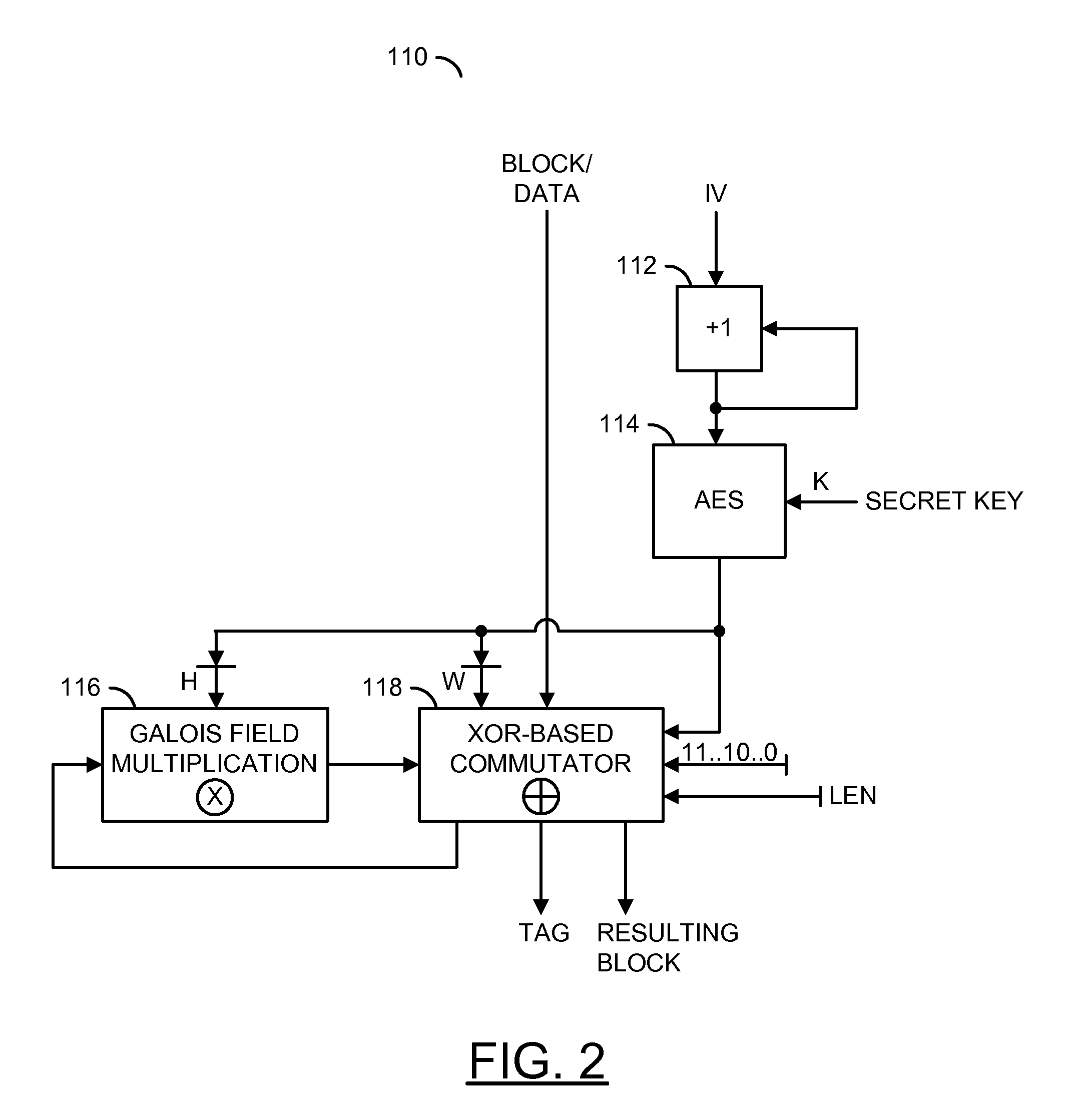
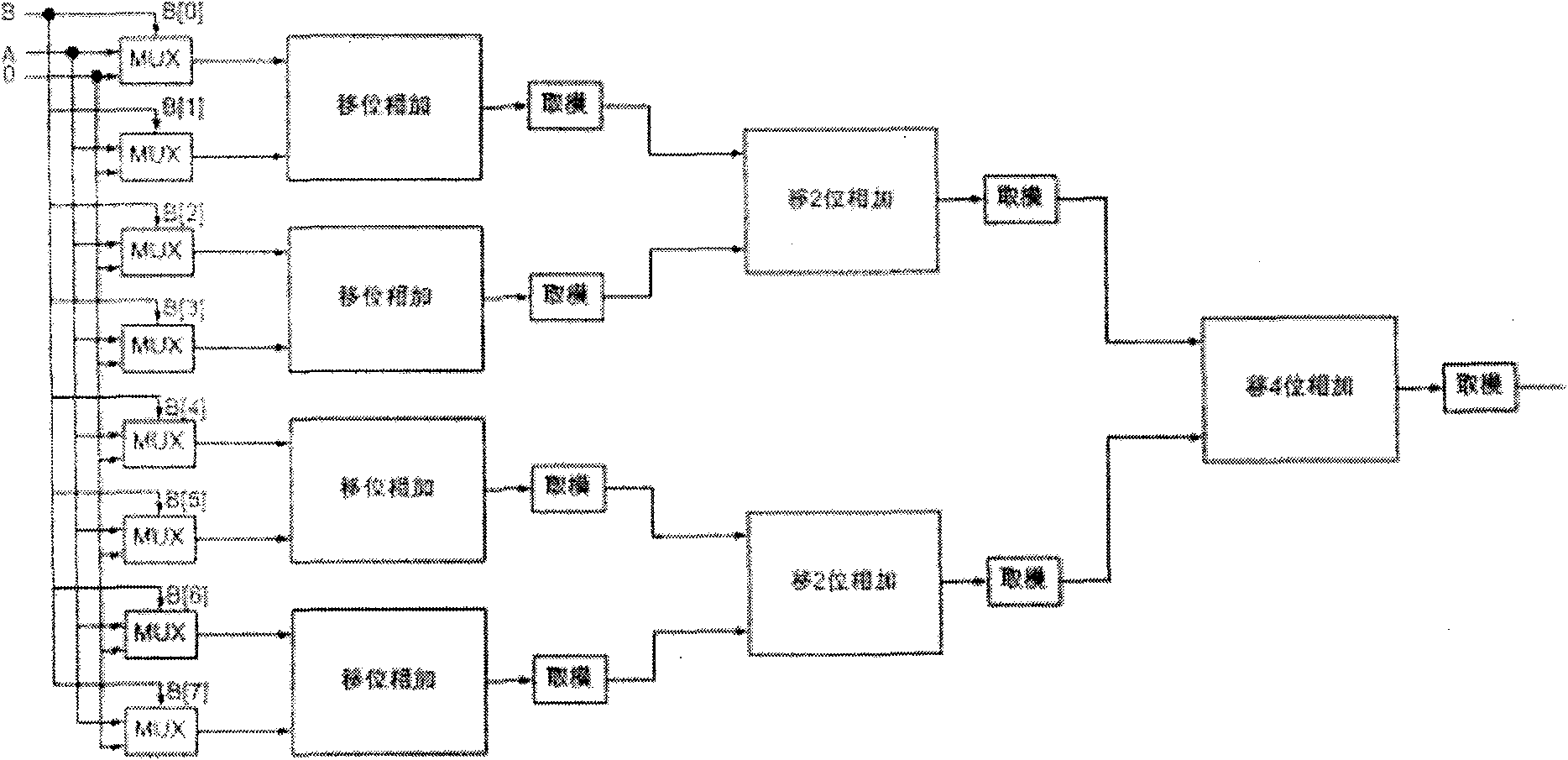
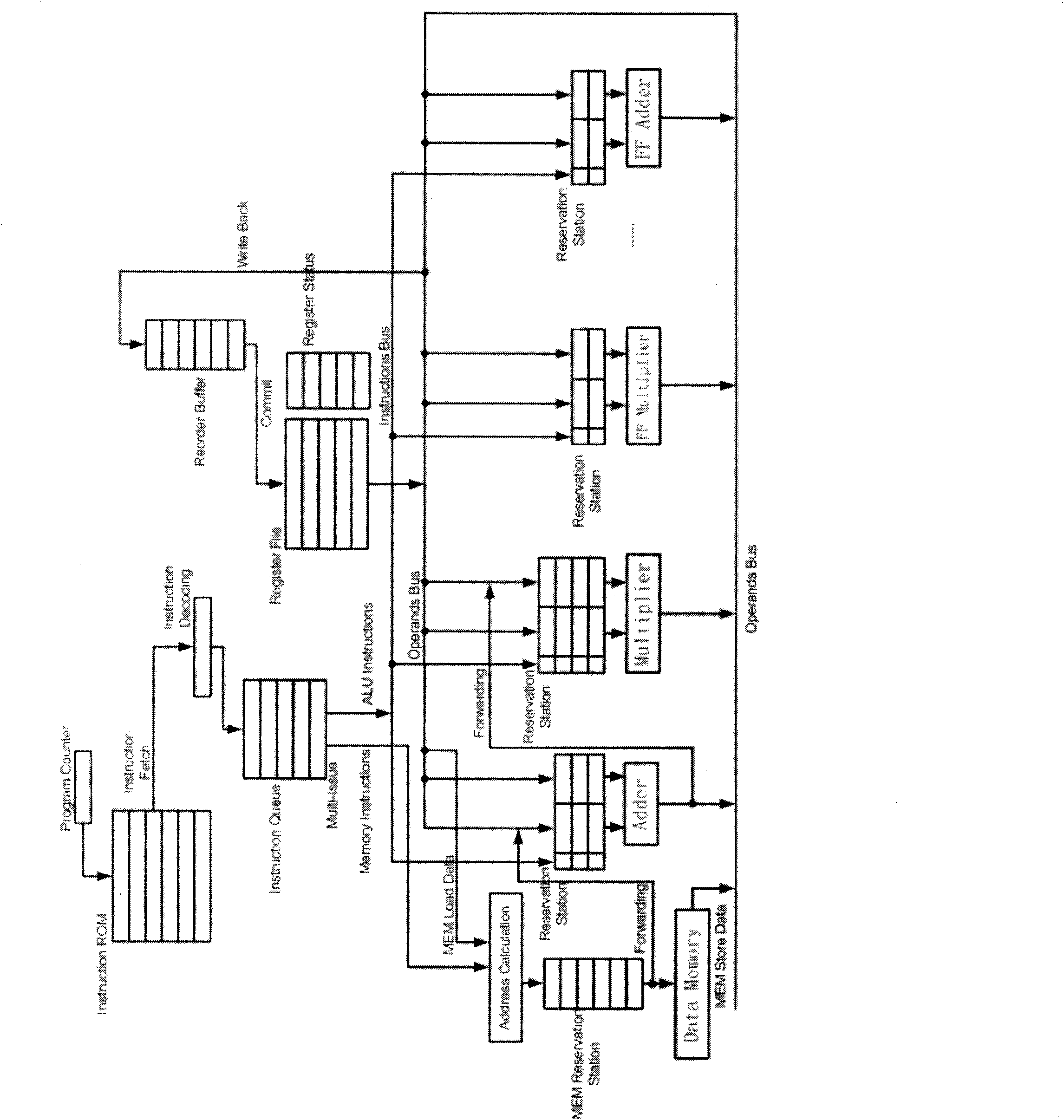
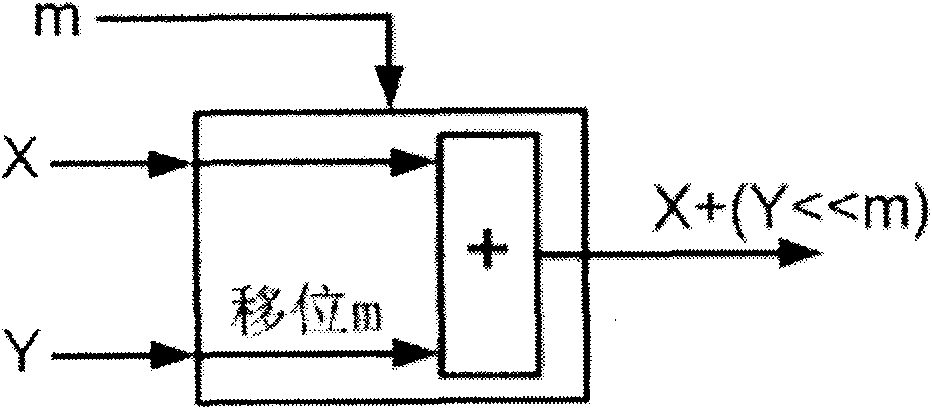
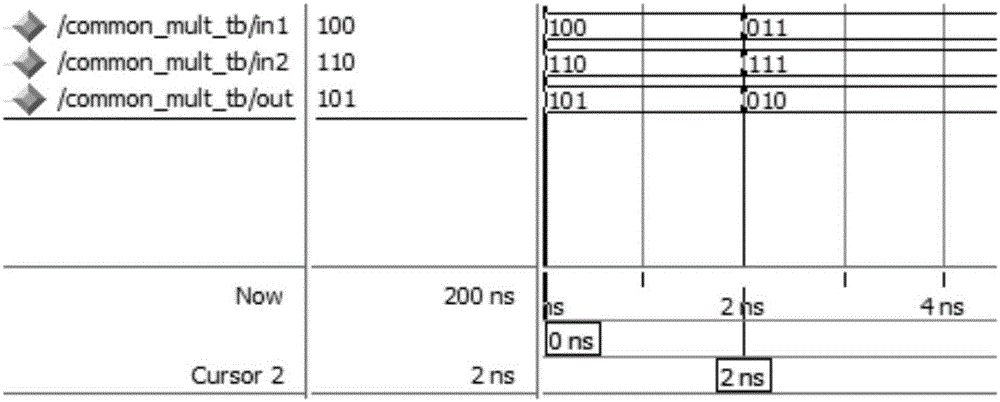
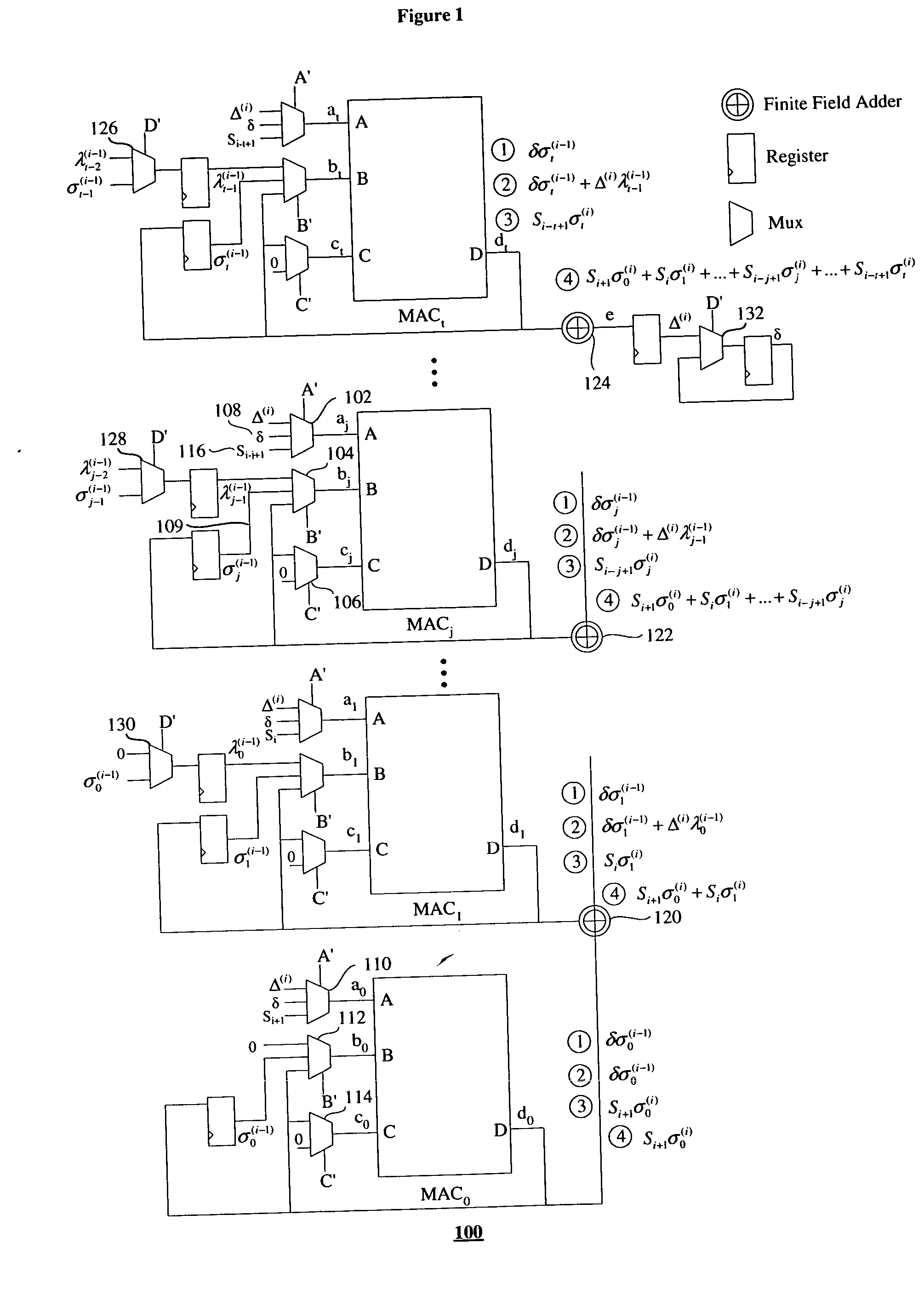
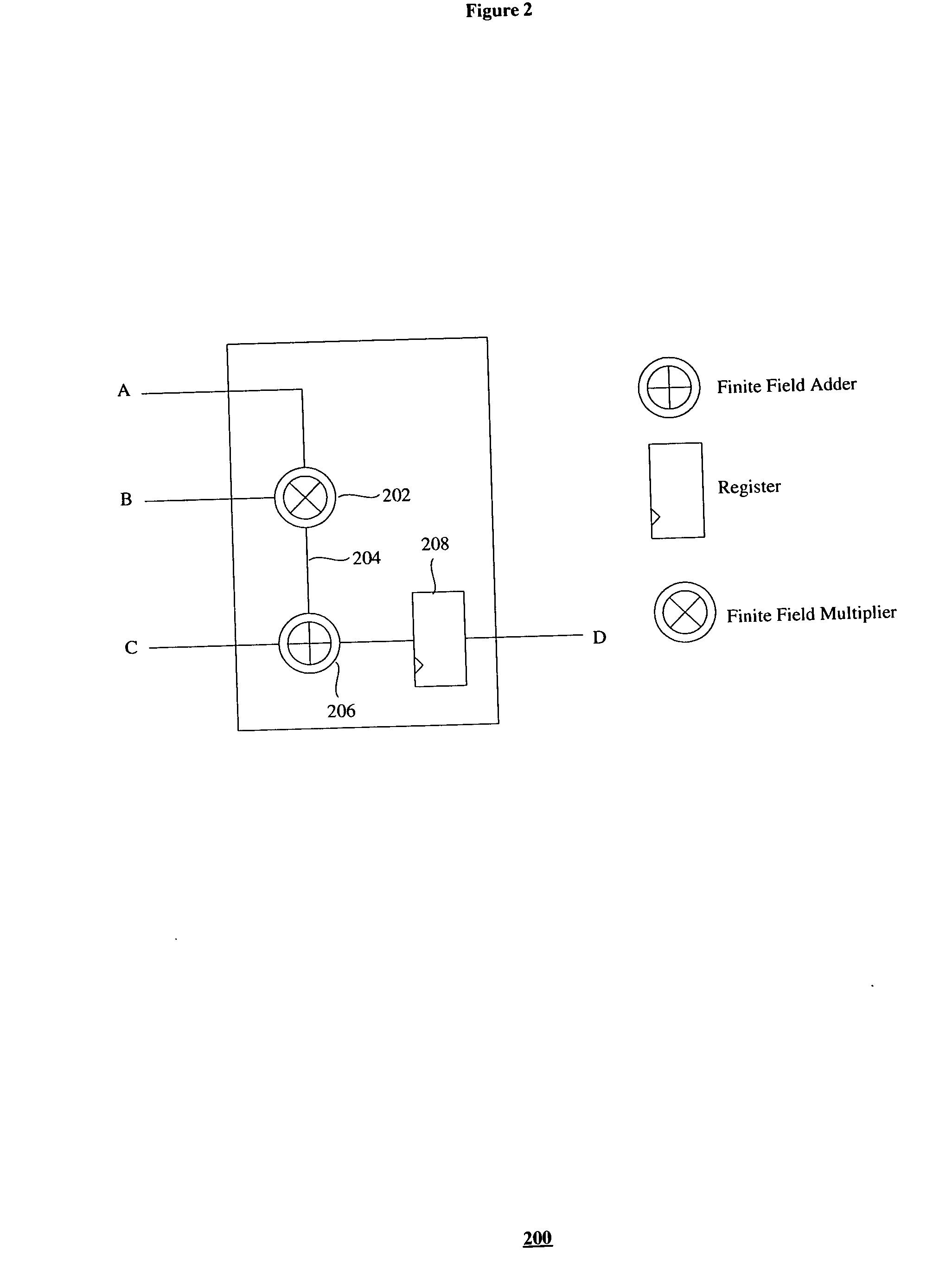
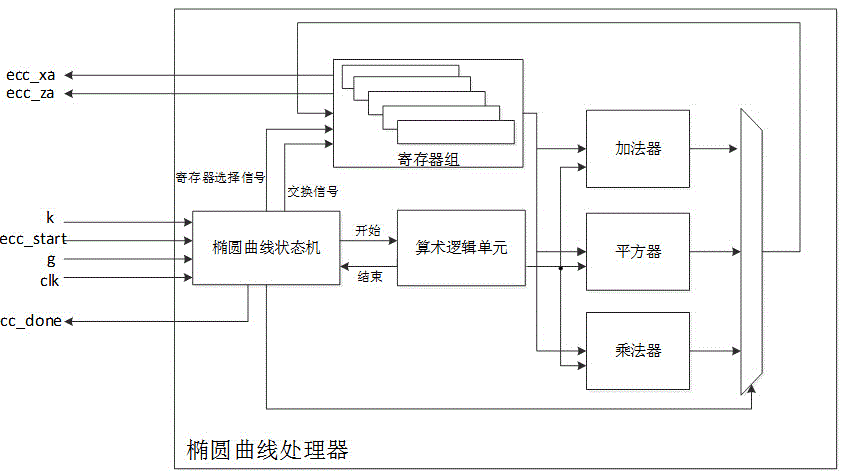
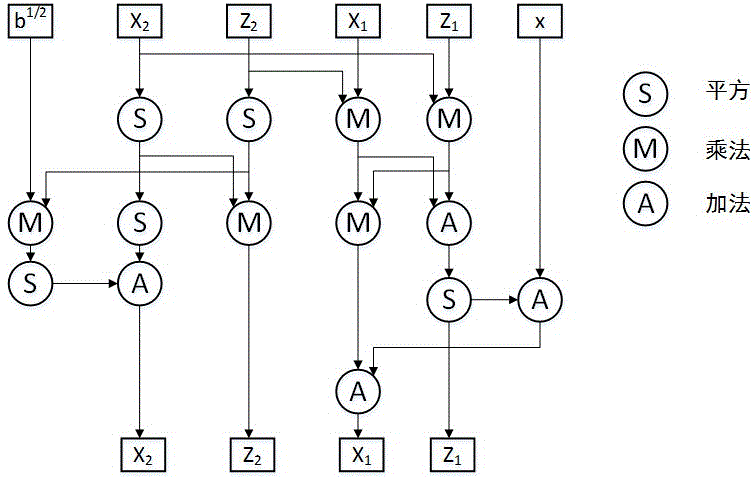
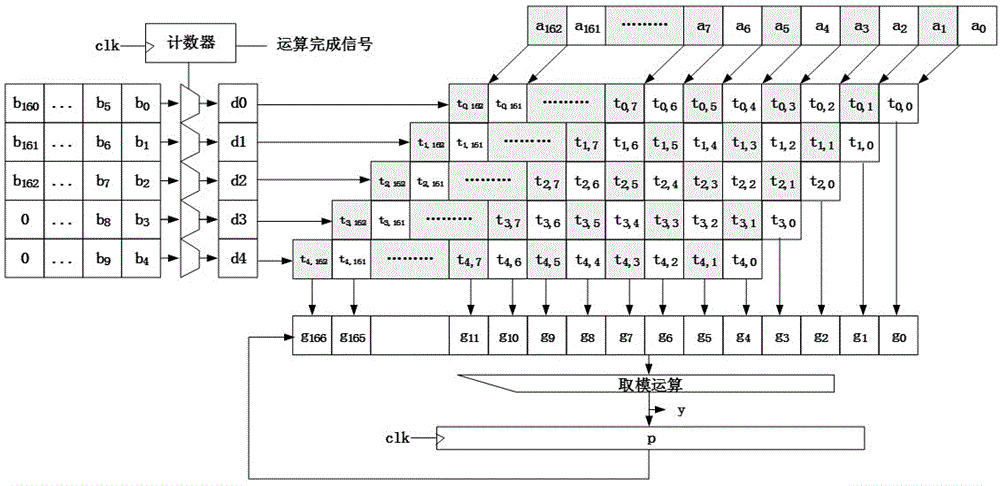
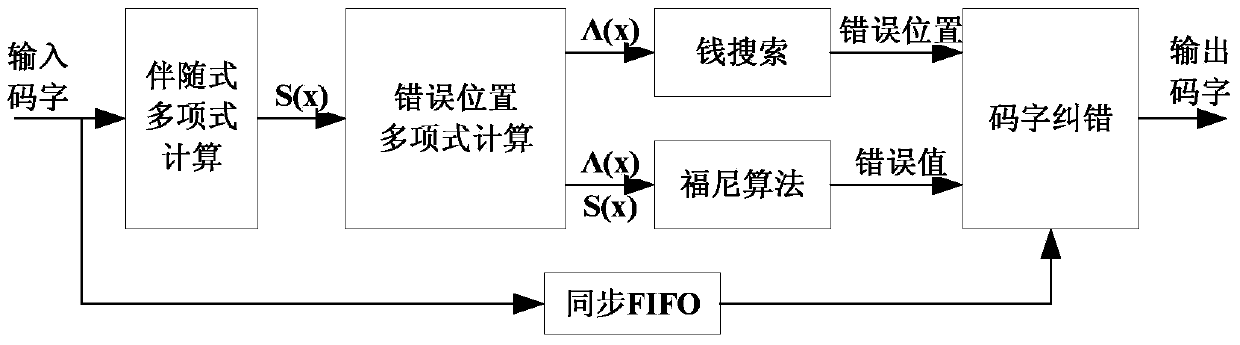
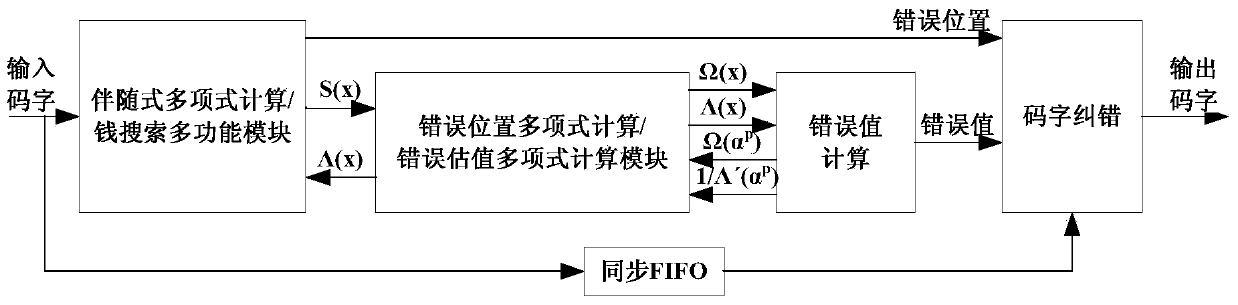
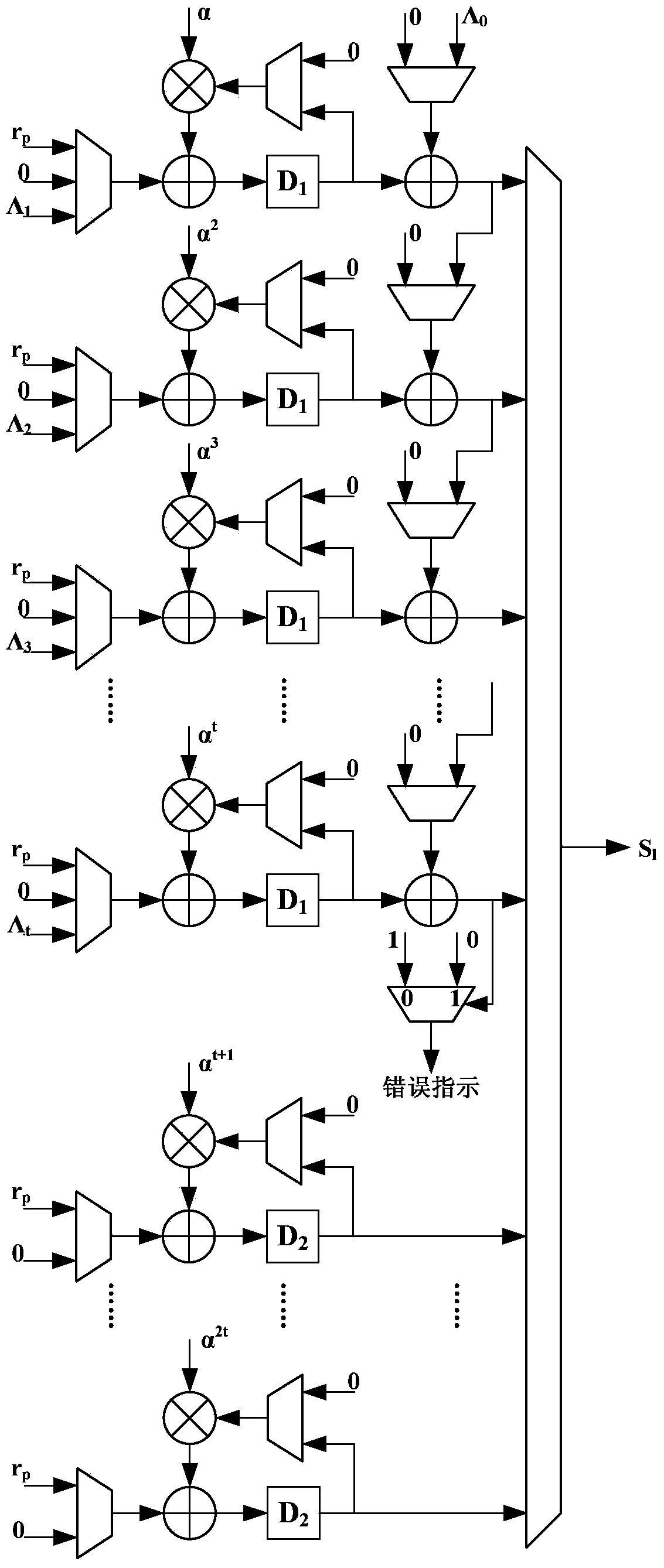
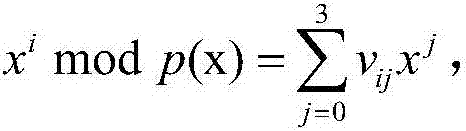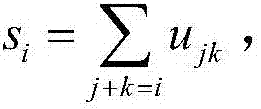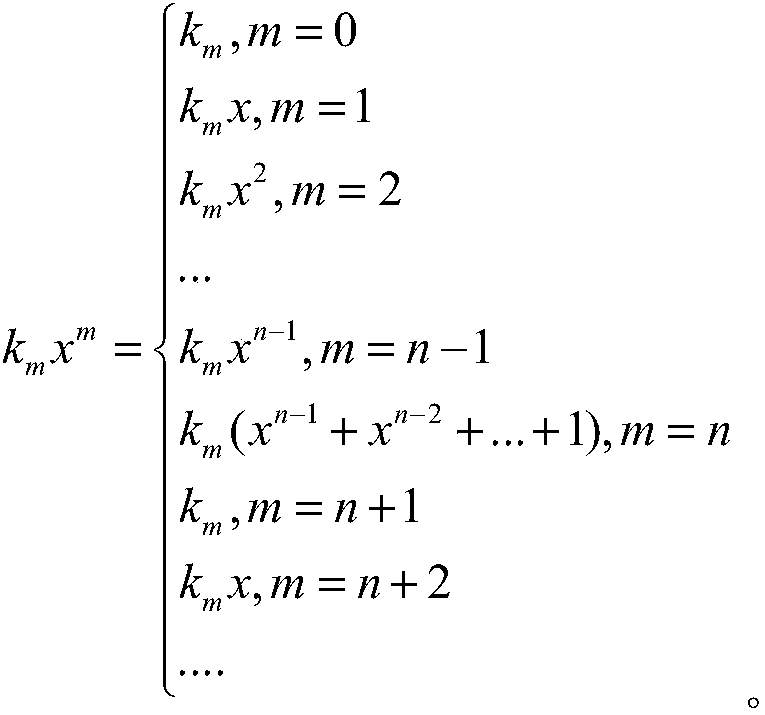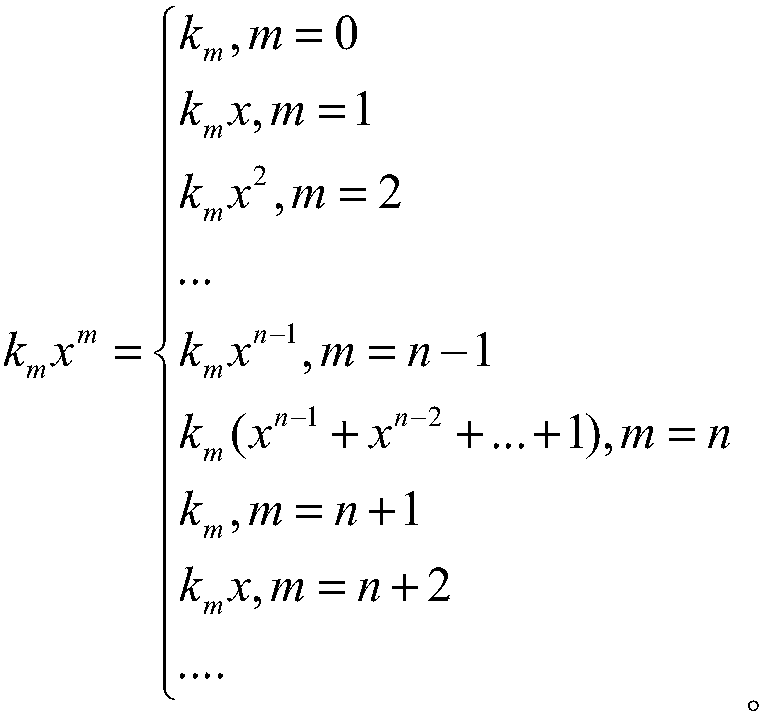Patents
Literature
45 results about "Finite field multiplier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
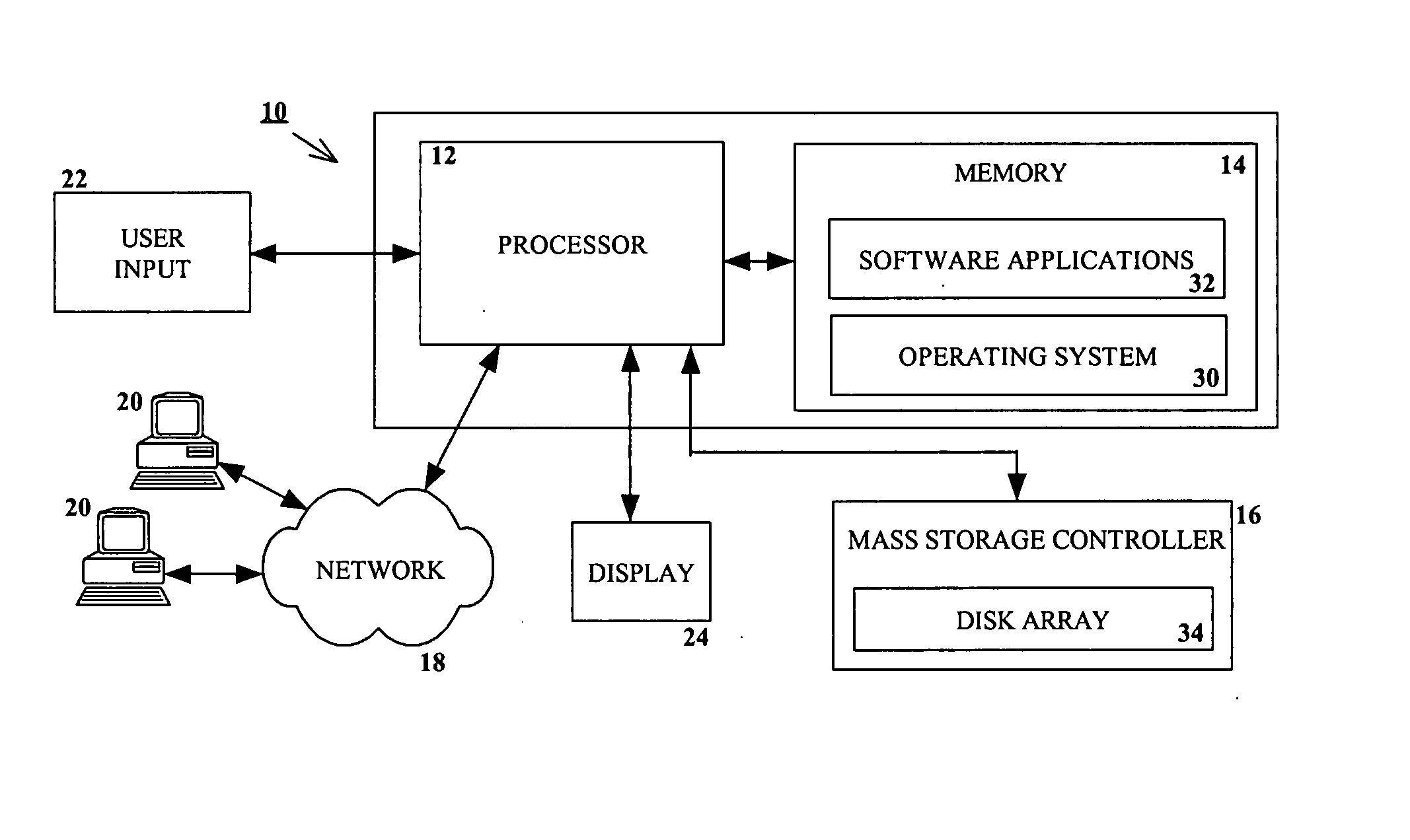
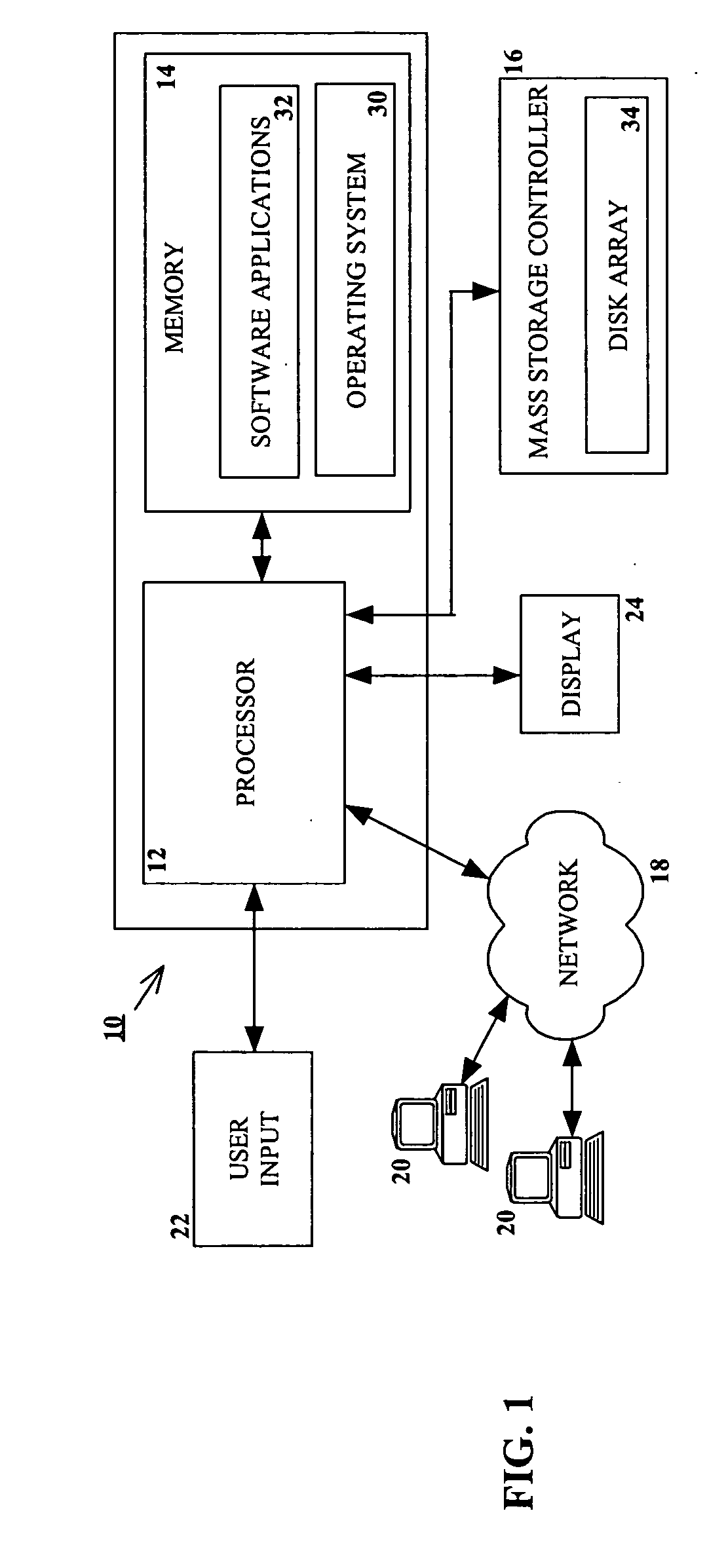
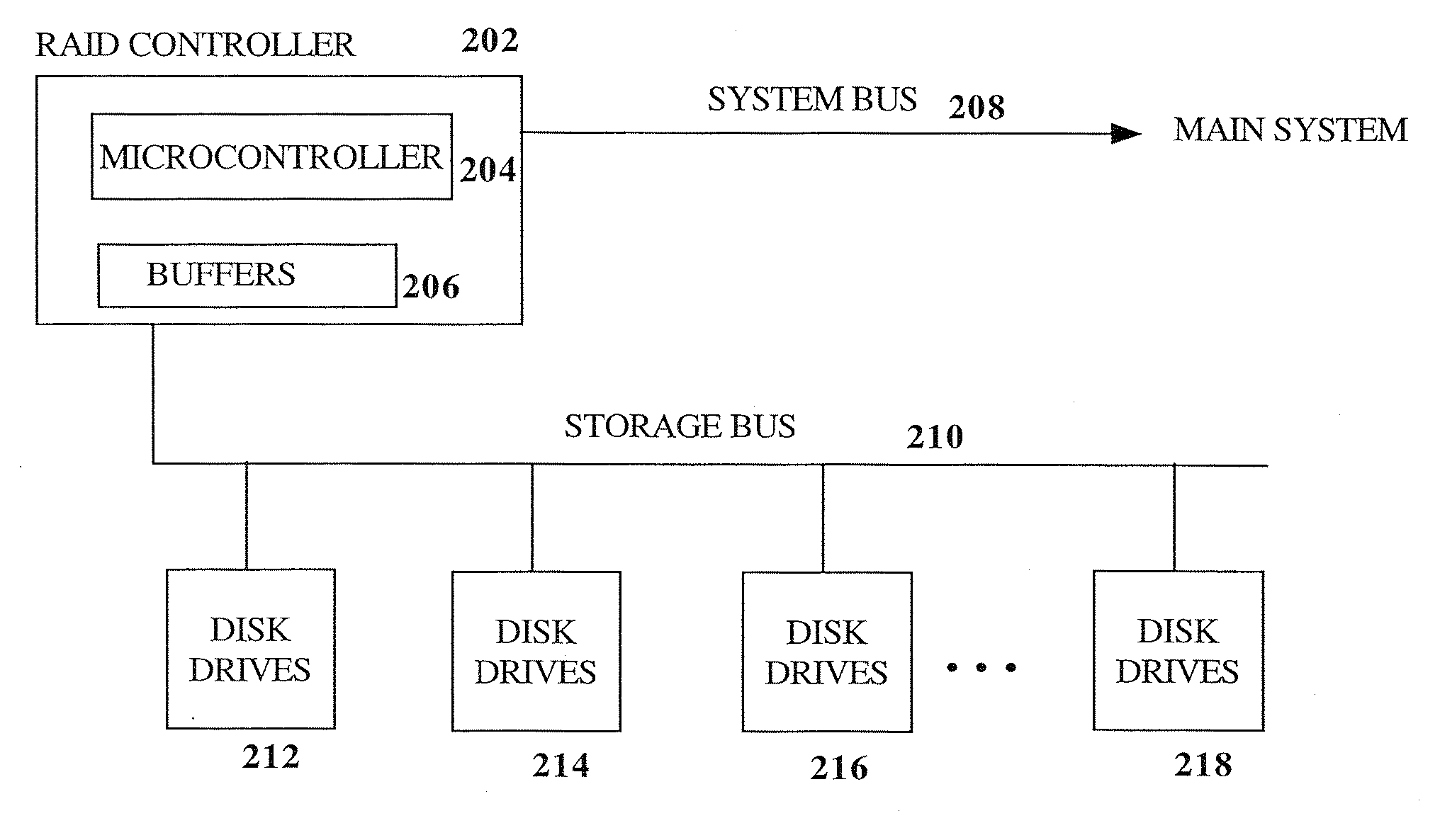
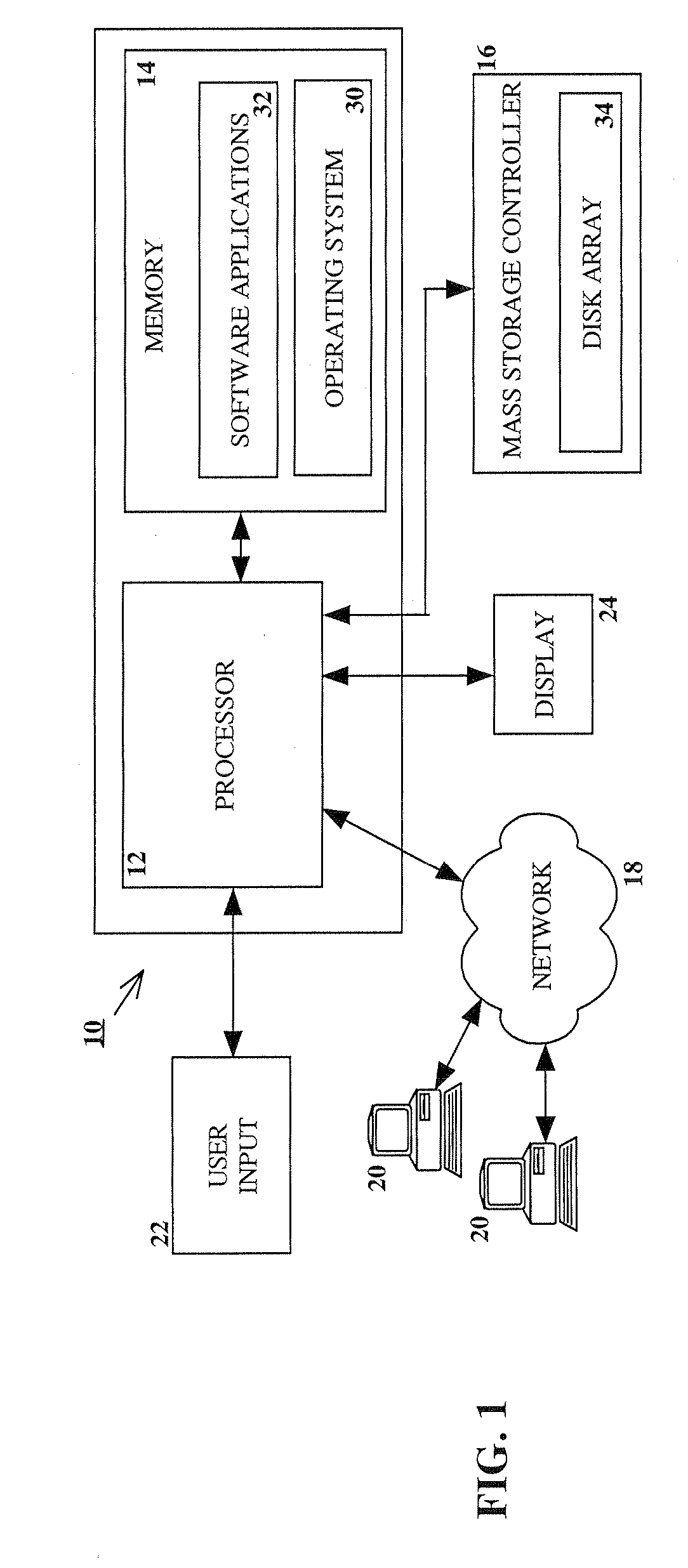
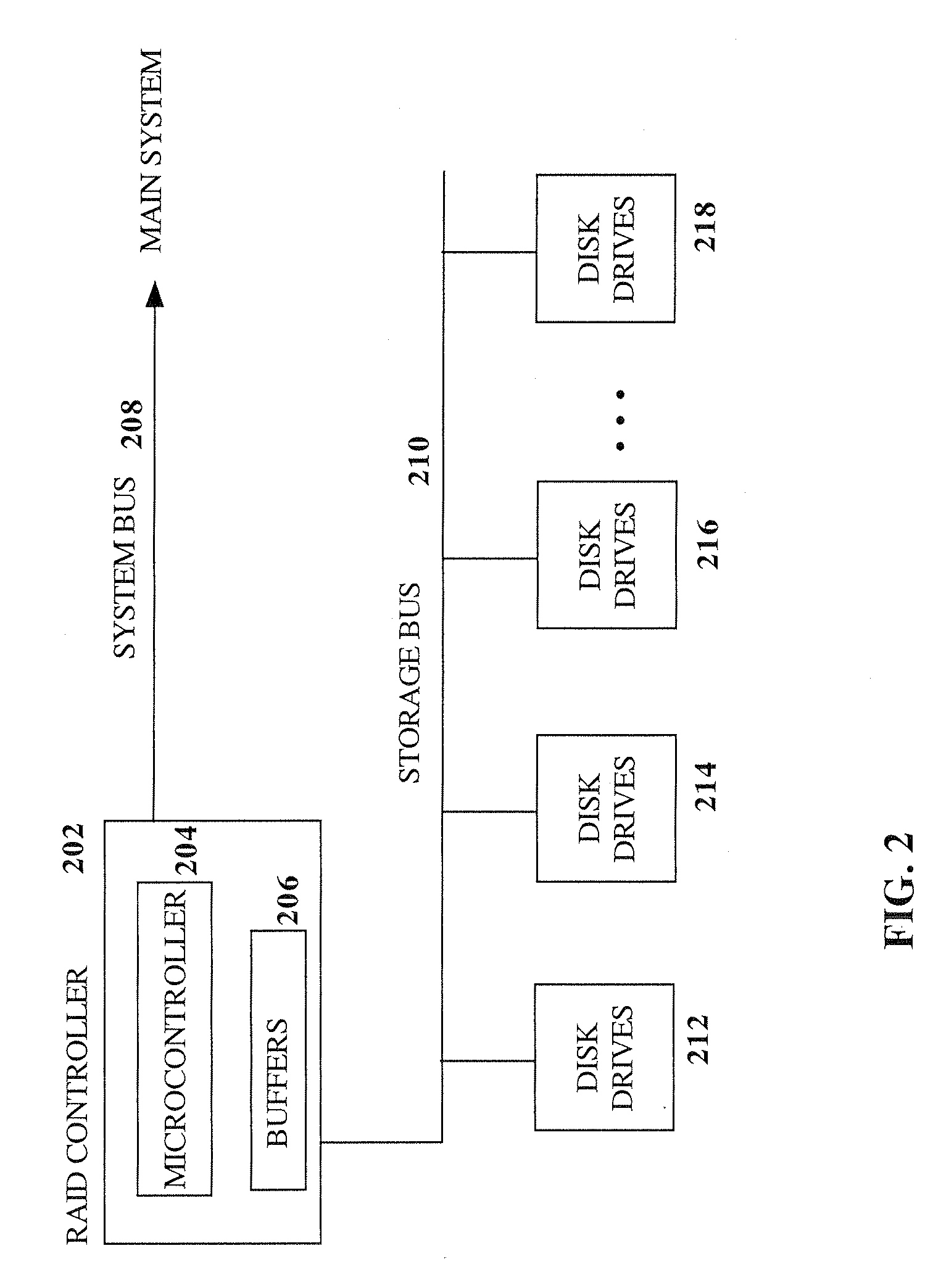
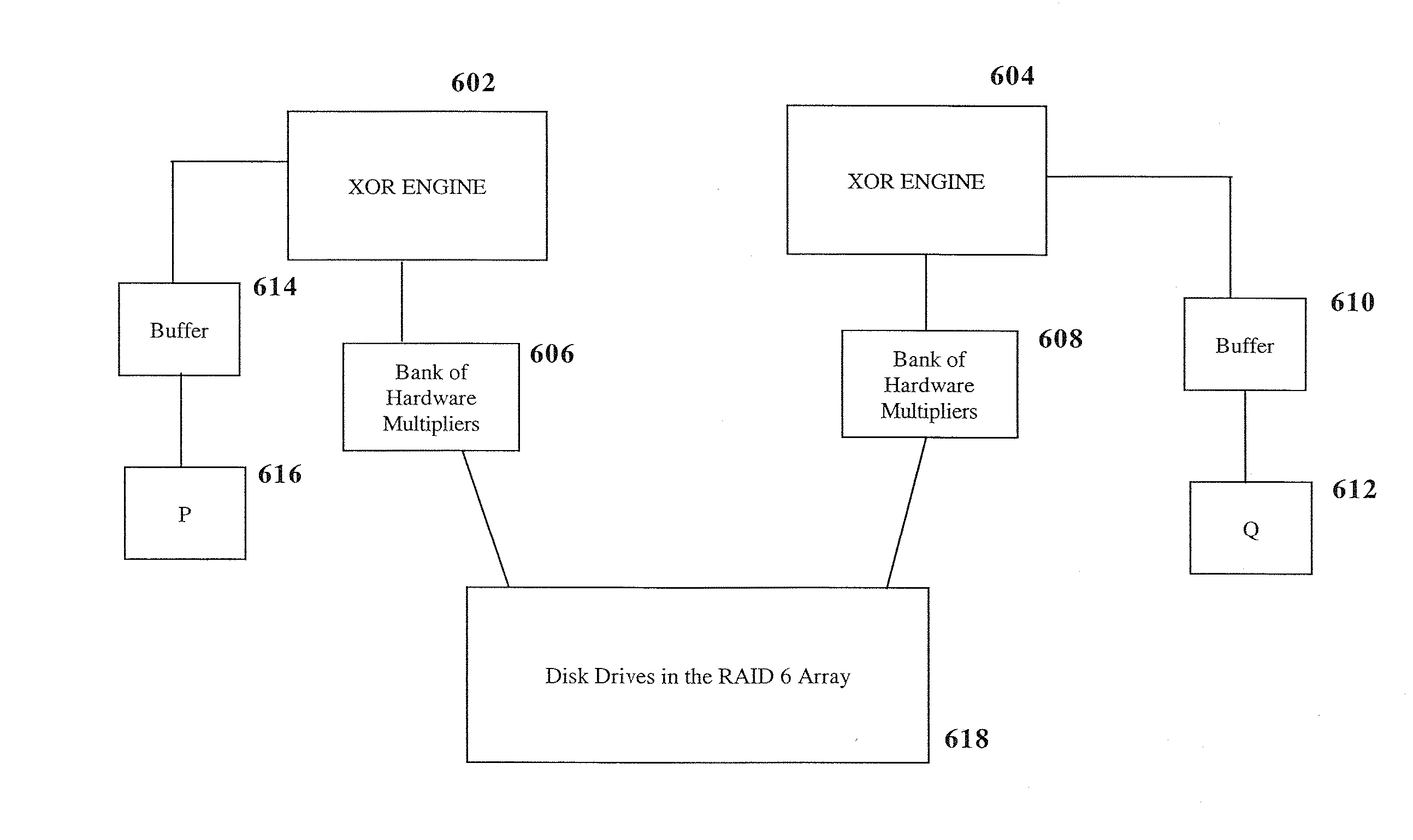
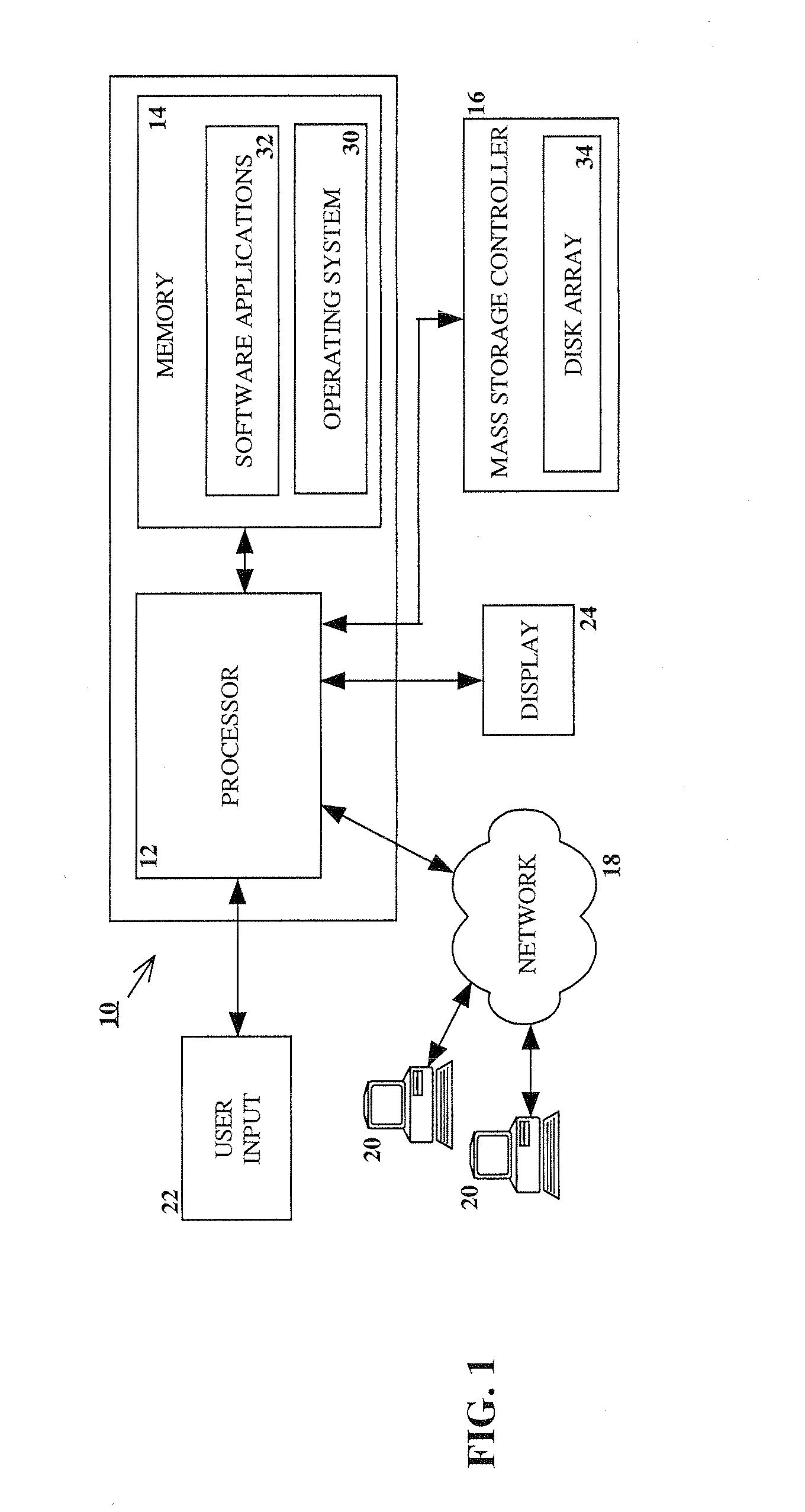
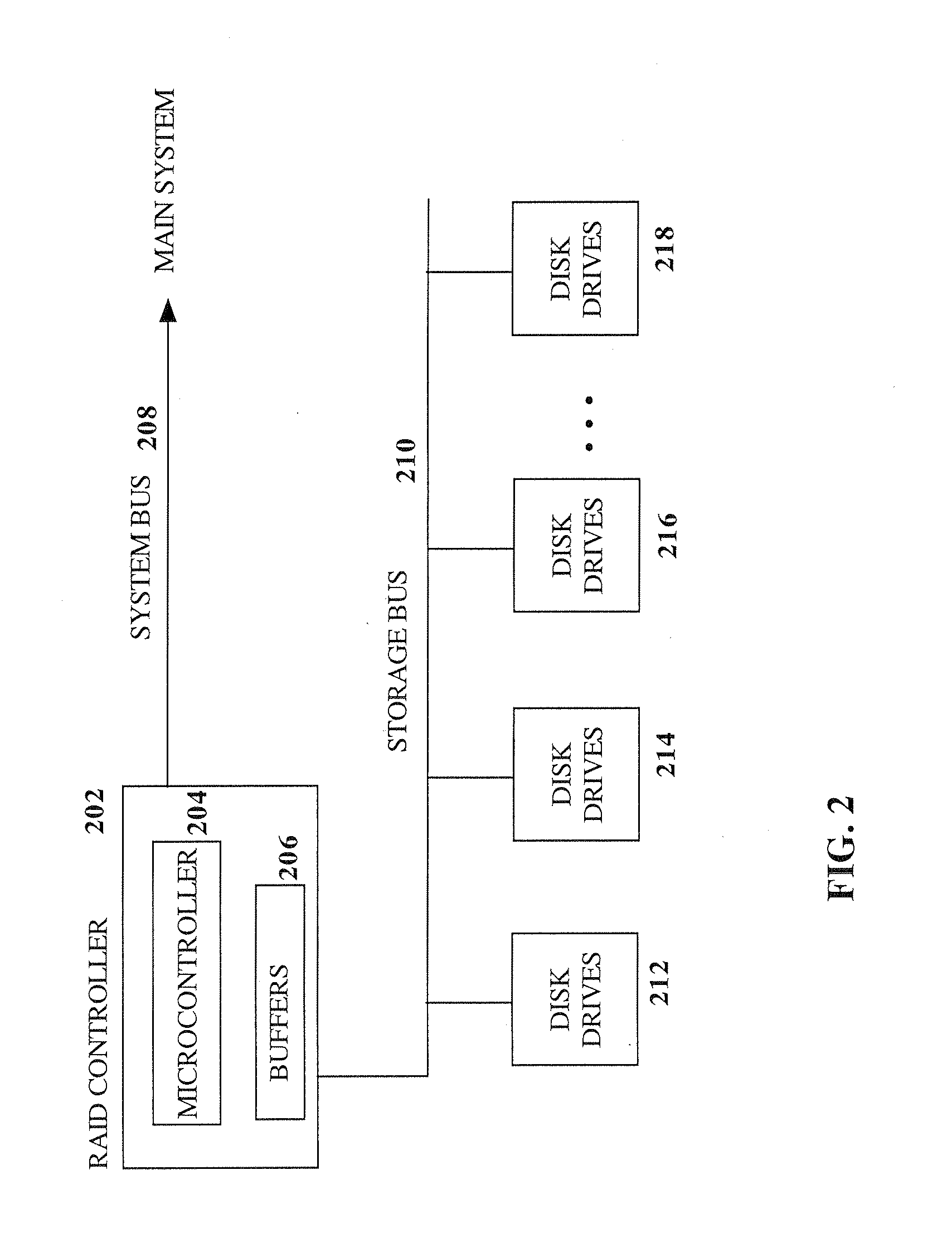
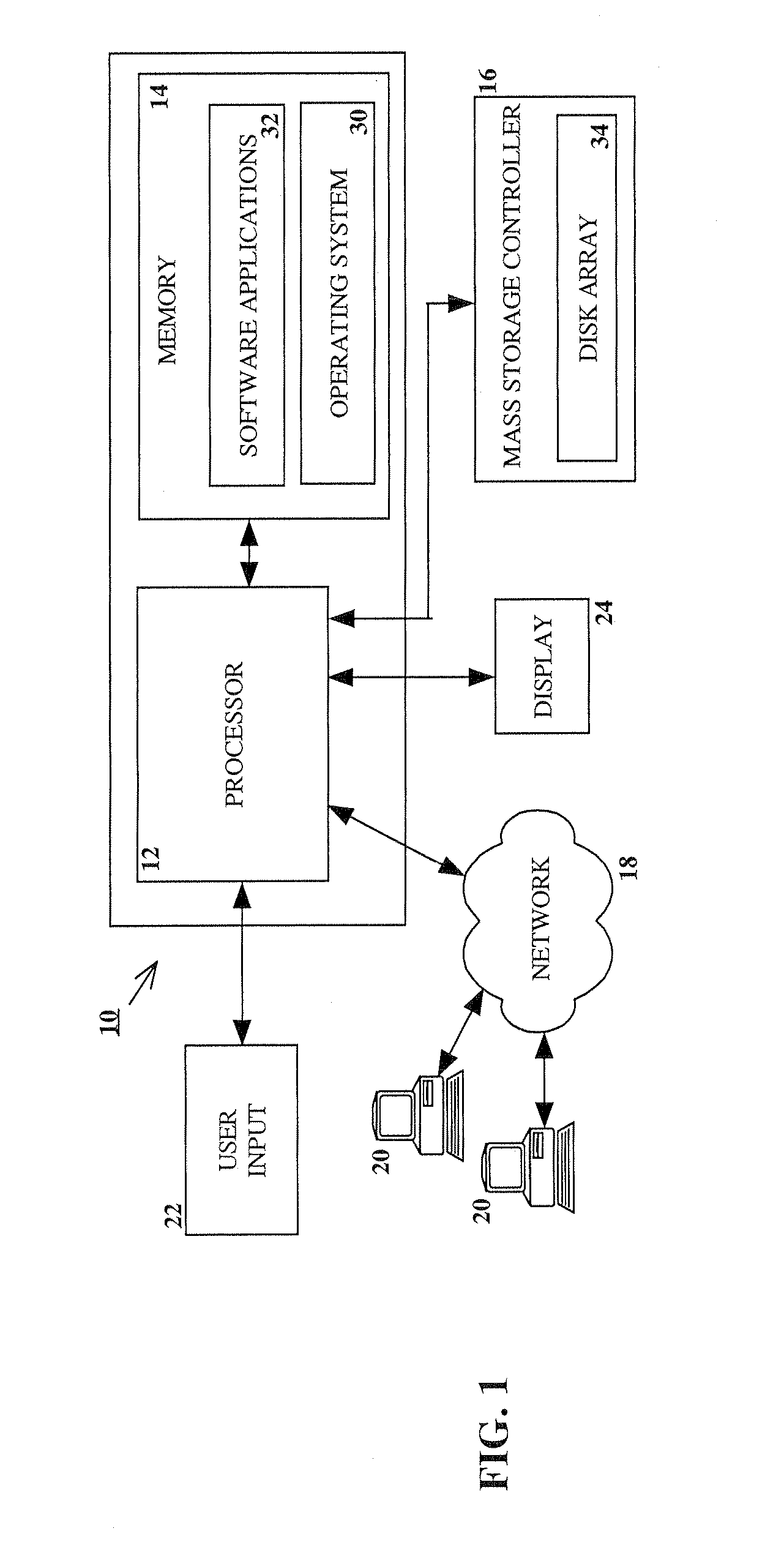
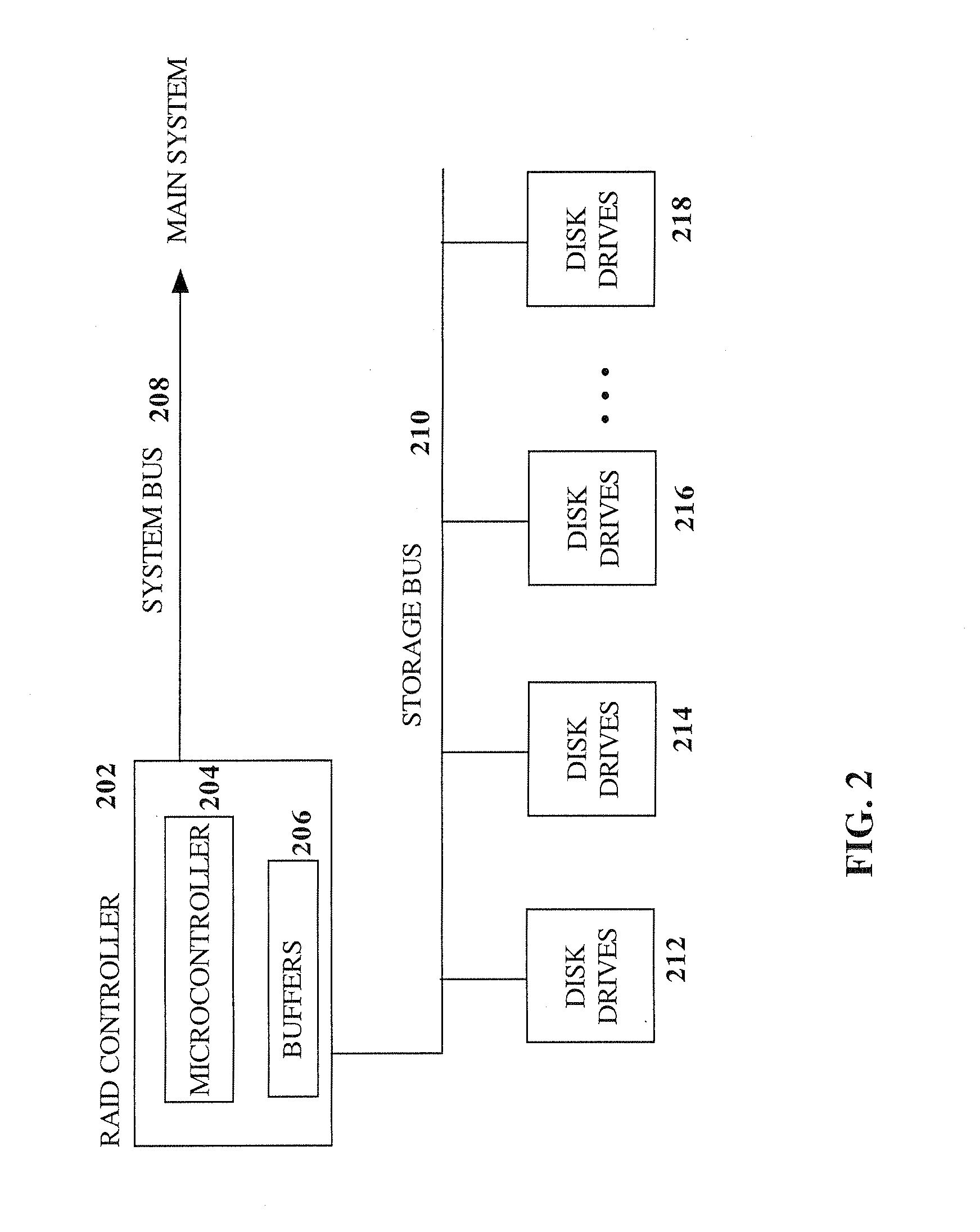
