Patents
Literature
210 results about "Small field of view" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
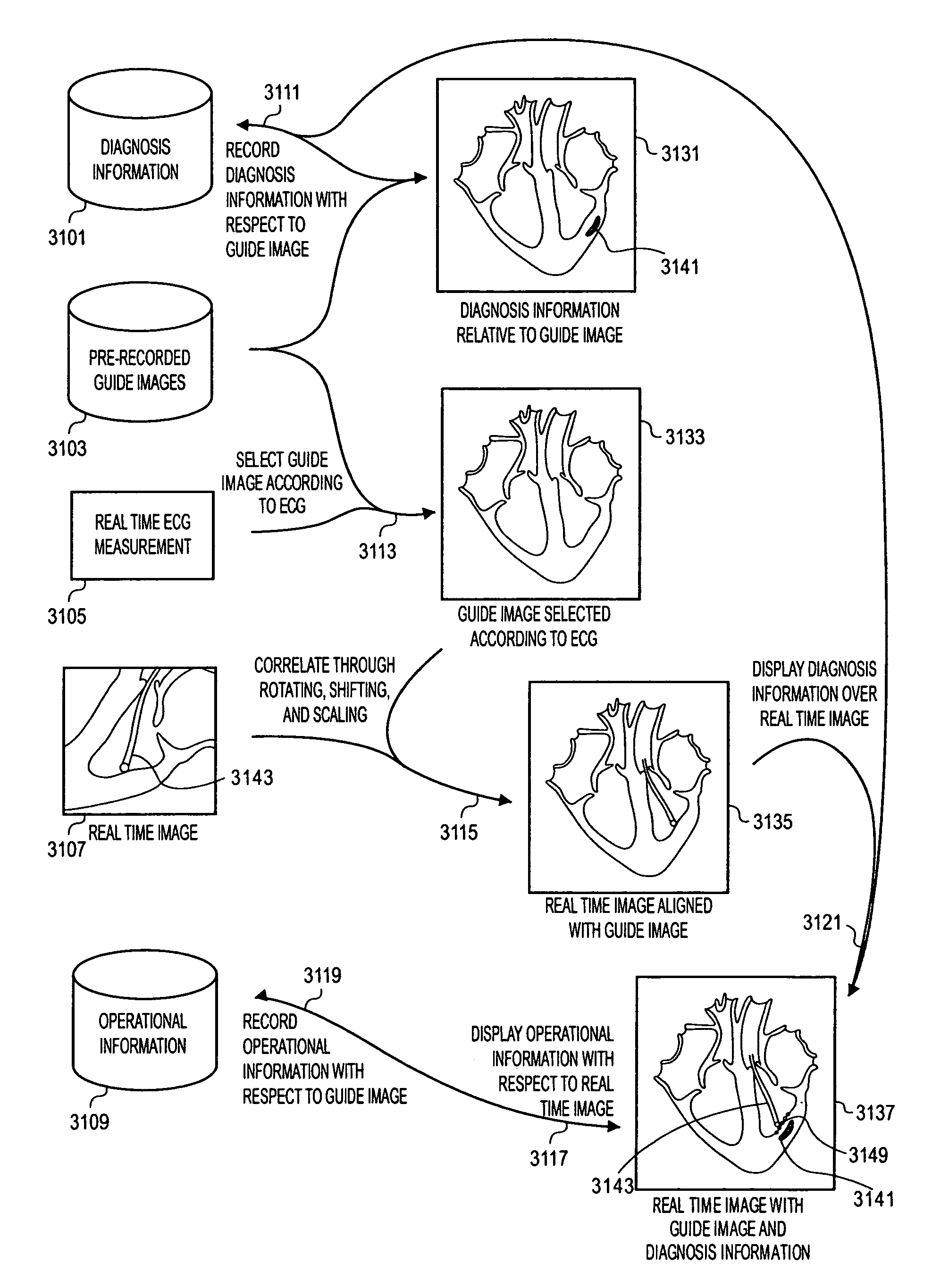
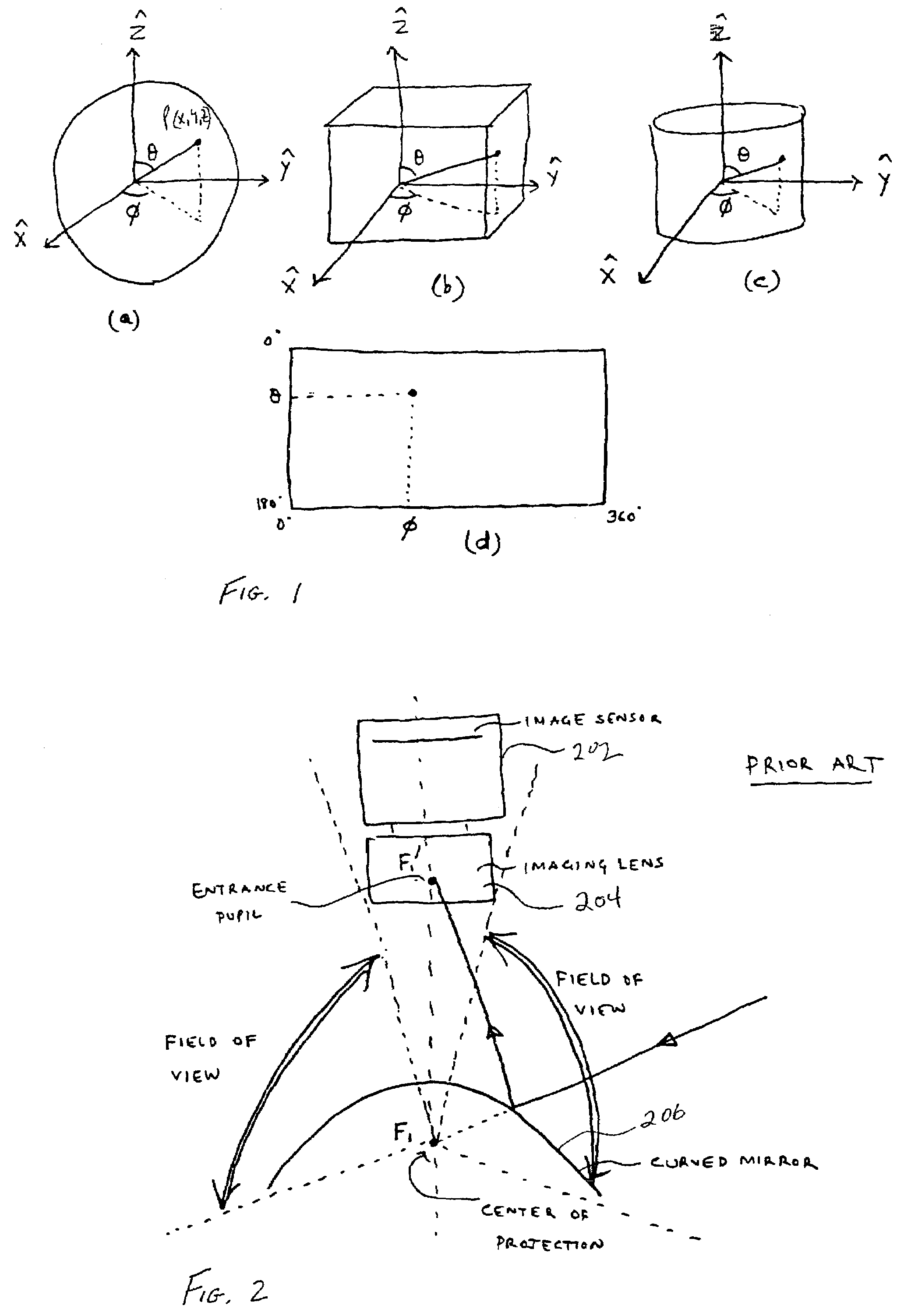
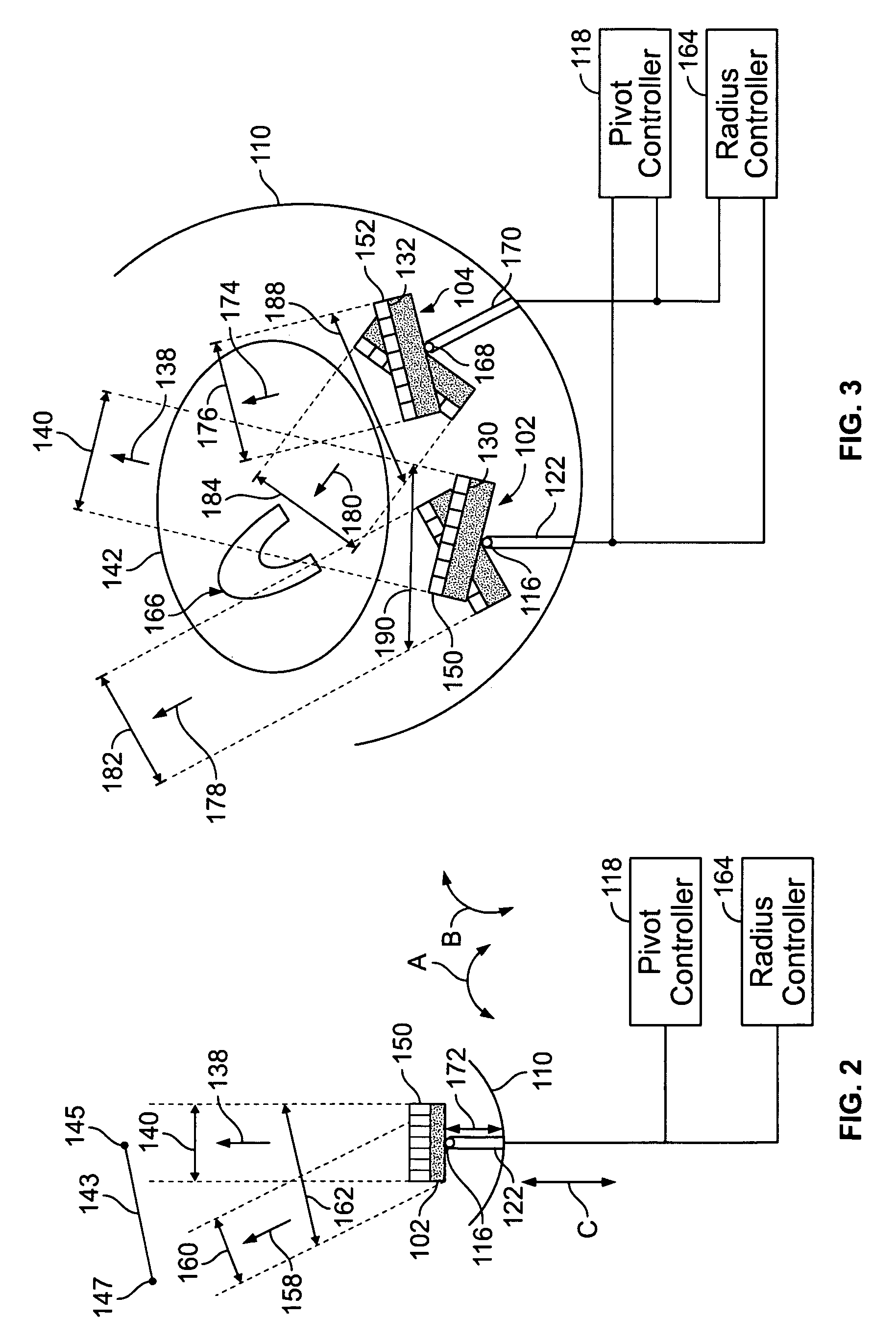
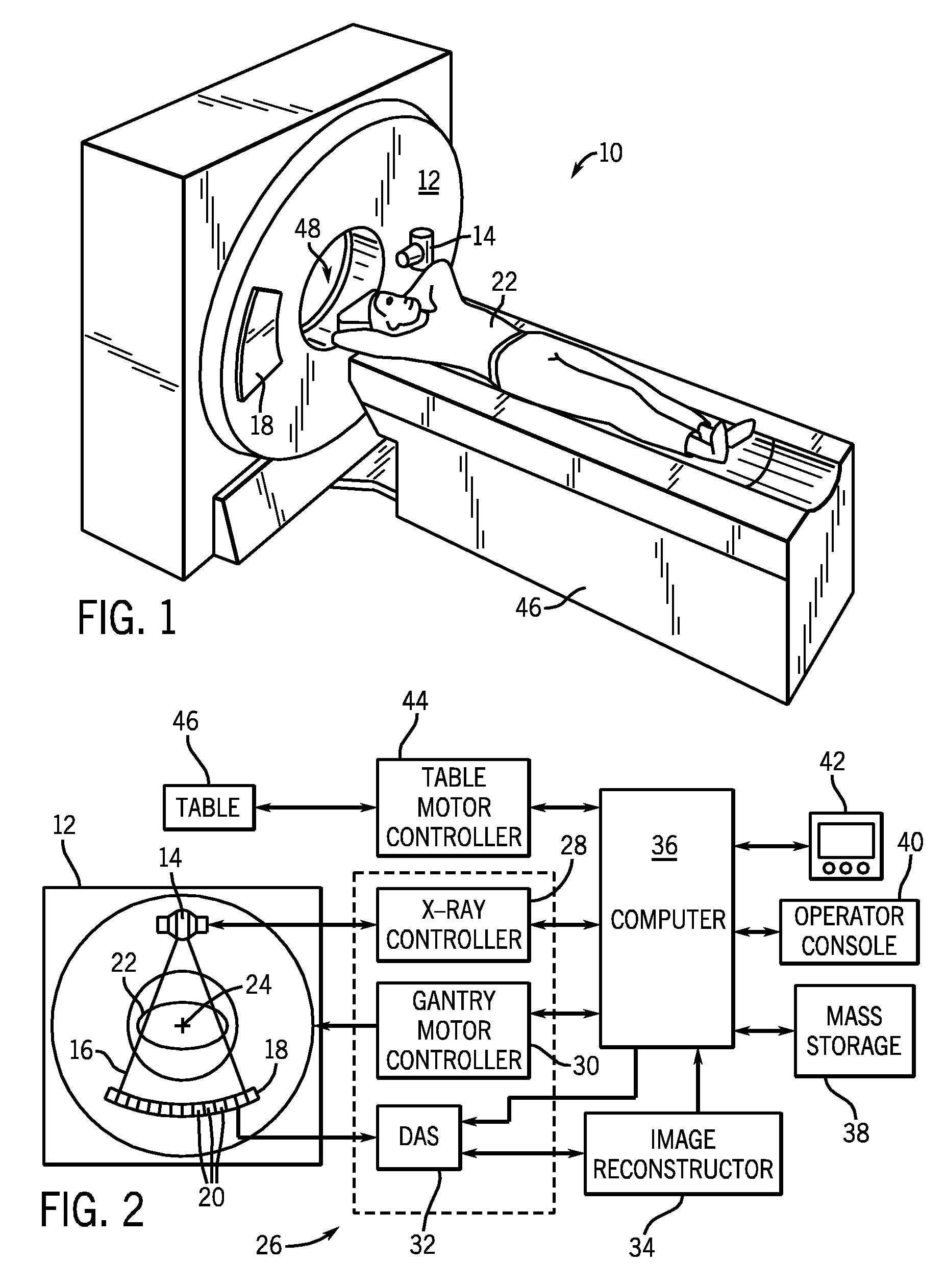
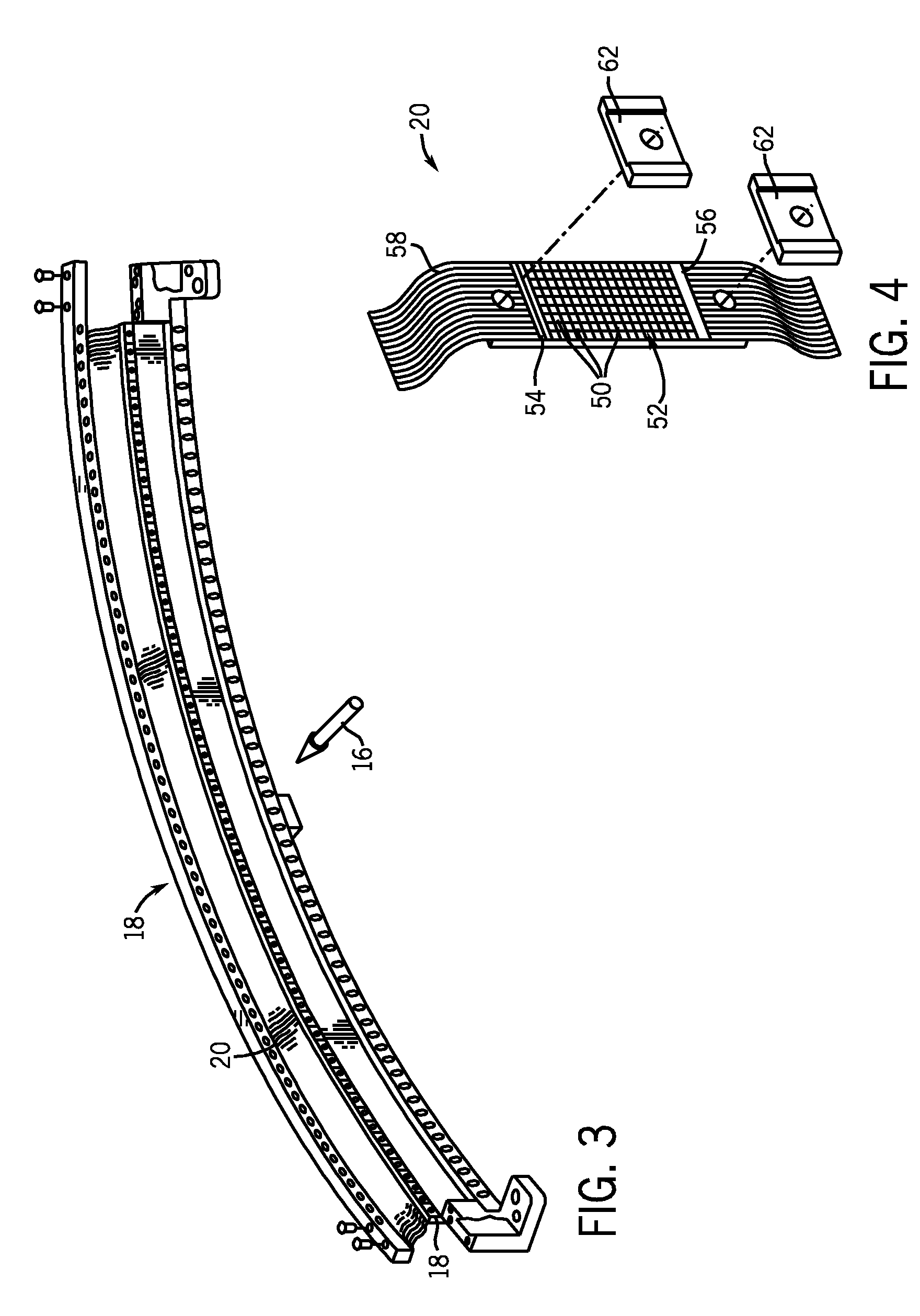
Methods and apparatuses for image guided medical procedures
ActiveUS8303505B2Uncertainty errorLocation uncertaintyMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTime informationImaging data
Methods and apparatuses for the image guidance and documentation of medical procedures. One embodiment includes combining small field of view images into a recorded image of with a large field of view and aligning the small field of view real time image with the recorded image through correlation of imaging data. A location and orientation determination system may be used to track the imaging system and provide a starting set of image alignment parameters and / or provide change updates to a set of image alignment parameters, which is then further improved through correlating imaging data. The recorded image may be selected according to real time measurement of a cardiac parameter during an image guided cardiac procedure. Image manipulations planned based on the recorded image can be stored and applied to the real time information. The position of the medical device may be determined and recorded through manipulating a cursor in a 3-D image space shown in two non-parallel views.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
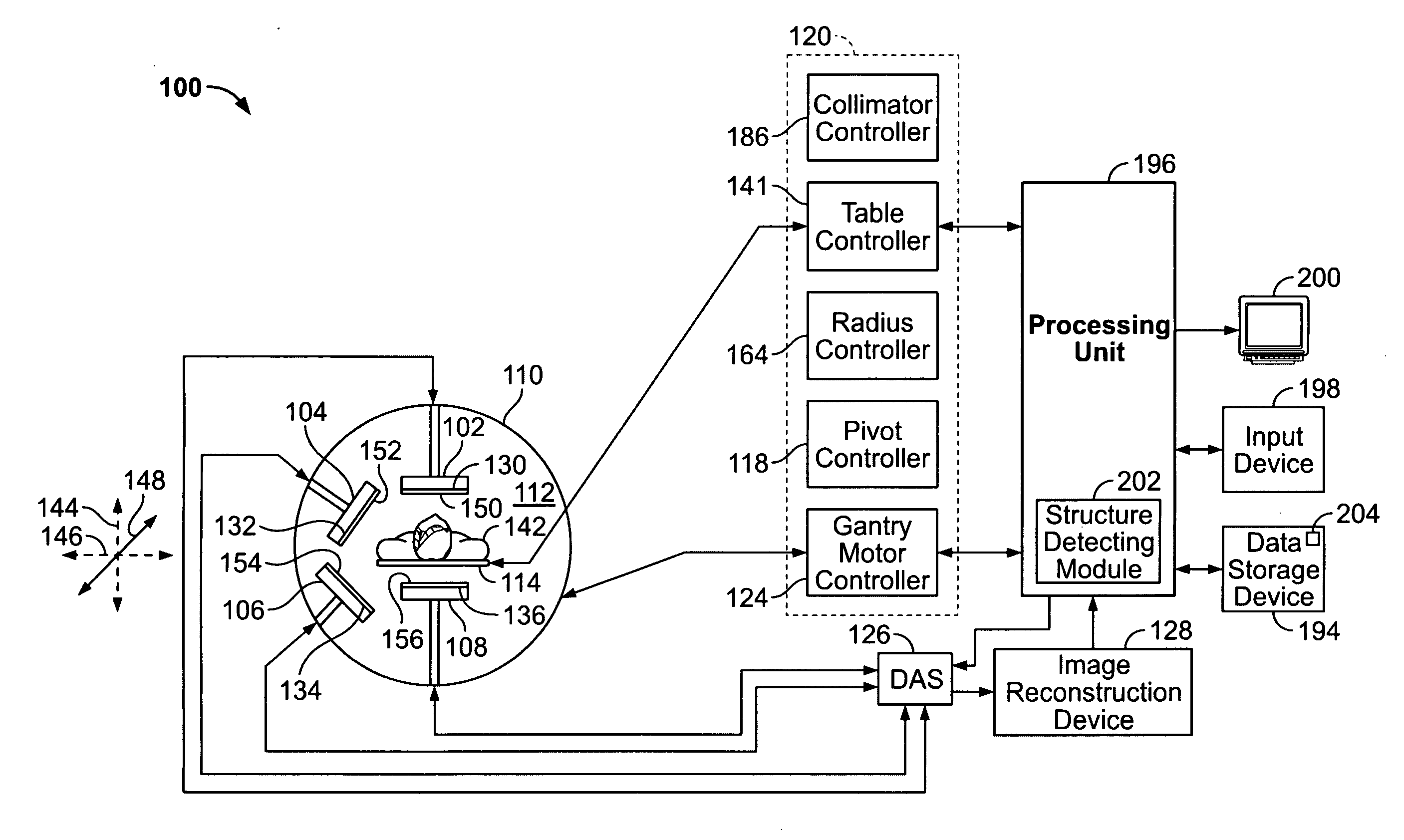
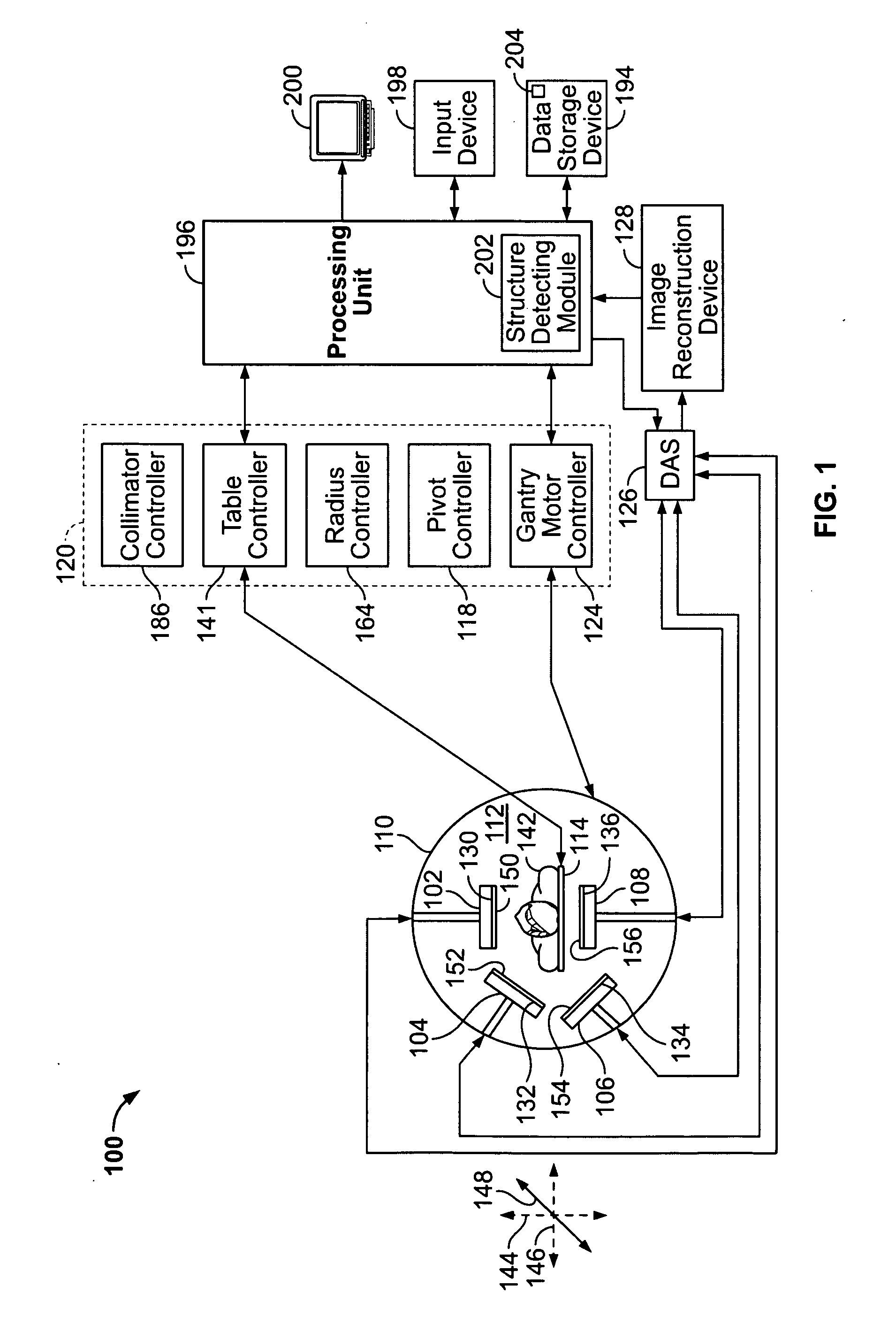
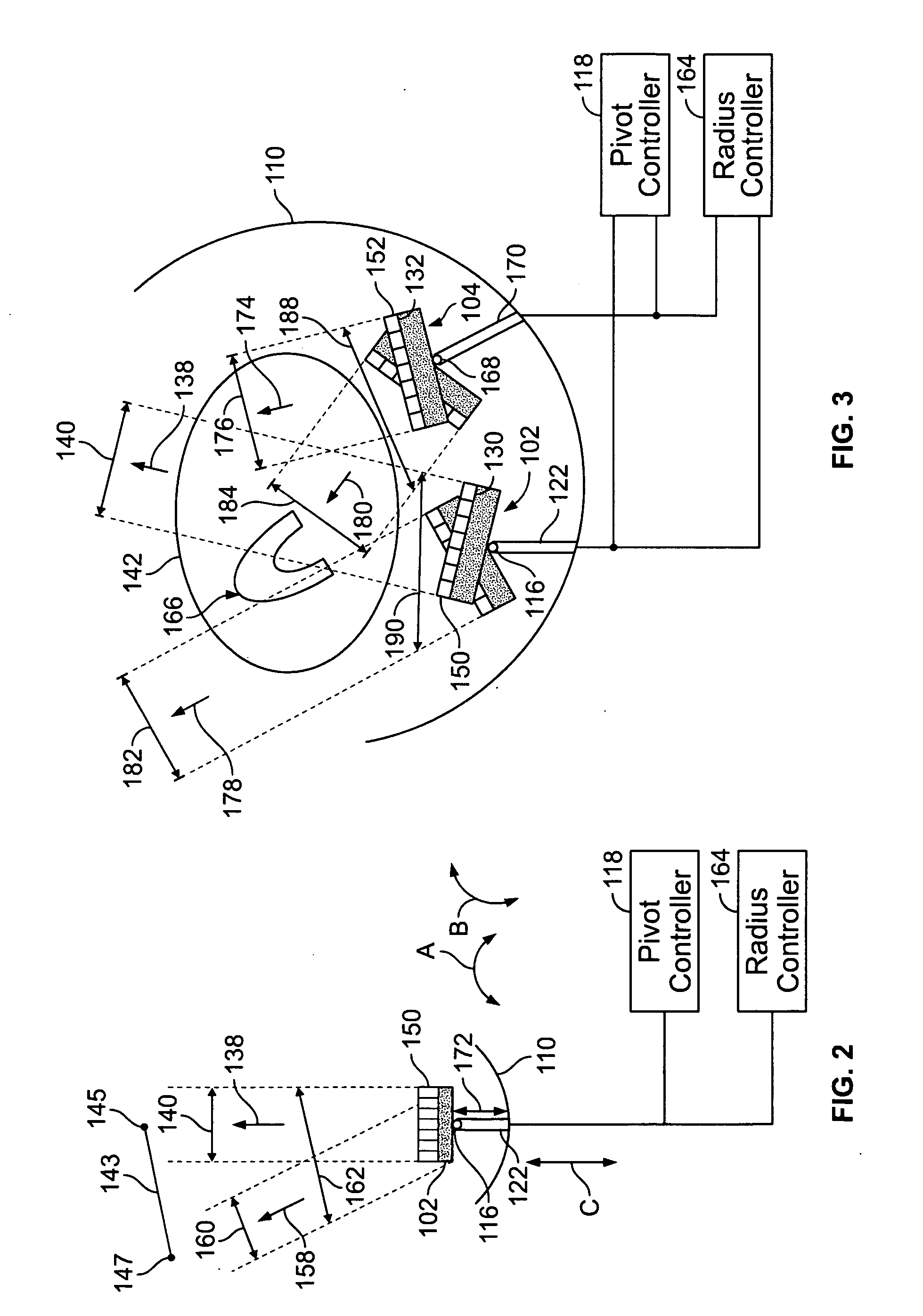
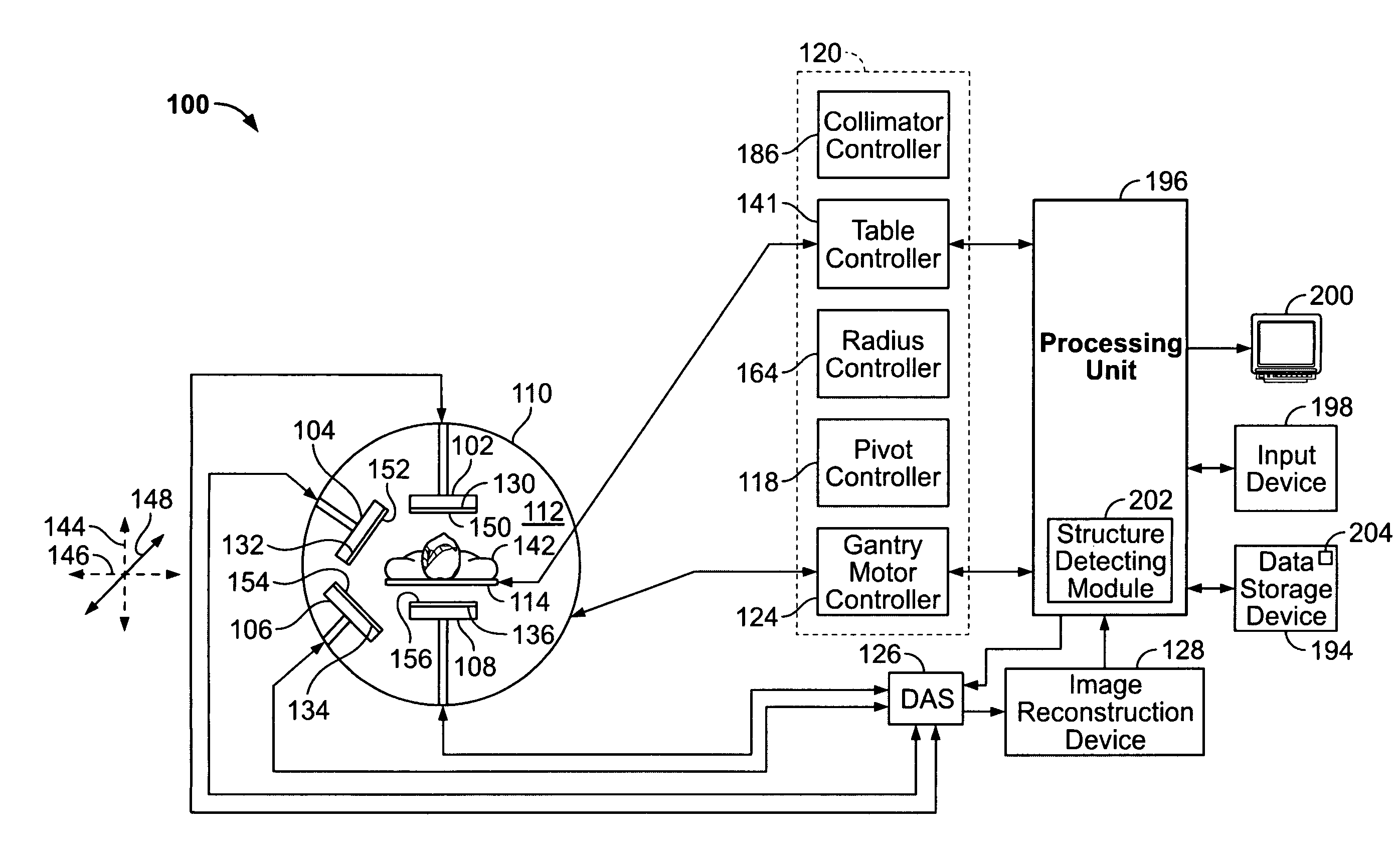
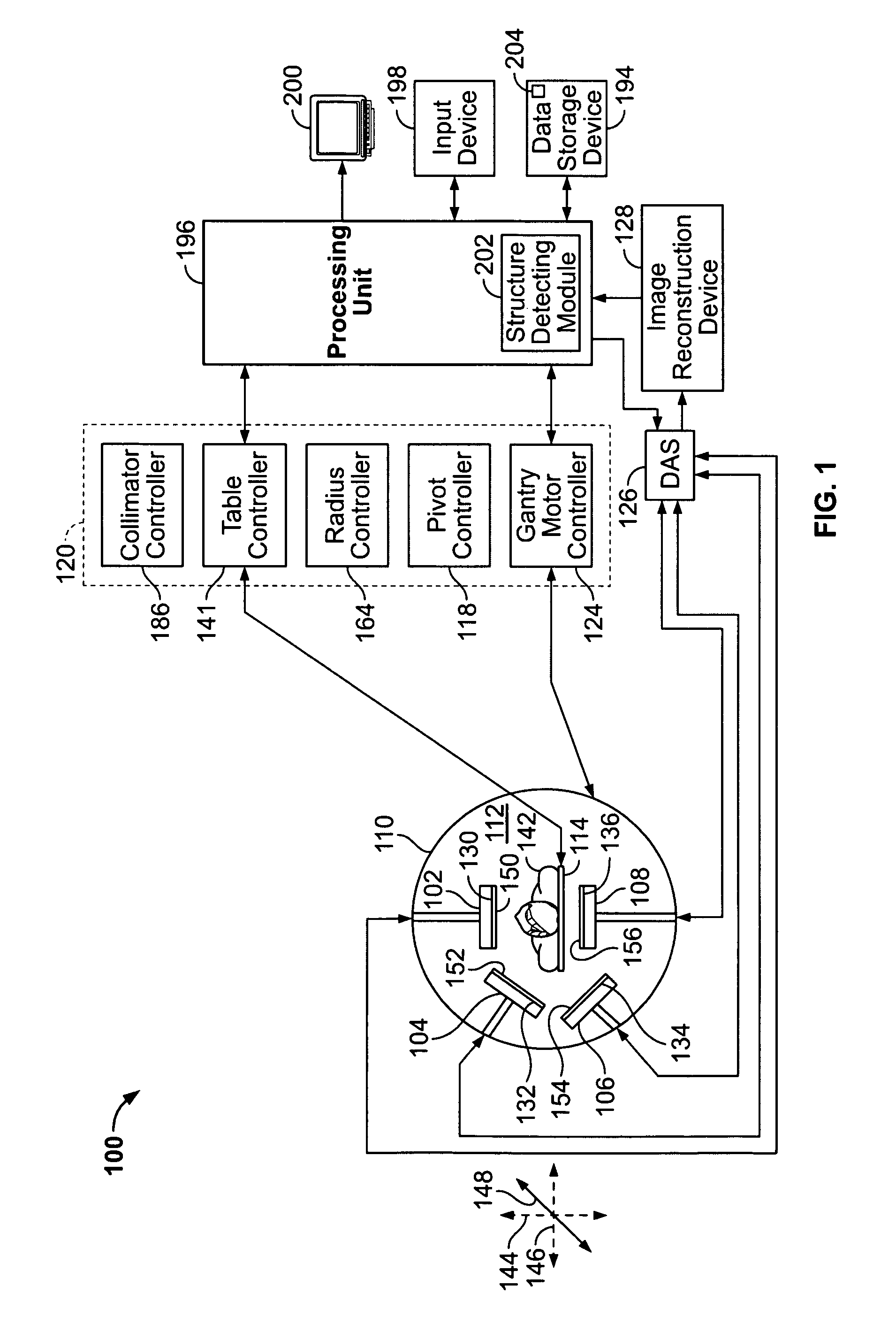
Method and apparatus for imaging with imaging detectors having small fields of view
ActiveUS20080029704A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansData acquisitionComputer science
An apparatus for imaging a structure of interest comprises a plurality of imaging detectors mounted on a gantry. Each of the plurality of imaging detectors has a field of view (FOV), is independently movable with respect to each other, and is positioned to image a structure of interest within a patient. A data acquisition system receives image data detected within the FOV of each of the plurality of imaging detectors.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE ISRAEL
Cardiovascular imaging and functional analysis system
