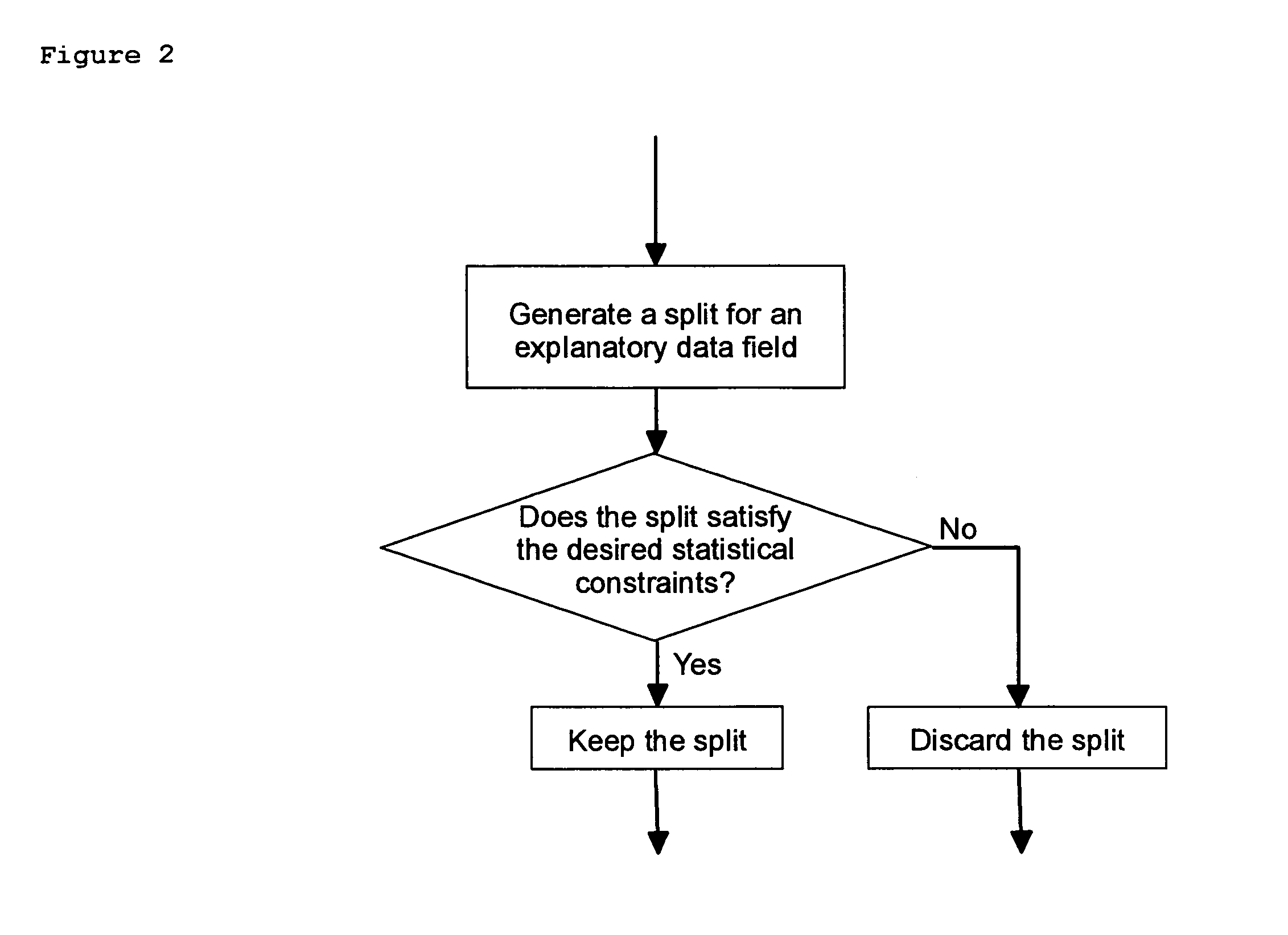
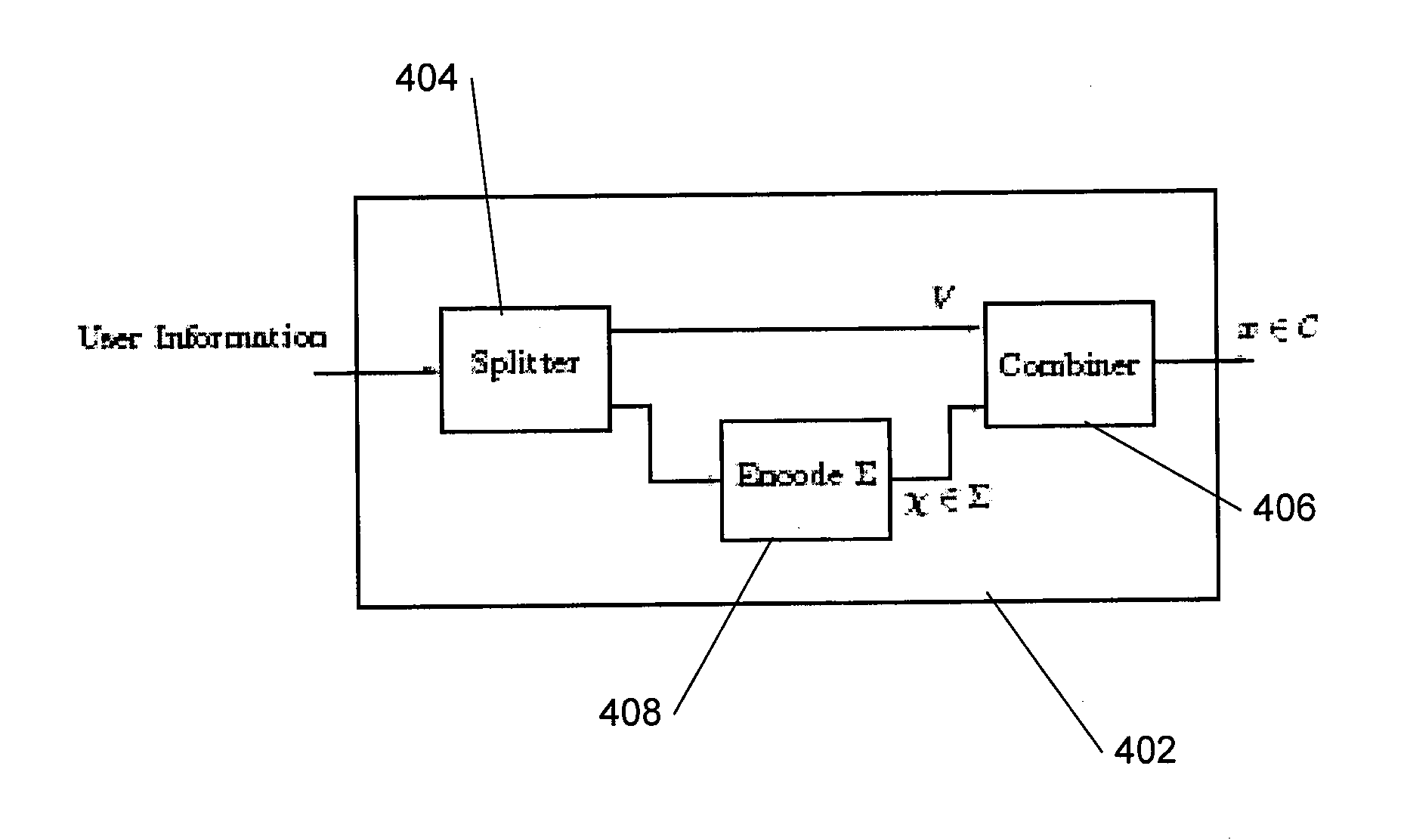
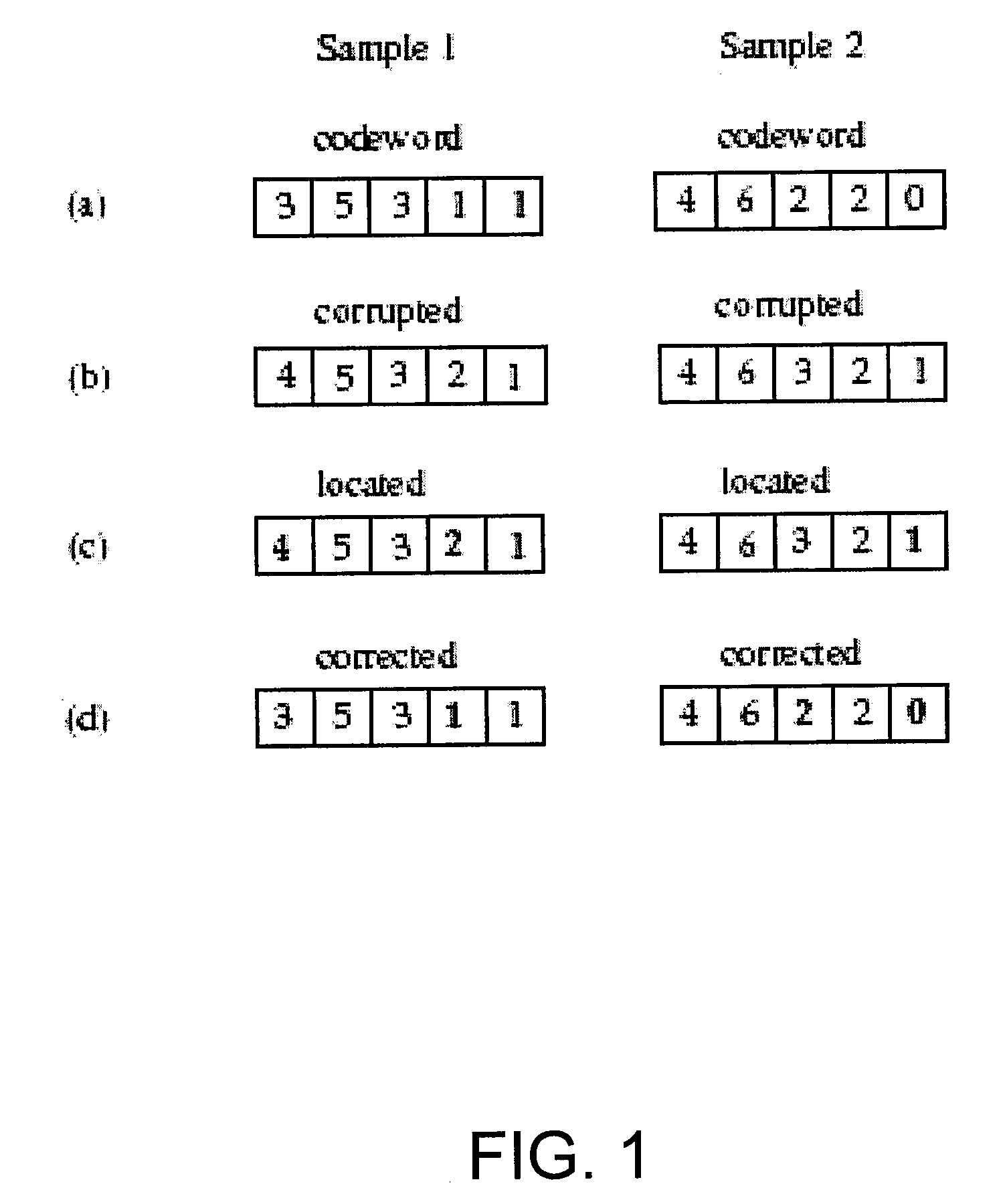
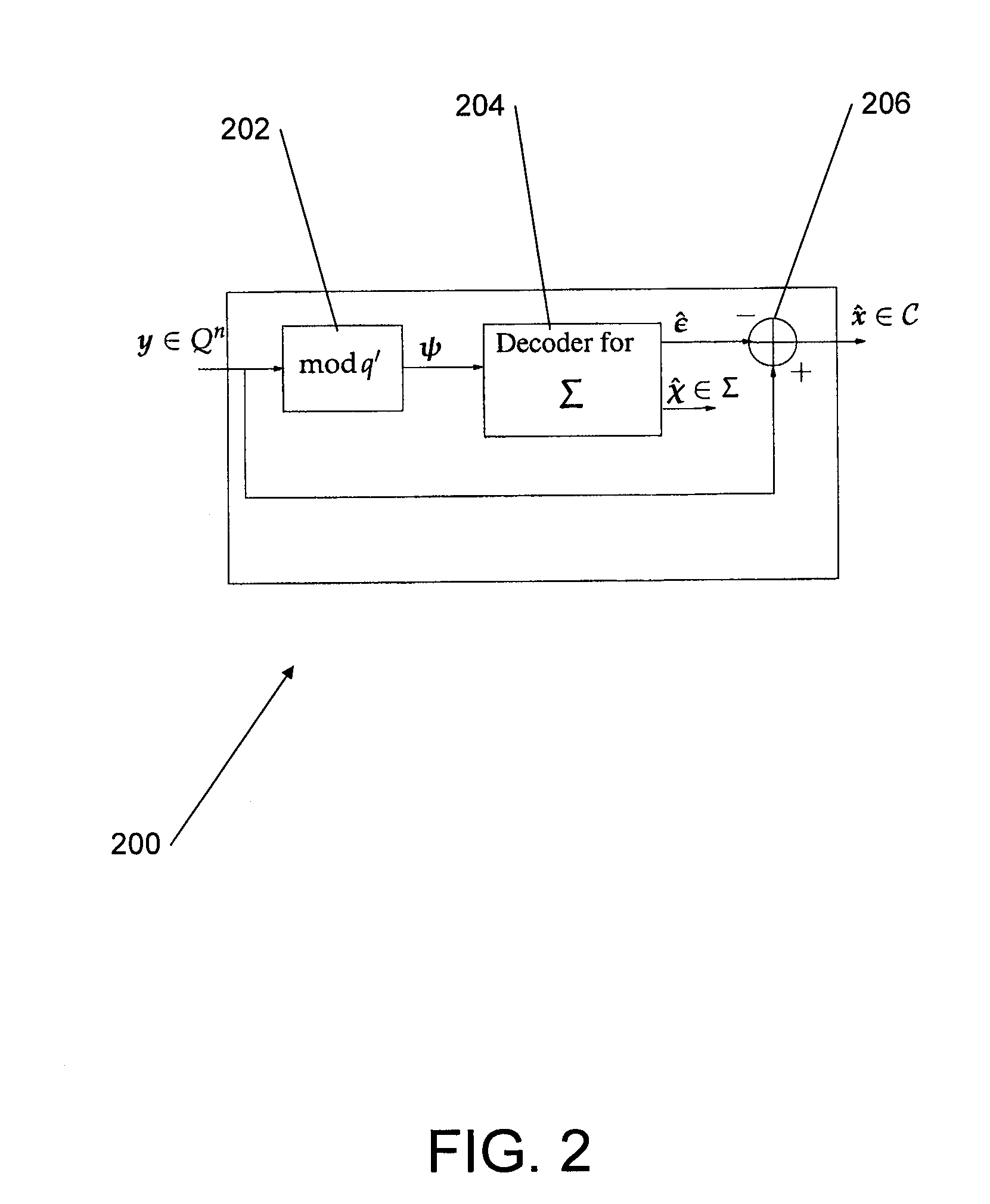
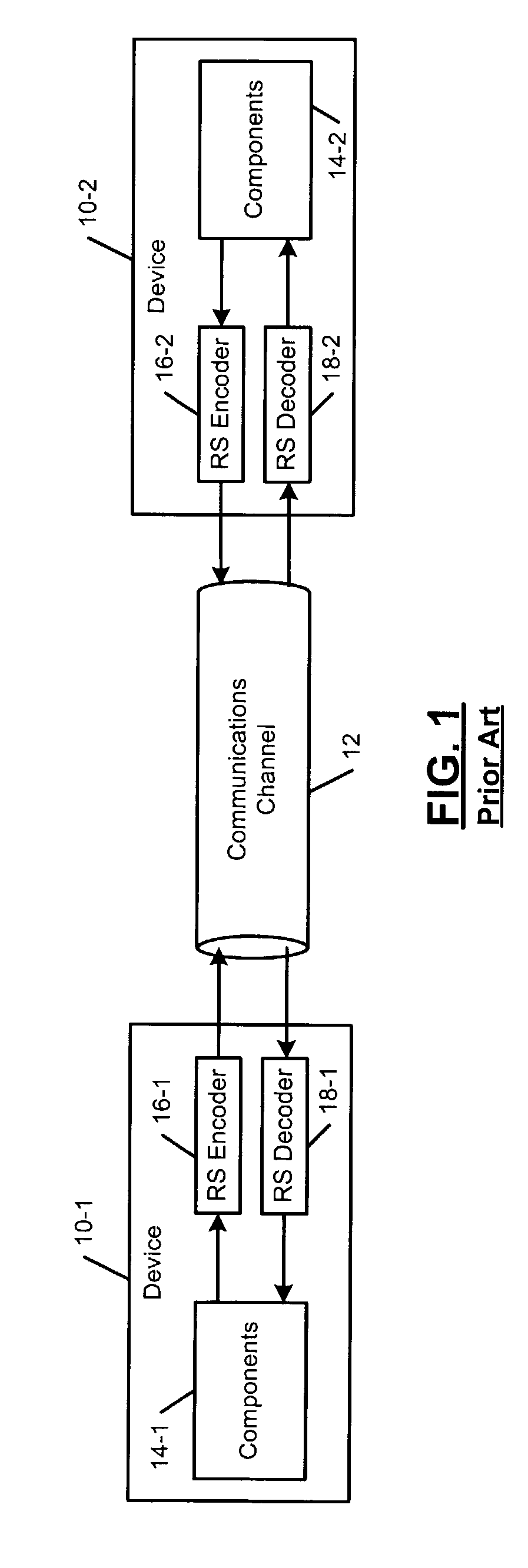
Patents
Literature
5807 results about "Errors and residuals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its "theoretical value". The error (or disturbance) of an observed value is the deviation of the observed value from the (unobservable) true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean), and the residual of an observed value is the difference between the observed value and the estimated value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals.
Method of Error Correction for 3D Imaging Device
A method is presented for correcting errors in a 3D scanner. Measurement errors in the 3D scanner are determined by scanning each of a plurality of calibration objects in each of a plurality of sectors in the 3D scanner's field of view. The calibration objects have a known height, a known width, and a known length. The measurements taken by the 3D scanner are compared to the known dimensions to derive a measurement error for each dimension in each sector. An estimated measurement error is calculated based on scans of each of the plurality of calibration objects. When scanning target objects in a given sector, the estimated measurement error for that sector is used to correct measurements obtained by the 3D scanner.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
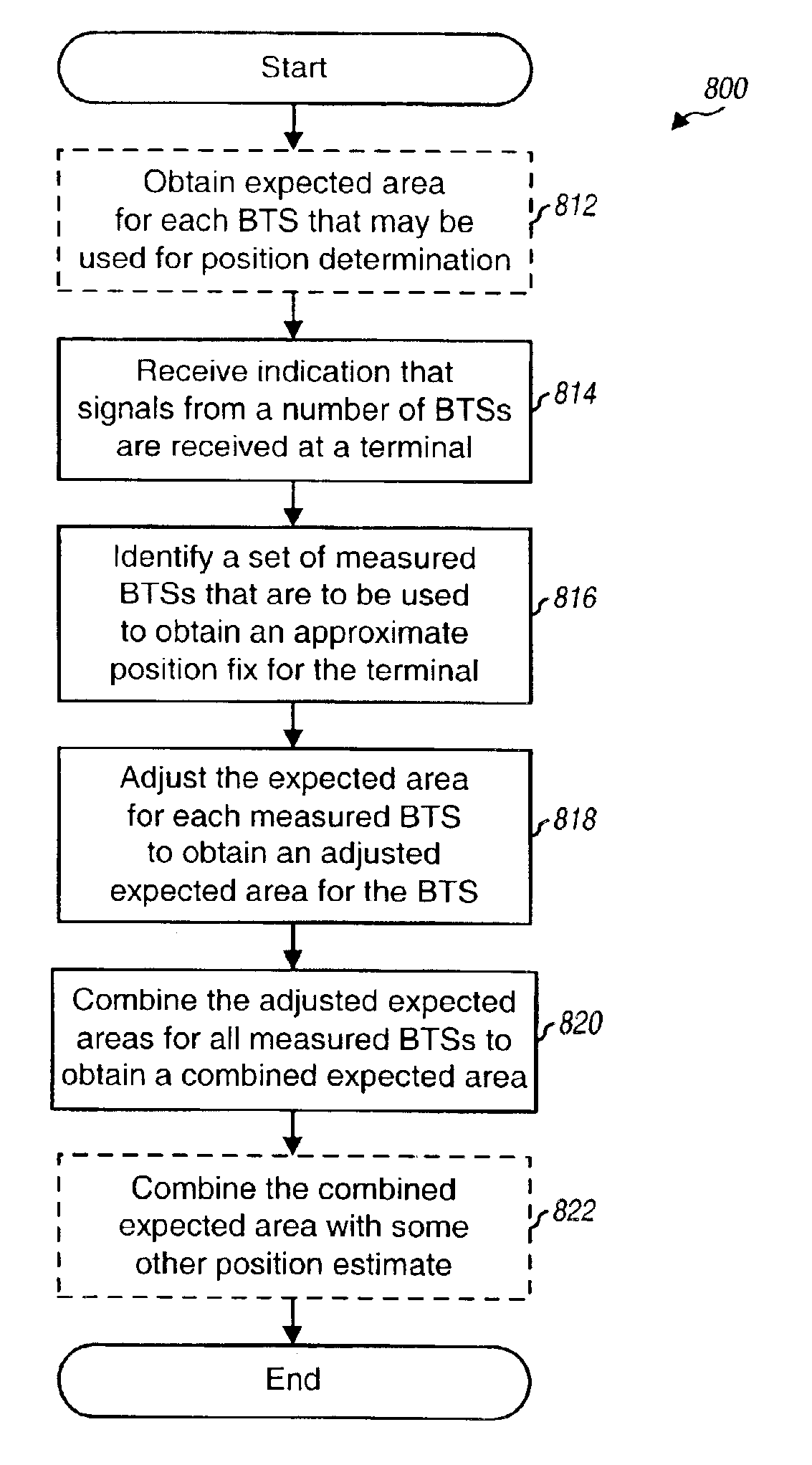
Area based position determination for terminals in a wireless network
InactiveUS6865395B2Accurate estimateDirection finders using radio wavesTelephonic communicationWireless mesh networkEngineering
Techniques to estimate the position of a wireless terminal. In a method, the identities of a number of transmitters (e.g., BTSs) to be used to estimate the position are initially received. Expected areas for these transmitters are then determined. The expected area associated with each transmitter is indicative of an area where the terminal is likely to be located given that the signal from the transmitter is received by the terminal. Each expected area may comprise a location (e.g., the expected area center) to be used as an estimated position of the terminal and an uncertainty (or error estimate) associated with that estimated position. The expected areas for the transmitters are then combined (e.g., based on a weighted average) to determine a combined expected area, which is then provided as the estimate of the position of the terminal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
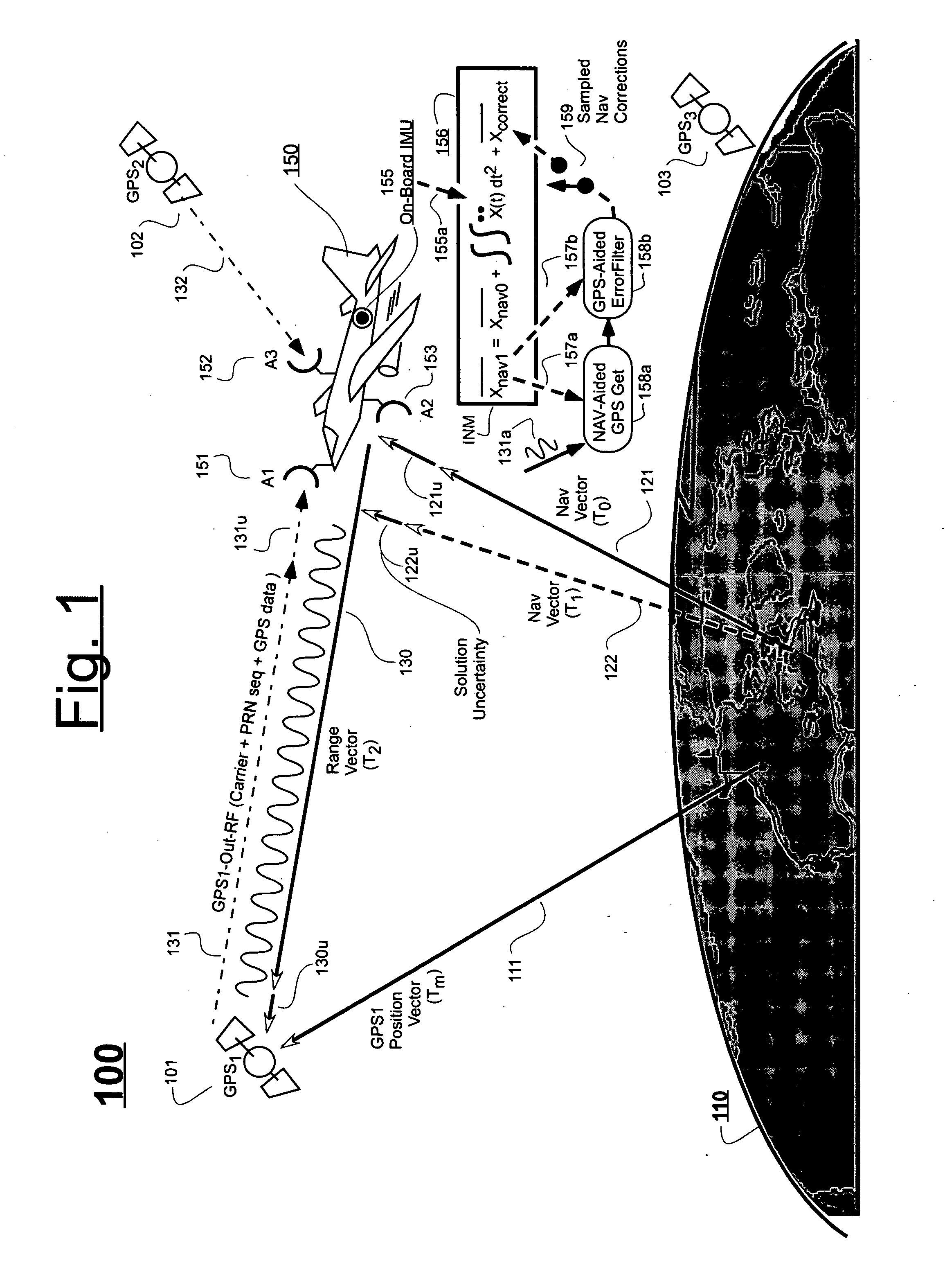
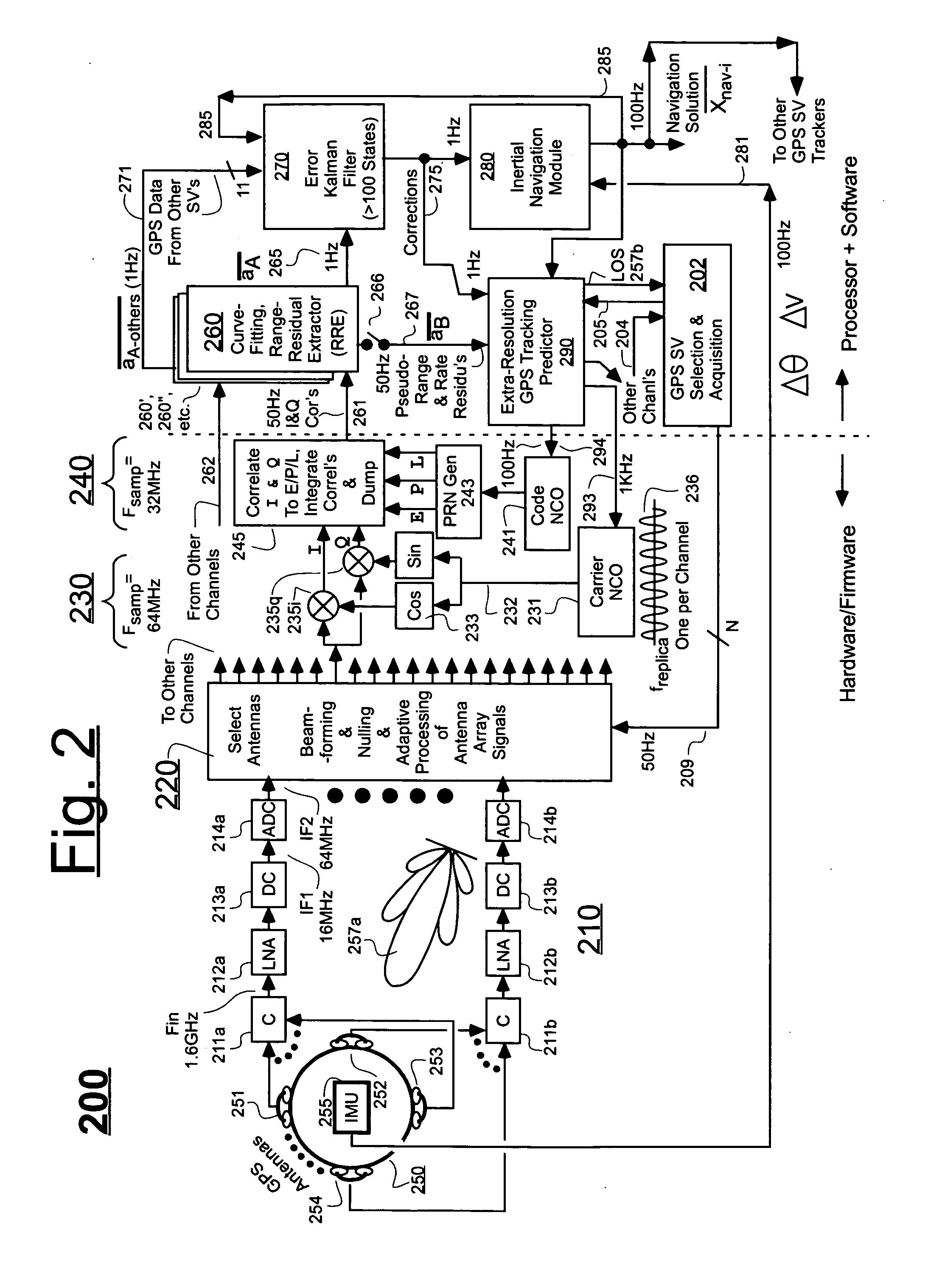
Ultra-tightly coupled GPS and inertial navigation system for agile platforms
InactiveUS20070118286A1Cancel noiseReduce computing timeDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCurve fittingCarrier signal
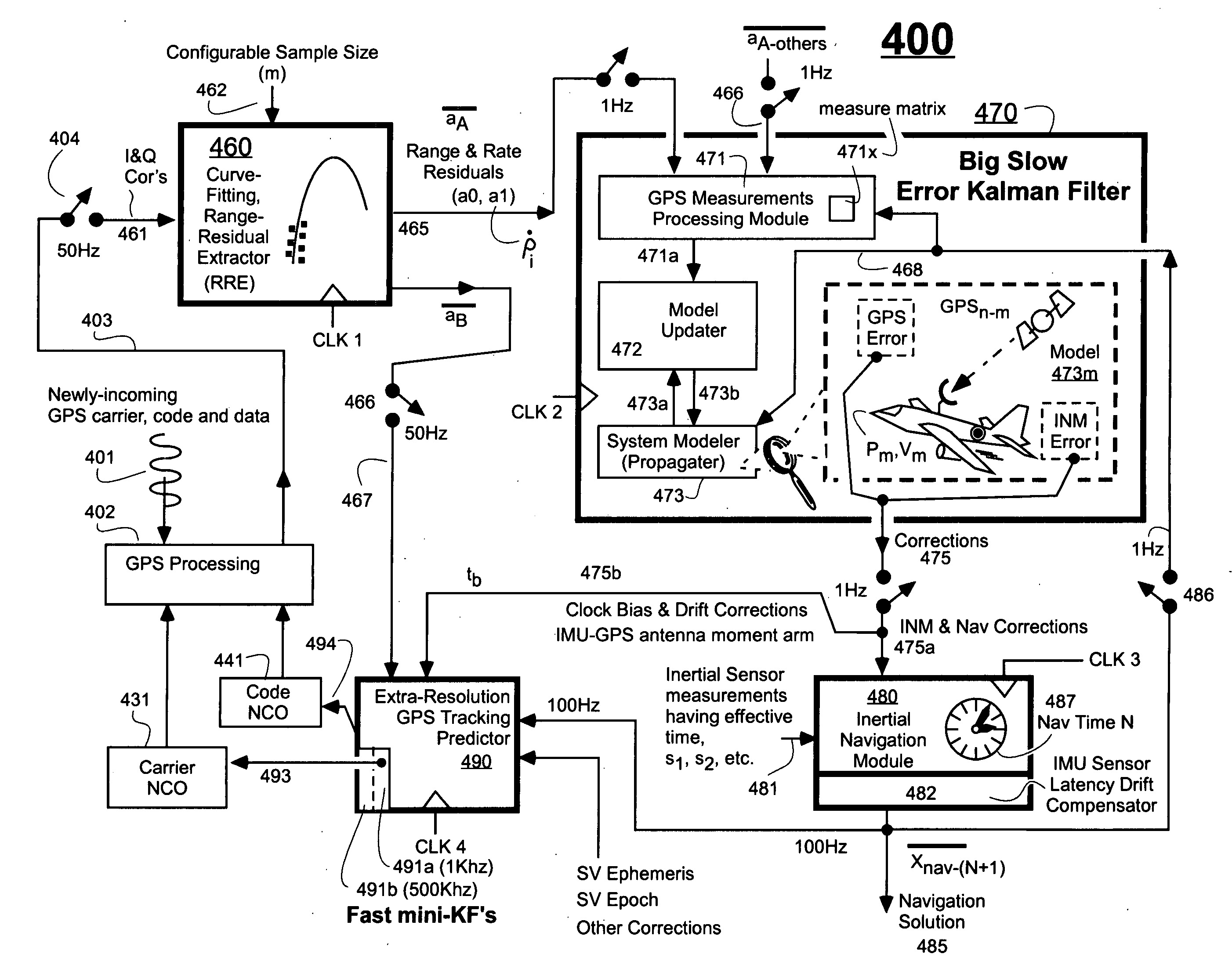
An Ultra-Tightly Coupled GPS-inertial navigation system for use in a moving agile platform includes a range residual extractor that uses best curve fitting of a third order polynomial for estimating range residual. The curve-fitted residual is used to update an error Kalman filter. The error Kalman filter includes correction for navigation solution, and IMU and GPS parameters. The navigation solution together with GPS parameter corrections are used in a Tracking Predictor to generate high-sampling-rate carrier and code replicas. The curve-fitting error covariance indicates signal to noise ratio for the tracked GPS signal and may be used for early indication of interference or jamming.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
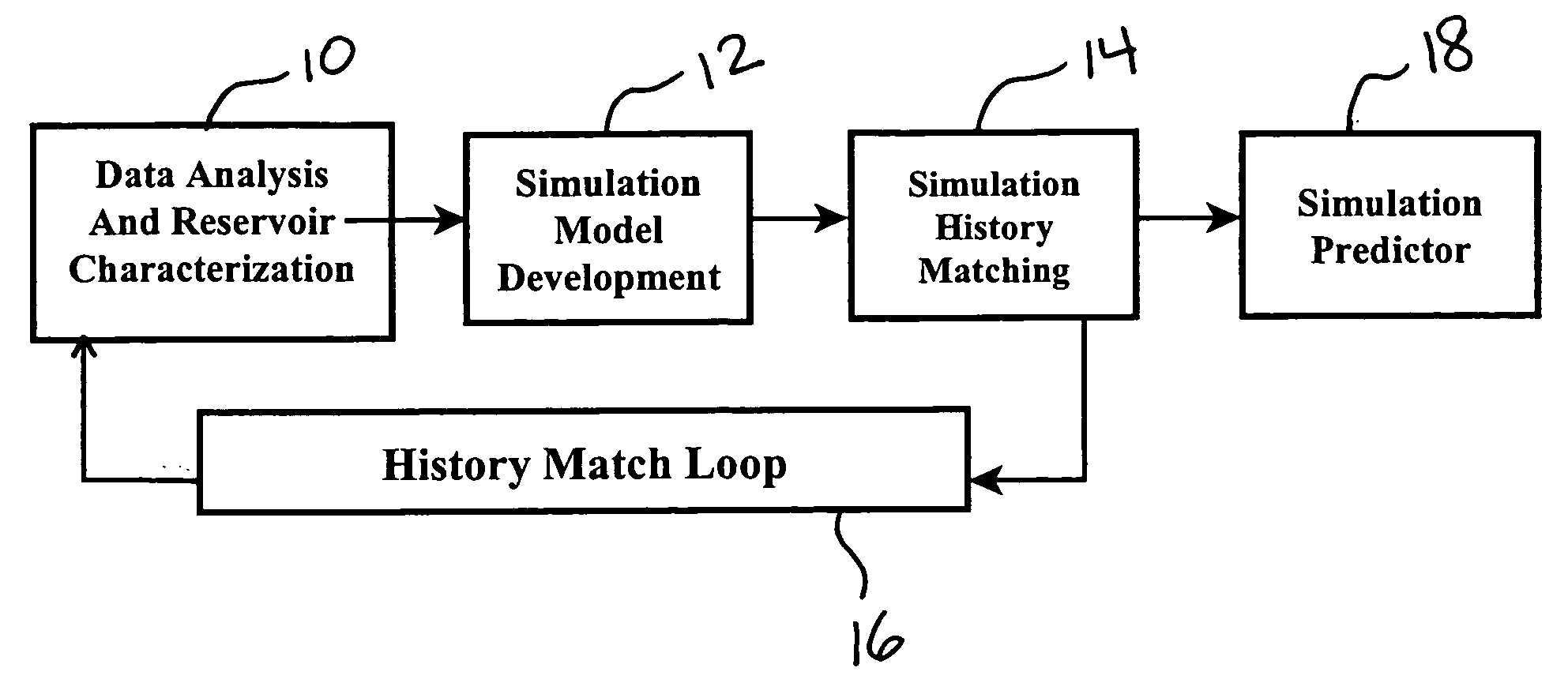
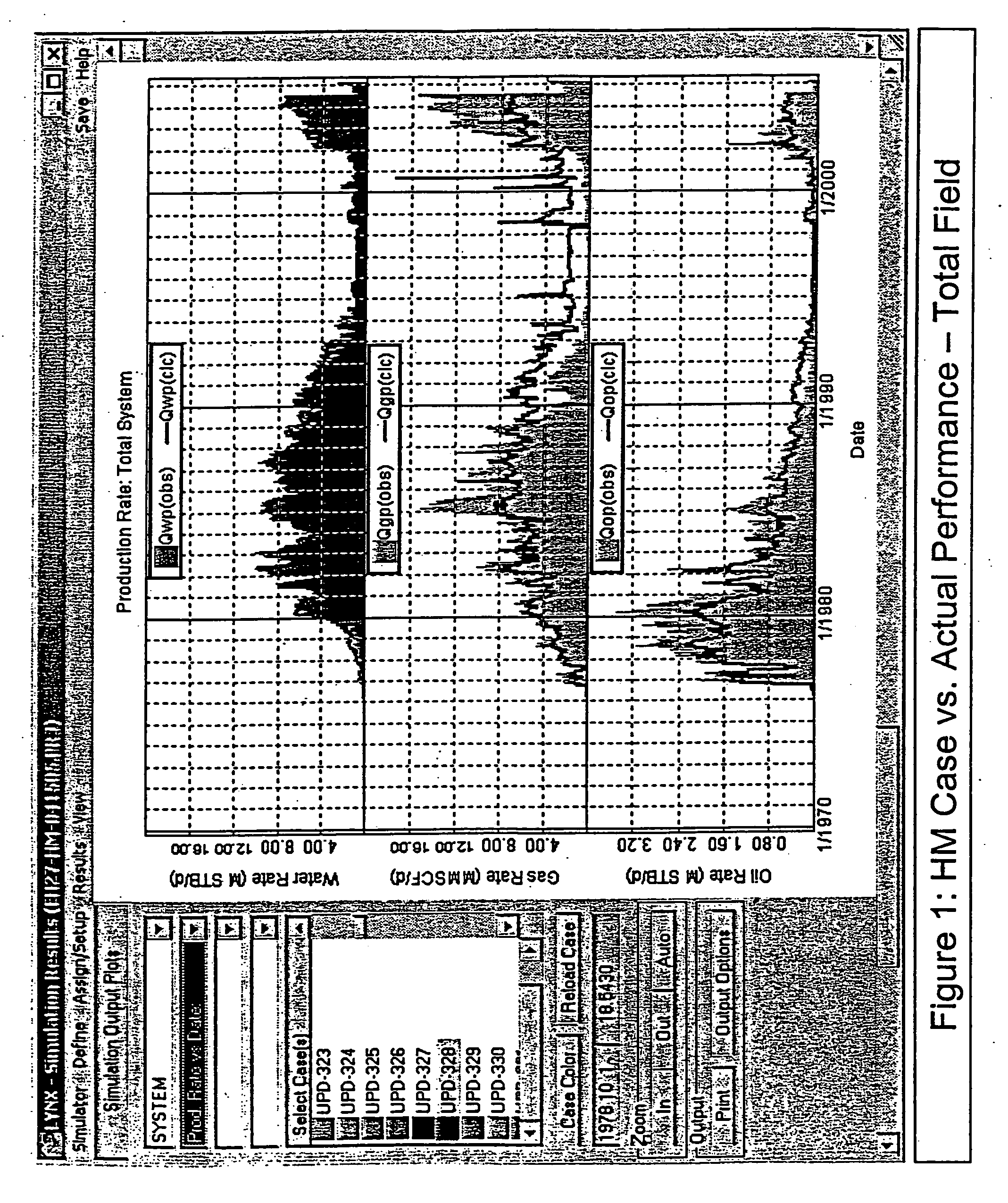
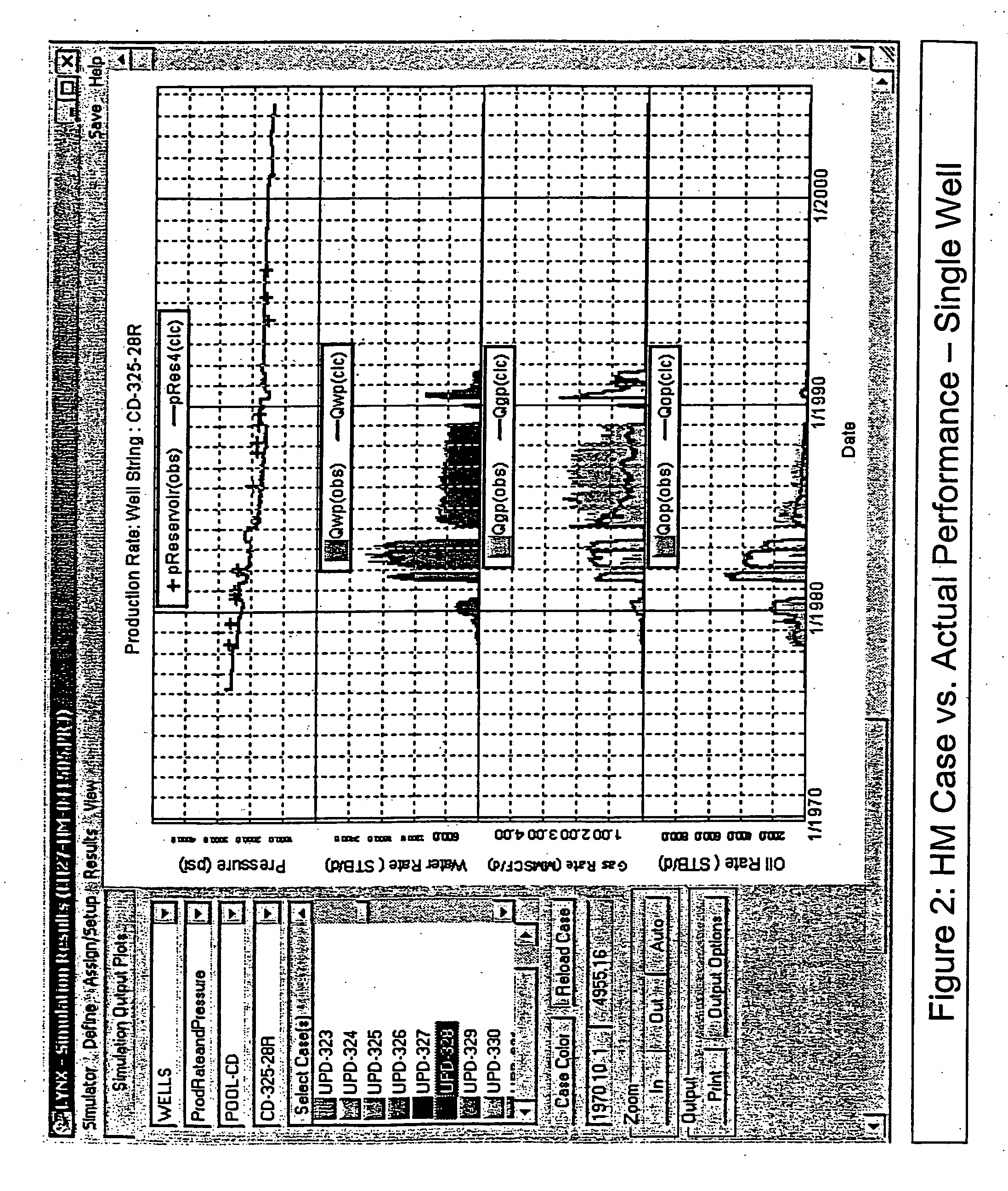