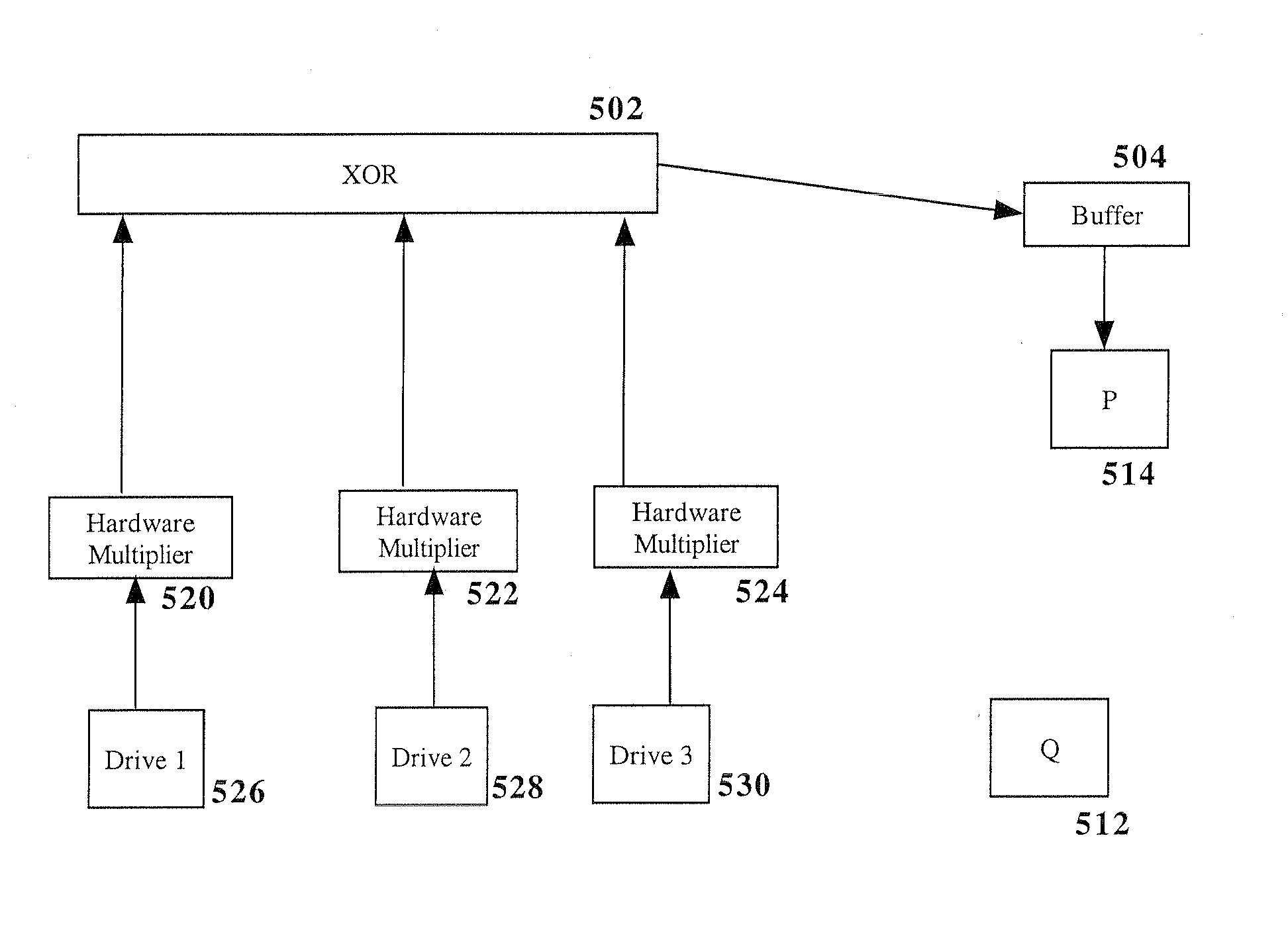
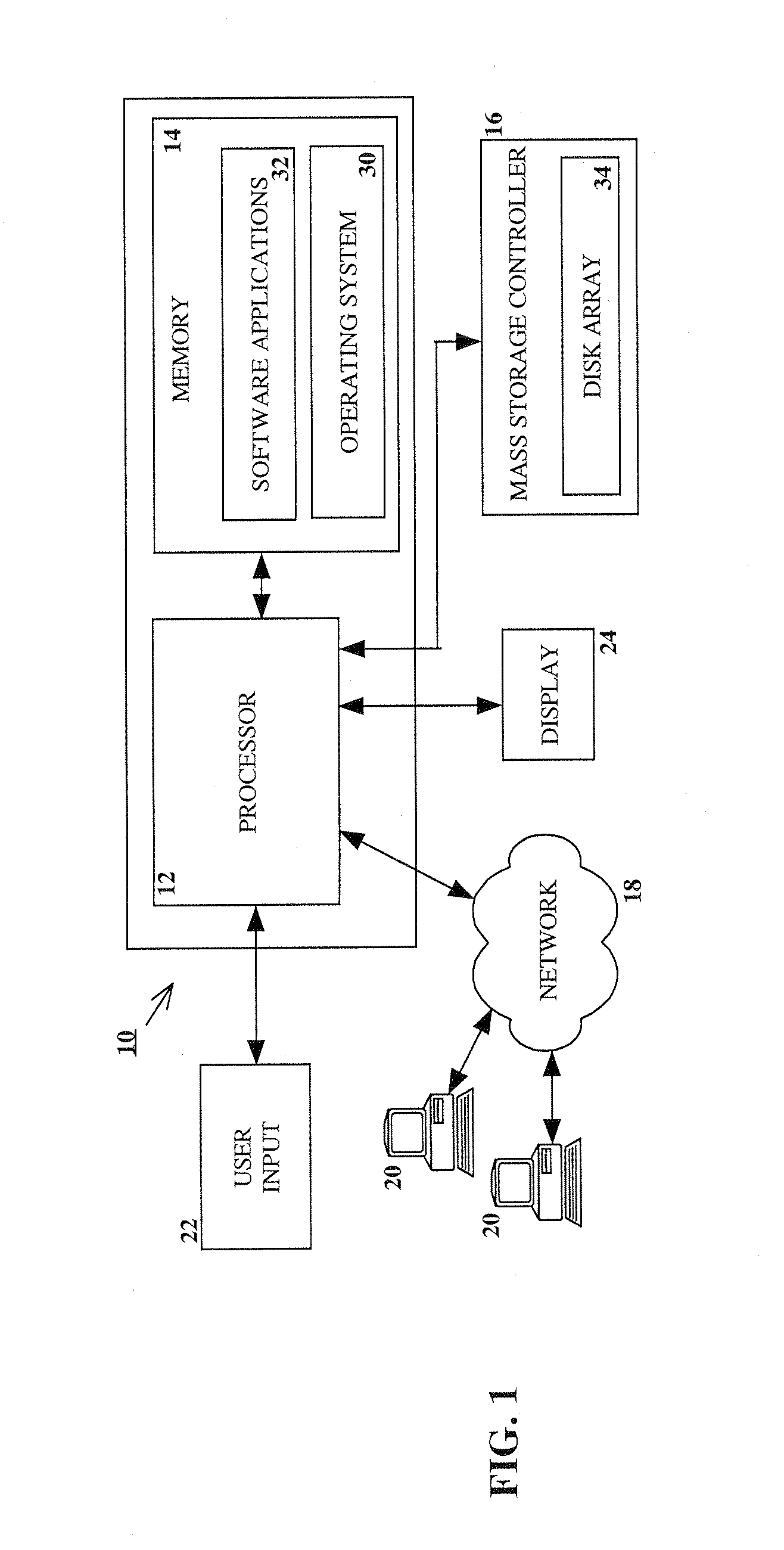
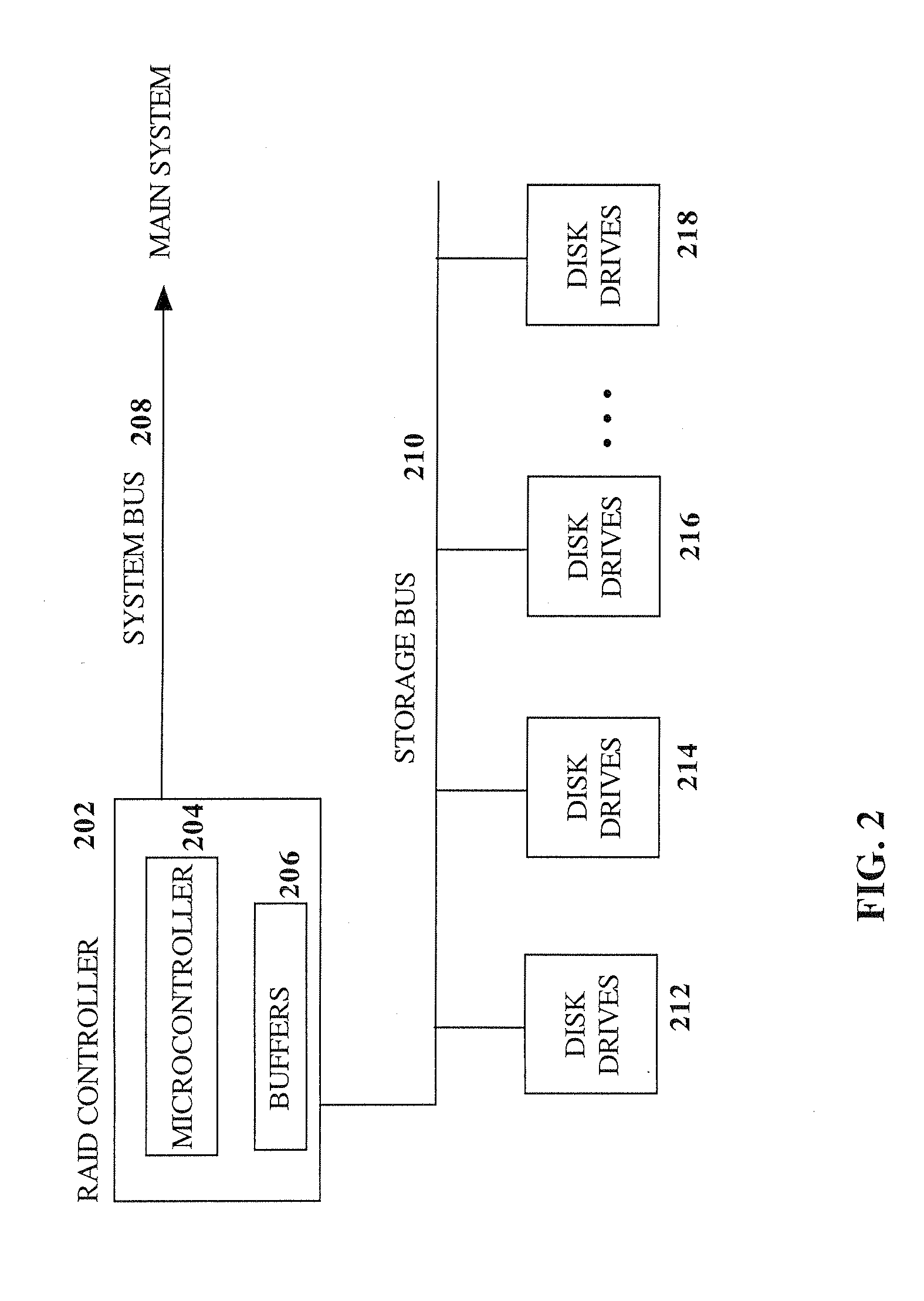
RAID environment incorporating hardware-based finite field multiplier for on-the-fly XOR
InactiveUS20060123271A1Improve parallelismReduce in quantityError detection/correctionRAIDParallel computing
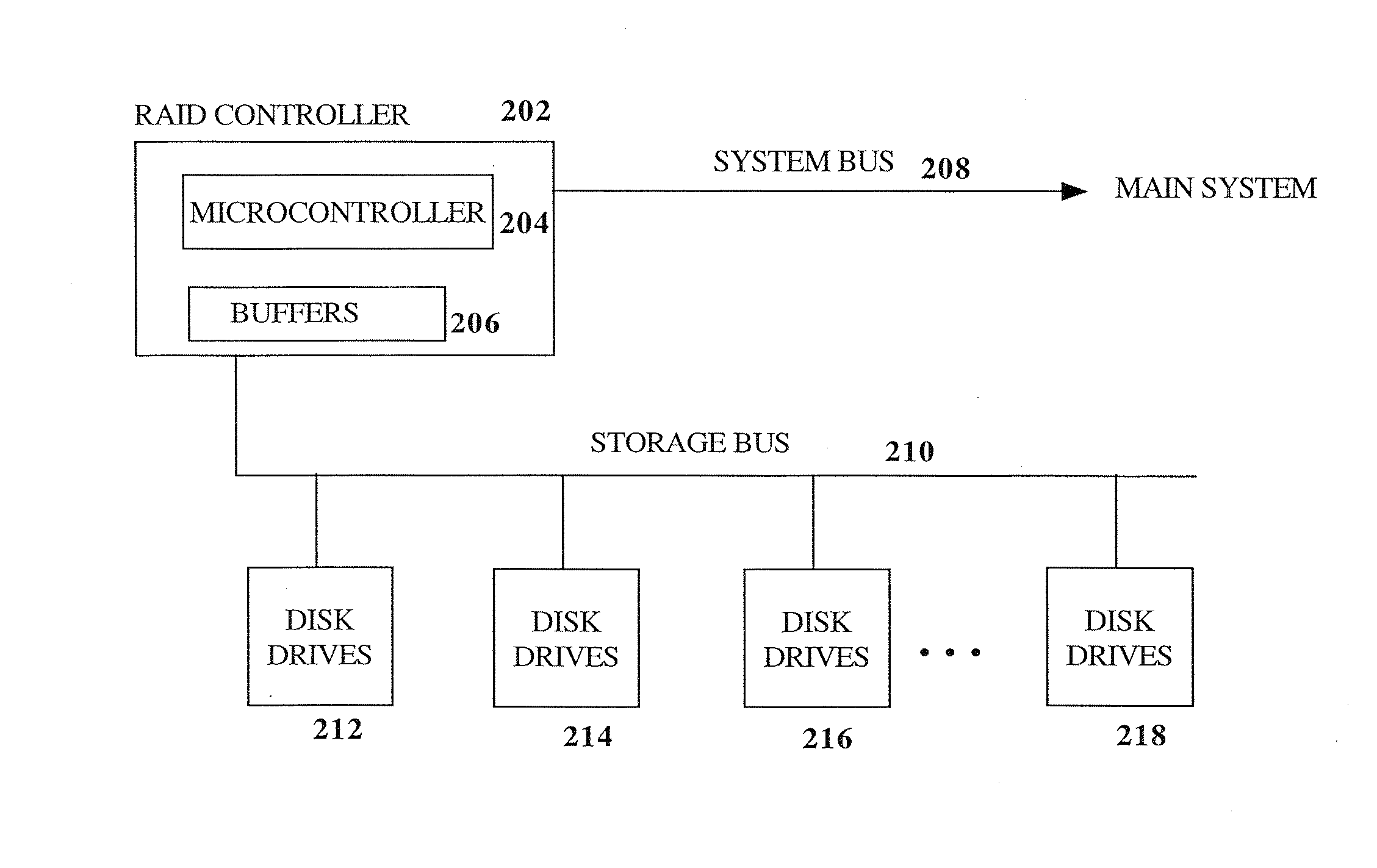
A hardware-based finite field multiplier is used to scale incoming data from a disk drive and XOR the scaled data with the contents of a working buffer when performing resync, rebuild and other exposed mode read operations in a RAID or other disk array environment. As a result, RAID designs relying on parity stripe equations incorporating one or more scaling coefficients are able to overlap read operations to multiple drives and thereby increase parallelism, reduce the number of required buffers, and increase performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
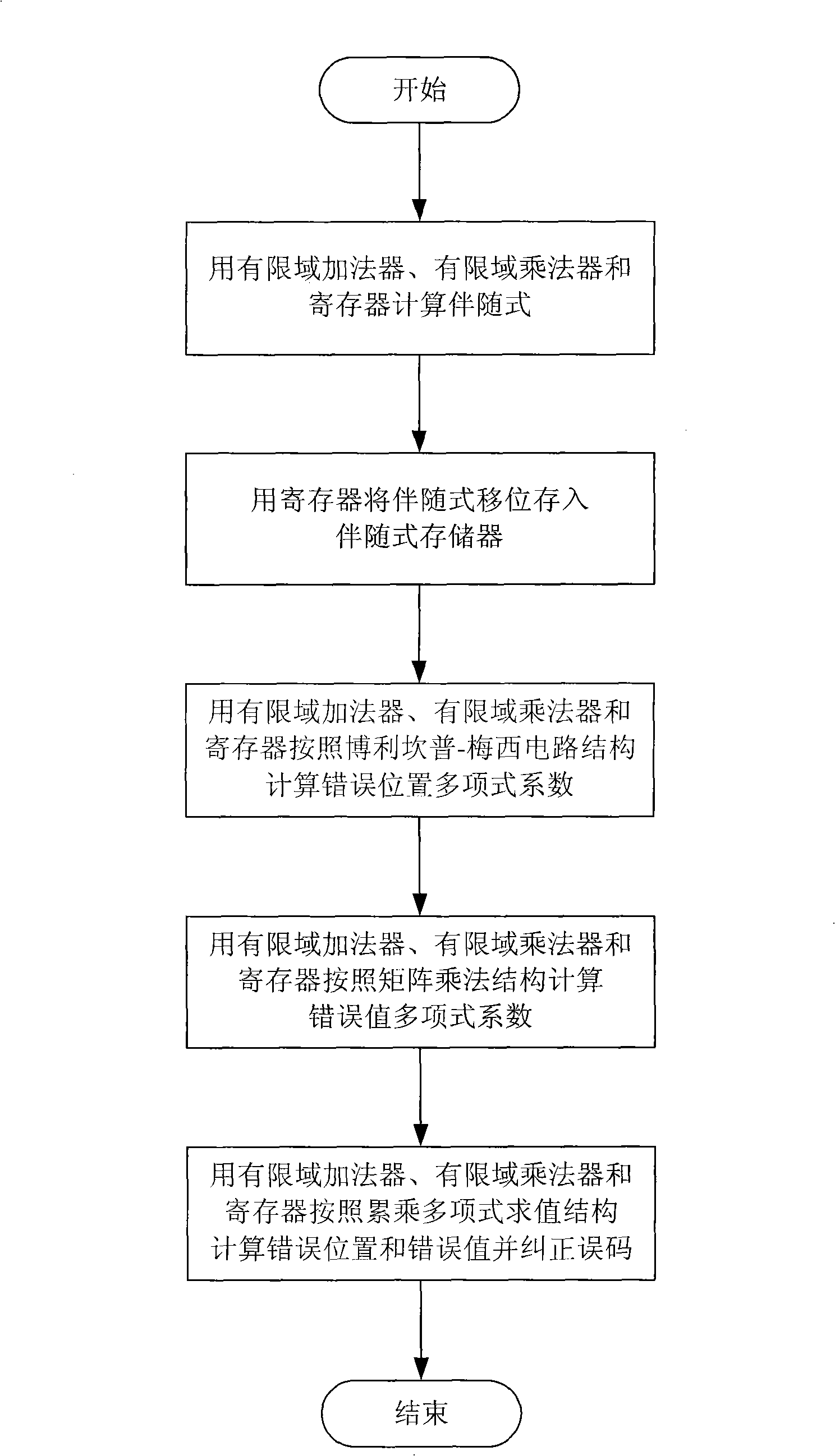
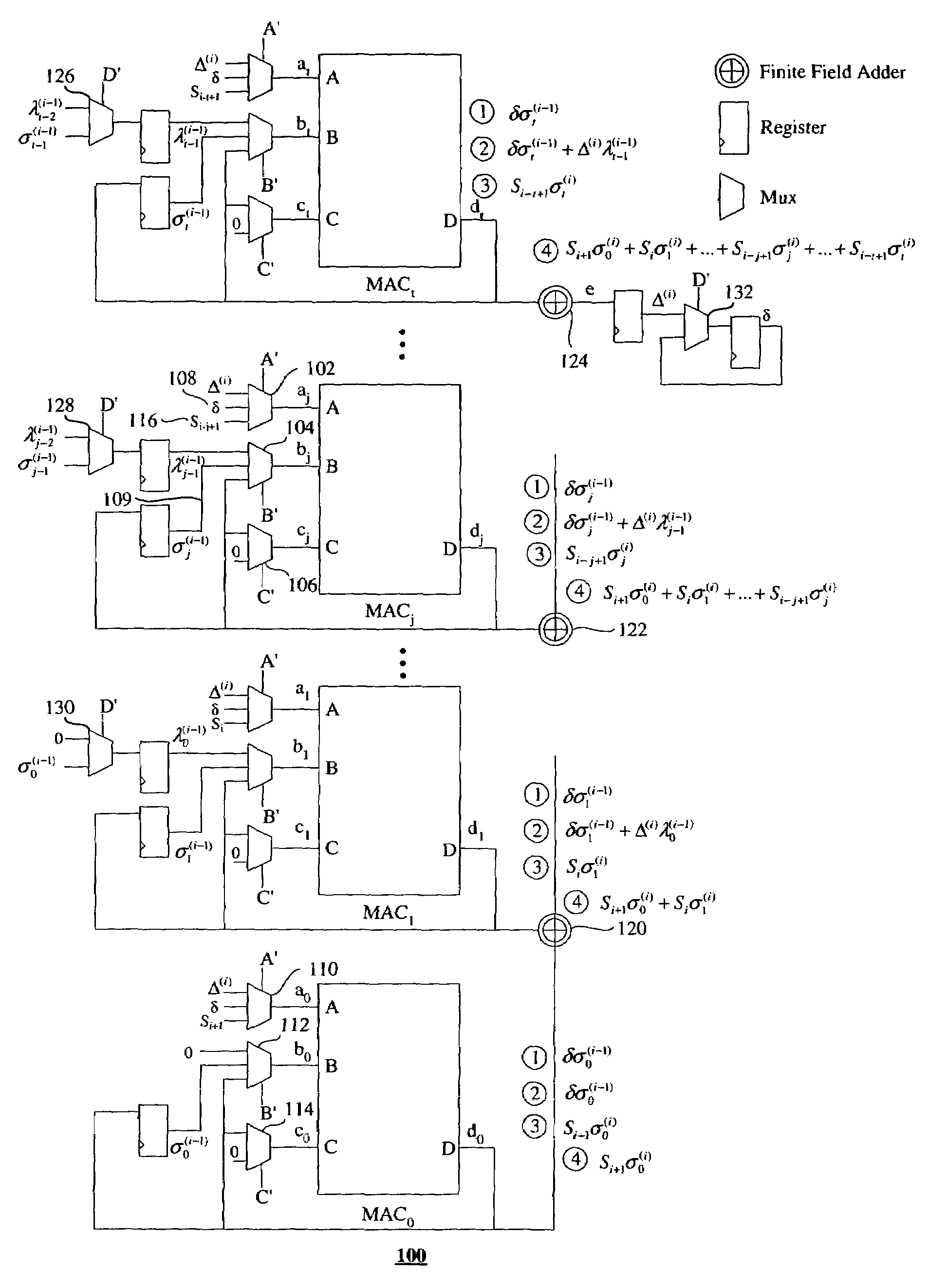
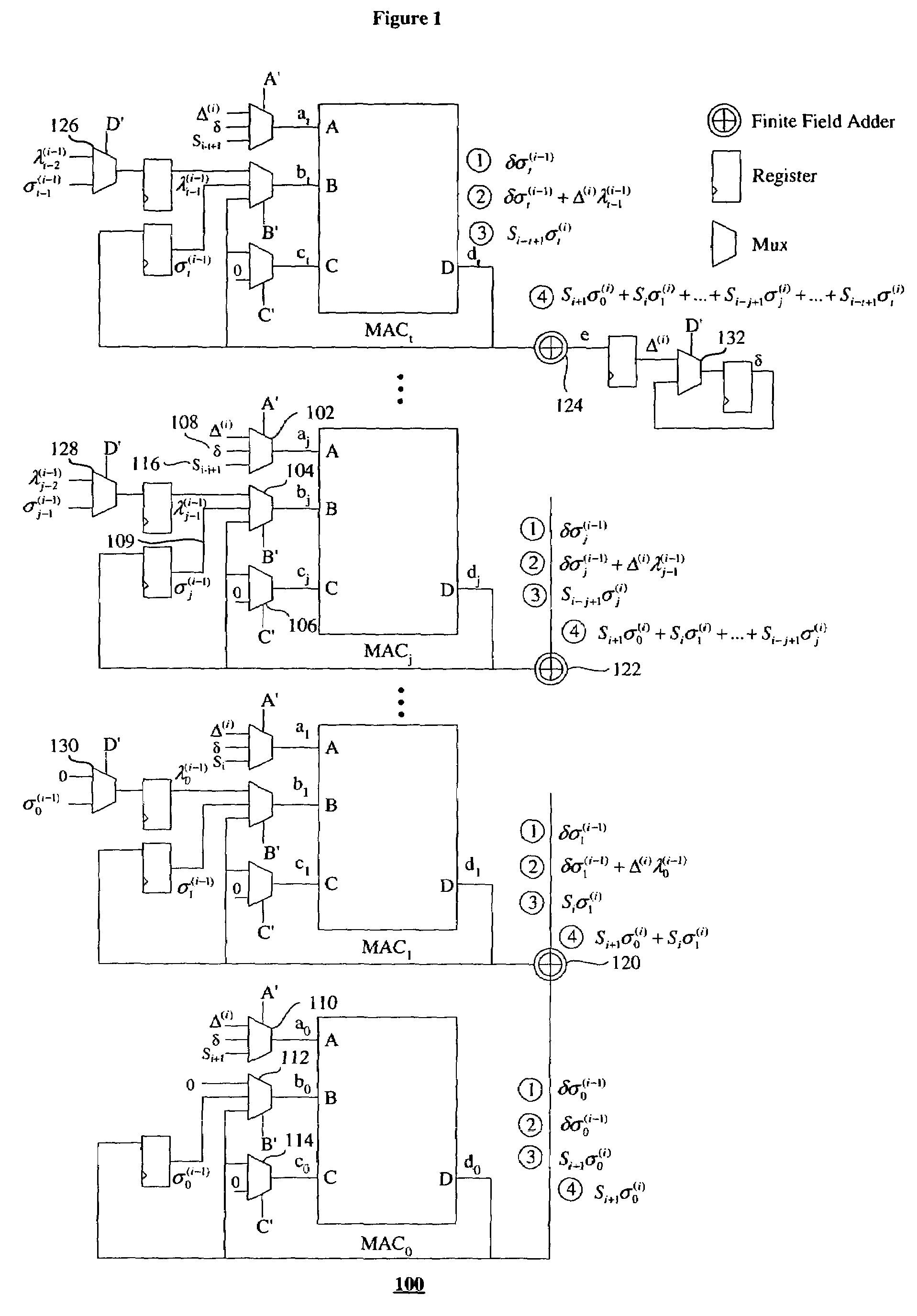
Method for complexing hardware of Reed Solomon code decoder as well as low hardware complex degree decoding device
