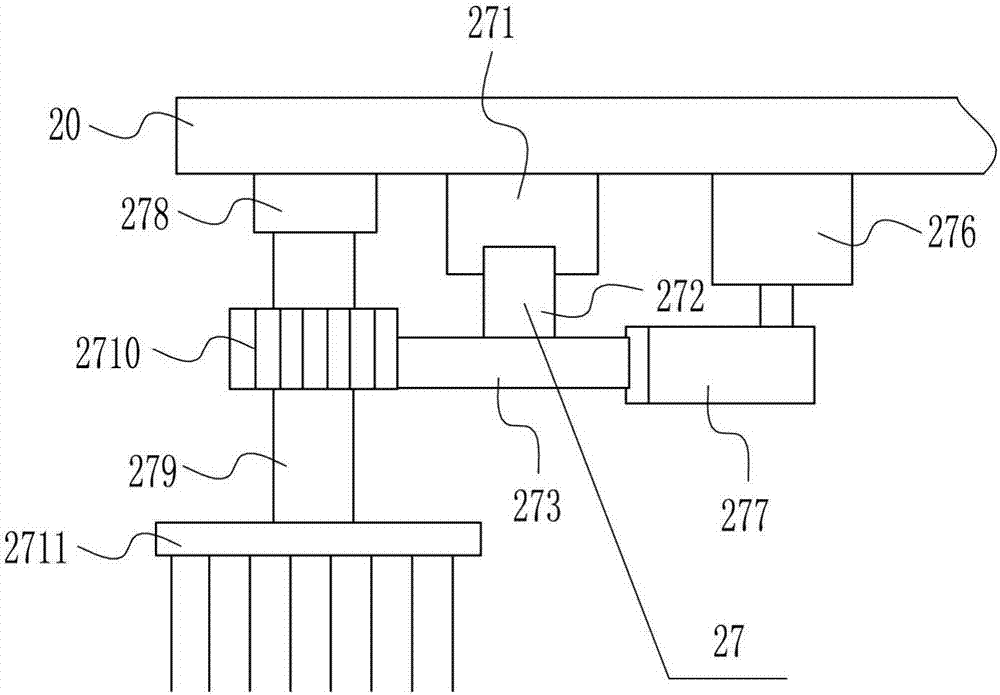
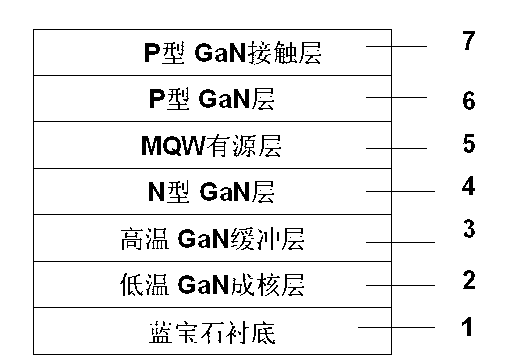
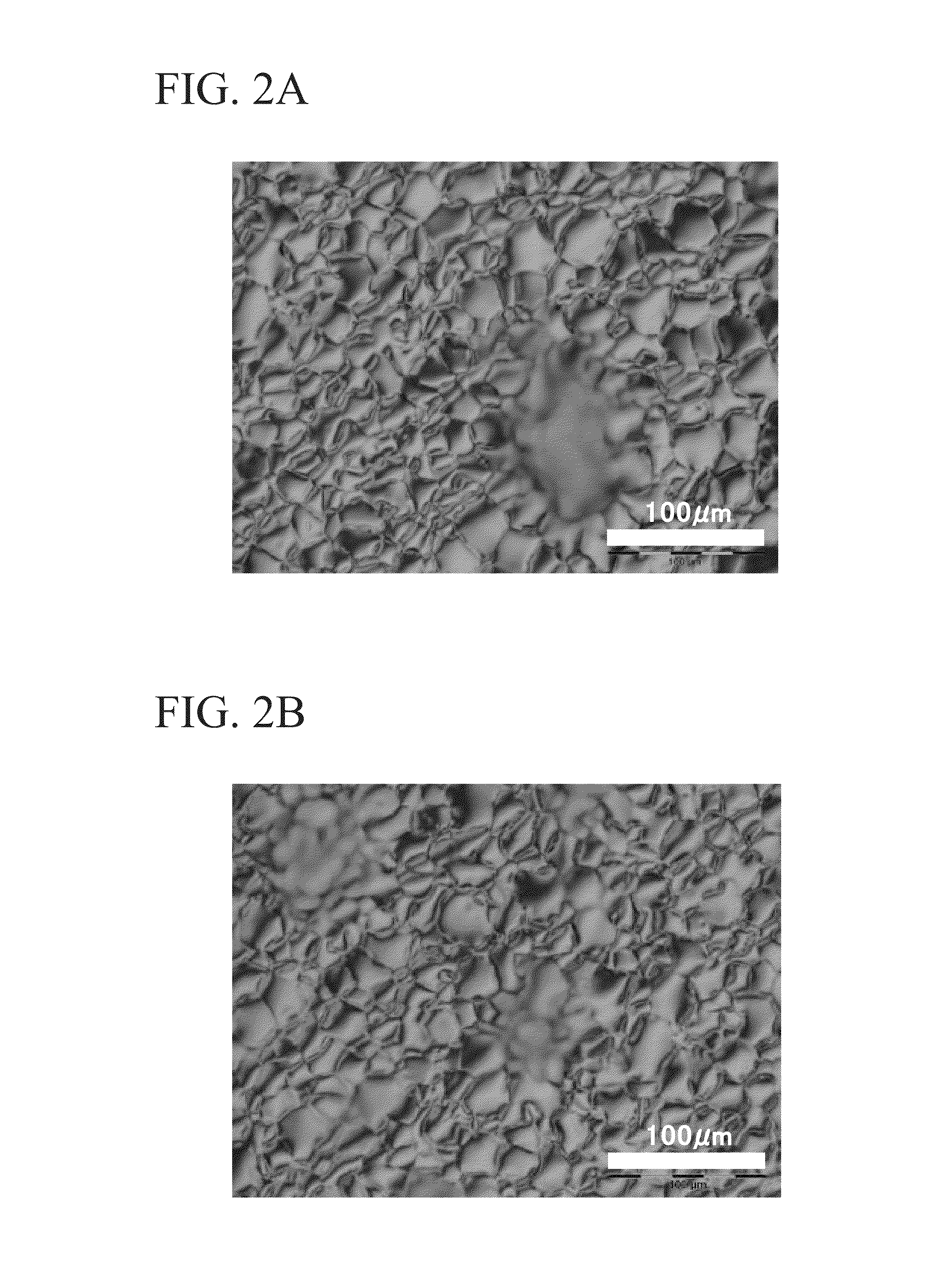
Patents
Literature
4352 results about "Epiwafer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An epitaxial wafer (also called epi wafer, epi-wafer, or epiwafer) is a wafer of semiconducting material made by epitaxial growth (epitaxy) for use in photonics, microelectronics, spintronics, or photovoltaics. The epi layer may be the same material as the substrate, typically monocrystaline silicon, or it may be a more exotic material with specific desirable qualities.
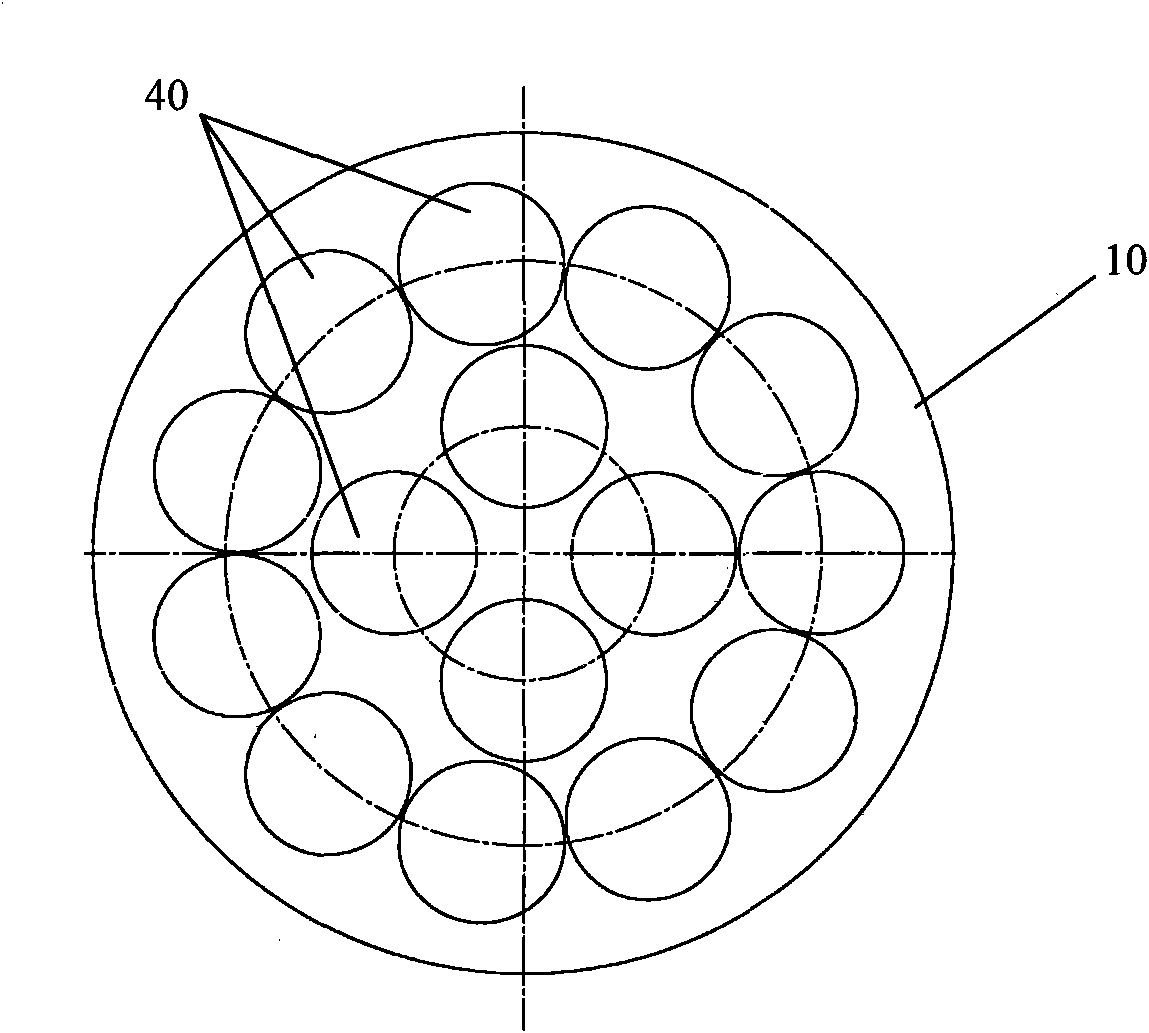
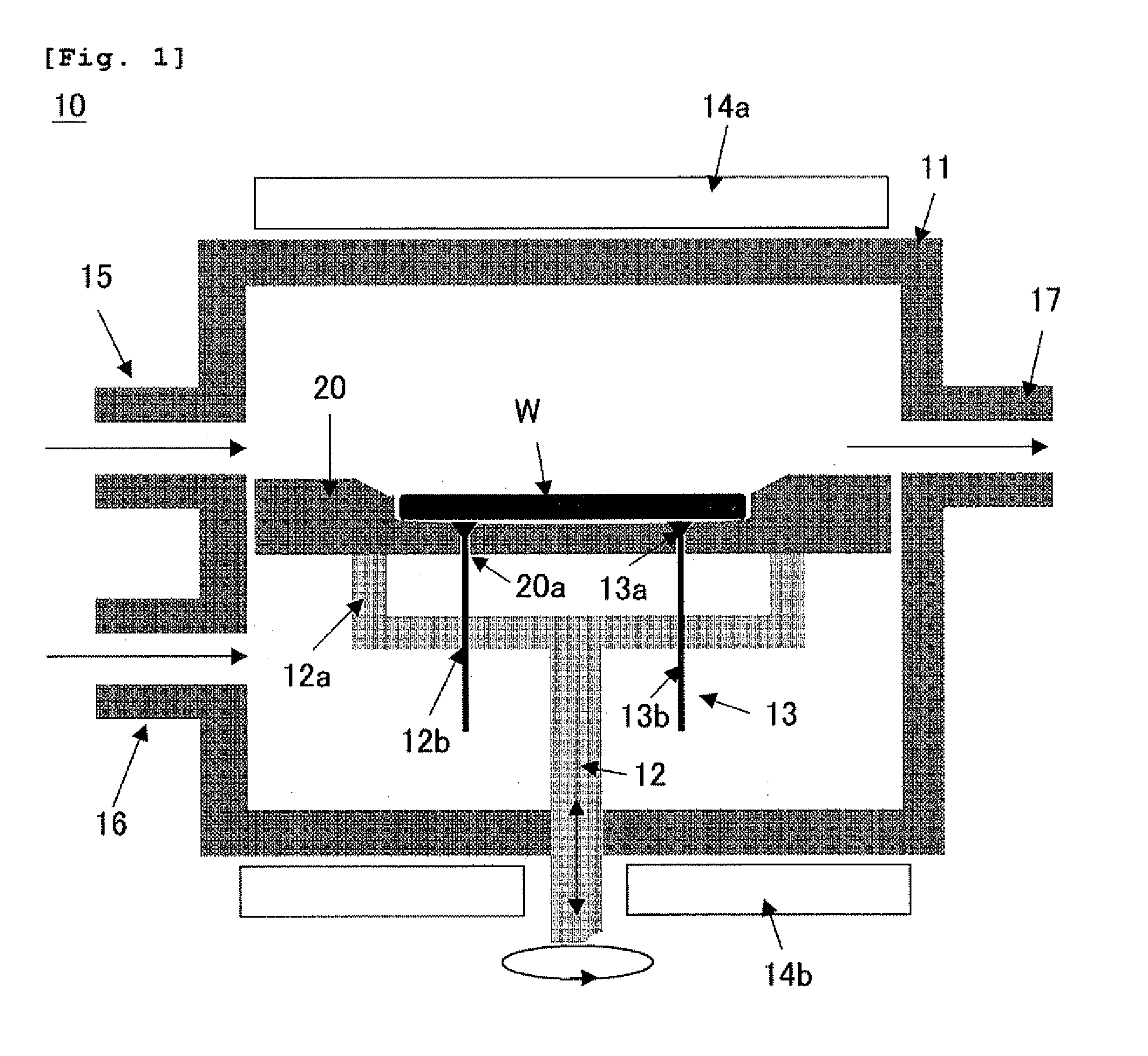
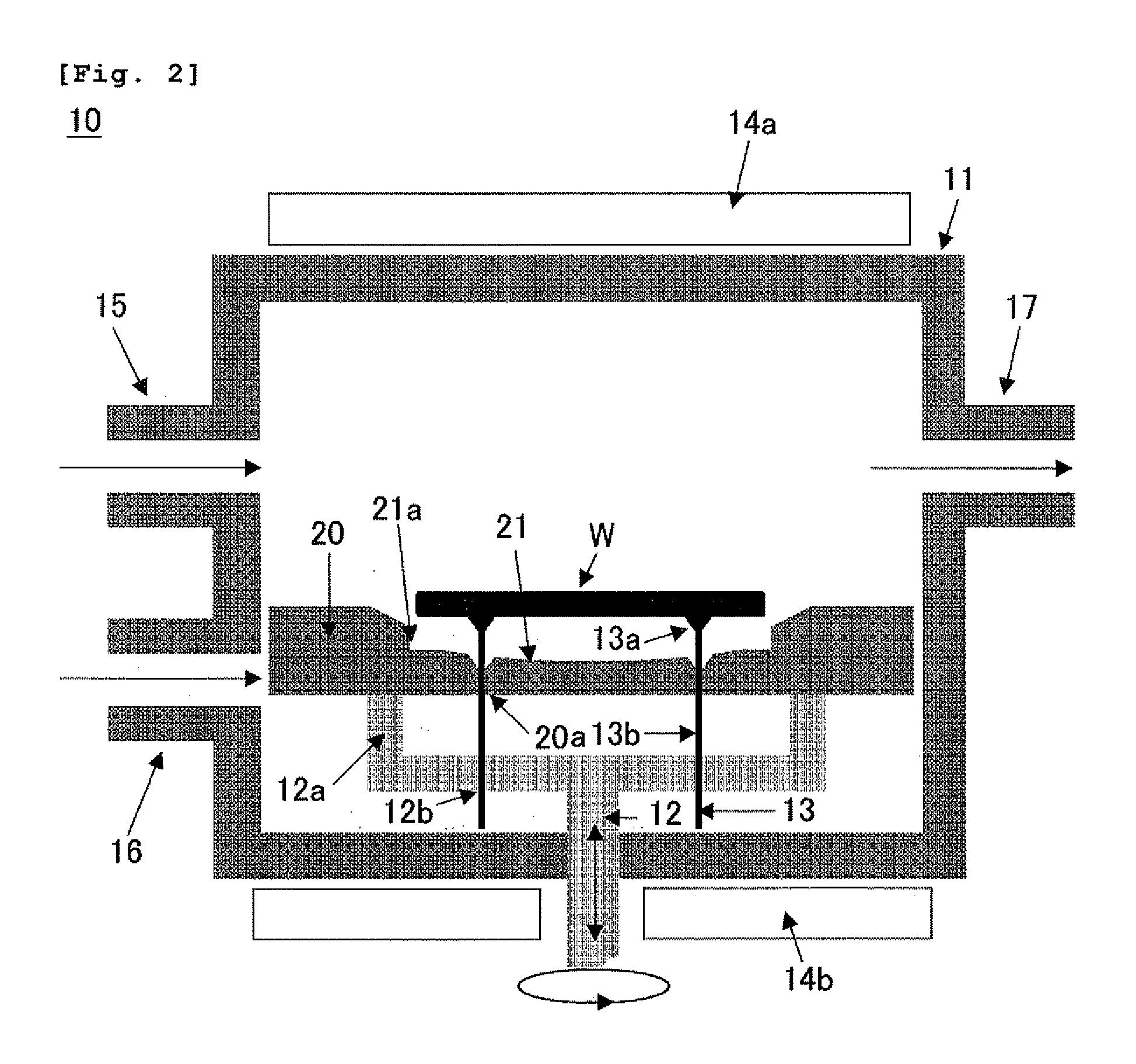
Susceptor and method for manufacturing silicon epitaxial wafer
ActiveUS20100129990A1Avoid stickingPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsSusceptorWafering
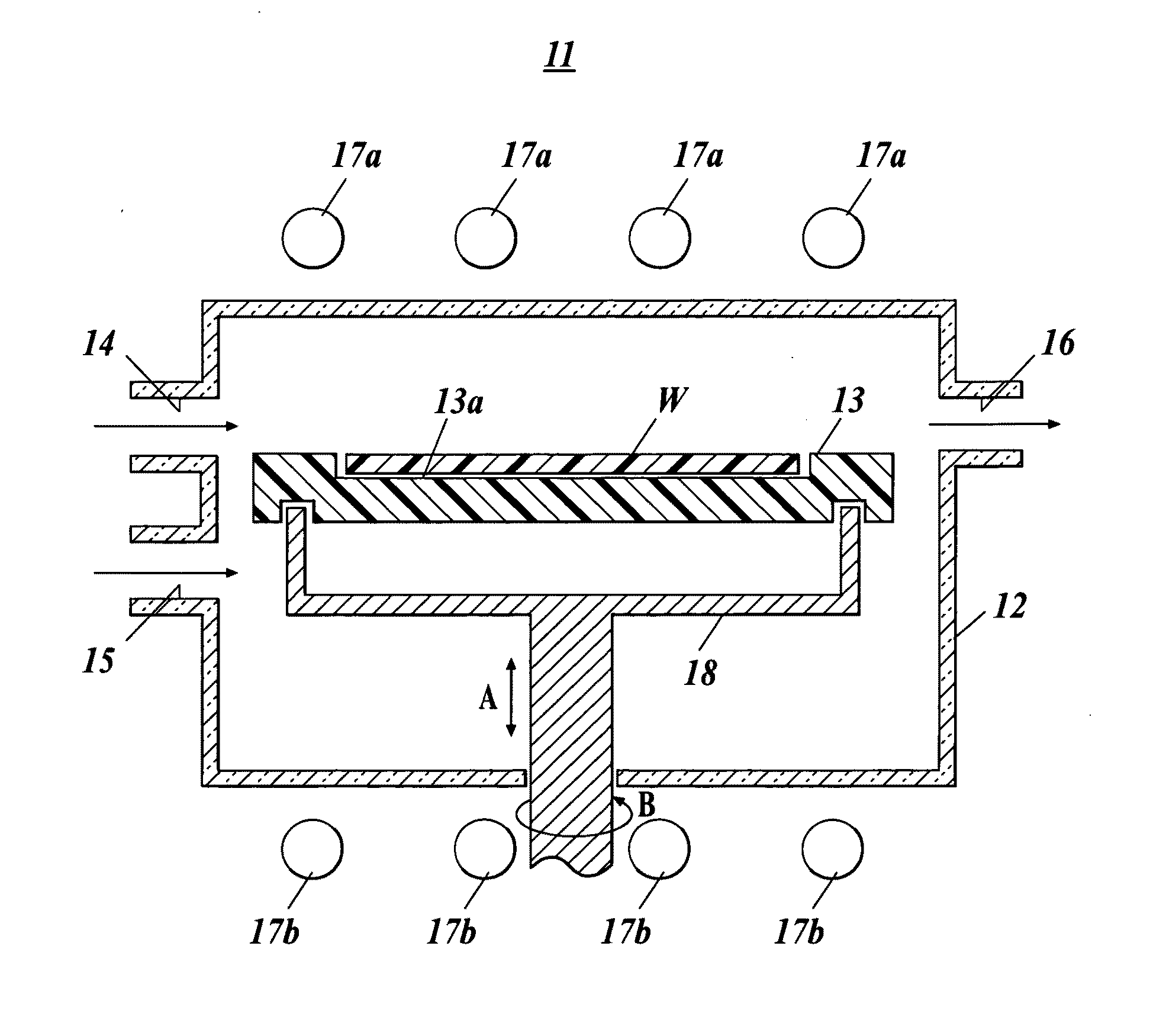
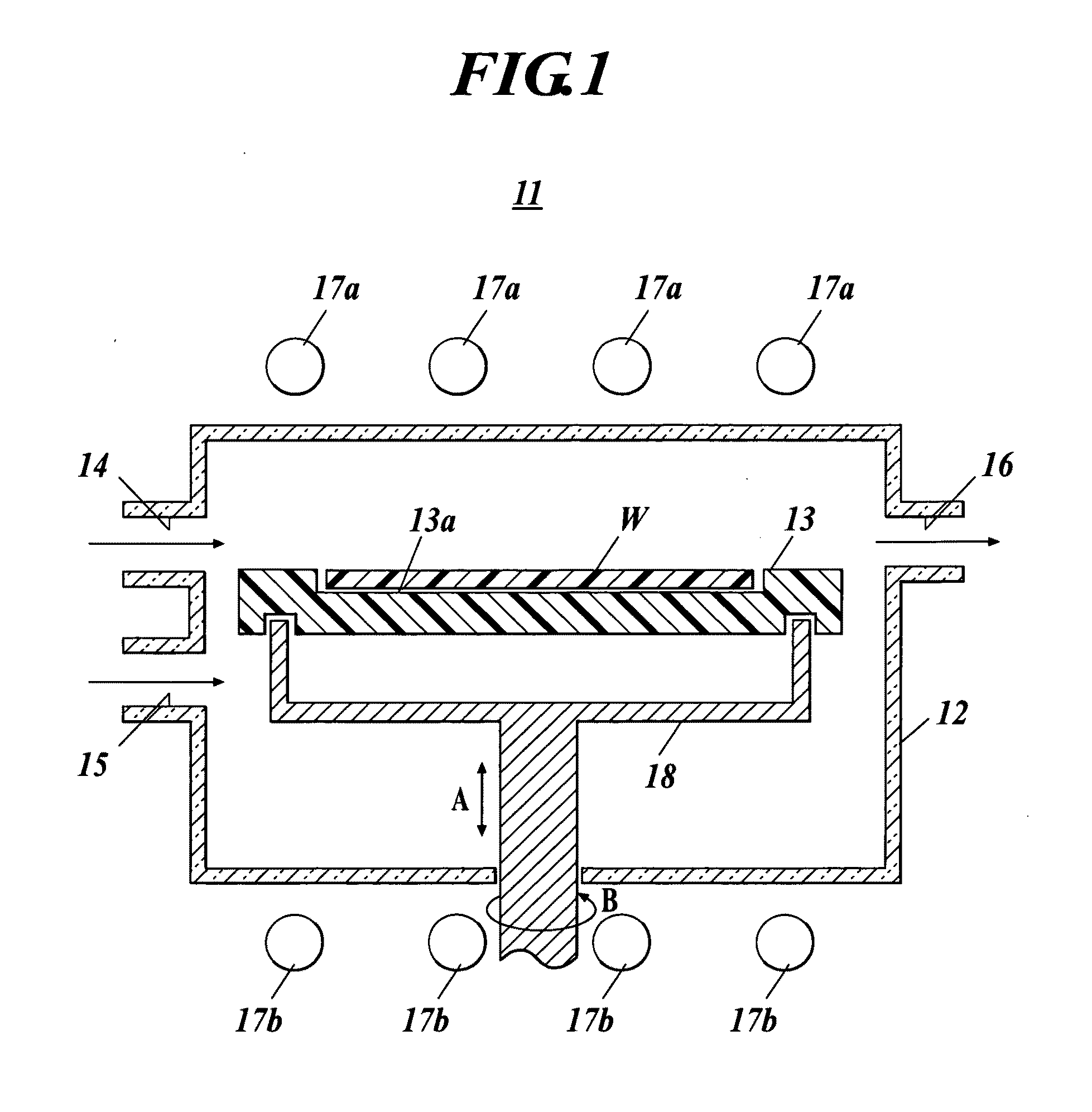
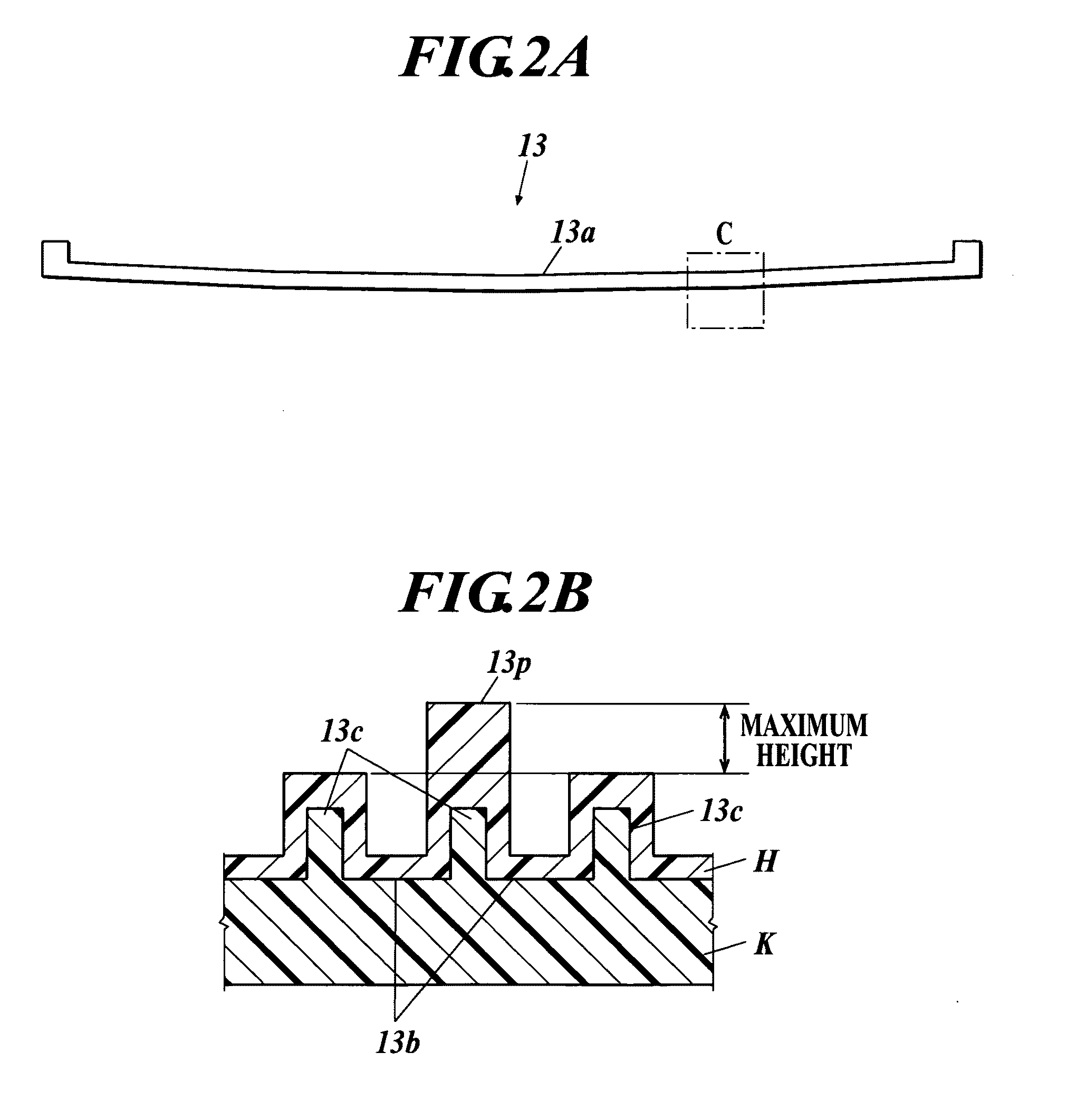
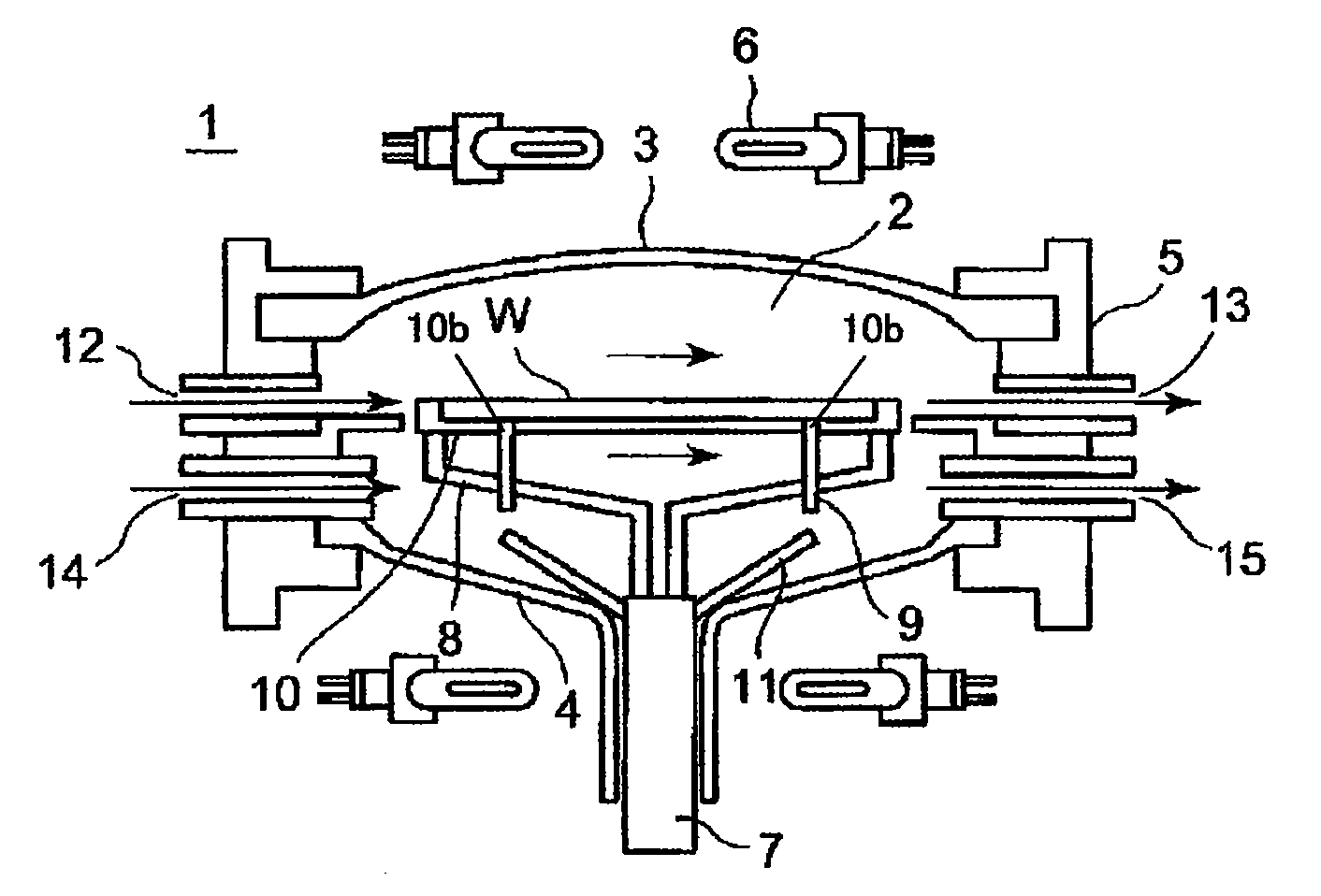
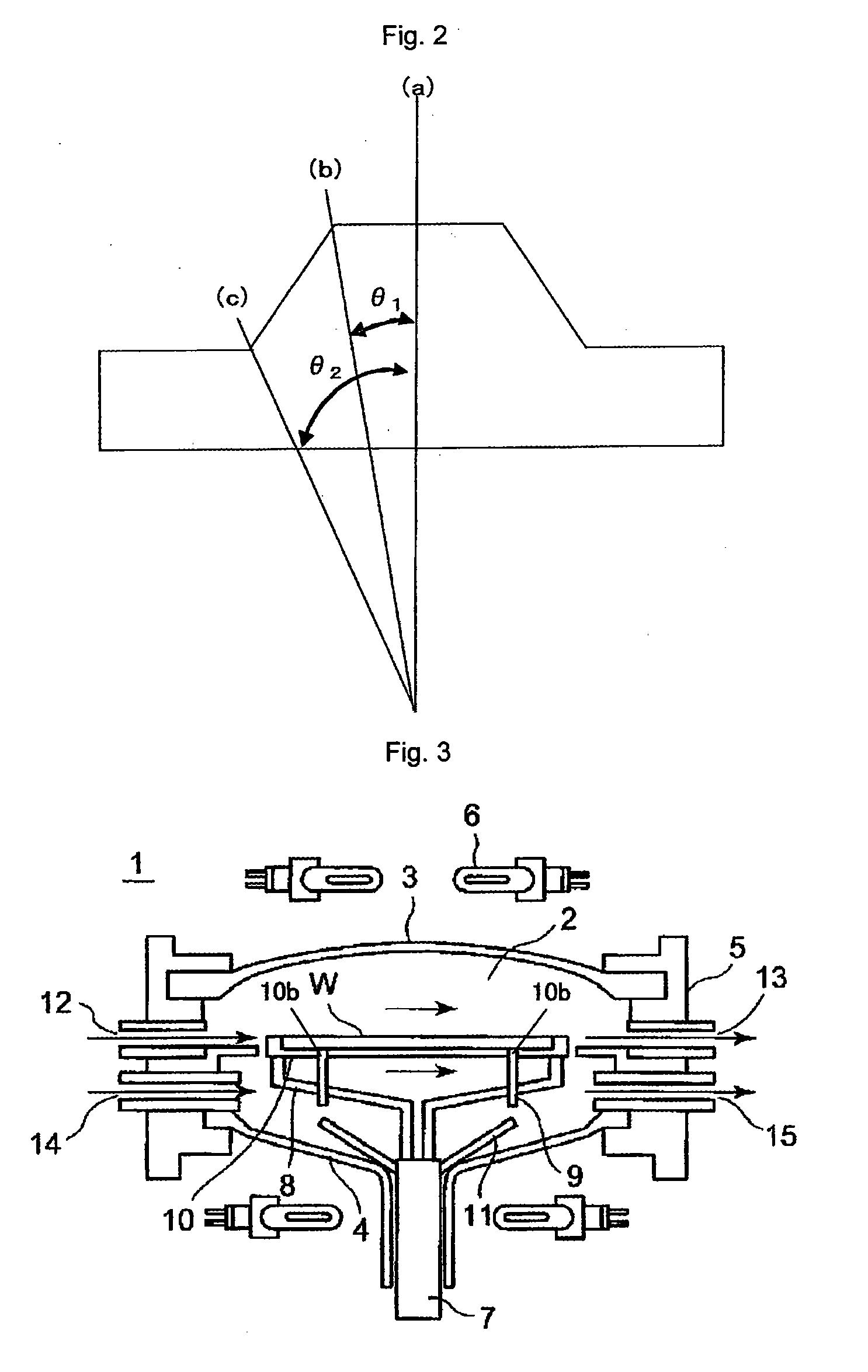
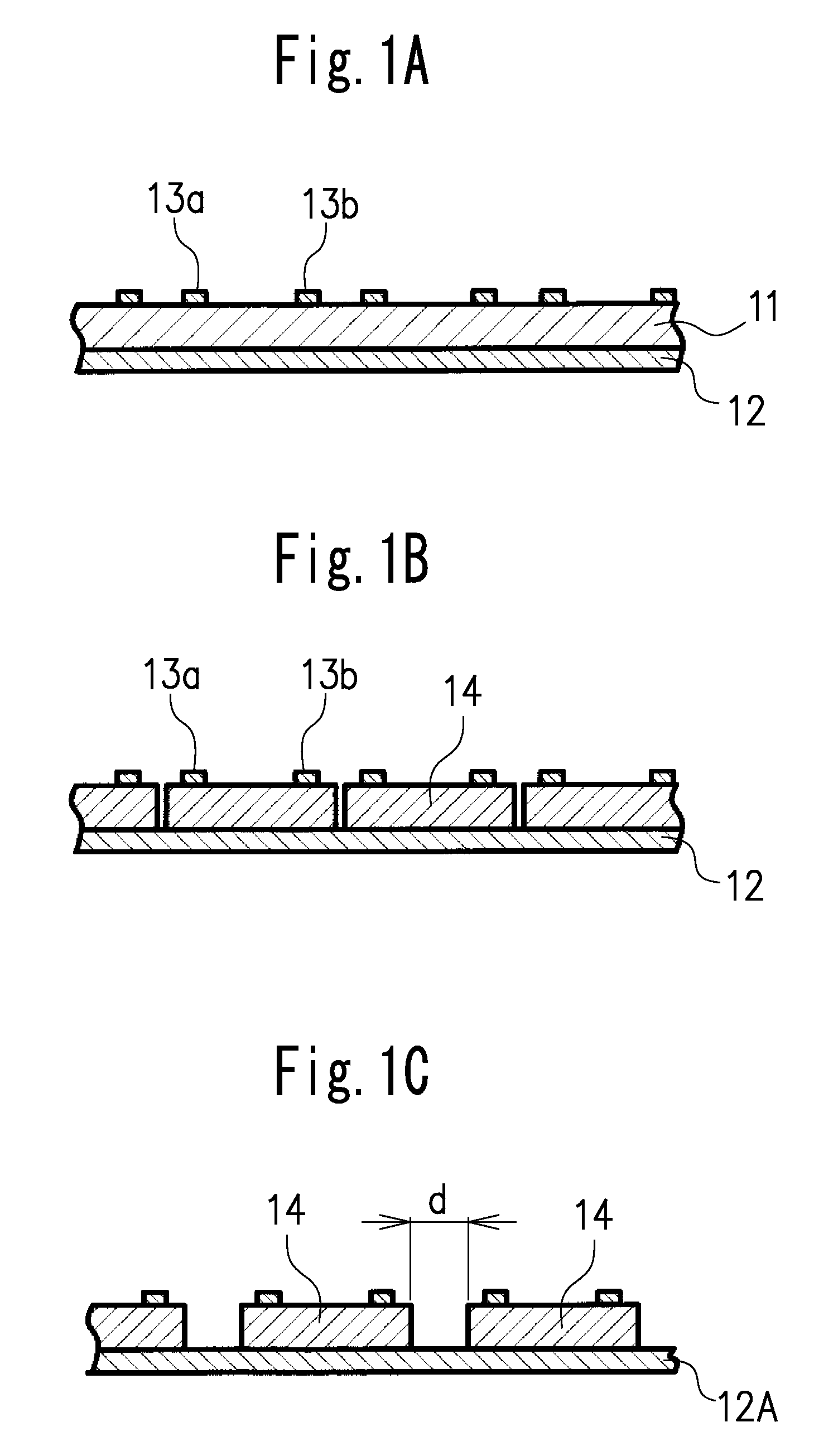
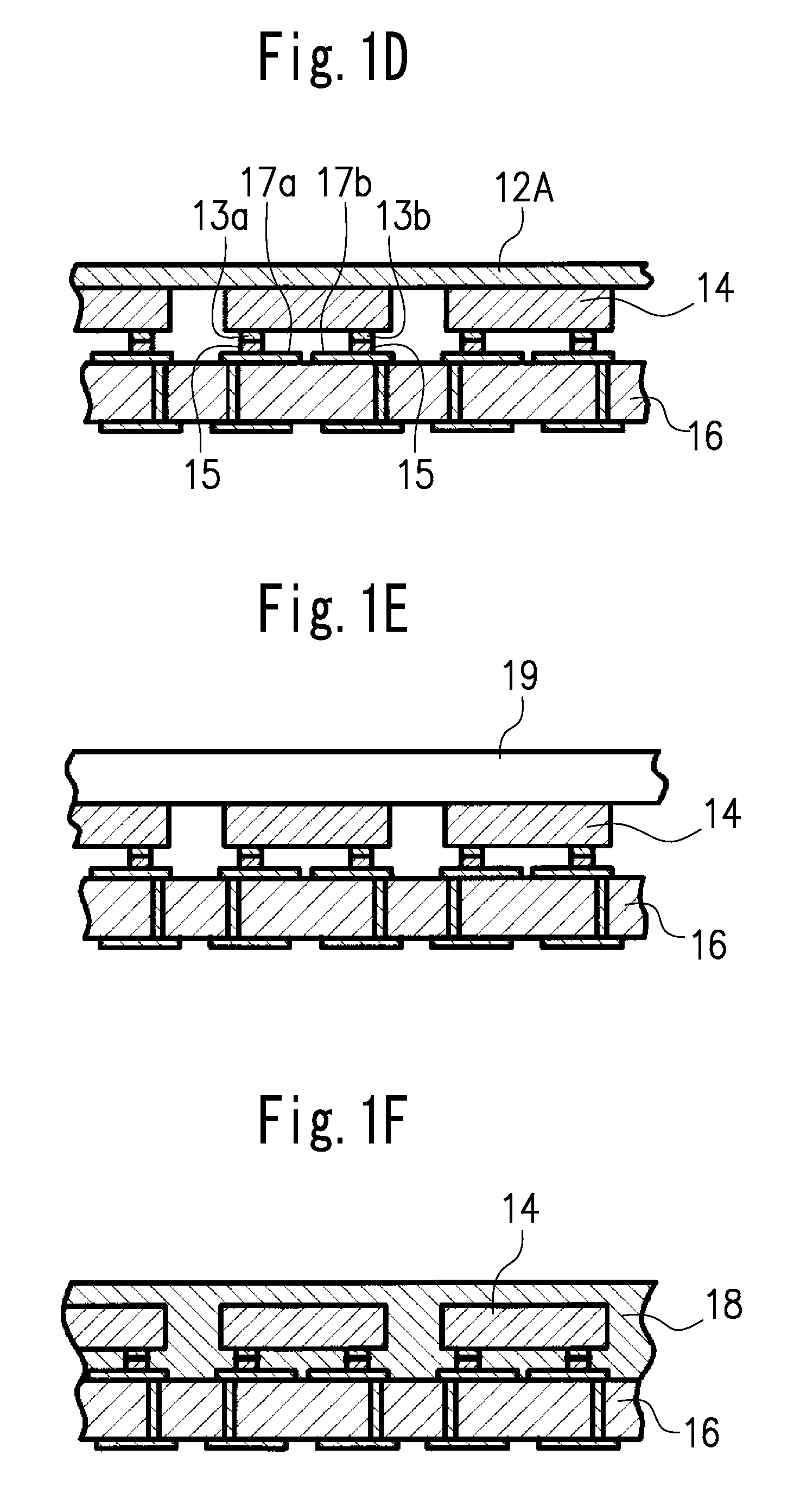
Provided is a susceptor 13 for manufacturing an epitaxial wafer, comprising a mesh-like groove 13b on a mount face on which a silicon substrate W is to be mounted, wherein a coating H of silicon carbide is formed on the mount face, and the coating has a surface roughness of 1 μm or more in centerline average roughness Ra and a maximum height of a protrusion 13p generated in forming the coating H of 5 μm or less. Thus, defects such as warping and slip as well as adhesion of the silicon substrate to the susceptor are prevented.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
