Patents
Literature
615 results about "Secondary phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
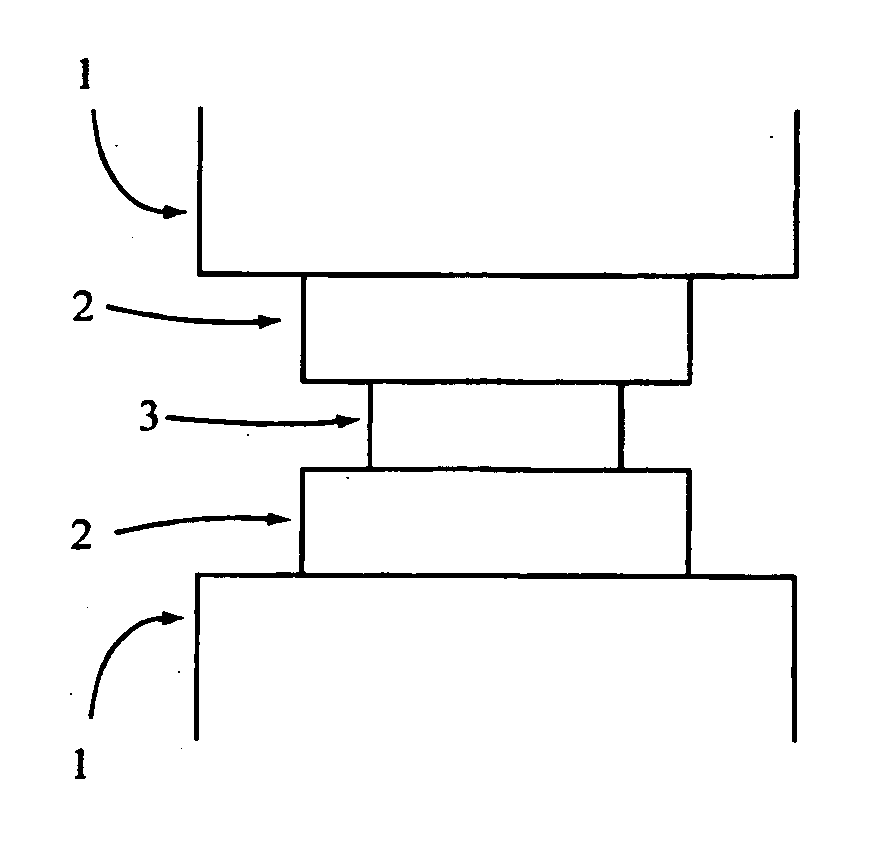
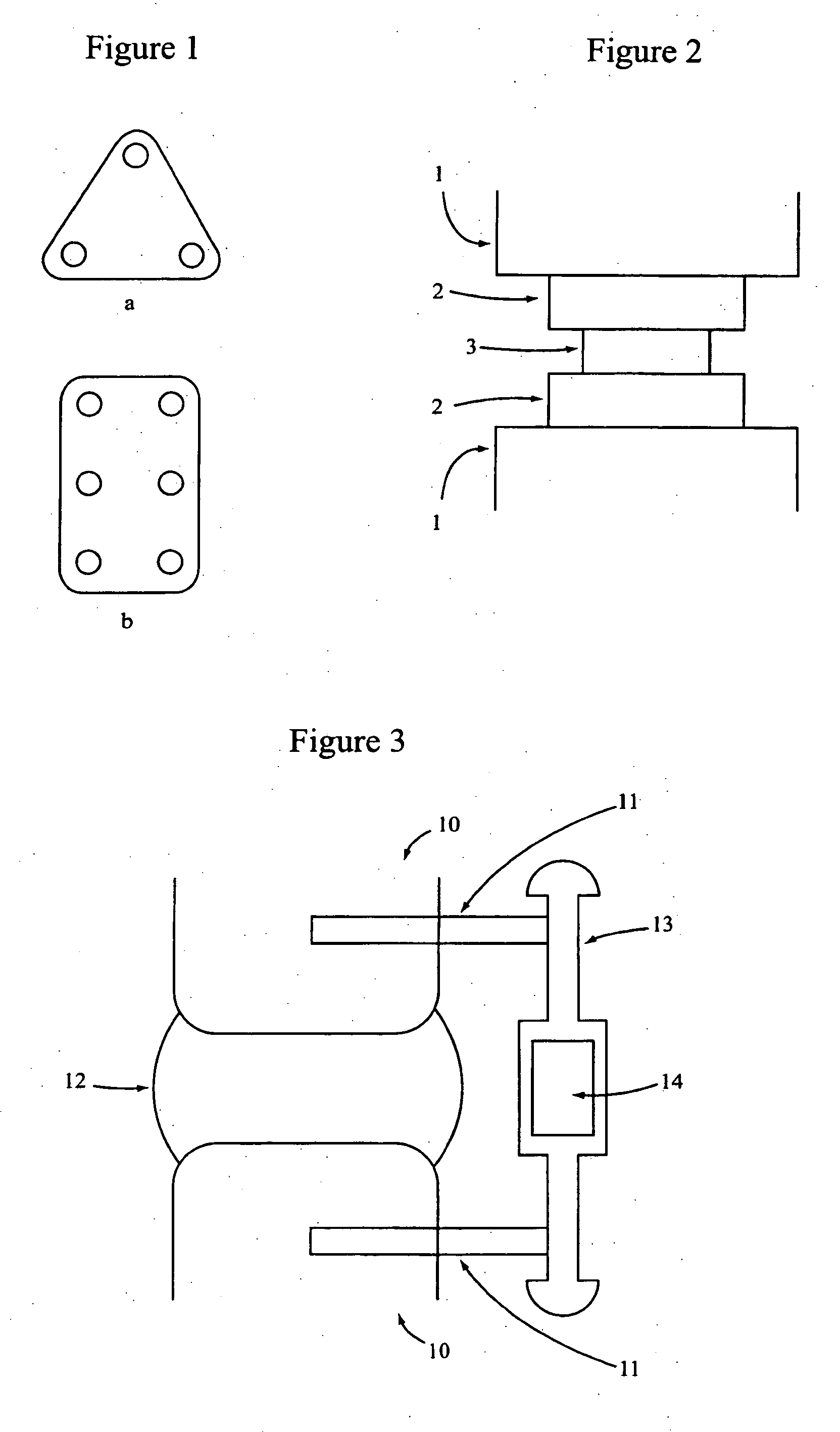
Materials, devices and methods for implantation of transformable implants
InactiveUS20060095134A1Easy to useQualityInternal osteosythesisLigamentsImplanted deviceSecondary phase
A transformable implantable device is disclosed comprising primary and secondary phases or materials. The secondary phase or material is relatively rigid compared to the primary phase or material and also renders the transformable implantable device relatively rigid compared to the primary phase or material. The secondary phase or material, upon implantation, becomes more flexible, thereby rendering the transformable implantable device more flexible also.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
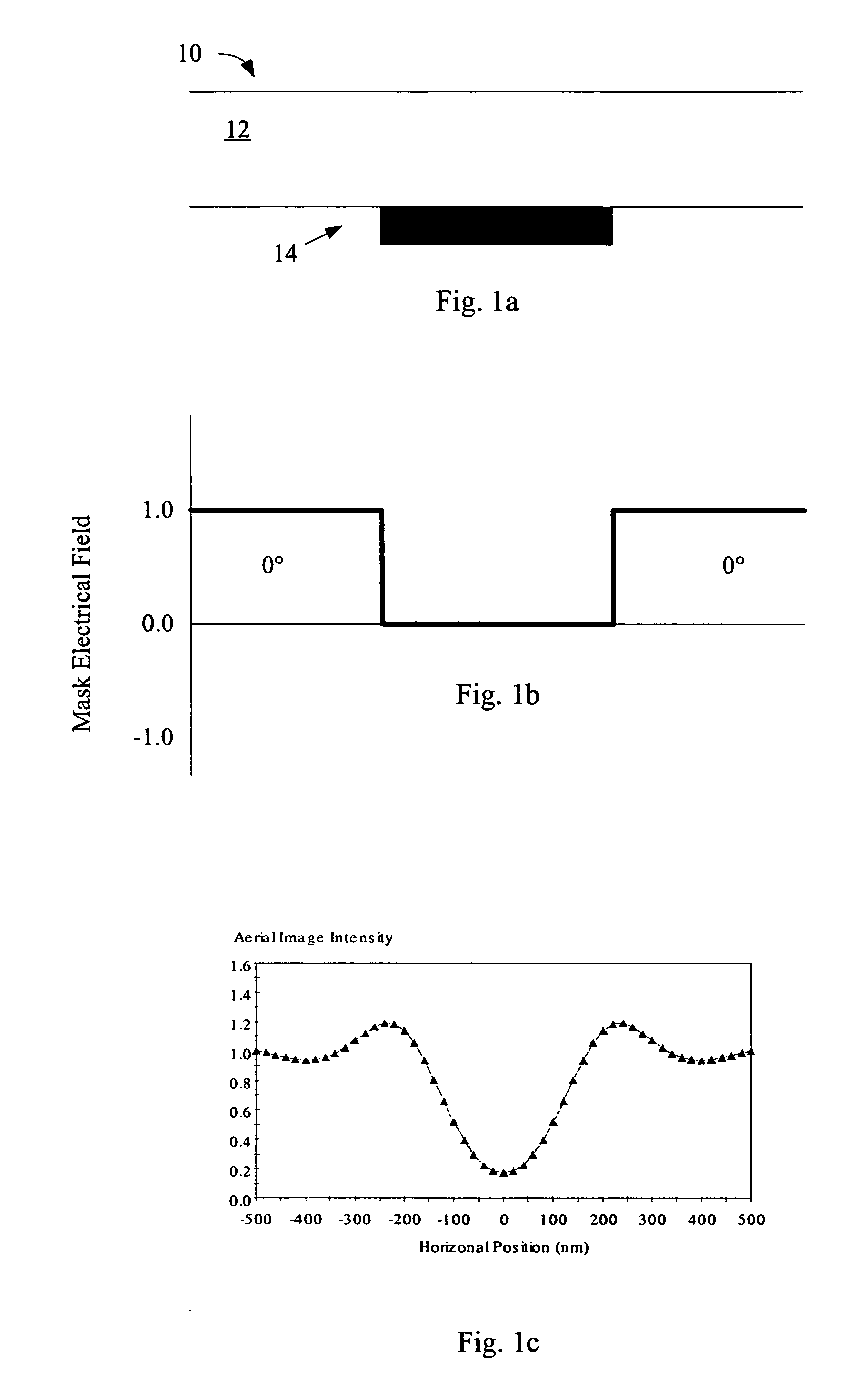
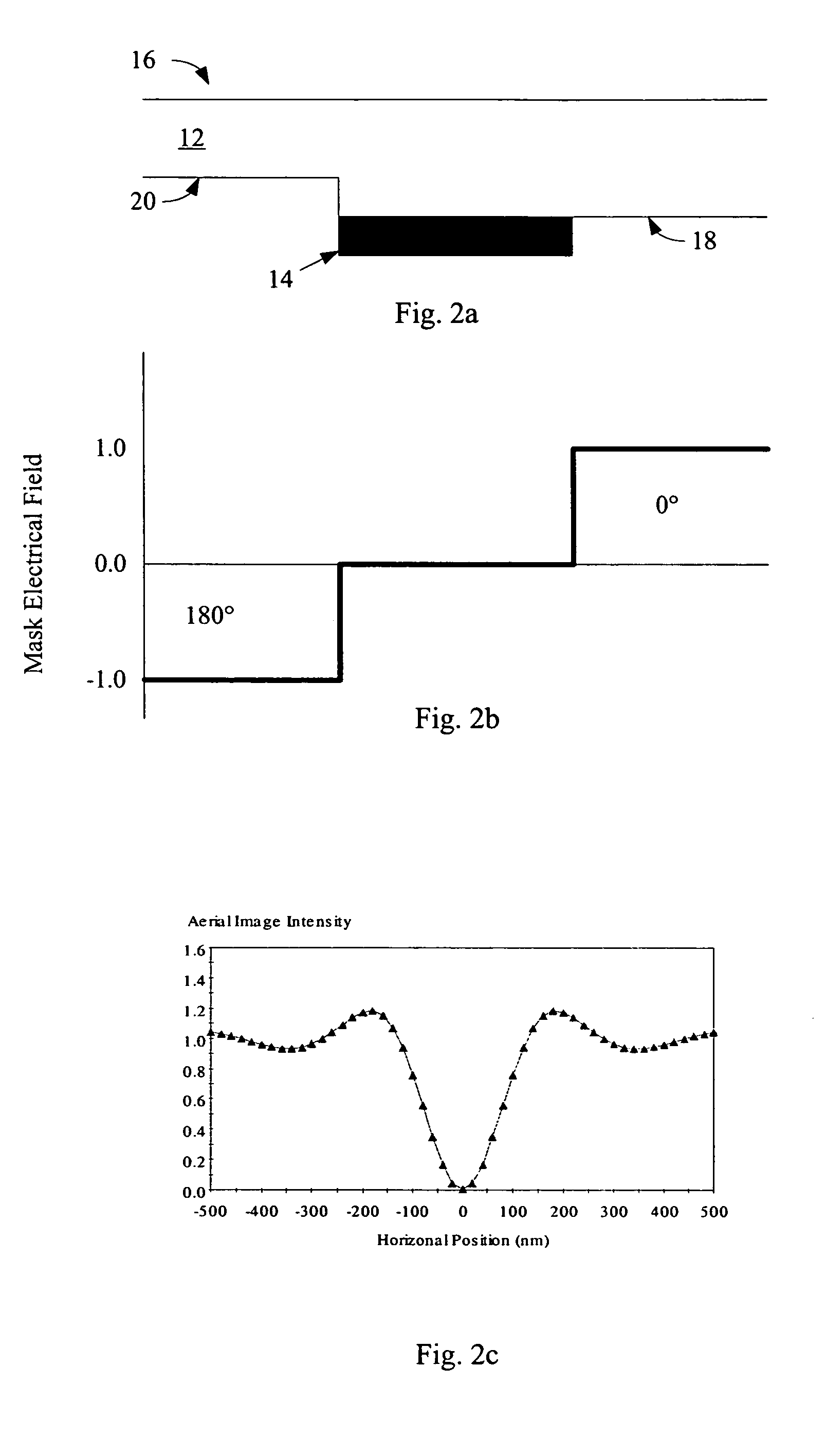
Photomask features with chromeless nonprinting phase shifting window
InactiveUS20050221200A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsPhase cancellationPhotoresist
Aspects of the present invention provide for a novel photomask for patterning features for an integrated circuit, the photomask including a first area transmitting light in a first phase surrounded by second area, the second area transmitting light in a second phase, the second phase opposite the first phase. No blocking material separates the first area from the second area. After development of photoresist, the transition between the first and second area causes formation of a residual photoresist feature on the photoresist surface due to phase canceling of light. If the first area is small enough, it is nonprinting, ie., the opposite sides of the residual photoresist feature formed at its perimeter merge, forming a contiguous photoresist feature, and thus a corresponding patterned feature after etch.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
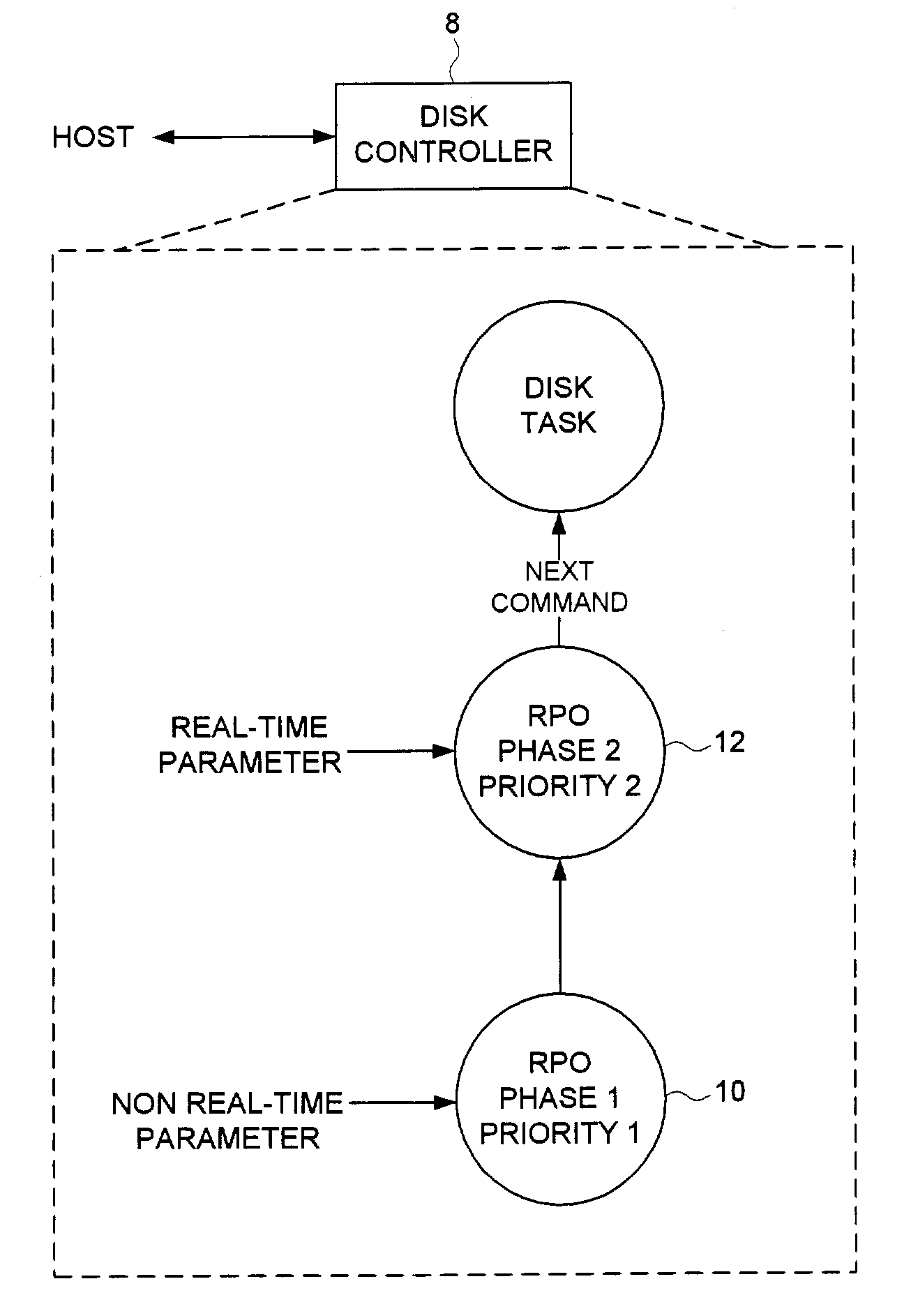
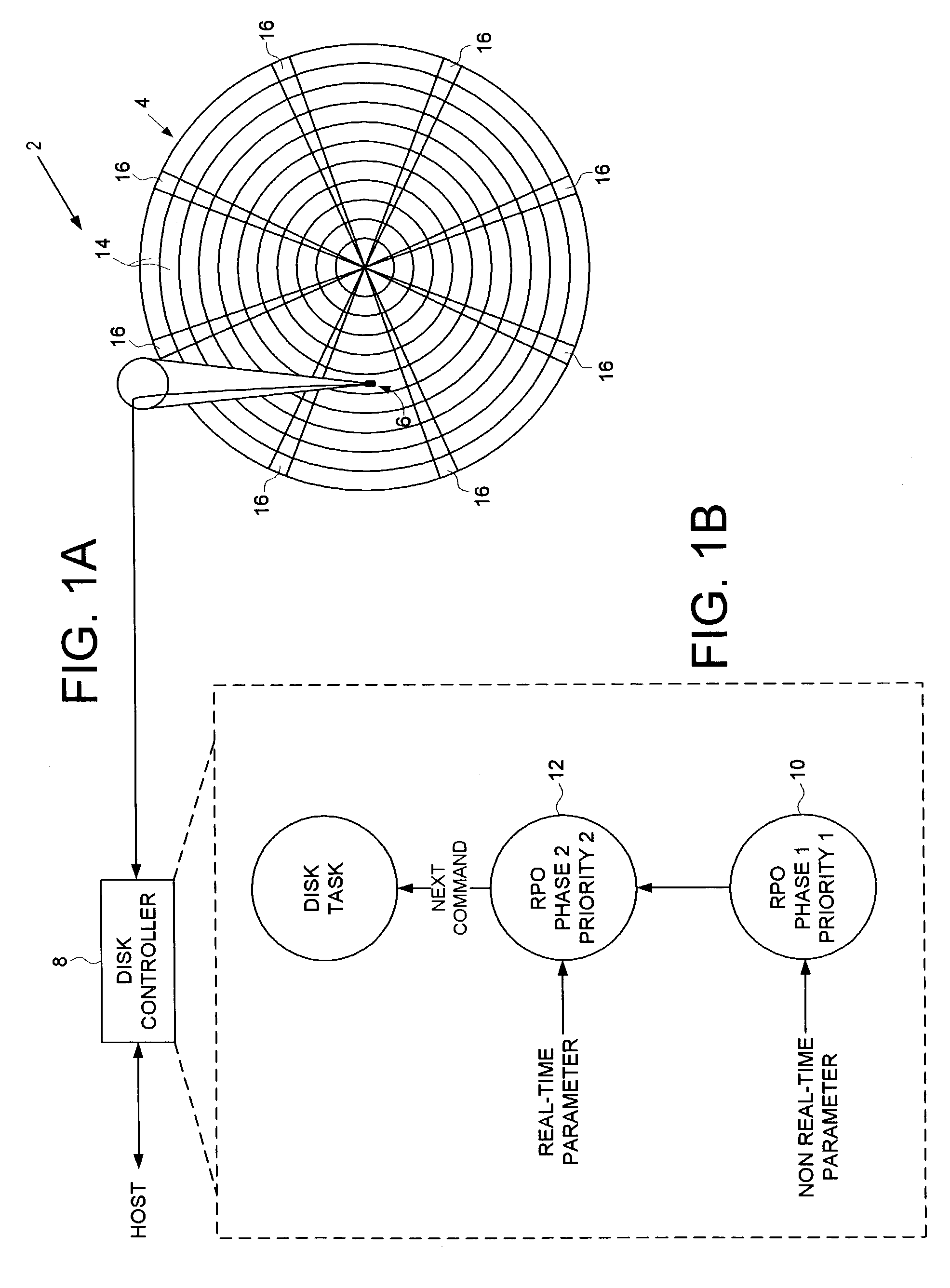
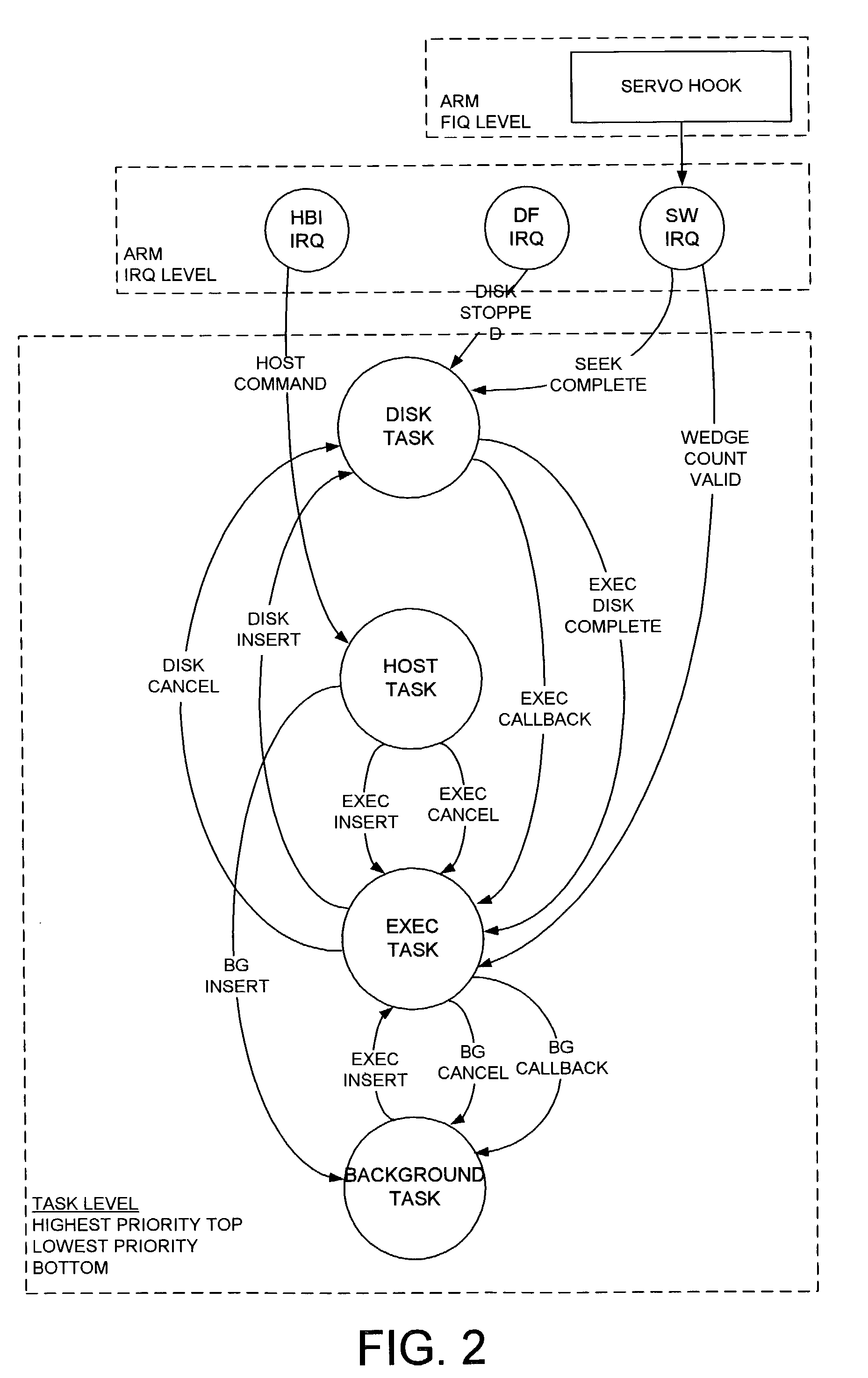
Disk drive employing a multi-phase rotational position optimization (RPO) algorithm
InactiveUS7114029B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksNon real timeMulti phase
A disk drive is disclosed which executes a rotational position optimization (RPO) algorithm for selecting a next command to execute out of a plurality of pending commands. The RPO algorithm comprises a first phase and a second phase. The first phase of the RPO algorithm is executed relative to a first priority and in response to at least one non-real-time parameter. The second phase of the RPO algorithm is executed relative to a second priority higher than the first priority and in response to at least one real-time parameter.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
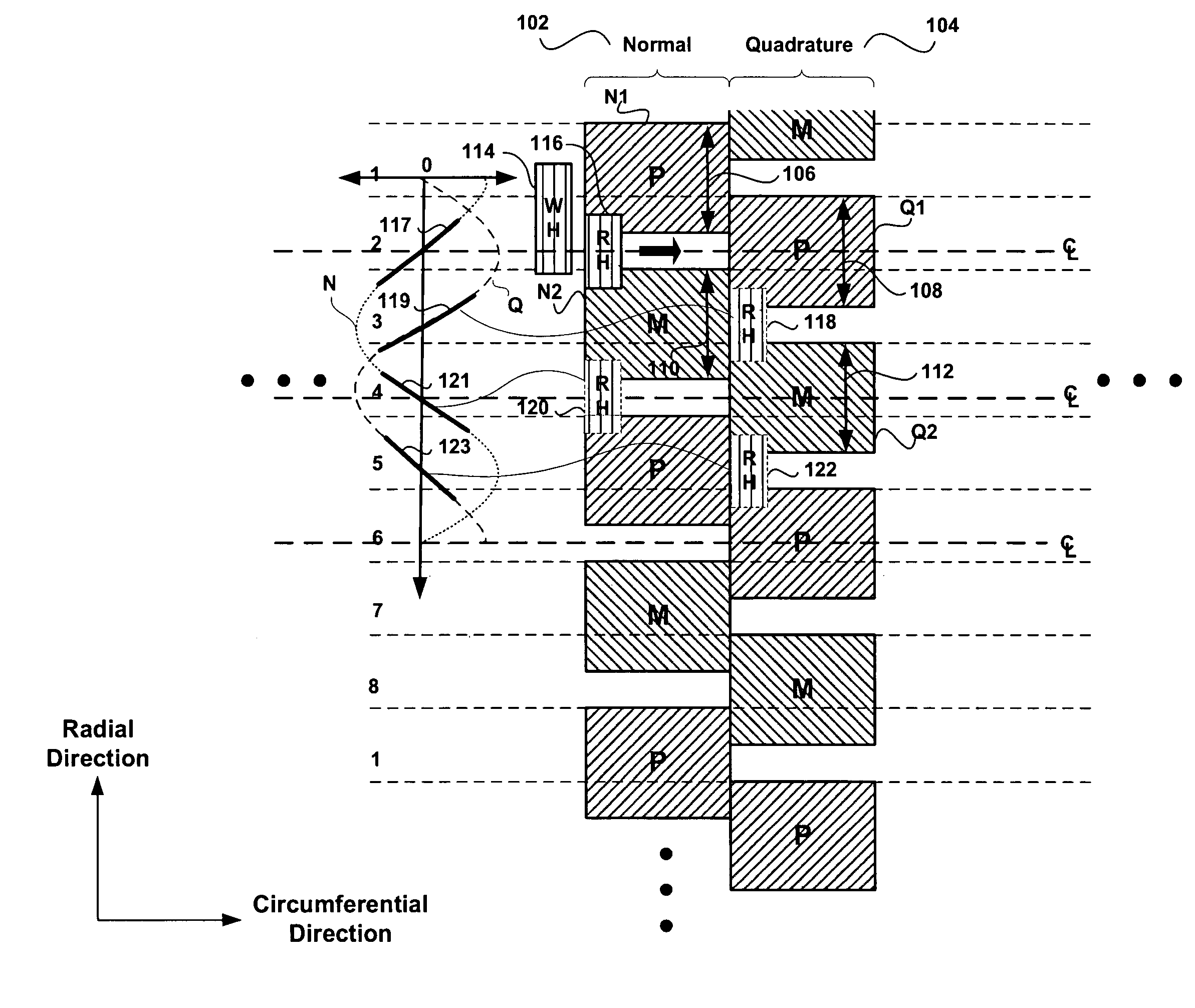
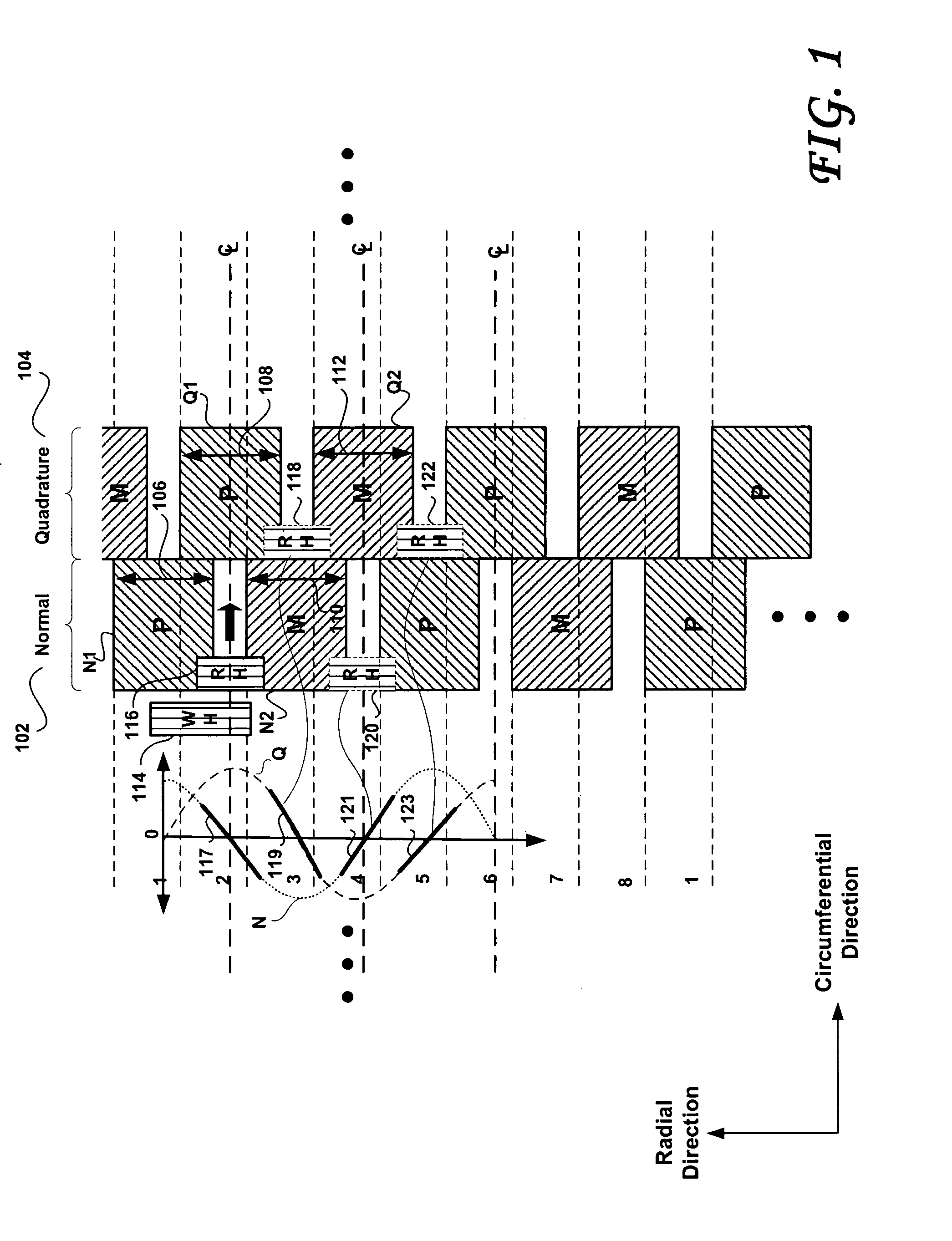
Disk drive having a disk including a servo burst pattern having a normal servo burst field and a quadrature servo burst field
InactiveUS6980389B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksEngineeringControl theory
A disk drive has a sampled servo system controller and a disk. The disk has a plurality a plurality servo burst fields, the plurality of servo burst field including first and second normal burst fields, and first and second quadrature burst fields. A portion of the first quadrature burst field is circumferentially contiguous with the first normal burst field and spans a portion of a radial extent of the first normal burst field. The second normal burst field is radially aligned with and away from the first normal burst field and spans a portion of a radial extent of the first quadrature burst field. The second quadrature burst field is radially aligned with and away from the first quadrature burst field and spans a portion of a radial extent of the second normal burst field. The first normal burst field and the first quadrature burst field have a same first phase and the second normal burst field and the first quadrature burst field have a same second phase. The first phase is different than the second phase.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
