Patents
Literature
390 results about "X ray analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Energy Dispersive X-Ray Analysis (EDX), referred to as EDS or EDAX, is an x-ray technique used to identify the elemental composition of materials. Applications include materials and product research, troubleshooting, deformulation, and more.
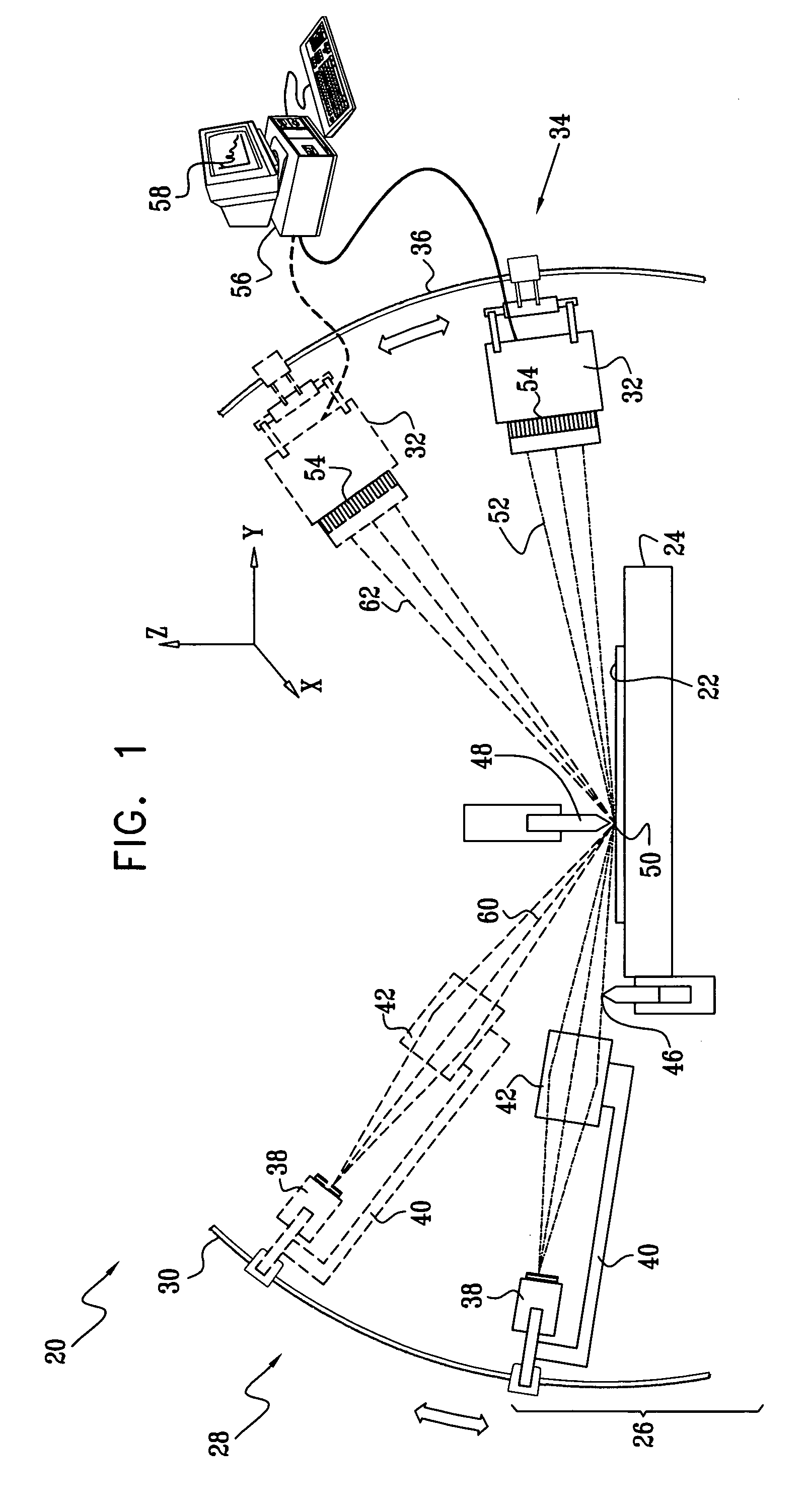
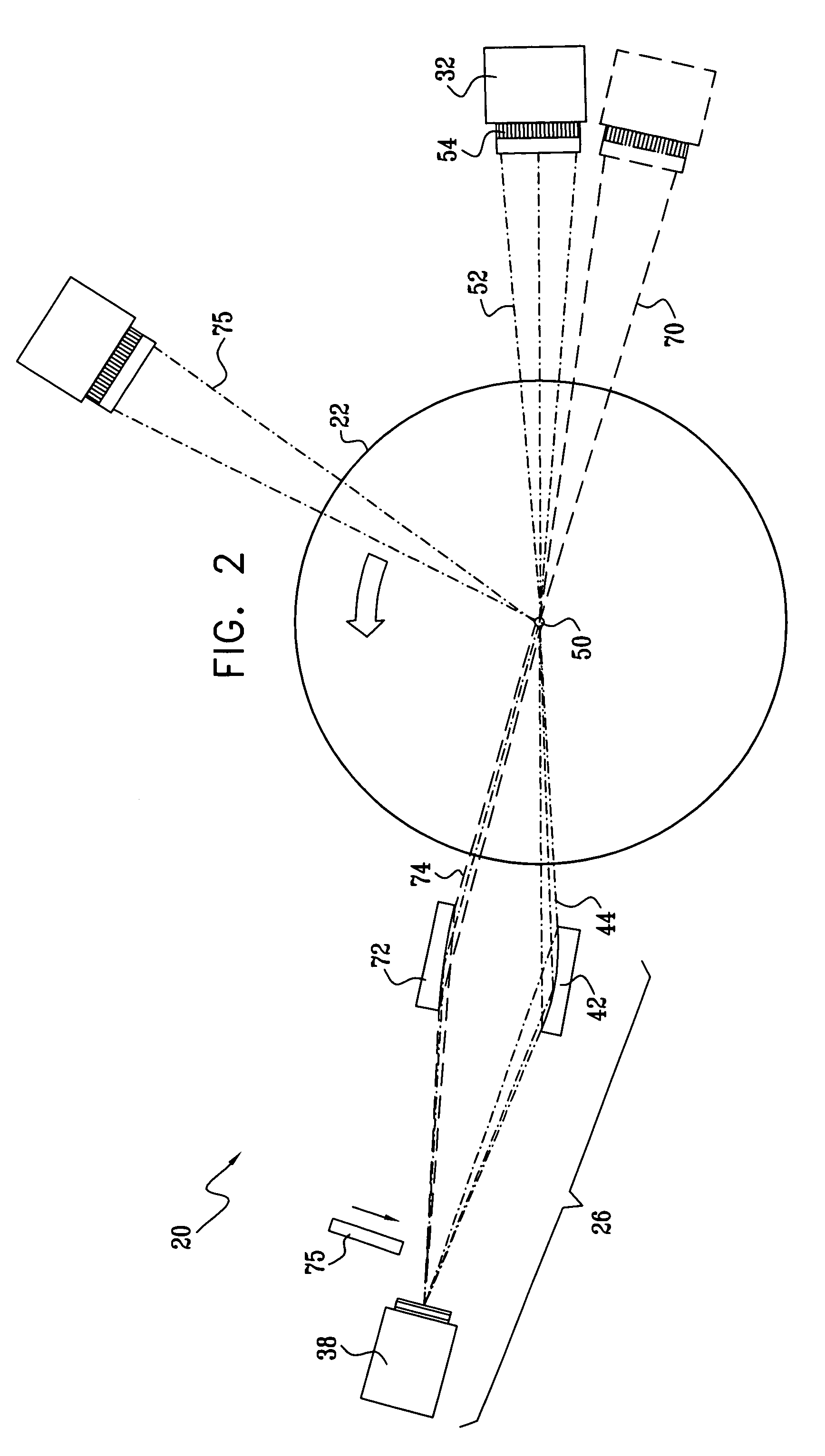
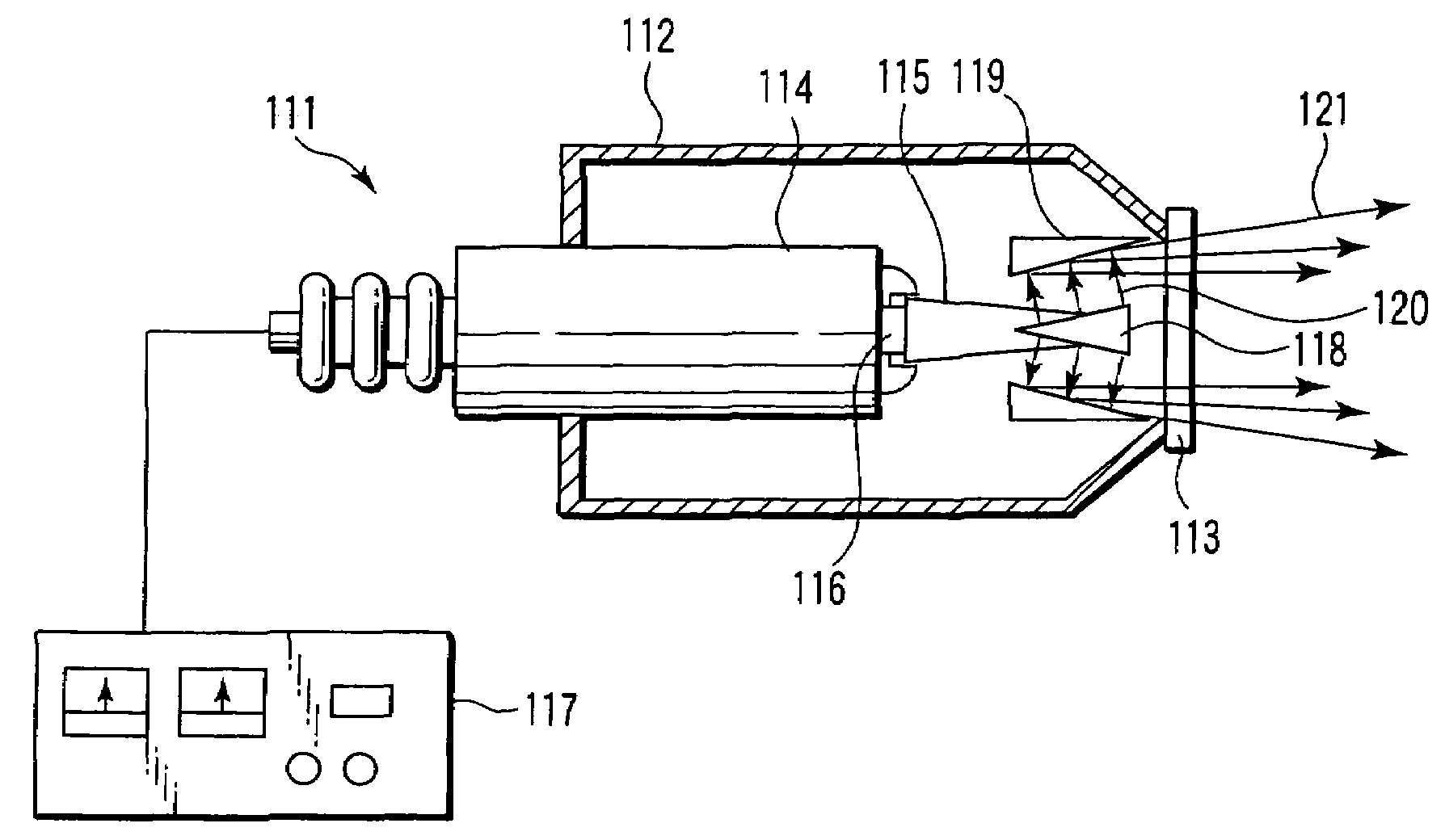
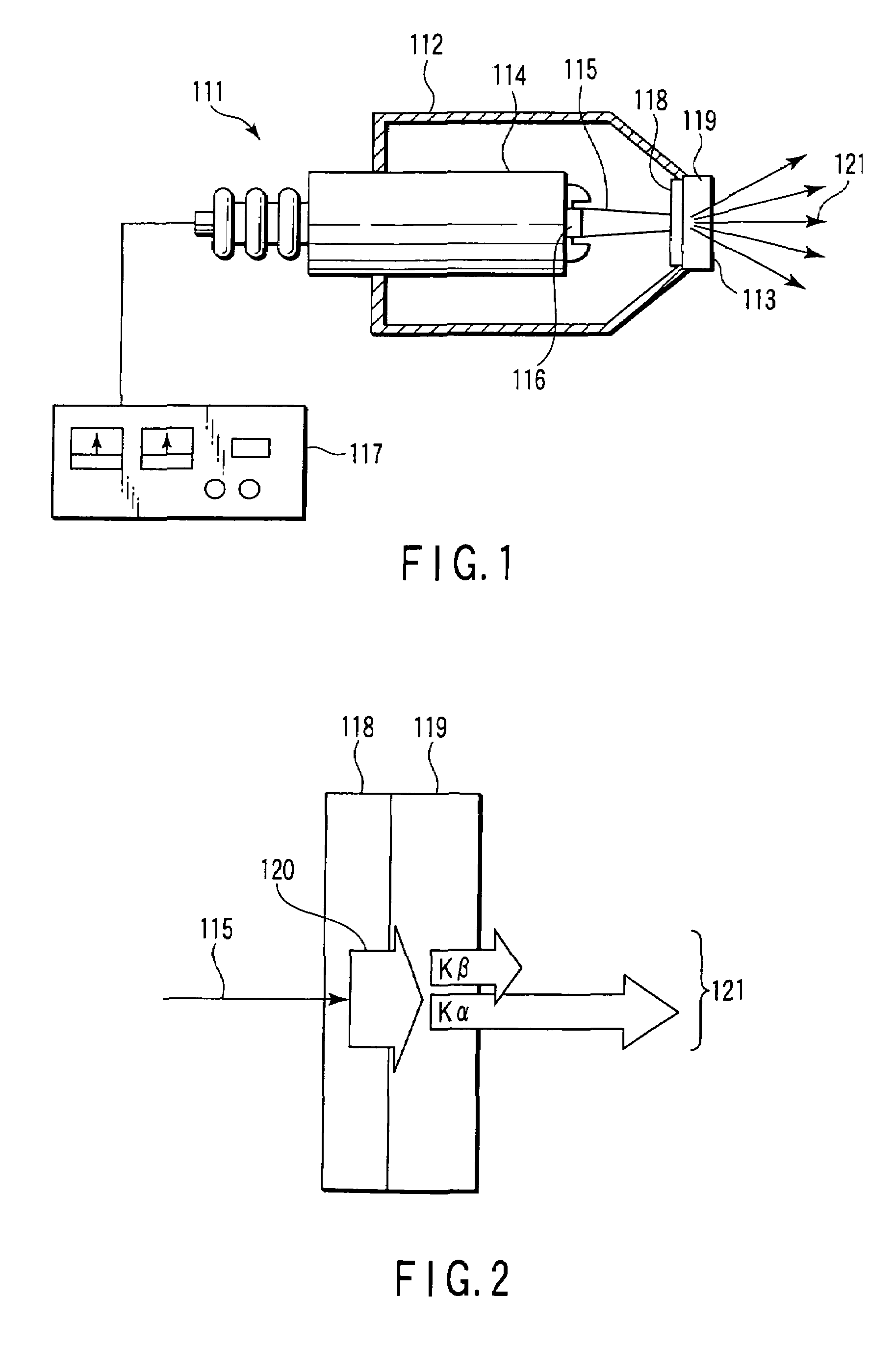
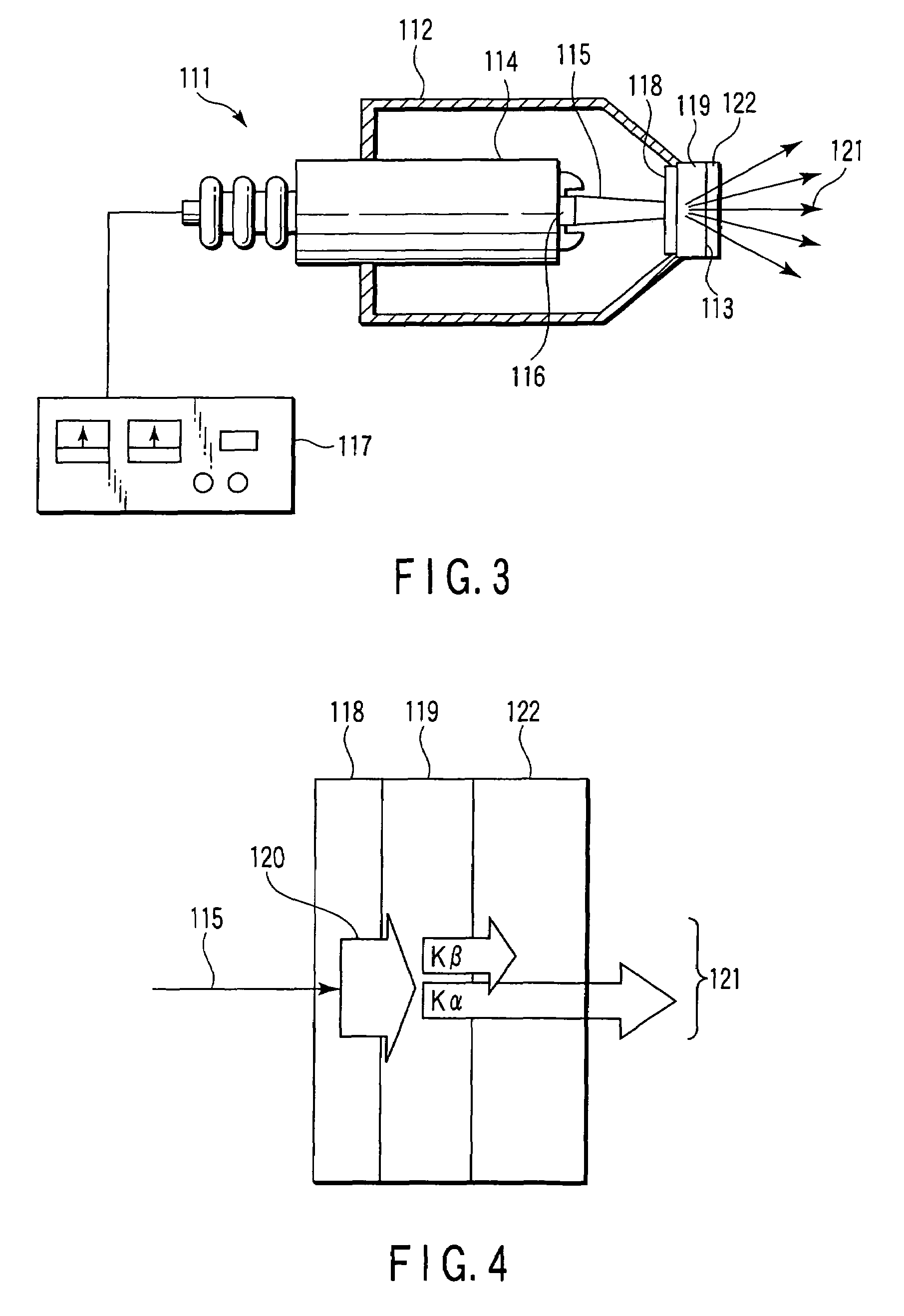
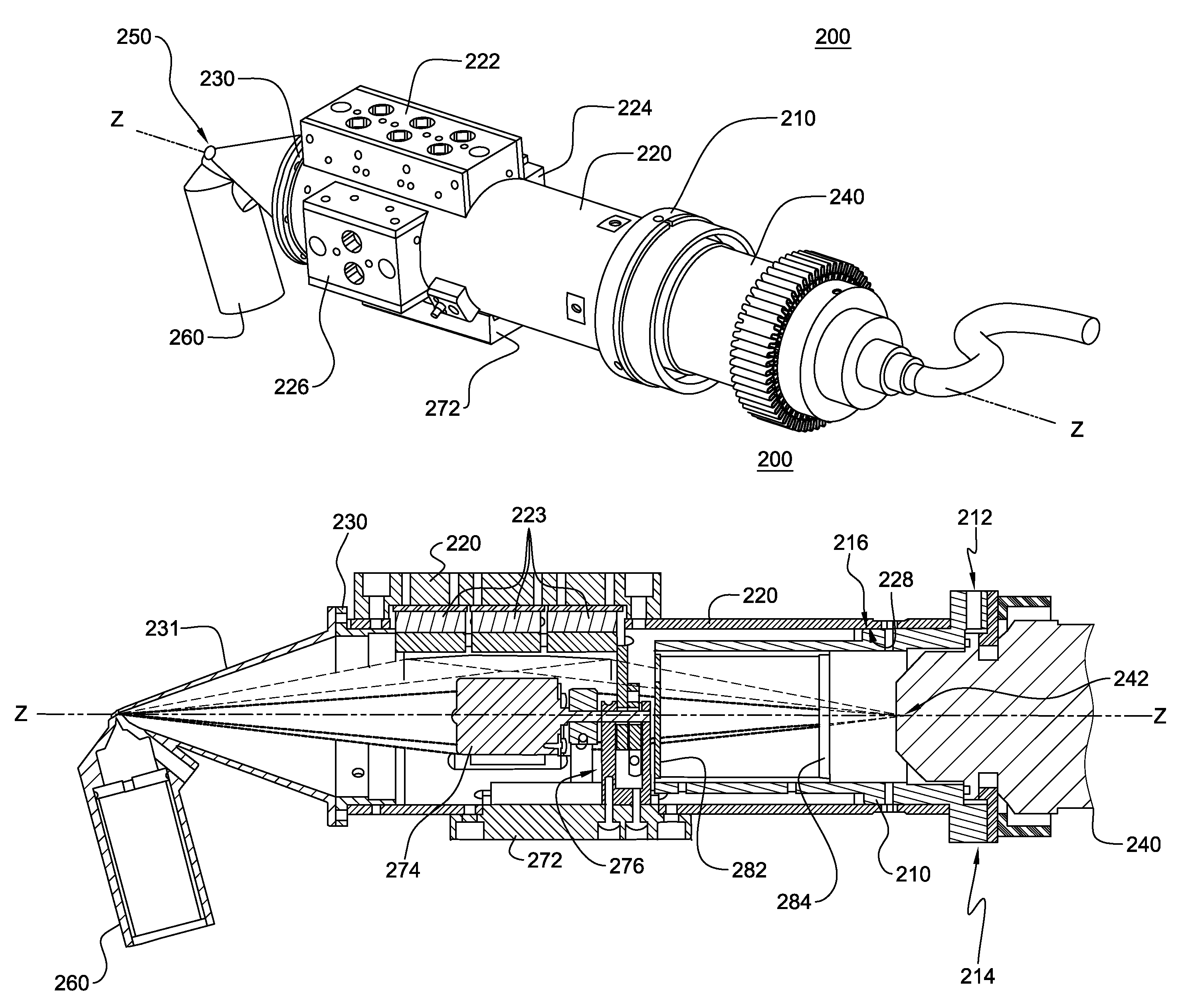
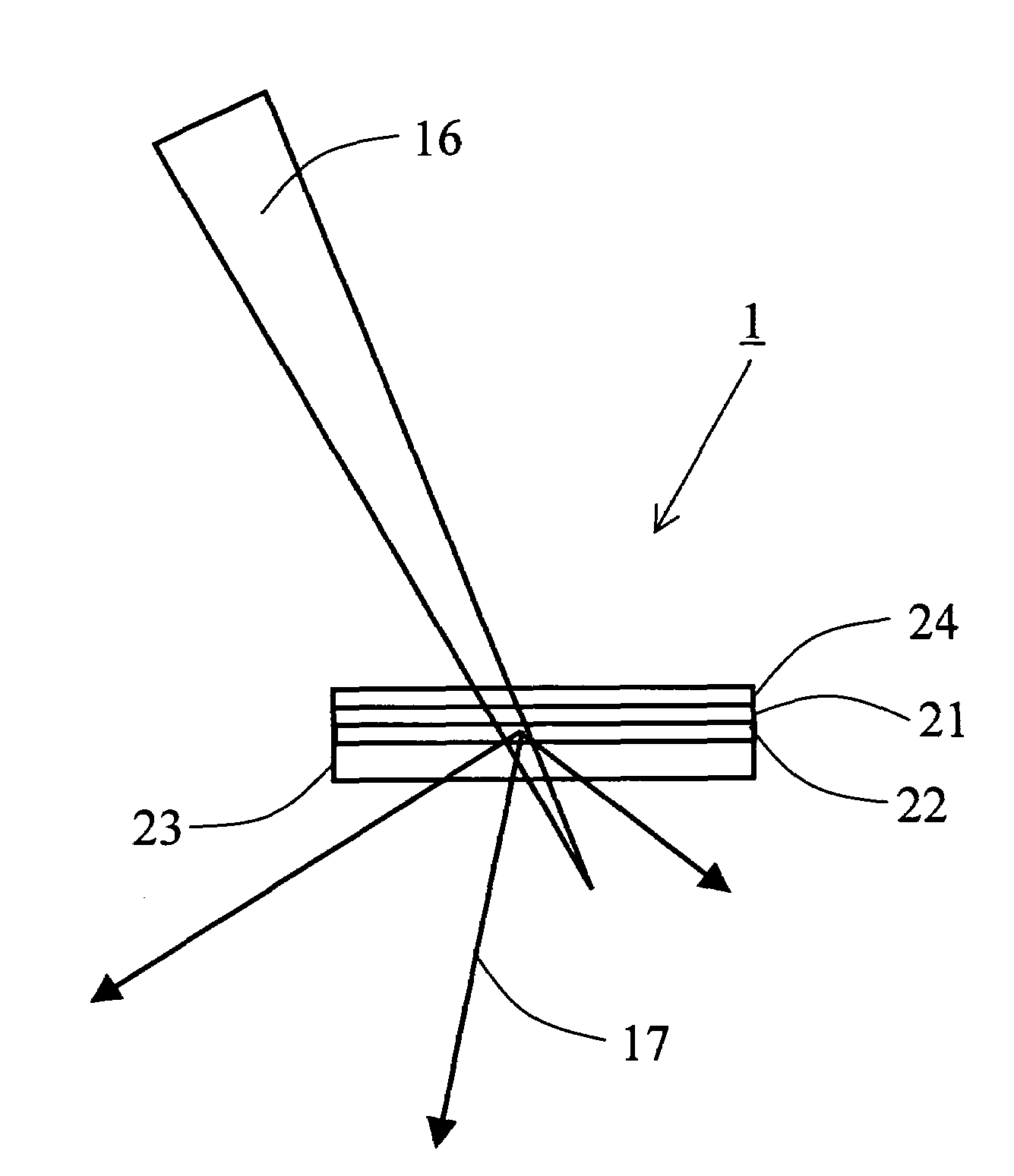
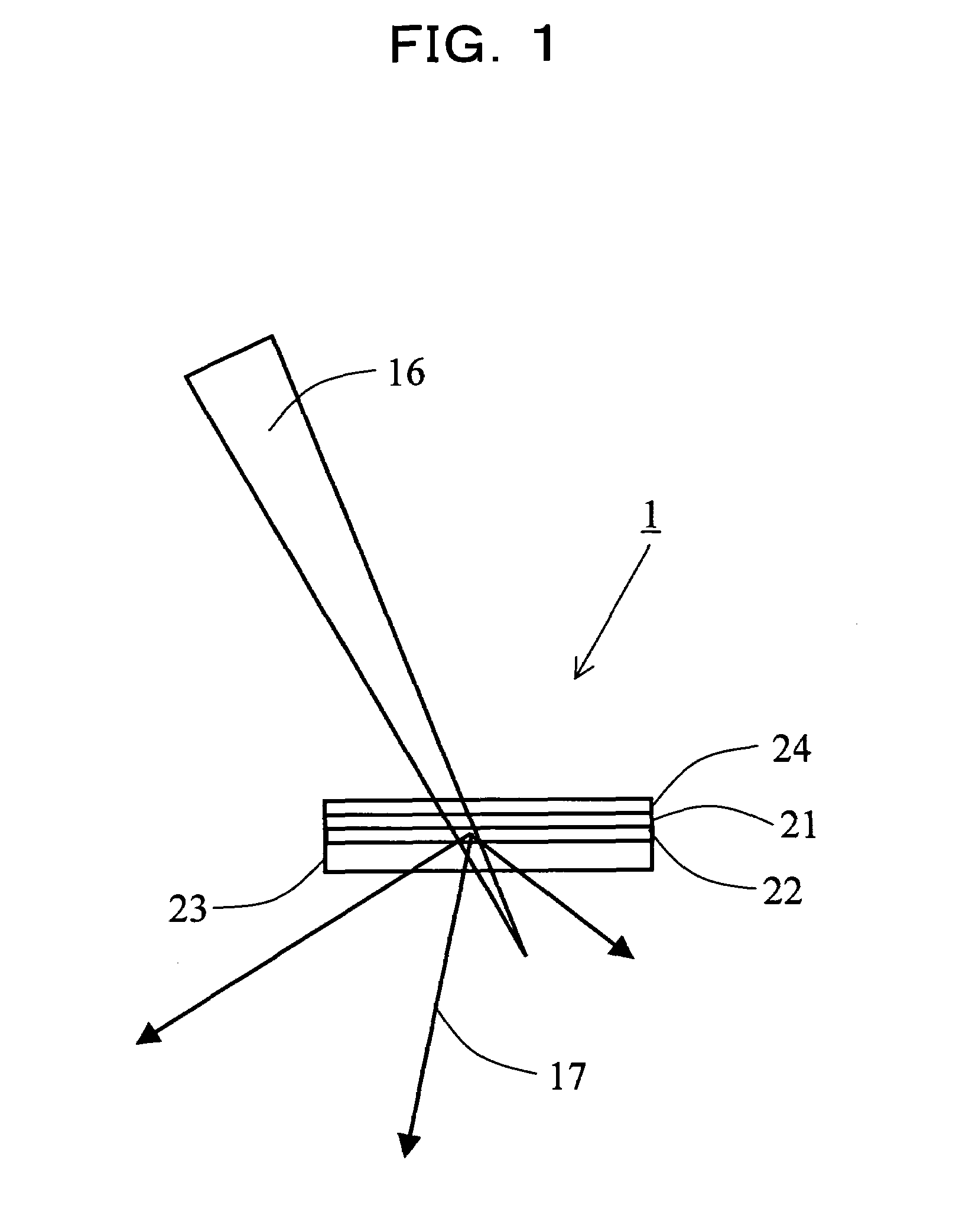
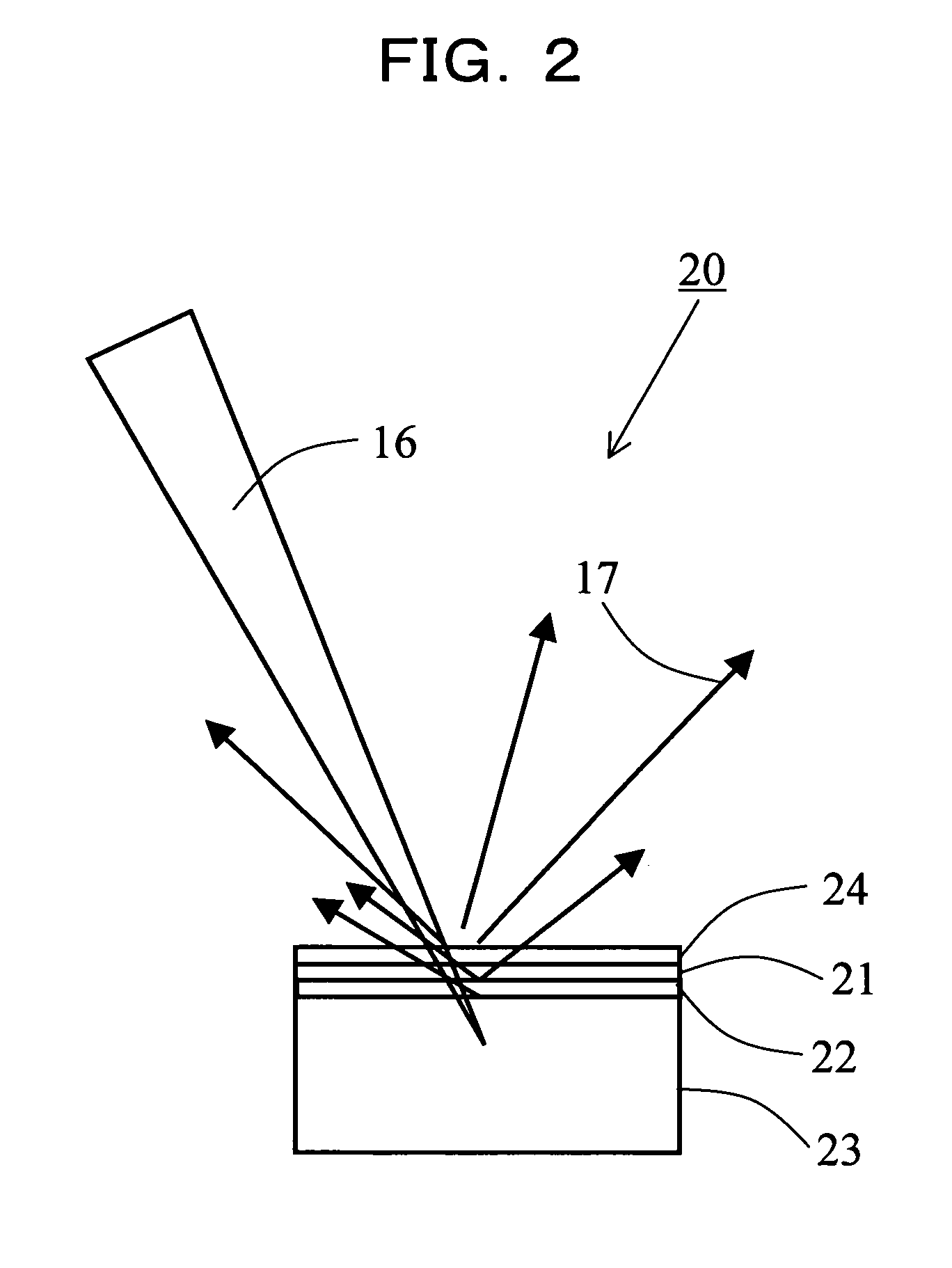
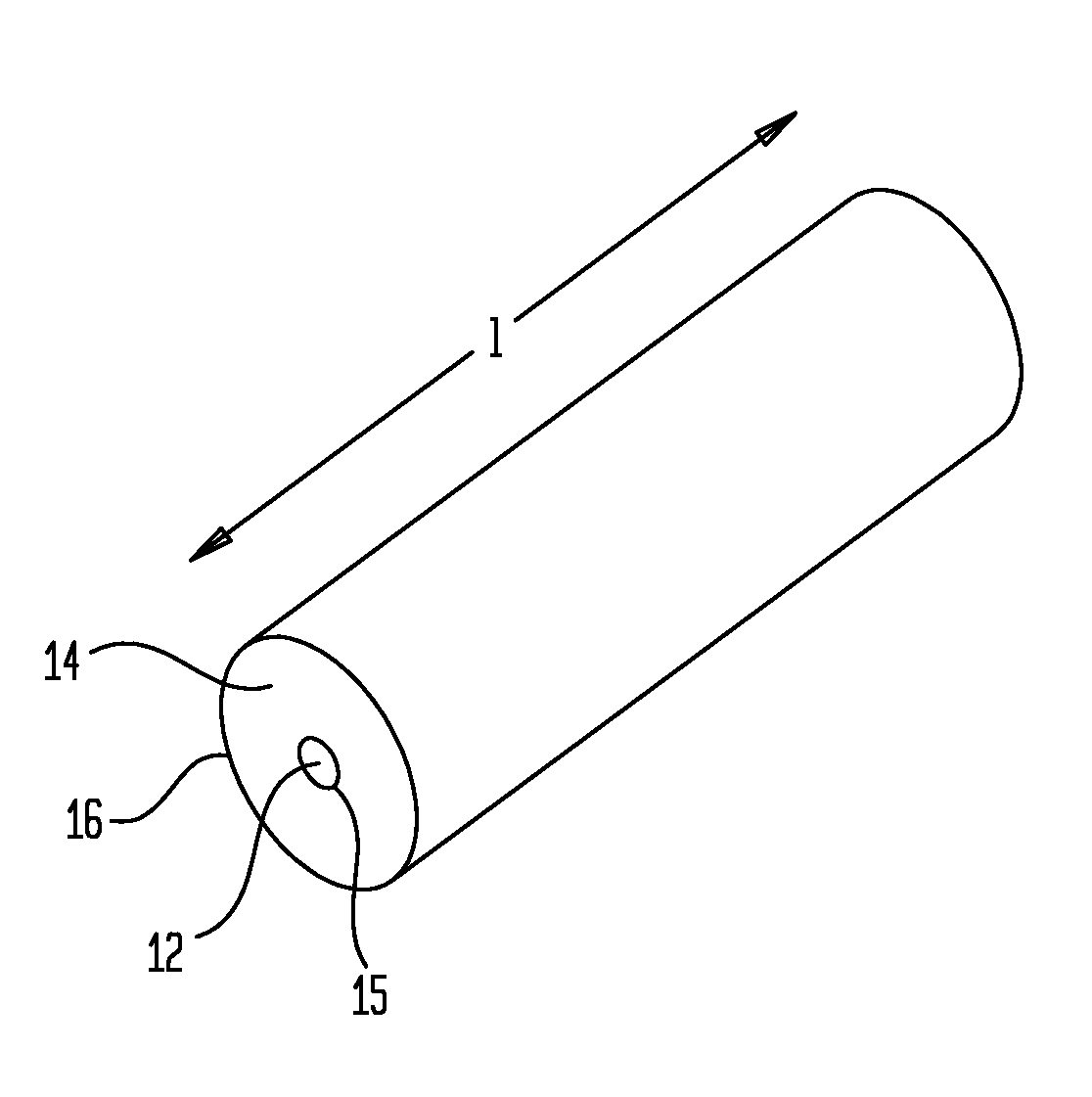
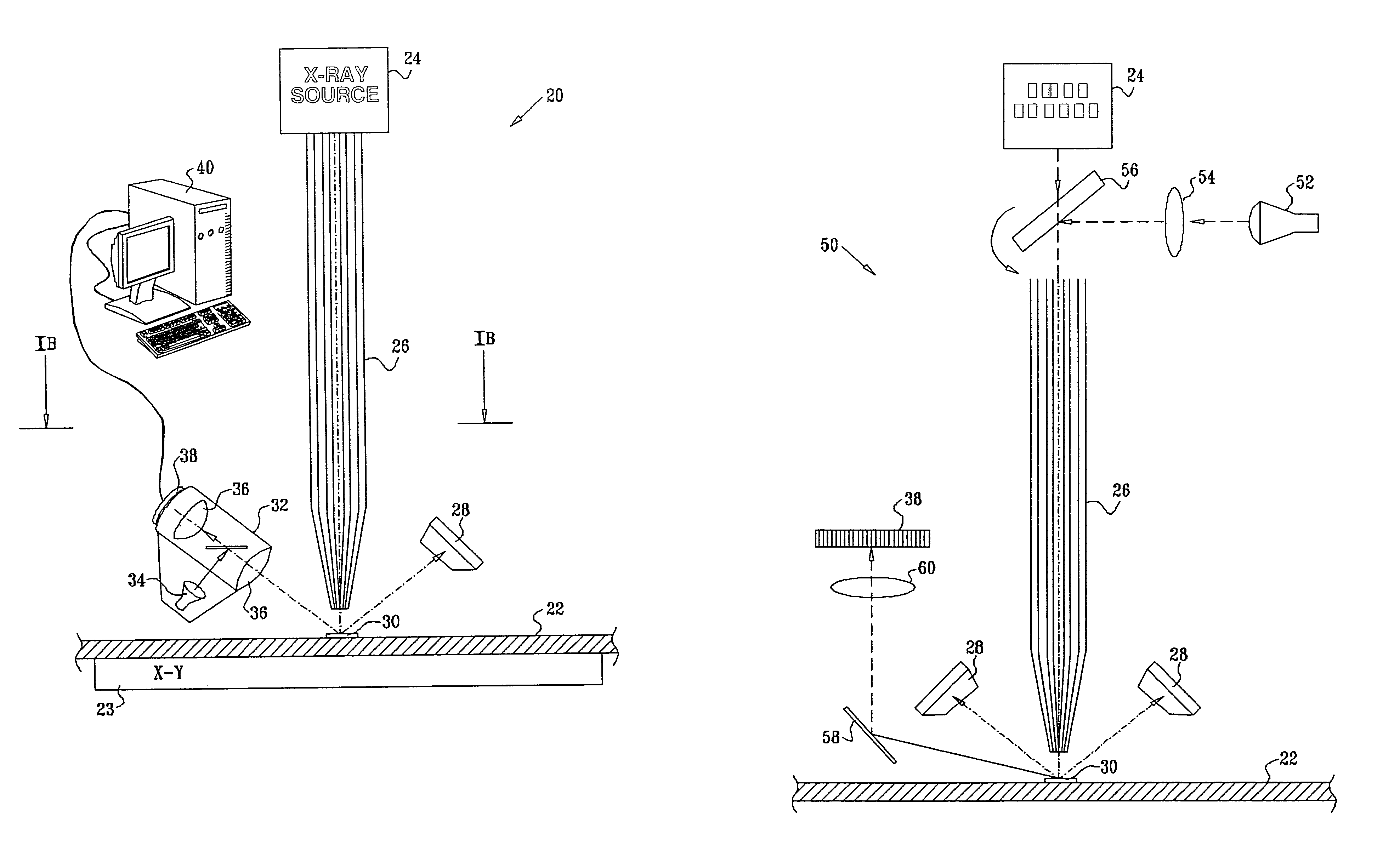
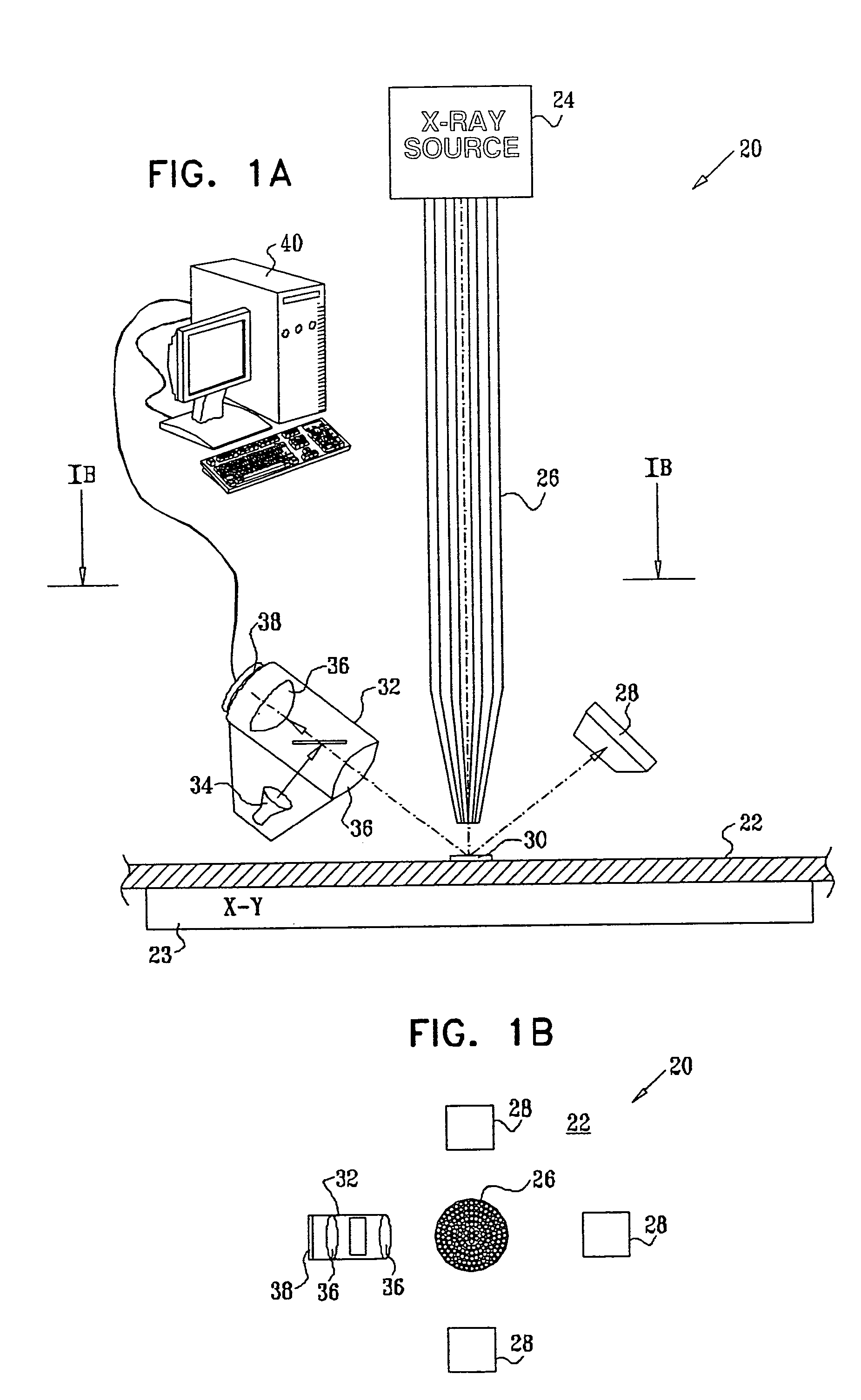
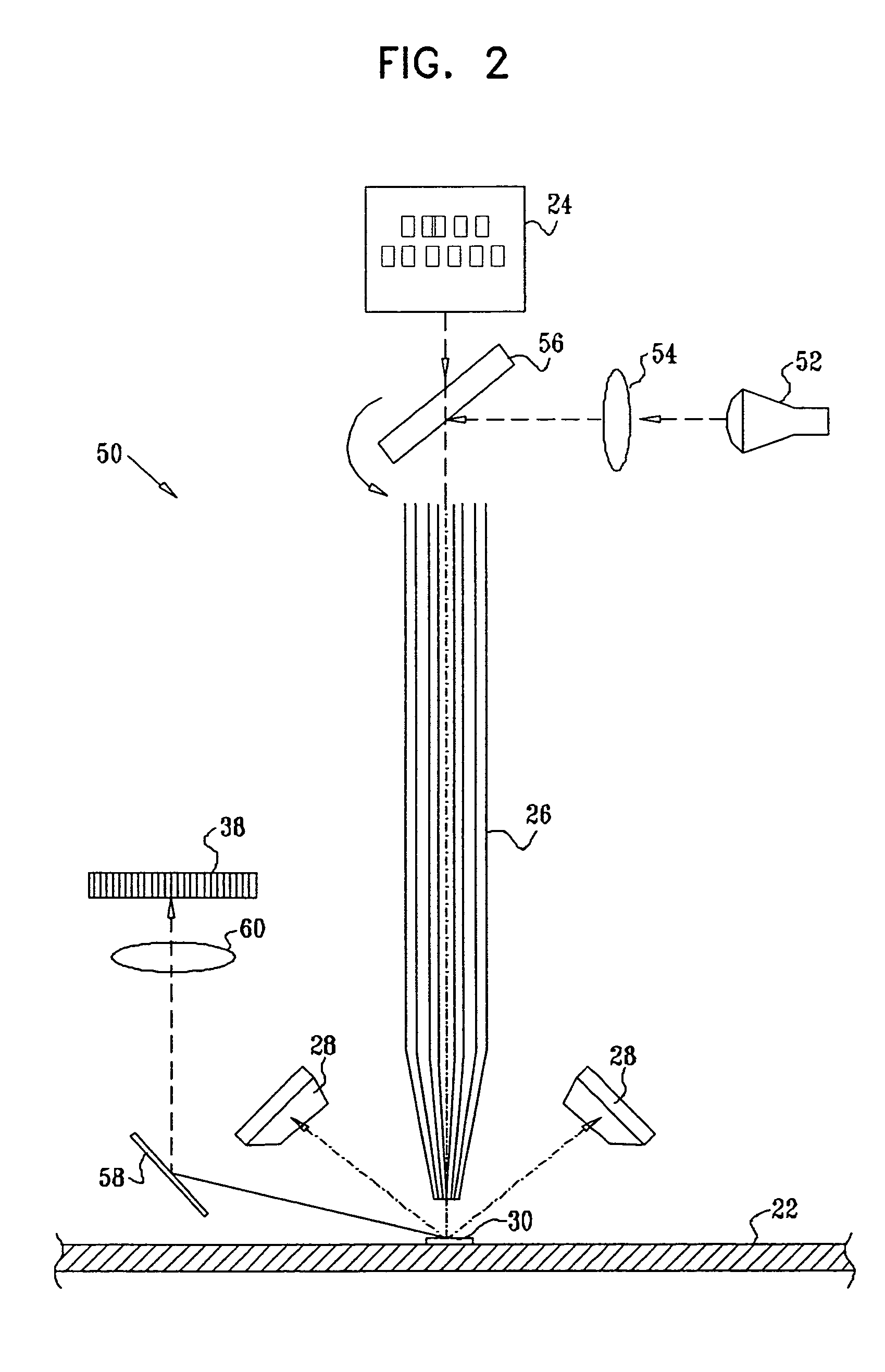
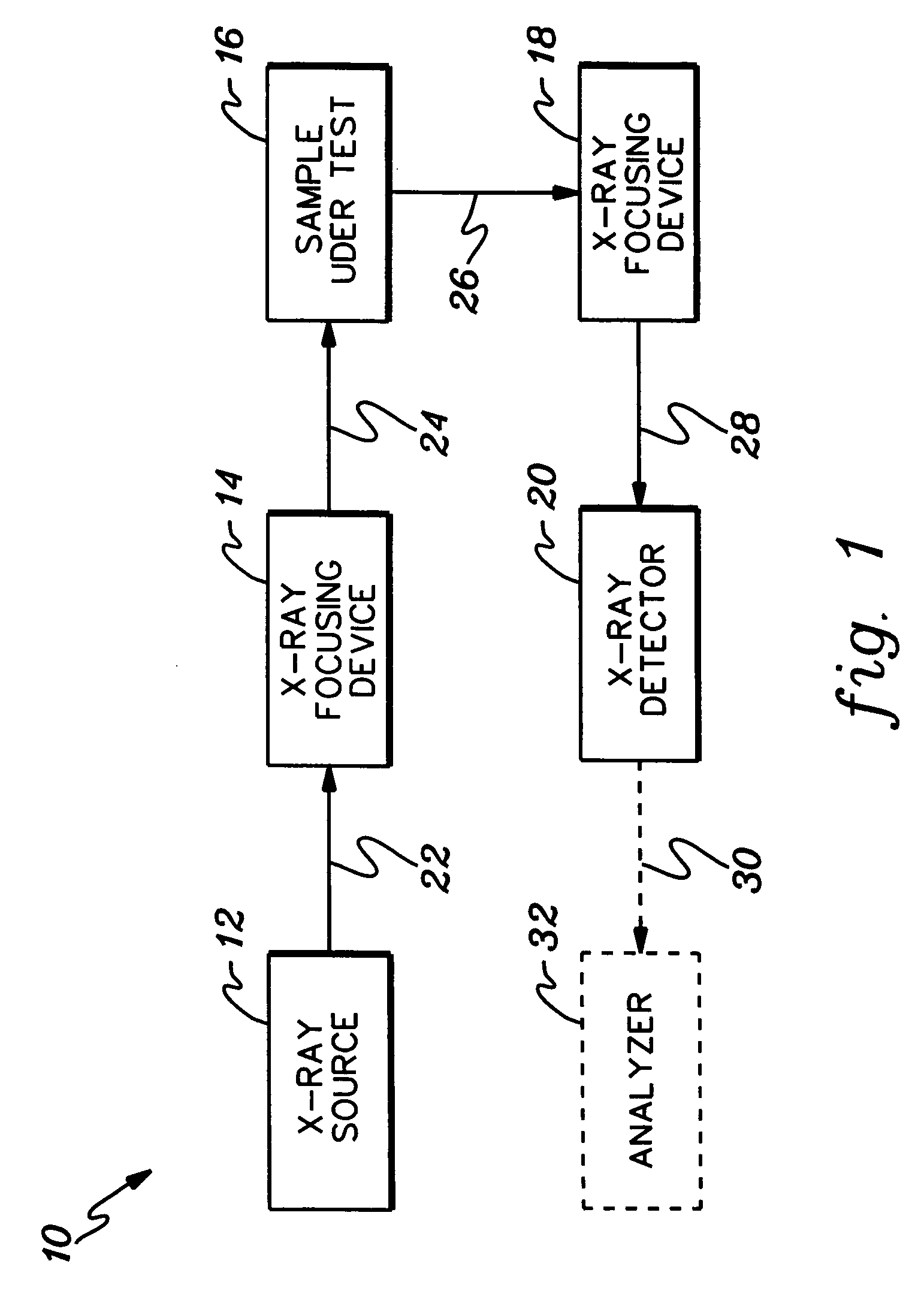
Multifunction X-ray analysis system
ActiveUS7551719B2Using wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSoft x rayX-ray
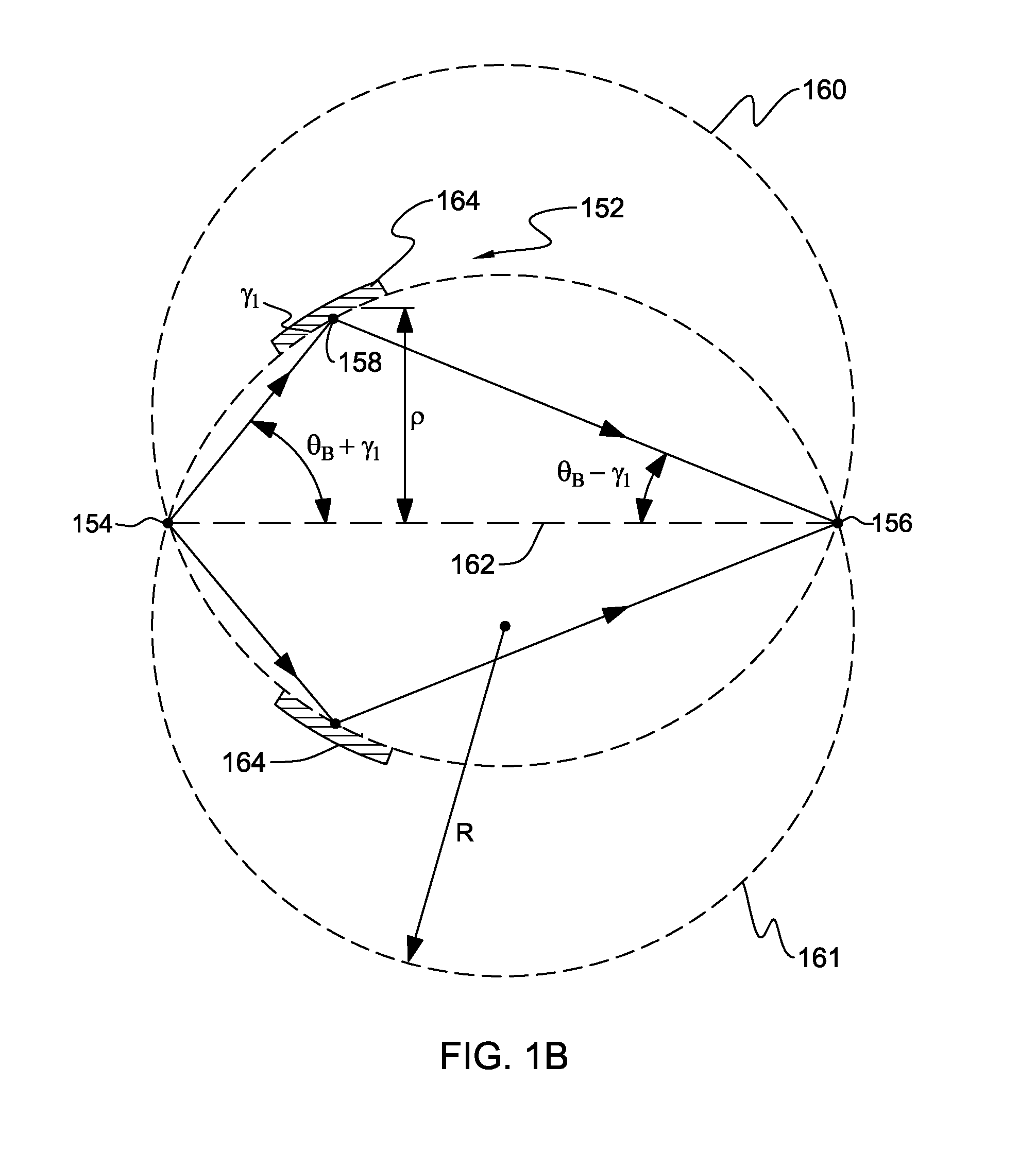
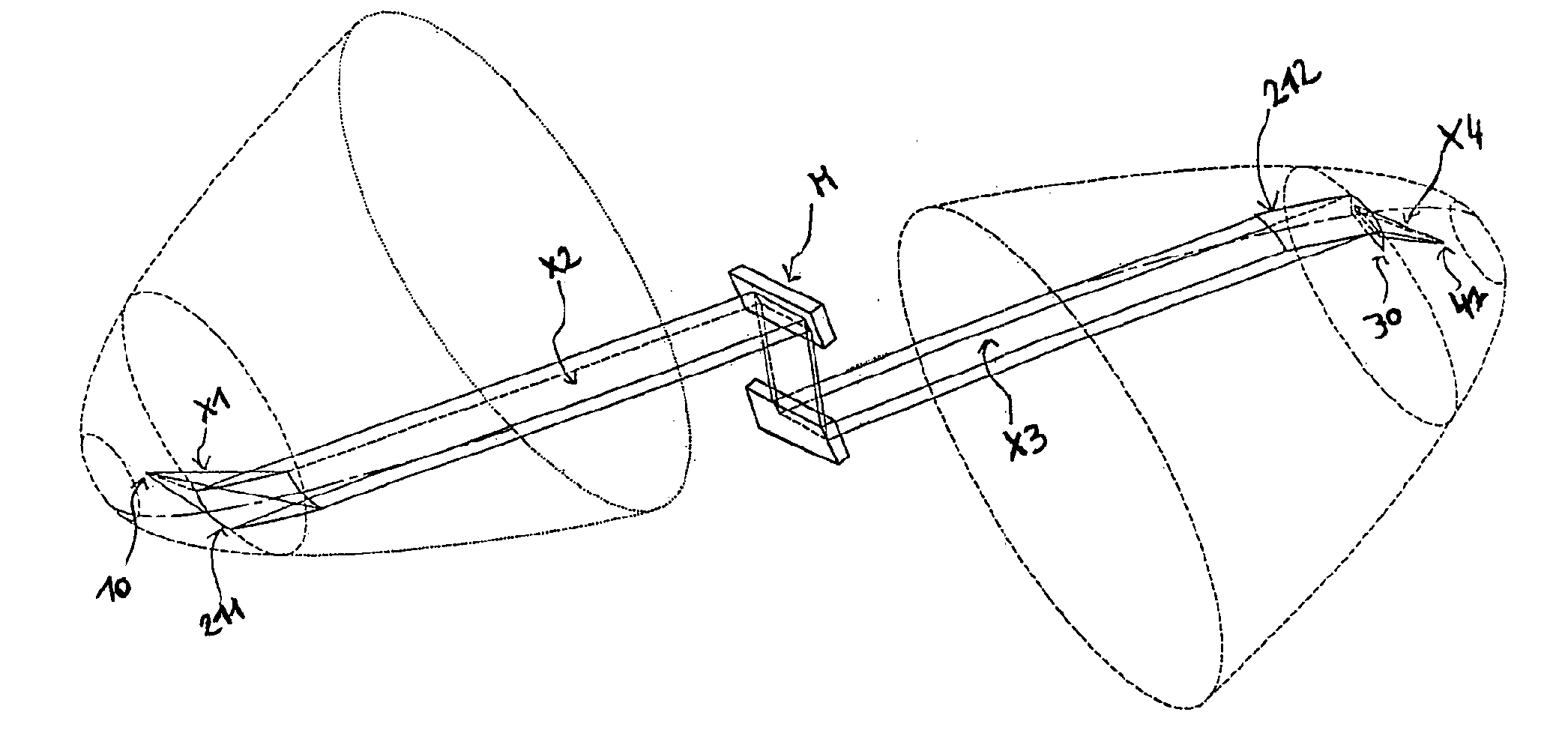
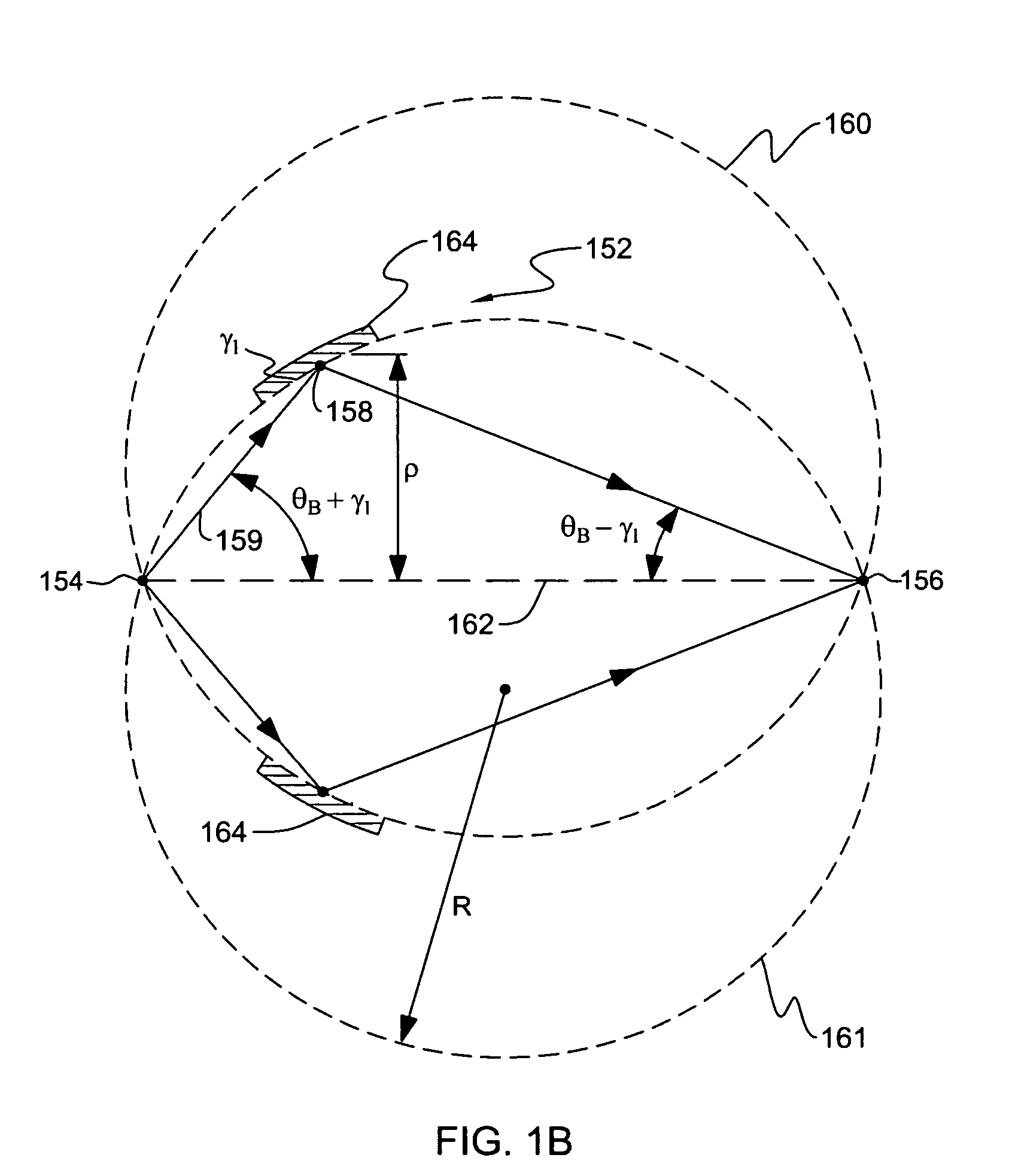
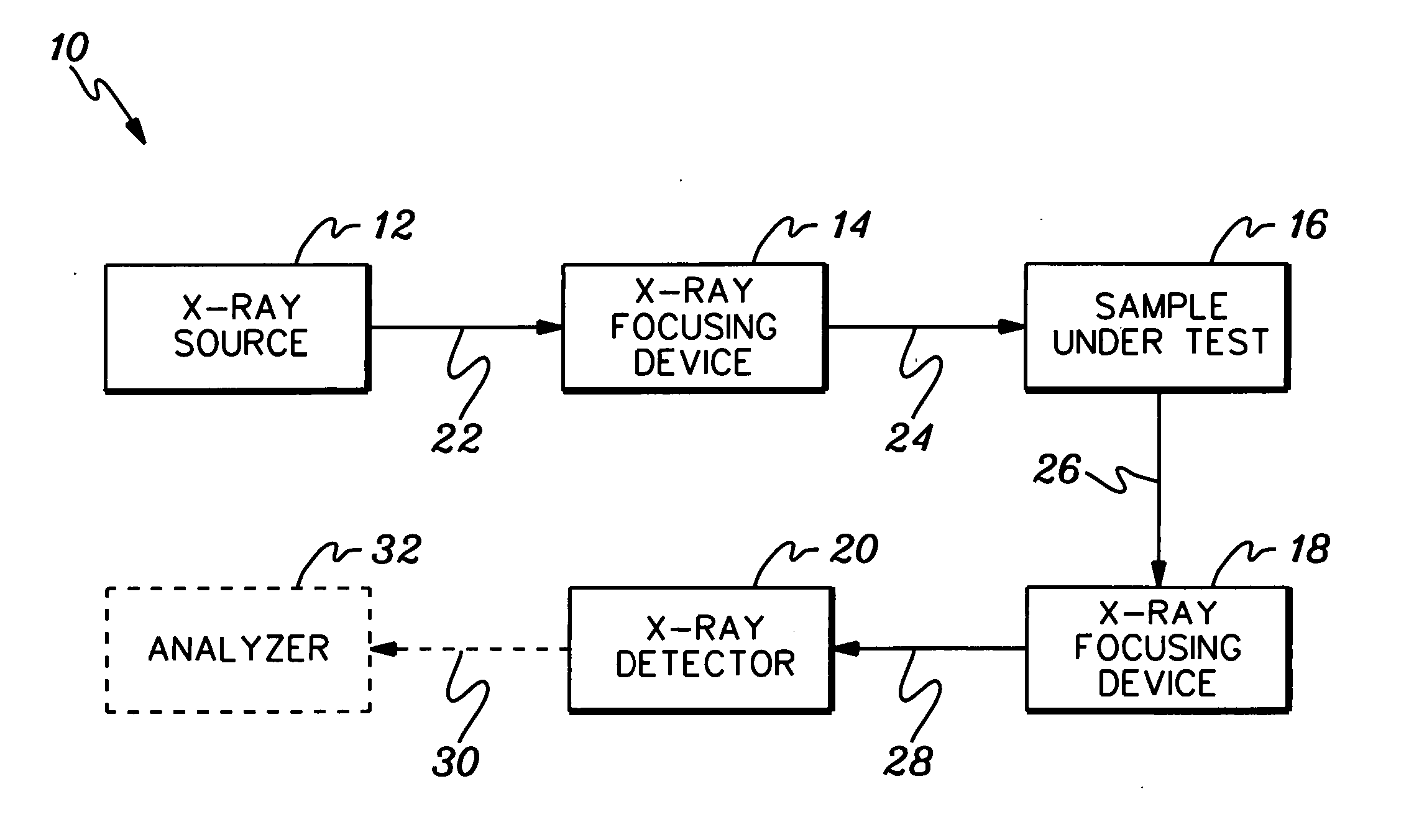
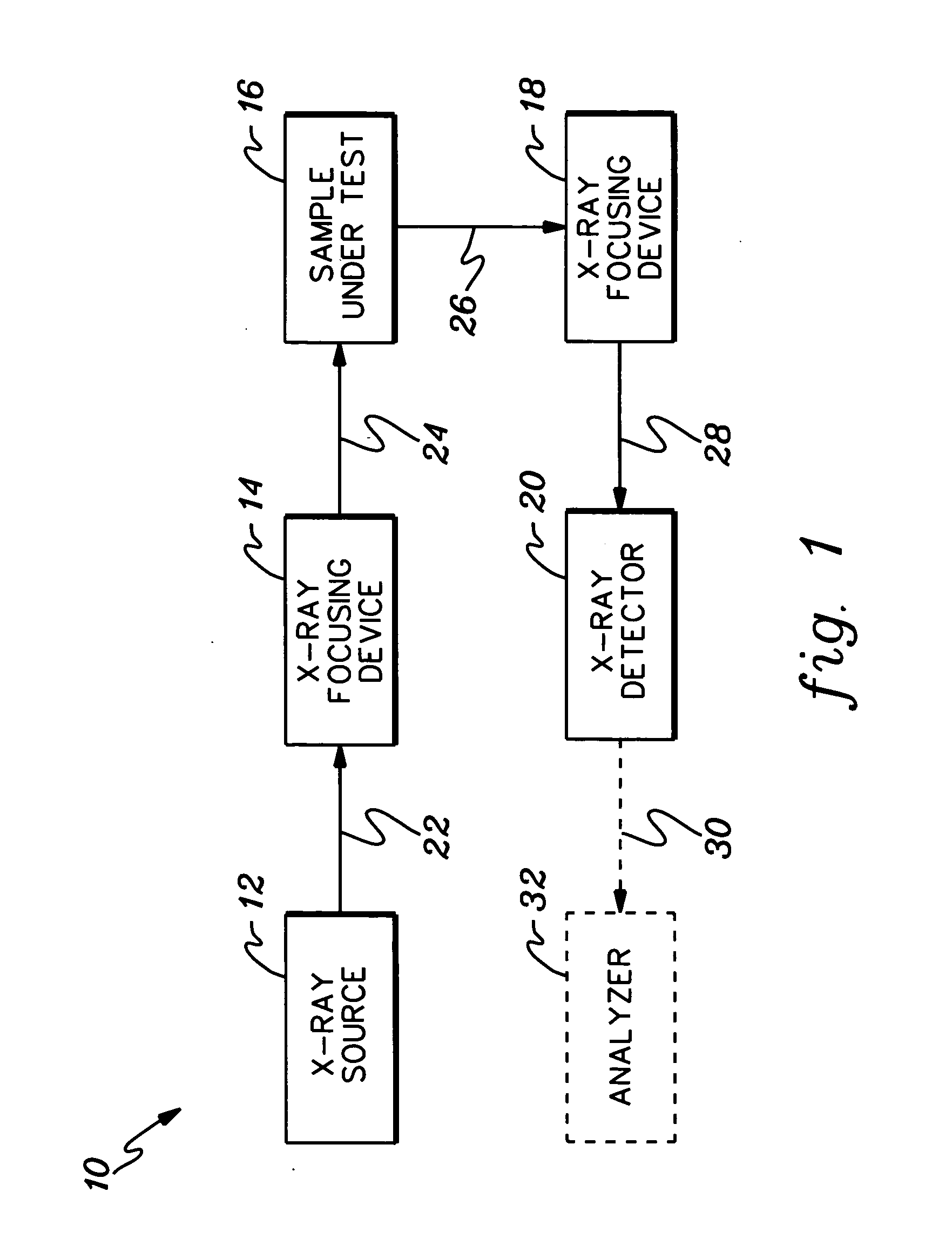
Apparatus for analysis of a sample includes a radiation source, which is adapted to direct a first, converging beam of X-rays toward a surface of the sample and to direct a second, collimated beam of the X-rays toward the surface of the sample. A motion assembly moves the radiation source between a first source position, in which the