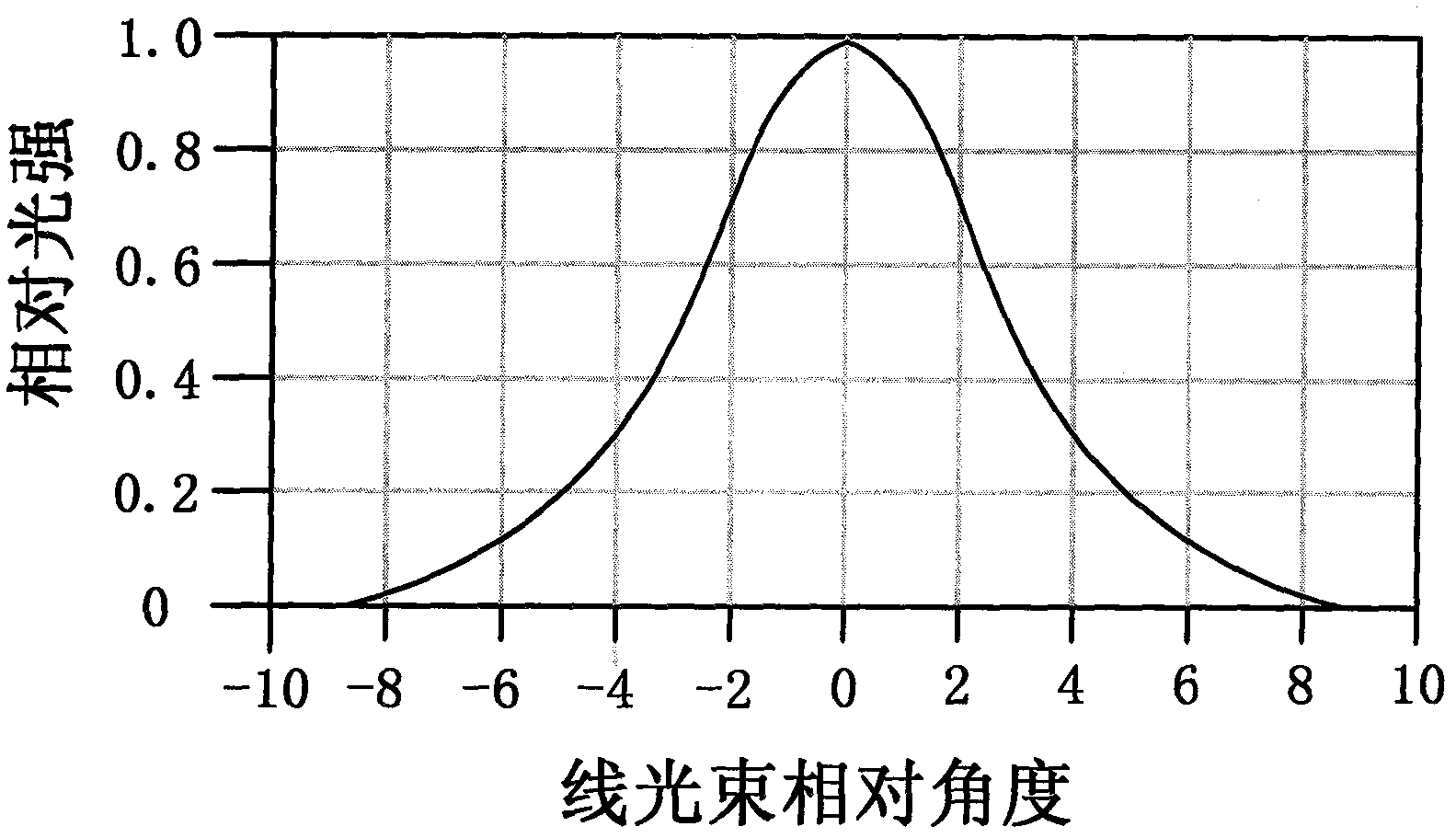
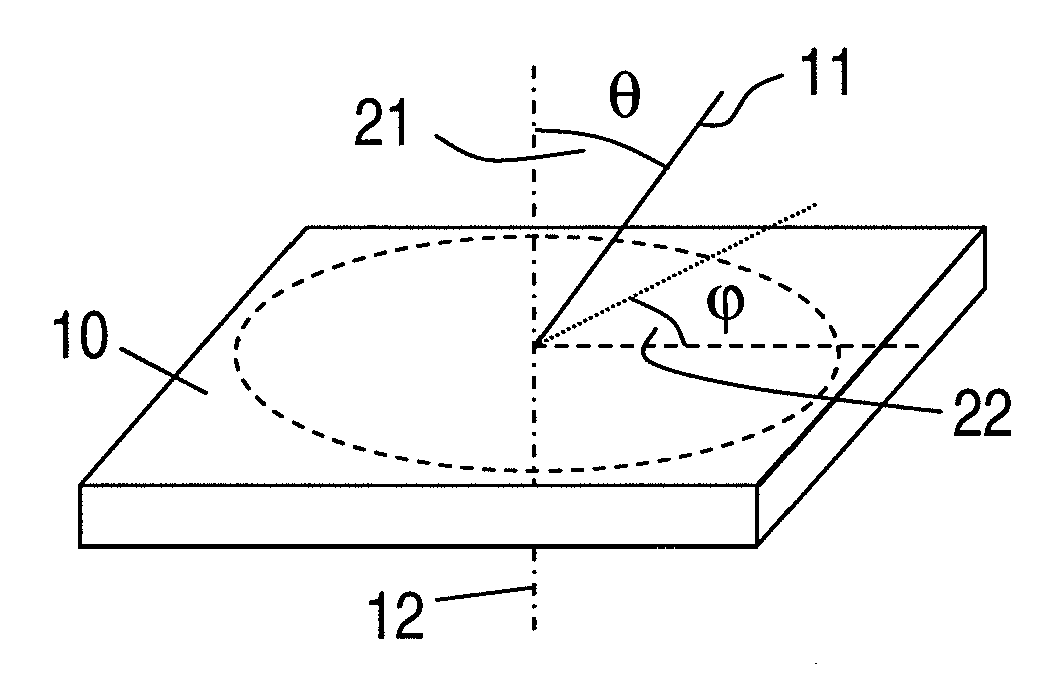
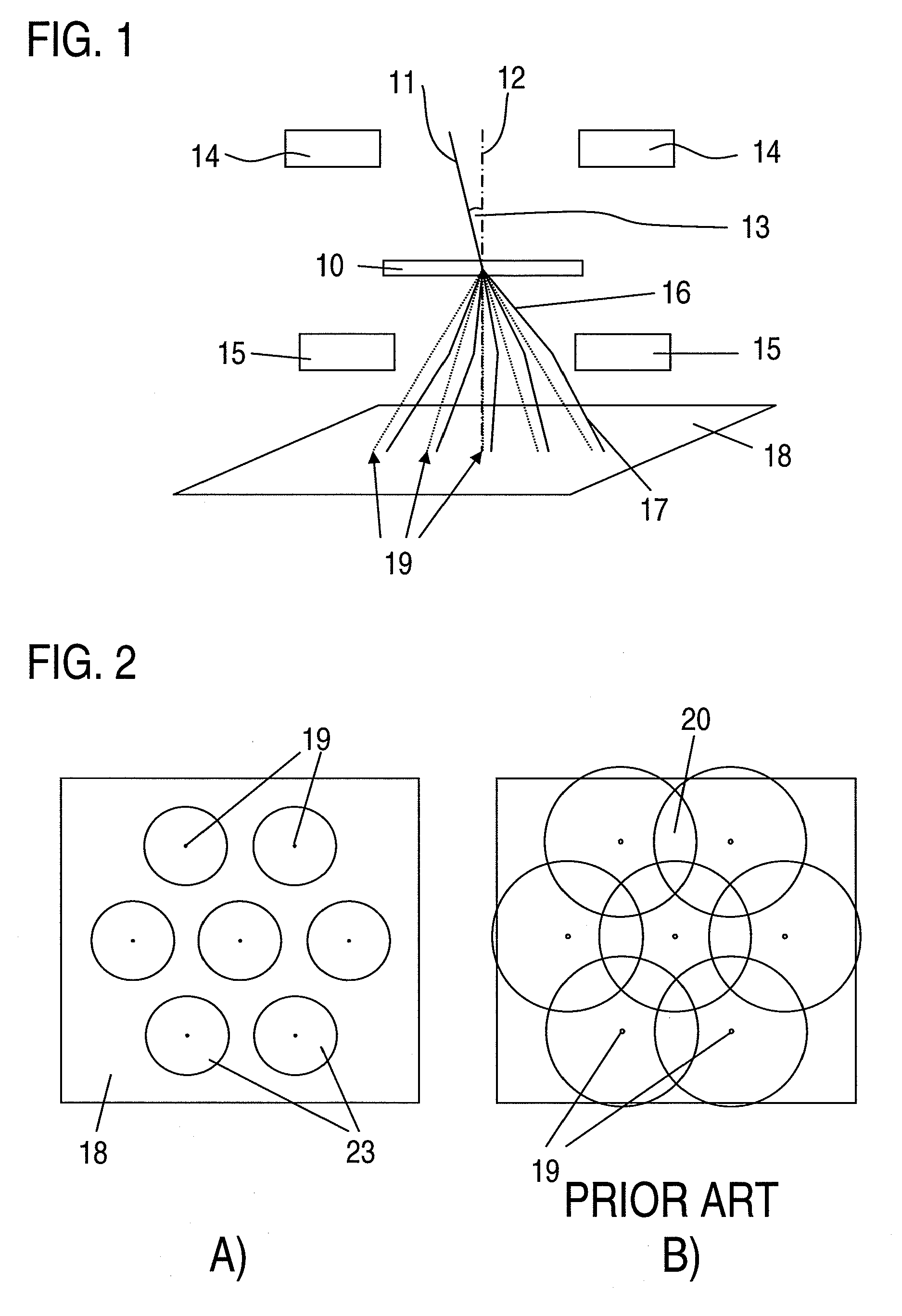
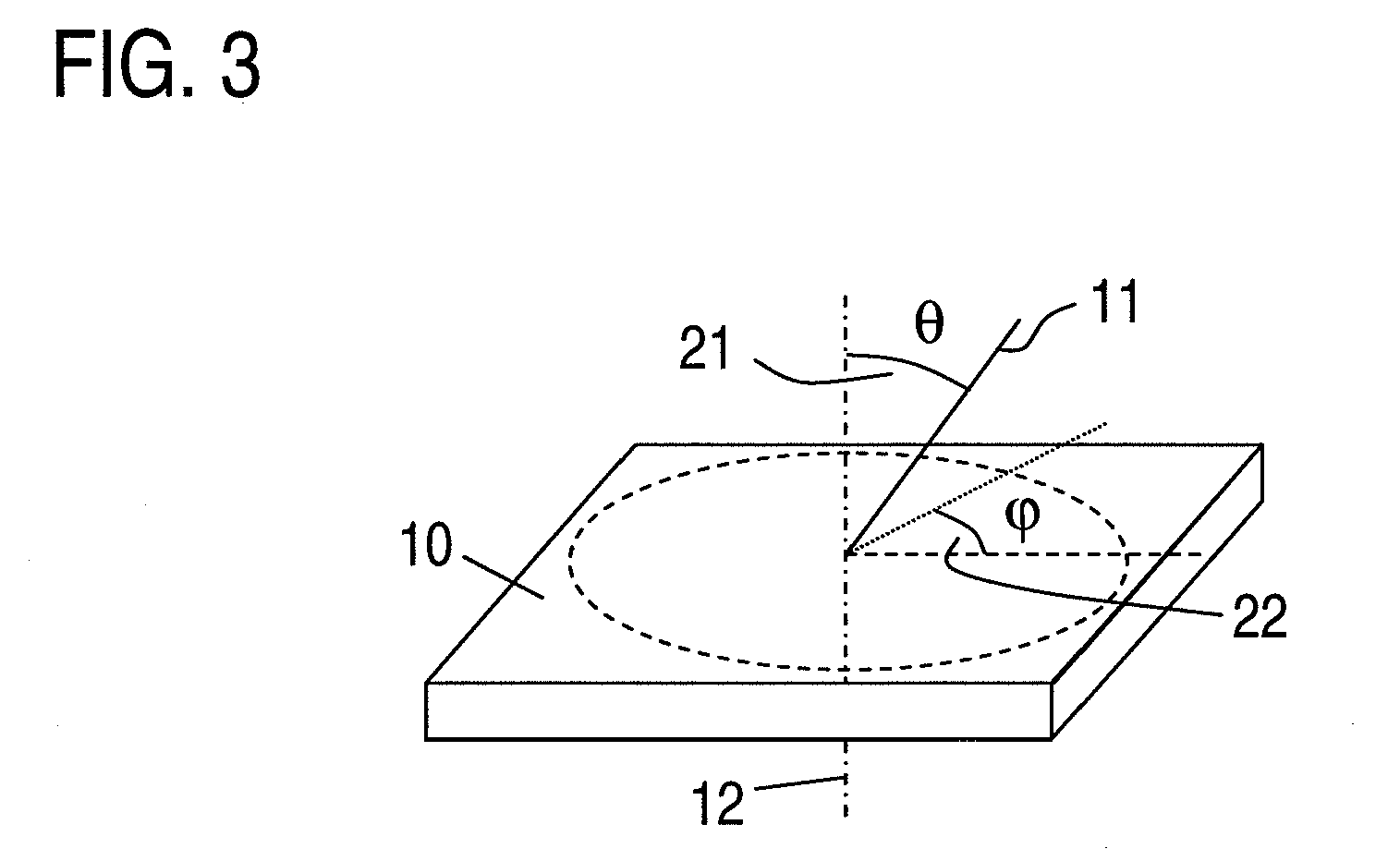
Patents
Literature
135 results about "Electron diffraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron diffraction refers to the wave nature of electrons. However, from a technical or practical point of view, it may be regarded as a technique used to study matter by firing electrons at a sample and observing the resulting interference pattern. This phenomenon is commonly known as wave–particle duality, which states that a particle of matter (in this case the incident electron) can be described as a wave. For this reason, an electron can be regarded as a wave much like sound or water waves. This technique is similar to X-ray and neutron diffraction.
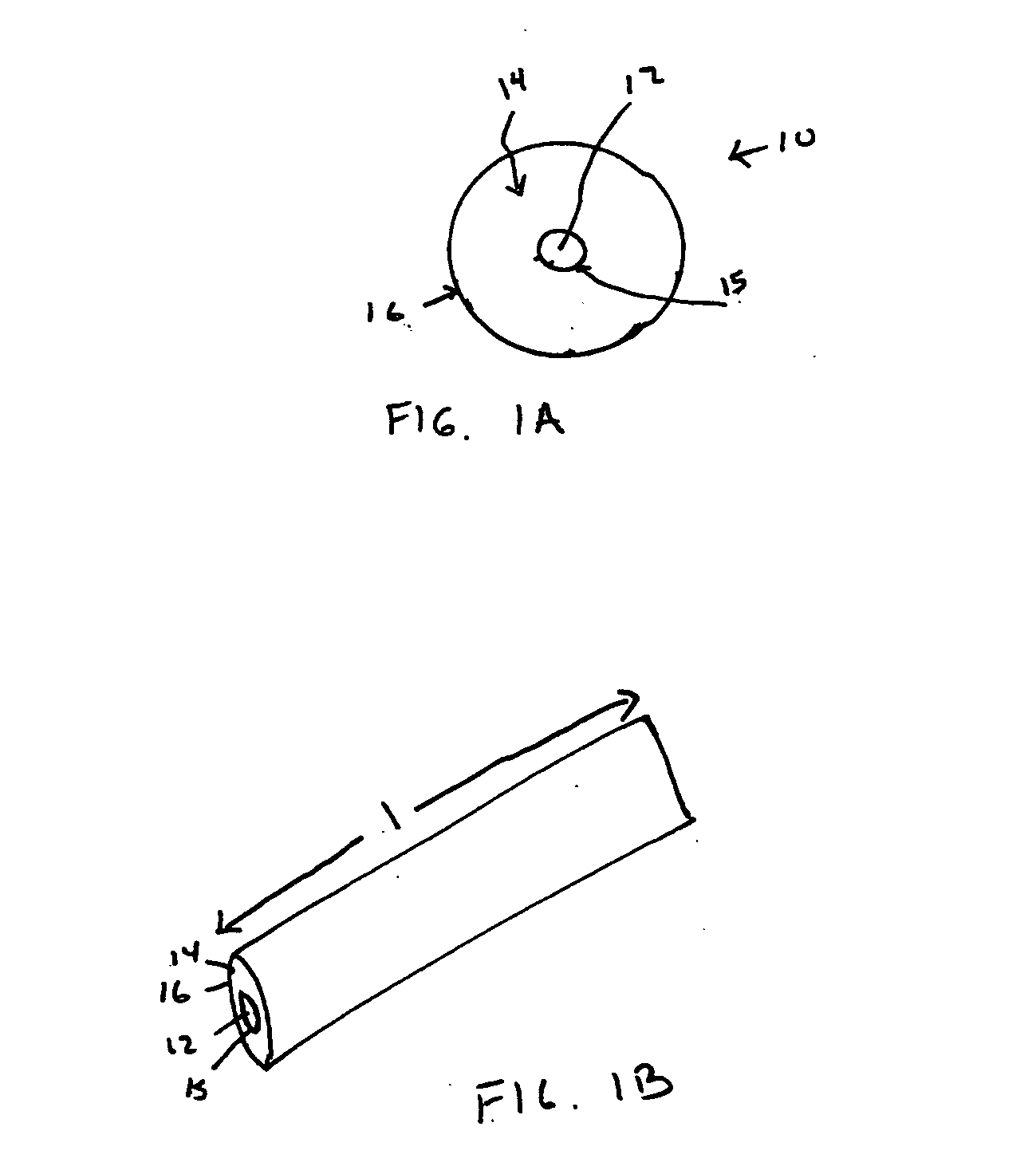
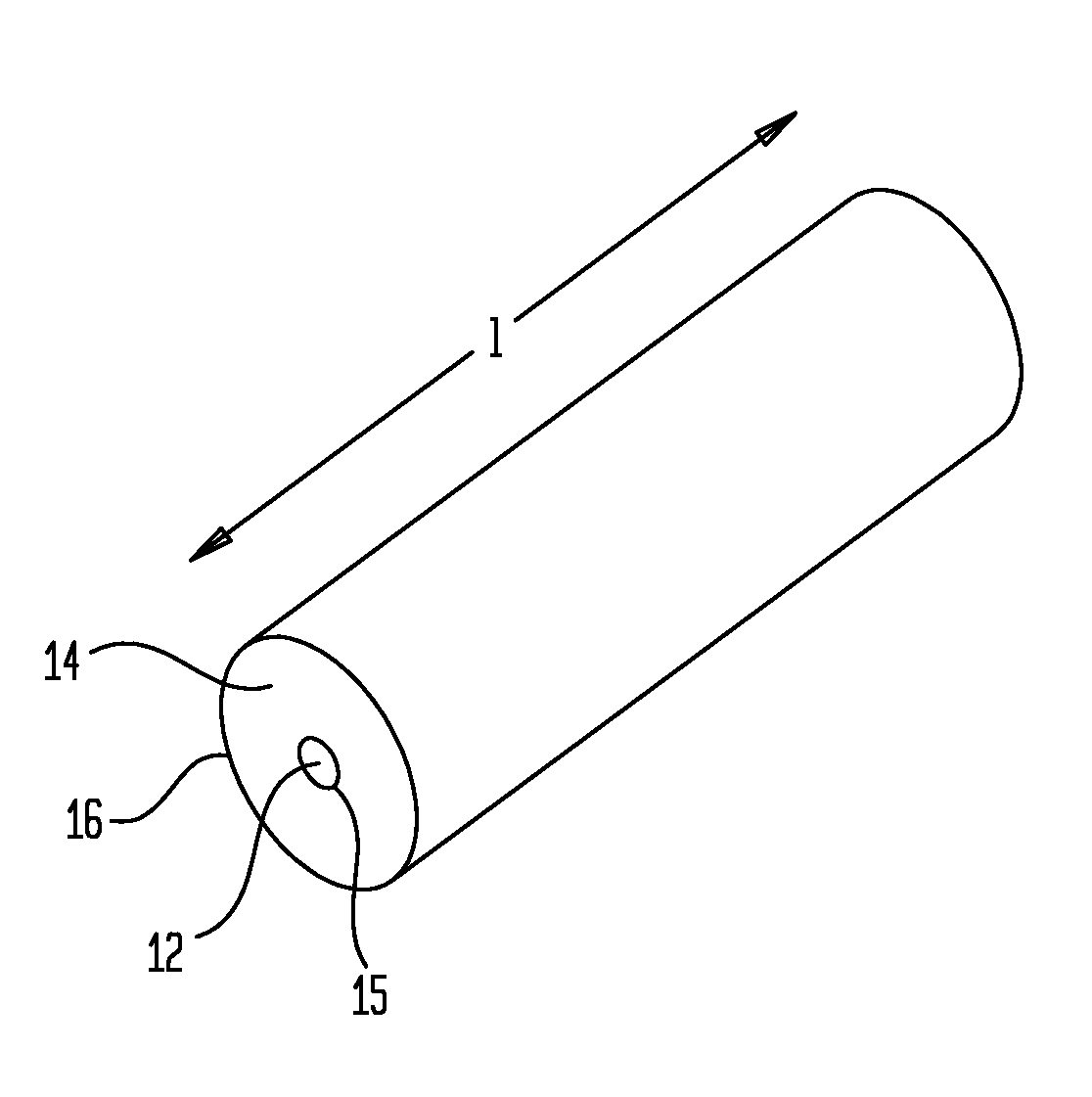
Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite nanotubes
ActiveUS20050036939A1Reduce the amount requiredThe instrumentation is simpleDigital storageGermanium dioxideStrontium titanateBarium titanate
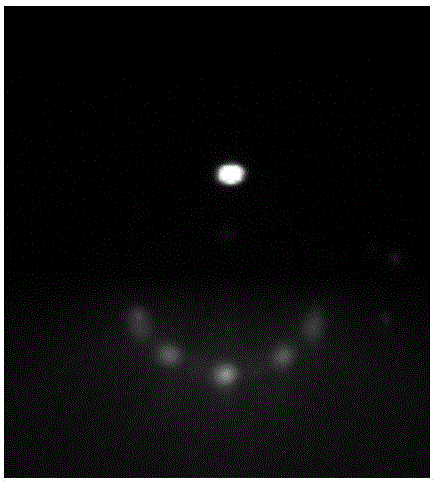
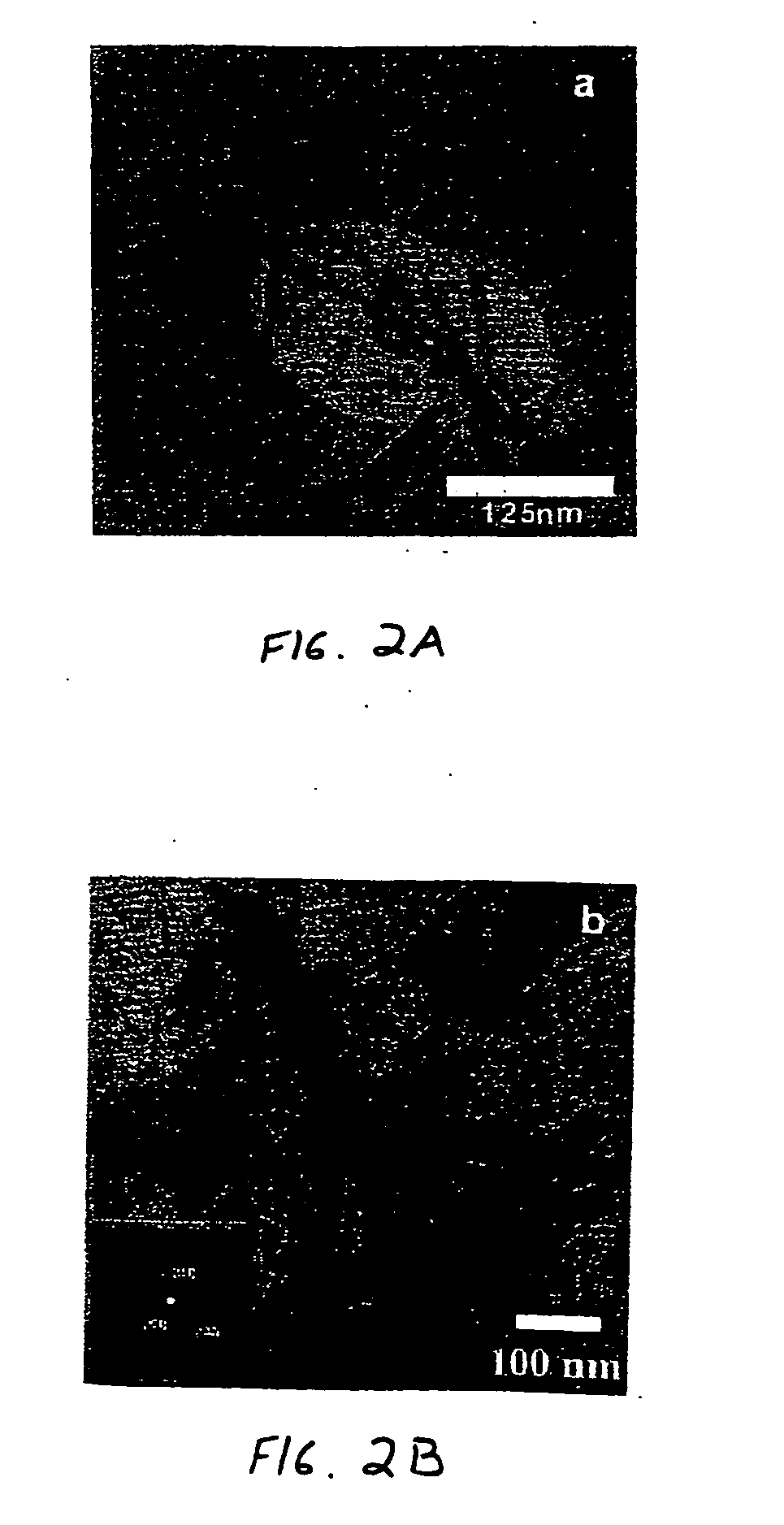
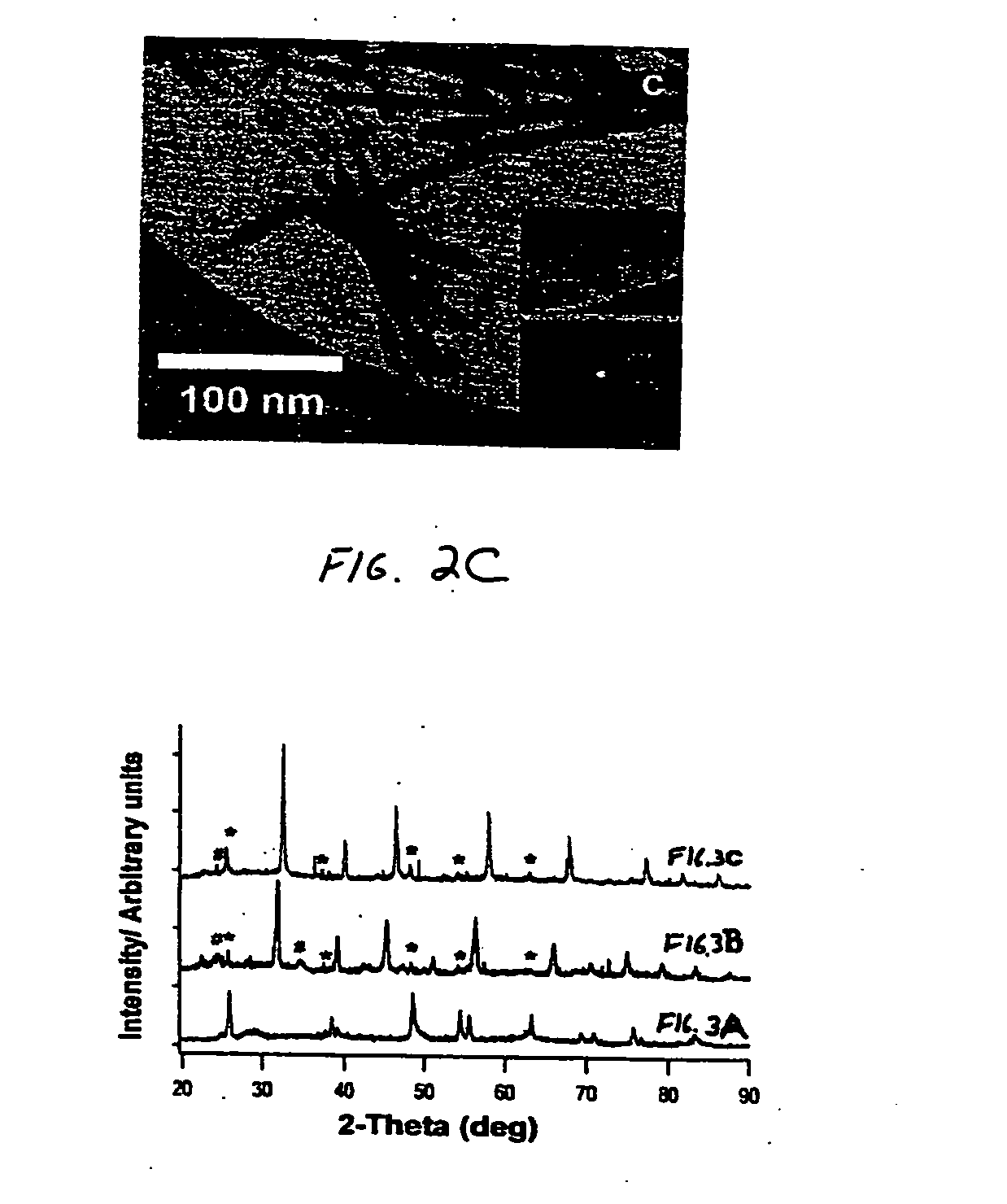
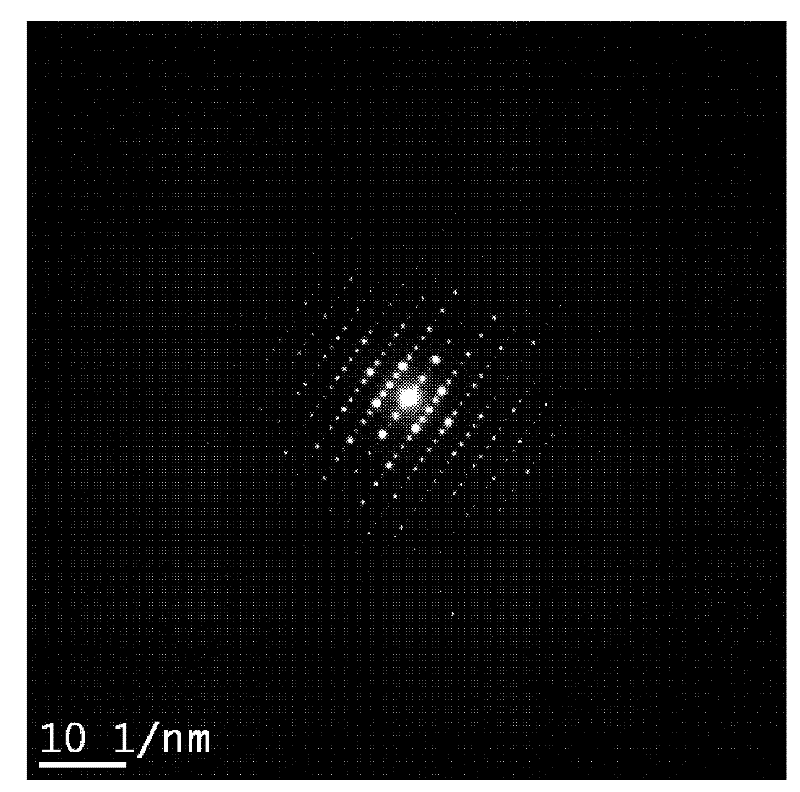
A low-temperature hydrothermal reaction is provided to generate crystalline perovskite nanotubes such as barium titanate (BaTiO3) and strontium titanate (SrTiO3) that have an outer diameter from about 1 nm to about 500 nm and a length from about 10 nm to about 10 micron. The low-temperature hydrothermal reaction includes the use of a metal oxide nanotube structural template, i.e., precursor. These titanate nanotubes have been characterized by means of X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy, coupled with energy dispersive X-ray analysis and selected area electron diffraction (SAED).
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite nanotubes
ActiveUS7147834B2The instrumentation is simpleReduce the amount requiredNanoinformaticsDigital storageStrontium titanateBarium titanate
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
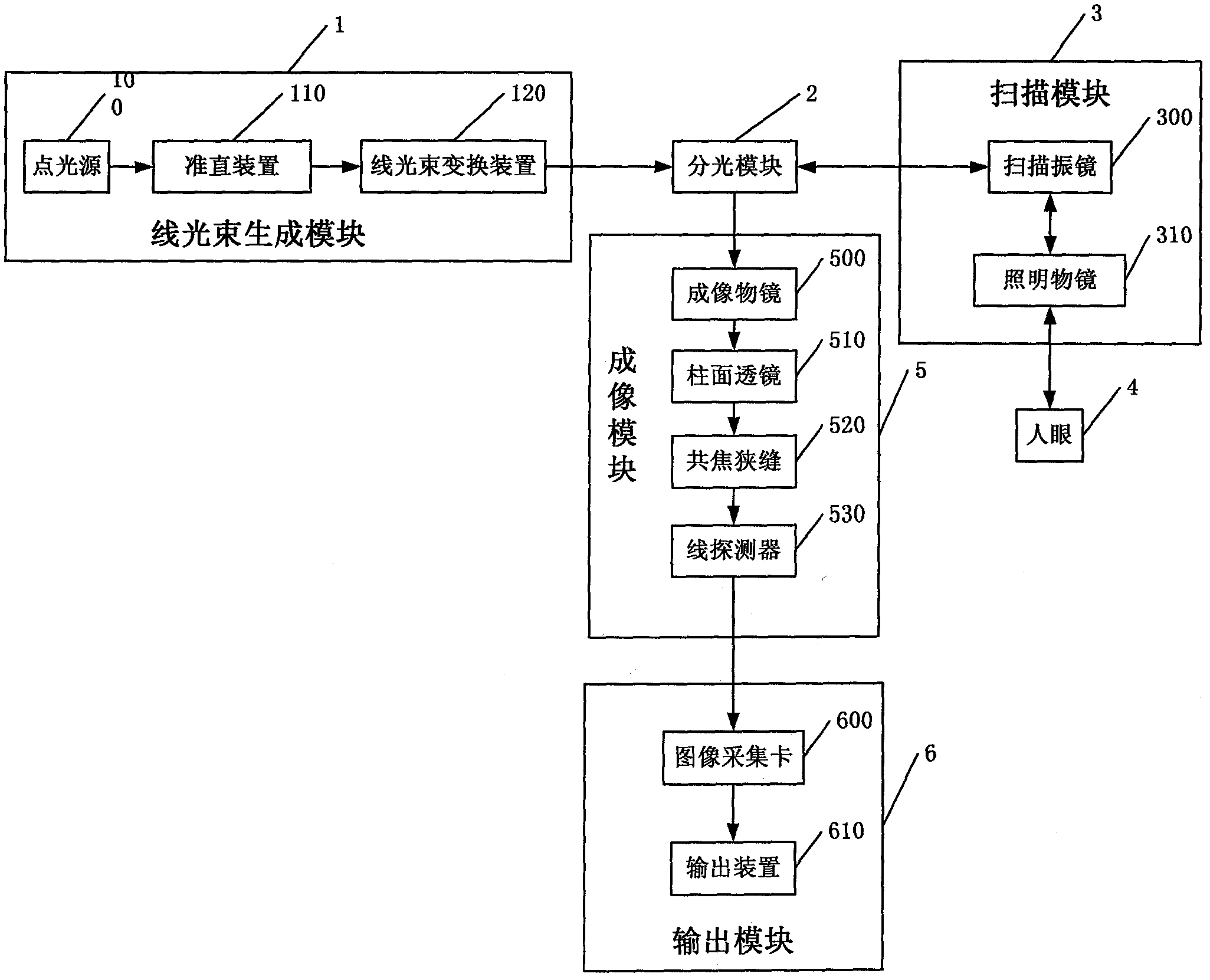
Line-scanning confocal ophthalmoscope system based on laser diffraction and method
InactiveCN102068236AEven energy distributionGood quality beamOthalmoscopesImaging qualityBeam splitting
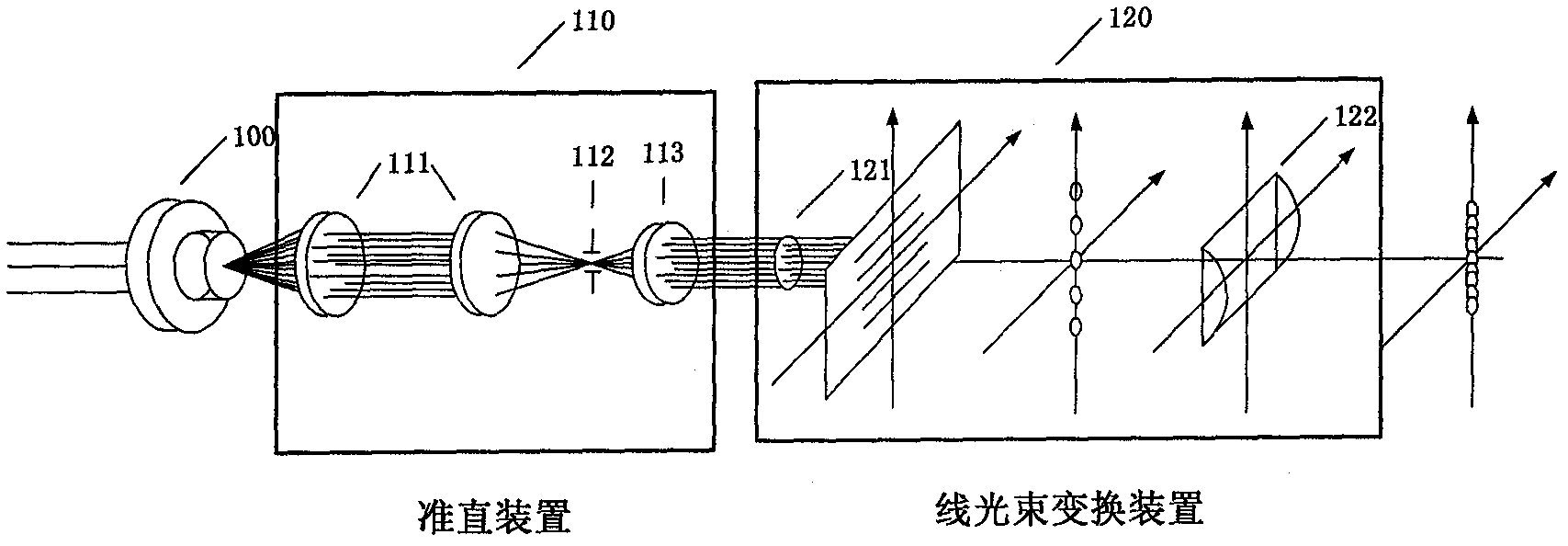
