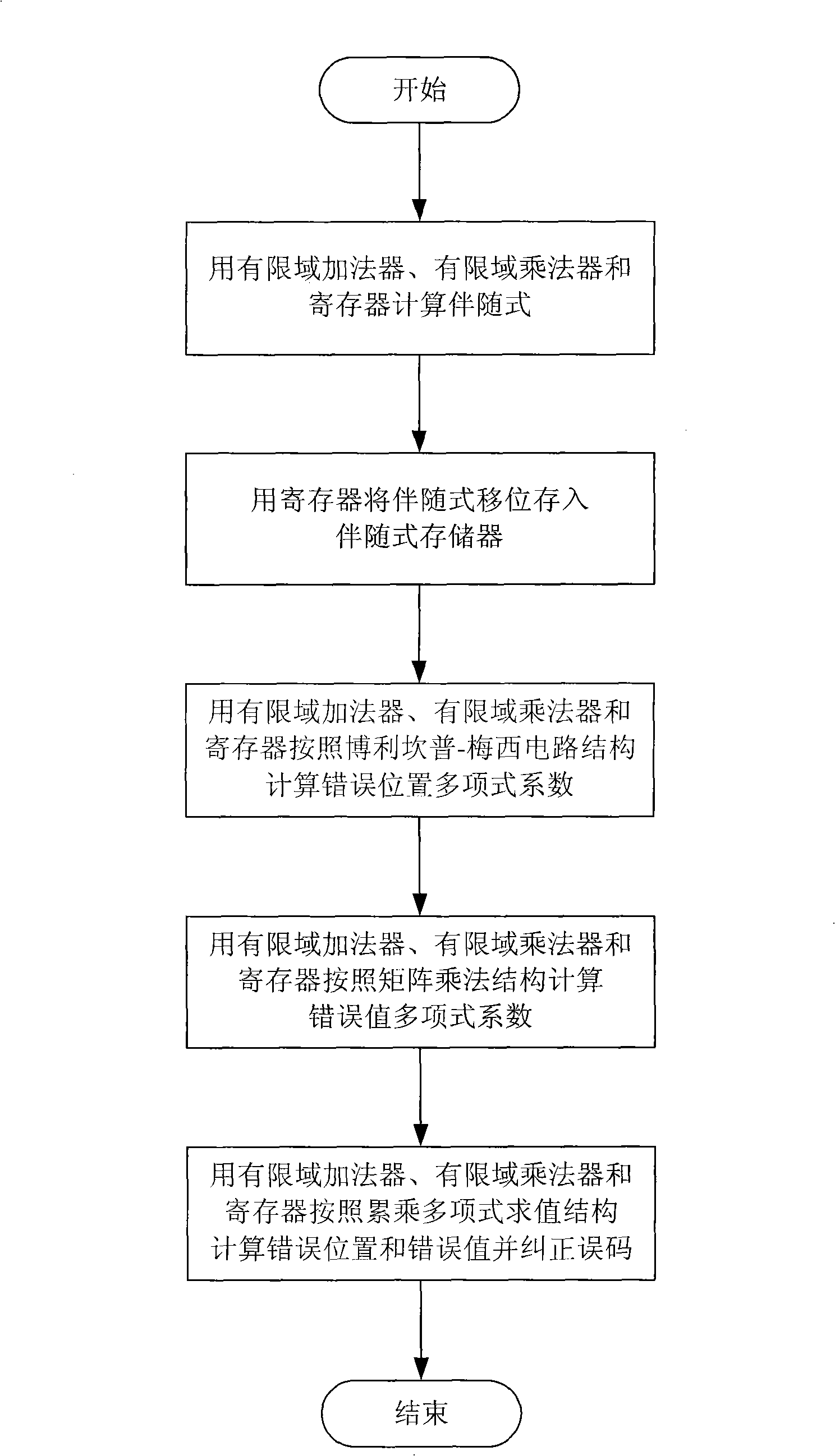
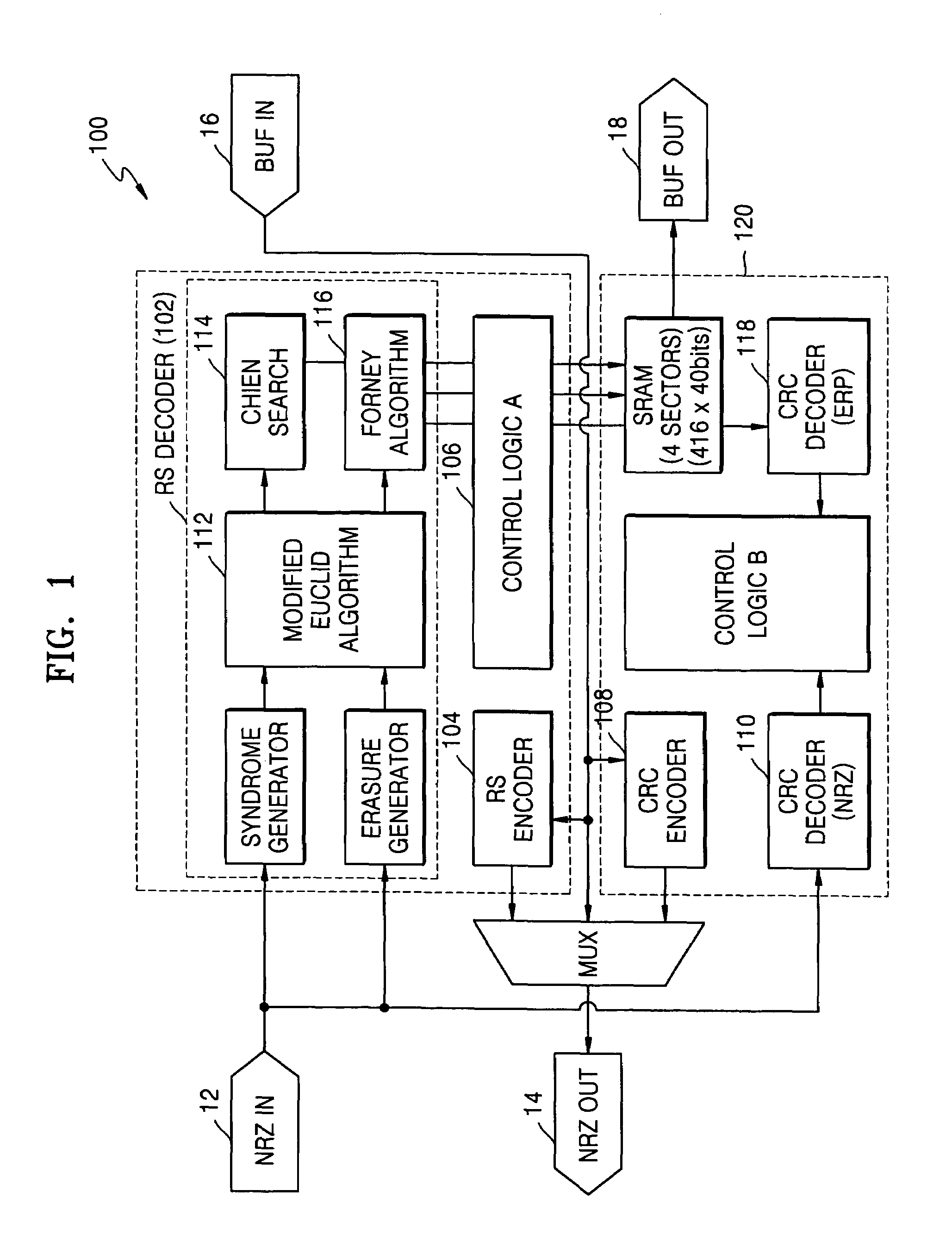
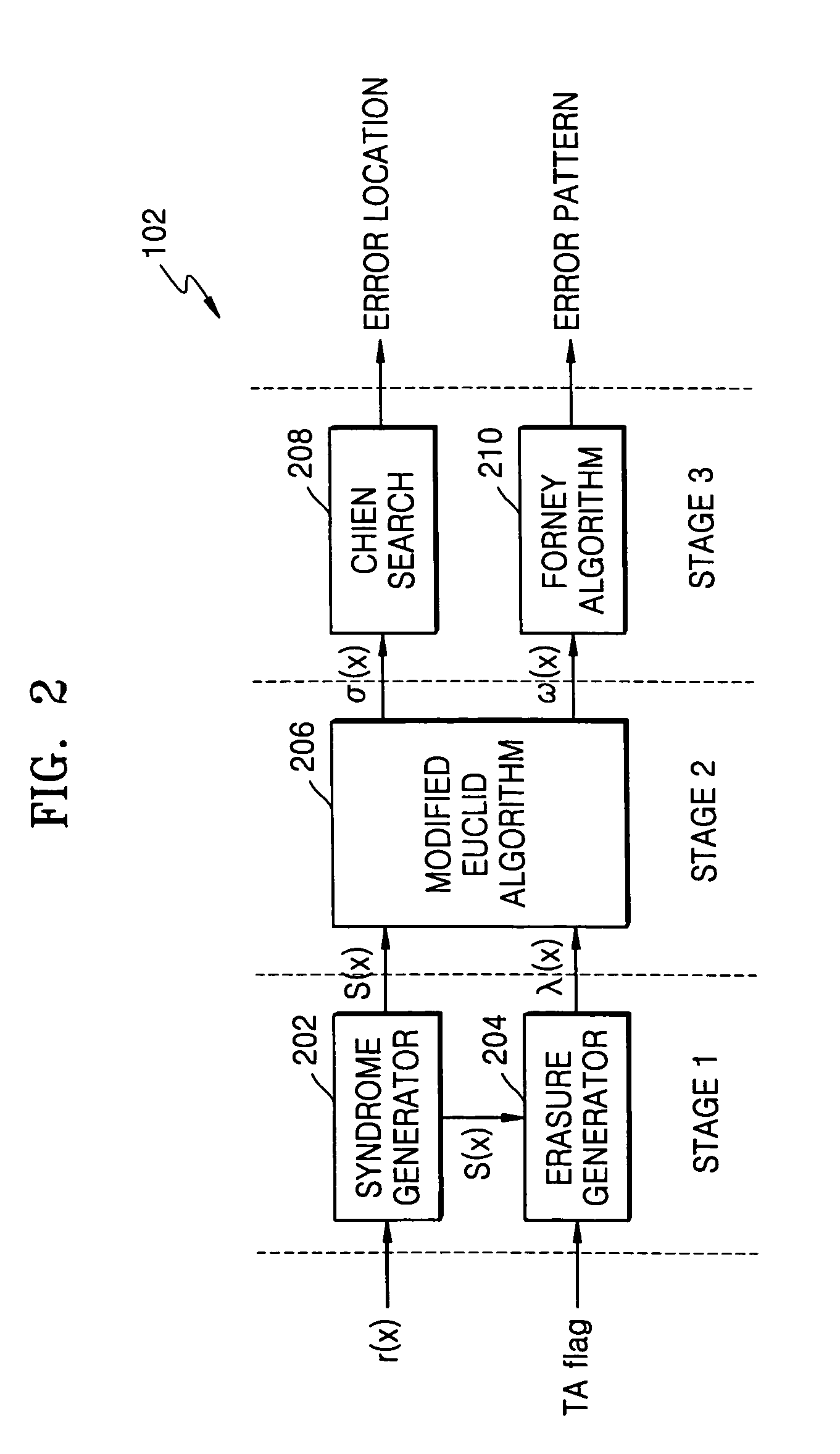
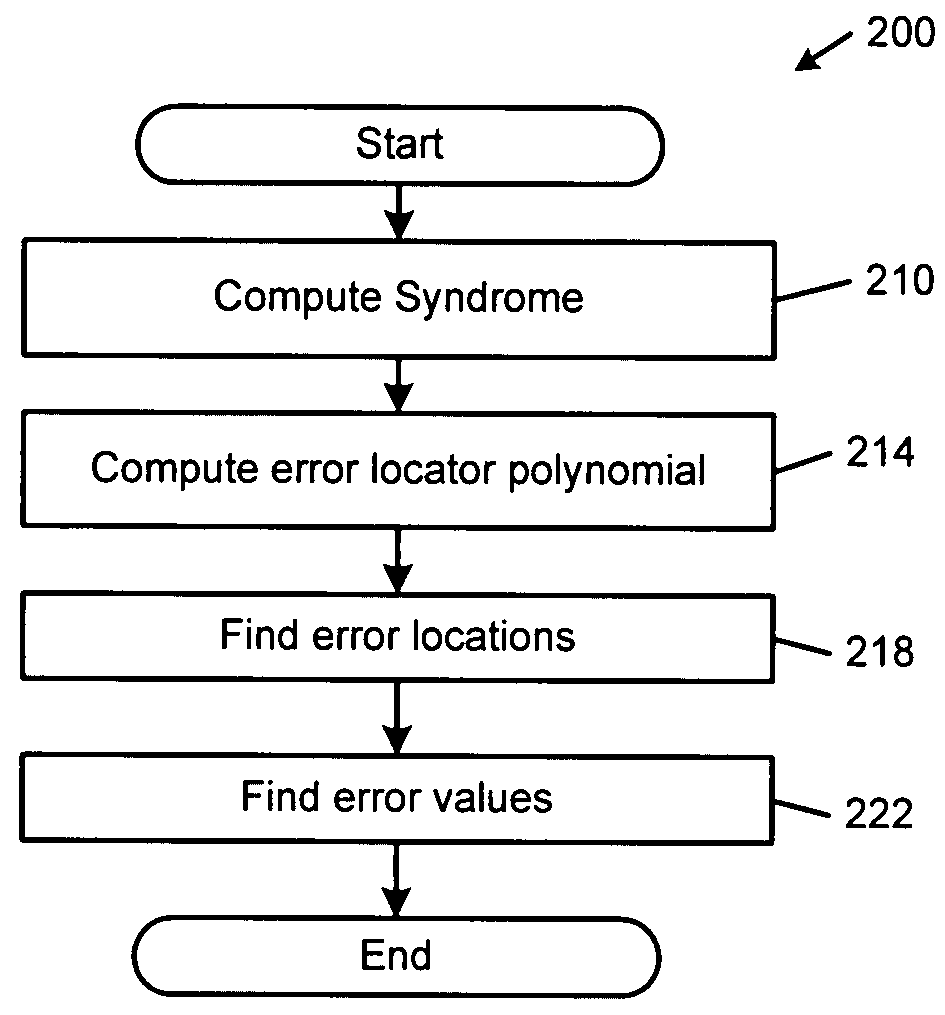
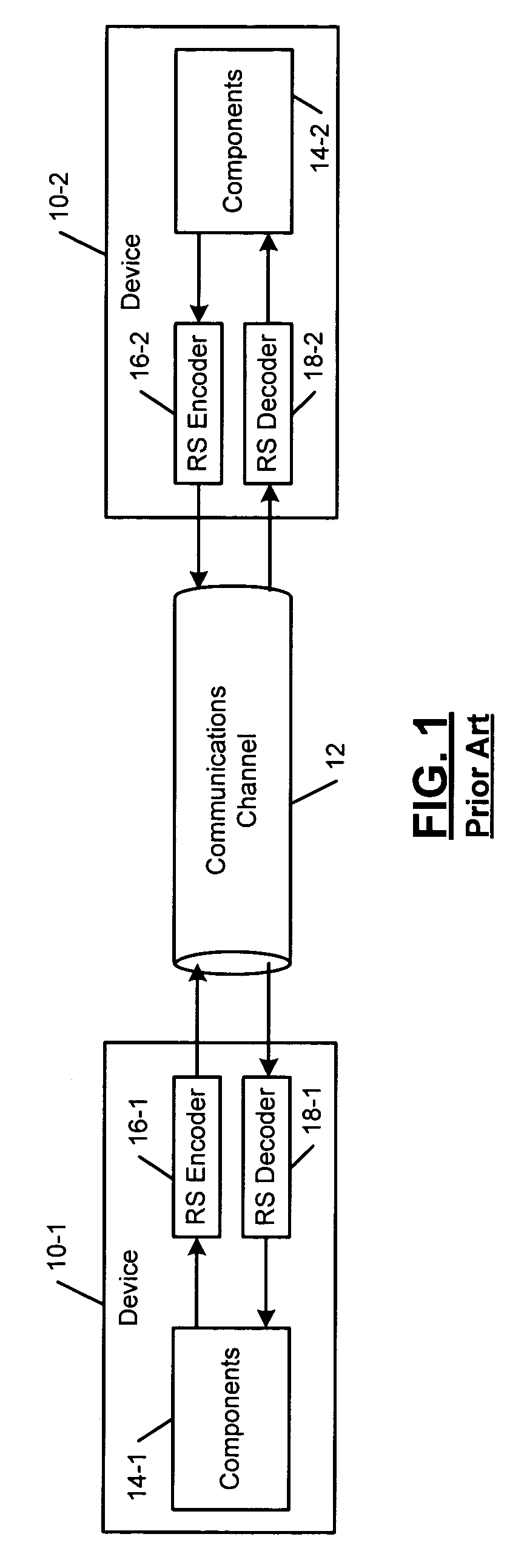
Patents
Literature
80 results about "Reed solomon decoder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
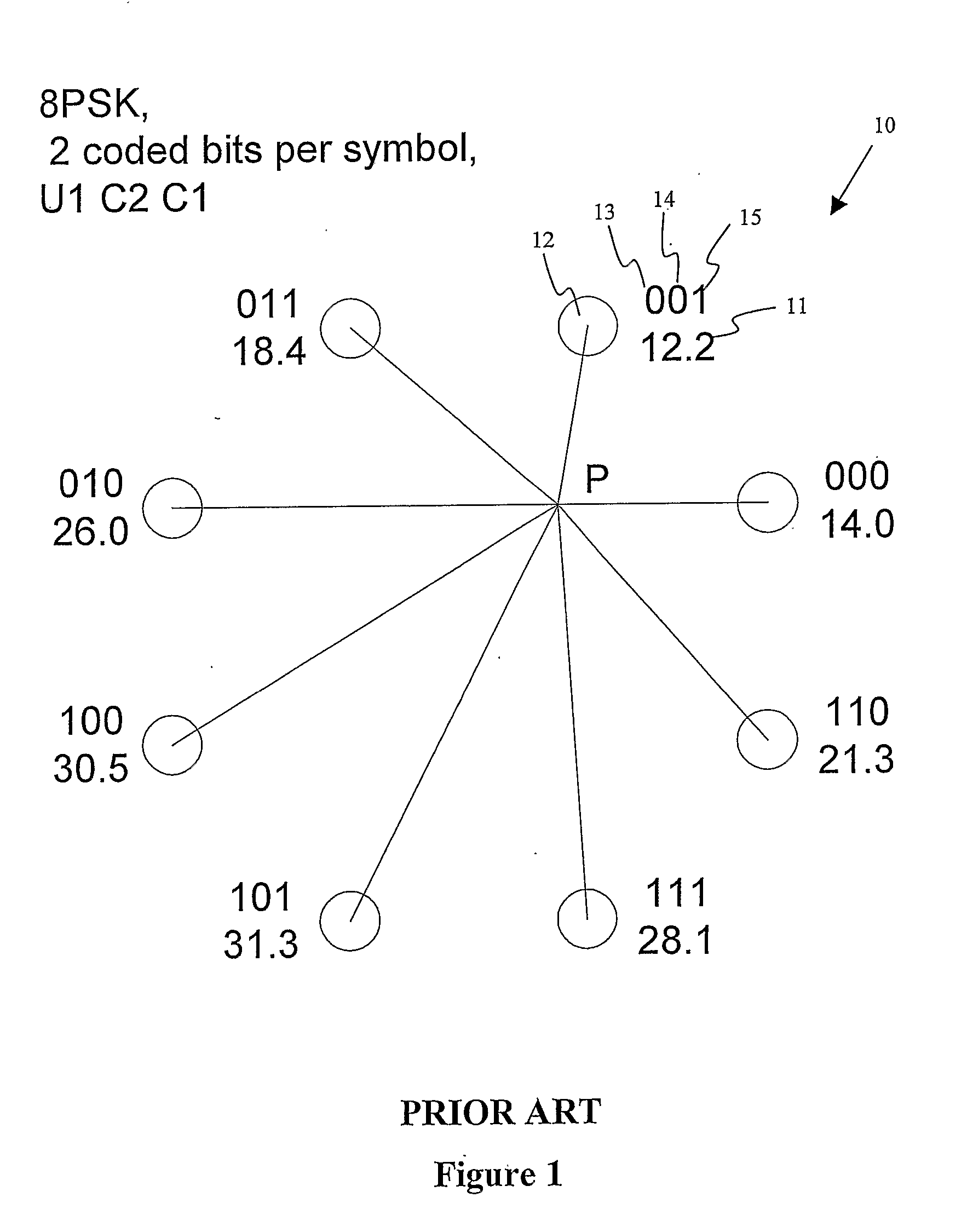
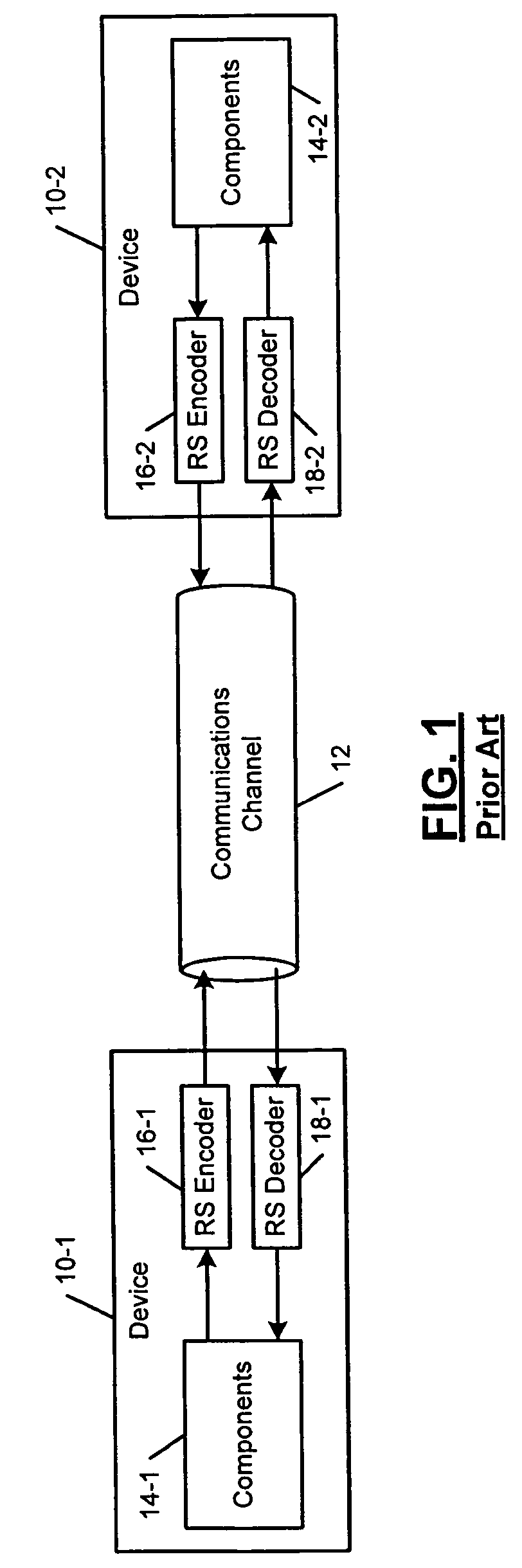
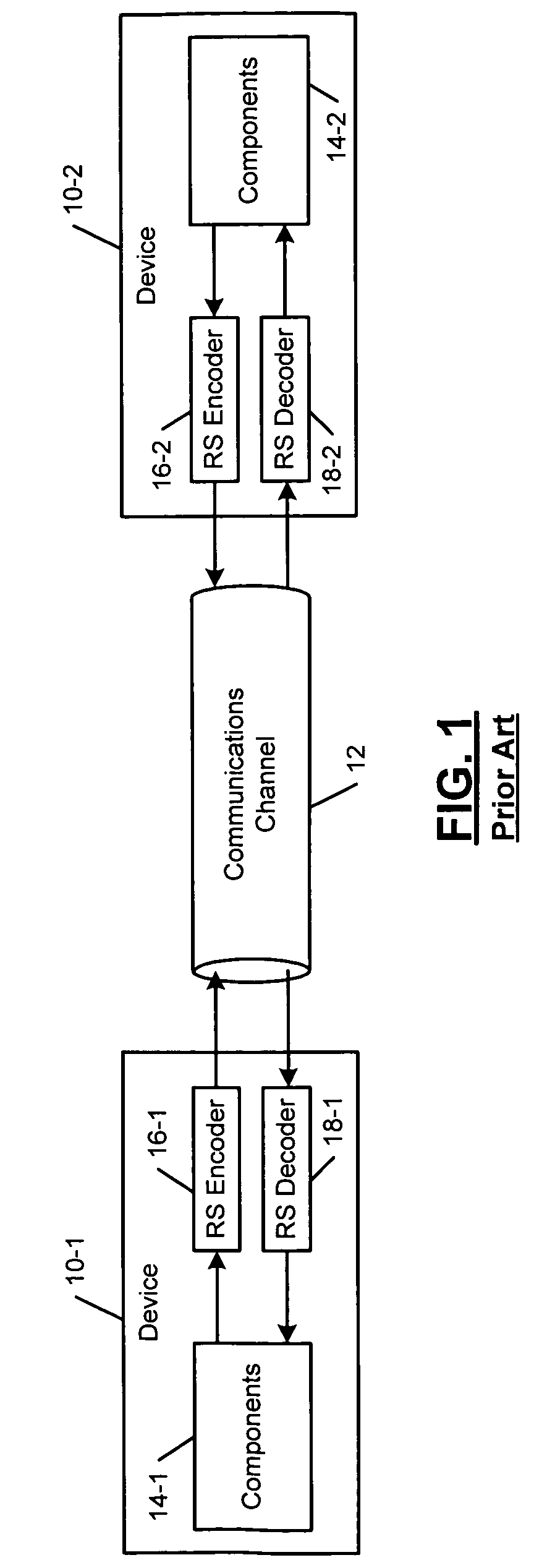
Head end receiver for digital data delivery systems using mixed mode SCDMA and TDMA multiplexing
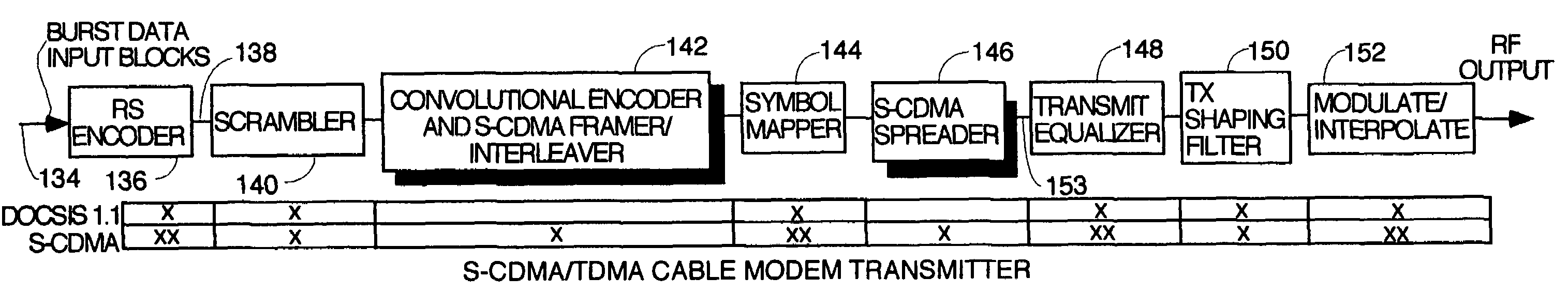
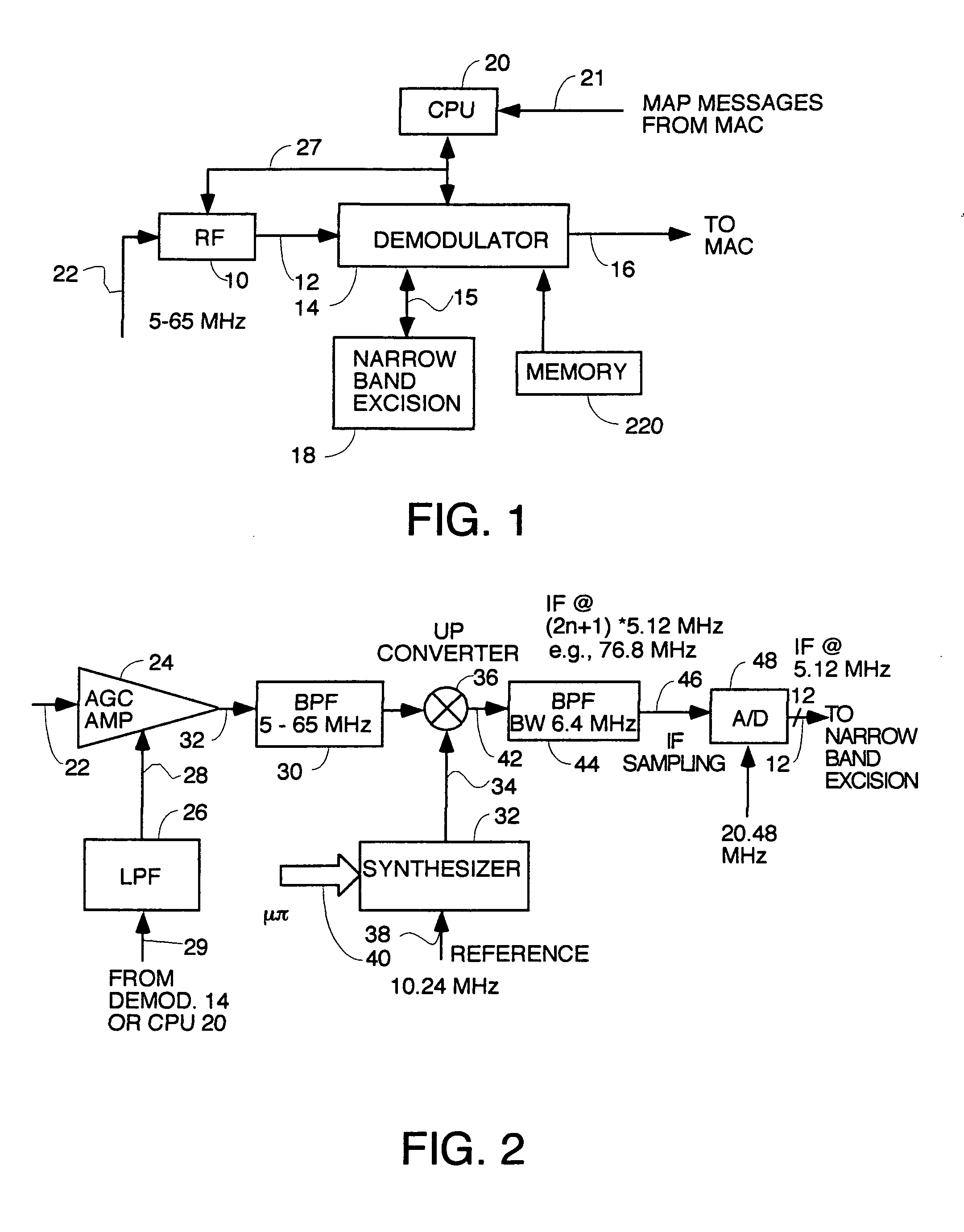
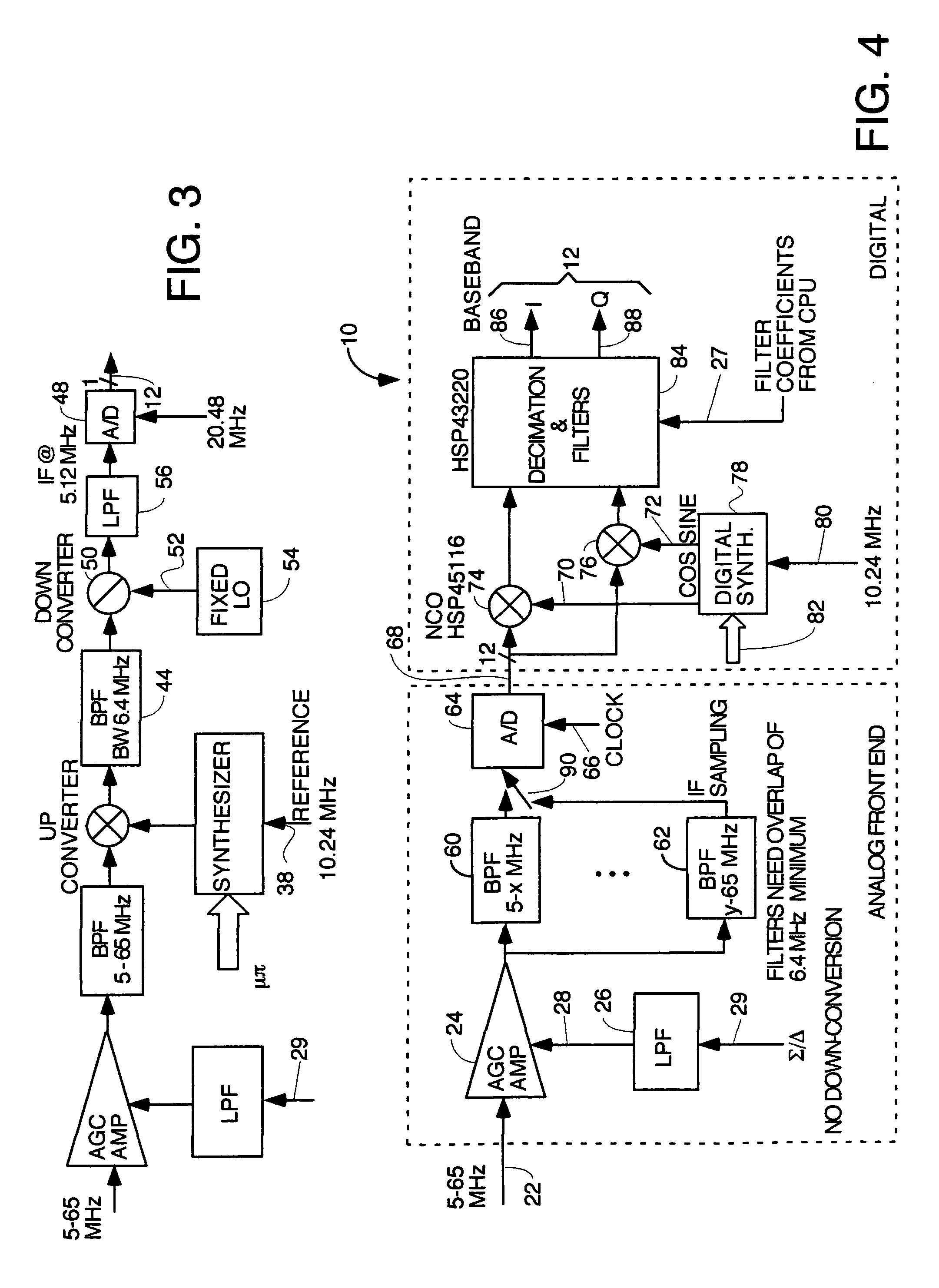
InactiveUS7050419B2Improve performance(SNR) ratioTransmission control/equlisationMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsDigital dataDOCSIS
A pipelined digital data receiver for a cable TV headend which is capable of receiving DOCSIS 1.0 or 1.1 or advanced PHY TDMA or SCDMA bursts having programmable symbol rates and programmable modulation types as well as a host of other burst parameters such at Trellis code modulation on or off, scrambling on or off, various values for Reed-Solomon T number and codeword length. The receiver has an RF section to filter and digitize incoming RF signals. It also has an input section to detect impulse noise and do match filtering and despread SCDMA bursts. A timing recovery section recovers the symbol clock and detects the start of bursts and collisions. A rotational amplifier and equalizer calculate and track gain, phase and frequency offsets and correct symbols and calculates equalization coefficients. A decoder section decodes TCM and non TCM bursts, and a Reed-Solomon decoder section reconstructs RS codewords and uses them to error correct the payload data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Reed-solomon decoder systems for high speed communication and data storage applications
InactiveUS20060059409A1Effective and reliable error correction functionalityReduce complexityCode conversionCoding detailsModem deviceHigh rate
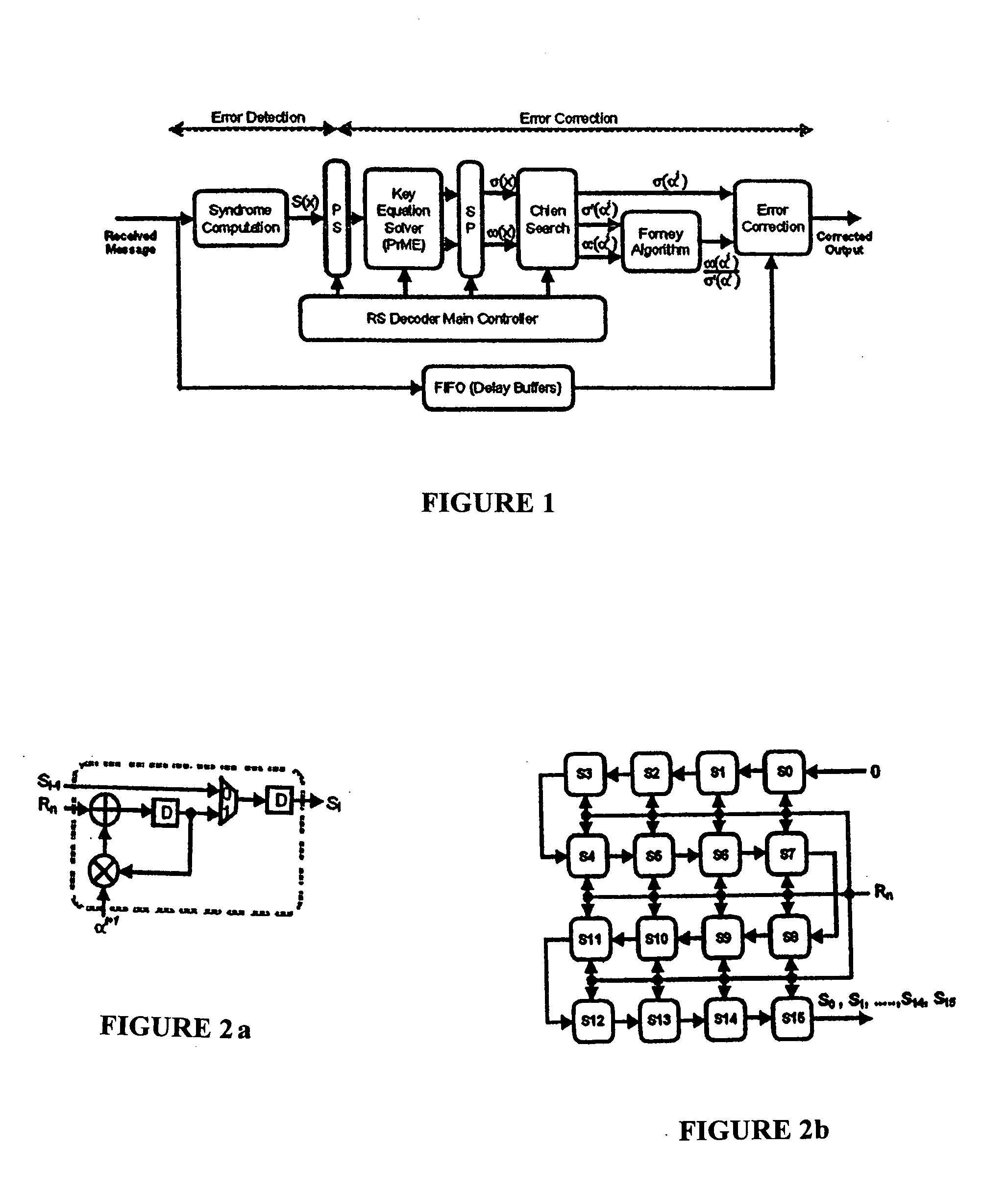
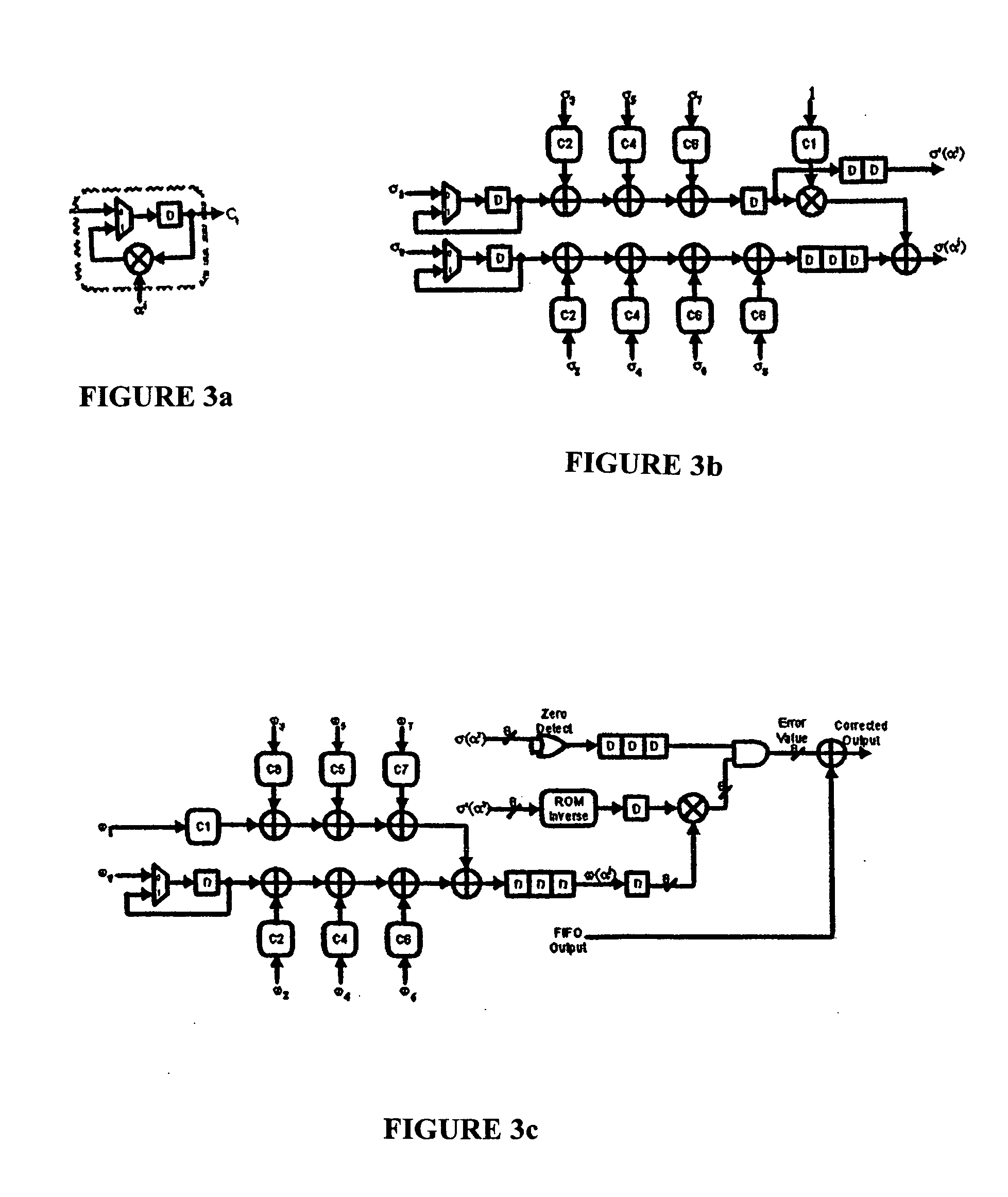
A high-speed, low-complexity Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder architecture using a novel pipelined recursive Modified Euclidean (PrME) algorithm block for very high-speed optical communications is provided. The RS decoder features a low-complexity Key Equation Solver using a PrME algorithm block. The recursive structure enables the low-complexity PrME algorithm block to be implemented. Pipelining and parallelizing allow the inputs to be received at very high fiber optic rates, and outputs to be delivered at correspondingly high rates with minimum delay. An 80-Gb / s RS decoder architecture using 0.13-μm CMOS technology in a supply voltage of 1.2 V is disclosed