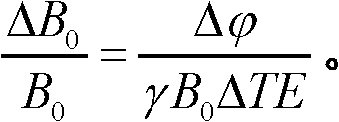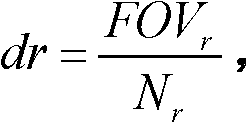Patents
Literature
925 results about "Phase synchronization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
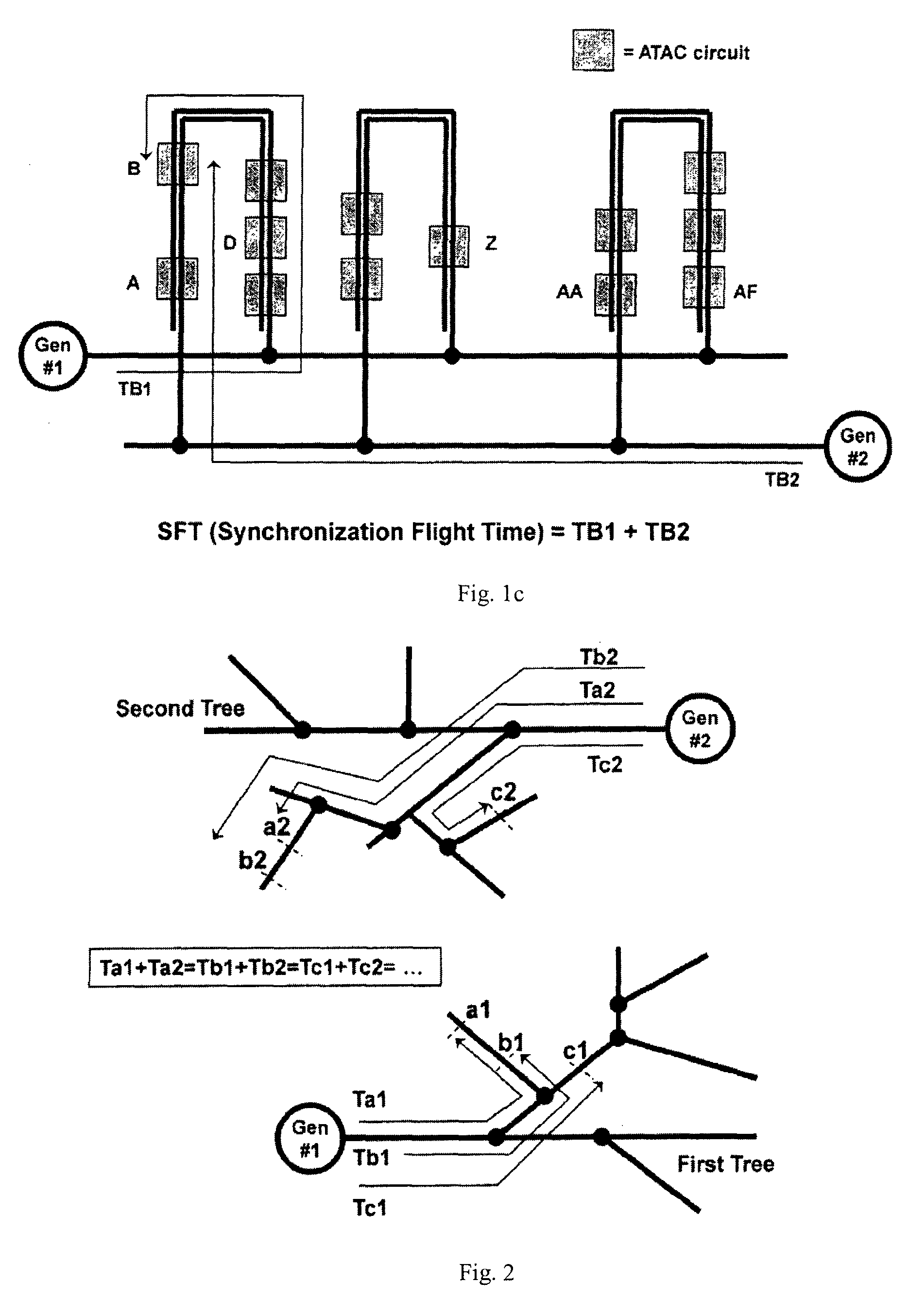
Phase synchronization is the process by which two or more cyclic signals tend to oscillate with a repeating sequence of relative phase angles. Phase synchronisation is usually applied to two waveforms of the same frequency with identical phase angles with each cycle. However it can be applied if there is an integer relationship of frequency, such that the cyclic signals share a repeating sequence of phase angles over consecutive cycles. These integer relationships are called Arnold tongues which follow from bifurcation of the circle map.
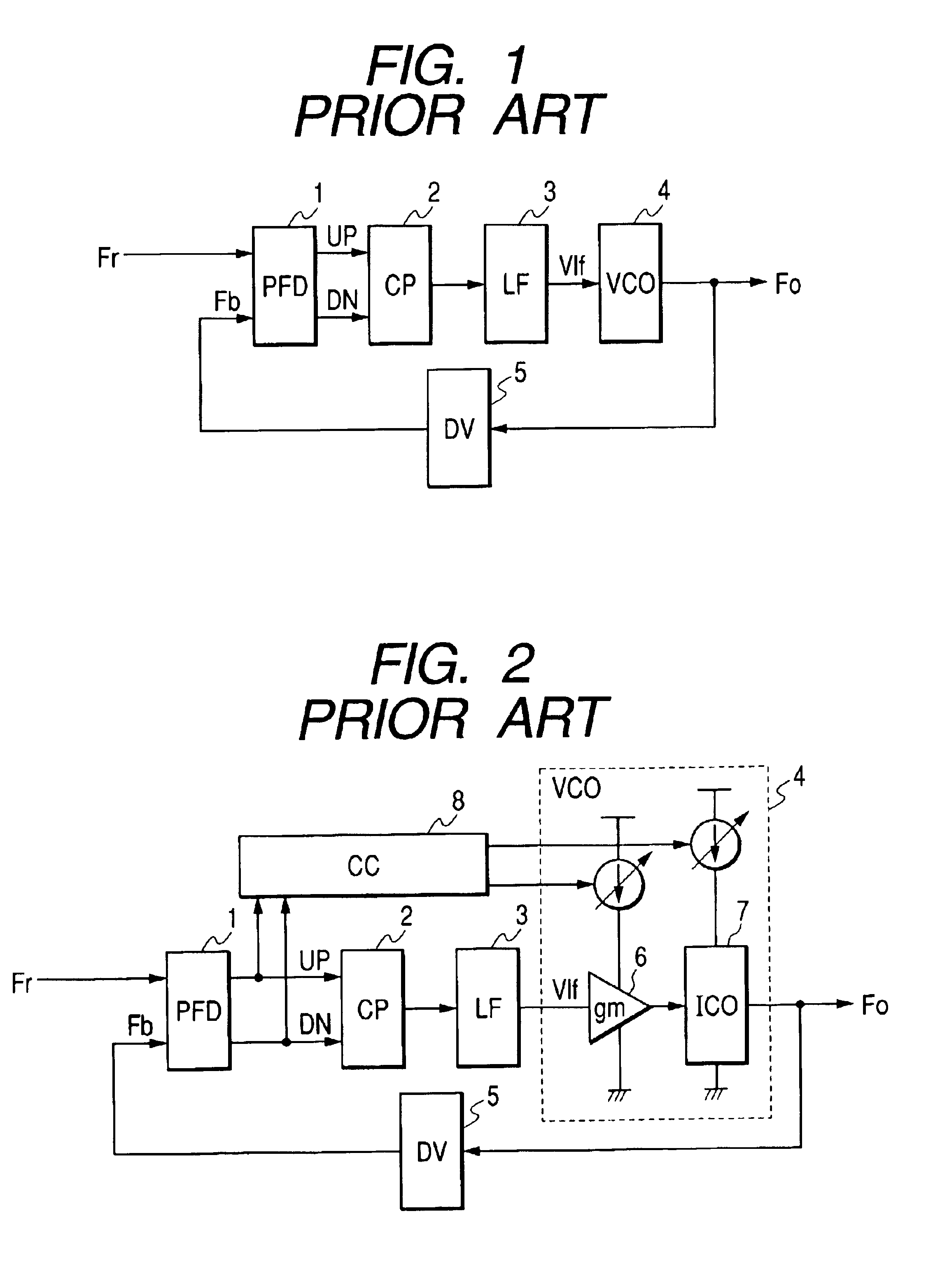
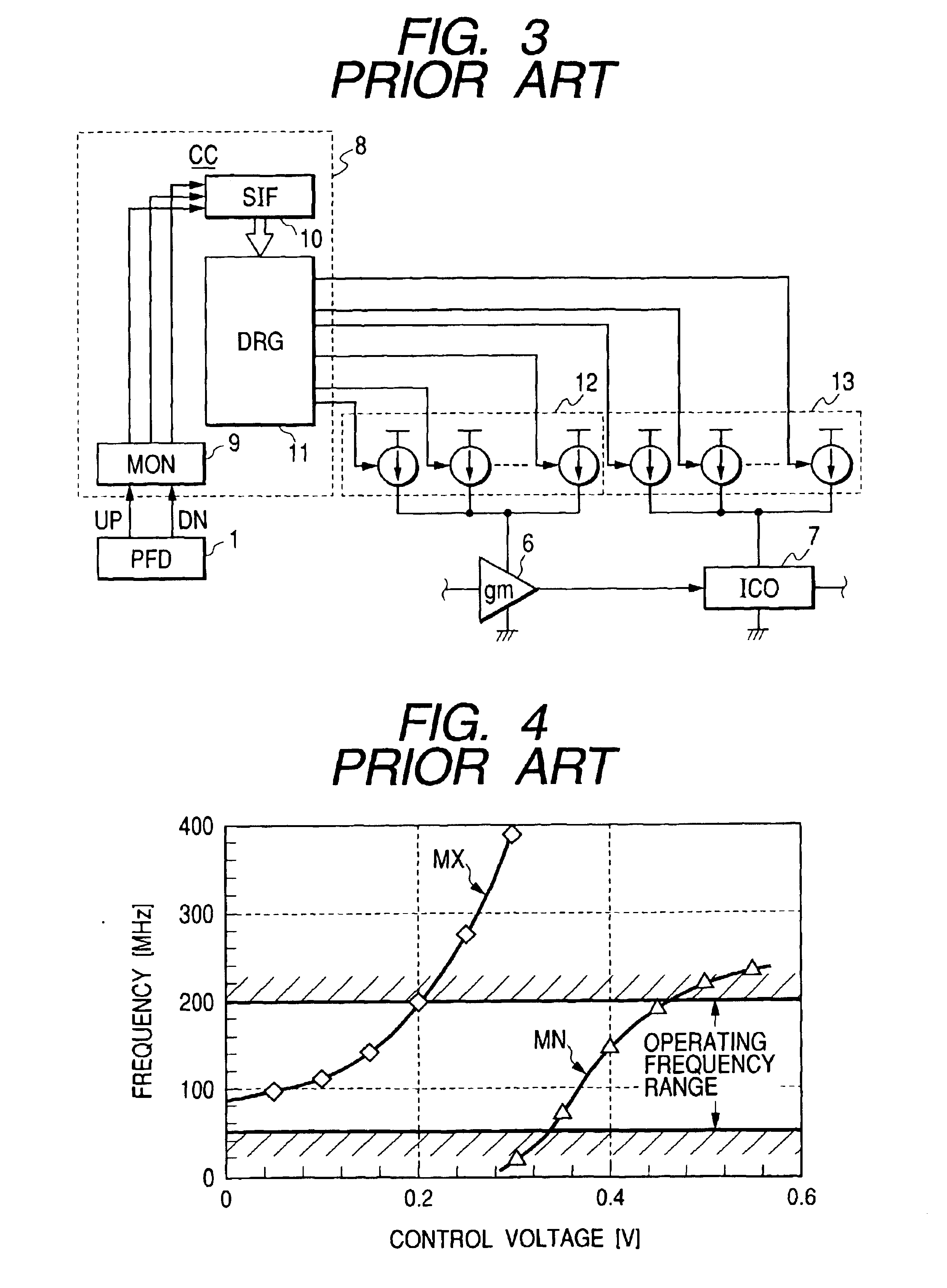
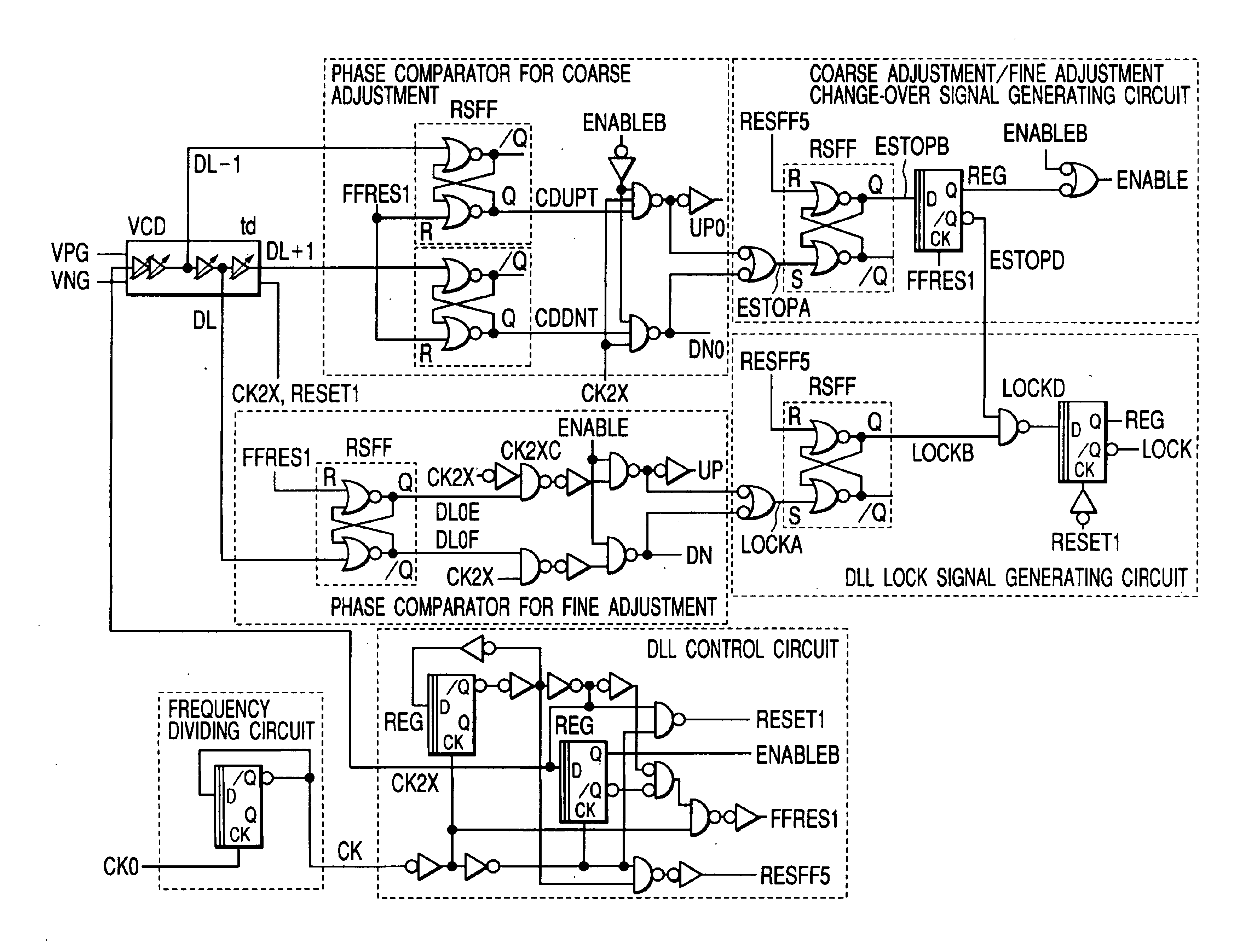
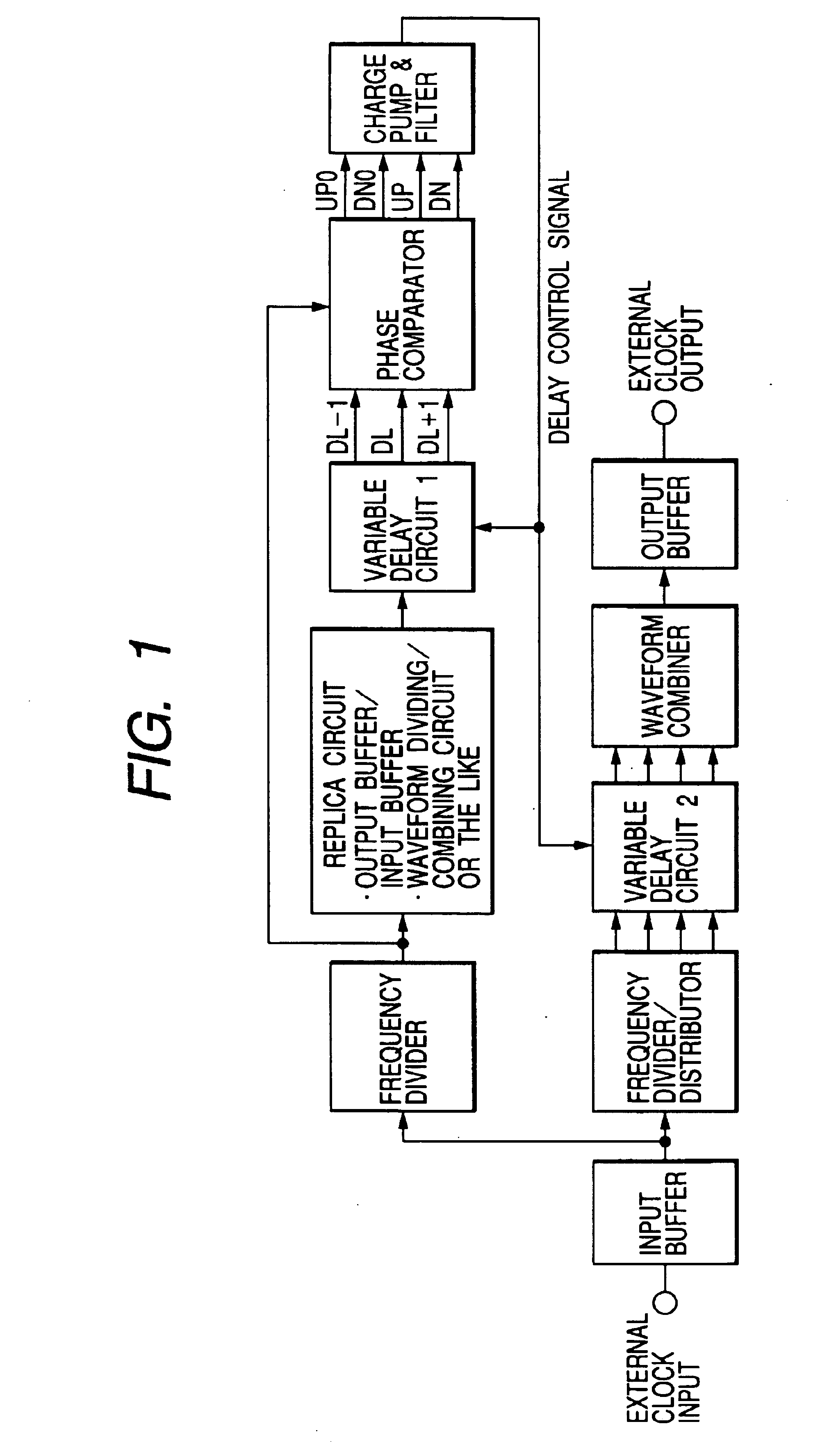
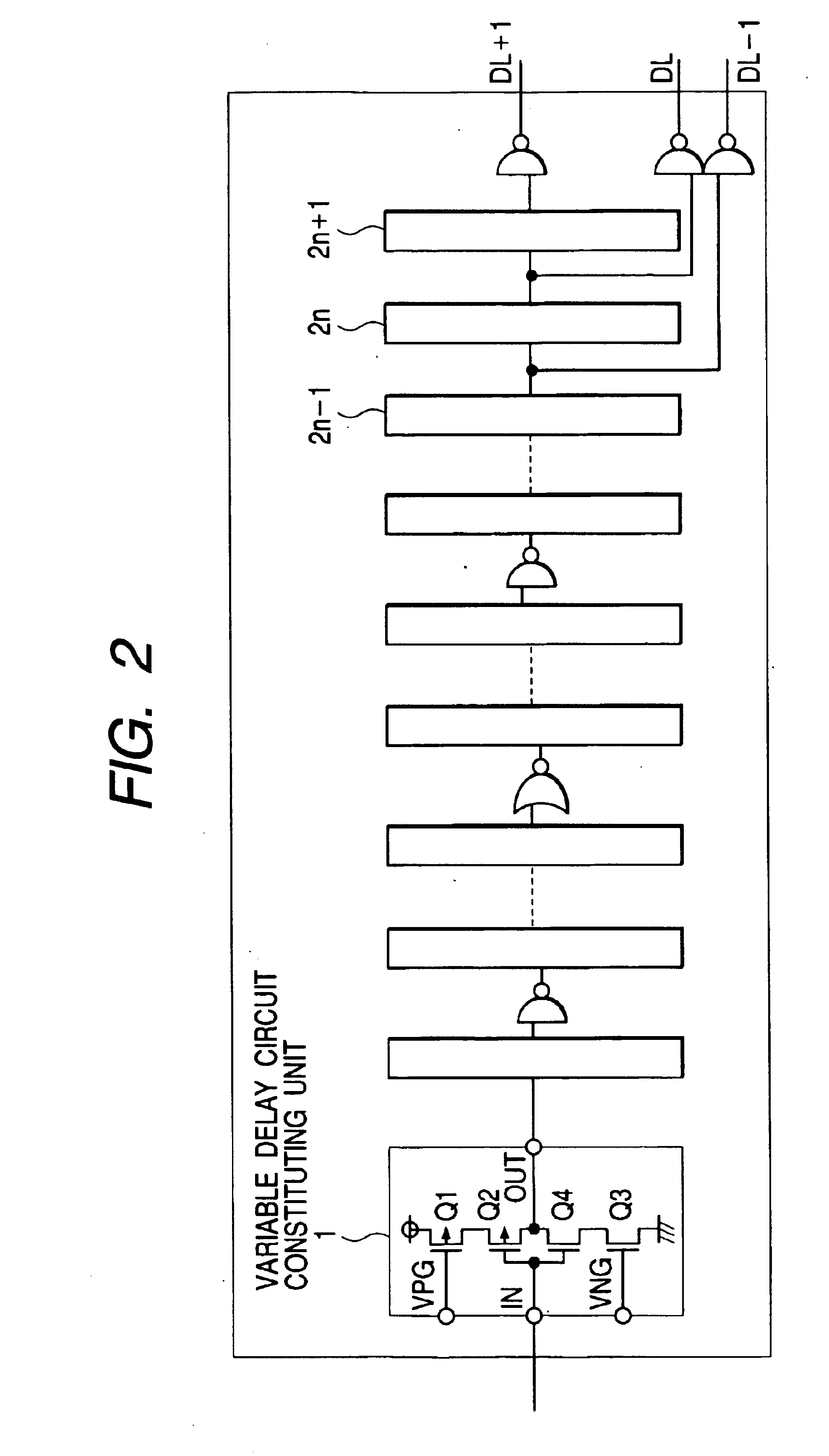
Clock reproduction circuit that can reproduce internal clock signal correctly in synchronization with external clock signal
InactiveUS6166990ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrequency determinationPhase synchronization
A frequency determination circuit generating a clock signal phase-locking with an external clock signal at a coarse precision and a fine adjust circuit generating an internal synchronizing signal phase-locking with the external clock signal at a fine precision are provided. The fine adjust circuit has a function of adjusting the phase of the frequency determination circuit when phase synchronization is to be carried out exceeding the adjust range thereof. The frequency determination circuit and the fine adjust circuit receive a clock power supply voltage. A clock reproduction circuit is provided which generates an internal clock signal phase-locking with an external clock signal or a reference clock signal stably even when the operating environment changes.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +2
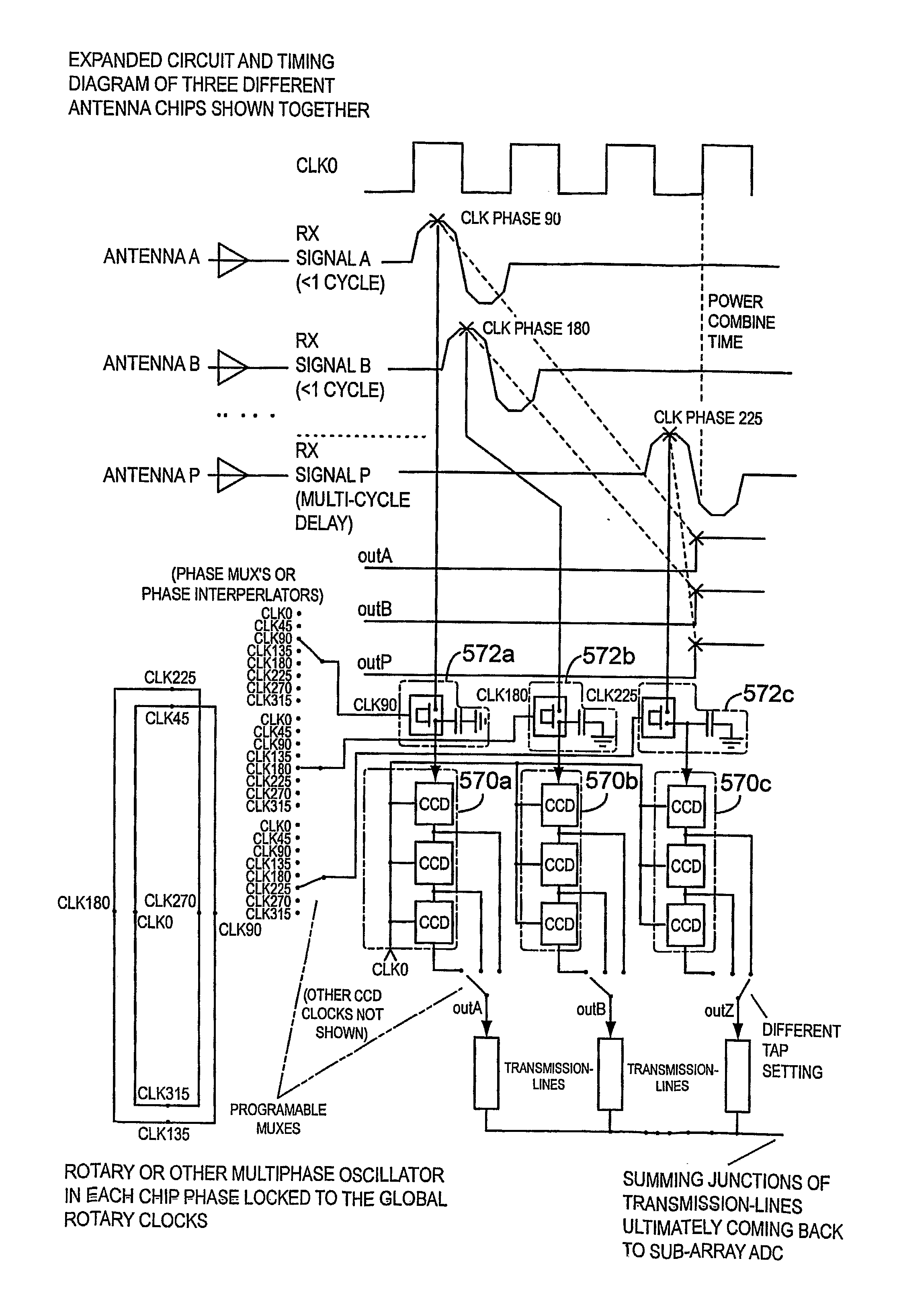
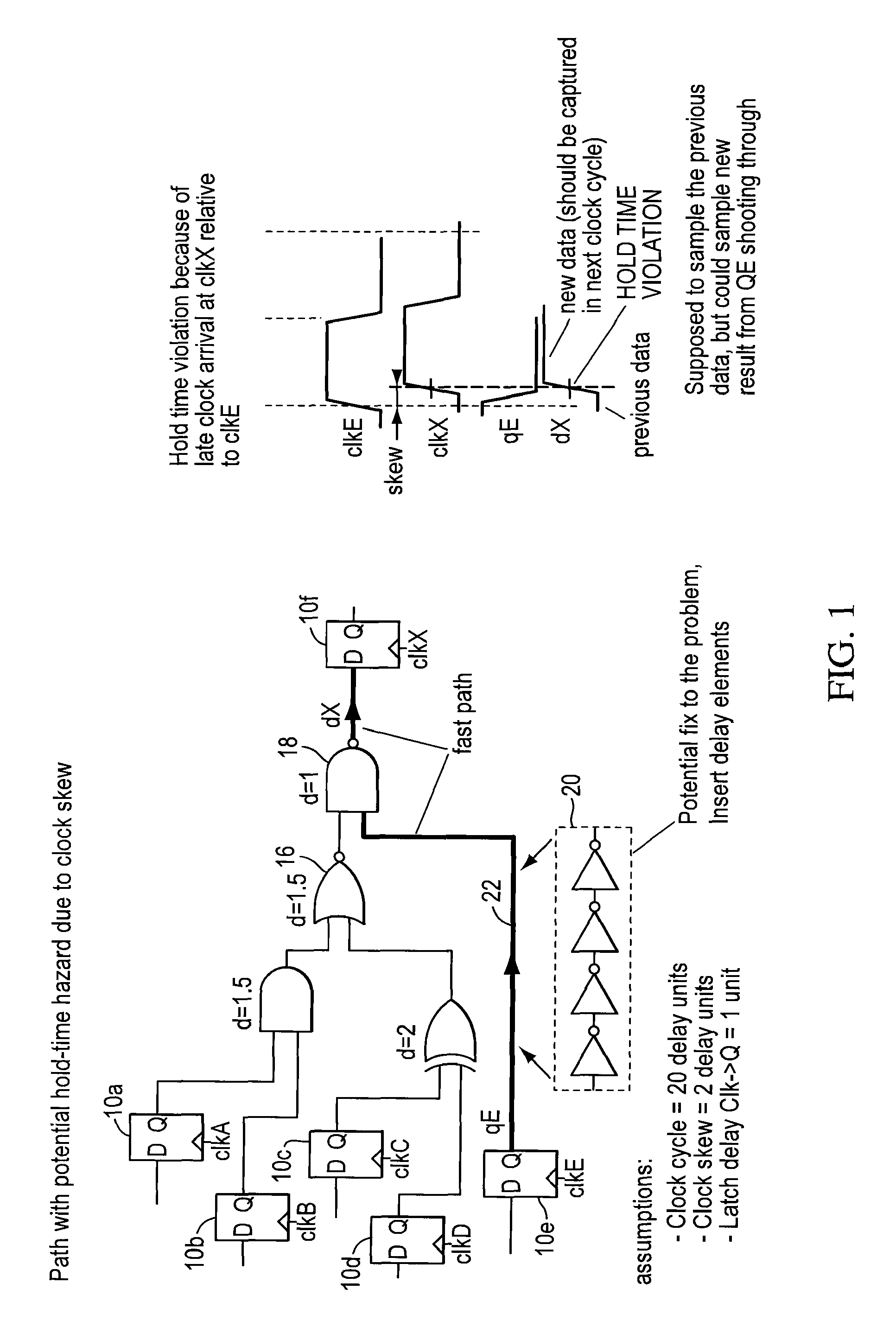
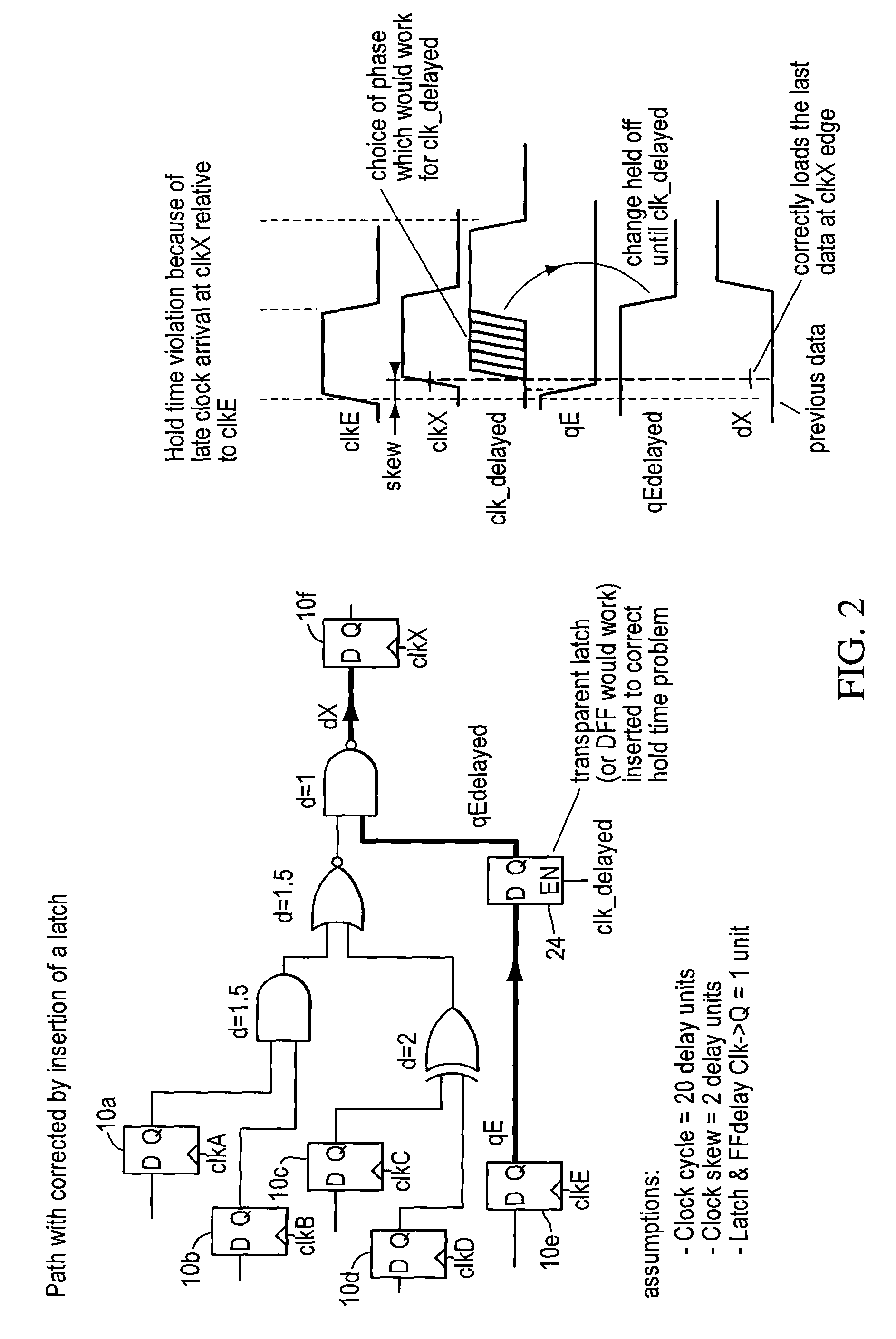
True time delay phase array radar using rotary clocks and electronic delay lines
ActiveUS20120039366A1Forming accuratelyEasy to moveAntenna arraysPulse automatic controlTime delaysAnalog delay line
Local oscillator circuitry for an antenna array is disclosed. The circuitry includes an array of rotary traveling wave oscillators which are arranged in a pattern over an area and coupled so as to make them coherent. This provides for a set of phase synchronous local oscillators distributed over a large area. The array also includes a plurality of phase shifters each of which is connected to one of the rotary oscillators to provide a phase shifted local oscillator for the array. The phase shifter optionally includes a cycle counter that is configured to count cycles of the rotary oscillator to which it is connected and control circuitry that is then operative to provide a shifted rotary oscillator output based on the count from the cycle counter. A system and method for operating a true-time delay phased array antenna system. The system includes a plurality of antenna element circuits for driving or receiving an rf signal from the elements of the array. Each element circuit has a transmit and a receive path and a local multiphase oscillator, such as a rotary traveling wave oscillator. Each