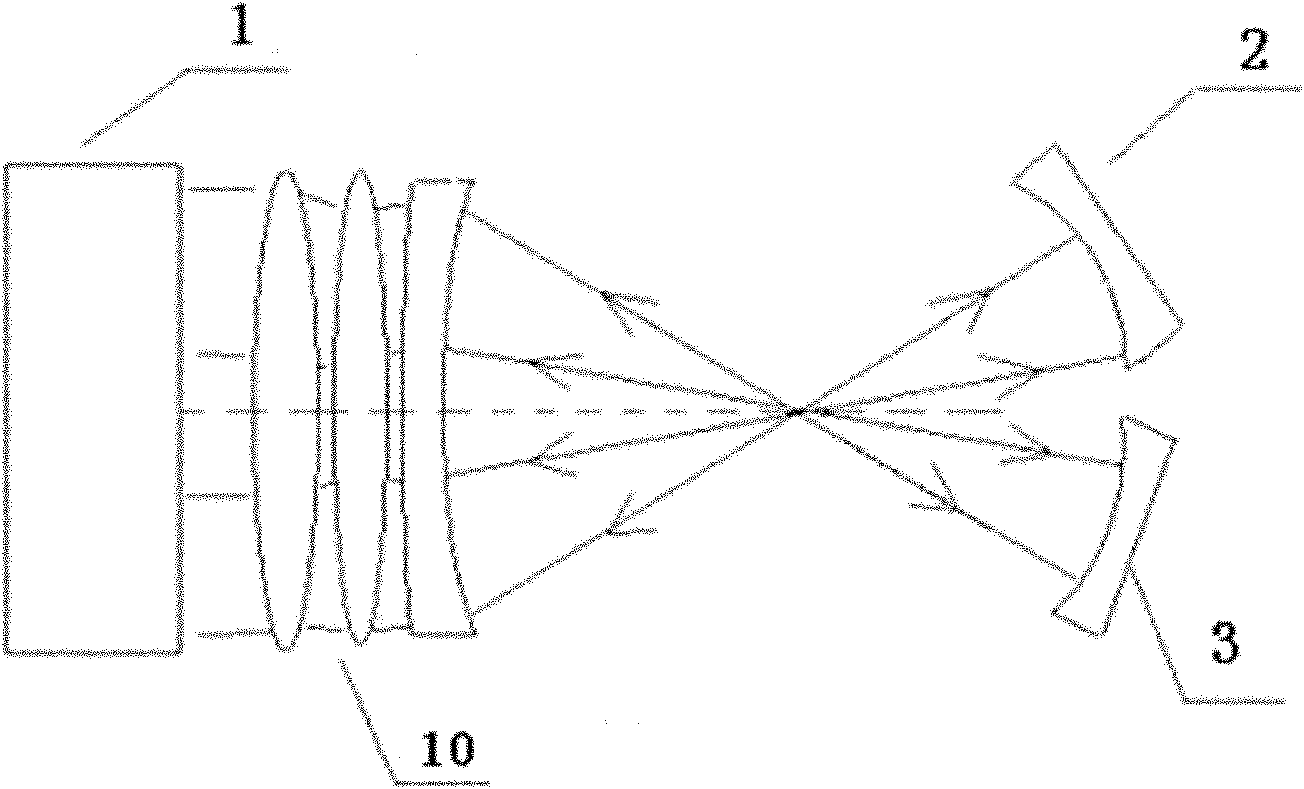
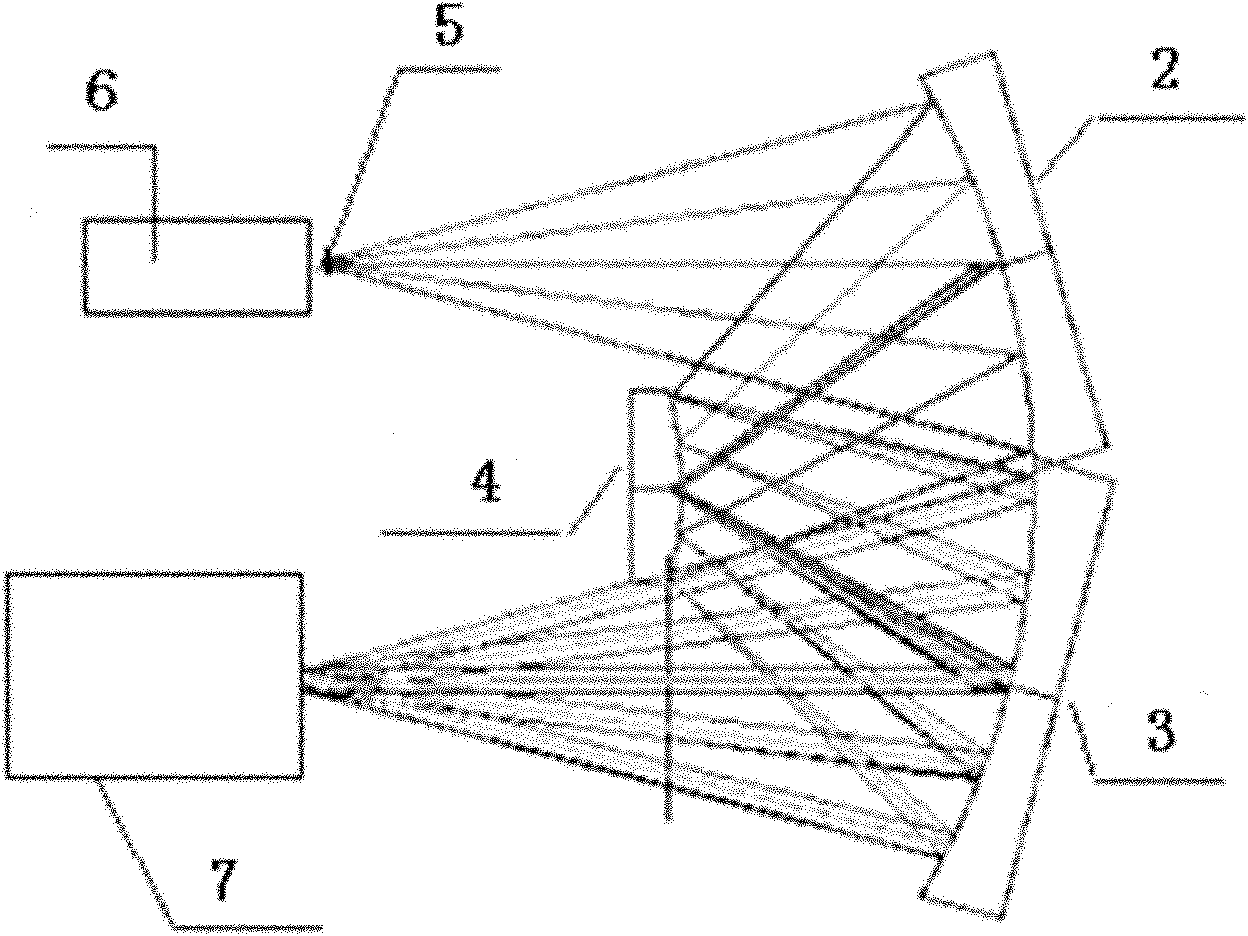
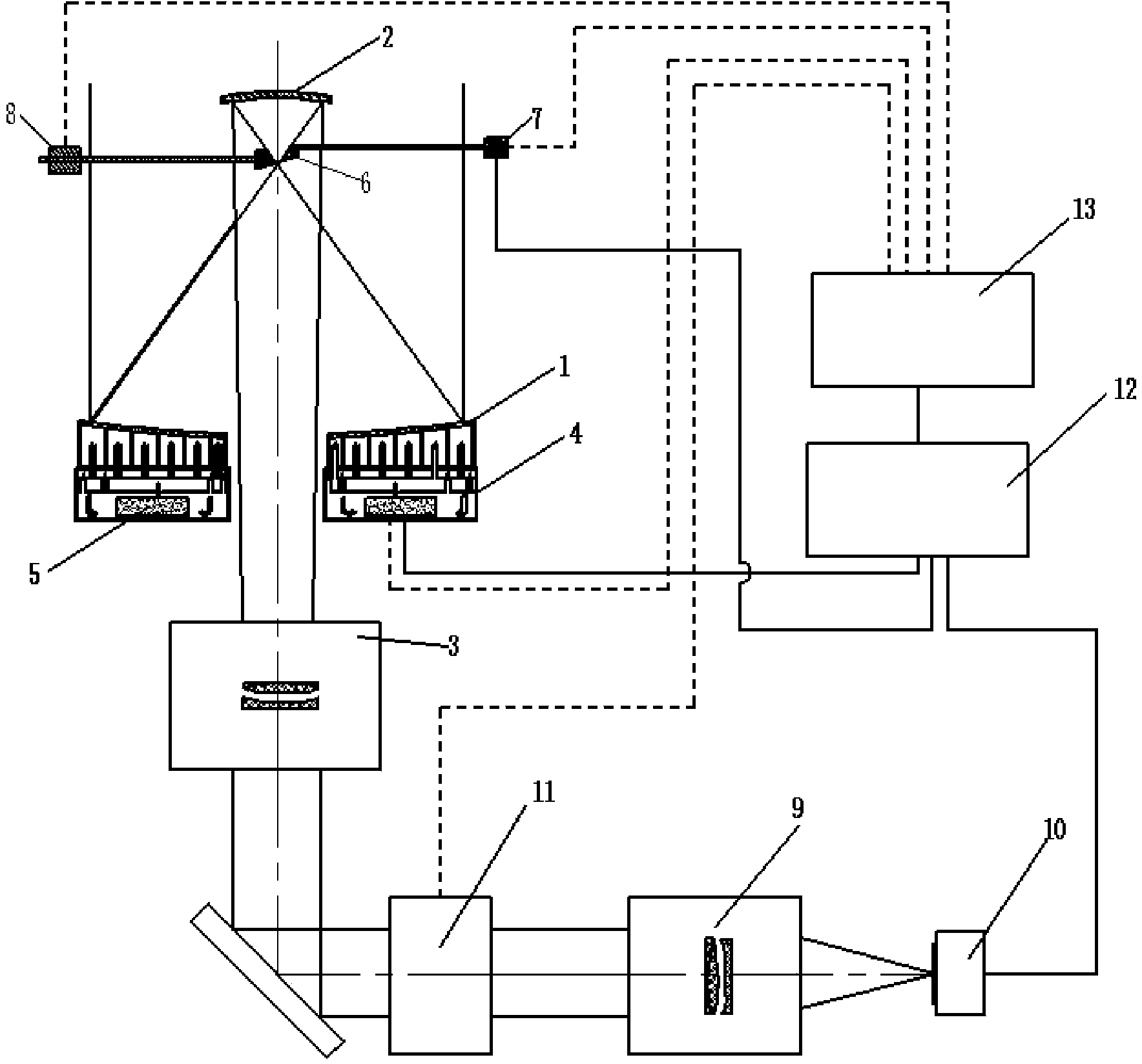
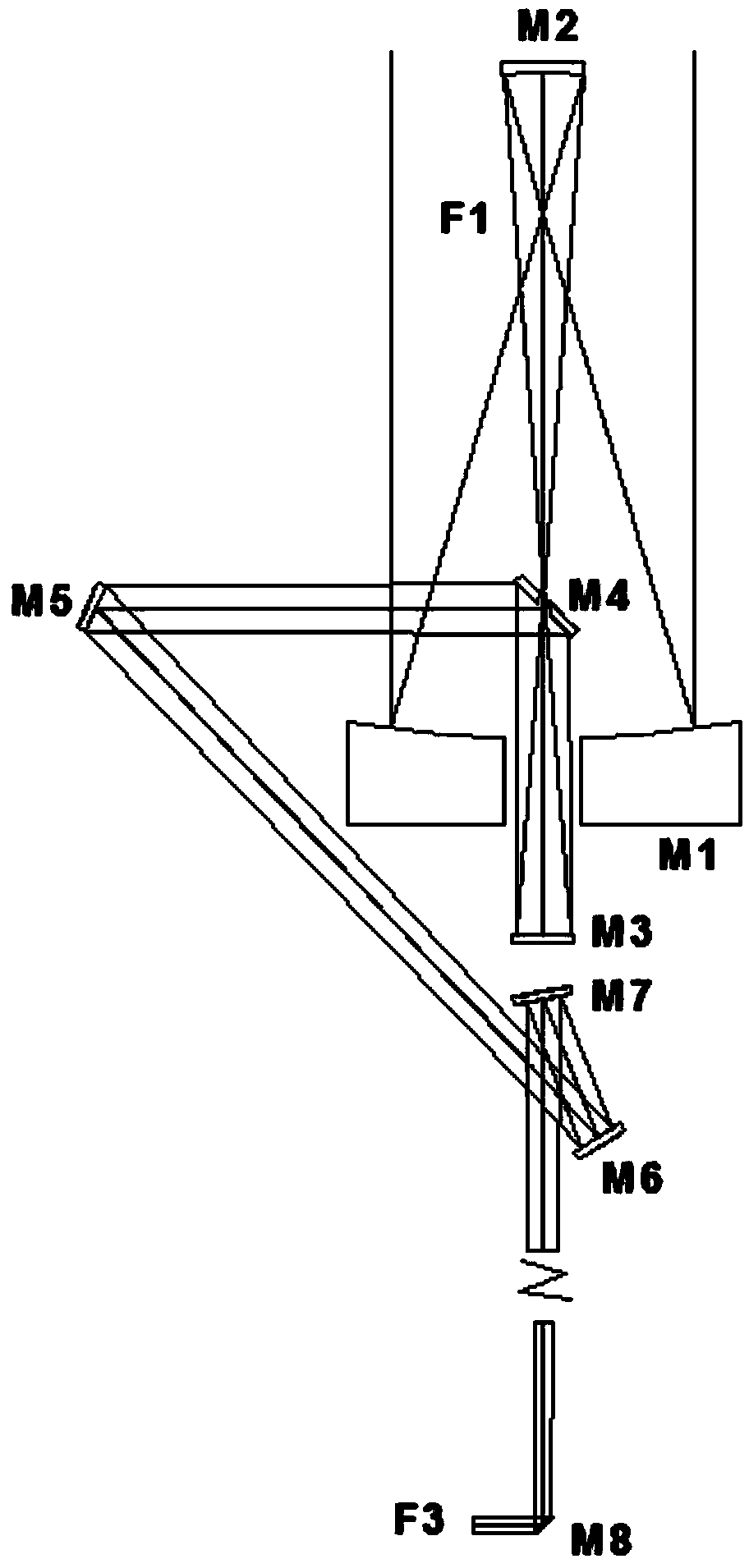
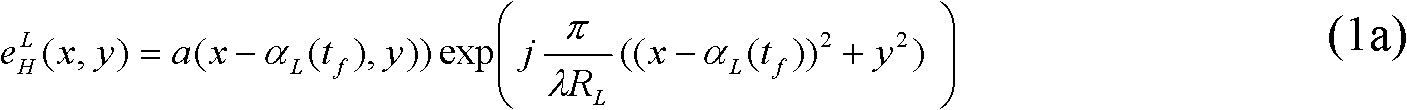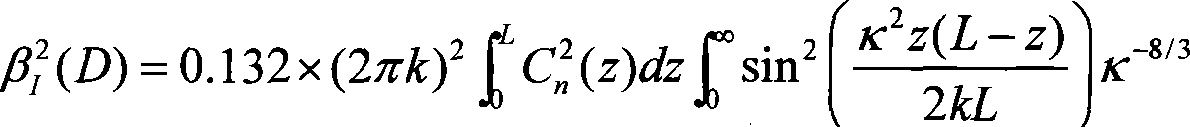Patents
Literature
701 results about "Primary mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A primary mirror (or primary) is the principal light-gathering surface (the objective) of a reflecting telescope.
Compound automotive rearview mirror
InactiveUS20080225421A1Inexpensive and easy to manufactureMirrorsOptical viewingMobile vehicleAuxiliary memory
A composite mirror adapted for use as an outside rearview mirror of a motor vehicle includes a main or primary viewing mirror and an auxiliary blindzone viewing mirror juxtaposed to expose the vehicle blindzone to the vehicle operator. The main viewing mirror is generally of unit magnification. The auxiliary mirror is composed of a planar array of reflecting facets mimicking a convex mirror. The main and auxiliary mirrors can be combined in constant or variable reflectivity applications.
Owner:PLATZER GEORGE E
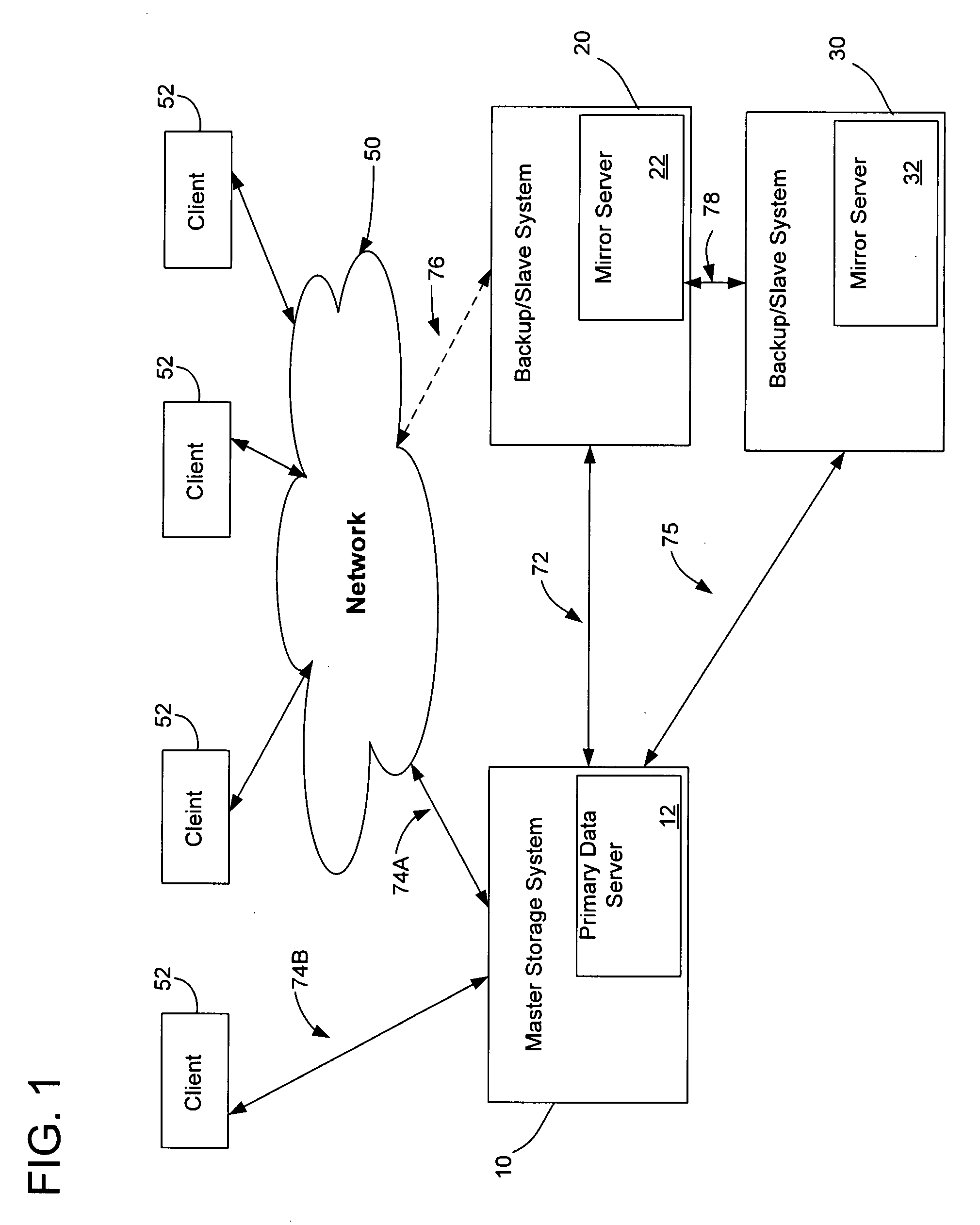
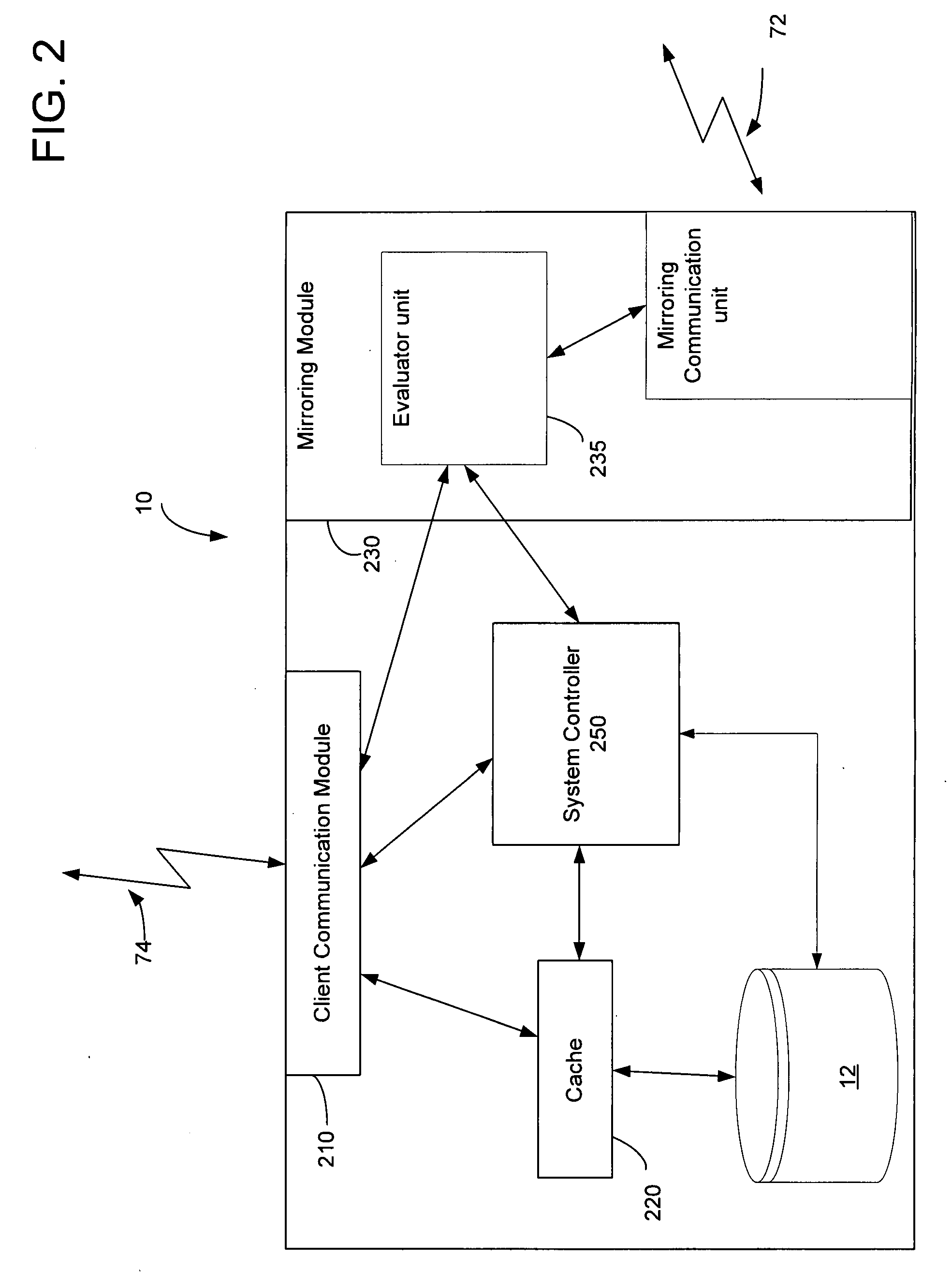
System method and circuit for differential mirroring of data
ActiveUS20070276983A1Lower latencyDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionSystems approachesMirror image
Disclosed is a system, method and circuit for mirroring data on a data server. According to some embodiments of the present invention, a primary mirroring module associated with a primary server may be adapted to establish data mirroring connections between the primary server and one or more mirror sever systems. According to some embodiments of the present invention, the primary mirroring module includes an evaluator unit which generates a delta file to be transmitted to the one or more mirror server systems.
Owner:IBM CORP
Monolithic Mirror Array
InactiveUS20090056790A1Easy to optimizeLow production costSolar heating energyMirrorsEngineeringThermal stability
The present invention is an improved solar concentrator array utilizing a monolithic array of primary mirrors fabricated from a single sheet of formable material. The material may include glass, plastic, and metal of a high thermal stability to be able to withstand a broad range of temperature conditions. The monolithic array of this invention may include integral alignment or attachment features for attachment to a supporting structure.
Owner:SOLFOCUS
Systems for cost effective concentration and utilization of solar energy
InactiveUS20120037206A1Reduce absorptionLow dispersionPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyHigh concentrationEngineering
The present invention is primarily directed to improvements to cost-effective systems for concentrating and using solar energy. The present invention co-optimizes the frame and the primary mirrors and secondary concentrator for a cost-effective very high concentration quasi-parabolic dish system that uses no moulded optics for the primary concentration, and also optimizes fabrication jigs for the main components of that design. The present invention also optimizes cell contacts and provides cost effective receiver cooling for dense receiver arrays for very high concentration photovoltaic systems. The present invention also includes a semi-dense receiver array that can provide a higher acceptance angle than a dense receiver array, and finally includes mutual-shading impact minimization methods and apparatus compatible with very high concentration photovoltaic systems.
