Patents
Literature
261 results about "Stacking fault" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
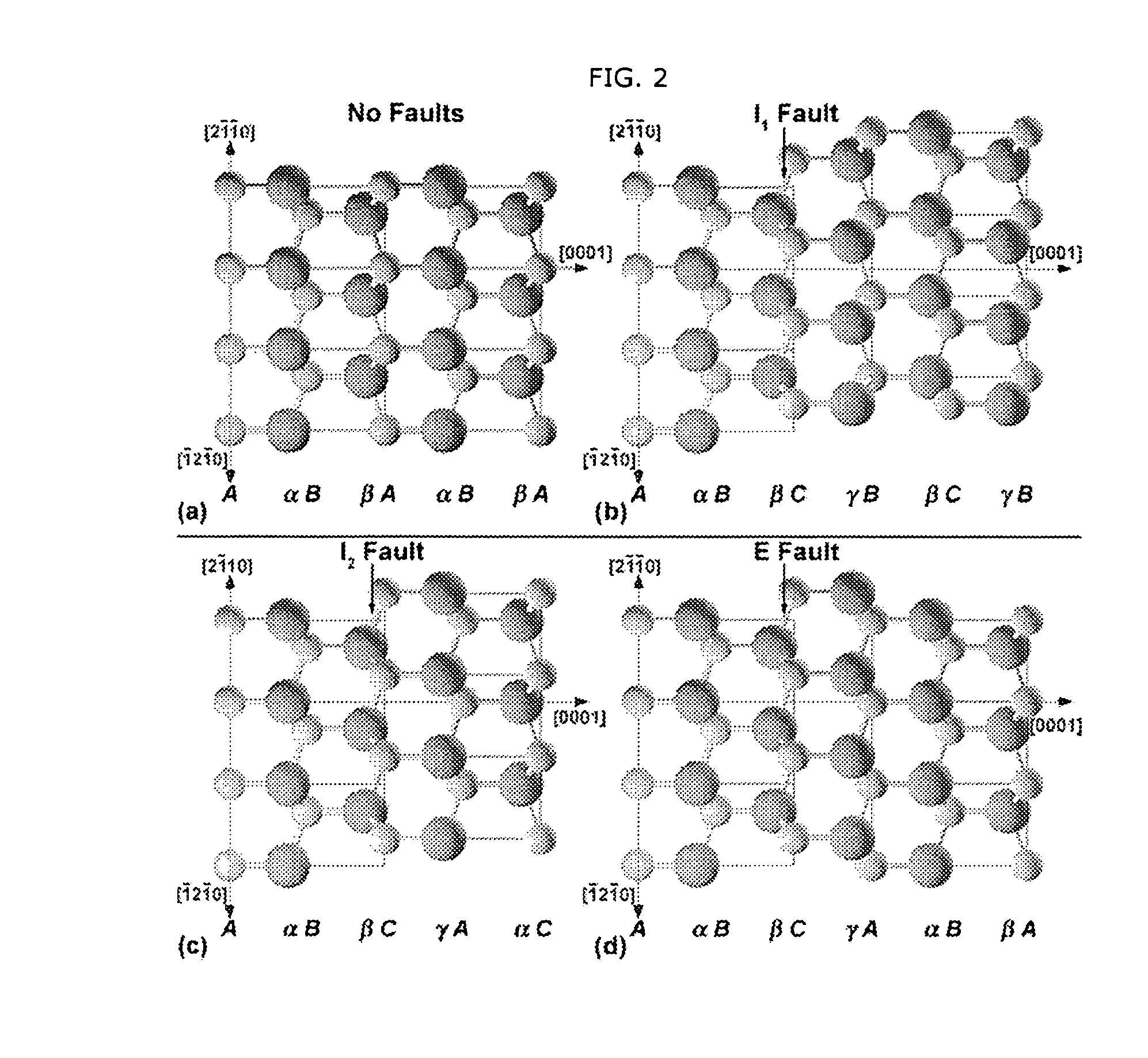
In crystallography, a stacking fault is a type of defect which characterizes the disordering of crystallographic planes. It is thus considered a planar defect. The most common example of stacking faults is found in close-packed crystal structures. Face-centered cubic (fcc) structures differ from hexagonal close packed (hcp) structures only in stacking order: both structures have close-packed atomic planes with sixfold symmetry — the atoms form equilateral triangles. When stacking one of these layers on top of another, the atoms are not directly on top of one another. The first two layers are identical for hcp and fcc, and labelled AB. If the third layer is placed so that its atoms are directly above those of the first layer, the stacking will be ABA — this is the hcp structure, and it continues ABABABAB. However, there is another possible location for the third layer, such that its atoms are not above the first layer. Instead, it is the atoms in the fourth layer that are directly above the first layer. This produces the stacking ABCABCABC, which is actually along the [111] direction of a cubic crystal structure. In this context, a stacking fault is a local deviation from one of the close-packed stacking sequences to the other one. Usually, only one- two- or three-layer interruptions in the stacking sequence are referred to as stacking faults. An example for the fcc structure is the sequence ABCABABCAB.
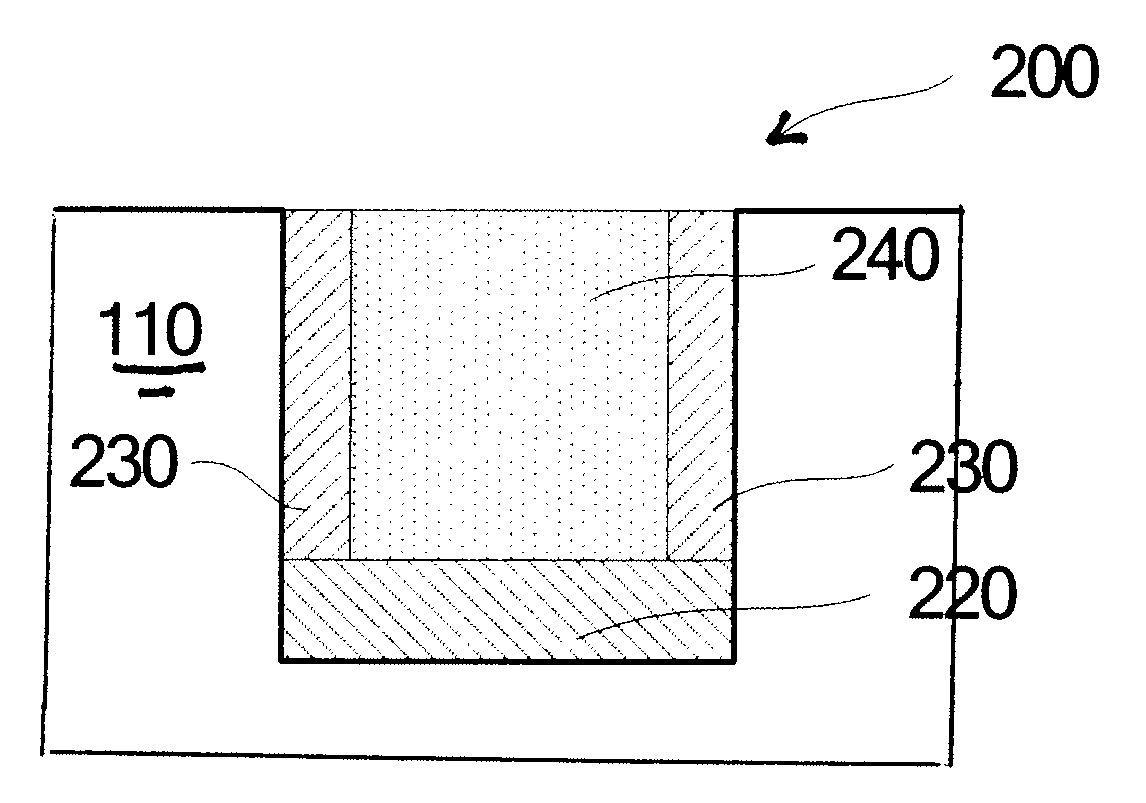
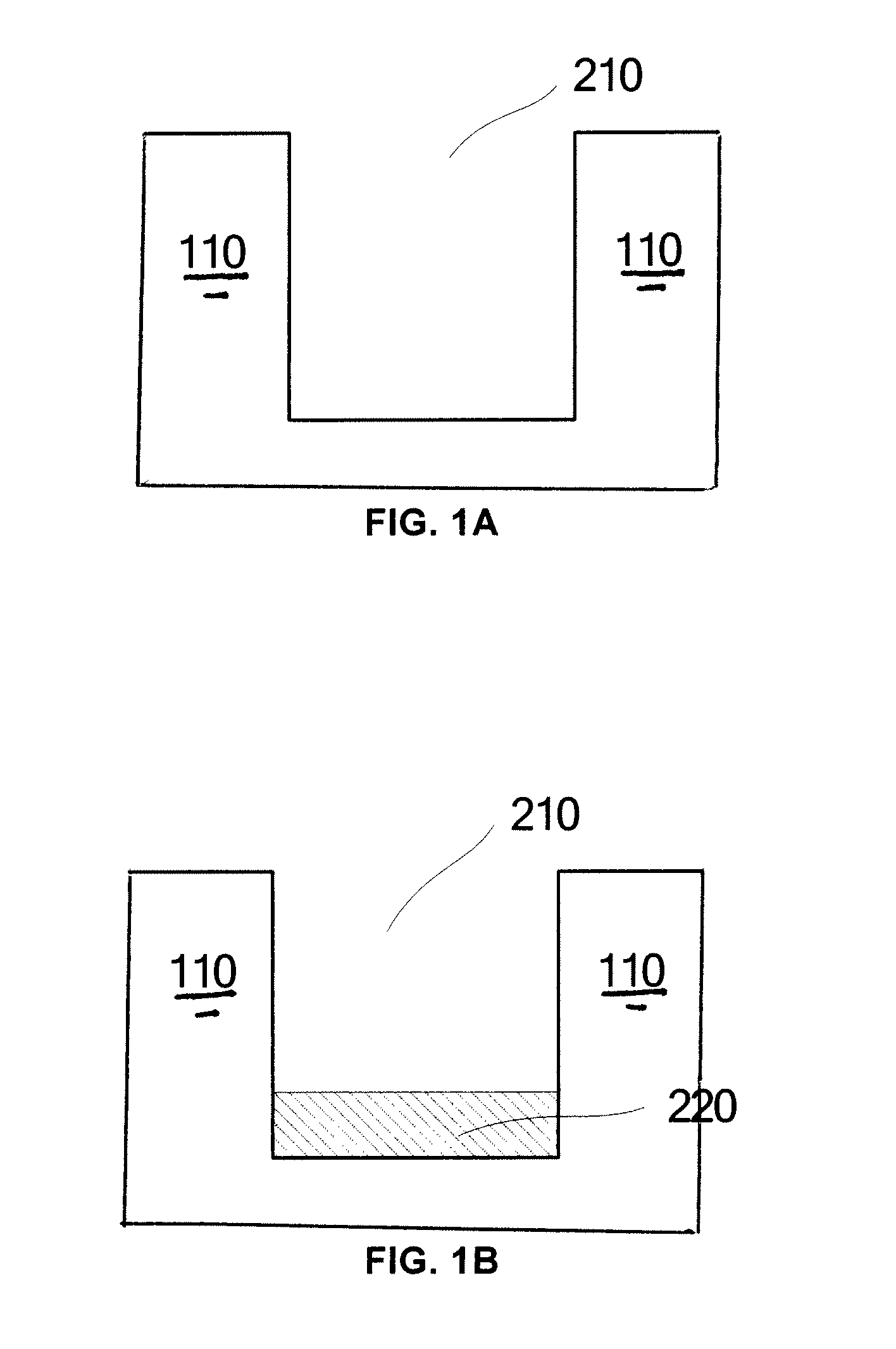
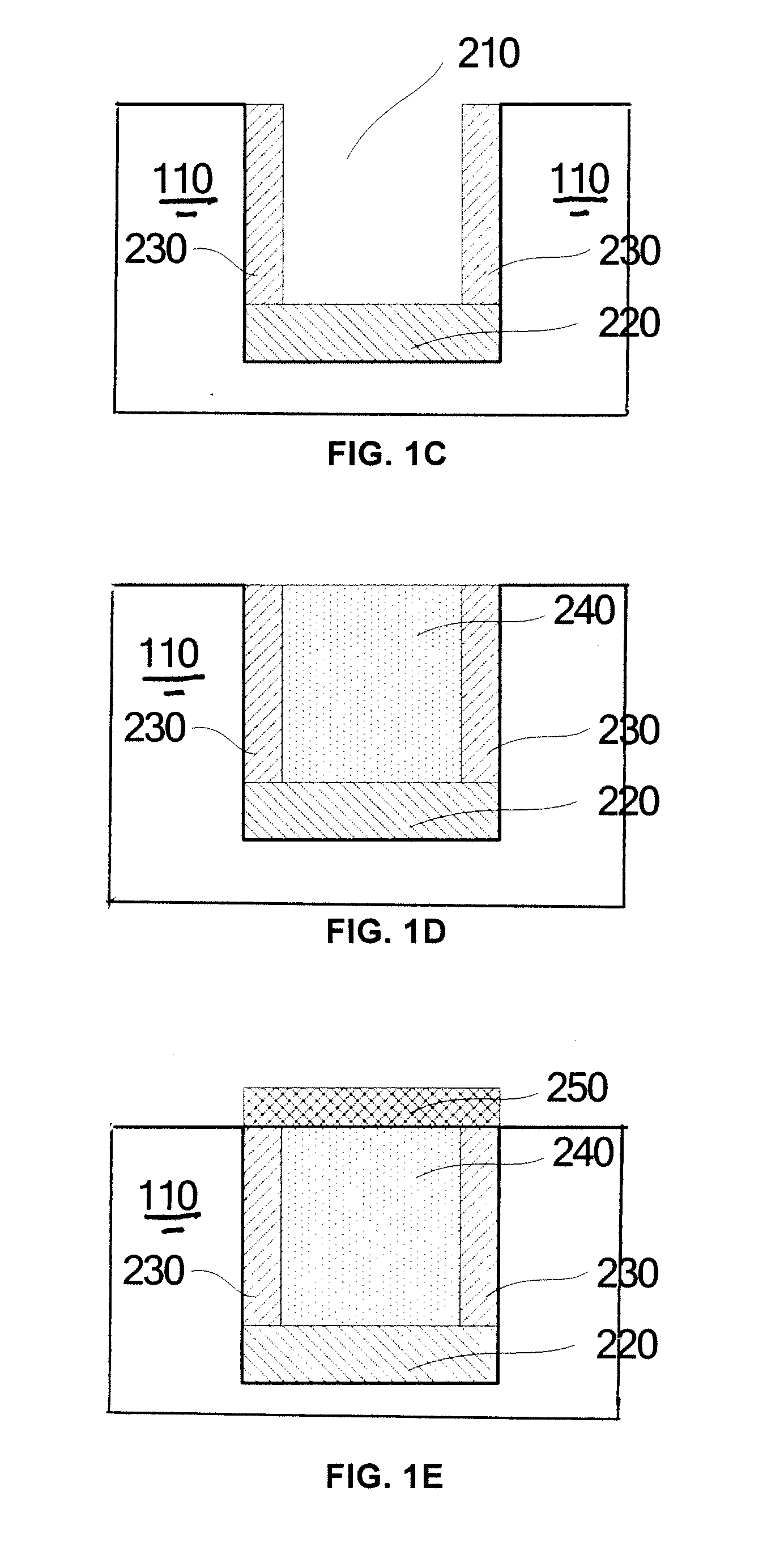
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20130037858A1Improving PMOS performanceIncrease contentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStacking faultDevice material
This invention relates to a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof for reducing stacking faults caused by high content of Ge in an embedded SiGe structure. The semiconductor device comprises a Si substrate with a recess formed therein. A first SiGe layer having a Ge content gradually increased from bottom to top is formed on the recess bottom, a SiGe seed layer is formed on sidewalls of the recess and a second SiGe layer having a constant content of Ge is formed on the first SiGe layer. The thickness of the first SiGe layer is less than the depth of the recess. The Ge content in the SiGe seed layer is less than the Ge content in the second SiGe layer and the Ge content at the upper surface of the first SiGe layer is less than or equal to the Ge content in the second SiGe layer.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
Ultra-thin, high quality strained silicon-on-insulator formed by elastic strain transfer
InactiveUS6991998B2Quantity minimizationReduce the temperatureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureStacking fault
A method of forming a semiconductor structure comprising a first strained semiconductor layer over an insulating layer is provided in which the first strained semiconductor layer is relatively thin (less than about 500 Å) and has a low defect density (stacking faults and threading defects). The method of the present invention begins with forming a stress-providing layer, such a SiGe alloy layer over a structure comprising a first semiconductor layer that is located atop an insulating layer. The stress-providing layer and the first semiconductor layer are then patterned into at least one island and thereafter the structure containing the at least one island is heated to a temperature that causes strain transfer from the stress-providing layer to the first semiconductor layer. After strain transfer, the stress-providing layer is removed from the structure to form a first strained semiconductor island layer directly atop said insulating layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Sic epitaxial wafer and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20120280254A1Improve uniformityQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingStacking fault
According to the present invention, there is provided an SiC epitaxial wafer which reduces triangular defects and stacking faults, which is highly uniform in carrier concentration and film thickness, and which is free of step bunching, and its method of manufacture. The SiC epitaxial wafer of the present invention is an SiC epitaxial wafer in which an SiC epitaxial layer is formed on a 4H—SiC single crystal substrate that is tilted at an off angle of 0.4°-5°, wherein the density of triangular-shaped defects of said SiC epitaxial layer is 1 defect / cm2 or less.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Directionally controlled growth of nanowhiskers
InactiveUS7354850B2Optimized structural formWell-defined surfaceMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthStacking faultOrganic vapor
Nanowhiskers are grown in a non-preferential growth direction by regulation of nucleation conditions to inhibit growth in a preferential direction. In a preferred implementation, <001> III-V semiconductor nanowhiskers are grown on an (001) III-V semiconductor substrate surface by effectively inhibiting growth in the preferential <111>B direction. As one example, <001> InP nano-wires were grown by metal-organic vapor phase epitaxy directly on (001) InP substrates. Characterization by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy revealed wires with nearly square cross sections and a perfect zincblende crystalline structure that is free of stacking faults.