that features a core gate count of 393 K and operates at a clock rate of 625 MHz. The RS decoder has a wide range of applications, including fiber optic telecommunication applications, hard drive or disk controller applications, computational storage system applications, CD or DVD controller applications, fiber optic systems, router systems, wireless communication systems, cellular telephone systems, microwave link systems, satellite communication systems, digital television systems, networking systems, high-speed modems and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
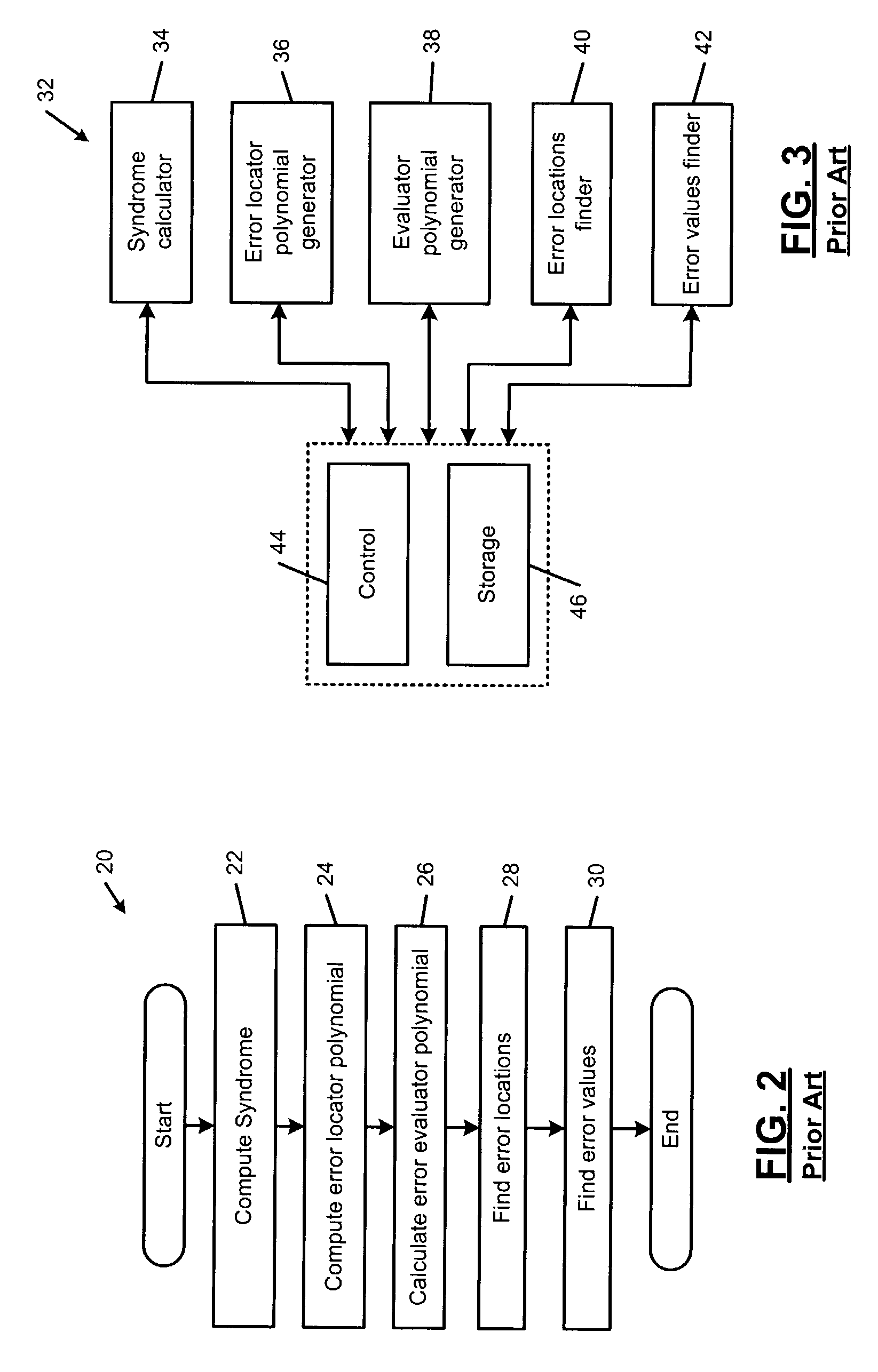
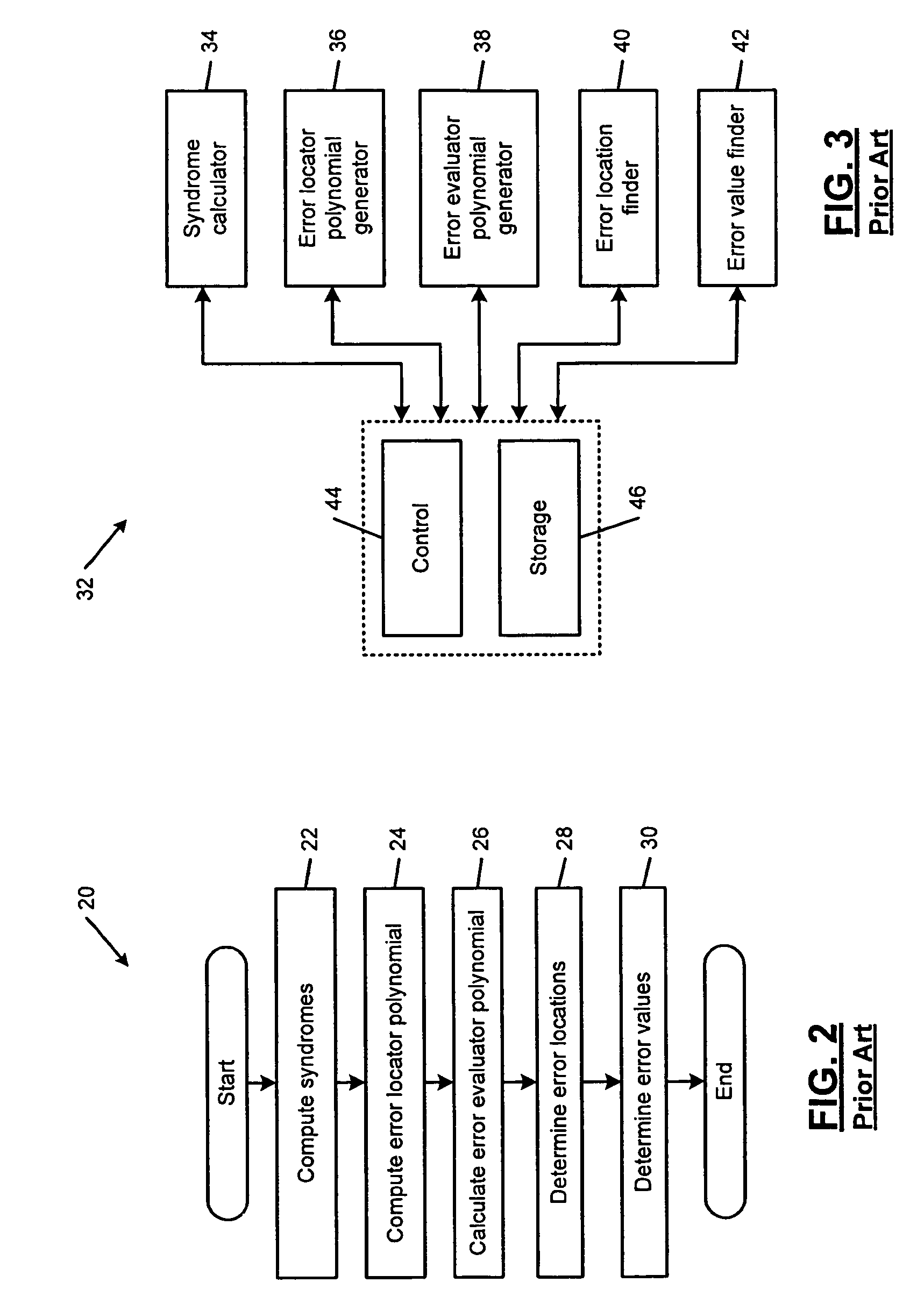
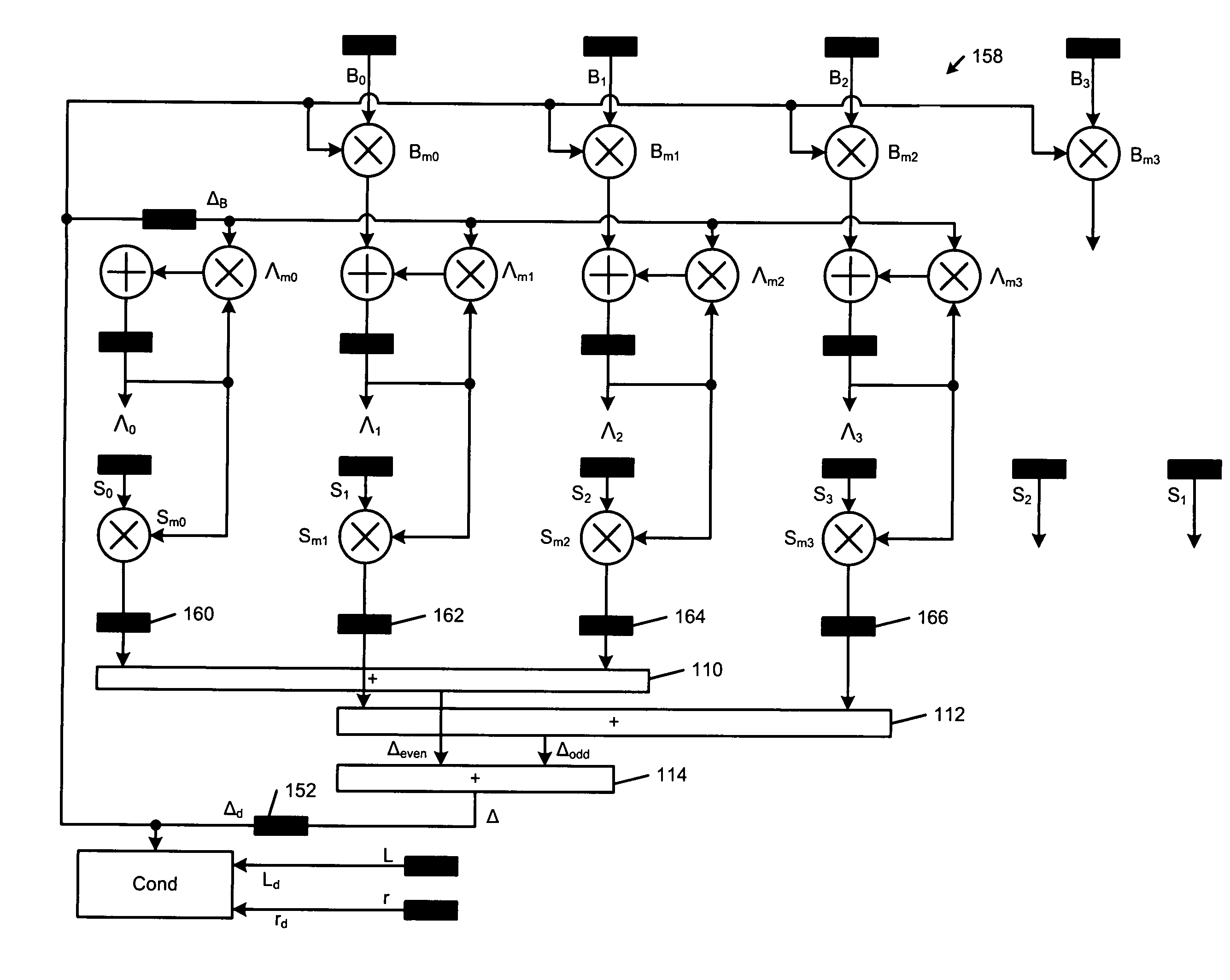
Error evaluator for inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm in Reed-Solomon decoders
ActiveUS7010739B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionError locationReed solomon decoder
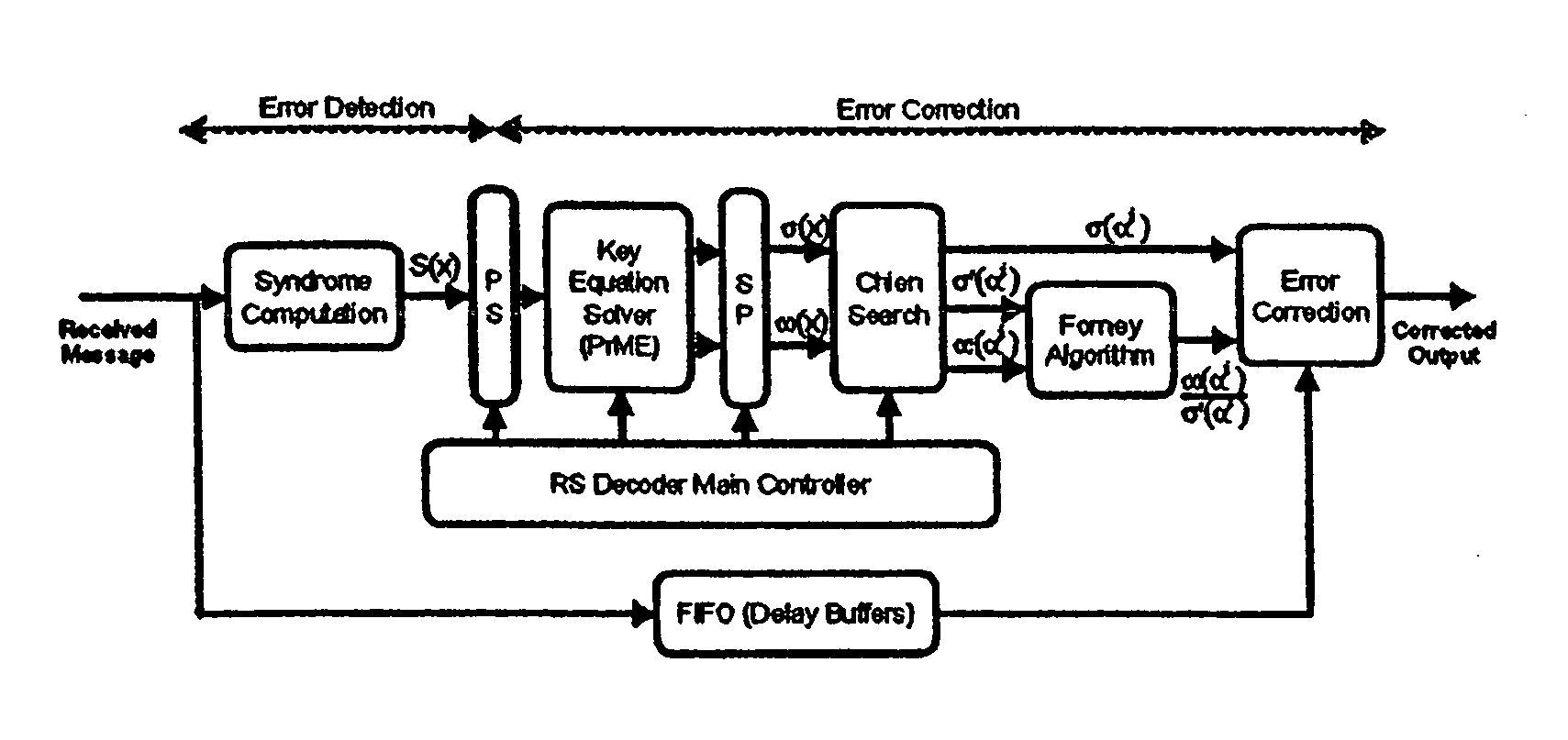
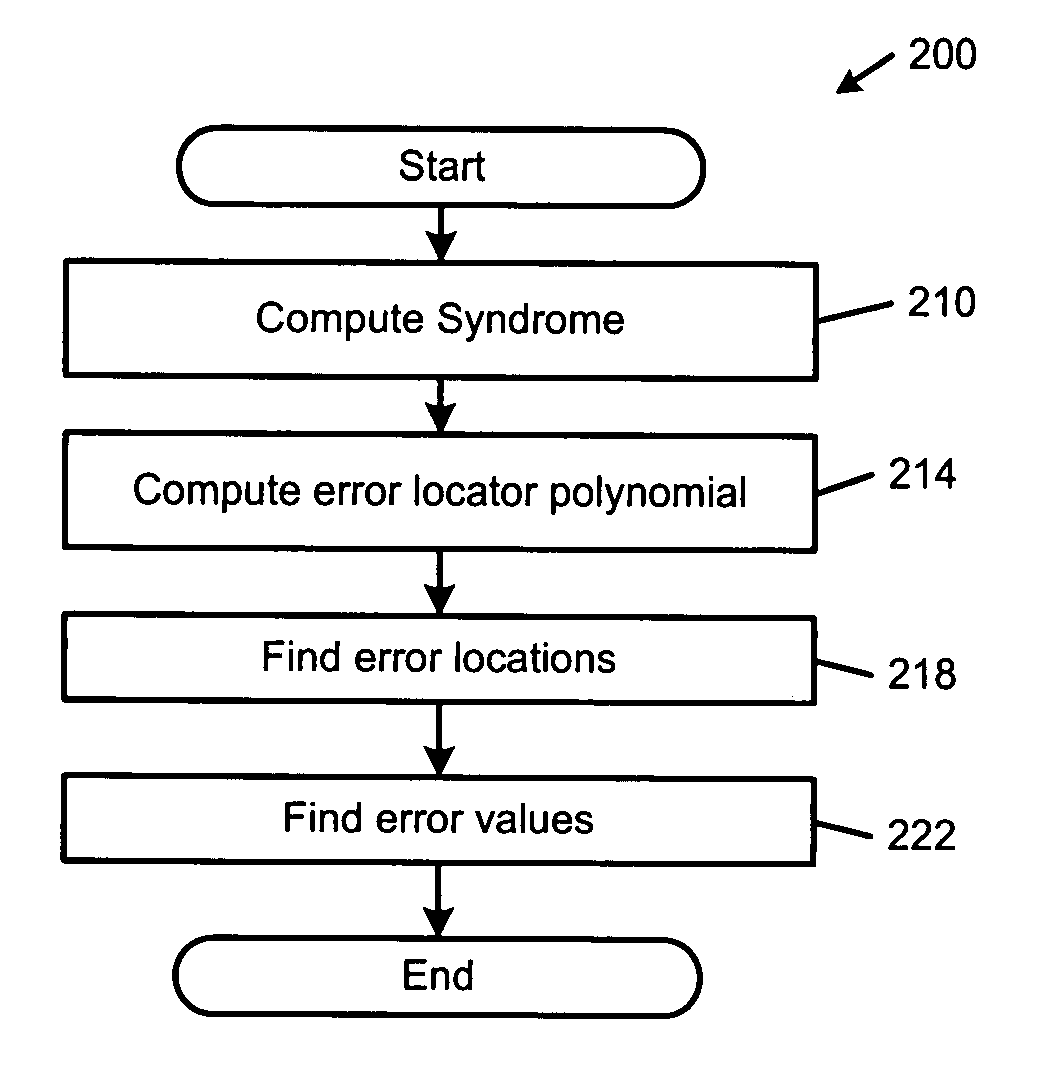
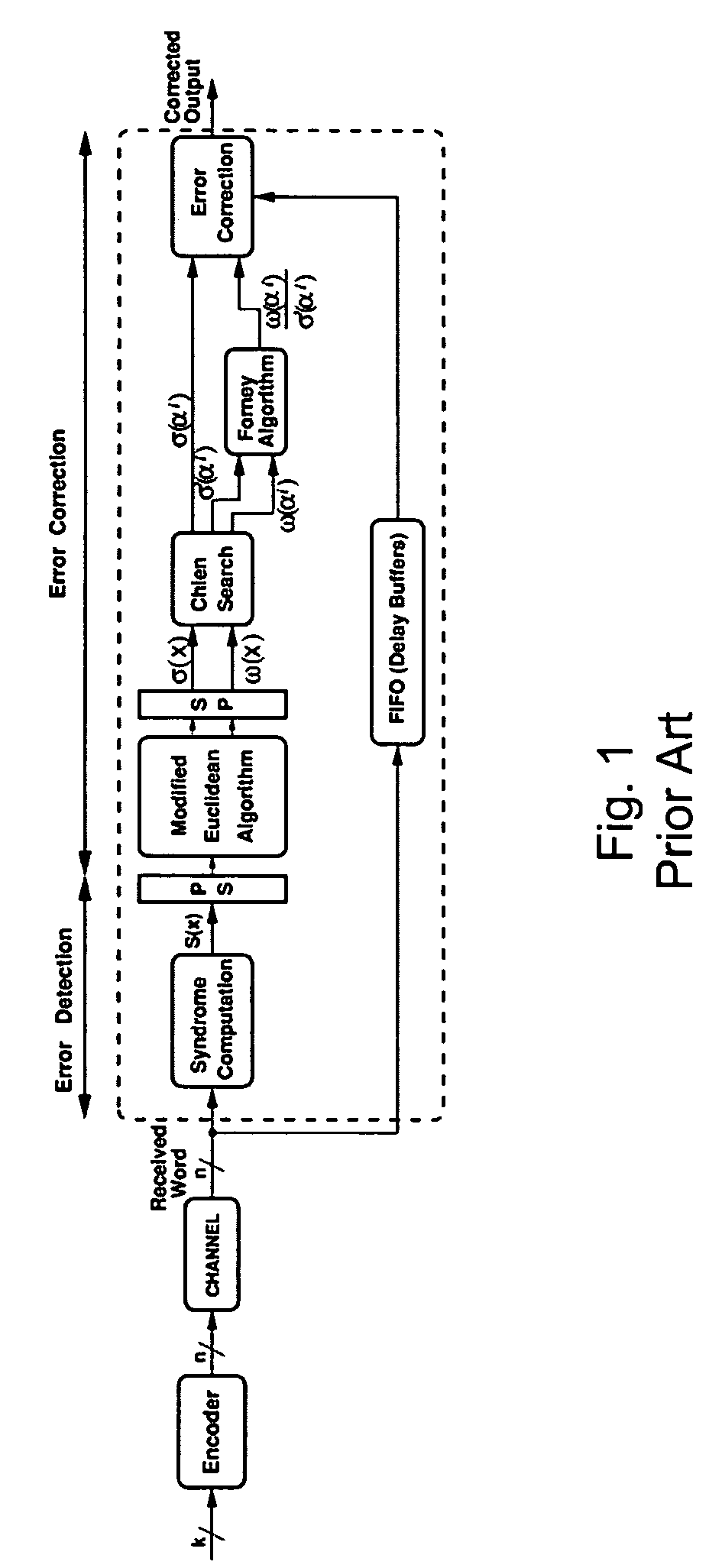
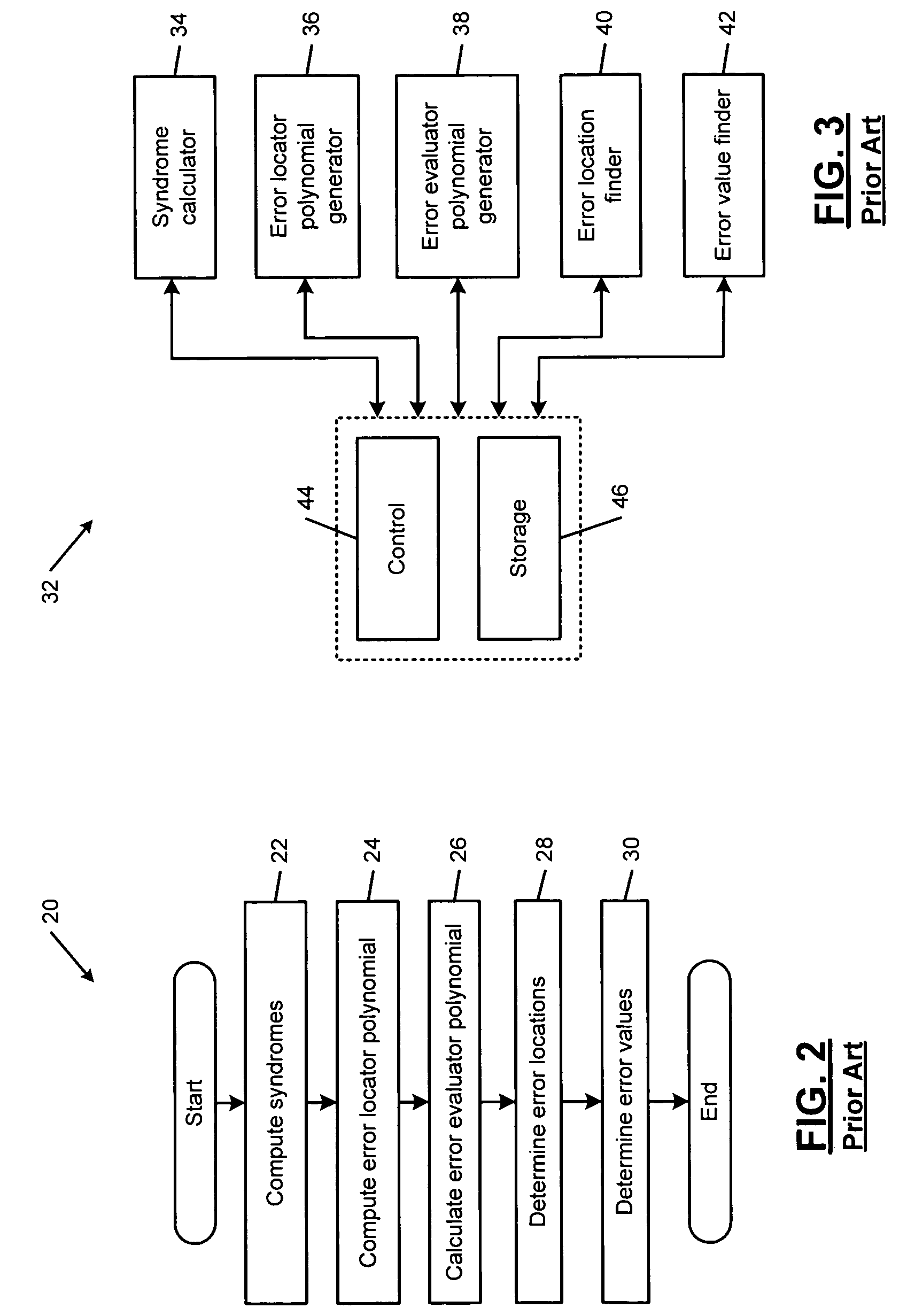
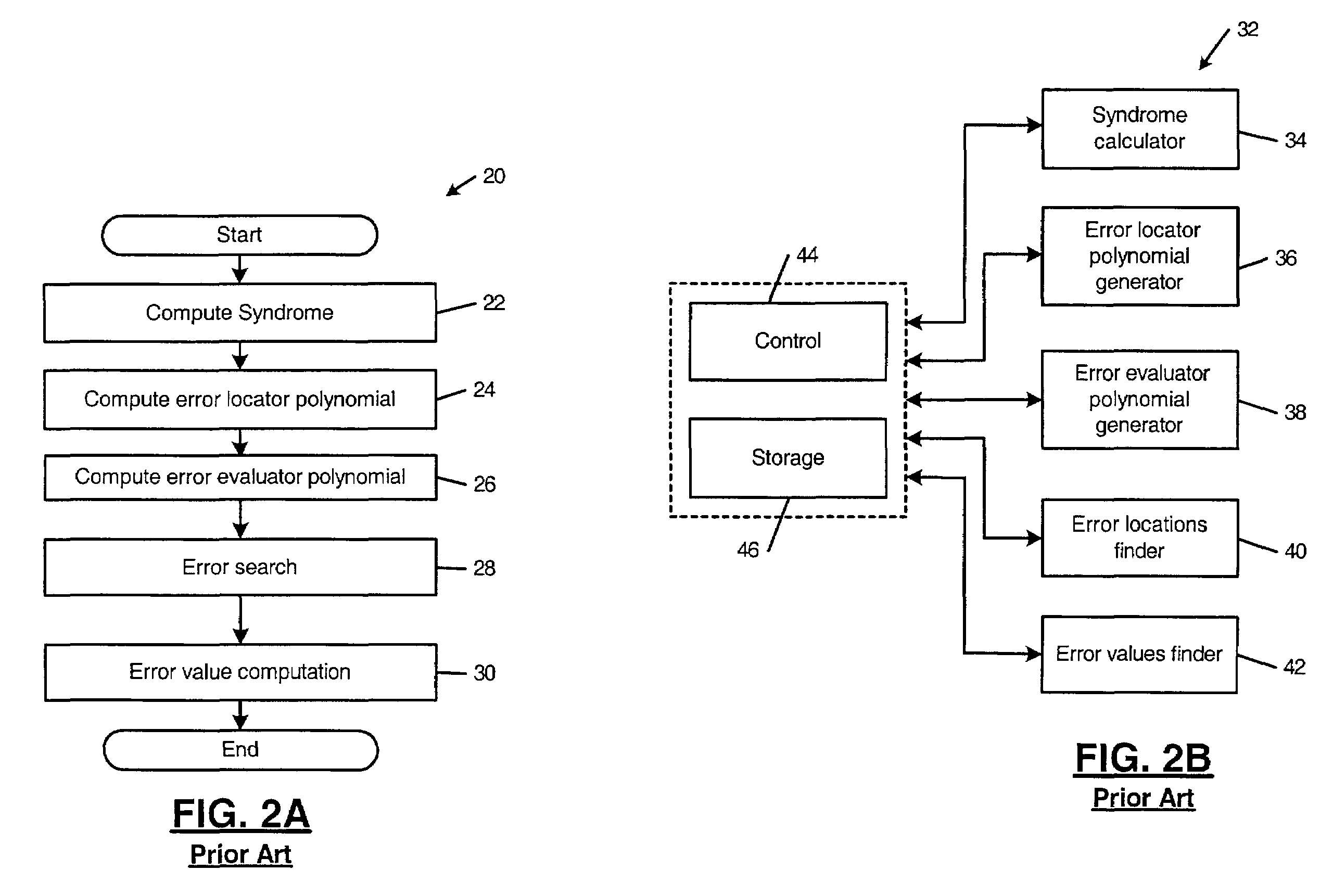
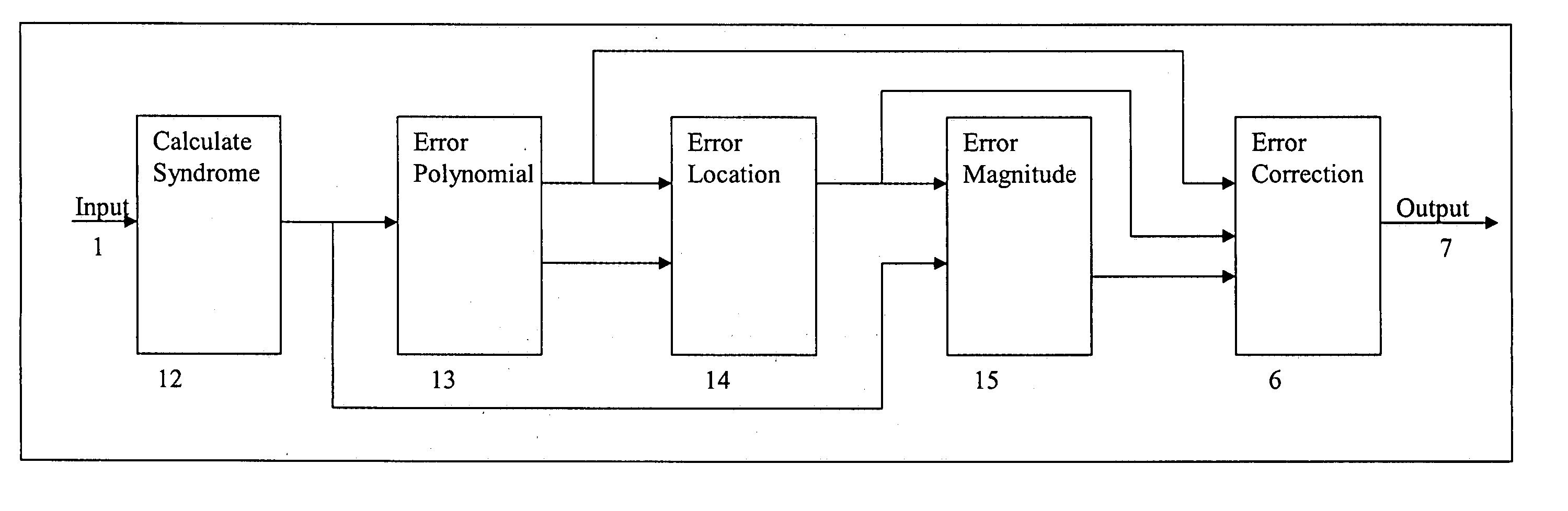
An error correcting Reed-Solomon decoder includes a syndrome calculator that calculates syndrome values. An error locator polynomial generator communicates with the syndrome calculator and generates an error locator polynomial. An error location finder communicates with at least one of the syndrome calculator and the error locator polynomial generator and generates error locations. An error values finder communicates with at least one of the syndrome calculator, the error location finder and the error locator polynomial generator and generates error values using an error value relationship that is not based on the traditional error evaluator polynomial. The error locator polynomial generator is an inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (iBMA), which calculates an error locator polynomial and a scratch polynomial. The error value relationship is based on the error locator polynomial and the scratch polynomial.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
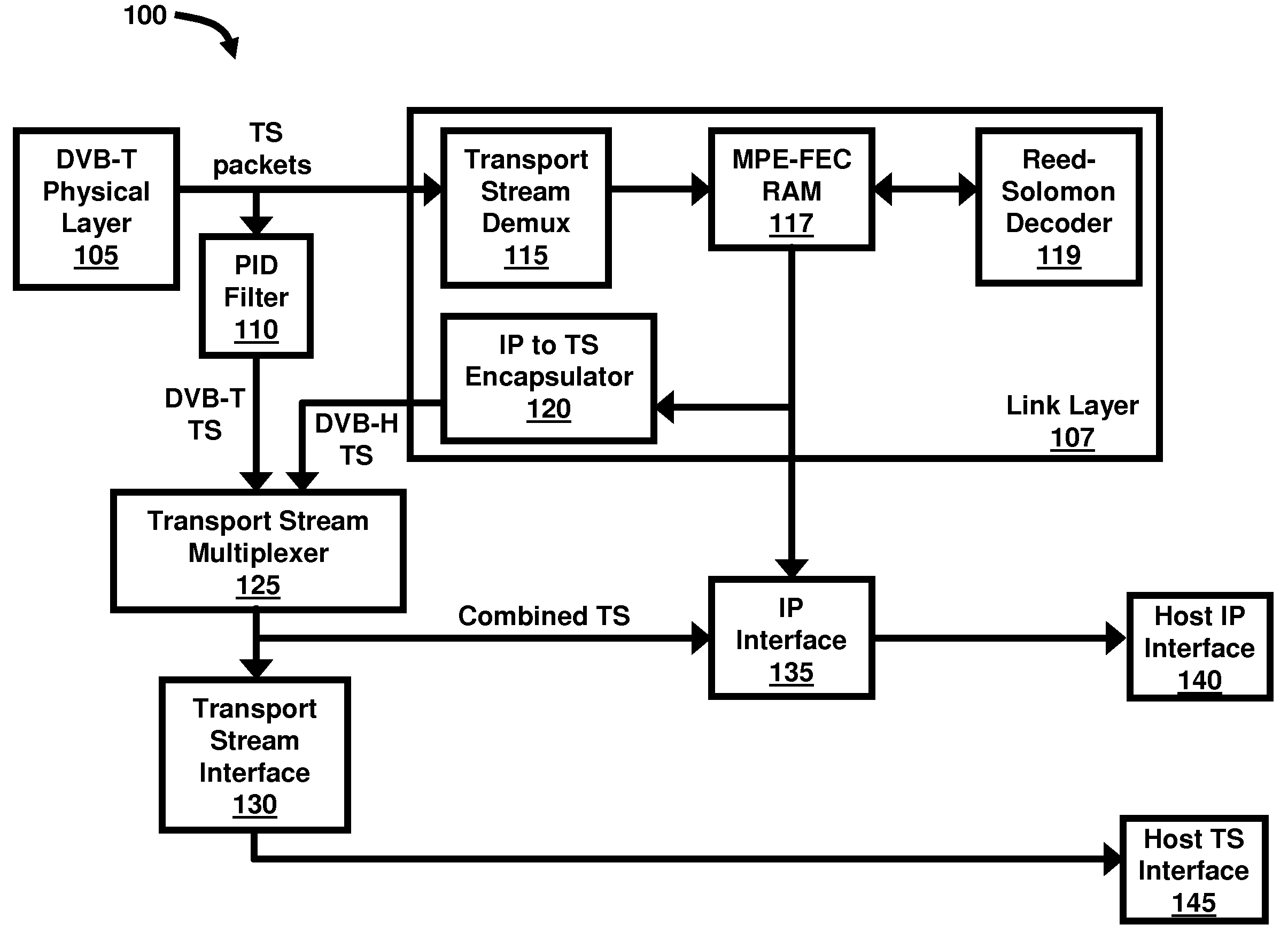
Unified interfacing for dvb-t/h mobile TV applications
InactiveUS20080159279A1Correction errorError preventionBroadcast information characterisationDigital videoComputer network
Transmitting data in a digital video broadcasting for handheld (DVB-H) receiver comprises a transport stream (TS) demultiplexer adapted to extract internet protocol (IP) datagrams from TS data packets; a packet identifier (PID) filter adapted to extract the TS data packets based on the PIDs of the TS data packets; a Multi Protocol Encapsulation-Forward Error Correction (MPE-FEC) random access memory (RAM) unit operatively connected to the TS demultiplexer; a