X-rays are directed toward the surface of the sample at a grazing angle, and a second source position, in which the X-rays are directed toward the surface in a vicinity of a Bragg angle of the sample. A detector assembly senses the X-rays scattered from the sample as a function of angle while the radiation source is in either of the first and second source configurations and in either of the first and second source positions. A signal processor receives and processes output signals from the detector assembly so as to determine a characteristic of the sample.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
Multifunction X-ray analysis system
ActiveUS20060062351A1Using wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayX ray analysis
Apparatus for analysis of a sample includes a radiation source, which is adapted to direct a first, converging beam of X-rays toward a surface of the sample and to direct a second, collimated beam of the X-rays toward the surface of the sample. a motion assembly moves the radiation source between a first source position, in which the X-rays are directed toward the surface of the sample at a grazing angle, and a second source position, in which the X-rays are directed toward the surface in a vicinity of a Bragg angle of the sample. A detector assembly senses the X-rays scattered from the sample as a function of angle while the radiation source is in either of the first and second source configurations and in either of the first and second source positions. A signal processor receives and processes output signals from the detector assembly so as to determine a characteristic of the sample.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
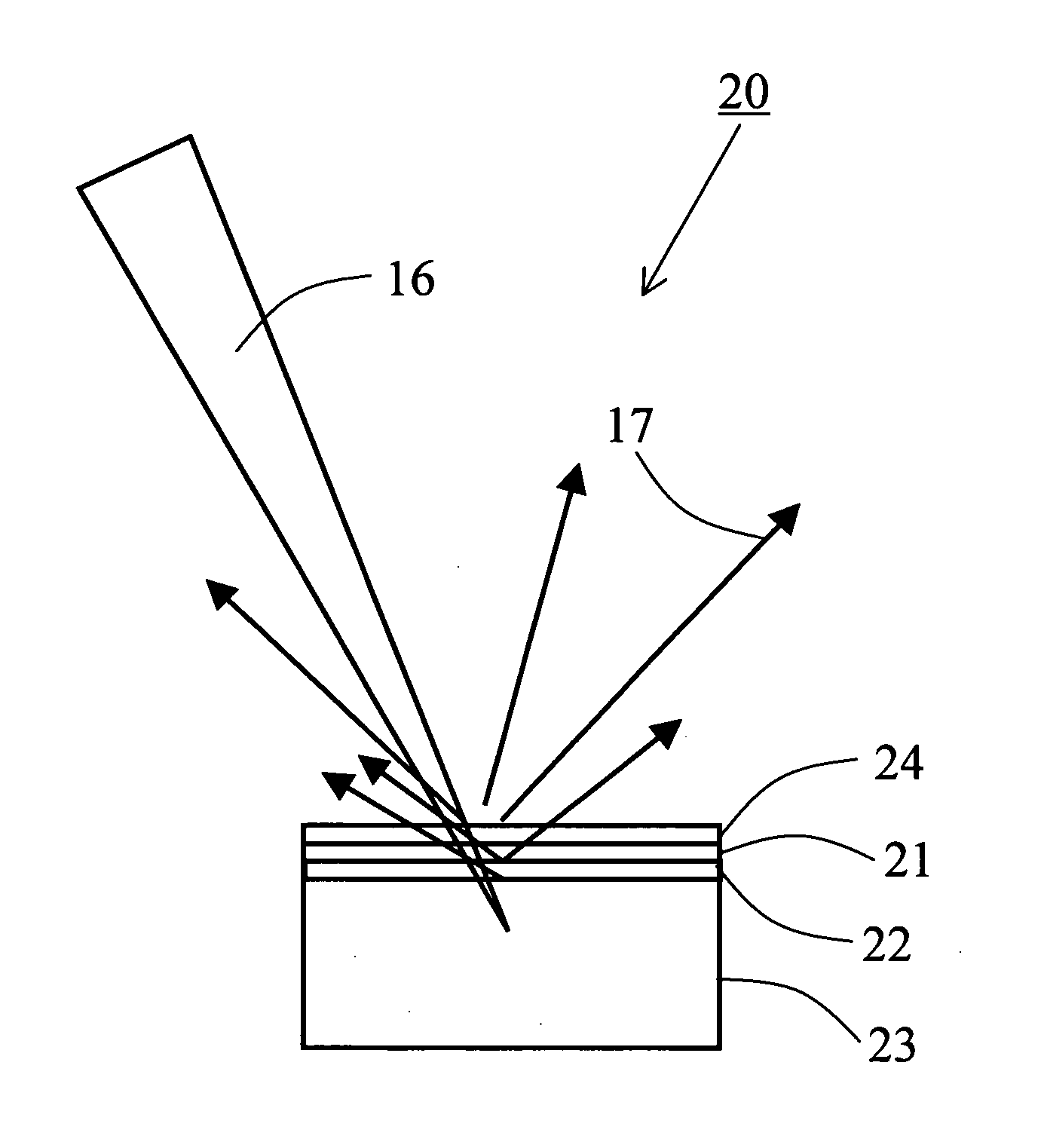
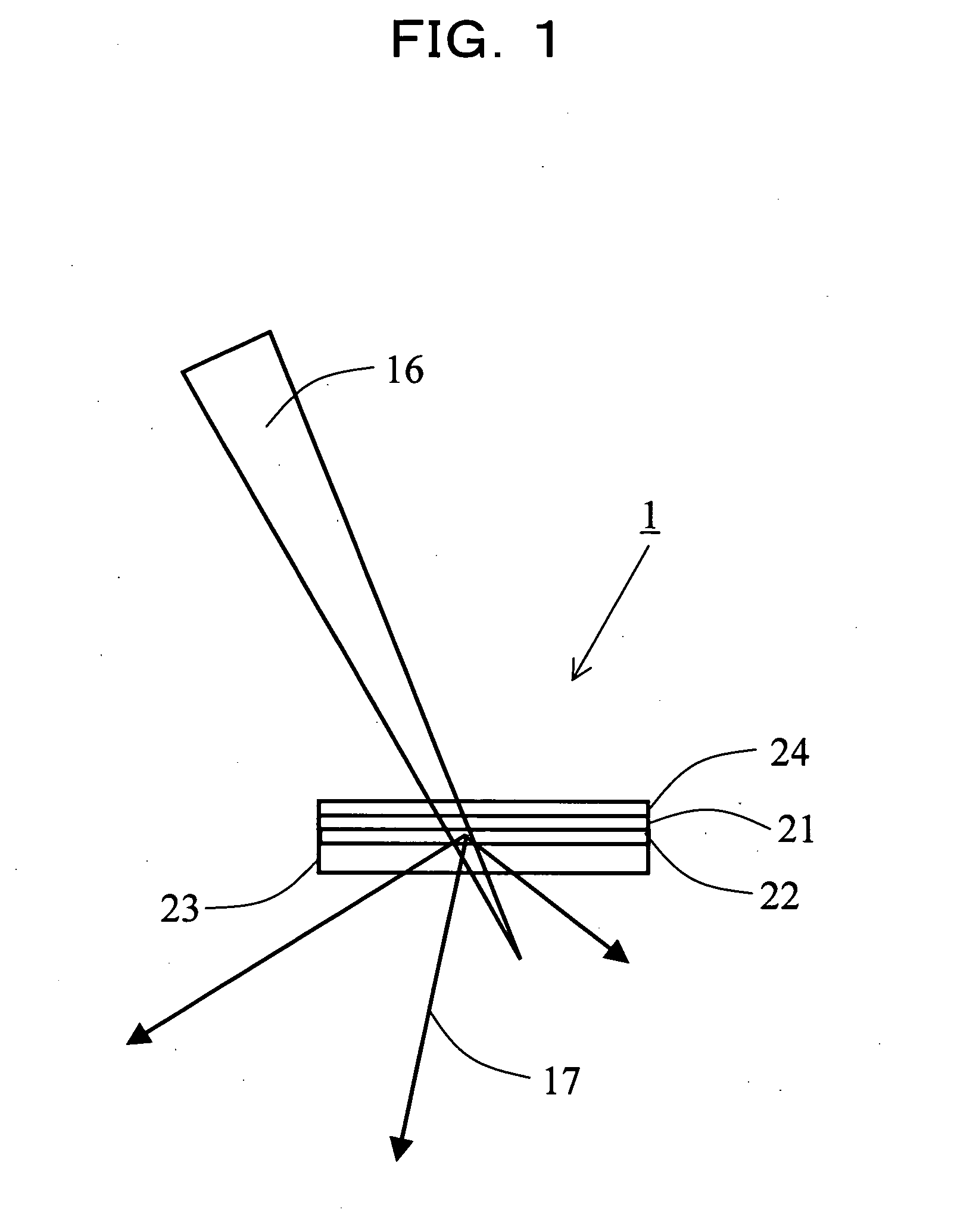
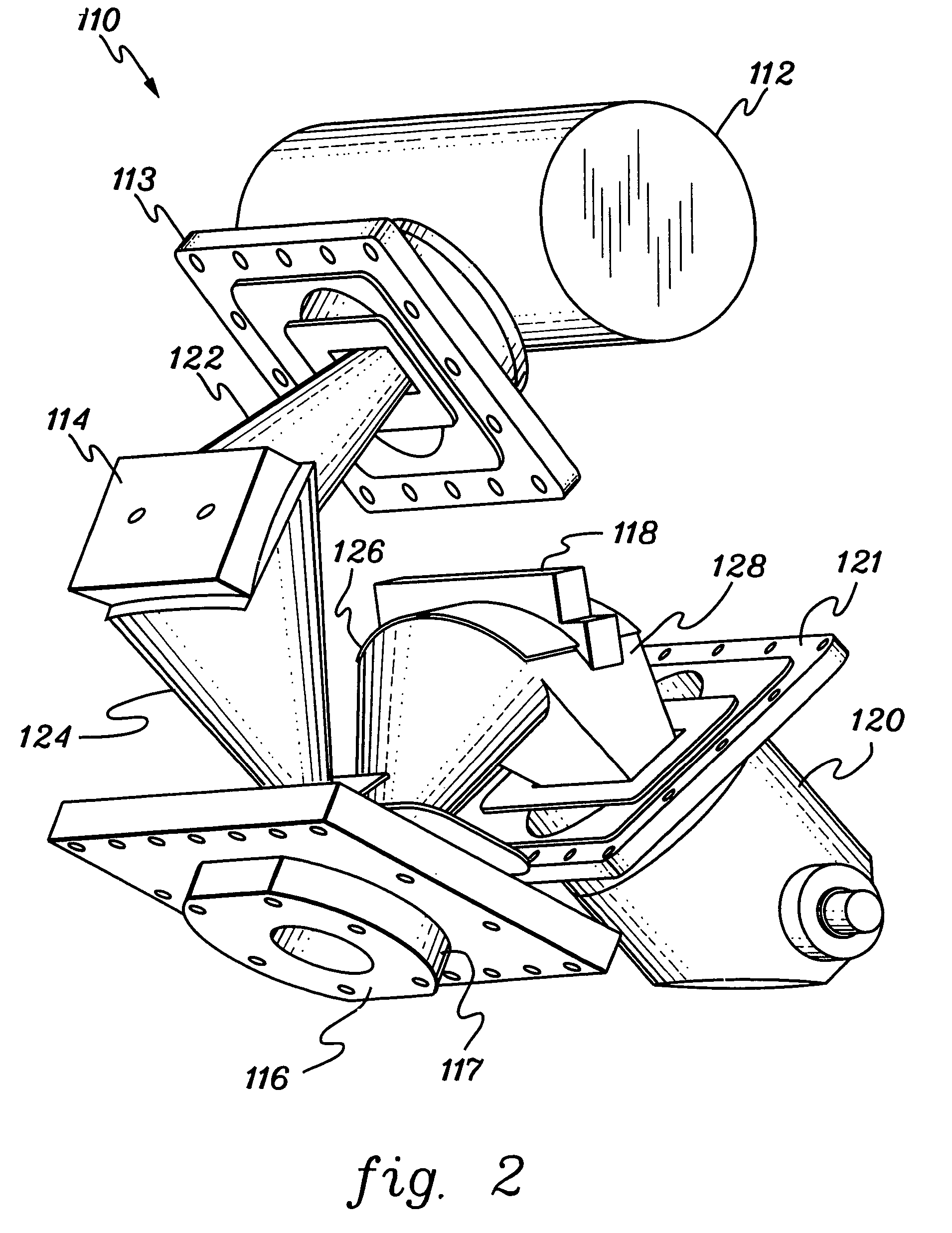
X-Ray Target and Apparatuses Using the Same
InactiveUS20070248215A1Highly convenientElectron beam absorptivityX-ray tube laminated targetsImaging devicesFluorescenceHigh intensity
Disclosed are an X-ray target having a micro focus size and capable of producing X-rays of high intensity, and apparatuses using such an X-ray target. The X-ray target (1) has a structure in which a first cap layer (21), a target layer (22), and a second cap layer (23) are successively laminated, wherein the first and second cap layers (21and 23) are each composed of a material which is lower in electron beam absorptivity than that of which the target layer (22) is composed. An X-ray generator using the X-ray target (1) can generate highly intense and nanofocus (several nm) X-rays (17). Using the X-ray generator, an X-ray microscope allows obtaining a high resolution transmission image, an X-ray diffraction apparatus allows obtaining an X-ray diffraction image of a very small area, and a fluorescent X-ray analysis apparatus allows making the fluorescent X-ray analysis of a minute area.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
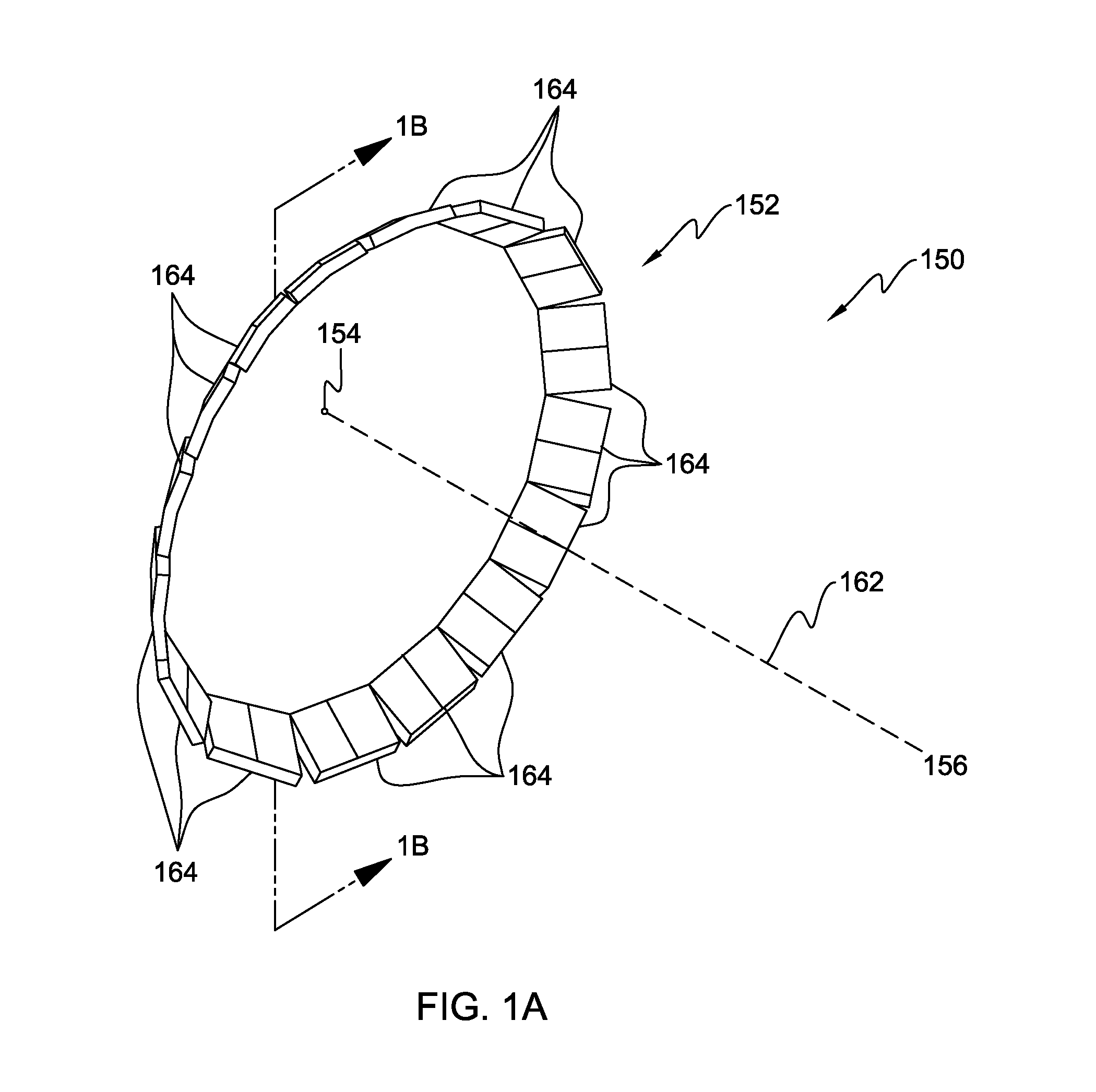
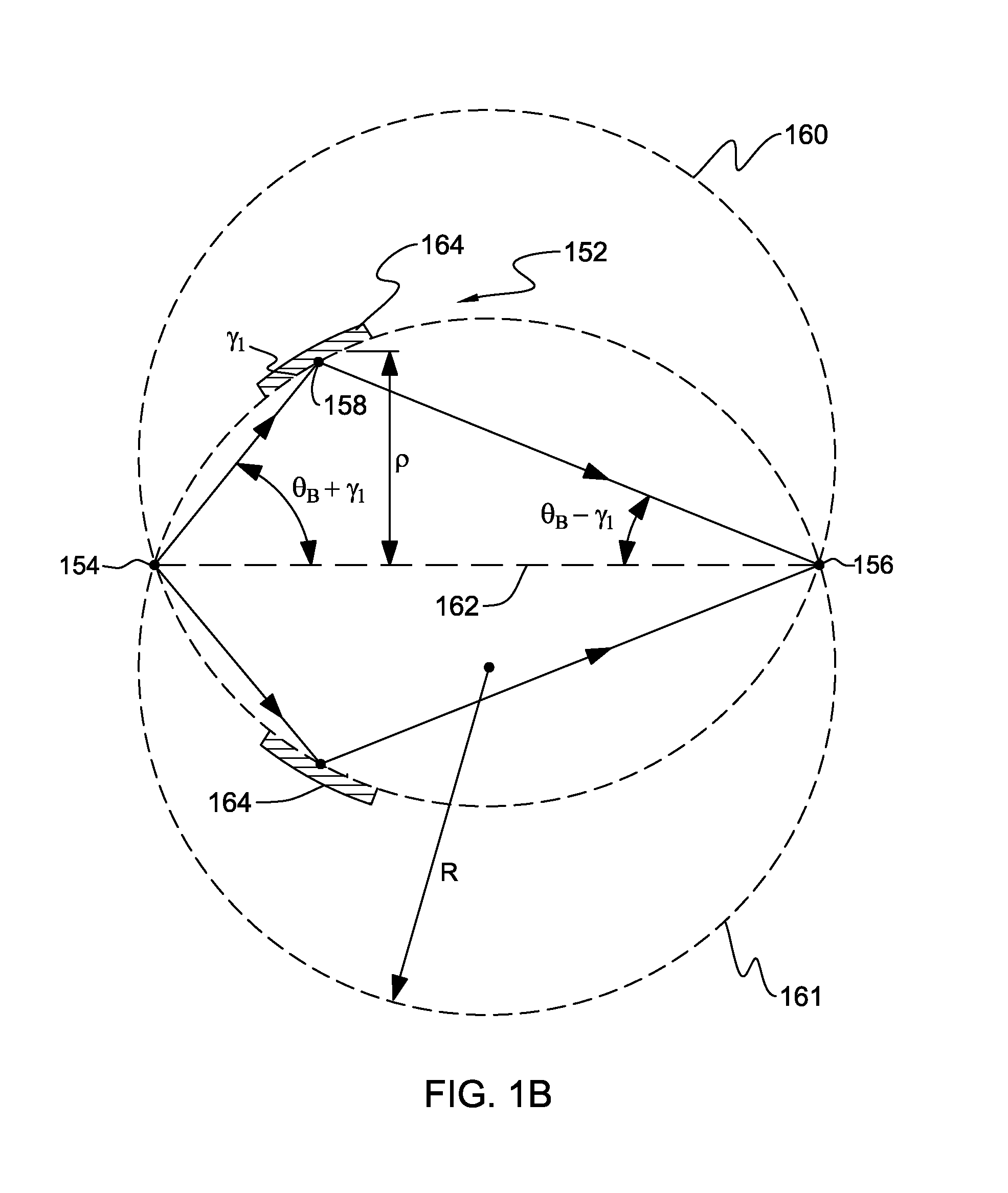
Fluorescent X-ray analyzer useable as wavelength dispersive type and energy dispersive type