A cardiovascular imaging and functional analysis system and method is disclosed, wherein a dedicated fast, sensitive, compact and economical imaging gamma camera system that is especially suited for heart imaging and functional analysis is employed. The cardiovascular imaging and functional analysis system of the present invention can be used as a dedicated nuclear cardiology small field of view imaging camera. The disclosed cardiovascular imaging system and method has the advantages of being able to image physiology, while offering an inexpensive and portable hardware, unlike MRI, CT, and echocardiography systems.The cardiovascular imaging system of the invention employs a basic modular design suitable for cardiac imaging with one of several radionucleide tracers. The detector can be positioned in close proximity to the chest and heart from several different projections, making it possible rapidly to accumulate data for first-pass analysis, positron imaging, quantitative stress perfusion, and multi-gated equilibrium pooled blood (MUGA) tests..In a preferred embodiment, the Cardiovascular Non-Invasive Screening Probe system can perform a novel diagnostic screening test for potential victims of coronary artery disease. The system provides a rapid, inexpensive preliminary indication of coronary occlusive disease by measuring the activity of emitted particles from an injected bolus of radioactive tracer. Ratios of this activity with the time progression of the injected bolus of radioactive tracer are used to perform diagnosis of the coronary patency (artery disease).
Owner:NORTH COAST IND INC
Cardiovascular imaging and functional analysis system
InactiveUS20020188197A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive tracerNon invasive
A Cardiovascular imaging and functional analysis system and method employing a dedicated fast, sensitive, compact and economical imaging gamma camera system that is especially suited for heart imaging and functional analysis. The system uses a dedicated nuclear cardiology small field of view imaging camera, allowing image physiology, while offering inexpensive and portable hardware. In some variations, a basic modular design suitable for cardiac imaging with one of several radionucleide tracers is used. The detector is positioned in close proximity to the chest and heart from several different projections, allowing rapid accumulation of data for first-pass analysis, positron imaging, quantitative stress perfusion, and multi-gated equilibrium pooled blood tests. In one variation, a Cardiovascular Non-Invasive Screening Probe system provides rapid, inexpensive preliminary indication of coronary occlusive disease by measuring the activity of emitted particles from an injected bolus of radioactive tracer.