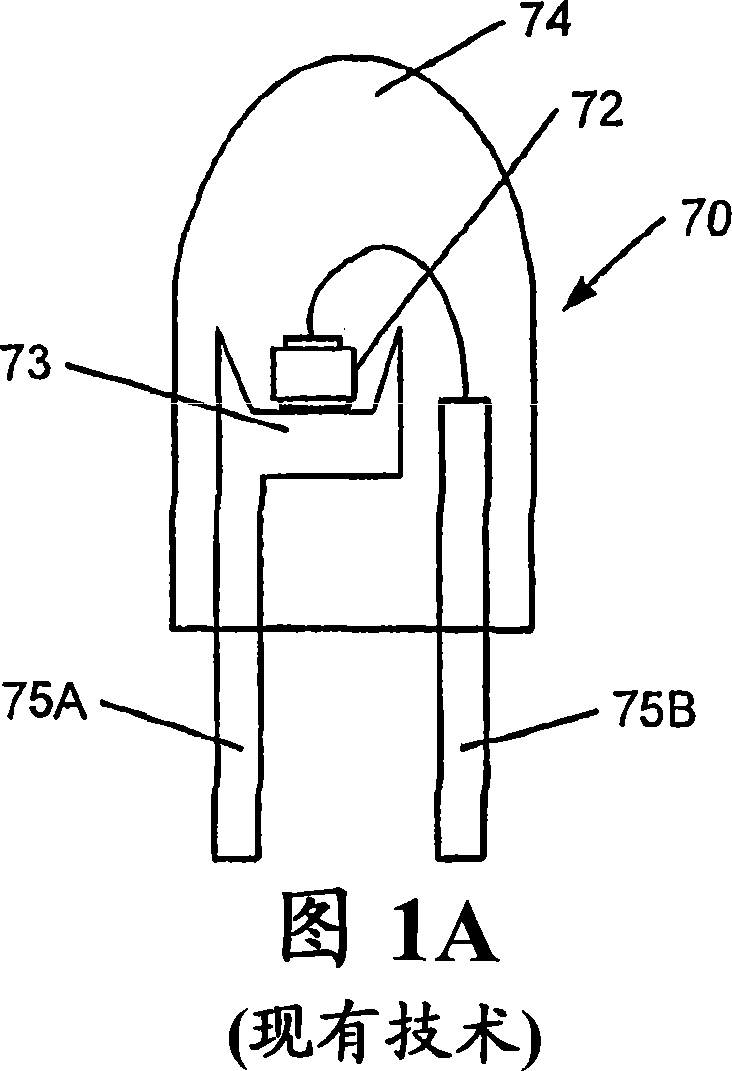
Flip chip light emitting diode devices having thinned or removed substrates
ActiveUS20050023550A1Reduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLight-emitting diodePhysics
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Method of recycling a delaminated wafer and a silicon wafer used for the recycling
InactiveUS6284628B1Easy to disassembleImprove surface roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateWafering
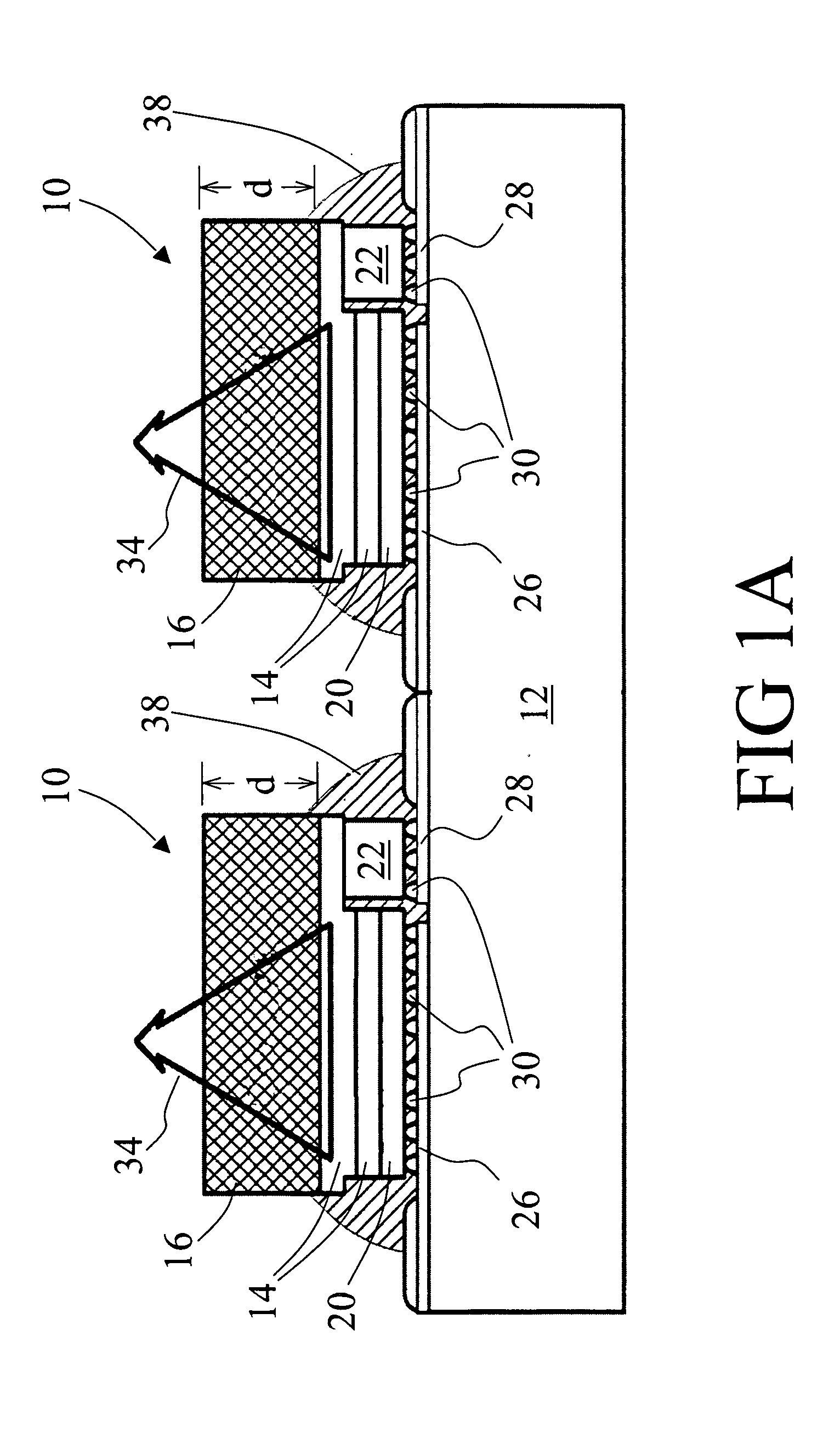
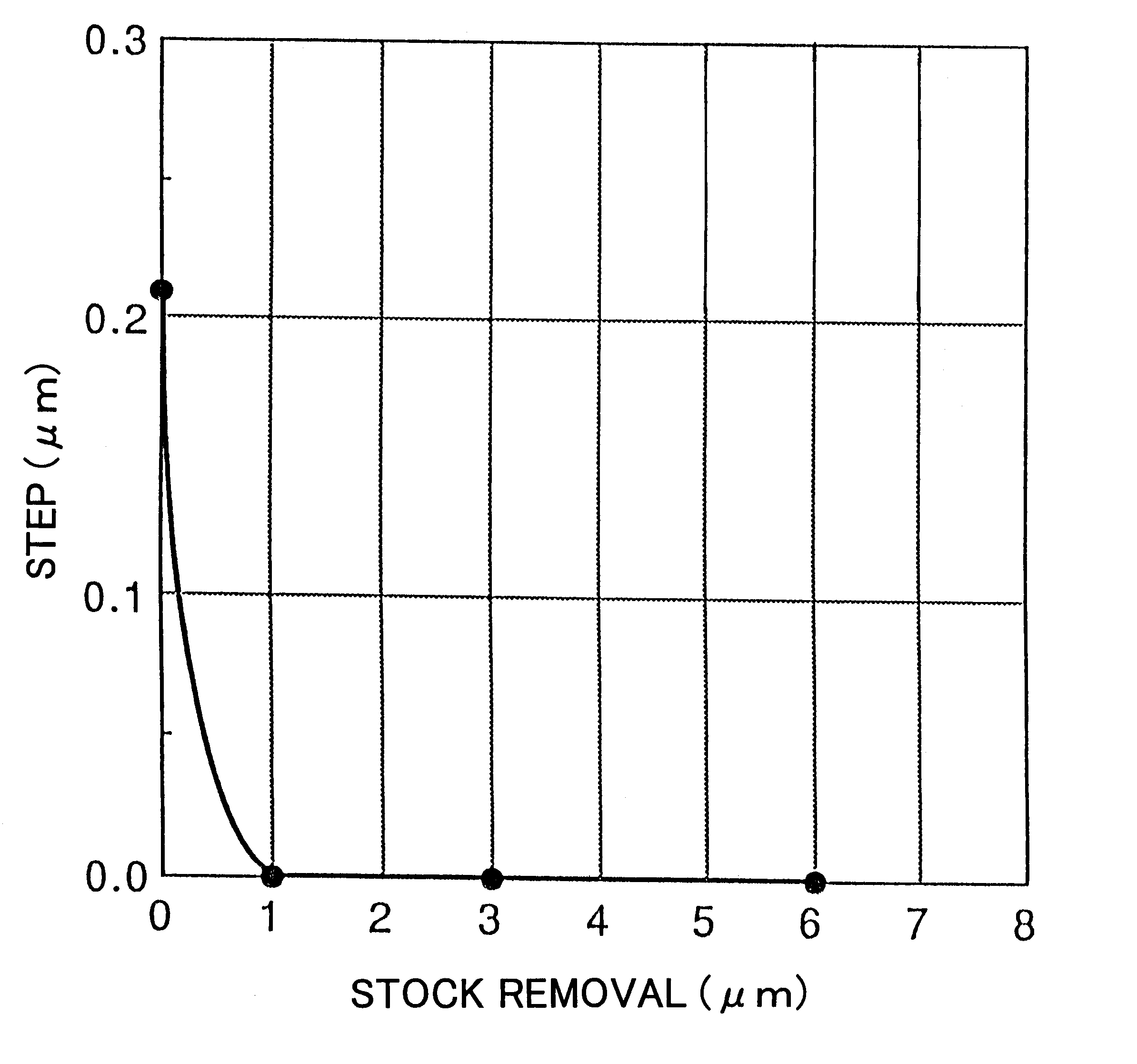
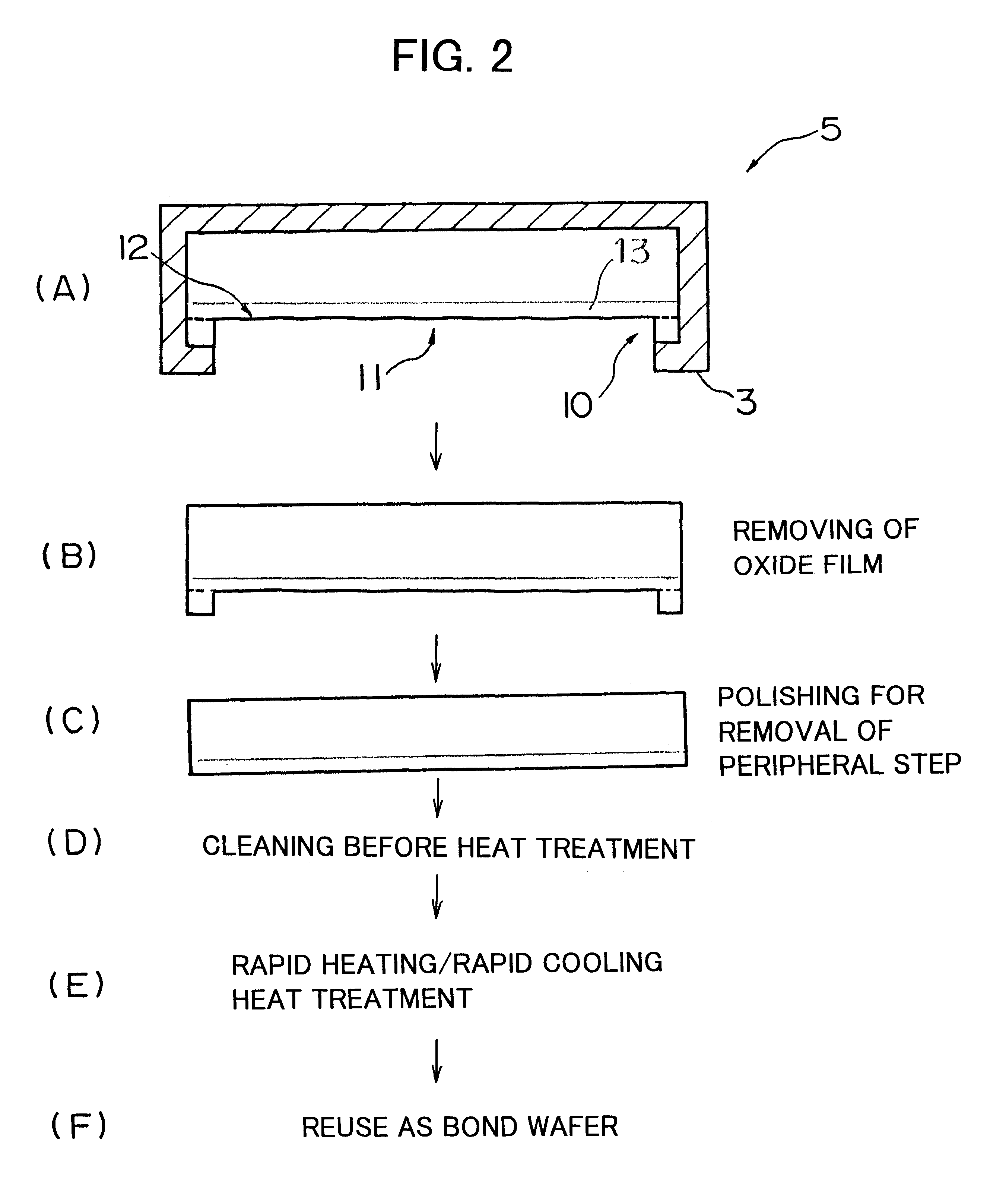
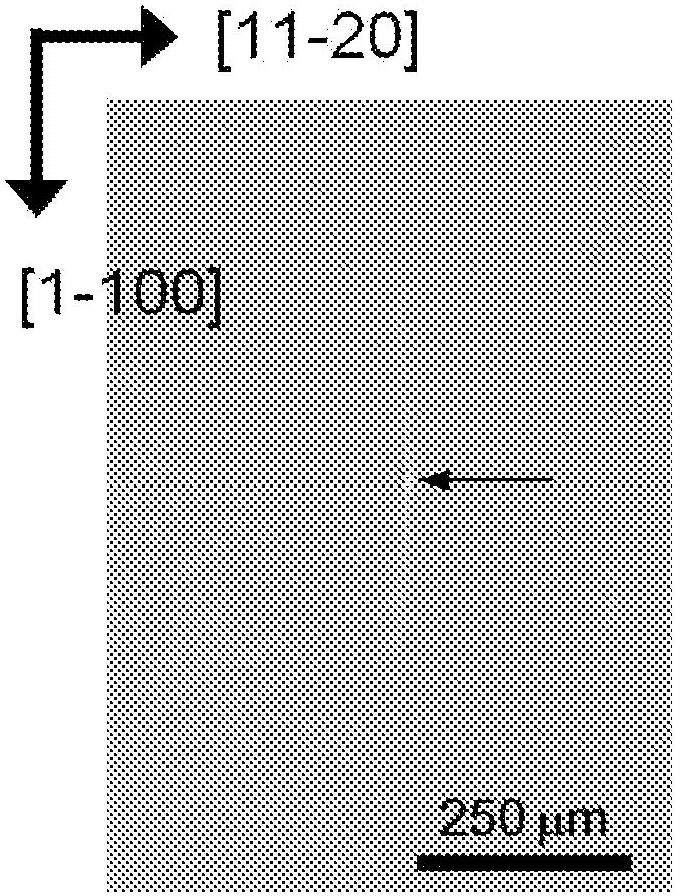
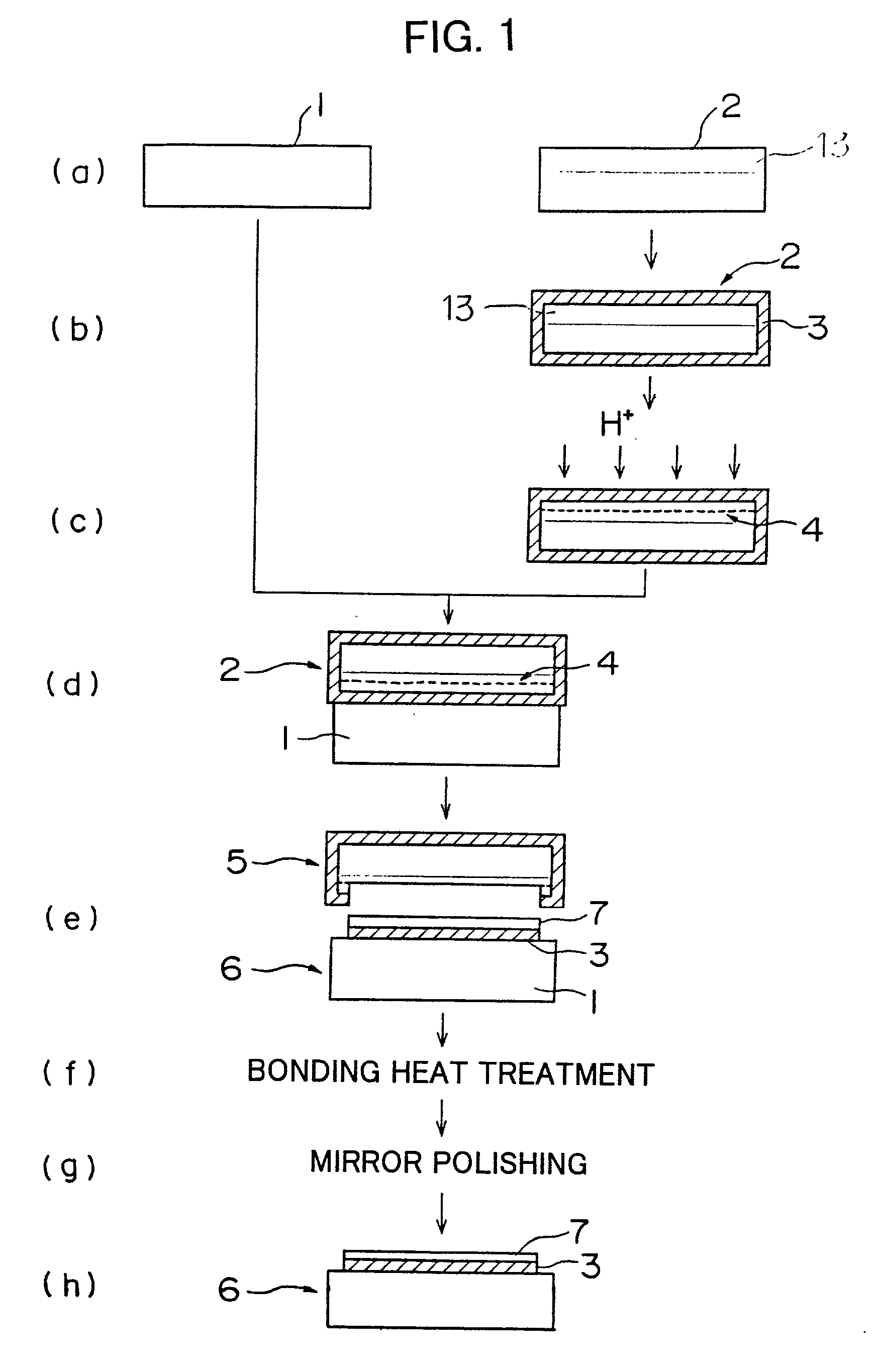
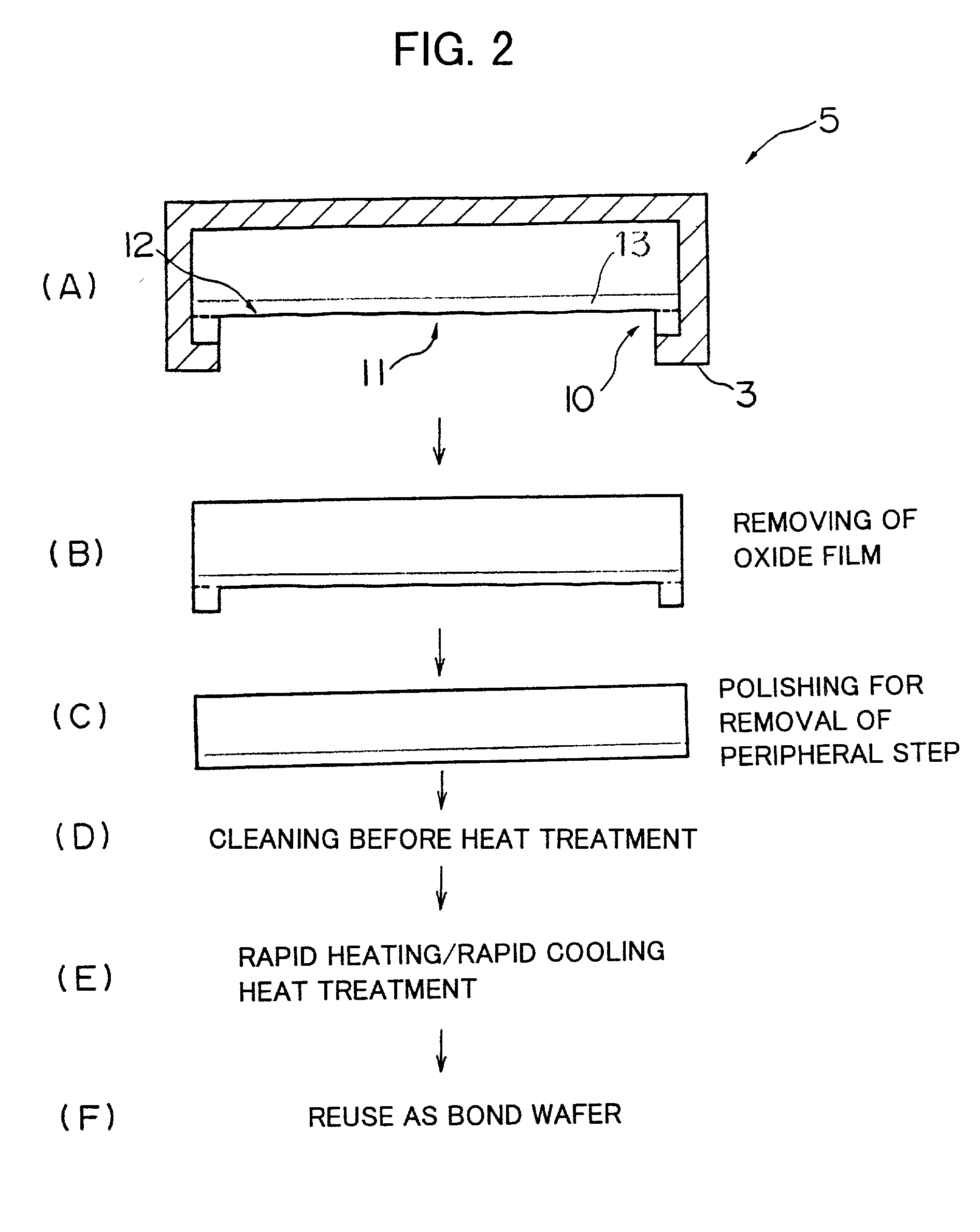
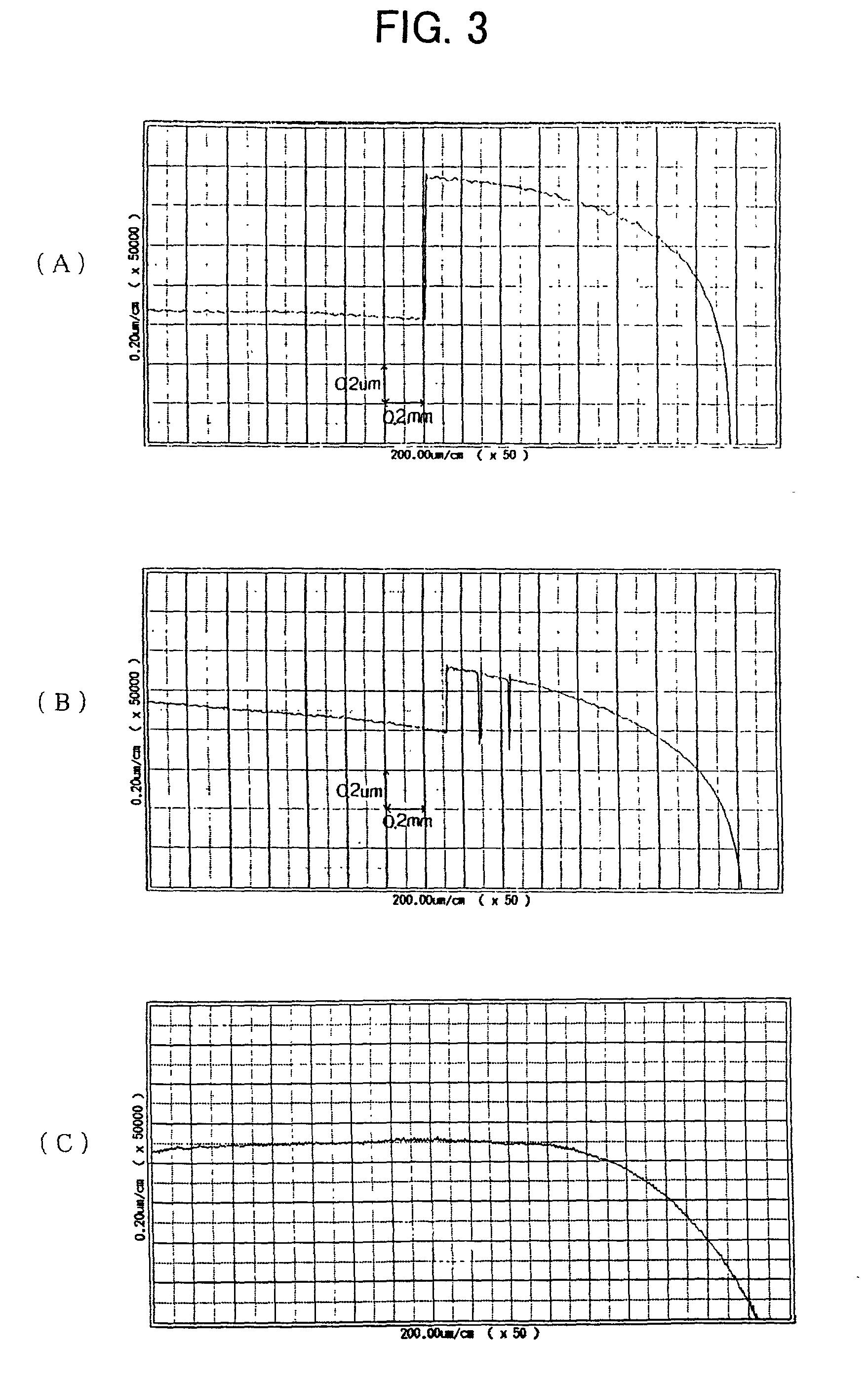
There is disclosed a method of recycling a delaminated wafer produced as a by-product in producing an SOI wafer according to a hydrogen ion delaminating method by reprocessing it for reuse as a silicon wafer, wherein at least polishing of the delaminated wafer for removing of a step in the peripheral part of the delaminated wafer and heat treatment in a reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen are conducted as the reprocessing. There are provided a method of appropriately reprocessing a delaminated wafer produced as a by-product in a hydrogen ion delaminating method to reuse it as a silicon wafer actually, and particularly, a method of reprocessing an expensive wafer such as an epitaxial wafer many times for reuse, to improve productivity of SOI wafer having a high quality SOI layer, and to reduce producing cost.