path has an analog delay line for providing a true-time delay for the antenna element. Preferably, the analog delay line is a charge coupled device whose control nodes are connected to phases of the local multiphase oscillator to implement a delay that is an integer number local multiphase oscillator periods. A fractional delay is also included in the path by using a sample and hold circuit connected to a particular phase of the oscillator. By delaying each antenna element by a true time delay, broadband operation of the array is possible.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Low cost, active antenna arrays
ActiveUS20120142280A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsSubstation equipmentElectricityCarrier signal
Owner:NEC ADVANCED NETWORKS INC
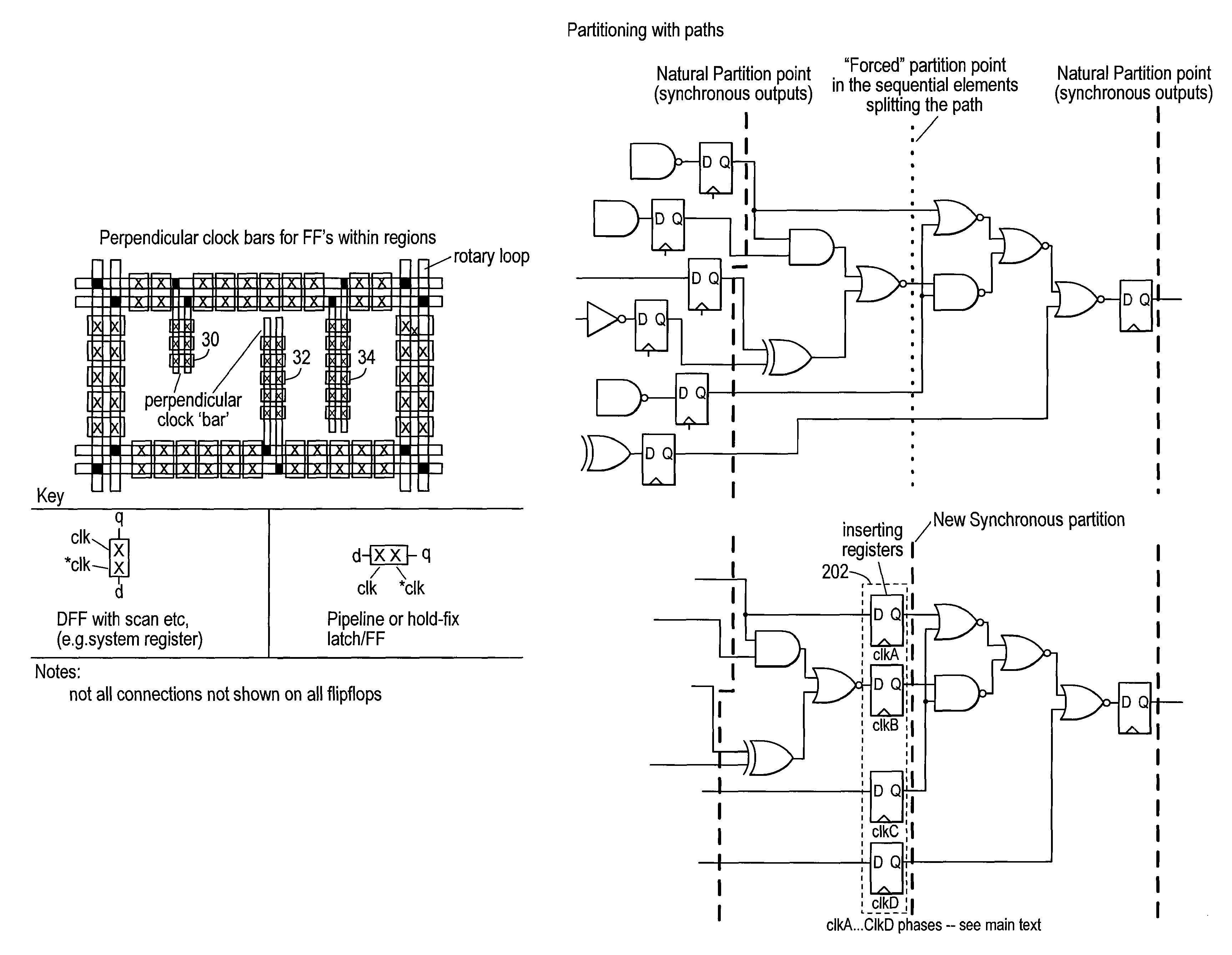
Rotary clock synchronous fabric
InactiveUS20050251775A1Minimize the numberComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringArray element
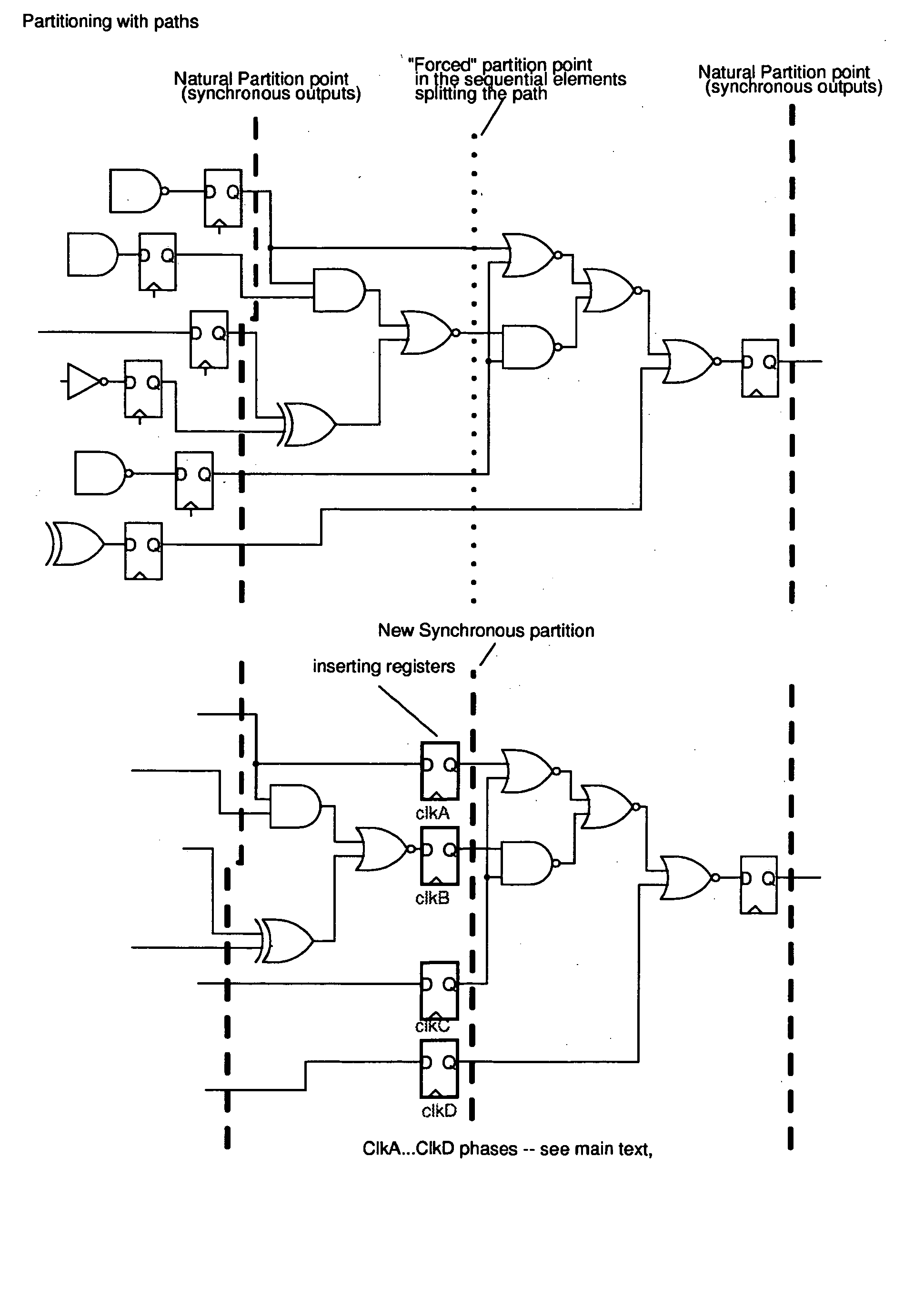
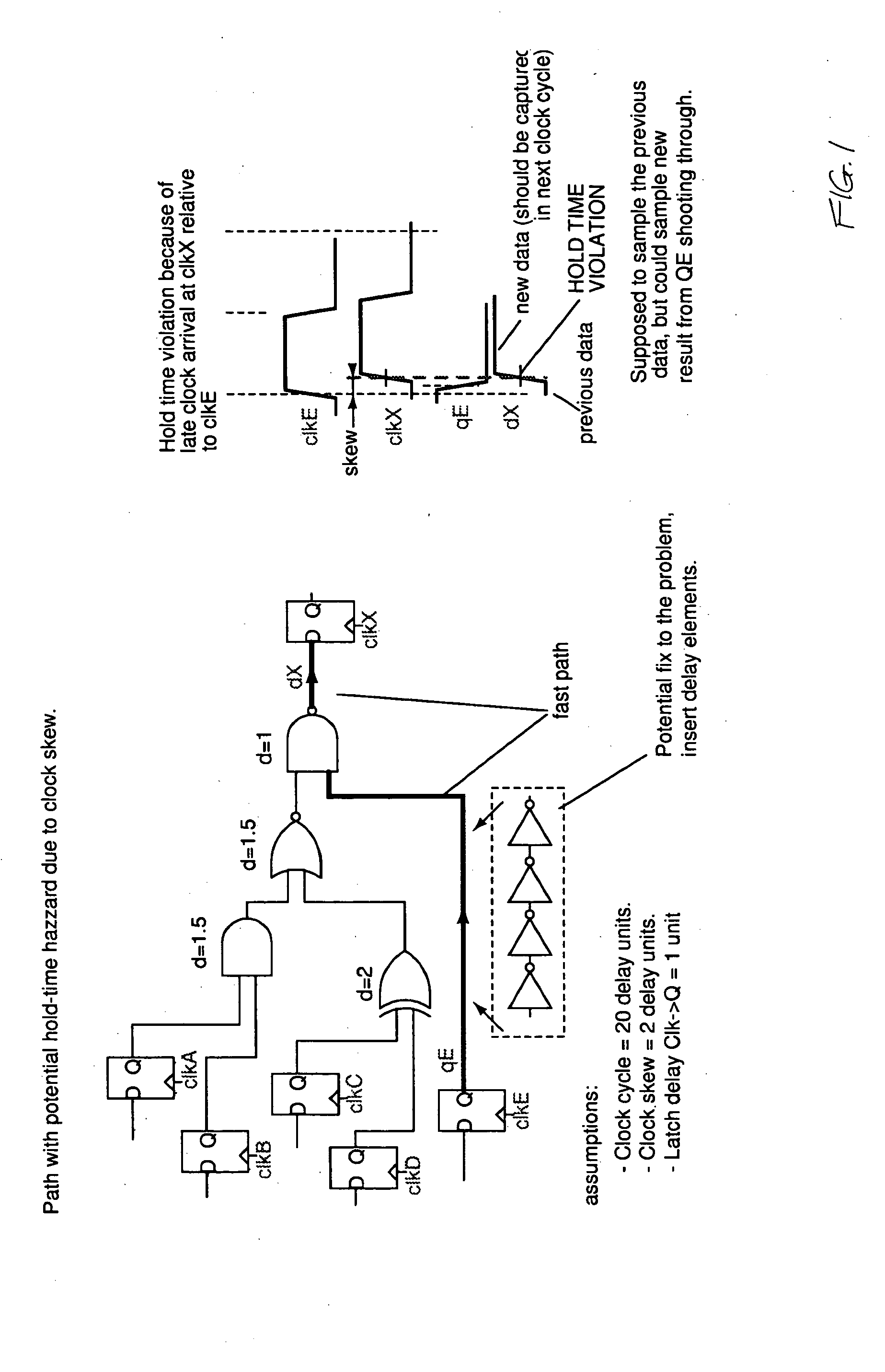
Methods for generating a design for logic circuitry using rotary traveling wave oscillators (RTWOs) are described. A plurality of RTWOs are is arranged into an array of rows and columns. Adjacent elements in the array are interconnected so that the clocks in adjacent element are phase synchronous. Clocked devices are placed along the signal path of each array element and each is connected to one of the multiple phases provided by the RTWO element. The logic circuitry, described by a netlist, is divided into a number of partitions and each of these partitions is mapped to one of the array elements. The logic circuitry of the partition is then placed within or about the element of the array to which the partition is mapped and the circuitry in the partition is connected between the clocked devices in the element of the array, according to the net list.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Clock generator for generating accurate and low-jitter clock
ActiveUS6900676B1Accurate and low jitterPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsControl signalPhase difference
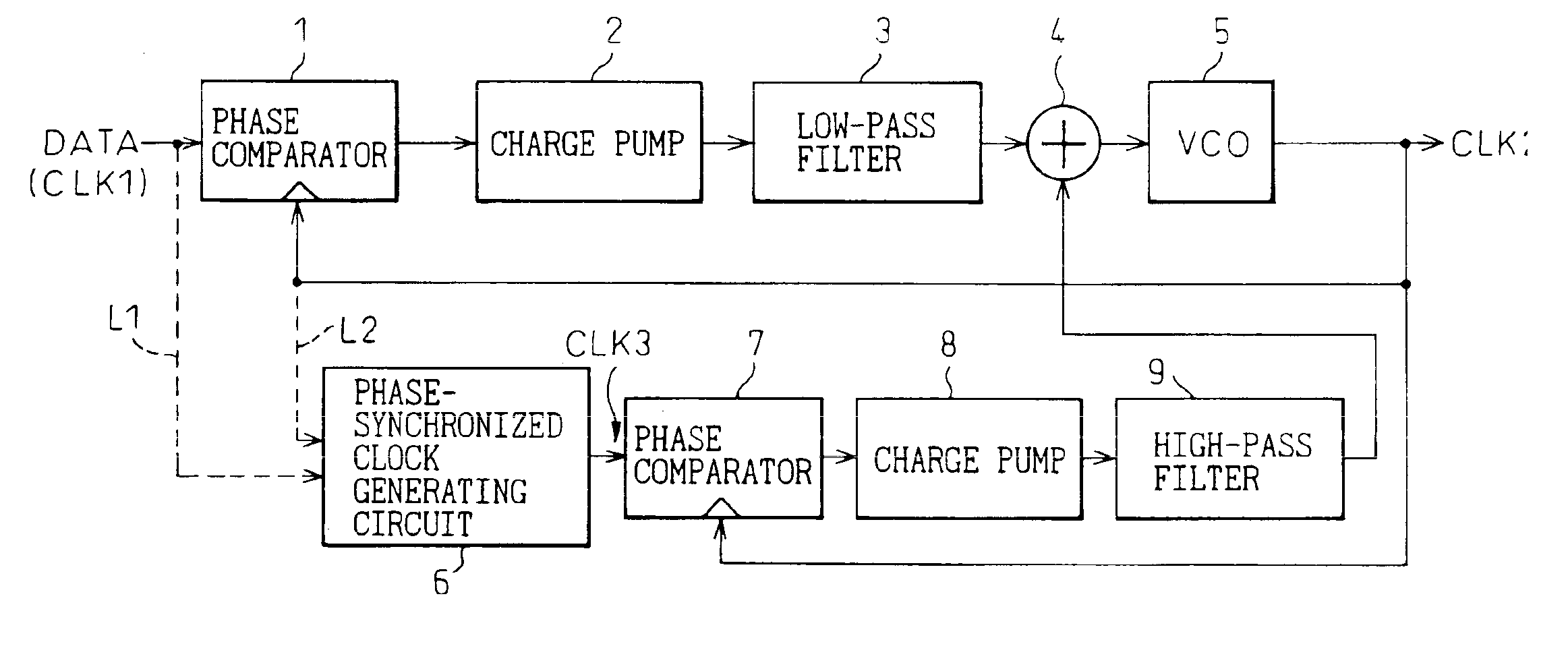
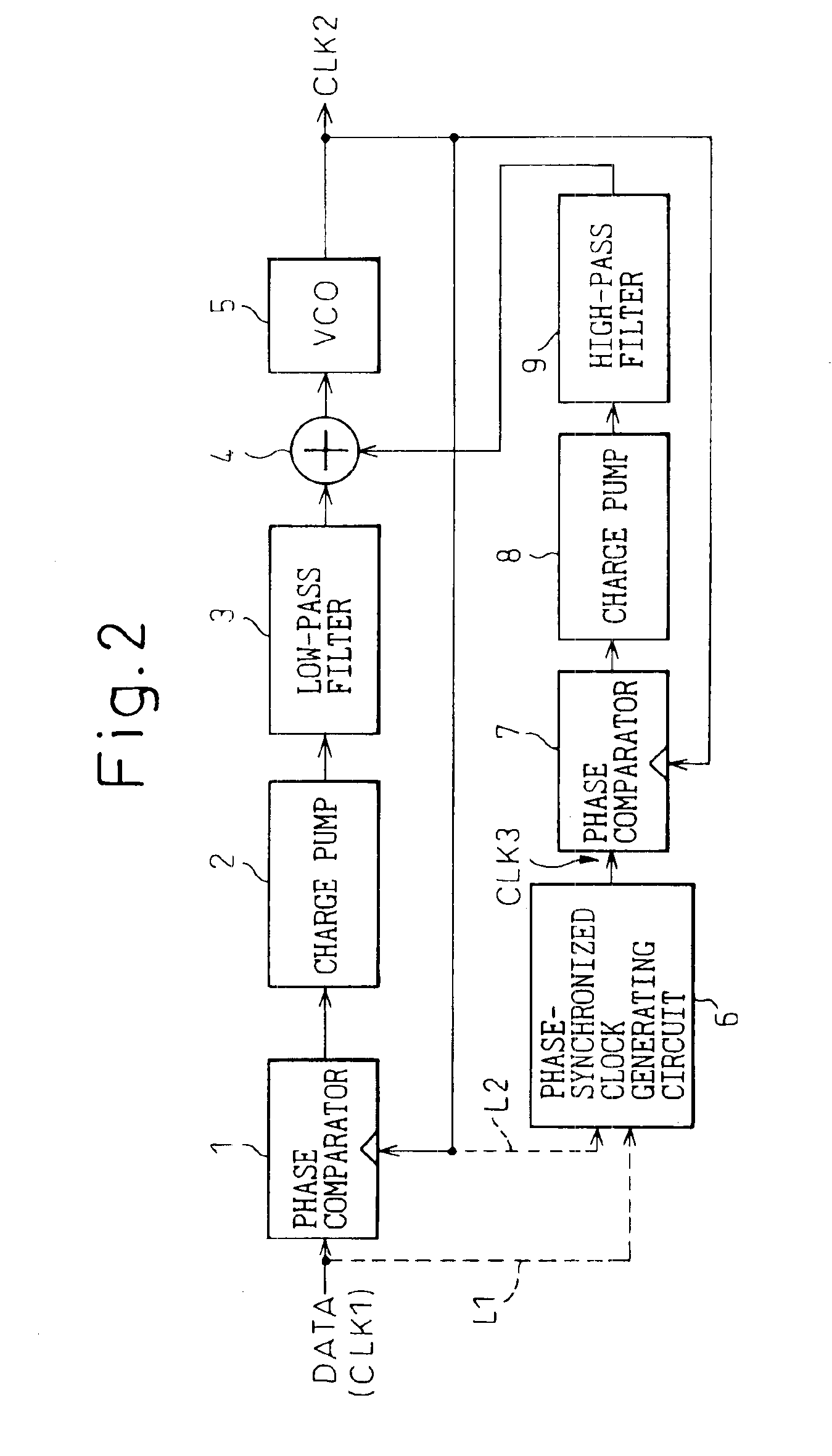
A clock generator has a clock generating circuit, a phase difference detection circuit, and a control signal generating circuit. The clock generating circuit has a function for varying a clock phase in accordance with a control signal, the phase difference detection circuit compars the clock phase output from the clock generating circuit with a phase of a reference waveform, and detecting a phase difference therebetween, and the control signal generating circuit generates a control signal for controlling the clock phase of the clock generating circuit, based on phase difference information obtained from the phase difference detection circuit. The phase difference detection circuit has a plurality of phase detection units, at least one of the plurality of phase detection units carries out a direct phase detection in which a phase of the clock is directly compared with the phase of the reference waveform, and at least the other one of the plurality of phase detection units carries out an indirect phase detection using a phase-synchronized waveform generating circuit generating a waveform synchronized in phase with the reference waveform or an output of the clock generating circuit and a phase information extracting circuit extracting phase information from the phase-synchronized waveform.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Phase synchronizing circuit