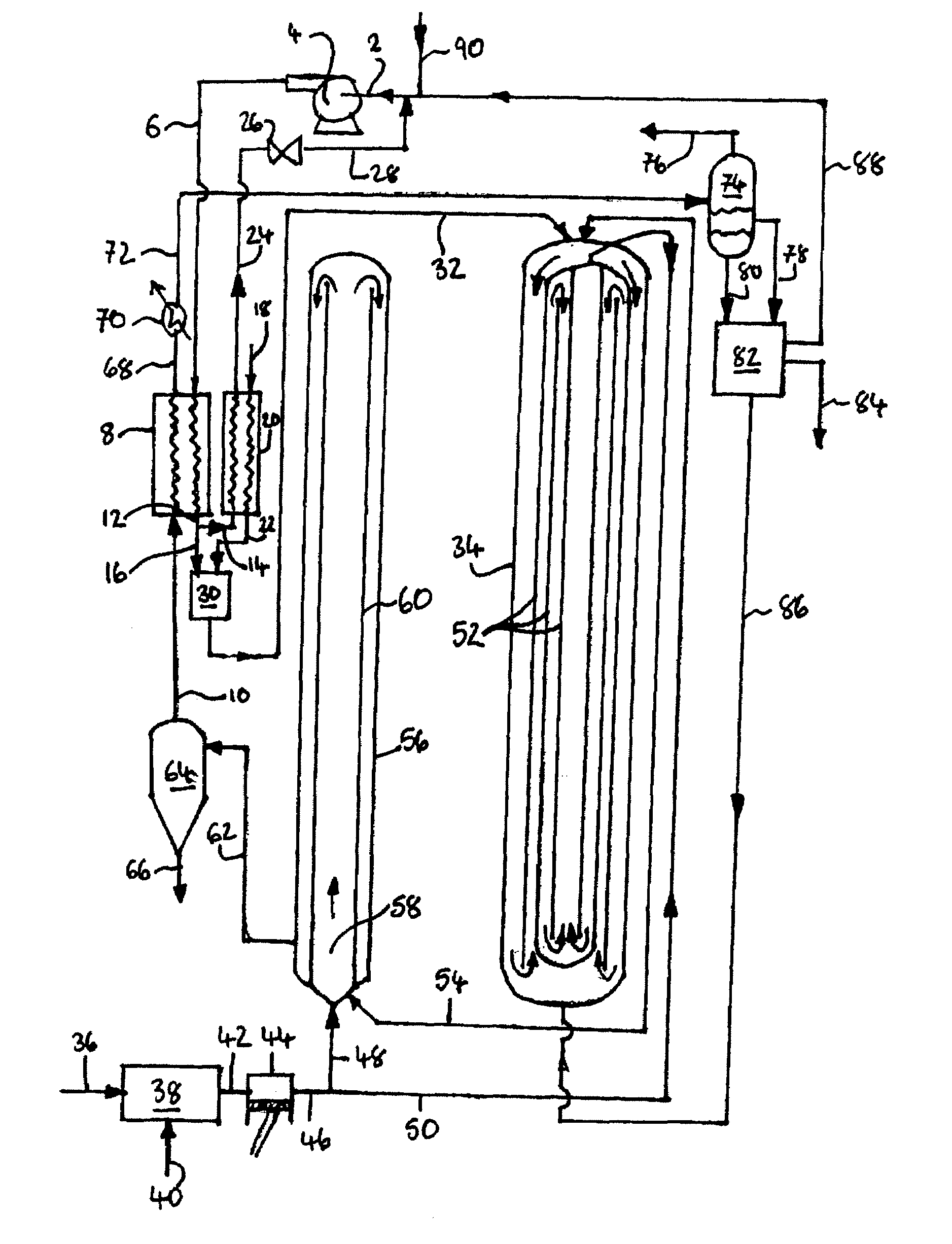
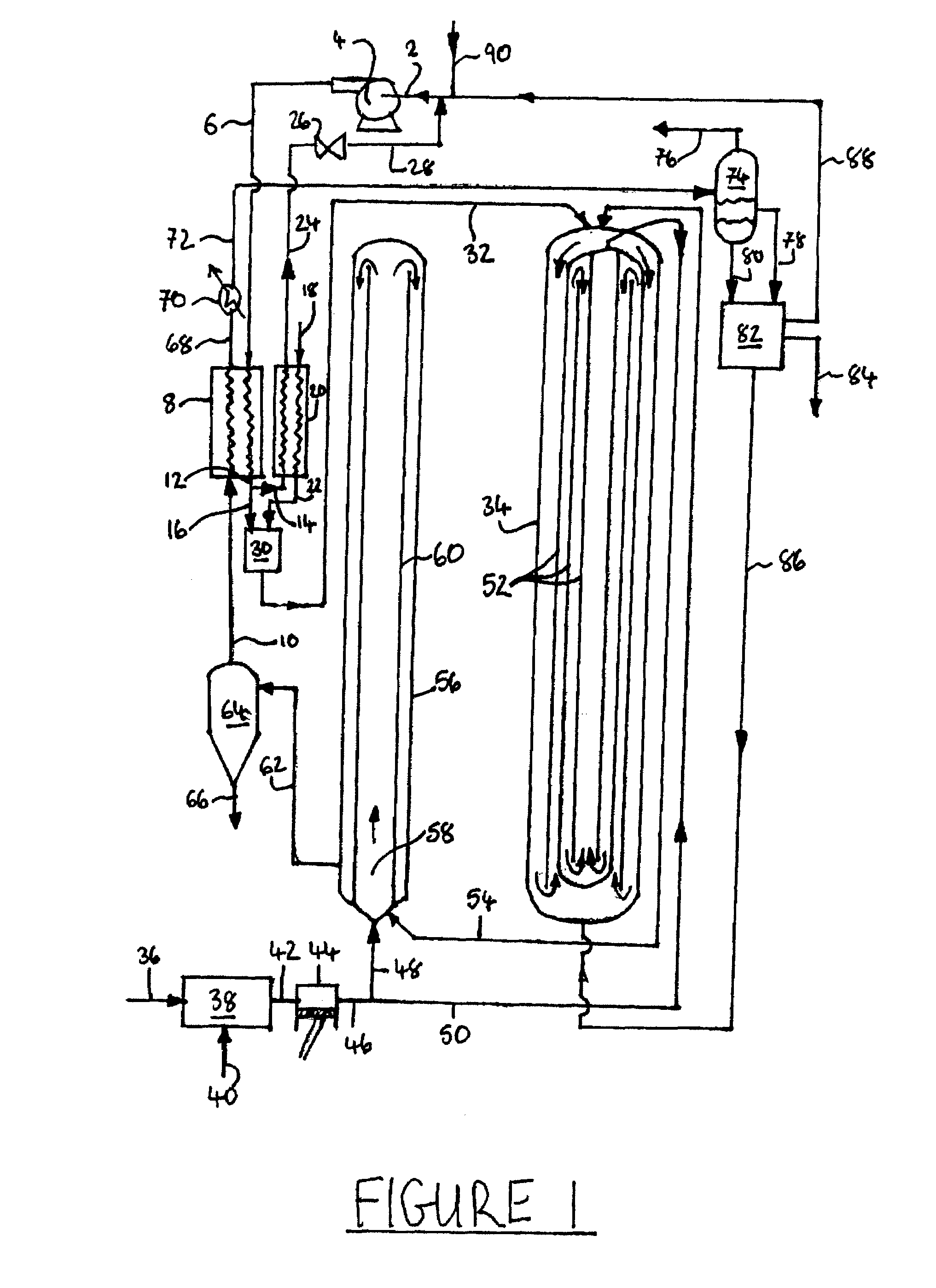
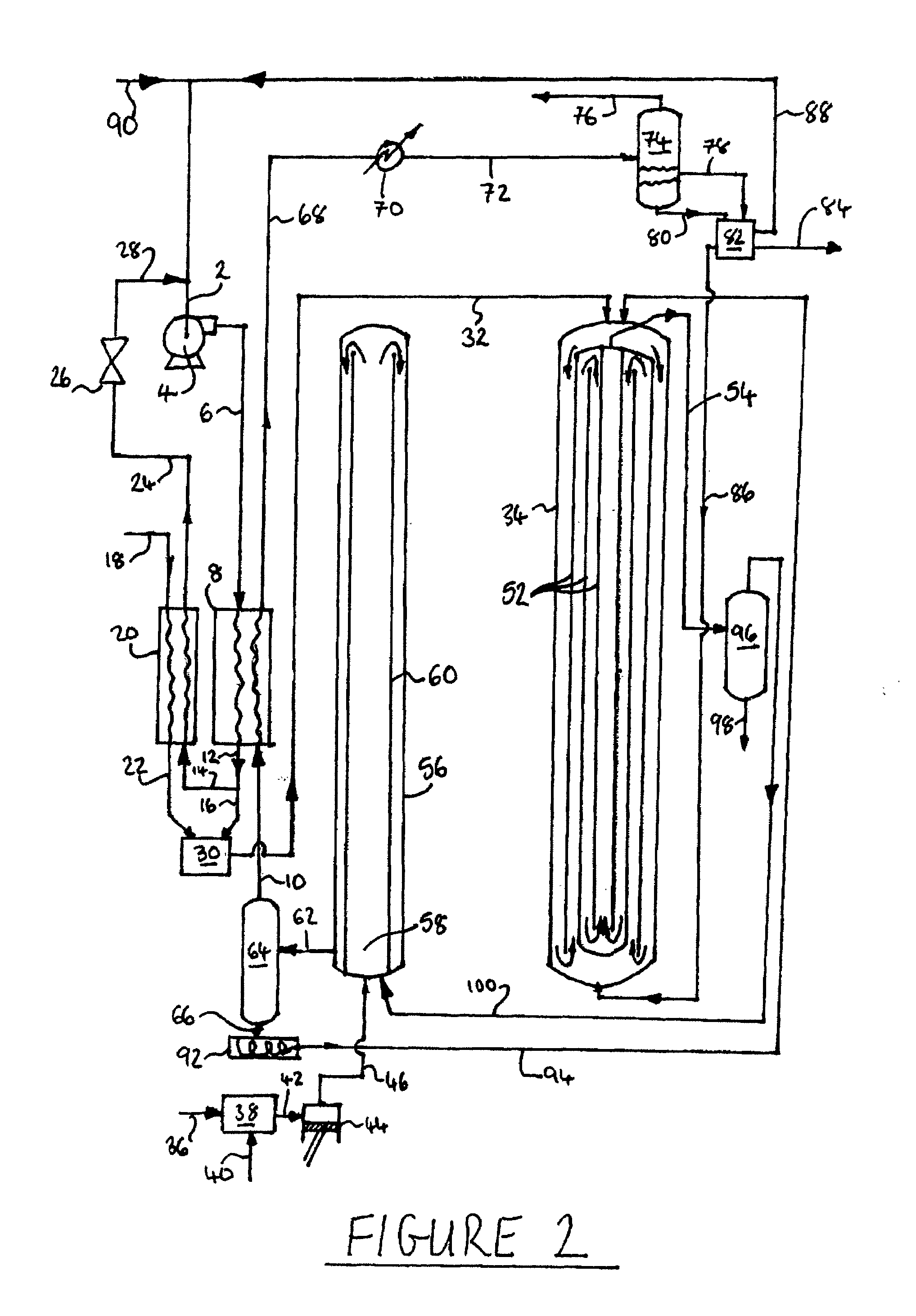
Process and apparatus for upgrading coal using supercritical water
Coal is converted into hydrocarbon compounds using supercritical water. The process involves two stages; a first stage in which carbonaceous material is reacted with supercritical water at above 850K to produce a first supercritical fluid reaction mixture comprising hydrocarbon compounds; and a second stage in which hydrocarbon compounds are extracted from coal mixed with at least a portion of the first supercritical fluid at a temperature within a range of from the supercritical temperature of water to about 695K. Char from the second stage is finely divided and may be either be used outside the process, e.g. in a coal fired power station or a gasifier, or used as at least a portion of the carbonaceous material used in the first stage.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
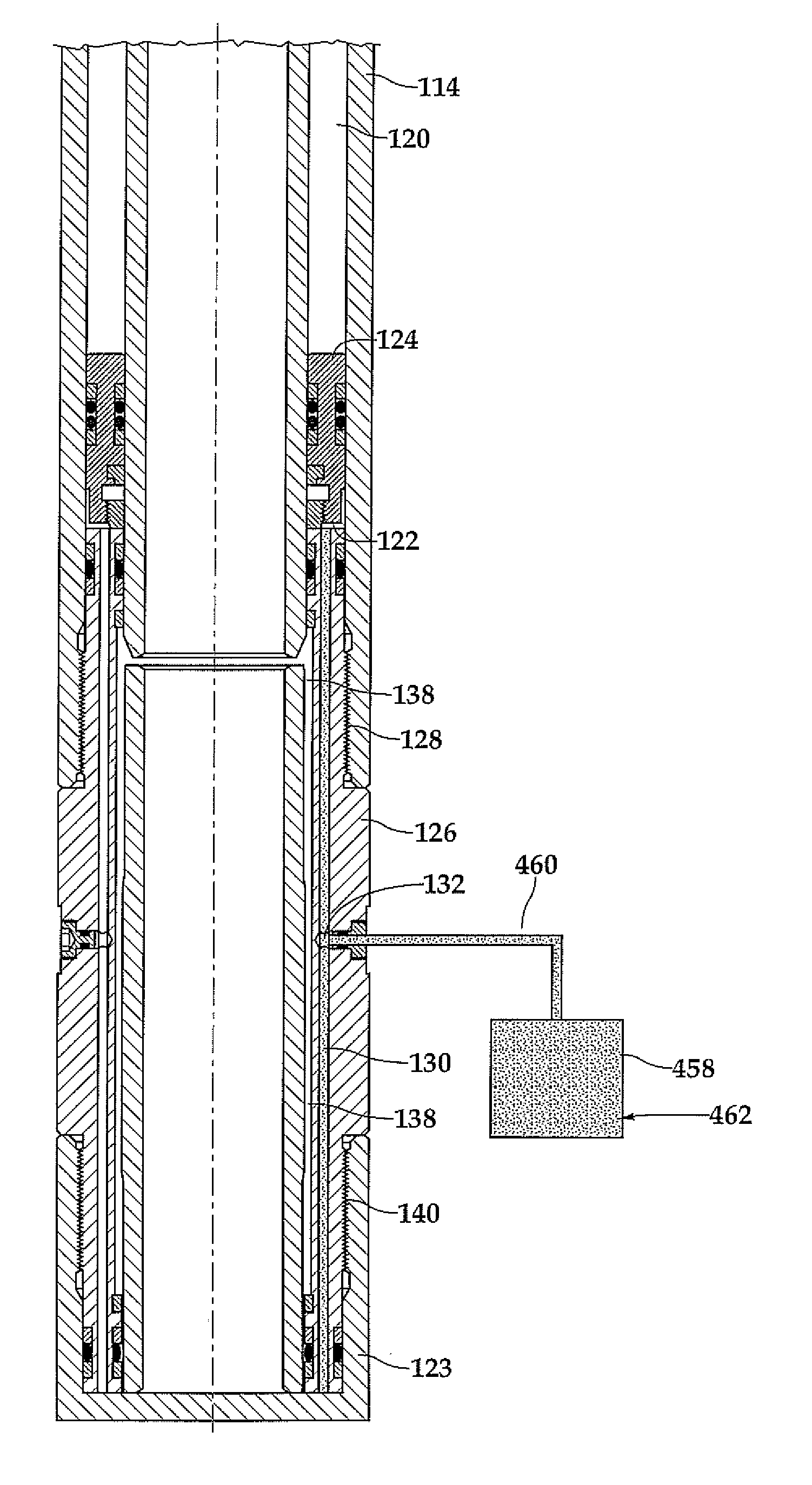
Phase Change Fluid Spring and Method for Use of Same
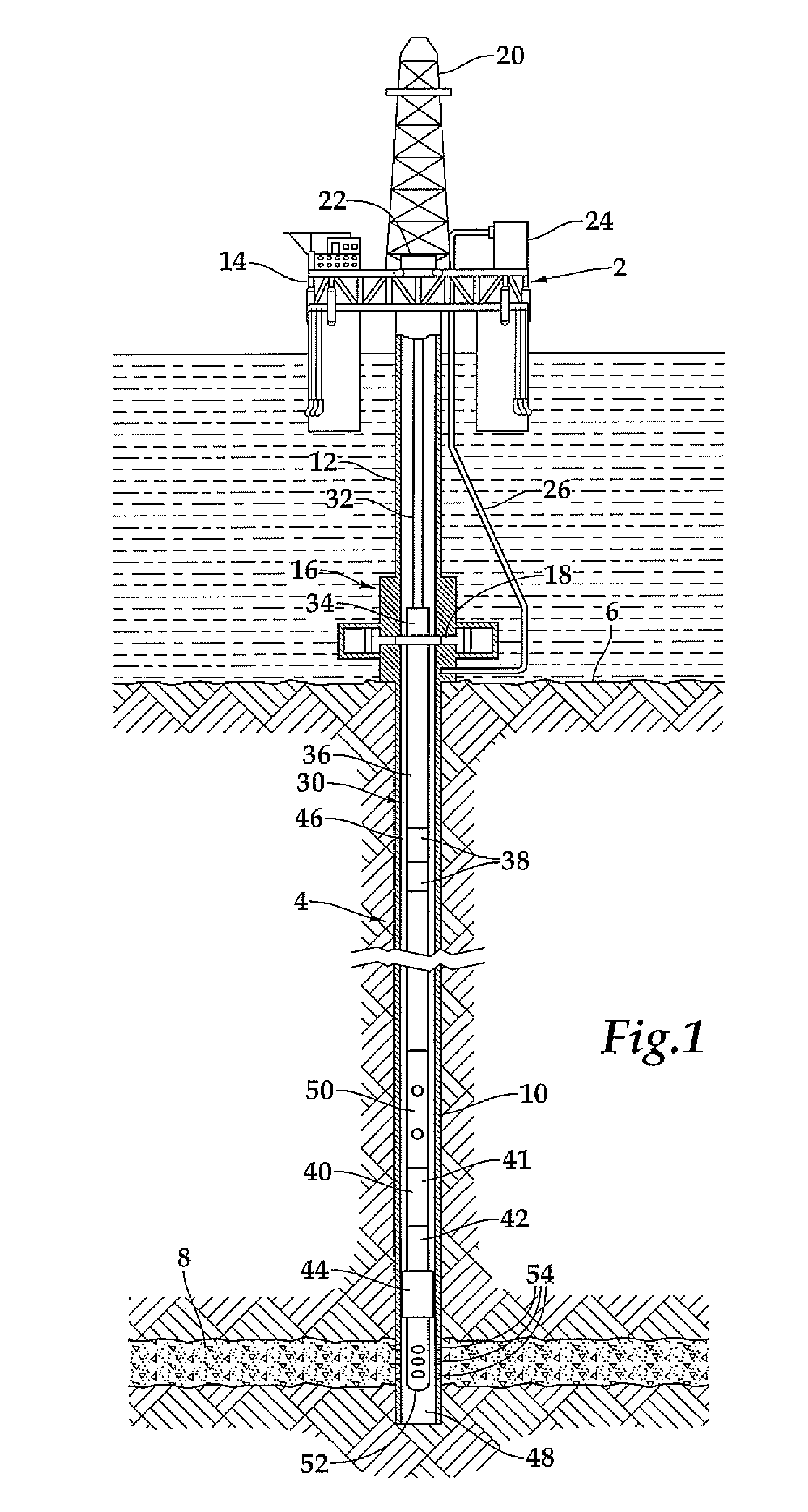
InactiveUS20090250224A1Reduce pressureIncrease pressureFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsEngineeringPhase change
A phase change fluid spring (450) for actuating a downhole tool (50) in a wellbore. The phase change fluid spring (450) includes a housing (114) defining a fluid chamber (120) and a phase change fluid disposed within the fluid chamber (120). The phase change fluid is in a first phase and at a first pressure at the surface. The phase change fluid is in a second phase and at a second pressure in the wellbore, the second pressure being greater than the first pressure. The phase change fluid is operable to store and release energy downhole to actuate the downhole tool (50).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Composite structure type high tensile strength steel plate, plated plate of composite structure type high tensile strength steel and method for their production
InactiveUS20030129444A1Lower yield stressImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingSheet steelHigh intensity
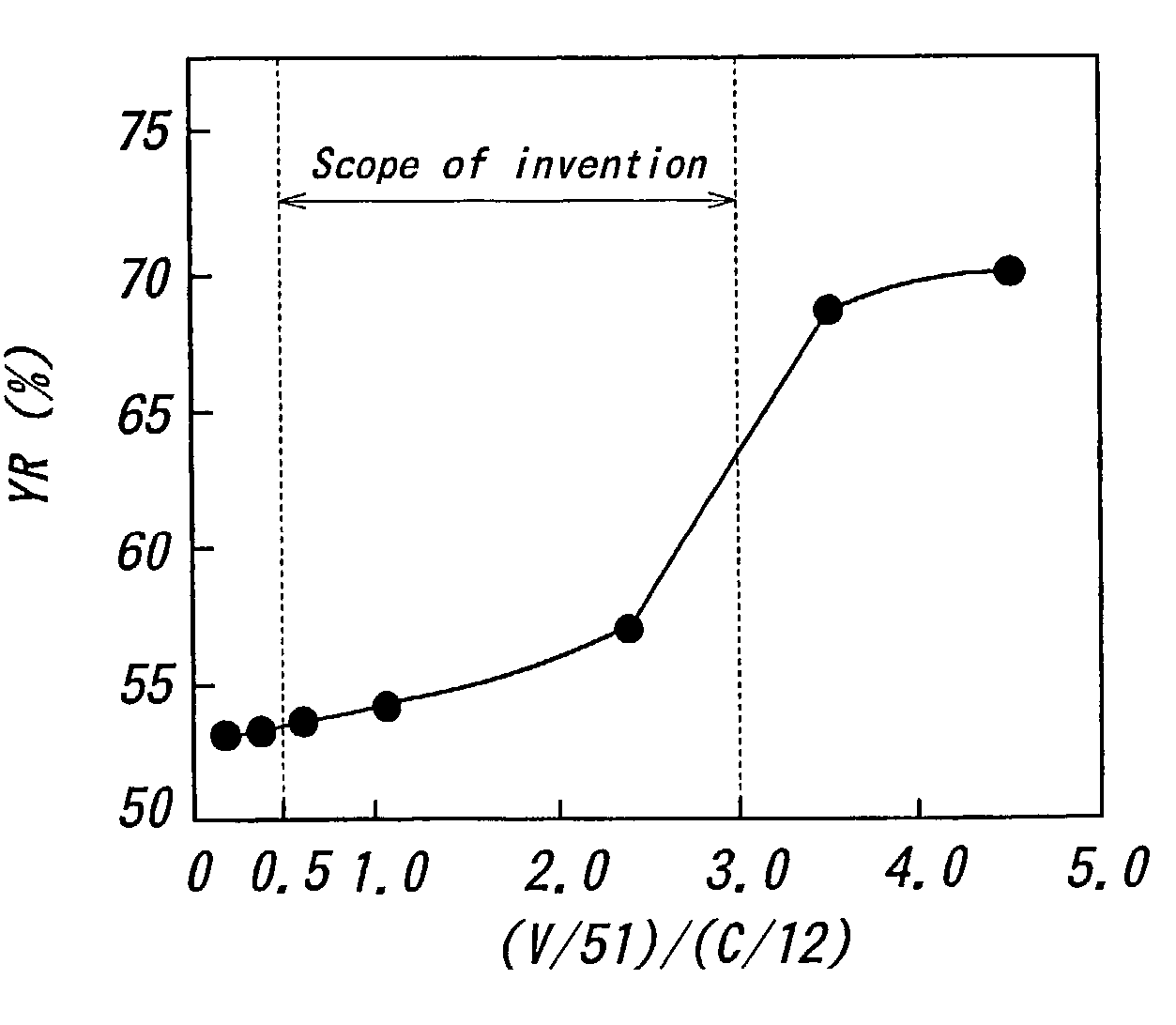
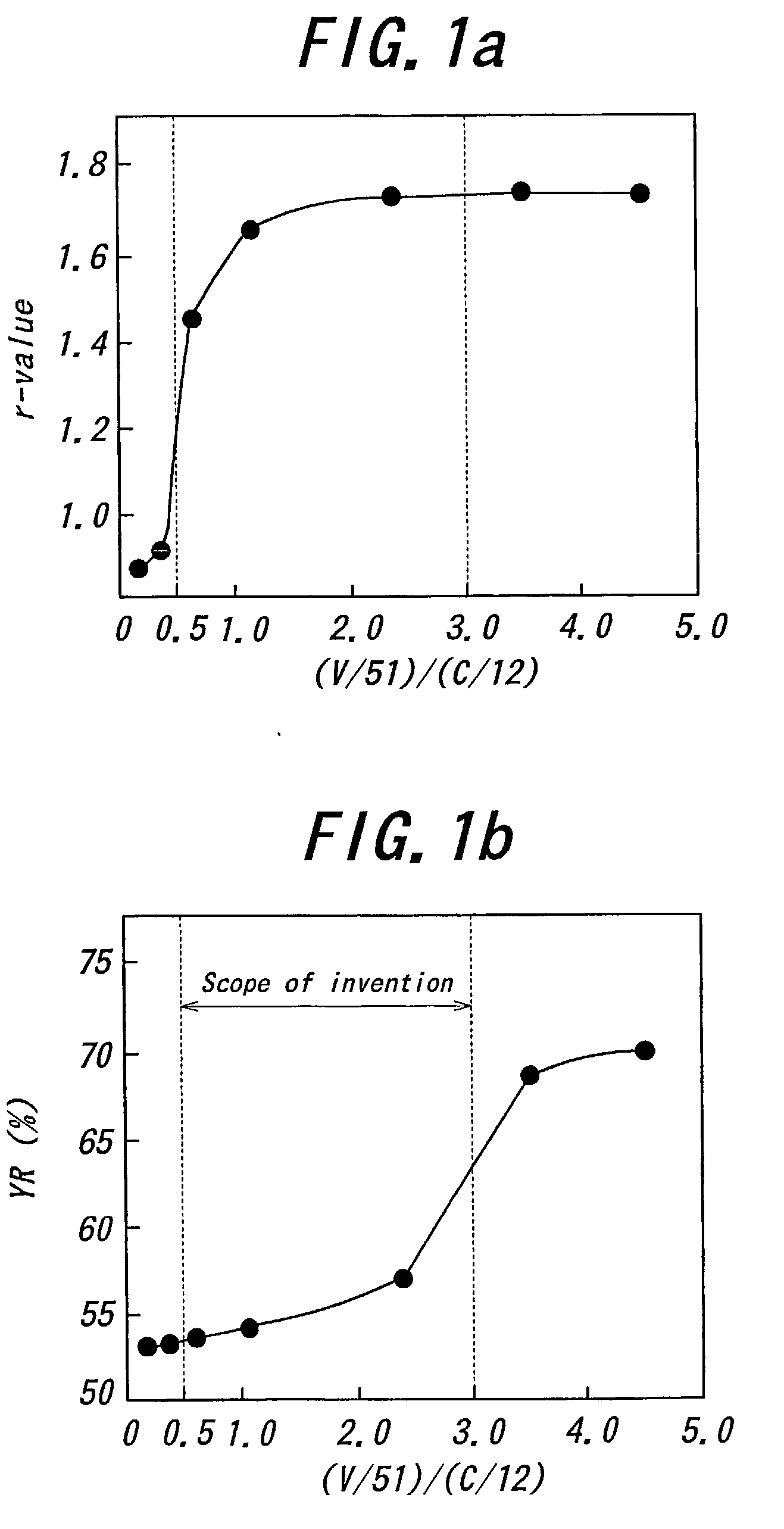
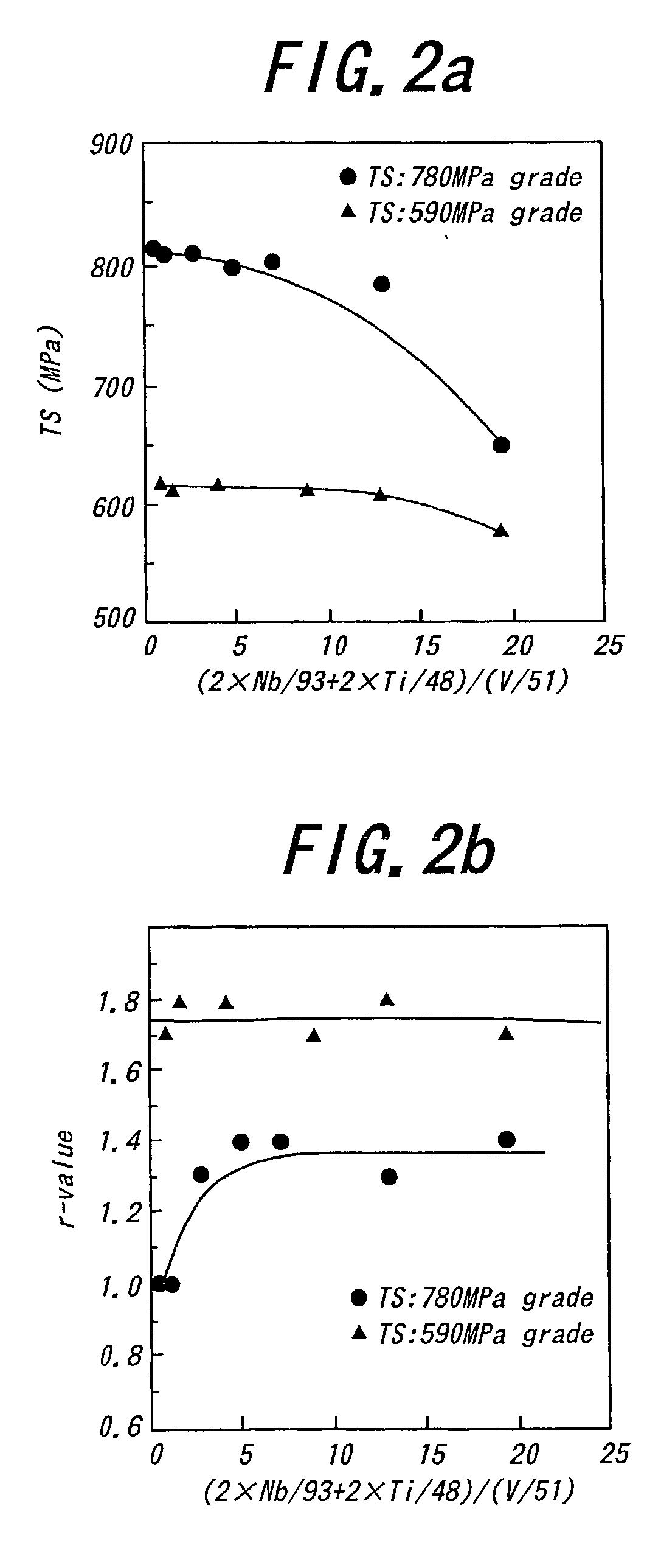
The invention proposes a high-strength dual-phase cold rolled steel sheet having an excellent deep drawability, wherein the steel sheet has a composition comprising C: 0.01-0.08 mass %, Si: not more than 2.0 mass %, Mn: not more than 3.0 mass %, P: not more than 0.10 mass %, S: not more than 0.02 mass %, A1: 0.005-0.20 mass %, N: not more than 0.02 mass % and V: 0.01-0.5 mass %, provided that V and C satisfy a relationship of 0.5xC / 12<=V / 51<=3xC / 12, and the remainder being Fe and inevitable impurities, and has a microstructure consisting of a ferrite phase as a primary phase and a secondary phase including martensite phase at an area ratio of not less than 1% to a whole of the microstructure and a high-strength dual-phase galvanized steel sheet comprising a galvanized coating on the above steel sheet as well as a method of producing the same.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Cell sorter chip having gel electrodes
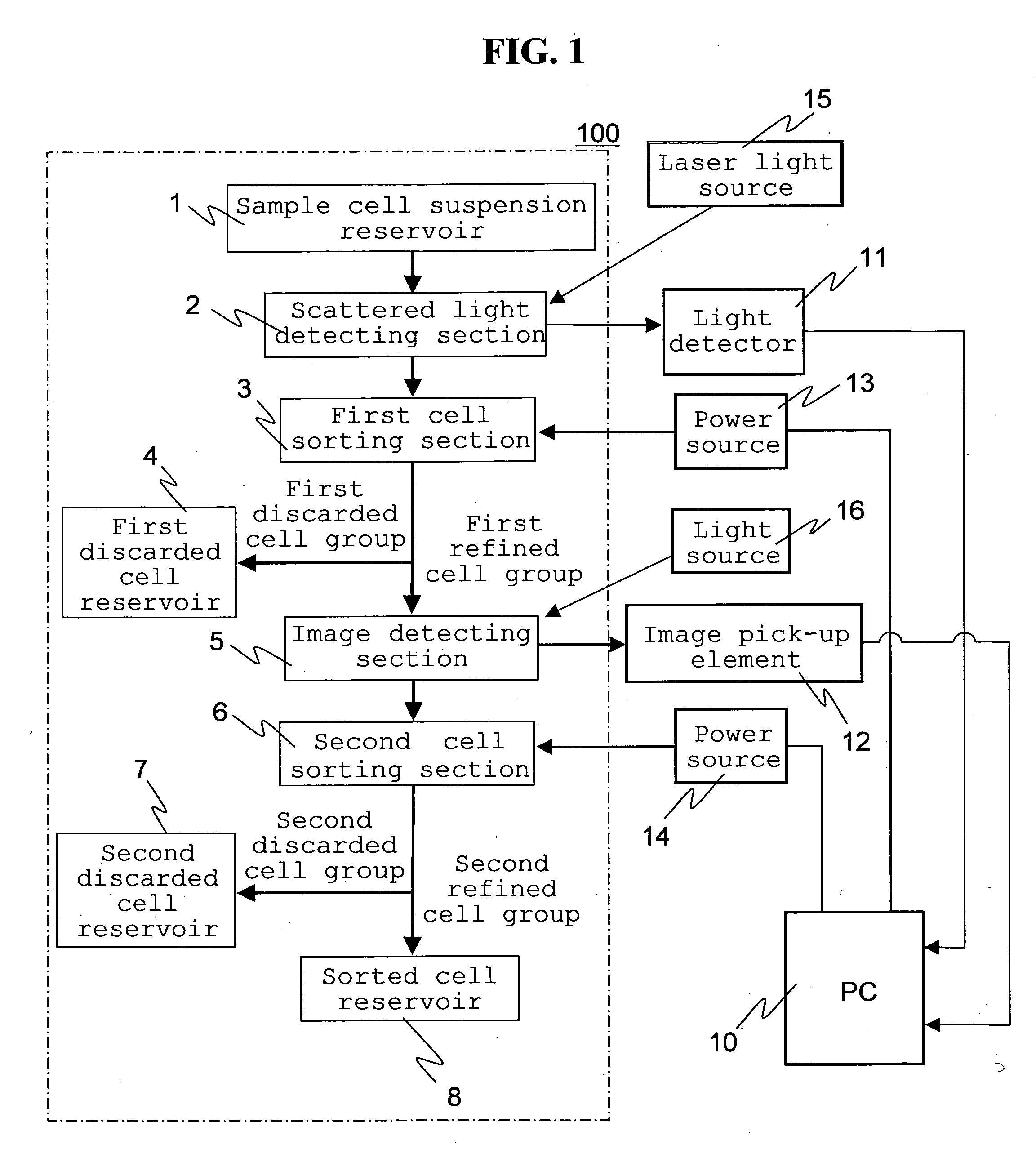