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Device and method for manufacturing a semiconductor wafer
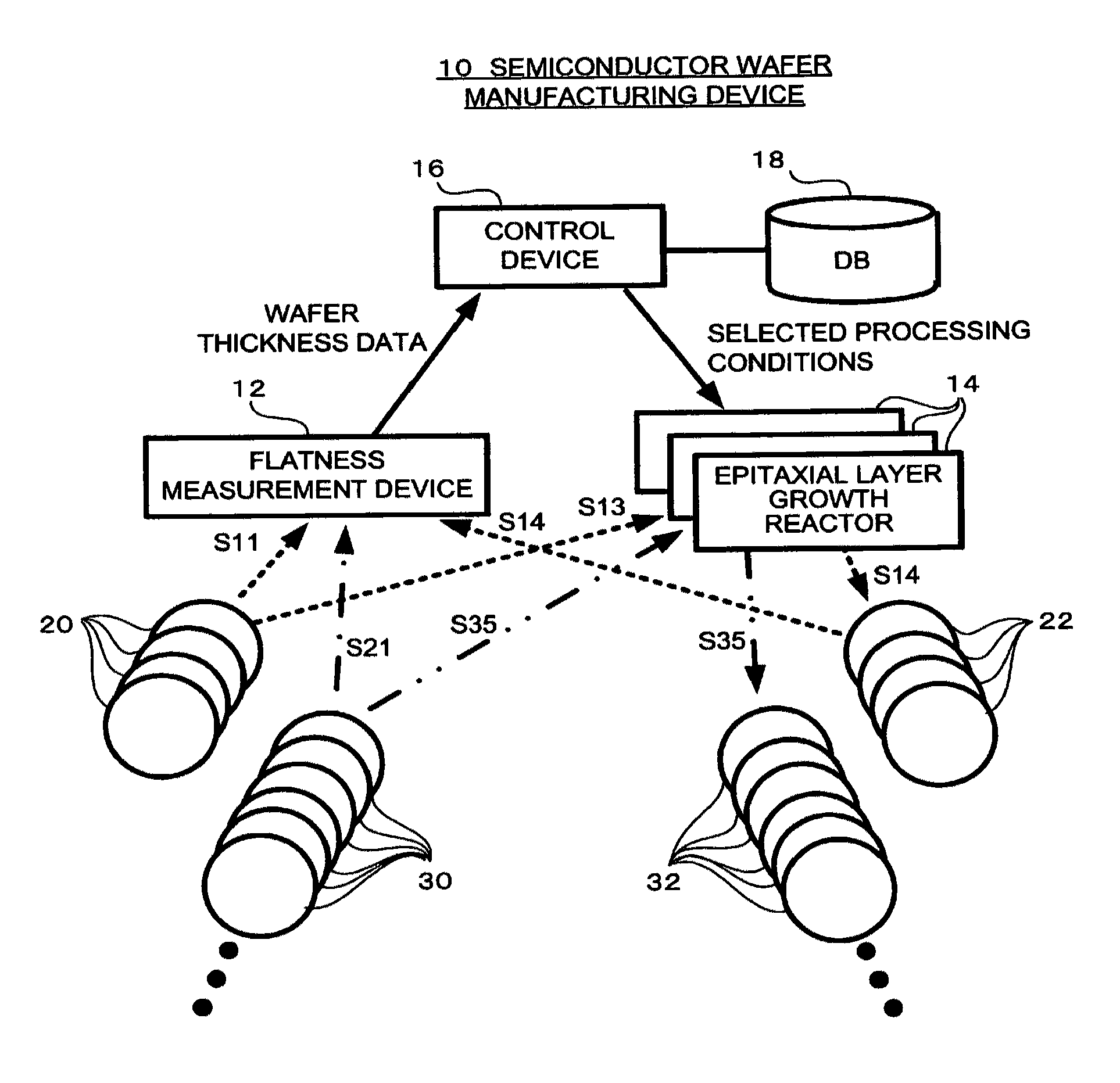
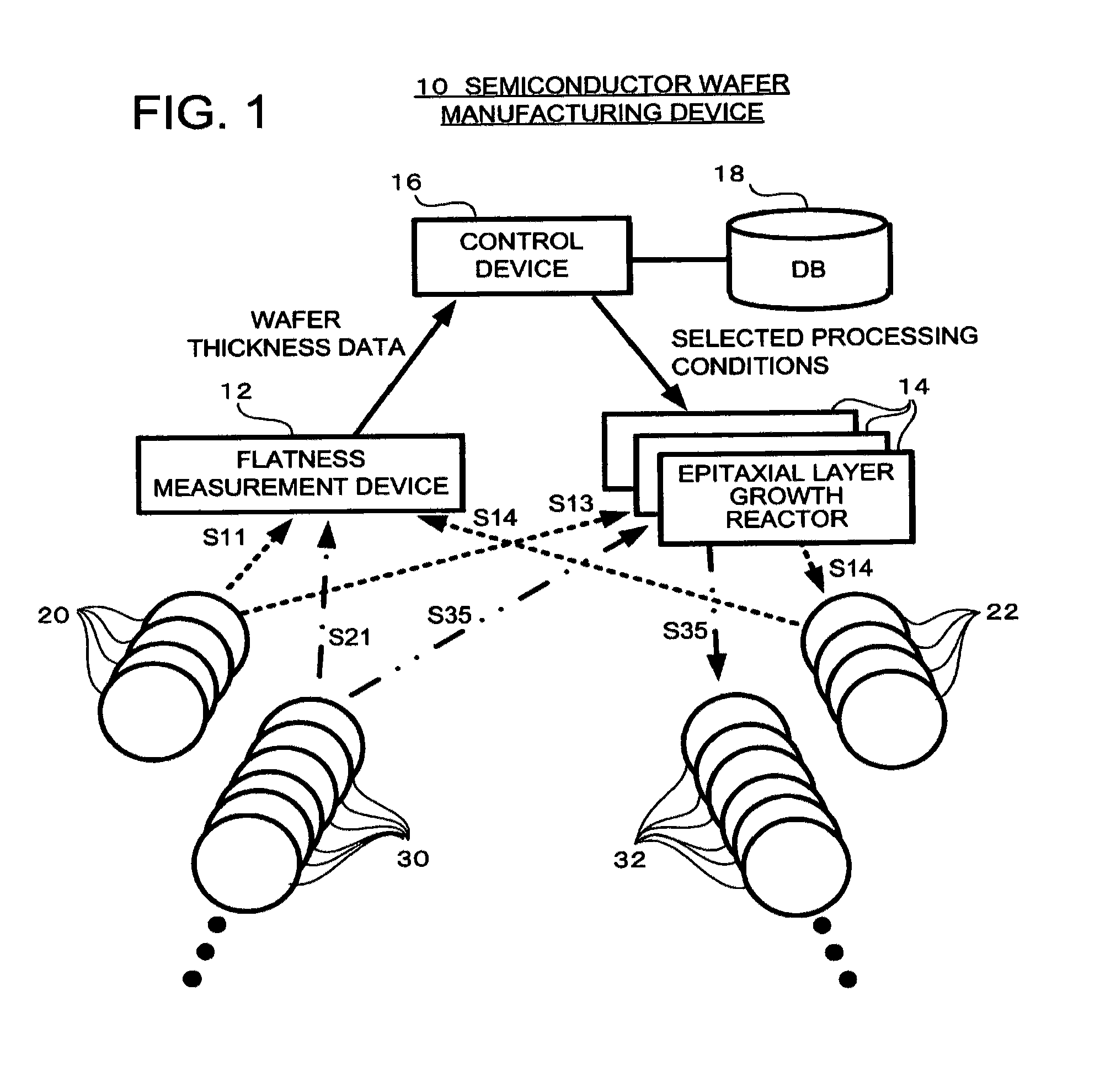
ActiveUS8196545B2Reliable manufacturingEnhance the imageProgramme controlLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringLayer thickness
Owner:SUMCO TECHXIV
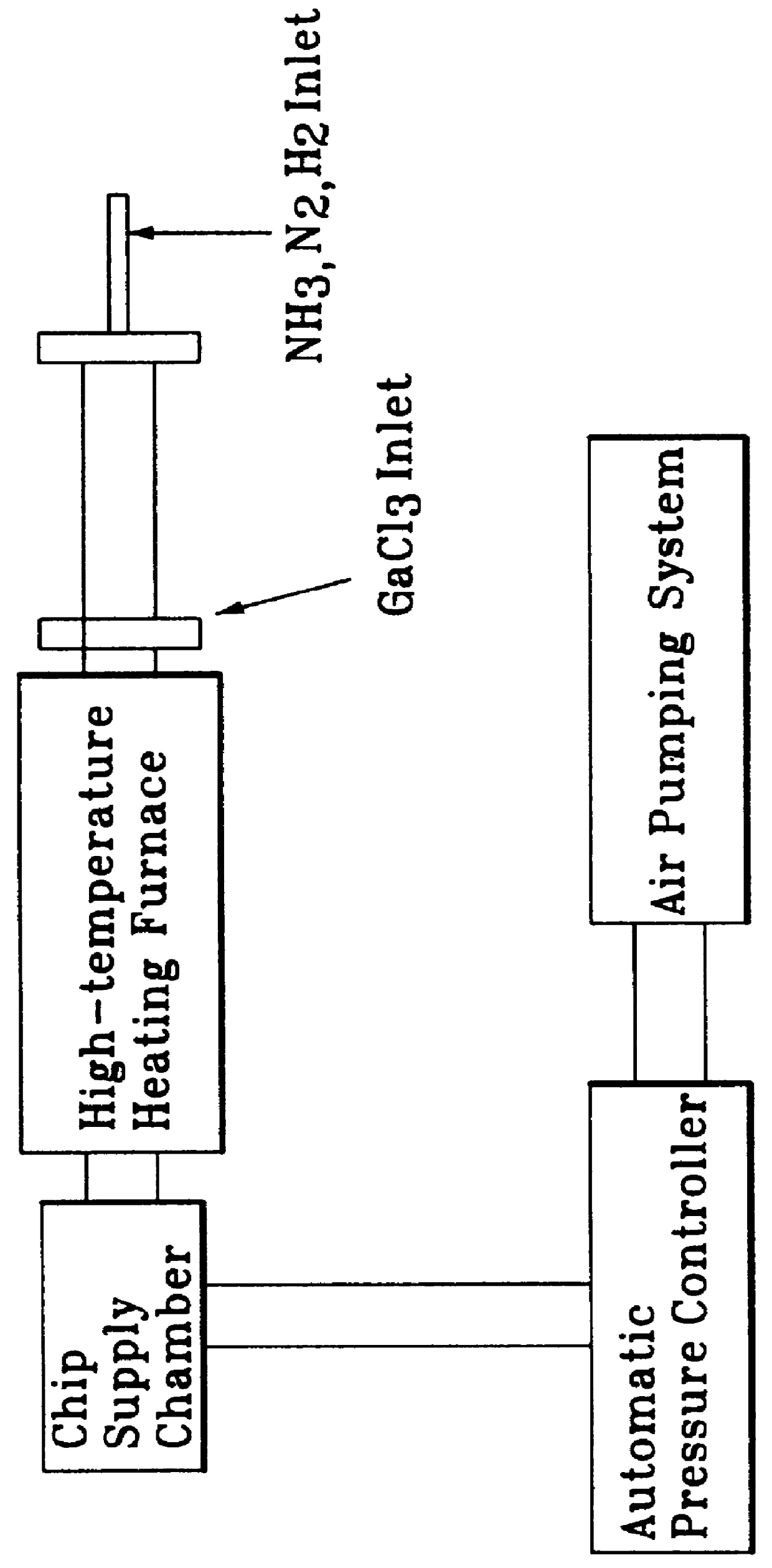
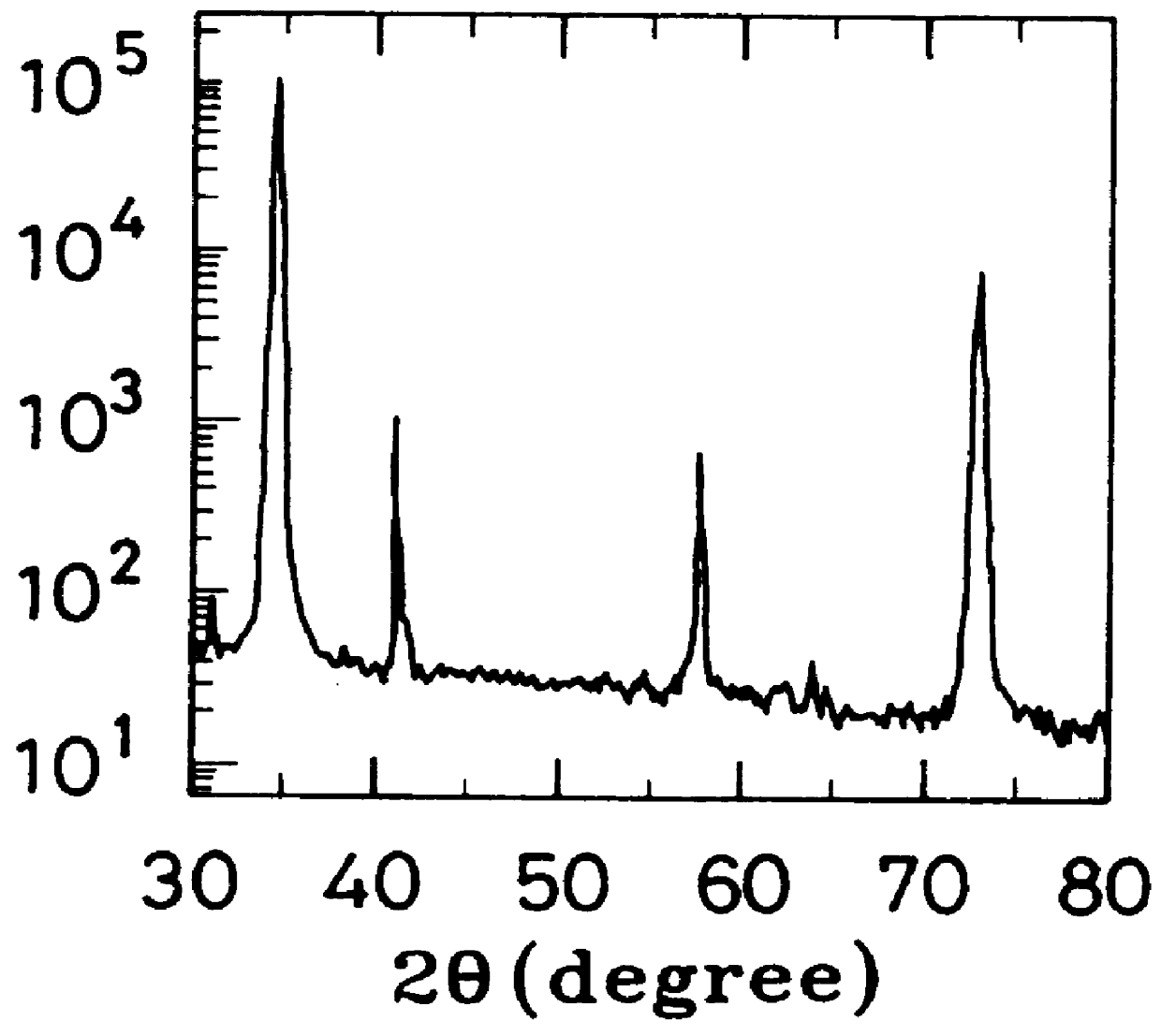
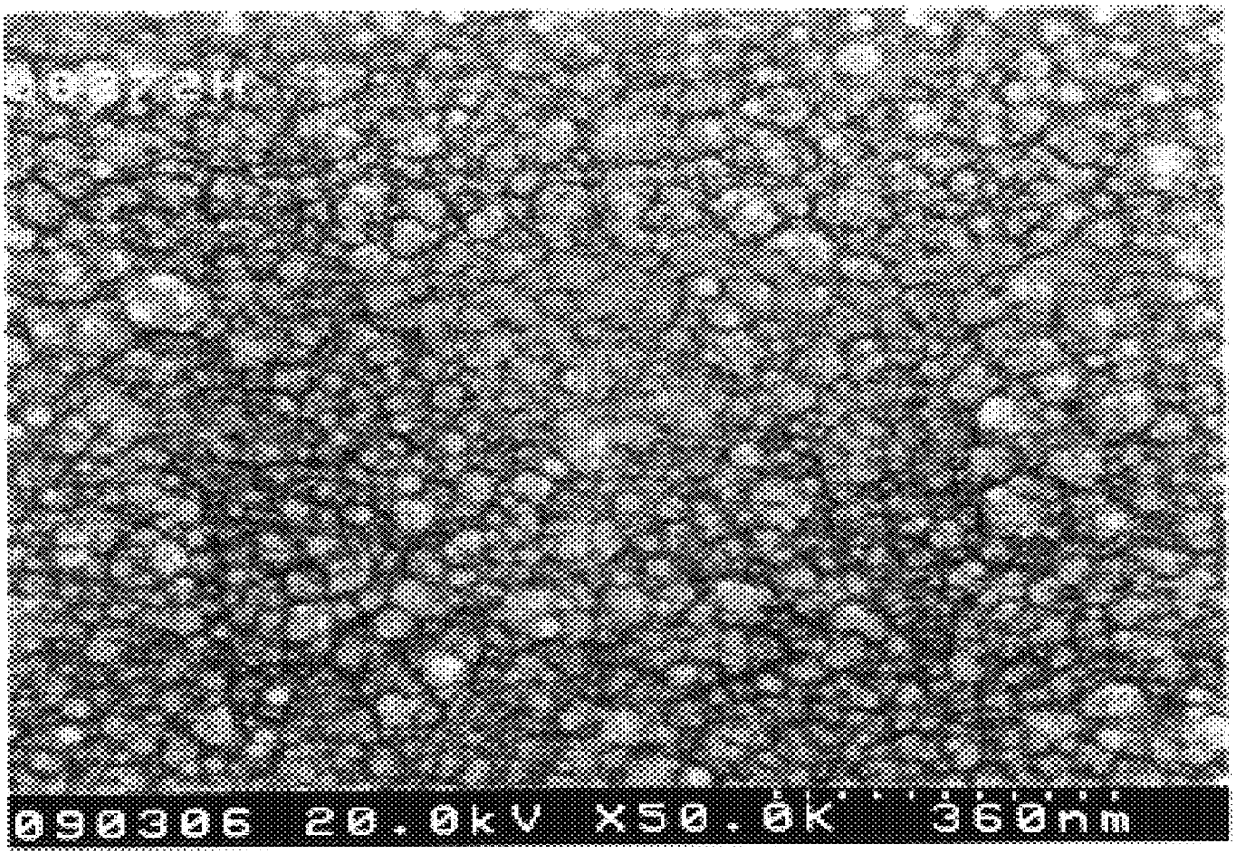
Method for manufacturing an epitaxial wafer with a group III metal nitride epitaxial layer
InactiveUS6110809APolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenNitride
A new method for manufacturing a Group III metal nitride epitaxial wafer comprises providing a first nitrogen-contained gas source, providing a second Group III metal trichloride-containing gas source, and causing said first gas to react with second gas in a heating region, thereby forming a Group III metal nitride epitaxial layer on a substrate. The formed epitaxial wafer can serve as a substrate of a laser diode.
Owner:SZE SIMON M +4
Sic epitaxial wafer and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20120280254A1Improve uniformityQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingStacking fault
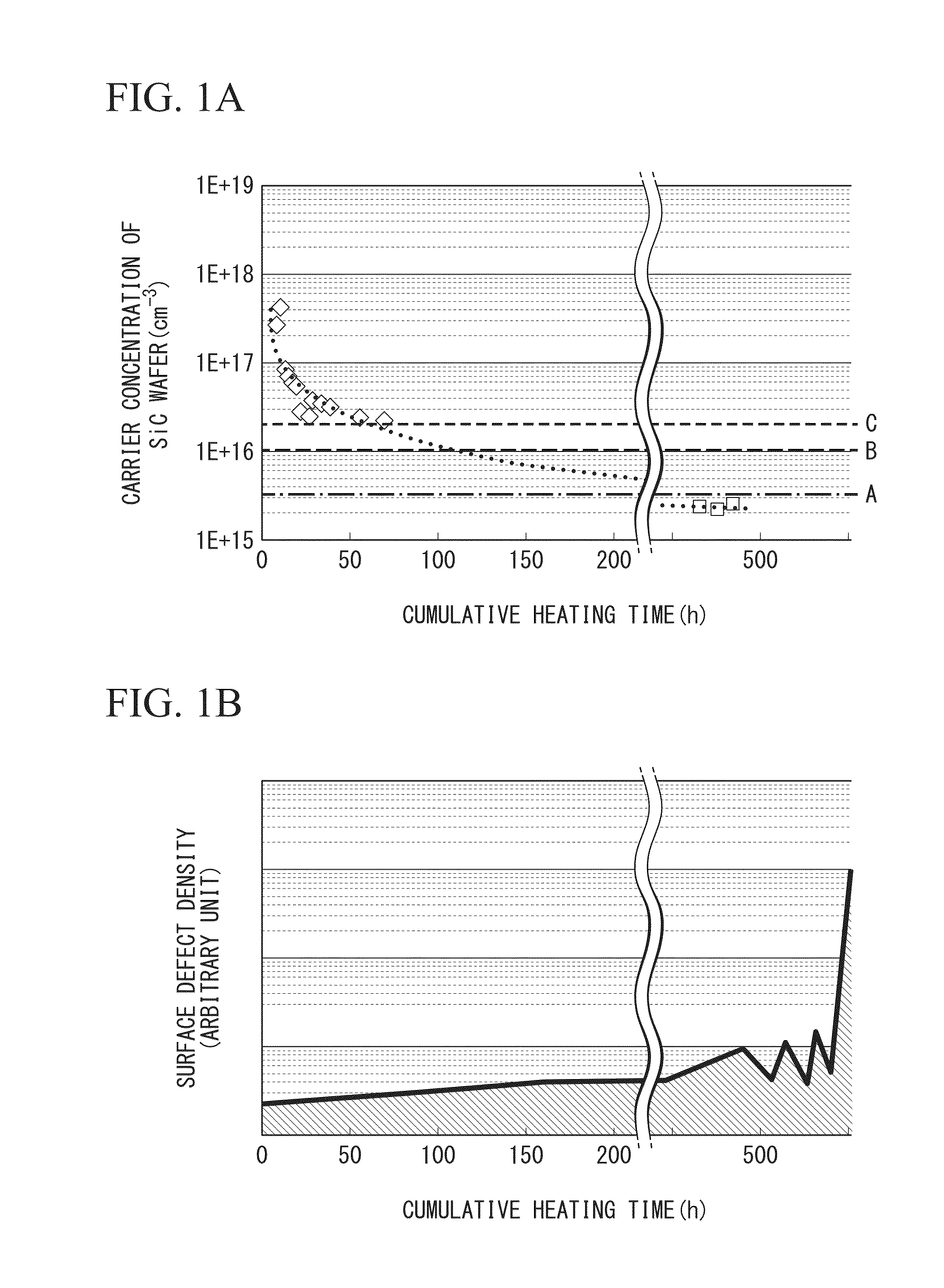