Method and system for accelerating and improving the history matching of a reservoir simulation model
InactiveUS20070016389A1Improve predicted recoveryFaster and reliable pressureSurveyGeomodellingNerve networkErrors and residuals
The present invention, in one embodiment, is directed to a method and system for accelerating and improving the history matching of a well bore and / or reservoir simulation model using a neural network. The neural network provides a correlation between the calculated history match error and a selected set of parameters that characterize the well bore and / or the reservoir. The neural network iteratively varies a selection and / or the value of the parameters to provide at least one set of history match parameters having a value that provides a minimum for the calculated history matching error.
Owner:OZGEN CETIN
Robust adaptive model predictive controller with tuning to compensate for model mismatch
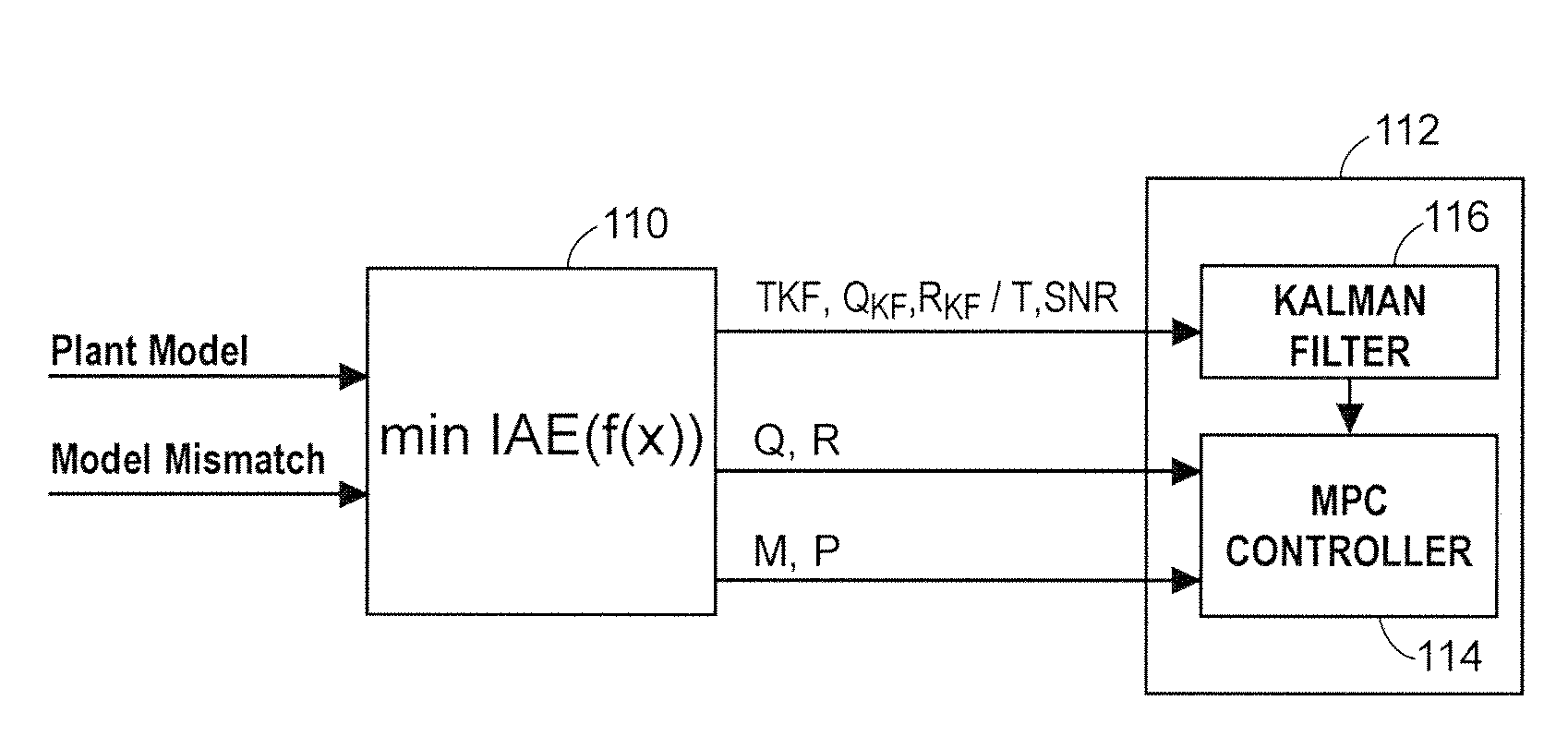
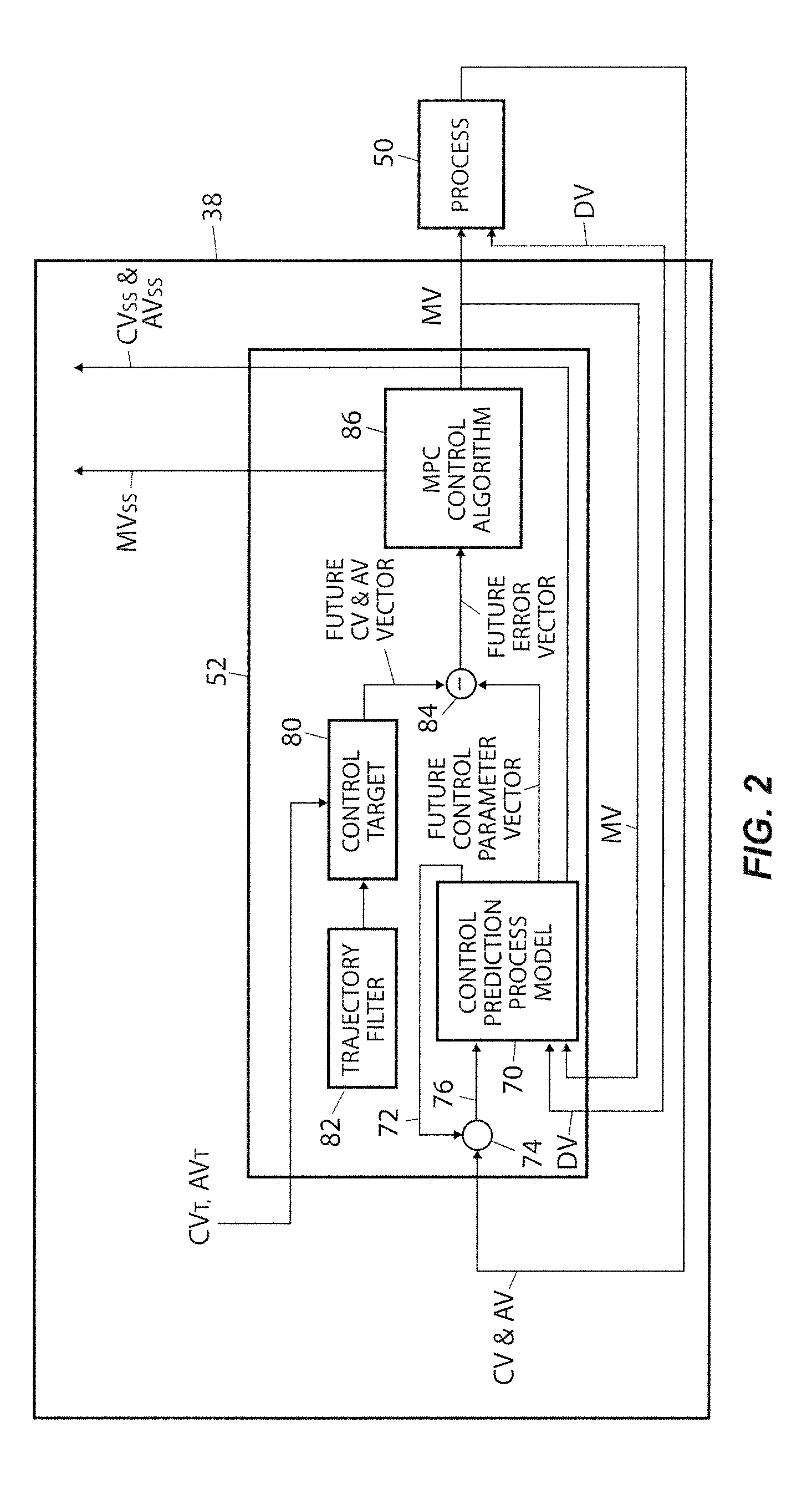
ActiveUS20090198350A1Improve immunityImprove performanceComputer controlSimulator controlClosed loopPredictive controller
An MPC adaptation and tuning technique integrates feedback control performance better than methods commonly used today in MPC type controllers, resulting in an MPC adaptation / tuning technique that performs better than traditional MPC techniques in the presence of process model mismatch. The MPC controller performance is enhanced by adding a controller adaptation / tuning unit to an MPC controller, which adaptation / tuning unit implements an optimization routine to determine the best or most optimal set of controller design and / or tuning parameters to use within the MPC controller during on-line process control in the presence of a specific amount of model mismatch or a range of model mismatch. The adaptation / tuning unit determines one or more MPC controller tuning and design parameters, including for example, an MPC form, penalty factors for either or both of an MPC controller and an observer and a controller model for use in the MPC controller, based on a previously determined process model and either a known or an expected process model mismatch or process model mismatch range. A closed loop adaptation cycle may be implemented by performing an autocorrelation analysis on the prediction error or the control error to determine when significant process model mismatch exists or to determine an increase or a decrease in process model mismatch over time.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Statistical combining of cell expression profiles
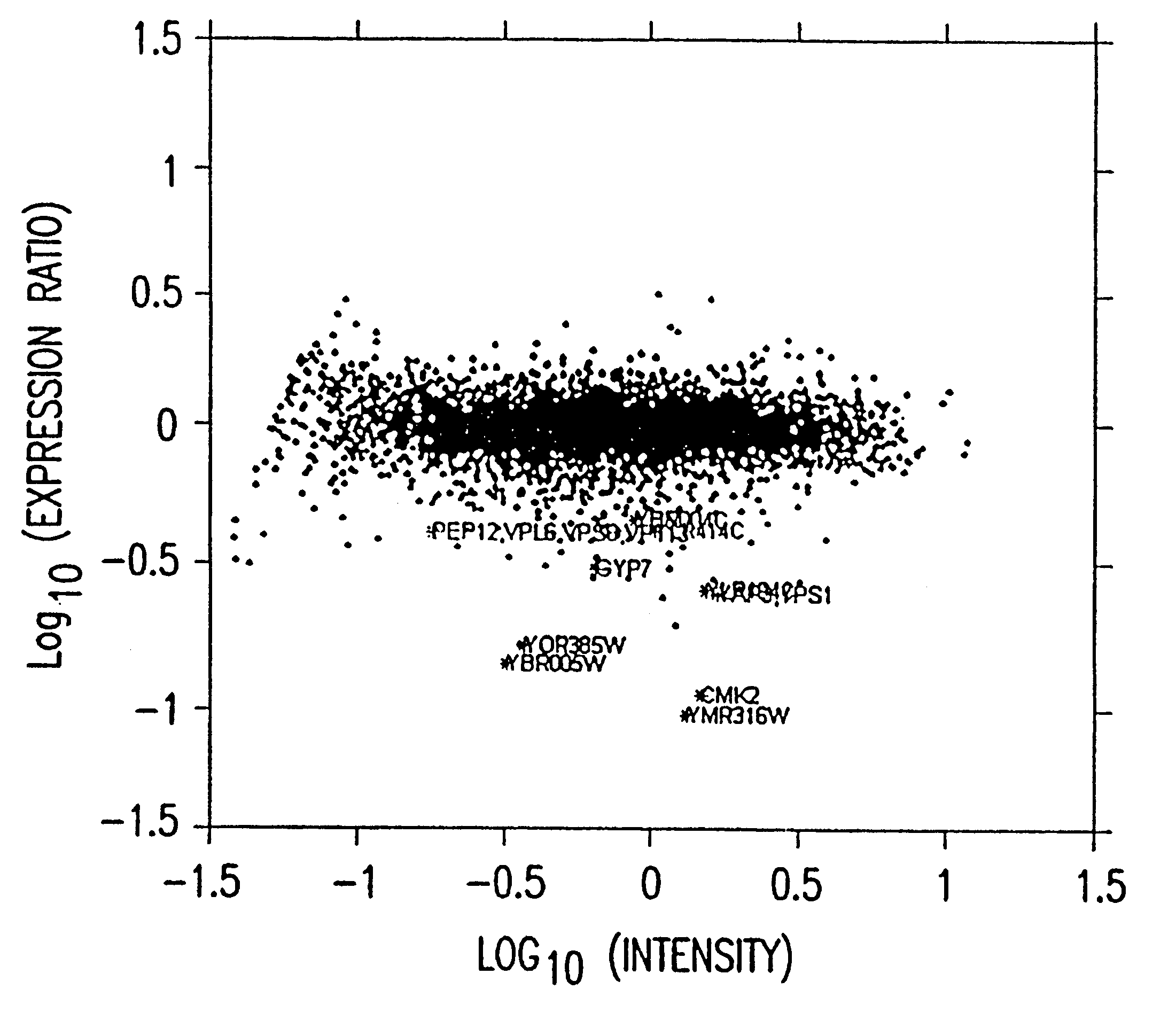
InactiveUS6351712B1Minimize repetitionEliminate errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyFluorophoreErrors and residuals
A method for fluorophore bias removal in microarray experiments in which the fluorophores used in microarray experiment pairs are reversed. Further, a method for calculating the individual errors associated with each measurement made in nominally repeated microarray experiments. This error measurement is optionally coupled with rank based methods in order to determine a probability that a cellular constituent is up or down regulated in response to a perturbation. Finally, a method for determining the confidence in the weighted average of the expression level of a cellular constituent in nominally repeated microarray experiments.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
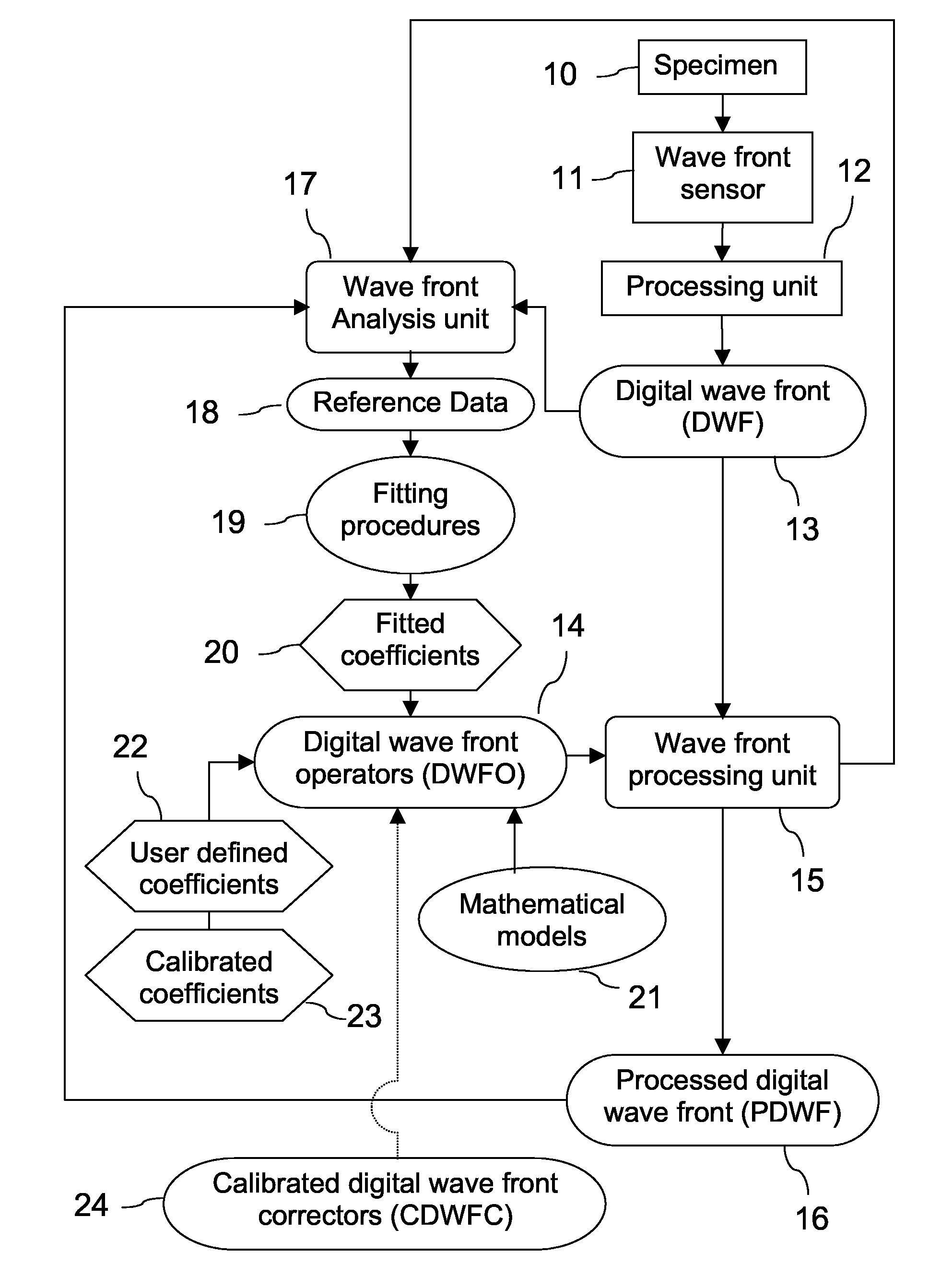
Wave front sensing method and apparatus
ActiveUS7649160B2Reduce fieldHigh resolutionImage enhancementOptical measurementsWavefront sensorMetrology
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Method and system to identify discrete trends in time series
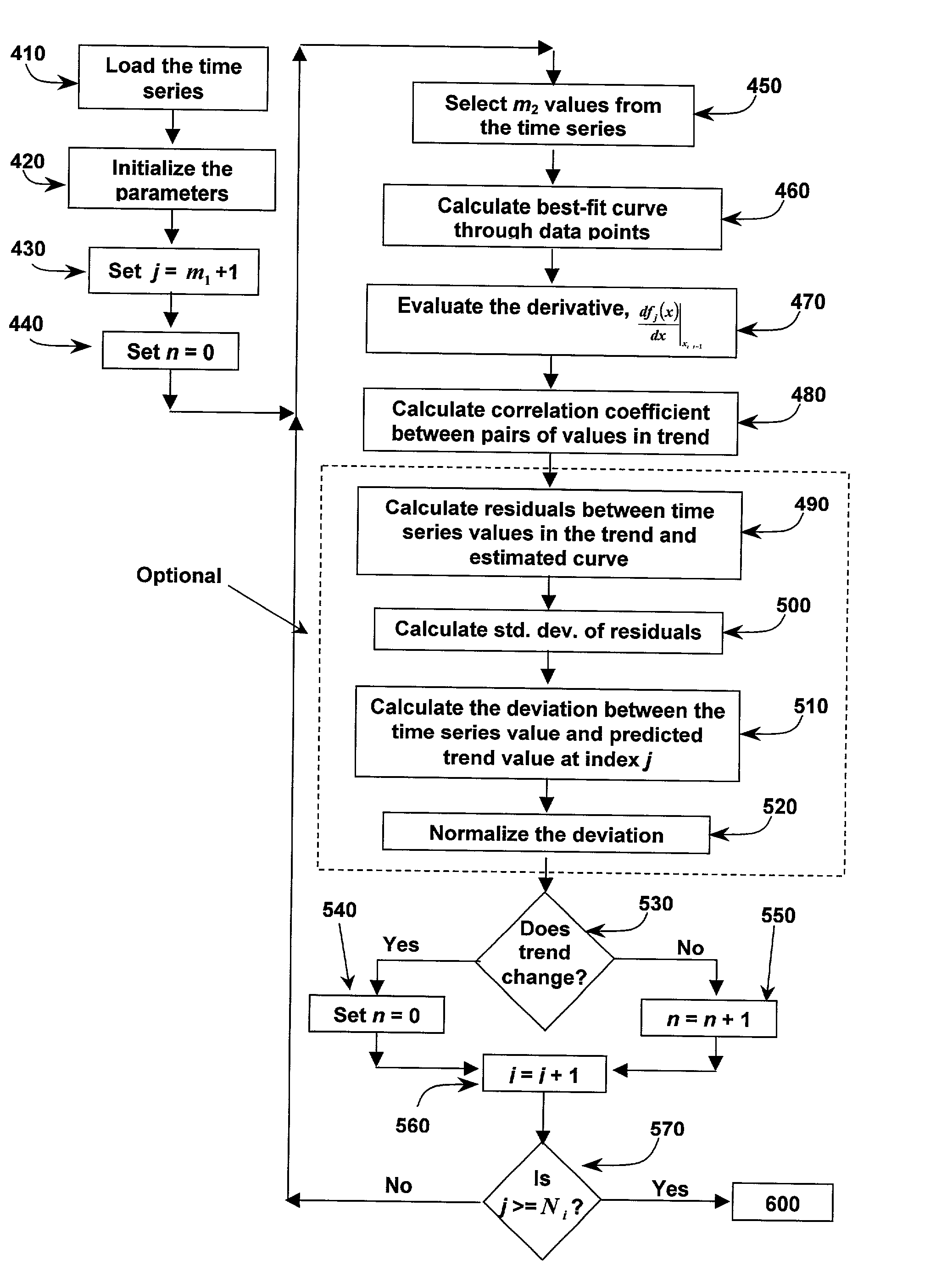
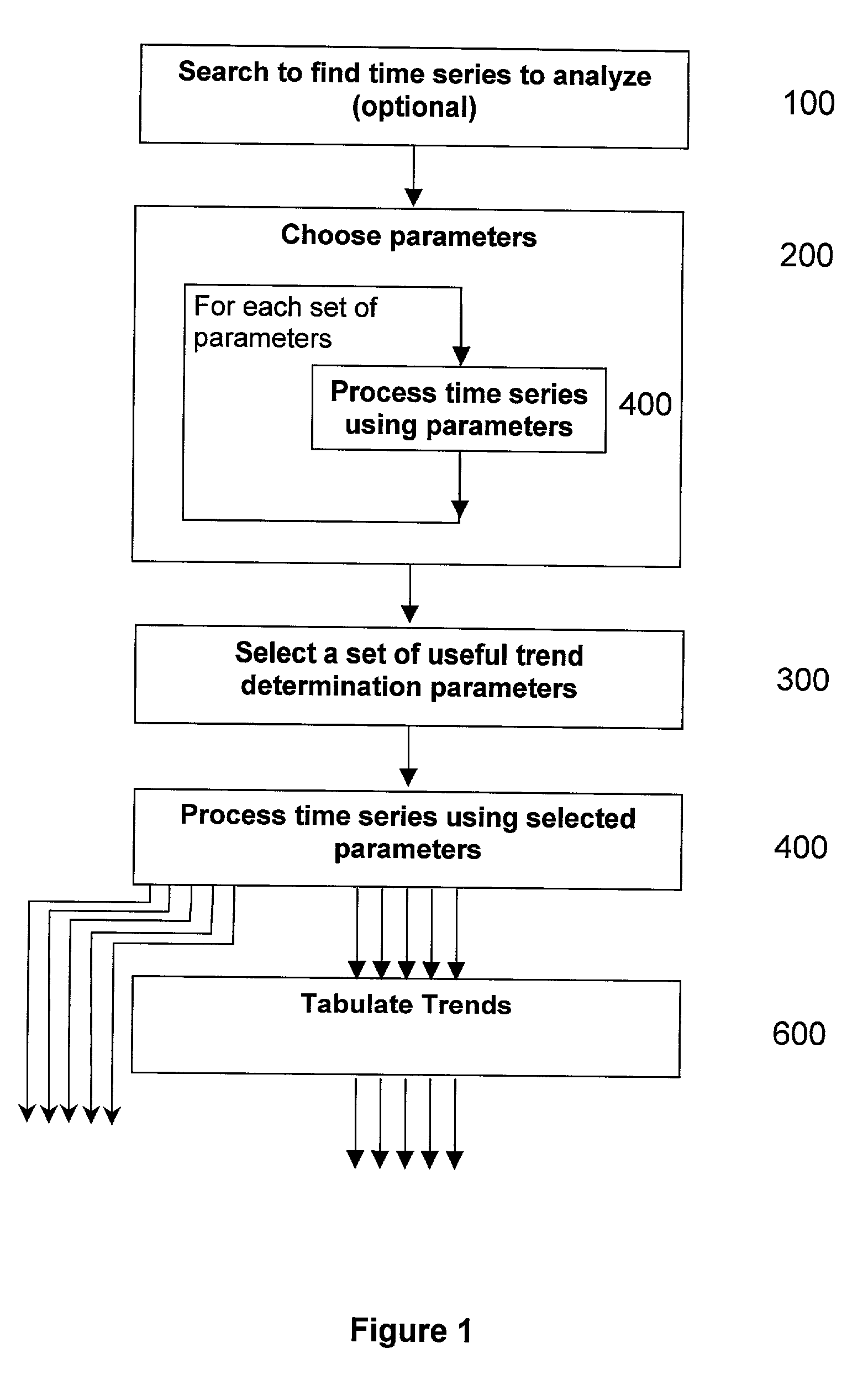
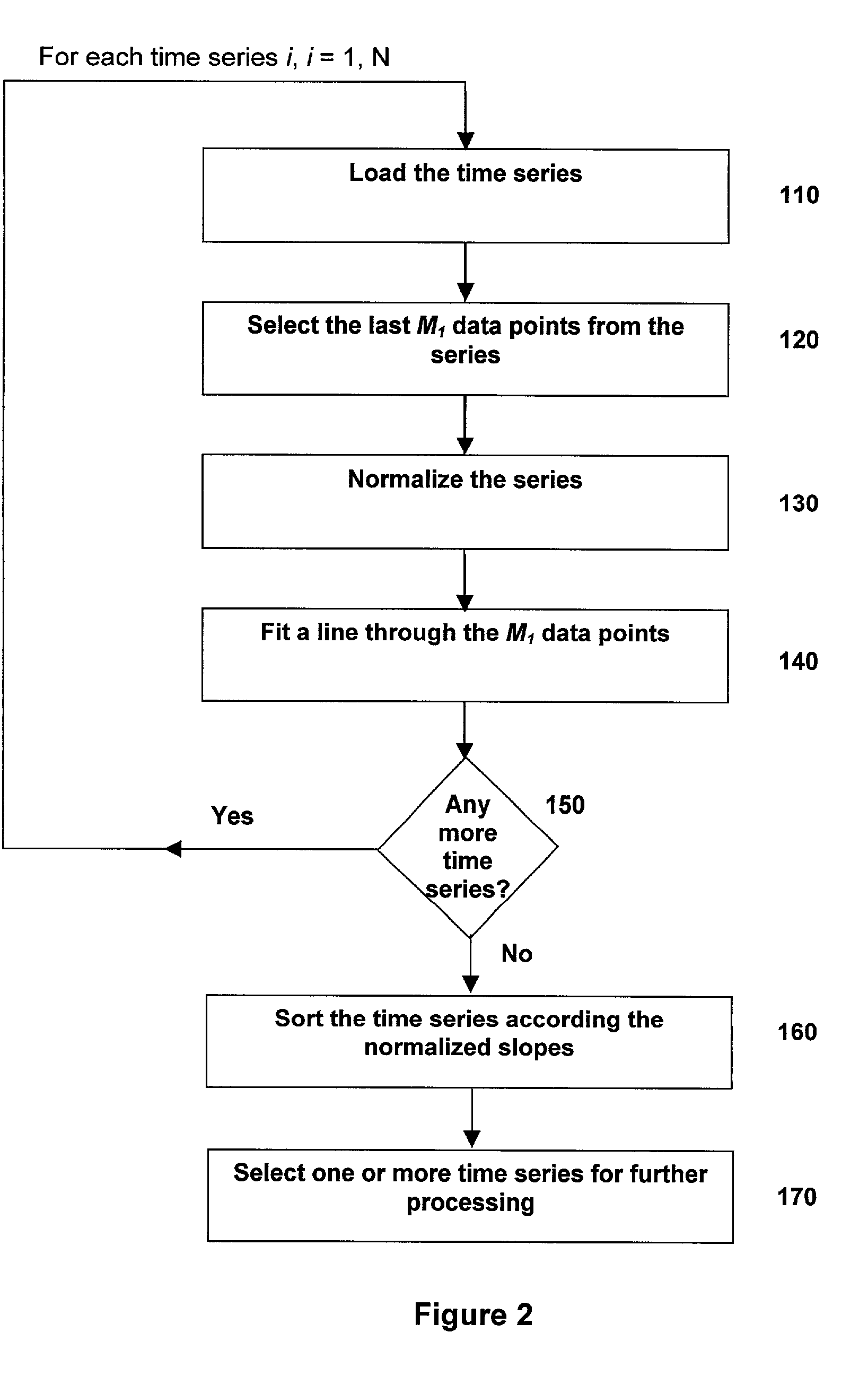