The invention relates to a line-scanning confocal ophthalmoscope system based on laser diffraction and a method. The system comprises a linear beam generation module, a beam-splitting module, a scanning module, an imaging module and an output module. The invention is characterized in that: the intensity of the linear beam generated by the line-scanning confocal ophthalmoscope system is uniformly distributed in a non-Gaussian form, a scanning galvanometer is adopted to scan the linear beam in a one-dimensional space to illuminate an ocular fundus retina, meanwhile, a linear detector is used for imaging the non-scanning linear beam reflected by the ocular fundus retina, and since the system only uses one scanning galvanometer and one linear detector, the number of the moving parts is less; meanwhile, a confocal slit is conjugated with the ocular fundus retina plane, consequently, the affection of the stay light of the non-retina plane on the imaging quality is eliminated, and thereby the high resolution of the confocal imaging principle. The system has the advantages of good linear beam quality, simple system structure, easy manufacturing, short light path, easy adjustment, small size, applicability, high stability and high imaging frame frequency.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
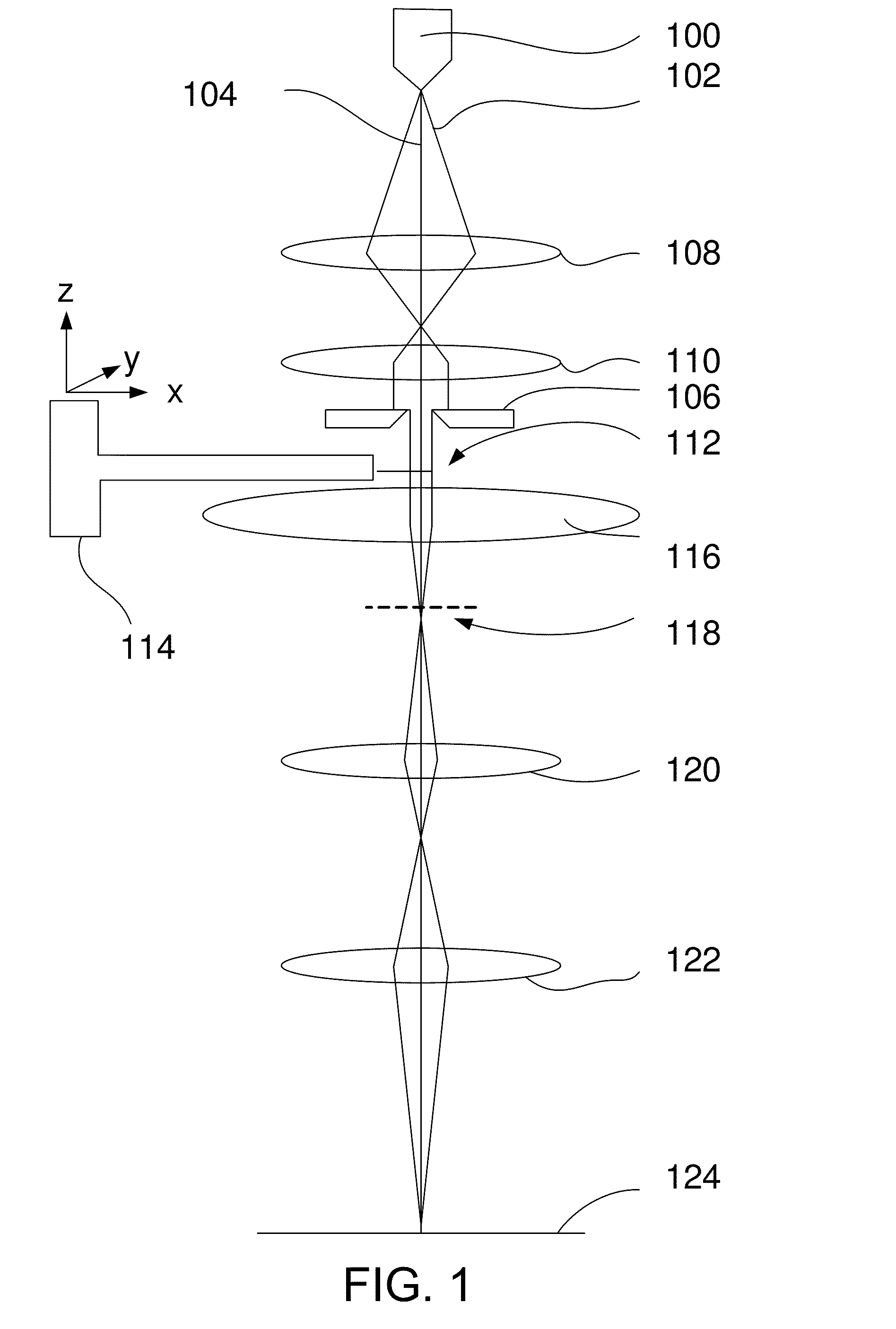
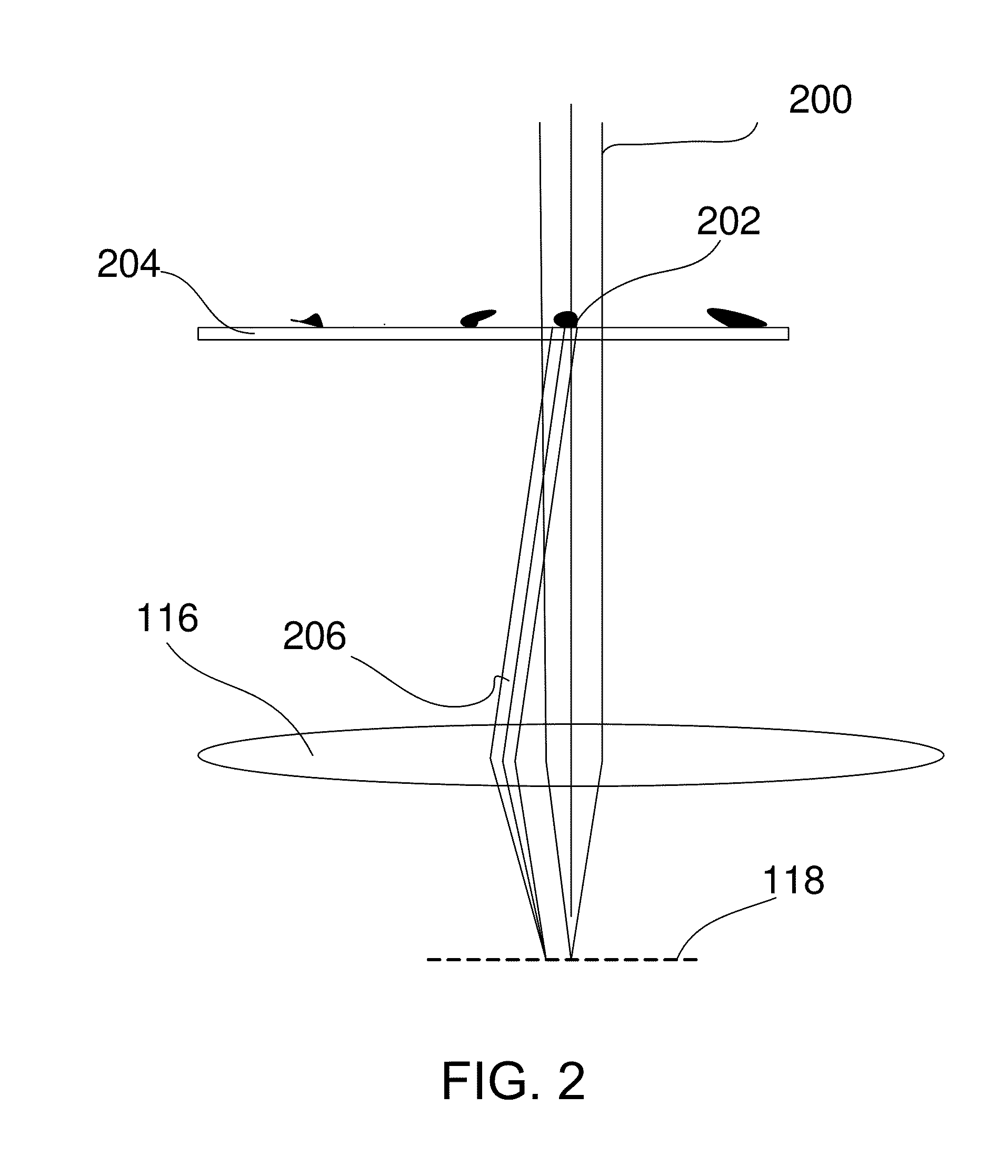
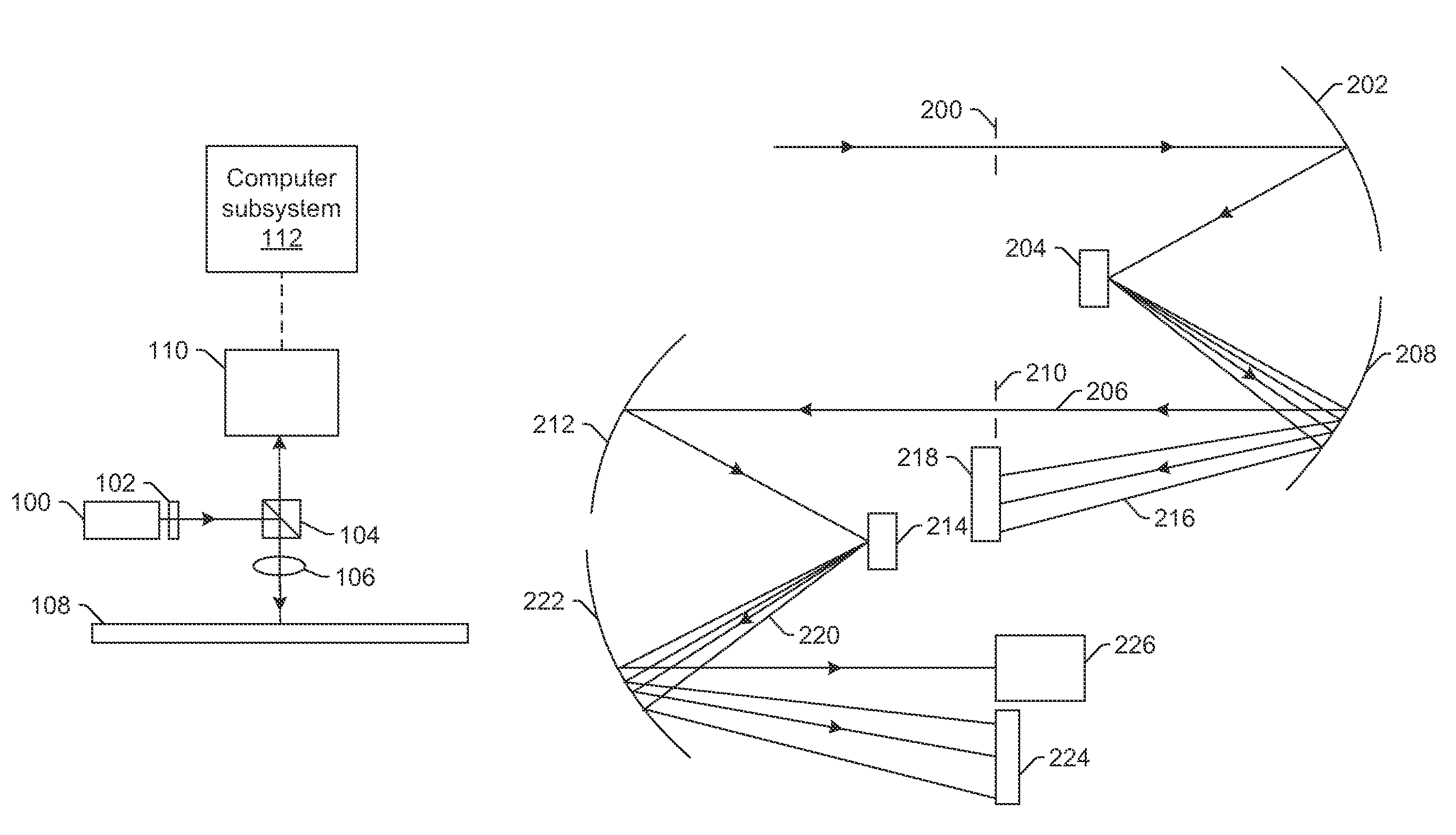
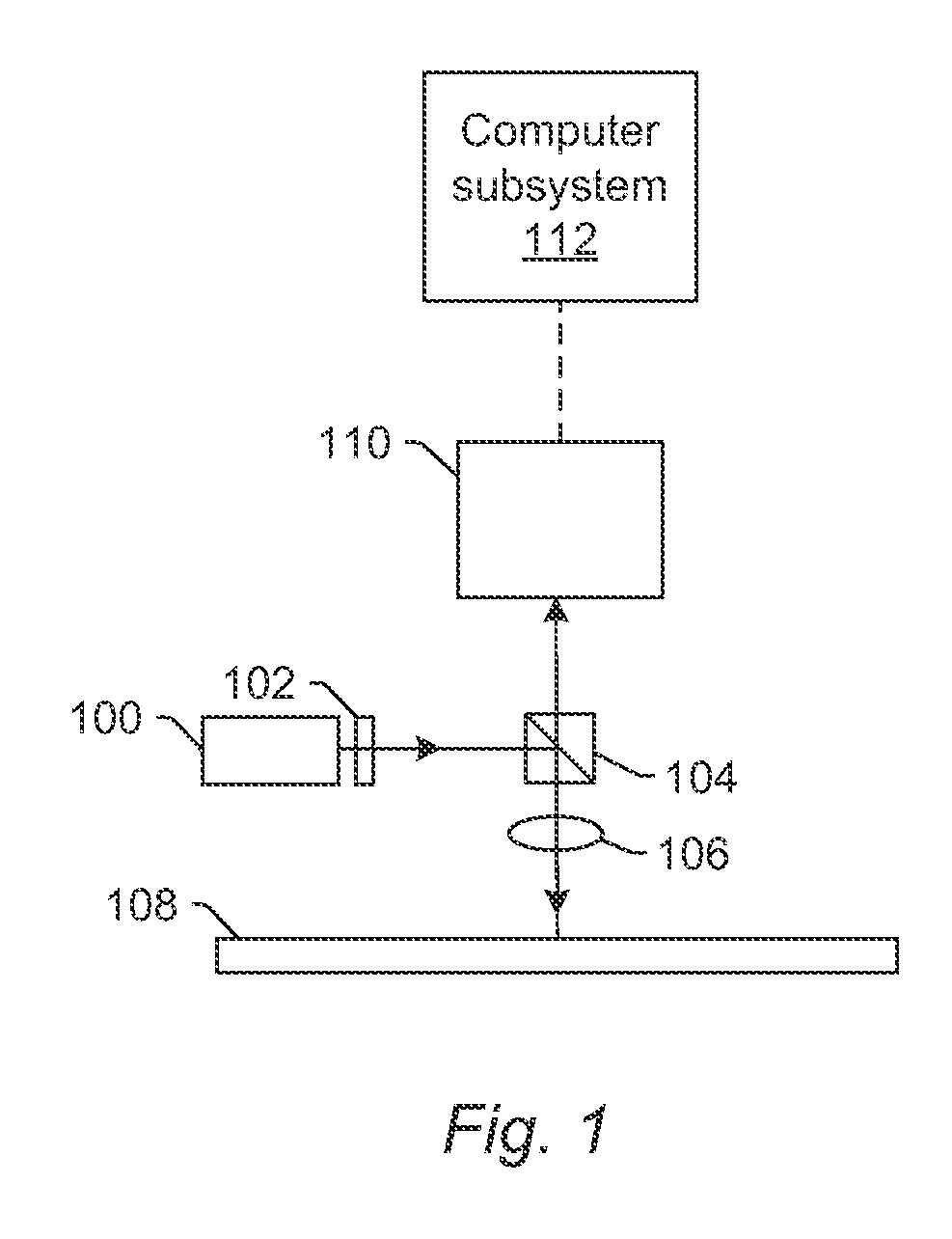
Method and device for measuring electron diffraction of a sample
ActiveUS20110049363A1Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAngle of incidenceLight beam
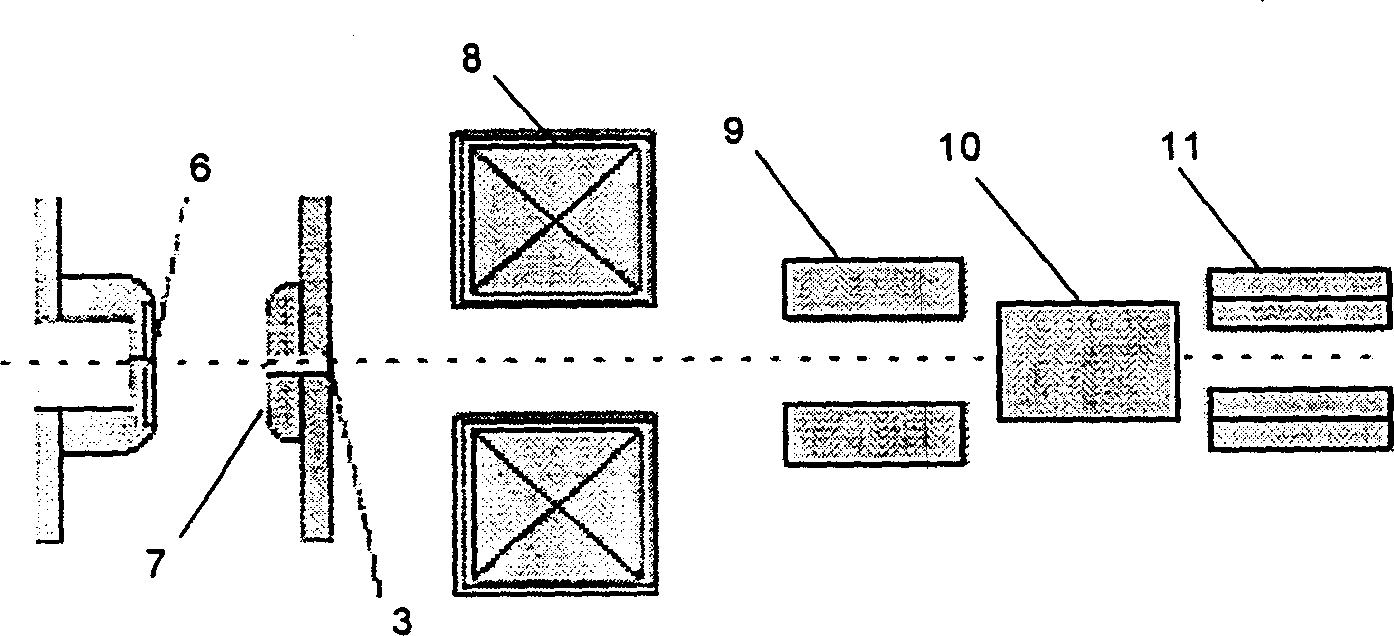
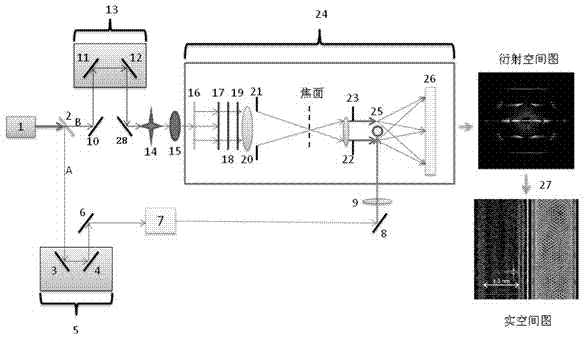
The invention relates to a method and a device for measuring electron diffraction of a sample, including the steps of illuminating the sample with an incident electron beam which is deflected from a sample axis to hit the sample at an angle of incidence relative to the sample axis, at least partially subjecting the incident electron beam to diffraction by the sample, subjecting the diffracted and undiffracted electron beams transmitted through the sample to a partial deflection compensation, detecting the intensity of the diffracted and undiffracted electron beams transmitted through the sample in dependency on the angle of incidence and a scattering angle of the diffracted beam. The invention also relates to a computer program for controlling a transmission electron microscope for carrying out the inventive method.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
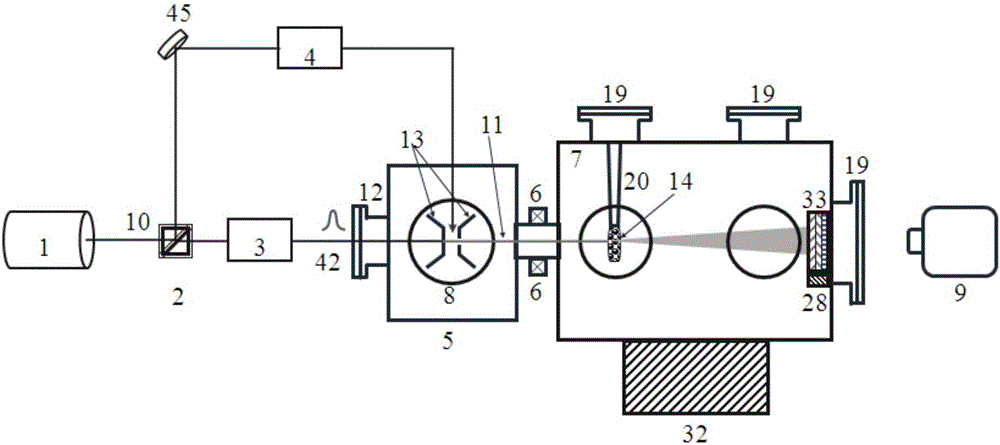
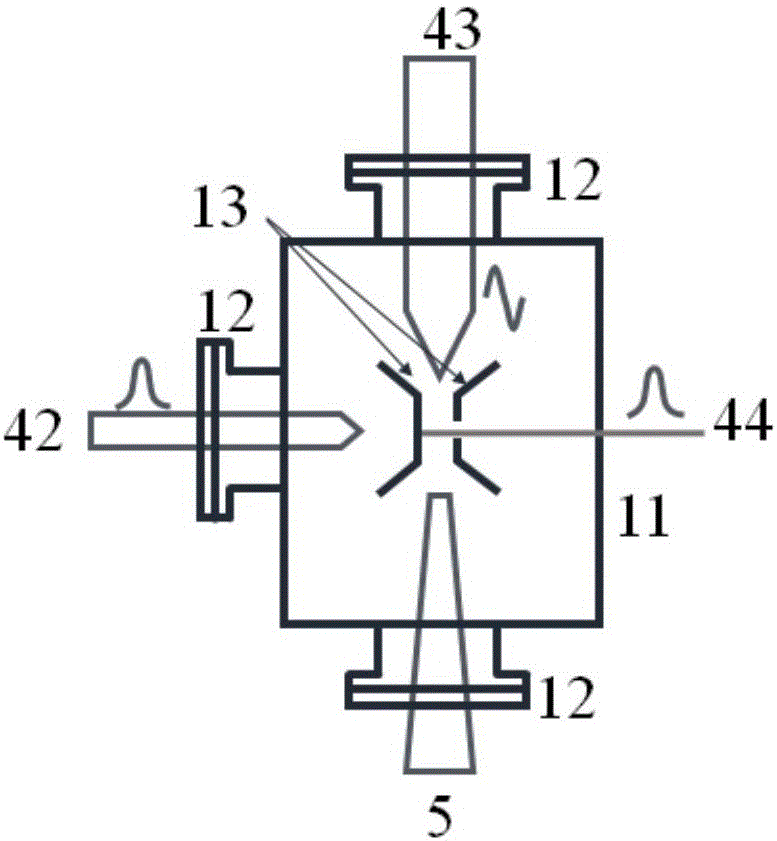
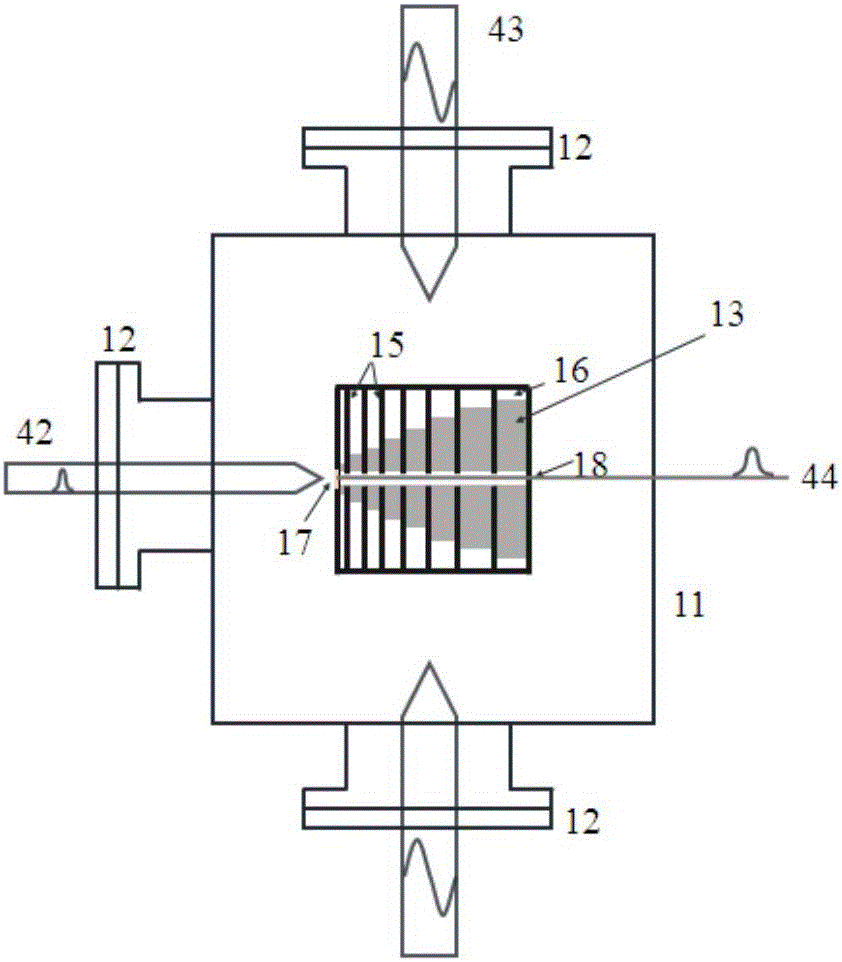
Femtosecond electronic diffraction device
InactiveCN1851450AImprove time resolutionImprove spatial resolutionElectrode and associated part arrangementsTube electron sourcesControl systemMagnetic lens
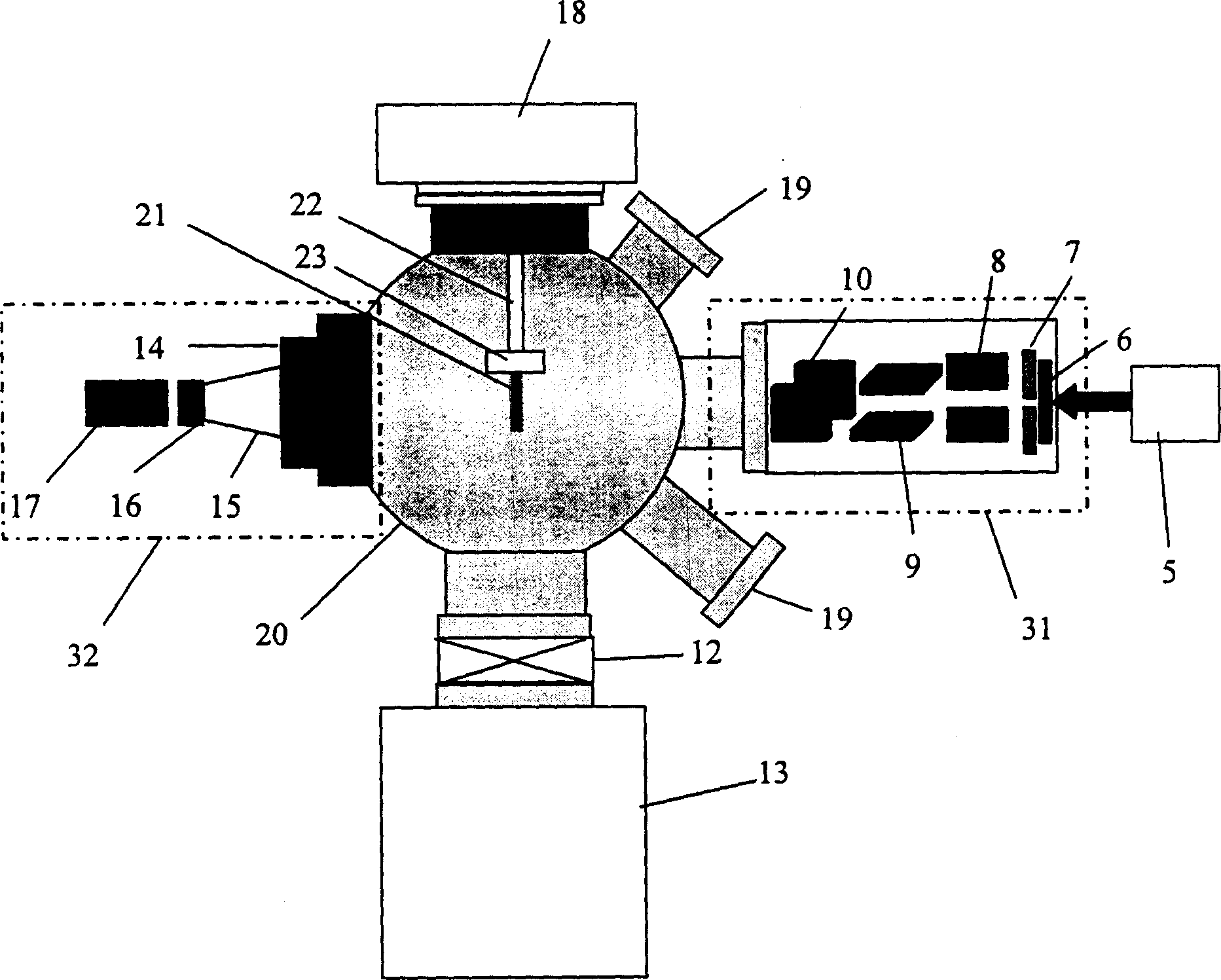
