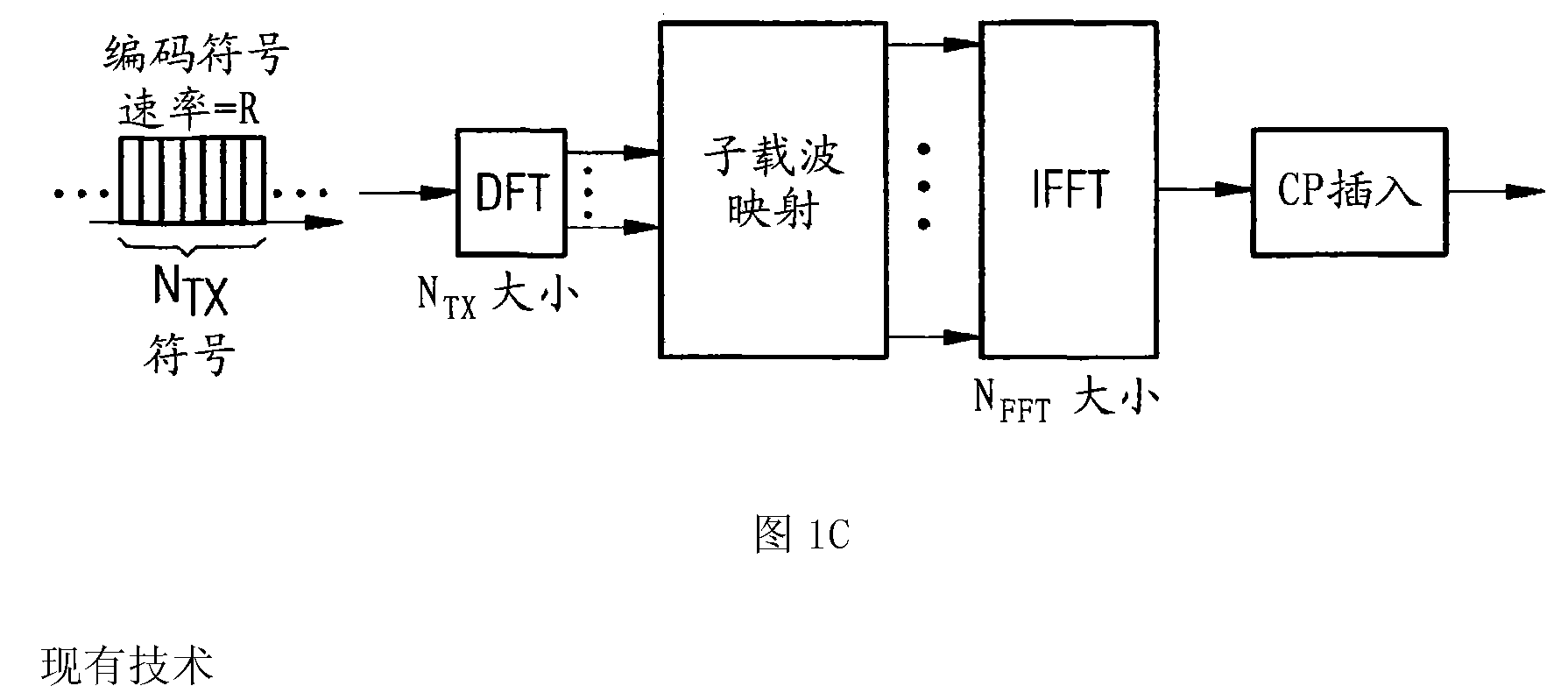
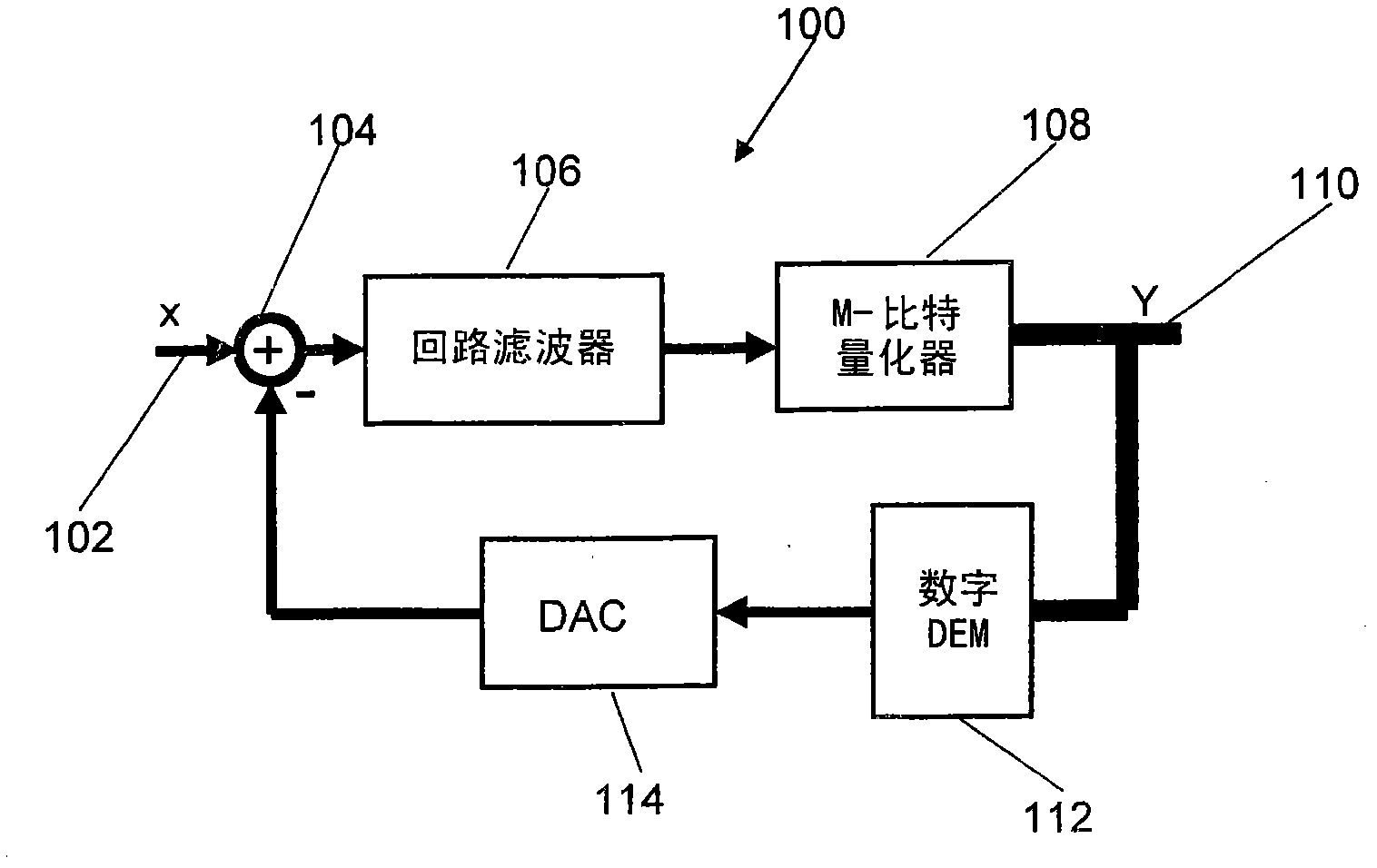
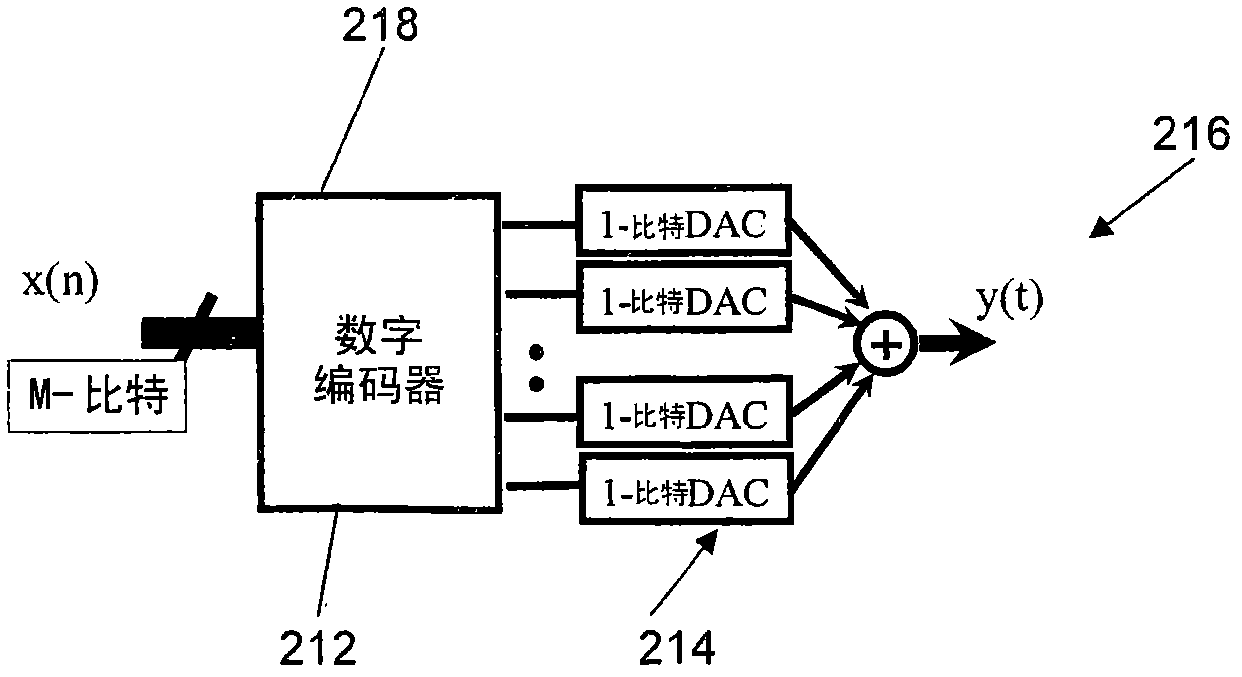
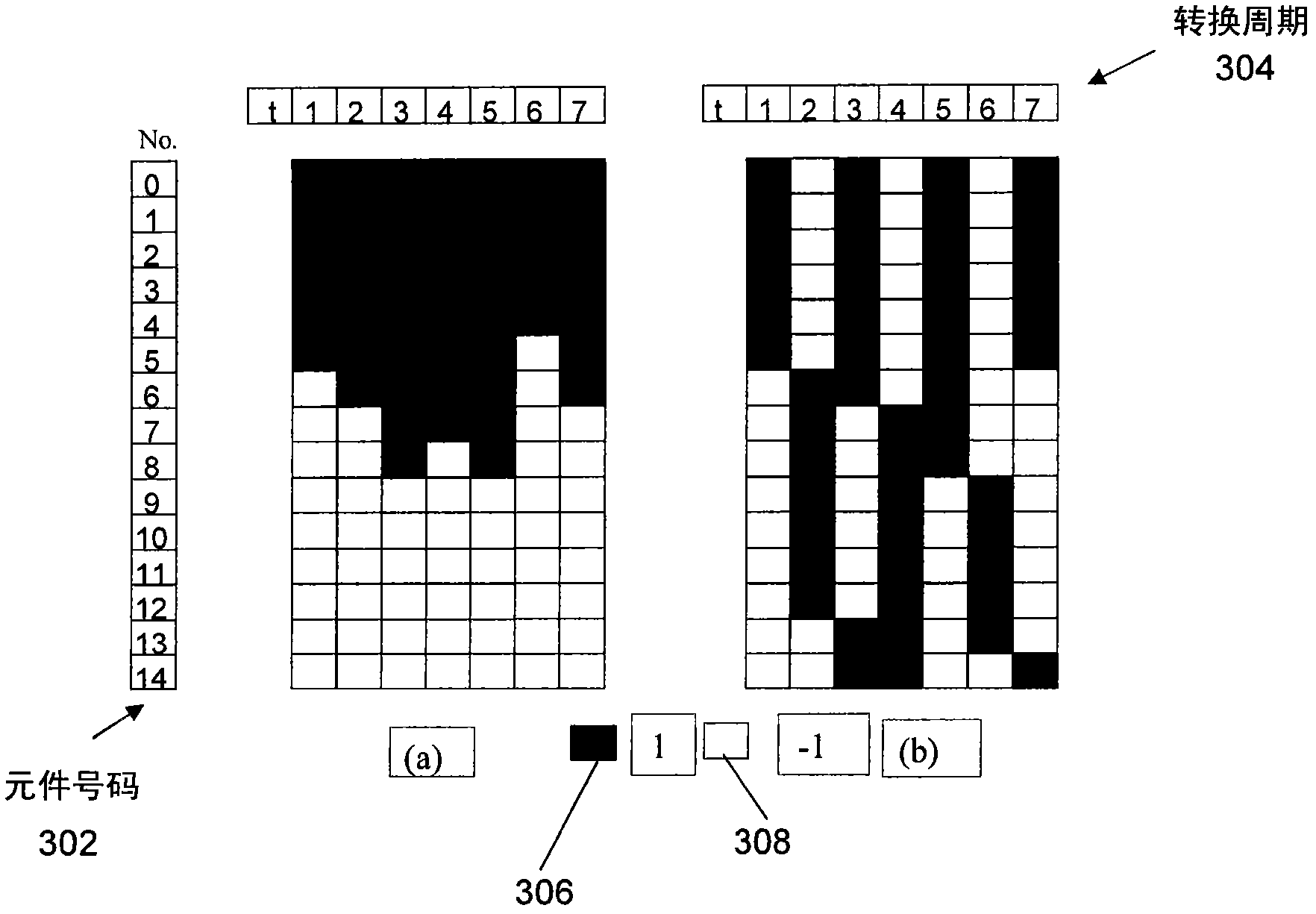
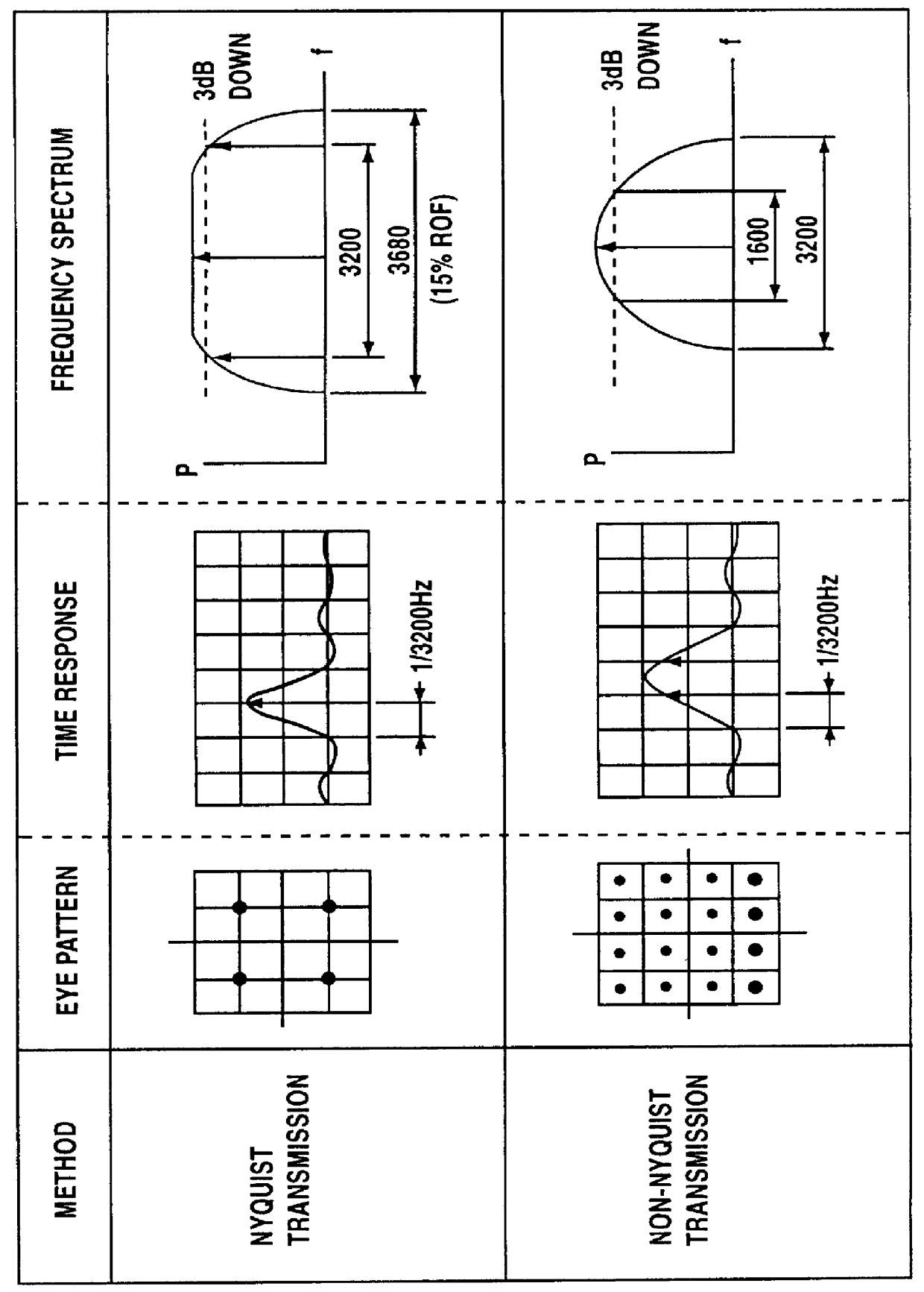
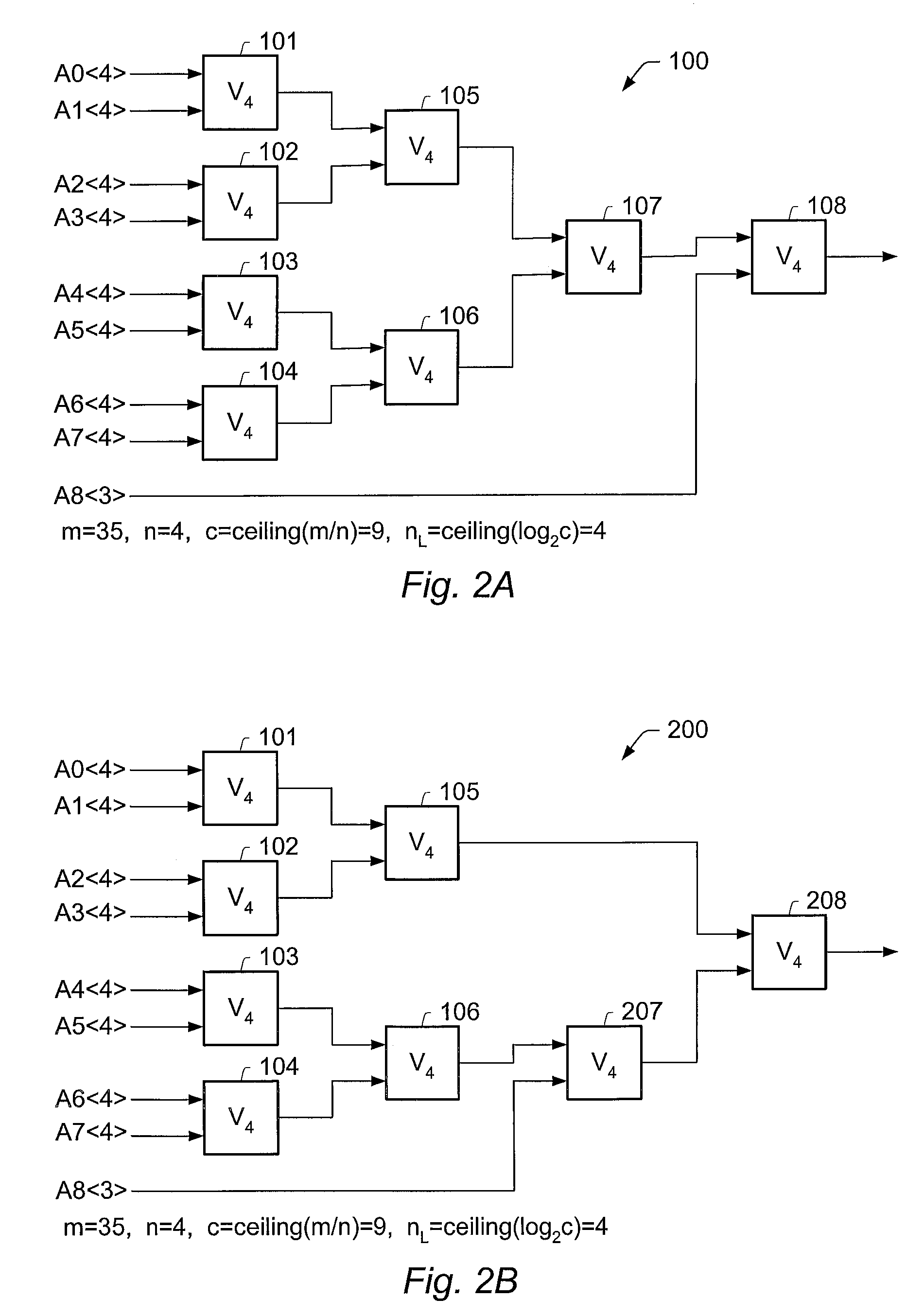
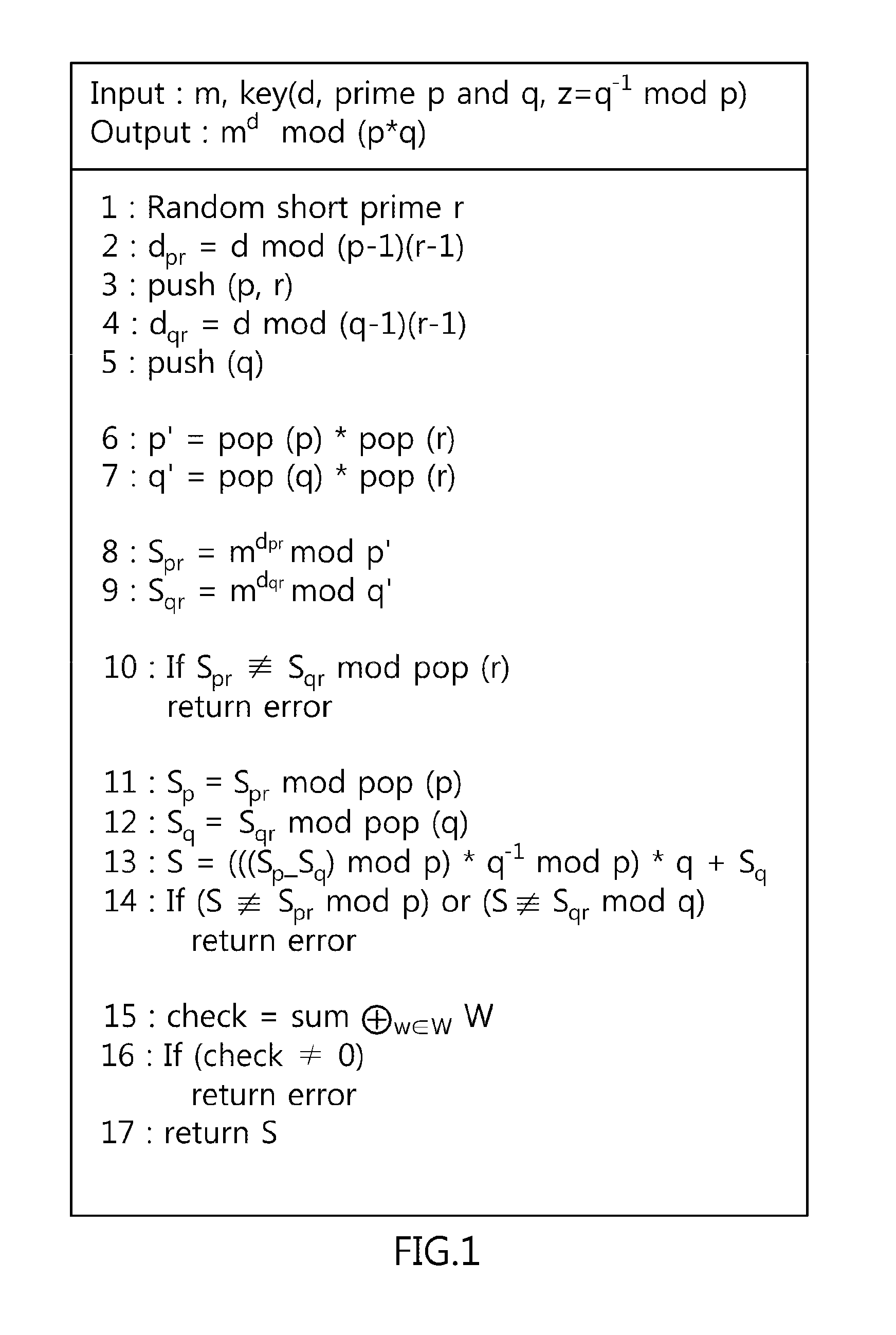Patents
Literature
248 results about "Modulo operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computing, the modulo operation finds the remainder after division of one number by another (called the modulus of the operation). Given two positive numbers, a and n, a modulo n (abbreviated as a mod n) is the remainder of the Euclidean division of a by n, where a is the dividend and n is the divisor.