According to the present invention, there is provided an SiC epitaxial wafer which reduces triangular defects and stacking faults, which is highly uniform in carrier concentration and film thickness, and which is free of step bunching, and its method of manufacture. The SiC epitaxial wafer of the present invention is an SiC epitaxial wafer in which an SiC epitaxial layer is formed on a 4H—SiC single crystal substrate that is tilted at an off angle of 0.4°-5°, wherein the density of triangular-shaped defects of said SiC epitaxial layer is 1 defect / cm2 or less.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
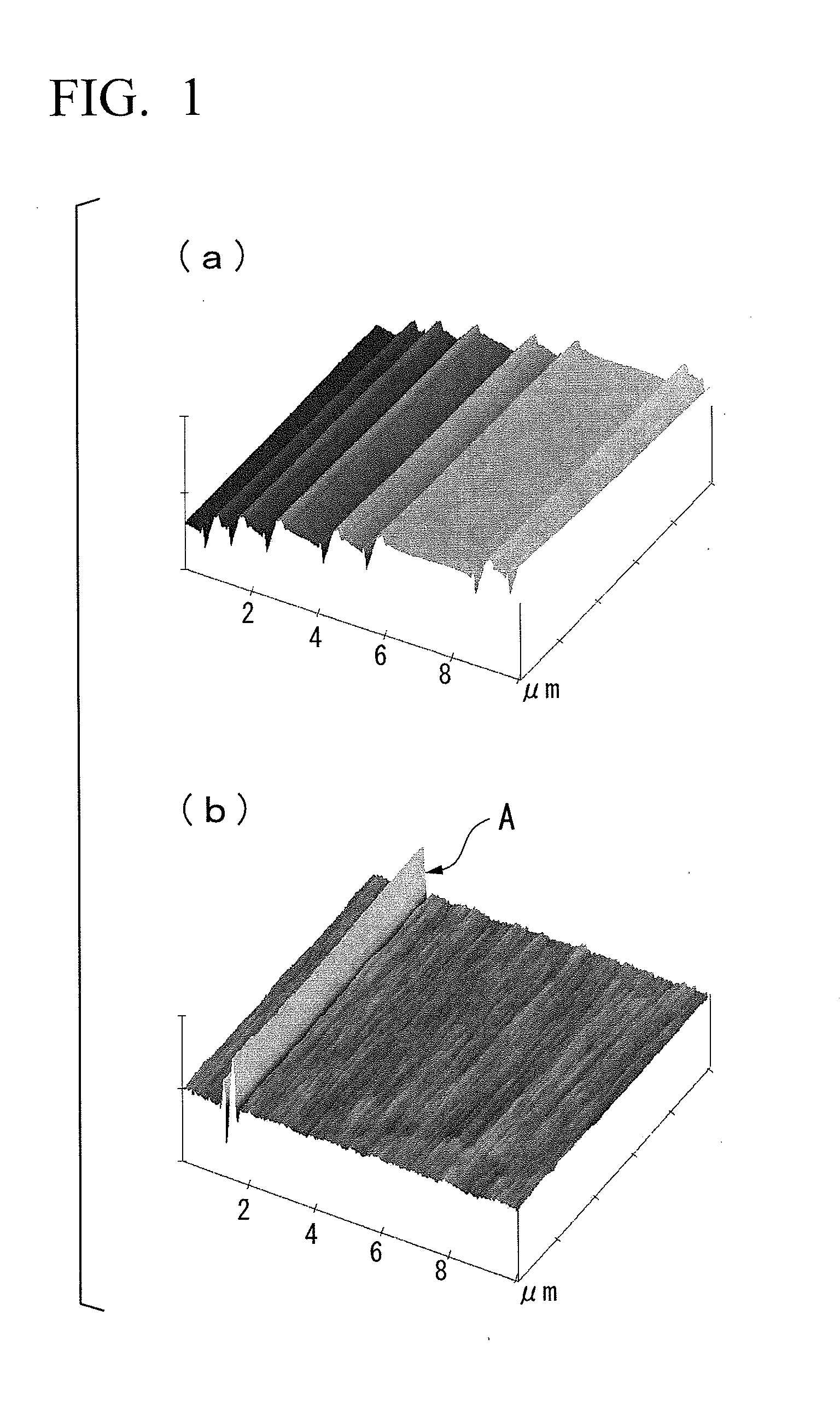
Method of manufacturing epitaxial silicon wafer and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20070227441A1Improve uniformityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorWafering
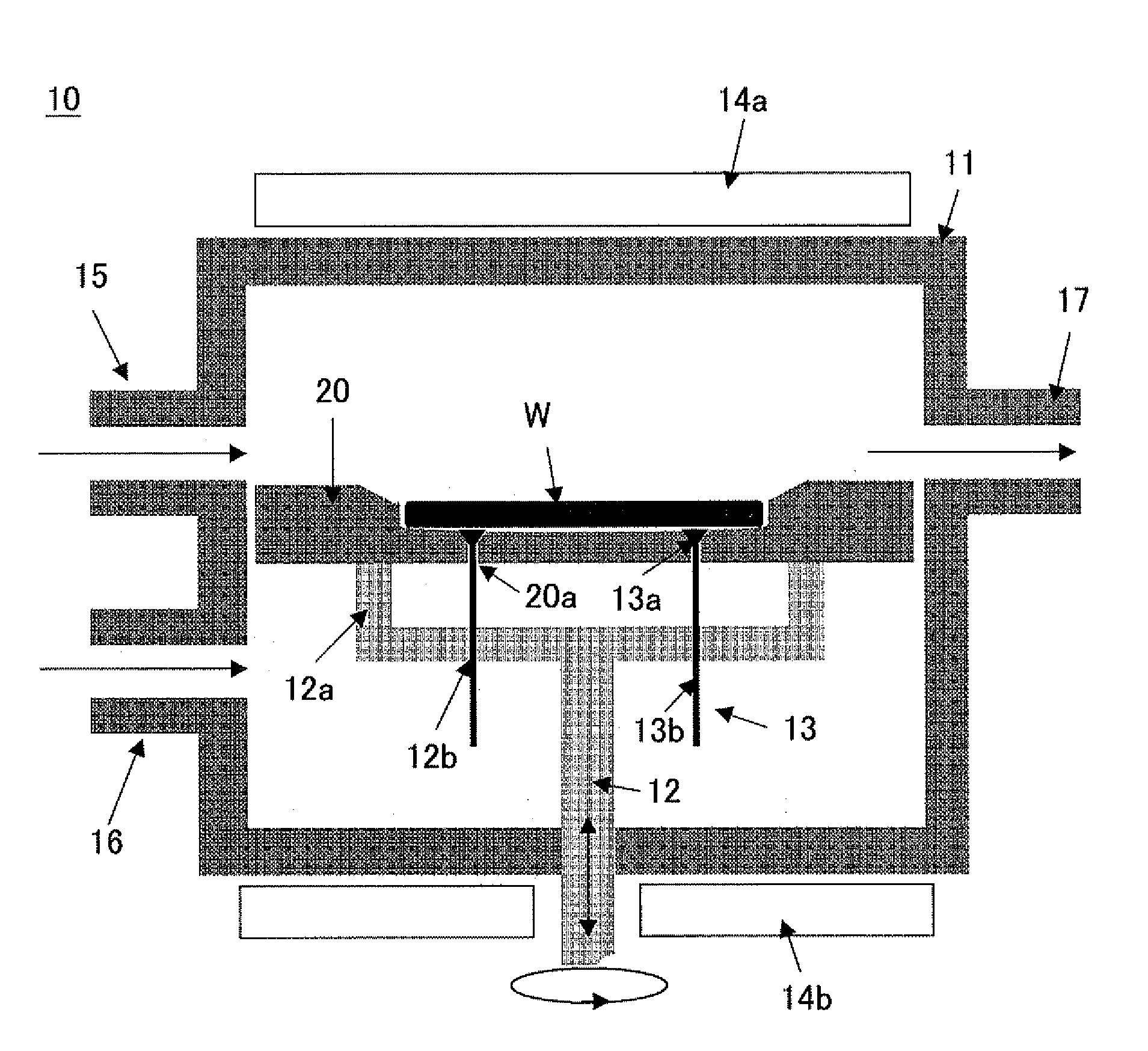
A method of forming an epitaxial layer to increase flatness of an epitaxial silicon wafer is provided. In particular, a method of controlling the epitaxial layer thickness in a peripheral part of the wafer is provided. An apparatus for manufacturing an epitaxial wafer by growing an epitaxial layer with reaction of a semiconductor wafer and a source gas in a reaction furnace comprising: a pocket in which the semiconductor wafer is placed; a susceptor fixing the semiconductor; orientation-dependent control means dependent on a crystal orientation of the semiconductor wafer and / or orientation-independent control means independent from the crystal orientation of the semiconductor wafer, wherein the apparatus may improve flatness in a peripheral part of the epitaxial layer.
