Patents
Literature
320 results about "Electrostatic lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
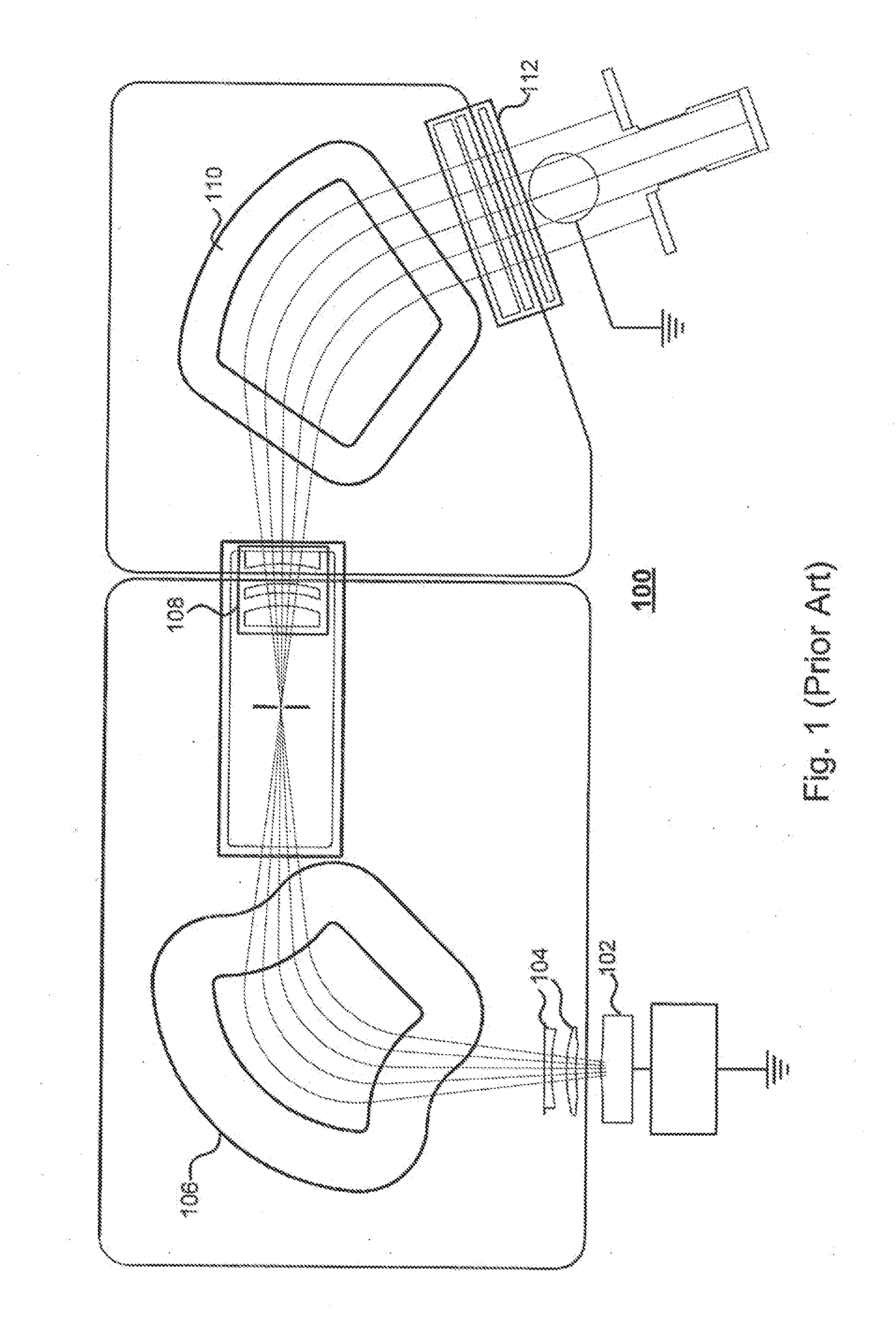
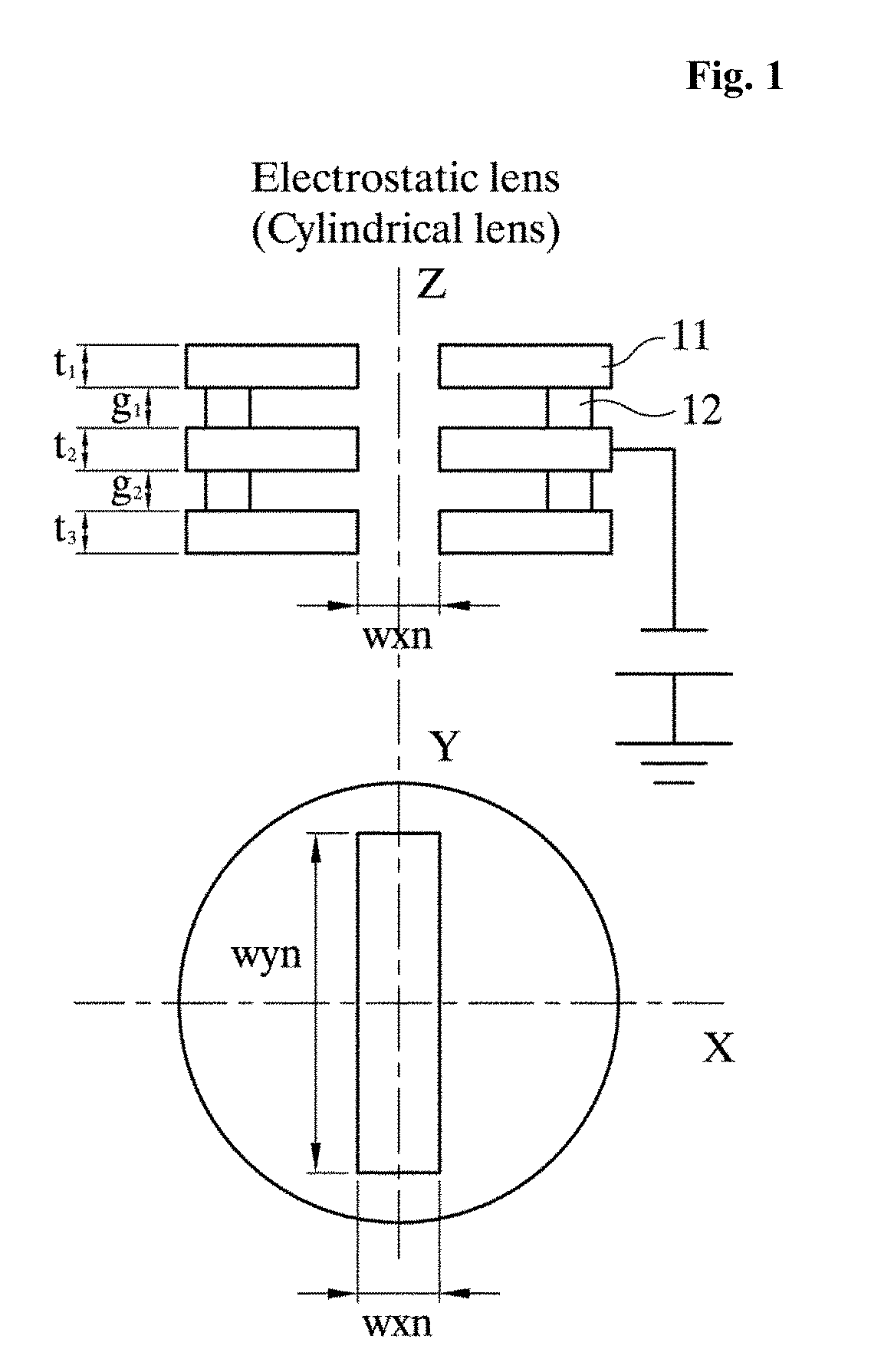
An electrostatic lens is a device that assists in the transport of charged particles. For instance, it can guide electrons emitted from a sample to an electron analyzer, analogous to the way an optical lens assists in the transport of light in an optical instrument. Systems of electrostatic lenses can be designed in the same way as optical lenses, so electrostatic lenses easily magnify or converge the electron trajectories. An electrostatic lens can also be used to focus an ion beam, for example to make a microbeam for irradiating individual cells.
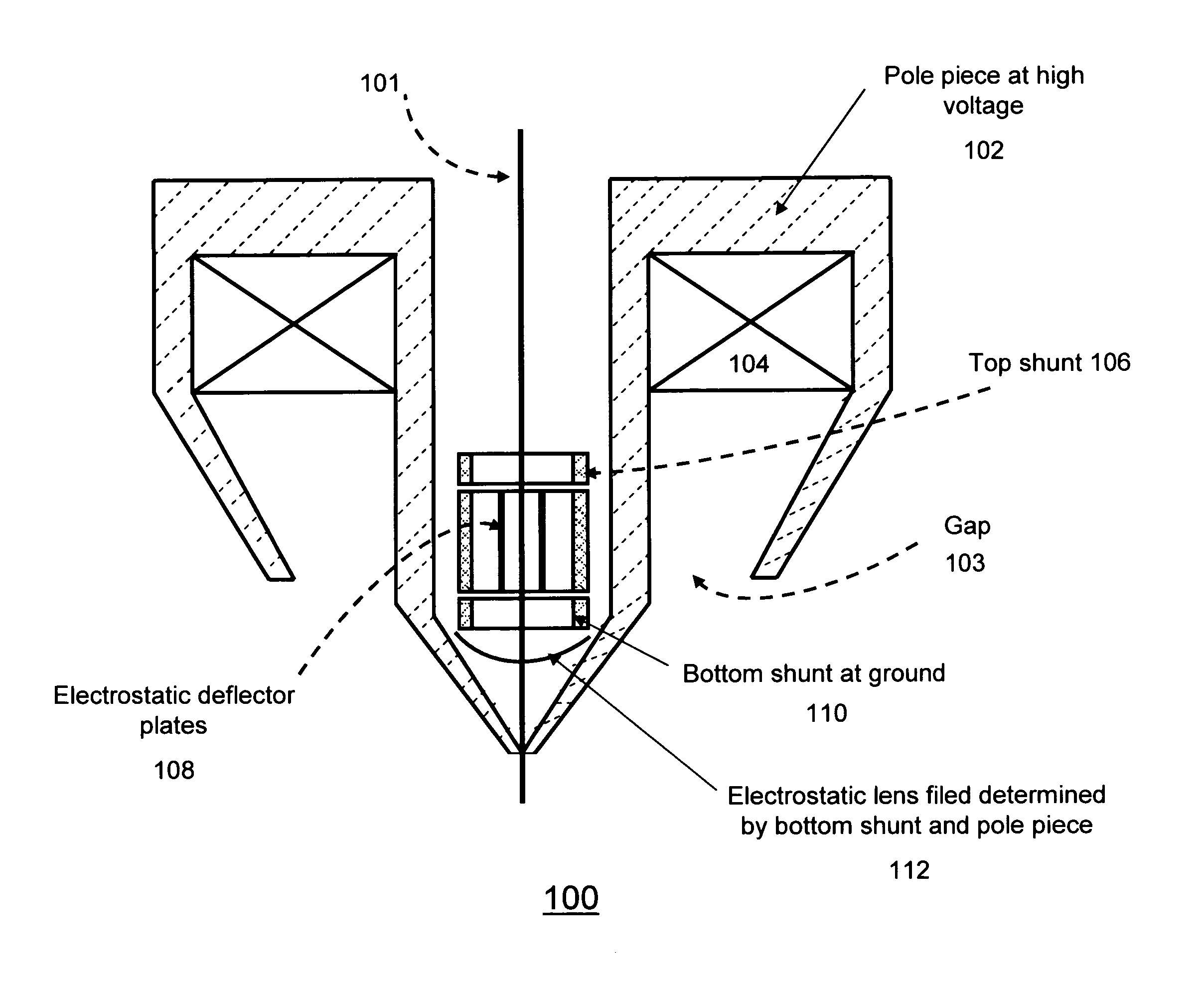
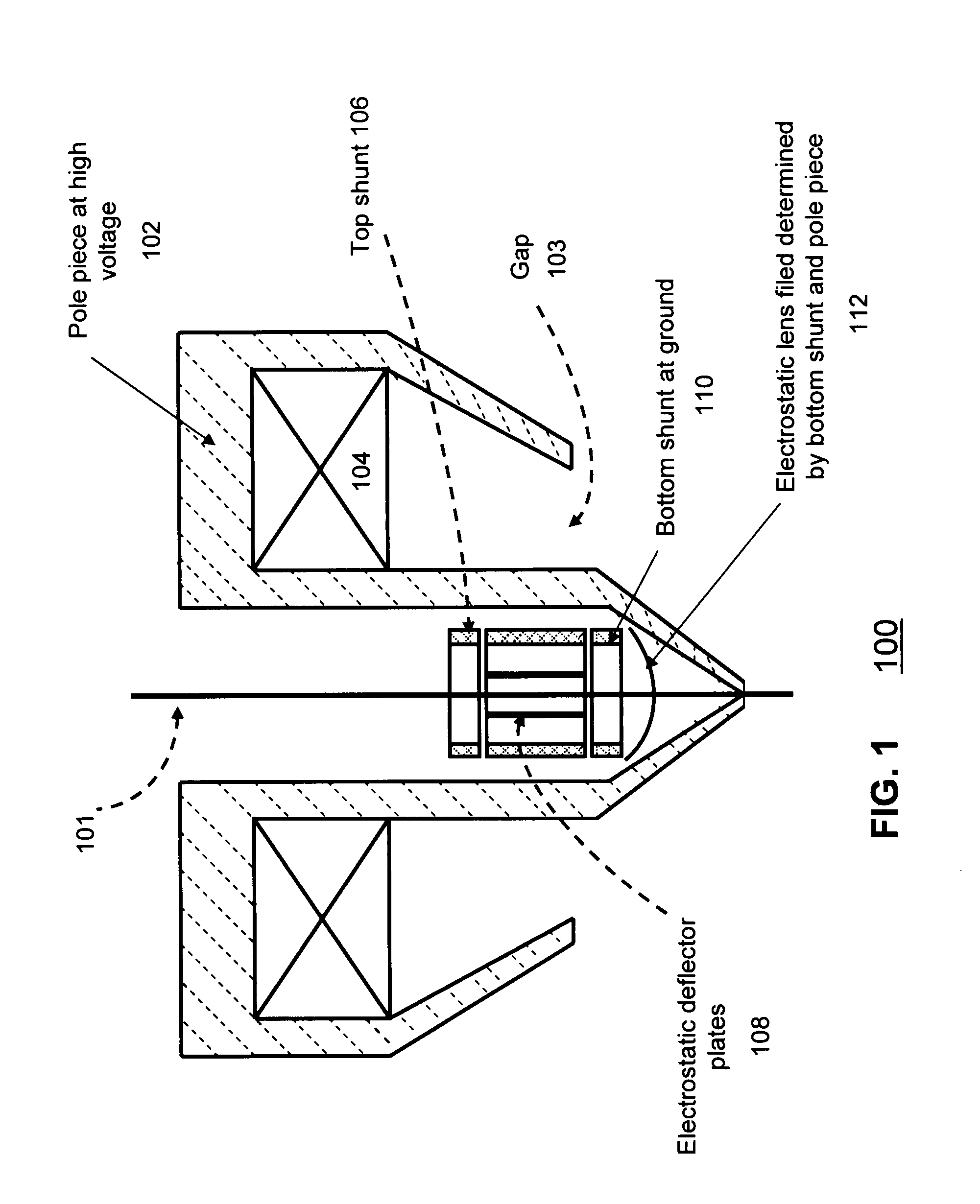
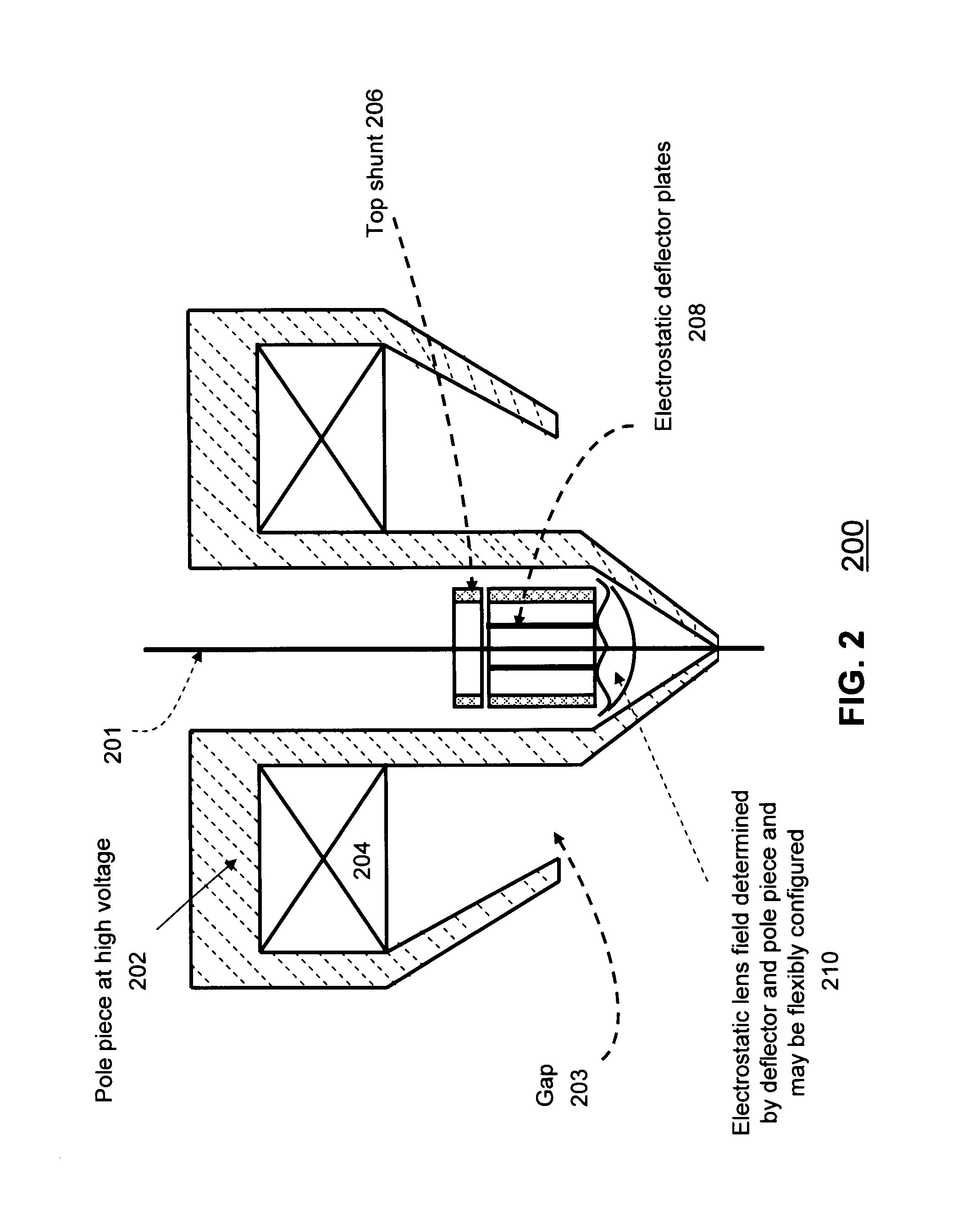
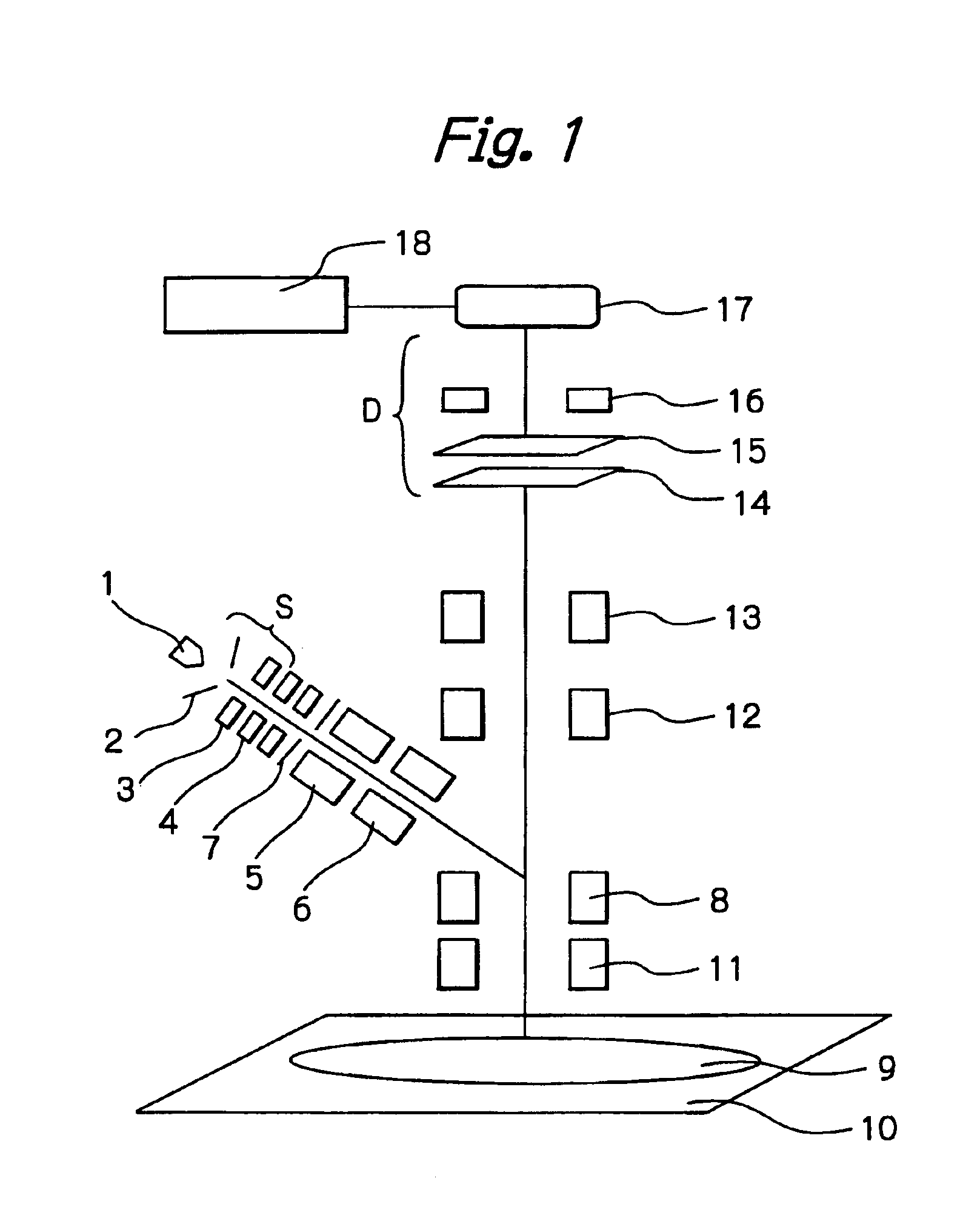
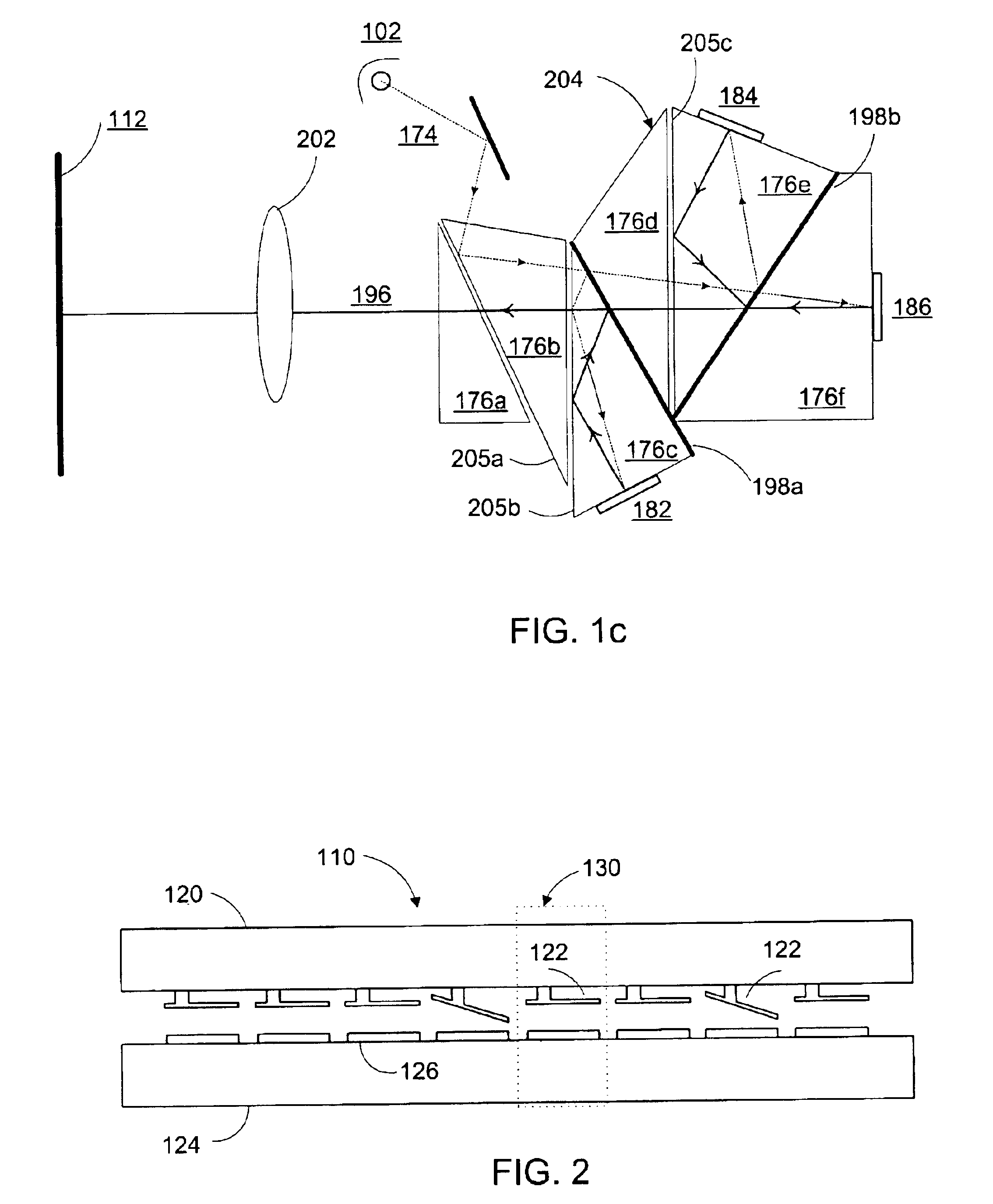
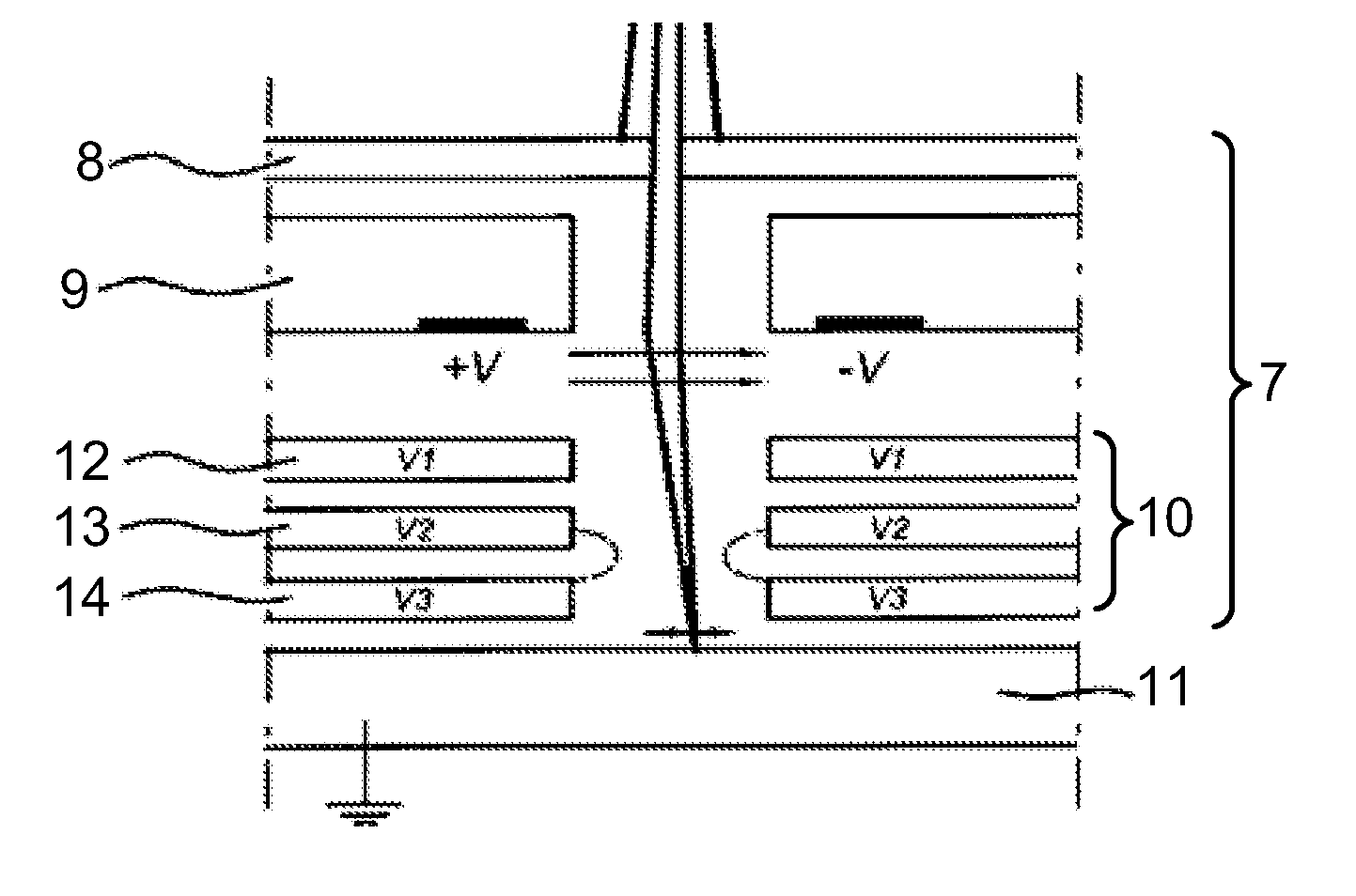
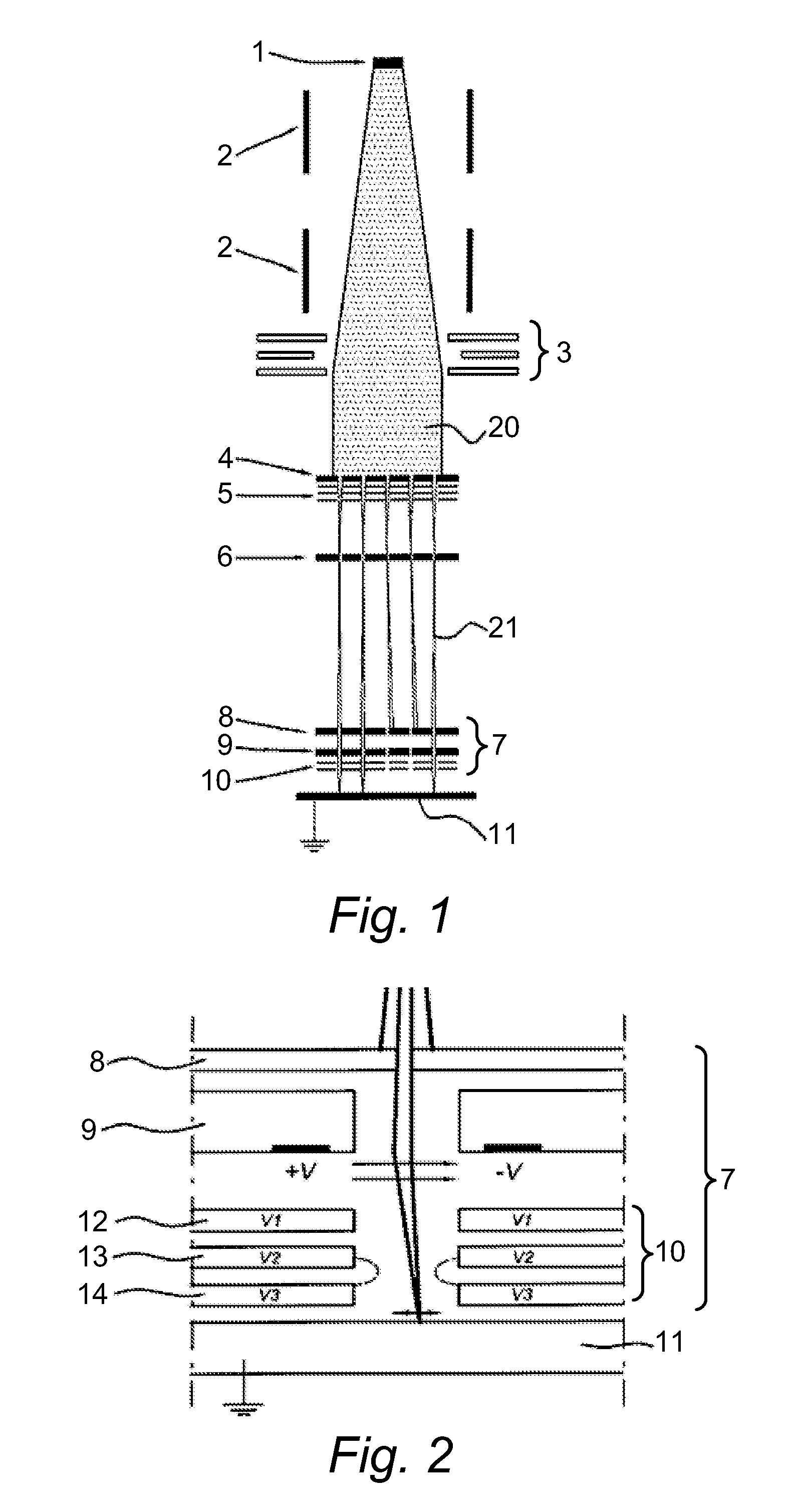
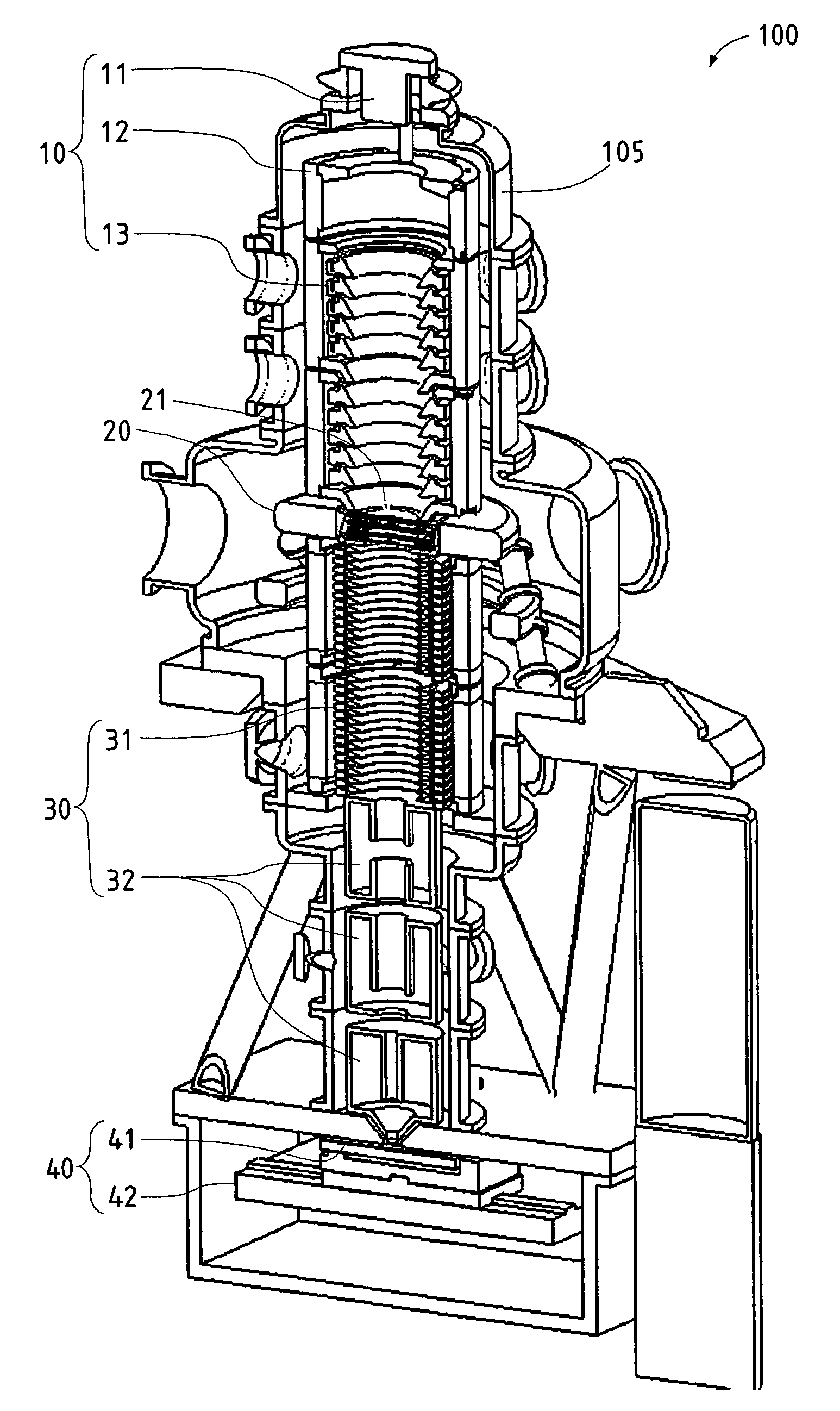
Objective lens with deflector plates immersed in electrostatic lens field
InactiveUS8698093B1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMagnetic polesPole piece
One embodiment relates to an objective lens utilizing magnetic and electrostatic fields which is configured to focus a primary electron beam onto a surface of a target substrate. The objective lens includes a magnetic pole piece and an electrostatic deflector configured within the pole piece. An electrostatic lens field is determined by the pole piece and the electrostatic deflector, and the electrostatic lens field is configured by adjusting offset voltages applied to plates of the electrostatic deflector. Other embodiments, aspects and features are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Electron beam apparatus and device manufacturing method using same
InactiveUS6909092B2Reduce image distortionLess aberrationThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectron sourceImaging processing
A defect inspecting apparatus is provided for generating a less distorted test image to reliably observe a surface of a sample for detecting defects thereon. The defect detecting apparatus comprises a primary electron beam source for irradiating a sample, electrostatic lenses for focusing secondary electrons emitted from the surface of the sample irradiated with the primary electron beam, a detector for detecting the secondary electrons, and an image processing unit for processing a signal from the detector. Further, a second electron source may be provided for emitting an electron beam irradiated to the sample, wherein the sample may be irradiated with the electron beam from the second electron source before it is irradiated with the primary electron beam from the first electron source for observing the sample. A device manufacturing method is also provided for inspecting devices under processing with high throughput using the defect detecting apparatus.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Focused ion beam system with coaxial scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS6900447B2Enhance the imageStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIon beamLight beam
A system including co-axial focused ion beam and an electron beam allows for accurate processing with the FIB using images formed by the electron beam. In one embodiment, a deflector deflects the electron beam onto the axis of the ion beam and deflects secondary particles collected through the final lens toward a detector. In one embodiment, a positively biased final electrostatic lens focuses both beams using the same voltage to allow simultaneous or alternating FIB and SEM operation. In one embodiment, the landing energy of the electrons can be varied without changing the working distance.
Owner:FEI CO
Charged particle beam apparatus
InactiveUS20060076489A1FunctionalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesElectron sourceSecondary electrons
A charged particle beam apparatus in which an electrostatic lens is used as a main focusing element to obtain a subminiature high-sensitivity high-resolution SEM, a drift tube for an electron beam is located inside a column between an electron source and a sample, and a detector for secondary electrons is located inside the drift tube. This solves the problem associated with the provision of a secondary electron detector, which heretofore has been a bottleneck in making a subminiature high-resolution SEM column.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Micromirror devices with in-plane deformable hinge
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV +1
Electron beam exposure system
InactiveUS20050211921A1Improve performanceHigh resolutionThermometer detailsNanoinformaticsTarget surfaceControl signal
The invention relates to an electron beam exposure apparatus for transferring a pattern onto the surface of a target, comprising: a beamlet generator for generating a plurality of electron beamlets; a modulation array for receiving said plurality of electron beamlets, comprising a plurality of modulators for modulating the intensity of an electron beamlet; a controller, connected to the modulation array for individually controlling the modulators, an adjustor, operationally connected to each modulator, for individually adjusting the control signal of each modulator; a focusing electron optical system comprising an array of electrostatic lenses wherein each lens focuses a corresponding individual beamlet, which is transmitted by said modulation array, to a cross section smaller than 300 nm, and a target holder for holding a target with its exposure surface onto which the pattern is to be transferred in the first focal plane of the focusing electron optical system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Micromirrors with mechanisms for enhancing coupling of the micromirrors with electrostatic fields
