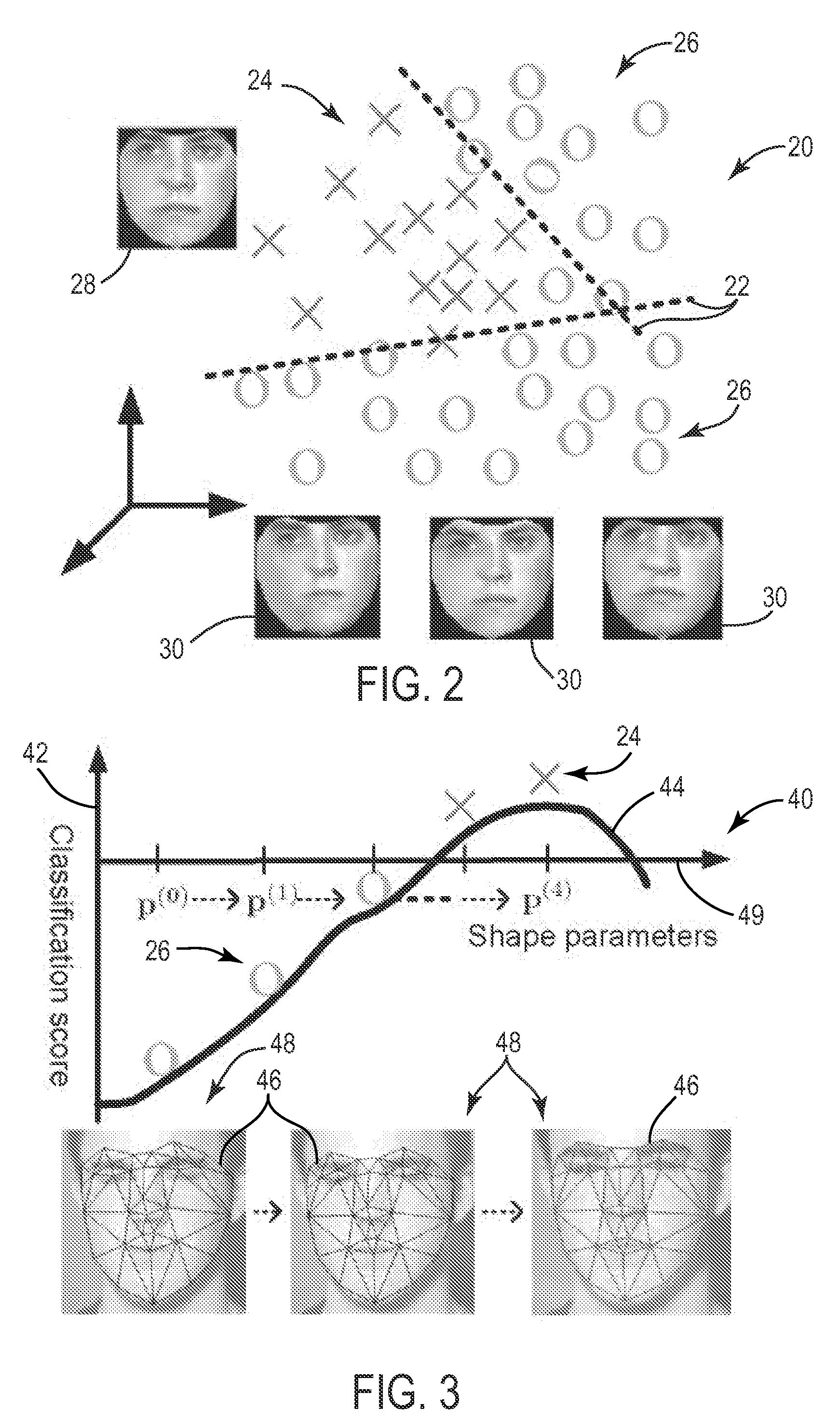
ActiveUS20080310759A1Maximizing a strong classifier scoreMaximizing a strong classifierCharacter and pattern recognitionGround truthPattern recognition
There is provided a discriminative framework for image alignment. Image alignment is generally the process of moving and deforming a template to minimize the distance between the template and an image. There are essentially three elements to image alignment, namely template representation, distance metric, and optimization method. For template representation, given a face dataset with ground truth landmarks, a boosting-based classifier is trained that is able to learn the decision boundary between two classes-the warped images from ground truth landmarks (e.g., positive class) and those from perturbed landmarks (e.g., negative class). A set of trained weak classifiers based on Haar-like rectangular features determines a boosted appearance model. A distance metric is a score from the strong classifier, and image alignment is the process of optimizing (e.g., maximizing) the classification score. On the generic face alignment problem, the proposed framework greatly improves the robustness, accuracy, and efficiency of alignment.