Owner:NORTH COAST IND INC
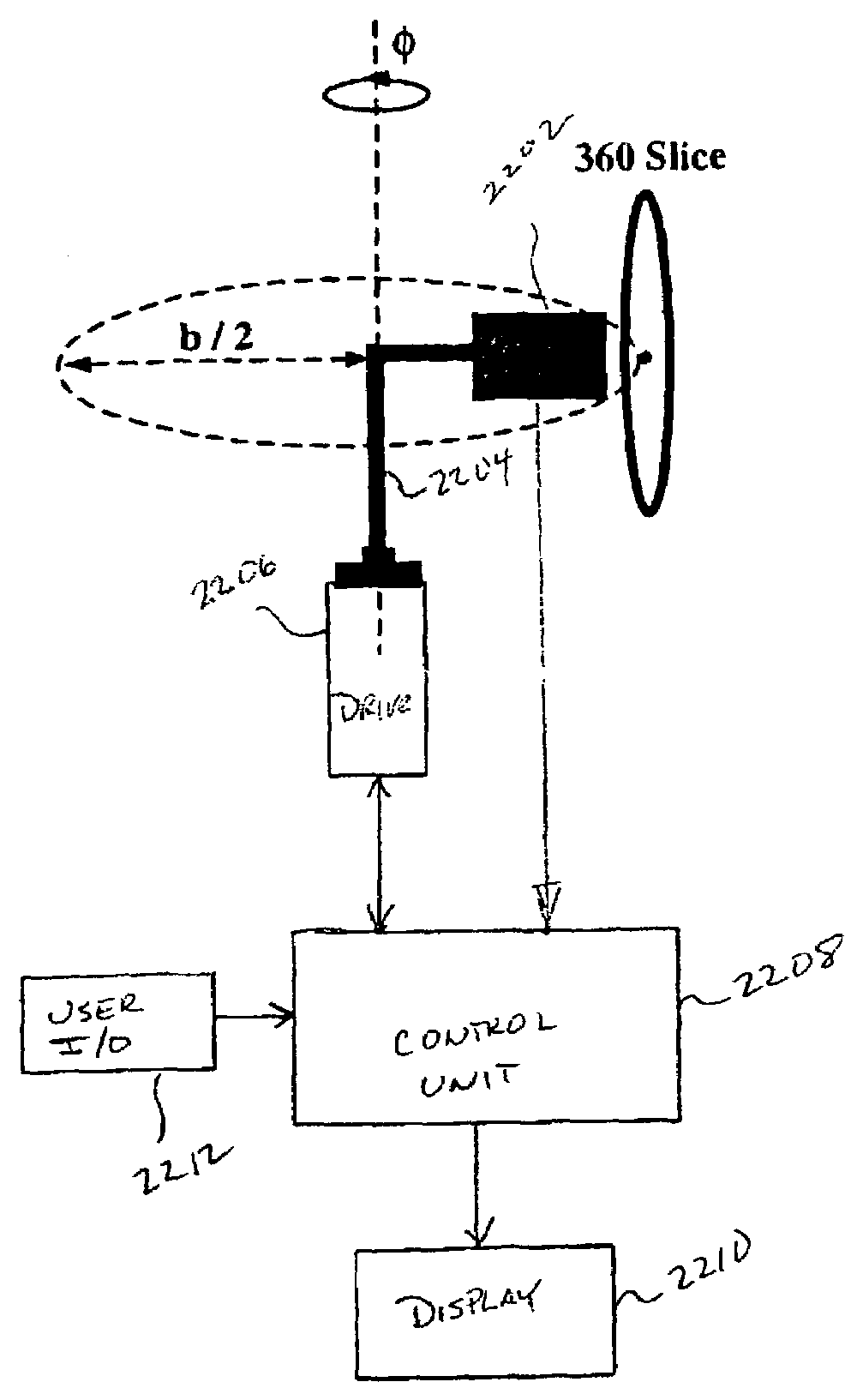
System and methods for generating spherical mosaic images
InactiveUS7176960B1Efficient scanningSmall sizeTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationSpherical formImage system
Systems and methods for generating an omnidirectional mosaic image are presented in which a number of images are acquired about an axis of rotational. The images have a large field of view along the axis of rotation and a small field of view or image width in a second direction. The images can be image strips, formed from non-parallel rays directed onto an image sensor (1008), which are formed from a narrow width of parallel rays directed onto imaging sensor (1008). The images are combined to form a spherical mosaic. In the case of overlapping image strips, image combination can be performed by identifying common features in the overlapping regions and aligning consecutive image strips accordingly. A blending algorithm can then be used to improve image fidelity in the overlapping regions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
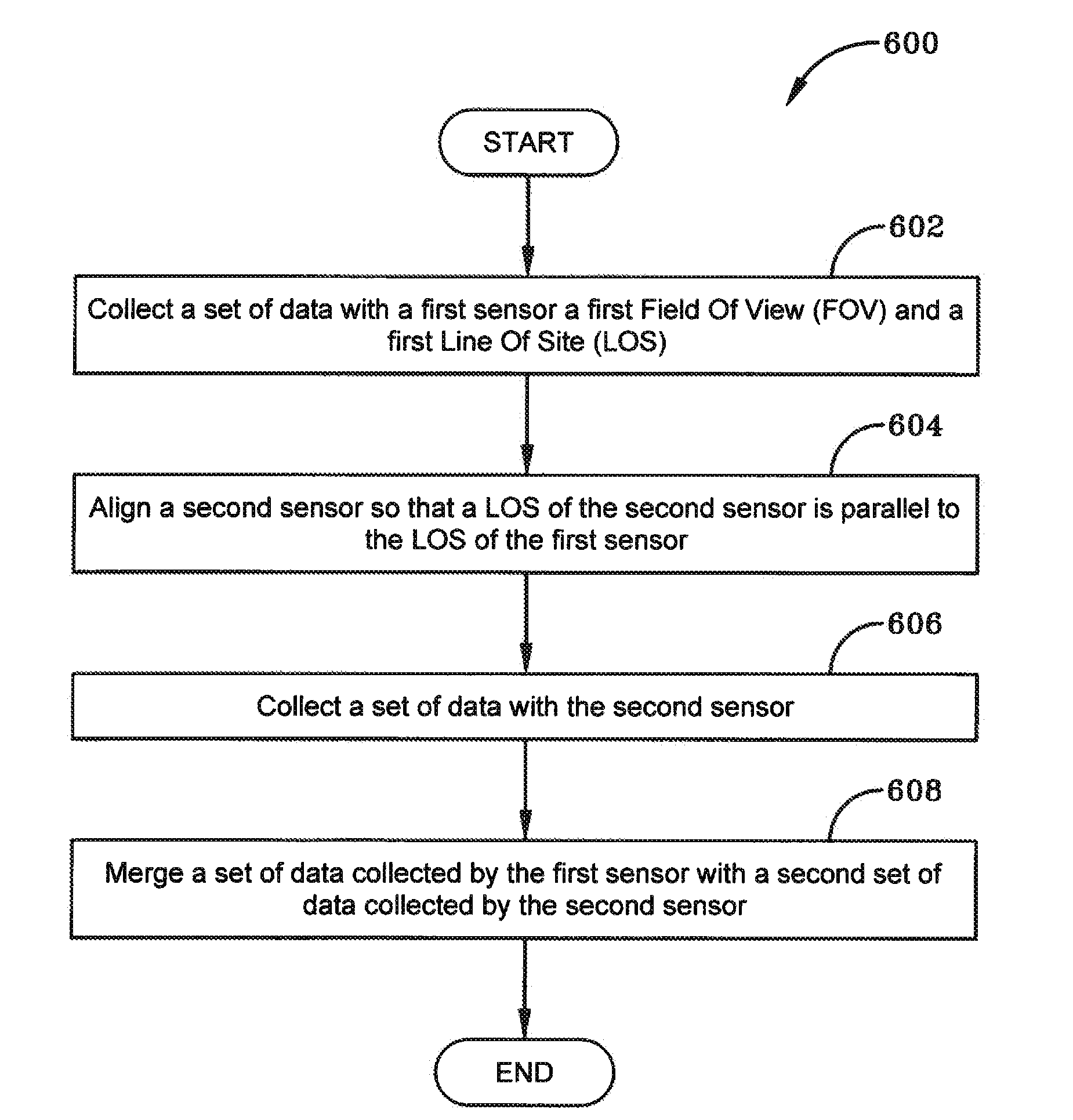
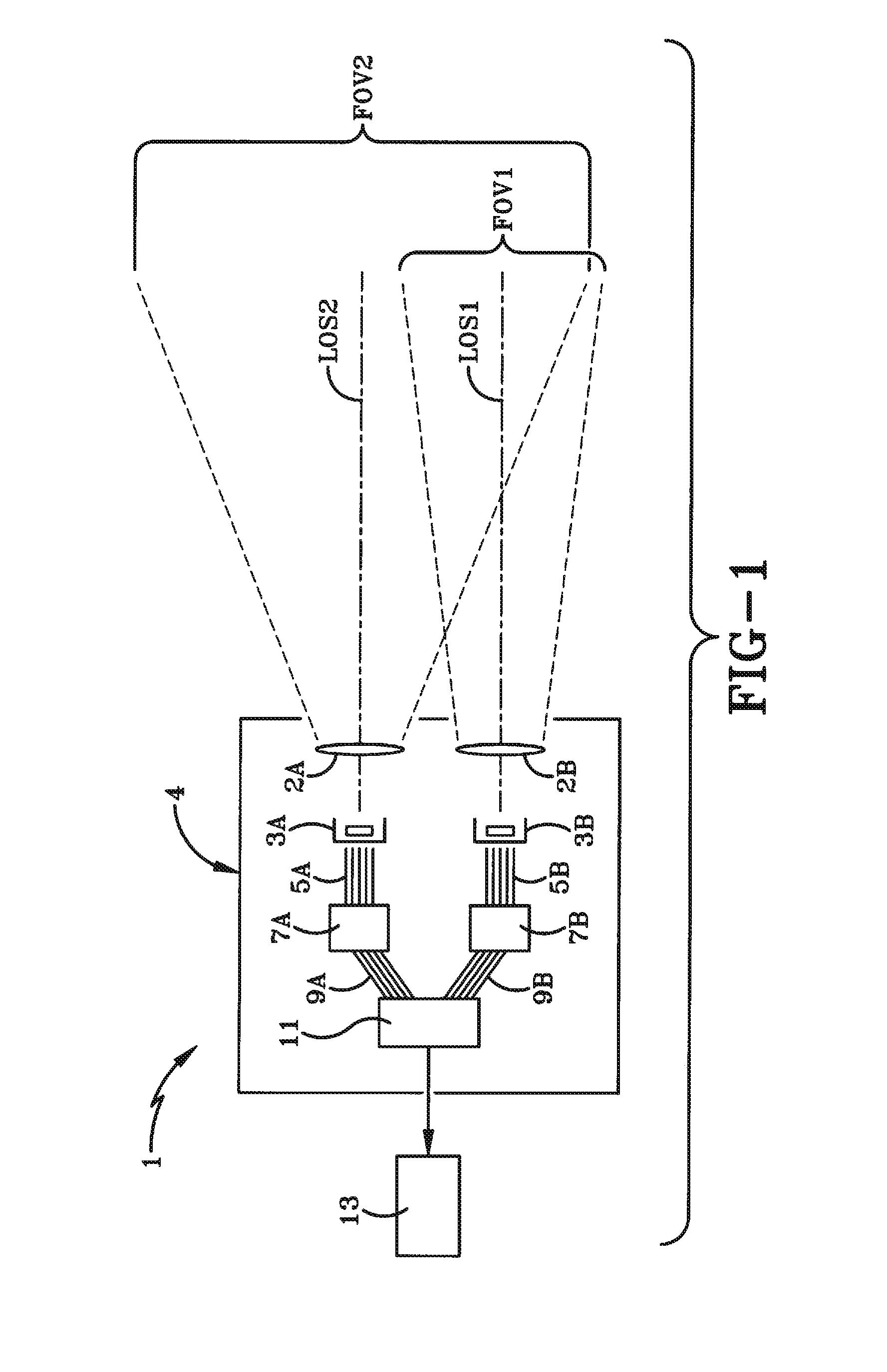
Multi field-of-view multi sensor electro-optical fusion-zoom camera
InactiveUS20150145950A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMulti fieldImage resolution
A system and method for creating an image is presented. The system includes a first camera, a second camera, and a fusion processor. The first camera has a small field-of-view (FOV) and an optical line of sight (LOS). The second camera has a large FOV that is larger than the small FOV and the second camera has an optical LOS. The first camera and second camera are mounted so that the optical LOS of the first camera is parallel to the optical LOS of the second camera. The fusion processor fuses a second image captured by the second camera with a first image captured by the first camera. The fused image has better resolution in a fused portion of the fused image than in unfused portion of the fused image.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method and apparatus for imaging with imaging detectors having small fields of view
ActiveUS7592597B2Material analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersData acquisitionField of view
An apparatus for imaging a structure of interest comprises a plurality of imaging detectors mounted on a gantry. Each of the plurality of imaging detectors has a field of view (FOV), is independently movable with respect to each other, and is positioned to image a structure of interest within a patient. A data acquisition system receives image data detected within the FOV of each of the plurality of imaging detectors.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE ISRAEL
Dual lens digital zoom
A camera with a pair of lens / sensor combinations, the two lenses having different focal lengths, so that the image from one of the combinations has a field of view approximately two to three times greater than the image from the other combination. As a user of the camera requests a given amount of zoom, the zoomed image provided will come from the lens / sensor combination having the field of view that is next larger than the requested field of view. Thus, if the requested field of view is less than the smaller field of view combination, the zoomed image will be created from the image captured by that combination, using cropping and interpolation if necessary. Similarly, if the requested field of view is greater than the smaller field of view combination, the zoomed image will be created from the image captured by the other combination, using cropping and interpolation if necessary.
Owner:DIGITALOPTICS CORPORATION
Architectures for cardiac CT based on area x-ray sources
InactiveUS7388940B1Improve time resolutionReducing conebeam artifactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLarge fovDetector array
A CT imaging system includes a rotatable gantry having an opening to receive an object to be scanned having a small field-of-view (FOV) inside a large FOV. A plurality of area sources is attached to the rotatable gantry, each area source includes a plurality of x-ray emission sources, wherein the plurality of area sources are configured to emit x-rays toward the object. A plurality of x-ray detector arrays is attached to the gantry and positioned such that at least a first detector array and a second detector array each receive x-rays that pass through at least the entire small FOV of the object.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
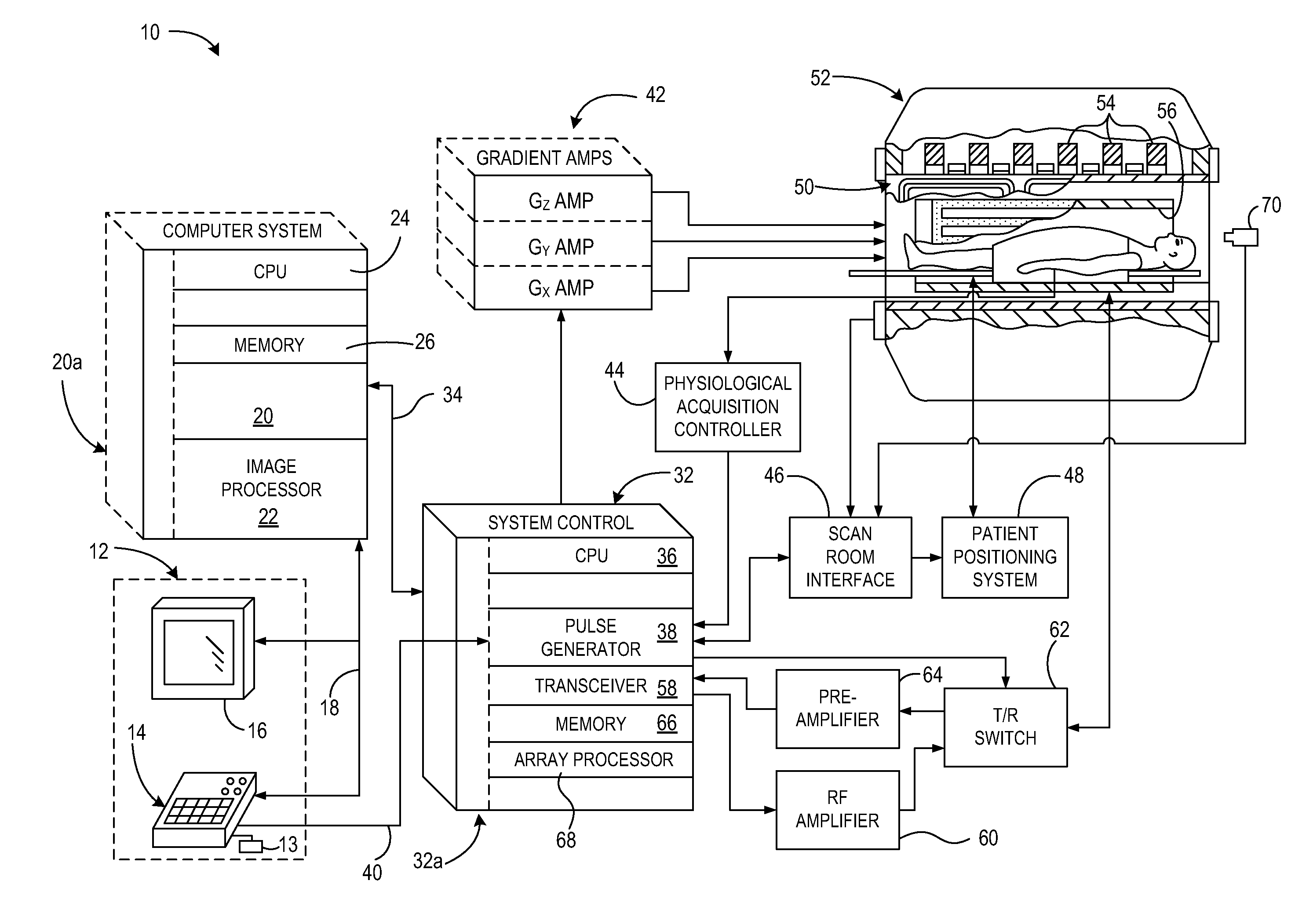
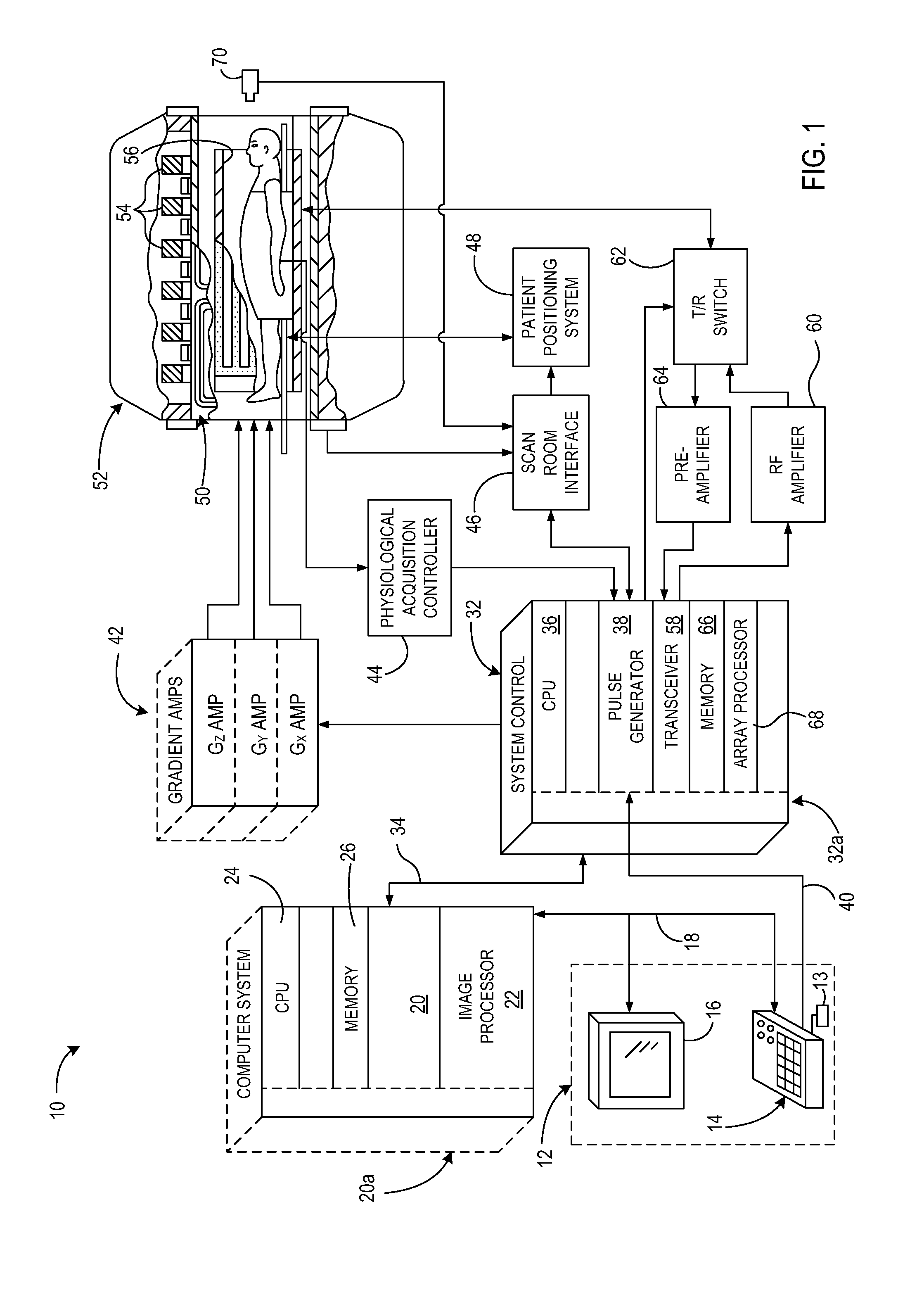
System and method for automatic computation of mr imaging scan parameters
InactiveUS20110228998A1Character and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsObject basedComputer science
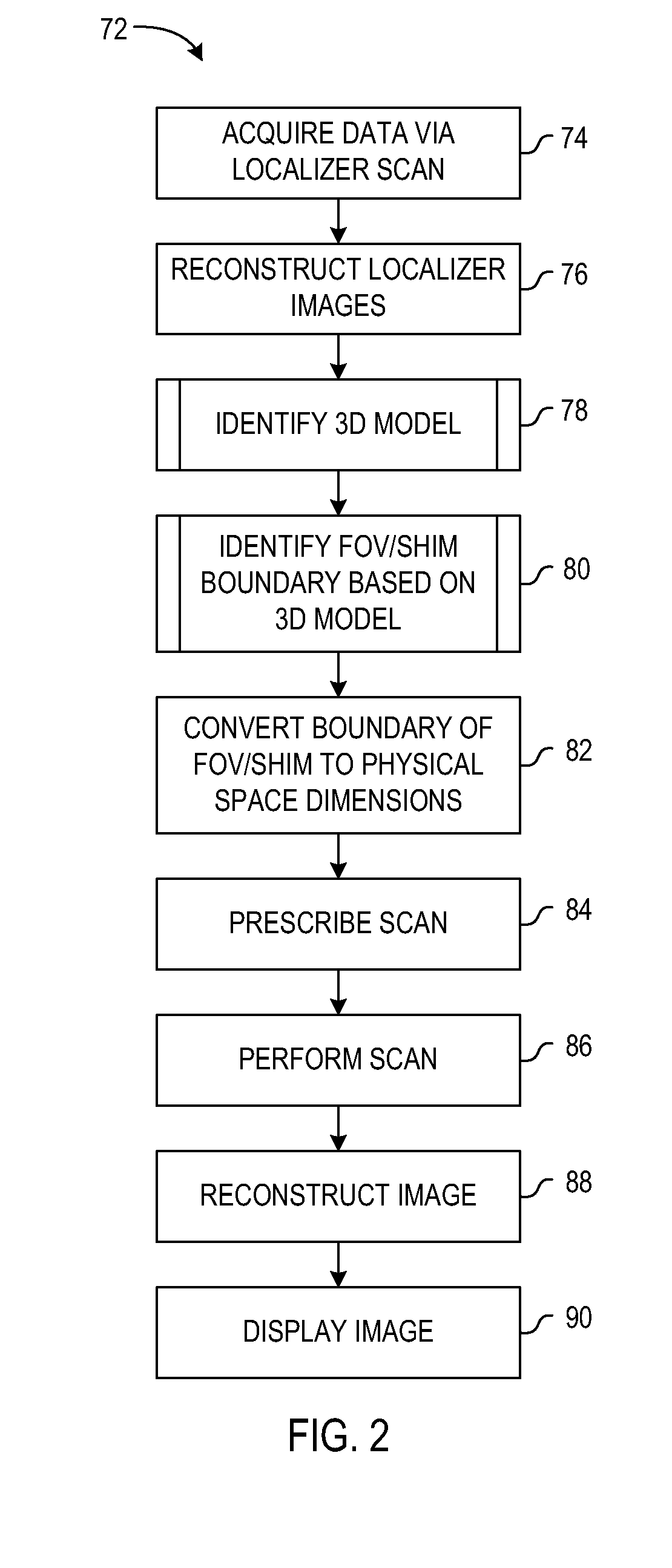
A system and method for automatic computation of MR imaging scan parameters include a computer programmed to acquire a first set of MR data from an imaging subject, the first set of MR data comprising a plurality of slices acquired at a first field-of-view. The computer is also programmed to reconstruct the plurality of slices into a plurality of localizer images and identify a 3D object based on the plurality of localizer images. The computer is further programmed to prescribe a scan, execute the prescribed scan to acquire a second set of MR data, and reconstruct the second set of MR data into an image. The prescribed scan includes one of a reduced field-of-view based on a boundary of the 3D object and a shim region based on the boundary of the 3D object.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tracking system for persons and/or objects
InactiveUS20120313759A1Reduce the numberData processing applicationsWireless architecture usageTriangulationField of view