InactiveUS6873450B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical elementsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A micromirror device is disclosed, along with a method of making such a micromirror device that comprises a mirror plate, a hinge and an extension plate. The extension plate is formed on the mirror plate and between the mirror plate and the electrode associated with the mirror plate for rotating the mirror plate. The extension plate can be metallic or dielectric. Also disclosed is a method of making such a micromirror device. In particular, the extension plate is formed after the formation of the mirror plate. Moreover, also disclosed is a projection system that comprises a spatial light modulator having an array of such micromirrors, as well as a light source, condensing optics, wherein light from the light source is focused onto the array of micromirrors, projection optics for projecting light selectively reflected from the array of micromirrors onto a target, and a controller for selectively actuating the micromirrors in the array.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV +1
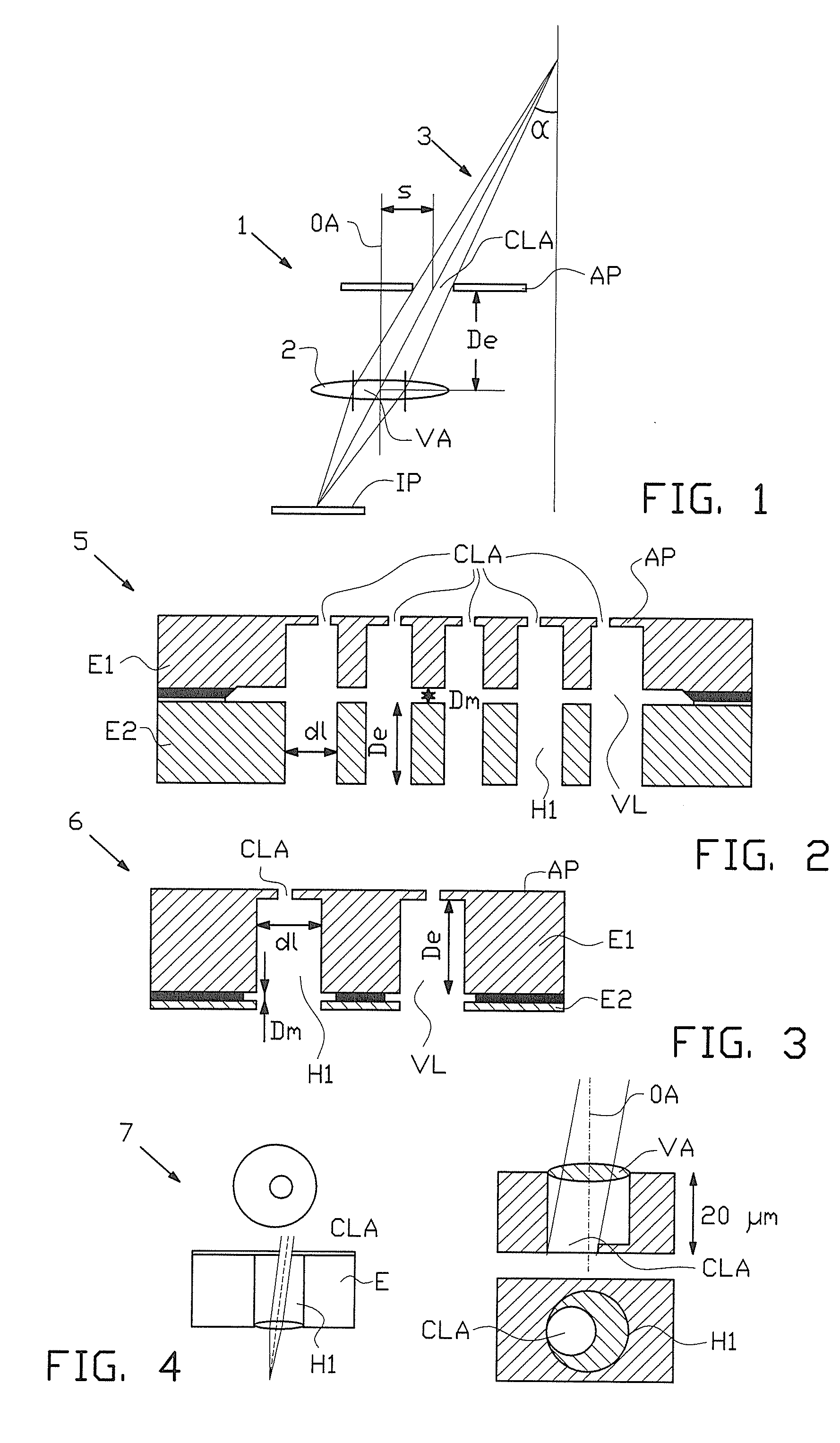
Method For The Production Of Multiplayer Electrostatic Lens Array
InactiveUS20100065741A1Simple and cost-effective methodHigh yieldLine/current collector detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron microscopeOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a method for the production of a multilayer electrostatic lens arrangement with at least one lens electrode in general, a method for the production of a phase plate in particular as well as the lens arrangement, the phase plate and a transmission electron microscope with the phase plate.The lens arrangement or the phase plate is produced from a thin self-supporting silicon nitride membrane which is fixed in a macroscopic chip with deposition of further layers. beam.The central bore as well as the aperture opening are milled out by means of an ion
Owner:GERTHSEN DAGMAR +2
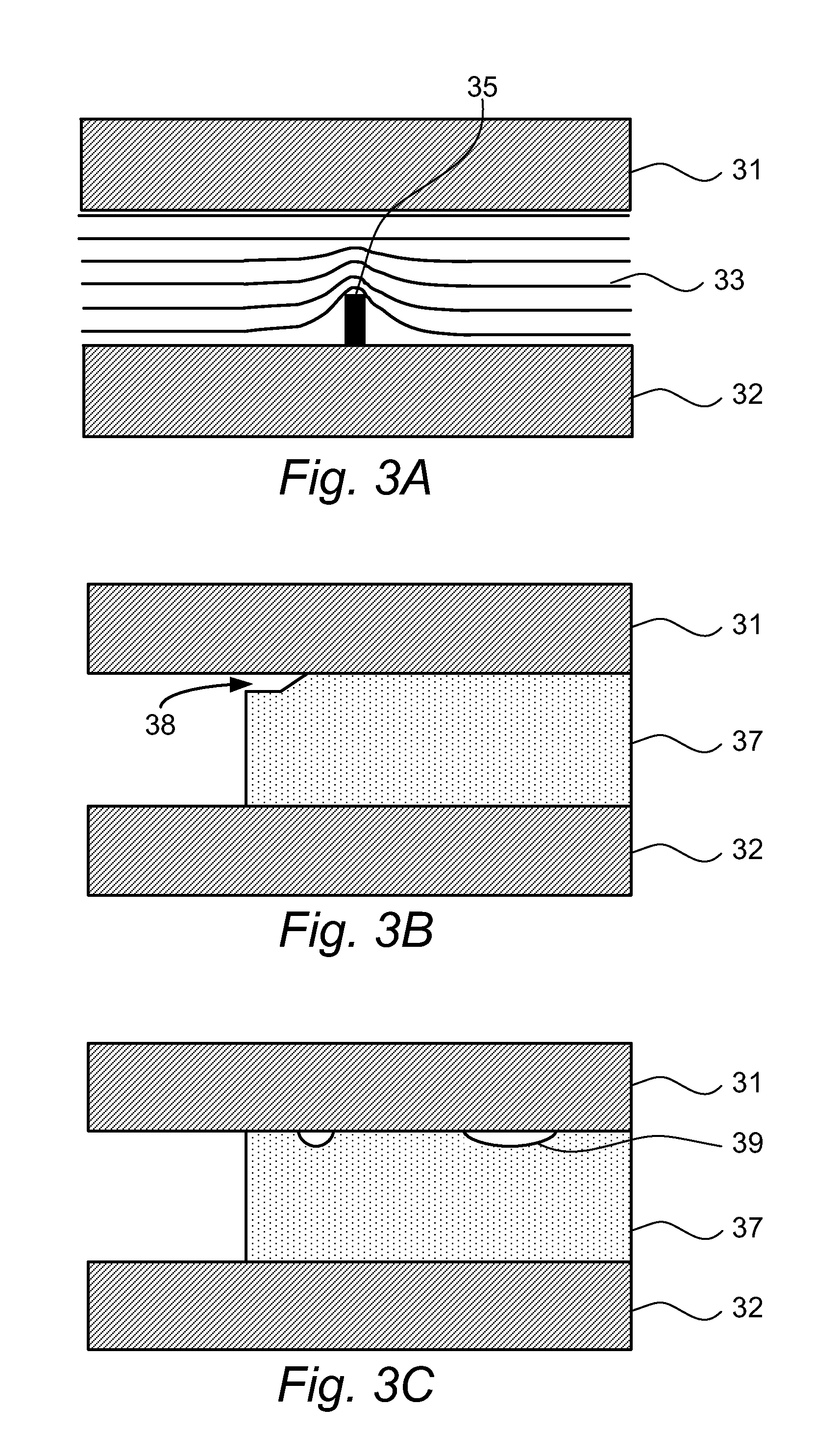
Electrostatic lens structure
ActiveUS20110216299A1Enhancement and elevation of electric fieldRaise the possibilityStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsEngineeringVoltage
An electrostatic lens comprising a first conductive plate with a first aperture, a second conductive plate with a second aperture, the second aperture being substantially aligned with the first aperture, a voltage supply for supplying a first voltage to the first conductive plate and a second voltage to the second conductive plate, the first voltage being lower than the second voltage, and an insulating structure for separating the first conductive plate from the second conductive plate. The insulating structure comprises a first portion in contact with the first conductive plate and a second portion in contact with the second conductive plate, the first portion having an overhanging portion and the second portion having an indented portion at an edge of the insulating structure, so that a gap is formed between the overhanging portion and the second conductive plate.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
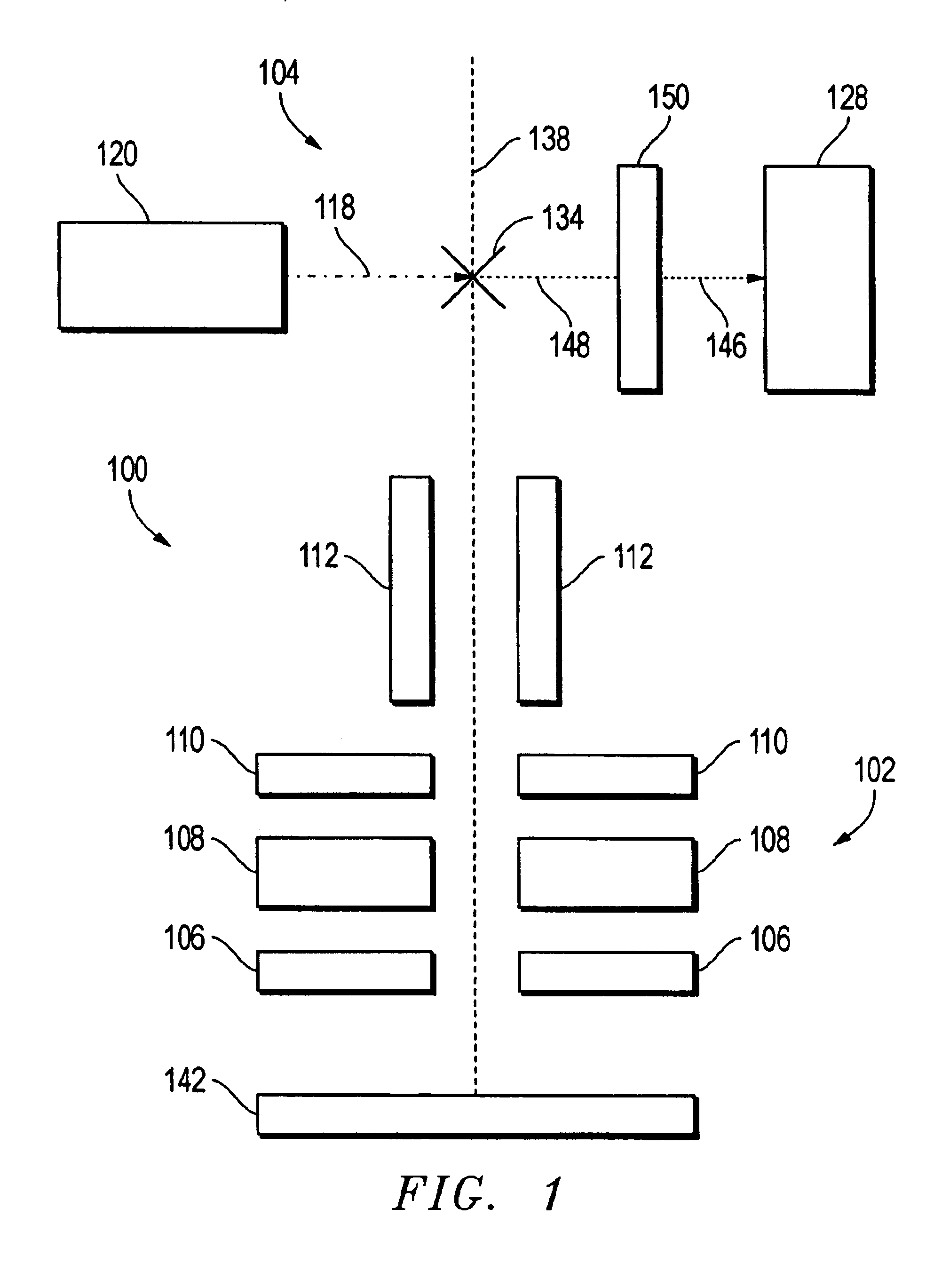
Method and apparatus for controlling an electrostatic lens about a central ray trajectory of an ion beam
ActiveUS20120168637A1Control deflectionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsIon beamElectric field
A method of controlling deflection of a charged particle beam in an electrostatic lens includes establishing a symmetrical electrostatic lens configuration comprising a plurality of electrodes disposed at unadjusted positions that are symmetric with respect to the central ray trajectory with applied unadjusted voltages that create fields symmetric with respect to the central ray trajectory. A symmetric electric field is calculated corresponding to the set of unadjusted voltages. A plurality of lower electrodes is arranged at adjusted positions that are asymmetric with respect to the central ray trajectory. A set of adjusted voltages is obtained for the plurality of lower electrodes, wherein the set of adjusted voltages corresponds to a set of respective potentials of the symmetric electric field at respective adjusted asymmetric positions. The adjusted voltages are applied to the asymmetric lens configuration when the charged particle beam passes therethrough.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
System and method for a charged particle beam
ActiveUS20080121810A1Large scanning rangeEfficient captureElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansPole pieceMagnetic lens
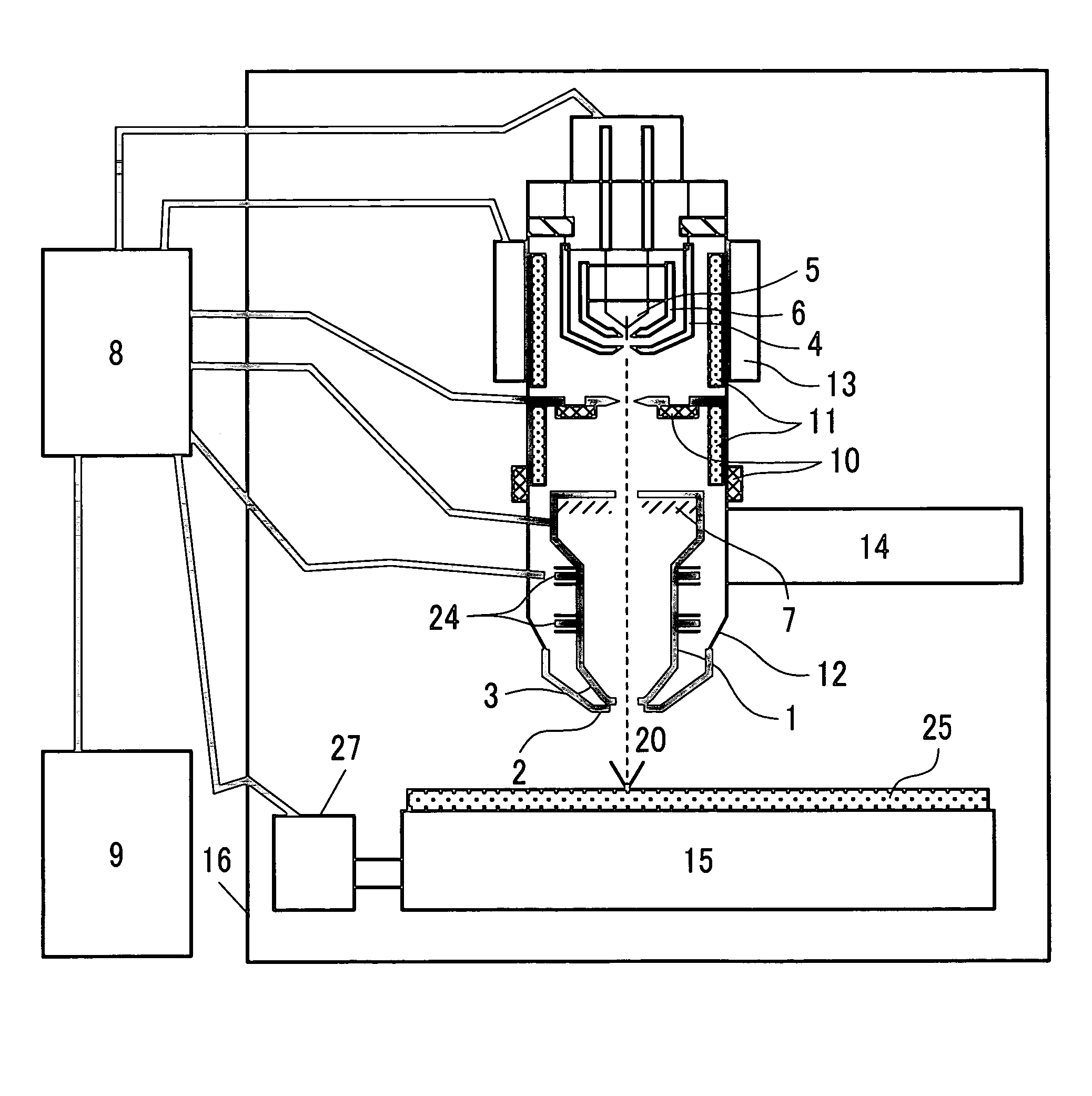
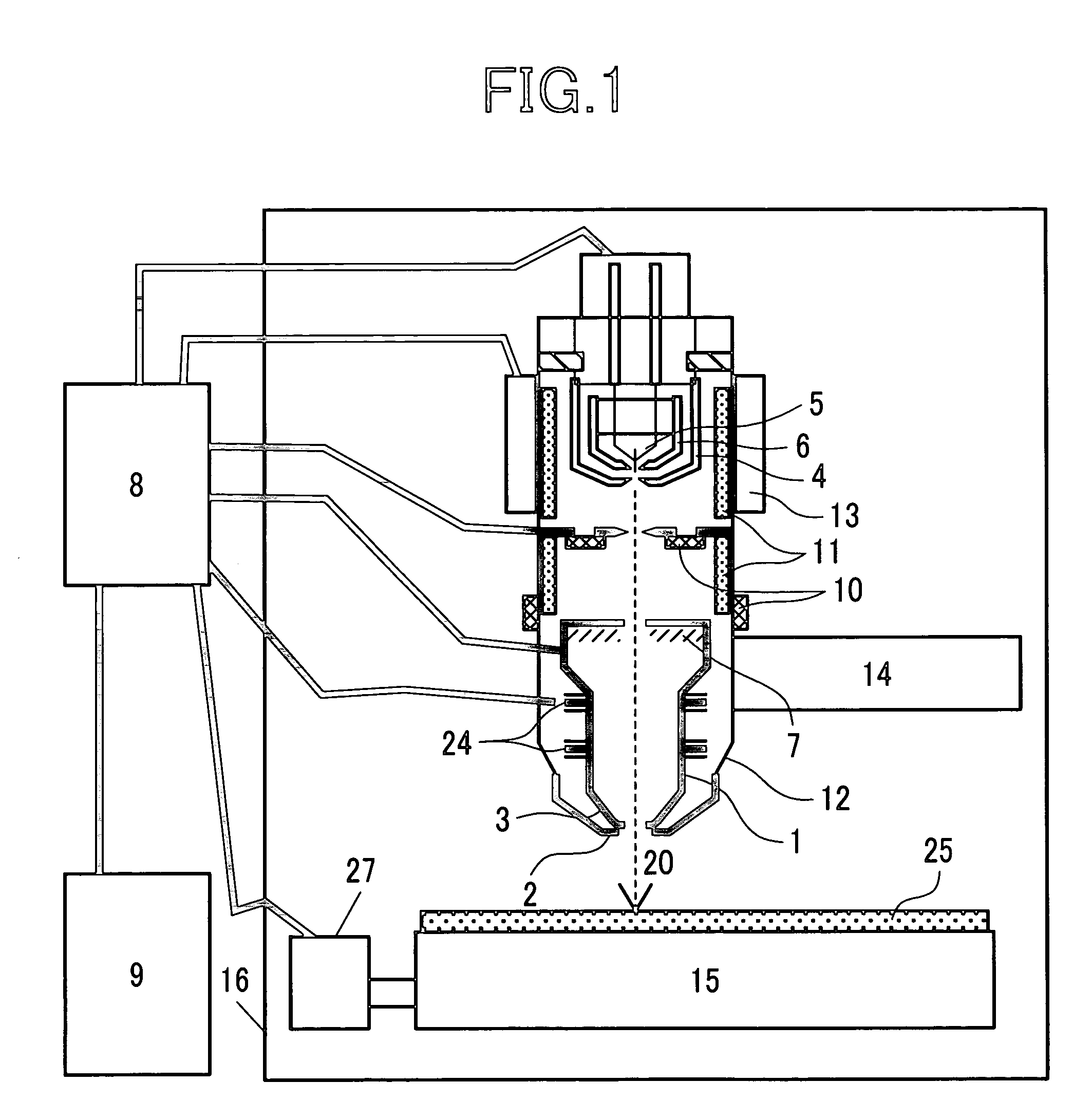
System and method for charged particle beam. According an embodiment, the present invention provides a charged particle beam apparatus. The apparatus includes a charged particle source for generating a primary charged particle beam. The apparatus also includes at least one condenser lens for pre-focusing the primary charge particle beam. Furthermore, the apparatus includes a compound objective lens for forming the magnetic field and the electrostatic field to focus the primary charged particle beam onto a specimen in the charged particle beam path. The specimen includes a specimen surface. The compound objective lens includes a conical magnetic lens, an immersion magnetic lens, and an electrostatic lens, the conical magnetic lens including an upper pole piece, a shared pole piece being electrically insulated from the upper pole piece, and an excitation coil.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Electron beam apparatus
ActiveUS20050253066A1Increase brightnessExtended service lifeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesImaging processingHigh flux
An electron beam apparatus is provided for evaluating a sample at a high throughput and a high S / N ratio. As an electron beam emitted from an electron gun is irradiated to a sample placed on an X-Y-θ stage through an electrostatic lens, an objective lens and the like, secondary electrons or reflected electrons are emitted from the sample. The primary electron beam is incident at an incident angle set at approximately 35° or more by controlling a deflector. Electrons emitted from the sample is guided in the vertical direction, and focused on a detector. The detector is made up of an MCP, a fluorescent plate, a relay lens, and a TDI (or CCD). An electric signal from the TDI is supplied to a personal computer for image processing to generate a two-dimensional image of the sample.