Owner:QUNANO
Method To Reduce Stacking Fault Nucleation Sites And Reduce Forward Voltage Drift In Bipolar Devices
ActiveUS20050064723A1Reduce nucleationReduce in quantityDecorative surface effectsElectrostatic cleaningStacking faultOptoelectronics
A method is disclosed for preparing a substrate and epilayer for reducing stacking fault nucleation and reducing forward voltage (Vf) drift in silicon carbide-based bipolar devices. The method includes the steps of etching the surface of a silicon carbide substrate with a nonselective etch to remove both surface and sub-surface damage, thereafter etching the same surface with a selective etch to thereby develop etch-generated structures from at least any basal plane dislocation reaching the substrate surface that will thereafter tend to either terminate or propagate as threading defects during subsequent epilayer growth on the substrate surface, and thereafter growing a first epitaxial layer of silicon carbide on the twice-etched surface.
Owner:CREE INC
Large Diameter, High Quality SiC Single Crystals, Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20130280466A1Increase temperaturePolycrystalline material growthLayered productsParticulatesStacking fault
A method and system of forming large-diameter SiC single crystals suitable for fabricating high crystal quality SiC substrates of 100, 125, 150 and 200 mm in diameter are described. The SiC single crystals are grown by a seeded sublimation technique in the presence of a shallow radial temperature gradient. During SiC sublimation growth, a flux of SiC bearing vapors filtered from carbon particulates is substantially restricted to a central area of the surface of the seed crystal by a separation plate disposed between the seed crystal and a source of the SiC bearing vapors. The separation plate includes a first, substantially vapor-permeable part surrounded by a second, substantially non vapor-permeable part. The grown crystals have a flat or slightly convex growth interface. Large-diameter SiC wafers fabricated from the grown crystals exhibit low lattice curvature and low densities of crystal defects, such as stacking faults, inclusions, micropipes and dislocations.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Stacking fault and twin blocking barrier for integrating III-V on Si
InactiveUS20080032478A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice defectsStacking fault
A stacking fault and twin blocking barrier for forming a III-V device layer on a silicon substrate and the method of manufacture is described. Embodiments of the present invention enable III-V InSb device layers with defect densities below 1×108 cm−2 to be formed on silicon substrates. In an embodiment of the present invention, a buffer layer is positioned between a III-V device layer and a silicon substrate to glide dislocations. In an embodiment of the present invention, GaSb buffer layer is selected on the basis of lattice constant, band gap, and melting point to prevent many lattice defects from propagating out of the buffer into the III-V device layer. In a specific embodiment, a III-V InSb device layer is formed directly on the GaSb buffer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Chabazite-containing molecular sieve, its synthesis and its use in the conversion of oxygenates to olefins
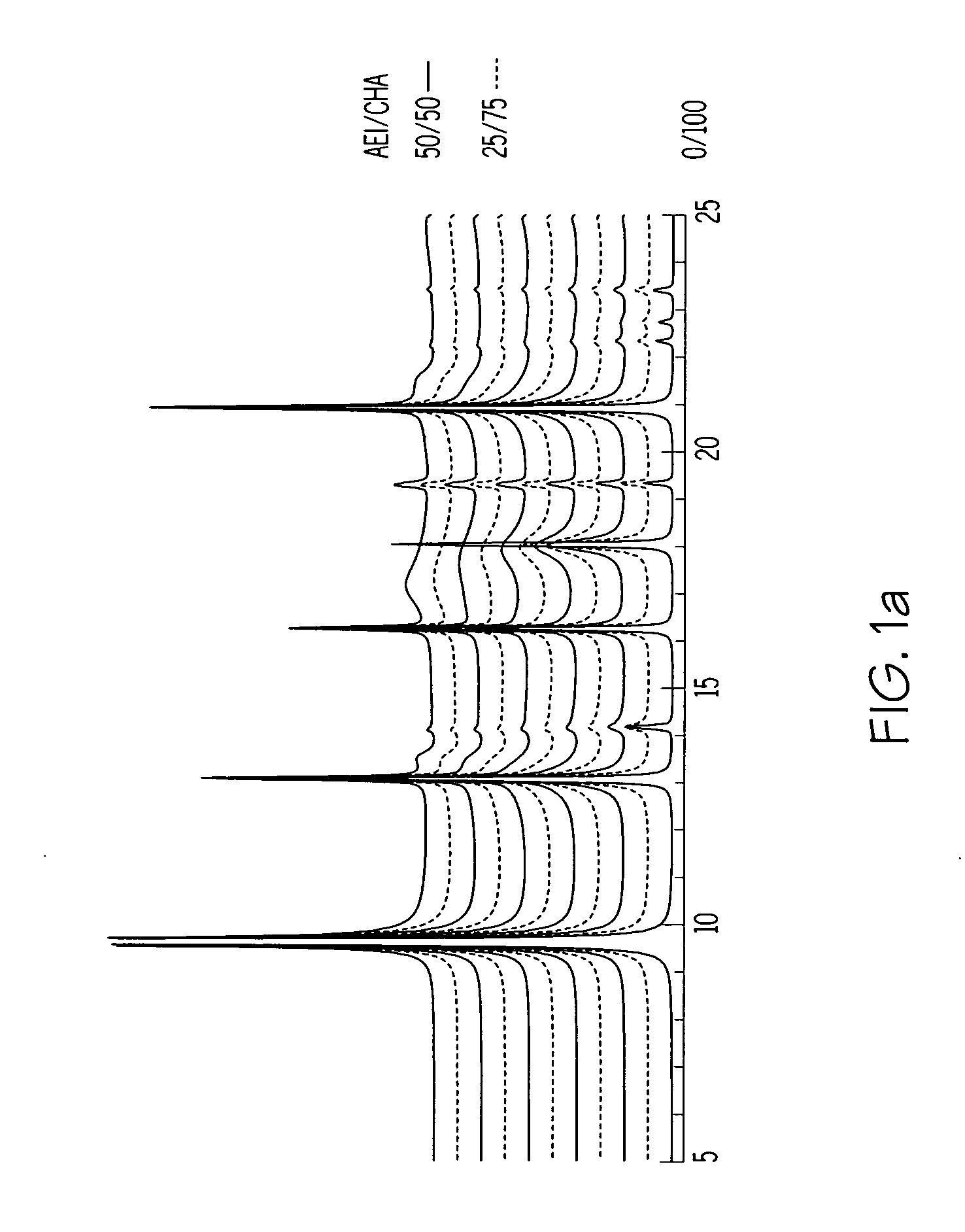
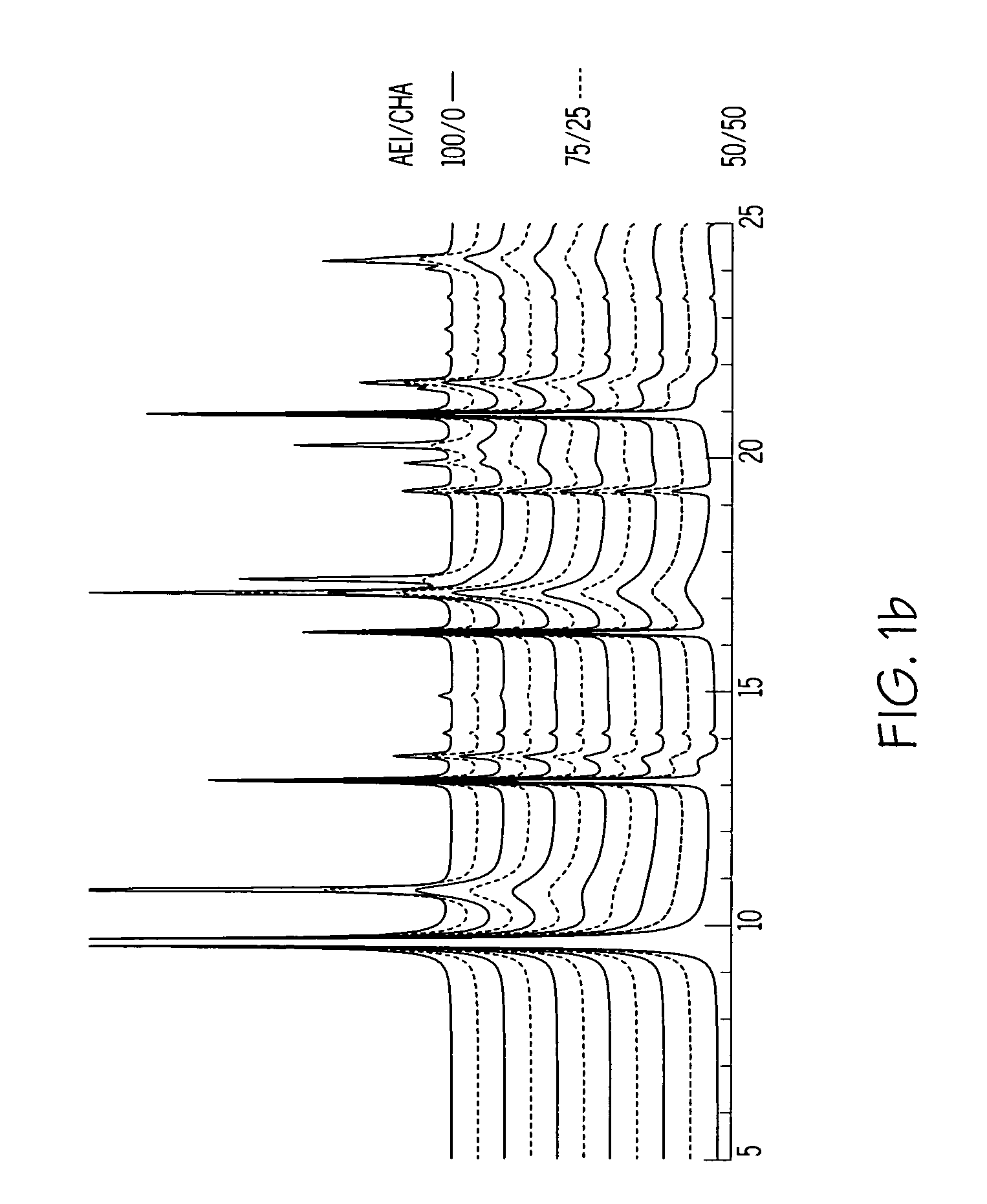
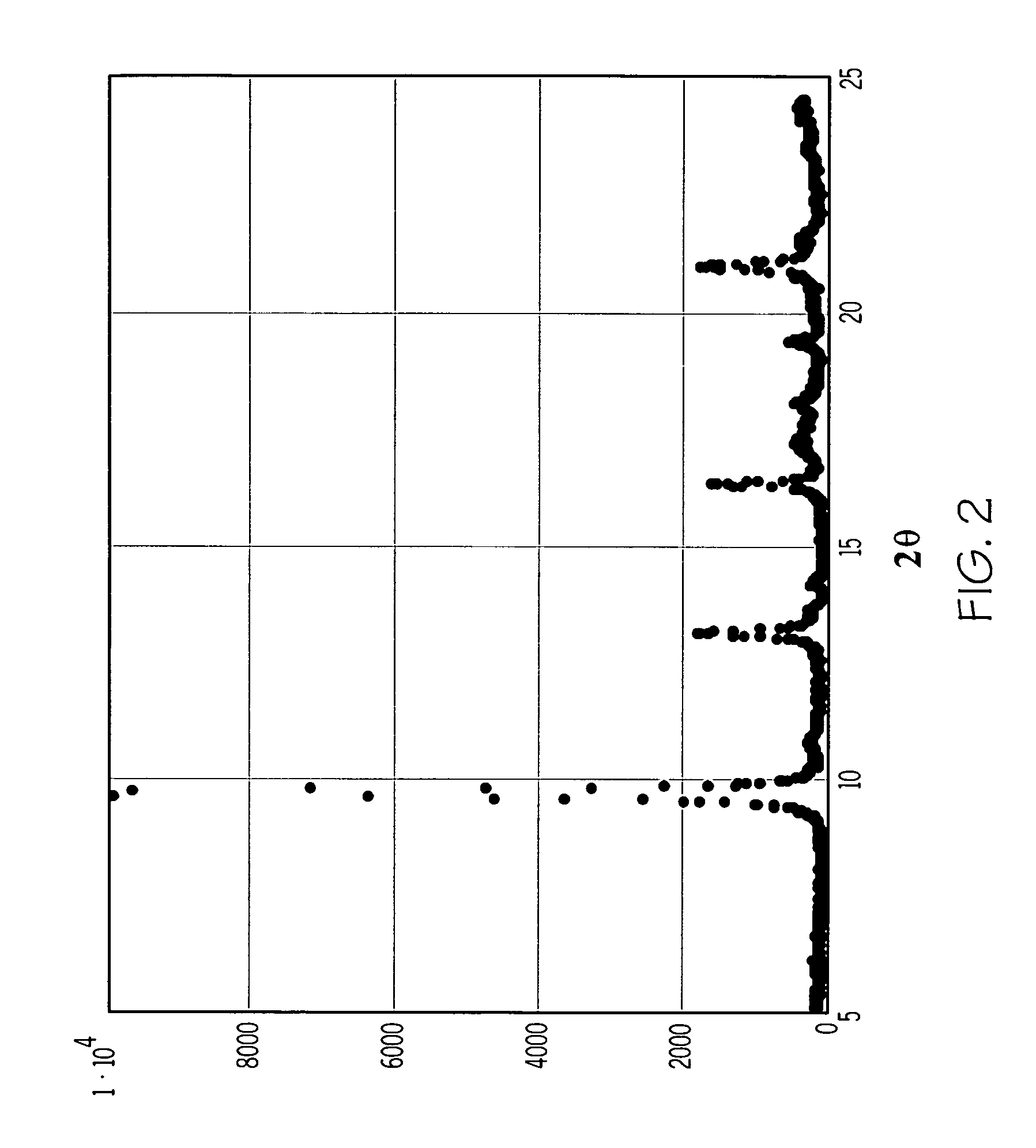
A crystalline material substantially free of framework phosphorus and comprising a CHA framework type molecular sieve with stacking faults or at least one intergrown phase of a CHA framework type molecular sieve and an AEI framework type molecular sieve, wherein said material, in its calcined, anhydrous form, has a composition involving the molar relationship: (n)X2O3:YO2, wherein X is a trivalent element; Y is a tetravalent element; and n is from 0 to about 0.5. The material exhibits activity and selectivity in the conversion of methanol to lower olefins, especially ethylene and propylene.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC +1
Directionally controlled growth of nanowhiskers
InactiveUS20060019470A1Well-defined surfaceReduce the temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanowireStacking fault
Nanowhiskers are grown in a non-preferential growth direction by regulation of nucleation conditions to inhibit growth in a preferential direction. In a preferred implementation, <001> III-V semiconductor nanowhiskers are grown on an (001) III-V semiconductor substrate surface by effectively inhibiting growth in the preferential <111>B direction. As one example, <001> InP nano-wires were grown by metal-organic vapor phase epitaxy directly on (001) InP substrates. Characterization by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy revealed wires with nearly square cross sections and a perfect zincblende crystalline structure that is free of stacking faults.