InactiveUS6870411B2Increase speedReduce the oscillation frequencyPulse automatic controlLower limitLoop filter
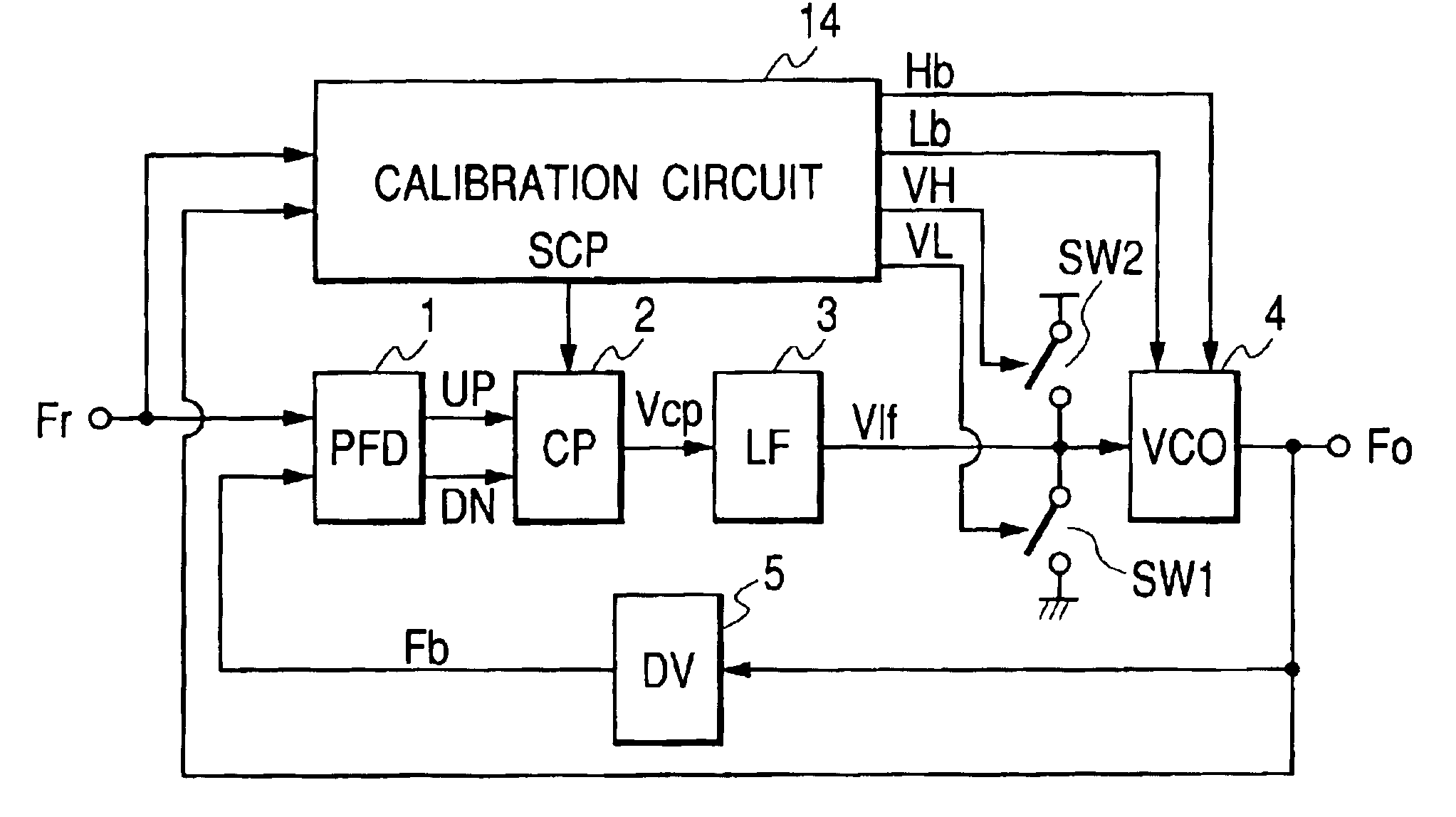
An object of this invention is to provide a phase synchronizing circuit capable of automatically adjusting a VCO such that the VCO satisfies a predetermined frequency range even in a frequency range in which the VCO oscillates by a leak current generated if a low threshold process is applied. The phase synchronizing circuit is composed of a PLL consisting of a phase comparator, a charge pump, a loop filter, a VCO, and a divider, and a calibration circuit for automatically adjusting a frequency range of the VCO. Before a convergence operation is started, a switch is closed in response to a signal Rst of the calibration circuit such that an output of the loop filter is leveled to the ground and the PLL is set to be an open loop. A VCO output Fo is set at an upper limit frequency or a lower limit frequency in response to a Vcal signal, and its frequency is measured by comparing its period with a period of a reference signal Fr, and signals Hb, Lb used for adjusting the frequency of the VCO are updated. The signals Hb, Lb are updated until the VCO satisfies the predetermined frequency range, and subsequently their values are maintained. The switch opens in response to the signal Rst, and the PLL is changed over to a close loop to start phase synchronization.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Airsync: enabling distributed multiuser MIMO with full multiplexing gain
InactiveUS8995410B2Spatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexData synchronizationCarrier signal
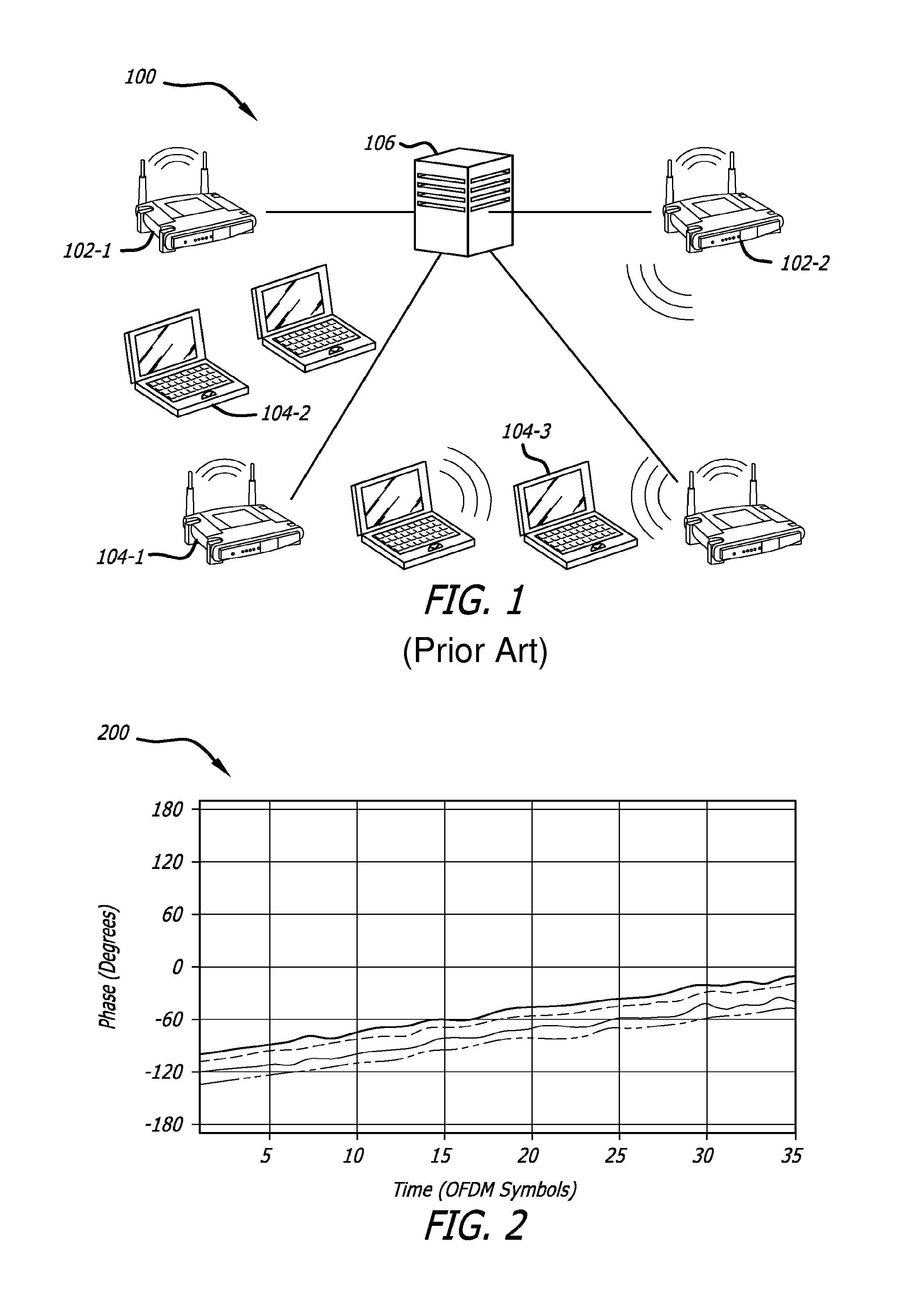
Time and phase synchronization may enable distributed multiuser multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) architectures and techniques, such as supported by the IEEE 802.11n standard, where several access points are connected to a central server and operate as a large distributed multi-antenna access point. The phase of all access points can be locked using a common reference (e.g., a synchronization tone) broadcasted over the air in conjunction with a predictive filter (e.g., a Kalman filter) which closely tracks the phase drift for each subcarrier channel.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Oversampling clock recovery having a high follow-up character using a few clock signals
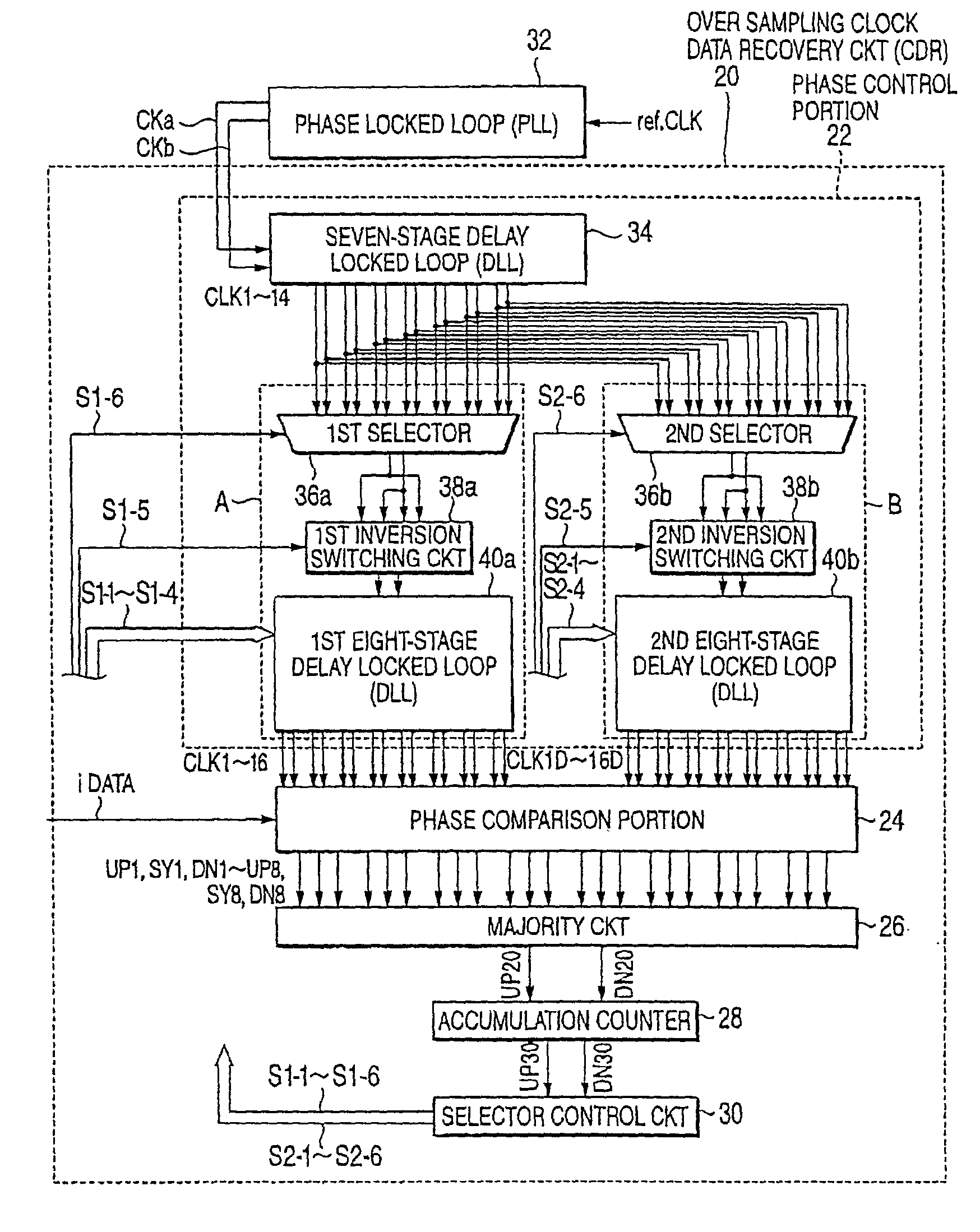
InactiveUS7010074B2High follow-up characterReduce the numberPulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexDelay-locked loopClock recovery
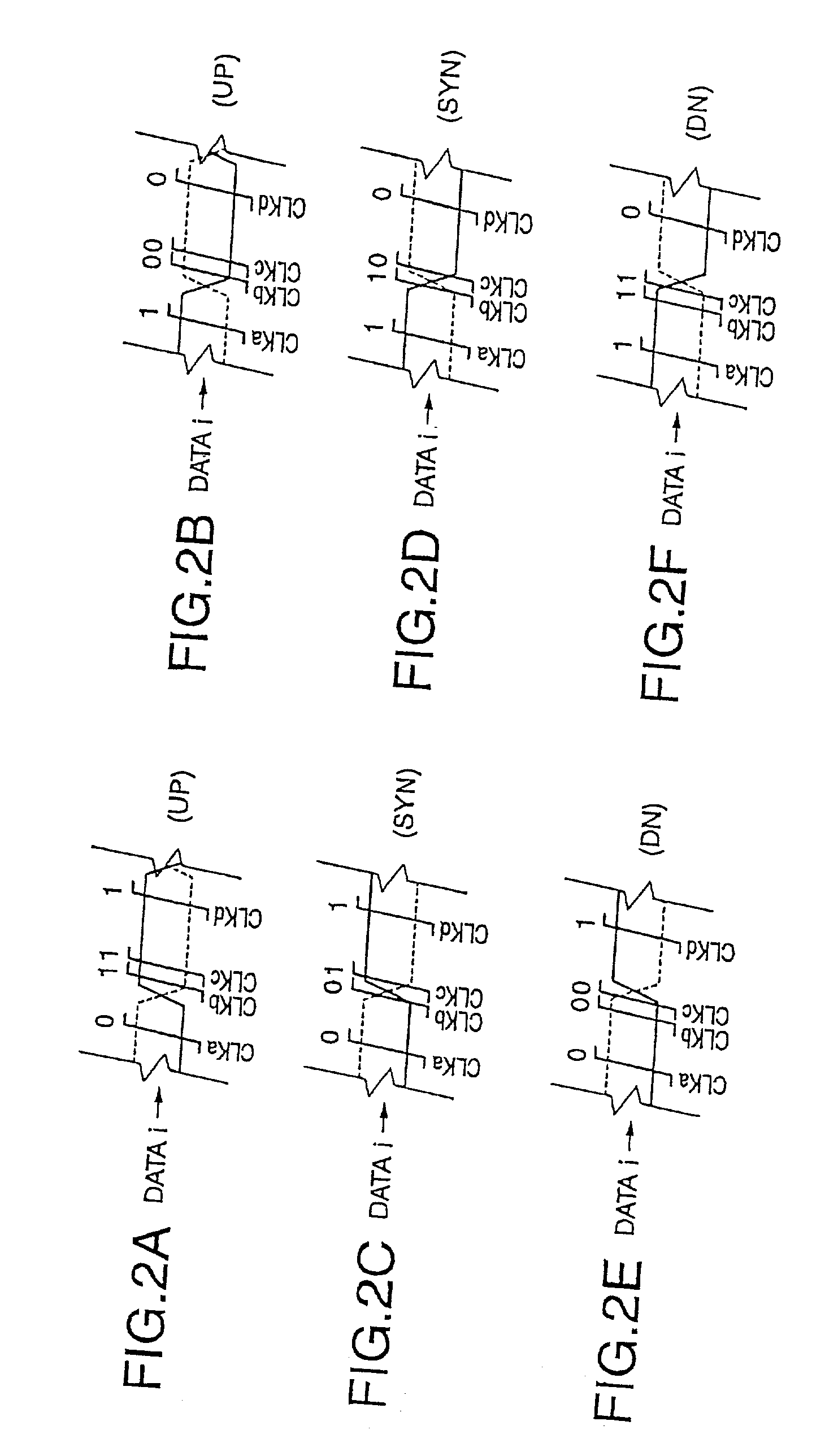
An oversampling clock recovery method according to this invention generates non-uniform three-phase clock signals CLKa, CLKb, and CLKc having non-uniform intervals for one bit of an input data i and controls phases of the clock signals so that either phase of two edges of two-phase clock signals CLKb and CLKc having a relatively narrower interval of 57 ps synchronizes with a phase of a transition point of the input data i. By changing clock signals to be phase-locked in three delay locked loops (DLLs), a phase interval of 57 ps is formed.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Dynamic shimming method of multi-order harmonics for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN102508182AImprove uniformityAccurate analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUniform fieldPower flow