Owner:EBARA CORP
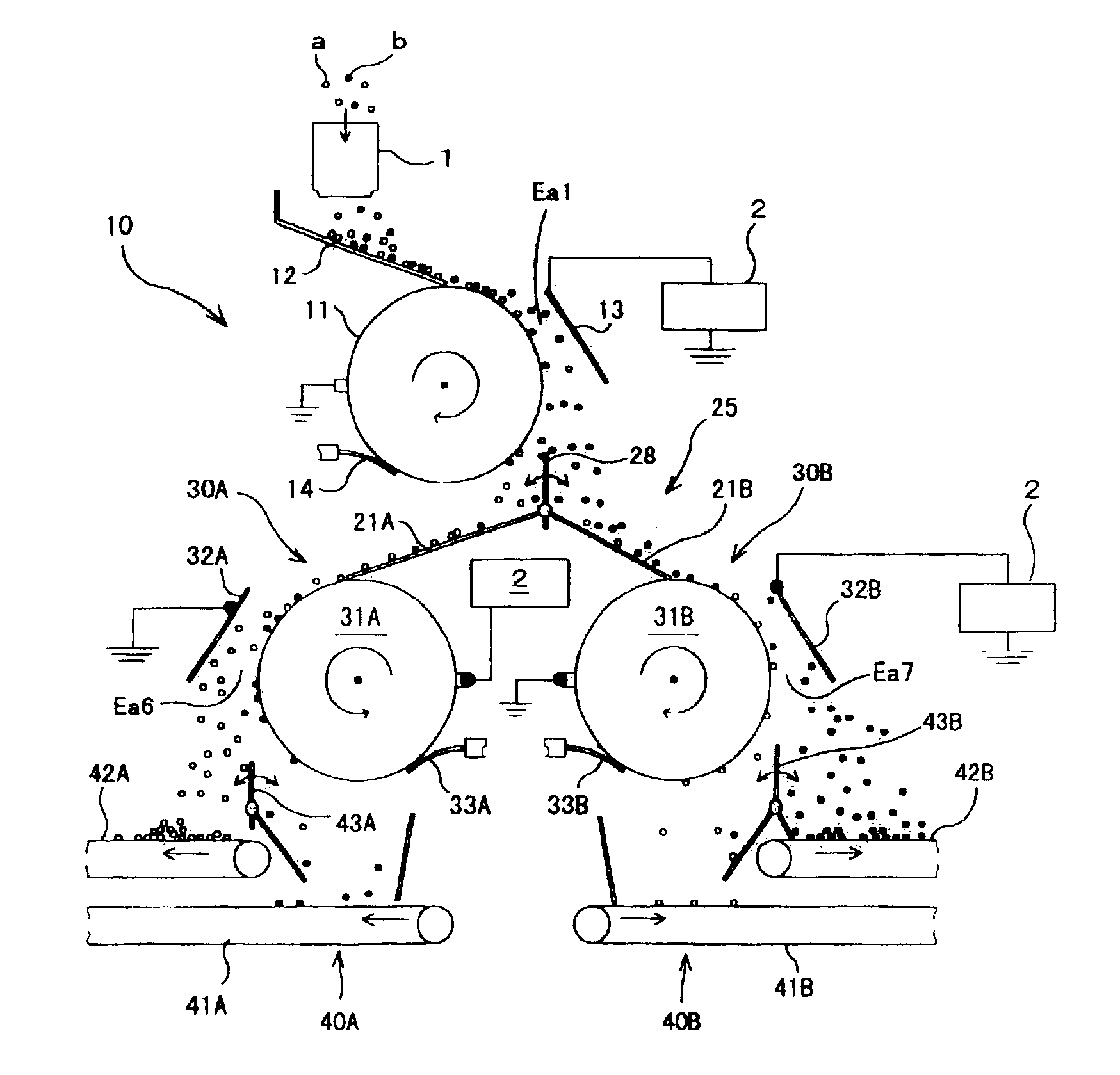
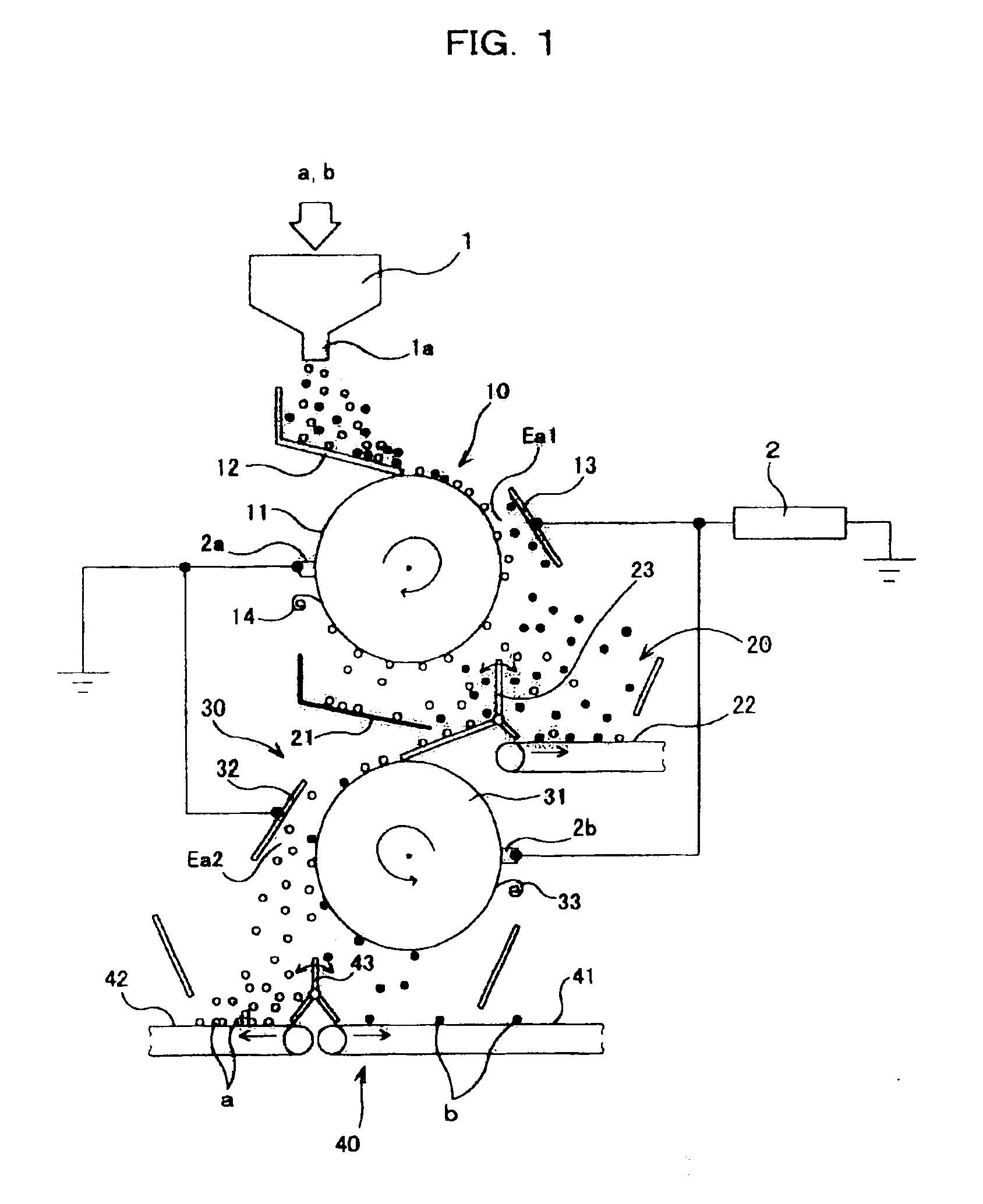
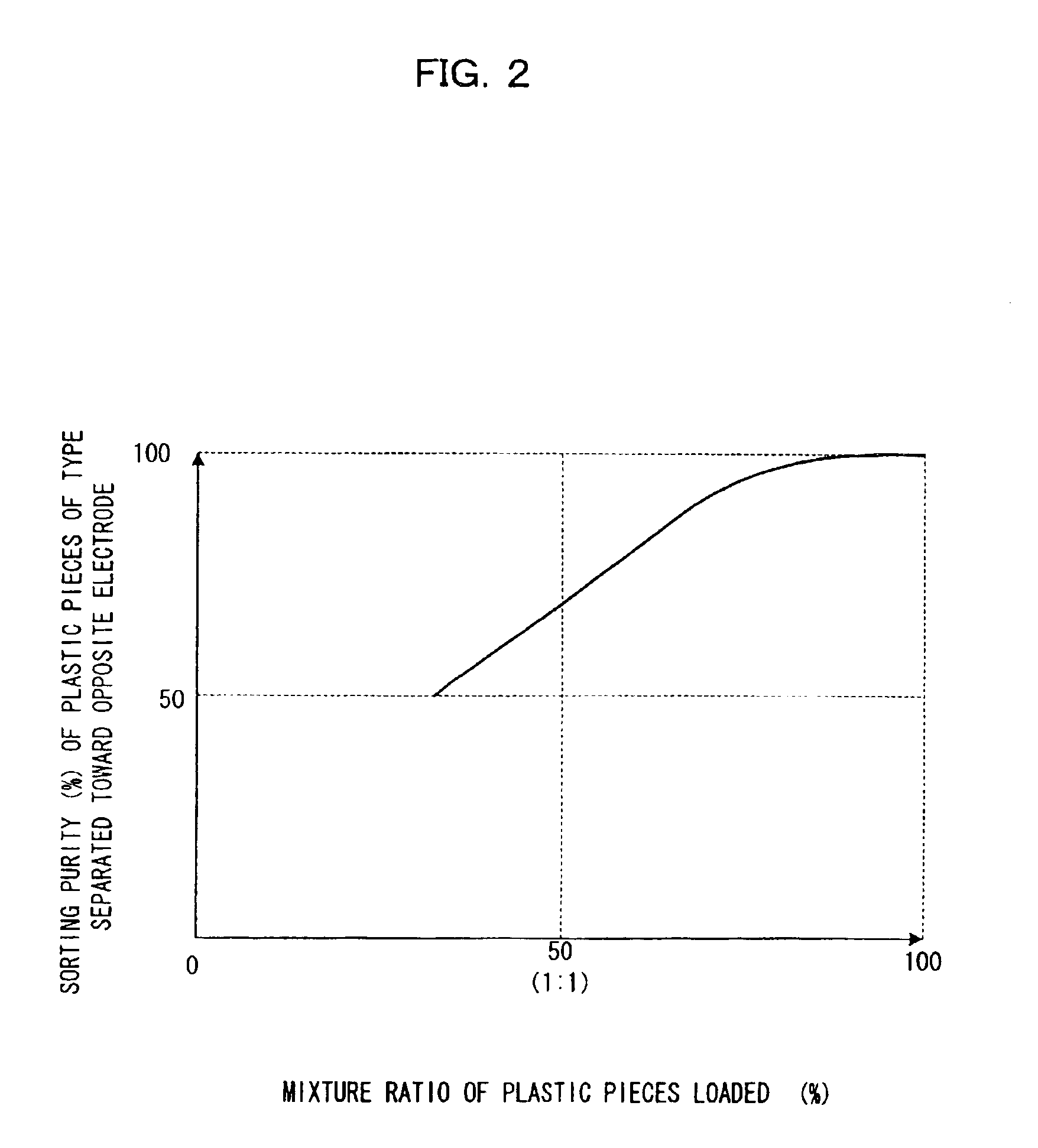
Apparatus for separating plastic chips
InactiveUS6903294B1High purityHigh recovery rateElectrostatic separationPlastic recyclingEngineeringStatic electricity
A first and second electrostatic sorting sections are arranged below a tribo-electrifying device in this order in a vertical direction to form a sorting electrostatic field between a drum electrode and an opposing electrode. Plastic pieces separated from the other plastic pieces by the sorting electrostatic field in the first electrostatic separating section are introduced into a sorting electrostatic field in the second electrostatic separating section for second separation, thereby increasing the separation purity and recovery rate of plastic pieces.
Owner:HITACHI ZOSEN CORP
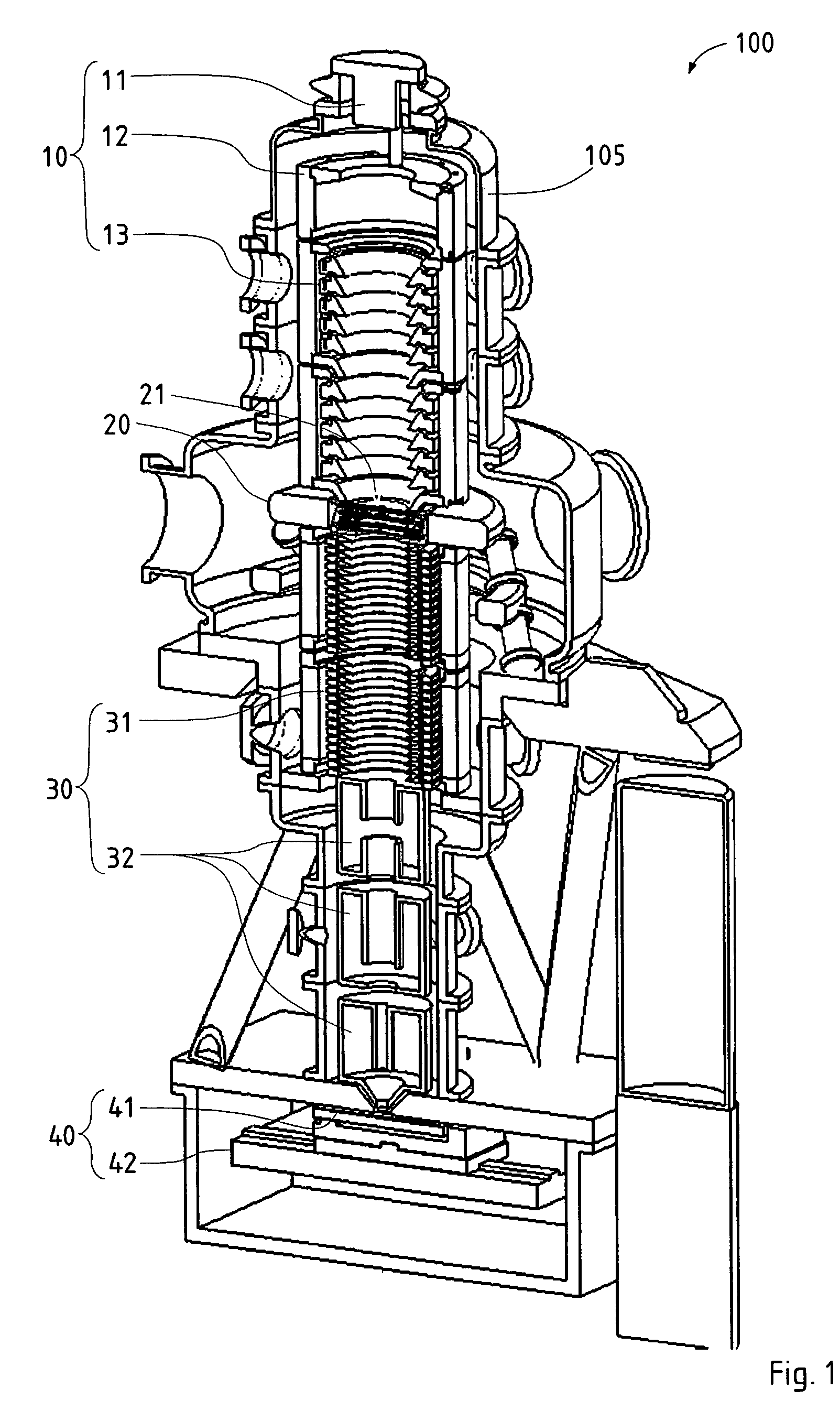
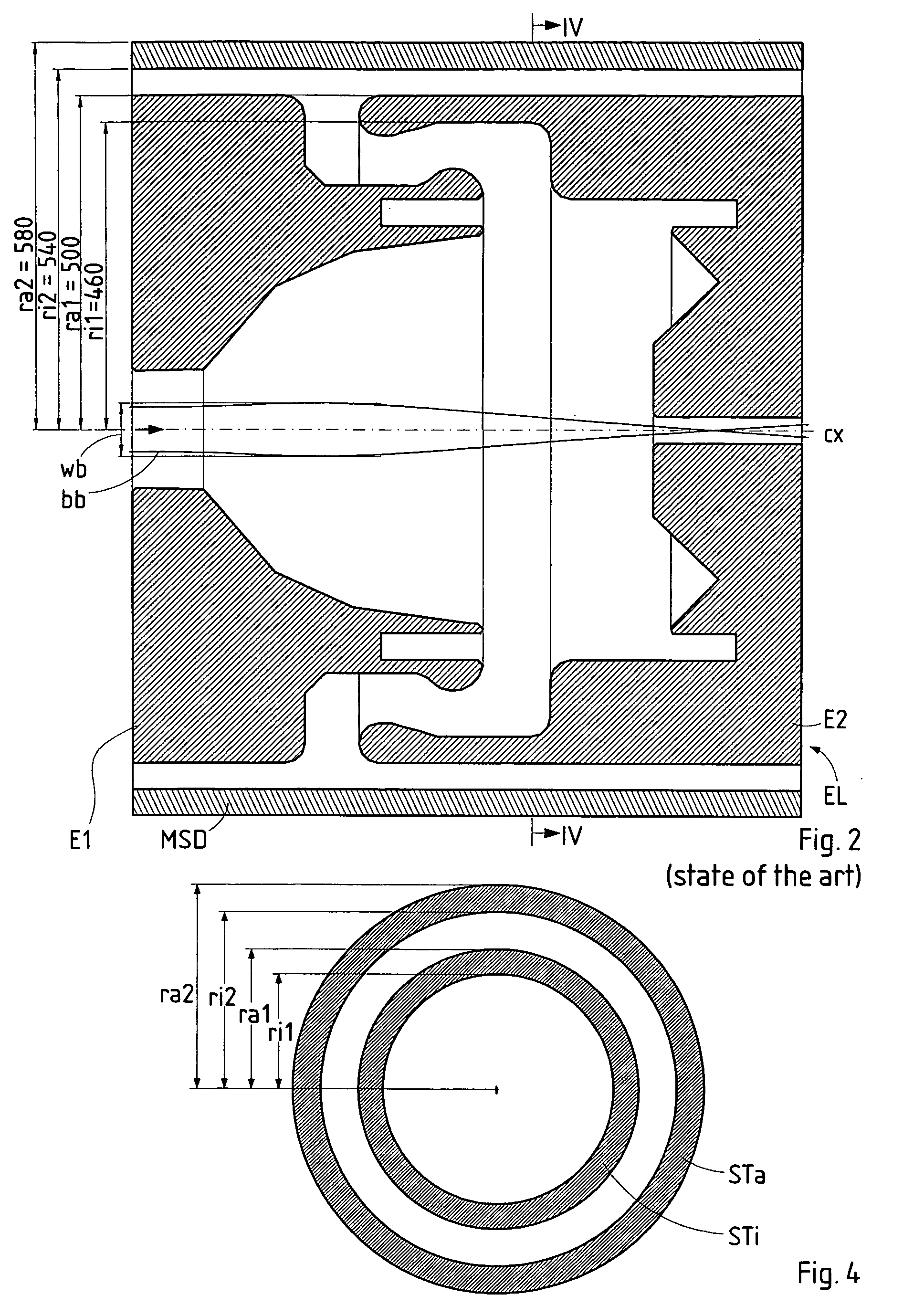
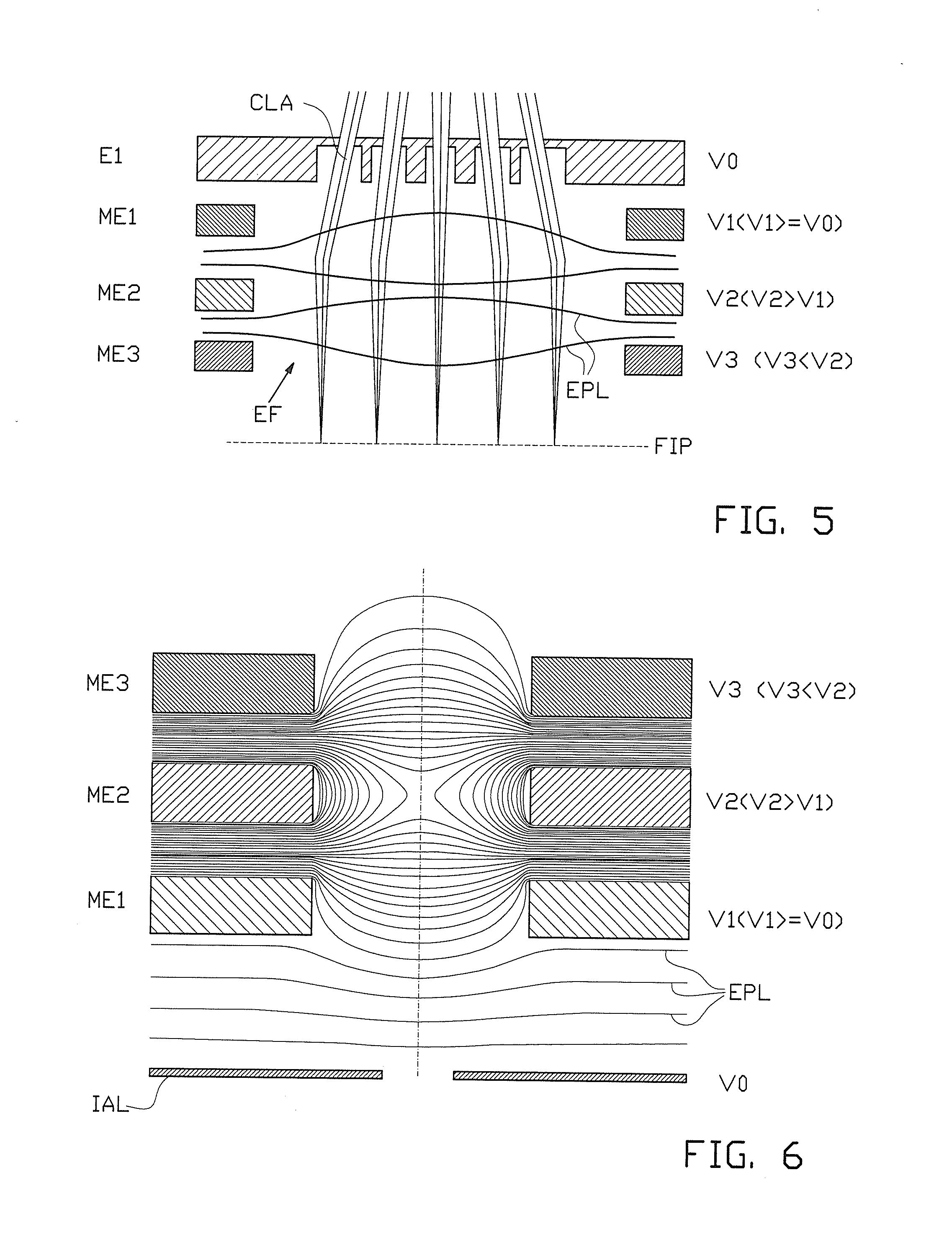
Particle-optic electrostatic lens
ActiveUS7199373B2Facilitate the magnetic shielding of an electrostatic lens systemReduce spacingStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsOptical axisParticle beam
In a charged-particle beam exposure device, an electrostatic lens (ML) comprises several (at least three) electrodes with rotational symmetry (EFR, EM, EFN) surrounding a particle beam path; the electrodes are arranged coaxially on a common optical axis representing the center of said particle beam path and are fed different electrostatic potentials through electric supplies. At least a subset of the electrodes (EM) form an electrode column realized as a series of electrodes of substantially equal shape arranged in consecutive order along the optical axis, wherein outer portions of said electrodes (EM) of the electrode column have outer portions (OR) of corresponding opposing surfaces (f1, f2) facing toward the next and previous electrodes, respectively. Preferably, the length of the electrode column is at least 4.1 times (3 times) the inner radius (ri1) of said surfaces (f1, f2).