Owner:QUNANO
Silicon wafers and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050054124A1Increased formationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStacking faultOxygen precipitates
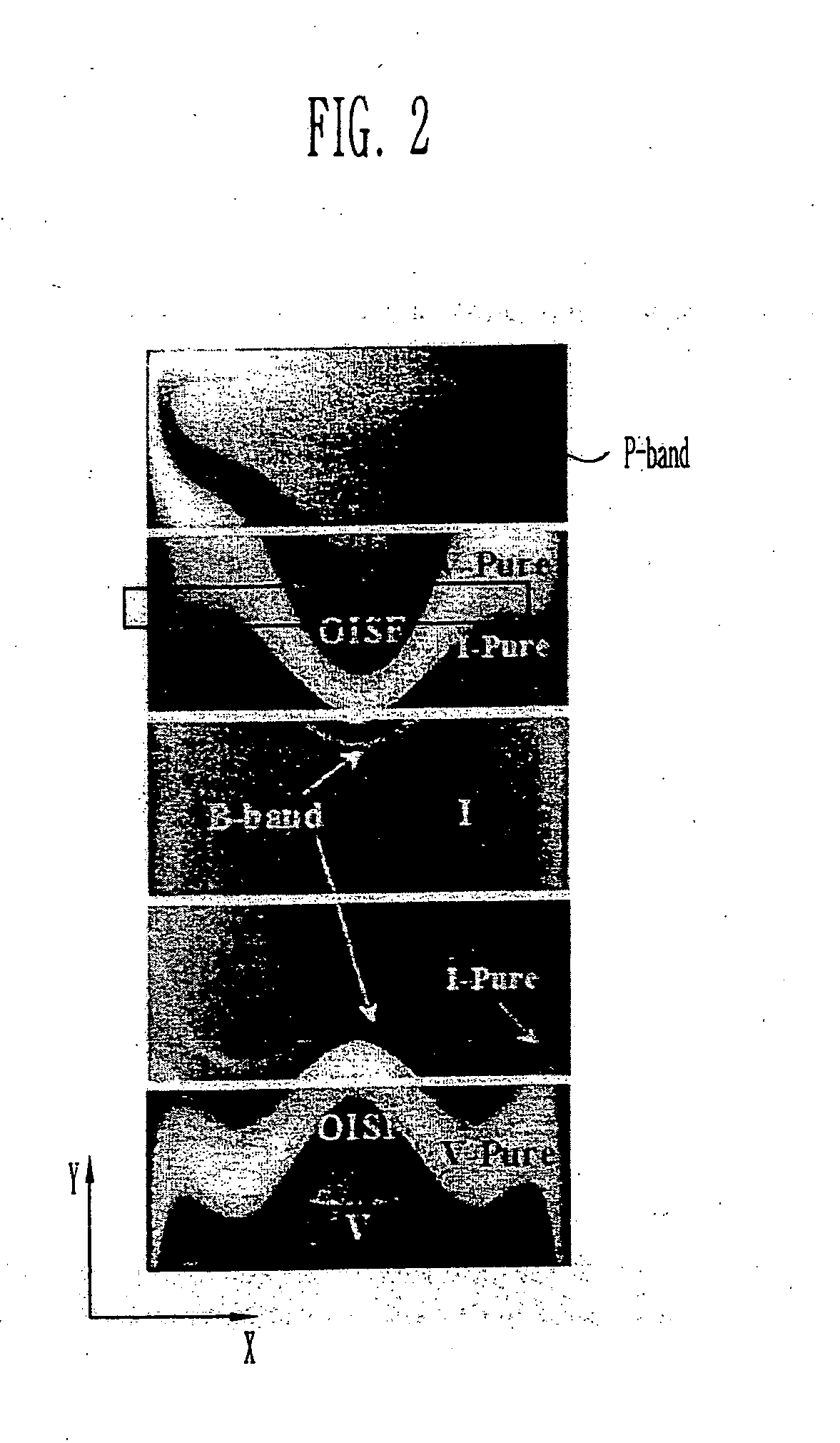
By using a two-step RTP (rapid thermal processing) process, the wafer is provided which has an ideal semiconductor device region secured by controlling fine oxygen precipitates and OiSFs (Oxidation Induced Stacking Fault) located on the surface region of the wafer. By performing the disclosed two-step rapid thermal process, the distribution of defects can be accurately controlled and an ideal device active zone can be formed up to a certain distance from the surfaces of the wafer. In addition, it is possible to maximize the internal gettering (IG) efficiency by enabling the oxygen precipitates and the bulk stacking faults to have constant densities in the depth direction in an internal region of the wafer, that is, the bulk region. In order to obtain the constant concentration profile of the oxygen precipitates and the bulk stacking faults in the bulk region, the wafer is subjected to the aforementioned two-step rapid thermal process in a predetermined mixed gas atmosphere.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
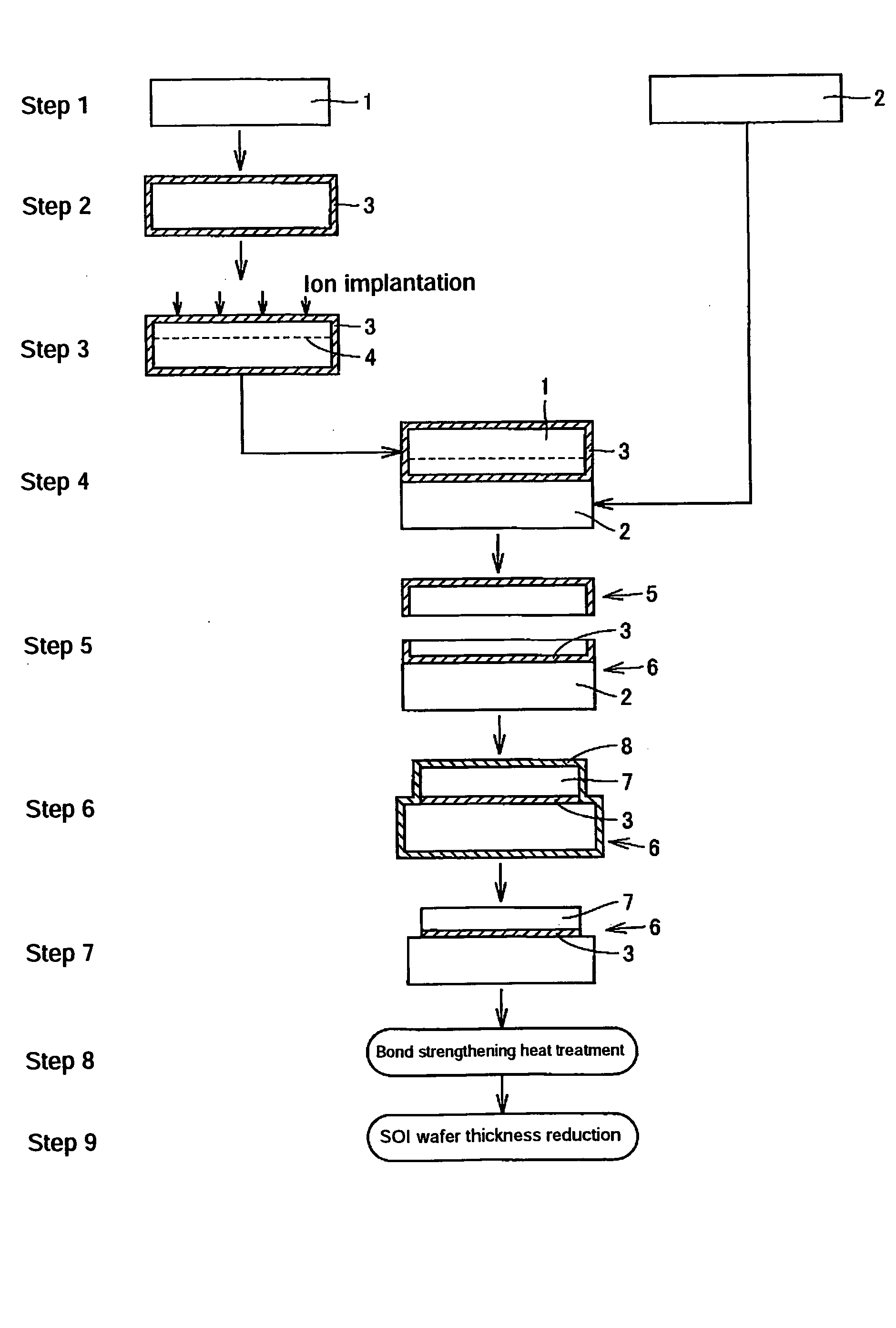
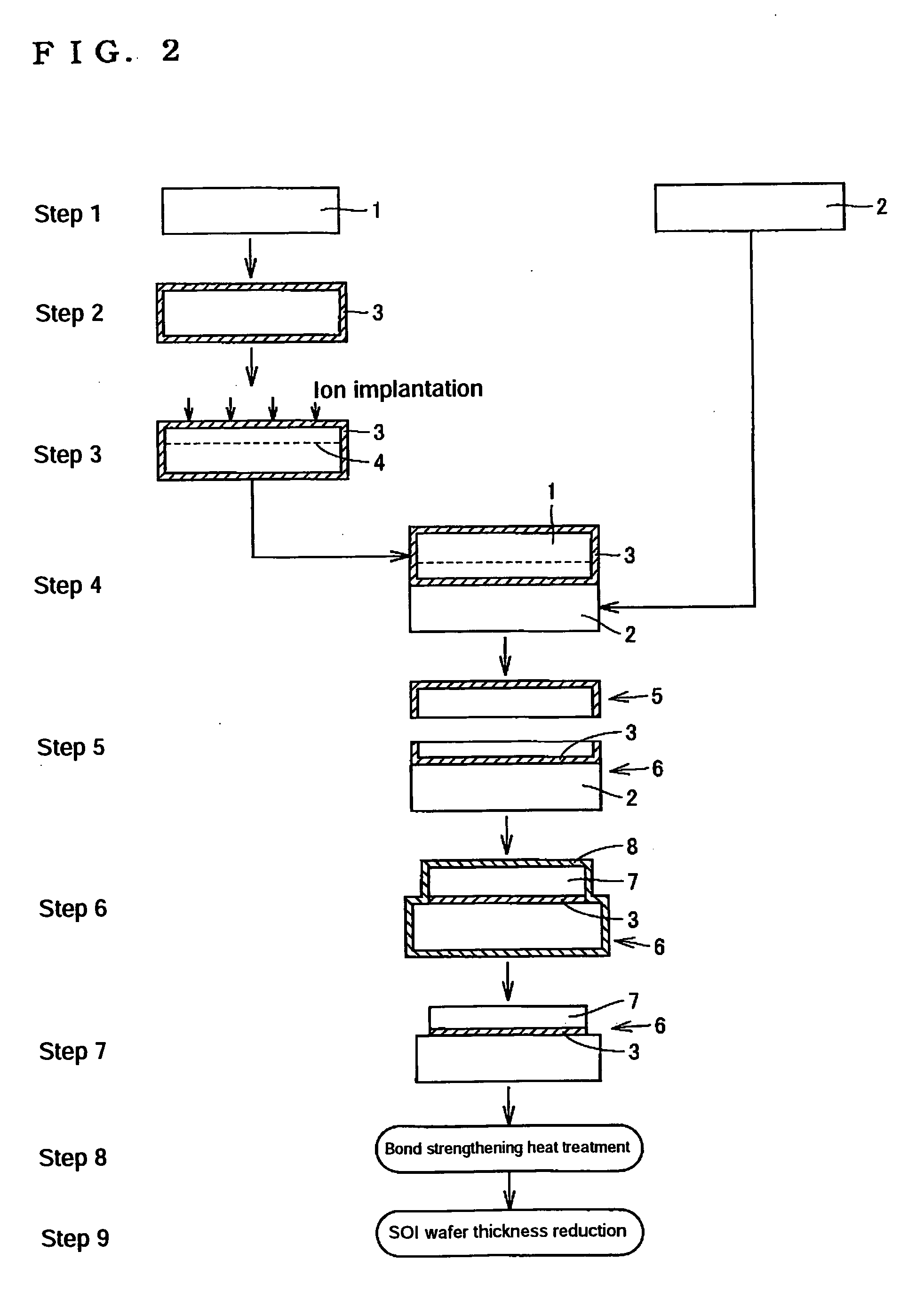
SOI wafer production method
InactiveUS20060177991A1Without deteriorating uniformity in SOI layer thicknessPromote lowerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingStacking fault
By using, in the so-called Smart Cut process comprising the steps of bonding an ion-implanted active layer wafer to a base wafer and later splitting off the base wafer to produce a SOI wafer, a wafer doped with C in a single crystal ingot growing process (desirably to a carbon concentration of not lower than 1×1016 atoms / cm3) as the active layer wafer, it becomes possible to exhibit the effect of inhibiting agglomeration of interstitial Si atoms and prevent development of stacking faults even when the SOI wafer is subjected to thermal oxidation treatment. Furthermore, the technique of sacrificial oxidation can be applied to production of SOI wafers and, thus, a damaged layer formed on the SOI layer surface can be removed and surface roughness can be improved without impairing crystalline integrity and, further, SOI layer thickness can be efficiently reduced.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Minimizing degradation of SiC bipolar semiconductor devices
A bipolar device has at least one p-type layer of single crystal silicon carbide and at least one n-type layer of single crystal silicon carbide, wherein those portions of those stacking faults that grow under forward operation are segregated from at least one of the interfaces between the active region and the remainder of the device.