Reed-Solomon decoder operatively connected to the MPE-FEC RAM unit; an IP to TS encapsulator operatively connected to the MPE-FEC RAM unit; a TS multiplexer operatively connected to each of the PID filter and the IP to TS encapsulator, wherein the TS multiplexer is adapted to combine both DVB-Terrestrial (DVB-T) and DVB-H TS data packets into a single combined TS data packet; and a host interface operatively connected to the TS multiplexer.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
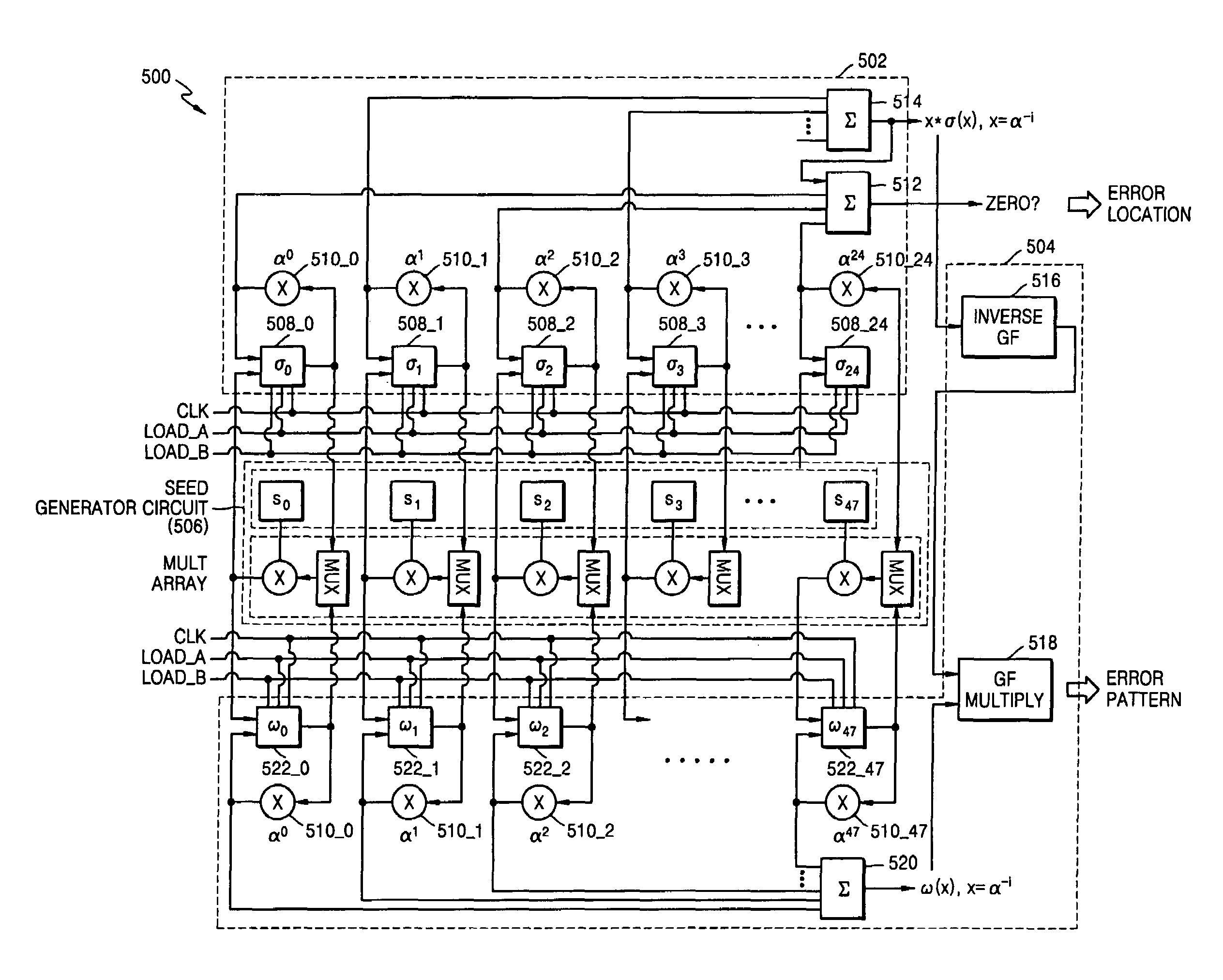
Forward Chien search type Reed-Solomon decoder circuit
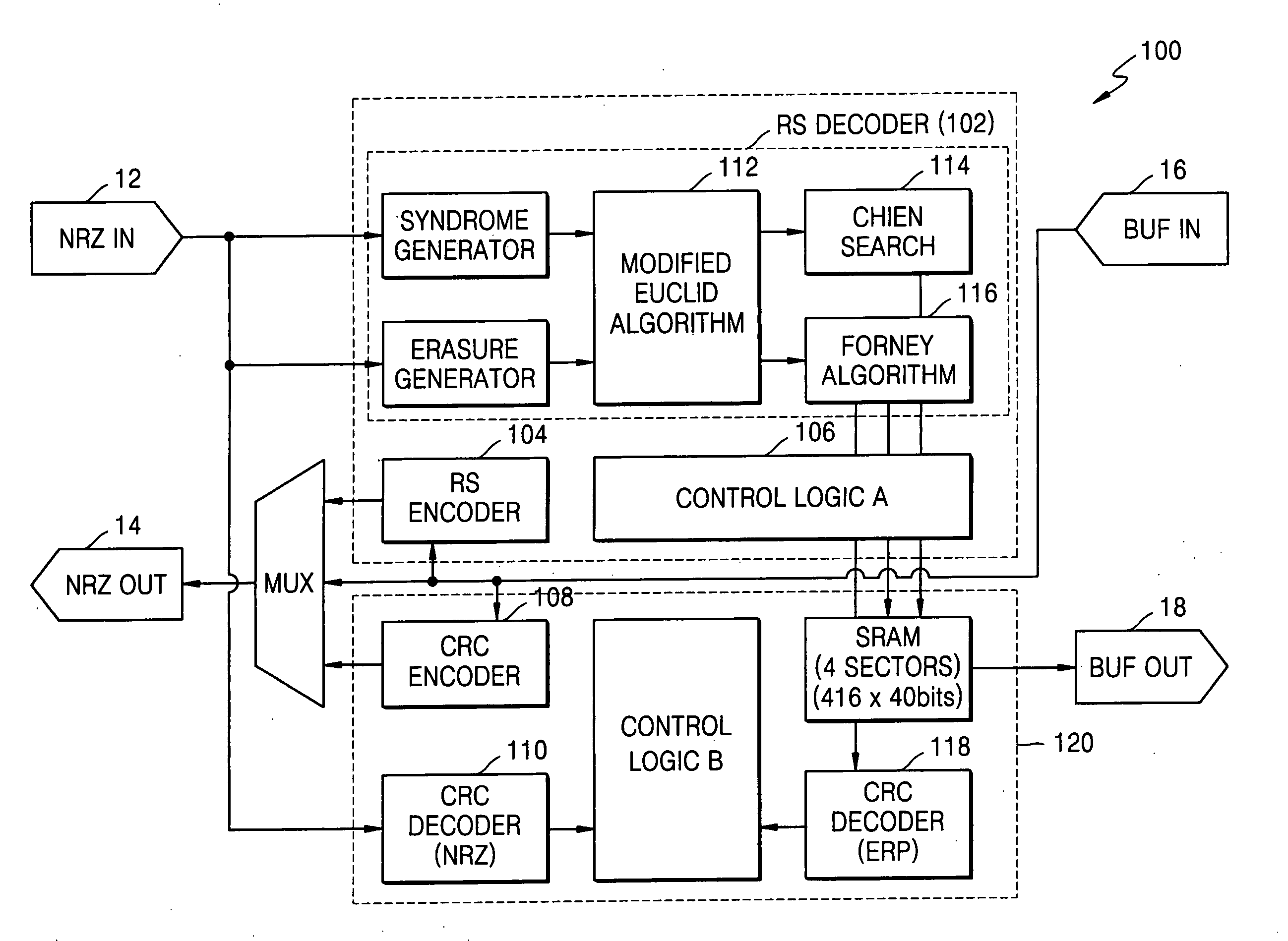
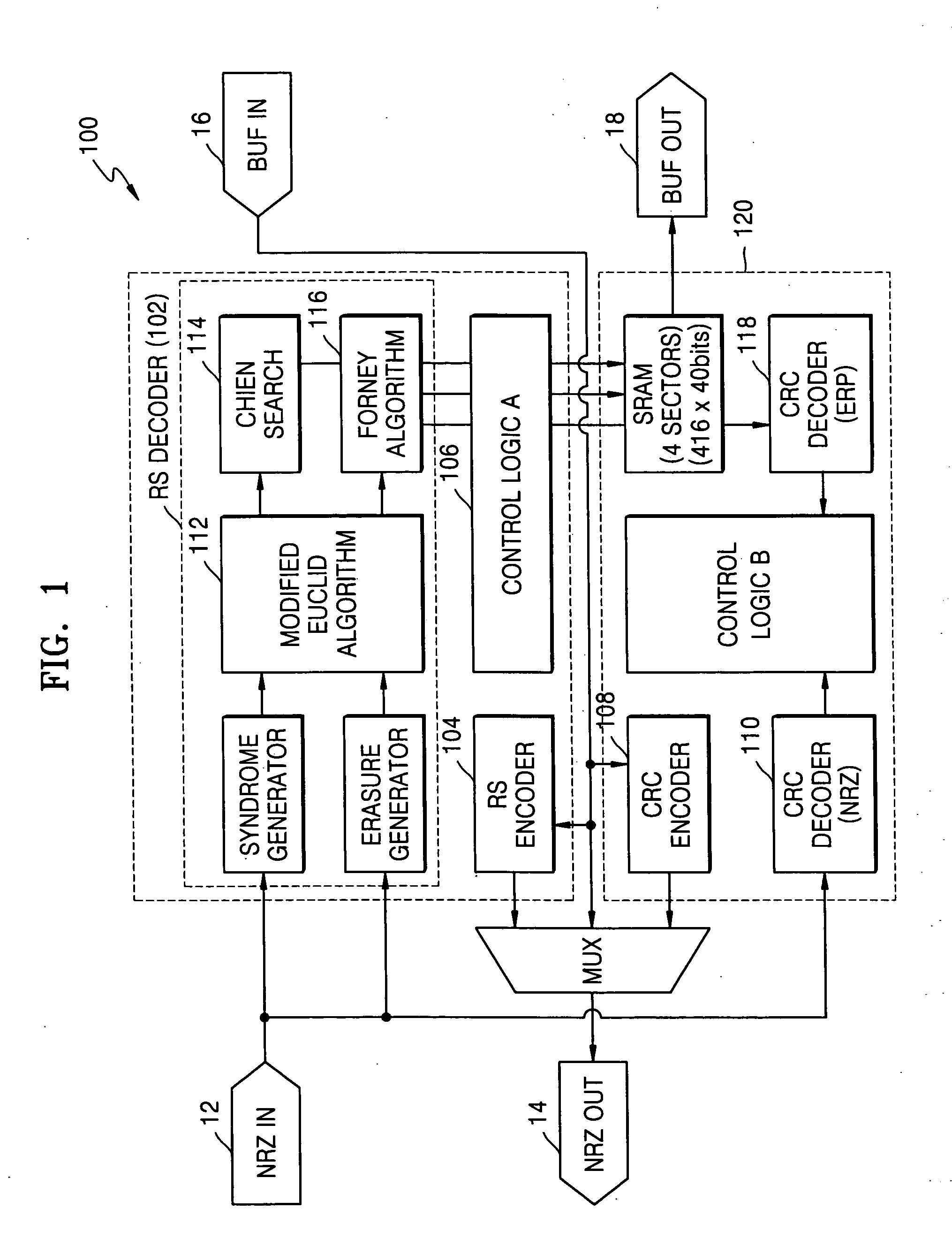
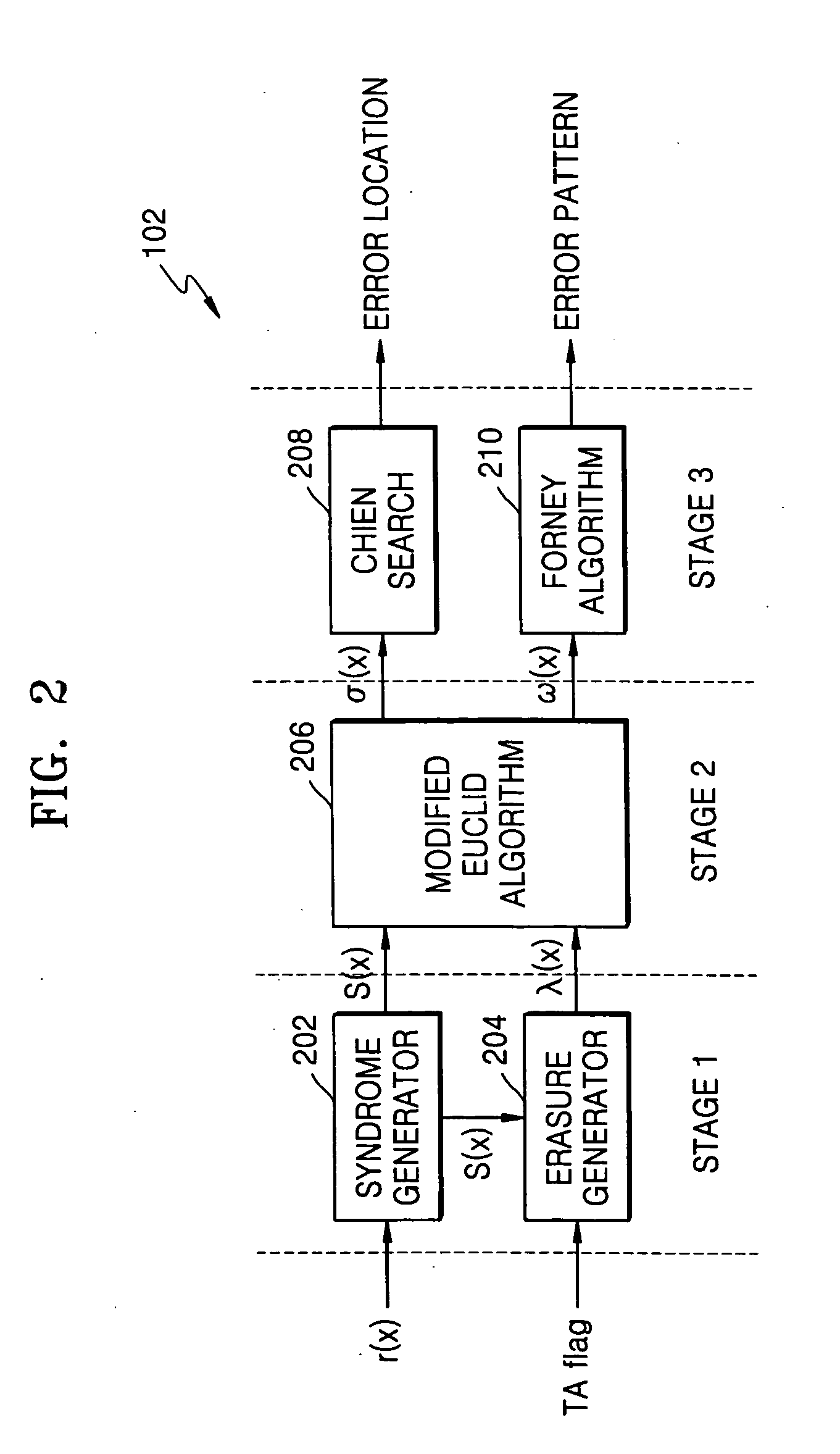
ActiveUS20050172208A1Reduce aggregation timeShorten the timeCode conversionCyclic codesError locationReed solomon decoder
A Reed-Solomon decoder includes a Chien search circuit to receive an error location polynomial function, performs Chien search, and finds an error location; a Forney algorithm circuit to receives an error pattern polynomial function and find an error pattern; and, a seed generator circuit to indicates a seed value corresponding to a codeword length for the input data. A Chien search is performed to obtain and outputs exponential terms related to variables for the polynomials, wherein the Chien search is performed in the same computational direction as an order for the input data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
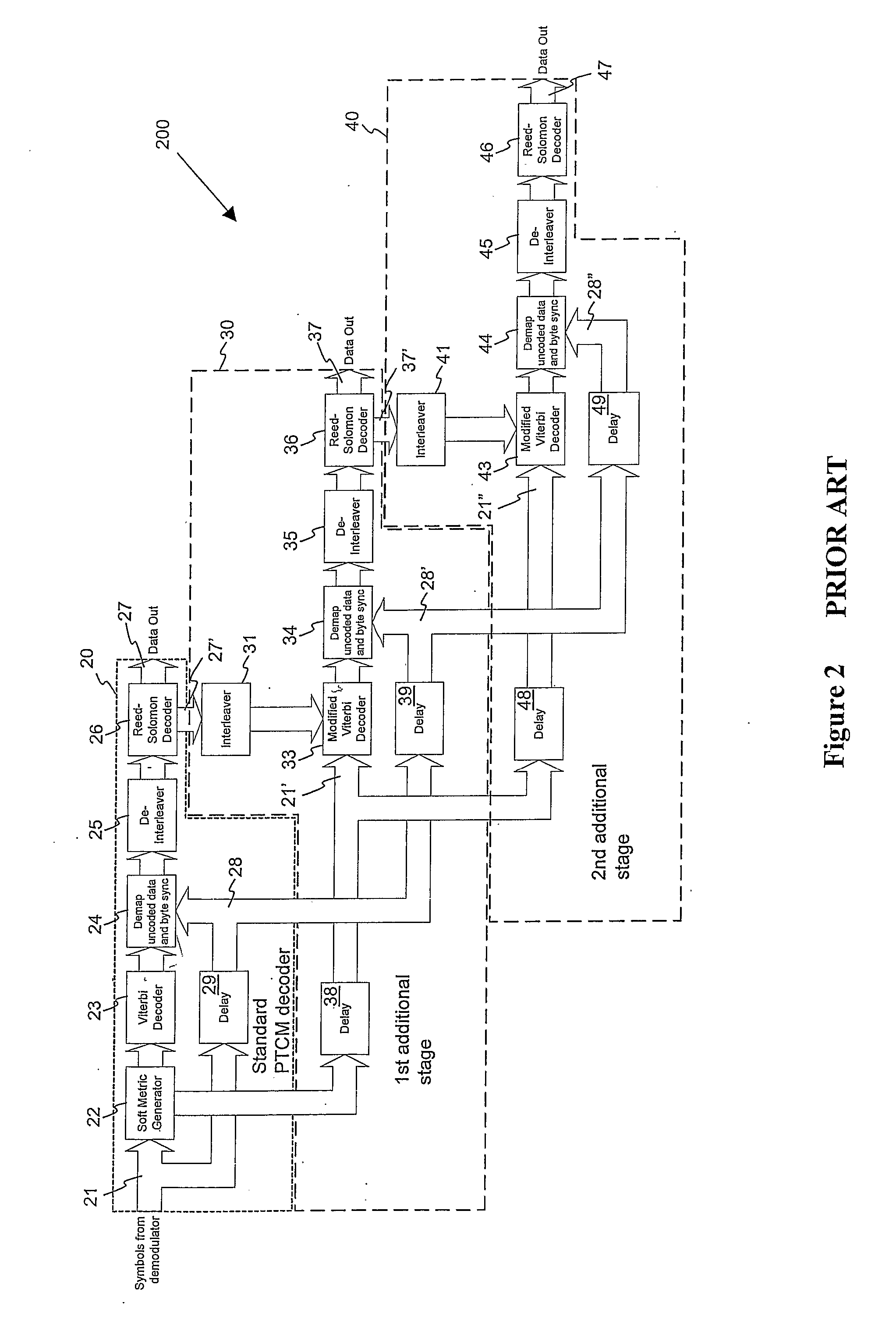
Decoding a Concatenated Convolutional-Encoded and Block Encoded Signal
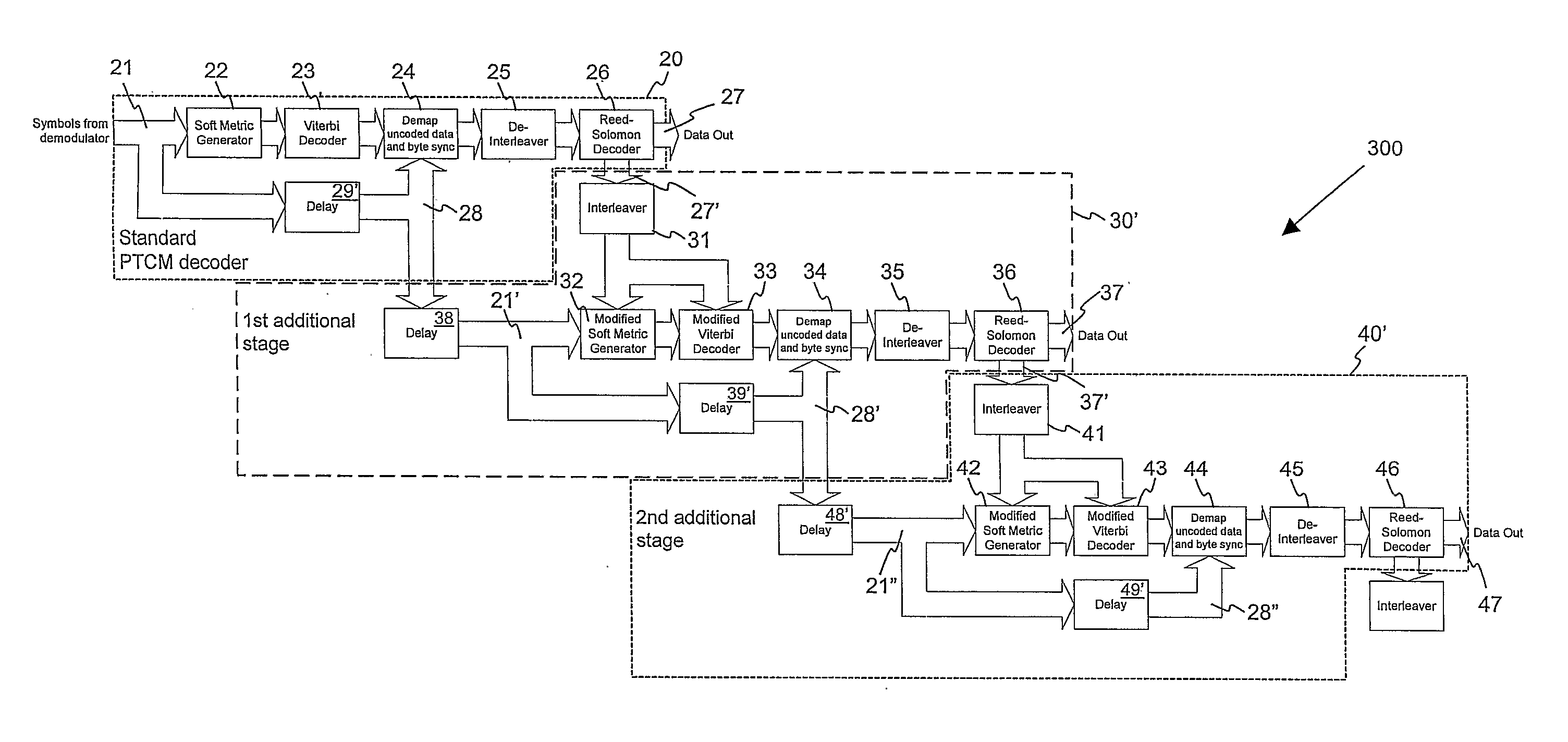
ActiveUS20070220408A1Improve efficiencySpeed up the decoding processData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesViterbi decoderReed solomon decoder
Encoded symbols of a concatenated convolutional-encoded and block encoded signal are presented to a conventional first stage of a concatenated decoder, comprising in sequence a soft metric generator, a Viterbi decoder, a first de-interleaver and a first block decoder such as a Reed-Solomon decoder. The encoded symbols are also presented to a delay chain to produce progressively delayed encoded symbols. Where an output block of the conventional decoder is indicated as being a valid codeword by the first block decoder, the bytes in this block are marked as being correct. These bytes that are known to be correct are then used after interleaving and serialisation as known bits input to a second stage of the decoder process operating on the delayed encoded symbols and incorporating a modified soft metric generator constrained by the known bits. This process can be extended to further iterations as required. A modified Viterbi decoder, which is also constrained by the known bits, may also be used in the second and subsequent iterative stages.