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
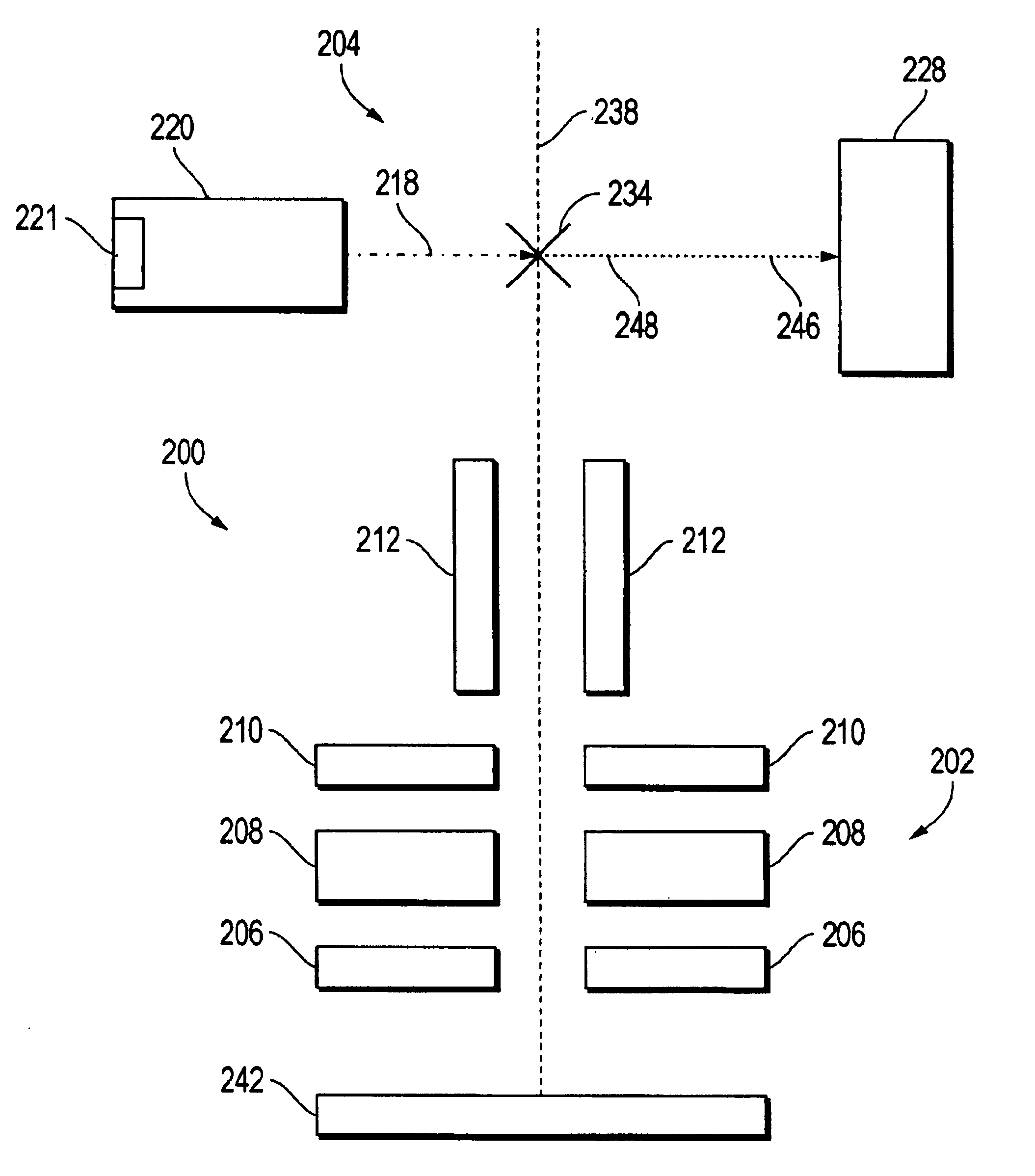
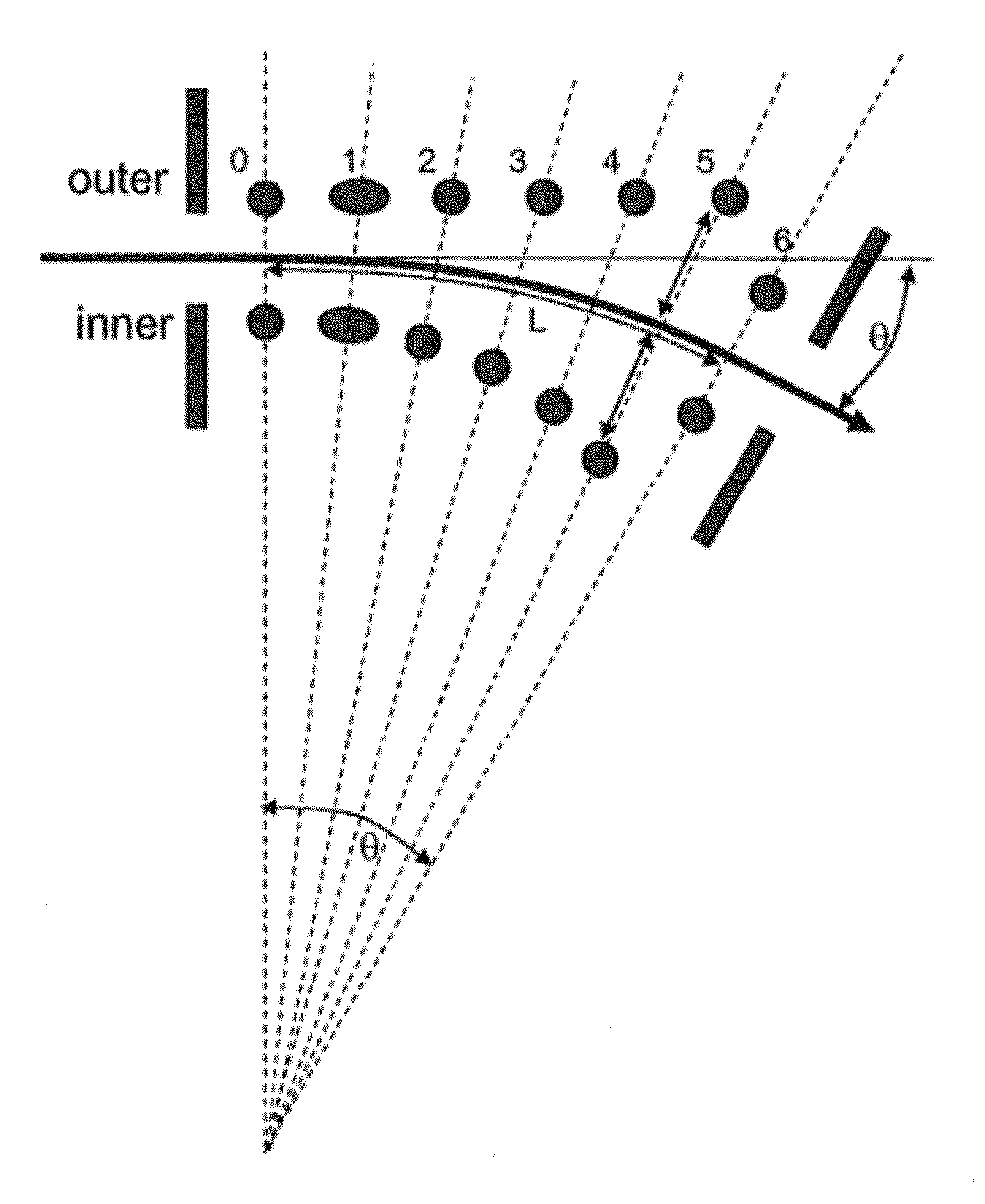
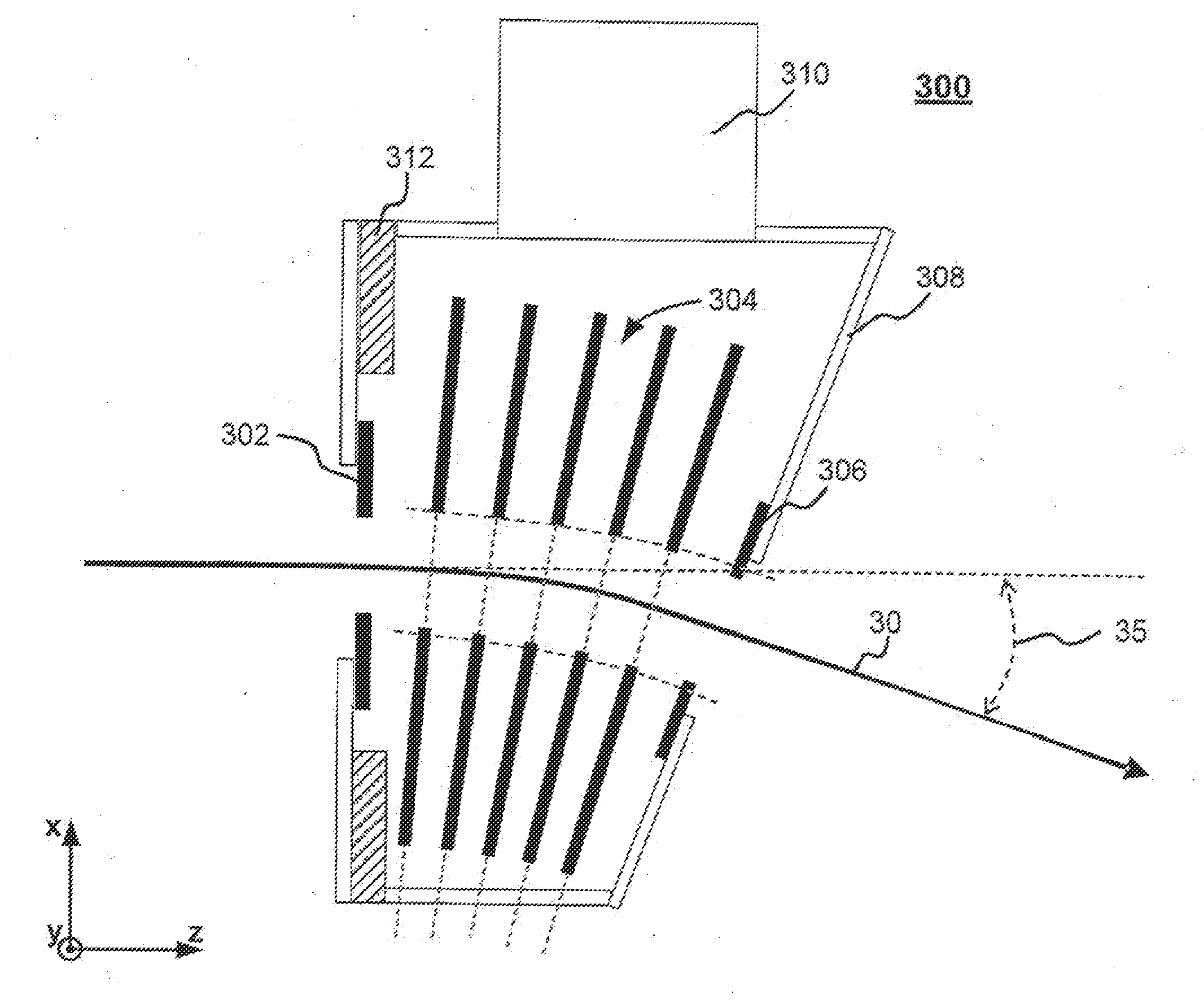
System and method for controlling deflection of a charged particle beam within a graded electrostatic lens
ActiveUS20110155921A1Small adjustmentKeep movingStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsControl systemLight beam
A method and apparatus for controlling deflection, deceleration, and focus of an ion beam are disclosed. The apparatus may include a graded deflection / deceleration lens including a plurality of upper and lower electrodes disposed on opposite sides of an ion beam, as well as a control system for adjusting the voltages applied to the electrodes. The difference in potential between pairs of upper and lower electrodes are varied using a set of “virtual knobs” that are operable to independently control deflection and deceleration of the ion beam. The virtual knobs include control of beam focus and residual energy contamination, control of upstream electron suppression, control of beam deflection, and fine tuning of the final deflection angle of the beam while constraining the beam's position at the exit of the lens. In one embodiment, this is done by fine tuning beam deflection while constraining the beam position at the exit of the VEEF. In another embodiment, this is done by fine tuning beam deflection while measuring the beam position and angle at the wafer plane. In a further embodiment, this is done by tuning a deflection factor to achieve a centered beam at the wafer plane.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Charged particle beam apparatus
InactiveUS7339167B2FunctionalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationThermometers using material expansion/contactionElectron sourceSecondary electrons
A charged particle beam apparatus in which an electrostatic lens is used as a main focusing element to obtain a subminiature high-sensitivity high-resolution SEM, a drift tube for an electron beam is located inside a column between an electron source and a sample, and a detector for secondary electrons is located inside the drift tube. This solves the problem associated with the provision of a secondary electron detector, which heretofore has been a bottleneck in making a subminiature high-resolution SEM column.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
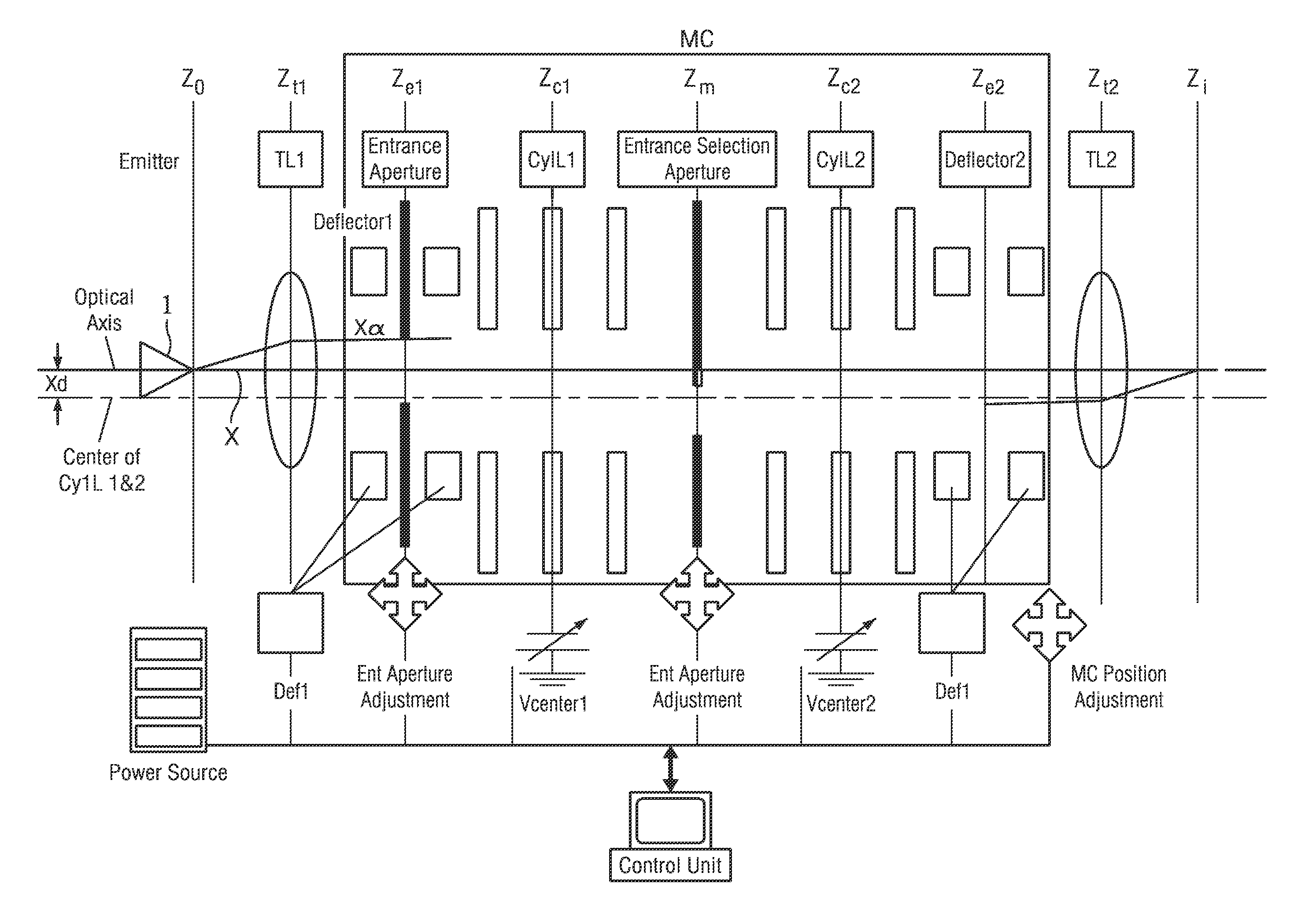
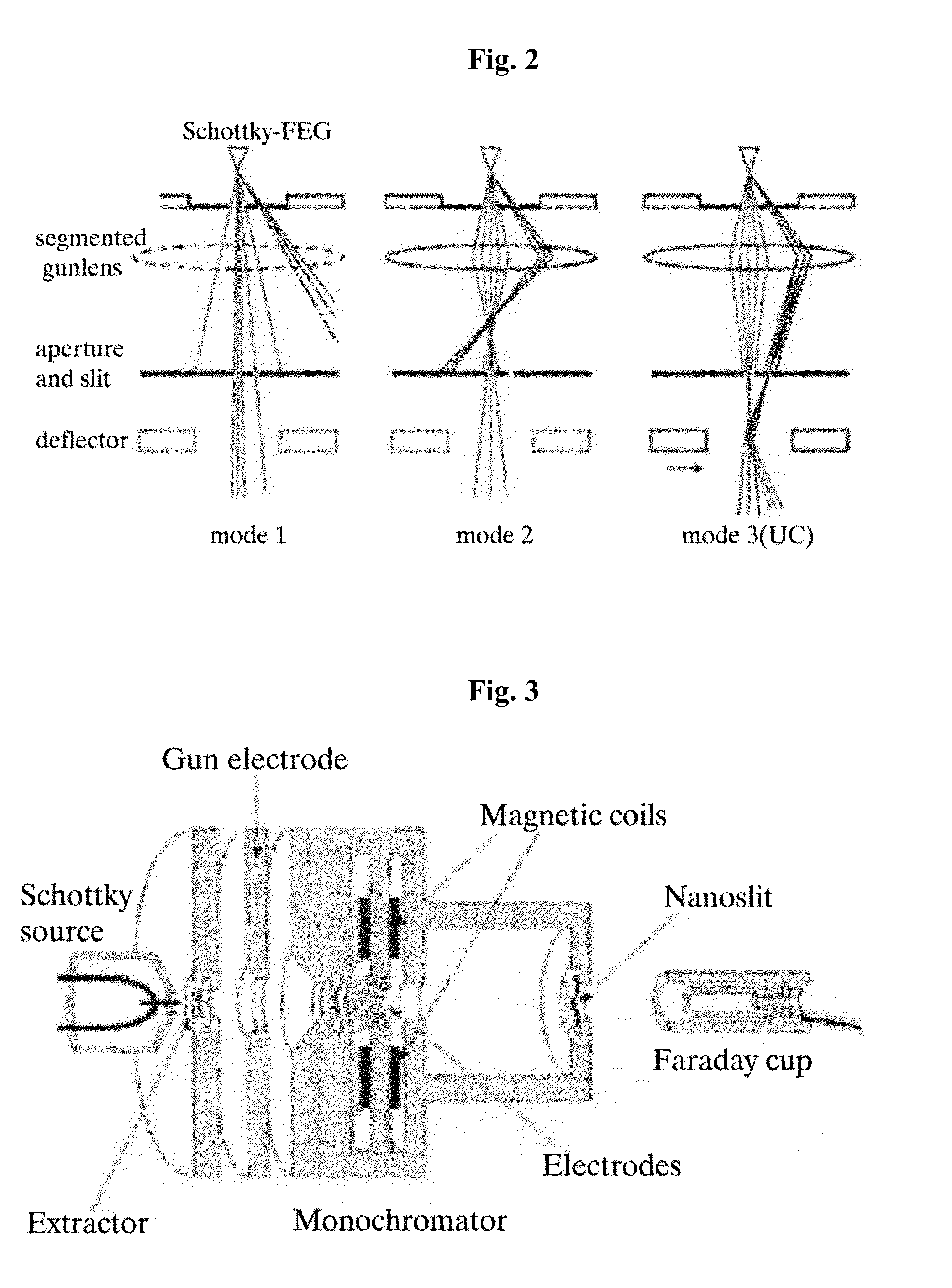
Monochromator and charged particle apparatus including the same
ActiveUS20150371811A1Enhance the imageStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMonochromatorMolecular physics
Disclosed herein are a monochromator and a charged particle beam apparatus including the same. The monochromator may include a first electrostatic lens configured to have a charged particle beam discharged by an emitter incident on the first electrostatic lens, refract a ray of the charged particle beam, and include a plurality of electrodes and a second electrostatic lens spaced apart from the first electrostatic lens at a specific interval and configured to have a central axis disposed identically with a central axis of the first electrostatic lens, have the charged particle beam output by the first electrostatic lens incident on the second electrostatic lens, refract the ray of the charged particle beam, and comprise a plurality of electrodes. Accordingly, there is an advantage in that a charged particle beam can have an excellent profile even after passing through the monochromator.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