A signal processing system and method for breaking a time series into piece-wise discrete trends and determining whether new data represents the continuation of a trend. The method identifies and utilizes at least one set of trend determination parameters, which have favorable trend fit characteristics relative to other possible sets of parameters. In a semi-automated embodiment, the error and trend length characteristics are cross-plotted for multiple sets of possible parameters, and one or more of the parameter sets is selected from the graph. In an automated embodiment, an objective function is formulated from the characteristics, and an optimization technique is applied to identify one or more good parameter sets.
Owner:BOERNER SEAN T
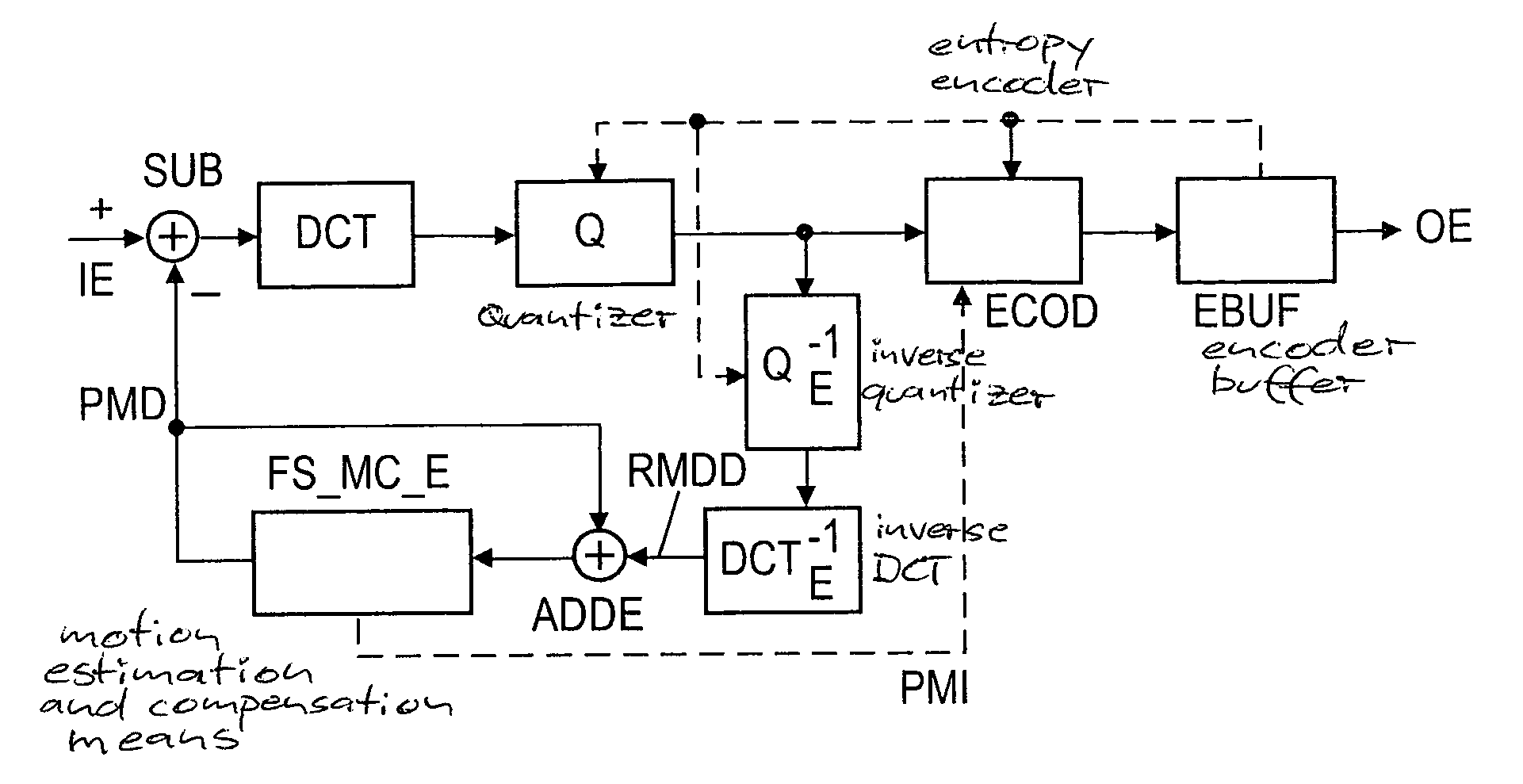
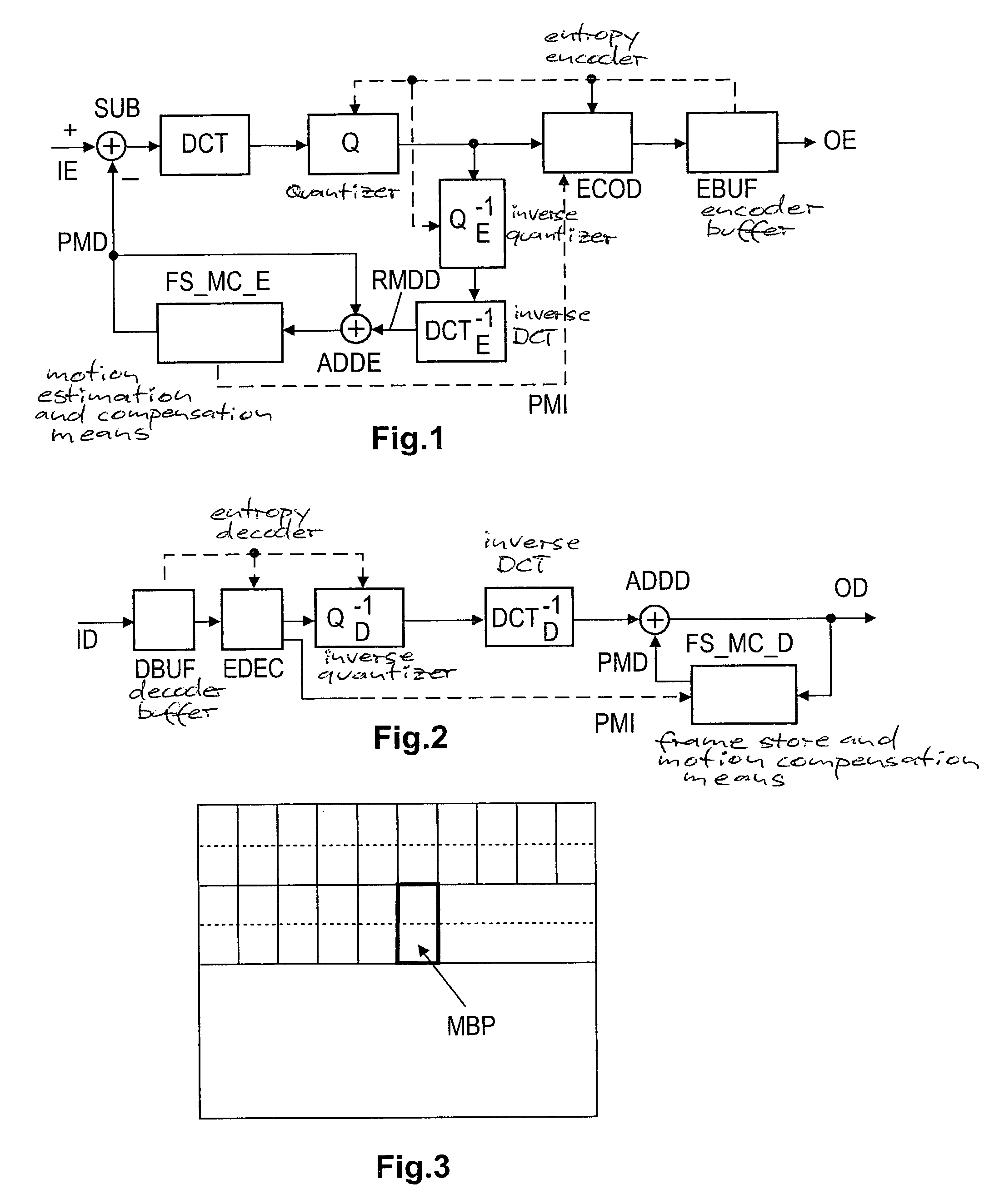
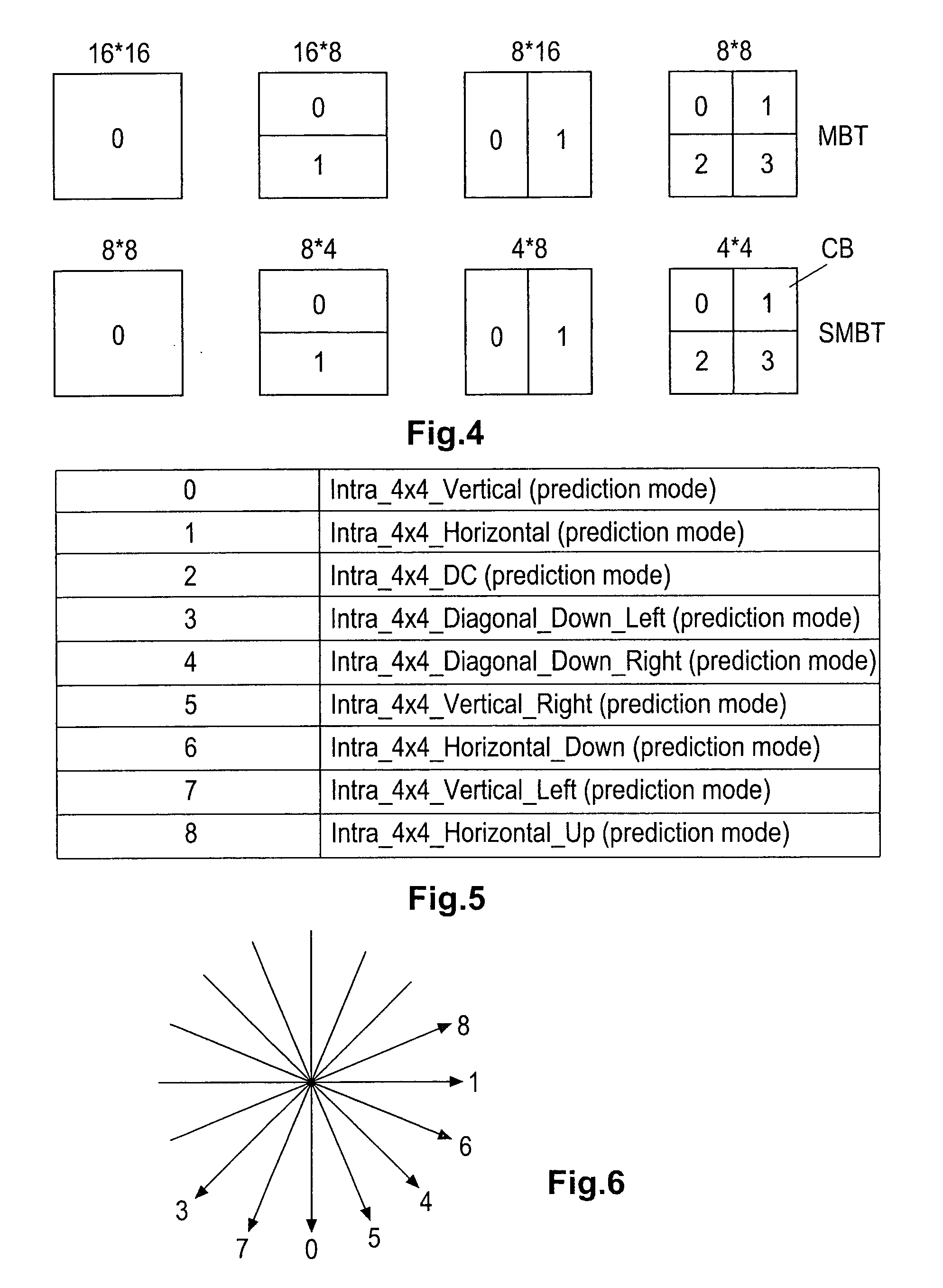
Method and apparatus for generating/evaluating in a picture signal encoding/decoding one or more prediction information items
ActiveUS20050157797A1Increase volumeReduces available data rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmVideo encoding
Advanced Video Coding uses intra prediction for 4*4 pixel blocks whereby reconstructed samples from adjacent pixel blocks are used to predict a current block. Nine different intra prediction modes are available in AVC. In order to save bits for signalling the prediction modes, a flag and a 3-bit parameter are used. If this flag is set the most probable prediction mode, which is calculated from previous predictions, is used by the encoder and the decoder to reconstruct the actual prediction mode. If the flag is cleared, the 3-bit parameter is sent to select the prediction mode independently. According to the invention, the flag is applied more frequently, based on a prediction error threshold, instead of applying the optimum prediction mode for a current pixel block.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Wave Front Sensing Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20080265130A1Improve performanceHigh imaging performanceImage enhancementPhotometry using reference valueWavefront sensorMetrology
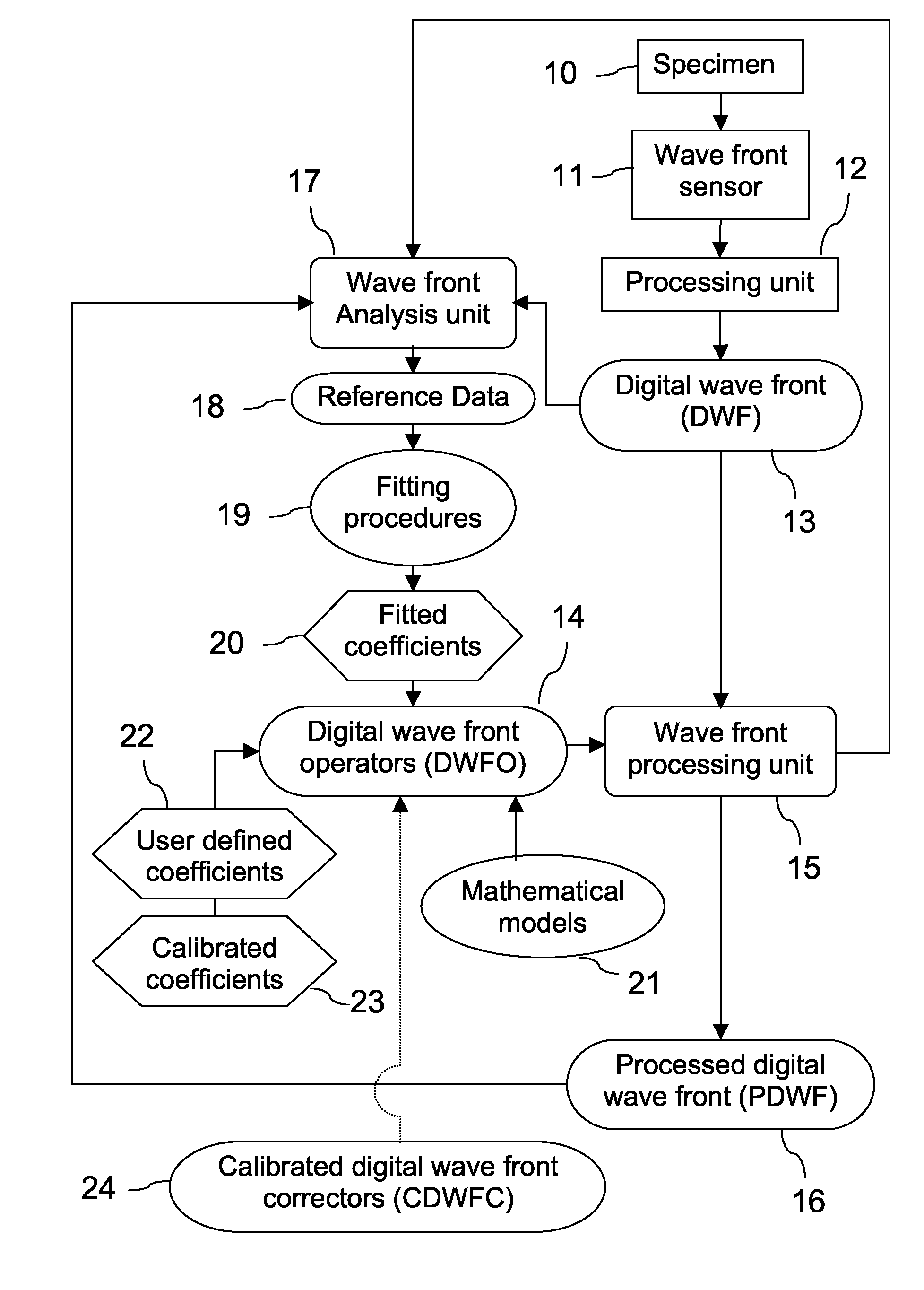
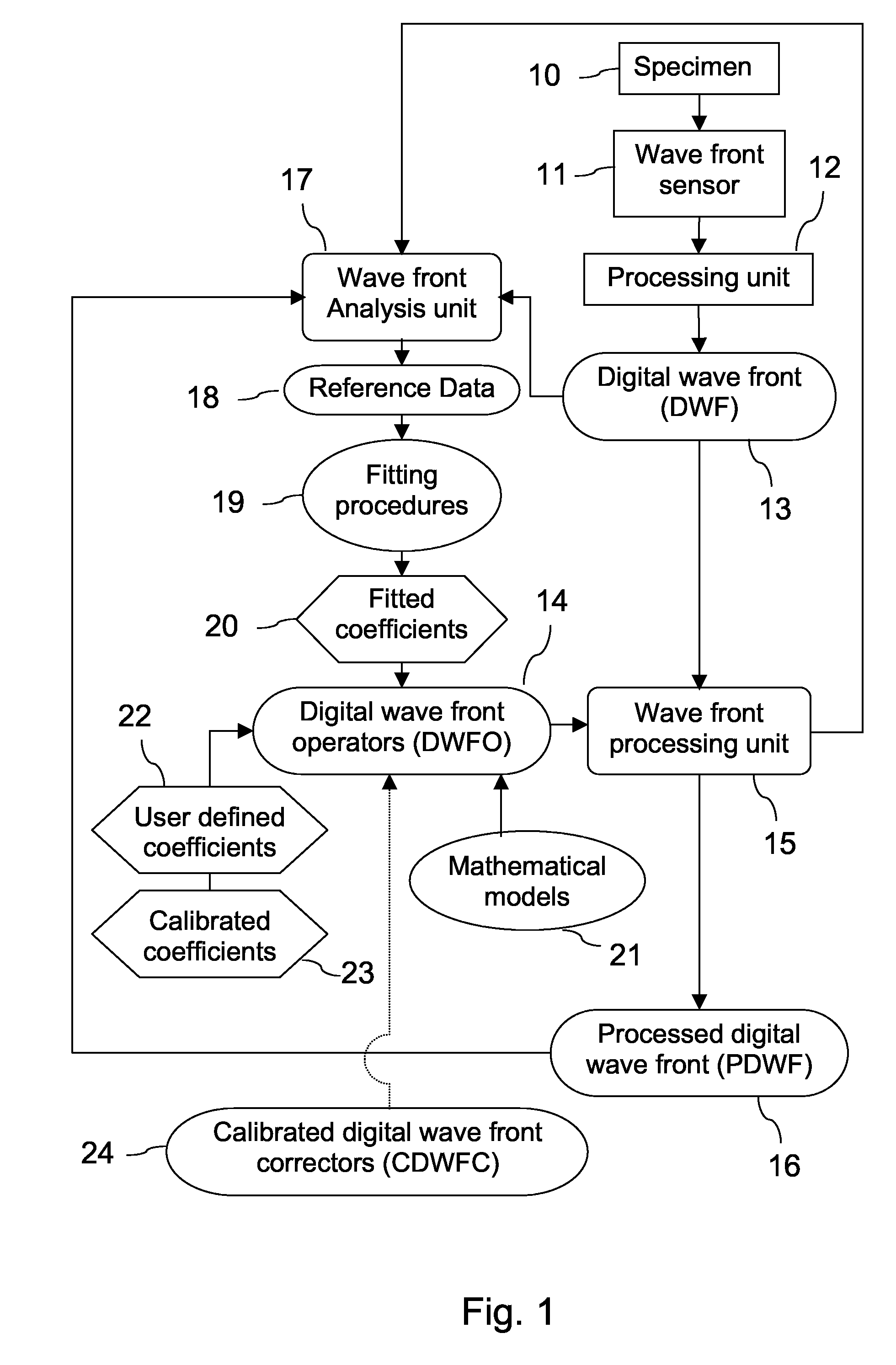
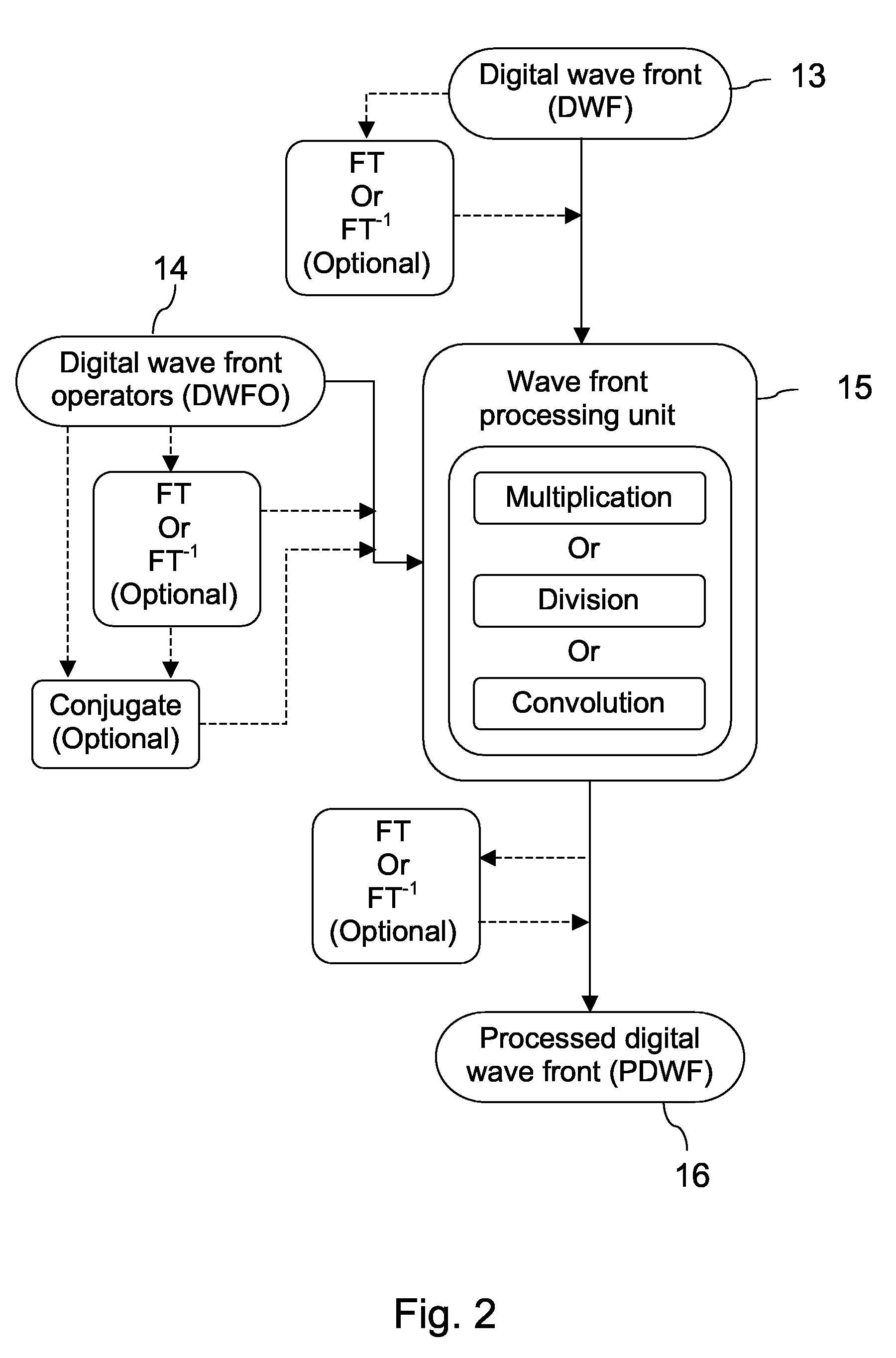
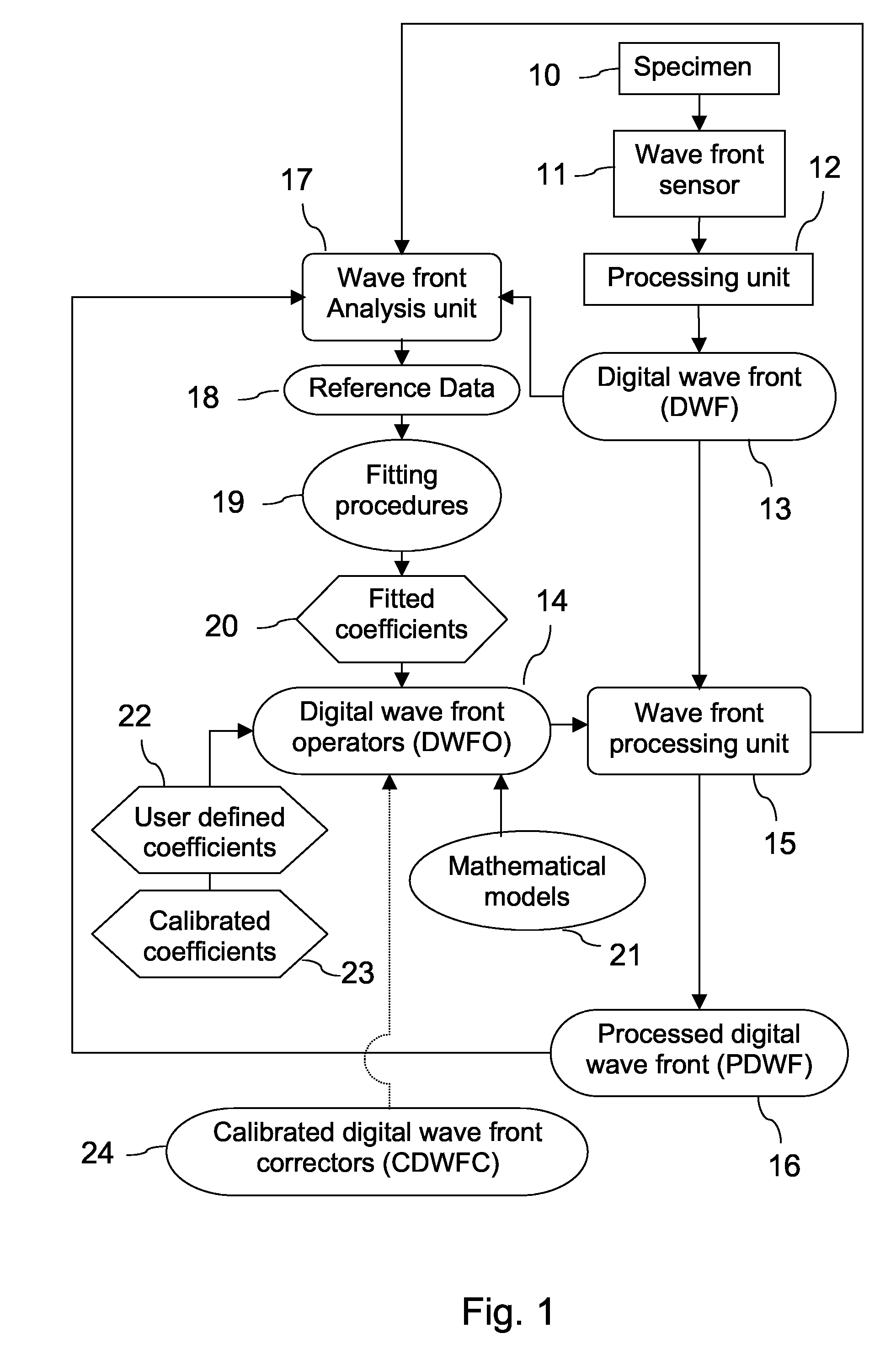
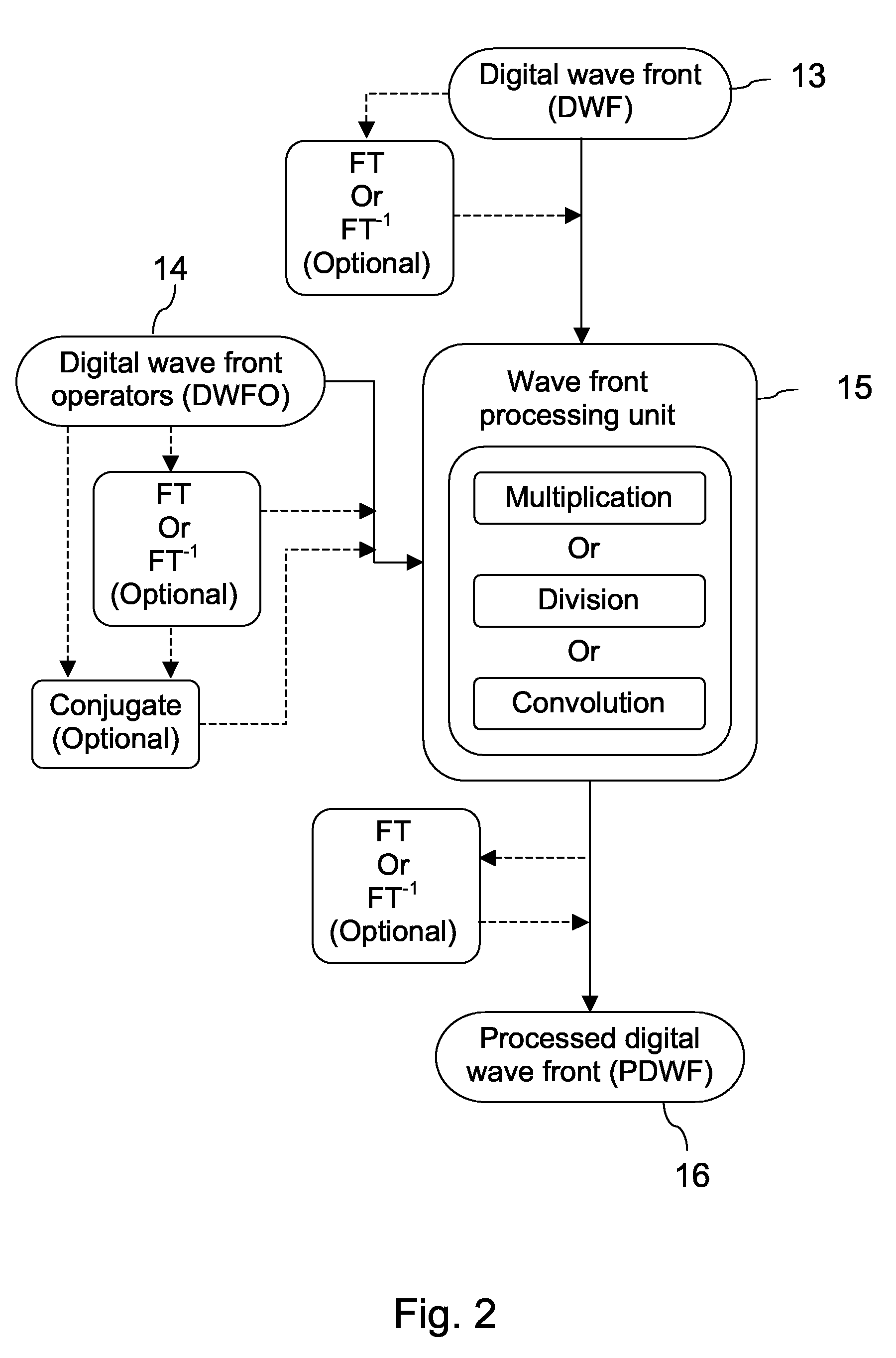
A new way of mixing instrumental and digital means is described for the general field of wave front sensing. The present invention describes the use, the definition and the utility of digital operators, called digital wave front operators (DWFO) or digital lenses (DL), specifically designed for the digital processing of wave fronts defined in amplitude and phase. DWFO are of particular interest for correcting undesired wave front deformations induced by instrumental defects or experimental errors. DWFO may be defined using a mathematical model, e.g. a polynomial function, which involves coefficients. The present invention describes automated and semi-automated procedures for calibrating or adjusting the values of these coefficients. These procedures are based on the fitting of mathematical models on reference data extracted from specific regions of a wave front called reference areas, which are characterized by the fact that specimen contributions are a priori known in reference areas. For example, reference areas can be defined in regions where flat surfaces of a specimen produce a constant phase function. The present invention describes also how DWFO can be defined by extracting reference data along one-dimensional (1D) profiles. DWFO can also be defined in order to obtain a flattened representation of non-flat area of a specimen. Several DWFO or DL can be combined, possibly in addition with procedures for calculating numerically the propagation of wave fronts. A DWFO may also be