Owner:NORMAN RICHARD
System and method for effecting high-power beam control with outgoing wavefront correction utilizing holographic sampling at primary mirror, phase conjugation, and adaptive optics in low power beam path
InactiveUS6849841B2Cancellation effectPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorPhased array
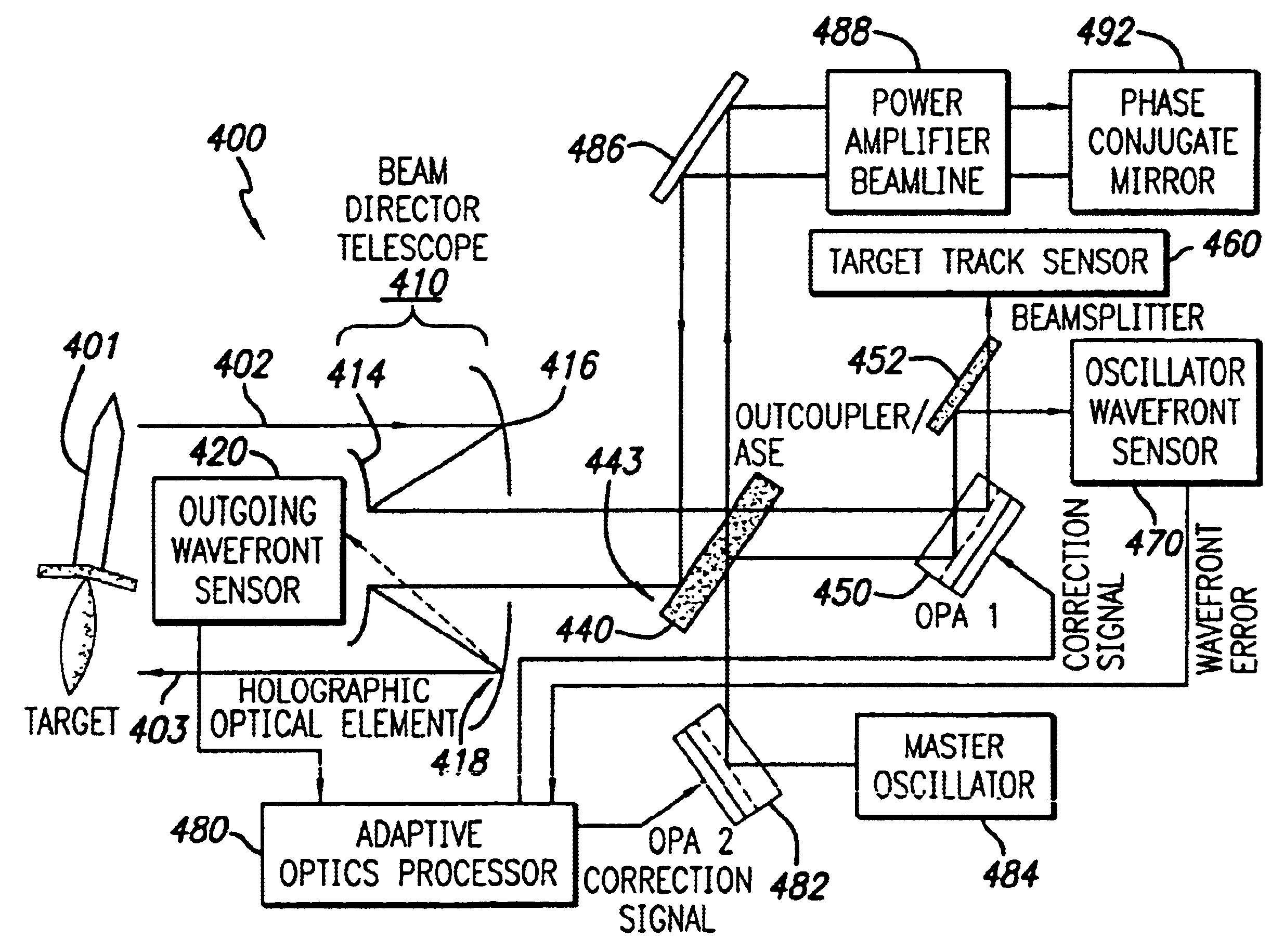
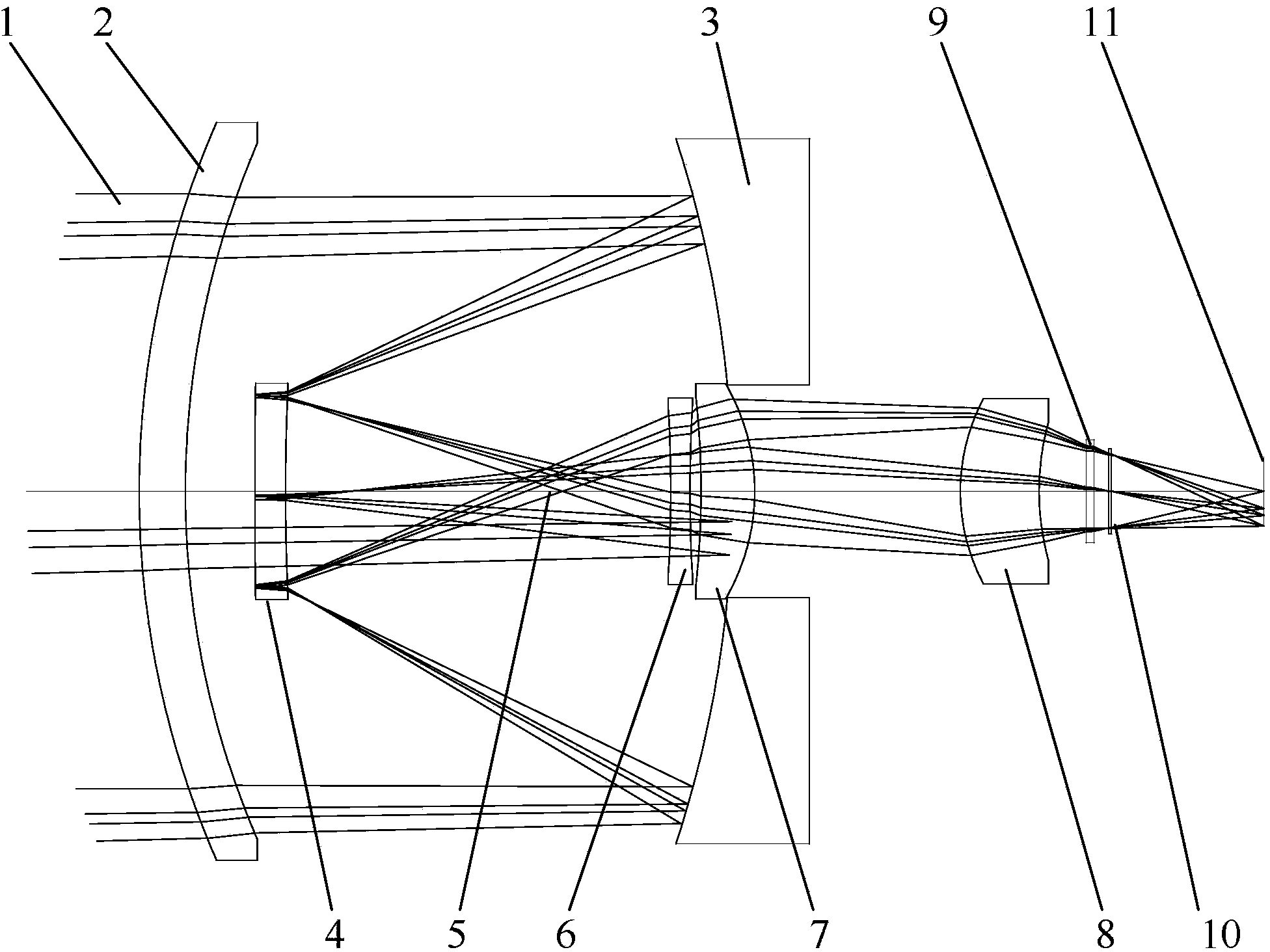
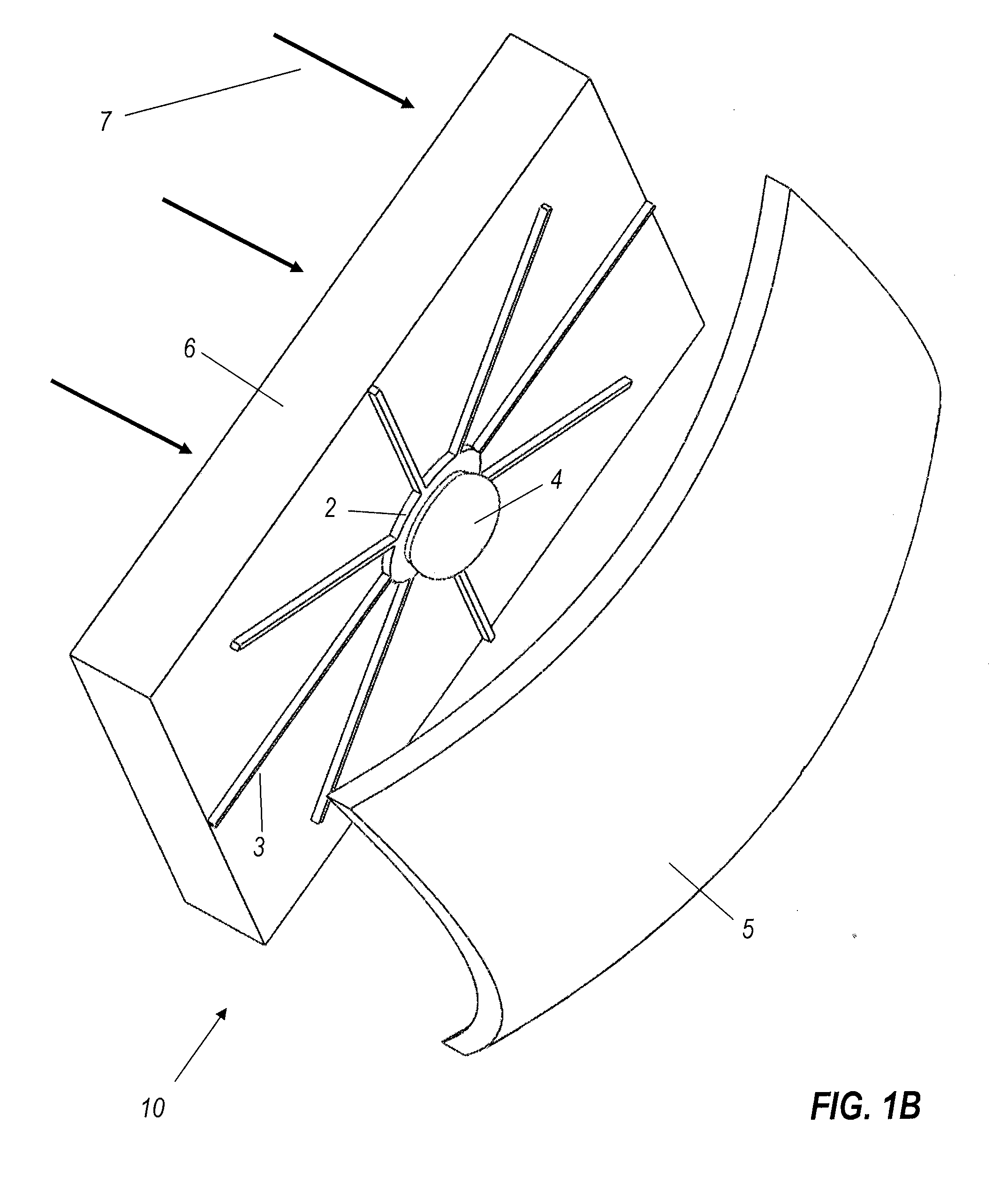
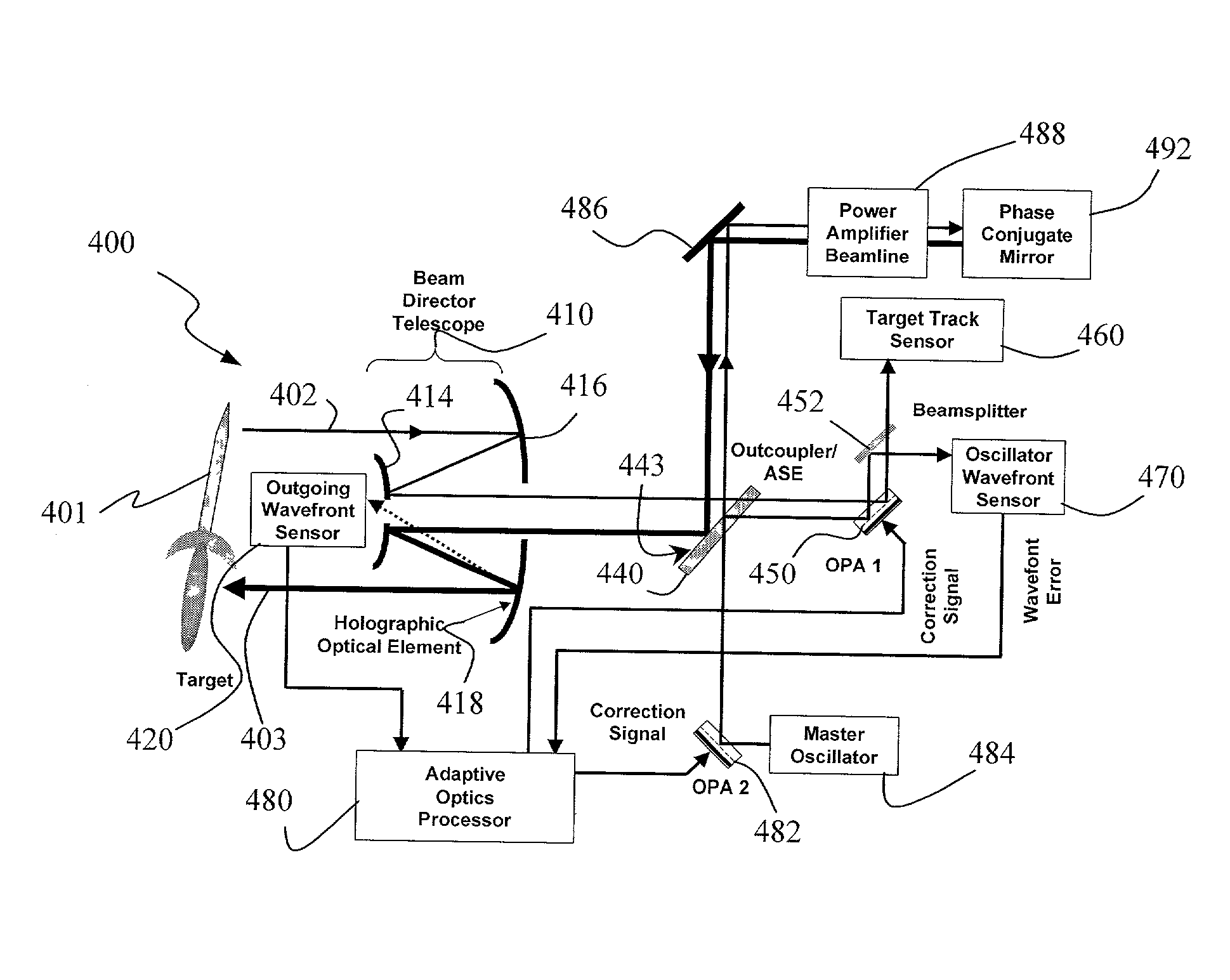
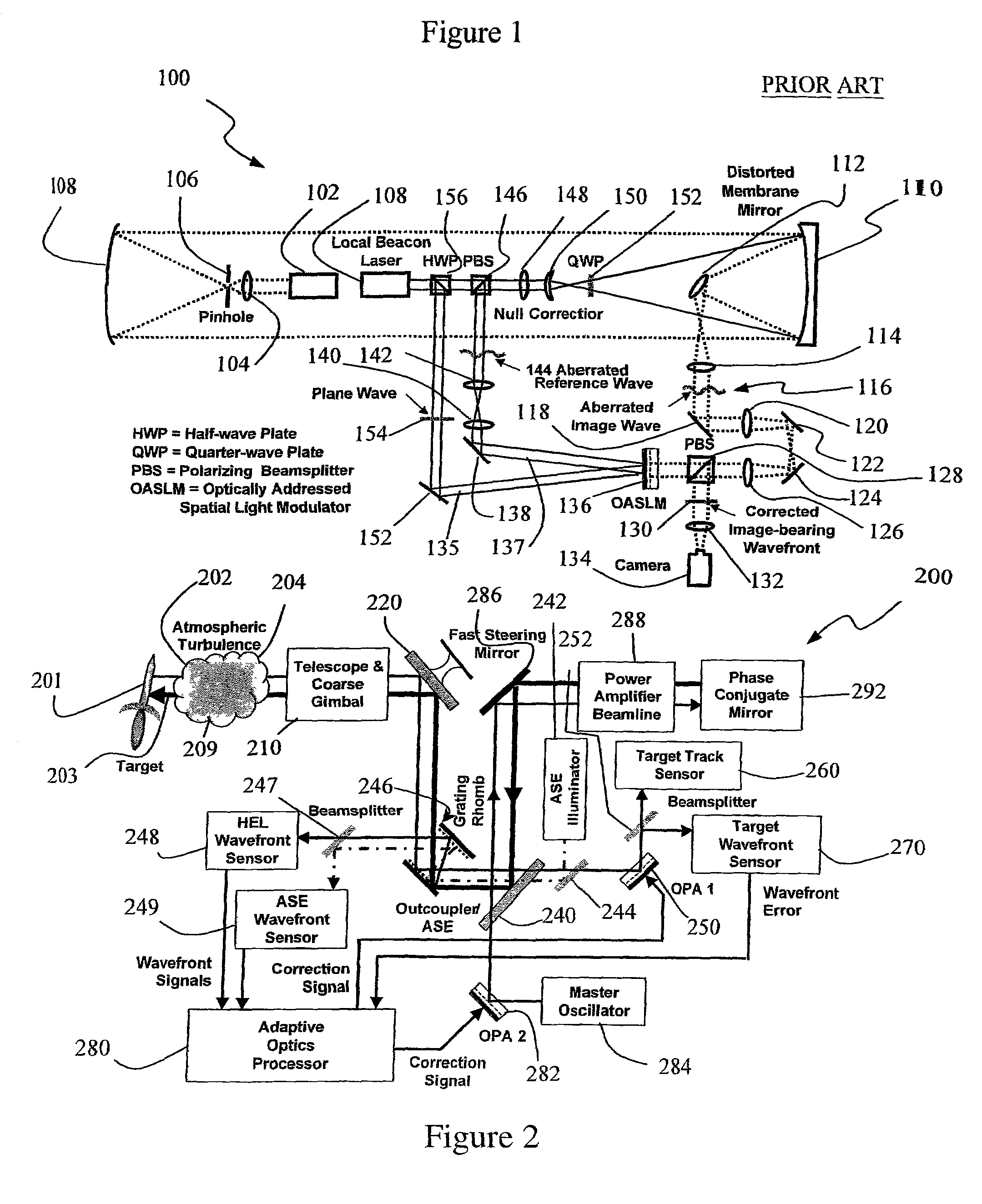
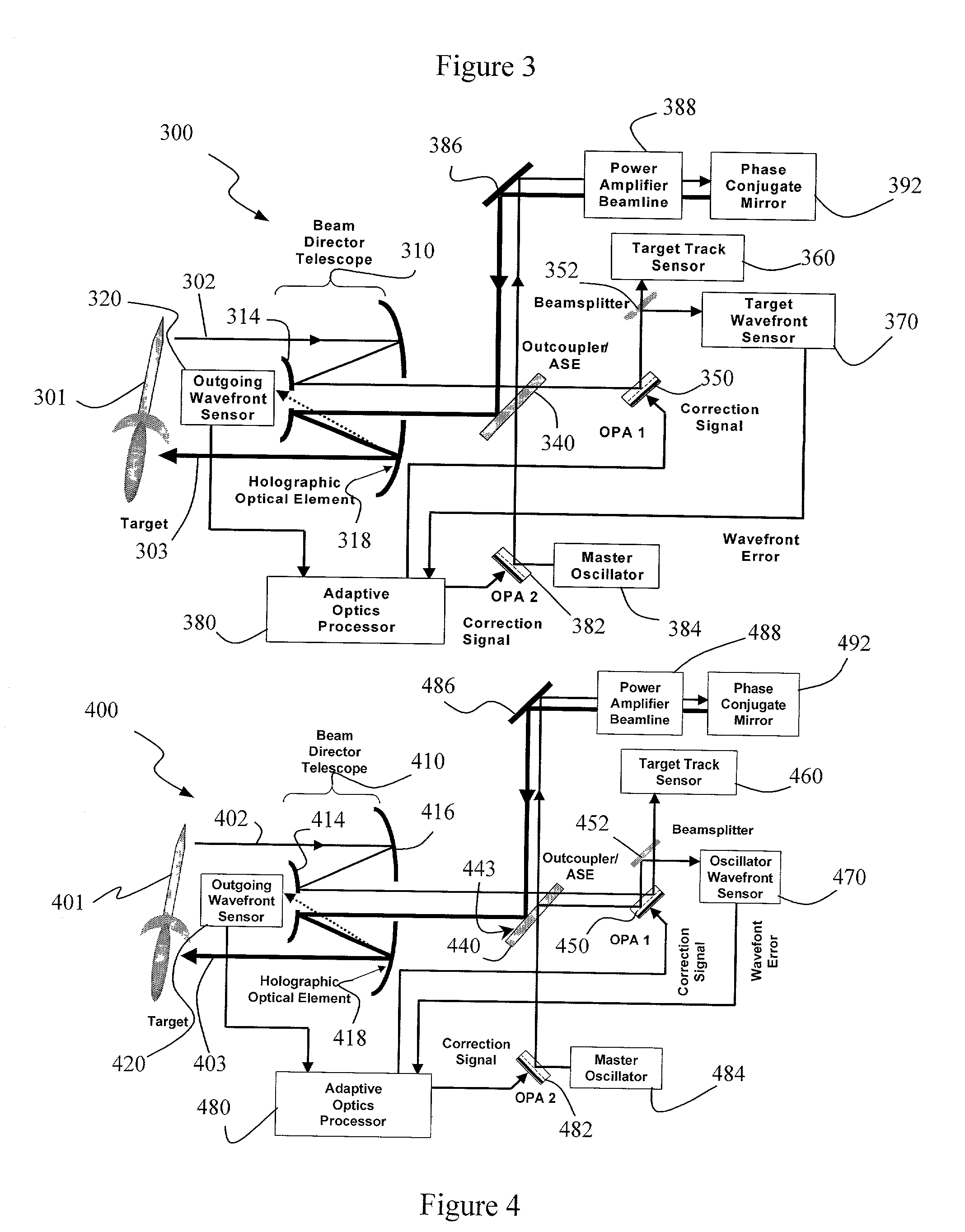
A beam control system and method. In an illustrative embodiment, the inventive system (500) provides a first beam of electromagnetic energy (503); samples the first beam (503) and provides a second beam (505) in response thereto; detects aberrations in the second beam (505); and corrects aberrations in the first beam (503) in response to the detected aberrations. In a specific implementation, the invention (500) includes a beam director telescope (510) having a primary mirror (516) on which a holographic optical element (518) is disposed. The holographic optical element (518) samples the output high-power beam and provides a sampled beam to a wavefront sensor (520). The wavefront sensor (520) provides signals to an adaptive optics processor (580). The adaptive optics processor (580) analyzes the sampled wavefront, detects aberrations therein and provides a correction signal to an optical phased array (550).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Spectral imaging method and spectrum imaging instrument of snapshot-type high throughput
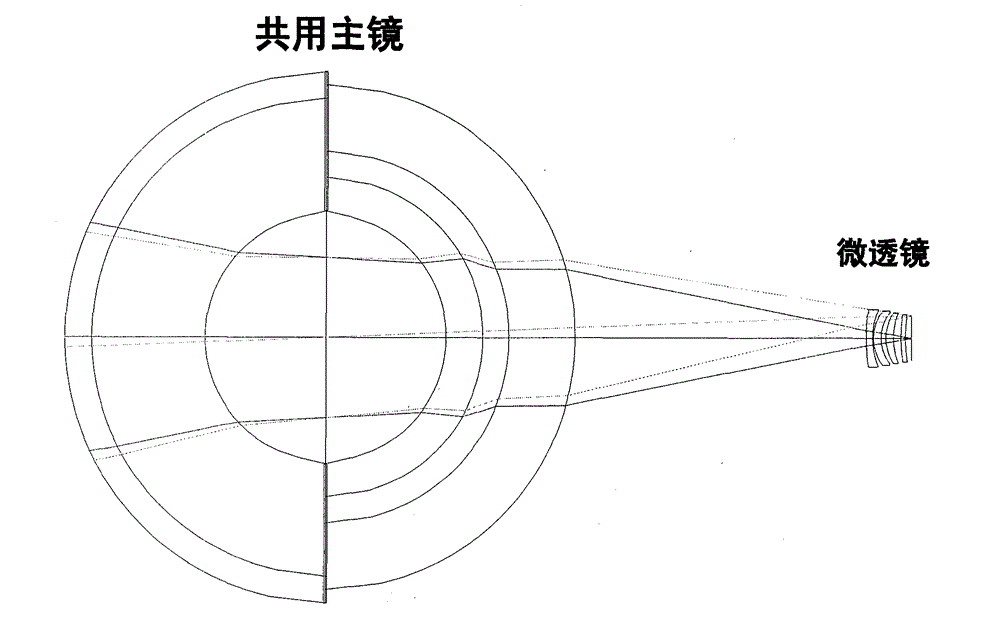
ActiveCN102944305AImprove throughputPixel Count ReductionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicro lens arrayPrimary mirror
The invention relates to a spectral imaging method and a spectrum imaging instrument of a snapshot-type high throughput, which aim at realizing a picture-type photograph. The spectrum instrument comprises a linear gradient filter array and an optical-field imaging mechanism, and the optical-field imaging mechanism comprises a primary mirror, a micro lens array and a detector. The filter array is arranged on an aperture diaphragm between lenses of the primary mirror, the filter array consists of a plurality of filters which have identical width and are arranged at intervals, and the filter is a linear gradient filter band with continuous spectrum. The micro lens array is arranged on an imaging surface of a front-mounted optical imaging system, and the detector is arranged on a focus plane of the micro lens array. The spectrum imaging method is characterized in that light in different directions transmitted or reflected by a target is imaged on one micro lens after being modulated by the primary mirror and the filter array, the light is dispersed by the micro lens onto a picture element of the detector to form a subimage, and finally three-dimensional spectrum image data is obtained. The complete spectrum image information of the target can be obtained through the photograph in one step, and the spectral imaging method and the spectrum imaging instrument can be used for monitoring and tracking a rapid variable or movable target.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar
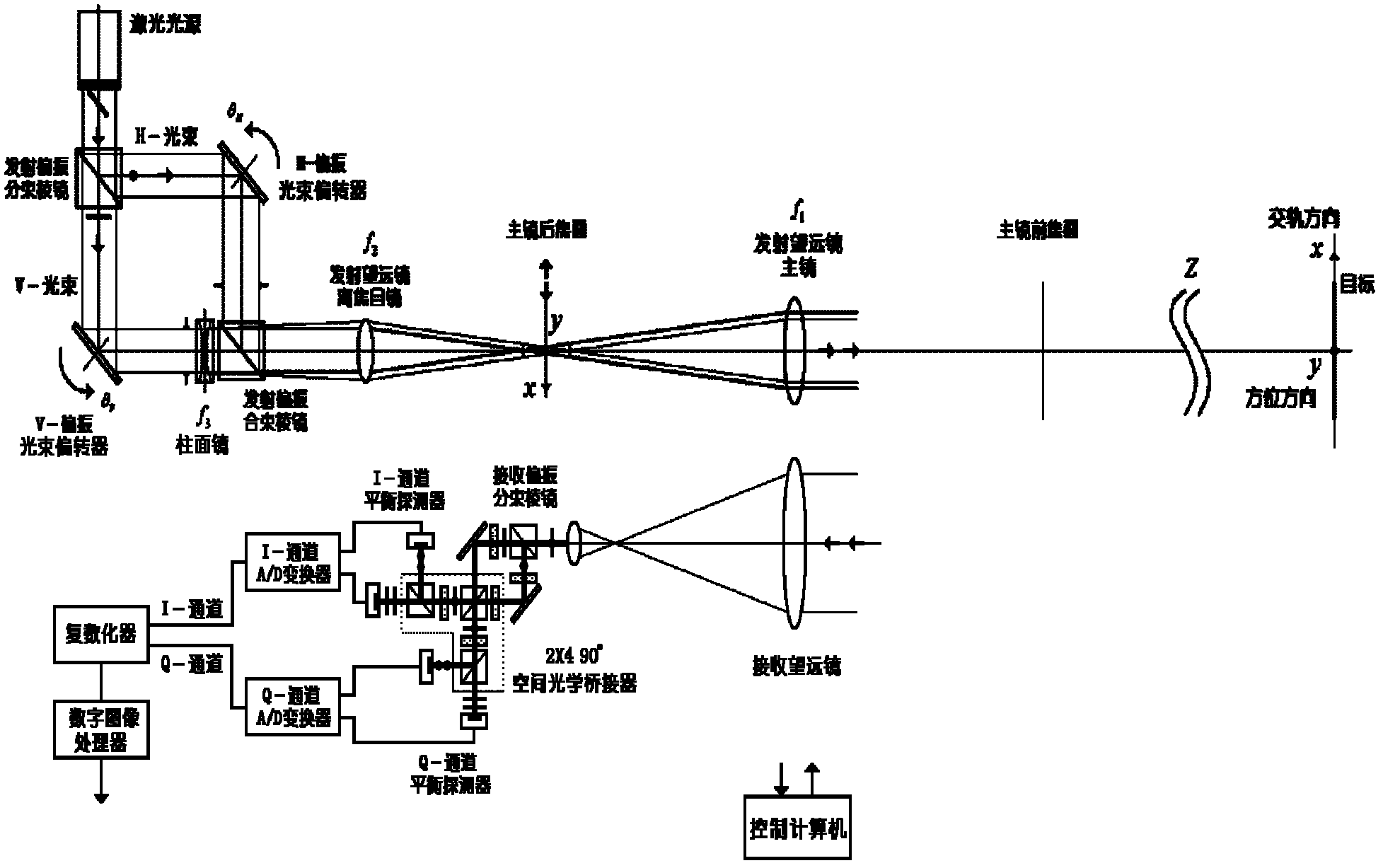
ActiveCN102435996AReduce the effects of phase interferenceBig optic toesElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh resolution imagingRadar systems
The invention relates to an orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar. The orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar comprises a laser light source, a transmission polarization beam splitter, a horizontal polarization optical path beam deflector, a horizontal polarization optical path transform lens, a vertical polarization optical path beam deflector, a vertical polarization optical path transform lens, a transmission polarization beam combiner, a transmitter telescope ocular, a transmitter telescope primary lens, a receiver telescope, a receiving polarization beam splitter, a 2 * 490 DEG optical bridge, an inphase channel balanced detector, an inphase channel A / D (analogue / digital) converter, a 90 DEG of phase shift channel balanced detector, a 90 DEG of phase shift channel A / D (analogue / digital) converter, a pluralizing processor, a digital image processor and a control computer. The orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar automatically eliminates phase changes and interference of atmosphere, motion platforms, optical radar systems and speckles, has high resolution imaging in larger optical footprint and larger receiving aperture, does not need optical delay lines, does not need real-time beat frequency signal phase synchronization, does not have shadows during imaging, and can be used for various lasers with single-module and single-frequency properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-cost refracting-reflecting athermalizing medium wave infrared lens
The invention provides a low-cost refracting-reflecting athermalizing medium wave infrared lens and aims at providing a low-cost refracting-reflecting optical lens which is small in aspherical mirror number, low in cost, made of a small amount of aspherical lenses and conventional silicon and germanium optical materials at a 3.7-4.8 [mu]m medium-wave infrared band and having the optical passive athermalizing performance. The technical scheme is that parallel light enters a main reflection spherical mirror (3) to form a converged light beam through a spherical cover (2) in an incidence mode, a convergence angle is decreased through a Mangin refracting-reflecting mirror (4), a primary mirror face (5) is formed by decreasing a part of aberration and increasing a part of balanced aberration and negative thermal difference of a lens to be arranged behind, the light beam is changed into divergent light, the divergent light enters a negative lens (6) made of an aspherical germanium material and a positive meniscus lens (7) made of a silicon material so as to reduce chromatic aberration and aberration, then converges through a positive convex lens (8) made of the silicon material, enters a detector window (9) and finally forms an image on a detector focal plane (11) through a cold light diaphragm (10), and the whole imaging process is finished.