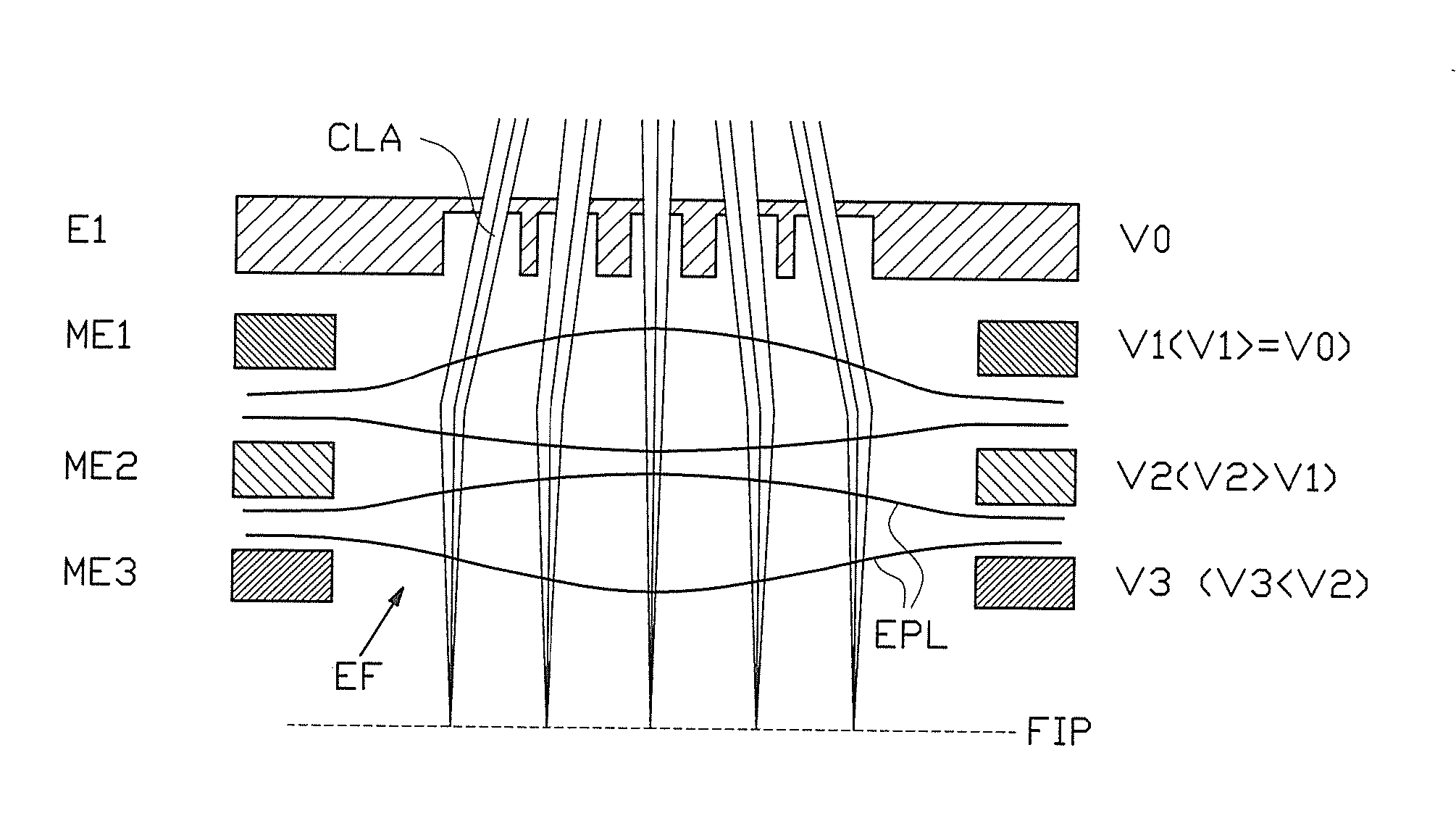
Multiple beam charged particle optical system
ActiveUS20080023643A1Small aperture lens strengthMinimize image aberrationStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCurrent limitingLight beam
The invention relates to a multiple beam charged particle optical system, comprising an electrostatic lens structure with at least one electrode, provided with apertures, wherein the effective size of a lens field effected by said electrode at a said aperture is made ultimately small. The system may comprise a diverging charged particle beam part, in which the lens structure is included. The physical dimension of the lens is made ultimately small, in particular smaller than one mm, more in particular less than a few tens of microns. In further elaboration, a lens is combined with a current limiting aperture, aligned such relative to a lens of said structure, that a virtual aperture effected by said current limiting aperture in said lens is situated in an optimum position with respect to minimizing aberrations total.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Multiple beam charged particle optical system
ActiveUS8294117B2Accurately determinedHighly accurate laser interferometersStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical axisMulti beam
The invention relates to a multiple beam charged particle optical system comprising:a charged particle source for generating a plurality of charged particle beamlets, andcharged particle optics for directing the charged particle beamlets from the charged particle source towards a target, wherein each charged particle beamlet defines a beamlet center line, said charged particle optics comprising one or more electrostatic lens arrays, each comprising two or more array electrodes for generating a plurality of electrostatic lenslets, wherein each lenslet is arranged for focusing a corresponding charged particle beamlet, and wherein each lenslet defines a lenslet optical axis, wherein at least one of said one or more electrostatic lens arrays comprises one or more off-axis electrostatic lenslets, wherein the beamlet center line of the corresponding charged particle beamlet passes through said off-axis electrostatic lenslet at a distance from its lenslet optical axis.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Multiple beam charged particle optical system
ActiveUS20110068276A1Accurately determinedHighly accurate laser interferometersStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical axisMulti beam
The invention relates to a multiple beam charged particle optical system comprising:a charged particle source for generating a plurality of charged particle beamlets, andcharged particle optics for directing the charged particle beamlets from the charged particle source towards a target, wherein each charged particle beamlet defines a beamlet centre line, said charged particle optics comprising one or more electrostatic lens arrays, each comprising two or more array electrodes for generating a plurality of electrostatic lenslets, wherein each lenslet is arranged for focusing a corresponding charged particle beamlet, and wherein each lenslet defines a lenslet optical axis, wherein at least one of said one or more electrostatic lens arrays comprises one or more off-axis electrostatic lenslets, wherein the beamlet centre line of the corresponding charged particle beamlet passes through said off-axis electrostatic lenslet at a distance from its lenslet optical axis.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Charged Particle System