Owner:UTC FIRE & SECURITY AMERICAS CORPORATION INC
Silhouette-based object and texture alignment, systems and methods
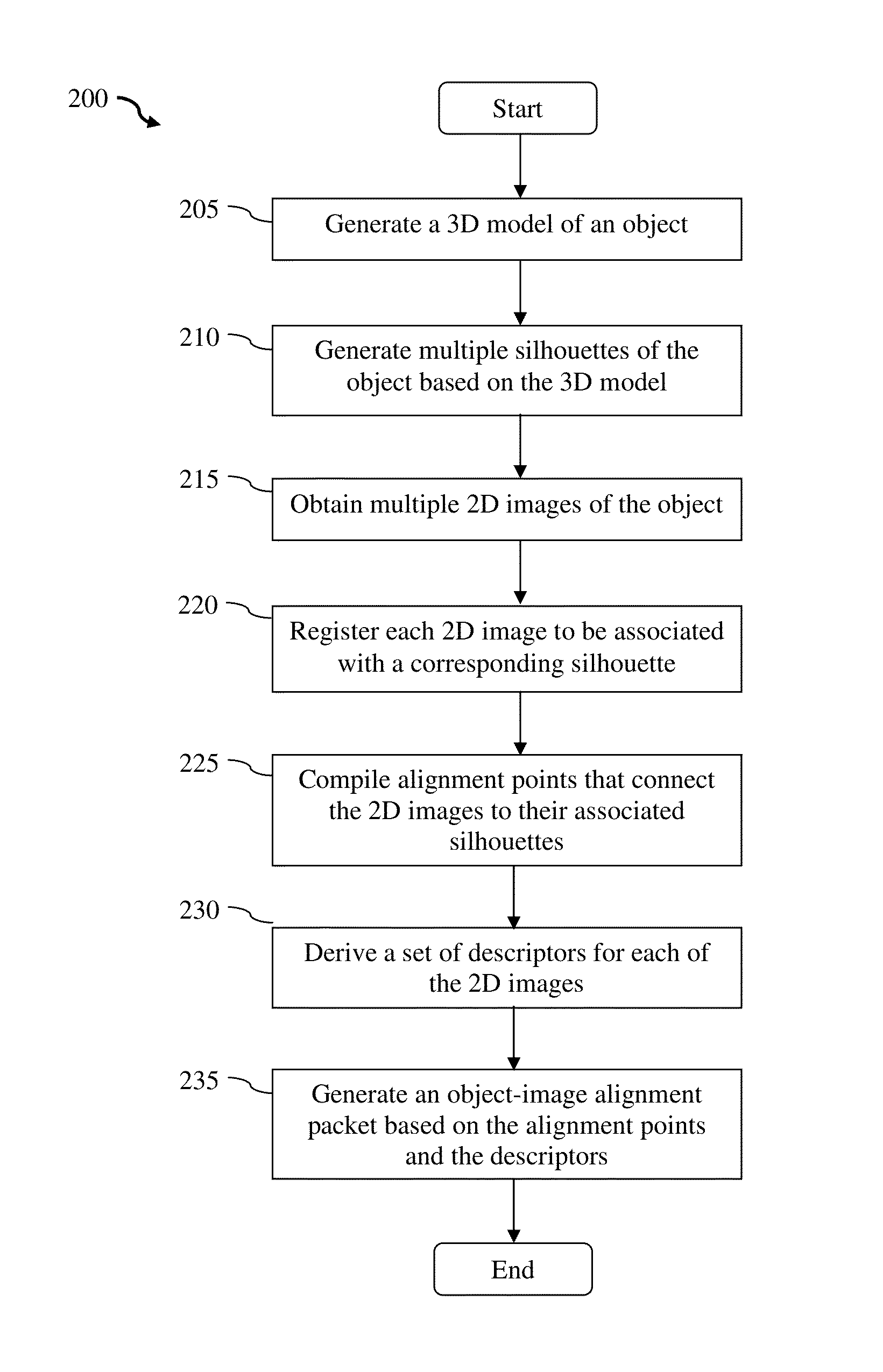
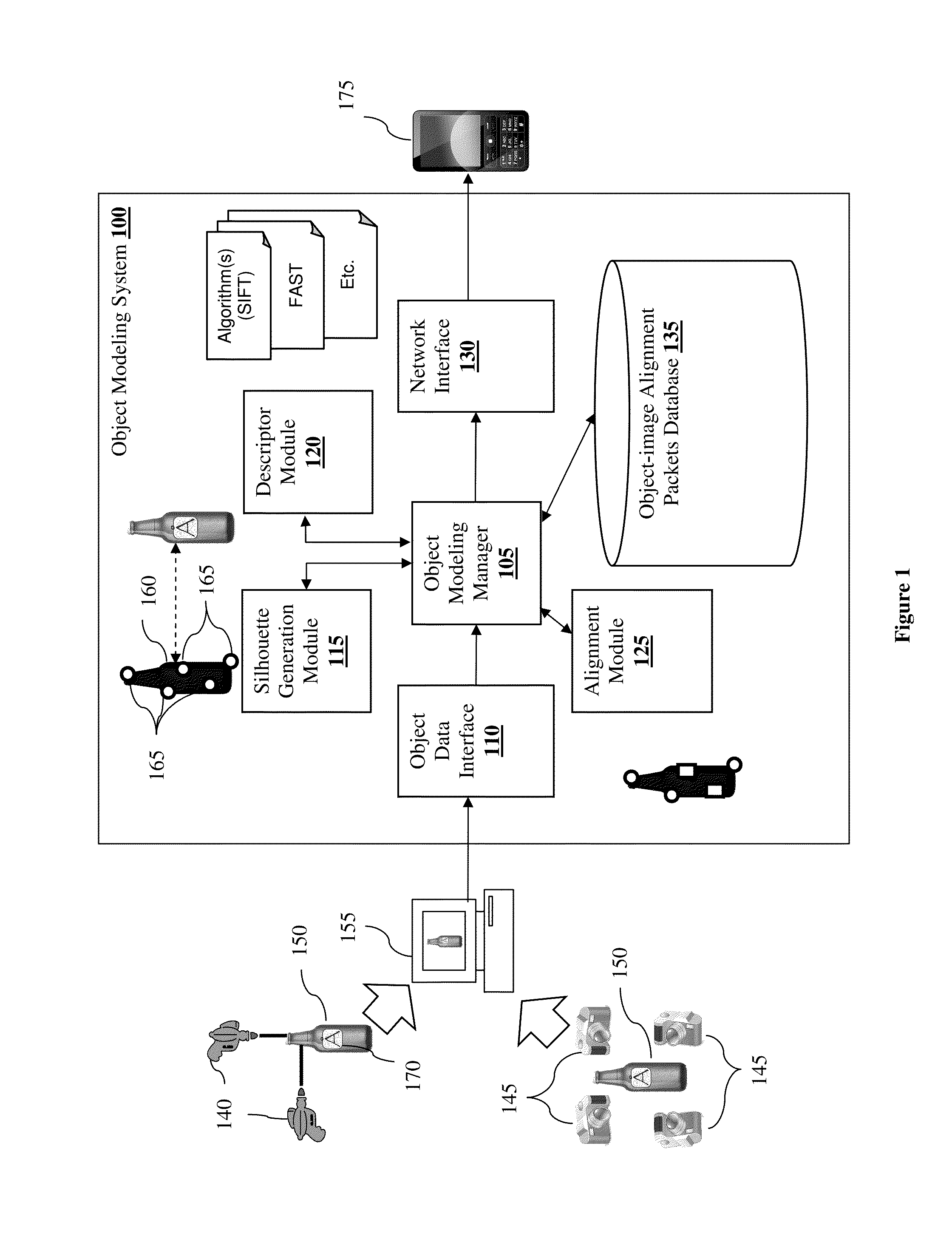
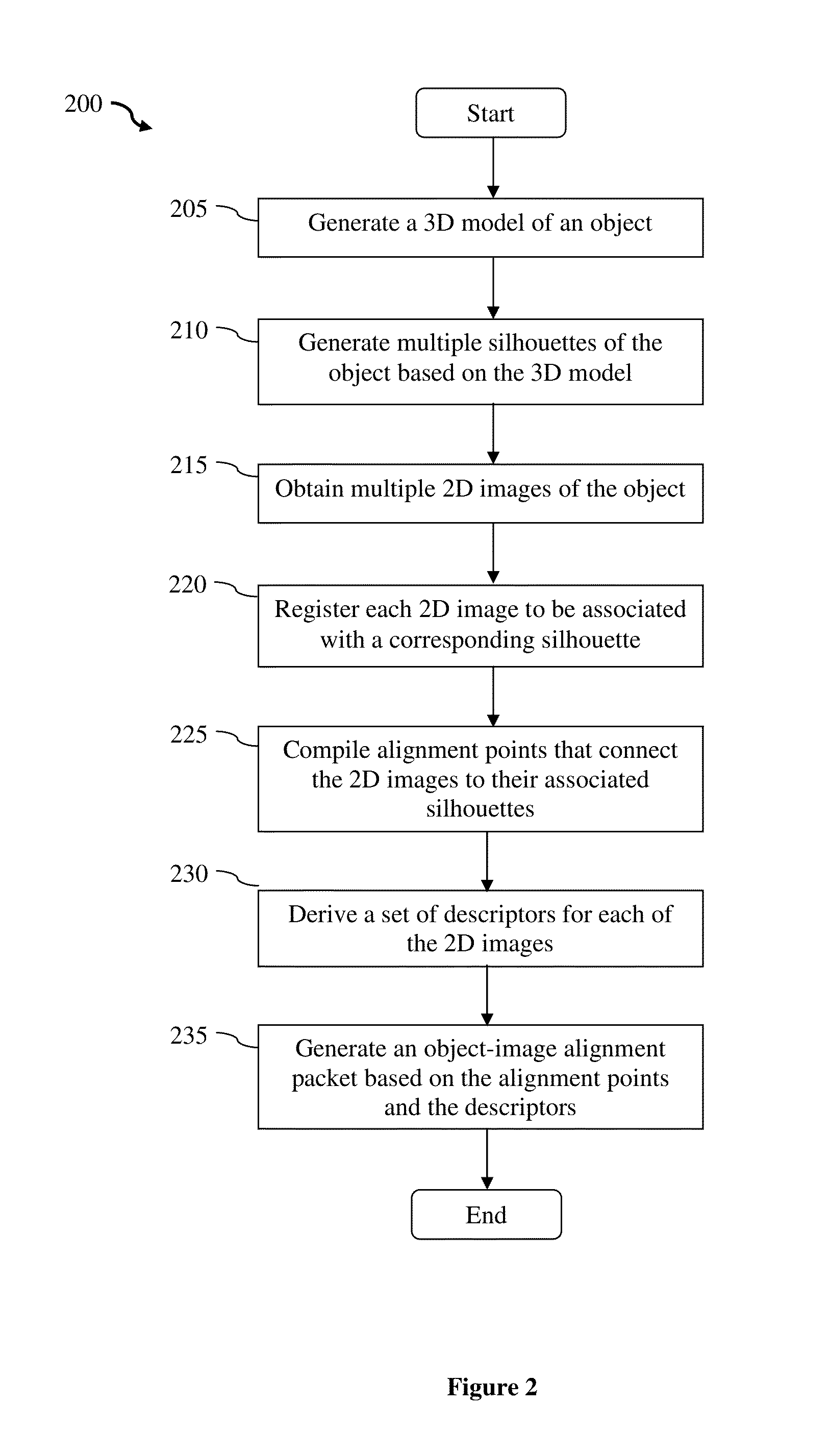
An object-image alignment data generating method for use in an object recognition system is presented. The method obtains a 3D model and a set of 2D images of the object. Each 2D image from the set is captured based on a particular camera point of view. The method then uses the 3D model of the object to generate multiple silhouettes of the object according to different camera point of views. Each silhouette is then matched and aligned with a 2D image based on the corresponding camera point of view. The method also derives at least one descriptor from the 2D images and compiles feature points that correspond to the descriptors. Each feature point includes a 2D location and a 3D location. The method then generates an object-image alignment packet by packaging the 2D images, the descriptors, and the feature points.