Owner:CREE INC
Silicon carbide substrate and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130071643A1Improve performanceImprove device performanceAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthStacking faultSingle crystal
A silicon carbide substrate capable of stably forming a device of excellent performance, and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. A silicon carbide substrate is made of a single crystal of silicon carbide, and has a width of not less than 100 mm, a micropipe density of not more than 7 cm−2, a threading screw dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a threading edge dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a basal plane dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a stacking fault density of not more than 0.1 cm−1, a conductive impurity concentration of not less than 1×1018 cm−2, a residual impurity concentration of not more than 1×1016 cm−2, and a secondary phase inclusion density of not more than 1 cm−3.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
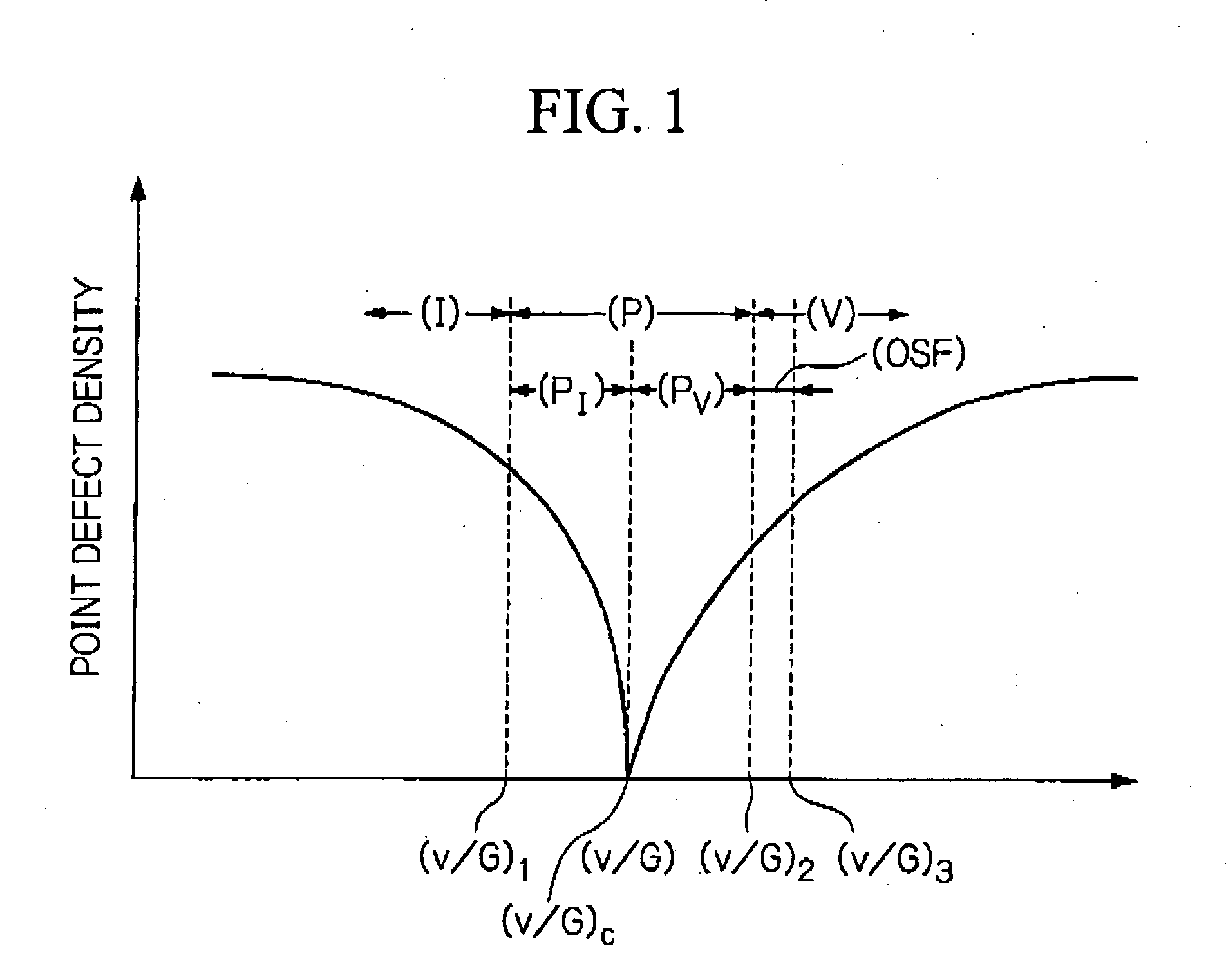
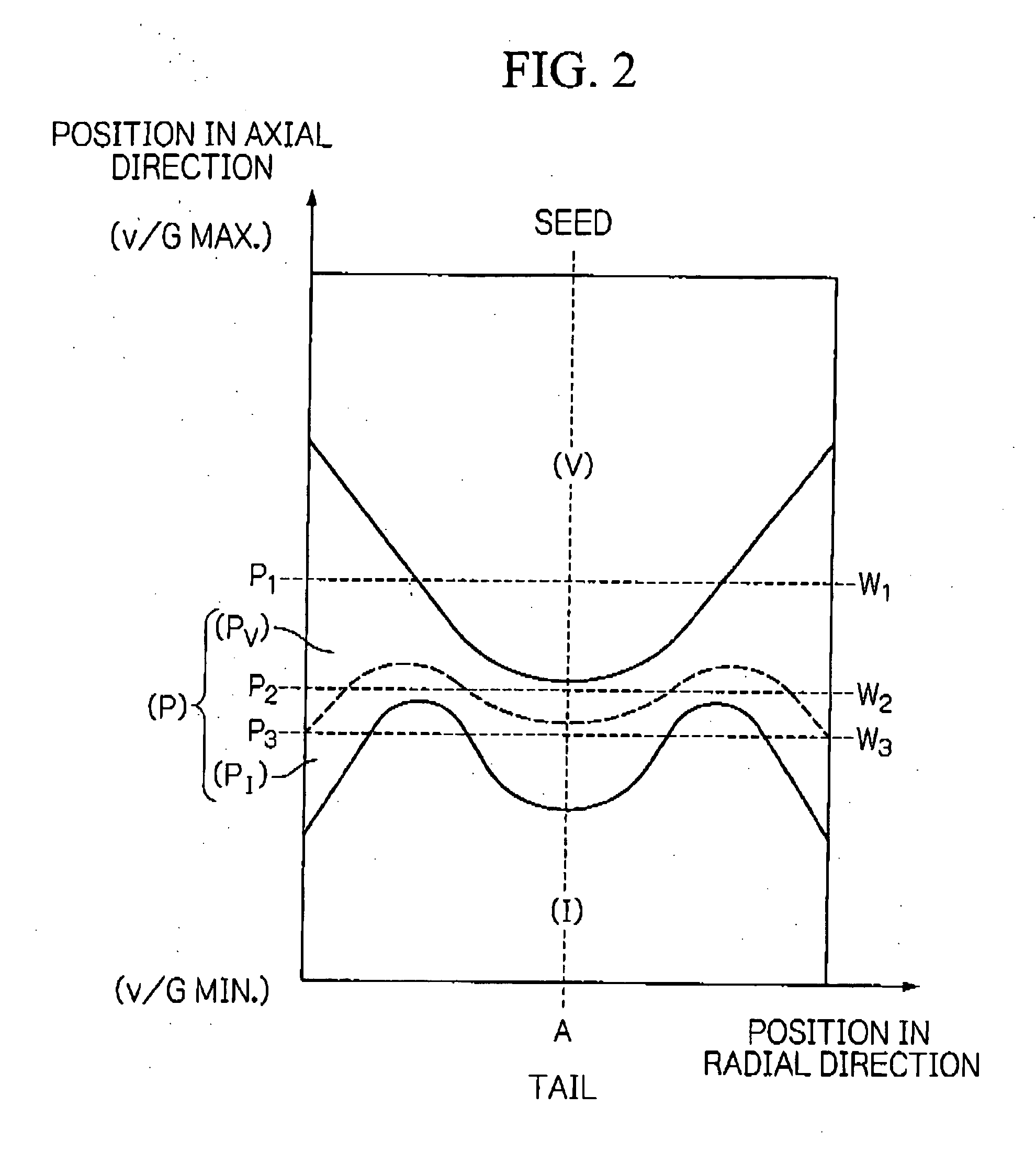
Low defect density silicon having a vacancy-dominated core substantially free of oxidation induced stacking faults
InactiveUS6846539B2Reduce concentrationPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsStacking faultIntrinsics
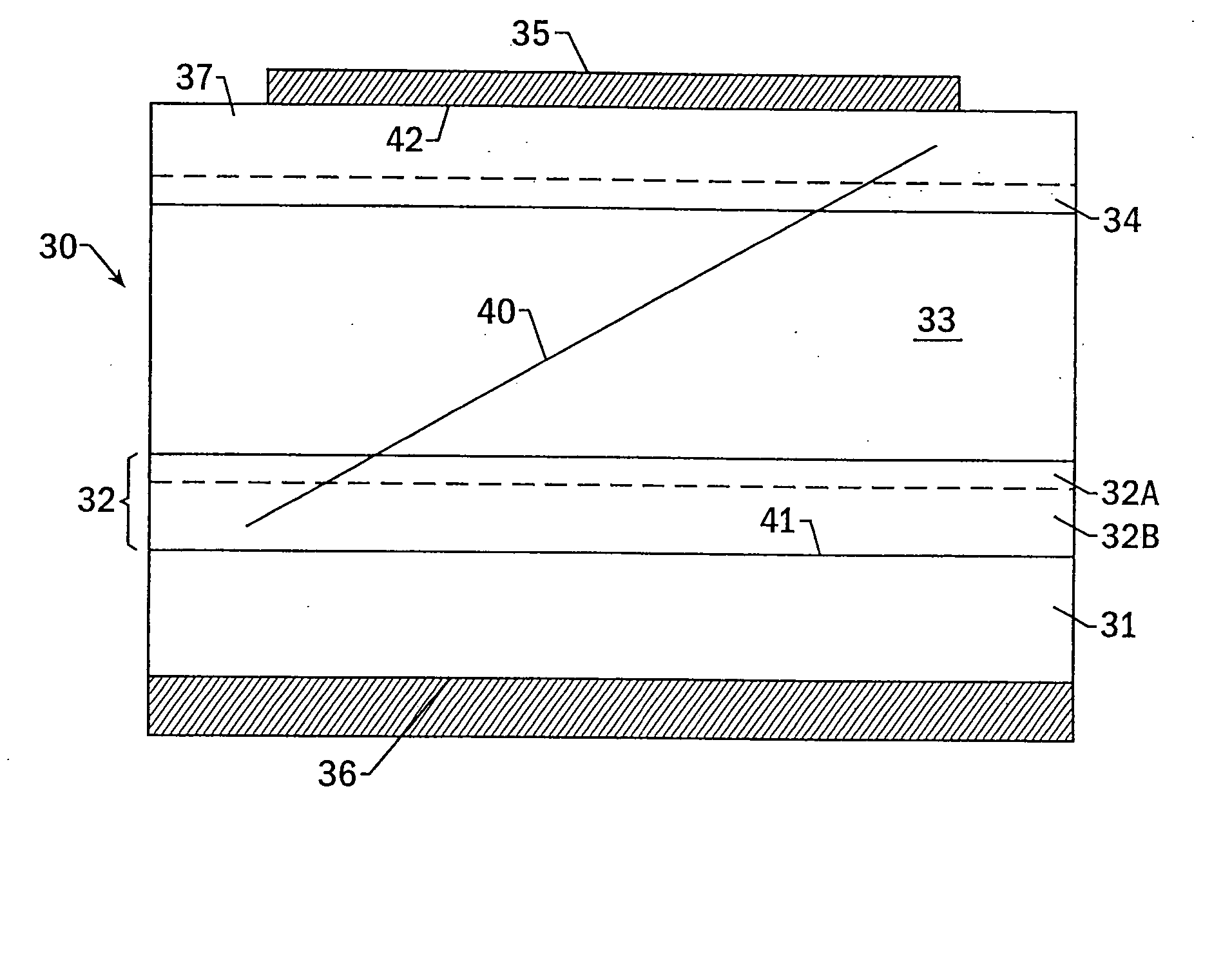
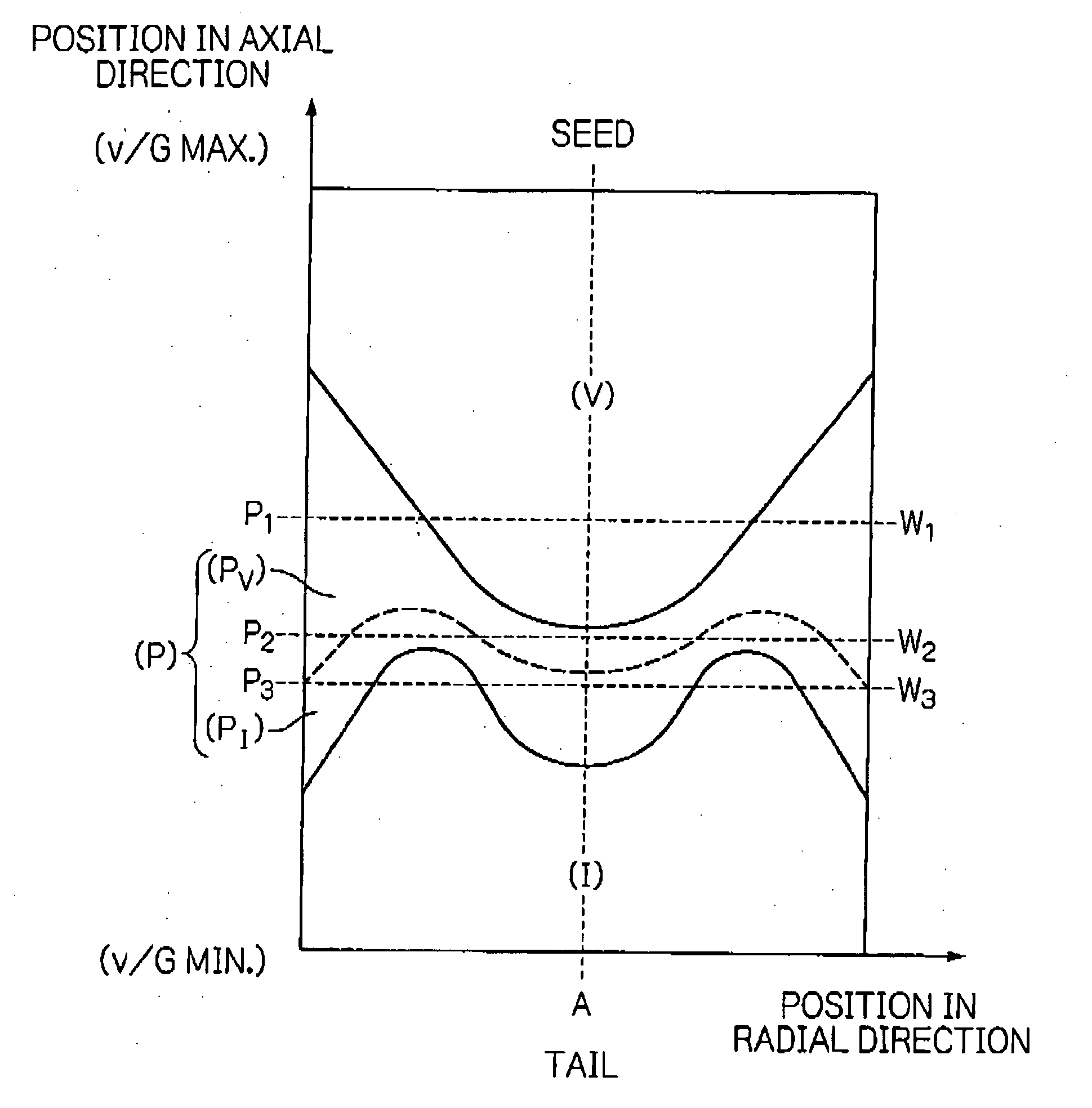
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a single crystal silicon ingot, as well as to the ingot or wafer resulting therefrom. The process comprises controlling (i) a growth velocity, v, (ii) an average axial temperature gradient, G0, and (iii) a cooling rate of the crystal from solidification to about 750° C., in order to cause the formation of a segment having a first axially symmetric region extending radially inward from the lateral surface of the ingot wherein silicon self-interstitials are the predominant intrinsic point defect, and a second axially symmetric region extending radially inward from the first and toward the central axis of the ingot. The process is characterized in that v, G0 and the cooling rate are controlled to prevent the formation of agglomerated intrinsic point defects in the first region, while the cooling rate is further controlled to limit the formation of oxidation induced stacking faults in a wafer derived from this segment, upon subjecting the wafer to an oxidation treatment otherwise suitable for the formation of such faults.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Electroluminescent phosphor, method for producing the same and device containing the same
InactiveUS20060192486A1Solve low luminous efficiencyIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorStacking fault
An electroluminescent phosphor comprising: ZnS-based phosphor particles and a coating layer provided on a surface of the particle, wherein the particles have an average particle size of from 0.1 to 20 μm, and a coefficient of variation in a particle size distribution of less than 35%, and a content of particles having 10 or more stacking faults with an interplanar spacing of 5 nm or less is 30% or more based on all of the ZnS-based phosphor particles.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Electroluminescent phosphor, process for producing the same, and electroluminescent device containing the same
InactiveUS20070001585A1High EL efficiencyIncreased durabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorStacking fault
An electroluminescent phosphor comprising ZnS-based phosphor core particles and a coating layer provided on the individual core particles, the core particles having a mean particle size of 0.1 to 15 μm with a coefficient of variation of particle size distribution less than 35% and containing at least 30%, based on total particles, of particles having at least 10 stacking faults with an interplanar spacing of 5 nm or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method to reduce stacking fault nucleation sites and reduce forward voltage drift in bipolar devices
InactiveUS7018554B2Reduce in quantityReduce nucleationDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStacking faultOptoelectronics
A method is disclosed for preparing a substrate and epilayer for reducing stacking fault nucleation and reducing forward voltage (Vf) drift in silicon carbide-based bipolar devices. The method includes the steps of etching the surface of a silicon carbide substrate with a nonselective etch to remove both surface and sub-surface damage, thereafter etching the same surface with a selective etch to thereby develop etch-generated structures from at least any basal plane dislocation reaching the substrate surface that will thereafter tend to either terminate or propagate as threading defects during subsequent epilayer growth on the substrate surface, and thereafter growing a first epitaxial layer of silicon carbide on the twice-etched surface.