Owner:MK SYST USA INC
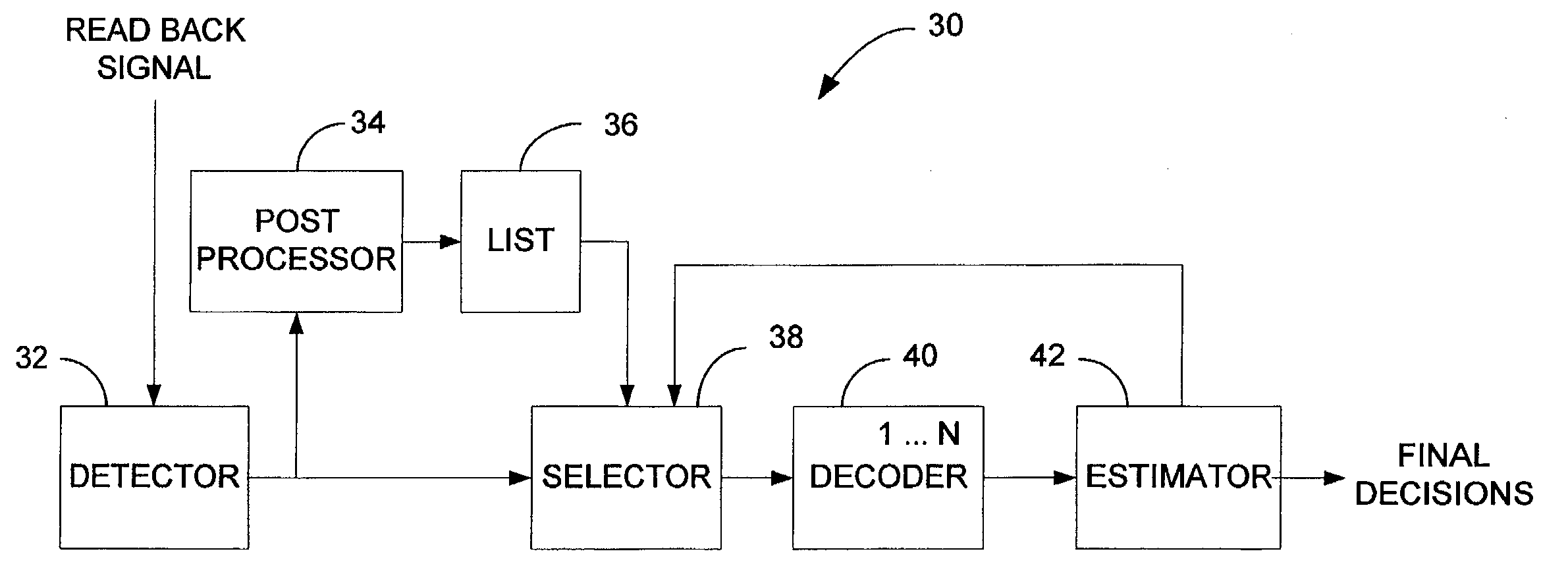
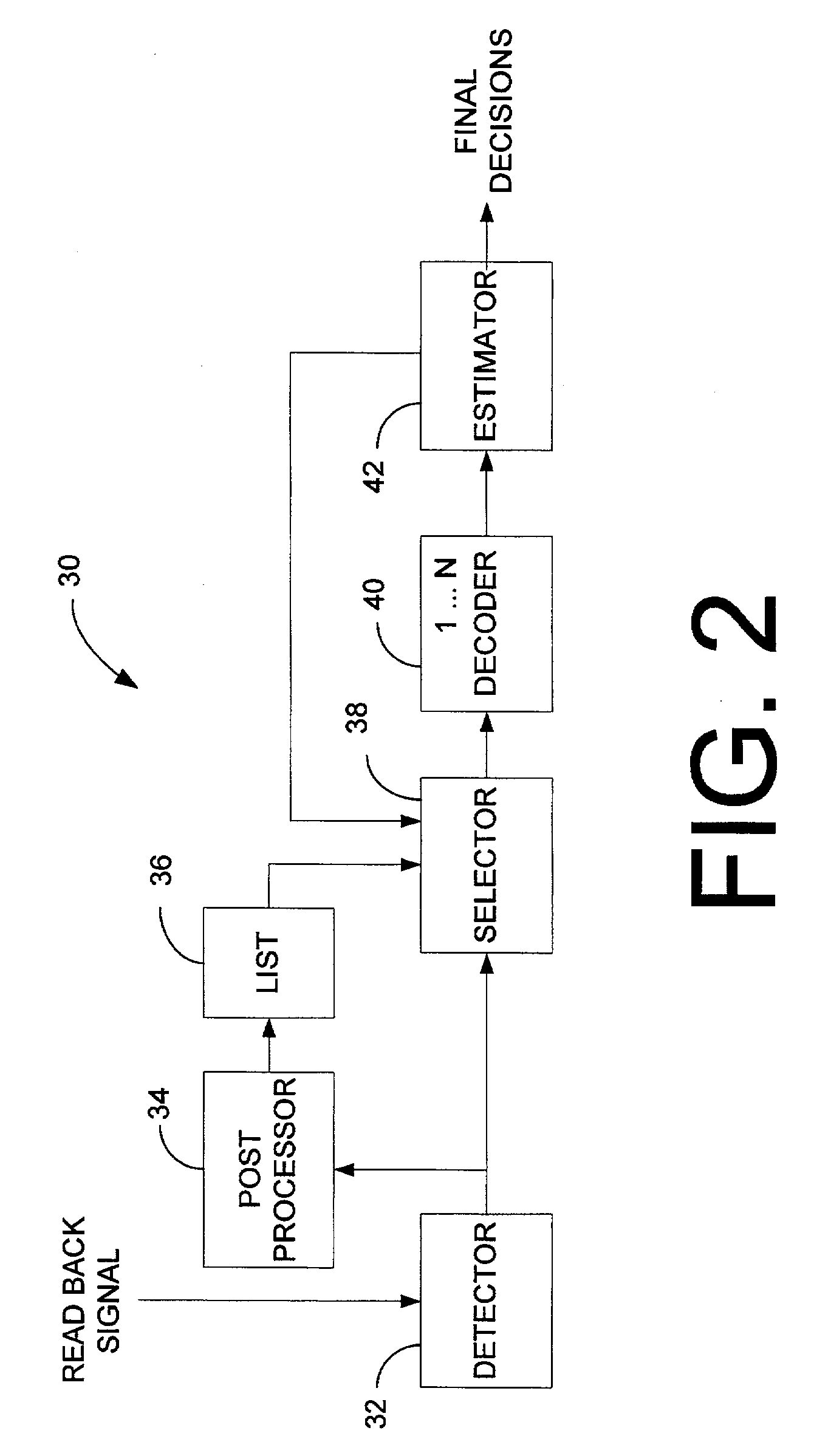
Correcting errors in disk drive read back signals by iterating with the Reed-Solomon decoder
A signal detector to detect symbols in a read back signal. The signal detector includes a first detector to generate raw decisions as a function of the read back signal. A post processor identifies possible defects in the raw decisions. A selector selects a portion of the possible defects and generates modified decisions based upon correcting the portion of the possible defects. At least one signal decoder generates final decisions as a function of the modified and raw decisions. A decision block returns control to the selector in response to detecting excess errors in the final decisions.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
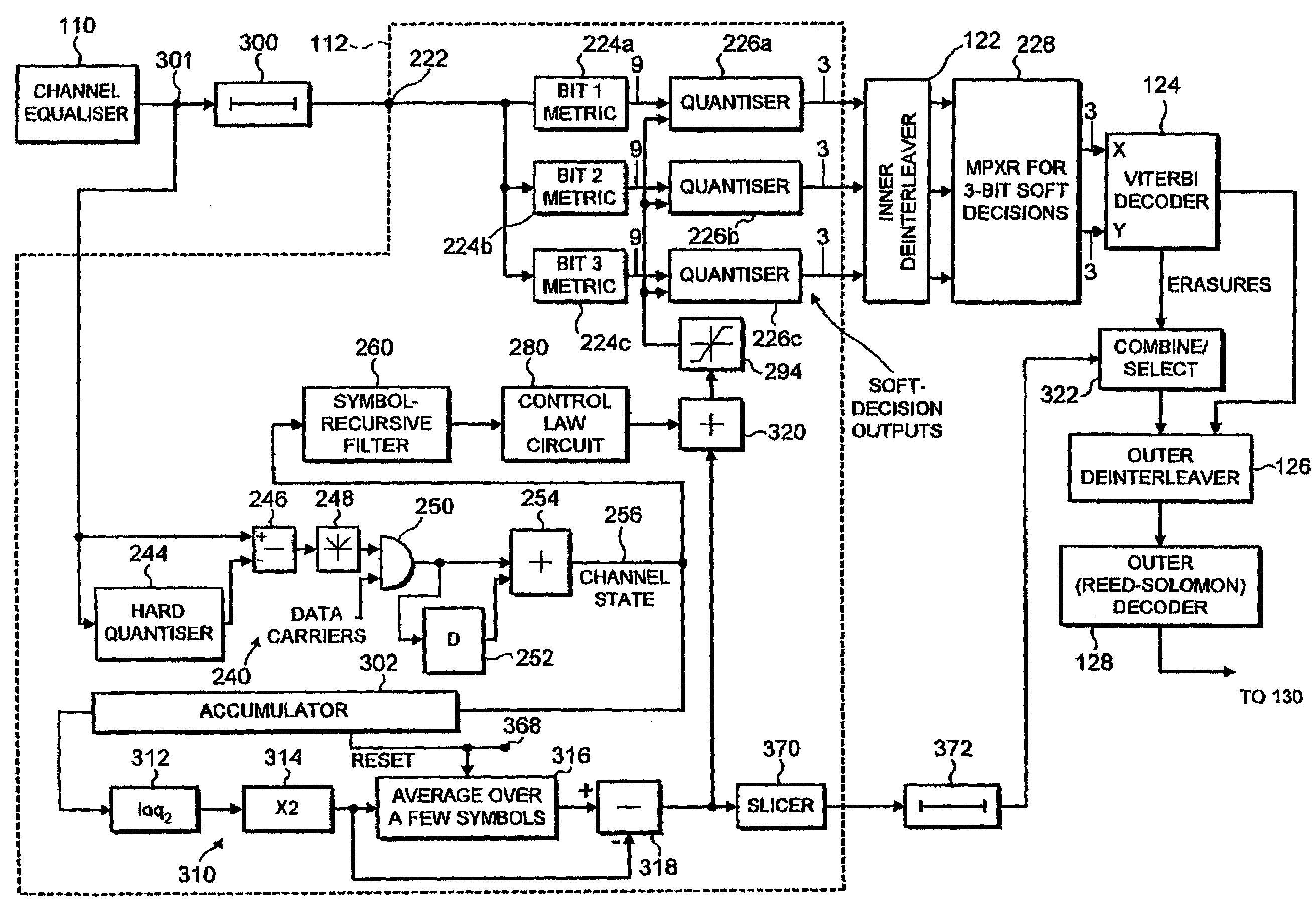
Decoders for many-carrier signals, in particular in DVB-T receivers
InactiveUS7221720B2Large memory requirementIncrease the number ofData representation error detection/correctionPulse modulation television signal transmissionViterbi decoderCarrier signal
A DVB-T receiver includes a channel equalizer, a metric assignment and demapping circuit, a Viterbi decoder and an outer Reed-Solomon decoder. The metric assignment and demapping circuit includes a soft-decision quantising arrangement which provides confidence values for the Viterbi decoder. The quantising arrangement receives a control input from channel state indication (CSI) measurement circuitry.A further channel state indication is obtained on a symbol-by-symbol basis. This is compared an average obtained over a few symbols, to detect impulsive interference, and applied as part of the control for the soft-decision quantiser.A signal derived from the further channel state indication is also applied to the erasures input of the Reed-Solomon decoder.
Owner:BRITISH BROADCASTING CORP
High speed hardware implementation of modified Reed-Solomon decoder
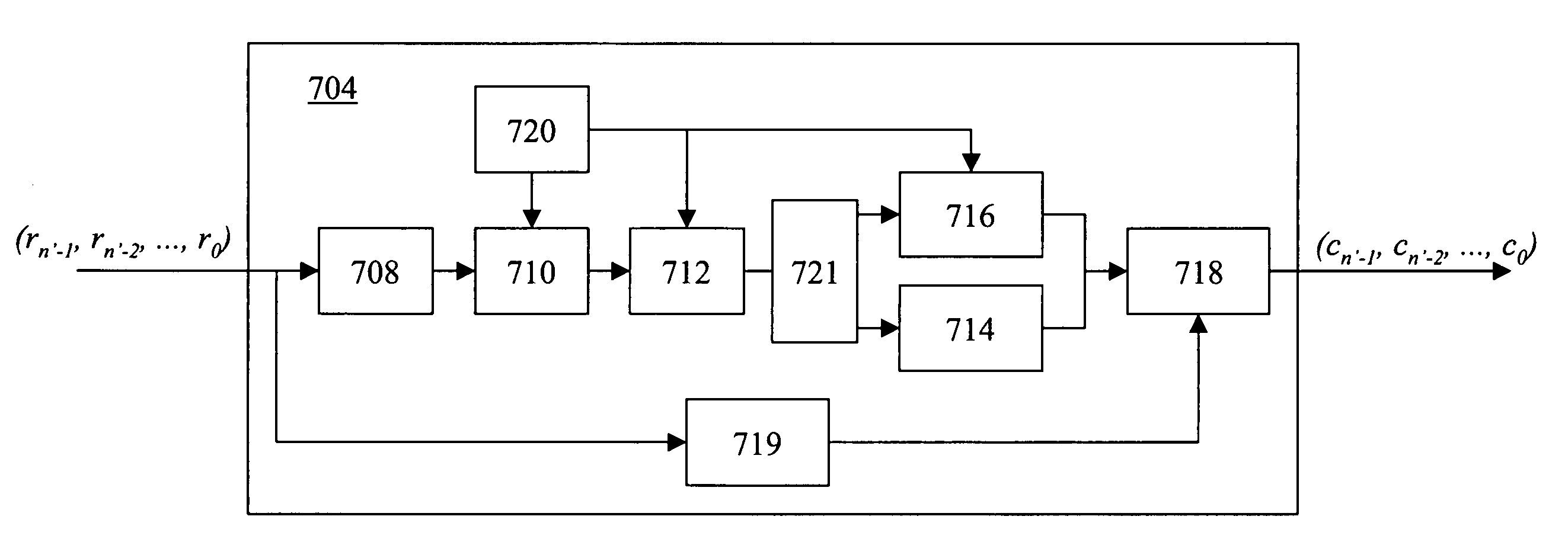
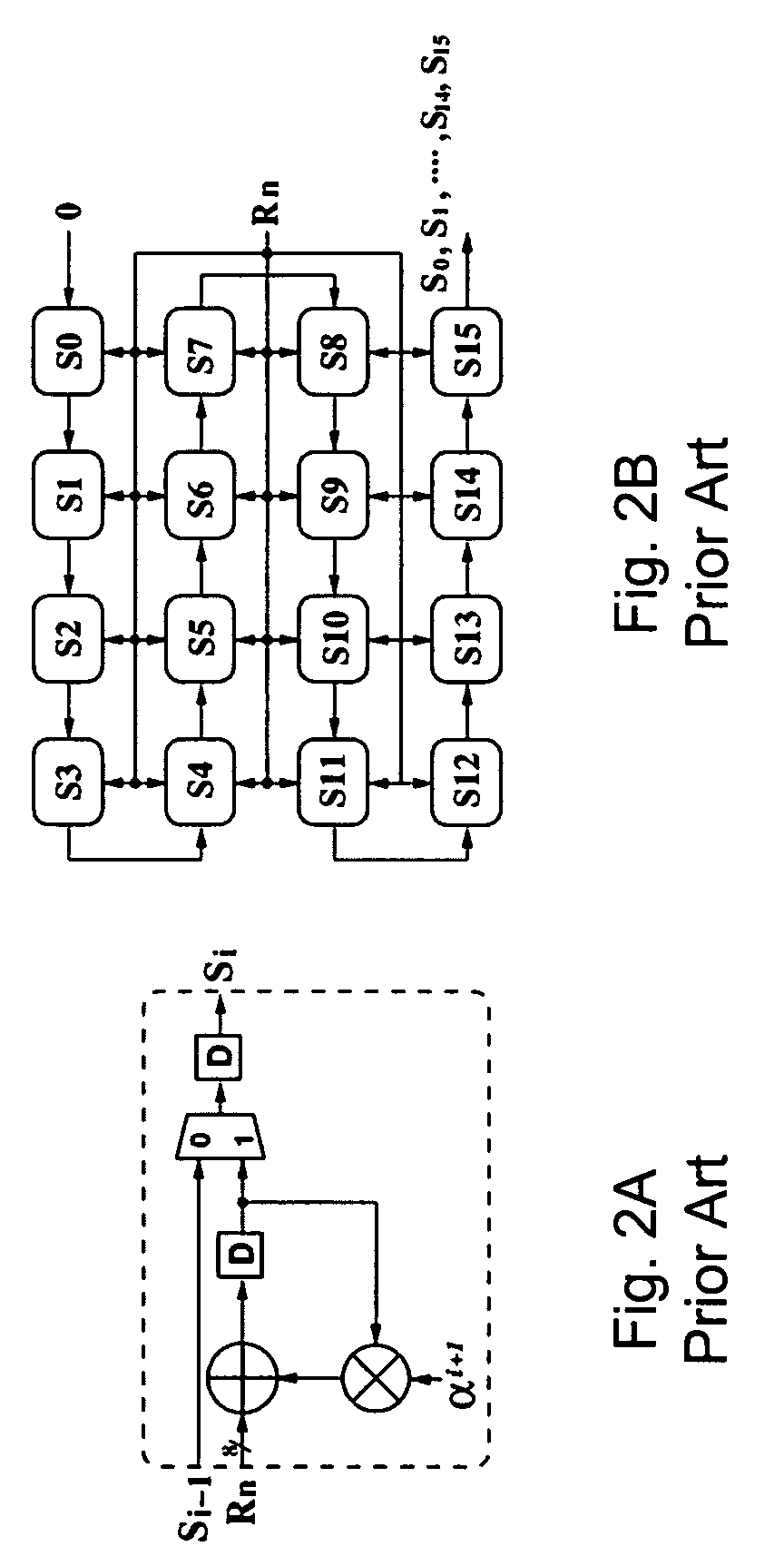
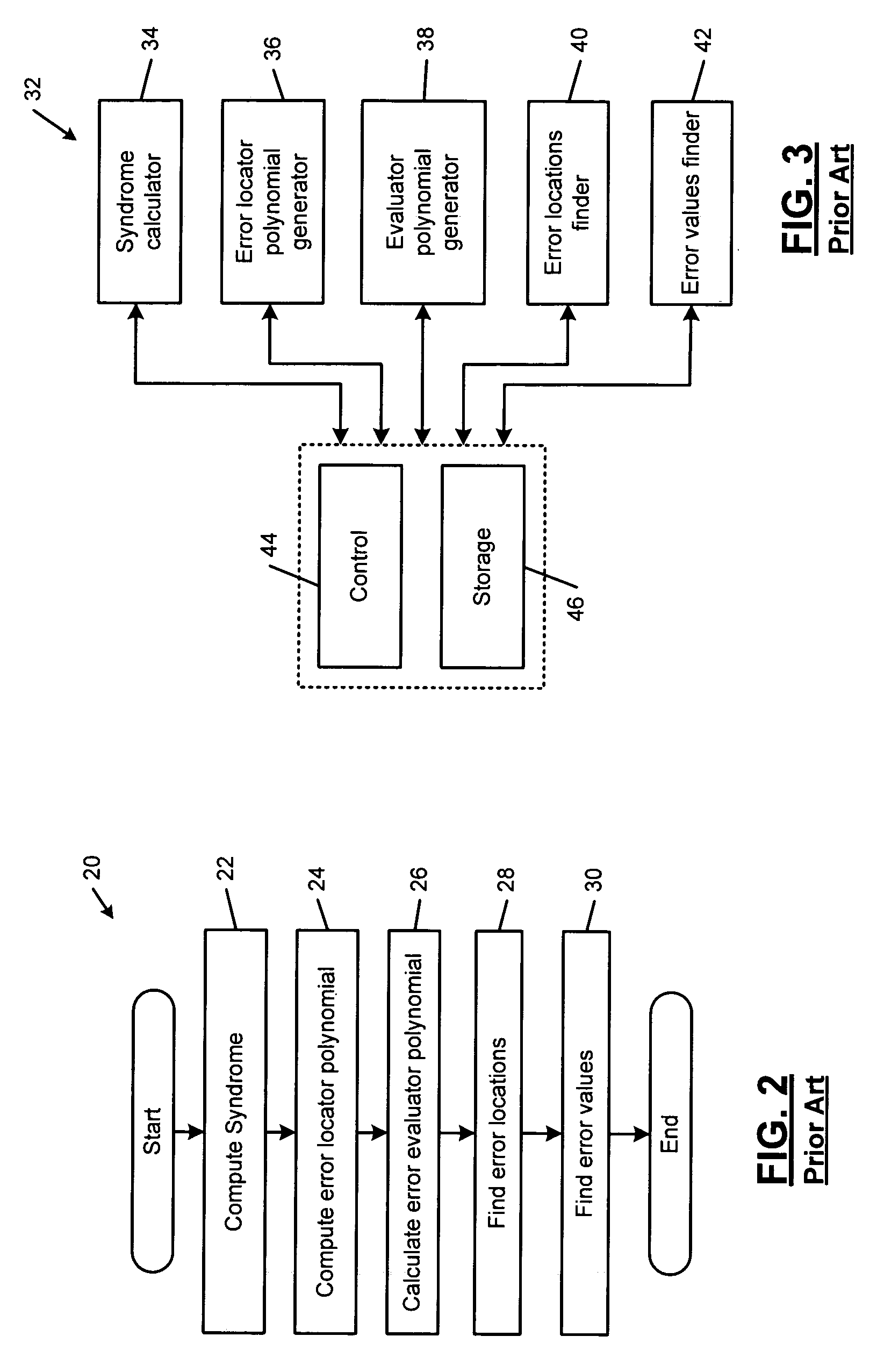
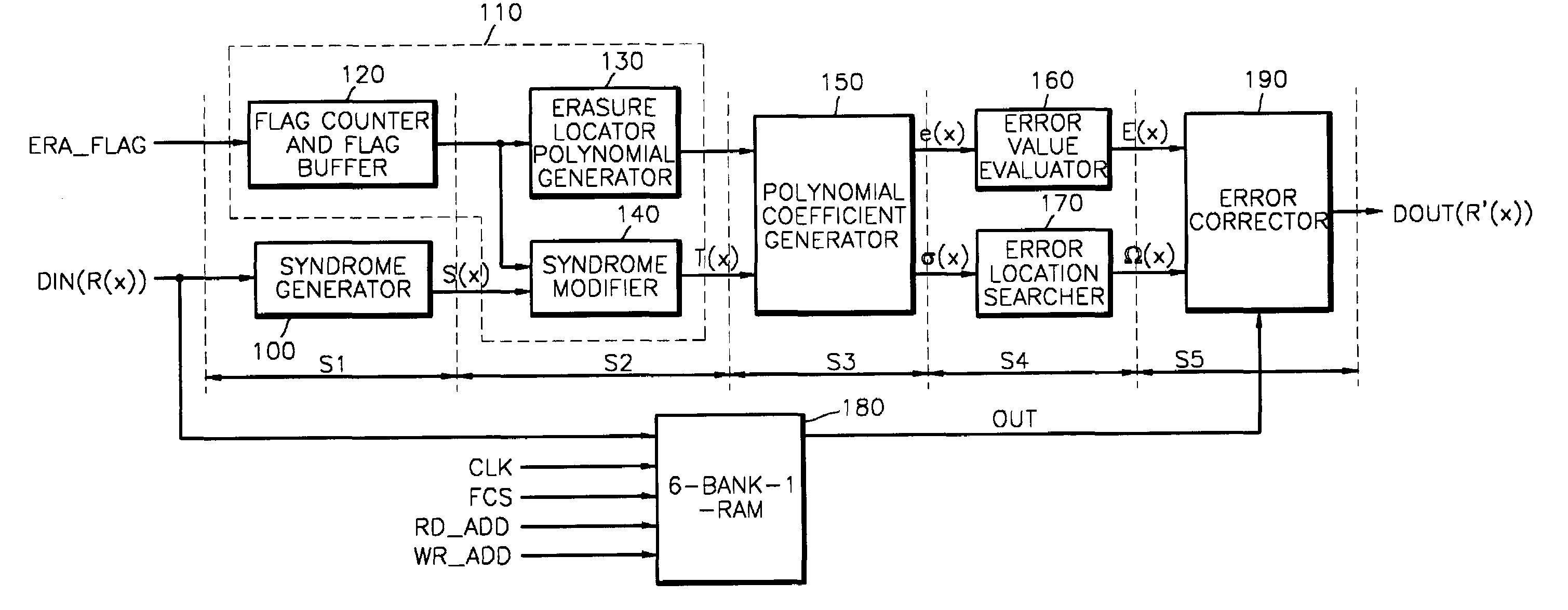
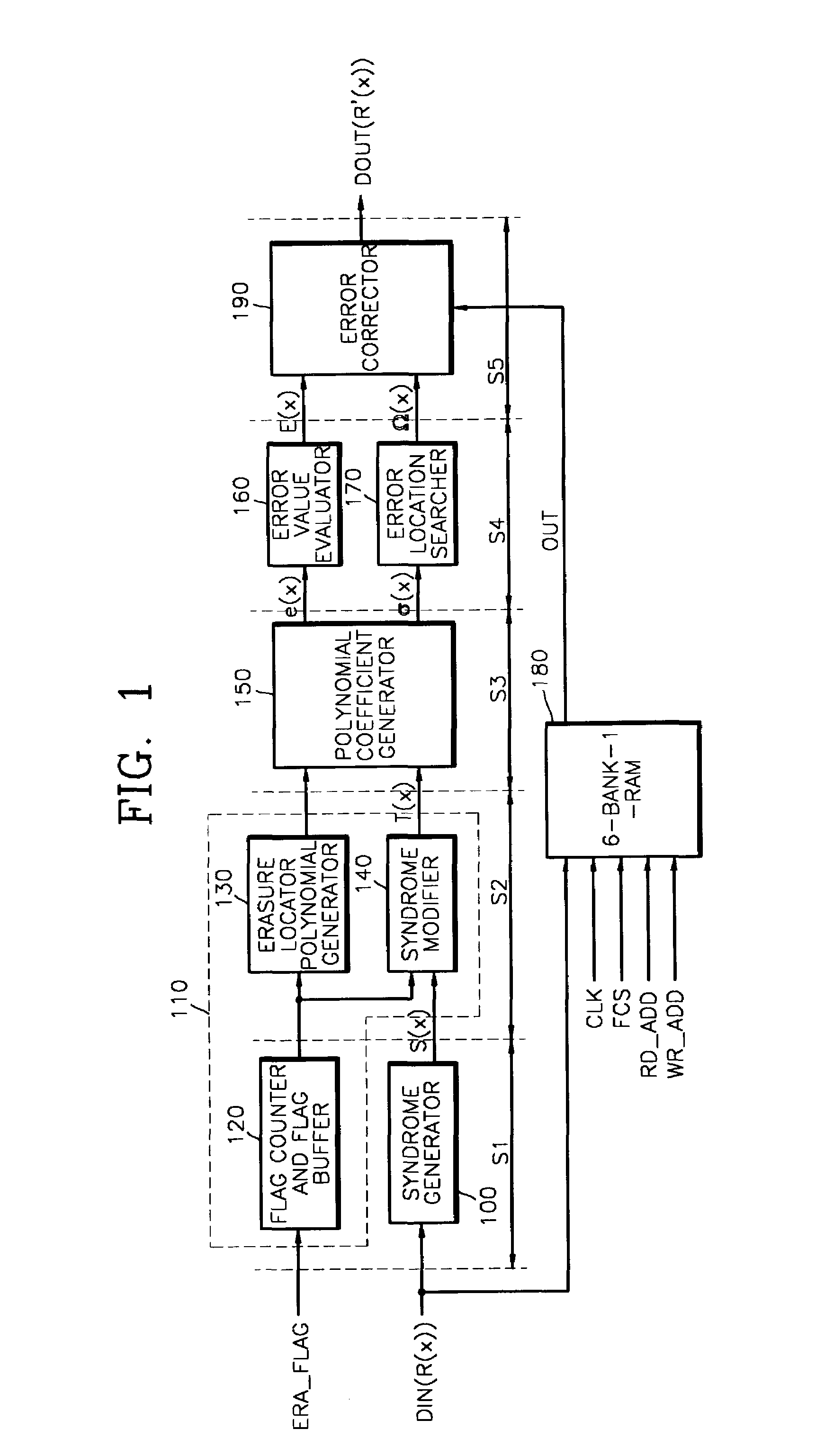
A decoder suitable for use in a digital communications system utilizing an RS(n′, k′) code modified from an RS(n, k) code receives n′-symbol vectors each including k′ message symbols and r′=n′−k′ parity symbols and decodes the n′-symbol vectors to correct errors therein, wherein n, k, n′, and k′ are integers, and k′<n′<n, k′<k<n, and wherein the decoder stores therein one erasure locator polynomial σ0(x). The decoder includes a syndrome calculator for receiving the n′-symbol vectors and for calculating syndromes of each n′-symbol vector, wherein the i-th syndrome Si of one n′-symbol vector R′, (rn′−1, rn′−2, . . . , r0), is Si=Rs(αi+1) for i=0, 1, . . . , n−k−1, wherein Rs(x)=rn′−1xn′−1+rn′−2xn′−2+ . . . +r0, and means for finding the locations and values of the errors in each n′-symbol vector using the syndromes thereof and the one erasure locator polynomial σ0(x).