Owner:SOUTH WEST INST OF TECHN PHYSICS
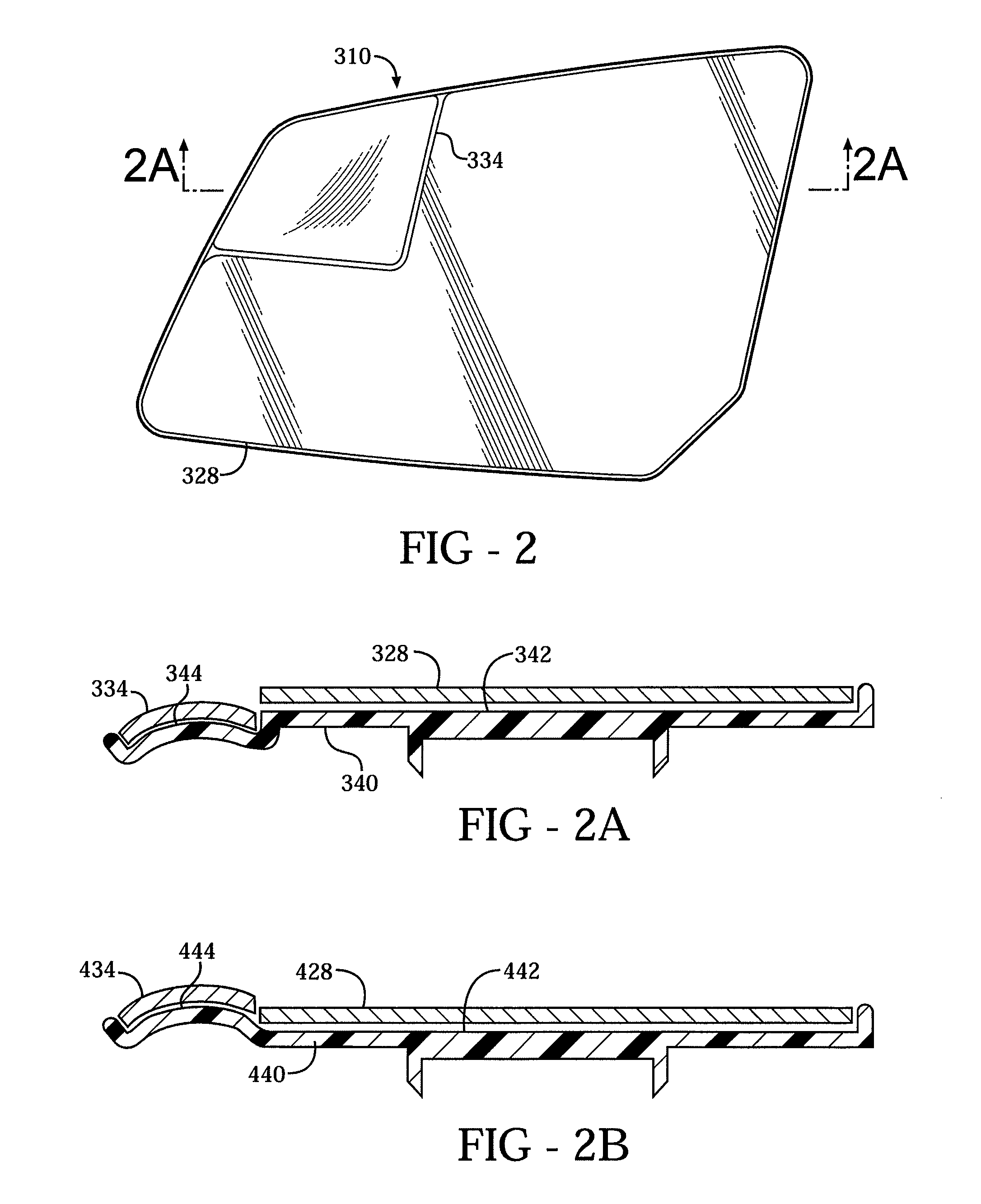
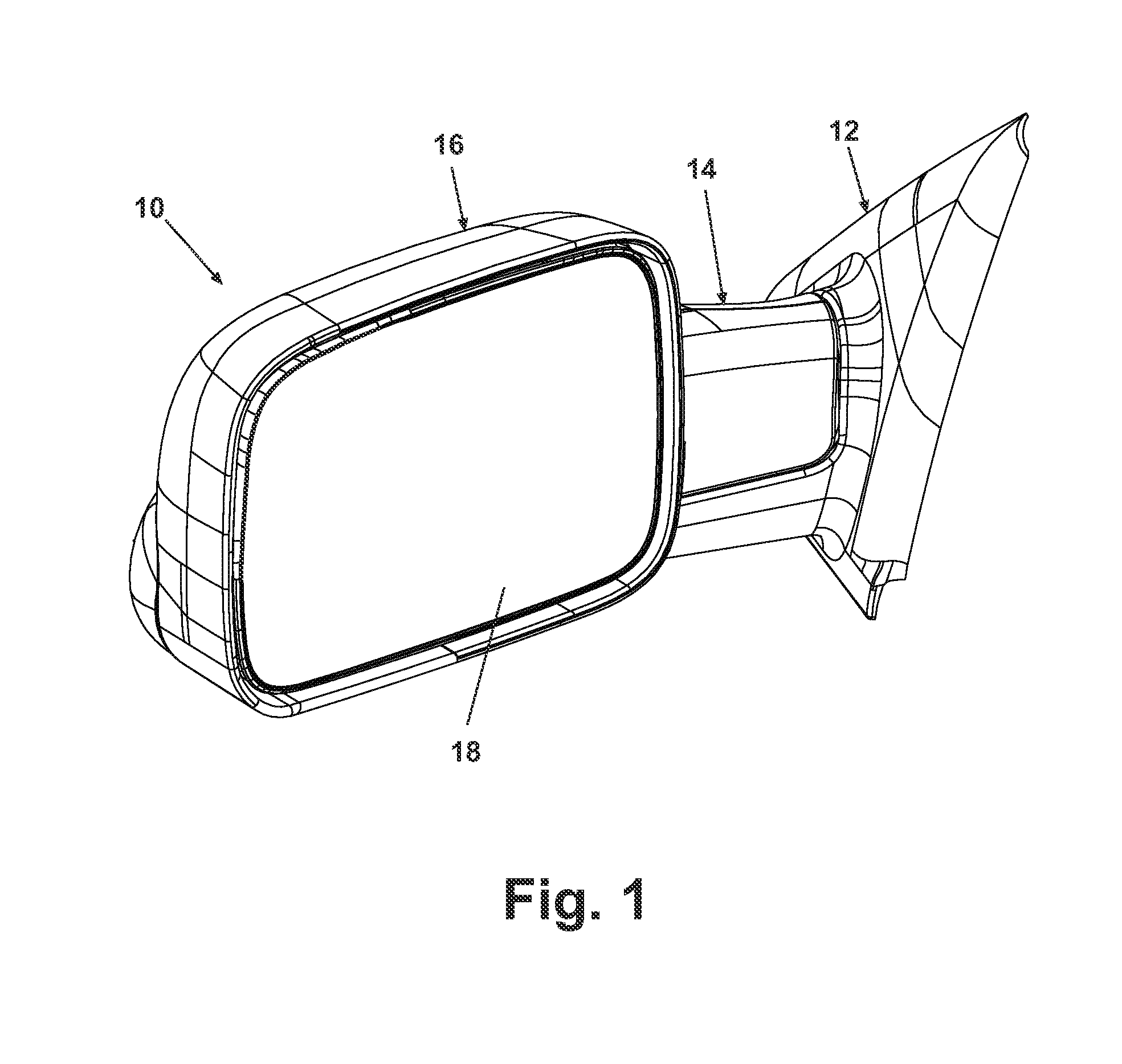
Exterior rearview mirror for motor vehicles
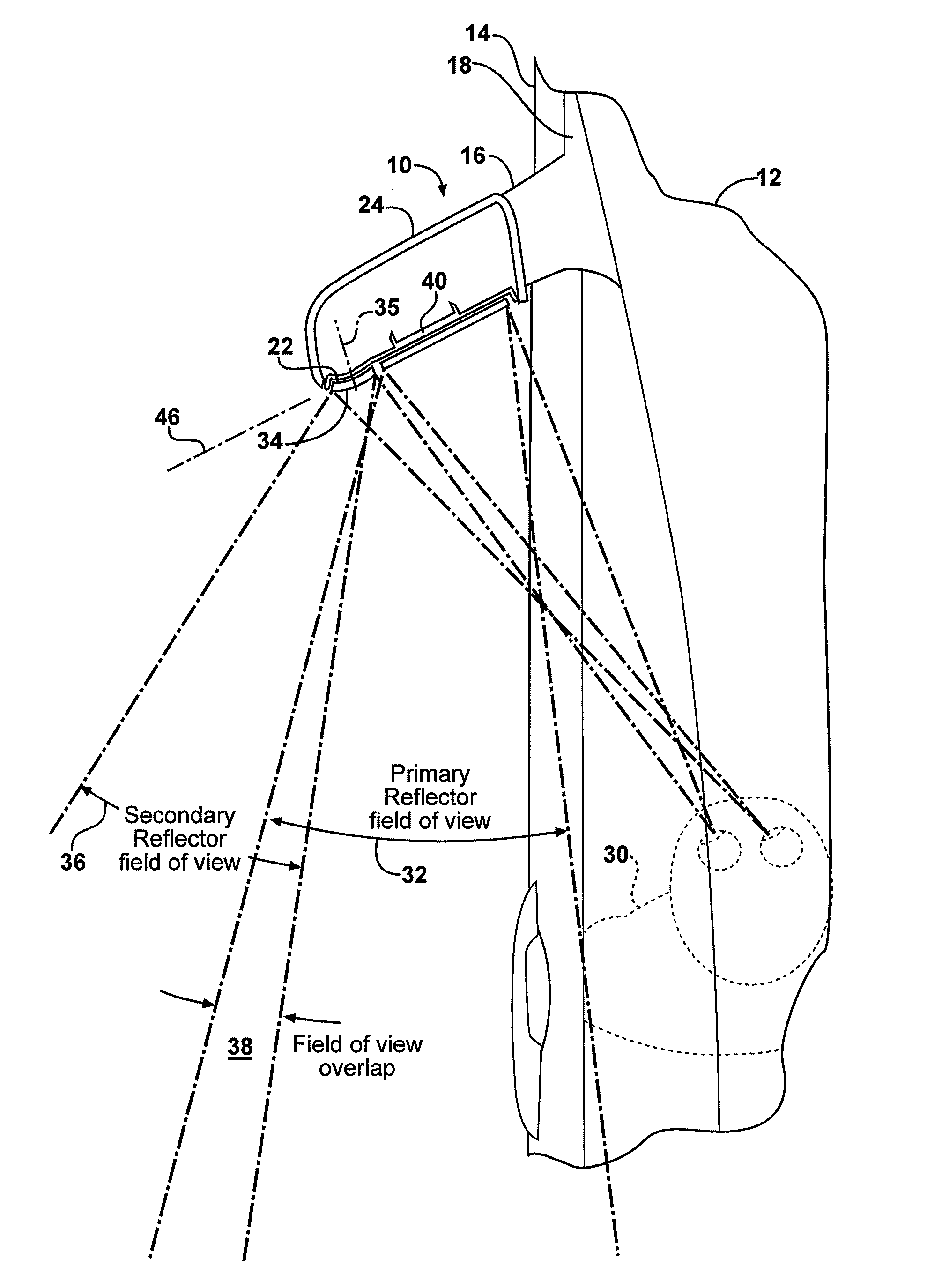
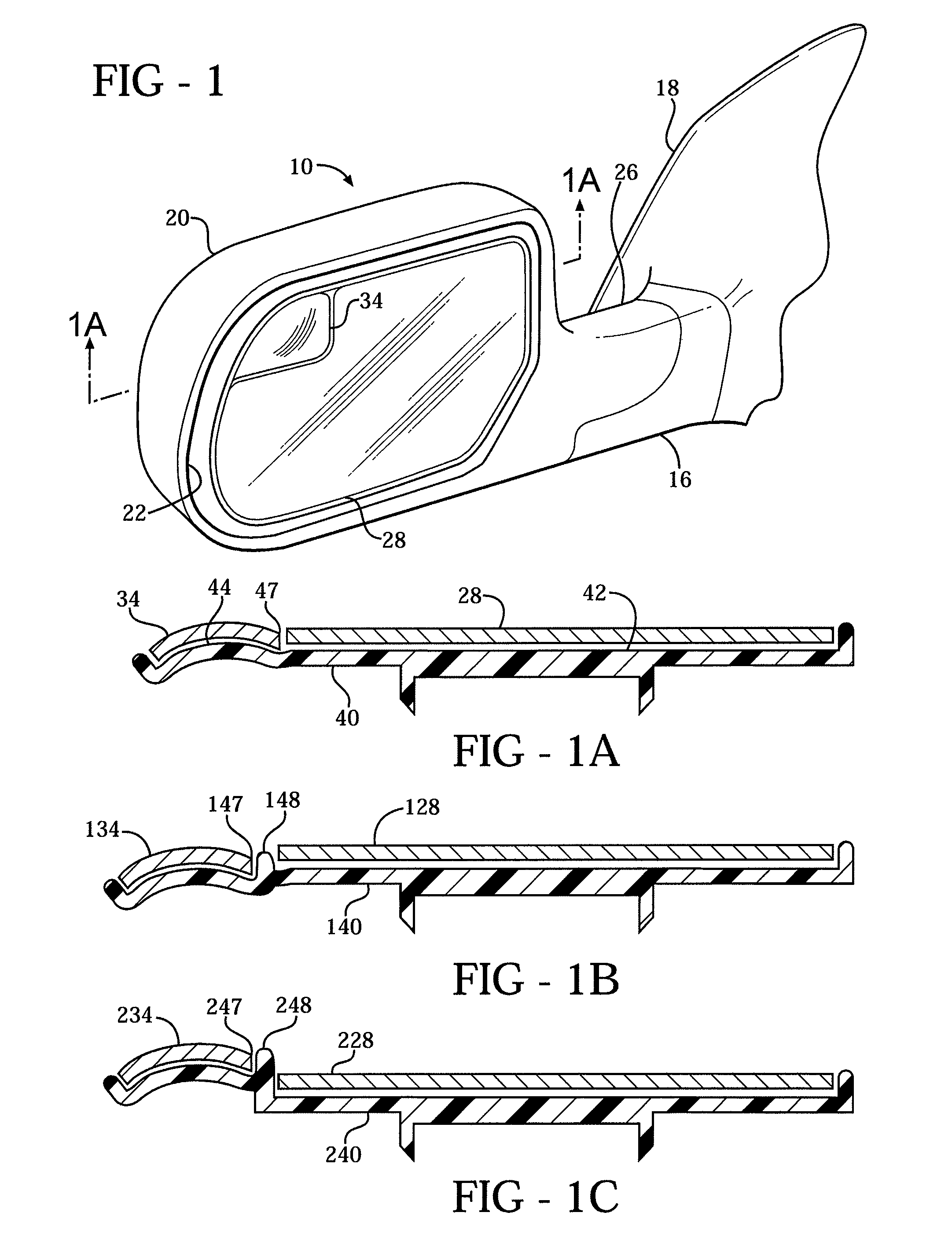
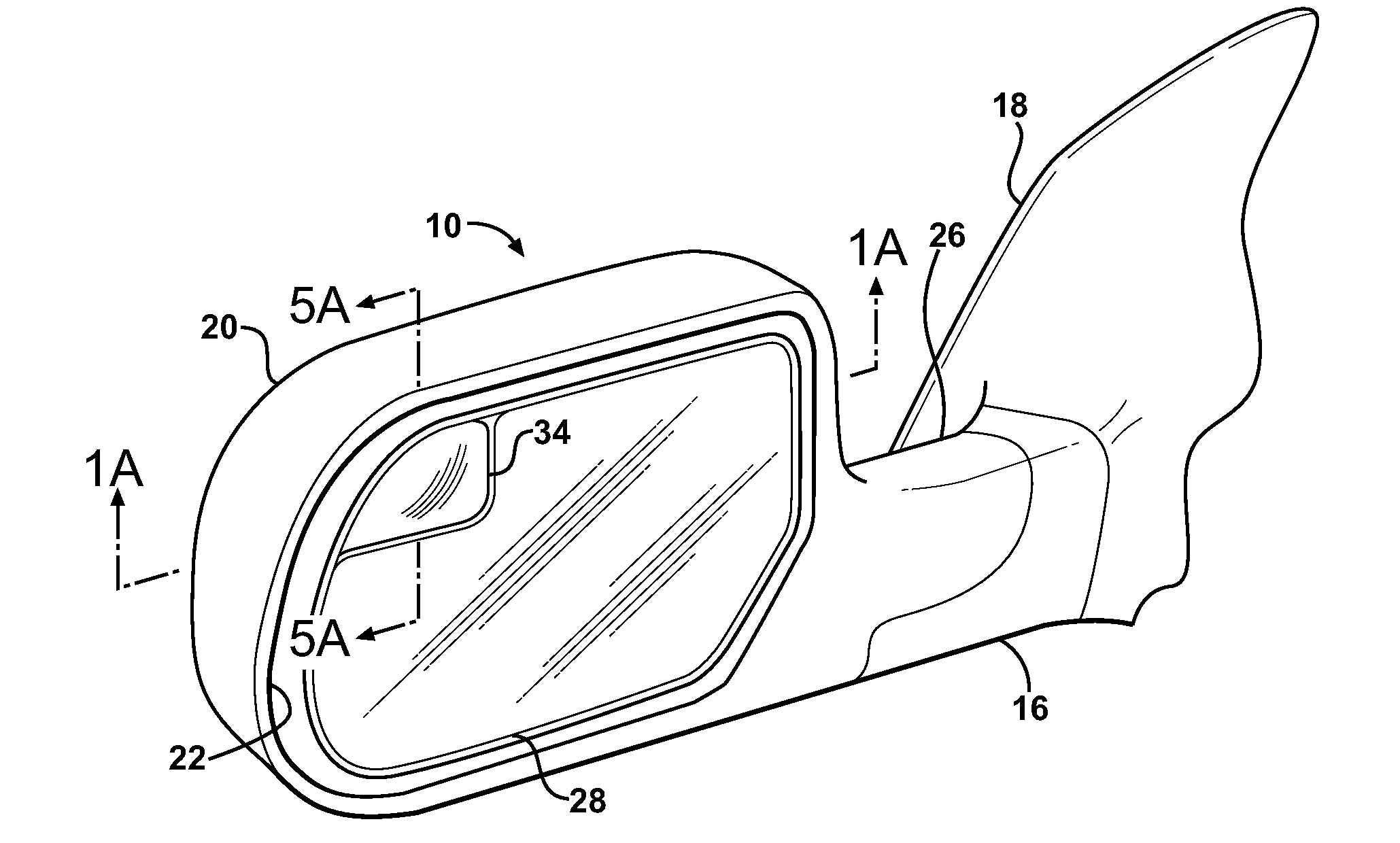
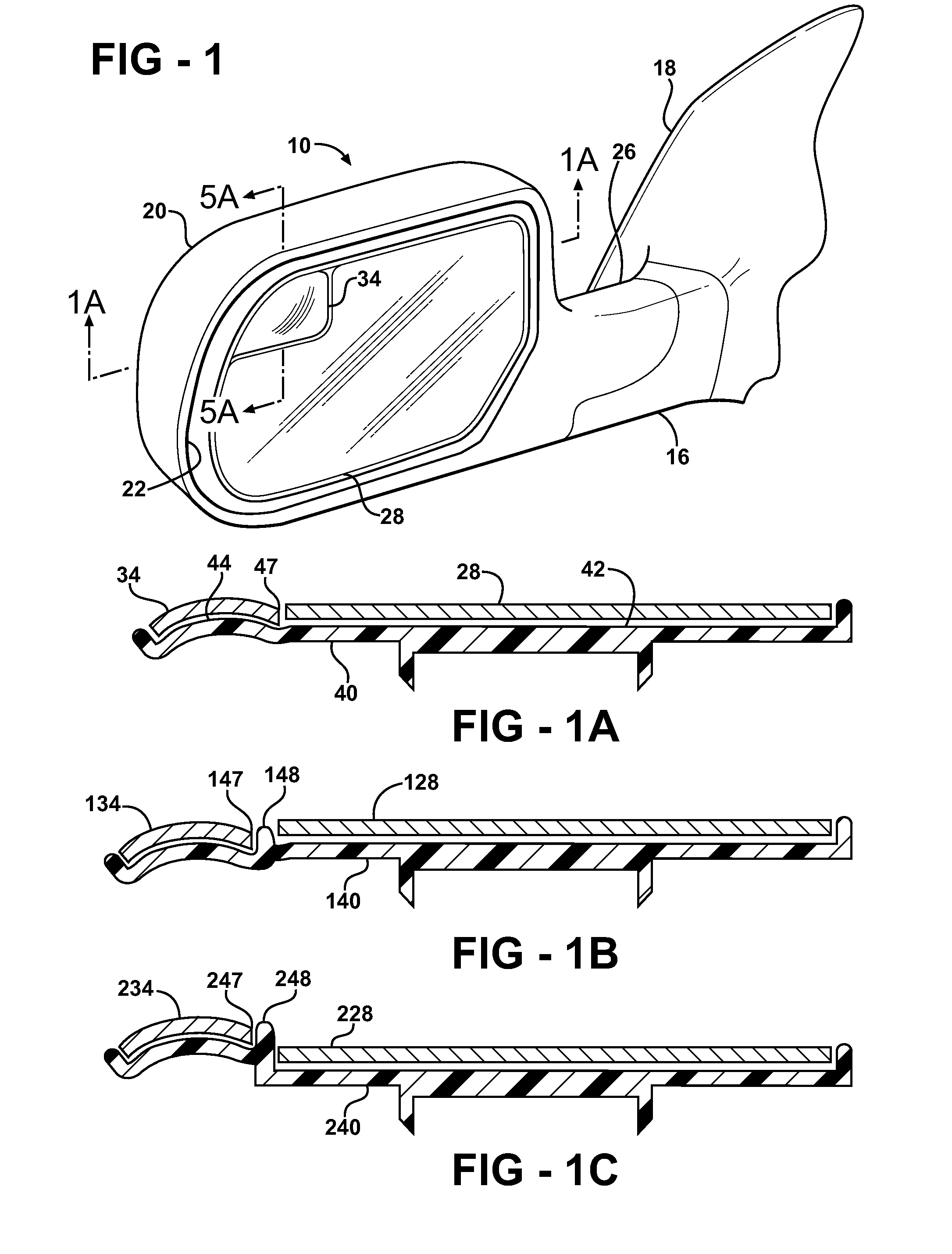
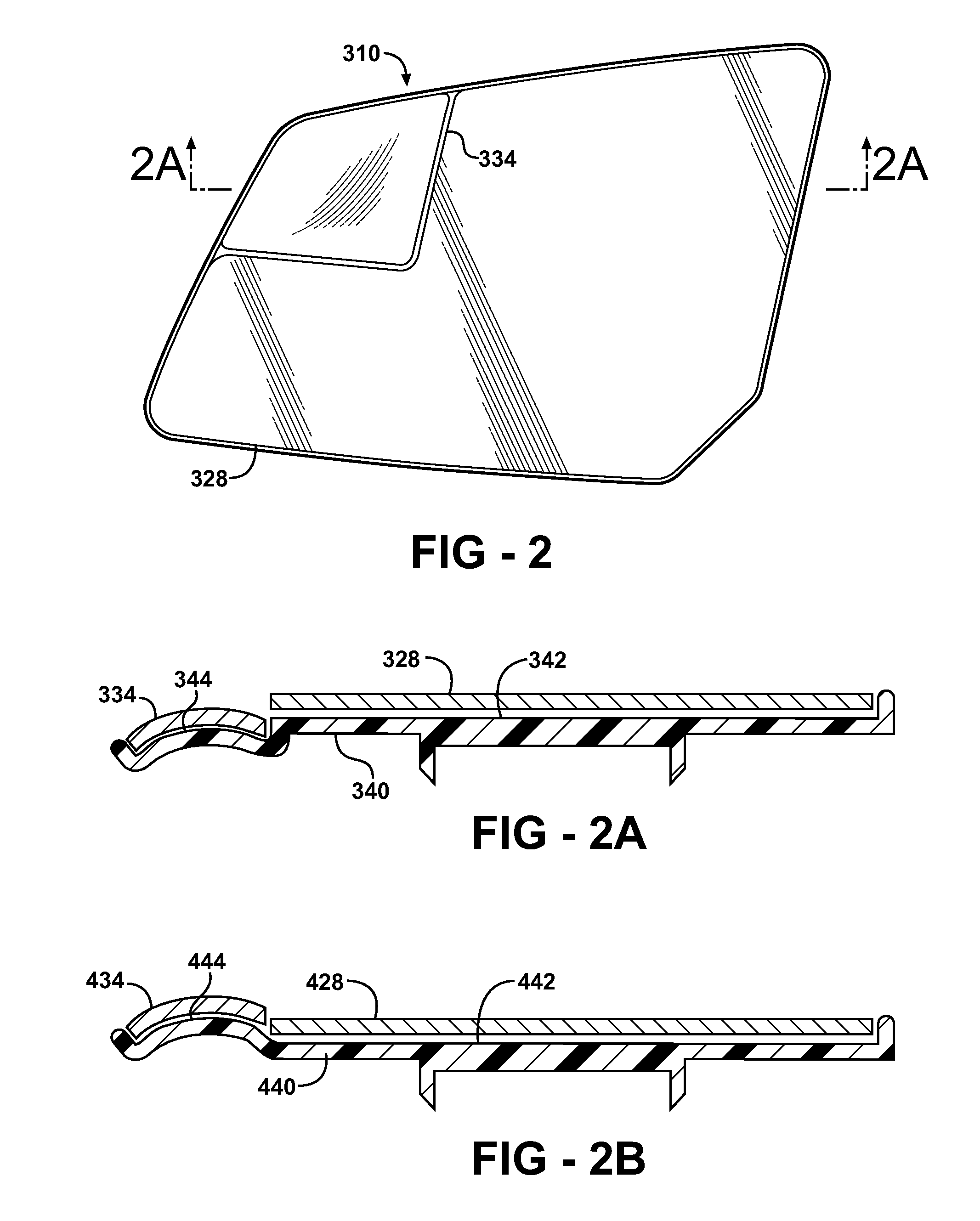
An exterior rearview mirror assembly for a motor vehicle is disclosed having a bracket which is fixedly secured to the motor vehicle. A mirror casing is secured to the bracket. The mirror casing defines a primary opening. A primary mirror is disposed within the primary opening and provides a view rearward of the motor vehicle through a primary field of view. A spotting mirror is disposed adjacent the primary mirror. The spotting mirror is defined by a single radius of curvature differing from the primary mirror such that the spotting mirror provides a secondary field of view rearward of the motor vehicle.