A cell sorting chip and a cell sorting technology are to be established which can positively detect and sort a specified cell for cell separation and detection using micro flow paths formed on a substrate, whereby a cell analyzing / sorting device is provided which uses an inexpensive disposable chip replaceable for each sample. To this end, micro flow paths formed on the substrate are formed, and cells are roughly sorted in a first stage and then finely sorted in a second stage. More specifically, cells are sorted roughly by using scattered light or according to intensity of luminescence in the first stage. In the second stage, the roughly sorted cells are sorted with high precision using image recognition.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +2
Process for in situ recovery of bitumen and heavy oil
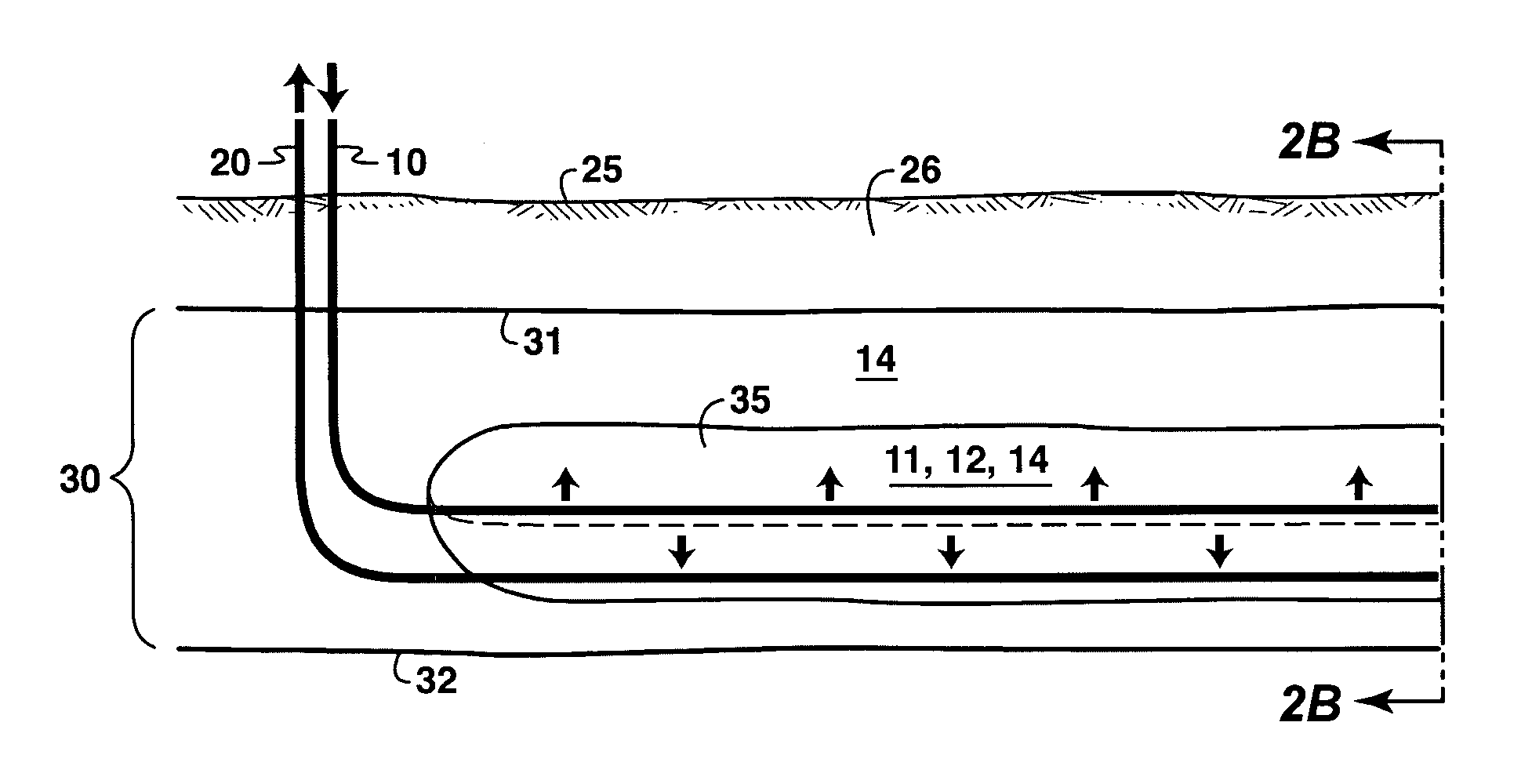
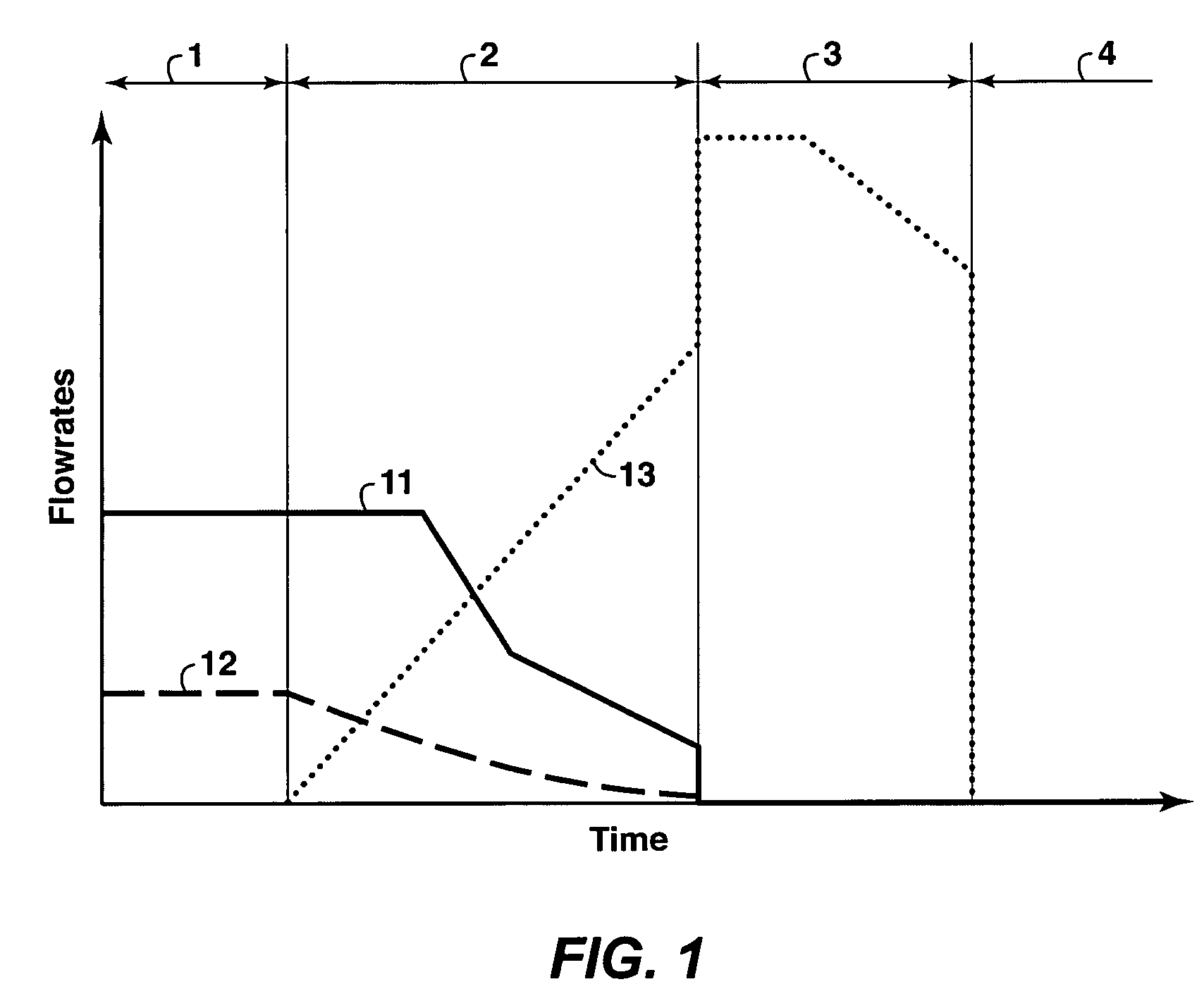
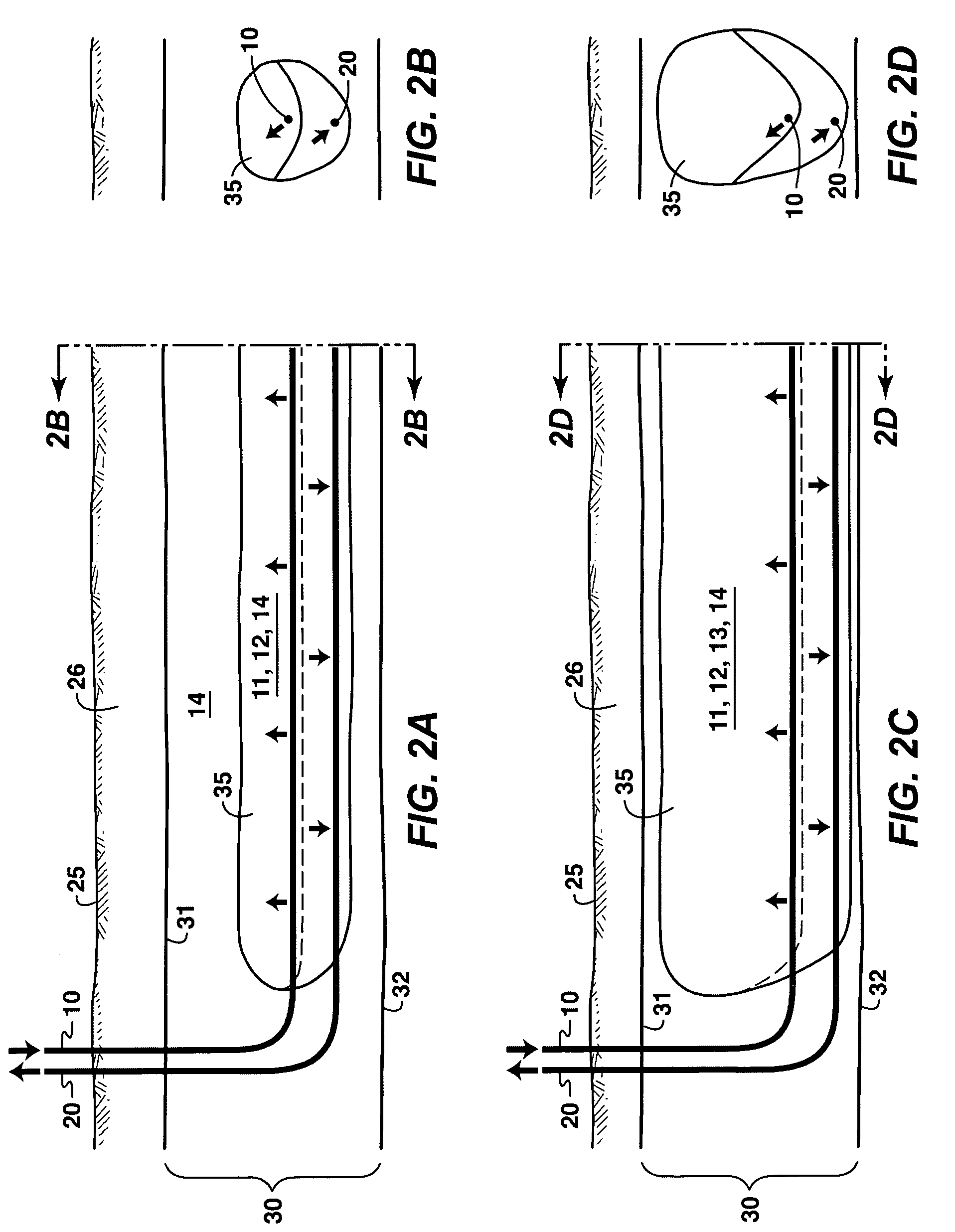
A process is described for in situ recovery of bitumen or heavy oil from a reservoir having a horizontal injection well and a horizontal production well. The process includes a first phase in which steam and a heavy hydrocarbon solvent are injected into the reservoir, a second phase in which the steam and heavy hydrocarbon injections are transitioned to a light hydrocarbon solvent injection, and a third phase in which a light hydrocarbon solvent is injected without further steam or heavy hydrocarbon injection. A displacement gas may be added during any of the phases, and production of hydrocarbons continues throughout all phases. The process employs a high-production start-up phase, followed by lower cost phases which progress a depletion chamber within the reservoir.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
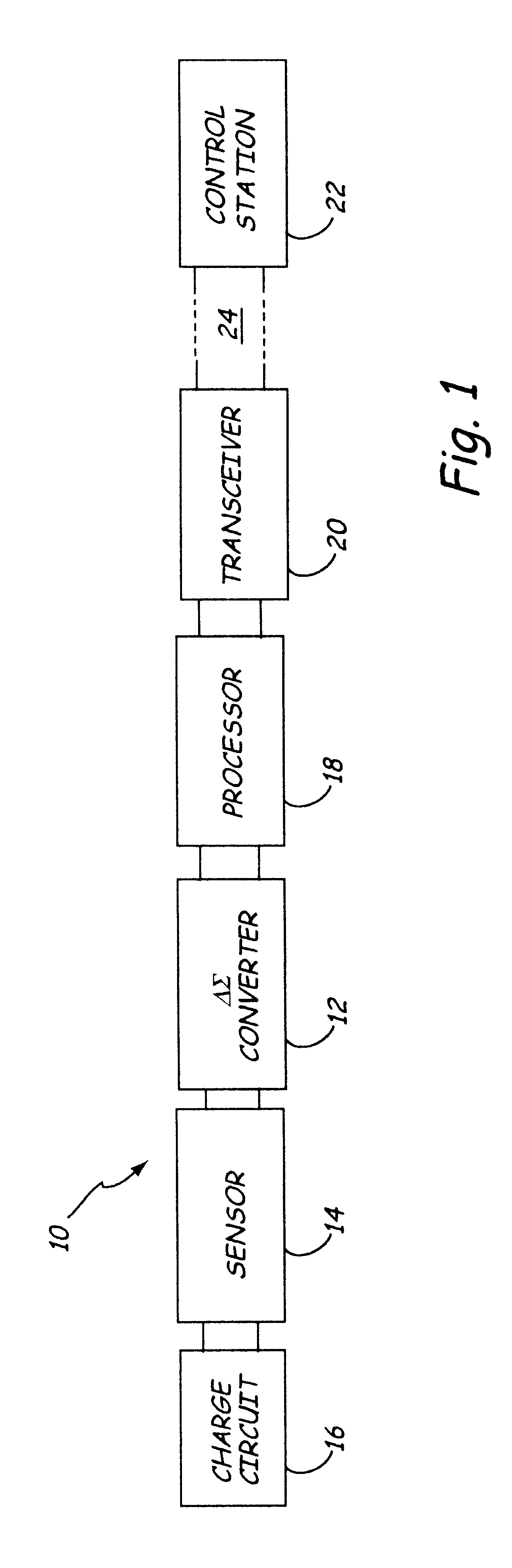
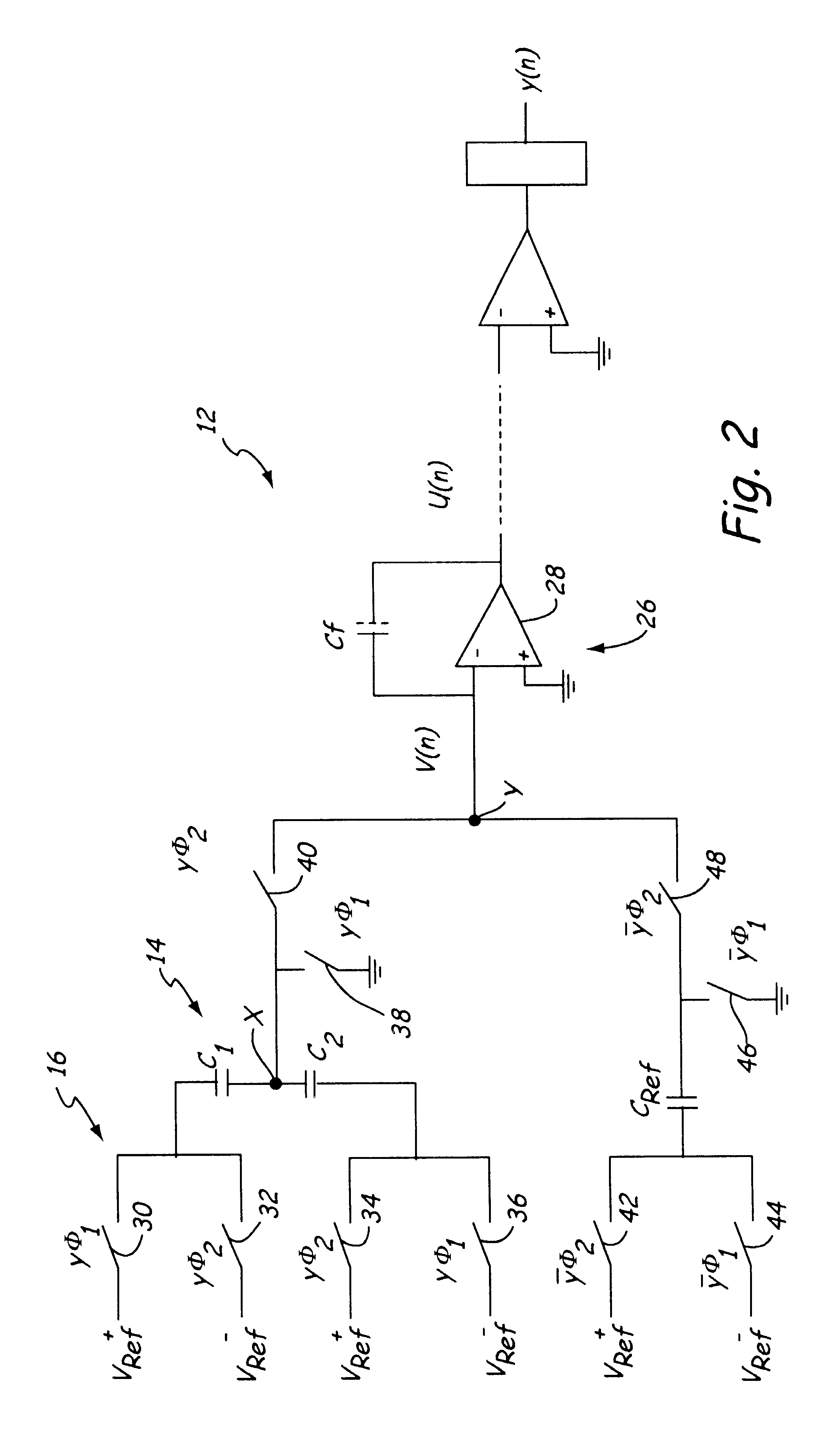
Bridged capacitor sensor measurement circuit
InactiveUS6720777B2Capacitance measurementsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsMaximum differenceCapacitance transducer
A pair of sensing capacitors, each having a capacitance C.sub.1 and C.sub.2 respectively, based on a process variable, are coupled to a bridge node which is coupled to a summing node. A reference capacitor, coupled to the summing node, has a capacitance C.sub.REF greater than an expected maximum difference between the capacitances of the pair of sensing capacitors. Switches selectively couple the sensing capacitors and the reference capacitor to at least first and second voltages to derive charges representative of C.sub.1 -C.sub.2 and C.sub.REF. In one embodiment the sensing capacitors are operated to charge and discharge during respective first and second phases of first cycles and the reference capacitor is operated to charge and discharge during respective first and second phases of second cycles. In another embodiment, the reference capacitor is operated to charge and discharge during alternate phases of the first and second cycles and the sensing capacitors are operated to charge and discharge during respective first and second phases of all cycles.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
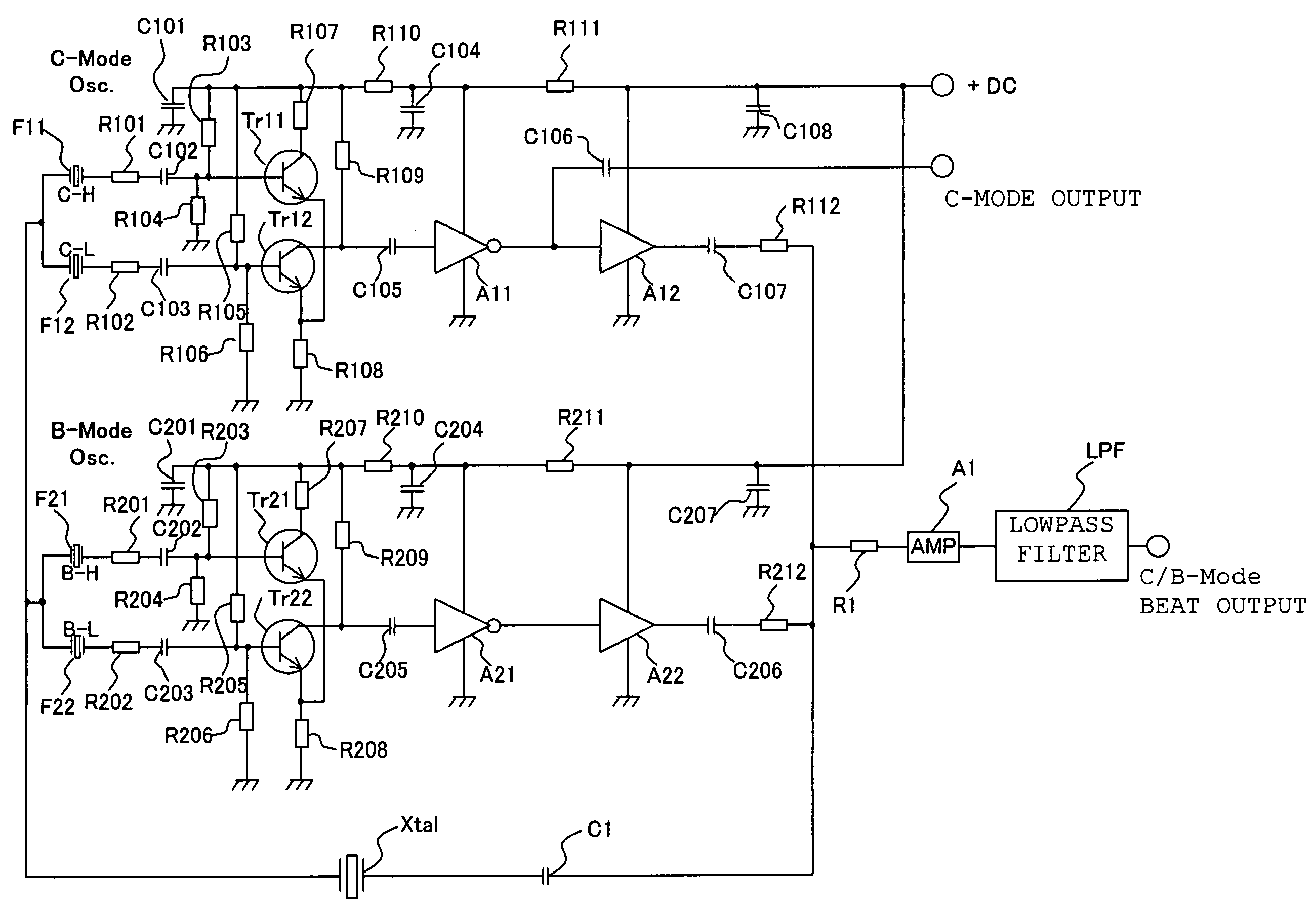
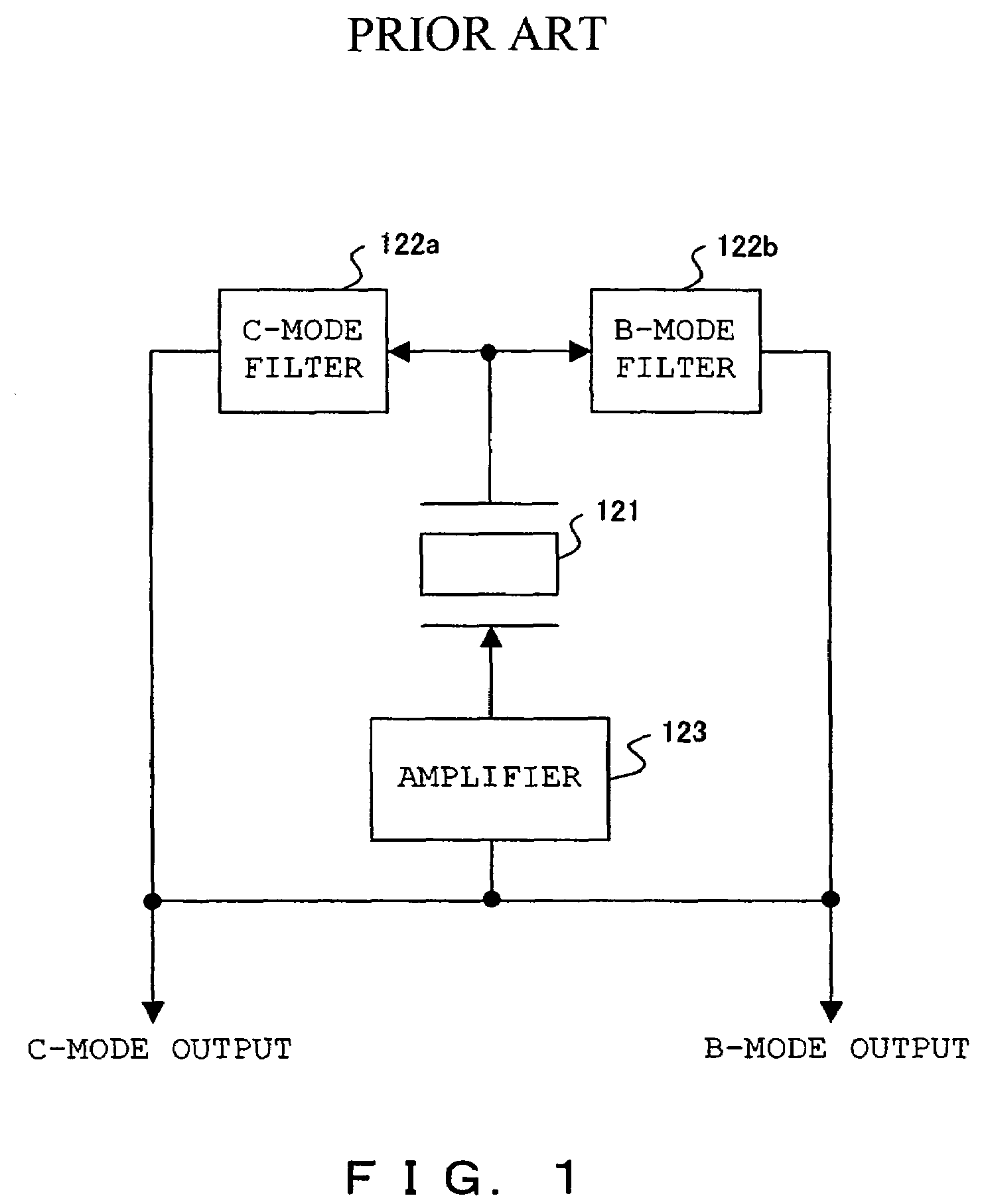
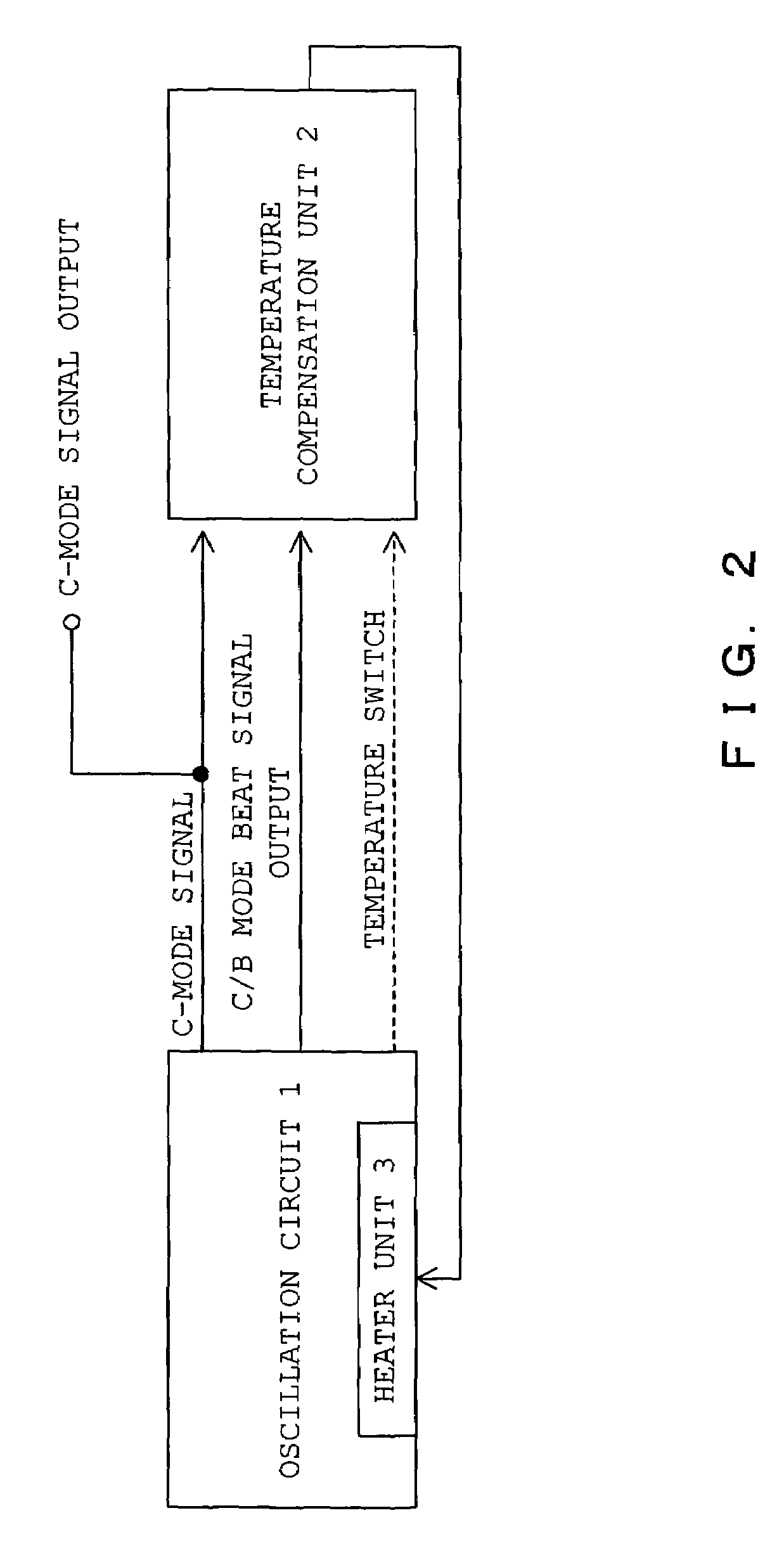
Crystal oscillator device, oscillation method and heater
InactiveUS7378916B2Improve thermal efficiencyImprove precision controlPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesOscillations generatorsResonanceQuantum electrodynamics