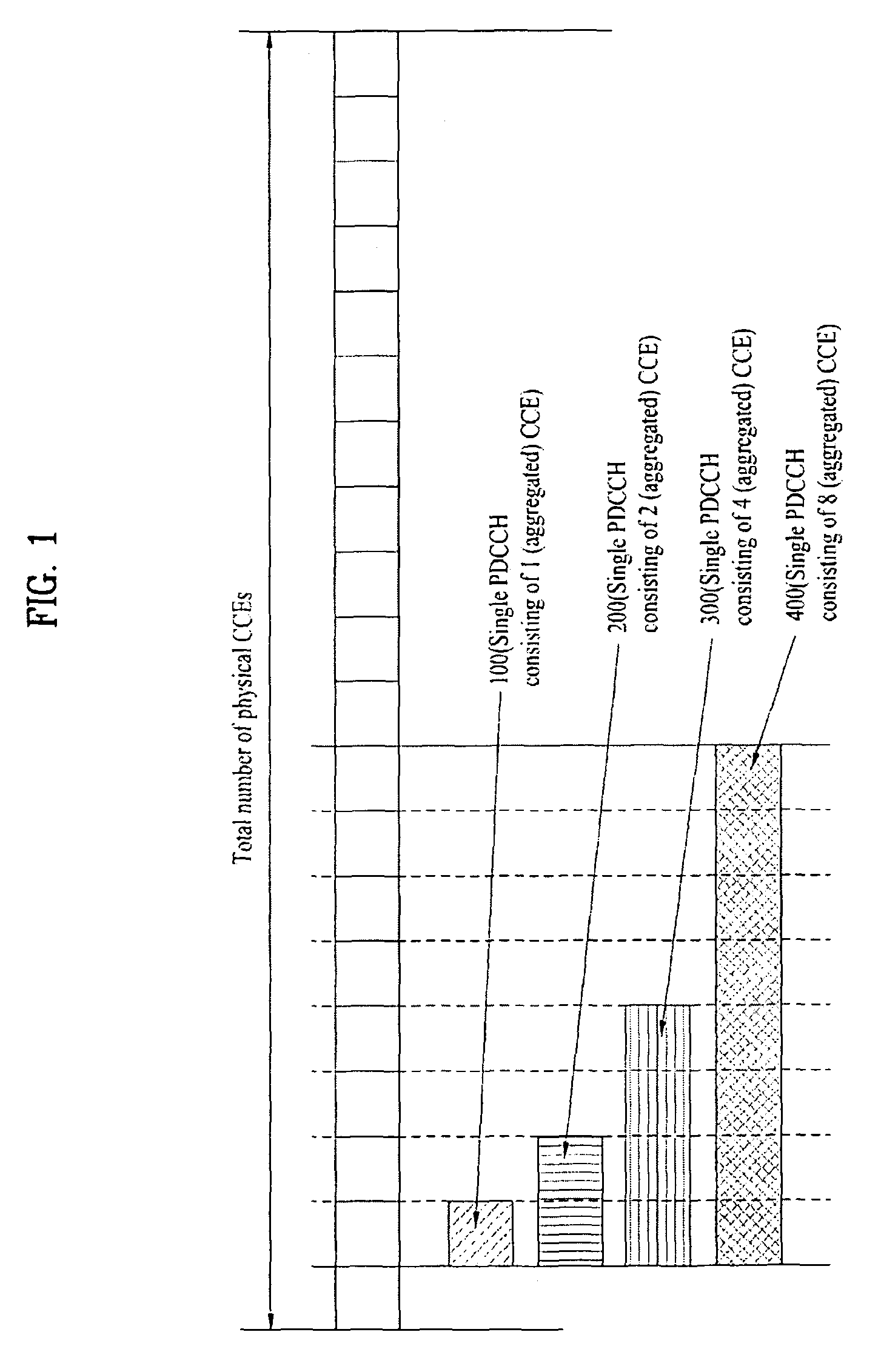
Method for monitoring downlink control channel in user equipements
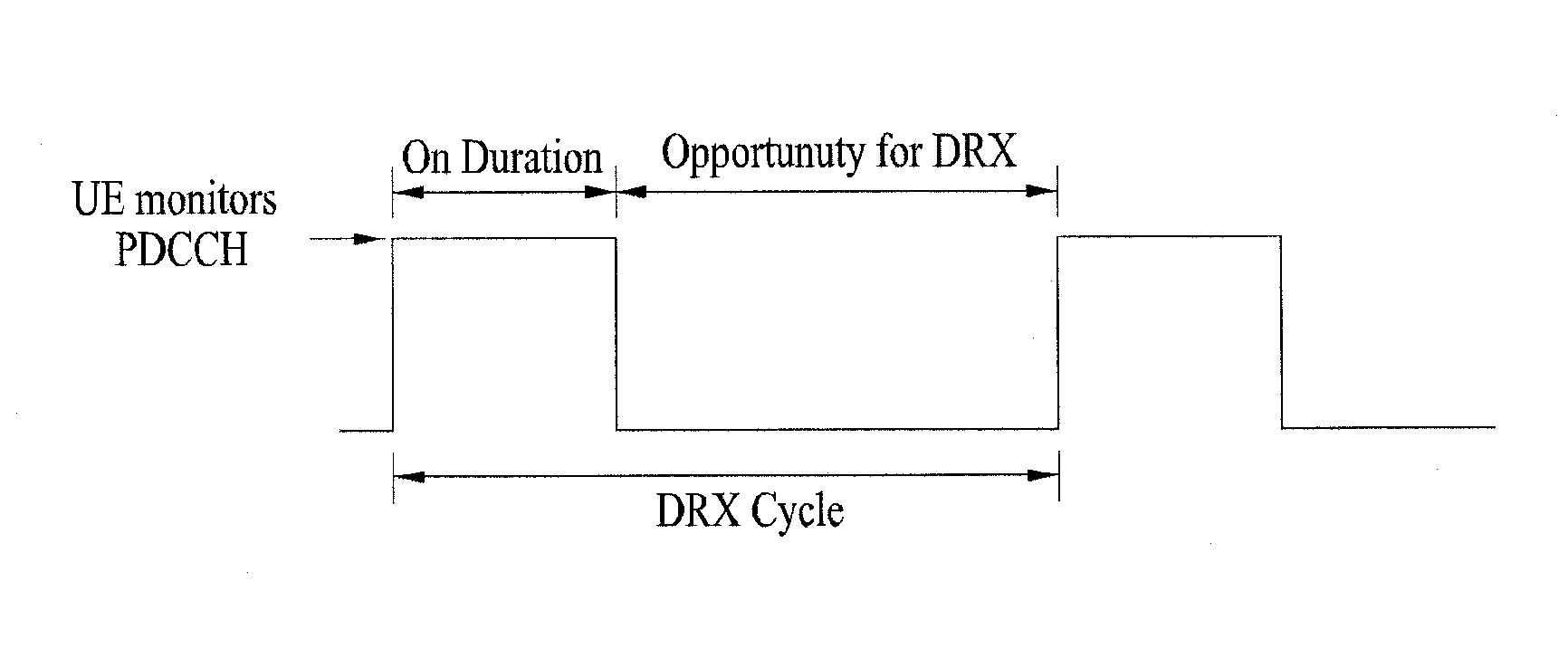
InactiveUS20100110897A1Rendering DRX operation can be reliableError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemControl channel
The method for discontinuously monitoring downlink control channel in a user equipment in a wireless communication system includes receiving a discontinuous reception (DRX) Start Offset from a base station to be used for both a first DRX Cycle and a second DRX Cycle, and starting an On Duration Timer at a subframe that satisfies either a first condition for the first DRX Cycle or a second condition for the second DRX Cycle, wherein a first DRX offset used in the first condition is based upon the DRX Start Offset received from the base station, and wherein a second DRX offset used in the second condition is based upon a remainder of the DRX Start Offset received from the base station after a modulo operation by the second DRX Cycle.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
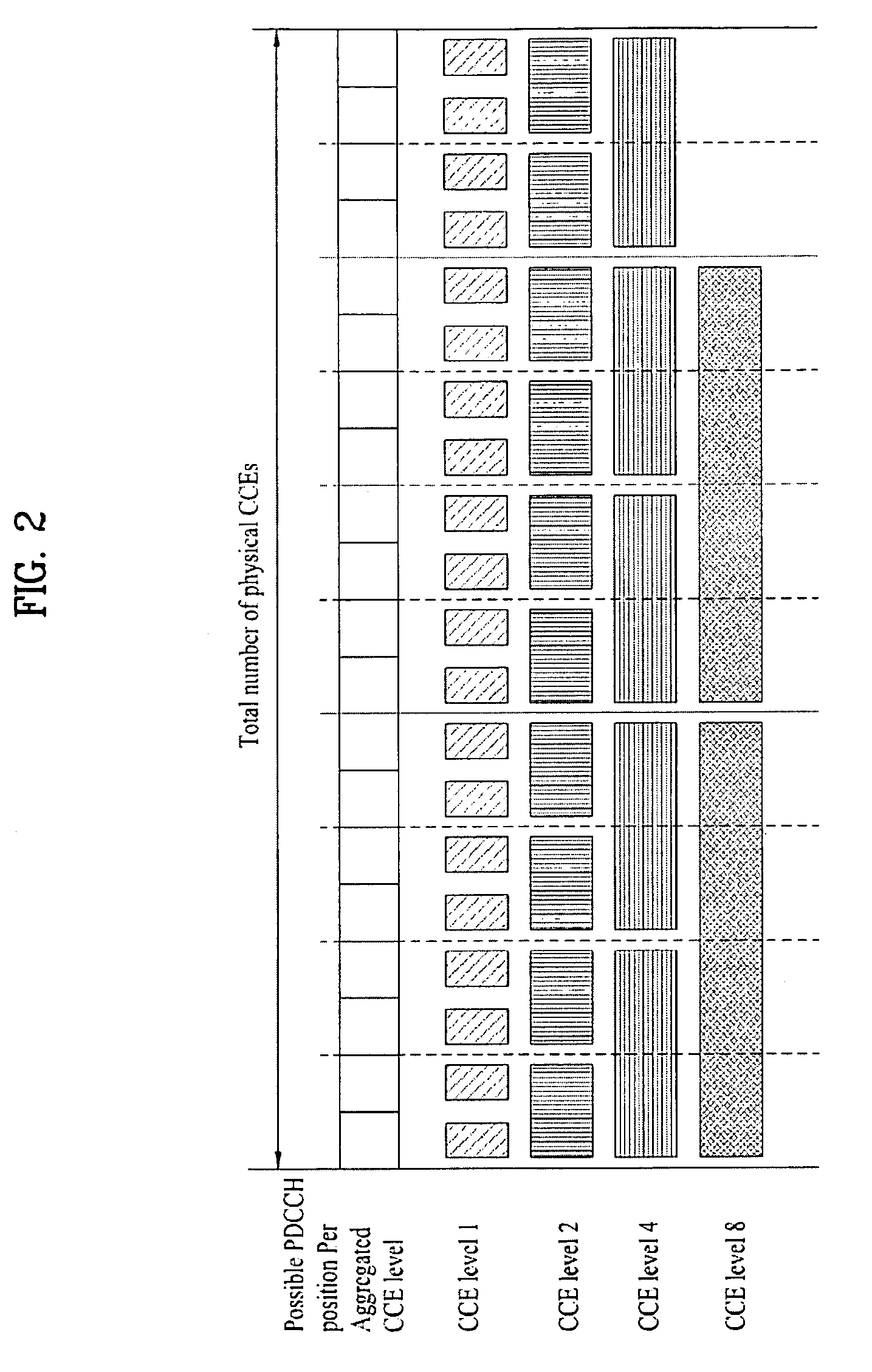
Method for transmitting and receiving control information through pdcch
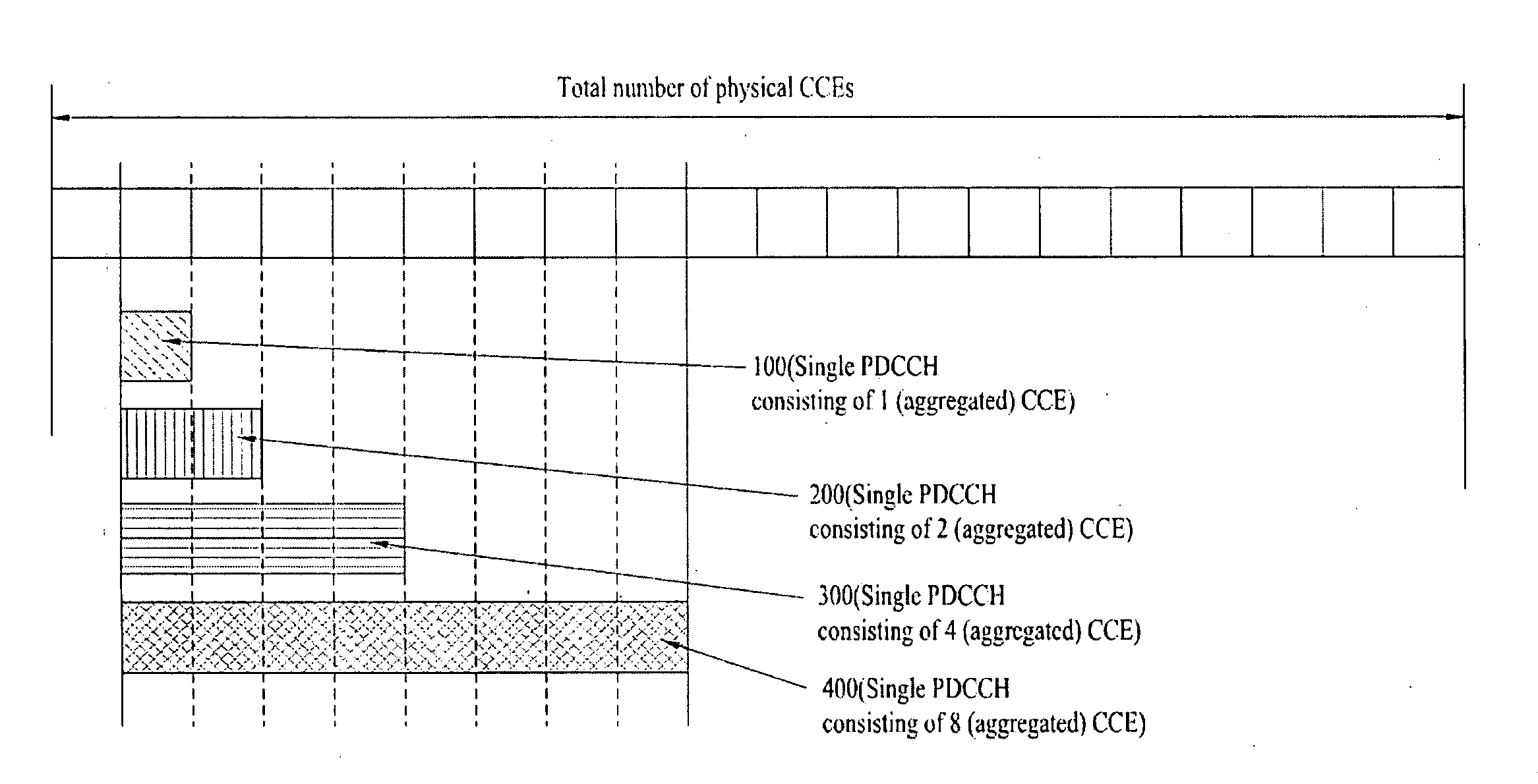
ActiveUS20090209247A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient receptionModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionControl channelData mining
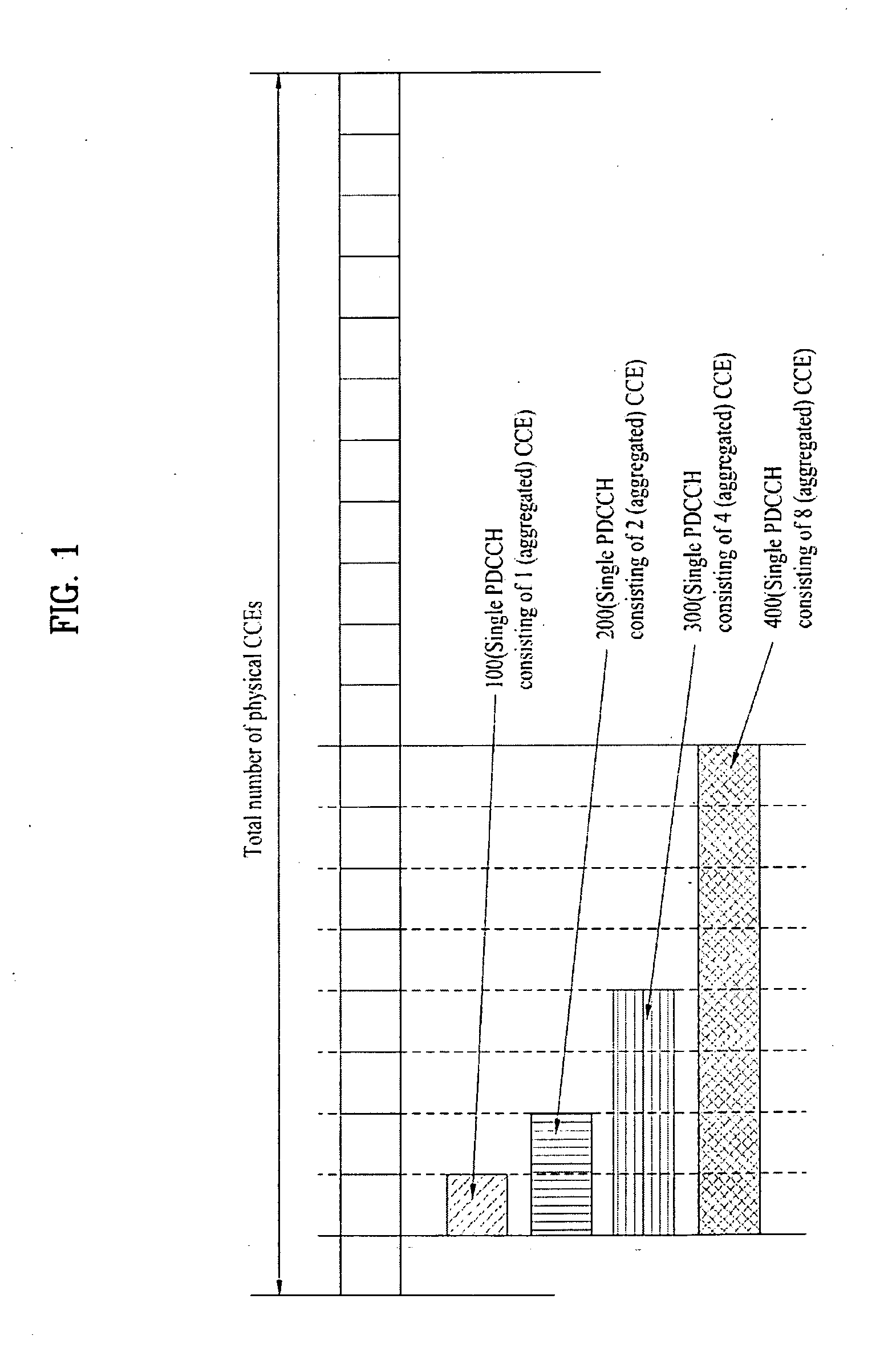
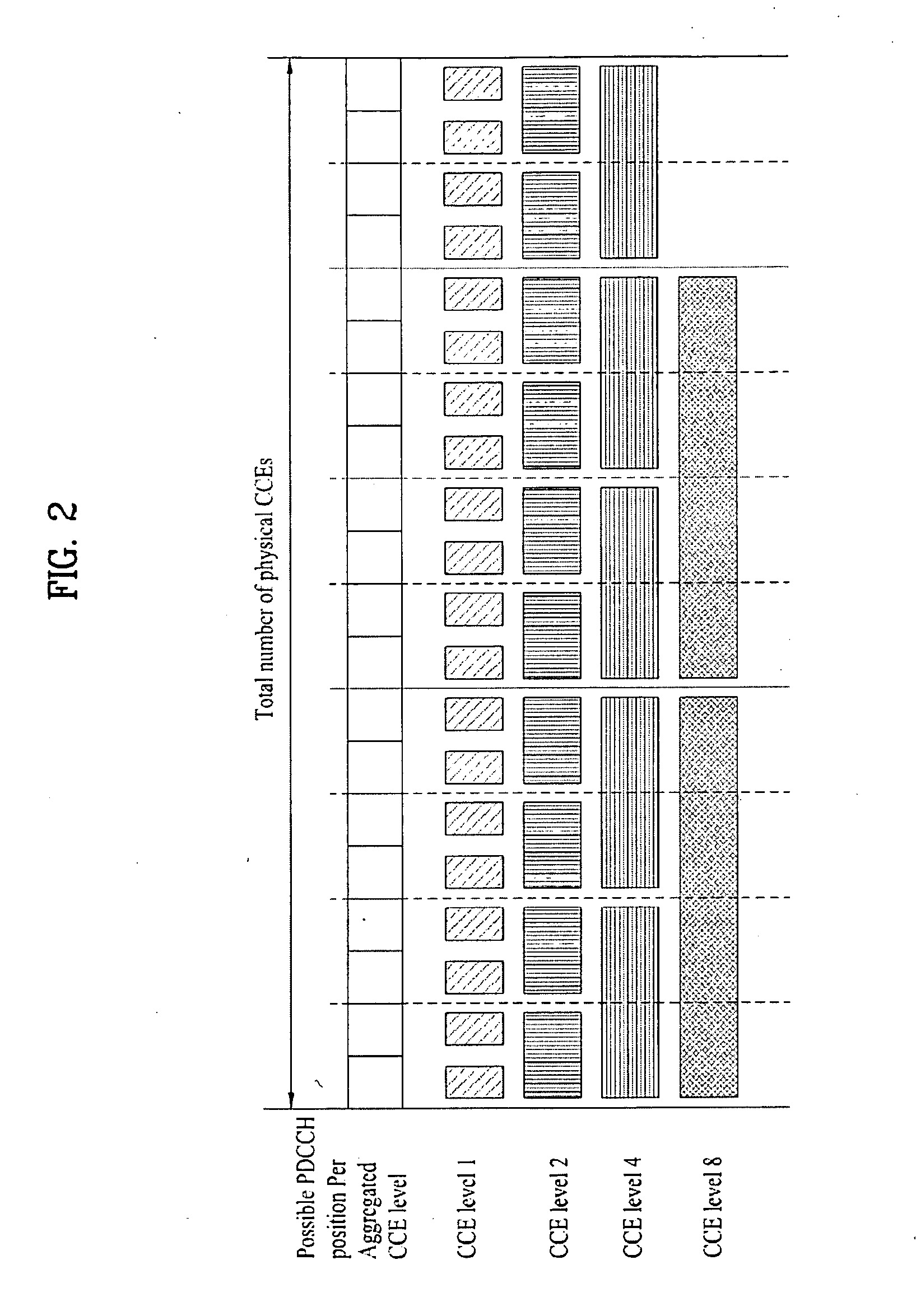
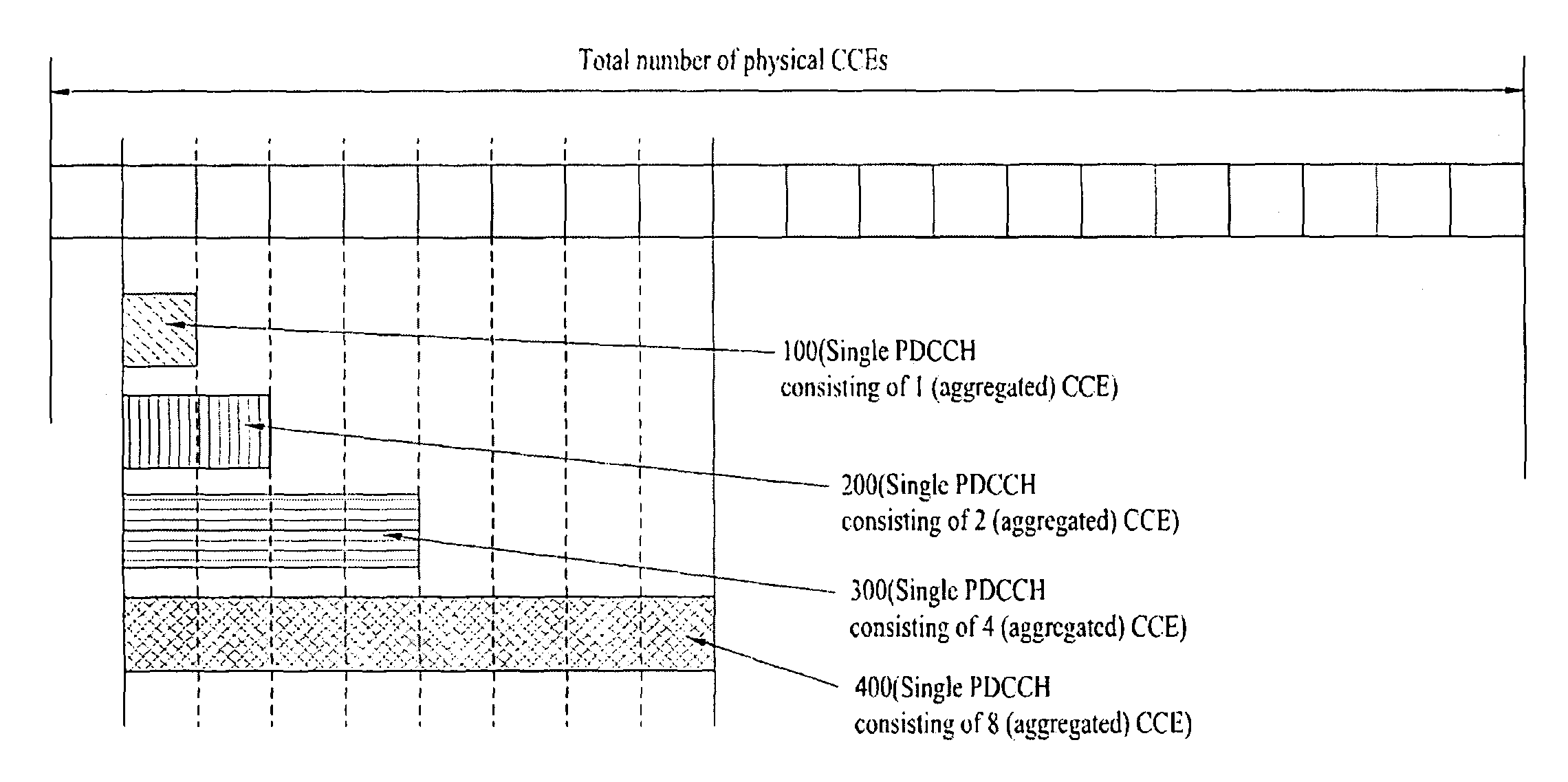
A method for efficiently transmitting and receiving control information through a Physical Downlink Control Channel (PDCCH) is provided. When a User Equipment (UE) receives control information through a PDCCH, the received control information is set to be decoded in units of search spaces, each having a specific start position in the specific subframe. Here, a modulo operation according to a predetermined first constant value (D) is performed on an input value to calculate a first result value, and a modulo operation according to a predetermined first variable value (C) corresponding to the number of candidate start positions that can be used as the specific start position is performed on the calculated first result value to calculate a second result value and an index position corresponding to the second result value is used as the specific start position. Transmitting control information in this manner enables a plurality of UEs to efficiently receive PDCCHs without collisions.