Owner:SMR PATENTS S A R L
Main mirror with pivot connection
A vehicular exterior rearview mirror system comprises a reflective element assembly, a base frame coupling the reflective element assembly to a vehicle, a support arm for coupling the reflective element assembly to the base frame, and a pivot connection for pivotally coupling the support arm to one of the base frame and the reflective element assembly. The pivot connection comprises a pedestal having at least two detent ribs, and an opening for receipt of the pedestal therethrough having at least two detent channels. Pivoting of one of the support arm relative to the base frame and the reflective element assembly relative to the support arm moves a first one of the at least two detent ribs out of a first one of the at least two detent channels and into a second one of the at least two detent channels.
Owner:MAGNA MIRRORS OF AMERICA INC
Single-lens-reflex digital camera
InactiveUS20070019945A1Avoid structureEasy to operateTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsReflexCamera lens
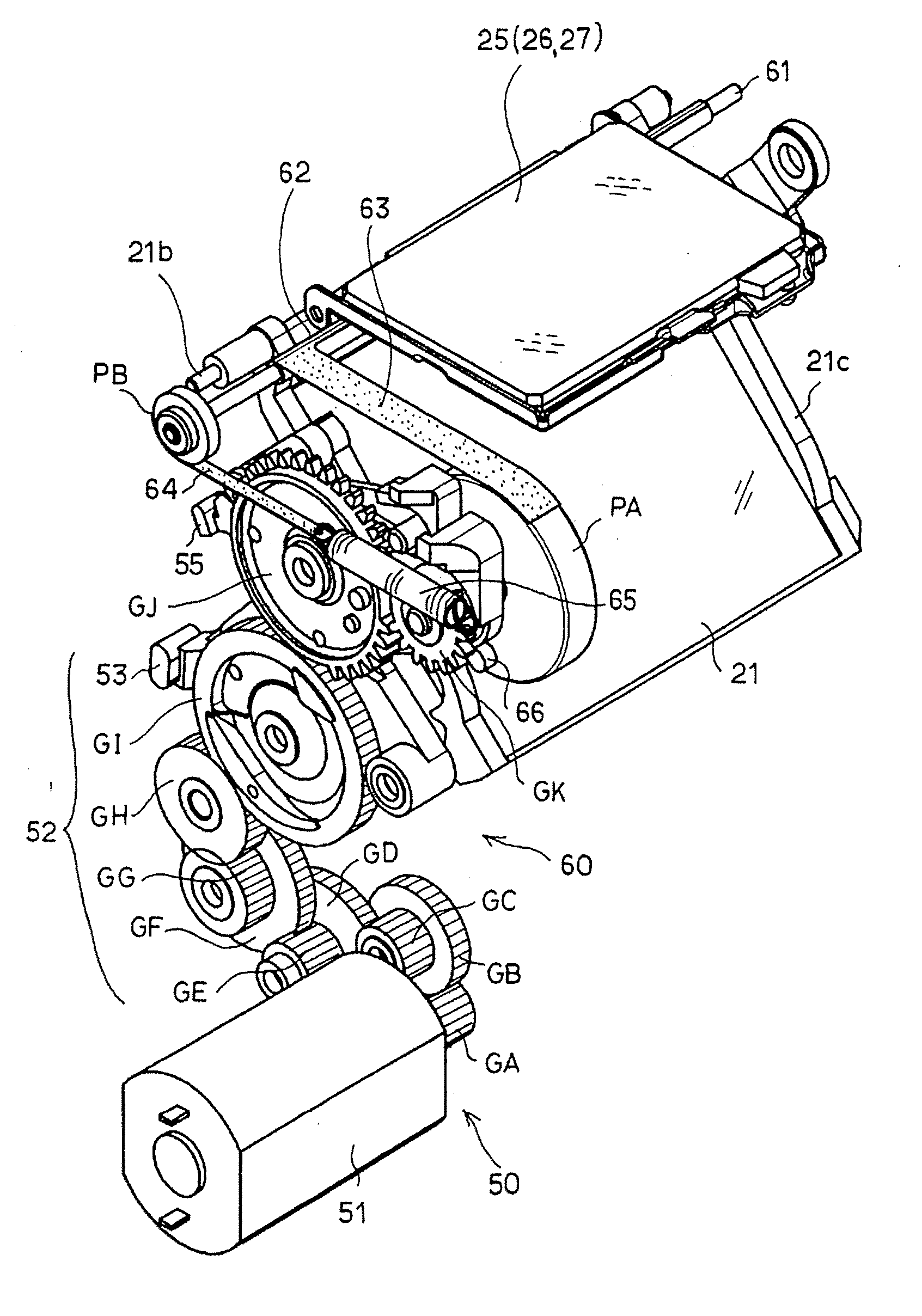
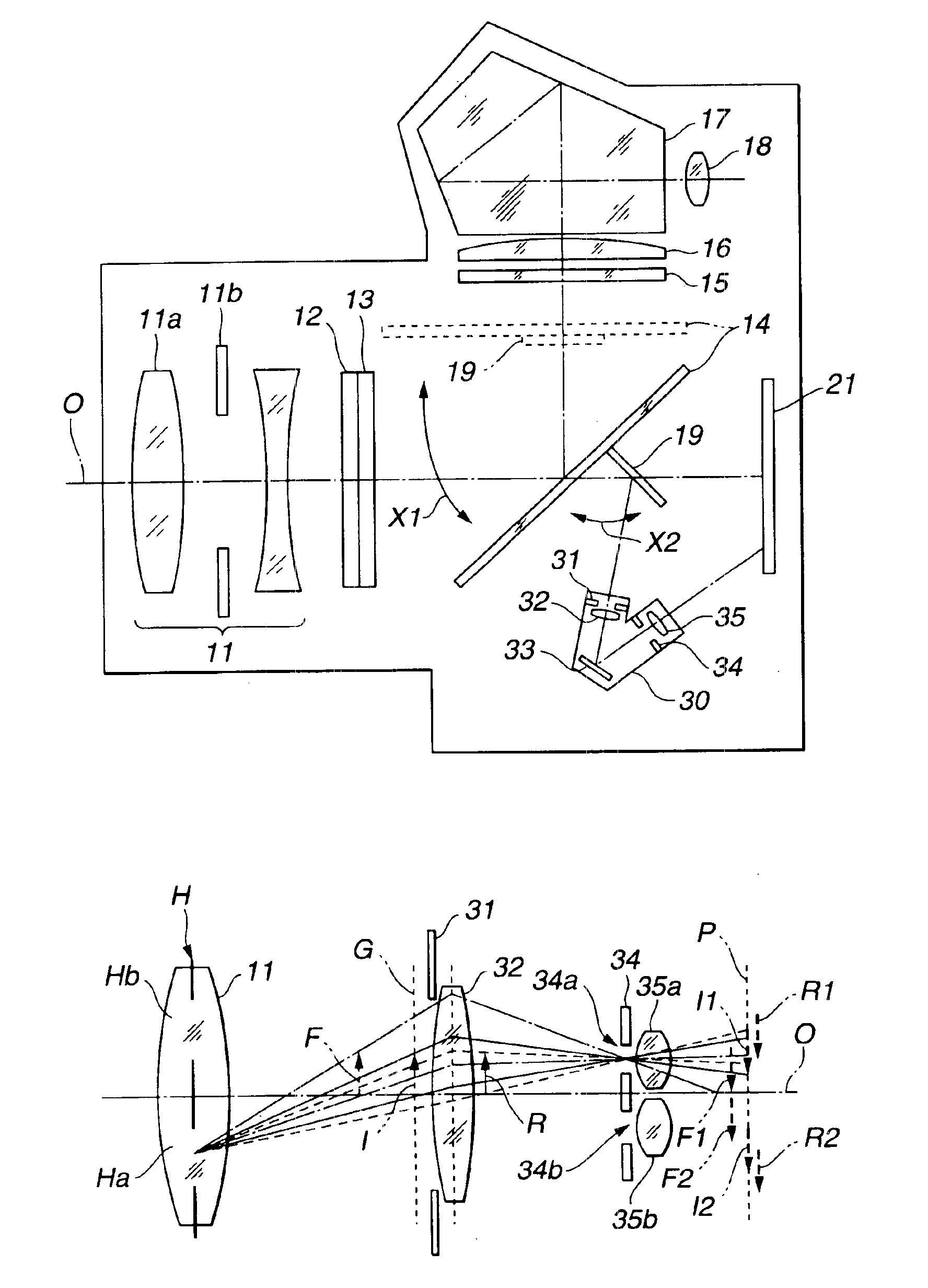
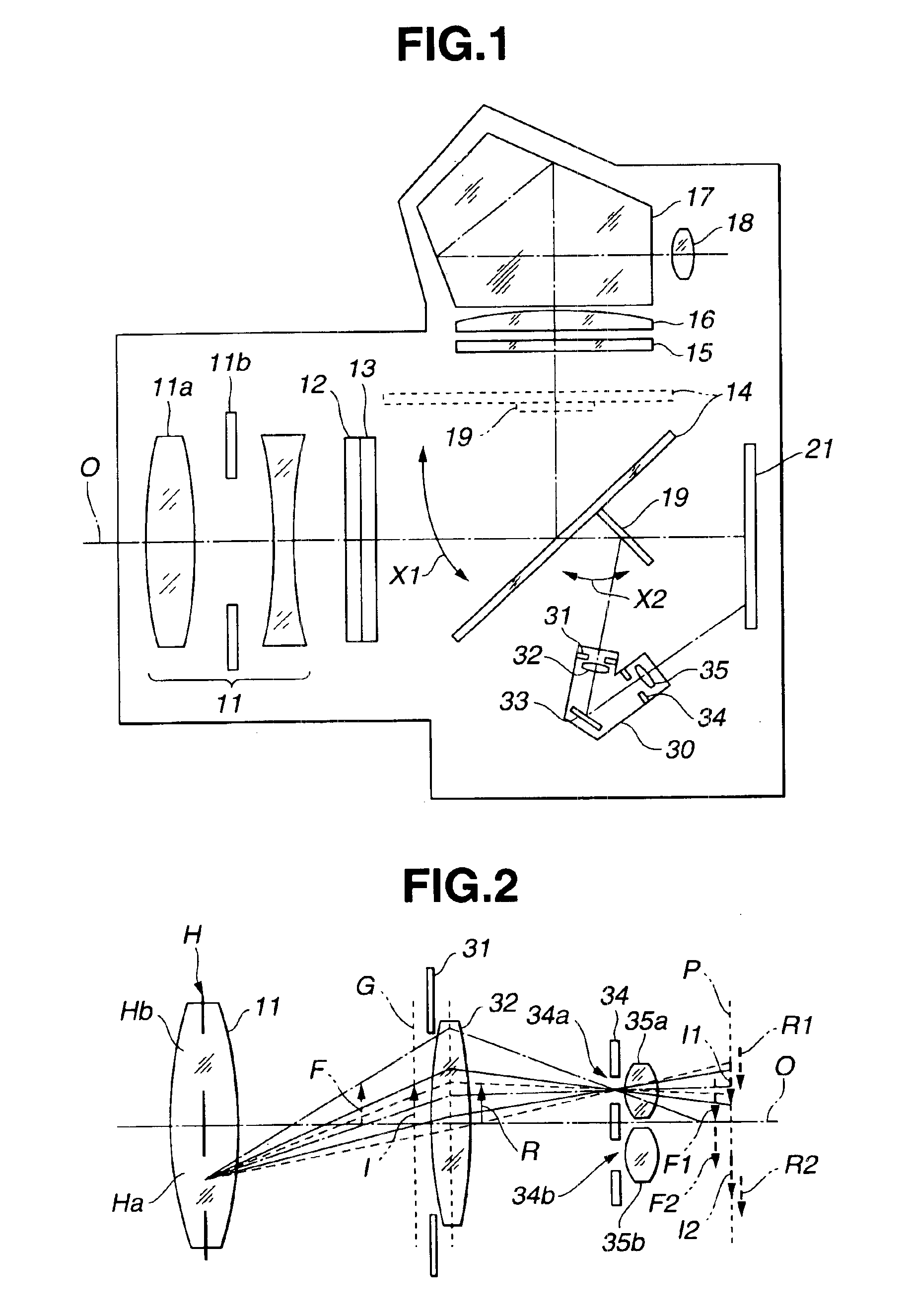
A single-lens-reflex digital camera in which an optical image of an object that is to be photographed via a photographing lens is reflected by a main mirror to be formed on a focusing screen so that the optical image is viewed through a viewfinder while the main mirror is retracted from an optical path of the photographing lens to capture an image of the object by an image pickup device, the single-lens-reflex digital camera includes an electroluminescent display provided on the focusing screen, wherein the electroluminescent display displays at least the object image captured by the image pickup device. The single-lens-reflex digital camera is configured to allow the object image displayed by the electroluminescent display and the optical image formed on the focusing screen to be viewed through the viewfinder.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
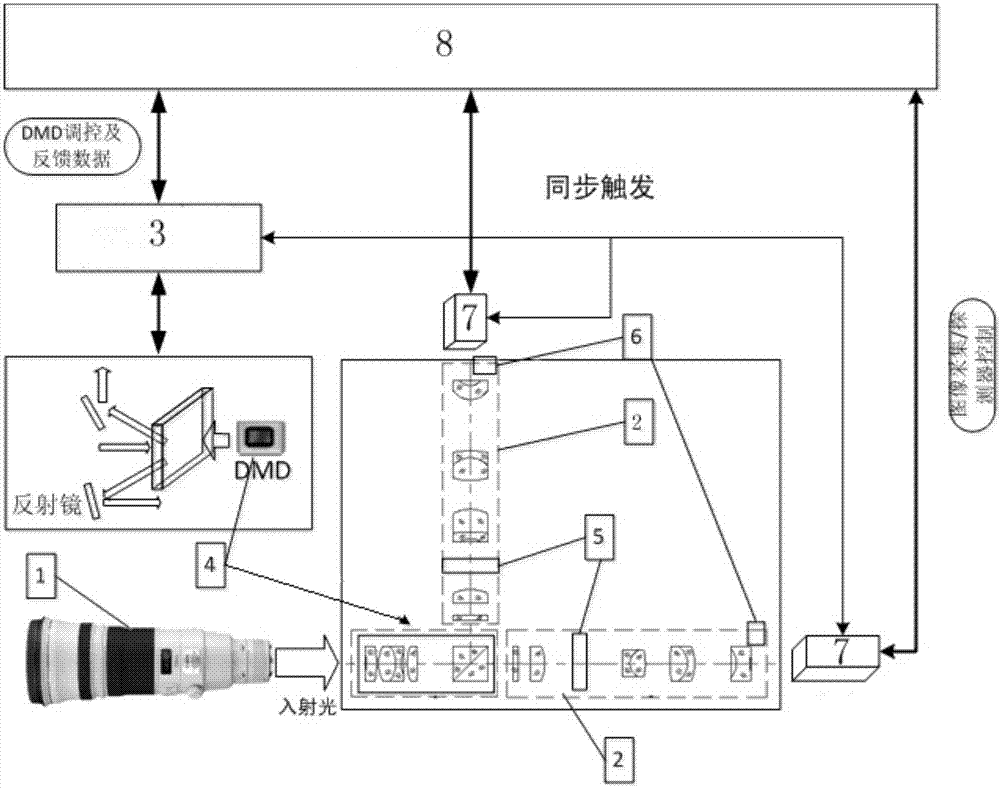
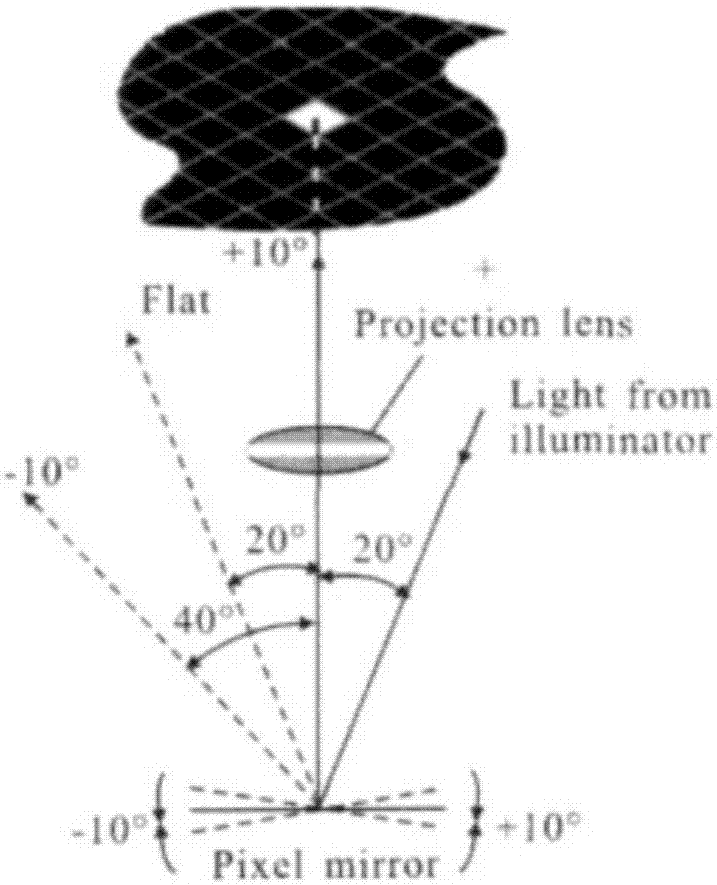
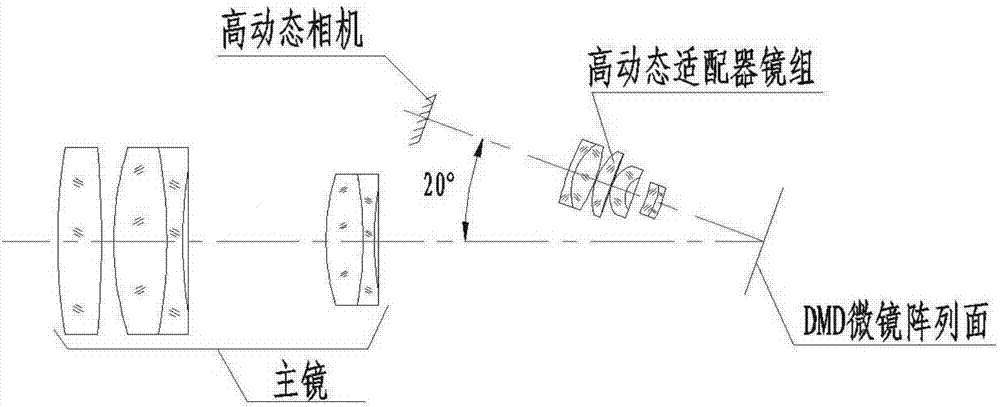
High dynamic imaging module based on DMD dynamic beam splitting
ActiveCN107343130AAchieve clear imagingGuaranteed full coverage of linear response dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh-dynamic-range imagingMulti camera
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
On-window solar-cell heat-spreader
InactiveUS20110120539A1Easy to cleanImprove isolationMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectrical conductorTransducer
An optoelectrical device, which may be a luminaire or a photovoltaic concentrator, has a transparent cover plate. A target with an optoelectrical transducer that produces waste heat in operation is mounted at an inside face of the transparent cover plate. A primary mirror reflects light between being concentrated on the target and passing generally collimated through the cover plate. A heat spreader is in thermal contact with the target. The heat spreader has heat conductors that thermally connect the target with the inside surface of the cover plate. The heat conductors may be arms extending radially outwards, and may be straight, zigzag, or branching. An array of targets may be mounted on a common cover plate, and their heat spreaders may be continuous from target to target.