Owner:SUMCO TECHXIV
Oxidized low density lipoprotein sensing device for gallium nitride process
InactiveUS7759710B1Detecting the level of protein oxidation in human body quickly, accurately and easilyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCatheterOxidized low density lipoproteinGallium nitride
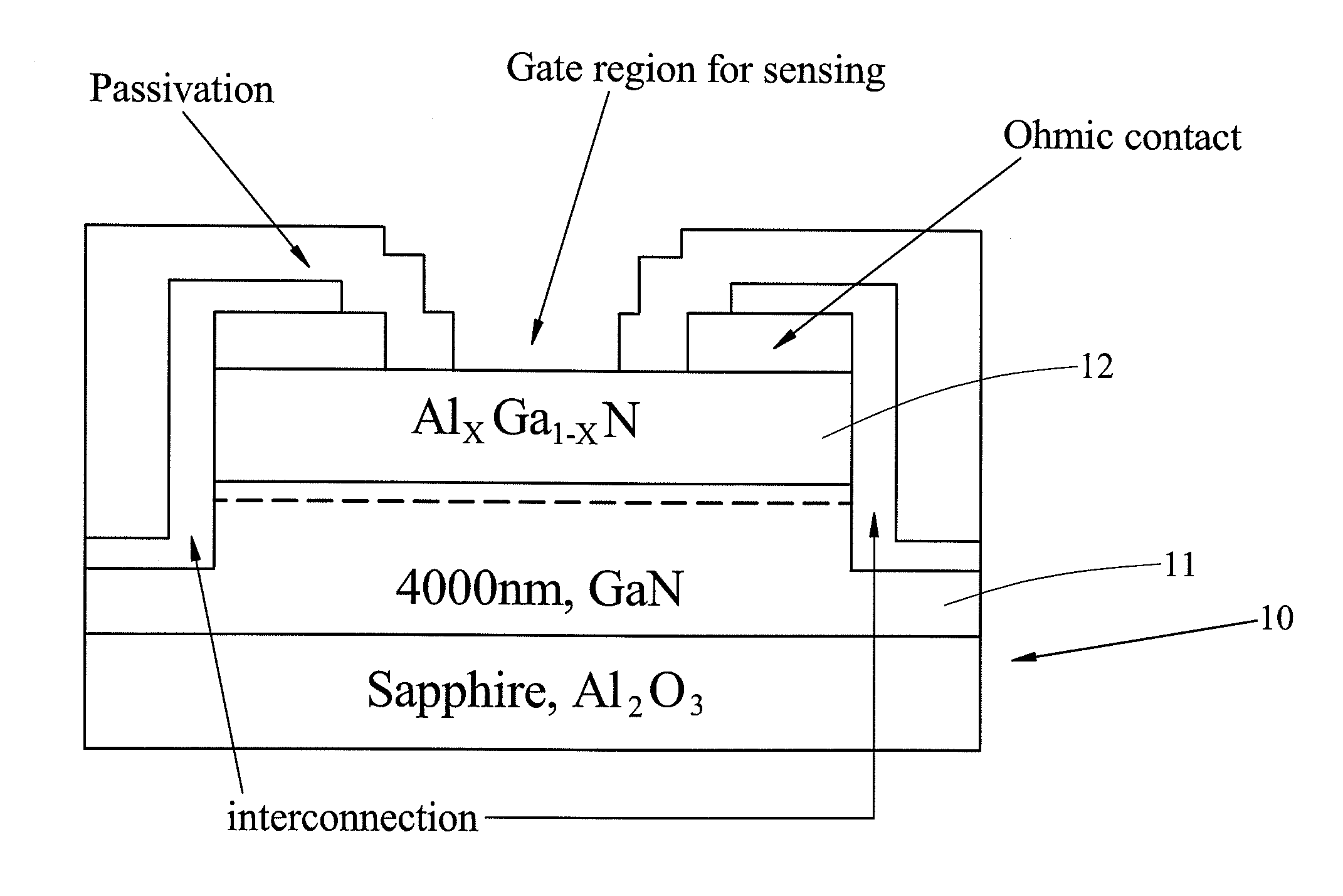
An oxidized low density lipoprotein sensing device for a gallium nitride process is a GaN HEMT device including: a gateless AlGaN / GaN sensing transistor device, a testing window, a source, a drain, two metal connecting wires and a passivation layer. The gateless AlGaN / GaN sensing transistor device has an epitaxial wafer structure including a GaN layer and an aluminum gallium nitride layer. The testing window is disposed on the epitaxial wafer structure. The metal connecting wire is disposed on a source and a drain. The passivation layer is covered onto a surface of the sensing device except the testing window. A built-in piezoelectric field is created by the properties of FET and the polarization effect of AlGaN / GaN to achieve the effect of sensing the level of oxidizing proteins in human body quickly, accurately and easily.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Method for enhancing antistatic ability of GaN-based light-emitting diode
ActiveCN101645480AImprove crystal qualityImprove antistatic performanceSemiconductor devicesGalliumContact layer
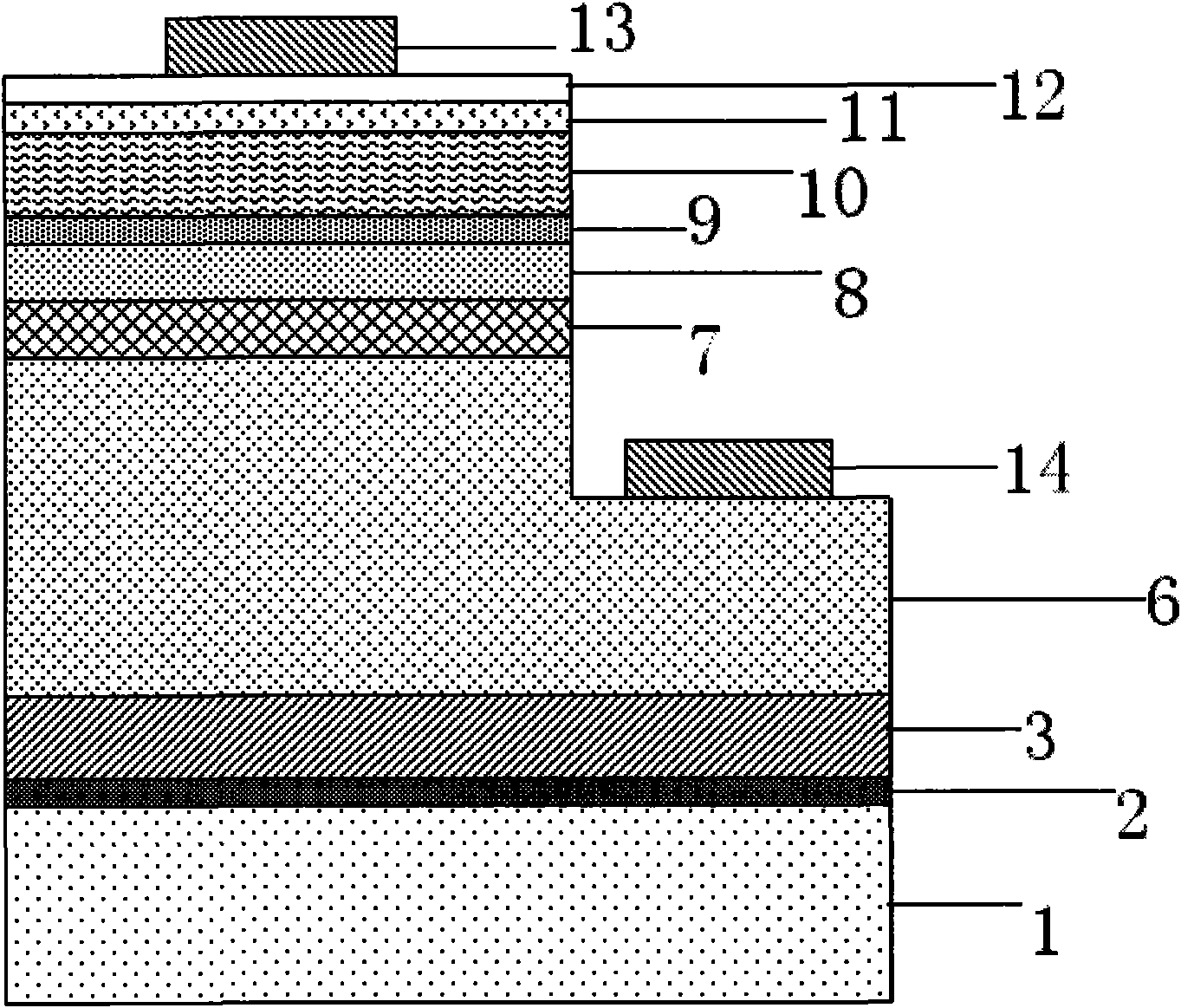
The invention discloses a method for enhancing the antistatic ability of GaN-based light-emitting diode. The epitaxial wafer structure of the light-emitting diode sequentially comprises an underlay, alow-temperature buffer layer, an unadulterated GaN high-temperature buffer layer, an aluminum gallium nitride / GaN superlattice structure, the unadulterated GaN high-temperature buffer layer, an N type contact layer, an N type GaN conductive layer, a light-emitting layer multiple quantum well structure MQW, a P type aluminum gallium nitride electric barrier layer, a P type GaN conductive layer and a P type contact layer in a sequence from down to up. In the invention, the aluminum gallium nitride / GaN superlattice periodic structure is inserted in the unalloyed GaN high temperature buffer layer. The insertion of the aluminum gallium nitride / GaN superlattice periodic structure can effectively improve crystal quality of materials, thereby enhancing the antistatic ability of the GaN-based light-emitting diode and improving the reliability and the stability of devices.
Owner:HC SEMITEK CORP
Methods of processing of gallium nitride
InactiveUS7015117B2Polycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateThermal energyElectrical conductor
A method for improving thermal dissipation in large gallium nitride light emitting diodes includes replacing sapphire with a better thermal conductor resulting in more efficient removal of thermal energy. A method for achieving a reliable and strong temporary bond between a GaN epitaxial layer and a support wafer. A method for transferring an epitaxial film from a growth substrate to a secondary substrate. An excimer laser initiates film delamination from the growth substrate. The laser beam is shaped by a shadow mask and aligned to an existing pattern in the growth substrate. A method for fabricating a LED that radiates white spectrum light. A phosphor that radiates a white spectrum after excitation in the blue or UV spectrum onto the GaN epitaxial wafer prior to die separation and packaging. A method for depositing a metal substrate onto a GaN epitaxy layer.
Owner:ALLEGIS TECH
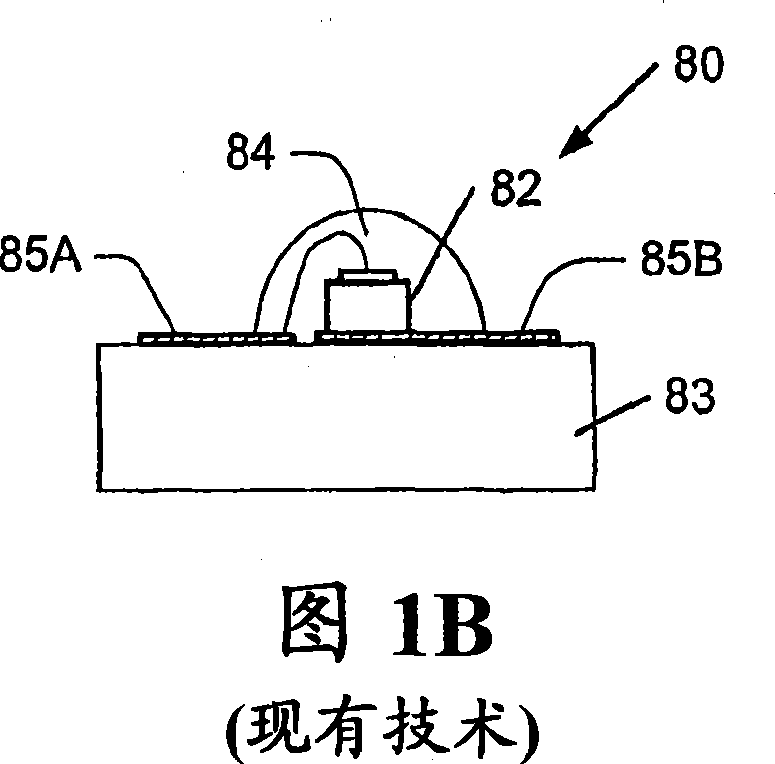
Chip-scale methods for packaging light emitting devices and chip-scale packaged light emitting devices
InactiveCN101032034AImprove reliabilityEasy to handleSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLight-emitting diodeLight emitting device
A packaged light emitting device includes a carrier substrate having a top surface and a bottom surface, first and second conductive vias extending from the top surface of the substrate to the bottom surface of the substrate, and a bond pad on the top surface of the substrate in electrical contact with the first conductive via. A diode having first and second electrodes is mounted on the bond pad with the first electrode is in electrical contact with the bond pad. A passivation layer is formed on the diode, exposing the second electrode of the diode. A conductive trace is formed on the top surface of the carrier substrate in electrical contact with the second conductive via and the second electrode. The conductive trace is on and extends across the passivation layer to contact the second electrode. Methods of packaging light emitting devices include providing an epiwafer including a growth substrate and an epitaxial structure on the growth substrate, bonding a carrier substrate to the epitaxial structure of the epiwafer, forming a plurality of conductive vias through the carrier substrate, defining a plurality of isolated diodes in the epitaxial structure, and electrically connecting at least one conductive via to respective ones of the plurality of isolated diodes.
Owner:CREE INC
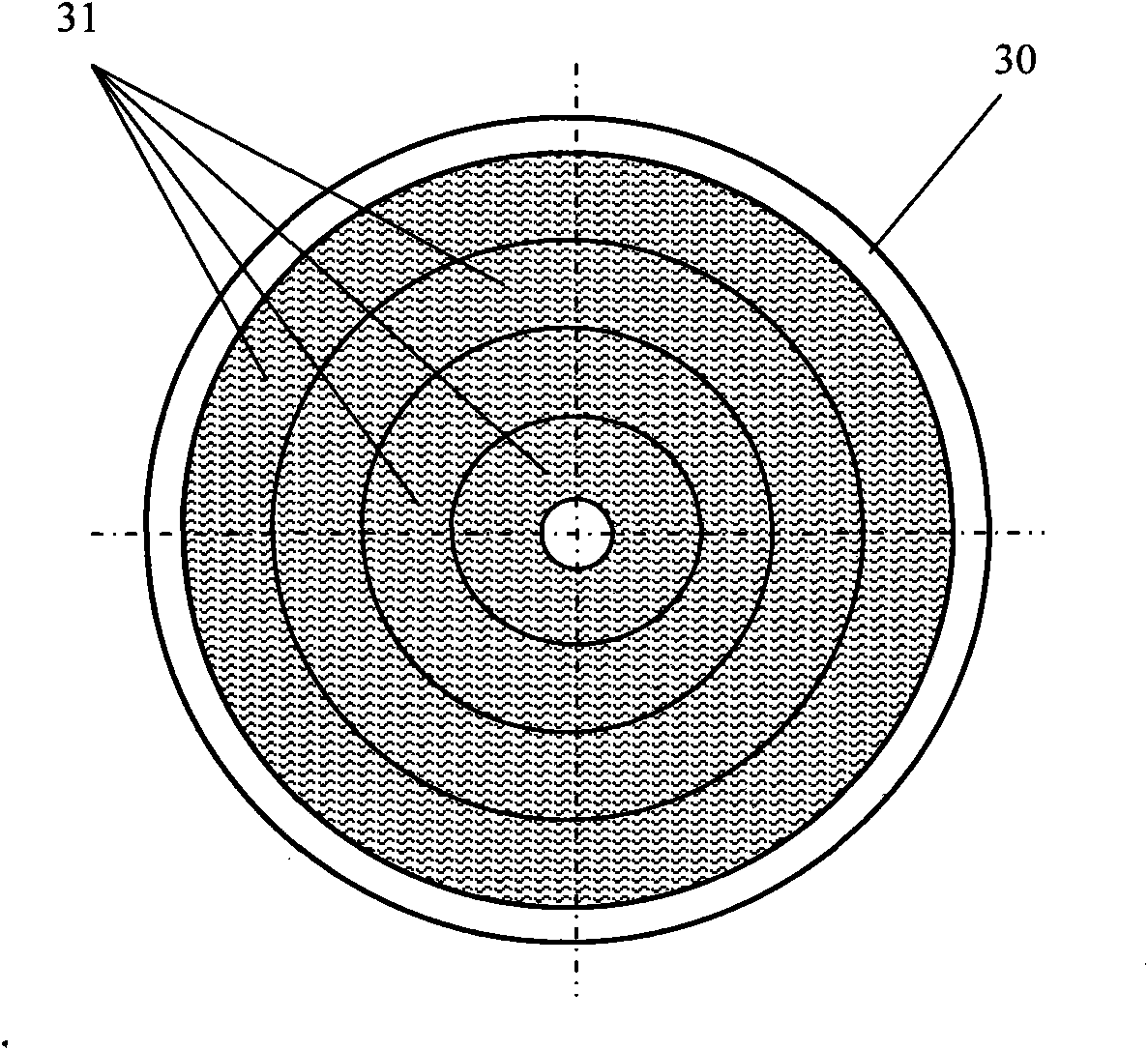
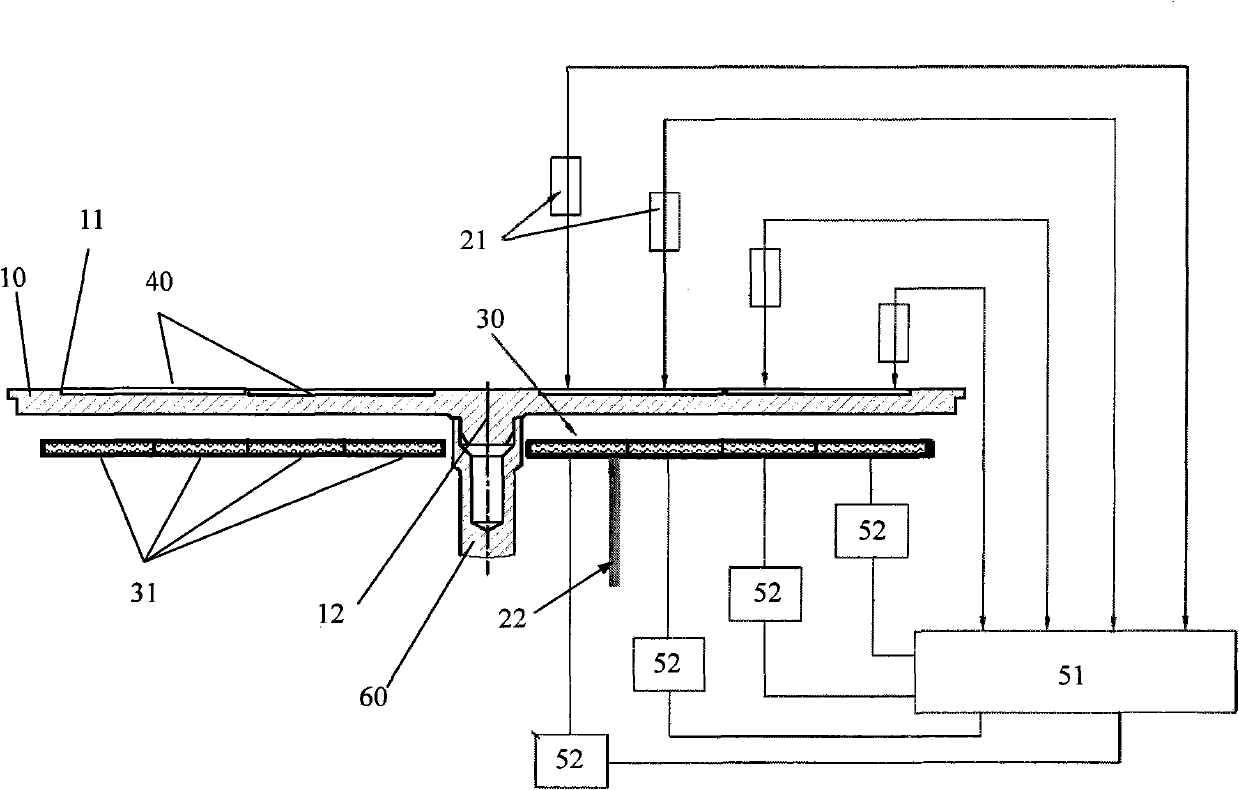
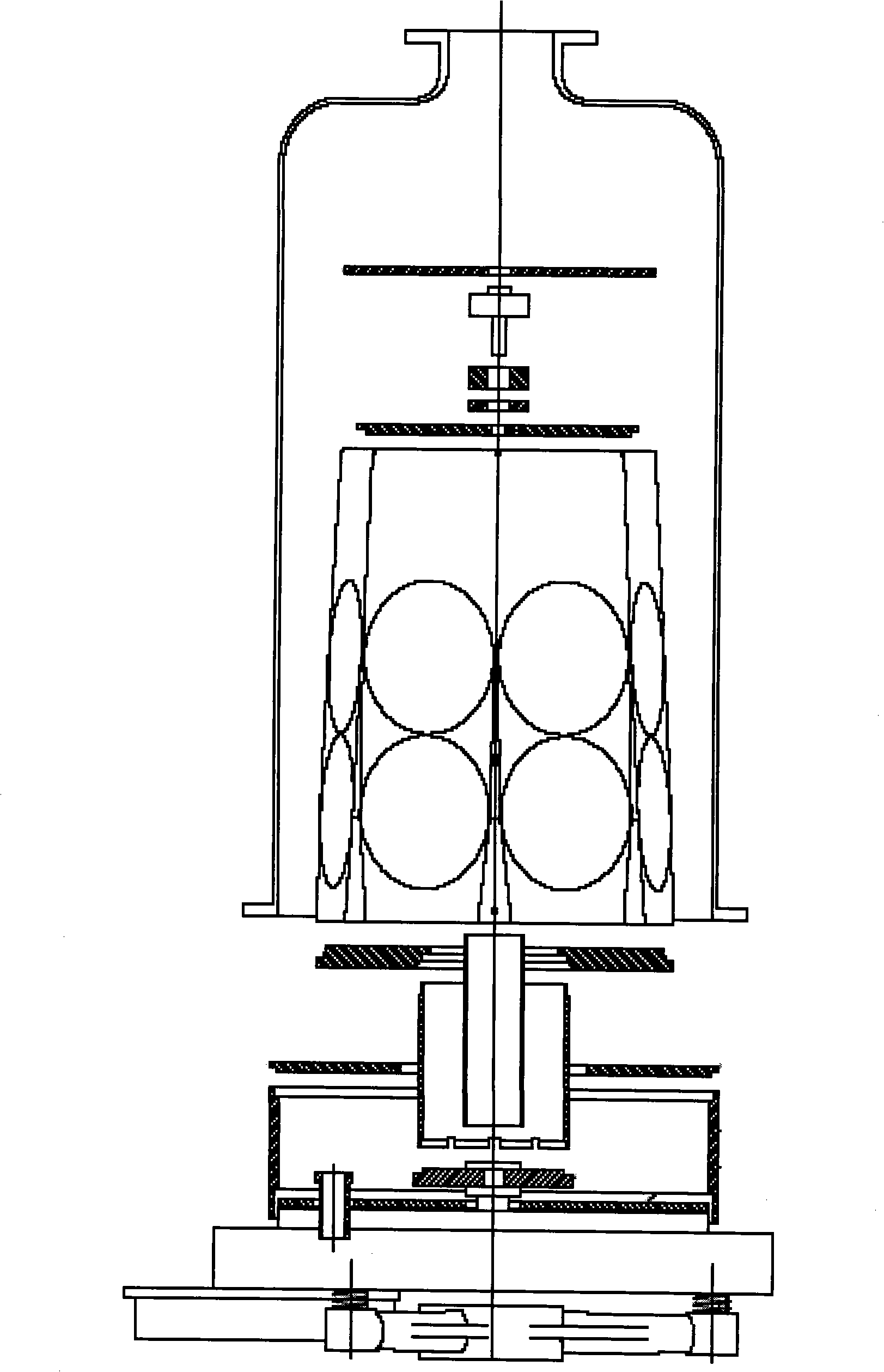
Device and method for controlling temperature and uniformity of epitaxial wafers in MOCVD system
ActiveCN101906622AGuaranteed accuracyAccurate measurementChemical vapor deposition coatingTemperature controlHeat losses
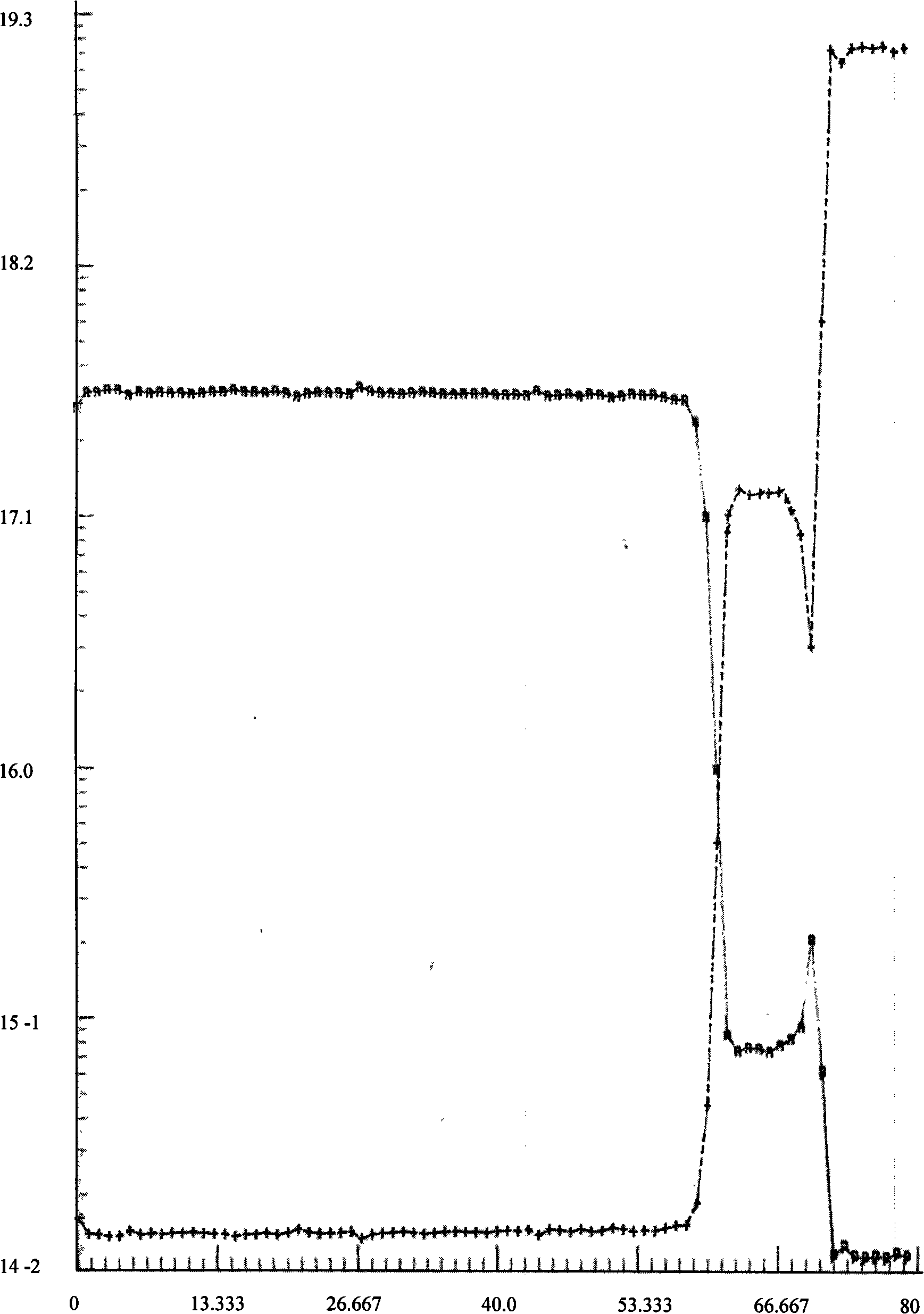
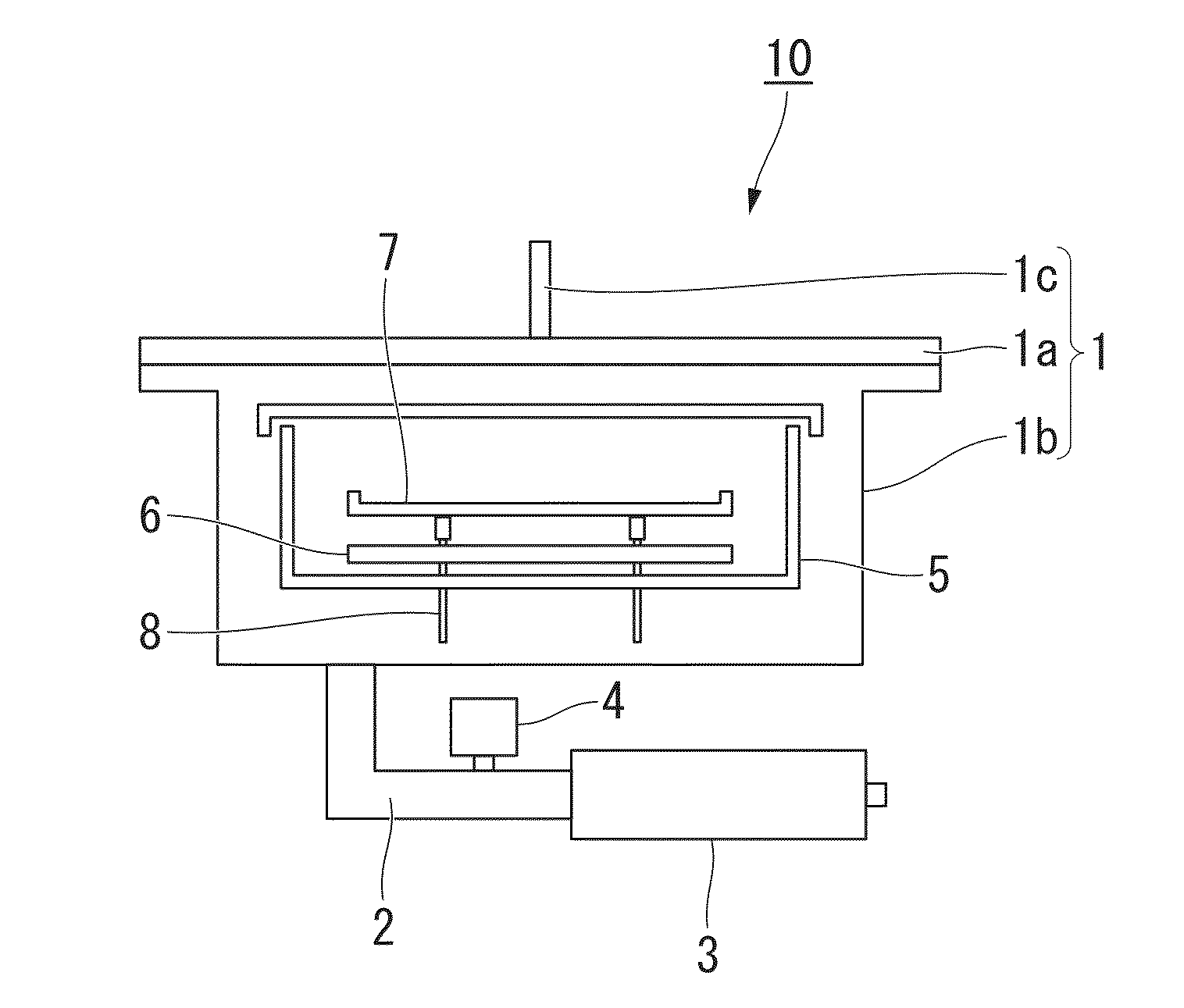
The invention discloses a device for controlling temperature and uniformity of epitaxial wafers in an MOCVD (metal organometallic chemistry vapor deposition) system. A group of non-contact optical thermometers is arranged above a tray along the radial direction to feed back the temperature of single or a plurality of epitaxial wafers in a plurality of annular areas. A temperature controller independently controls the power output of a plurality of heating elements below the tray by using difference minimization of a statistical average value of the temperatures of the epitaxial wafers and an epitaxial process specified temperature as a target. The plurality of epitaxial wafers in each annular area are correspondingly heated by using one or more lower adjacent heating elements which are arranged annularly and have small radial coverage area so as to effectively balance the radial heat loss of the epitaxial wafers and the tray under the process condition of different temperatures and realize accurate and stable control of the temperature and the uniformly between the single epitaxial wafers and the adjacent epitaxial wafers. The device is also provided with a contact thermocouple thermometer for measuring a heater temperature serving as a reference point of the epitaxial process specified temperature and meanwhile monitoring whether the heater works normally.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGSHENG SEMICON EQUIP
Method for improving LED external quantum efficiency
ActiveCN101521258AImprove yieldImprove light extraction efficiencySemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyLight emission
The invention discloses a method for improving the LED external quantum efficiency. The growth mode of a P-shaped layer in an LED epitaxial wafer structure adopts the following novel coarsening method: improving the doping concentration of Mg in the P-shaped layer so as to reach the effect of coarsening the surface of the epitaxial wafer. The coarsened layer can be any layer or any multiple layersin the P-shaped composite layer, or a certain area in a certain layer. The method not only ensures a higher hole concentration, but also provides a coarsened surface. The LED surface coarsened layercan change the direction of light rays meeting a total reflection law, break down the total reflection of the light rays inside the LED, improve the light emission efficiency, and consequently improvethe external quantum efficiency.