InactiveCN101277119AReduce consumptionReduce hardware complexityCyclic codesComputer hardwareMultiplexing
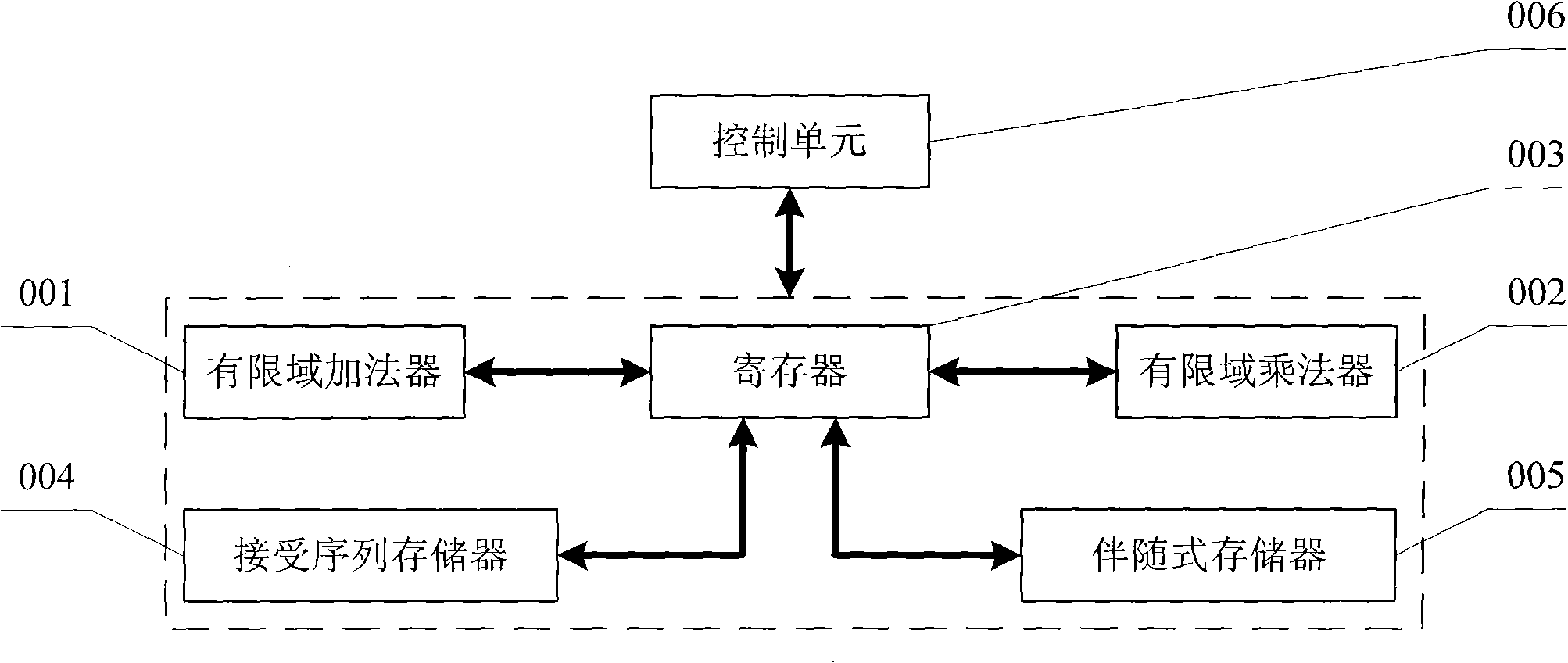
A Reed Solomon code decoder hardware multiplexing method and a low hardware complexity decoding device thereof belong to the technical field of digital information transmission technique. The hardware resource multiplexing method complexes a finite field adder, a finite field multiplier and a register to complete syndrome calculating, syndrome storing, error position polynomial calculating, error value polynomial calculating and error code correcting in the Reed Solomon decoding calculation. The hardware resource multiplexing method is universal to various Reed Solomon decoders with different code rates and parameters. The decoding device comprises the following components: a finite field adder, a finite field multiplier, a register, a receiving sequence memorizer, a syndrome memorizer and the like. The Reed Solomon decoding calculation is realized according to the multiplexing method. The multiplexing method and decoding device disclosed in the invention can evidently reduce the complexity of the hardware for decoding Reed Solomon code.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Low depth combinational finite field multiplier
