Patents
Literature
468 results about "Catoptrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
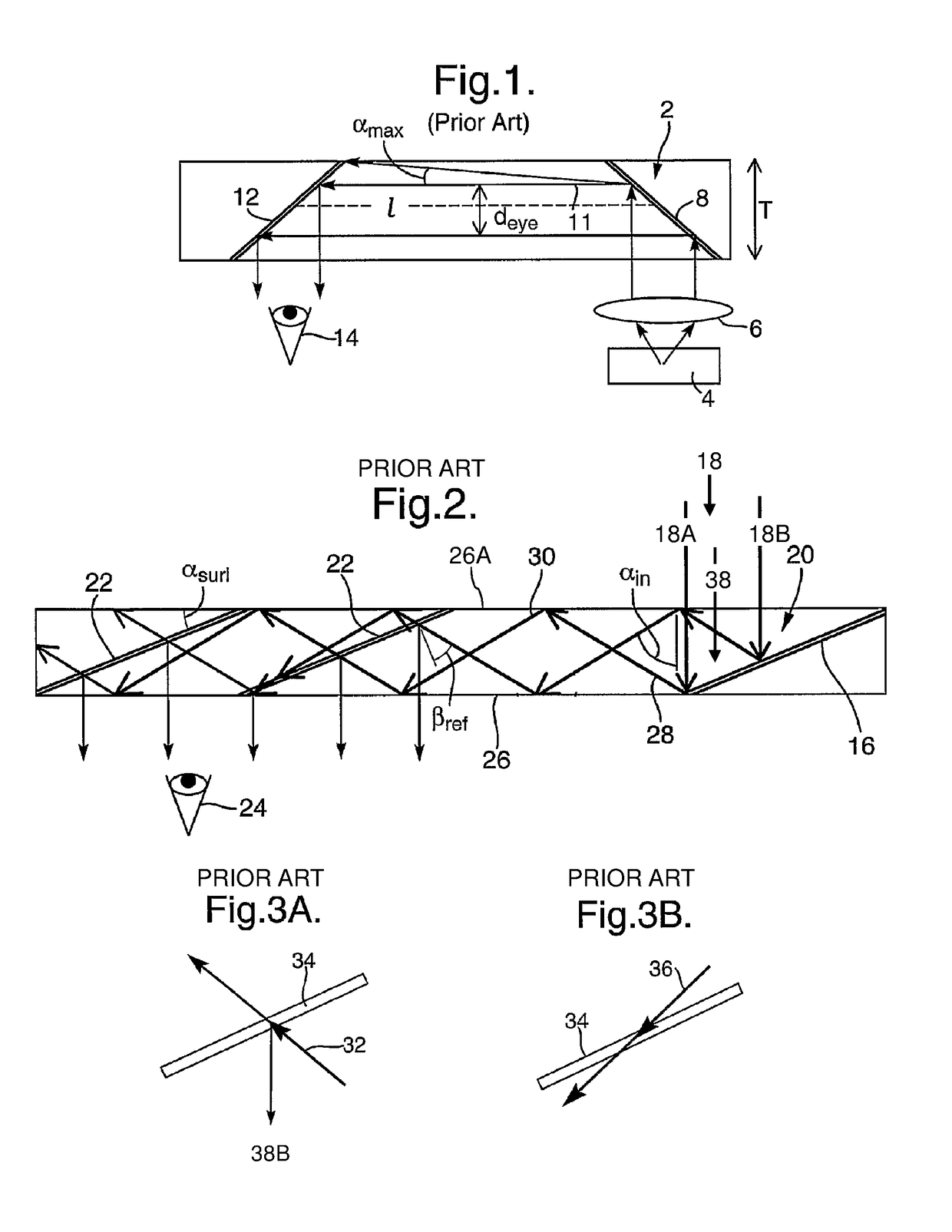
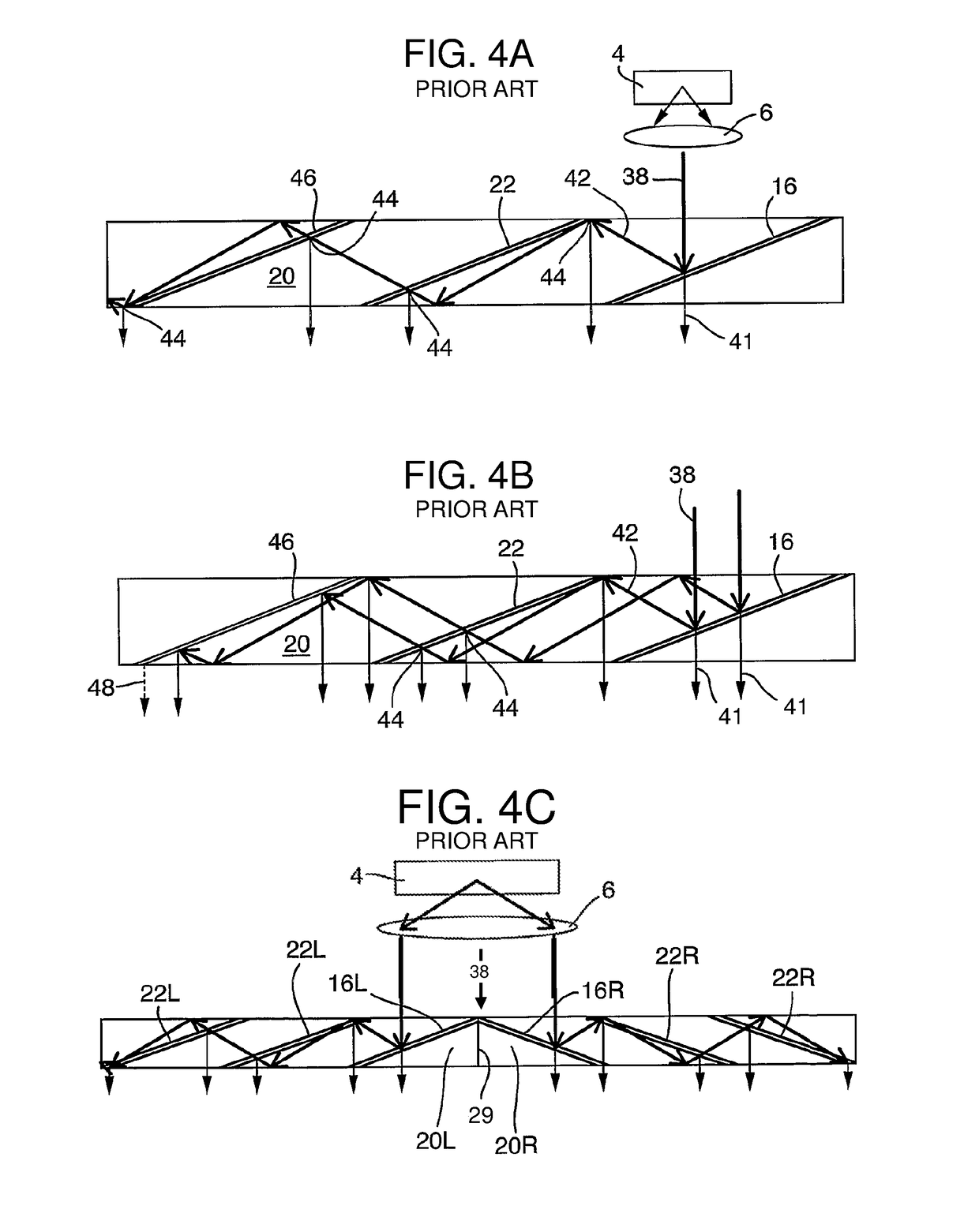
Catoptrics (from Greek: κατοπτρικός katoptrikós, "specular", from Greek: κάτοπτρον katoptron "mirror") deals with the phenomena of reflected light and image-forming optical systems using mirrors. A catoptric system is also called a catopter (catoptre).
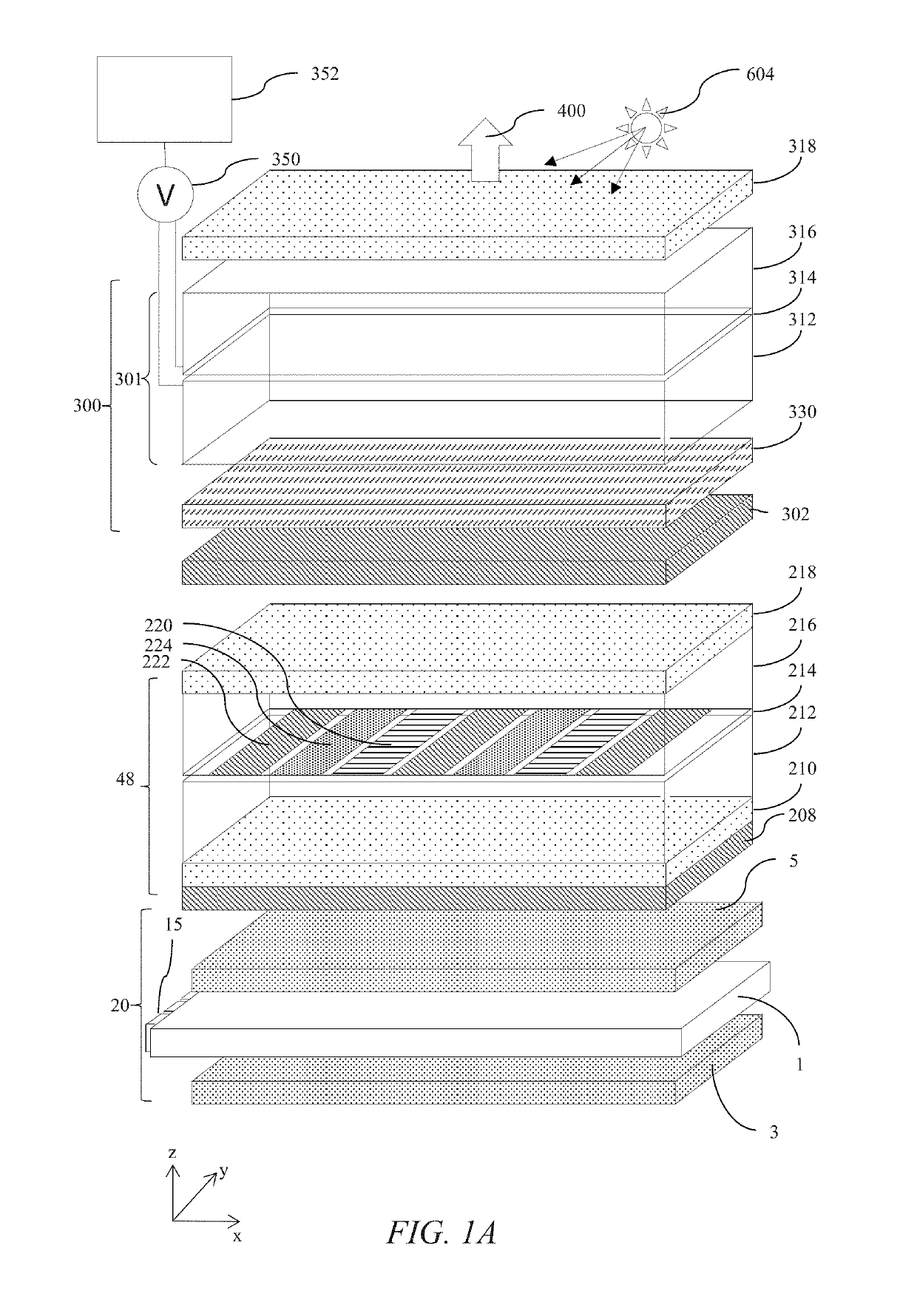
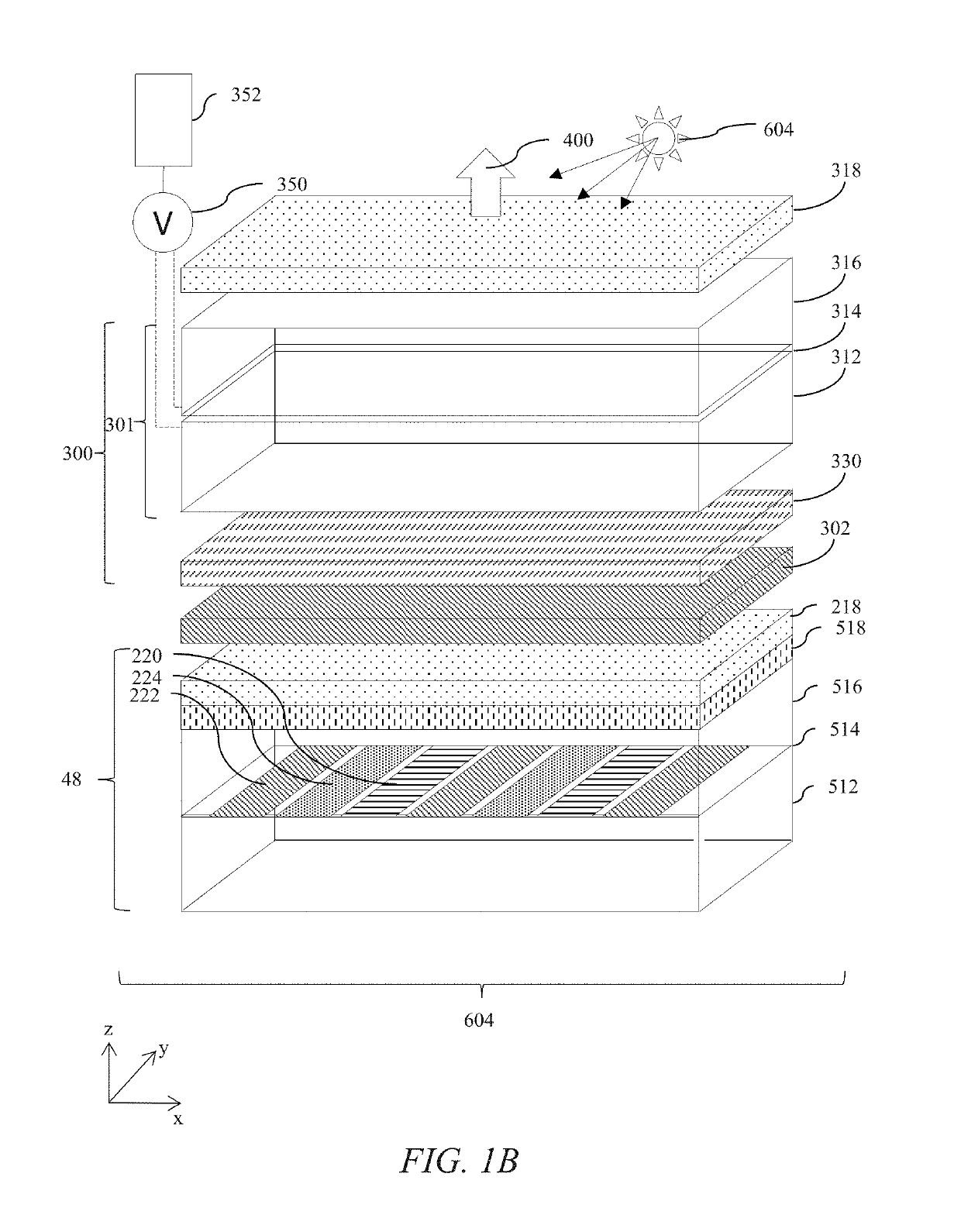
Electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20120293858A1Rule out the possibilityNon-linear opticsOptical elementsCatoptricsSelective reflection
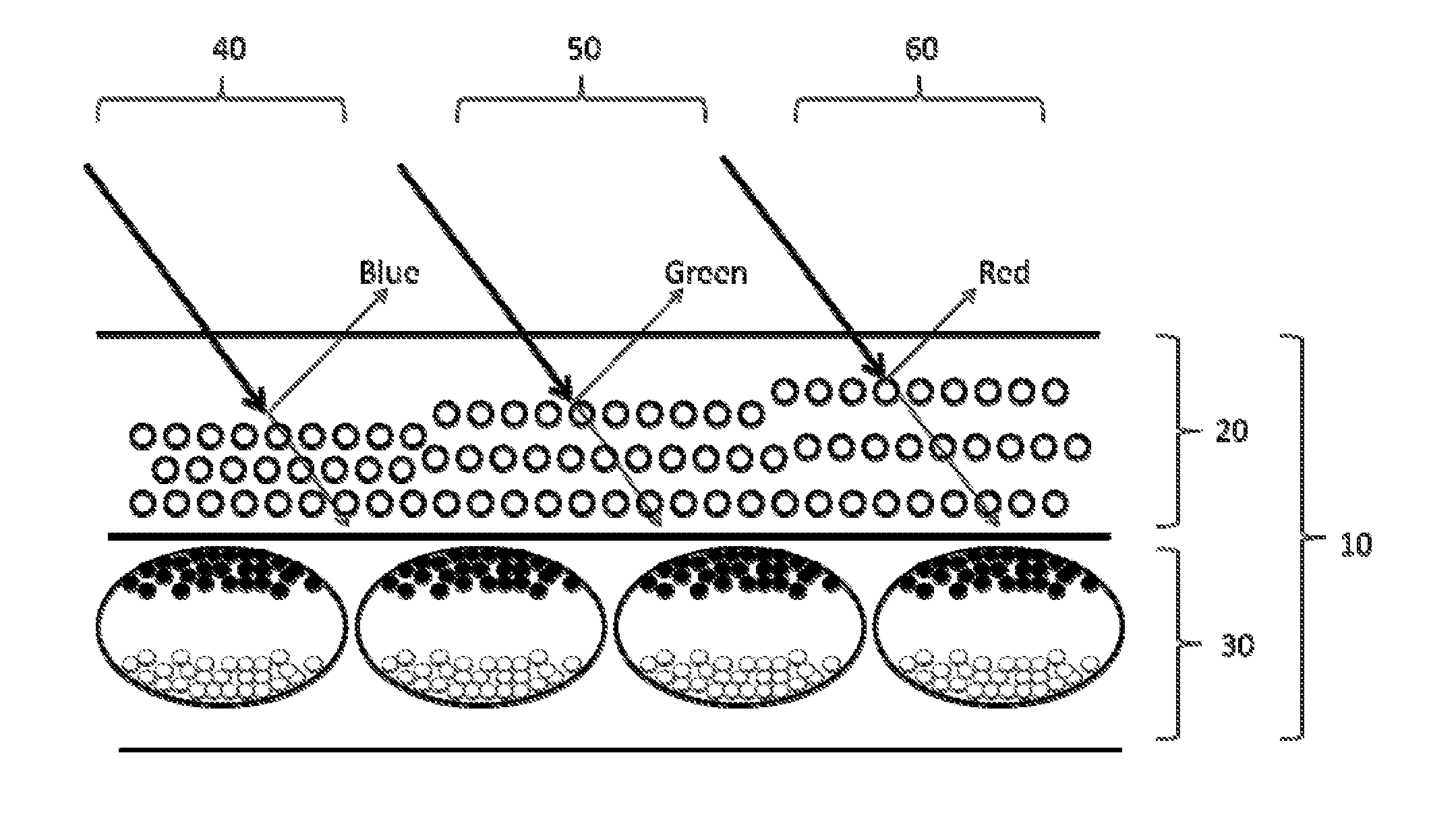
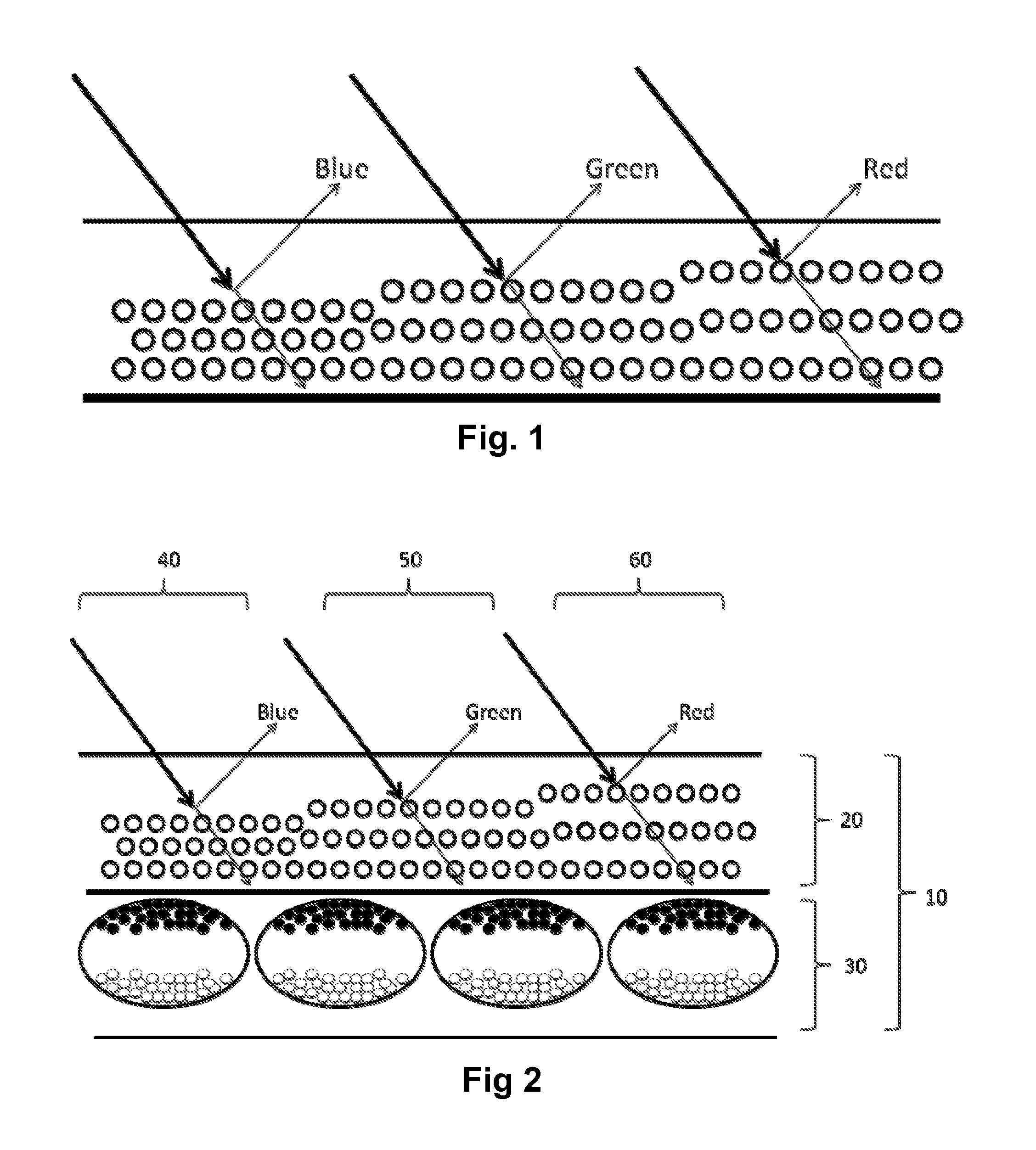
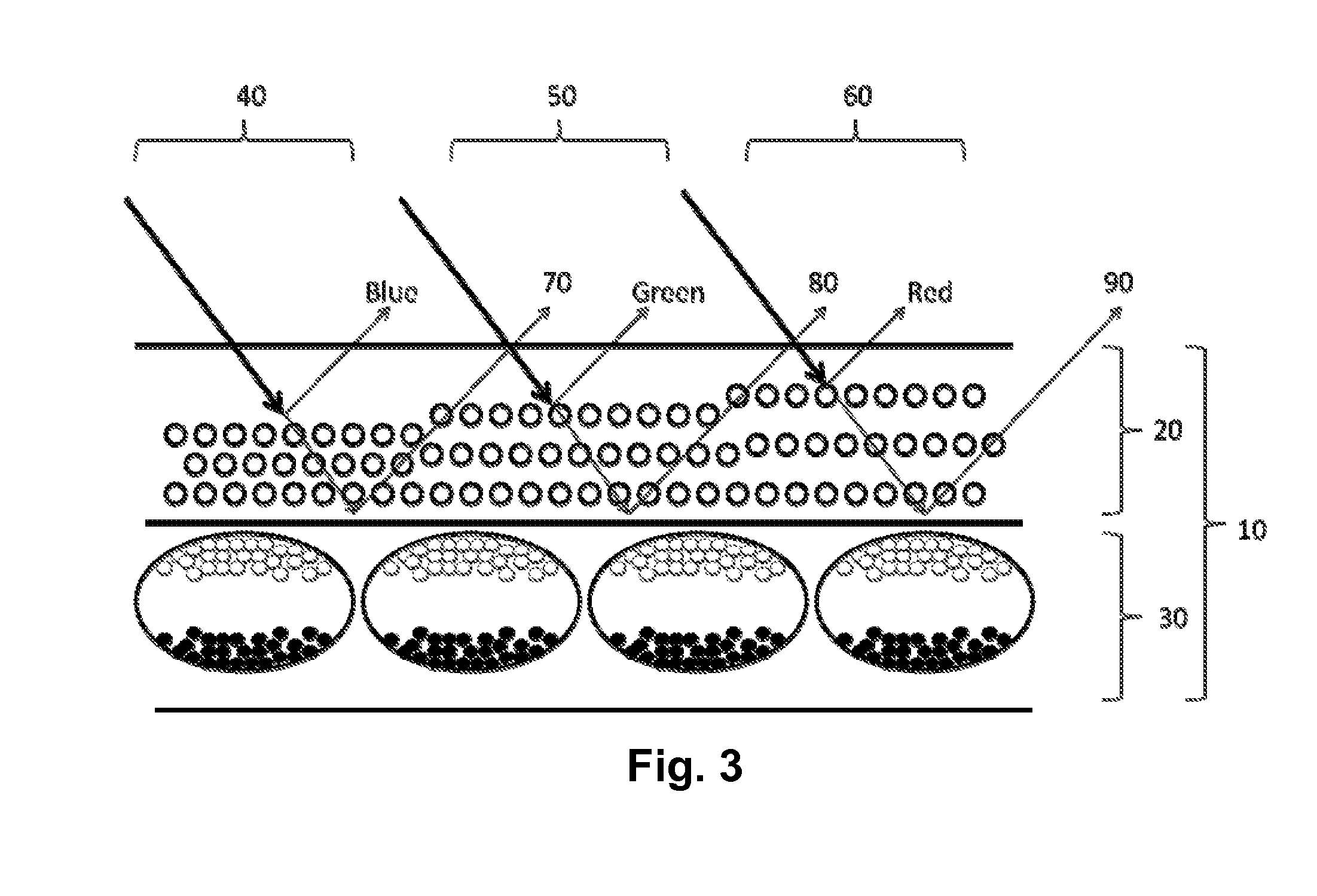
A wavelength selective reflection display (10) comprises a wavelength selective reflection medium (20) and a backing member (30) having a first, non-reflective optical state, and a second, reflective optical state. Both the wavelength selective reflection medium (20) and the backing member (30) are divided into pixels (40, 50, 60), and the backing member (30) is switchable between its first and second optical states on a pixel-by-pixel basis. The pixels of the backing member (30) are substantially aligned with those of the wavelength selective reflection medium (20).