ActiveUS20080210887A1Enhance the imageImprove imaging effectElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsPole pieceProjection system
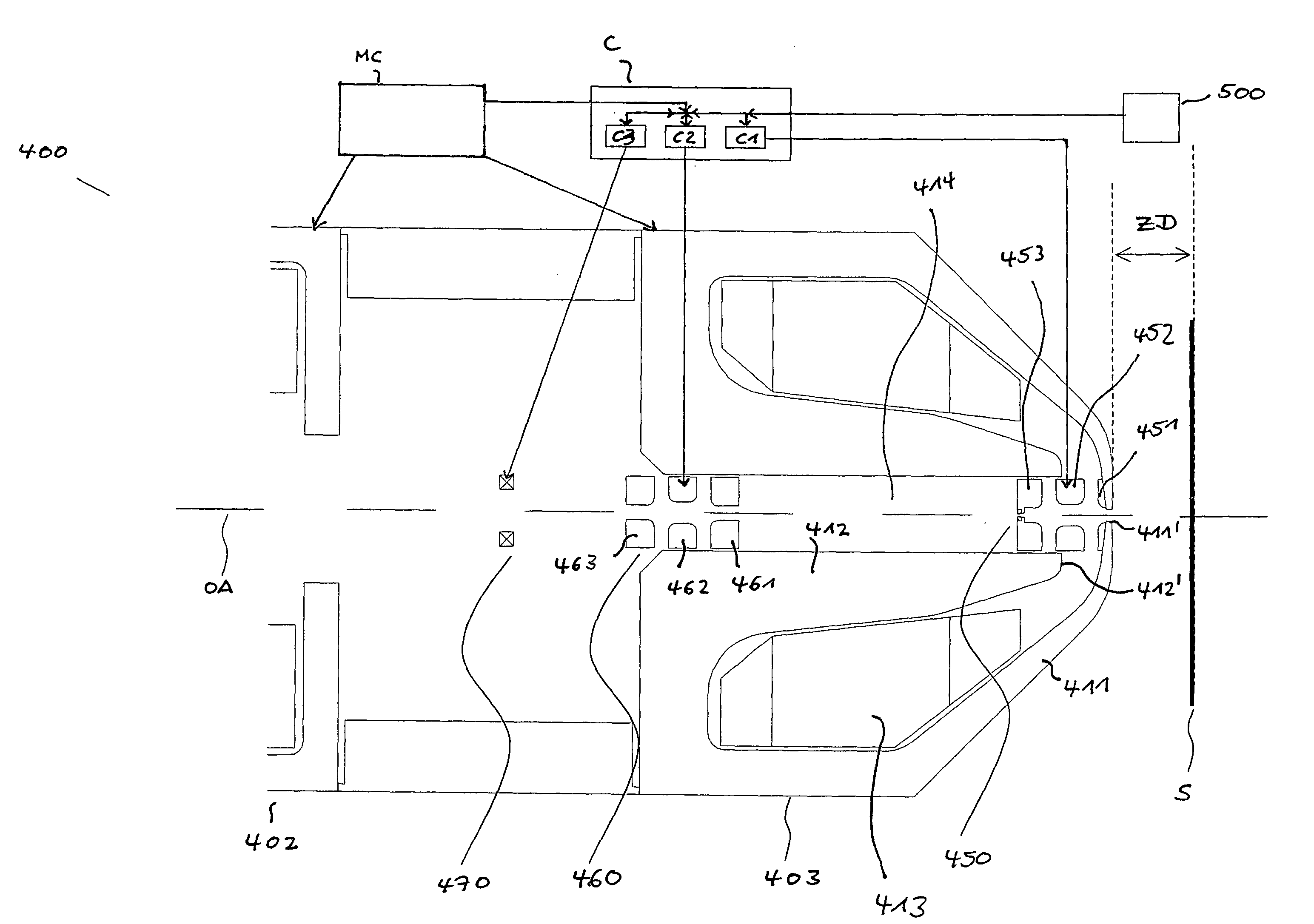
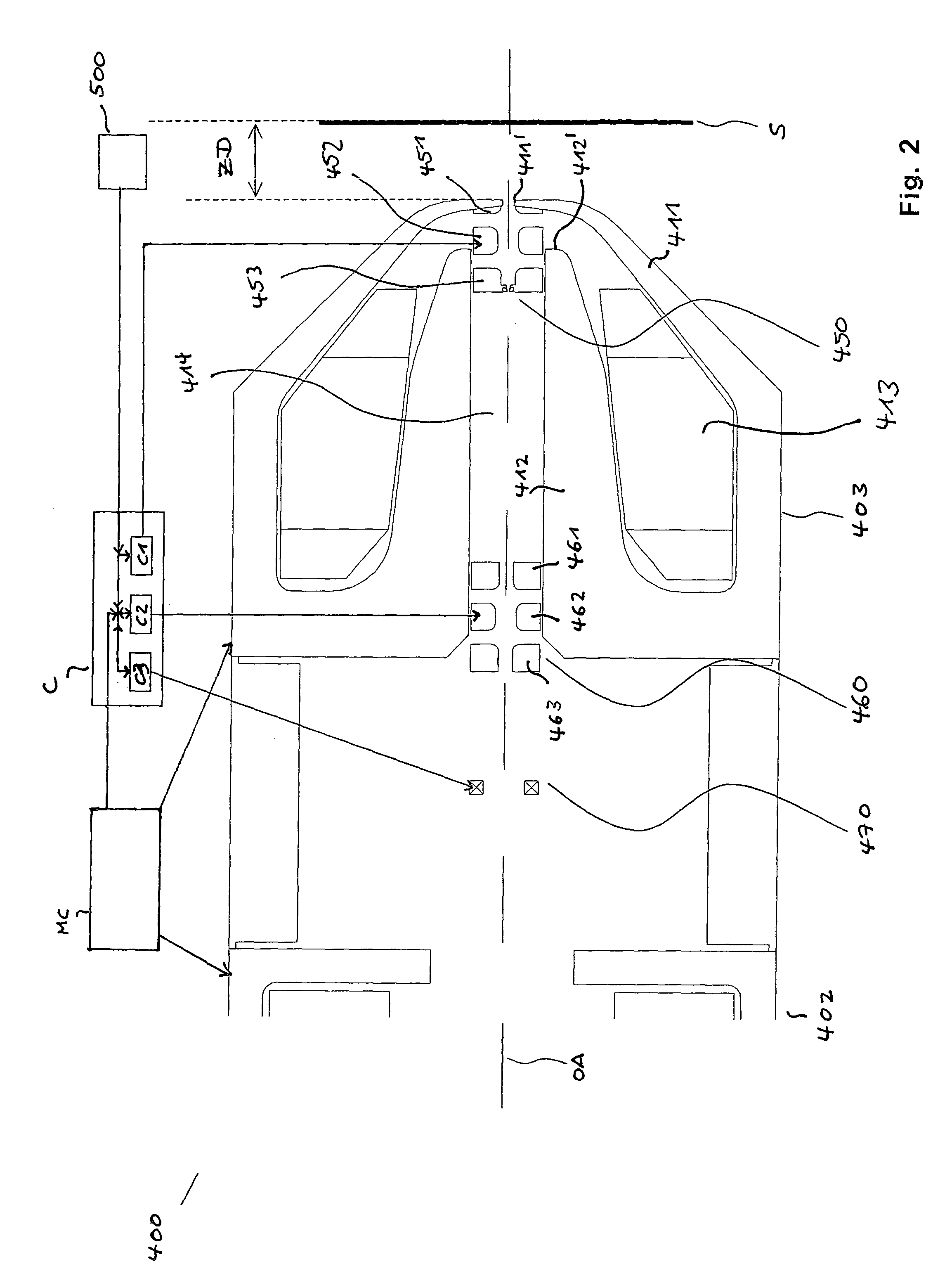
A charged particle system comprises a particle source for generating a beam of charged particles and a particle-optical projection system. The particle-optical projection system comprises a focusing first magnetic lens (403) comprising an outer pole piece (411) having a radial inner end (411′), and an inner pole piece (412) having a lowermost end (412′) disposed closest to the radial inner end of the outer pole piece, a gap being formed by those; a focusing electrostatic lens (450) having at least a first electrode (451) and a second electrode (450) disposed in a region of the gap; and a controller (C) configured to control a focusing power of the first electrostatic lens based on a signal indicative of a distance of a surface of a substrate from a portion of the first magnetic lens disposed closest to the substrate.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Electron beam apparatus to collect side-view and/or plane-view image with in-lens sectional detector
ActiveUS7705301B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron sourceSecondary electrons
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
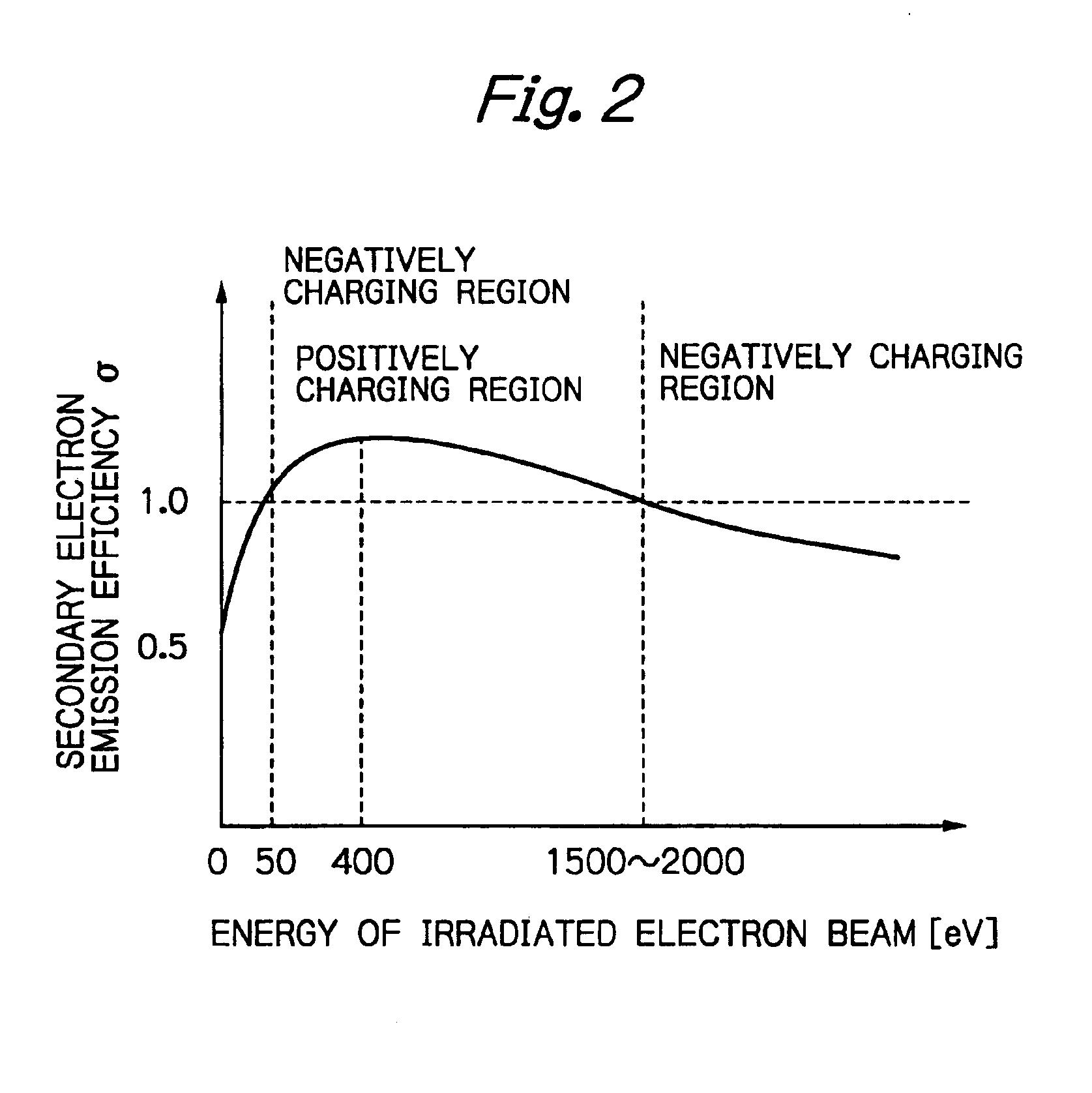
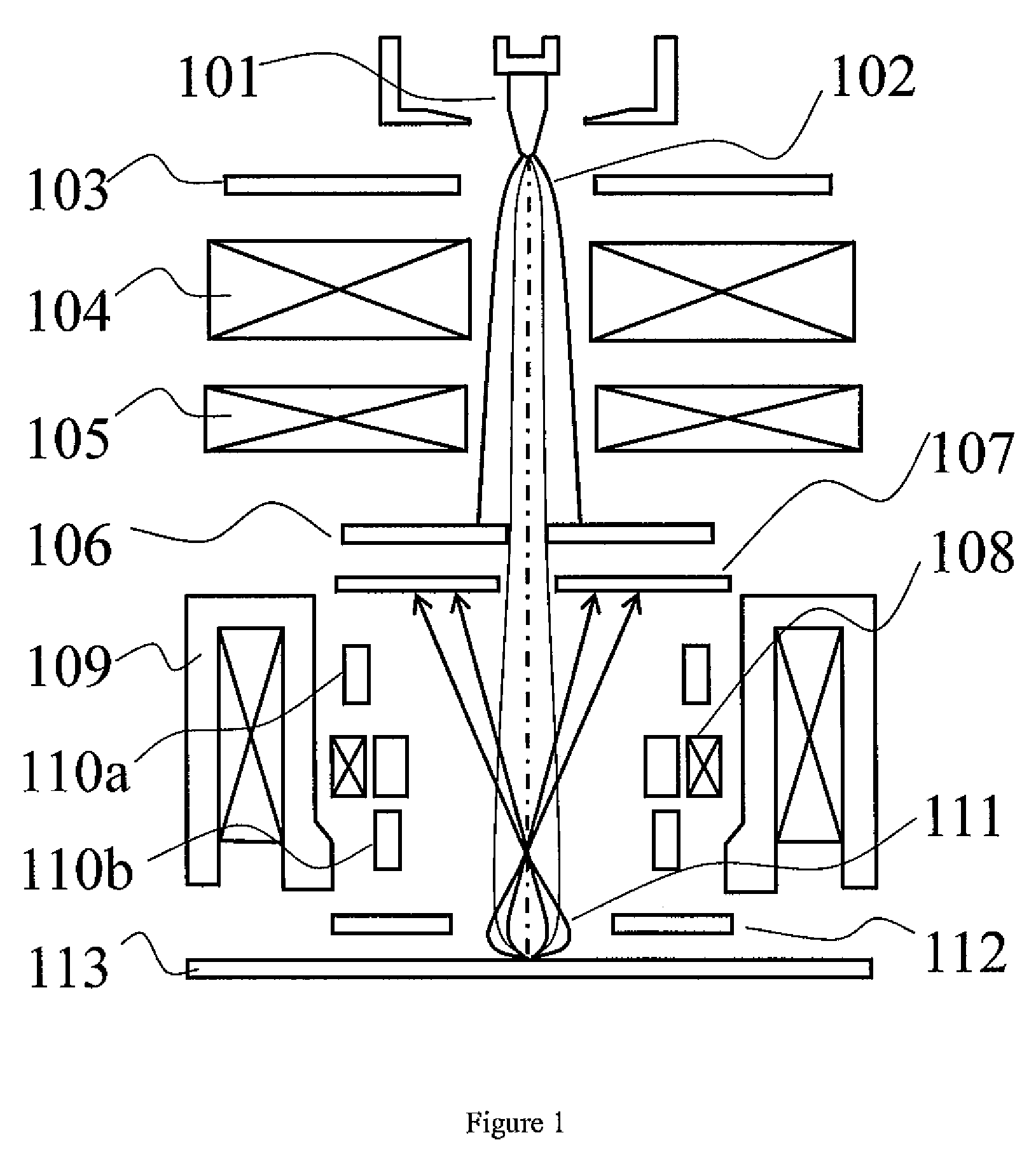
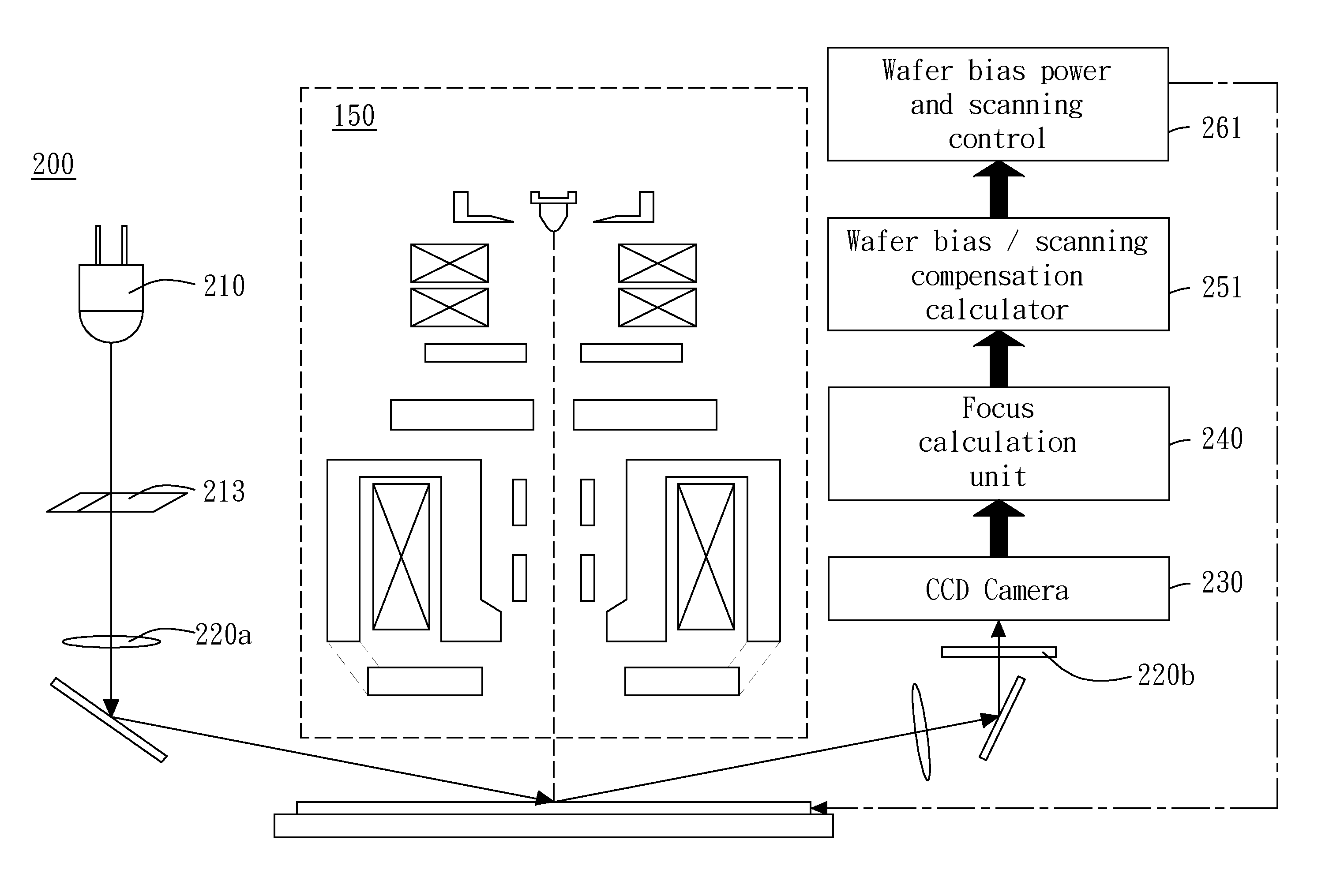
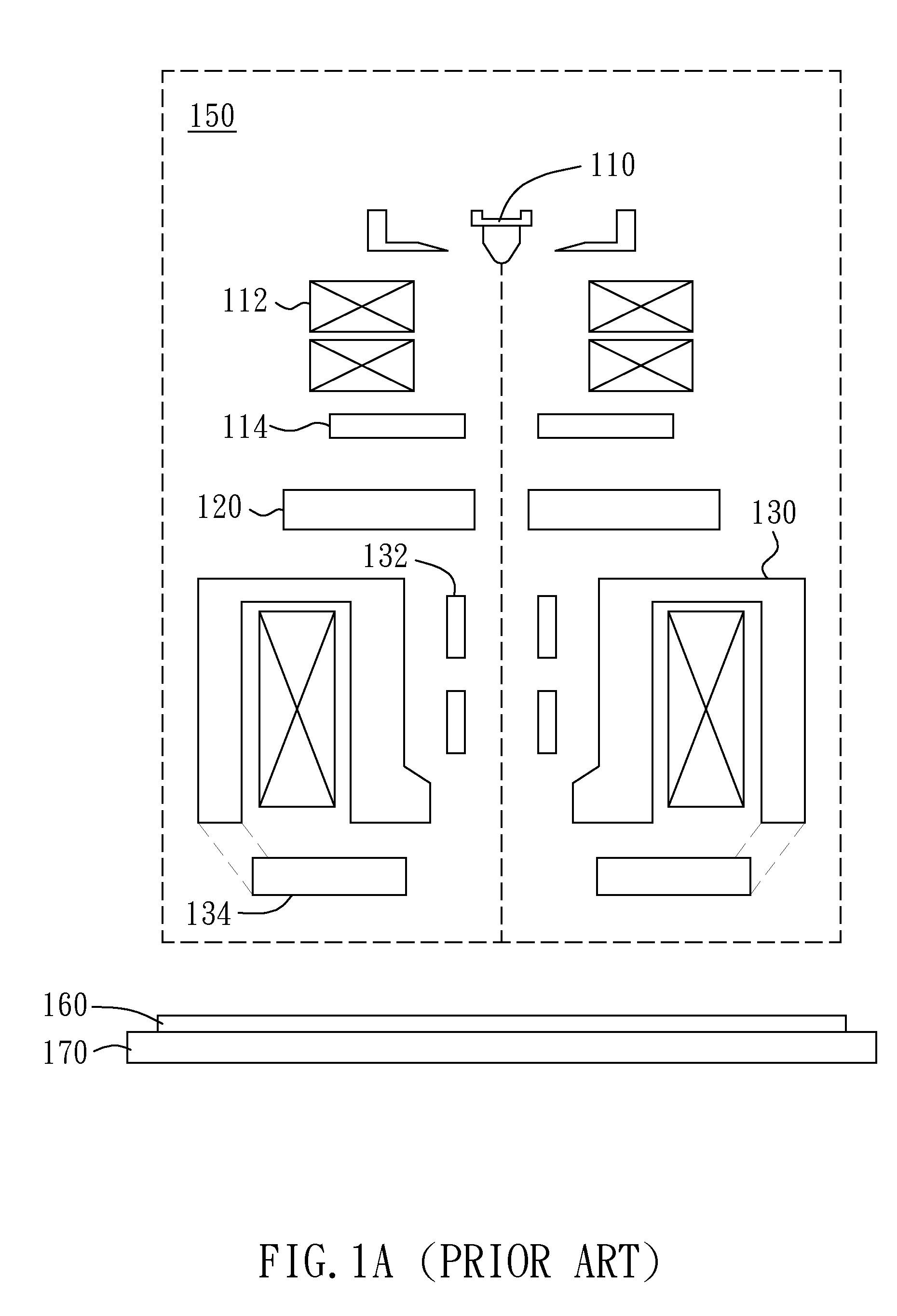
Dynamic Focus Adjustment with Optical Height Detection Apparatus in Electron Beam system
ActiveUS20110260055A1Adjust focusElectric discharge tubesUsing optical meansField strengthImage system
The present invention generally relates to dynamic focus adjustment for an image system. With the assistance of a height detection sub-system, present invention provides an apparatus and methods for micro adjusting an image focusing according the specimen surface height variation by altering the field strength of an electrostatic lens between objective lens and sample stage / or a bias voltage applied to the sample surface. Merely by way of example, the invention has been applied to a scanning electron inspection system. But it would be recognized that the invention could apply to other system using charged particle beam as observation tool with a height detection apparatus.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Semiconductor wafer metrology apparatus and method
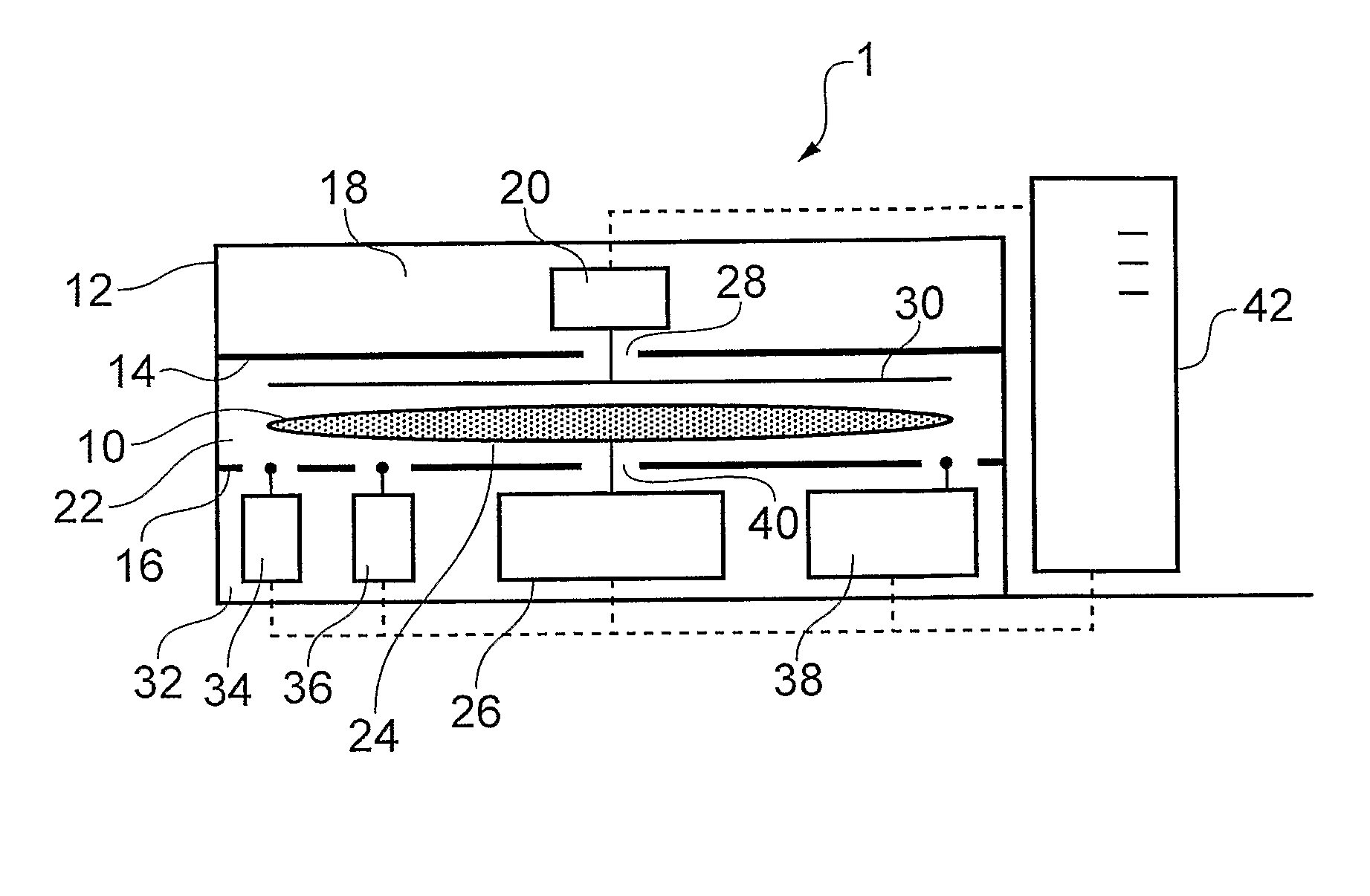
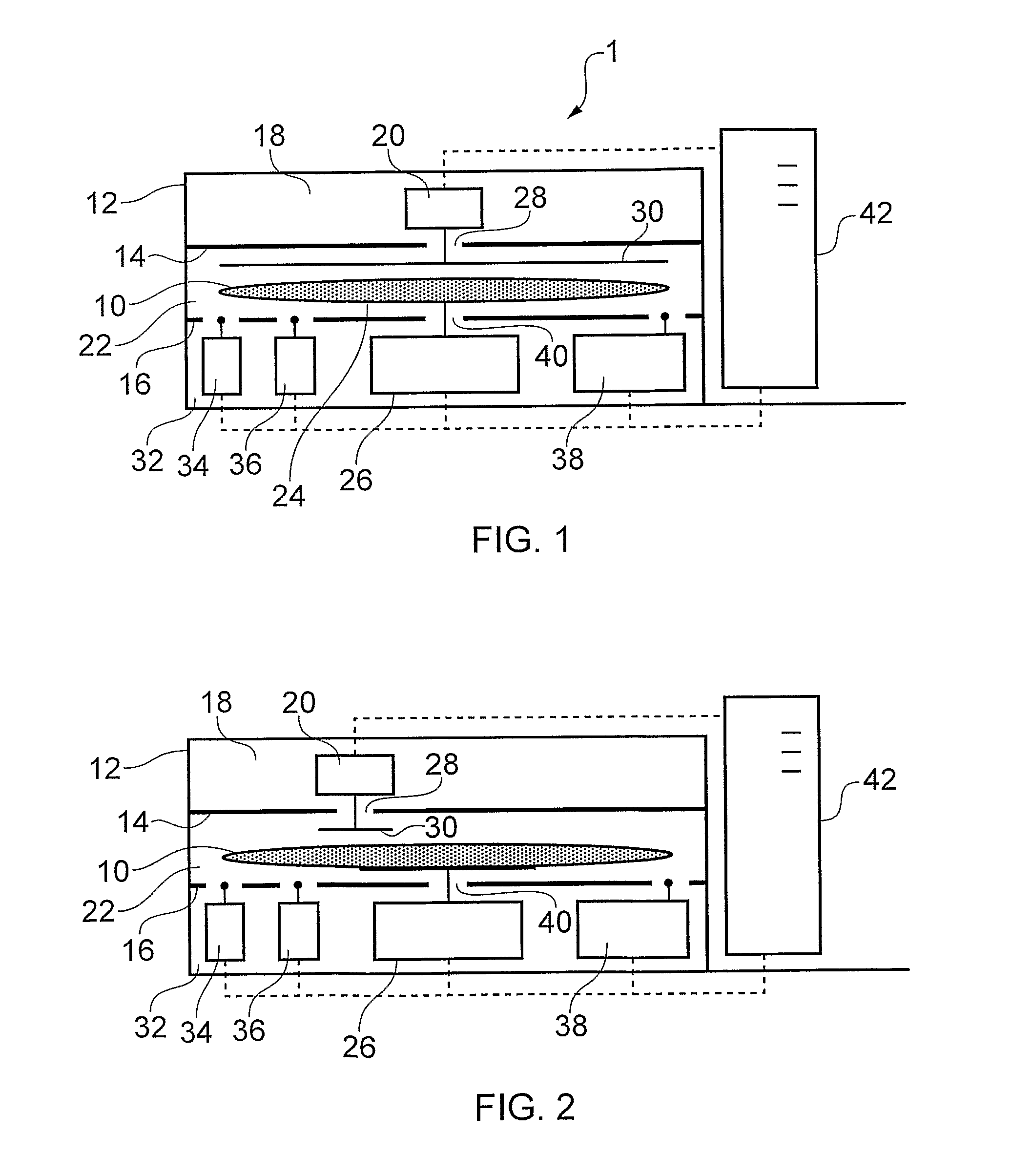
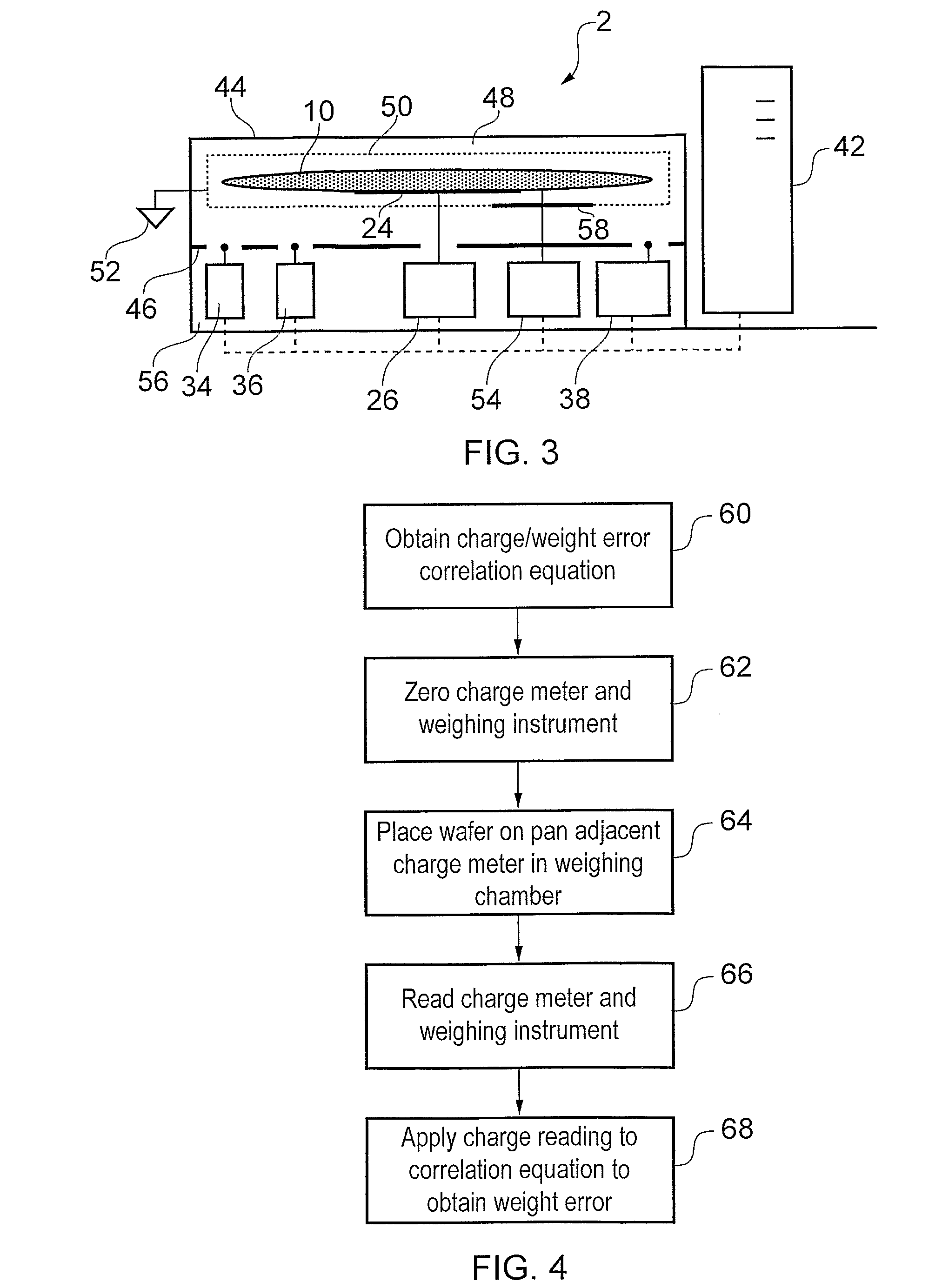
ActiveUS20100206098A1Eliminate the effects ofThe effect is accurateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWeighing auxillary devicesMetrologySemiconductor
A semiconductor wafer metrology technique which corrects for the effect of electrostatic forces on an atmospheric buoyancy compensated weight force measurement of a semiconductor wafer. In one aspect a wafer is weighed in a faraday cage whose is measured independently. A change in the measured weight of the faraday cage can be used to correct the measure weight the wafer. In another aspect a direct electrostatic measurement can be converted into a weight correction using a predetermined correlation between an electrostatic charge measured by the charge meter and a weight error force. In another aspect the electrostatic measurement may be indirect, e.g. derived from varying the distance between the wafer and a grounded plate parallel to the wafer to effect a change in an electrostatic force between the grounded plate and the wafer.