Owner:CREE INC
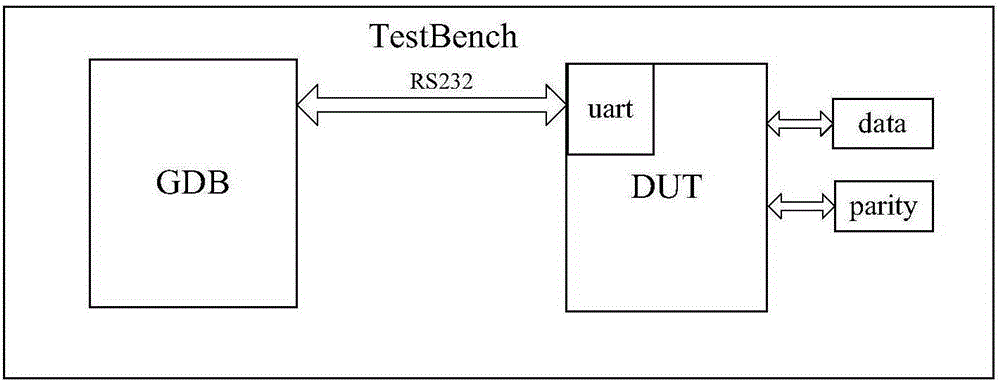
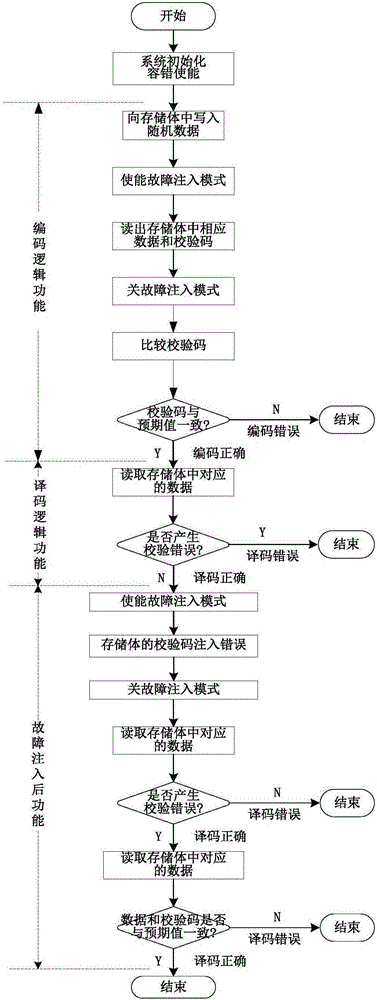
Automatic verification platform and method for on-chip memory management unit fault-tolerant structure
ActiveCN105185413AAchieve correctnessAchieve reliabilityStatic storageSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureStacking fault
The invention provides an automatic verification platform and method for an on-chip memory management unit fault-tolerant structure. The automatic verification platform and method can conduct random fault injection verification on the fault-tolerant structure and are high in verification coverage rate. The platform comprises a debugging host and a to-be-tested host connected through a serial port. The debugging host is used for flow control verification, encoding result checking, fault injection, decoding result checking in the verification process, and monitoring and debugging of a processor. The on-chip memory stack fault-tolerant structure is integrated in the to-be-tested host and used for generation of check codes, decoding verification after decoding logic and fault injection and loading of an automatic verification program for the memory stack fault-tolerant structure. The memory stack fault-tolerant structure comprises a memorizer control module, a fault-tolerant module, a selector and a memory stack. The memorizer control module and the fault-tolerant module conduct read-write control over the memory stack through the selector to control the working mode and the failure mode of the on-chip memory stack fault-tolerant structure.
Owner:NO 771 INST OF NO 9 RES INST CHINA AEROSPACE SCI & TECH
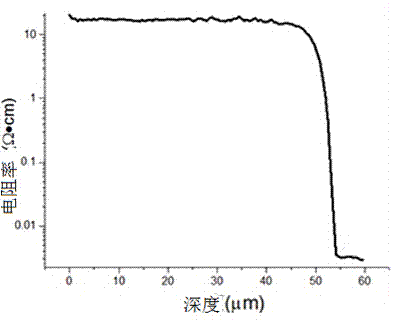
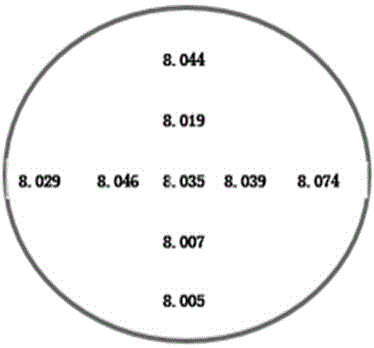
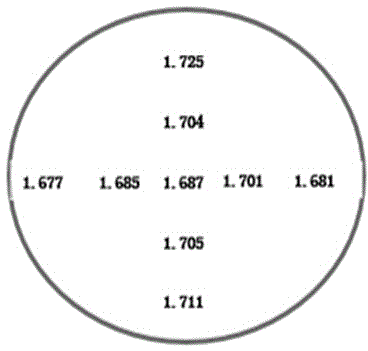
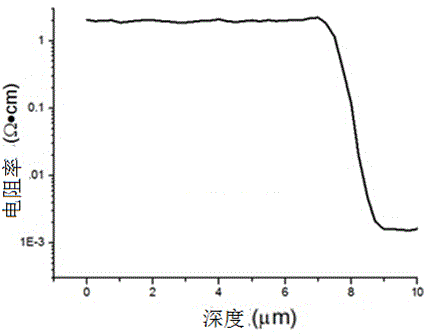
Method for growing high-resistance thick layer silicon epitaxy on 6-inch heavily As-doped silicon substrate
ActiveCN104851784AInactive doping effect suppressionImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSlip lineHigh resistance
The invention relates to a method for growing a high-resistance thick layer silicon epitaxy on a 6-inch heavily As-doped silicon substrate. In the method, a normal-pressure flat plate type epitaxial furnace is adopted. The method comprises the following steps: (1) corroding an epitaxial furnace base by using hydrogen chloride with the purity of not less than 99.99 percent at a high temperature; (2) loading a silicon substrate sheet in the epitaxial furnace, purging a cavity of the epitaxial furnace for 8-10min by sequentially using nitrogen and hydrogen with purities of not less than 99.99 percent; (3) performing in-situ corrosion on the surface of the silicon substrate sheet by using hydrogen chloride gas; (4) purging the surface of the silicon substrate sheet by large-flow hydrogen; (5) growing an intrinsic epitaxial layer on the substrate by using non-doped trichlorosilane; (6) growing a doped epitaxial layer; and (7) cooling after the epitaxial layer reaches a preset temperature during growing. The method has the beneficial effects of being used for successfully preparing a high-resistance thick layer silicon epitaxy structure with thickness non-uniformity of less than 1 percent and specific resistance non-uniformity of less than 1 percent, without defects of a stacking fault, dislocation, a slip line and fog, with an optimal transition region width of less than 4 micrometers, good uniformity and a narrow transition region, and capable of completely meeting a requirement of a power MOS device on a silicon epitaxial material in an aspect of a parameter.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST +1