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Light-modulating element, display element, and exposure element
InactiveUS7050219B2Shorten the light pathImprove efficiencyNon-linear opticsOptical elementsCatoptricsCoupling
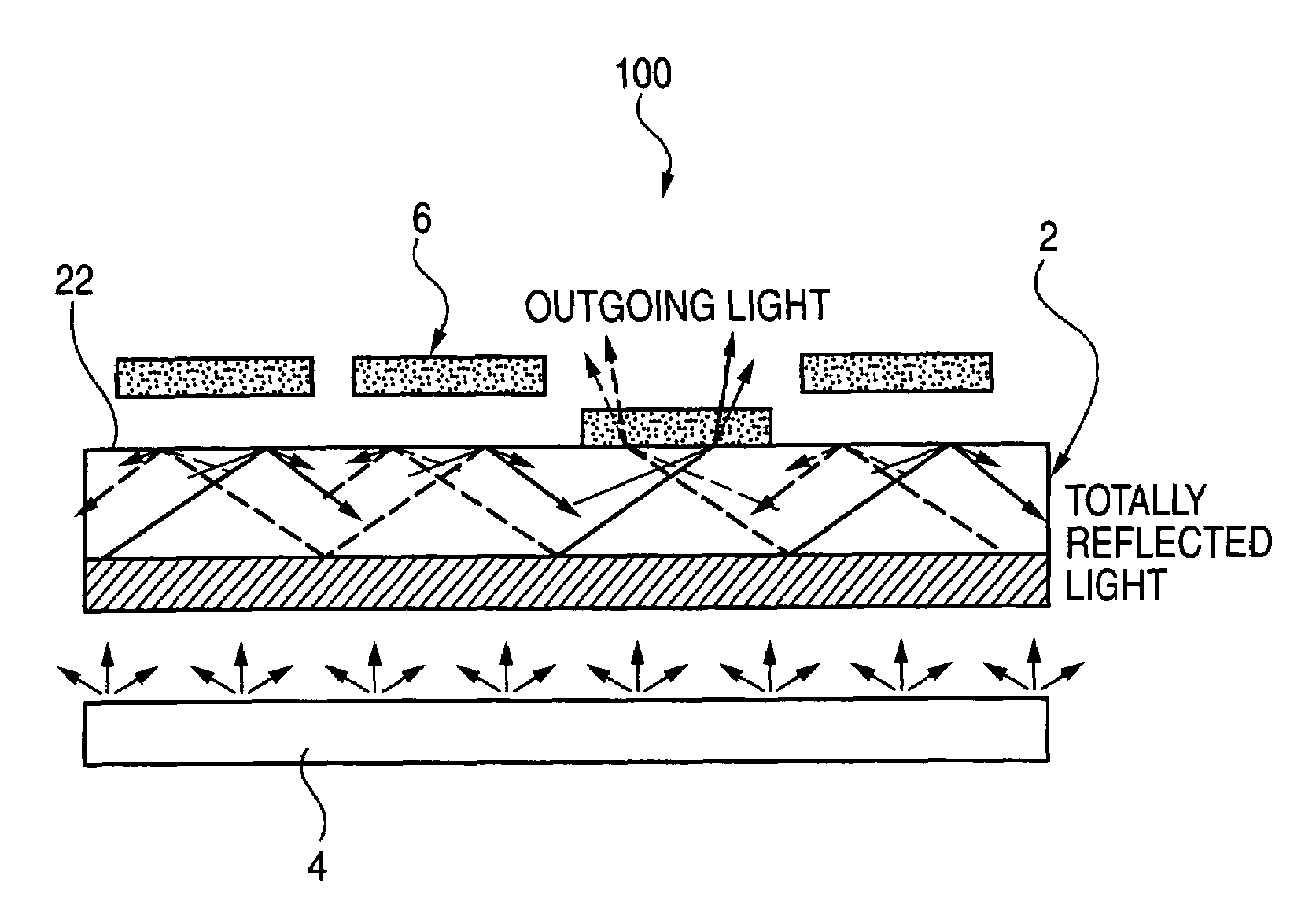
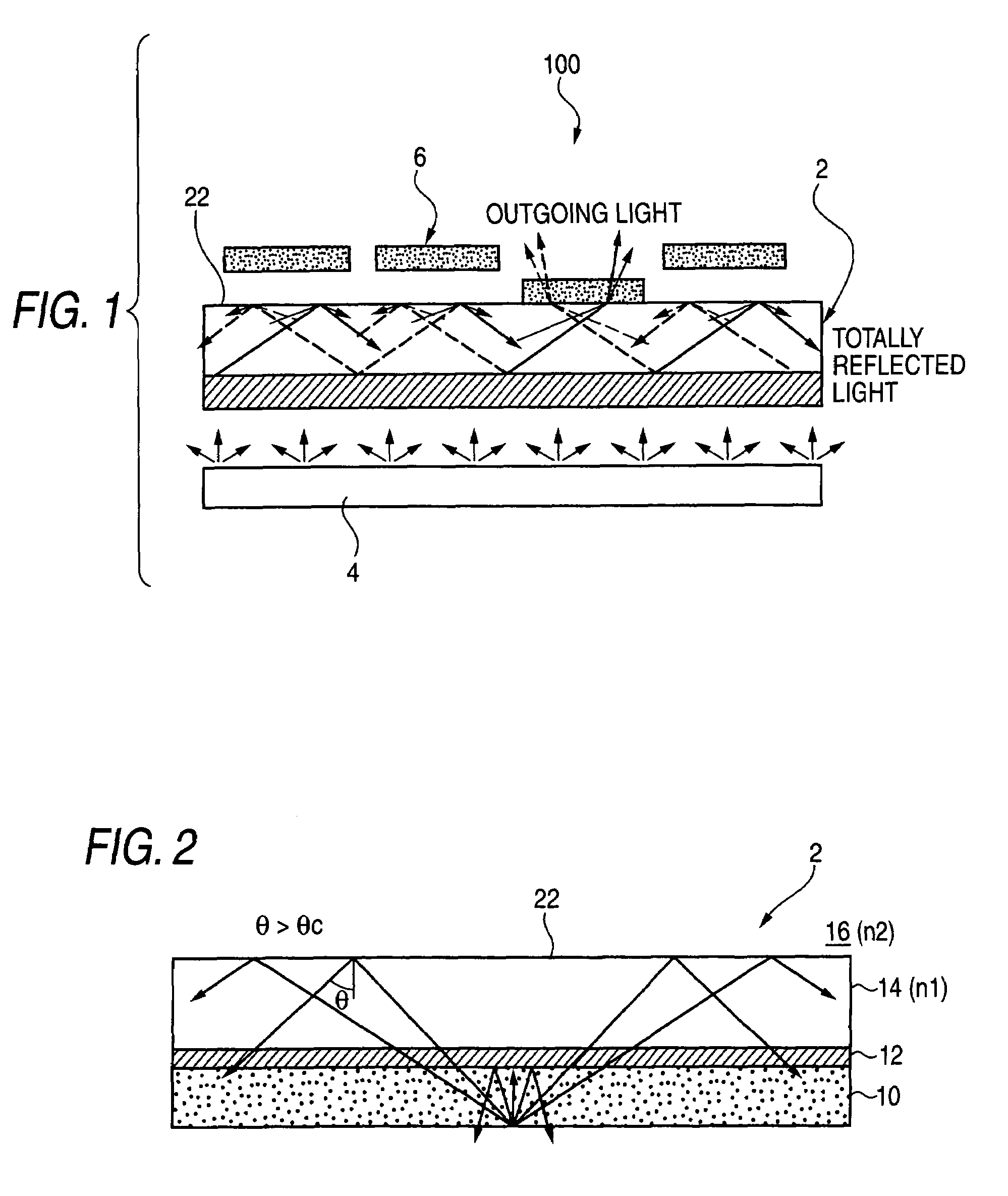
Subjects for the invention are to provide a light-modulating element having an elevated energy efficiency while preventing a decrease in contrast at low cost without using a display technique employing a waveguide or lightguide plate, and to provide a display element capable of producing high-quality display images and an exposure element capable of exposure treatment.In the invention, the light-modulating element comprises: a total-reflection optical member 2 having such a property that at least part of planar incident light introduced into the light-modulating element is totally reflected at an interface (total reflection plane) 22 of a layer constituted by the light-modulating element and the incident light does not substantially go out through the side opposite to the incident-light introduction side; and light-coupling elements 6 which are disposed on the total reflection plane 22 side of the total-reflection optical member 2 and serve to selectively couple with the incident light and take out the same from the total reflection plane 22.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Reflective multi-turn encoder
InactiveUS20090152452A1Material analysis by optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyCatoptricsEngineering
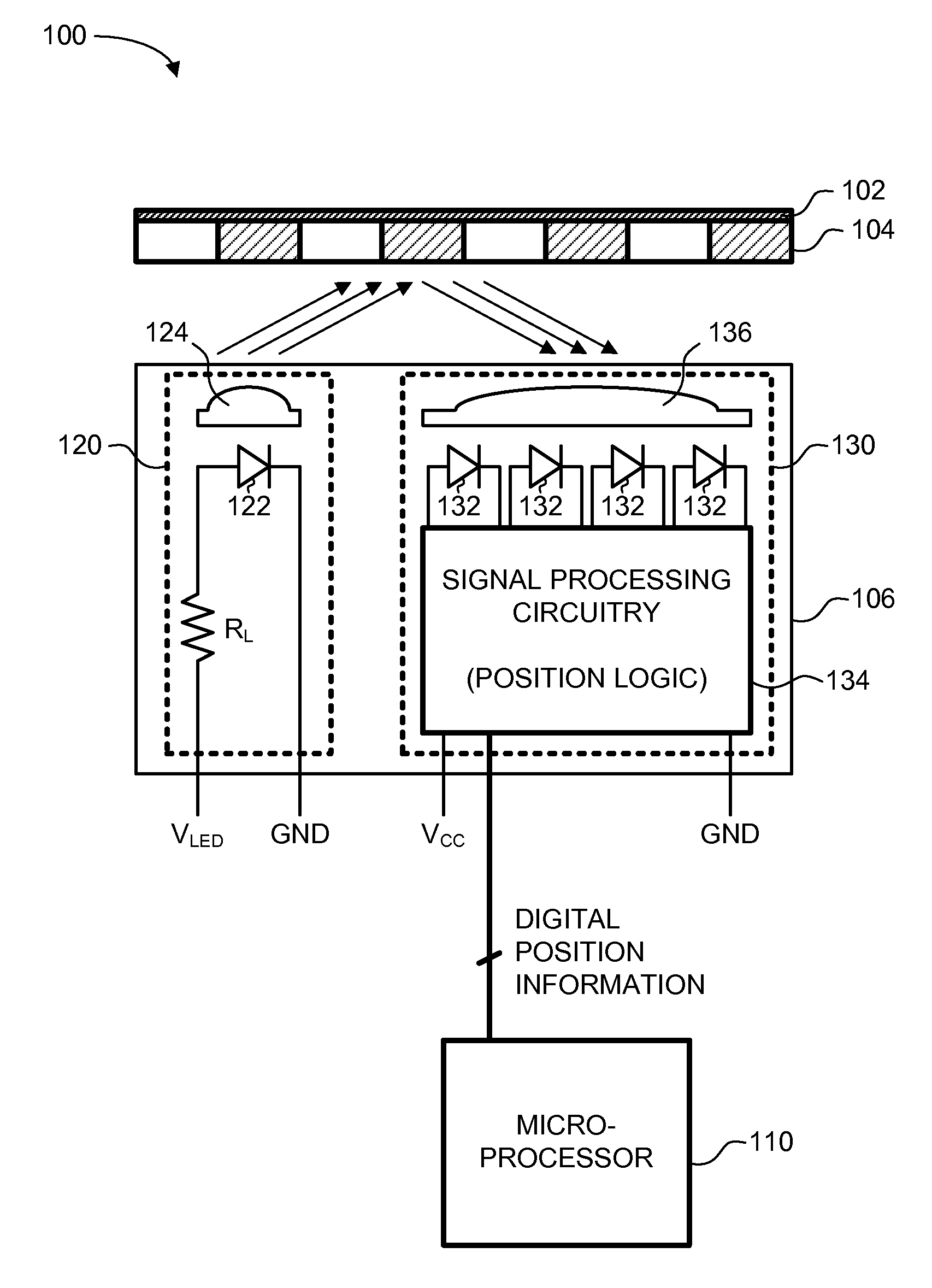