InactiveUS6292532B1X-ray spectral distribution measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansSoft x rayFluorescence
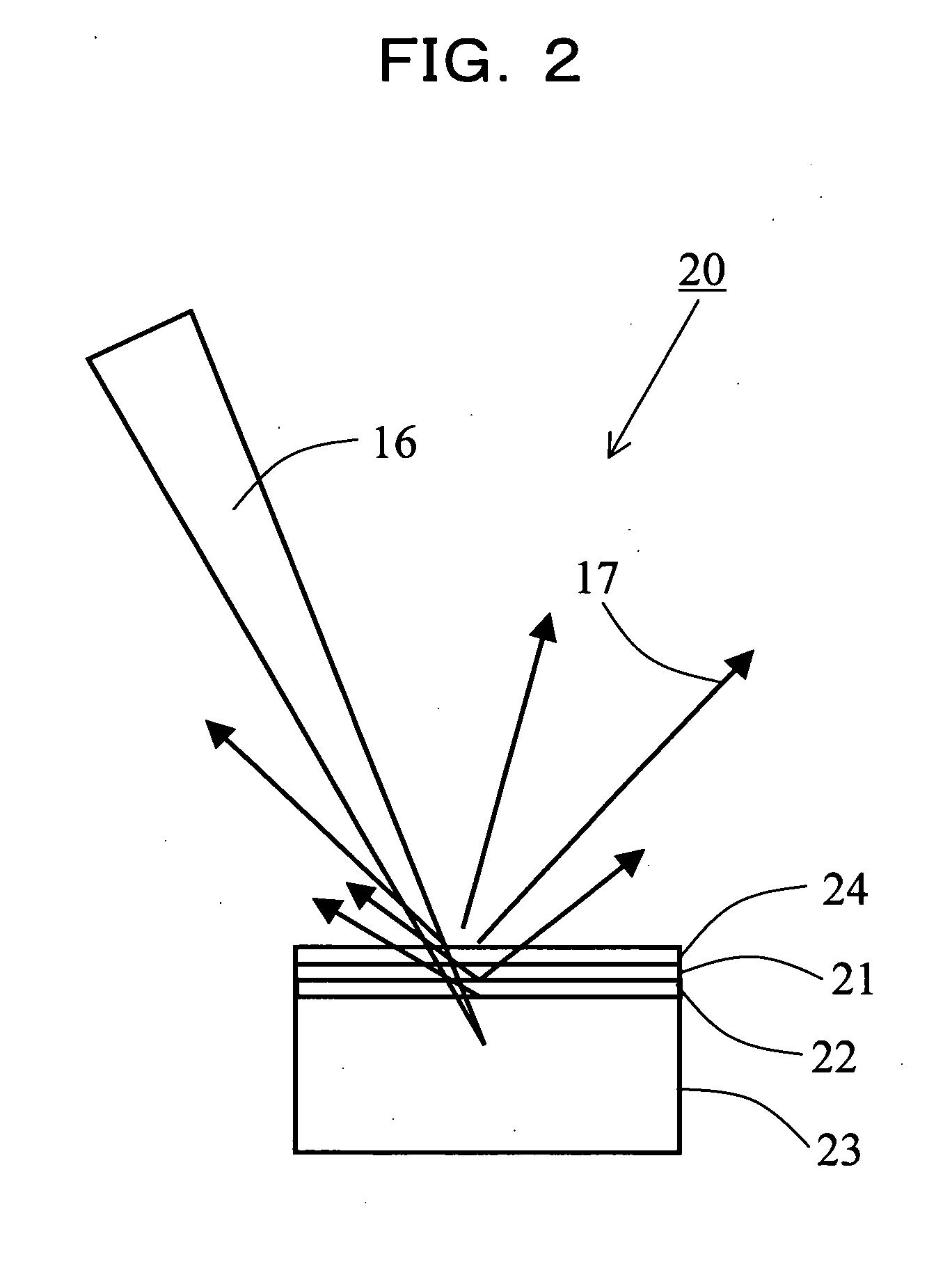
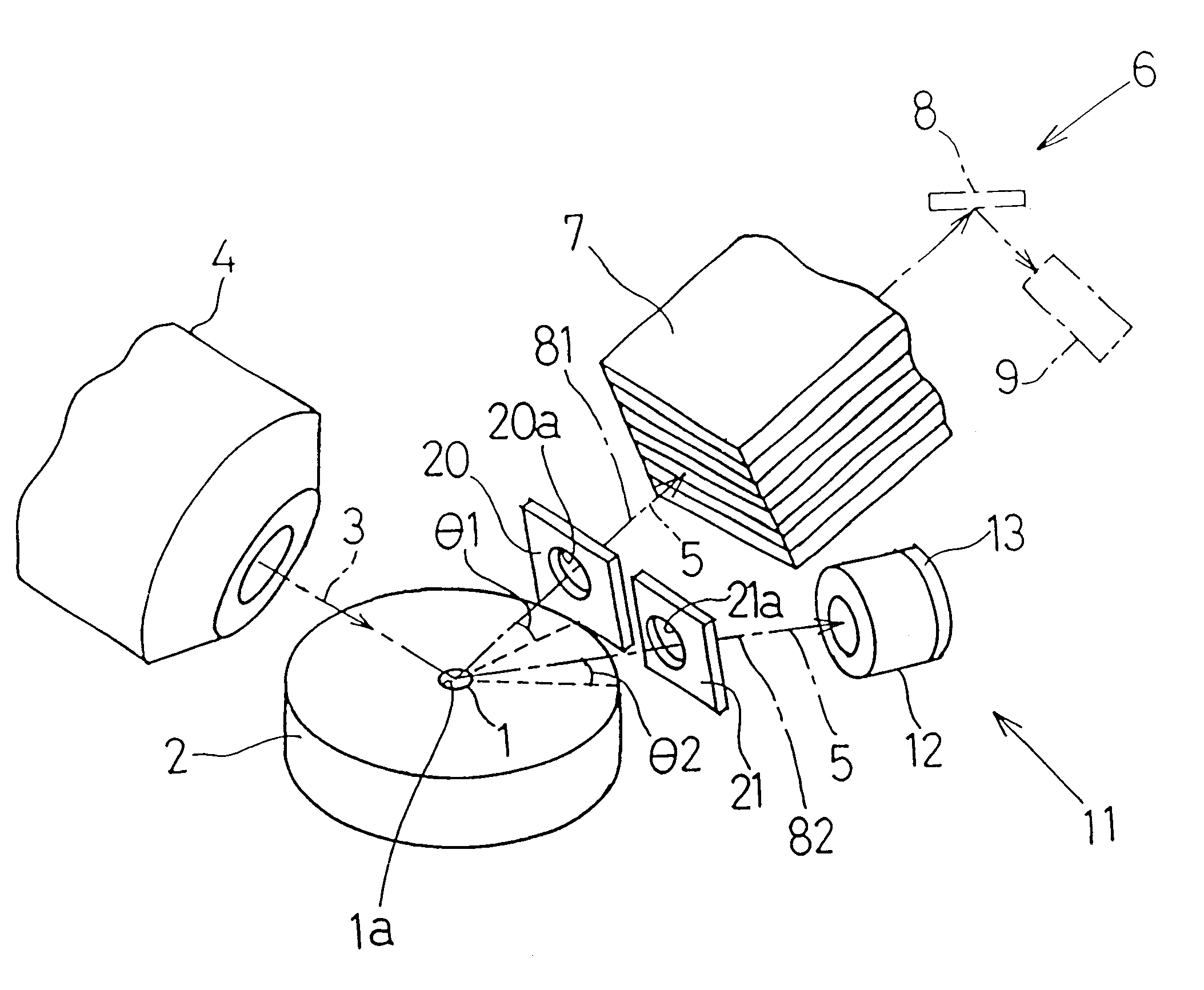
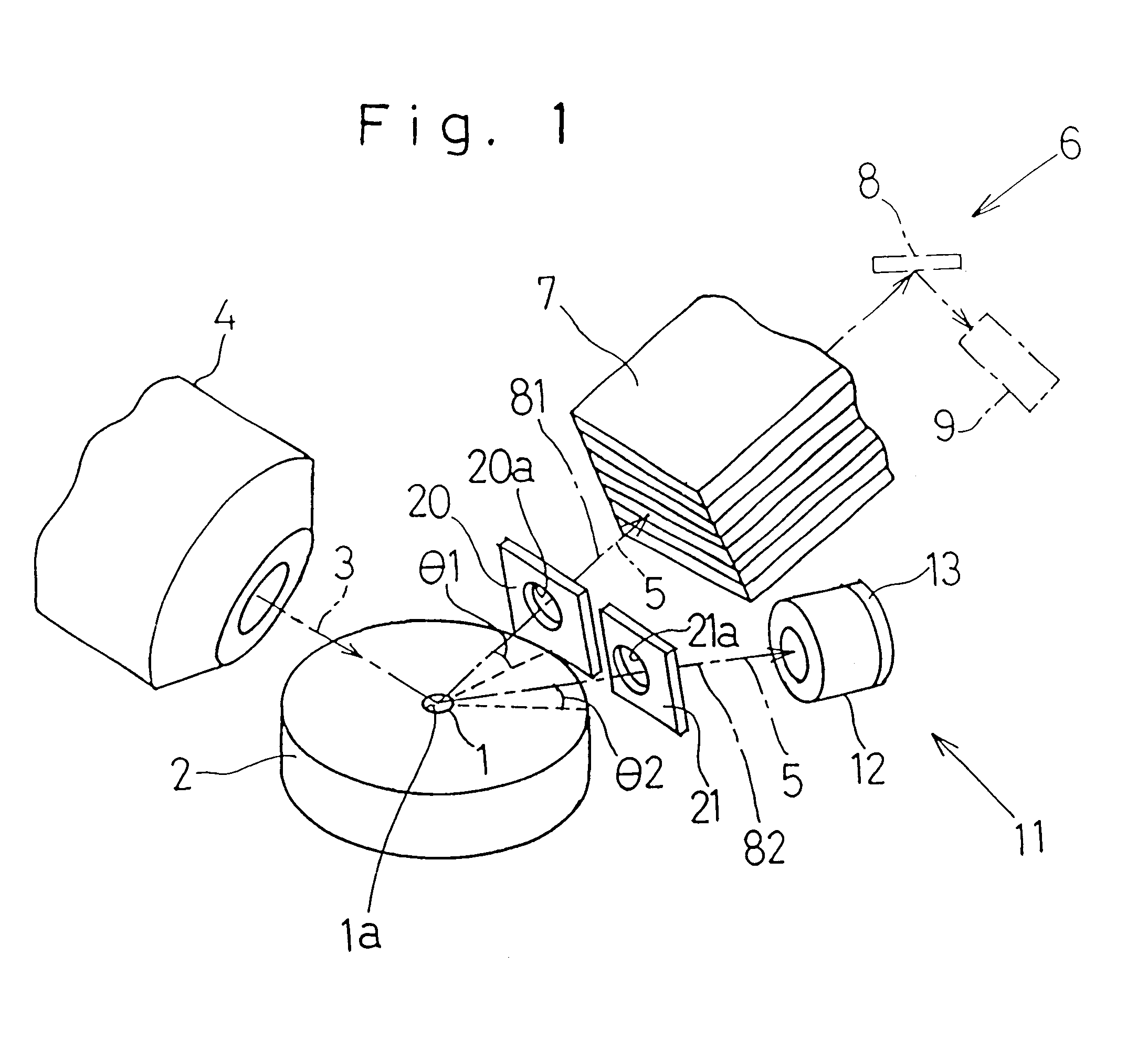
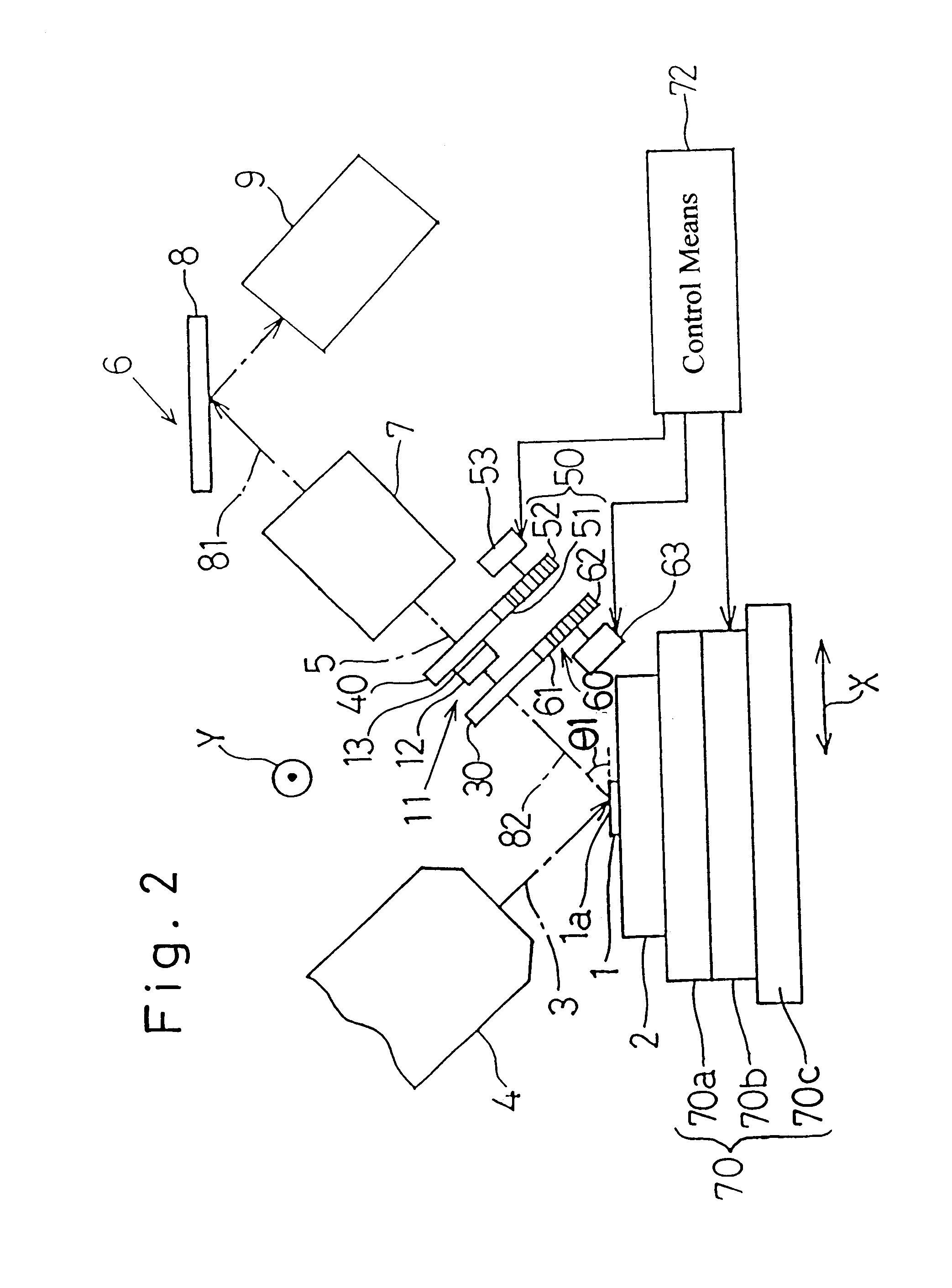
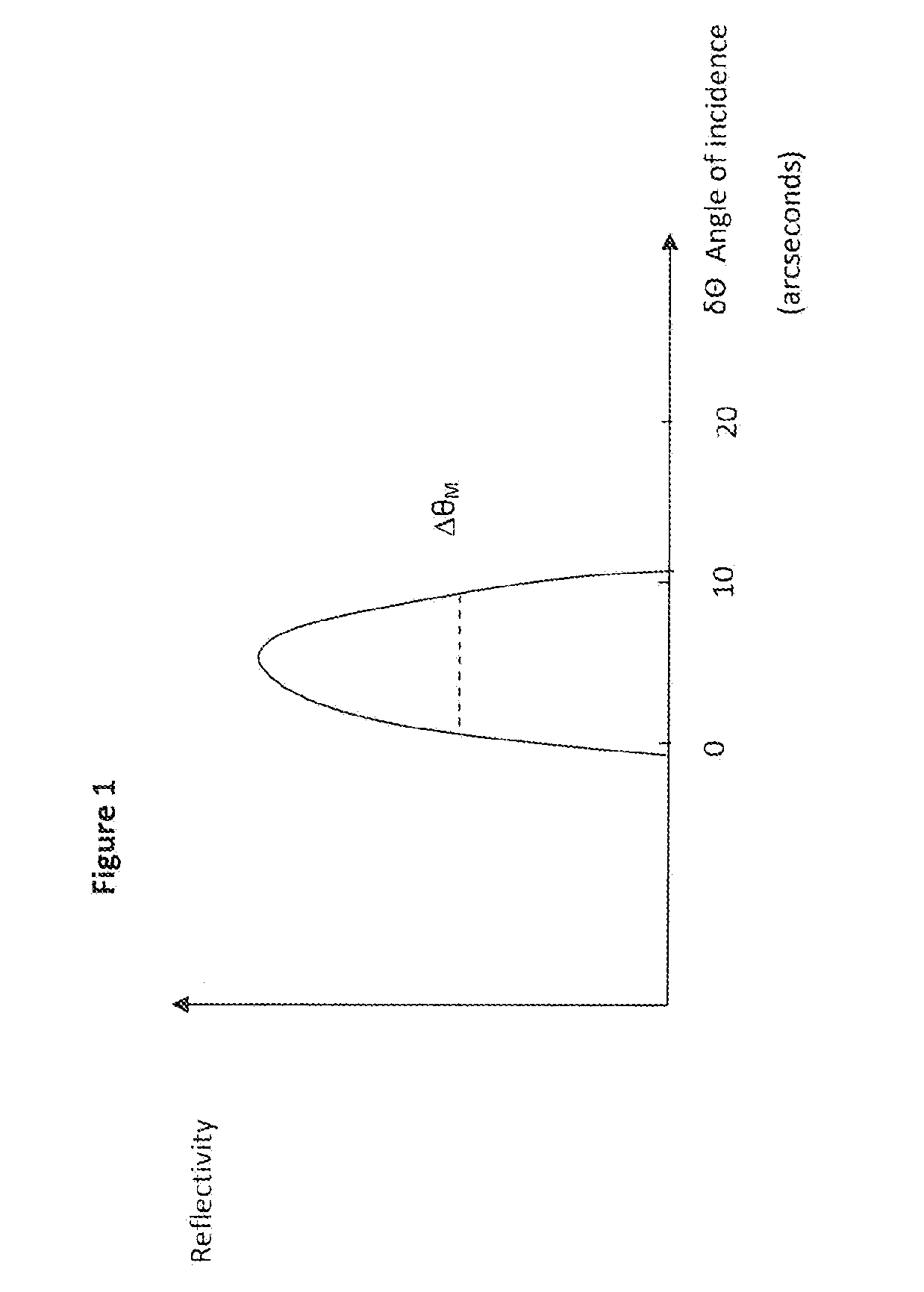
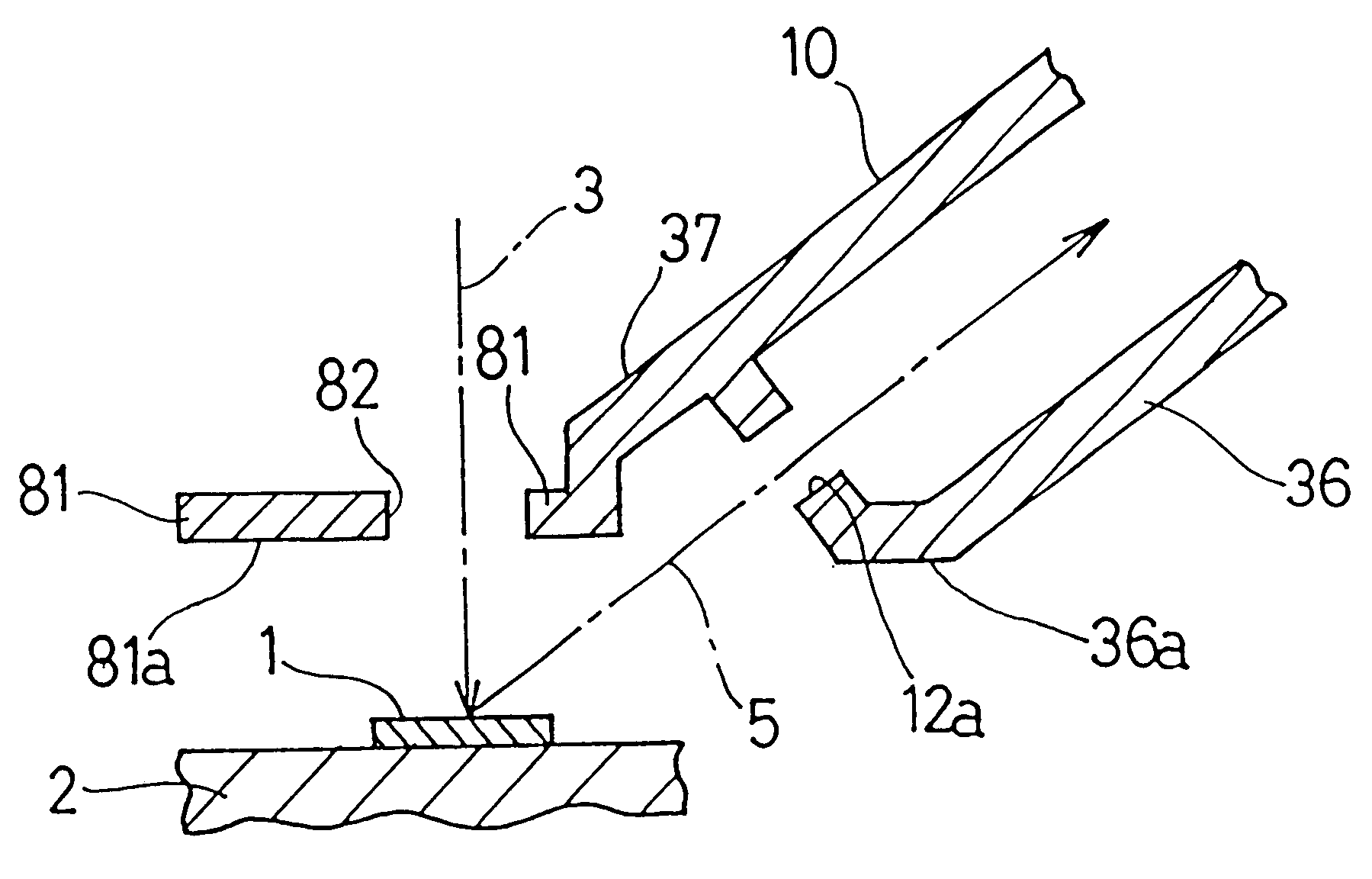
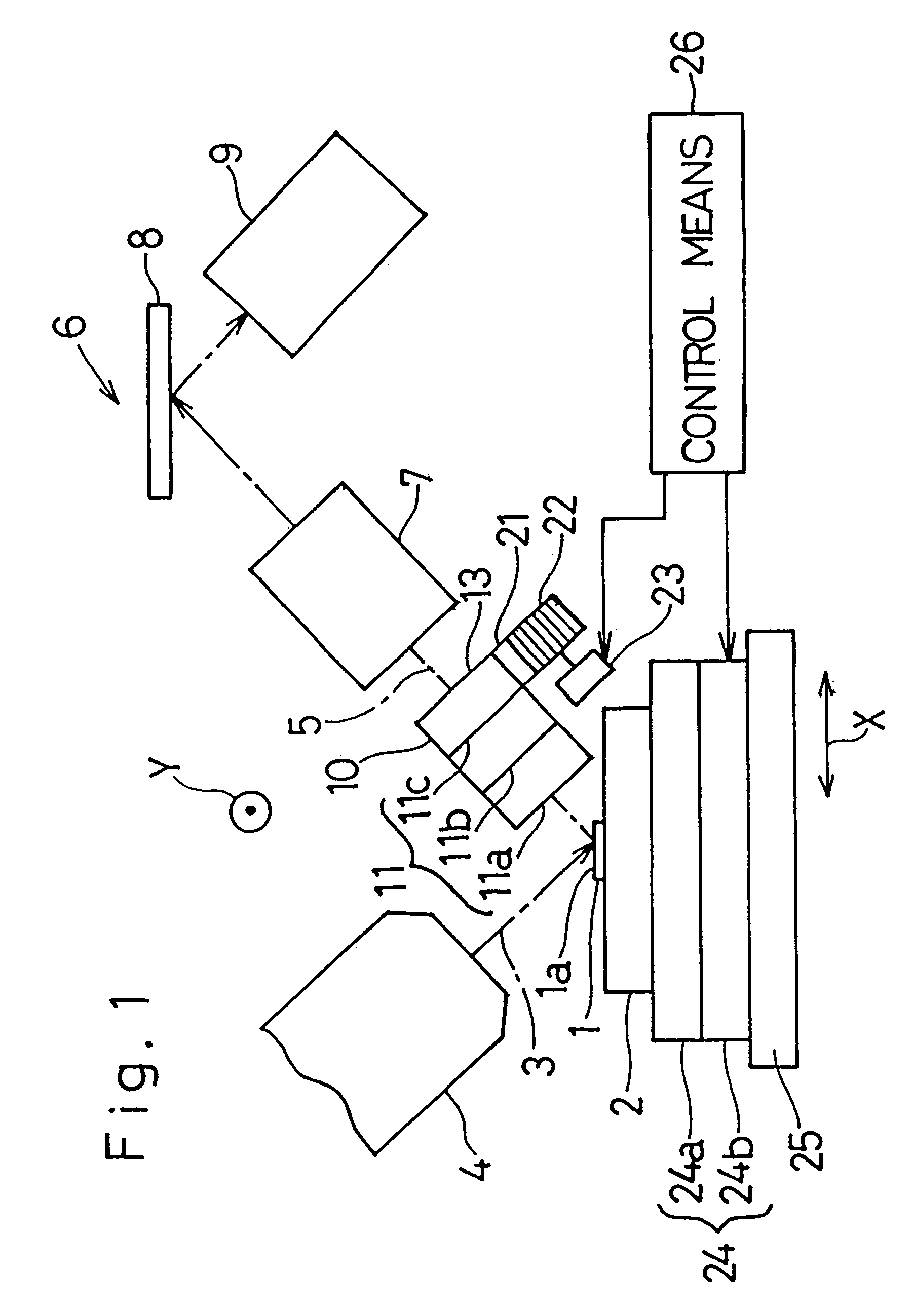
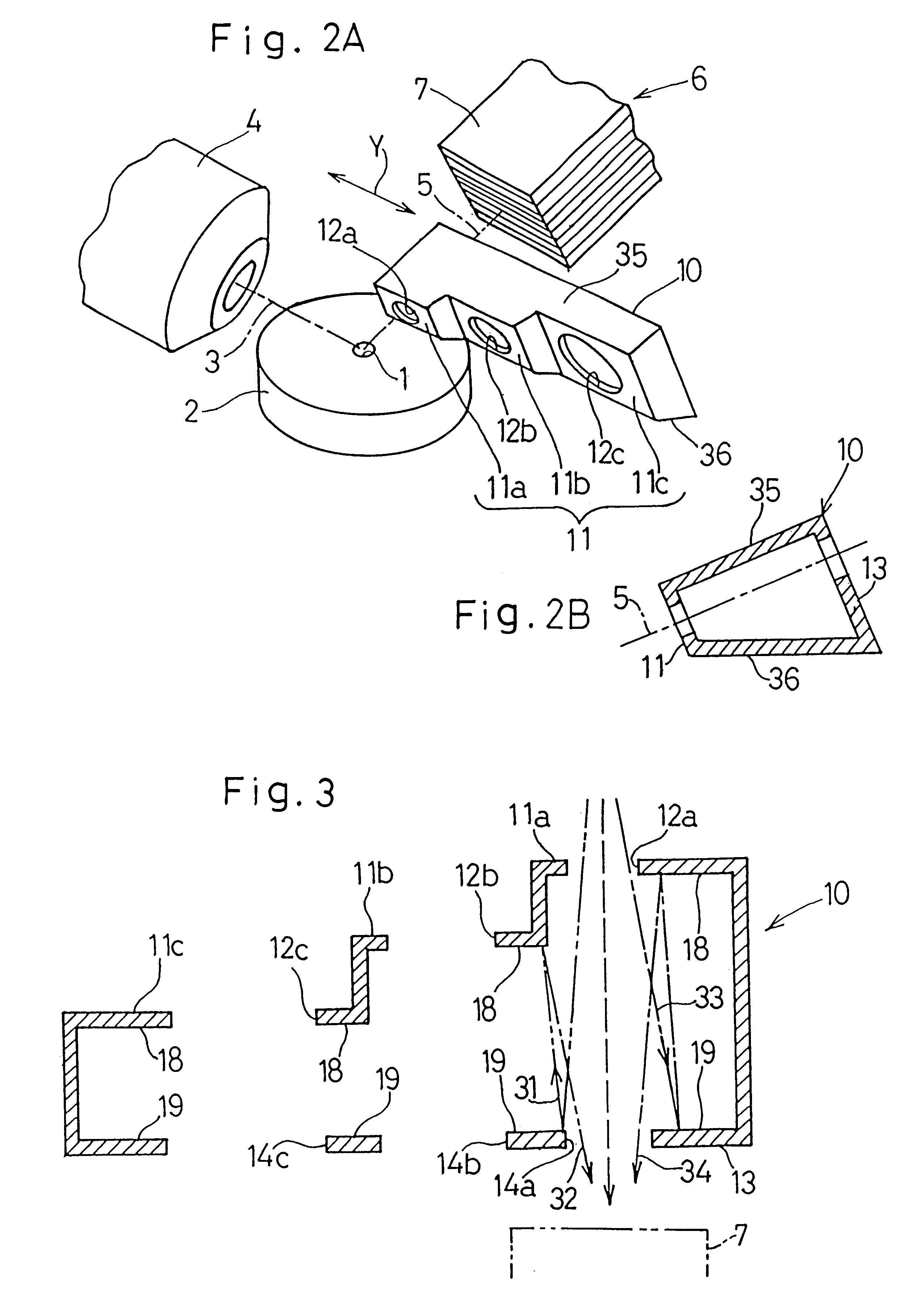
A fluorescent X-ray analyzing apparatus capable of being used as either a wavelength dispersive type or an energy dispersive type is provided, with which the analysis can be performed quickly and accurately. The fluorescent X-ray analyzing apparatus includes a detecting unit for detecting and analyzing fluorescent X-ray (5) emitted from at least one target area (1a) of a sample (1) to be analyzed as a result of excitation of such target area (1a) with a primary X-ray (3). The detecting unit includes a wavelength dispersive type detecting unit (6) including a spectroscope (8) and a first detector (9), and an energy dispersive type detecting unit (11) including a second detector (12) of an energy dispersive type. The angle theta1 formed between a first path (81) of travel of the fluorescent X-ray from the target area (1a) towards the spectroscope (8) and a surface of the sample (1) is equal to the angle theta2 formed between a second path (82) of travel of the fluorescent X-ray from the target area (1a) towards the second detector (12) of the energy dispersive type and a surface of the sample (1), but the second path (82) is shorter than the first path (81).
