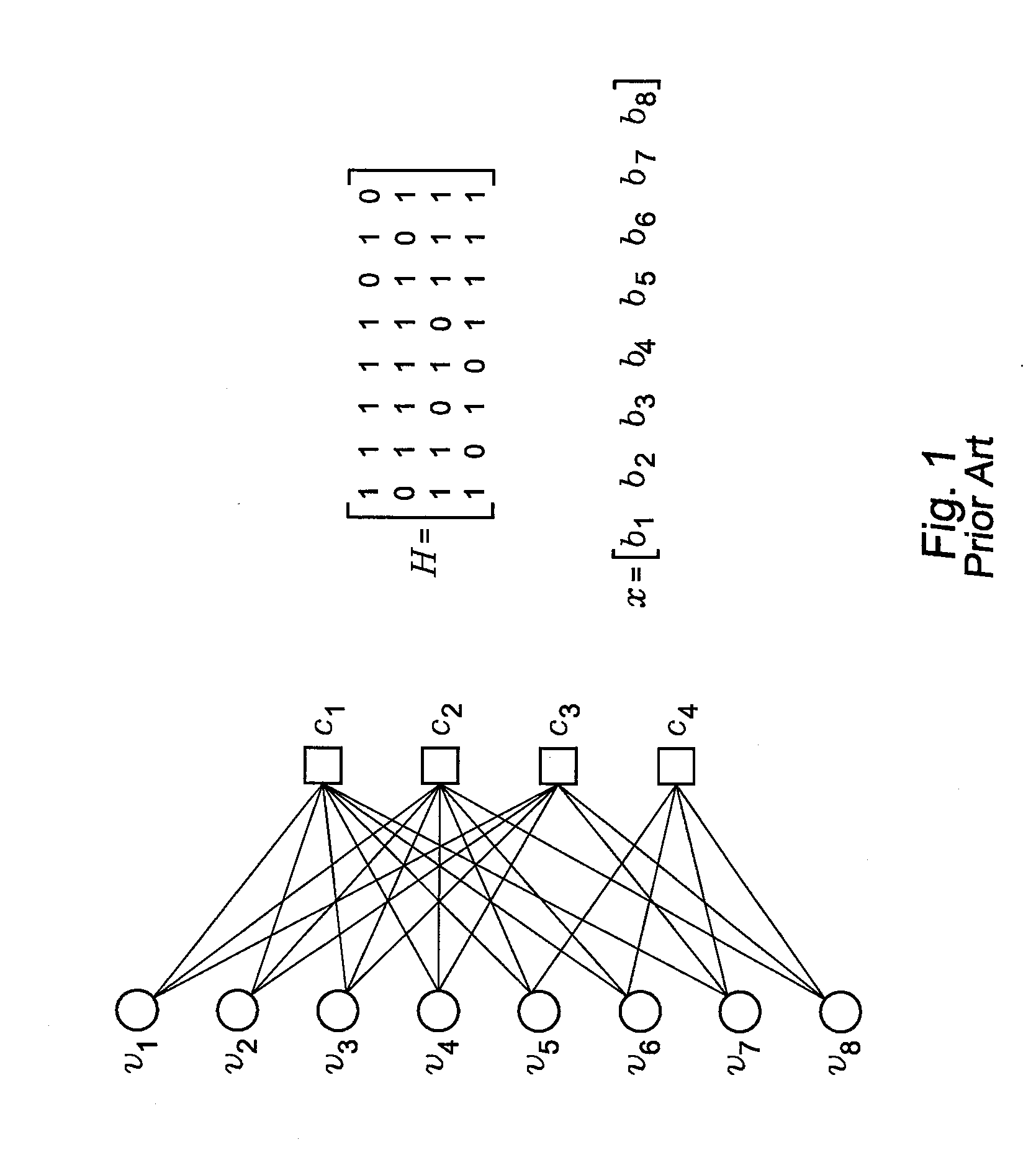
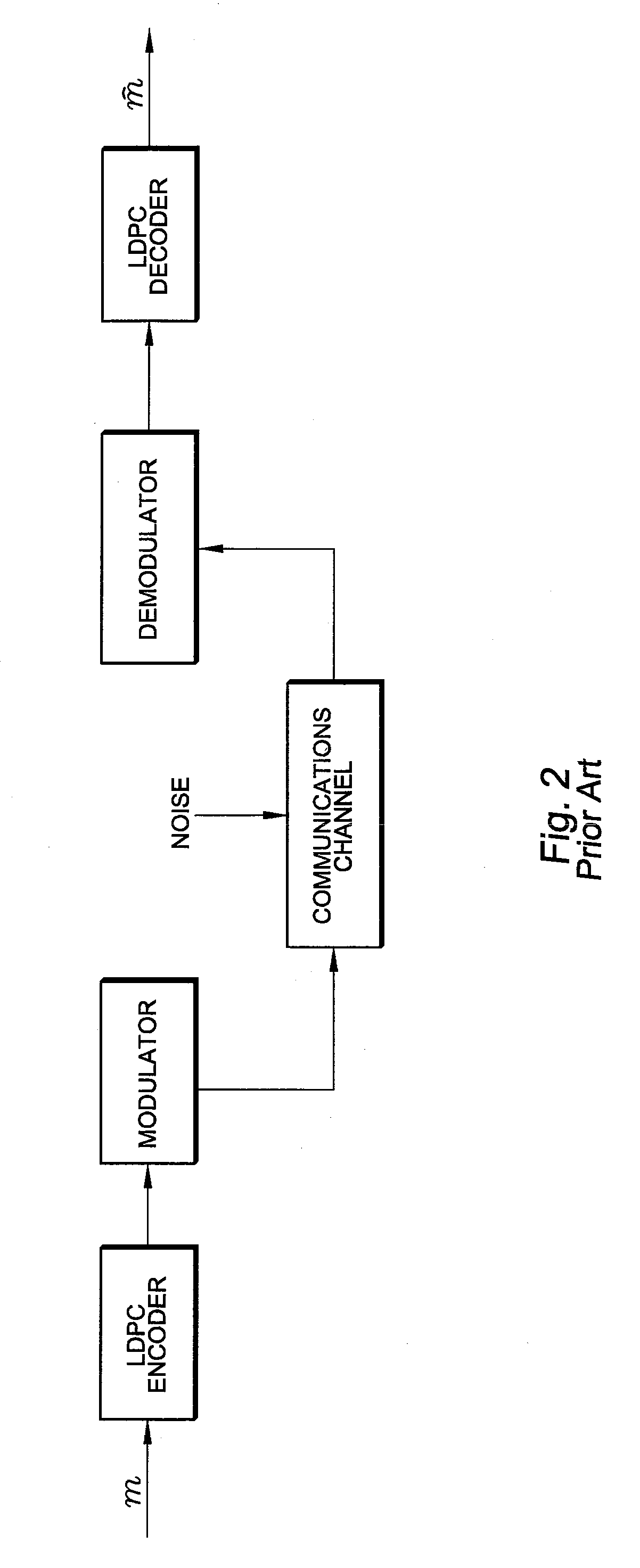
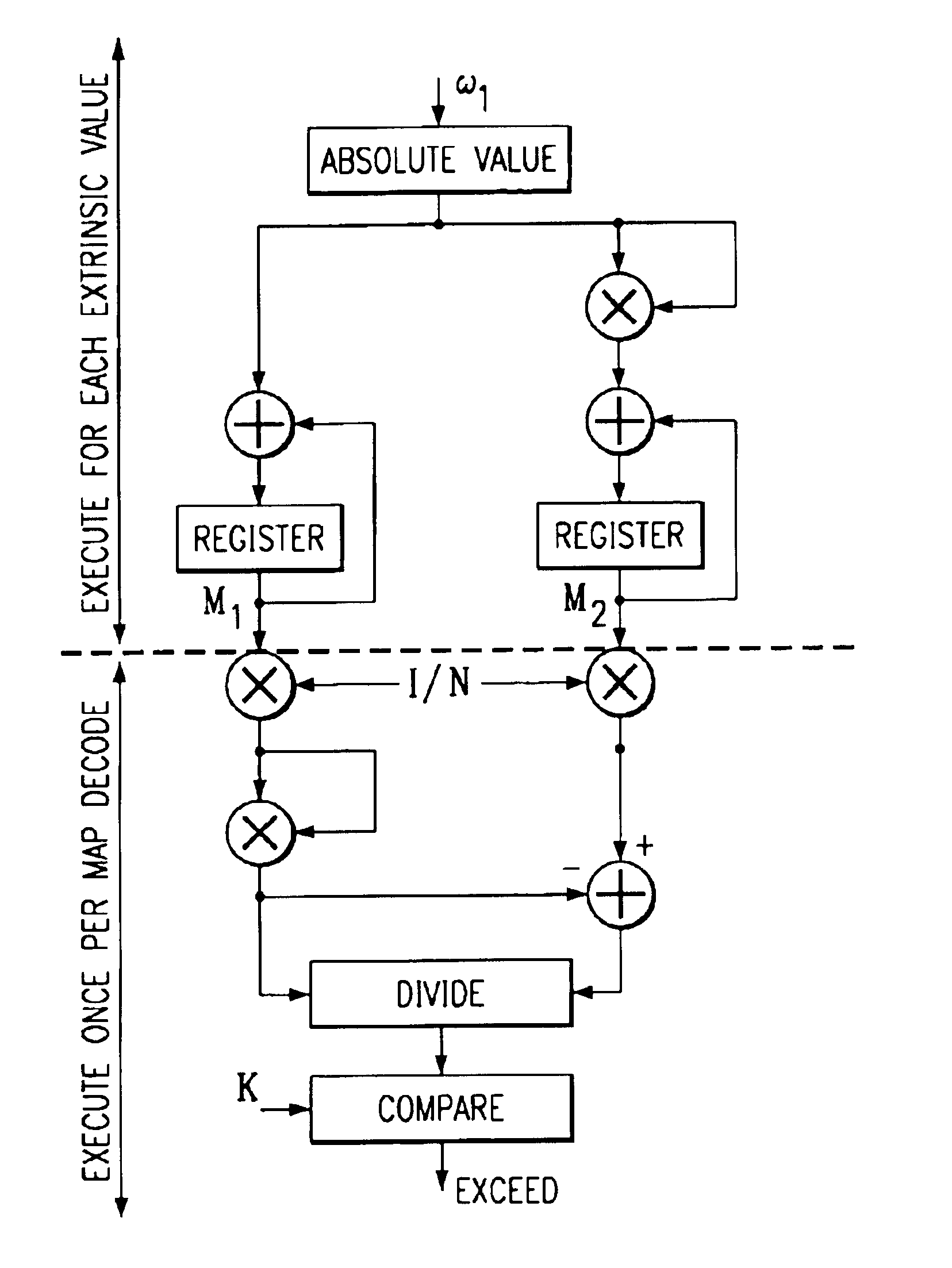
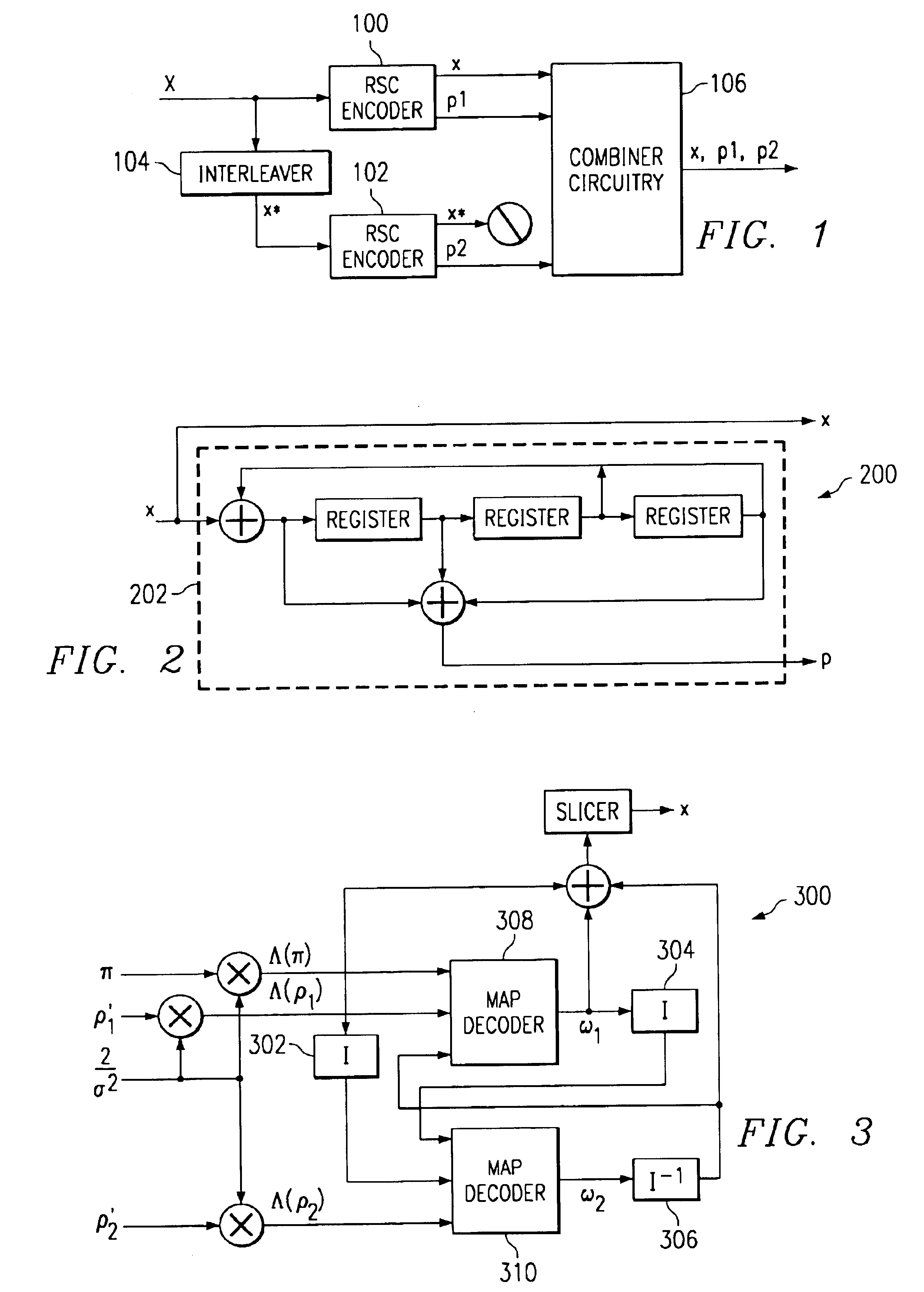
Patents
Literature
79results about How to "Simple hardware implementation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
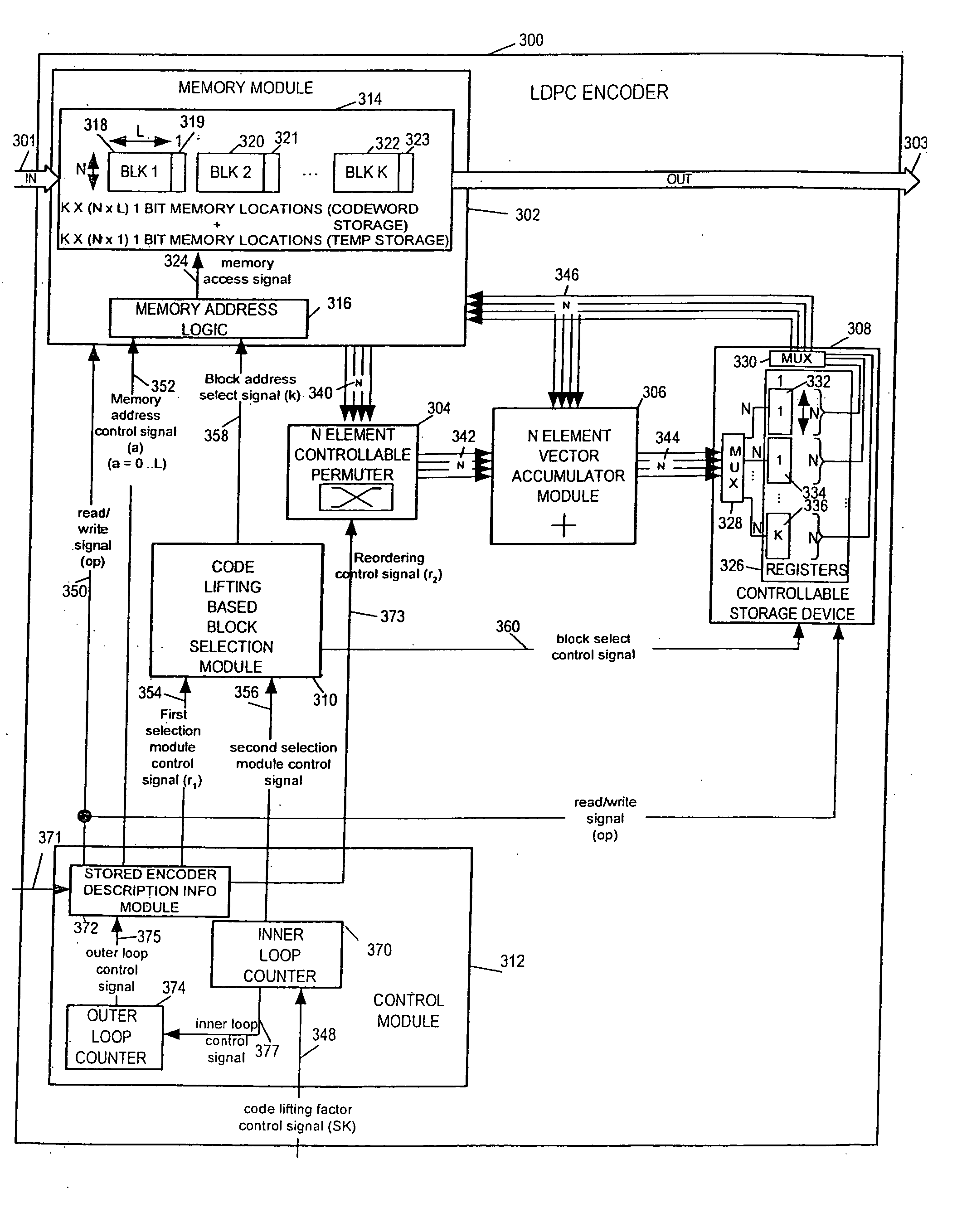
LDPC encoding methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20060020872A1Simple microcodeEasy to modifyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDegree of parallelismInstruction set
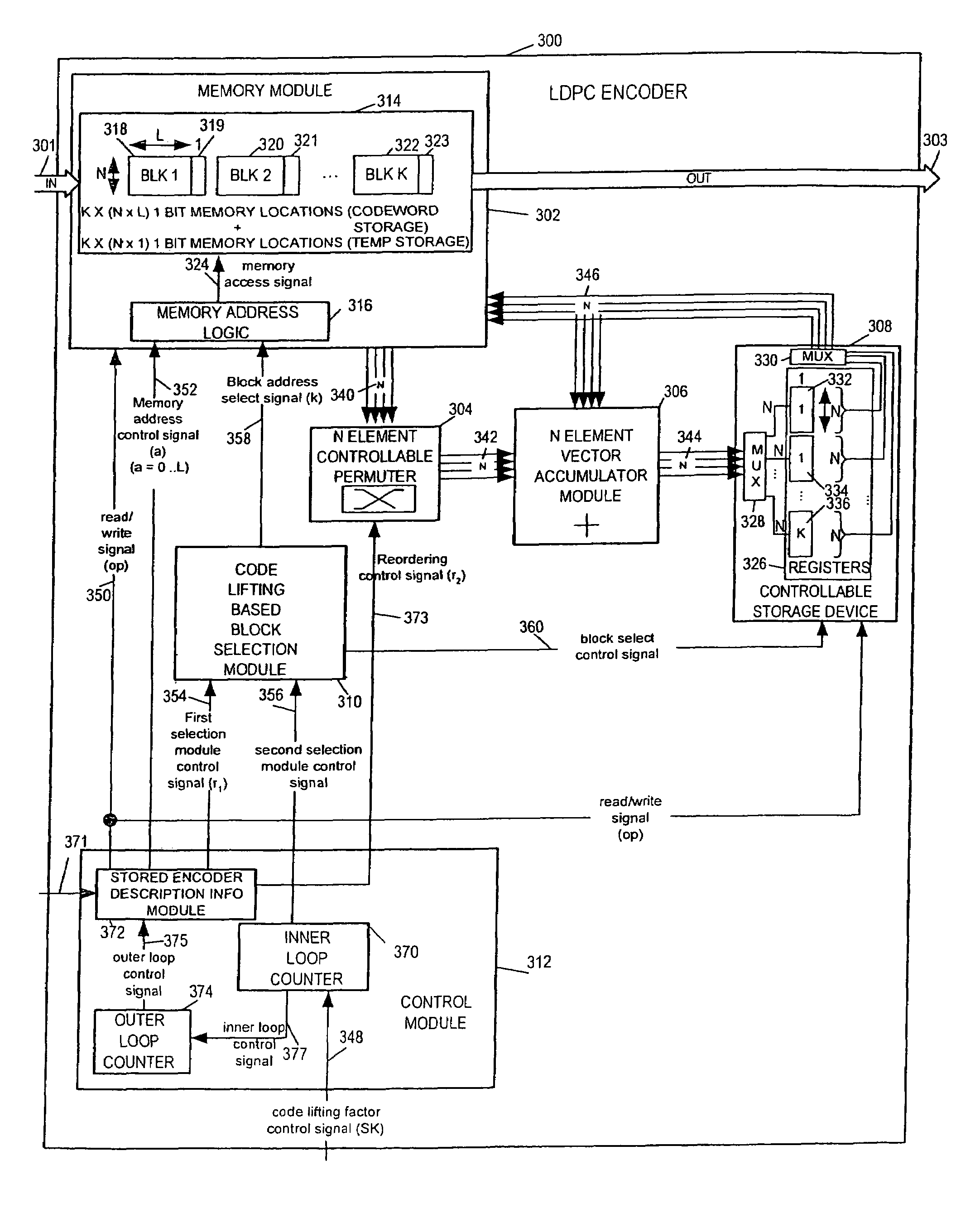
A flexible and relatively hardware efficient LDPC encoder is described. The encoder can be implemented with a level of parallelism which is less than the full parallelism of the code structure used to control the encoding process. Each command of a relatively simple microcode used to describe the code structure can be stored and executed multiple times to complete the encoding of a codeword. Different codeword lengths can be supported using the same set of microcode instructions but with the code being implemented a different number of times depending on the lifting factor selected to be used. The LDPC encoder can switch between encoding codewords of different lengths, without the need to change the stored code description information, by simply changing a code lifting factor used to control the encoding processes. When coding codewords shorter than the maximum supported codeword length some block storage locations and / or registers may go unused.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
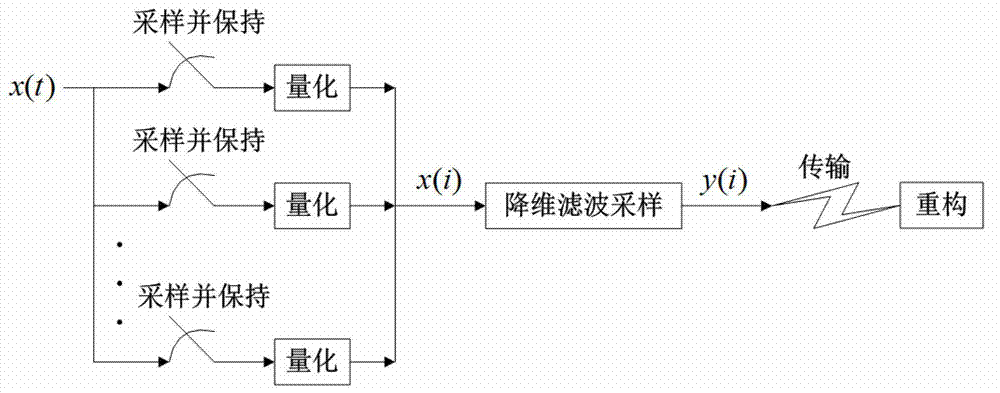
Compressed sensing signal collection method based on filtering
InactiveCN103036573AEfficient acquisitionSimple hardware implementationCode conversionOptimization problemCompressed sensing
A compressed sensing signal collection method based on filtering includes the following steps: firstly, sensing equipment is used for collecting target signals x (t) in an independent sampling period and carries out digital quantification on the signals in an analog / digit (A / D) mode. Secondly, the dimension of the quantified signals x (i) is reduced. Lastly, the signals with the reduced dimension are reconfigured. The t means the sampling time, and the i means the sequence of the quantified signals. The detailed method of dimension-reduction of the quantified signals is that the quantified signals respond to a difference equation of a filter through finite impulse, and the difference equation is that i= 1, ..., M, wherein h (0), ..., h (L-1) is the coefficients of the filter. The design constructs a following toeplitz measurement array based on a compressed sensing signal collection framework of the filter, and the toeplitz measurement array is that i= 1, ..., M is observed, wherein b1,..., bL are treated as coefficients of the filter. The singular value of a sub-array phi FT is an arithmetic value of a characteristic value of a Gramm array which is that G (phi F, T) = phi ` FT phi FT, all the characteristic values that lambada i belongs to (1- delta K, 1+ delta K), wherein i= 1, ..., T of G (phi F, T) are tested, and the original signals are reconfigured by solving the following l1 optimization problems.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Soft, prioritized early packet discard system
InactiveUS6980516B1Simple hardware implementationRiskMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionSatelliteReal-time computing
A Soft, Prioritised Early Packet Discard System is provided, which is suitable for satellite onboard switching and very-high-speed terrestrial switching applications. The system counts the number of newly arriving packets, calculates and regularly updates an average queue size, which is used in setting a packet-count threshold via a descending staircase function. When the number of newly arriving packets reaches the packet-count threshold and when the average queue size reaches or exceeds the congestion threshold; a packet is discarded and the packet-counter is reset to zero. The counting of packets is halted while the average queue size remains below the congestion threshold. The regular dropping of packets allows simplified hardware implementations. In calculating the average queue size, a progressively higher exponential queue-length averaging parameter is used for higher instantaneous queue length, to provide faster reaction to congestion situations. The averaging parameters and packet-count thresholds are implemented using lookup tables. A priority-based method is incorporated to better match the Quality of Service requirements associated with a service class.
Owner:SPACEBRIDGE SEMICON CORP
Method and system for a sharing buffer
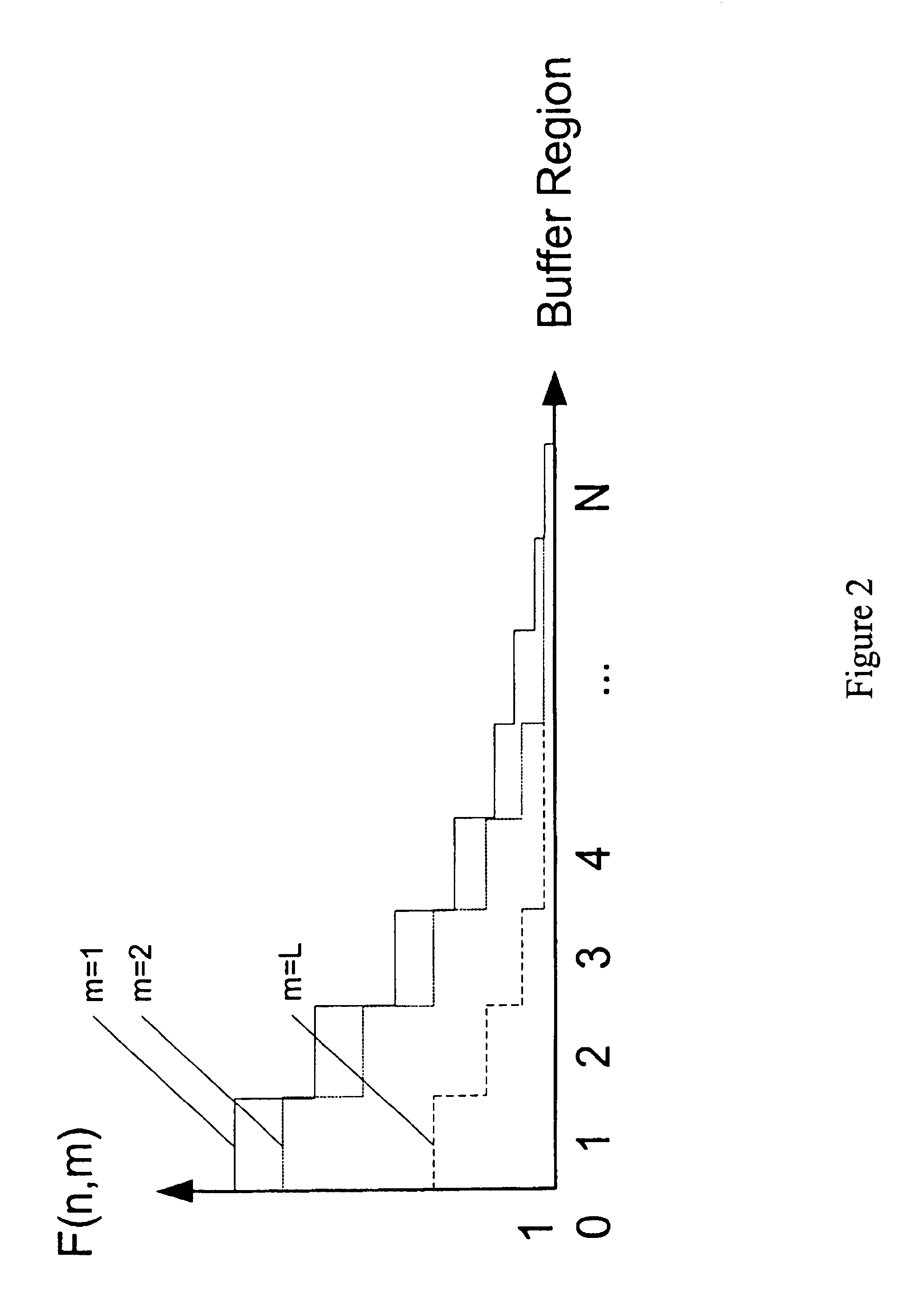
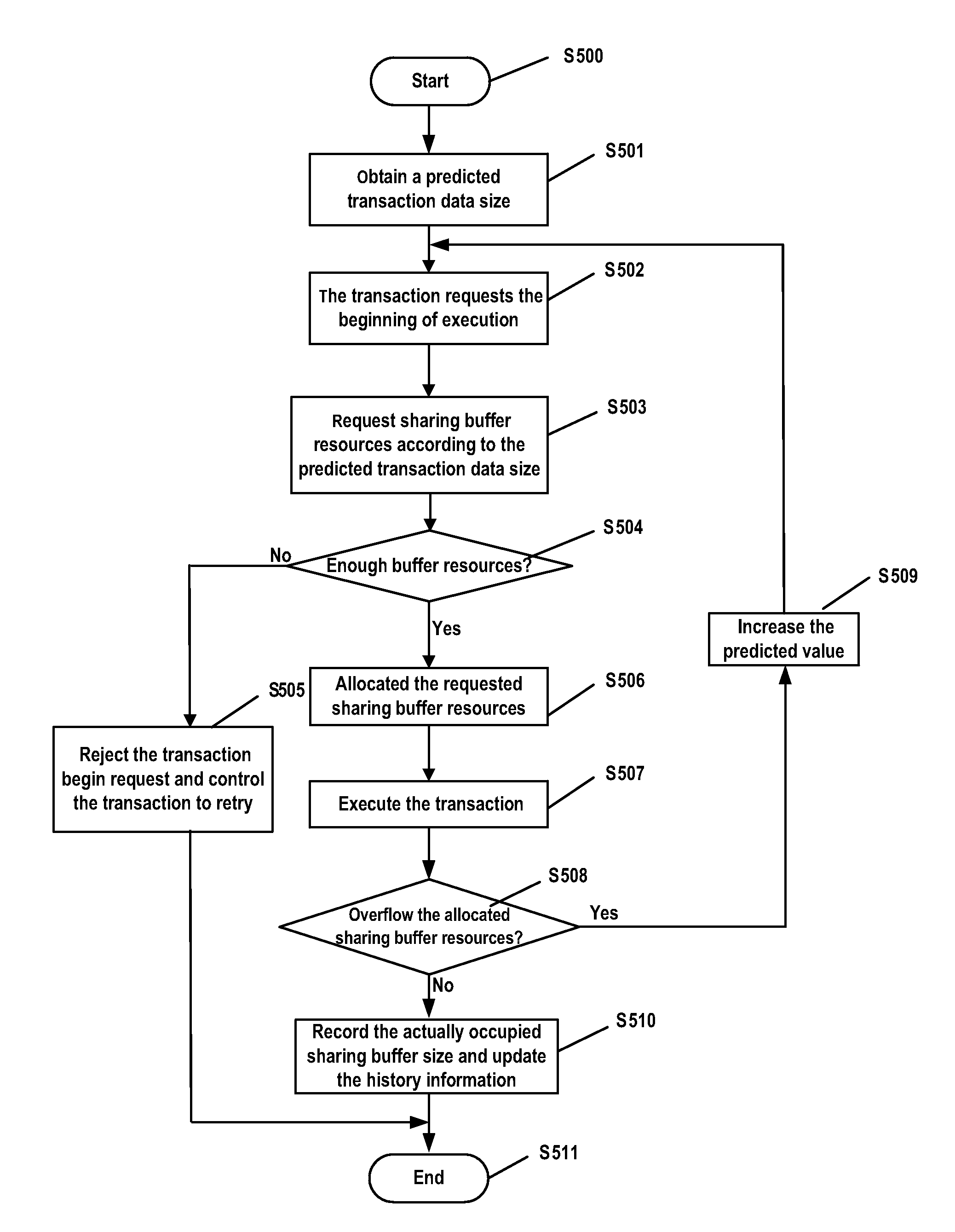
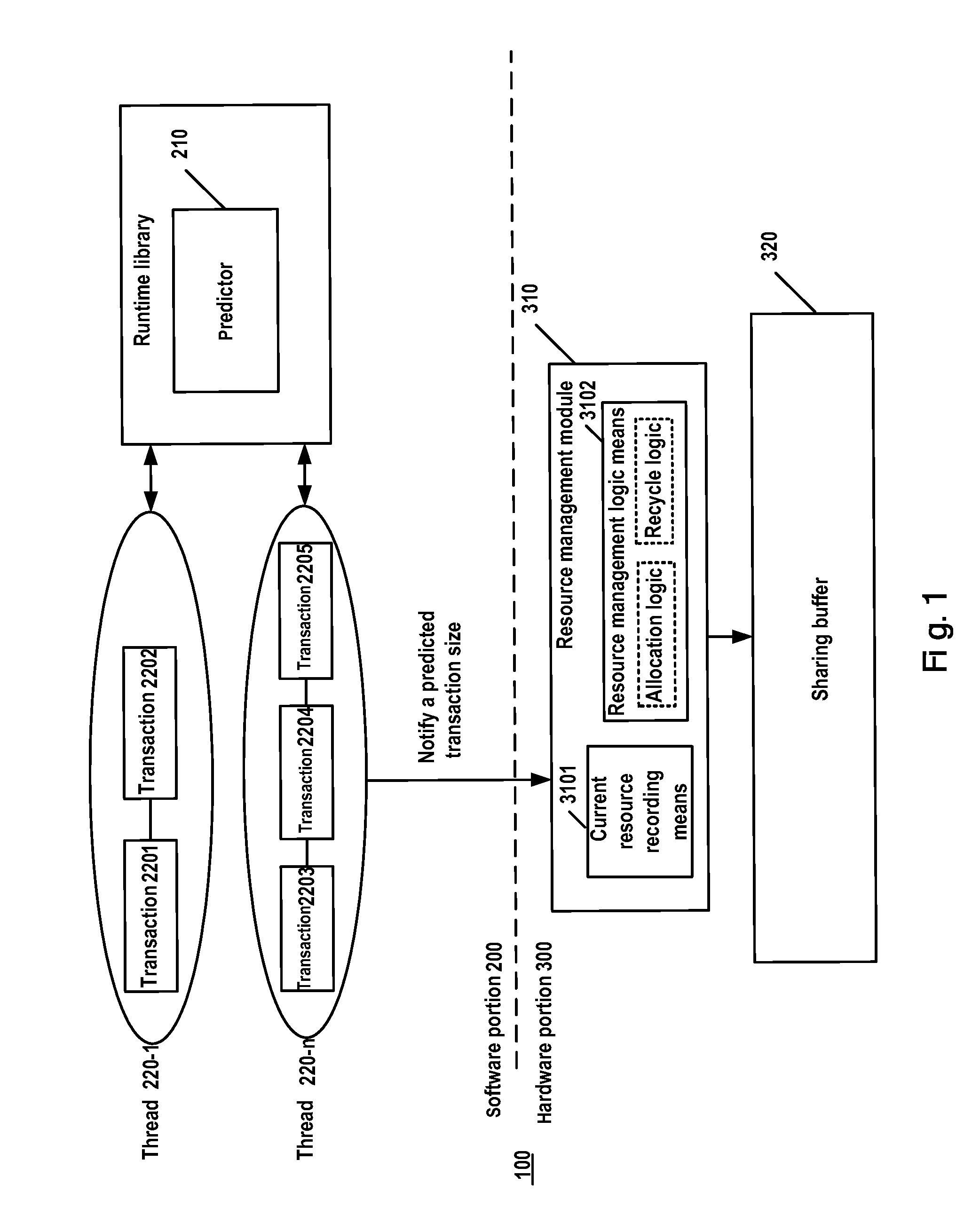
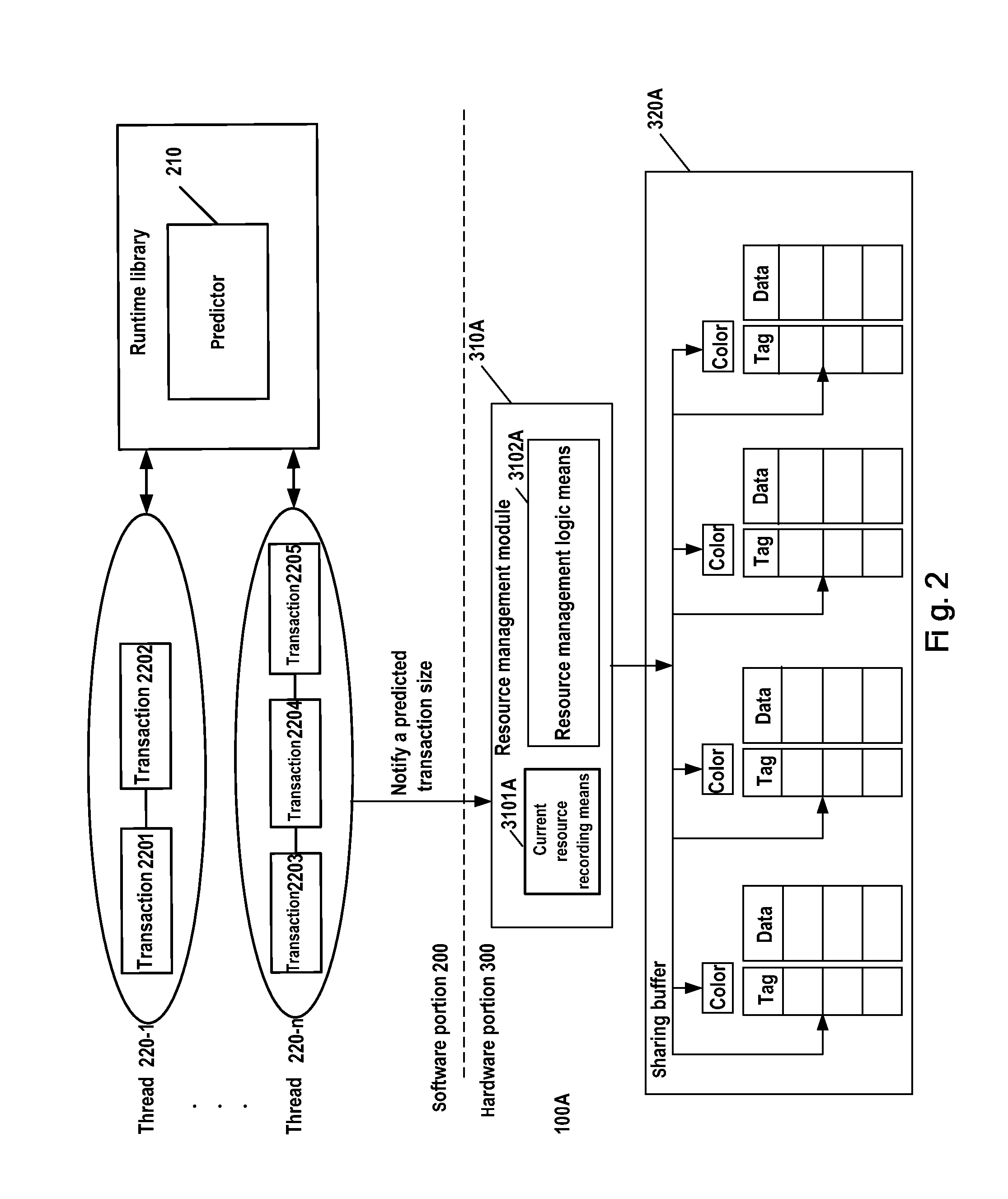
InactiveUS20100138571A1Shift complexityWithout performanceMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingTransaction dataResource management
A system, method, and computer readable article of manufacture for sharing buffer management. The system includes: a predictor module to predict at runtime a transaction data size of a transaction according to history information of the transaction; and a resource management module to allocate sharing buffer resources for the transaction according to the predicted transaction data size in response to beginning of the transaction, to record an actual sharing buffer size occupied by the transaction in response to the successful commitment of the transaction, and to update the history information of the transaction.