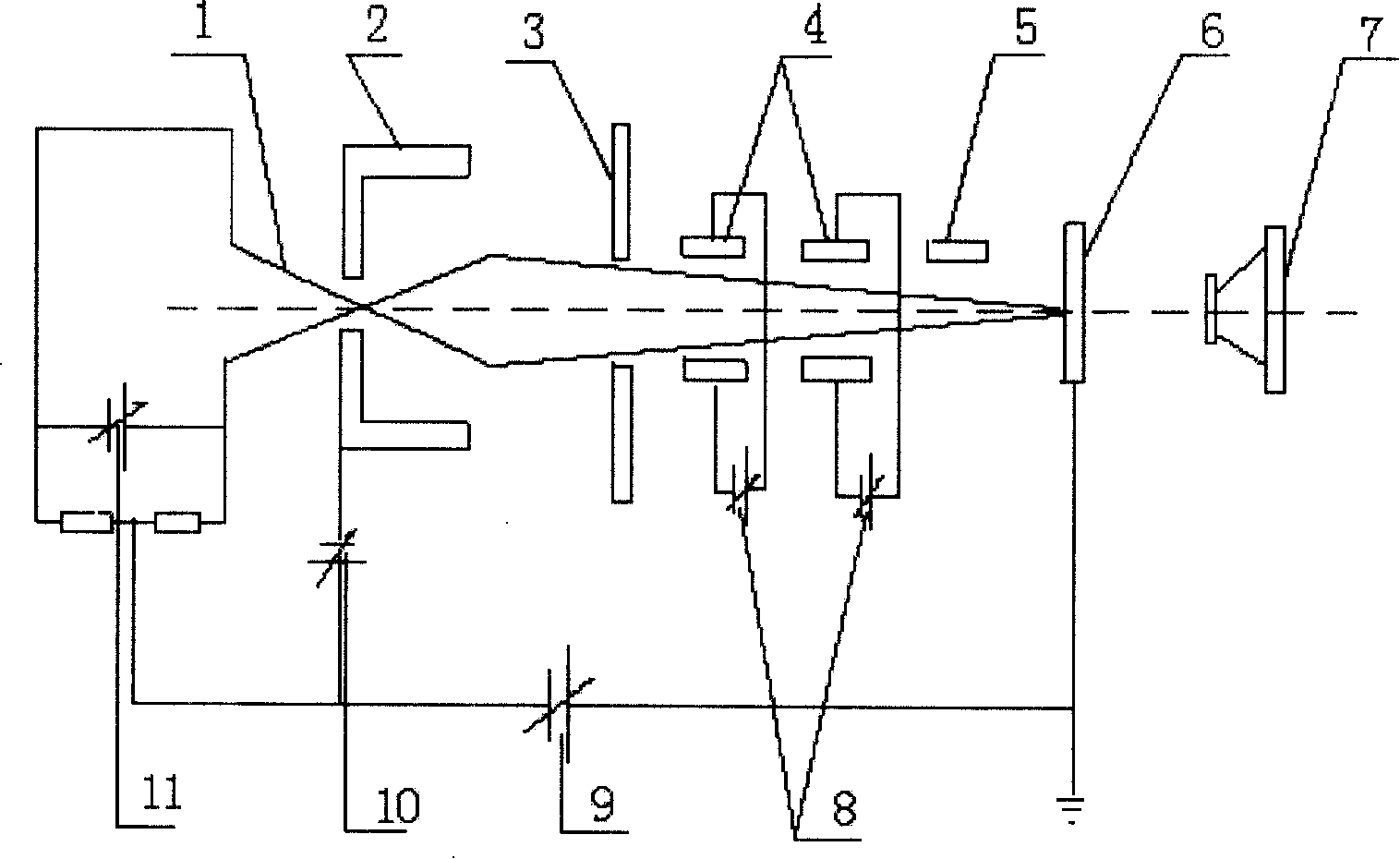
The invention discloses a femtosecond electron diffraction device that includes light resource, electron generate and control system, sample room, electron measuring and imaging system, vacuum system and five shafts control system. The electron generating and controlling system includes photo cathode, anode, magnetic lens, X direction deflecting plate and Y direction deflecting plate. The invention decreases the distance from the cathode to sample and improves the time resolving power. The invention could be used to measure the structure dynamic information of transmission diffraction and reflection diffraction of the sample.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
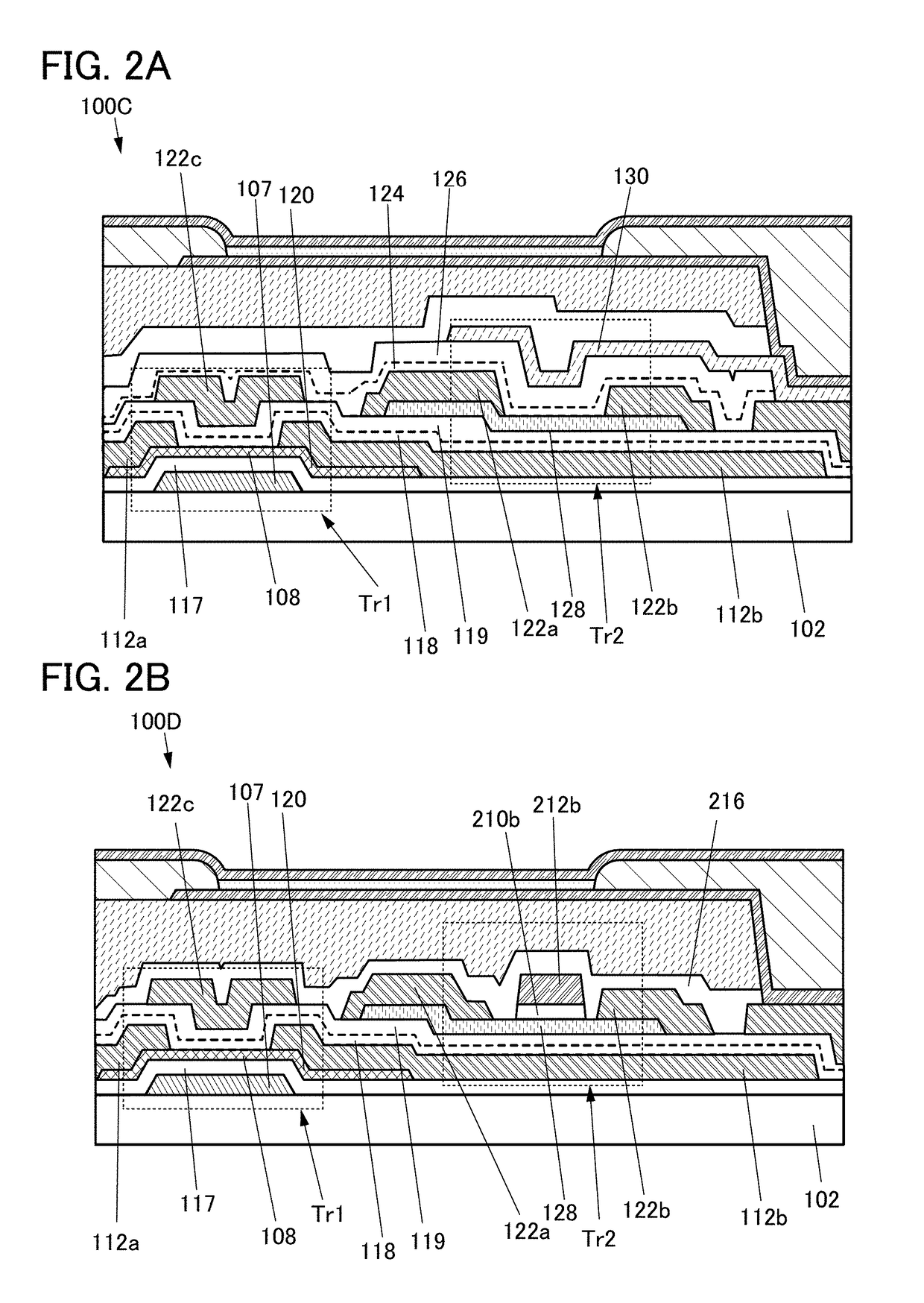
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20150084045A1Reduce the density of defect statesImprove featuresSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceLow density
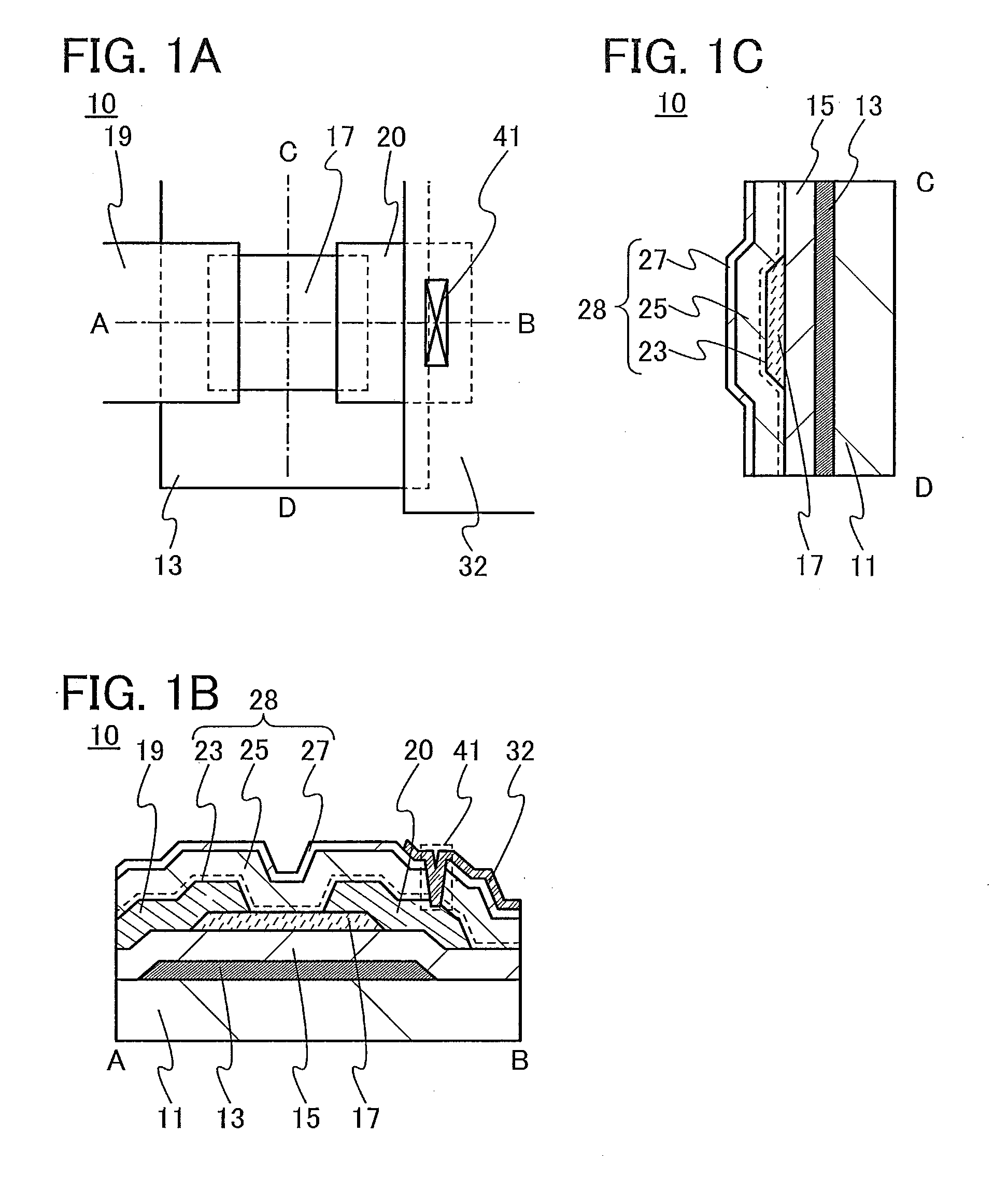
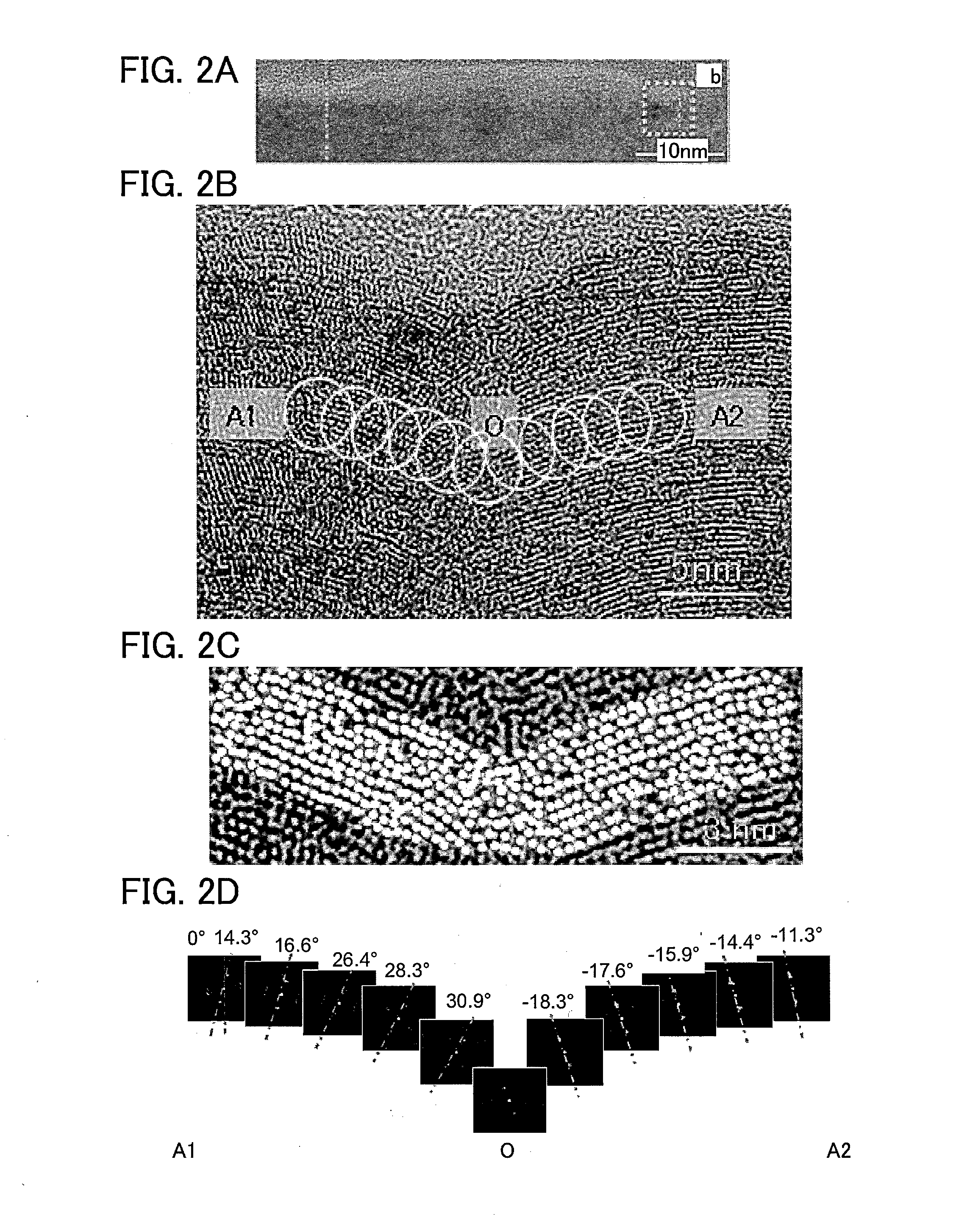
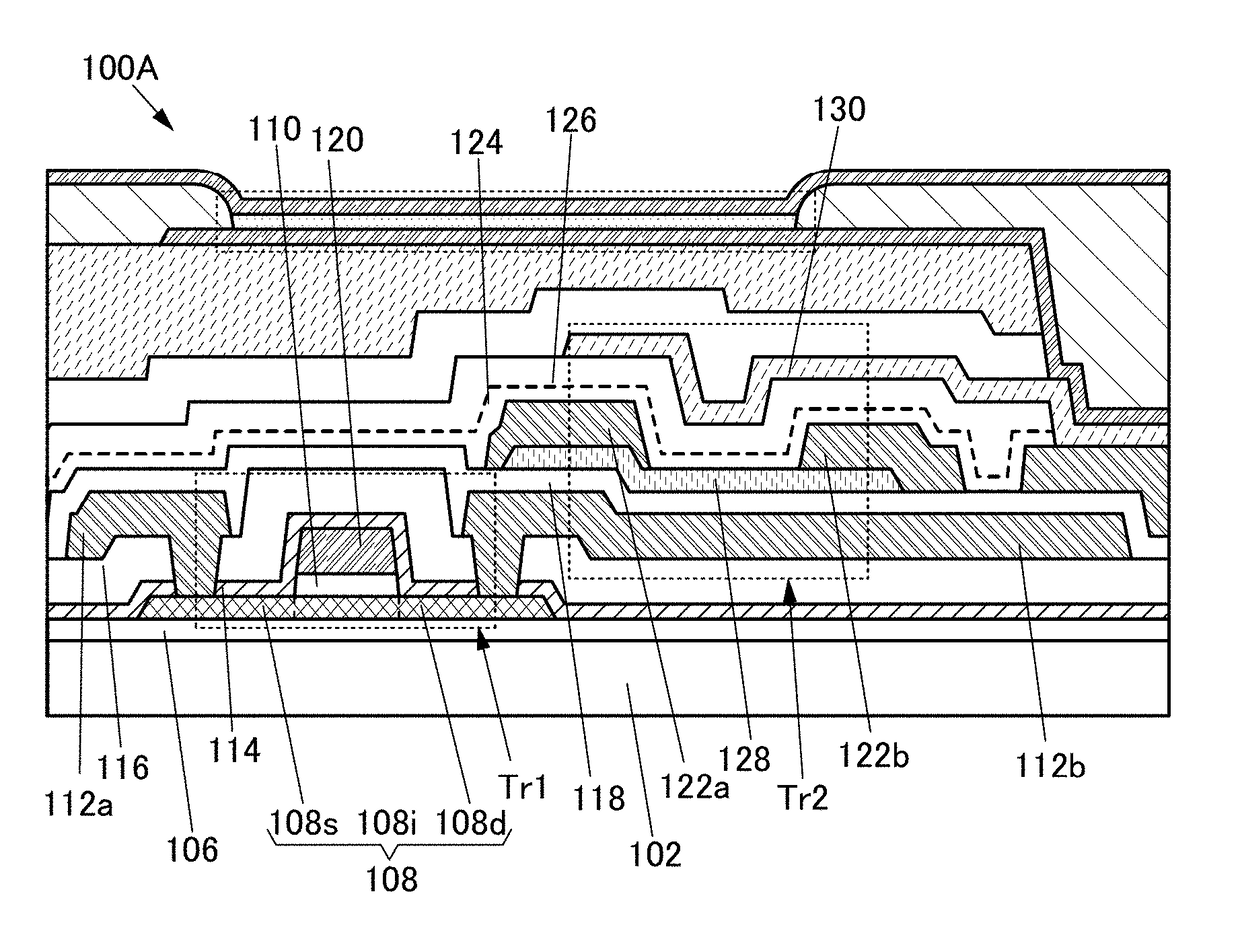
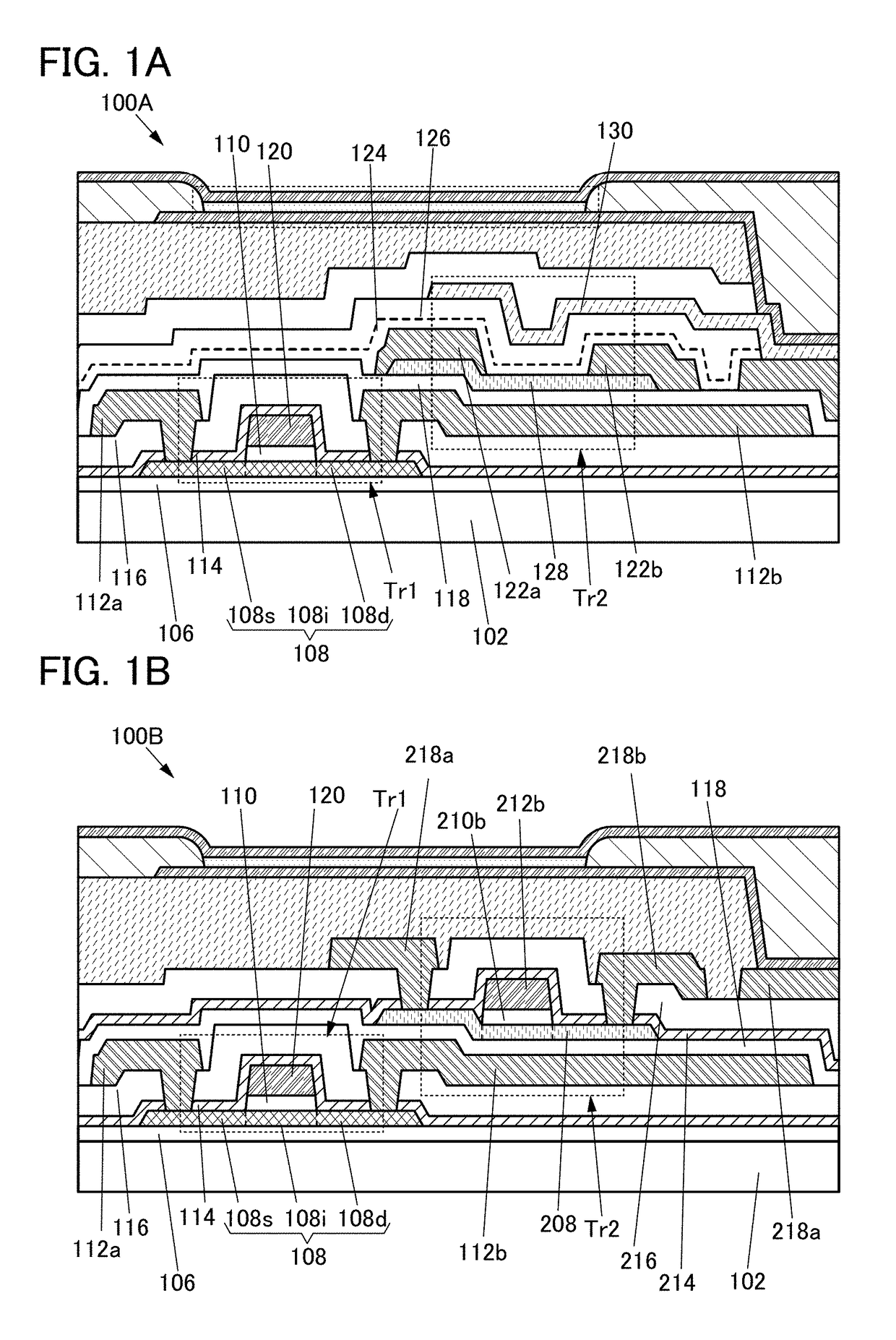
An oxide semiconductor film with a low density of defect states is formed. In addition, an oxide semiconductor film with a low impurity concentration is formed. Electrical characteristics of a semiconductor device or the like using an oxide semiconductor film is improved. A semiconductor device including a capacitor, a resistor, or a transistor having a metal oxide film that includes a region; with a transmission electron diffraction measurement apparatus, a diffraction pattern with luminescent spots indicating alignment is observed in 70% or more and less than 100% of the region when an observation area is changed one-dimensionally within a range of 300 nm.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electronic gun power supply for reflected high energy electron diffraction instrument
ActiveCN101178371AImprove reliabilityReduce volumeAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHigh energyLow voltage
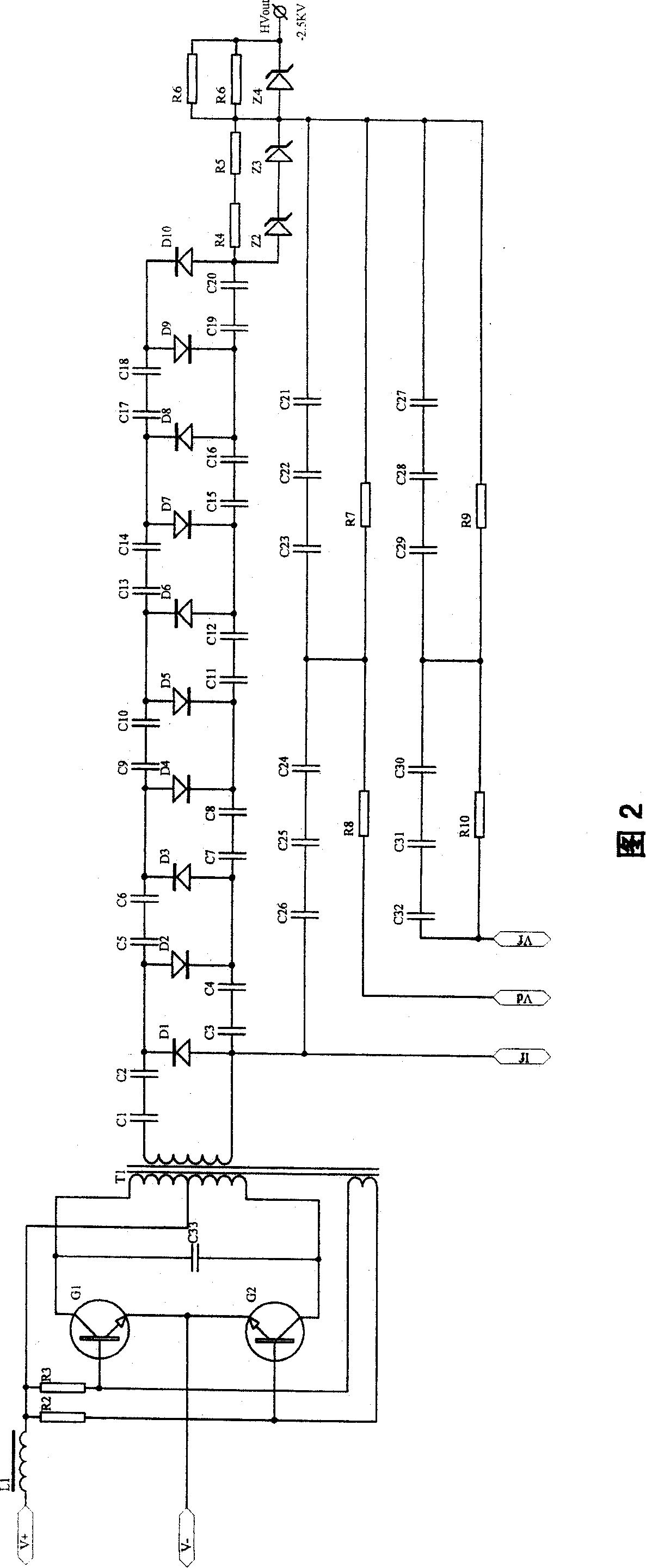
The invention discloses a power supply of an electron gun for a reflection high-energy electron diffractometer, wherein, the high-voltage power supply which consists of a high-voltage part and a low-voltage adjusting part is minus 25 KV,, the output of a resonance circuit of the high-voltage part is connected on a lamp wire of the electron gun and a grid by generating the high voltage of minus 25KV by a 10-time rectifier filter; the low-voltage adjusting part is connected with the high-voltage part and a second driving tube by an adjusting tube, an input signal which is connected