defined experimentally, e.g. by calibration procedures using reference specimens. A method for generating a DWFO by filtering in the Fourier plane is also described. All wave front sensing techniques may benefit from the present invention. The case of a wave front sensor based on digital holography, e.g. a digital holographic microscope (DHM), is described in more details. The use of DWFO improves the performance, in particular speed and precision, and the ease of use of instruments for wave front sensing. The use of DWFO results in instrumental simplifications, costs reductions, and enlarged the field of applications. The present invention defines a new technique for imaging and metrology with a large field of applications in material and life sciences, for research and industrial applications.
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Method for constructing segmentation-based predictive models from data that is particularly well-suited for insurance risk or profitability modeling purposes
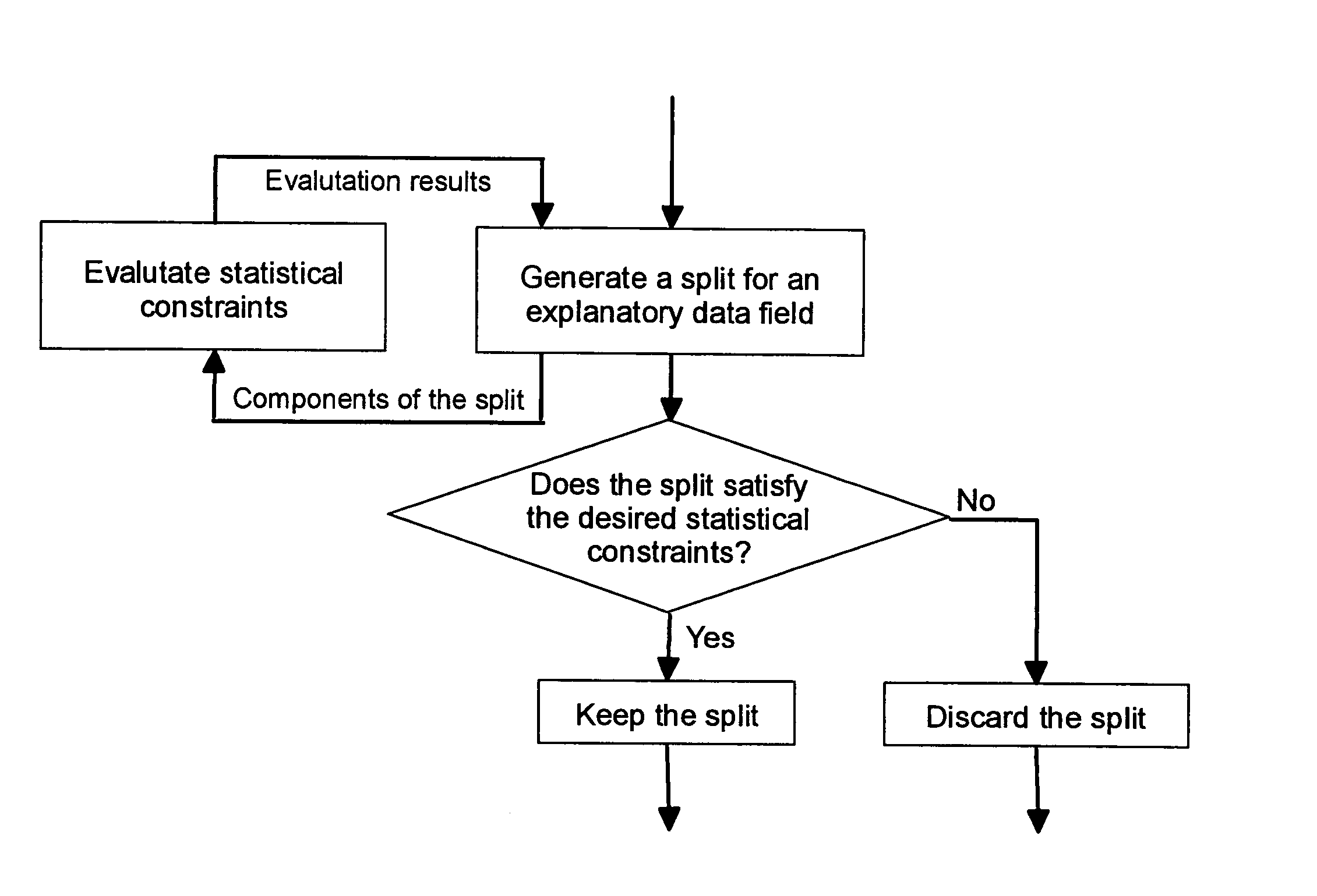
The invention considers a widely applicable method of constructing segmentation-based predictive models from data that permits constraints to be placed on the statistical estimation errors that can be tolerated with respect to various aspects of the models that are constructed. The present invention uses these statistical constraints in a closed-loop fashion to guide the construction of potential segments so as to produce segments that satisfy the statistical constraints whenever it is feasible to do so. The method is closed-loop in a sense that the statistical constraints are used in a manner that is analogous to an error signal in a feed-back control system, wherein the error signal is used to regulate the inputs to the process that is being controlled.
Owner:IBM CORP
Codes For Limited Magnitude Asymetric Errors In Flash Memories
ActiveUS20080168320A1Increase speedReach levelError preventionTransmission systemsReduced sizeErrors and residuals
Error correction is tailored for the use of an ECC for correcting asymmetric errors with low magnitude in a data device, with minimal modifications to the conventional data device architecture. The technique permits error correction and data recovery to be performed with reduced-size error correcting code alphabets. For particular cases, the technique can reduce the problem of constructing codes for correcting limited magnitude asymmetric errors to the problem of constructing codes for symmetric errors over small alphabets. Also described are speed up techniques for reaching target data levels more quickly, using more aggressive memory programming operations.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
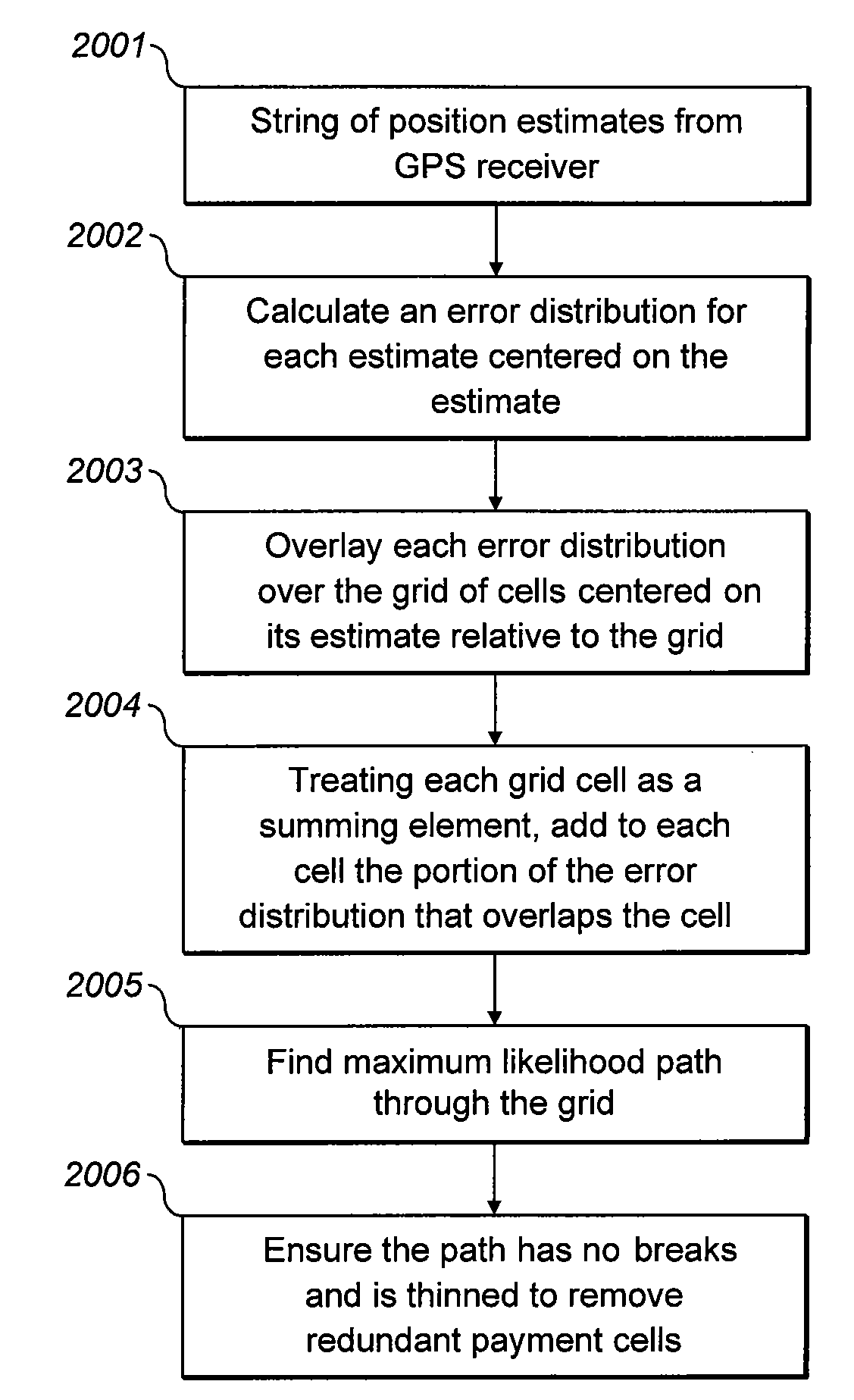
Method and process to ensure that a vehicular travel path recording that includes positional errors can be used to determine a reliable and repeatable road user charge
InactiveUS20090157566A1Instruments for road network navigationTicket-issuing apparatusRoad userReal representation
The invention relates to a system and a method for addressing three problems:(A) generate a tollpath of consistent length by determining one of a possible set of paths which are all the same length in cell-count every time the same journey is taken,(B) determine a consistent price for each tollpath by setting pre-determined values on those cells such that every possible path variant of a specific journey produces the same toll, and(C) determine the correct price for each tollpath by adjusting prices in each cell to account for the exact distance actually represented (some roads pass through a cell parallel to the cell edges and some pass through at an angle) so that the toll calculated exactly matches the toll that would be calculated had the exact linear, analogue distance been measured on the actual road.