Owner:NANT HLDG IP LLC
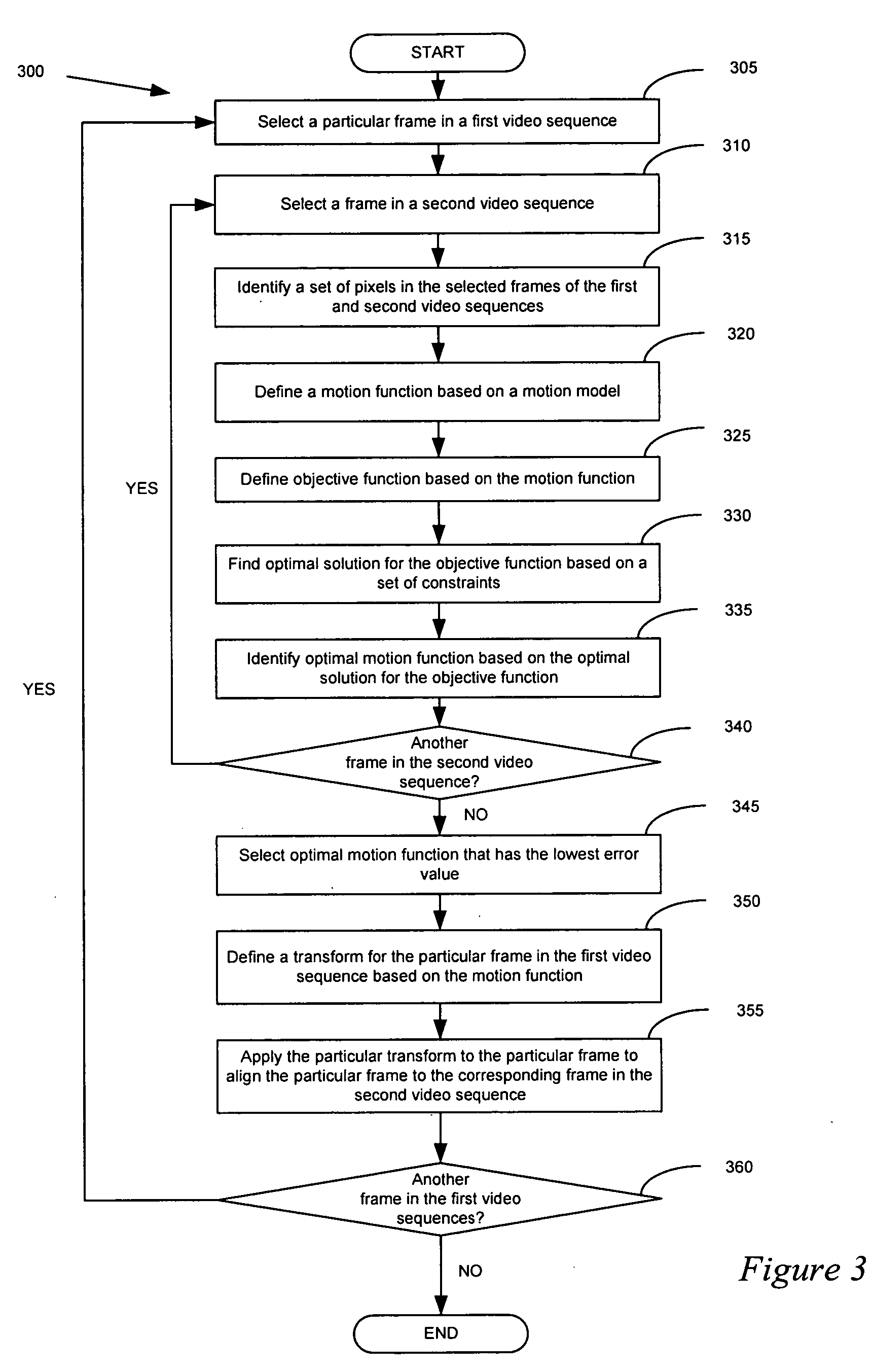
Spatial and temporal alignment of video sequences
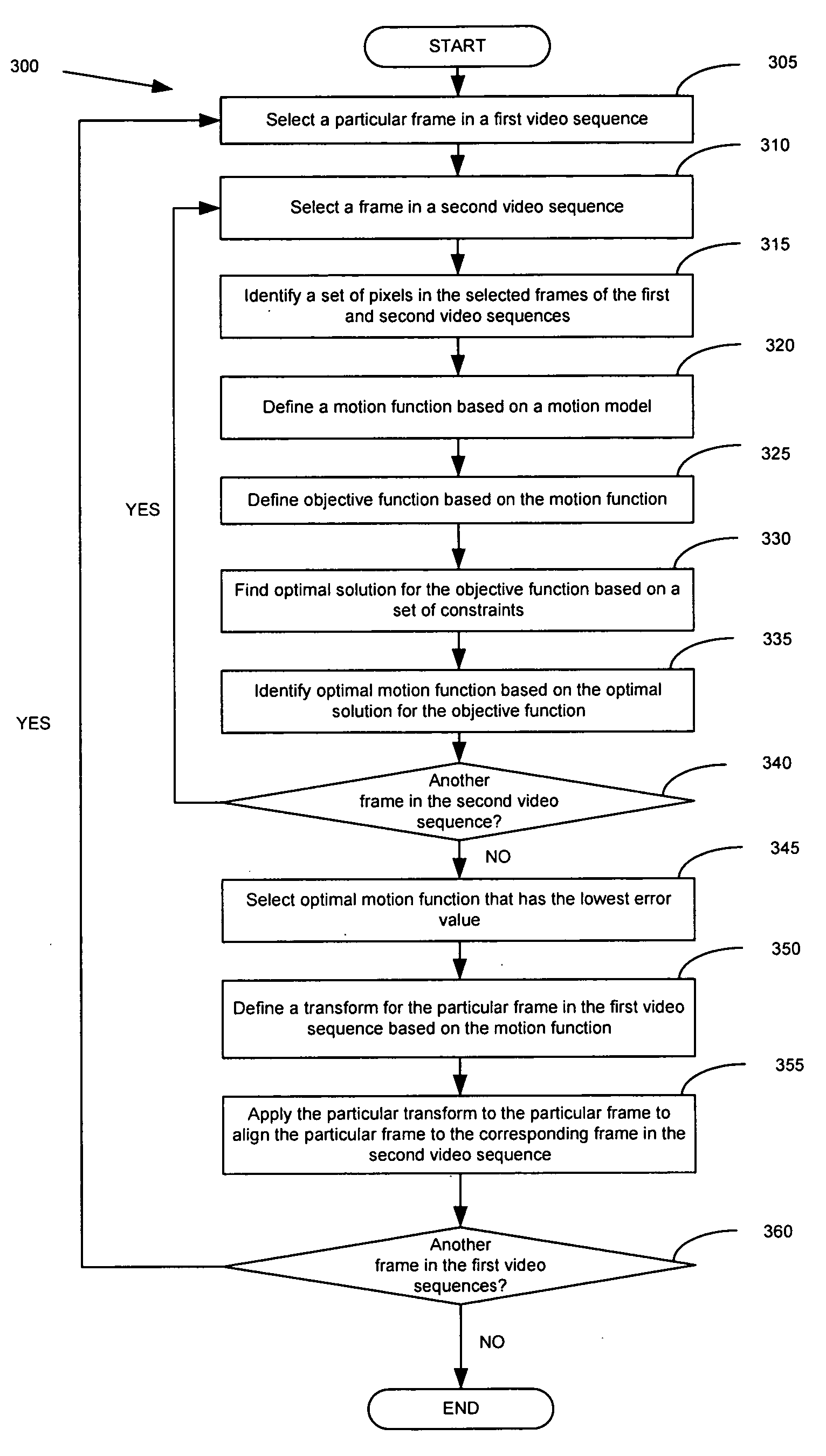
Some embodiments allow a video editor to spatially and temporally align two or more video sequences into a single video sequence. As used in this application, a video sequence is a set of images (e.g., a set of video frames or fields). A video sequence can be from any media, such as broadcast media or recording media (e.g., camera, film, DVD, etc.). Some embodiments are implemented in a video editing application that has a user selectable alignment operation, which when selected aligns two or more video sequences. In some embodiments, the alignment operation identifies a set of pixels in one image (i.e., a “first” image) of a first video sequence and another image (i.e., a “second” image) of a second video sequence. The alignment operation defines a motion function that describes the motion of the set of pixels between the first and second images. The operation then defines an objective function based on the motion function. The operation finds an optimal solution for the objective function. Based on the objective function, the operation identifies a transform, which it then applies to the first image in order to align the first image with the second image.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods of monitoring effects of chemical agents on a sample
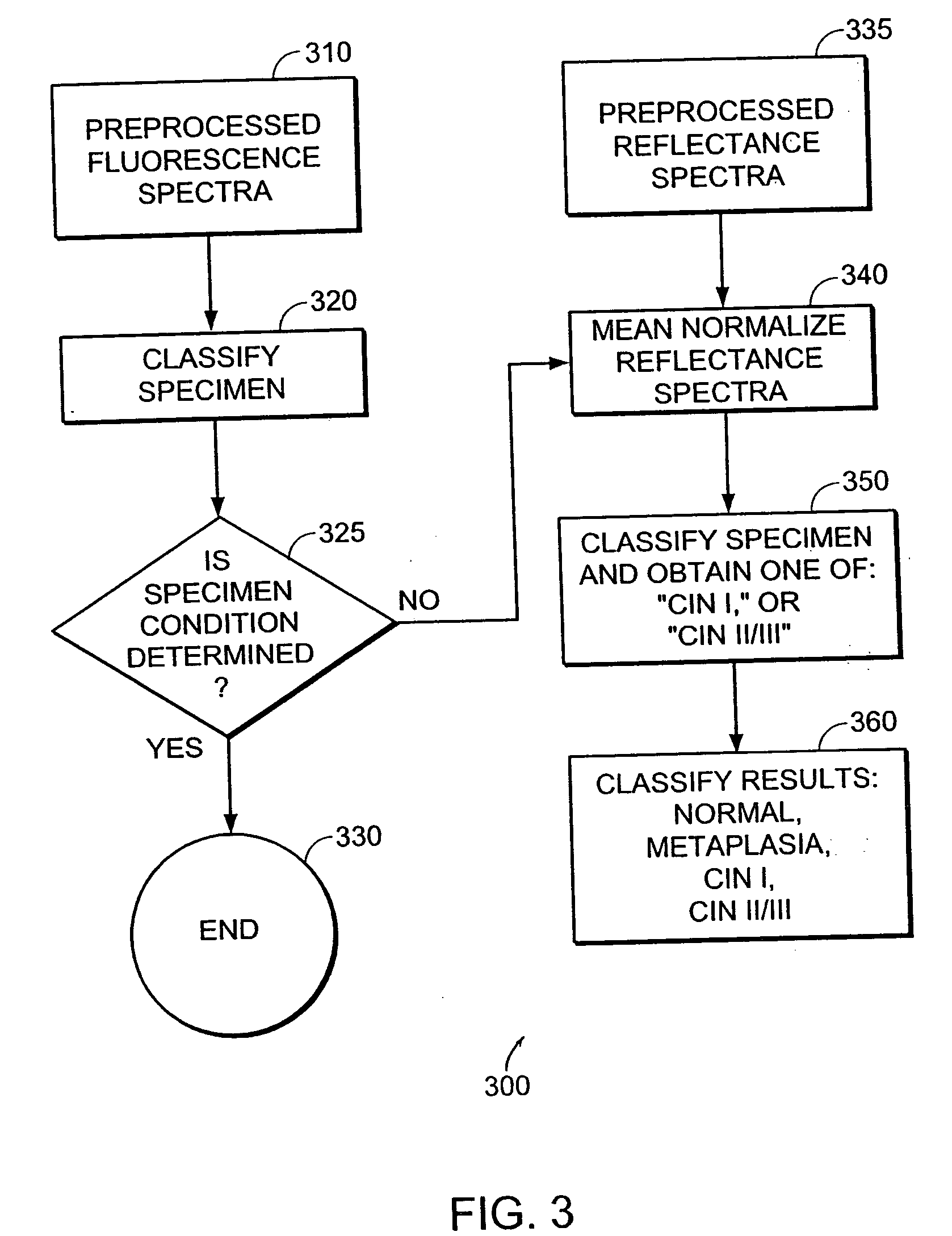
Owner:MEDISPECTRA
Apparatus and method for fingerprint recognition system
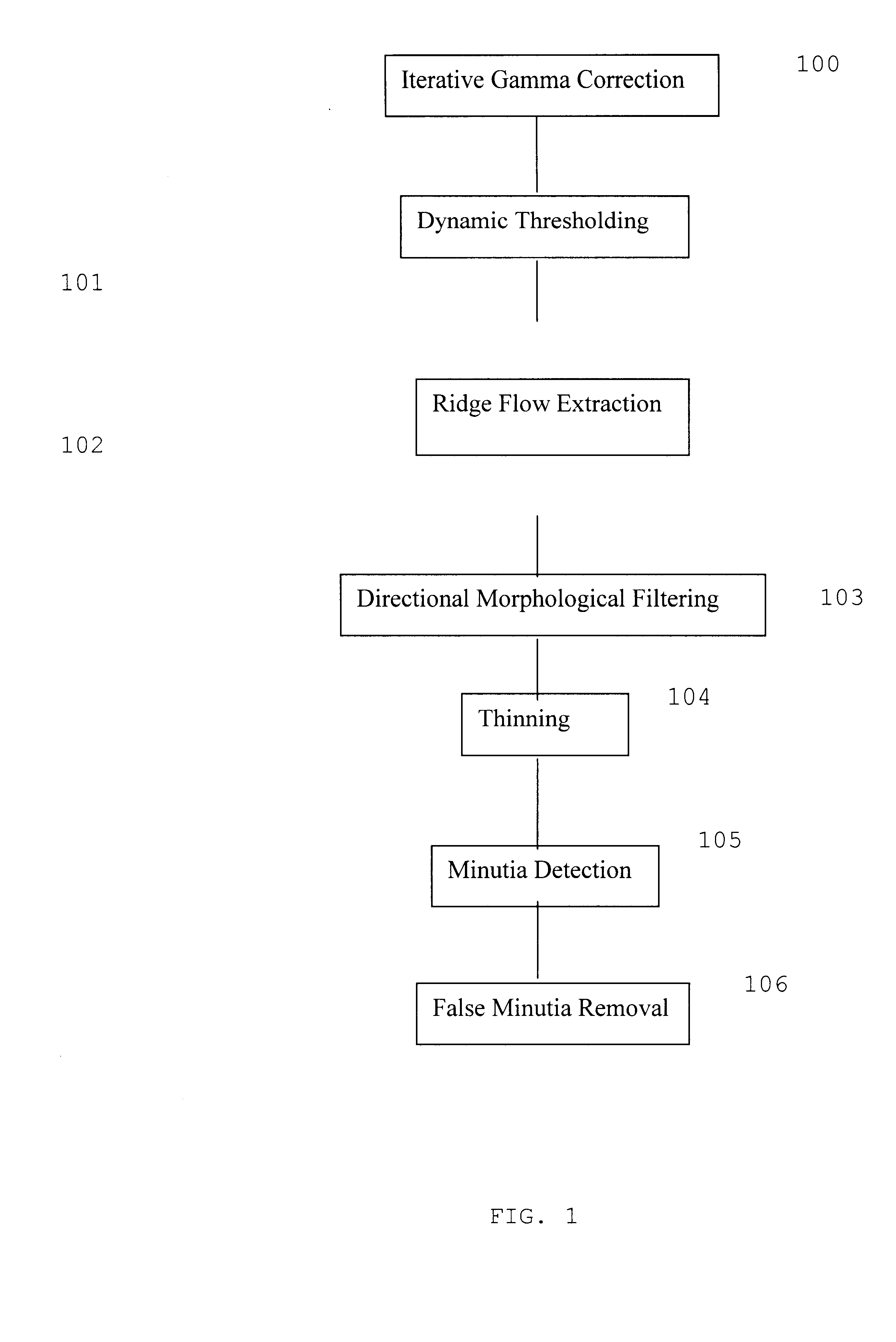
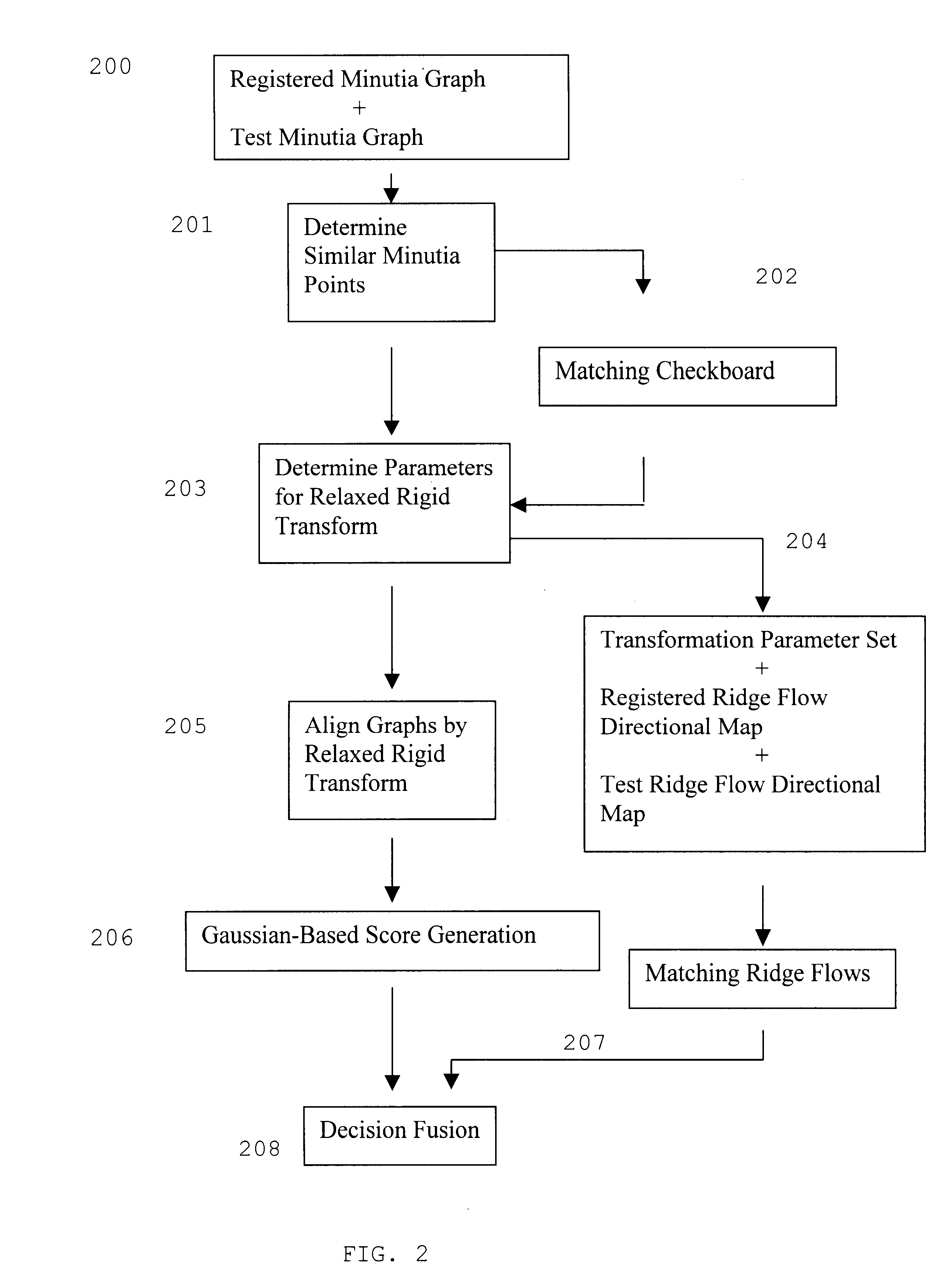
InactiveUS6763127B1Compensation effectMatching and classificationFeature extractionMorphological filtering