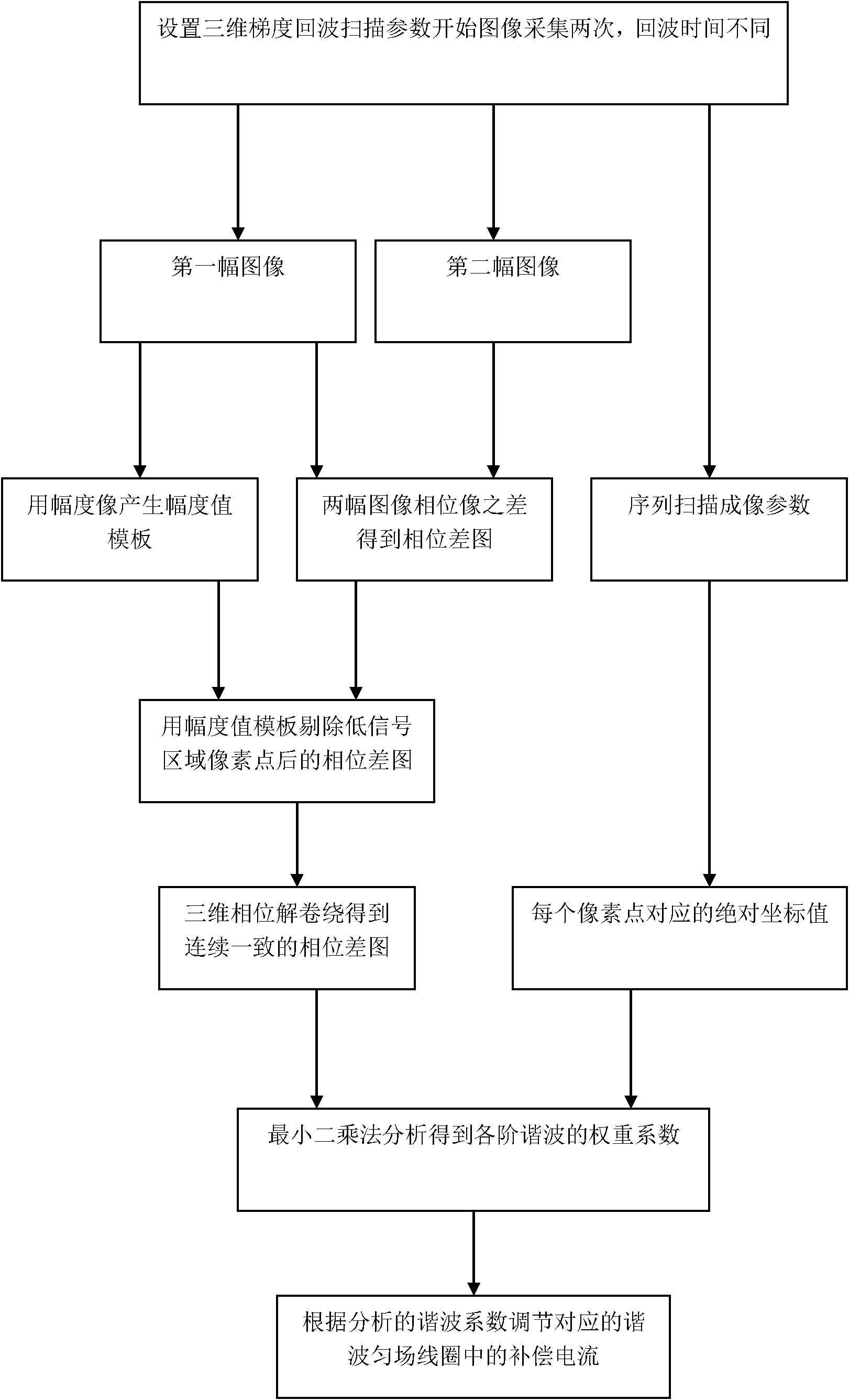
The invention discloses a method for carrying out dynamic and real-time shimming on any multi-order harmonic component in a selected area for magnetic resonance imaging, and the method can be used for improving the uniformity degree of a main magnetic field in an imaging area through cancelling out non-uniform harmonic items. According to the method provided by the invention, the weight distribution of any-order harmonic of the main magnetic field in the selected area can be analyzed once through phase information of images which are acquired by a three-dimensional gradient echo sequence twice, wherein a series of technical means of carrying out water-fat phase synchronization, eliminating low-signal noise pollution by virtue of an amplitude template and unwinding a three-dimensional phase are adopted, so that the weight component coefficient of any-order harmonic in the selected imaging area can be accurately and rapidly analyzed; a reversed compensating current is added into a corresponding harmonic shimming coil so as to accurately cancel out non-uniform high-order harmonics and only reserve zero-order harmonics, namely a uniform field; and the method provided by the invention has the advantage of maximally improving the uniformity degree of the main magnetic field by combining owned hardware conditions.
Owner:SUZHOU LONWIN MEDICAL SYST
Rotary clock synchronous fabric
Methods for generating a design for logic circuitry using rotary traveling wave oscillators (RTWOs) are described. A plurality of RTWOs are is arranged into an array of rows and columns. Adjacent elements in the array are interconnected so that the clocks in adjacent element are phase synchronous. Clocked devices are placed along the signal path of each array element and each is connected to one of the multiple phases provided by the RTWO element. The logic circuitry, described by a netlist, is divided into a number of partitions and each of these partitions is mapped to one of the array elements. The logic circuitry of the partition is then placed within or about the element of the array to which the partition is mapped and the circuitry in the partition is connected between the clocked devices in the element of the array, according to the net list.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
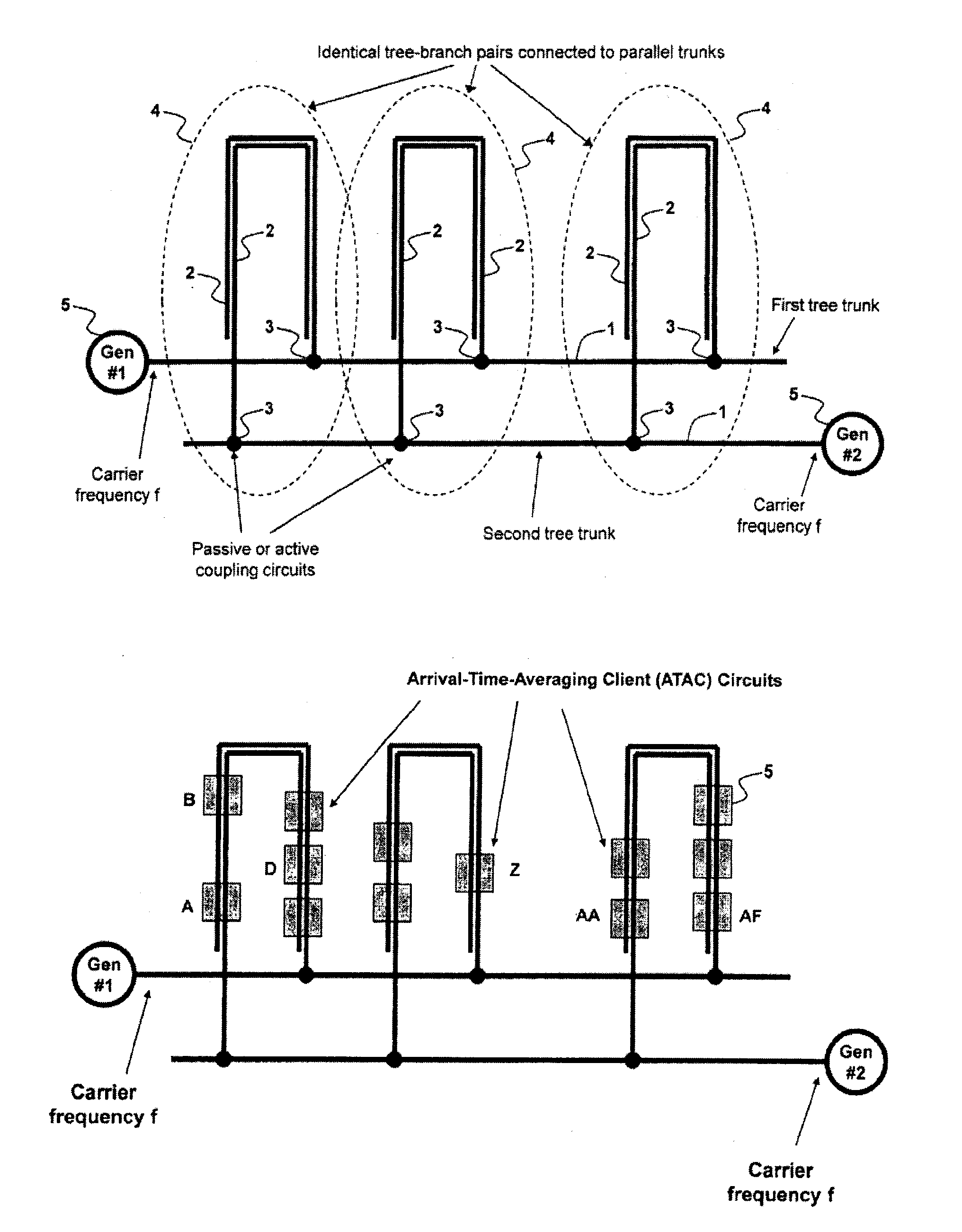
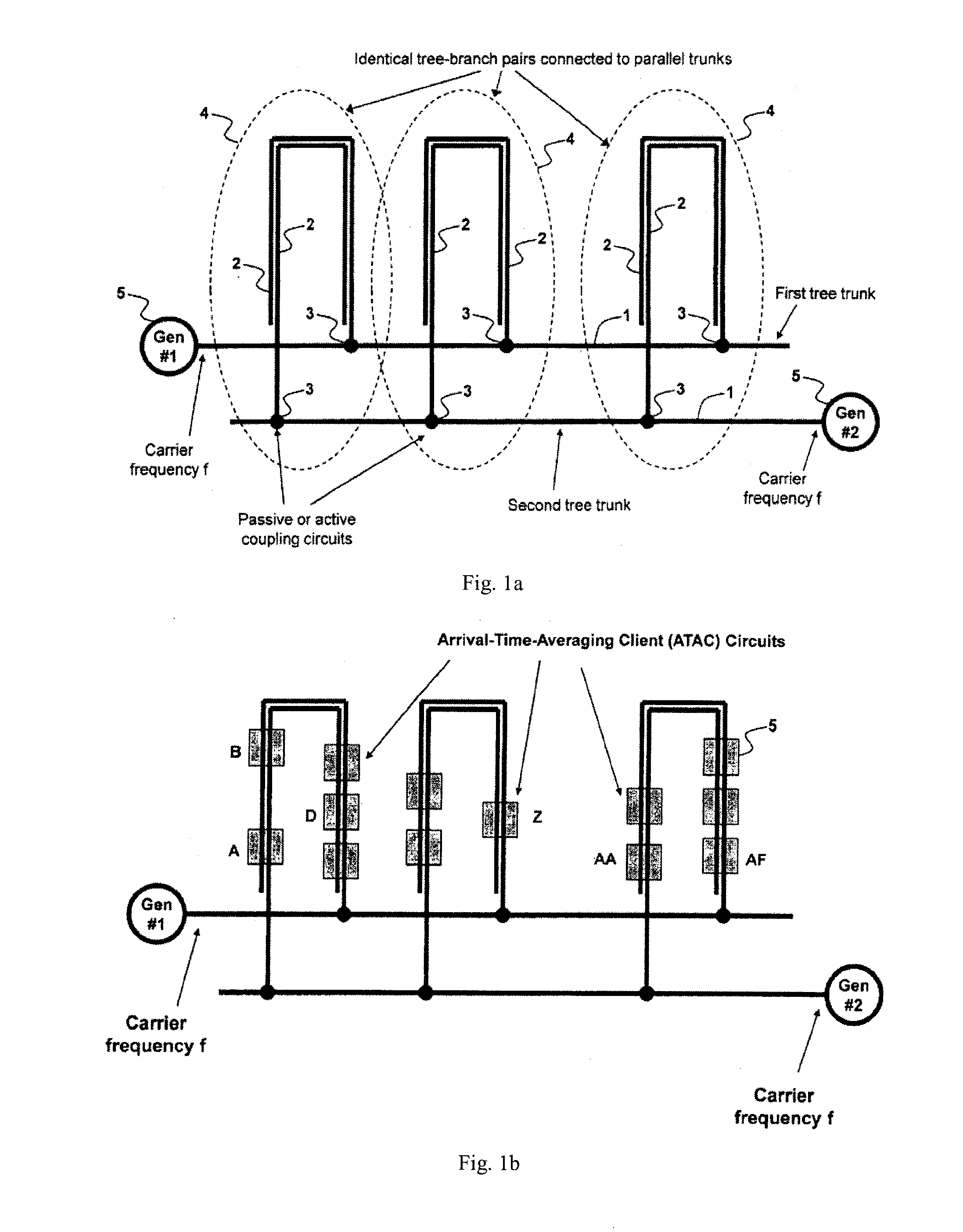
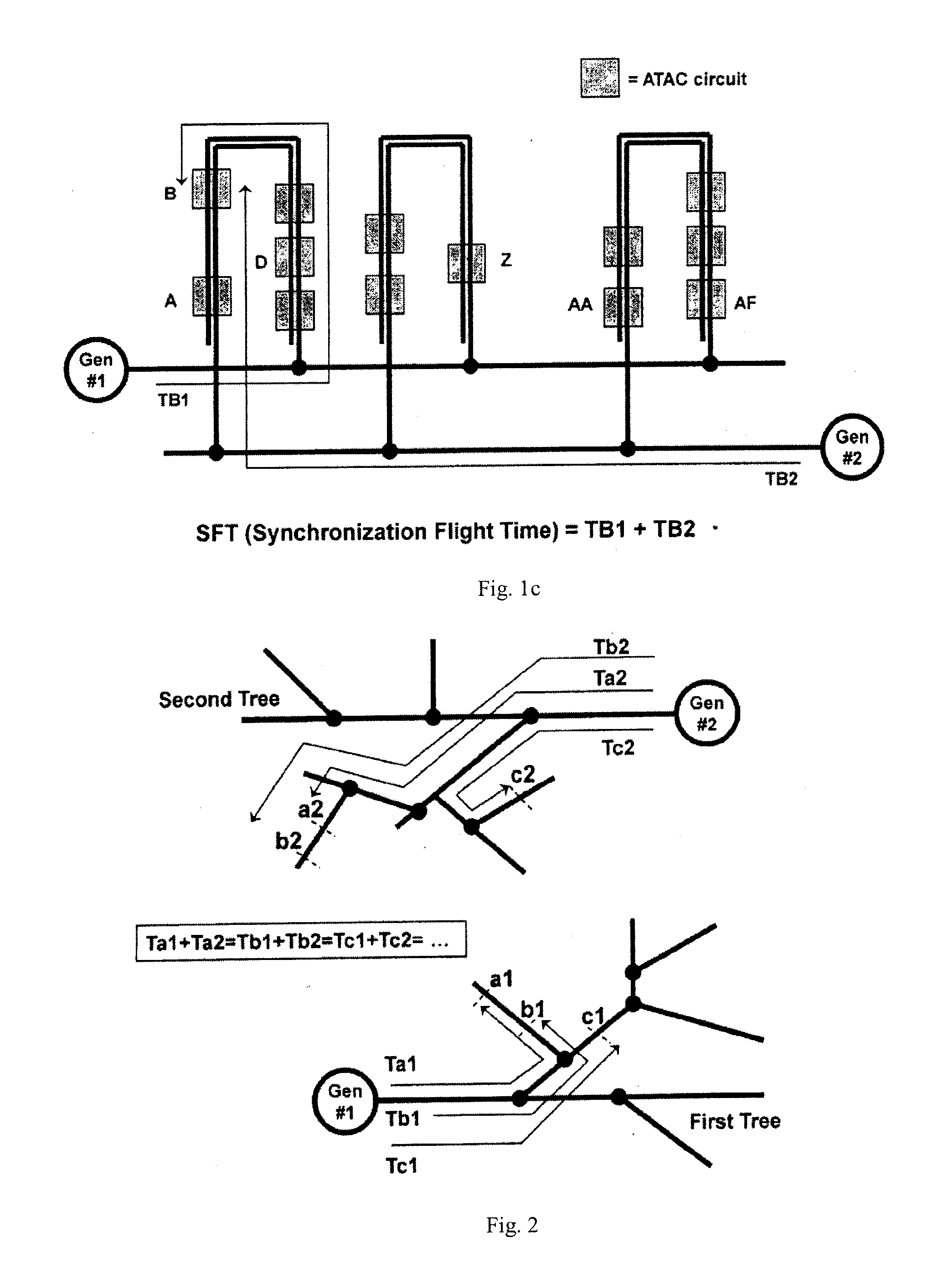
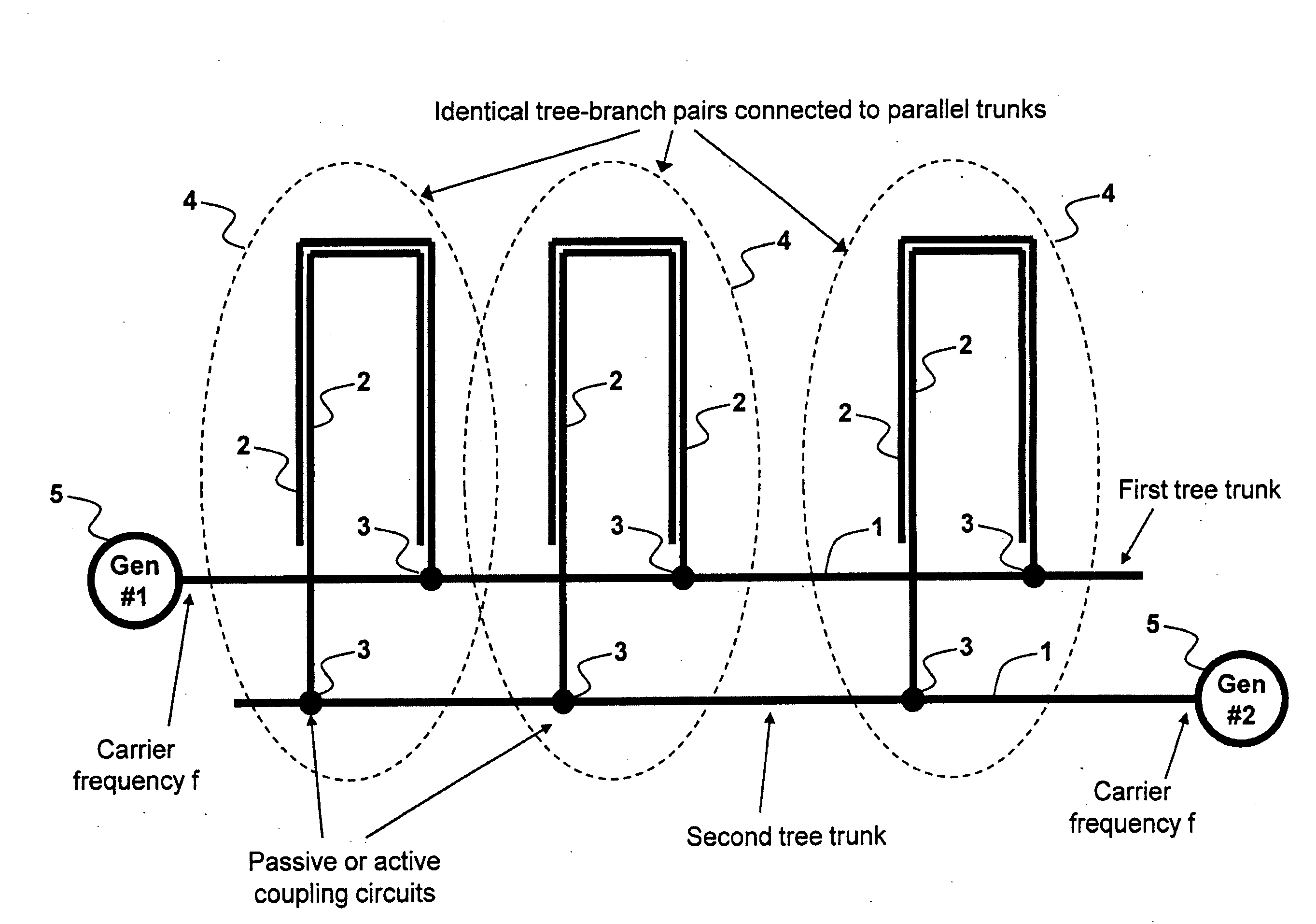
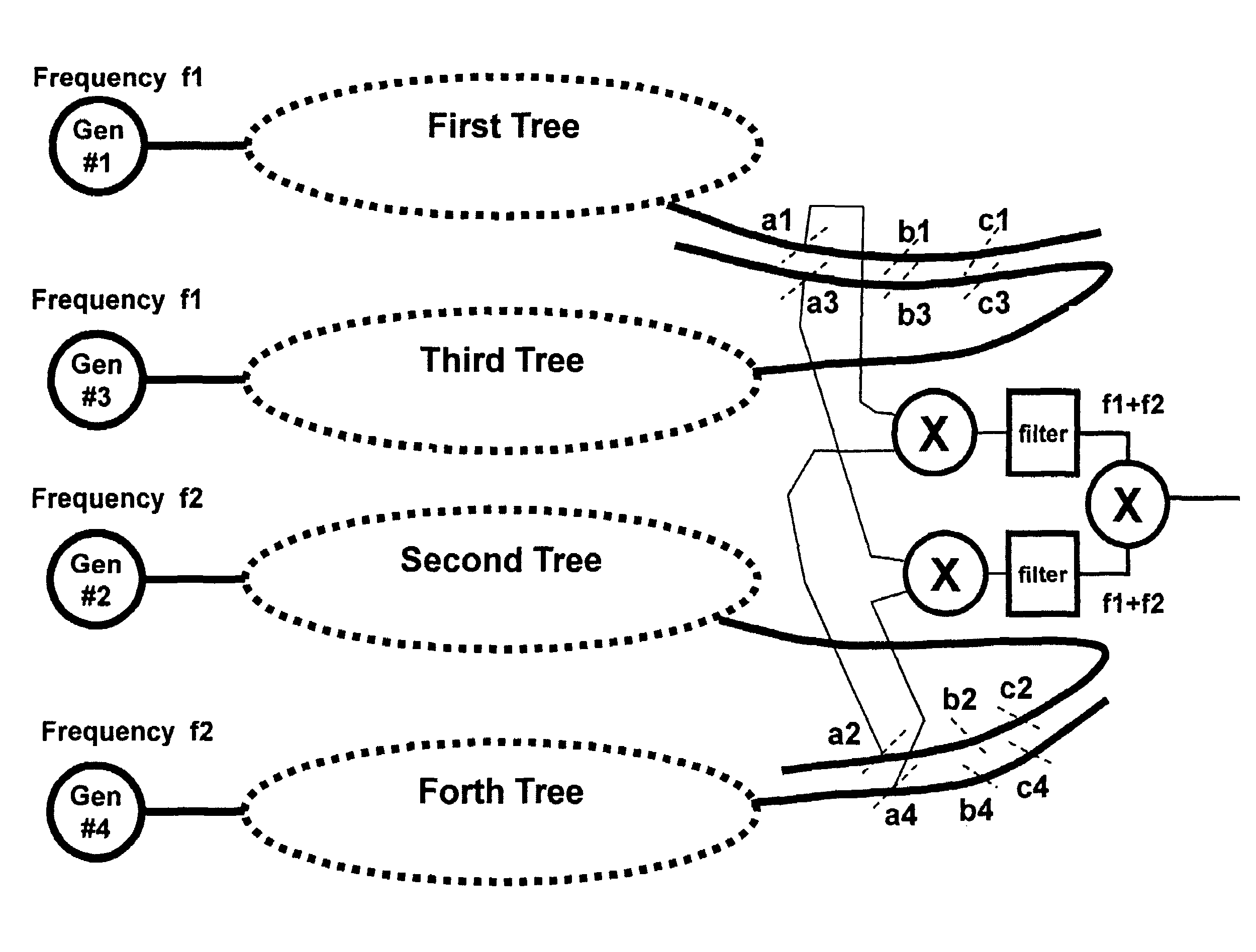
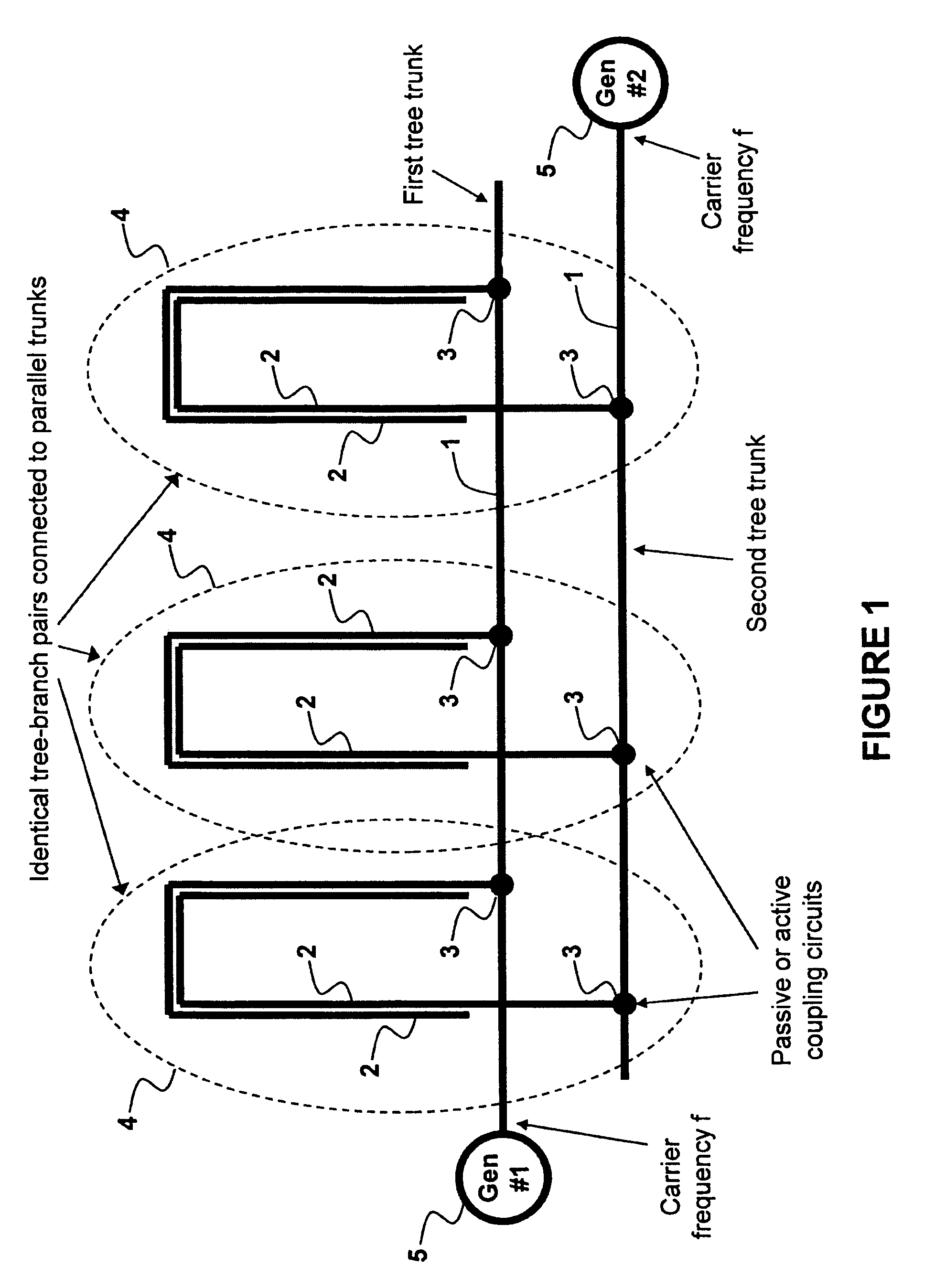
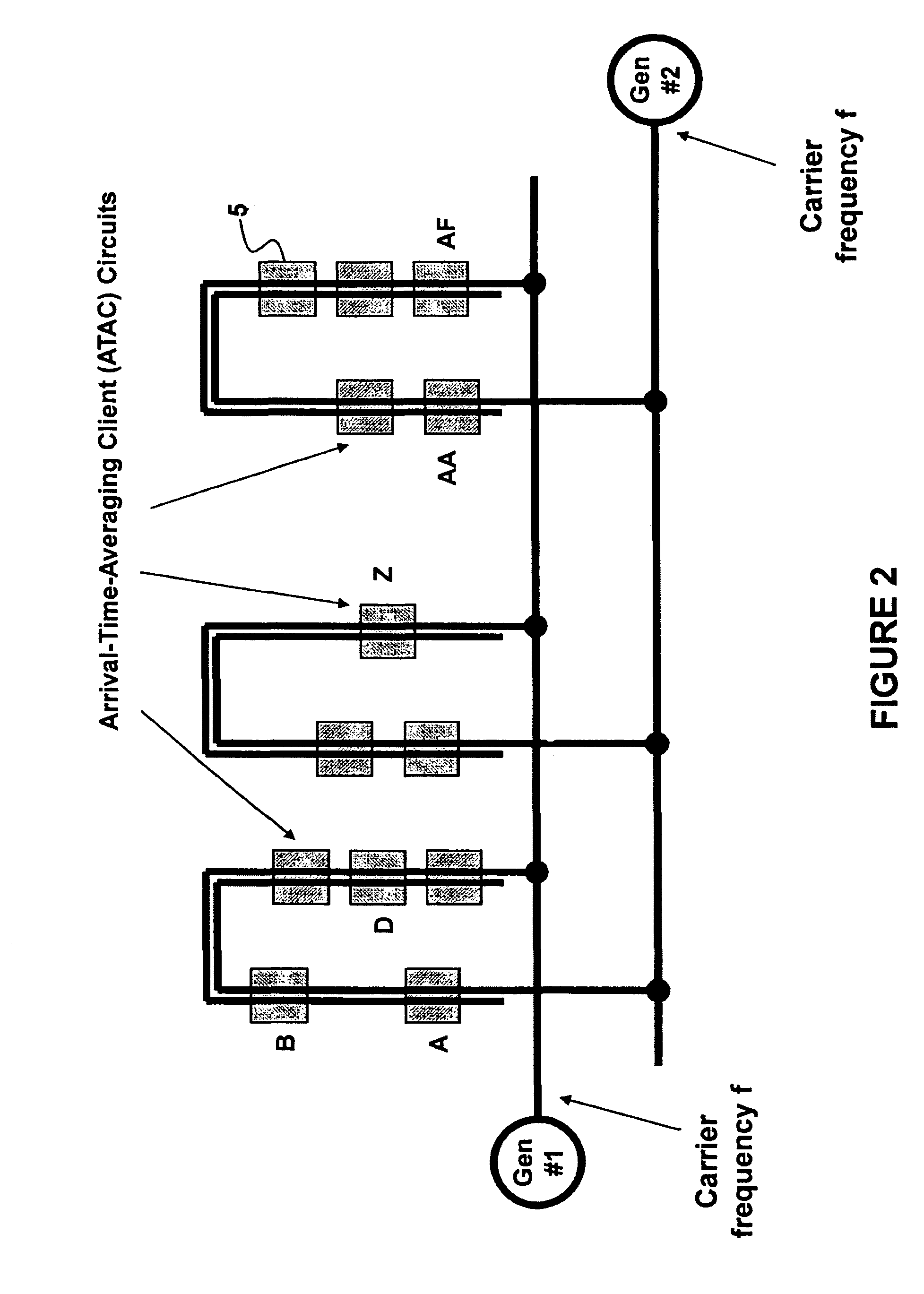
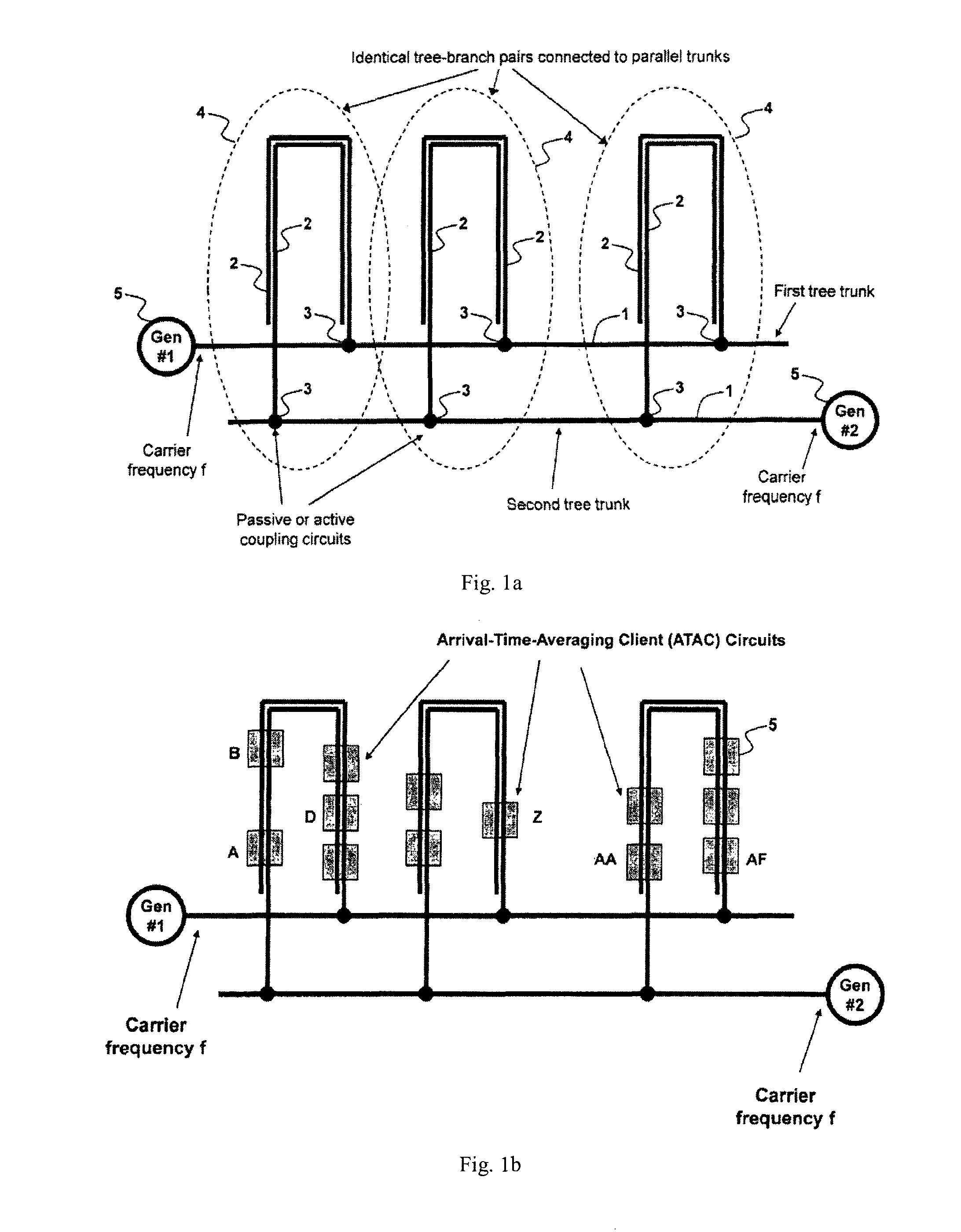
Method and System for Multi-Point Signal Generation with Phase Synchronized Local Carriers
ActiveUS20090086867A1Reduce transmissionReduce signal lossPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsCarrier signalEngineering
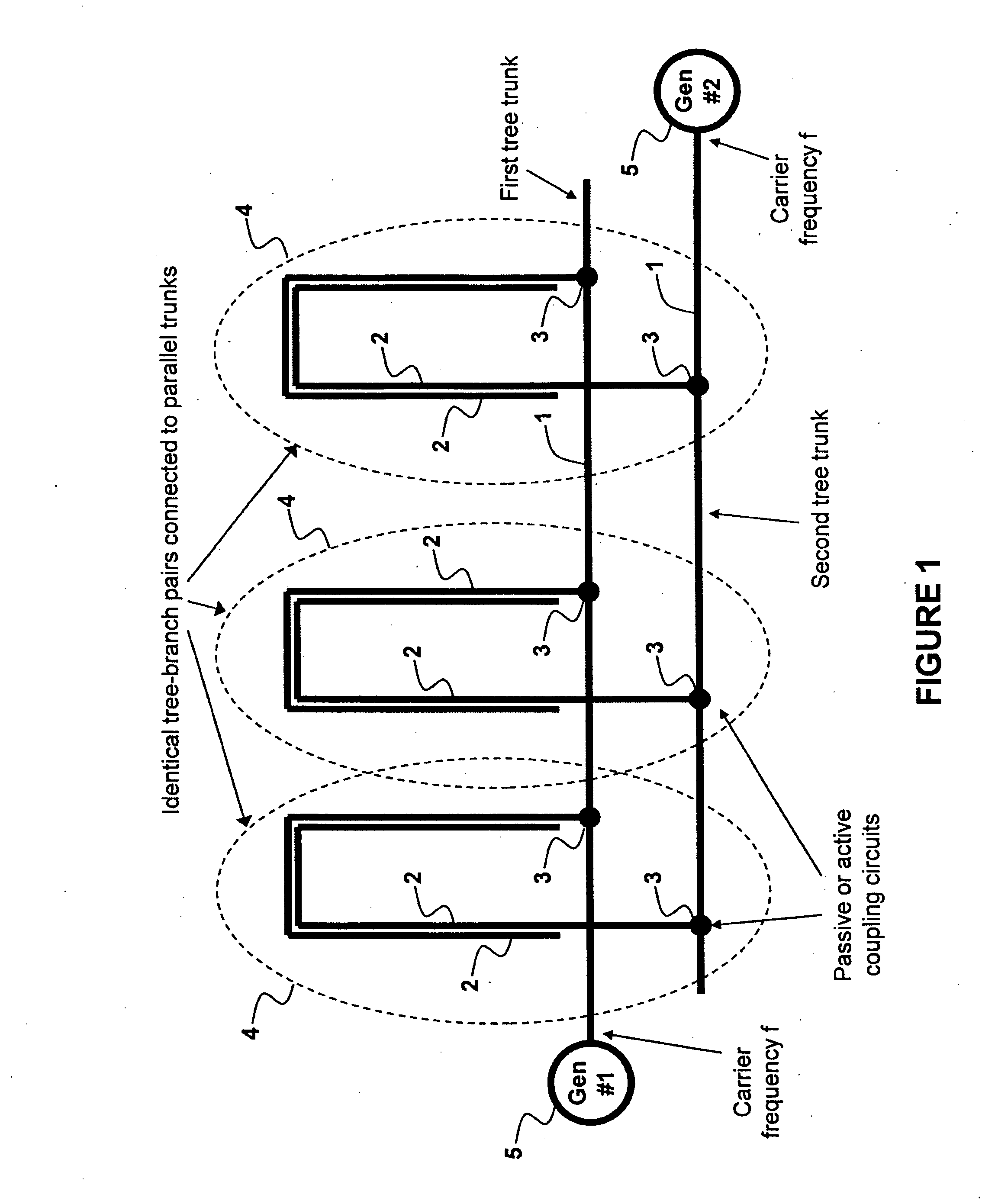
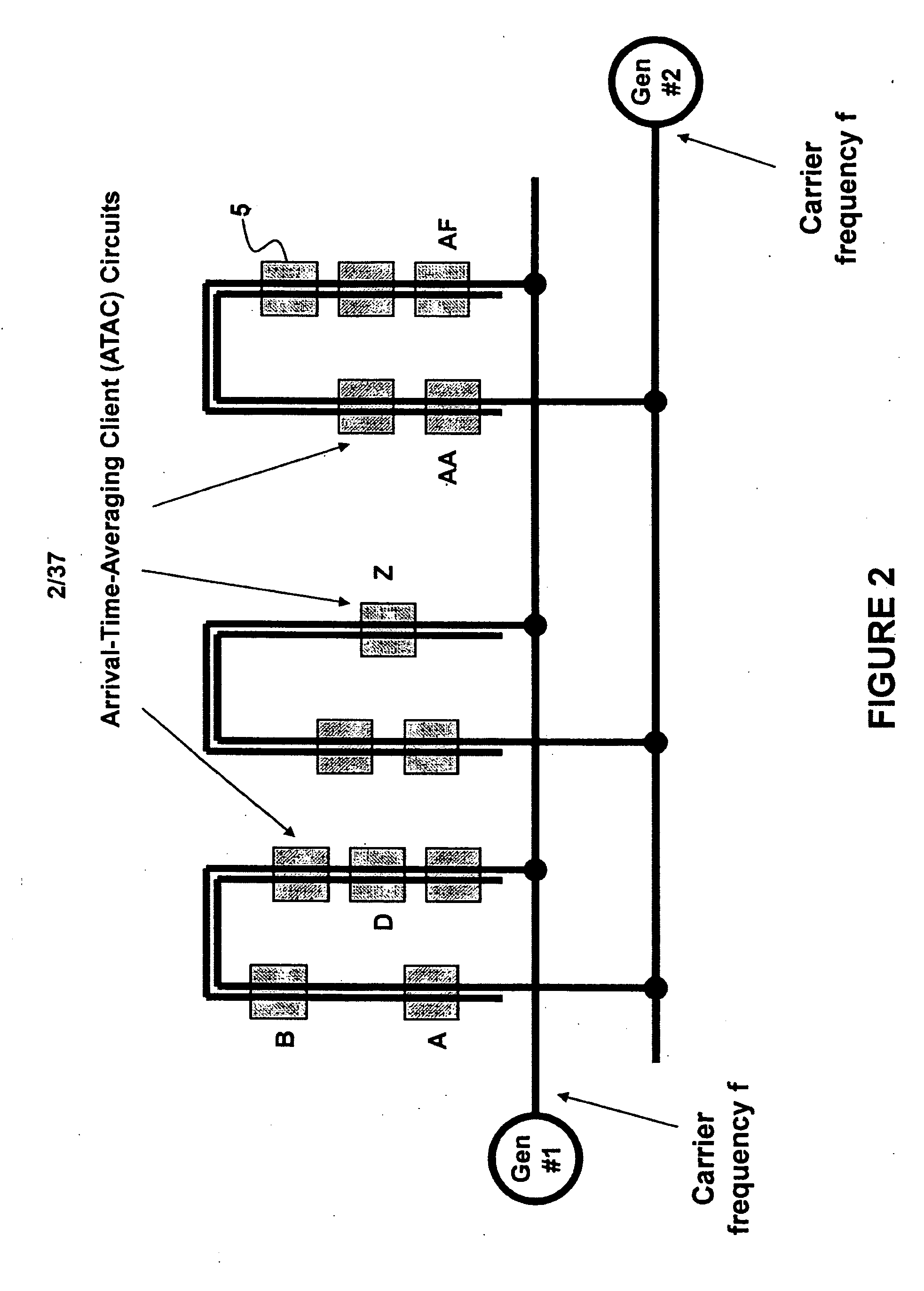
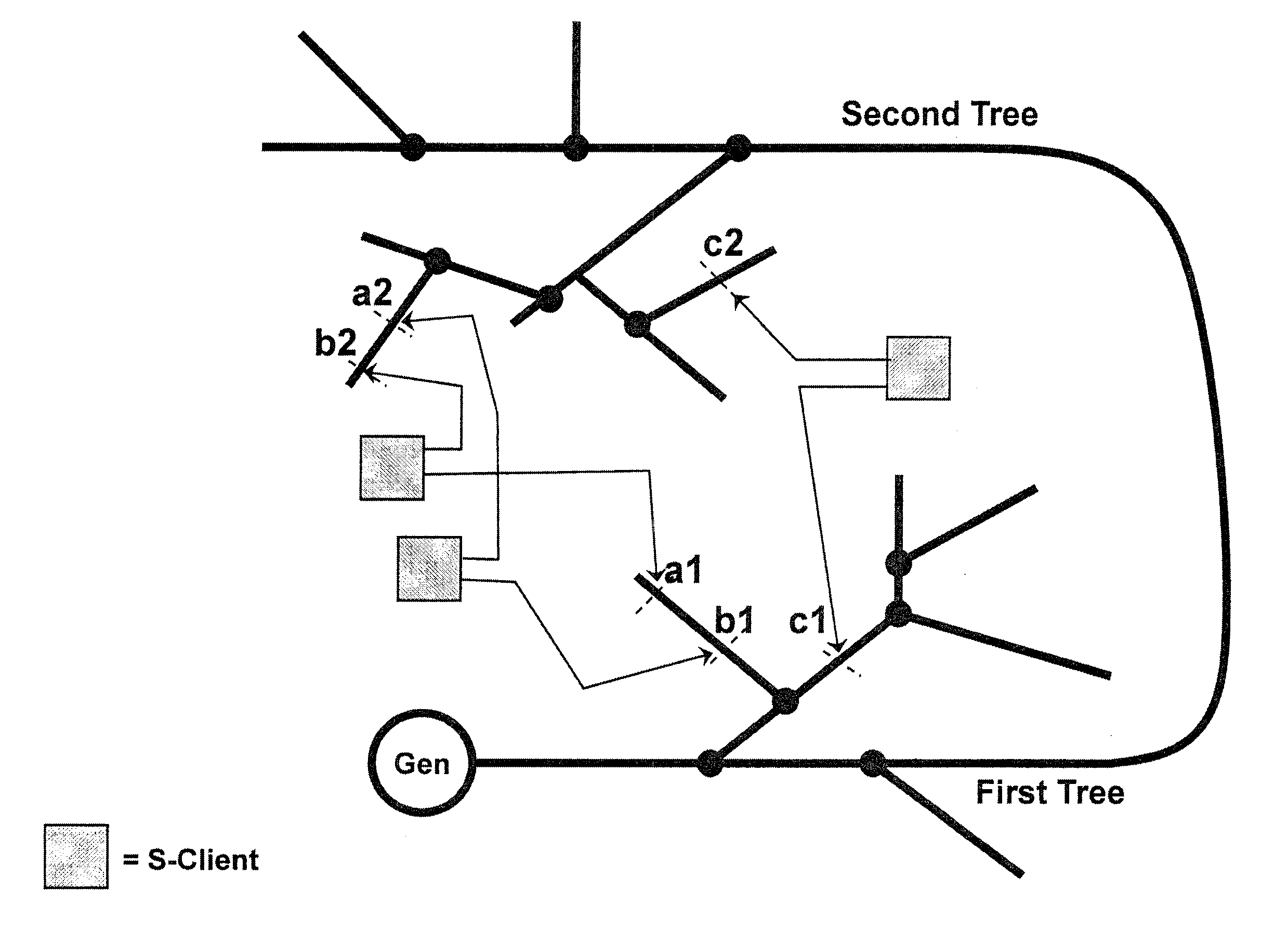
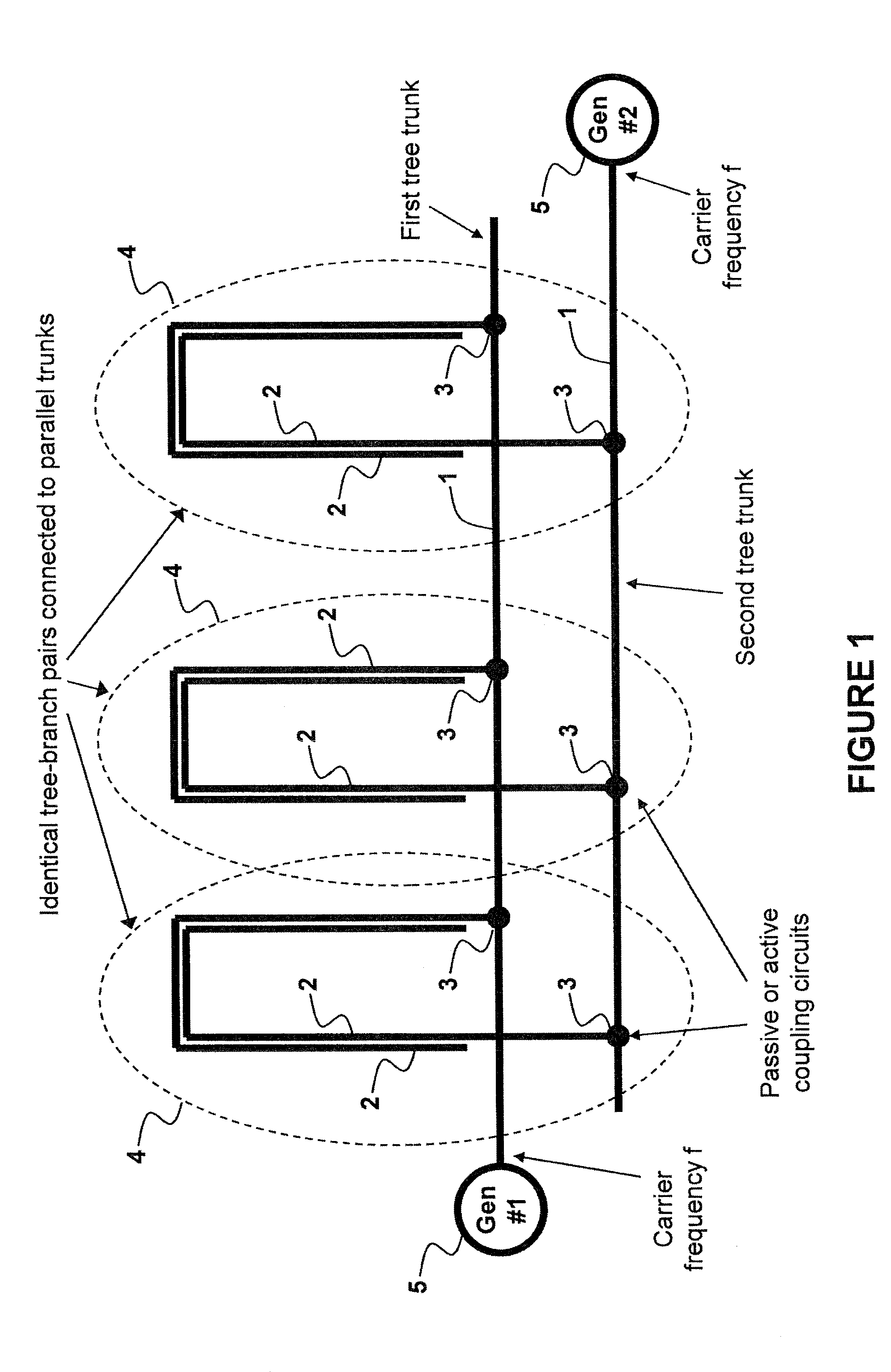
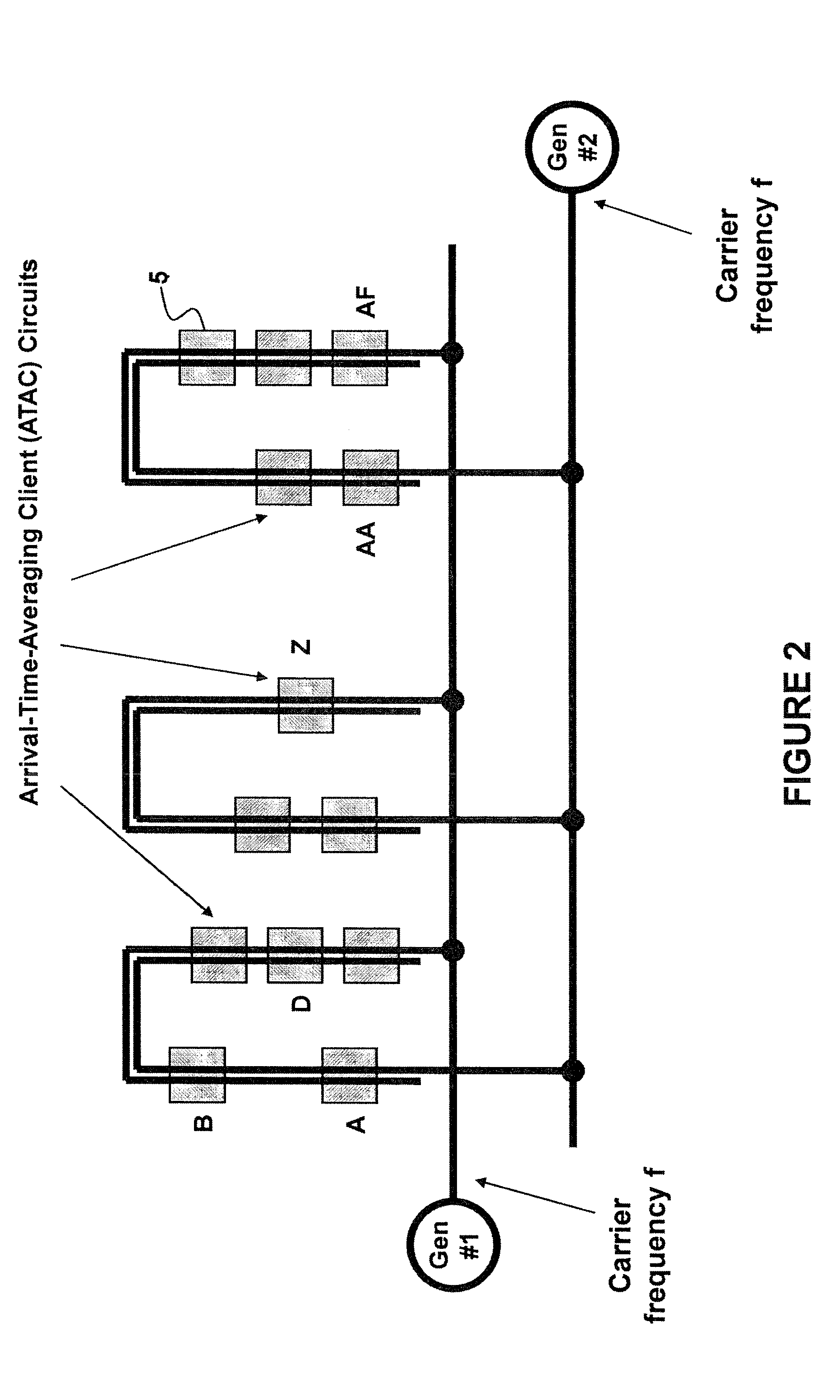
A method and system of applying modulated carrier signals to tree networks and processing signals tapped from the tree networks to generate output signals with phase-synchronized carriers are disclosed.