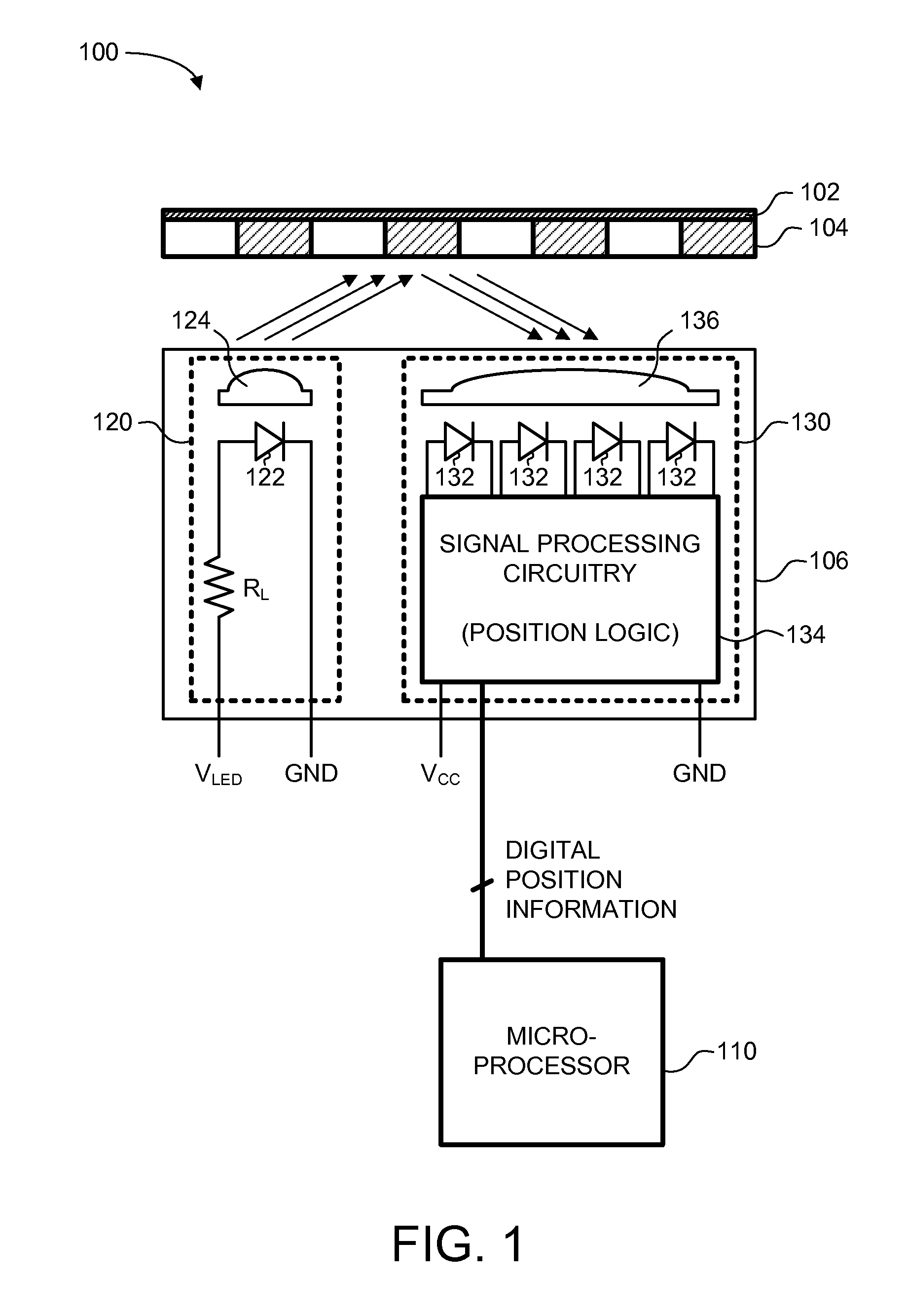
A reflective optical encoder for a gear train. The reflective optical encoder includes a gear train with a plurality of gears. Each of the gears is operably coupled to at least one other gear of the plurality of gears. A reflective code pattern is accessible on a surface of at least one of the gears. A reflective optical sensor detects light reflected by the reflective code pattern. Position logic coupled to the optical sensor determines a rotational parameter of the gear train based on the light reflected by the reflective code pattern. Additionally, the position logic may determine rotational parameter of a pinion coupled to the gear train based on the rotational parameter of the gear train.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Waveguide design incorporating reflective optics
This invention relates to devices for coupling light between an optical waveguide and an optical element in a manner that is substantially independent of temperature, using reflective optics. Certain embodiments of the invention concern improved designs for the transmit and receive optics of a waveguide-based optical touch screen sensor, incorporating reflective optics. The improved designs have substantially temperature independent operation and reduced optical losses. In one preferred embodiment the improved design incorporates a parabolic or quasi-parabolic reflector. In another preferred embodiment the improved design incorporates an elliptical or quasi-elliptical reflector. The transmit and receive elements and associated waveguides preferably comprise photo-patternable polymers.