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Optimized Reed-Solomon decoder
ActiveUS7788570B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionError locationReed solomon decoder
A modified Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder comprises a syndrome calculation module that calculates a plurality of syndromes from a received codeword; a syndrome modification module that cyclically modifies the plurality of syndromes; an error correction module that selectively removes a set of error values from the received codeword at a set of error locations to create a corrected codeword; and a control module that determines whether the corrected codeword is valid, generates a success signal if the corrected codeword is valid, and selectively actuates the syndrome modification module if the corrected codeword is invalid.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
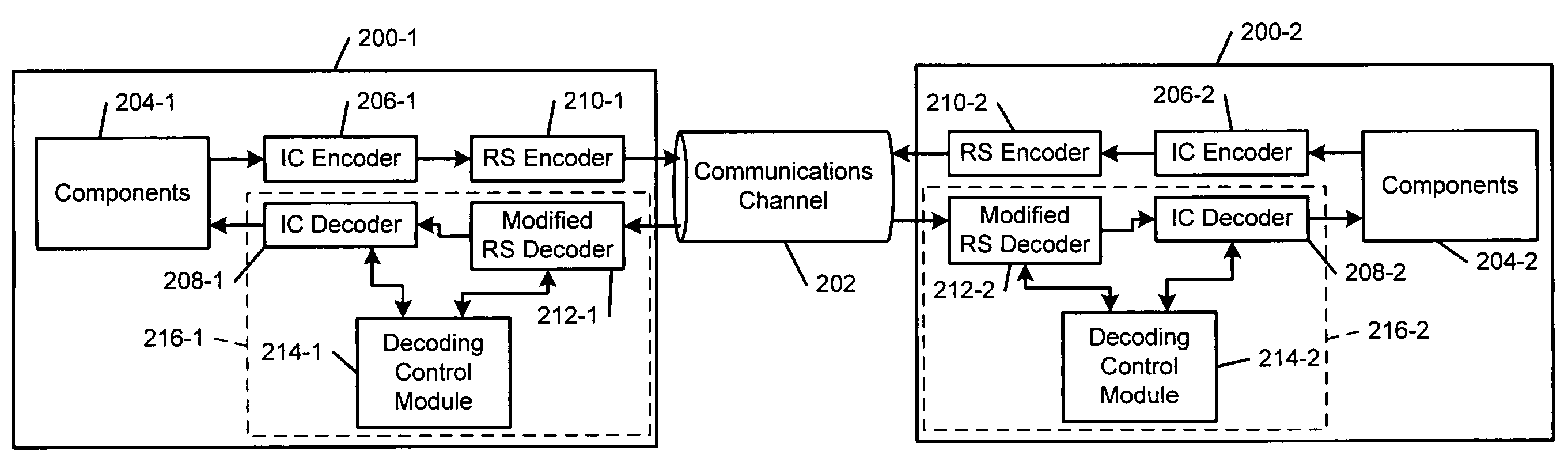
Optimized reed-solomon decoder
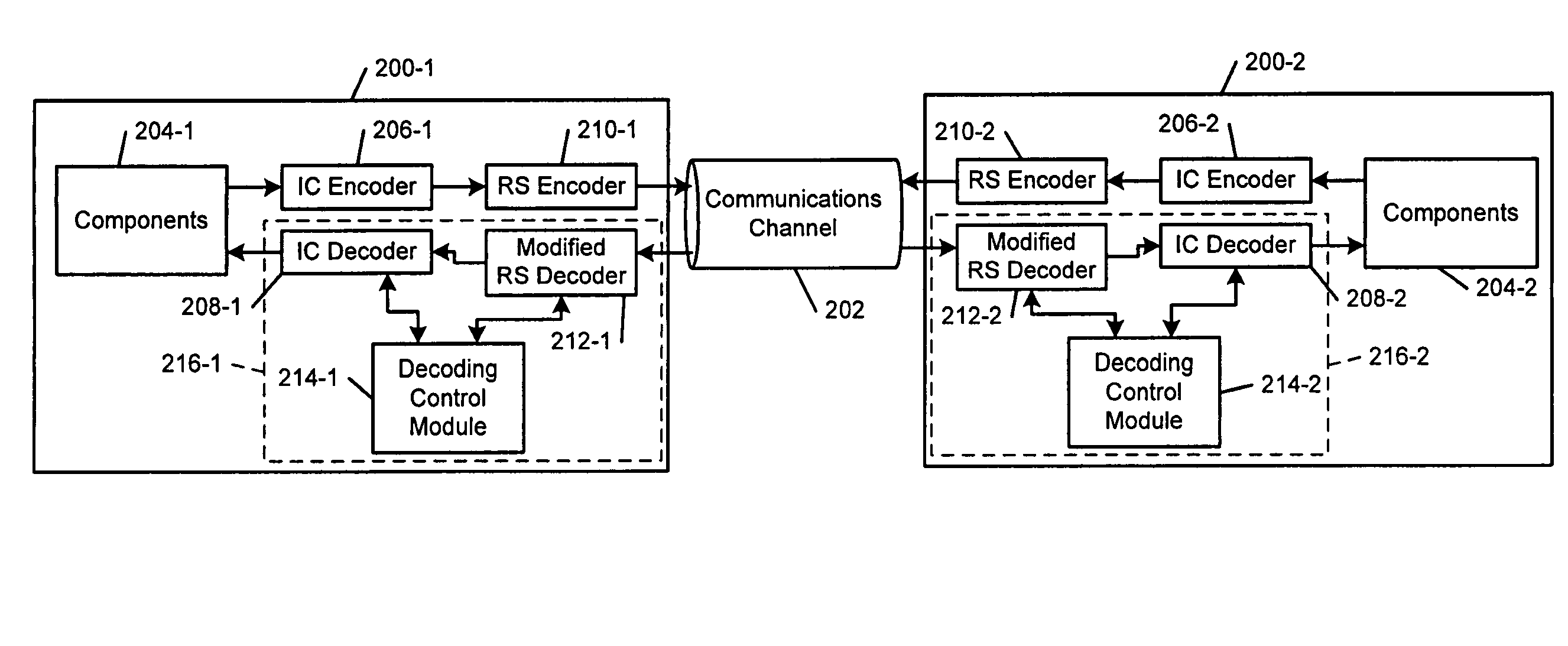
An error decoding system that comprises a first Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder that receives an encoded codeword and generates a decoded codeword. An inner code (IC) decoder checks the decoded codeword for uncorrected errors. A decoding control module communicates with the first RS decoder and the IC decoder, iteratively modifies a parameter of the first RS decoder if the IC decoder detects uncorrected errors in the decoded codeword, and instructs the first RS decoder to decode the encoded codeword again after modifying the parameter.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Efficient high-speed Reed-Solomon decoder
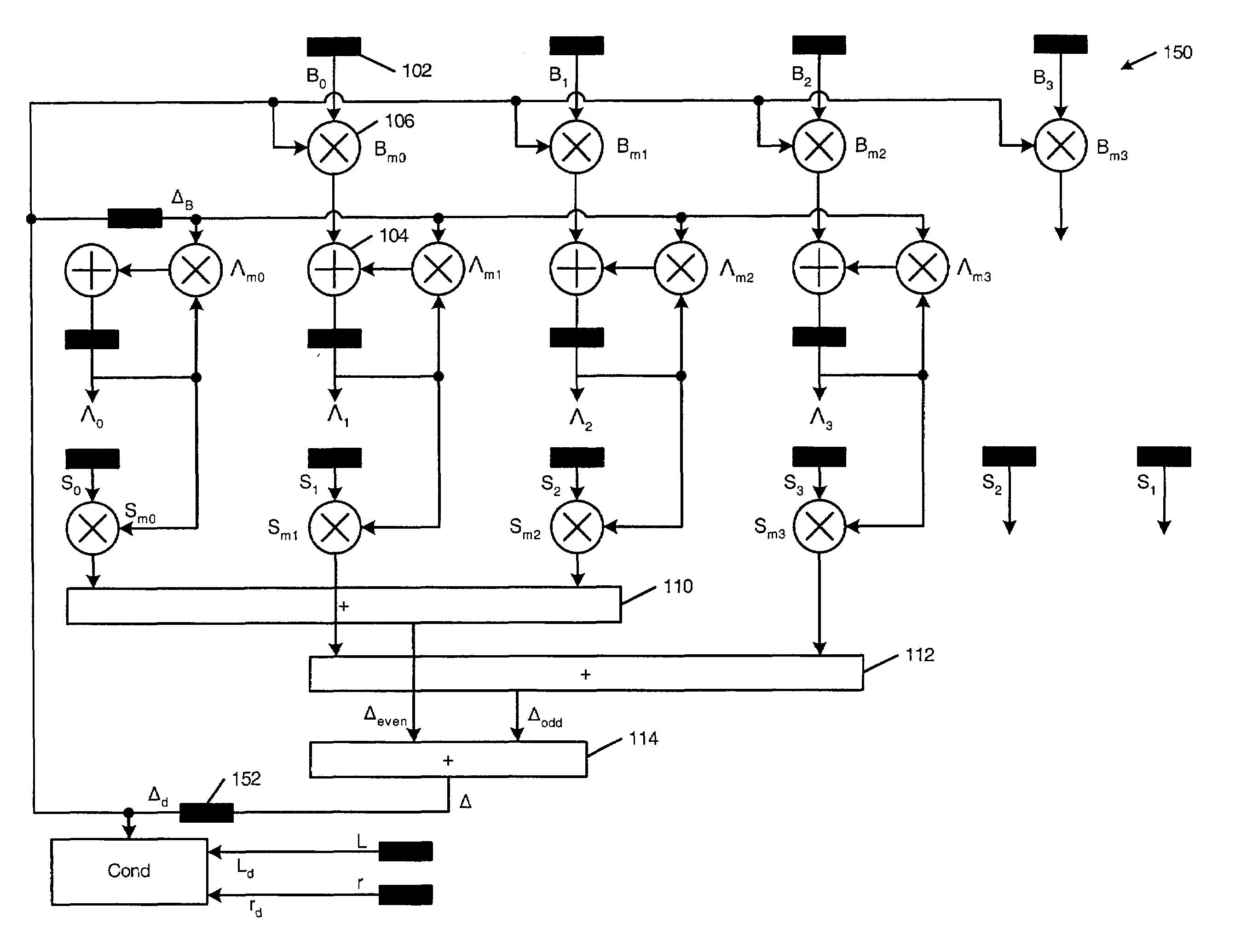
A Reed-Solomon decoder includes an inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (iBMA) circuit with a pipelined feedback loop. An error locator polynomial generator generates error locator polynomial values. A scratch polynomial generator generates scratch polynomial values. A discrepancy generator generates discrepancy values based on the error locator polynomial values and the scratch polynomial values. Multipliers used to generate the discrepancy values are also used to generate the error locator polynomial to reduce circuit area. A first delay circuit delays the discrepancy values. A feedback loop feeds back the delayed discrepancy values to the error locator polynomial generator and the scratch polynomial generator. An error location finder circuit communicates with the iBMA circuit and identifies error locations. An error value computation circuit communicates with at least one of the error location finder circuit and the iBMA circuit and generates error values.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
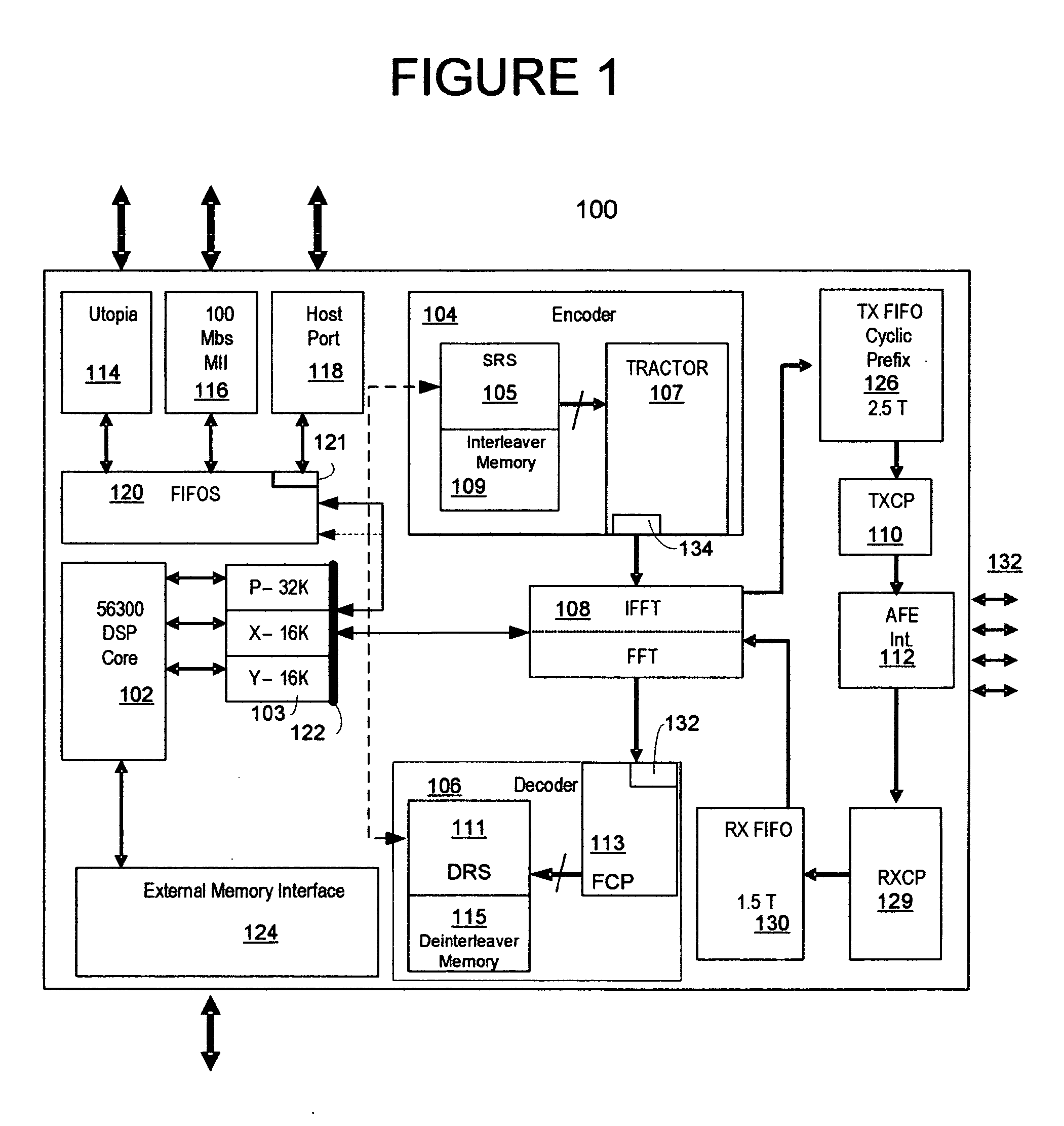
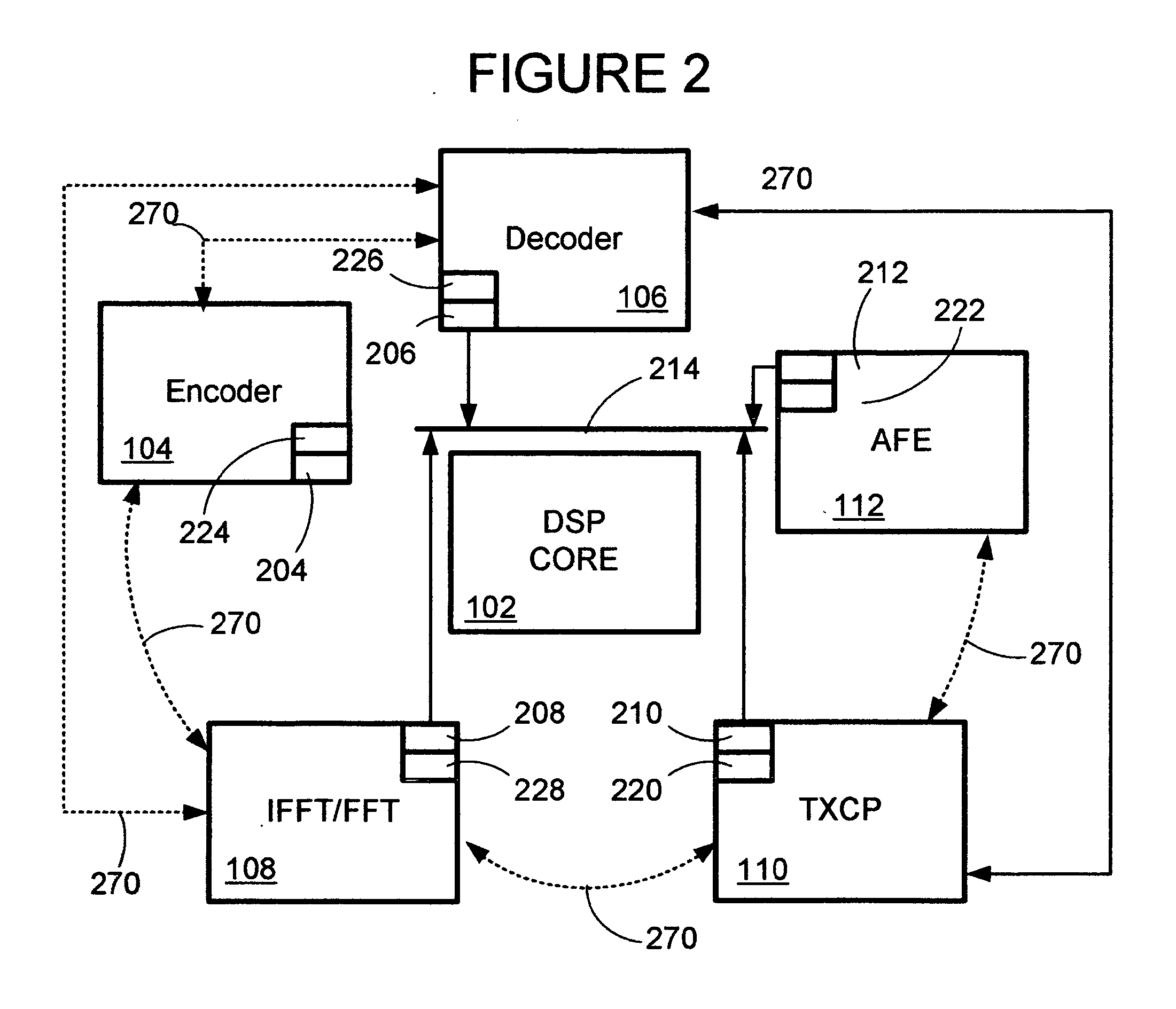
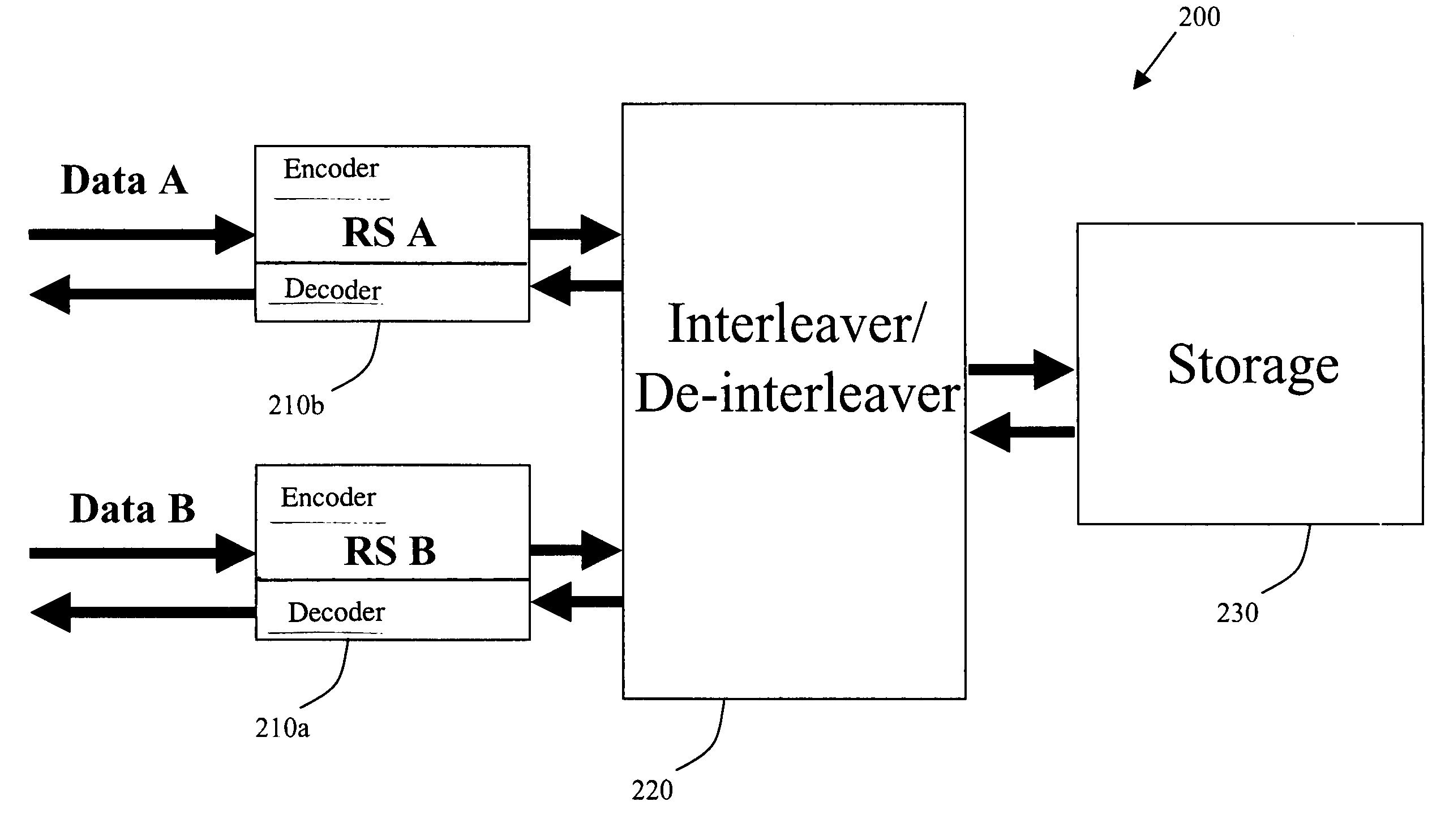
Multiple channel digital subscriber line framer/deframer system and method
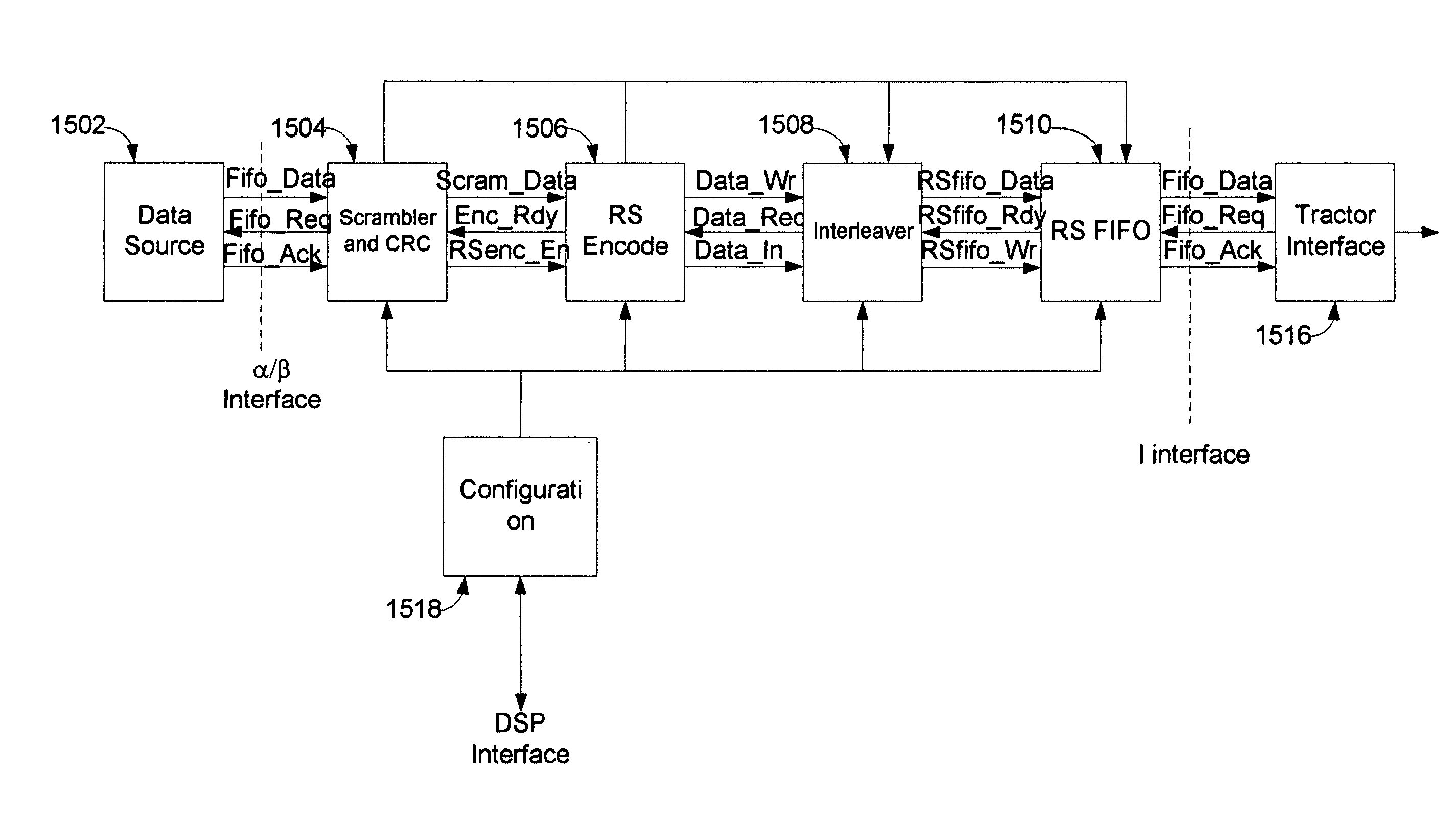
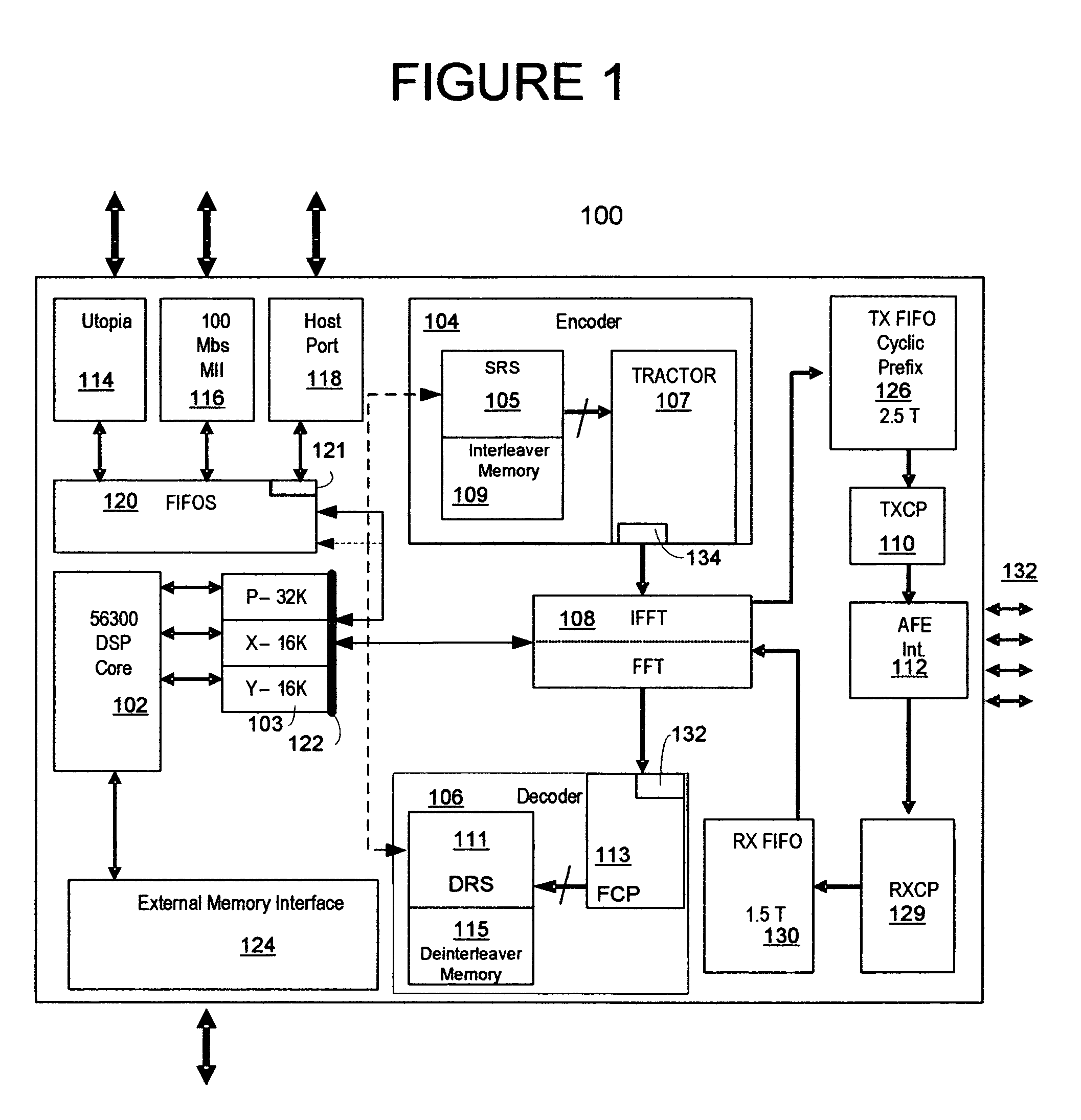
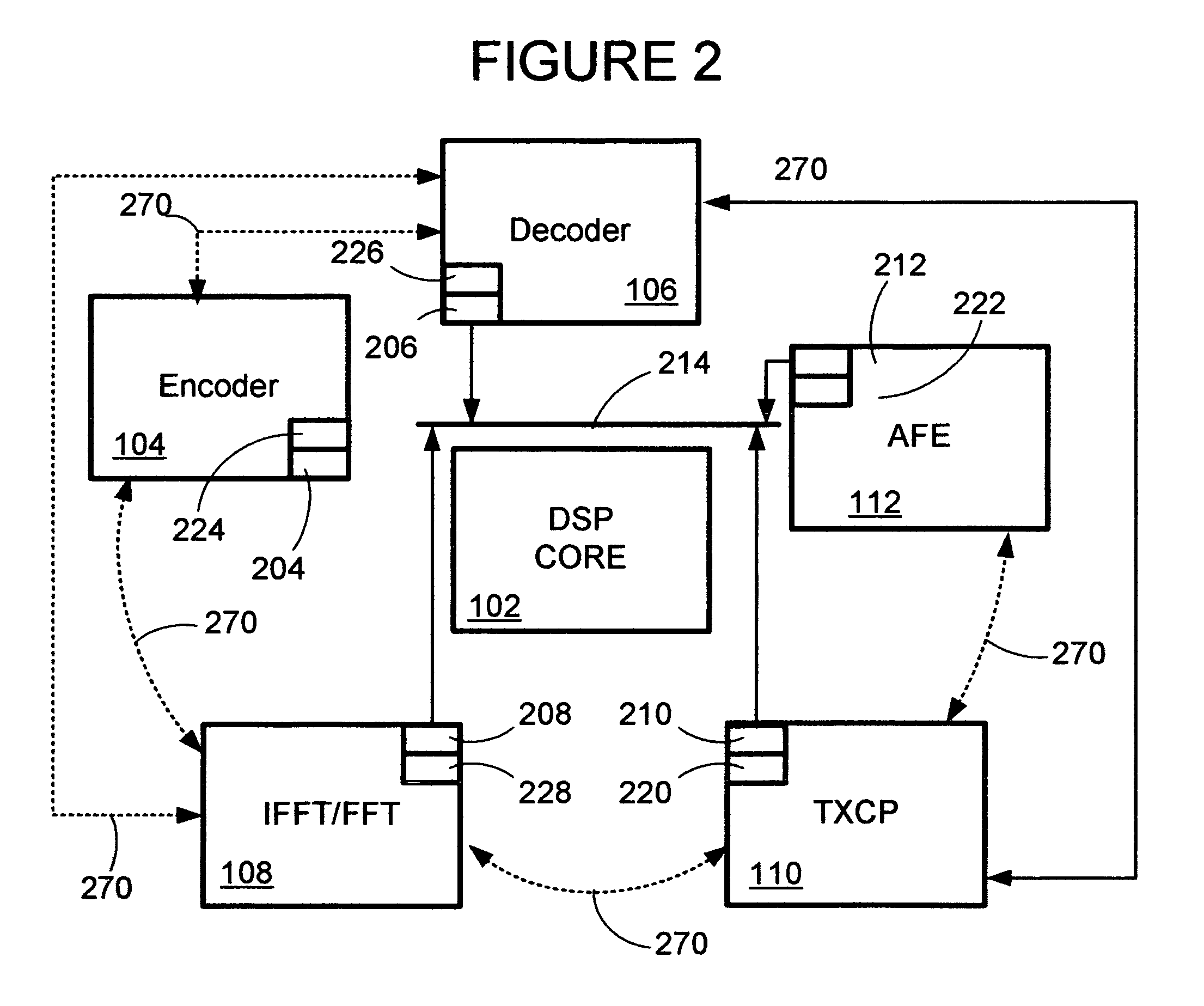
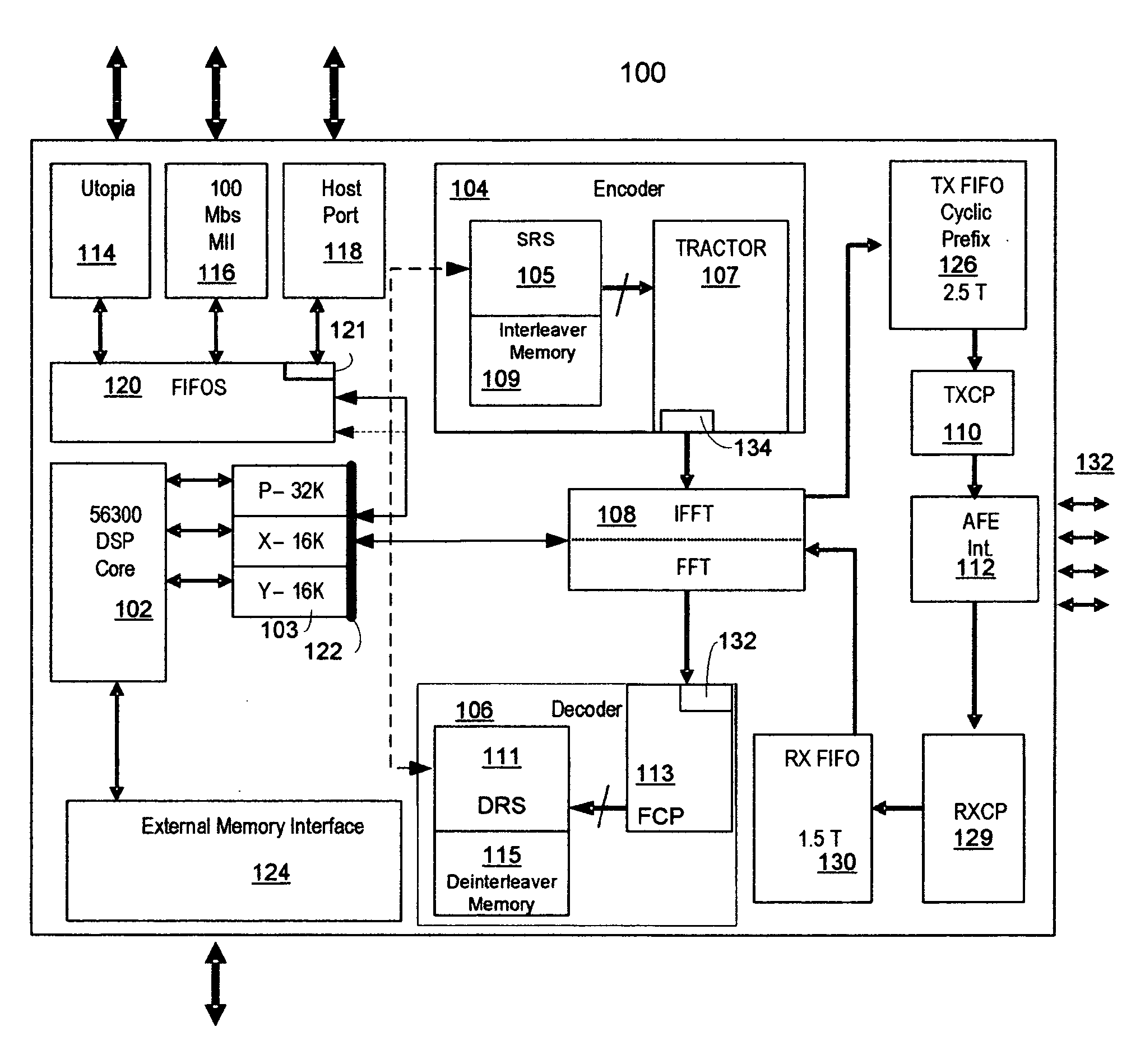
The framer, also referred to as the scrambler / Reed-Solomon encoder (SRS), is a part of the transmitter and accepts user and control data in the form of one or more logical channels, partitions this data into frames, adds error correction codes, randomizes the data through a scrambler, and multiplexes logical channels into a single data stream. The multiplexed data is then passed to the constellation encoder as the next step in the formation of the VDSL symbol. The deframer, also referred as the descrambler / Reed-Solomon decoder (DRS), is part of the receiver and performs the inverse function of the framer. Disclosed is a highly configurable hardware framer / deframer that includes a digital signal processor interface configured to provide high level control, a FIFO coupled to data interfaces, a scrambler and CRC generator, a Reed-Solomon encoder, an interleaver, a data interface coupled to a constellation encoder, a data interface coupled to a constellation decoder, a deinterleaver, a Reed-Solomon decoder, descrambler and CRC check, an interface to external data sync, methods for control of configuration of data paths between hardware blocks, and methods for control and configuration of the individual hardware blocks in a manner that provides compliance with VDSL and many related standards.