The crystal oscillator device for simultaneously generating oscillator signals with a plurality of oscillation modes of a crystal unit, comprising: a primary resonator unit filtering the oscillator signal with a primary oscillation mode, which is one of the oscillation modes, from the output of the crystal unit, a secondary resonator unit filtering the oscillation signal, bearing a different resonance frequency from that of the primary resonator unit, with the primary oscillation mode from the output of the crystal unit, a primary phase synthesis unit, synthesizing the phases of the output signal of the primary resonator unit and the output signal of the secondary resonator unit, a tertiary resonator unit, a quaternary resonator unit, and a secondary phase synthesis unit.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
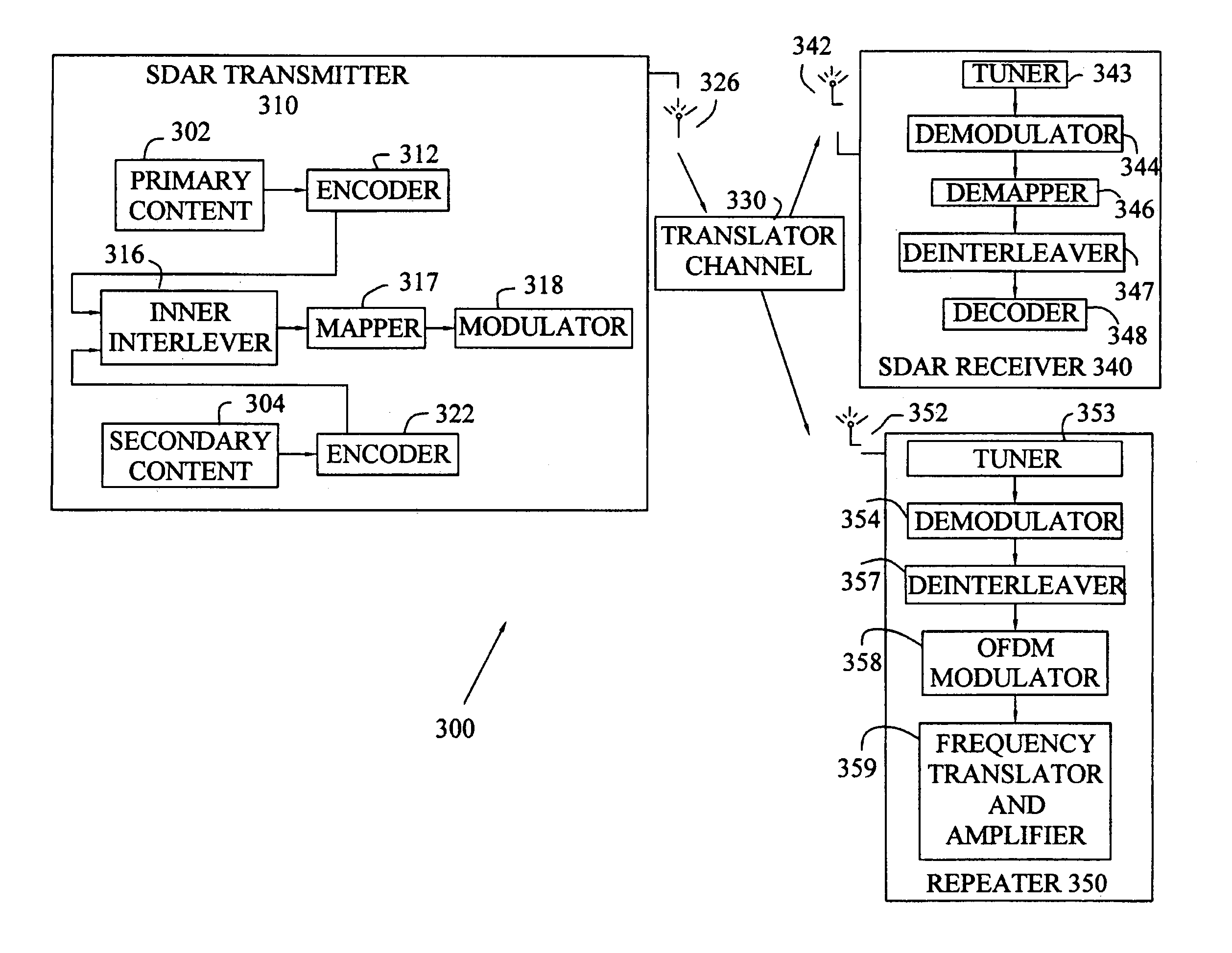
Method to minimize compatibility error in hierarchical modulation
ActiveUS7215713B2Increase volumeIncrease the amount of dataLeaf springsMultiplex communicationData signalData rate
The present invention involves a method and system for transmitting two levels of data in a hierarchical transmission schema. A first modulated signal is generated based on first input. A second modulation signal is generated based on a second input that has a data rate that is a fraction of the data rate of the first modulated signal. The second modulation signal has known instances where the second modulation signal has no energy. In a system where the first modulation is quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK), the second modulation signal can be a secondary phase offset. A receiver in the system that has a priori knowledge about the timing relationship between the first data signal and the instances when the second data signal is present will be able to detect both data signals optimally.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
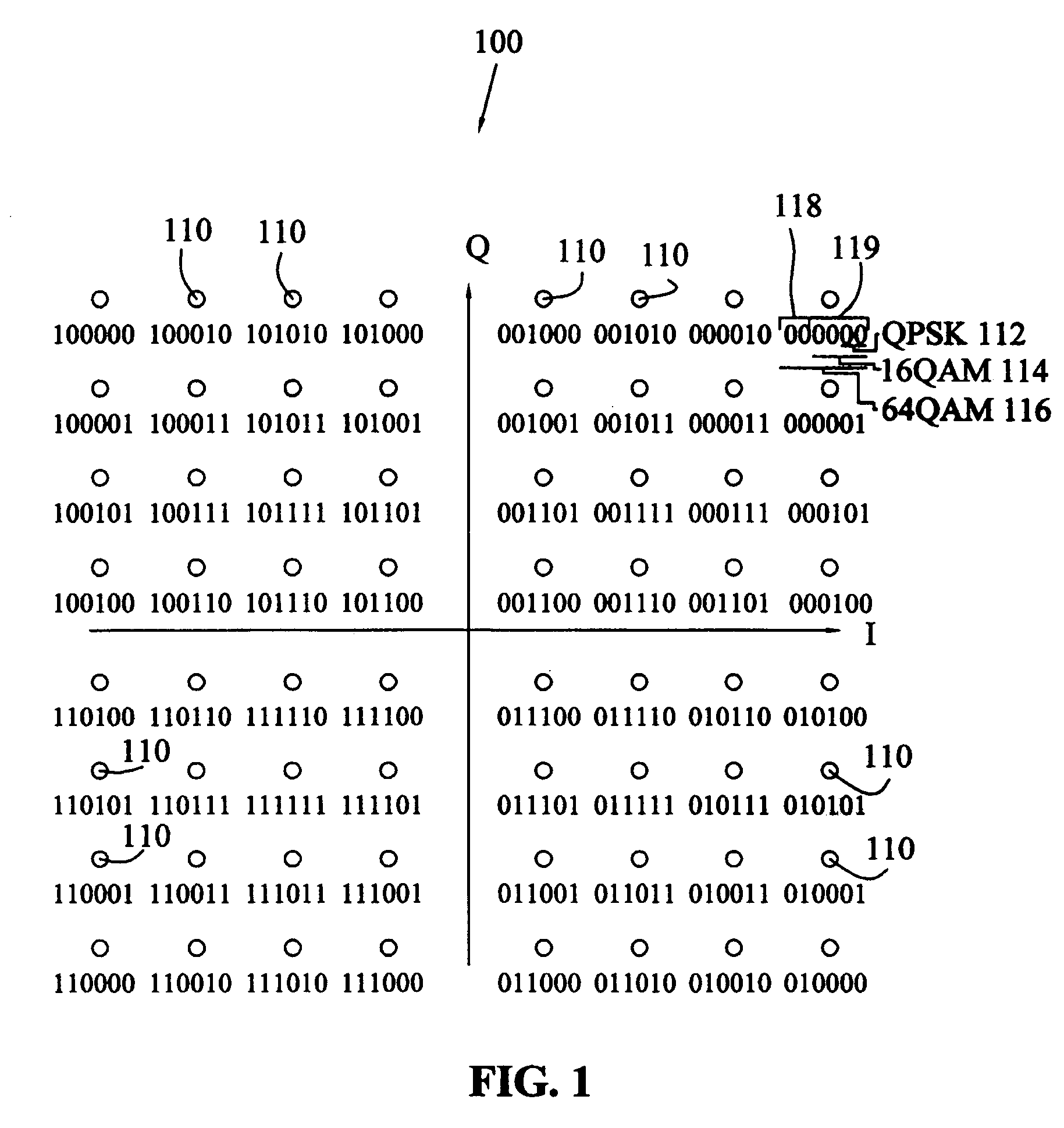
Display device, terminal device, display panel, and display device driving method
ActiveUS20090096726A1Improve image qualityInhibit deteriorationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsImaging qualityComputer graphics (images)
To provide a plural-viewpoint display device having an image separating optical element such as a lenticular lens or a parallax barrier, which is capable of achieving a high image quality by suppressing deterioration in the display image quality caused when a block division driving method is employed, and to provide a terminal device, a display panel, and a driving method thereof, which can be preferably used for those devices. A pixel group configured with pixels for displaying a right-eye image includes a pixel connected to a data line phase-deployed in the first phase of a block division driving method, and a pixel connected to a data line phase-deployed in the third phase, and a pixel connected to a data line phase-deployed in the second phase. In this manner, it is designed to have no deviation in the phase deployment orders in the pixel groups for each viewpoint.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
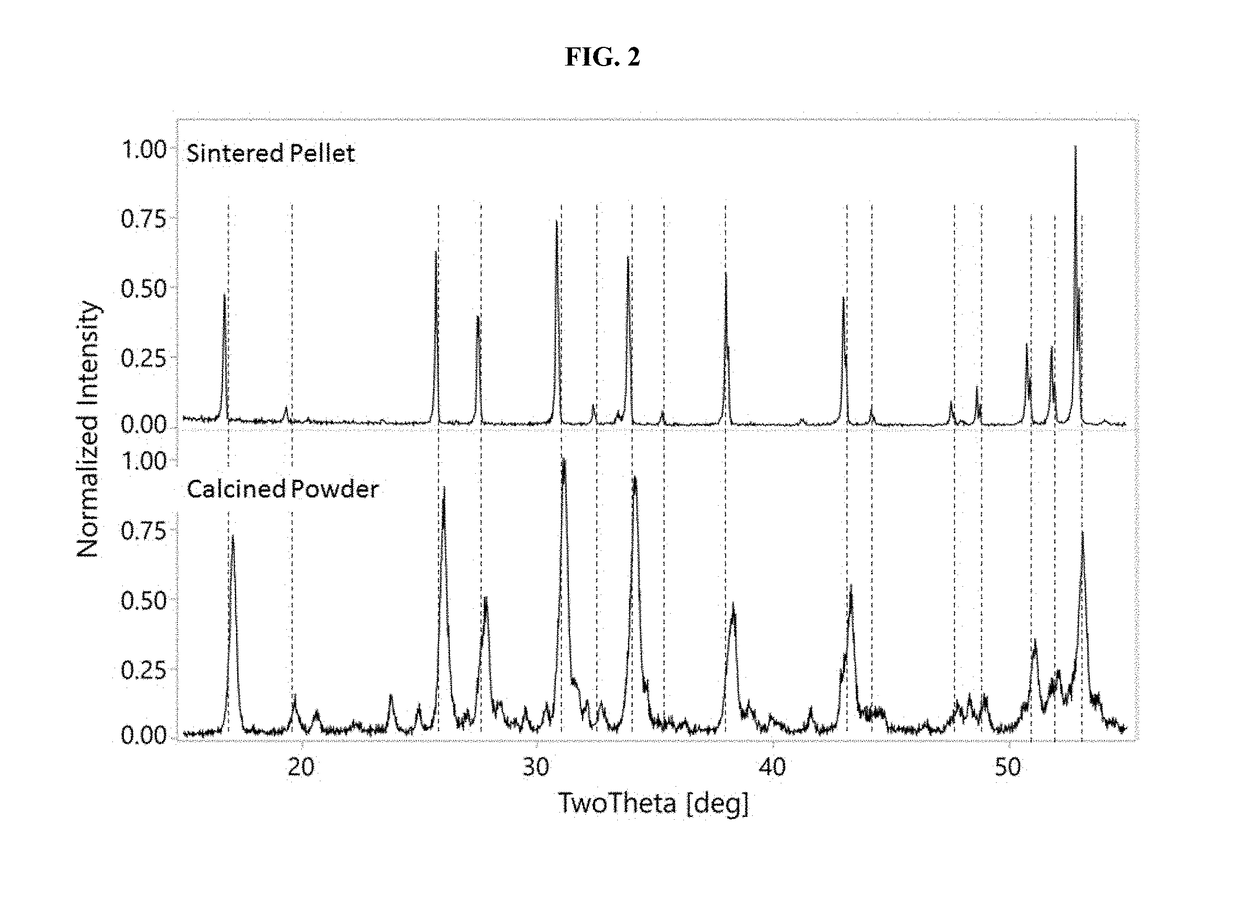
Lithium-stuffed garnet electrolytes with secondary phase inclusions
The instant disclosure sets forth multiphase lithium-stuffed garnet electrolytes having secondary phase inclusions, wherein these secondary phase inclusions are material(s) which is / are not a cubic phase lithium-stuffed garnet but which is / are entrapped or enclosed within a lithium-stuffed garnet. When the secondary phase inclusions described herein are included in a lithium-stuffed garnet at 30-0.1 volume %, the inclusions stabilize the multiphase matrix and allow for improved sintering of the lithium-stuffed garnet. The electrolytes described herein, which include lithium-stuffed garnet with secondary phase inclusions, have an improved sinterability and density compared to phase pure cubic lithium-stuffed garnet having the formula Li7La3Zr2O12.