Owner:NEC ADVANCED NETWORKS INC
Phase synchronization circuit and receiver having the same
InactiveUS20090207961A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase detectorPhase difference
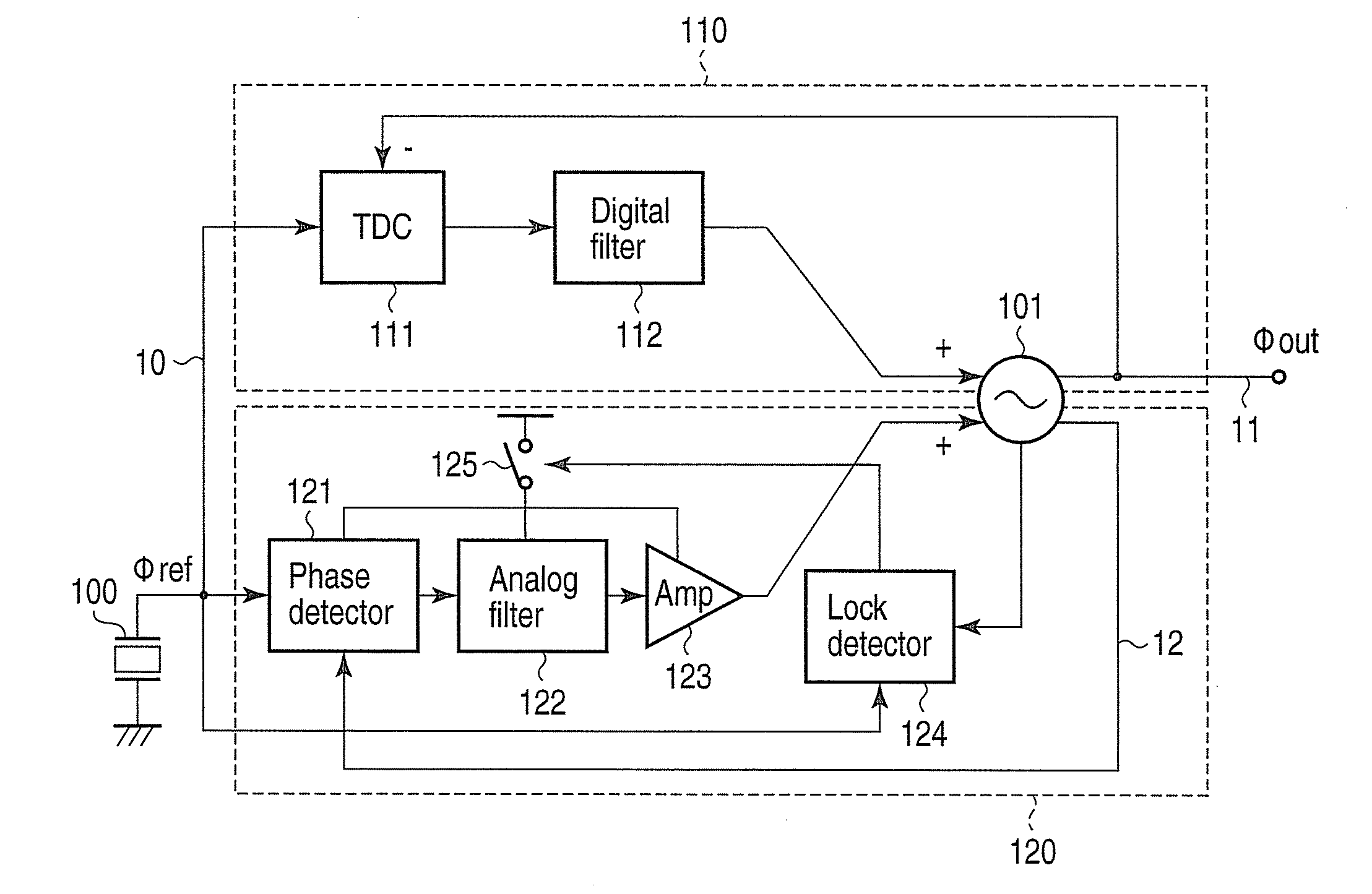
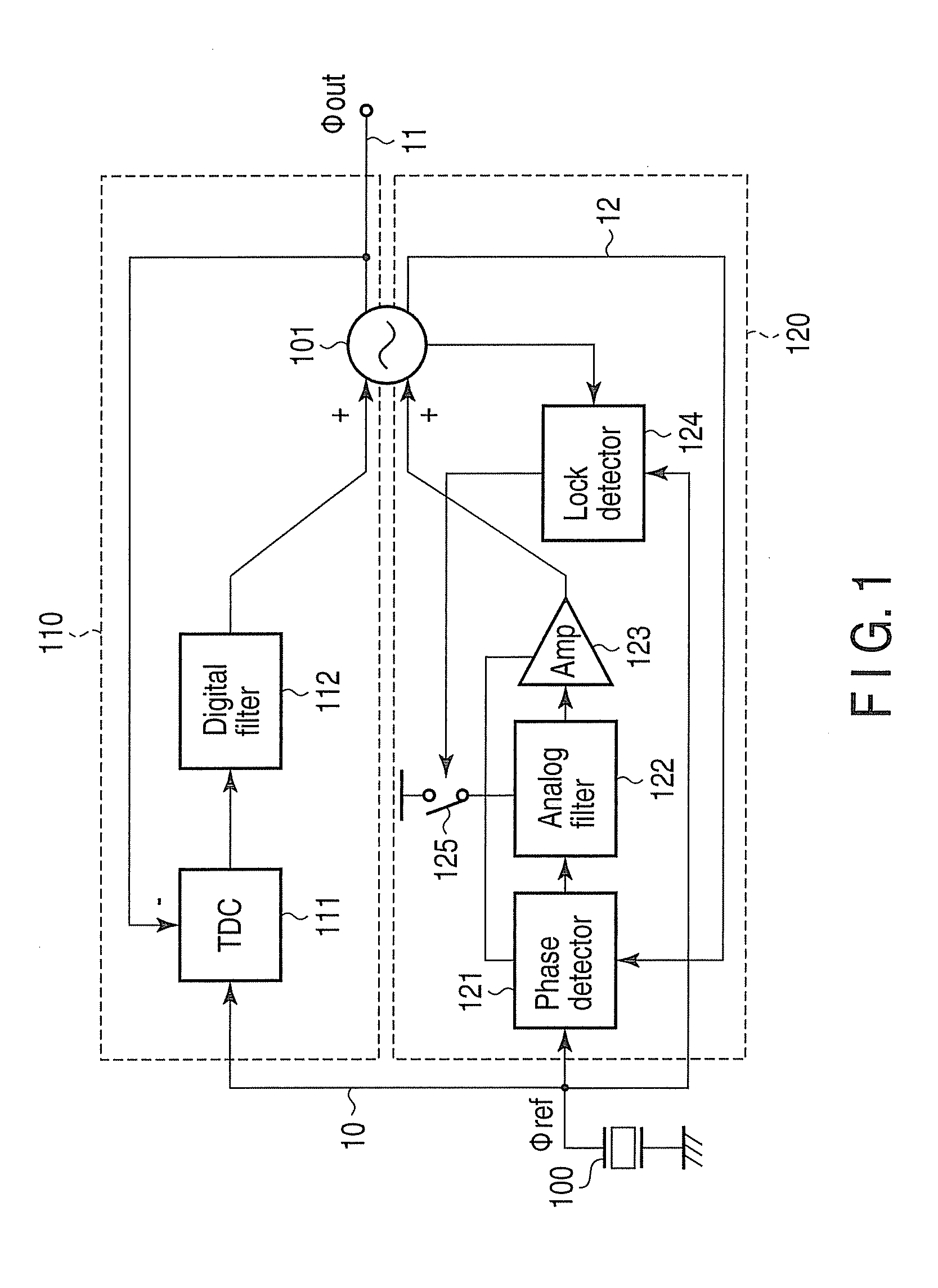
A phase synchronization circuit includes a controlled oscillator configured to generate a first oscillation signal and a second oscillation signal that have a common frequency but different phase controlled by a combination of a first control signal and a second control signal, a digital phase frequency detector configured to detect a frequency difference and a first phase difference between a reference signal and the first oscillation signal to generate the first control signal, an analog phase detector configured to detect a second phase difference between the second oscillation signal and the reference signal to generate the second control signal, and a lock detection unit configured to detect a lock of the first oscillation signal with the reference signal in terms of frequency and phase, in order to set the analog phase detector in an active state.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
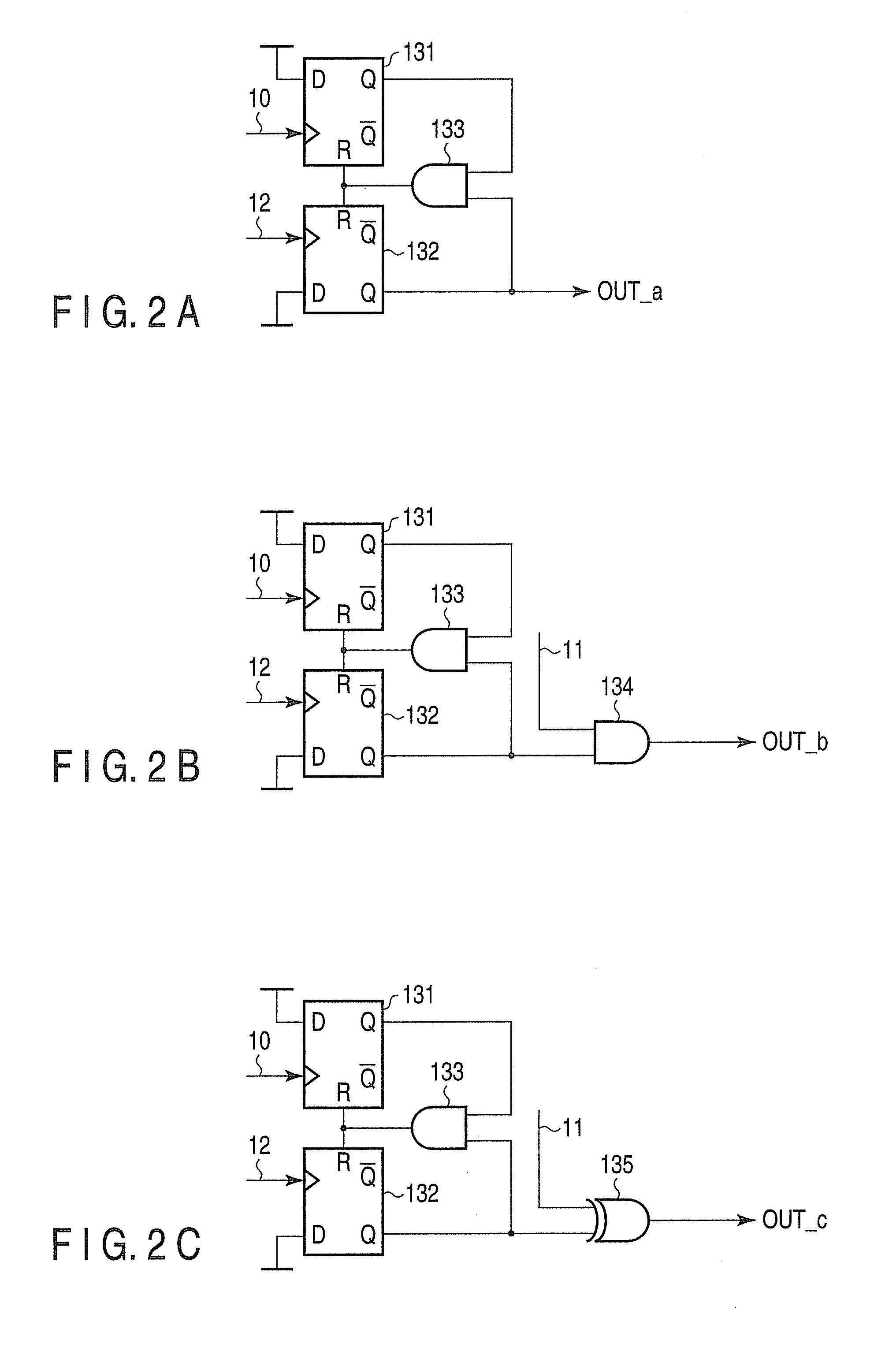
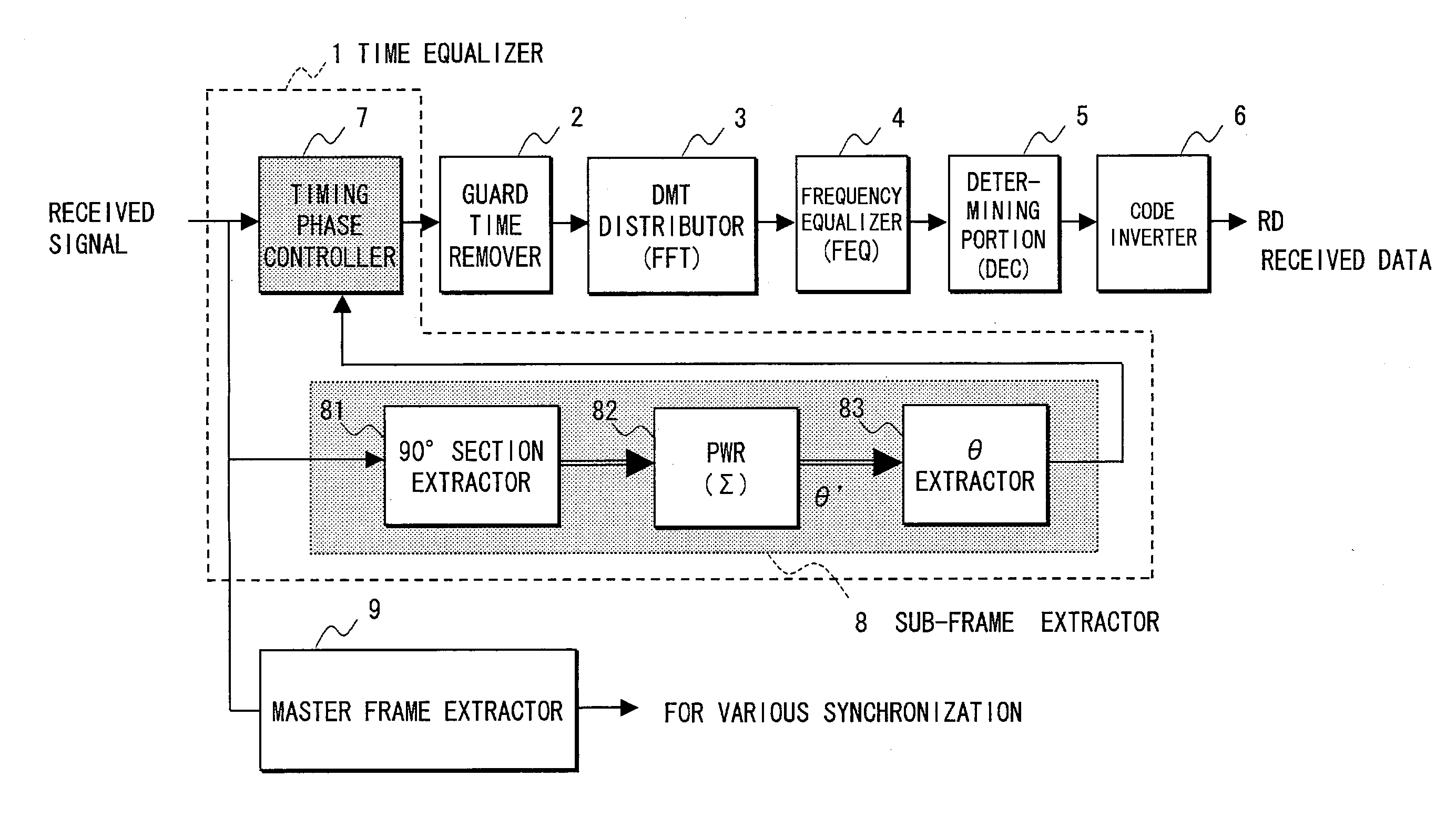
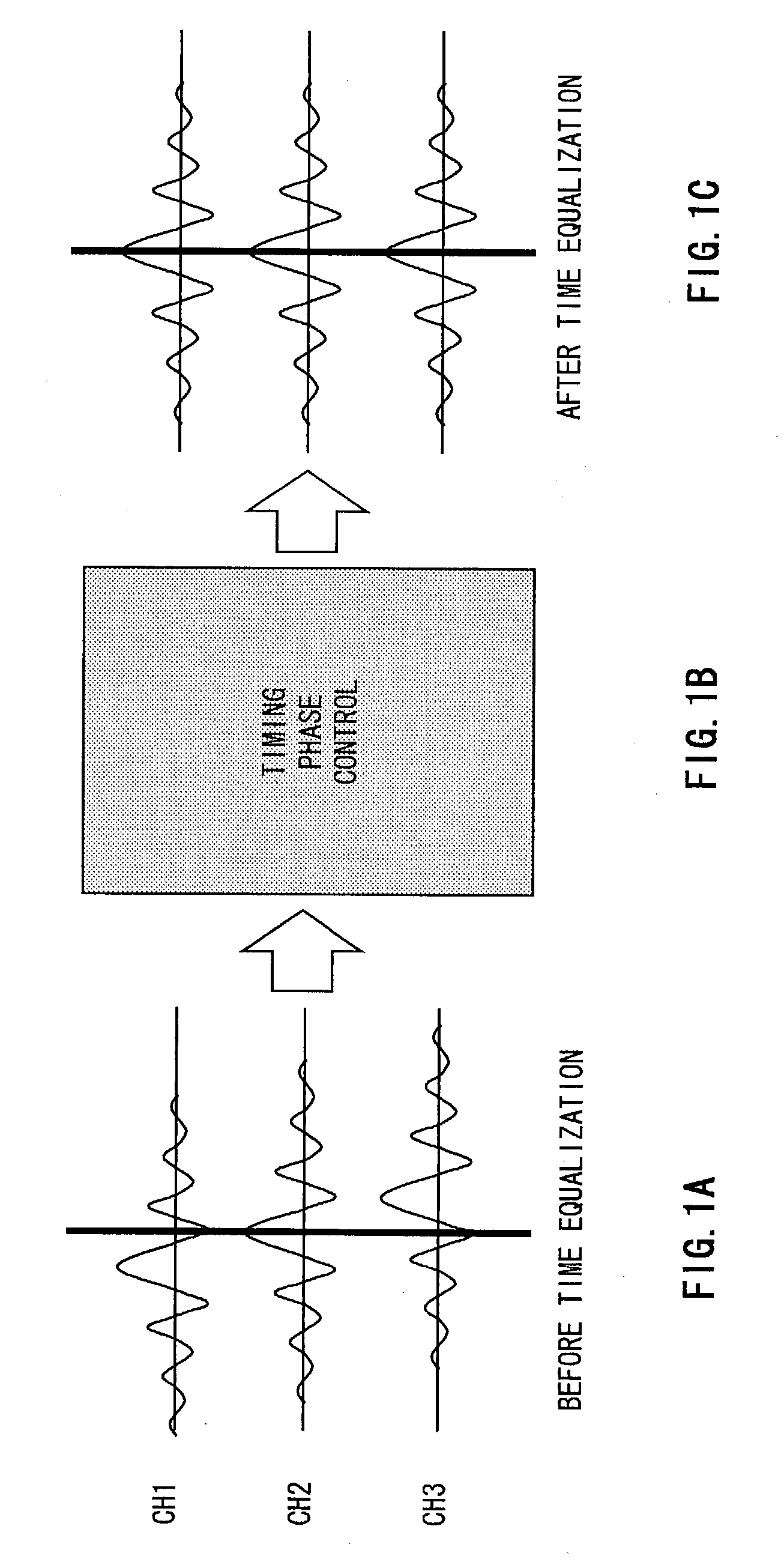
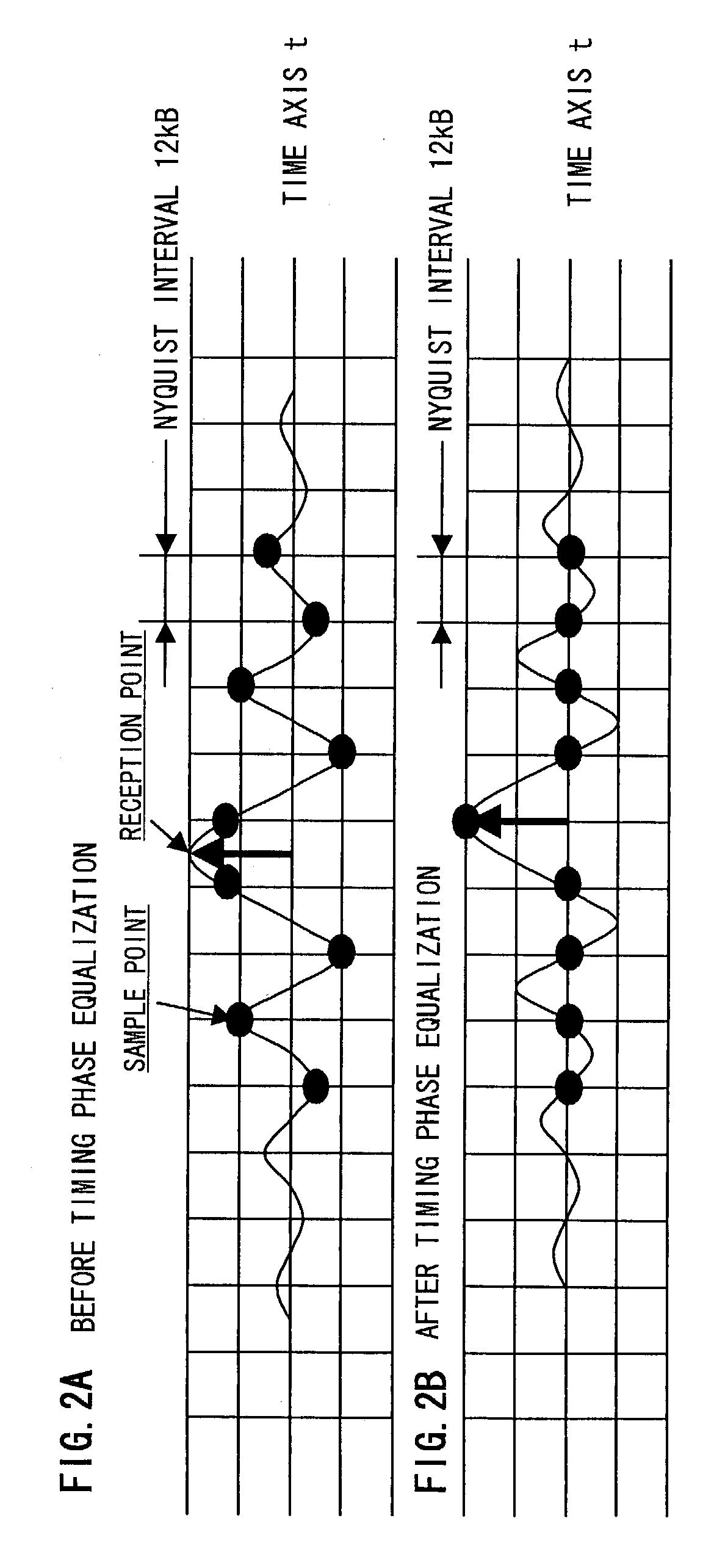
Method and apparatus for time equalization
InactiveUS20030138037A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPhase synchronizationEqualization
Timing phase information is extracted from a power spectrum of a received signal whose amplitude is modulated per frame or sub-frame, and timing phase synchronization of the received signal is performed with the timing phase information. Also, a vector signal of the power spectrum is generated, the vector signal is multiplied by another vector signal to be rotated, a sign decision of the rotated vector signal is performed, a result of the sign decision is integrated to be outputted as the timing phase information, and a vector conversion is performed to the integrated value to be fed back as the other vector signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Synchronization circuit and synchronization method
InactiveUS6909312B2Simple structurePulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase synchronizationPulse delay
Phase synchronization is achieved by forming a first pulse to be synchronized with a reference pulse, a second pulse leading in phase for a certain period relative to said first pulse and a third pulse delayed in phase for a certain period from said first pulse; comparing said reference pulse with said first pulse in a first comparing; comparing said reference pulse with said second pulse and said third pulse in a second comparing; and forming a control voltage by giving priority to a comparison output of said second comparing with respect to a comparison output of said first comparing, matching the phase of said reference pulse with the phrase of said second pulse or said third pulse, and matching, after said matching of phases, the phrase of said reference pulse with the phase of said first pulse by forming said control, voltage from the comparison output of said first comparing.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
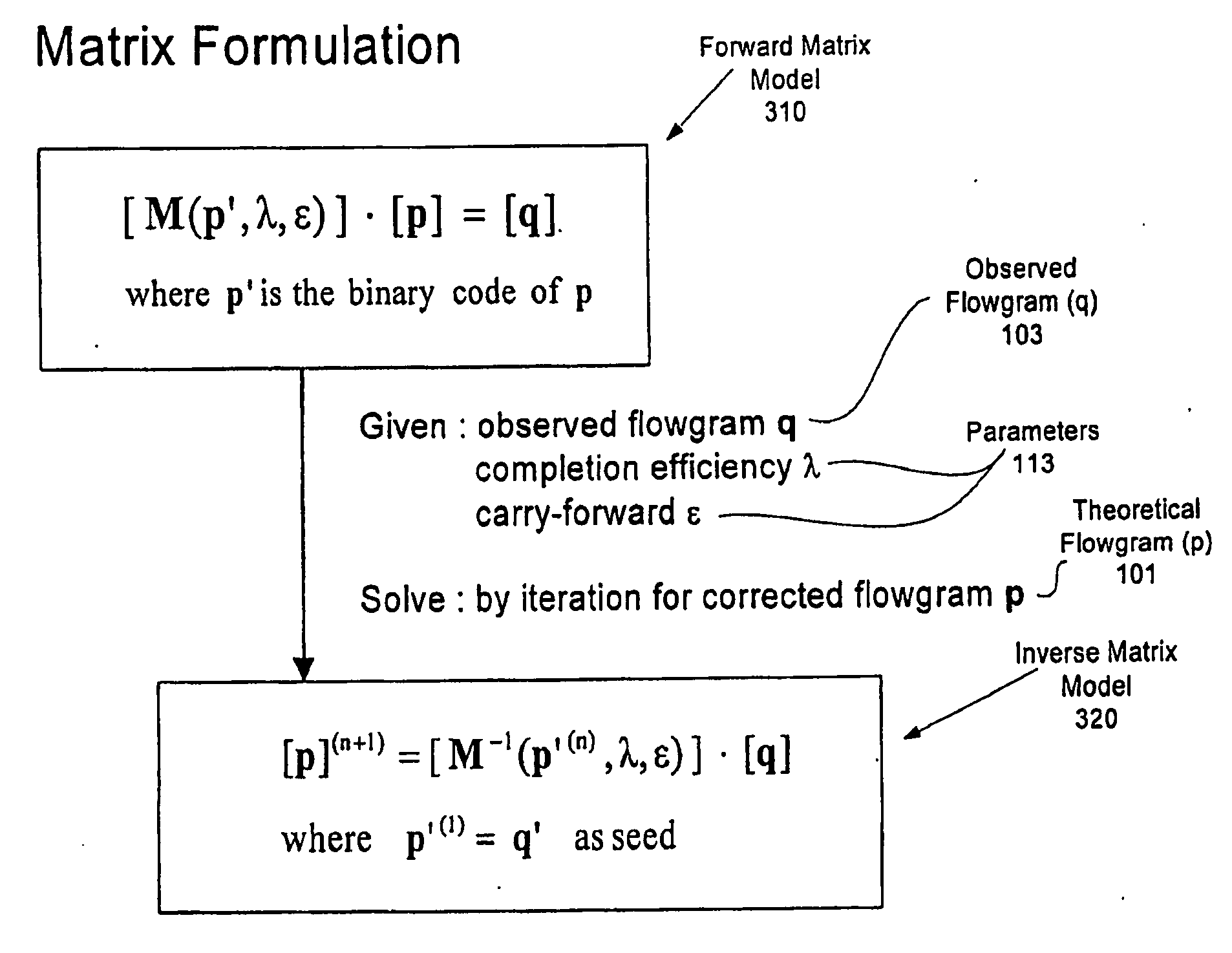
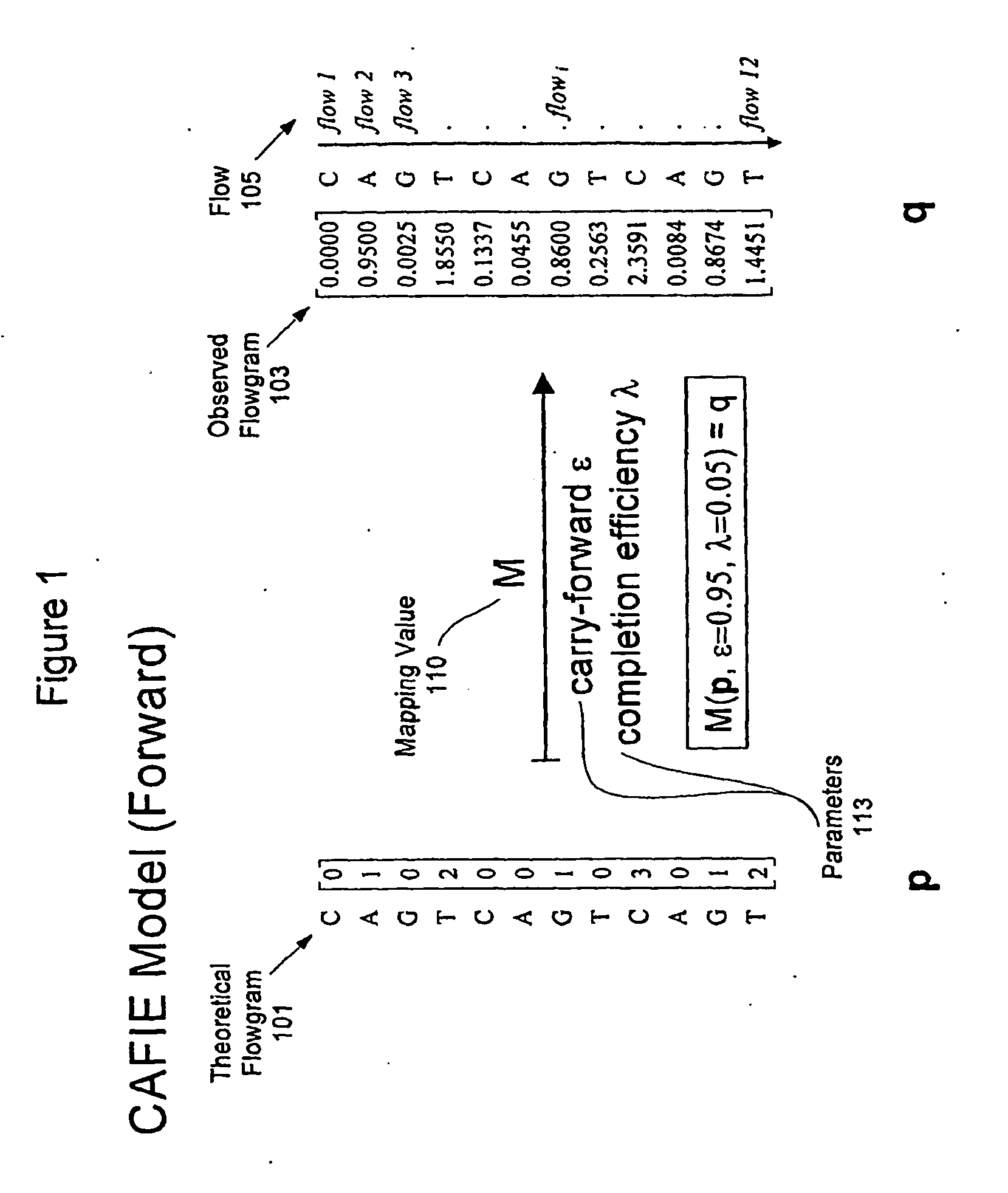
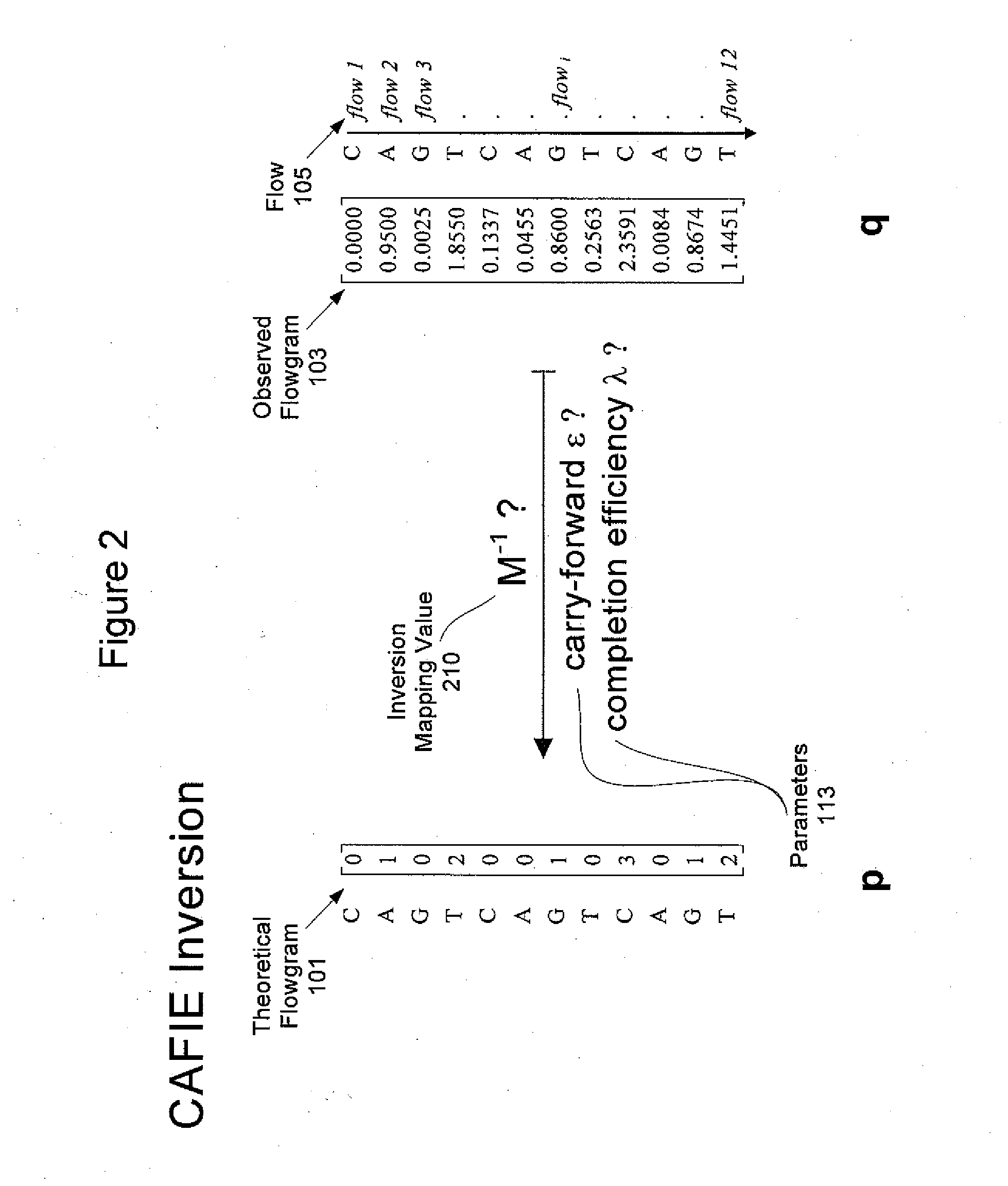
System and Method for Correcting Primer Extension Errors in Nucleic Acid Sequence Data
ActiveUS20100192032A1Quality improvementAvoid excessive depthError preventionTransmission systemsNucleic acid sequencingComputer science
An embodiment of method for correcting an error associated with phasic synchrony of sequence data generated from a population of substantially identical copy of a template molecule is described that comprises (a) detecting a signal generated in response to an incorporation of one or more nucleotides in a sequencing reaction; (b) generating a value for the signal; and (c) correcting the value for the phasic synchrony error using a first parameter and a second carry forward parameter.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
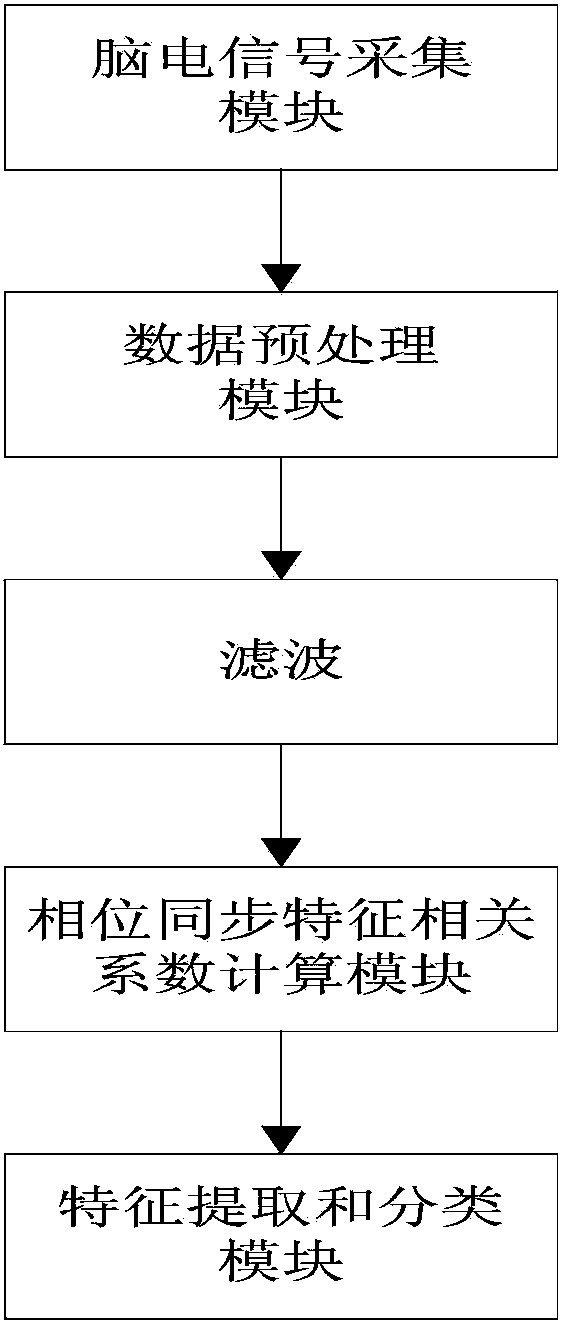
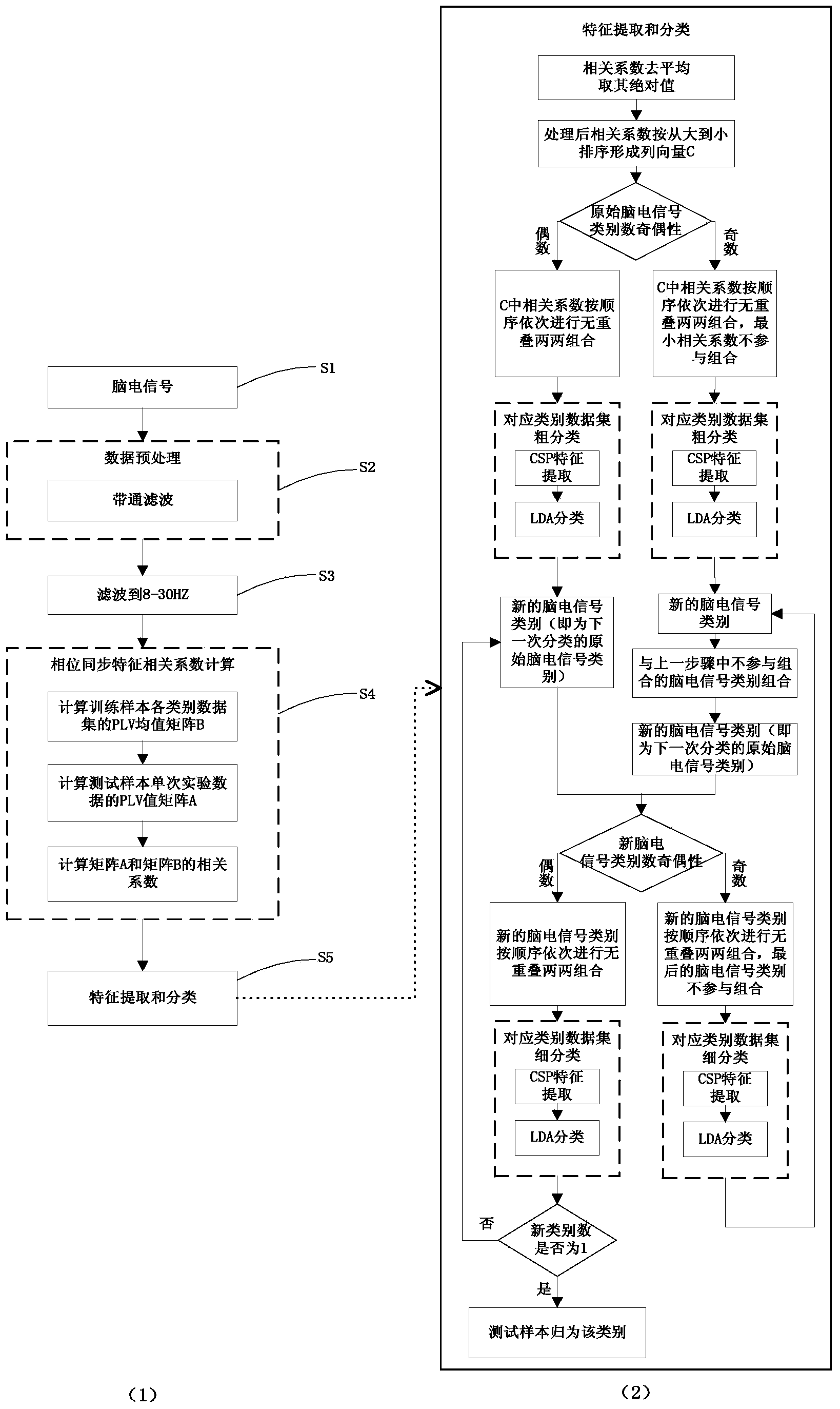
Multi-class motor imagery brain electrical signal classification method based on phase synchronization
ActiveCN103971124AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionData synchronizationSignal classification
The invention relates to a multi-class motor imagery brain electrical signal classification method based on phase synchronization. According to the method, firstly, phase synchronization features of a training sample and a test sample are calculated respectively through a phase locking value; secondly, correlation coefficients of the training sample and the test sample are calculated and arrayed from large to small after an average value is removed and an absolute value is obtained; thirdly, brain electrical signals are roughly classified according to the arrayed correlation coefficients, and then disaggregated classification is conducted according to the brain electrical signals which are roughly classified, wherein the process is involved in a shared airspace mode feature extraction method and a linear discriminant analysis and classification method. The method comprises the steps of brain electrical signal collection, data pre-processing, filtering, calculation of the correlation coefficients of the phase synchronization features, feature extraction and classification and classification accuracy calculation. Classification results show that by the adoption of the brain electrical signal classification method based on phase synchronization, the classification results are good, the rough class where the test sample belongs can be efficiently and accurately determined through brain electrical signal rough classification based on phase synchronization, and the calculated amount is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
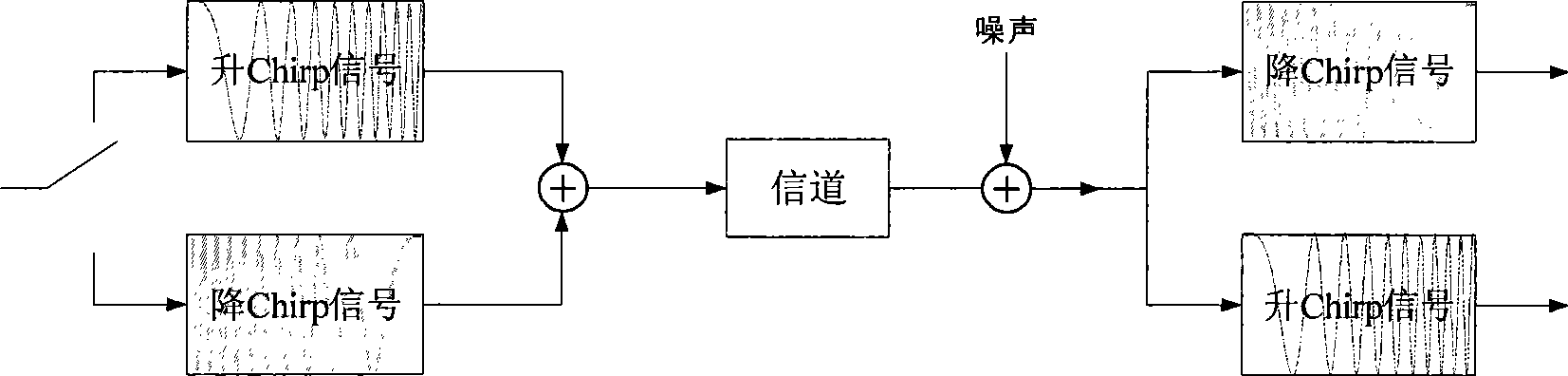
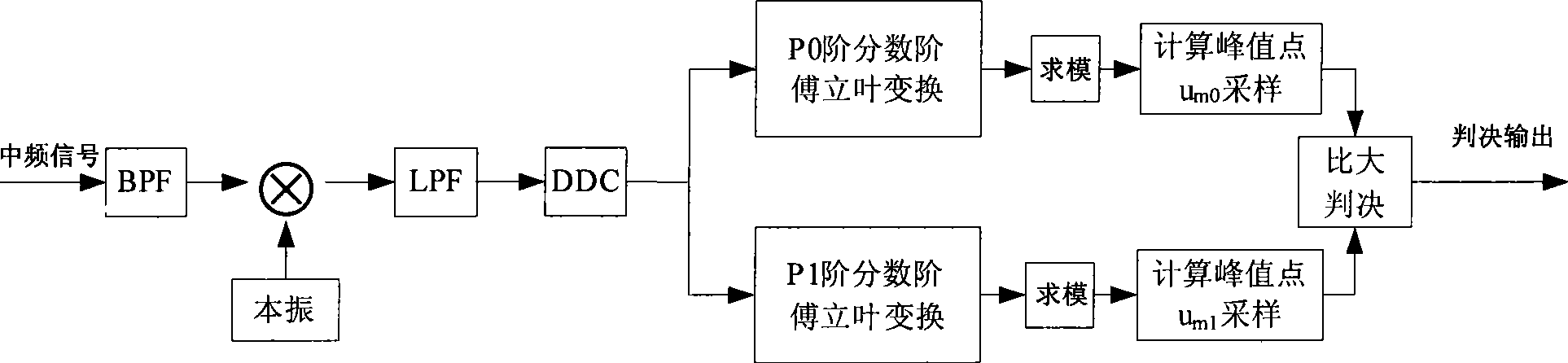
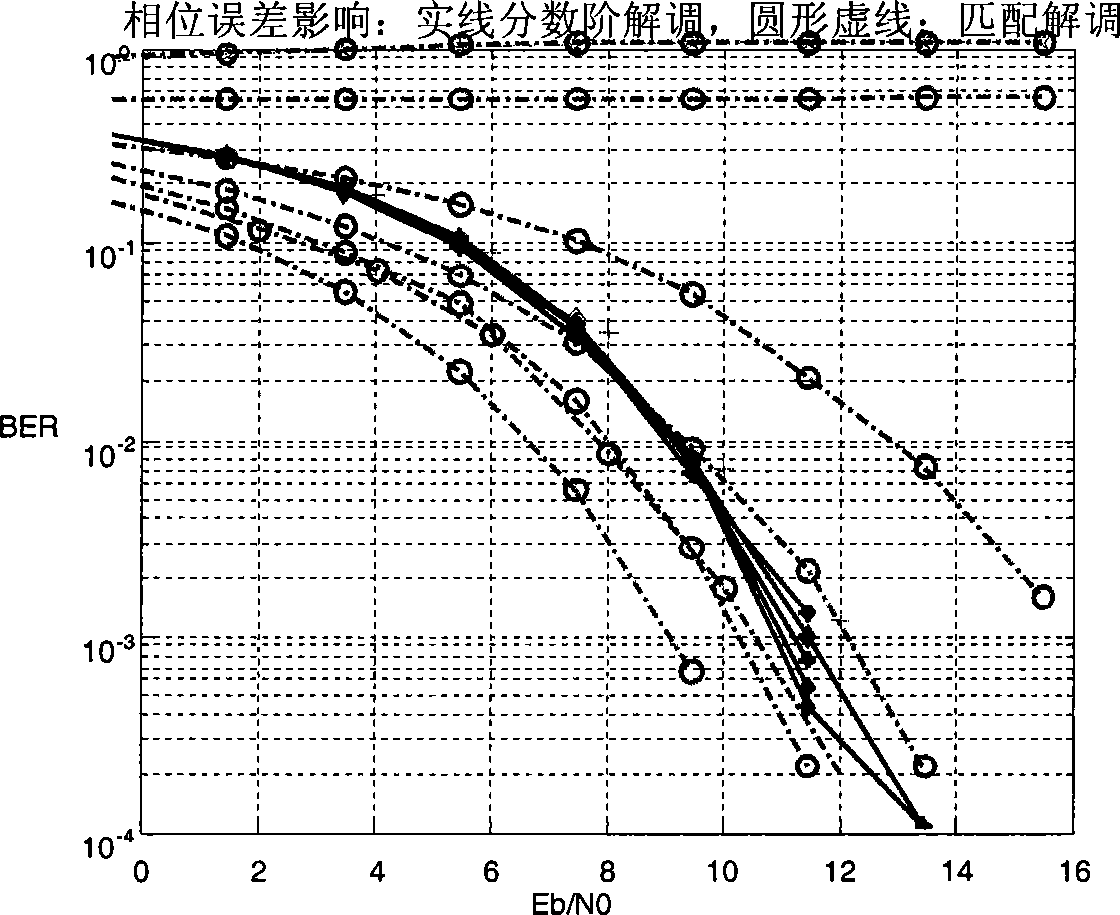
Chirp spread spectrum technique non-coherent demodulation method based on fractional Fourier transform
InactiveCN101388877AReduce the difficulty of implementationSmall phase shift errorMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFourier transform on finite groupsCoded element