Owner:METRYX
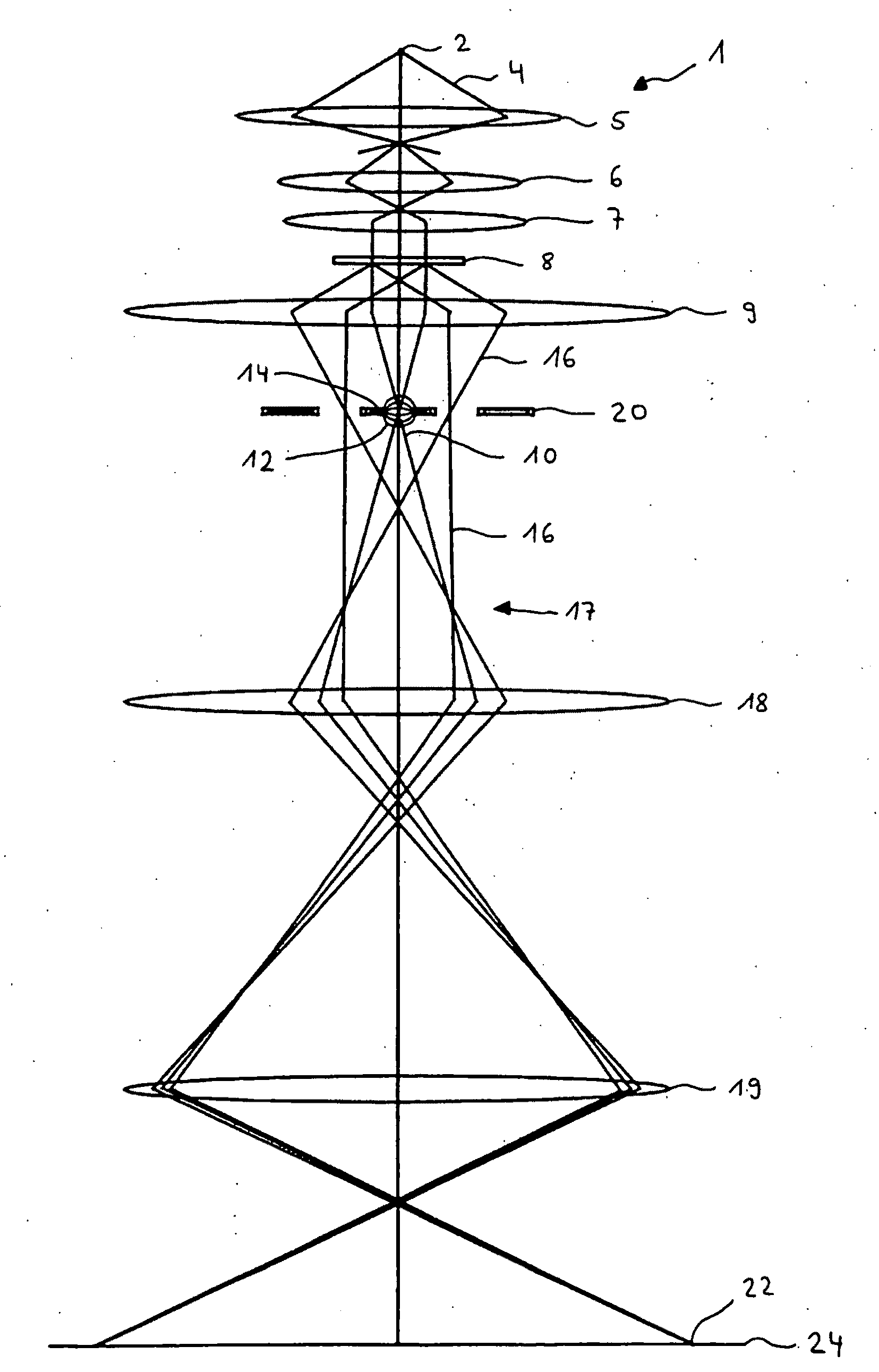
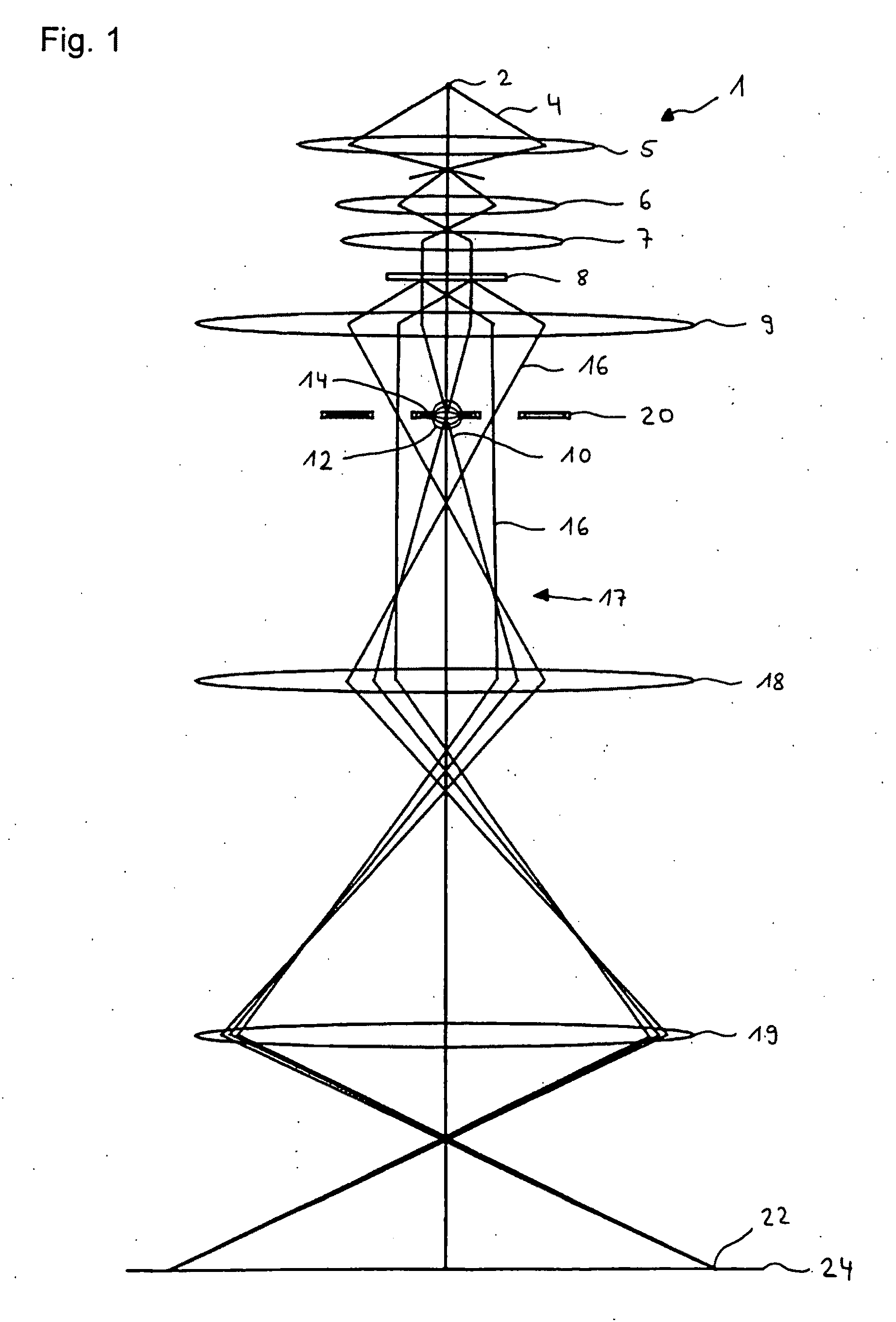
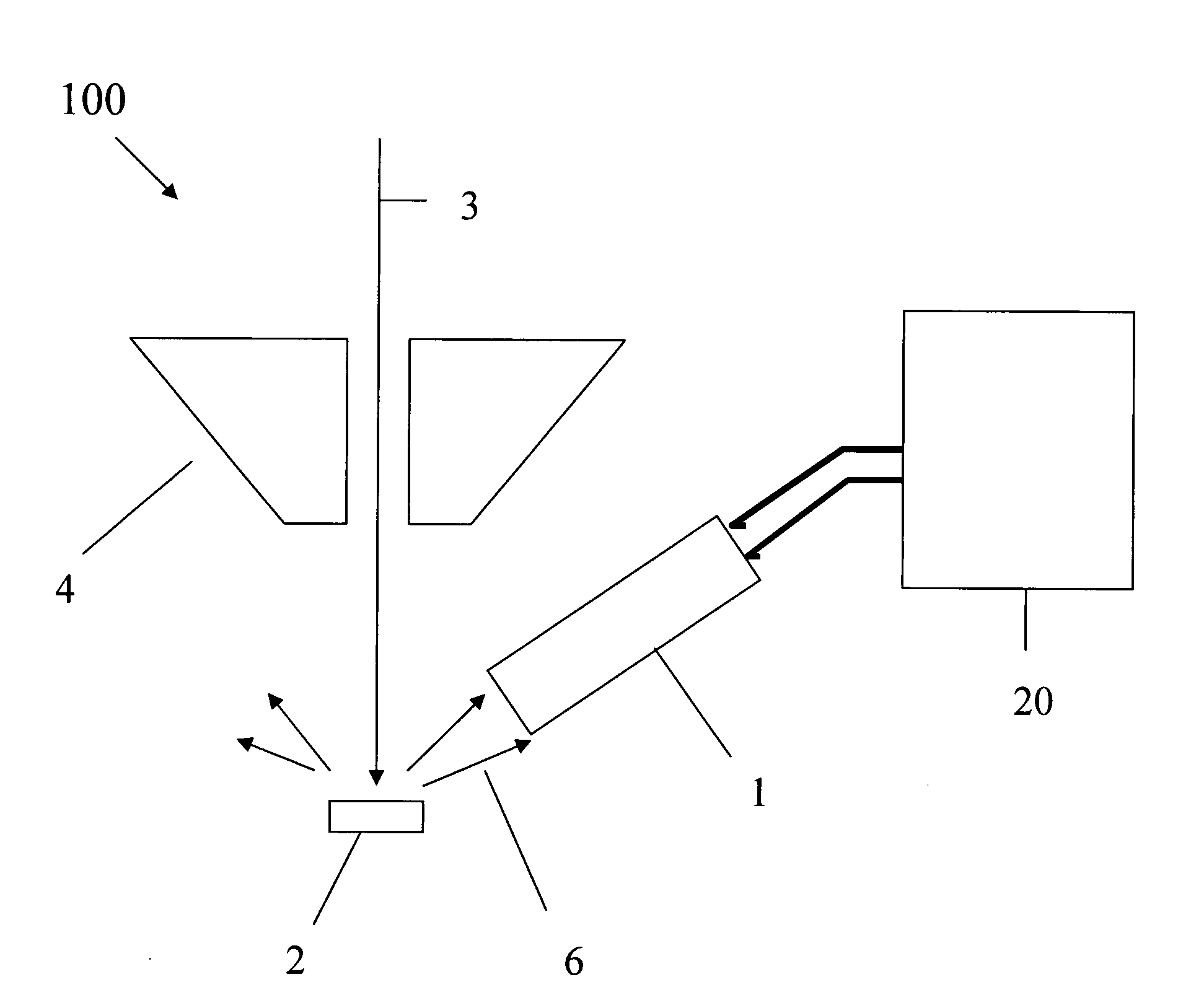
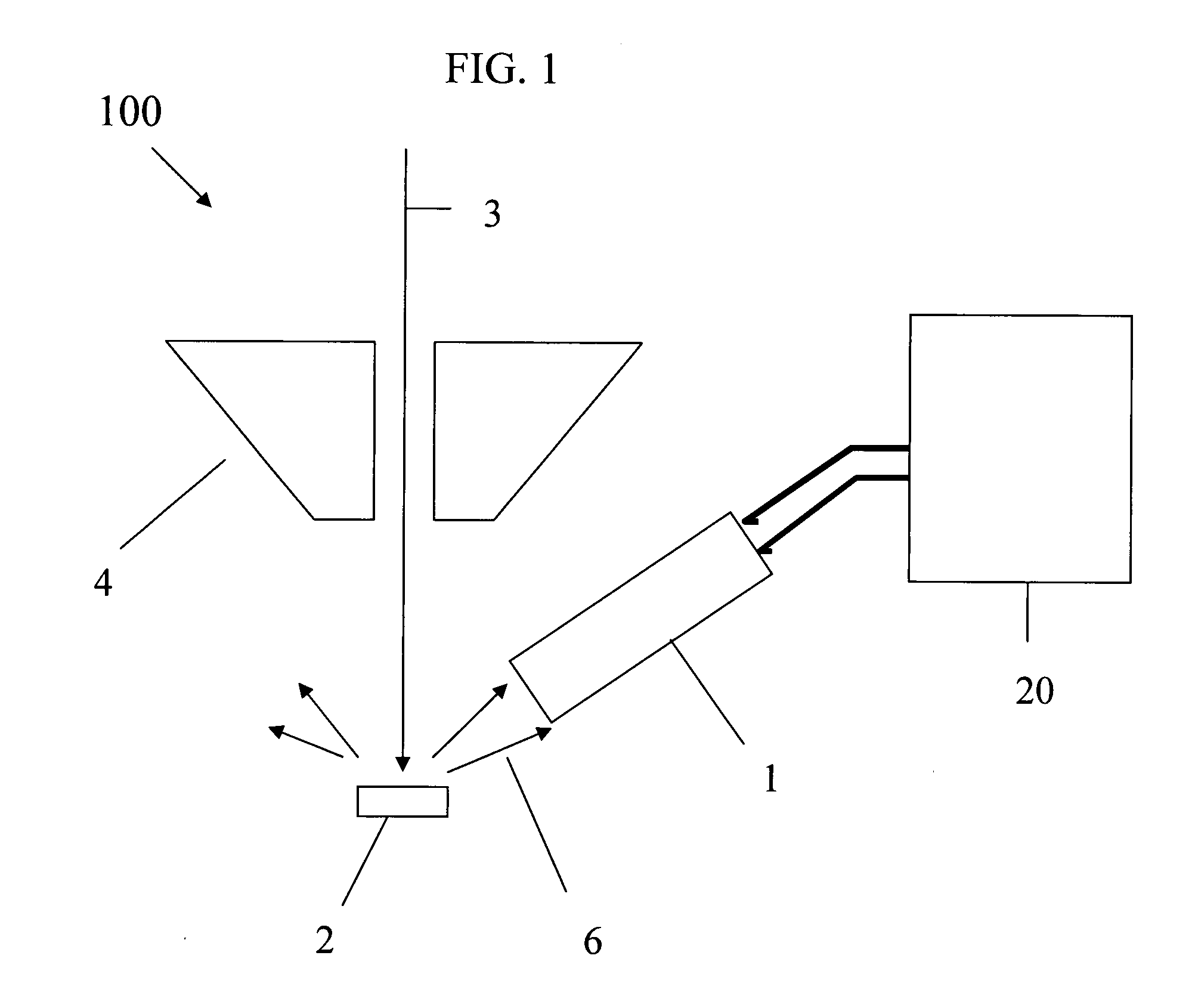
Charged particle analyser and method
ActiveUS20100163725A1High acceptance angleReduce lossParticle separator tubesPhotoelectric discharge tubesCharged particle detectorsParticle physics
A charged particle analyser (1) comprises a first non-imaging electrostatic lens (8, 9) for receiving charged particles having divergent, trajectories and for converting the said trajectories into substantially parallel trajectories. At least one planar filter (10) is provided for receiving the charged particles having the substantially parallel trajectories and for filtering the charged particles in accordance with their respective energies. A second non-imaging electrostatic lens (11) receives the energy filtered charged particles and selectively modifies their trajectories as a function of their energies. A charged particle detector (12) then receives the charged particles in accordance with their selectively modified trajectories.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR NANOTECH TOOLS
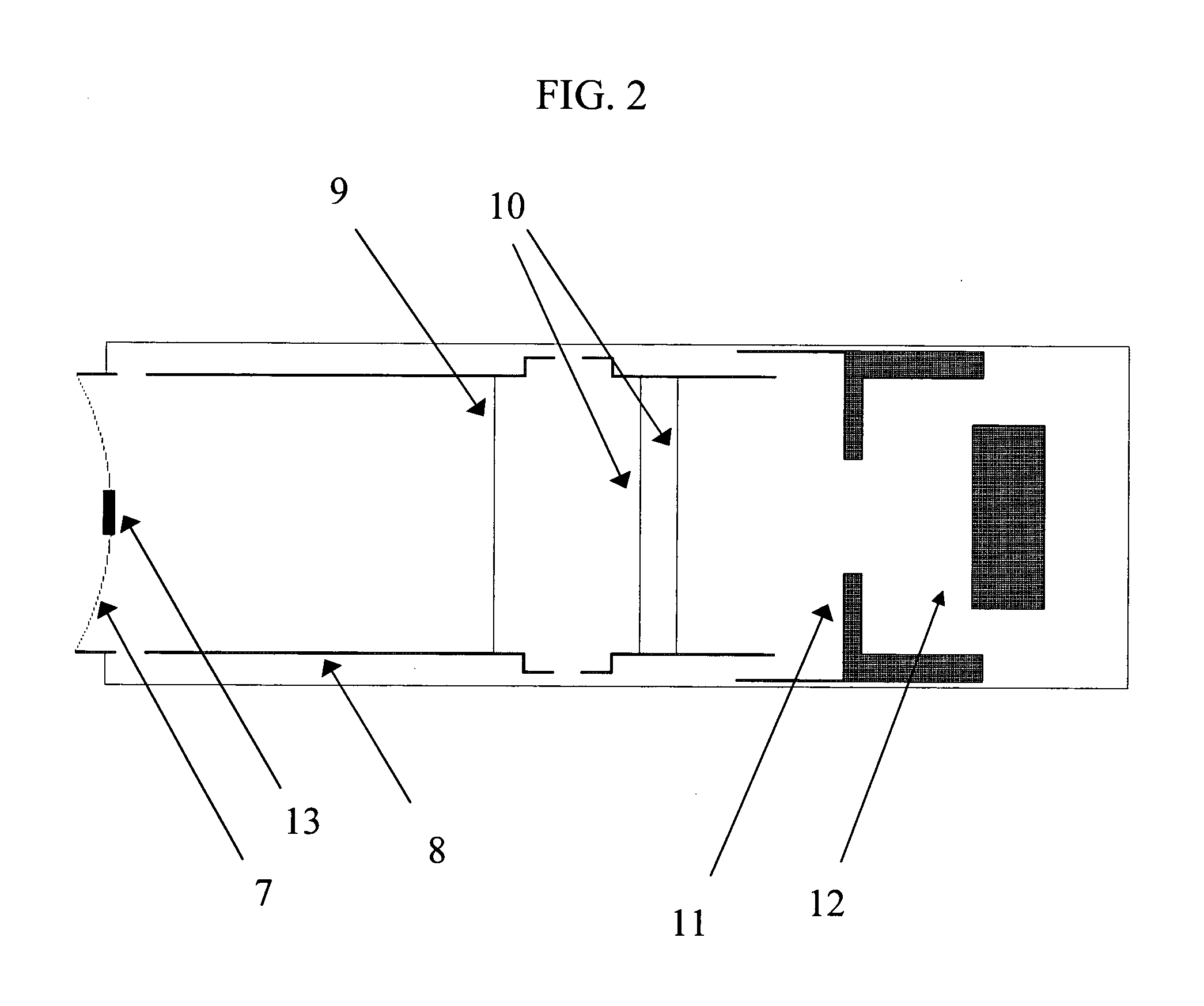
Aberration-correcting cathode lens microscopy instrument
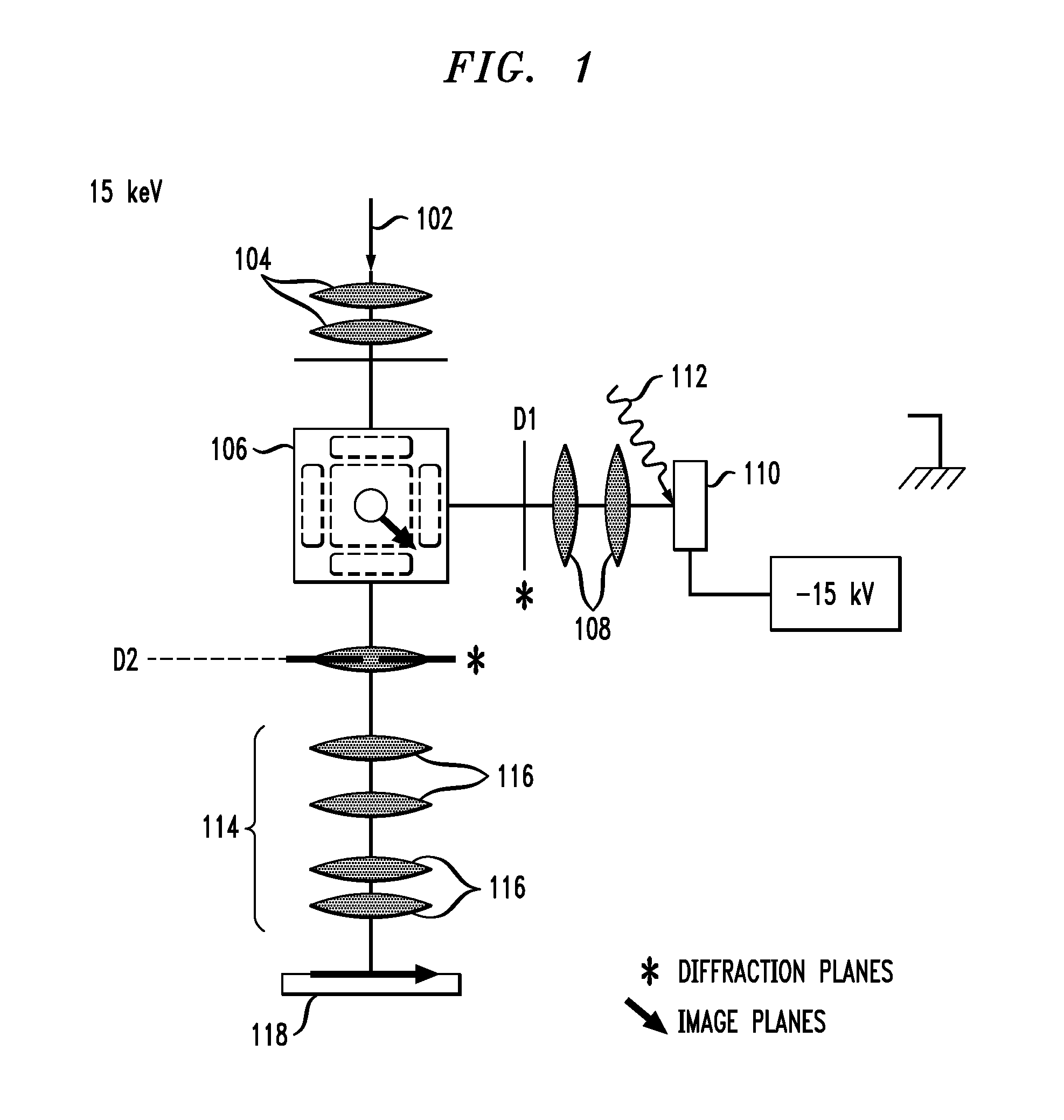
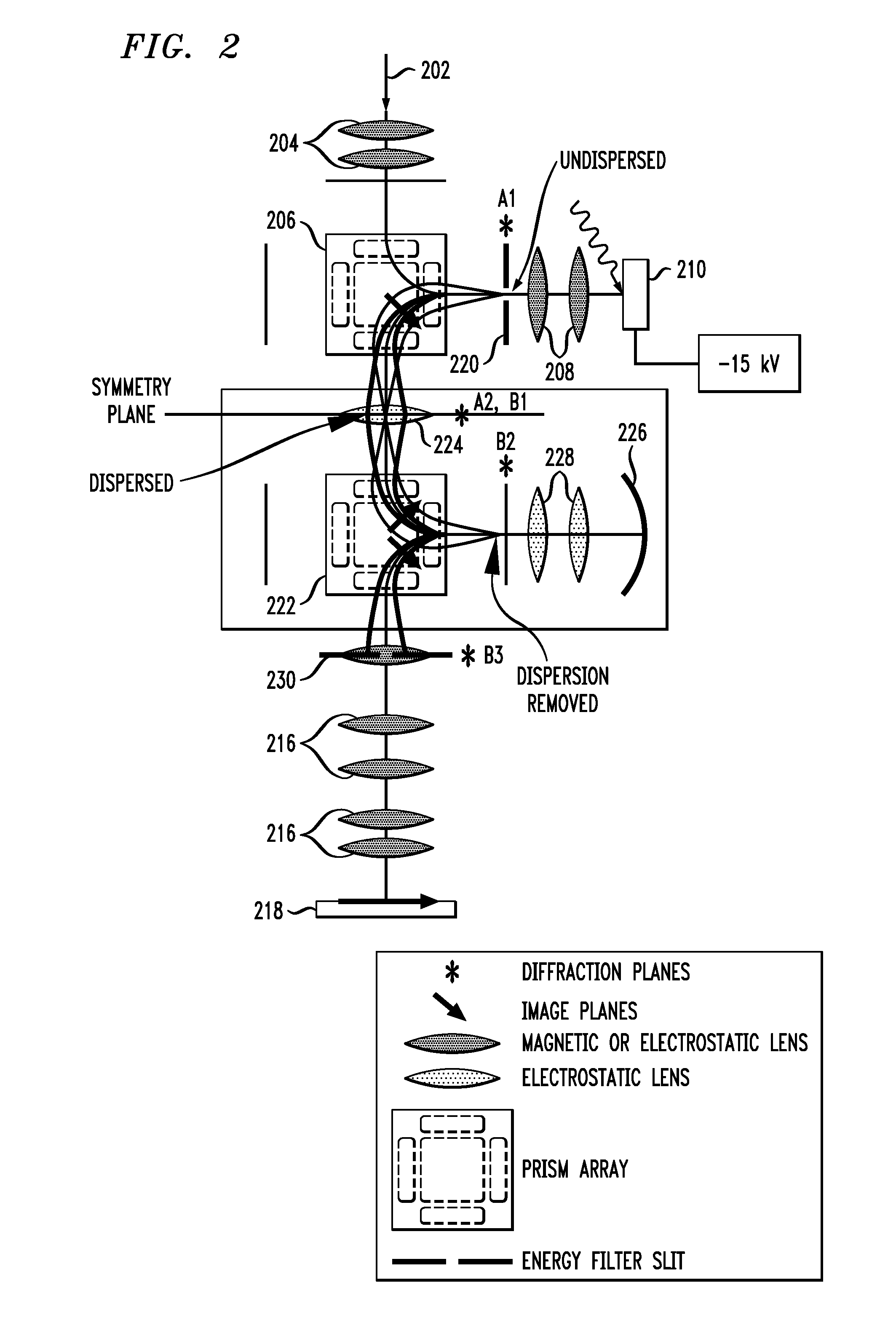
ActiveUS20070200070A1Stability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationExit planeElectron diffraction pattern
An aberration-correcting microscopy instrument is provided. The instrument has a first magnetic deflector disposed for reception of a first non-dispersed electron diffraction pattern. The first magnetic deflector is also configured for projection of a first energy dispersed electron diffraction pattern in an exit plane of the first magnetic deflector. The instrument also has an electrostatic lens disposed in the exit plane of a first magnetic deflector, as well as a second magnetic deflector substantially identical to the first magnetic deflector. The second magnetic deflector is disposed for reception of the first energy dispersed electron diffraction pattern from the electrostatic lens. The second magnetic deflector is also configured for projection of a second non-dispersed electron diffraction pattern in a first exit plane of the second magnetic deflector. The instrument also has an electron mirror configured for correction of one or more aberrations in the second non-dispersed electron diffraction pattern. The electron mirror is disposed for reflection of the second non-dispersed electron diffraction pattern to the second magnetic deflector for projection of a second energy dispersed electron diffraction pattern in a second exit plane of the second magnetic deflector.
Owner:IBM CORP
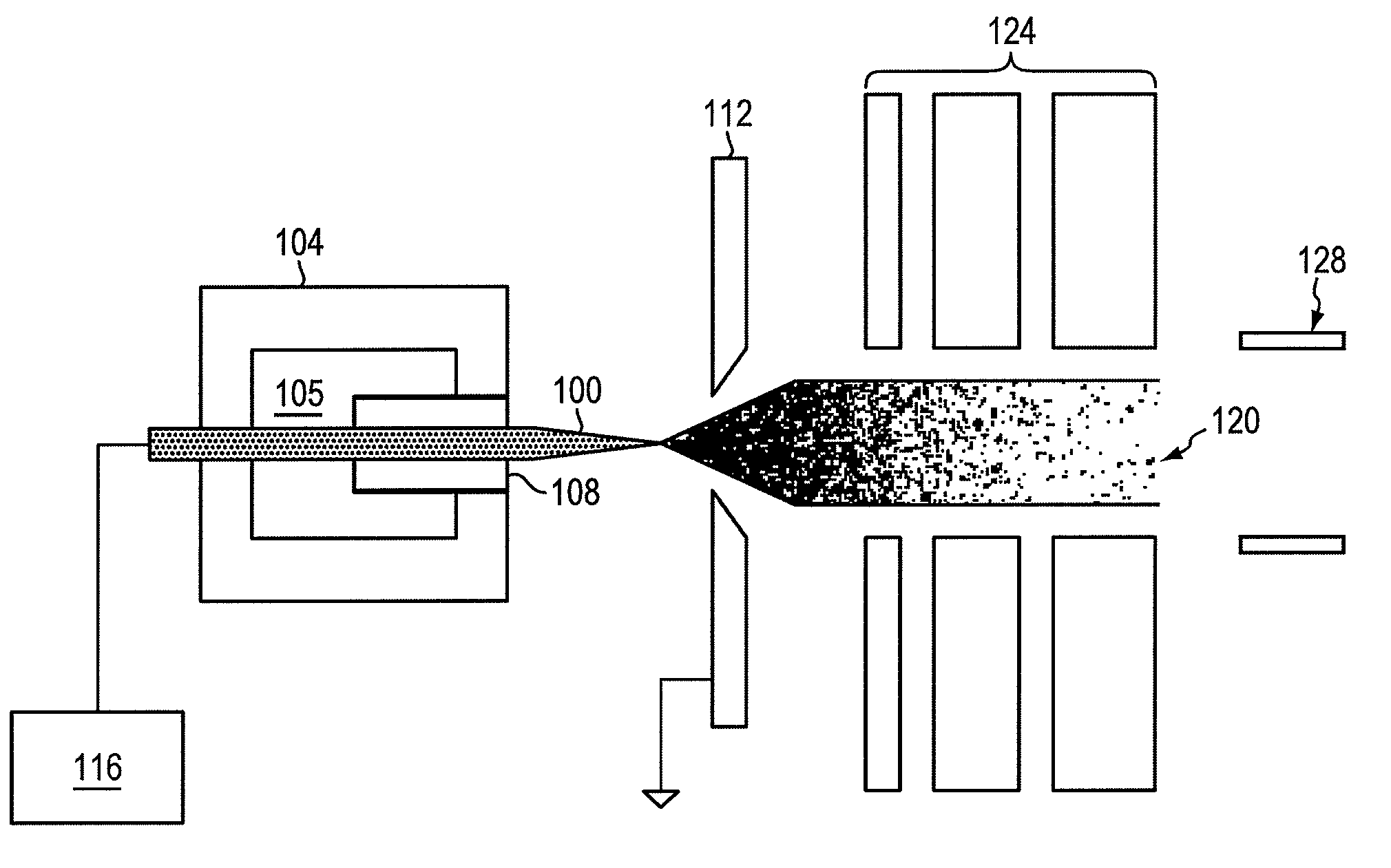
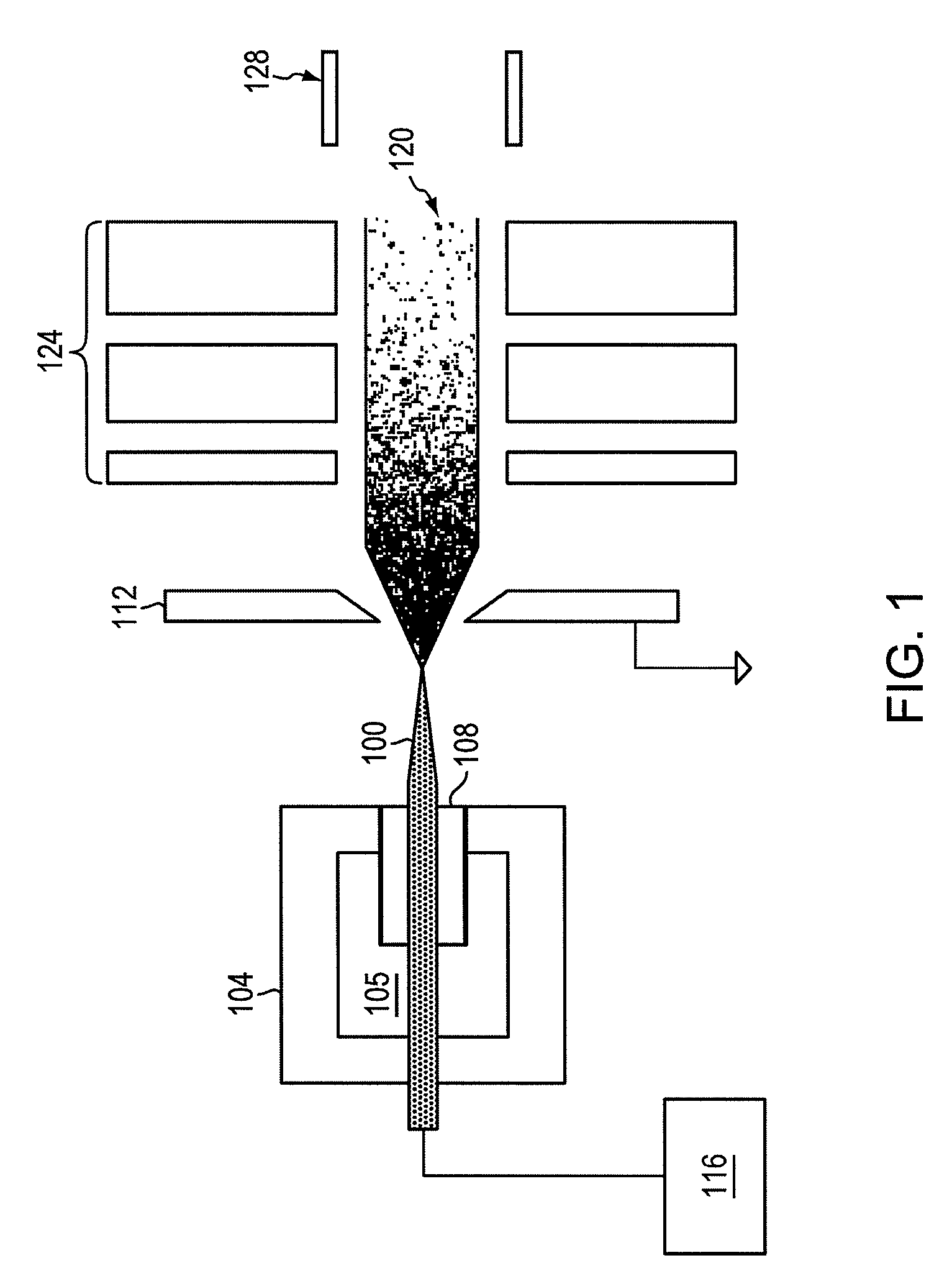
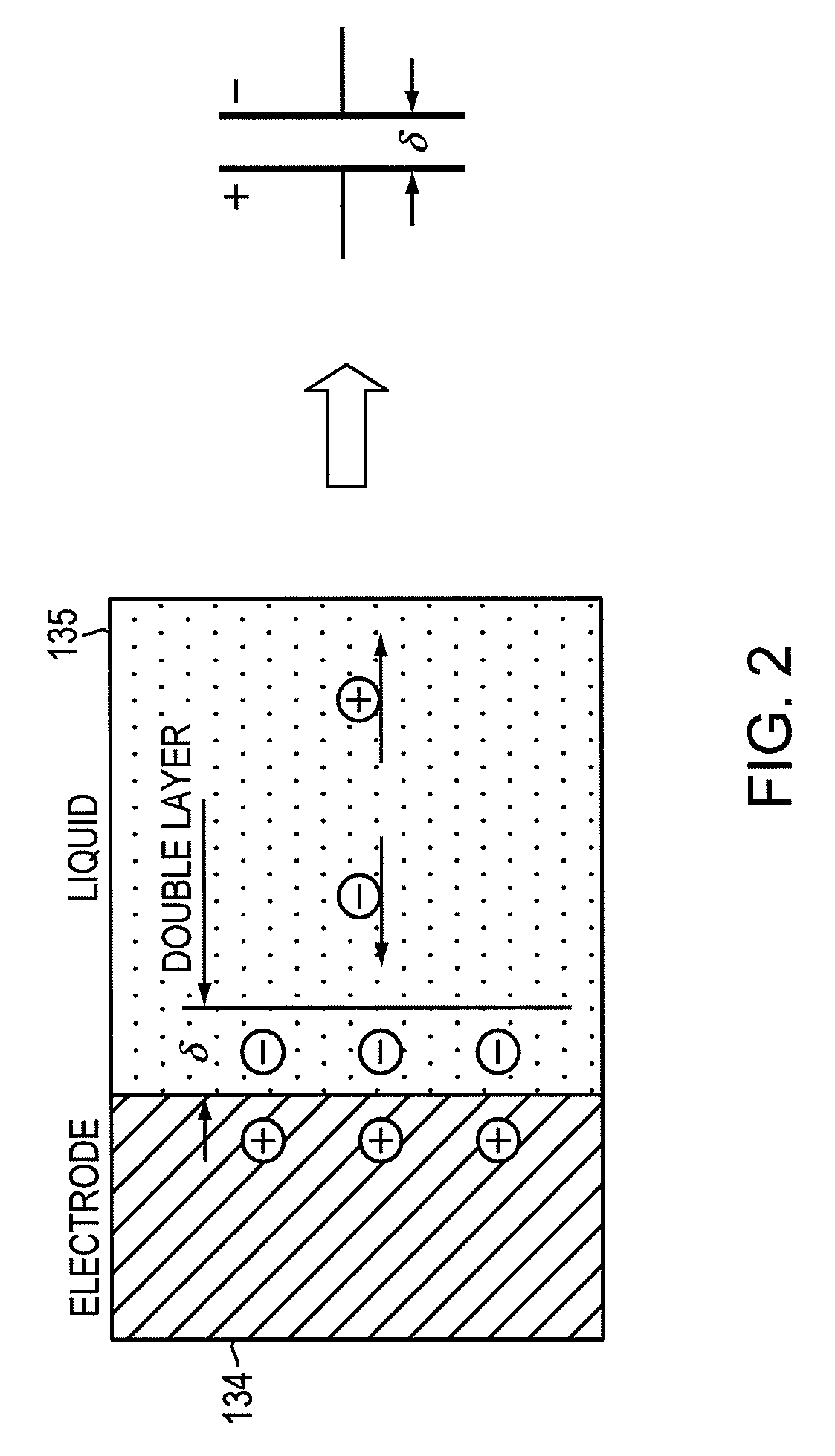
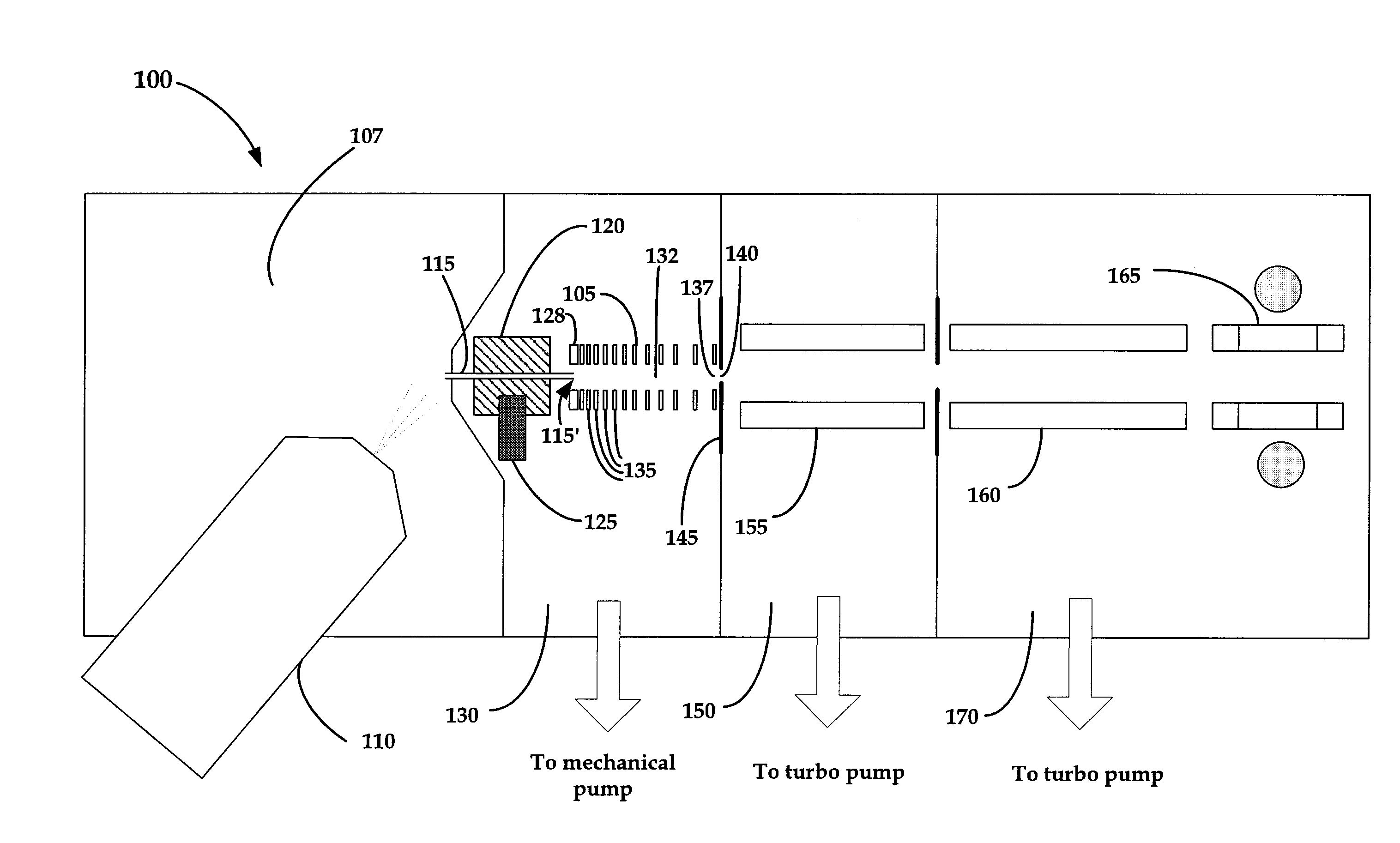
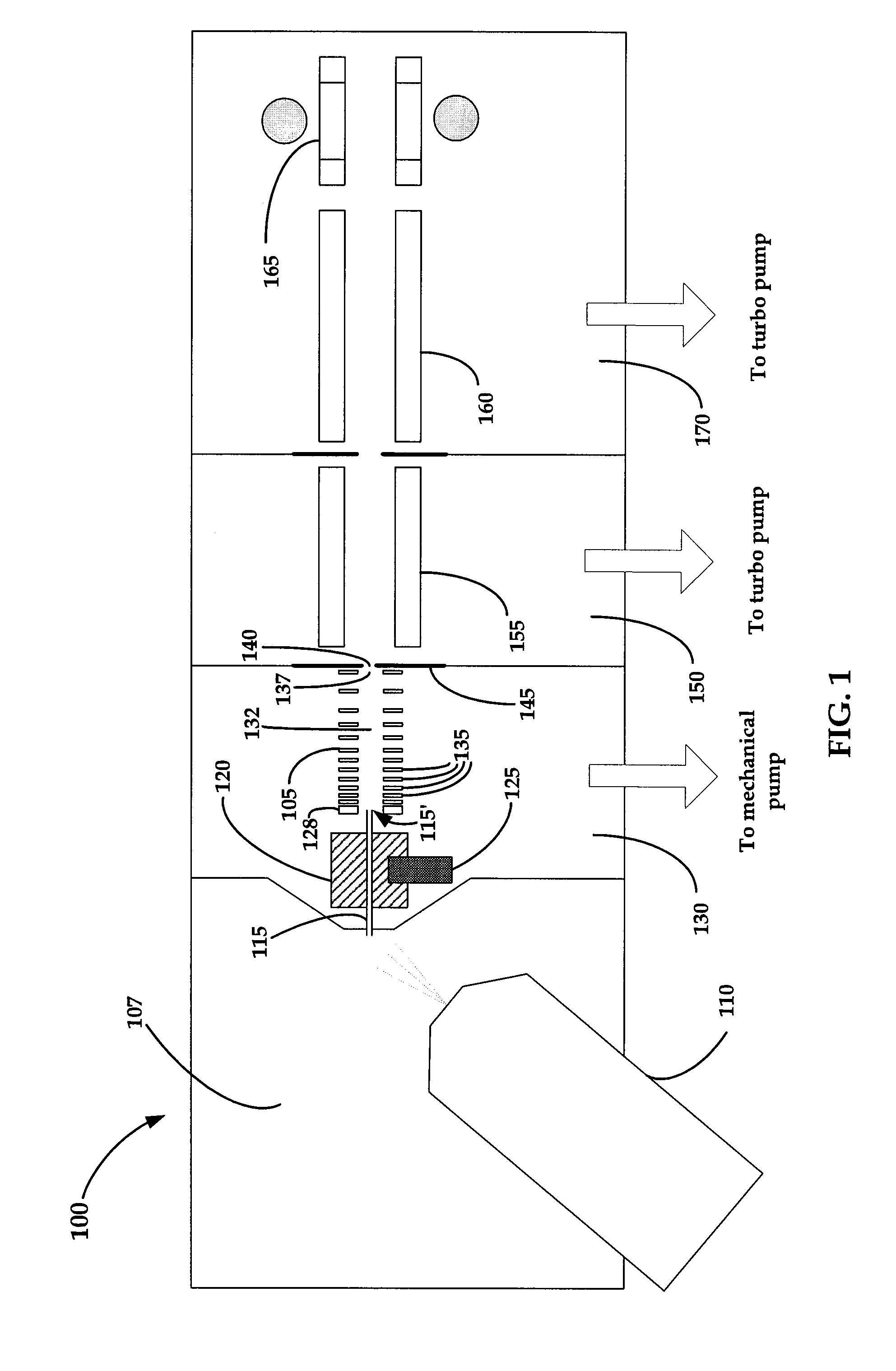
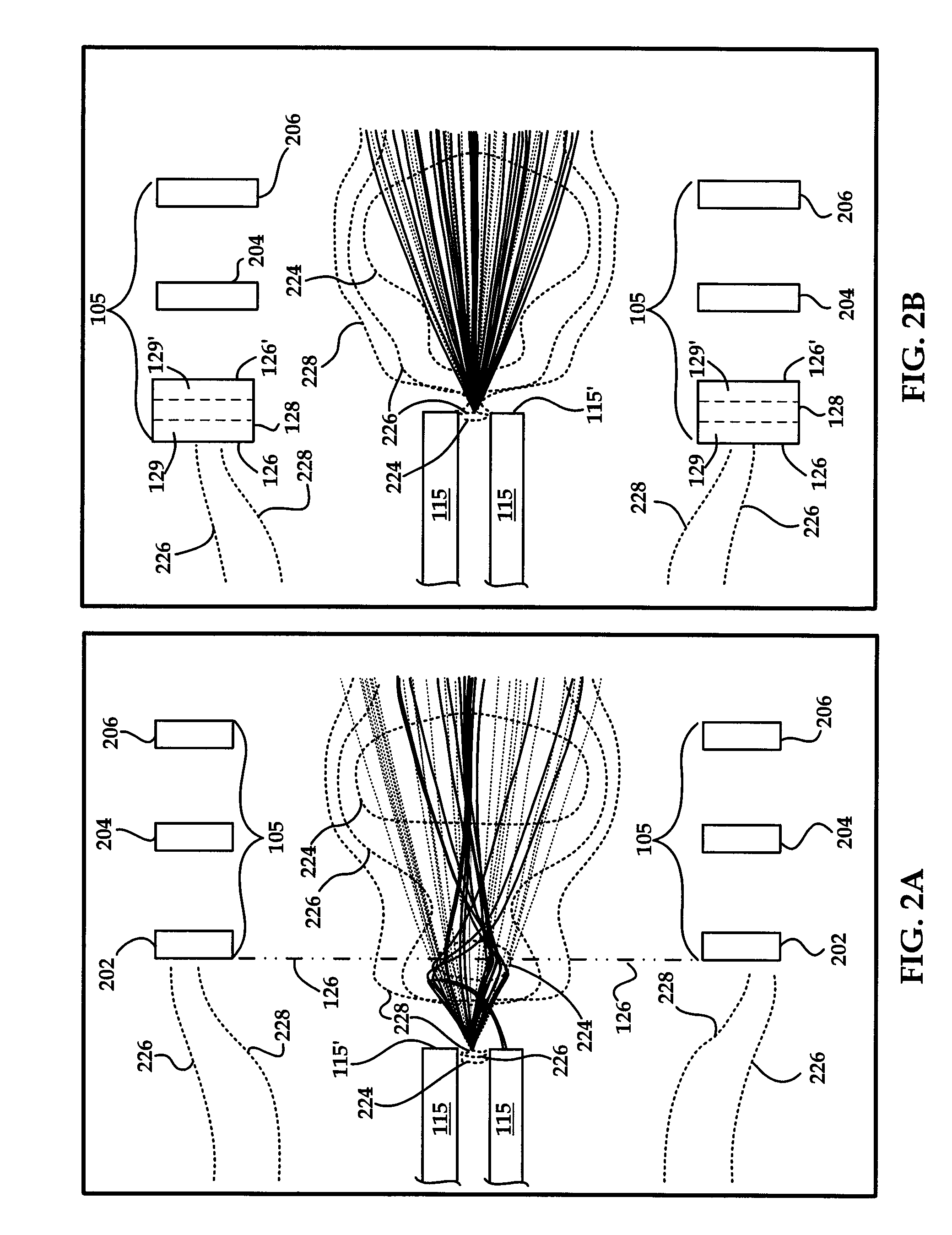
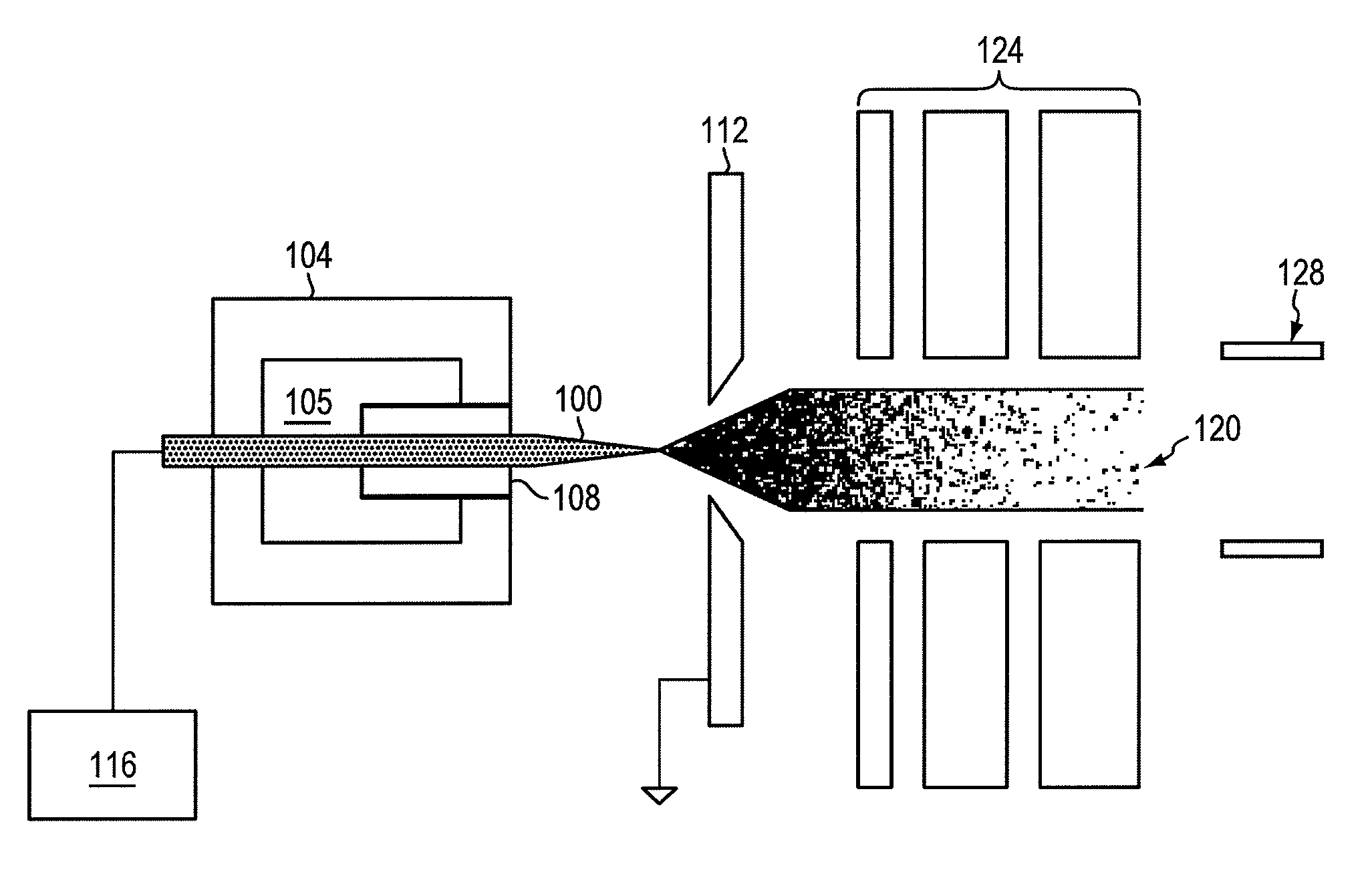
Focused negative ion beam field source
ActiveUS7863581B2Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRoom temperatureIon beam