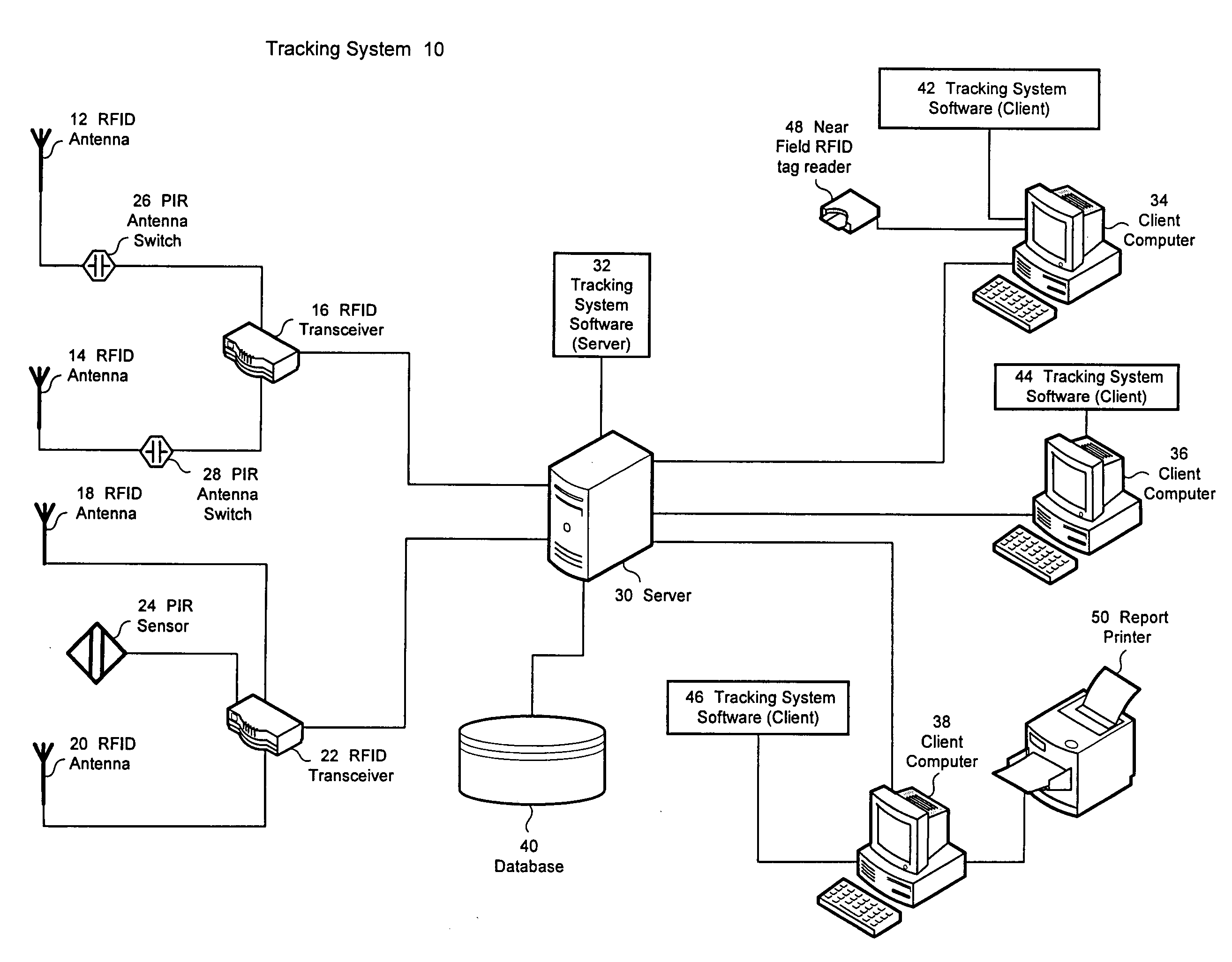
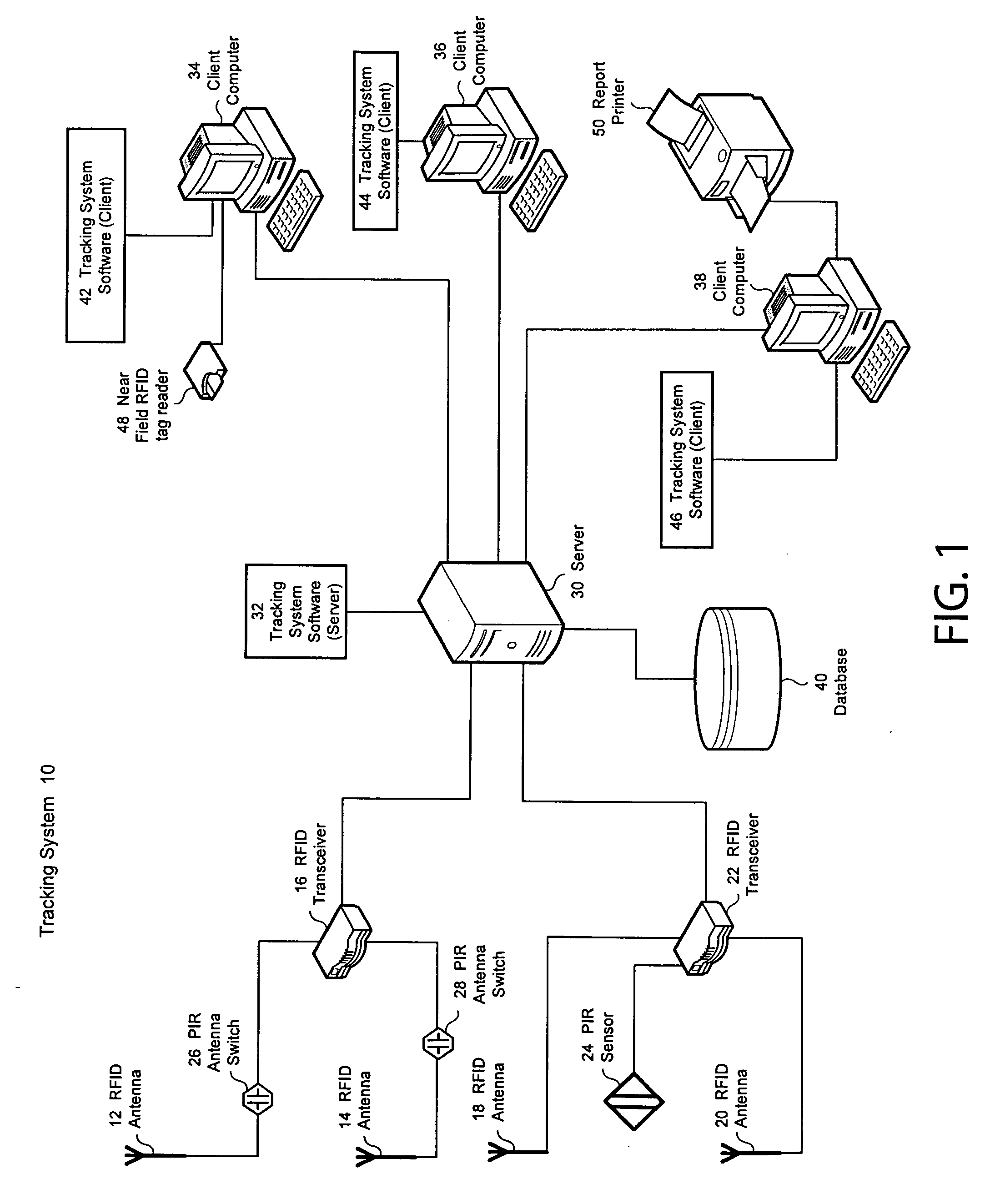
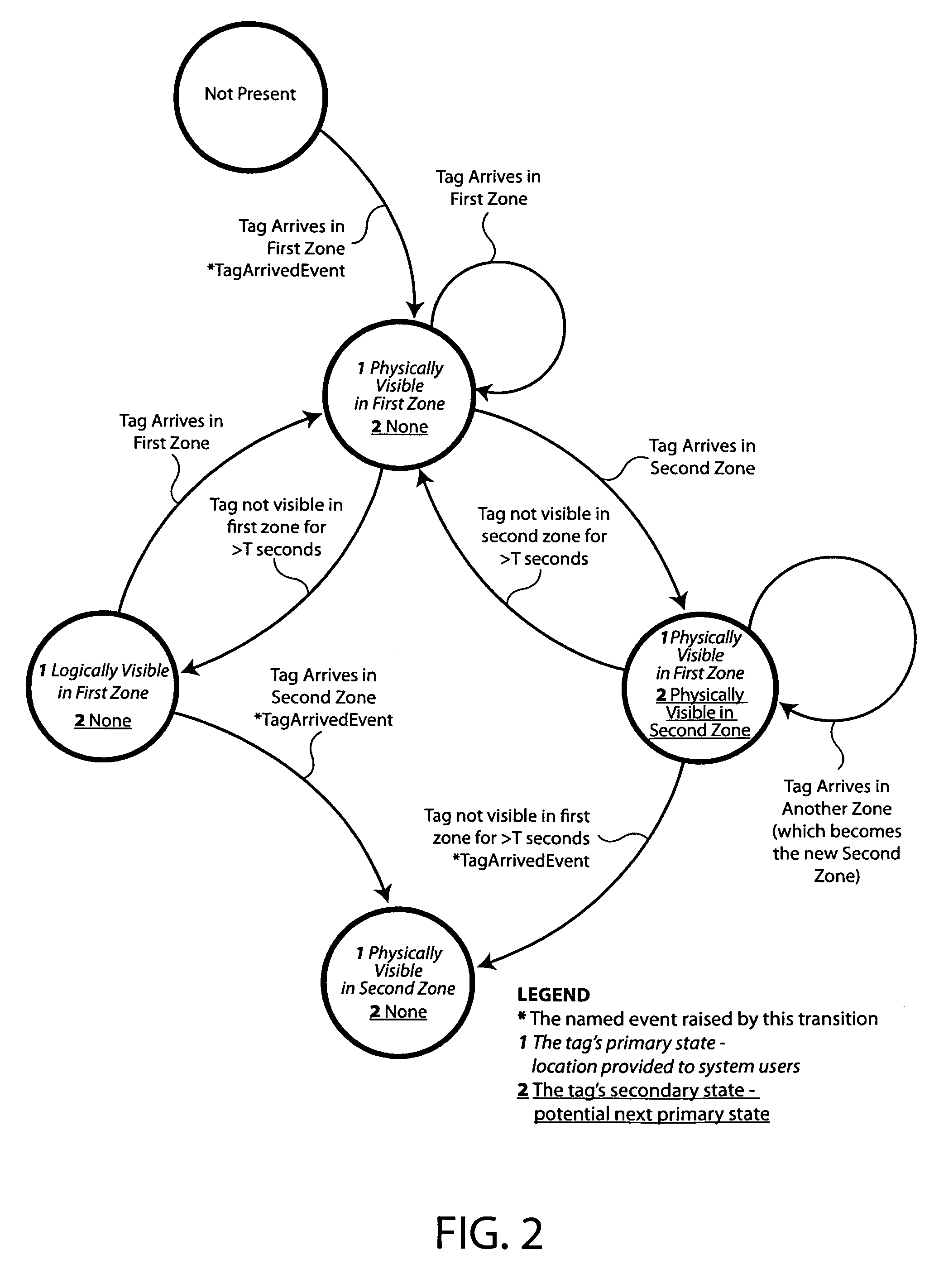
An RFID-based tracking system that tracks persons and / or objects of interest without the need for triangulation techniques is disclosed. The system tracks persons and / or objects of interest by utilizing RFID antennas having a relatively small field of view and positioned relative to functional areas of a facility and / or within passageways between functional areas of the facility. The persons and / or objects of interest to be tracked are provided with an RFID tag. The present invention provides the system user with the ability to determine whether the persons and / or objects of interest are present within a particular functional area of the facility regardless of whether the presence of the person and / or object of interest is continuously detected by the system.
Owner:TIMEKEEPING SYST
A spliced large area array digital aerial survey camera
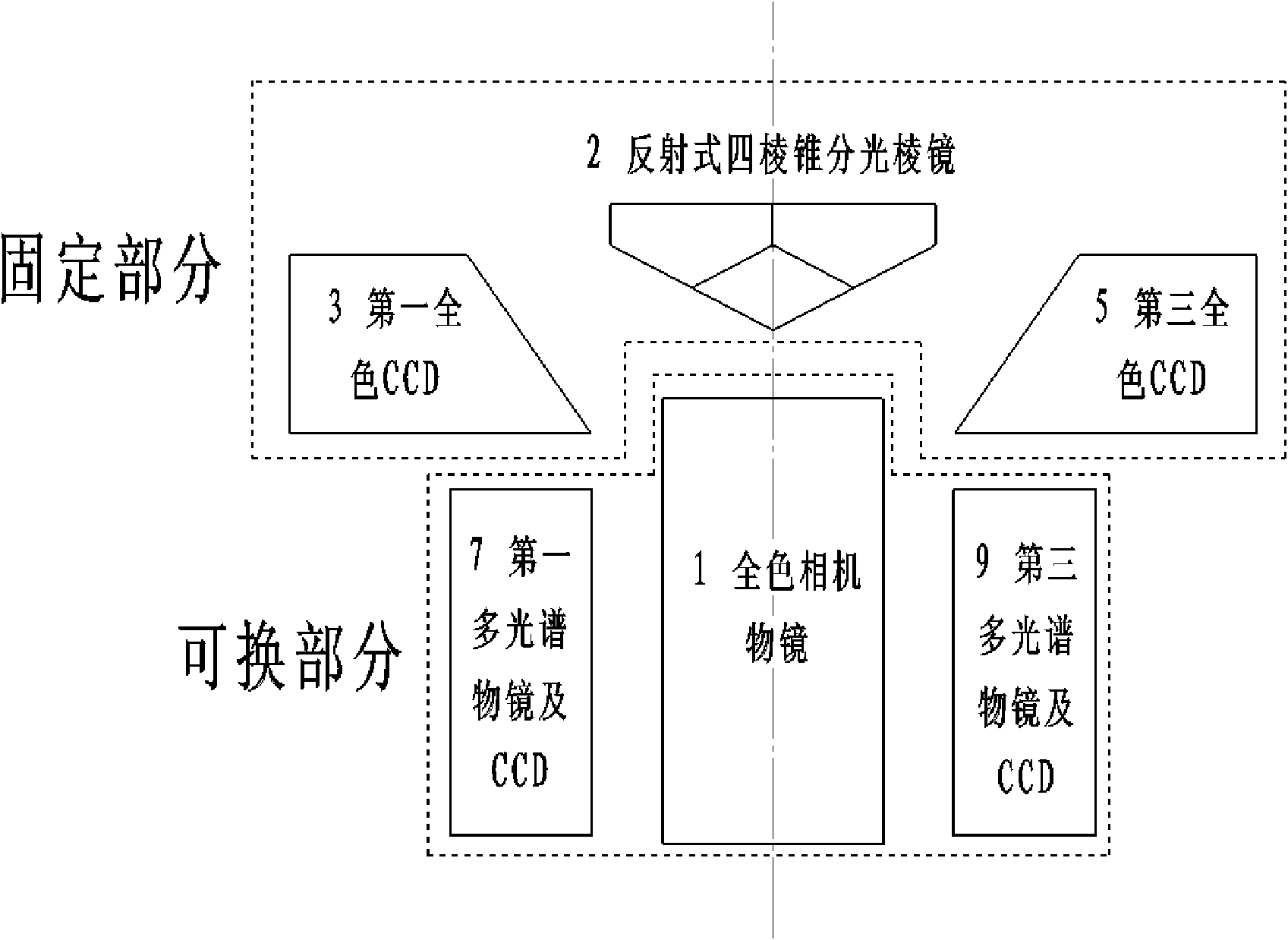
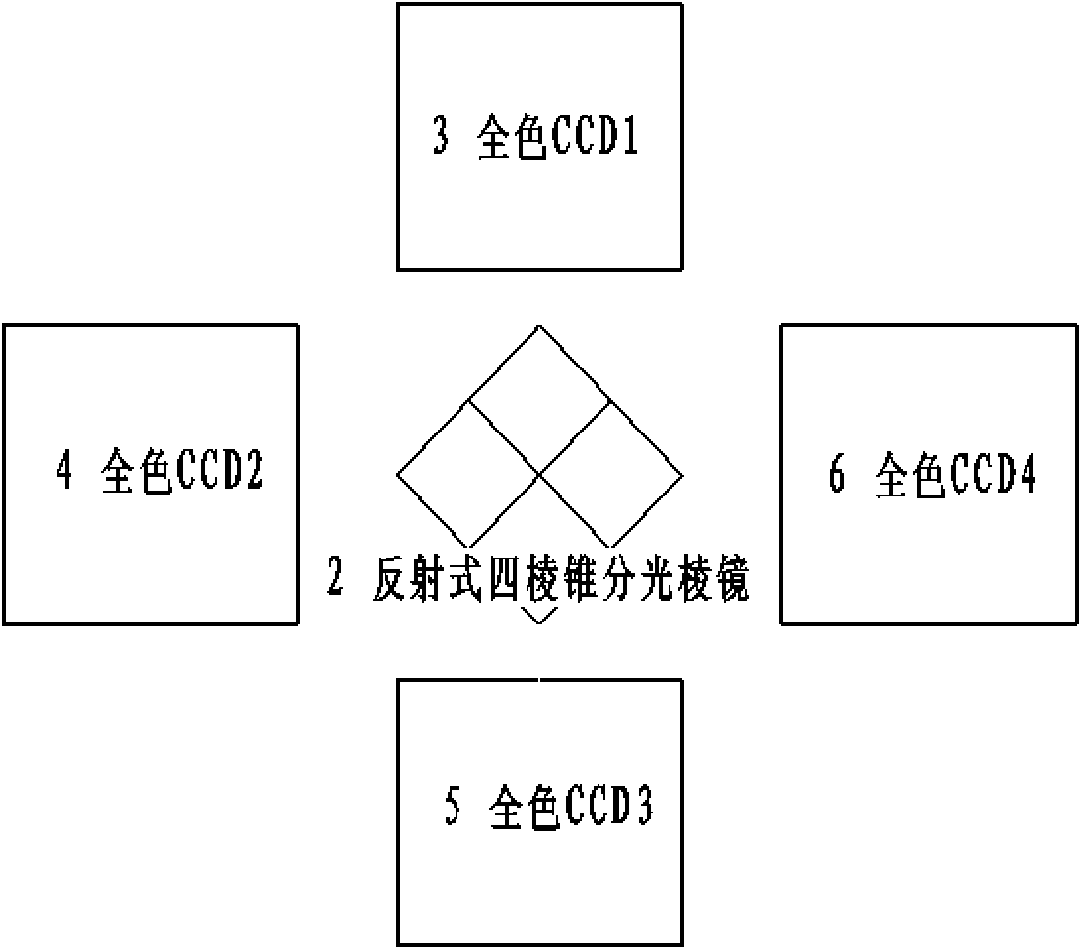
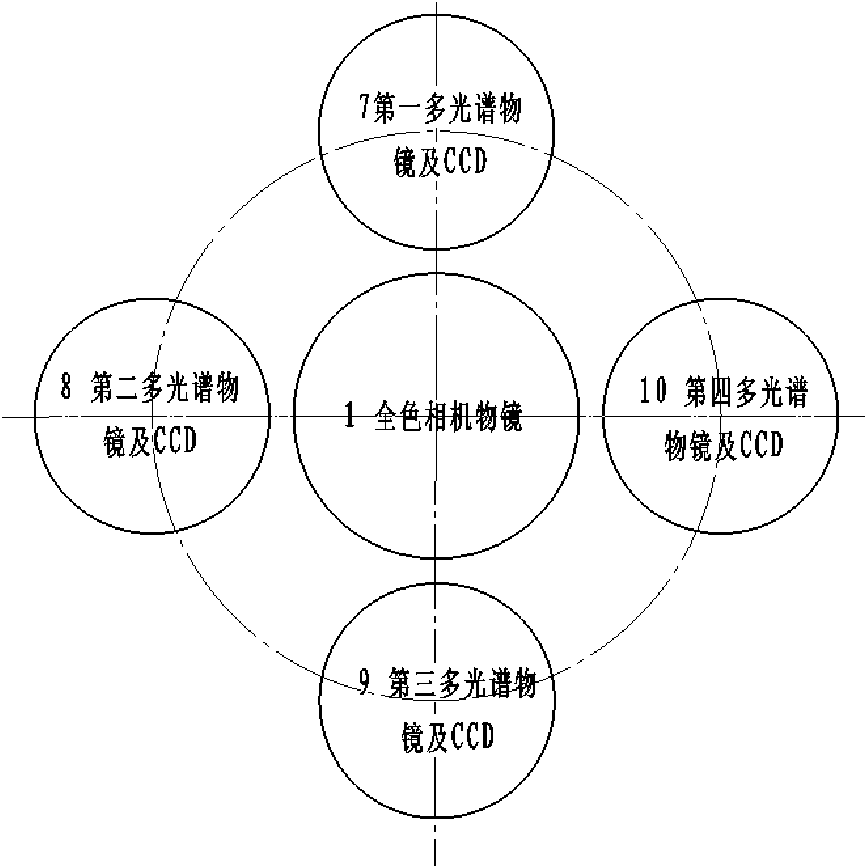
InactiveCN102261909AImprove resolutionSolve small format problemsPicture taking arrangementsCamera body detailsBeam splittingPrism
The invention discloses a spliced large area array digital aerial camera, which comprises a full color camera module and a multispectral camera module, wherein the full color camera module comprises a full color camera objective lens, a reflective pyramid beam splitting prism and four full color charge coupled devices (CCDs); and the multispectral camera module comprises four multispectral objective lenses and a CCD; the full color camera objective lens is positioned in the middle, and the four multispectral objective lenses and the CCD are symmetrically arranged at the periphery of the full color camera objective lens; the rear of the full color camera objective lens is provided with the reflective pyramid beam splitting prism; and the periphery of the reflective pyramid beam splitting prism is provided with the four full color CCDs. By the camera, the problem that a digital aerial camera has small breadth is solved, and a 20k*20k large-breadth high-resolution aerial image is provided; the camera comprises wide-angle, middle-angle and normal-angle full color camera objective lenses and multispectral objective lenses; and during work, the full color camera objective lenses at different angles can be flexibly selected according to different mapping applications, the angles of the multispectral objective lenses are matched with those of the full color camera objective lenses, and the problem that the conventional area array digital aerial camera has small field of view and single objective lens type is solved. Meanwhile, due to a mode of splicing a single full color objective lens and multiple full color CCDs, the image splicing difference caused by exposure difference of various full color cameras in the mode of splicing the multispectral objective lenses and the multiple CCDs is avoided.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
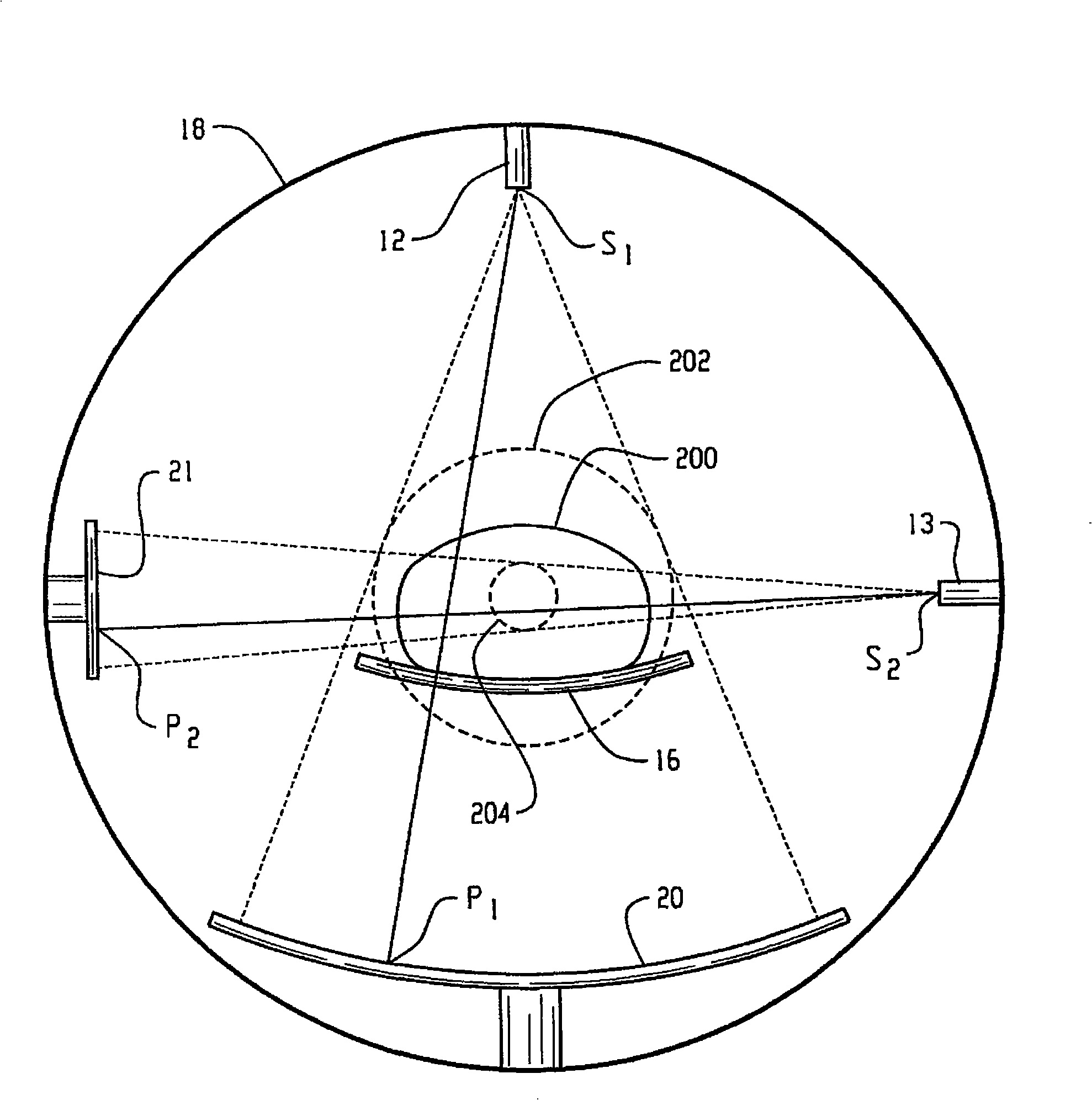
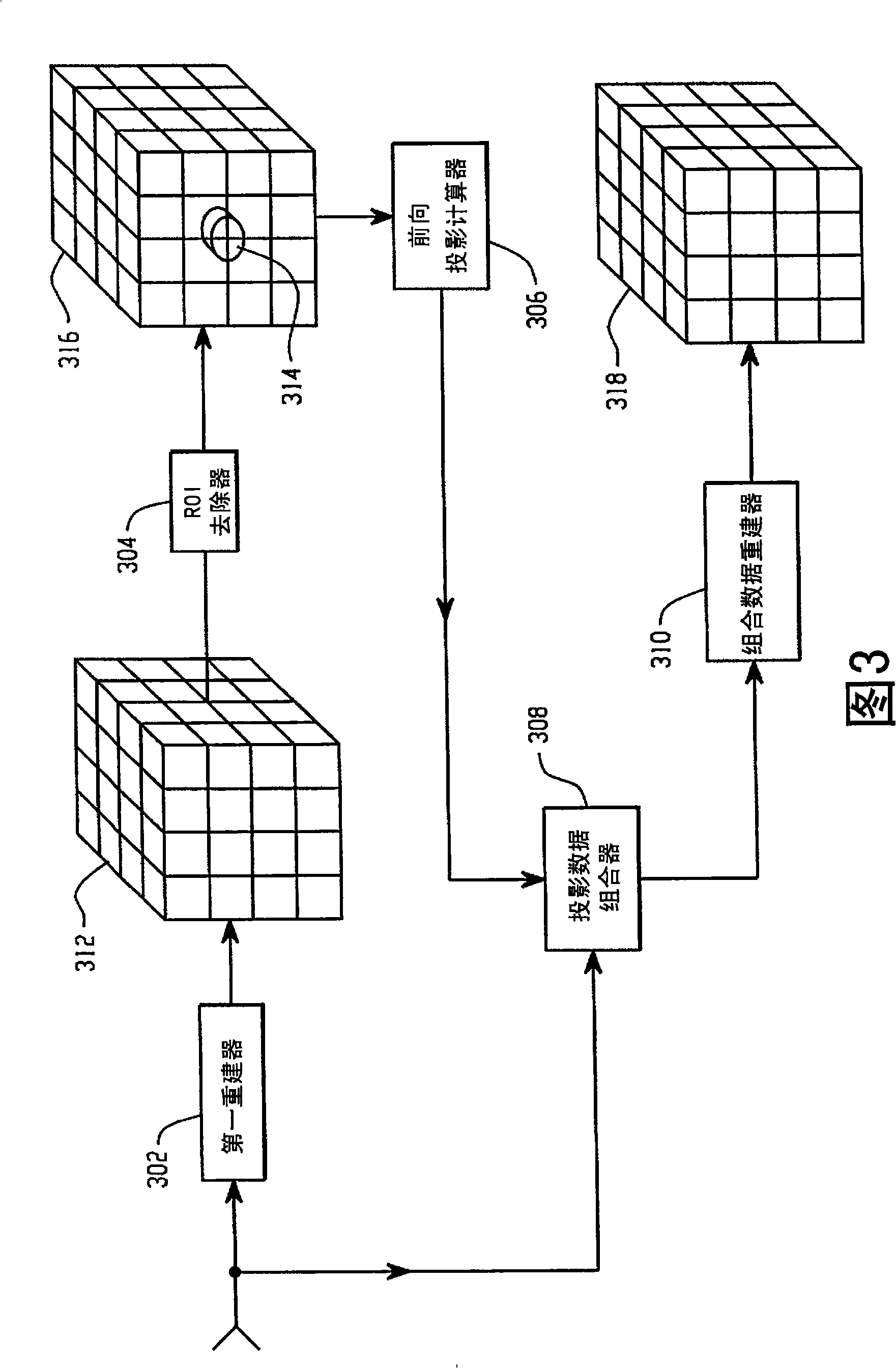
Computed tomography data acquisition apparatus and method
InactiveCN101405619ATomographyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentData acquisitionComputed tomography scanner
A computed tomography scanner includes a first (20) and second (21) detectors. The second detector (21) has a relatively higher spatial resolution and a relatively smaller field of view (204) than that of the first detector (20). Projection data generated by the detectors (20, 21) is combined and reconstructed so as to generate relatively high resolution volumetric data (318) indicative of a region of interest (314) in an object under examination.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
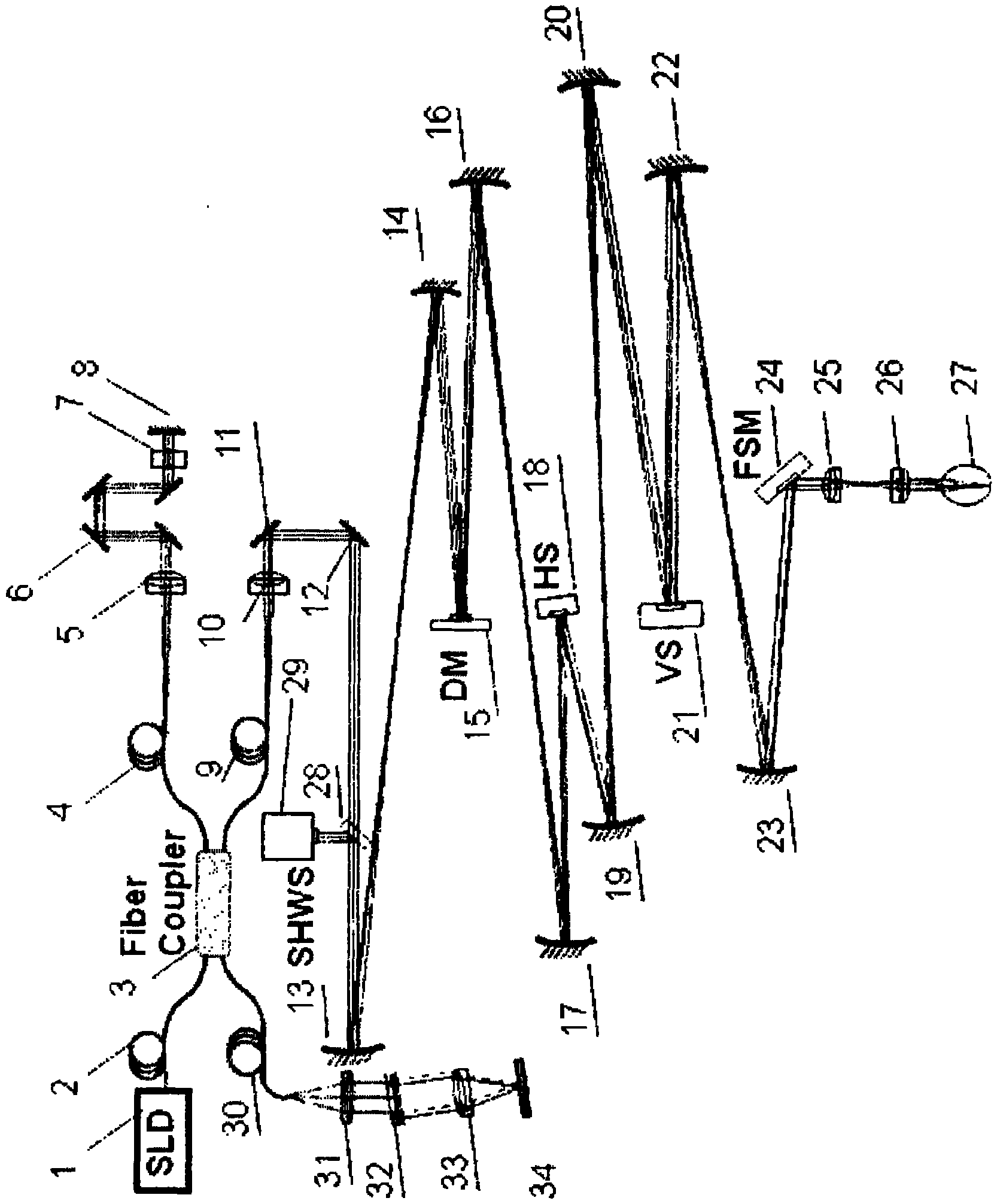
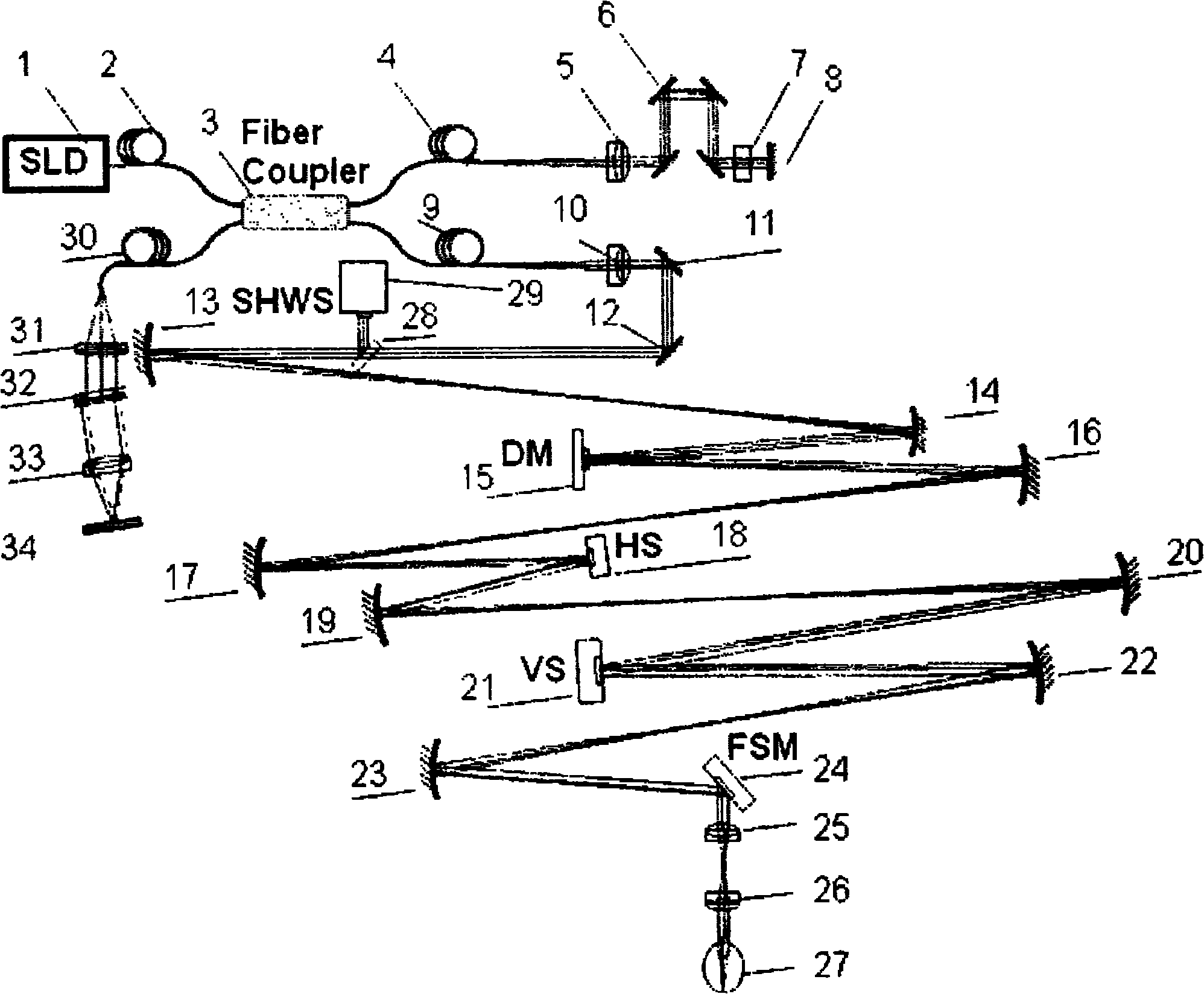
Wide field of view optical coherence tomographic instrument based on adaptive optical technology
InactiveCN101884524ALarge imaging field of viewImproved imaging field of viewPhase-affecting property measurementsOthalmoscopesSystems designImaging quality
The invention relates to a wide field of view optical coherence tomographic instrument based on the adaptive optical technology, which comprises an optical source assembly, a reference arm assembly, an aberration detecting and correcting assembly, a two-dimensional imaging and scanning assembly, a wide field of view scanning assembly and a detector assembly. In the optical coherence tomographic instrument provided by the invention, an optical signal receiving part of a system mainly utilizes optical fibers and optical fiber couplers, so that the system has compact design. A lighting optical path part is designed by mainly using spherical reflector telescopes, so that the higher order aberration of the system is avoided. Meanwhile, the adaptive optical technology is introduced to detect and correct wave-front aberration, so that the light beam quality of the lighting optical path and an imaging optical path both achieve the level of diffraction limits. Through the synchronous operation of a fast tilting mirror and the two-dimensional imaging and scanning assembly, the high-resolution tomographic image of the human eye ground (or a sample to be measured) in a wide field of view range by using the automatic mosaic technology on the basis of the acquisition of a small field of view single-frame image. The invention mainly solves the difficulty of high-resolution and wide field of view synchronous imaging, the wide field of view optical coherence tomographic instrument with compact design and high imaging resolution and wide imaging field of view is realized, and the imaging field of view and the imaging quality of the traditional optical coherence tomographic instrument are greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