Owner:HC SEMITEK SUZHOU
SiC epitaxial wafer and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN102656297AImprove uniformityImprove stabilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingSingle crystal substrate
Disclosed is an SiC epitaxial wafer, which has reduced triangular defects and lamination defects, high carrier concentration uniformity and high film thickness uniformity, and is step-bunching-free. Also disclosed is a method for manufacturing the wafer. In the SiC epitaxial wafer, an SiC epitaxial layer is formed on a 4H-SiC single crystal substrate which is tilted by an off-angle of 0.4-5 DEG. The defect density of the triangular defects on the surface of the SiC epitaxial layer is 1 defect / cm2 or less.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Method of recycling a delaminated wafer and a silicon wafer used for the recycling
InactiveUS20010029072A1Easy to disassembleImprove surface roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateHydrogen
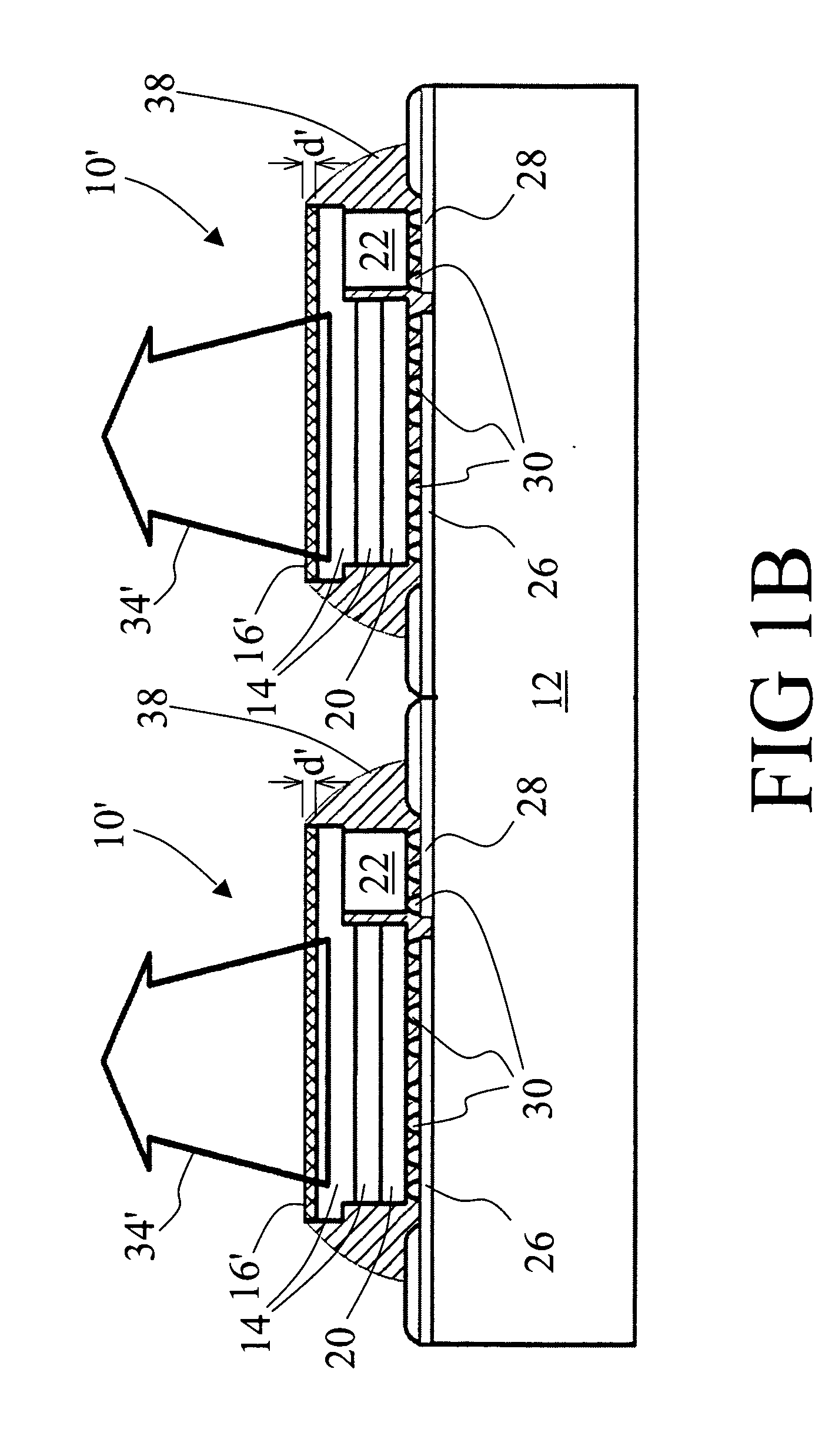
There is disclosed a method of recycling a delaminated wafer produced as a by-product in producing an SOI wafer according to a hydrogen ion delaminating method by reprocessing it for reuse as a silicon wafer, wherein at least polishing of the delaminated wafer for removing of a step in the peripheral part of the delaminated wafer and heat treatment in a reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen are conducted as the reprocessing. There are provided a method of appropriately reprocessing a delaminated wafer produced as a by-product in a hydrogen ion delaminating method to reuse it as a silicon wafer actually, and particularly, a method of reprocessing an expensive wafer such as an epitaxial wafer many times for reuse, to improve productivity of SOI wafer having a high quality SOI layer, and to reduce producing cost.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Method and system for magnetically assisted statistical assembly of wafers
InactiveUS20030186469A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectretDielectric layer
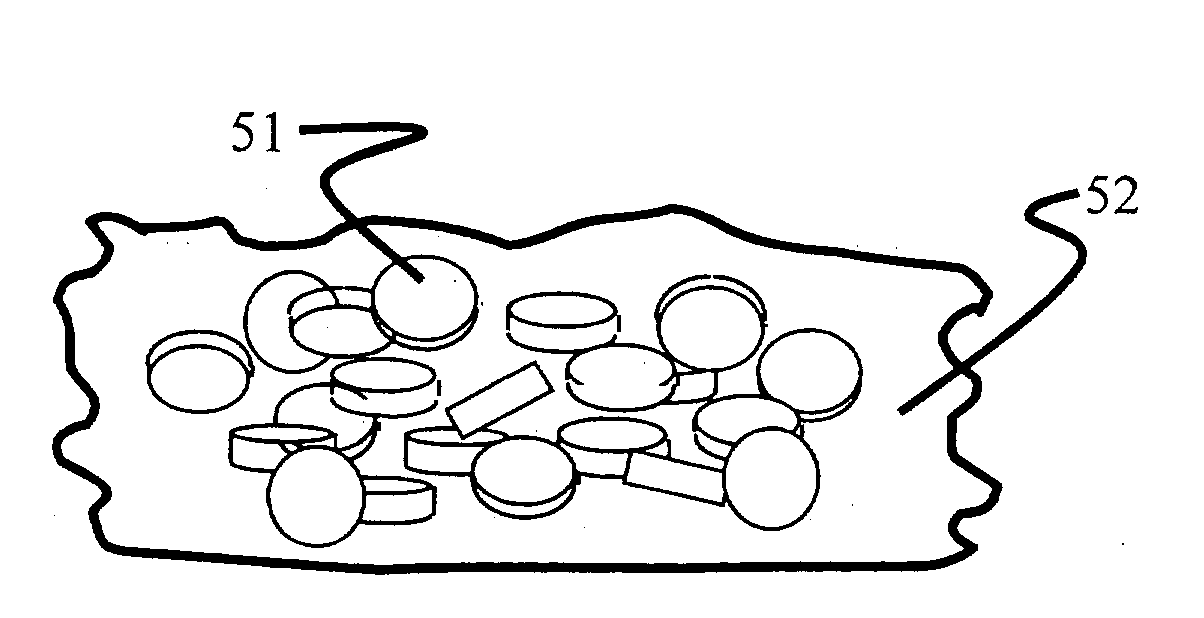
A wafer having heterostructure therein is formed using a substrate with recesses formed within a dielectric layer. A magnetized magnetic layer or a polarized electret material is formed at the bottom of each recess. The magnetized magnetic layer or a polarized electret material provides a predetermined magnetic or electrical field pattern. A plurality of heterostructures is formed from on an epitaxial wafer wherein each heterostructure has formed thereon a non-magnetized magnetic layer that is attracted to the magnetized magnetic layer formed at the bottom of each recess or dielectric layer that is attracted to the polarized electret material formed at the bottom of each recess. The plurality of heterostructures is etched from the epitaxial wafer to form a plurality of heterostructure pills. The plurality of heterostructure pills is slurried over the surface of the dielectric layer so that individual heterostructure pills can fall into a recess and be retained therein due to the strong short-range magnetic or electrical attractive force between the magnetized magnetic layer in the recess and the non-magnetized magnetic layer on the heterostructure pill or between the polarized electret material in the recess and the dielectric on the heterostructure pill. Any excess heterostructure pills that are not retained in a recess formed within the dielectric layer are removed and an overcoat is applied to form a substantial planar surface.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
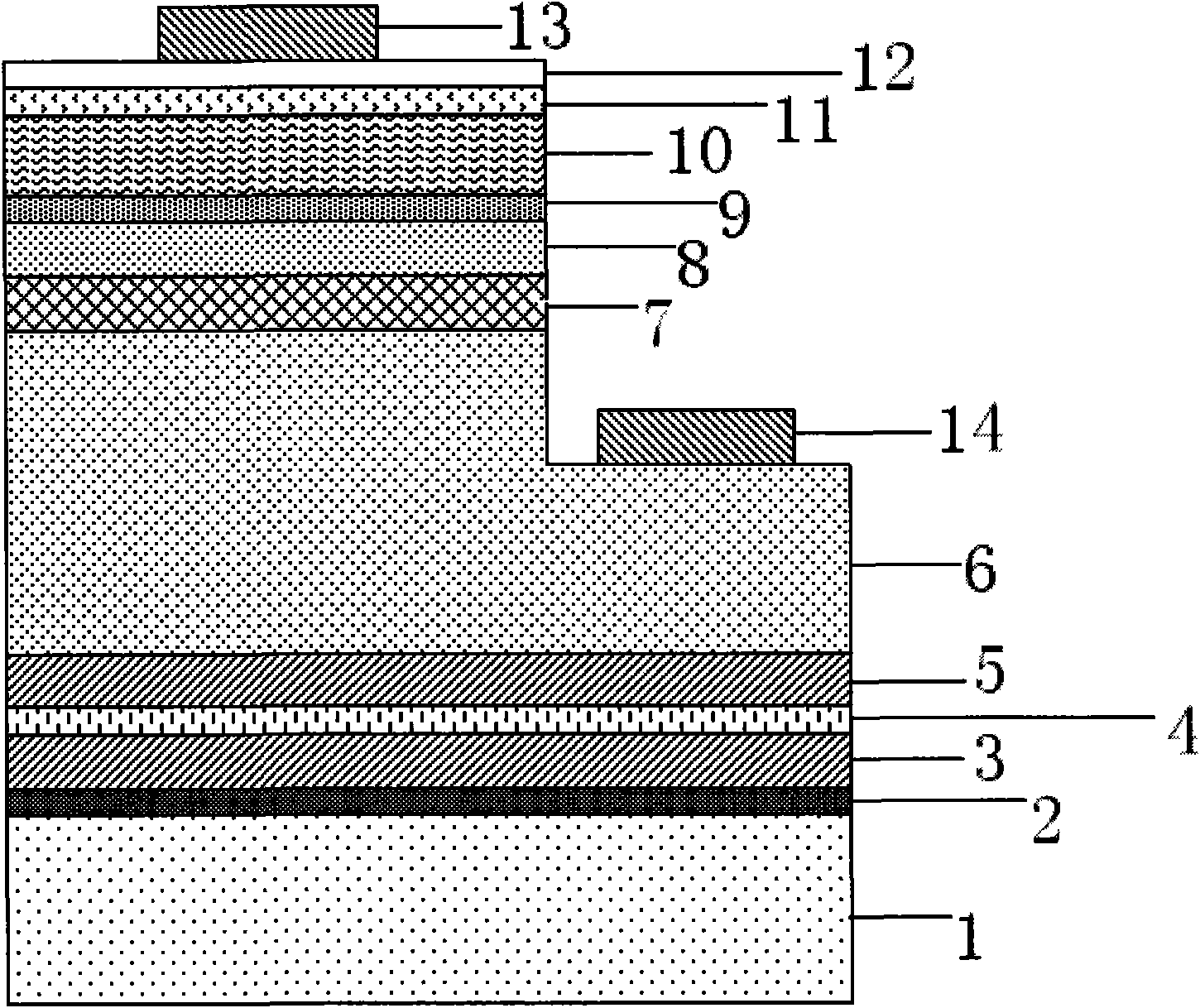
Single-mode high-power vertical cavity surface emitting laser and manufacturing method thereof
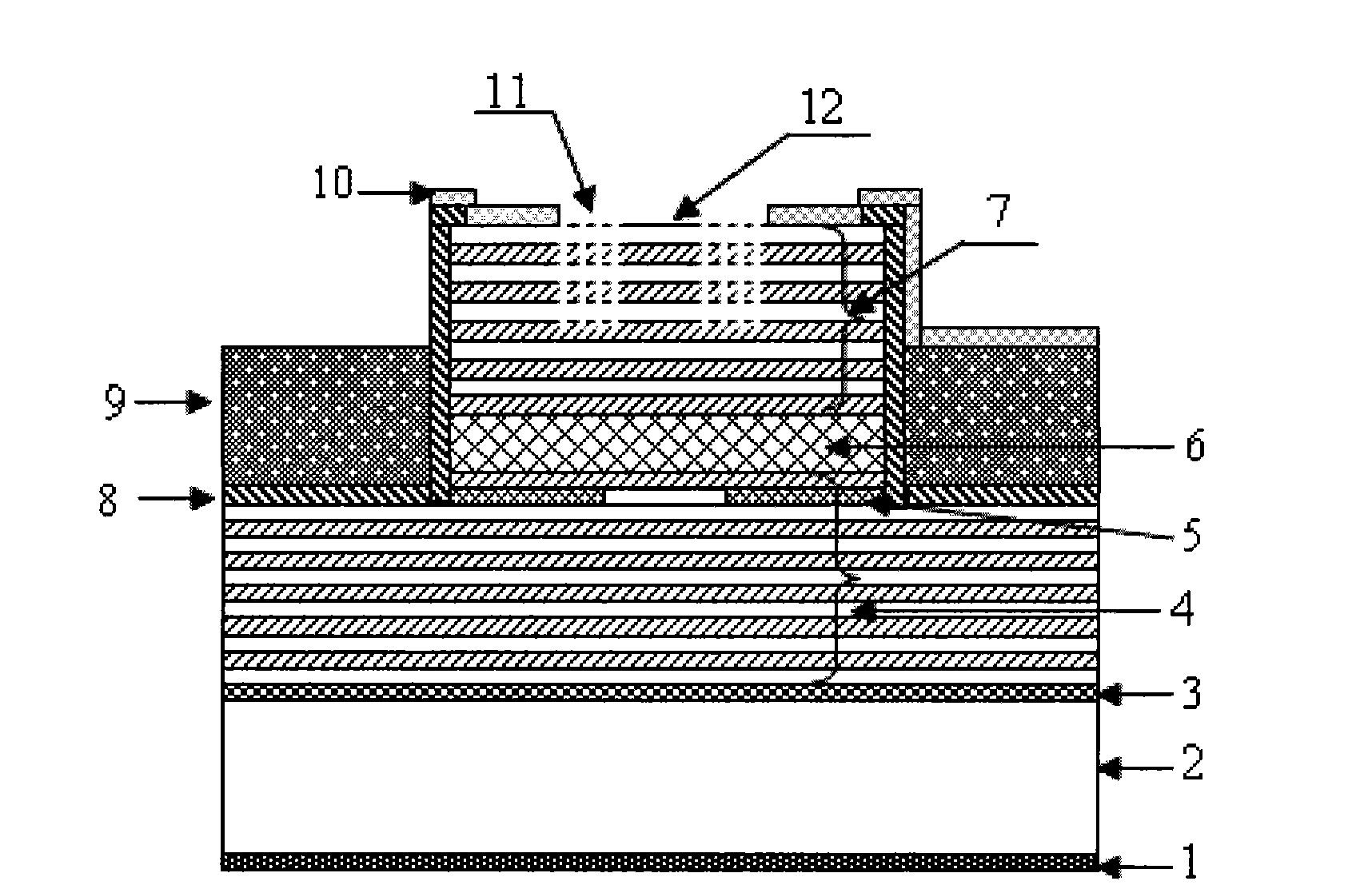
ActiveCN101667715AIncrease output powerImprove thermal propertiesLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserElectron
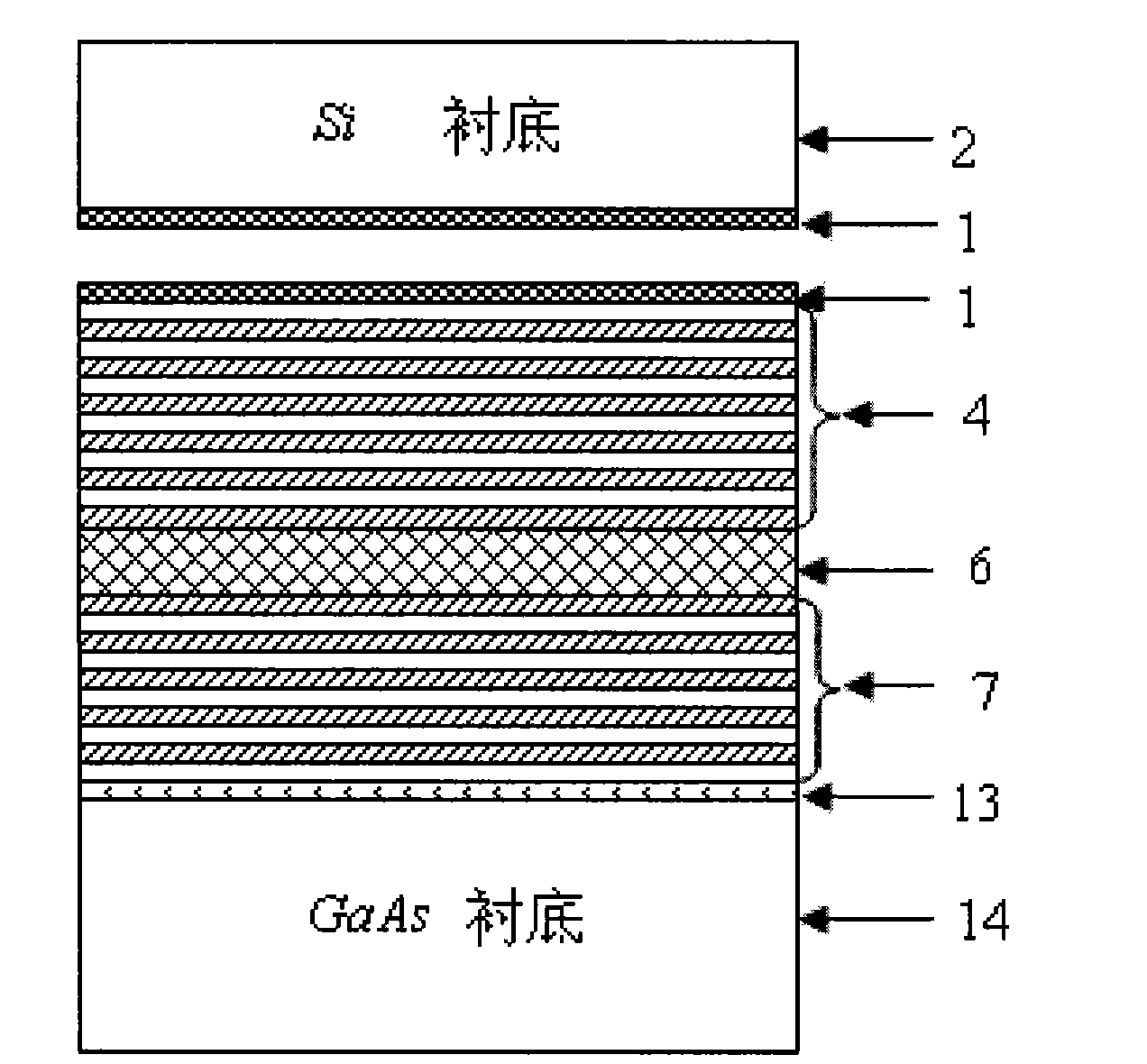
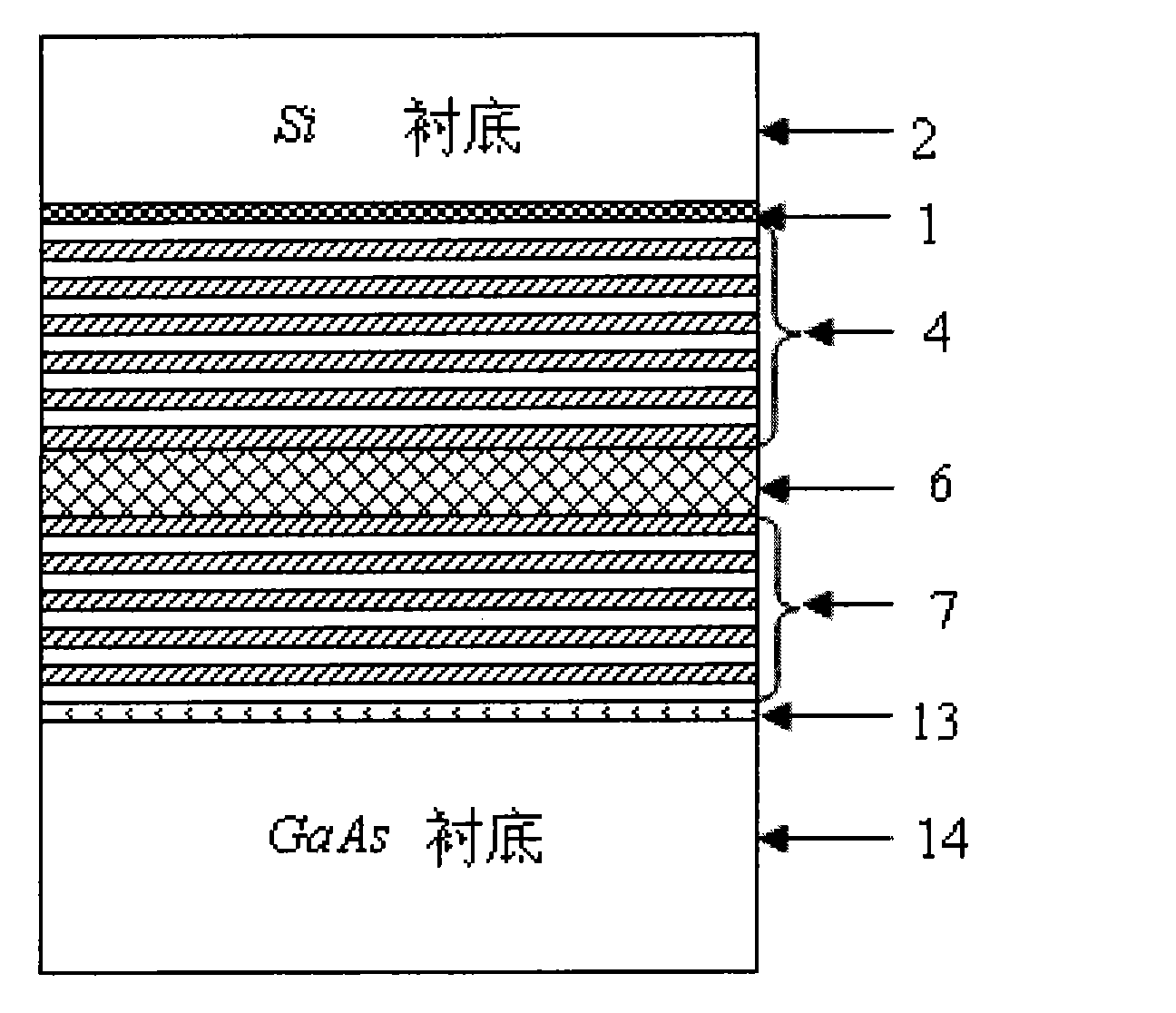
The invention relates to a single-mode high-power vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL), which belongs to the field of semiconductor photoelectronics. The laser is characterized by comprisinga P-type electrode (1), a P-type Si substrate (2), a metal bonding layer (3), a P-type distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) (4), an oxide limiting layer (5), an active area (6), an N-type DBR (7), a SiO2 mask (8), polymide or benzocyclobutene (BCB) (9), an N electrode (10), a photonic crystal (11) and a light-exiting window (12). The introduction of the photonic crystal into the vertical cavity surface emitting laser with the structure can enlarge an oxidation aperture and improve the single-mode output power; and at the same time, the transfer of the conventional VCSEL epitaxial wafer to the Sisubstrate by adopting bonding technology and the adoption of a design of exiting light at the bottom are convenient for narrowing the distance between a VCSEL epitaxial wafer active area and the Si substrate, improving the thermal characteristics of devices and further improving the single-mode output power.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device for controlling delivery and uniform distribution of reaction gases in MOCVD reaction chamber
ActiveCN101914761AReduce manufacturing costControl consumptionChemical vapor deposition coatingSystem capacityEngineering
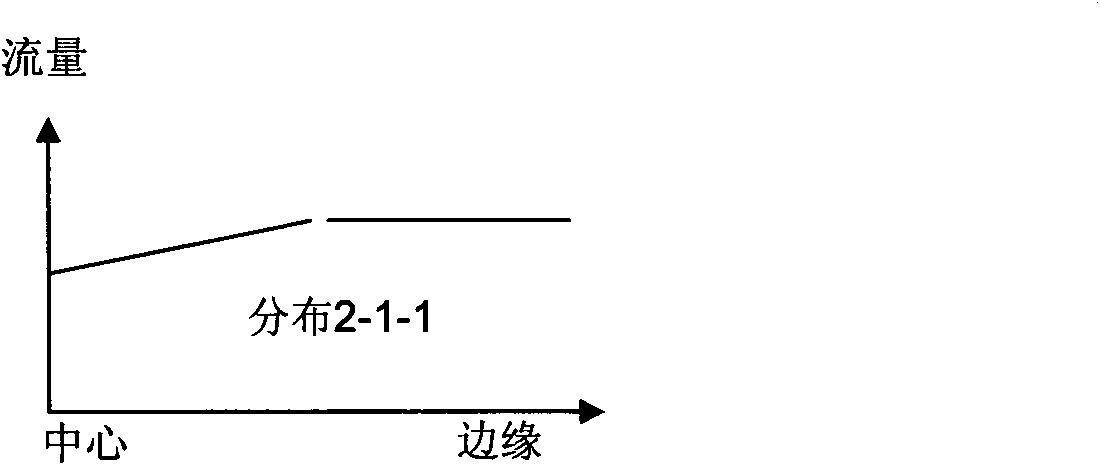
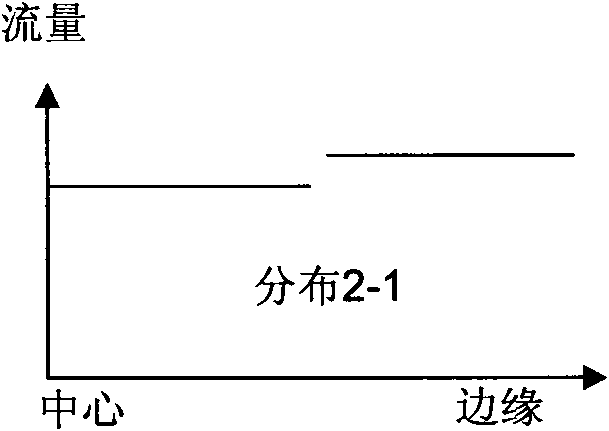
The invention discloses a device for controlling the delivery and the uniform distribution of reaction gas in a MOCVD reaction chamber. By respectively controlling the flow of gas passages non-uniformly distributed radially on a front gas homogenizing plate and input passages at different positions, at least two reaction gases are respectively introduced into two paths which are radially and axially crossed on a spray header, and can be secondarily distributed by nozzles in different shapes, so the uniformly distributed boundary layer concentration, speed and temperature required are achieved on the surface of a rotary epitaxial wafer, the quality of massively produced epitaxial films and the finished product ratio of massively produced epitaxial wafers are improved, the consumption of expensive reaction gases can be effectively controlled and the epitaxial production cost is reduced. By properly increasing the distance between the surface of the spray header and the epitaxial wafer, deposits generated on the surface of the spray header and the nozzles in the epitaxial growth are reduced, the cleaning period is prolonged, and the production efficiency and system capacity are improved. The device also can reduce the processing difficulty and manufacturing cost of the nozzles of the spray header and cooling medium passages.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGSHENG SEMICON EQUIP
Method for enhancing luminous efficiency of multiquantum well of semiconductor diode
ActiveCN102368519AImprove crystal qualityBlock pass chanceSemiconductor devicesElectron holeQuantum well