The invention relates to a non coherent demodulation method, which belongs to the signal processing field, is used in Chirp spread spectrum technology demodulation, can reduce phase shift error, multipath time delay error and Doppler shift effect, and achieves better performance over multipath fading channels and IEEE802.15.4a S-V standard channels. The fundamental principle of the invention is: utilizing a Chirp signal as an impulse function in a proper fractional Fourier domain, i.e. fractional Fourier transformation achieves an excellent focusing ability to the Chirp signal sent by the CCS system. For the advantage of Chirp signal processing in fractional Fourier transformation, the fractional Fourier transformation can be used in CSS spread spectrum technology to demodulate Chirp signals with different modulation frequencies. The demodulation to CCS system is realized by implementing fractional Fourier transformation to the received base band data, and judging the code element by detecting the peak value of the focusing order. The method reduces the demand to frequency synchronization, needs no phase synchronization, and achieves better performance over multipath frequency selectively fading channels.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
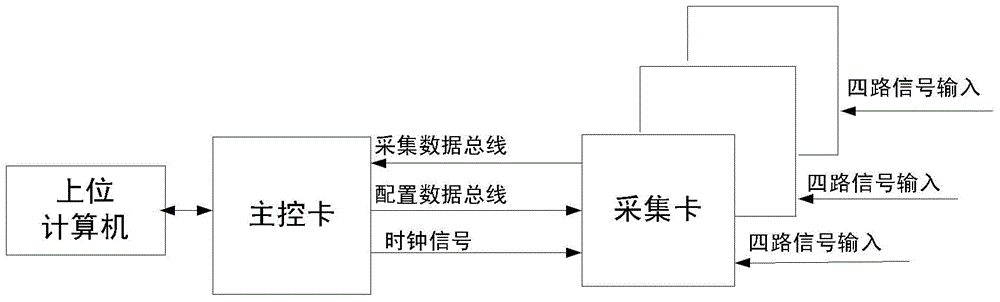
General multi-channel data collection system
ActiveCN103336667AFunction independentStrong targetingEnergy efficient computingInput/output processes for data processingData acquisitionDigital signal
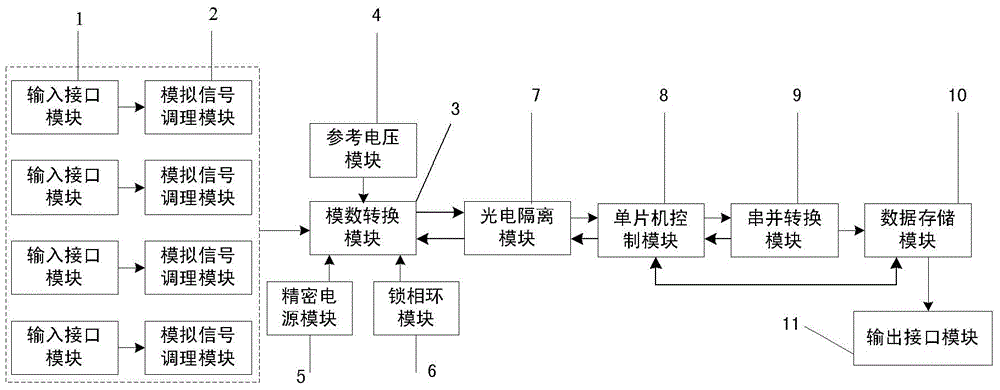
The invention discloses a general multi-channel data collection system. The general multi-channel data collection system comprises a collection card and a master control card. The collection card collects analog signals transmitted from a collection sensor, and the analog signals are collected and converted into digital signals. The master control card carries out denoising and filtering on data in the digital signals, so that real-time correction of the data is achieved, an upper computer is connected with the master control card, and configuration information is written from the master control card, so that control over the work of a whole system is achieved. An analog-digital conversion module of the collection card converts the analog signals into the digital signals, and a photoelectric isolation module of the collection card isolates the analog portion from the digital portion of the whole data collection system completely, so that the transmission of the analog signals is not interfered by noise of a digital circuit. The photoelectric isolation module is used for reducing the influence of the noise of the analog portion on the digital portion, a precision power module of the collection card reduces the influence of power supply noise, and a phase-locked loop of the collection card guarantees phase synchronization of clock signals among the collection cards.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZUOANXINHUI ELECTRONICS TECH
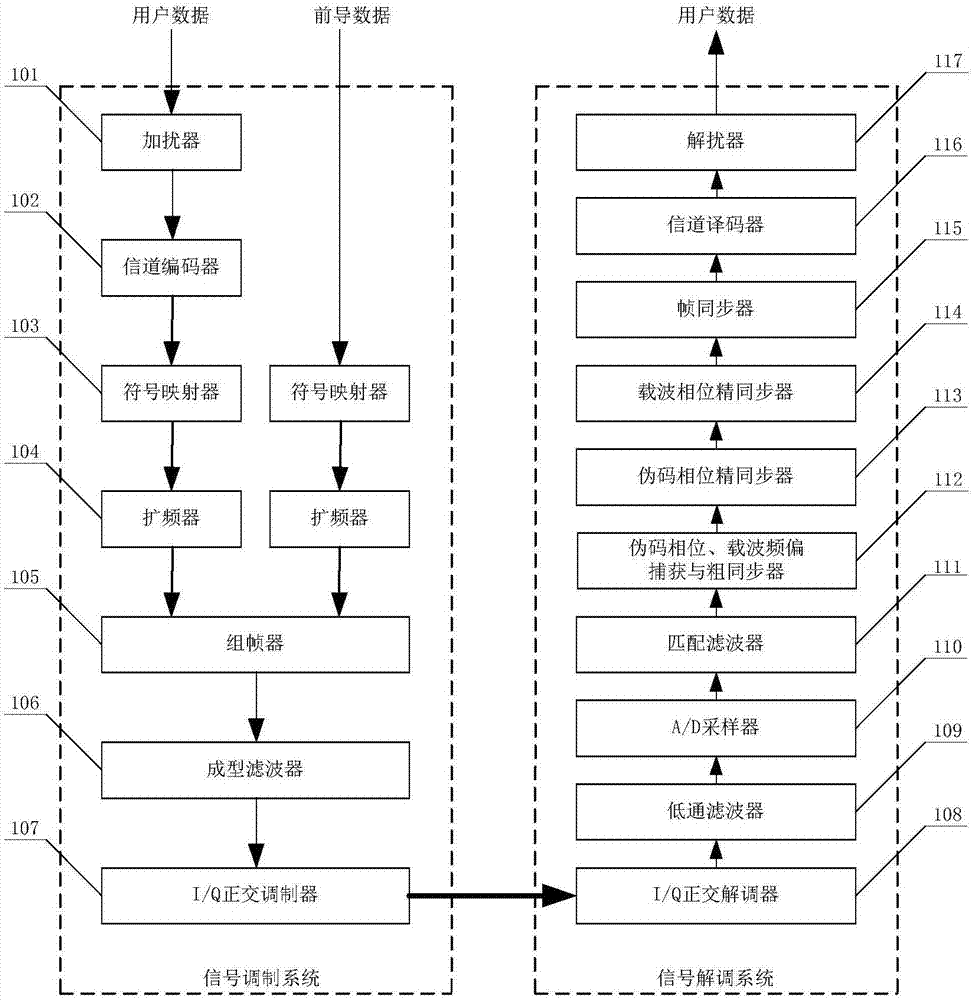
Burst direct sequence spread spectrum system and pseudo code synchronization method of burst direct sequence spread spectrum waveform thereof
InactiveCN107026810ASimple structureQuick captureMulti-frequency code systemsData segmentCarrier frequency offset
The invention discloses a burst direct sequence spread spectrum system and a pseudo code synchronization method of a burst direct sequence spread spectrum waveform thereof. By adoption of the burst direct sequence spread spectrum system disclosed by the invention, the capturing, tracking and convergence times of a burst direct sequence spread spectrum signal can be greatly shortened, and the frequency offset estimation precision is relatively high. The burst direct sequence spread spectrum system disclosed by the invention is realized by the following technical scheme: in a signal modulation system, a specific segment of lead data is added in front of user data after scrambling and channel encoding are carried out on the user data for accomplishing signal capture and synchronization; and in a signal demodulation system, pseudo code phase capture and carrier frequency offset capture are carried out on a digital baseband signal to accomplish signal capture, coarse pseudo code phase synchronization and coarse frequency offset compensation with a coarse synchronizer, precise signal synchronization of a coarse synchronization signal is separately accomplished by pseudo code phase and carrier phase synchronization loops, identification information and a starting position of a user data segment are determined from a precise synchronization signal by a frame synchronizer, and the user data are restored by channel decoding and descrambling.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
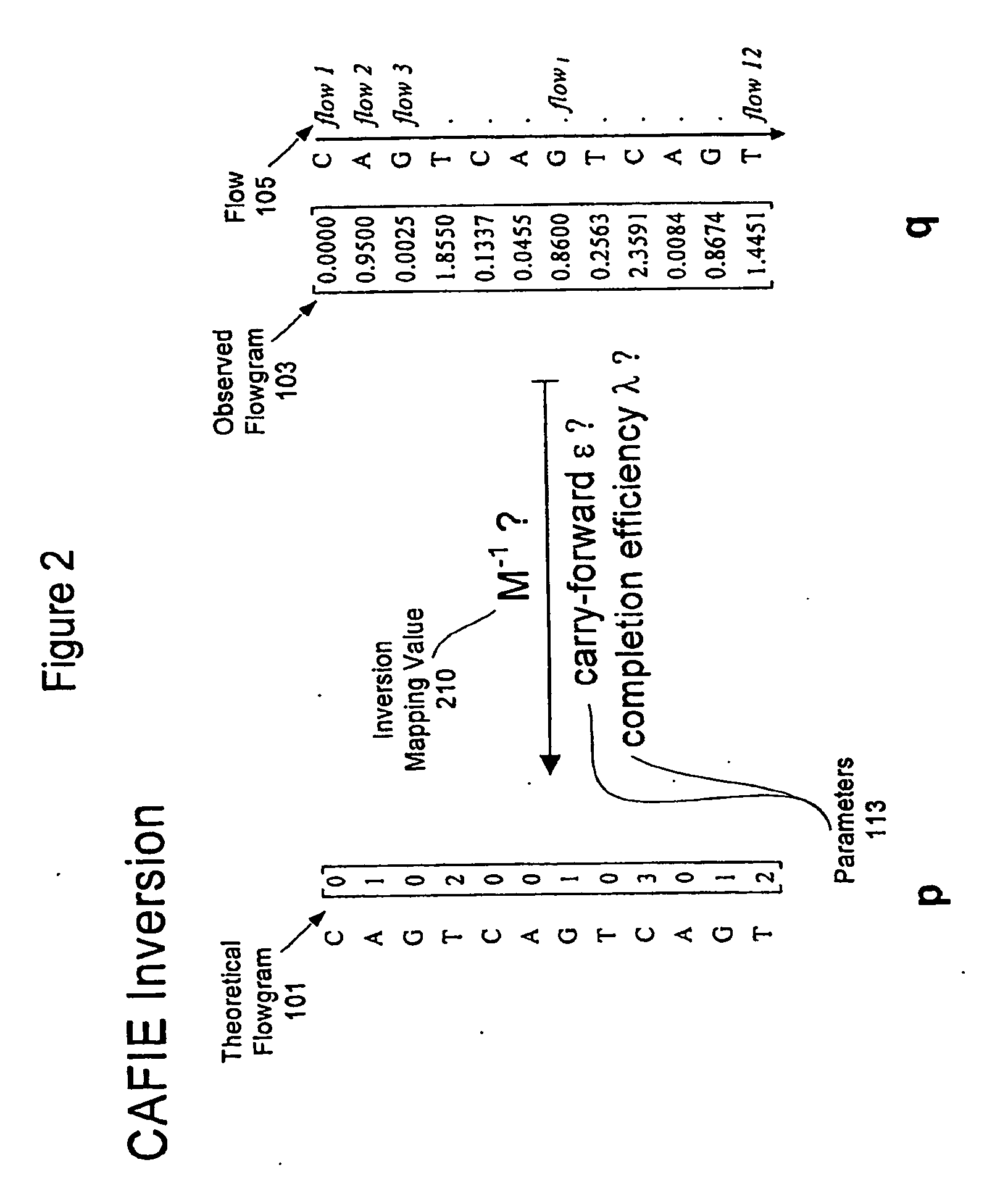
System and method to correct out of phase errors in DNA sequencing data by use of a recursive algorithm
InactiveUS20110213563A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAlgorithmErrors and residuals
An embodiment of a method for correcting an error associated with phasic synchrony of sequence data generated from a population of template molecules is described that comprises the steps of detecting signals generated in response to nucleotide species introduced during a sequencing reaction; generating an observed value for the signal detected from each of the nucleotide species; defining positive incorporation values and negative incorporation values from the observed values using a carry forward value and an incomplete extension value; revising the carry forward value and the incomplete extension value using a noise value that is derived from observed values associated with the negative incorporation values; re-defining the positive incorporation values and the negative incorporation values using the revised carry forward value and the revised incomplete extension value; and repeating the steps of revising and re-defining until convergence of the positive incorporation values and the negative incorporation values
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Method and system for multi-point signal generation with phase synchronized local carriers
ActiveUS8259884B2Reduce transmissionReduce signal lossPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsCarrier signalPhase synchronization
A method and system of applying modulated carrier signals to tree networks and processing signals tapped from the tree networks to generate output signals with phase-synchronized carriers are disclosed.
Owner:NEC ADVANCED NETWORKS INC
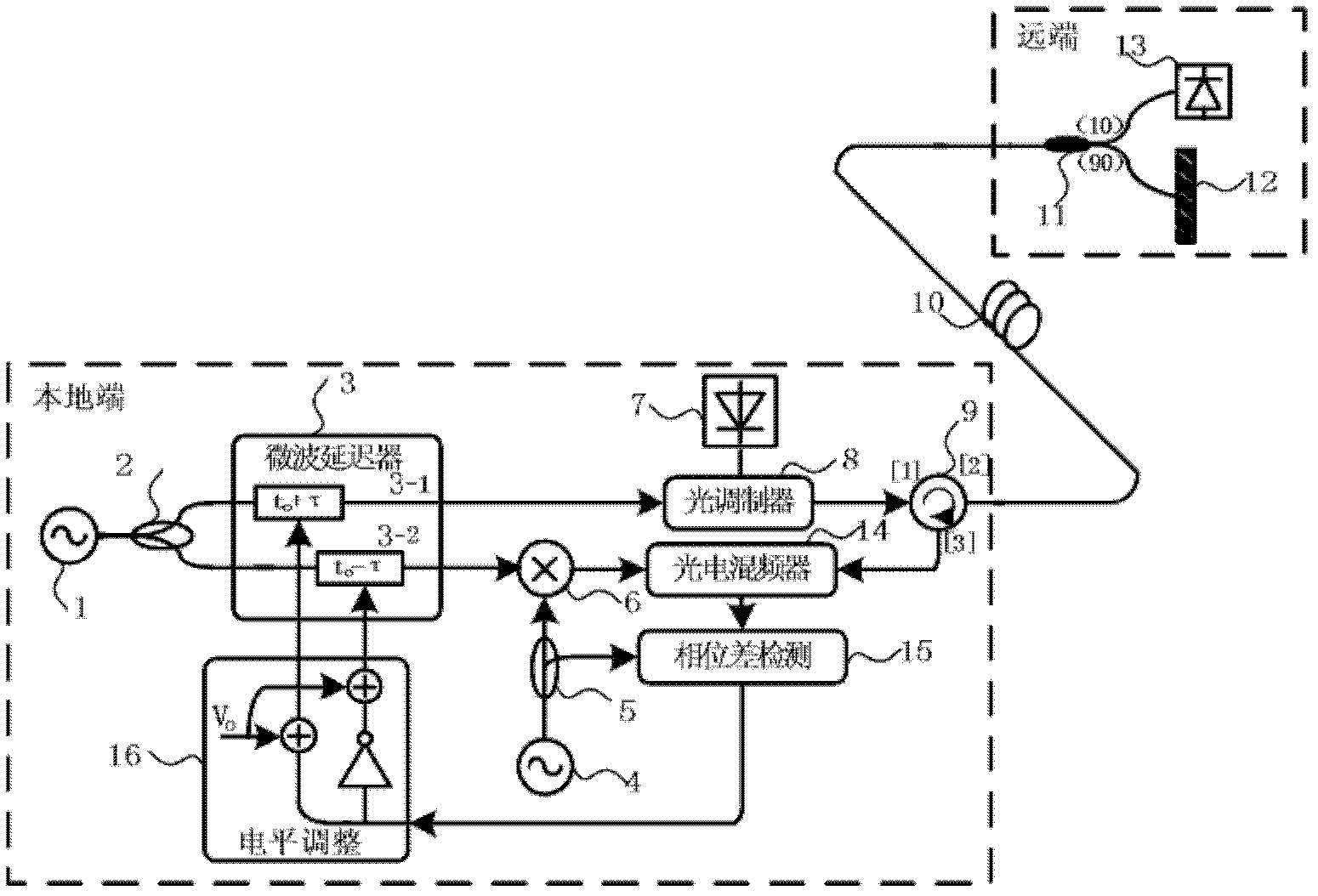
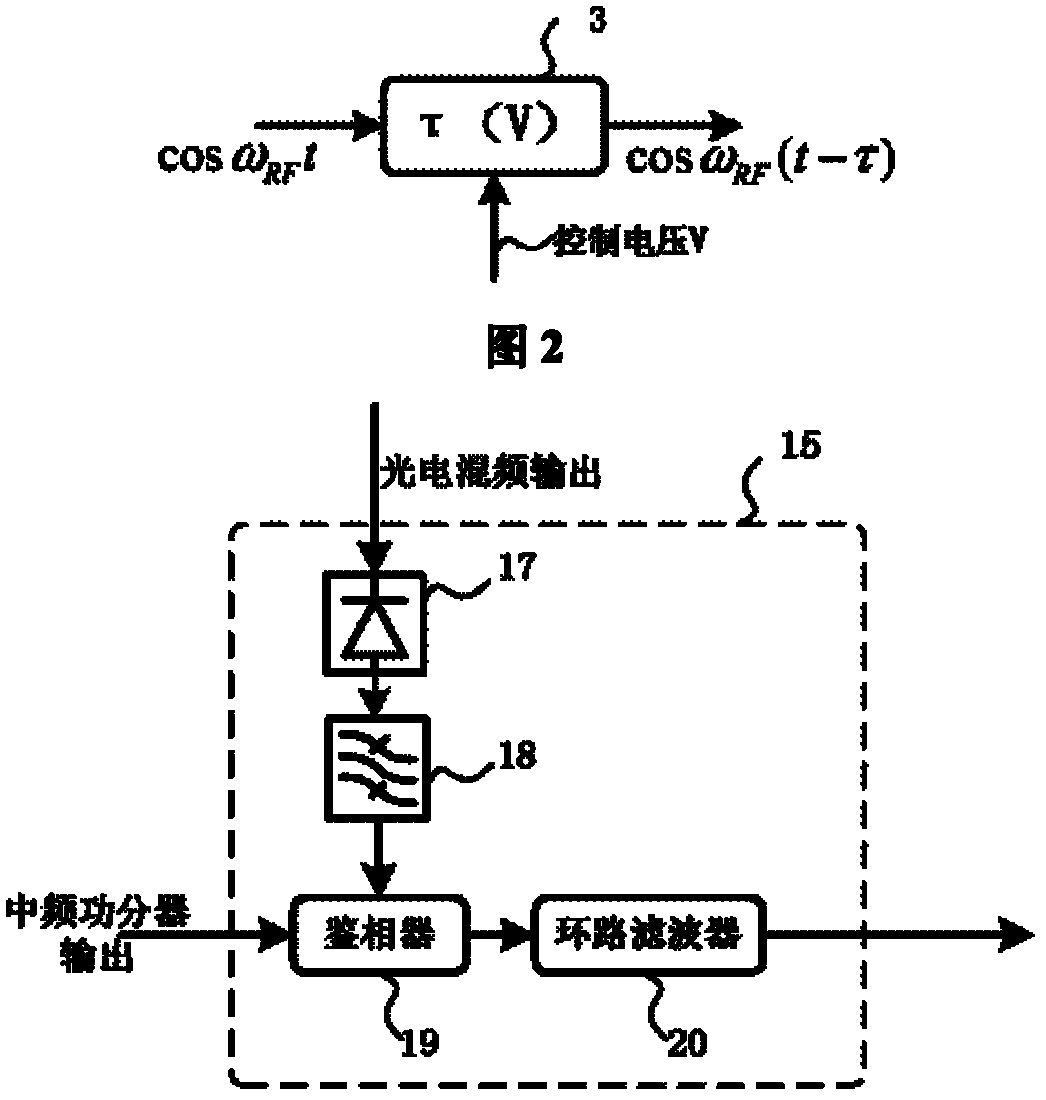
Delay-locked-loop-based remote microwave signal phase-stabilized optical fiber transmission device
InactiveCN102215104ALow signal to noise ratioAvoid disadvantages such as phase polarity ambiguityFibre transmissionSynchronising arrangementPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