Vertebral feature identification
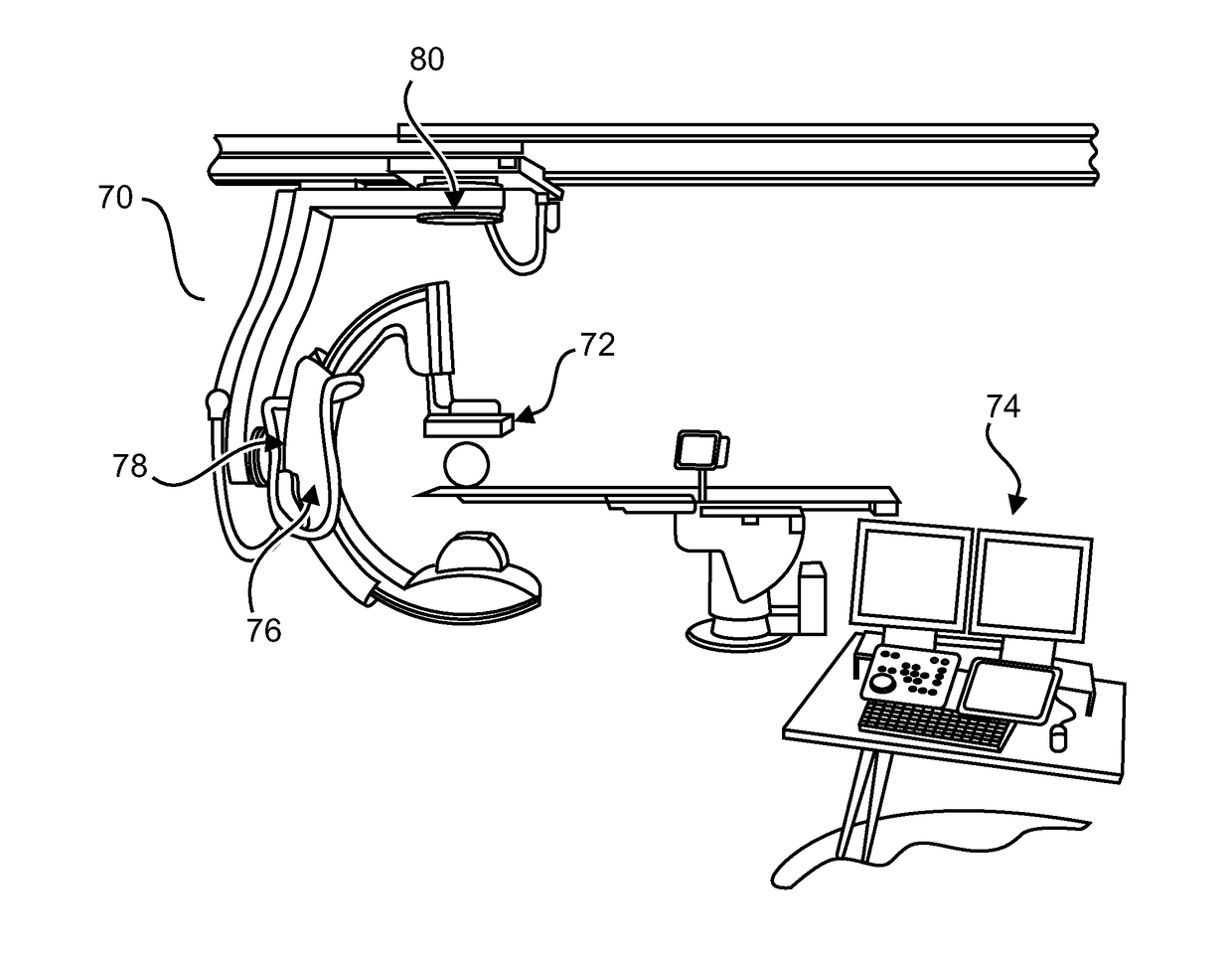
ActiveUS20170367645A1Easy to optimizeWiden perspectiveImage enhancementMedical imagingSpinal columnFluoroscopic imaging
Minimally-invasive spinal inventions are often performed using fluoroscopic imaging methods, which can give a real-time impression of the location of a surgical instrument, at the expense of a small field of view. When operating on a spinal column, a small field of view can be a problem, because a medical professional is left with no reference vertebra in the fluoroscopy image, from which to identify a vertebra, which is the subject of the intervention. Identifying contiguous vertebrae is difficult because such contiguous vertebrae are similar in shape. However, characteristic features, which differentiate one vertebra from other vertebra, and which are visible in the fluoroscopic view, may be used to provide a reference.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Camera mixing calibration method based on quadratic curve and straight lines
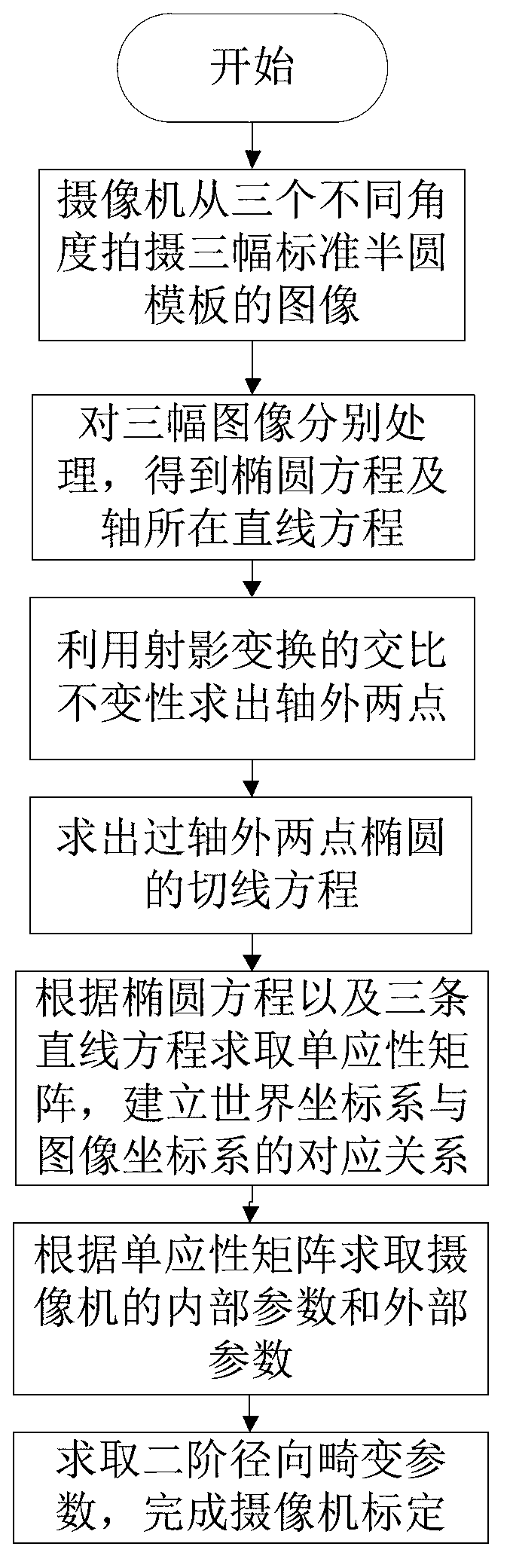
InactiveCN103247048AAccurate internal and external parametersSolve the problem that the calibration cannot be completedImage analysisPartition of unityAngular degrees
A camera mixing calibration method based on a quadratic curve and straight lines aims to enable a camera to exactly complete calibration in a small field of view environment so as to accurately perform subsequent three-dimensional measurement. According to the invention, a brand-new standard circle calibration template is designed; the template is shot from any three different angles; an equation of a circle and linear equations of the radius are detected out; then anharmonic ratio invariance of projective transformation is utilized to accurately obtain two points outside the circle; accordingly, a tangential equation passing through the two points outside the circle is obtained; combining the equation of the circle and the three linear equations, so as to obtain a homography matrix; establishing a corresponding relation of the world coordinate system and an image coordinate system; calculating inside parameters and outside parameters of the camera by using unit orthogonality of a rotation matrix; and finally considering a second-order radial distortion to optimize a calibration result, so as to complete the whole calibration process of the camera.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Small-view-field magnetic resonance imaging method based on single-sweep super-speed orthogonal space-time coding
ActiveCN103809140AImprove spatial resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpatial encodingField of view
The invention discloses a small-view-field magnetic resonance imaging method based on single-sweep super-speed orthogonal space-time coding. The method comprises the following steps of: enabling protons in a space to automatically rotate in an excitation phase by virtue of the organic combination of an orthogonally-distributed space coding gradient and a linear frequency sweep pulse to acquire a secondary phase related to a space position, thus carrying out two-dimensional space-time coding on the automatic rotation of the protons in an imaging plane; for the automatic rotation of the protons in an orthogonal space-time coding space, only the automatic rotation of the protons with static phase distribution can be detected during a decoding sampling period, and according to the characteristic of orthogonal space-time coding, decoding sampling can be carried out on a plurality of randomly-distributed areas in the space by designing a decoding sampling gradient, thus acquiring the magnetic resonance data of a plurality of areas of interest finally. High-resolution reconstruction is sequentially carried out on acquired magnetic resonance data of the plurality of areas, and then the high-resolution small-view-field magnetic resonance images of the plurality of areas can be obtained finally.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Small-sized optical system for infrared medium wave detector
ActiveCN102621669AImprove transmittanceHigh temperature sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMountingsIntermediate imageObject point
The invention discloses a small-sized optical system for an infrared medium wave detector, which comprises four lenses which are sequentially arranged from an object point to an image point along the same optical axis. Focal powers of the four lenses are positive, negative, positive and positive respectively, and a second lens is located at one of two positions which enable the object point and the image point to be conjugated; the object point performs imaging for the first time at a position of an intermediate image surface between a first lens and a third lens, and an image formed for the first time is subjected to further imaging on a photosensitive surface of the infrared medium wave detector through a fourth lens; and the focal distance of the optical system is set as fn in a working state of a small field of view, the diameter of the first lens is set as D1, the focal distance of the first lens is set as f1, the magnification of the fourth lens is set as m4, then the f1 / fn is larger than or equal to 0.2 and smaller than or equal to 0.3, f1 / D1 is larger than or equal to 0.7 and smaller than or equal to 1.2, and m4 is larger than or equal to -3 and smaller than or equal to -1.5. The small-sized optical system for the infrared medium wave detector has the advantages that miniaturization of infrared cameras is achieved, and simultaneously the optical system is guaranteed to have a large aperture, a long focal distance, double fields of view, and good imaging qualities.