A fingerprint recognition method includes iterative gamma correction that compensates moisture effect, feature extraction operations, directional morphological filtering that effectively links broken ridges and breaks smeared ridges, adaptive image alignment by local minutia matching, global matching by relaxed rigid transform, and statistical matching with Gaussian weighting functions.
Owner:KIOBA PROCESSING LLC
Digital camera and method for in creating still panoramas and composite photographs
ActiveUS7656429B2High resolutionPrecise alignmentTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage resolutionGlyph
Digital cameras and methods that help a user accurately align sequential photographs to create large panoramas and composite photographs derived from a sequence of smaller photographs. This effectively creates a higher resolution, or larger, photograph from a zigzag series of photographs using a low resolution camera. An algorithm running on the camera guides a user through the image-taking procedure, allowing him or her to select if a panoramic or composite photograph is to be taken, and optionally the number of images (width and height) needed to create the final image. The algorithm displays indicia, such as marks or a shadow (transparent) image, that are overlaid and moved over the live image during the image-taking process to help align the subsequent image to be taken with the previously recorded image.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Full speed lane sensing with a surrounding view system
ActiveUS20130293717A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsView cameraImage alignment
A system and method for providing lane sensing on a vehicle by detecting roadway lane-markers, where the system employs a surround view camera system providing a top-down view image around the vehicle. The method includes detecting left-side and right-side lane boundary lines in the top-down view image, and then determining whether the lane boundary lines in the image are aligned from one image frame to a next image frame and are aligned from image to image in the top-down view image. If the boundary lines are not aligned, then calibration of one or more of the cameras is performed, and if the lines are aligned, then a model fitting process is used to specifically identify the location of the boundary lines on the roadway.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Image alignment method, comparative inspection method, and comparative inspection device for comparative inspections
InactiveUS7020350B2Solve the small densityLittle in luminance luminanceImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageImage alignment
The present invention provides a high-precision alignment method, device and code for inspections that compare an inspection image with a reference image and detect defects from their differences. In one embodiment an inspection image and a reference image are divided into multiple regions. An offset is calculated for each pair of regions. Out of these multiple offsets, only the offsets with high reliability are used to determine an offset for the entire image. This allows high-precision alignment with little or no dependency on pattern density or shape, differences in luminance between images, and uneven luminance within individual images. Also, detection sensitivity is adjusted as necessary by monitoring alignment precision.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