InactiveUS20120226731A1Easy to testLow overall depthComputation using non-contact making devicesSpecial data processing applicationsBinary multiplierTheoretical computer science
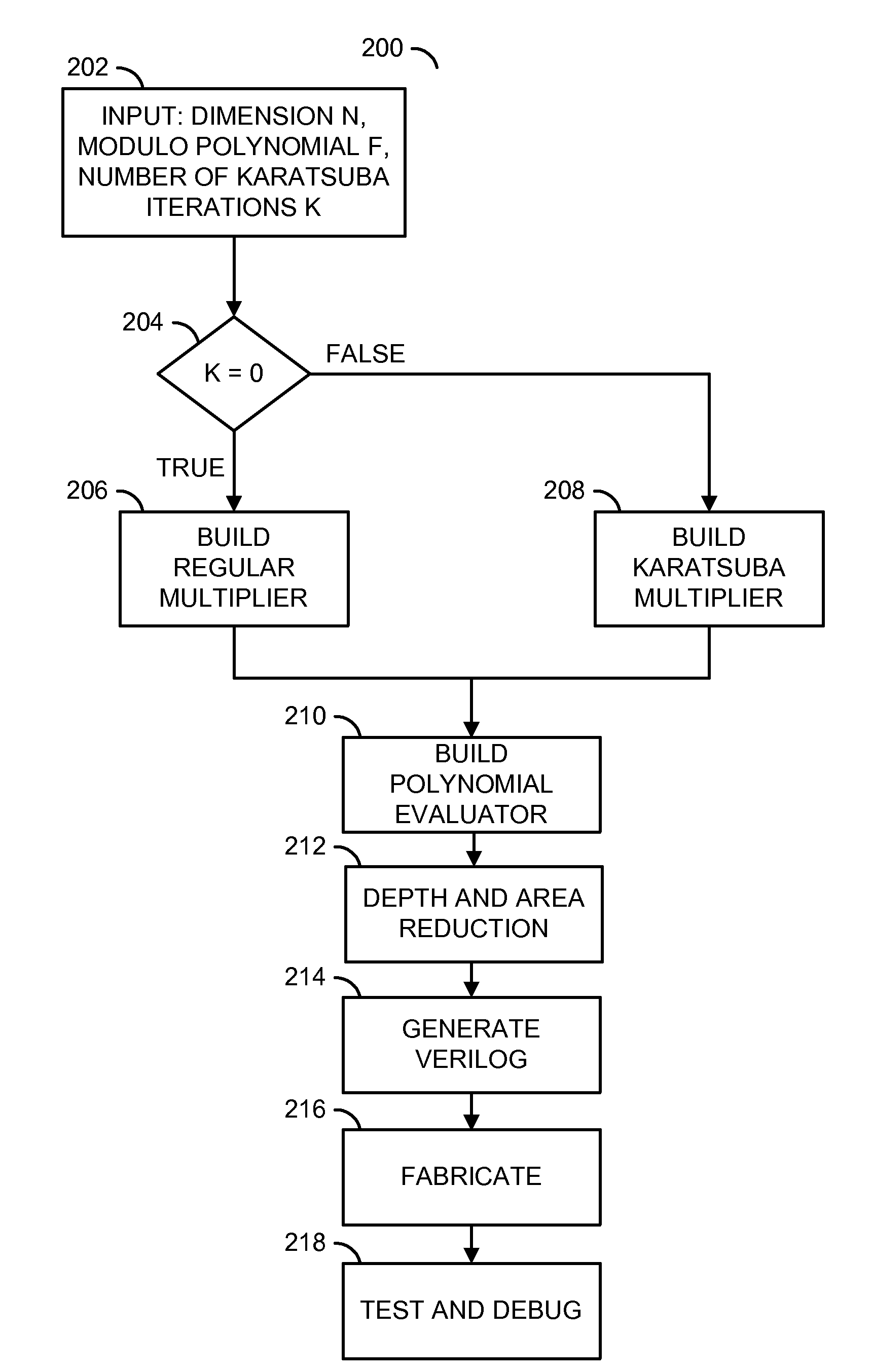
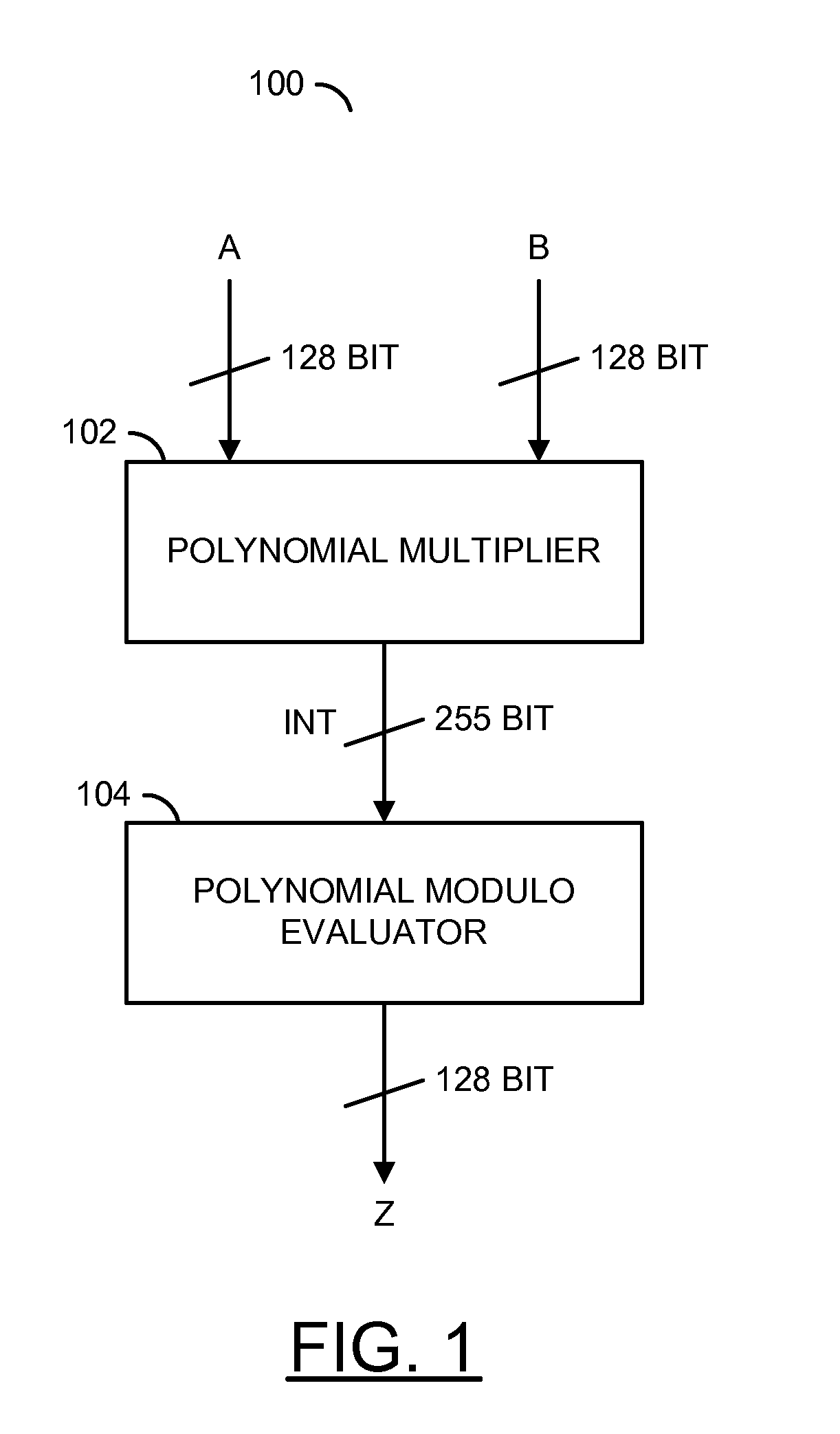
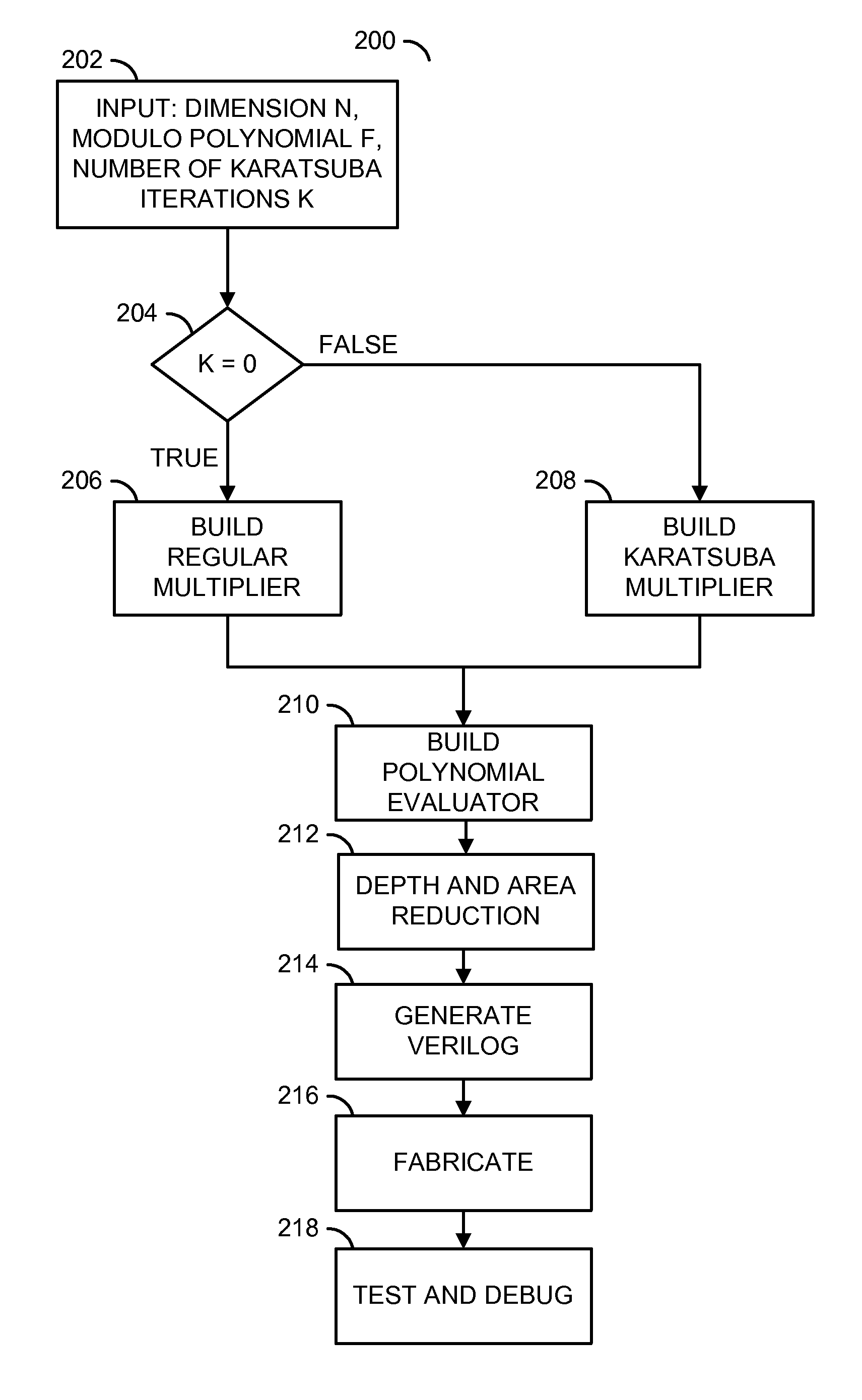
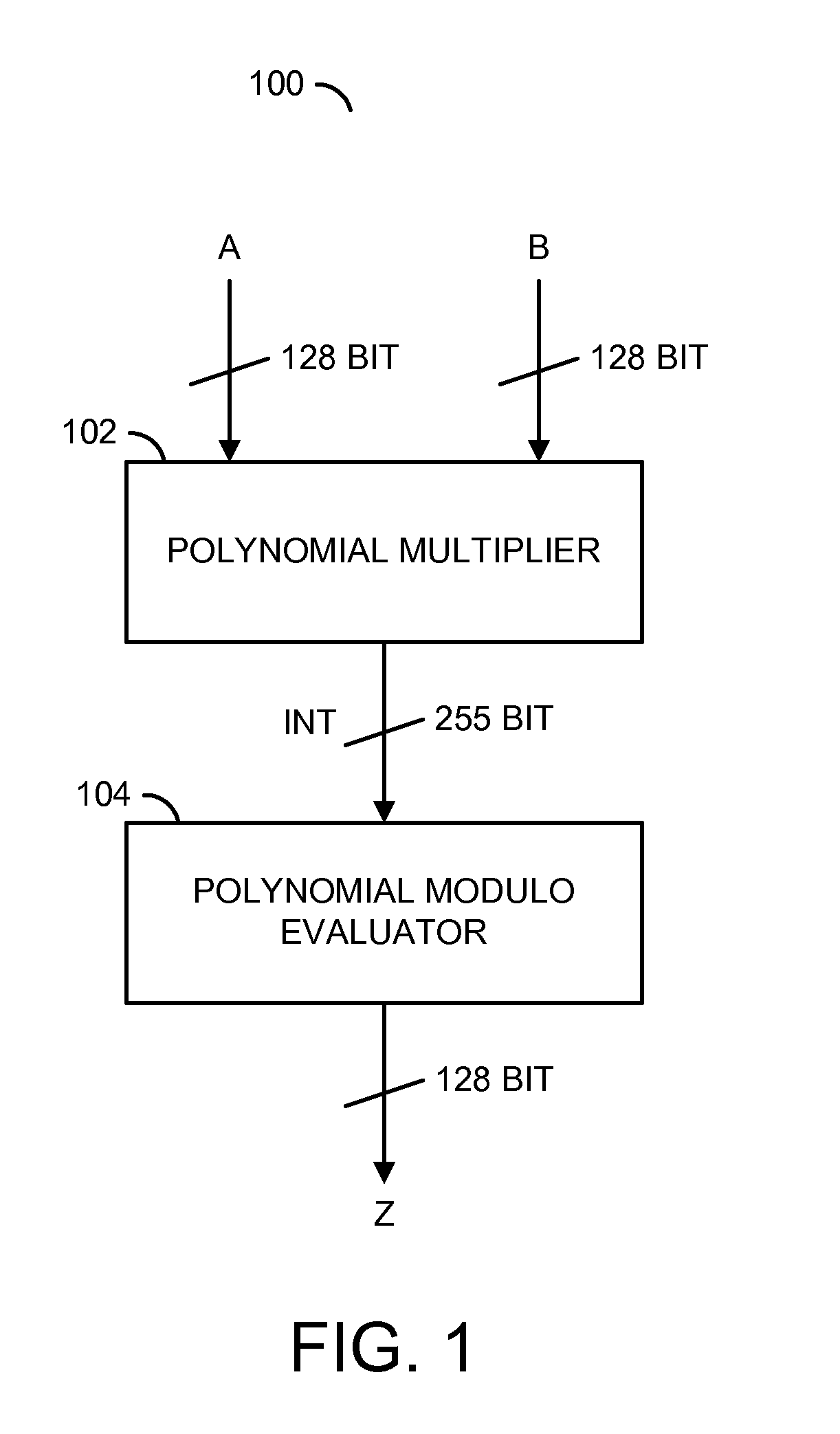
A method for generating a design of a multiplier is disclosed. The method generally includes steps (A) to (C). Step (A) may generate a first circuit comprising a plurality of polynomial results of a particular multiplier scheme based on a plurality of parameters of the multiplier. The first circuit is generally configured to multiply a plurality of polynomials. Step (B) may generate a second circuit comprising a plurality of polynomial evaluators based on the parameters. The second circuit may be (i) connected to the first circuit and (ii) configured to evaluate a polynomial modulo operation. Step (C) may generate the design of the multiplier in combinational logic by optimizing a depth of a plurality of logic gates through the first circuit and the second circuit. A product of the polynomials generally resides in a finite field.