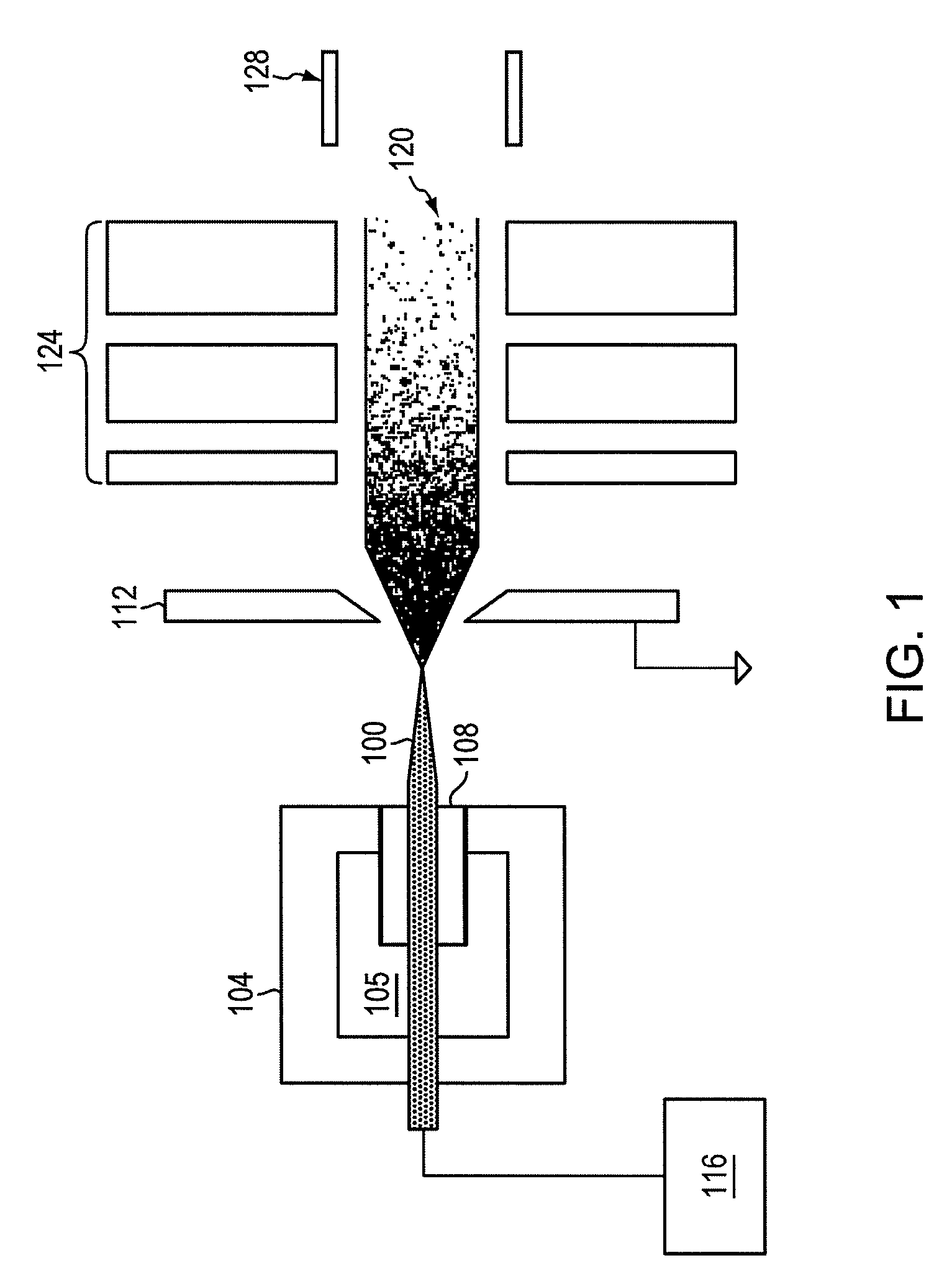
An apparatus for producing negative ions including an emitter coated with an ionic liquid room-temperature molten salt, an electrode positioned downstream relative to the emitter, a power supply that applies a voltage to the emitter with respect to the electrode. The power supply is sufficient to generate a stable high brightness beam of negative ions having minimal chromatic and spherical aberrations in the beam. An electrostatic lens and deflector is used to focus and direct the beam to a target.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Electro-dynamic or electro-static lens coupled to a stacked ring ion guide
InactiveUS20100090104A1Improve permeabilityParticle separator tubesIsotope separationIon transferLow vacuum
A device for improved transportation and focusing of ions in a low vacuum or atmospheric-pressure region of a mass spectrometer is constructed from one or more electro-dynamic or electrostatic focusing lenses that is / are coupled to the first electrode of a stacked ring ion guide (SRIG) to which oscillatory (e.g., radio-frequency) voltages are applied. Such configurations as disclosed herein, minimizes deleterious field effects and / or repositioning problems of desired ion transfer instruments that utilize such stacked ring ion guides by generally configuring the outlet end of the ion transfer device to a desired position within the electro-dynamic or electro-static focusing lens(es).
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
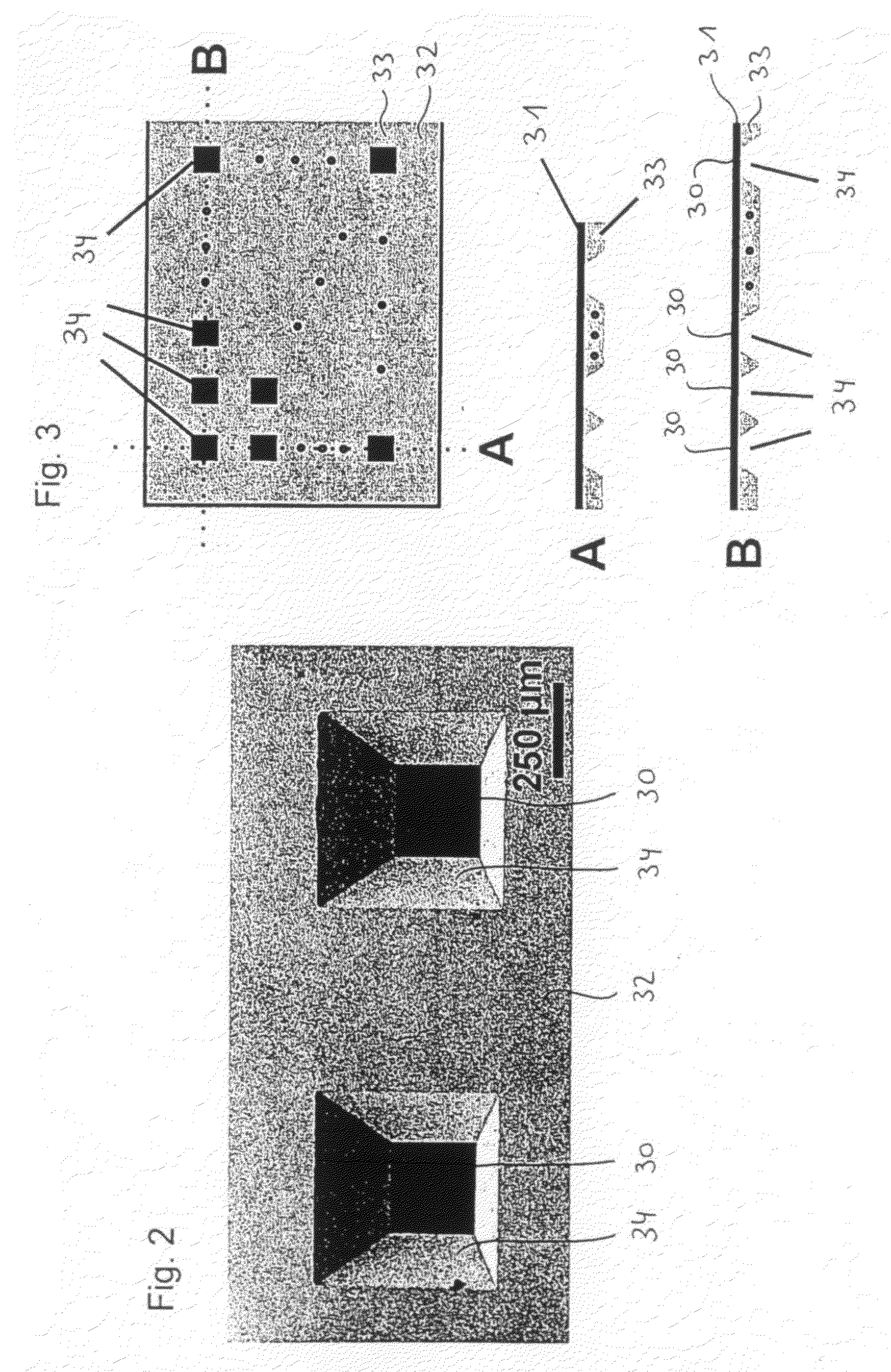
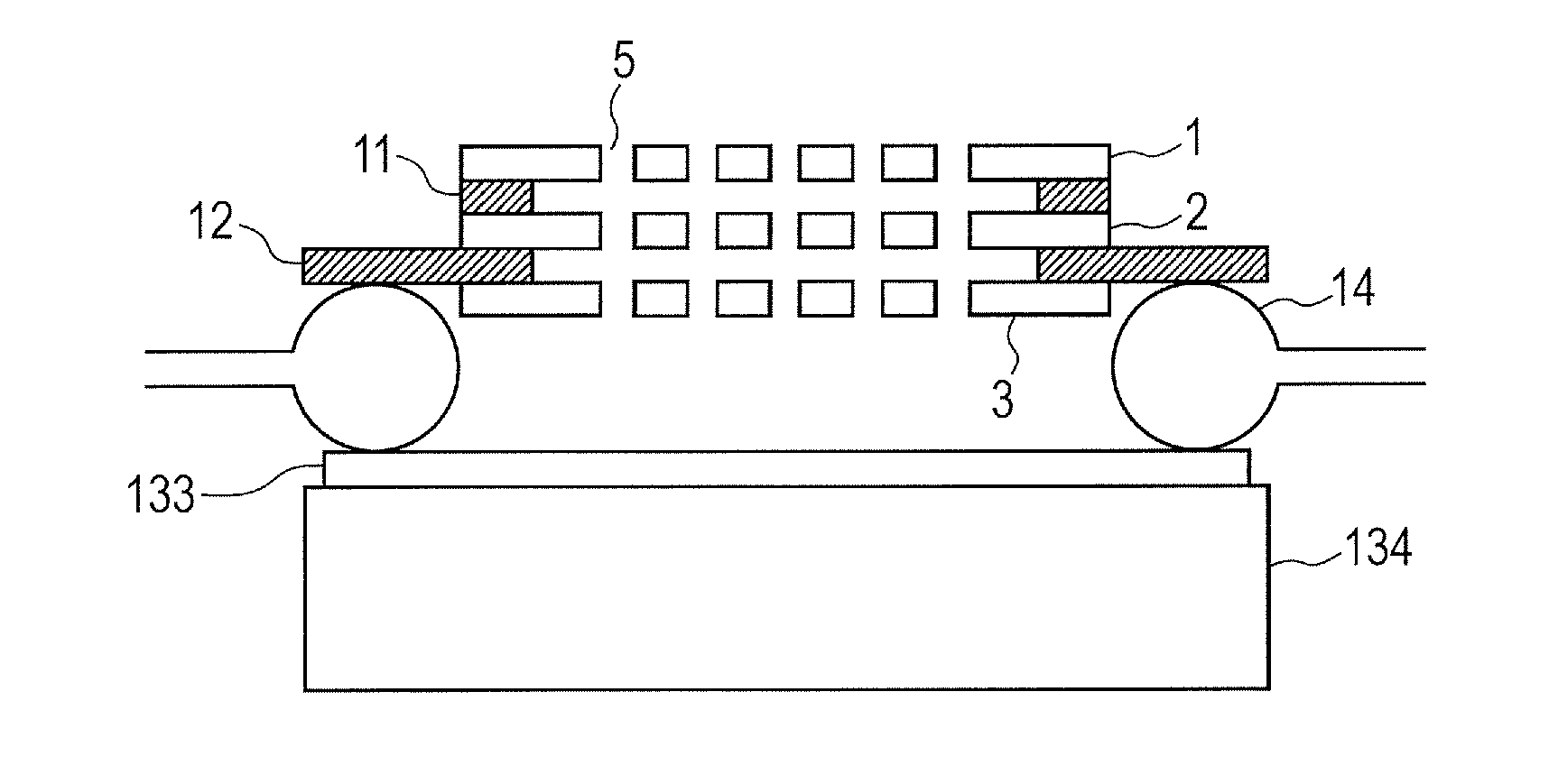
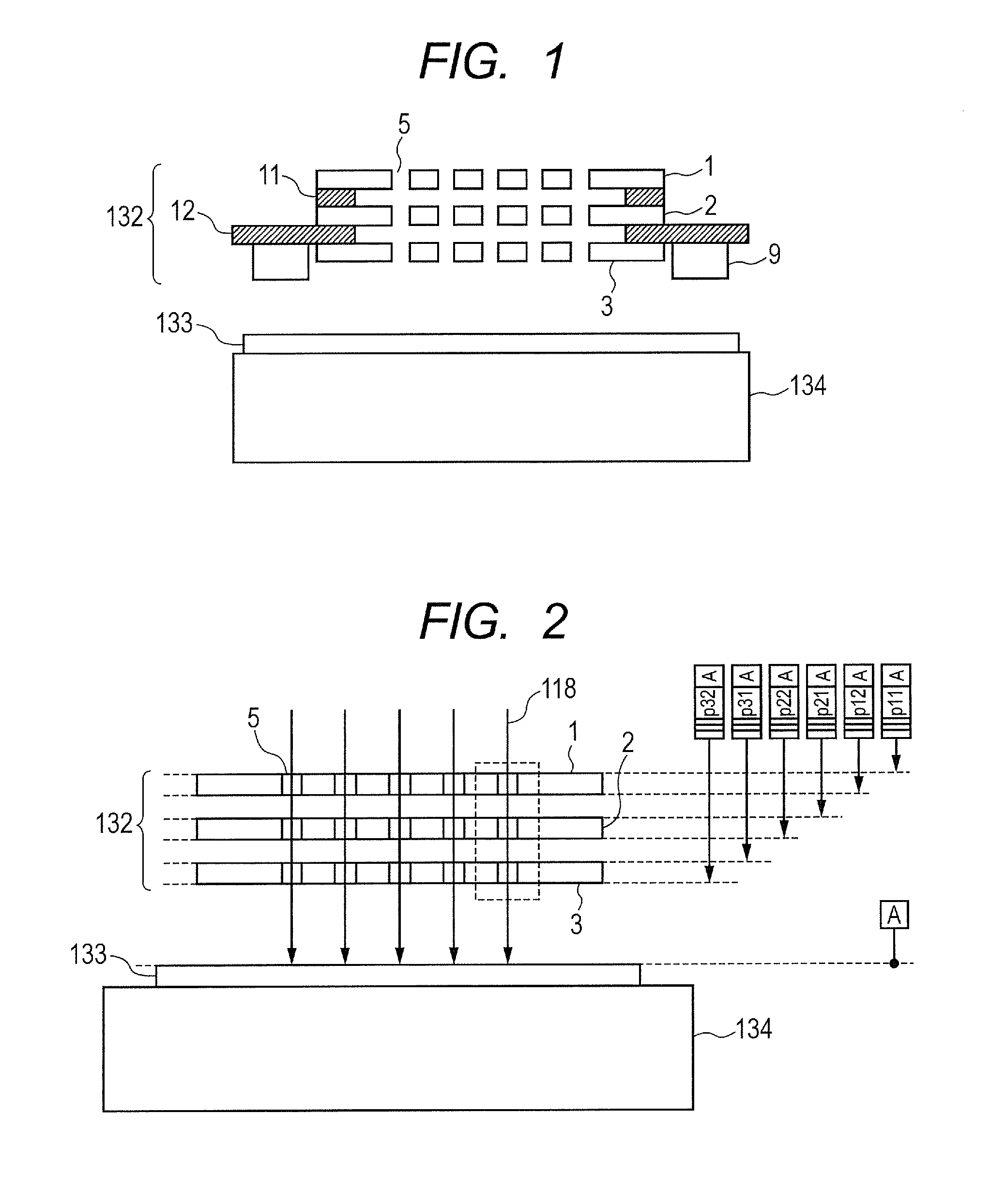
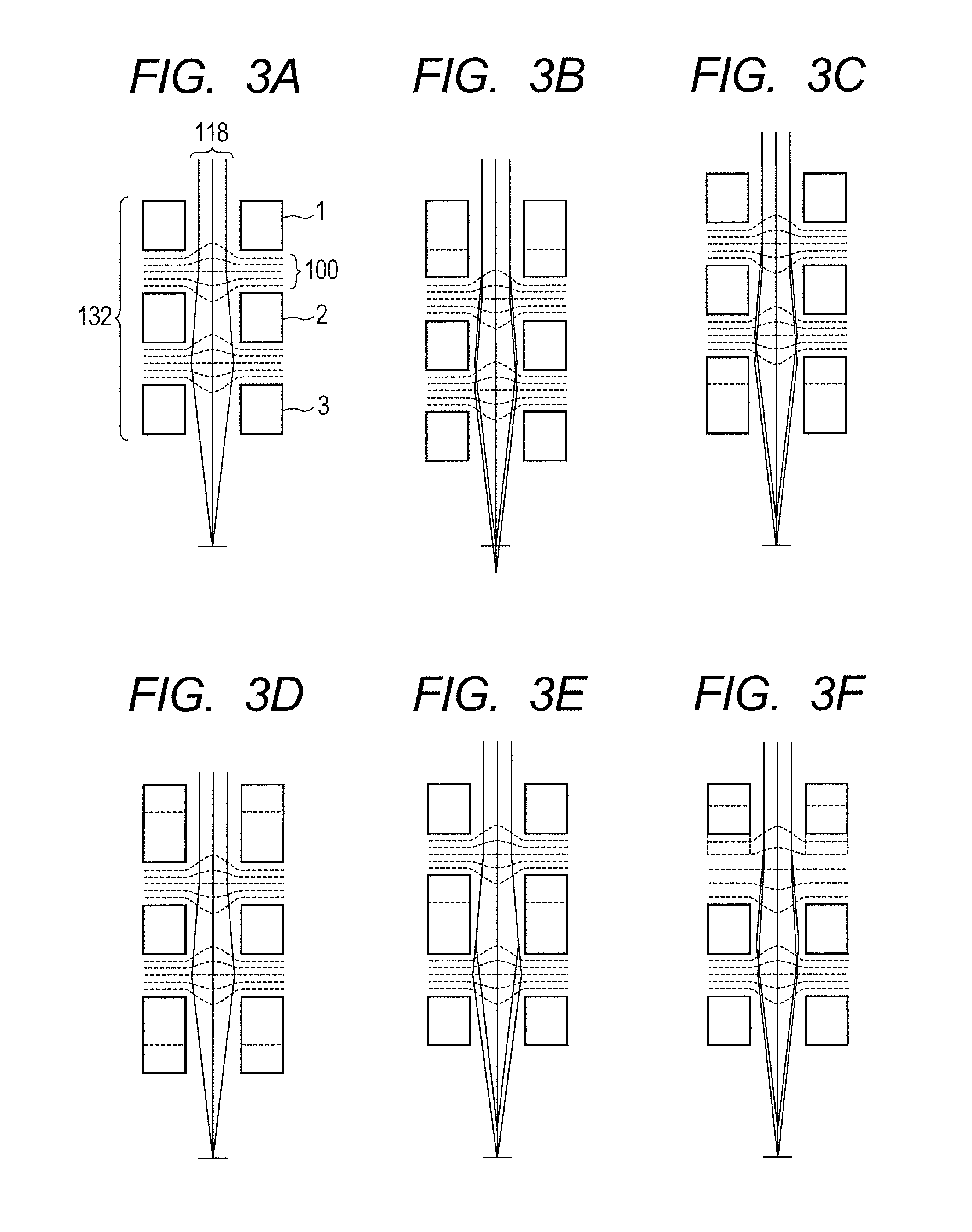
Electrostatic lens array
InactiveUS8748842B2Easy to adjust focusThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersCharged particle beamContour line
Provided is an electrostatic lens array, including multiple substrates arranged with intervals, each of the multiple substrates having an aperture for passing a charged particle beam, in which: in a travelling direction of the charged particle beam, a peripheral contour line formed by any one of surfaces of the multiple substrates other than an upper surface of a most upstream substrate and a lower surface of a most downstream substrate has a protruding portion protruding from a peripheral contour line of one of the upper surface of the most upstream substrate and the lower surface of the most downstream substrate; and a position of the protruding portion is defined by a position regulating member, whereby parallelism is adjustable so that a surface including the protruding portion is parallel to a surface to be irradiated with the charged particle beam after passing through the aperture.
Owner:CANON KK
Focused negative ion beam field source
ActiveUS20090032724A1Increase brightnessThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsIon beamMolten salt
An apparatus for producing negative ions including an emitter coated with an ionic liquid room-temperature molten salt, an electrode positioned downstream relative to the emitter, a power supply that applies a voltage to the emitter with respect to the electrode. The power supply is sufficient to generate a stable high brightness beam of negative ions having minimal chromatic and spherical aberrations in the beam. An electrostatic lens and deflector is used to focus and direct the beam to a target.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com