Owner:IBM CORP
LDPC encoding methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7346832B2Simple microcodeEasy to modifyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionProcessor registerDegree of parallelism
A flexible and relatively hardware efficient LDPC encoder is described. The encoder can be implemented with a level of parallelism which is less than the full parallelism of the code structure used to control the encoding process. Each command of a relatively simple microcode used to describe the code structure can be stored and executed multiple times to complete the encoding of a codeword. Different codeword lengths can be supported using the same set of microcode instructions but with the code being implemented a different number of times depending on the lifting factor selected to be used. The LDPC encoder can switch between encoding codewords of different lengths, without the need to change the stored code description information, by simply changing a code lifting factor used to control the encoding processes. When coding codewords shorter than the maximum supported codeword length some block storage locations and / or registers may go unused.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
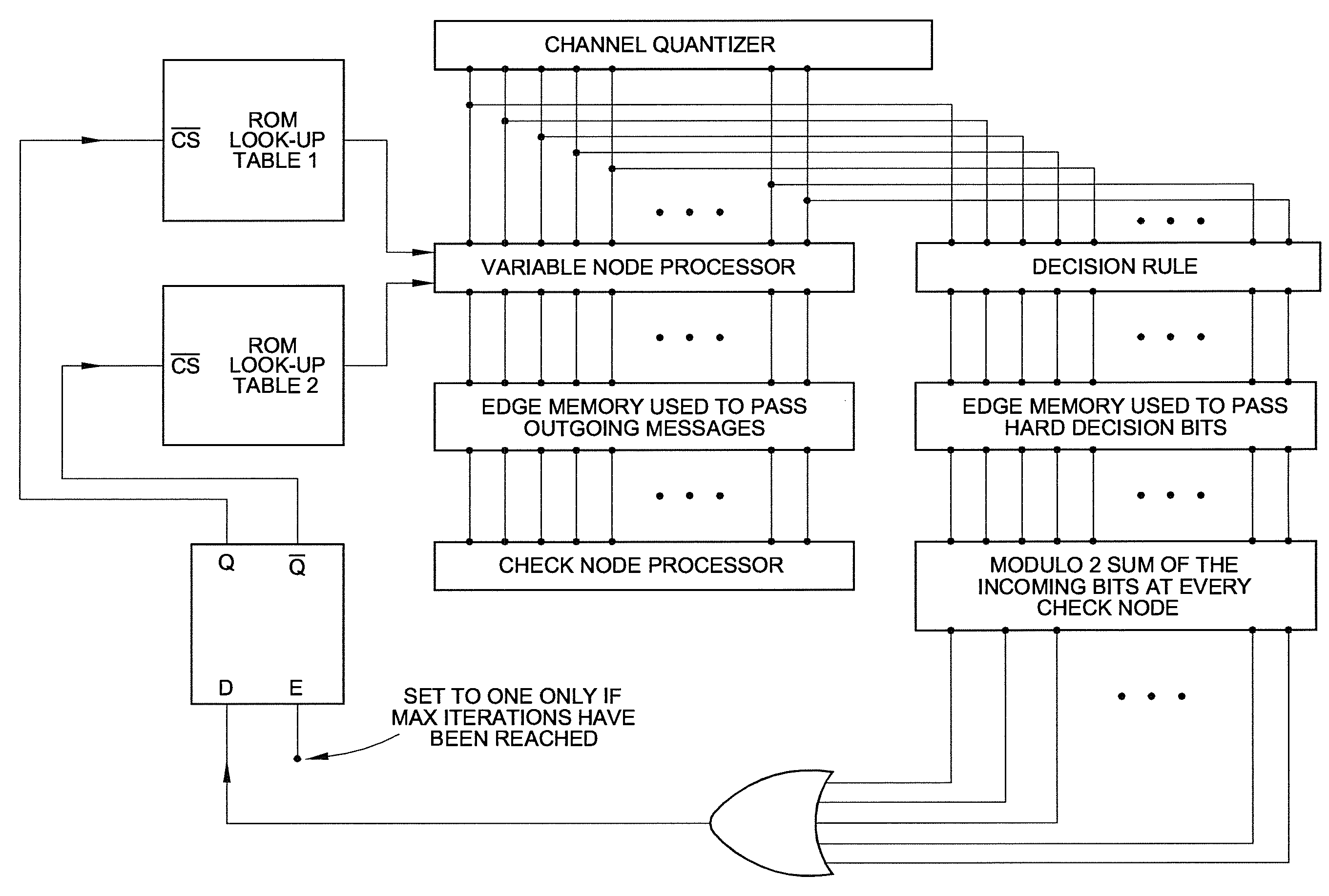
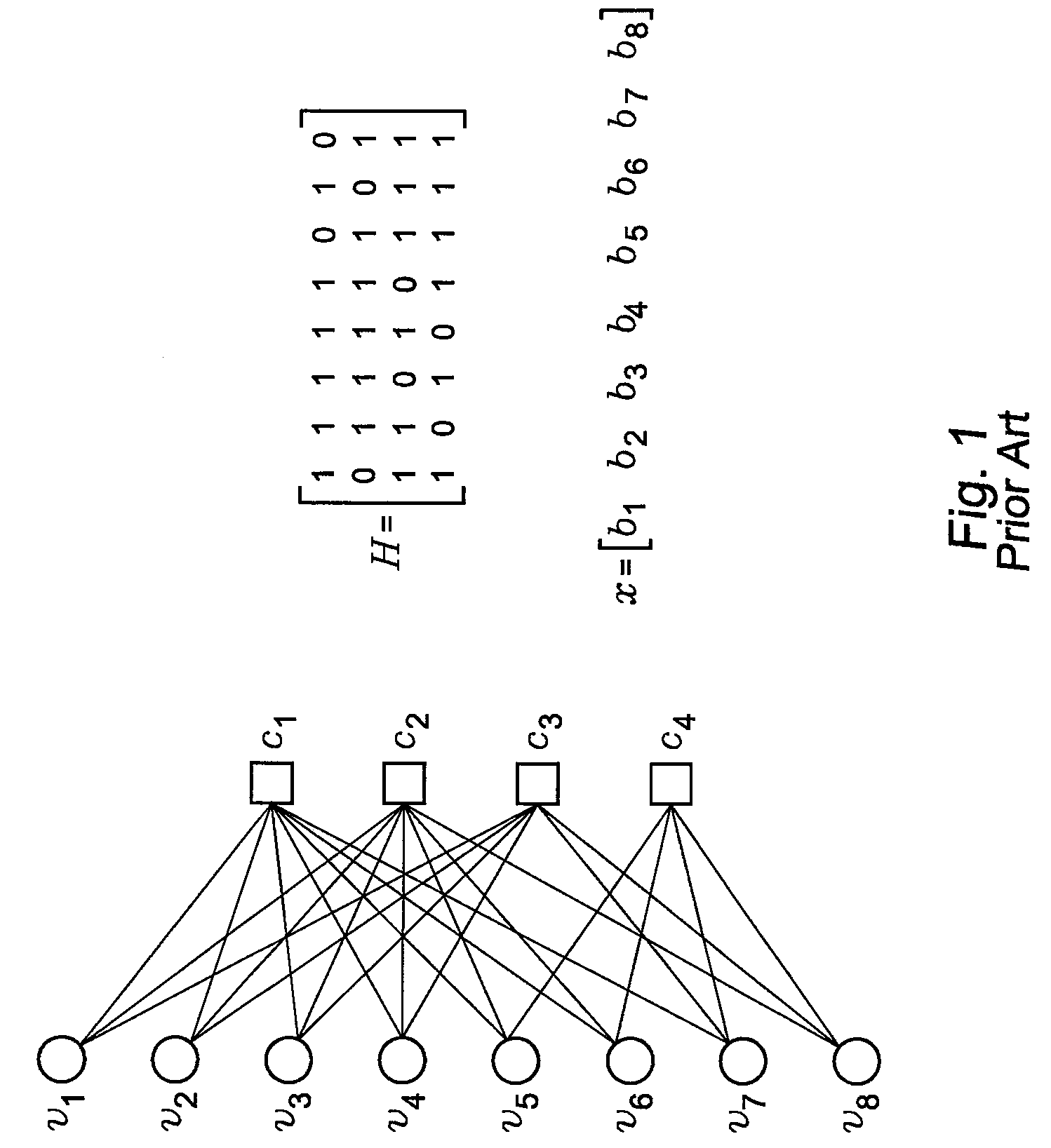
Low complexity finite precision decoders and apparatus for LDPC codes
ActiveUS20110087946A1Improving message-passing processLow failure rateCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesNODALRound complexity
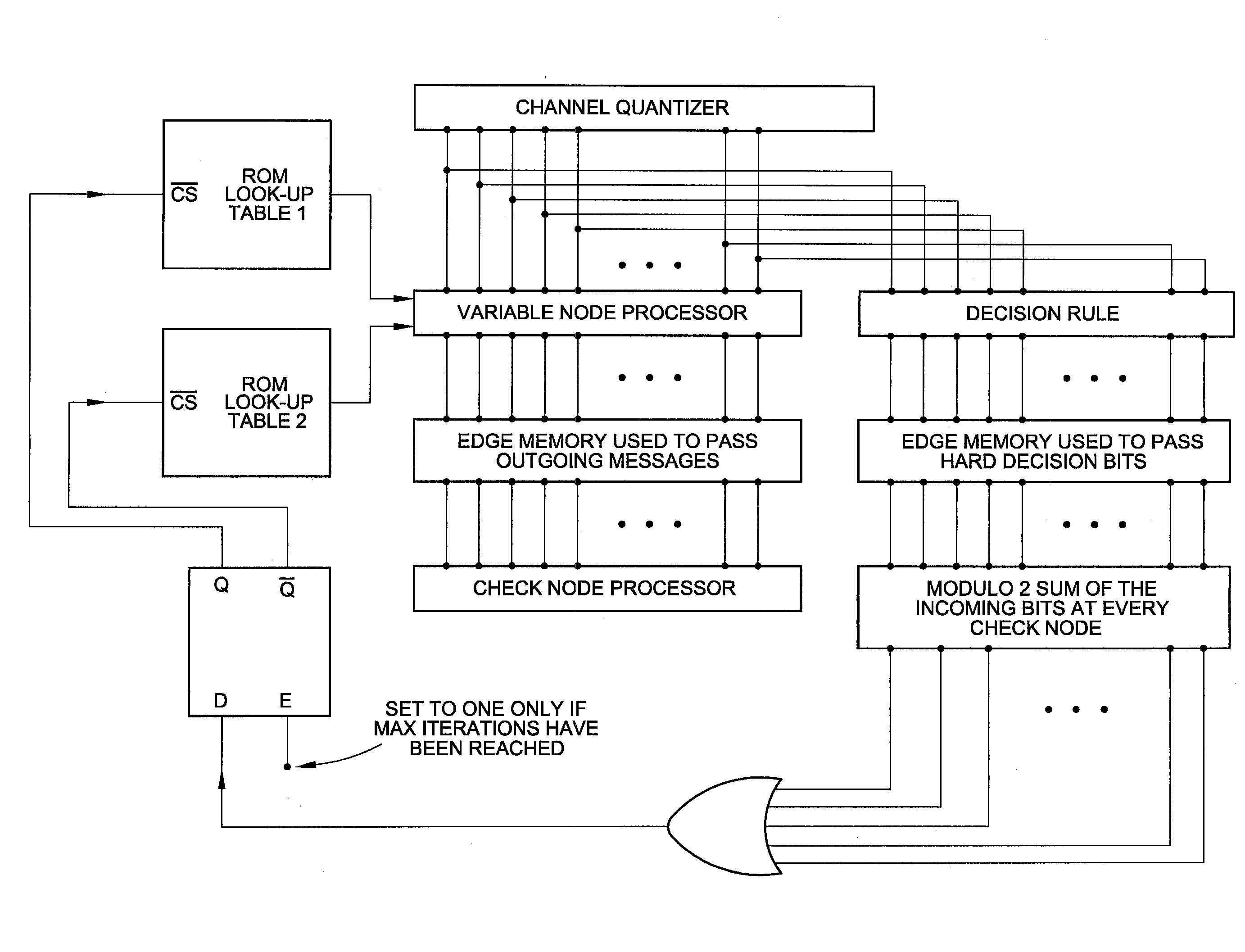
In this invention, a new class of finite precision multilevel decoders for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes is presented. These decoders are much lower in complexity compared to the standard belief propagation (BP) decoder. Messages utilized by these decoders are quantized to certain levels based on the number of bits allowed for representation in hardware. A message update function specifically defined as part of the invention, is used to determine the outgoing message at the variable node, and the simple min operation along with modulo 2 sum of signs is used at the check node. A general methodology is provided to obtain the multilevel decoders, which is based on reducing failures due to trapping sets and improving the guaranteed error-correction capability of a code. Hence these decoders improve the iterative decoding process on finite length graphs and have the potential to outperform the standard floating-point BP decoder in the error floor region. The description and apparatus of 3-bit decoders for column-weight three LDPC codes is also presented.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +2
Turbo decoder stopping criterion improvement
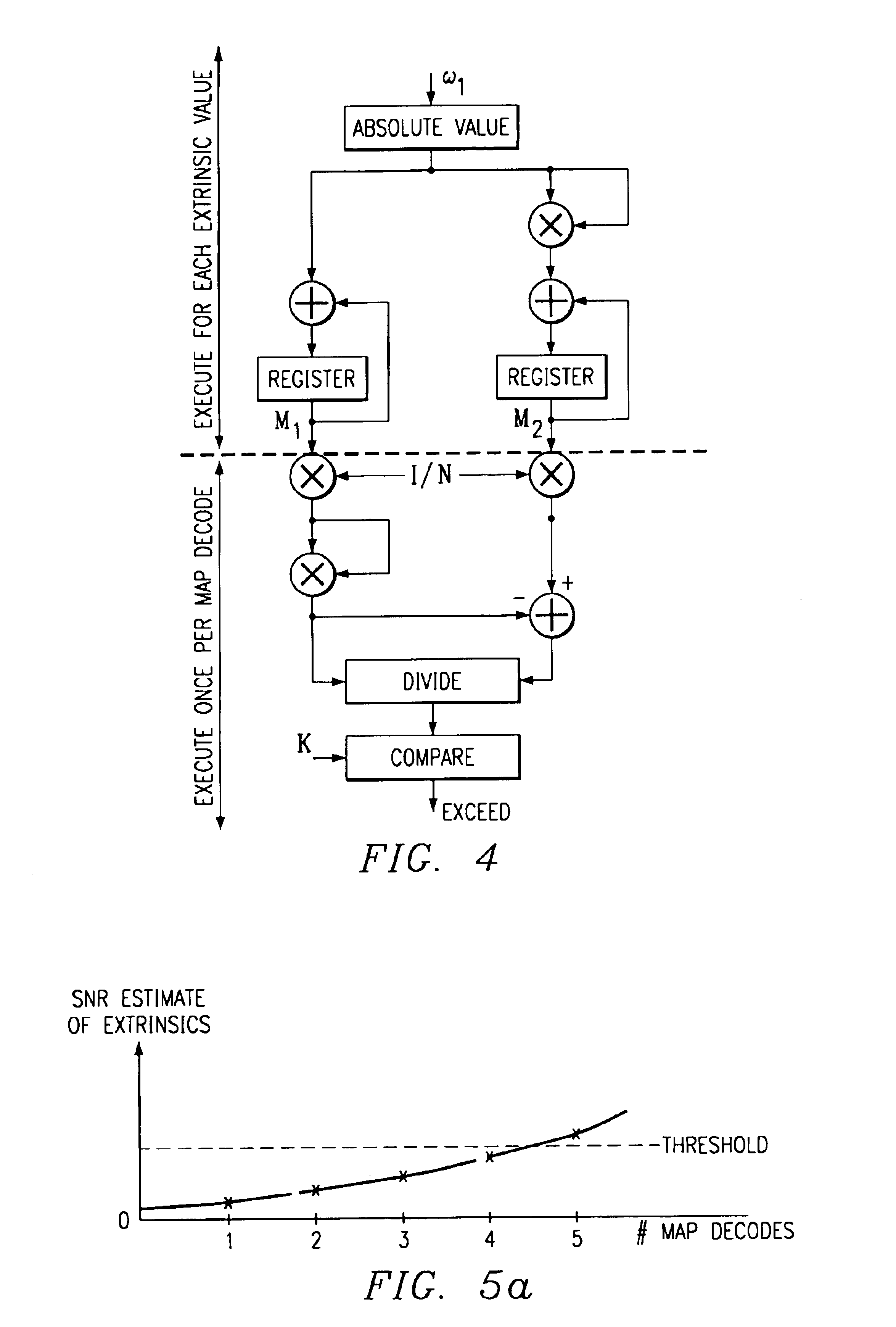
InactiveUS6898254B2Simple hardware implementationImprove processing speedData representation error detection/correctionError preventionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
A stopping criterion improvement for a turbo decoder that does not require division by a variable quantity. The stopping criterion improved upon generates a signal-to-noise ratio based on the mean and variance of soft-output estimates. The decoding process is aborted based on a comparison of the generated signal-to-noise ratio to a predetermined threshold.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
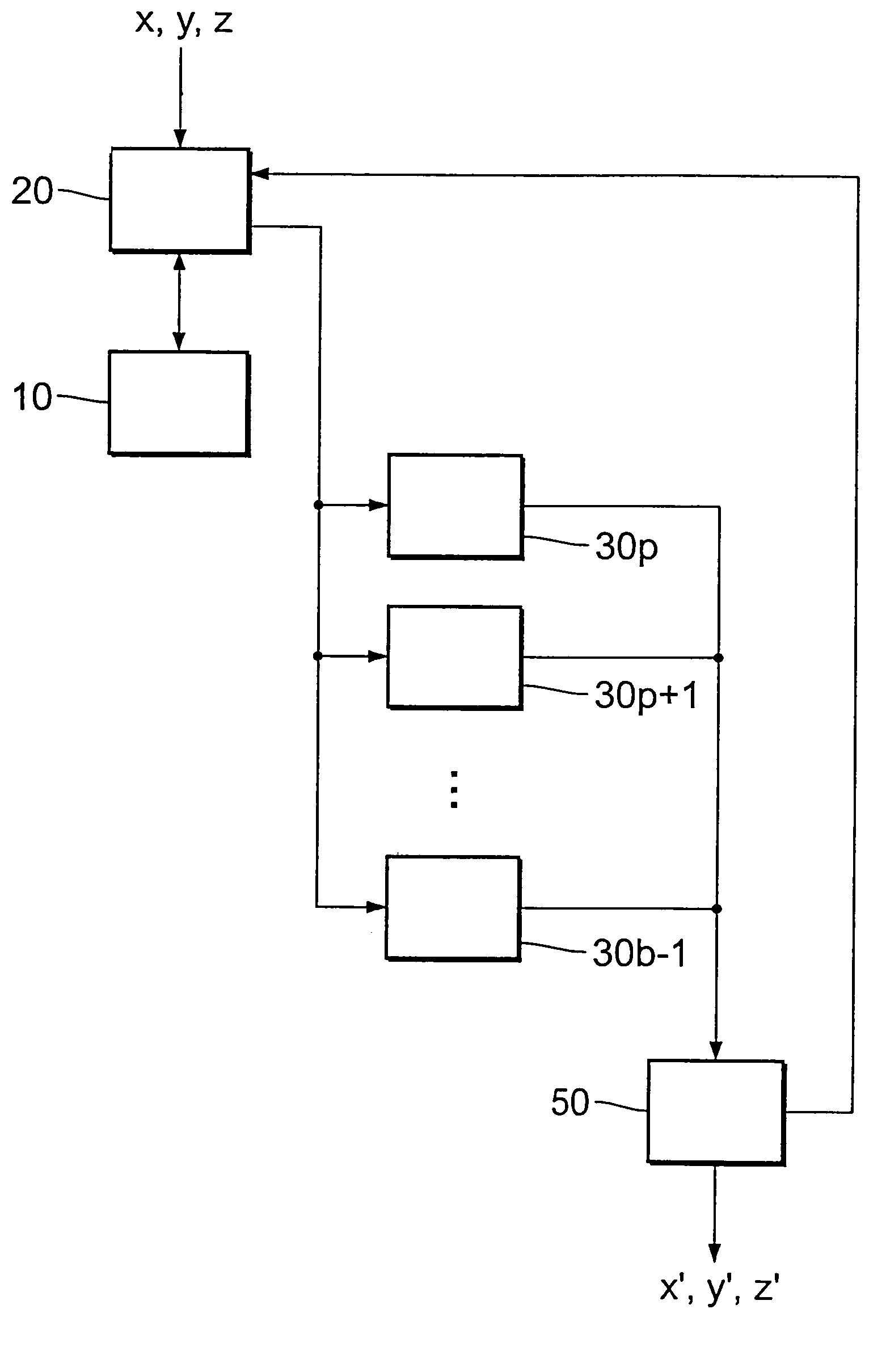
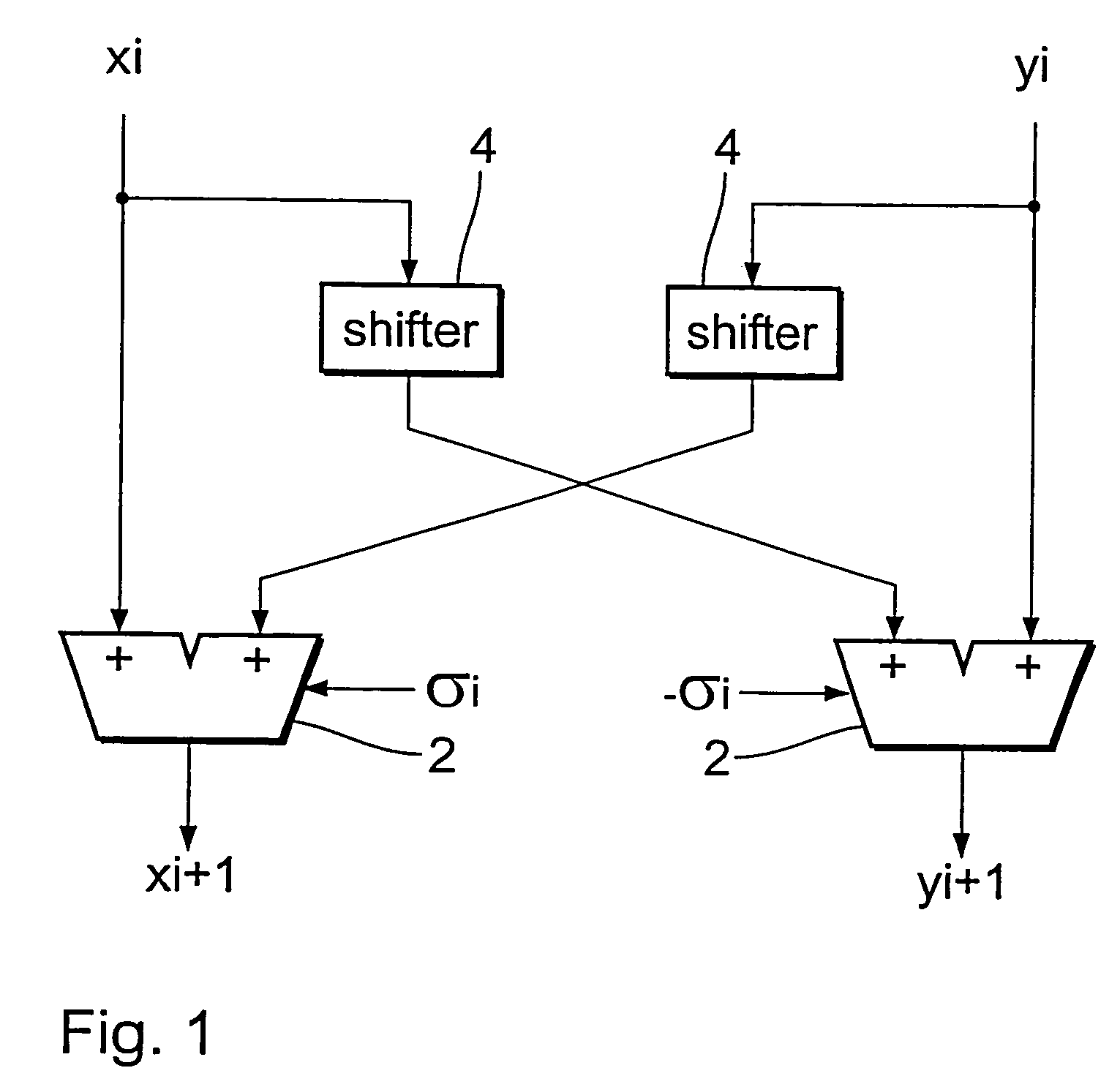
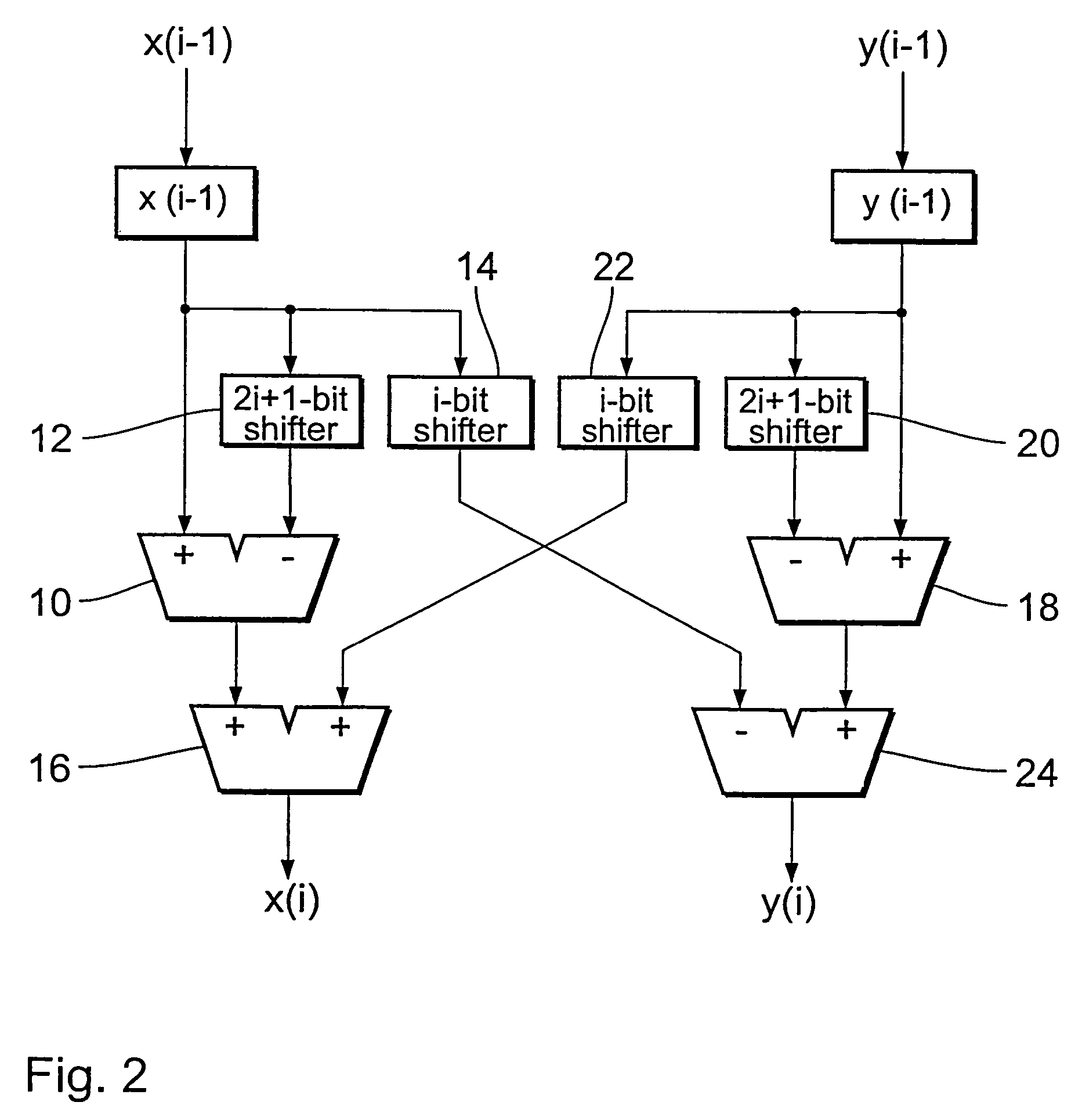
Cordic unit
InactiveUS20060059215A1Reduced activityReduce consumptionDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsParticle physicsTriggering device
A CORDIC unit for the iterative approximation of a vector rotation through a rotary angle θ by a number of elementary rotations through elementary angles αi, including elementary rotation stages for respectively effecting an elementary rotation through an elementary angle αi as an iteration step in the iterative approximation. After such an elementary rotation there remains a residual angle through which rotation is still to be effected. The elementary rotation stages of the CORDIC unit are adapted for rotation through elementary angles a( given by powers of two with a negative integral exponent. The CORDIC unit can also include a triggering device for triggering the elementary rotations, a triggering device which is adapted prior to each iteration step to compare the residual angle to at least one of the elementary angles and to omit those elementary rotation stages whose elementary angles are greater than the residual angle.