Owner:ZETTA RES & DEV LLC RPO SERIES
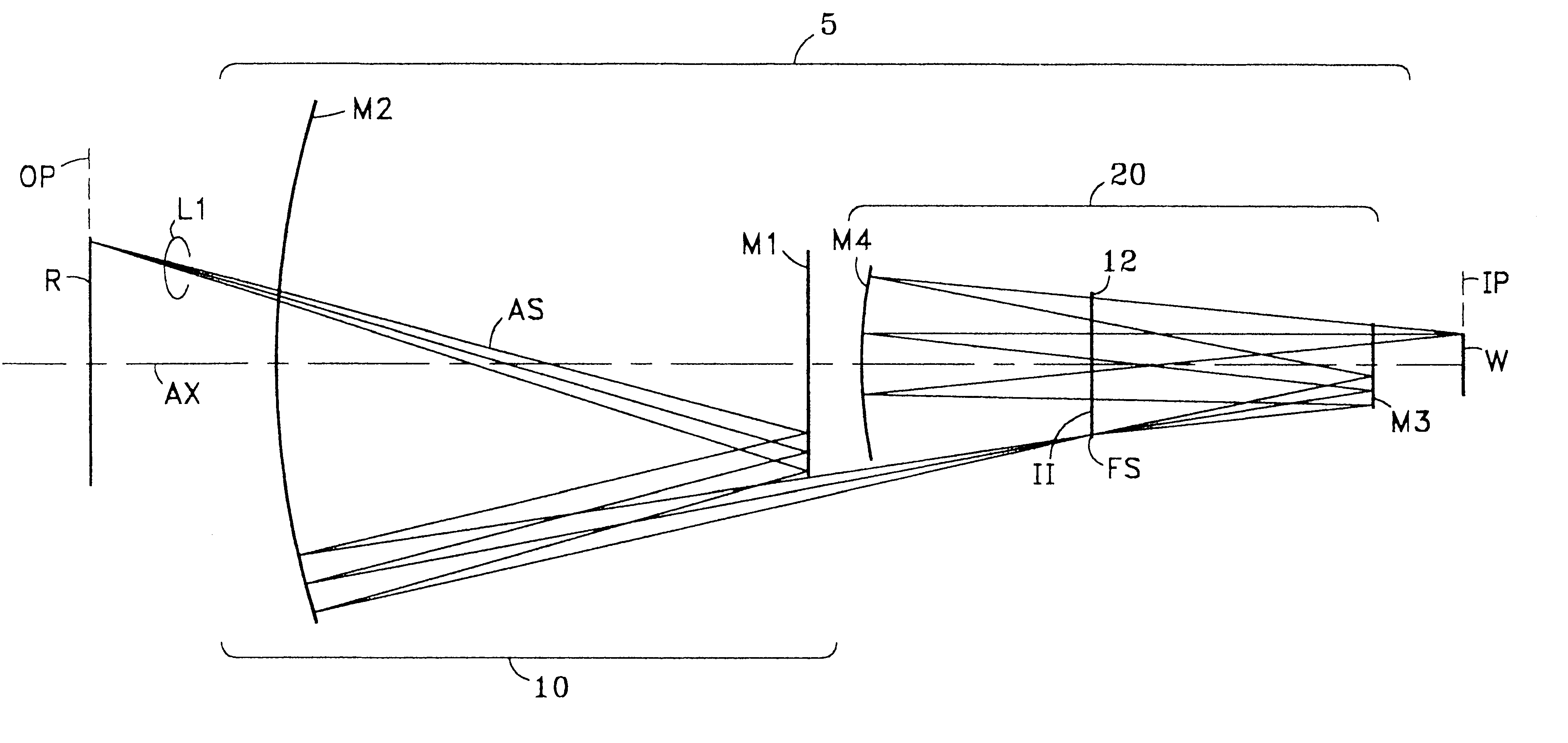
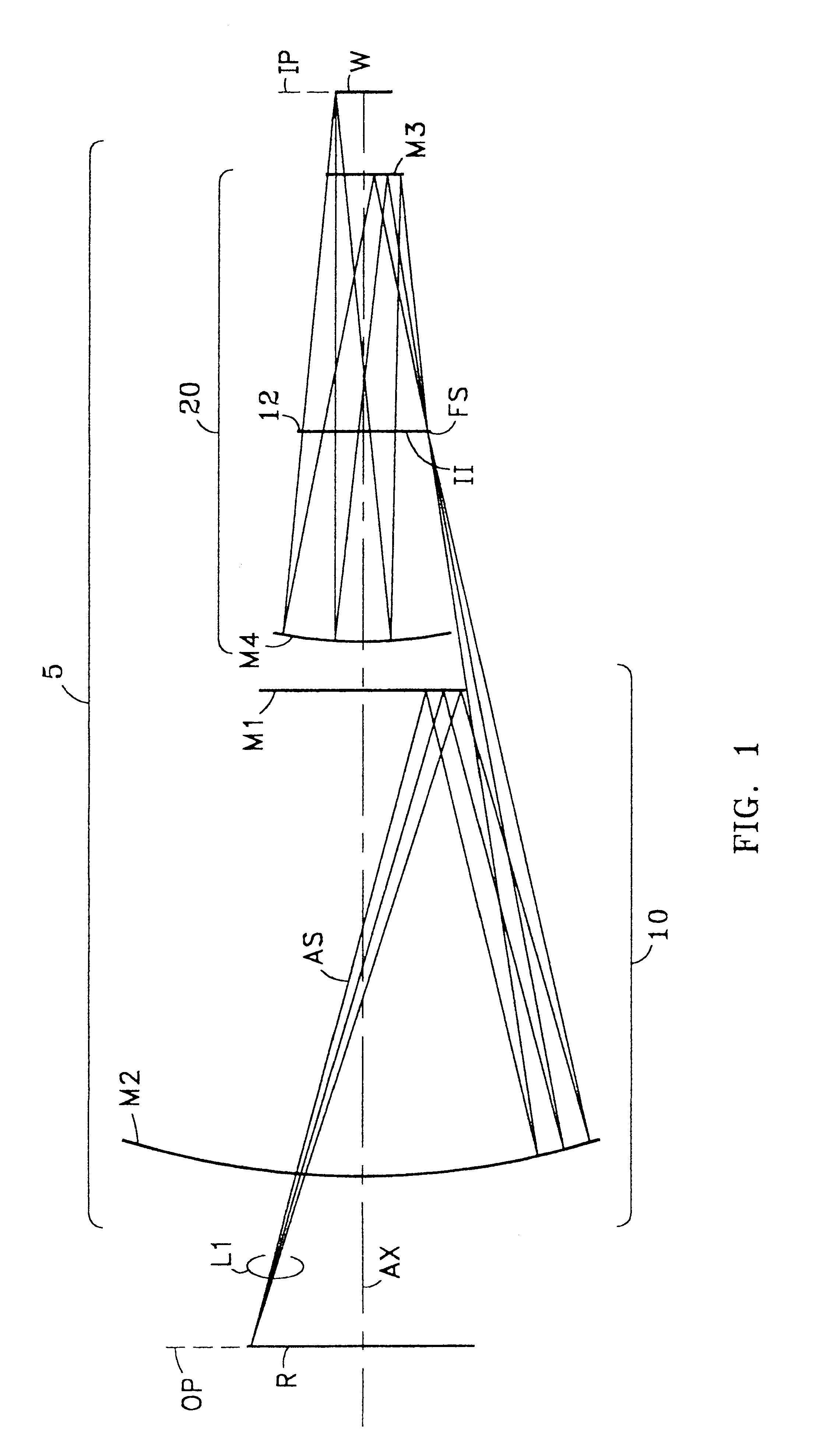
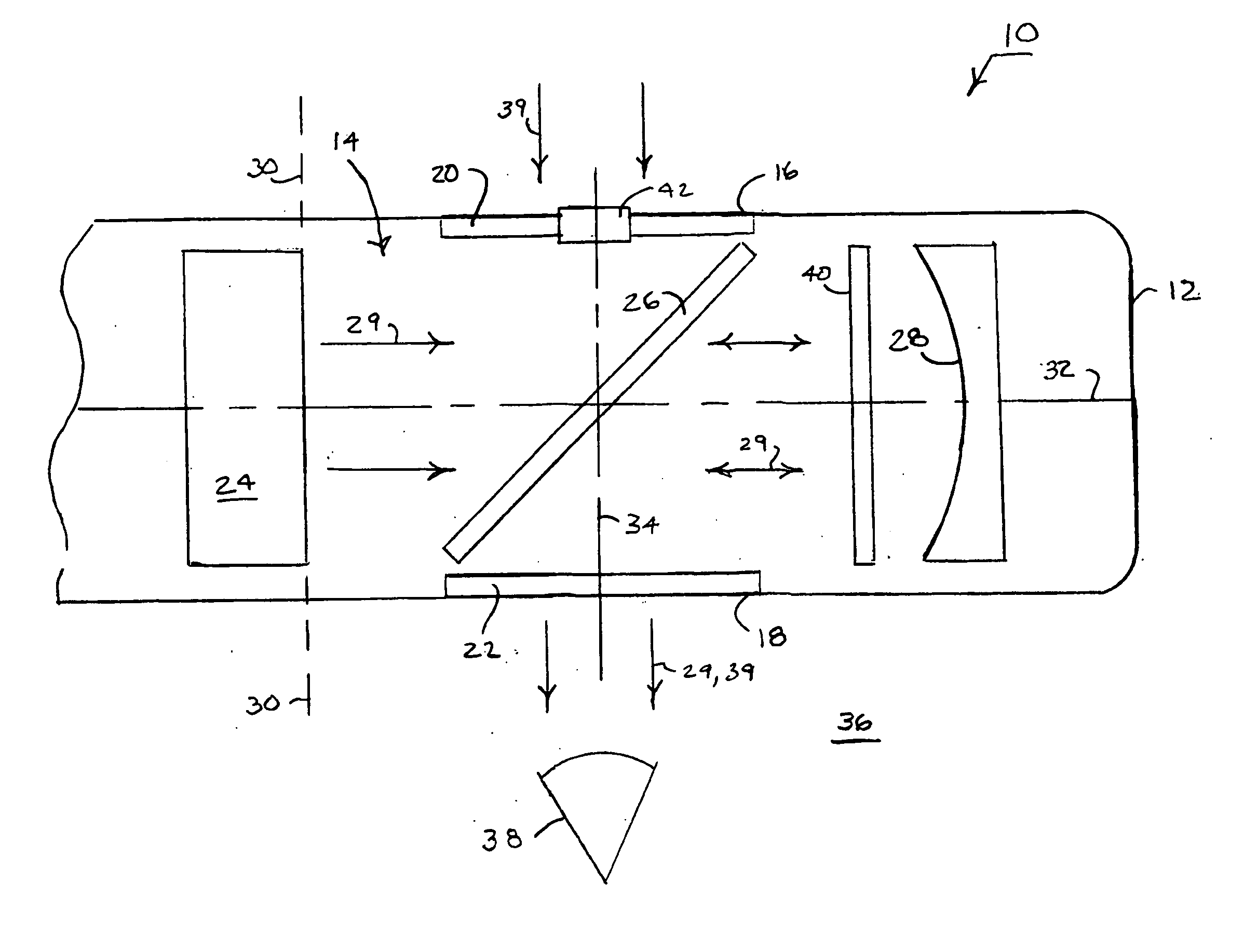
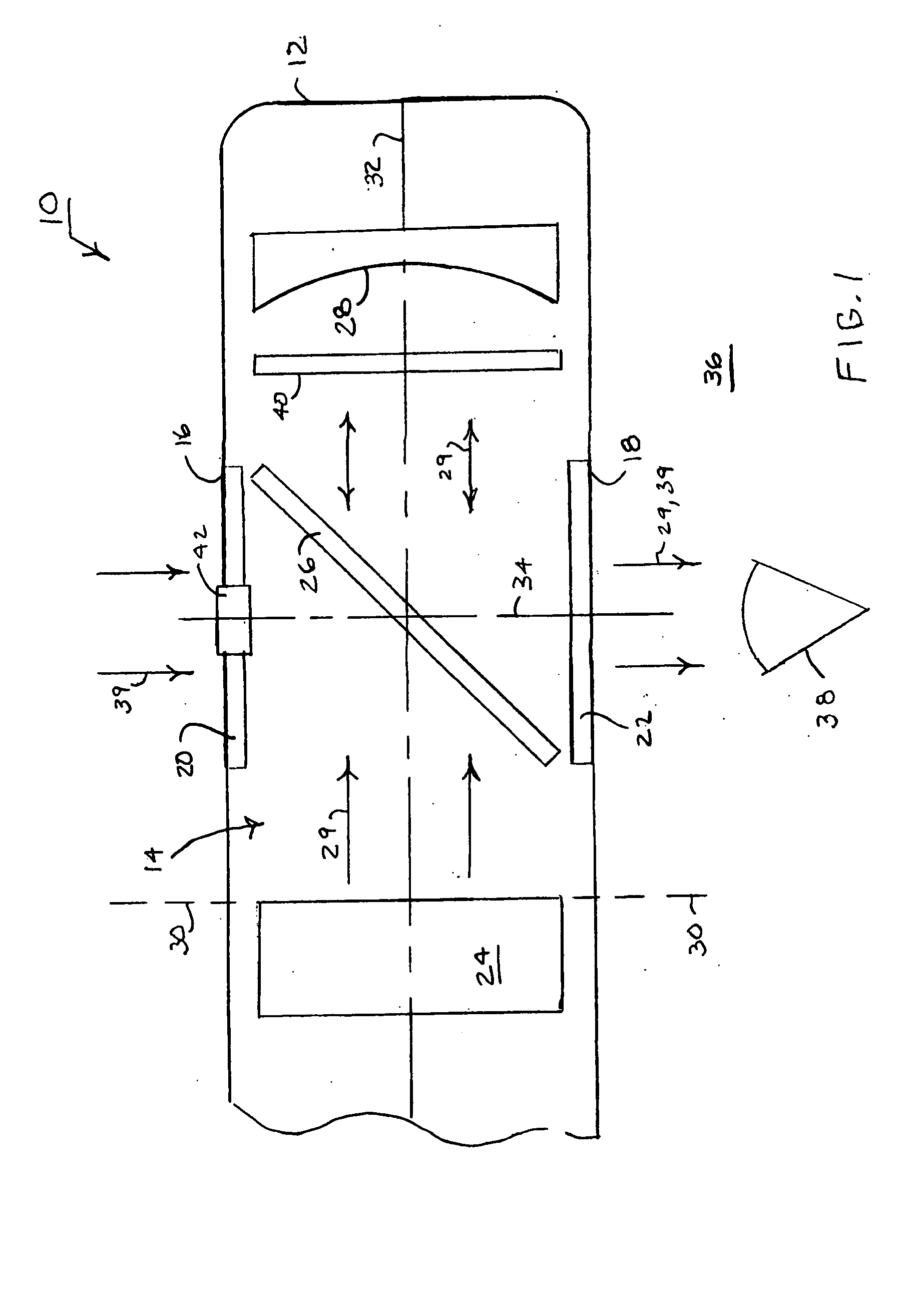
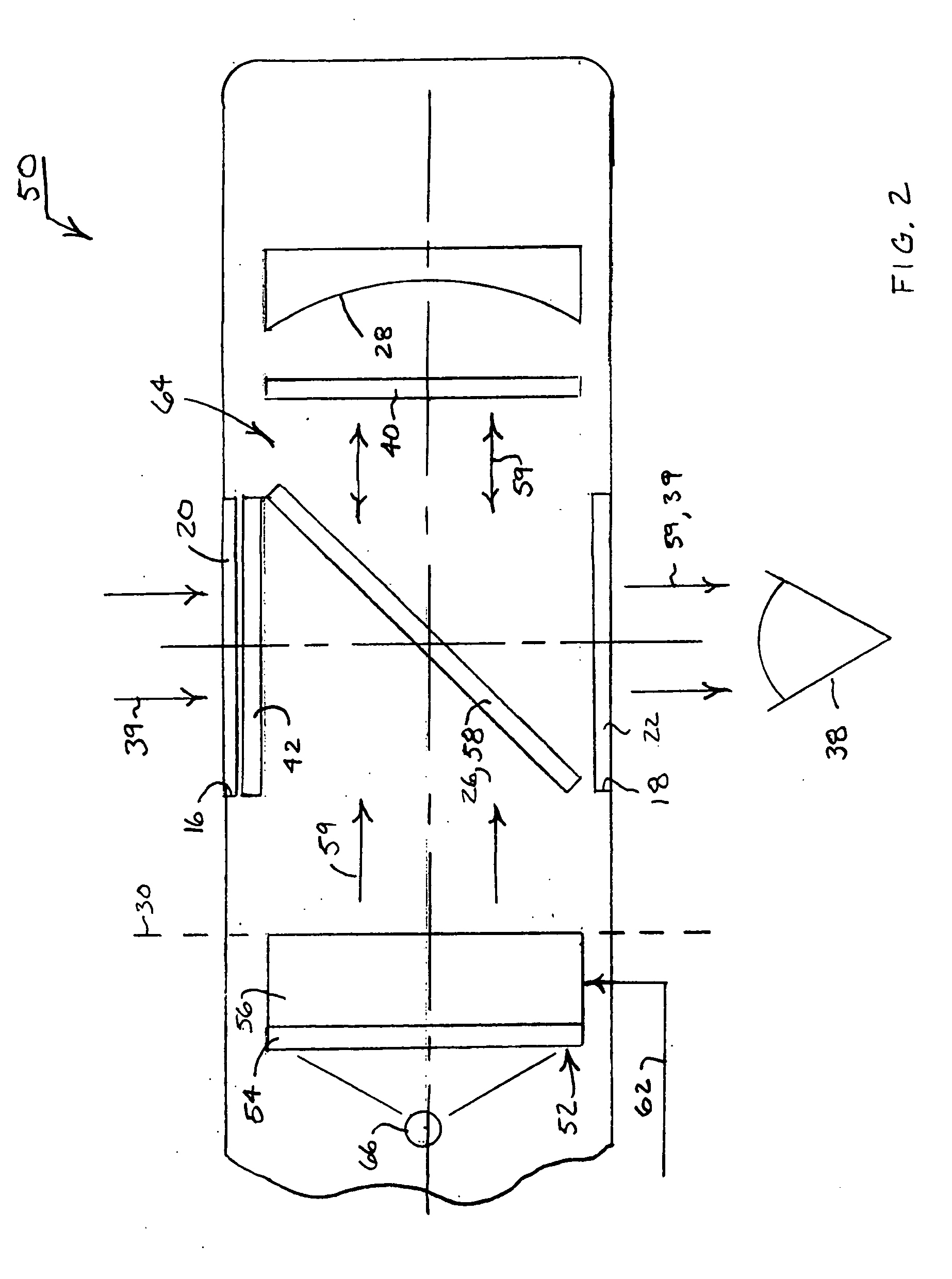
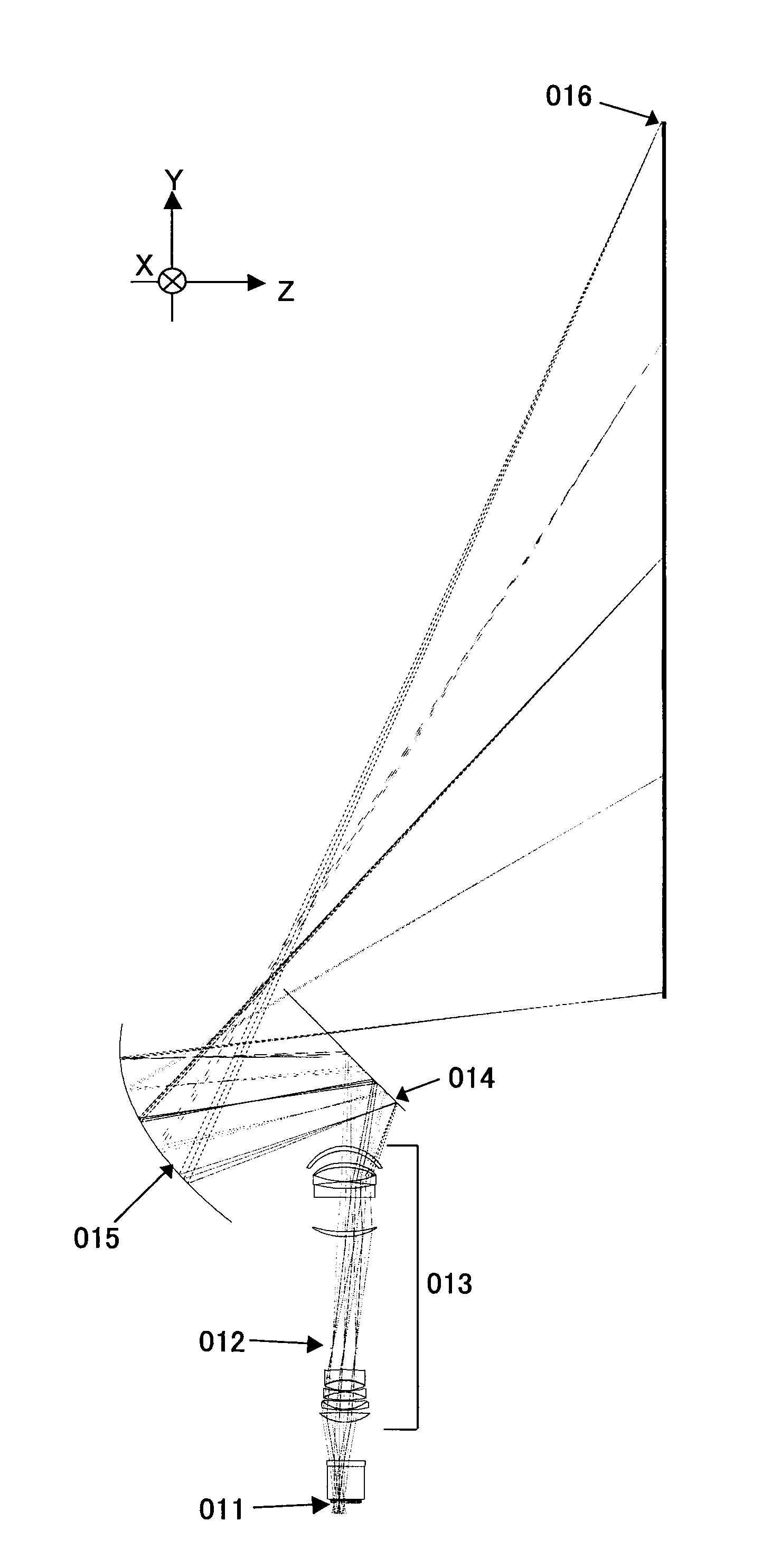
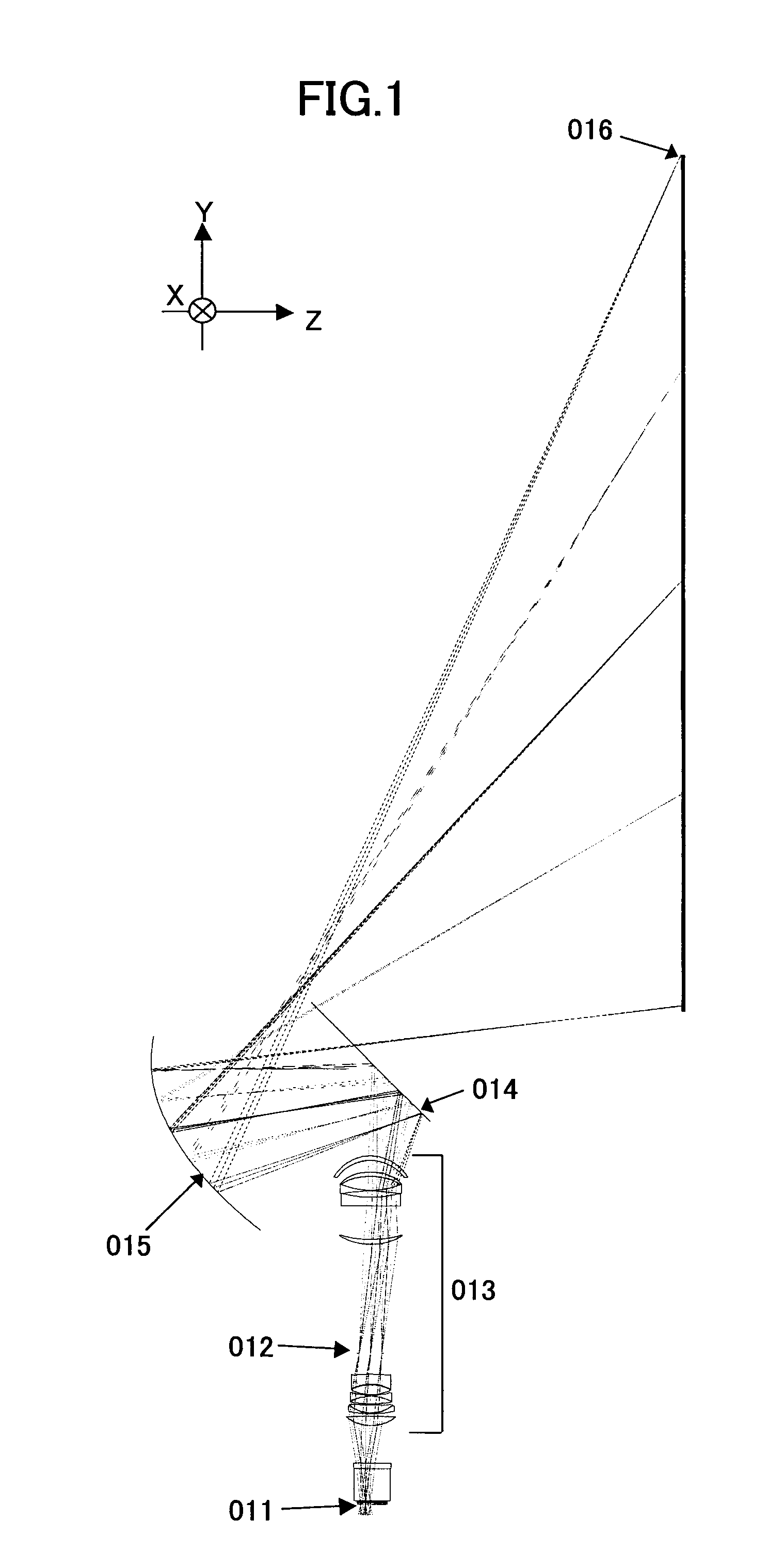
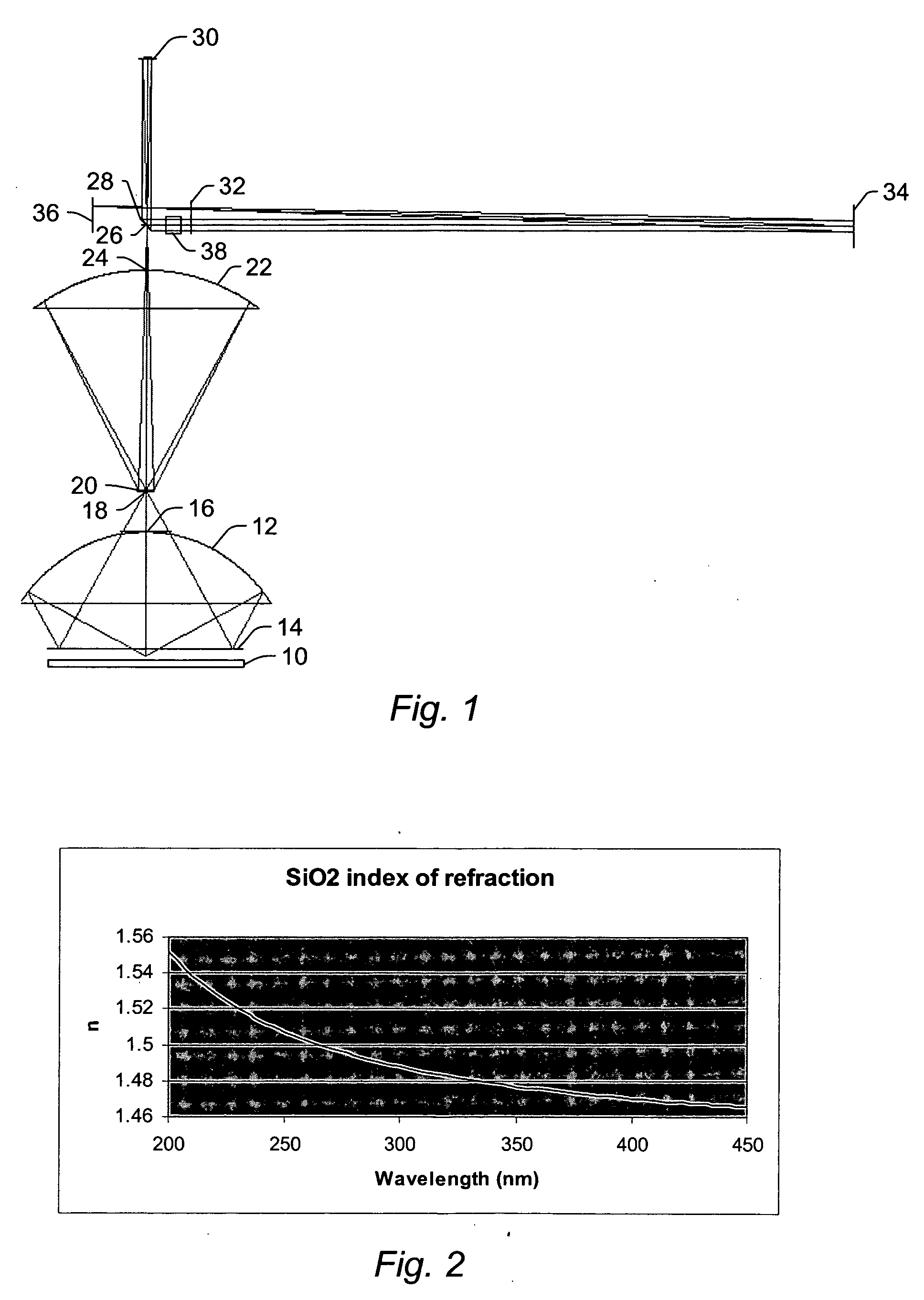
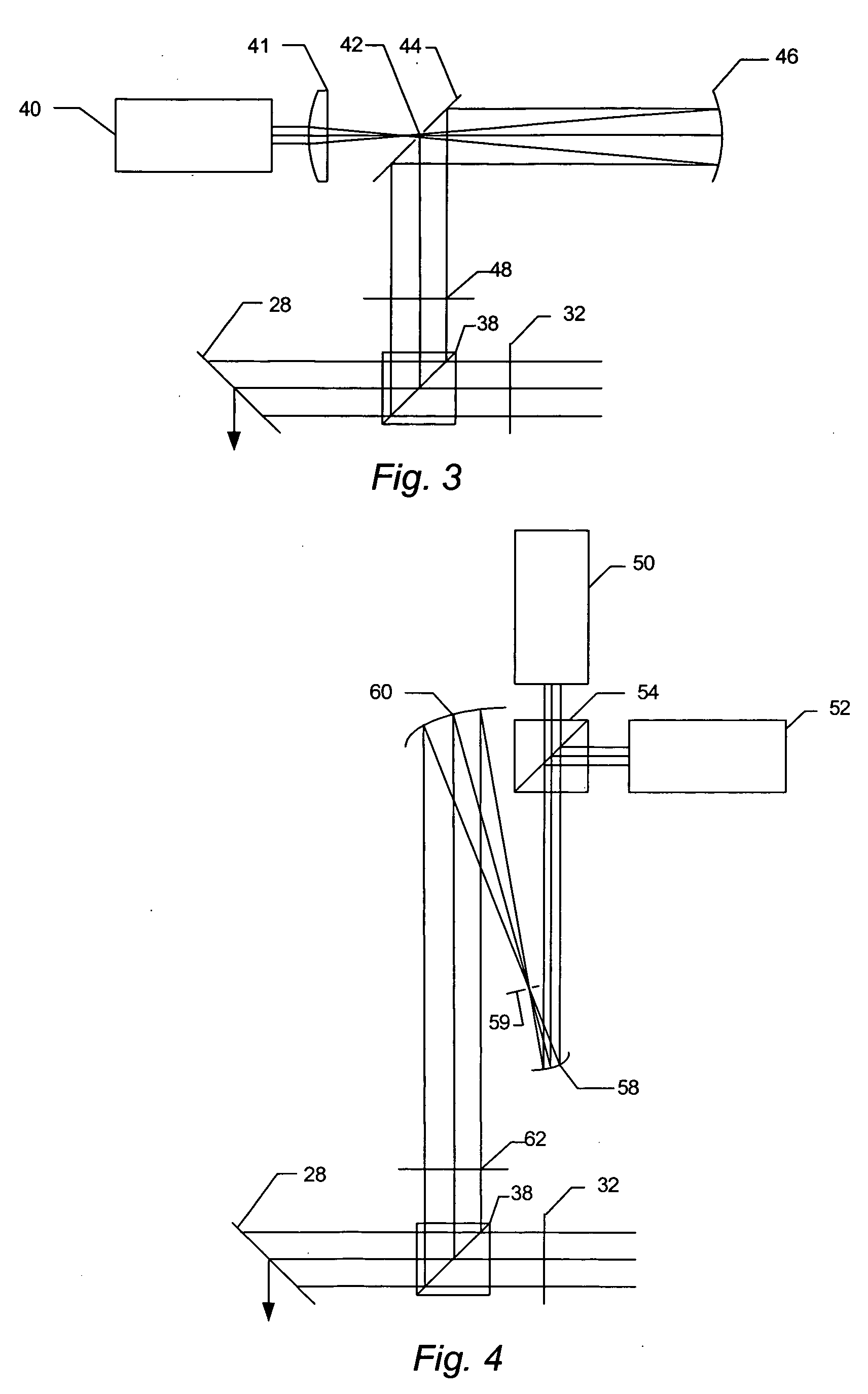
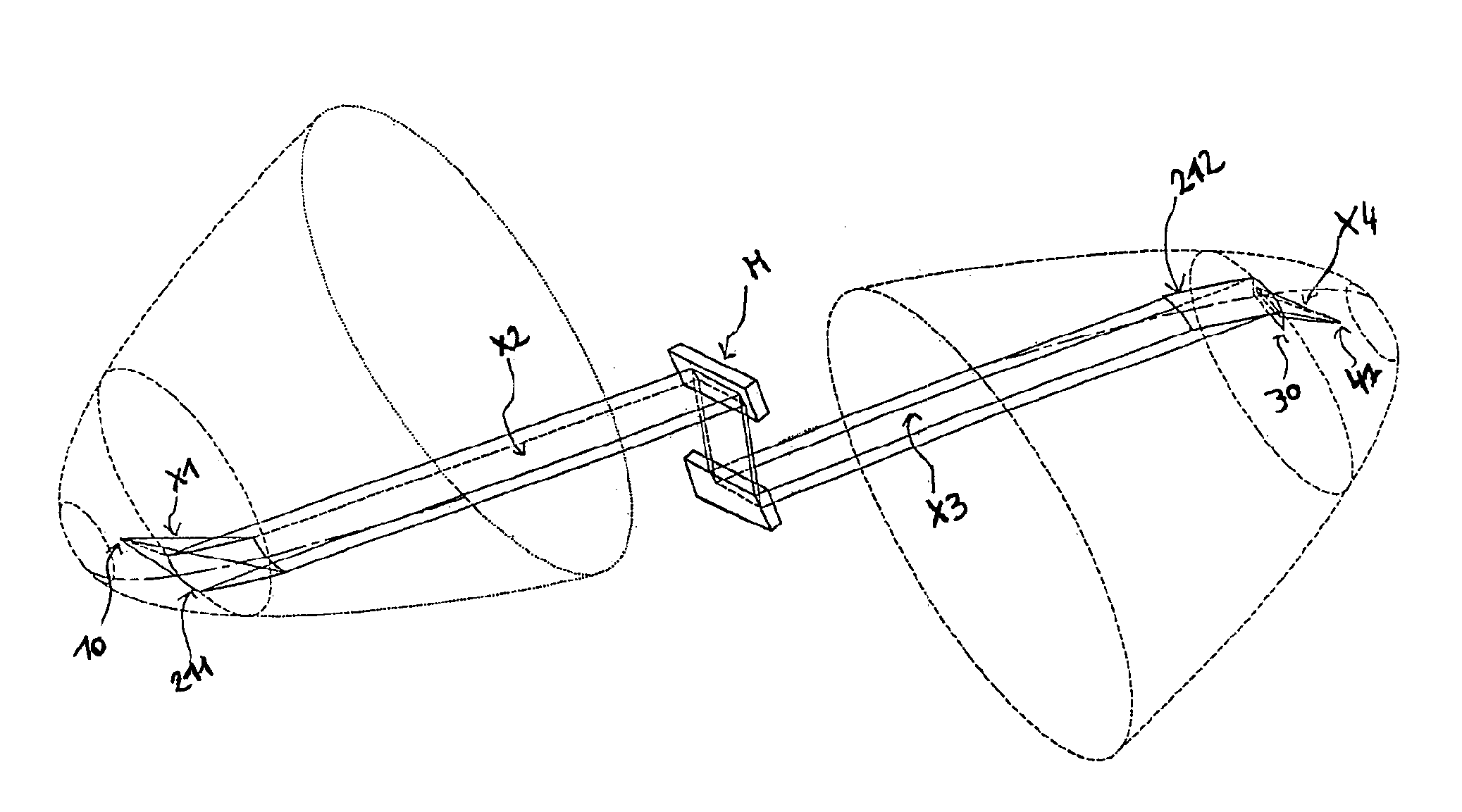
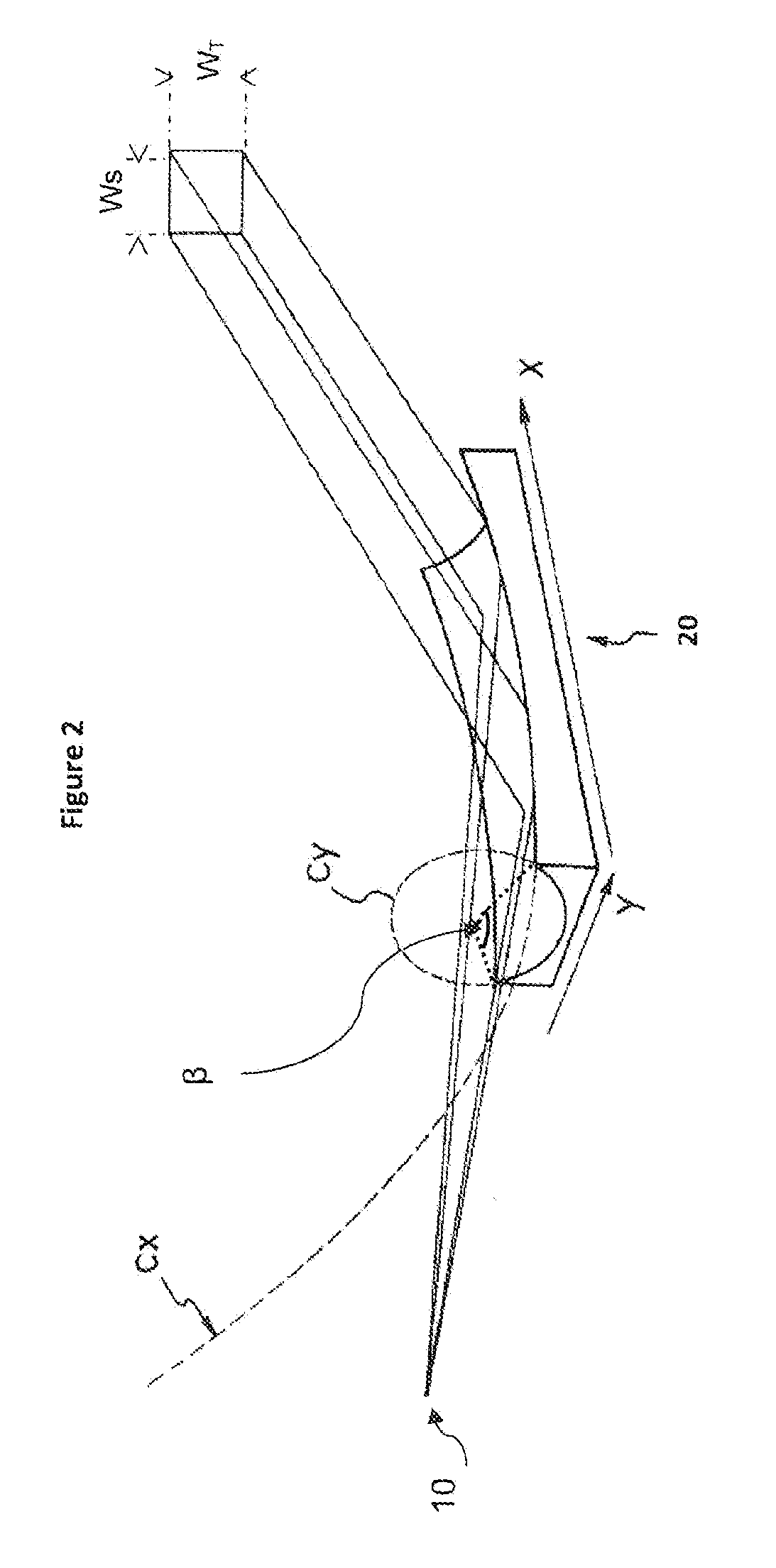
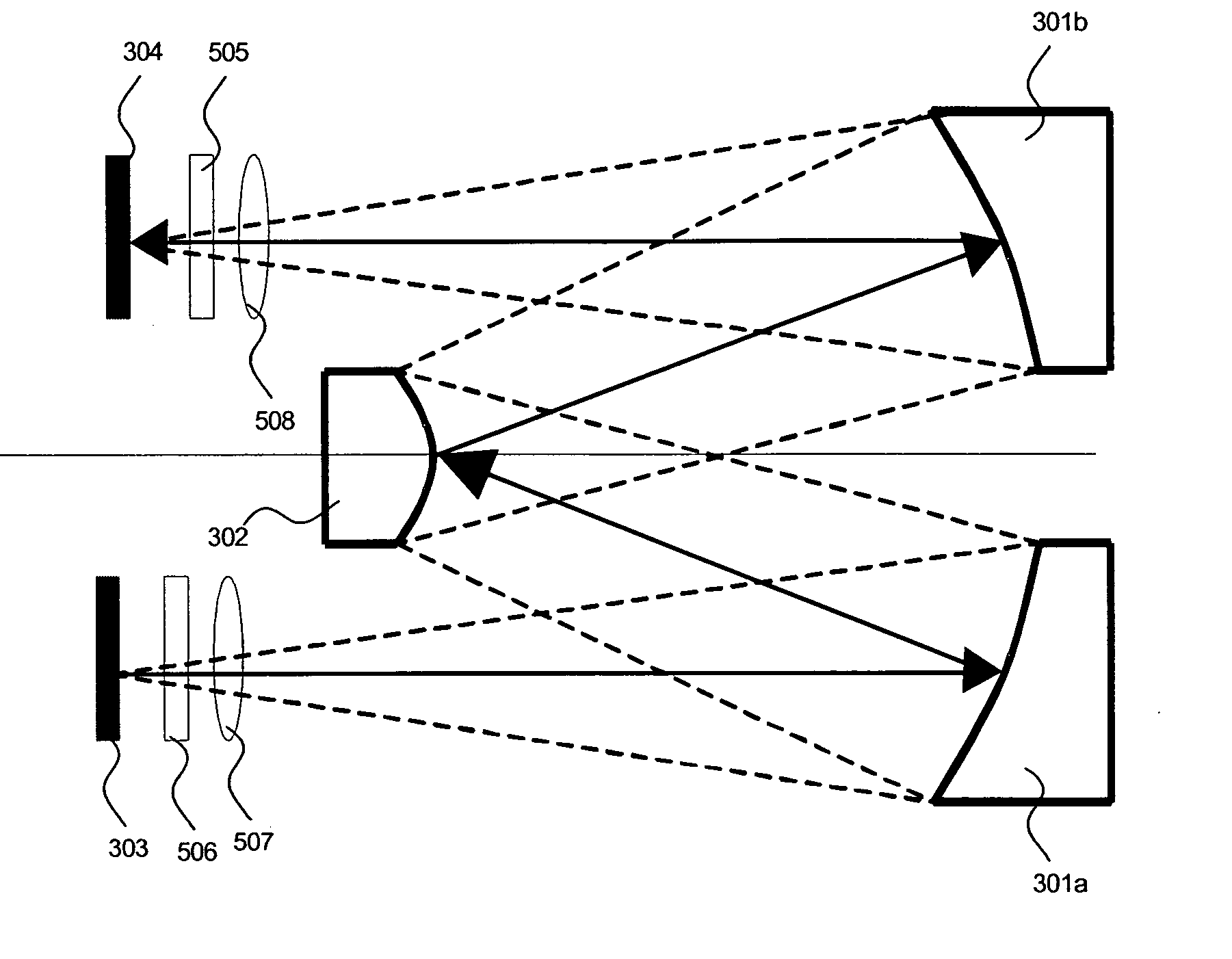
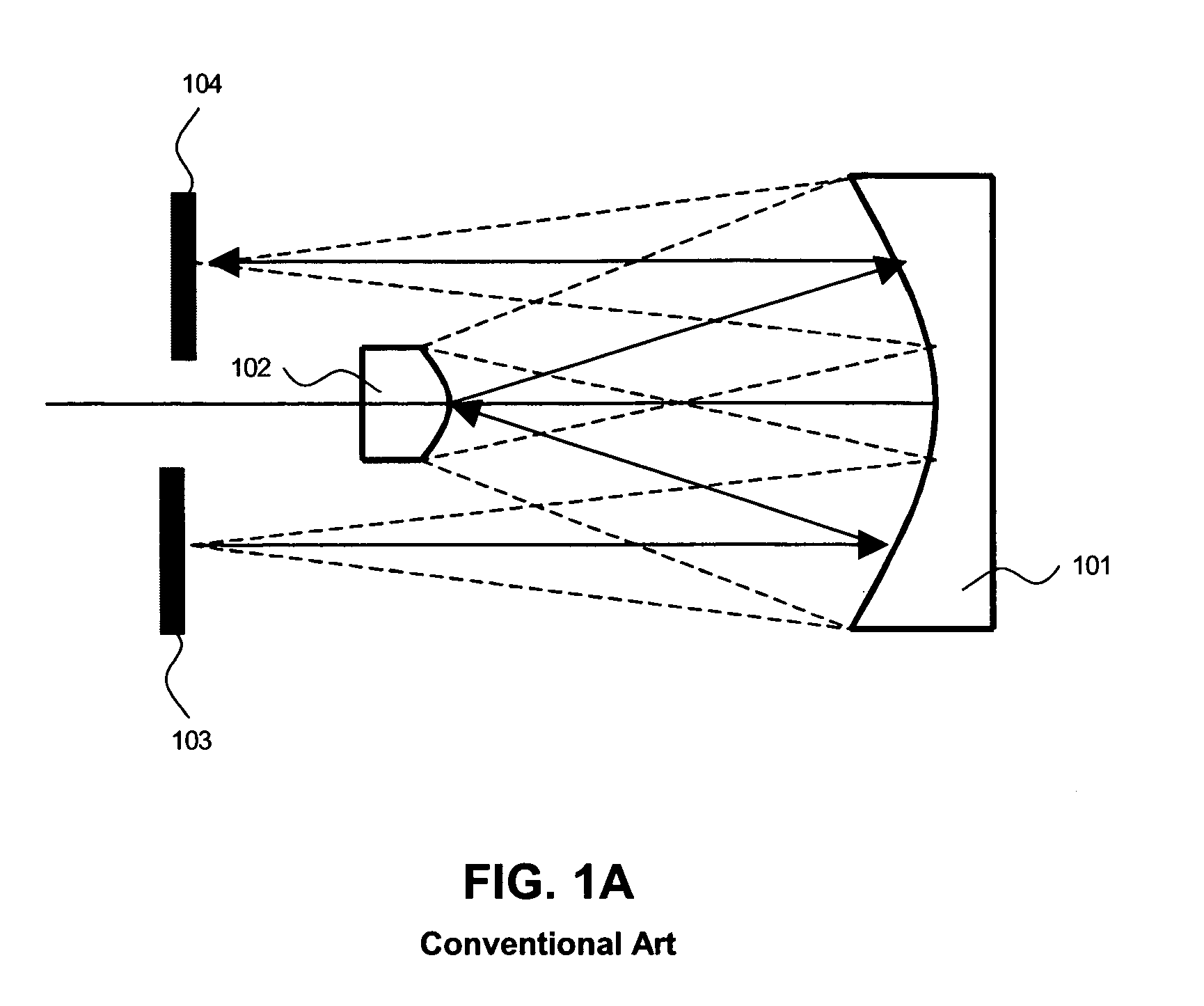
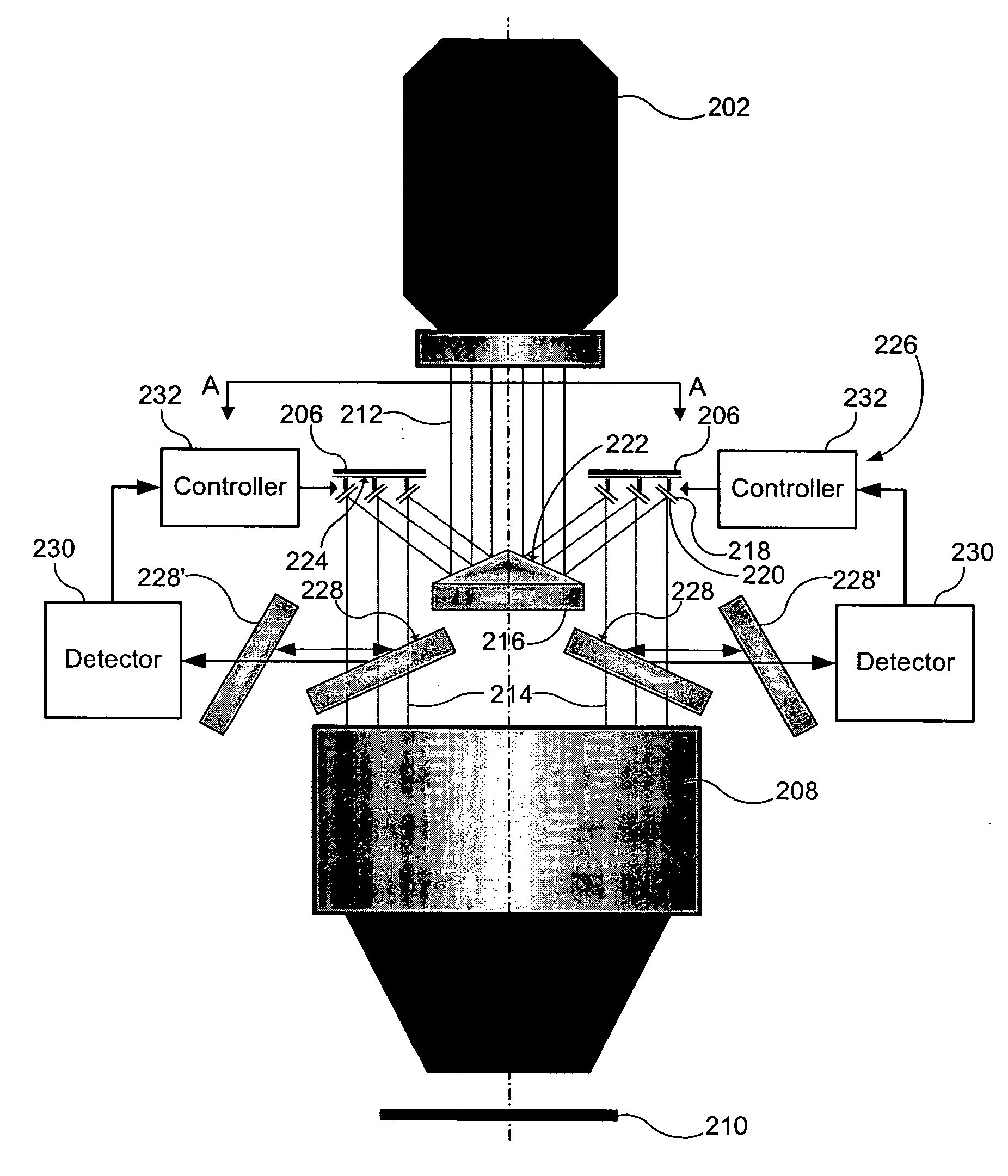
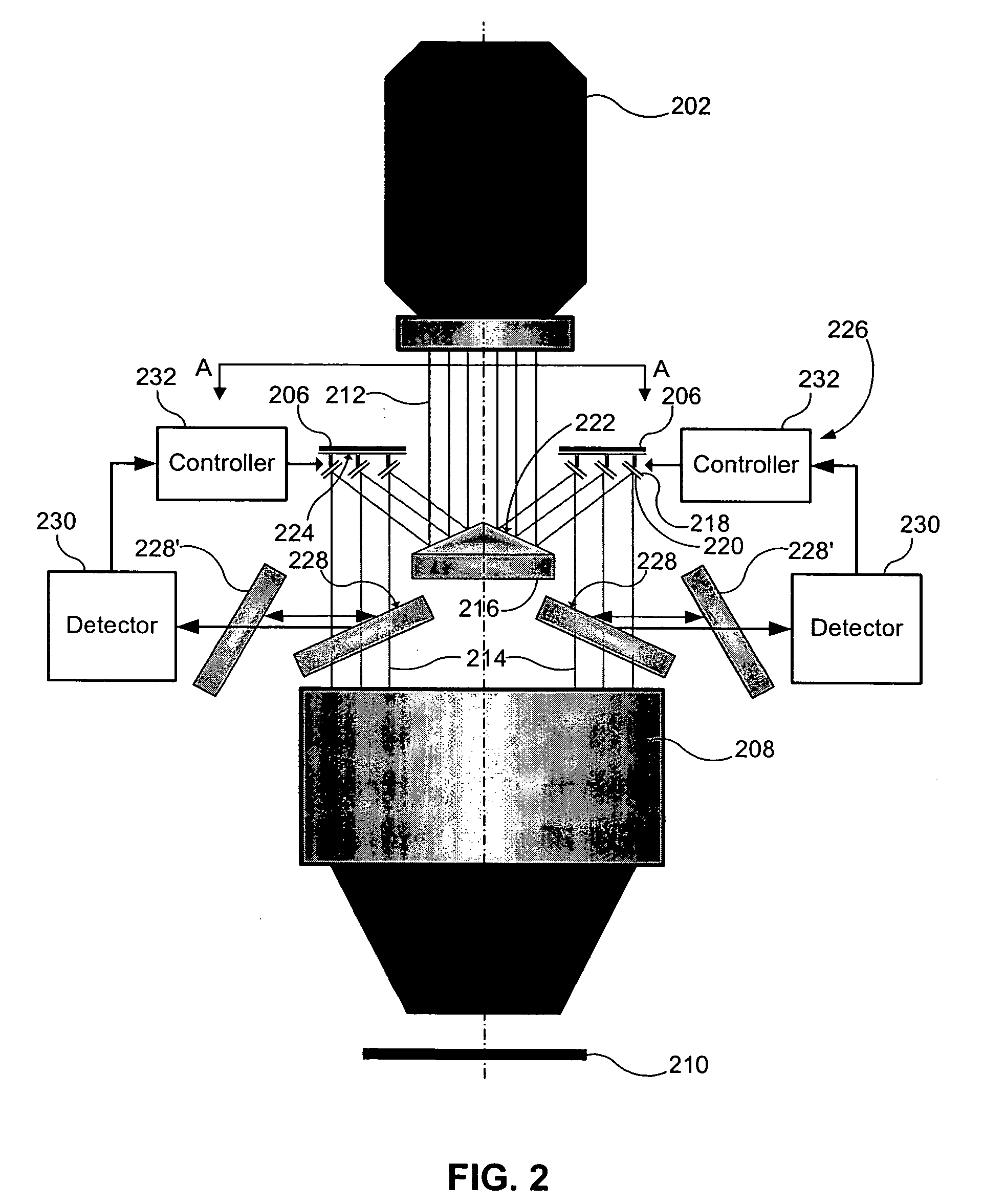
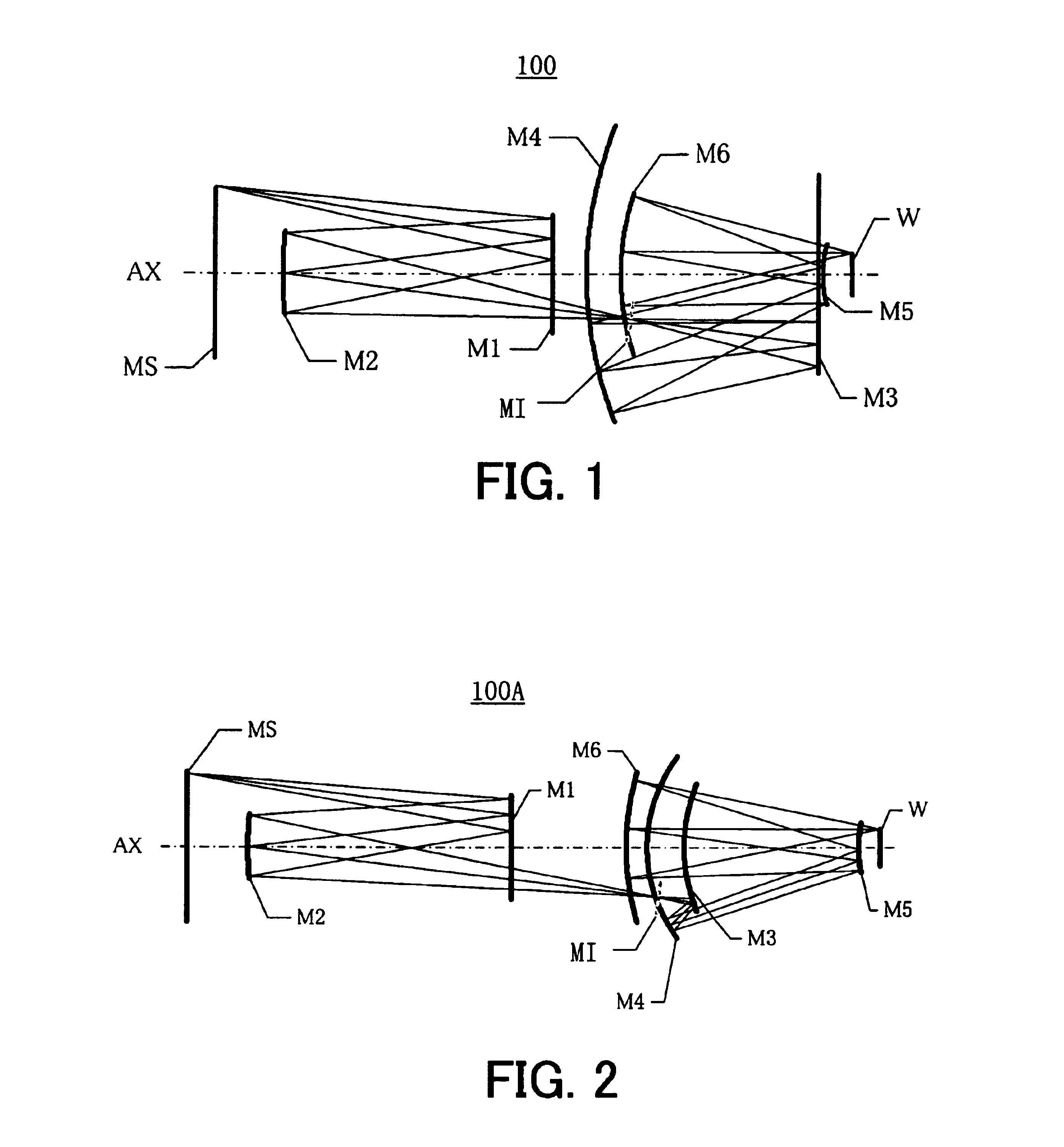
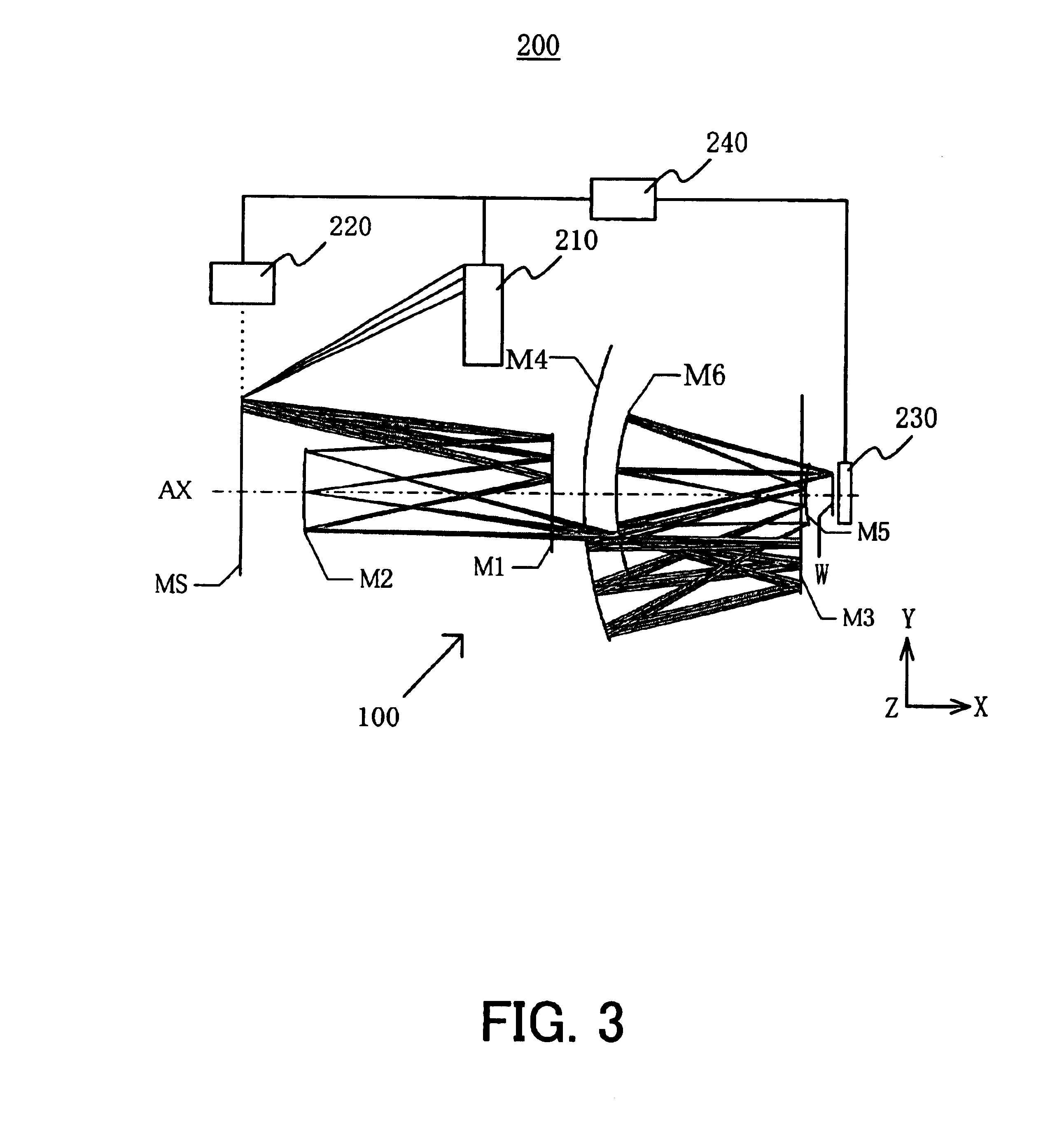
Catoptric reduction projection optical system and exposure apparatus and method using same
A catoptric reduction projection optical system (5) is provided with a first catoptric optical system (10) that images an object (R) in first (object) plane (OP) into a second plane (12) and forming an intermediate image (II) therein, and a second catoptric optical system (20) that images the intermediate image in the second plane onto a third (image) plane (IP), thereby forming a reduced image of the object in the first (object) plane onto the third (image) plane. The first catoptric optical system comprises a first mirror pair comprising two reflective mirrors (M1, M2). The second catoptric optical system comprises a second mirror pair comprising a convex mirror (M3) and a concave mirror (M4). The system also preferably satisfied a number of design conditions.