Owner:SKYMETER
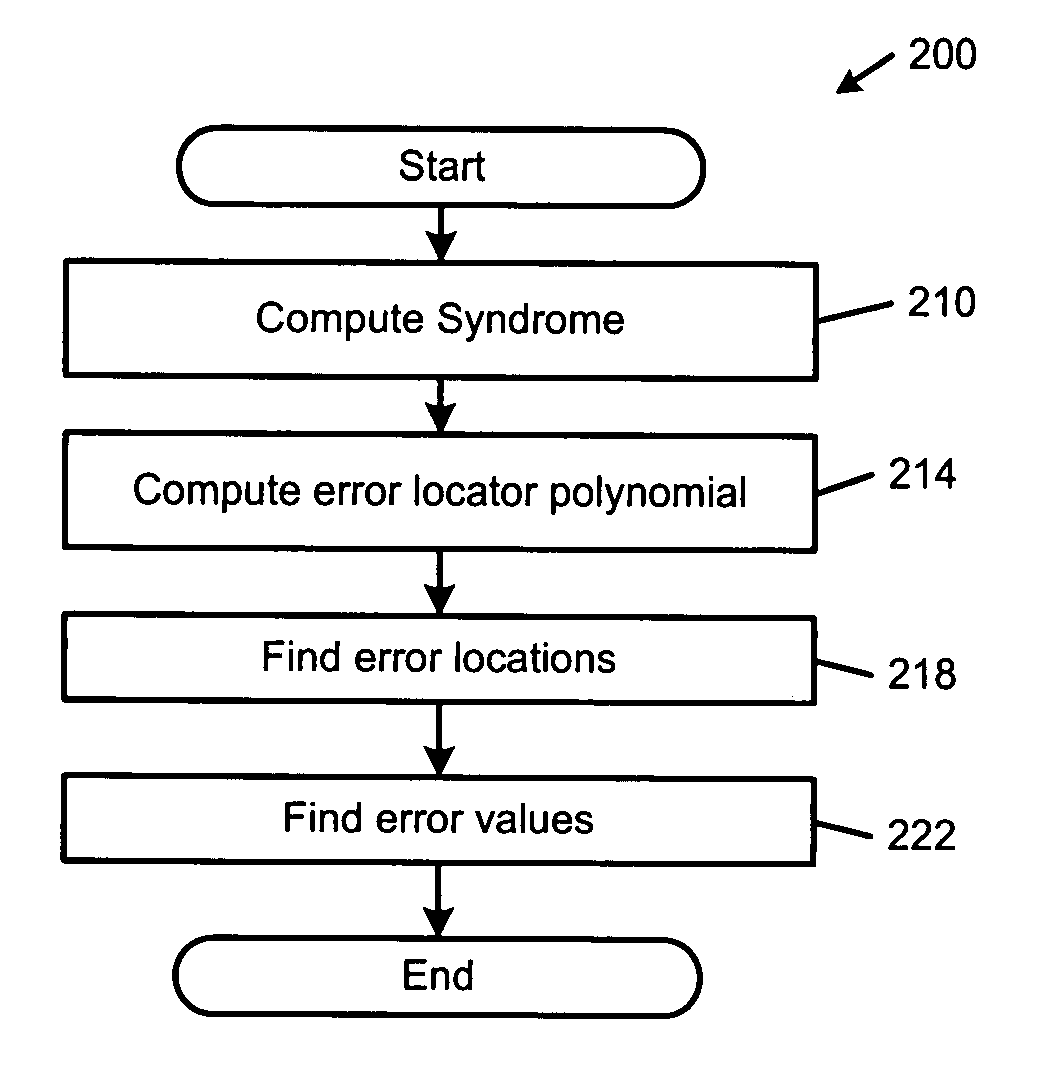
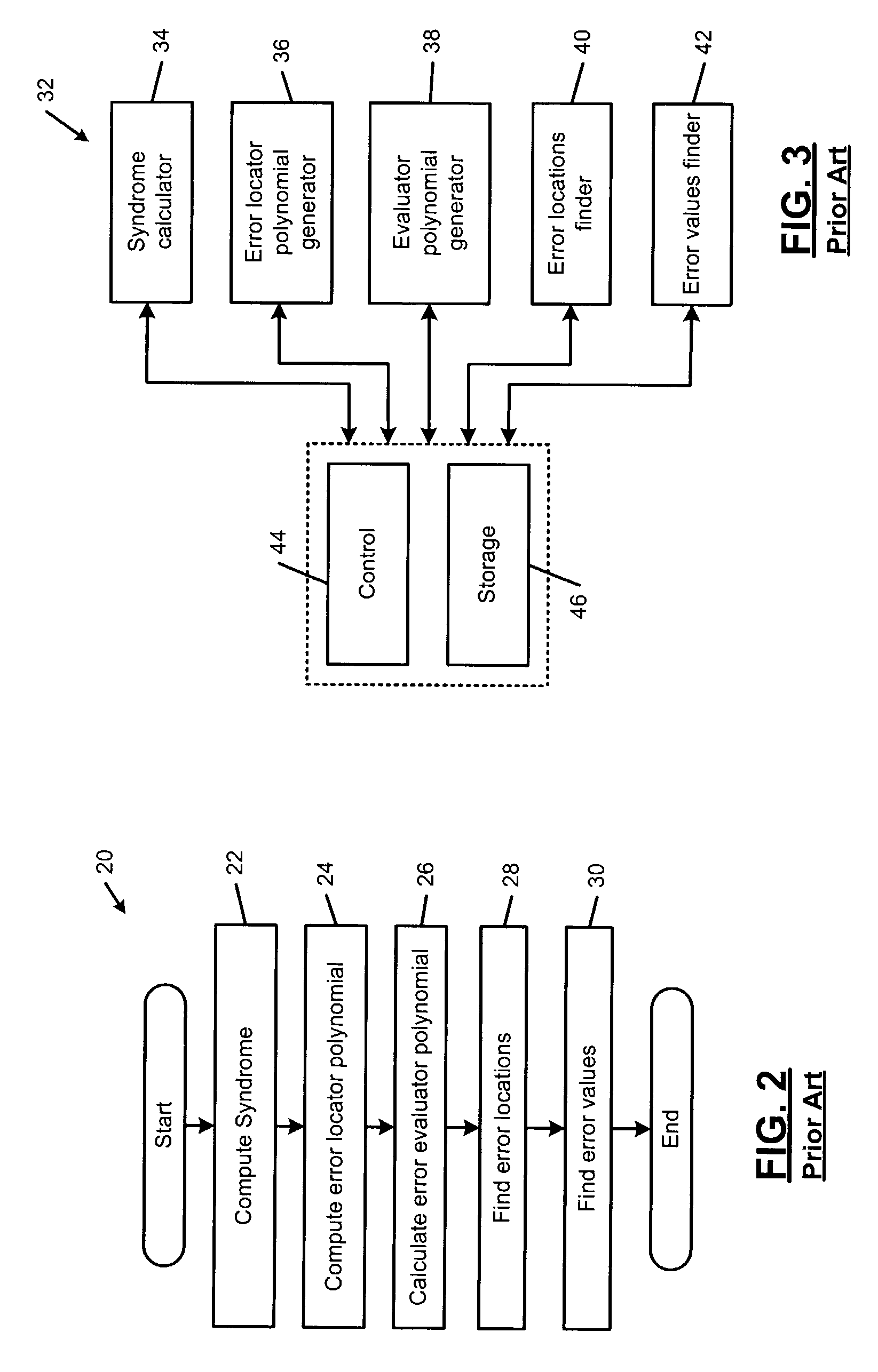
Error evaluator for inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm in Reed-Solomon decoders
ActiveUS7010739B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionError locationReed solomon decoder
An error correcting Reed-Solomon decoder includes a syndrome calculator that calculates syndrome values. An error locator polynomial generator communicates with the syndrome calculator and generates an error locator polynomial. An error location finder communicates with at least one of the syndrome calculator and the error locator polynomial generator and generates error locations. An error values finder communicates with at least one of the syndrome calculator, the error location finder and the error locator polynomial generator and generates error values using an error value relationship that is not based on the traditional error evaluator polynomial. The error locator polynomial generator is an inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (iBMA), which calculates an error locator polynomial and a scratch polynomial. The error value relationship is based on the error locator polynomial and the scratch polynomial.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
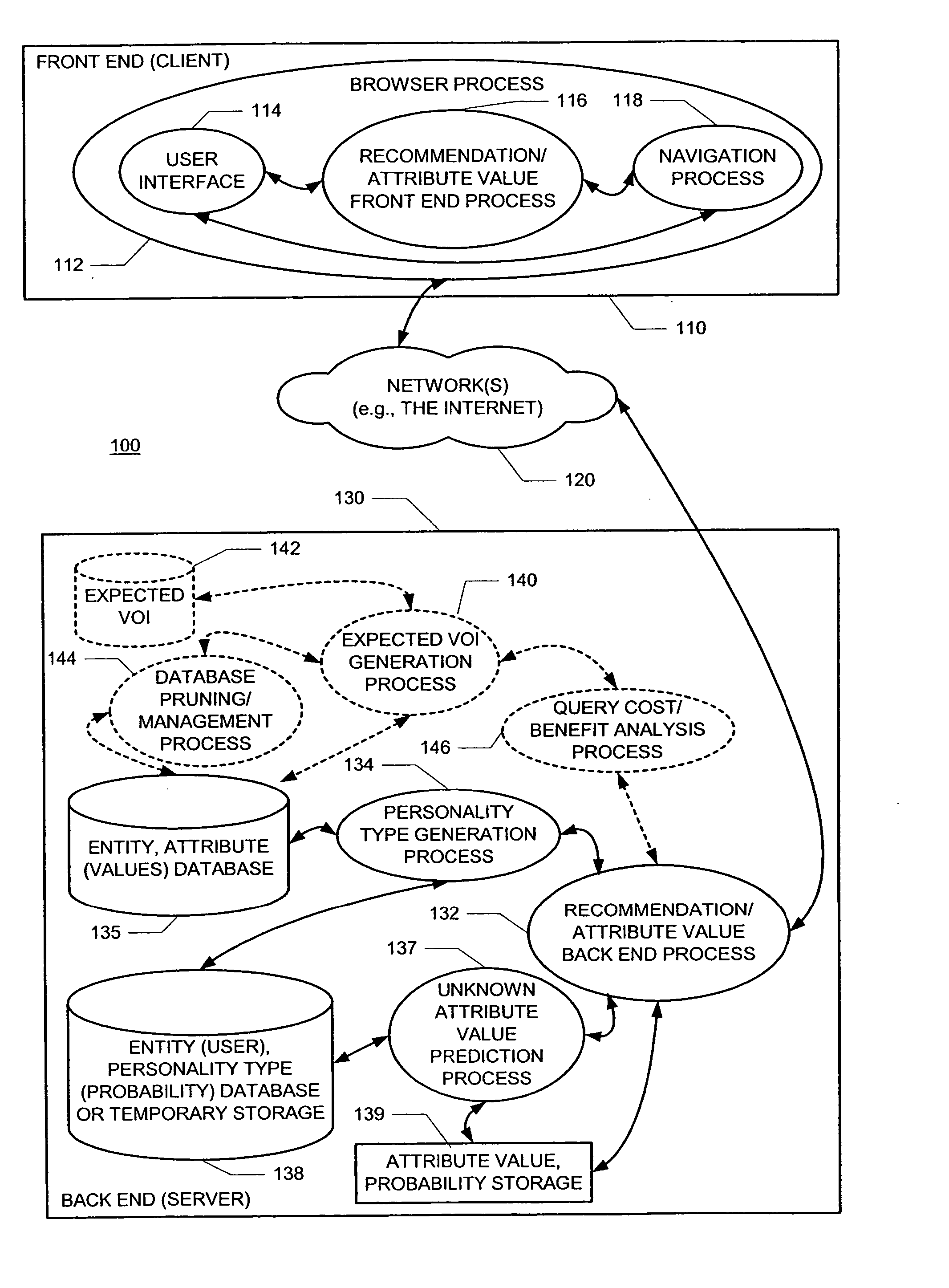
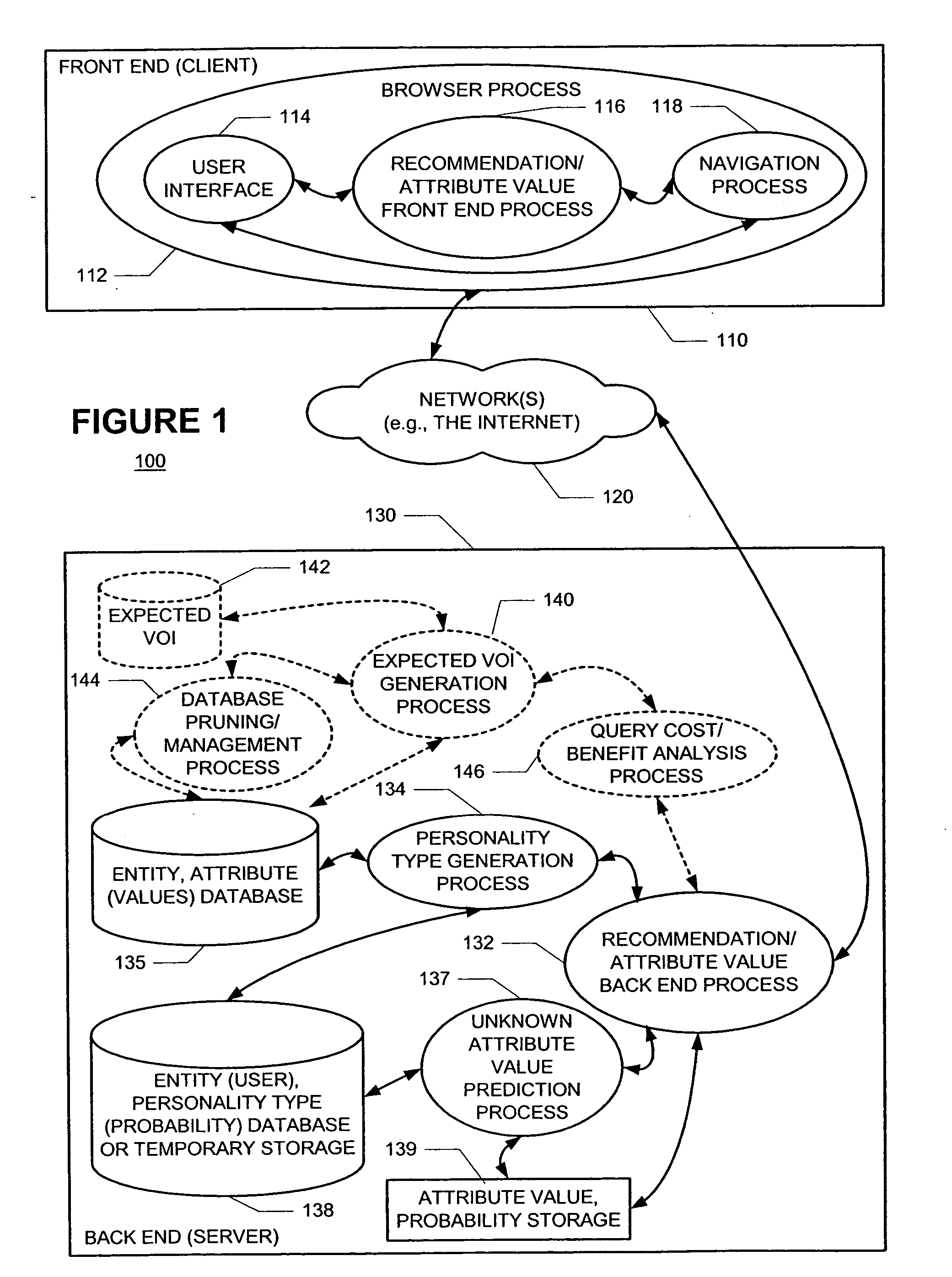
Methods and apparatus for predicting and selectively collecting preferences based on personality diagnosis
InactiveUS20040076936A1Minimal effectCumbersome processMarket predictionsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsProbabilistic semanticsValue of information
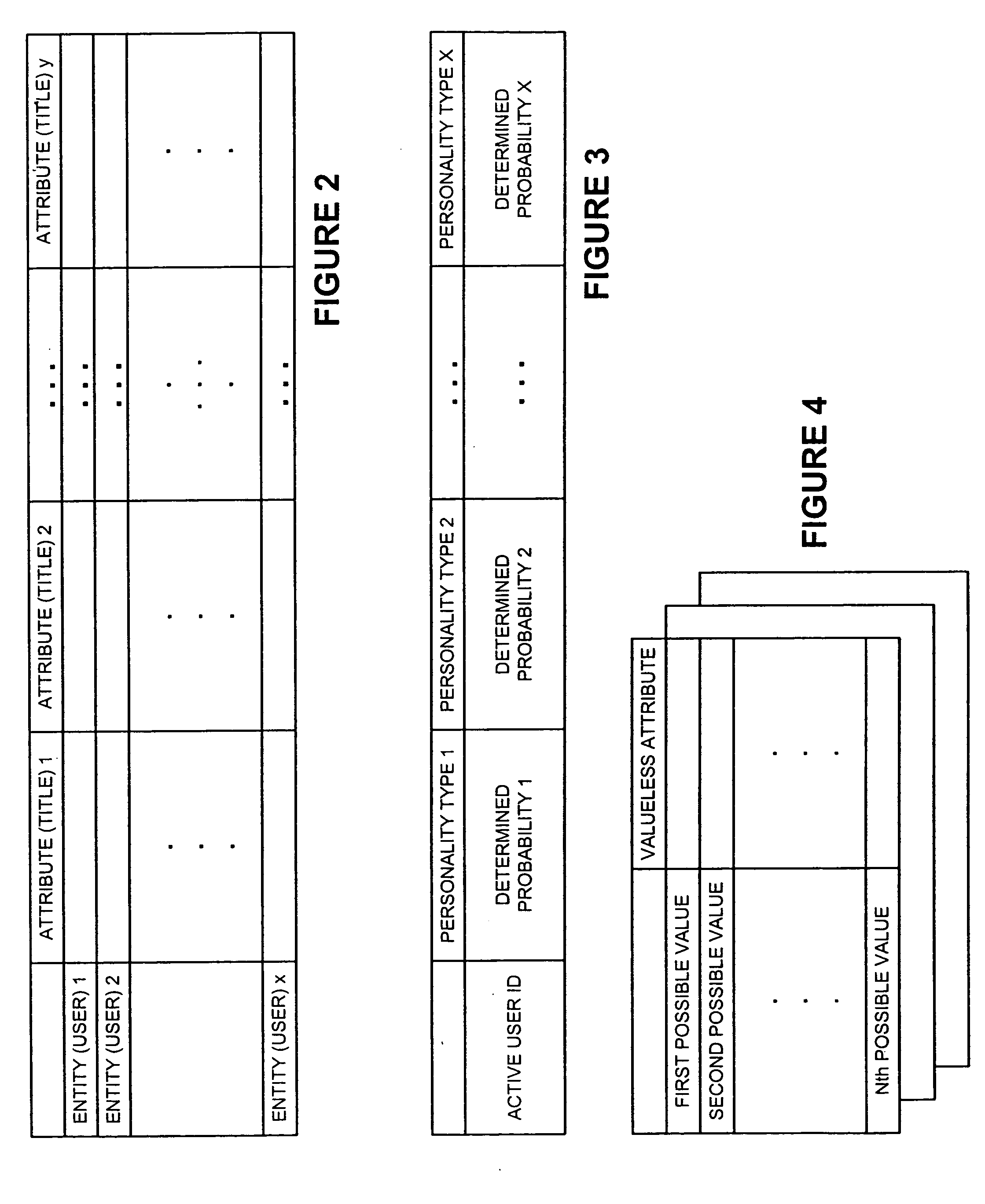
A new recommendation technique, referred to as "personality diagnosis", that can be seen as a hybrid between memory-based and model-based collaborative filtering techniques, is described. Using personality diagnosis, all data may be maintained throughout the processes, new data can be added incrementally, and predictions have meaningful probabilistic semantics. Each entity's (e.g., user's) reported attributes (e.g., item ratings or preferences) may be interpreted as a manifestation of their underlying personality type. Personality type may be encoded simply as a vector of the entity's (e.g., user's) "true" values (e.g., ratings) for attributes (e.g., items) in the database. It may be assumed that entities (e.g., users) report values (e.g., ratings) with a distributed (e.g., Gaussian) error. Given an active entity's (e.g., user's) known attribute values (e.g., item ratings), the probability that they have the same personality type as every other entity (e.g., user) may be determined. Then, the probability that they will have a given value (e.g., rating) for a valueless (e.g., unrated) attribute (e.g., item) may then be determined based on the entity's (e.g., user's) personality type. The probabilistic determinations may be used to determine expected value of information. Such an expected value of information could be used in at least two ways. First, an interactive recommender could use expected value of information to favorably order queries for attribute values (e.g., item ratings), thereby mollifying what could otherwise be a tedious and frustrating process. Second, expected value of information could be used to determine which entries of a database to prune or ignore-that is, which entries, which if removed, would have a minimal effect of the accuracy of recommendations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D artifact reducing for encoded image signal
InactiveUS20060050783A1Efficient reductionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementRandom noiseNoise reduction
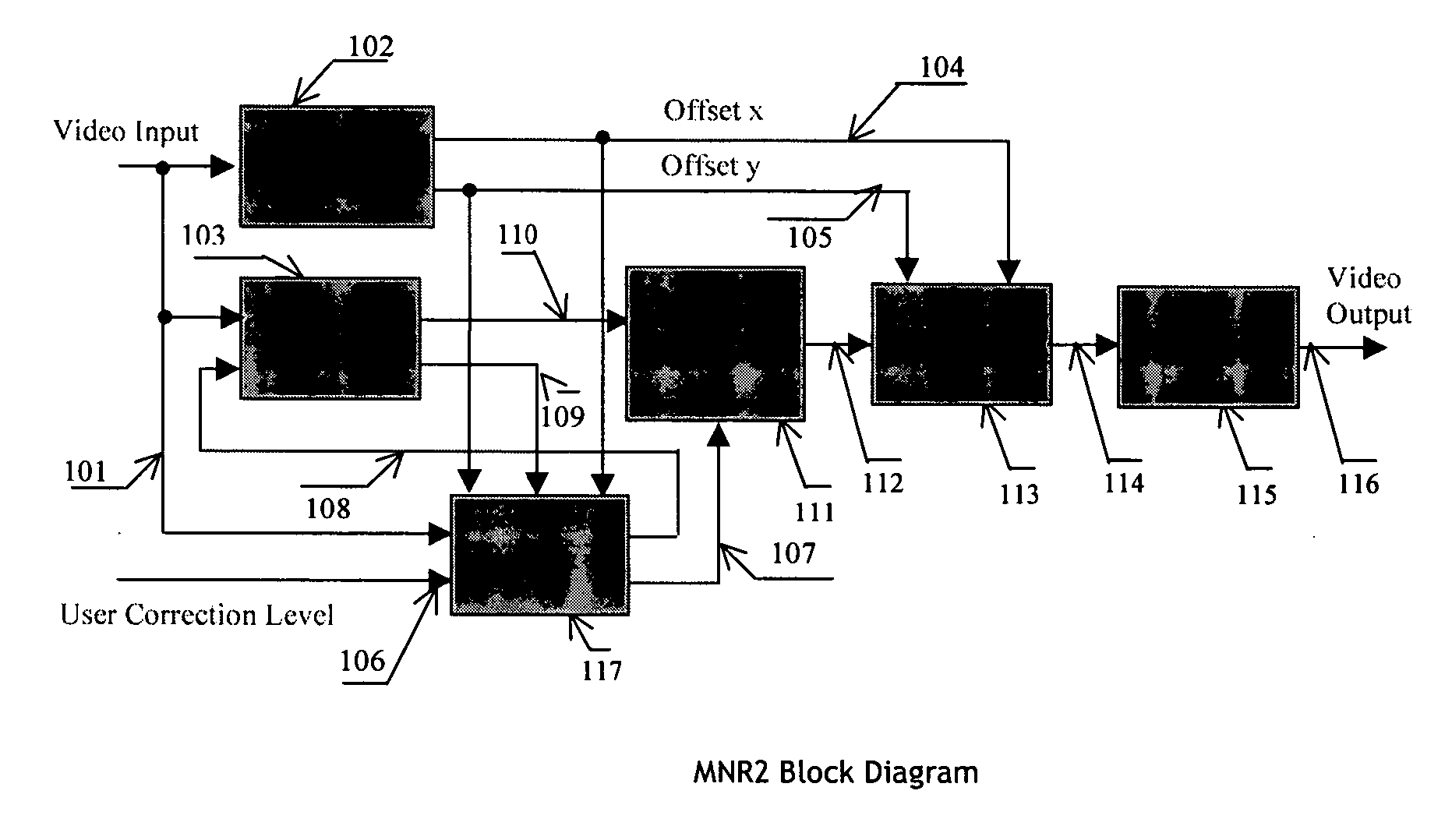
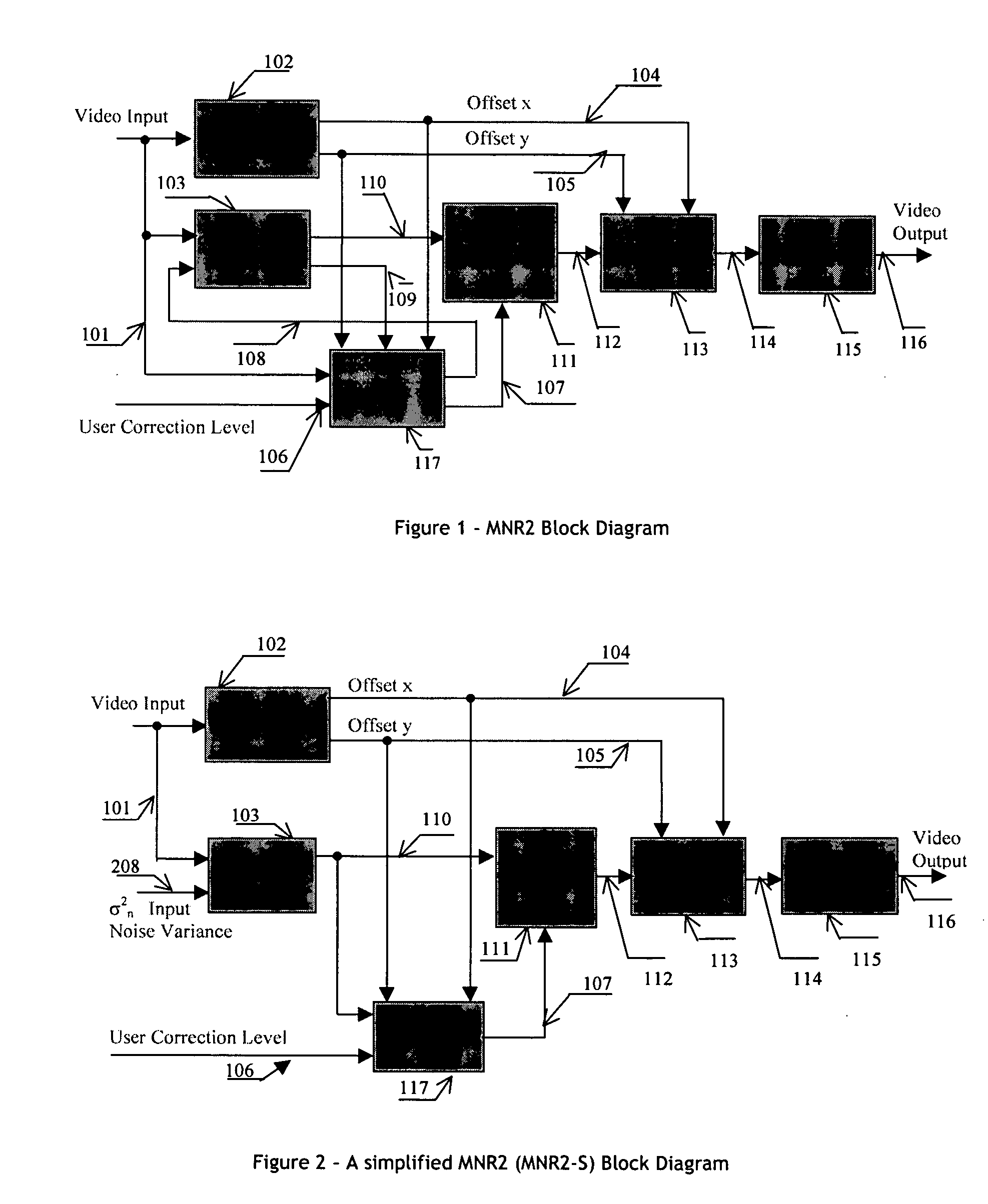
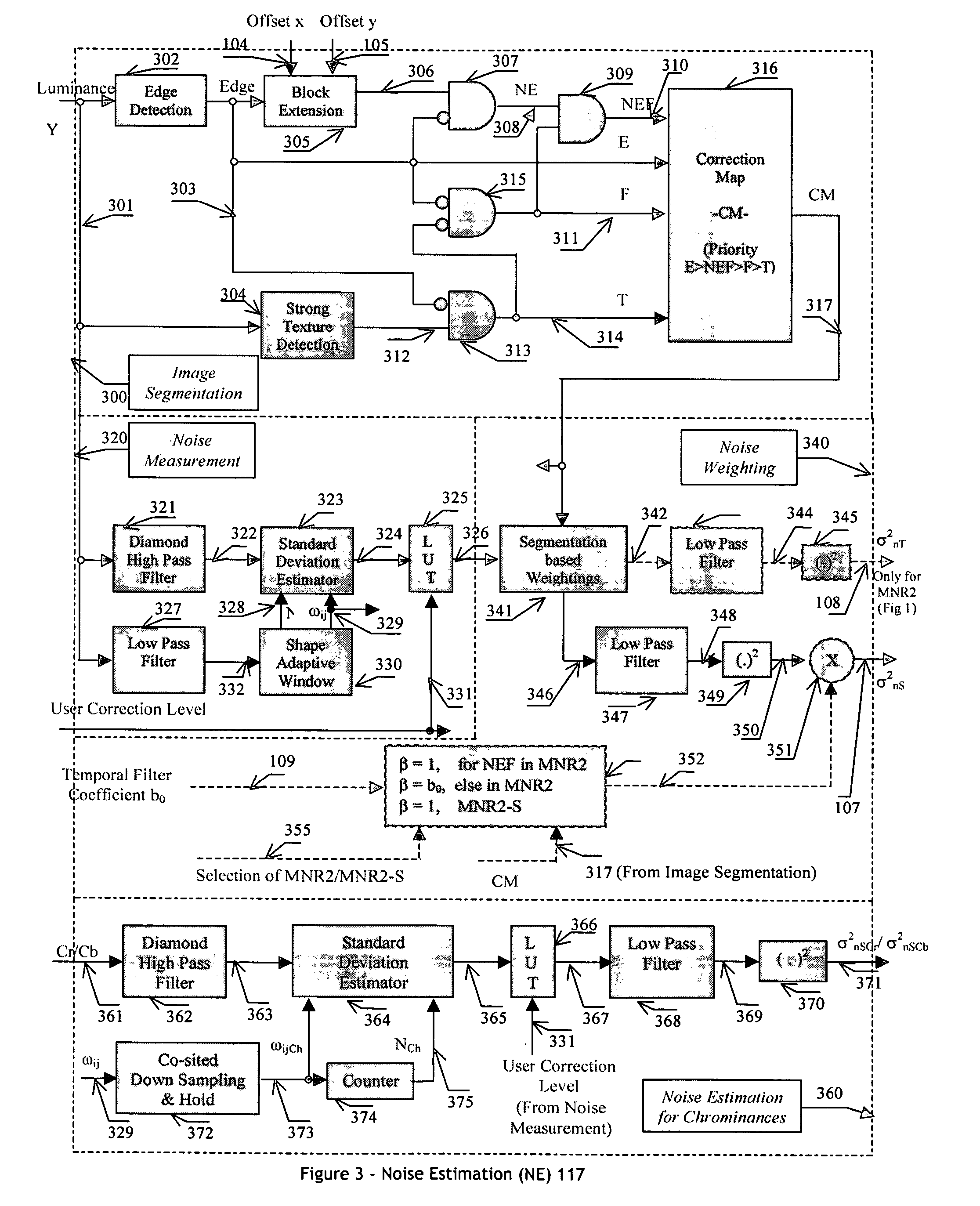
An efficient and non-iterative 3D post processing method and system is proposed for mosquito noise reduction, block localization and correction in DCT block-based decoded images. The 3D post processing is based on a simple classification that segments a picture in multiple regions such as Edge, Near Edge, Flat, Near Flat and Texture regions. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient and shape adaptive local power estimation for equivalent additive noise and provides simple noise power weighting for each above cited region. Temporal filtering configurations using Minimum Noise Variance Criterion are proposed for reducing temporally varying coding artifacts. A Minimum Mean Square Error or Minimum Mean Square Error-like noise reduction with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing is utilized for smoothing mosquito and / or random noise for the whole image, particularly for Edge regions. The proposed technique comprises also signal domain histogram analysis based Block Localization and adaptive edge based Block artifact correction. Finally, is also proposed an optional adaptive detail enhancer which can enhances the luminance signal in eight directions differently.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