Owner:HIGHBRIDGE PRINCIPAL STRATEGIES LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
Efficient techniques for sharing a secret
InactiveUS7167565B2Adequate protection against disk attackComputationally efficientKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageKey distributionModulo operation
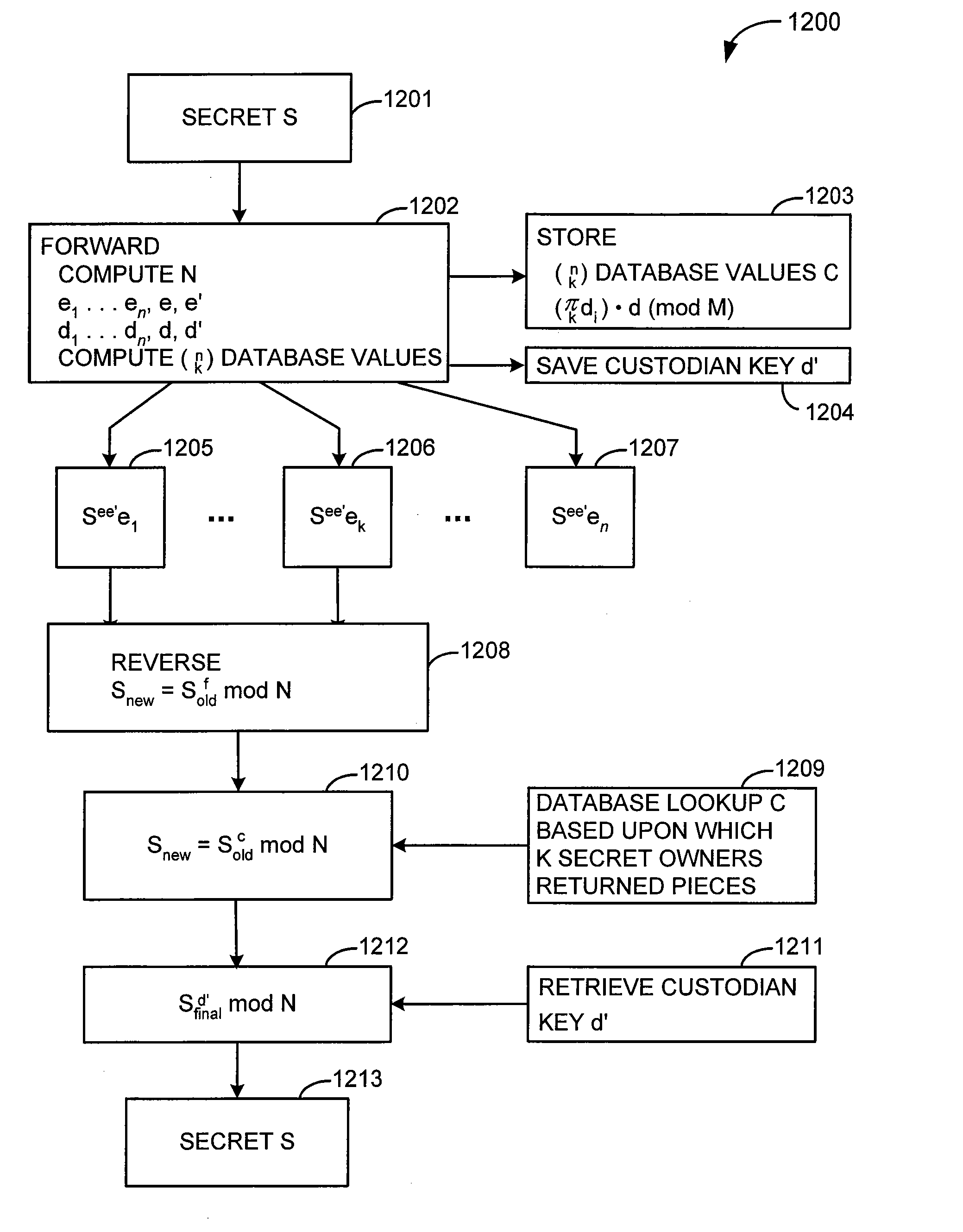
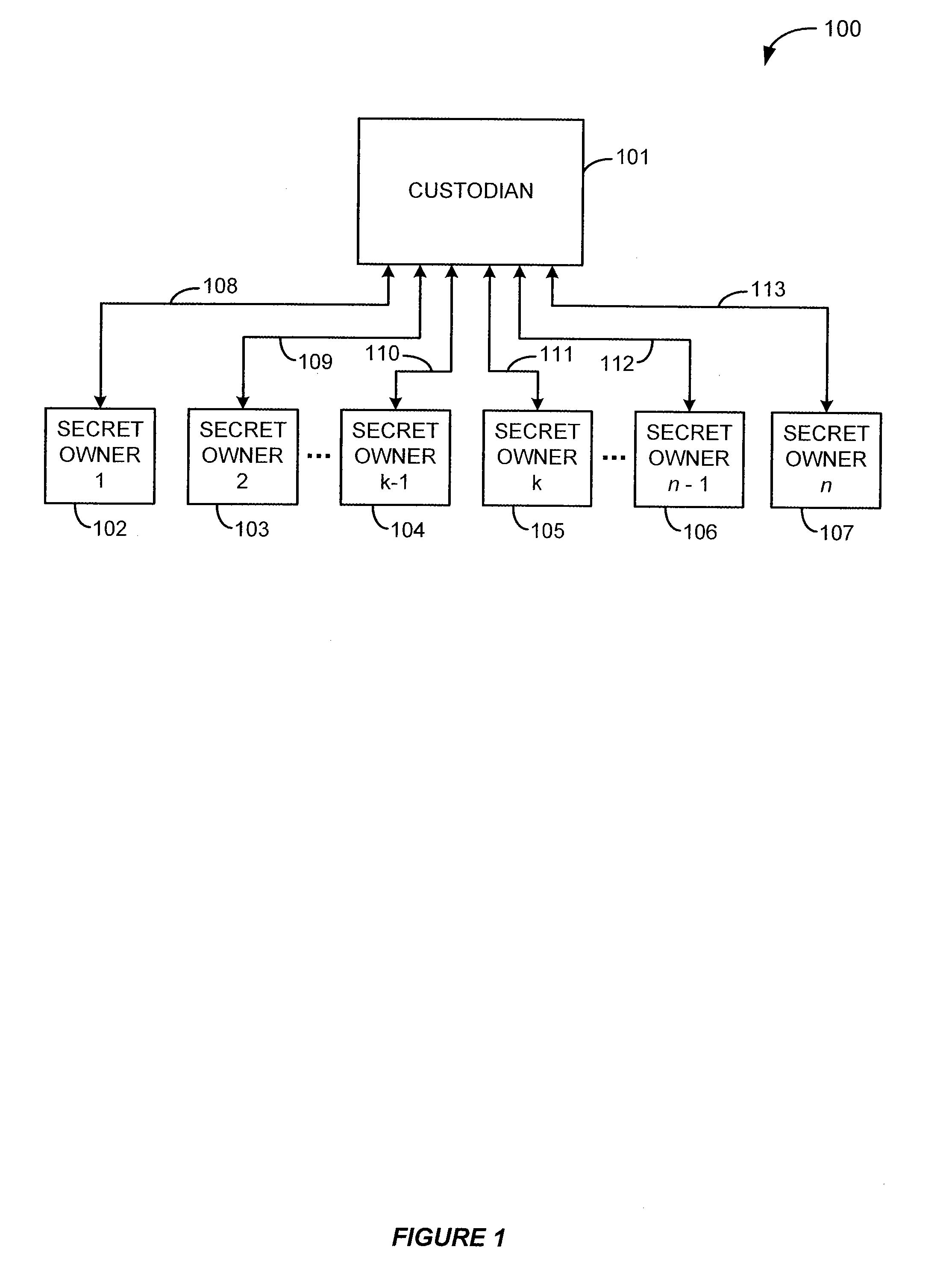
An n person secret sharing solution computes n unique keys to be distributed to the secret owners along with an exponentiated version of the secret. The custodian performs an exponent / modulo operation each time one of the keys is received from one of the secret owners. Alternatively, n+1 keys are created by the custodian, and the custodian retains one key after distributing the remaining n keys to the secret owners. After the custodian has received and processed the n keys from the secret owners, he performs an exponent / modulo operation using his own retained key. According to another aspect, a k out of n secret sharing solution involves computing and storing a database having an entry for each unique combination of k keys that could be returned from among the n keys. After k keys have been received, the custodian looks up in the database the entry corresponding to the particular unique combination of secret owners who returned keys. The custodian performs another exponent / modulo operation using the entry retrieved from the database in order to reconstruct the original secret. According to an embodiment, the custodian computes n+1 keys, distributes n of the keys to the secret owners, and keeps one of the keys for himself. The custodian retrieves his own key and performs a final exponent / modulo operation in order to reconstruct the original secret. According to another aspect, a k out of n secret sharing solution involves encrypting the original secret before applying any conventional k out of n secret sharing solution.
Owner:CA TECH INC
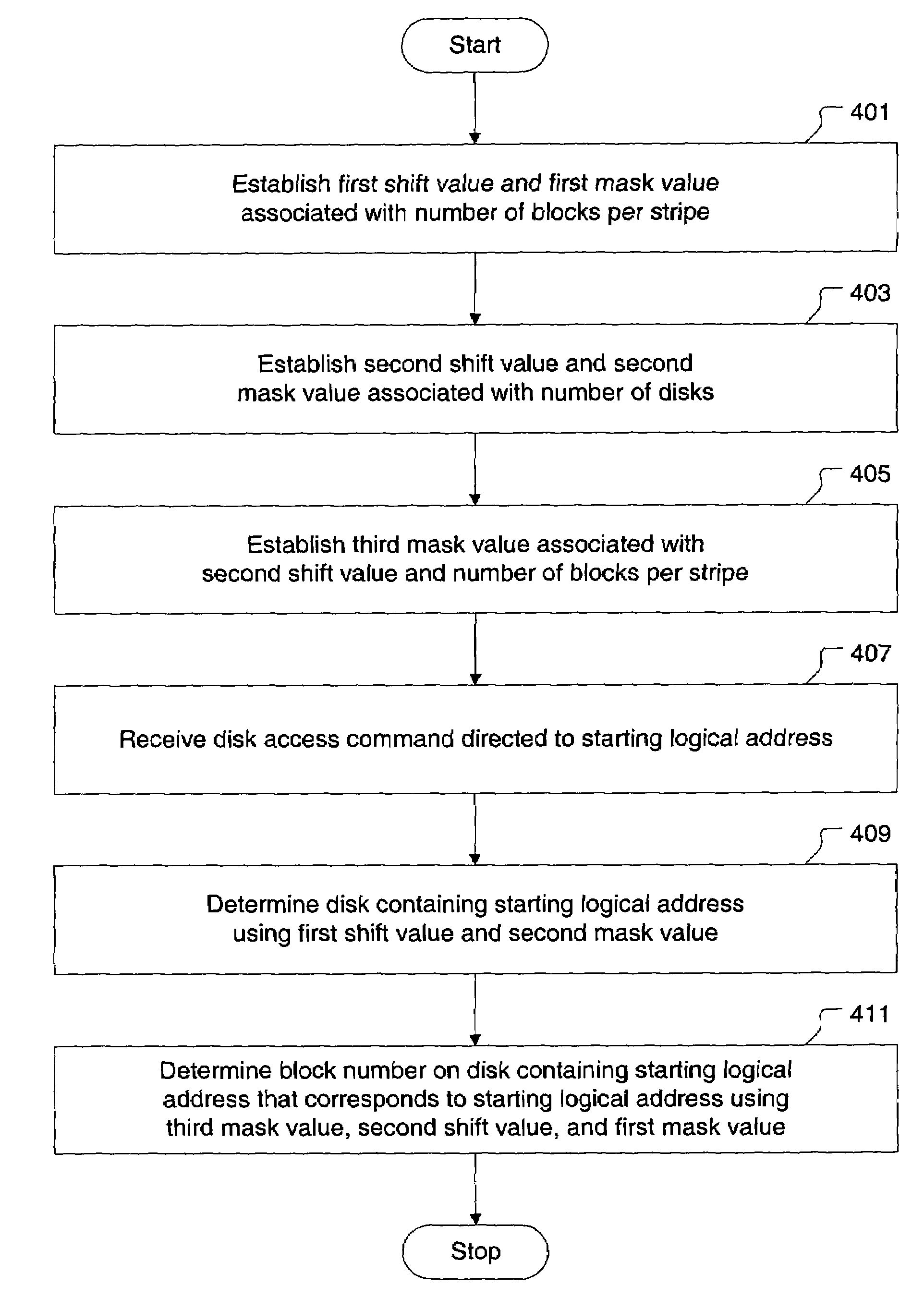
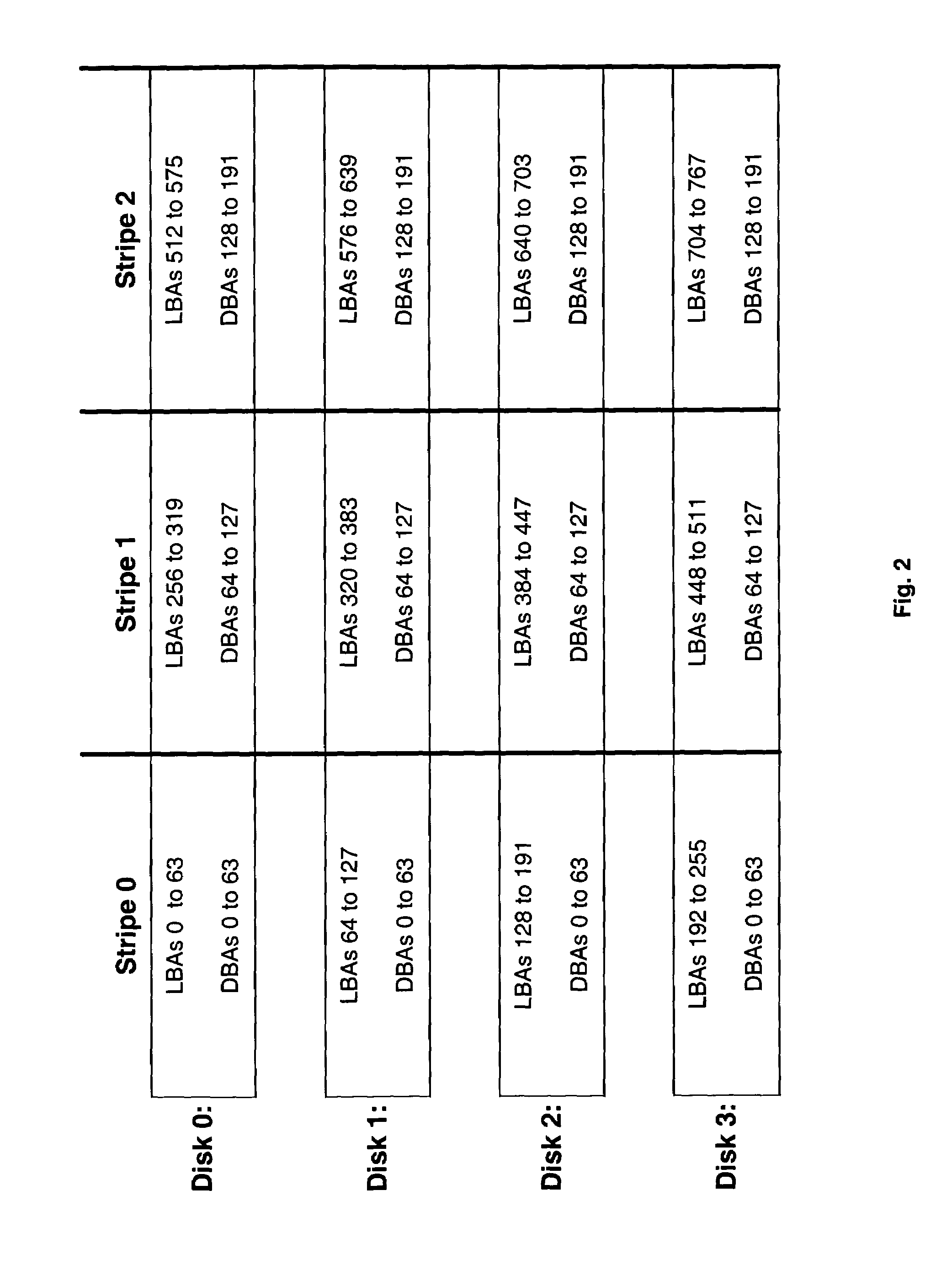
Method and apparatus for accessing a striped configuration of disks
InactiveUS7406563B1Efficient processingEasy to implementMemory loss protectionInput/output processes for data processingRAIDModulo operation
Broadly speaking, a method and an apparatus is provided for processing access commands directed to a striped configuration of disks. More specifically, the method and apparatus determines a physical block address corresponding to a logical address in a redundant array of independent disks level 0 (RAID 0) system. Bit-level operations are incorporated to determine a disk in the RAID 0 system and a block number on the disk that corresponds to a particular logical address. Since the bit-level operations replace traditionally required division and modulo operations, the method and apparatus provides for more efficient processing of access commands directed to the RAID 0 system.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
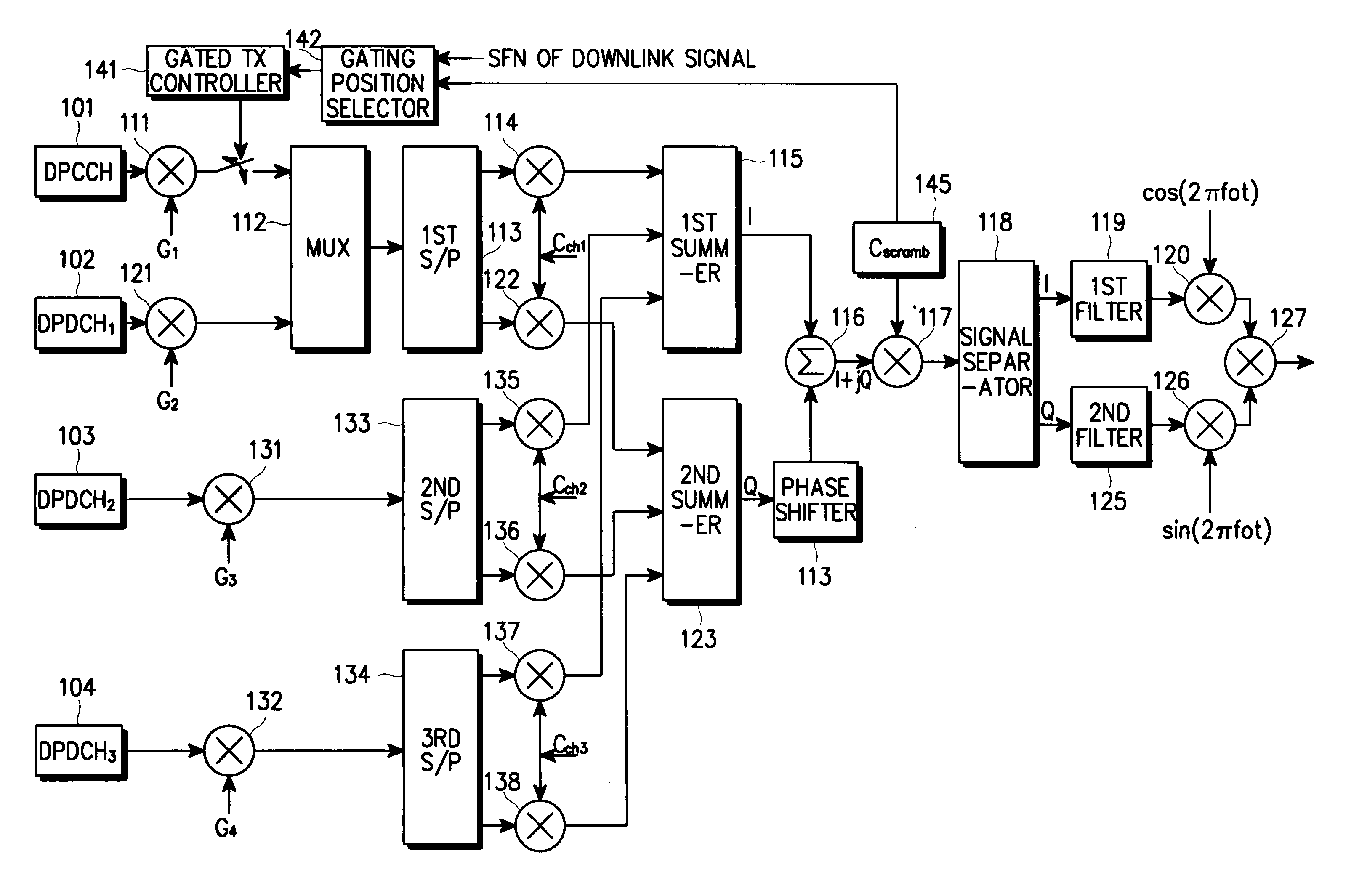
Apparatus and method for gating data on a control channel in a CDMA communication system
A method for transmitting control data on a downlink and / or uplink channel in a base station and / or mobile station in a mobile communication system. In one embodiment, the base station determines whether there is downlink channel data to transmit to a mobile station. If there is no data to be transmitted over the downlink channel for a predetermined time period, the base station drives a random gating position selector to determine a random gating slot position, gates on the control data at the determined slot position, and gates off the control data at other slot positions. The random position selector determines the gating slot position by calculating a value x by multiplying a system frame number (SFN) of a received signal by a specific integer; selecting n bits starting from a position which is at an x-chip distance from the start point of a scrambling code, which has a period equal to one frame, before a plurality of gating durations used in generating a downlink signal; and determining a gating slot position of a corresponding gating slot group by performing a modulo operation on the selected n bits, where the module operation is by the number of slots in a gating slot group.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for transmitting and receiving control information through PDCCH
ActiveUS7873004B2Efficiently transmitting and receiving control informationEfficient settingsModulated-carrier systemsTransmission systemsControl channelUser equipment
A method for efficiently transmitting and receiving control information through a Physical Downlink Control Channel (PDCCH) is provided. When a User Equipment (UE) receives control information through a PDCCH, the received control information is set to be decoded in units of search spaces, each having a specific start position in the specific subframe. Here, a modulo operation according to a predetermined first constant value (D) is performed on an input value to calculate a first result value, and a modulo operation according to a predetermined first variable value (C) corresponding to the number of candidate start positions that can be used as the specific start position is performed on the calculated first result value to calculate a second result value and an index position corresponding to the second result value is used as the specific start position. Transmitting control information in this manner enables a plurality of UEs to efficiently receive PDCCHs without collisions.
Owner:HIGHBRIDGE PRINCIPAL STRATEGIES LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
Systems and methods for determining a good rss key
ActiveUS20110153861A1Optimize allocationDigital data processing detailsGeneral purpose stored program computerHash functionTheoretical computer science
The present application is directed towards systems and methods for ensuring equal distribution of packet flows among a plurality of cores in a multi-core system by identifying a rank of a matrix created from a hash key. If the rank of the matrix is equal to or greater than a divisor of a modulo operation applied to the results of the hash function, then the hash key may be used to ensure equal distribution of packet flows.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
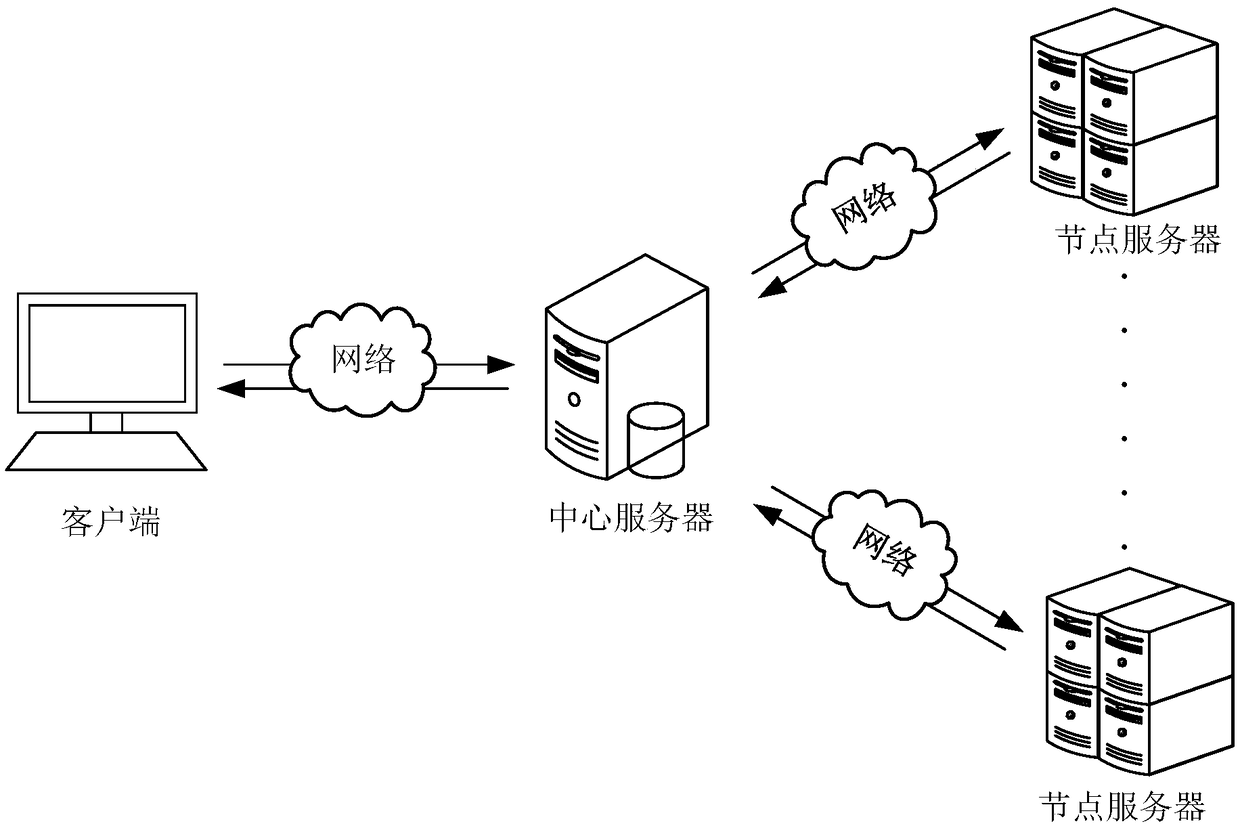
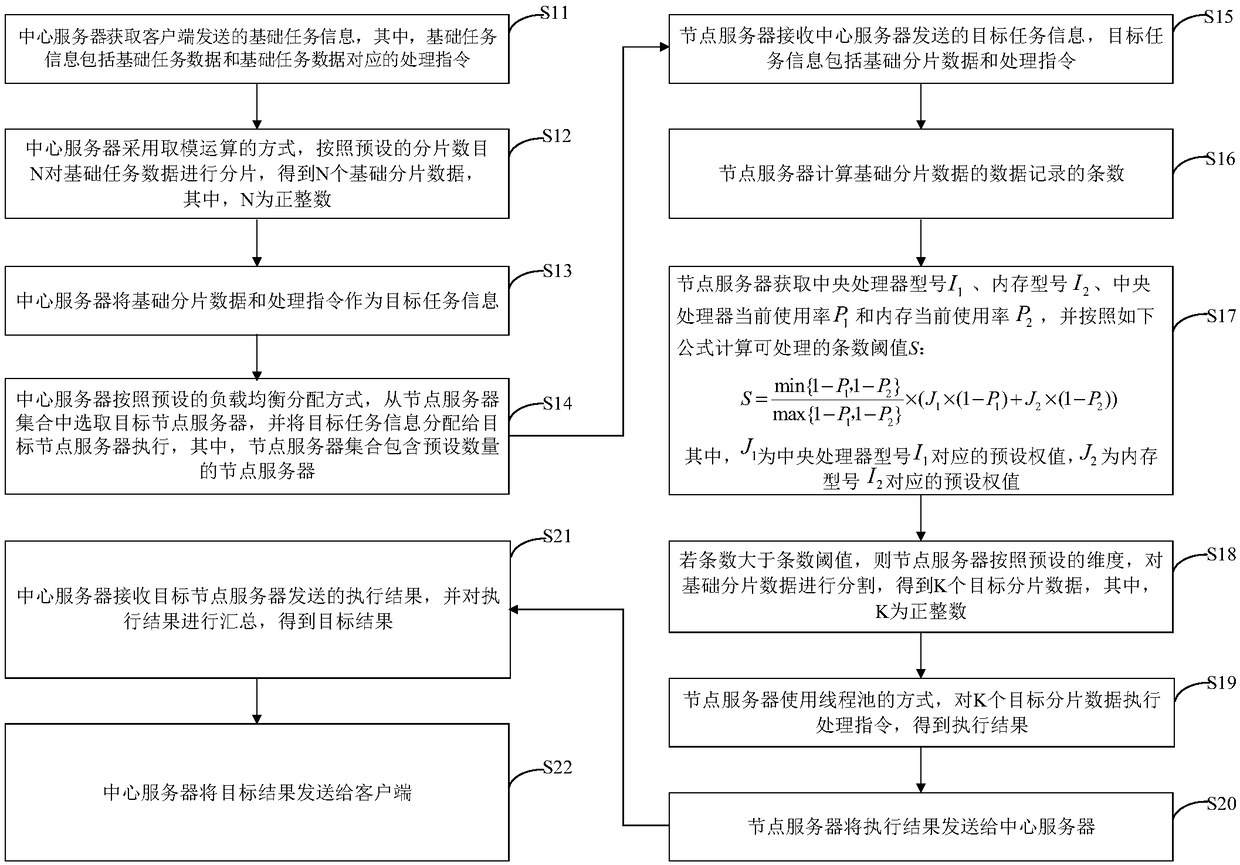
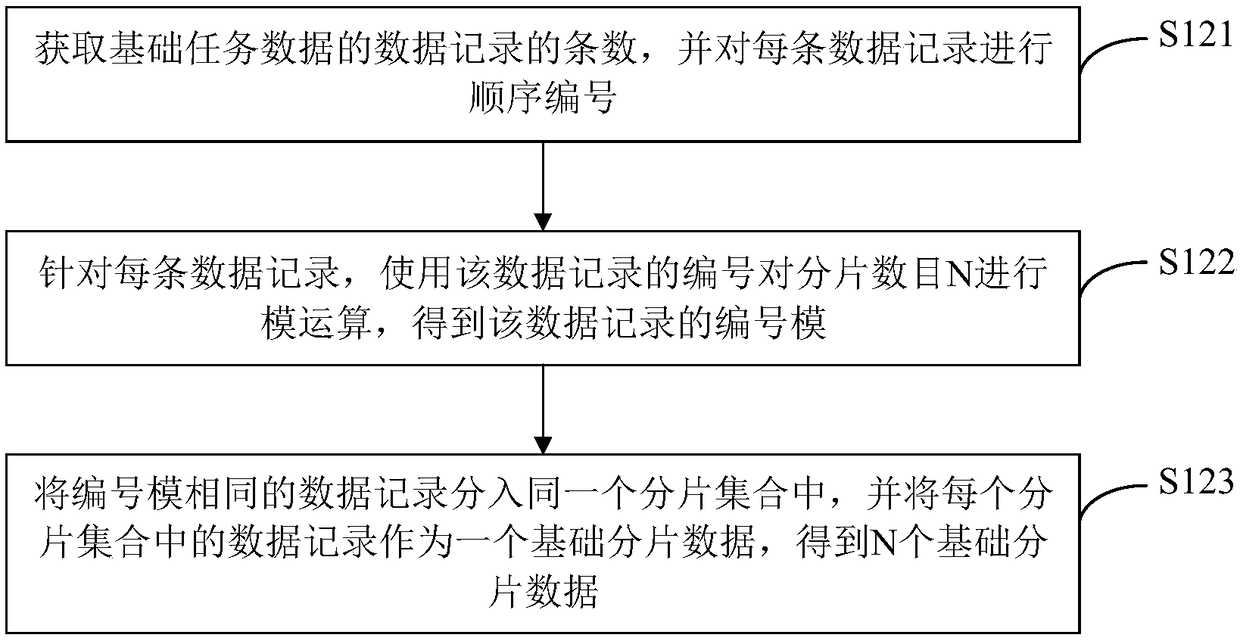
DATA PROCESSING METHOD, device, COMPUTER device, AND STORAGE MEDIUM
PendingCN109144731AGuaranteed stabilityImprove processing efficiencyProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationProcessing InstructionModulo operation
The invention discloses a method for processing data, a DEVICE, a COMPUTER DEVICE AND a STORAGE MEDIUM. The method comprises: the central server obtains the basic task information sent by the client,the basic task data is sliced by modulo operation, and the sliced data and processing instructions are sent to the node server as the target task information for execution. The task with large amountof data is reasonably distributed to the distributed node server for execution, and the data processing efficiency is improved. After receiving the target task information, depending on the running state of the current node server, the threshold number of strips that can be processed is calculated, and tasks that exceed the number threshold are segmented, the task data after segmentation is executed in the way of thread pool, and the execution result is returned to the central server, so that the node server can dynamically set the threshold value of the number of pieces according to its own running state, and use multi-threads to process, thus improving the stability and processing efficiency in the data processing process.