Owner:IHP GMBH INNOVATIONS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE MICROELECTRONICS LEIBNIZ INST FUR INNOVATIVE
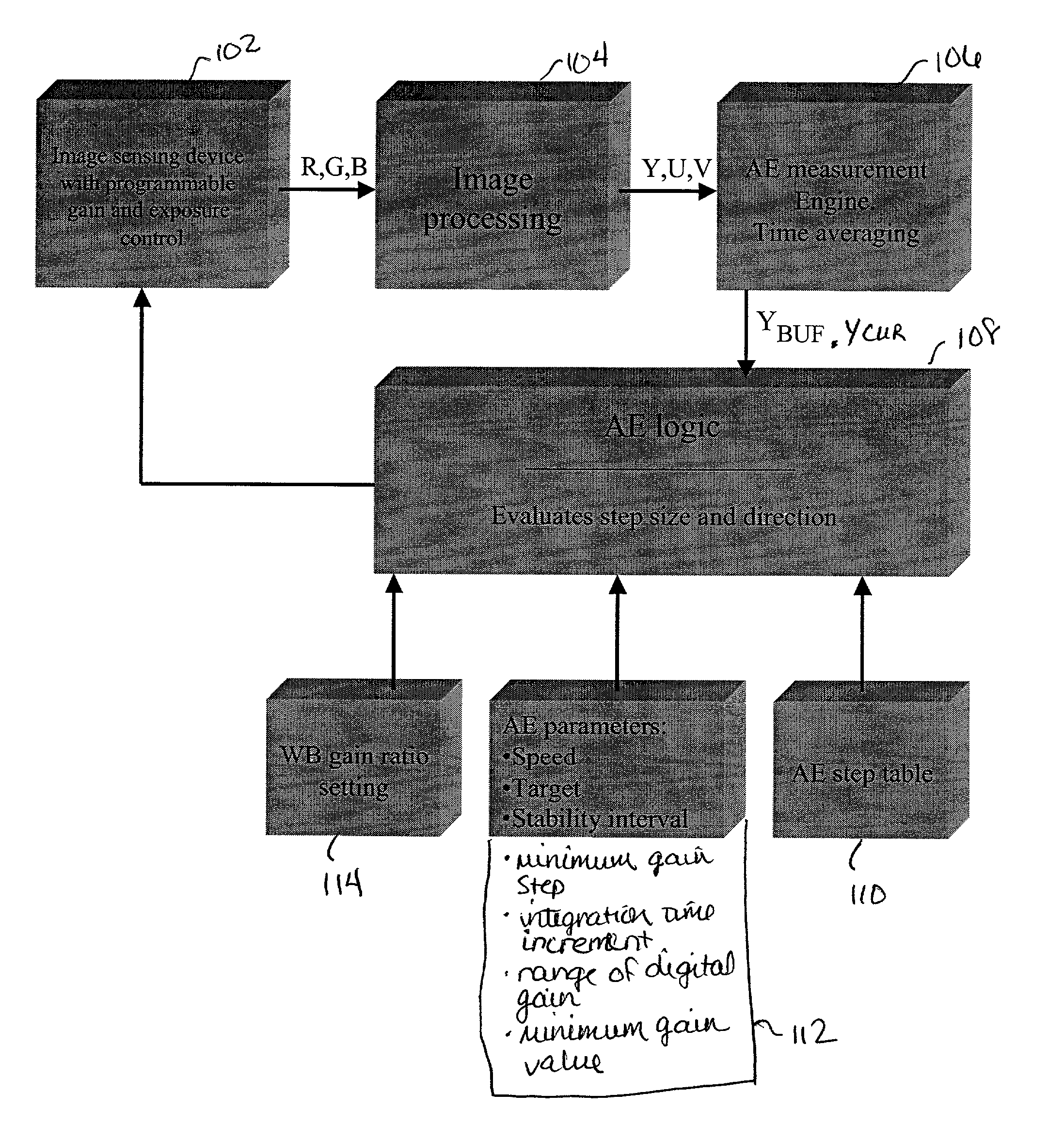
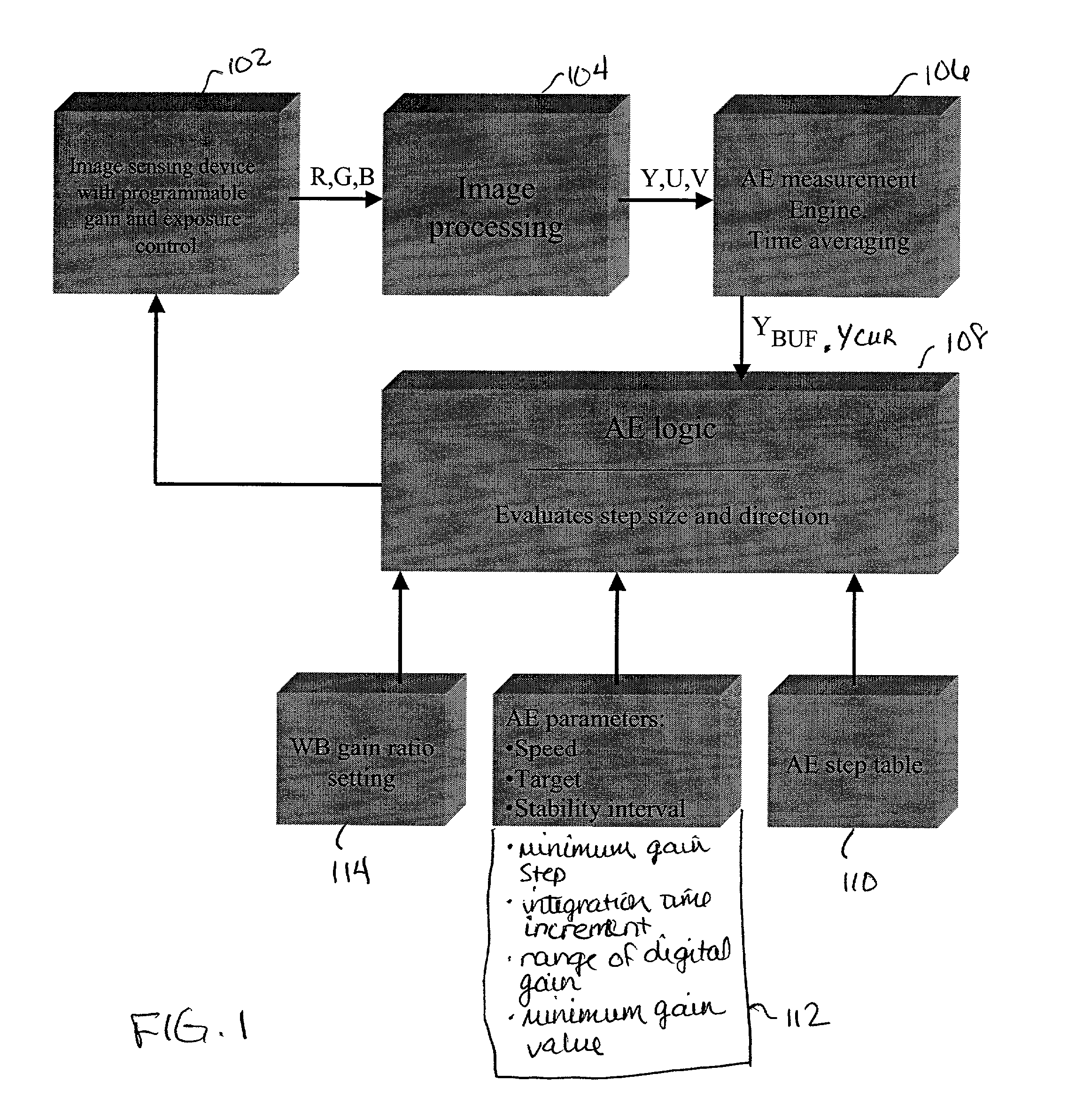
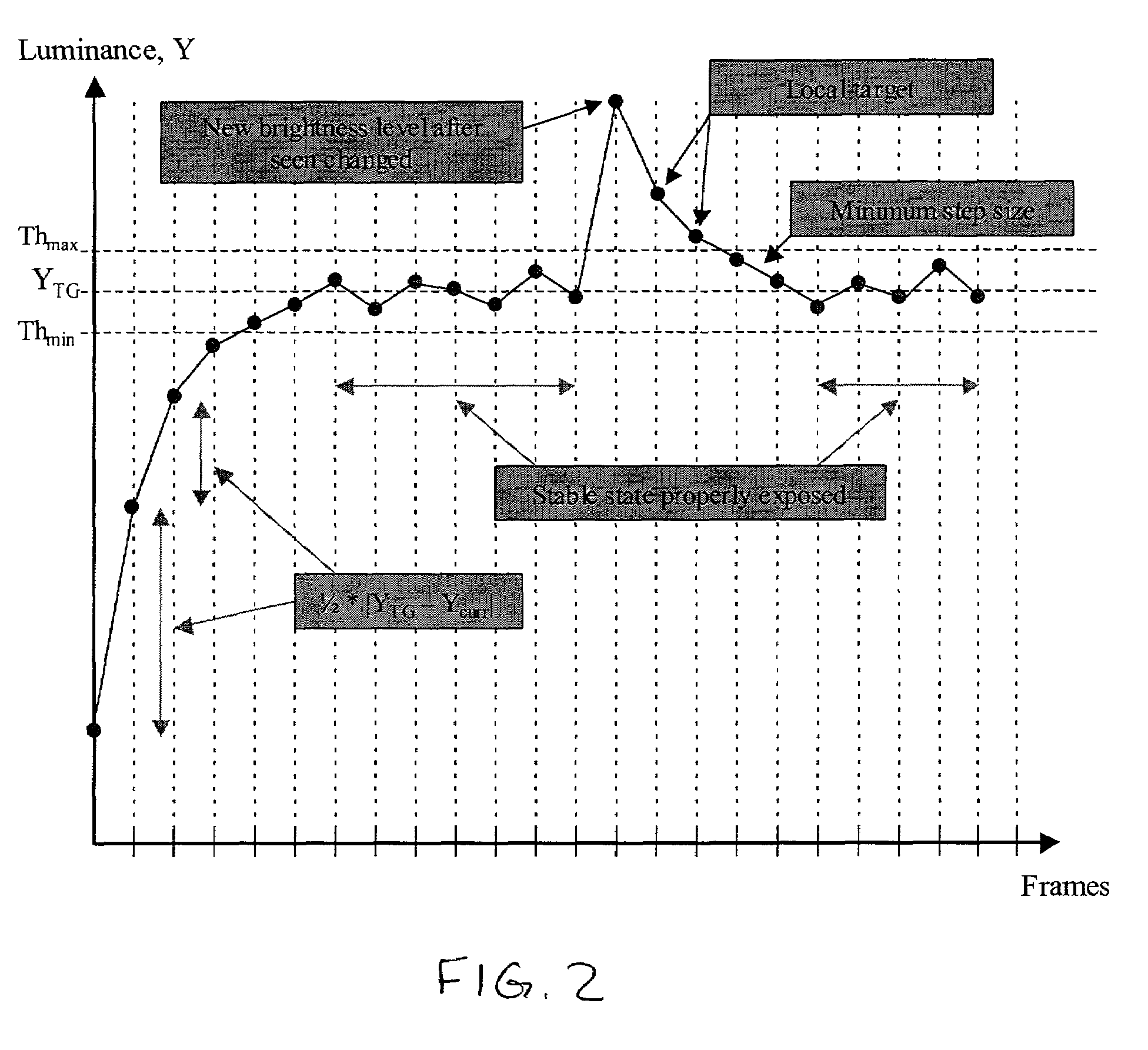
Method and apparatus for automatic gain and exposure control for maintaining target image brightness in video imager systems
ActiveUS7245320B2Maximize signal to noise ratioEfficiently maintaining a target image brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Imaging processing
In an image processing system, the imager gain and the exposure time are adjusted based on a predefined stepping sequence using a stepping table designed to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio in the image. This is achieved by providing a stepping sequence with each step having the largest suitable integration time (exposure) and an appropriate amplifier and digital gain setting, while achieving an equal relative percentage change in image brightness between adjacent sequence steps. The size of the executed AE steps is proportional to the distance between a current image luminance and the target luminance. This is achieved by the capability to skip one or more steps in the stepping sequence, if appropriate, for each relevant executed step, with the number of skipped steps, if any, being proportional to the magnitude of the deviation from the target brightness.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
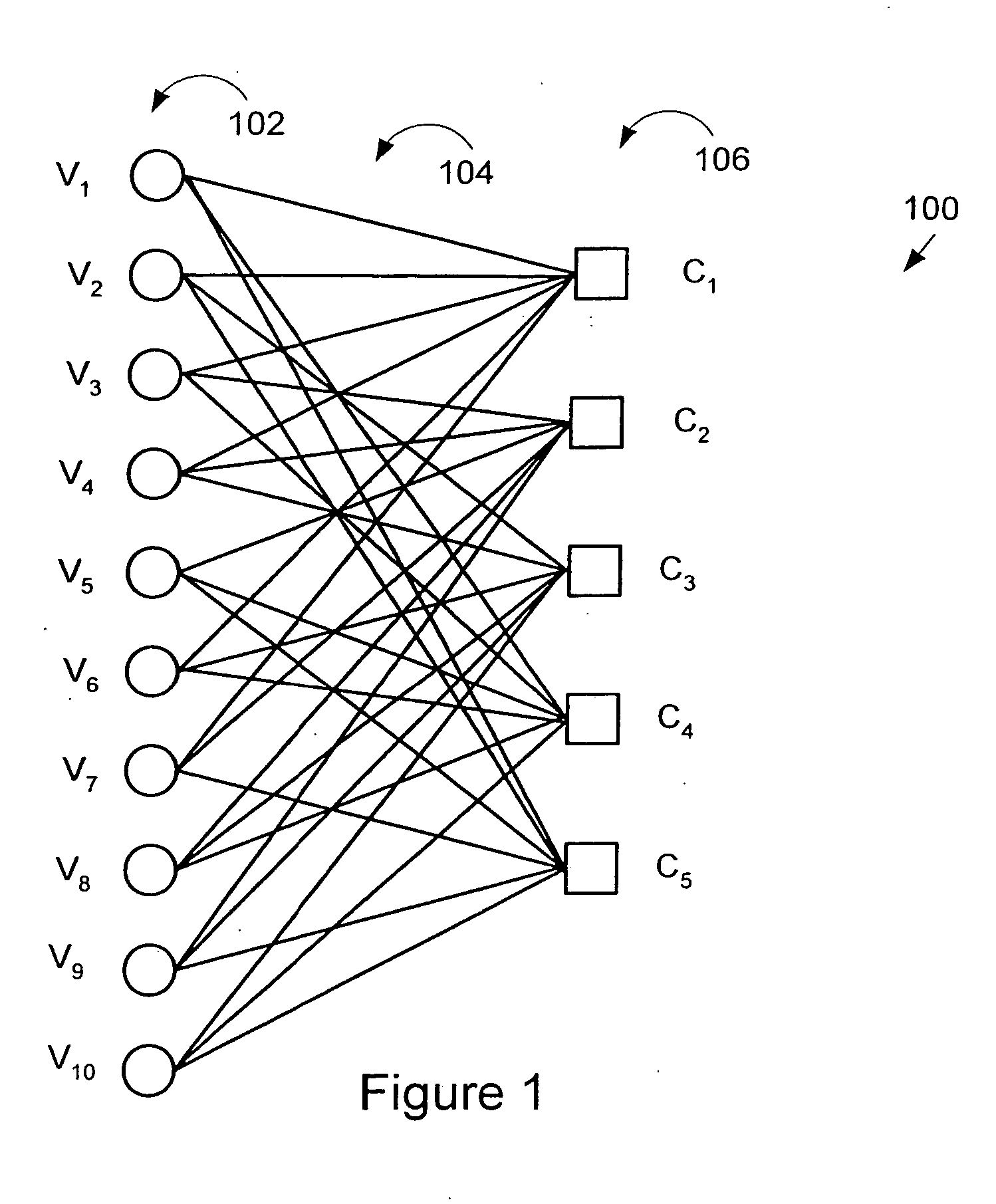
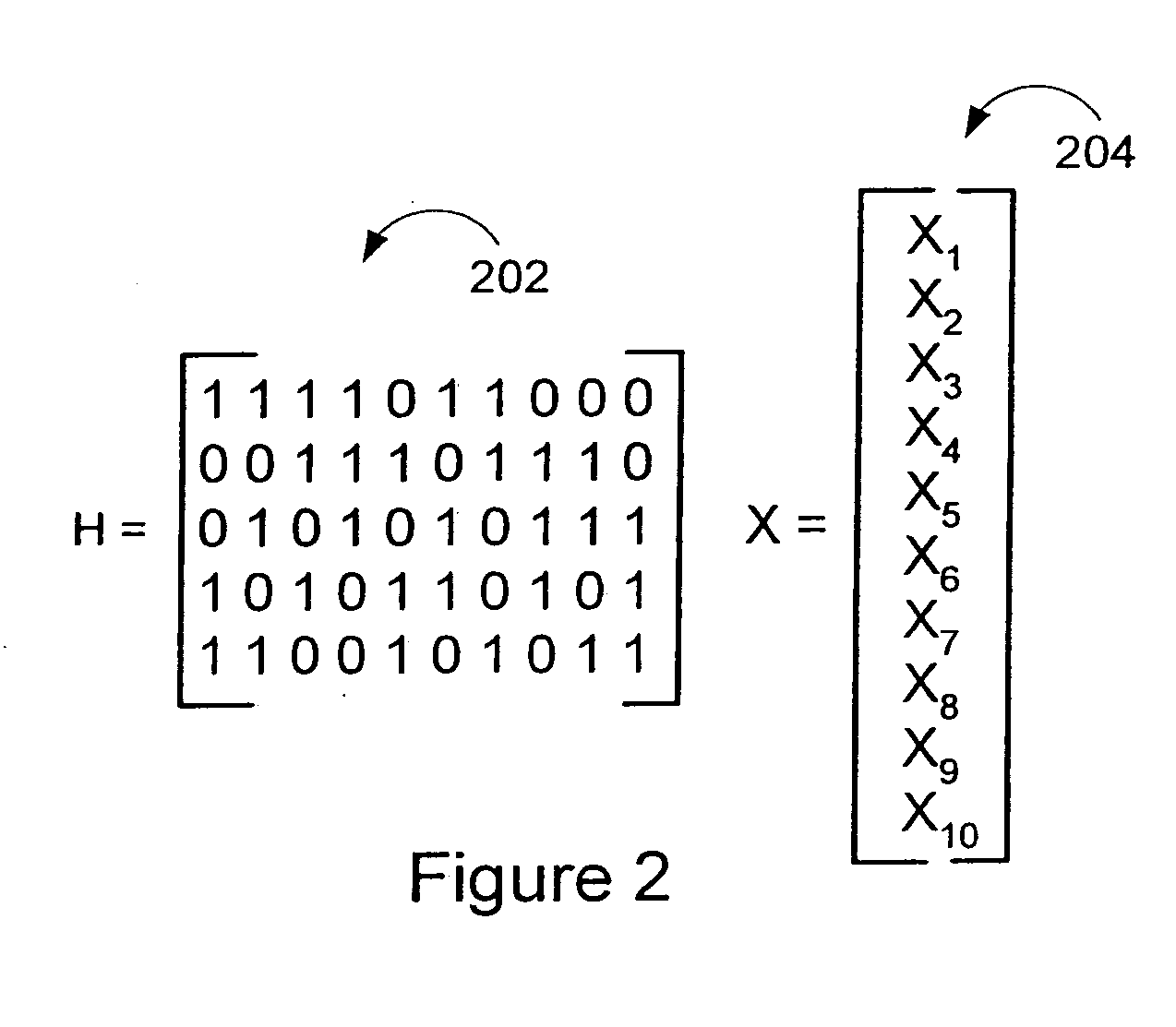
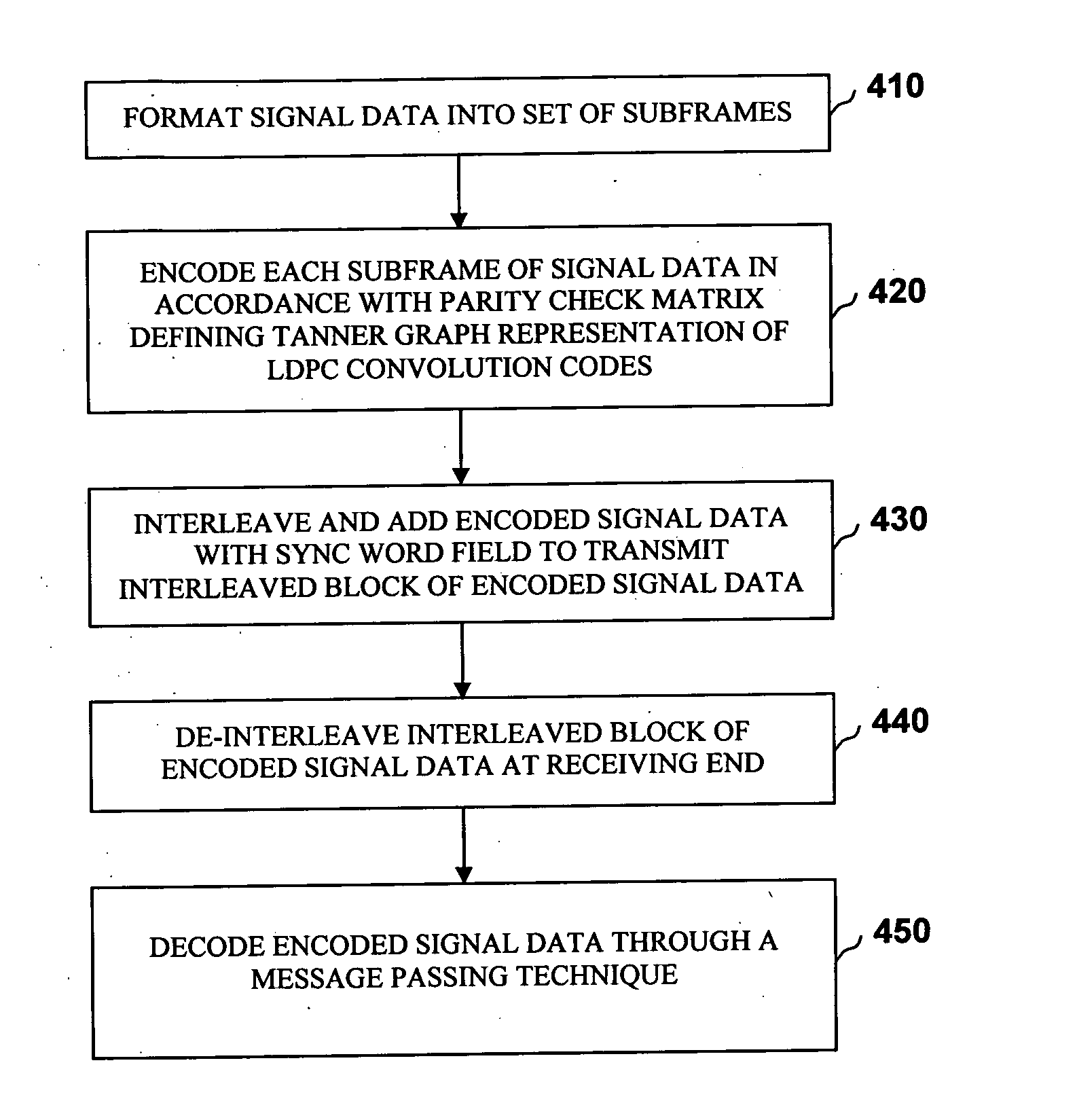
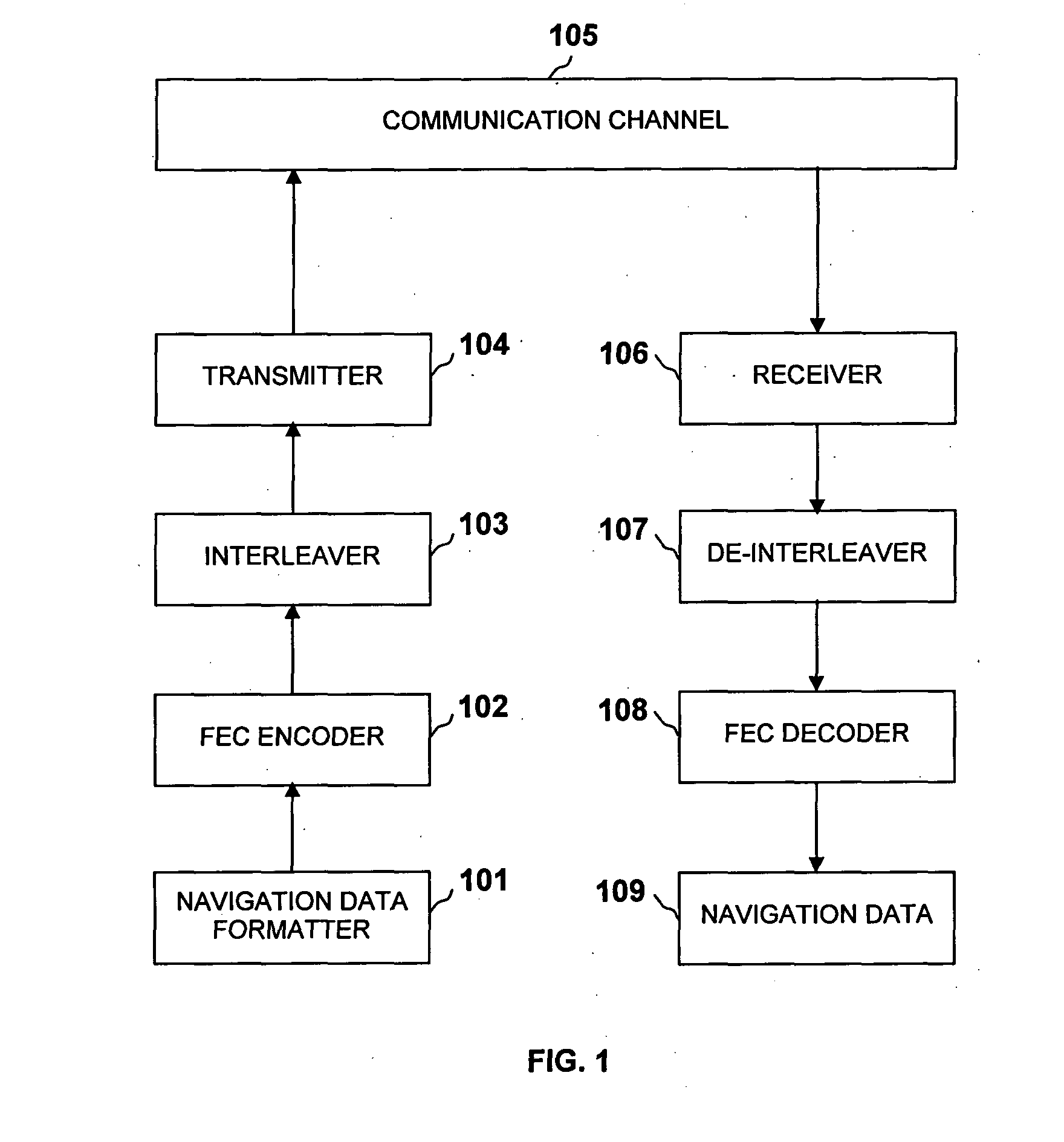
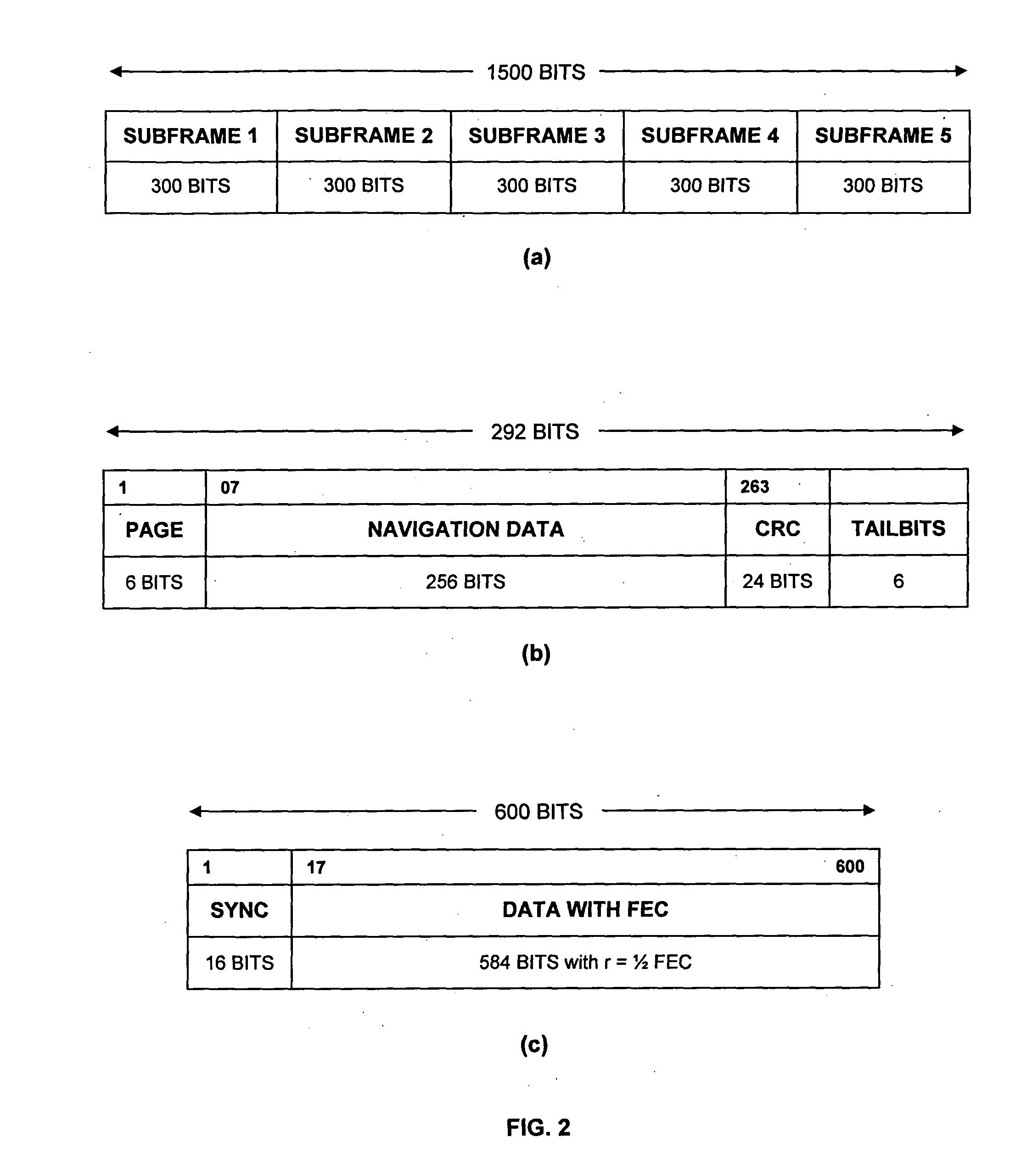
Method of communicating signal data in GNSS using LDPC convolution codes and a system thereof
InactiveUS20120198307A1Effective navigation data communicationError free performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputer hardwareLdpc convolutional codes
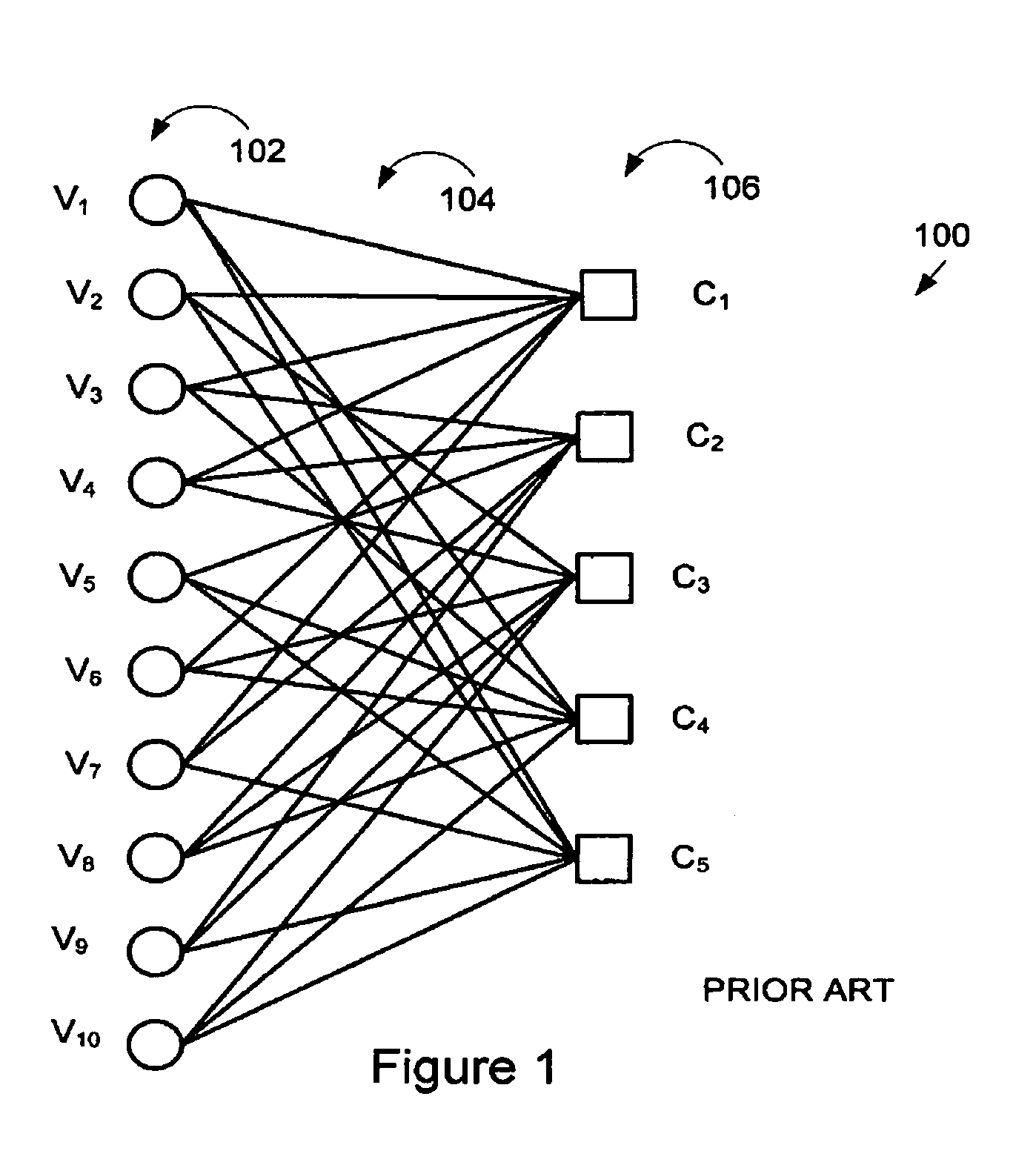
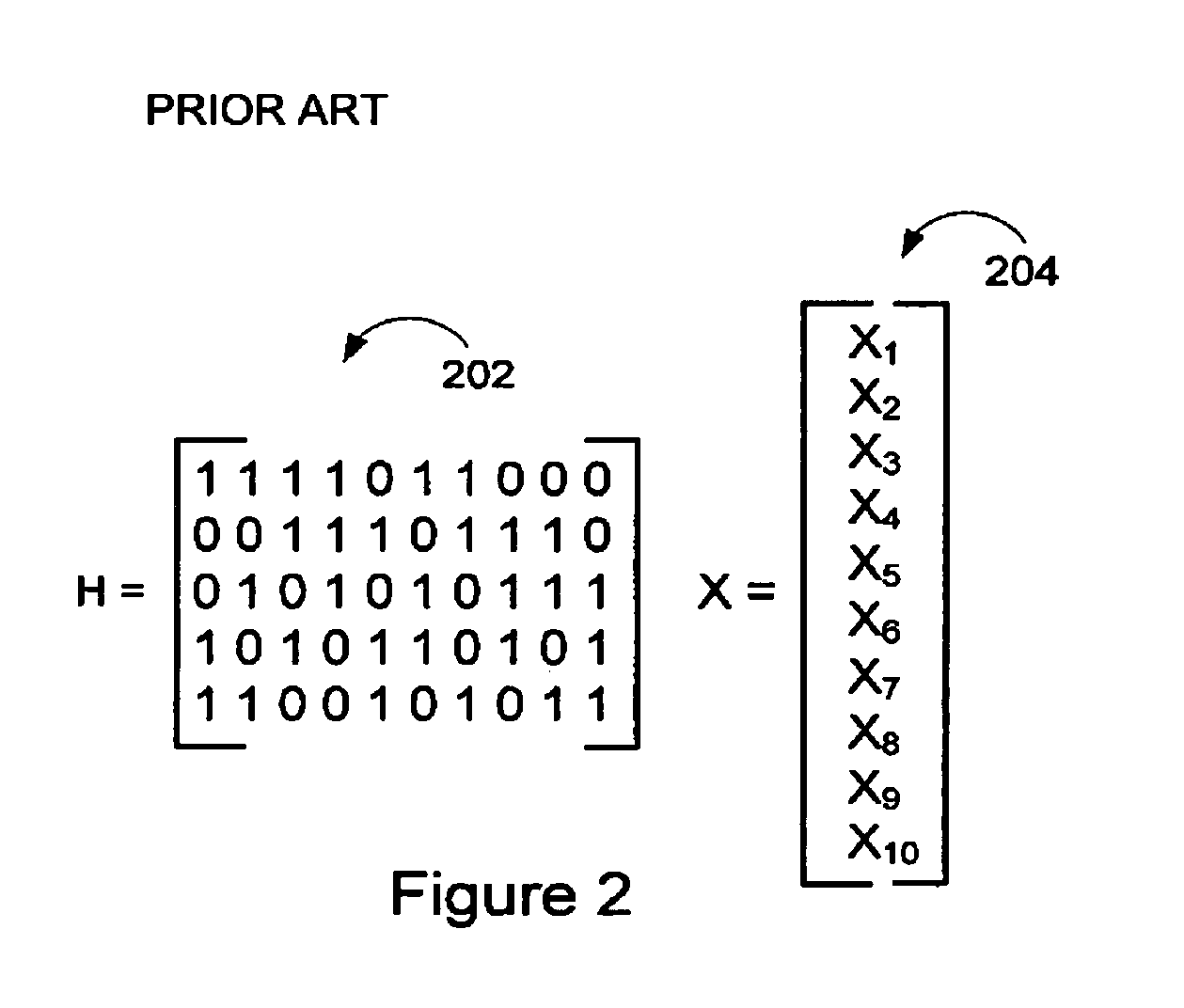
A method and system for communicating signal data in GNSS system using LDPC convolution codes. The method involves, at transmitting end, formatting signal data into a set of subframes. Each subframe of the signal data can be encoded in accordance with a parity check matrix defining Tanner graph representation of LDPC convolution codes. The encoded signal data can be interleaved and added with a Sync word field to transmit an interleaved block of encoded signal data through a communication channel. At receiving end, the interleaved block of encoded signal data can be de-interleaved after it is received from the communication channel. The Tanner Graph shows the connectivity in time invariant parity check matrix. A message passing technique is used to decode the LDPCCC encoded message. The encoded signal data can be decoded through the message passing technique to obtain the signal data primitively transmitted at the transmitting end. Such method and system are capable of achieving error free performance over the GNSS communication channel for effective navigation data communication, and also provide good BER performance over a wide range of Signal-to-Noise ratios.