with the second driving tube comes from the high-voltage part and an overflow protection and fault alarm circuit of a current sampling amplifying circuit, a slow starting circuit is connected with the overflow protection and fault alarm circuit and a voltage sampling amplifying circuit; the input of a high-voltage measurement display circuit is the high-voltage part, the output thereof is connected with a display; a deflection power supply includes a low-voltage signal circuit and a high-voltage amplifying circuit, the low-voltage signal circuit provides the voltage signals with two reverse polarities andis connected with the high-voltage amplifying circuit and is finally connected with a deflection plate. The invention has reliable work and simple structure.
Owner:SHENYANG SCI INSTR RES CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for electron back scattered diffraction test sample of zirconium oxide thermal barrier coating
InactiveCN104089801ANo pollution in the processNo residual shear stressPreparing sample for investigationPollutionElectron
The invention relates to a preparation method for an electron back scattered diffraction test sample of a zirconium oxide thermal barrier coating. The preparation method comprises the steps of a. performing surface treatment on the electron back scattered diffraction test sample of the zirconium oxide thermal barrier coating; b. fixing the electron back scattered diffraction test sample of the zirconium oxide thermal barrier coating on a sample table of an argon ion beam grinder, and adjusting the center of the electron back scattered diffraction test sample of the zirconium oxide thermal barrier coating; c. vacuumizing to form a pressure being 1*10<-5>-1*10<-3>Pa, adjusting an inclination angle of the sample table for three times, wherein the inclination angle of the sample table is adjusted to be 60-85 degrees each time, and performing argon ion beam grinding on the electron back scattered diffraction test sample of the zirconium oxide thermal barrier coating; and d. resetting the inclination angle of the electron back scattered diffraction test sample of the zirconium oxide thermal barrier coating to zero degree, and performing spray-plating on the electron back scattered diffraction test sample of the zirconium oxide thermal barrier coating. The preparation method has the characteristics of no shear stress residue, no grinding material pollution, no scratches, low injury to the test sample and the like; a kikuchi band is relatively high in definition; the calibration rate of an electronic diffraction pattern is over 95 percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH +1