Owner:QUANTUMSCAPE BATTERY INC
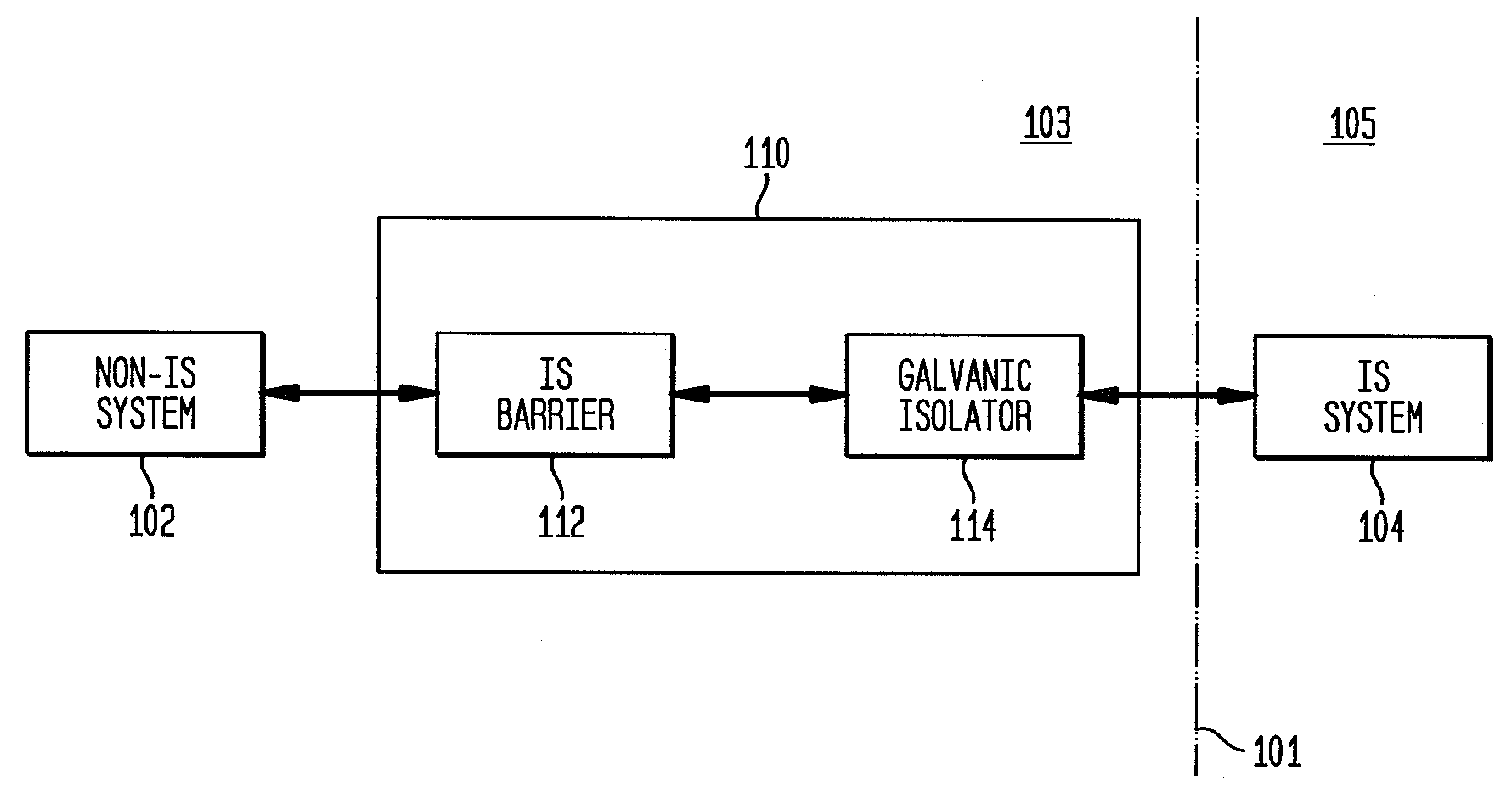
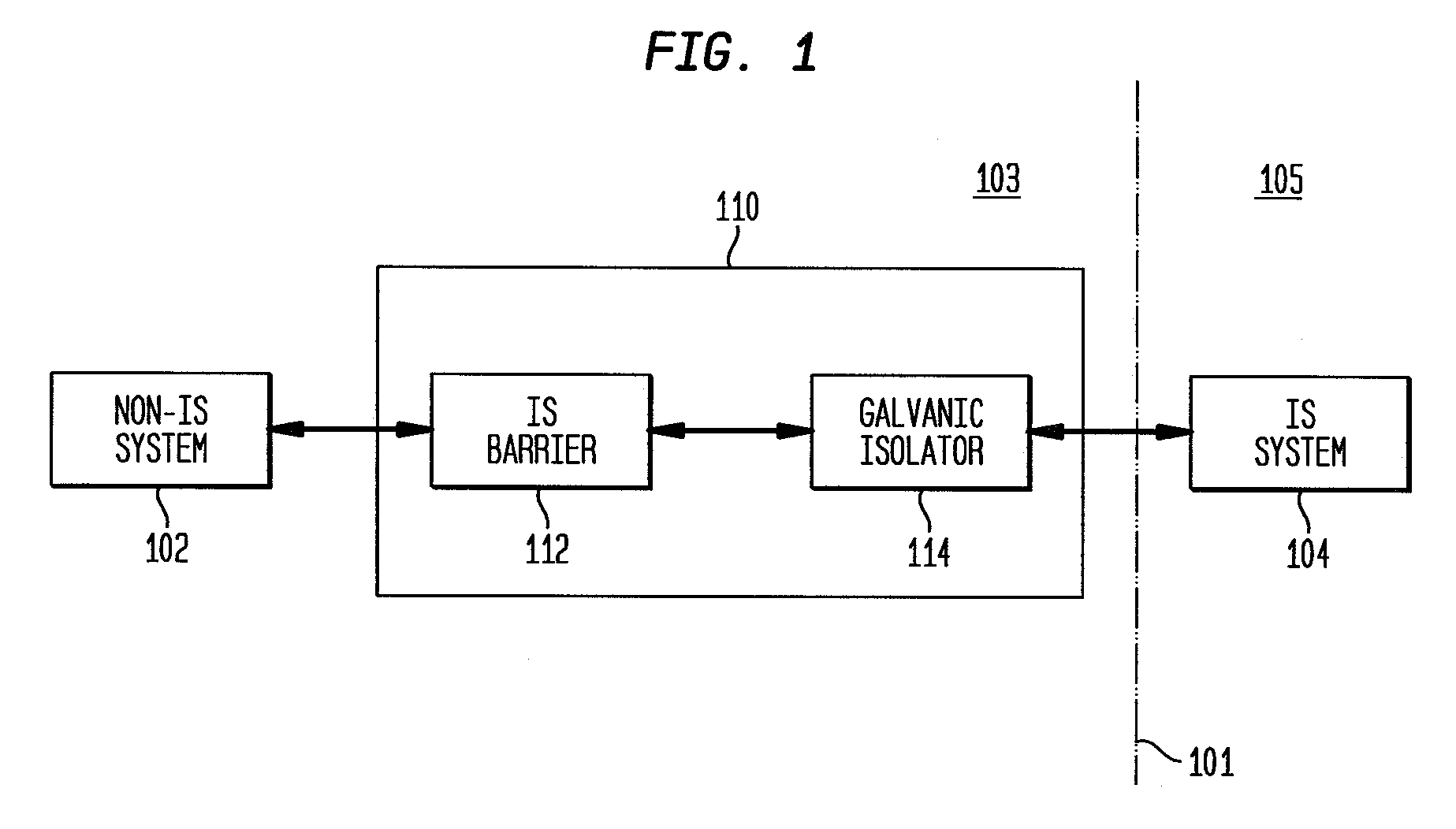
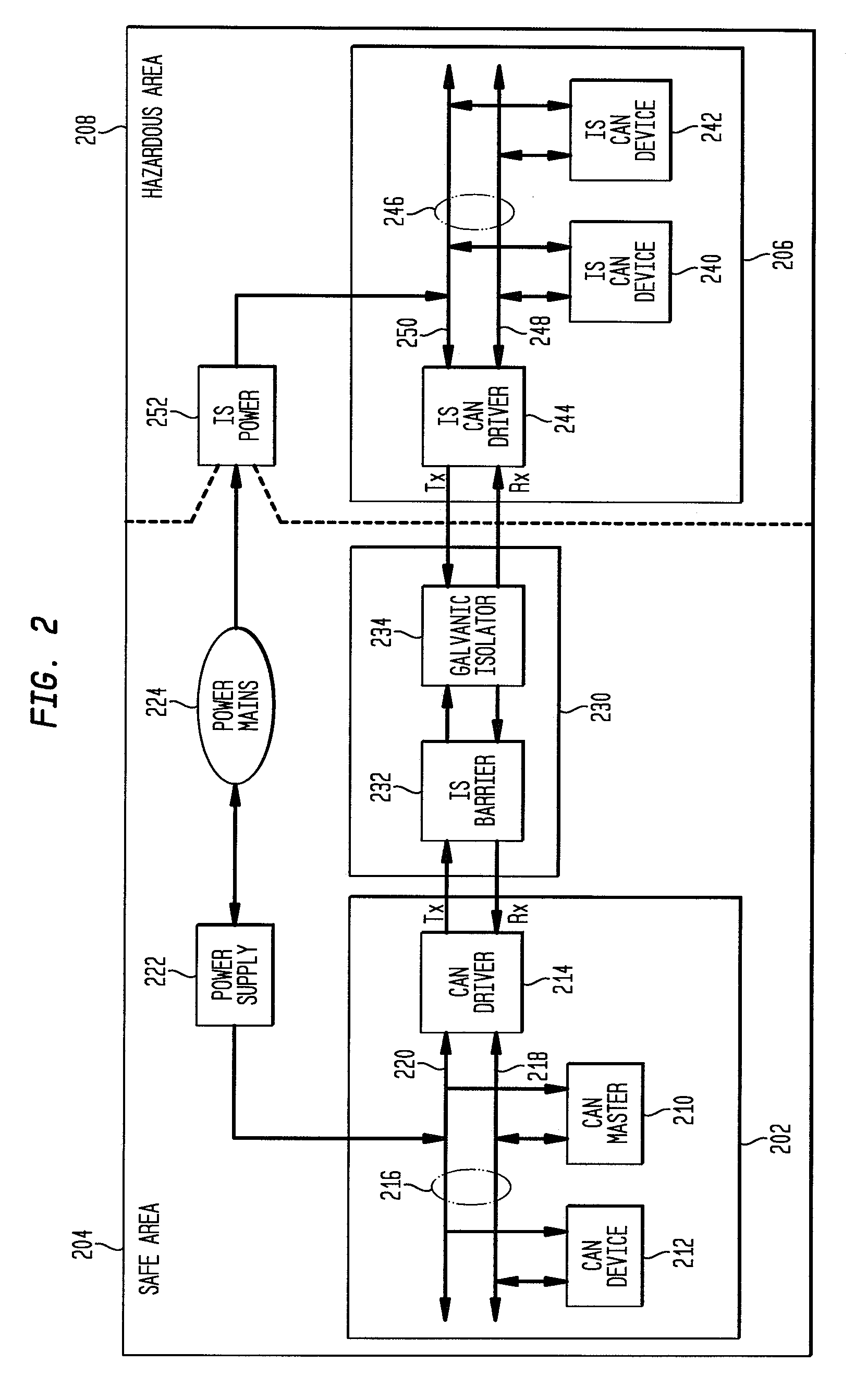
Intrinsically safe galvanically isolated barrier device and method thereof
ActiveUS20080180226A1Increase speedProgramme controlEmergency protective arrangement detailsIntrinsic safetyElectricity
A system and method for providing an intrinsically safe (IS) galvanically isolated barrier device. An IS barrier device provides IS galvanic isolation between a non-IS system and an IS system using a two-stage approach. In the first stage, a non-galvanically isolated IS barrier limits energy of electrical transmissions received from the non-IS system to convert such electrical transmissions into IS transmissions. In the second stage, the IS transmissions are transmitted through a galvanic isolator to the IS system to galvanically isolate the IS system from the non-IS system. A digital monolithic isolator cannot be IS certified to be the single bridge between IS and non-IS systems, however, it can be used in a certifiable fashion to isolate between IS systems. When used in conjunction with a non-galvanic IS barrier that is capable meeting the IS certification as non-IS to IS barrier, a digital monolithic isolator can be used to implement the galvanic isolator such that high speed, low cost galvanic isolation is possible. Such a galvanically isolated barrier device can be used to implement an IS galvanically isolated high speed communication bus for sample system control.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and materials for bonding electrodes to interconnect layers in solid oxide fuel cell stacks
ActiveUS20070111069A1Reliable electrical connectionStrong adhesive bondFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesBond propertiesElectrical integrity
A method and related bonding compositions for use in assembling a solid oxide fuel cell (“SOFC”) stack having thermally and chemically stable and electrically conductive bonds between alternating fuel cells and interconnect components in the stack. The improved method and materials allow for the assembly of solid oxide fuel cells having a stronger and more reliable bond with good electrical contact in situ between the SOFC interconnect layers (plates) and the electrodes. The bonding materials and method according to the invention provide good electrical performance while maintaining the mechanical and electrical integrity of SOFC stacks without requiring excessive mechanical compression of the stack as exemplified by prior art systems. The preferred bonding agents comprise a primary phase that provides the electrical conduction path during fuel cell operation, as well as the mechanical strength necessary to insure a reliable connection between the interconnect and the relevant anode or cathode surfaces of the fuel cell. Secondary phases can be added in small amounts to the primary phase to improve adhesion. An exemplary method according to the invention also contemplates various different steps for pre-treating the surfaces of the interconnect plates and electrodes to improve their surface bonding properties.
Owner:CUMMINS ENTERPRISE LLC
Emulsion and suspension polymerization processes, and improved electrochemical performance for carbon derived from same
The present application is directed to methods for preparation of polymer particles in gel form and carbon materials made therefrom. The carbon materials comprise enhanced electrochemical properties and find utility in any number of electrical devices, for example, as electrode material in ultracapacitors or batteries. The methods herein can also be employed generally to improve emulsion and / or suspension polymerization processes by improved control of diffusion of acidic and basic species between the polymer and secondary phases.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
Improved emulsion and suspension polymerization processes, and improved electrochemical performance for carbon derived from same
The present application is directed to methods for preparation of polymer particles in gel form and carbon materials made therefrom. The carbon materials comprise enhanced electrochemical properties and find utility in any number of electrical devices, for example, as electrode material in ultracapacitors or batteries. The methods herein can also be employed generally to improve emulsion and / or suspension polymerization processes by improved control of diffusion of acidic and basic species between the polymer and secondary phases.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
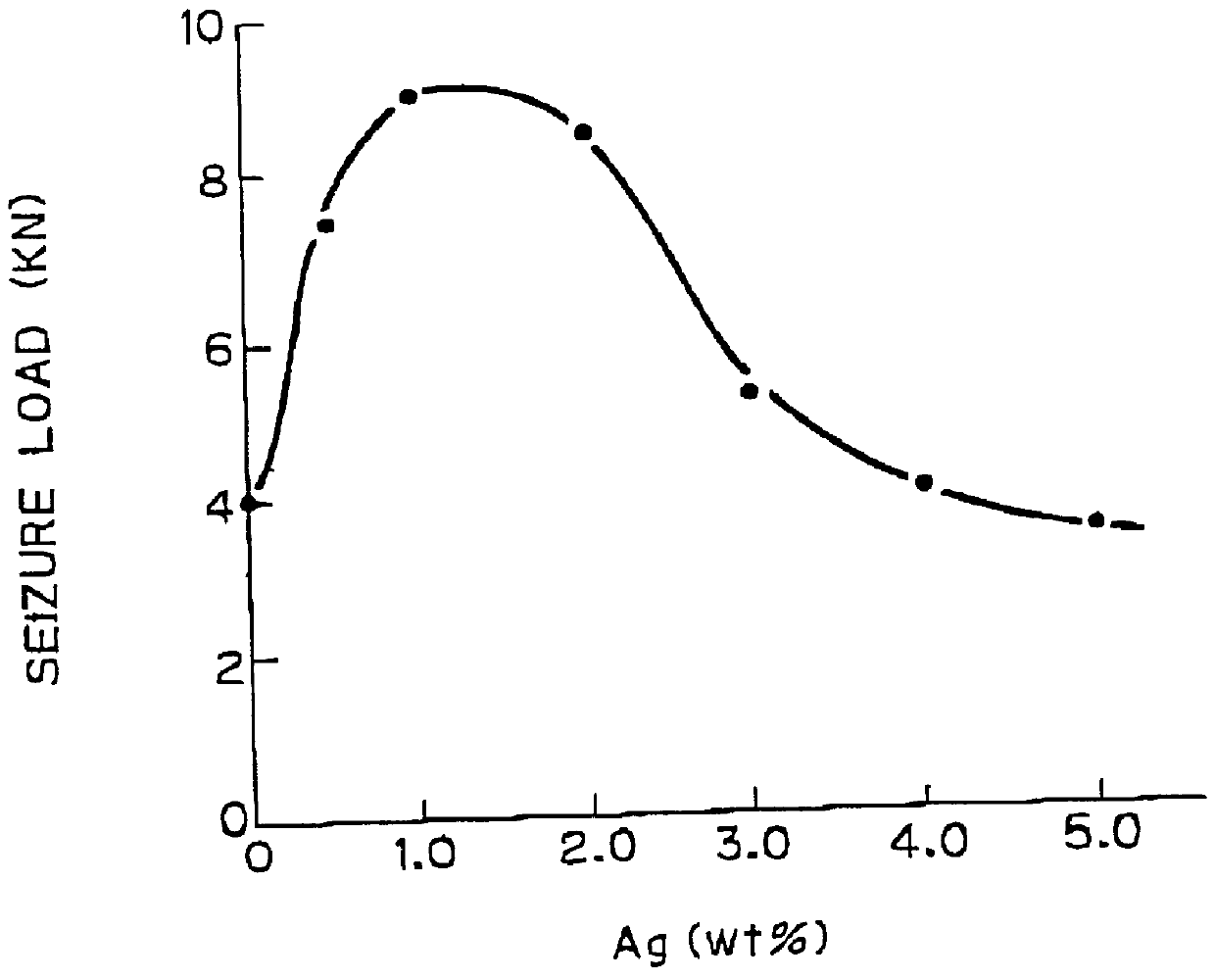
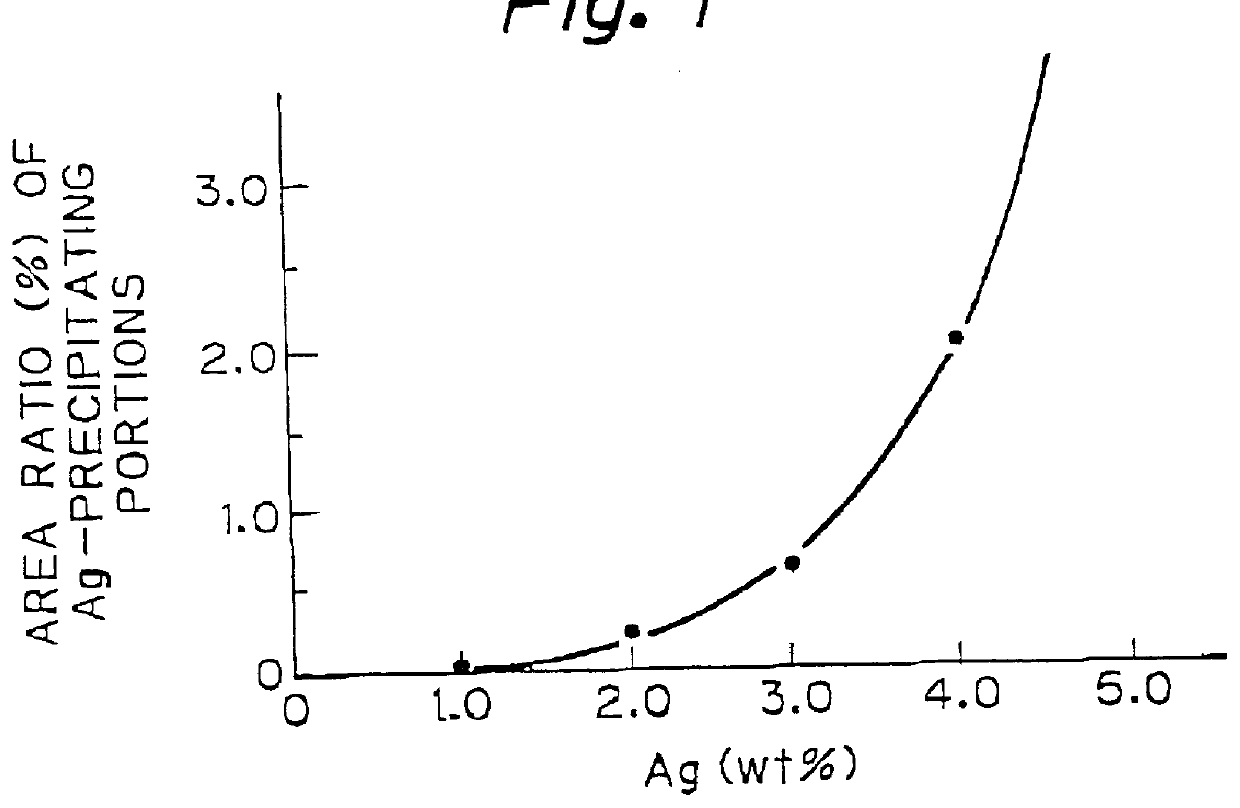
Copper-based bearing material and sliding bearing for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS6025081AEasy to slideFree cutting propertyConnecting rod bearingsCasingsCombustionInternal combustion engine