Owner:INDIAN SPACE RES ORG
Low complexity finite precision decoders and apparatus for LDPC codes
ActiveUS8458556B2Improving message-passing processLow failure rateCode conversionCoding detailsNODALRound complexity
In this invention, a new class of finite precision multilevel decoders for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes is presented. These decoders are much lower in complexity compared to the standard belief propagation (BP) decoder. Messages utilized by these decoders are quantized to certain levels based on the number of bits allowed for representation in hardware. A message update function specifically defined as part of the invention, is used to determine the outgoing message at the variable node, and the simple min operation along with modulo 2 sum of signs is used at the check node. A general methodology is provided to obtain the multilevel decoders, which is based on reducing failures due to trapping sets and improving the guaranteed error-correction capability of a code. Hence these decoders improve the iterative decoding process on finite length graphs and have the potential to outperform the standard floating-point BP decoder in the error floor region. The description and apparatus of 3-bit decoders for column-weight three LDPC codes is also presented.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +2
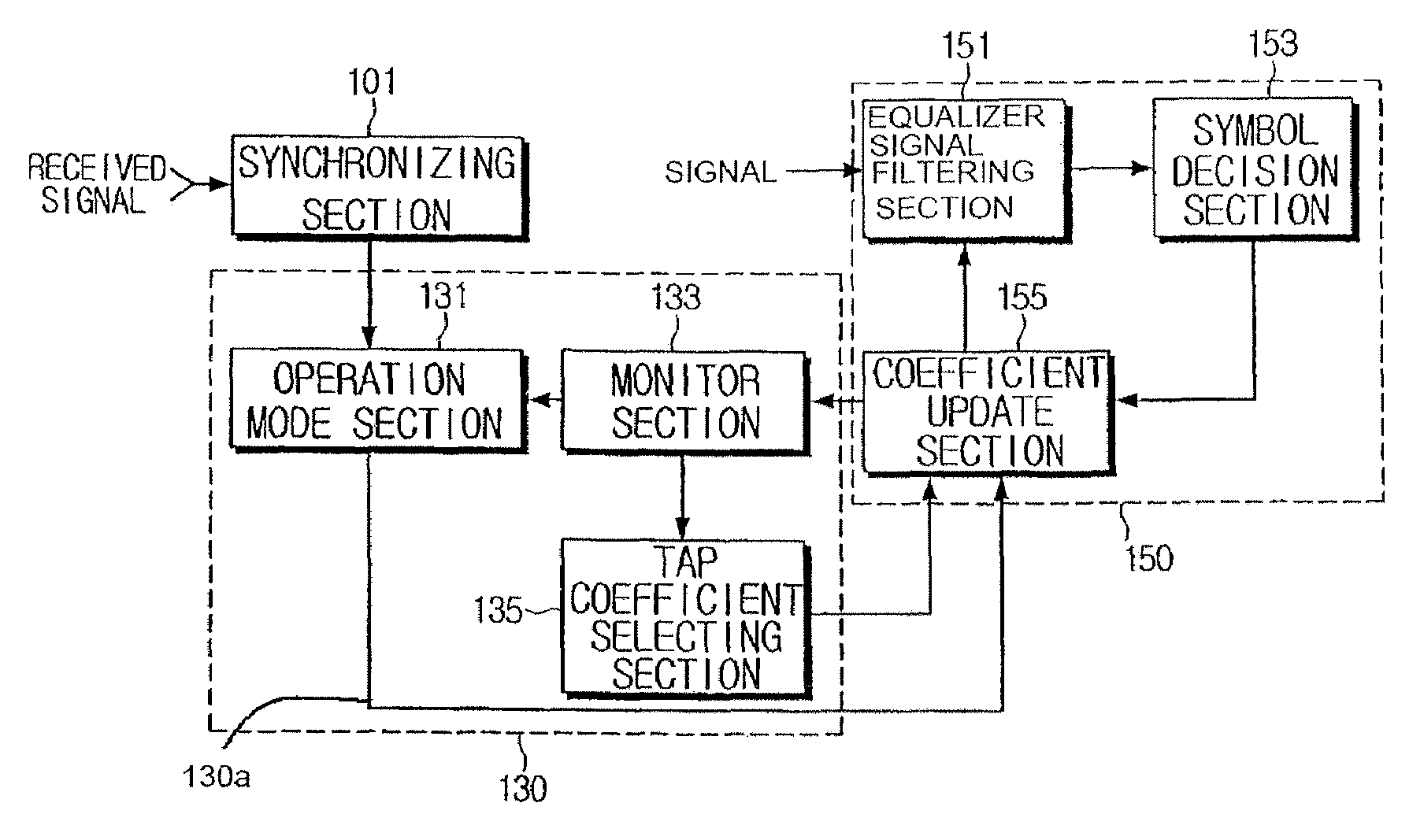
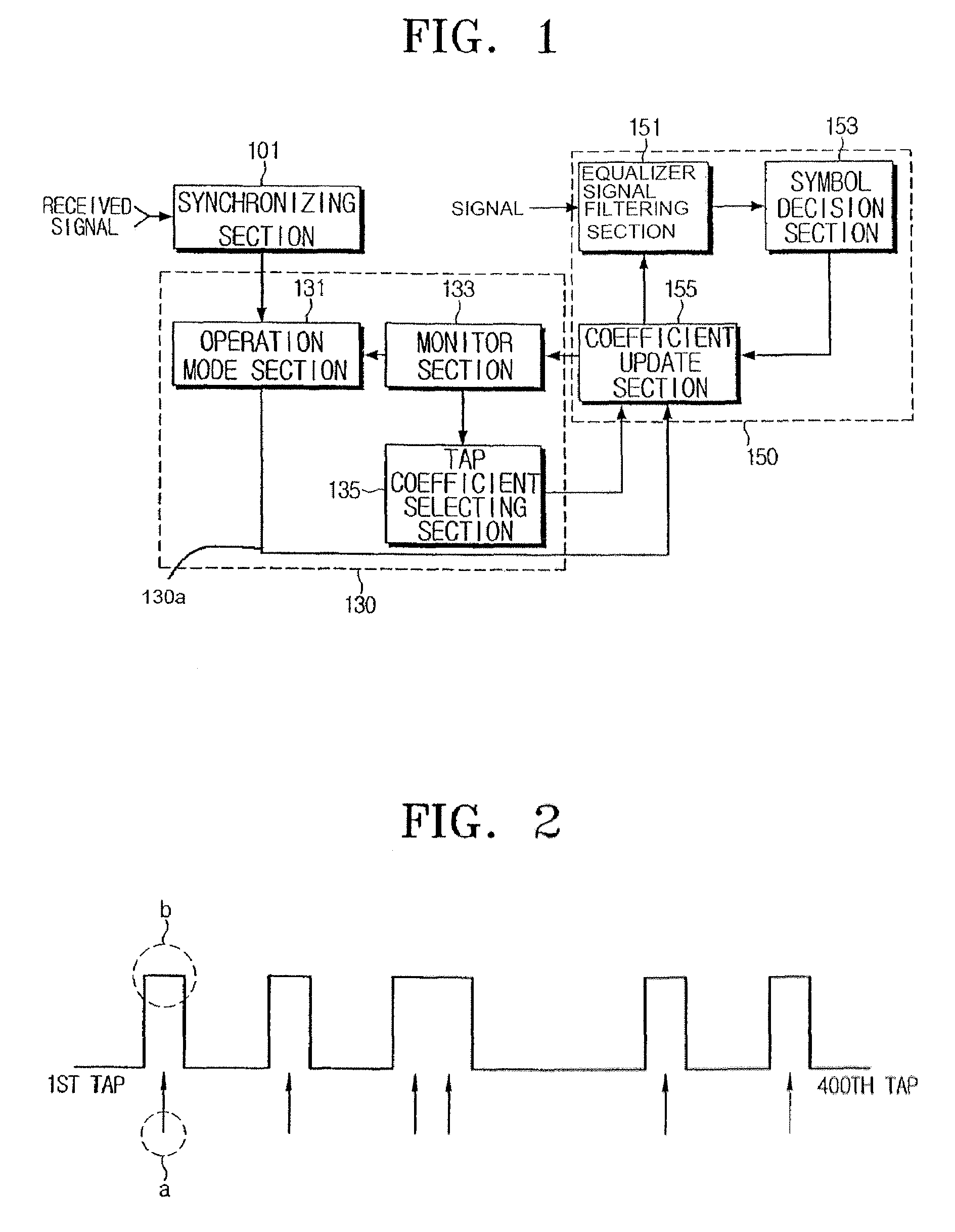
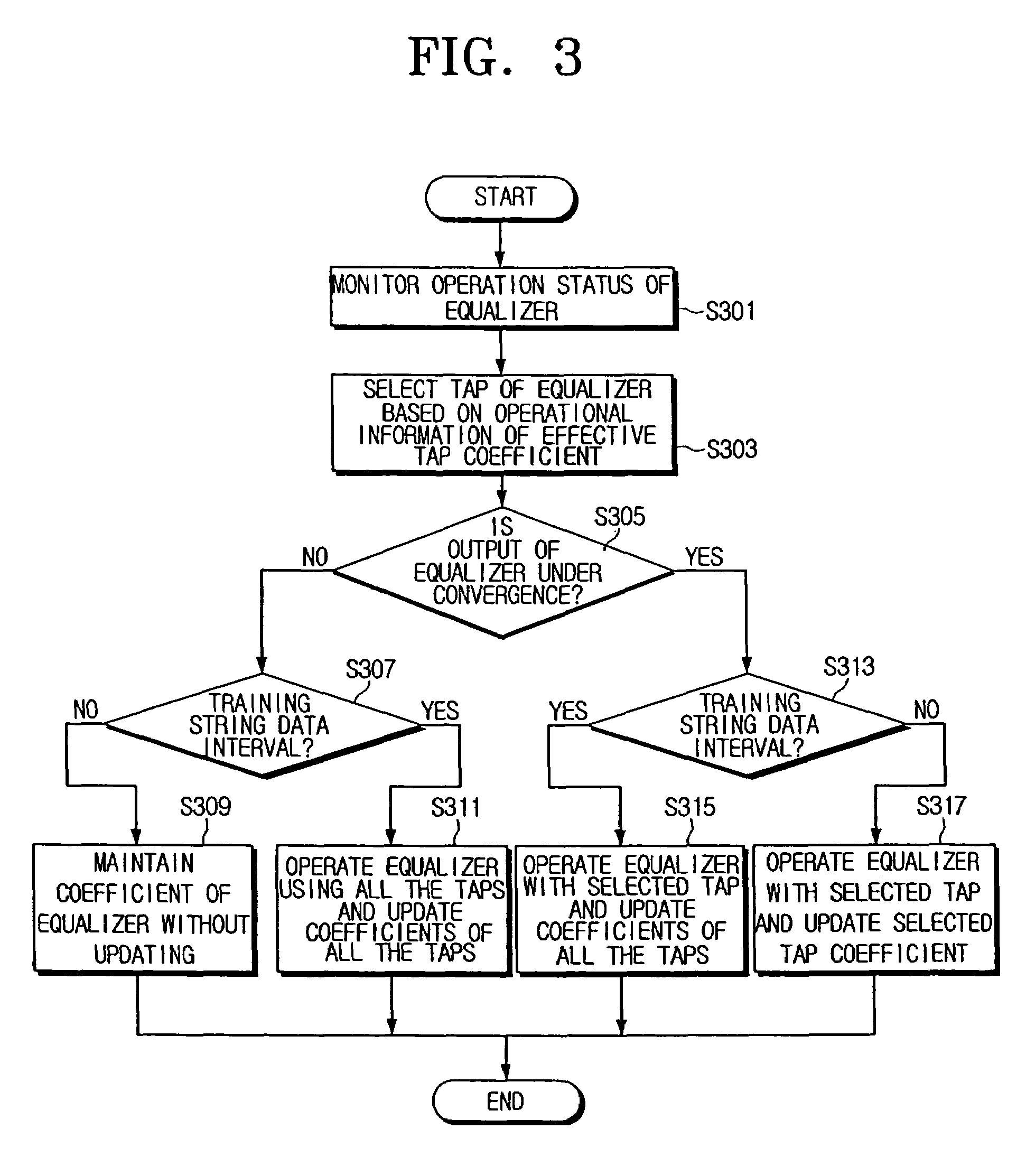
Method and apparatus to control operation of an equalizer
InactiveUS7486728B2Simple hardware implementationMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
A method and an apparatus to control an equalizer. A signal to noise ratio of an output of the equalizer is measured, the measured signal to noise ratio is fed back to the equalizer controlling apparatus, and convergence information of the equalizer is monitored and at the same time effective tap information of the equalizer is monitored. Accordingly, one or more taps can be selected to perform equalization in the equalizer and to control operation of the equalizer. Thus, it is not necessary to estimate channel information in order to properly operate the equalizer. Thus, since the channel information need not be estimated, a configuration of the equalizer is relatively simple. Additionally, it is possible to select a proper tap depending on a change in a channel environment and to update a corresponding tap coefficient. Accordingly, performance can be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Spreading code hopping for synchronous DS-CDMA system to mitigate interference effects
InactiveUS7099372B2Improve performanceMitigation of adjacent cell interferenceAntenna supports/mountingsRadio transmissionCommunications systemData rate
Disclosed is a method for operating a code division multiple access communications system, and a system that operates in accordance with the method. The method operates within a coverage area of a base station by assigning a set of spreading codes to individual ones of a plurality of subscriber stations and then, during transmissions within the cell, by periodically hopping amongst spreading code within the set of spreading codes such that at any given time no two subscriber stations operate with the same spreading code. The set of spreading codes may include the all one's spreading code. The step of periodically hopping preferably changes from a currently used spreading code to a next spreading code at a symbol rate or at a multiple of the symbol rate. The set of spreading codes may be a hopped sub-set of a larger set of spreading codes, and in this case the method further operates to assign a non-hopped sub-set of the larger set of spreading codes to individual ones of the plurality of subscriber stations for use on a system access channel and / or on a system control channel or, more generally, for use on a non-traffic channel. The system may be a fixed data rate system or a variable data rate system. In the latter case the step of periodically hopping may change from a currently used spreading code to a next spreading code at the symbol rate, or at a multiple of the symbol rate of the lowest or the highest symbol rate users.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
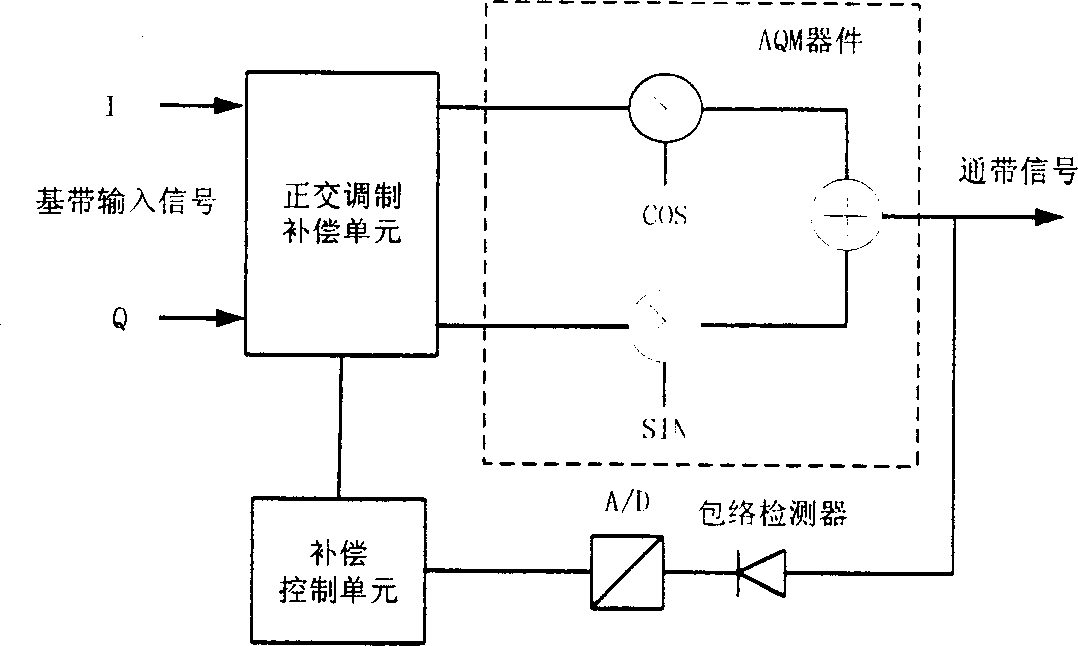
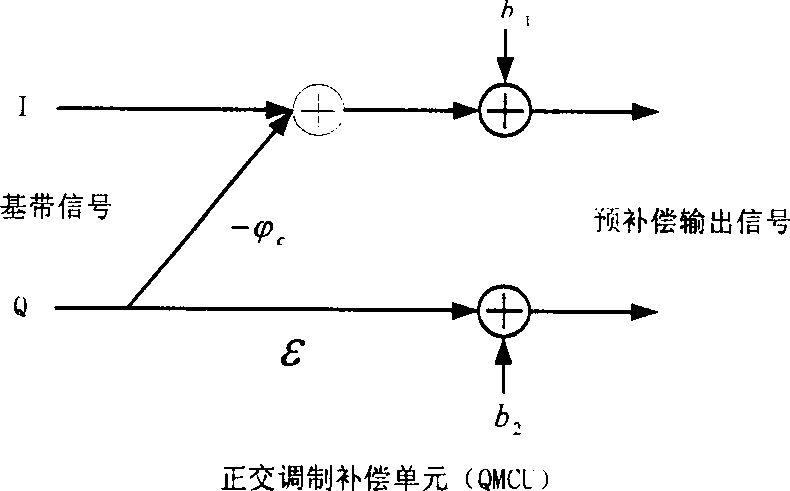
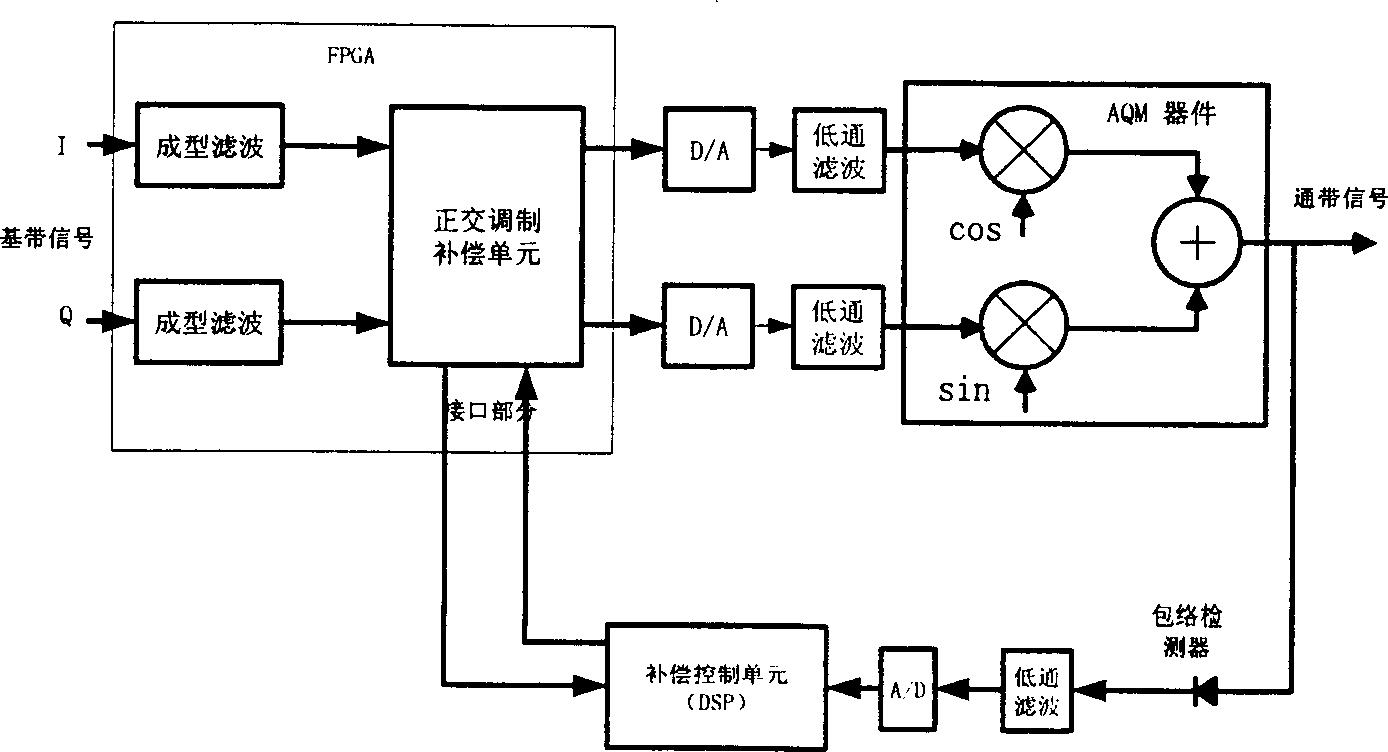
Analog orthogonal modulation unbalance compensating method
InactiveCN1392691ASimple hardware implementationSmall amount of calculationTransmission control/equalisingTransmission monitoringCarrier signalQuadrature modulation
This invention relates to an analog compensation method for quadrature modulation of unbalance using the following steps: substep unbalance compensation based on testing phoneme in the switch-on stage and unbalance compensation based on analog Newton iteration in the receiving and sending process, a compensation control unit uses envelope detector to detect the analog quadrature-modulated signal for its peak envelope to get IQ two routes DC bias compensation coefficient, phase unbalance compensation coefficient, and gain unbalance coefficient. The base-band signals to be delivered in first sent to QMCU for pretreatment, then to analog quadrature modulator modulated on the pass-band to make output signals reach or be approximate to the performance of ideal quadrature modulators.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
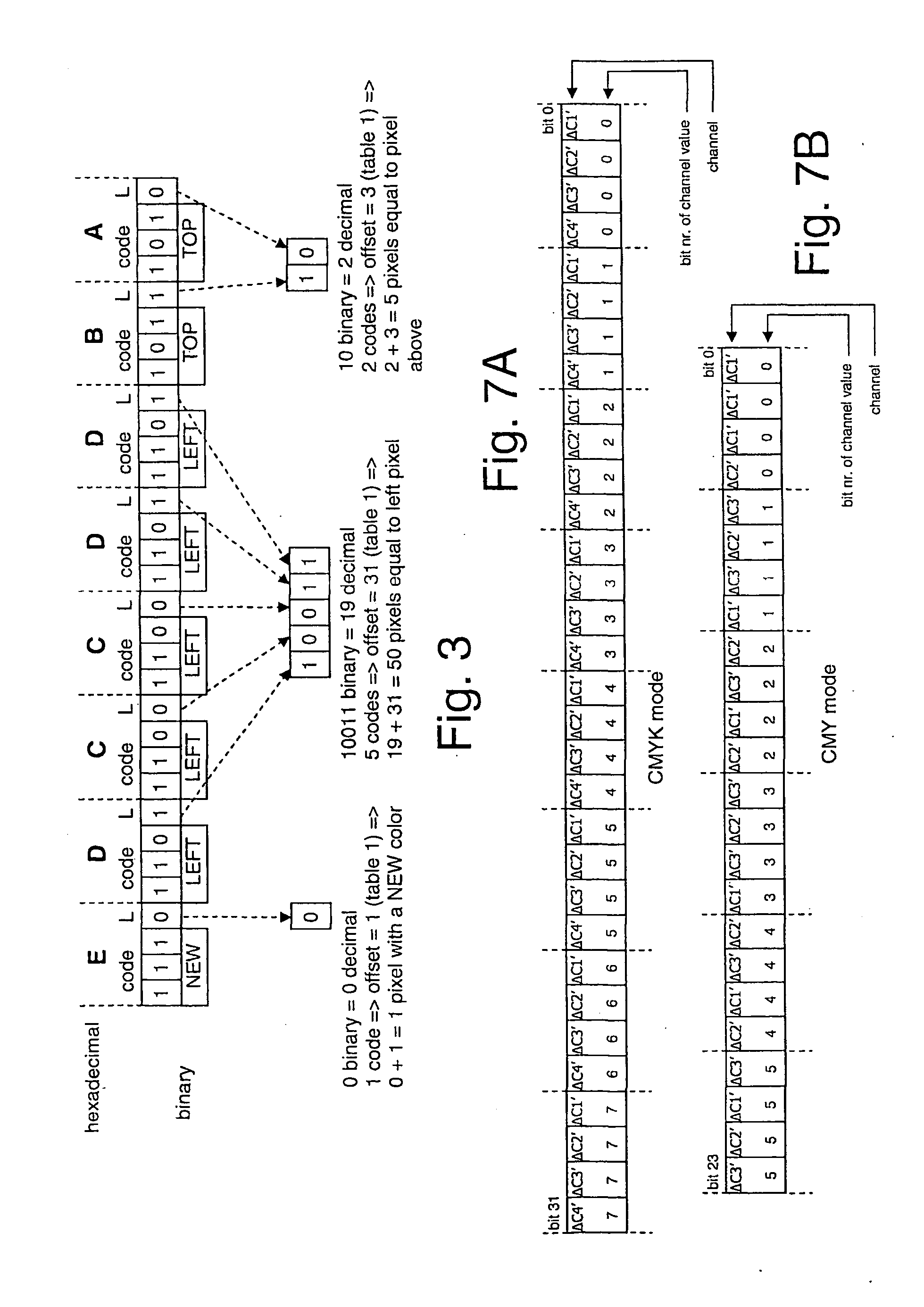
Lossless Compression of Color Image Data Using Entropy Encoding
ActiveUS20090129691A1Reduce complexityCompression can be losslessColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionColor imageScan line
A method compresses a digital continuous tone image of pixels situated on scan lines. The method includes the steps of, for a current pixel to be encoded, said current pixel having an actual pixel value, predicting a predicted pixel value based on pixel values of at least one previously processed pixel from the same image, using a fixed rule, determining a difference parameter based on a difference value of said predicted pixel value and the actual pixel value of said current pixel to be encoded, and inspecting the difference parameter for existence of an uninterrupted series of highest order bits having a value equal to zero, removing at least part of said highest order zero bits, and, if a number of bits within predetermined limits remains, generating a compression code having a predetermined fixed length, said code indicating the number of remaining bits.