Owner:METANOIA TECH
Multiple Channel Digital Subscriber Line Framer/Deframer System and Method
InactiveUS20100246585A1Code conversionData switching by path configurationData streamReed solomon decoder
Owner:METANOIA TECH
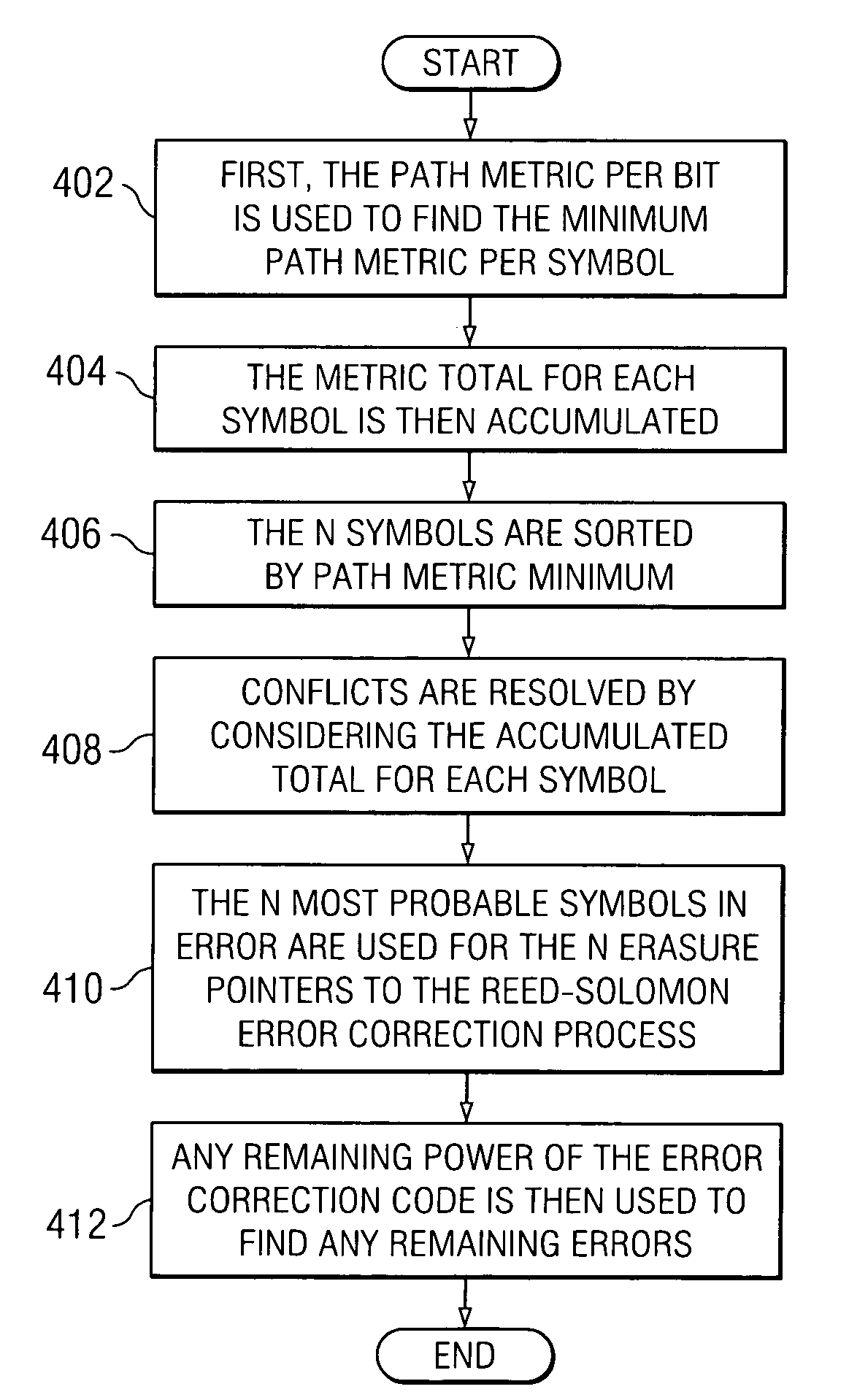
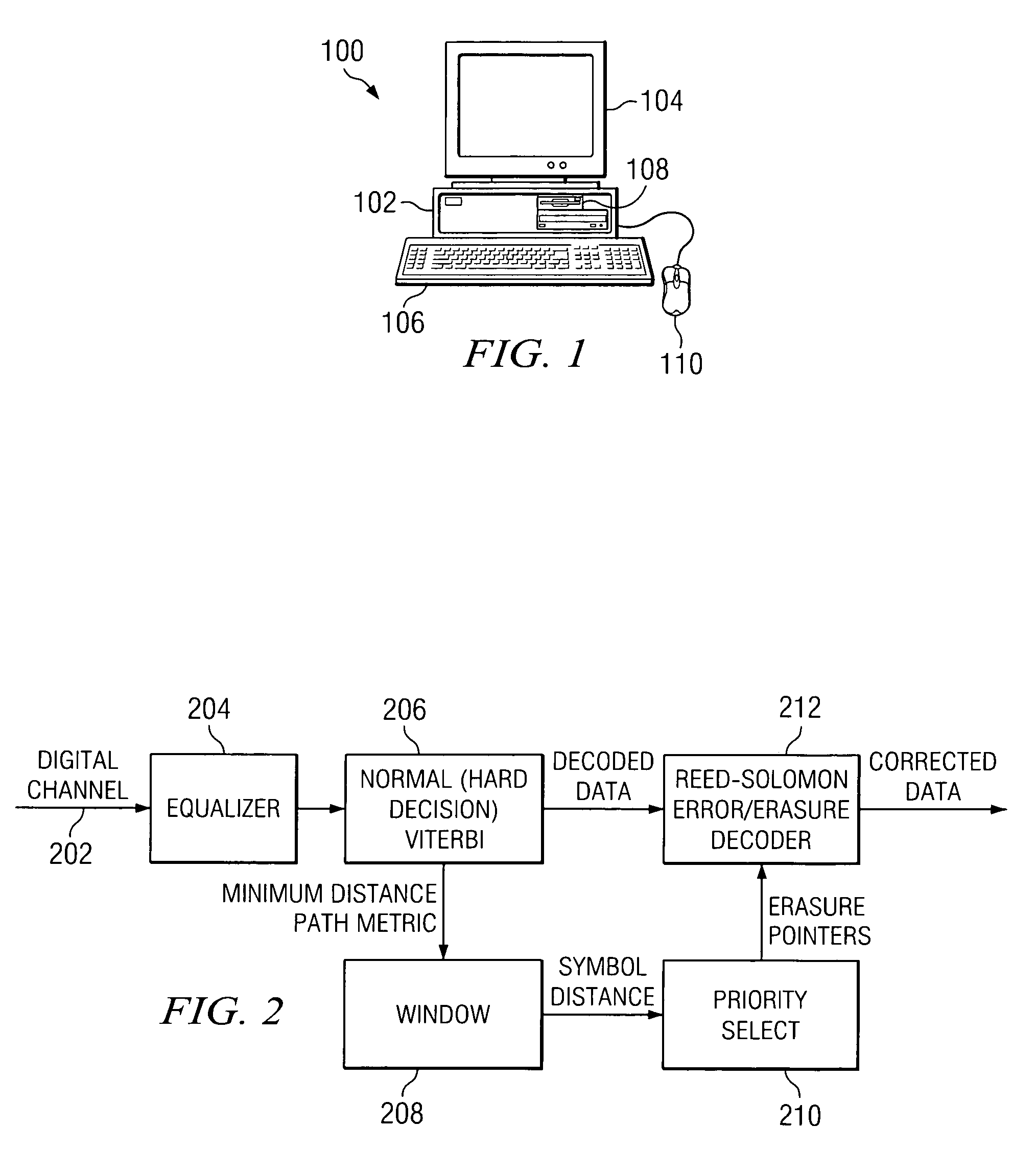
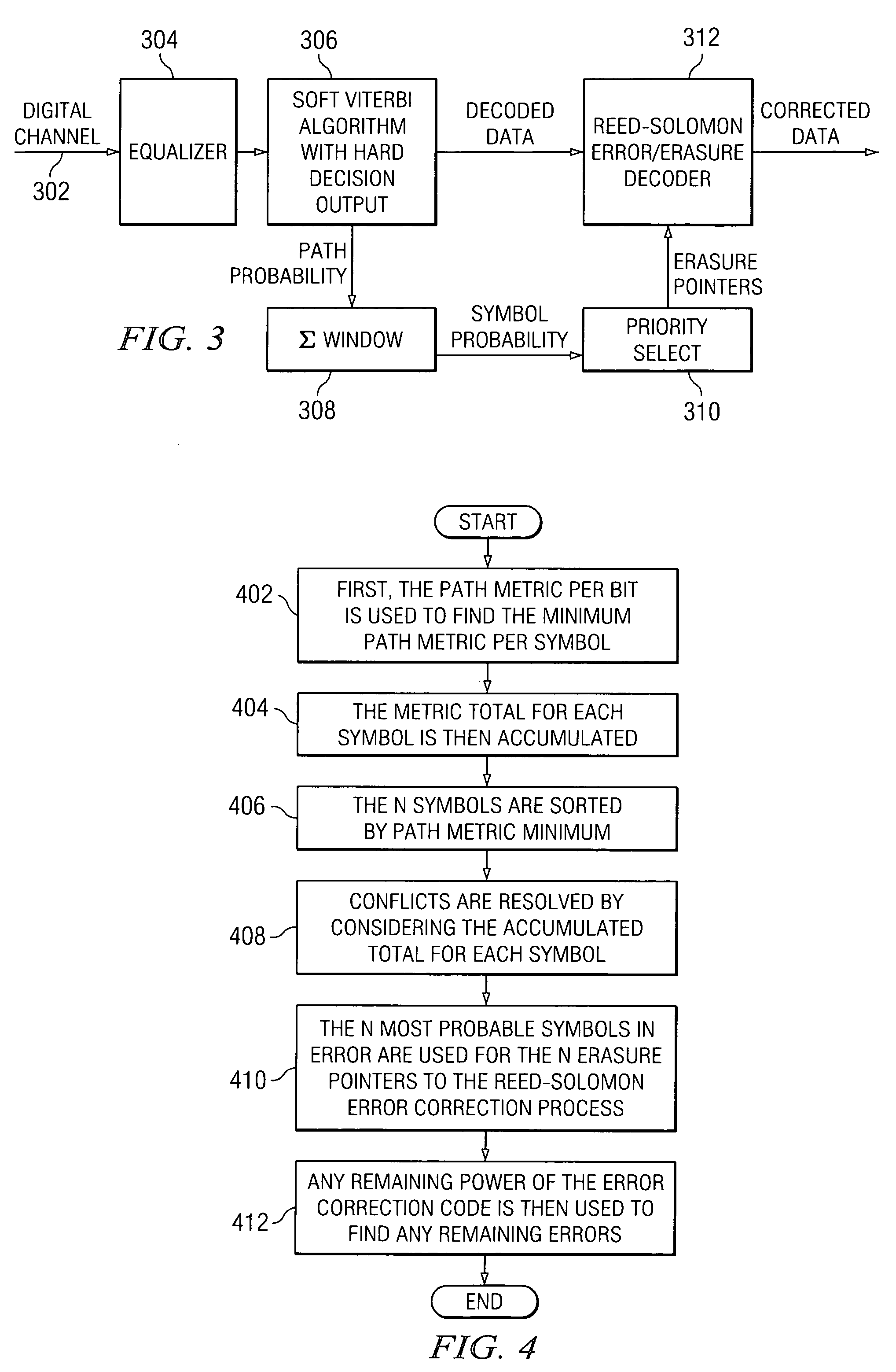
Soft viterbi Reed-Solomon decoder
ActiveUS7228489B1Television system detailsData representation error detection/correctionViterbi decoderAlgorithm
A Viterbi decoder is used to provide erasure information to a symbol based decoder. In a preferred embodiment, a Viterbi decoder is used to provide either minimum distance path metric information or path probability information, which is summed over a symbol window to derive erasure information for the symbol based decoder.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
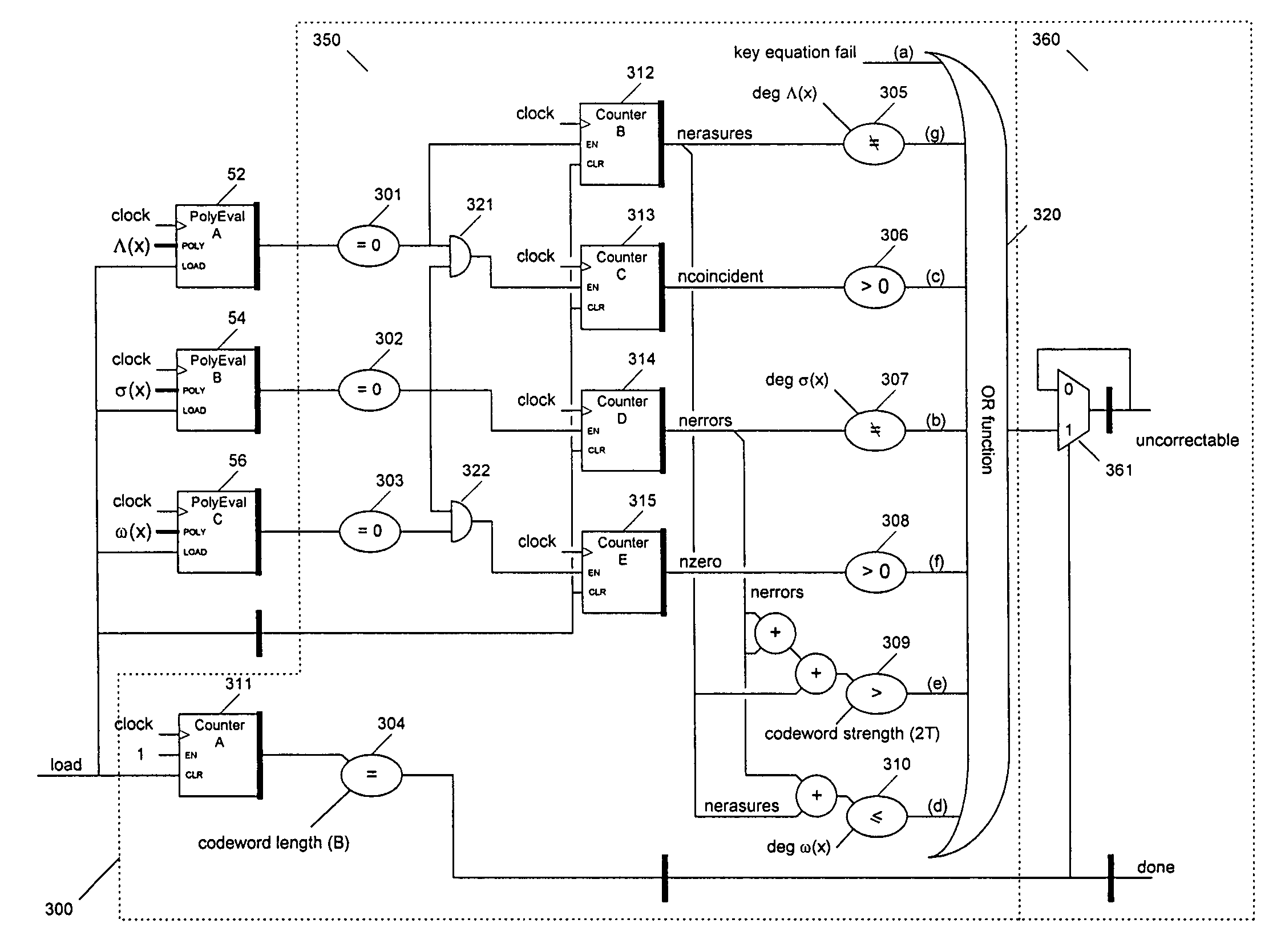
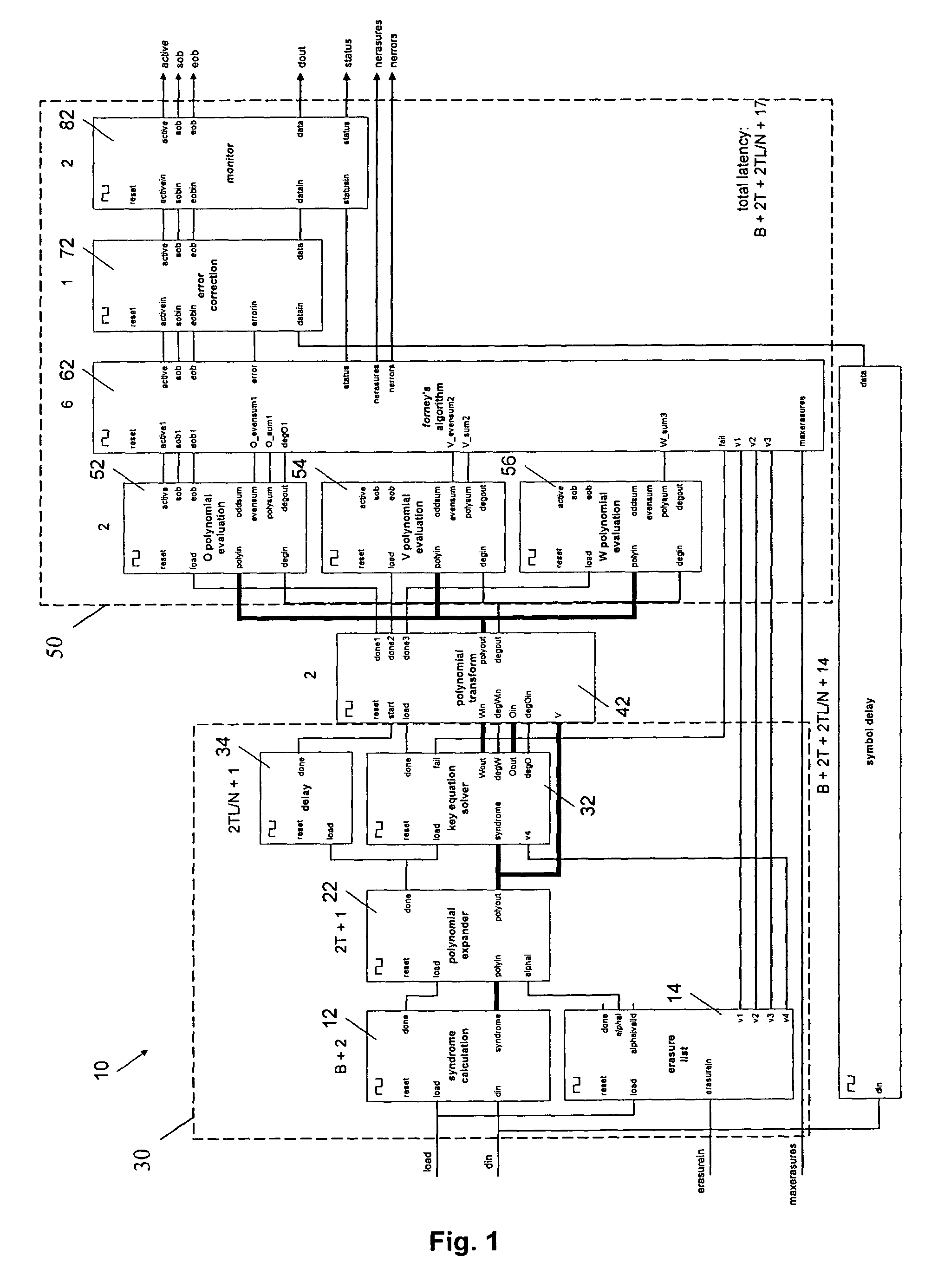
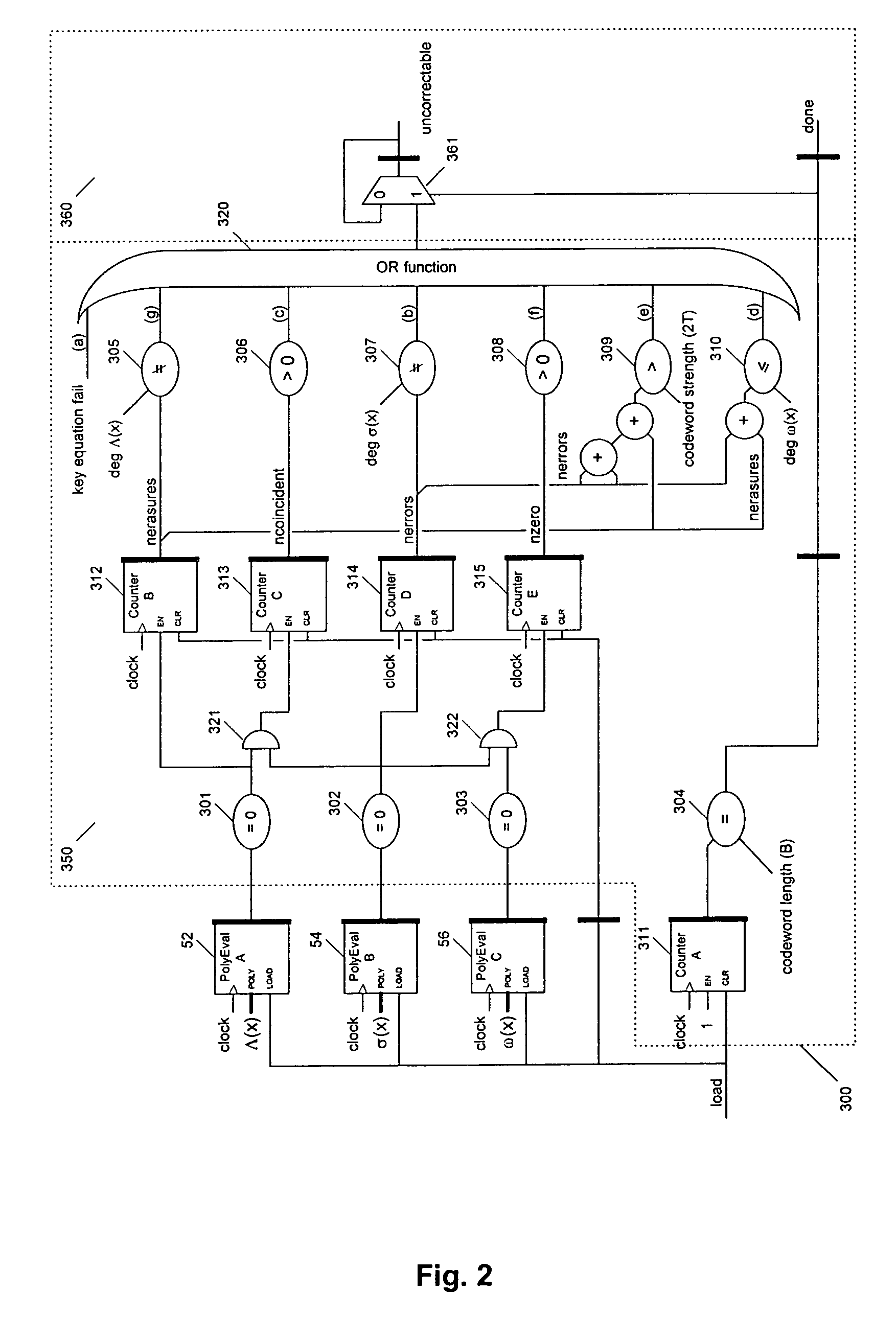
Identifying uncorrectable codewords in a Reed-Solomon decoder for errors and erasures
InactiveUS7278086B2Error detection/correctionCode conversionReed solomon decoderArtificial intelligence
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method for complexing hardware of Reed Solomon code decoder as well as low hardware complex degree decoding device
InactiveCN101277119AReduce consumptionReduce hardware complexityCyclic codesComputer hardwareMultiplexing
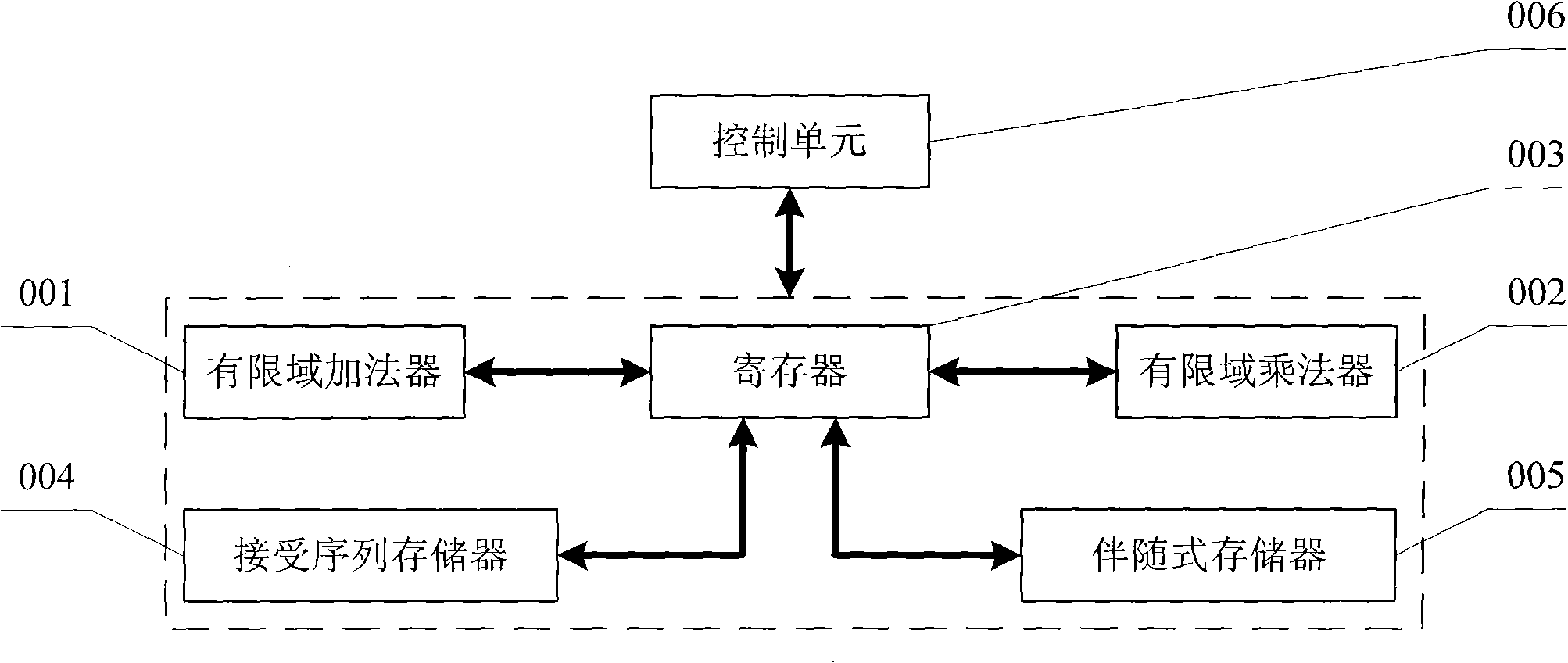
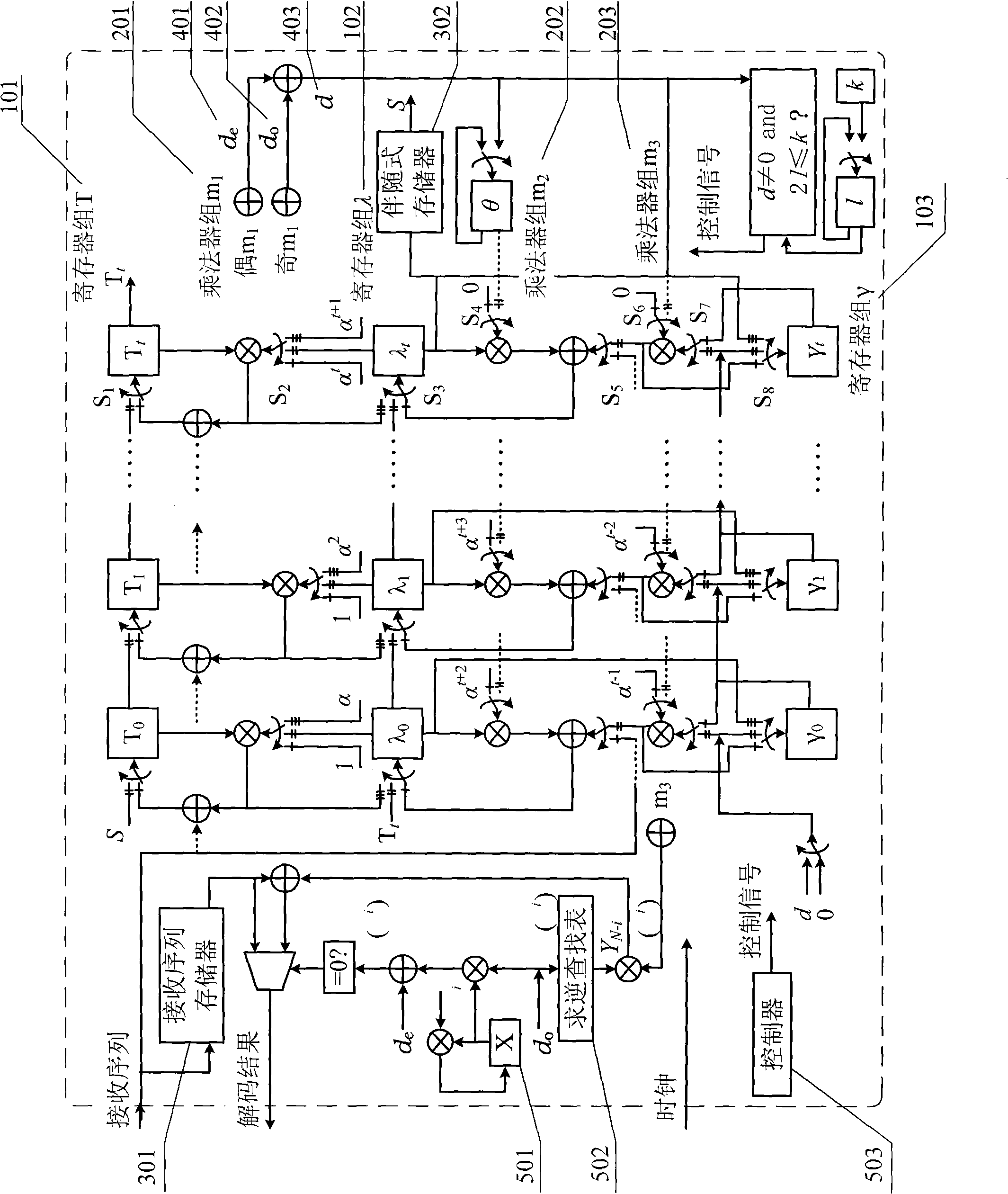
A Reed Solomon code decoder hardware multiplexing method and a low hardware complexity decoding device thereof belong to the technical field of digital information transmission technique. The hardware resource multiplexing method complexes a finite field adder, a finite field multiplier and a register to complete syndrome calculating, syndrome storing, error position polynomial calculating, error value polynomial calculating and error code correcting in the Reed Solomon decoding calculation. The hardware resource multiplexing method is universal to various Reed Solomon decoders with different code rates and parameters. The decoding device comprises the following components: a finite field adder, a finite field multiplier, a register, a receiving sequence memorizer, a syndrome memorizer and the like. The Reed Solomon decoding calculation is realized according to the multiplexing method. The multiplexing method and decoding device disclosed in the invention can evidently reduce the complexity of the hardware for decoding Reed Solomon code.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
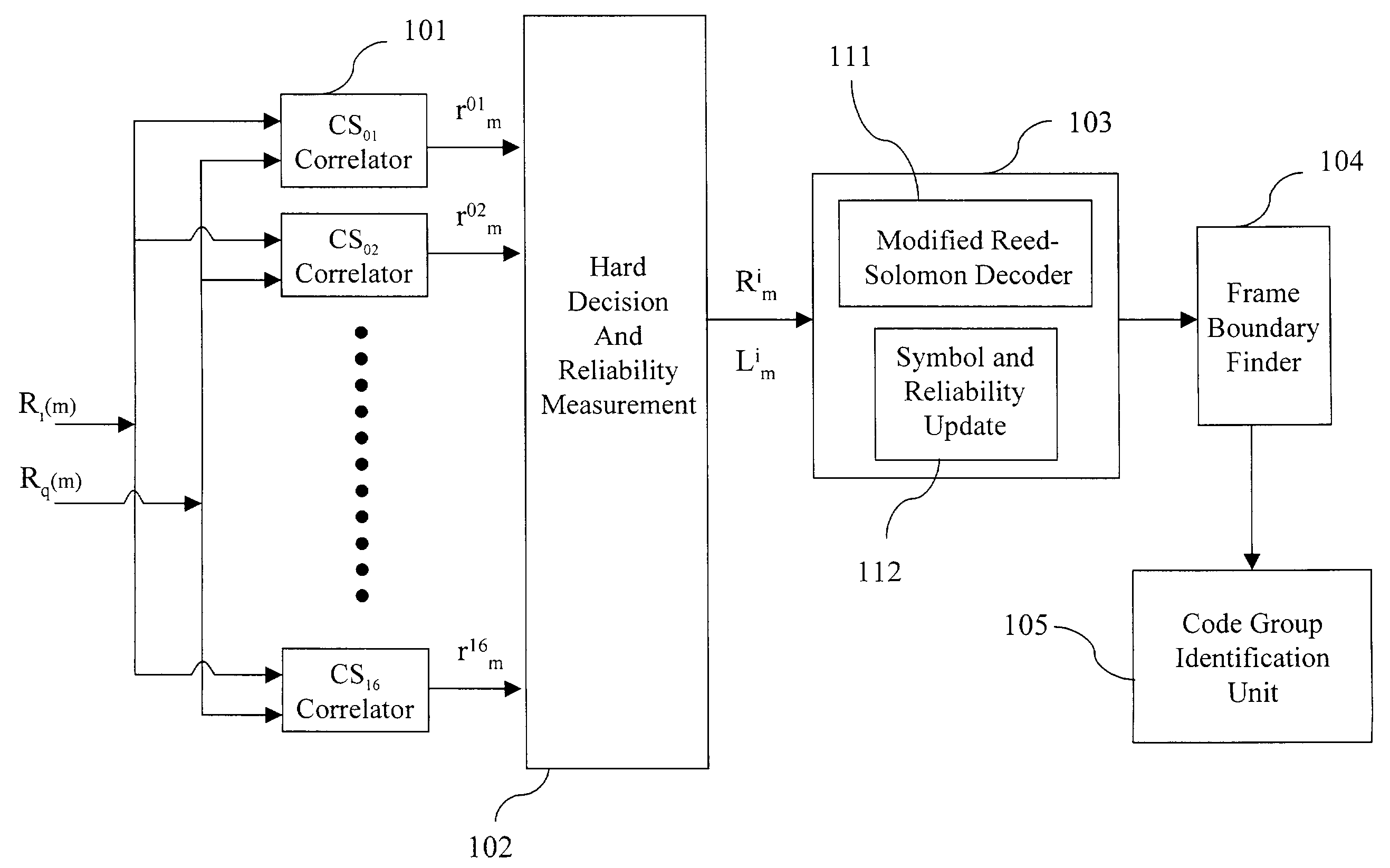
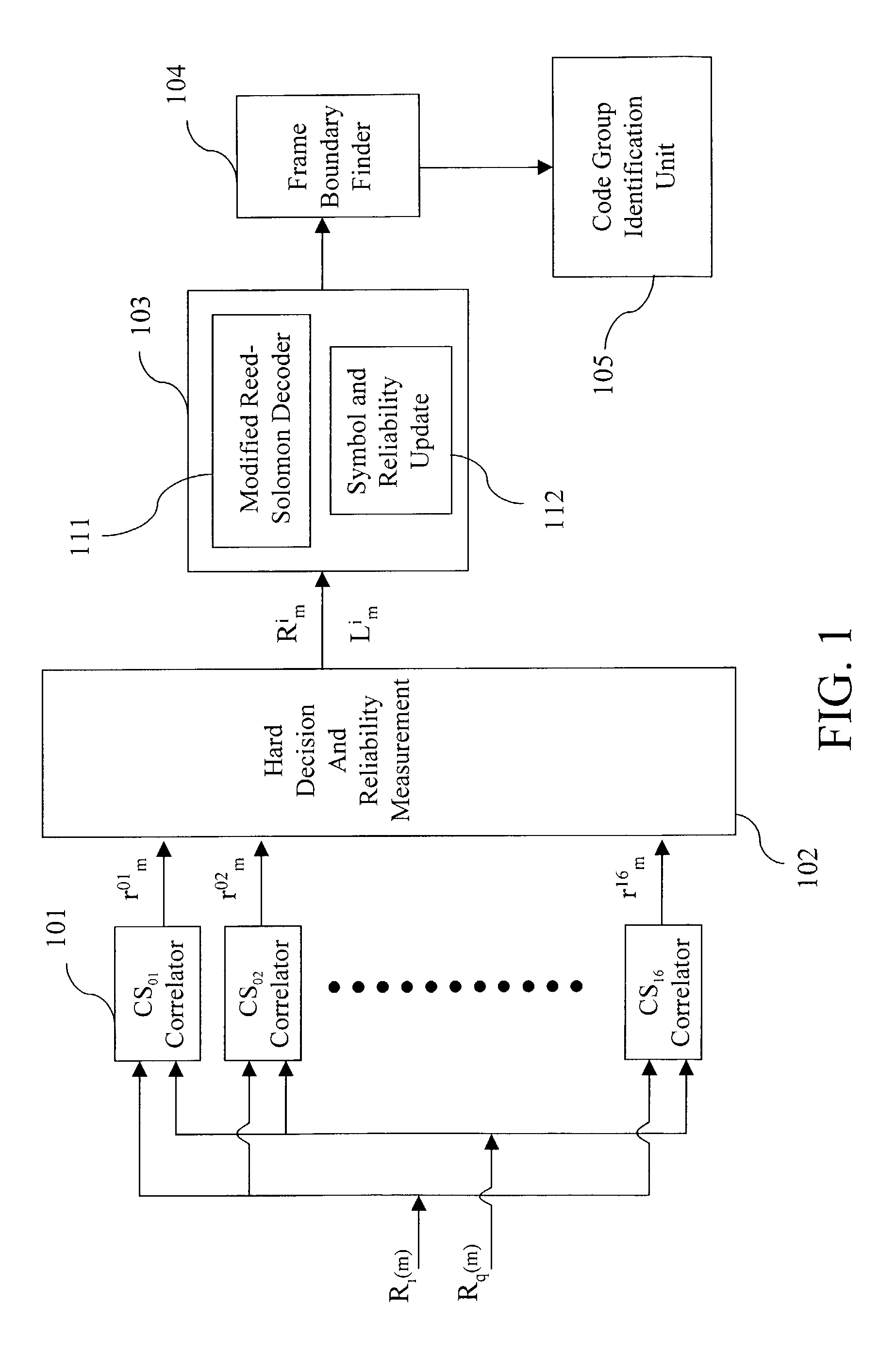
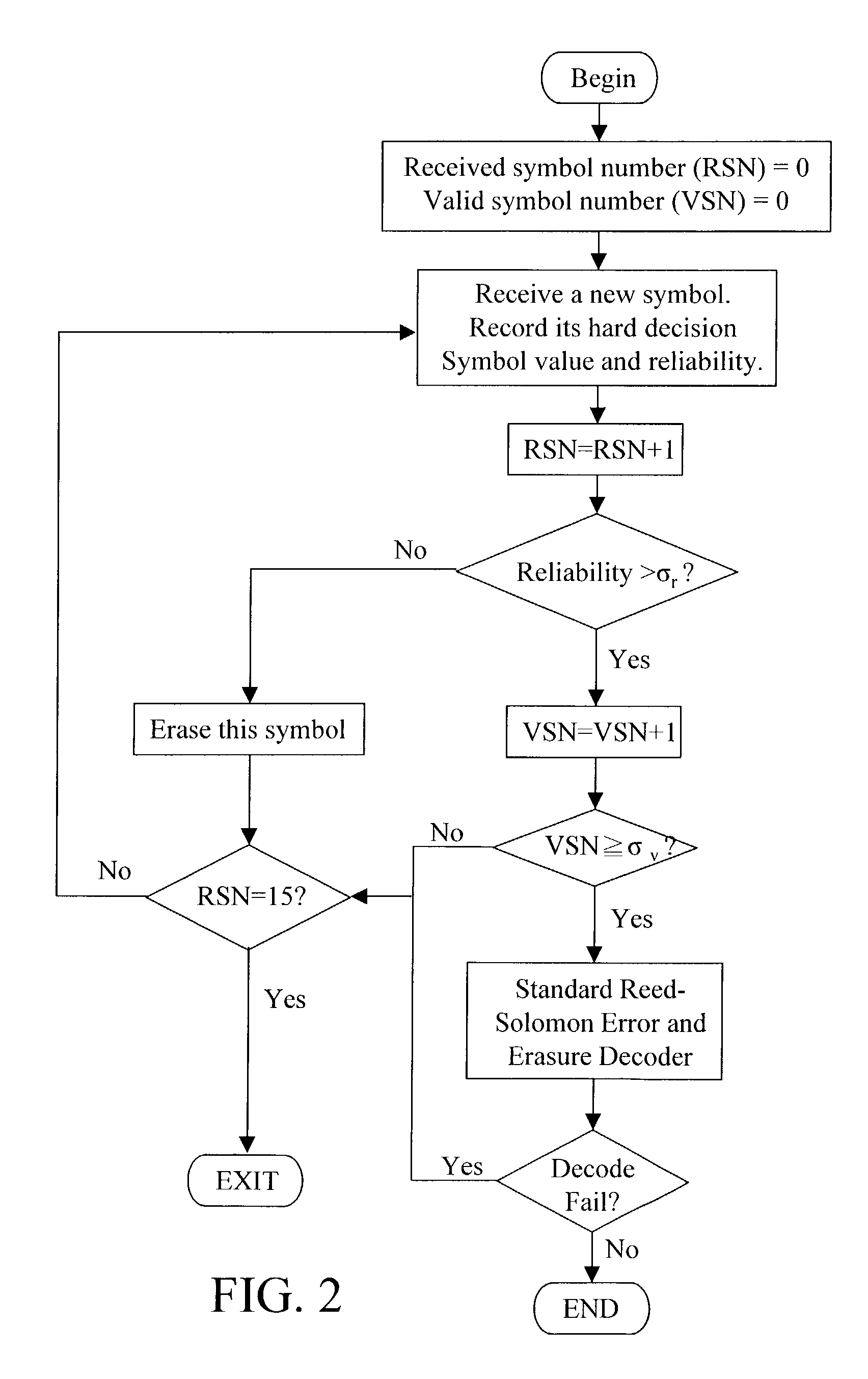
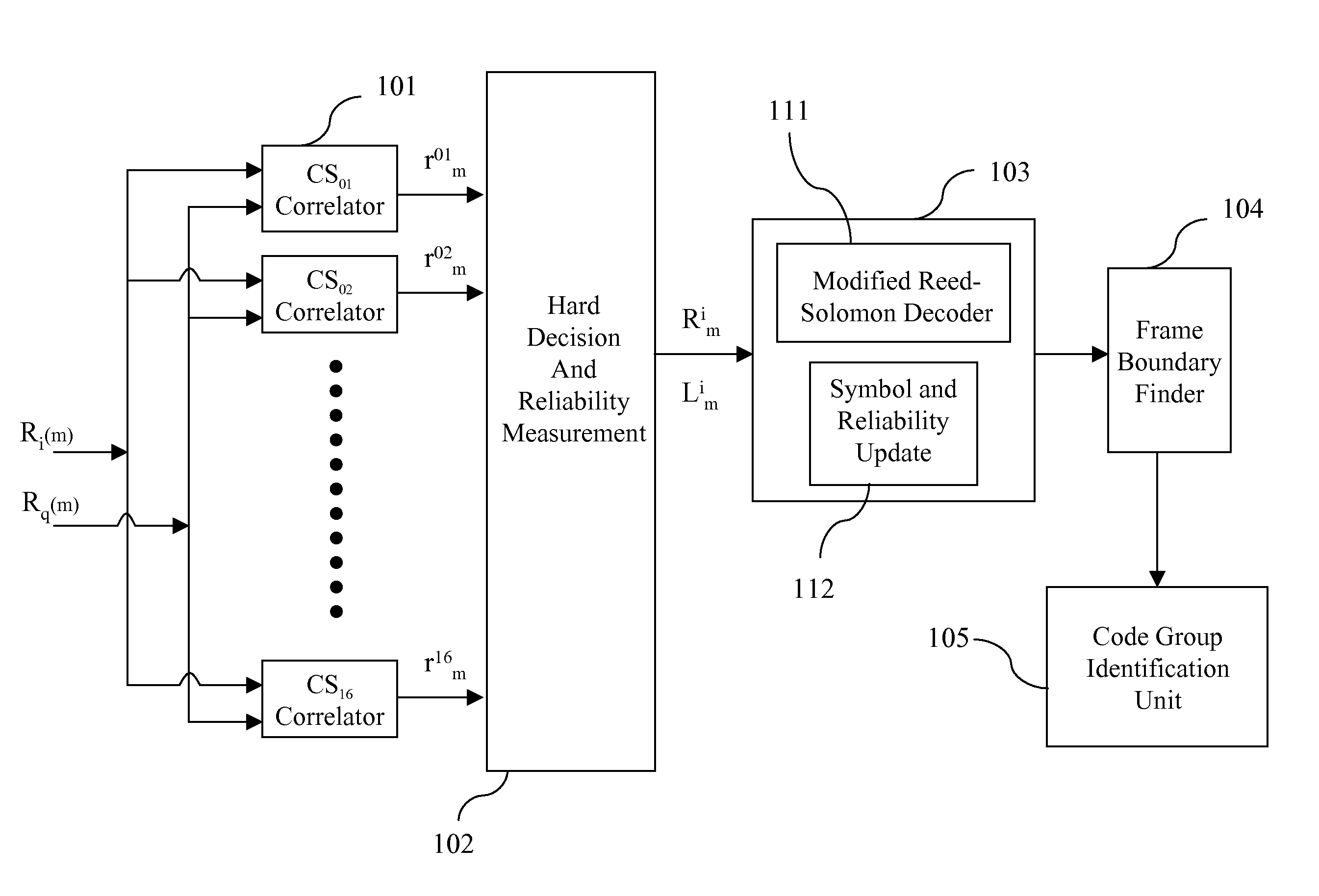
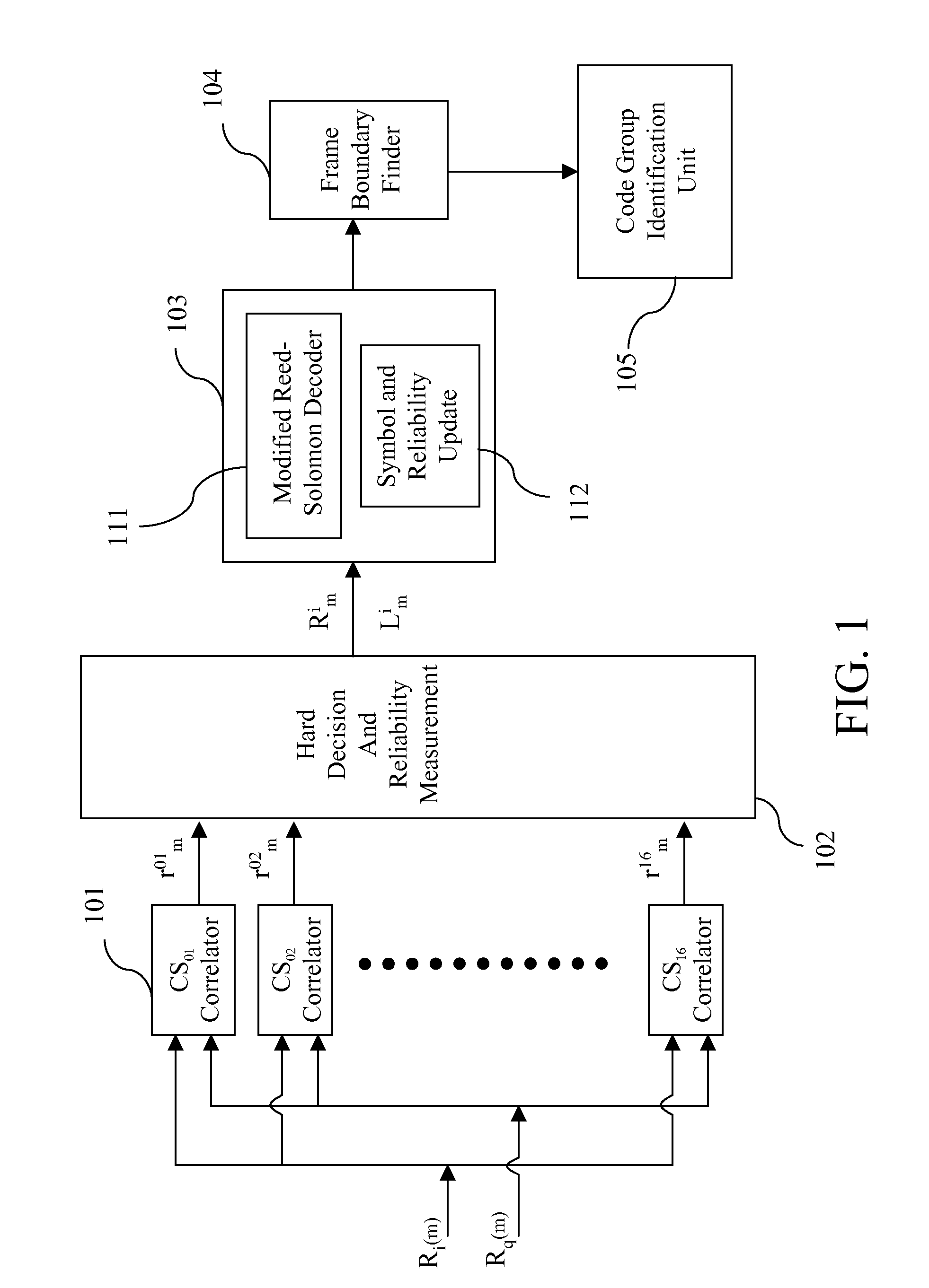
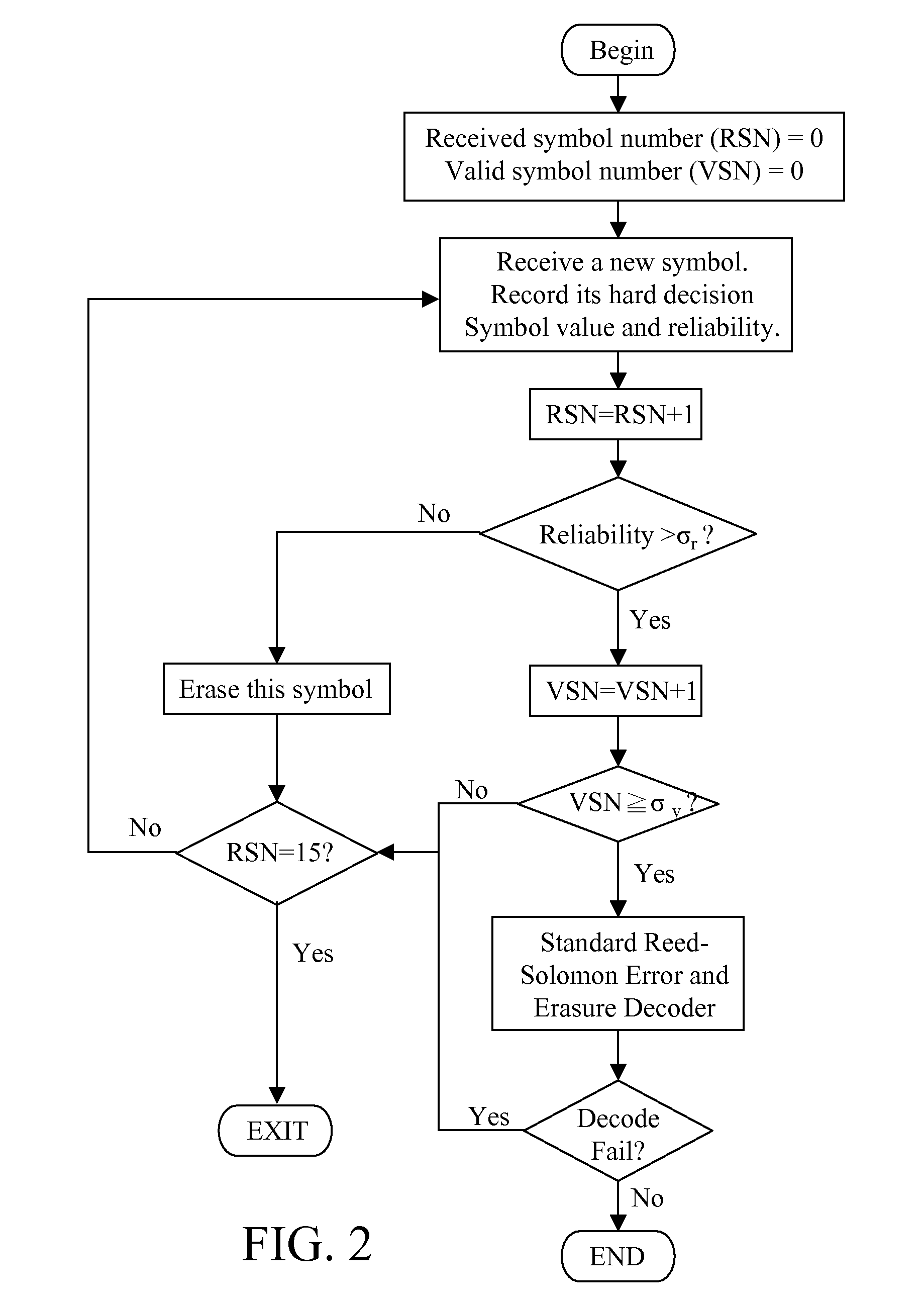
Method and apparatus for code group identification and frame synchronization by use of Reed-Solomon decoder and reliability measurement for UMTS W-CDMA
InactiveUS7633976B2Improve performanceReduce error rateError preventionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesReed solomon decoderComputer science
A method and apparatus having a modified Reed-Solomon decoder is used for finding a specific code group used by a base station and the frame timing synchronization with the base station. The modified Reed-Solomon decoder uses a standard Reed-Solomon decoder and some reliability measurements computed from the received code word symbols. If the reliability of a received symbol is too low, this symbol is considered as erasure. By selecting code word symbols with higher reliabilities and erasing code word symbols with lower reliabilities, the symbol error probability is reduced and the performance is improved. Several modified Reed-Solomon decoders and a few decoding strategies are introduced in order to decode the received code word sequences with a power- and memory-effective method.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Semiconductor memory with reed-solomon decoder
InactiveUS20100107039A1Code conversionError correction/detection using block codesError checkingReed solomon decoder
A semiconductor memory device with an error checking / correction system includes a memory cell array. The error checking / correction system is capable of symbolizing data to a symbol, searching errors of data read from the memory cell array by solving equations with decoders representing a solution, correcting data based on the searched errors, and outputting the corrected data in parallel with the other process to the other data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Reed-solomon decoder using a configurable arithmetic processor
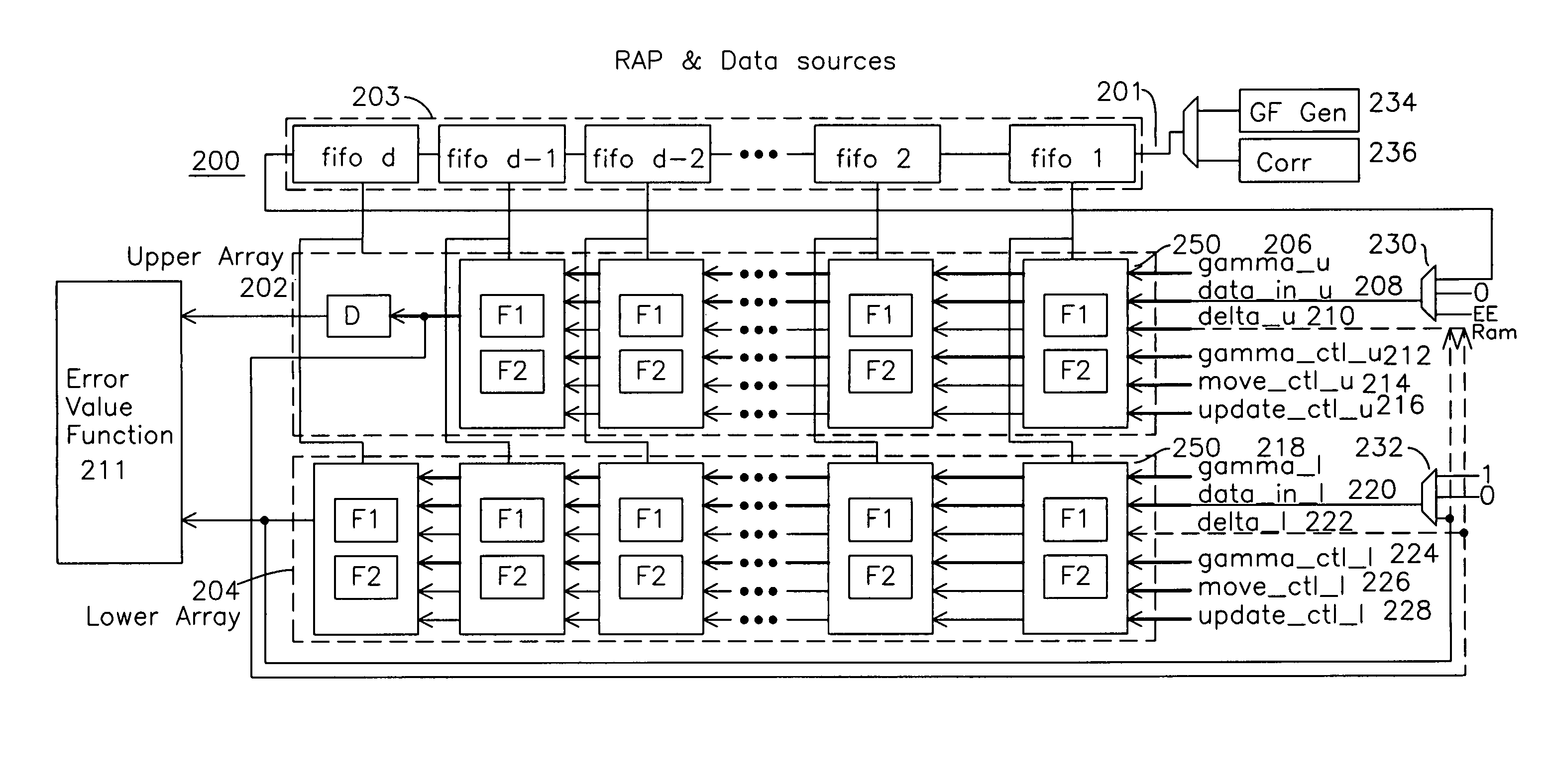