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
System and method for effecting high-power beam control with outgoing wavefront correction utilizing holographic sampling at primary mirror, phase conjugation, and adaptive optics in low power beam path
InactiveUS20030062464A1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorPhased array
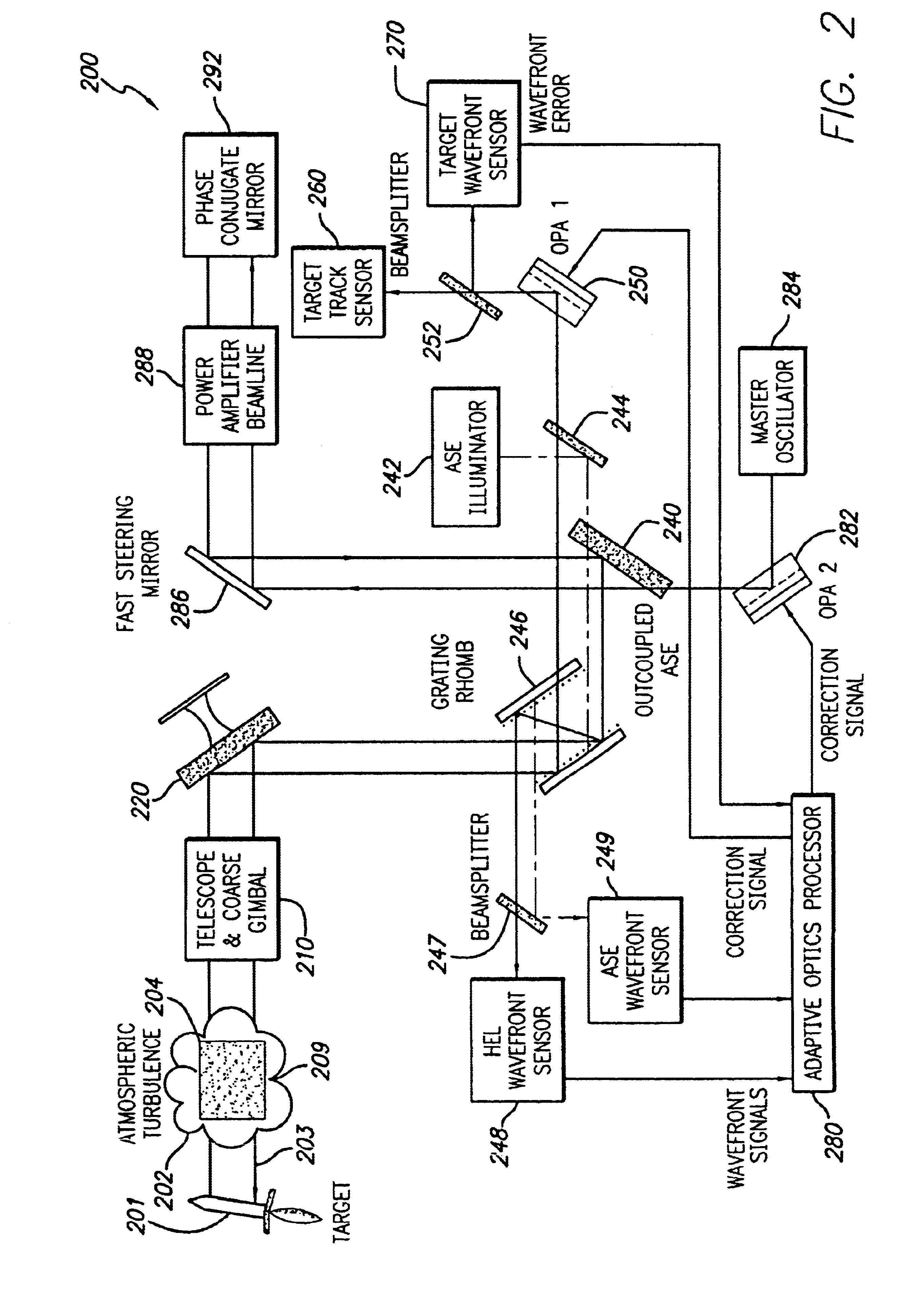
A beam control system and method. In an illustrative embodiment, the inventive system (500) provides a first beam of electromagnetic energy (503); samples the first beam (503) and provides a second beam (505) in response thereto; detects aberrations in the second beam (505); and corrects aberrations in the first beam (503) in response to the detected aberrations. In a specific implementation, the invention (500) includes a beam director telescope (510) having a primary mirror (516) on which a holographic optical element (518) is disposed. The holographic optical element (518) samples the output high-power beam and provides a sampled beam to a wavefront sensor (520). The wavefront sensor (520) provides signals to an adaptive optics processor (580). The adaptive optics processor (580) analyzes the sampled wavefront, detects aberrations therein and provides a correction signal to an optical phased array (550). A master oscillator (552) provides a reference beam, which reads the optical phased array (550) and is back reflected off a front surface of an aperture sharing element (540). The resulting beamfront is conjugated by a first phase conjugate mirror (546) and then again by a second phase conjugate mirror (556). The output of the second phase conjugate mirror (556) is amplified and reflected off the front surface of the aperture sharing element (540). The aperture sharing element (540) outputs the high power beam via the telescope (510) which is corrected for the optical distortions in the telescope and beam path.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Novel high resolution large visual field optical imaging system
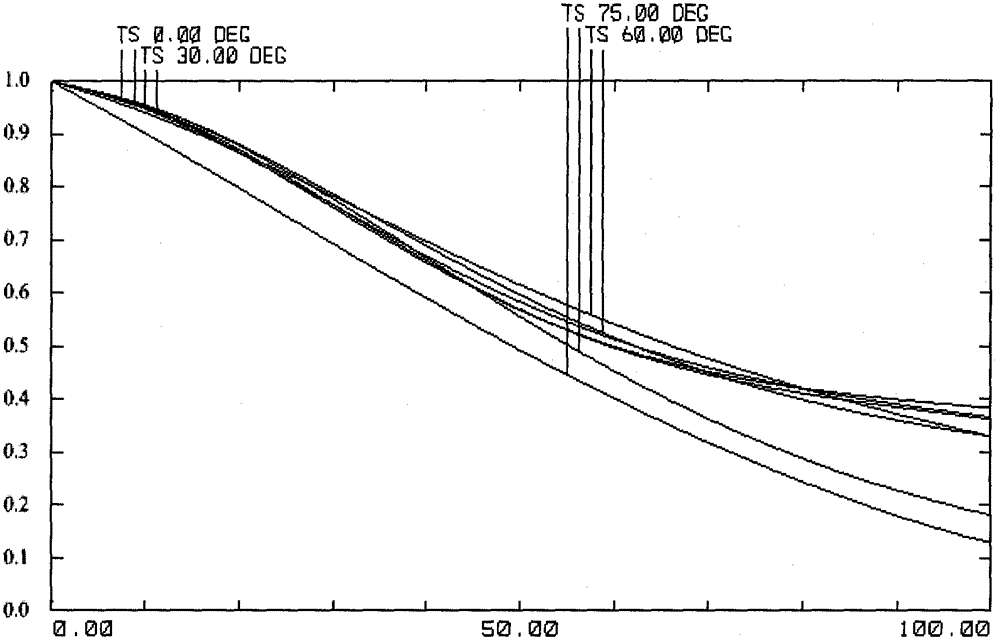
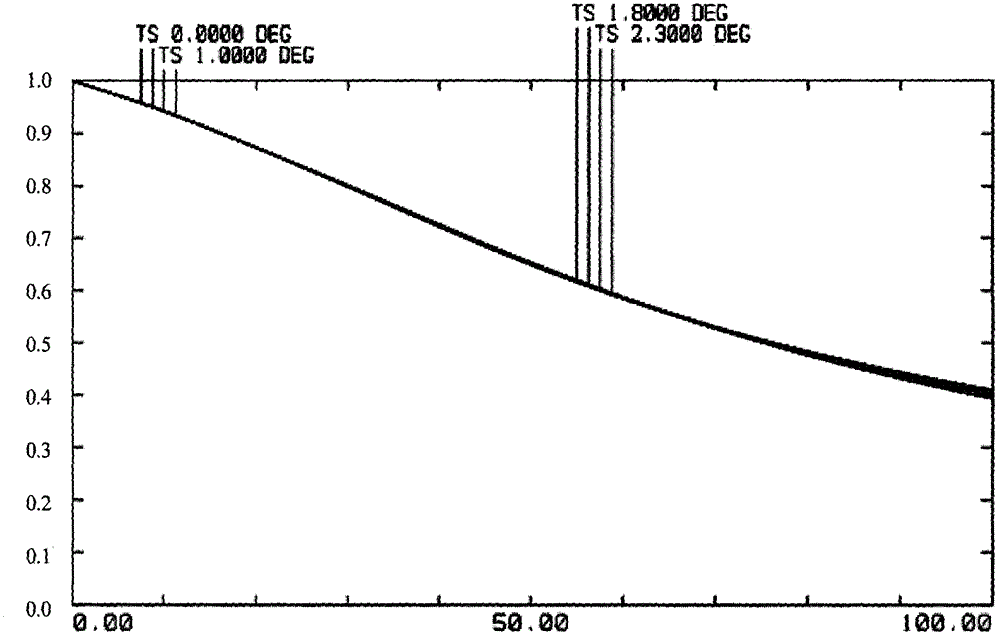
ActiveCN103064171AAchieve super large field of viewHigh-resolutionOptical elementsAir monitoringImaging quality
A novel high resolution large visual field optical imaging system is composed of a share primary mirror, a microlens array and a detector array. The share primary mirror is in a holocentric spherical mirror structure, and the center of the share primary mirror is a spherical mirror. Two meniscus lenses are wrapped on two sides of the share primary mirror, and incident rays respectively pass through the share primary mirror and the microlens array, and finally reach the detector array for imaging. Through the computed imaging technology, image restoration is carried out on every sub-image (eliminating impact of spherical difference on image quality), and all sub-images are subjected to registration recombination to obtain a complete clear image. The novel high resolution large visual field optical imaging system is simple in structural type, and the visual field can reach 180 degrees in theory. The full visual field has a uniform resolution ratio, and combines with the computed image post processing technology, the systematic resolution ratio can be close to a diffraction limit in theory. The novel high resolution large visual field optical imaging system has the advantages of having an extra large visual field, a high resolution ratio, and the like, and particularly suitable for researching and finding of space targets in a wide range, air monitoring for a stratosphere, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Ultra-small angle x-ray scattering measuring apparatus
ActiveUS7646849B2Accurate captureSuppressing the smearing phenomenonRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsLattice planeSmall-angle X-ray scattering
An ultra-small angle X-ray scattering measuring apparatus includes a detector for detecting X-rays emitted from a sample, an X-ray collimating mirror arranged between the X-ray real focus and the sample, a monochromator arranged between the X-ray collimating mirror and the sample and an analyzer arranged between the sample and the detector. The X-ray collimating mirror includes a pair of X-ray mirrors that are arranged orthogonally relative to each other. The X-ray mirrors are multilayer film mirrors and their X-ray reflection surfaces are paraboloidal. The interplanar spacing of lattice planes of each of the multilayer films is continuously changed along the paraboloid so as to meet the Bragg's condition. The monochromator and the analyzer are formed by using a channel-cut crystal. The analyzer is driven to rotate for scanning around a 2θ-axial line and diffracted rays reduced to a spectrum by the analyzer are detected by the detector.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
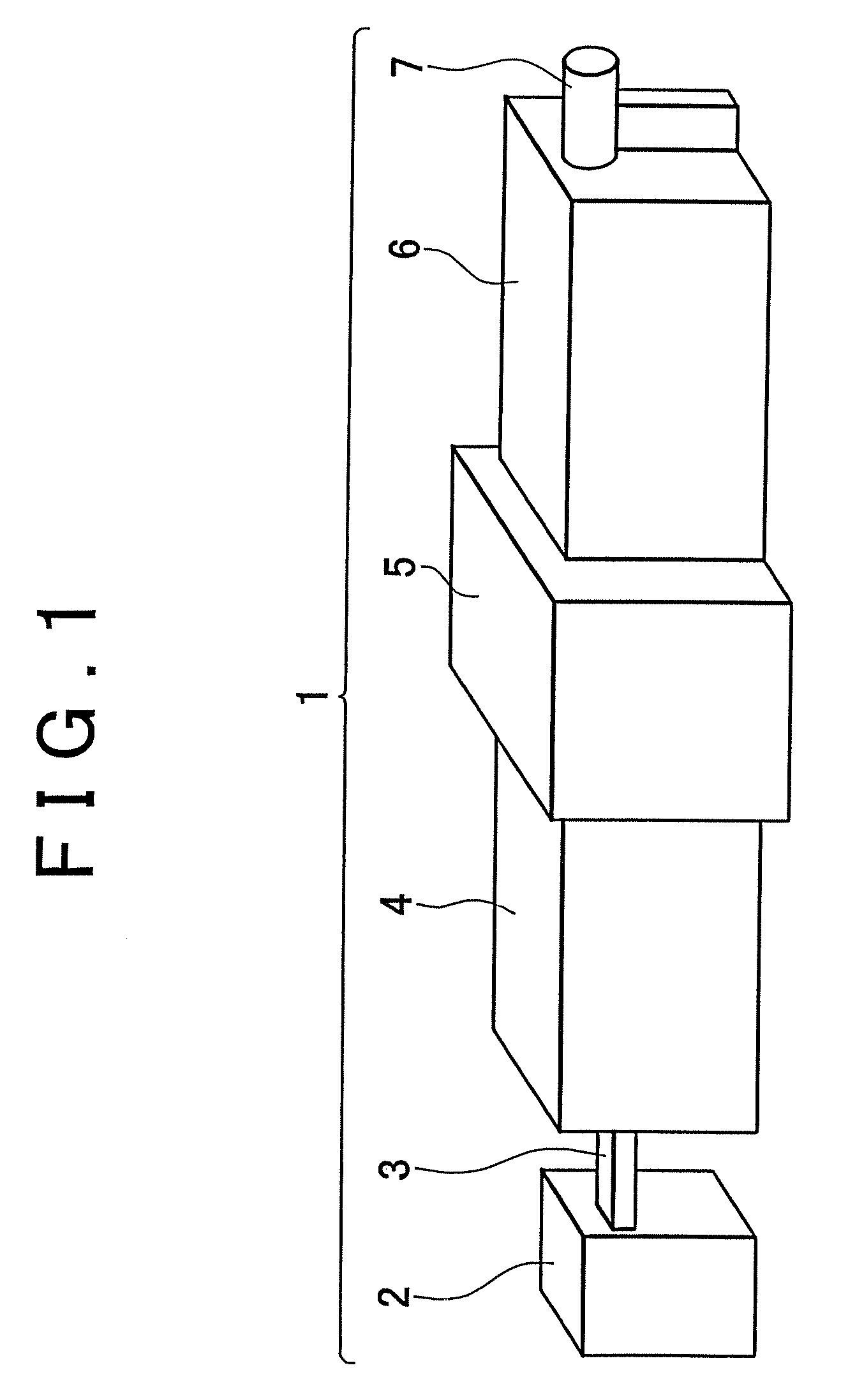
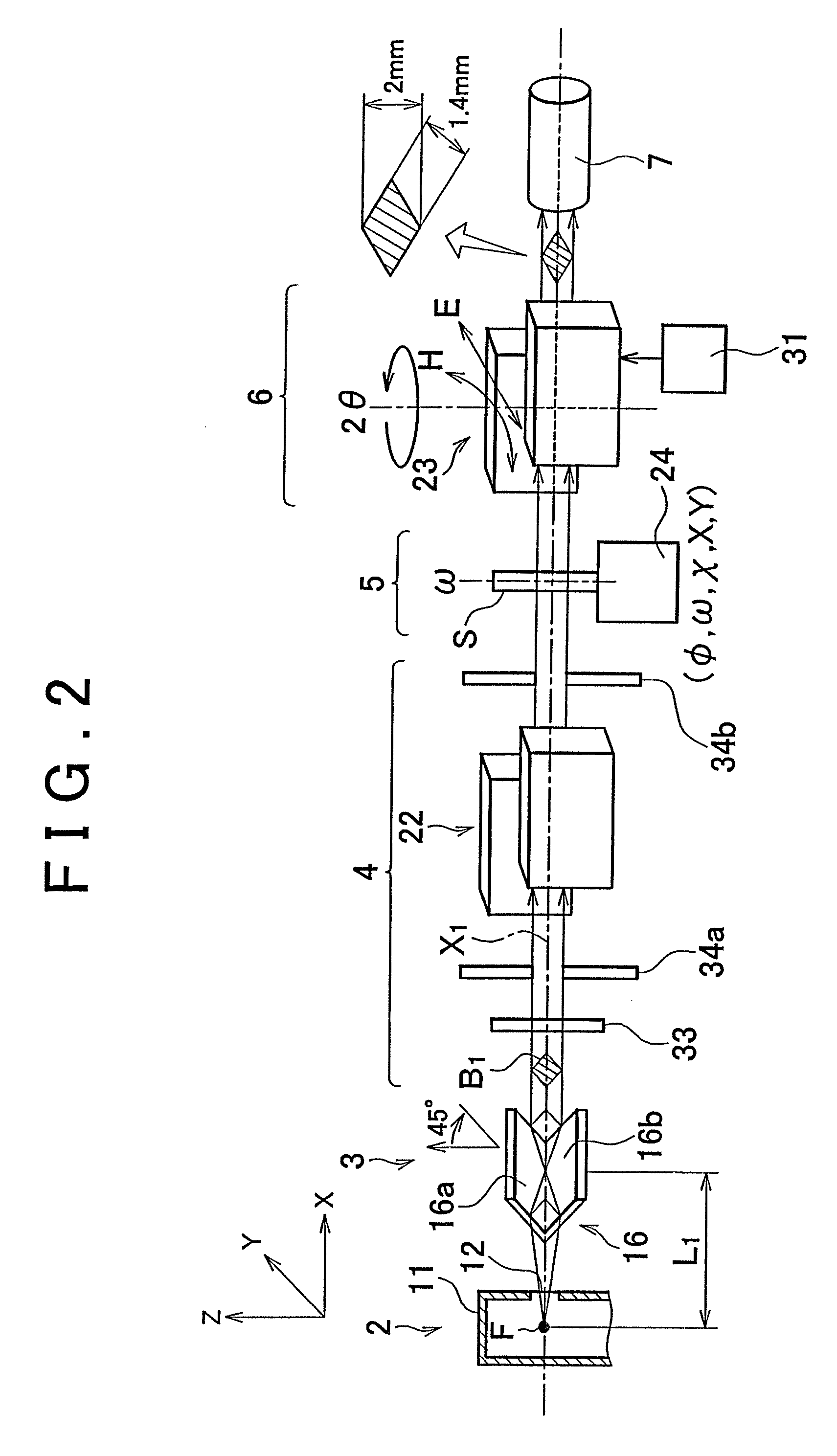
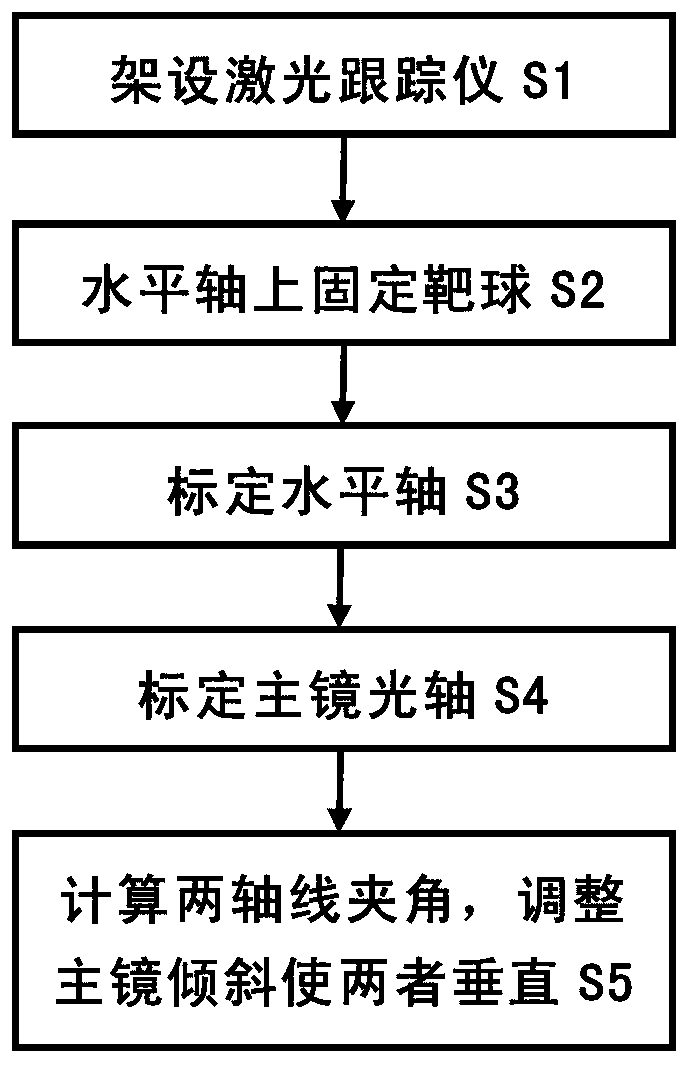
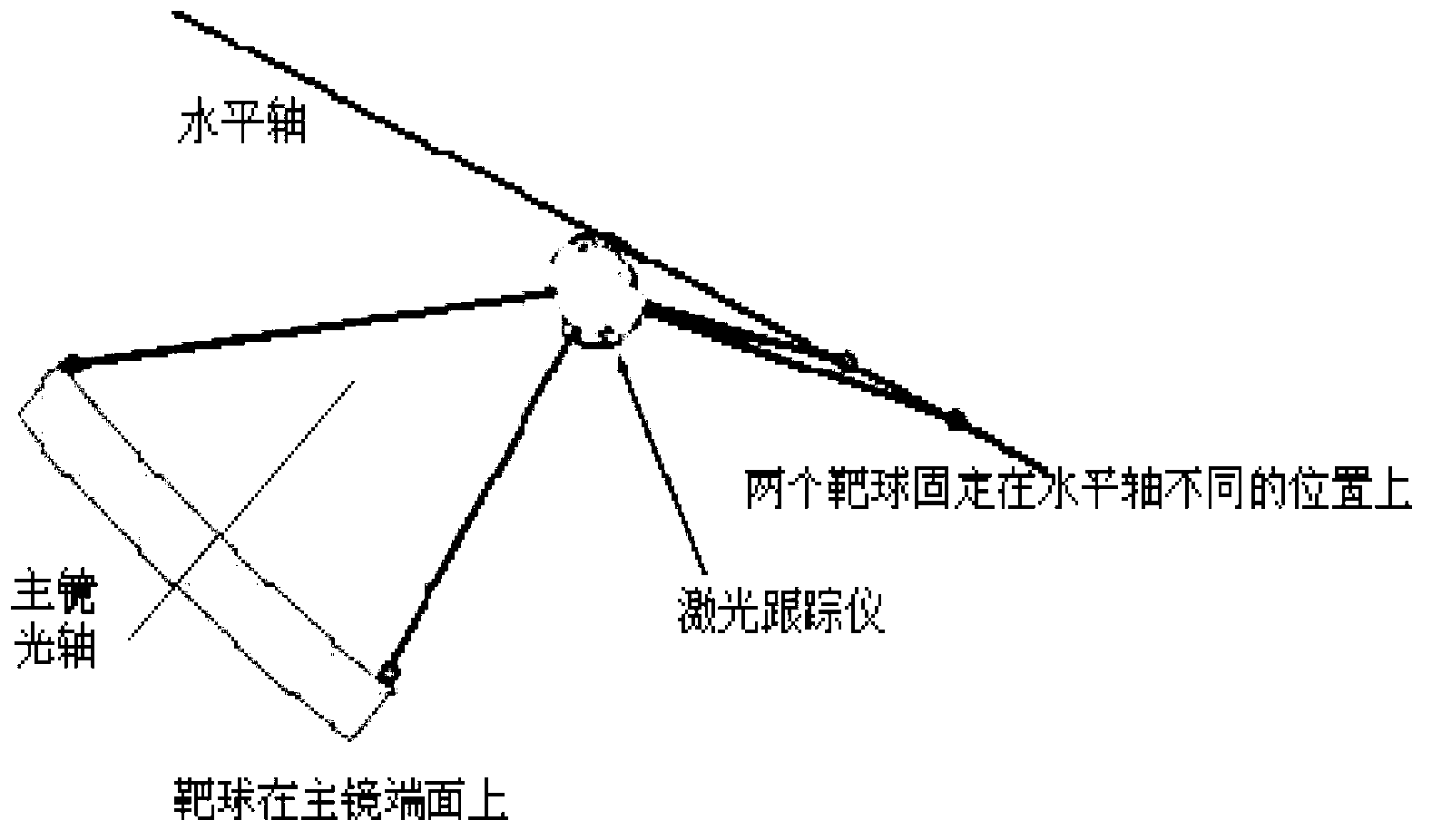
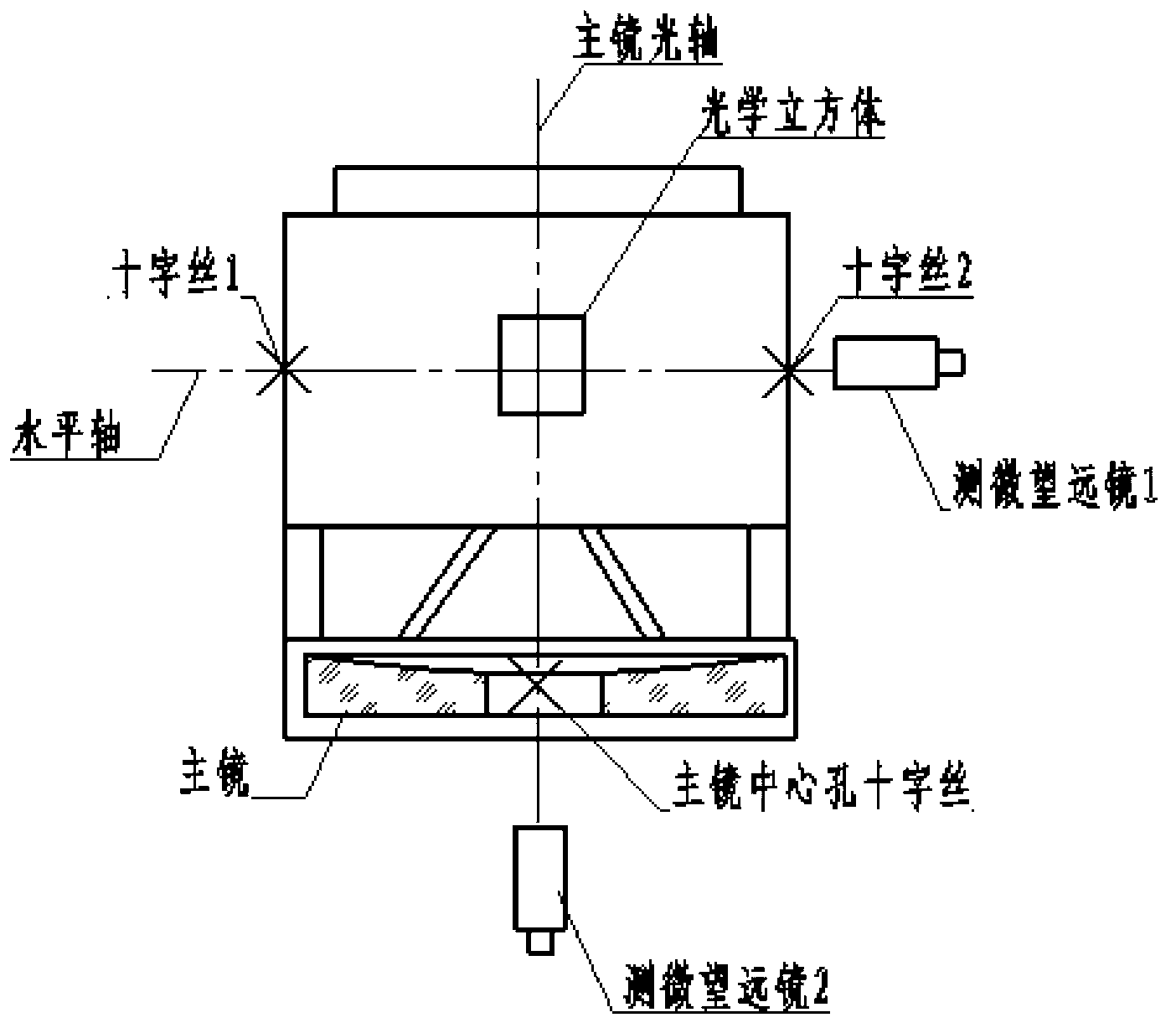
Method for adjusting primary mirror optical axis to be perpendicularly to horizontal axis by using laser tracker
InactiveCN103017686AOvercoming the need to designOvercoming processabilityUsing optical meansOptical axisHorizontal axis