Owner:OCE TECH
Method and apparatus for generating a composite signal
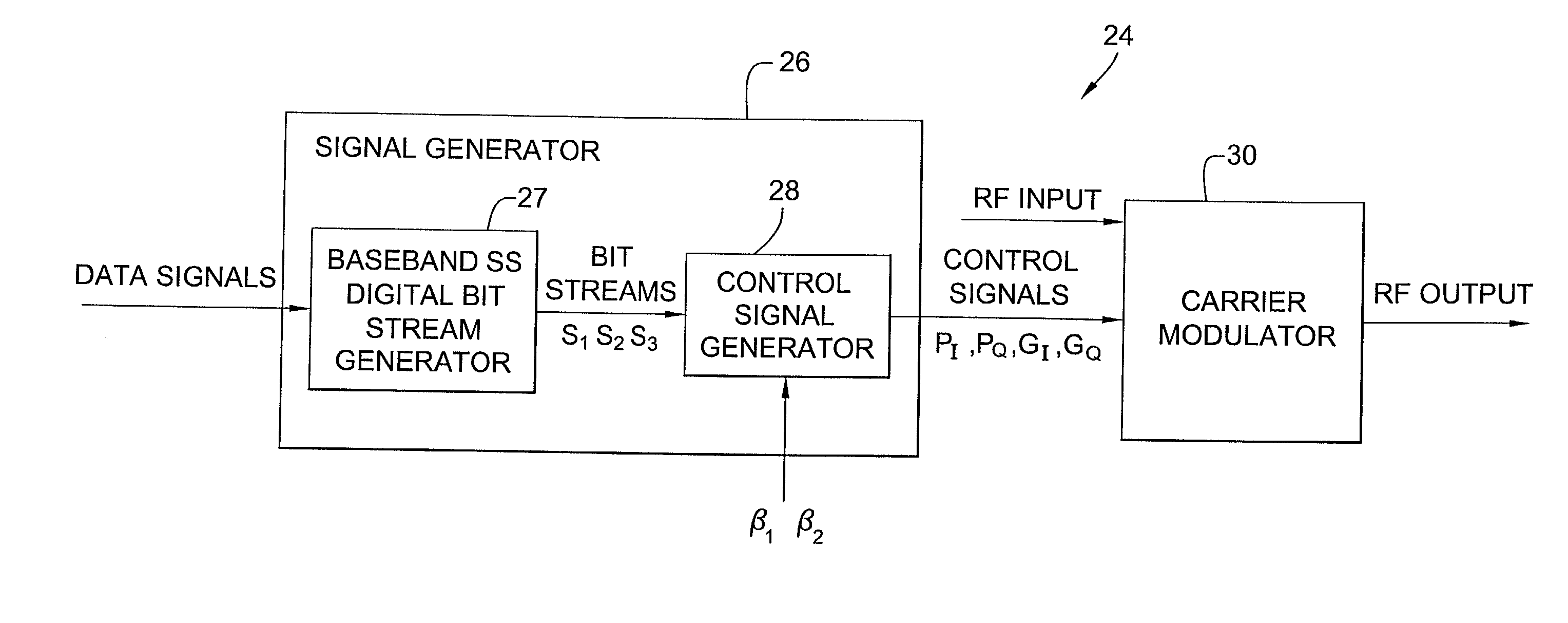
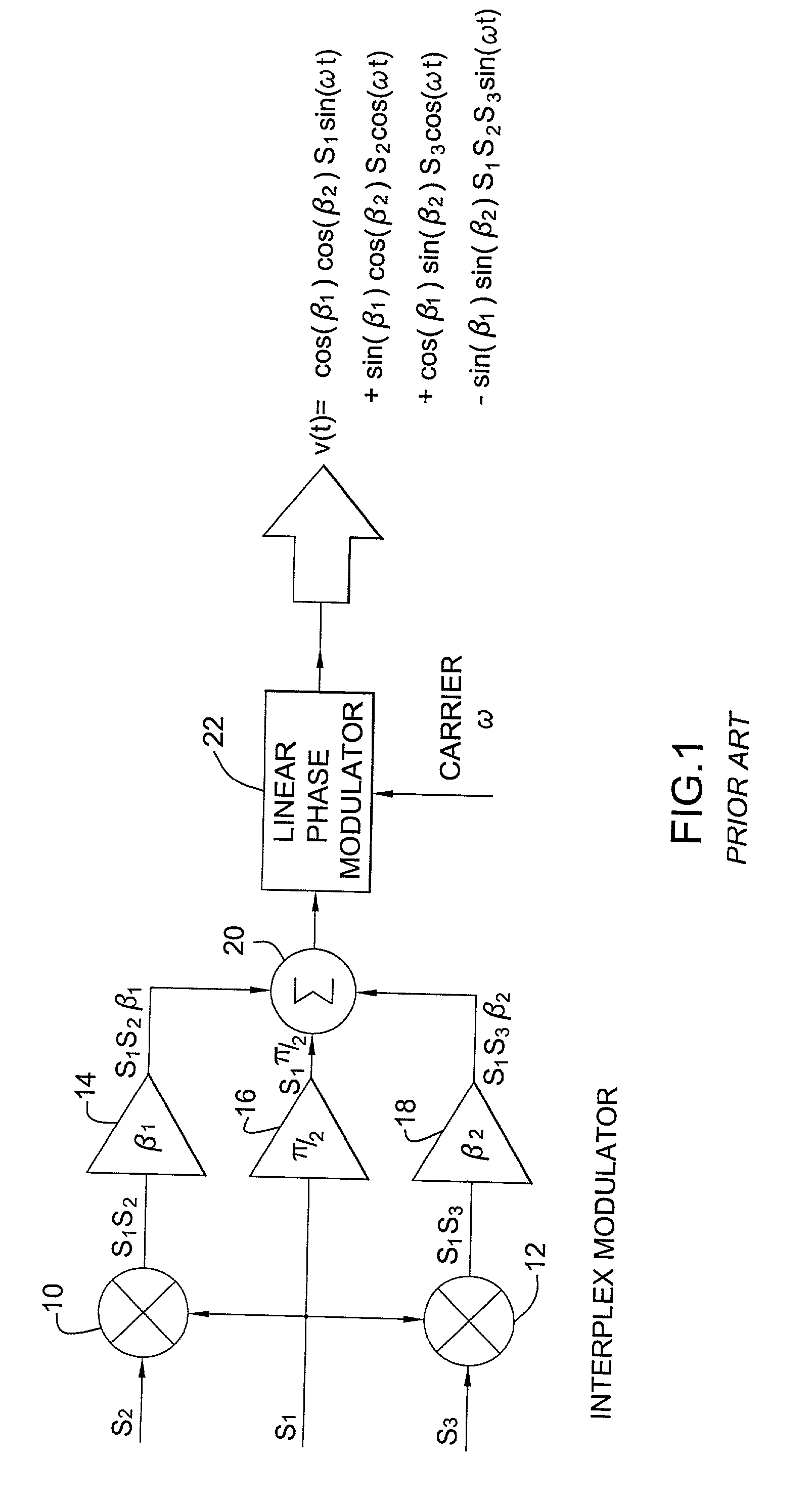
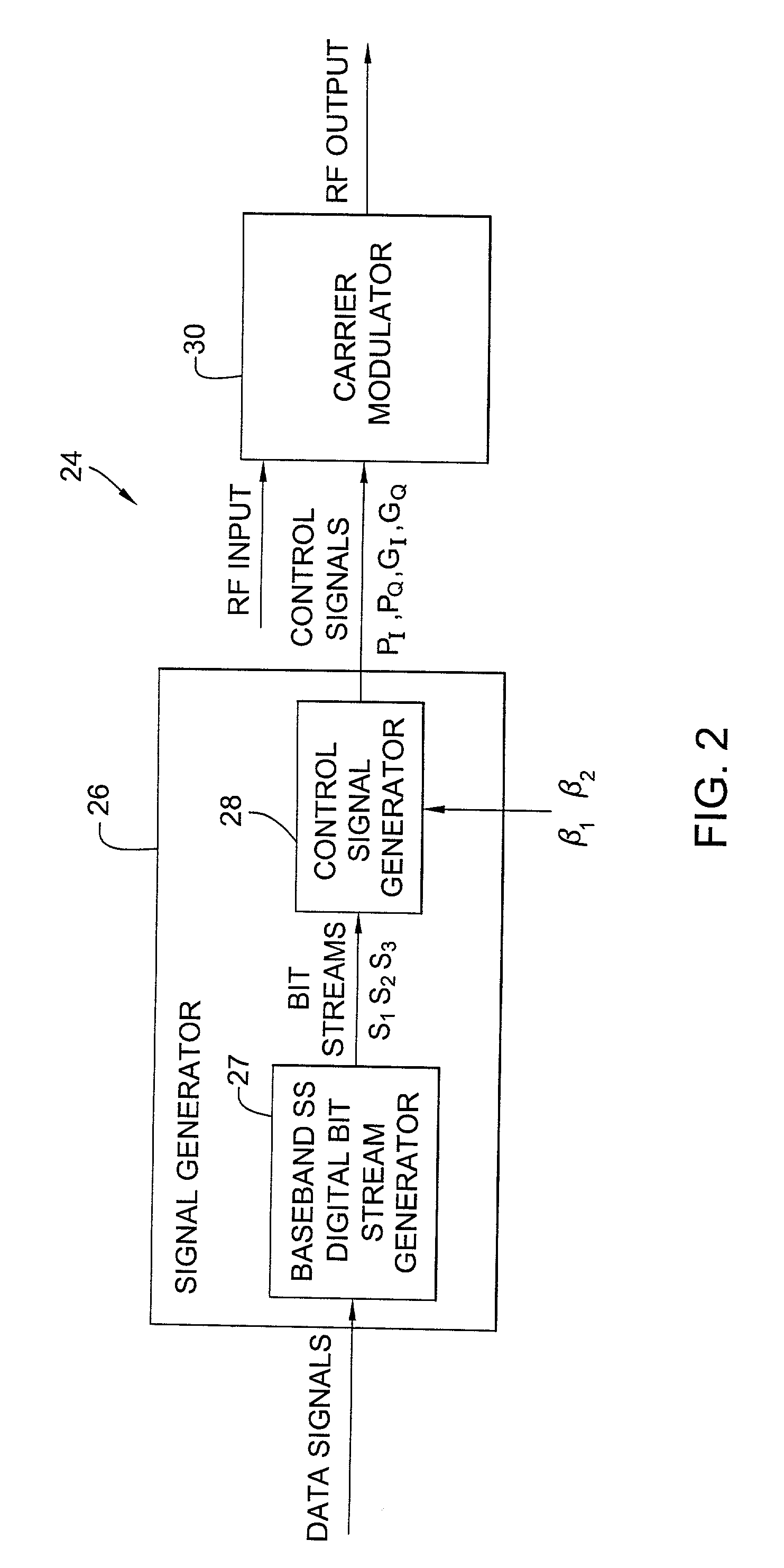
ActiveUS7039122B2Simple hardware implementationEasy to adjustElectric signal transmission systemsEqual length code transmitterCarrier signalDirect-sequence spread spectrum
A programmable waveform generator forms a composite transmission signal containing multiple information signals using a reduced number of hardware components to modulate the phase and amplitude of the carrier signal. A signal generator develops baseband direct sequence spread spectrum digital bit streams from corresponding input data signals. The values of the digital bit steams are used to simultaneously control states of phase modulators and variable attenuators which modulate the phase and amplitude of the in-phase and quadrature carrier components. The programmable waveform generator can be used to implement an interplex modulator producing a constant-envelope composite signal with fewer phase modulators and attenuators.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
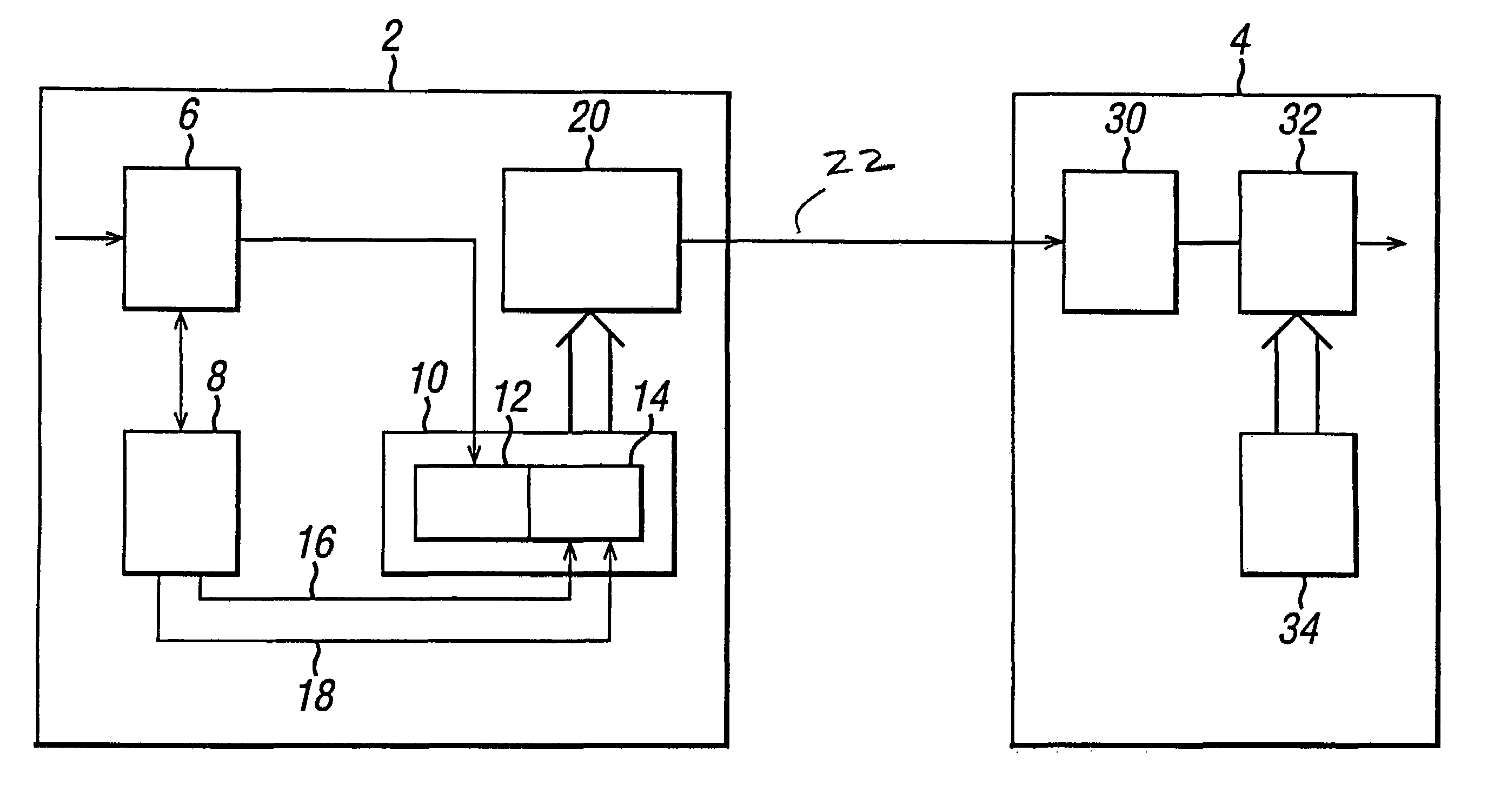
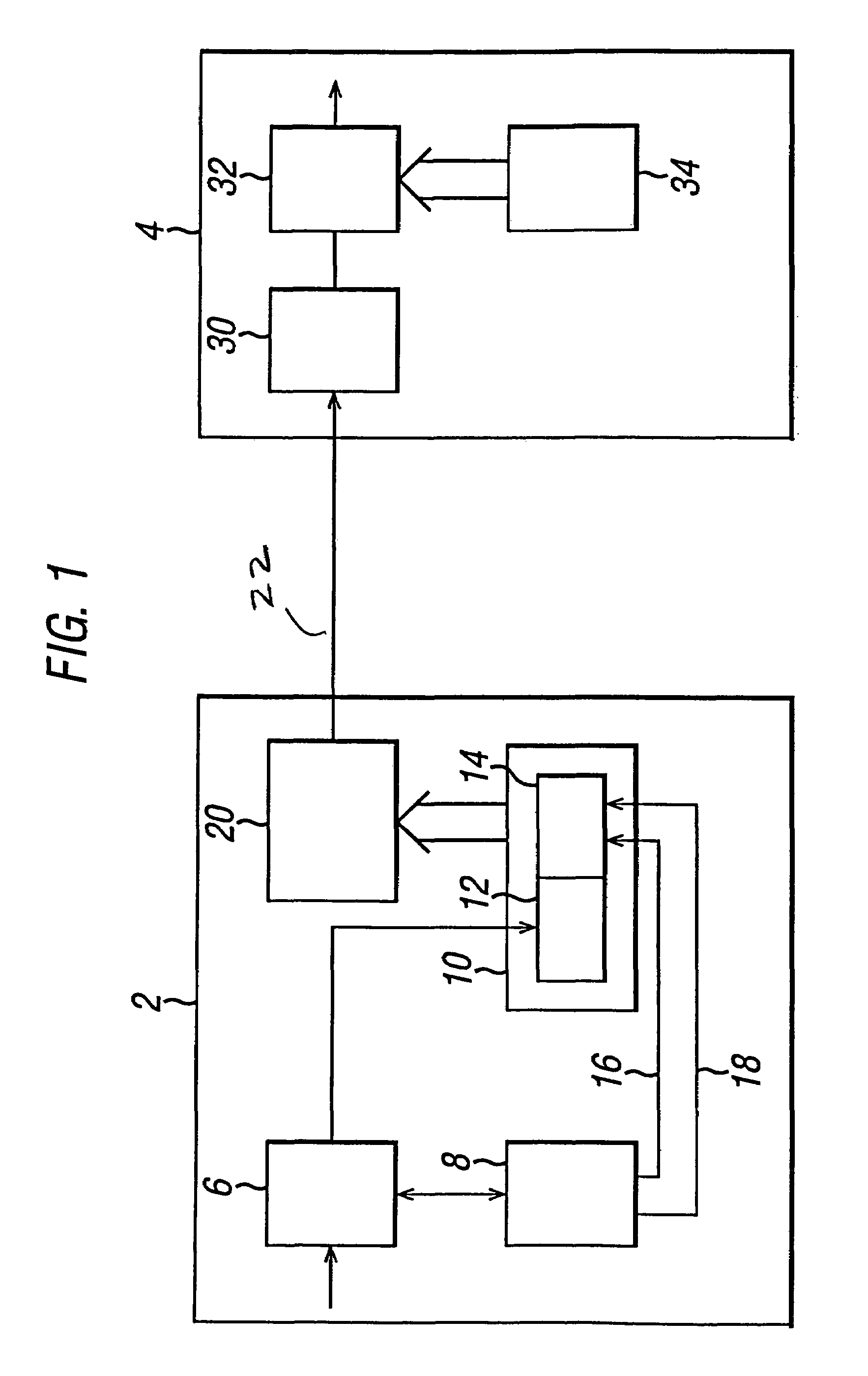
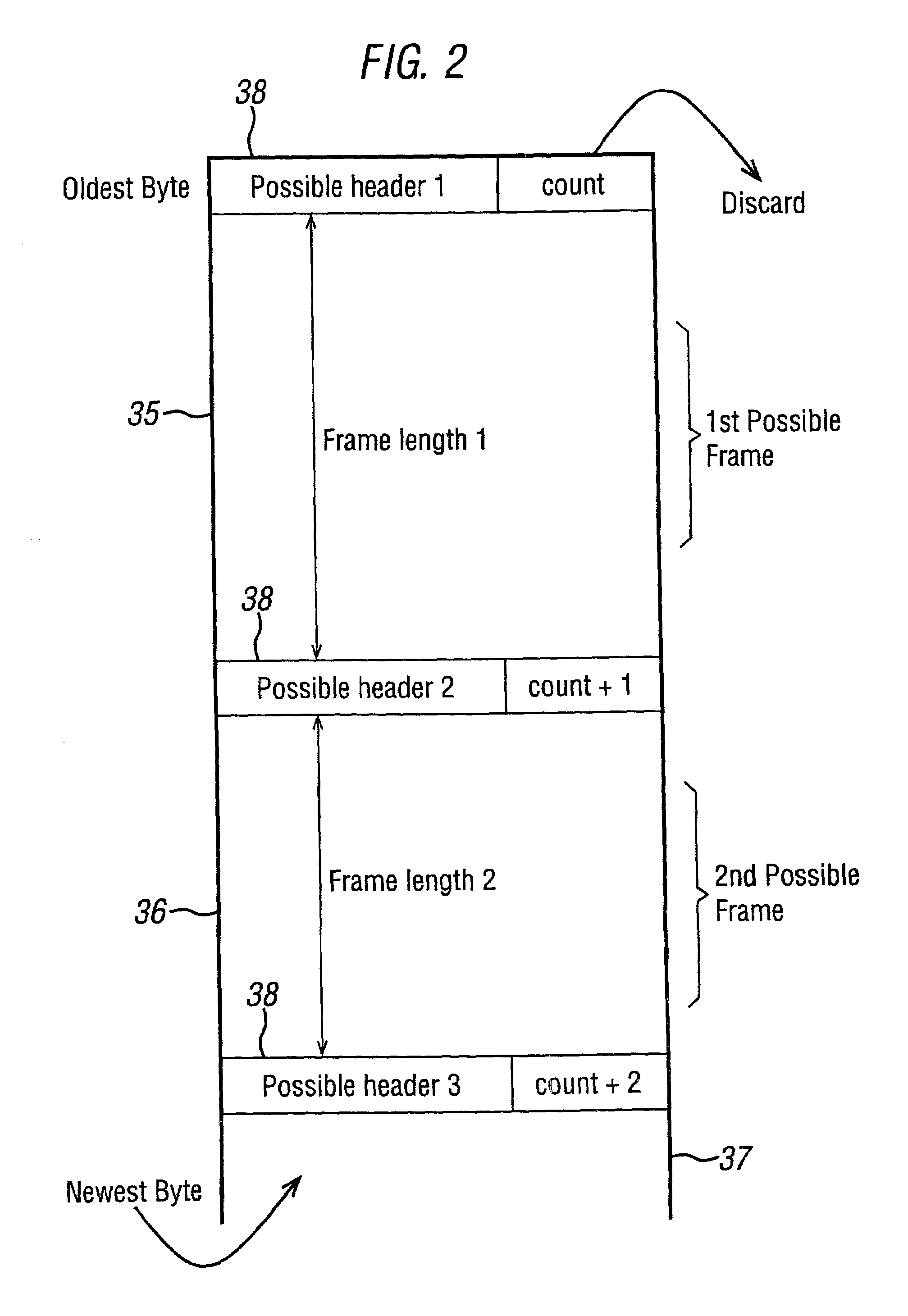
Frame synchronization in data communication system
InactiveUS6983031B2Easy to implementSimple hardware implementationTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementCommunications systemConsecutive frame
In order to provide a simple and reliable means of frame synchronization in a serial data communication system, which avoids the problem of ‘bit-stuffing’ in known HDLC systems, the data communication system comprises a transmitter arranged to transmit data as a sequence of frames, each frame comprising a synchronization section and a payload section of data, and the transmitter including in the synchronization section of each frame a count value of a sequence of count values (a part of a predetermined code sequence), wherein successive frames contain successive count values (other parts of the predetermined code sequence) The receiver includes a FIFO buffer for storing three successively received frames, and a processor for assessing the stored data within the frames in order to locate and recognize the count values, whereby to synchronize to the received frames.
Owner:AGERE SYST GUARDIAN
Method and system for performing snore recognition and strength output and breathing machine
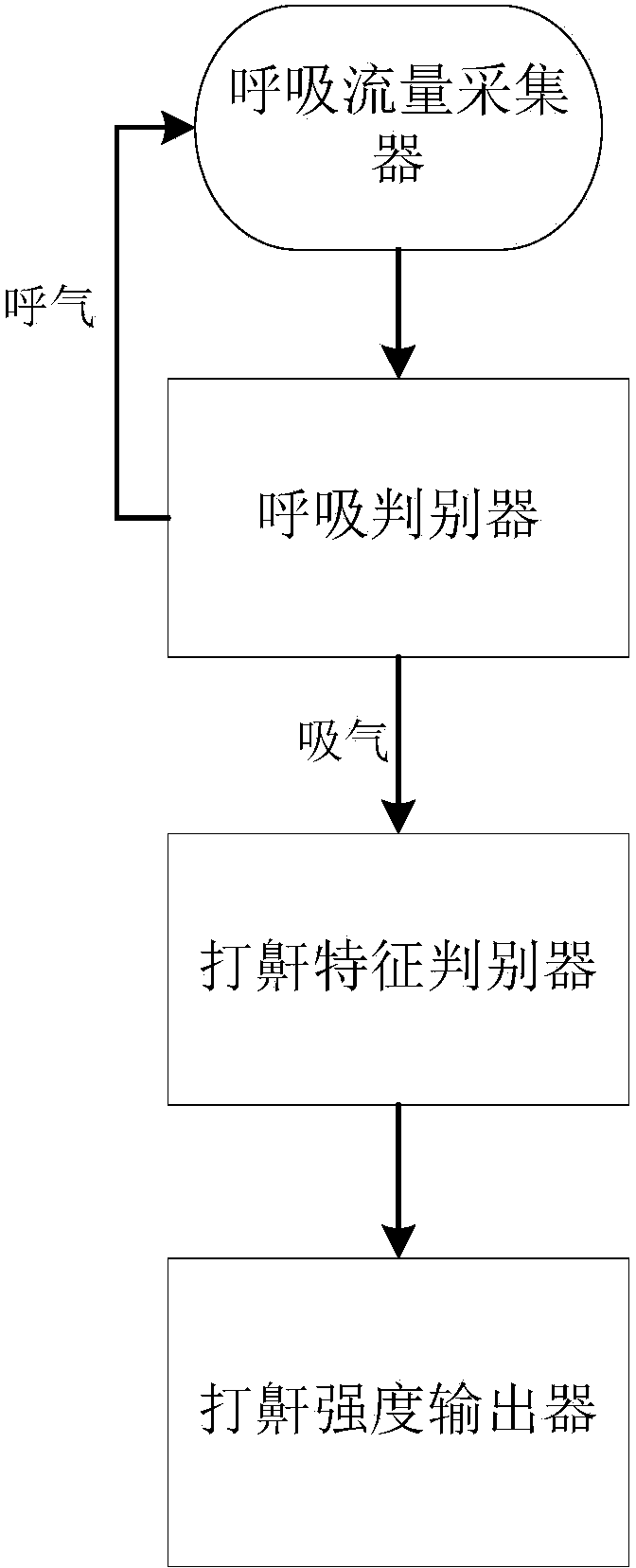
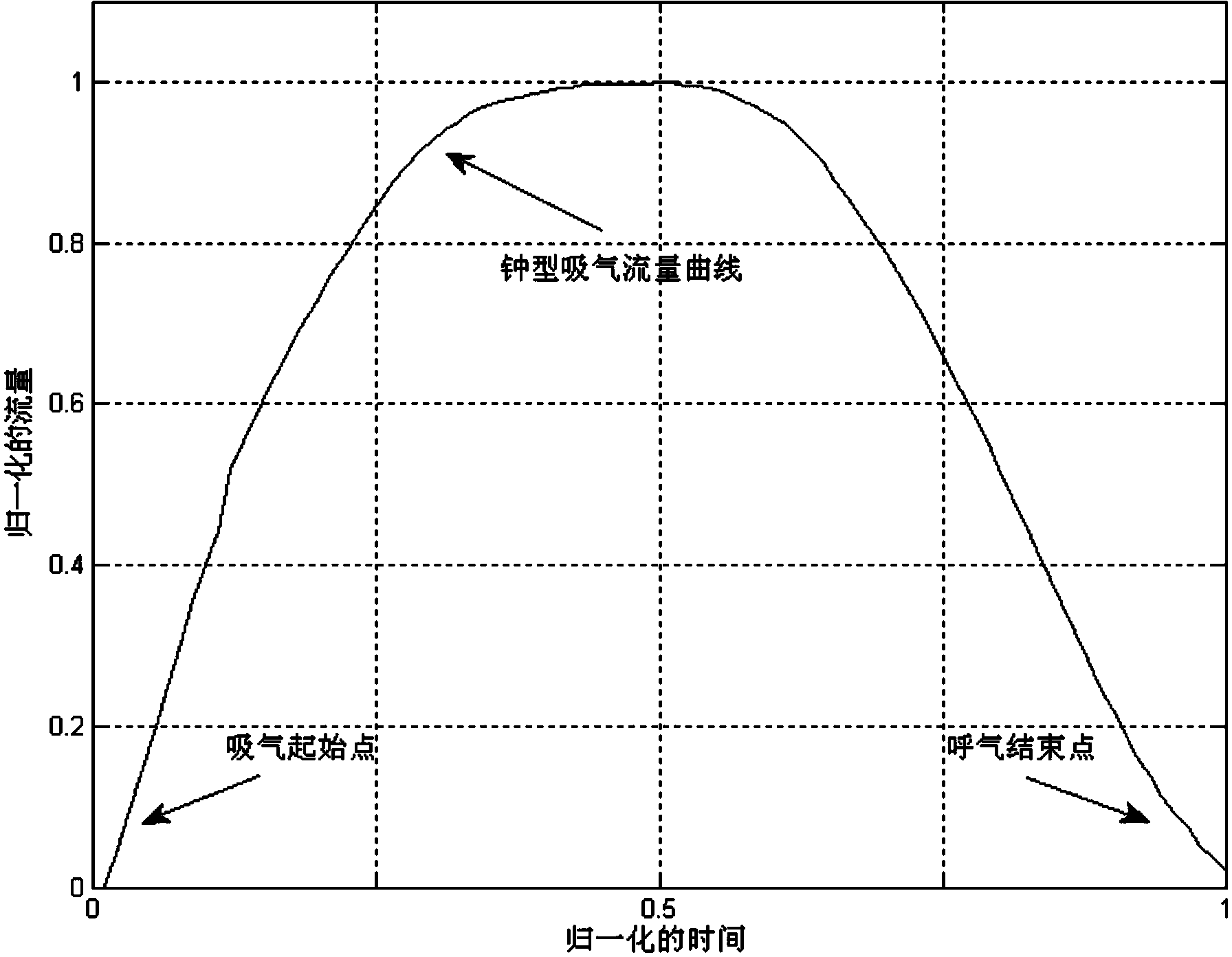
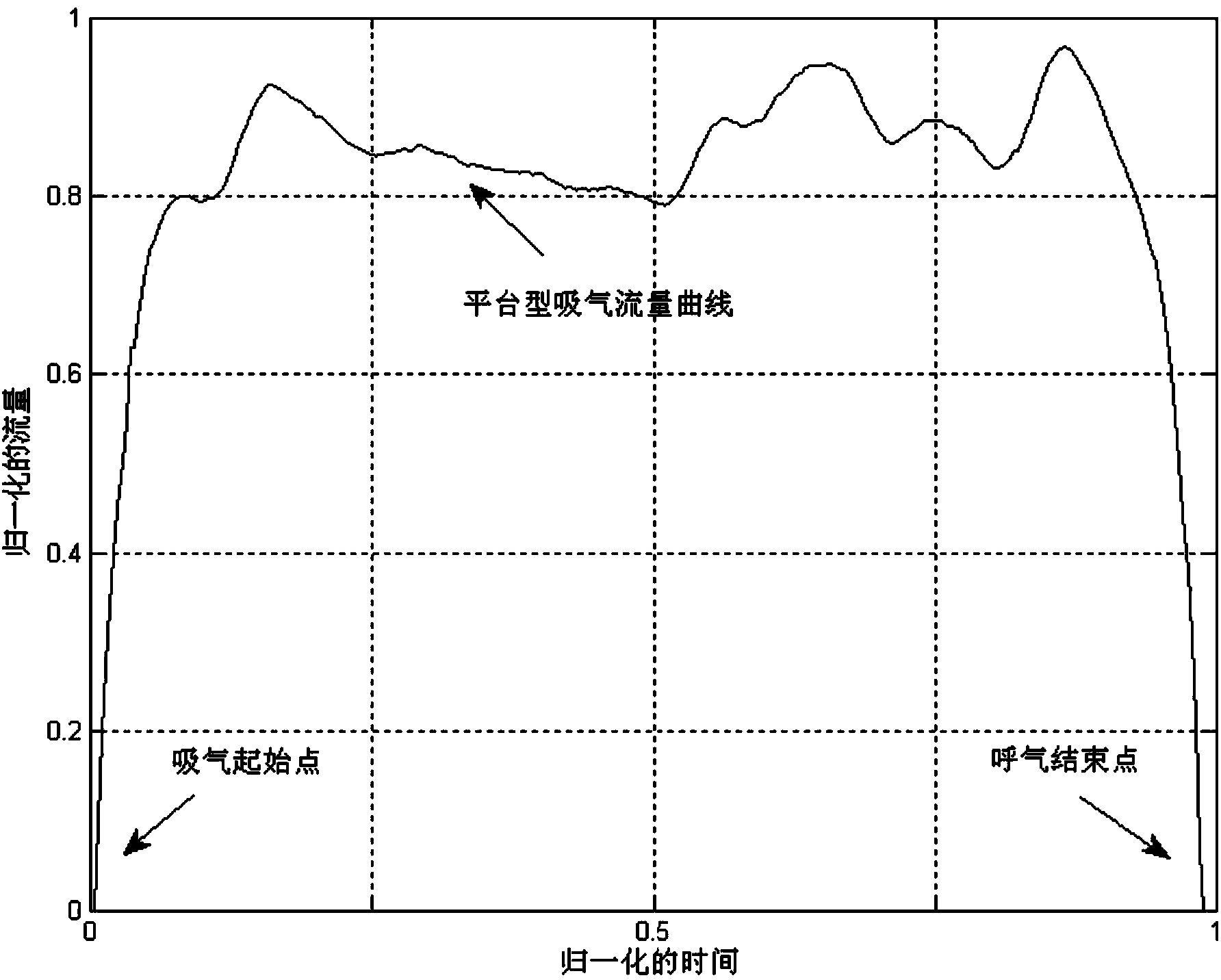
ActiveCN103961105AEliminate environmental noise interferenceSimple hardware implementationRespiratorsDiagnostic recording/measuringTraffic volumeInspiratory flow
The invention discloses a method and a system for performing snore recognition and strength output and a breathing machine. The system mainly comprises a breathing flow collector, a breathe recognizer, a snore feature recognizer and a snore strength output device which are connected in sequence, wherein the breathing flow collector collects expiration and inspiration flows in the breathing process and sends the flows to the breathe recognizer. The breathe recognizer is used for recognizing an inspiration starting point and an inspiration ending point in a breathing period. When the inspiration starting point is detected, the snore feature recognizer is started, and the snore strength output device is closed. When the inspiration ending point is detected, the snore feature recognizer is closed, and the snore strength output device is started. The snore feature recognizer analyzes flowing speed change characteristics in an inspiration period and recognizes whether snoring occurs or not. The snore strength output device judges recognized snore and then outputs normalized snore strength indexes. By adopting the method and the system for performing the snore recognition and the strength output, the success rate of accurate judgment is improved, the hardware cost is saved, and the achieving complexity is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN DYMIND BIOTECH
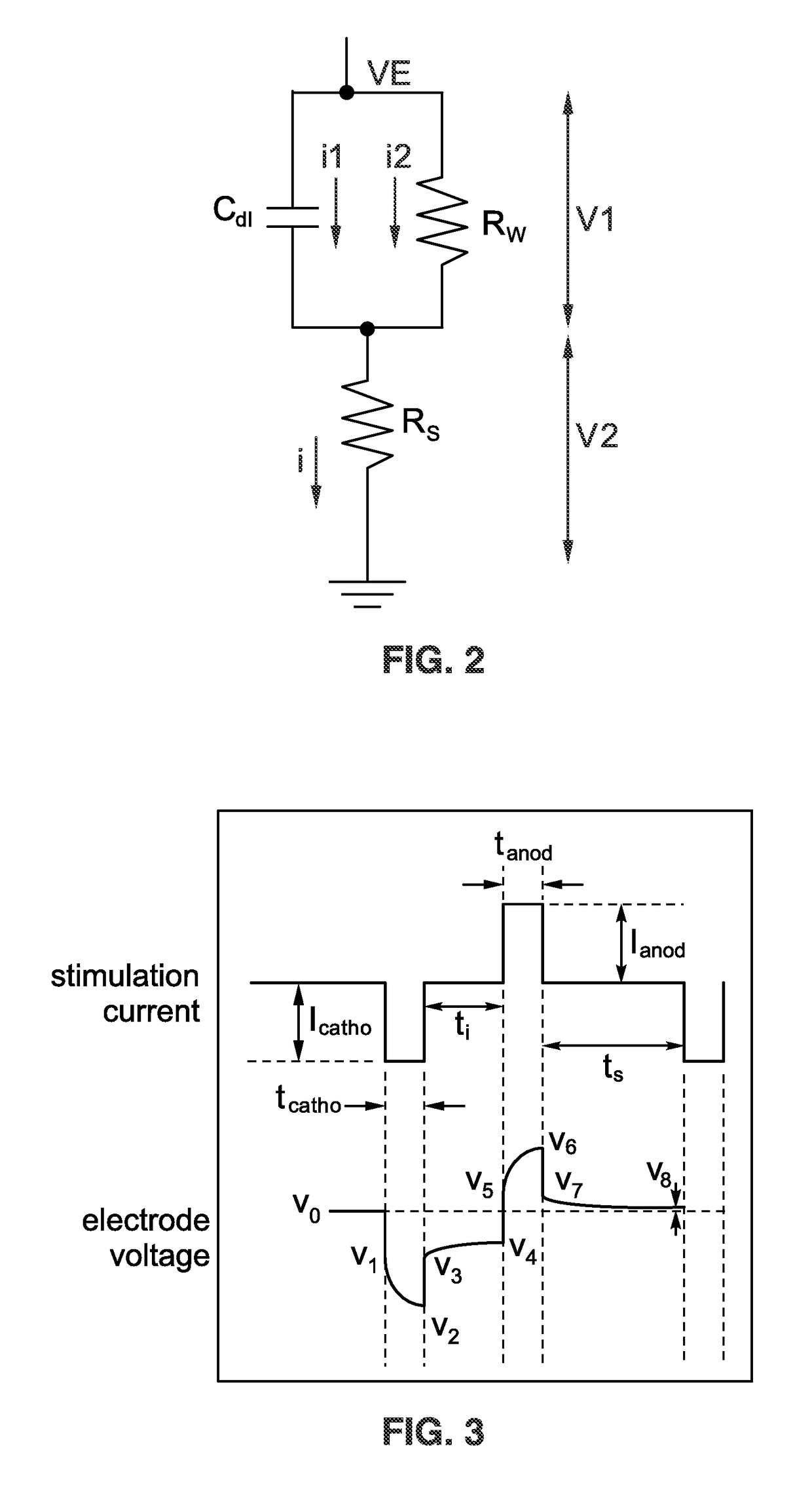
Electrical charge balancing method and apparatus for functional stimulation using precision pulse width compensation