Owner:INTEL CORP
High-performance superscalar elliptic curve cryptographic processor chip
ActiveCN102682232AFast operationEasy programmingPlatform integrity maintainanceComputer hardwareFinite field arithmetic
The invention designs a high-performance superscalar elliptic curve cryptographic processor chip shown as in the figure and relates to the technical fields of information security, encryption and decryption and chips. The chip designed by the invnetion adopts the modern processor superscalar technology,fully utilizes an instruction set to double the operational performance; a high-speed finite field multiplier greatly improves the computational efficiency, and properly solves the performance bottleneck of an elliptic curve cryptographic processor; the instruction set including the finite field arithmetic operation supported by the processor not only ensures that an elliptical curve cryptographic algorithm is more convenient to realize, but also makes necessary preparation for the future standardization; and the chip has a wide application prospect in the fields requiring information security, such as finance, communication and national defense.
Owner:赛芯半导体技术(北京)有限公司
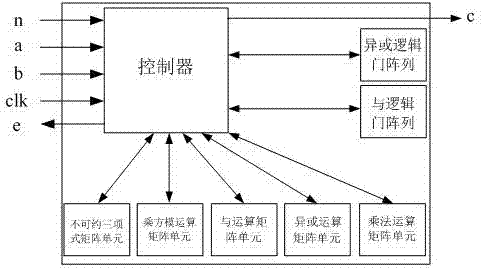
Finite field multiplier based on irreducible trinomial
InactiveCN107015782AObvious speed advantageDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierExclusive or
The invention provides a finite field multiplier based on an irreducible trinomial. The multiplier comprises a controller, an input port, an output port, an exclusive or logic gate array, an and logic gate array, an irreducible trinomial matrix, a power modular arithmetic matrix, an and operation matrix, an exclusive or operation matrix and a multiplication operation matrix; the input port comprises a port for inputting a multiplication operand a(x), a port for inputting a b(x), a port for inputting the size of GF(2n) where the multiplication is located, and a port for inputting a clock signal; the output port comprises a port for outputting a multiplication result c(x), and a port for outputting feedback information about whether operation is within the multiplier operation range or not; the controller comprises a processor and an analyzer which are connected and is connected with the other components; the irreducible trinomial matrix stores the irreducible trinomial on different GF(2n); the and operation matrix stores the and operation results among bits of the a(x) and bits of the b(x). Compared with an existing multiplier, the finite field multiplier has the obvious speed advantage on multiplication on GF(2n) calculation.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
Raid environment incorporating hardware-based finite field multiplier for on-the-fly xor
InactiveUS20080040646A1Reduce in quantityImprove parallelismError detection/correctionStatic storageRAIDParallel computing
A hardware-based finite field multiplier is used to scale incoming data from a disk drive and XOR the scaled data with the contents of a working buffer when performing resync, rebuild and other exposed mode read operations in a RAID or other disk array environment. As a result, RAID designs relying on parity stripe equations incorporating one or more scaling coefficients are able to overlap read operations to multiple drives and thereby increase parallelism, reduce the number of required buffers, and increase performance.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
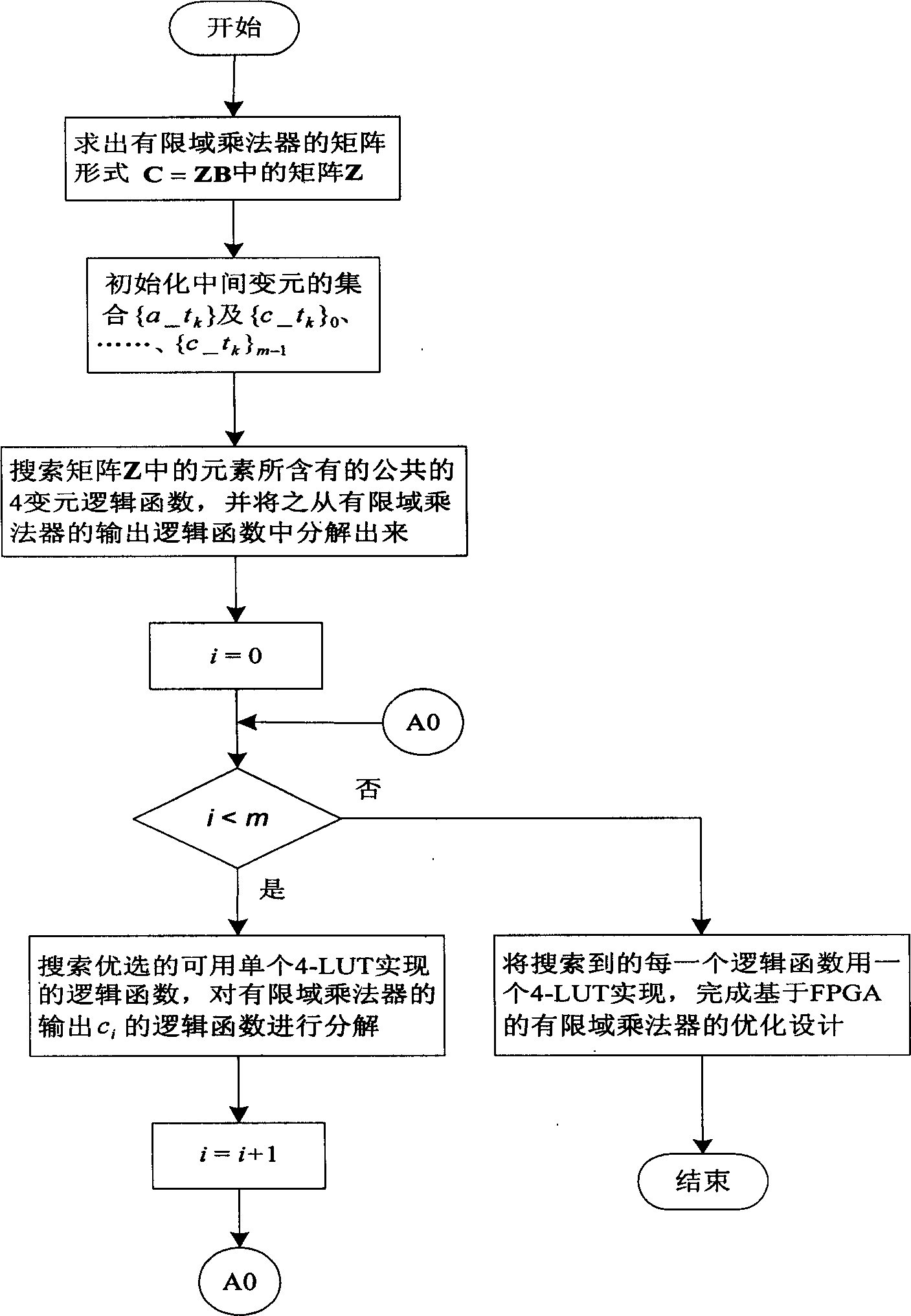
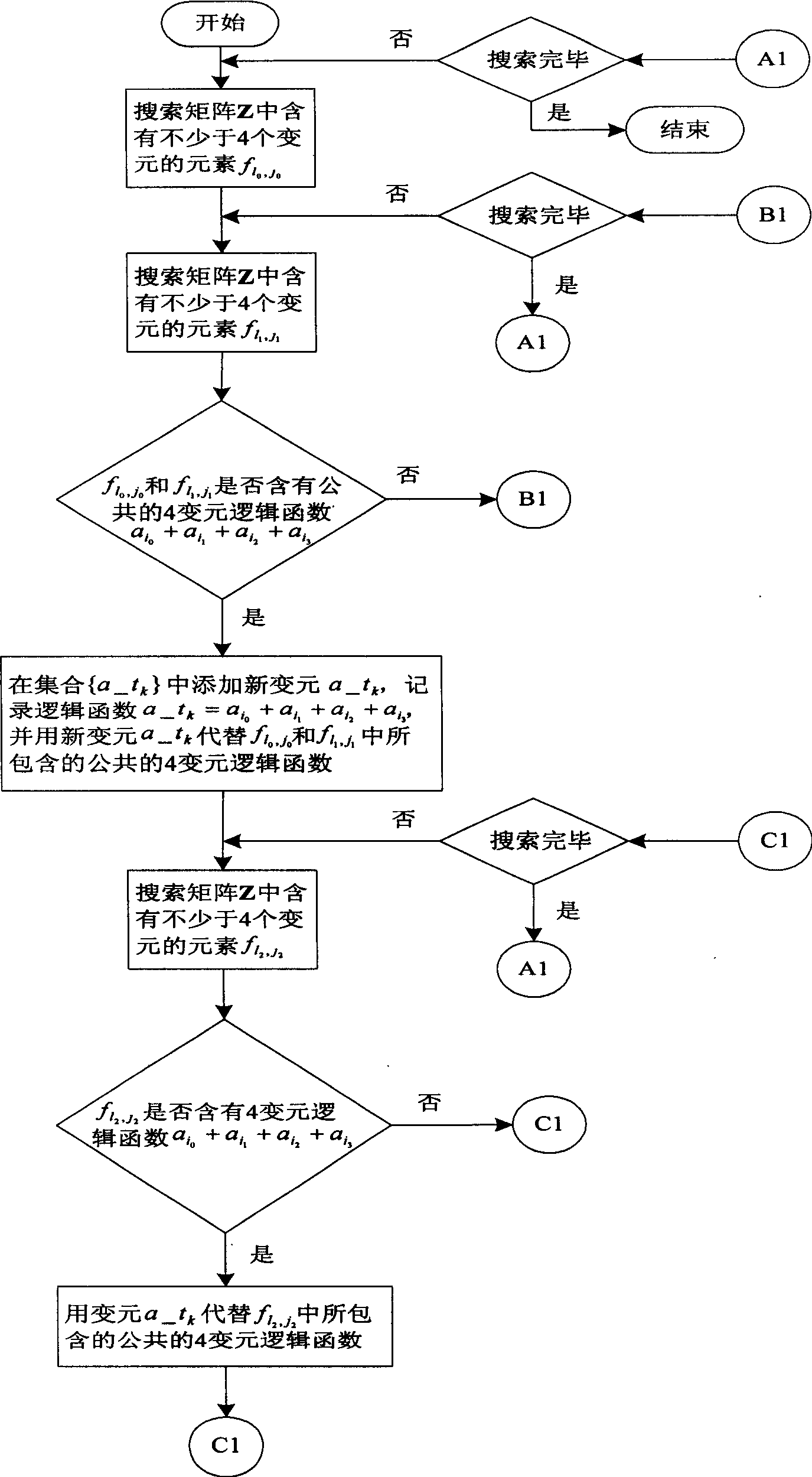
Optimization design method based on FPGA finite field multipier
InactiveCN1658200AShorten the lengthReduce resource usageSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceCritical path method
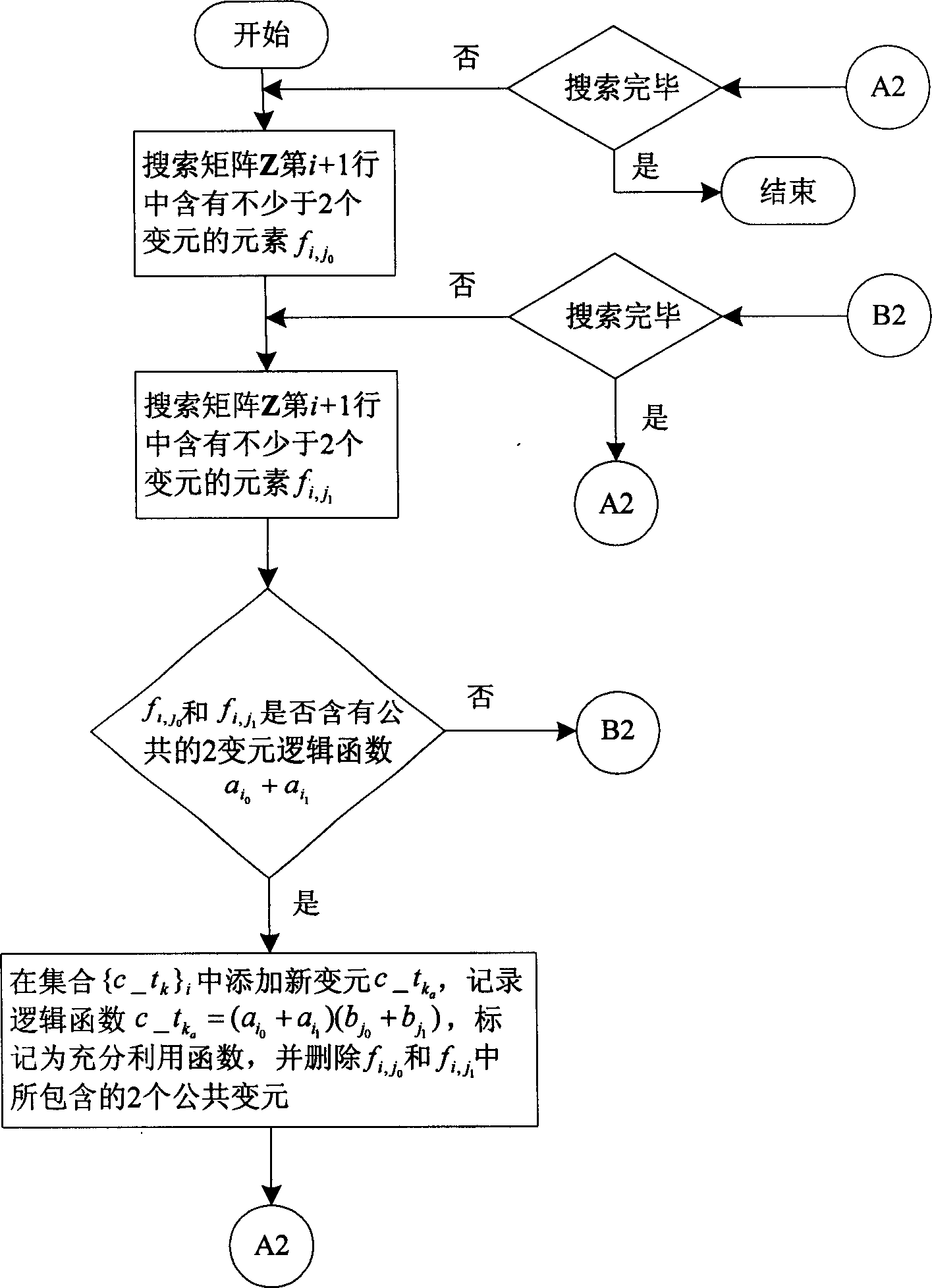
This invention discloses a optimum design method for the finite field multiplier on the base of FPGA. This invention defines those logic functions which can be realized with a single 4-LUT into 7 styles, and it will follow some steps to realize the optimization for the finite field multiplier. Firstly, it figures out the matrix form of the finite field multiplier according to the generator polynomial and initialize the integration of middle variables. Secondly, it will repeatedly search for the common logic functions in the elements in the Matrix Z, bringing in a new middle variable, and it will use this new middle variable to represent the output variable of those logic functions, modifying the Matrix Z. Finally, it will find out preferred logic functions that can be realized by a single 4-LUT. Then those logic functions will be decomposed into a series of logic functions that can be realized by a single 4-LUT, and Matrix Z and the integration of middle variables will be modified. After all above, we finally get a optimized finite field multiplier on the base of FPGA. The advantages are short key route and time delay.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Serial finite field multiplier
ActiveUS6917218B2Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsArray data structureTheoretical computer science
The present invention relates to a finite field multiplier used for implementing an encrypting algorithm circuit, thereby minimizing power consumption and circuit area in implementing the finite field multiplier with a LFSR (Linear Feedback Shift Register) structure. The Finite field multiplier of the present invention is an operator performing a modular operation on the multiplication result of two data represented on a polynomial basis in a Galois Field into an irreducible polynomial. The LFSR structure is a serial finite field multiplication structure, and has a merit over an array structure and a hybrid structure in application to systems that are limited in size and power due to its simplicity of circuits and also its capability of being implemented in a small size.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
General finite-field multiplier and method of the same
InactiveUS6925479B2Facilitate performance improvementsDigital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticBinary multiplierField element
A general finite-field multiplier and the method of the same are disclosed for the operation of the finite-field multipliers of various specifications. In the multiplier, AND gates and XOR gates are used as primary components, and the inputs include two elements A and B to be multiplied and the coefficients of a variable polynomial p(x). This multiplier can be applied to the finite-field elements of different bit number. After all the coefficients of the A, B and p(x) are input, the values of a desired C can be obtained rapidly. Since the output values are parallel output, the application is very convenient. Furthermore, the multiplier can be used in the RS chip for different specifications.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
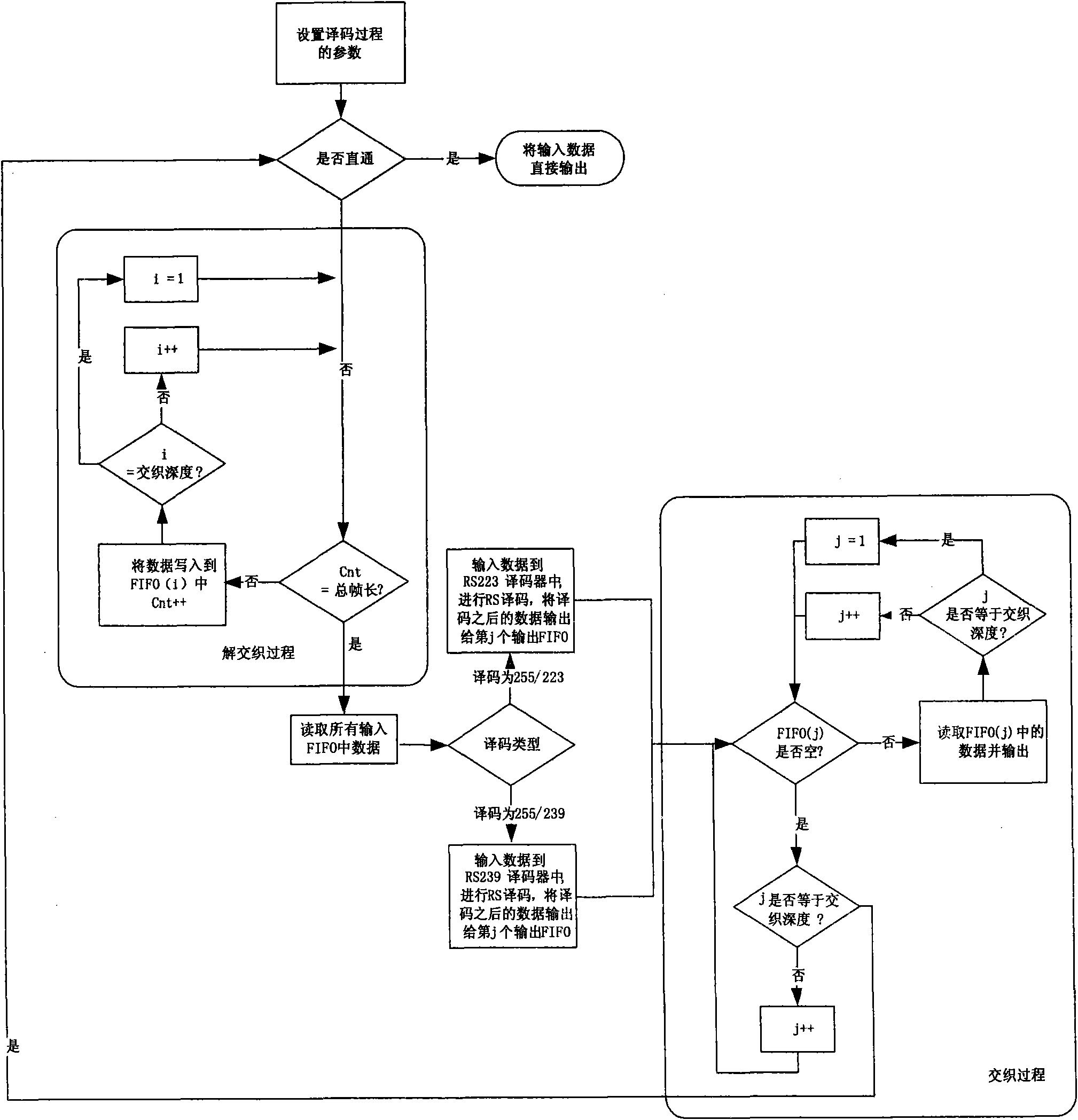
High-speed parallel RS decoding method for space communication
ActiveCN101969358AFlexibility to adapt to encoding formatsMinimizeError preventionData systemDegree of parallelism
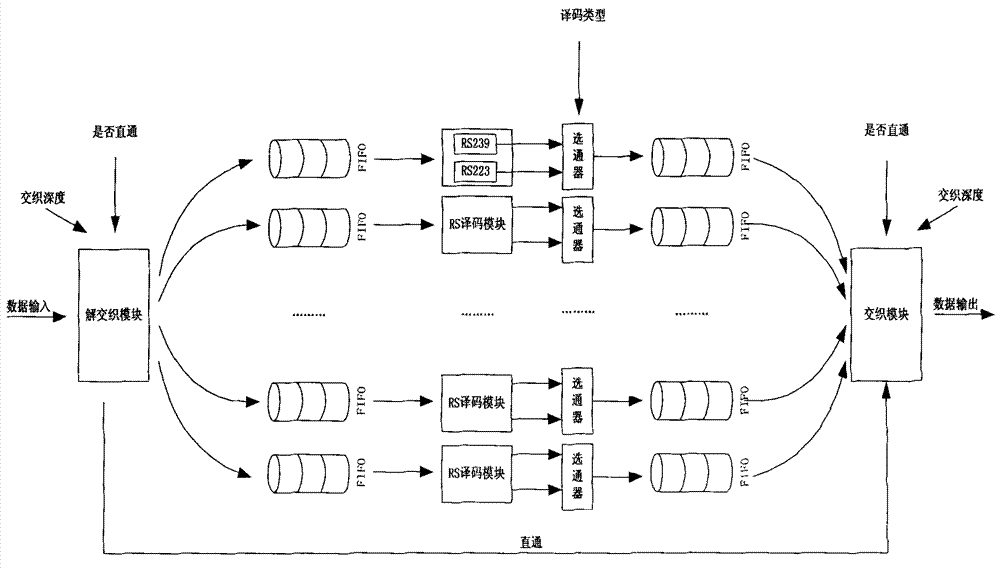
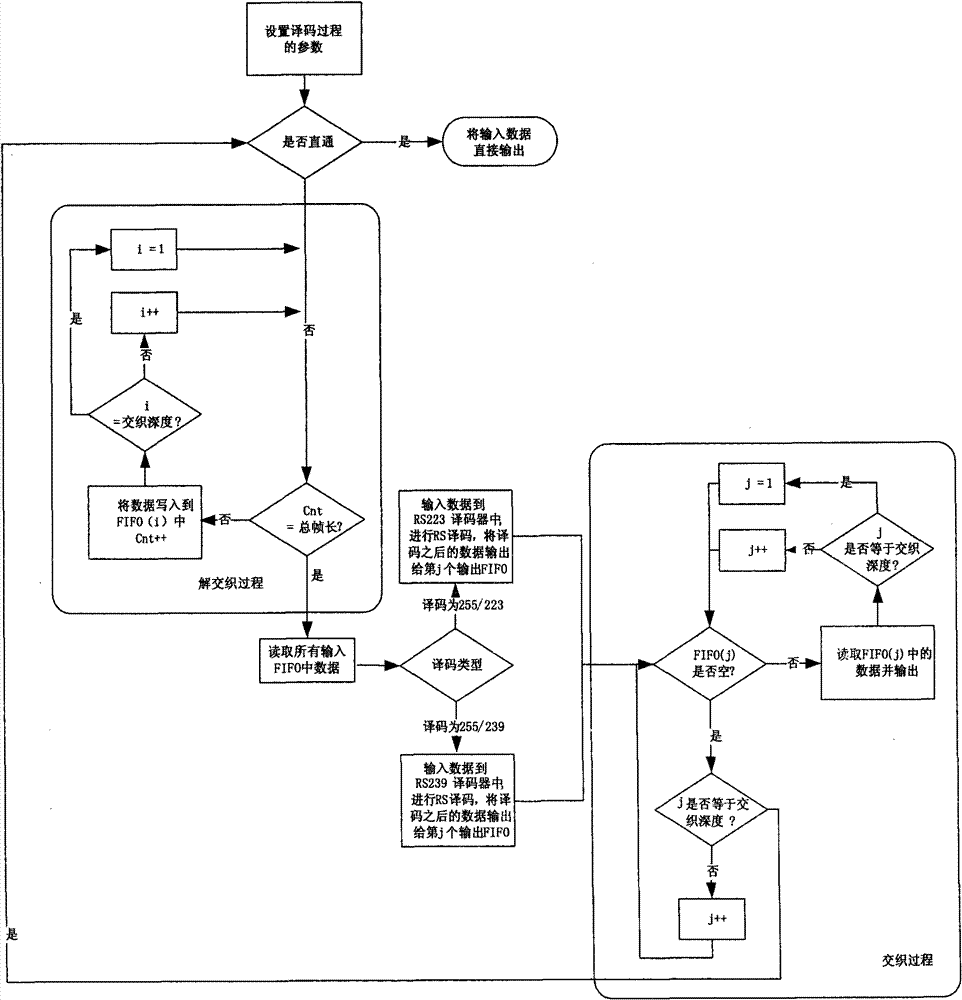
The invention relates to a high-speed parallel Reed-Solomon (RS) decoding method for space communication. In the method, two decoding modules RS (255, 223) and RS (255, 239) are configured simultaneously, so that a decoder can configure decoding types on line according to coding parameters to flexibly adapt to two coding formats specified by the consultative committee for space data system (CCSDS) standard; input data is filled and acquired in first in first out (FIFO) by ping-pong operation during deinterlacing and interlacing, a multi-channel parallel pipeline mode is adopted during decoding, and a composite structure ensures the maximization of system performance and realizes the minimization of resources and is suitable for 1 to 8 arbitrary interlacing depths; and measures such as multi-channel parallel RS decoding, the optimization of realization logic of a finite field multiplier, and the like are adopted, so that decoding rate is greatly improved. The method can be directly applied to a high-code-rate remote sensing satellite ground receiving system and can further increase parallelism degree and improve performance when necessary by modular design.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
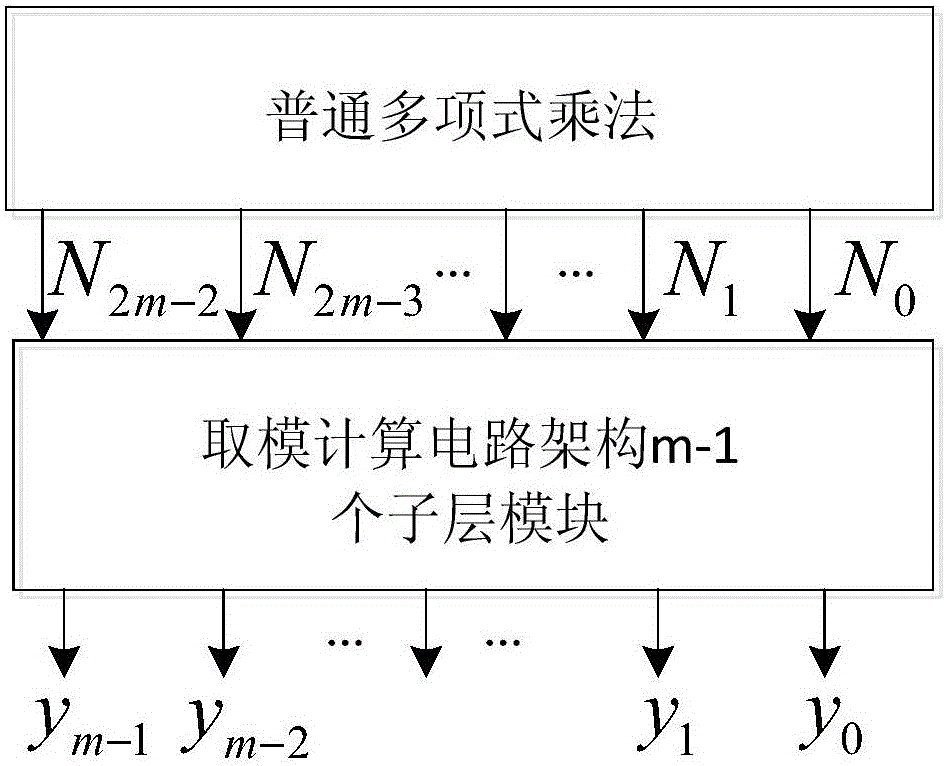
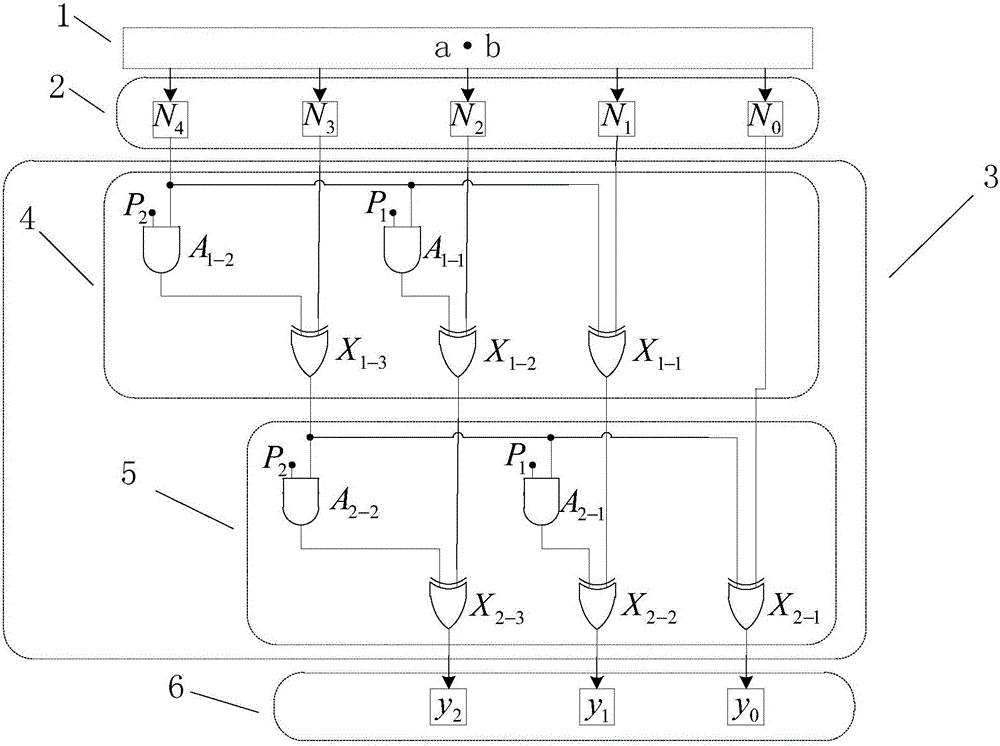
Finite field multiplier based on RS (reed-solomon) code
ActiveCN106201433ASatisfy the urgent need of easy-to-implement designSatisfy urgent needs that are easy to implementComputation using non-contact making devicesCommunications systemTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a finite field multiplier based on an RS (reed-solomon) code. The finite field multiplier based on the RS code is composed of two partial operations, firstly a common polynomial multiplication is carried out, and the obtained result is a polynomial with the highest order of 2m-2, wherein m is bit width of two finite field multipliers; and secondly, modular operation is carried out on the primitive polynomial p(x) by adopting the product polynomial, and the obtained remainder coefficient is namely final result of a finite field multiplication. The invention innovatively provides a two-step implementation method of the finite field multiplier. A modulus calculating circuit is composed of sublayers of the same structures, structure is regular, expansion is easy, engineering realization is applicable, the finite field multiplier with any bit width can be realized by regulating sublayers in a modulus obtaining circuit framework, and the finite field multiplier is especially applicable to error control code field such as application of the RS code and can meet urgent demand of easy implementation of VLSI (very large scale integration) design in a communication system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Finite field multiplier based on binary tree structure
InactiveCN106909339AImplement multiplicationSimple structureComputation using non-contact making devicesNODALTheoretical computer science
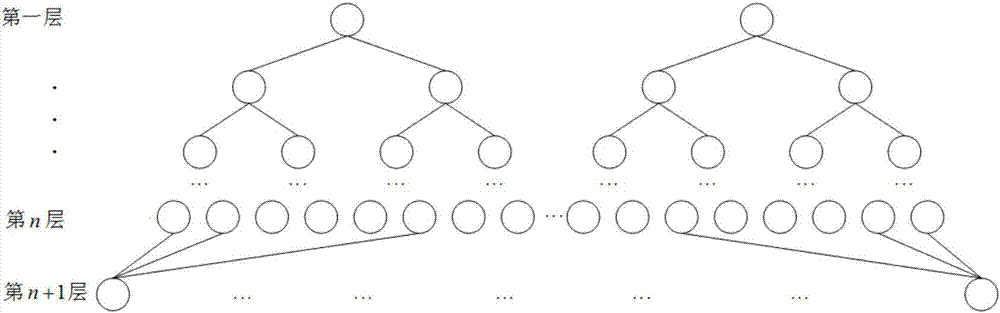
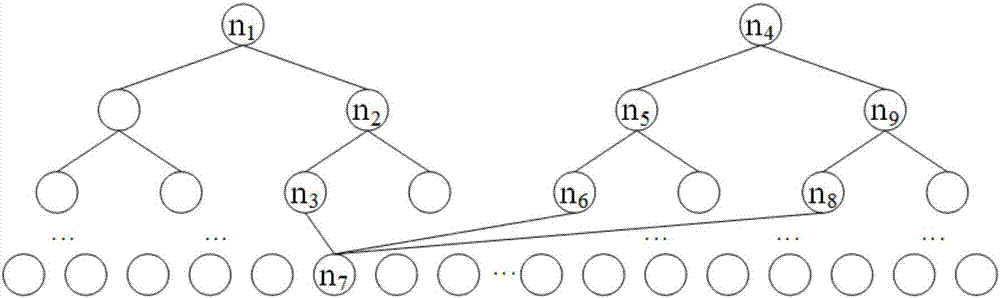
The invention provides a finite field multiplier based on a binary tree structure. The finite field multiplier comprises an input port used for inputting the operand a(x) and the operand b(x) of a finite field GF(2<n>), an output port used for outputting the multiplying result c(x) of the operand a(x) and the operand b(x), and a binary tree structure used for executing the multiplying of GF(2<n>) with the operand a(x) and the operand b(x). The binary tree structure comprises n+1 layers, from top to bottom, the layers numbered from 1 to n include a left binary tree and a right binary tree, and the bottommost layer is the (n+1)th layer; each node of the (n+1)th layer is connected with three nodes of the nth layer. Multiplying of the finite field is achieved with the binary tree structure, the structure is simple, and the finite field multiplier has obvious speed advantages in multiplying of GF(2<n>) compared with an existing finite field multiplier, and can be widely applied to various engineering fields.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
Data processing system and method
ActiveUS20050050131A1Favourable area-latency productLower areaCode conversionDigital computer detailsData processing systemFinite field arithmetic
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a data processing system comprising a first arithmetic unit comprising at least one finite field multiplier and at least one finite field adder for selectively performing at least two finite field arithmetic calculations; the data processing system comprising means to use a previous finite field arithmetic calculation result in a current finite field arithmetic calculation to determine at least part of a polynomial.