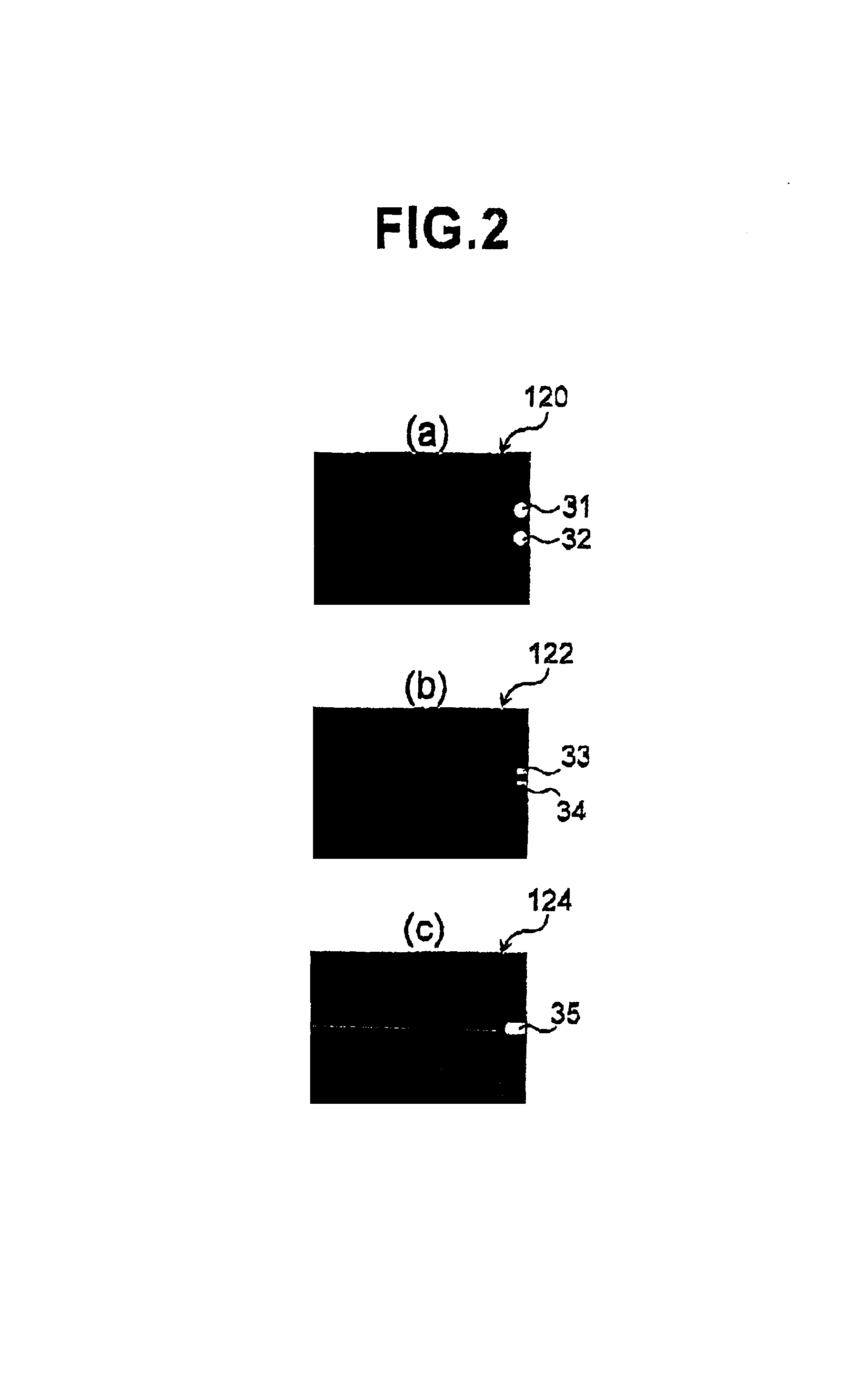
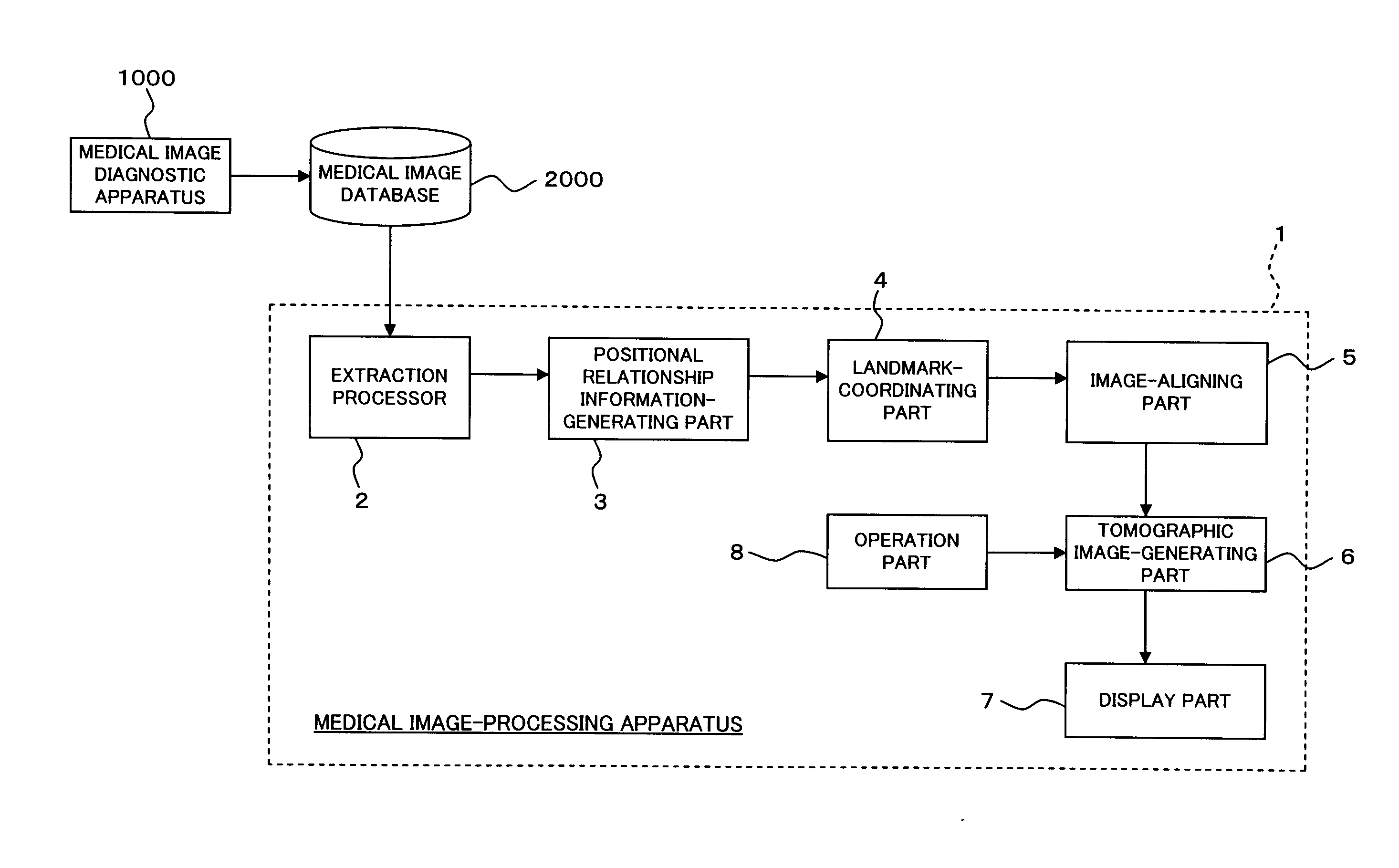
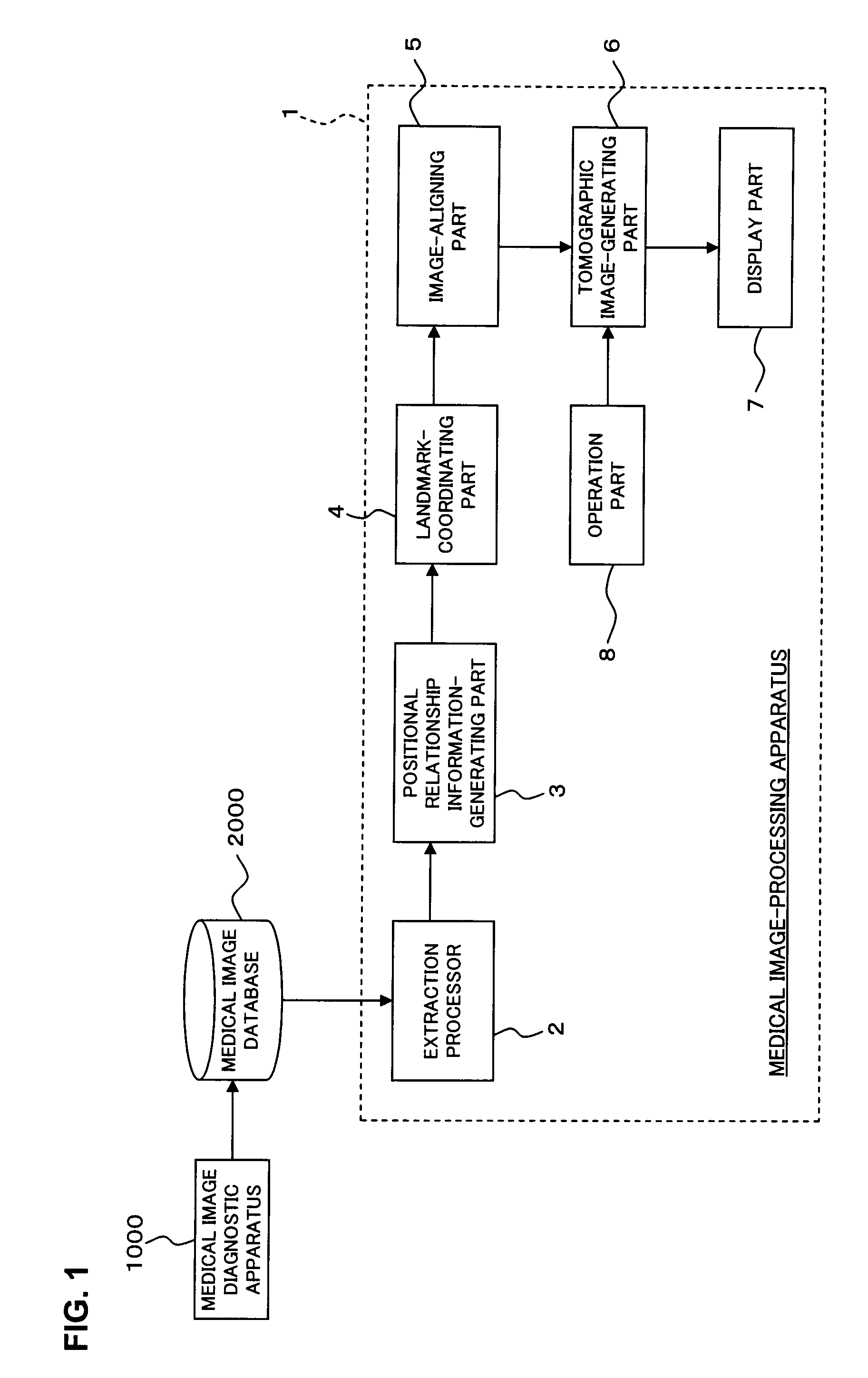
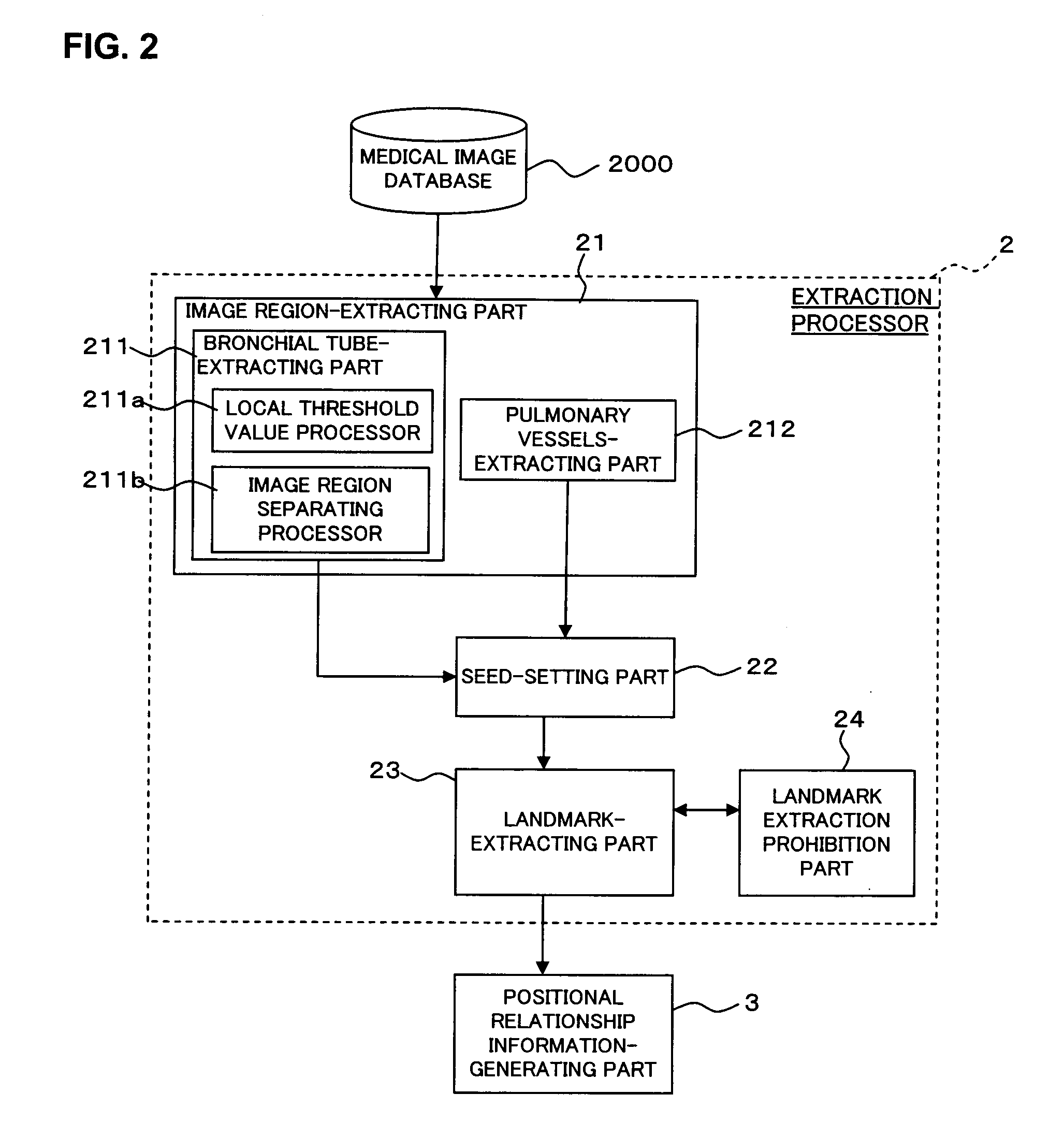
Medical image-processing apparatus and a method for processing medical images
InactiveUS20080019580A1Long processing timeShorten the timeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImage alignmentImage based
The extraction processor of the medical image-processing apparatus sets landmarks of each medical image based on volume data of two medical images. The positional relationship information-generating part generates positional relationship information that indicates positional relationship of the landmarks for each of the two medial images. The landmark-coordinating part eliminates one or more landmarks from each medical image based on the positional relationship information. Further, the landmark-coordinating part coordinates the landmarks of two medical images that remained after the elimination. The image-aligning part aligns the two sets of volume data based on the result of the coordination of landmarks.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Image alignment method based on novel end-to-end face super-resolution network
InactiveCN107958246AGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionPrior information
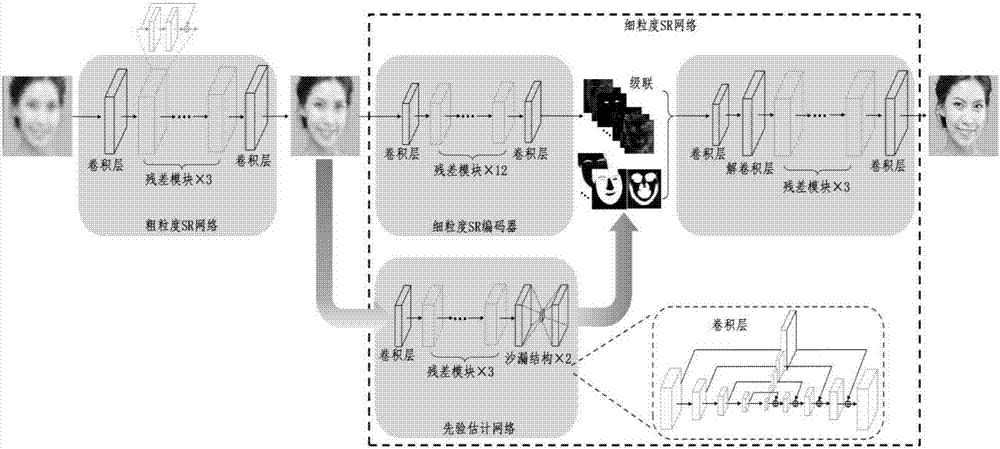
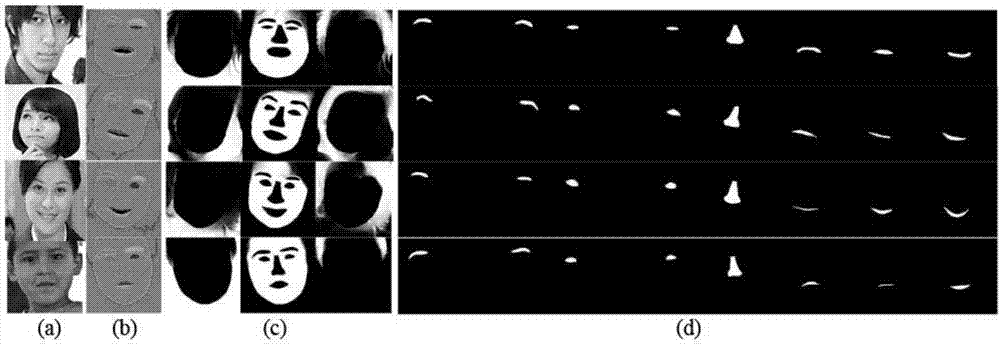
The invention provides an image alignment method based on a novel end-to-end face super-resolution network. In the image alignment method, a face super-resolution network and a face super-resolution generative adversarial network are mainly involved; the image alignment