The invention discloses a method for enhancing the luminous efficiency of a multiquantum well of a semiconductor diode. A novel gradient growth method is adopted as a multiquantum well growth manner of an epitaxial wafer structure of a light emitting diode; in the multiquantum well structure, InGaN components in the first several periods are gradually increased, so that the stress generated in the growth process of suddenly transferring GaN to InGaN with high In components is eased, and thus the polarization effect is reduced, the crystal quality of the quantum well is improved, and the compounding possibility is increased. In addition, the thicknesses of barrier layers in the first several periods are gradually reduced, the speed of electrons and the traversing possibility of electrons can be reduced by the barrier layers with larger thickness, the traversing possibility of electron holes can be increased by the barrier layers with smaller thickness, so that the electrons and the electron holes are distributed more uniformly and the problem of the reduced efficiency under high current injection is avoided, and therefore the luminous efficiency of the multiquantum well is improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
Gallium nitride based LED chip and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1738066AReduce thermal resistanceImprove cooling effectSemiconductor devicesContact layerGallium nitride
The invention discloses a gallium nitride light-emitting diode and its manufacturing method. Wherein, the light-emitting active region 3, P contact layer 4, P contact electrode 6 discrete array are arranged on the N contact layer 2; the N contact electrode 7 is arranged as net structure; by face-down bonding technique and the welded material protruded block 13 of tube corn supporter, the P electrode thickened metallic layer 9 is connected to the contact electrode layer 12 of P region and the N electrode thickened reflective metallic layer 14 is connected to the contact electrode layer 15 of N region; the contact electrode layer 12 of P region and the contact electrode layer 15 of N region are arranged on the isolated layer 11 which is over the substrate 10 of tube corn supporter. First, processing the epitaxial sheet of gallium nitride light-emitting diode into the body of tube corn; then, forming the tube corn supporter on the substrate of tube corn supporter; at last, connecting the body of tube corn with the tube corn supporter by the technique of face-down bonding. Said invention can improve the luminous efficiency, the diffusion of current, and increase the heat conductance.
Owner:东莞市福地电子材料有限公司
Method for manufacturing IGBT silicon epitaxial wafer
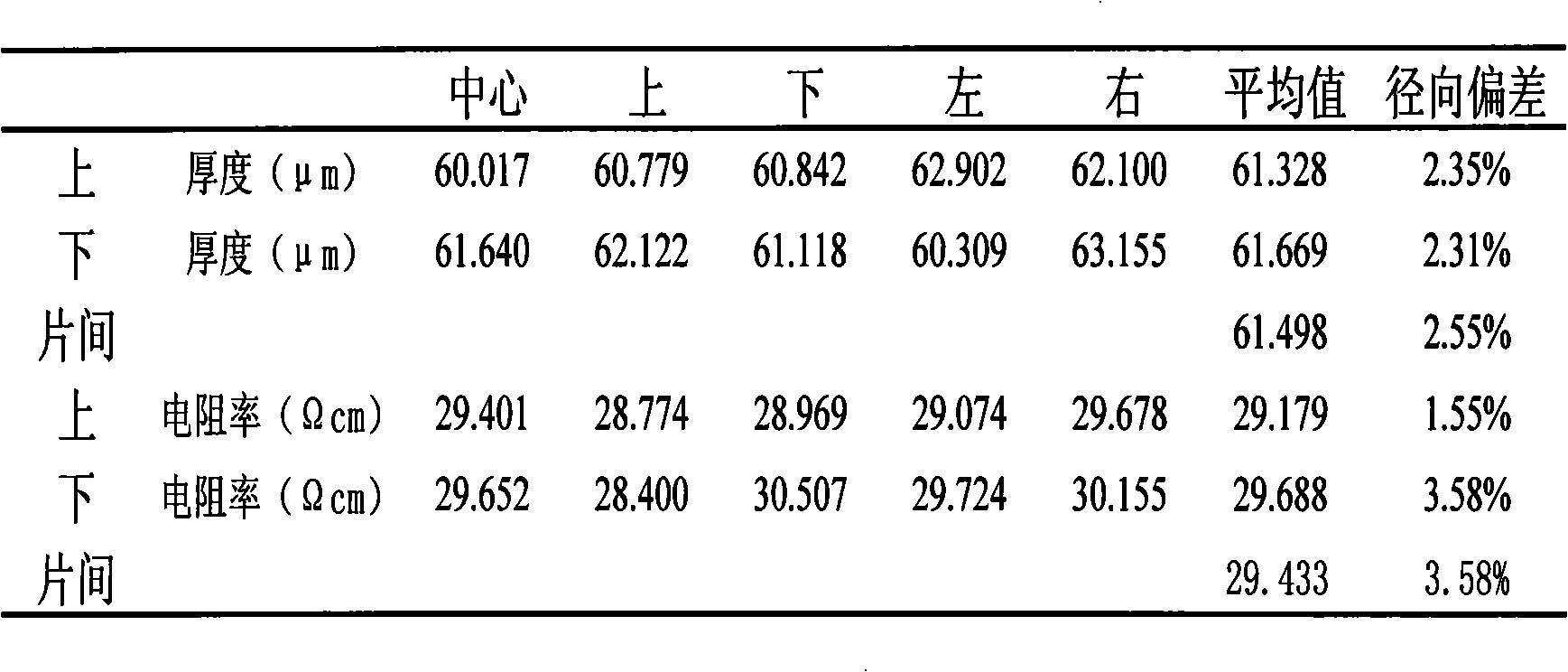
ActiveCN101256958AImprove uniformityGood repeatabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGrowth controlBoron
The present invention discloses a manufacturing method of IGBT silicon epitaxial wafer, the selecting P type of the heavily Boron-doped & 1t; 100 &g t; the polished piece, the electrical resistivity <= 0.02 Omega cm, the partial flatness <= 1.5 mm, the backing layer of oxide at side edge without the width <= 1mm; appropriate increasing polished time and improving the technique temperature, selecting appropriate HC1 flow quantity 8-10L at 1180 EDG C, polishing time 10 min, sweeping more than 10min by using high flow rate H2 after polishing; synthetic considering factors such as self-doping, crystal lattice quality, electric resistivity control and production efficiency, etc, selecting appropriate epitaxial process condition with double-layer, silicon source using ultra-pure trichlorosilane, first step developing temperature 1080-1100 EDG C, developing rate-controlling 0.8-1.0 Mu m, second step developing temperature 1120-1150 EDG C, developing rate-controlling 1.2-1.6 Mu m, the double-layer epitaxial growth controlled by different adulterate source accurately.
Owner:NANJING GUOSHENG ELECTRONICS
Epitaxial slice cleaning device for LED lamp production
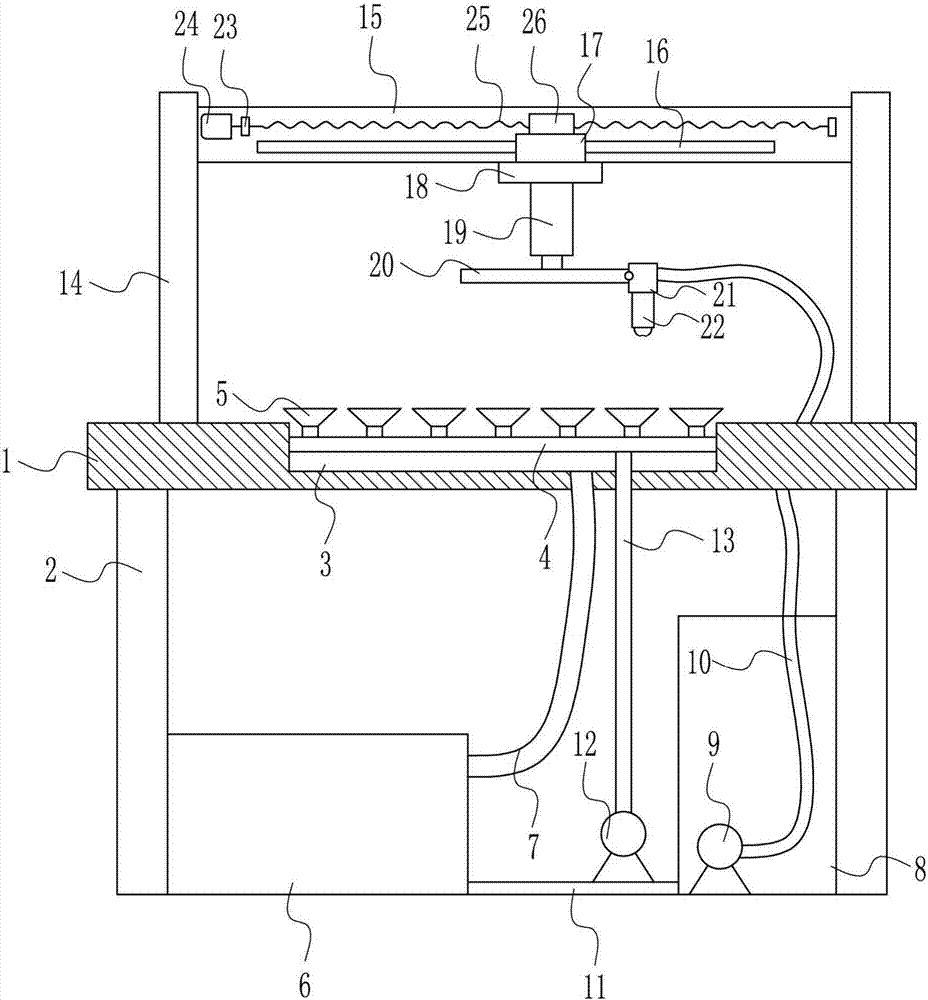
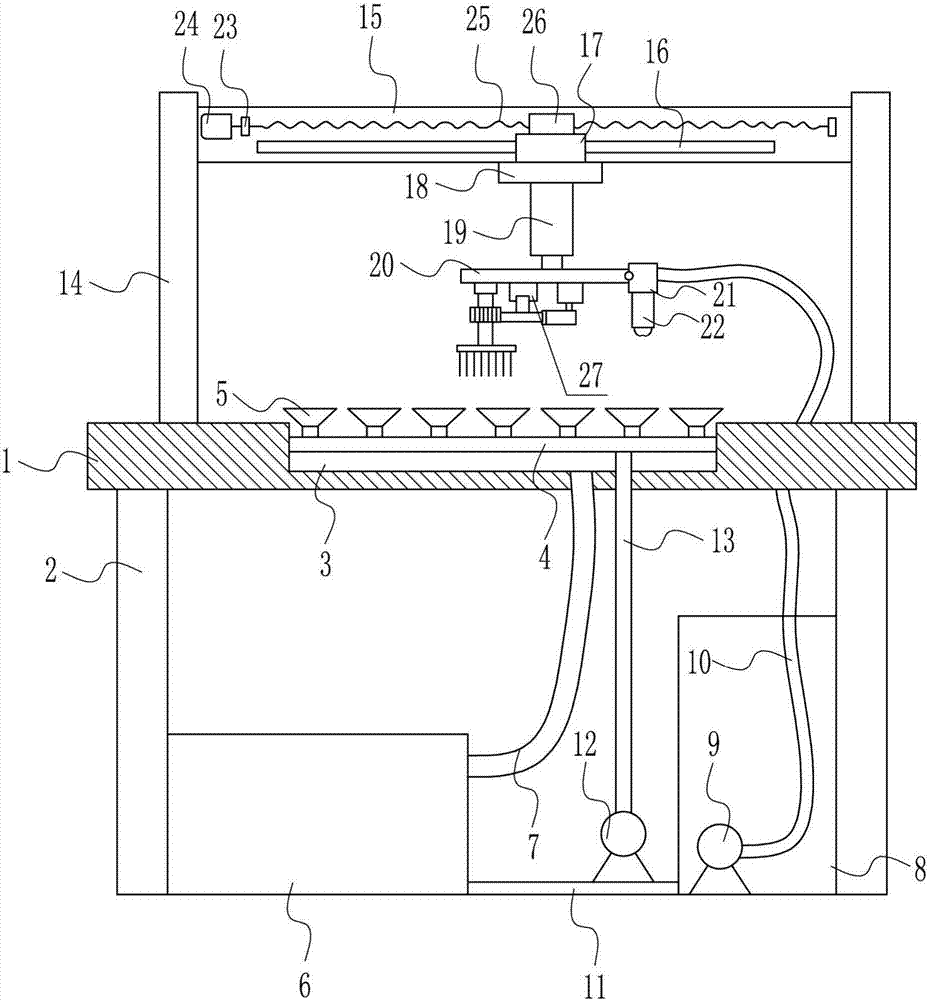
InactiveCN106964588APrevent splashExpand the spraying areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using toolsRefluxEngineering
The invention relates to an LED lamp production device, in particular to an epitaxial slice cleaning device for LED lamp production. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide the epitaxial slice cleaning device for LED lamp production capable of saving both time and labors, improving the cleaning efficiency and protecting the health of workers. In order to solve the technical problem, the invention provides the epitaxial slice cleaning device for LED lamp production. The device comprises a worktable tabletop, support legs, a first air pipe, a vacuum sucker, a recovery water tank, a reflux water pipe, a solution tank, a water pump, a water outlet pipe, a support plate, a vacuum pump and the like; and the support legs are connected to the bottom of the worktable tabletop through a bolt connecting mode. A nozzle sprays out cleaning solution, and moves left and right to once clean more epitaxial slices, so that the effect of saving both time and labors is achieved, and the cleaning efficiency can be improved.
Owner:冯晓栋
LED (light emitting diode) epitaxy structure and preparation method thereof
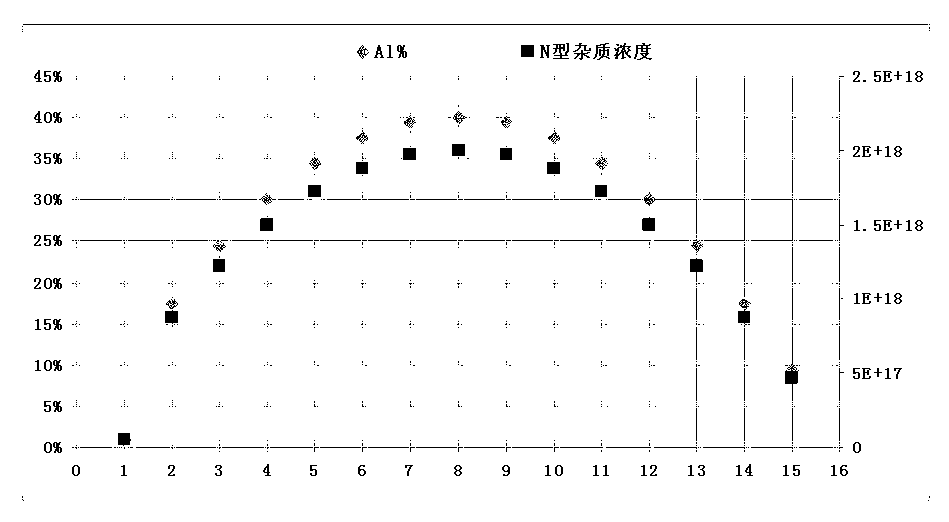
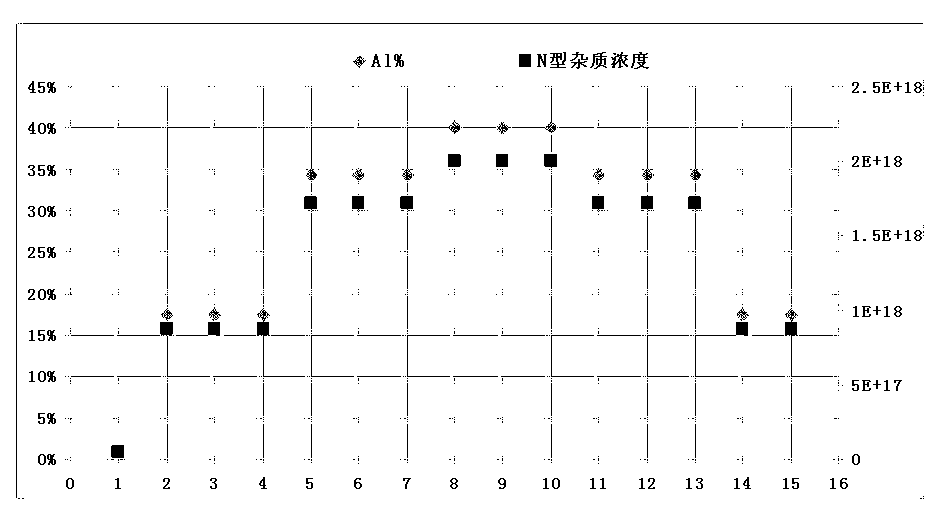
ActiveCN103236477AReduce dislocationAvoid warping effectSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystallographyLattice mismatch
The invention discloses an LED (light emitting diode) epitaxy structure and a preparation method thereof. The LED epitaxy structure successively comprises a substrate, a GaN nucleating layer, multiple pairs of superlattice buffer layers, an n-GaN layer, an MQW luminescent layer, a p-GaN layer and a p-type contact layer from bottom to top, wherein each superlattice buffer layer is formed by an AlGaN / n-GaN alternately stacked structure. The LED epitaxy structure is characterized in that Al(n) is defined to represent an Al component value in the nth pair of AlGaN / n-GaN superlattice buffer layer; N(n) represents the n-type impurity concentration value in the nth pair of AlGaN / n-GaN superlattice buffer layer; the variation trend of Al(n) is gradually lowered after being gradually raised; and the variation trend of N(n) is gradually lowered after being gradually raised. According to the LED epitaxy structure provided by the invention, lattice stress caused by lattice mismatch due to that a sapphire substrate and the GaN lattice are not matched can be effectively and fully released on a bottom layer growth section so as to greatly lower the warping of an epitaxial wafer in the whole high-temperature growth process and improve the wavelength concentricity and yield of the epitaxial wafer. Meanwhile, the GaN lattice quality is effectively improved, the lattice dislocation density is reduced, and the optical-electrical characteristic of the device is more stable.