Method for in-situ processing and structural characterization of composite inclusion in steel
InactiveCN104458781AAvoid Analysis Interference ProblemsImprove analysis accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionDistribution characteristicX-ray
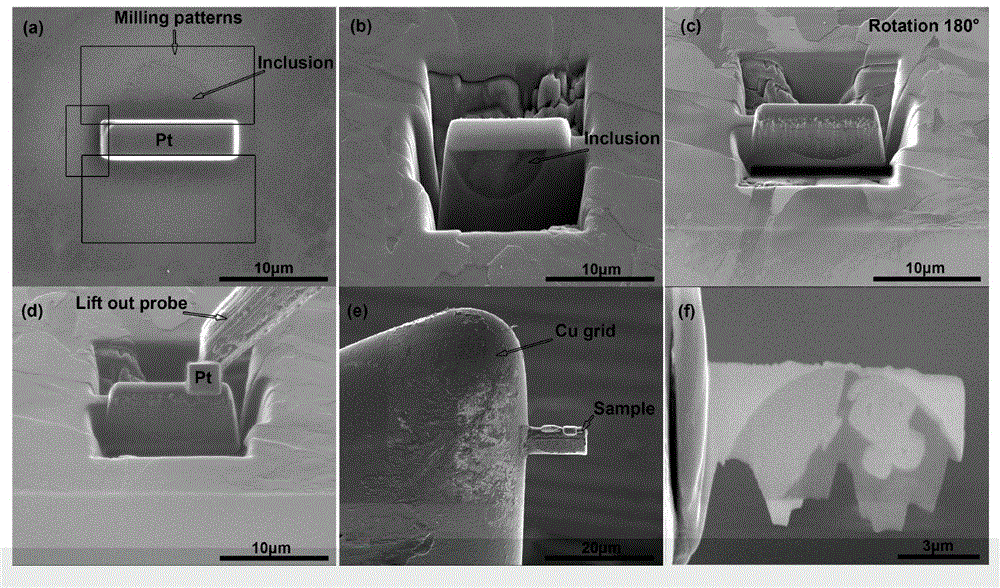
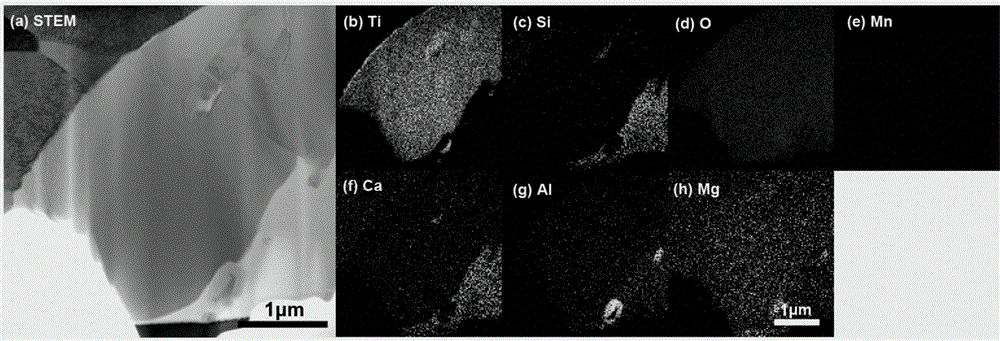
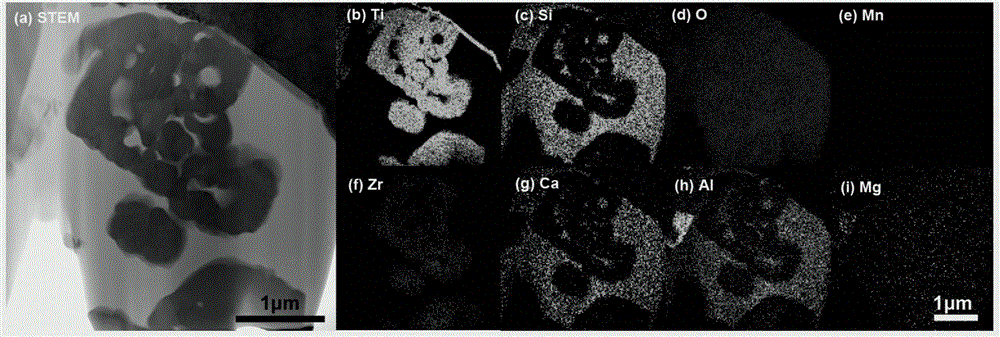
The invention relates to a method for in-situ processing and structural characterization of a composite inclusion in steel. The method comprises the following steps: (1) accurately positioning and in-situ preparing a transmission electron microscope profile sample of an interesting composite inclusion by utilizing a focused ion beam; (2) analyzing element composition and element area distribution of the inclusion by virtue of an X-ray spectrometer attached on the transmission electron microscope; (3) obtaining a diffraction pattern of the low-index surface of each element gathered area in the inclusion by utilizing the electron diffraction technology of the transmission electron microscope; and (4) calibrating the phase corresponding to each diffraction spectrum by utilizing the diffraction pattern and combining the element composition and area distribution characteristics of the inclusion. According to the method, the phase distribution and composition of the interesting composite inclusion from core to surface can be quickly accurately obtained, a novel method is provided to studies on phase composition and formation mechanism inside the composite inclusion, and the defects of high randomness, low success rate, difficult inclusion completeness guarantee and the like of the composite inclusion transmission electron microscope sample can be overcome.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
Method of Electron Diffraction Tomography
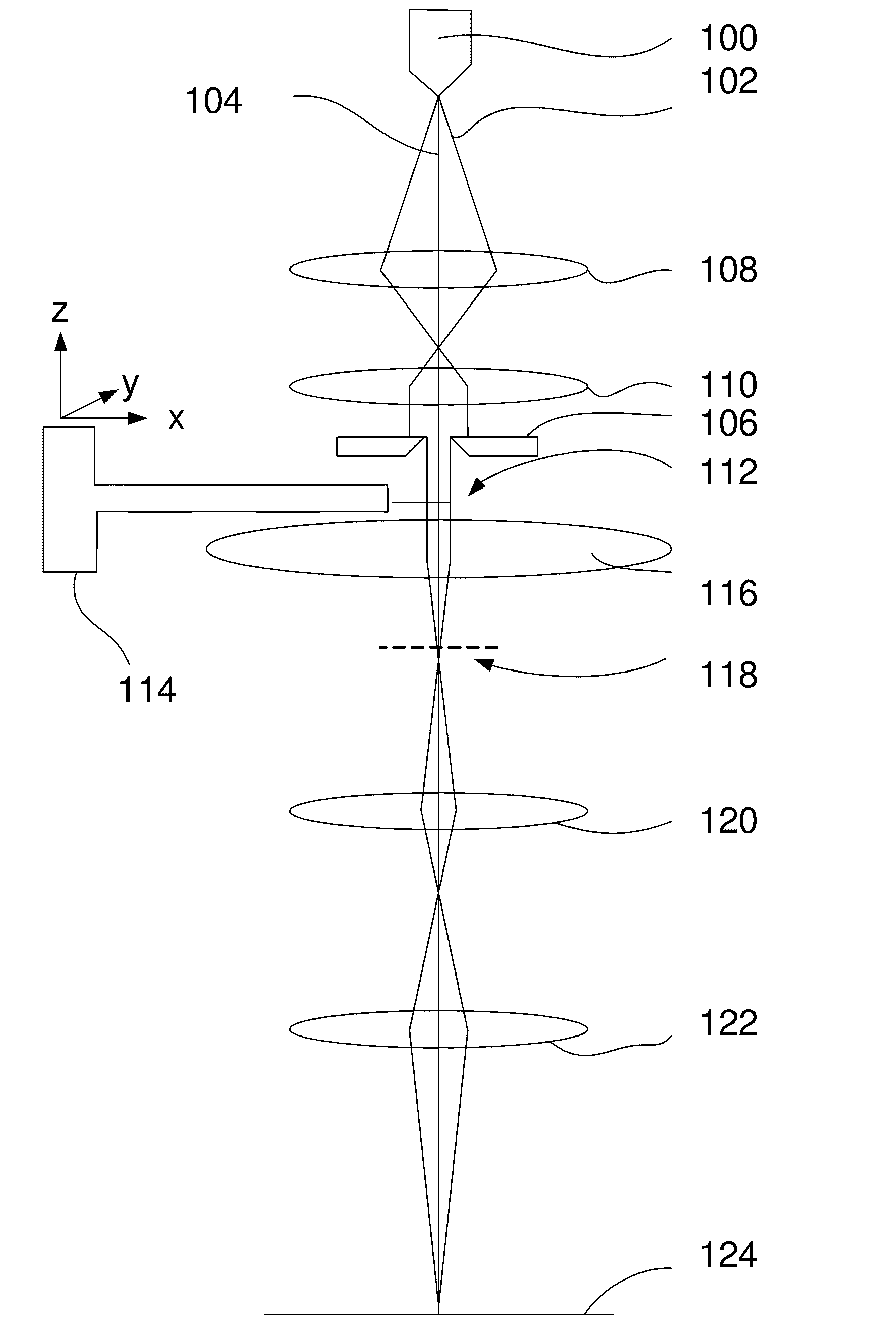
ActiveUS20120001068A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeLight beam
The invention relates to a method for electron diffraction tomography in a Transmission Electron Microscope. Known methods involve using Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope, and use the scanned beam for STEM diffraction. The invention proposes to form the diffraction patterns with a stationary beam with a diameter slightly larger than the crystal, as a result of which a TEM without STEM unit can be used. Finding the crystal is done in TEM mode. Advantages of the method according to the invention are: a TEM without scanning unit can be used, and the diffraction volume is not depending on the orientation of the crystal, as the whole crystal is illuminated while obtaining the diffraction pattern.