Owner:CHINA PING AN LIFE INSURANCE CO LTD
Consensus Verification Method Based on Block Chain, Digger and Block Chain System
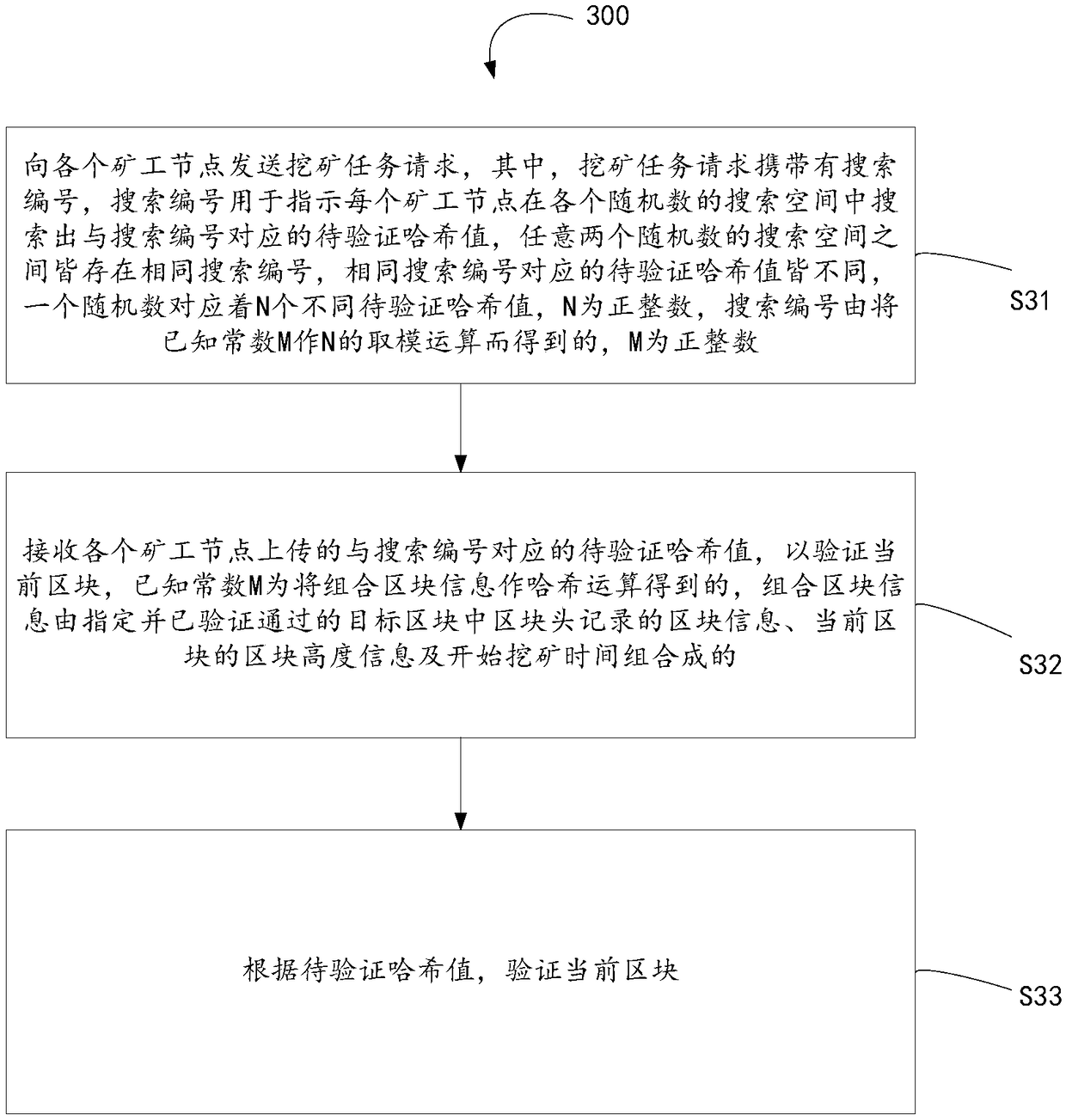
InactiveCN109146484AReduce consumptionBlock out smoothlyPayment protocolsPayment circuitsStart timeValidation methods
The invention relates to the technical field of block chains, in particular to a consensus verification method based on block chains, a mining machine and a block chain system. The method comprises the following steps of: sending a mining task request to each miner node, wherein the mining task request carries a search number, and the search number being obtained by performing a modulo operation of N on a known constant M; the hash value to be verified corresponding to the search number uploaded by each miner node being received, and the known constant M being obtained by hashing the combinedblock information, which is composed of the block information recorded by the block head in the current block, the block height information of the current block and the mining start time; validating the current block based on the hash value to be validated. Because the hash values corresponding to the same search number are different, the proxy node can avoid repeating the same verification work,thereby saving energy consumption relatively.
Owner:SHENZHEN FIIIPAY CO LTD
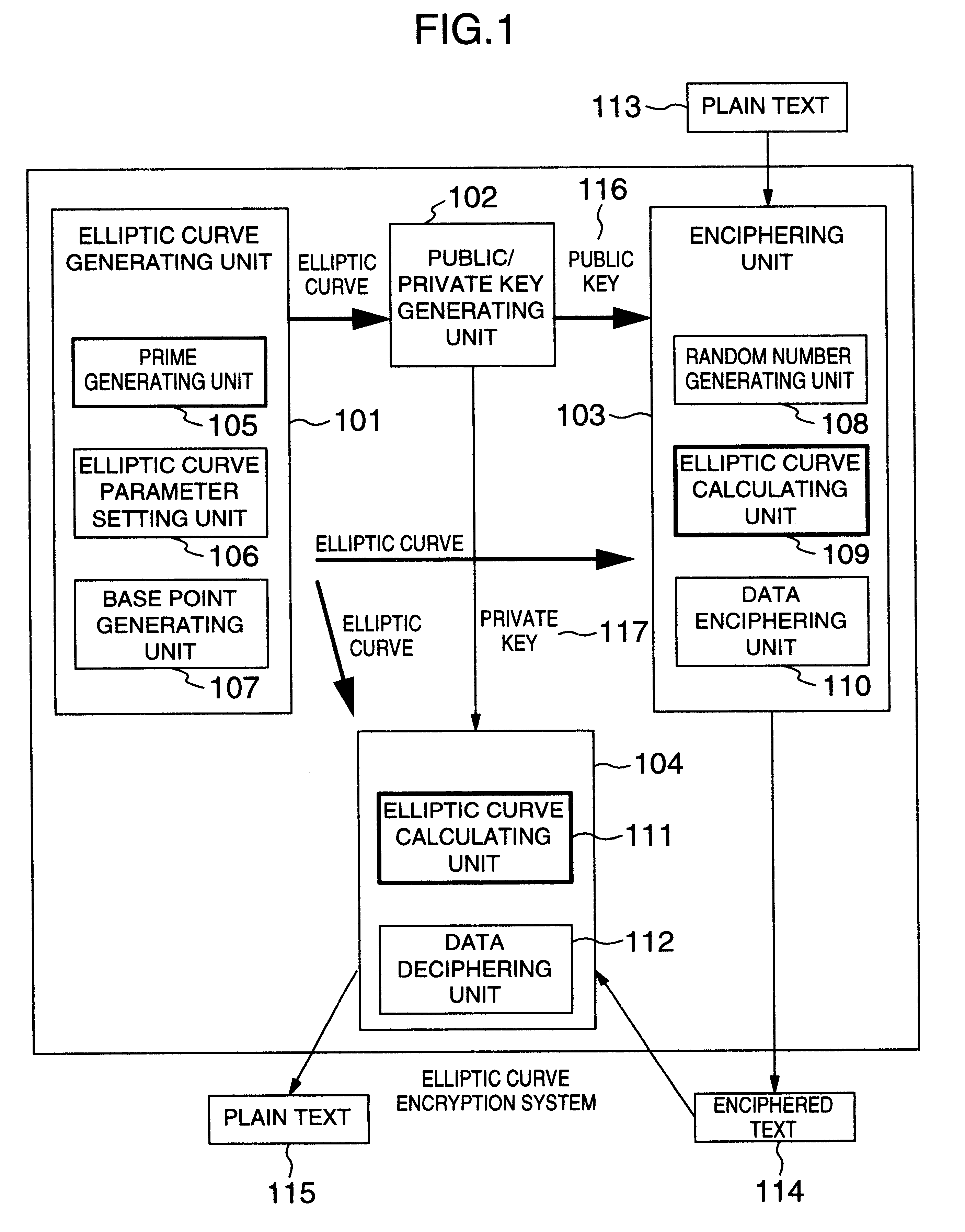
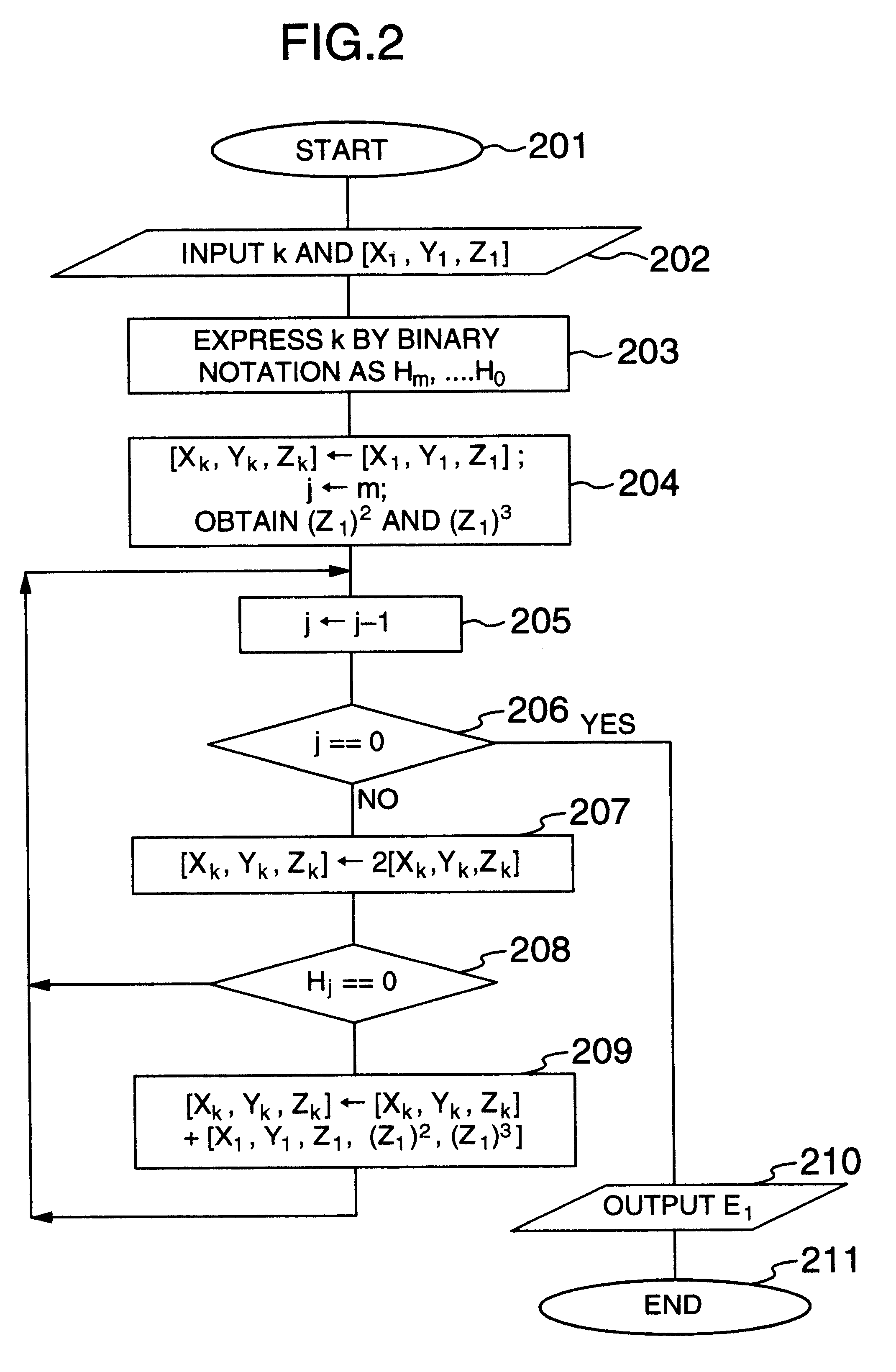
Elliptic curve encryption method and system
InactiveUS6480606B1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationEncryptionModulo operation
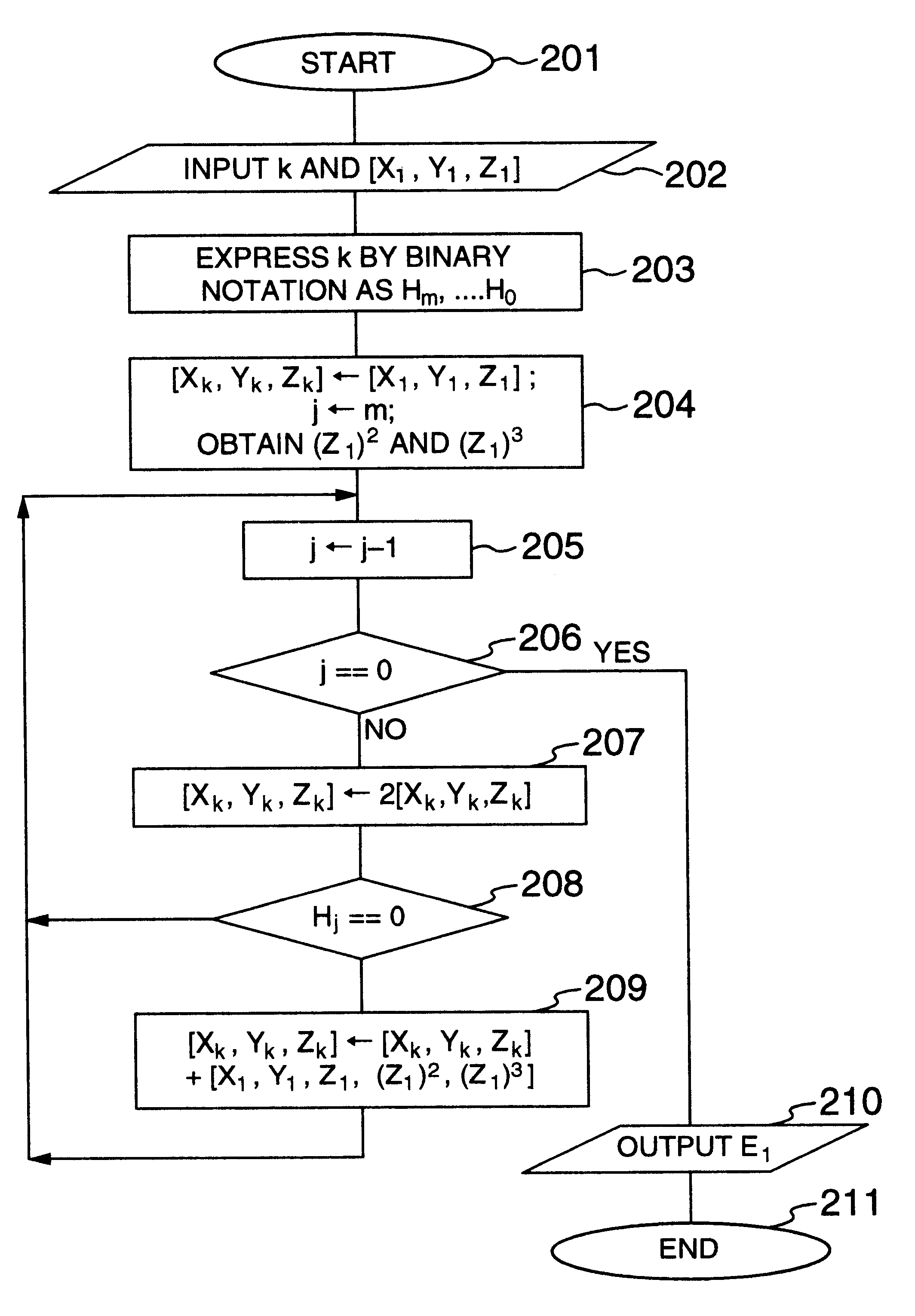
In encryption techniques using an elliptic curve, in order to use a homogeneous coordinate system [X, Y, Z], a high speed [X1, Y1, Z1, (Z1)2, (Z1)3] for the addition and a high speed [X1, Y1, Z1] for the doubling the following schemes are provided: (1) Addition is executed by [X3, Y3, Z3]=[X1, Y1, Z1, (Z1)2, (Z1)3]+[X2, Y2, Z2]. (2) Doubling is executed by a conventional [X3, Y3, Z3]=2[X1, Y1, Z1] and an addition operation is executed by [X3, Y3, Z3]=[X1, Y1, Z1, (Z1)2, (Z1)3]+[X2, Y2, Z2]. It is also required to speed up the multiplication modulo operation. The Montgomery multiplication modulo operation is speeded up by using the following forms of the definition order (prime): (3) the multiplication modulo operation is executed at high speed by using a prime having a form of p=Abn+B where 0<A<2w, 0<B<2w, b=2w; and w, A, b, n and B are positive integers.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Coordinated cyclic shift and sequence hopping for ZADOFF-CHU, modified ZADOFF-CHU, and block-wise spreading sequences
InactiveCN101926112ARadio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsCell specificRandom frequency hopping
A cyclic shift of a reference signal is quantized as a combination of a cell specific cyclic shift with an outcome of a pseudo-random hopping, and an indication of the cell specific cyclic shift is broadcast in the cell. In one embodiment the cyclic shift is quantized as a modulo operation on a sum of the cell specific cyclic shift, the outcome of the pseudo-random hopping, and a user specific cyclic shift, in which case an indication of the user specific cyclic shift is sent in an uplink resource allocation and a user sends its cyclically shifted reference signal in the uplink resource allocated by the uplink resource allocation. The cyclic shift may also be quantized according to length of the reference signal as cyclic_shift_symbol= (cyclic_shift_value * length of the reference signal) / 12; where cyclic_shift_value is between zero and eleven and cyclic_shift_symbol is the amount of cyclic shift given in reference signal symbols.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
Method of preventing fault-injection attacks on chinese remainder theorem-rivest shamir adleman cryptographic operations and recording medium for storing program implementing the same
InactiveUS20130208886A1Computationally efficientAvoid attackDigital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareChinese remainder theorem
Disclosed herein are a method of preventing fault-injection attacks on Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT)-Rivest Shamir Adleman (RSA) cryptographic operations, and a recording medium for storing a program implementing the same. First, the method receives first and second primes, that is, different primes, and a randomly selected prime, that is, a random prime, which are used for CRT-RSA cryptographic operations. Thereafter, a cumulative value is calculated by performing an XOR (Exclusive OR) operation on the first prime, the second prime, and the random prime using a push function. Thereafter, the first prime, the second prime, and the random prime are loaded by performing an XOR operation on the cumulative value using a pop function corresponding to the push function. Finally, CRT-RSA operations are executed by computing modulo operations based on the first prime and the second prime.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
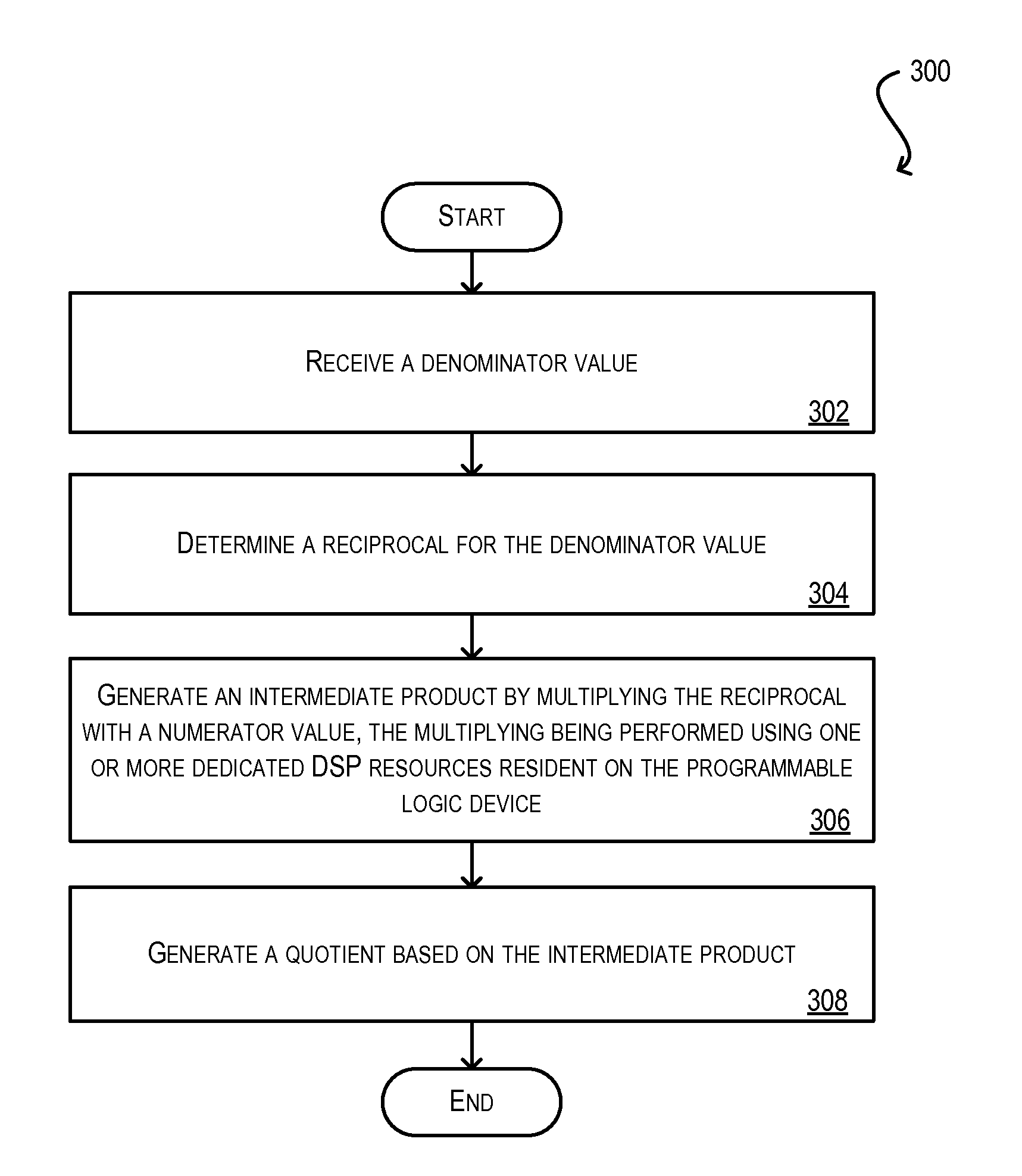
High speed design for division & modulo operations
InactiveUS20120166512A1Efficient executionHigh speed machiningComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital signal processingProgrammable logic device