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
X-ray source and fluorescent X-ray analyzing apparatus
InactiveUS7809113B2Eliminates unwanted noise componentGenerate efficientlyX-ray tube laminated targetsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayX-ray
Owner:TOSHIBA ELECTRON TUBE & DEVICES
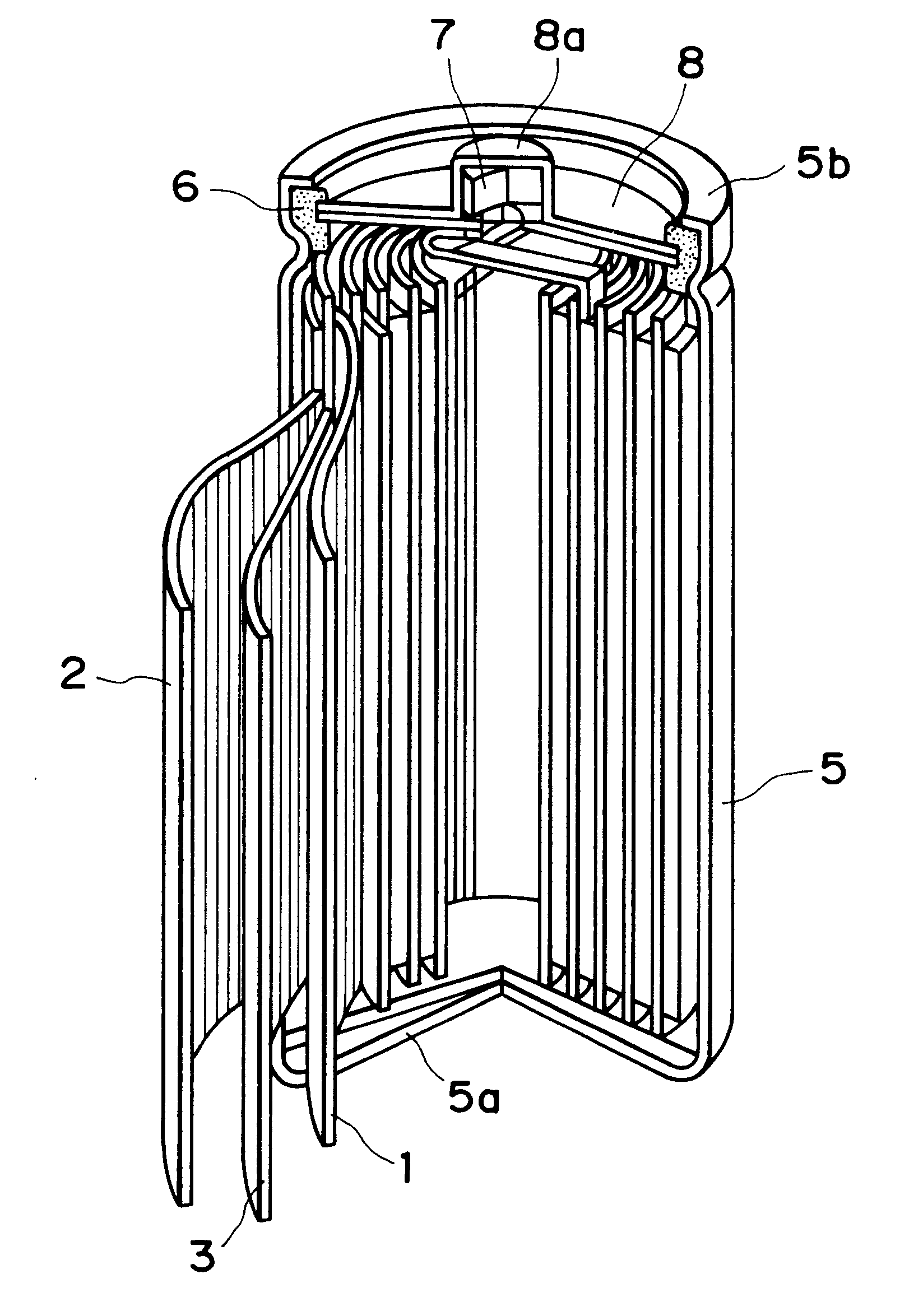
Carbonaceous electrode material for secondary battery and process for production thereof
InactiveUS6303249B1Small non-dedoping capacityLarge capacityNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLi-accumulatorsPotassiumSolvent
A carbonaceous electrode having improved capacities for doping and dedoping of a cell active substance, such as lithium, and suitable for a non-aqueous solvent-type secondary battery, is constituted by a carbonaceous material having a pore volume of at least 0.55 ml / g of pores having a pore diameter of at most 5 mum as measured by mercury injection method, a potassium content of at most 0.5 wt. % as measured by fluorescent X-ray analysis, and a specific surface area of at most 100 m2 / g as measured by nitrogen adsorption BET method. The carbonaceous material is advantageous produced by carbonizing a carbon precursor of plant origin having a potassium content of at most 0.5 wt. % as measured by fluorescent X-ray analysis, in contact with a stream of an inert gas optionally containing a halogen gas at a temperature of 700-1500° C.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite nanotubes
ActiveUS20050036939A1Reduce the amount requiredThe instrumentation is simpleDigital storageGermanium dioxideStrontium titanateBarium titanate
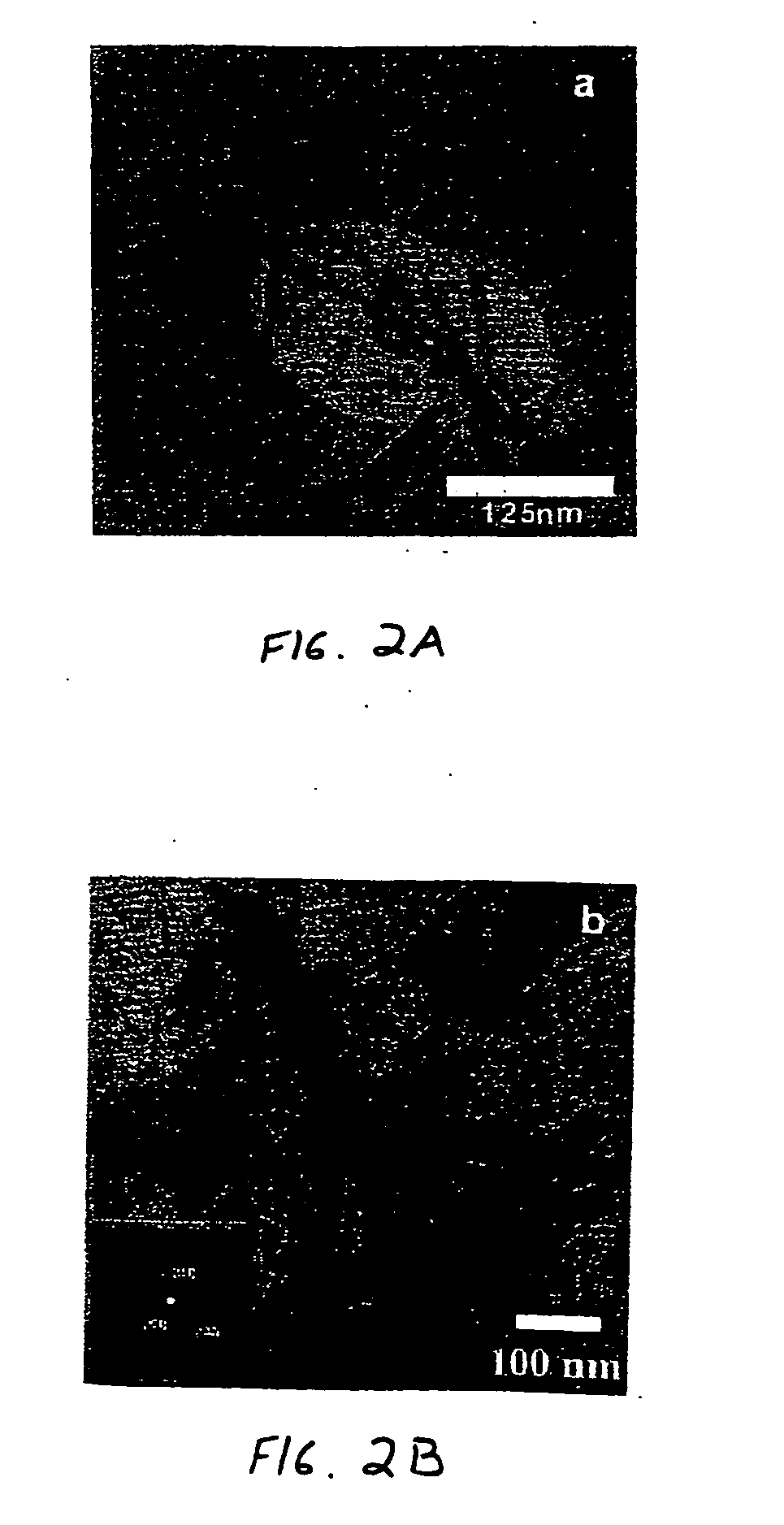
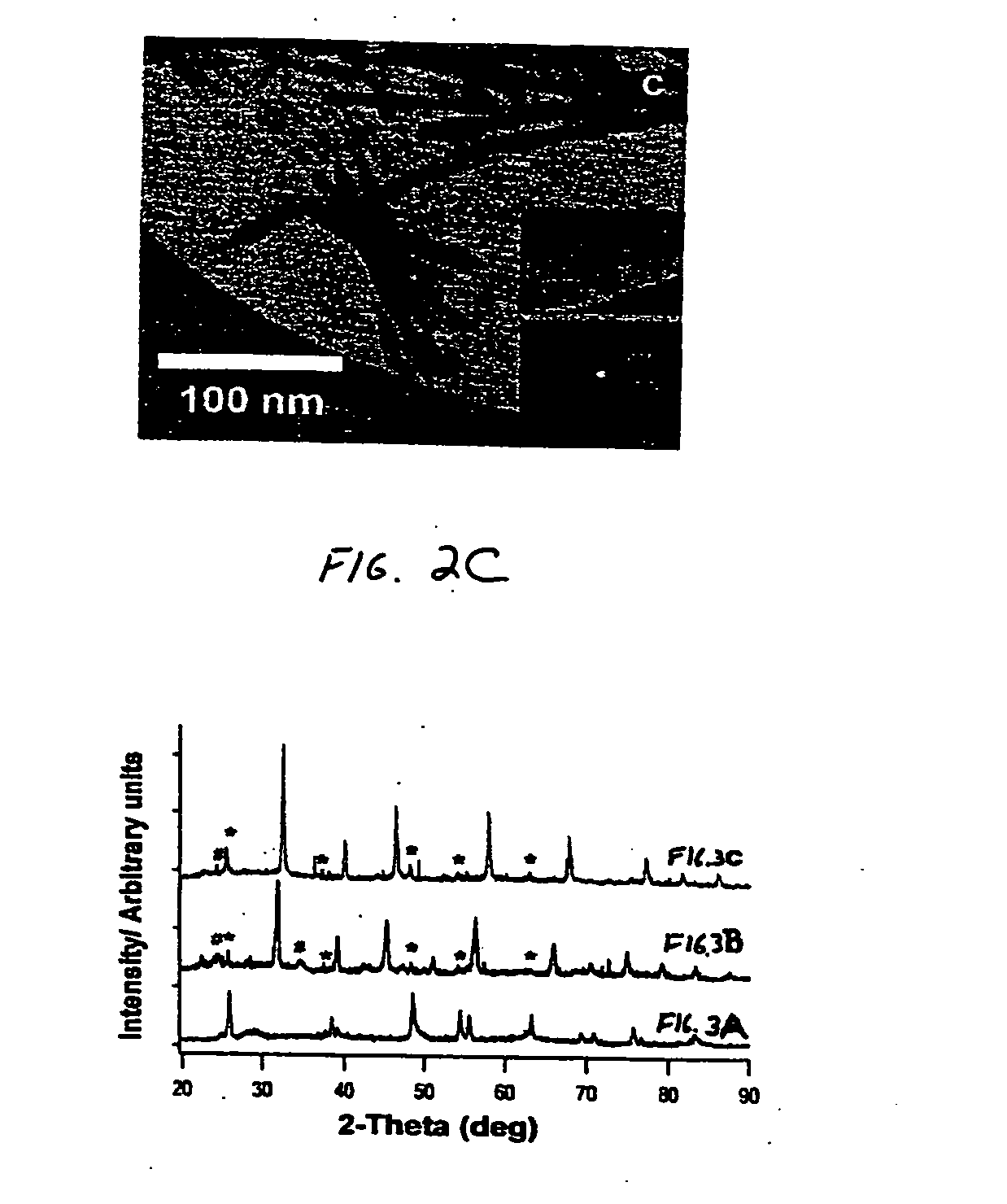
A low-temperature hydrothermal reaction is provided to generate crystalline perovskite nanotubes such as barium titanate (BaTiO3) and strontium titanate (SrTiO3) that have an outer diameter from about 1 nm to about 500 nm and a length from about 10 nm to about 10 micron. The low-temperature hydrothermal reaction includes the use of a metal oxide nanotube structural template, i.e., precursor. These titanate nanotubes have been characterized by means of X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy, coupled with energy dispersive X-ray analysis and selected area electron diffraction (SAED).
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
XRF system having multiple excitation energy bands in highly aligned package
ActiveUS8559597B2Increased signal noiseSmall intensityX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX ray analysisX-ray optics
An x-ray analysis apparatus for illuminating a sample spot with an x-ray beam. An x-ray tube is provided having a source spot from which a diverging x-ray beam is produced having a characteristic first energy, and bremsstrahlung energy; a first x-ray optic receives the diverging x-ray beam and directs the beam toward the sample spot, while monochromating the beam; and a second x-ray optic receives the diverging x-ray beam and directs the beam toward the sample spot, while monochromating the beam to a second energy. The first x-ray optic may monochromate characteristic energy from the source spot, and the second x-ray optic may monochromate bremsstrahlung energy from the source spot. The x-ray optics may be curved diffracting optics, for receiving the diverging x-ray beam from the x-ray tube and focusing the beam at the sample spot. Detection is also provided to detect and measure various toxins in, e.g., manufactured products including toys and electronics.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
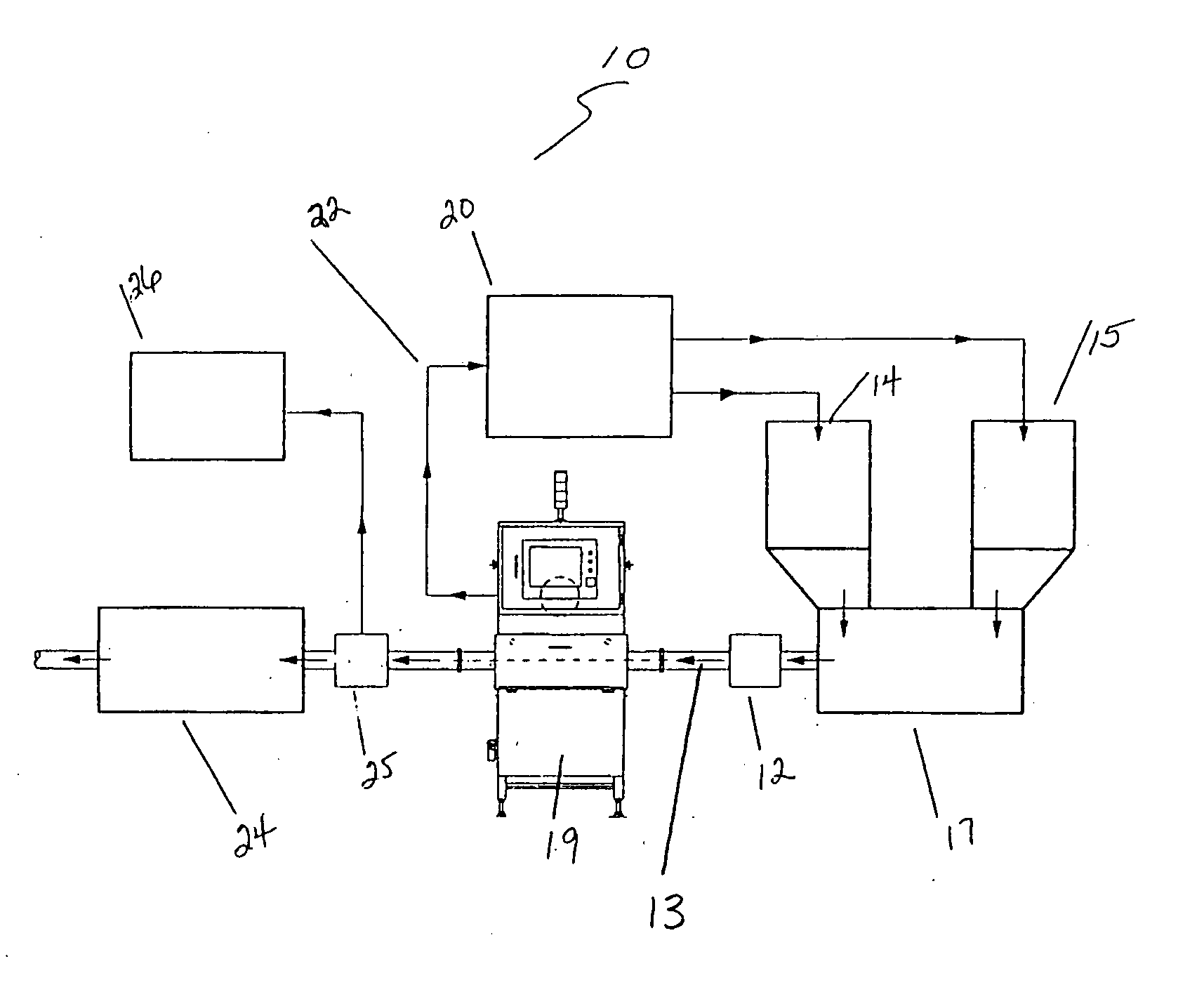
Method and apparatus for meat scanning
A system and apparatus for scanning food products to determine at least one property of the food product. In one embodiment, two sources of the food product, such as a low fat and a high fat source, controllably feed into a grinder. The grinder feeds into an x-ray analysis apparatus which is adapted to determine the desired property of the food product by x-ray analysis. A controller then forms a feedback loop which controls the relative amount of food product being feed from each of the food product sources.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO INC +1
System and method for fuel cell material x-ray analysis
ActiveUS7499521B2Shorten development timeImprove reliabilityRadiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansHard X-raysMetrology
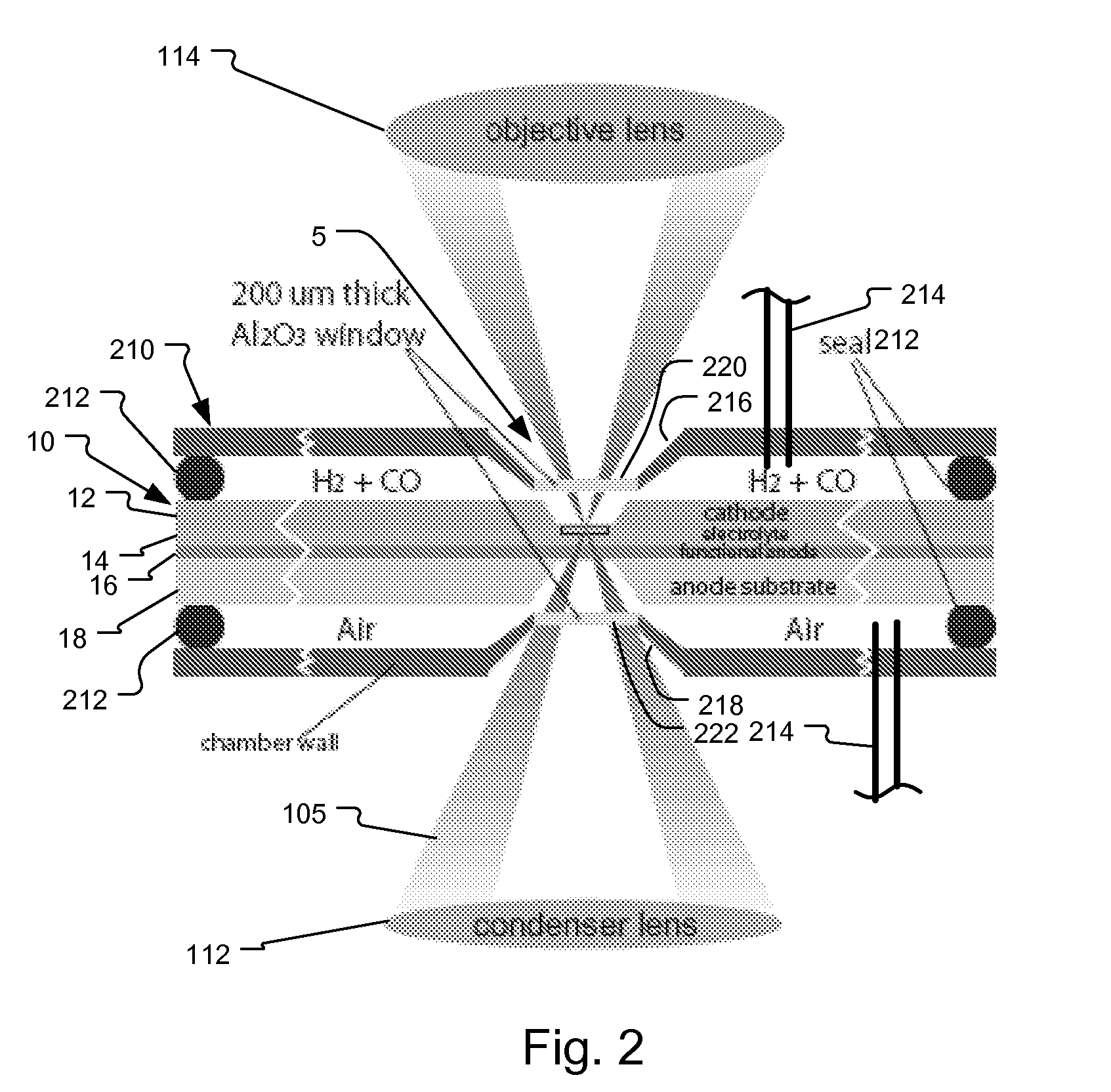
An imaging technology for fuel cells is based on x-ray microscopy. A metrology system images the electro-chemical interaction areas of solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFC) in-situ. This system takes advantage of both the penetrating power and elemental absorption contrast of hard x-ray radiation to image the internal interaction areas in a SOFC. The technology can further take advantage of the strong dependence of the x-ray absorption on material type and energy to distinguish the four major material types: cathode, electrolyte, air, and low-Z contaminants such as sulfur.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
X-ray beam device
ActiveUS8422633B2Improve throughputIncreased collecting angleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayCatoptrics
The invention refers to an X-ray beam device for X-ray analytical applications, comprising an X-ray source designed such as to emit a divergent beam of X-rays; and an optical assembly designed such as to focus said beam onto a focal spot, wherein said optical assembly comprises a first reflecting optical element, a monochromator device and a second reflecting optical element sequentially arranged between said source and said focal spot, wherein said first optical element is designed such as to collimate said beam in two dimensions towards said monochromator device, and wherein said second optical element is designed such as to focus the beam coming from said monochromator device in two dimensions onto said focal spot.
Owner:XENOCS
X-ray target and apparatuses using the same
InactiveUS7551722B2Electron beam absorptivitySmall in focus sizeX-ray tube laminated targetsImaging devicesHigh intensityX ray analysis
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite nanotubes
ActiveUS7147834B2The instrumentation is simpleReduce the amount requiredNanoinformaticsDigital storageStrontium titanateBarium titanate
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
X-ray analyzer having multiple excitation energy bands produced using multi-material x-ray tube anodes and monochromating optics
ActiveUS20150043713A1Lower levelX-ray tube laminated targetsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMulti materialFluorescence
An x-ray tube includes a target on which electrons impinge to form a diverging x-ray beam. The target has a surface formed from first and second target materials, each tailored to emit a respective x-ray energy profile. A first x-ray optic may be provided for directing the beam toward the sample spot, the first x-ray optic monochromating the diverging x-ray beam to a first energy from the energy emitted by the first target material; and a second x-ray optic may be provided, for directing the beam toward the sample spot, the second x-ray optic monochromating the diverging x-ray beam to a second energy from the energy emitted by the second target material. Fluorescence from the sample spot induced by the first and second monochromated energies is used to measure the concentration of at least one element in the sample, or separately measure elements in a coating and underlying substrate.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
Sample module with sample stream spaced from window, for x-ray analysis system
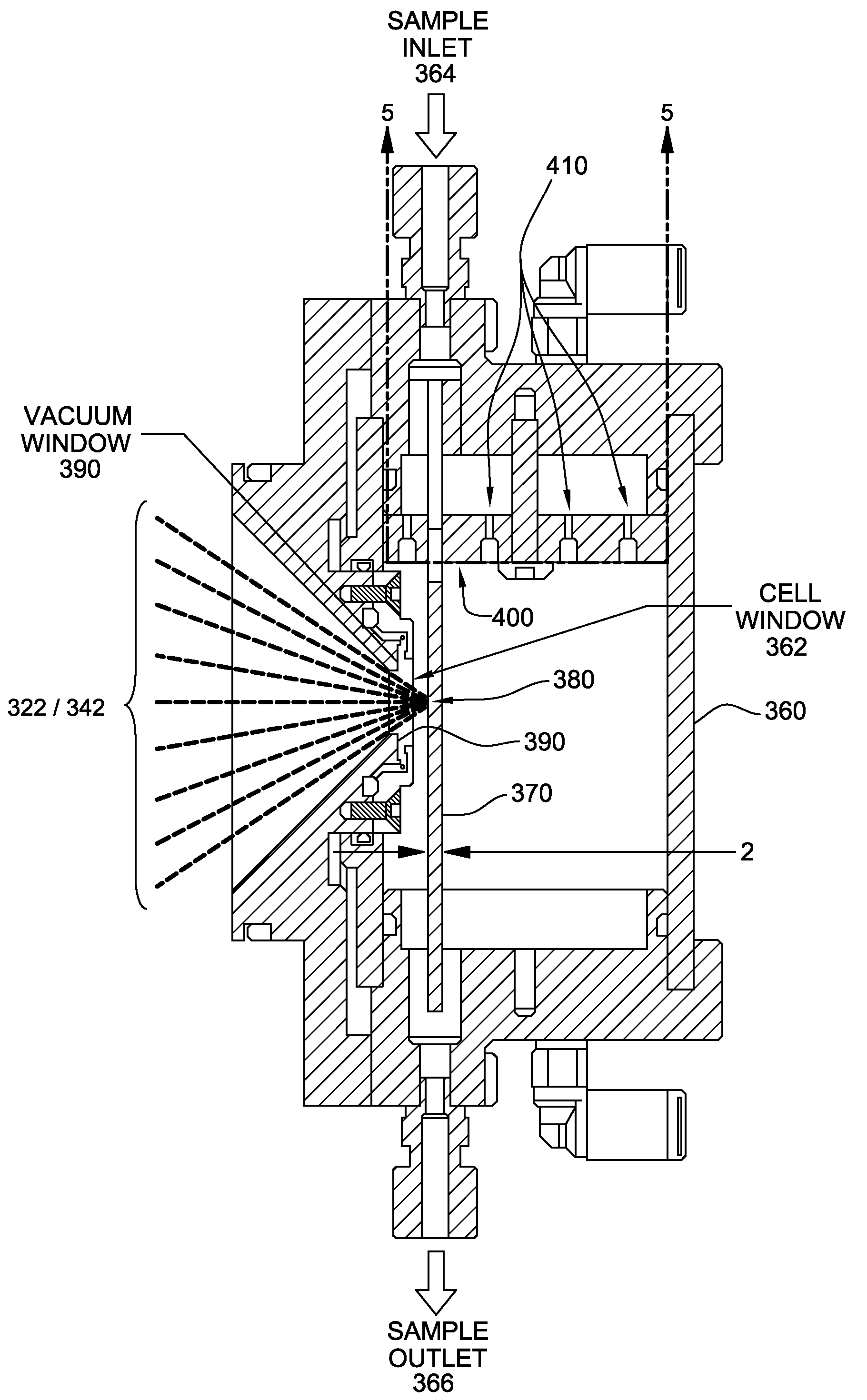
ActiveUS20090213988A1Low costX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationExcitation beamSoft x ray
An x-ray analysis system with an x-ray source for producing an x-ray excitation beam directed toward an x-ray analysis focal area; and a sample chamber for presenting a fluid sample to the x-ray analysis focal area. The x-ray excitation beam is generated by an x-ray engine and passes through an x-ray transparent barrier on a wall of the chamber, to define an analysis focal area within space defined by the chamber. The fluid sample is presented as a stream suspended in the space and streaming through the focal area, using a laminar air flow and / or pressure to define the stream. The chamber's barrier is therefore separated from both the focal area and the sample, resulting in lower corruption of the barrier.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
X-ray beam device
ActiveUS20100272239A1Reduce divergenceImprove throughputHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSoft x rayX-ray
The invention refers to an X-ray beam device for X-ray analytical applications, comprising an X-ray source designed such as to emit a divergent beam of X-rays; and an optical assembly designed such as to focus said beam onto a focal spot, wherein said optical assembly comprises a first reflecting optical element, a monochromator device and a second reflecting optical element sequentially arranged between said source and said focal spot, wherein said first optical element is designed such as to collimate said beam in two dimensions towards said monochromator device, and wherein said second optical element is designed such as to focus the beam coming from said monochromator device in two dimensions onto said focal spot.