The invention discloses a delay-locked-loop-based remote microwave signal phase-stabilized optical fiber transmission device, which realizes the phase synchronization of a local microwave signal and a remote microwave signal by utilizing a delay-locked loop. The device realizes optoelectronic heterodyne mixing by utilizing the nonlinear effects of an optoelectronic modulator for phase detection, drives and controls a microwave delayer by feeding a phase difference signal back, performs phase change on the microwave signals, compensates microwave signal phase disturbance caused by the delay change of a transmission link, keeps a phase synchronism relationship between the local microwave signal and the remote microwave signal, solves the problem of phase asynchronism between the local microwave signal and the remote microwave signal, fulfills the aim of phase-stabilized transmission of the microwave signals, adopts noncoherent correction, and has the advantages of wide dynamic range, high stability and the like, besides a long phase-stabilized transmission distance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
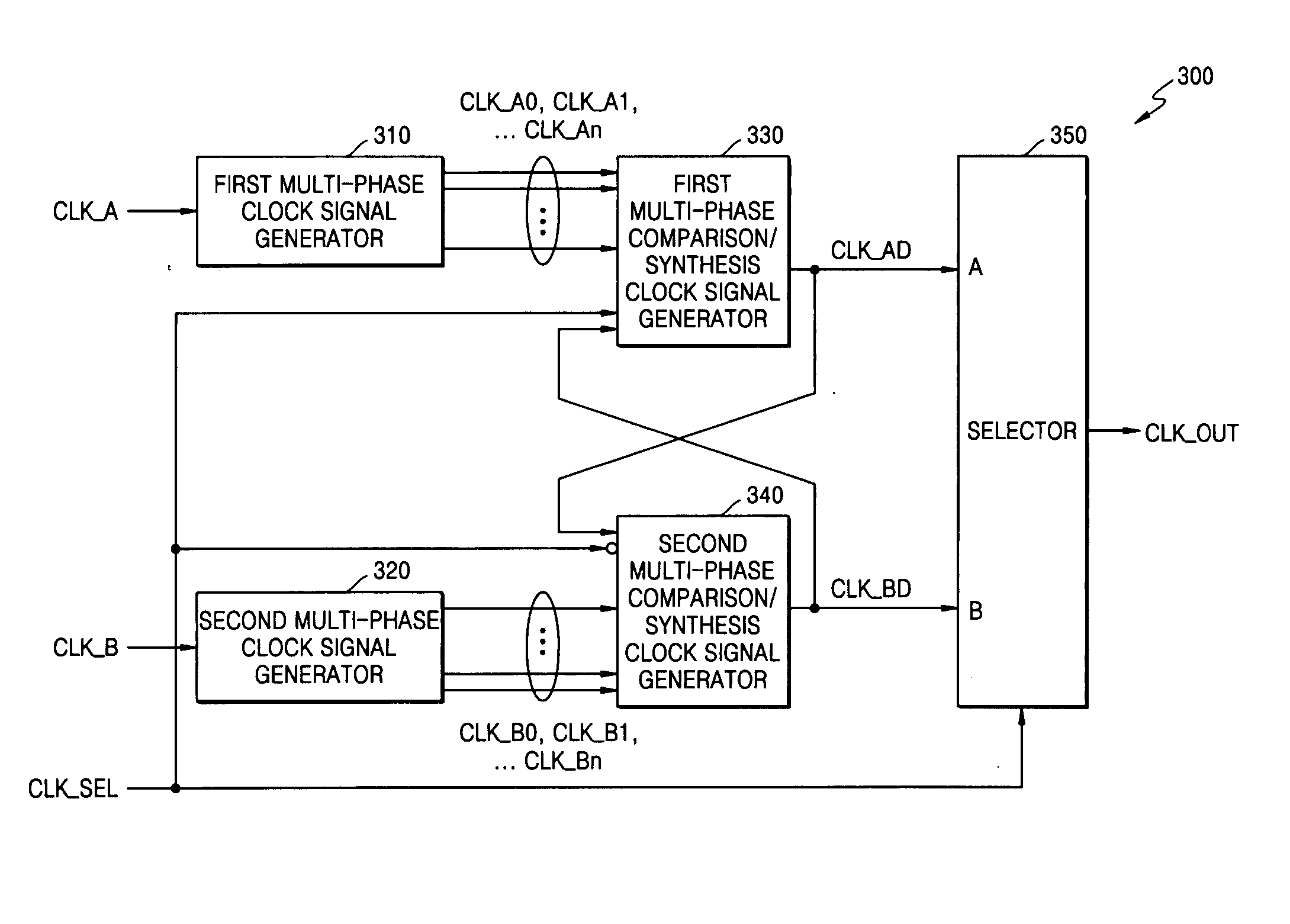
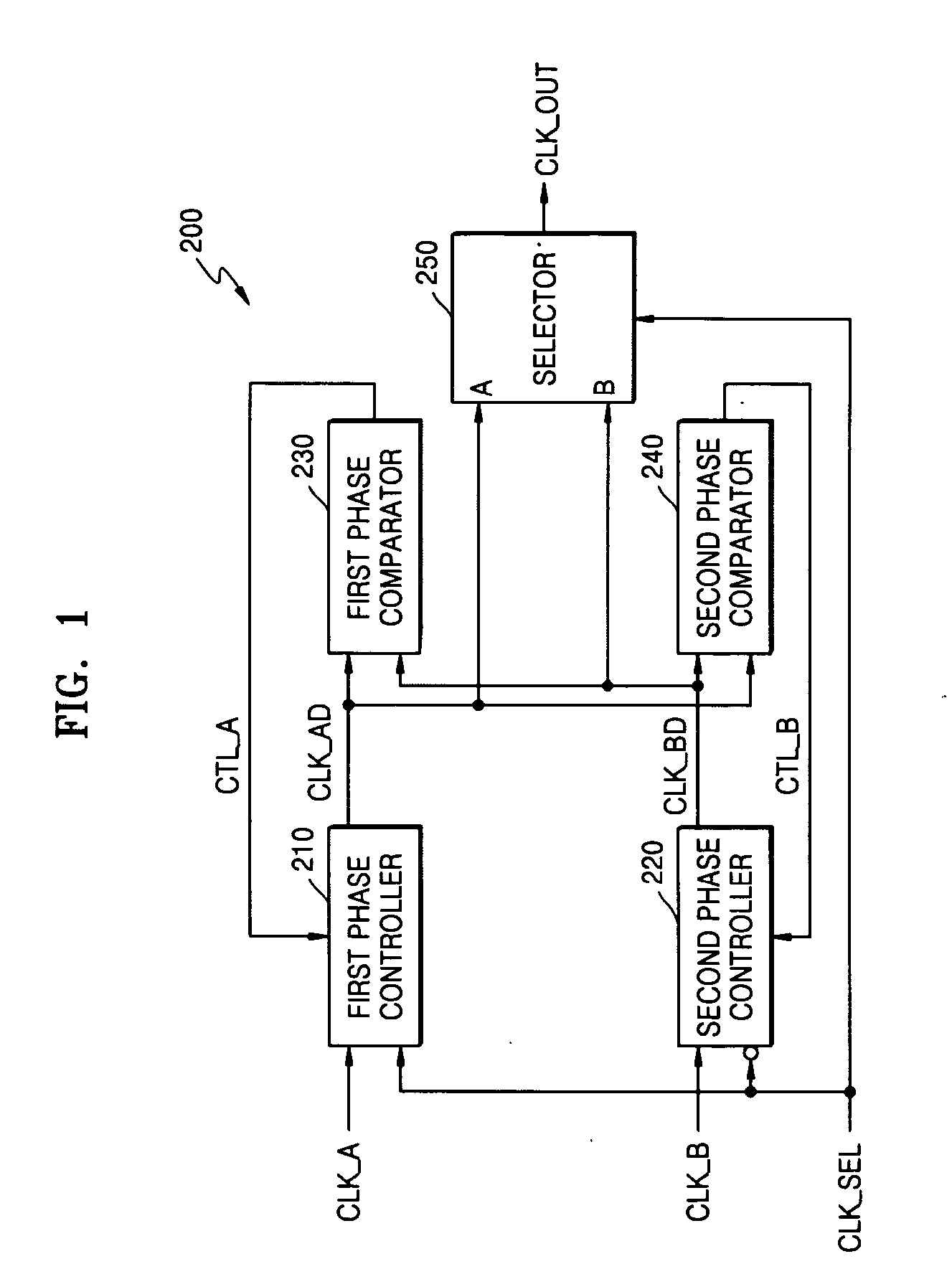
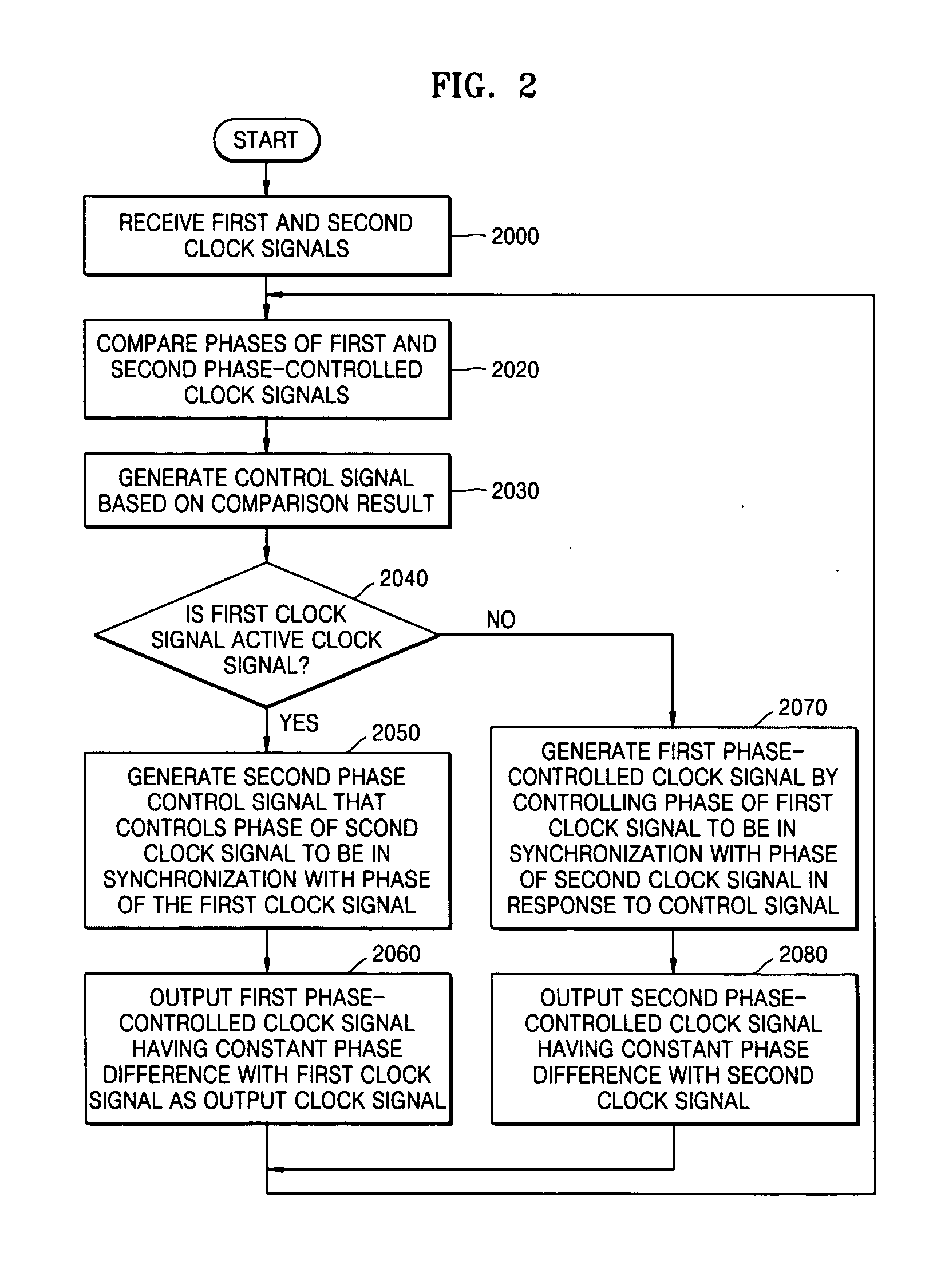
Clock signal selecting apparatus and method that guarantee continuity of output clock signal
InactiveUS20050084050A1Guaranteed continuityPulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexEngineeringPhase synchronization
Provided are a clock signal selecting apparatus and method that can guarantee the continuity of an output clock signal. The clock signal selecting apparatus and method can synchronize the phases of at least two clock signals by continuously controlling the phases of the clock signals. Accordingly, even when an active clock signal and a standby clock signal have different frequencies, it is possible to guarantee the continuity of the output clock signal regardless of whether the clock signals are switched from one to another. In addition, it is possible to guarantee the stability of the output clock signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar
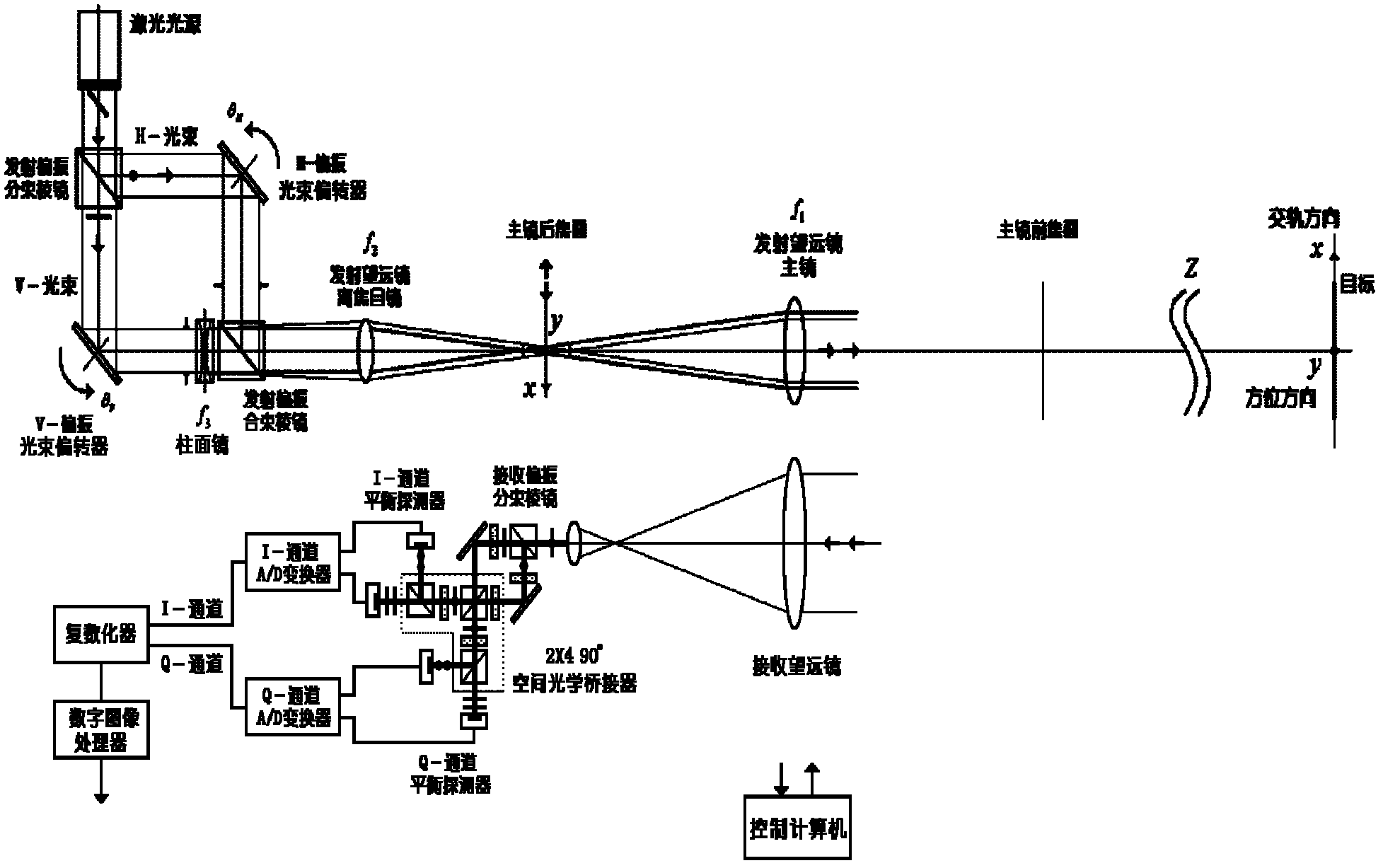
ActiveCN102435996AReduce the effects of phase interferenceBig optic toesElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh resolution imagingRadar systems
The invention relates to an orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar. The orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar comprises a laser light source, a transmission polarization beam splitter, a horizontal polarization optical path beam deflector, a horizontal polarization optical path transform lens, a vertical polarization optical path beam deflector, a vertical polarization optical path transform lens, a transmission polarization beam combiner, a transmitter telescope ocular, a transmitter telescope primary lens, a receiver telescope, a receiving polarization beam splitter, a 2 * 490 DEG optical bridge, an inphase channel balanced detector, an inphase channel A / D (analogue / digital) converter, a 90 DEG of phase shift channel balanced detector, a 90 DEG of phase shift channel A / D (analogue / digital) converter, a pluralizing processor, a digital image processor and a control computer. The orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar automatically eliminates phase changes and interference of atmosphere, motion platforms, optical radar systems and speckles, has high resolution imaging in larger optical footprint and larger receiving aperture, does not need optical delay lines, does not need real-time beat frequency signal phase synchronization, does not have shadows during imaging, and can be used for various lasers with single-module and single-frequency properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Digital receive phase lock loop with cumulative phase error correction and dynamically programmable correction rate
InactiveUS6701140B1Pulse automatic controlSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlCurrent sampleData signal
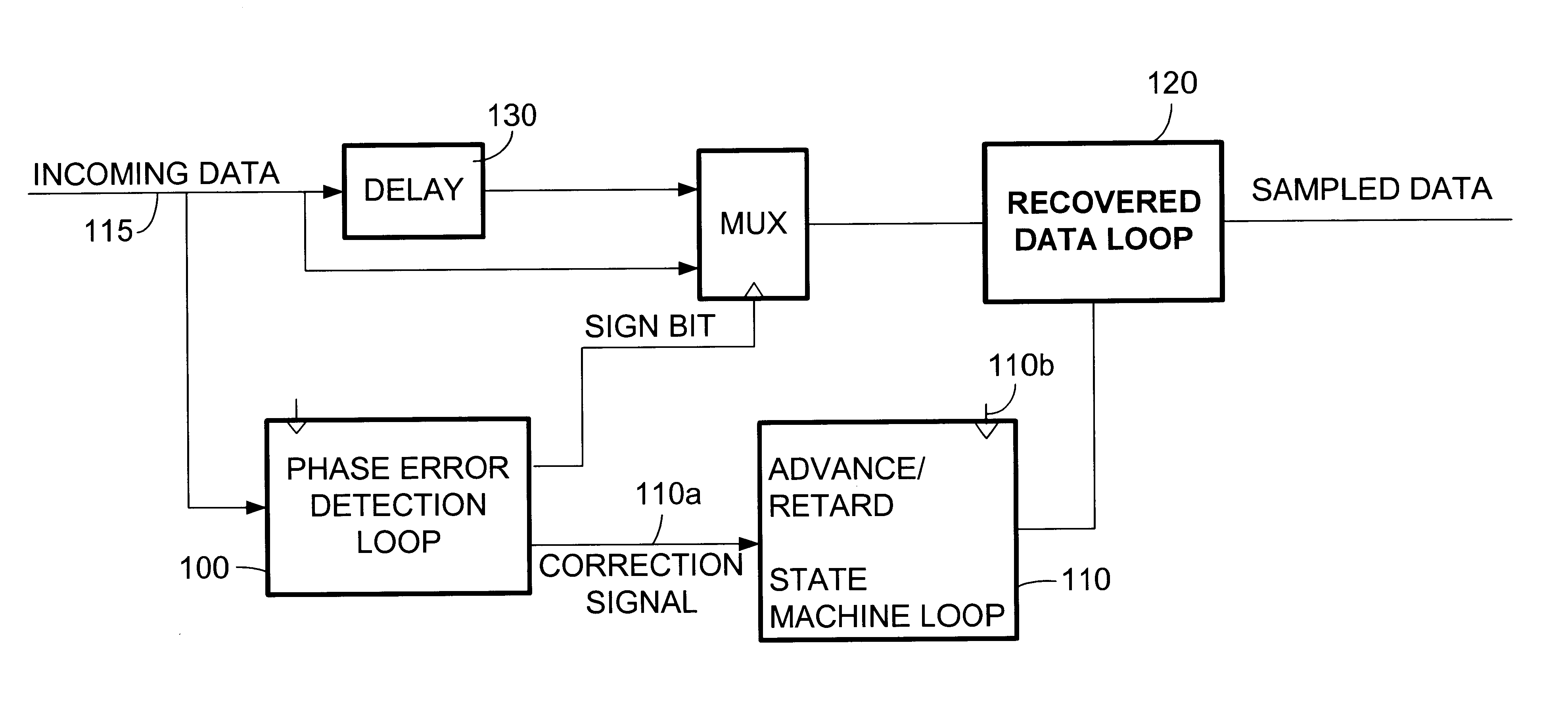
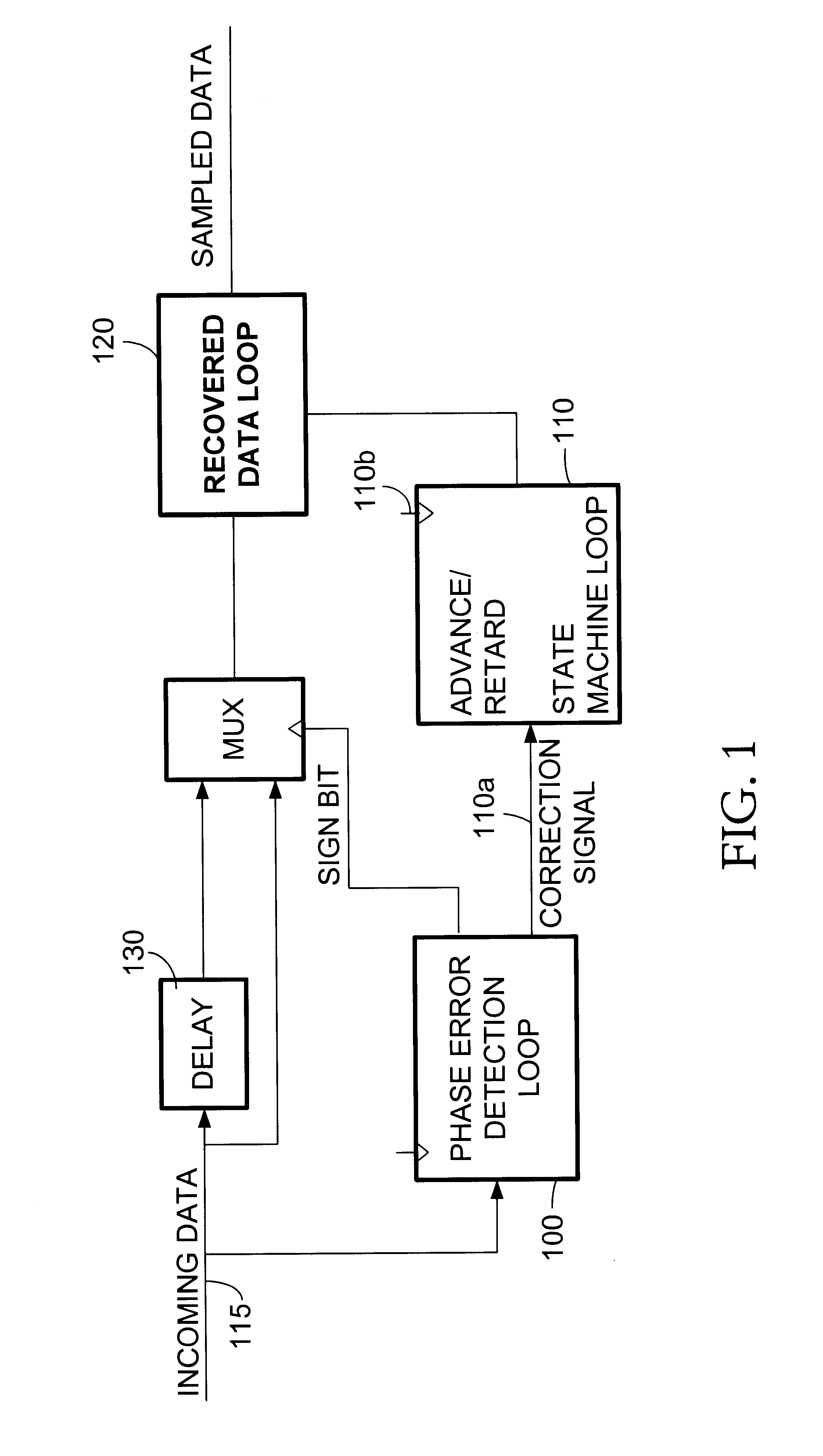
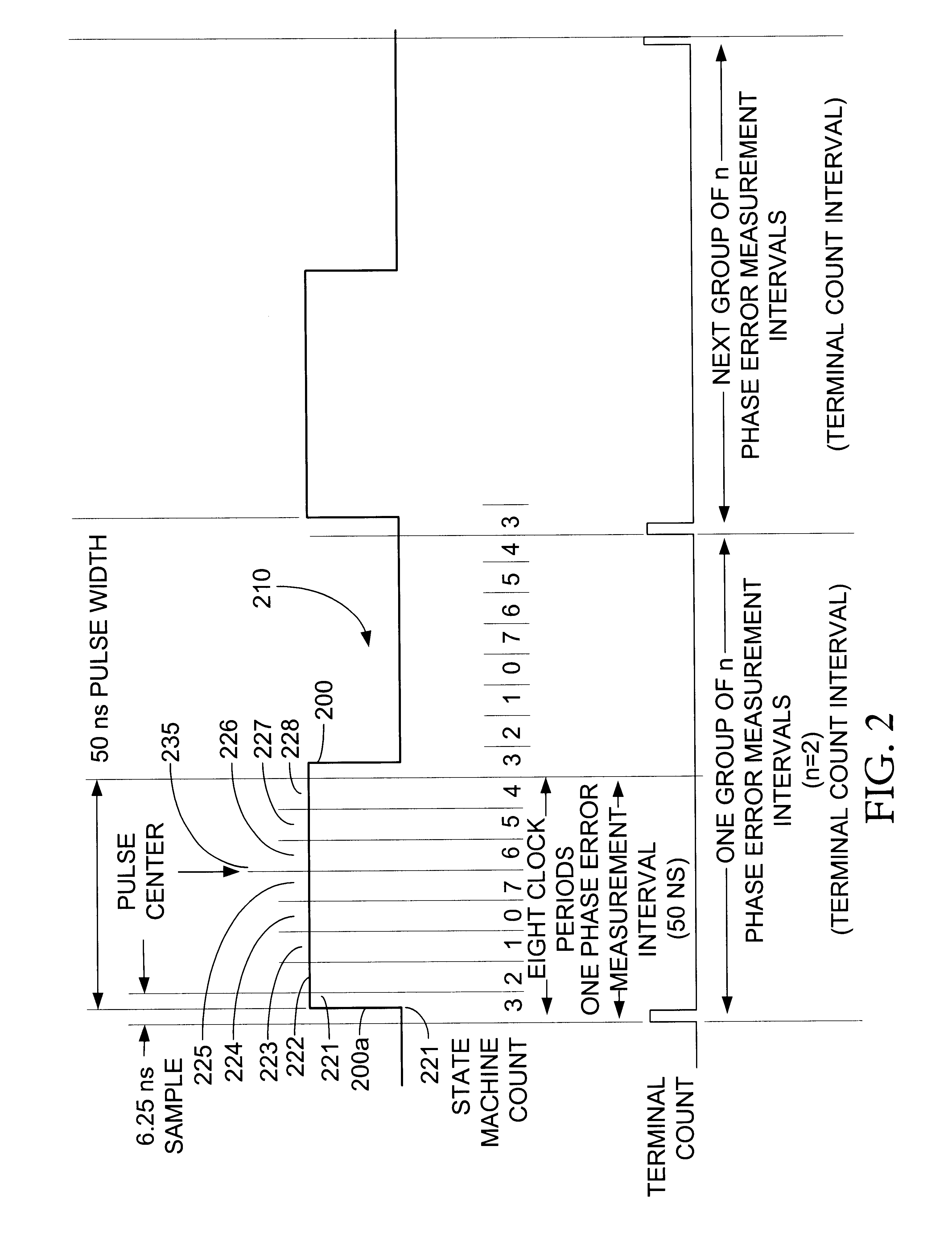
A digital phase lock loop (PLL) for maintaining synchronization with the phase of a received data signal including a preamble and an information-containing data frame, by incrementing a state machine through an internal cyclic count, each cycle thereof including a center count tending to coincide with center regions of the successive pulses and an edge count tending to coincide with edges of the successive pulses. The PLL selects a current sample of the signal whenever the internal count reaches the predetermined center count value. The state machine internal count is updated in accordance with a cumulative phase error obtained by summing the phase errors detected over successive edges between each edge and the corresponding center count. The interval over which the cumulative phase error is computed depends upon the number of received edges during the preamble and depends upon elapsed time during the data frame.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Method and system for multi-point signal generation with phase synchronized local carriers
ActiveUS20120294400A1Reduce transmissionReduce signal lossPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsCarrier signalEngineering
A method and system of applying modulated carrier signals to tree networks and processing signals tapped from the tree networks to generate output signals with phase-synchronized carriers are disclosed.
Owner:NEC ADVANCED NETWORKS INC
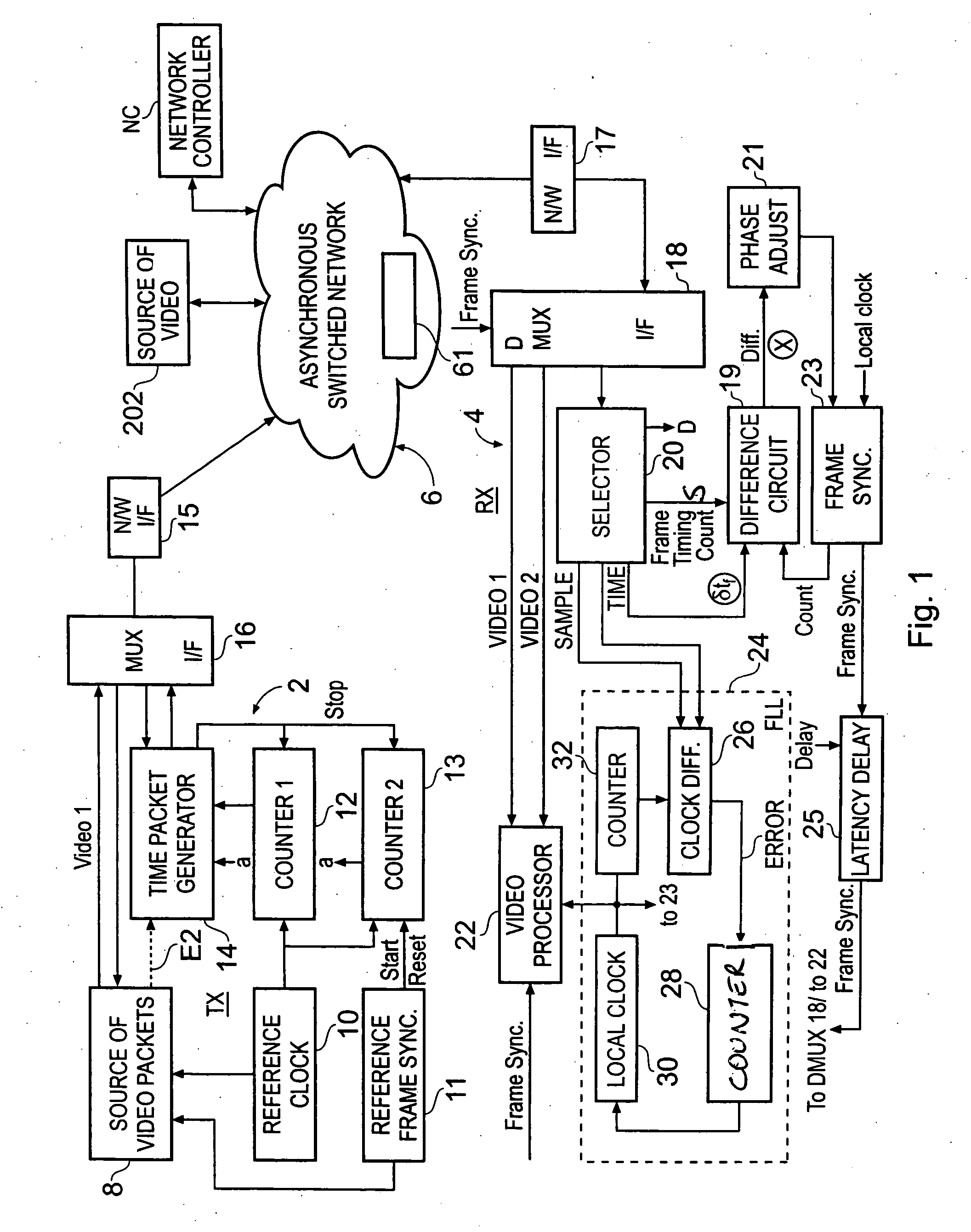
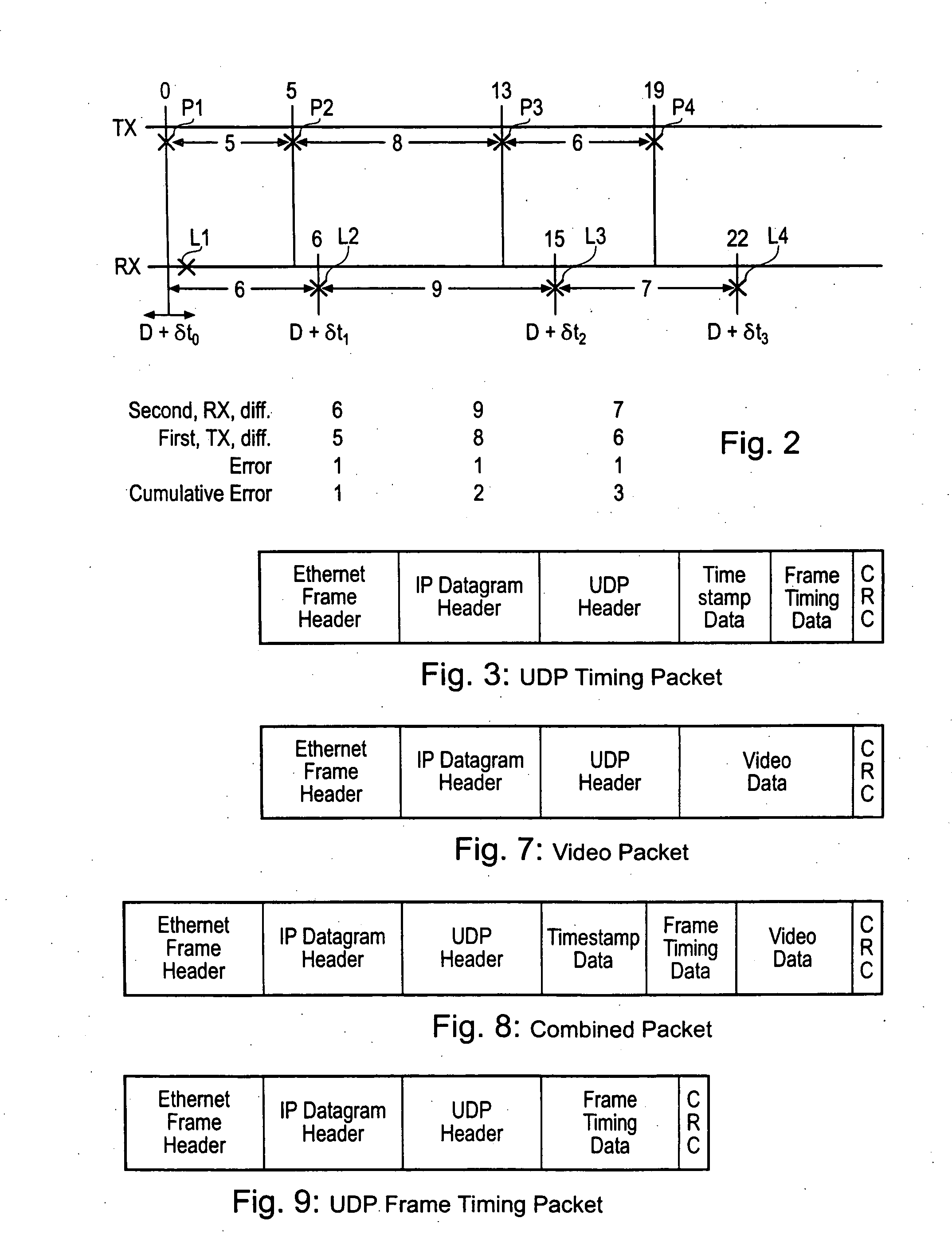
Video snychronisation
ActiveUS20040257469A1Reduce dataEliminate the effects ofTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionReference imageData treatment
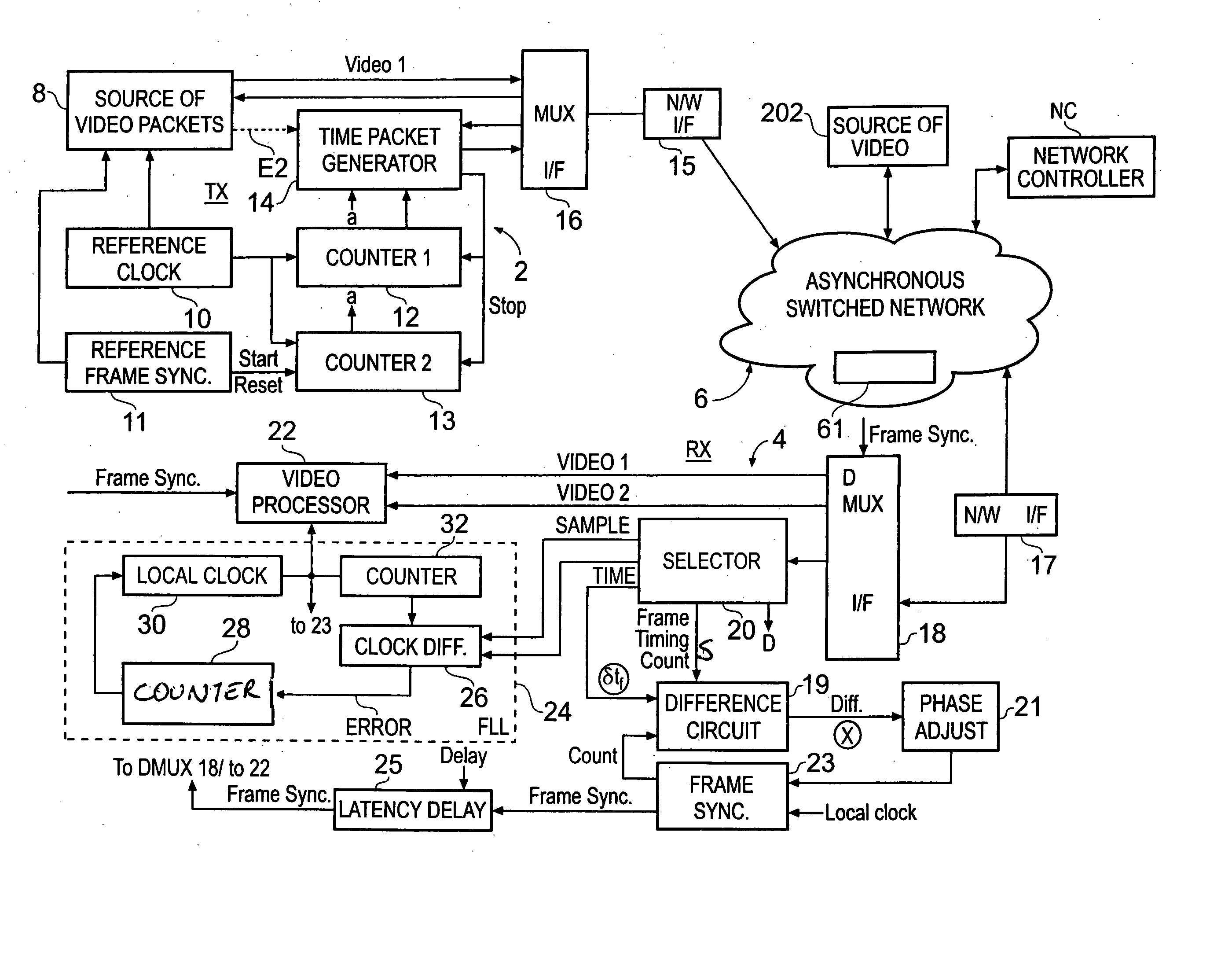
A method of synchronising the phase of a local image synchronisation signal generator of a local video data processor in communication with an asynchronous switched packet network to the phase of a reference image synchronisation signal generator of a reference video data processor also coupled to the network, the local and reference processors having respective clocks, the reference and local image synchronisation signal generators generating periodic image synchronisation signals in synchronism with the reference and local clocks respectively comprises the steps of: frequency synchronising the local and reference clocks; the reference video data processor sending, via the network, to the local data processor an image timing packet providing reference image synchronisation data indicating the difference in timing, measured with respect to the reference processor's clock, between the time at which the image timing packet is launched onto the network and the time of production of a reference image synchronisation signal; and the local processor controlling the timing of the production of the local image synchronisation signal in dependence on the reference image synchronisation data and the time of arrival of the timing packet.