Owner:NANJING WAVELENGTH OPTO ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
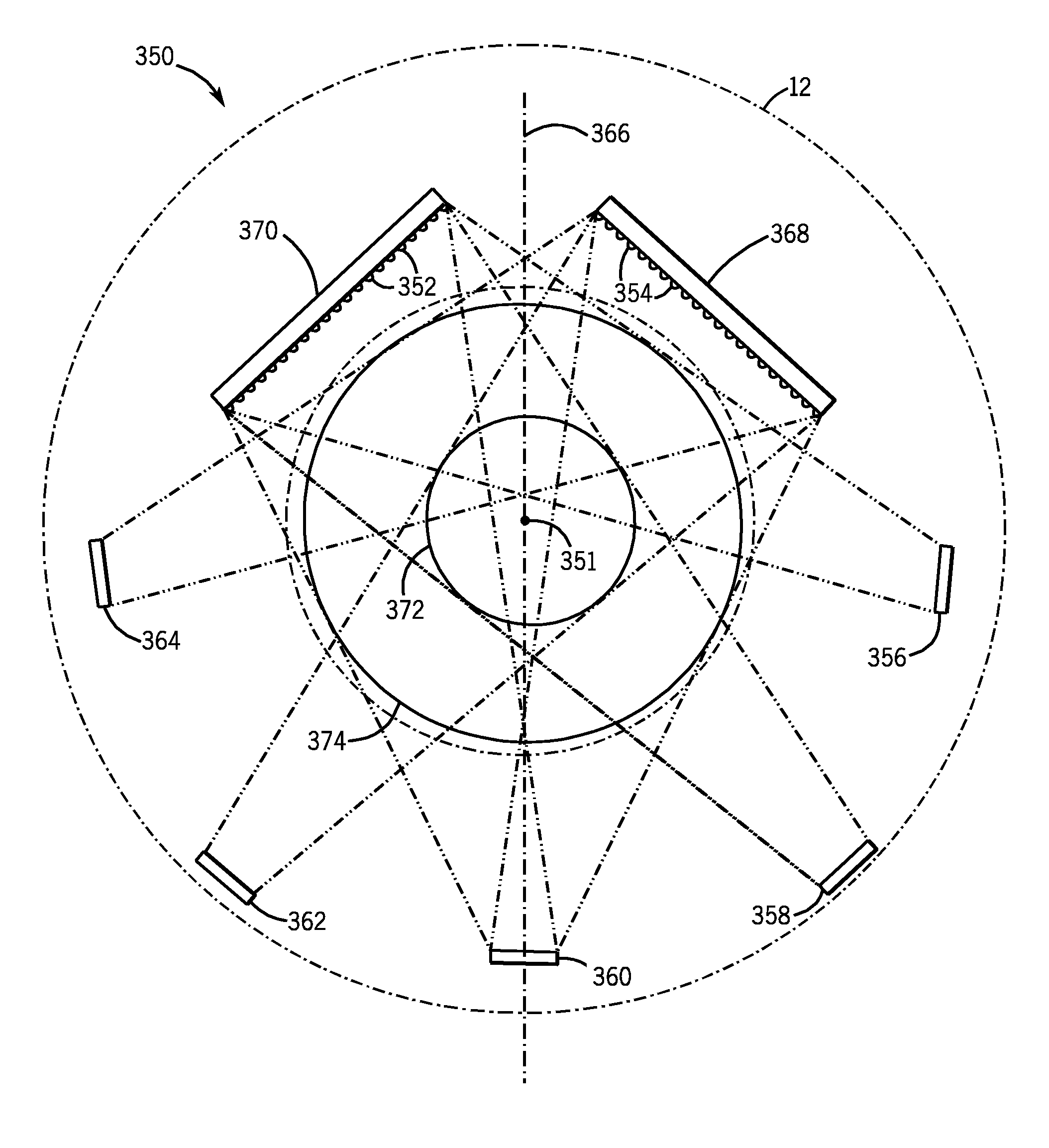
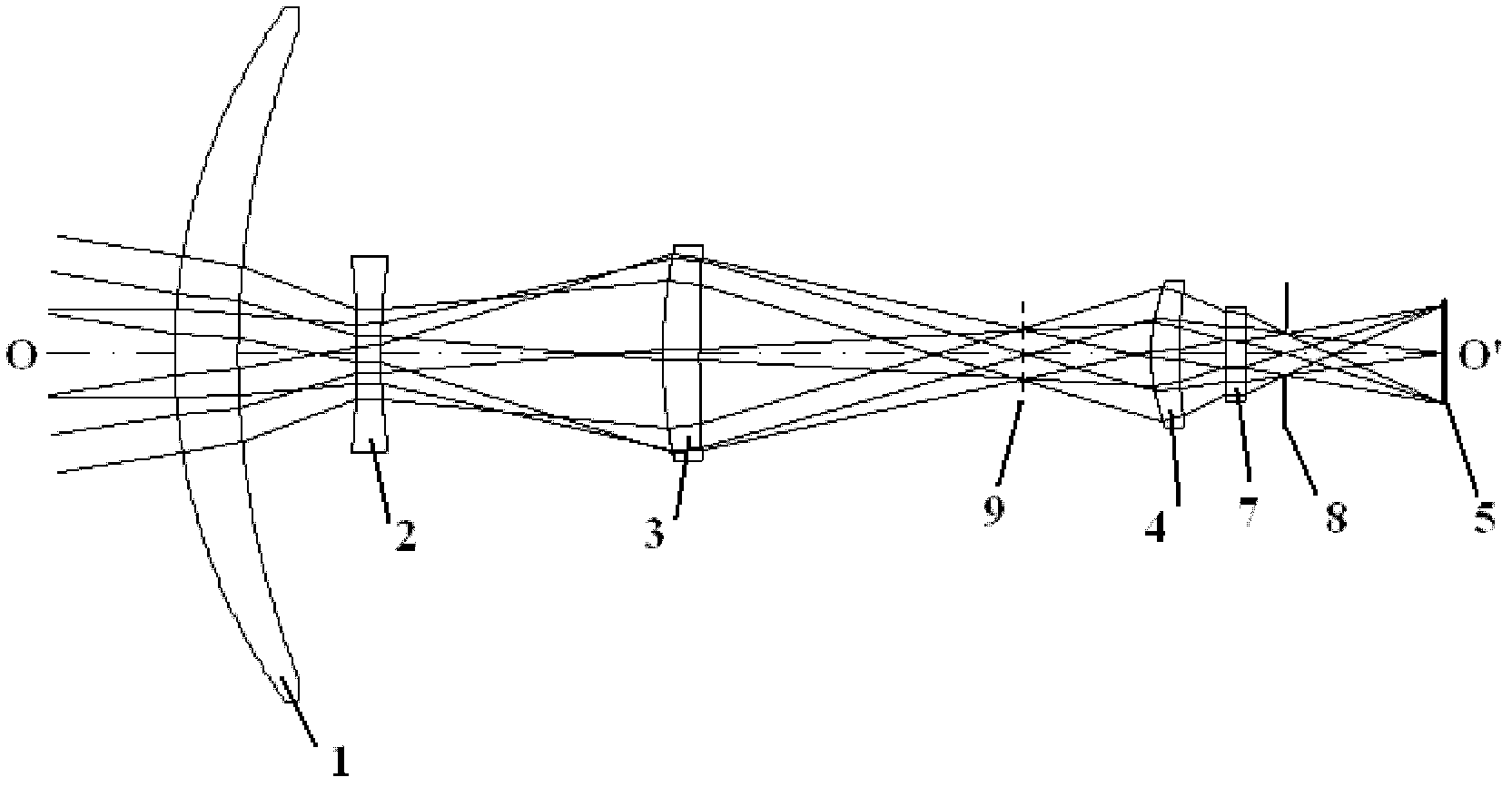
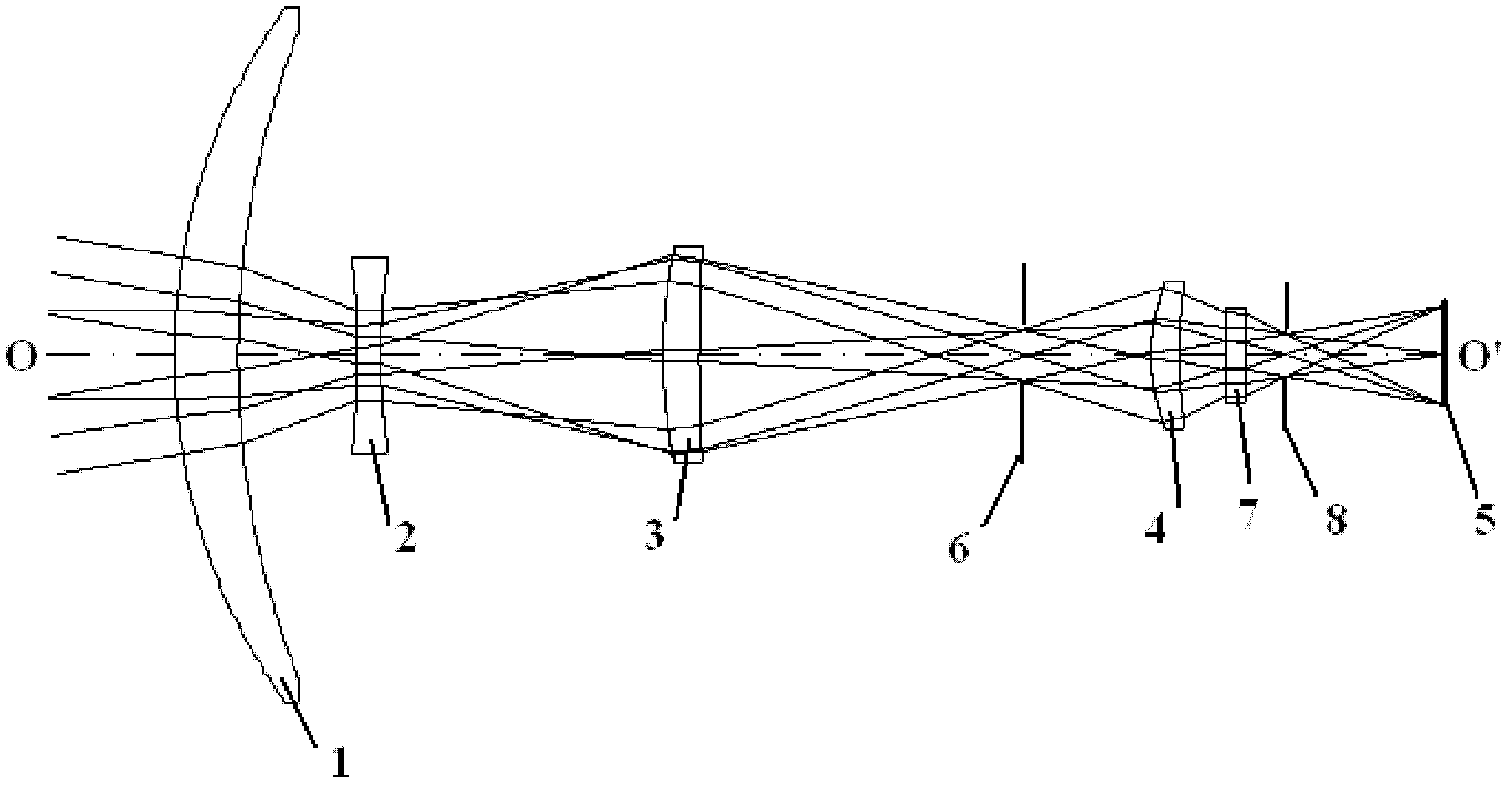
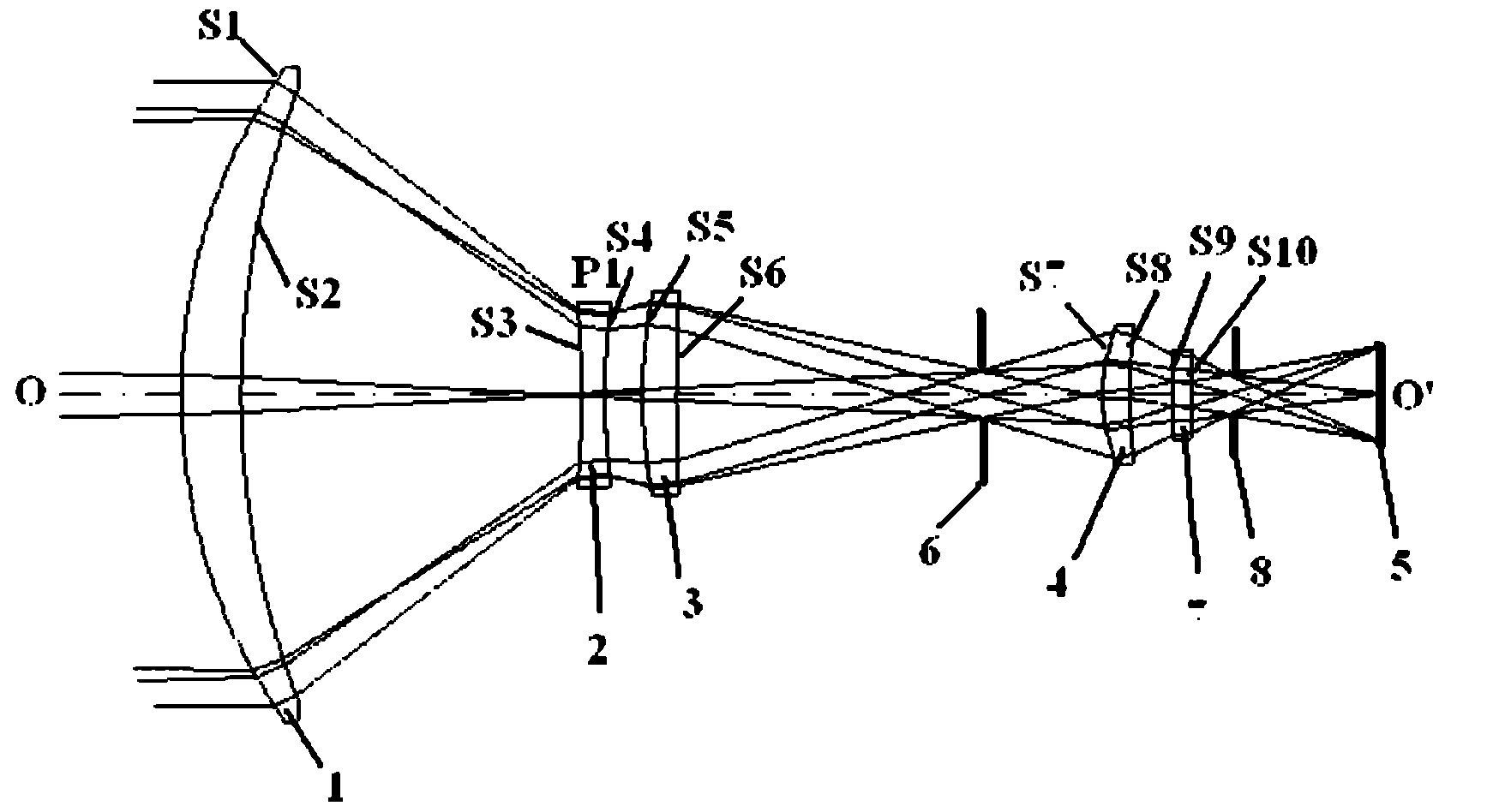
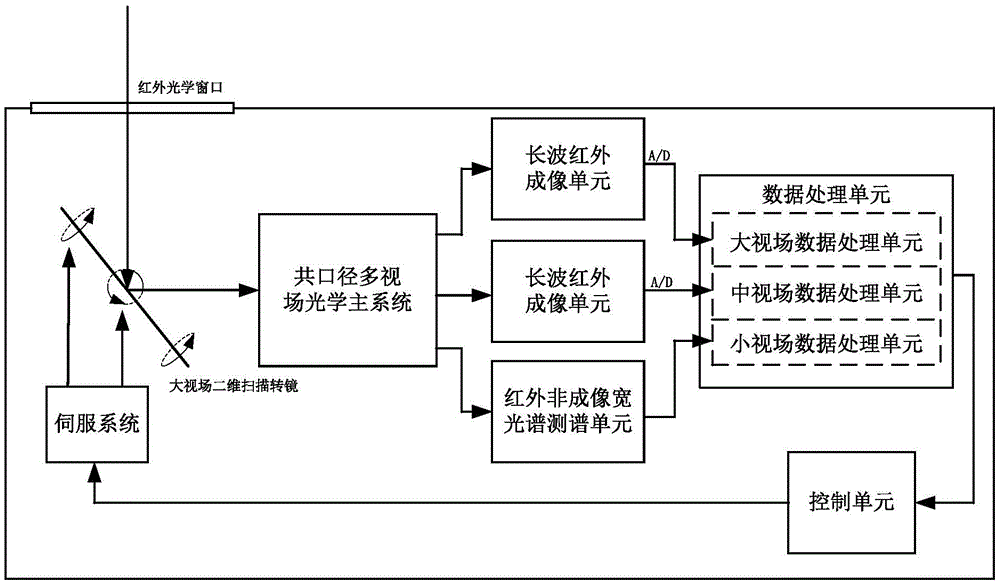
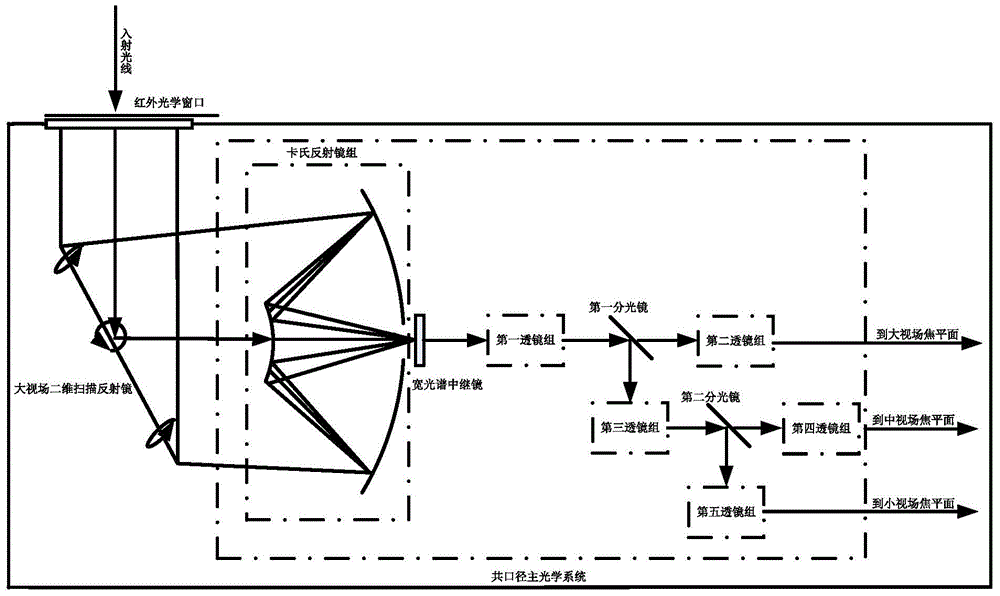
Common-caliber multi-field-of-view atlas cooperative detection system, and method thereof
ActiveCN105676305AStrong ability to detect and identify objects with remote sensingHigh detection sensitivityTelevision system detailsOptical detectionStaringMulti field
The invention discloses a common-caliber multi-field-of-view atlas cooperative detection system. The common-caliber multi-field-of-view atlas cooperative detection system includes an infrared optical window, a large field of view two dimension scanning rotating mirror, a common-caliber multi-field-of-view main optical system, a large field of view scanning detector, a staring infrared detector, an infrared non-imaging broadband spectrum measuring unit, a data processing unit, a control unit and a servo system. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a method based on the common-caliber multi-field-of-view atlas cooperative detection system. The common-caliber multi-field-of-view atlas cooperative detection system, and the method thereof can search the target area through large field of view scanning, and then can identify the target through middle field of view staring infrared detection, and finally can perform small field-of-view fine detection of the area. By means of combination with spectral data analysis, the common-caliber multi-field-of-view atlas cooperative detection system, and the method thereof are high in the sensitivity for identification and detection of the target, can be more accurate and stable for capturing and tracking the target, and solve the technical problem that conventional remote sensing detection cannot research change of motion of the movable target and the dynamic situation and cannot search and track the object with small scale, thus being high in the actionability and the practical promotion value.