Techniques for efficiently performing division and modulo operations in a programmable logic device. In one set of embodiments, the division and modulo operations are synthesized as one or more alternative arithmetic operations, such as multiplication and / or subtraction operations. The alternative arithmetic operations are then implemented using dedicated digital signal processing (DSP) resources, rather than non-dedicated logic resources, resident on a programmable logic device. In one embodiment, the programmable logic device is a field-programmable gate array (FPGA), and the dedicated DSP resources are pre-fabricated on the FPGA. Embodiments of the present invention may be used in Ethernet-based network devices to support the high-speed packet processing necessary for 100G Ethernet, 32-port (or greater) trunking, 32-port / path (or greater) load balancing (such as 32-path ECMP), and the like.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
Method and device for synchronously capturing pseudo codes in real time
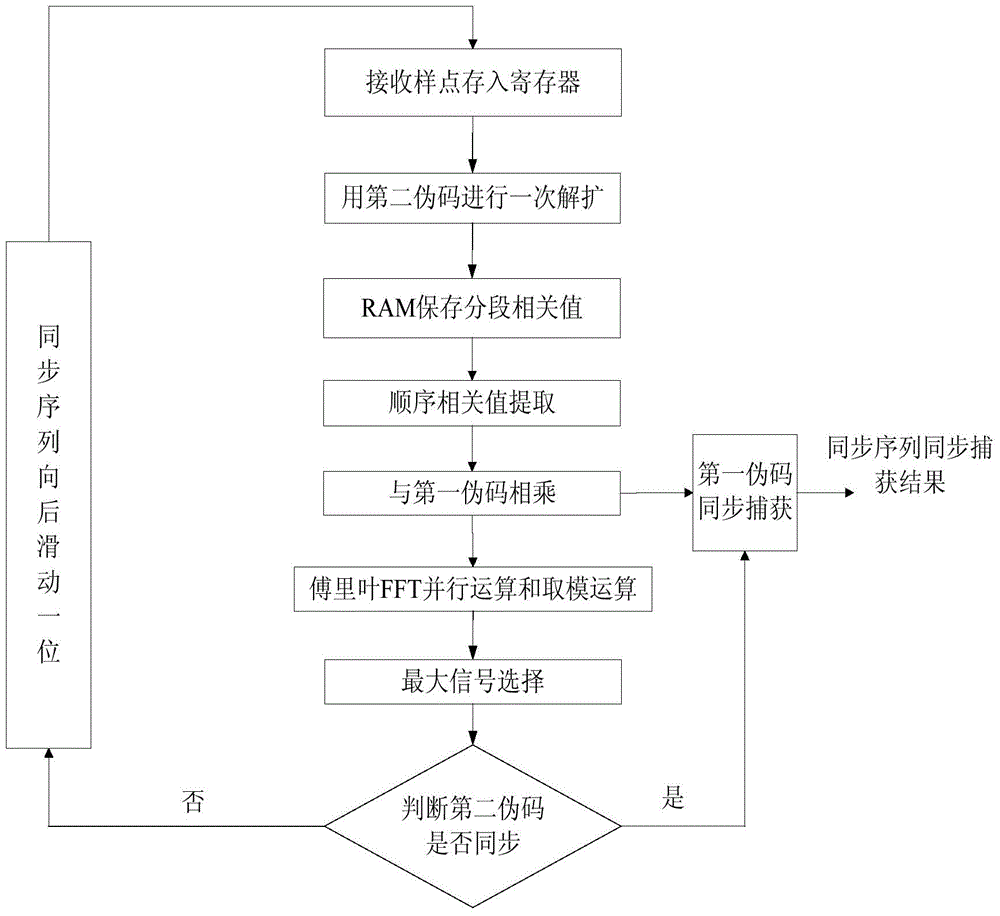
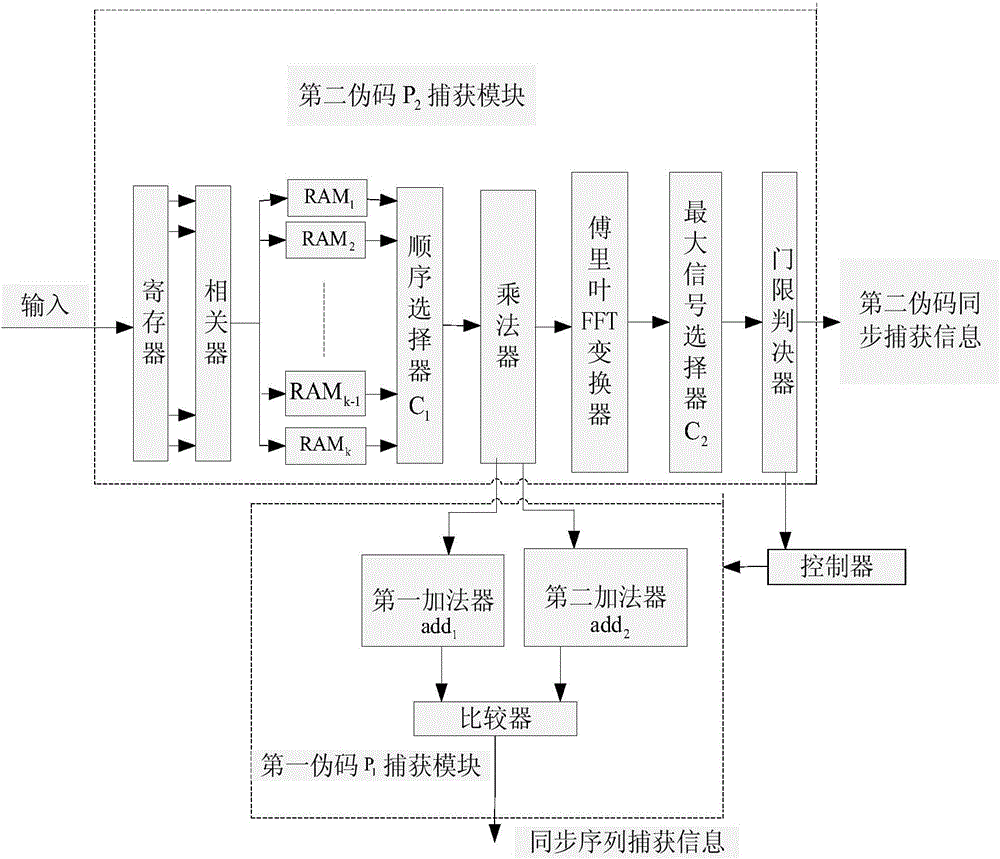
InactiveCN104065397ASolve the problem of blurred sync positionImprove capture success rateTransmissionPseudo-codeComputer science
The invention discloses a method and a device for synchronously capturing pseudo codes in real time and mainly aims to solve the problem that real-time capture of long-period pseudo codes is difficult in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: first, a synchronous head is spectrum-spread by adoption of a first pseudo code and a second pseudo code to generate a synchronization sequence, and the synchronization sequence is transmitted; second, a receiving end de-spreads a received signal to obtain segment correlation values and stores the segment correlation values; third, the segment correlation values are sequentially extracted and multiplied by the second pseudo code to obtain part of a correlation value sequence; fourth, modulo operation is performed on the sequence after FFT operation, the peak of the module value is selected and compared with a set threshold, the second pseudo code is successfully captured if the peak is greater than or equal to the threshold, or the method returns to the second step until the second pseudo code is synchronously captured; and fifth, the first half of a superposition value and the second half of the superposition value of the part of correlation value sequence are compared, synchronous capture succeeds if the two are approximately equal, or synchronous capture fails. The method and the device of the invention has the advantages of being capable of capturing long-period pseudo codes in real time, and can be used for real-time synchronous capture in burst communication.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Improved re-transmission capability in semi-persistent transmission
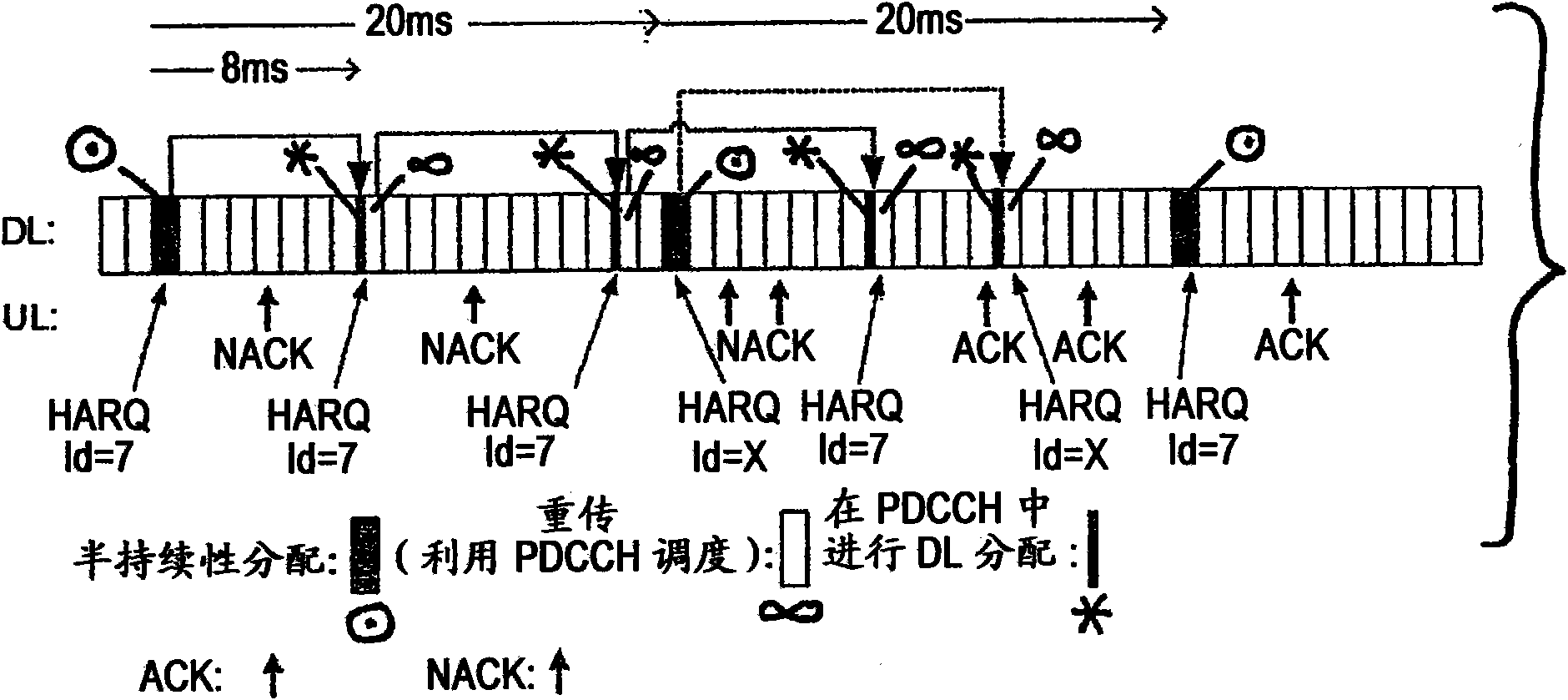
InactiveCN101874377AError prevention/detection by using return channelControl signalProcess identification
One or more hybrid automatic repeat request process identifications are configured for scheduling without associated control signaling. A particular HARQ process ID to be assumed for a given subframe is determined based on at least one of: a) system frame number; b) number of hybrid automatic repeat request processes that are allocated for semi- persistent scheduling; and c) periodicity for semi-persistent scheduling. In various embodiments: a) is broadcast and b) and c) are sent via RRC signaling; and the assumed particular HARQ process ID is determined as a function of [Current TTI / SP_Period] mod Num_SP_HARQ: wherein Current TTI is a number for the given subframe derived from the system frame number and the term [Current TTI / SP_Period] is rounded to an integer prior to the modulo operation; SP_Period is the periodicity of the semi-persistent scheduling; and Num_SP_HARQ is the number of hybrid automatic repeat request processes that are allocated for semi-persistent scheduling.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
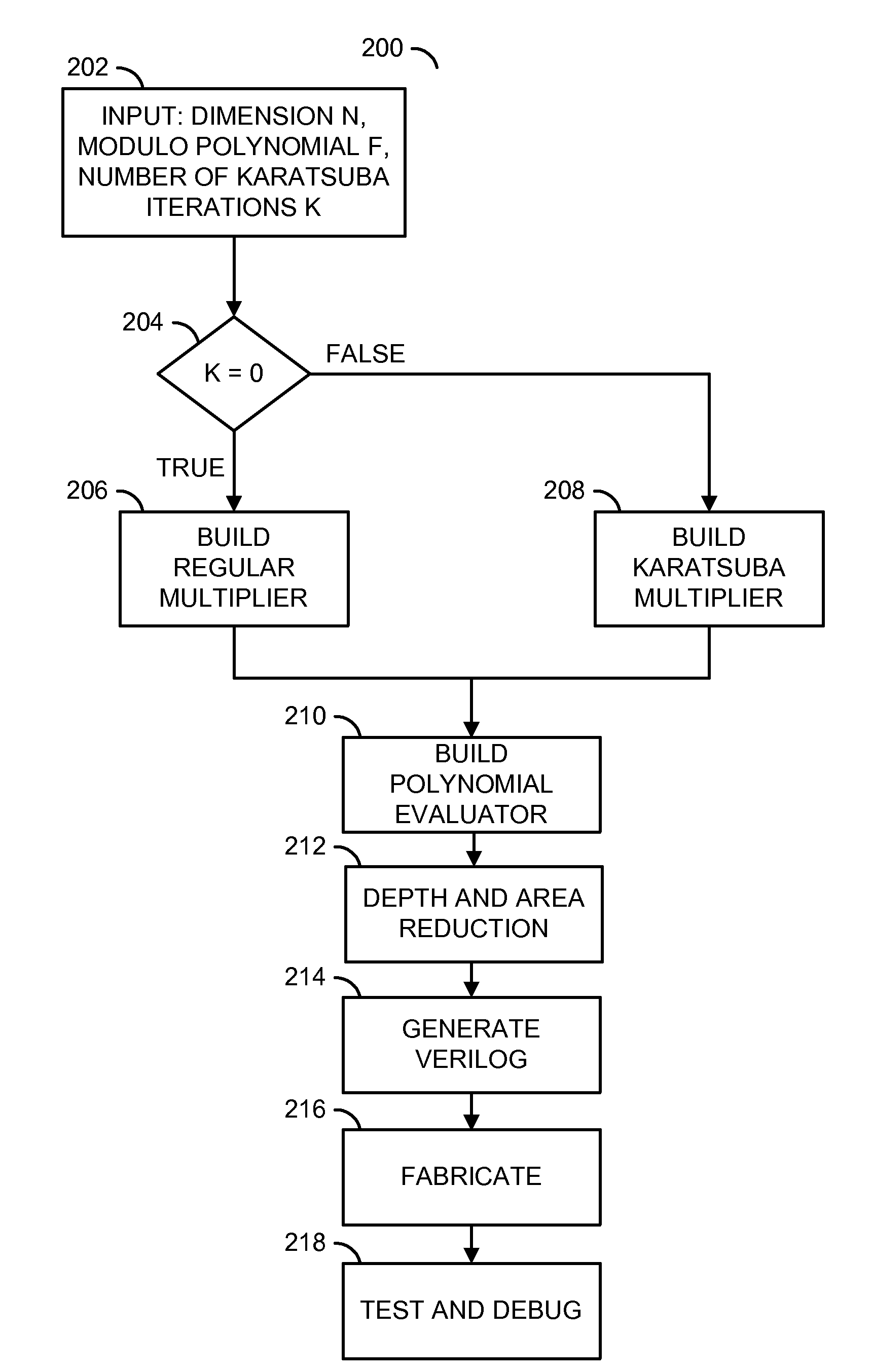
Low depth combinational finite field multiplier
InactiveUS20120226731A1Easy to testLow overall depthComputation using non-contact making devicesSpecial data processing applicationsBinary multiplierTheoretical computer science
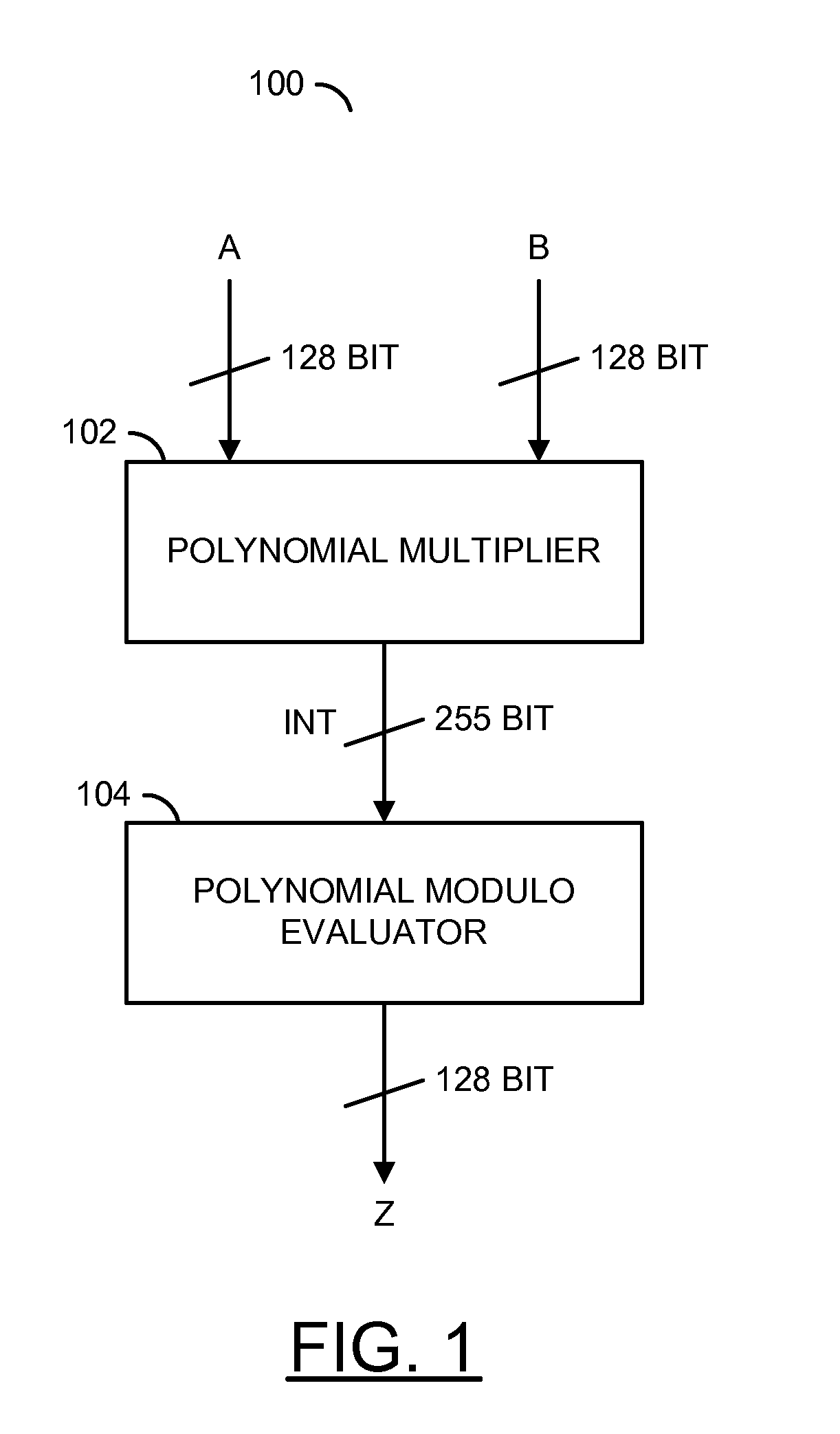
A method for generating a design of a multiplier is disclosed. The method generally includes steps (A) to (C). Step (A) may generate a first circuit comprising a plurality of polynomial results of a particular multiplier scheme based on a plurality of parameters of the multiplier. The first circuit is generally configured to multiply a plurality of polynomials. Step (B) may generate a second circuit comprising a plurality of polynomial evaluators based on the parameters. The second circuit may be (i) connected to the first circuit and (ii) configured to evaluate a polynomial modulo operation. Step (C) may generate the design of the multiplier in combinational logic by optimizing a depth of a plurality of logic gates through the first circuit and the second circuit. A product of the polynomials generally resides in a finite field.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Data block interleaving and deinterleaving method and apparatus for communication equipments
ActiveUS20150263765A1Simple hardware implementationReduce hardware complexityBurst error correctionCode conversionHardware implementationsComputer science
The present invention relates to communication field, disclosing a data block interleaving and deinterleaving method and apparatus for communication equipments. In the present invention, a recursive method for calculating interleaver or deinterleaver addresses for existing power line communication standards is proposed. The complex modulo operation is simplified to a series of Add-Compare-Subtract operations. Therefore, the hardware implementation complexity is significantly reduced.