Owner:XENOCS
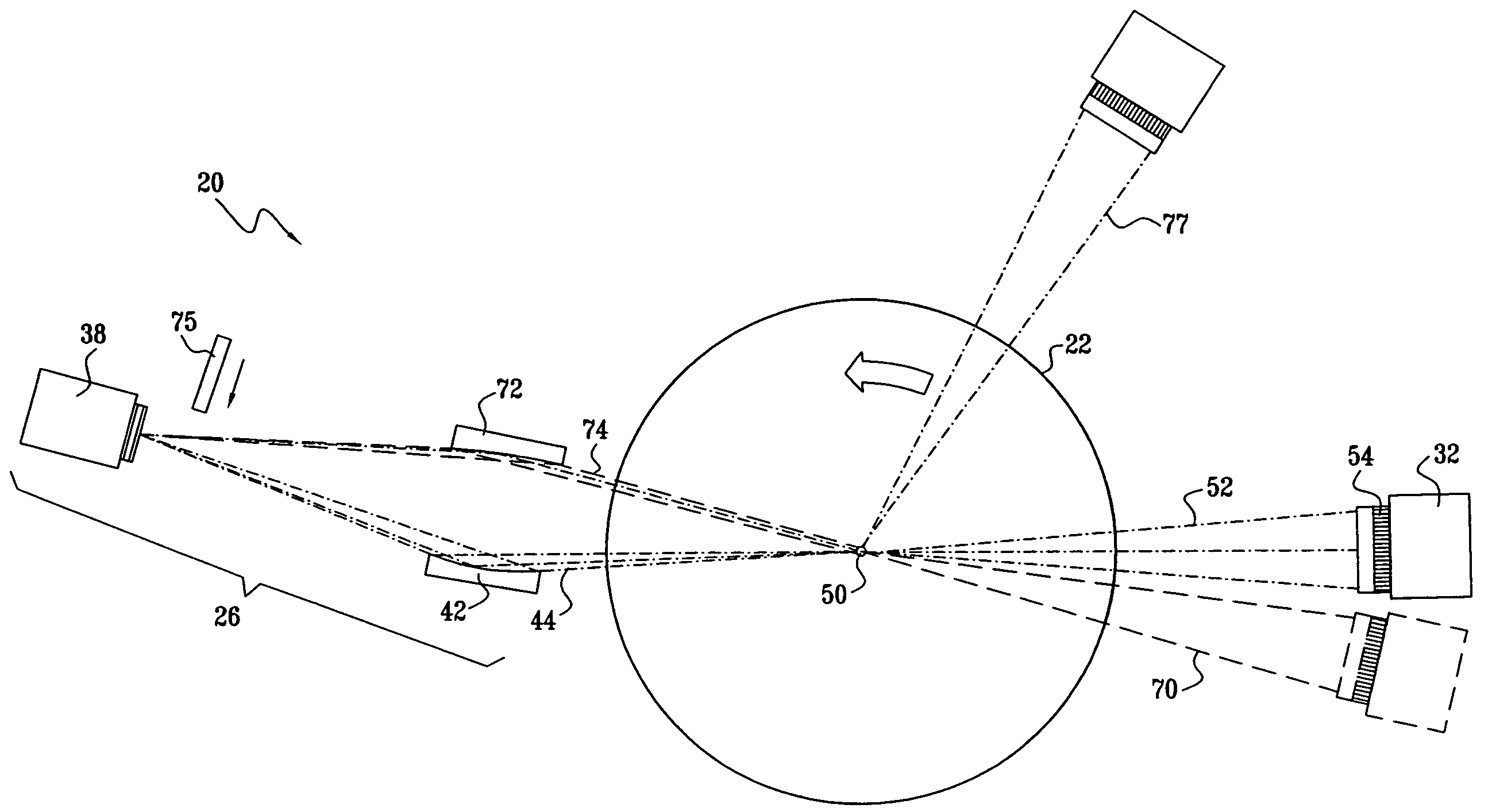
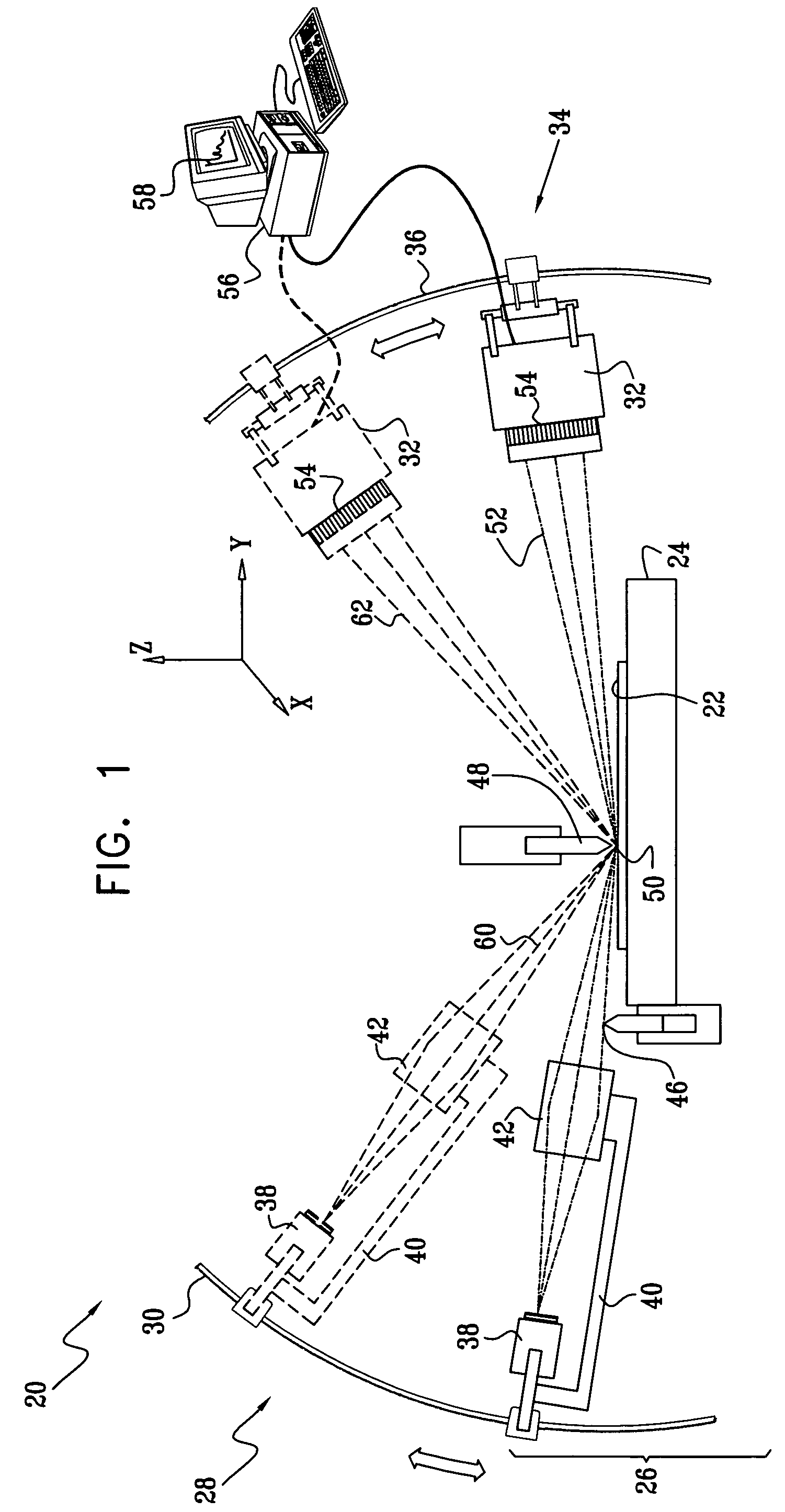
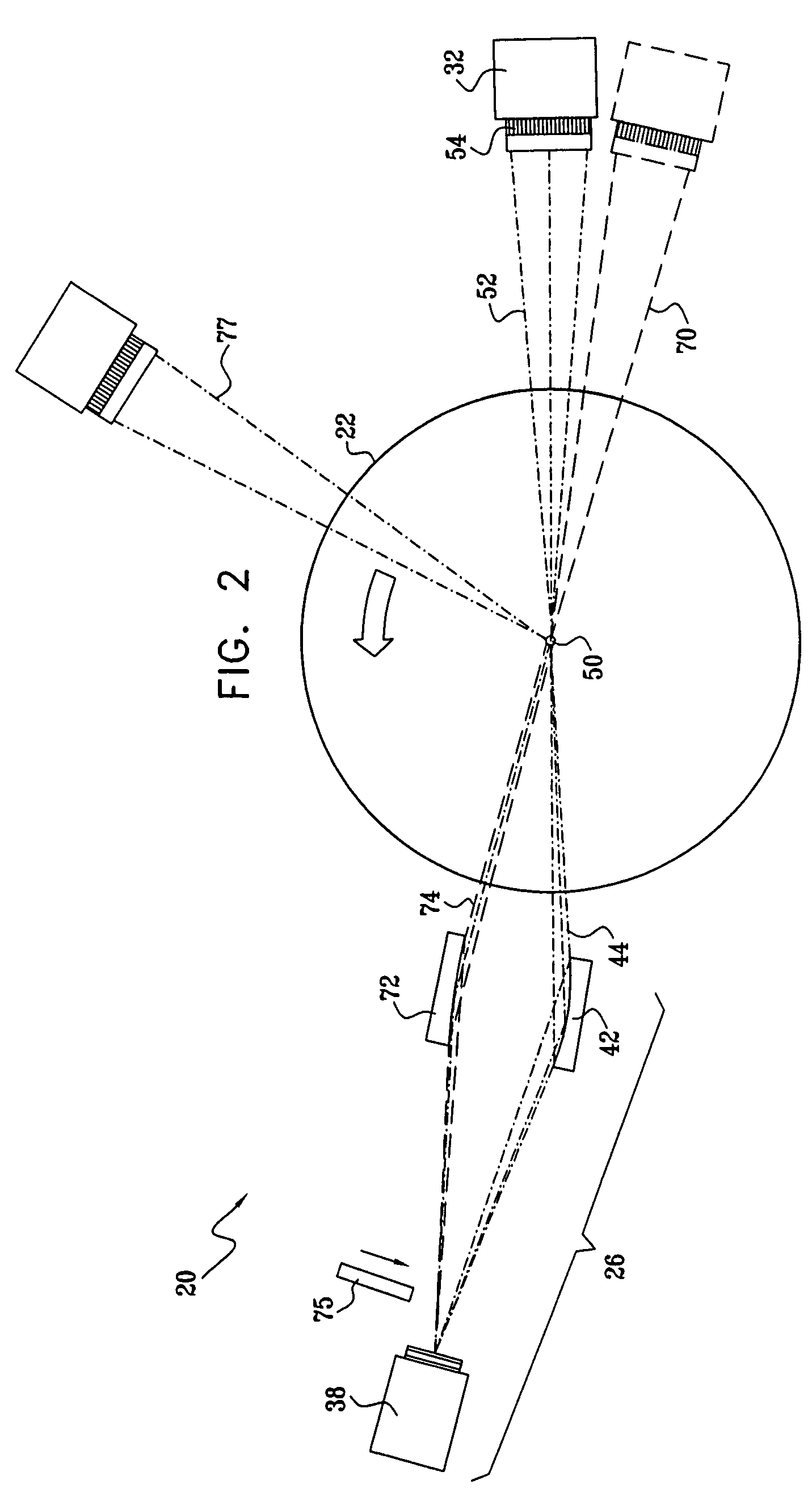
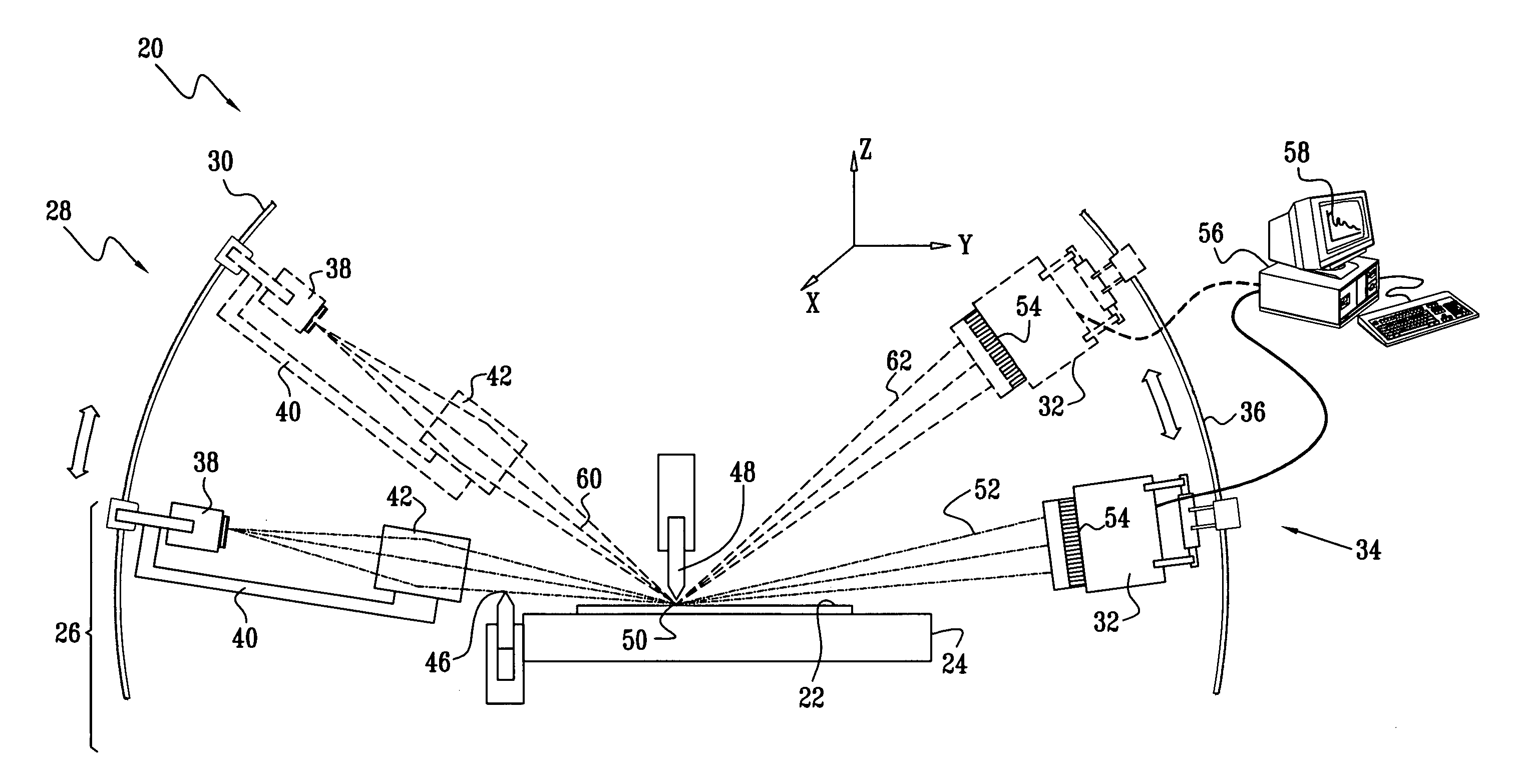
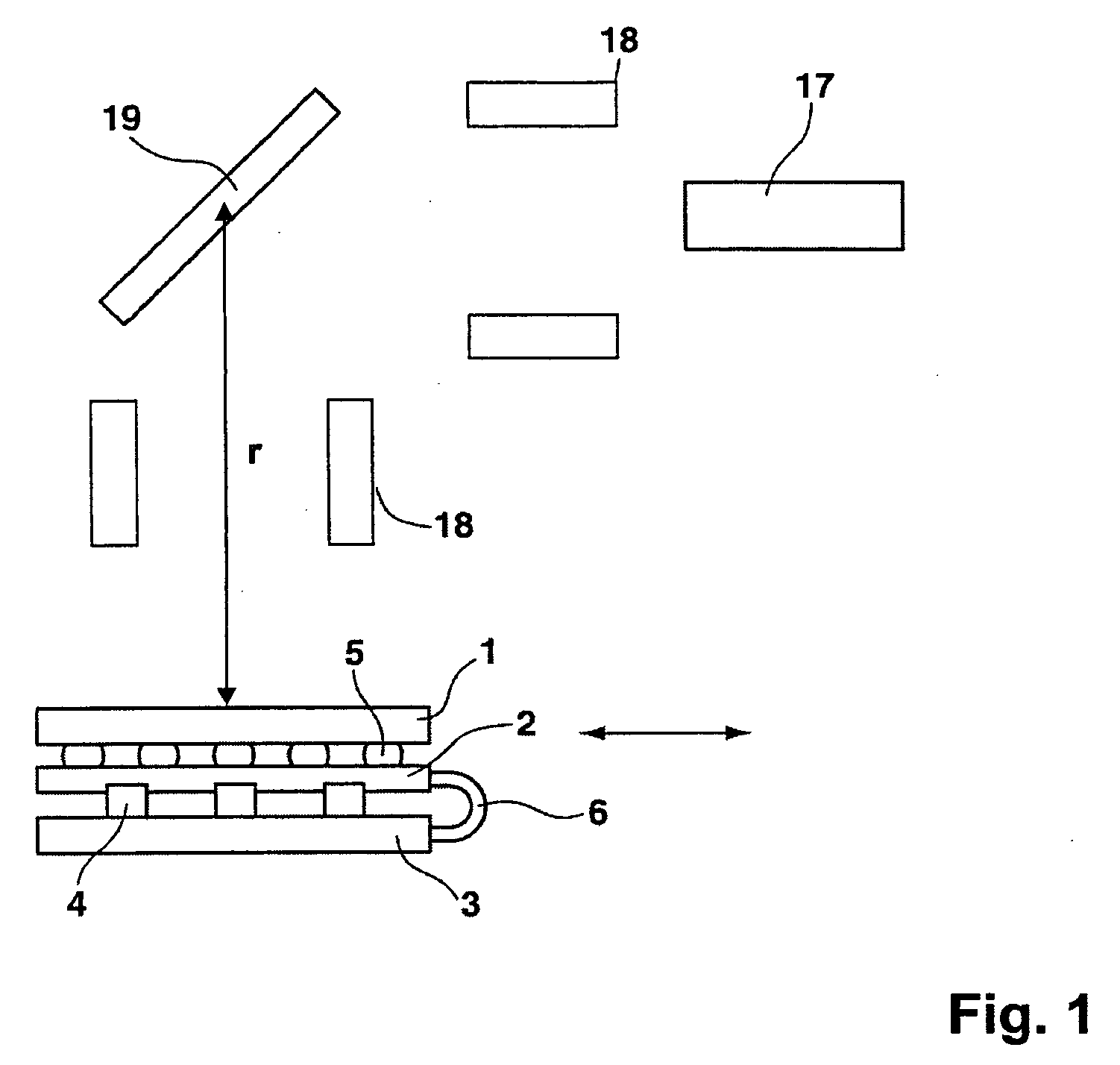
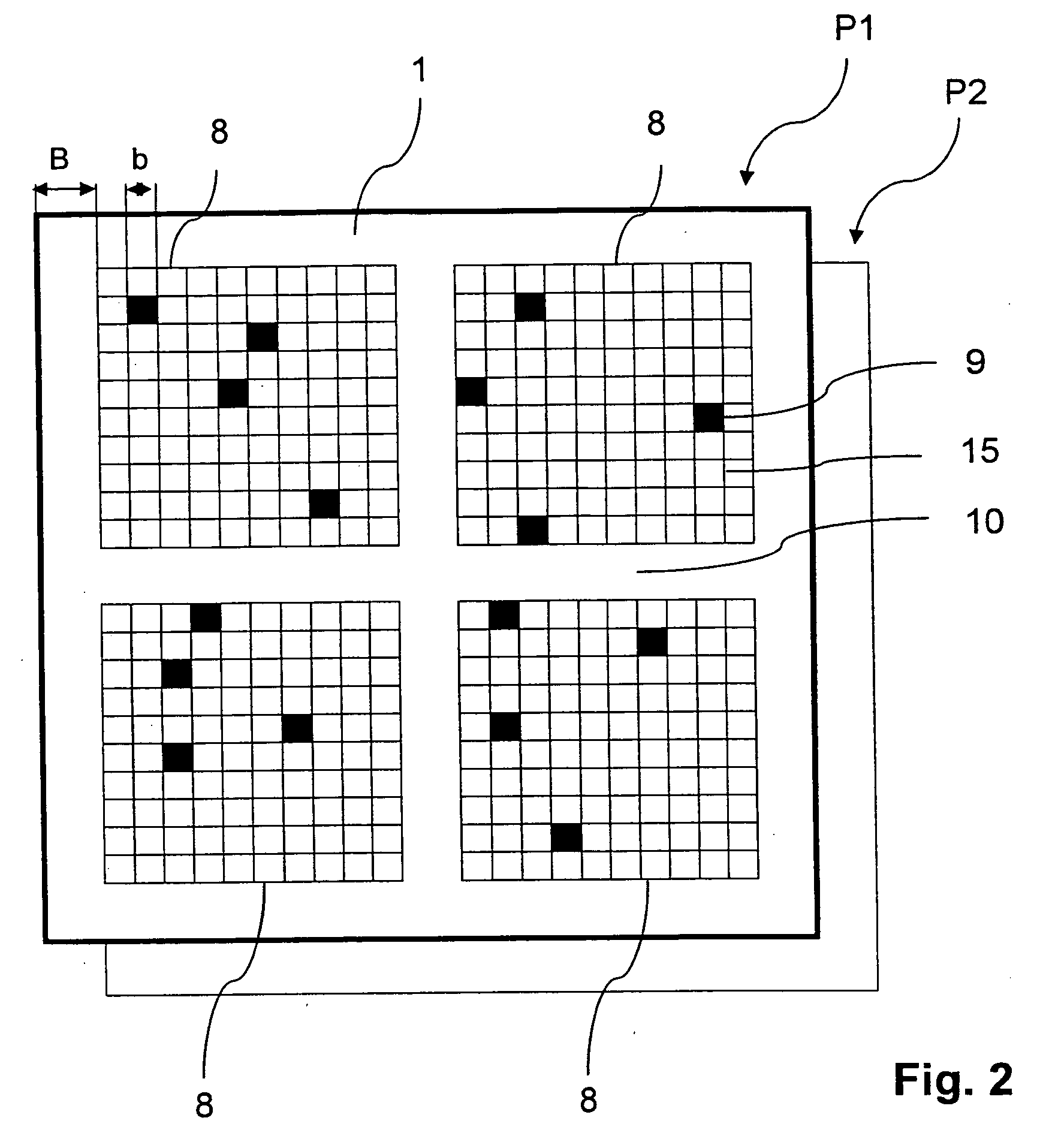
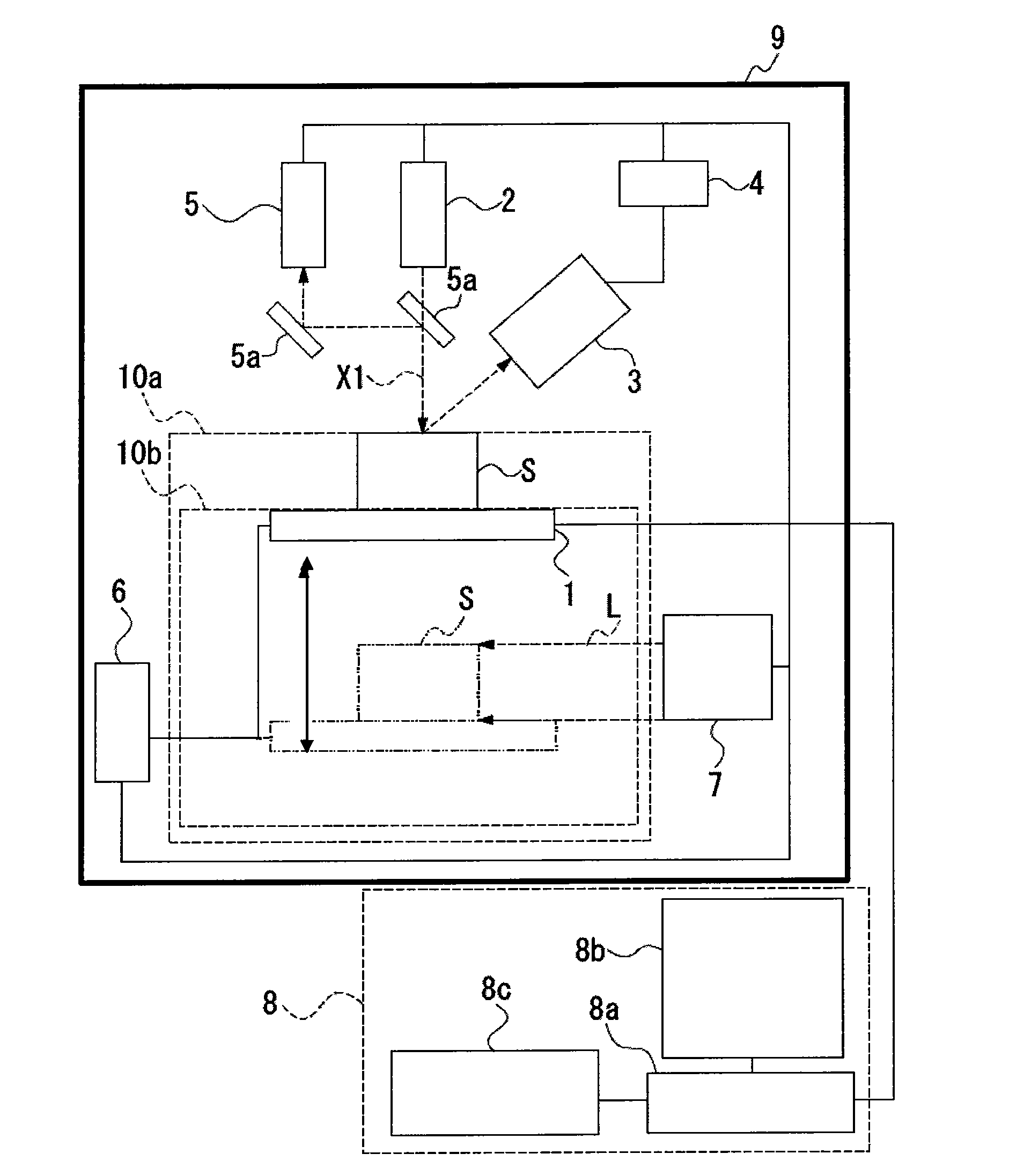
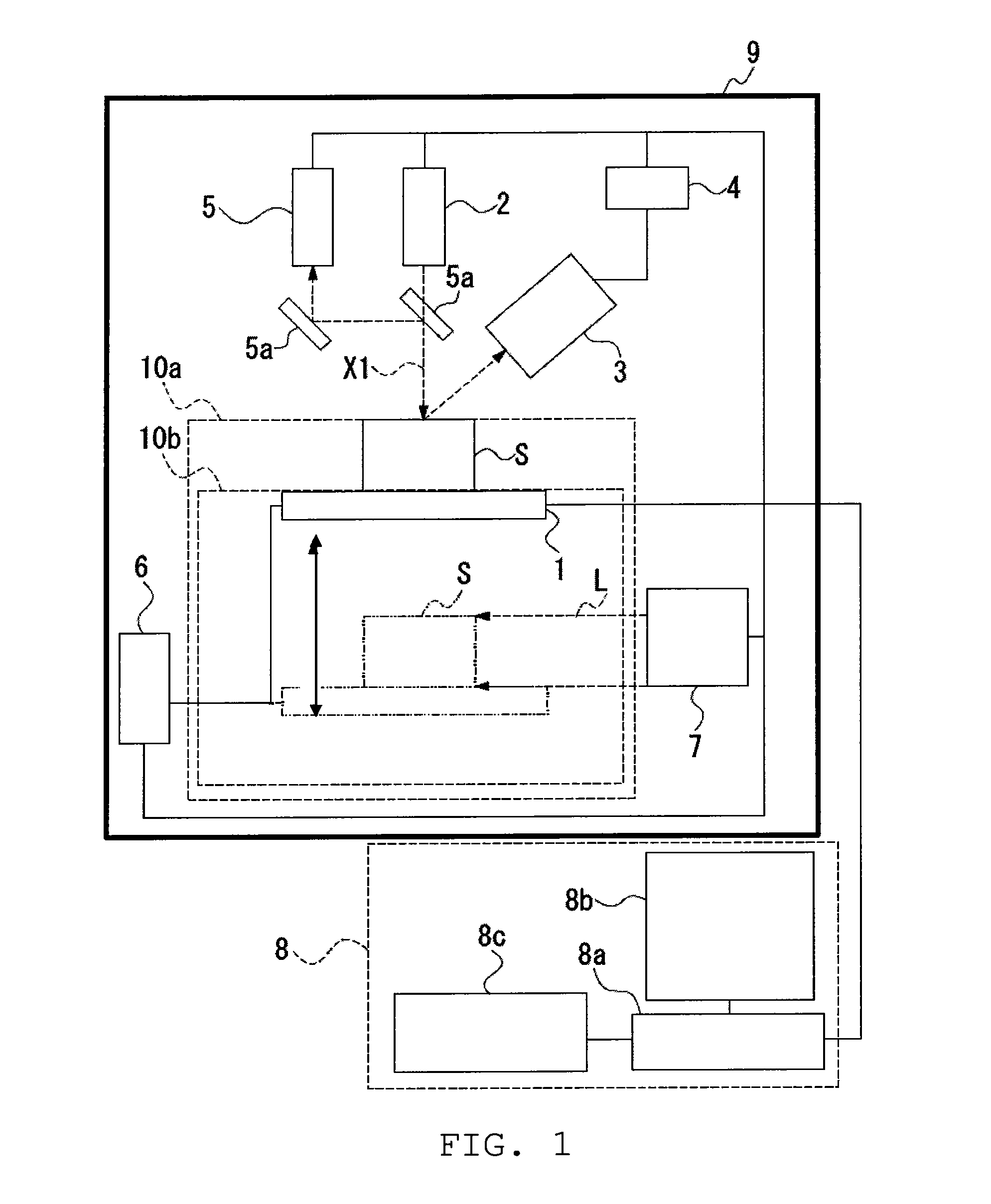
Method for operating an X-ray analysis apparatus with two-dimensional array detector and X-ray analysis apparatus for carrying out the method
ActiveUS20050259790A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMovabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSpatially resolvedData set
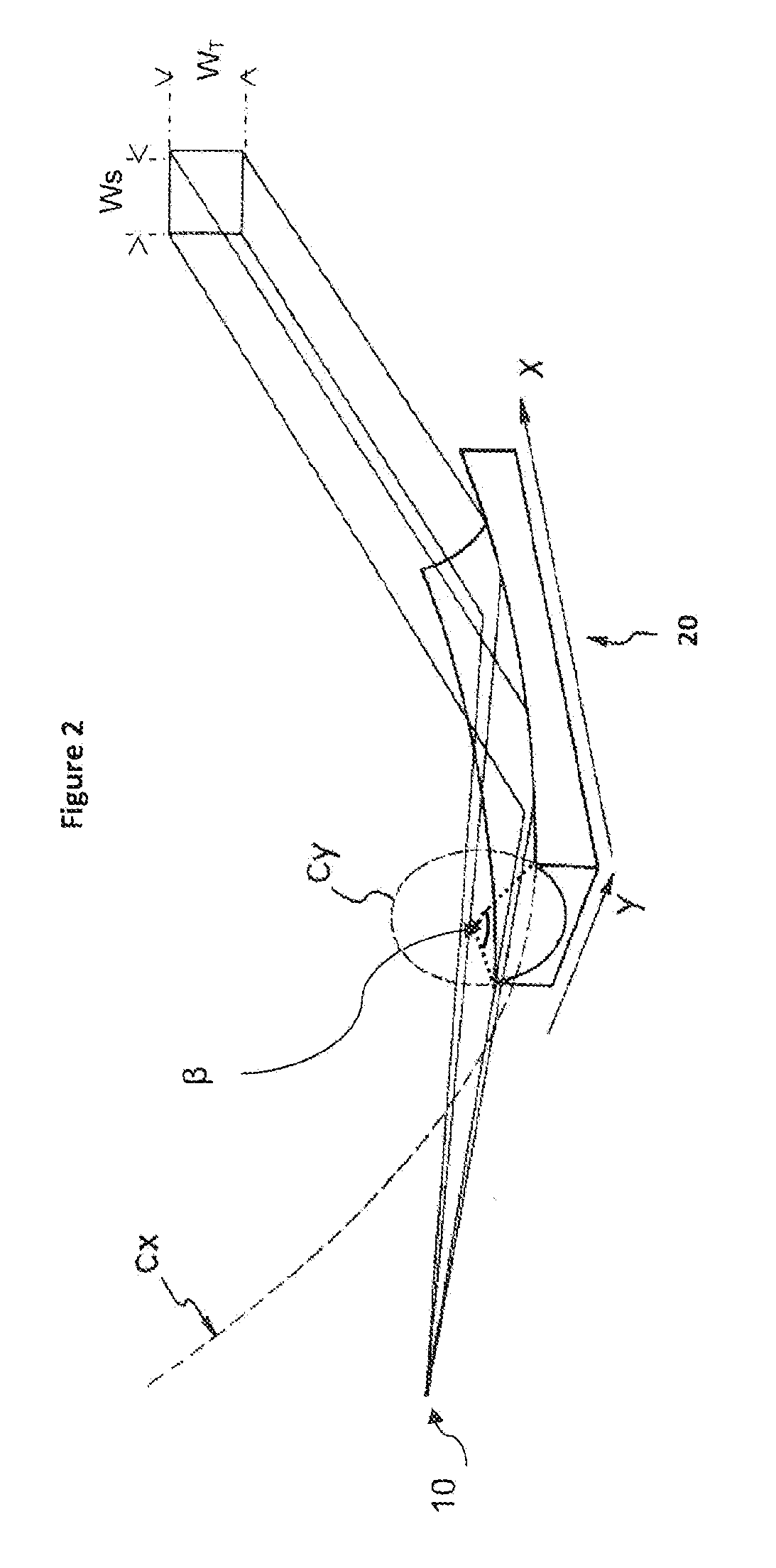
A method for operating an X-ray analysis device with a source (17) for X-ray radiation, an object (19) under investigation which is irradiated with X-ray radiation, and a planar two-dimensional array detector with pixel elements (7) for spatially resolved detection of the X-ray radiation emitted by the object (19), whereby a data set, in particular, in the form of a digitized diffractogram and / or spectrum is obtained, characterized by the following steps: a) recording a first data set (11) in a first relative spatial position (P1) of source (17), object (19) and detector; b) displacement and / or rotation of the detector in the detector plane relative to the source (17) and the object (19), whereby the relative position of source (17) and object (19) is not changed; c) recording a second data set (11) in the position (P2) displaced according to step b); and d) superposition of the recorded data sets (11) to form an overall data set (13), wherein the pixels of the recorded data sets are combined corresponding to their actual relative position with respect to the source (17) and object (19). The inventive method or the inventive X-ray analysis device comprising means for carrying out this method reduces the dead pixels in a data set due to faulty pixel elements or pixel elements weighted with 0 in a simple manner. The use of individual detectors composed of several sensor chips eliminates disturbing influences of the edge regions during generation of data sets. Moreover, the recording region is increased and, with suitable selection of displacement of the sensor chips, the spatial resolution of the measurement is also improved.