A Reed Solomon decoder utilizes re-configurable and re-usable components in a granular configuration which provides an upper array and a lower array of repeated Reconfigurable Elementary Units (REU) which in conjunction with a FIFO can be loaded with syndromes and correction terms to decode Reed Solomon codewords. The upper array of REUs and lower array of REUs handle the Reed Solomon decoding steps in a pipelined manner using systolic REU structures. The repeated REU includes the two registers, two Galois Field adders, a Galois Field multiplier, and multiplexers to interconnect the elements. The REU is then able to perform each of the steps required for Reed-Solomon decoder through reconfiguration for each step using the multiplexers to reconfigure the functions. In this manner, a reconfigurable computational element may be used for each step of the Reed-Solomon decoding process.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
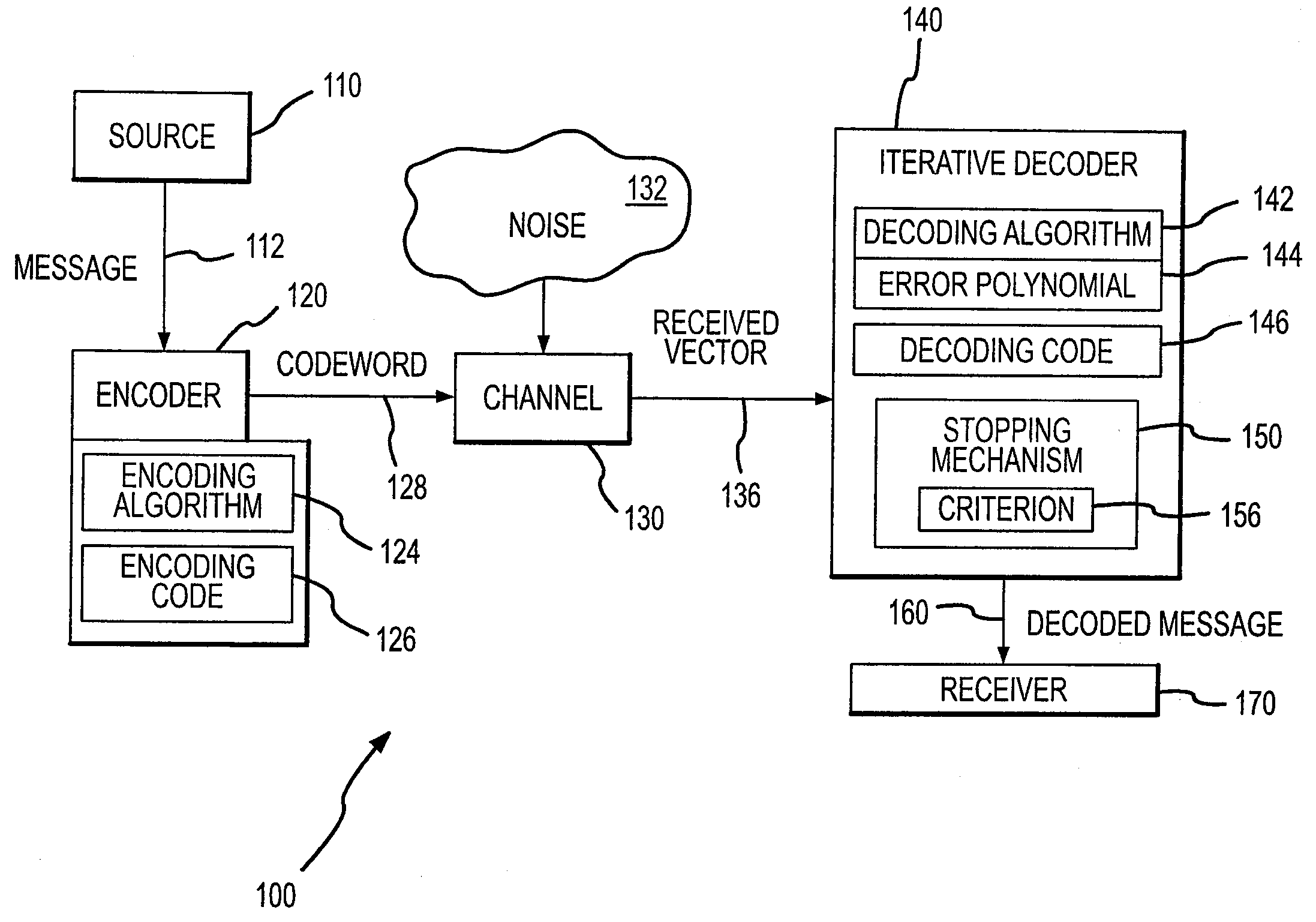
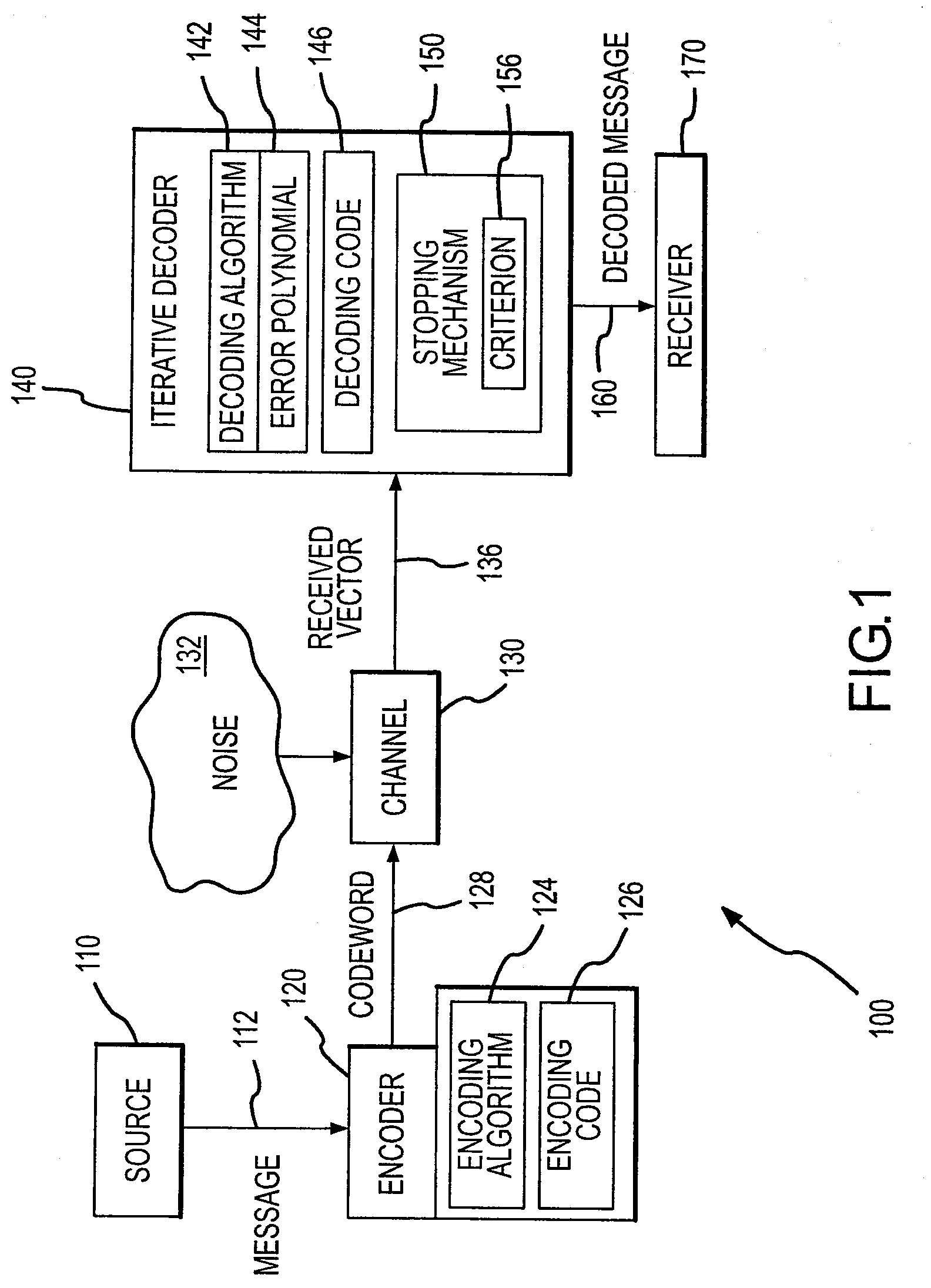
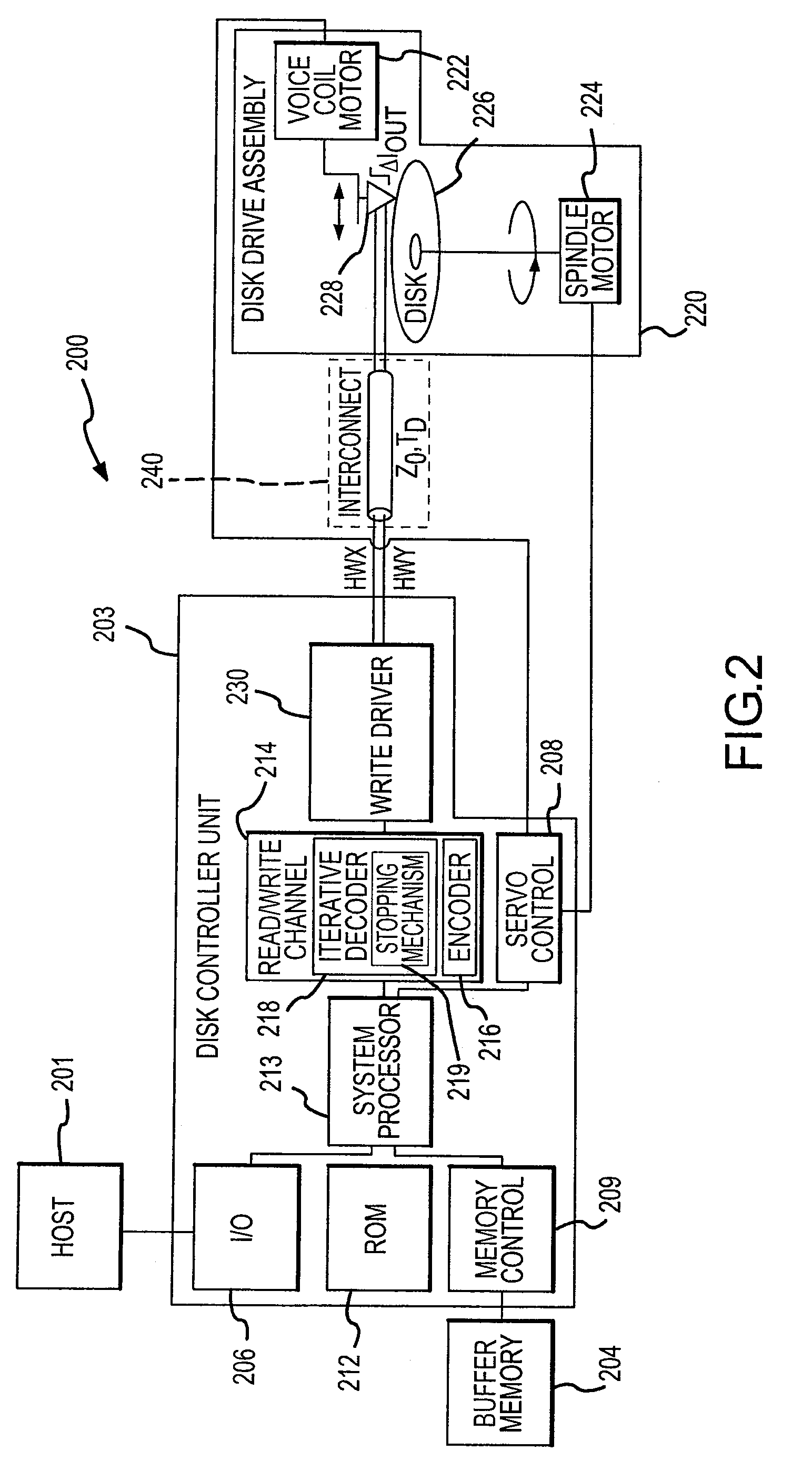
Iterative decoder with stopping criterion generated from error location polynomial
InactiveUS7904795B2Reduce in quantityEnhanced stopping criterionData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer hardwareTurbo encoder
A decoder for error correction an encoded message, such as one encoded by a turbo encoder, with reduced iterations due to an improved stopping criterion. The decoder includes an error correction loop that iteratively processes a message that is encoded prior to transmittal over a communication channel. The error correction loop generates, such as with a Reed-Solomon decoder, an error location polynomial in each iterative process. A stopping mechanism in the decoder allows an additional iteration of the message decoding based on the error location polynomial, such as by obtaining the degree of the error location polynomial and comparing it to a threshold. In one example, the threshold is the maximum number of symbol errors correctable by the Reed-Solomon code embodied in the decoder. The stopping mechanism allows additional iterations when the stopping criterion (or polynomial degree) is greater than the maximum number of symbol errors correctable by the Reed-Solomon code.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Forward Chien search type Reed-Solomon decoder circuit
A Reed-Solomon decoder includes a Chien search circuit to receive an error location polynomial function, performs Chien search, and finds an error location; a Forney algorithm circuit to receives an error pattern polynomial function and find an error pattern; and, a seed generator circuit to indicates a seed value corresponding to a codeword length for the input data. A Chien search is performed to obtain and outputs exponential terms related to variables for the polynomials, wherein the Chien search is performed in the same computational direction as an order for the input data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Error evaluator for inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm in Reed-Solomon decoders
InactiveUS7249310B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionError locationReed solomon decoder
An error correcting Reed-Solomon decoder includes an error locator polynomial generator that generates an error locator polynomial and a scratch polynomial based on an inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (iBMA). An error location finder communicates with the error locator polynomial generator and generates error locations. An error values finder communicates with the error locator polynomial generator and generates error values directly from the error locator polynomial and the scratch polynomial.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Memory device for use in high-speed block pipelined Reed-Solomon decoder, method of accessing the memory device, and Reed-Solomon decoder having the memory device
InactiveUS7055087B2Fast memory accessHigh speedCode conversionCyclic codesMemory bankRandom access memory
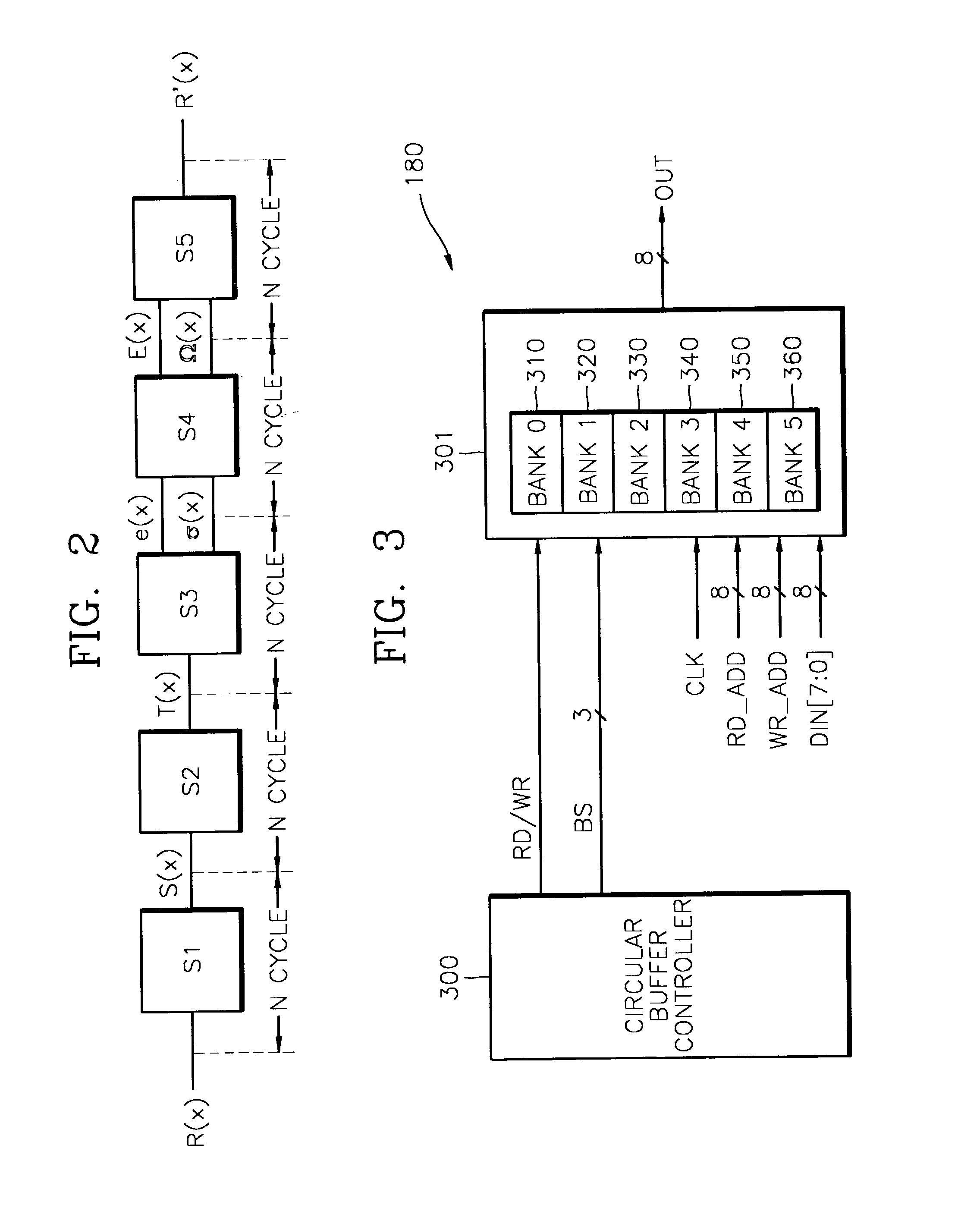
A random access memory (RAM) device for use in a high-speed pipelined Reed-Solomon decoder, a method of accessing the memory device, and a Reed-Solomon decoder having the memory device are provided. The memory device, which data is written to and read from at the same time during decoding of one frame of data, includes a random access memory (RAM) having a plurality of banks; and a control circuit for setting a first bank pointer, which selects a first bank among the plurality of banks, and a second bank pointer which selects a second bank among the plurality of banks, wherein the first and second bank pointers are set to banks with a predetermined offset every frame of data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Efficient high-speed Reed-Solomon decoder
A Reed-Solomon decoder includes an inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (iBMA) circuit with a pipelined feedback loop. A first polynomial generator generates error locator polynomial values. A discrepancy generator generates discrepancy values based on the error locator polynomial values and the scratch polynomial values. Arithmetic units are used to generate the discrepancy values are also used to generate the error locator polynomial to reduce circuit area. A first delay circuit delays the discrepancy values. A feedback loop feeds back the delayed discrepancy values to the error locator polynomial generator. An error location finder circuit communicates with the iBMA circuit and identifies error locations. An error value computation circuit communicates with at least one of the error location finder circuit and the iBMA circuit and generates error values.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Reed-Solomon decoder with low hardware spending