Owner:HI TREND TECH SHANGHAI
System and method for connection identifier synchronization in a communication system
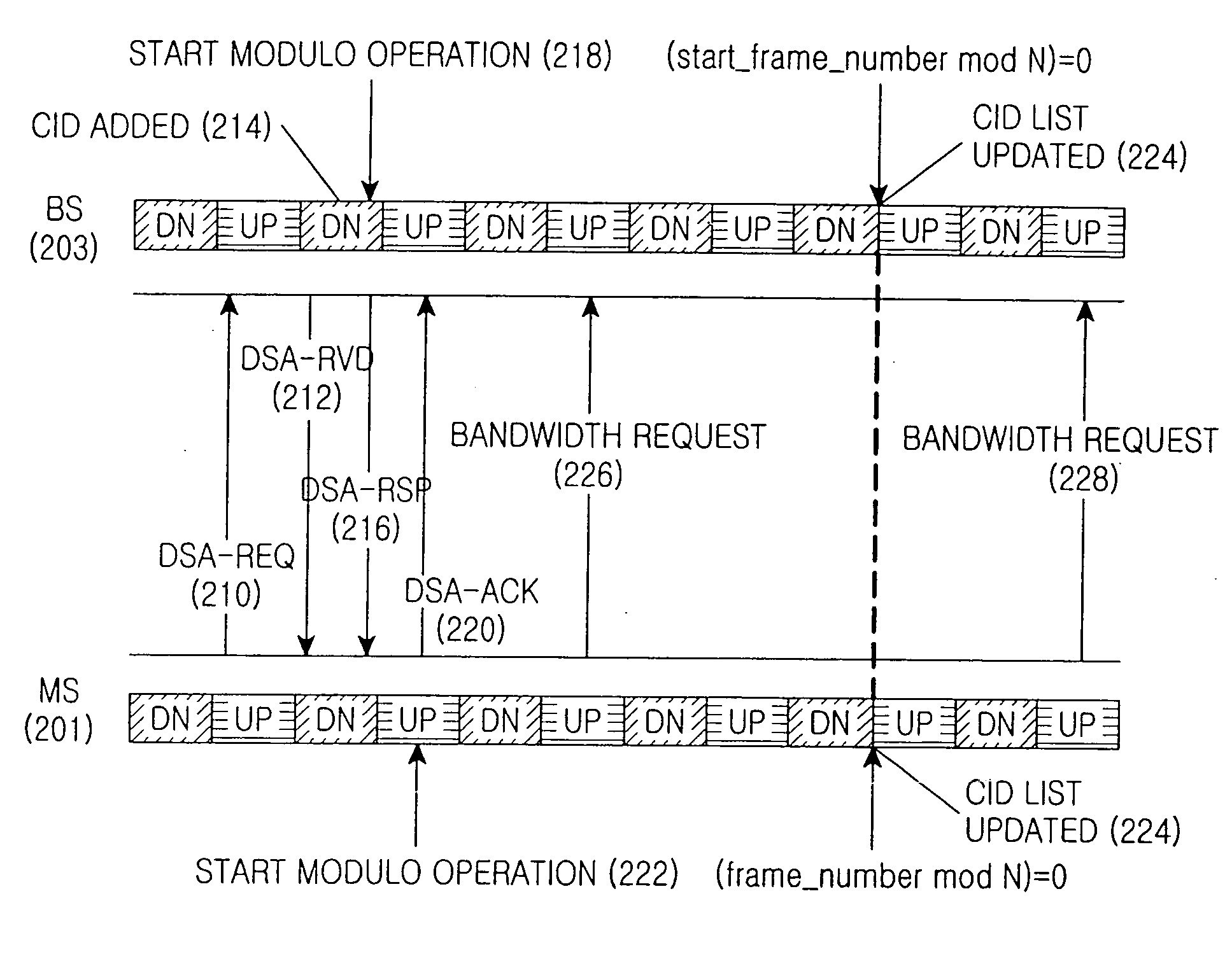
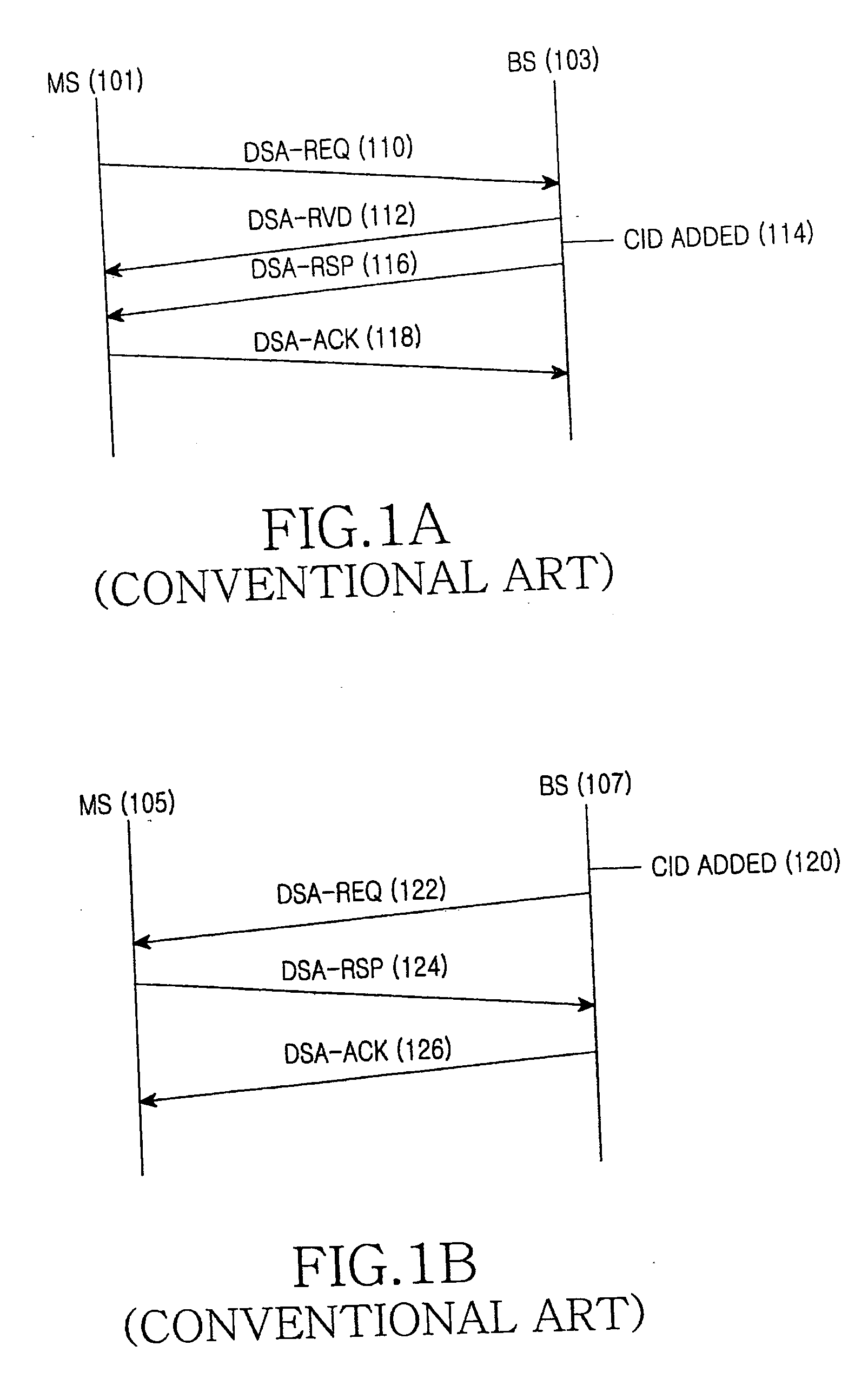
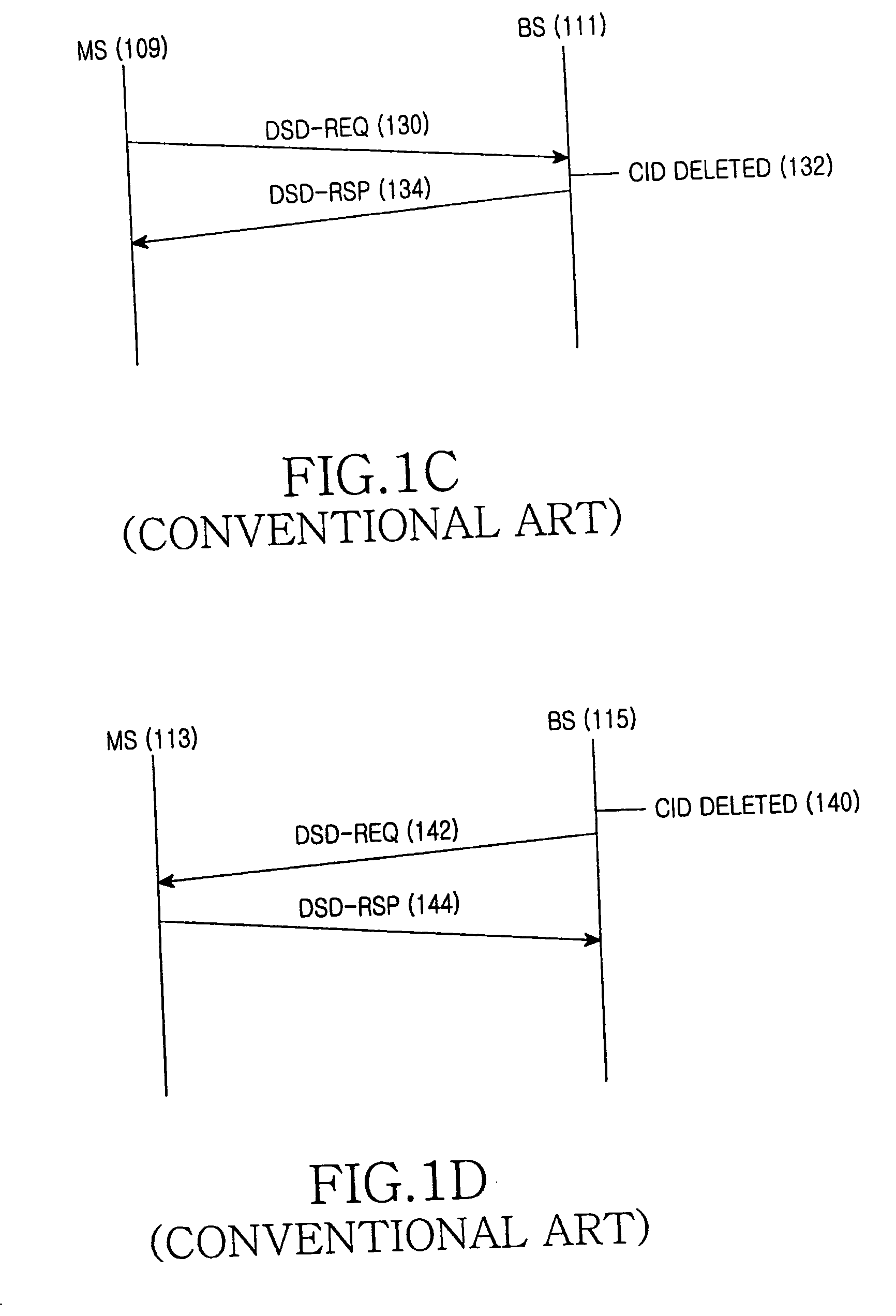
A method is provided for synchronizing Connection IDentifiers (CIDs) of a first station and a second station in a communication system. The CID synchronization method includes sending, by the first station, a first message for requesting addition of a service flow identified by a CID to the second station; sending, by the second station, a second message which is a response message to the first message, and at the same time, setting a number of a frame where the second message is transmitted as a first start frame number; sending, by the first station, a third message for acknowledging receipt of the second message to the second station, and at the same time, setting a number of a frame where the third message is transmitted as a second start frame number; performing, by each of the first station and the second station, a modulo operation on a frame having the first or second start frame number and its succeeding frames using a positive integer for each frame, and detecting a number of a frame where a result value of the modulo operation becomes zero (0); and simultaneously updating CID lists of the first station and the second station at a frame having the detected frame number with regard to a CID of the added service flow.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for mapping memory addresses to corresponding cache entries
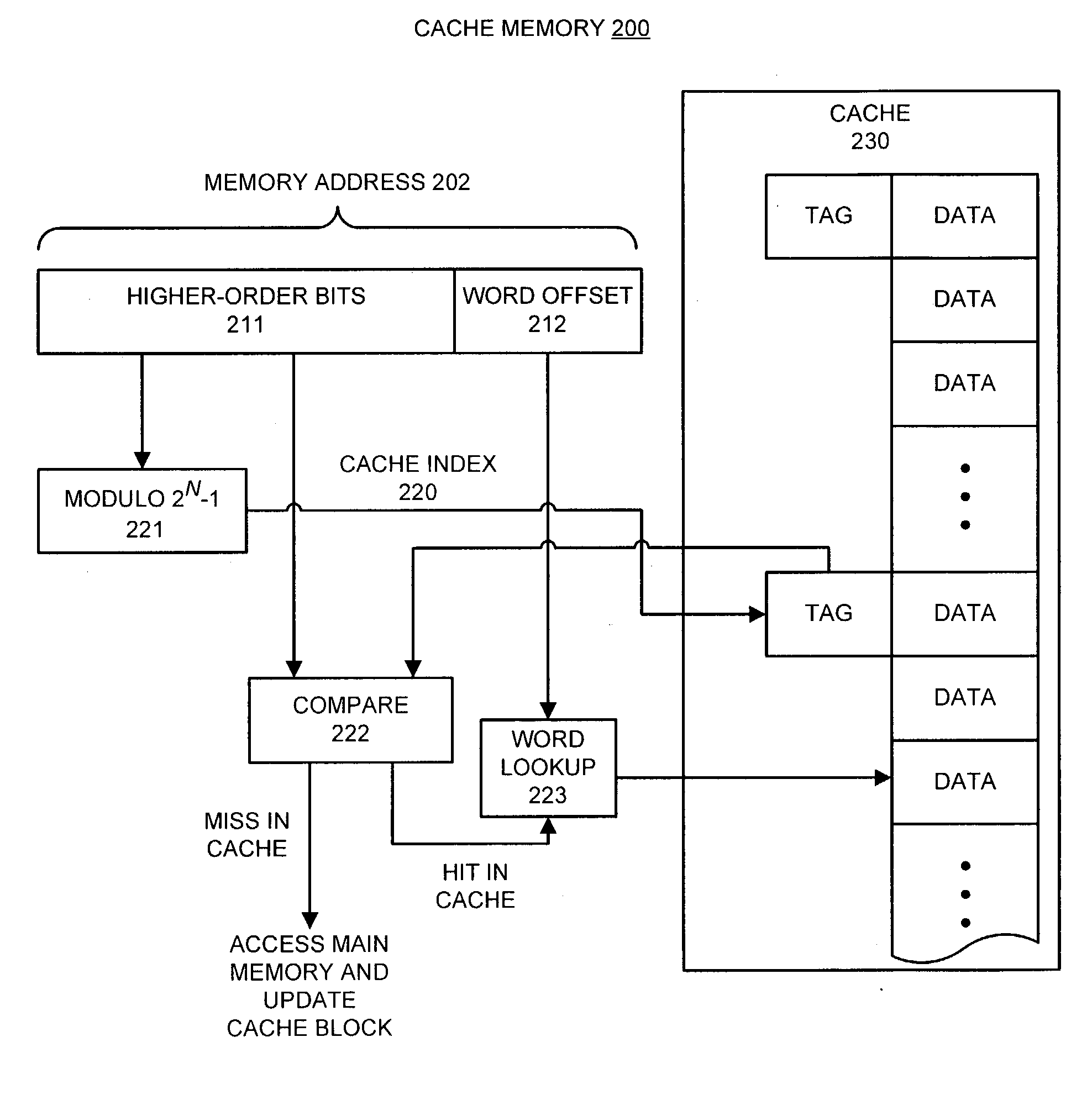
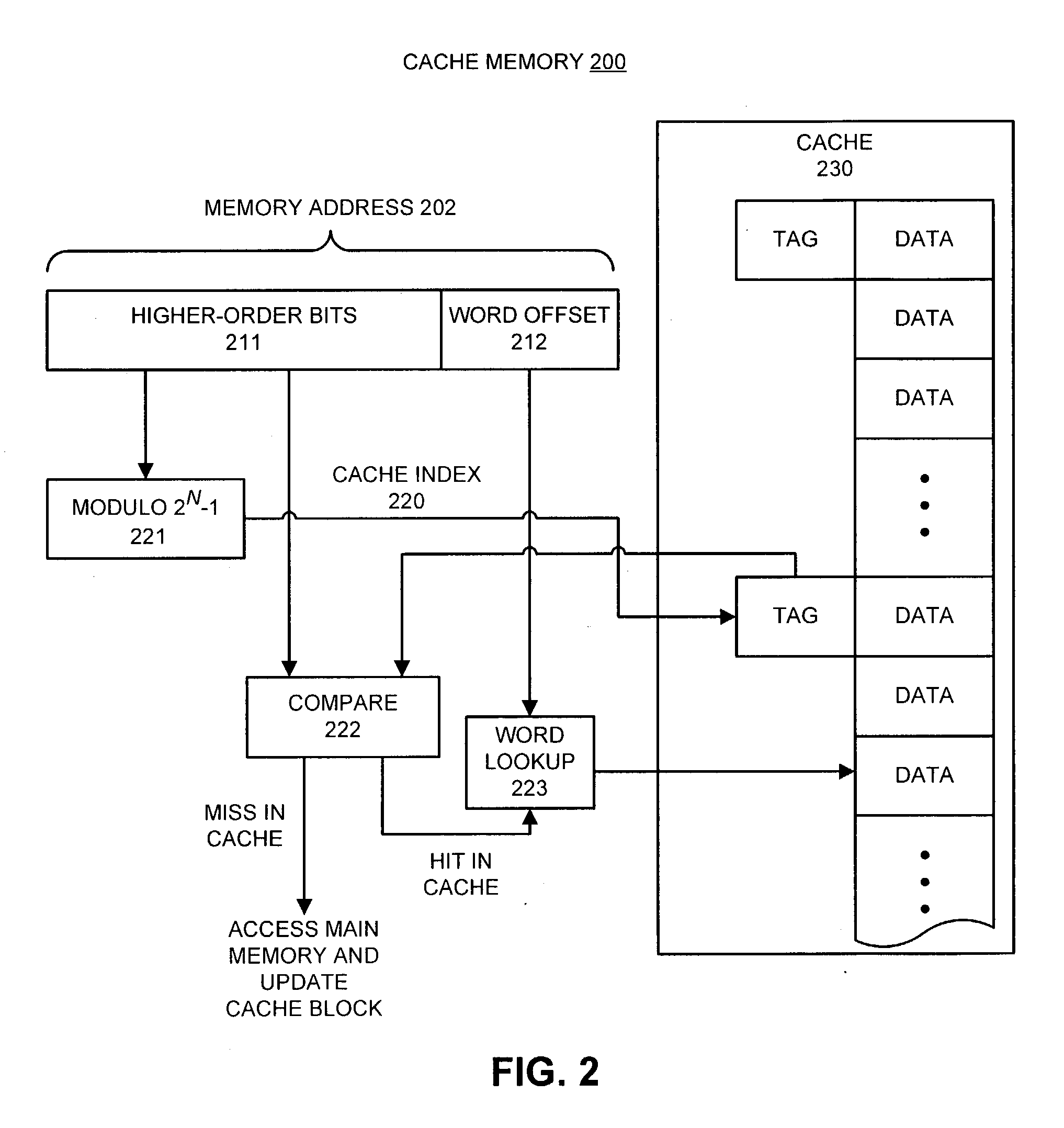
ActiveUS20040225859A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationMemory addressParallel computing
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for mapping memory addresses to cache entries. The system operates by first receiving a memory request at the cache memory, wherein the memory request includes a memory address. The system then partitions the memory address into a set of word offset bits and a set of higher-order bits. Next, the system maps the memory address to a cache entry by computing a modulo operation on the higher-order bits with respect to an integer and using the result as the cache index.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Encryption domain image reversible data hiding method based on neighborhood prediction
ActiveCN109803142AIncrease embedding capacityImprove forecast accuracyDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionImage segmentation
The invention discloses an encrypted domain image reversible data hiding method based on neighborhood prediction. The method comprises three steps including Image Encryption reversible data hiding and; secret information extraction; In the image encryption part, an image is segmented into image blocks; the pixel value of each pixel point in each image block and the value of one element in the random sequence are added for encryption, and modulo operation is performed on 256 to realize encryption ; the linear prediction difference values meeting the specific conditions in the image blocks arekept consistent before and after encryption; data hiding in the encrypted image can be ensured; The method has the advantages that hidden information extraction and image decryption are achieved, complete separation of hidden information extraction and image decryption is guaranteed, hidden information can be effectively extracted in an encryption domain, hidden information can also be effectivelyextracted in a decryption domain, the practicability is higher, and meanwhile it can be guaranteed that an original image can be restored without distortion after the hidden information is extracted.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A converter
InactiveCN102111155AImprove Noise PerformanceProcessing satisfactionAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsNoise shapingTheoretical computer science
A method of providing a value for each element of a sequence of elements in a converter, comprising: calculating a pointer position for the present conversion cycle (Pi+1) in accordance with an Nth order noise shaped function based on pointer positions for N previous conversion cycles (Pi to Pi-(N-1)); determining if the pointer position for the present conversion cycle (Pi+1) is in excess of the number of elements in the sequence; attributing a first component-value to all of the elements, updating the new pointer position (Pi+1) by performing a modulo operation and replacing the new pointer position (Pi+1) with the remainder value; attributing a second component-value to the elements in accordance with a (N-1)th order algorithm; attributing a third component-value to the elements in accordance with the inverse of the second component-value for the previous conversion cycle; and adding the first, second and third component-values for each element.
Owner:NXP BV
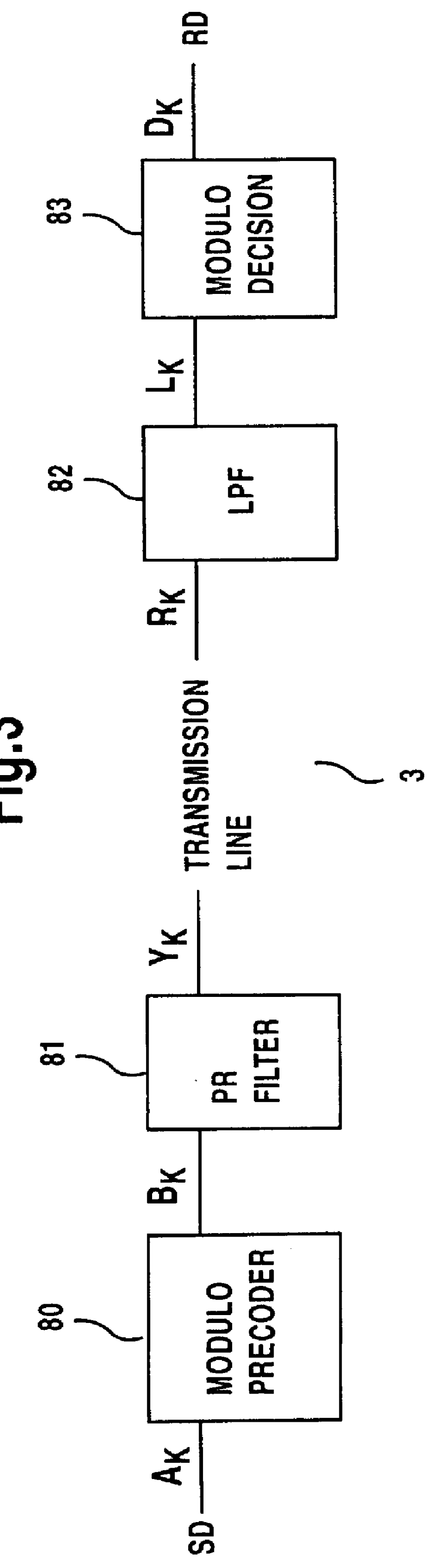
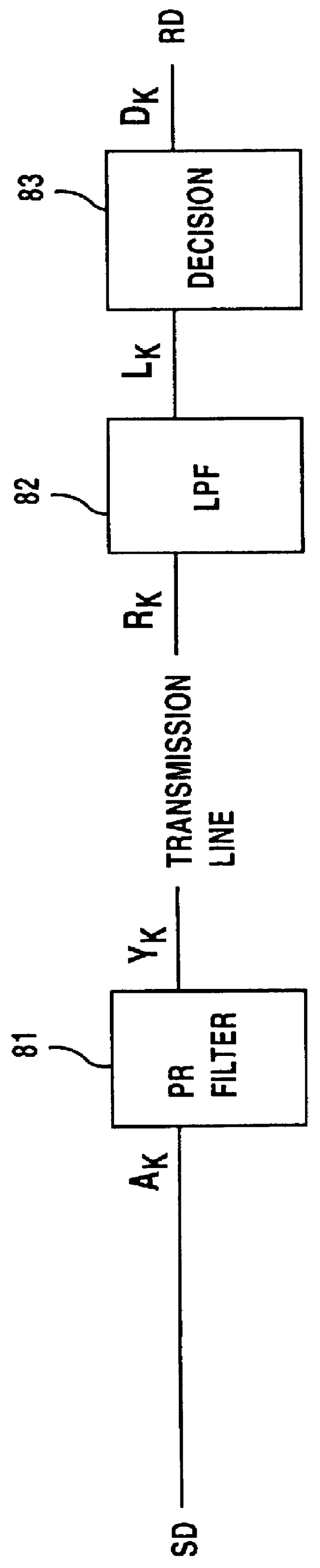
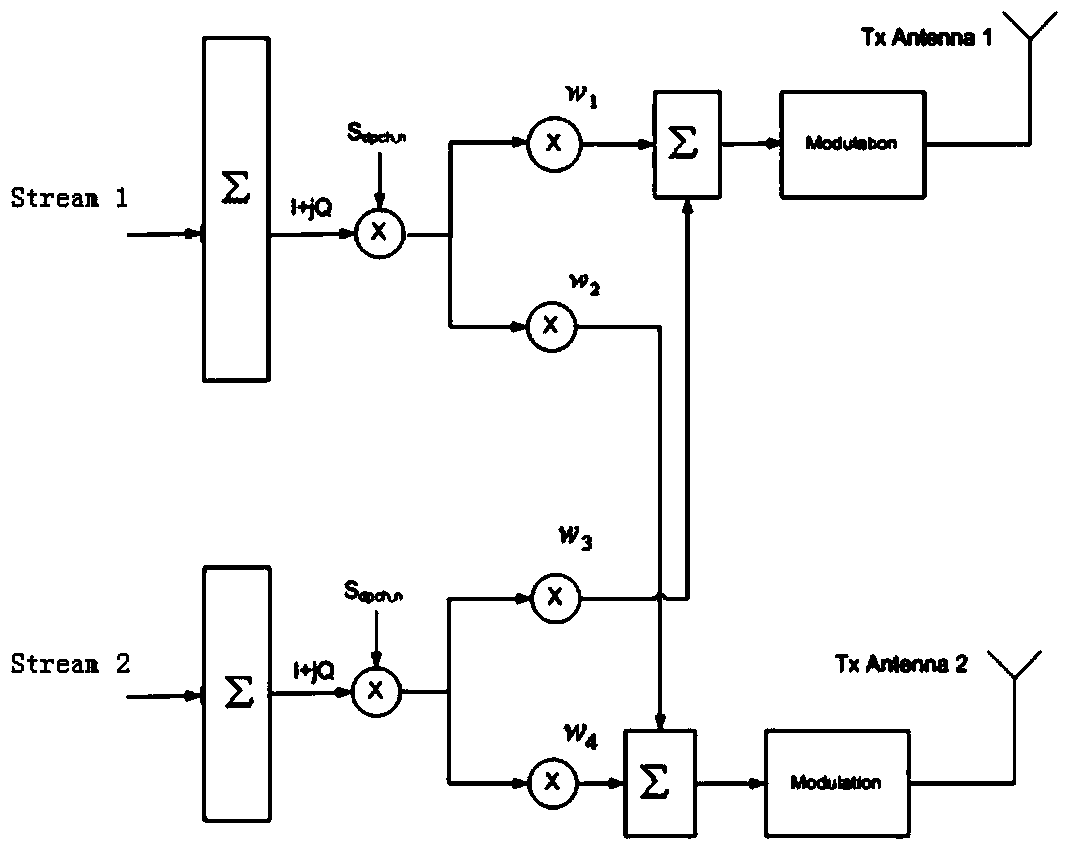
Process and system for transferring vector signal with precoding for signal power reduction
A transfer process in which, an original vector signal is precoded to an intermediately-precoded vector signal, and the extended modulo operation is performed when the intermediately-precoded vector signal is located outside a predetermined extended-modulo limit area, and the precoded vector signal is transferred through a system having a predetermined filtering characteristic. From the transferred vector signal, the original vector signal is detected, based on a relationship between the vector components of the original vector signal and the transferred vector signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