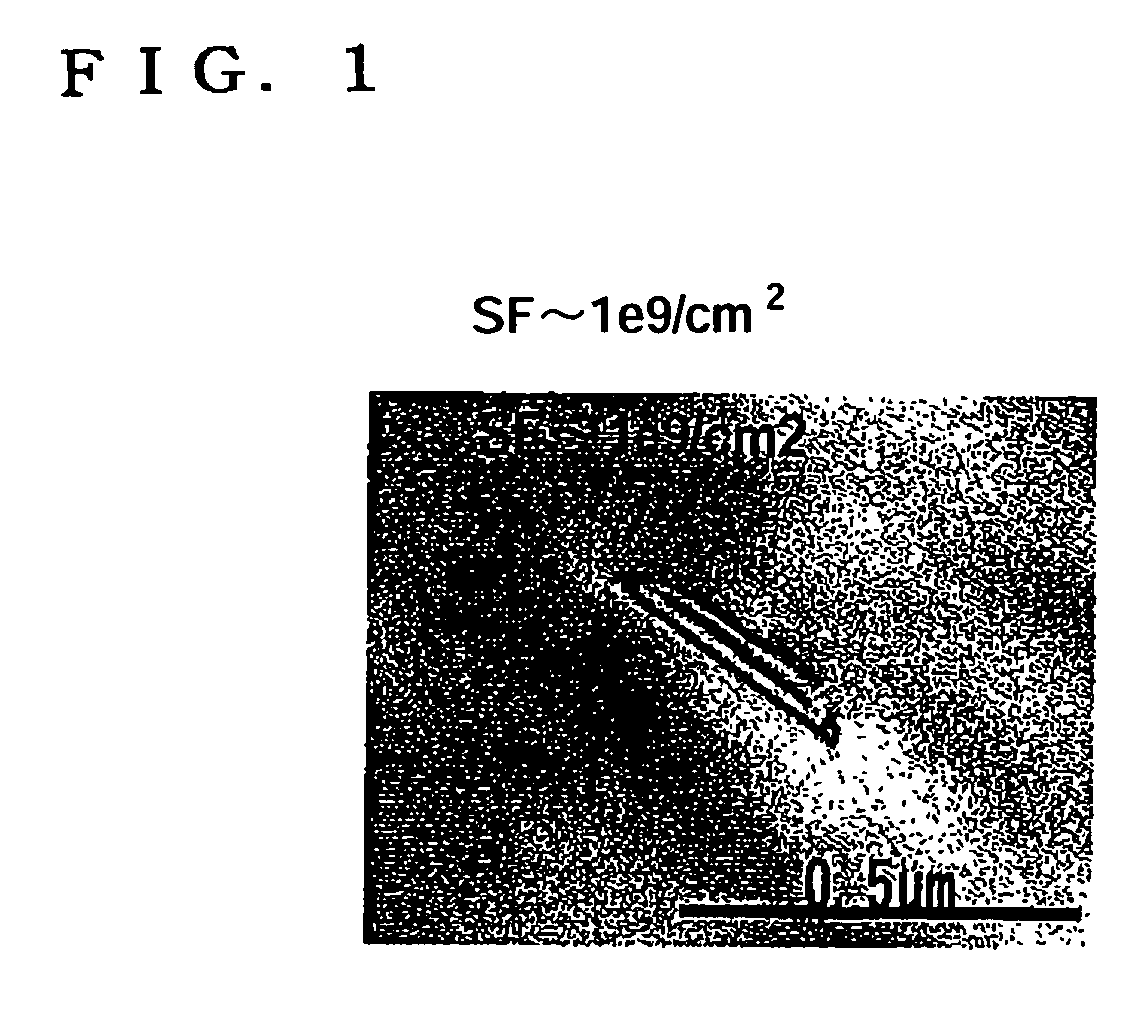
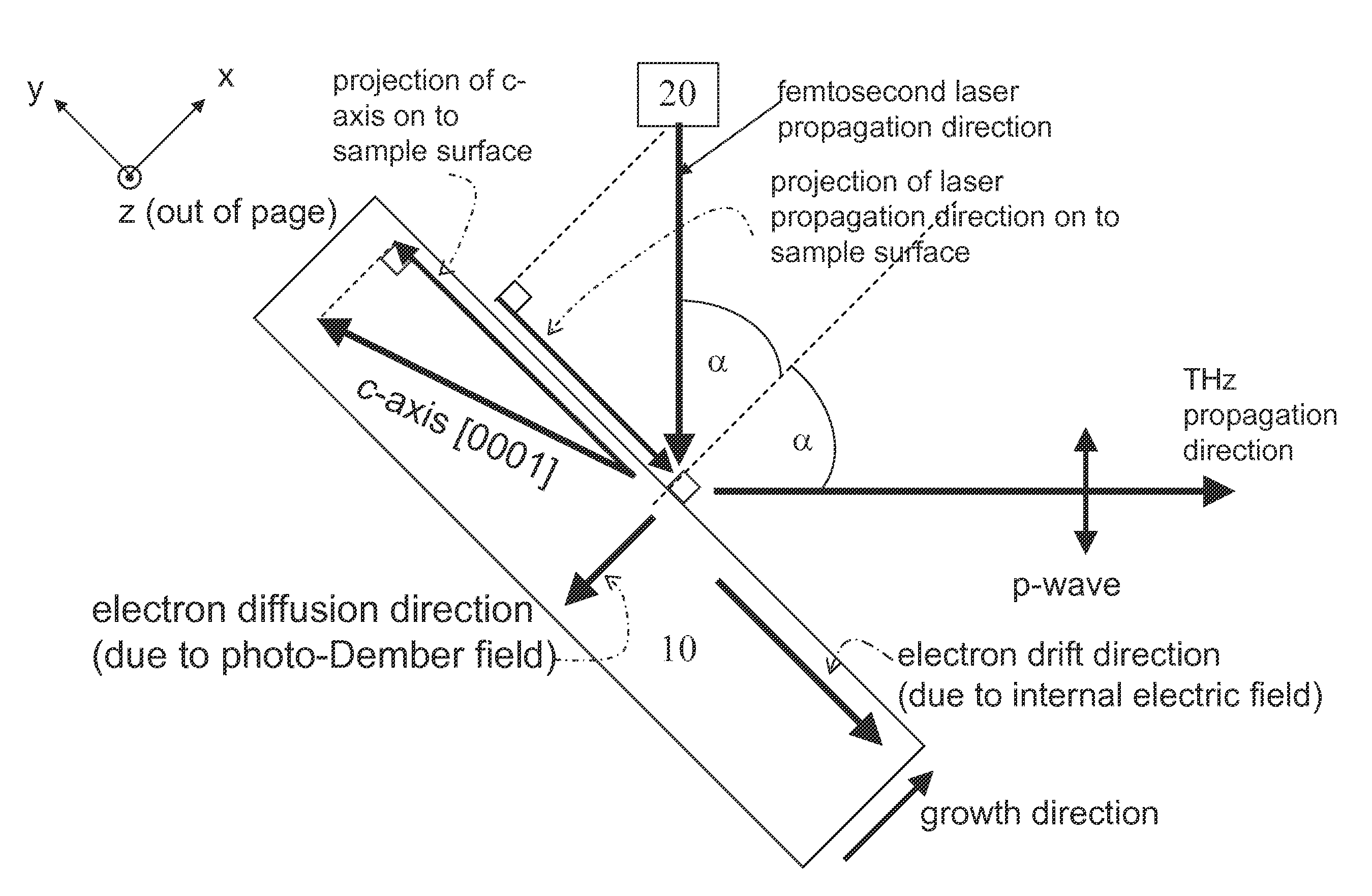
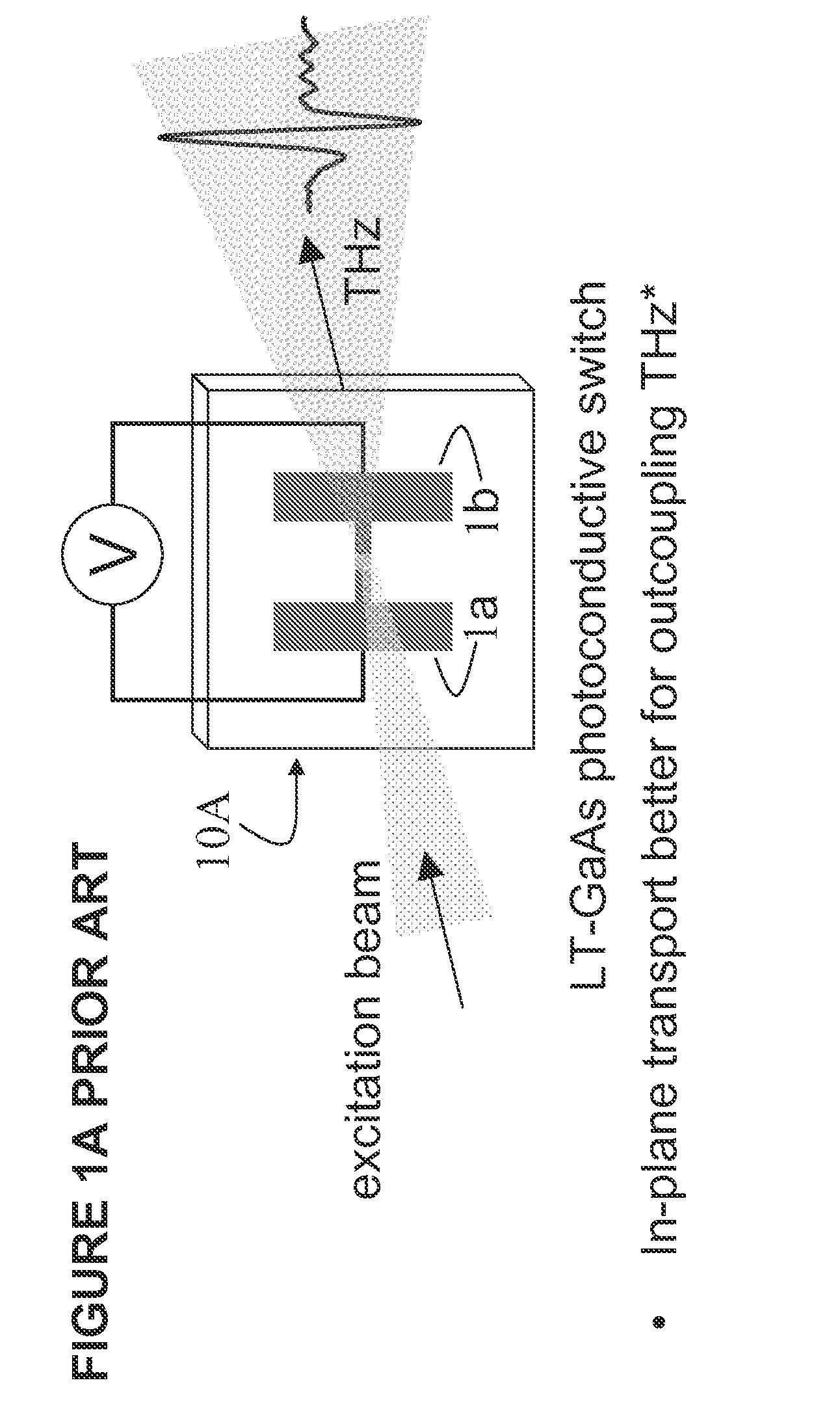
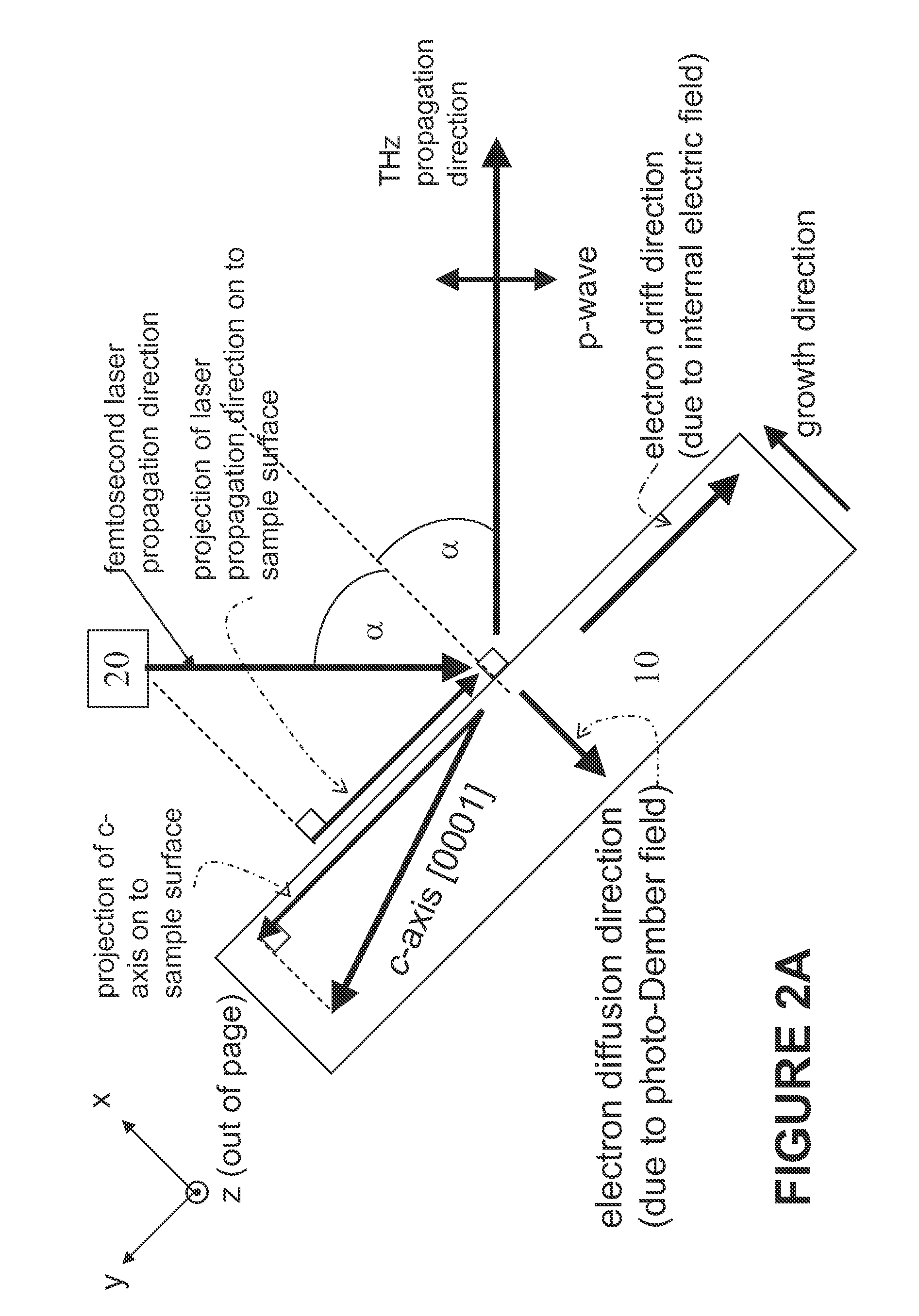
Method and Apparatus for Enhanced Terahertz Radiation from High Stacking Fault Density
ActiveUS20100006780A1Enhanced levelImprove efficiencyRadiation pyrometrySolid masersStacking faultTerahertz radiation
A method and device for generating terahertz radiation comprising a polar crystal material layer operative to emit terahertz radiation; the polar crystal material layer comprising a plurality of stacking faults; the stacking faults lying substantially perpendicular to the polar axis and forming boundaries at which the internal electric polarization terminates leading to charges accumulating at the boundaries, and creation of internal electric fields oriented along the polar axis; a pulsed radiation source for creating photogenerated carriers in the polar crystal material; whereby the photogenerated carriers accelerate in the internal electric fields associated with the termination of the internal electric polarization by the stacking faults to thereby generate terahertz radiation.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
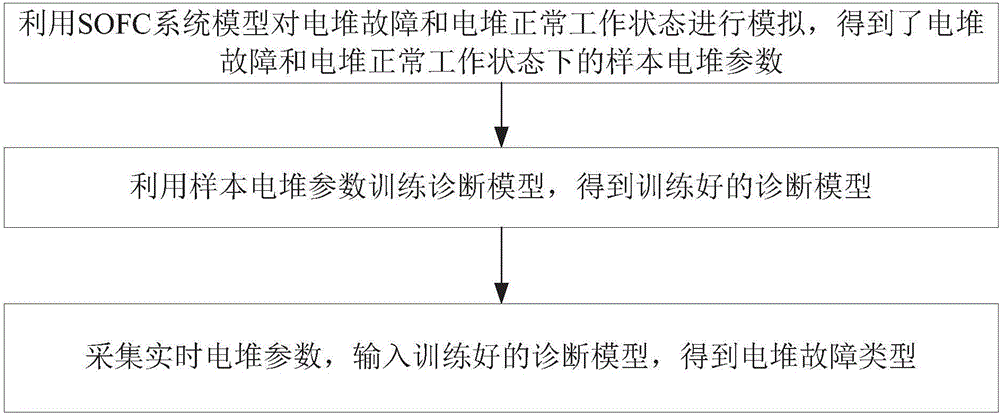
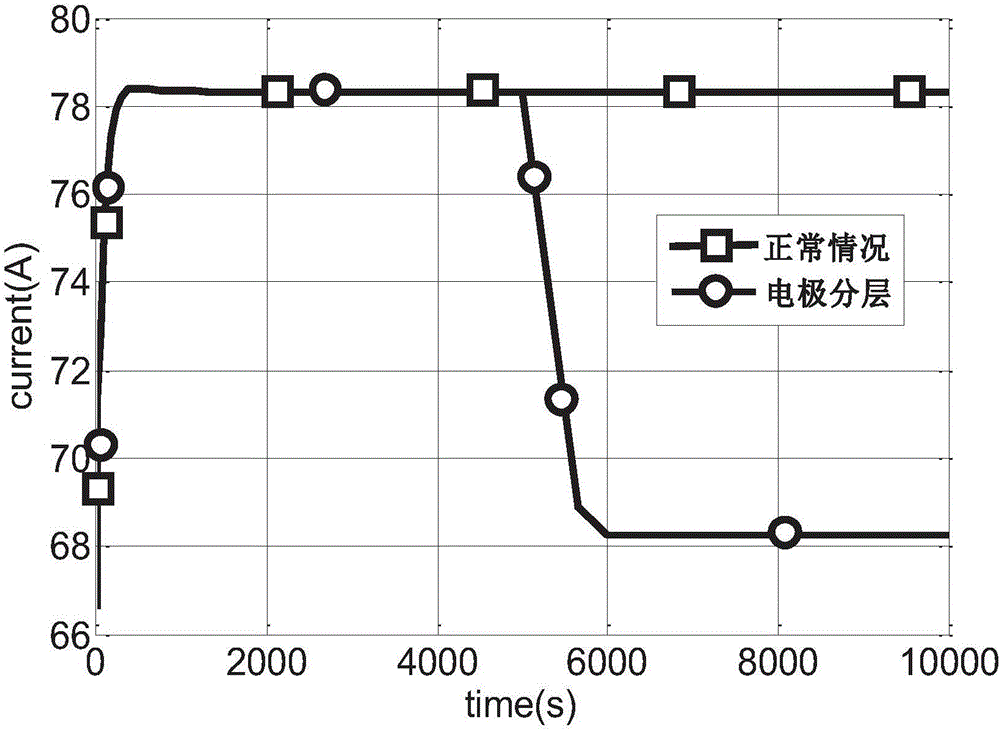
Solid oxide fuel cell stack fault diagnosis method and system
ActiveCN107180983AImprove accuracyEasy to identifySolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsStacking fault
The invention discloses a solid oxide fuel cell stack fault diagnosis method and system, wherein the method comprises: using an SOFC (solid oxide fuel cell) system model to simulate fault state and normal running state of a stack so as to obtain sample stack parameters under the fault state and normal running state of the stack; using the sample stack parameters to train a diagnosis model to obtain the strained diagnosis model; collecting real-time stack parameters, and entering in the trained diagnosis model to obtain a stack fault type. The SOFC system model is used herein to simulate the fault state and normal running state of the stack so as to obtain the stack parameters under the fault state and normal running state of the stack, and the collected stack parameters are entered in the trained diagnosis model to obtain one stack fault type. The diagnosis model herein is effective in diagnosing the normal running and fault type of the stack, the diagnostic results are highly accurate, and the method is high in practicality, identifiability and accuracy.
Owner:浙江国氢能源科技发展有限公司
Nitride substrates, thin films, heterostructures and devices for enhanced performance, and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20080296626A1Reduce threading dislocation densityImprove electricity efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThreading dislocationsStacking fault
The present invention provides nitride semiconductors having a moderate density of basal plane stacking faults and a reduced density of threading dislocations, various products based on, incorporating or comprising the nitride semiconductors, including without limitation substrates, template films, templates, heterostructures with or without integrated substrates, and devices, and methods for fabrication of templates and substrates comprising the nitride semiconductors.