The invention discloses a method for adjusting a primary mirror optical axis to be perpendicularly to a horizontal axis by using a laser tracker and belongs to the technical field of optical installation and adjustment. The method is used for adjusting the primary mirror optical axis of a photoelectric device to be perpendicularly to the horizontal axis and comprises the steps of (1) erecting the laser tracker; (2) fixing two target balls of the laser tracker at different positions of the horizontal axis; (3) rotating the horizontal axis to drive target balls, and using the laser tracker to calibrating the horizontal axis; (4) moving target balls on a primary mirror, and using the laser tracker to calibrating the primary mirror optical axis; and (5) calculating the included angle formed by the primary mirror optical axis and the horizontal axis, and adjusting the primary mirror to incline, so that the primary mirror optical axis is perpendicularly to the horizontal axis. The method solves the problems that existing technologies are complex in tooling, miscellaneous in operation process and large in reference error and is simple to operate, safe and high in efficiency.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Foldable spectacle frame with engaging means for maintaining the spectacle frame in unfolded state while wearing
Owner:HUANG DAVID
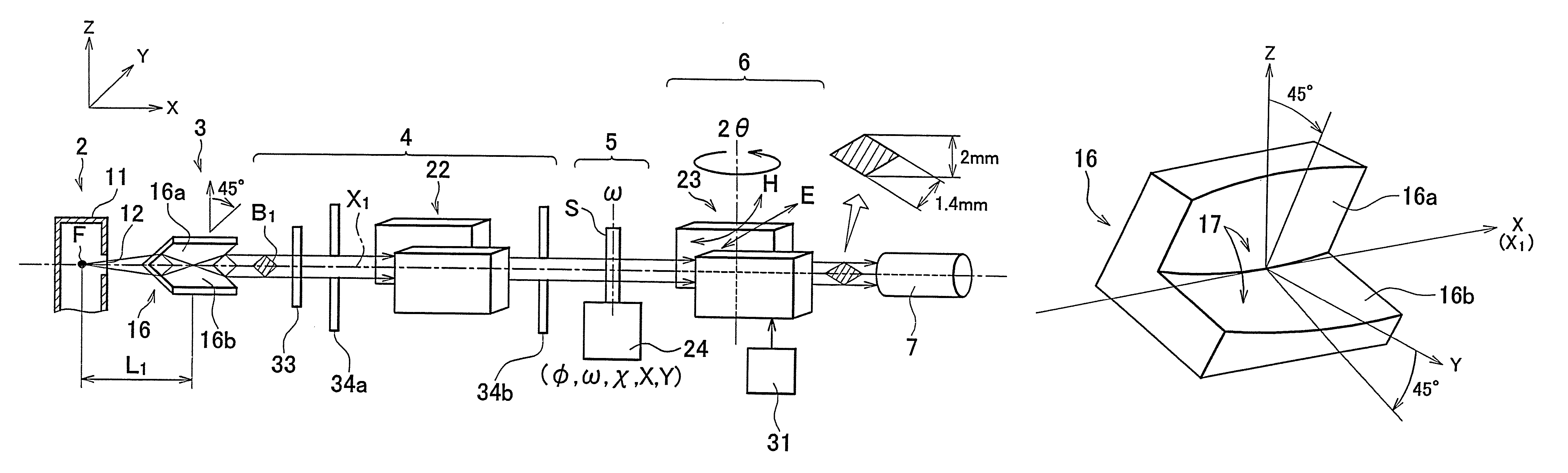
Direct wave face conversion scanner for direct sight synthetic aperture laser imaging radar emitting light beam
ActiveCN103245939AThe overall structure is simple and reliableReduce volumeWave based measurement systemsWork patternRadar imaging
The principle of a direct wave face conversion scanner for a direct sight synthetic aperture laser imaging radar emitting light beam is that a Mach-Zehnder polarized interferometer is adopted to divide an incident light beam into two cross-polarization separated space channels, each of the channel is internally provided with a track-along cylindrical mirror needed by phase quadratic term traversing and a track-crossing cylindrical mirror needed by phase line modulating, the track-crossing cylindrical mirror is provided with a scanning driver, and wave face conversion is performed on the light beam by combining the cylindrical mirrors of the two channels to generate two coaxial cross-polarization scanning emitting wave faces which are imaged to a target face by an emitting optical main mirror. The direct wave face conversion scanner for the direct sight synthetic aperture laser imaging radar emitting light beam has the advantages of simple and reliable structure, small size, small transmission loss, vibration resistance, realizing precise phase quadratic term by adopting a high-precision non-spherical optical element, and capability of changing the work mode and the running performance parameters of a radar by adopting the cylindrical mirrors with different focal lengths and different scanning directions without changing the whole structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Telescopic truss type binary optical space camera and on-orbit work method thereof
The invention provides a telescopic truss type binary optical space camera and an on-orbit work method thereof and belongs to the field of spaceflight space repeatable unfolding. The telescopic truss type binary optical space camera aims to solve the problems that an existing space foldable and spreadable framework type supporting arm is complicated in structure, heavy and difficult to repeatedly fold and unfold. A partitioned type spreadable optical main lens of the telescopic truss type binary optical space camera is installed on a supporting arm through three ball hinges. The supporting arm comprises multiple framework type foldable units. The on-orbit work method comprises the steps that during launching, the supporting arm and the partitioned type spreadable optical main lens are in a folded mode, and the optical camera is in a launch closed mode; after injection, the supporting arm is switched to a unfolding mode and is unfolded; after the supporting arm is unfolded appropriately, the space camera is switched to an on-orbit operation mode, and the partitioned type spreadable optical main lens is unfolded; when the space camera is switched to an on-orbit closed mode, the supporting arm is folded, and the partitioned type spreadable optical main lens is unfolded. The telescopic truss type binary optical space camera is a large-caliber space camera.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
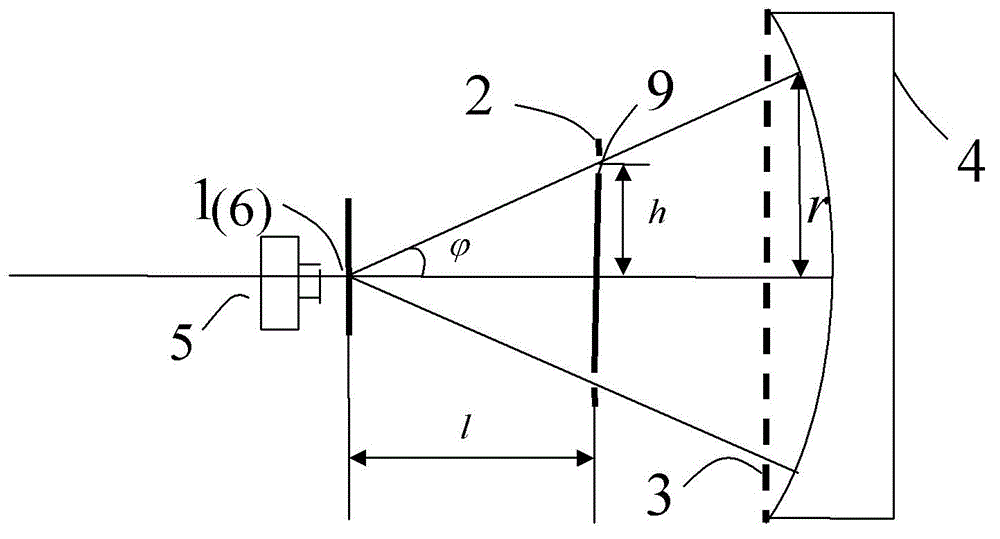
Large-caliber aspheric surface primary mirror detection device and method
ActiveCN103335613AAccurately determineAvoid Diffraction PhenomenaUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsSpecular reflection
The invention relates to a large-caliber aspheric surface primary mirror detection device and method. The device includes a point light source, a baffle, a measuring scale, a CCD (charge coupled detector) and a thin wire. According to the method, a spherical wave emitted by the point light source passes through an annular seam in the baffle and irradiates the mirror surface of a to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror; then the spherical wave is reflected by the mirror surface; the position of the baffle is adjusted, so that the light reflected by the mirror surface of the to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror can pass through the annular seam in the baffle; a circle of bright ray is formed at the point light source; the thin wire is used for cutting at the point light source; observing from the back of the thin wire, a user can see that the bright ray disappears; the CCD positioned behind the point light source is used for shooting and recording images of the bright ray; the radius of the annulus of the bright ray and the distance from the light point source to the to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror are measured. The position of the point light source or the baffle is adjusted, and the radius of the annulus of the bright ray and the distance from the light point source to the to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror are measured, so that the radius of curvature of a vertex of the to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror, a secondary constant and a surface shape are figured out according to the aspheric surface primary mirror surface shape formula.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electronic image pickup apparatus