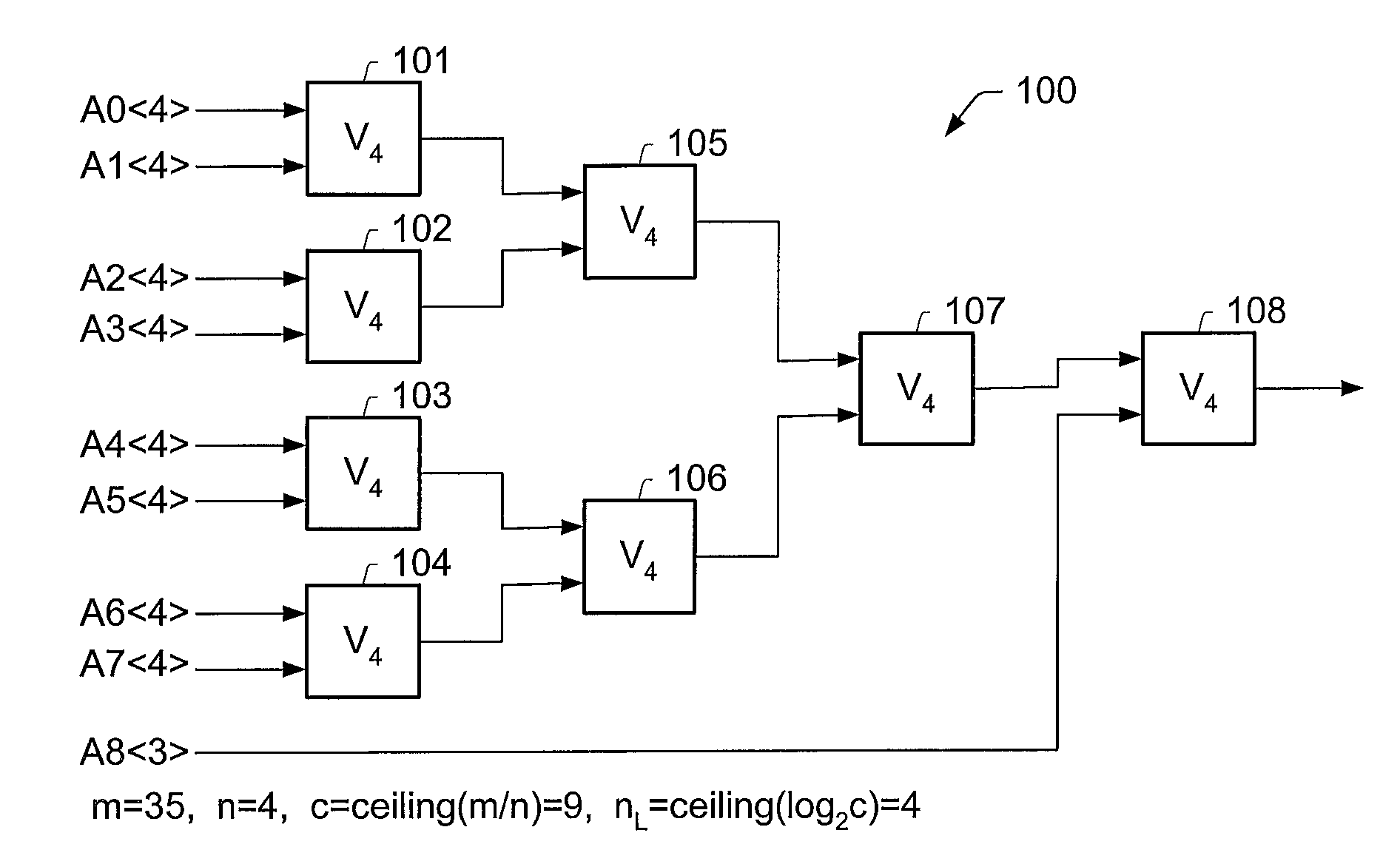
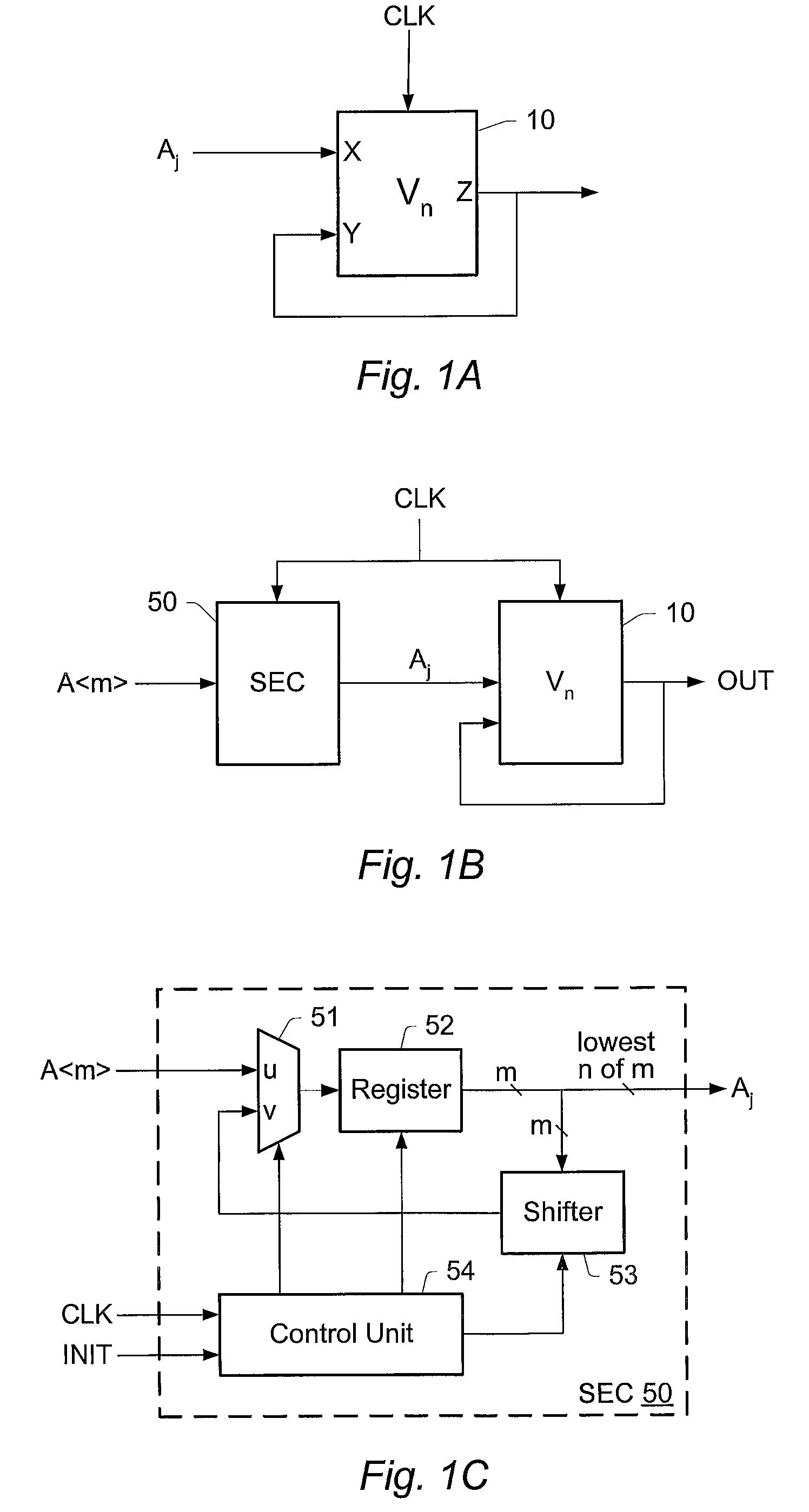
Efficient computation of the modulo operation based on divisor (2n-1)
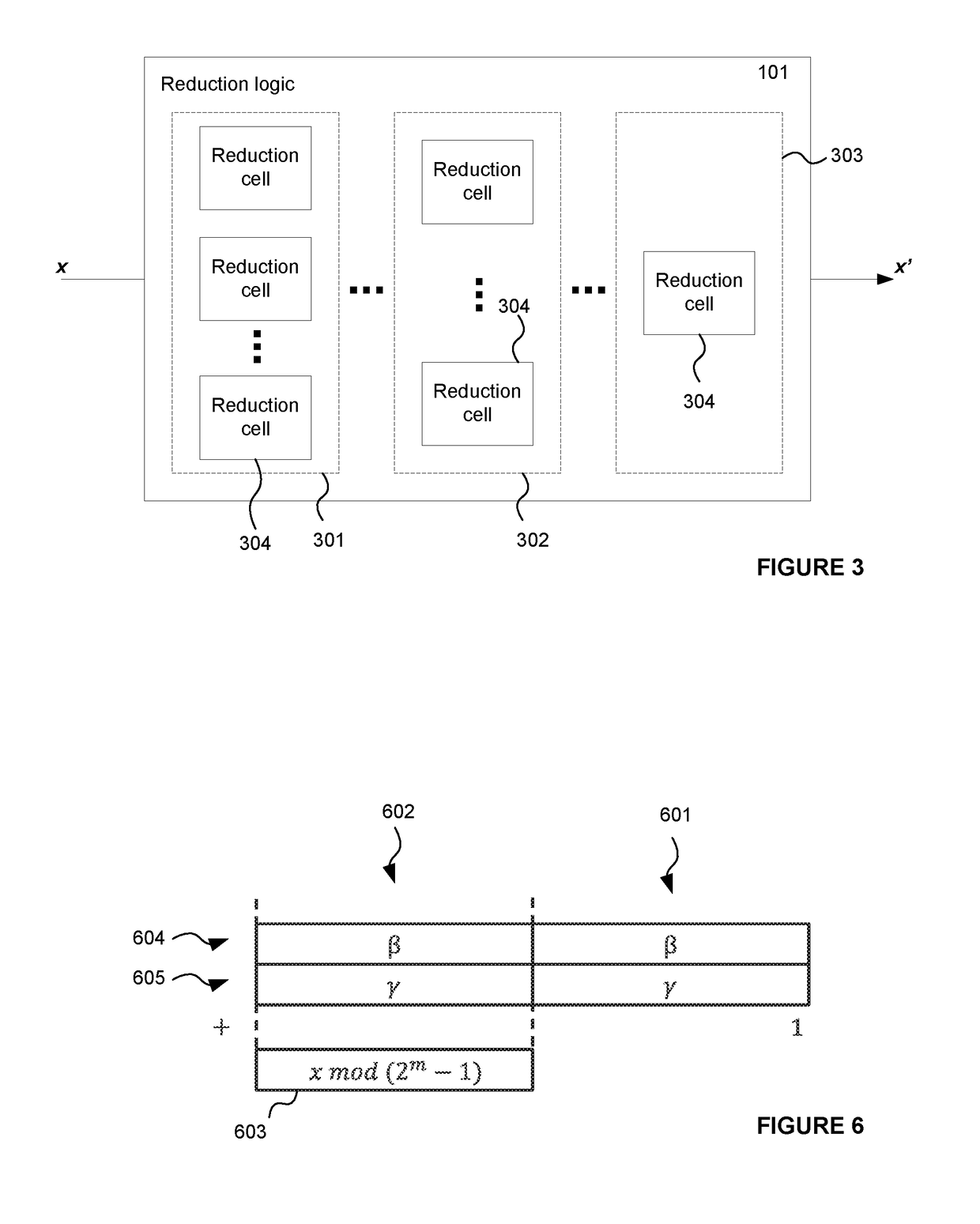
InactiveUS7849125B2Computations using residue arithmeticComputation using denominational number representationComputer scienceModulo operation
A system and method for computing A mod (2n−1), where A is an m bit quantity, where n is a positive integer, where m is greater than or equal to n. The quantity A may be partitioned into a plurality of sections, each being at most n bits long. The value A mod (2n−1) may be computed by adding the sections in mod(2n−1) fashion. This addition of the sections of A may be performed in a single clock cycle using an adder tree, or, sequentially in multiple clock cycles using a two-input adder circuit provided the output of the adder circuit is coupled to one of the two inputs. The computation A mod (2n−1) may be performed as a part of an interleaving / deinterleaving operation, or, as part of an encryption / decryption operation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Video format converter
InactiveUS6501509B1Promote conversionColor signal processing circuitsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer hardwareImage resolution
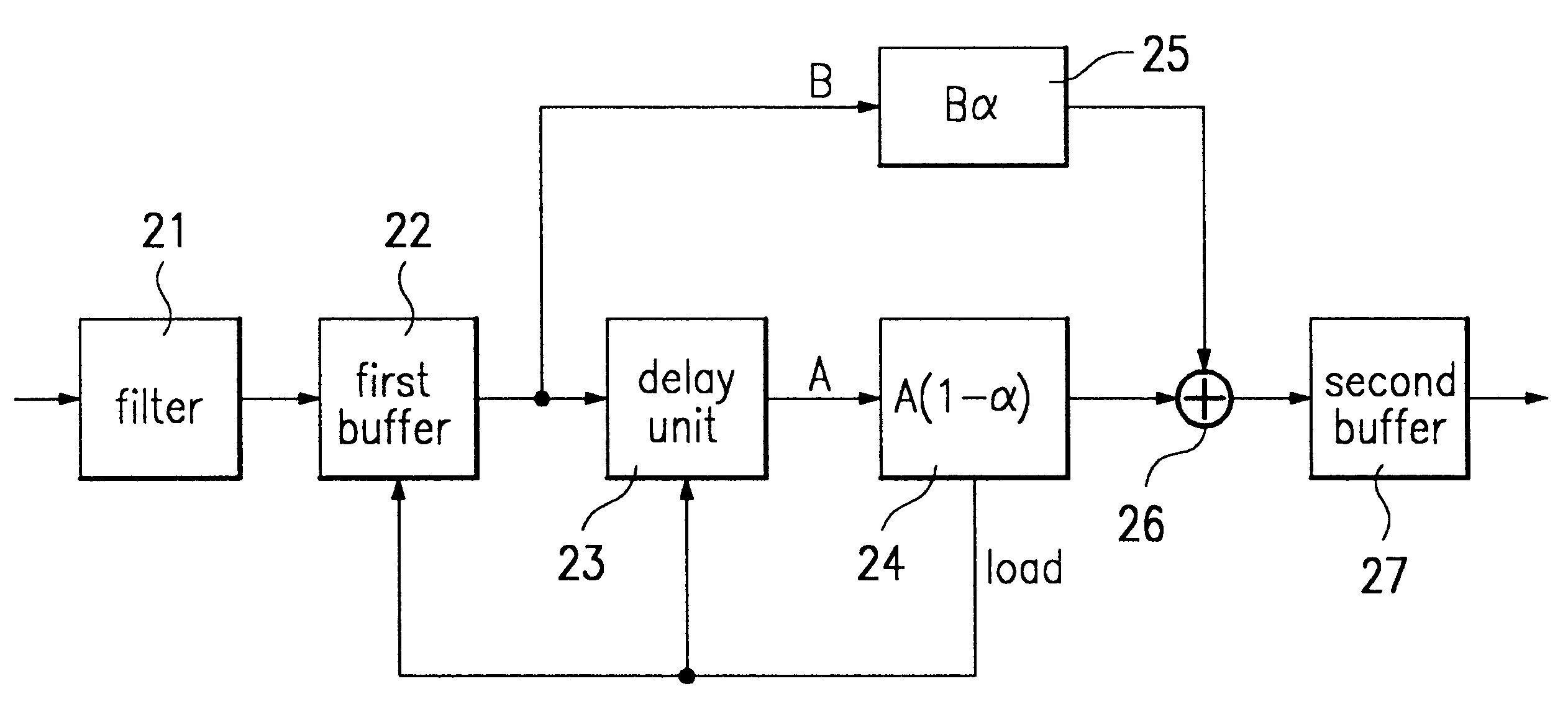
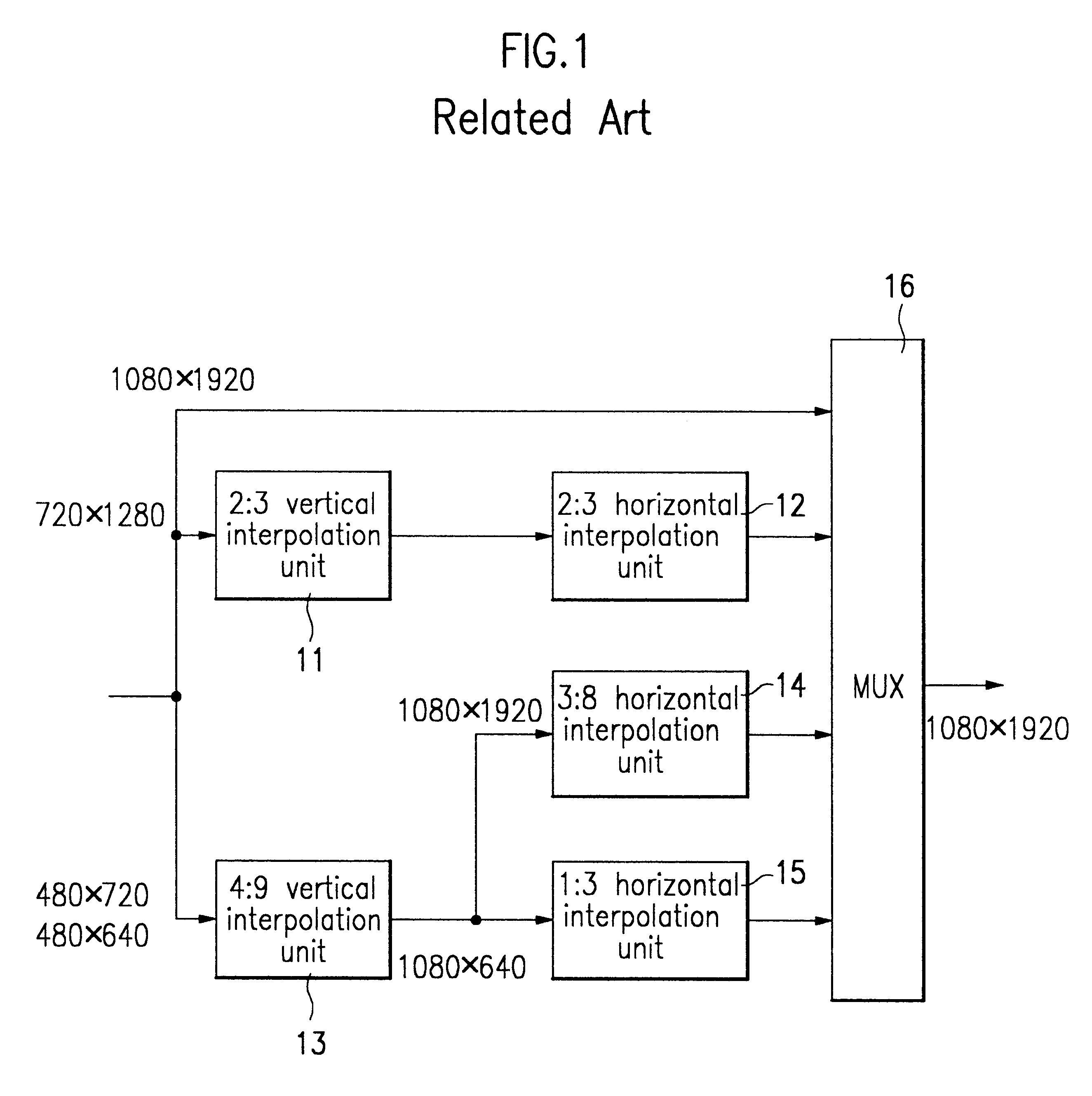
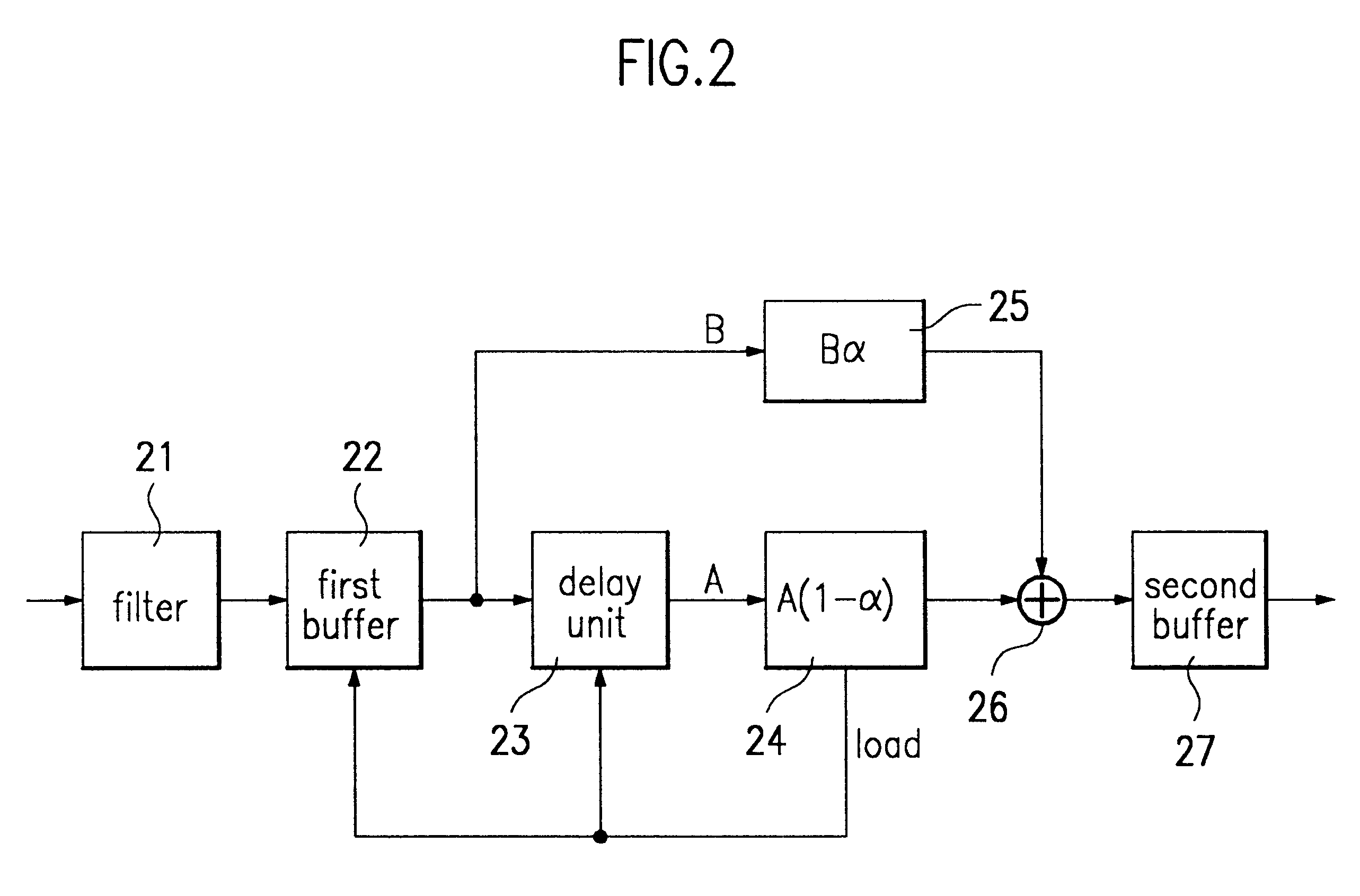
A video format converter for converting resolution of an input digital image to a different resolution includes an adder for adding the number of input pixels L to a feedback value, a modulo operation unit for allowing an output value of the adder as a numerator value to be feedback to the adder if the output value of the adder is smaller than the number of output pixels, but outputting a load signal so that a new data is loaded into them if the output value of the adder is greater than the number of output pixels M, and at the same time for outputting the remainder divided the output value of the adder by the number of output pixels to the adder, and a divider for performing division using the output value of the modulo operation unit as a numerator value and the number of output pixels as a denominator value and for outputting the resultant value as a weighted value alpha. Since the video format converter has a simple structure, a small amount of hardware can be realized. Also, since there are provided various input / output formats, it is not necessary to correct hardware due to a newly added format. Since differences in color coordinate sampling and scanning types as well as format size are considered, all kinds of format conversion can be realized without addition of a separate hardware.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
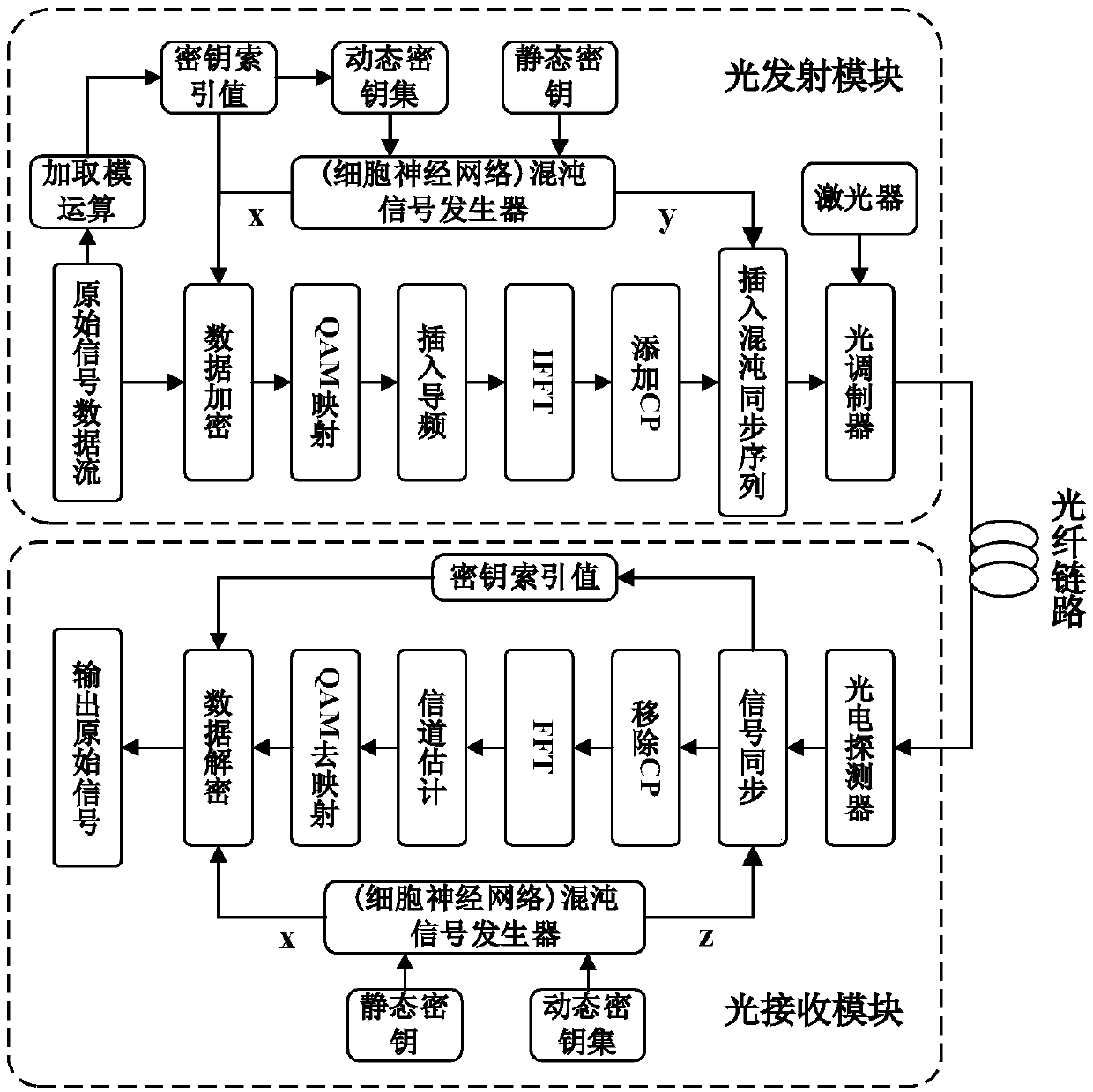
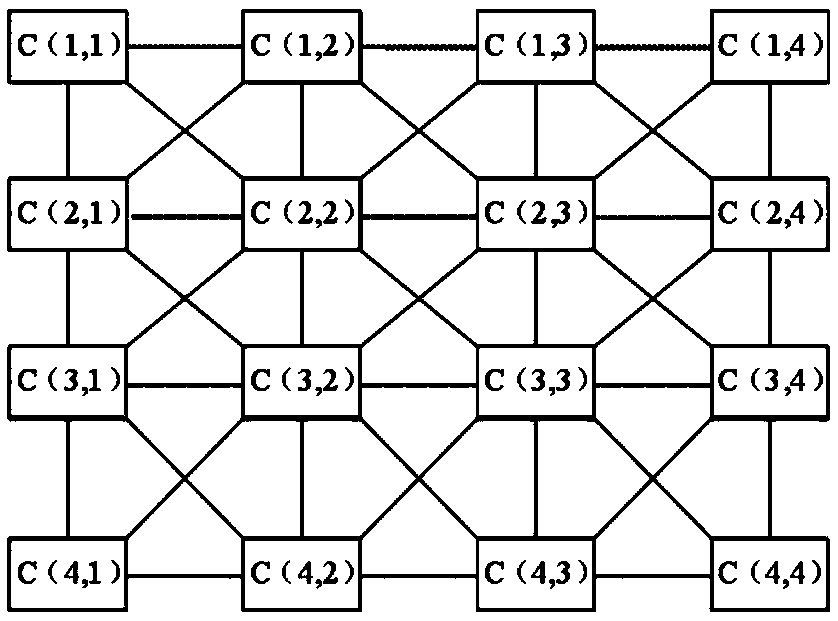
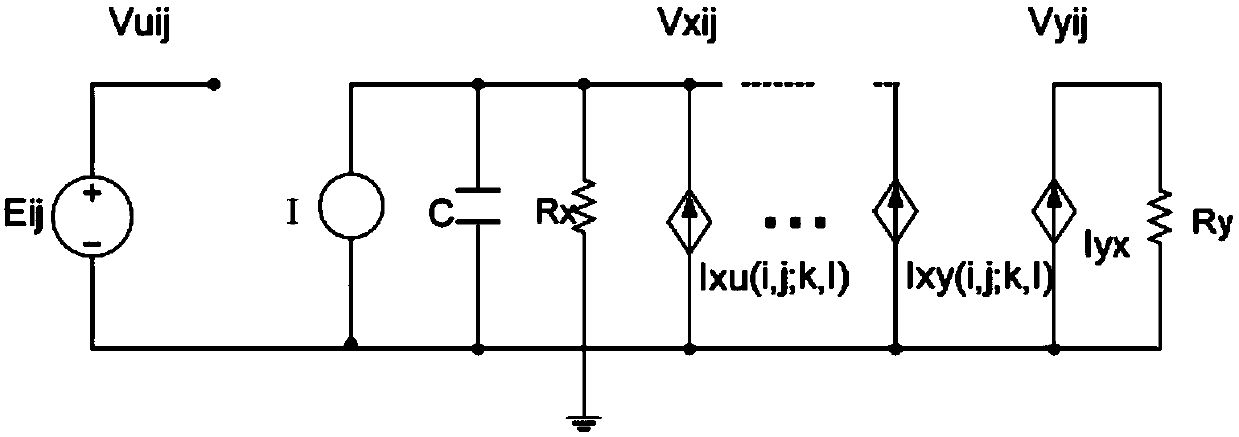
Encryption and decryption method of OFDM-PON system based on cell neural network
ActiveCN109672517AStrong randomnessHigh degree of hardware implementationElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsSecuring communication by chaotic signalsChosen-plaintext attackNerve network
The invention belongs to the technical field of the optical communication encryption, and specifically relates to an encryption and decryption method of an OFDM-PON system based on a cell neural network. The encryption method comprises the following steps: constructing a dynamic key set of the cell neural network, performing summation and modulo operation on input digital signals, and taking an obtained value as an index value of the dynamic key set of the cell neural network; determining an initial value of the cell neural network through the index value, thereby generating a corresponding chaotic sequence as a synchronization sequence of the OFDM-PON system; performing plaintext-chosen attack resistant encryption on the original data by utilizing the chaotic sequence generated by the cell neural network and the index value; and entering optical fiber transmission after the OFDM modulation and electro-optical modulation conversion. By utilizing the chaotic characteristic of the cell neural network, multiple initial values are combined as a key set, the key is randomly selected every time to improve the dynamic feature of the key; and a plaintext-chosen attack resistant encryptionscheme is constructed by utilizing the randomness of plaintext sending, and the security is high.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
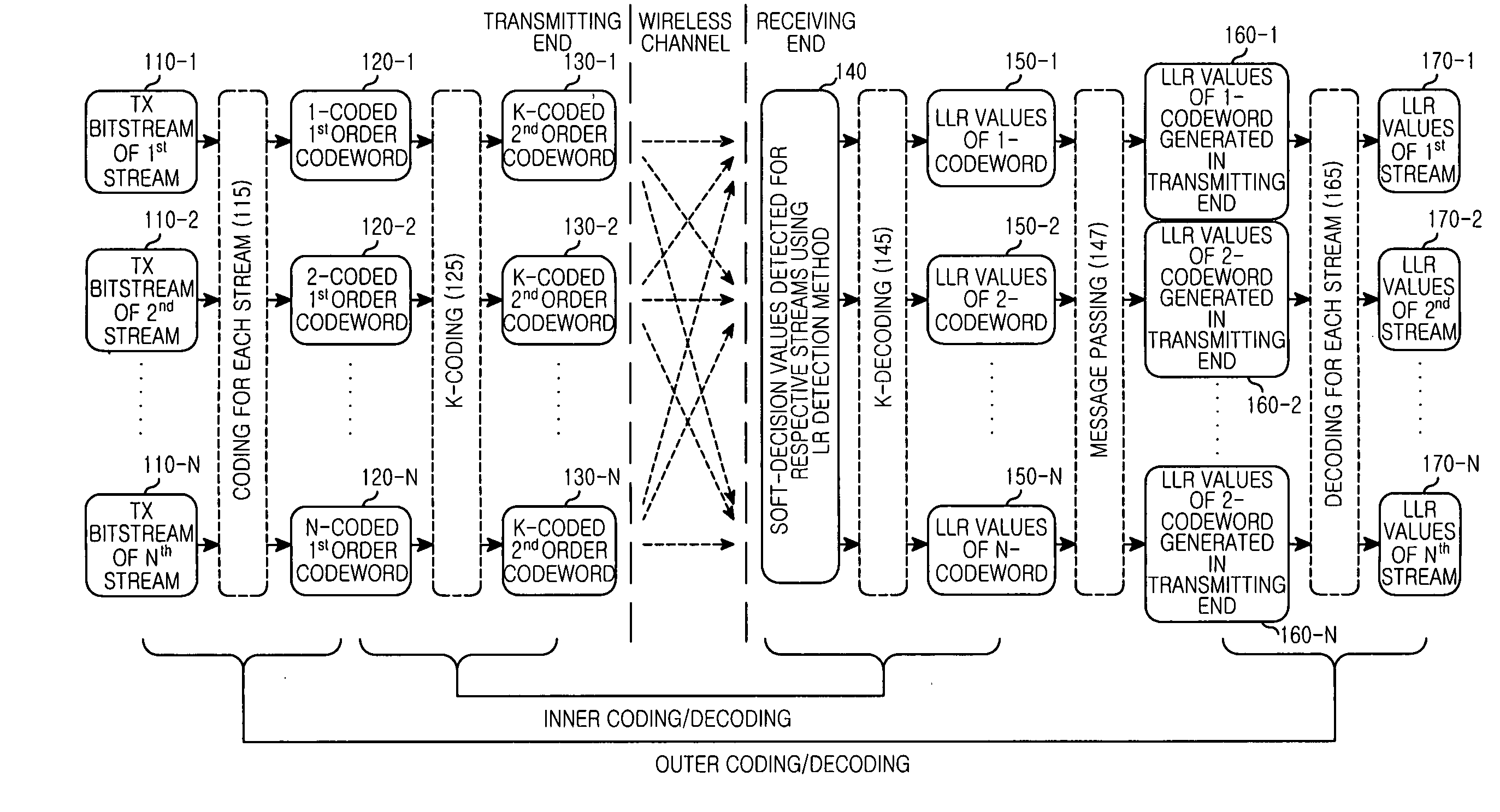
Apparatus and method for detecting signal based on lattice reduction to support different coding scheme for each stream in multiple input multiple output wireless communication system
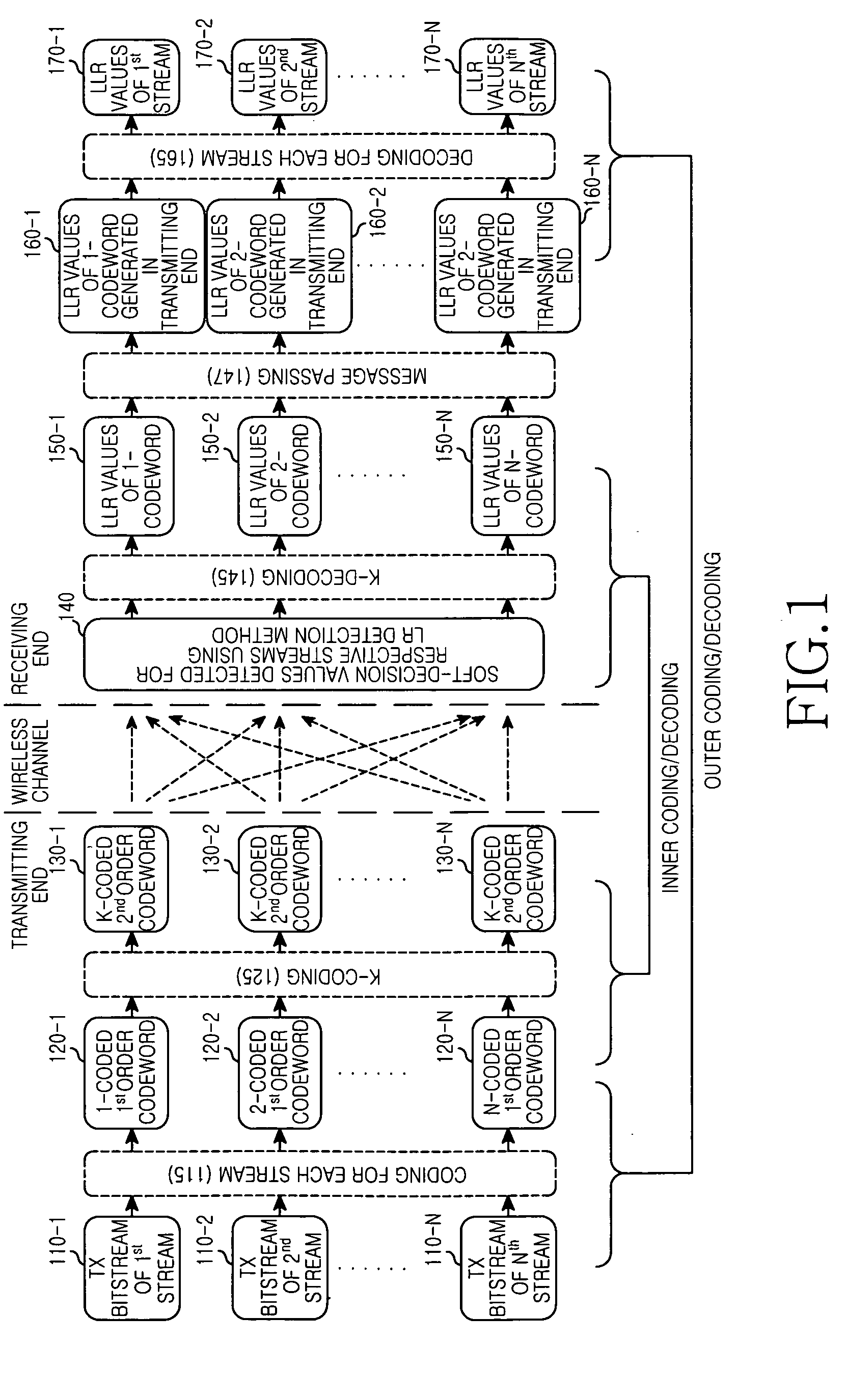
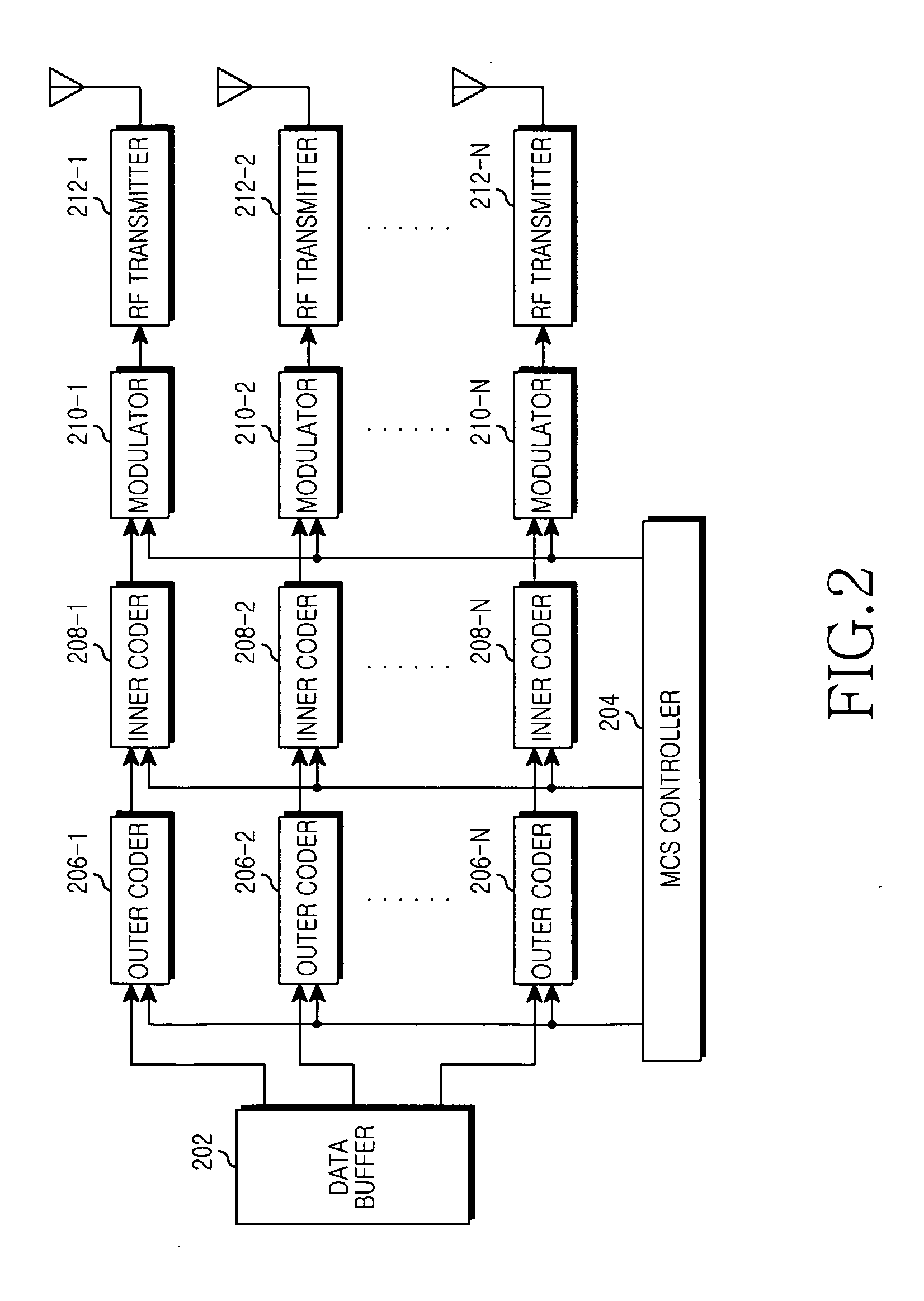
ActiveUS20090252242A1Spatial transmit diversityCode conversionCommunications systemLattice reduction