Owner:FEI CO
Selective diffraction with in-series gratings
Systems and methods for determining information for a wafer are provided. One system includes a first grating that diffracts light from a wafer having wavelengths in a first portion of a broadband range and does not diffract the light from the wafer having wavelengths in a second portion of the broadband range. The system also includes a second grating positioned in the path of the light that is not diffracted by the first grating. The second grating diffracts the light from the wafer having the wavelengths in the second portion of the broadband range. The system further includes a first detector configured to generate first output responsive to the light diffracted by the first grating and a second detector configured to generate second output responsive to the light diffracted by the second grating.
Owner:KLA CORP
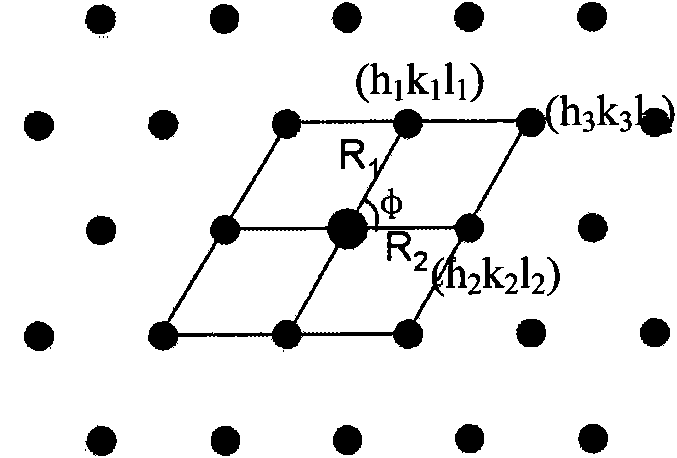
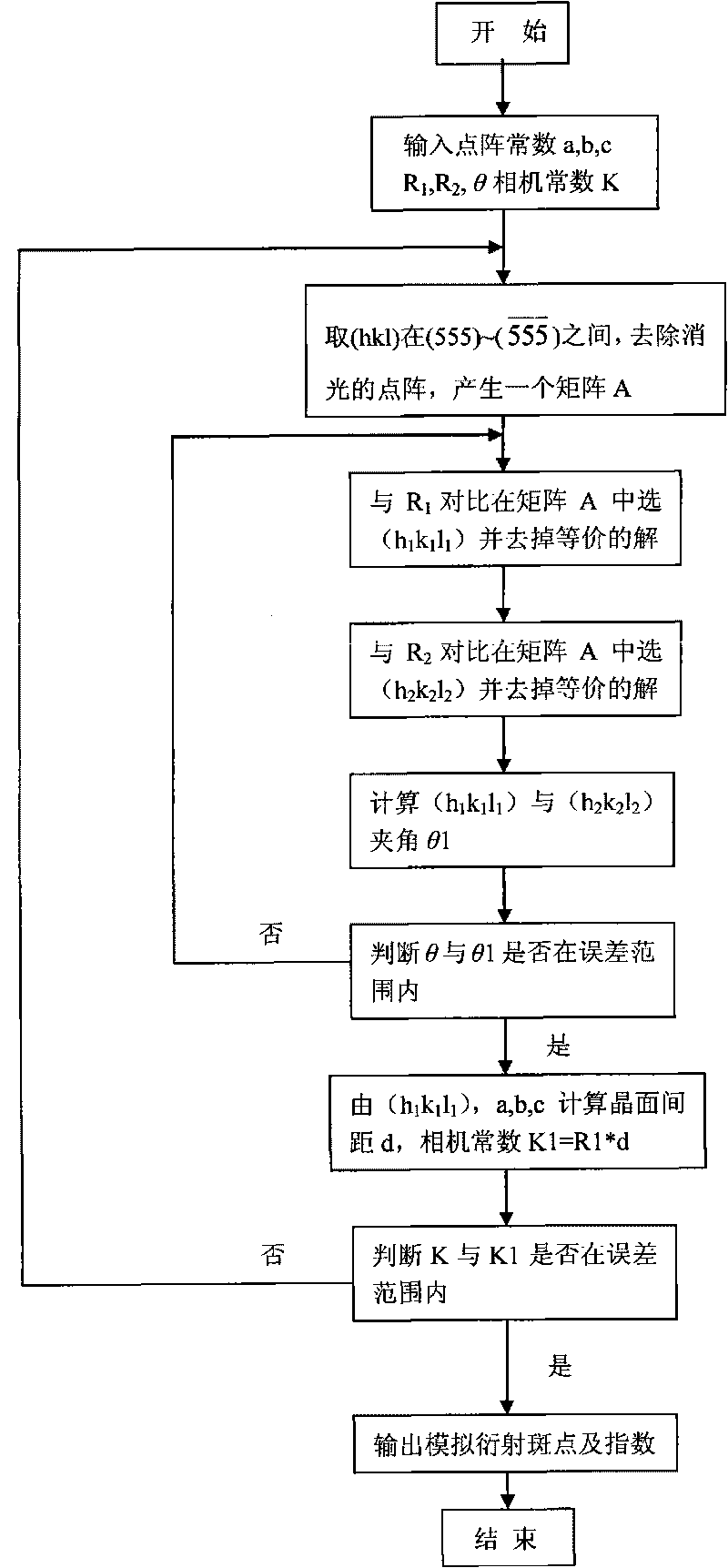
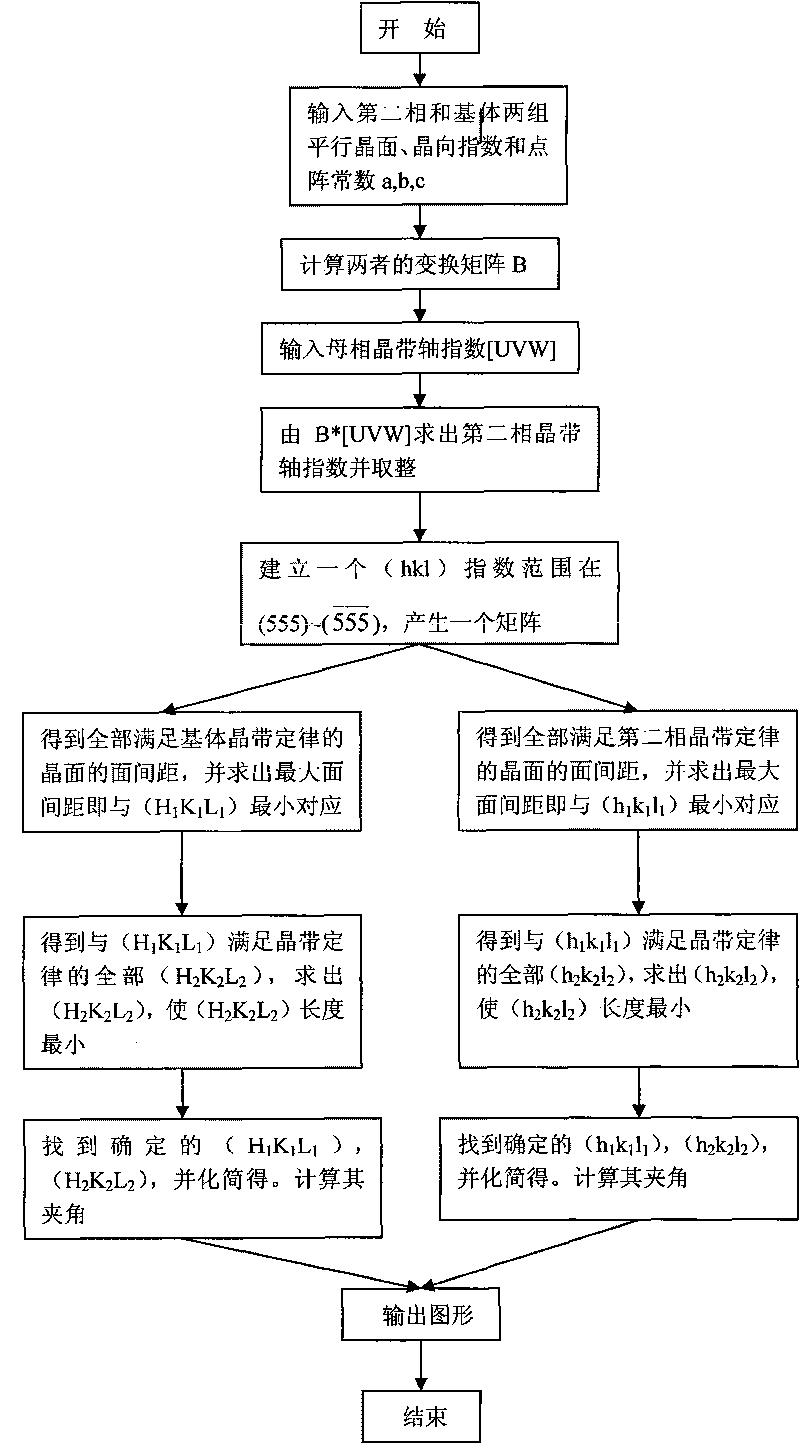
Electronic diffraction index calibrating method based on Matlab
InactiveCN101710085AEasy CalibrationQuick calibrationSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionMATLABDiffraction spectrum
The invention belongs to the field of scientific analysis of materials, in particular to an electronic diffraction index calibrating method based on Matlab. The zero-order electronic pattern index calibration and the index calibration of electronic simulating diffraction spots of two substances with a specific orientation relationship are carried out on a sample material by using a transmission electronic microscope, a computer and Matlab software. The invention mainly relates to a calibrating method of a monocrystal diffraction spectrum and the drawing of a standard electronic diffraction spectrum. Compared with the traditional calibrating method, the invention saves more time, can conveniently draw a zero-order and high-order simulating spot chart and an orientation relationship chart of a second phase and a base body and provides the beneficial technical basis for the computer to recognize the monocrystal diffraction spectrum.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
In-situ temperature loading device for neutron diffraction
InactiveCN105388074AEffective isolationGuaranteed reliabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesNeutron diffractometerEngineering
The invention provides an in-situ temperature loading device for neutron diffraction. The device comprises a furnace body cavity, a base, an incidence window plate, an emergence window plate, a high-temperature extensometer, a support leg A window film, a support leg B window film, a left-side fixture, a right-side fixture, a left-side fixture gasket, a right-side fixture gasket, a left-side cooling water jacket, a right-side cooling water jacket and an upper cooling water jacket. The device is characterized in that a neutron incidence hole, a neutron emergence hole, two fixture holes and two extensometer measuring support leg insertion holes are formed in the furnace body cavity, so that measurement neutrons can pass through directly, and meanwhile sample deformation can be measured in real time. When the in-situ temperature loading device is applied to a neutron diffraction in-situ mechanics-temperature composite environment loading experiment conforming to the national high-temperature tensile test standard together with a neutron diffractometer and a neutron diffraction in-situ mechanics device, the acting mechanism of a temperature-mechanics composite condition on the internal microstructure of a sample material is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Method for reconstructing three-dimensional reciprocal space of material with complex structure
For some materials with complex structures or abnormal flaw distribution, the reciprocal spaces thereof may have locality constitution distribution or local paracycle modulation. The invention provides a method for reconstructing a three-dimensional reciprocal space of a material with a complex structure for confirming the kind of complex structures, the method carries out the pre-quantization through the matched value of a main tilt angle Alpha (titling step Delta Alpha i) and a vice tilt angle Beta ( titling offset angle Delta Beta i) of a sample platform in the process of tilting operation, so the operation and record of the whole tilting reconstruction experiment can be accurate and efficient. The invention solves the problems that the kind of complex structures is time-consuming and has poor precision, and the like. Since the quantity offset of the vice tilt angle Delta Beta i is adopted, the gained serial selected-area electron diffraction spectrum can accurately maintain the same titling axis, and also provides a practical method which can conform the dynamic range of intensity of a negative. On the basis of theoretical analysis, the method can simultaneously be matched with the experiment measurement, and quantificationally confirm the value range of diffracted intensity gray level, which accords with the intensity dynamic range of the record negative.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrafast lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging method and device
InactiveCN102903591AImprove time resolutionLow costElectric discharge tubesImage resolutionBack calculation
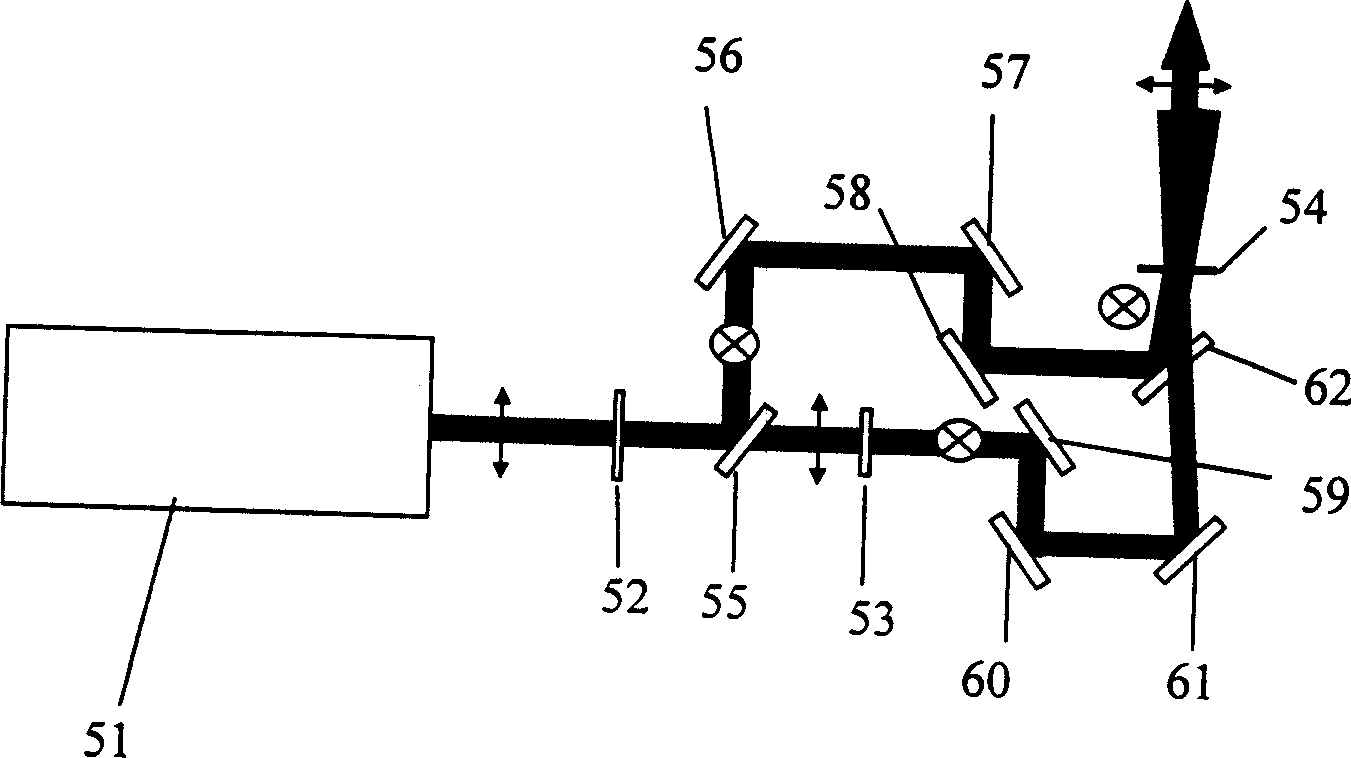
The invention discloses an ultrafast lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging method and device. The method is combined with the electronic pulse which is in precise synchronization with process exciting sources (such as femtosecond laser pulses) and a lens-free coherent electron diffraction imaging technology, and comprises the steps of analyzing the strength distribution of the diffracted coherent electronic pulses, and carrying out back calculation to determine the electronic scattering phase, so as to achieve the reconstruction of the structure and the appearance of three-dimensional transient atomic scale. By adopting the method and device disclosed by the invention, the technical problem that the conventional electronic microimaging method has no high time resolution or the existing ultrafast electronic imaging time and space resolution are limited can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Semiconductor device and display device including the semiconductor device
InactiveUS20170271378A1Transistor area can be reducedNumber of mask increaseTransistorSolid-state devicesOxide semiconductorElectron diffraction
A semiconductor device with a reduced layout area of transistors is provided. The semiconductor device includes a first transistor including a first oxide semiconductor film and a second transistor including a second oxide semiconductor film over a substrate. When the oxide semiconductor films are subjected to electron diffraction, the ratio of the integrated intensity of luminance of a diffraction spot derived from c-axis alignment to the integrated intensity of luminance of a diffraction spot derived from alignment in any direction in the first oxide semiconductor film is higher than that in the second oxide semiconductor film. In addition, part of the first transistor is located between the second transistor and the substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Terahertz-driven electronic pulse accelerating femtosecond electron diffraction device
ActiveCN106384704AOvercoming spark-through problemsRemove time jitterElectric discharge tubesBeam splitterTemporal resolution