method comprises the following process: constructing a coarse-grained super-resolution (SR) network for recovering a coarse-grained high-resolution (HR) image; sending the coarse-grained HR image to a fine-grained SR encoder and a prior information estimating network respectively, wherein the fine-grained SR encoder is used forextracting image features and the prior information estimating network is used for estimating a critical point heat map; restoring the HR image by using the image features and prior information in adecoder, wherein in order to further generate a realistic face, the face super-resolution generative adversarial network is provided and adversarial loss is brought into the face super-resolution network. A network consisting of the face super-resolution network and the face super-resolution generative adversarial network is used for image alignment, so that the imaging quality can be effectivelyimproved and the image alignment method is simplified.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Method for fast constructing high-accuracy personalized face model on basis of facial images
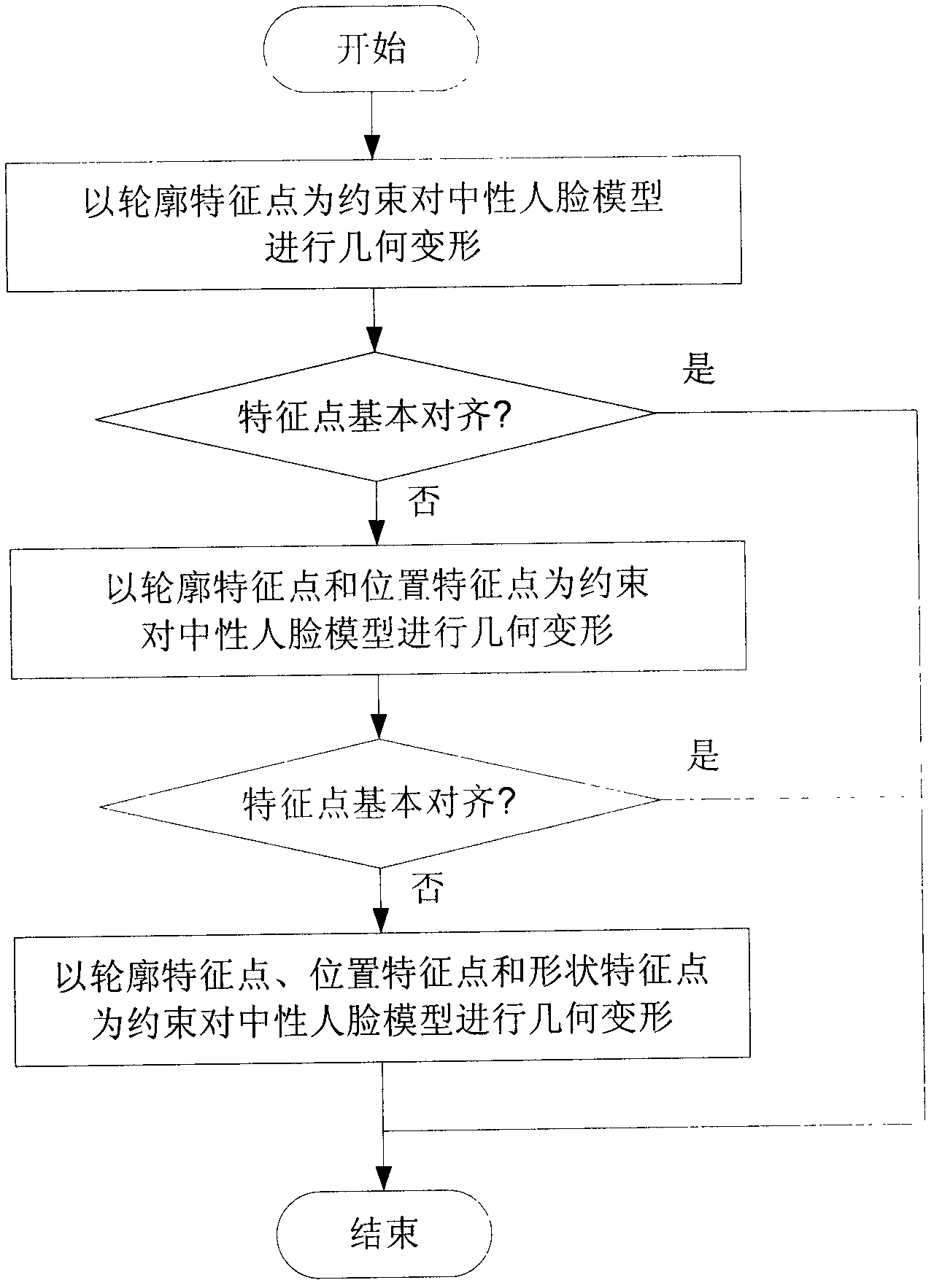
InactiveCN102222363AFast preparationReduce modeling costs3D modellingPattern recognitionPersonalization
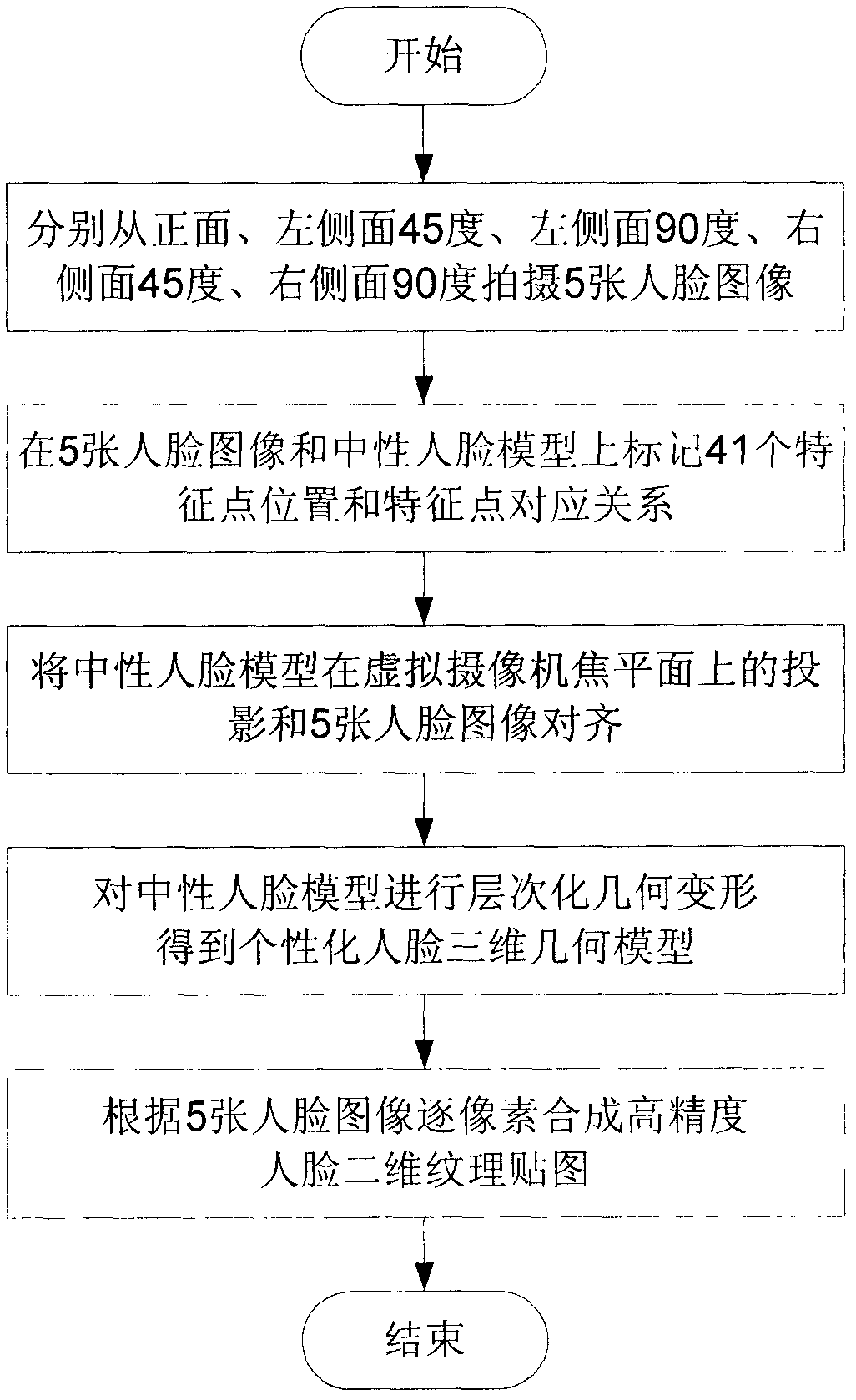
The invention discloses a method for fast constructing a high-accuracy personalized face model on the basis of facial images, which belongs to the cross field of computer vision and computer graphics, and aims at achieving the purposes of fast reconstructing a personalized 3D geometrical facial model and a high-accuracy 2D facial texture mapping on the basis of real facial images. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, shooting five facial images from multiple angles; secondly, marking positions and corresponding relationships of forty-one characteristic points on the facial images and a neutral facial model; thirdly, aligning the projection of the neutral facial model on a virtual camera focal plane with the facial images; fourthly, carrying out hierarchical geometrical deformation on the neutral facial model to obtain the personalized geometrical facial model; and finally, synthesizing the high-accuracy facial texture mapping according to the five facial images. The face modeling method has the advantages of convenience for data acquisition, high modeling speed and modeling accuracy, and the like, and achieves higher practical values in the fields of video communication, electronic games, man-machine interaction, and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU REALTIME DIGITAL MEDIA
Progressive self-learning defect review and classification method
ActiveUS7162071B2Improve loading timeExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingClassification methods
A progressive self-learning (PSL) method is provided for enhancing wafer or mask defect inspection review and classification by identifying a plurality of wafer or mask defects, and by classifying each of the plurality of defects according to an extent of resemblance of each defect. The method having the steps of: performing image processing on a scanned defect image; aligning the scanned defect image with a just-stored digitized defect image; matching the scanned defect image with a just-stored digitized defect image; and classifying the scanned defect image.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com