An apparatus and method for detecting signals based on a Lattice Reduction (LR) algorithm in a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) wireless communication system are provided. The apparatus includes a plurality of operators for determining soft-decision values for respective streams by performing a soft modulo operation on respective symbol values included in a Receive (Rx) signal block multiplied by a lattice transformation matrix T, a plurality of inner decoders for determining Log Likelihood Ratio (LLR) values of codewords according to coding schemes for the respective streams by decoding the soft-decision values for the respective streams according to identical decoding scheme, a passer for restoring the LLR values representing the codewords generated in a transmitting end using the LLR values, and a plurality of outer decoders for determining LLR values of Transmit (Tx) bitstreams for the respective streams by decoding the LLR values representing the codewords generated in the transmitting end for the respective streams according to decoding schemes for the respective streams.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
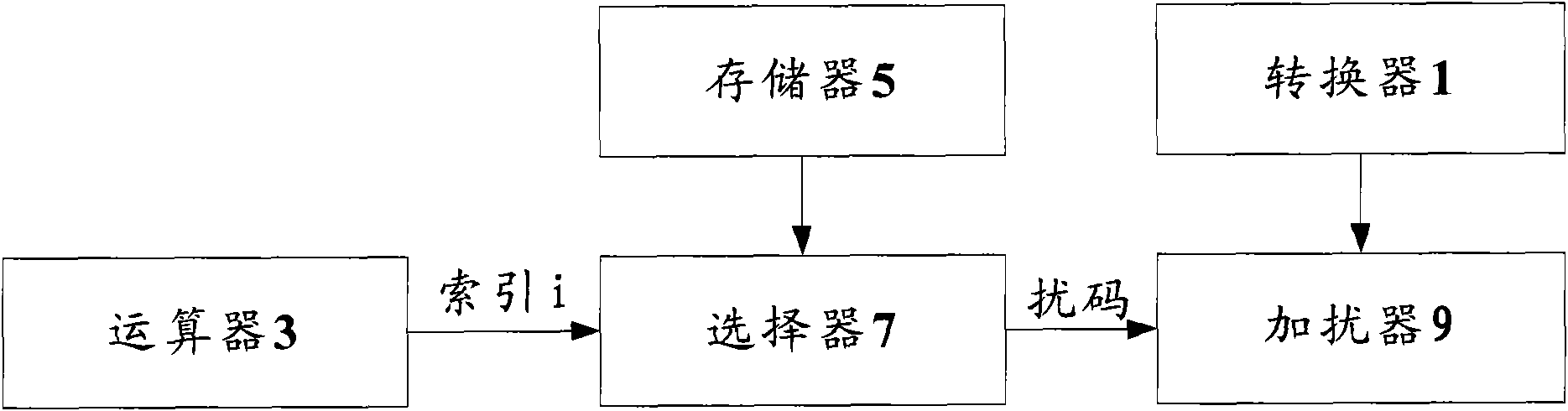
Scrambling code selection method and scrambling device
ActiveCN101938340AImprove reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCoding blockComputer science
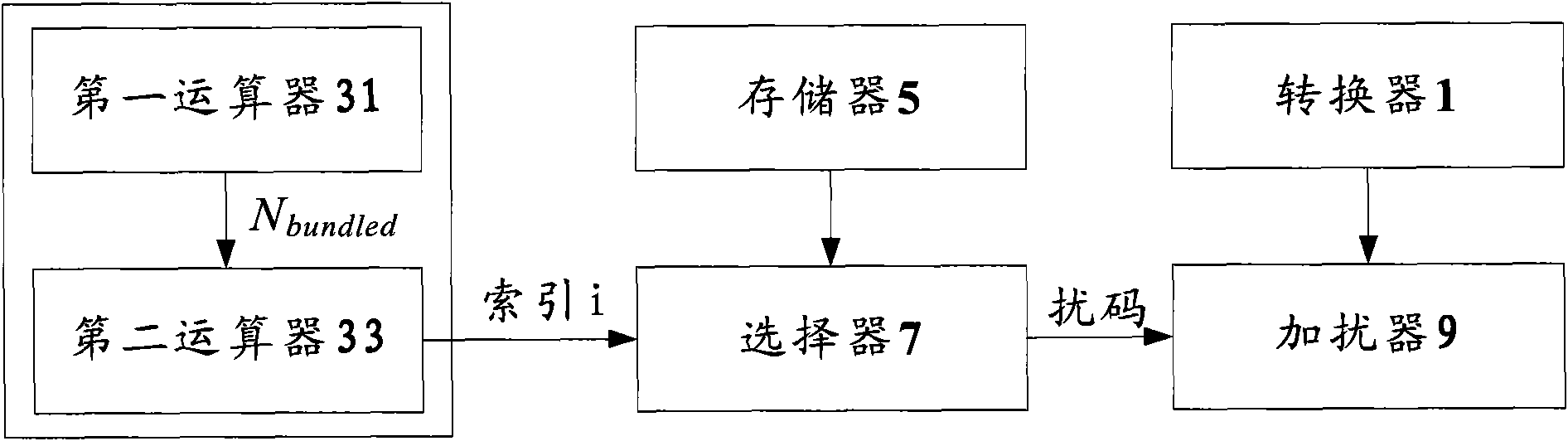
The invention discloses a scrambling code selection method and a scrambling device. The scrambling code selection method comprises the following processing steps: cascading multiple ACK / NACK coding blocks to obtain a sequence to be scrambled; calculating the number Nbundled of physical downlink shared channels corresponding to ACK / NACK messages according to the number of the transmitted physical downlink shared channels VDAIUL corresponding to subframes indicated in an uplink authorization signaling and the fact whether downlink assignment loss is detected, and further calculating an index i; and selecting a scrambling code corresponding to the index i to scramble the sequence to be scrambled from the mapping relation between the index and the scrambling code, wherein the index i is determined according to the following rule: i=(Nbundled-1)mod4, if user equipment detects that at least one downlink assignment losses, Nbundled=VDAI+1 or Nbundled=VDAI+3, otherwise, Nbundled=VDAI, and mod represents modulo operation. The invention can improve the system reliability.
Owner:NANTONG HUAXIN CENT AIR CONDITIONER
Pre-coding matrix selection method, device and system
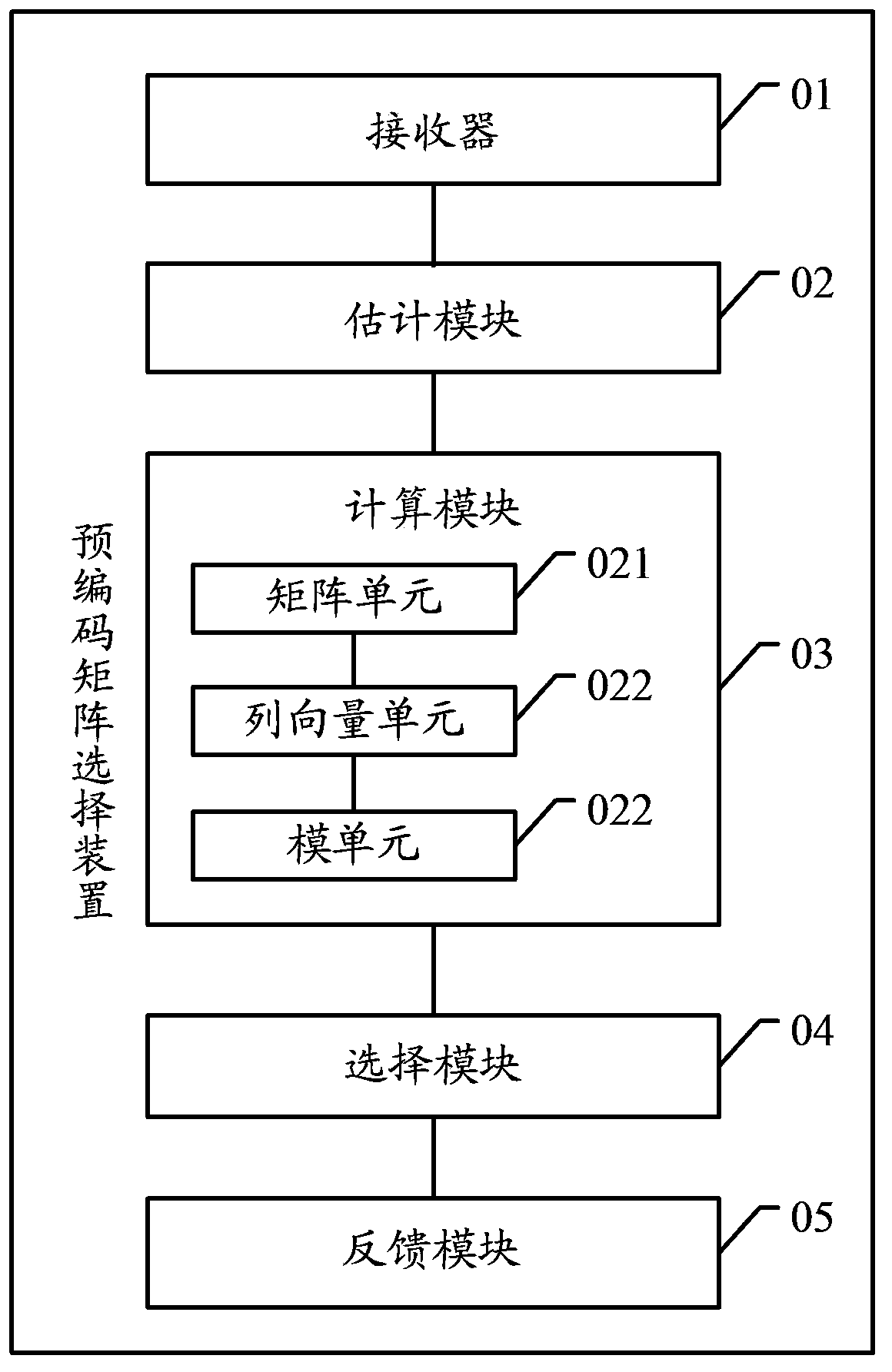
InactiveCN103634071ASimplify the selection processSmall amount of calculationError prevention/detection by diversity receptionCurrent channelEngineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses a pre-coding matrix selection method, a device and a system. The method comprises the steps that pilot frequency information sent by a sending end is received through the current channel; according to the pilot frequency information, an equivalent channel matrix of the current channel is estimated; inner product and modulo operation are respectively carried out on the equivalent channel matrix and each pre-coding matrix in a preset pre-coding codebook collection, so as to acquire a number of module values; the pre-coding matrix corresponding to the maximum module value in a number of module values is selected as a target matrix; and the target matrix is fed back to the sending end, so that the sending end selects the target matrix to carry out pre-coding on a signal sent through the current channel. The embodiment of the invention further discloses a pre-coding matrix selection device and system. According to the invention, the pre-coding matrix selection method, device and system are provided; a pre-coding selection process can be simplified; the calculation amount in the pre-coding selection process is reduced; and the problems of large calculation amount and complicated operation of the pre-coding matrix selection method in the prior art, are solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for giving the compressed encryption functionality to integer-based homomorphic encryption schemes
InactiveUS20150180659A1Improve storage efficiencyReduce volumeKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesPlaintextCiphertext
The present invention relates to a compressed encryption and decryption apparatus comprising: an interface receiving a public key, a secret key and a compression ratio; a memory storing instructions for encryption and decryption of plaintexts; and a processor encrypting and decrypting plaintexts according to the instruction, wherein the instruction comprises instructions performing; generating an extended public key and an extended secret key by revising the public key and the secret key according to the compression ratio; outputting the extended public key; receiving compressed ciphertext; and decrypting the compressed ciphertext using modulo operation for multiplication of the extended secret key and the compressed ciphertext.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
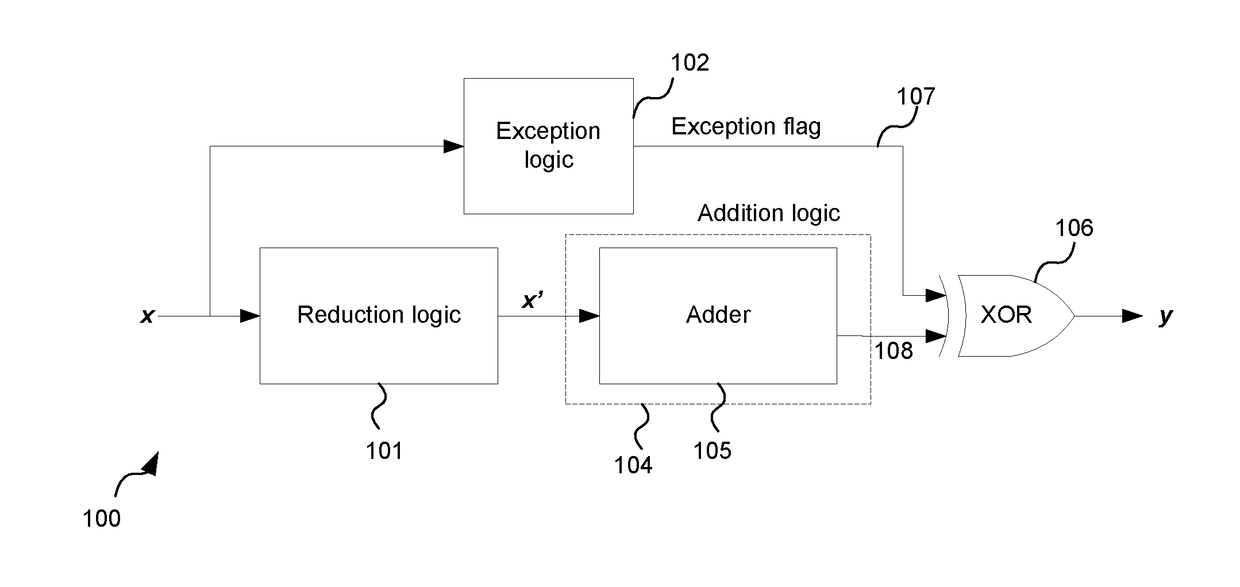
Division Synthesis
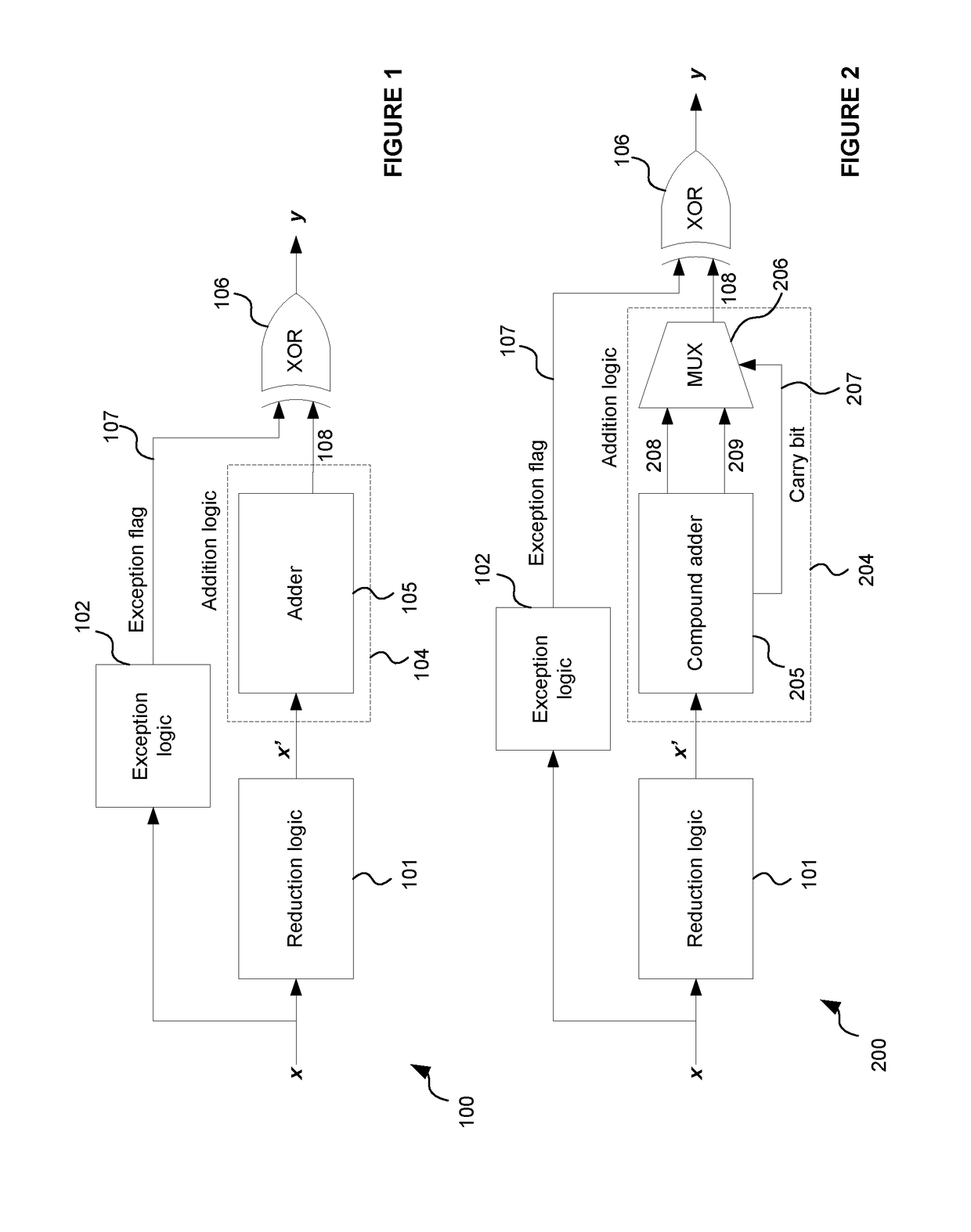
A binary logic circuit for determining the ratio x / d in accordance with a rounding scheme, where x is a variable integer input of bit length w and d is a fixed positive integer of the form 2n±1, the binary logic circuit being configured to form the ratio as a plurality of bit slices, the bit slices collectively representing the ratio, wherein the binary logic circuit is configured to generate each bit slice according to a first modulo operation for calculating mod(2n±1) of a respective bit selection of the input x and in dependence on a check for a carry bit, wherein the binary logic circuit is configured to, responsive to the check, selectively combine a carry bit with the result of the first modulo operation.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com