Error estimate concerning a target device's location operable to move in a wireless environment
ActiveUS20050131635A1Improve efficiencyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlProbit modelPosition error
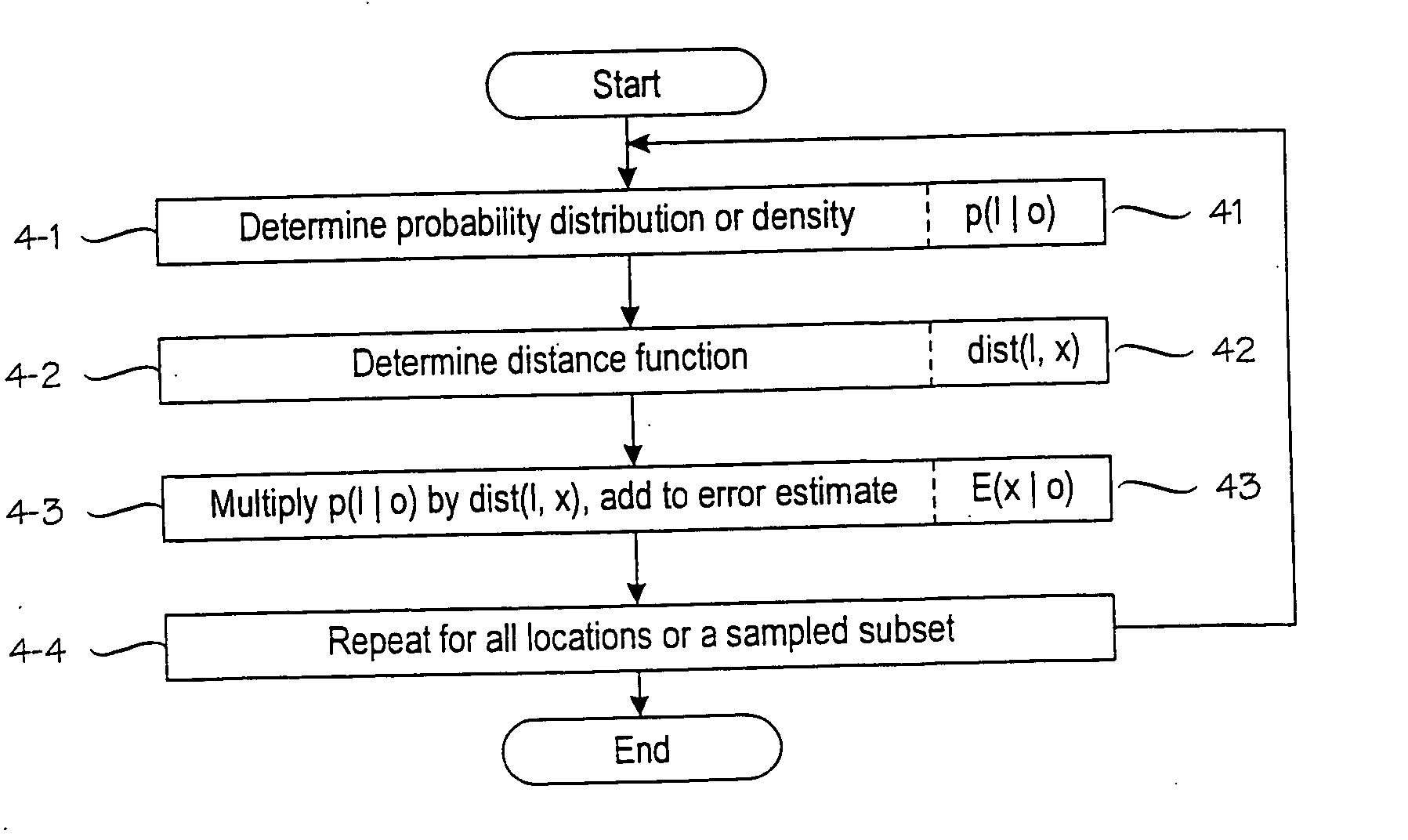
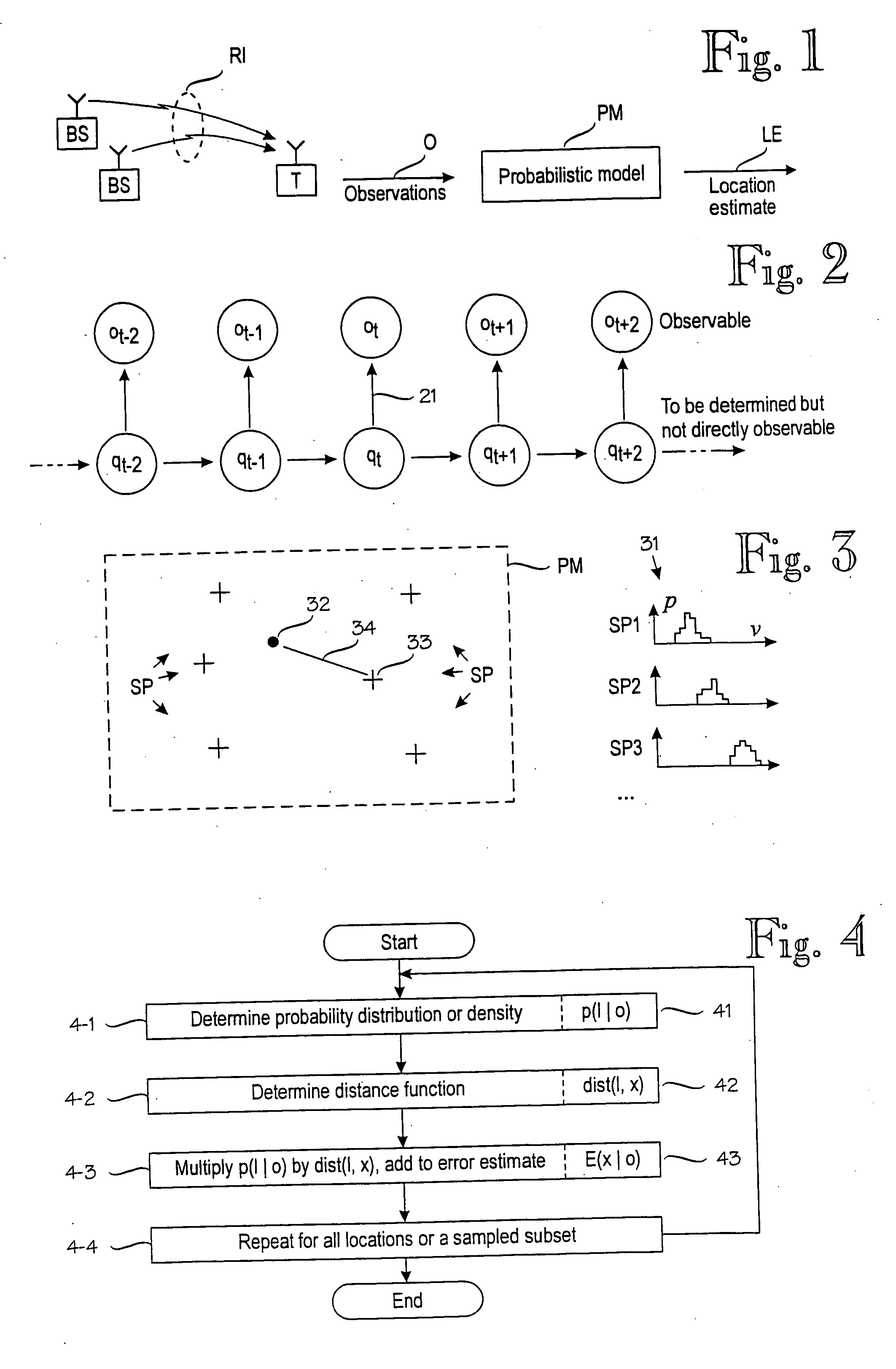
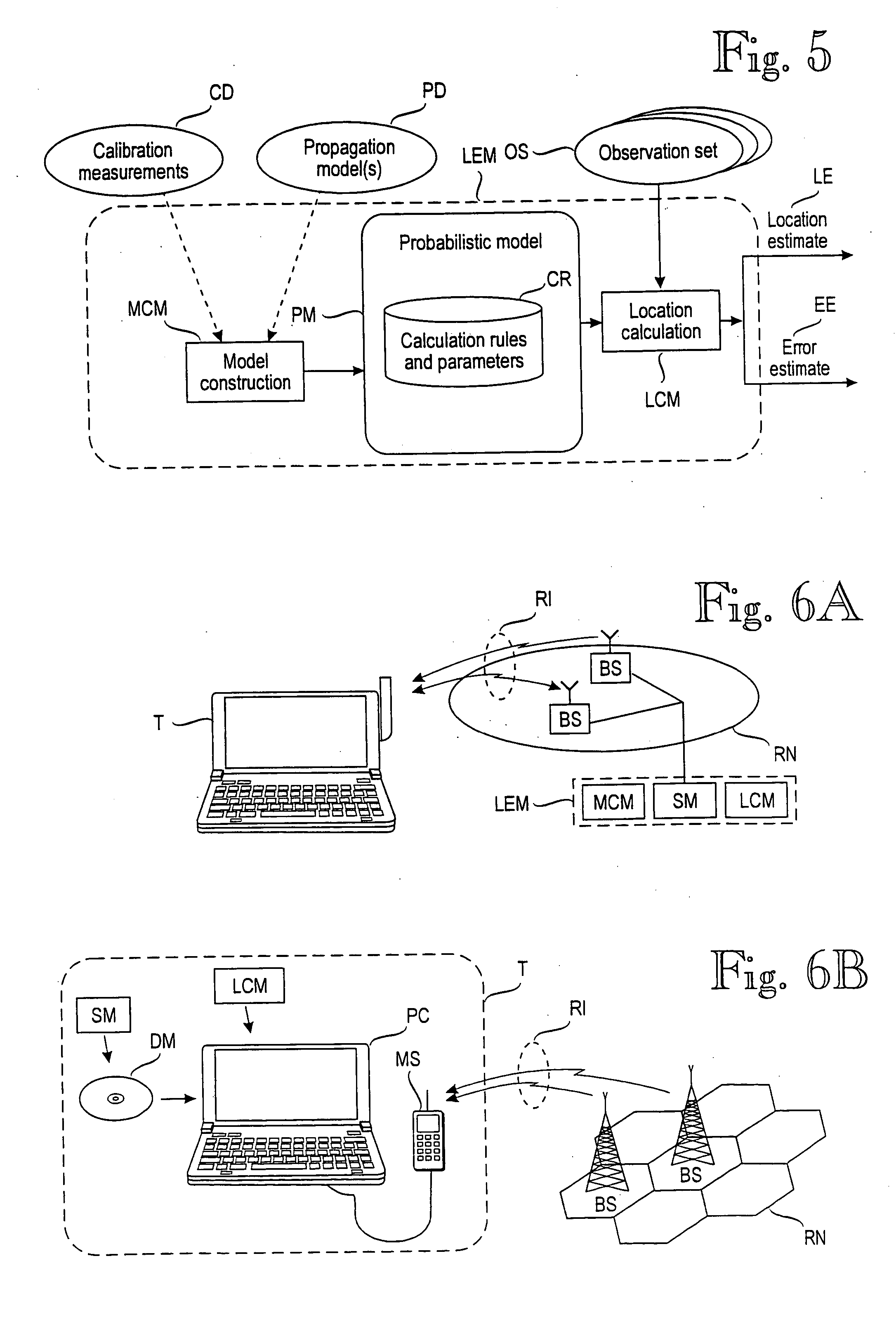
A method for determining an error estimate concerning a target device's location. The target device moves and communicates in a wireless environment using signals having at least one measurable signal value. A probabilistic model of the wireless environment indicates a probability distribution for signal values at several sample points in the wireless environment. A set of observations of signal values is made and the target device's location is estimated based on the probabilistic model and the set of observations. The error estimate (43) is determined as a combination of products over several sample points (SP). Each product comprises a probability distribution (41) for the sample point in question being the target device's location and a distance function (43) between the sample point in question and the target device's estimated location.
Owner:AIRISTA FLOW INC +1
Method and Apparatus for Determining an Overlay Error
ActiveUS20120013881A1Scattering properties measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusAsymmetric inductionScatterometer
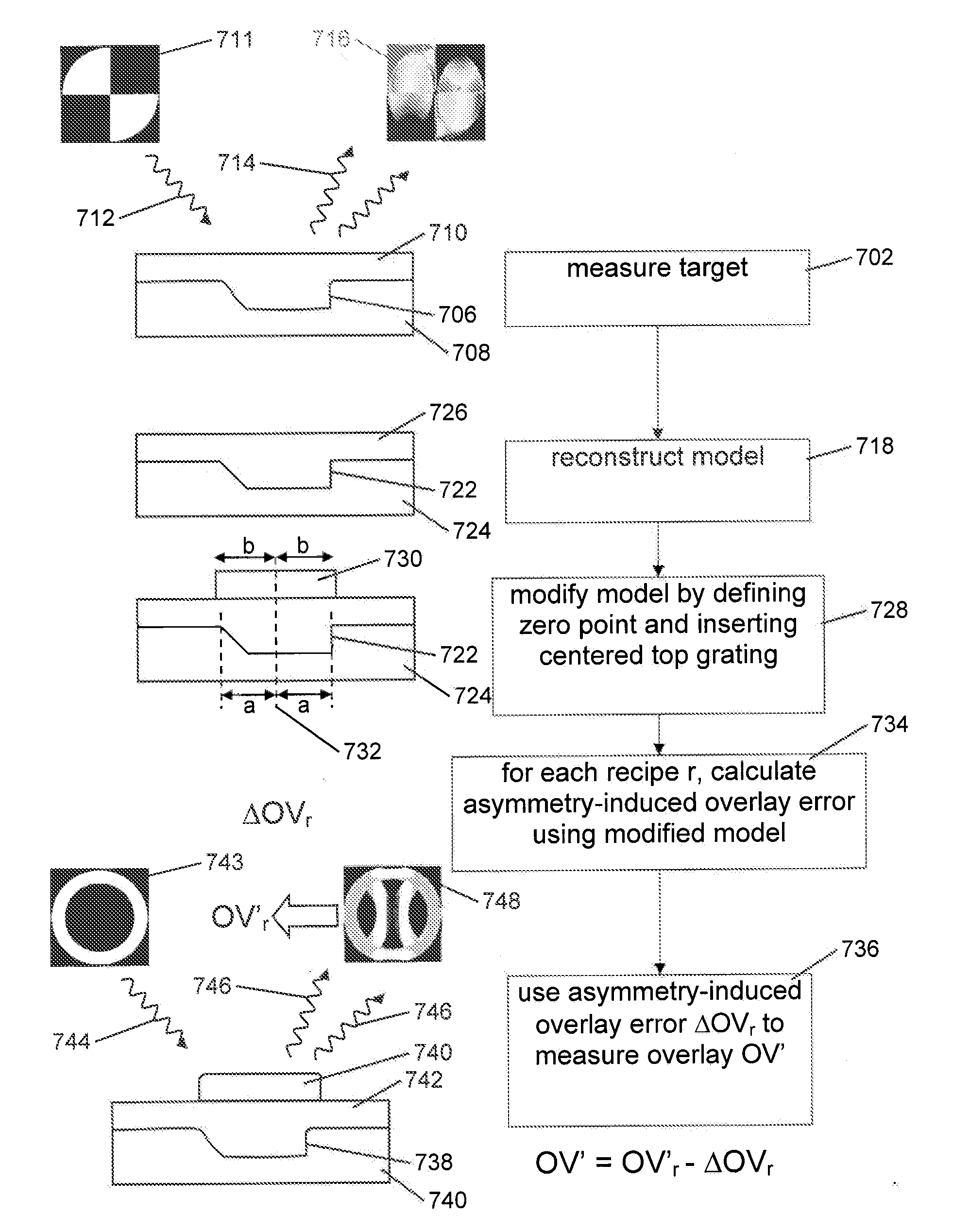
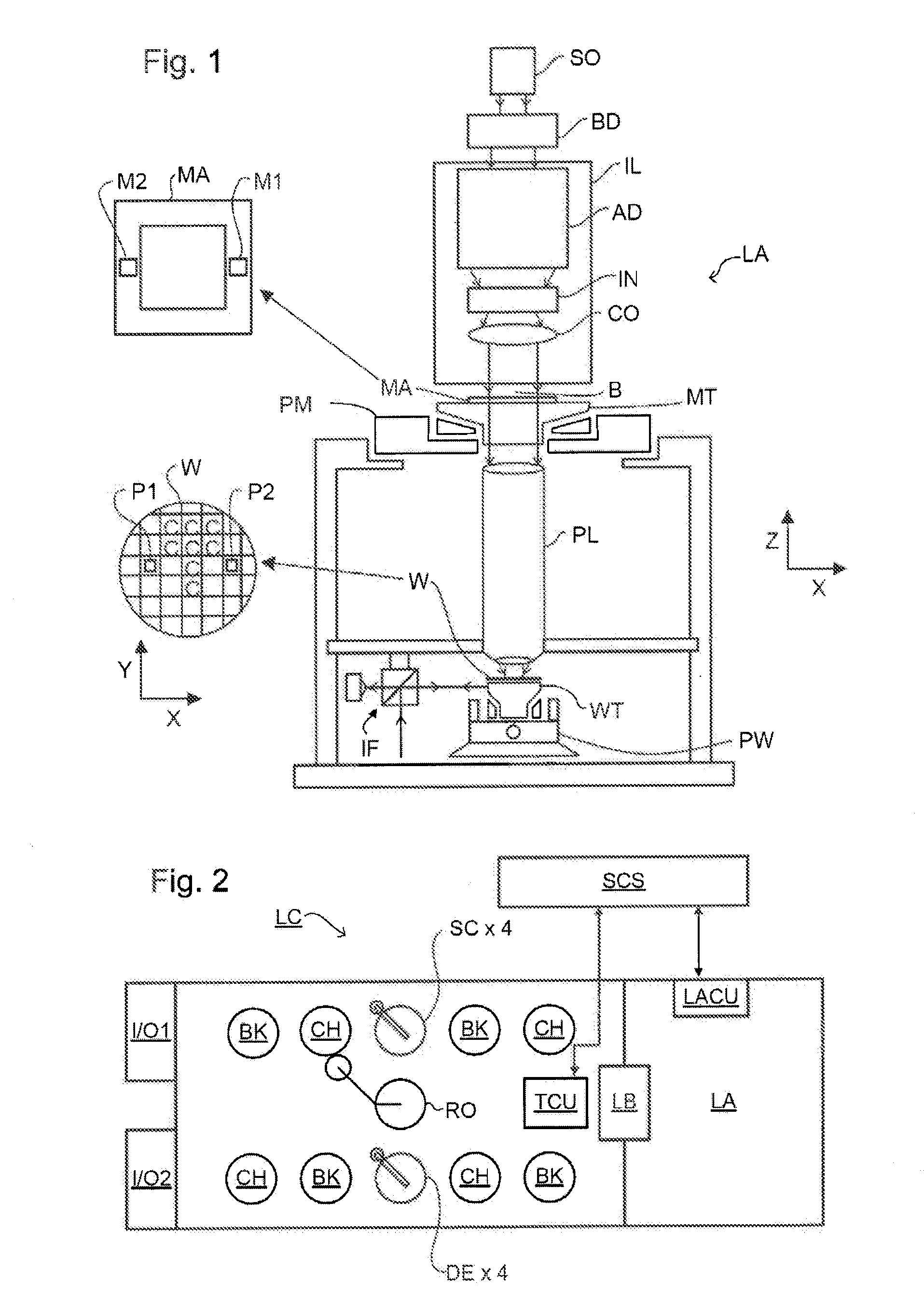
A method of determining an overlay error. Measuring an overlay target having process-induced asymmetry. Constructing a model of the target. Modifying the model, e.g., by moving one of the structures to compensate for the asymmetry. Calculating an asymmetry-induced overlay error using the modified model. Determining an overlay error in a production target by subtracting the asymmetry-induced overlay error from a measured overlay error. In one example, the model is modified by varying asymmetry p(n′), p(n″) and the calculating an asymmetry-induced overlay error is repeated for a plurality of scatterometer measurement recipes and the step of determining an overlay error in a production target uses the calculated asymmetry-induced overlay errors to select an optimum scatterometer measurement recipe used to measure the production target.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Motion estimation and compensation device with motion vector correction based on vertical component values
InactiveUS20060023788A1Color television with pulse code modulationImage analysisMotion vectorErrors and residuals
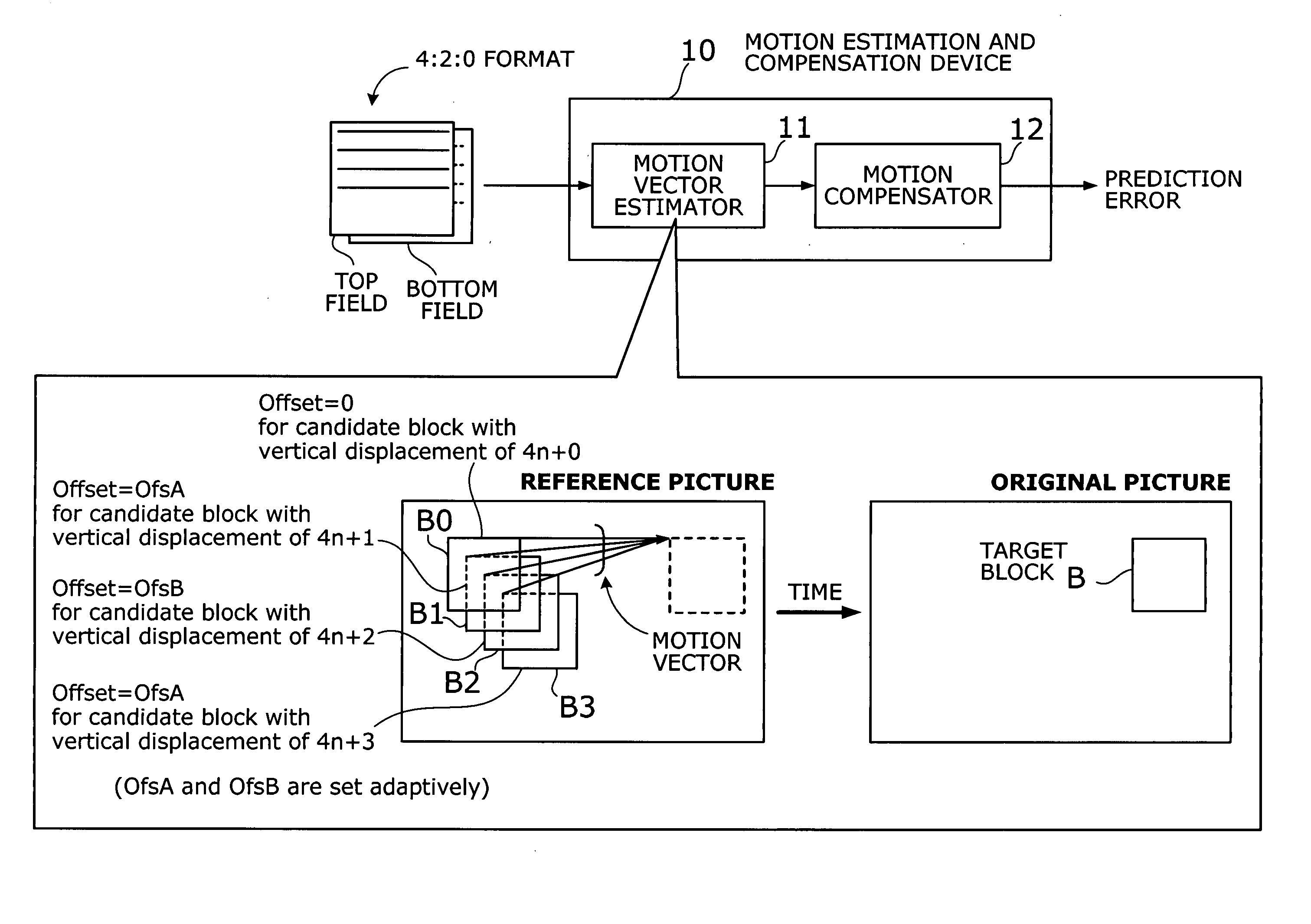
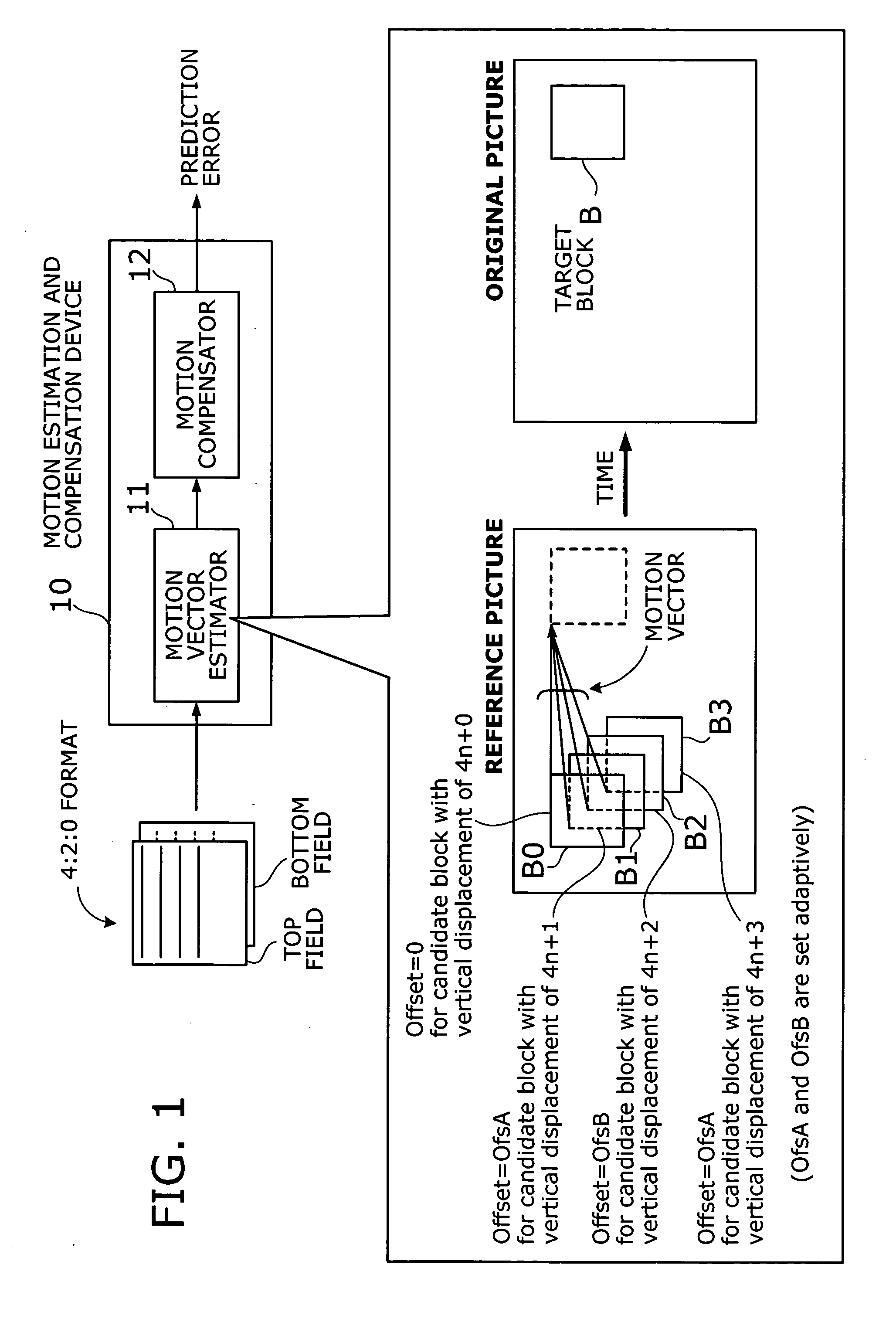
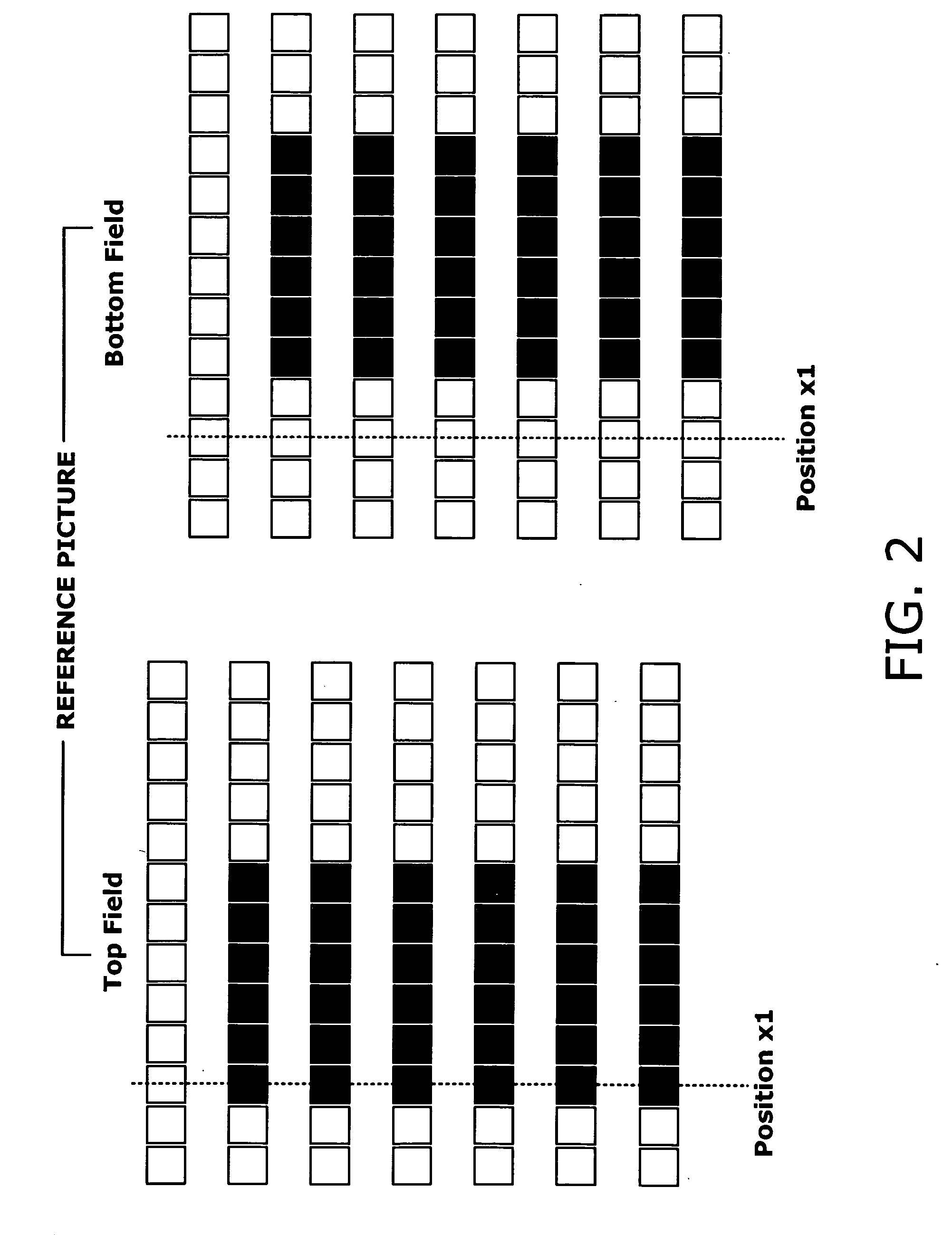
A motion estimation and compensation device that avoids discrepancies in chrominance components which could be introduced in the process of motion vector estimation. The device has a motion vector estimator for finding motion vectors in given interlace-scanning chrominance-subsampled video signals. The estimator compares each candidate block in a reference picture with a target block in an original picture by using a sum of absolute differences (SAD) in luminance as similarity metric, chooses a best matching candidate block that minimizes the SAD, and determines its displacement relative to the target block. In this process, the estimator gives the SAD of each candidate block an offset determined from the vertical component of a corresponding motion vector, so as to avoid chrominance discrepancies. A motion compensator then produces a predicted picture using such motion vectors and calculates prediction error by subtracting the predicted picture from the original picture.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
Methods and apparatus for utilizing a proportional hazards model to evaluate loan risk
InactiveUS7392216B1Increase valueAccurate identificationFinanceProportional hazards modelErrors and residuals
Systems and processes for more accurate mortgage scoring are described. A proportional hazards model is employed in which not only the occurrence of an event, but also the time to an event such as default of a loan, is considered. In this approach, a hazard rate can be viewed as the chance that an observation will experience an event in the next instant. There are two components to the response, and a binary variable is utilized to indicate whether the event was observed or not, and a time variable. As a result, the number of loans used for modeling is greatly increased, and the time it takes to observe the event, a valuable piece of information in itself, is included in the process. In addition, nonlinear effects are advantageously modeled in a continuous fashion using hat functions to map a series of independent variables. This approach typically yields smaller prediction errors near boundary points.