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 03118 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 8, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 8, 1998 PCT Filed Oct. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 15695 PCT Pub. Date May 1, 1997The copper-based sliding material has improved seizure resistance, even if it is free of Pb, and enables thinning of the overlay. The copper alloy provided consists of from 0.1 to 2% of Ag, from 1 to 10% of Sn, and the balance consisting of Cu and unavoidable impurities and, further said Ag and Sn do not essentially form the secondary phases but are in complete or essentially solid-solution state in the Cu matrix.
Owner:TAIHO INDUSTRIES CO LTD
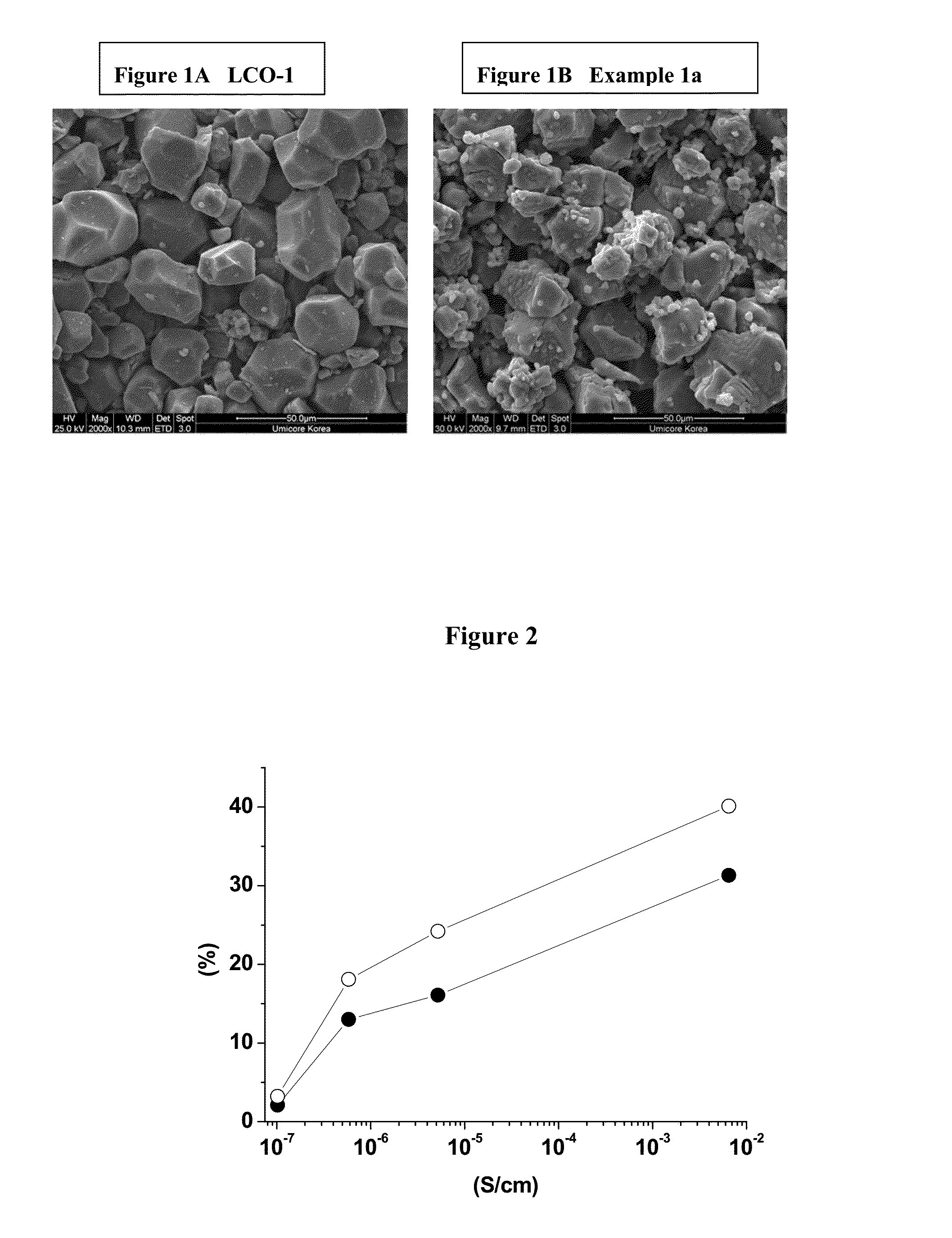
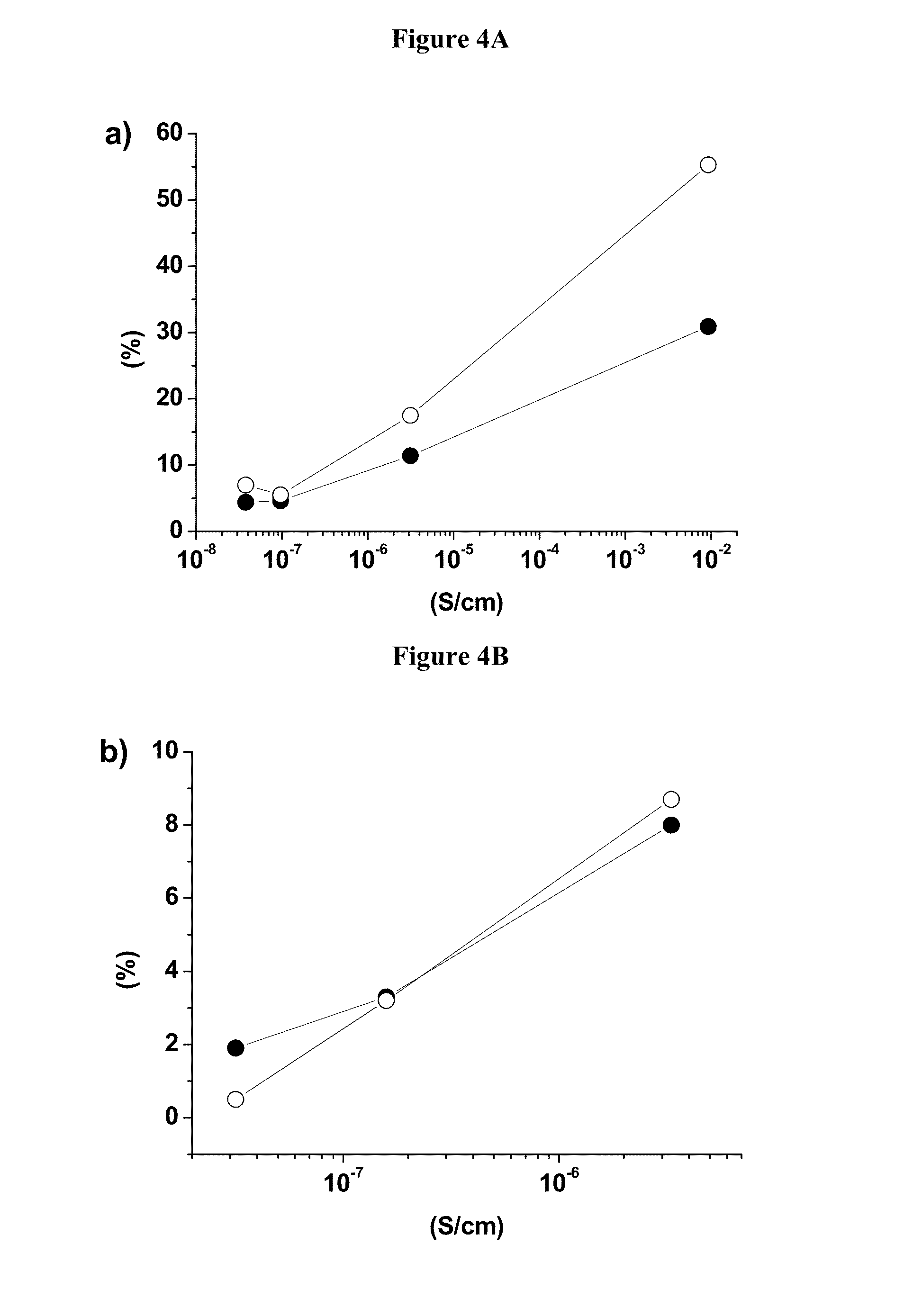
Cathode Material for Lithium-Ion Rechargeable Batteries
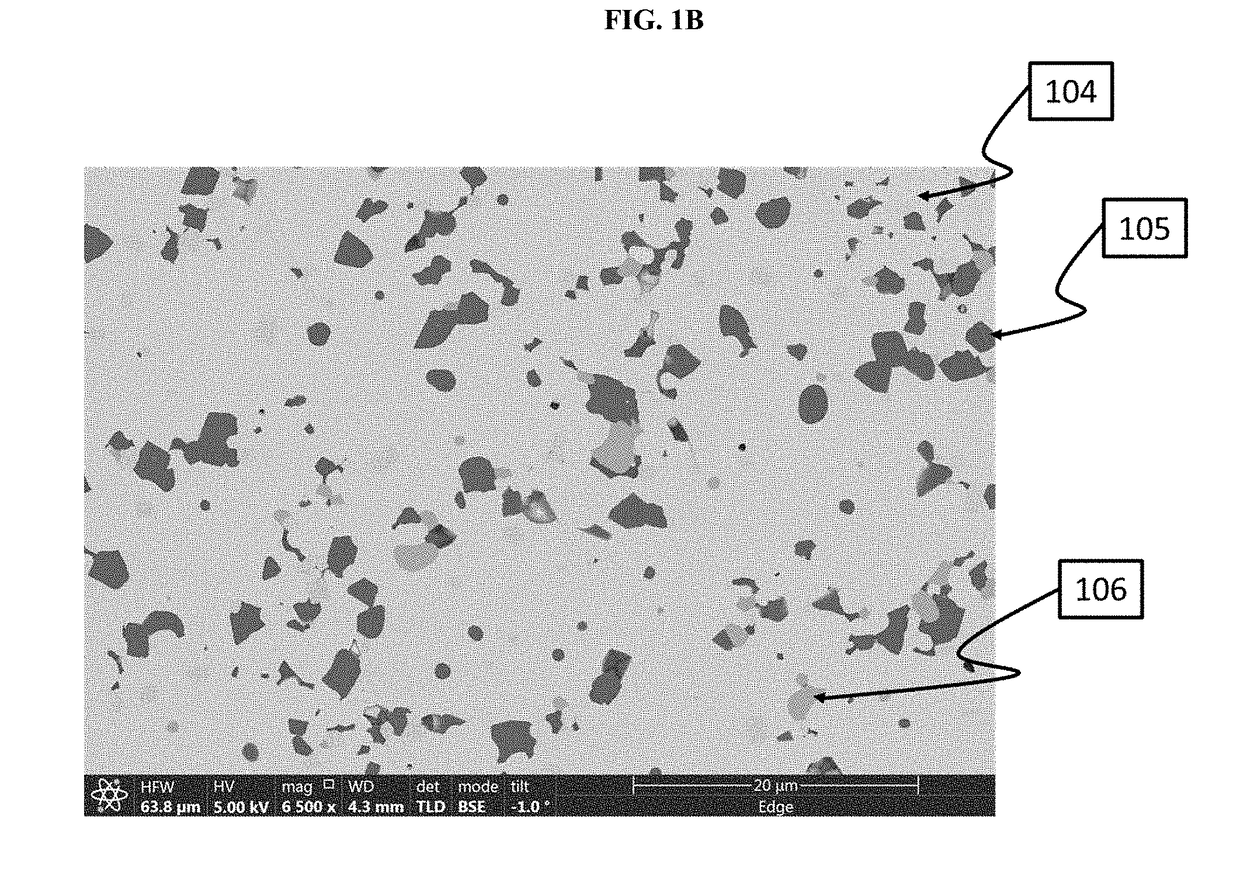
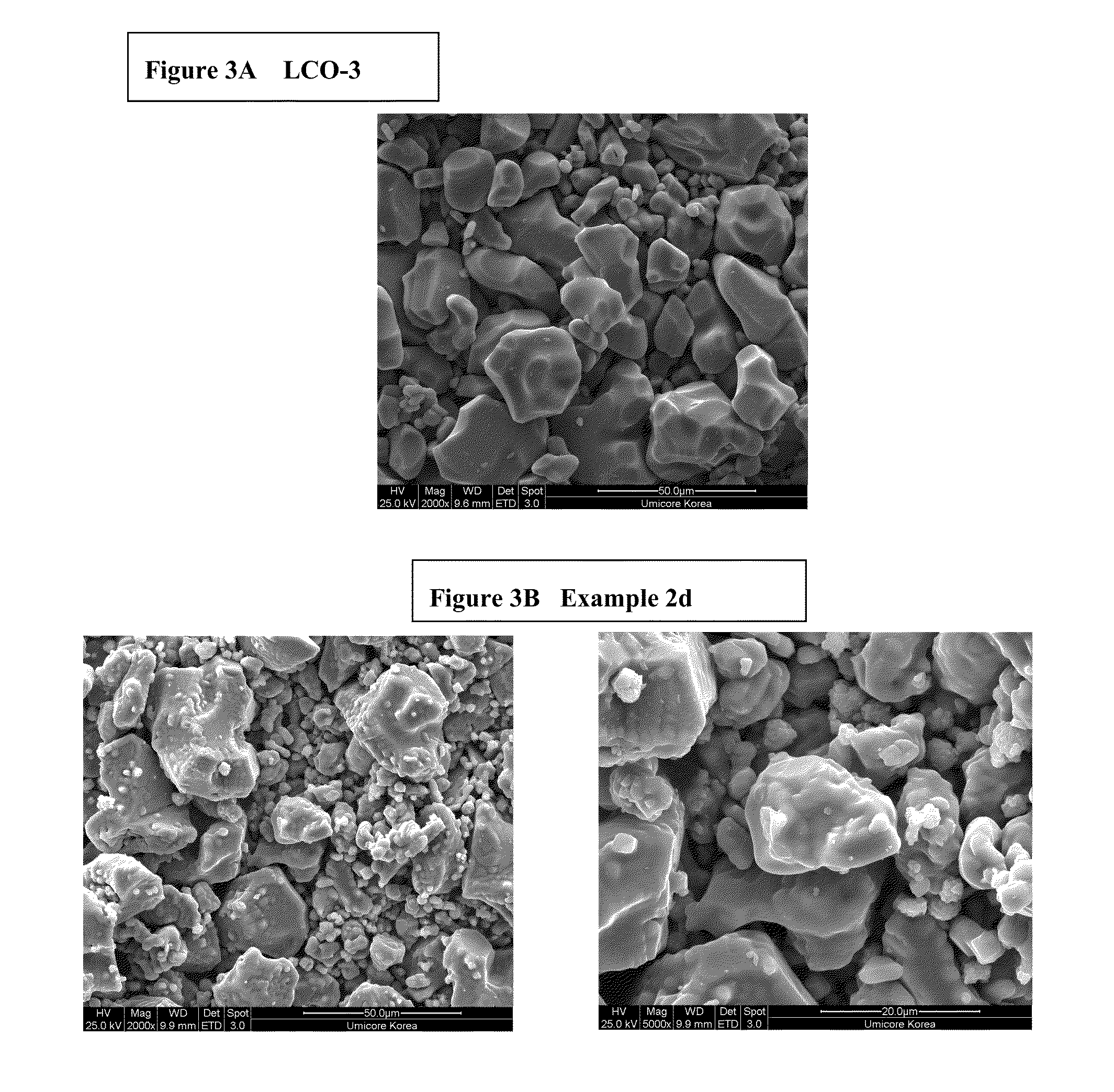
Disclosed are a cathode active material and a method to produce the same at low cost. The cathode powder comprises modified doped LiCoO2 carrying a secondary phase having either one of space groups Fm-3m or Fd-3 mS. The modified LiCoO2 is Ni and Mn bearing and has regions of low and high manganese content, where regions with high manganese content are located in islands on the surface. The cathode material has high cycling stability, a very high rate performance and good high temperature storage properties.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
High strength thin steel sheet, high strength alloyed hot-dip zinc-coated steel sheet, and method for producing them
InactiveUS6410163B1Improve the plating effectImproving threadabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsSheet steelHigh intensity
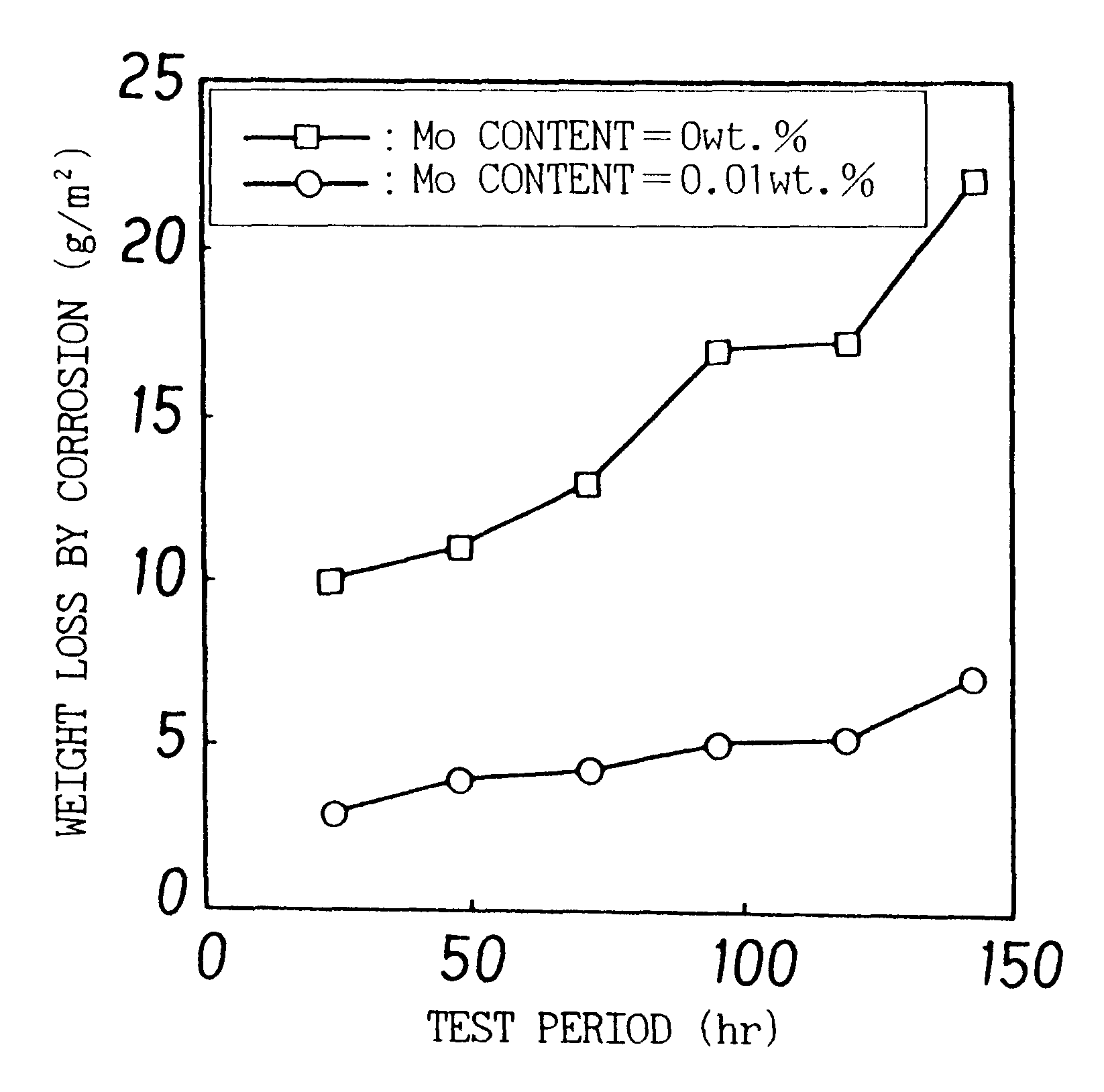
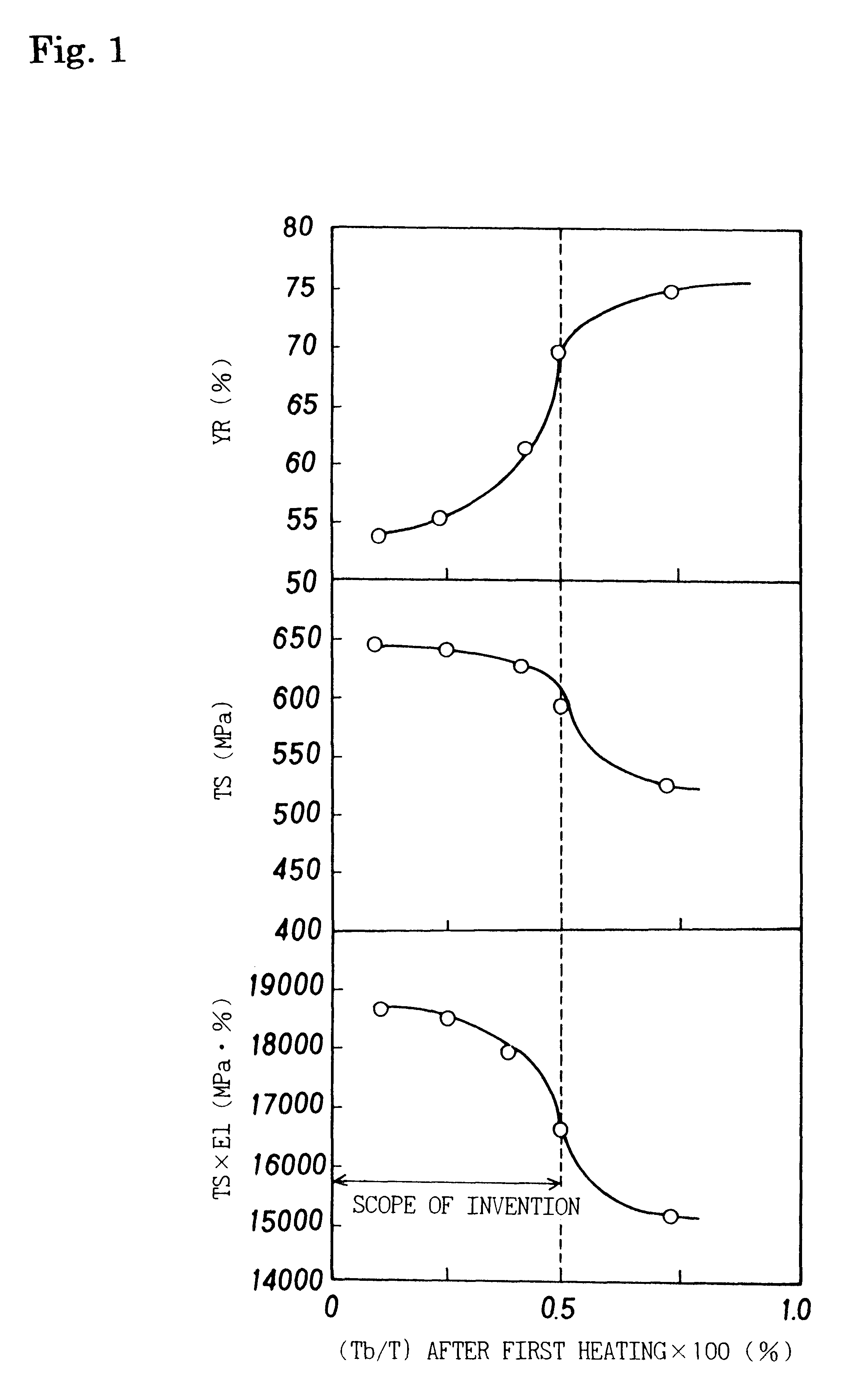
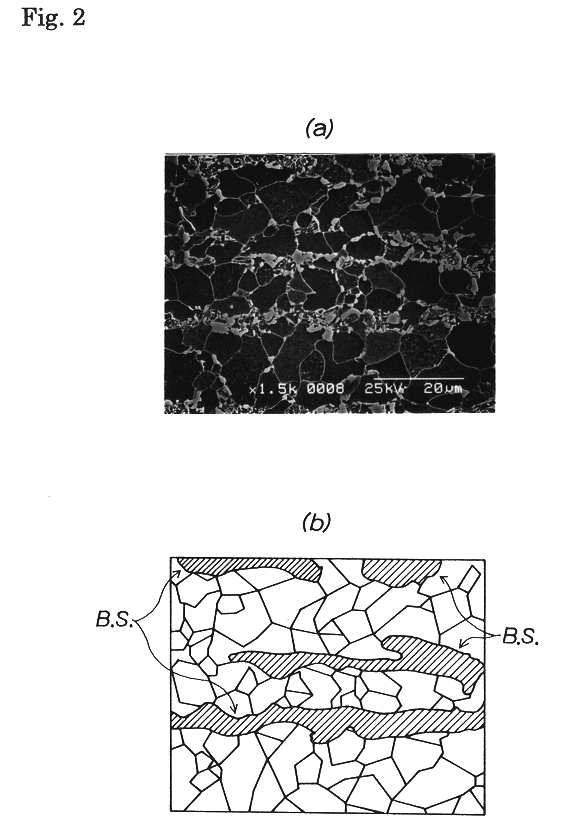
The present invention provides a high strength thin excellent workability and galvanizability, having a composition comprising from 0.01 to 0.20 wt. % C, up to 1.0 wt. % Si, from 1.0 to 3.0 wt. % Mn, up to 0.10 wt. % P, up to 0.05 wt. % S, up to 0.10 wt. % Al, up to 0.010 wt. % N, up to 1.0 wt. % Cr, from 0.001 to 1.00 wt. % Mo, and the balance Fe and incidental impurities, wherein a band structure comprising a secondary phase has a thickness satisfying the relation Tb / T<=0.005 (where, Tb: average thickness of the band structure in the thickness direction of steel sheet; T: steel sheet thickness), and a manufacturing method thereof, and a manufacturing method of a high strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet or a high strength galvannealed steel sheet applying hot-dip galvanizing or further galvannealing, and giving an excellent workability, a high tensile strength, and excellent galvanizability, coating adhesion and corrosion resistance.
Owner:KAWASAKI STEEL CORP
Method and Apparatus for Measuring the Flow Rates of the Individual Phases of a Multiphase Fluid Mixture
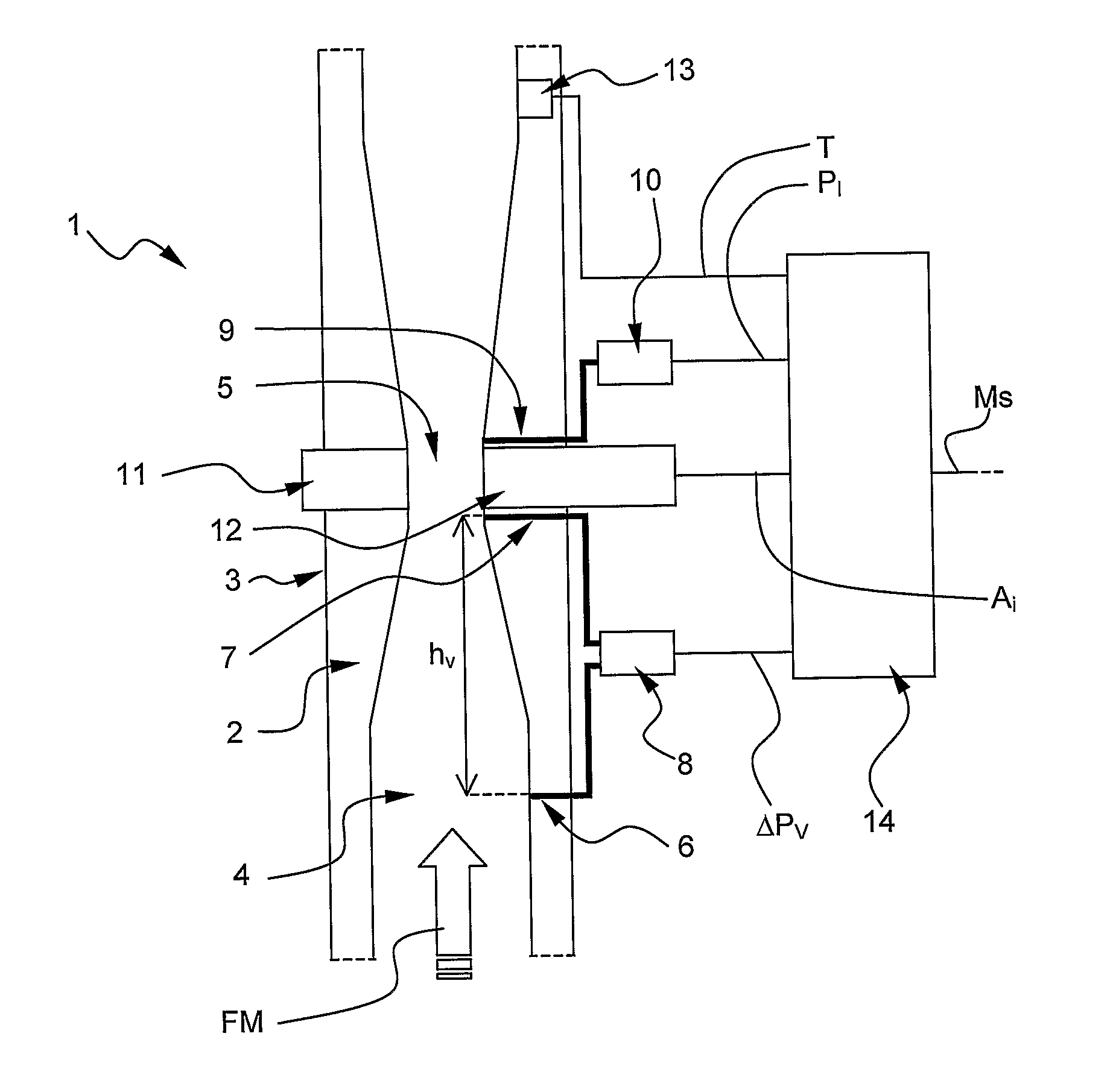
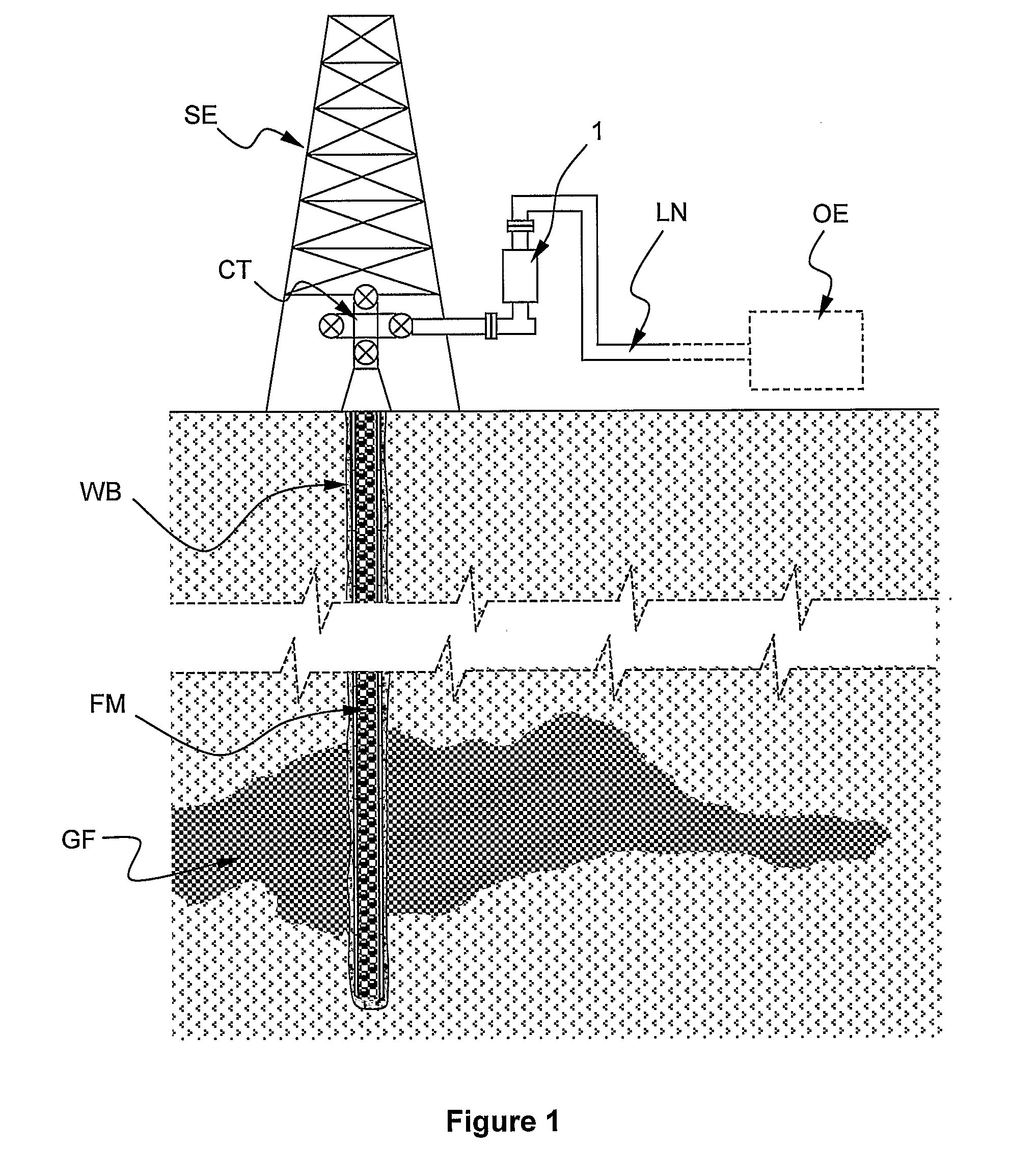
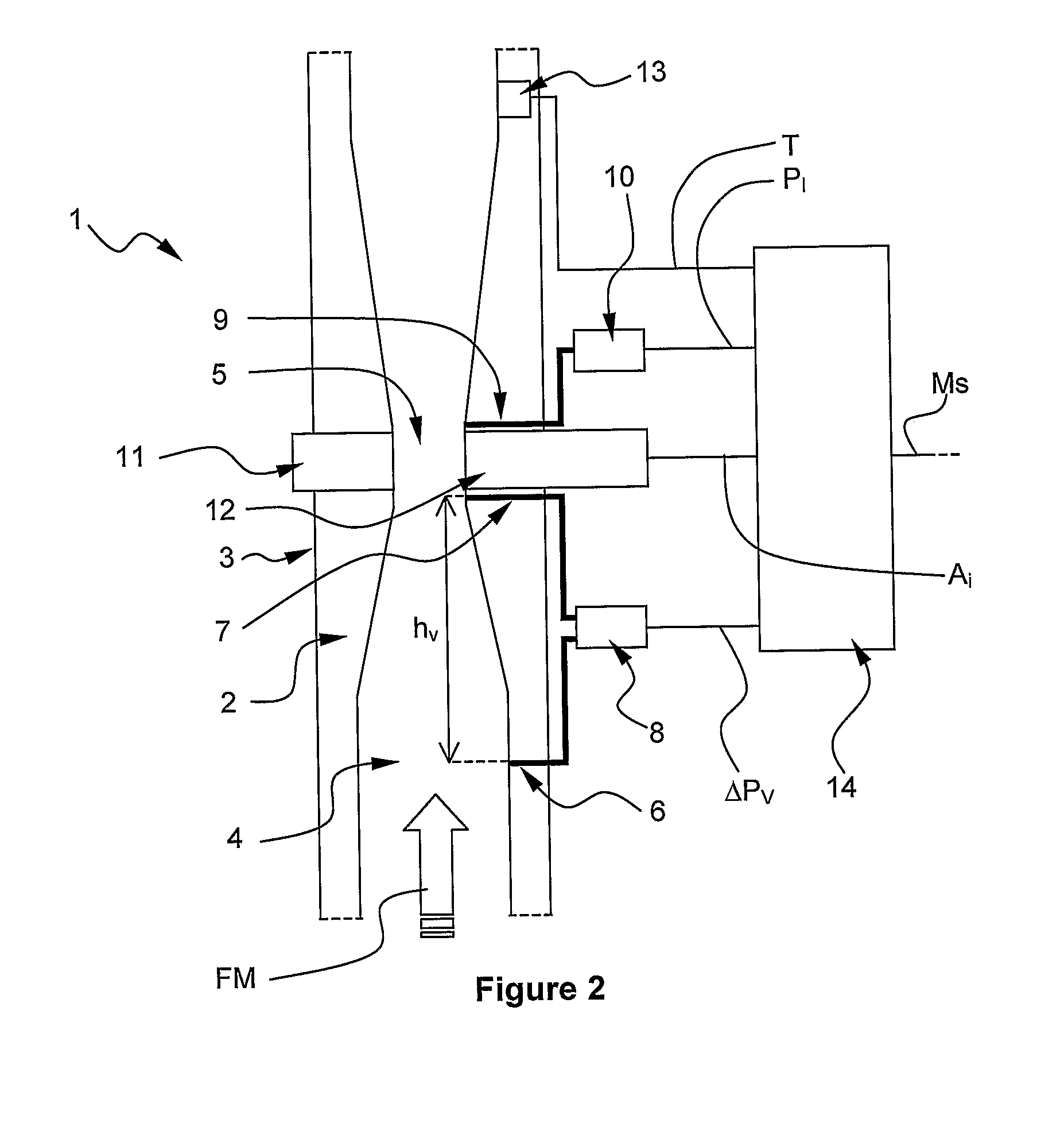
InactiveUS20090000390A1Less-expensive to implementSimilar accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVolume/mass flow by differential pressureContinuous measurementLine tubing
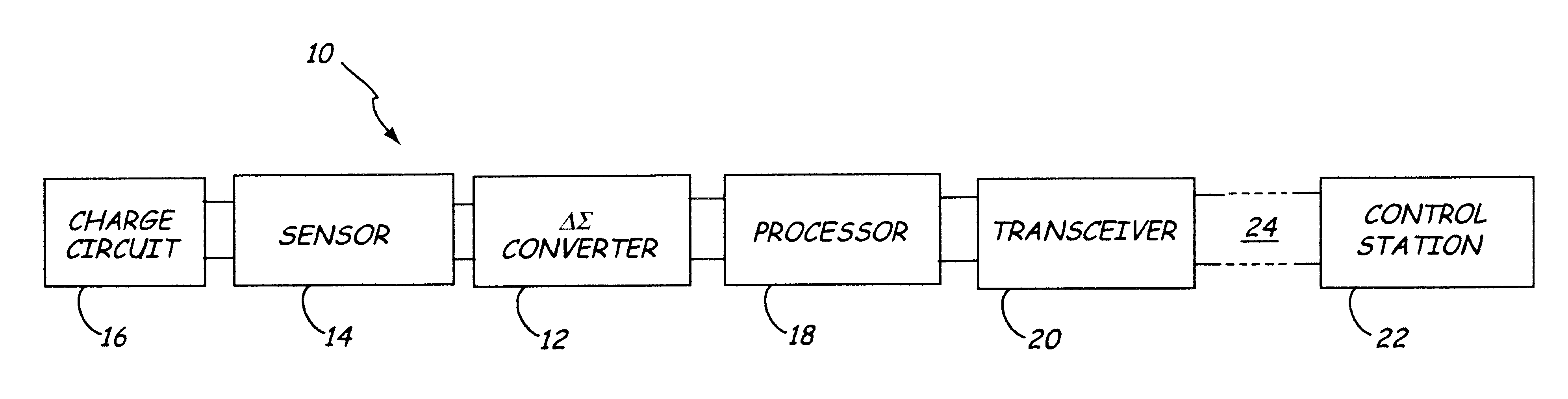
A flow rate measuring method for a multiphase fluid mixture FM flowing into a line LN, the fluid mixture FM comprising at least a first and a second phase, the method comprising the steps of: passing the fluid mixture through a Venturi tube in which the fluid mixture is subjected to a pressure drop, continuously measuring by means of said Venturi tube permanently installed on the line a differential pressure across the Venturi tube ΔPv and a line pressure of the fluid mixture in the line Pi, punctually measuring at a determined instant by means of a second measuring device removably installed on the line at least one measured parameter of the fluid mixture correlated to the first phase quantity relatively to the second phase quantity, continuously determining at least one estimated parameter of the fluid mixture correlated to the first phase quantity relatively to the second phase quantity based on the punctually measured parameter and an extrapolating scheme, and determining at least one phase flow rate based on the differential pressure across the Venturi ΔPv, the line pressure of the fluid mixture into the line Pi and the at least one measured parameter of the fluid mixture when the second device is installed on the line, and determining at least one phase flow rate based on the differential pressure across the Venturi ΔPv, the line pressure of the fluid mixture into the line Pi and the at least one estimated parameter of the fluid mixture when the second device is removed from the line.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Silicon carbide substrate and method of manufacturing the same
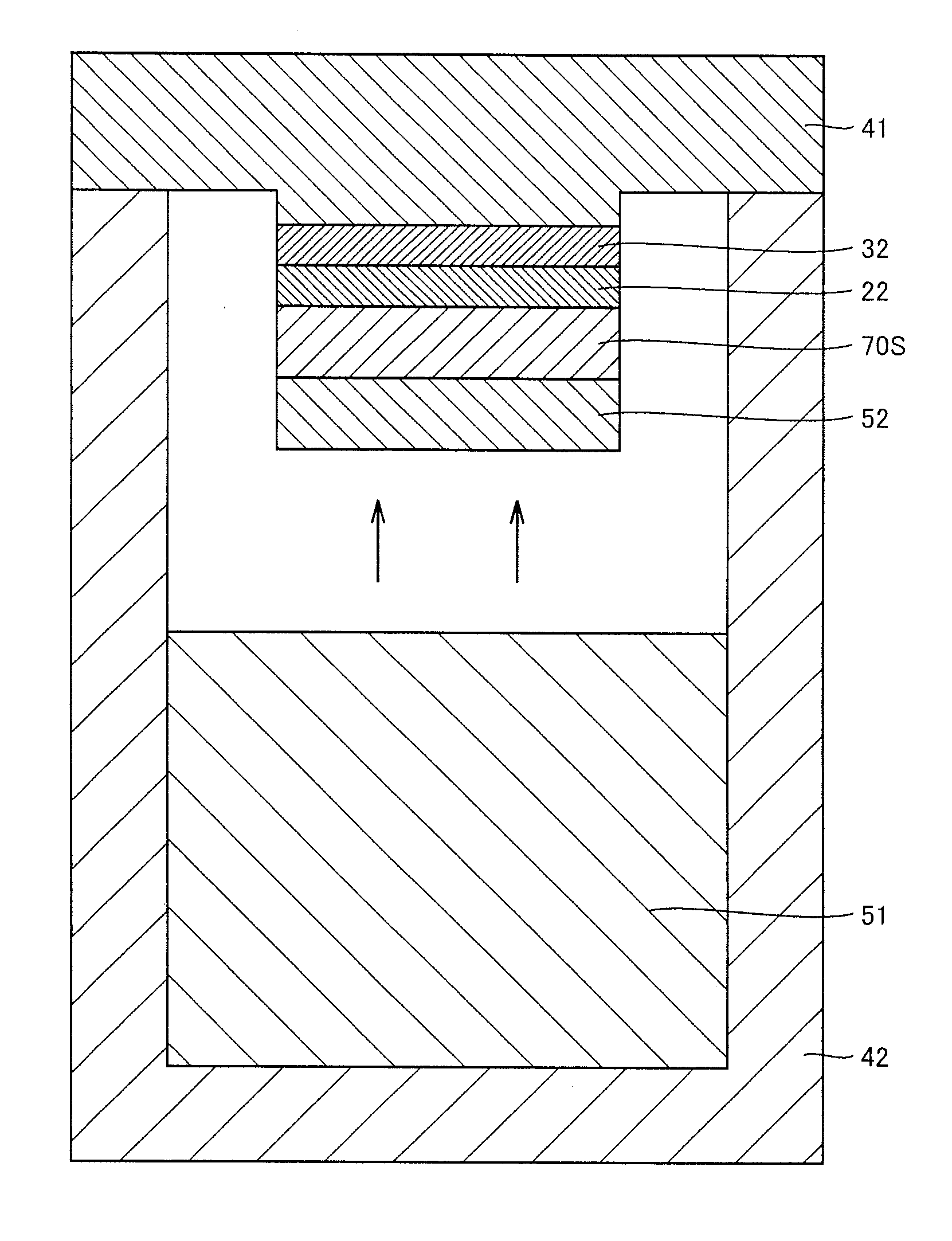
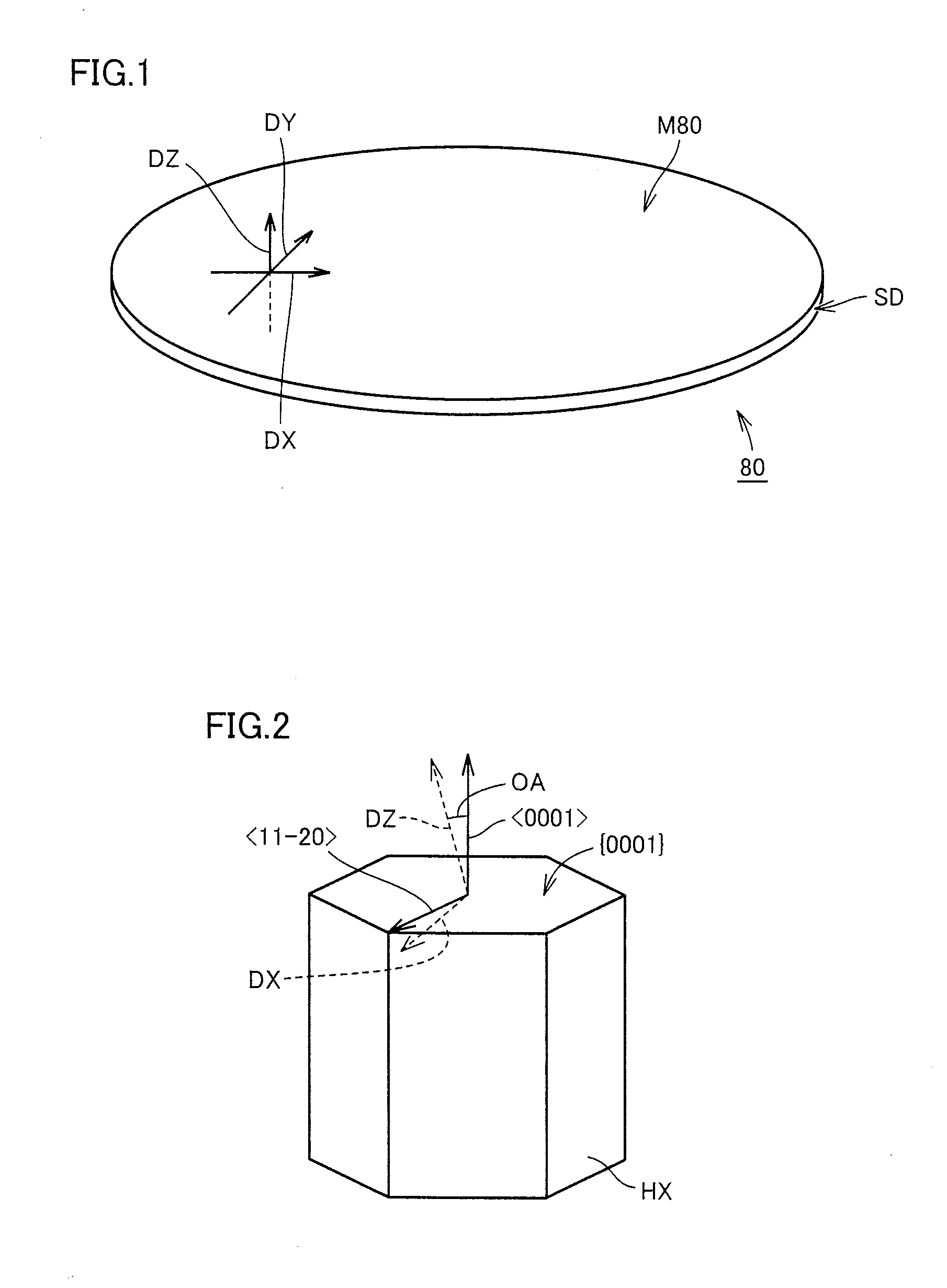
ActiveUS20130071643A1Improve performanceImprove device performanceAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthStacking faultSingle crystal