Owner:NANJING HUATU INFORMATION TECH
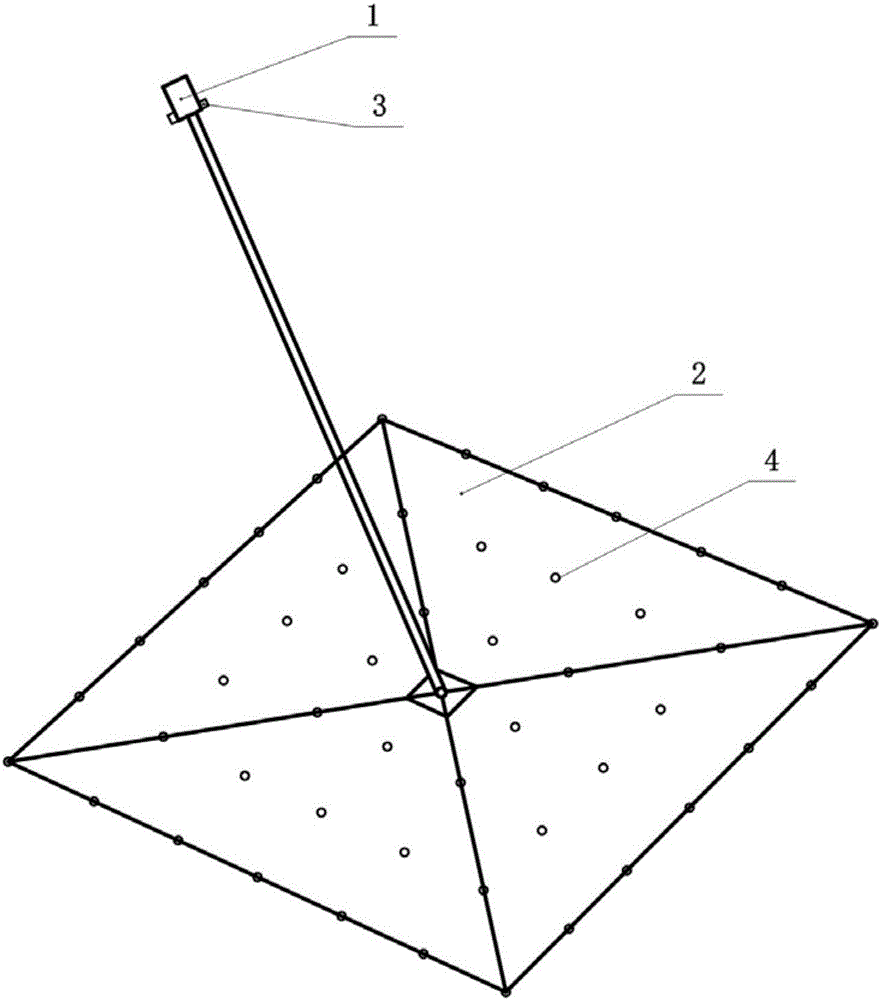
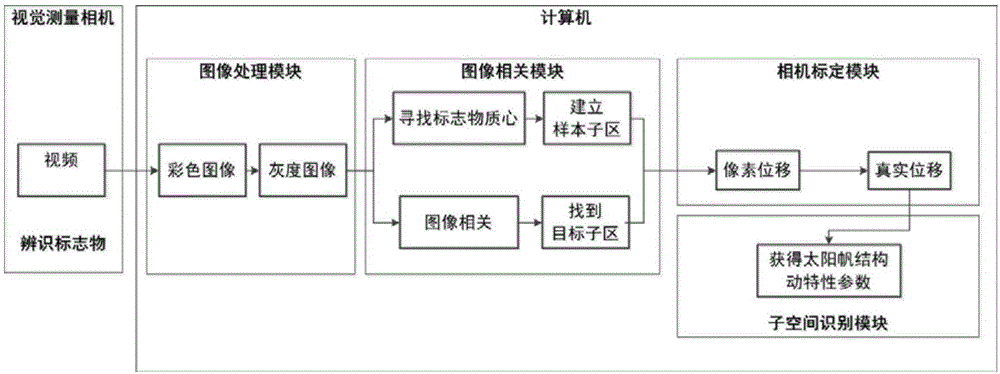
Solar sail spread structure dynamic characteristic in-orbit identification method based on binocular vision measurement
ActiveCN106408570ARealize full field monitoringImprove recognition accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCamera lensFull field
The invention discloses a solar sail spread structure dynamic characteristic in-orbit identification method based on binocular vision measurement in order to solve the technical problem that the existing solar sail spread structure dynamic characteristic in-orbit identification method has small field of view for single measurement and is difficult to implement. The technical scheme is as follows: two cameras are used as vision sensors, vibration displacement information of a structure is extracted directly from images by use of image processing, digital image correlation, sub-pixel positioning and other methods, the dynamic characteristics of the structure are acquired in real time through an operational modal analysis technology, and thus, in-orbit identification of the dynamic characteristics of the structure is realized, and high identification precision is achieved. The cameras are fixed on a camera support fixedly connected with a solar sail spacecraft structure, and the structure of the whole sail surface can be monitored in an all-round way by finely tuning the locations and directions of the camera lenses. The method is easy to implement.
Owner:西北工业大学太仓三角研究院
Galvanometer scanning system and scanning method for dual optical path imaging
ActiveCN106405826AEasy to monitor the marking situationImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansLaser technologyGalvanometer
The invention relates to the field of laser technology, and discloses a galvanometer scanning system for dual optical path imaging. The galvanometer scanning system comprises a first lens, a second lens, a large field of view imaging unit, a small field of view imaging unit, a focusing mirror, an XY scanning galvanometer, and an optical source. An external laser optical path reaches the XY scanning galvanometer through the first lens, and after reflection, acts on an object to be marked to conduct marking sequentially through the focusing mirror and the second lens. The optical source is lit up to send out a lighting optical path to illuminate the object to be marked, the lighting optical path is reflected onto the second lens, a part of the lighting optical path is reflected through the second lens into the large field of view imaging unit to image for monitoring the marking condition. The other part of the lighting optical path is focused through the second lens and the focusing mirror onto the XY scanning galvanometer, and reflected through the first lens into the small field of view imaging unit to image for detecting the marking condition. The invention can improve the detection accuracy and detection efficiency of the scanning system.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD +1
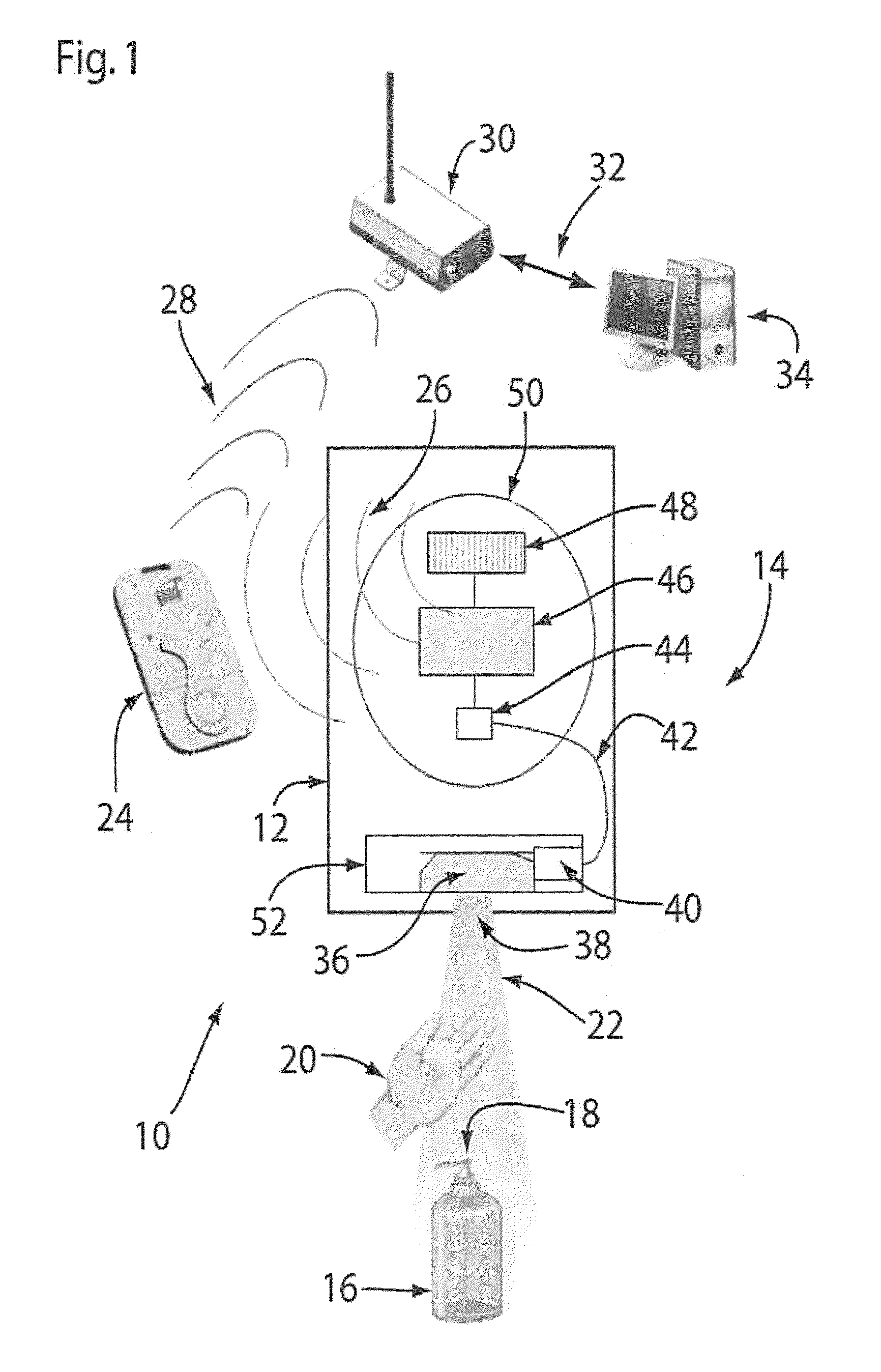
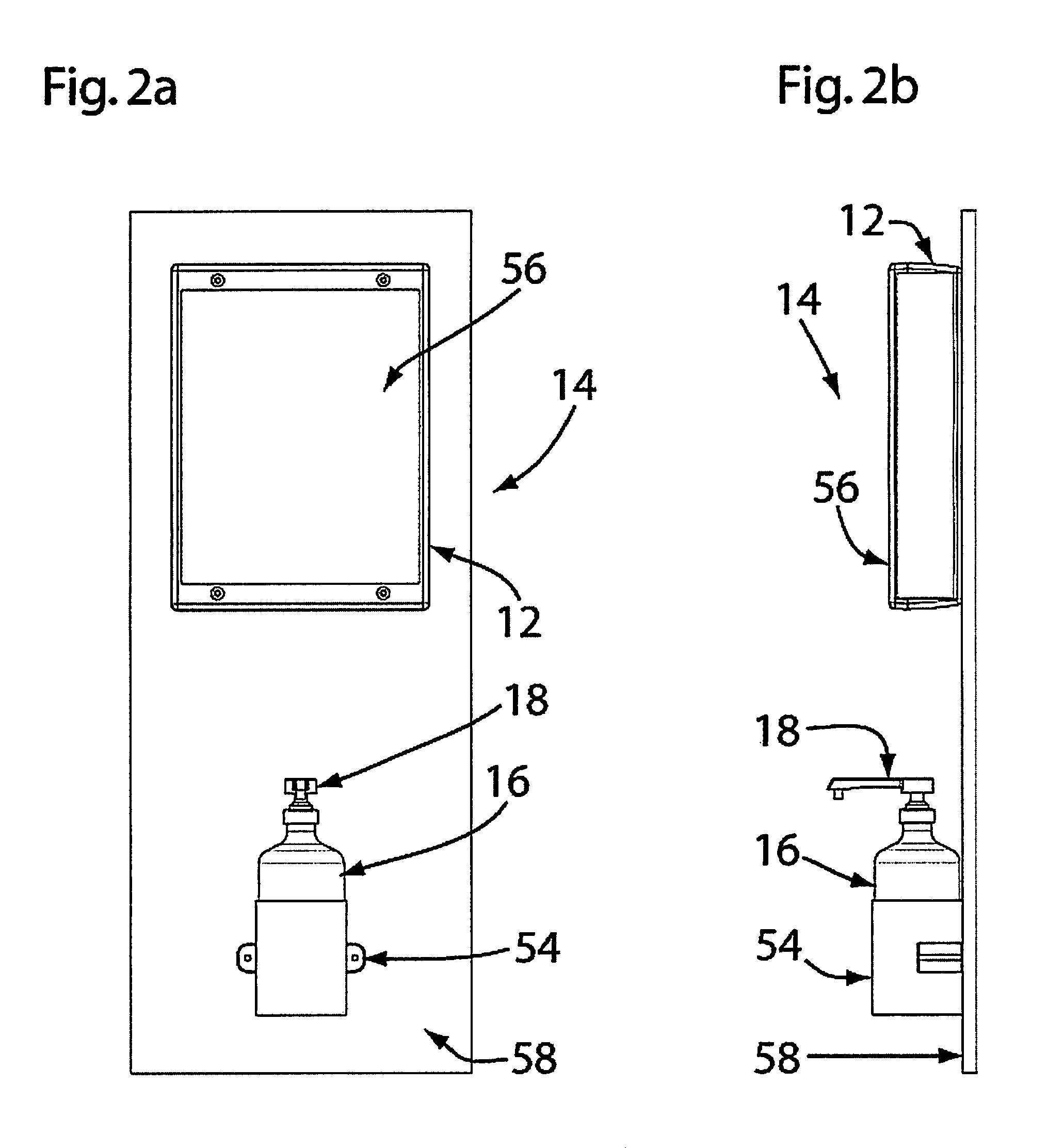
Hand sanitizer compliance detection system
ActiveUS8994537B2Accurate and reliable monitoringAccurate compliance monitoring is improvedElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingLiquid transferring devicesHand sanitizerField of view
A hand sanitizer compliance detection system for RFID-tagged employees comprises a hand sanitizer station with a detector enclosure having a sensor and an aperture that narrows a field of view by the sensor to define a hand detection zone.
Owner:GUARD RFID SOLUTIONS INC
Illumination test apparatus and test method for illumination uniformity and stray light
ActiveCN105319858ASolve the problem of insufficient sampling frequencyShort test timePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusComputational physicsPoint energy
The invention provides an illumination test apparatus and a test method for illumination uniformity and stray light. A special detecting light path is added for realizing energy detection, and the problem of an insufficient sampling frequency in an image plane space is solved; a high-precision measurement for the illumination uniformity and stray light in small fields of view can be realized at the same time; compared with the conventional test method carried out by driving a point energy sensor through a motion table, the test method provided by the invention makes the test time shorter; and the stray light can be monitored in real time without requiring to load a mask.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Intelligent control system and method for double-field of view thermal imager
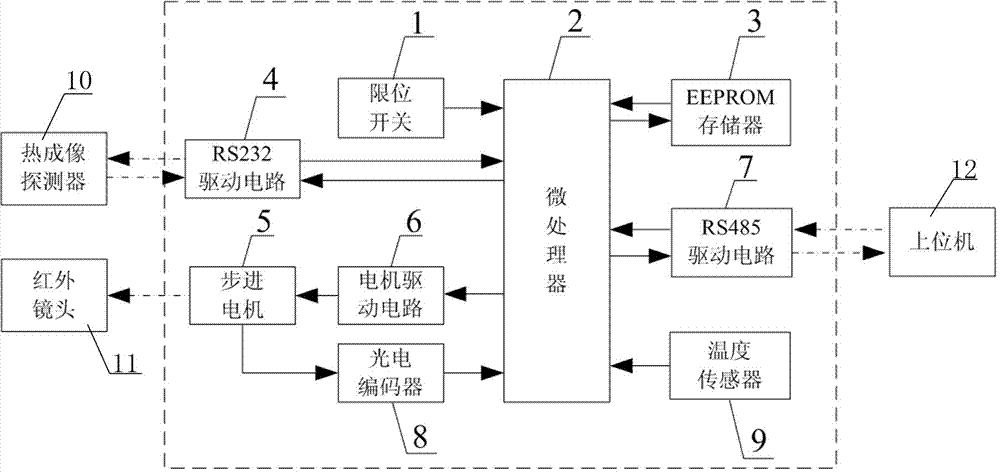
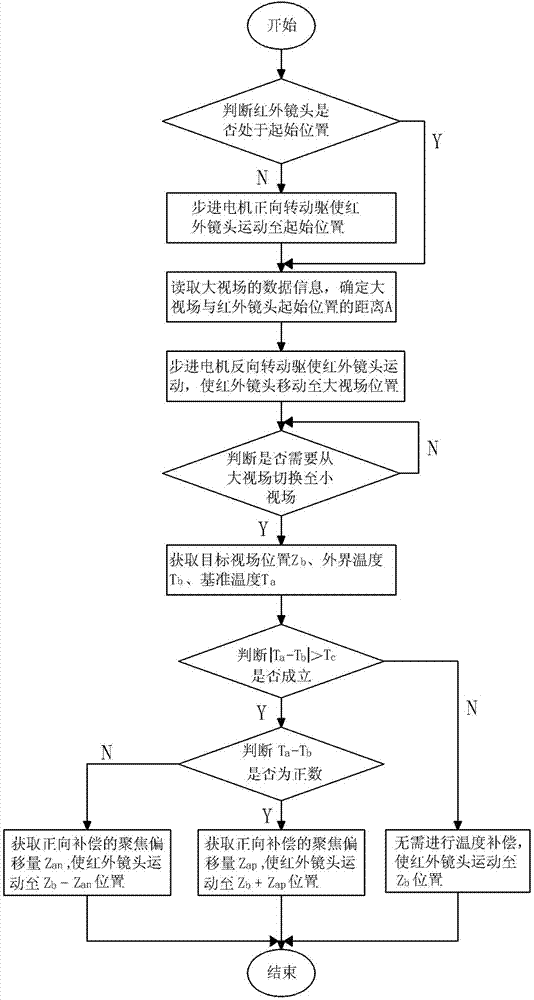
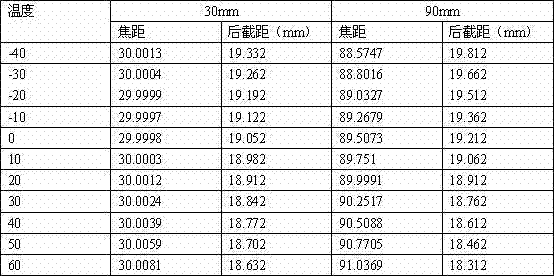
ActiveCN103616897ASwitch accuratelyRealize intelligent compensationControl using feedbackEngineeringIntelligent control system
The invention discloses an intelligent control system of a double-field of view thermal imager. The intelligent control system comprises an infrared lens, a thermal imaging detector, a microprocessor, a stepping motor and a limit switch. The intelligent control system is characterized in that the microprocessor drives the stepping motor to operate through a motor driving circuit, and the input end of the microprocessor is connected with a photoelectric encoder and a temperature sensor. A control method of the intelligent control system of the double-field of view thermal imager comprises the steps of (a) detecting states, (b) moving to a starting position, (c) determining the distance of a large field of view, (d) moving to the position of the large field of view, (e) judging whether switching of fields of view is needed, (f) determining the position and temperature, (g) acquiring a reference temperature, (h) judging whether position compensation is needed, (i) switching to a small field of view, (j) determining focus bias quantity, (k) conducting forward compensation, and (l) conducting reverse compensation. The double-field of view thermal imager can be used for focus position compensation of the fields of view at different temperatures, is accurate, reliable, stable in operation, capable of meeting quick switching between the fields of view, and capable of being widely applied to many fields including weaponry, scout monitoring, people search and rescue and the like.