The invention relates to a terahertz-driven electronic pulse accelerating femtosecond electron diffraction device which comprises a femtosecond laser, a beam splitter, an ultraviolet laser pulse generator, a terahertz pulse generator, an electron gun, an electron focusing device, a sample room, an imaging device and a camera. After the femtosecond laser emitted by the femtosecond laser passes through the beam splitter, one beam of femtosecond laser enters the ultraviolet laser pulse generator, and the other beam of femtosecond laser enters the terahertz pulse generator through a mirror. An ultraviolet laser pulse and a terahertz pulse received by the electron gun enter the cavity of the electron gun to produce an electronic pulse. The electron focusing device is mounted between the cavity of the electron gun and the sample room. A sample assembly and the imaging device are placed inside the sample room in sequence along the emitting direction of the electronic pulse. The camera is placed at a position, facing the imaging device directly, outside the sample room. The device can run in a reflection or transmission mode, can be used in research of both a reversible process and an irreversible process, and is of high brightness and high spatial-temporal resolution.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Co-B/CeO2-SiO2 alloy catalyst, its preparation process and application
InactiveCN1698957ANo pollution in the processSimple and fast operationOrganic chemistryCatalyst activation/preparationAlloy catalystX-ray
This invention discloses a Co-B / CeO2-SiO2 amorphous alloy catalyst, in addition to a preparing method and its uses. The mole percent of each component is: Co:13.8-18.5%, Ce:0-9.72%, B: 0.9-1.75%. By the test of X-ray diffraction and selected area electron diffraction, the catalyst has obvious amorphous structure, and the specific surface area is 37- 87m2 / gCo. The catalyst can be used for furfural liquidoid selectively hydrogenation preparing furfuryl alcohol. Said method has good catalytic activity and selective not only to furfural hydrogenation, but also to acetonitrile hydrogenation, amylaceum hydrogenation and benzalacet aldehyde hydrogenation.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Electron diffractometer capable of realizing automatic defect regulation
ActiveCN107655909AAchieving Regulatory RepairQuantity is easy to controlMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDiffractometerPulse energy
The invention relates to an electron diffractometer and provides an electron diffractometer capable of realizing automatic defect regulation. The electron diffractometer comprises a vacuum sample room, and also comprises a testing optical path, a detect regulation optical path and a processing unit. Frequency tripled laser of the testing optical path is transmitted from a first incidence window into the vacuum sample room. Frequency doubled laser of the defect regulation optical path is transmitted from a second incidence window into a sample stage inside the vacuum sample room. An electronicgun is also arranged inside the vacuum sample room. A cathode of the electronic gun is positioned on the testing optical path. The defect regulation optical path is provided with a laser pulse energyregulator and a laser pulse scanning device. The processing unit comprises a receiving component and a control center. The electron diffractometer of the invention can achieve in-situ real-time nondestructive measurement of the micro- and nano-fabrication process and realize growth while testing. In addition, sample surface defect information is obtained through processing of diffraction images, and femtosecond laser pulse energy and scanning position are regulated according to the invention so as to repair defects, thus achieving the purpose of testing while regulating.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for improving mechanical property of FSW (friction stir welding) magnesium alloy joint
InactiveCN102528271AAdjust angleSolve the problem that the mechanical properties are lower than the magnesium alloy base metalNon-electric welding apparatusFriction weldingButt welding
The invention discloses a method for improving the mechanical property of an FSW (friction stir welding) magnesium alloy joint. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1), a magnesium alloy plate is taken and is rolled, compressed or forged until the grain orientations in the magnesium alloy plate are consistent, and the grain orientations in the magnesium alloy plate is detected through X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) or backscattered-electron diffraction (BSED) to obtain a magnesium alloy plate 1 of which the grain orientation is trimmed; 2), the magnesium alloy plate 1 is cut to obtain magnesium alloy plates 2 of which the grain orientations form included angles with the horizontal surface of the magnesium alloy plate respectively; and 3), and the two magnesium alloy plates 2 are butt-welded in an FSW method to obtain a magnesium alloy FSW joint with an excellent mechanical property. According to the method, before FSW, the grain orientation of the transition area of the joint is improved by adjusting the initial grain orientation of magnesium alloy, so that the mechanical property of the magnesium alloy joint is improved greatly, and the strength of the joint is close to that of base metal to ensure the application of magnesium alloy FSW piece.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
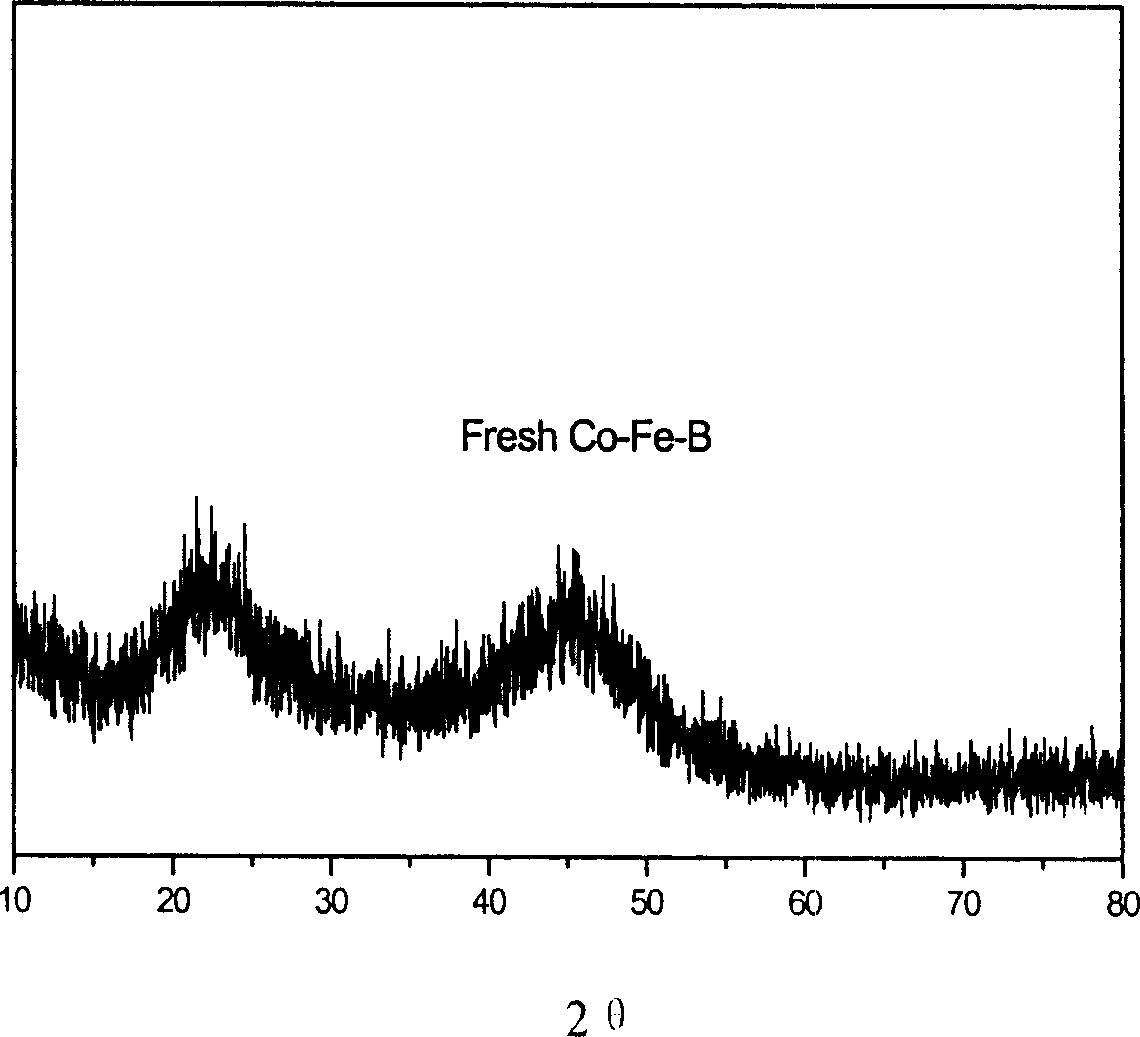
Co-Fe-B amorphous alloy catalyst, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1666816ANo pollution in the processSimple and fast operationOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationAlloy catalystX-ray
The invention discloses Co-Fe-B amorphous alloy catalyst and its preparation. The mole ratios of the components are: Co: 0-32%, Fe: 0.1-32%, B: 67-70%. The catalyst of the invention passes X-ray diffraction and selective-area electronic diffraction tests, and has apparent non-crystal structure and 19-71m2 / g surface area. The catalyst is utilized to acetonitrile election hydro-preparation of ethamine. The method has simple operation and the good catalyzing and active selection to the reactions of hydro-furfural, hydro-dextrose and cinnamaldehyde.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
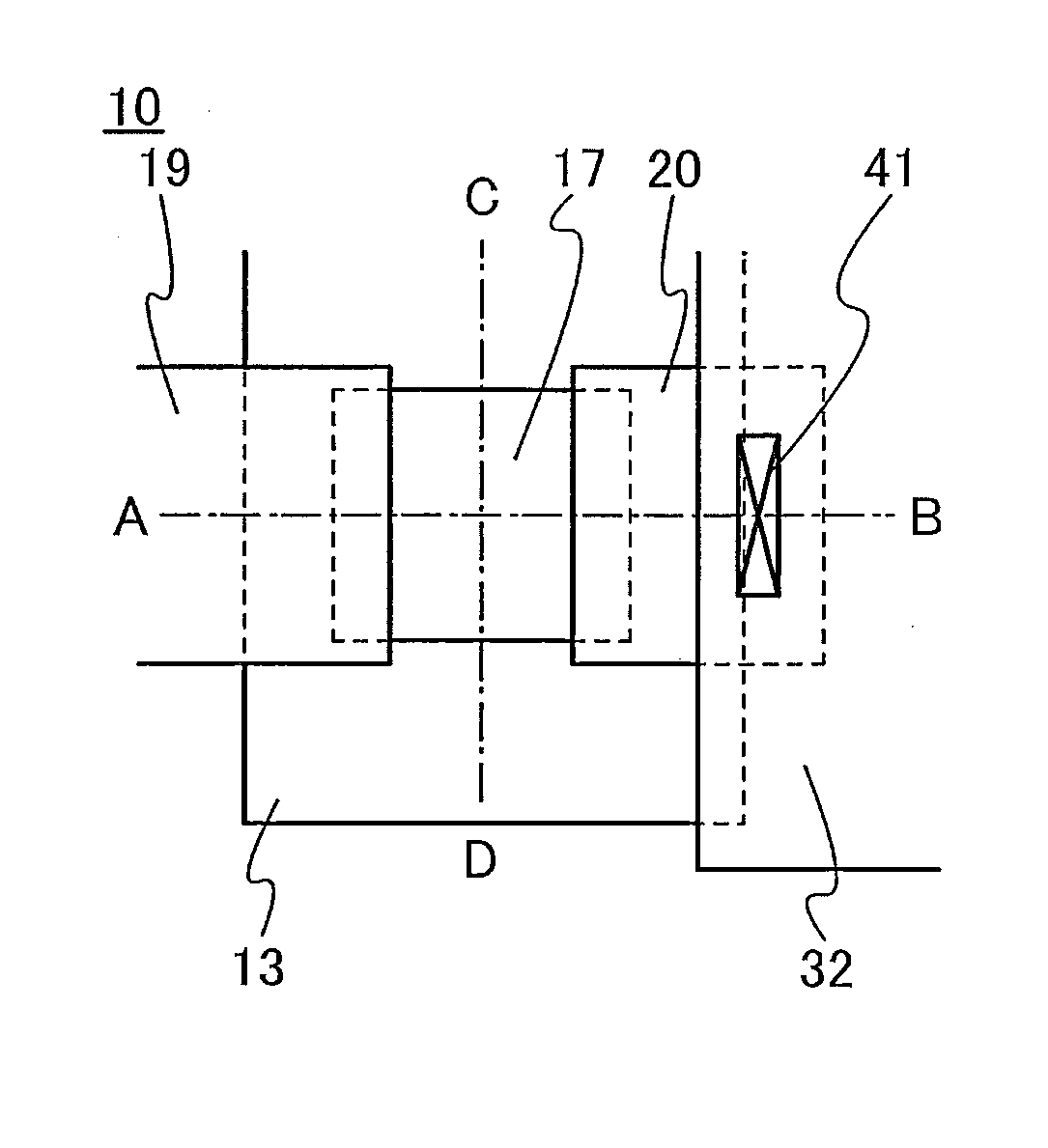
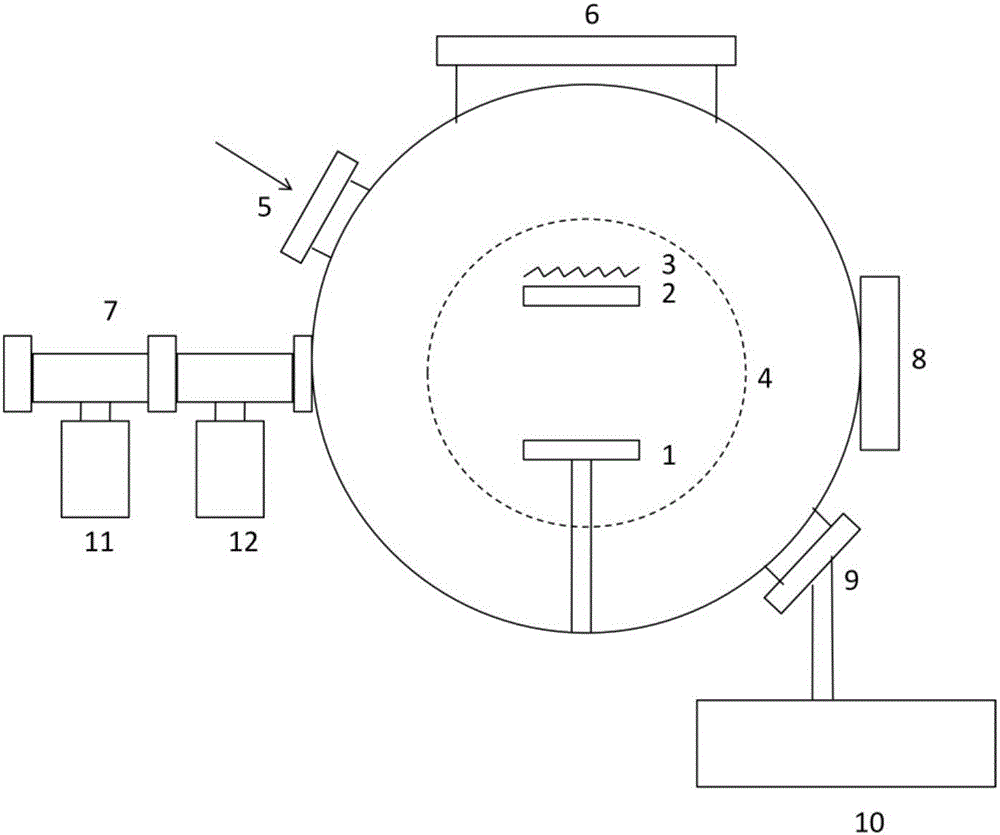
Sample platform and microscope system
The invention provides a sample platform and a microscope system. The sample platform is applicable to an electronic back-scattering diffraction-type work mode and a transmission electronic diffraction work mode. The sample platform includes a support frame, and a sample sink assembled on the support frame. The support frame includes a jack stand and a support rod. The support rod is connected with the jack stand. The jack stand forms an angle of 142 degrees with the support rod. When the sample platform is used, the sample platform is fixed on an object table of a secondary electronic microscope and the support rod is made form an angle of 90 degrees with the object table. Through a structure in which the angle between the jack stand and the support rod is designed to be 142 degrees and the angle between the support rod and the object table to be 90 degrees, when a sample is loaded on the sample platform for test analysis, through adjustment of tilting and / or rotation of the object table, a tilt angle between the sample and the horizontal plane can be adjusted in a large range so that switching between the electronic back-scattering diffraction-type work mode and the transmission electronic diffraction work mode can be carried out according to practical demands.
Owner:胜科纳米(苏州)股份有限公司
Method of electron diffraction tomography
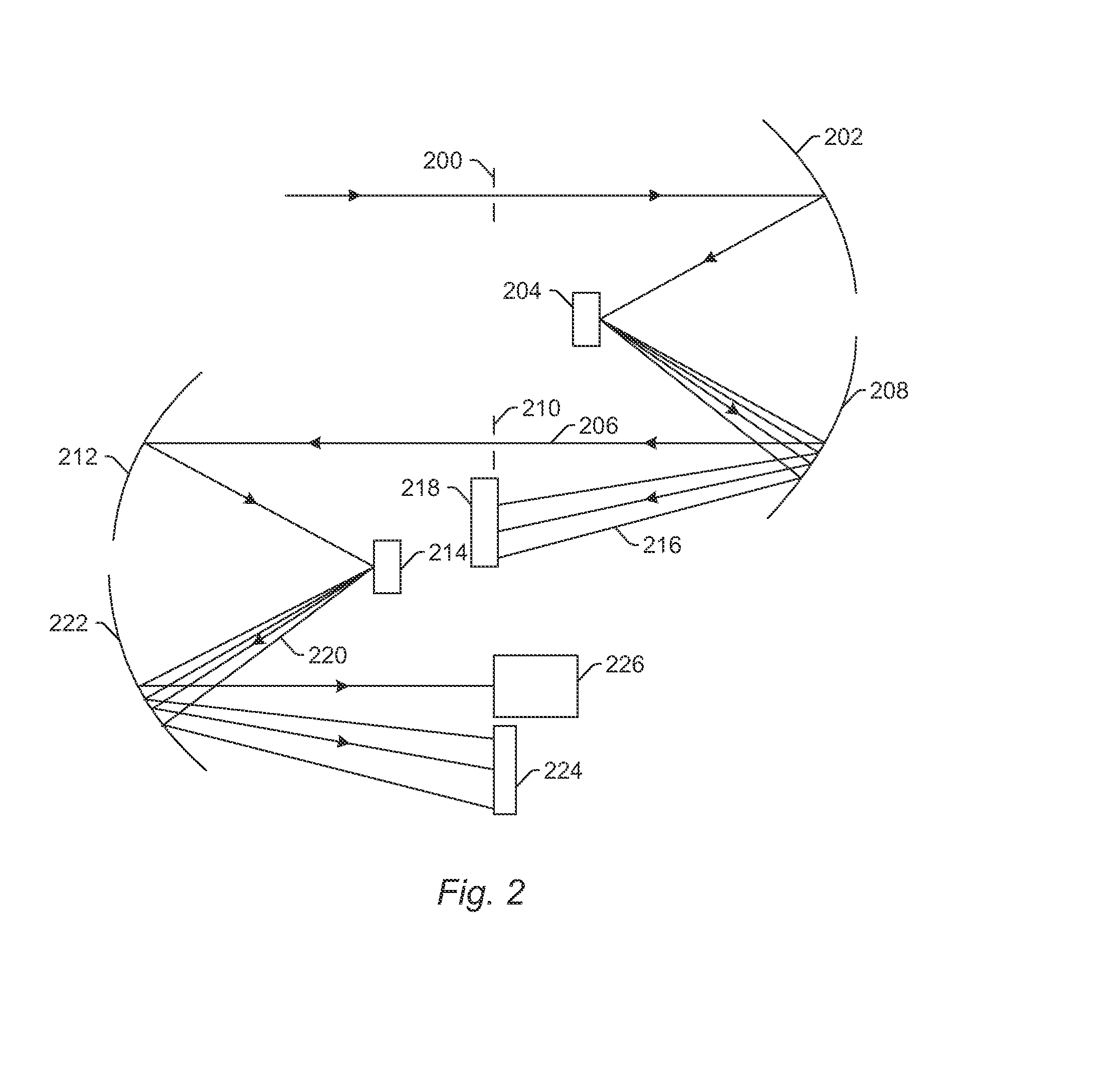
InactiveCN102313755AElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionElectron microscopeTomography
Discloded is a method of electron diffraction tomography. The invention relates to a method for electron diffraction tomography in a Transmission Electron Microscope. Known methods involve using Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope, and use the scanned beam for STEM diffraction. The invention proposes to form the diffraction patterns with a stationary beam 200 with a diameter slightly larger than the crystal, as a result of which a TEM without STEM unit can be used. Finding the crystal is done in TEM mode. Advantages of the method according to the invention are: a TEM without scanning unit can be used, and the diffraction volume is not depending on the orientation of the crystal, as the whole crystal is illuminated while obtaining the diffraction pattern.