Owner:NIKON CORP
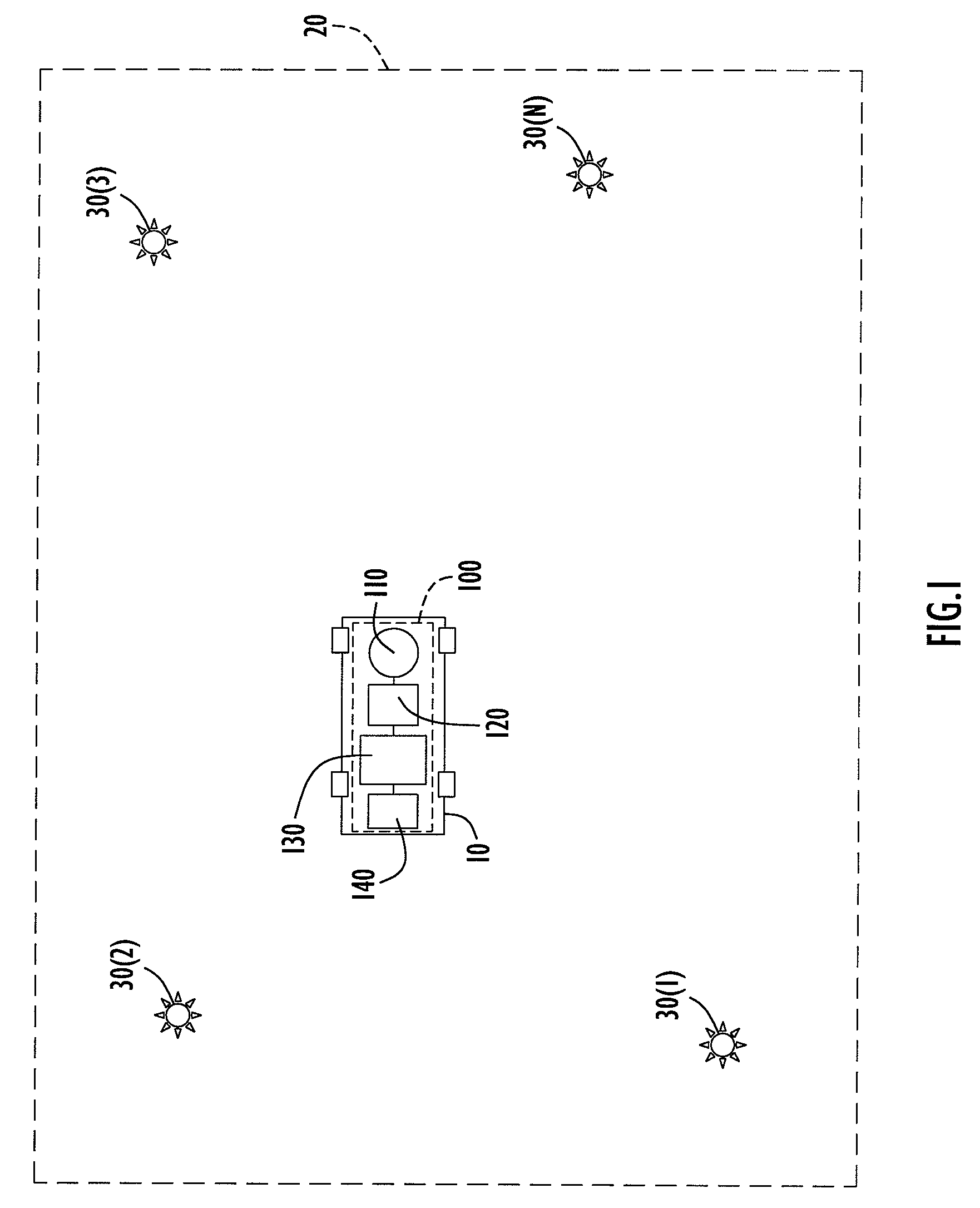
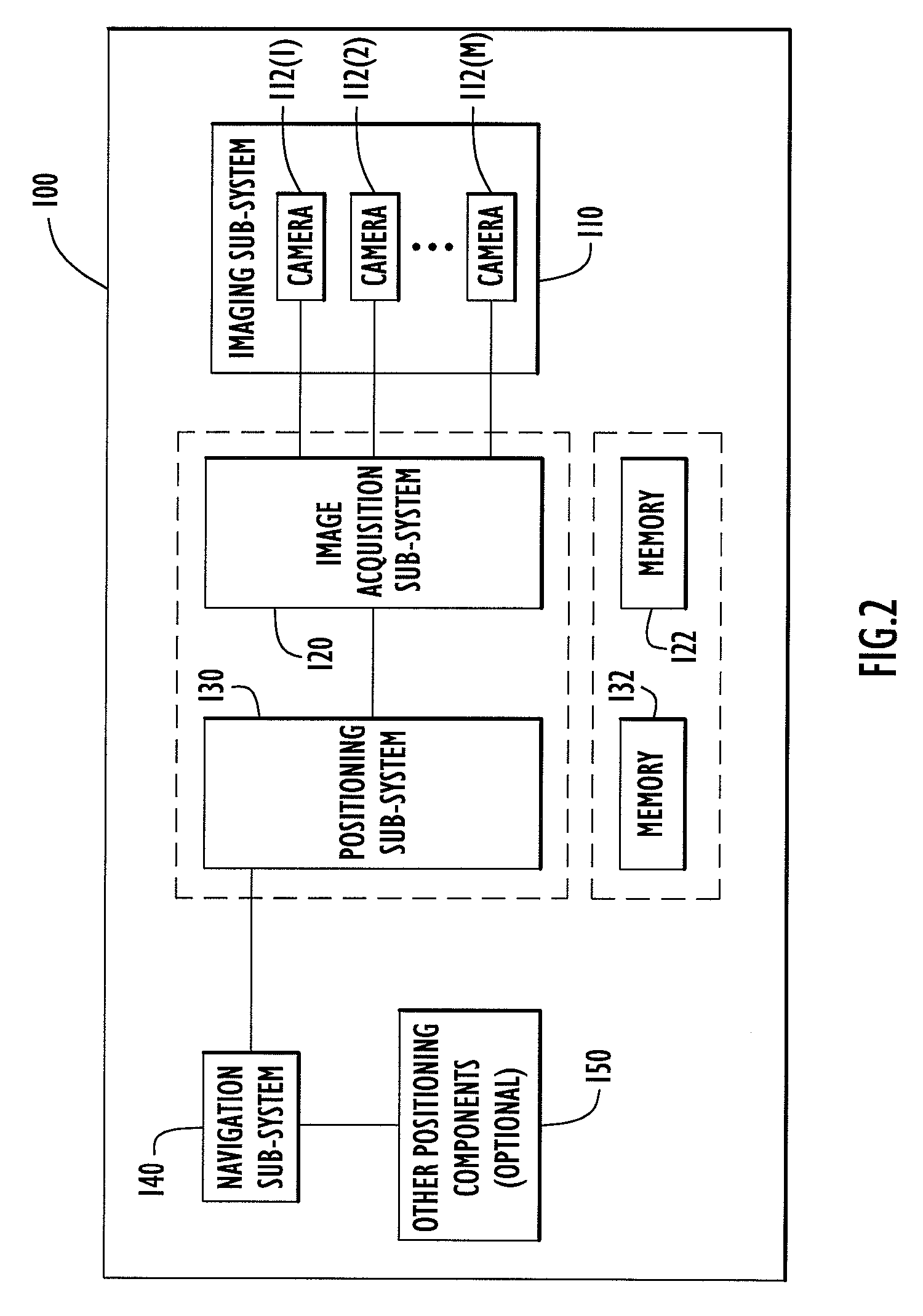
Landmark Navigation for Vehicles Using Blinking Optical Beacons
ActiveUS20080262718A1Road vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsBlink frequencyComputer science
A system and method for landmark navigation employing optical beacons deployed at locations throughout a field of operation of a vehicle. The optical beacons emit or reflect an optical signal at a predetermined blink frequency. The locations of the optical beacons may or may not be known to the vehicle. At least one imaging device on the vehicle, such as a digital camera, captures images in the field of operation, and in particular a pair of image frames such that the time interval between the image frames of the pair is equal to one-half of the blink period of the optical signal. Data is generated that represents a difference frame between two image frames captured by the imaging device. Pixel locations of optical beacons in the difference frame are identified. The position and orientation of the vehicle is determined from data representing pixel locations of optical beacons in the difference frame.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Reflective optical stack for privacy display
A privacy display comprises a polarized output spatial light modulator, reflective polarizer, switchable liquid crystal retarder and polarizer. In a privacy mode of operation, on-axis light from the spatial light modulator is directed without loss, whereas off-axis light has reduced luminance. Further, display reflectivity is reduced for on-axis reflections of ambient light, while reflectivity is increased for off-axis light. The visibility of the display to off-axis snoopers is reduced by means of luminance reduction and increased frontal reflectivity to ambient light. In a wide angle mode of operation, the liquid crystal retardance is adjusted so that off-axis luminance and reflectivity are unmodified.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Reflective optical system, tracking system and holographic projection system and method
ActiveUS8120828B2Computational load requiredReduce demandStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical reflectionVisibility
The invention relates to an optical reflection system with a reflection element for reflecting reconstruction light waves, an entry-side focal point, from which the reconstruction light waves come when they hit the reflection element, and an exit-side focal point, to which the reconstruction light waves propagate after being reflected from the reflection element. The invention further relates to a tracking system and a holographic projection system with such optical reflection system, and a corresponding holographic projection method. In order to achieve with such an optical reflection system an aberration correction and a tracking of the visibility region and a reconstruction larger than with prior art devices, the optical reflection system according to this invention comprises a deflection element with optically controllable deflection properties and a deflection control means for optically controlling the deflection properties of the deflection element which controls the position of at least the exit-side focal point of the optical reflection system.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
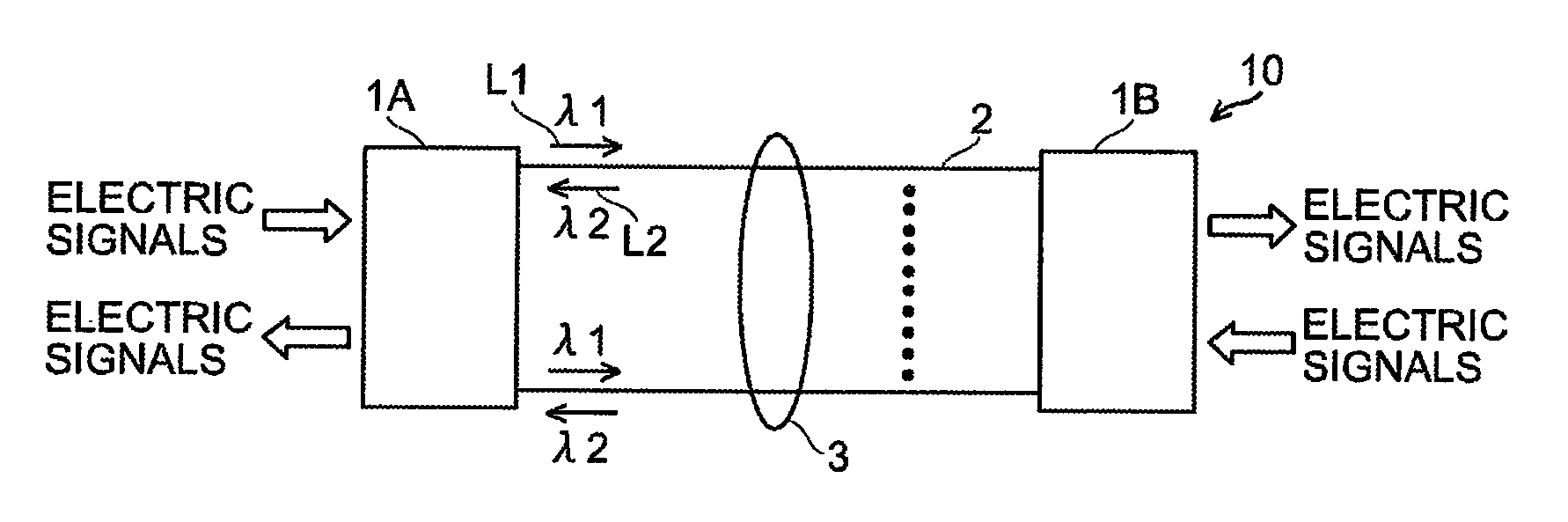
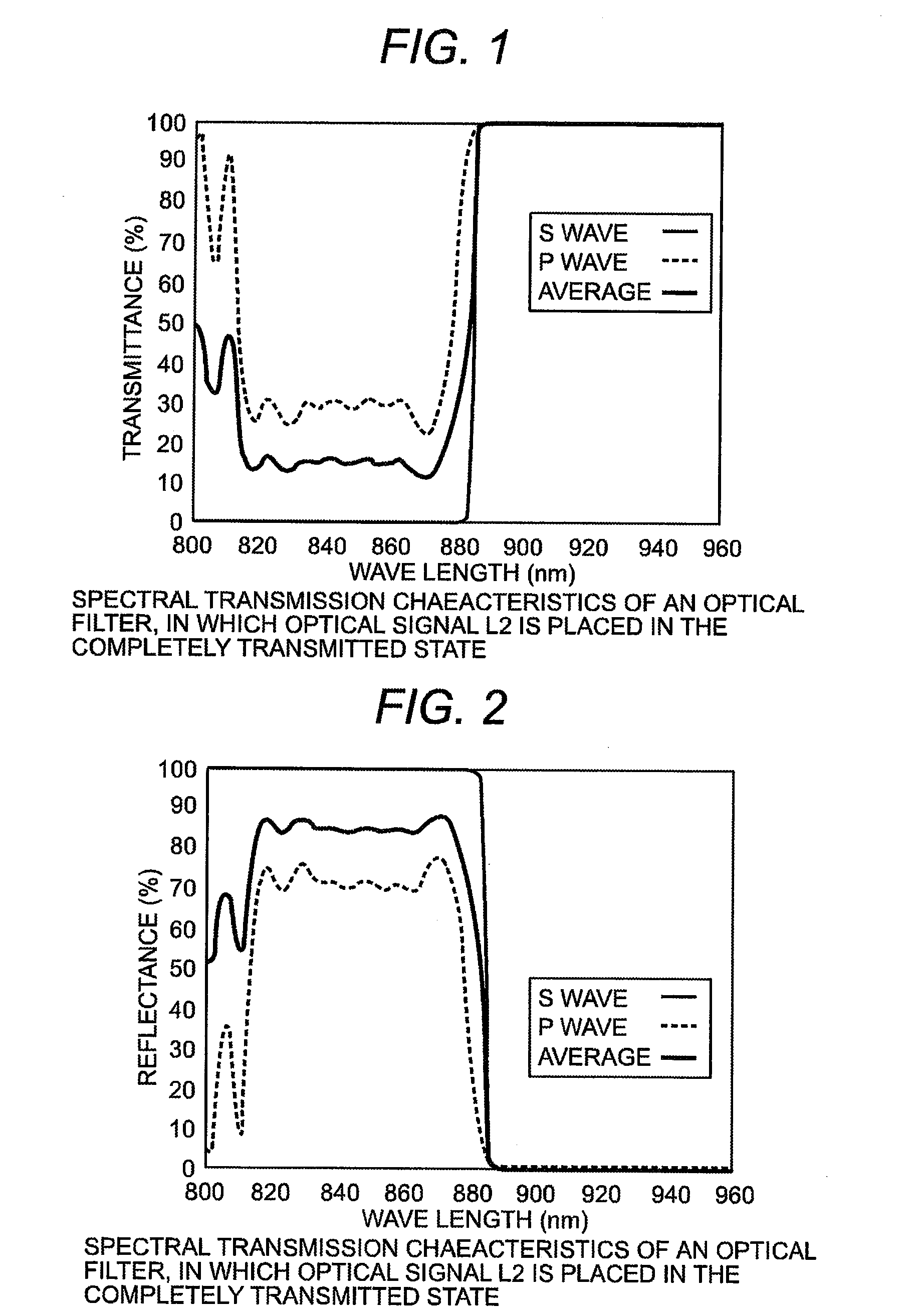
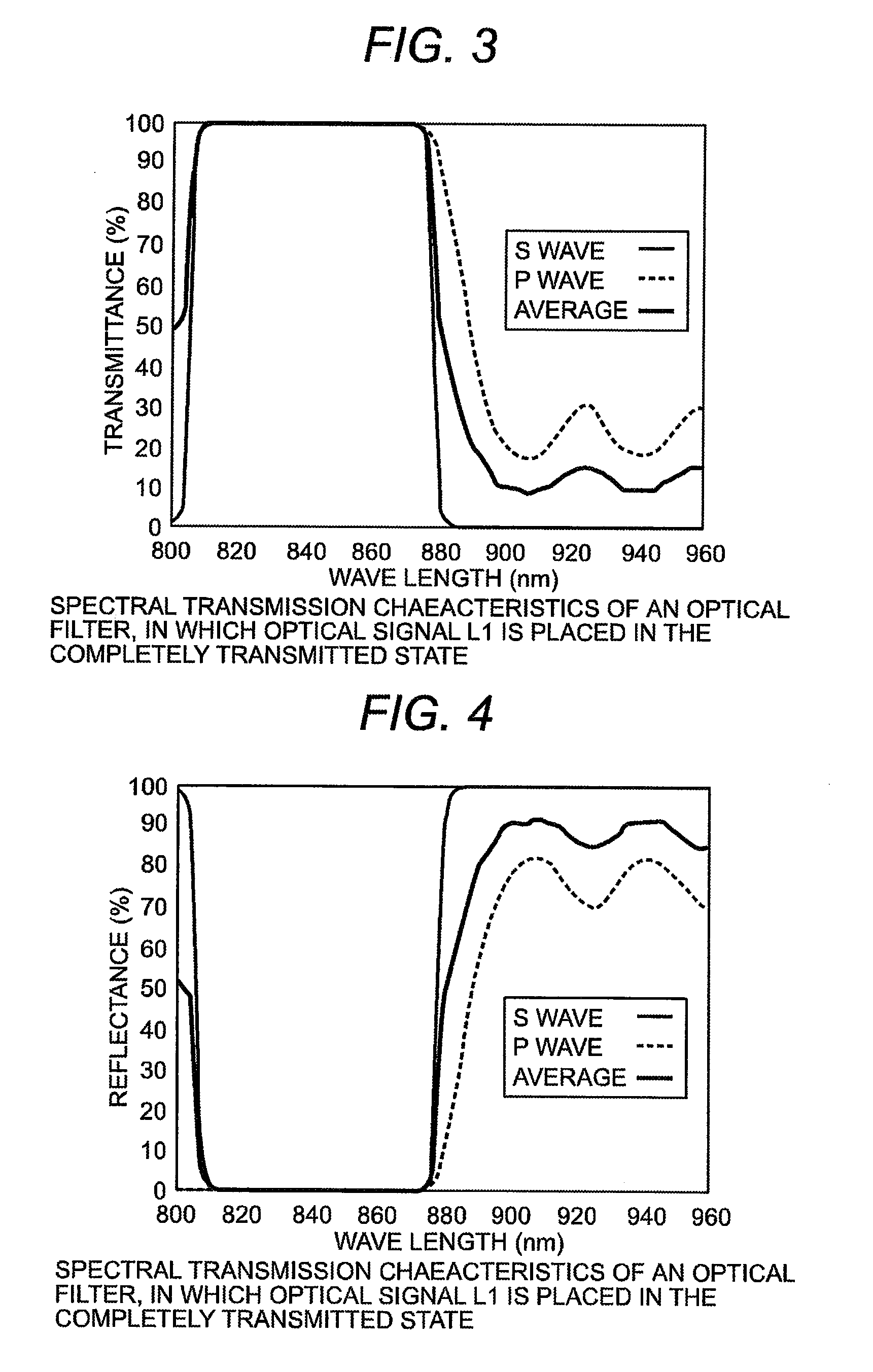
Optical transmission module and optical transmission system
An optical transmission module includes one or more transmission optical devices for transmitting an optical signal L1, one or more reception optical devices for receiving another optical signal L2, and an optical member for converting optical paths for one or more optical signals L1 and one or more optical signals L2 having a different wavelength from the optical signal L1. The optical transmission module includes two or more inclined planes angled relative to the optical axis of the optical fiber, one of the two or more inclined planes has an optical filter for allowing these optical signals to partially or almost completely pass or partially reflect the optical signals L1 and L2; a reflecting plane for reflecting the optical signal L1 or L2 is formed on another one of the two or more inclined planes; a fiber lens is provided at a fiber-side end facing the optical fiber.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Light guide optical assembly
An optical assembly for optical aperture expansion combines facet reflective technology with diffractive technology. At least two diffractive components having opposite optical power (matching) are used, so that chromatic dispersion introduced by the first diffractive component will then be cancelled by the second diffractive component. The two diffractive components are used in combination with a reflective optical component to achieve more efficient aperture expansion (for near eye display), reducing distortions and noise, while also reducing design constraints on the system and individual components, as compared to conventional techniques. The assembly eliminates and / or reduces the need for polarization management, while enabling wider field of view. In addition, embodiments can have reduced nonuniformity, as compared to conventional single technology implementations, since the distortion patterns of the two technologies do not correlate.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Reflective optical element for EUV lithography device
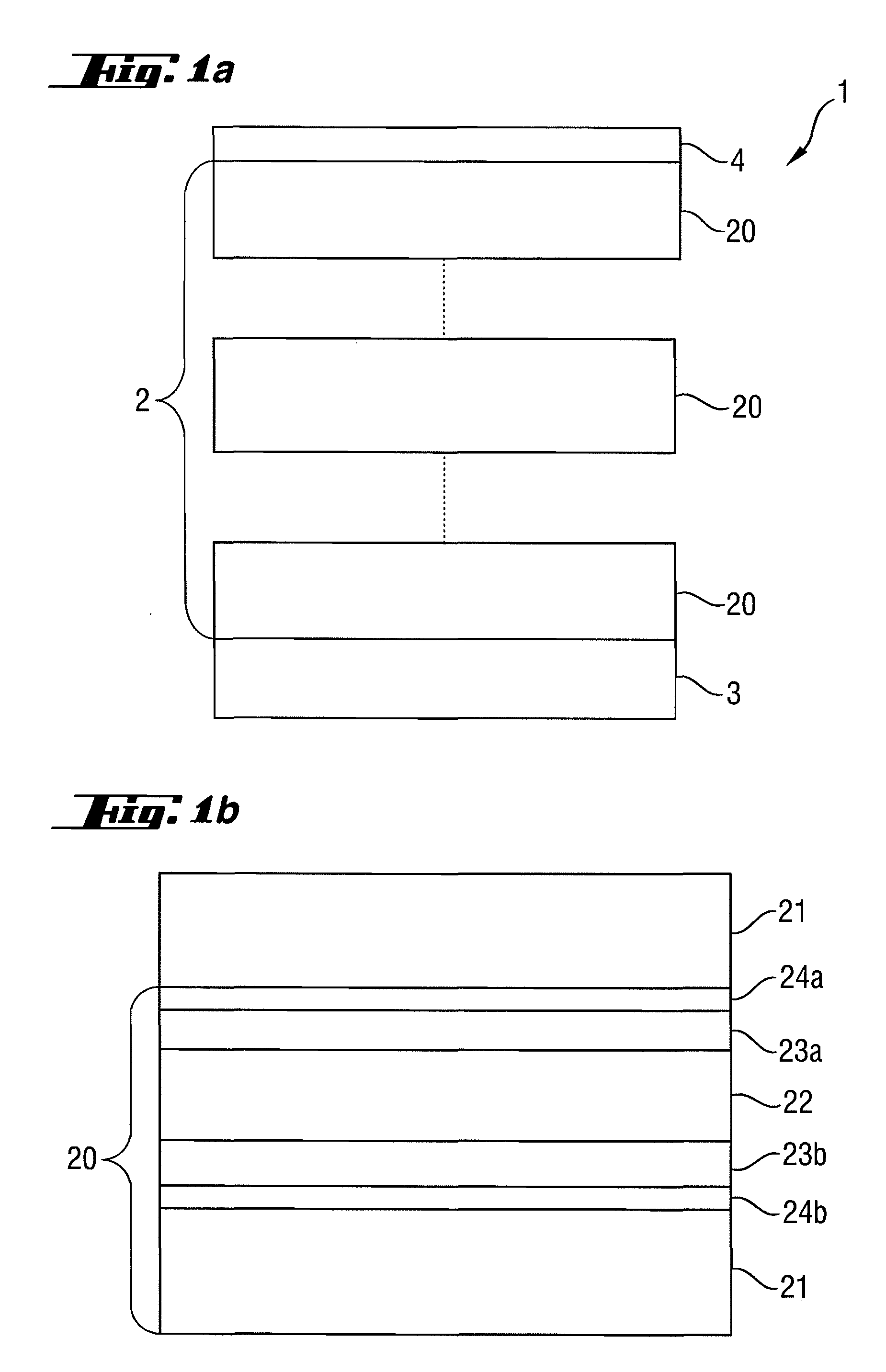
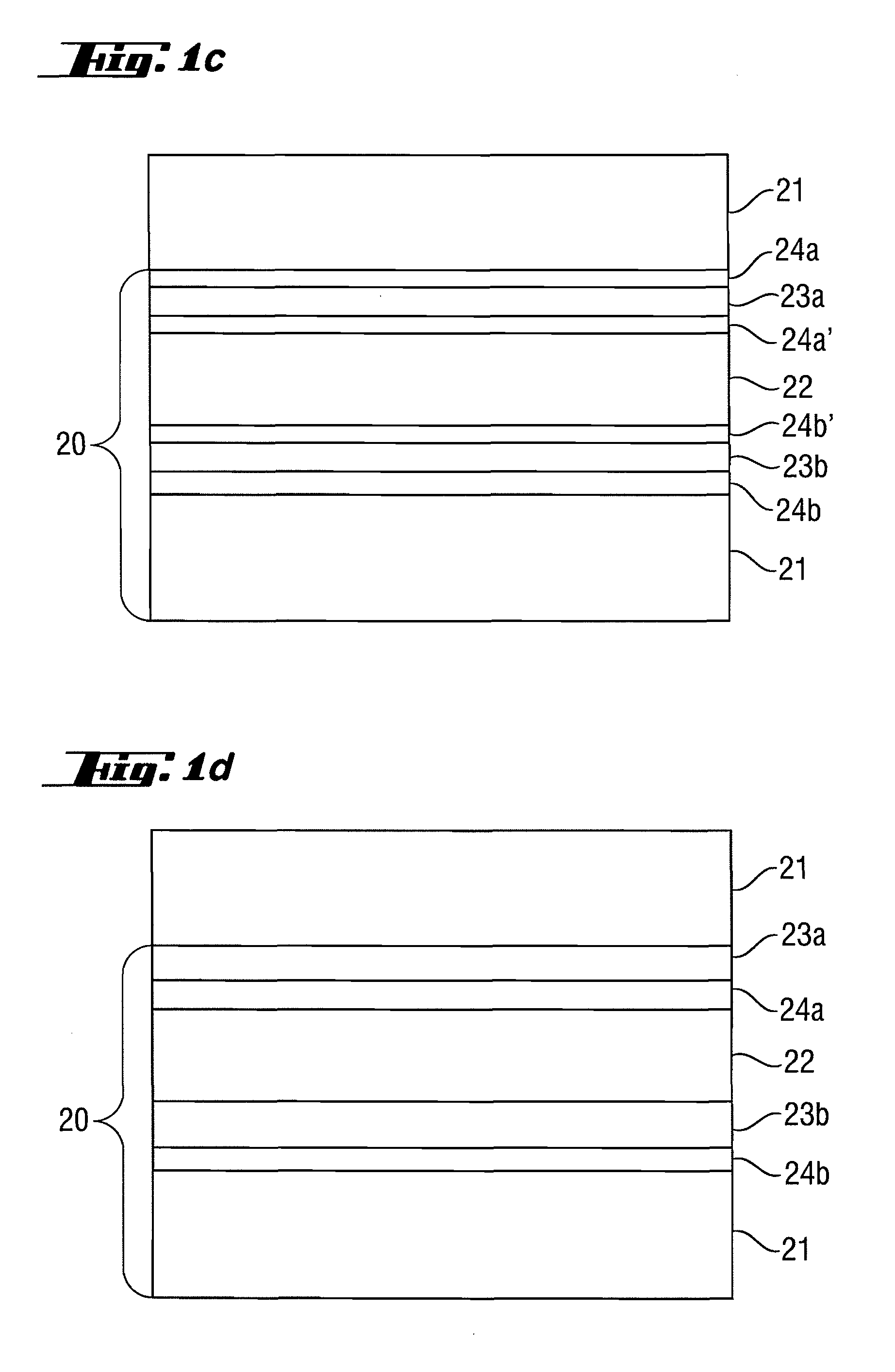
ActiveUS20100027107A1Improve reflectivityIncrease of maximum reflectivityMirrorsNanoinformaticsCatoptricsComputational physics
A reflective optical element exhibits an increase in the maximum reflectivity at operating wavelengths in the extreme ultraviolet or soft x-ray wavelength range. A first additional intermediate layer (23a, 23b) and a second additional intermediate layer (24a, 24b) are provided between the absorber layer (22) and the spacer layer (21), wherein the first additional intermediate layer increases the reflectivity and the second additional intermediate layer (24a,b) prevents chemical interaction between the first additional intermediate layer (23a,b) and the adjoining spacer layer (21) and / or the absorber layer (22).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Micro-display engine
ActiveUS20050180021A1Improve efficiencyImprove performancePolarising elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsCatoptricsImage formation
Virtual displays with micro-display engines are arranged in compact, lightweight configurations that generate clear virtual images for an observer. The displays are particularly suitable for portable devices, such as head-mounted displays adapted to non-immersive or immersive applications. The non-immersive applications feature reflective optics moved out of the direct line of sight of the observer and provide for differentially modifying the amount or form of ambient light admitted from the forward environment with respect to image light magnified within the display. Micro-display engines suitable for both non-immersive and immersive display applications and having LCD image sources displace polarization components of the LCD image sources along the optical paths of the engines for simplifying engine design. A compound imaging system for micro-display engines features the use of reflectors in sequence to expand upon the imaging possibilities of the new micro-display engines. Polarization management also provides for differentially regulating the transmission of ambient light with respect to image light and for participating in the image formation function of the image source.
Owner:TDG ACQUISITION COMPANY
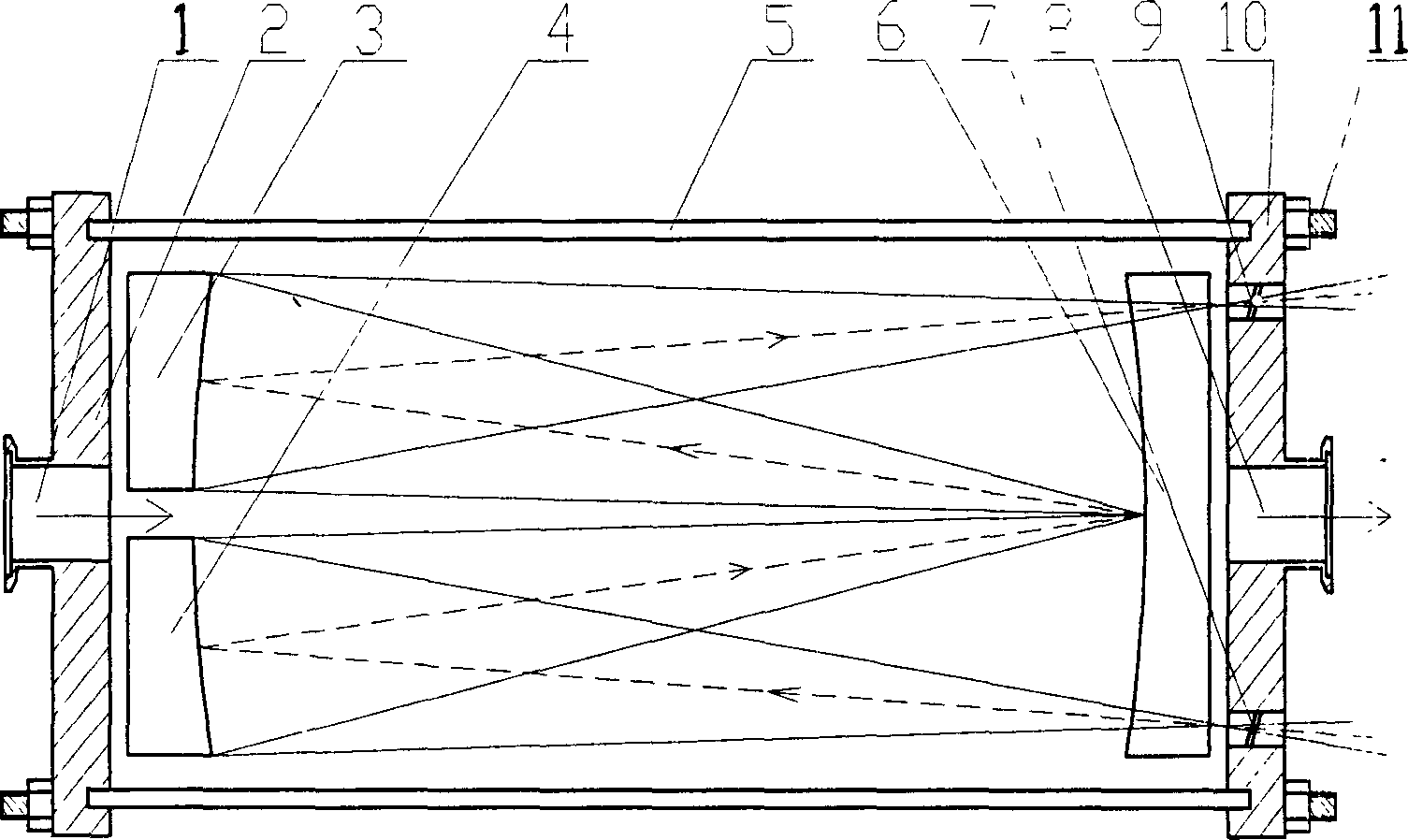
Method and apparatus for adjustable multiple reflection optical absorptions
InactiveCN1699971AIncrease the number of reflectionsColor/spectral properties measurementsBackground spectrumCatoptrics
The invention discloses a apparatus and method for adjustable multiple reflection optical absorption, which adopts the principle of multiple reflection to design a optical absorbing pool; light beam multiple reflects by main reflector and two auxiliary reflectors so as to effectively accrete the length of detecting optical path in a small spacing. The multiple reflection optical absorbing pool has compact structure and can do alternative measurement to sample spectrum and background spectrum.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Projection optical system and image projecting apparatus
A projection optical system including a first optical system configured to form a second image conjugate to a first image and a second optical system configured to include a reflective optical element which reflects light from the second image and to project a third image conjugate to the second image onto a projection surface is provided, wherein the first optical system includes a stop and at least one optical element with a positive refractive power and at least one optical element with a negative refractive power which are provided between the stop and the second image, and an optical element with a strongest positive refractive power in the at least one optical element with a positive refractive power is provided between the stop and an optical element with a strongest negative refractive power in the at least one optical element with a negative refractive power.