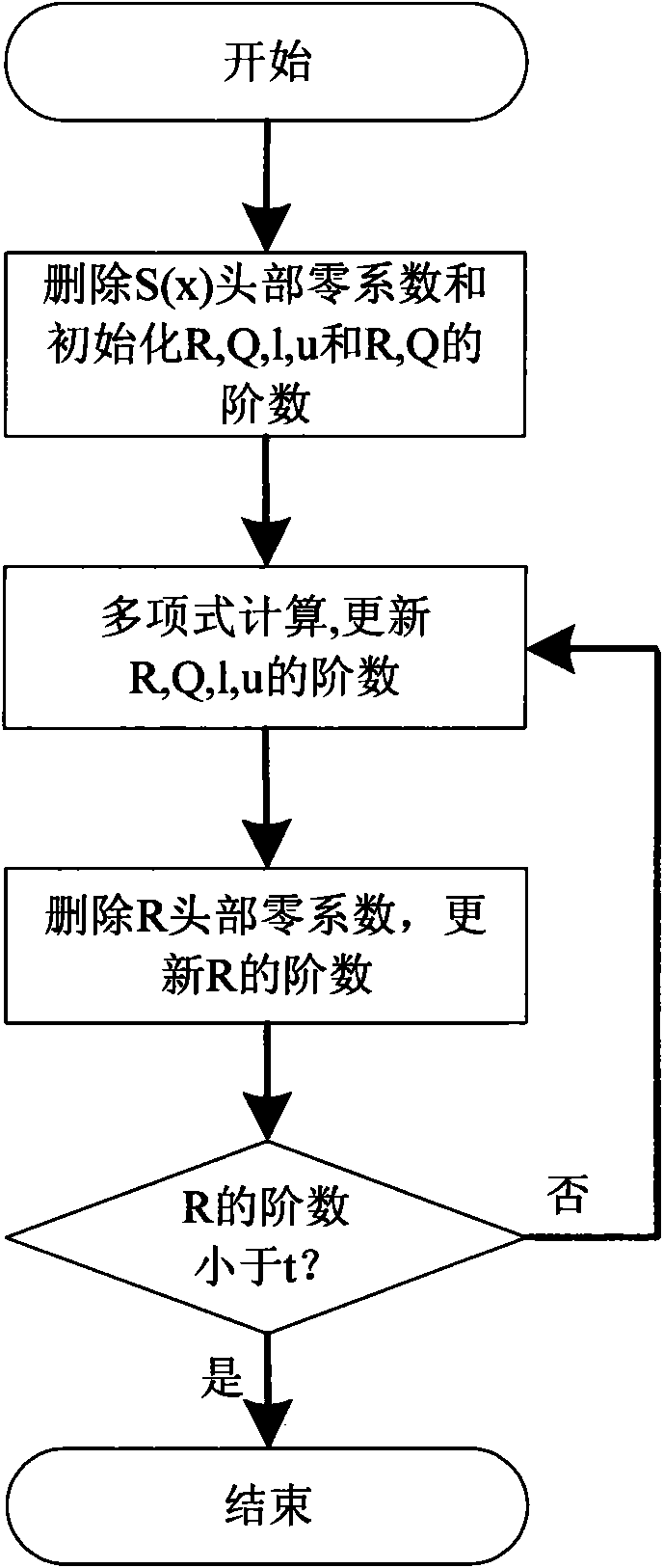
ActiveCN101325706AOptimized decoding algorithmIncreased complexityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRound complexityHardware complexity
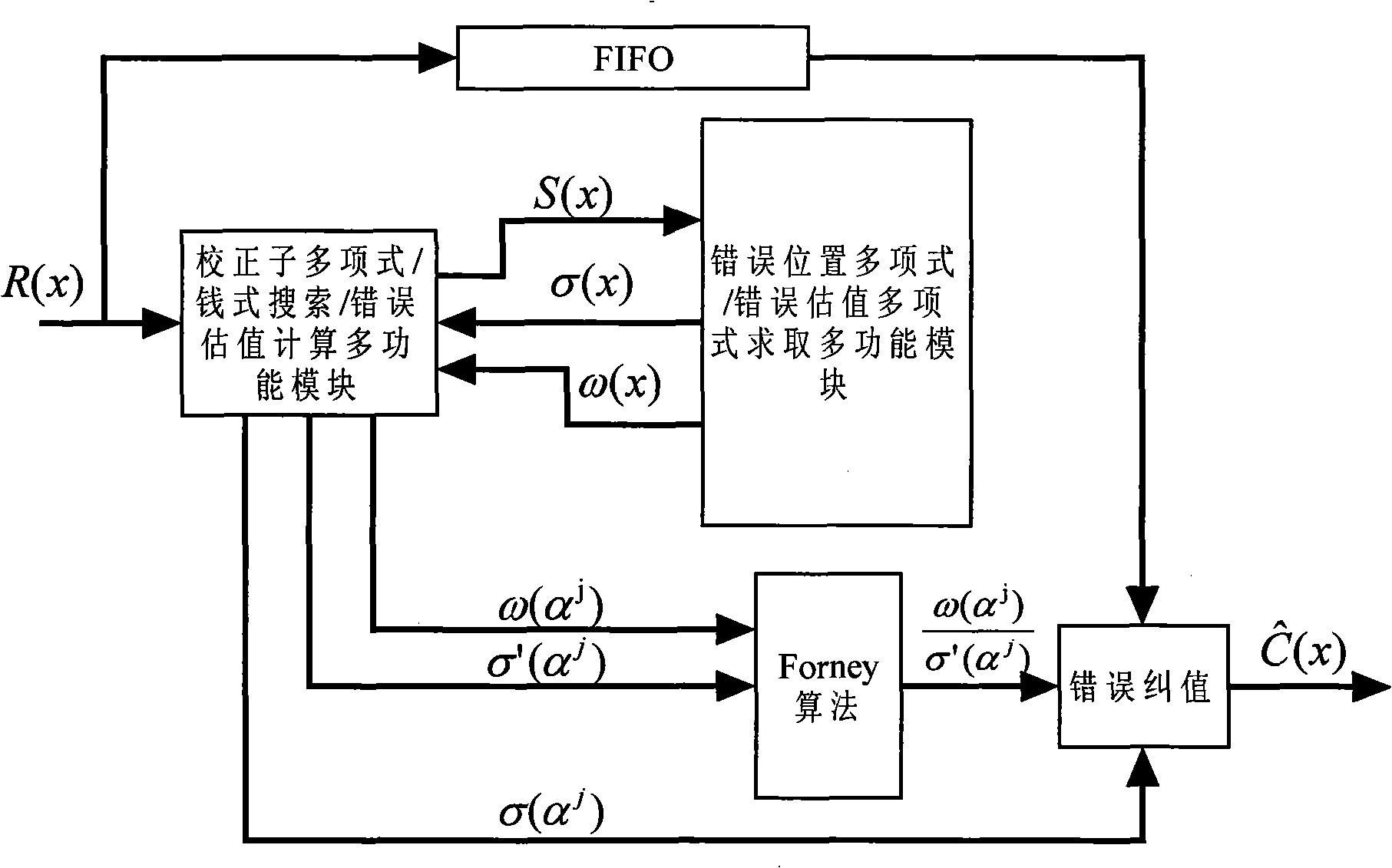
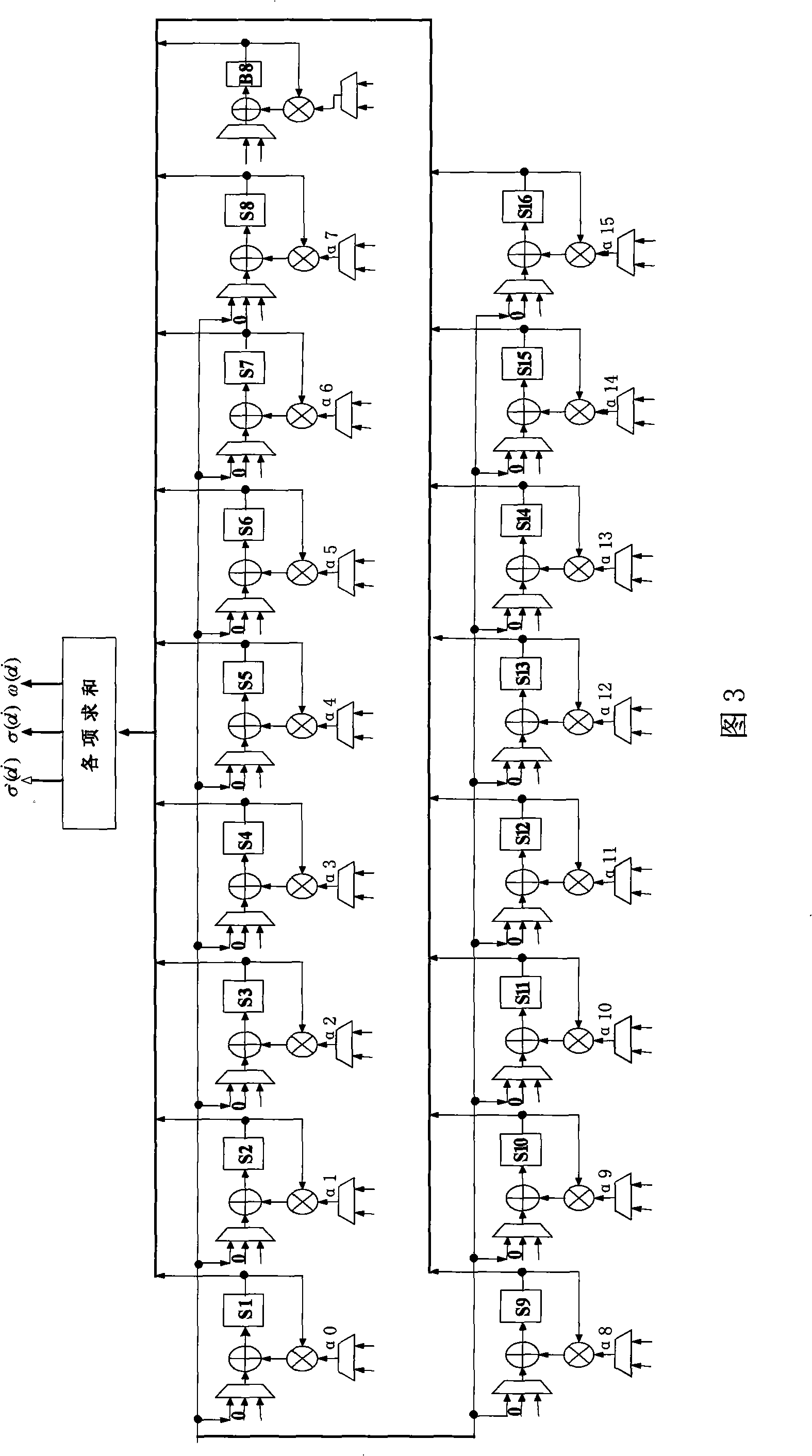
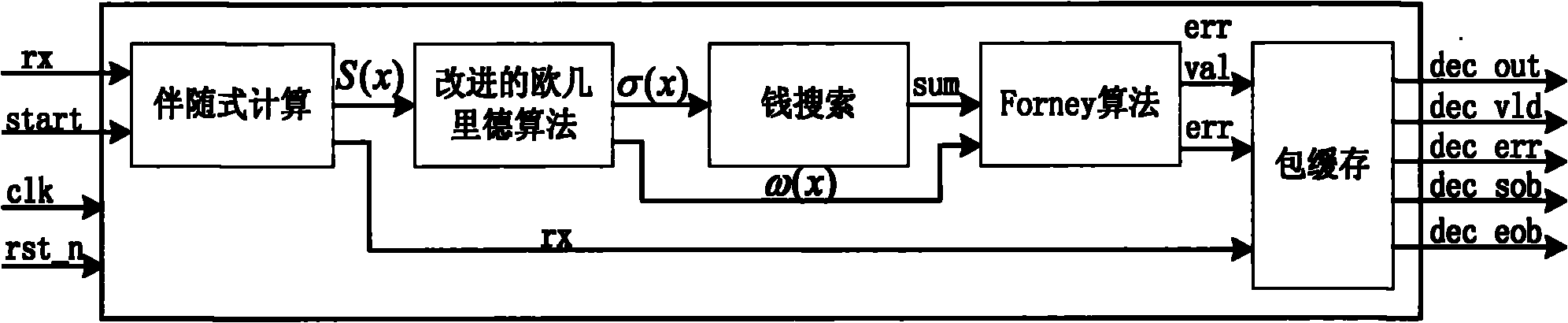
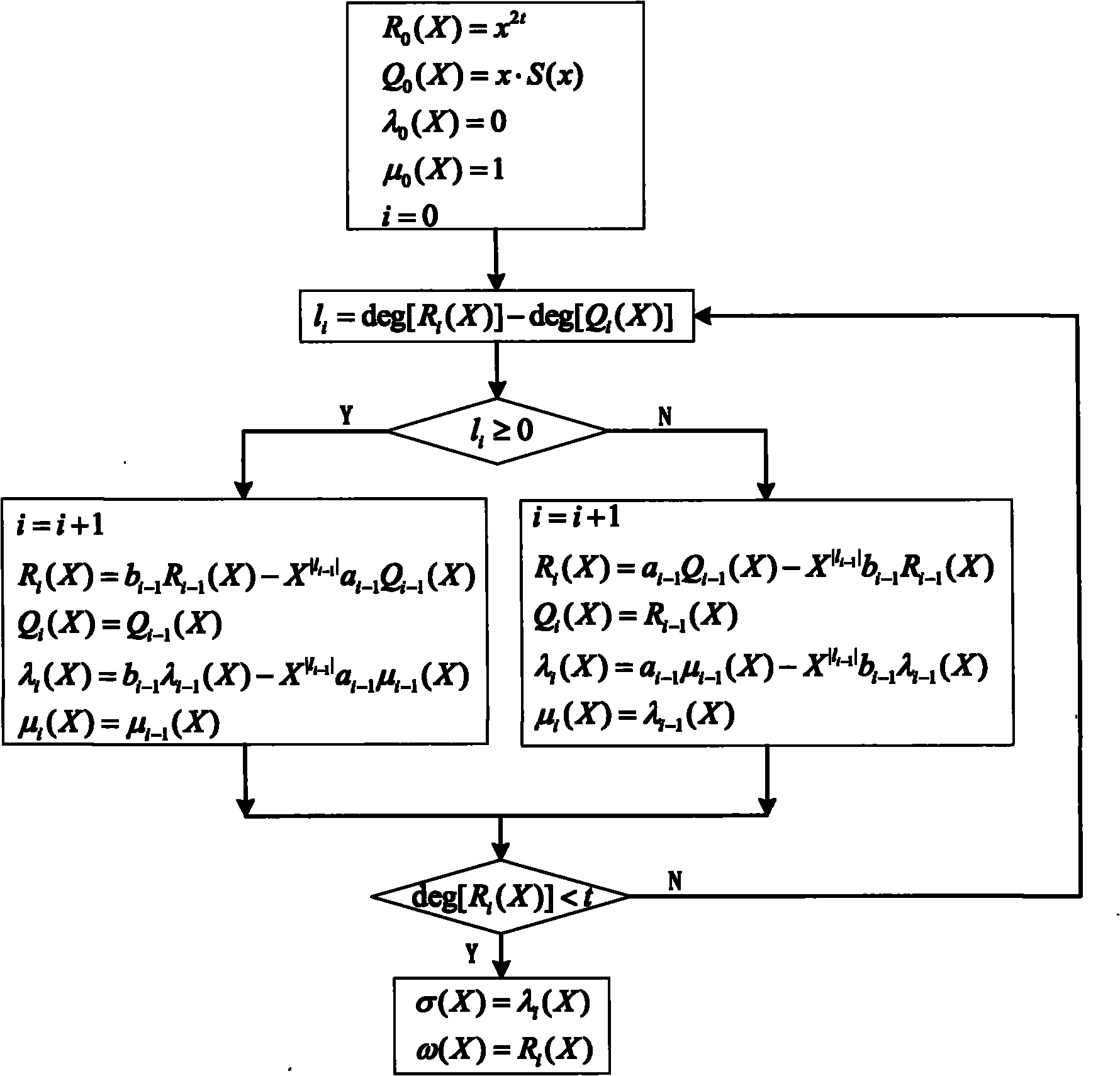
The invention claims a low hardware overhead Reed-Solomon decoder, comprising: a syndrome multinomial / chain search / error estimated value calculation multifunctional module, which realizes calculation of syndrome multinomial through algorithm S=((r<n-1>alphai-1+r<n-2>)alphai-1+...+r<1>)alphai-1+r<0> 1<=i<=2t, and is used for timely realizing functions of hidden search and error evaluation calculation etc; error position multinomial / error estimated value multinomial acquisition multifunctional module which has no need for iterating transfer inversion operation every time when performing solving using error position multinomial iteration algorithm through improved smooth Berlekamp-Massey algorithm so as to save the hardware resource, meanwhile, it can further timely realize acquisition of error position multinomial / error estimated value multinomial. The invention optimized decoding algorithm of Reed-Solomon decoder, reduces complexity of decoded hardware, greatly reduces the expenditure on hardware, and reduces the chip area and power consumption of the decoder.
Owner:MAXSCEND MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Implementation method of Reed-Solomon decoder
InactiveCN101834616AEasy to decodeDecoder implementation is easyCyclic codesReed solomon decoderDelayed time
The invention discloses an implementation method of a Reed-Solomon decoder. The Reed-Solomon decoder realizes solving on an error location polynomial and an error value polynomial by a controller, an arithmetic device and four shifting registers, and can decode a plurality of symbols of a Reed-Solomon code, thus achieving small and fixed delay time for decoding and regular structure.
Owner:高通创锐讯通讯科技(上海)有限公司
Even-load software reed-solomon decoder
A software implementation of a Reed-Solomon decoder placing a constant load on the processor of a computer. A Berlekamp-Massey Algorithm is used to calculate the coefficients of the error locator polynomial, a Chien Search is used to determine the roots of the error locator polynomial, and a Forney Algorithm is used to determine the magnitude of the errors in the received digital code word. Each step is divided into m small tasks where m is the number of computational blocks it takes to read in a code word and the processor can pipeline or parallel process one task from each step each time a block is read.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Method And Apparatus For Code Group Identification And Frame Synchronization By Use Of Reed-Solomon Decoder And Reliability Measurement For UMTS W-CDMA
InactiveUS20080244364A1Improve performanceLarge amount of memoryError preventionFault responseReed solomon decoderDependability
A method and apparatus having a modified Reed-Solomon decoder is used for finding a specific code group used by a base station and the frame timing synchronization with the base station. The modified Reed-Solomon decoder uses a standard Reed-Solomon decoder and some reliability measurements computed from the received code word symbols. If the reliability of a received symbol is too low, this symbol is considered as erasure. By selecting code word symbols with higher reliabilities and erasing code word symbols with lower reliabilities, the symbol error probability is reduced and the performance is improved. Several modified Reed-Solomon decoders and a few decoding strategies are introduced in order to decode the received code word sequences with a power- and memory-effective method.
Owner:SHIEH SHIN LIN +2
Error detection and correction method and system for memory devices
ActiveUS7475326B2Increasing costIncrease the number ofError detection/correctionStatic storageComputer hardwareData set
A method and a system for the detection and correction of errors in memory systems is disclosed. In one embodiment, a method of error detection in a memory system having a plurality (m>1) of memory devices includes generating check bits for each of a plurality of data sets, dividing each memory device into a plurality (n>1) of segments. The plurality of data sets are interleaved to form a plurality (p>1) of words. Each word includes at least one segment from two or more of the memory devices. Detection and correction may utilize oneor more parallel Reed-Solomon decoder and encoder. The system and method allow for the efficient detection and / or correction of memory device errors and bit errors in one or more memory devices.
Owner:DATA DEVICE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com