Owner:NXP BV
Low power elliptical curve encryption engine for electronic label rapid identity discrimination
InactiveCN105471855AEnsure safetyIncrease added valueMemory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsComputer hardwareMontgomery ladder
The invention belongs to the radio frequency identification technology field and particularly relates to a low power elliptical curve encryption engine for rapid electronic label identity discrimination. The ECC encryption engine comprises an arithmetic operation module, a register set module and a logic control module, wherein the arithmetic operation module comprises three sub modules of a finite field adder, a finite field multiplier and a finite field square arithmetic unit. Batch labels can be rapidly identified by employing the low power technology in combination with algorithm simplification, elliptical curve system configuration optimization and module realization; elliptical curve engine design can not only guarantee communication safety of labels and reader-writers, and design requirements in speed, area and power consumption can be further satisfied. The ECC encryption engine is suitable for realization schemes based on the Lopez-Daha elliptical curve system and the Montgomery step algorithm, effective support is provided for rapid false-proof verification on high additional value articles, and thereby article flow safety is enhanced.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
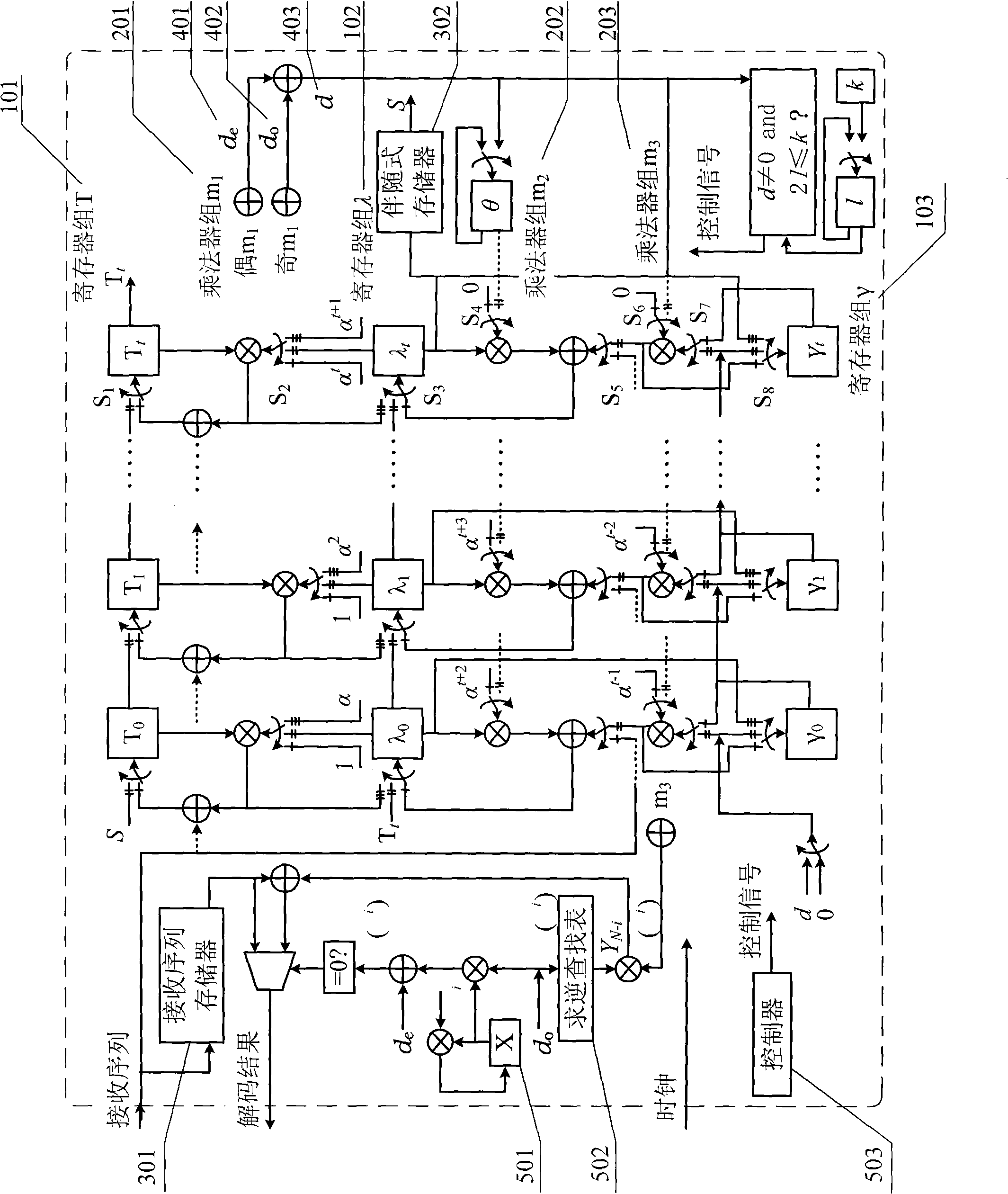
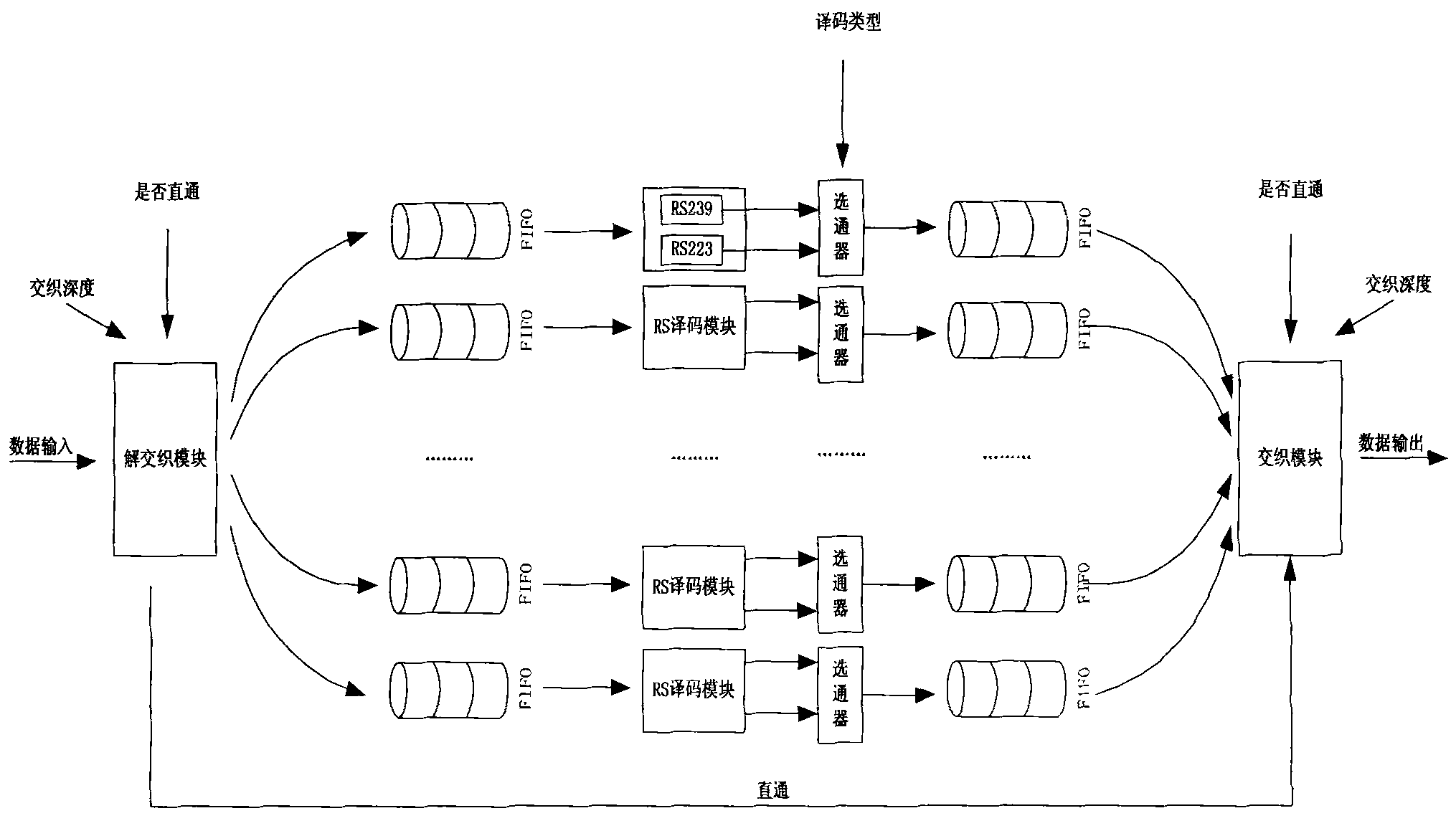
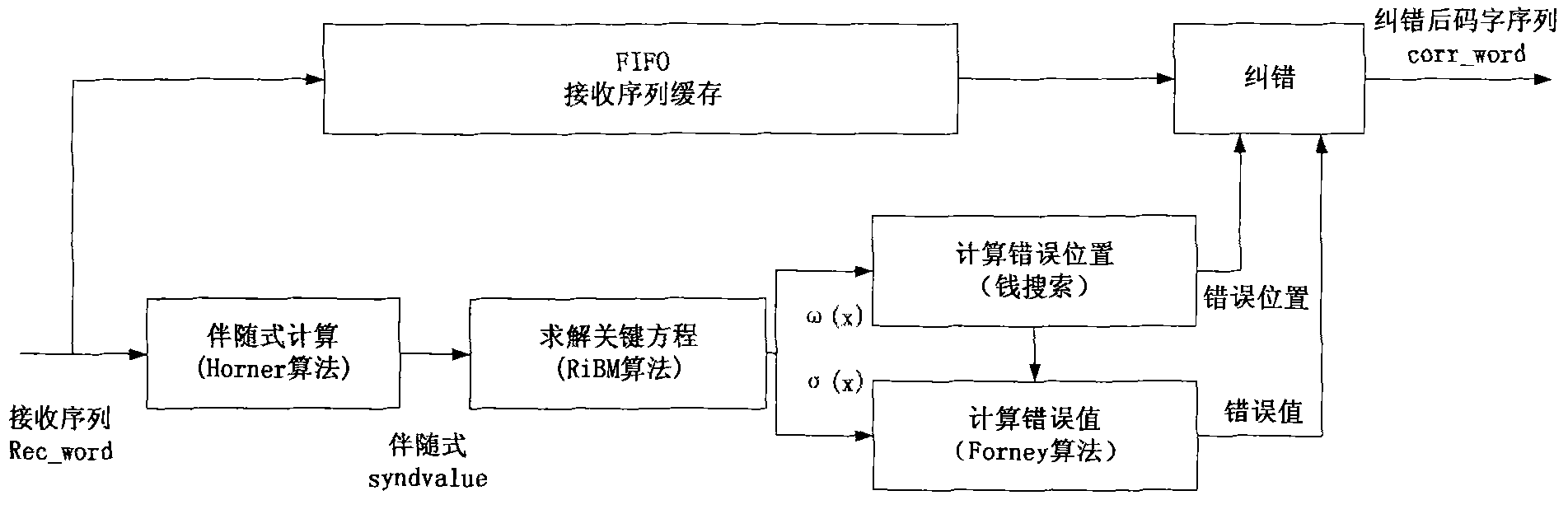
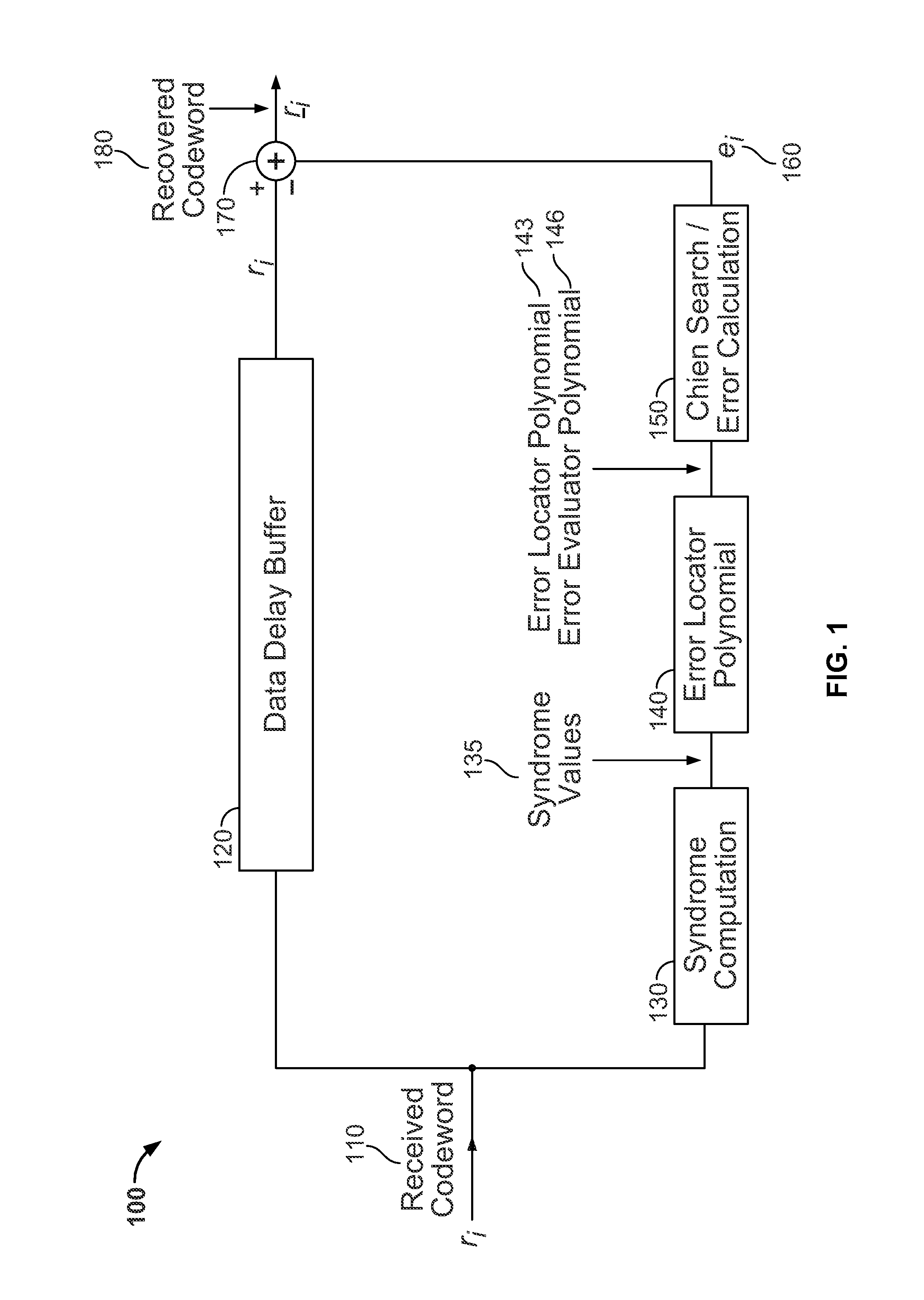
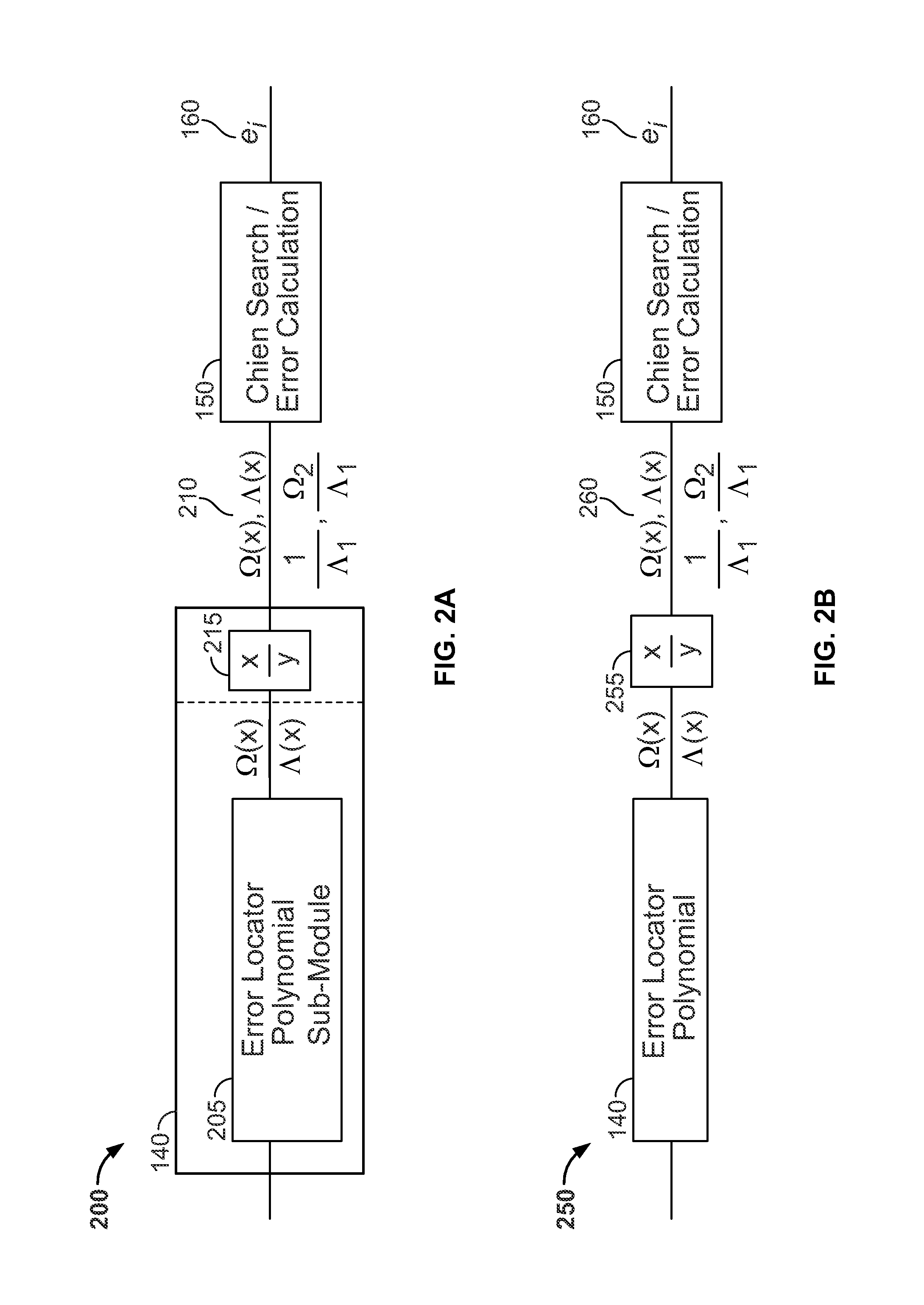
RS decoder low in hardware complexity
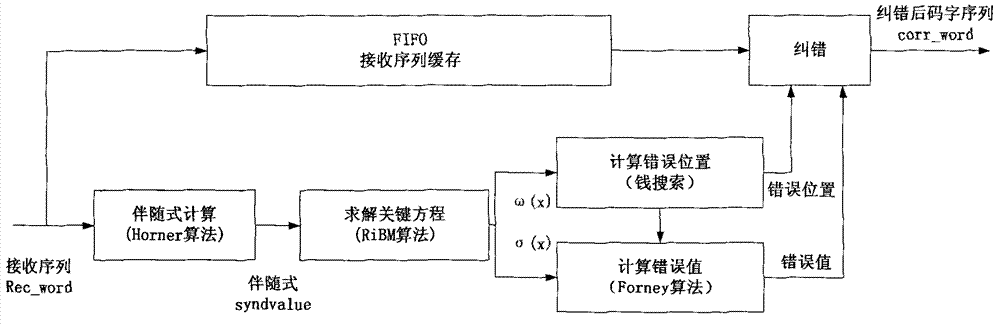
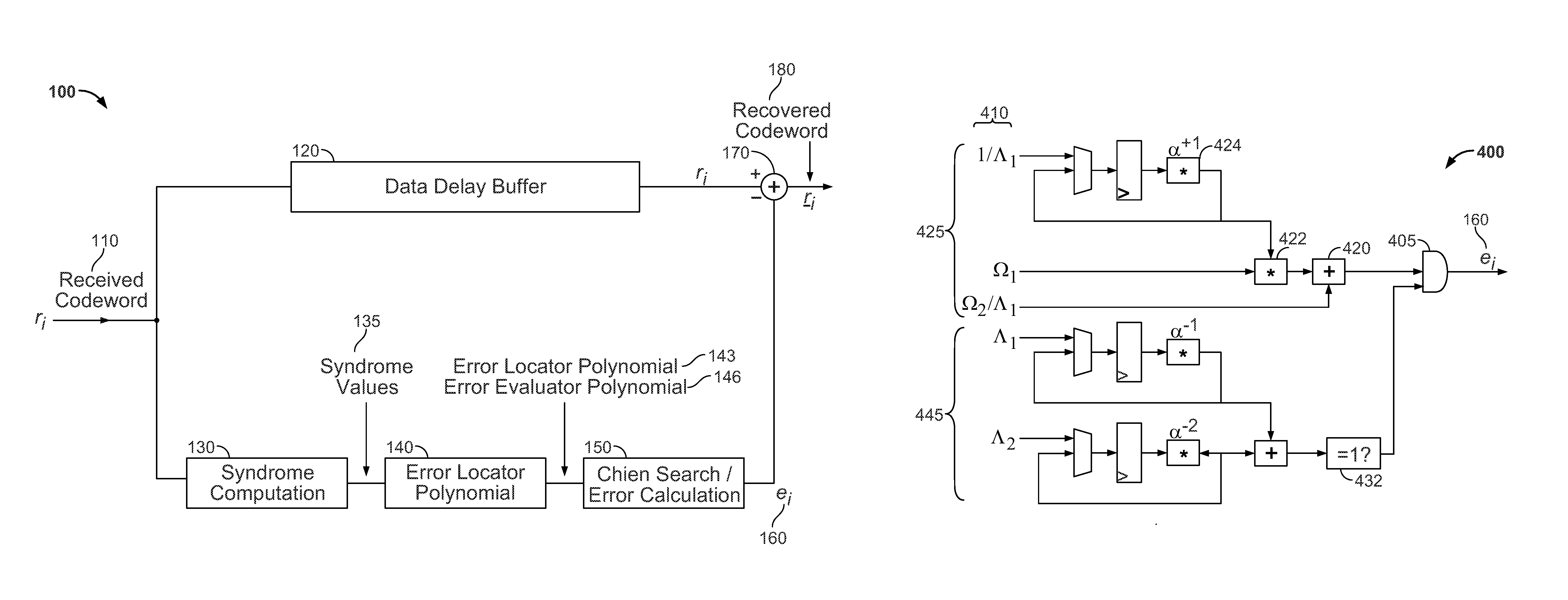
The invention discloses an RS decoder low in hardware complexity. Received code words are stored; syndrome polynomial coefficient of the code words is calculated by utilizing Horner rules and used for time division to realize a chien searching function, and an error position is determined; polynomial coefficient of the error position is iteratively calculated according to the syndrome polynomial coefficient through a decomposed non-inversion Berlekamp-Massey algorithm, and polynomial calculation of an error estimated value is realized according to syndrome polynomial and error position polynomial time division; an error value on the error position is calculated; corresponding code words in a synchronous FIFO are corrected according to the error position and the error value. According to an iBM algorithm in the form of decomposition, inversion operation is eliminated during iterative solving of error position polynomial, and iteration is performed through decomposition, so that number of finite field multipliers is reduced, hardware complexity is lowered, hardware resources are saved to a great extent, and area and power consumption of a decoder chip is reduced.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
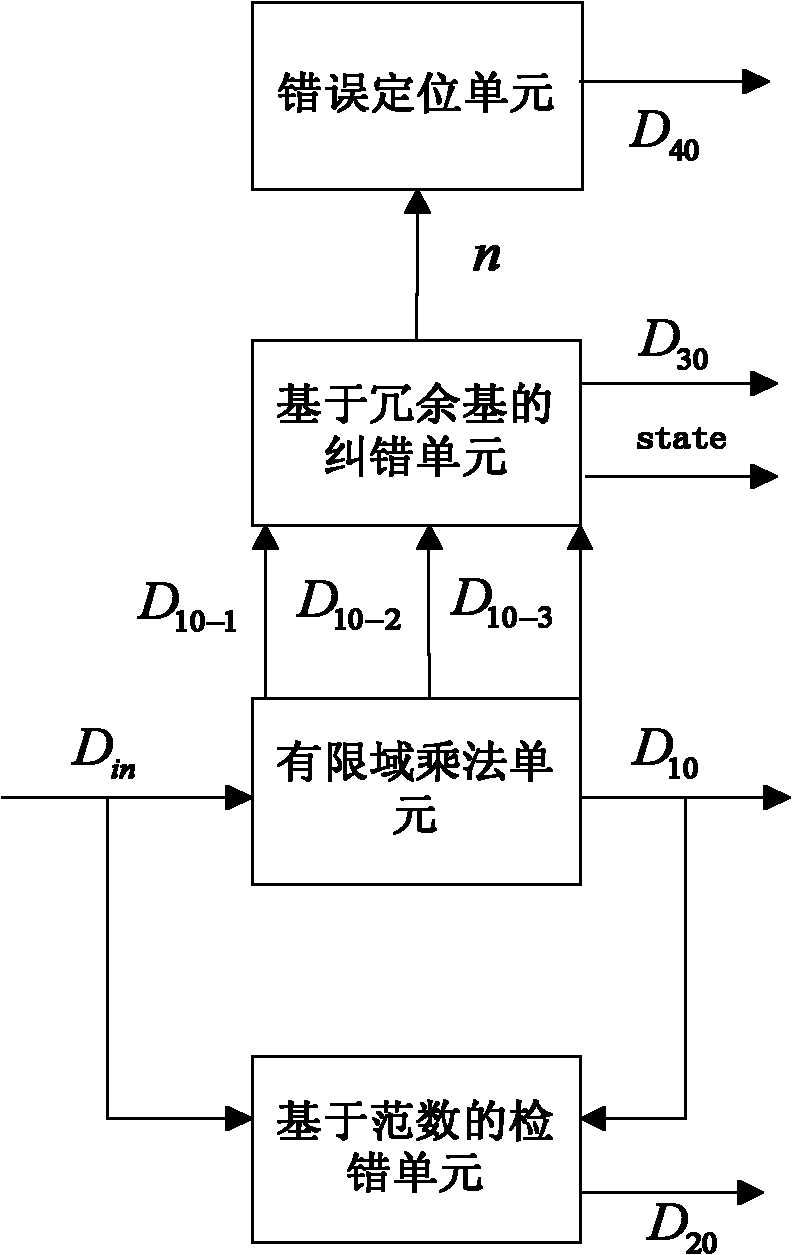
Implementation method of finite field multiplying unit with functions of detecting, correcting and locating error
InactiveCN102073477AIncrease data processing rateStrong error detection abilityError correction/detection using linear codesComputations using residue arithmeticComputer scienceCorrection code
The invention provides an implementation method of a finite field multiplying unit with functions of detecting, correcting and locating an error. The finite field multiplying unit comprises an error locating unit, an error correction unit based on a redundant base, a finite field multiplication unit and an error detecting unit based on norm; and the finite field multiplying unit has the functions of detecting, correcting and locating the error. The finite field multiplying unit generated by the method has the function of locating the error so as to be convenient for dealing with hardware failure, and has the function of error correction so as to effectively resist the failure attack of an opponent.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Raid environment incorporating hardware-based finite field multiplier for on-the-fly xor
InactiveUS20080040416A1Reduce in quantityImprove parallelismDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionRAIDParallel computing
A hardware-based finite field multiplier is used to scale incoming data from a disk drive and XOR the scaled data with the contents of a working buffer when performing resync, rebuild and other exposed mode read operations in a RAID or other disk array environment. As a result, RAID designs relying on parity stripe equations incorporating one or more scaling coefficients are able to overlap read operations to multiple drives and thereby increase parallelism, reduce the number of required buffers, and increase performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
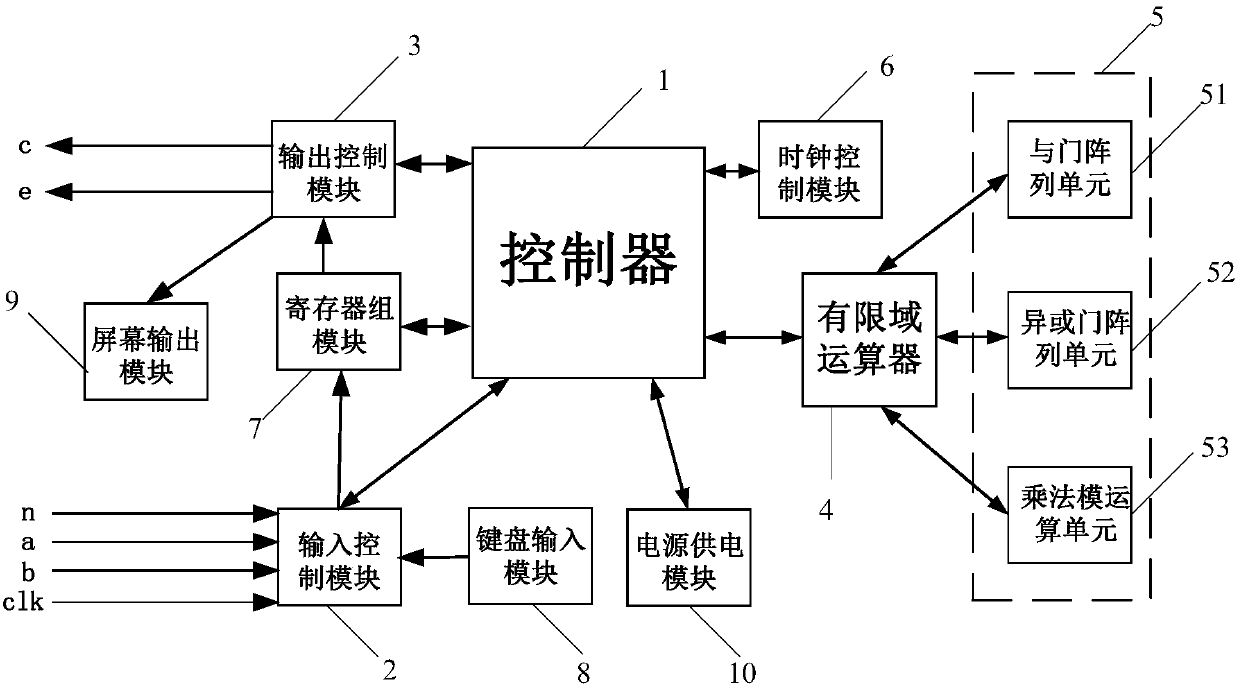
All-in-one irreducible polynomial based finite field multiplier
The invention relates to an all-in-one irreducible polynomial based finite field multiplier which comprises a controller, an input control module, an output control module, a finite field multiplier and an operation module, wherein the controller is used for controlling and scheduling data transmission among the input control module, the output control module and the finite field multiplier; the input control module is used for inputting a multiplication operation number a(x) and a multiplication operation number b(x) when detecting that a finite field GF(2n) has an all-in-one irreducible polynomial; the finite field multiplier is used for calling the operation module to carry out finite field multiplication operation on the multiplication operation number a(x) and the multiplication operation number b(x) to obtain a multiplication operation result c(x); the operation module is used for implementing and logical operation, exclusive or logic operation and modular operation; the output control module is used for outing the multiplication operation result c(x). By adopting the multiplier, the operation efficiency of finite field multiplication is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