Owner:RICOH KK
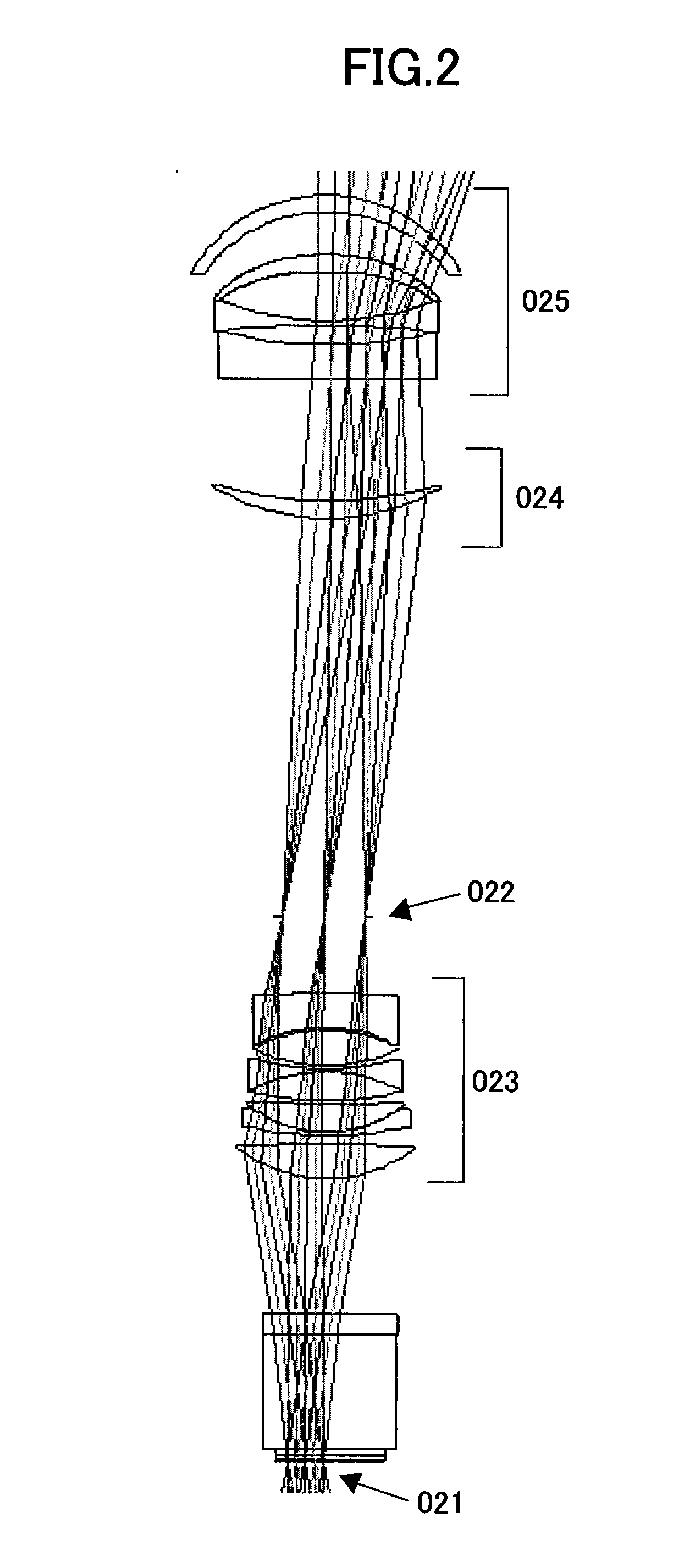
Toner-density calculating method, reflective optical sensor, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20100266302A1Solve problemsScattering properties measurementsElectrographic process apparatusCatoptricsElectro-optical sensor
Owner:RICOH KK
Active optical zoom system
An active optical zoom system changes the magnification (or effective focal length) of an optical imaging system by utilizing two or more active optics in a conventional optical system. The system can create relatively large changes in system magnification with very small changes in the focal lengths of individual active elements by leveraging the optical power of the conventional optical elements (e.g., passive lenses and mirrors) surrounding the active optics. The active optics serve primarily as variable focal-length lenses or mirrors, although adding other aberrations enables increased utility. The active optics can either be LC SLMs, used in a transmissive optical zoom system, or DMs, used in a reflective optical zoom system. By appropriately designing the optical system, the variable focal-length lenses or mirrors can provide the flexibility necessary to change the overall system focal length (i.e., effective focal length), and therefore magnification, that is normally accomplished with mechanical motion in conventional zoom lenses. The active optics can provide additional flexibility by allowing magnification to occur anywhere within the FOV of the system, not just on-axis as in a conventional system.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
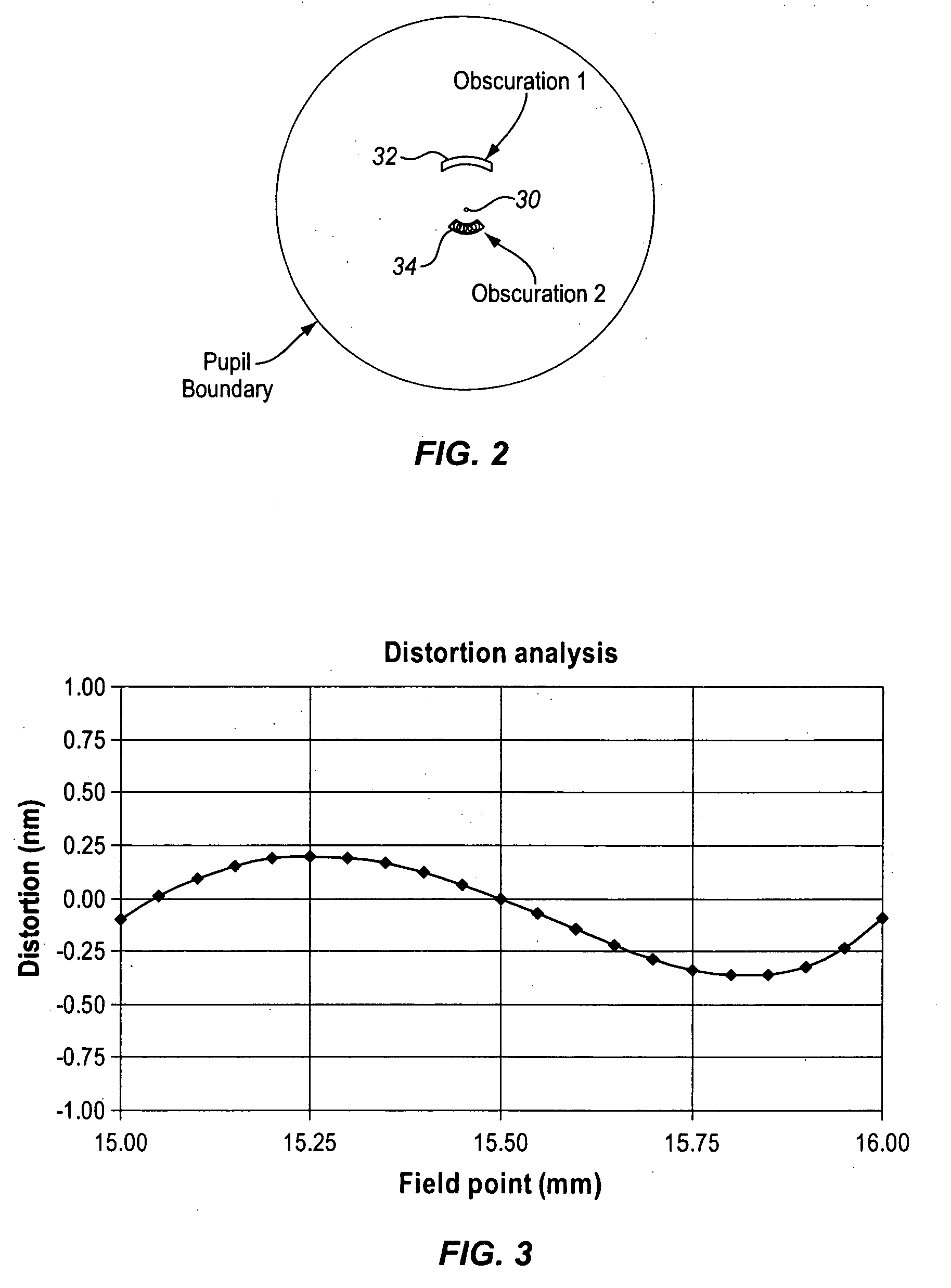
All-reflective optical systems for broadband wafer inspection
ActiveUS20060219930A1Low central obscurationReduce distortion problemsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsCatoptricsBroadband
All-reflective optical systems for broadband wafer inspection are provided. One system configured to inspect a wafer includes an optical subsystem. All light-directing components of the optical subsystem are reflective optical components except for one or more refractive optical components, which are located only in substantially collimated space. The refractive optical component(s) may include, for example, a refractive beamsplitter element that can be used to separate illumination and collection pupils. The optical subsystem may also include one or more reflective optical components located in substantially collimated space. The optical subsystem is configured for inspection of the wafer across a waveband of greater than 20 nm. In some embodiments, the optical subsystem is configured for inspection of the wafer at wavelengths less than and greater than 200 nm.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
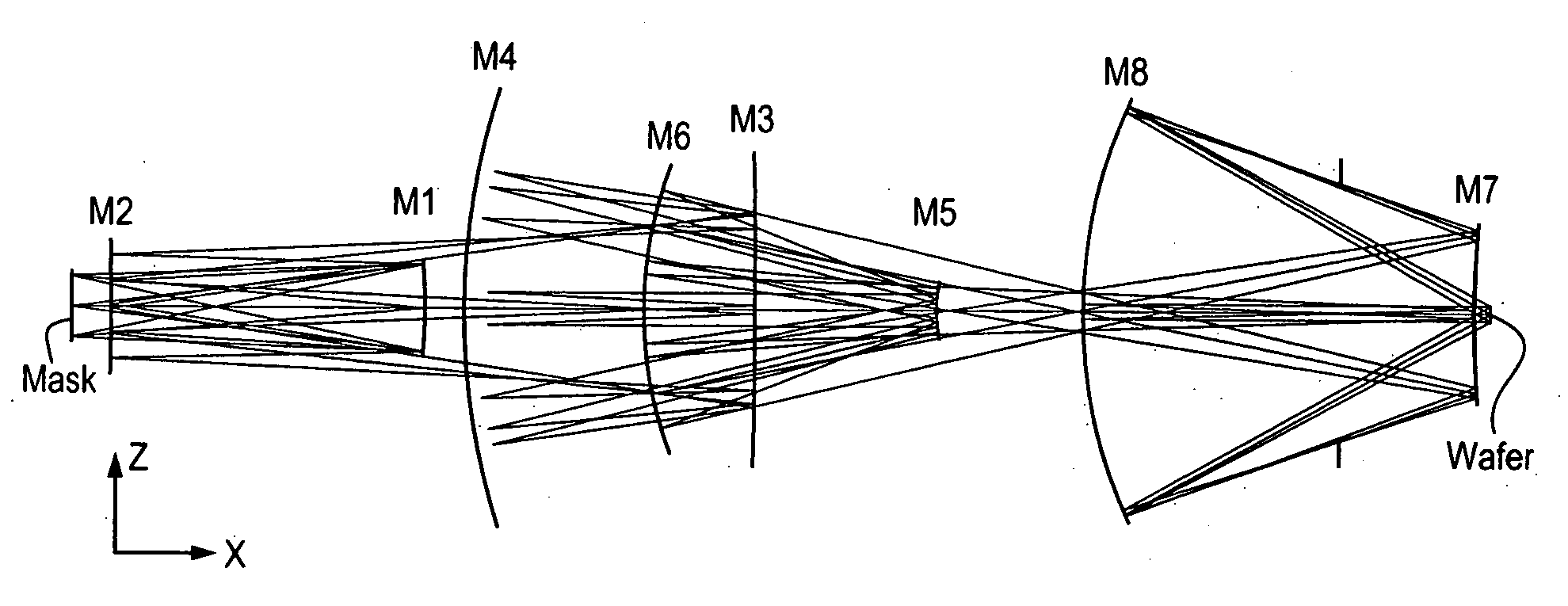
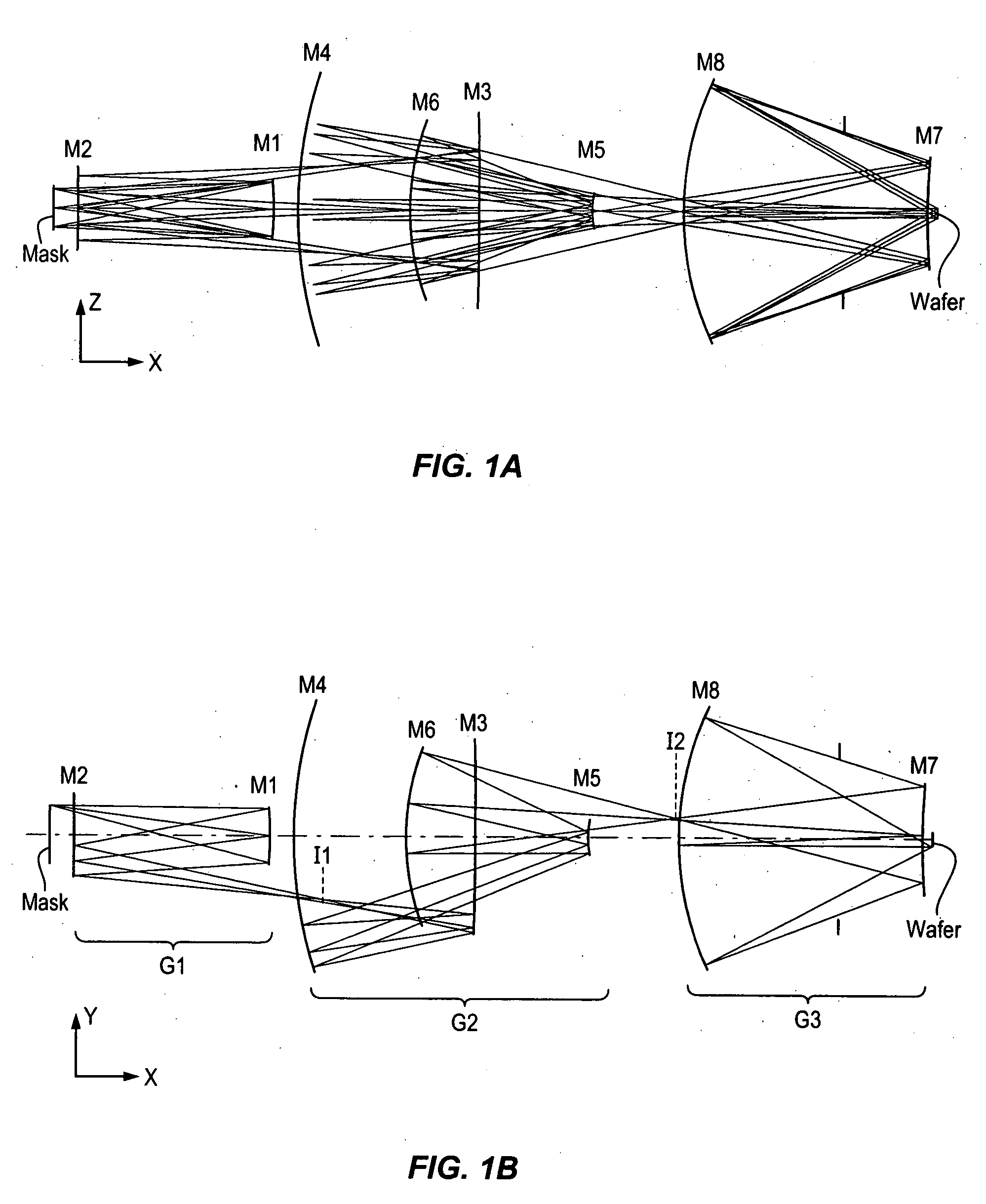
6-Mirror projection objective with few lenses
There is provided a projection objective for wavelengths of <=193 nm for imaging an object field in an object plane into an image field, in an image plane. The projection objective includes a first reflective optical element, a second reflective optical element, a third reflective optical element, a fourth reflective optical element, a fifth reflective optical element, and a sixth reflective optical element, and a refractive optical element. The reflective and refractive optical elements each have an off axis segment with a diameter. The projection objective has an image-side numerical aperture >=0.65, and the off axis segment of the refractive optical element has a diameter that is less than 1 / 3<rd >of the distance from the object plane to the image plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Reflective optical system for a photolithography scanner field projector
InactiveUS20080118849A1Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCatoptricsComputational physics
A reflective optical system for a photolithography scanner field projector is described. In one example, the optical projection system has at least eight reflecting surfaces for imaging a reflection of a photolithography mask onto a wafer and the system has a numerical aperture of at least 0.5.
Owner:INTEL CORP
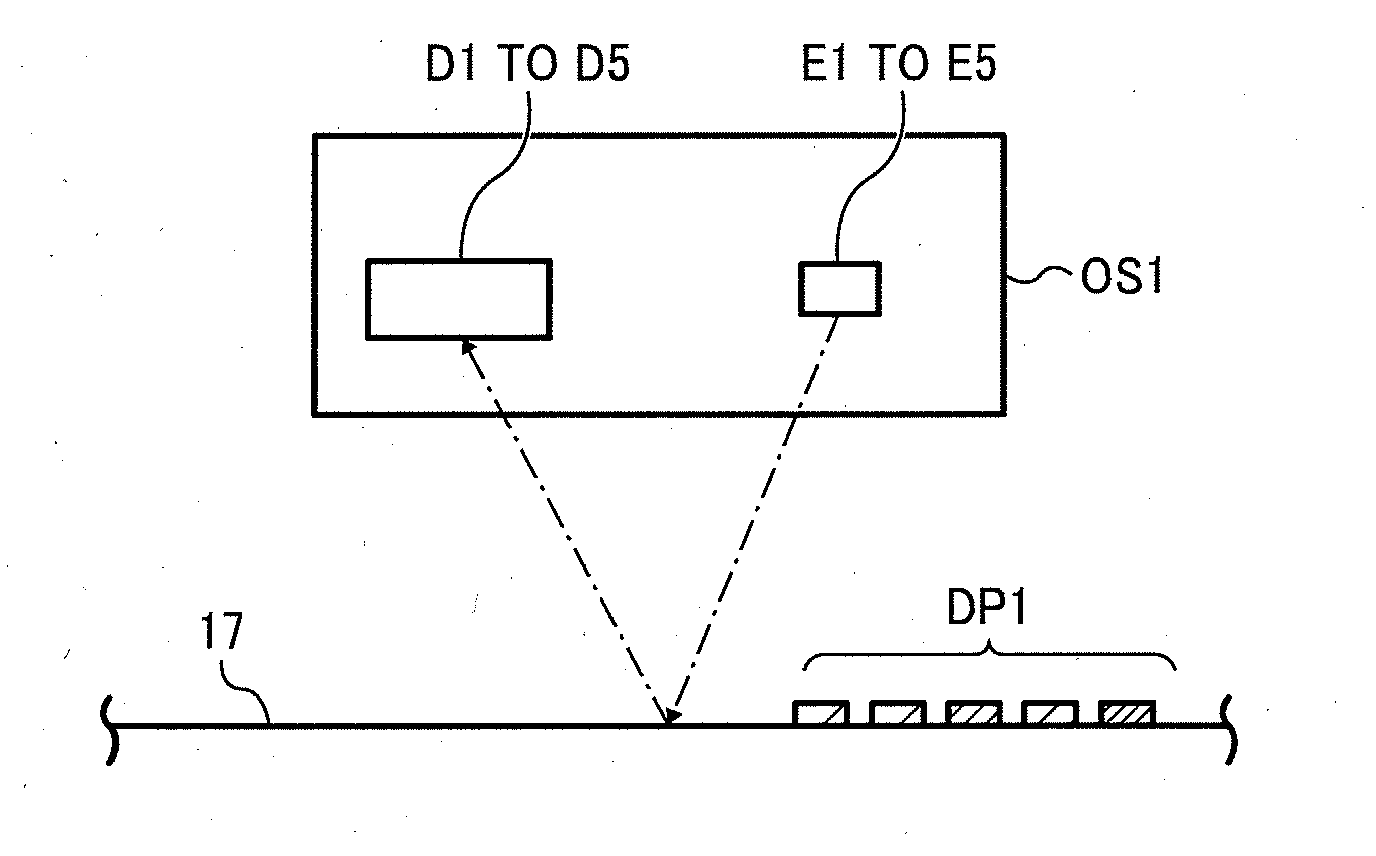
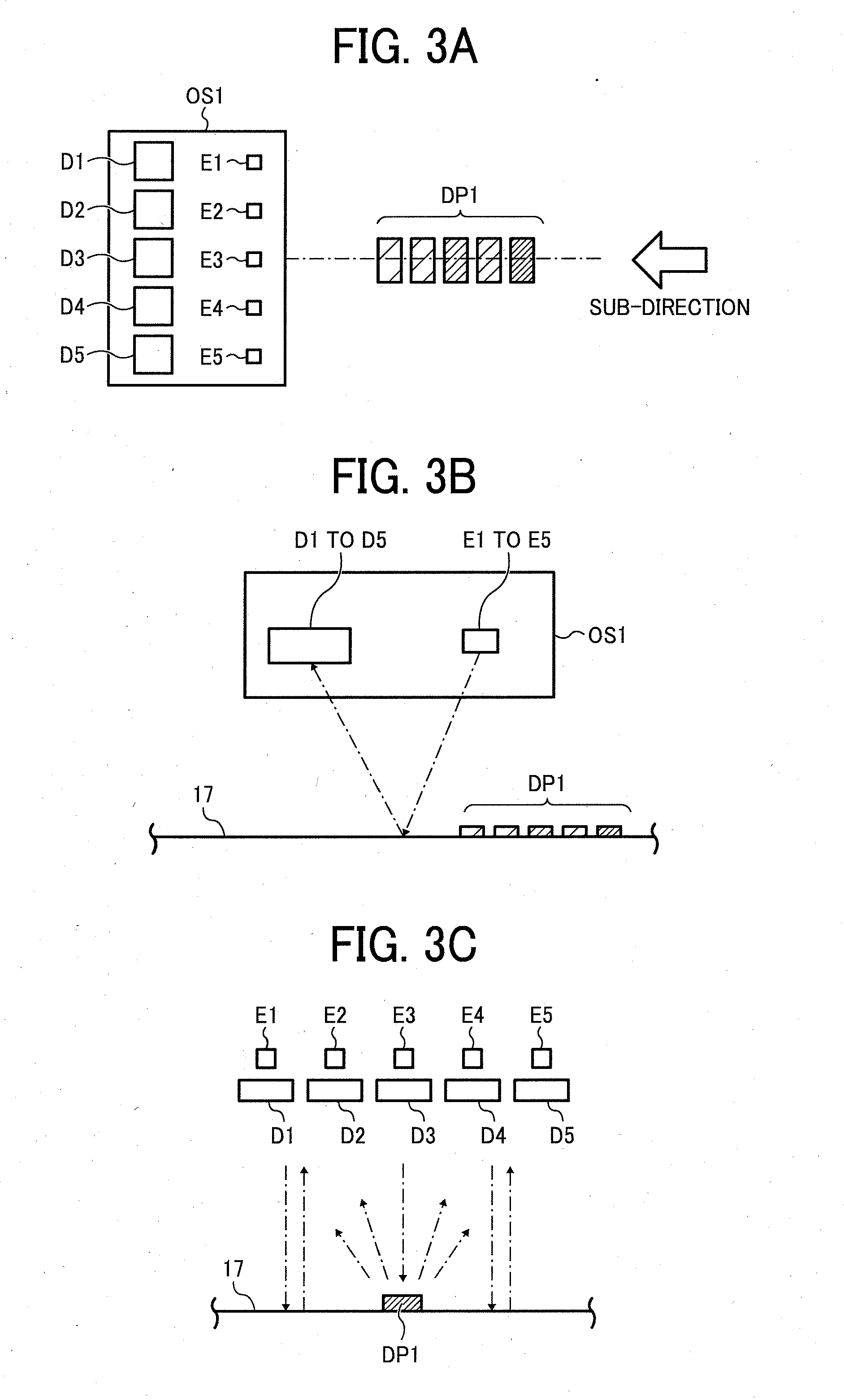
Toner-density calculating method, reflective optical sensor, reflective optical sensor device, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20090238590A1Solve problemsScattering properties measurementsDigital computer detailsCatoptricsLight spot