A silicon carbide substrate capable of stably forming a device of excellent performance, and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. A silicon carbide substrate is made of a single crystal of silicon carbide, and has a width of not less than 100 mm, a micropipe density of not more than 7 cm−2, a threading screw dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a threading edge dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a basal plane dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a stacking fault density of not more than 0.1 cm−1, a conductive impurity concentration of not less than 1×1018 cm−2, a residual impurity concentration of not more than 1×1016 cm−2, and a secondary phase inclusion density of not more than 1 cm−3.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
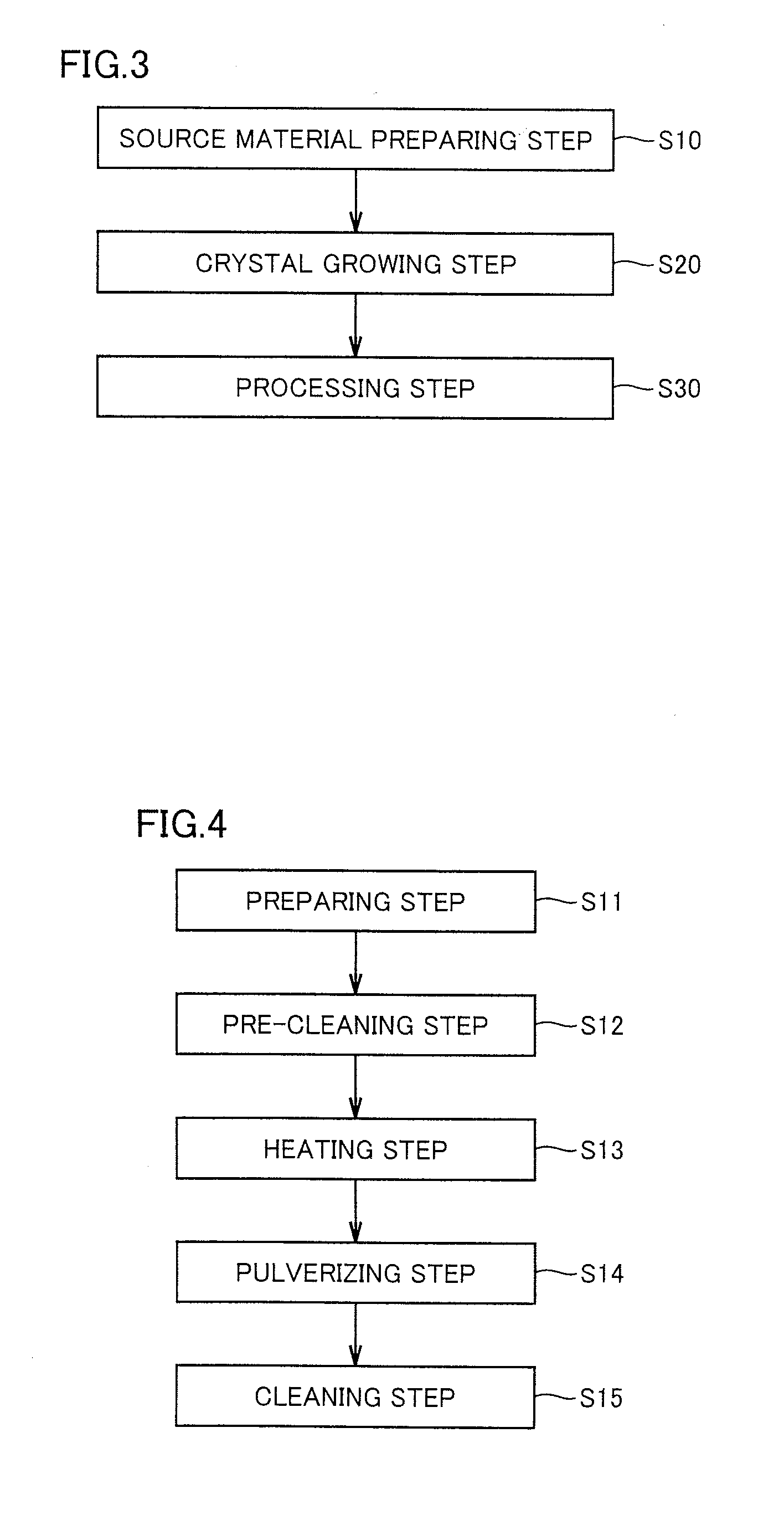
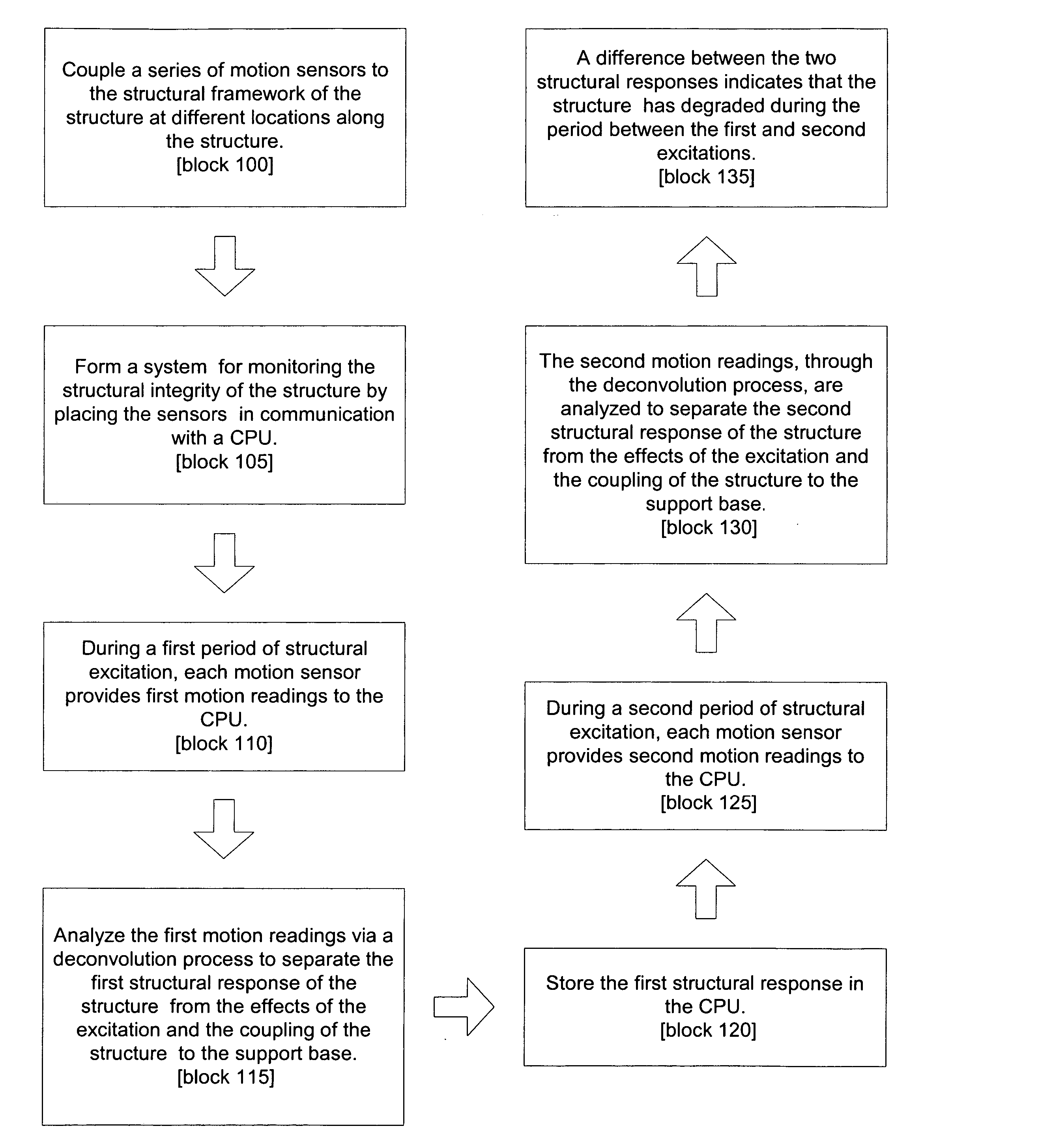
System for and method of monitoring structural integrity of a structure
InactiveUS20060248954A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMaterial analysis by using resonanceEngineeringStructural framework
The present invention, in one embodiment, is a system for determining the structural change (e.g., degradation) of a structural framework coupled to a support base, wherein the structural framework is subjected to first and second periods of excitation. The system comprises a plurality of motion sensors and a CPU. The plurality of motion sensors are distributed along the structural framework. The CPU is in communication with the motion sensors. The plurality of sensors provides to the CPU first motion data that is associated with the first period of excitation. The CPU deconvolves the first motion data to separate a first structural response pertaining to the structural framework from an effect of the first excitation and an effect of the structural framework being coupled to the support base. The plurality of sensors provides to the CPU second motion data that is associated with the second period of excitation. The CPU deconvolves the second motion data to separate a second structural response pertaining to the structural framework from an effect of the second excitation and an effect of the structural framework being coupled to the support base. The CPU compares the first and second structural response to determine whether the structural framework has structurally changed (e.g., degraded).
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
Method for continuous production hydrolysate by methylchlorosilane concentrated acid hydrolyzing
ActiveCN101323666AThe new hydrolysis process is excellentReduce or completely avoid entrainmentChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideDecompositionHydrolysate
The invention relates to a method for hydrolyzing methyl chlorosilane with concentrated acids to obtain hydrolysate, wherein, the methyl chlorosilane and the acidic oil-contained aqueous solution separated from the primary phase separator and the secondary phase separator from the hydrolysate are mixed, pass through a preheater, enter a concentrated-acid hydrolysis reaction system and undergo a circular reaction operation; the hydrogen chloride generated in the hydrolysis reaction is released from the top of a tower, goes through a defroster and a condensator and then becomes qualified HCI gas to be used in the production of methyl chloride. Qualified hydrolysate used for decomposition process is obtained after the hydrolysate of methyl chlorosilane goes through four phase separators and a steam tower.
Owner:BEIJING PETROCHEM ENG +1
Two phase anaerobic contact sequencing batch reactor (ACSBR) system for treating wastewater containing simple and complex organic constituents
InactiveUS20060175252A1Improve efficiencyEfficient digestionWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSequencing batch reactorSuspended solids
A two-phase anaerobic treatment system and method for the treatment of wastewaters containing simple and complex organic constituents is provided wherein the complex organic constituents are broken down into simple organic constituents by acidogenic bacteria in a Phase One reactor and the simple organic constituents from the Phase One reactor are converted into biogas, mainly methane, in a Phase Two reactor by methanogenic bacteria. The method includes the steps of feeding wastewater to the Phase One reactor either in an intermittent batch mode or semi-continuous mode, and withdrawing effluent from the Phase One reactor preferably in a batch mode. Effluent from the Phase One reactor is fed to the Phase Two reactor in an intermittent batch mode while effluent from the Phase Two reactor is withdrawn in a batch mode. The method minimizes the transfer of suspended solids from the Phase One reactor to the Phase Two reactor.
Owner:UPENDRAKUMAR K C +2
Method and apparatus to reduce bias temperature instability (BTI) effects
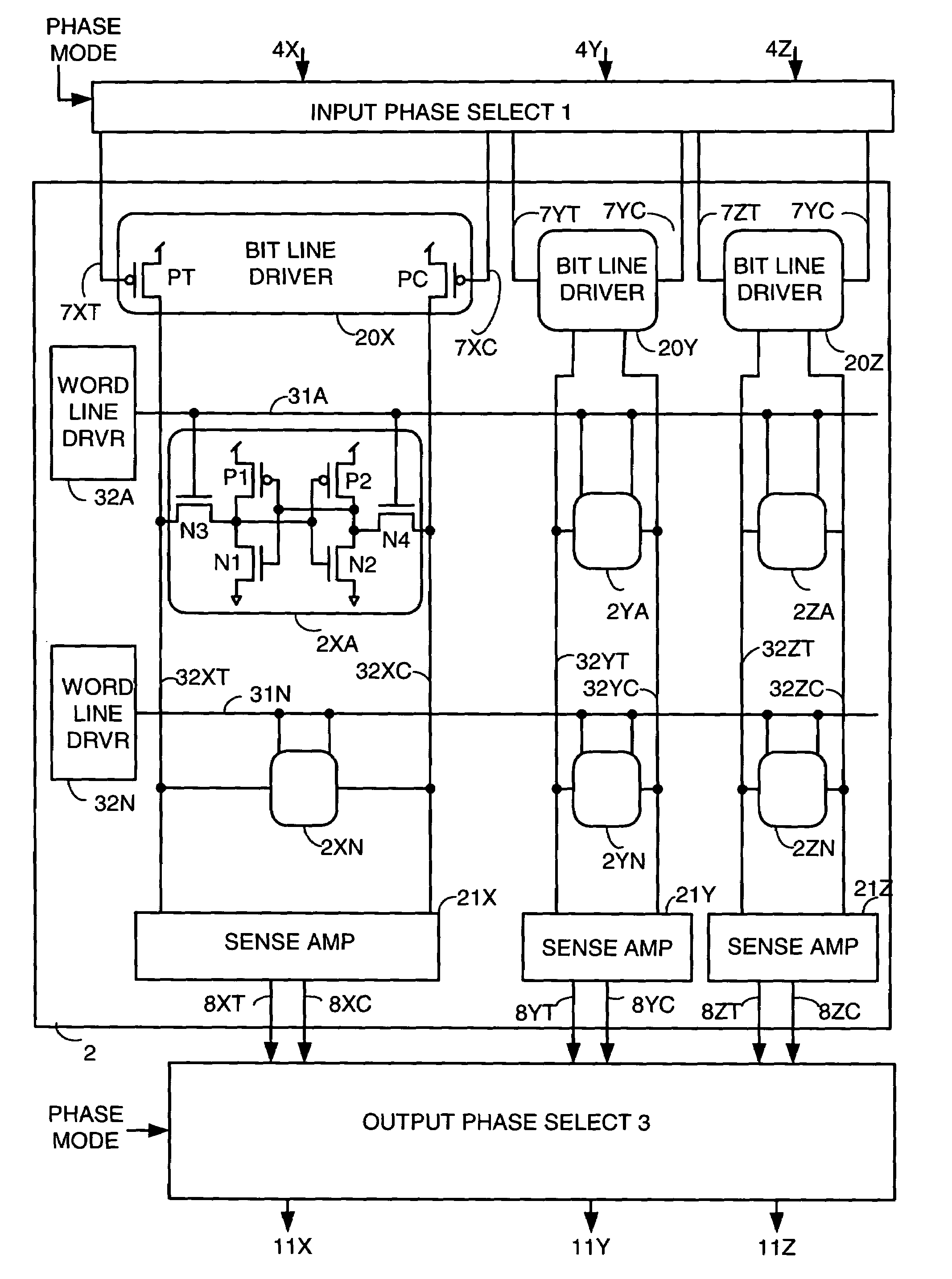
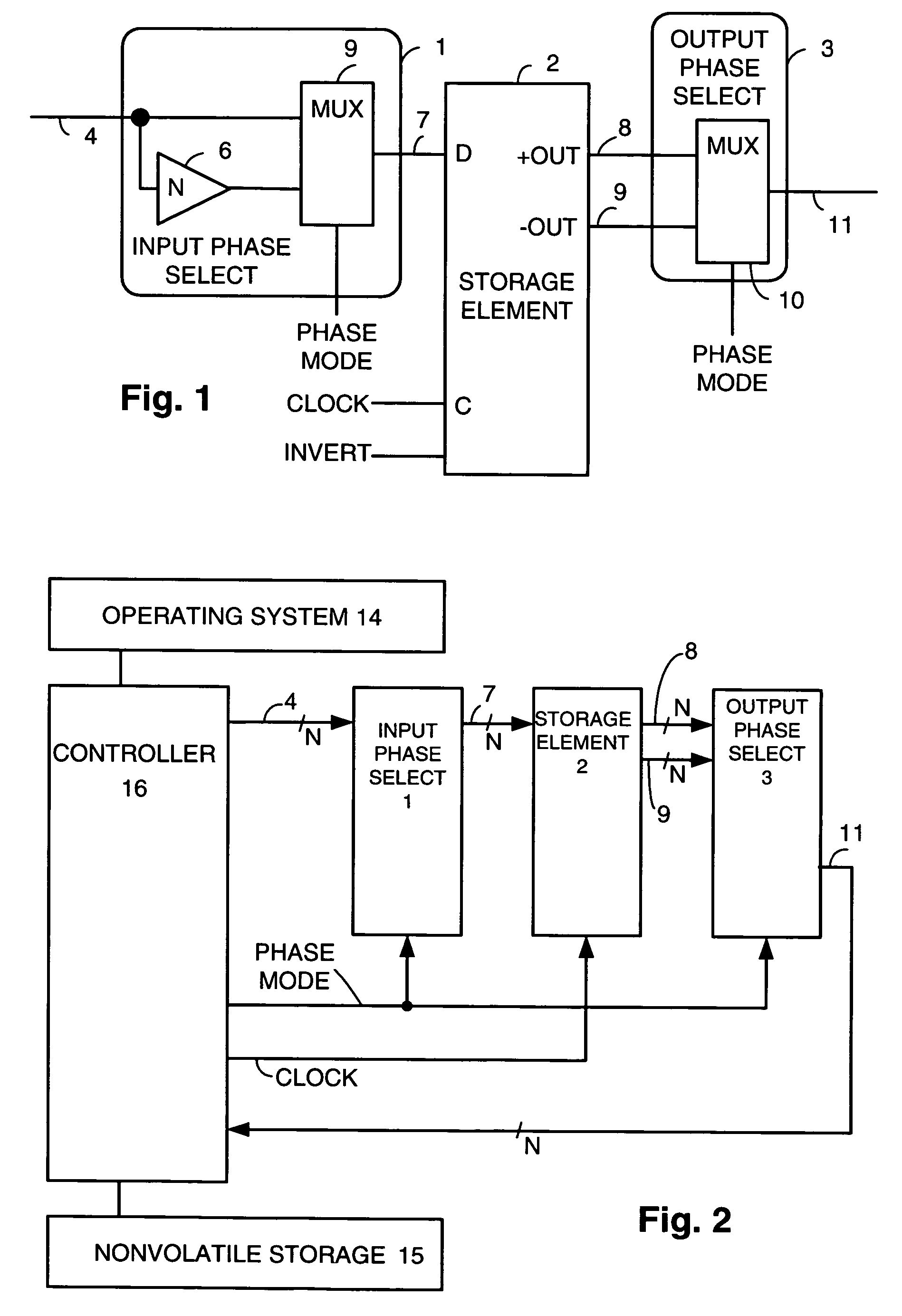
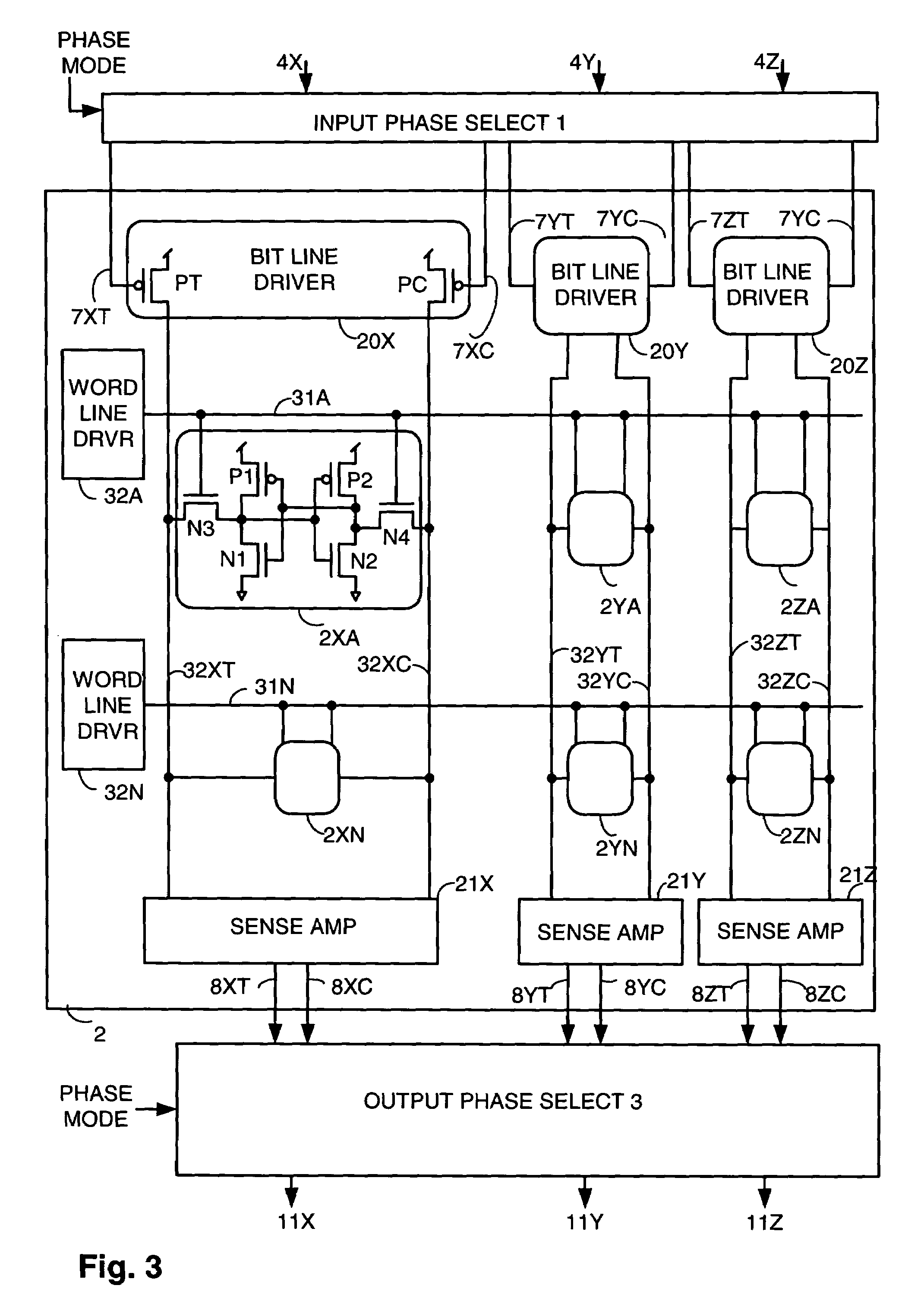