High-speed parallel RS encoder and encoding method for consultative committee for space data system (CCSDS) system
ActiveCN103117752AReduce the amount of calculationReduce implementation complexityCyclic codesShift registerData system
The invention provides a high-speed parallel RS encoding scheme for a consultative committee for space data system (CCSDS). The high-speed parallel RS encoder and an encoding method for the CCSDS are characterized in that the encoder is mainly composed of a finite field multiplying unit, a finite field adding device and a shifting register. Change of base is synthesized to a constant coefficient matrix of the finite field multiplying unit, a correctional coefficient matrix is produced, and the process of change of base is removed. The high-speed parallel RS encoder and the encoding method for the CCSDS has the advantages of being low in calculated amount, easy to achieve, capable of effectively reducing calculated amount of encoding and achieving complexity, and capable of improving encoding speed.
Owner:苏州威士达信息科技有限公司
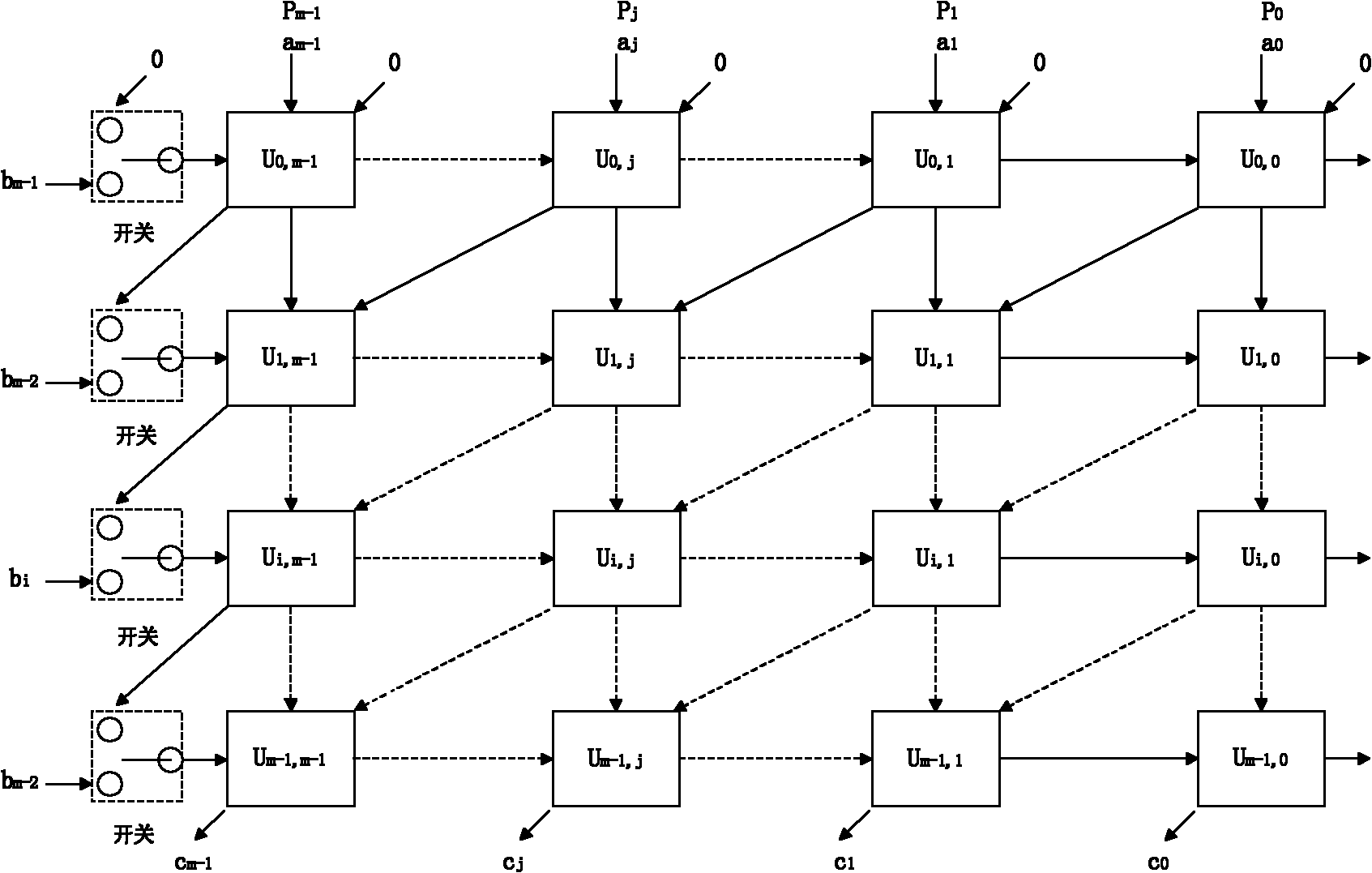
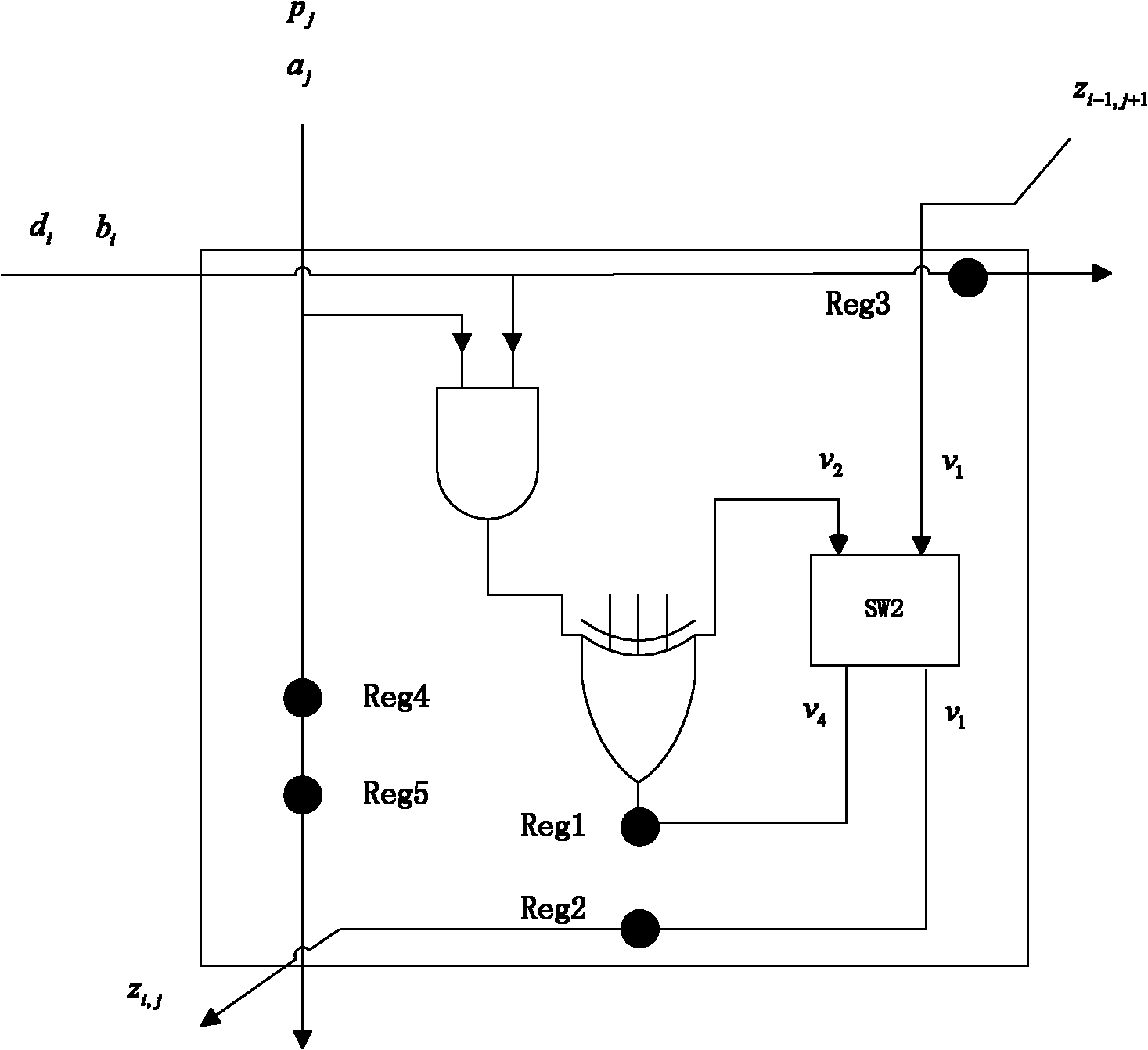
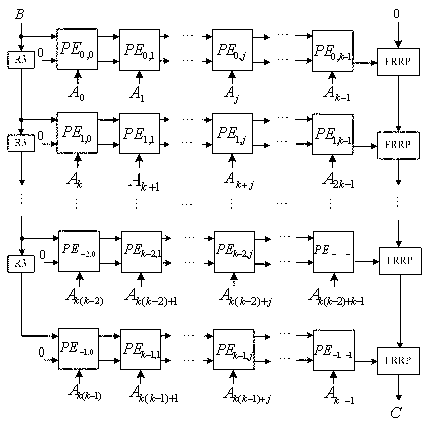
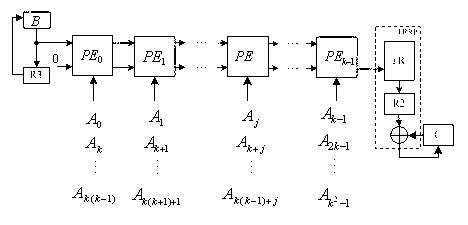
Fast arithmetic multi-bit serial pulse dual-base binary finite field multiplier
InactiveCN103186360AComputation using non-contact making devicesTheoretical computer scienceComputer module
The invention relates to a fast arithmetic multi-bit serial pulse dual-base binary finite field multiplier, comprising an input end B, k PE modules, an FRRP module and an R3 module. The k PE modules are connected in series, the k PE modules pass through k cycles, in the first cycle, the input of A is that B is directly input, and the calculation result is restored and input into a temporary register C through the FRRP module; in the second cycle, the input of A is that B is input through the R3 module, the calculation result is also restored through the FRRP module, and is added to the calculation result of the first cycle and stored in the temporary register C; so, in the k cycle, the input of A is that B is input after passing through the R3 module for (k-1) times, the calculation result is restored through the FRRP module, added to the accumulation result of the previous (k-1) times and stored in the temporary register C, and the temporary register C outputs the result.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Raid environment incorporating hardware-based finite field multiplier for on-the-fly xor
InactiveUS20080040542A1Reduce in quantityImprove parallelismError detection/correctionMemory systemsRAIDParallel computing
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Raid environment incorporating hardware-based finite field multiplier for on-the-fly xor
InactiveUS20080040415A1Reduce in quantityImprove parallelismError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsRAIDParallel computing
A hardware-based finite field multiplier is used to scale incoming data from a disk drive and XOR the scaled data with the contents of a working buffer when performing resync, rebuild and other exposed mode read operations in a RAID or other disk array environment. As a result, RAID designs relying on parity stripe equations incorporating one or more scaling coefficients are able to overlap read operations to multiple drives and thereby increase parallelism, reduce the number of required buffers, and increase performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
Parallel encoder of multi-code rate reed-solomon (RS) codes in china mobile multimedia broadcasting (CMMB) and encoding method
The invention relates to a scheme for solving a problem of parallel encoding of three kinds of reed-solomon (RS) codes in a china mobile multimedia broadcasting (CMMB) system and is characterized in that a parallel encoder of the multi-code rate RS codes of the system is manly composed of four parts including a shifting register, an eight-bit dual-input exclusive-or-gate, a summation array and product selectors. All finite field multiplying units share one 255 multiple-input exclusive-or-gate in the summation array. Each product selector selects eight outputs of the multiple-input exclusive-or-gate to form a result of the finite field multiplying units, and all product selectors completes parallel computation of the 64 finite field multiplying units simultaneously. A single encoder is compatible to three kinds of code rate, is simple in control logic, can greatly reduce resource needs on the premise of keeping encoding speed to be unchanged, and has the advantages of being low in cost, small in power dissipation and the like.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Low depth combinational finite field multiplier
InactiveUS9417847B2Easy to testLow overall depthComputation using non-contact making devicesComputations using residue arithmeticBinary multiplierEngineering
A method for generating a design of a multiplier is disclosed. The method generally includes steps (A) to (C). Step (A) may generate a first circuit comprising a plurality of polynomial results of a particular multiplier scheme based on a plurality of parameters of the multiplier. The first circuit is generally configured to multiply a plurality of polynomials. Step (B) may generate a second circuit comprising a plurality of polynomial evaluators based on the parameters. The second circuit may be (i) connected to the first circuit and (ii) configured to evaluate a polynomial modulo operation. Step (C) may generate the design of the multiplier in combinational logic by optimizing a depth of a plurality of logic gates through the first circuit and the second circuit. A product of the polynomials generally resides in a finite field.