Owner:GE MORTGAGE HLDG
Model predictive control system and method for reduction of steady state error
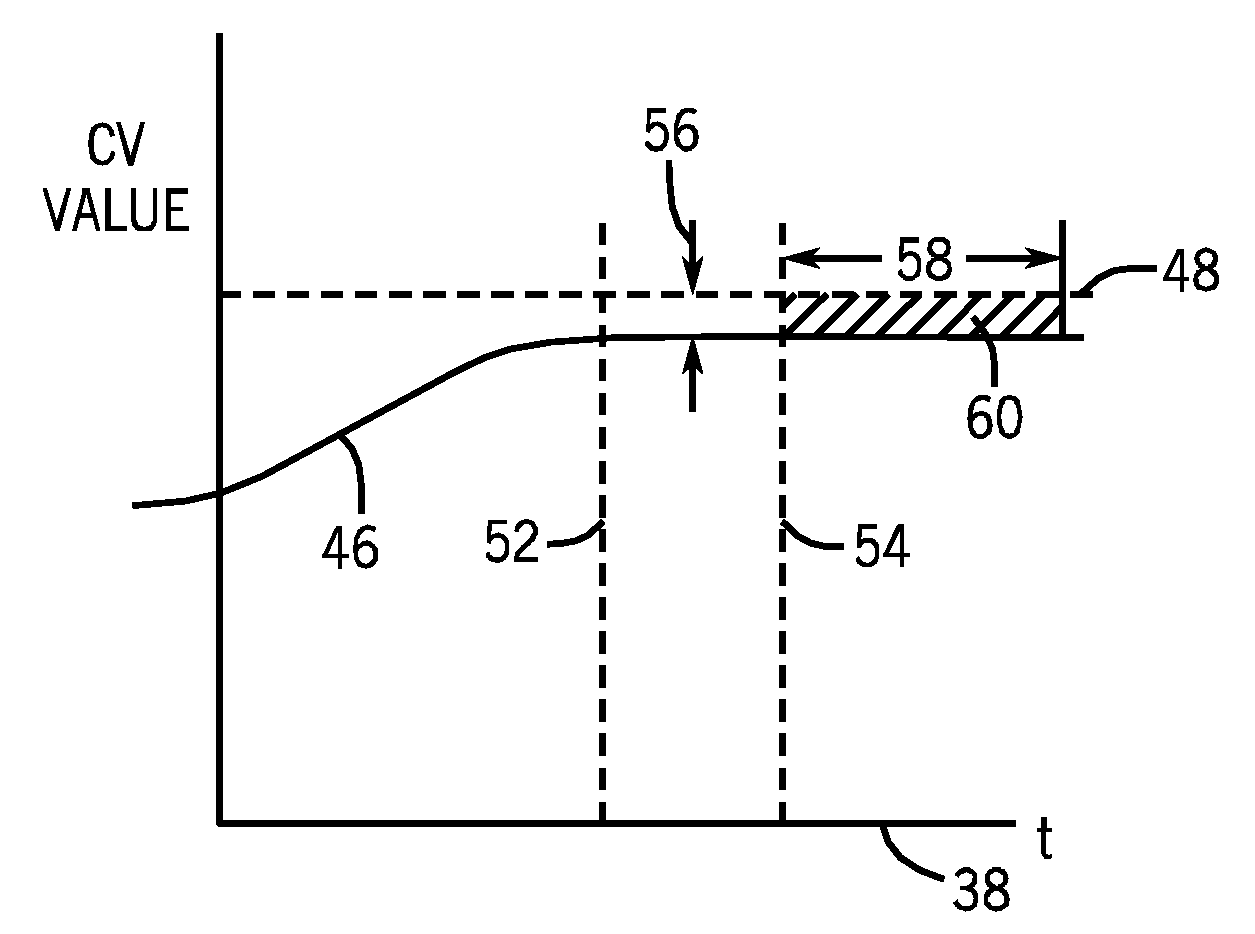
ActiveUS8032235B2Reducing steady state errorReduce errorsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisHorizonControl system
A technique is disclosed for reducing an error in a controlled variable via model predictive control. A predicted error in the controlled variable is determined for a forward-looking control horizon based upon measured or computed variables. The integral of the predicted error is computed. If the error or the integral exceed a tolerance for a determined time period, the model predictive control algorithm is modified to drive the error or the integral to within a tolerance. The modifications to the control algorithm may include changes to coefficients for terms based upon the error and / or the integral of the error.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Rapid target detection method based on convolutional neural network
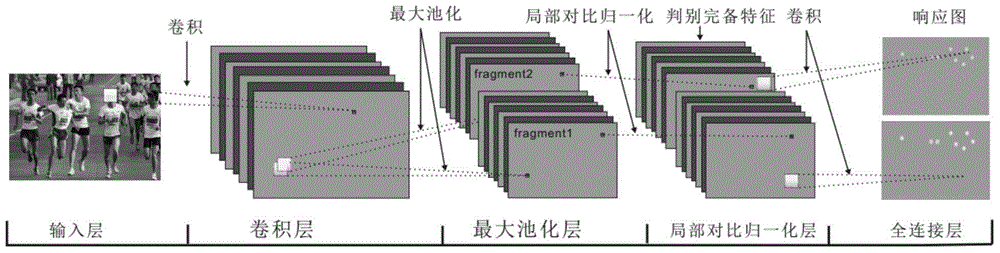
ActiveCN104573731ASolve the feature loss problemImprove detection efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionGeneralization errorVisual technology
The invention relates to a rapid target detection method based on a convolutional neural network, and relates to the computer vision technology. The rapid target detection method comprises the following steps: training convolutional neural network parameters by utilizing a training set; solving the problem of max-pooling losing feature by using an expander graph and generating a discriminative complete feature graph; regarding the full-connection weight of the convolutional neural network as a linear classifier, and estimating the generalization error of the linear classifier on the discriminative complete feature by using a probable approximately correct learning framework; estimating the required number of the linear classifiers according to the generalization error and the expected generalization error threshold value; and finally, completing the target detection on the discriminative complete feature graph by using the linear classifiers on the basis of a smooth window. The detection efficiency and the target detection precision are obviously improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
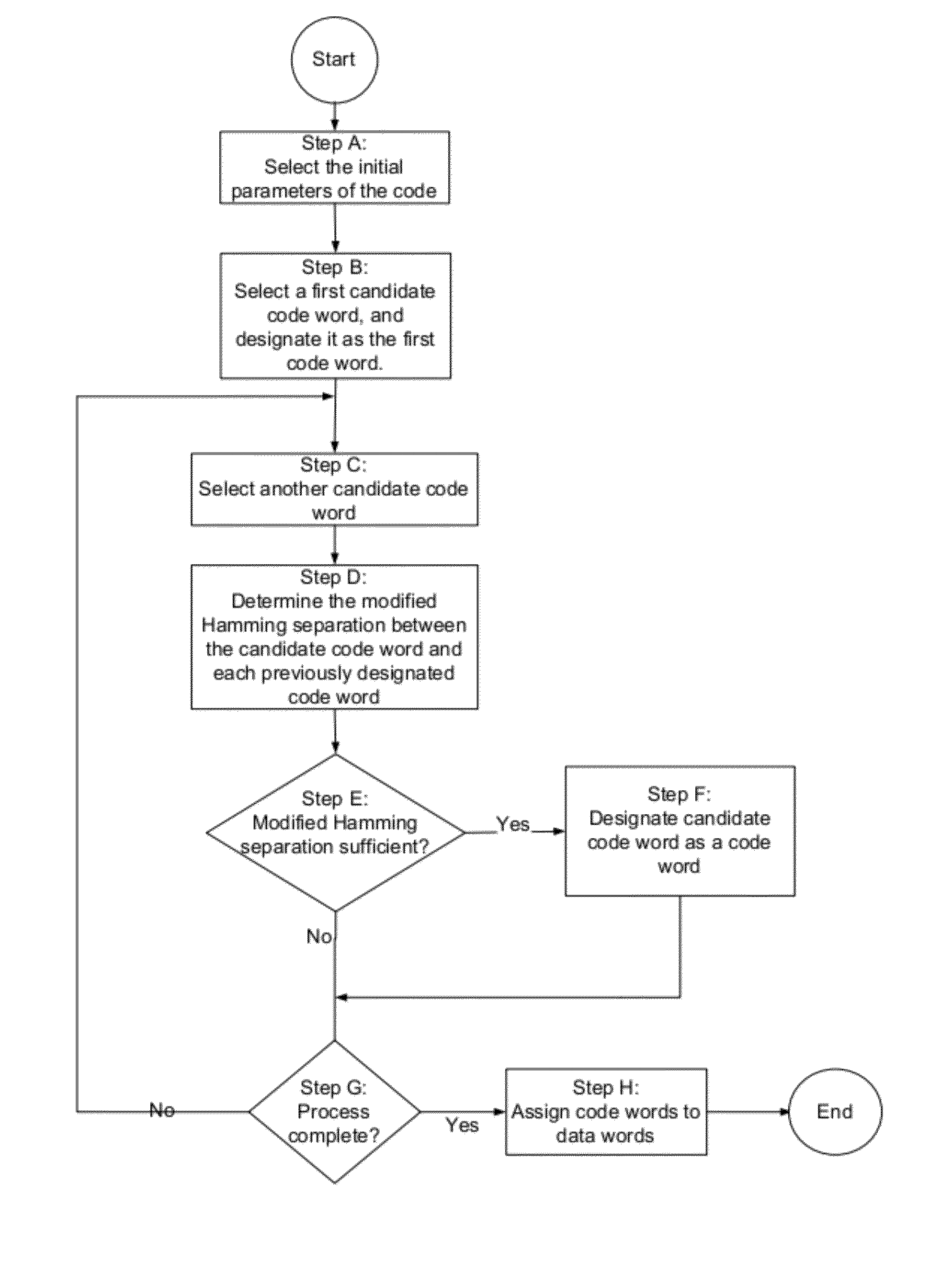
Error detection and correction codes for channels and memories with incomplete error characteristics
InactiveUS8429495B2Efficient error-correcting codeOther error detection/correction/protectionCode conversionParallel computingErrors and residuals
A channel has a first and a second end. The first end of the channel is coupled to a transmitter. The channel is capable of transmitting symbols selected from a symbol set from the first end to the second end. The channel exhibits incomplete error introduction properties. A code comprises a set of code words. The elements of the set of code words are one or more code symbols long. The code symbols are members of the symbol set. The minimum modified Hamming separation between the elements of the set of code words in light of the error introduction properties of the channel is greater than the minimum Hamming distance between the elements of the set of code words. A memory device, a method of using the channel, and a method of generating the code are also described.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Methods of filtering and determining cofidence factors for reference points for use in triangulation systems based on Wi-Fi access points
Methods and systems for classifying WLAN access points according to the quality of estimation of characteristics of the WLAN access points are provided. The classifications may be used to scale a reference database and quantify an expected error of estimation of the characteristics of the access points. WLAN access points may be classified based on their impact on a user's position, speed of travel, and direction of travel estimation accuracy in a WLAN positioning system. A method for determining a quality of estimation of characteristics of a Wi-Fi access point comprises a Wi-Fi enabled scanning device measuring a number of received signal strength (RSS) samples of the Wi-Fi signal transmitted by the Wi-Fi access point. A total distance traveled by the Wi-Fi enabled scanning device while measuring the number of RSS samples is estimated and used to estimate the quality of estimation of characteristics of the Wi-Fi access point.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
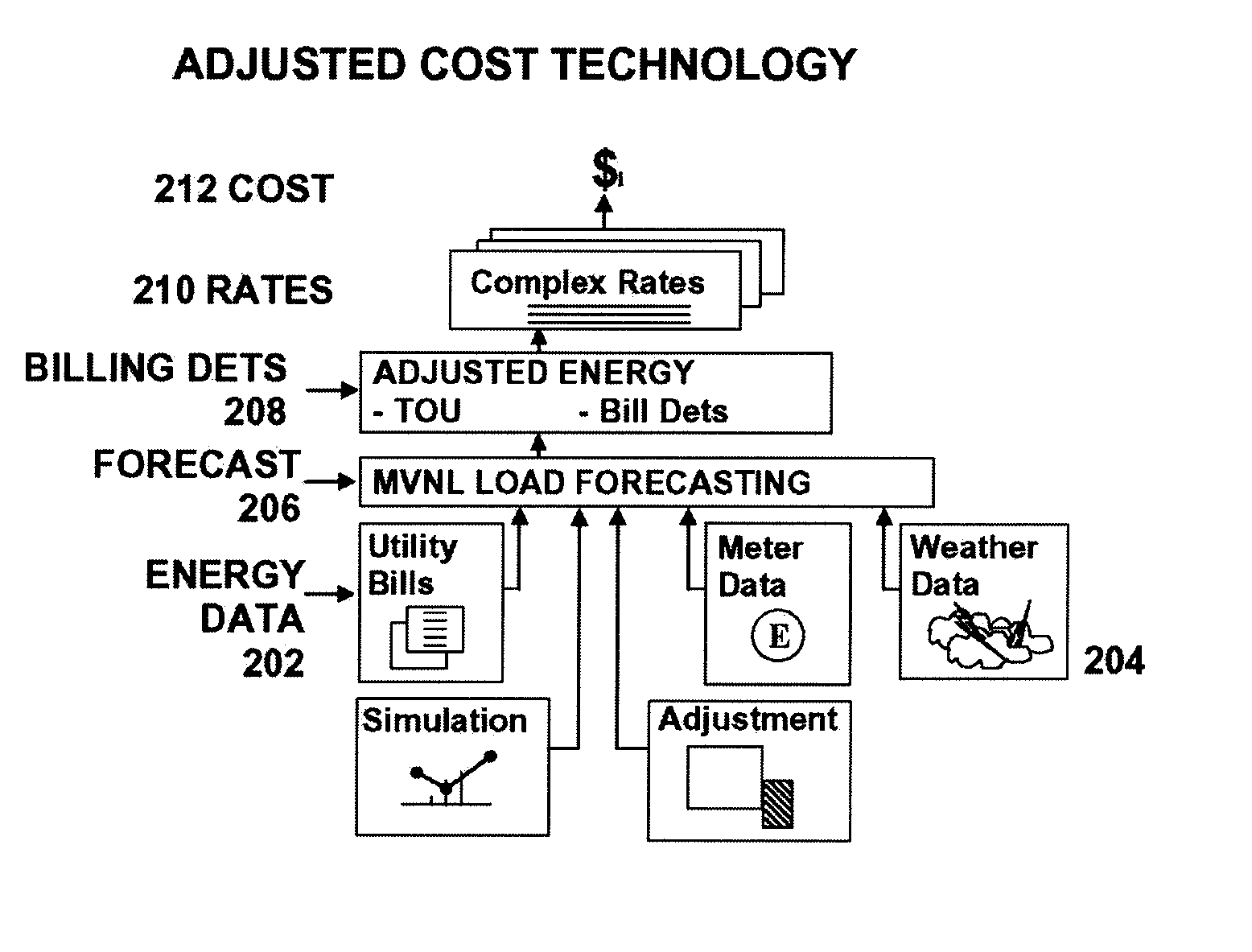
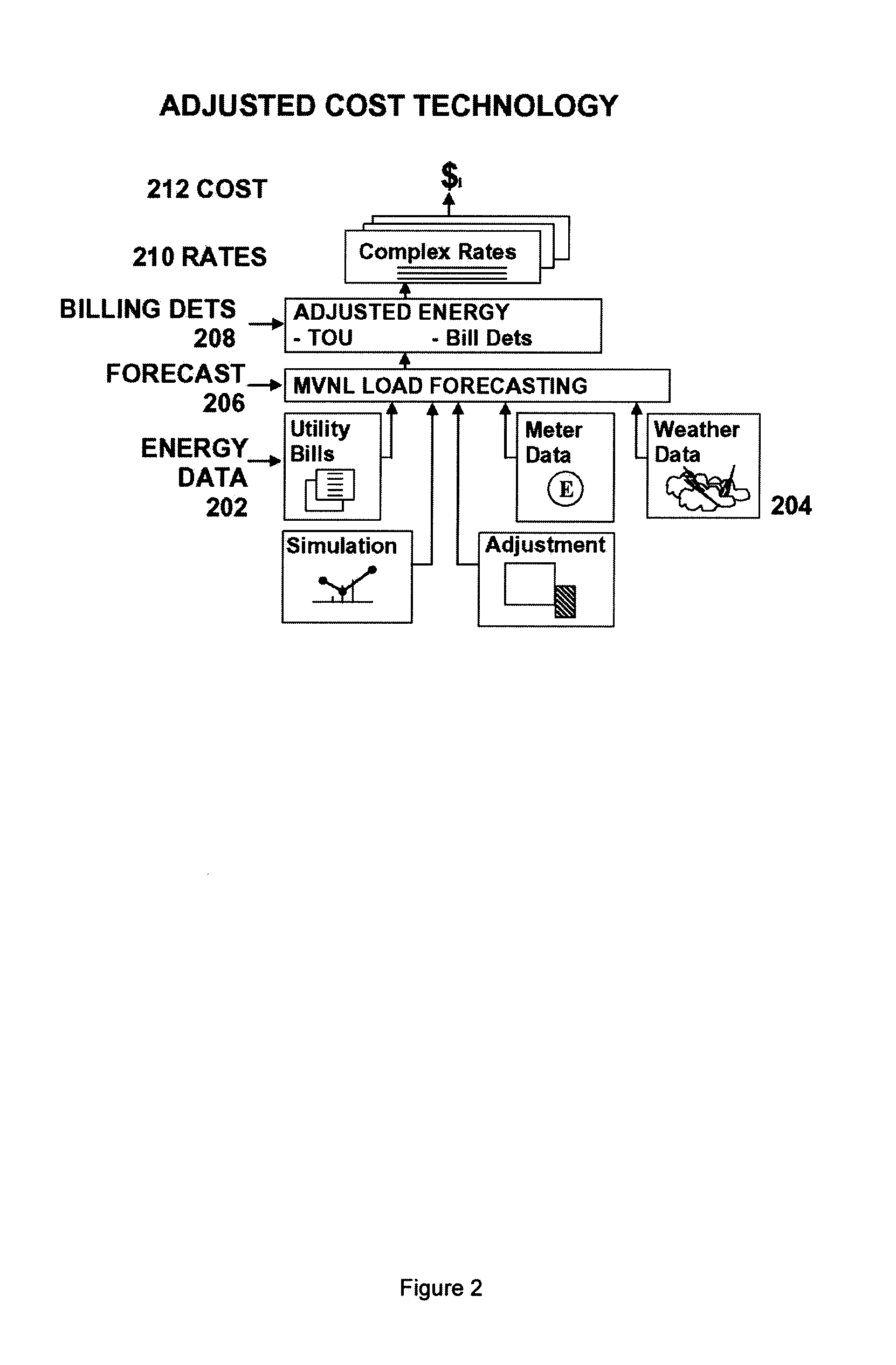
Energy and cost savings calculation system
ActiveUS20070244604A1Save energyAccurate and reliable and costLevel controlTemperatue controlEngineeringTime of use
An Energy and Cost Savings Calculation System is provided that automates the determination of energy and cost savings due to energy conservation measures. The system provides Multi-Variant, Non-Linear (MVNL) load forecasting techniques, energy and cost savings calculations, and Weather Ranking. The load forecasting technique may accept numerous external parameters as input. The technique may use multiple Baselines. It may also use multiple Basic Reference Periods to reduce the load forecasting error. The load forecasting technique may utilize external parameters that are updated on a daily basis, such as dry bulb temperature, dew point temperature, solar condition, and interval meter data. The technique may use Baseline Extensions to perform forecasts and Reference Period Modifications to enhance accuracy. The system may calculate energy and cost savings using Complex Rates and time-of-use (TOU) energy data. The system may rank a plurality of sources providing weather data to identify the most accurate weather data.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
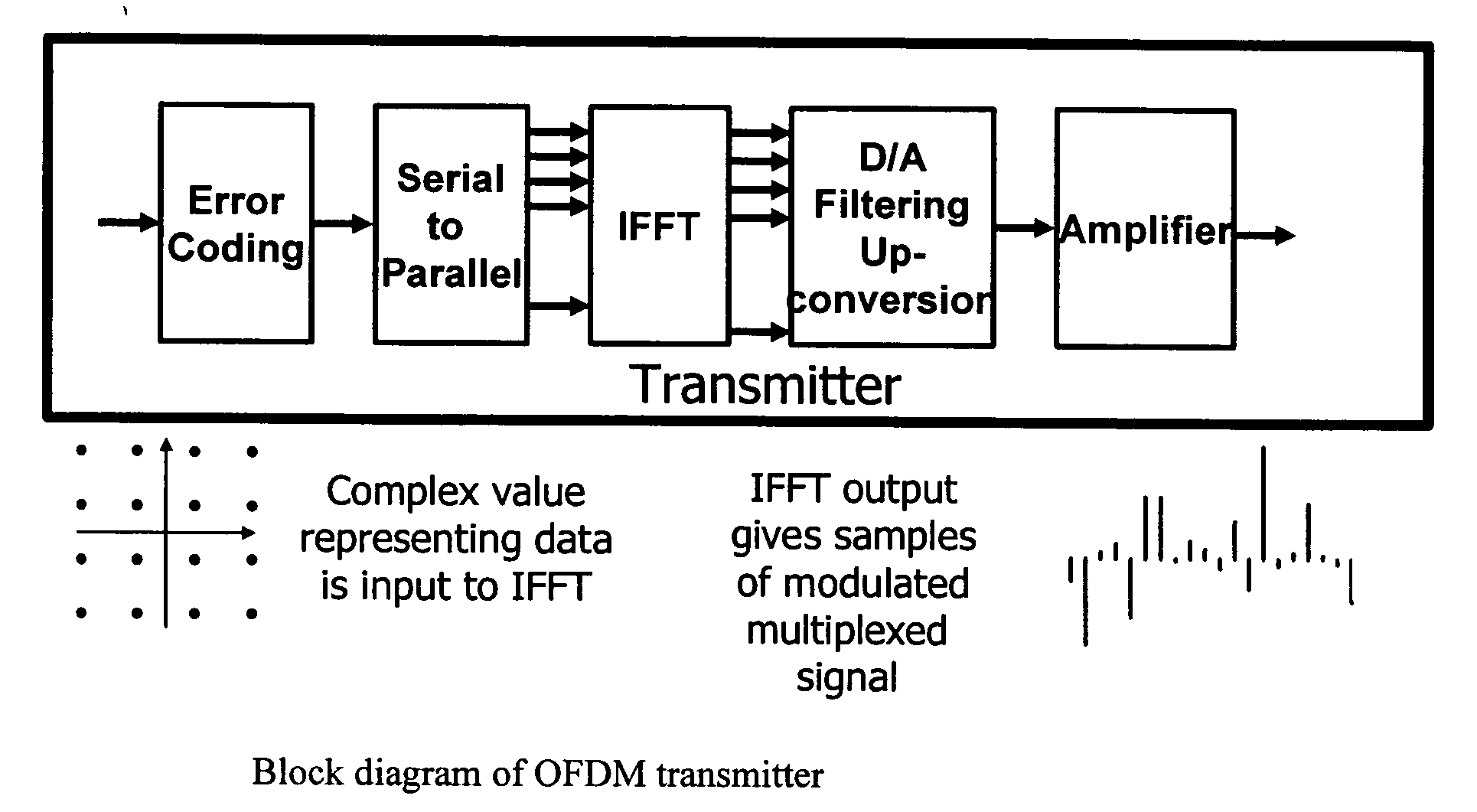
Multicarrier modulation systems
ActiveUS20050243938A1Reduce probabilityMinimize degradationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCarrier signalEngineering
The invention provides a new approach which is better suited to FFT design as applied to multicarrier modulation systems such as OFDM. The signals are scaled so that overflow, rather than being completely avoided, occurs with low probability throughout the IFFT and FFT structures. The size of the error that results from an overflow depends on how overflow is handled in the DSP. To minimize the degradation, overflow should result in saturation of the value at the maximum positive or negative value option. This is equivalent to clipping the signal. Using the new technique, signals within the FFT structure are scaled to balance the effect of clipping and round-off. Clipping may result in comparatively large errors in a few signal values but because of the spreading effect of the FFT and because OFDM systems typically include error coding / correction, system performance depends on the total error or, in other words the total noise power, across all of the FFT outputs rather than on any individual value.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Method of generating a smooth image from point cloud data
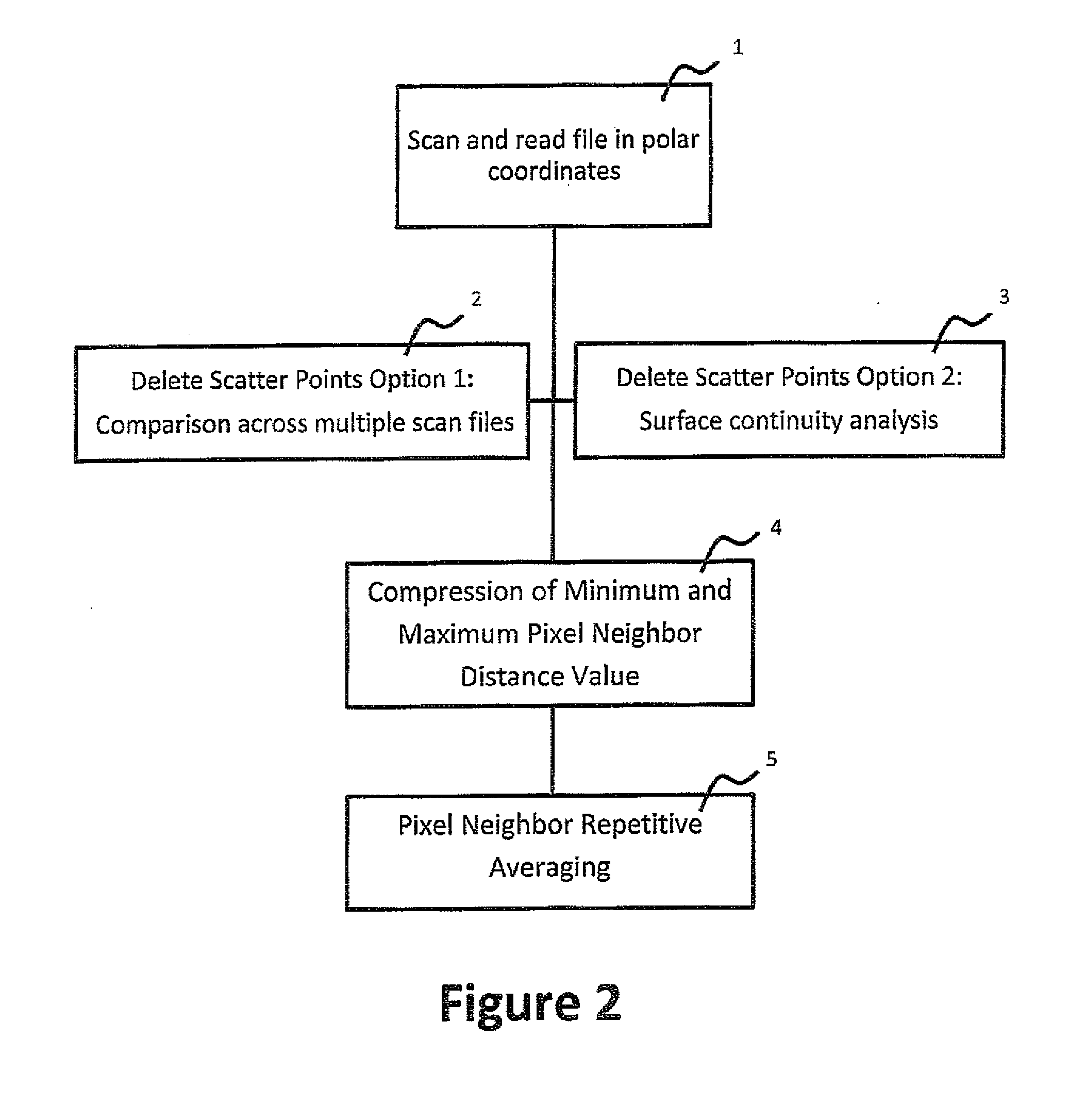
A method for processing an array of pixels in a point cloud, comprises calculating local error limits for each distance value for each pixel in the processed point cloud data set. One may then determine the error bar. One begins a distance value adjusting loop by for each pixel in the processed point cloud data set by calculating the difference between the distance value in the pixel of the point cloud data set being processed and each of the neighboring pixels or the most suitable neighboring pixel distance value is determined whether the difference is within the range defined by the error bar. It the difference is not within the error bar, the distance value is changed for the pixel being processed by a small fraction while keeping the new distance value within the range defined by the original distance value for the pixel being processed plus or minus the error bar. If the difference is within the error bar the distance value in the pixel being processed is replaced by a weighted average value. The number of neighboring pixels with their distance values within the error bar for the pixel being processed is counted and if the count is greater than a predetermined threshold, average the counted distance values and substitute the average for the pixel distance value, but if the count is below the threshold leave the pixel distance value unchanged. It is determined whether loop exit criteria have been met and if loop exit criteria have not been met beginning the loop again, and if loop exit criteria have been met, terminating the loop.