Owner:RICOH KK
Method For Manufacturing Reflective Optical Element, Reflective Optical Elements, Euv-Lithography Apparatus And Methods For Operating Optical Elements And Euv-Lithography Apparatus, Methods For Determining The Phase Shift, Methods For Determining The Layer Thickness, And Apparatuses For Carrying Out The Methods
InactiveUS20070285643A1Large intensityPhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansCatoptricsLayer thickness
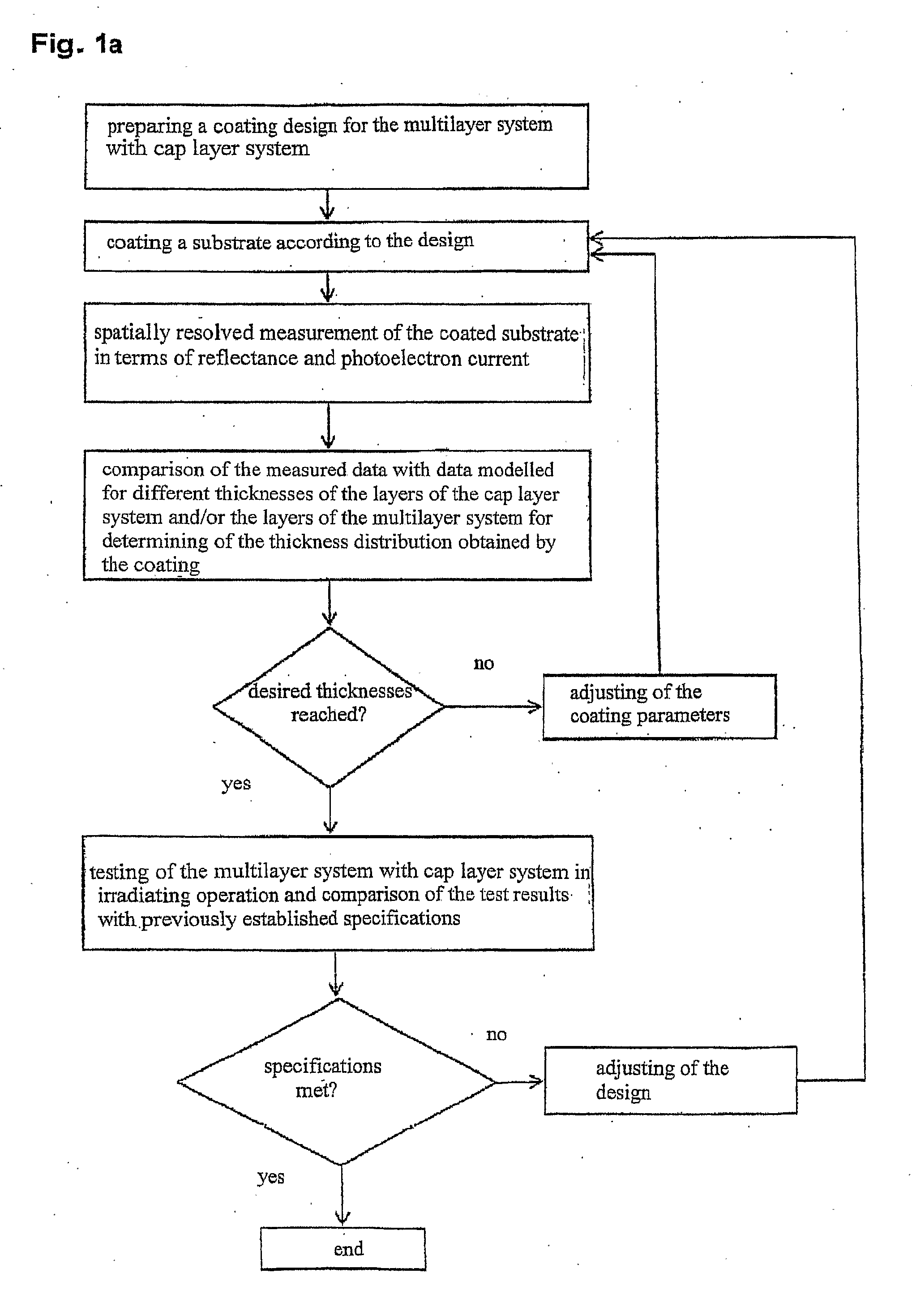
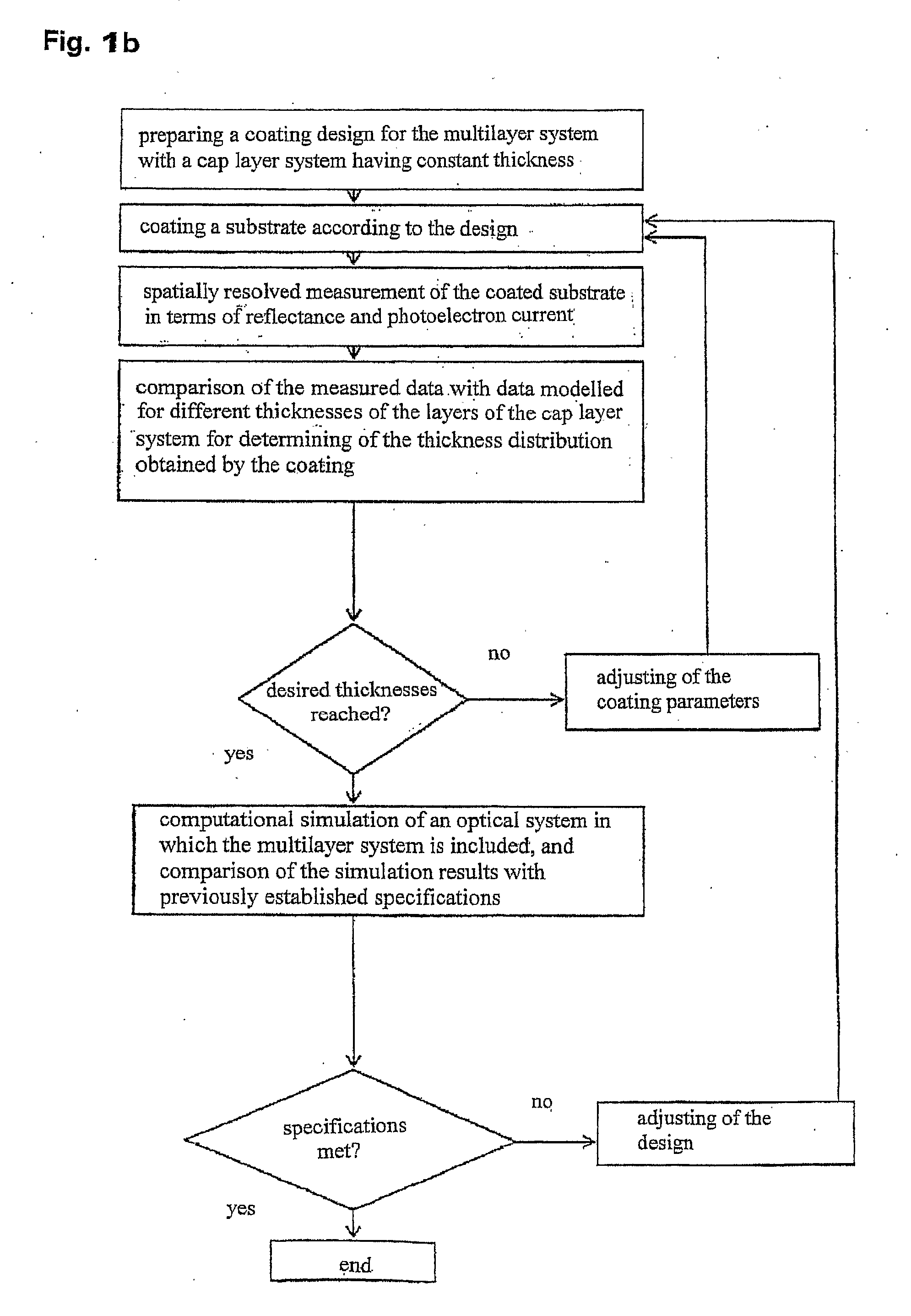
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing of a multilayer system (25) with a cap layer system (30), in particular for a reflective optical element for the extreme ultraviolet up to the soft x-ray wavelength range, comprising the steps of: 1. preparing a coating design for the multilayer system (25) with cap layer system (30); 2. coating a substrate (20) with the multilayer system (25) with cap layer system (30); 3. spatially resolved measurement of the coated substrate in terms of reflectance and photoelectron current in at least one surface point; 4. comparison of the measured data with data modelled for different thicknesses of the layers (31, 32, 33) of the cap layer system (30) and / or the layers (21, 22, 23, 24) of the multilayer system (25) for determining of the thickness distribution obtained by the coating; 5. if necessary, adjusting of the coating parameters and repeating steps 2 to 5 until the coated thickness distribution coincides with the design. The invention also relates to further manufacturing methods, reflective optical elements, EUV-lithography apparatuses, and methods for operating optical elements and EUV-lithography apparatuses as well as methods for determining the phase shift, methods for determining the layer thickness, and apparatuses for carrying out the methods.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
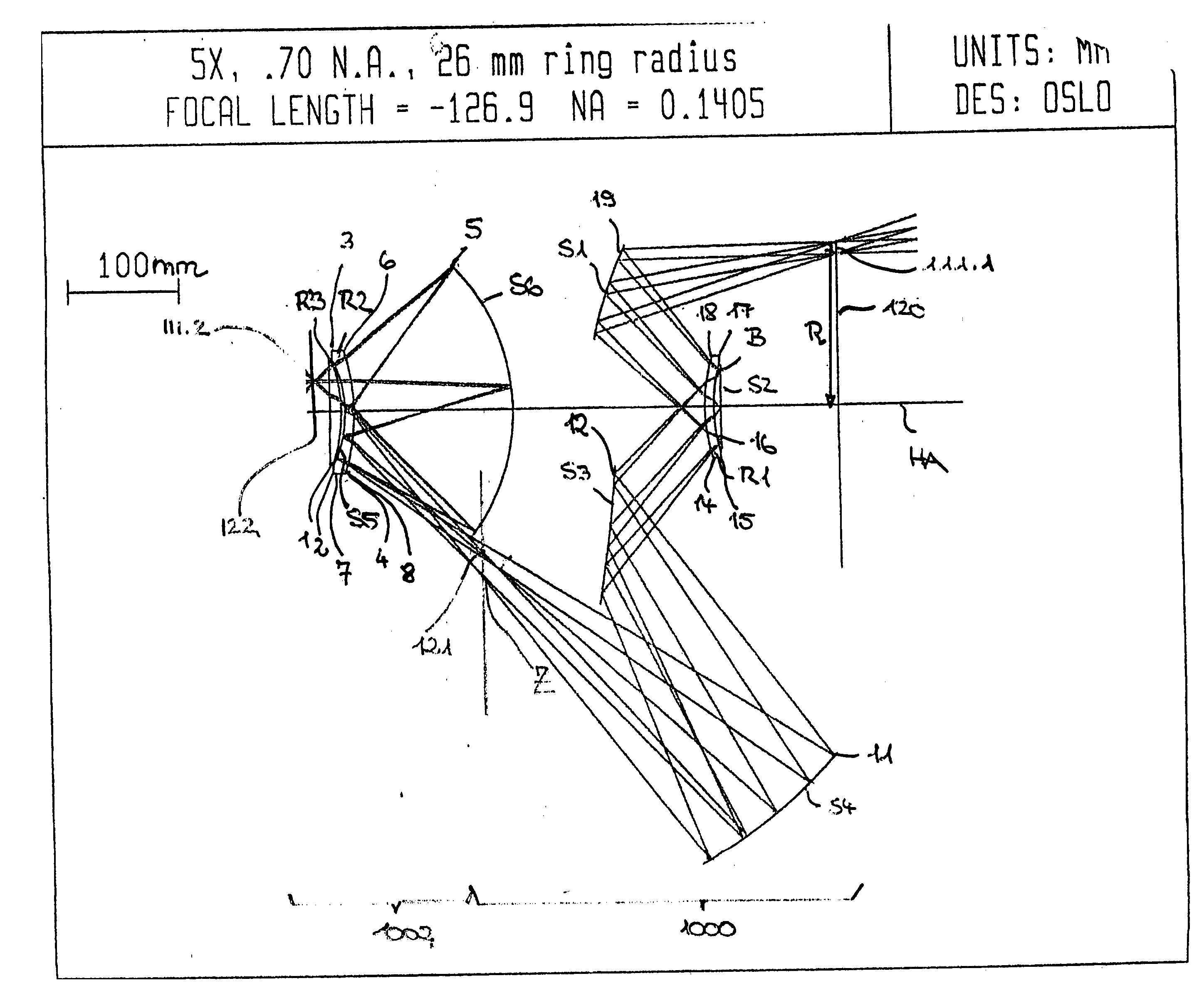
Projection optical system, exposure apparatus, and exposure method
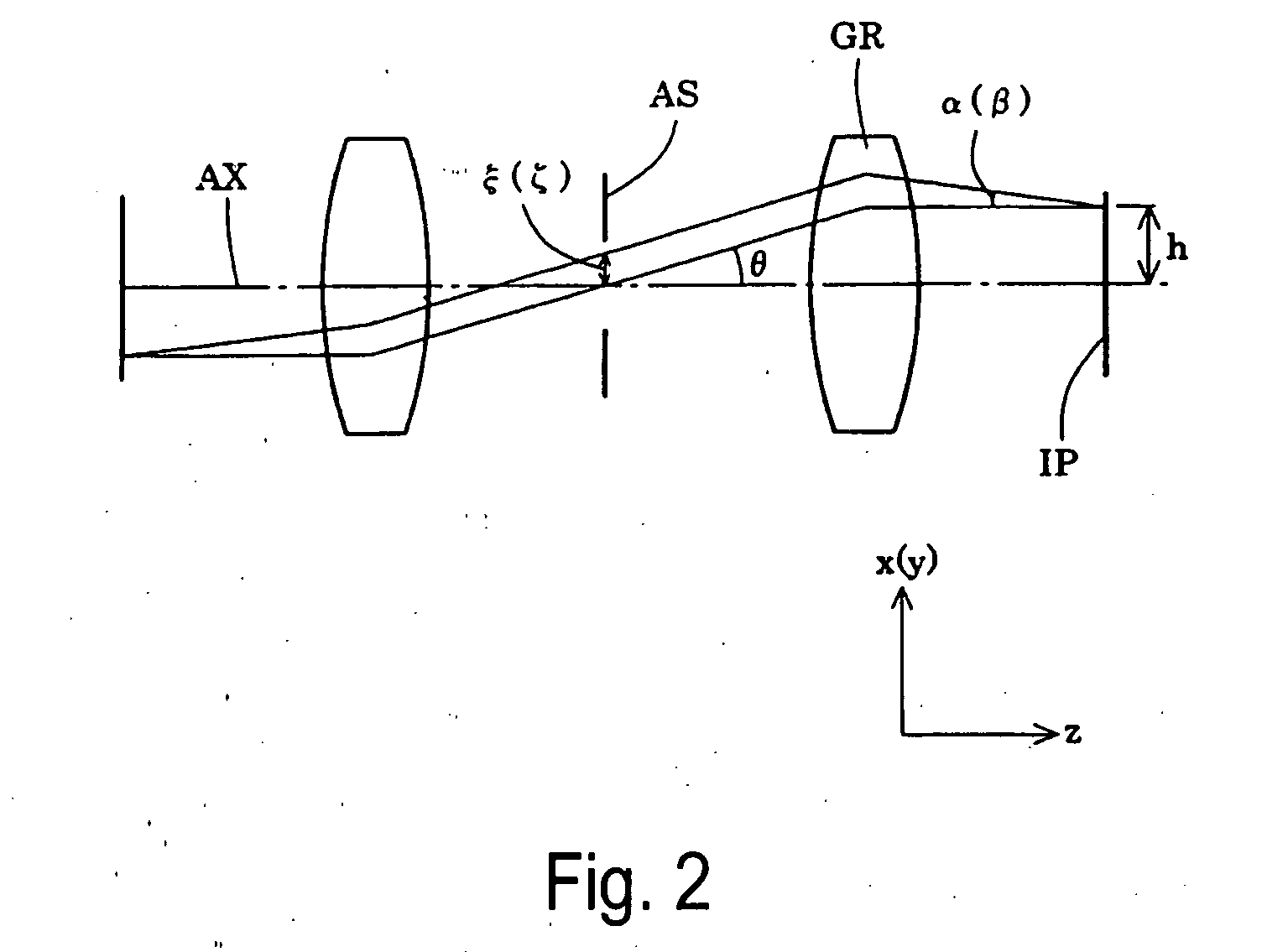
ActiveUS20060012767A1High resolutionUniform numberPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingOptical axisField of view
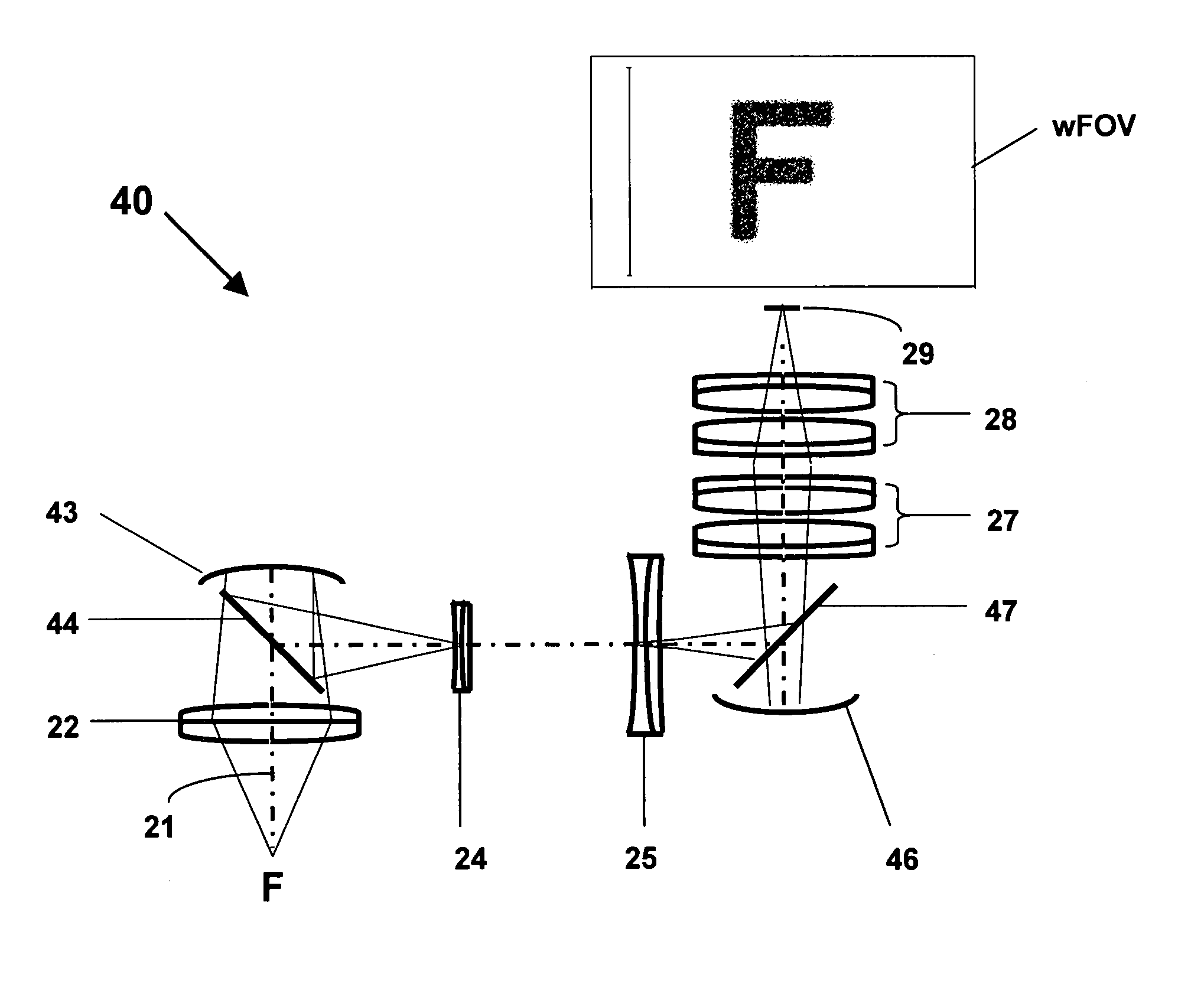
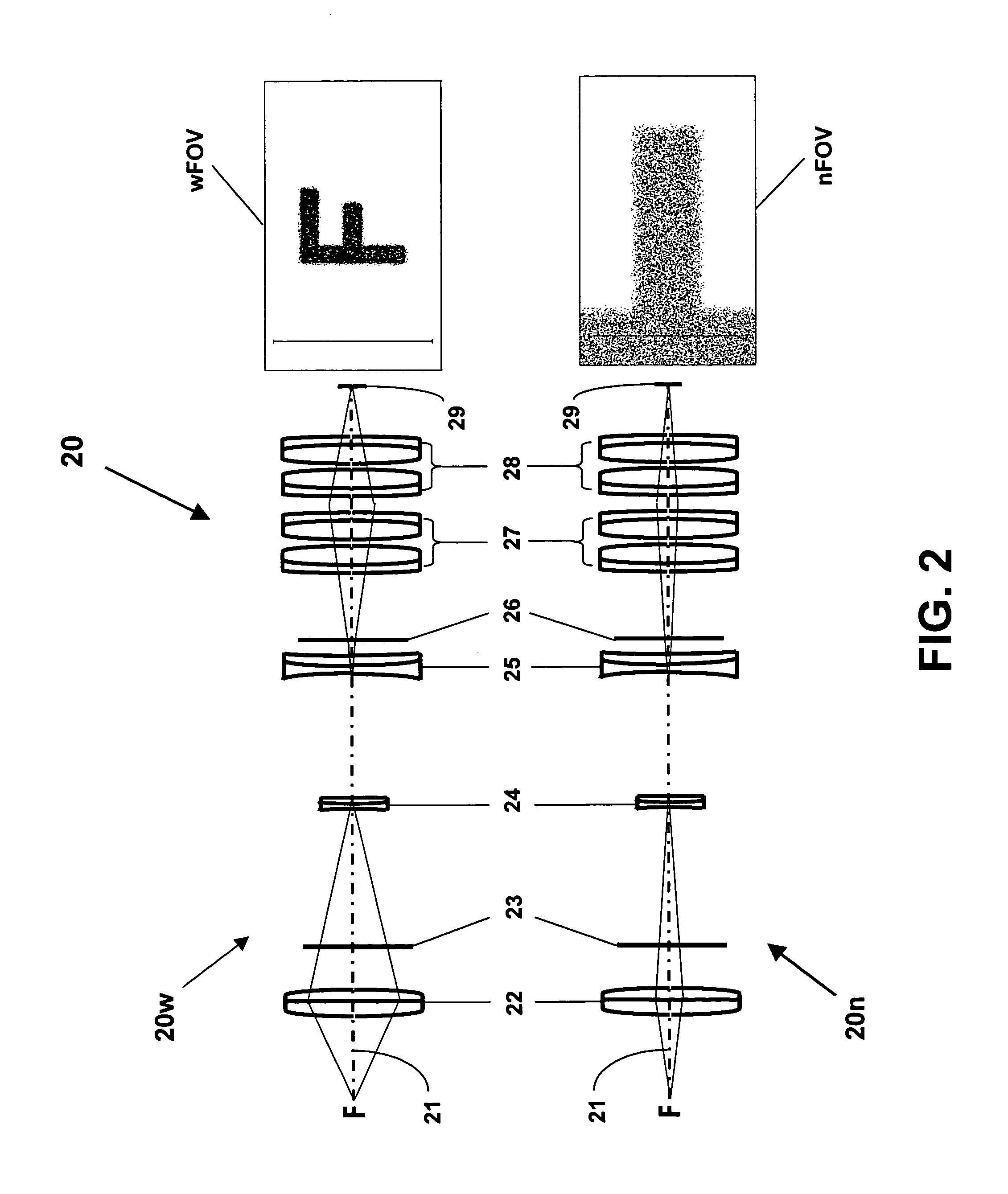
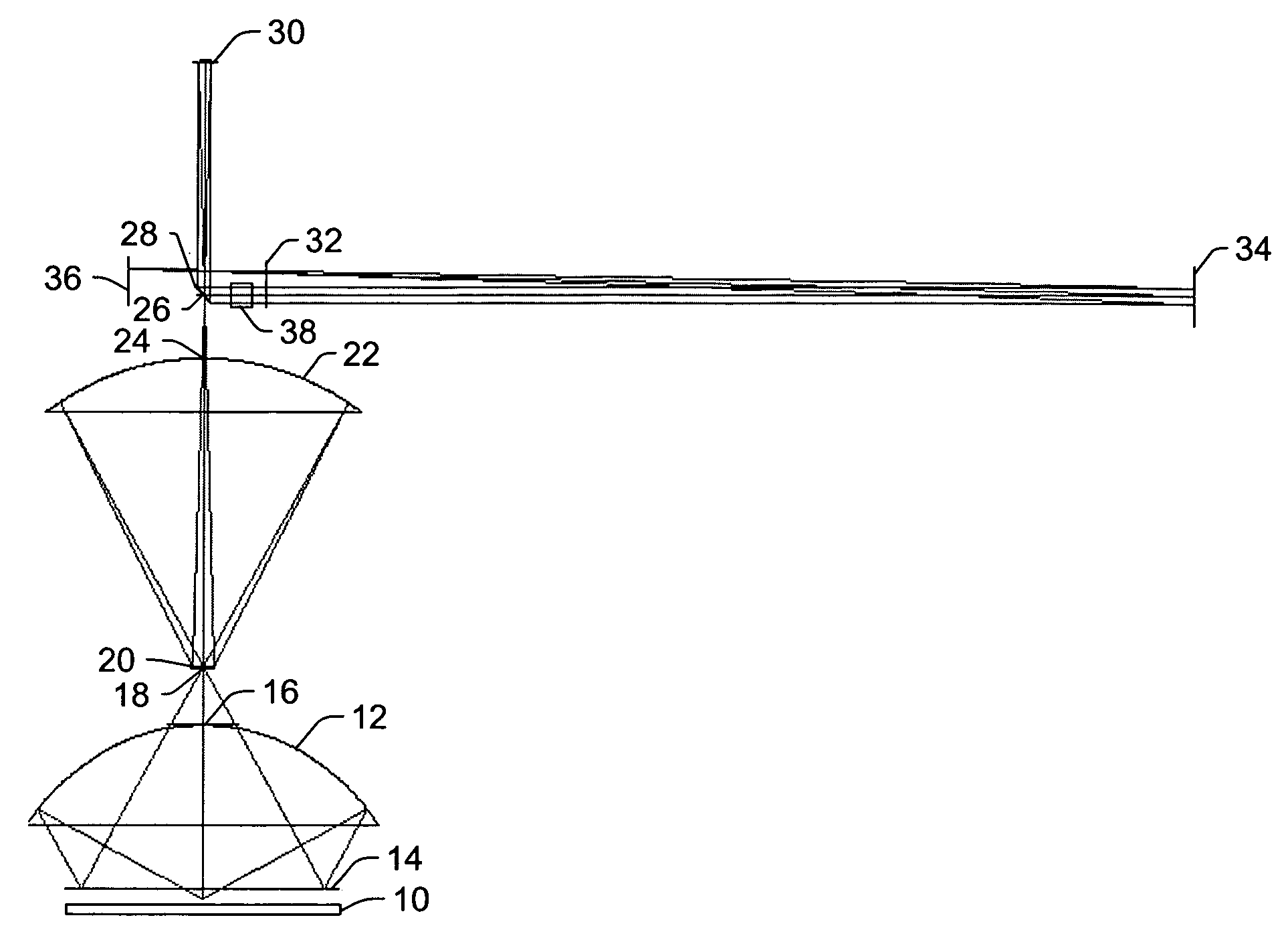
A projection optical system is a catoptric system in which a field of view region and an imaging region are located spaced from an optical axis, in which a numerical aperture of light reaching each point on an image plane is substantially uniform regardless of an image height and a direction. An aperture stop for defining the numerical aperture of the projection optical system is provided, and the aperture stop is provided with an aperture portion in a predetermined shape in which the numerical aperture of light reaching each point within a predetermined region is substantially uniform over the predetermined region, that is, in a shape in which dimensions concerning two directions perpendicular to each other are different from each other. A predetermined shape of the aperture portion is defined so as to compensate for the effect of non-uniformity of the numerical aperture of light reaching each point within a predetermined region due to a partial optical system arranged between the aperture stop and an image plane not satisfying a desired projective relationship.
Owner:NIKON CORP
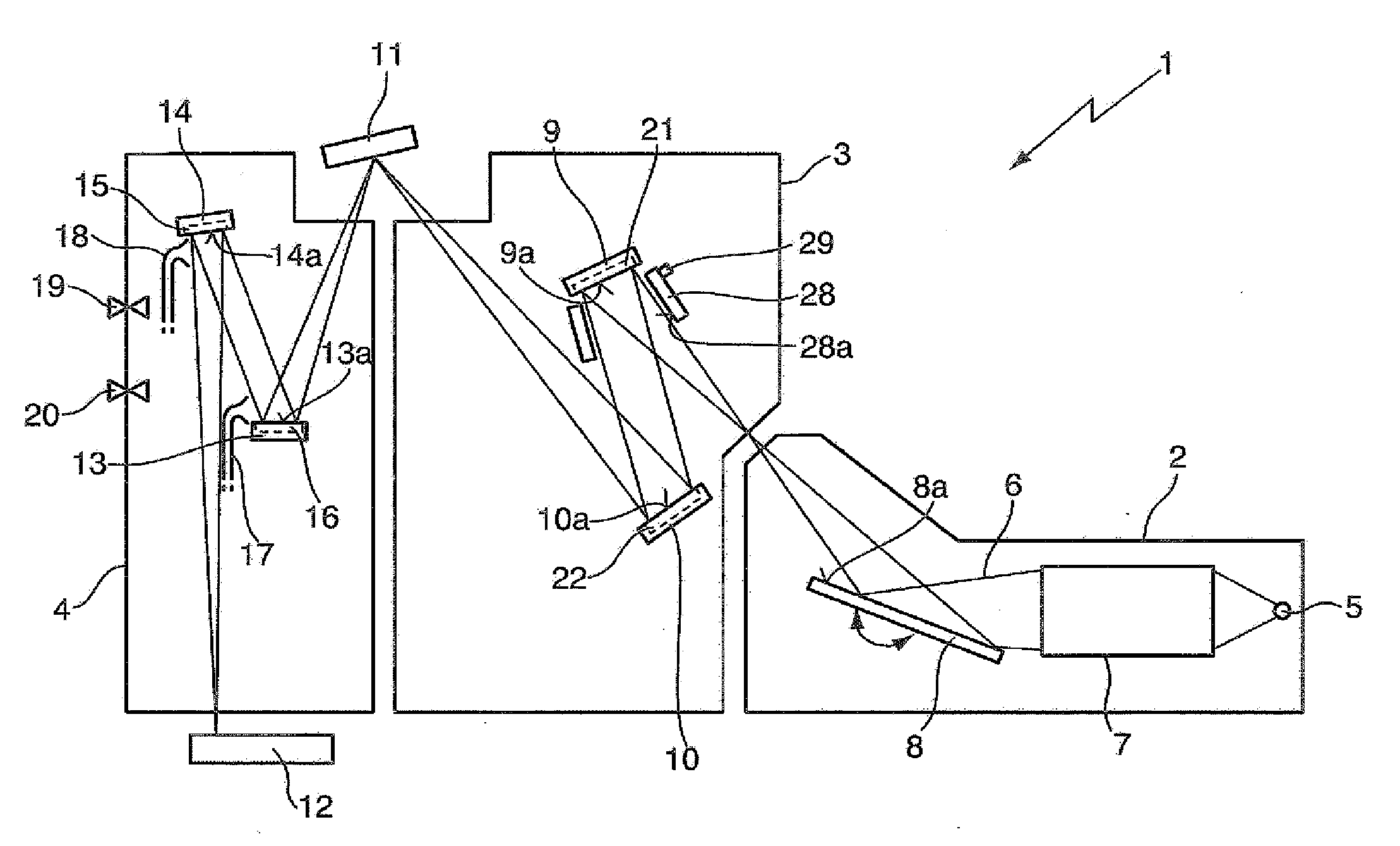
X-ray beam device
ActiveUS8422633B2Improve throughputIncreased collecting angleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayCatoptrics
The invention refers to an X-ray beam device for X-ray analytical applications, comprising an X-ray source designed such as to emit a divergent beam of X-rays; and an optical assembly designed such as to focus said beam onto a focal spot, wherein said optical assembly comprises a first reflecting optical element, a monochromator device and a second reflecting optical element sequentially arranged between said source and said focal spot, wherein said first optical element is designed such as to collimate said beam in two dimensions towards said monochromator device, and wherein said second optical element is designed such as to focus the beam coming from said monochromator device in two dimensions onto said focal spot.