Owner:INTEL CORP
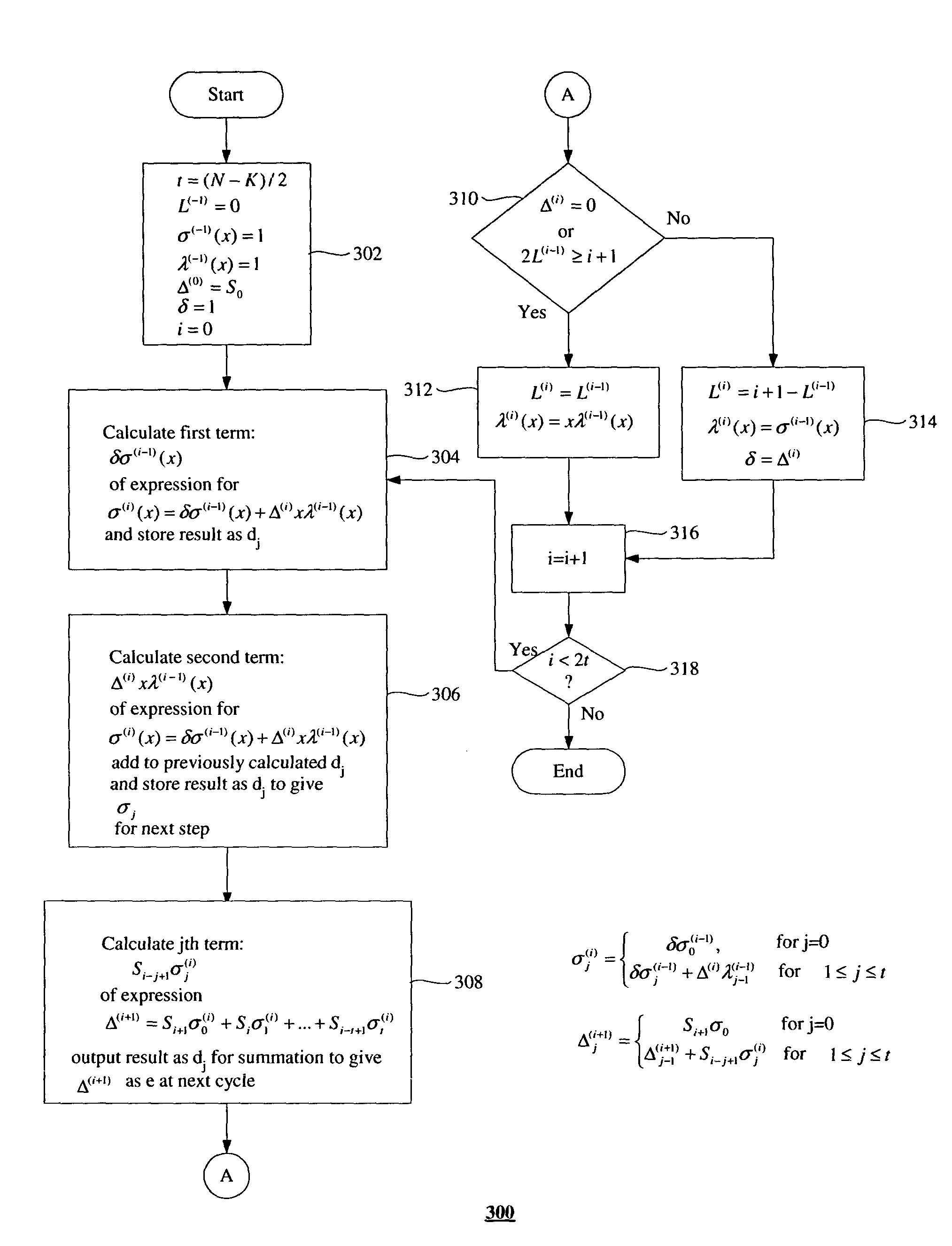
Key equation solving circuit of read-solomon decoder
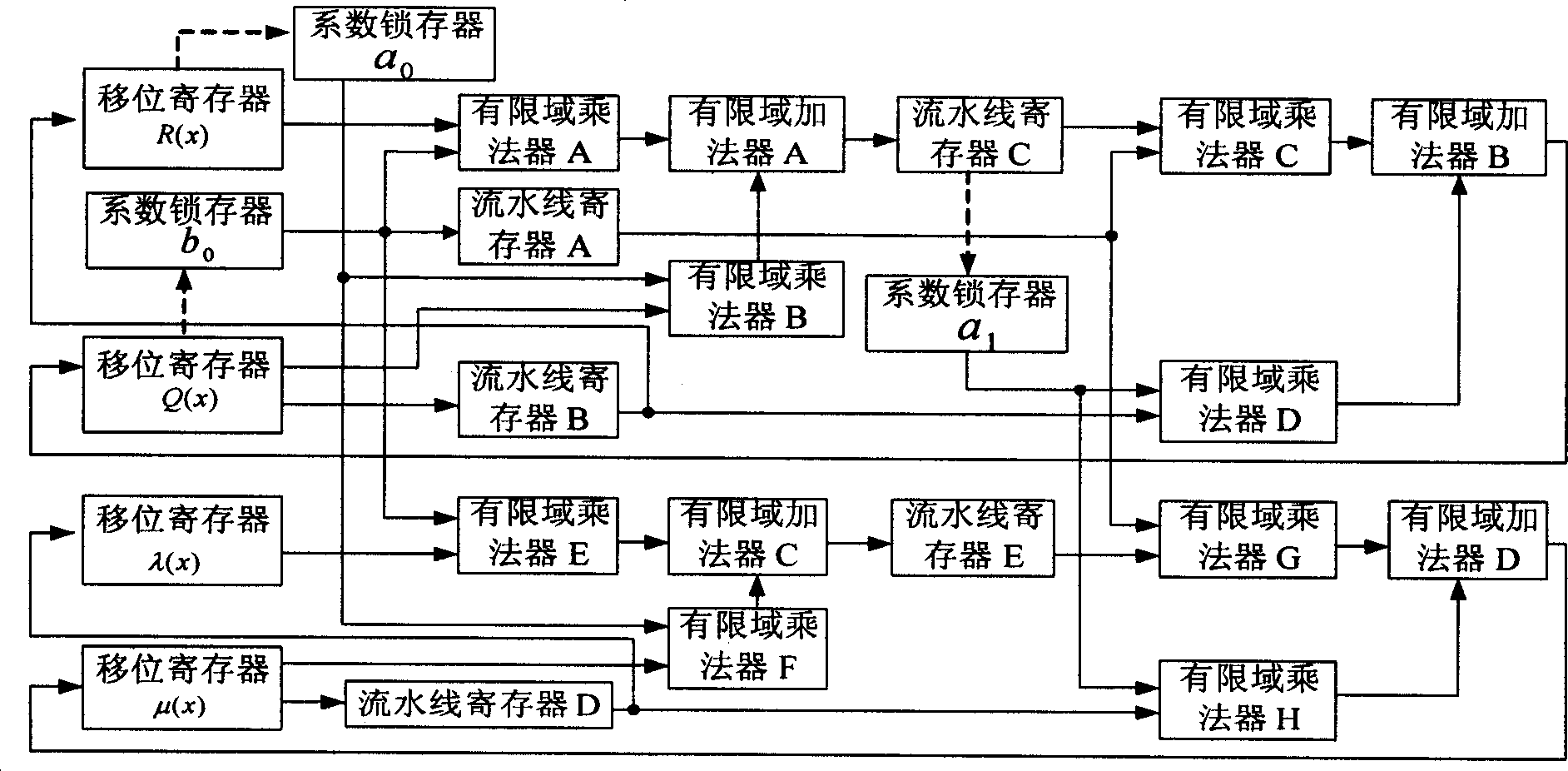
InactiveCN1658515AMeet processing speed requirementsCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesShift registerProcessor register
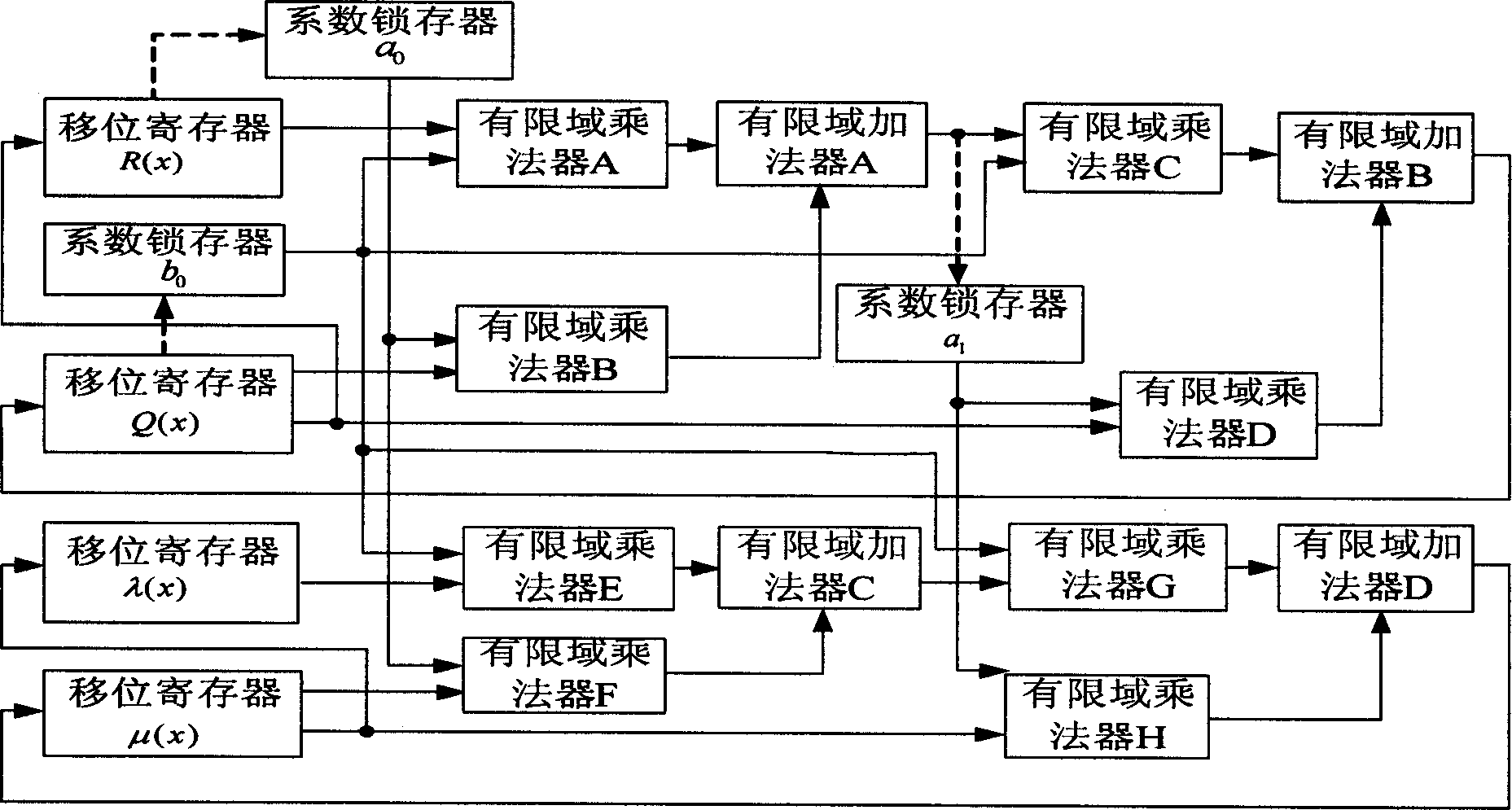
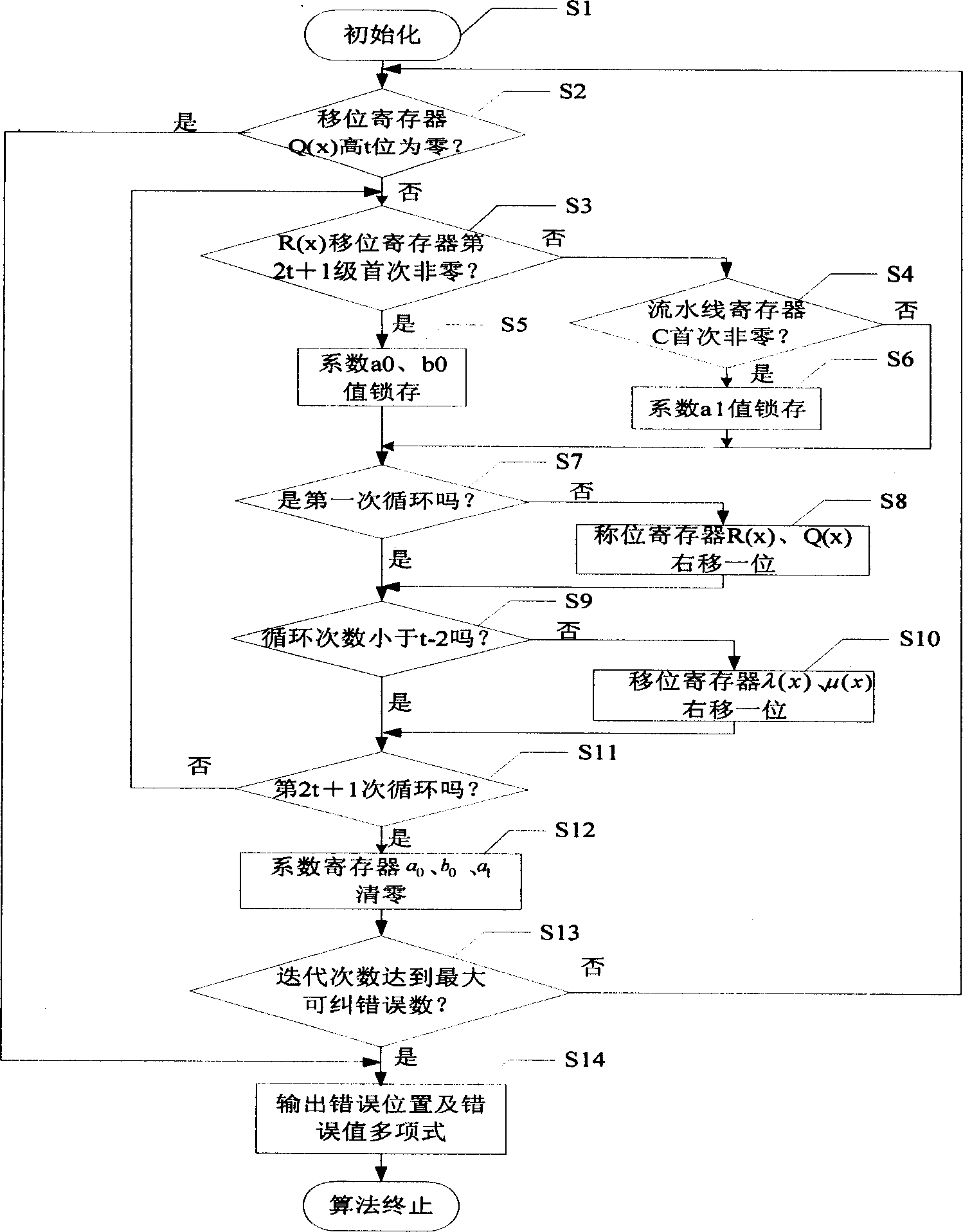
This invention discloses a Read-Solomon decoder key equation solution circuit. The aim is to avoid the long key path between the present registers, and the low working frequency of internal part of decoders. It includes R(x) shift register, Q(x) shift register, lambda(x) shift register, mu(x) shift register, the finite extent multiplier, the finite extent adder, the coefficient latch a0, b0 and a1. The characteristics are: it also includes the pipeline register C and E, the input end of the pipeline register C connects the finite extent adder A, the output end of the pipeline register C respectively connects the coefficient latch a1 and the finite extent multiplier C, the input end of the pipeline register E connects the finite extent adder C, the output end of the pipeline register E connects the finite extent multiplier G. Because increasing the number of the pipeline registers, the key path are shortened from '2XTmult+2XTadd' to 'Tmult+Tadd'. The highest working frequency of internal clock is 204.79MHz, and increases 63.6% of the present 133.33MHz.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Bit displacement processing method and device based on RS coding blind synchronization
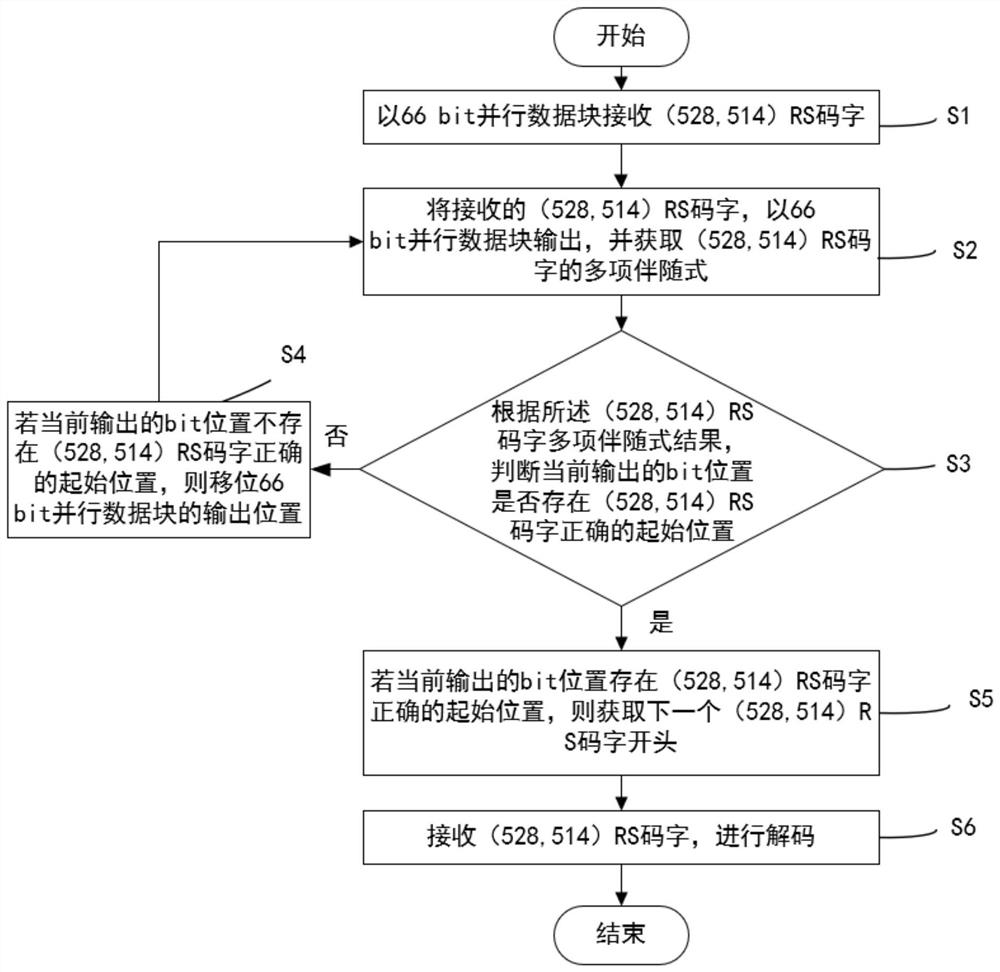
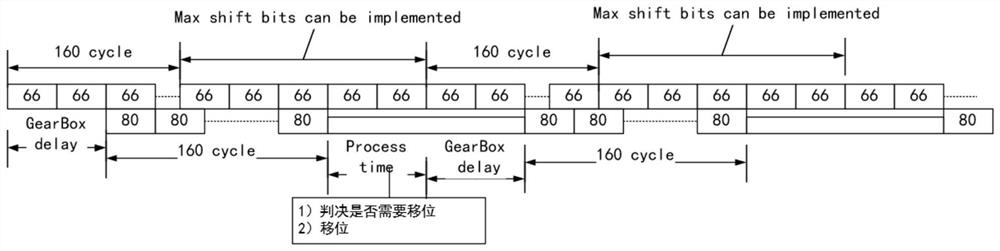
ActiveCN114205052ASimple structureEasy to integrateReceiver specific arrangementsComputer hardwareBinary multiplier
The invention discloses a bit shift processing method based on RS (Reed-Solomon) coding blind synchronization. The bit shift processing method comprises the following steps of: receiving RS code words by using 66bit parallel data blocks; outputting in a 66bit parallel data block manner, and acquiring an RS code word syndrome; according to the syndrome result, judging whether the currently output bit position has a correct initial position of the RS code word or not; if not, shifting the output position of the 66bit parallel data block; if yes, obtaining the beginning of the next RS code word; and receiving the RS code word and decoding the RS code word. According to the method, the rate of finding the correct code word beginning in the received bit stream is improved, the calculation speed is improved, the calculation period is shortened, and the descrambling and decoding efficiency is greatly improved. The invention further discloses a bit displacement processing device based on RS coding blind synchronization, the structure is simple, the bit displacement processing device can be conveniently realized in finite field multipliers with different bit widths, and circuit integration is facilitated.
Owner:SHENZHEN PANGO MICROSYST CO LTD
Data processing system and method
ActiveUS7693927B2Favourable area-latency productLower areaCode conversionDigital computer detailsData processing systemFinite field arithmetic
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a data processing system comprising a first arithmetic unit comprising at least one finite field multiplier and at least one finite field adder for selectively performing at least two finite field arithmetic calculations; the data processing system comprising means to use a previous finite field arithmetic calculation result in a current finite field arithmetic calculation to determine at least part of a polynomial.
Owner:NXP BV
High-speed parallel RS decoding method for space communication
ActiveCN101969358BFlexibility to adapt to encoding formatsMinimizeError preventionDecoding methodsStructure of Management Information
The invention relates to a high-speed parallel Reed-Solomon (RS) decoding method for space communication. In the method, two decoding modules RS (255, 223) and RS (255, 239) are configured simultaneously, so that a decoder can configure decoding types on line according to coding parameters to flexibly adapt to two coding formats specified by the consultative committee for space data system (CCSDS) standard; input data is filled and acquired in first in first out (FIFO) by ping-pong operation during deinterlacing and interlacing, a multi-channel parallel pipeline mode is adopted during decoding, and a composite structure ensures the maximization of system performance and realizes the minimization of resources and is suitable for 1 to 8 arbitrary interlacing depths; and measures such as multi-channel parallel RS decoding, the optimization of realization logic of a finite field multiplier, and the like are adopted, so that decoding rate is greatly improved. The method can be directly applied to a high-code-rate remote sensing satellite ground receiving system and can further increase parallelism degree and improve performance when necessary by modular design.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Parallel low and asymmetric rate Reed Solomon coding
ActiveUS9032277B1Error preventionTransmission systemsSymbol of a differential operatorComputer science
Owner:ALTERA CORP
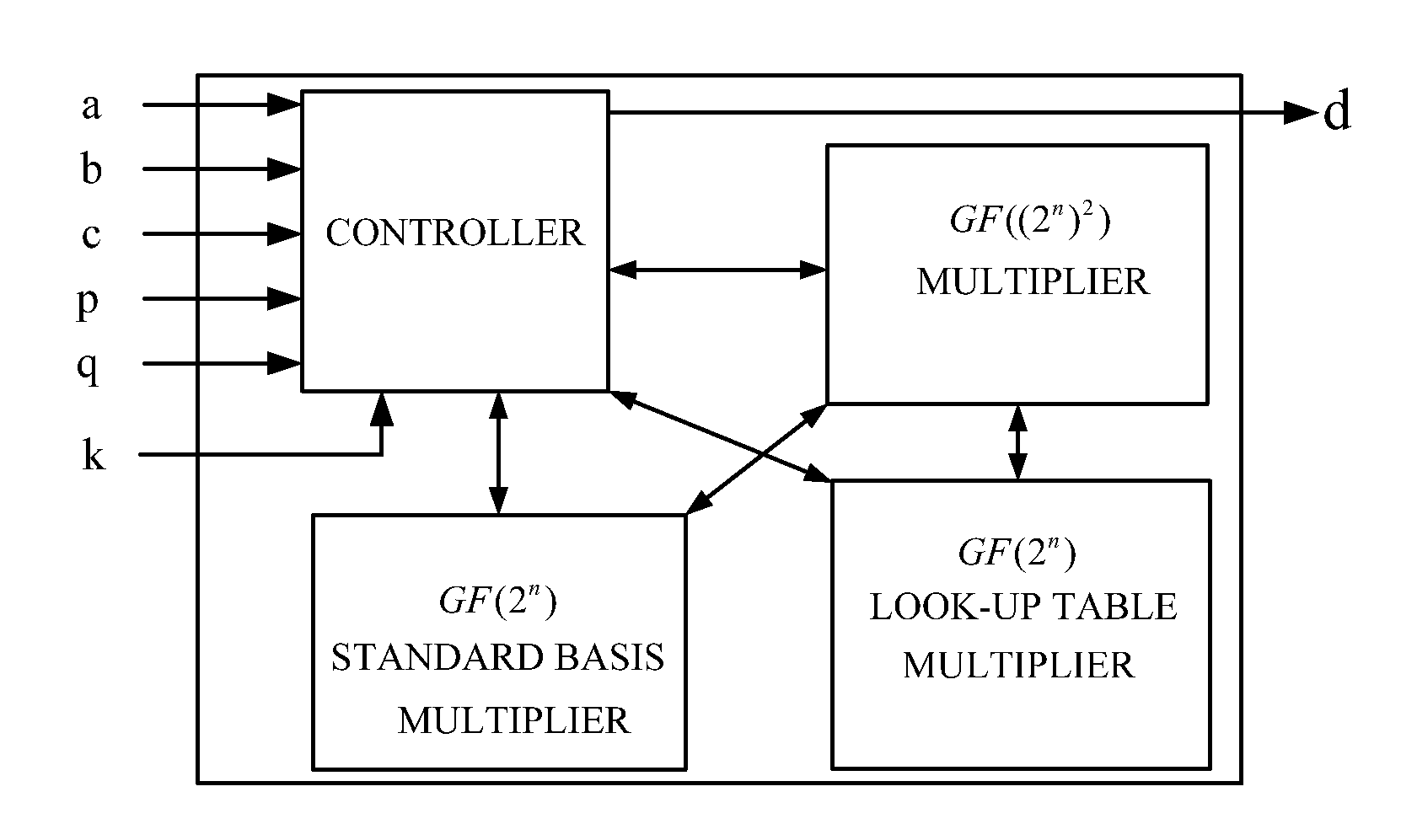
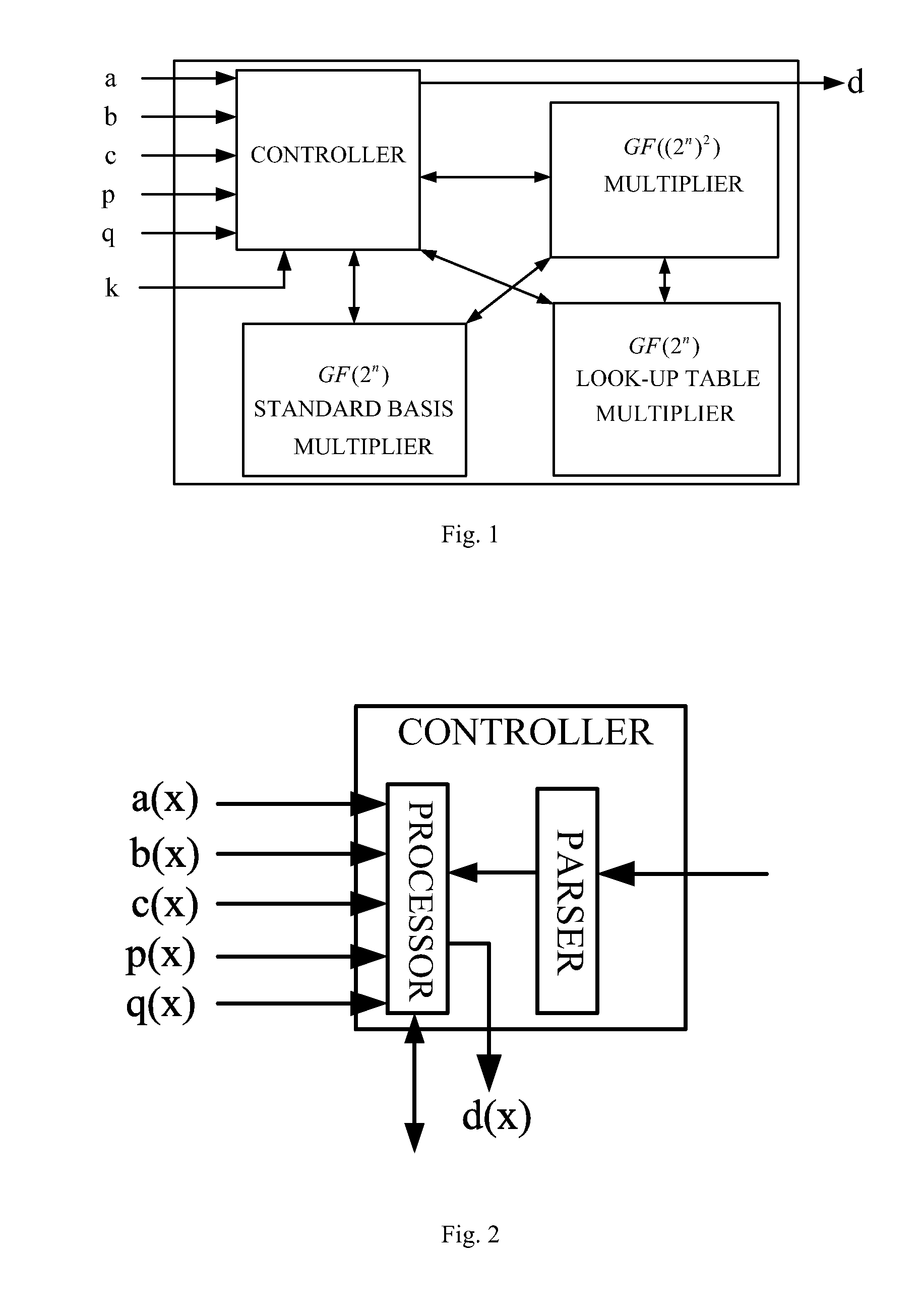
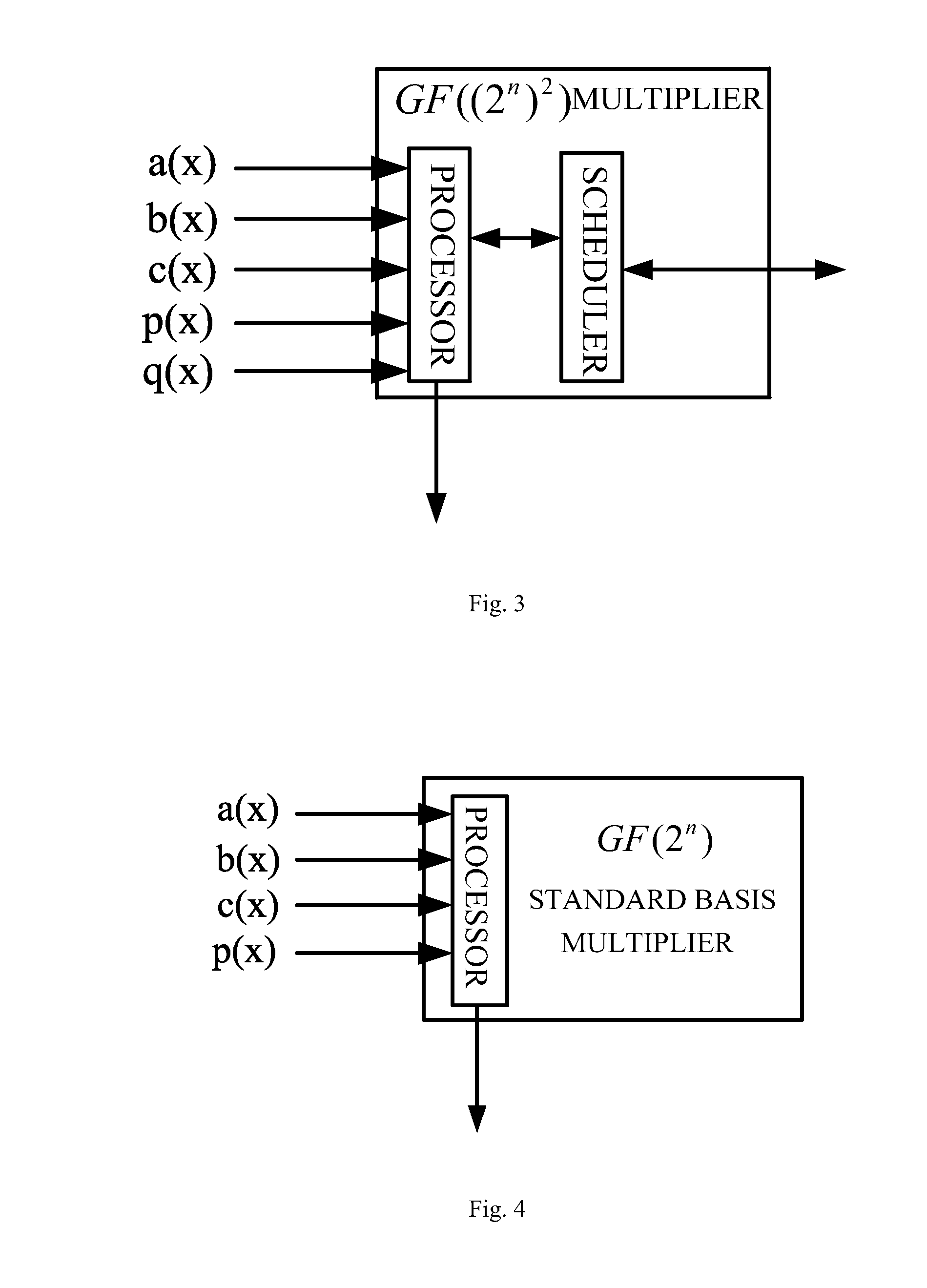
Composite finite field multiplier
ActiveUS20140101220A1Significant speedEasy to useComputation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsBinary multiplierEngineering
A composite finite field multiplier is disclosed. The multiplier includes a controller, an input port, an output port, a GF((2n)2) multiplier, a GF(2n) standard basis multiplier, and a GF(2n) look-up table multiplier; the controller is connected respectively to the input port, the output port, the GF((2n)2) multiplier, the GF(2n) standard basis multiplier and the GF(2n) look-up table multiplier; the GF((2n)2) multiplier is connected respectively to the GF(2n) standard basis multiplier and the GF(2n) look-up table multiplier. By using the GF((2n)2) multiplier, the GF(2n) standard basis multiplier and the GF(2n) look-up table multiplier, the multiplication of three operands is realized. Compared with the existing multiplier, the multiplier of the present invention has significant advantages in the speed of multiplying three operands over GF((2n)m).
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com