Owner:FEI CO
Epitaxial growth method of yttrium iron garnet film
ActiveCN106048726AInsulationRoom temperature ferromagneticPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesHigh energyRoom temperature
An epitaxial growth method of a yttrium iron garnet film comprises the following steps: vacuumizing a vacuum cavity with a treated yttrium iron garnet substrate to be 8.6+ / -1*10-6 Pa, and heating the yttrium iron garnet substrate to the constant temperature which is 736 DEG C; in a heating process, feeding ozone when heating to the temperature of 250 DEG C; after heating to the temperature of 736 DEG C, maintaining air pressure of the vacuum cavity, adjusting the mass fraction of the ozone to be 40%, meanwhile insulating for half a hour, and starting a reflective high-energy electron diffraction instrument (RHEED) to adjust so as to obtain diffraction spots of a substrate; maintaining real-time and in-situ monitoring of the RHEED in the whole process, and focusing laser onto a YIG target through a lens by using a KrF excimer laser of which the wavelength is 248 nm; after growth of the film is finished, maintaining the temperature of the substrate unchanged, annealing in situ for 15 minutes, then naturally cooling the film to the temperature about 250 DEG C, stopping protective gas and cooling to the room temperature. The obtained YIG film has uniform components, is controllable in thickness and good in process repeatability, and has high preparation efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for detecting formation of nanocrystals on 690 high-strength steel surfaces
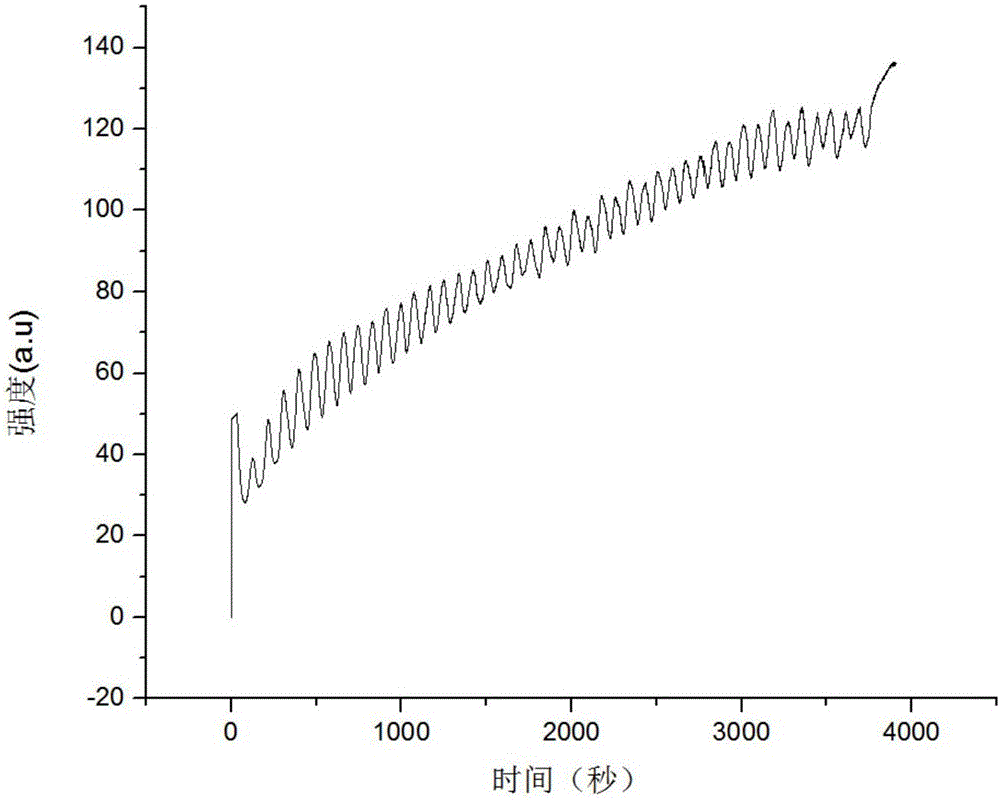
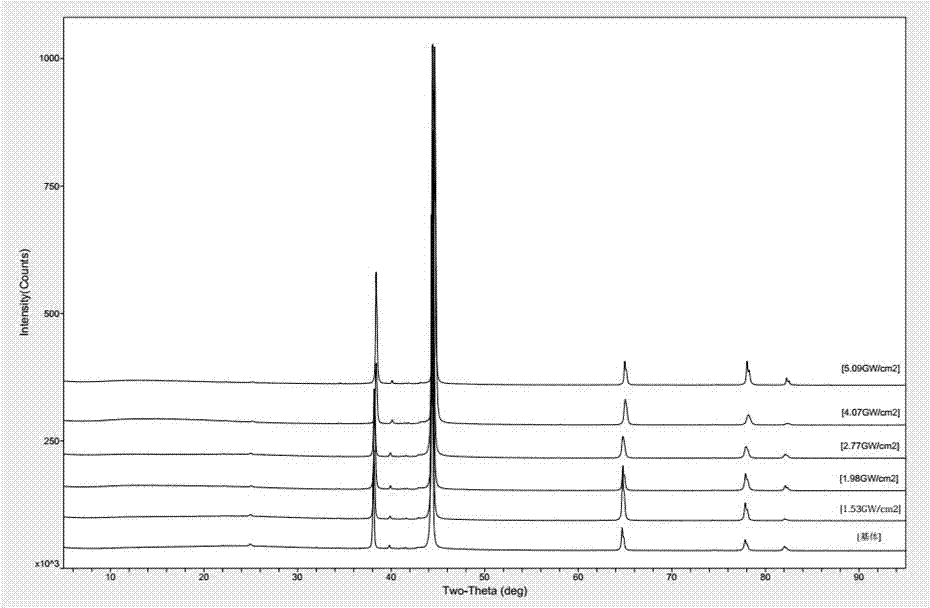
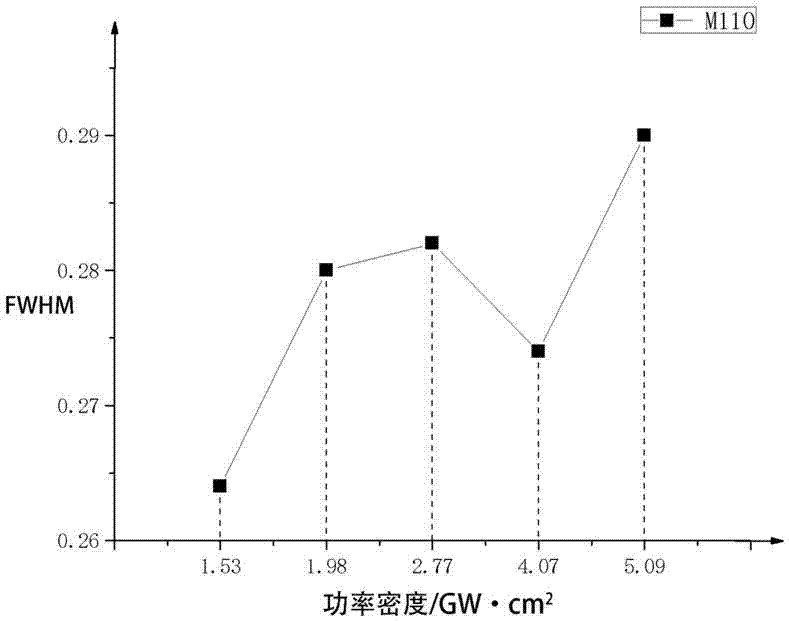
ActiveCN107290362AVerify reliabilityApplicable to the actual production processPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFull width at half maximumX-ray
The invention discloses a method for detecting formation of nanocrystals on 690 high-strength steel surfaces. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out extreme plastic strain on a plurality of 690 high-strength steel samples under the same process and different process parameters; carrying out X-ray diffraction on the samples after extreme plastic strain to obtain a group of X-ray diffraction patterns; calculating the full width at half maximum of the same crystal surface under each process parameter; and drawing a curve graph of the full width at half maximum changing along with each process parameter and finding out an increase inflection point and verifying that the process parameter of the extreme plastic strain corresponding to the increase inflection point is the minimal process parameter for forming the nanocrystals on the 690 high-strength steel surfaces through a transmission electron microscope and an electron diffraction experiment. According to the method for detecting formation of the nanocrystals on the 690 high-strength steel surfaces, the nanocrystals can be formed on the 690 high-strength steel surfaces through the extreme plastic strain carried out by adopting the process parameter exceeding the minimal process parameter for forming the nanocrystals on the 690 high-strength steel surfaces; detection is carried out without destroying the 690 high-strength steel surfaces; and the method is suitable for the practical production process.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method of MBE isoepitaxial growth SrTiO3 film
InactiveCN102492984AHigh sensitivityLower requirementPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsHigh energySurface reconstruction
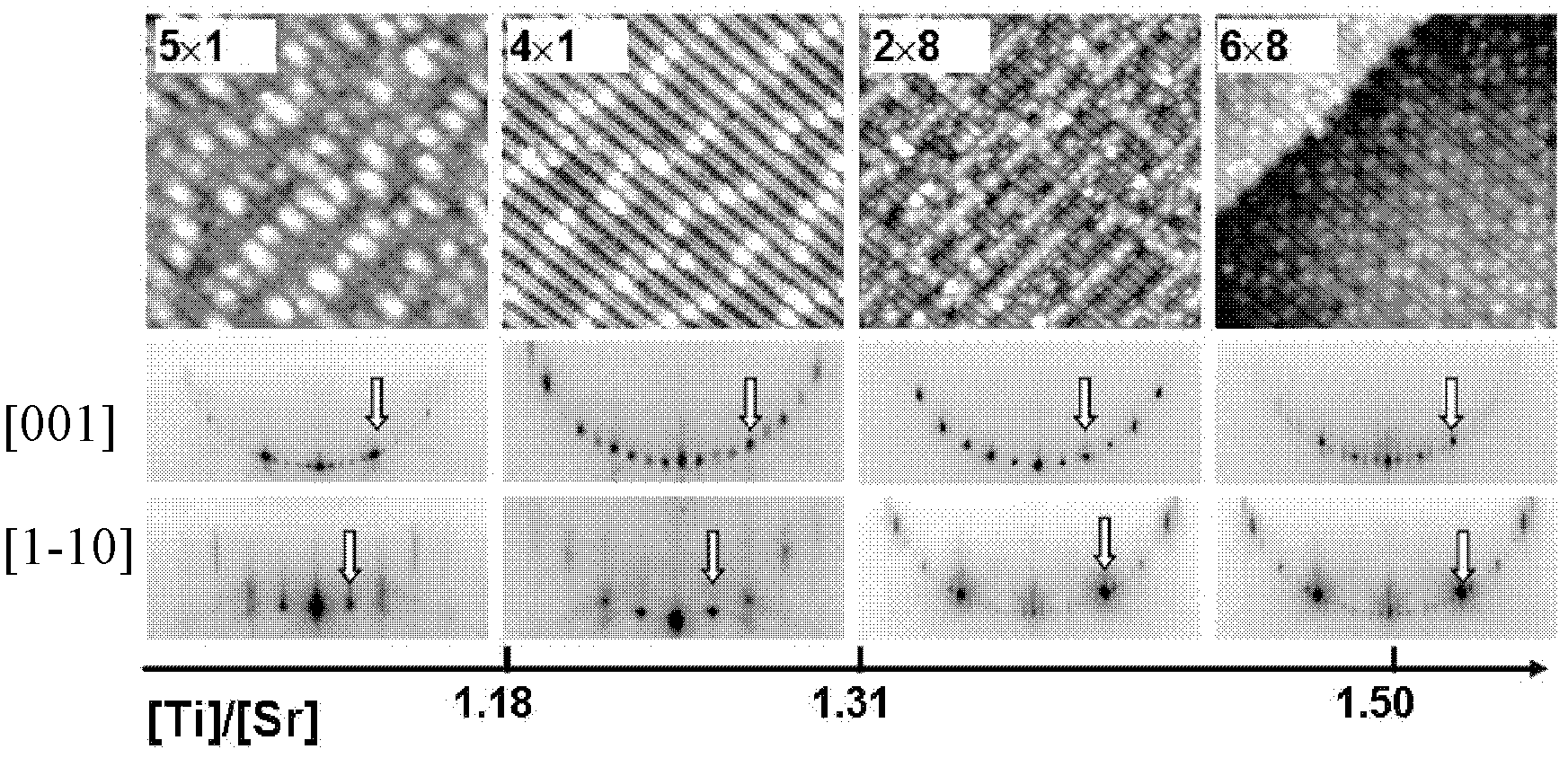
The invention provides a method of an MBE isoepitaxial growth SrTiO3 film. The method comprises steps of: 1) carrying out codeposition of Ti and Sr on a SrTiO3 substrate (110) in an oxygen atmosphere and carrying out real time monitoring of reflective high energy electron diffraction on a sample; and 2) adjusting a beam proportion of Ti and Sr according to brightness of characteristic strips of the reflective high energy electron diffraction to realize a film surface reconstruction the same as a substrate surface reconstruction.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Neutron diffraction method for welding residual stress of duplex stainless steel thick plate
ActiveCN108490009AStrong penetrating powerReduce time errorMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationApparatus for force/torque/work measurementThick plateWelding residual stress
The invention discloses a neutron diffraction method for welding residual stress of a duplex stainless steel thick plate. The method comprises the following steps: determining stress testing crystal faces in different directions and a wavelength changing manner, so that a penetration depth of the neutron in the duplex stainless steel thick plate is increased, and testing time and testing errors are reduced; accurately calculating a two-phase ratio in a standard volume of the neutron diffraction test by virtue of transformation of diffraction peak intensity; and simultaneously testing two-phasestresses under specific equipment and diffraction conditions. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the penetration depth of the neutron can be effectively improved by virtue of a variable wavelength manner; the residual stress time of the duplex stainless steel thick plate in the neutron diffraction test can be reduced; the testing error of the residual stress of the duplex stainless steel thick plate can be reduced; the two-phase ratio in the standard volume can be accurately calculated by utilizing data of the diffraction peak intensity obtained by the neutron diffraction; and the influence produced by micro stress caused by two-phase performance mismatching is clear, and macro welding residual stress distribution of the duplex stainless steel is accurately calculated.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Microscopy characterization and evaluation method of homogeneity of carbon fibers
InactiveCN103884551APreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionFiber structureElectron diffraction
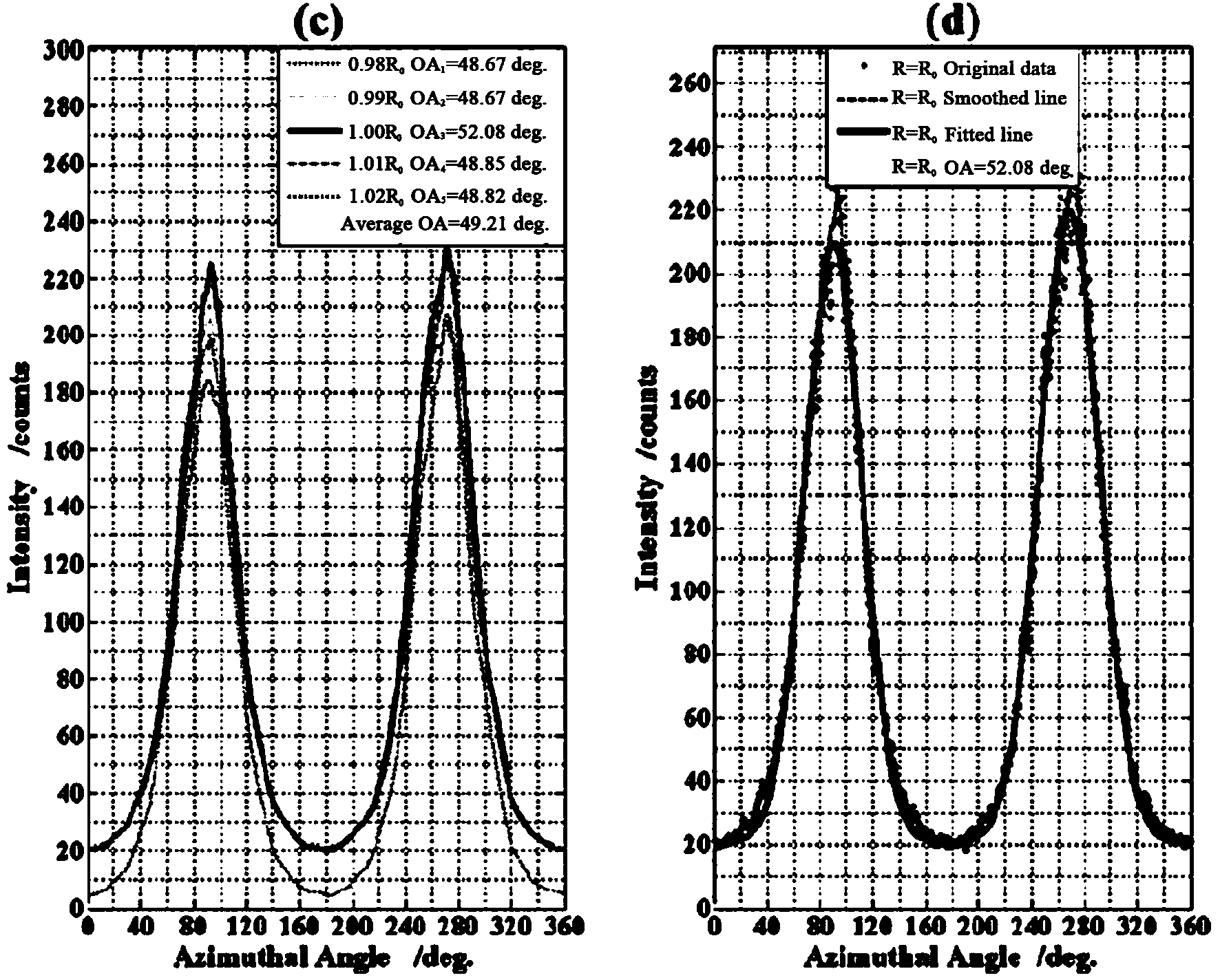
The invention aims to provide a microscopy characterization and evaluation method of homogeneity of carbon fibers. The method has the advantages that the homogeneity of a carbon fiber structure can be systematically evaluated, the method is not limited by the structures of the carbon fiber products of different diameters, different densities, different batches and different corporations, meanwhile, a condition that the carbon fibers are high modulus or high strength carbon fibers is not distinguished, and a simple, convenient and feasible evaluation standard is provided for evaluating the homogeneity of the carbon fiber structure in a qualitative manner. The evaluation method comprises the following specific steps of collecting an axially horizontal slice sample of carbon fibers, and collecting a series of continuous selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns on slices the sizes of which are same with the longitudinal sections of the carbon fibers by using a transmission electron microscope; respectively reading diffracted intensity values of the positions (0002) of the periphery along each diffraction arc to obtain a preferred orientation angle OA map, wherein the preferred orientation angle directly corresponds to the arrangement orientation degree of a (0002) carbon atom layer of the carbon fibers; accurately and quantitatively characterizing a texture degree of the carbon fibers by using the orientation angle.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring layer number of graphene on silicon carbide substrate
InactiveCN105717148AQuick measurementAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayElectron
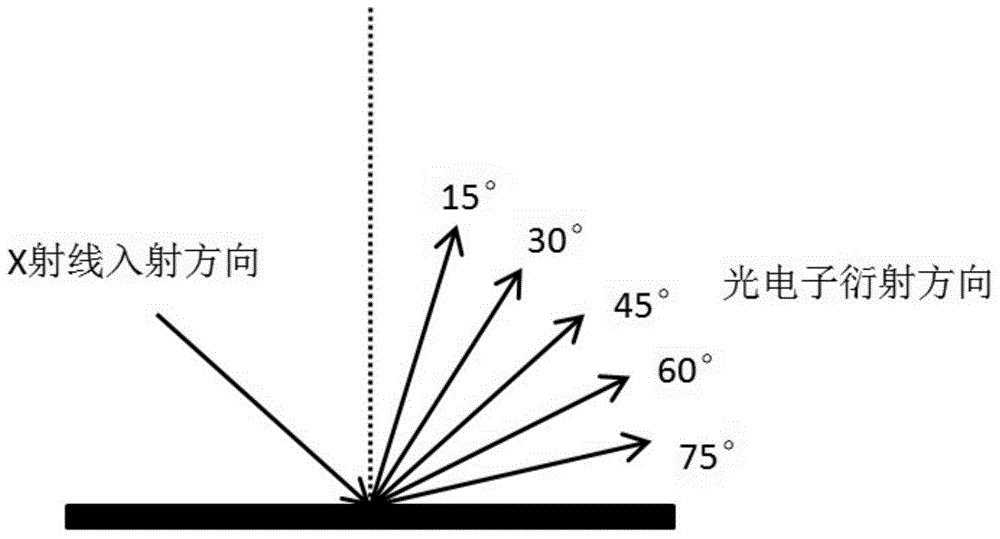
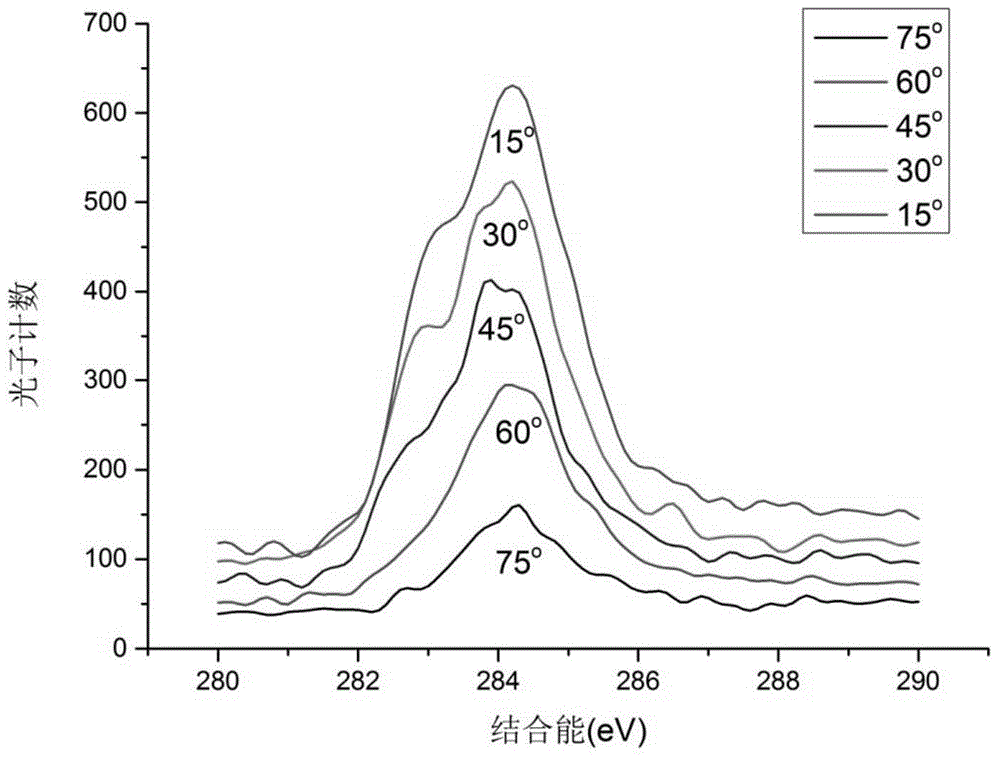
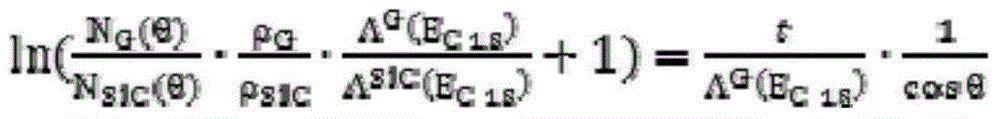
The invention relates to a method for measuring the layer number of graphene on a silicon carbide substrate. The invention belongs to the technical field of spectral analysis. The method comprises 1, forming a graphene sample with a multilayer structure and a certain thickness on a silicon surface of silicon carbide through a thermal decomposition epitaxy method, 2, measuring the sample through an X ray photoelectron spectroscopy, 3, calculating C1s electron diffraction photon integrated intensity in a C-C bond at 284.5eV and C1s electron diffraction photon integrated intensity in a Si-C bond at 282.9eV through a scanned XPS energy spectrum, 4, substituting the diffraction photon integrated intensities into a function equation of the diffraction photon integrated intensity and graphene thickness and calculating sample graphene thickness and 5, comparing the graphene thickness and graphene atom interlayer space to obtain the layer number of the graphene sample. The method is fast, realizes accurate measurement, is free of peeling of graphene from a substrate, realizes lossless measurement and is convenient for device processing and performance test.
Owner:天津恒电空间电源有限公司 +1
Transmission electron microscope electron diffraction CCD imaging device
InactiveCN105575749ARetain scattered lightEffective protectionElectric discharge tubesImage resolutionDrive shaft
The invention relates to a transmission electron microscope electron diffraction CCD imaging device. The transmission electron microscope electron diffraction CCD imaging device comprises a transmission shaft and a protection sleeve; one end of the transmission shaft is an enlarged portion, and the other end of the transmission shaft is connected with a shielding portion; the protection sleeve is fixed at one side surface of a vacuum protection box; a coaxial through hole is formed in the protection sleeve and the vacuum protection box; the transmission shaft is inserted in the through hole of the protection sleeve and the vacuum protection box; the enlarged portion of the transmission shaft is arranged to one side of the protection sleeve; the shielding portion is arranged to one side of the vacuum protection box; the vacuum protection box is connected with the lens barrel of a transmission electron microscope electron; and the shielding portion extends into the transmission electron microscope electron so as to shield a transmission light source. With the transmission electron microscope electron diffraction CCD imaging device of the invention adopted, the problems of complex negative film shooting and high possibility of data loss in existing electron diffraction CCD imaging can be solved, and the influence of the noises of a mechanical pump of a negative film chamber on the resolution of the transmission electron microscope can be avoided, and a transmission electron microscope electron diffraction CCD imaging function can be realized.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com