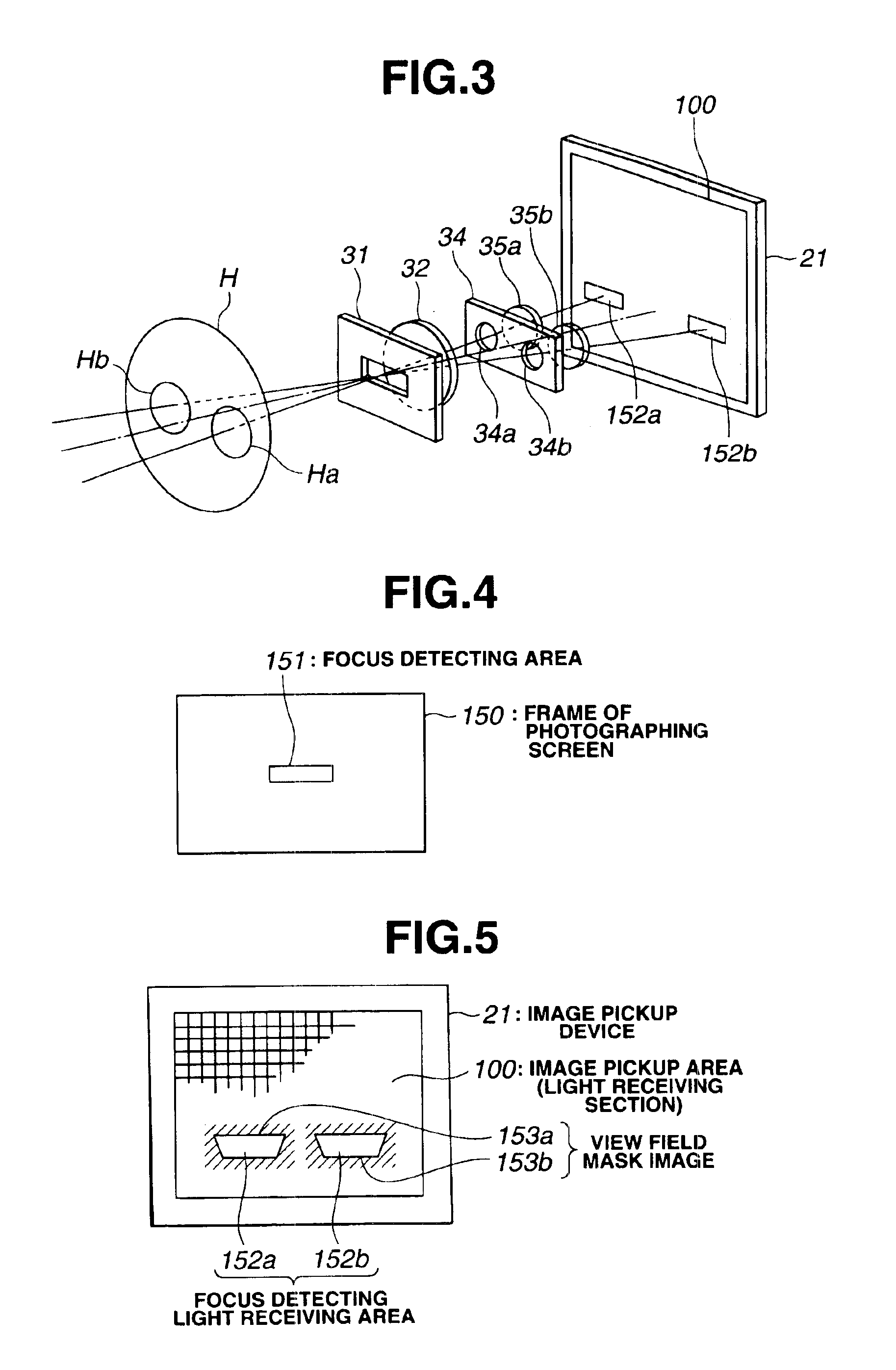
InactiveUS6897899B1Low production costEquipment miniaturizationTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementLight beamOptic system
An electronic image pickup apparatus comprises a photographic optical system; solid state image pickup devices disposed on a plant where a subject image formed by subject beams which have passed through the photographic optical system is formed; a main mirror disposed between the photographic optical system and the solid state image pickup devices, wherein a part of the main mirror is formed of a half mirror to divide the subject beams which have passed through the photographic optical system into an observing beam and a focus detecting beam; a sub-mirror for reflecting the subject beam which has passed through the part of the main mirror; a focus detecting optical system for forming an image of the subject beam reflected by the sub-mirror on a partial area of the solid image pickup devices; and an electrical circuit for outputting focus detecting information based on image signals of the partial areas of the solid image pickup devices. The structure provides an electronic image pickup apparatus which contributes to the down-sizing of the apparatus and to the reduction of production cost by eliminating an image pickup device which is dedicated for focus detection.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
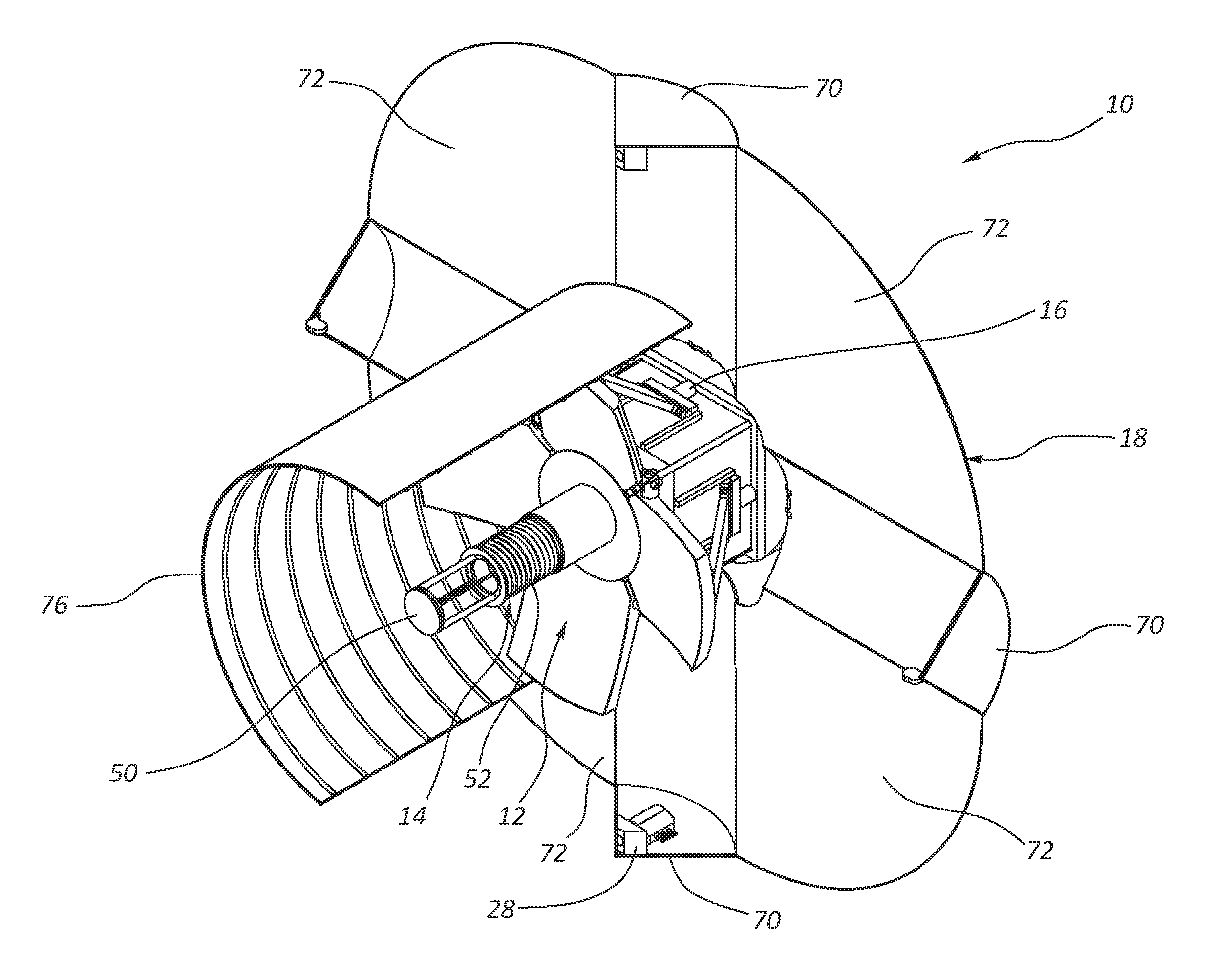
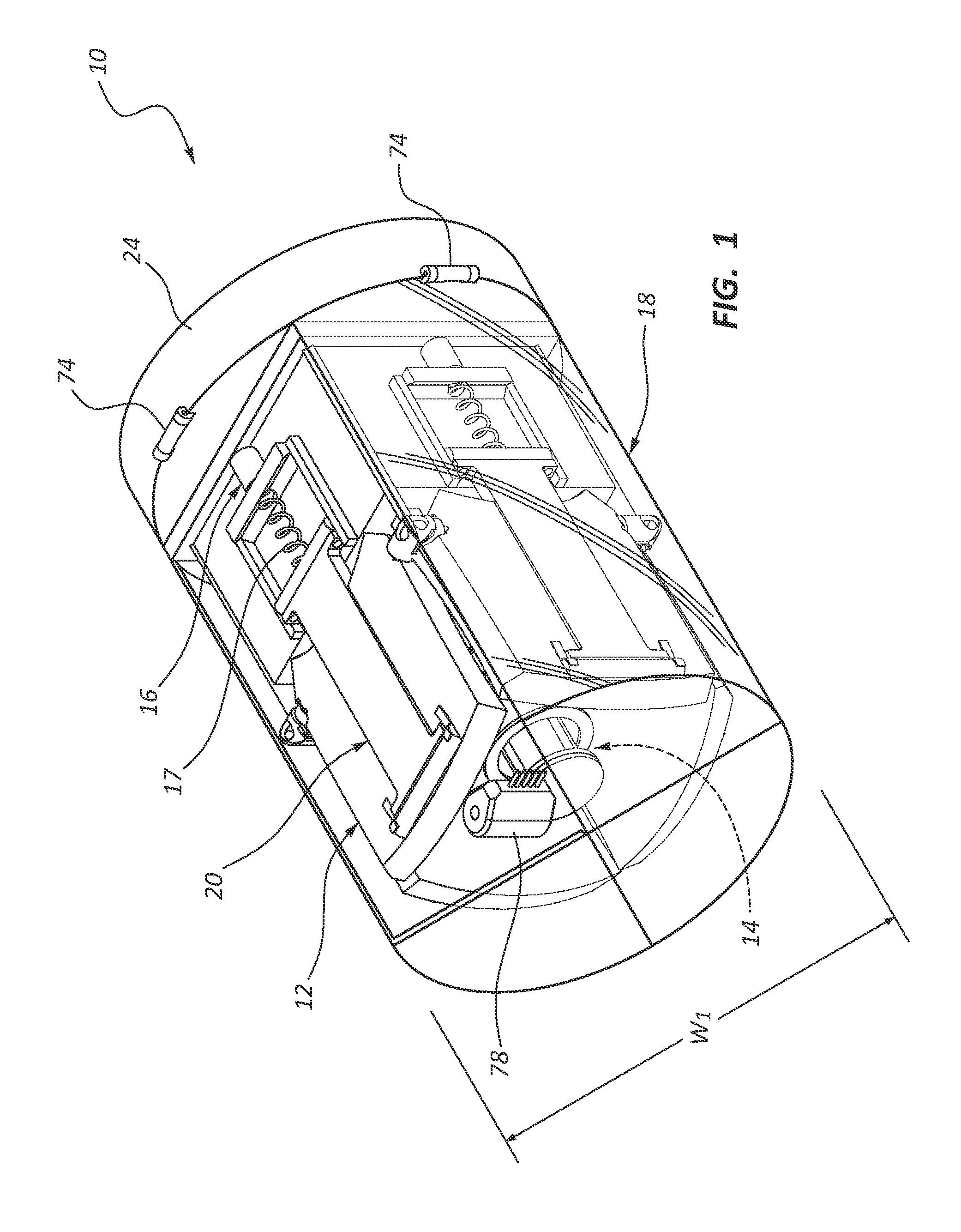
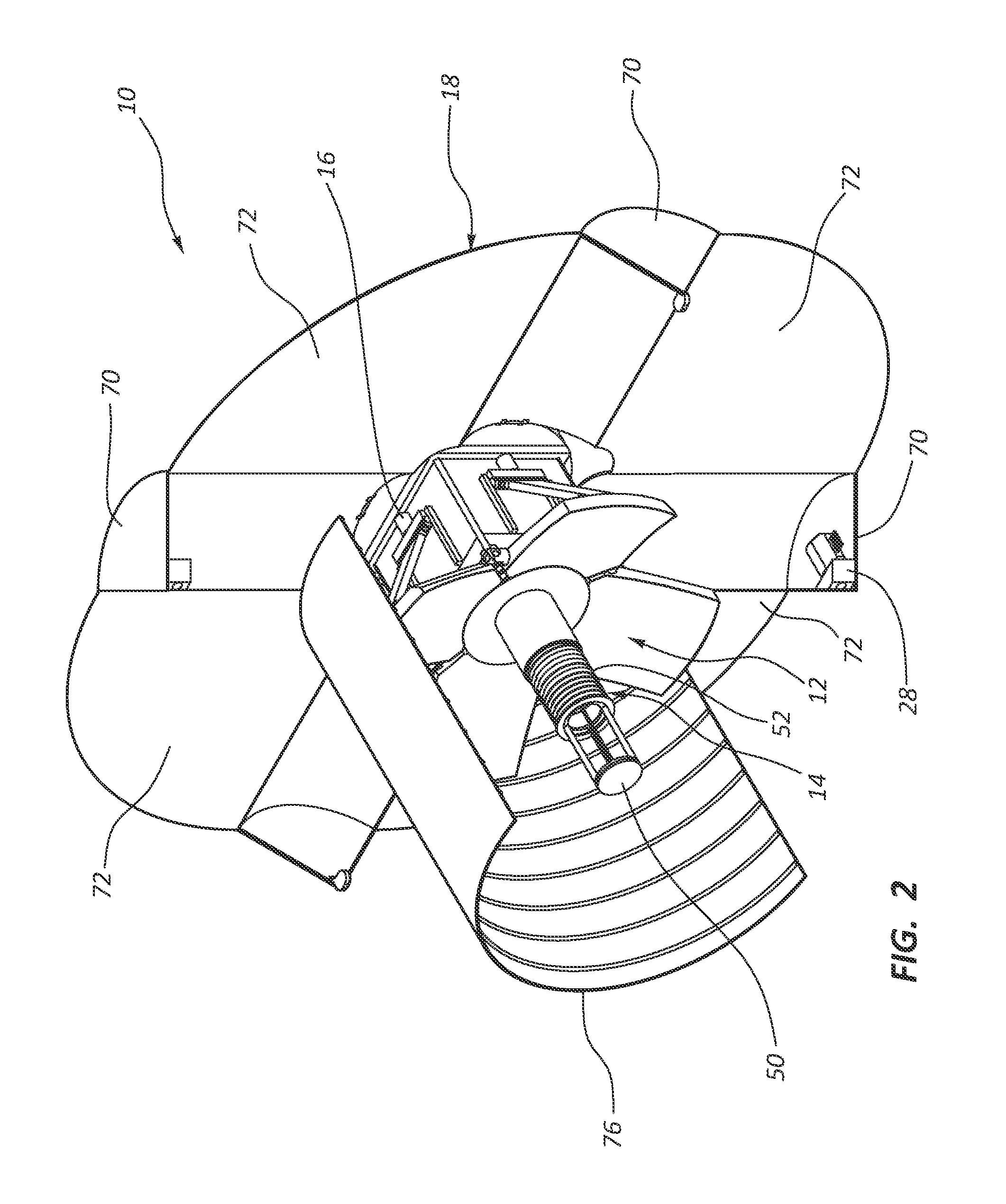
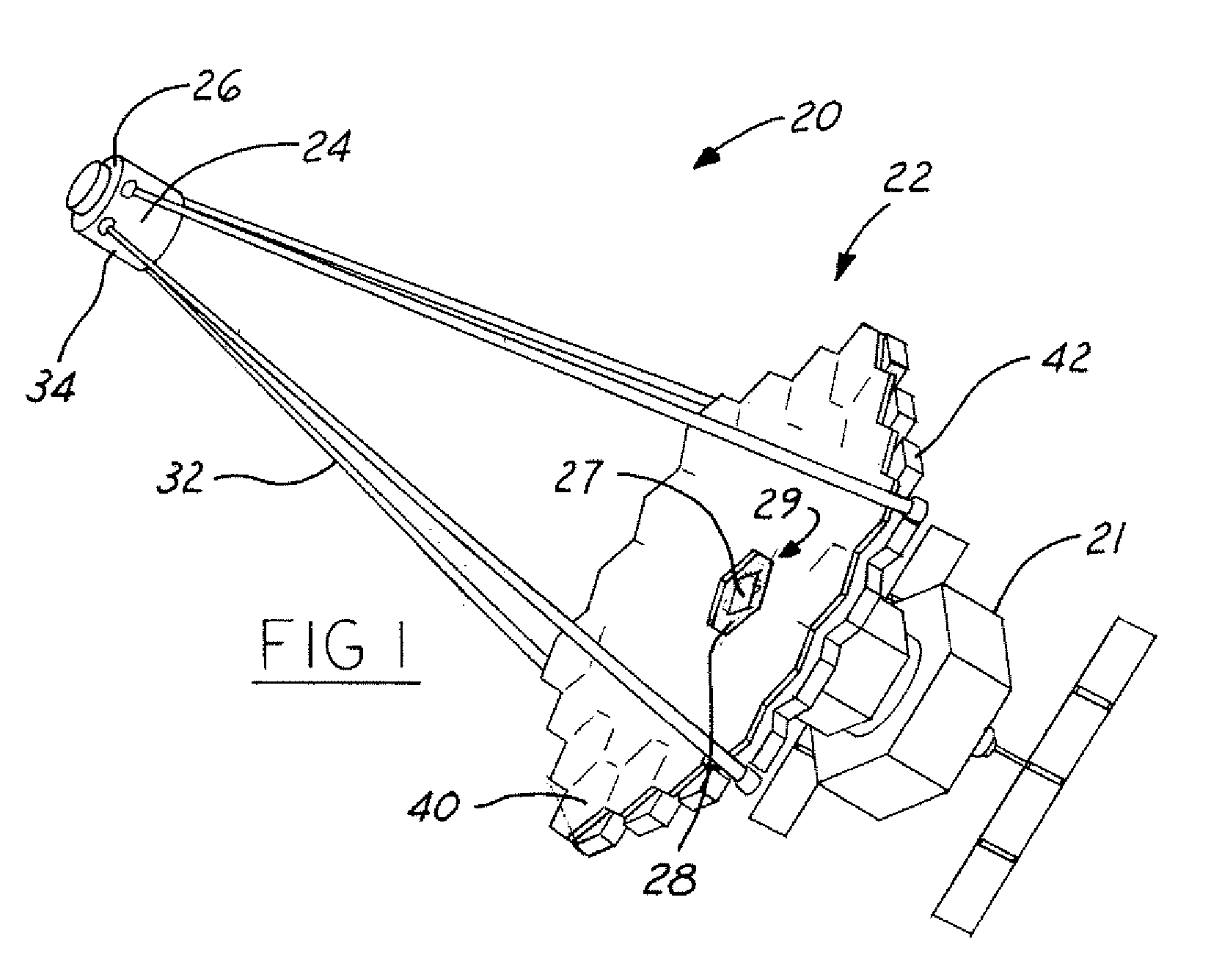
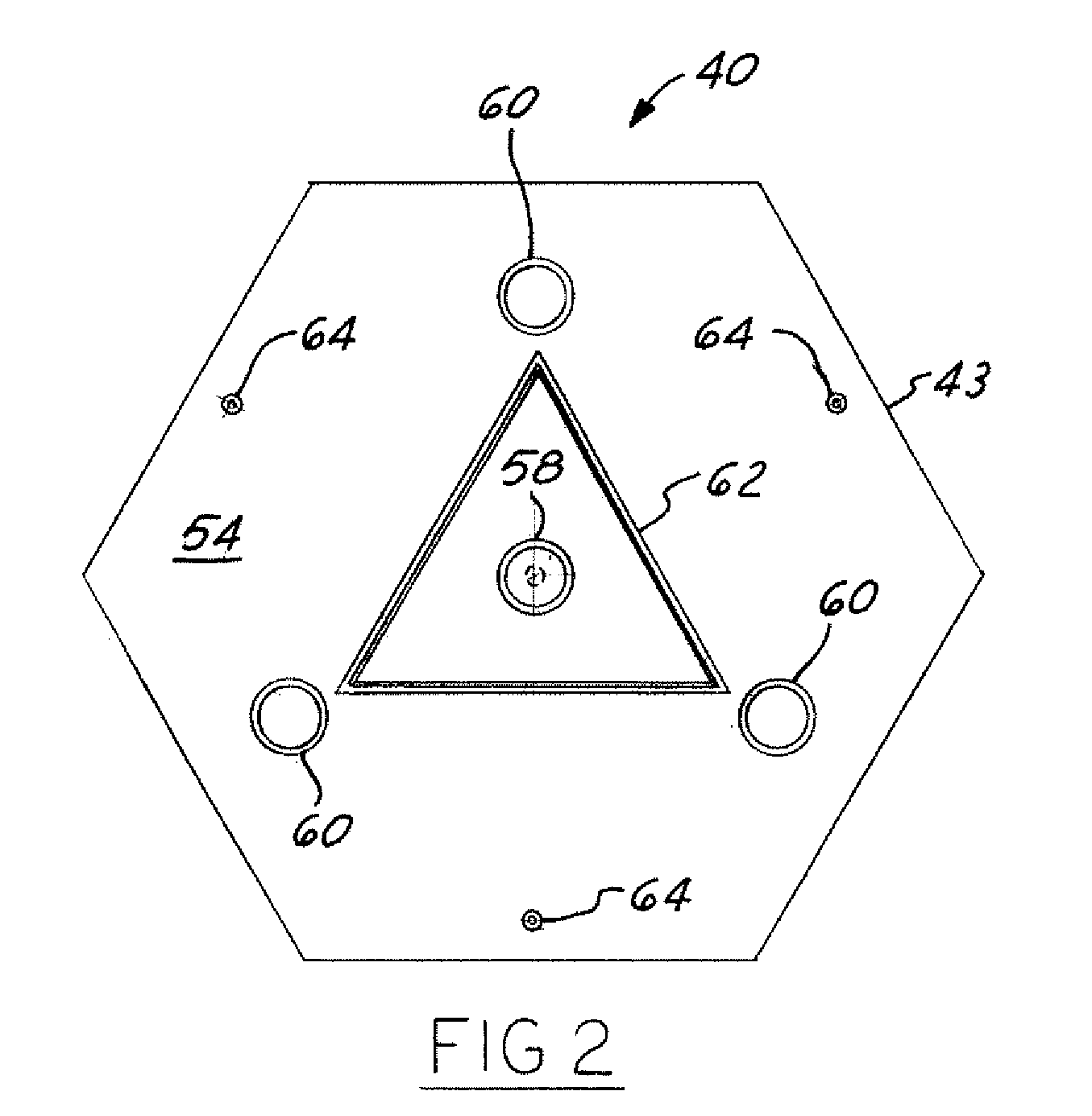
Multiple Petal Deployable Telescope
An opto-mechanical deployable telescope includes a hub, at least one deployable multiple petal primary mirror mounted to the hub, a deployment assembly, and a deployment engine assembly. The deployment assembly is operable to move the at least one primary mirror between a stowed position and a deployed position. The deployment engine assembly is operable to power the deployment assembly using stored mechanical energy. The deployment assembly includes a kinematic or semi-kinematic interface between the hub and the at least one primary mirror to hold petals of the at least one primary mirror in alignment relative to each other in the deployed position.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
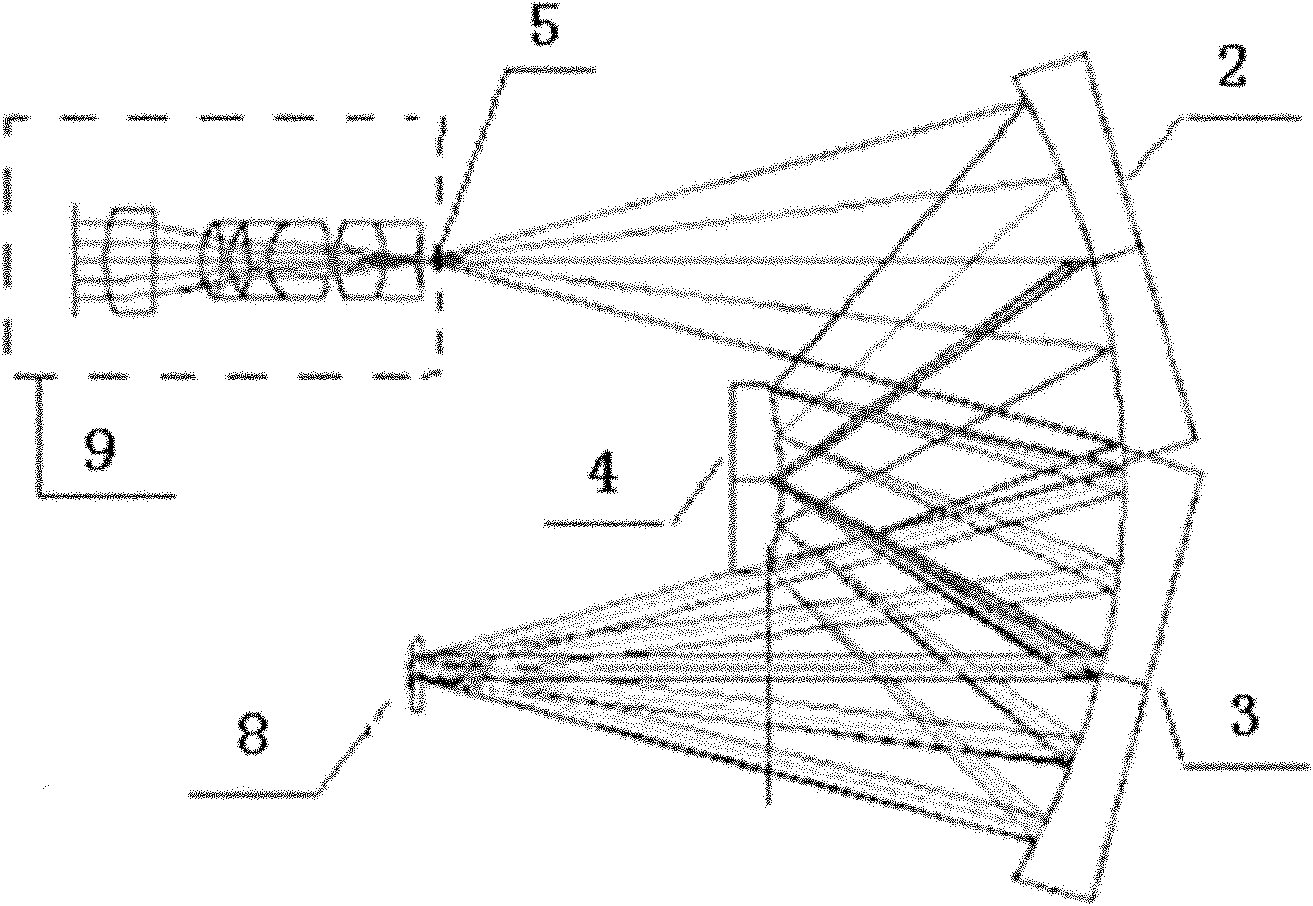
Method for assembling convex grating imaging spectrometer
InactiveCN102141439ATroubleshoot assembly methodsHigh implementabilitySpectrum investigationTelephoto lensGrating
The invention discloses a method for assembling a convex grating imaging spectrometer, and the method provided by the invention belongs to the field of optical instruments, and is used for solving the problems that the existing convex grating concentric beam-splitting system is difficult to install and adjust, so that the concentric accuracy of the system is low and the practical applicability of the system is poor. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: configuring an interferometer and a standard compensating mirror; arranging a primary mirror and a triangular mirror of a convex grating beam splitting system in front of the interferometer, adjusting the positions of the primary mirror and the triangular mirror, so that an interference fringe occurs to the interferometer; arranging a mercury lamp in front of a slit, arranging a grating between the primary mirror and the triangular mirror, arranging a reading microscope at the image surface of the convex grating beam splitting system, and then adjusting the grating, so that the reading microscope can read out the zero-level and minus-one-level spectrums of the mercury lamp; and arranging a detector and a telephoto lens, and then adjusting the detector and the telephoto lens, so that the detector can accept an ideal spectral image of a detected target. In the method disclosed by the invention, because the assembling of the grating and the detector are realized by using a spectrogram direct-reading method, the method is strong in practicability and high in accuracy.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
All-day multifunctional telescope device capable of being both used for solar active region observation and night astronomical observation
ActiveCN103901601AReduce the temperatureSeeing effect controlTelescopesTemperature controlControl system
An all-day multifunctional telescope device capable of being both used for solar active region observation and night astronomical observation comprises an optical telescope system, a lightweight cellular main lens and temperature control system, a thermovision field diaphragm and temperature control system, a thermovision field diaphragm adjusting structure, an achromatic imaging system, a light filter, a rotating rack and a data processing and control system. According to the all-day multifunctional telescope device capable of being both used for solar active region observation and night astronomical observation, under the condition that cost and system complexity are not obviously increased, the effective observation time of the telescope device is changed to achieve daytime and night continuous observation from only daytime or night observation, the effective observation time is effectively prolonged, the observation efficiency is improved, important reference is provided for development of telescopes, in particular to development of large-diameter telescopes, and the innovativeness and practicability are achieved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large-caliber laser isotope scanner and method for measuring structure constant atmosphere index of refraction