Owner:INLUSTRA TECH
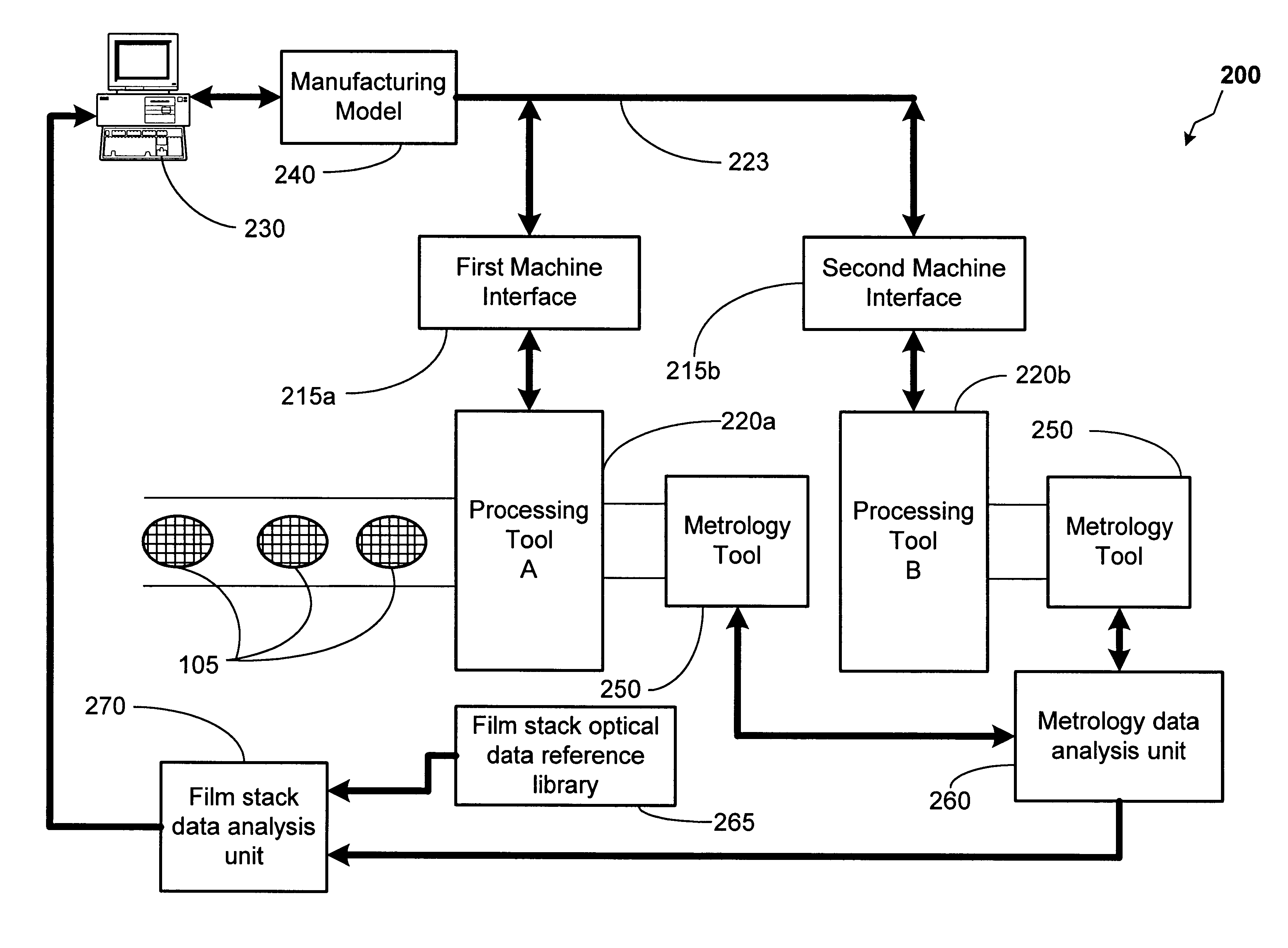
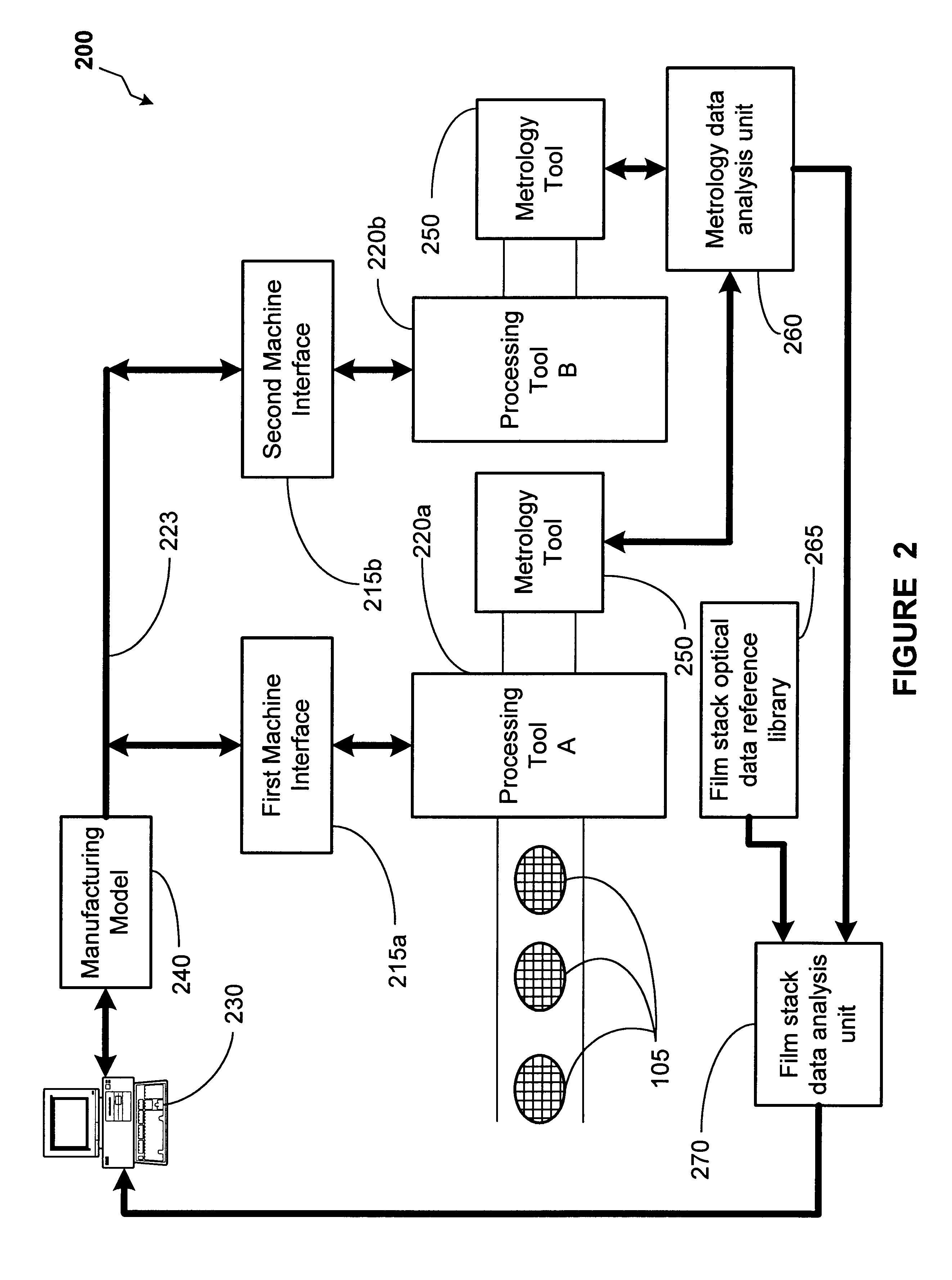
Method and apparatus for optical film stack fault detection
InactiveUS6458610B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesMetrologyStacking fault
A method and an apparatus for performing film stack fault detection. At least one semiconductor wafer is processed. Metrology data from the processed semiconductor wafer is acquired. Data from a reference library comprising optical data relating to a film stack on the semiconductor wafer is accessed. The metrology data is compared to data from the reference library. A fault-detection analysis is performed in response to the comparison of the metrology data and the reference library data.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
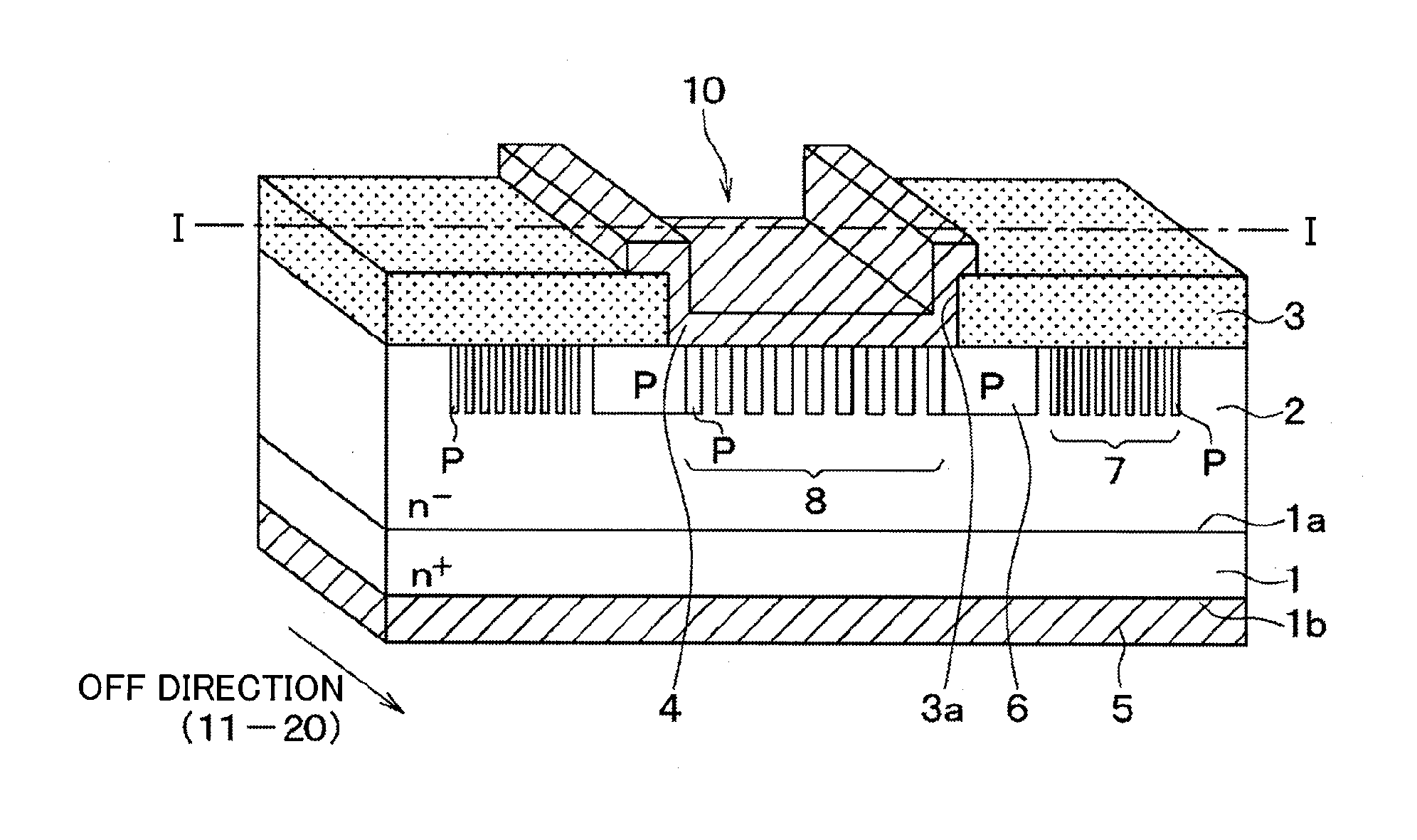
Silicon carbide semiconductor device having junction barrier schottky diode
ActiveUS20150206941A1Improve device yieldTotal current dropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierStacking fault
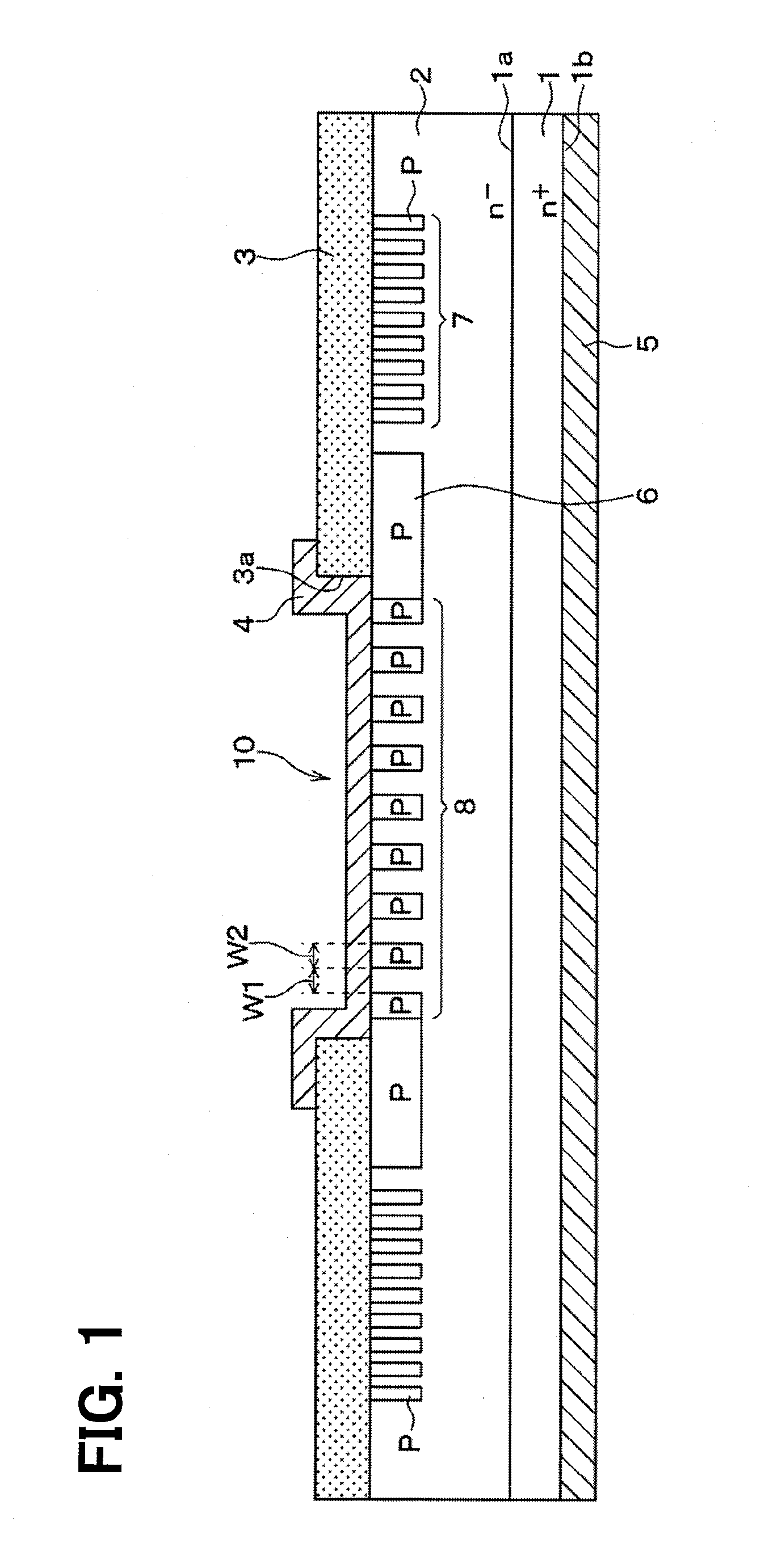
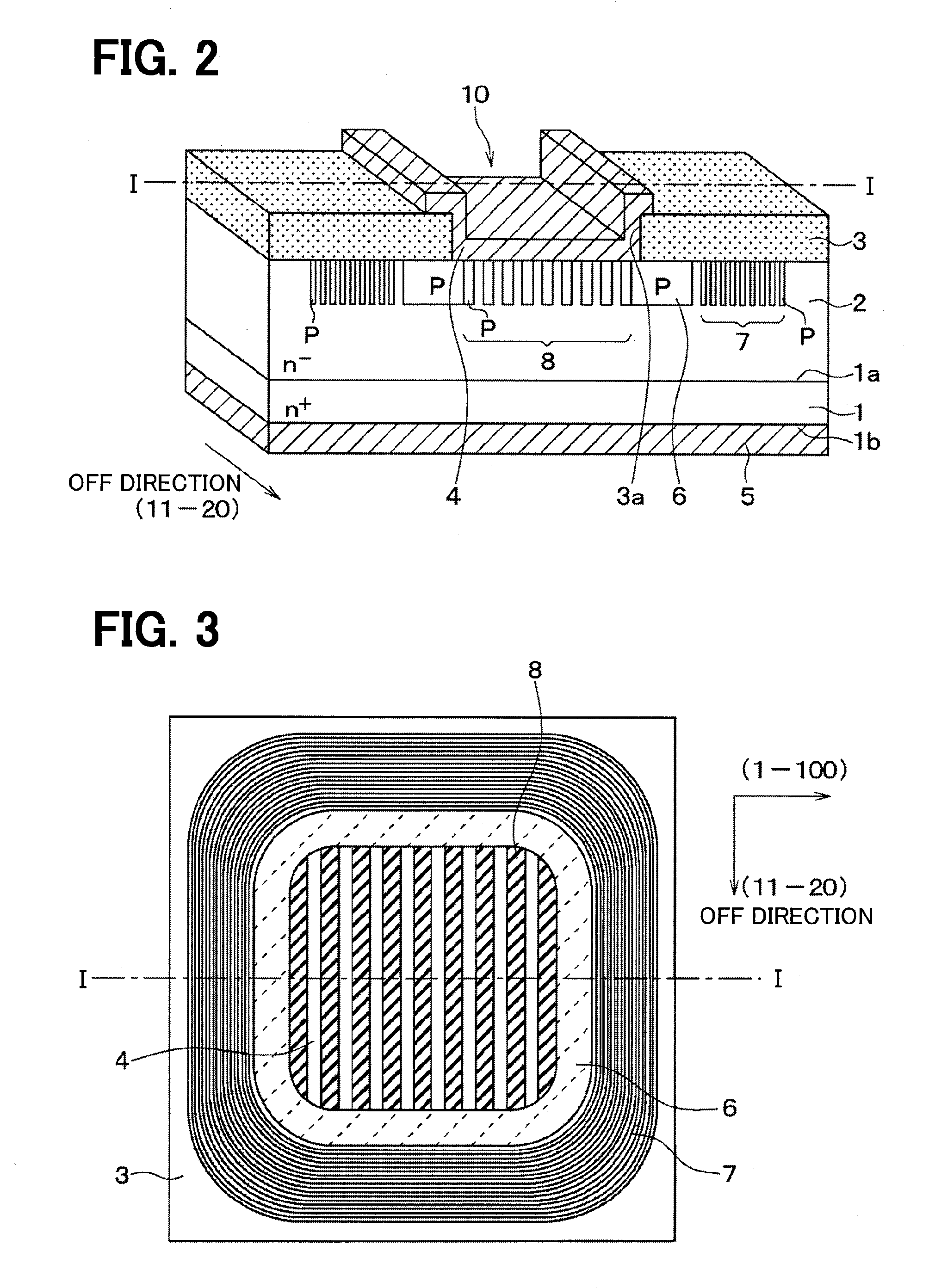
A silicon carbide semiconductor device includes a junction barrier Schottky diode including a substrate, a drift layer, an insulating film, a Schottky barrier diode, and a plurality of second conductivity type layers. The Schottky barrier diode includes a Schottky electrode and an ohmic electrode. A PN diode is configured by the plurality of second conductivity type layers and the drift layer, and the plurality of second conductivity type layers is formed in stripes only in a direction parallel to a rod-shaped stacking fault.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Sequential lithographic methods to reduce stacking fault nucleation sites and structures having reduced stacking fault nucleation sites
ActiveUS20050205872A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom chemically reactive gasesStacking faultCarbide
An epitaxial silicon carbide layer is fabricated by forming first features in a surface of a silicon carbide substrate having an off-axis orientation toward a crystallographic direction. The first features include at least one sidewall that is orientated nonparallel (i.e., oblique or perpendicular) to the crystallographic direction. A first epitaxial silicon carbide layer is then grown on the surface of the silicon carbide substrate that includes first features therein. Second features are then formed in the first epitaxial layer. The second features include at least one sidewall that is oriented nonparallel to the crystallographic direction. A second epitaxial silicon carbide layer is then grown on the surface of the first epitaxial silicon carbide layer that includes the second features therein.
