Small-view-field magnetic resonance imaging method based on single-sweep super-speed orthogonal space-time coding
A technology of orthogonal space-time coding and magnetic resonance imaging, which is applied in the direction of using nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system for measurement, magnetic resonance measurement, magnetic variable measurement, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of improving the spatial resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
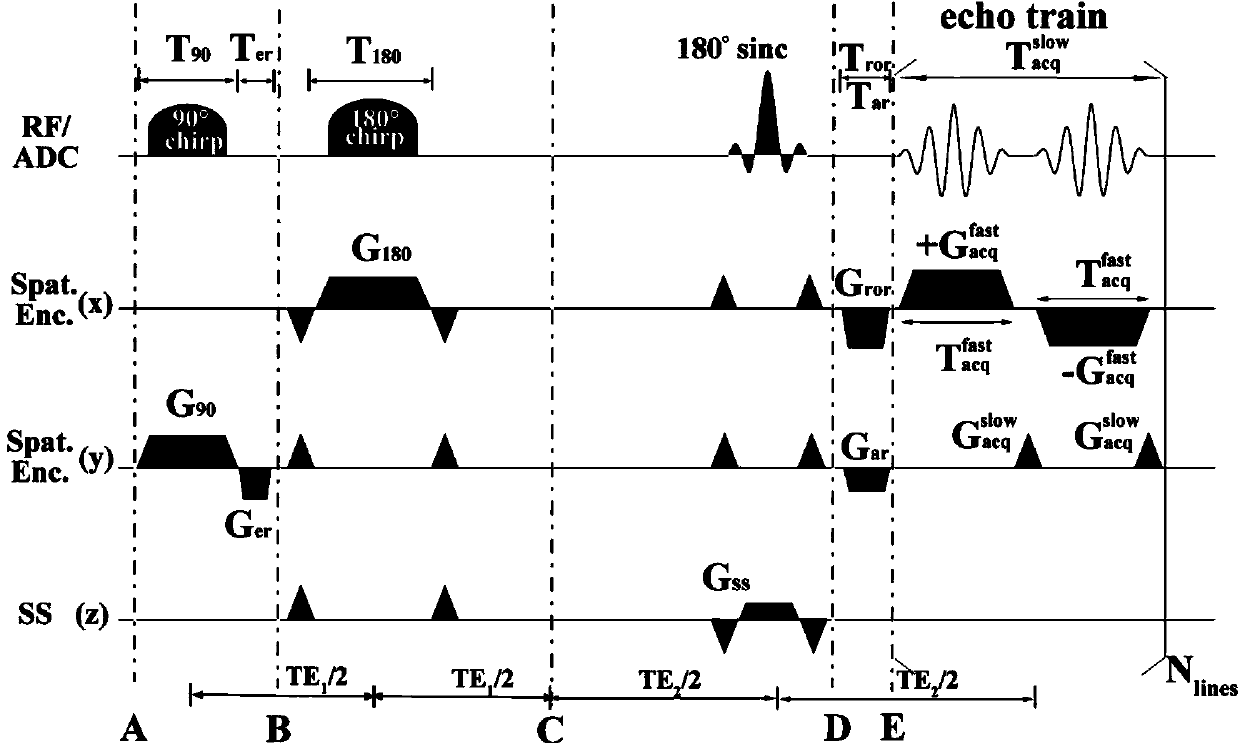
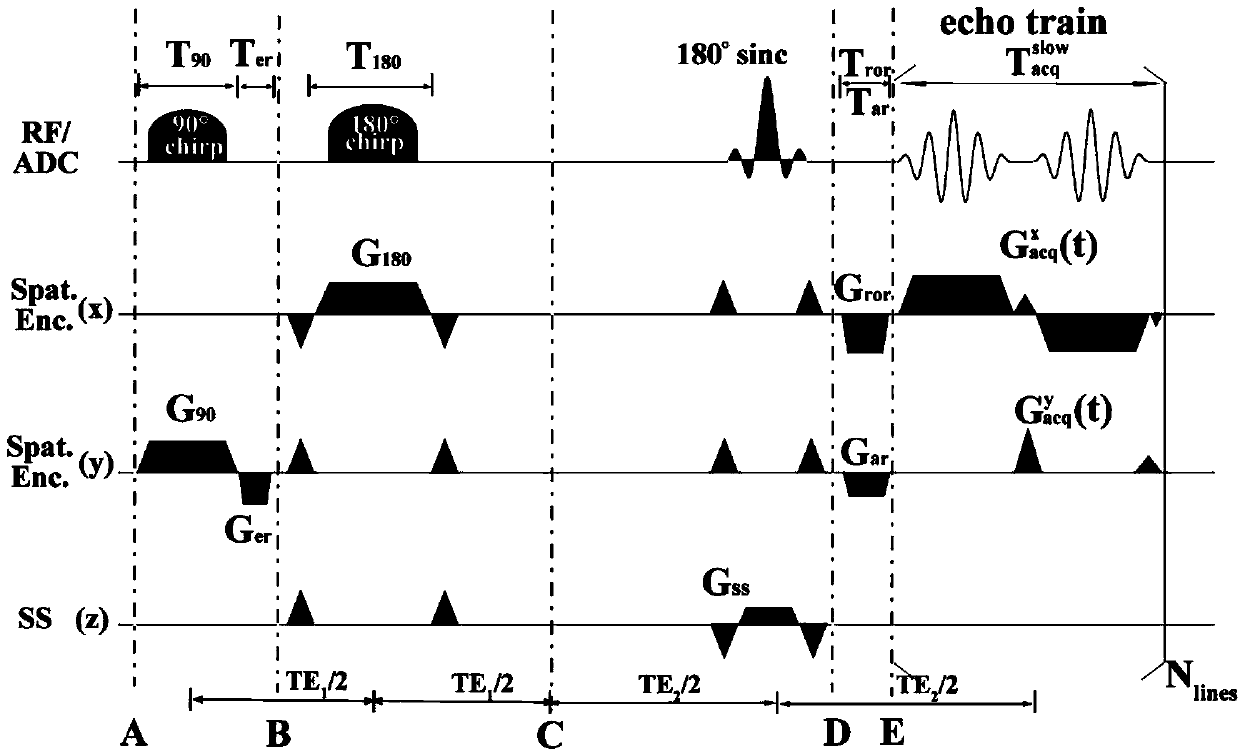
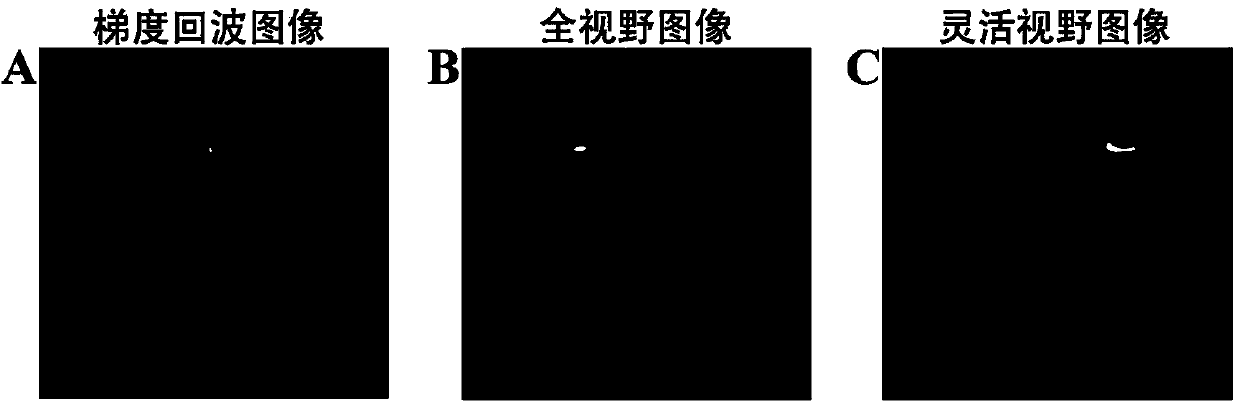
[0047] We will demonstrate the small field of view magnetic resonance imaging method based on single-scan ultra-fast orthogonal spatio-temporal encoding in live SD rats to verify the feasibility of the present invention. Experimental tests were performed on a Varian7T imager (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The imaging sample used in the experiment was about 250 grams of living SD rats. Before the experiment, the rats were injected with 10% chloral hydrate solution at a ratio of 0.4mg / 100g to anesthetize the rats. experiment of. Before the experiment, the rat was fixed on the experimental bed and then introduced into the imager. On the operating table of the magnetic resonance imager, open the corresponding operating software of the imager, and locate the rat site of interest. Here we choose to perform coronal imaging on the brain of the rat. Then we perform tuning, shimming, frequency and power correction. According to the operation process of the flexible fie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com