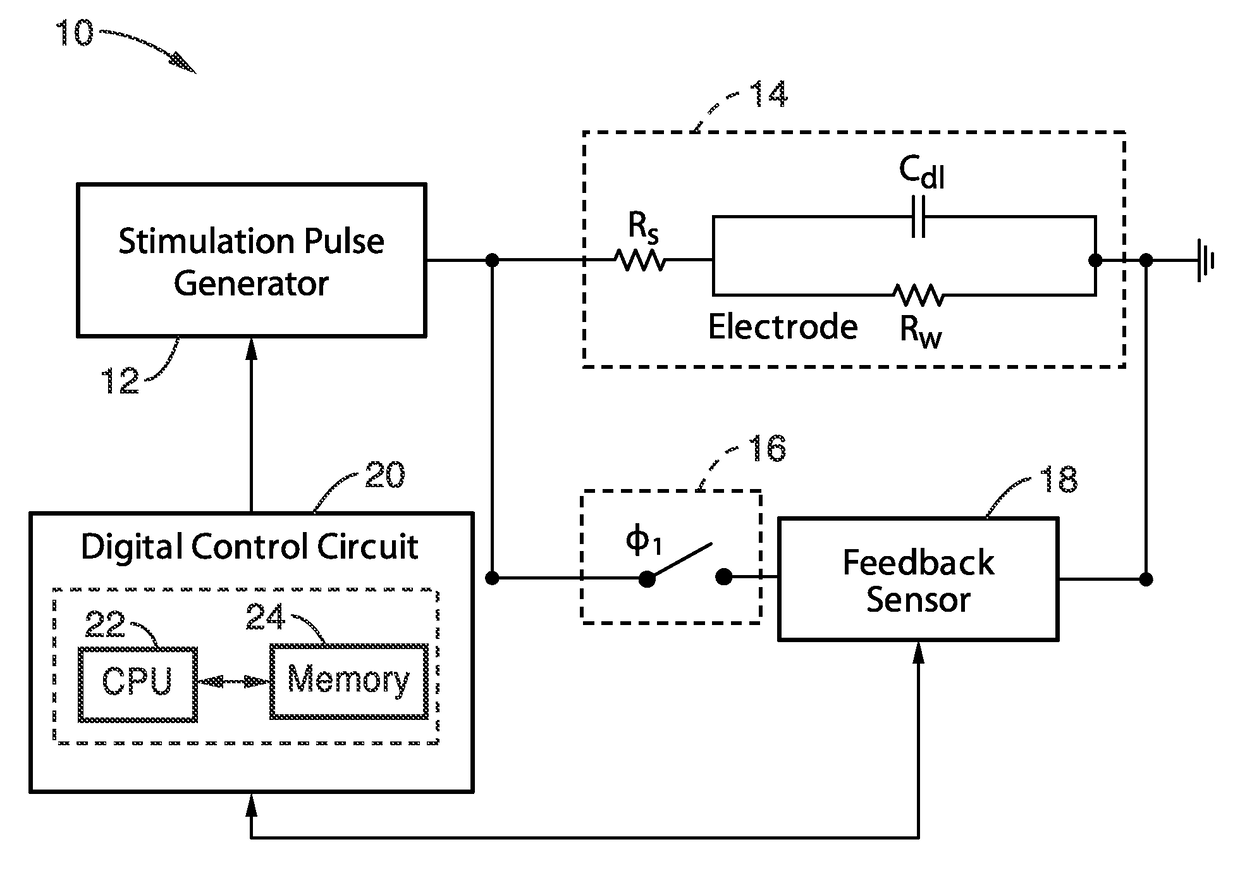
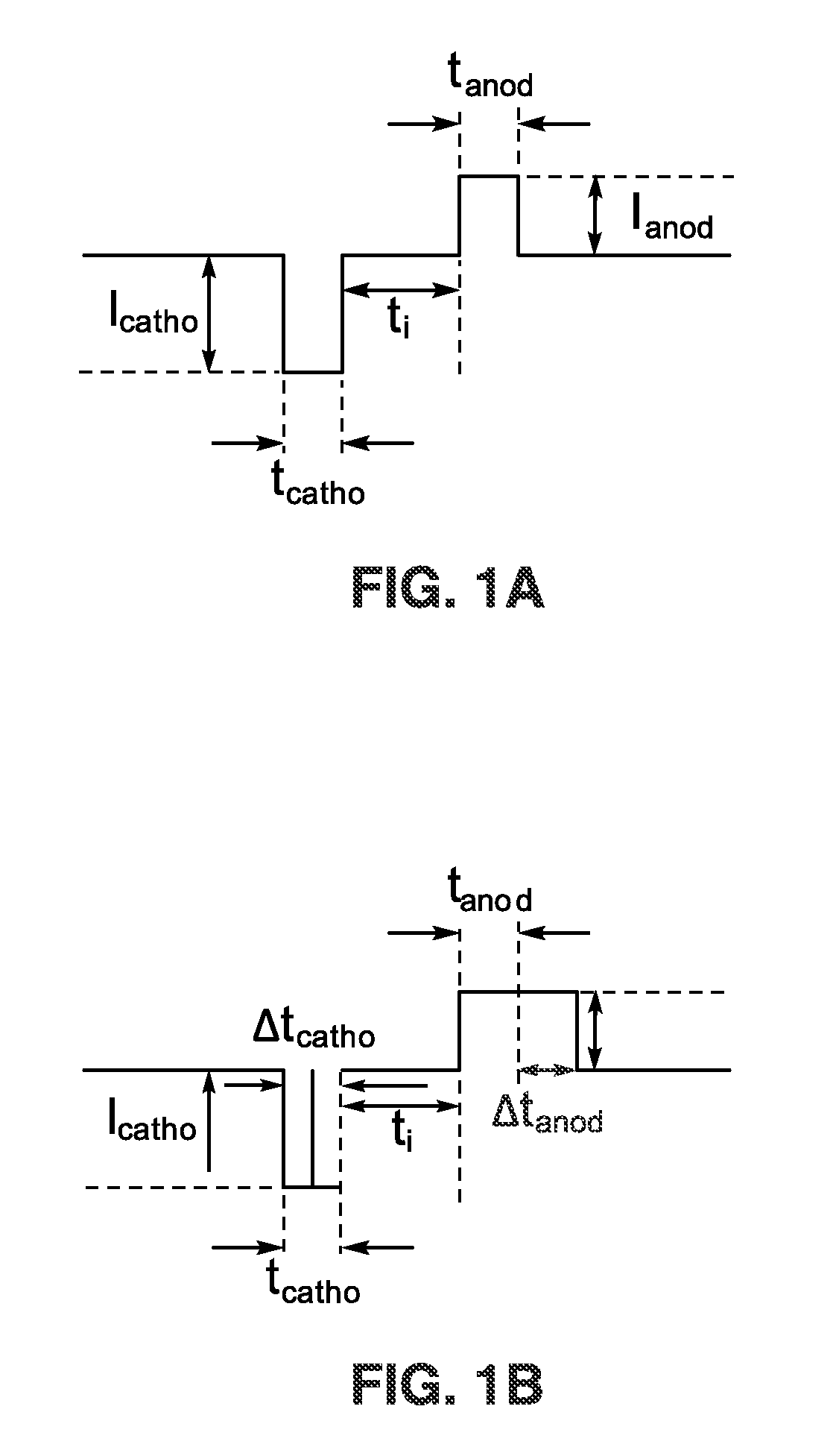
ActiveUS9700724B2Simple hardwareEliminate residual chargeElectrotherapyArtificial respirationElectrical polarityEngineering
An apparatus and method for electrical charge balancing when generating a stimulus during functional neural stimulation is presented. A stimulus pulse is generated (cathodic or anodic), and after a selected delay a charge compensating pulse is generated of an opposite polarity. The electrode circuit discontinuously examines electrode voltage after termination of the stimulus pulse, and utilizes this voltage to determine how long to extend the width of the charge compensating pulse. The electrode circuit thus performs accurate electrical charge cancellation to remove residual charges from the electrode by precisely controlling pulse width for an opposing polarity compensating pulse that need not have the same current level as the stimulus pulse.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
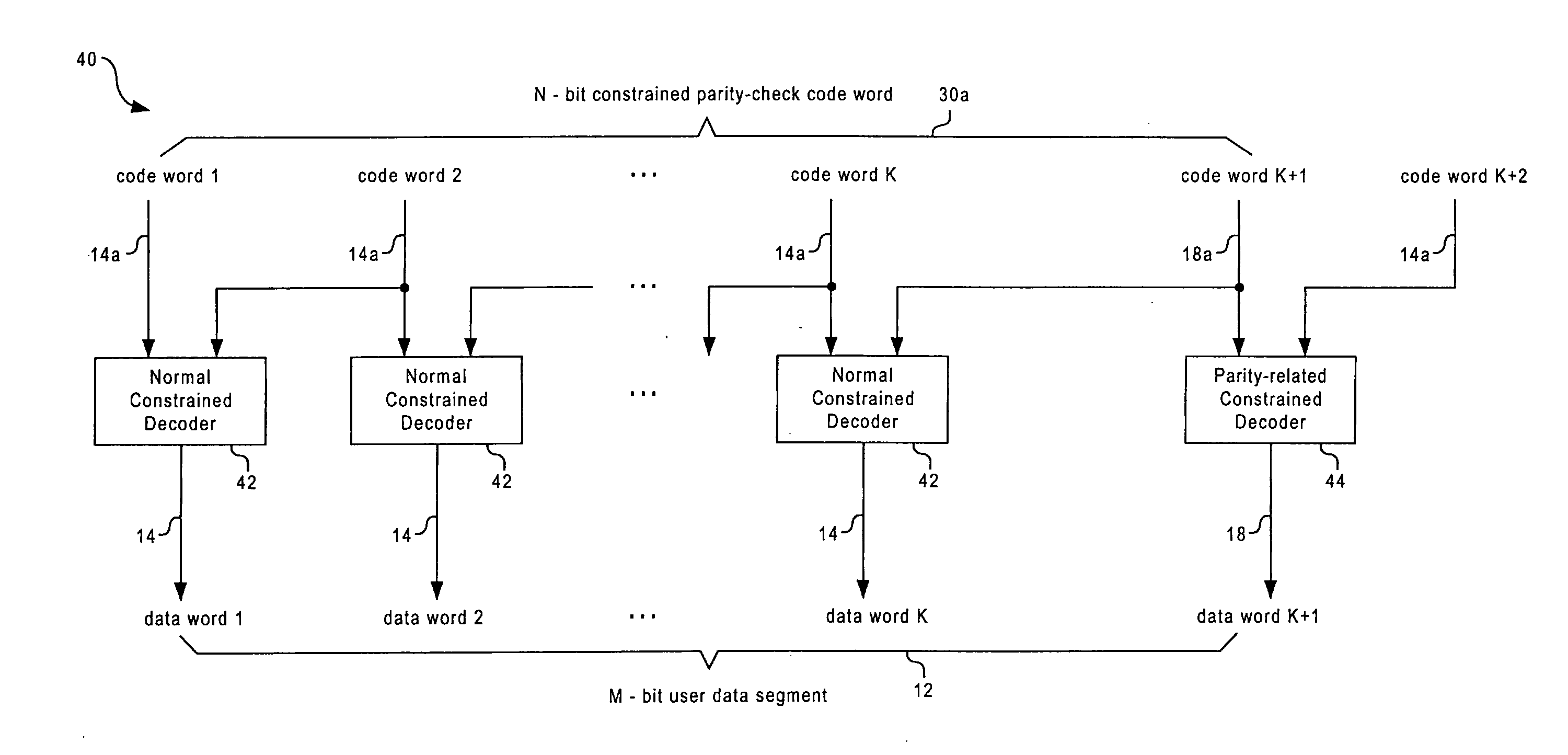
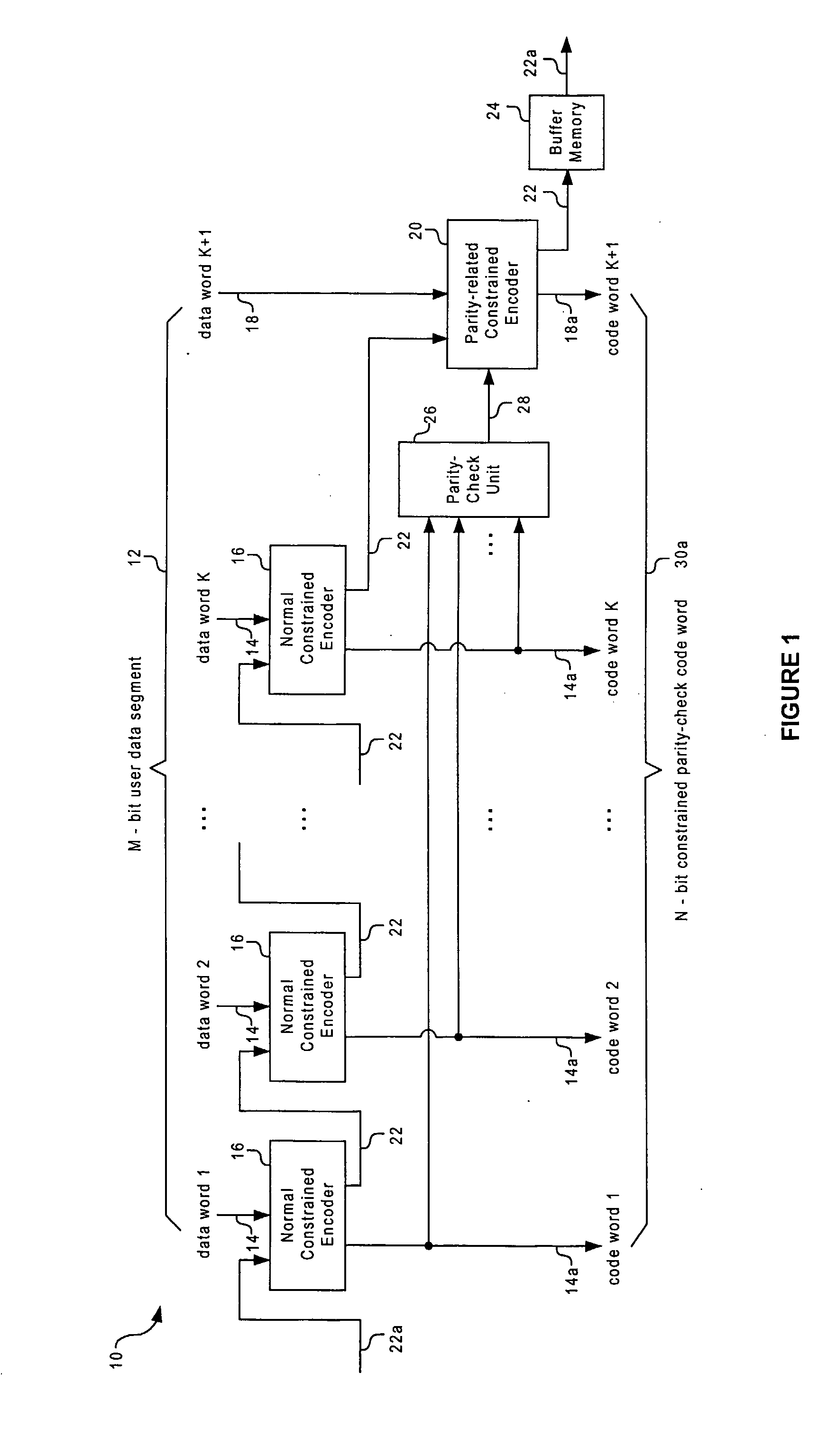
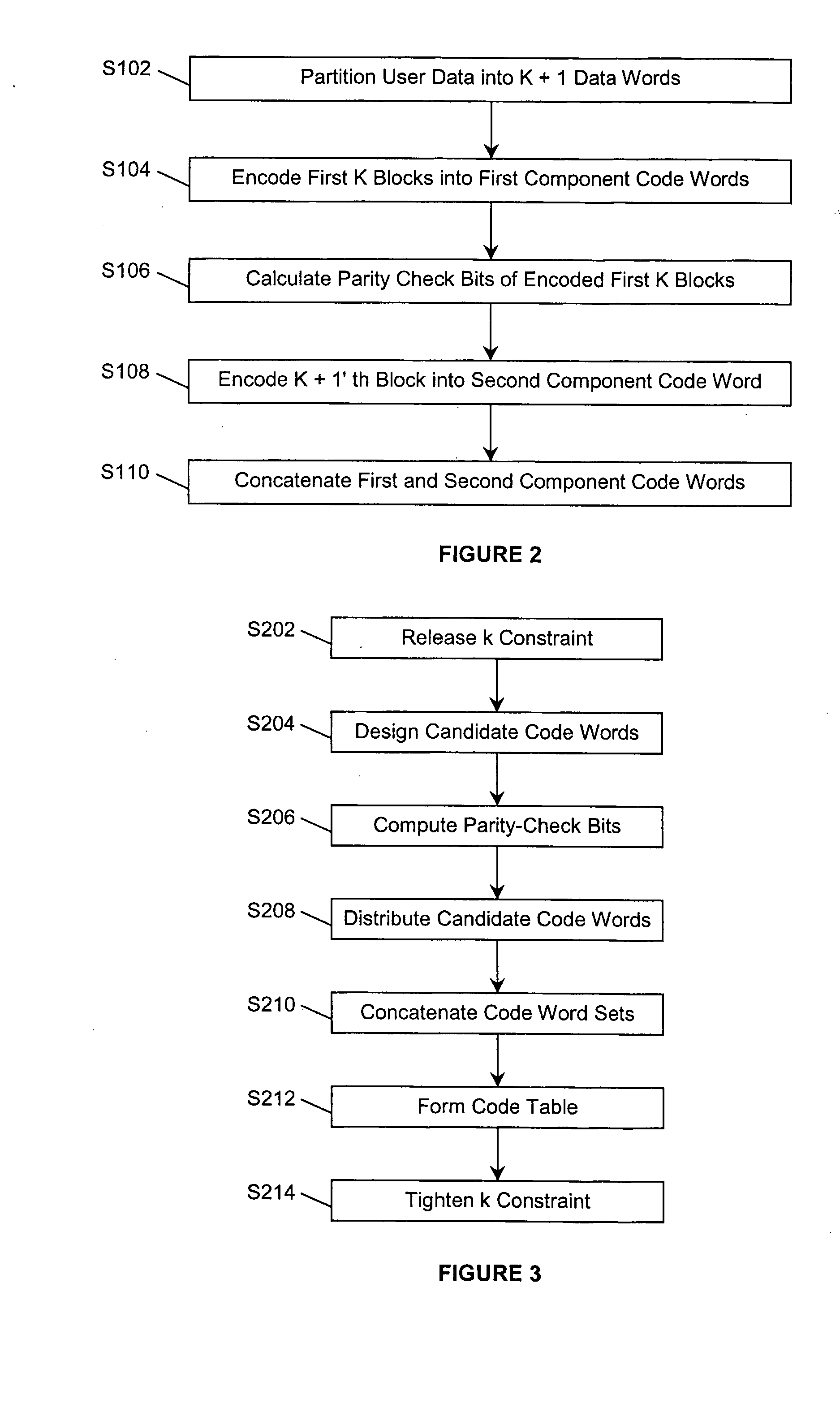
Method And System For Encoding And Decoding Information With Modulation Constraints And Error Control
InactiveUS20080141095A1Simple hardware implementationReduce in quantityError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRecord information storageBlock codeTheoretical computer science
A method and system for encoding a segment of user data words into a segment of code words so that both modulation constraints and a predetermined parity-check constraint are satisfied. Each segment of the user data is partitioned into several data words, and encoded separately by first and second types of component code, which are referred to as the normal constrained code and the parity-related constrained code, respectively. The parity-check constraint over the combined code word is achieved by concatenating the sequence of normal constrained code words with a specific parity-related constrained code word chosen from a candidate code word set. Both the component codes are finite-state constrained codes, which are designed to have rates close to the Shannon capacity. Furthermore, they are based on the same finite state machine (FSM), which enables them to be connected seamlessly, without violating the modulation constraints. Two preferred embodiments are provided to design a code in the non-return-to-zero inverted (NRZI) format and the non-return-to-zero (NRZ) format, respectively. Designing the codes in NRZ format may reduce the number of parity-check bits required for error detection and simplify error correction or post-processing. The parity-check constraint is defined by the parity-check polynomial or parity-check matrix of a systematic linear block code, which could detect any type of dominant error event as well as error event combinations of a given optical recording system. As a result, the information density of the system is improved.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Identification arrangement and method
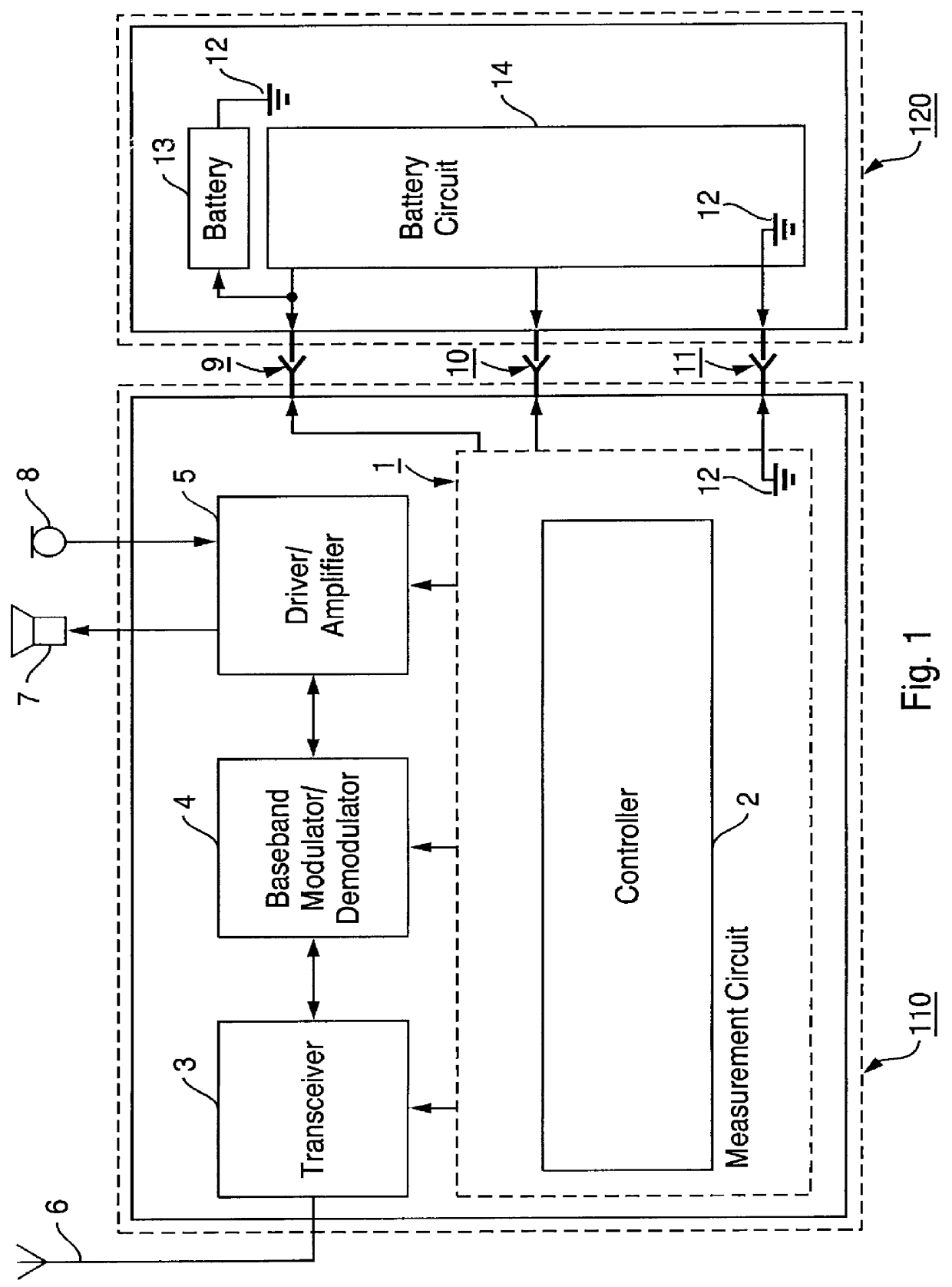
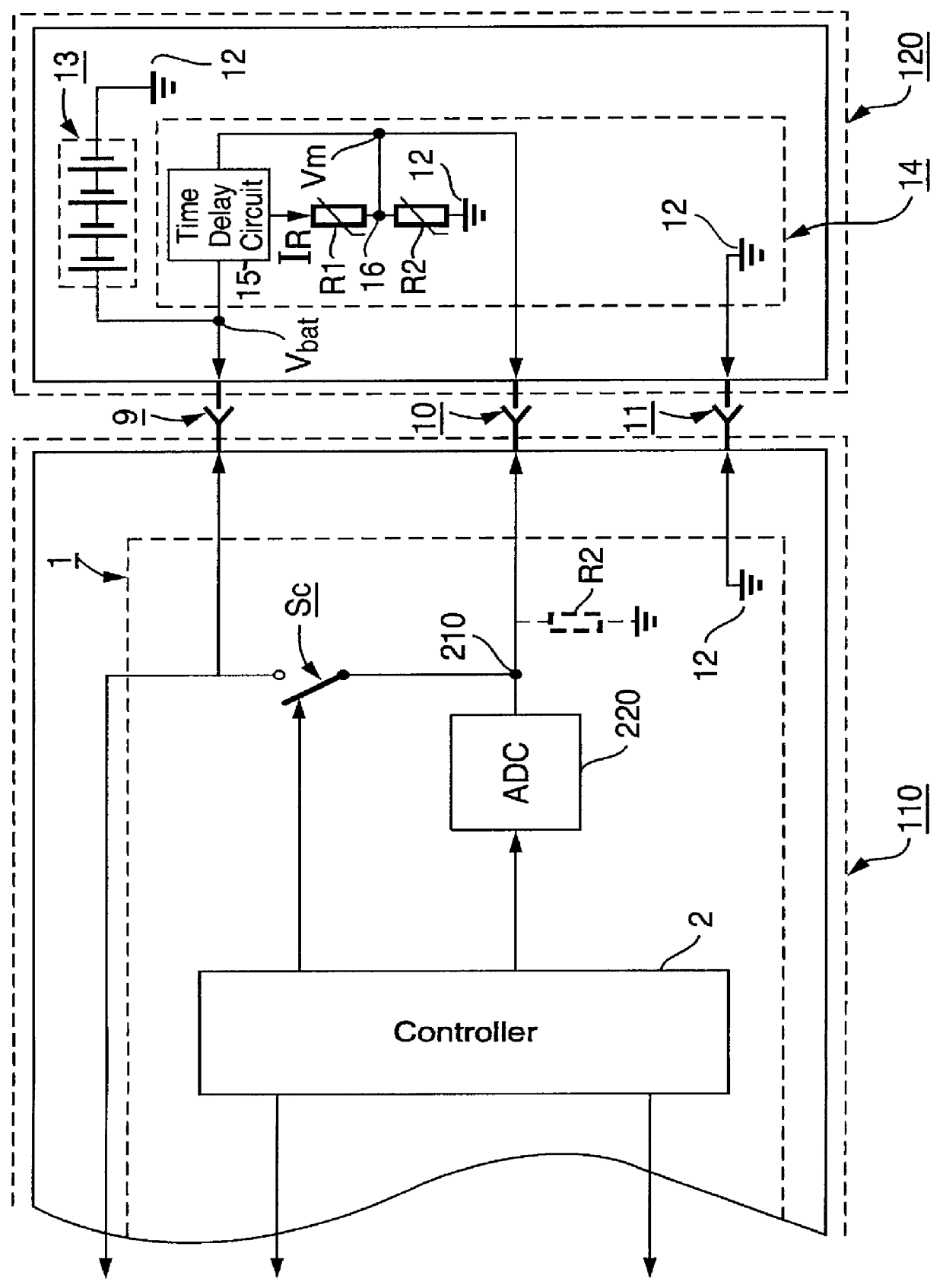
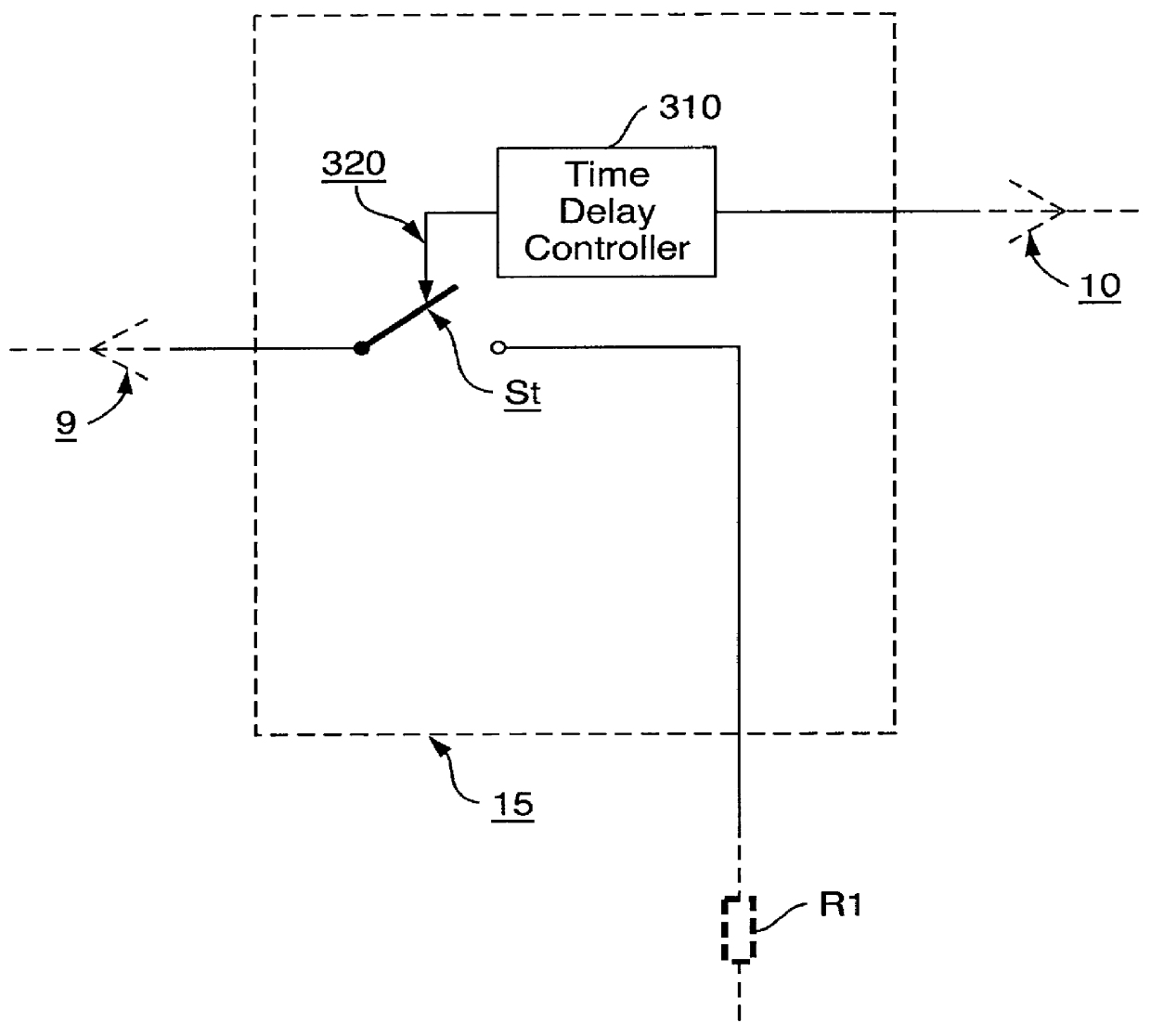
InactiveUS6112105ASimple hardware implementationEasy to implementResonant long antennasPrimary cell maintainance/servicingEngineeringMobile station
The invention provides a battery identification arrangement, a battery equipment (120) suitable for identification and a battery identification method for implementation in an electronic equipment (110) such as a mobile station or a charger with a battery (13). The present invention also relates to a method to measure the temperature of a battery (13) connected to an electronic equipment (110). The battery identification arrangement includes both a measurement circuit (1) of the electronic equipment (110) and a battery circuit (14) of a battery equipment (120). On identifying, means in the measurement circuit (1) measure at least one identification voltage (Vid) which is generated by dividing a battery voltage (Vbat) into a division ratio by means of in series connected resistors (R1, R2) connected to ground (12). The resistors (R1, R2) are connected to the battery (13) only during measurement of the identification voltage (Vid) and the battery voltage (Vbat).