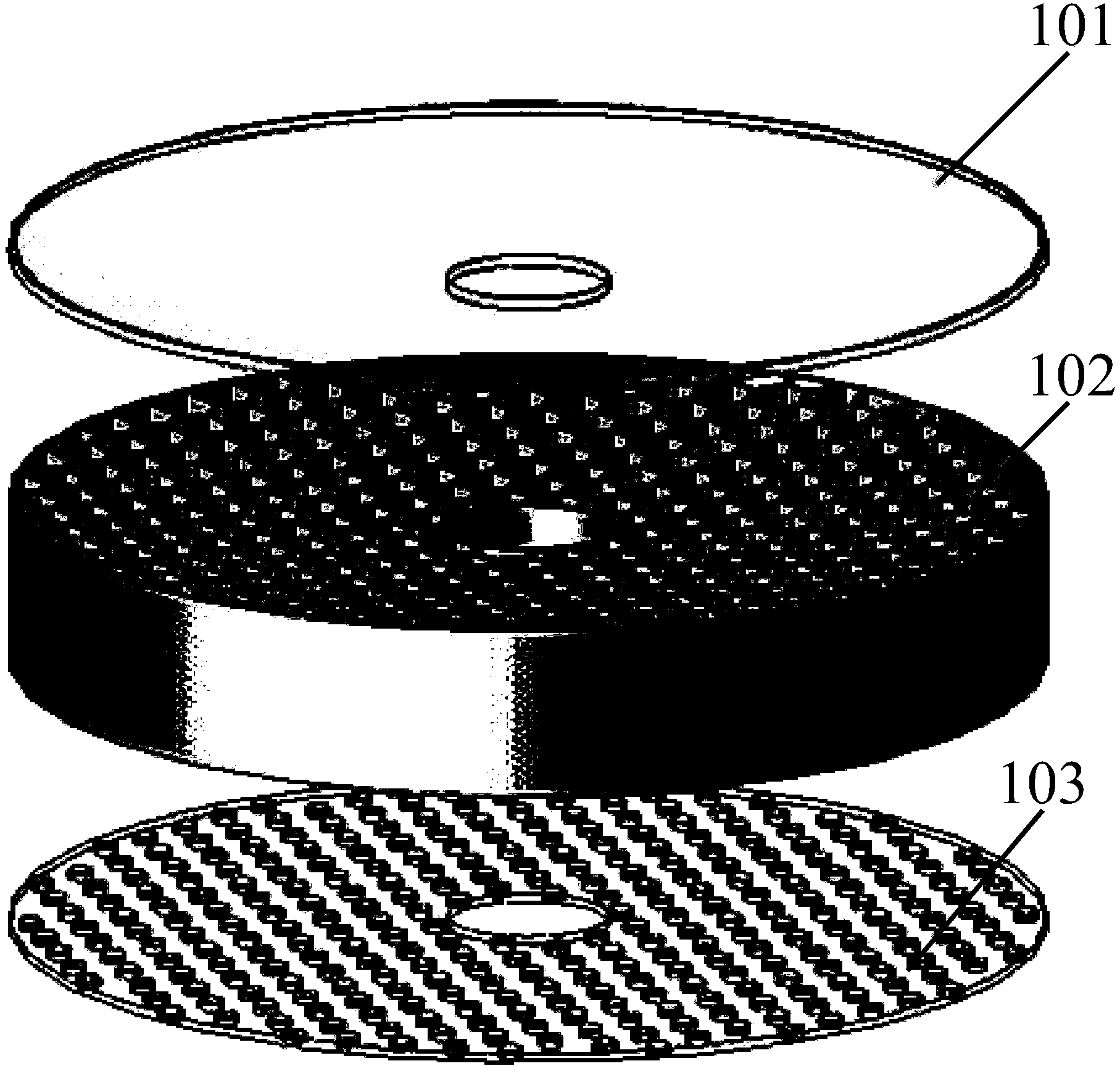
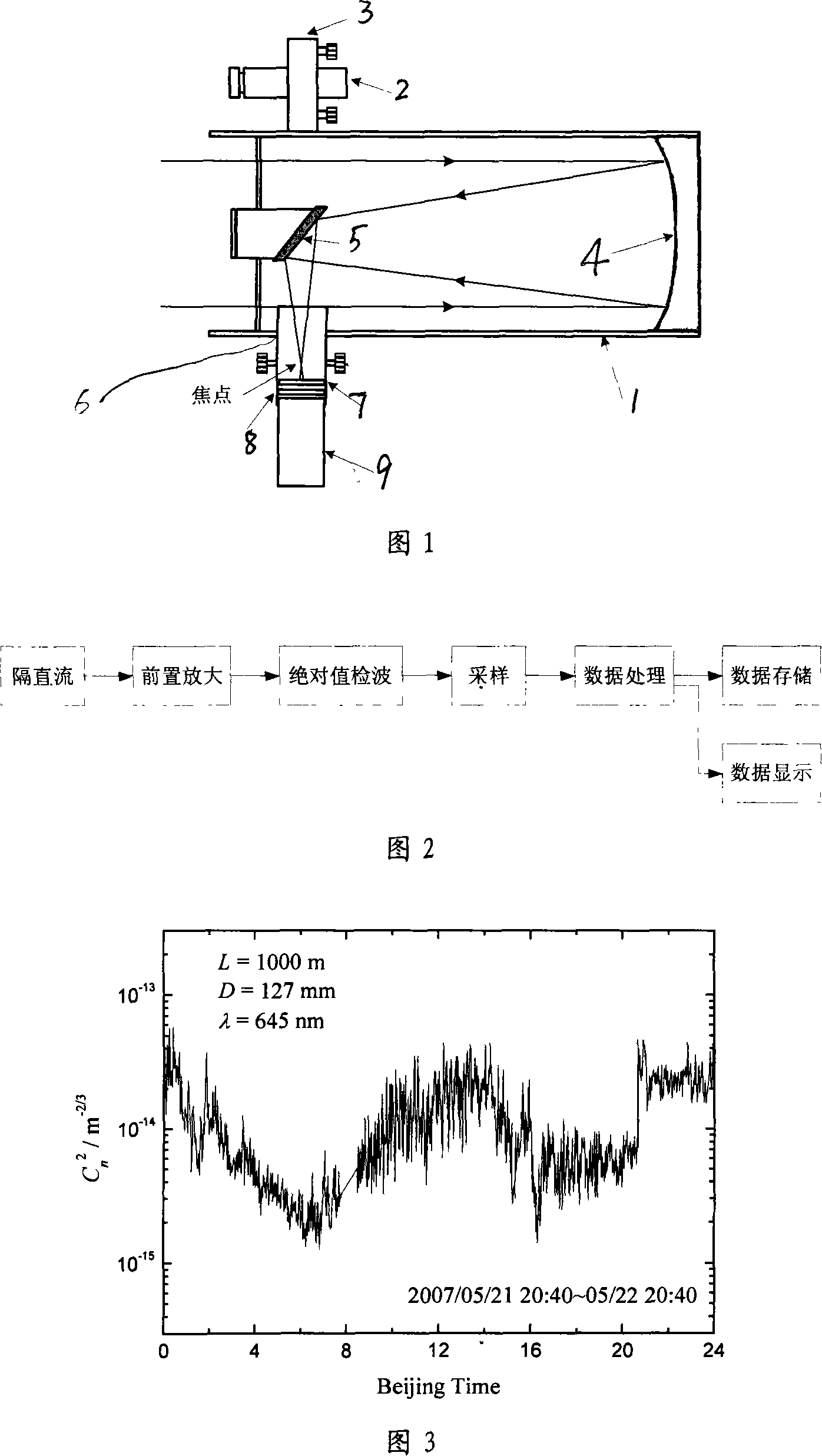
InactiveCN101109702AAvoid saturationImprove signal-to-noise ratioPhase-affecting property measurementsReflecting telescopePlane mirror
The invention discloses a laser flasher with big diameter for measuring the structure constant of atmospheric refractivity as well as the method for that. The laser flasher comprises two opposite-arranged reflecting telescopes and lasers on the lens cones. The incident lights reach to the secondary plane mirror after being reflected by a main parabolic mirror in the lens cones, pass the openings, attenuating pieces and narrow-band interference filters on the lens cones, and then are converged on a photoelectric detector. At transmission test, two arrangements are placed at the two ends of the transmission path; the emitting system at one end of the path gives out modulated laser signals, after being transmitted by a turbulent atmosphere, the light signals are collected by the telescope at anther end, and go through photoelectric conversion by the photoelectric multiplier near to the focus; then the electric signals enter into a built-in control system for demodulation, sampling, processing, saving and displaying. The invention is of high accuracy and improves the accuracy in the measurements.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
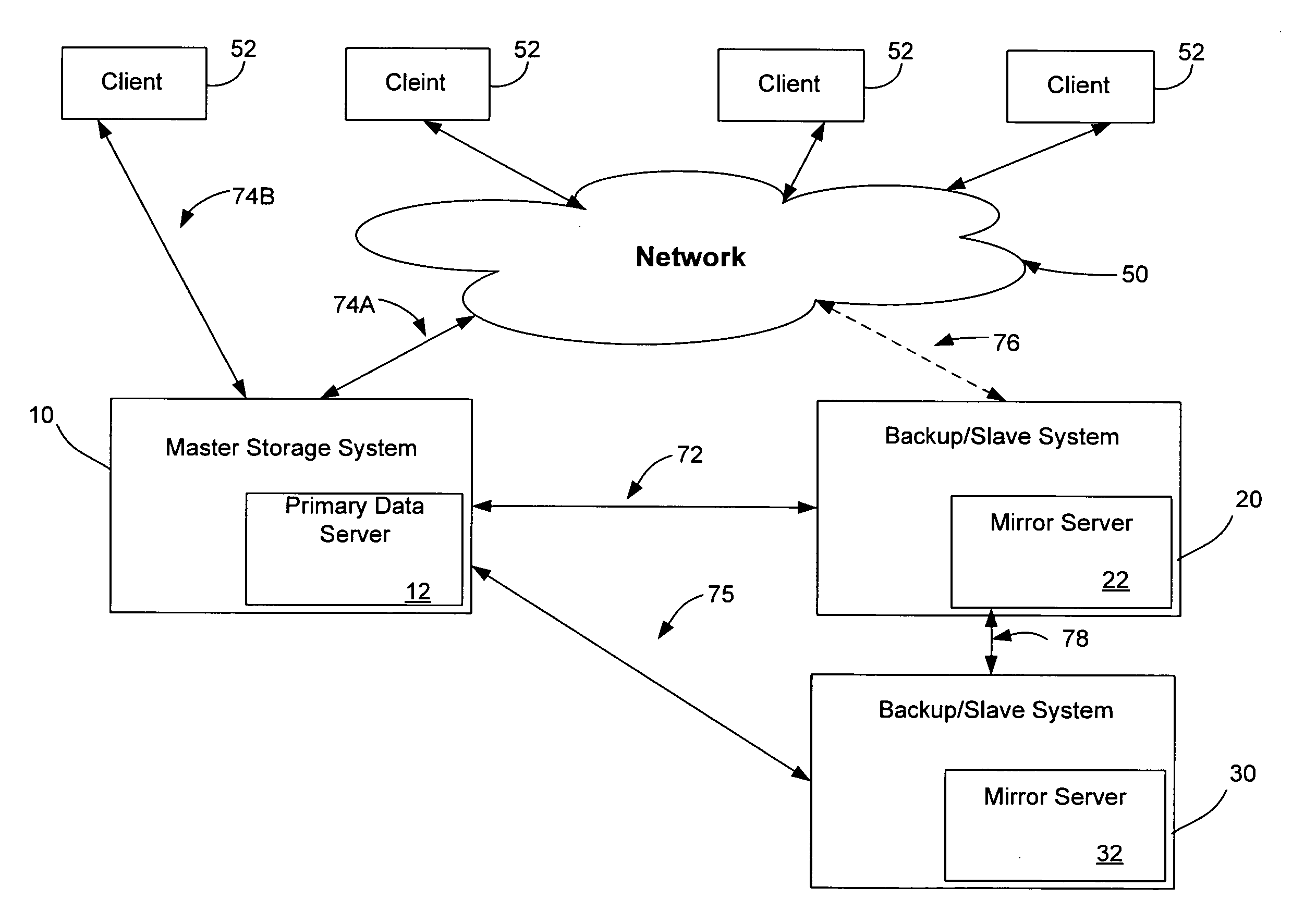
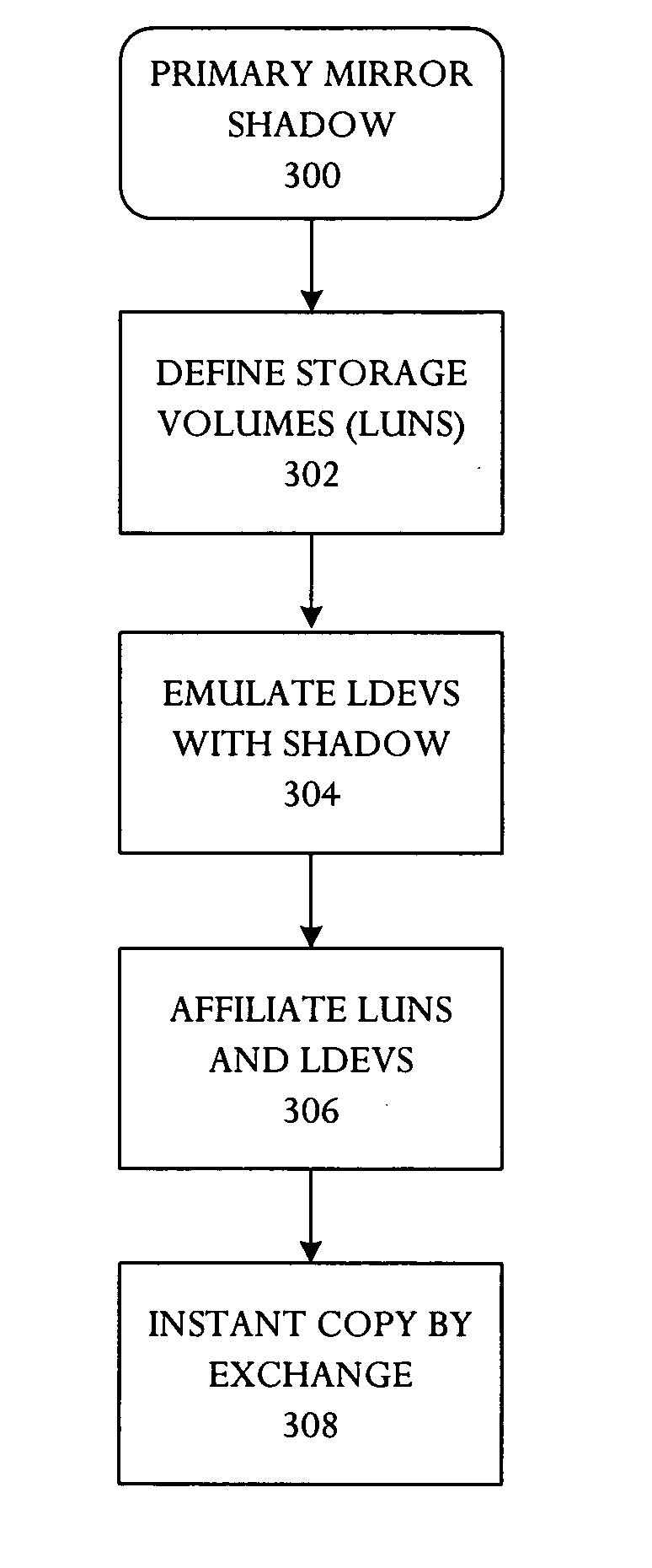
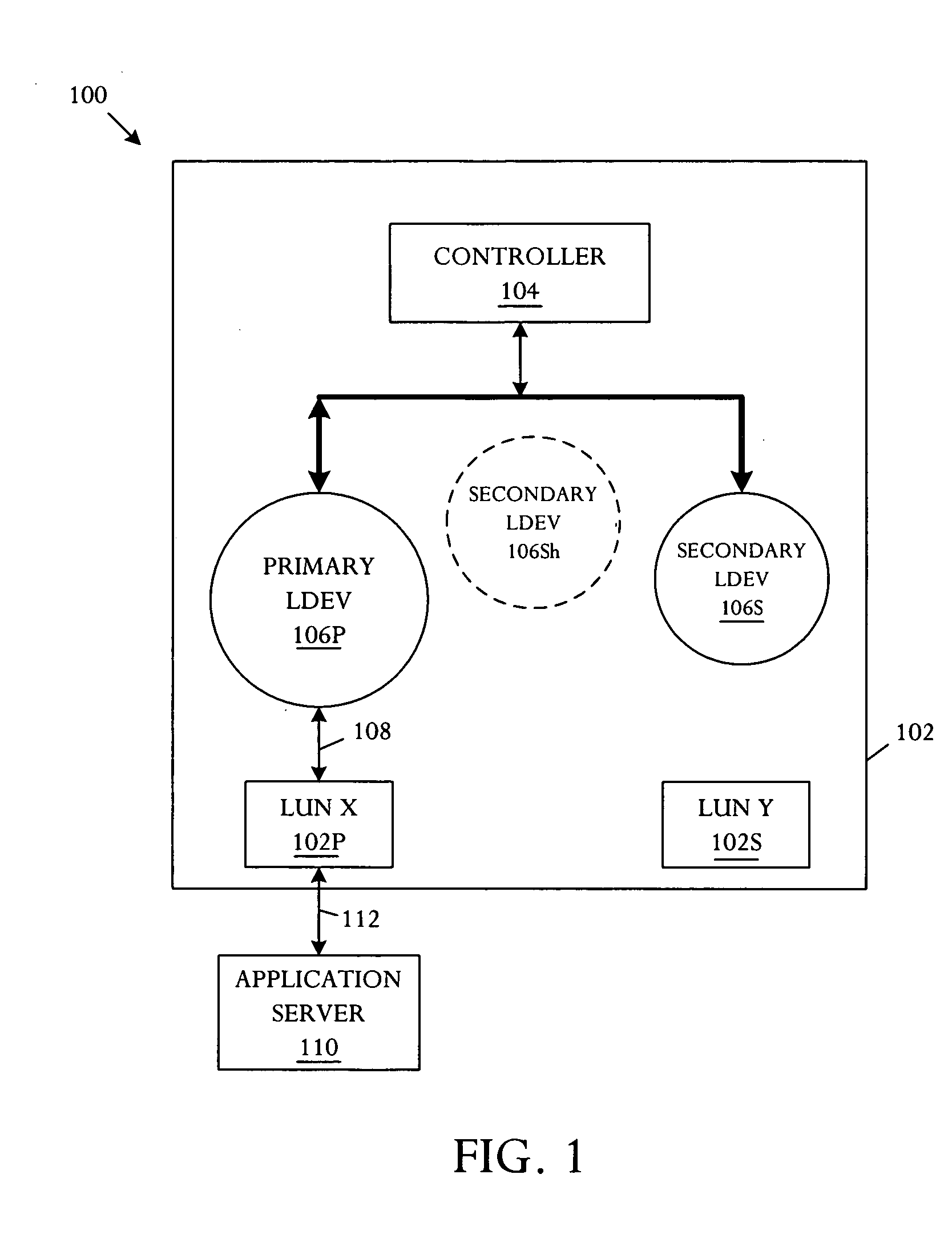
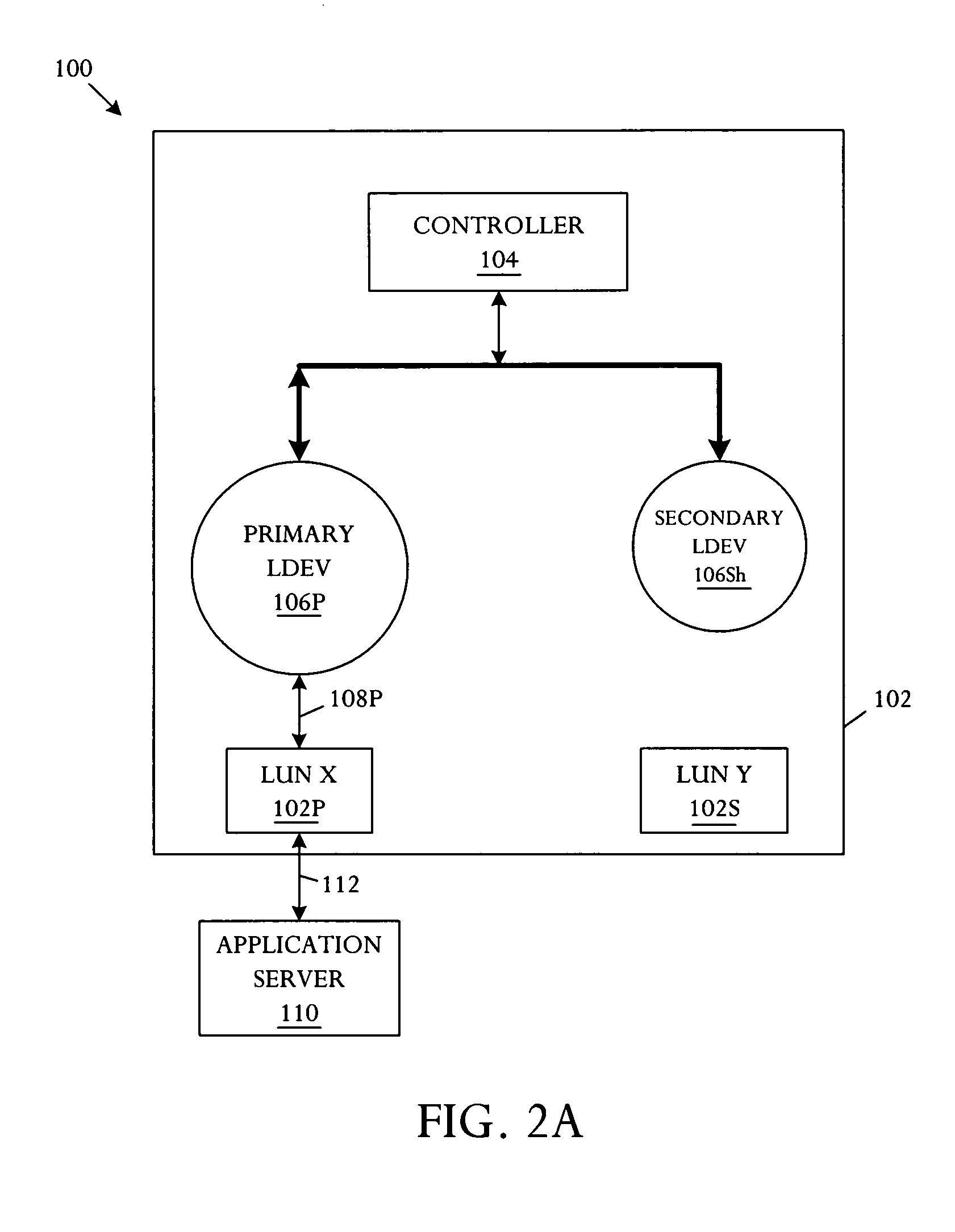
Storage system with primary mirror shadow
A storage system with primary mirror shadow comprises a storage array, and a controller. The controller is capable of predefining storage array volumes as a primary volume that is subsequently paired with a secondary volume, emulating a primary logical device and a plurality of secondary logical devices including a shadow logical device, tracking volumes and logical devices using a pointer, and instantaneously evoking a volume copy by a pointer exchange.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Autonomously assembled space telescope
InactiveUS20050088734A1High resolutionGood optical performanceMirrorsTelescopesModular unitModularity
A method for autonomously assembling a segmented filled aperture telescope (“AAST”) in space using modular components that are launched into orbit using multiple launches. In one embodiment, a plurality of interlocking modular mirror backing structure segments, with or without an edge truss, are introduced to a satellite. To this are coupled a plurality of modular segmented optics to form a primary concave mirror. In another embodiment, the mirror backing structure and modular optics segments are formed as a single modular unit, with a plurality of these units coupled together to form the primary concave mirror. The modular concept allows primary mirrors of virtually limitless size to be formed in space with or without using astronauts.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
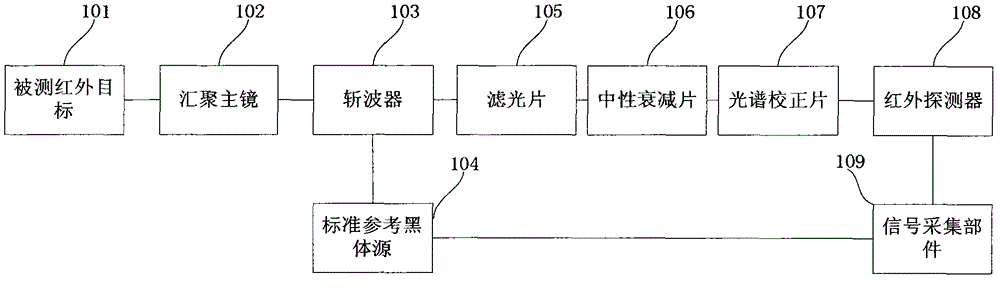
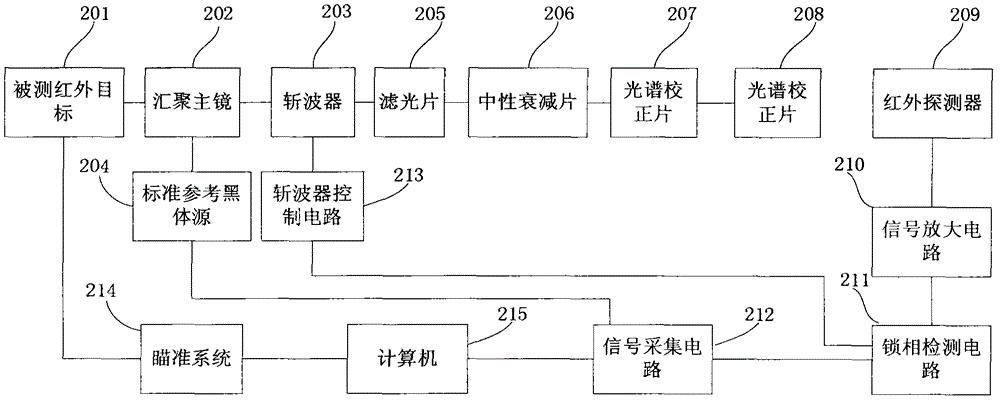
External field type infrared radiometer
The invention relates to the technical field of optical tests, in particular to an external field type infrared radiometer. According to the infrared radiometer, a main convergence mirror is connected with a wave chopper; the wave chopper is connected with a standard reference black body source and light filters; the light filters are connected with neutral attenuation pieces; the neutral attenuation pieces are connected with optical spectrum correcting pieces; the optical spectrum correcting pieces are connected with an infrared detector; a signal acquisition part is connected with the infrared detector and the wave chopper respectively. Through the embodiment, a corresponding optical spectrum curve of a whole system in a measurement waveband can be enabled to be a flat curve through the optical spectrum correcting piece, the linearity and the measurement accuracy of the whole system are improved, and the influence of a radiation spectrum of a tested object on a measurement structure is avoided; the neutral light filters with different attenuation ratios are adopted and the dynamic range of equipment is expanded. Therefore, the equipment has a plurality of ranges and strong and weak radiation targets can be measured.
Owner:BEIJING ZHENXING METROLOGY & TEST INST
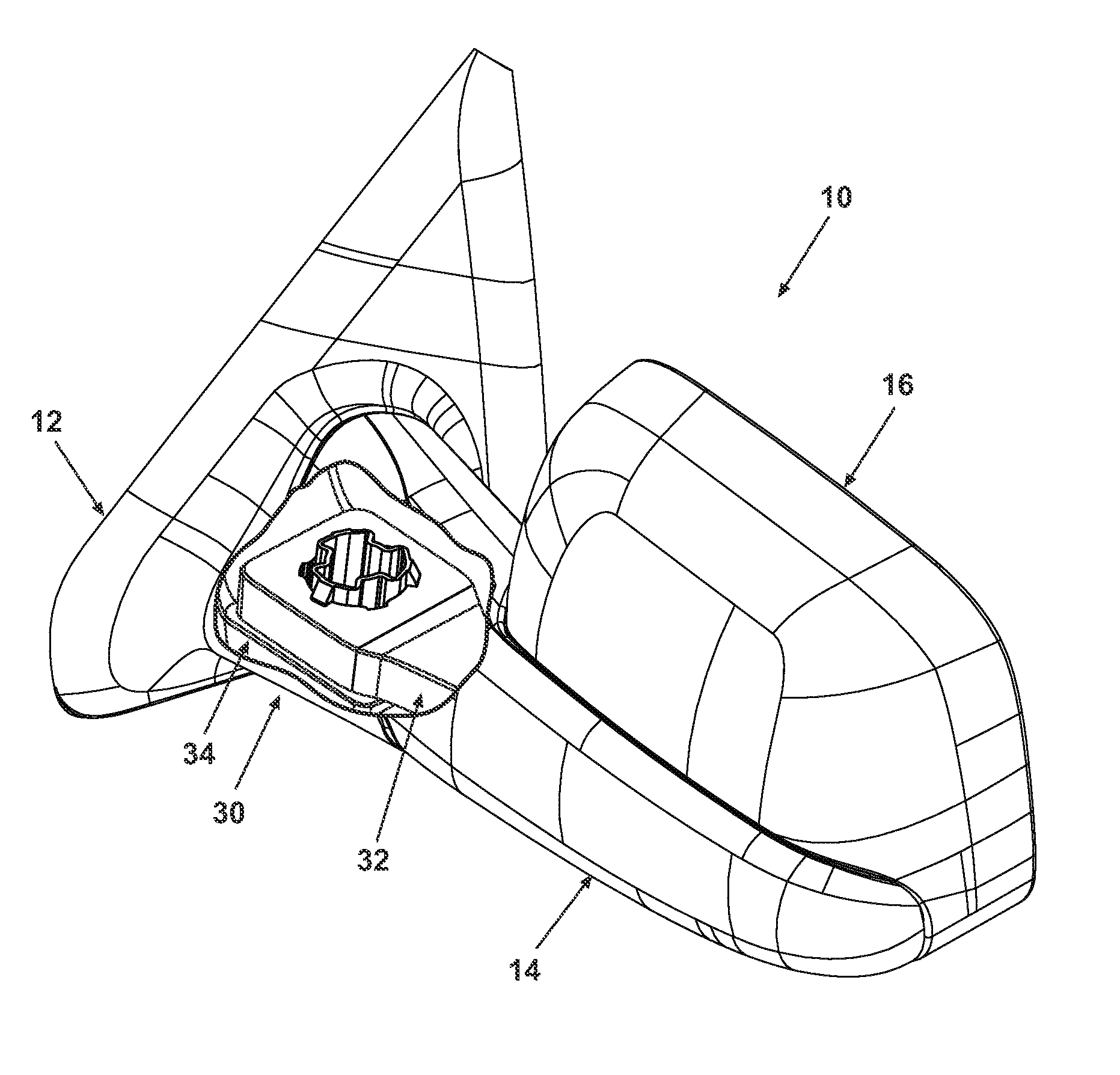
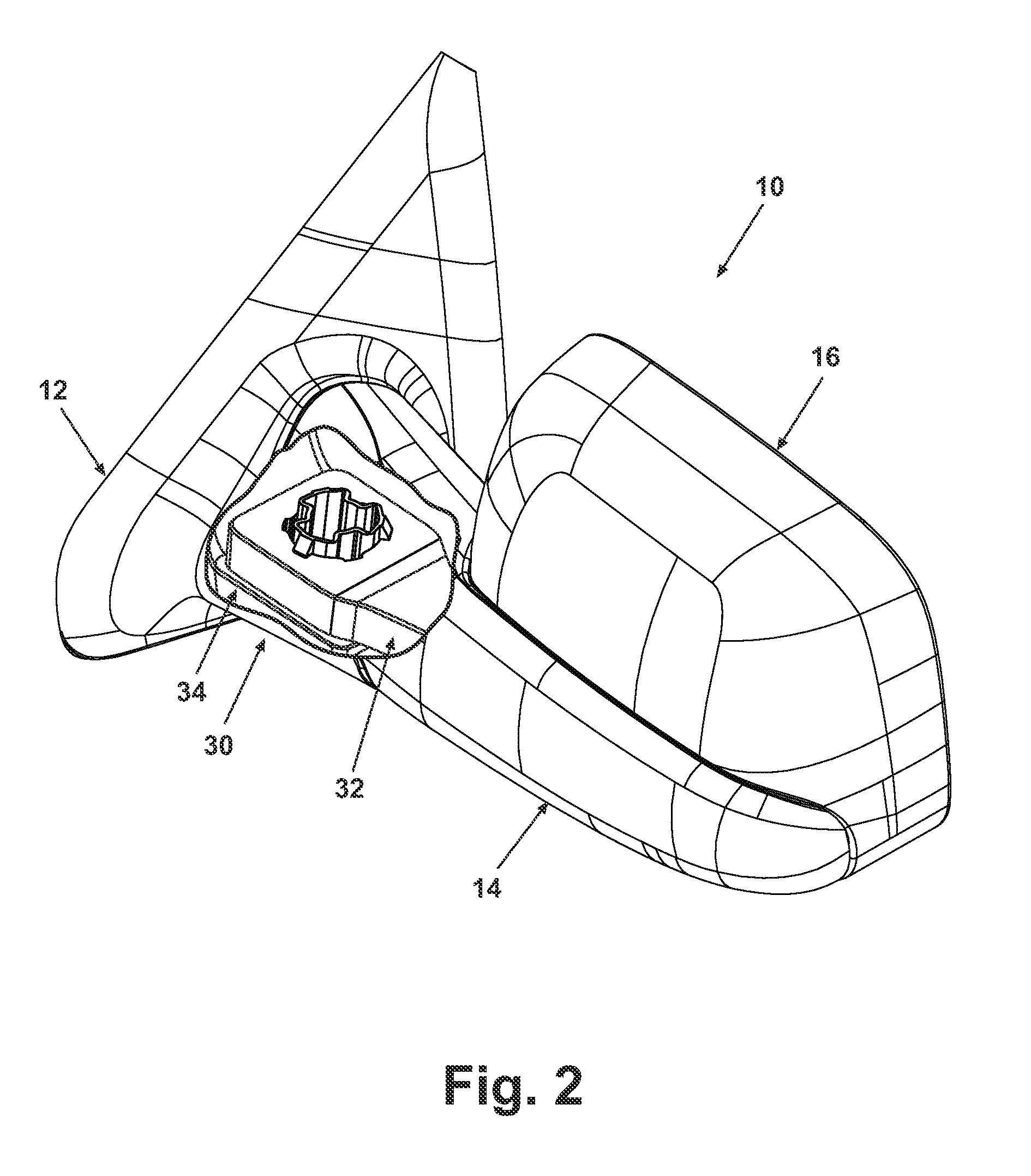
Exterior Rearview Mirror for Motor Vehicles
An exterior rearview mirror assembly for a motor vehicle is disclosed having a primary mirror and a spotting mirror. Both the primary mirror and the spotting mirror are secured to the same single mirror support, or backing plate. The spotting mirror is snap fit to the backing plate by having a monolithic structure which is receivable by a recess or hole in the backing plate. The recess acts as a securing device by receiving an abutment surface extending outwardly away from the monolithic structure which snaps over the backing plate and prevents the spotting mirror from moving away from the backing plate.
Owner:SMR PATENTS S A R L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com