Owner:SONY EUROPE BV
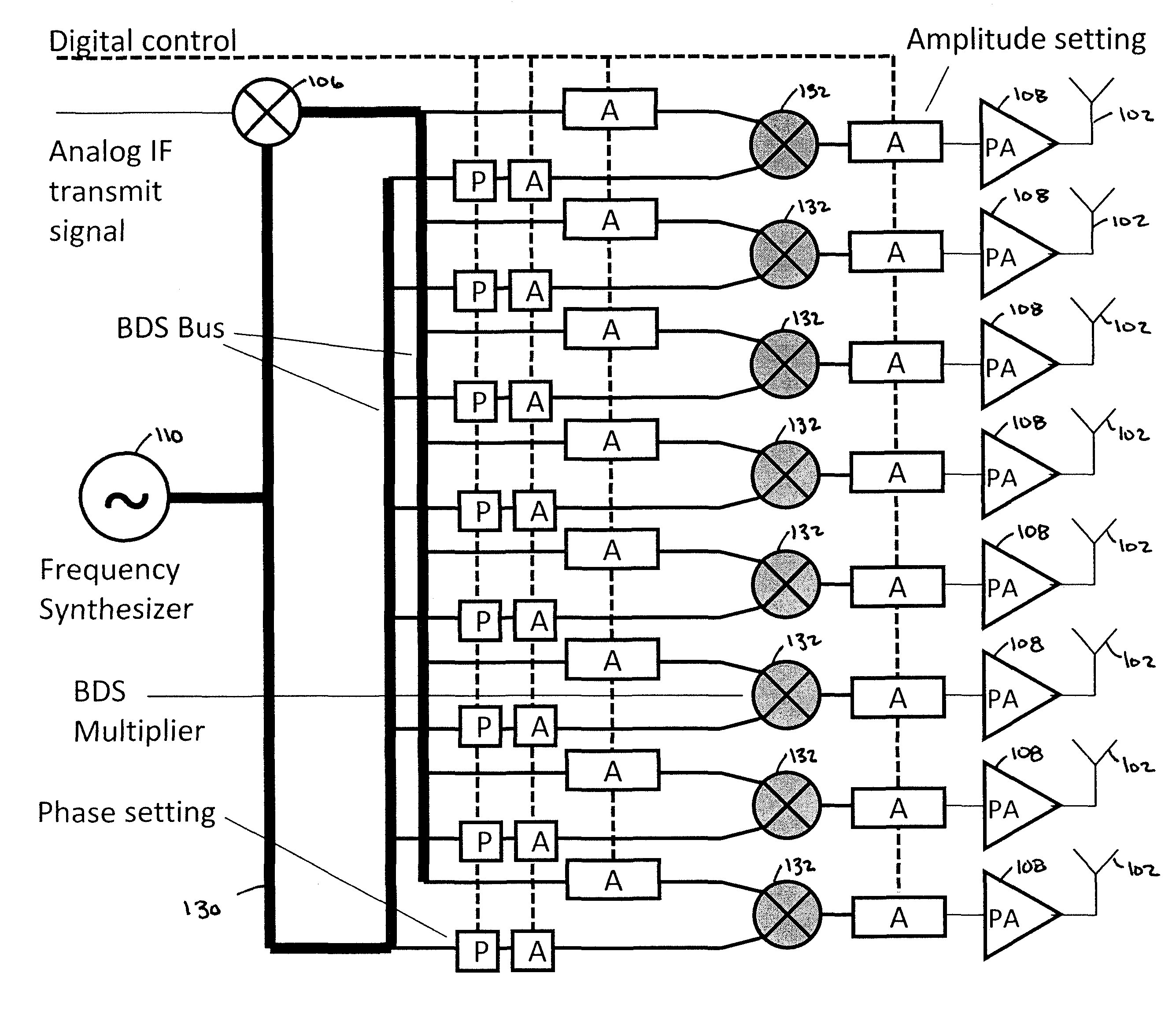
Low cost, active antenna arrays
ActiveUS8611959B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsSubstation equipmentElectricityCarrier signal
A transmitter system including: a bidirectional signaling (BDS) network having first and second networks for carrying first and second carrier signals, and having a set of n phase synchronous location pairs (ai, bi); and also including tunable transmitter circuits for driving an antenna array, each tunable transmitter circuit having an output line for carrying an output signal and first and second input lines electrically connected to the first and second networks of the BDS network at locations of a corresponding one of the set of phase synchronous location pairs, and including a multiplier having a first input electrically connected to the first input line of that tunable transmitter circuit; a phase setting circuit electrically connected to the multiplier for controlling the phase of the output signal of that tunable transmitter circuit; and an amplitude setting circuit for controlling the amplitude of the output signal of that tunable transmitter circuit.
Owner:NEC ADVANCED NETWORKS INC
Distributed vision system with multi-phase synchronization
ActiveUS20110157389A1Promote recoveryOvercome disadvantagesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsUnique identifierEngineering
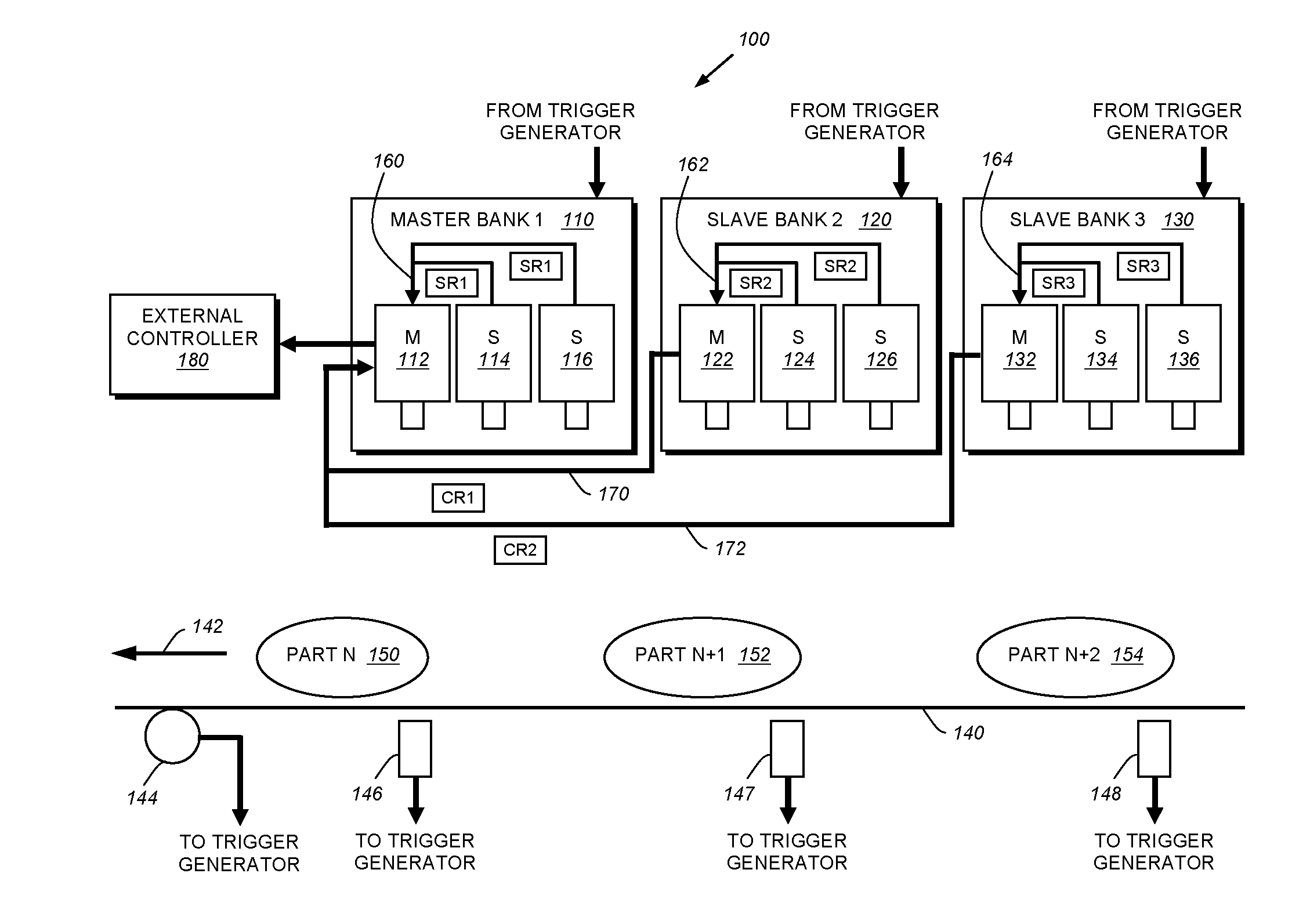
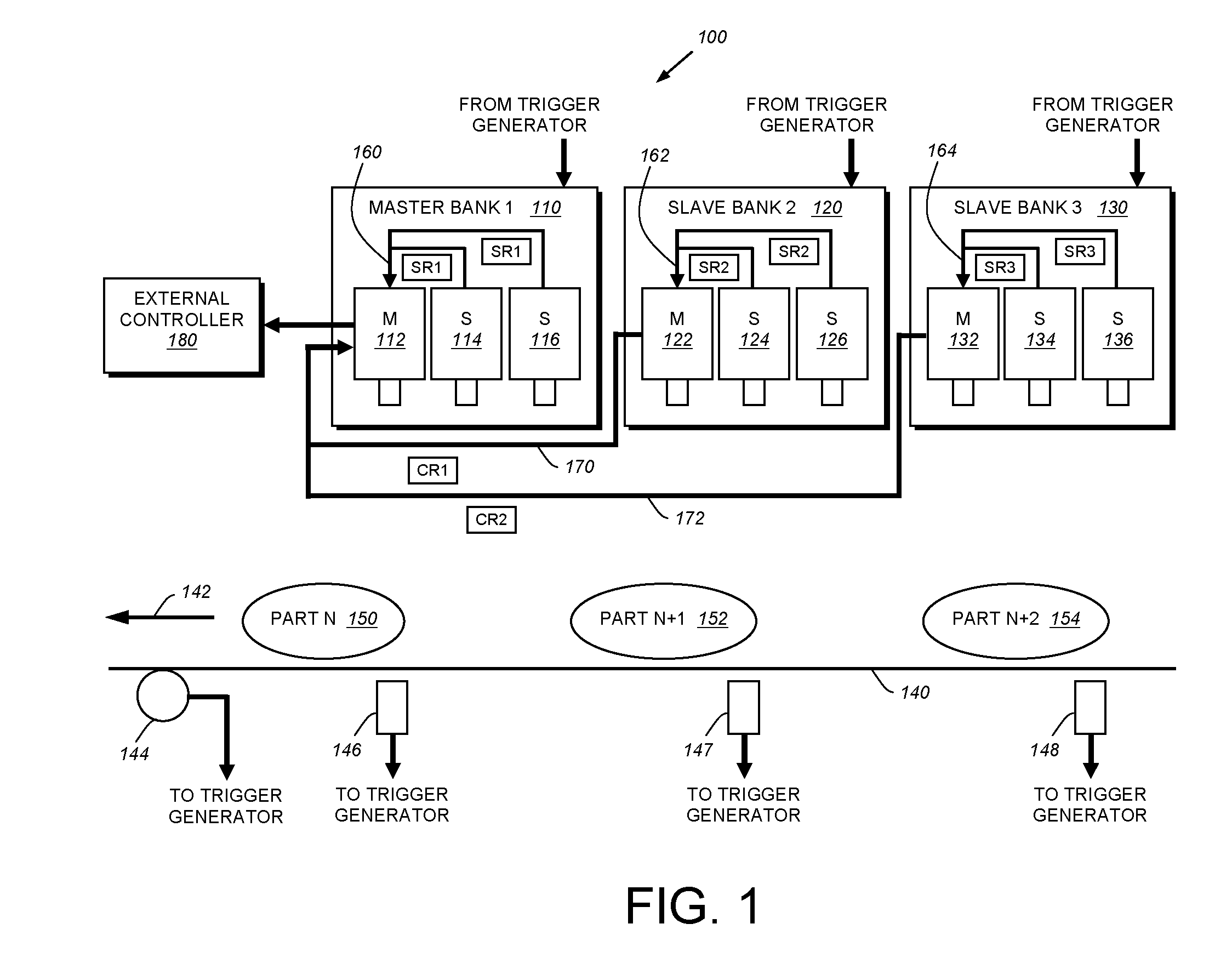
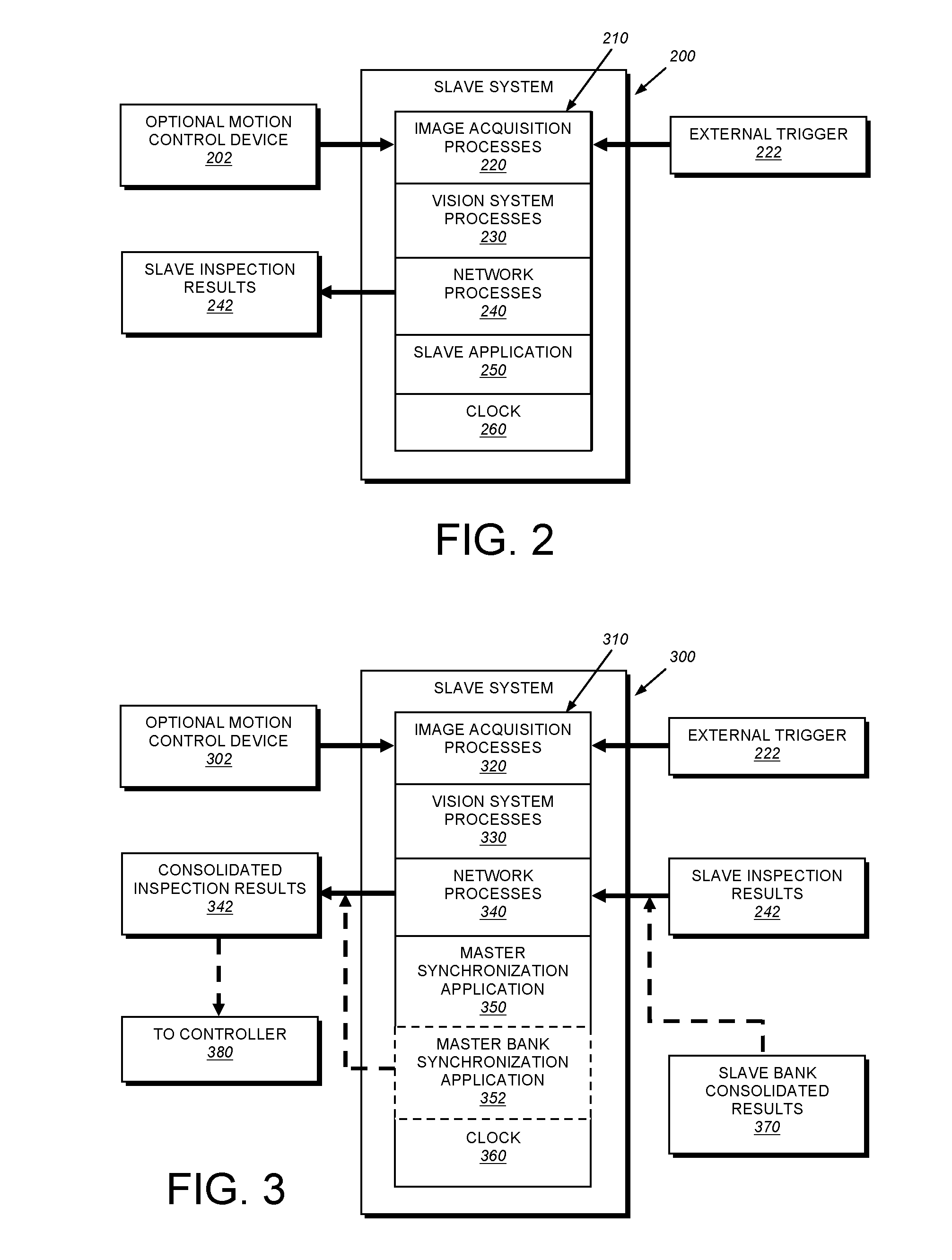
This invention provides a system and method for synchronization of vision system inspection results produced by each of a plurality of processors that includes a first bank (that can be a “master” bank) containing a master vision system processor and at least one slave vision system processor. At least a second bank (that can be one of a plurality of “slave” banks) contains a master vision system processor and at least one slave vision system processor. Each vision system processor in each bank generates results from an image acquired and processed in a given inspection cycle. The inspection cycle can be based on an external trigger or other trigger signal, and it can enable some or all of the processors / banks to acquire and process images at a given time / cycle. In a given cycle. each of the multiple banks can be positioned to acquire an image of a respective region of a plurality of succeeding regions on a moving line. A synchronization process (a) generates a unique identifier and that passes a trigger signal with the unique identifier associated with the master processor in the first bank to each of the slave processor in the master bank and each of the master and slave processor and (b) receives consolidated results via the master processor of the second bank, having the unique identifier and consolidated results from the results from the first bank. The process then (c) consolidates the results for transmission to a destination if the results are complete and the unique identifier of each of the results is the same.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
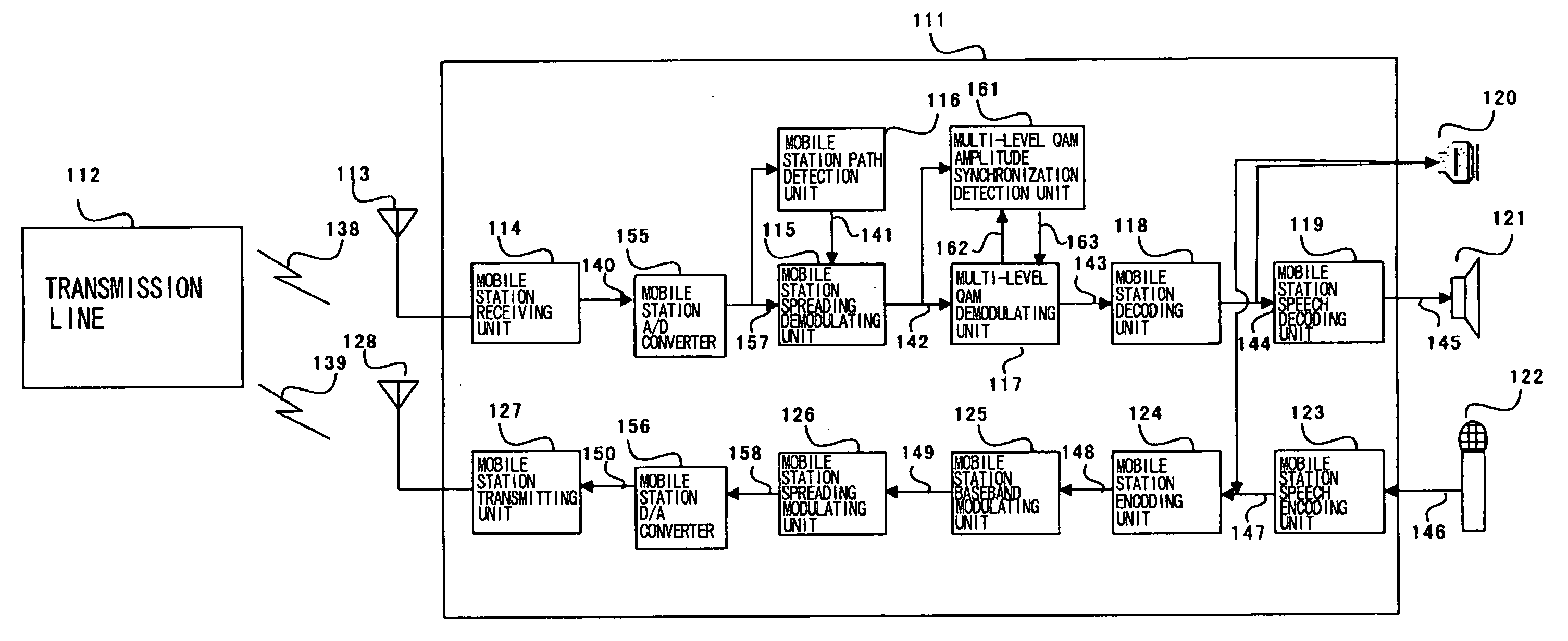
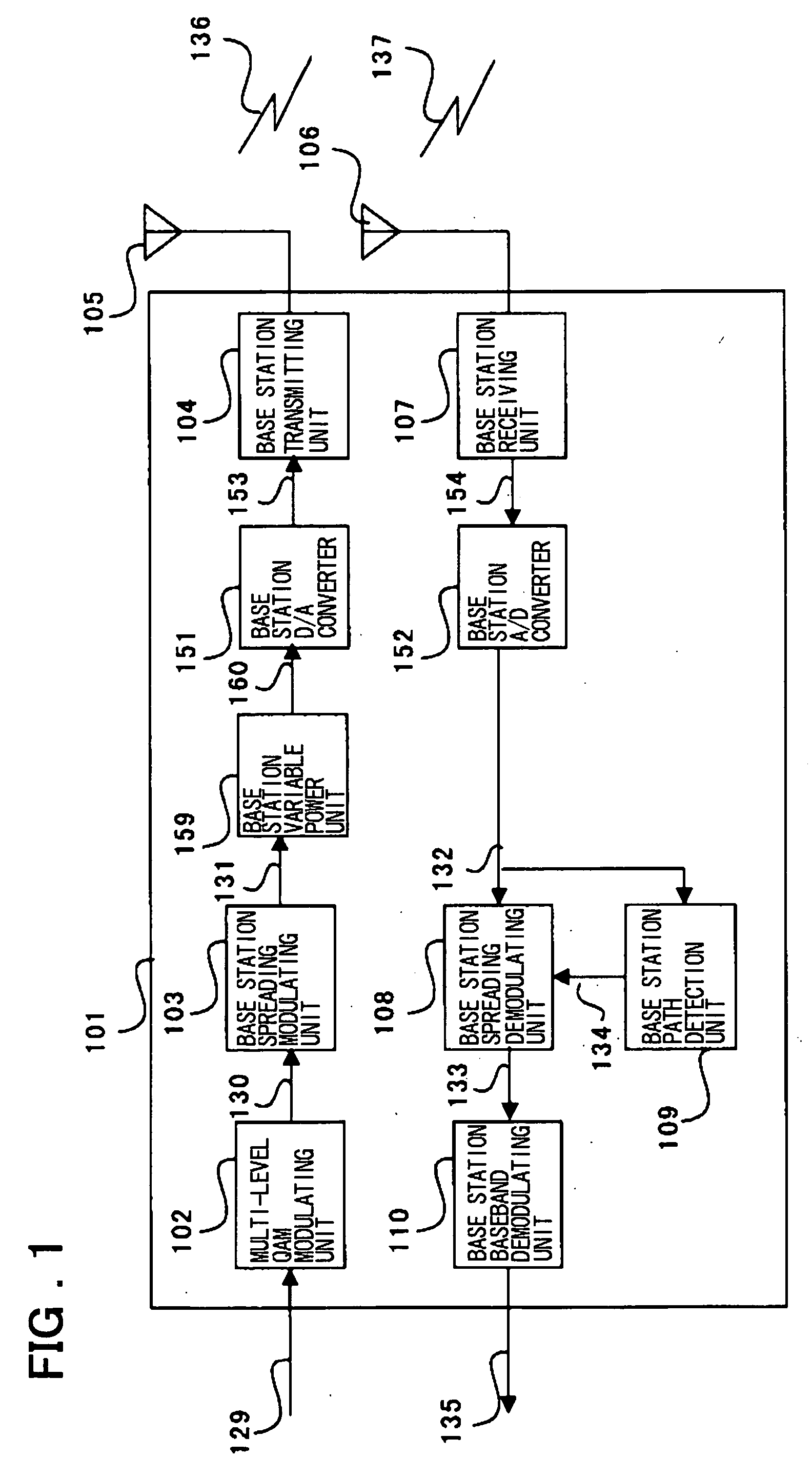
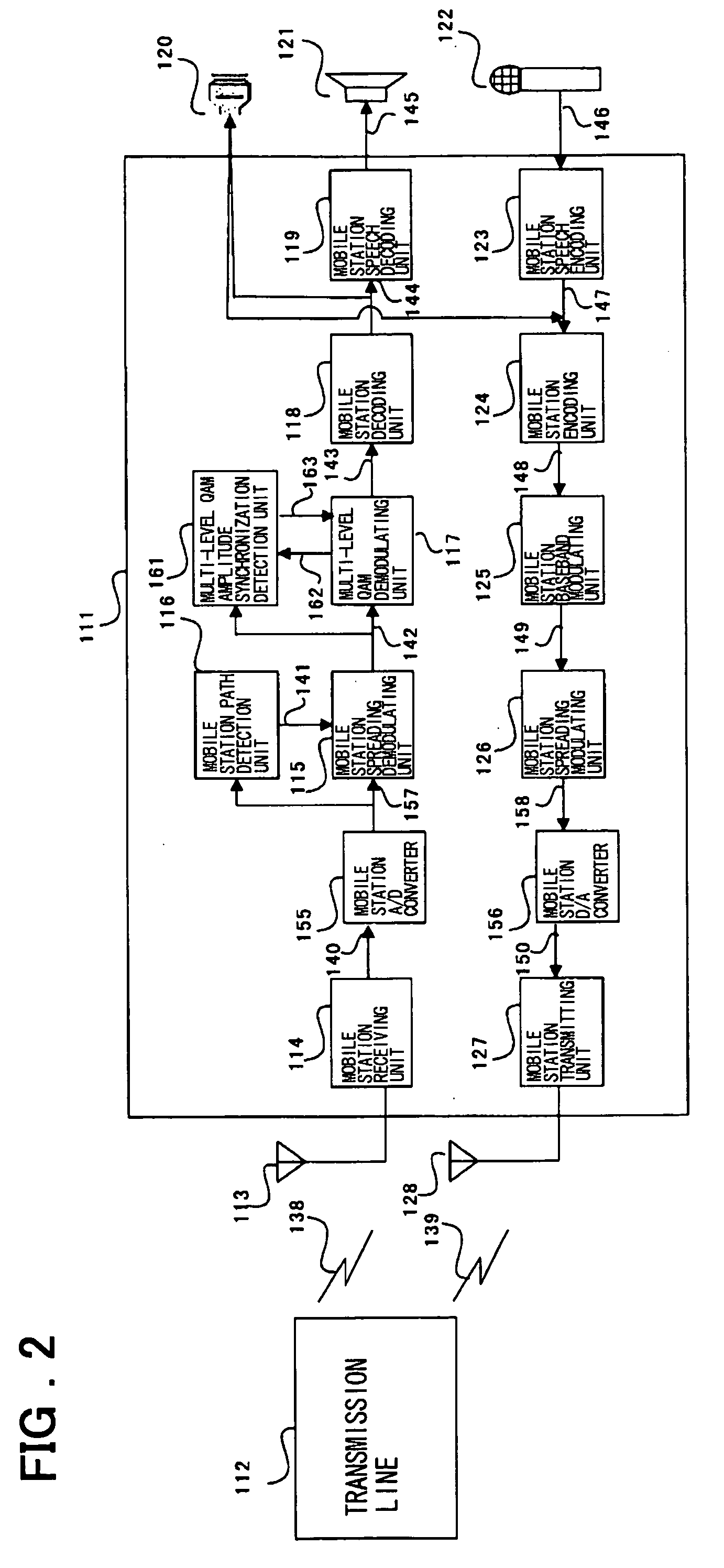
Wireless apparatus employing multi-level QAM and method for estimating threshold value
InactiveUS20040114692A1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionTransmission monitoringTelecommunicationsEngineering
An wireless terminal includes a demodulating unit which comprises an FV (fading vector) estimating unit for receiving a CPICH spread / demodulated signal to output an FV signal with a reduced noise ratio; a phase synchronization unit for multiplying a PDSCH spread / demodulated signal with a complex conjugate of the FV signal to correct the phase offset of the PDSCH I and Q signals to send the resulting PDSCH I and Q signals to a multi-level QAM amplitude synchronization detection unit and to an amplitude demodulating unit; a first-quadrant transformation unit for collecting the second to fourth quadrant signals of the phase-synchronized PDSCH I and Q signals; and a threshold value detecting unit for calculating a multi-level QAM threshold value from the first quadrant signals and the FV signals to send the threshold signal to an amplitude demodulating unit. The amplitude demodulating unit effects amplitude demodulation to output multi-level QAM demodulated signals. The threshold value detecting unit previously assumes a plural number of probabilities as to which of the levels received data belongs to and, using a plural number of the data, raises the precision of the assumed data. The threshold value is estimated, using the frequencies and differences of the respective levels, from the assumed plural threshold values.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com