Owner:BRUKER AXS
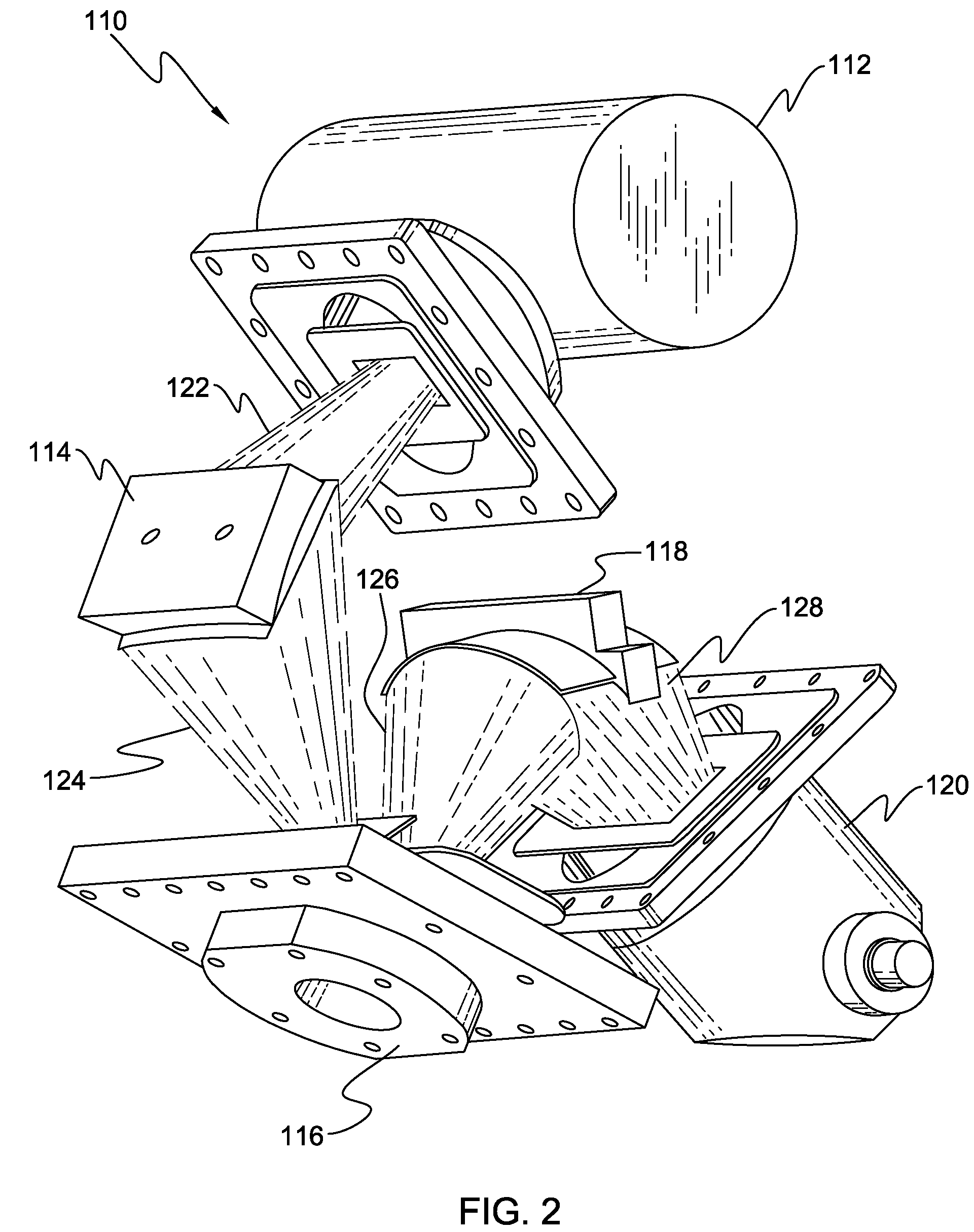
Highly aligned x-ray optic and source assembly for precision x-ray analysis applications
InactiveUS7738630B2NanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX ray analysisX-ray optics
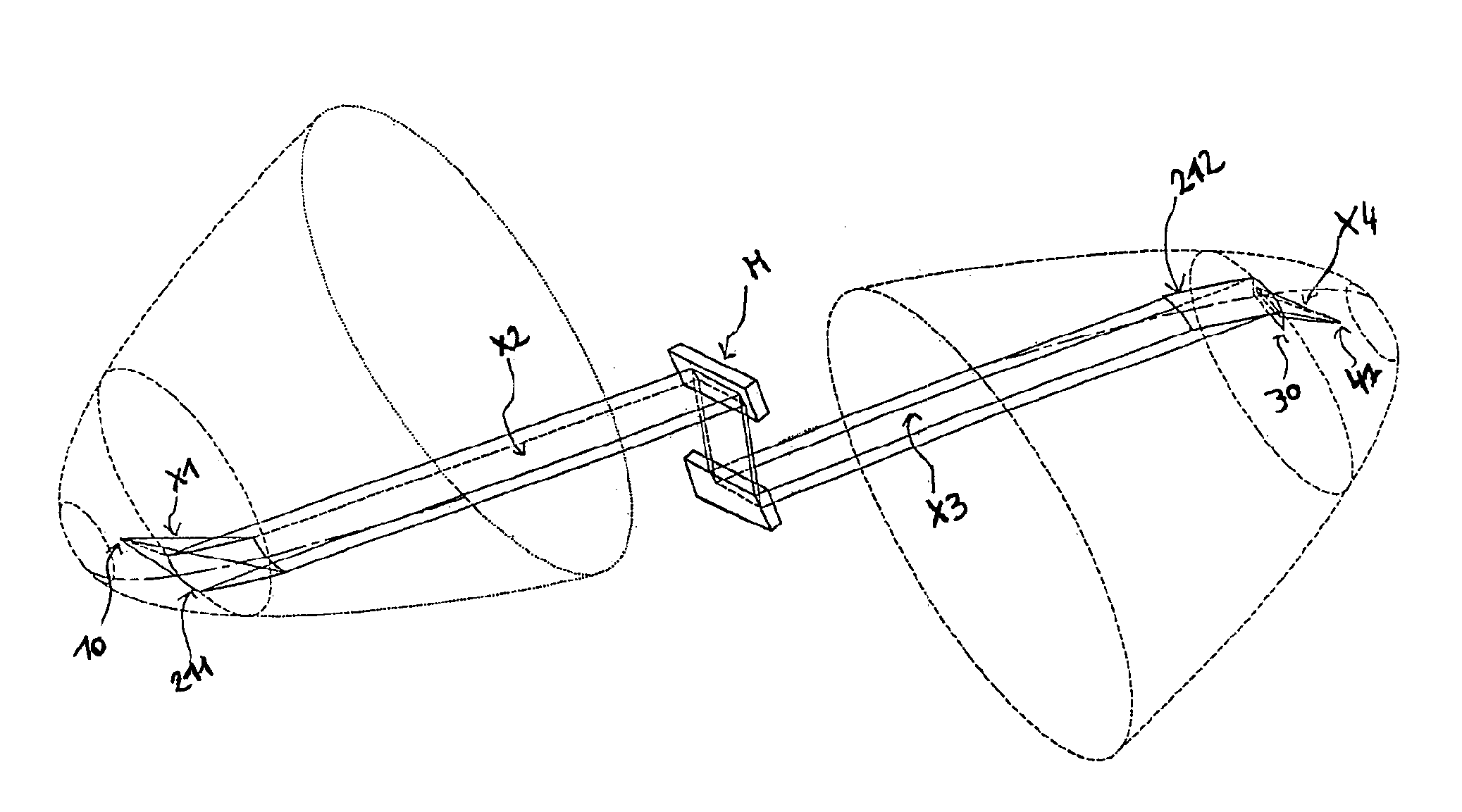
An x-ray analysis apparatus for illuminating a sample spot with an x-ray beam. An x-ray tube is provided having a source spot from which a diverging x-ray beam is produced, the source spot requiring alignment along a transmission axis passing through the sample spot. A first housing section is provided, to which the x-ray tube is attached, including mounting features for adjustably mounting the x-ray tube therein such that the source spot coincides with the transmission axis. A second housing section includes a second axis coinciding with the transmission axis; and at least one x-ray optic attached to the second housing section for receiving the diverging x-ray beam and directing the beam toward the sample spot. Complimentary mating surfaces may be provided to align the first and second sections, and the optics, to the transmission axis. A third housing section may also be provided, including an aperture through which the x-ray beam passes, and to which a detector may be attached.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
High strength tape articles from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
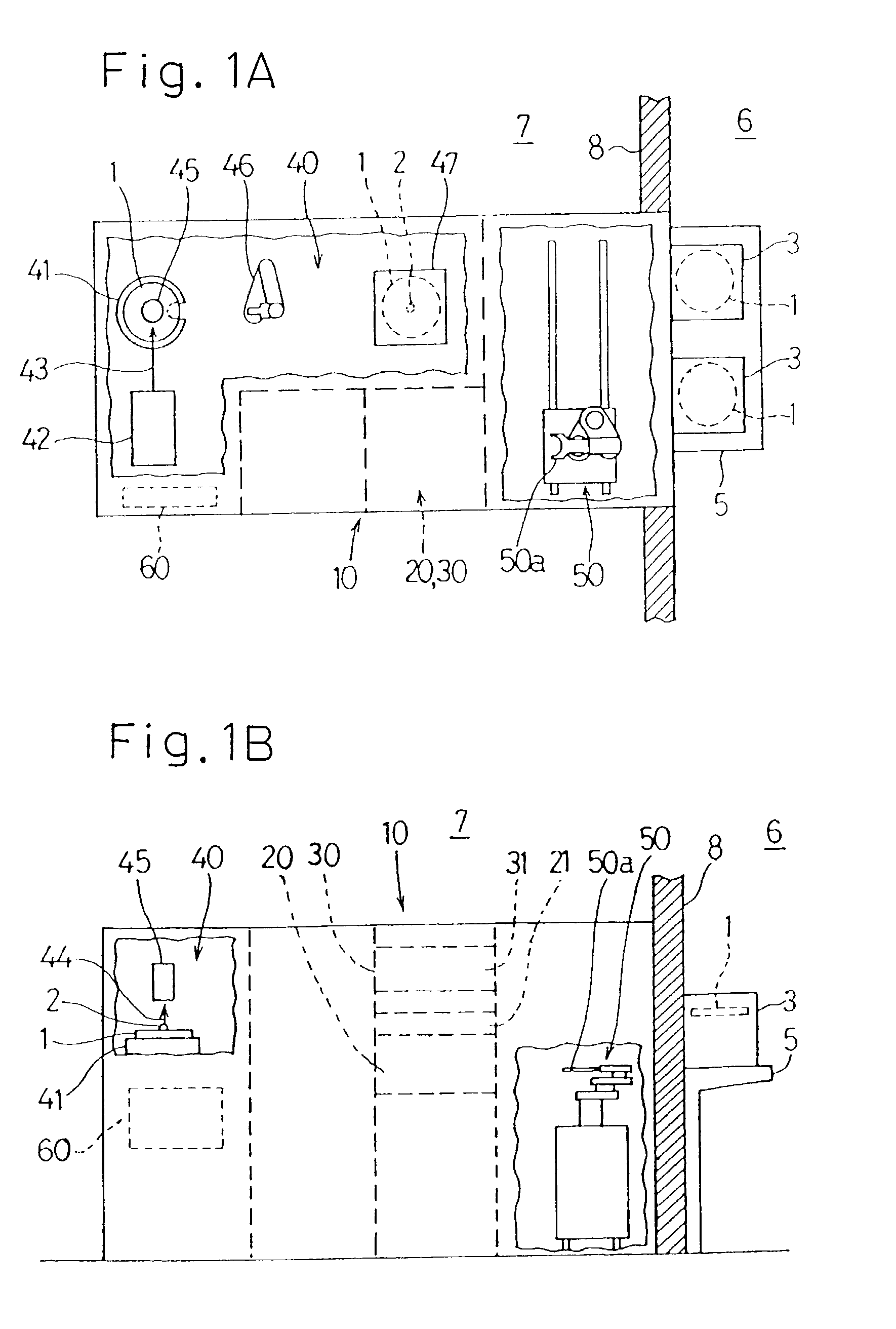
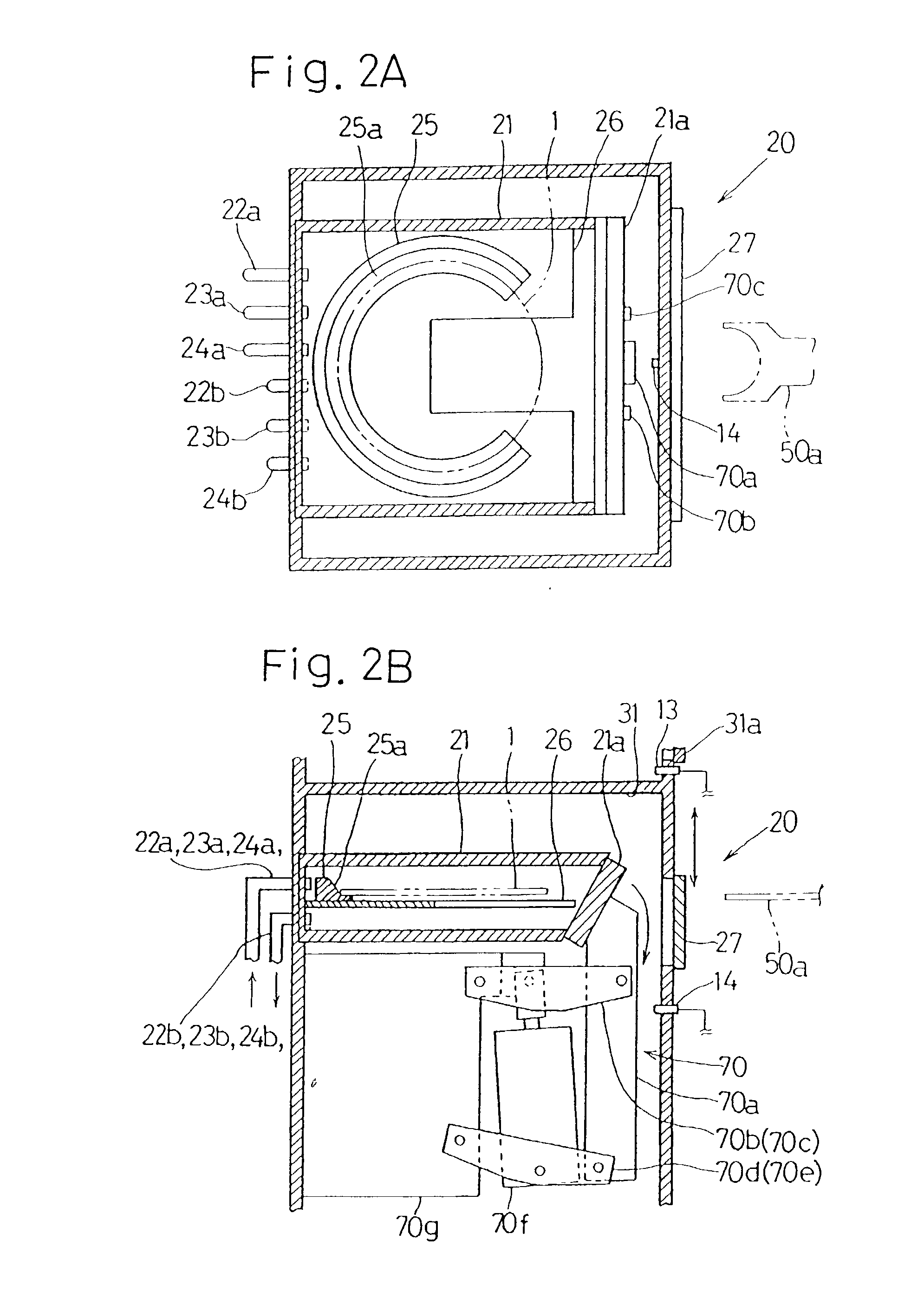
Sample preprocessing system for a fluorescent X-ray analysis and X-ray fluorescence spectrometric system using the same
InactiveUS20030053589A1Extended service lifeLiquid surface applicatorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationReactive gasFluorescence spectrometry
A sample preprocessing system for a fluorescent X-ray analysis includes a sample preprocessing apparatus for retaining on a surface of a substrate a substance to be measured that is found on the surface of the substrate, after such substance has been dissolved and subsequently dried, a transport apparatus for transporting the substrate, and a control apparatus for controlling the sample preprocessing apparatus and the transport apparatus. The control apparatus 60 after having confirmed that the pressure difference between inside and outside of the apparatus 10 (20, 30) and the concentration of the reactive gas within the apparatus are within a predetermined range causes automatically opening and closing shutters 21a, 27 and 31a to thereby avoid a possible corrosion of the apparatuses positioned outside the sample preprocessing apparatus while increasing the service lifetime thereof.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
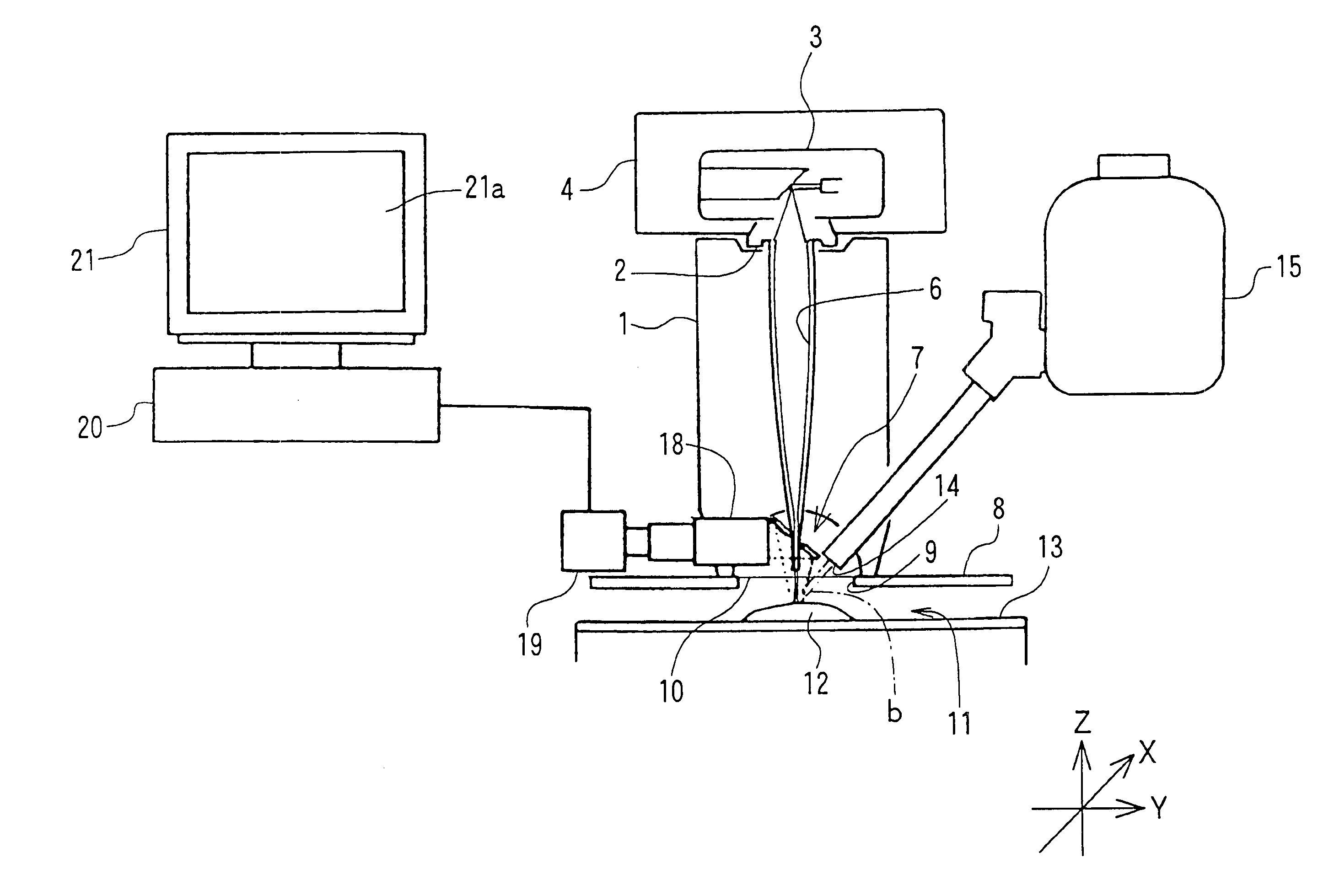
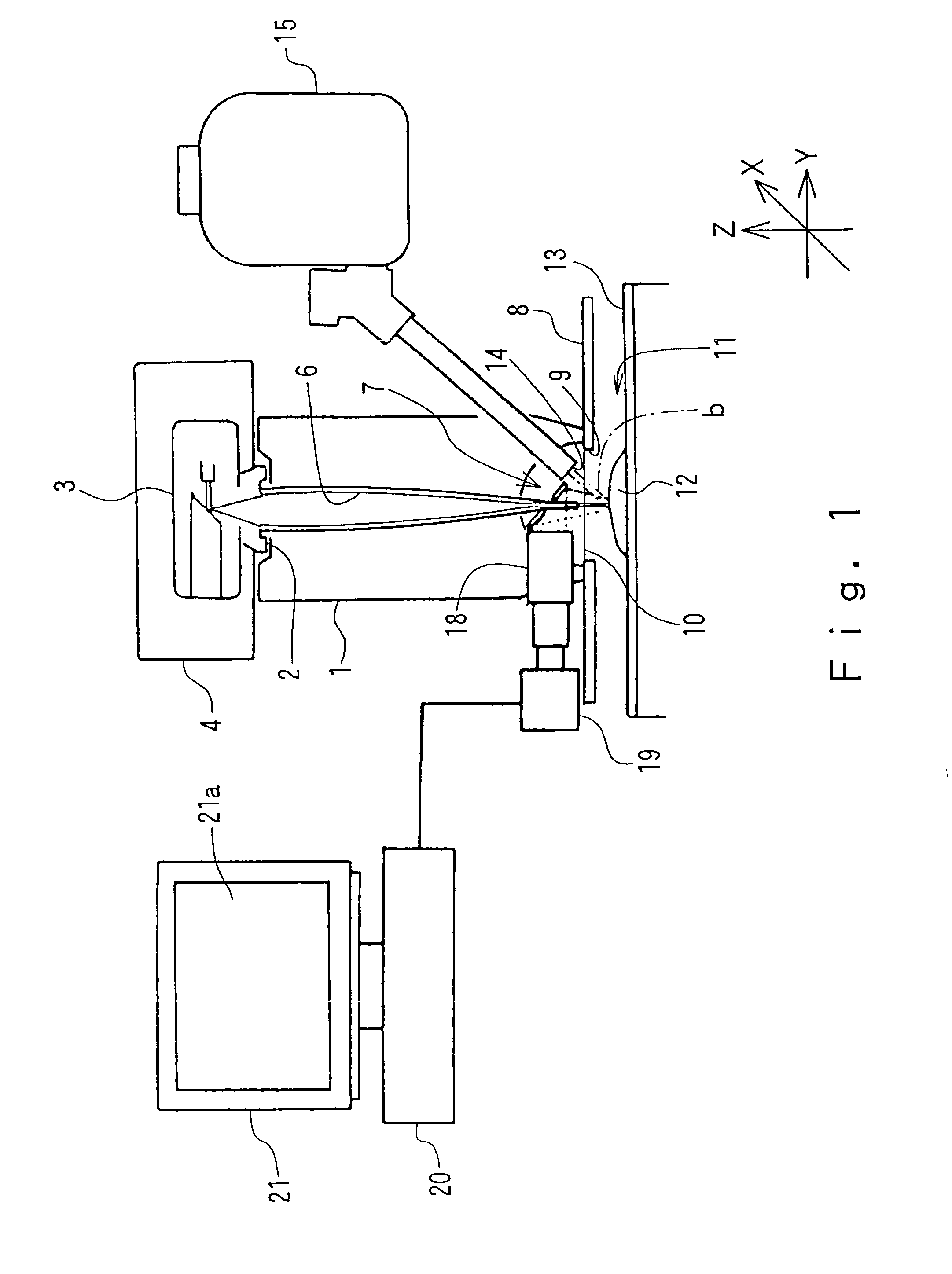
X-ray analyzer and x-ray analysis method
ActiveUS20100046700A1Avoid collisionEasy to analyzeX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayX-ray
An X-ray tube which irradiates a primary X-ray to an irradiation point on a sample, an X-ray detector which detects a characteristic X-ray and a scattered X-ray emitted from the sample and outputs a signal including energy information on the characteristic X-ray and scattered X-ray, an analyzer which analyzes the signal, a sample stage on which the sample is placed, a moving mechanism which moves the sample on the sample stage, the X-ray tube, and the X-ray detector relative to each other, a height measuring mechanism which measures a maximum height of the sample, and a control unit which adjusts the distance between the sample and the X-ray tube and the distance between the sample and the X-ray detector by controlling the moving mechanism on the basis of the measured maximum height of the sample, are included.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
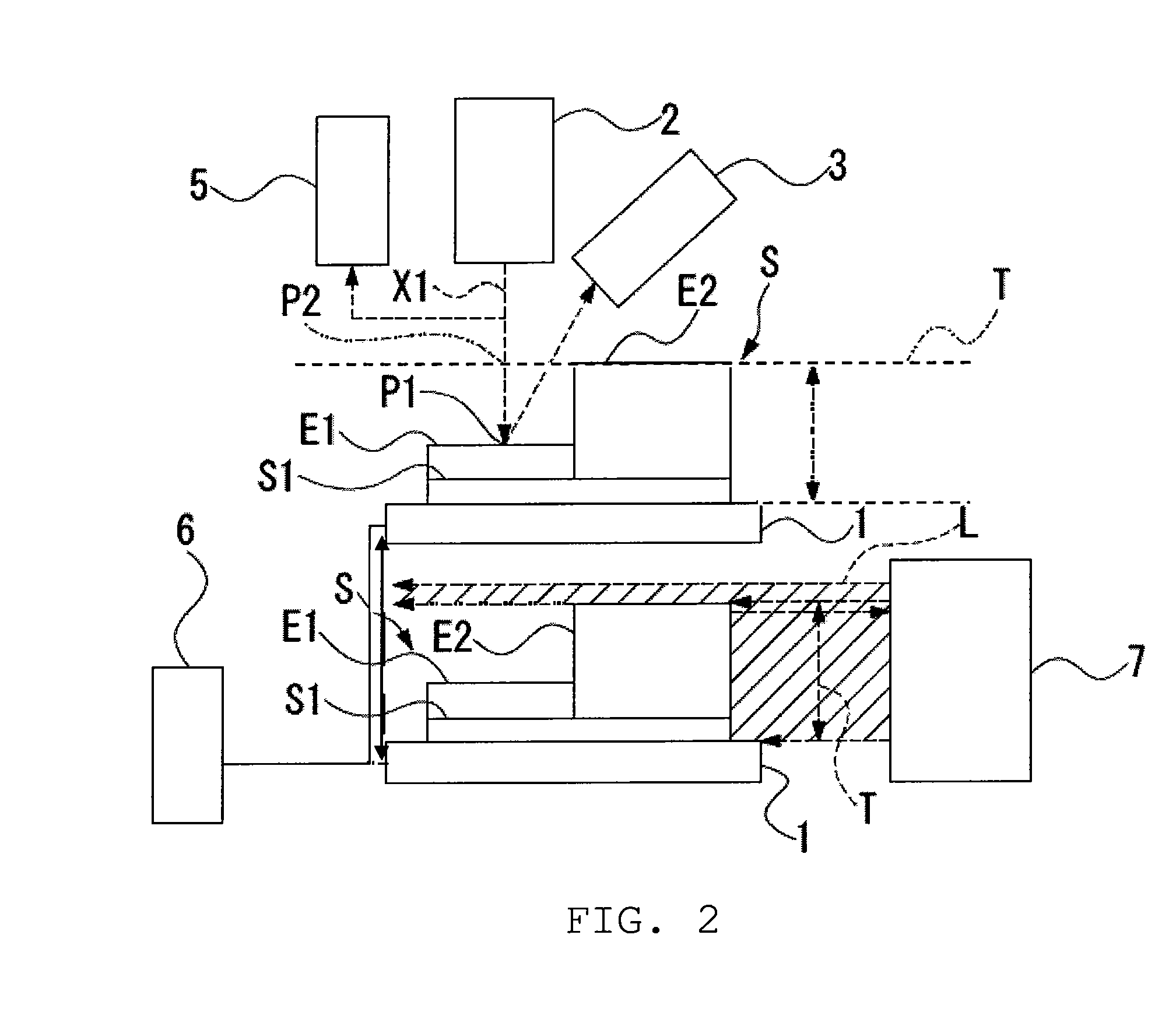
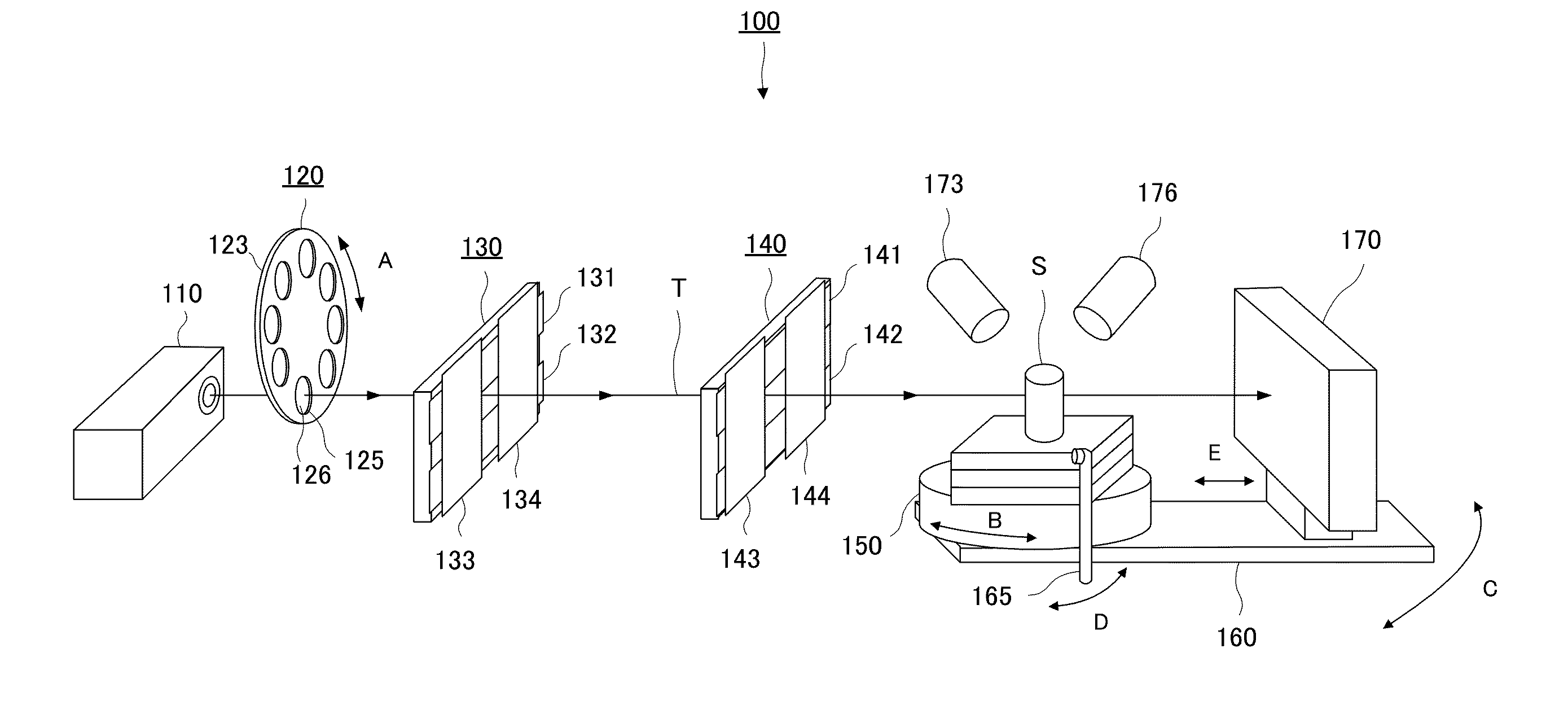
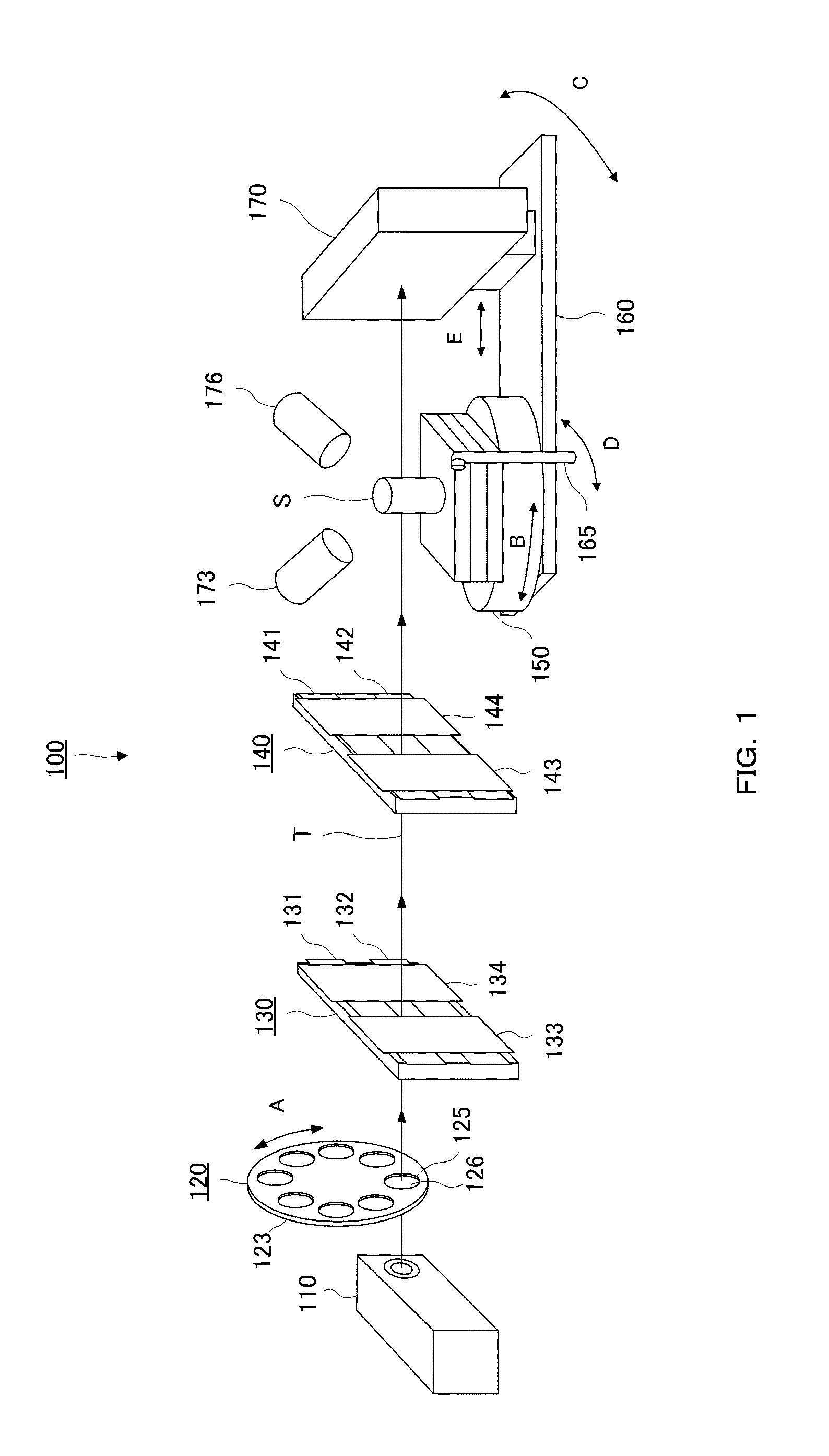
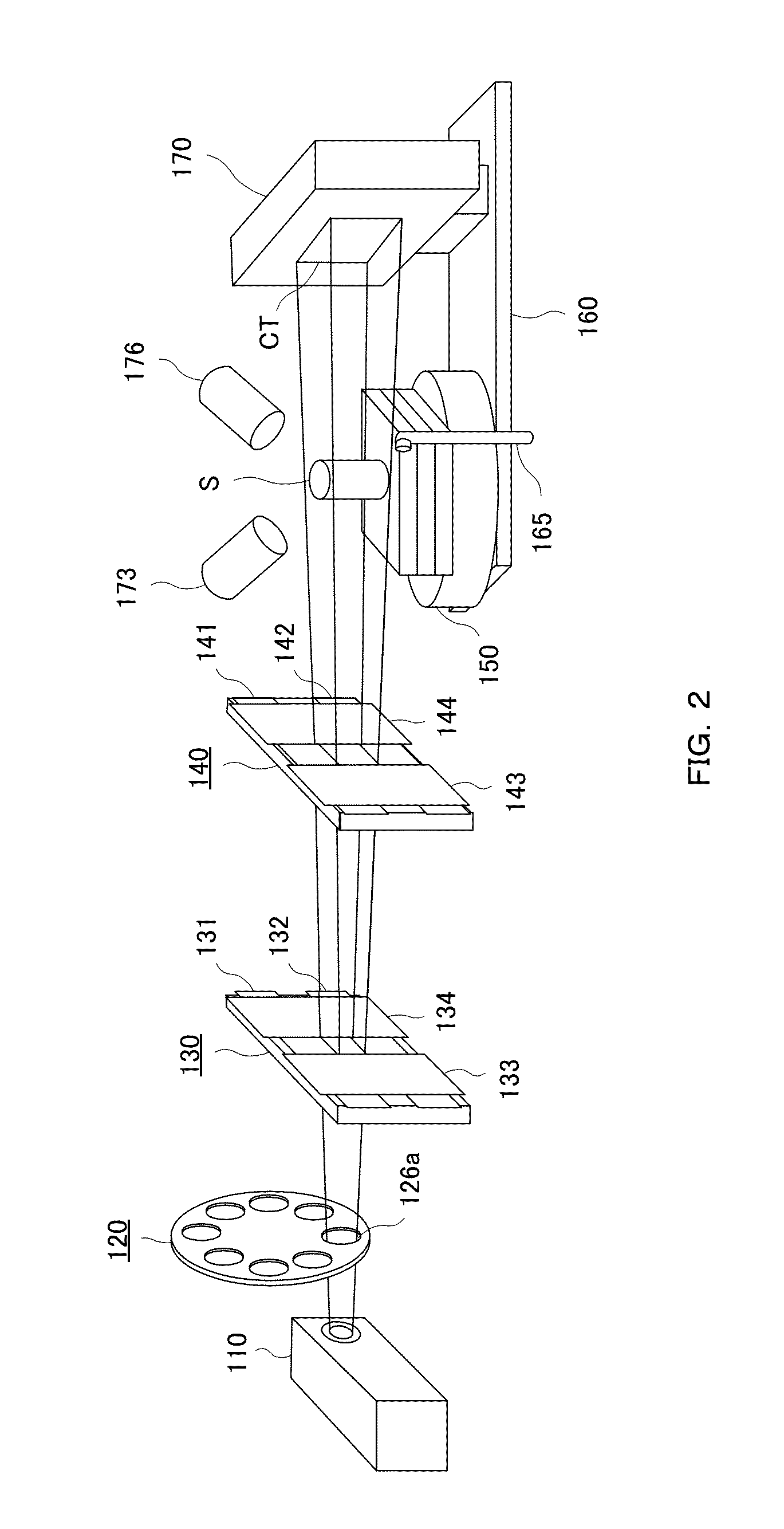
X-ray composite apparatus
InactiveUS20130251100A1Efficient executionRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusTwo dimensional detectorFluorescence
There is provided an X-ray composite apparatus capable of performing, with one unit, X-ray CT and element analysis by fluorescent X-rays. The X-ray composite apparatus 100 includes an X-ray source 110 generating cone beam X-rays, a sample support 150 holding a sample S, collimator parts 130 and 140 capable of narrowing the cone beam X-rays to form parallel X-rays, depending on the intended use, between the X-ray source and the sample support 150, a two-dimensional detector 170 detecting the cone beam X-rays transmitted through the sample S, and a fluorescent X-ray detector 176 detecting fluorescent X-rays radiated from the sample S, and when the apparatus is used for X-ray CT, the apparatus irradiates the sample with the cone beam X-rays, while when the apparatus is used for fluorescent X-ray analysis, the apparatus irradiates the sample S with the parallel X-rays.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Fluorescent X-ray analyzer
InactiveUS6337897B1X-ray spectral distribution measurementHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionFluorescenceX-ray
A fluorescent X-ray analyzer includes a detector (6) for detecting fluorescent X-rays (5) emitted from a sample piece (1) to be analyzed, and a first collimator (10) disposed between the sample piece (1) and the detector (6) supported for movement between inserted and retracted positions with respect to a path of travel of the fluorescent X-rays (5) towards the detector (6). The first collimator (10) comprises a wall (11) adjacent the sample piece (1) that is stepped to provide stepped wall segments (11a, 11b, 11c) having respective apertures (12a, 12b, 12c) of varying diameters defined therein. The smaller the aperture, the closer it is to the sample piece (1) when one of the apertures (12a, 12b, 12c) is selected according to a size of a target area of the sample piece (1) to be measured and is then brought in register with the path of travel of the fluorescent X-rays (5) towards the detector (6).