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
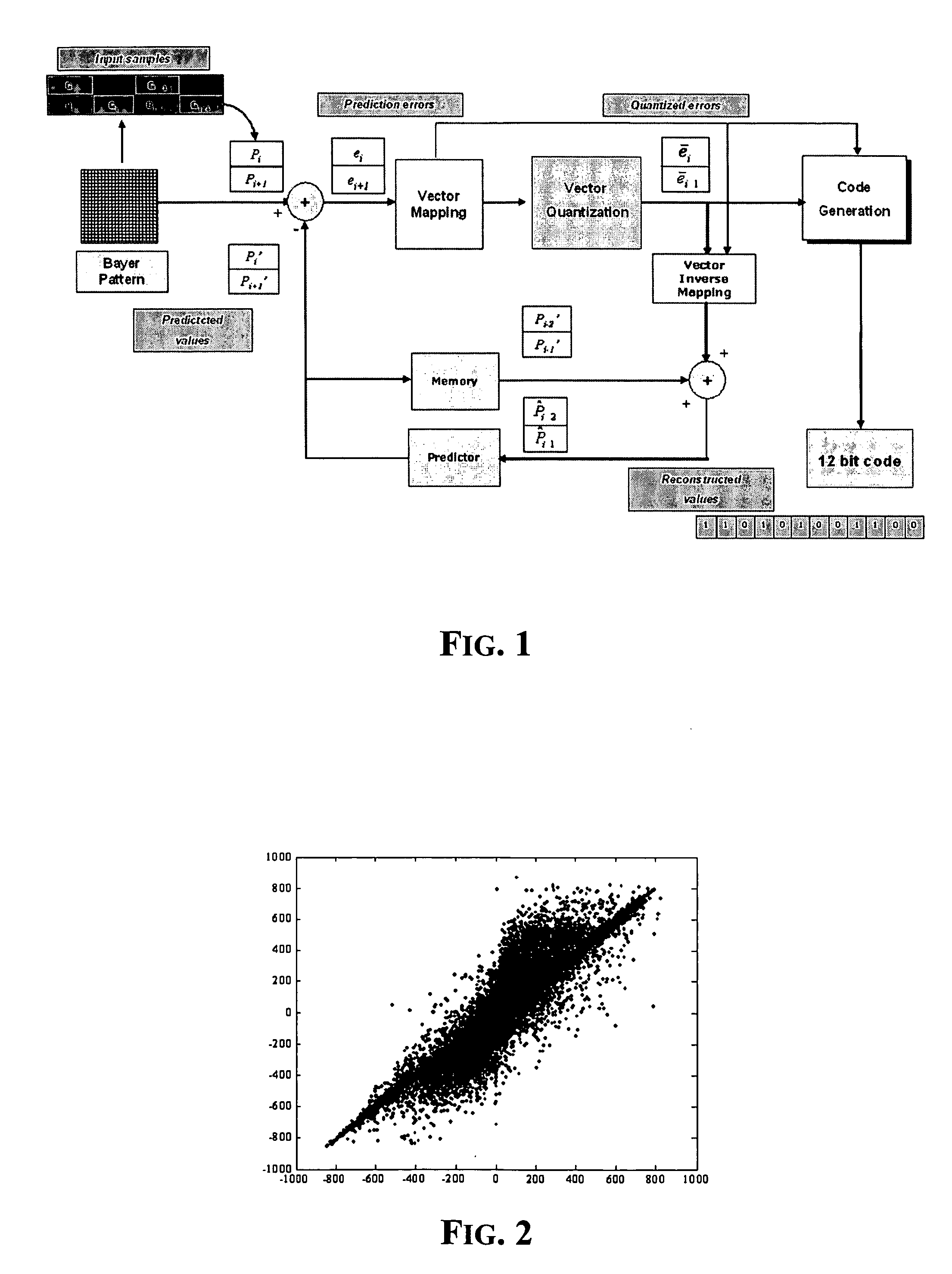
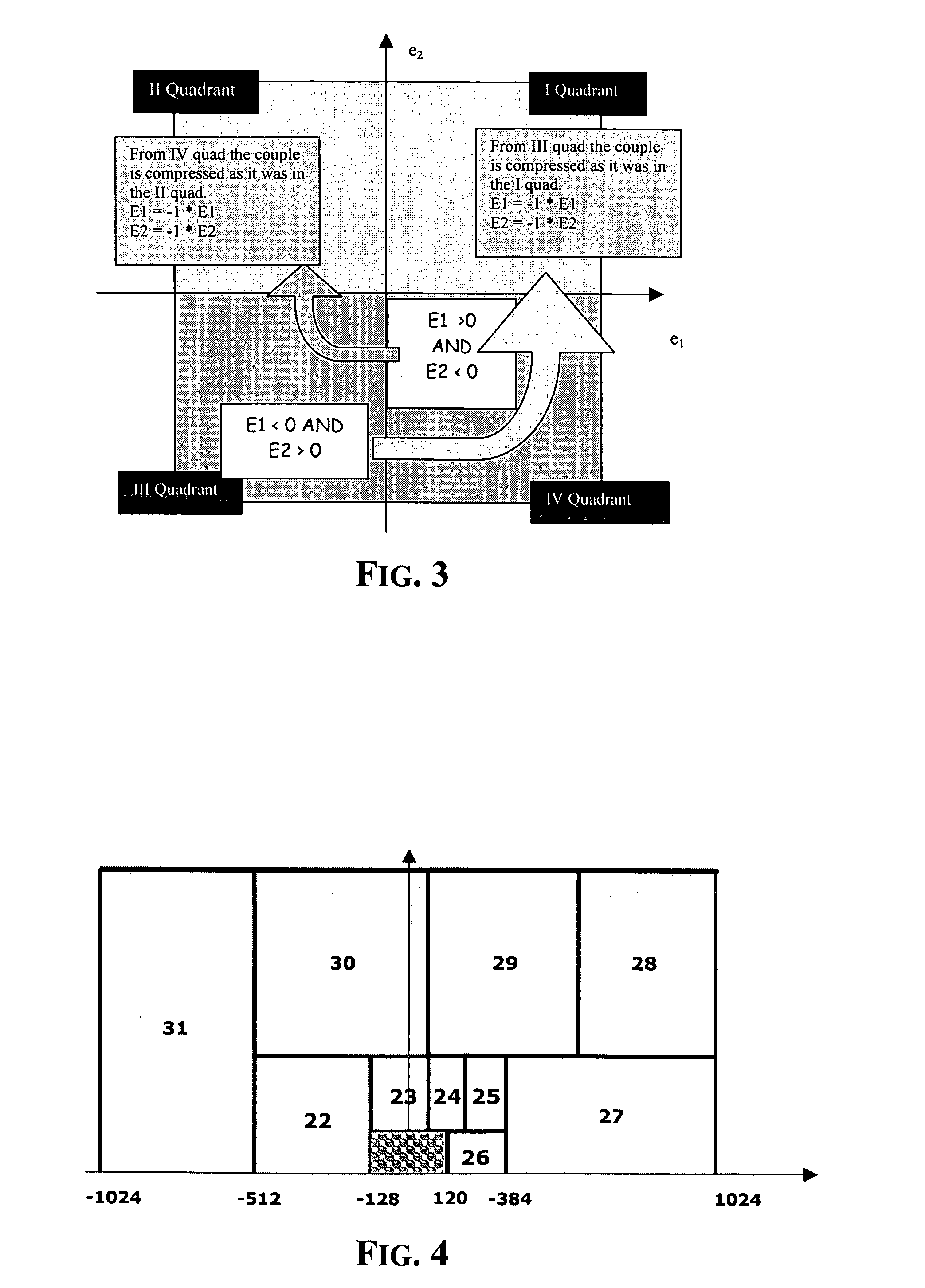
Method and architecture for compressing image data acquired from a bayer color filter array
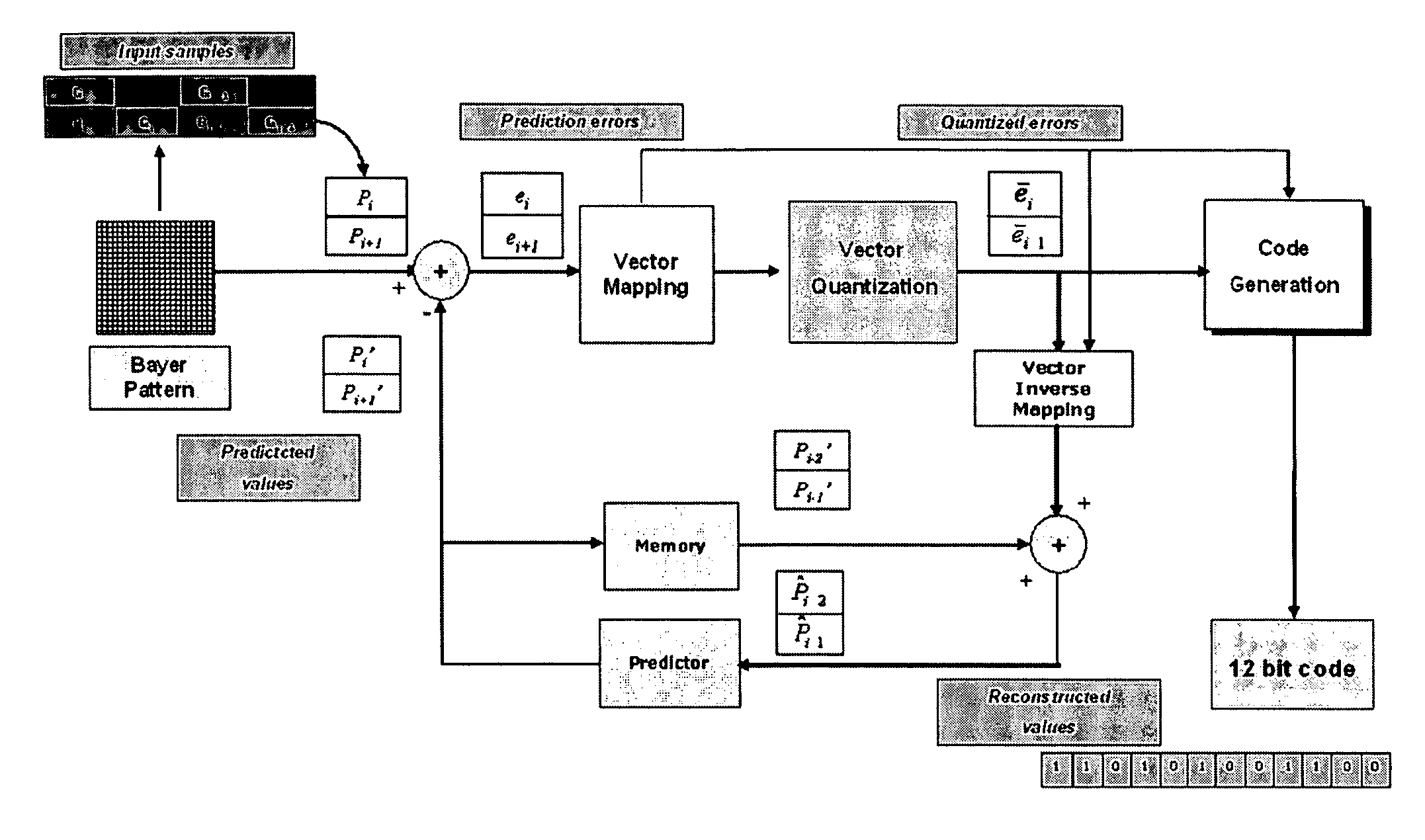
InactiveUS20060013314A1Small errorNegligible computational complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer visionColor filter array
For each color channel, the process includes gathering Bayer pattern pixel values by pairs, each pair being composed by two successive pixels belonging to the channel along the scanning direction of the pixels of the image, thus each pair of values representing a current input vector, and calculating a predictor vector of the input vector in terms of the differences between the values defining the input vector and a pair of prediction values generated according to a certain criterion, for representing a prediction error. The process further includes quantizing each so calculated predictor vector according to a heavier or lighter degree of quantization depending on whether the predictor vector is representative of an area of relatively uniform color of the image or of an area of relatively abrupt changes of colors of the image, and generating a multibit code representative of the quantized predictor vector of the input vector according to a certain compression ratio.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
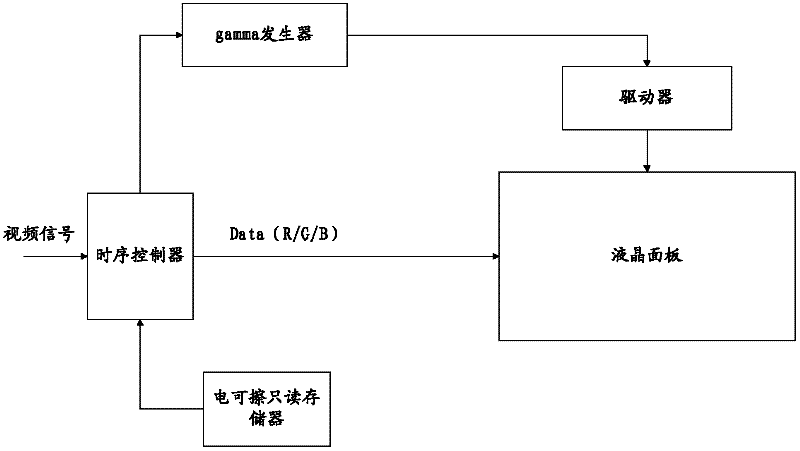
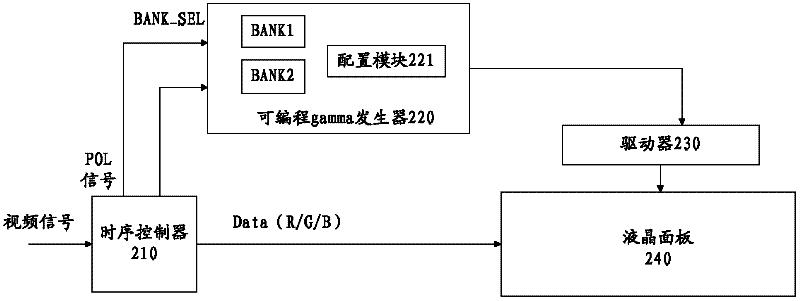
Liquid crystal display and method for improving contrast ratio of image
InactiveCN102237066AImprove image contrastSimple hardware implementationStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayLiquid crystal
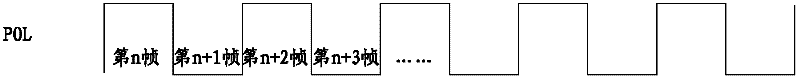
The invention relates to a liquid crystal display and a method for improving contrast ratio of an image. The liquid crystal display comprises a gamma generator and a liquid crystal panel. The gamma generator stores a plurality of groups of gamma voltage values and periodically acquires one group of gamma voltage values from a plurality of groups of gamma voltages based on control of a polarity overturn POL signal. The liquid crystal panel displays an image based on a plurality of groups of gamma voltage values. By adopting the liquid crystal display provided by the invention, the contrast ratio of the image is improved, thus the liquid crystal display can be widely applied to display equipment.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Trie-Type Memory Device With a Compression Mechanism
ActiveUS20070011577A1Simple hardware implementationImprove device speedStatic storageData switching networksTrieComputer science
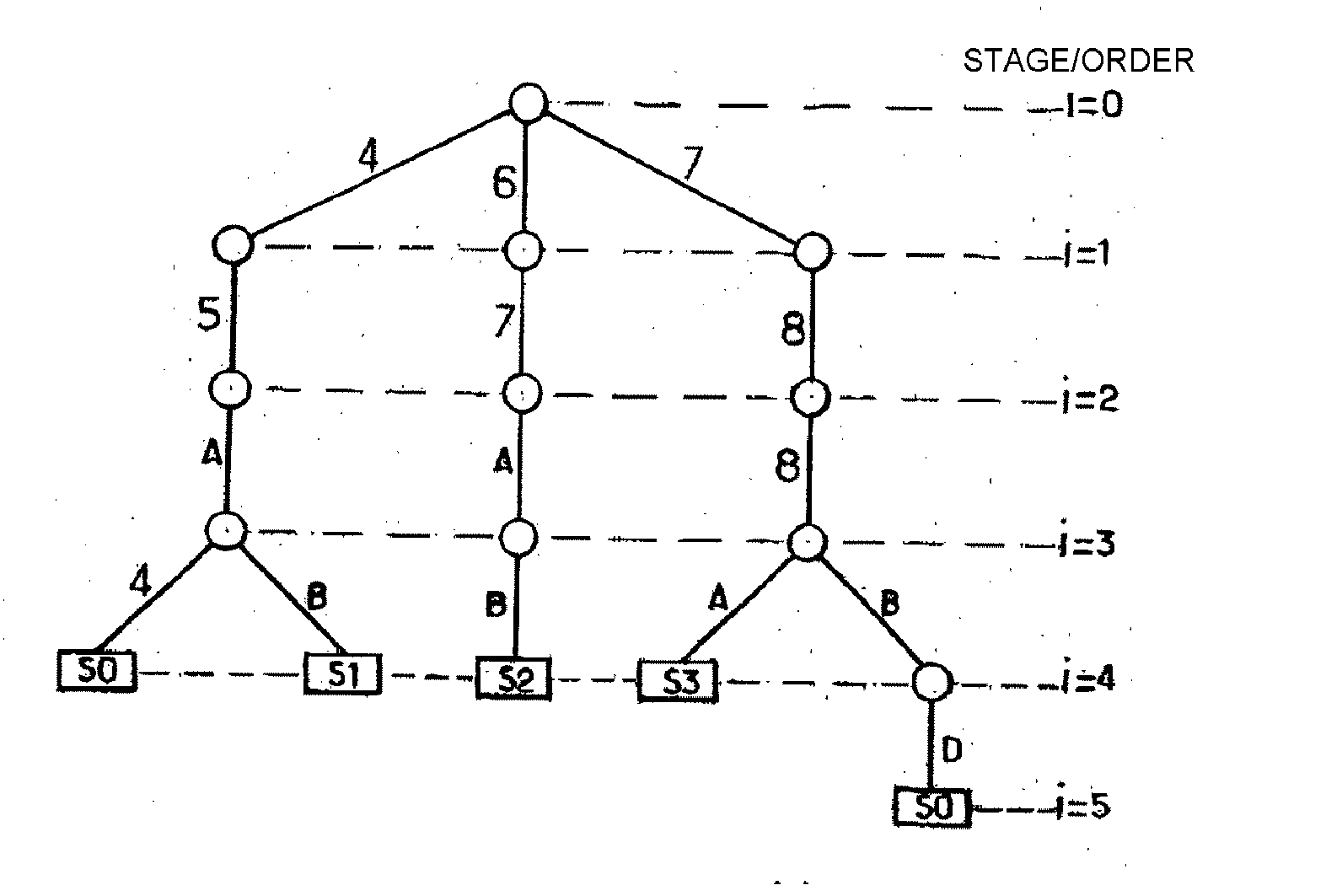
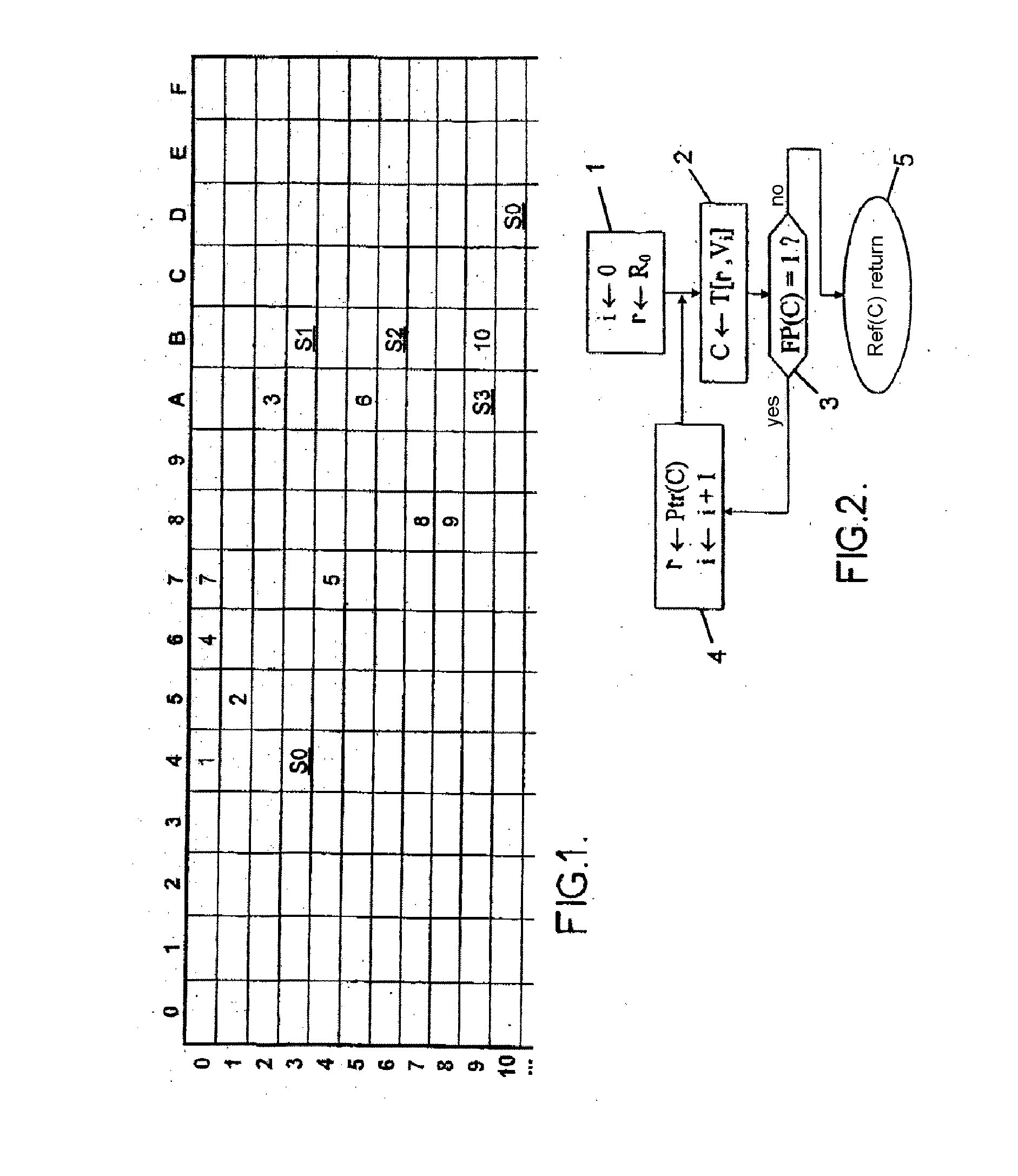
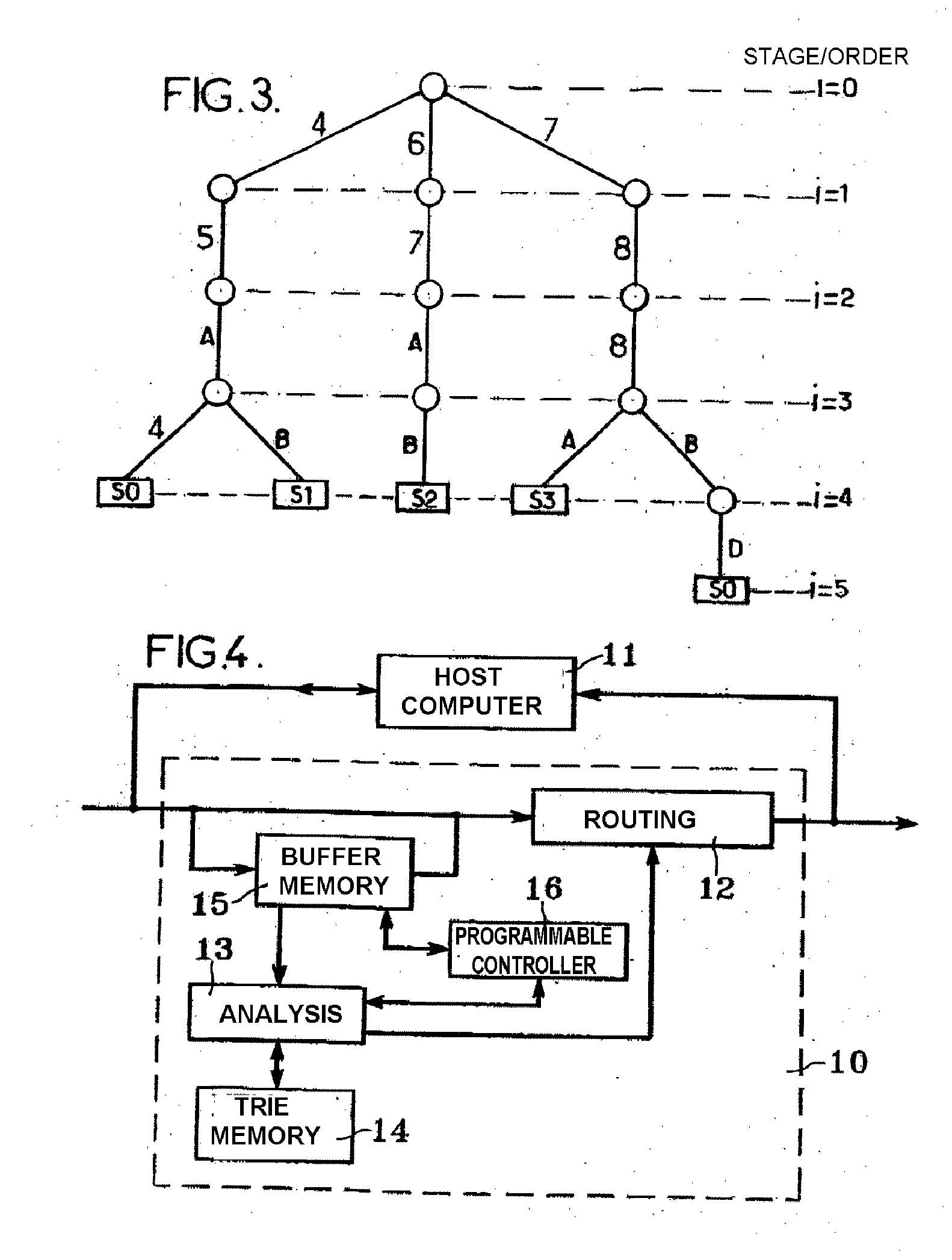
The invention relates to a tri-type memory device comprising a compression mechanism. According to the invention, the memory stores binary patterns that are associated with respective references. Data chains are analyzed by successive section of K bits (K>1) in order to extract one of the references when there is a match with a stored binary pattern associated with said reference. The memory is organized into several successive memory cell states, the analysis of the (i+1)-th section of a chain providing access to a cell of stage i≧0. Each non-empty cell of a stage i≧0 contains one of the following: a register-type analysis tracking pointer designating a register of 2K cells of stage i+1; a linear-type analysis tracking pointer designating a zone of one or two cells forming a reduced register of stage i+1; or a reference associated with a stored binary pattern.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
CORDIC unit
InactiveUS7606852B2Reduced activityReduce consumptionDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsPartition of unityIterative approximation
A CORDIC unit for the iterative approximation of a vector rotation through a rotary angle θ by a number of elementary rotations through elementary angles αi, including elementary rotation stages for respectively affecting an elementary rotation through an elementary angle αi as an iteration step in the iterative approximation. After such an elementary rotation there remains a residual angle through which rotation is still to be affected. The elementary rotation stages of the CORDIC unit are adapted for rotation through elementary angles αi given by powers of two with a negative integral exponent. The CORDIC unit can also include a triggering device for triggering the elementary rotations, a triggering device which is adapted prior to each iteration step to compare the residual angle to at least one of the elementary angles and to omit those elementary rotation stages whose elementary angles are greater than the residual angle.