Owner:XENOCS
Large field of view protection optical system with aberration correctability for flat panel displays
InactiveUS7158215B2Improve performanceReadingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCatoptricsDisplay device
An exposure system for manufacturing flat panel displays (FPDs) includes a reticle stage adapted to support a reticle. A substrate stage is adapted to support a substrate. A reflective optical system is adapted adapted to image the reticle onto the substrate. The reflective optical system includes a primary mirror including a first mirror and a second mirror, and a secondary mirror. The reflective optical system has sufficient degrees of freedom for both alignment and correction of third order aberrations when projecting an image of the reticle onto the substrate by reflections off the first mirror, the secondary mirror, and the second mirror.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Optical arrangement and EUV lithography device with at least one heated optical element, operating methods, and methods for cleaning as well as for providing an optical element
InactiveUS20080143981A1Improve optical characteristic of optical and of opticalAvoid optical distortionMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingCatoptricsProjection system
An optical arrangement, in particular a projection system, illumination system or beam shaping system for EUV lithography, including at least one optical element that is arranged in a beam path of the optical arrangement and that reflects radiation in the soft X-ray- or EUV wavelength range, wherein at least during operation of the optical arrangement at least one of, preferably each of, the reflective optical elements in the beam path, at least at the optical surface, has an operating temperature of approximately 30° C. or more, preferably of approximately 100° C. or more, particularly preferably of approximately 150° C. or more, and even more preferably of approximately 250° C. or more, and wherein the optical design of the at least one reflective optical element is selected such that its optical characteristics are optimised for operation at the operating temperature. Also presented is a method for providing a reflective optical element with such an optical design.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
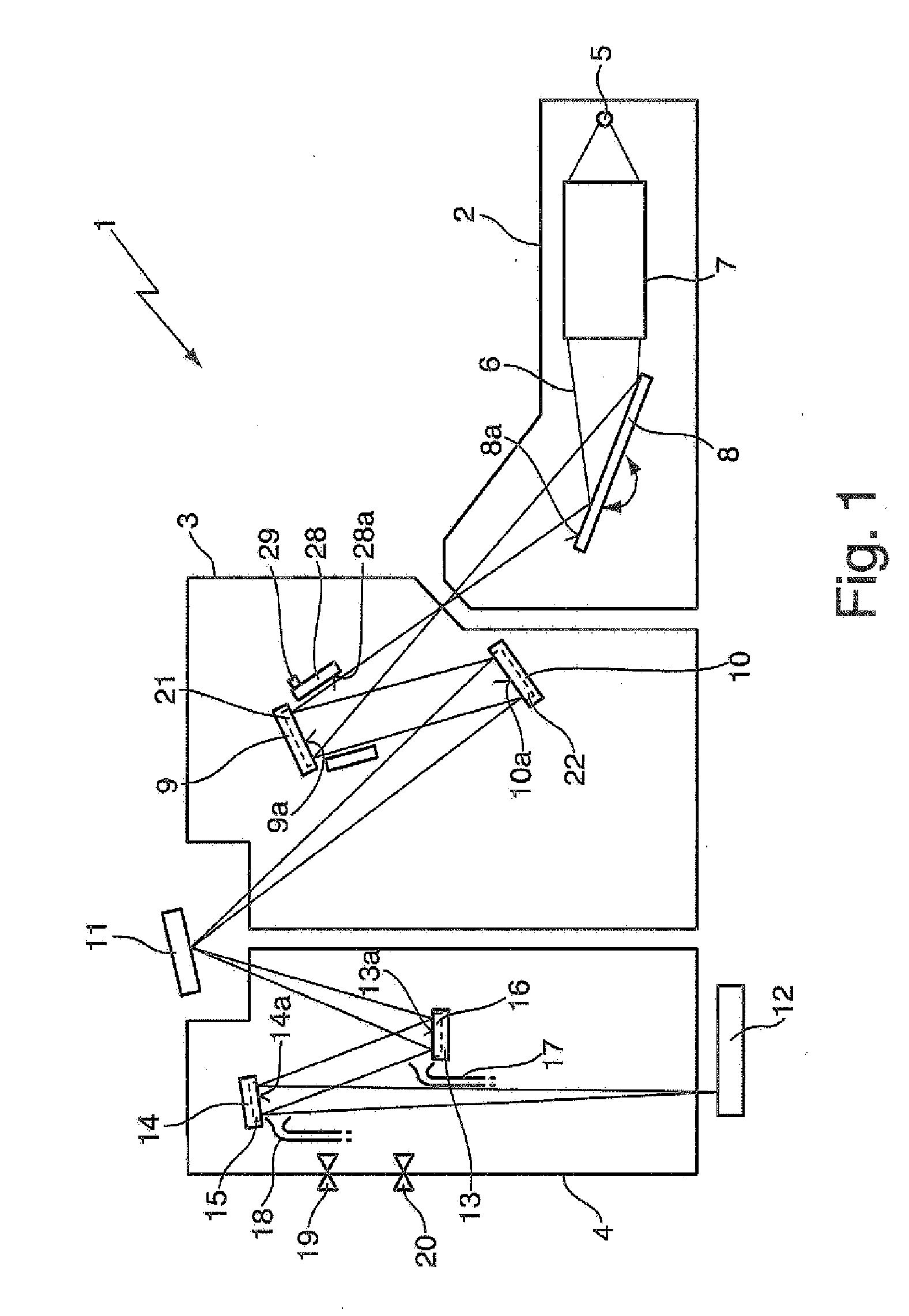
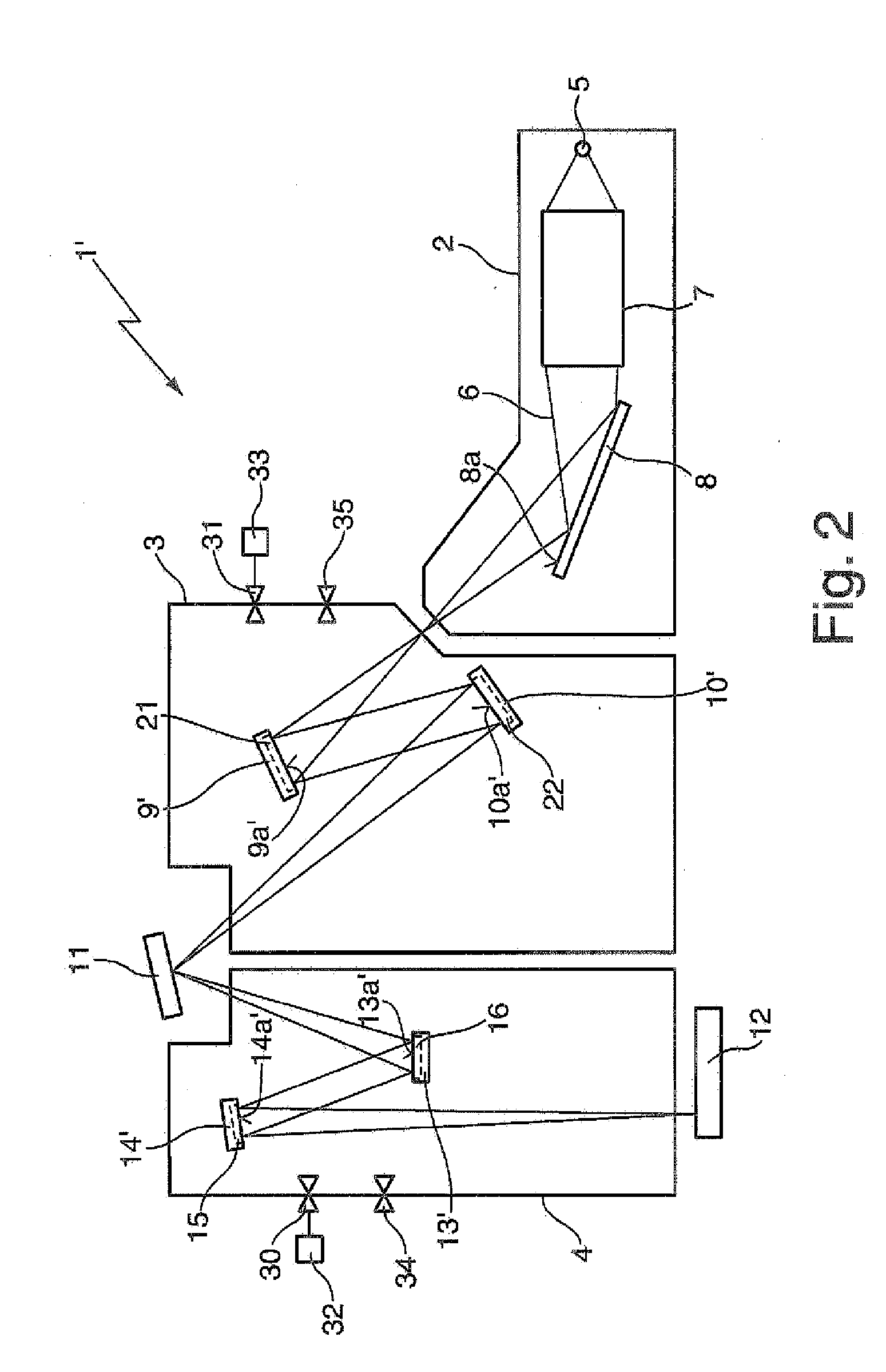
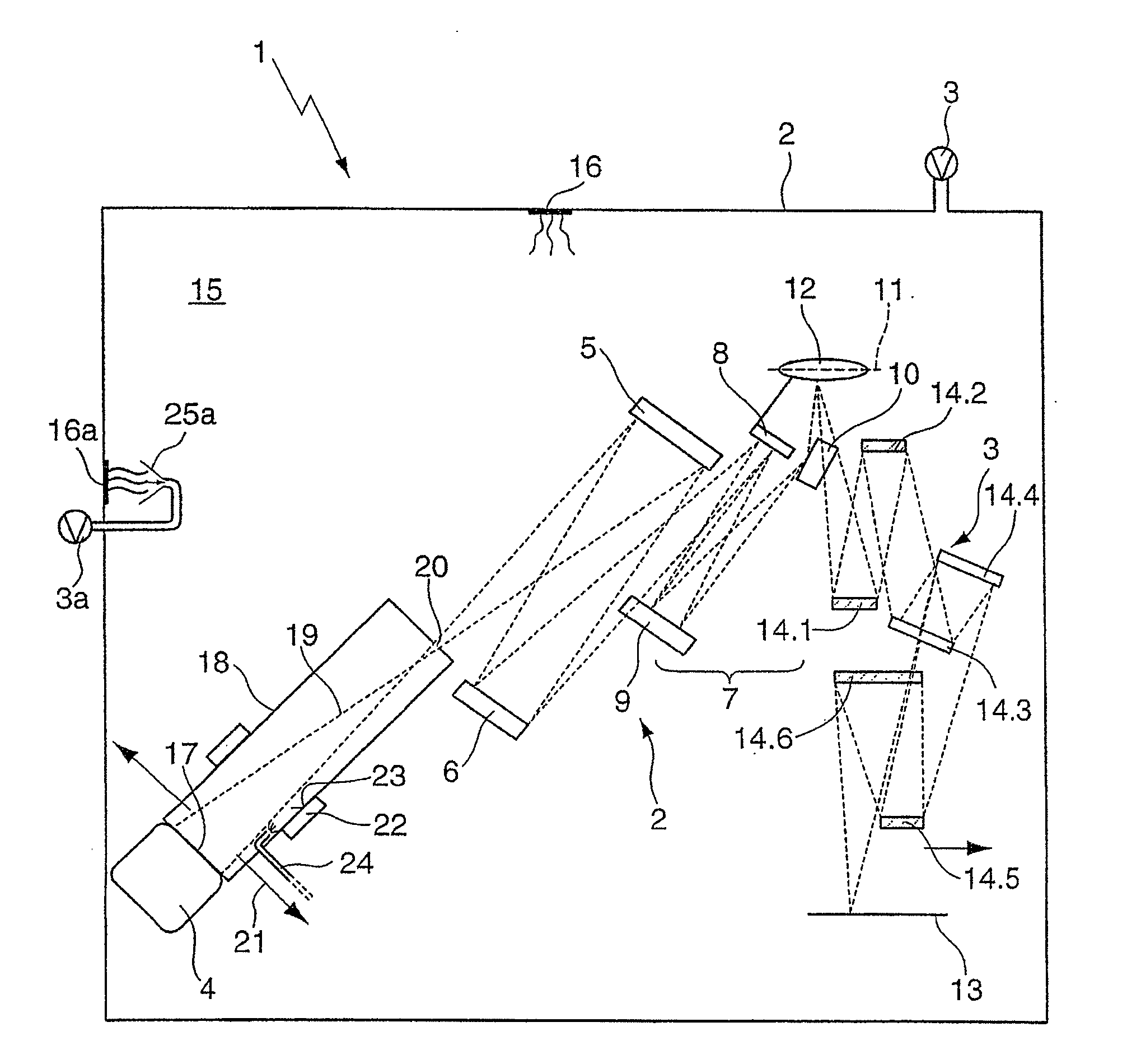
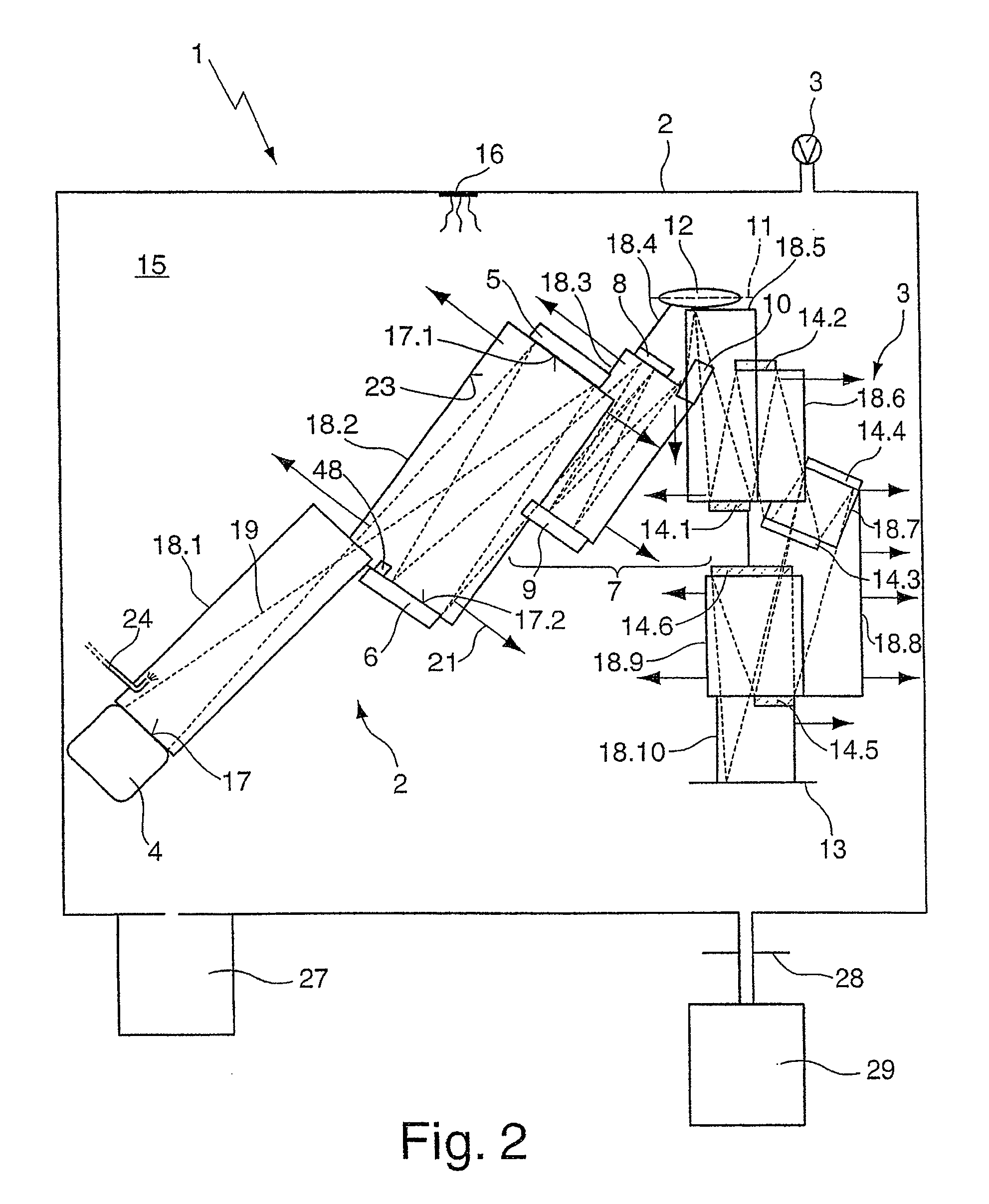
Optical arrangement, in particular projection exposure apparatus for EUV lithography, as well as reflective optical element with reduced contamination
ActiveUS20090231707A1Reduce adhesionReduce pollutionMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingInterior spaceLithographic artist
An optical arrangement, in particular a projection exposure apparatus (1) for EUV lithography, includes: a housing (2) that encloses an interior space (15); at least one, in particular reflective, optical element (4 to 10, 12, 14.1 to 14.6) that is arranged in the housing (2); at least one vacuum generating unit (3) for generating a vacuum in the interior space (15) of the housing (2); and at least one vacuum housing (18, 18.1 to 18.10) that is arranged in the interior space (15) of the housing (2) and that encloses at least the optical surface (17, 17.1, 17.2) of the optical element (4 to 10, 12, 14.1 to 14.5), wherein a contamination reduction unit is associated with the vacuum housing (18.1 to 18.10), which contamination reduction unit reduces the partial pressure of contaminating substances, in particular of water and / or hydrocarbons, at least in close proximity to the optical surface (17, 17.1, 17.2) in relation to the partial pressure of the contaminating substances in the interior space (15).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV +1
All-reflective optical systems for broadband wafer inspection
ActiveUS7351980B2Color/spectral properties measurementsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsCatoptricsBroadband
All-reflective optical systems for broadband wafer inspection are provided. One system configured to inspect a wafer includes an optical subsystem. All light-directing components of the optical subsystem are reflective optical components except for one or more refractive optical components, which are located only in substantially collimated space. The refractive optical component(s) may include, for example, a refractive beamsplitter element that can be used to separate illumination and collection pupils. The optical subsystem may also include one or more reflective optical components located in substantially collimated space. The optical subsystem is configured for inspection of the wafer across a waveband of greater than 20 nm. In some embodiments, the optical subsystem is configured for inspection of the wafer at wavelengths less than and greater than 200 nm.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Lithographic apparatus having double telecentric illumination
A system and method are used to pattern illumination to form one or more devices on a substrate using a reflecting system, a pattern generator that defines an objection plane, a projection system, and the substrate that defines an image plane. A reflecting portion of the reflecting system is substantially parallel to a reflecting portion of the pattern generator. The reflecting portion of the pattern generator patterns the illumination beam and directs the patterned illumination beam towards the substrate via the projection system. Based on the relationship of the reflecting system and the pattern generator, the illumination beam is telecentric proximate the object plane and the patterned illumination beam is telecentric proximate the image plane. Through use of a reflecting optic and not a transmissive optic to direct light between the illuminator and the projection system, illumination efficiency is increased and errors imparted on the illumination are decreased.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
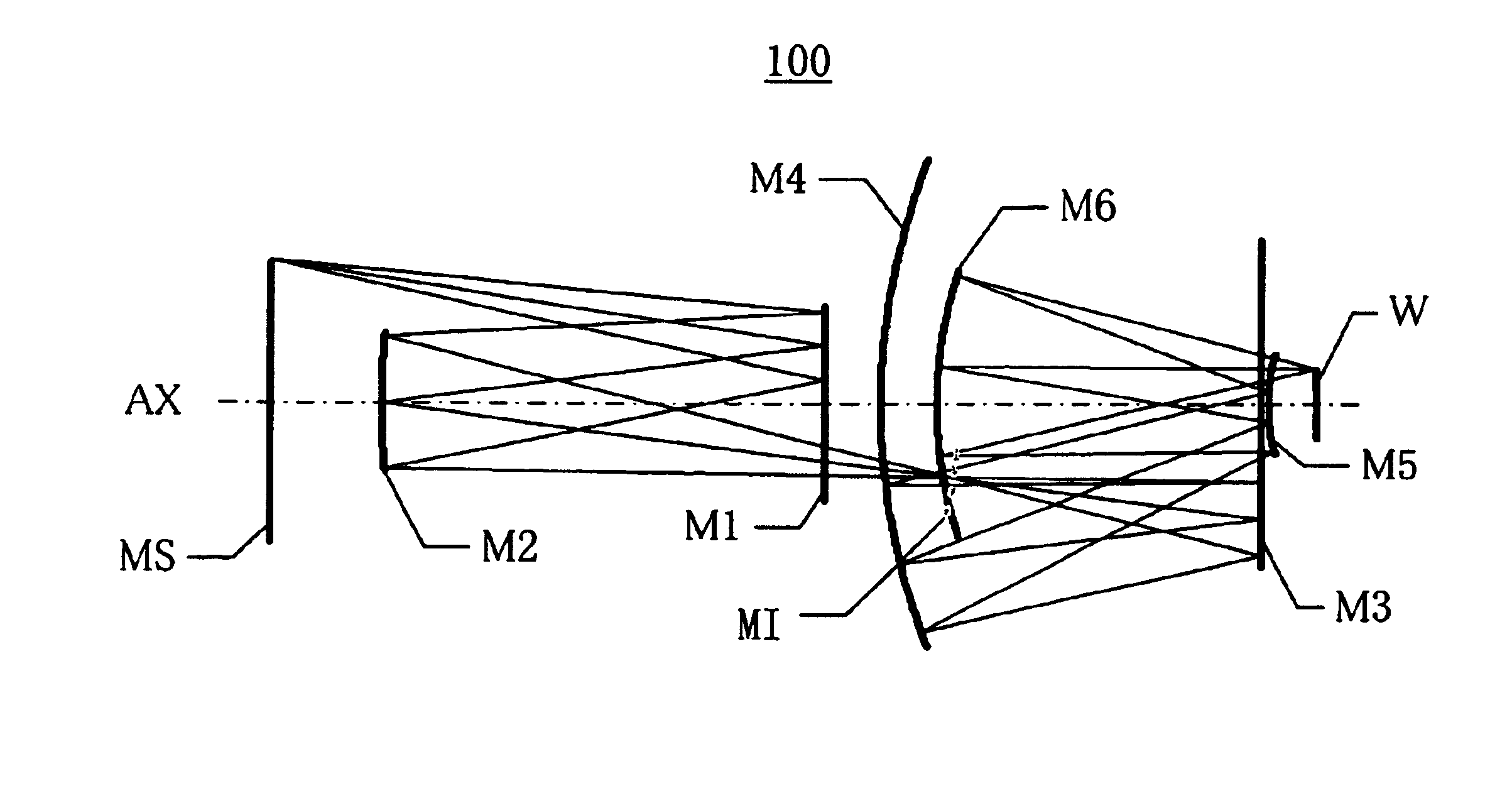
Catoptric projection optical system and exposure apparatus
InactiveUS6922291B2Large numerical apertureImprove imaging effectMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntermediate imageExit pupil
A catoptric projection optical system for projecting a reduced size of a pattern on an object surface onto an image surface and for serving as an imaging system that forms an intermediate image between the object surface and image surface, includes six or more mirrors, wherein a position of an exit pupil with respect to the intermediate image is located between the object surface and image surface, and wherein the largest angle between principal rays and an optical axis for angles of view at the position of the exit pupil is sin−1NA or smaller, where NA is a numerical aperture at the side of the image surface.
Owner:CANON KK
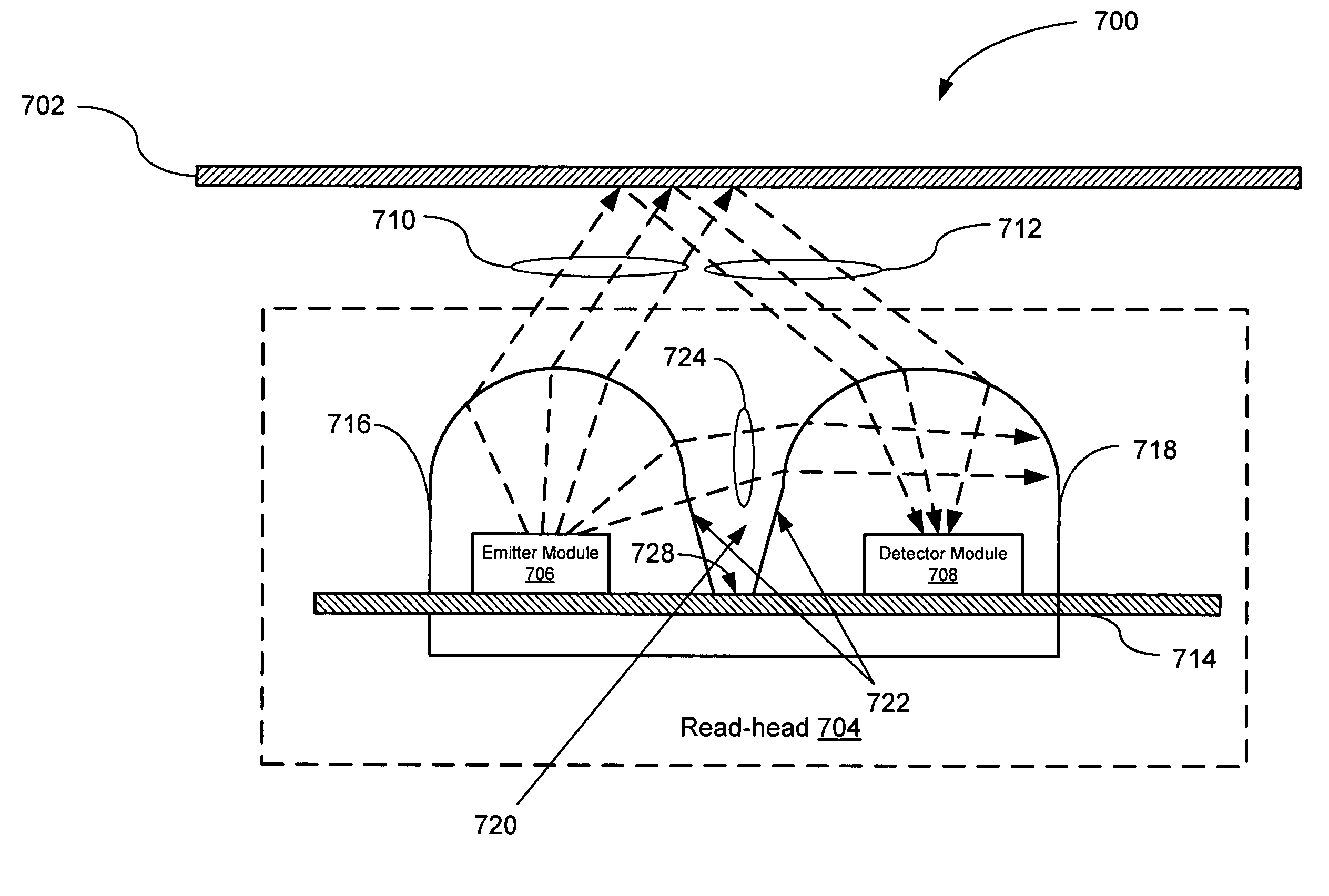
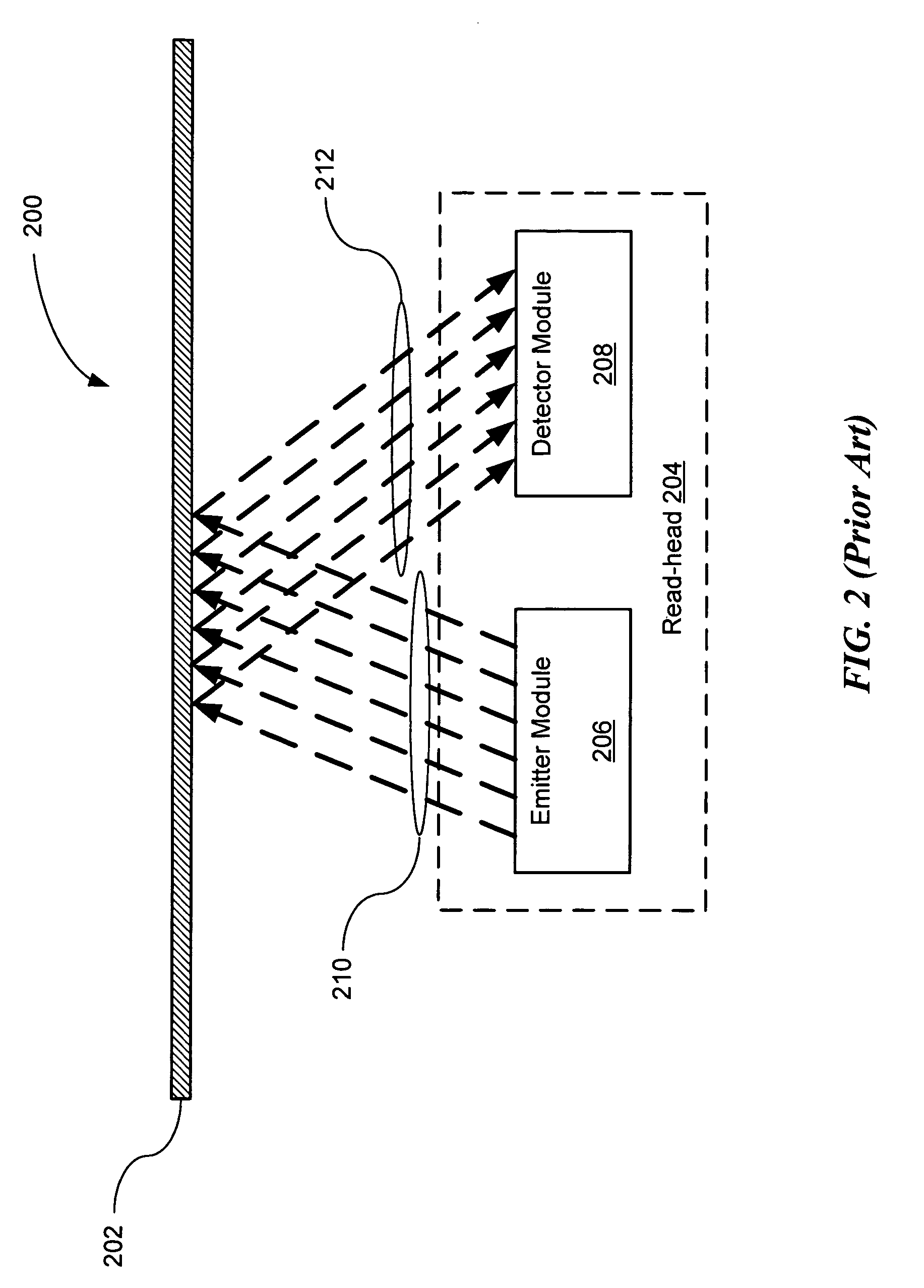
Enhanced reflective optical encoder
ActiveUS20060097051A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical radiationCatoptrics
An Enhanced Reflective Optical Encoder (“EROE”) having an emitter module for transmitting emitted optical radiation to an encoded media and a detector module for receiving reflected optical radiation from the encoded media. The EROE may include a transmissive layer covering both the emitter module and the detector module, and an optical isolation element located within the transmissive layer and located between the emitter module and the detector module. The optical isolation element reduces undesired optical radiation transmitted from the emitter module to the detector module, where the undesired optical radiation is a portion of the emitted optical radiation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com