Methods and apparatus are disclosed that allow an electronic system implemented with field effect transistors (FETs) to reduce threshold voltage shifts caused by bias temperature instability (BTI). BTI caused VT shifts accumulate when an FET is in a particular voltage stress condition. Many storage elements in an electronic system store the same data for virtually the life of the system, resulting in significant BTI caused VT shifts in FETs in the storage elements. An embodiment of the invention ensures that a particular storage element is in a first state for a first portion of time the electronic system operates, during which data is stored in a storage element in a first phase, and that the particular storage element is in a second state for a second portion of time the electronic system operates, during which data is stored in the storage element in a second phase.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
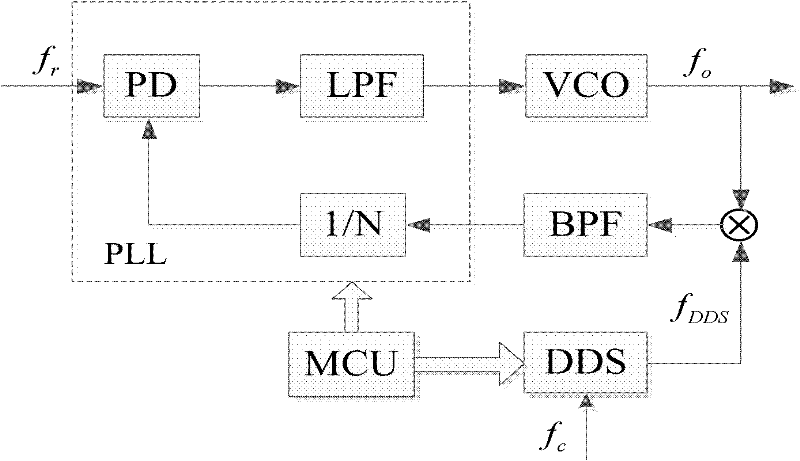
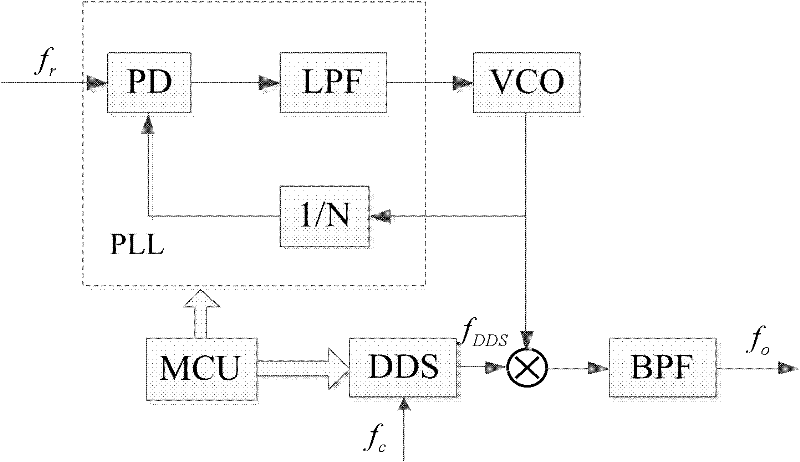
Design method of low-phase-noise microwave wideband frequency combiner
ActiveCN102651649AGuaranteed normal outputLow spuriousPulse automatic controlMicrocontrollerPhase noise
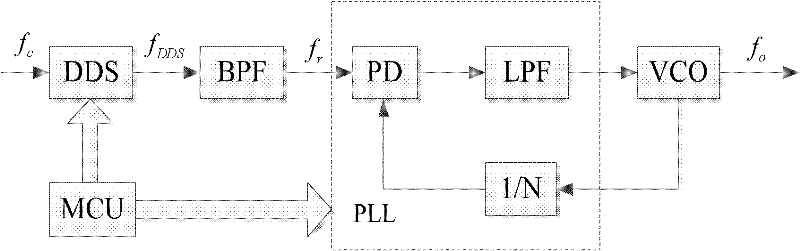
The invention relates to a design method of a microwave wideband frequency combiner applied to the field of signal interference. According to the method, a DDS (Direct Digital Synthesis) + PLL (Phase Locked Loop) + DAFS (Direct Analog Frequency Synthesis) hybrid frequency synthesis mode is utilized to synthesize a 0.1-18GHz ultra wide band microwave frequency, wherein the frequency band comprises working frequencies of most of microwave signals, can meet the frequency requirement for interfering with most of the microwave signals and especially can be applied to the field of satellite interference; in a DDS+PLL link, a 4-10GHz waveband is synthesized, a double phase locked loop internal mixing synthesis mode is adopted, a secondary phase locked loop adopts a mode of stimulating PLL by DDS, and a main phase locked loop is inserted into an output frequency so as to be mixed with the output frequency; in a DAFS link, DDS+PLL output is utilized as input and expanded to a 0.1-18GHz band width by virtue of a frequency multiplication, frequency demultiplication and down frequency conversion mode so as to be output; and in the whole frequency synthesis process, through carrying out frequency control by virtue of a singlechip and an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) and reasonably selecting the output frequency, frequency multiplication times and mixing frequency of each link, the final output frequency has the characteristics of low phase noise and wide band, and simultaneously the output of strays and harmonic waves can be well restrained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
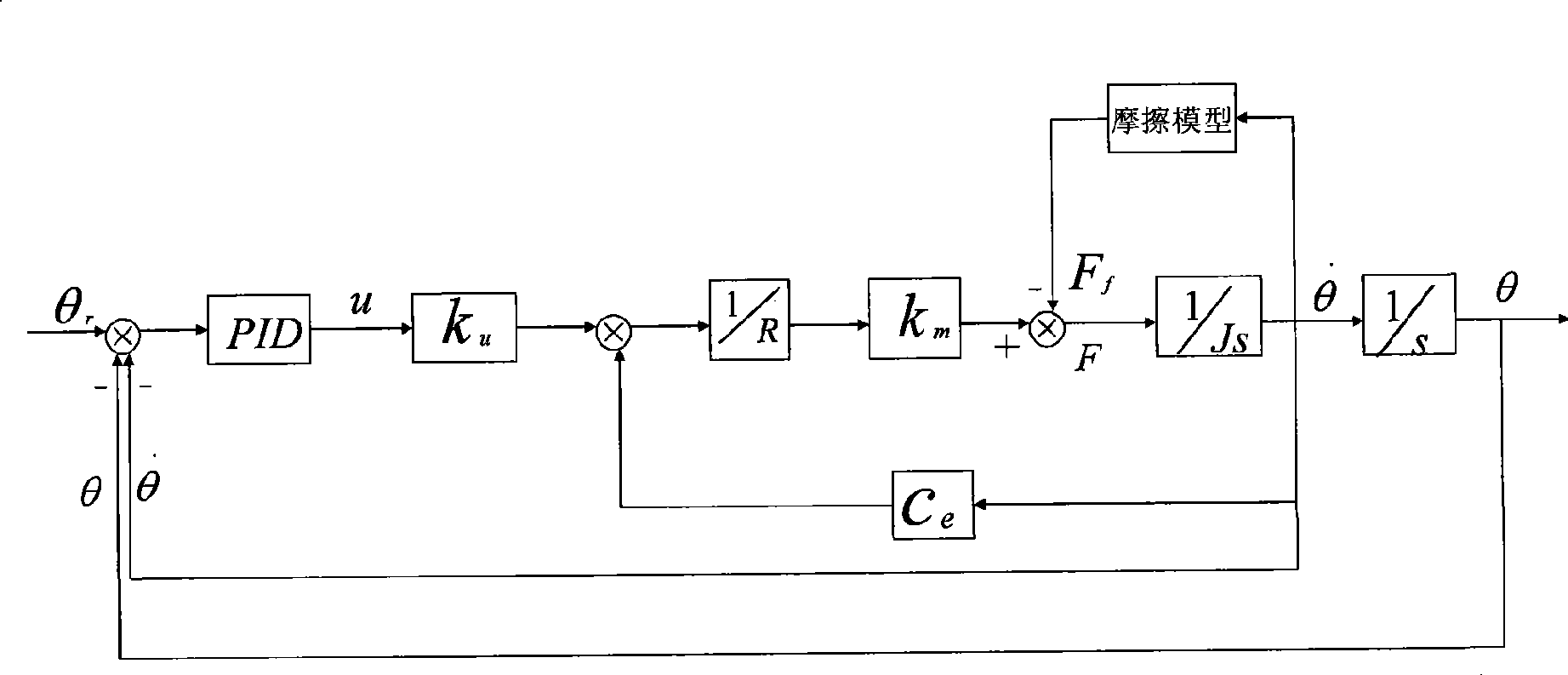
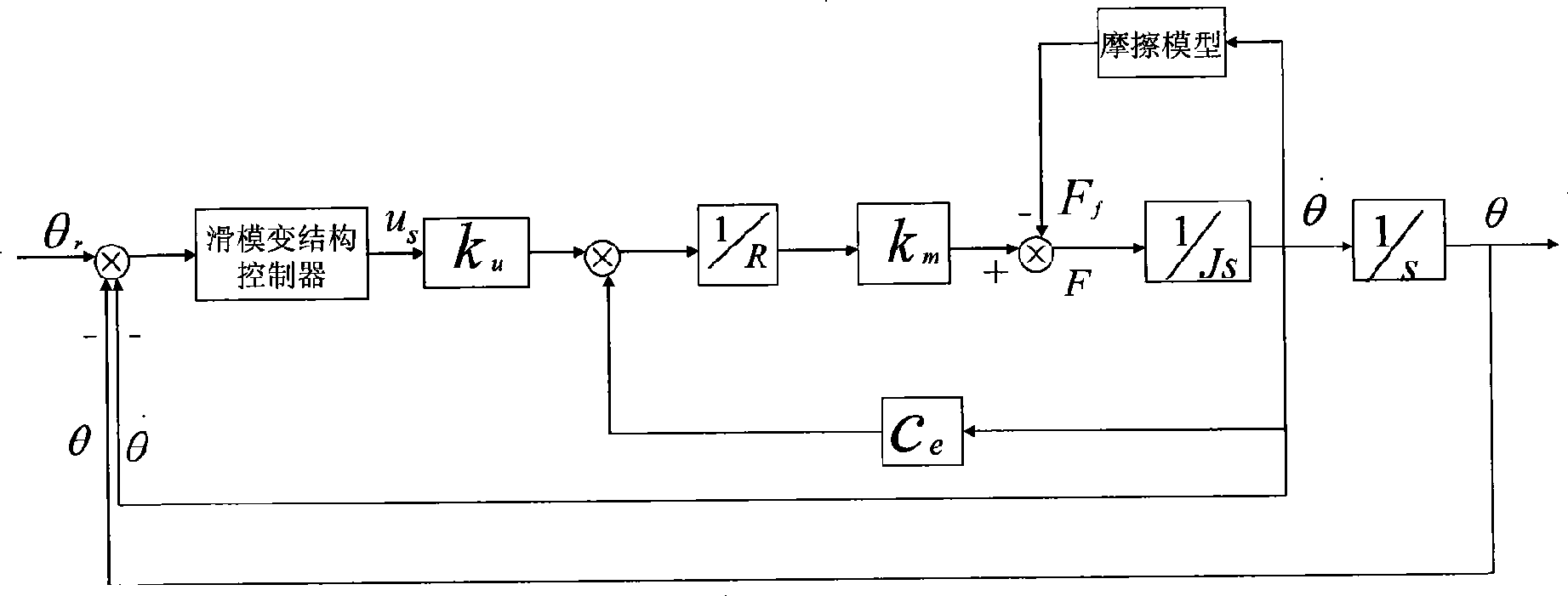
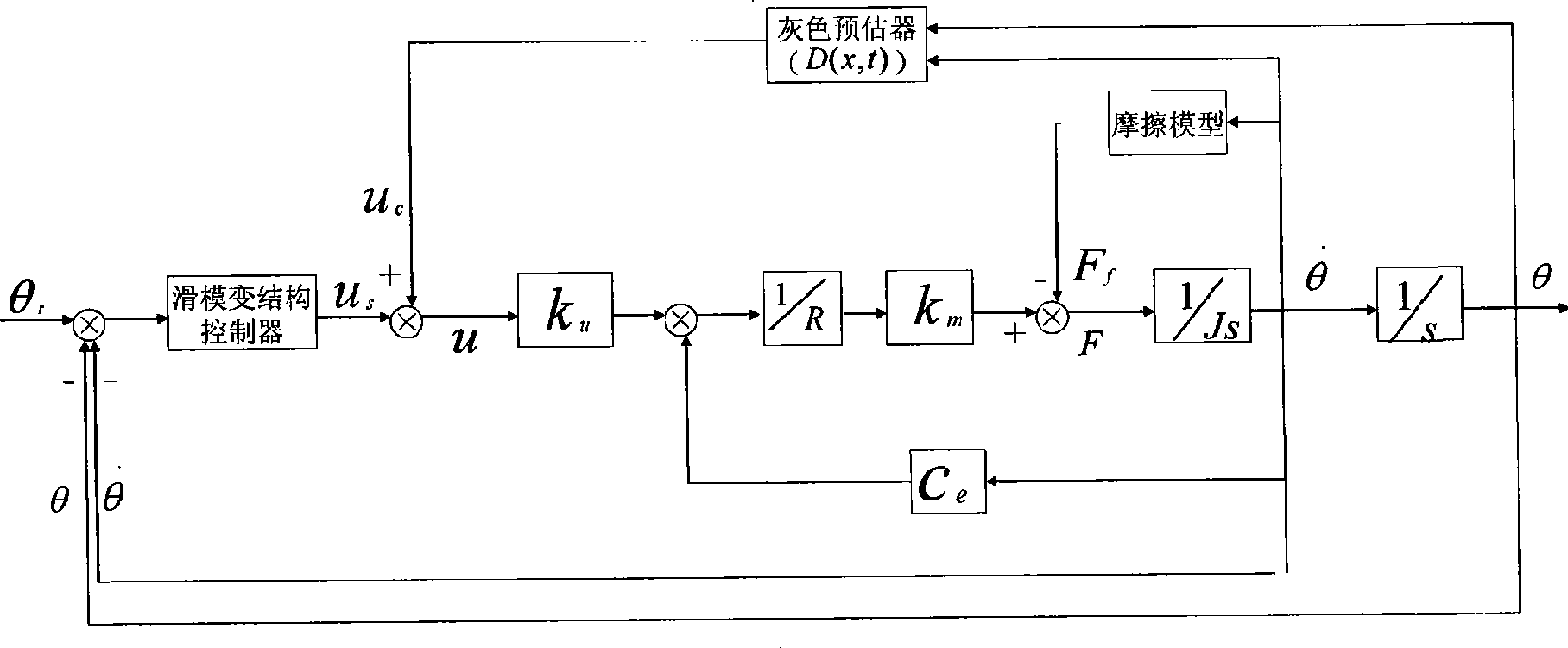
Low speed friction servo system sliding-mode variable structure control method based on grey prediction device
The invention relates to a sliding mode variable structure control method for a low-speed friction servo system which is based on a gray predictor. The method comprises two stages: the first stage, the sliding mode variable structure control method of the exponential approach rate is adopted to control the servo system, simultaneously, the gray control theory is utilized to estimate the uncertain part of the servo system and the outside unknown interference model parameter; the second stage, after former steps, based on the control law at the first stage, the gray predicting compensation control quantity can be calculated according to the estimate parameter, and can take part in controlling the servo system along with the control quantity of the fist stage. The control method can guarantee the low-speed friction servo system to also obtain better robust even though the effects of the uncertain part and the outside unknown interference model parameter are considered, so as to reach high precision tracing effect. The control method has the simple and pellucid program, provides a new control strategy for systems which have nonlinear and uncertain control objects as well as outside unknown interference, thereby having certain practical engineering value.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
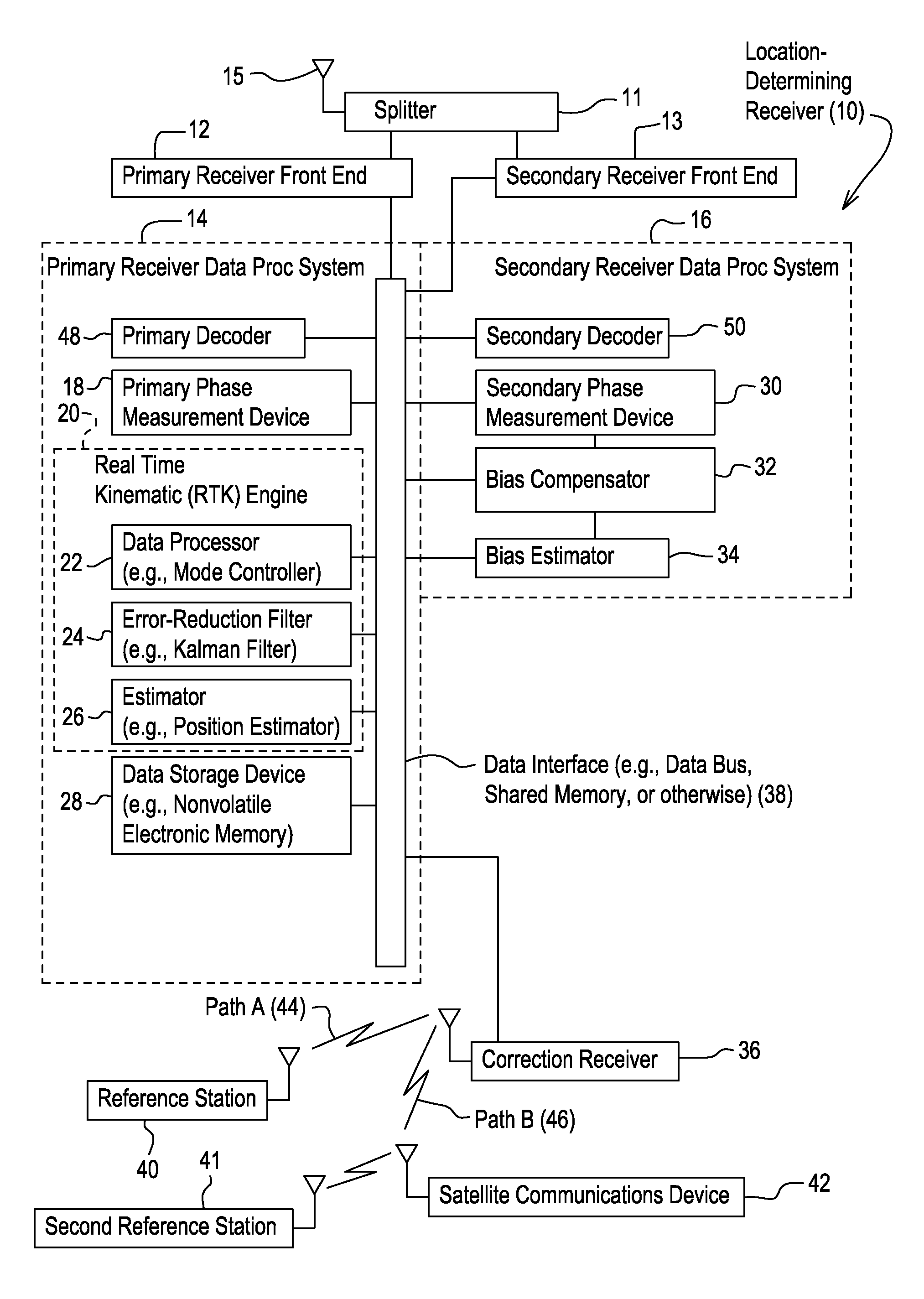
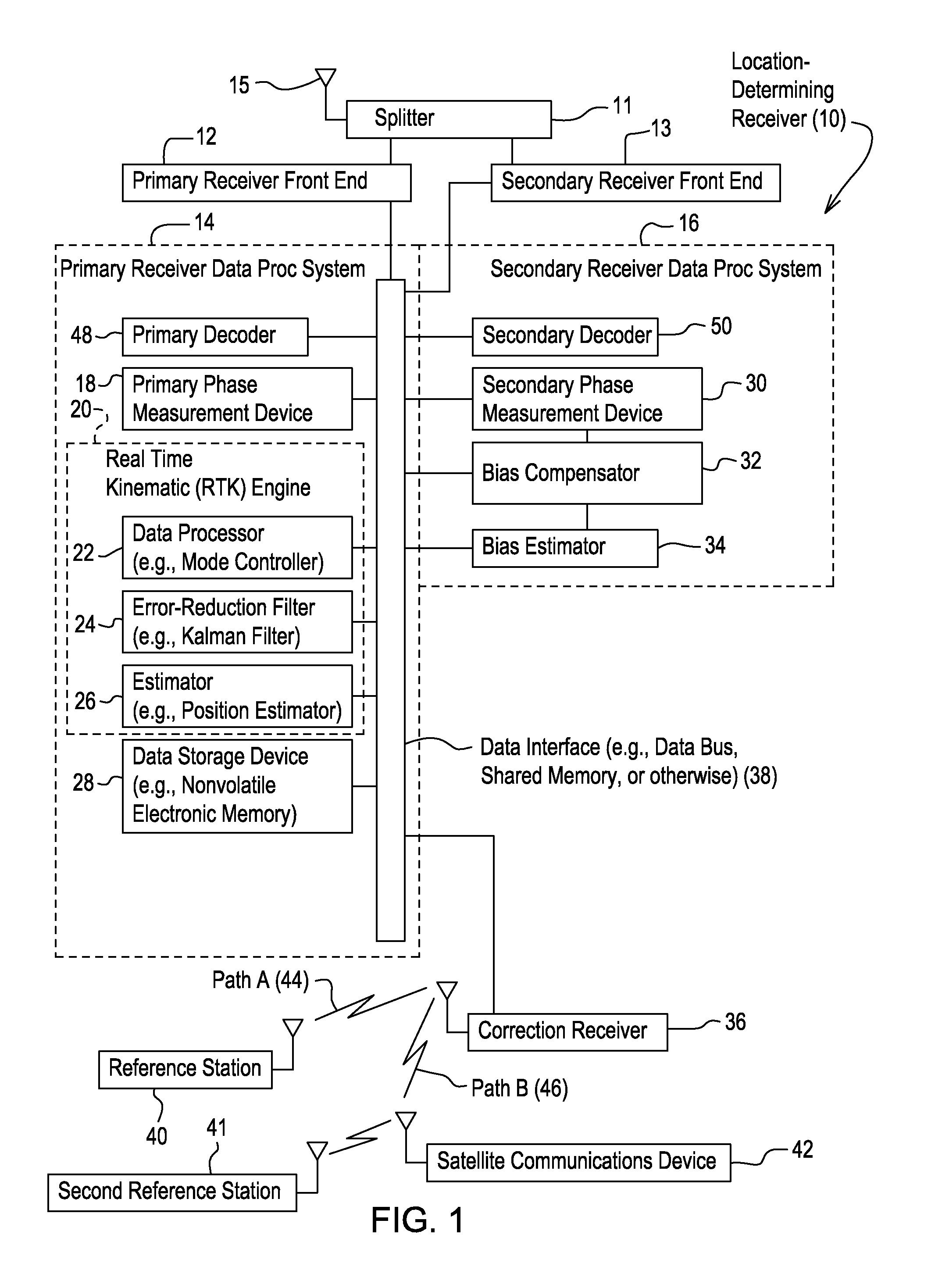
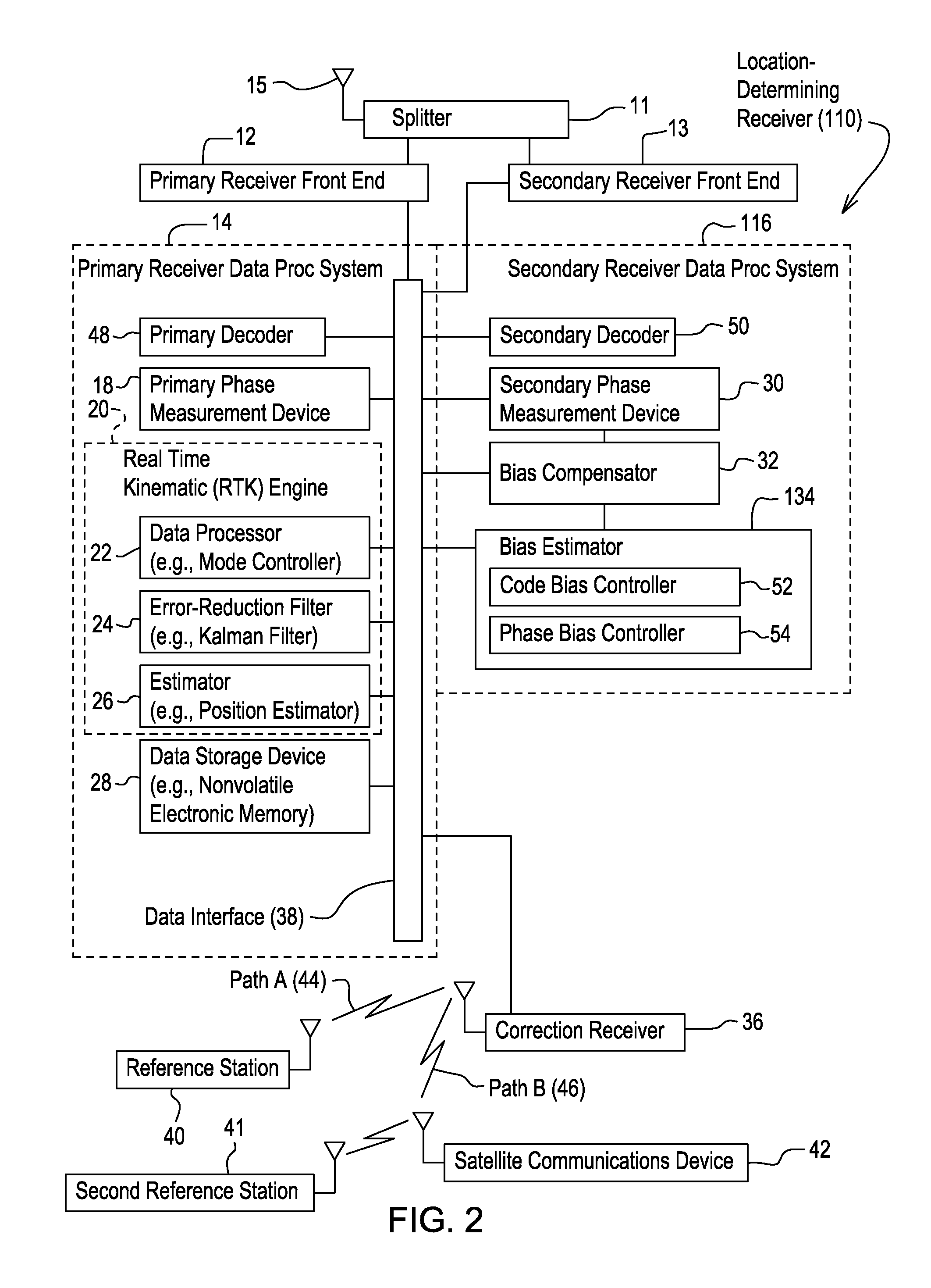
Method and system for estimating position with bias compensation
A primary phase measurement device measures a first carrier phase and a second carrier phase of carrier signals received by the location-determining receiver. A secondary phase measurement device measures the third carrier phase and the fourth carrier phase of other carrier signals. A real time kinematic engine estimates a first integer ambiguity set associated with the measured first carrier phase and a second integer ambiguity set associated with the measured second carrier phase. The real time kinematic engine estimates a third ambiguity set associated with the measured third carrier phase and a fourth ambiguity set associated with the measured fourth carrier phase. A compensator is capable of compensating for the inter-channel bias in at least one of the third ambiguity set and the fourth ambiguity set by modeling a predictive filter in accordance with various inputs or states of the filter estimated by an estimator.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com