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
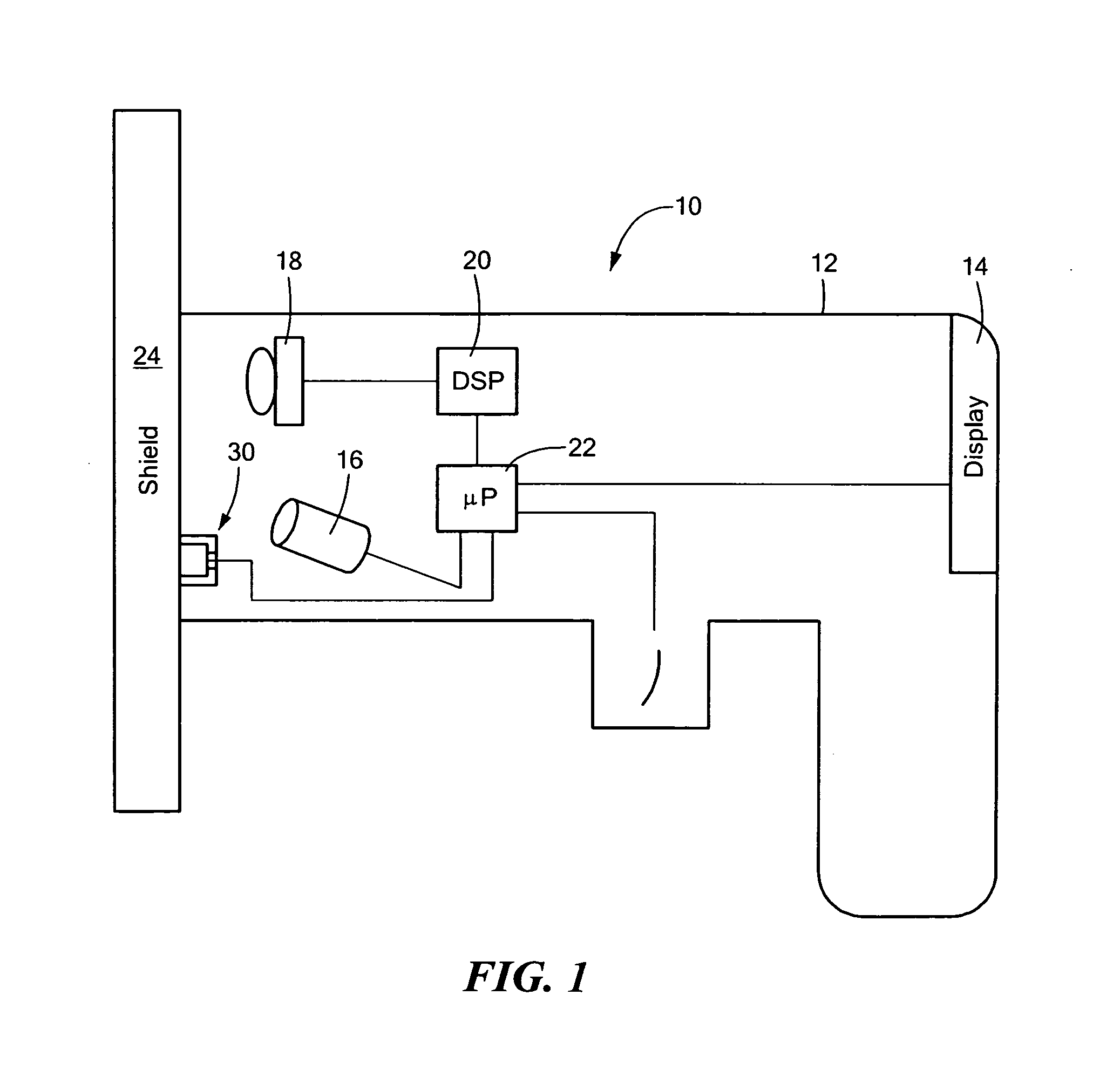
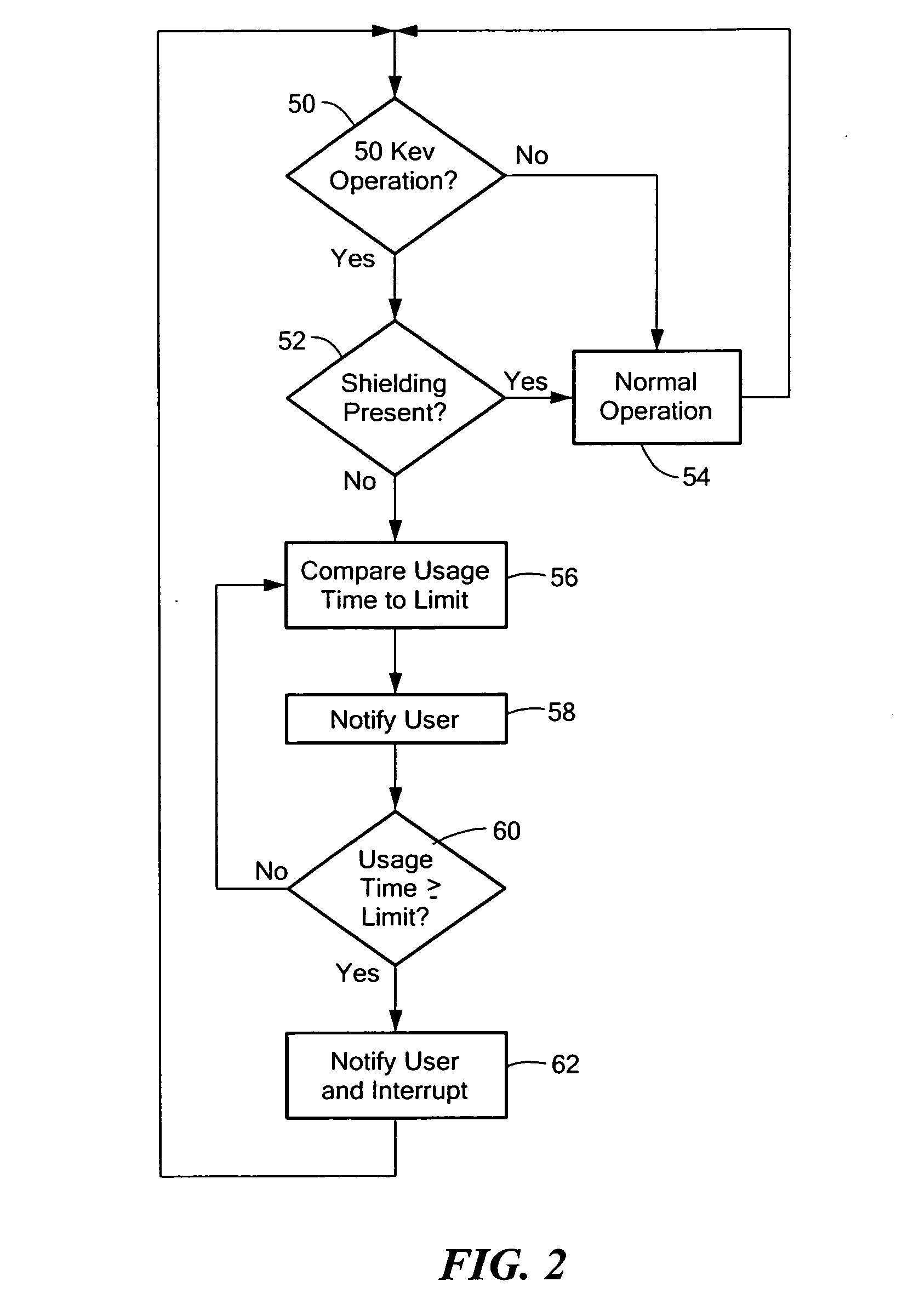
X-ray analysis apparatus with radiation monitoring feature
ActiveUS20130003923A1Reduce radiation levelsWeight increaseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementFluorescenceEngineering
An XRF analysis apparatus includes a housing with a source of penetrating radiation to be directed at a sample and a detector for detecting fluoresced radiation from the sample. A shield is attachable to the housing to protect the user from radiation and a safety interlock is configured to detect whether or not the shield is attached to the housing. A controller is responsive to the safety interlock, and configured to monitor usage of the source of radiation at or above a predetermined power level when the shield is not attached to the housing and provide an output signal when the monitored usage of the source of penetrating radiation at or above the predetermined power level without the shield attached to the housing exceeds one or more predetermined thresholds.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA
X-ray analysis apparatus and method
InactiveUS6965663B2Accurately determinedHigh sensitivityX-ray spectral distribution measurementElectrode and associated part arrangementsSoft x rayImage resolution
This invention provides an X-ray analysis apparatus and method capable of simply and accurately determining the position of analysis in a sample from an optical image of it without lowering the sensitivity and / or the spatial resolution in light element analysis. The X-ray analysis apparatus of the present invention irradiates a sample with X-rays narrowed down by means of an X-ray guide member from above the sample in which said sample is directly irradiated with X-rays from said X-ray guide member and an optical image of said sample is obtained in the direction coaxial with said X-ray guide member.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
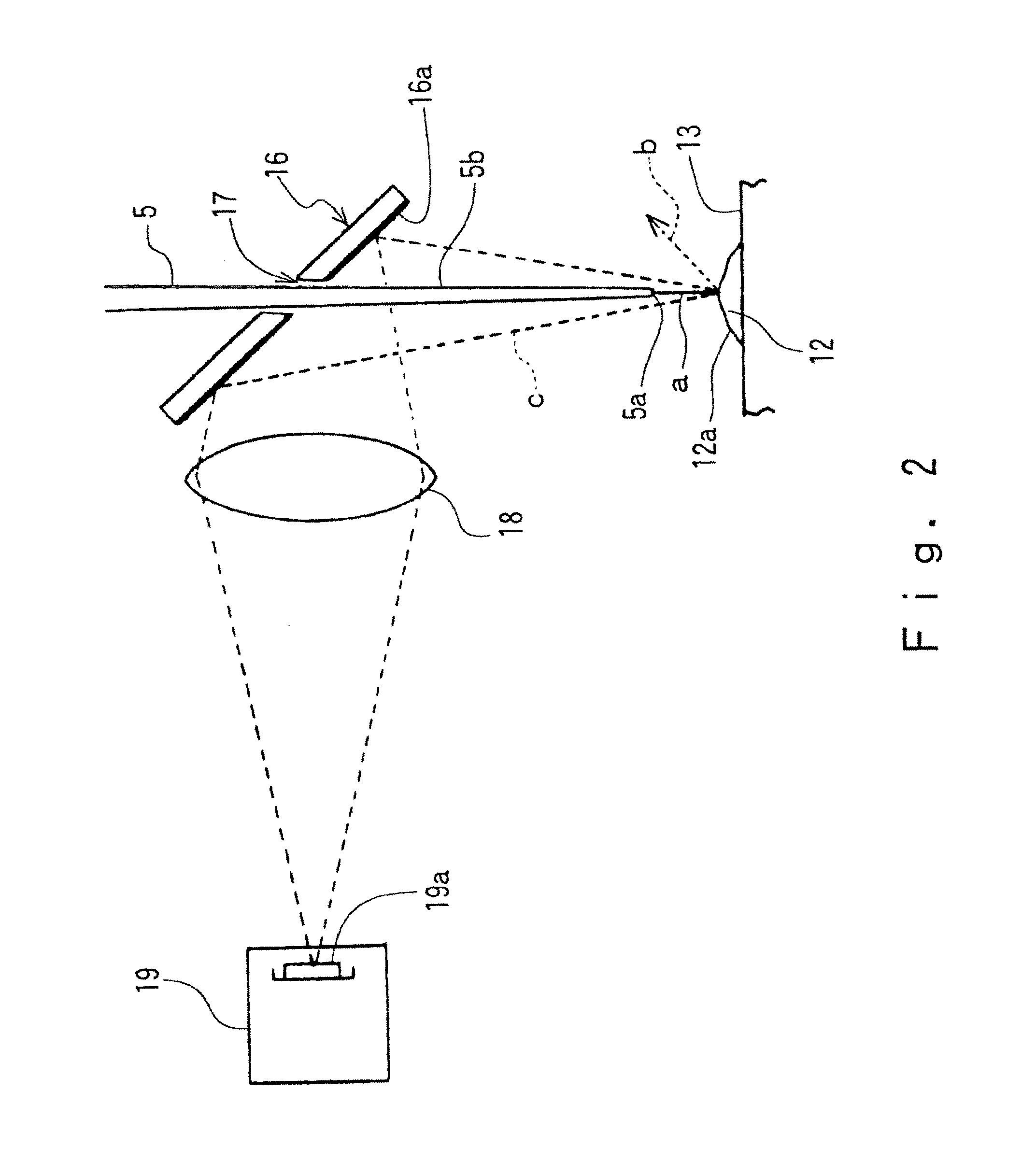
Optical alignment of X-ray microanalyzers
InactiveUS7023954B2Precise alignmentX-ray spectral distribution measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansSoft x rayOptical radiation
A method for X-ray analysis of a sample includes aligning an optical radiation source with an X-ray excitation source, so that a spot on the sample that is irradiated by an X-ray beam generated by the X-ray excitation source is illuminated with optical radiation generated by the optical radiation source. Optical radiation that is reflected from the sample is used to generate a first signal, which is indicative of an alignment of the spot on the sample. The X-ray beam is aligned, responsively to the first signal, so that the spot coincides with a target area of the sample. X-ray photons received from the spot on the sample, after aligning the X-ray beam, are used in generating a second signal that is indicative of a characteristic of the target area.
Owner:BRUKER TECH LTD
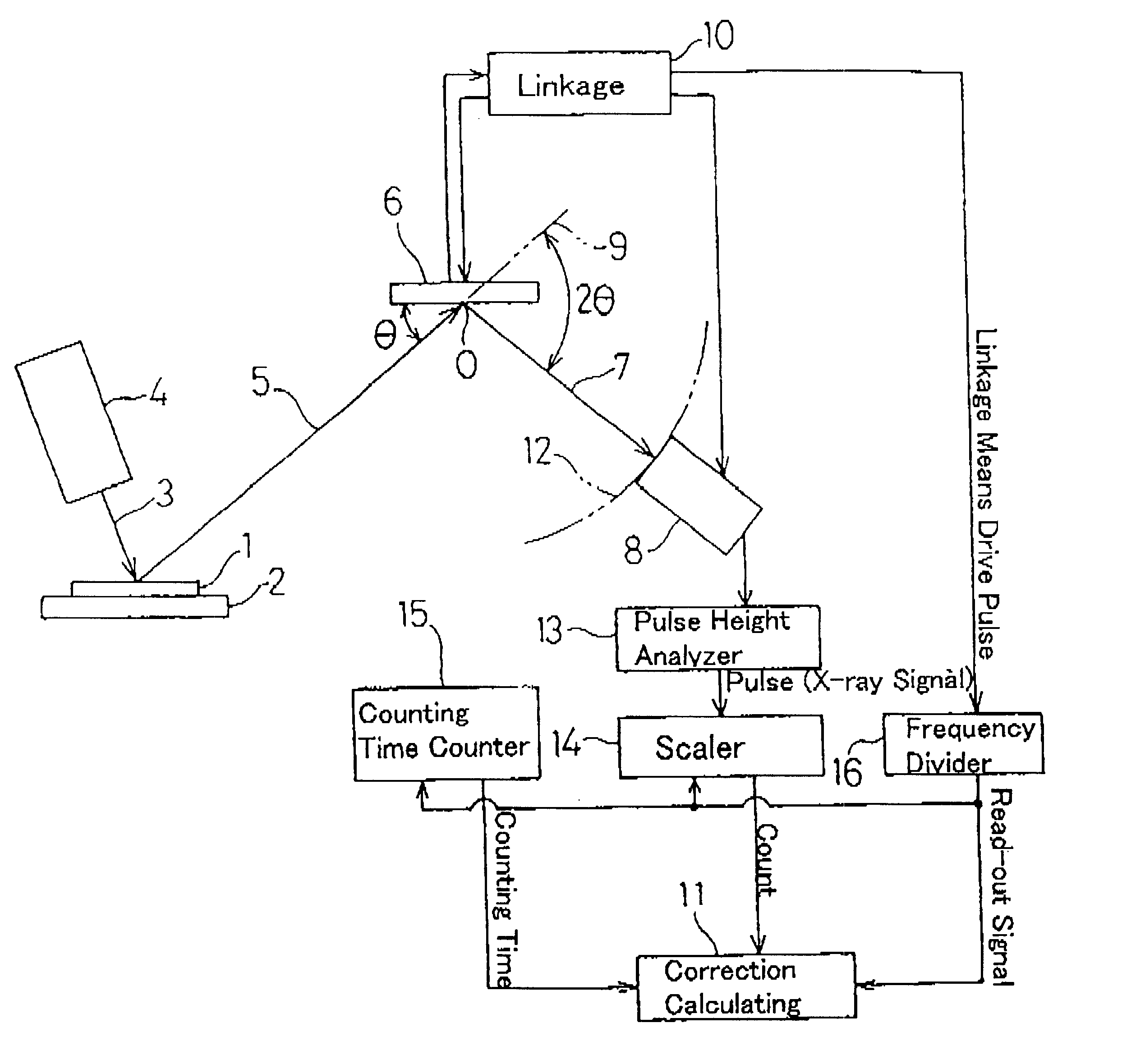
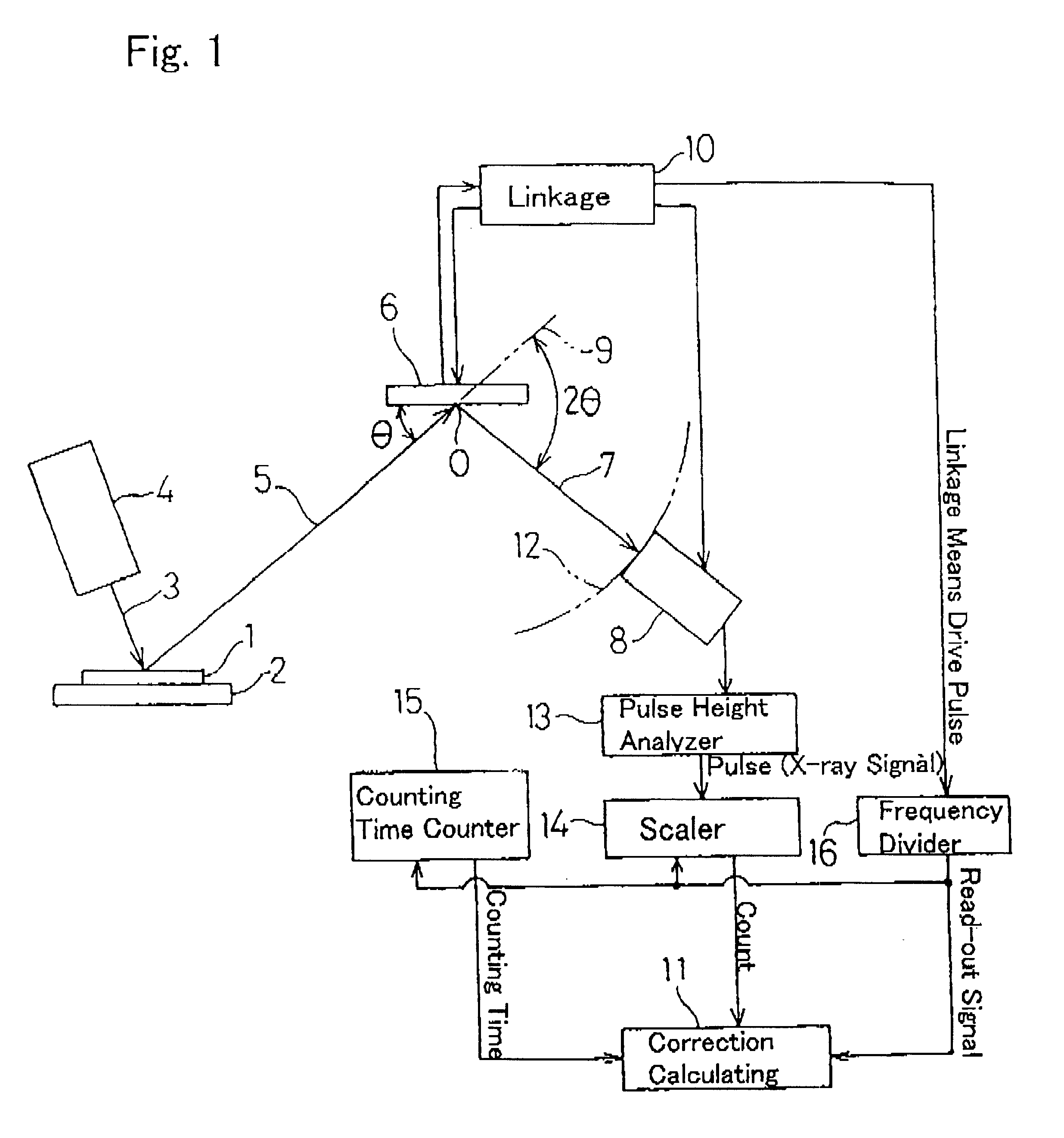
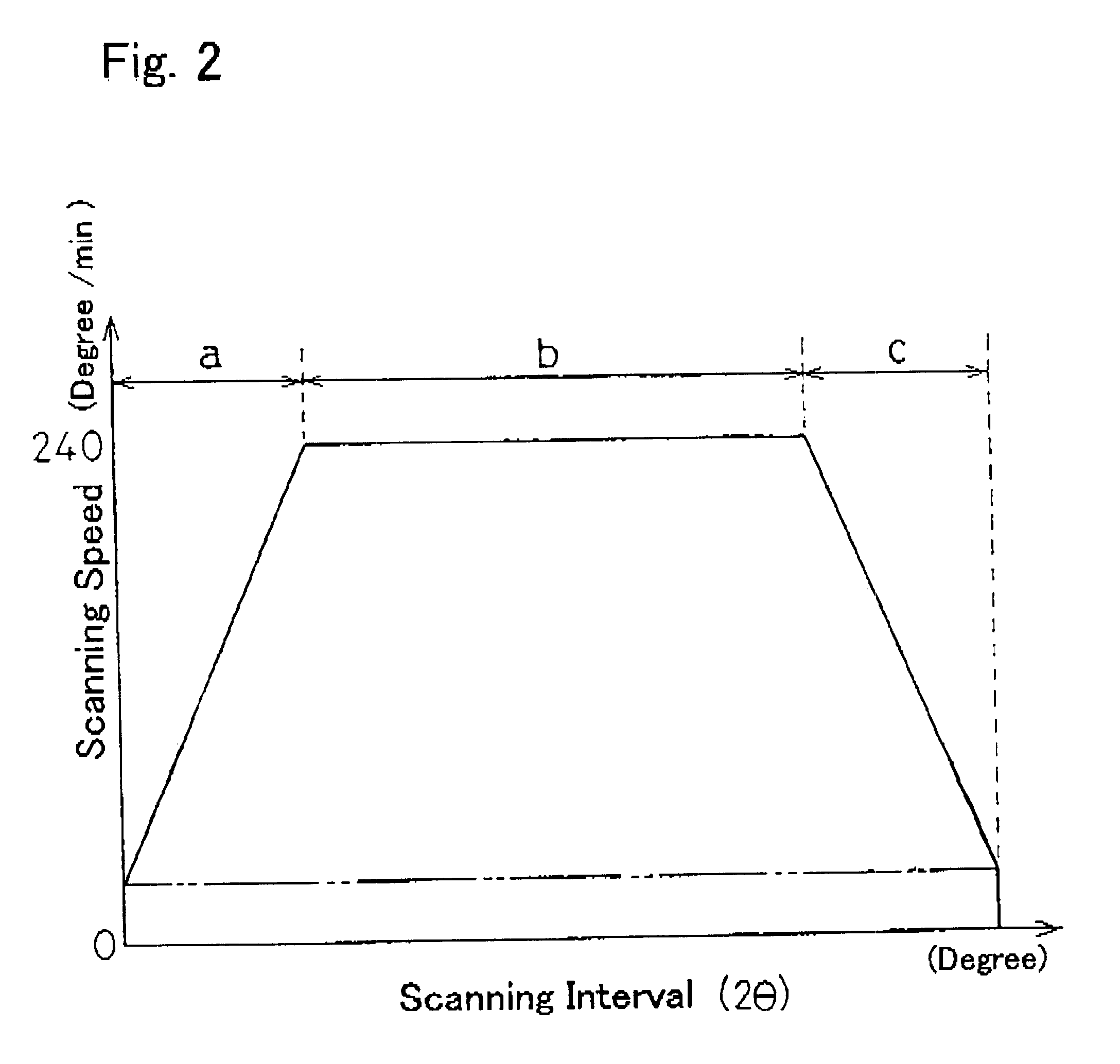
Continuously scanning X-ray analyzer having improved readiness and accuracy
InactiveUS6404847B1X-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSoft x rayContinuous scanning
An X-ray analyzing apparatus capable of accomplish a rapid and accurate analysis is provided in which a detector for X-rays is rotated or shuttled to perform a continuous scanning. Determining a counting time for each of fixed scanning intervals by means of a counting time counter 15 and a frequency divider 16, correction of a count for each scanning interval is made by a correction calculating means 11 on the basis of the corresponding counting time.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Moveable transparent barrier for x-ray analysis of a pressurized sample
ActiveUS7277527B2Increase and decrease pressureReduce frictionX-ray spectral distribution measurementX-ray tube electrodesParticle beamX-ray
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
Sliding sample cell insertion and removal apparatus for x-ray analyzer
A sample cell insertion and removal apparatus for an analysis instrument, including a horizontally sliding frame; a sample cell carriage movably mounted to the sliding frame, the sample cell carriage including an area to hold a sample cell; wherein upon sliding into and out of the instrument, the sample cell carriage is moved horizontally and vertically into and out of an analysis position. This instrument may include a radiation shielded enclosure into and out of which the apparatus slides, and an x-ray analysis engine which transmits x-rays upwards towards the sample cell which projects from a bottom of the apparatus. The disclosed sample cell is especially suited for an x-ray analysis engine having a focal spot requiring alignment with the sample in the sample cell.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
X-ray tube and method and apparatus for analyzing fluid streams using x-rays
InactiveUS20050031073A1Improve stabilityX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation/particle handlingX-rayPetroleum
A method and apparatus for analyzing fluids by means of x-ray fluorescence. The method and apparatus are applicable to any fluid, including liquids and gases, having at least one component that emits x-ray fluorescence when exposed to x-rays. The apparatus includes an x-ray source (82) including an x-ray tube (64) having improved heat dissipating properties due to the thermal coupling of the x-ray tube with a thermally-conductive, dielectric material (70, 1150). The x-ray tube also includes means for aligning (100, 2150, 2715) the x-ray tube with the x-ray source housing whereby the orientation of the x-ray beam produced by the x-ray source can be optimized, and stabilized various over operating conditions. The method and apparatus may also include an x-ray detector having a small-area, for example, a PIN-diode type semiconductor x-ray detector (120), that can provide effective x-ray detection at room temperature. One aspect of the disclosed invention is most amenable to the analysis of sulfur in petroleum-based fuels.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com