Owner:ASKAN YOLDAS
Product authentication
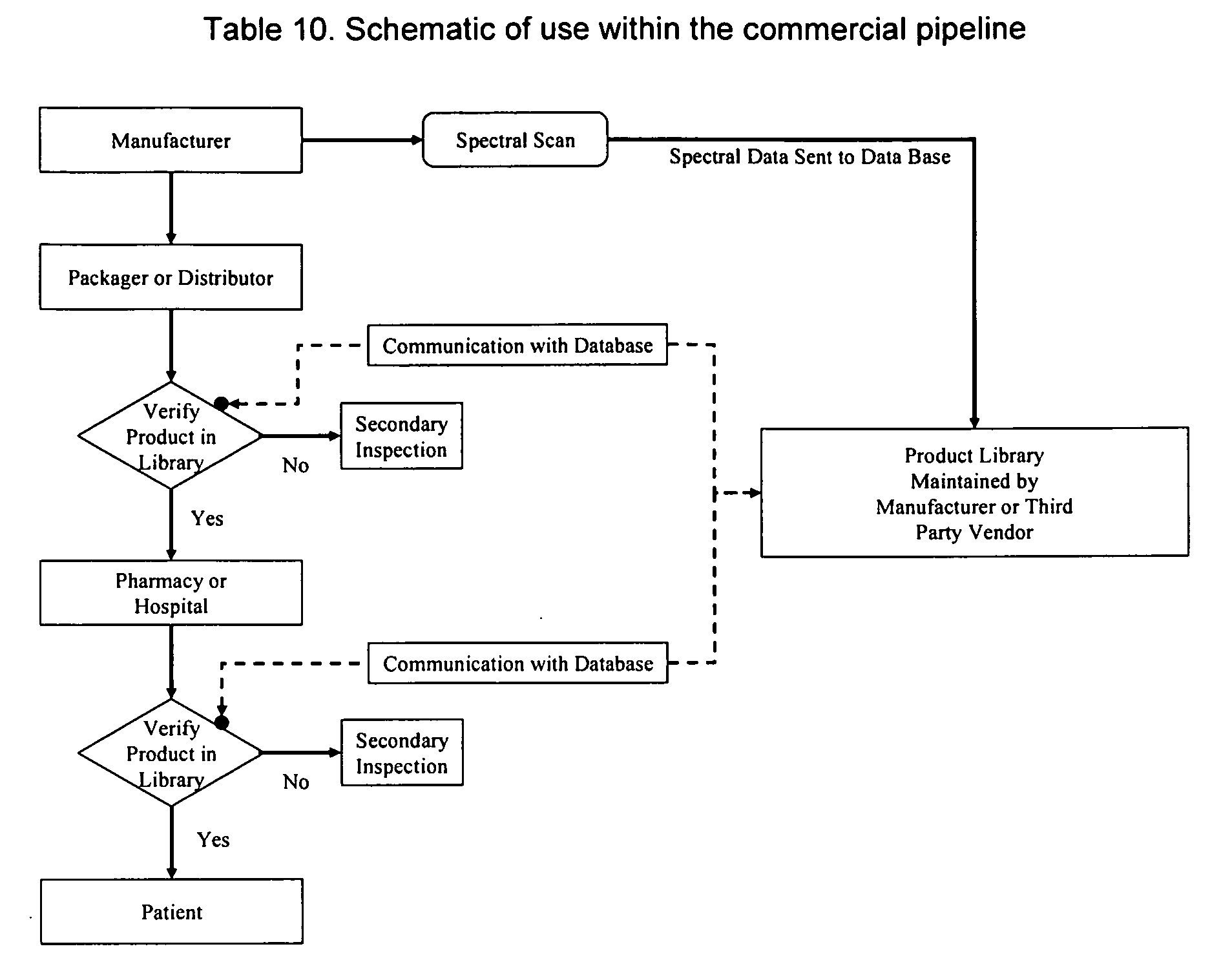
InactiveUS20060283931A1Rapid accurate approachPrevent the pharmaceutical product from being counterfeitedStampsRaman scatteringEngineeringErrors and residuals
A method is disclosed to verify and identify products through their product signatures in order to combat counterfeiting and reduce dispensing errors, using methods such as spectral analysis (e.g., near infrared spectroscopy). Furthermore, in order to actively evade product counterfeiting, a method is disclosed where an amount of one or more components of the product are varied (e.g., over time); the variation provides a different product signature, but falling within a desirable or necessary range.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
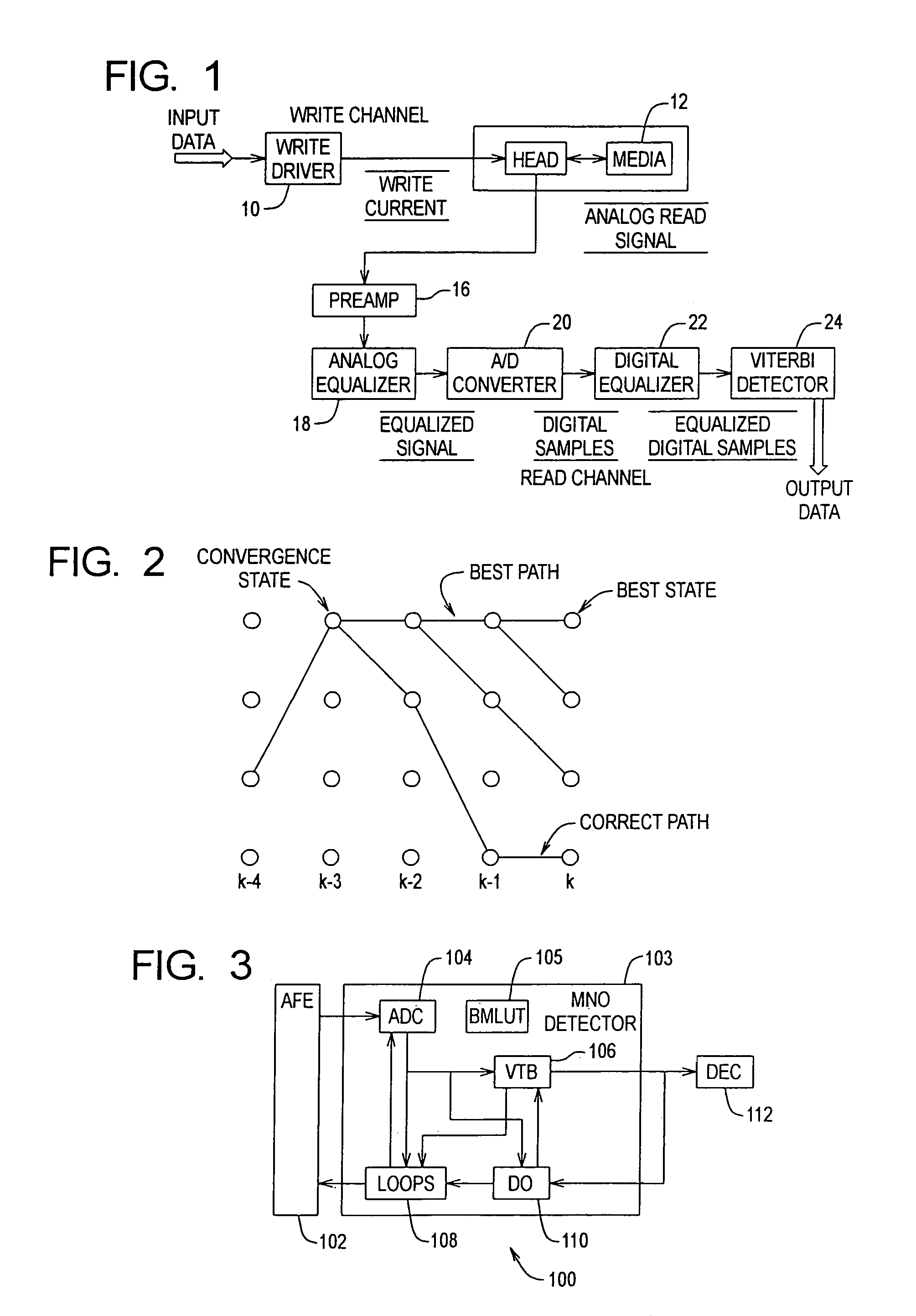
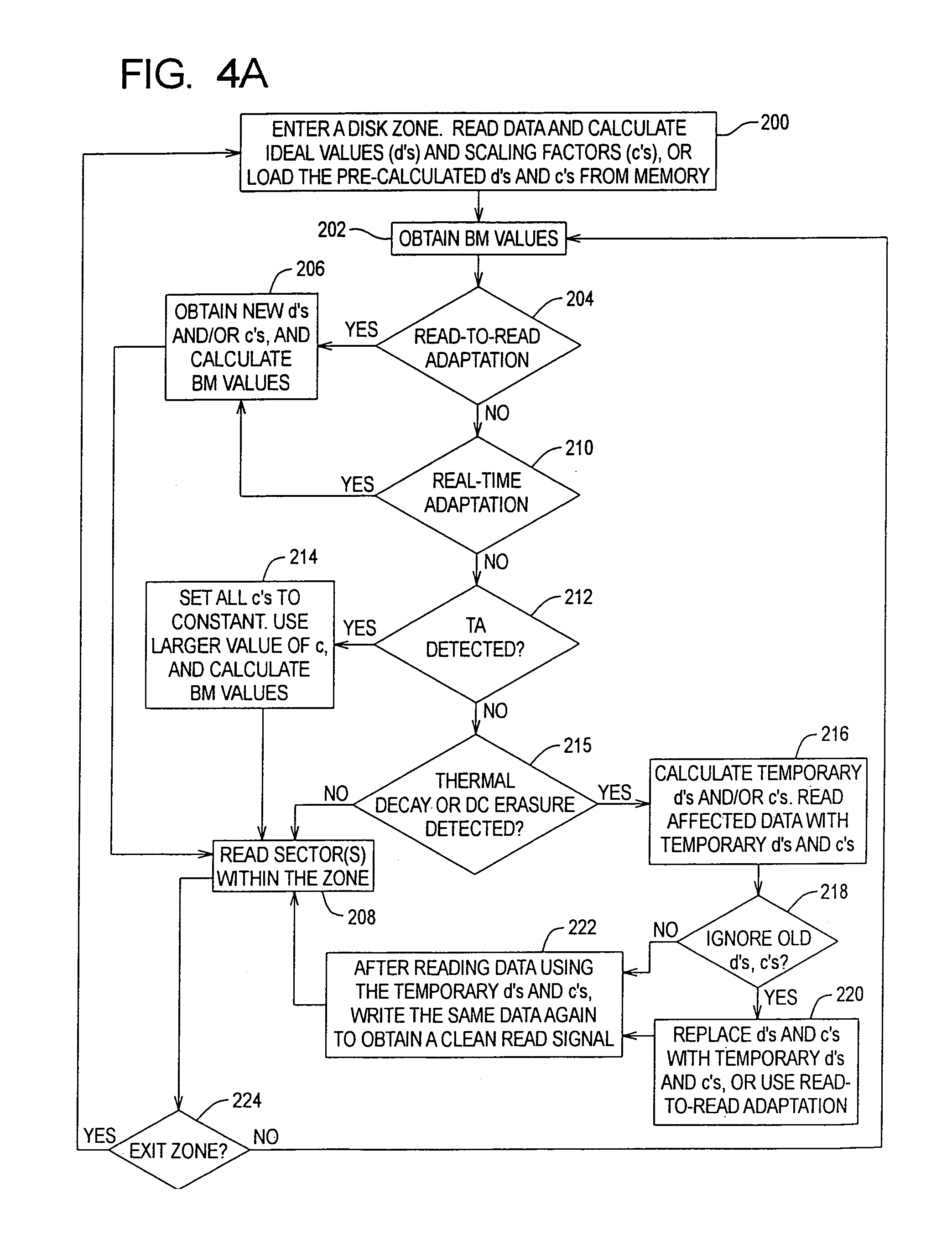
Media noise optimized detector for magnetic recording
InactiveUS7173783B1Significant disk drive yield benefitImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsModification of read/write signalsPattern recognitionViterbi detector
A media noise optimized (MNO) detector for a read channel compensates for pattern dependent media noise, and compensates for nonlinearities from many sources such as residual MR nonlinearity, residual nonlinear transition shift, partial erasure, write-induced nonlinearity, and steady-state mis-equalization. The MNO detector is implemented by adjusting a conventional Viterbi detector branch metric so that the channel output value (ideal value) can be a nonlinear function of the state / branch bits, and the branch metric scaling factor is a function of the state / branch. For a given state / branch, the ideal value is the mean of analog-to-digital converter samples for the pattern corresponding to the state / branch, and the branch metric scaling factor is proportional to the noise variance for the pattern corresponding to that state / branch.
Owner:MAXTOR
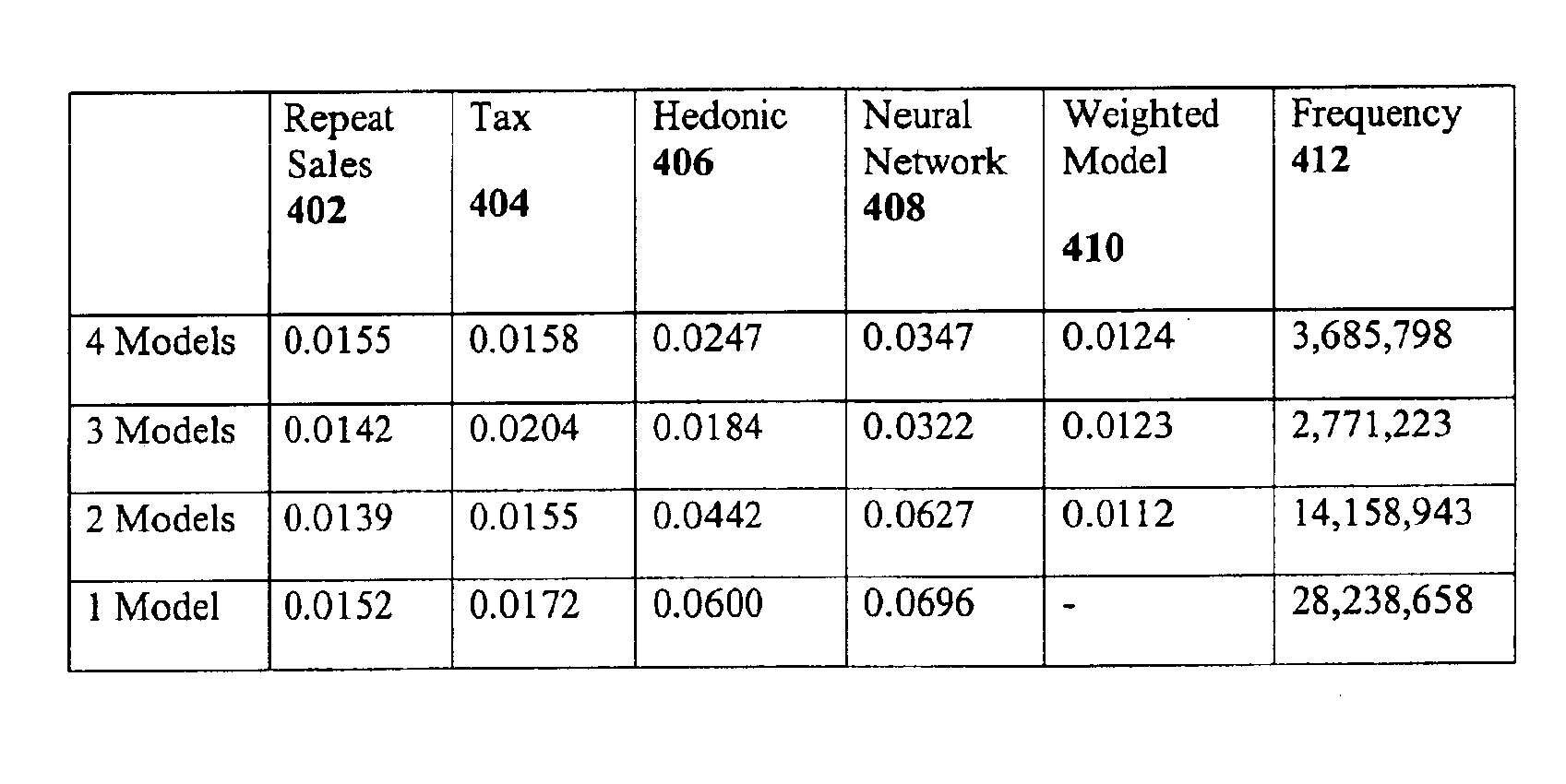
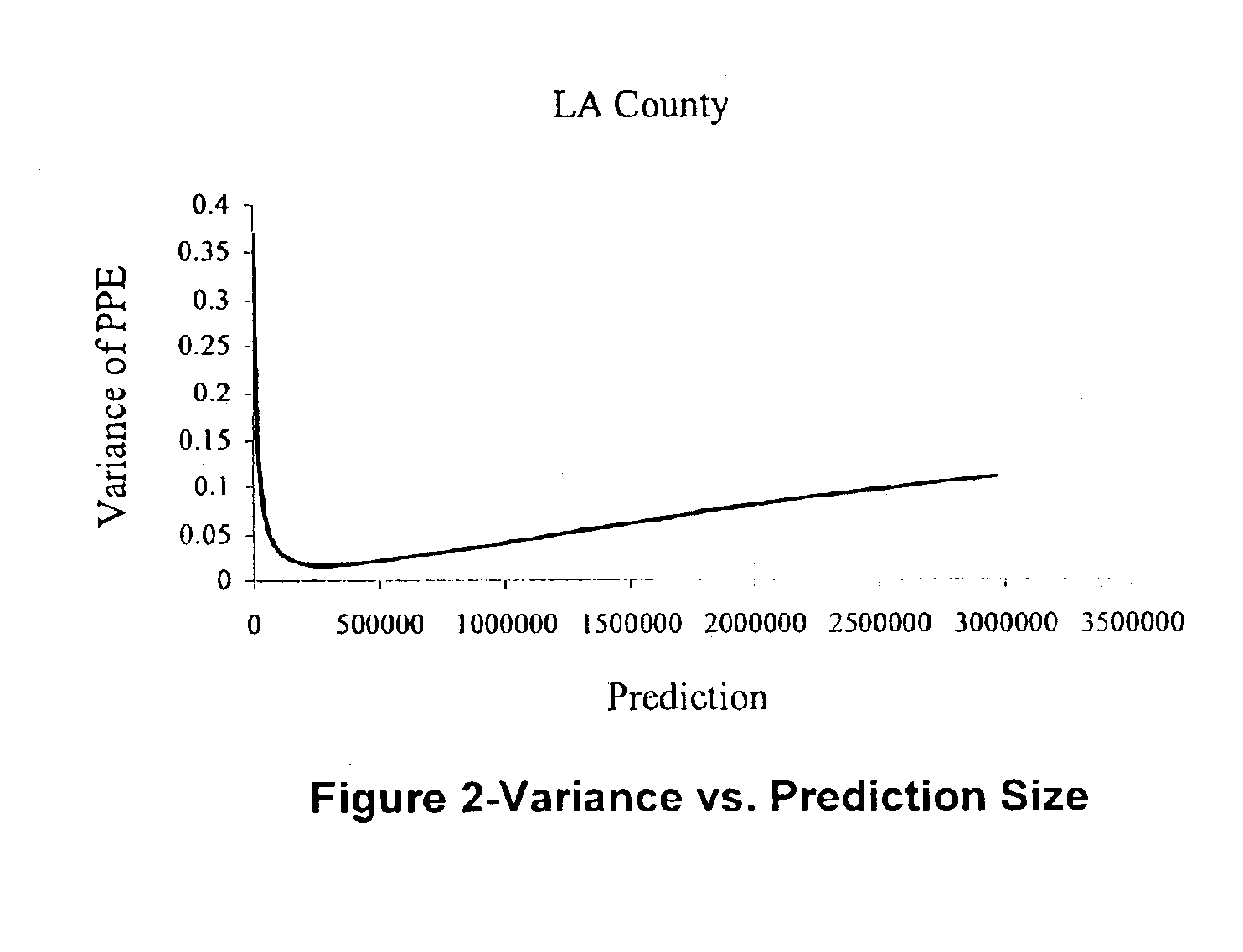
Method and apparatus for predicting and reporting a real estate value based on a weighted average of predicted values
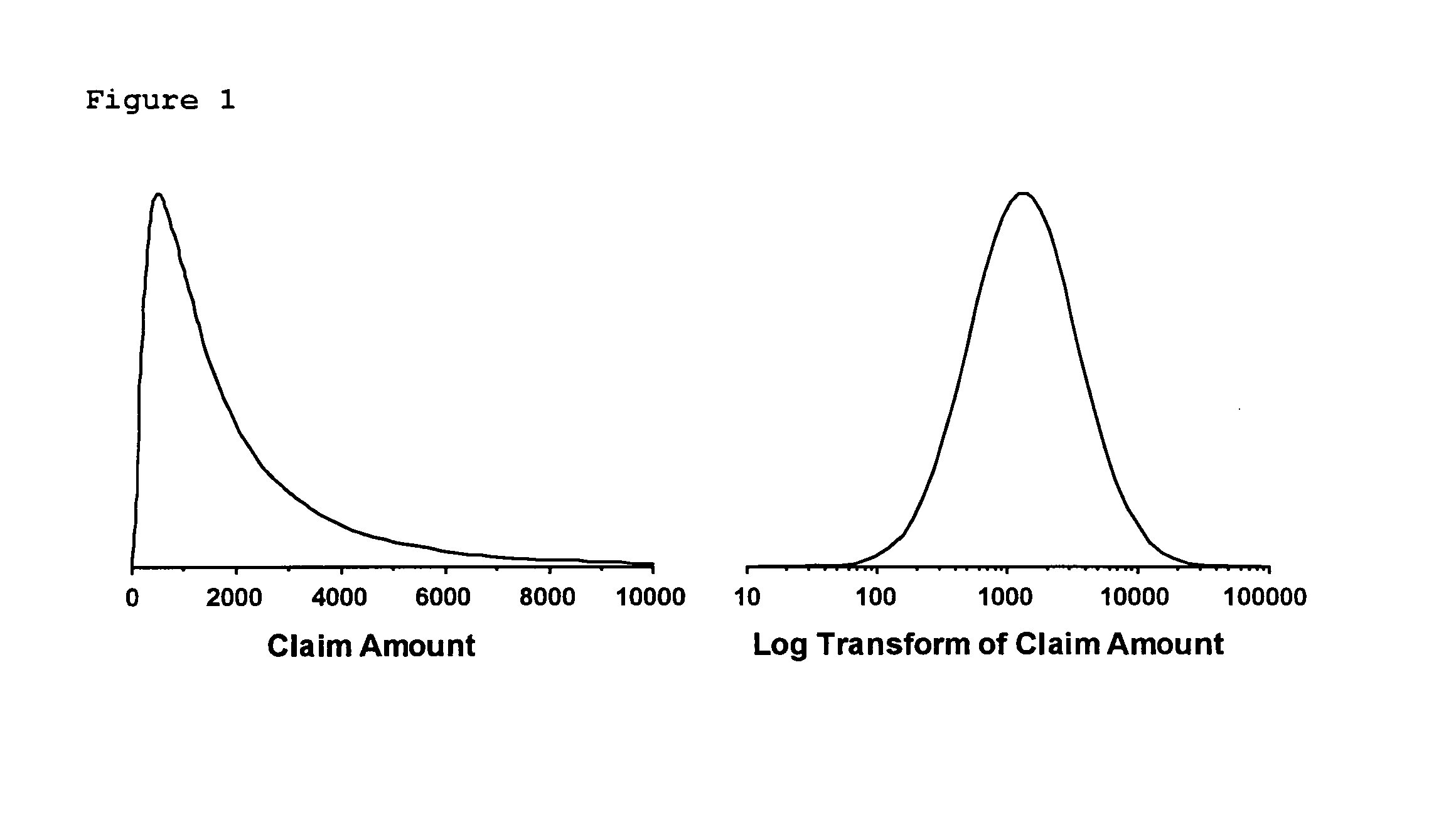
InactiveUS6876955B1Accurate predictionAccurately reportingFinanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceProperty valueErrors and residuals
A system and method of accurately predicting and reporting a value of a property based on a weighted average of values predicted by at least two prediction models. The system and method include the steps of accessing predicted values, determined by the prediction models, for the property; determining property-specific proportional prediction error distribution information for each predicted value determined by each prediction model; assigning a weight to the predicted value determined by each prediction model by using the property-specific proportional prediction error distribution information; and generating a property-specific weighted average value based on combination of the weight and the predicted value determined by each prediction model and reporting the property-specific weighted average value to minimize prediction error during prediction of the property value.
Owner:FANNIE MAE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com