Owner:山东神戎电子股份有限公司
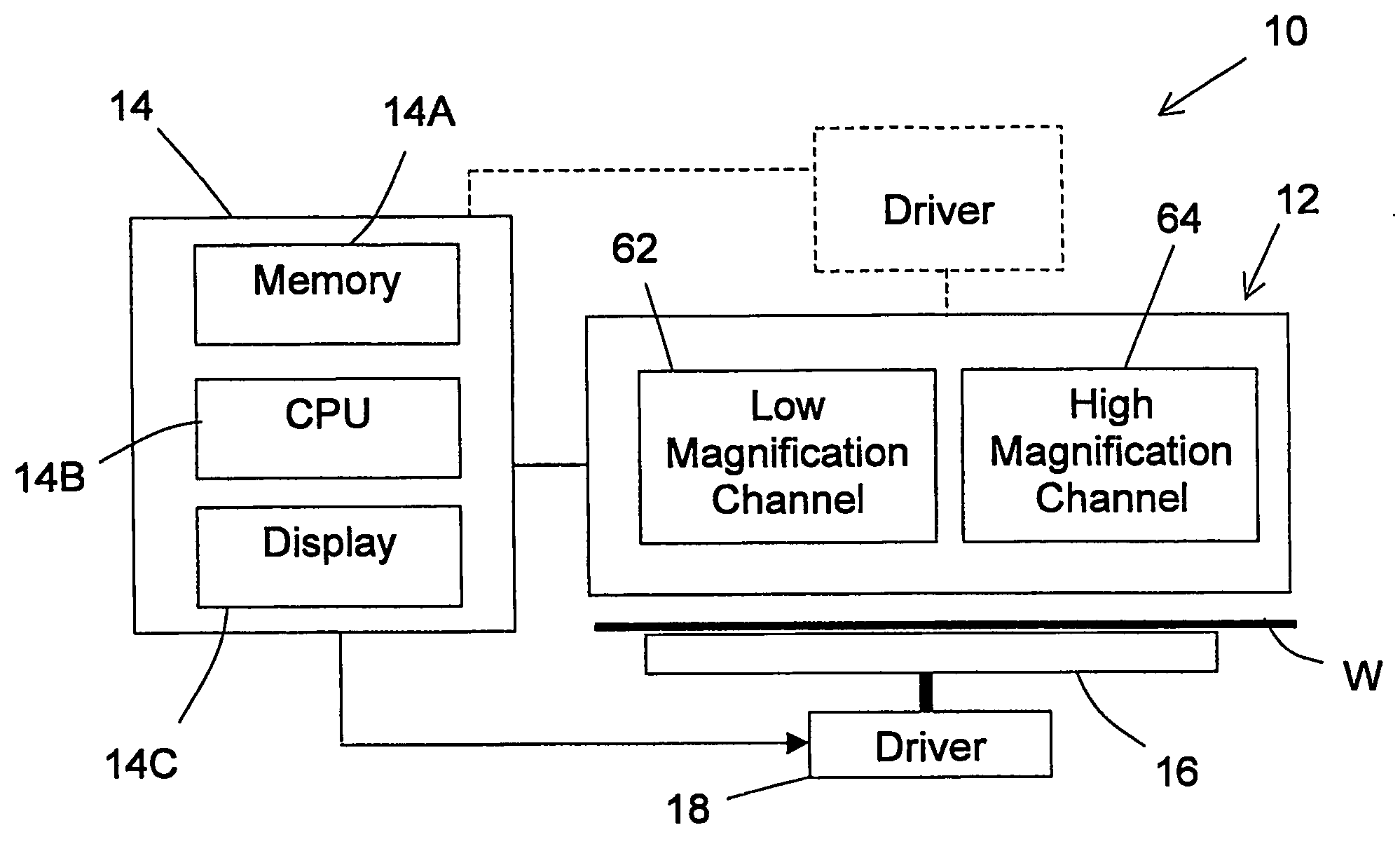
Method and system for automatic target finding
InactiveUS20060232777A1Enhance the imageHigh magnification imagingPhotomechanical apparatusCharacter and pattern recognitionRegion of interestSmall field of view
A method and system are presented for automatic target finding by using two imaging channels with relatively low and high magnifications, using the low magnification channel (relatively large field of view) for finding a region of interest (i.e., that of the targets location within the field), scanning this zone by grabbing images via the high magnification channel (relatively small field of view) and marking the overlay targets using image processing algorithms.
Owner:NOVA MEASURING INSTR LTD
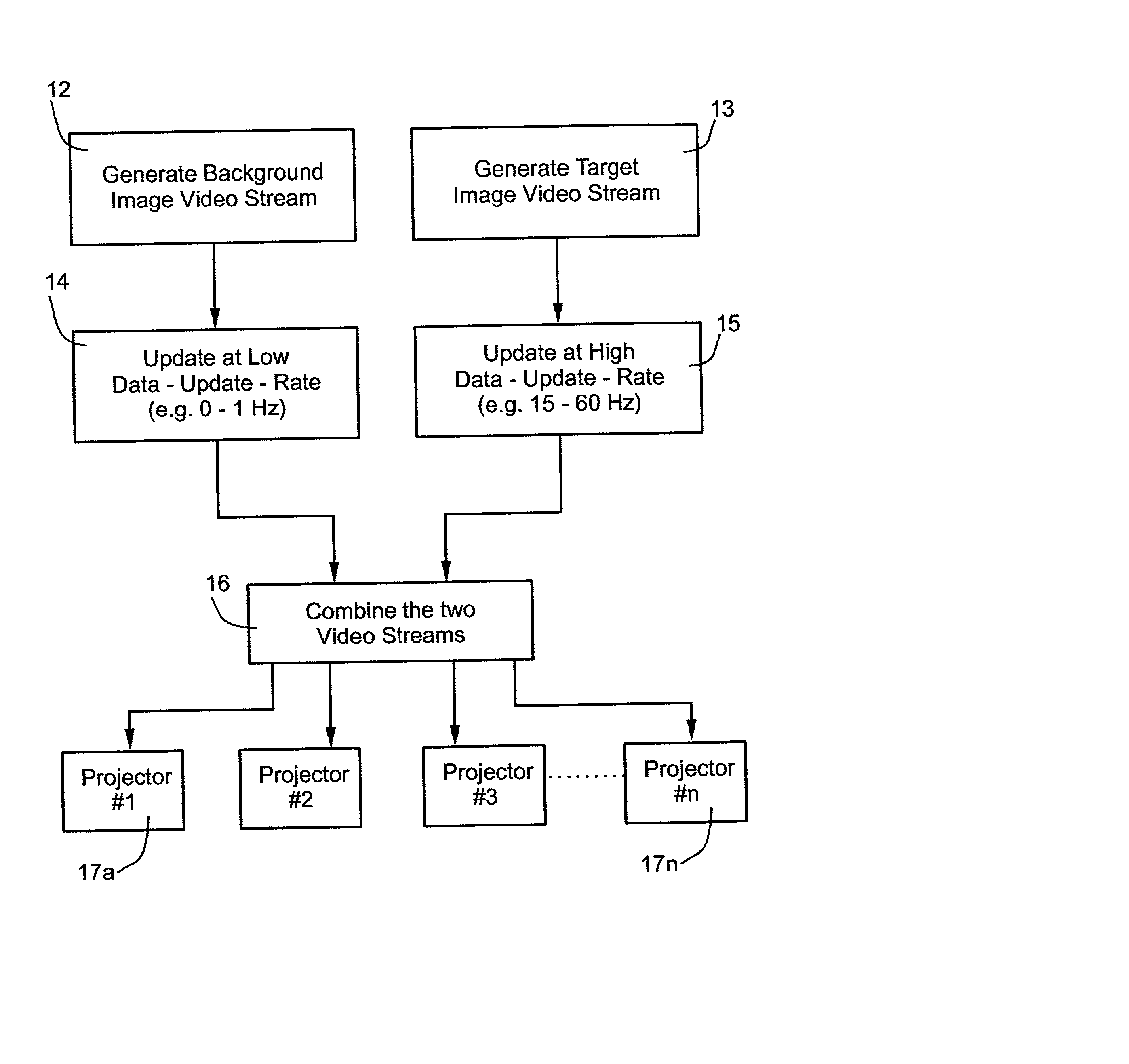
Display apparatus and method particularly useful in simulators
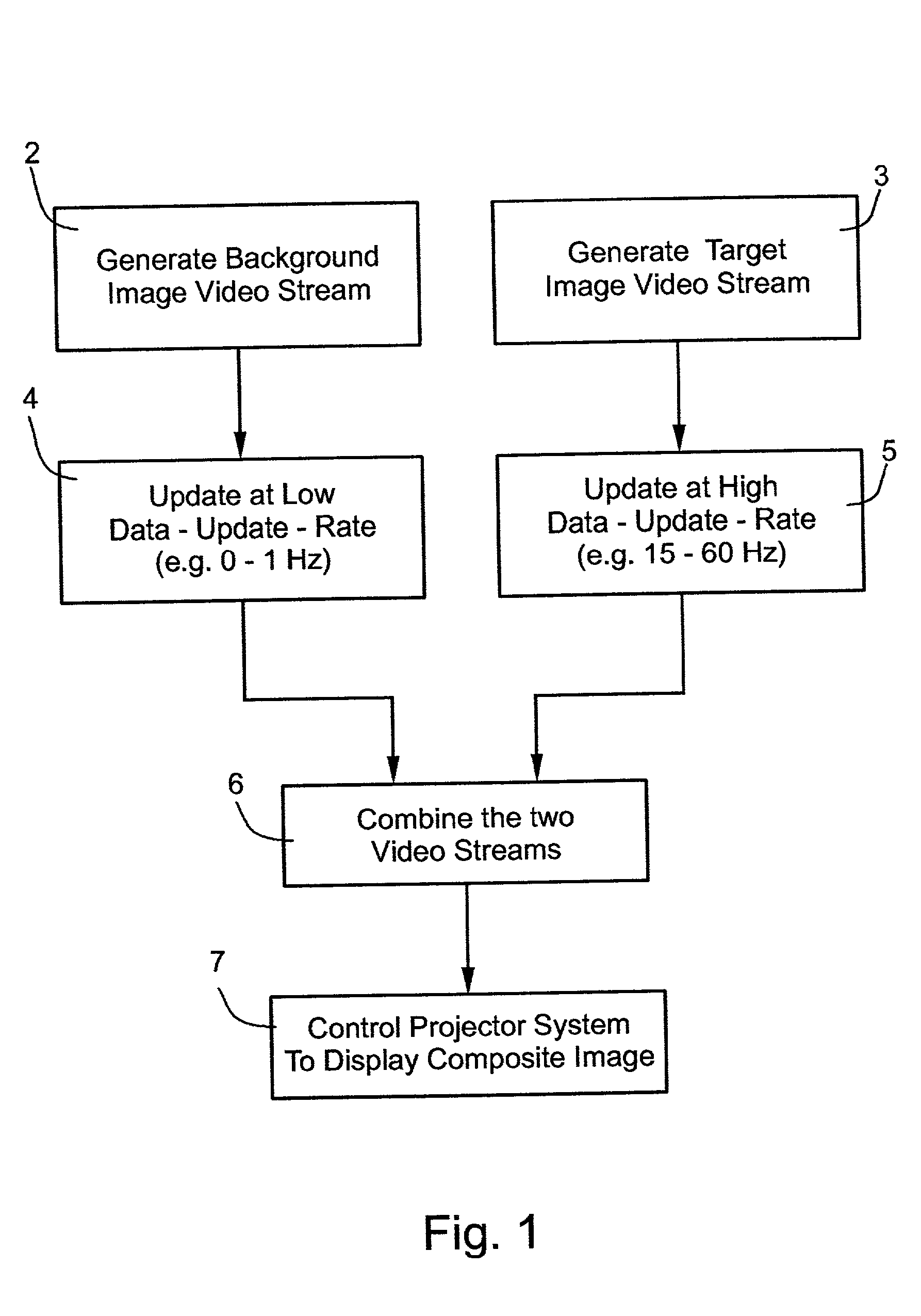
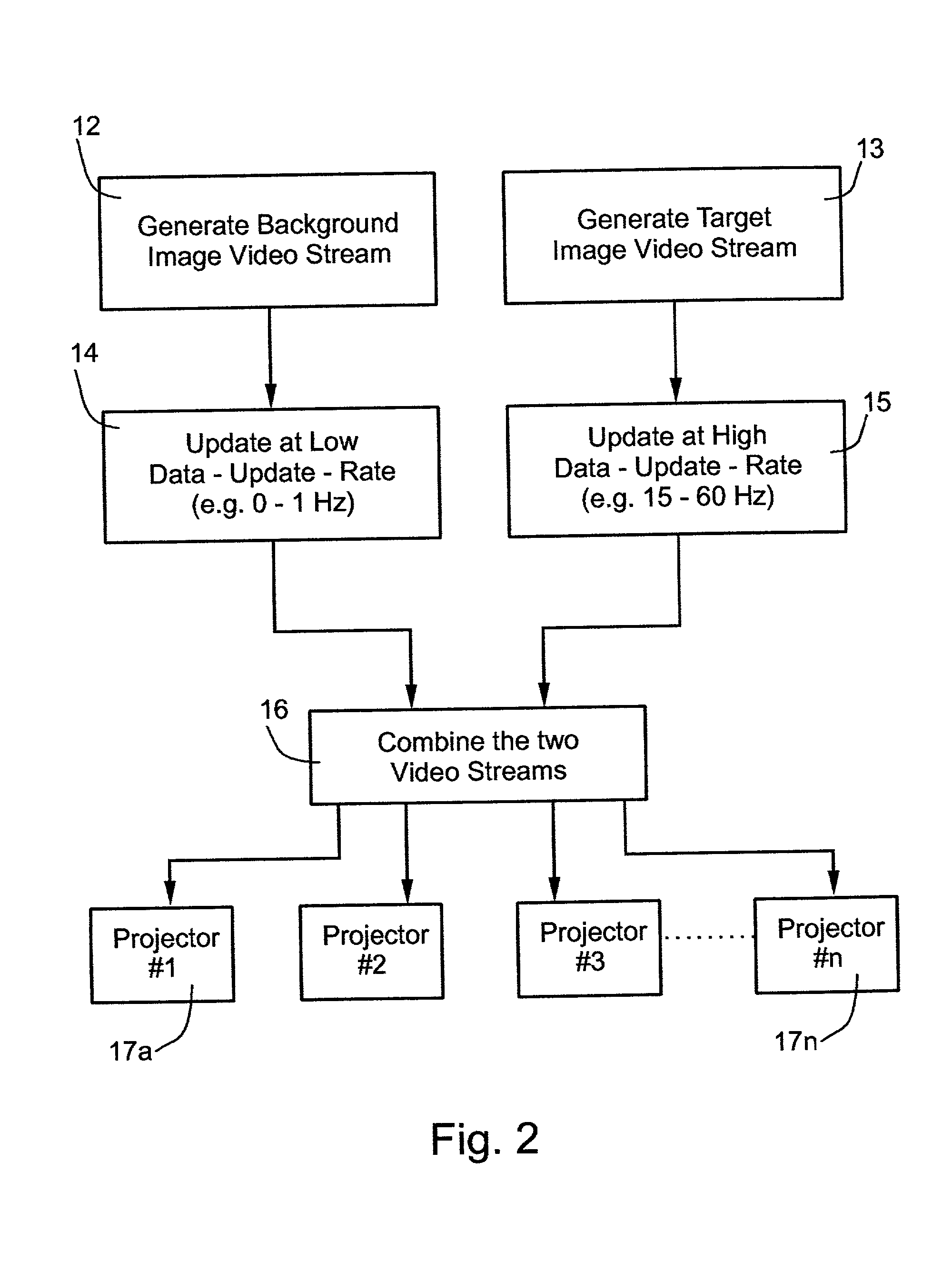
InactiveUS20030011750A1Reduce resolutionIncrease costTelevision system detailsProjectorsComputer graphics (images)Background image
A method and apparatus for displaying composite images, as viewed from a relatively stationary eye point, including a moving target image of relatively small field-of-view overlaid on a background image of relatively large field-of-view, by generating a background image video stream of image data for the background image; updating the background image video stream at a zero or low data update-rate; generating a target image video stream of image data for the target image; updating the target image video stream at a relatively high data update-rate; combining the background and target image video streams to produce a combined video stream; and feeding the combined video stream to a display system for displaying the composite images. The described preferred embodiment is a simulator, wherein the display system includes a plurality of projectors each projecting a predetermined section of the composite image including the background of the respective section, and the portion of the target in the respective section.
Owner:COMVIEW VISUAL SYST
Large-view-field wavefront detection method based on focal plane Hartmann wavefront sensor
InactiveCN111458045AEffective correction and recovery in real timeIncrease profitOptical measurementsWavefront sensorSingle exposure
The invention discloses a large-view-field wavefront detection method based on a focal plane Hartmann wavefront sensor, and the method comprises the steps: recording the spatial information through alight spot array image detected by a CCD detector in the focal plane Hartmann wavefront sensor, and recording the phase information through a microlens array, i.e., incident light waves of different view fields or angles. Based on the special optical structure, wavefront information of multiple fields of view can be measured at a time, and therefore the effect of a large field of view is achieved.However, a traditional wavefront detector generally has a small field of view or a zero-degree field of view and can only detect a middle field of view. According to the invention, the problem of wavefront error large-view-field measurement is solved, and under the condition that the detection caliber of the wavefront detector is fixed, the view field range of wavefront information which can be restored by single exposure is increased, and the image restoration precision is enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
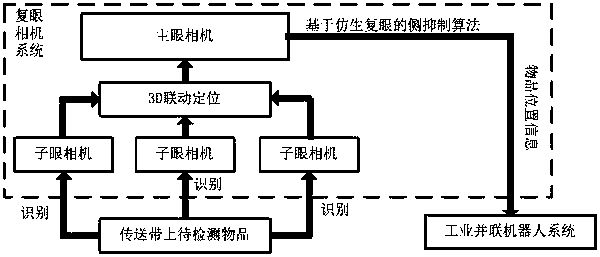
Industrial parallel robot fast visual inspection algorithm based on bionic compound eye structure
InactiveCN107610086ARecognition speed is fastEasy to identifyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionEngineering
An industrial parallel robot fast visual inspection algorithm based on bionic compound eye structure is provided. A compound eye camera system includes multiple sub-eye cameras and a main eye camera mounted on the front end of an industrial parallel robot, and a lateral inhibition algorithm based on bionic compound eyes. The algorithm can rapidly capture the contours of objects on a conveyor beltunder the global field of view, and make the industrial parallel robot vision system extremely sensitive to a target contour. After the sub-eye cameras obtain a target position quickly, a coordinate mapping relationship is adopted so that the main eye camera after receiving a command can rapidly magnify and locate the target position so as to perform further small field of view and large-target recognition and improve the visual recognition rate and efficiency of the industrial parallel robot.
Owner:TIANJIN SUPER ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Method for optimizing freeform surface optical system in combination with surface form and field-of-view optimization strategy
ActiveCN107219626AFast optimizationImprove optimization speedOptical elementsFast optimizationWave aberration
The invention discloses a method for optimizing a freeform surface optical system in combination with a surface form and a field-of-view optimization strategy. The method uses the respective coefficients of a Zernike standard polynomial representing an optical system wave aberration as an evaluation basis, develops a optimization process by a successive approximation strategy combining surface form optimization and field of view optimization, and comprises steps of: firstly, selecting an initial small field of view, searching out the maximum item of system aberration targetedly in each optimization step according to an established XY polynomial and a polynomial relation model, selecting a corresponding XY polynomial item in the freeform surface as a new-added variable to optimize and balance the aberration, and synchronously adjusting the weight of each field of view according to the wave aberration rms values of respective fields of view of the system; after a structure satisfying a performance index is optimized and acquired within a small field of view range, gradually expanding the field of view and repeating the optimization steps until optical system structure parameters within all field of view range are obtained. The method has a large field of view, fast optimization speed, aberration pertinence and guidance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical imaging lens and imaging equipment
ActiveCN110632743ACompact structureDimensional ConstraintsOptical elementsCamera lensImage resolution
The invention provides an optical imaging lens and imaging equipment, and the optical imaging lens comprises, in order from the object side to the image side, the following parts of a first lens having focal power, wherein the object side is convex, and the image side is concave; a second lens having negative focal power, wherein the object side is concave, and the image side is concave; a third lens having positive focal power, wherein the object side is convex, and the image side is convex; a fourth lens having positive focal power, wherein the object side is convex, and the image side is convex; a fifth lens having positive focal power, wherein the object side is convex, and the image side is convex; a sixth lens having negative focal power, wherein the object side is concave, the imageside is concave, and the fifth lens and the sixth lens constitutes a cemented body; a seventh lens having a negative focal power, wherein the object side is concex, and the image side is concave; anda diaphragm. The optical imaging lens provided by the invention has the characteristics of a large aperture, a long focal length, high resolution, and the like, and can meet the requirements of a small field of view and a high resolution lens in the automotive field.
Owner:JIANGXI LIANCHUANG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com