Owner:CREE INC
Seed crystal of silicon carbide single crystal and method for producing ingot using same
InactiveUS20050160965A1Few defectSuitable for practicalPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateWaferingStacking fault
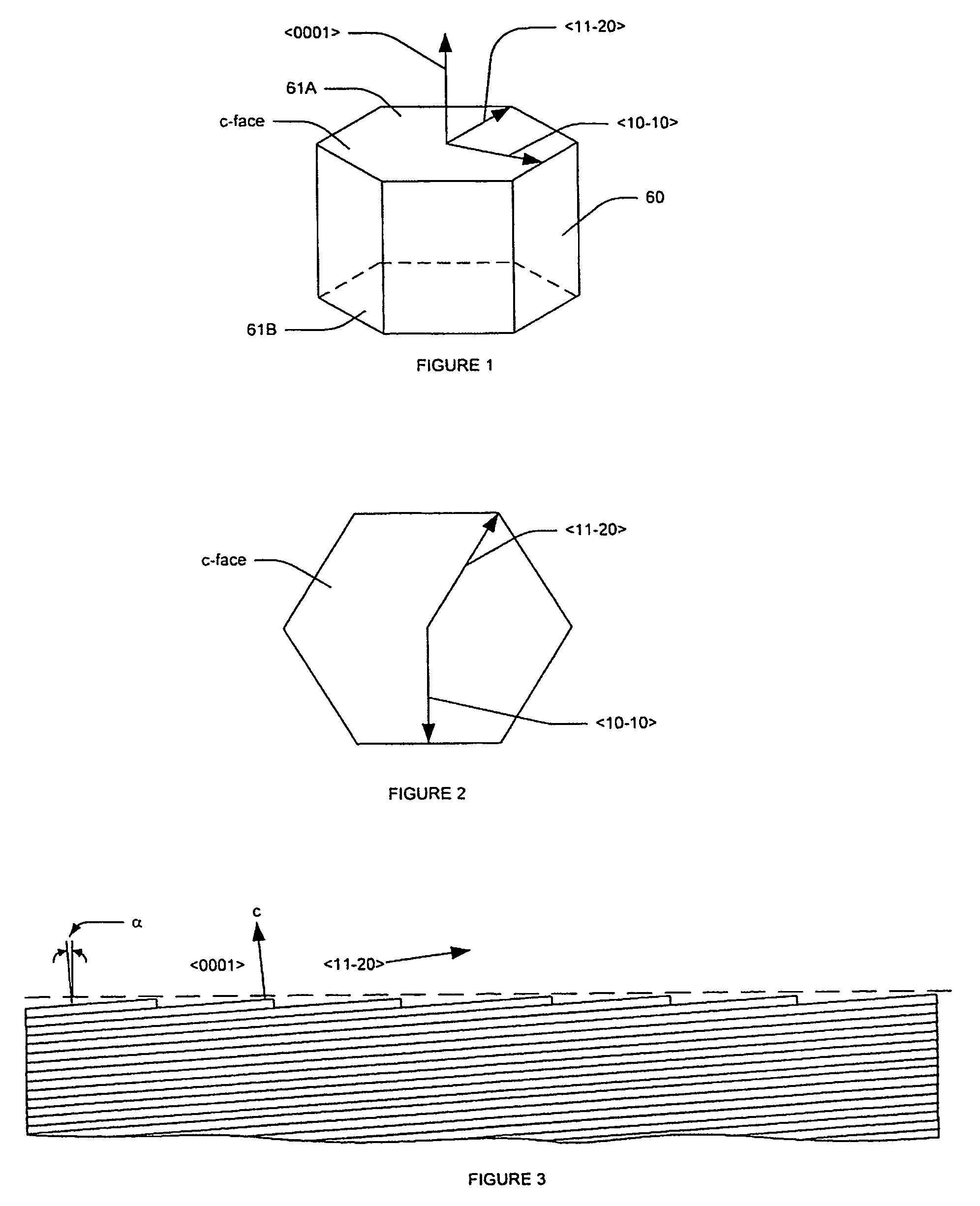
The present invention relates to a seed crystal consisting of a silicon carbide single crystal suitable for producing a substrate (wafer) for an electric power device, a high-frequency device or the like, and a method for producing an ingot using the same. A single crystal growing face of a seed crystal consisting of a silicon carbide single crystal is inclined at an angle ranging from 3 degrees or more to 60 degrees or less with respect to the (11-20) face to a direction inclined at an angle ranging from −45 degrees or more to 45 degrees or less from a <0001> direction to the [1-100] direction. By performing crystal growth using such a seed crystal, a high quality silicon carbide single crystal ingot can be obtained. According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain material consisting of a silicon carbide single crystal of favorable quality, which has few crystal defects such as micropipe defects and stacking faults, and the diameter is suitable for practical application.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Minimizing degradation of SiC bipolar semiconductor devices
Owner:SUMAKERIS JOSEPH J +6
Silicon wafer production process and silicon wafer
ActiveUS20060027159A1Reduce impactEasy to optimizePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsManufacturing technologyStacking fault
This silicon wafer production process has a step of cutting a silicon wafer from a silicon single crystal ingot in a perfect region which includes a perfect region P free of agglomerates of interstitial-silicon-type point defects and agglomerates of vacancy-type point defects and / or a region R in which there is occurrence of ring-shaped oxidation induced stacking faults, and a step of performing rapid thermal annealing on the silicon wafer in a hydrogen atmosphere, an argon atmosphere or an atmosphere containing a mixed gas thereof.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
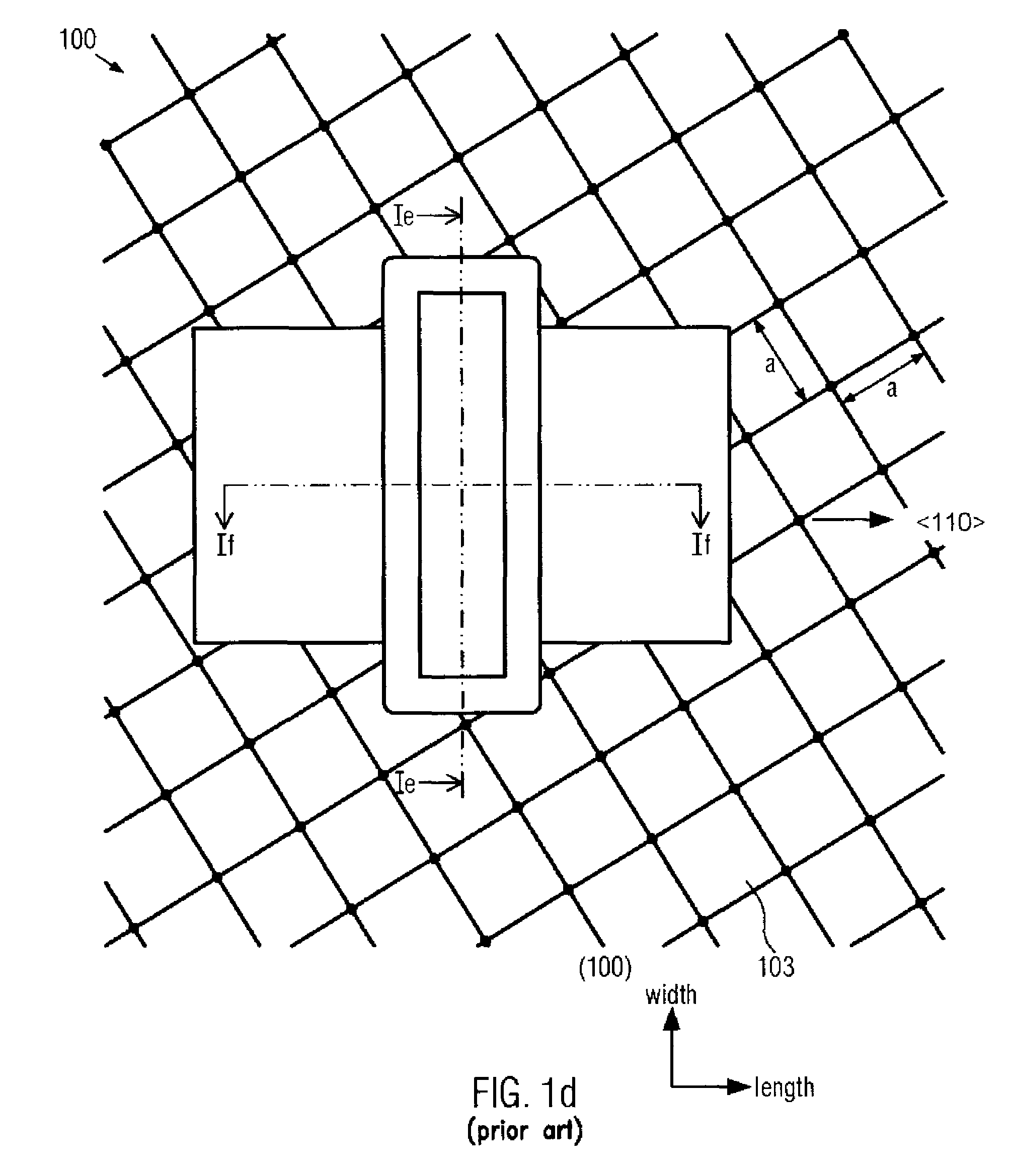
Method for reducing crystal defects in transistors with re-grown shallow junctions by appropriately selecting crystalline orientations
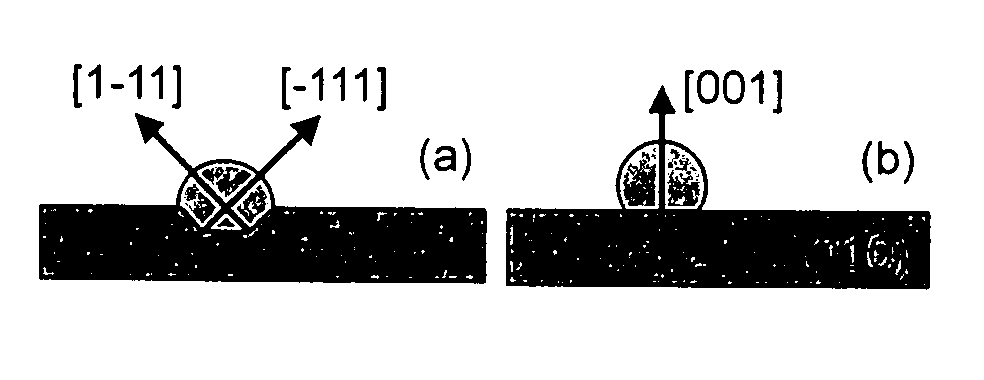
ActiveUS7763505B2Enhance re-crystallization processAvoid undue crystalline defectTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSide effectSemiconductor materials
By appropriately adapting the length direction and width directions of transistor devices with respect to the crystallographic orientation of the semiconductor material such that identical vertical and horizontal growth planes upon re-crystallizing amorphized portions are obtained, the number of corresponding stacking faults may be significantly reduced. Hence, transistor elements with extremely shallow PN junctions may be formed on the basis of pre-amorphization implantation processes while substantially avoiding any undue side effects typically obtained in conventional techniques due to stacking faults.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Production method of heavily phosphorus-doped thin substrate silicon epitaxial layer for Schottky devices
ActiveCN104947183AInactive doping effect suppressionImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom chemically reactive gasesSlip lineHydrogen
The invention relates to a production method of a heavily phosphorus-doped thin substrate silicon epitaxial layer for Schottky devices. The method adopts a normal-pressure flat plate type epitaxial furnace, and comprises the following steps: 1, polishing the pedestal of the epitaxial furnace at a high temperature by using hydrogen chloride with the purity being not lower than 99.99%; 2, filling the epitaxial furnace with a phosphorus-doped silicon substrate slice, and sequentially purging the cavity of the epitaxial furnace by nitrogen and hydrogen, wherein the purities of nitrogen and hydrogen are not lower than 99.999% respectively; 3, polishing the surface of the silicon substrate slice by using a hydrogen chloride gas; 4, purging the surface of the silicon substrate slice by using a bulk flow of hydrogen; 5, growing an intrinsic epitaxial layer; 6, carrying out variable flow purging on the reaction cavity of the epitaxial furnace; and 7, growing a doped epitaxial layer. The thickness inhomogeneity of the epitaxial layer is smaller than 1%, the resistivity inhomogeneity of the epitaxial layer is smaller than 1%, the surface of the epitaxial layer has no stacking fault, dislocation, slip lines, mist or other defects, the width of a transition region under optimum conditions can be smaller than 1[mu]m, and requirements of the silicon epitaxial layer by the Schottky devices can be completely met, so the performances and the yield of the Schottky devices are improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com