Owner:IHP GMBH INNOVATIONS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE MICROELECTRONICS LEIBNIZ INST FUR INNOVATIVE
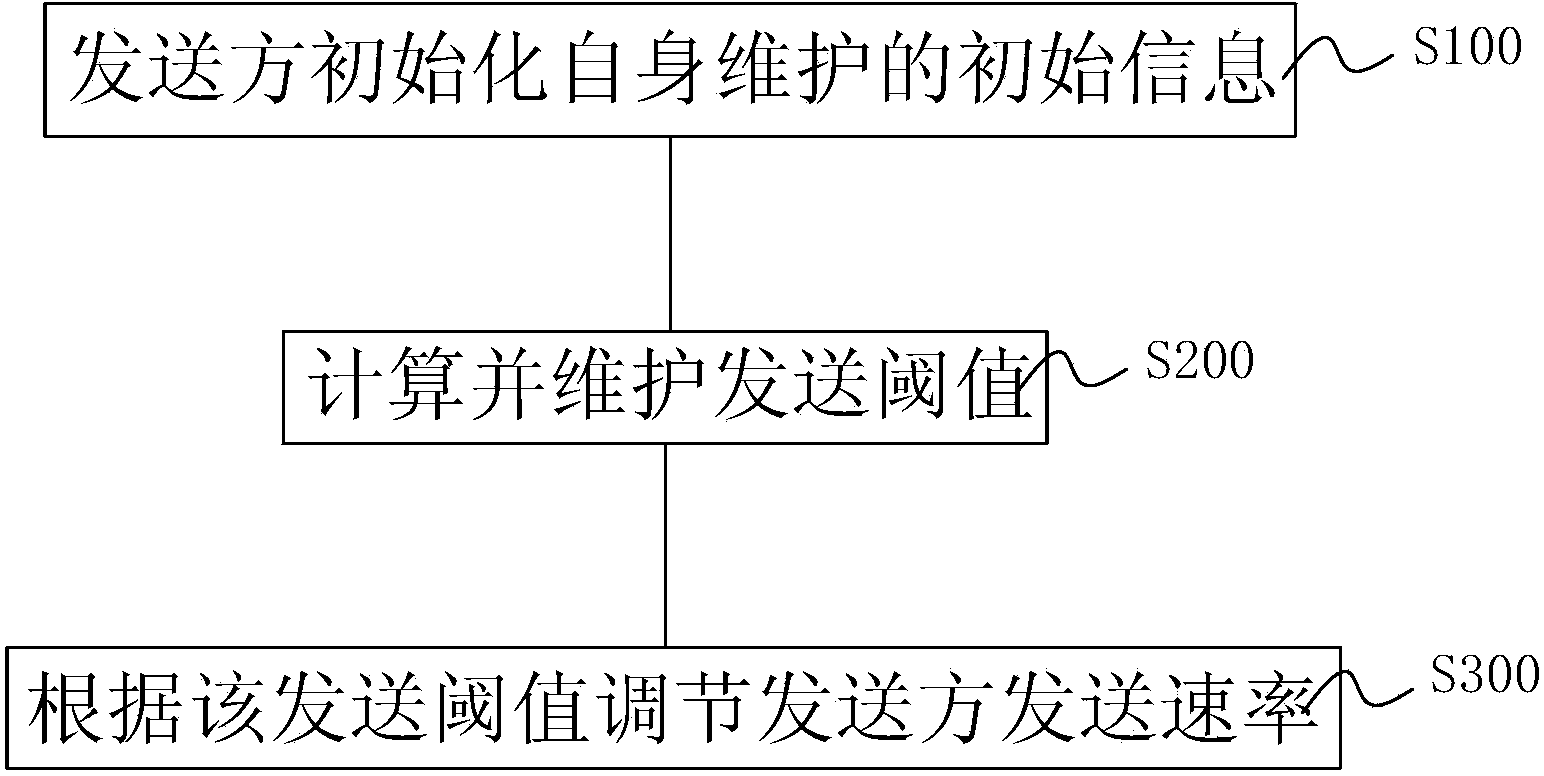
Reputation-based link congestion control method
ActiveCN103647722ALink packet loss avoidanceSimple hardware implementationData switching networksNetwork congestionTransmission rate
Disclosed is a reputation-based link congestion control method, in which congestion control and reputation flow control are integrated between hops of a link and a transmission rate of a sender is adjusted through a reputation value of a receiver to avoid link congestion. The method comprises the steps of initializing initial information the sender maintains by the sender, the initial information including a transmission count, the reputation value of the receiver and a current transmission window size; calculating and maintaining transmission thresholds, determining a transmission threshold based on the number of receivable buffers of the receiver, and considering the transmission threshold as a basis for adjusting the transmission rate of the sender; and adjusting the transmission rate of the sender according to the transmission threshold, and automatically adjusting the transmission window size based on the transmission threshold to avoid packet loss due to a buffer overflow of the receiver.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
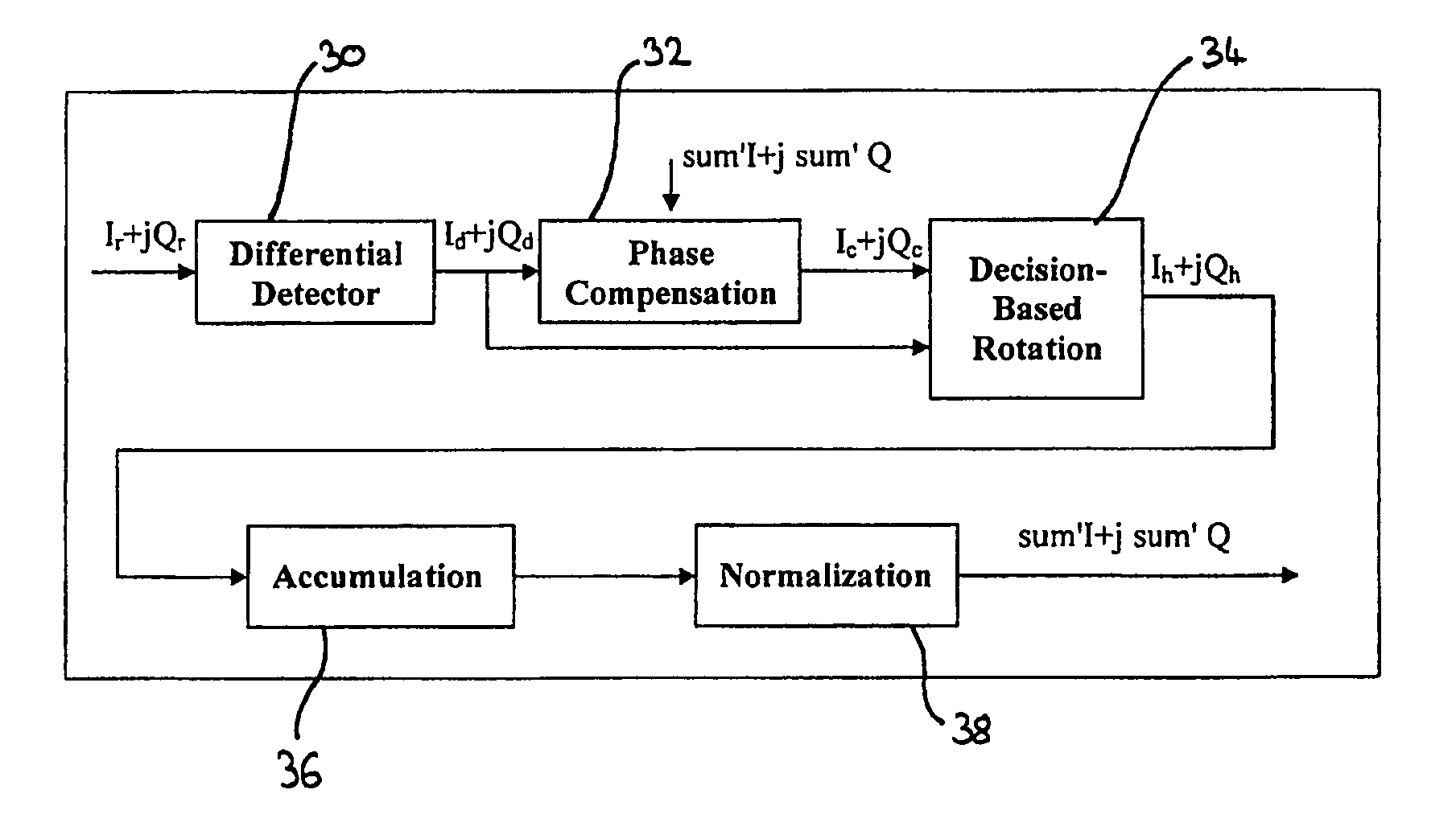
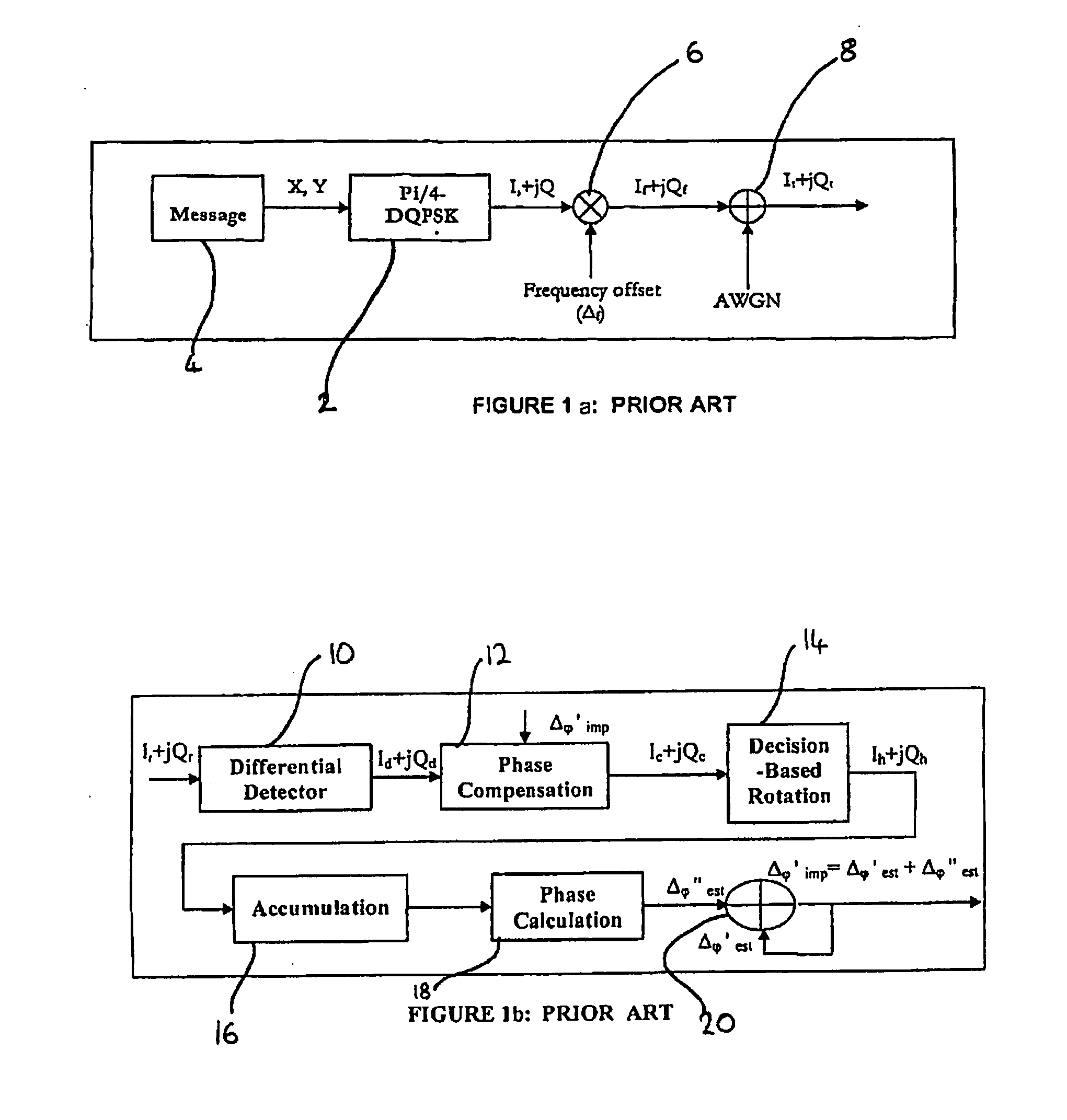
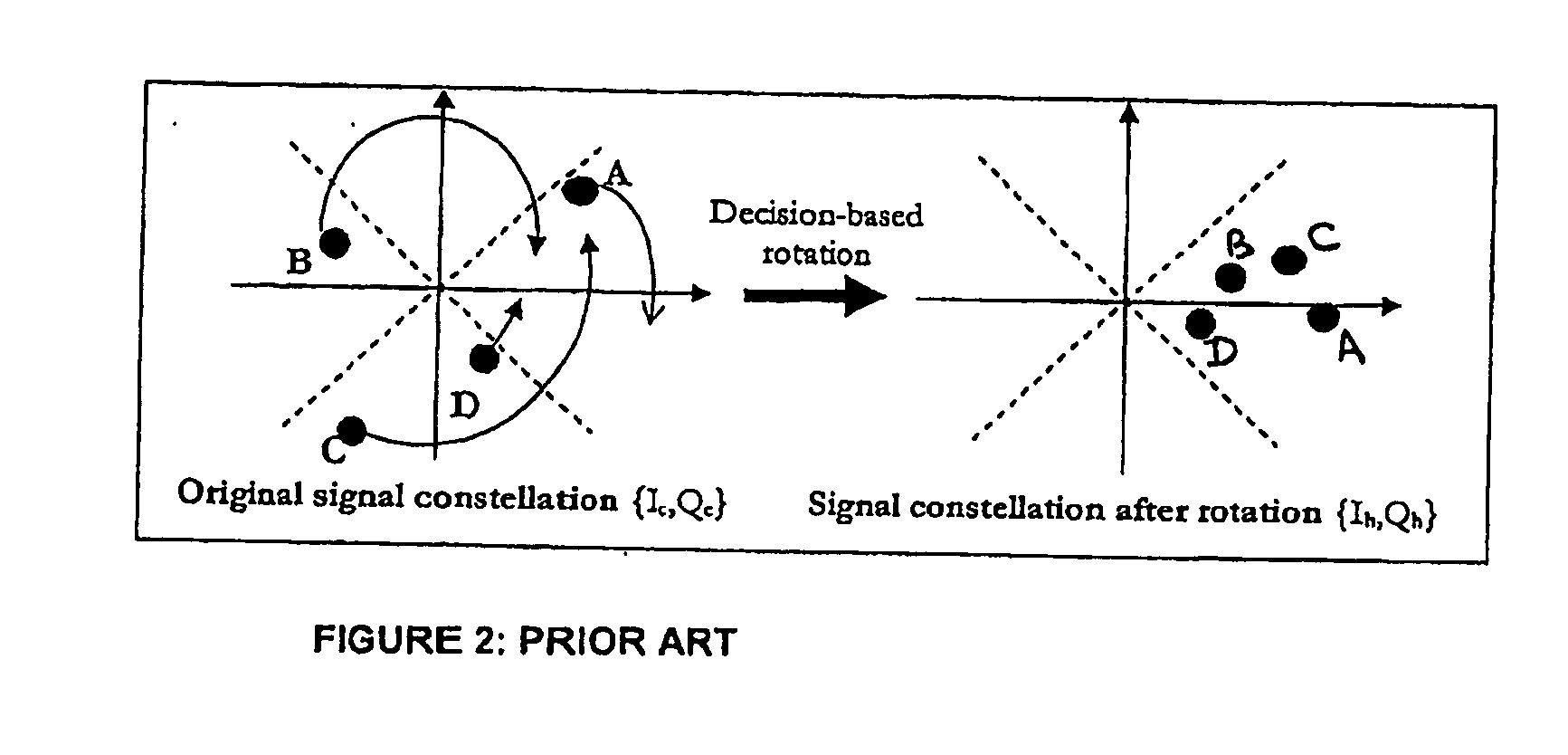
System and method for estimating phase offset in a communication system
InactiveUS20070192048A1Simple hardware implementationPhase accurateNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCommunications systemLocal oscillator
A system and method for estimating phase offset between a local oscillator and a transmitted input signal in a communication system comprises a differential detector and a phase compensation stage for compensating for phase errors in an output signal from the differential detector. The output signal from the differential detector is rotated in a decision-based rotation stage coupled to the outputs of the differential detector and the phase compensation stage. The rotation is based on a decision made using the output signal from the phase compensation stage. An accumulation stage accumulates the output signal from the decision-based rotation stage for a number of symbols in the transmitted input signal. A normalization stage normalizes the output signal from the accumulation stage and the normalized output signal corresponds to a phase offset of the local oscillator relative to the transmitted input signal. The phase compensation stage has a further input to which the phase offset is applied to compensate the phase of a subsequently received symbol in the transmitted input signal. The phase offset between the local oscillator and the transmitted input signal is then estimated.
Owner:OKI TECHNO CENT SINGAPORE PTE
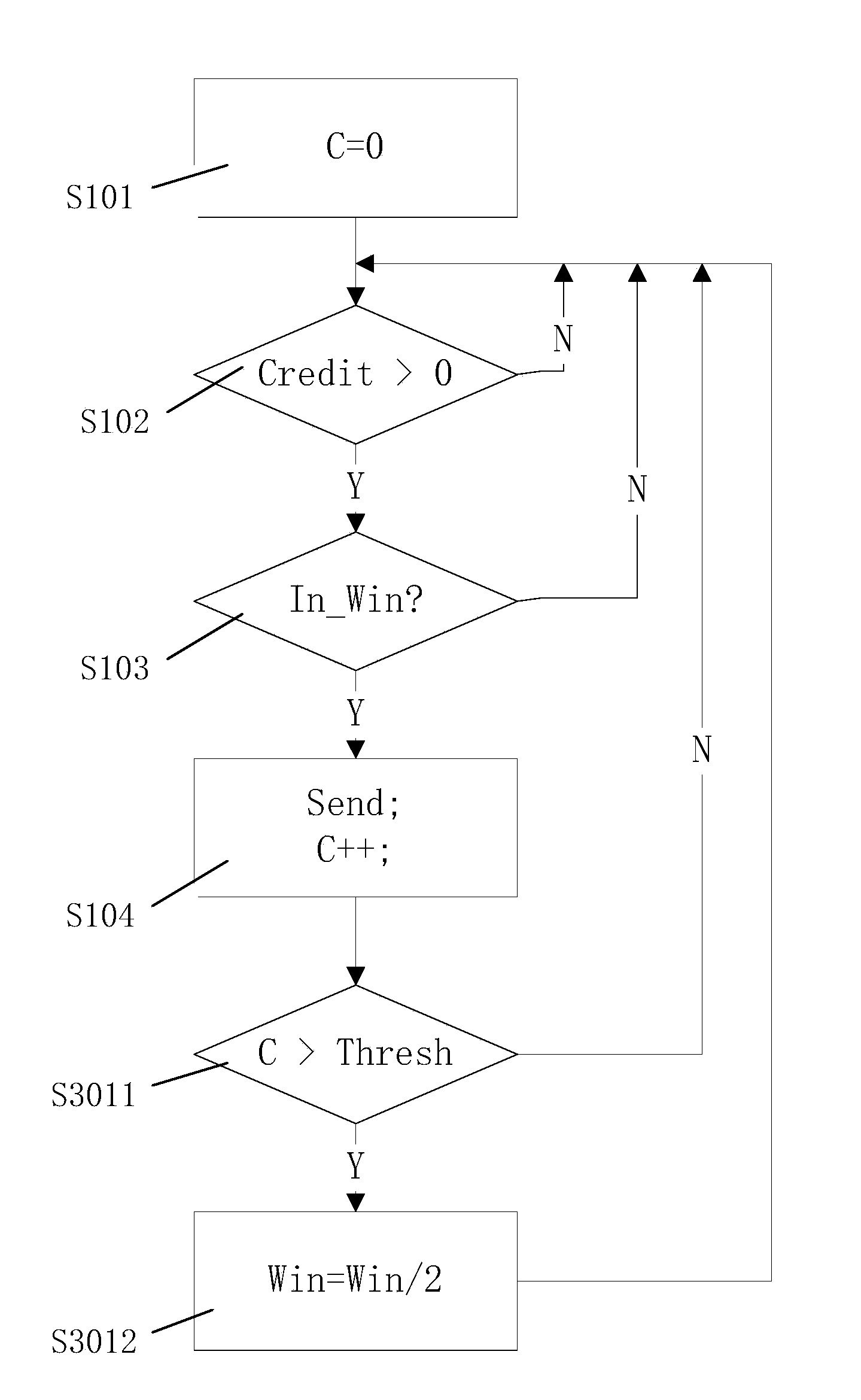
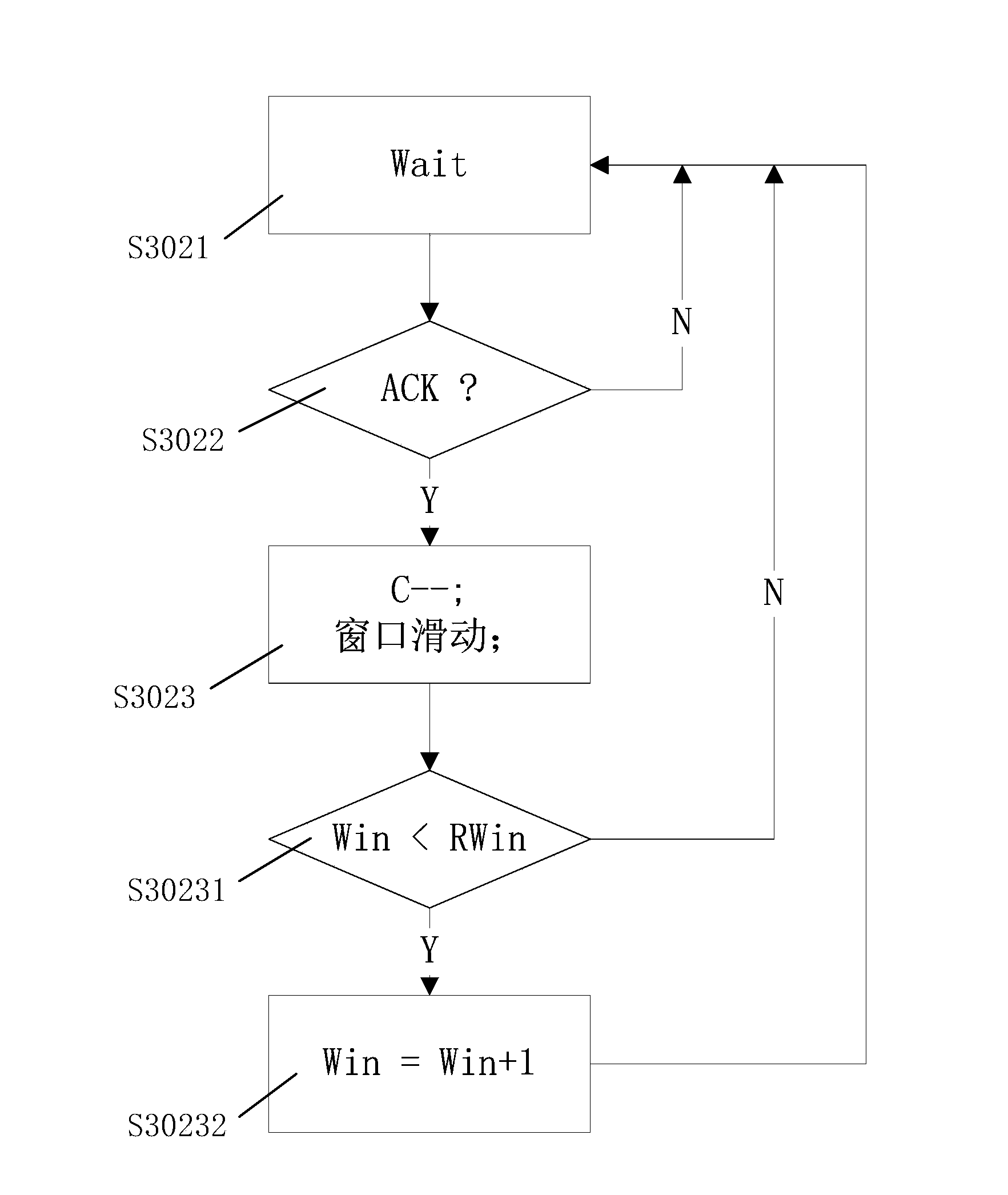
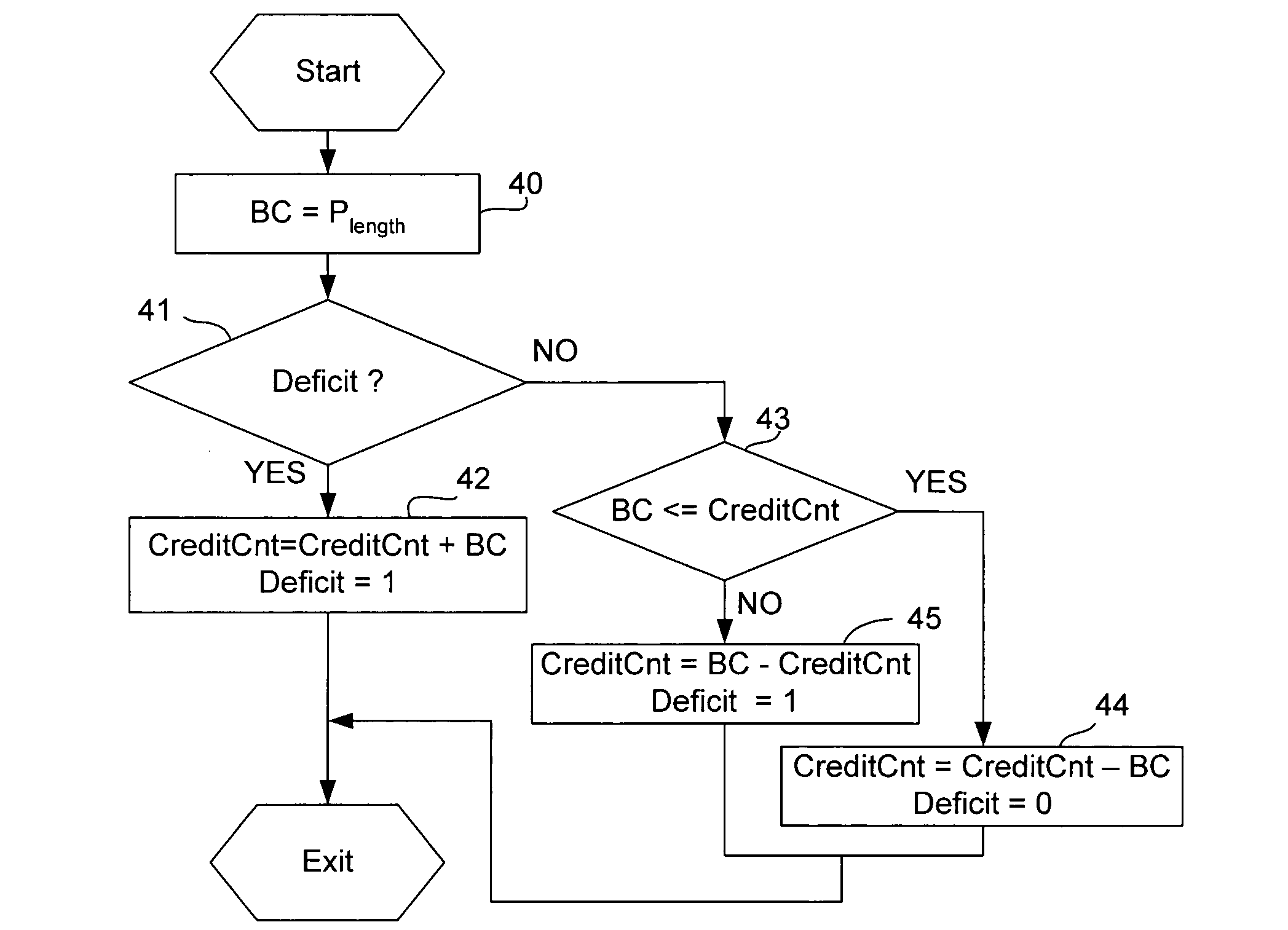
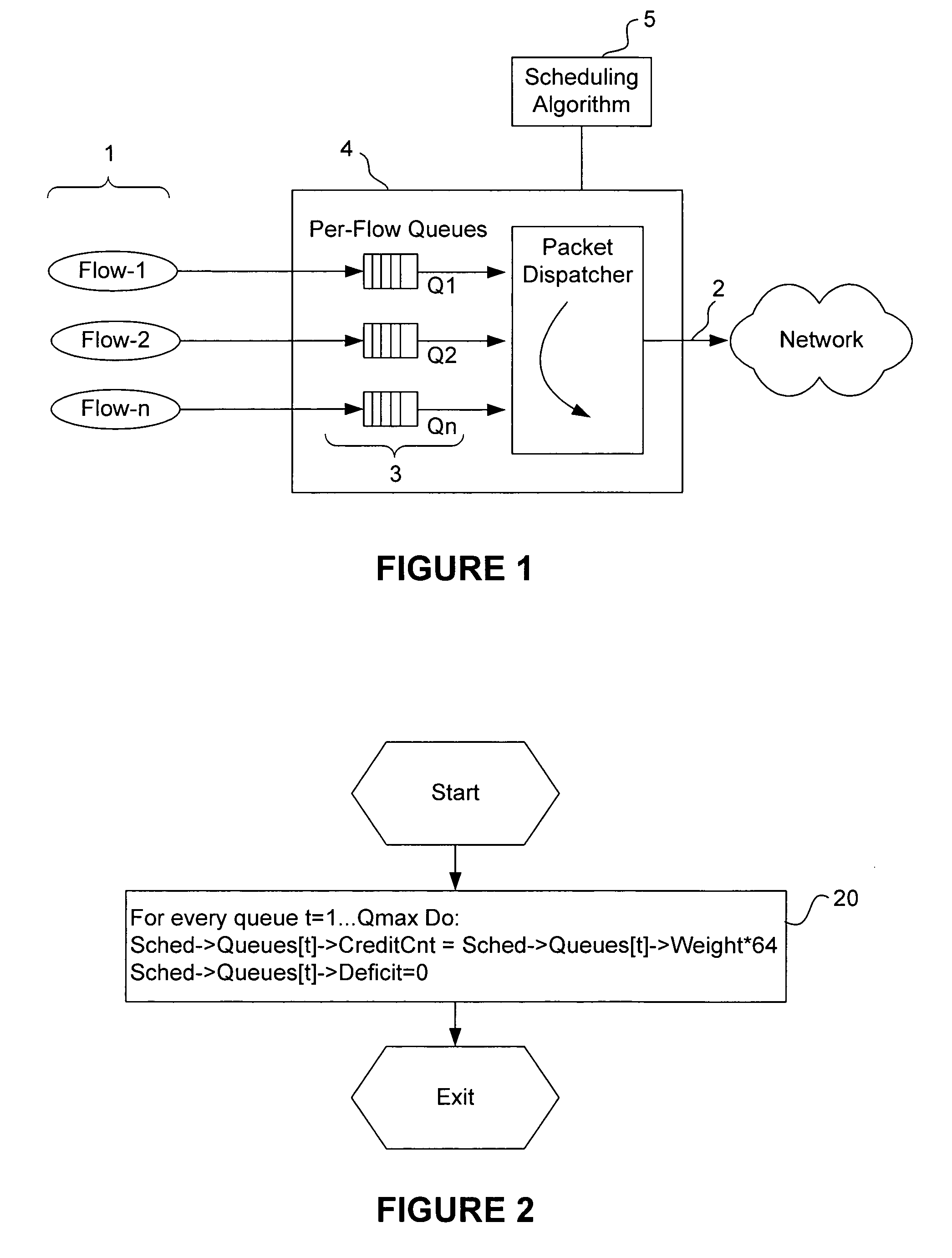
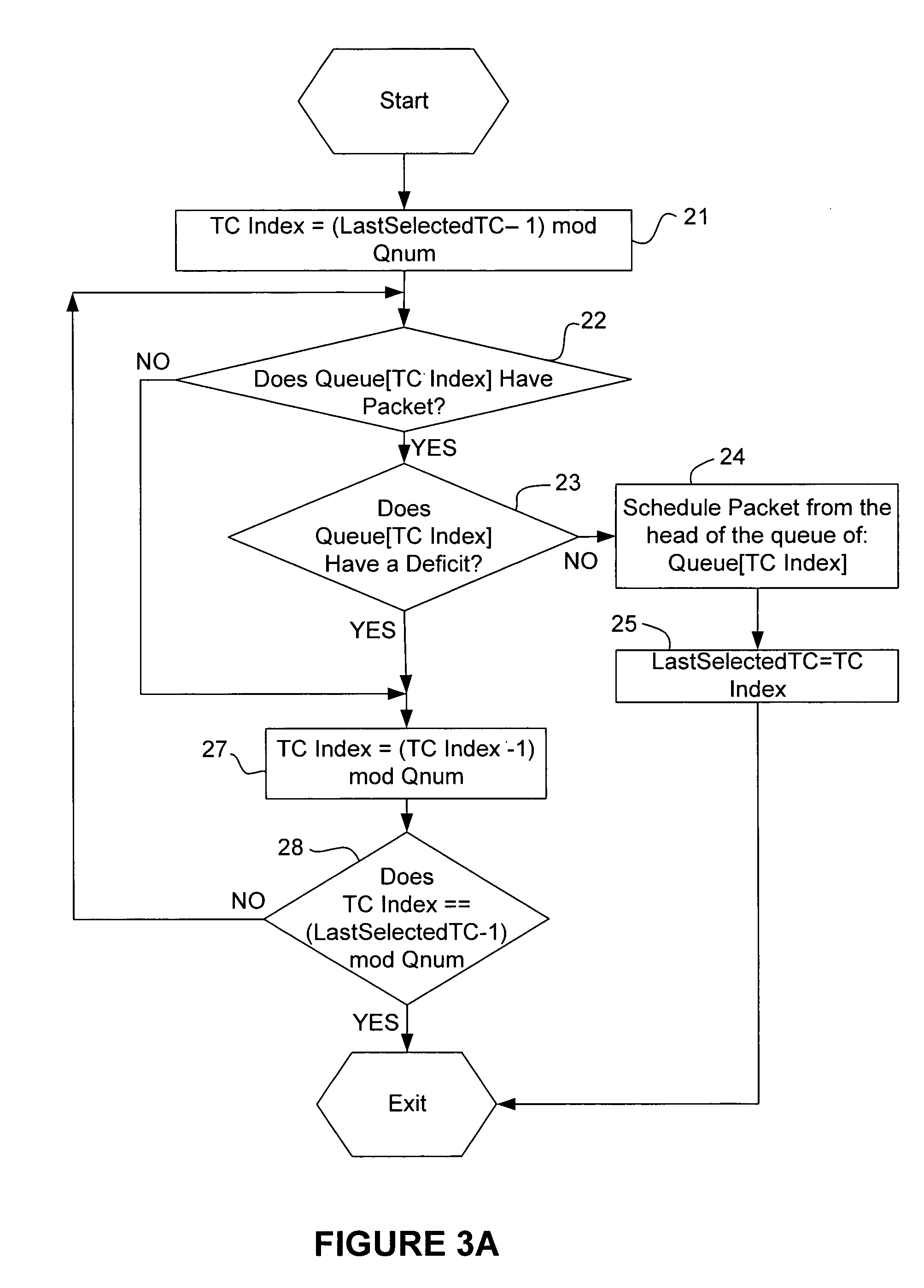
Method and apparatus for packet scheduling
ActiveUS7646717B1Fair distributionReduce complexityCoupling device connectionsError preventionData packPacket scheduling
A methods, apparatus and computer memory are provided for packet scheduling. A processor polls queues in a round robin fashion and schedules for transmission onto a link a packet in each queue with no deficit before scheduling for transmission onto the link a packet in each queue with a deficit. A credit is allocated to each queue with the deficit based on a proportional weight, until each queue with the deficit has a credit.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD +1
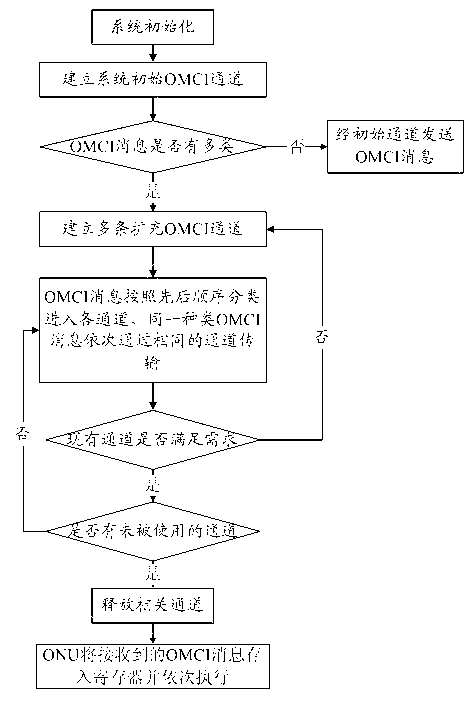
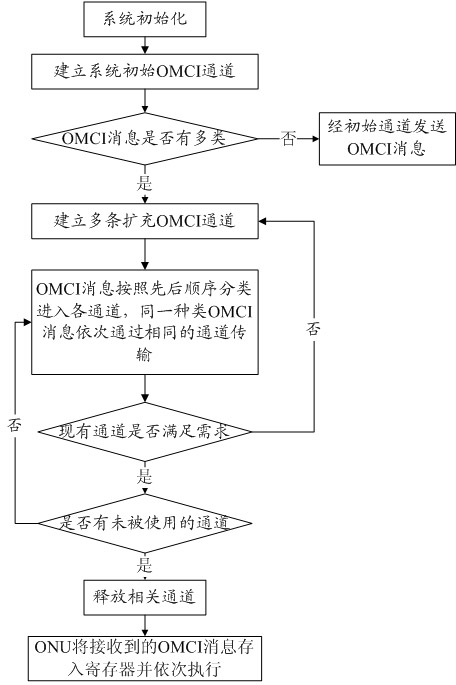
Method for transmitting and processing OMCI (ont management and control interface) messages in GPON (gigabit passive optical network)
InactiveCN102710999AImprove configuration management efficiencyImprove work efficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsProcessor registerGigabit
The invention discloses a method for transmitting and processing OMCI (ont management and control interface) messages in a GPON (gigabit passive optical network). The GPON comprises an optical line terminal (OLT) and at least one optical network unit (ONU) connected with the OLT through optical fibers. The method comprises the following steps: an initial OMCI channel communicated with the ONU is established by the OLT firstly, then a plurality of expansion OMCI channels are established according to the types of OMCI messages, and the OMCI messages are simultaneously sent to the ONU by the OLT by utilizing the plurality of OMCI channels, so that under the condition that more OMCI messages are needed to be sent to the ONU, the efficiency of configuring and managing the ONU by the OLT is effectively improved, and the integral working efficiency of the system is improved. Moreover, only one register is needed to be arranged in the ONU, so that the method has the advantages of simple hardware implementation mode, low cost and wider application range. The invention also discloses the GPON using the method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Error Correction Circuit for Data Communication Providing Parallelizable Linear Programming Decoding
ActiveUS20140089759A1Improve scalabilityImprove execution speedError preventionCode conversionElectronic circuitBelief propagation
An error detection / correction system provides an electronic circuit detecting and correcting transmission errors using linear programming. Linear programming techniques are made practical for real-time error correction and decoding by dividing the linear programming problem into independent parallelizable problems so that separate independent portions of the electronic circuit may simultaneously address solutions related to individual bits and / or parity rules. Linear programming is believed to avoid error floors inherent in conventional belief propagation error detection and correction techniques providing a decoding system suitable for high reliability applications.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com