Owner:ANHUI SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
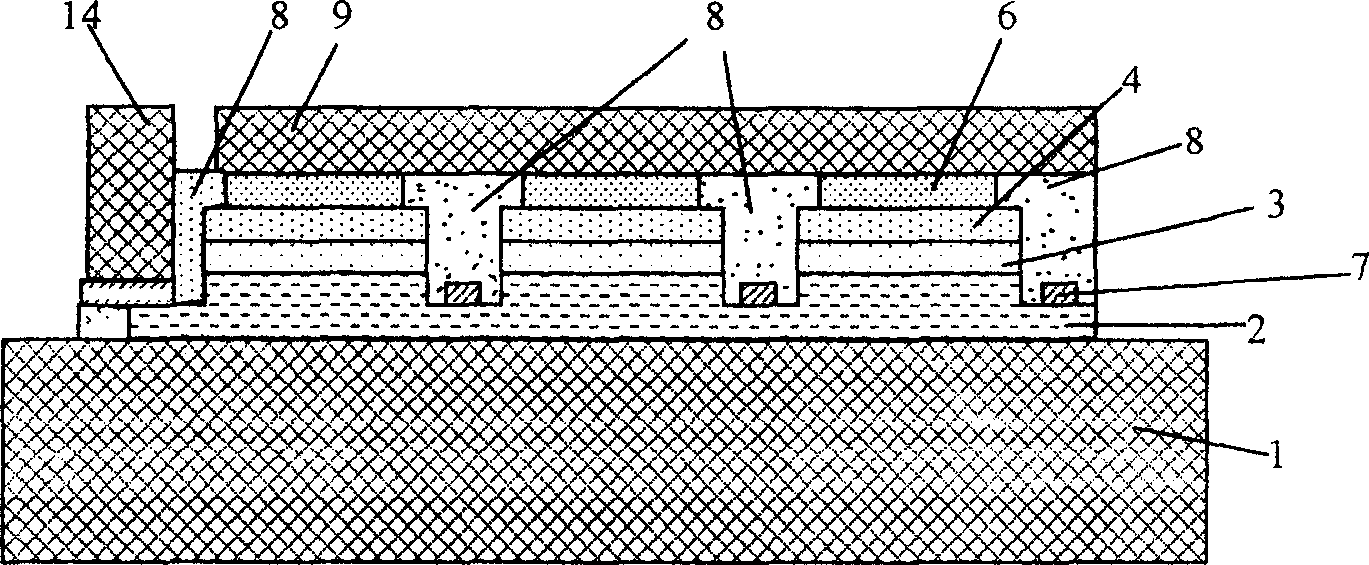
Susceptor, vapor phase growth apparatus, and method of manufacturing epitaxial wafer
InactiveUS20100029066A1Reduce the crystal defects in a semiconductor elementHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorWafering
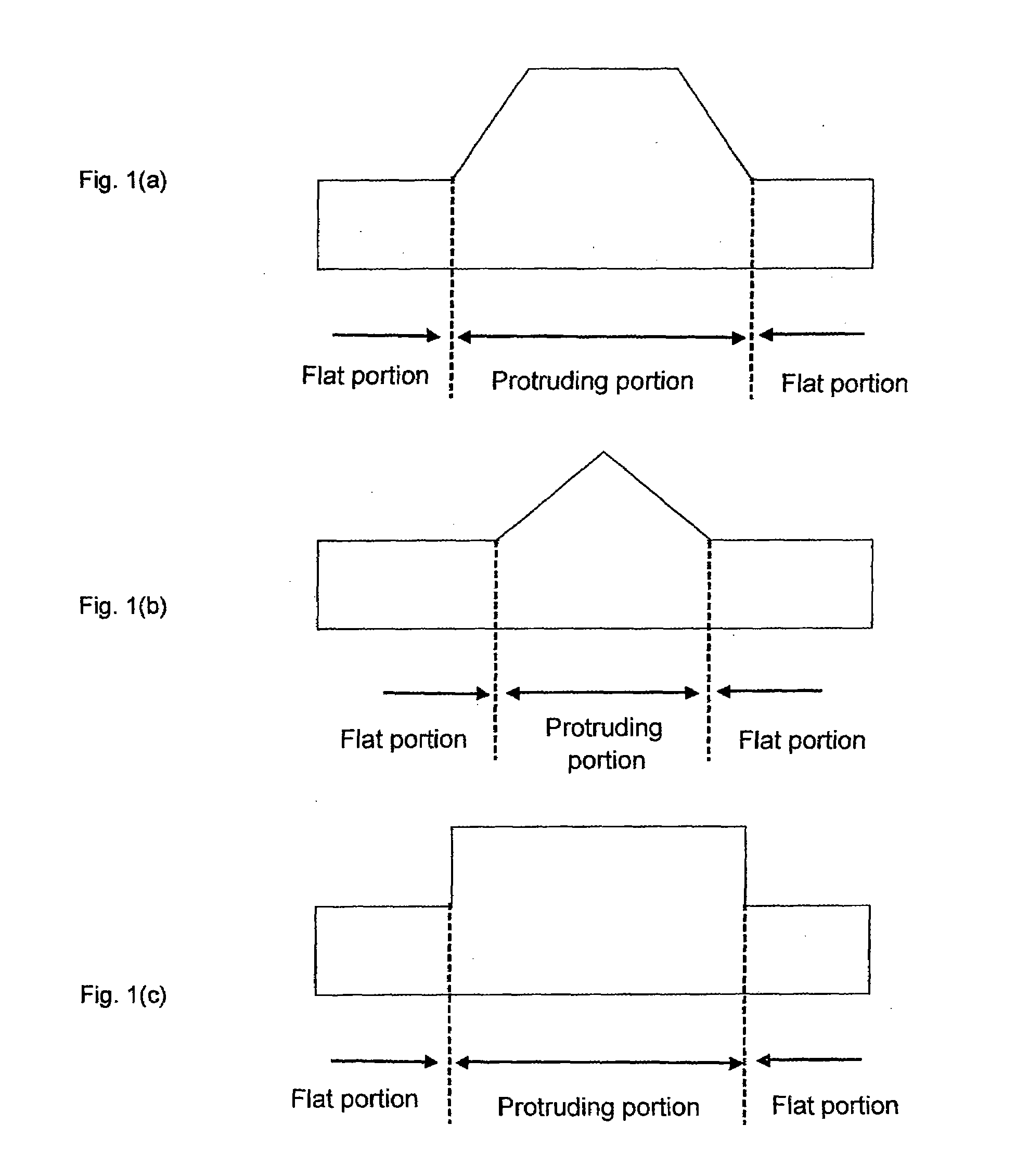
An aspect of the present invention relates to a susceptor comprising a counterbored groove receiving a semiconductor wafer in the course of manufacturing an epitaxial wafer by vapor phase growing an epitaxial layer on a surface of the semiconductor wafer, wherein a lateral wall of the counterbored groove is comprised of at least one flat portion and at least one protruding portion being higher than the flat portion, and a height of the flat portion is equal to or greater than a thickness of the semiconductor wafer.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
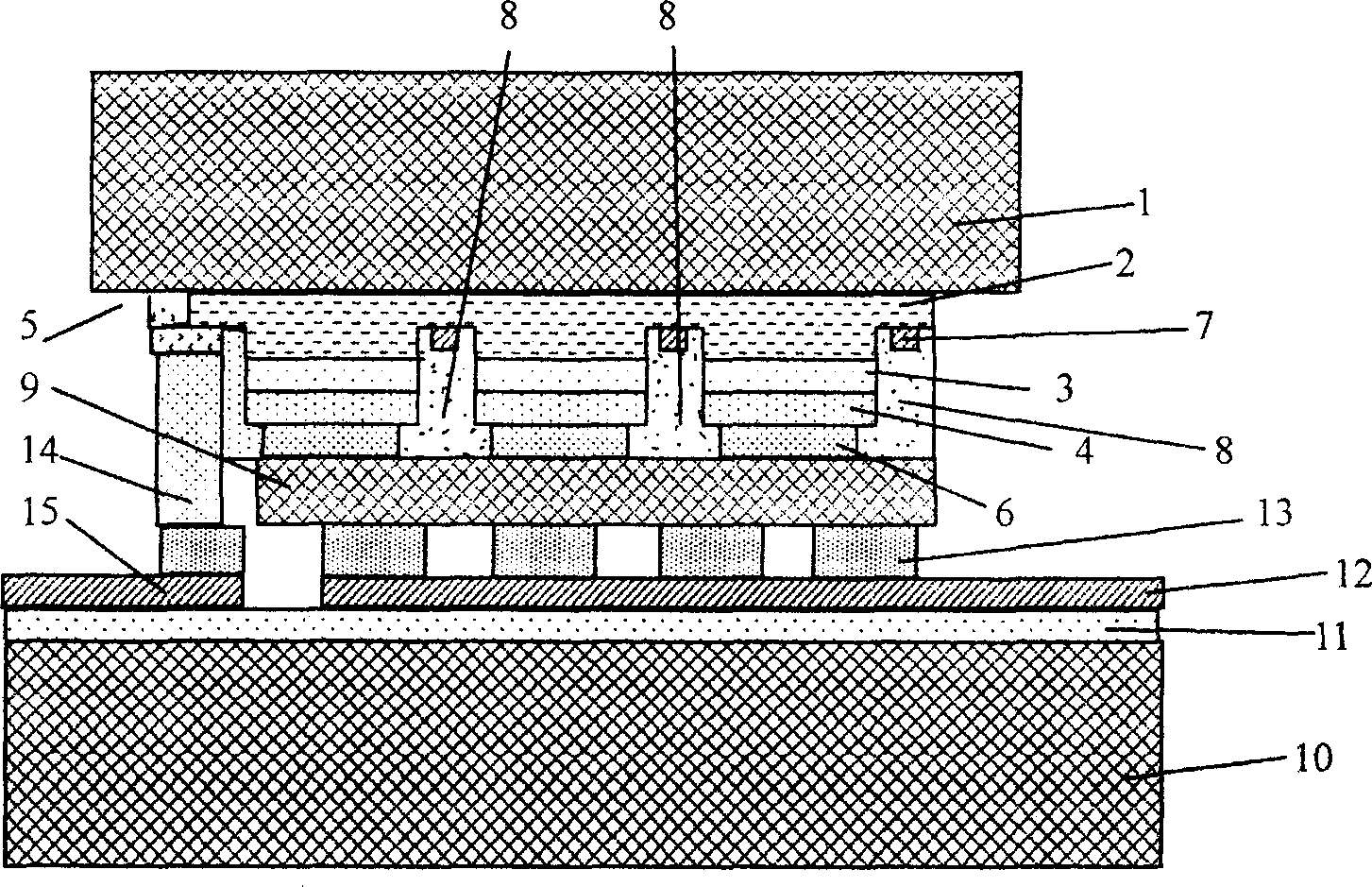
Vapor-phase growth semiconductor substrate support susceptor, epitaxial wafer manufacturing apparatus, and epitaxial wafer manufacturing method
InactiveUS20120309175A1Improve flatnessStable supplySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom chemically reactive gasesSusceptorGas phase
According to the present invention, there is provided a vapor-phase growth semiconductor substrate support susceptor for supporting a semiconductor substrate at the time of vapor-phase growth, wherein the susceptor comprises a pocket portion in which the semiconductor substrate is arranged and has a taper portion having a taper formed such that an upper surface of the susceptor is inclined upwards or downwards from an edge of the pocket portion to an outer side. As a result, there can be provided the susceptor for supporting the semiconductor substrate at the time of vapor-phase growth that can improve flatness of an epitaxial wafer by controlling a layer thickness of an epitaxial layer at a peripheral portion on a main front surface side of the epitaxial wafer, and the epitaxial wafer manufacturing apparatus using this susceptor.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Light-emitting diode with distributed electric conducting hole structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104300059AReduce invalid injectionSolving recognition difficultiesSemiconductor devicesSurface layerOhmic contact
The invention provides a light-emitting diode with a distributed electric conducting hole structure and a manufacturing method of the light-emitting diode, and belongs to the technical field of photoelectrons. According to the method, a mirror surface reflecting layer is manufactured on an epitaxial wafer, a substrate is bonded on the mirror surface reflecting layer, a base plate, a buffering layer and a cut-off layer on the epitaxial wafer are removed, an N-GaAs ohmic contact layer is exposed, and then a graphical N-GaAs ohmic contact layer, an extension electrode, a main electrode and a back electrode are manufactured. According to the light-emitting diode, the mirror surface reflecting layer is formed by all through holes in a SiO2 electric conducting hole layer and the mirror surface layer, and AuZn in a SiO2 hole and a P-GaP current extension layer form good electricity contact; as no electric conducting holes are formed in a cutting channel and schottky junctions are formed below the electrodes, ineffective injection of currents is reduced, and the light-emitting efficiency is improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU CHANGELIGHT
Flip-chip GAN LED fabrication method
InactiveUS20110294242A1Minimize forward voltageMinimize power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactConductive materials
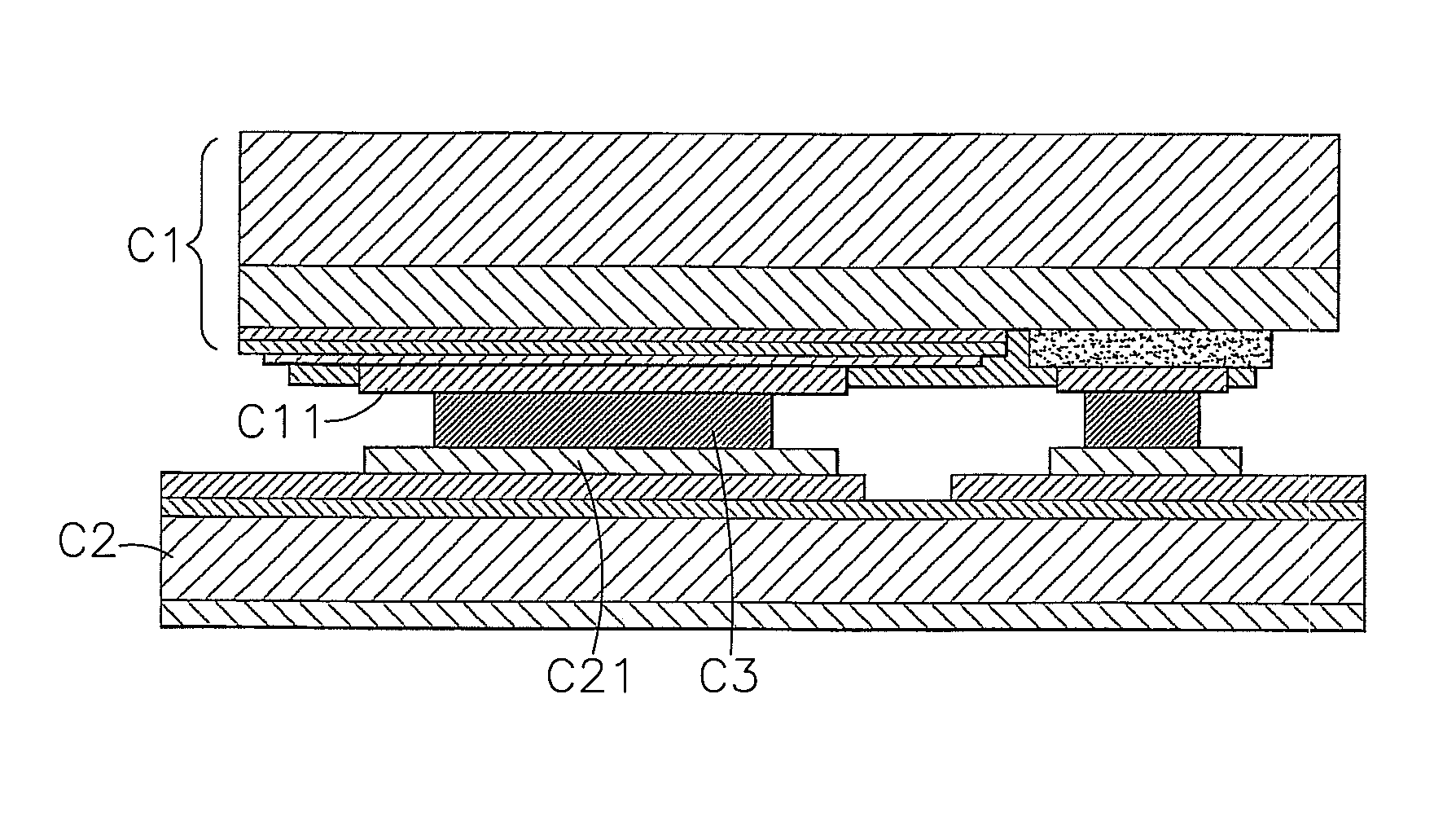
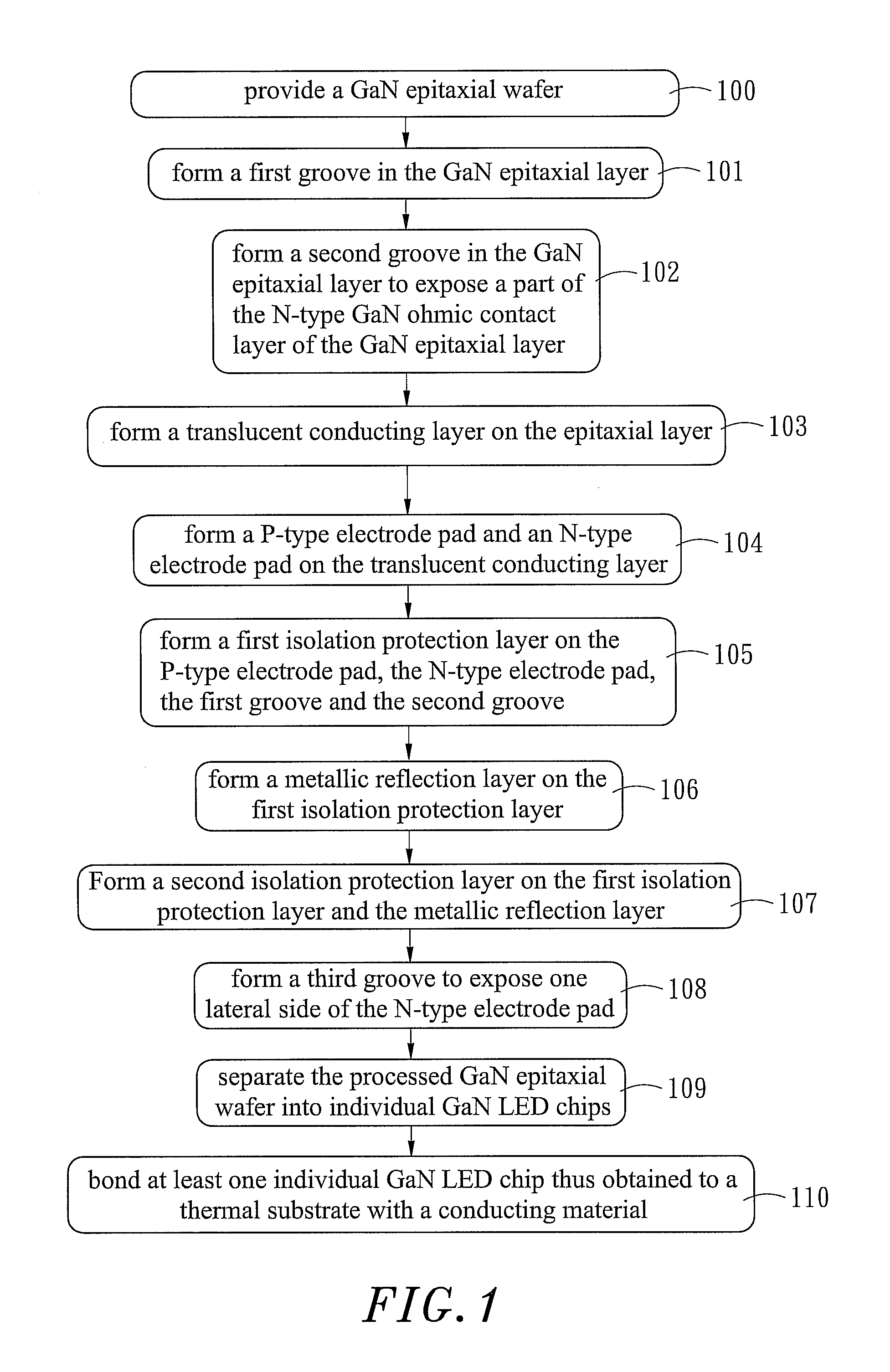
A flip-chip LED fabrication method includes the steps of (a) providing a GaN epitaxial wafer, (b) forming a first groove in the GaN epitaxial layer, (c) forming a second groove in the GaN epitaxial layer to expose a part of the N-type GaN ohmic contact layer of the GaN epitaxial layer, (d) forming a translucent conducting layer on the epitaxial layer, (e) forming a P-type electrode pad and an N-type electrode pad on the translucent conducting layer, (f) forming a first isolation protection layer on the P-type electrode pad, the N-type electrode pad, the first groove and the second groove, (g) forming a metallic reflection layer on the first isolation protection layer, (h) forming a second isolation protection layer on the first isolation protection layer and the metallic reflection layer, (i) forming a third groove to expose one lateral side of the N-type electrode pad, (j) separating the processed GaN epitaxial wafer into individual GaN LED chips, and (k) bonding at least one individual GaN LED chip thus obtained to a thermal substrate with a conducting material.
Owner:ENERLIGHTING CORP
Manufacturing method of light-emitting diode
ActiveUS20100190280A1Inhibition of attachmentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPrinted circuit board
A manufacturing method of an LED comprises attaching an LED epitaxial wafer (LED wafer) to an expanding tape, dicing the LED wafer on the expanding tape longitudinally and laterally to a certain element size to divide into a plurality of LED elements, expanding the expanding tape to a certain size to form an enlarged expanding tape, placing respective pairs of element electrodes of the plurality of LED elements that are attached to the enlarged expanding tape on respective pairs of electrodes on a printed-circuit board assembly collectively to perform a bonding, and removing the enlarged expanding tape from the plurality of the LED elements.
Owner:CITIZEN ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
METHOD FOR PRODUCING SiC EPITAXIAL WAFER
InactiveUS20160208414A1Eliminate occupation timeIncrease productivityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingManufactured apparatus
The method for producing an SiC epitaxial wafer according to the present invention includes: a step of vacuum baking a coated carbon-based material member at a degree of vacuum of 2.0×10−3 Pa or less in a dedicated vacuum baking furnace; a step of installing the coated carbon-based material member in an epitaxial wafer manufacturing apparatus; and a step of placing an SiC substrate in the epitaxial wafer manufacturing apparatus and epitaxially growing an SiC epitaxial film on the SiC substrate.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
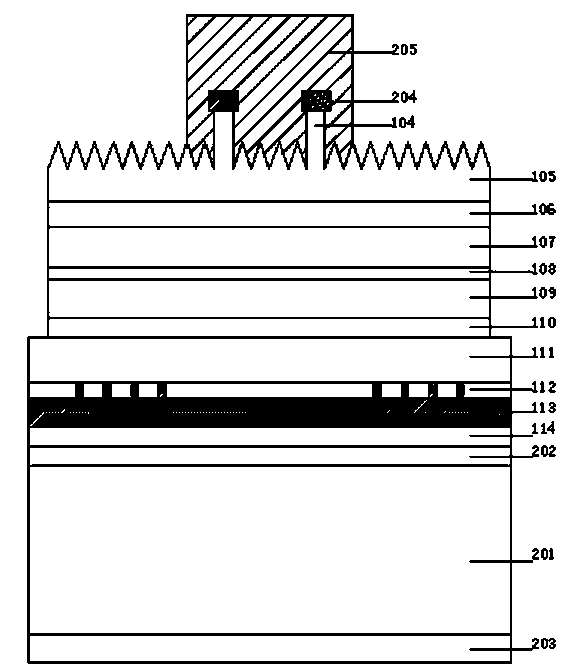
GaN based LED epitaxial wafer of graphical substrate and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101740677AImprove light extraction efficiencyImprove crystal qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexReflective layer
The invention provides a GaN based LED epitaxial wafer of a graphical substrate and a method for preparing the same. In the GaN based LED epitaxial wafer of the graphical substrate, the substrate of the epitaxial wafer comprises a distributed DBR reflecting layer which has a layering structure formed by periodical alternative growth of two transparent materials with different refractive indexes, and the DBR reflecting layer having the layering structure forms at least two graphical structures, which are spaced, on the substrate; a window area is formed between the graphical structures, and the GaN epitaxial layer can be epitaxially grown from the window area; because the growing direction of the crystals is vertical to the original motion direction of dislocations, and a mask layer blocks the majority of motion of the extended dislocations, so that the epitaxial growth of the invention can greatly reduce the density of the extended dislocations in the epitaxial layer, and improve the crystal quality of the GaN epitaxial film; and simultaneously, because the DBR reflecting layer structure on the graphical substrate is the layering structure formed by the periodical alternative growth of two materials with different refractive indexes, the light transmitted downward by an active area can be reflected to the upper surface of the output light and the light outputting efficiency of the LEDs is greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN CENTURY EPITECH LEDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com